Microscopic particle rotator of bidirectional conical optical fibers
A technology of tiny particles and rotators, applied in the directions of cladding fibers, radiation/particle processing, optical waveguides and light guides, etc., can solve the problems of difficult movement, bulky laser tweezers, and high cost, and achieves easy modification, large control range, High mixing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The present invention is described in more detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing example:
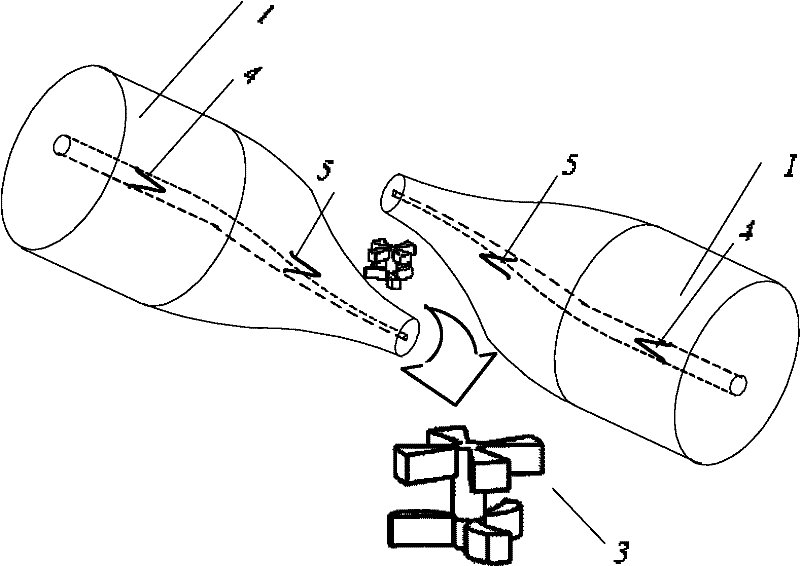
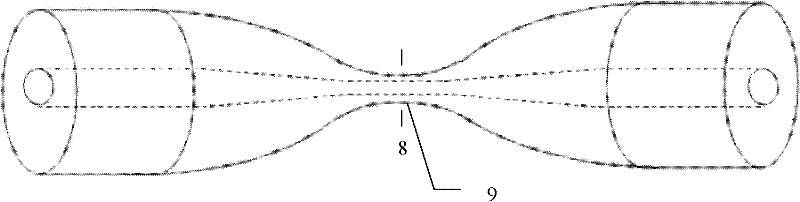
[0033] combine figure 1 , the first embodiment of the present invention is composed of two standard single-mode optical fibers 1, which are made of a tapered optical fiber 2 and a double-body microparticle 3, which are cut by fusion tapering, and inject light into the two tapered optical fibers . Because of the special structure of the tapered fiber, the transmitted light 4 in the fiber core is transmitted out of the cladding in the form of evanescent waves 5 and acts on the tiny particles 3, and this part of the transmitted evanescent field generates light radiation pressure on the tiny particles 3 Torsion torque is formed to realize rotation.
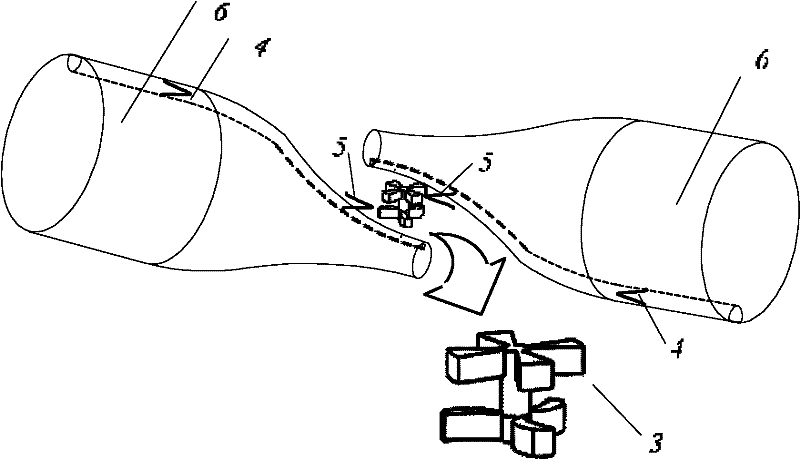
[0034] combine figure 2 , The second embodiment of the present invention is composed of two surface single-core optical fibers 6 which are made of a tapered optical fiber and double-body micro-particles 3 after fusion...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com