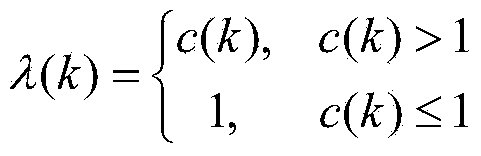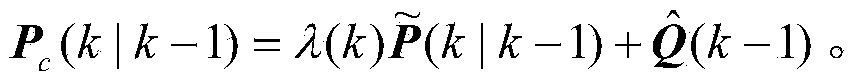Patents
Literature
91 results about "Noise statistics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Statistical noise is unexplained variability within a data sample. The term noise, in this context, came from signal processing where it was used to refer to unwanted electrical or electromagnetic energy that degrades the quality of signals and data.
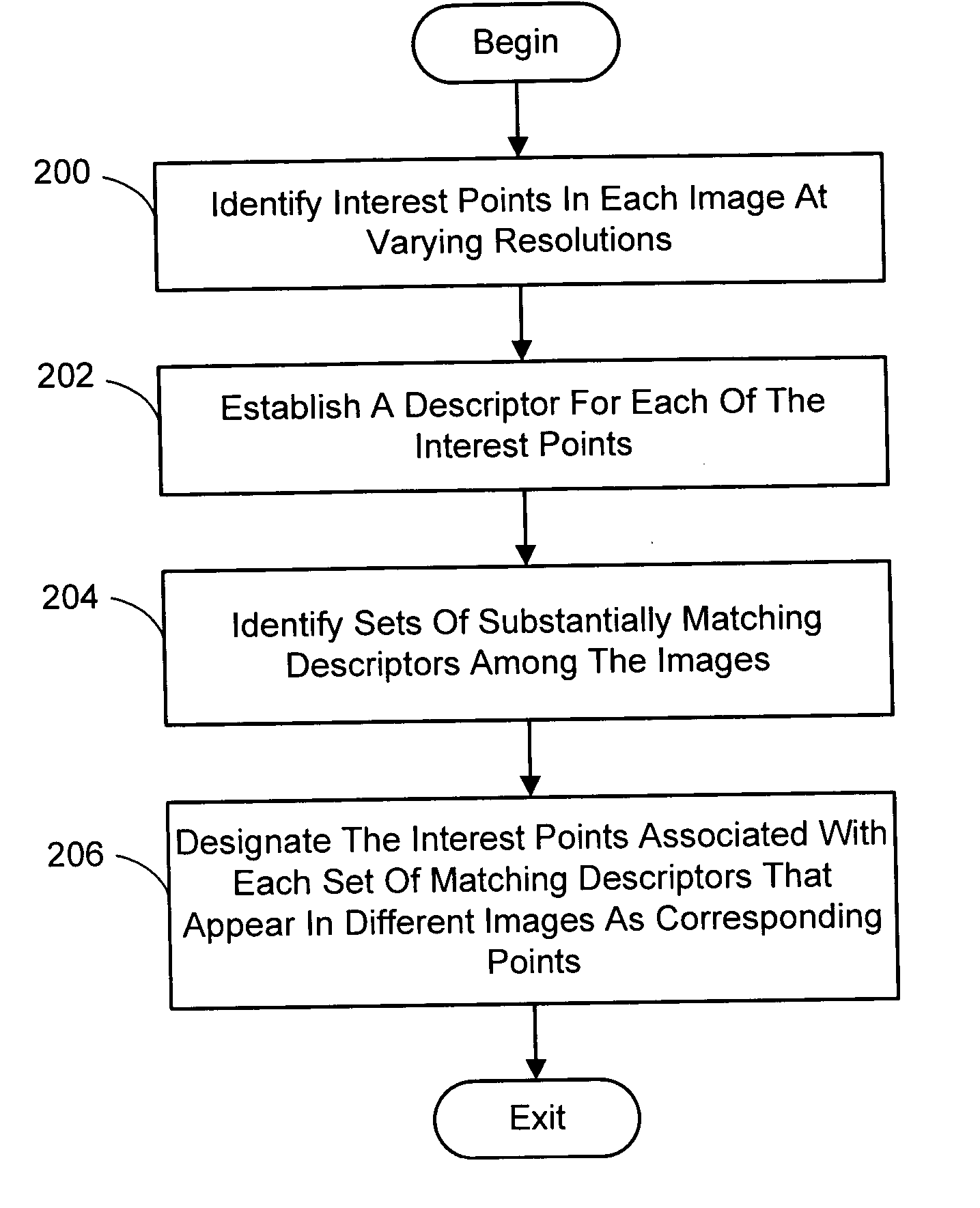
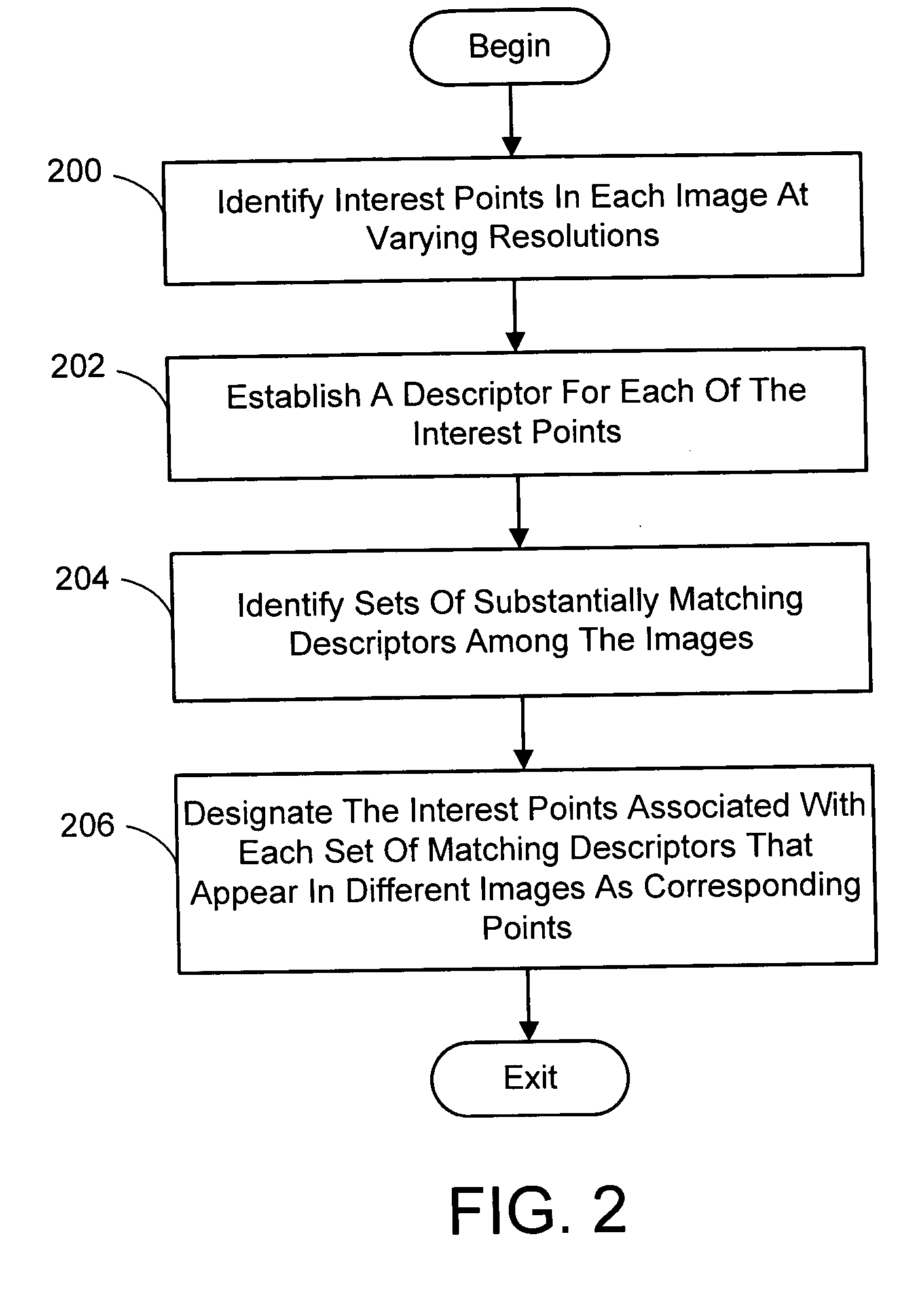
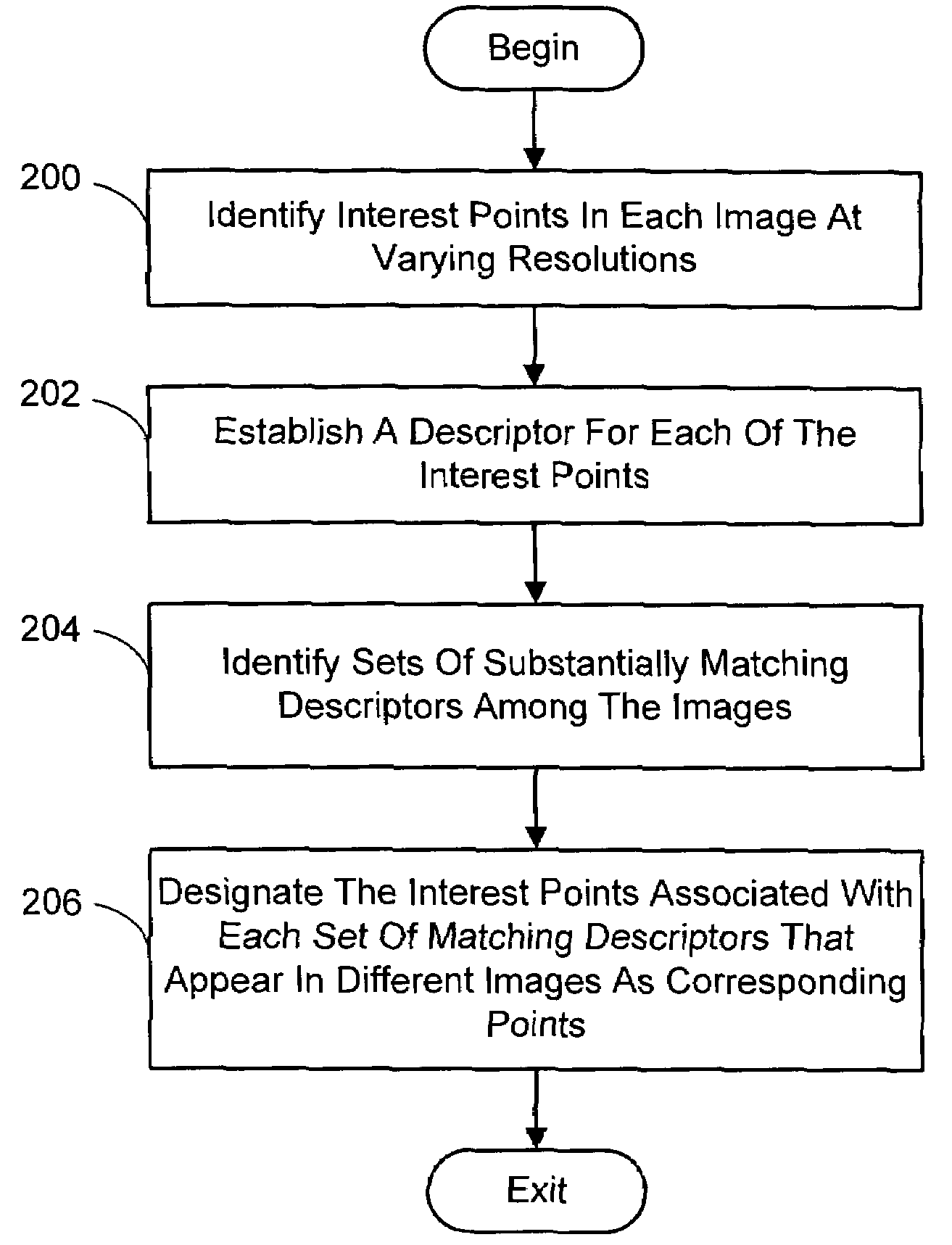
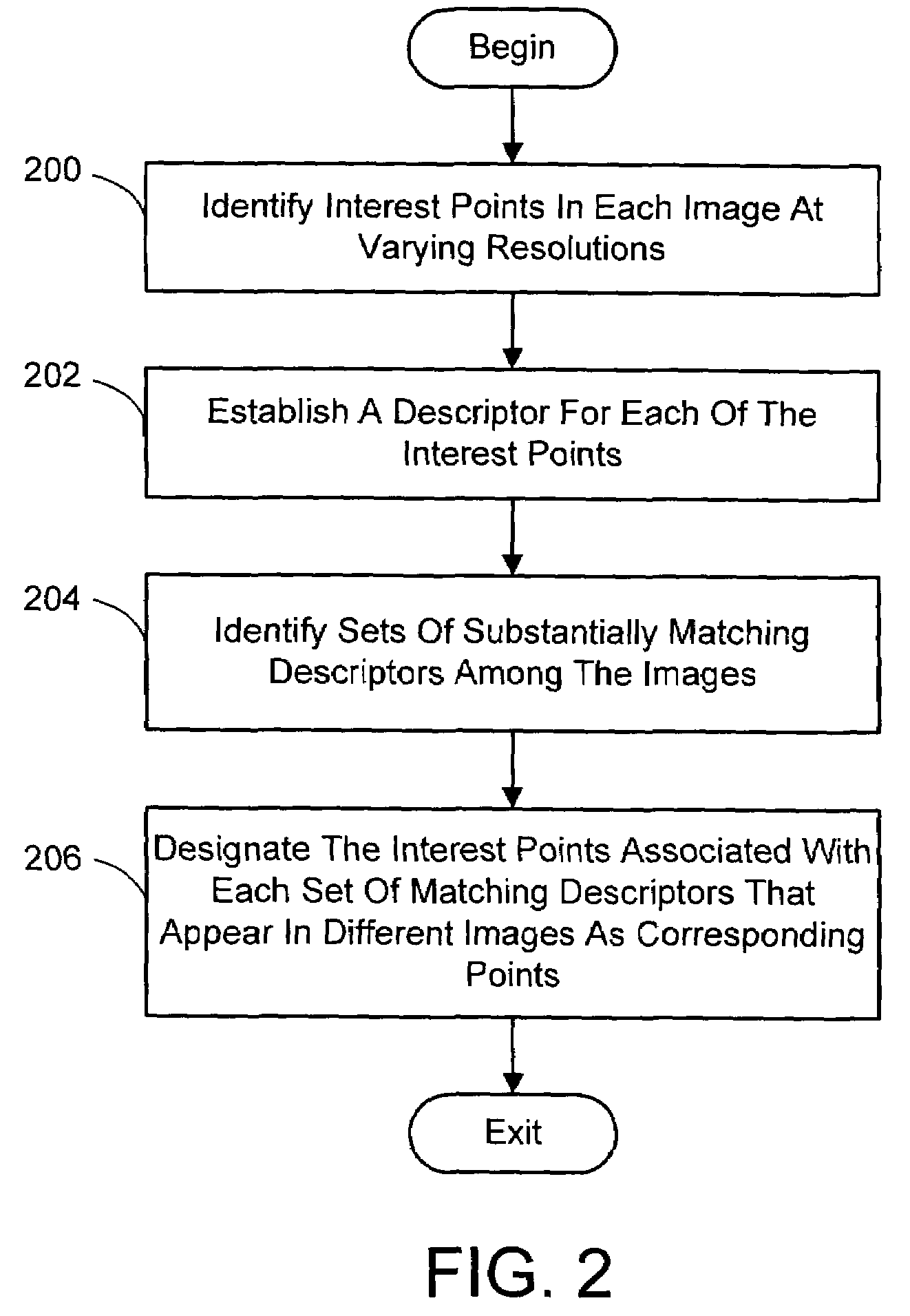
Multi-image feature matching using multi-scale oriented patches
InactiveUS20050238198A1Quick extractionEasy to liftConveyorsImage analysisPattern recognitionNear neighbor
A system and process for identifying corresponding points among multiple images of a scene is presented. This involves a multi-view matching framework based on a new class of invariant features. Features are located at Harris corners in scale-space and oriented using a blurred local gradient. This defines a similarity invariant frame in which to sample a feature descriptor. The descriptor actually formed is a bias / gain normalized patch of intensity values. Matching is achieved using a fast nearest neighbor procedure that uses indexing on low frequency Haar wavelet coefficients. A simple 6 parameter model for patch matching is employed, and the noise statistics are analyzed for correct and incorrect matches. This leads to a simple match verification procedure based on a per feature outlier distance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
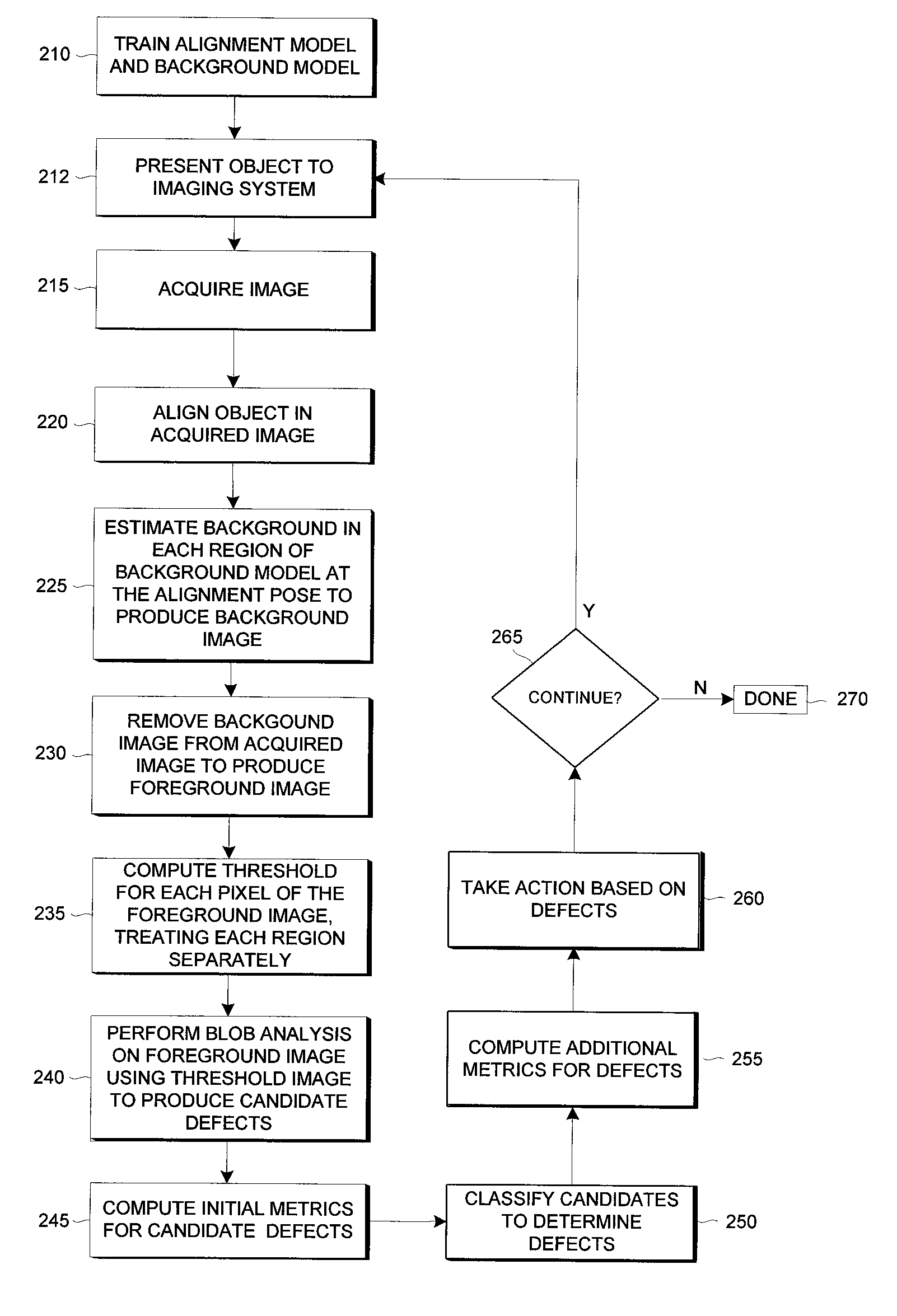
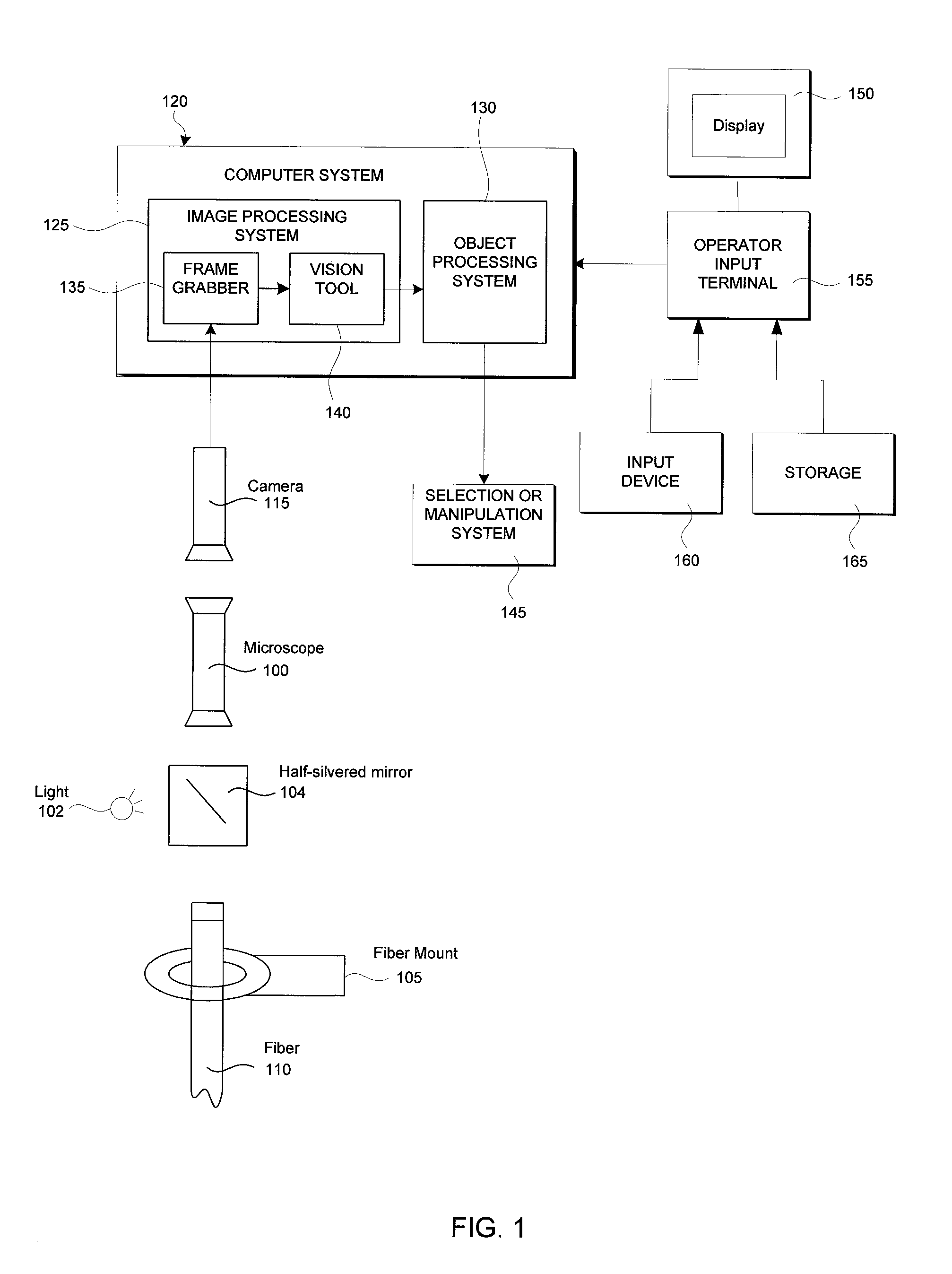
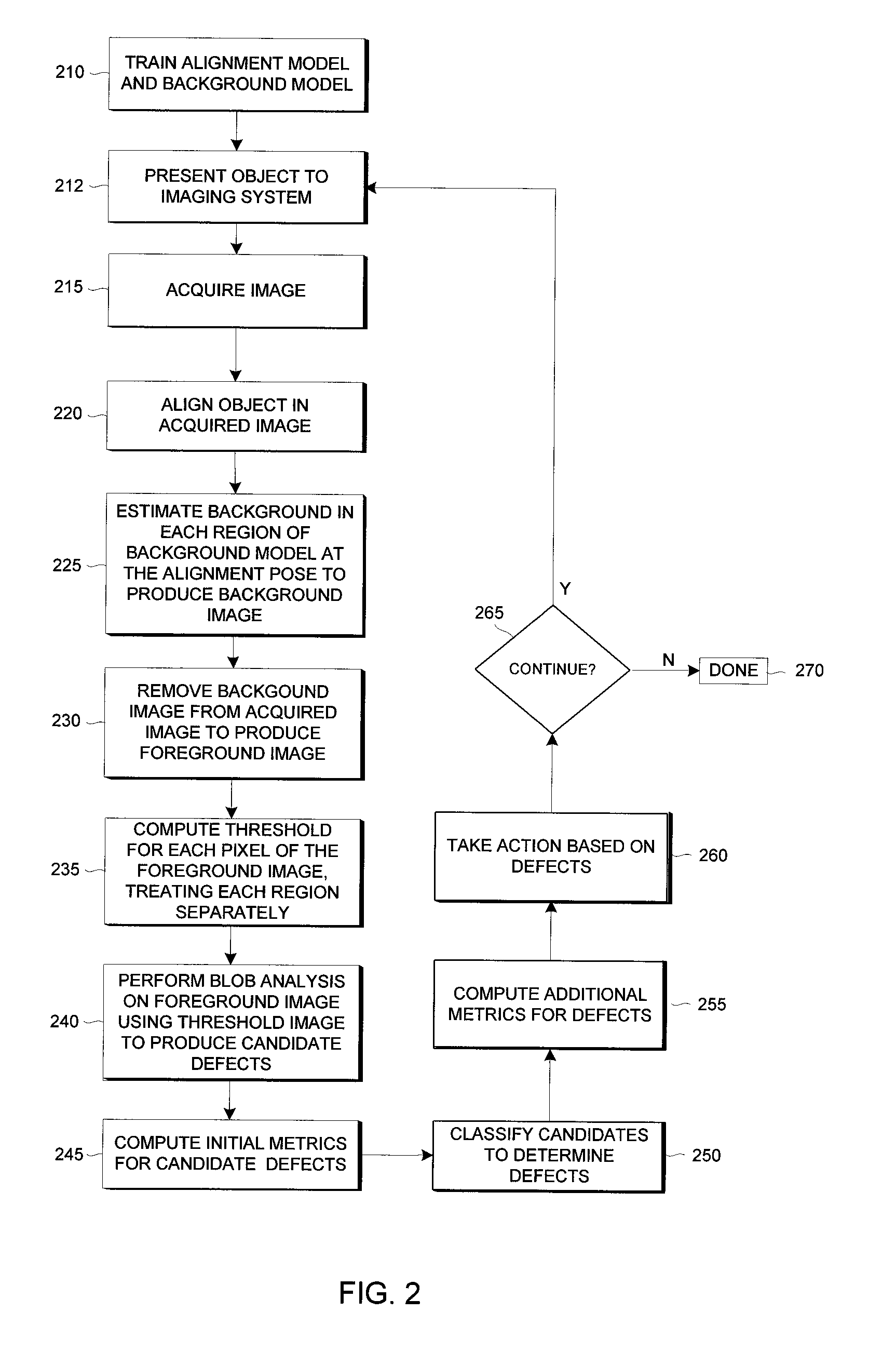
Methods and apparatuses for detecting classifying and measuring spot defects in an image of an object
InactiveUS7162073B1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisFiberComputer vision
A method is provided for detecting spot defects on an object when an allowable variation (called the “background”) in the appearance of the object can be modeled. Methods are also provided for measuring and classifying detected spot defects. An alignment model is used to align the image of the object, a background model is then used to estimate the (possibly different) background in each region, and each background is substantially removed from the image so as to form a foreground image on which blob analysis can be applied to detect spot defects, the blob analysis using a threshold image that accommodates different noise statistics for each region. The method facilitates robust spot defect inspection of fiber optic end faces, or of any object with different object regions. The method also allows use of blob analysis over a larger range of conditions, including conditions that make simple blob analysis infeasible.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
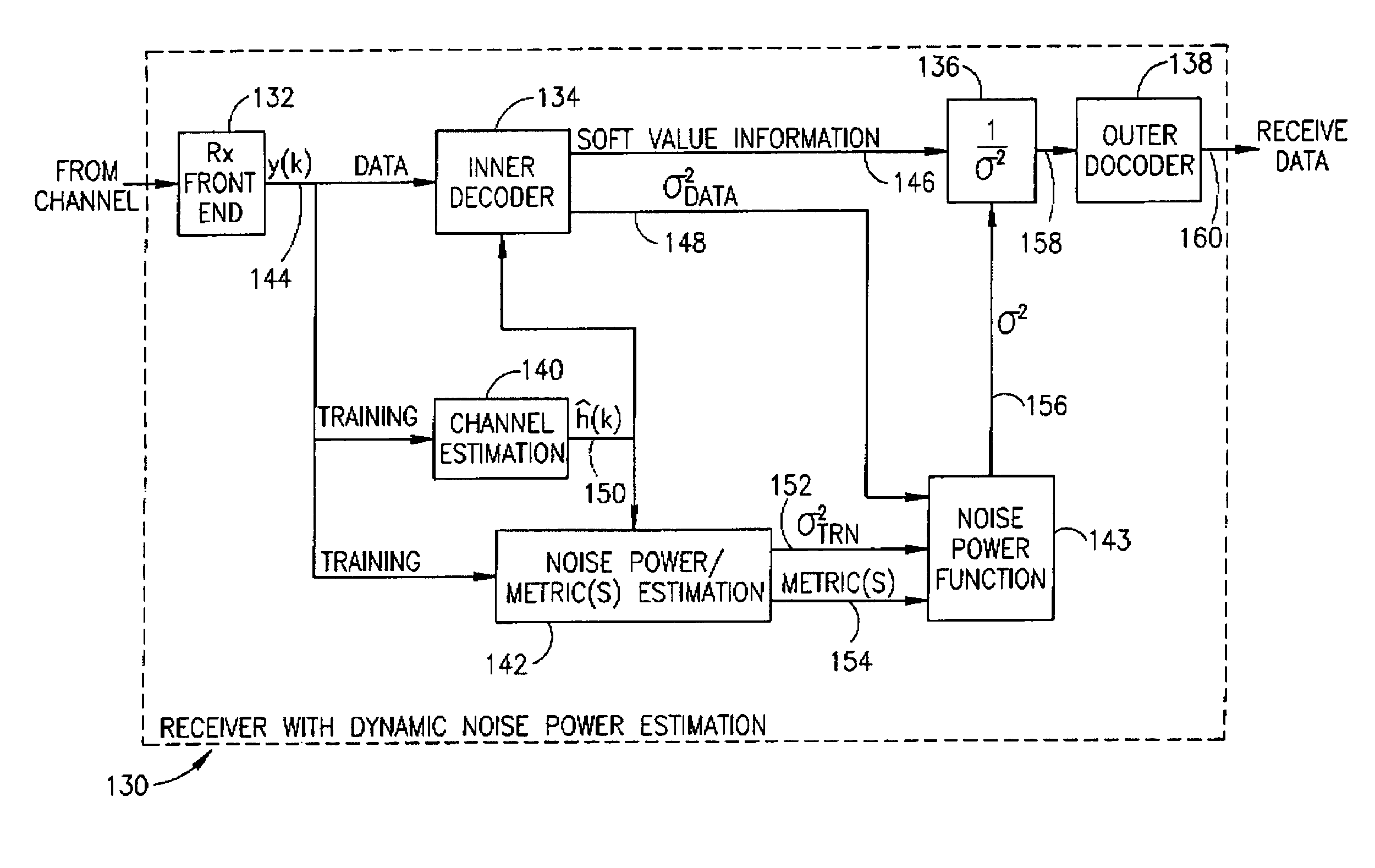
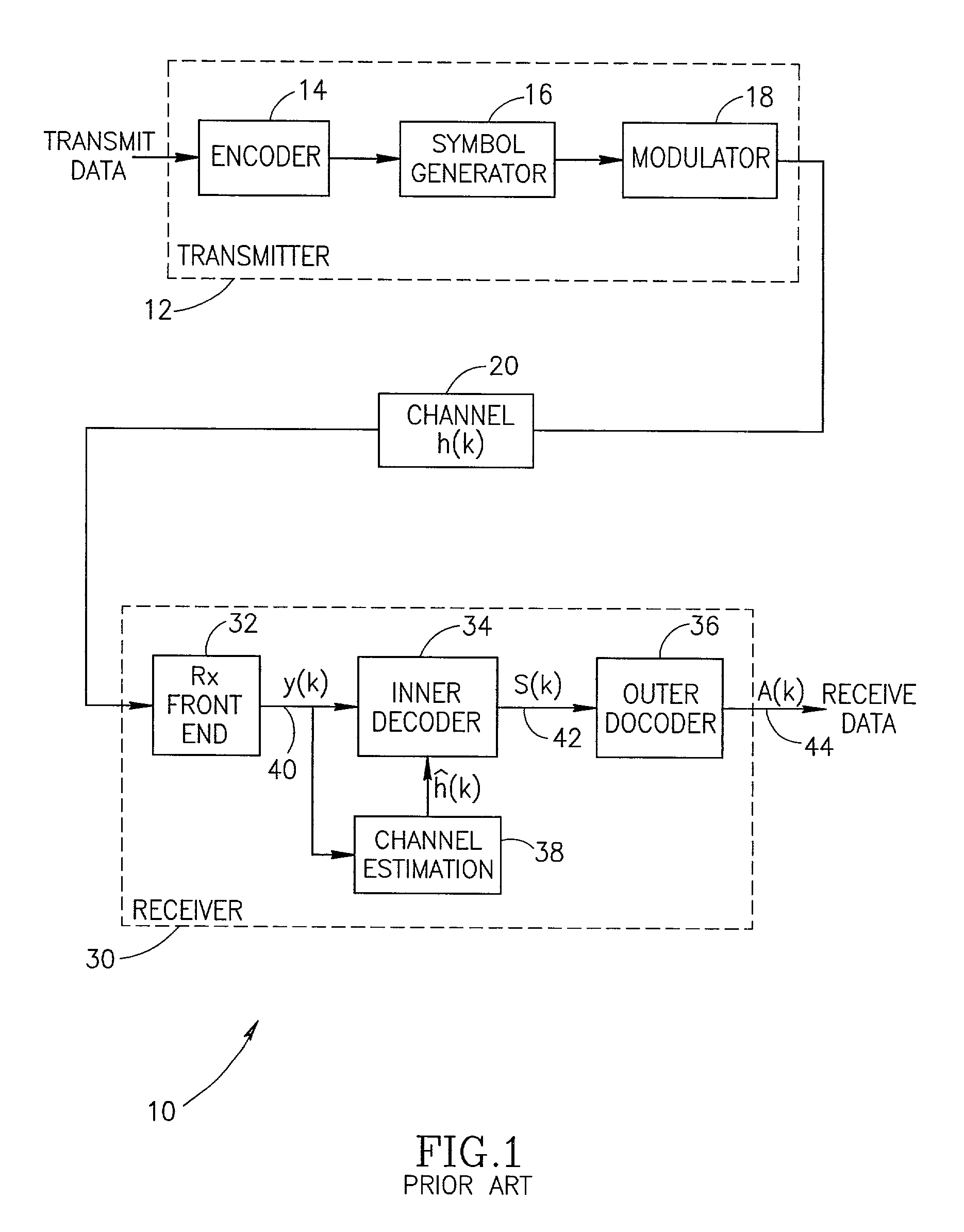
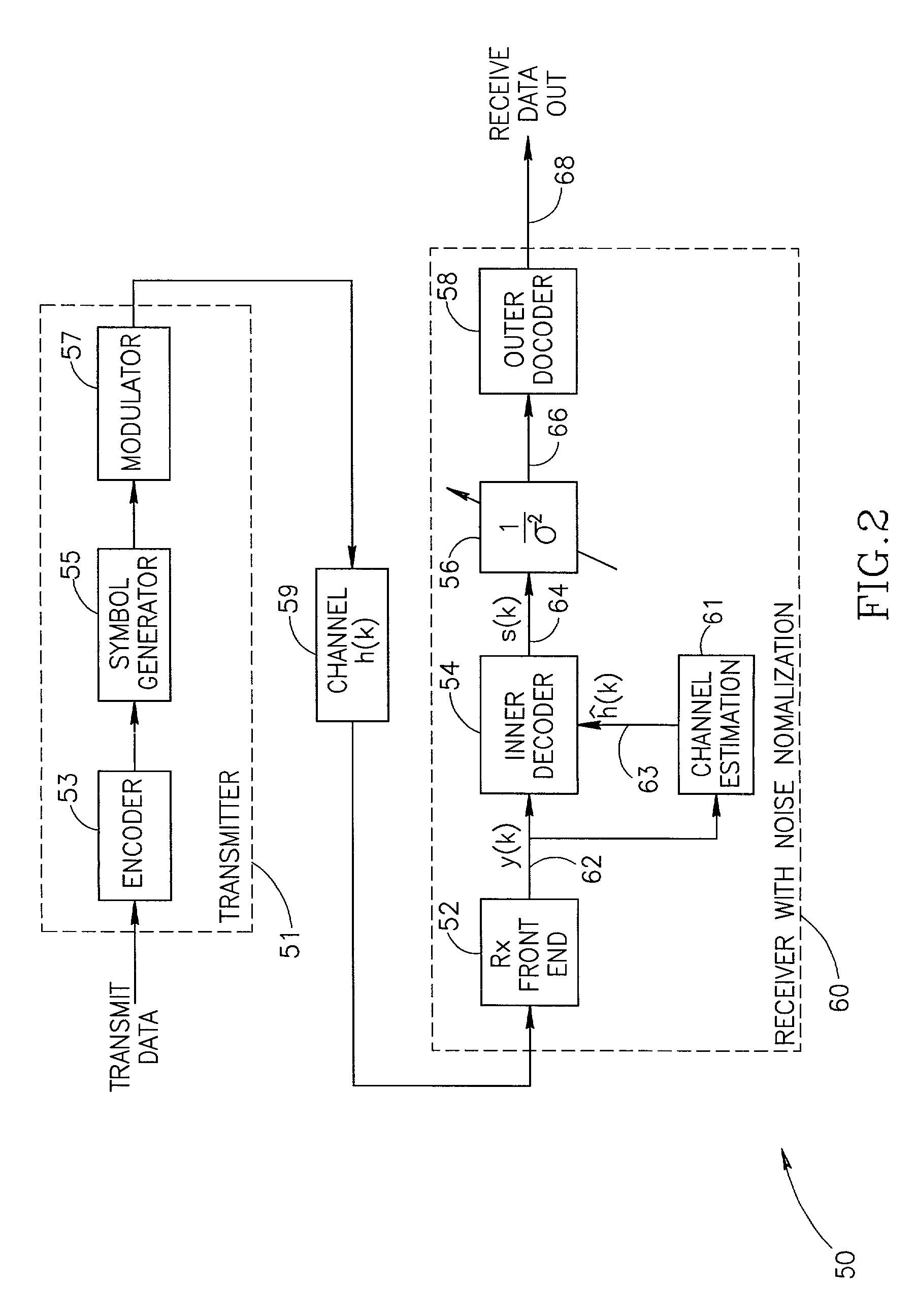
Normalization of equalizer soft output for channels with varying noise power
InactiveUS6980602B1Overcome disadvantagesSuitable for useData representation error detection/correctionError preventionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Computer science
An apparatus for and method of generating normalized soft decision information output from an inner decoder (i.e. equalizer) in a communications receiver. The invention is operative to normalize the soft decision information before it enters a soft outer decoder. The normalization is performed using a noise power estimate that is dynamically calculated in response to changing noise statistics on the channel. The normalized soft decision output is then applied to the soft outer decoder thus realizing maximum performance therefrom. The noise power estimate is derived from the training sequence and / or the data portion of the received signal. Both types of estimates are calculated. A binary or smoothly weighted average is calculated using both types of estimates. The weighting factor is determined based on one or more performance metrics, such as the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR).
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
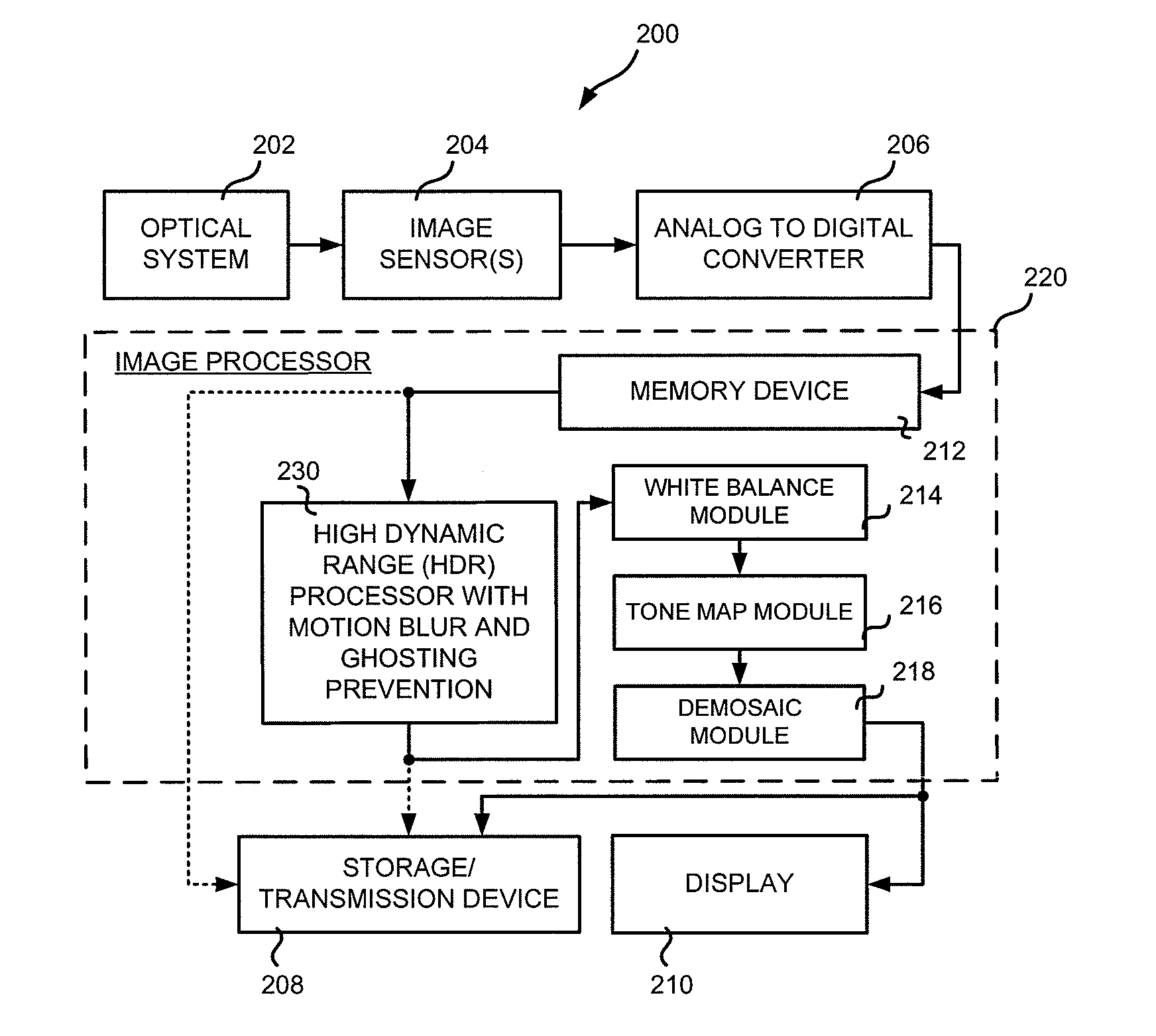
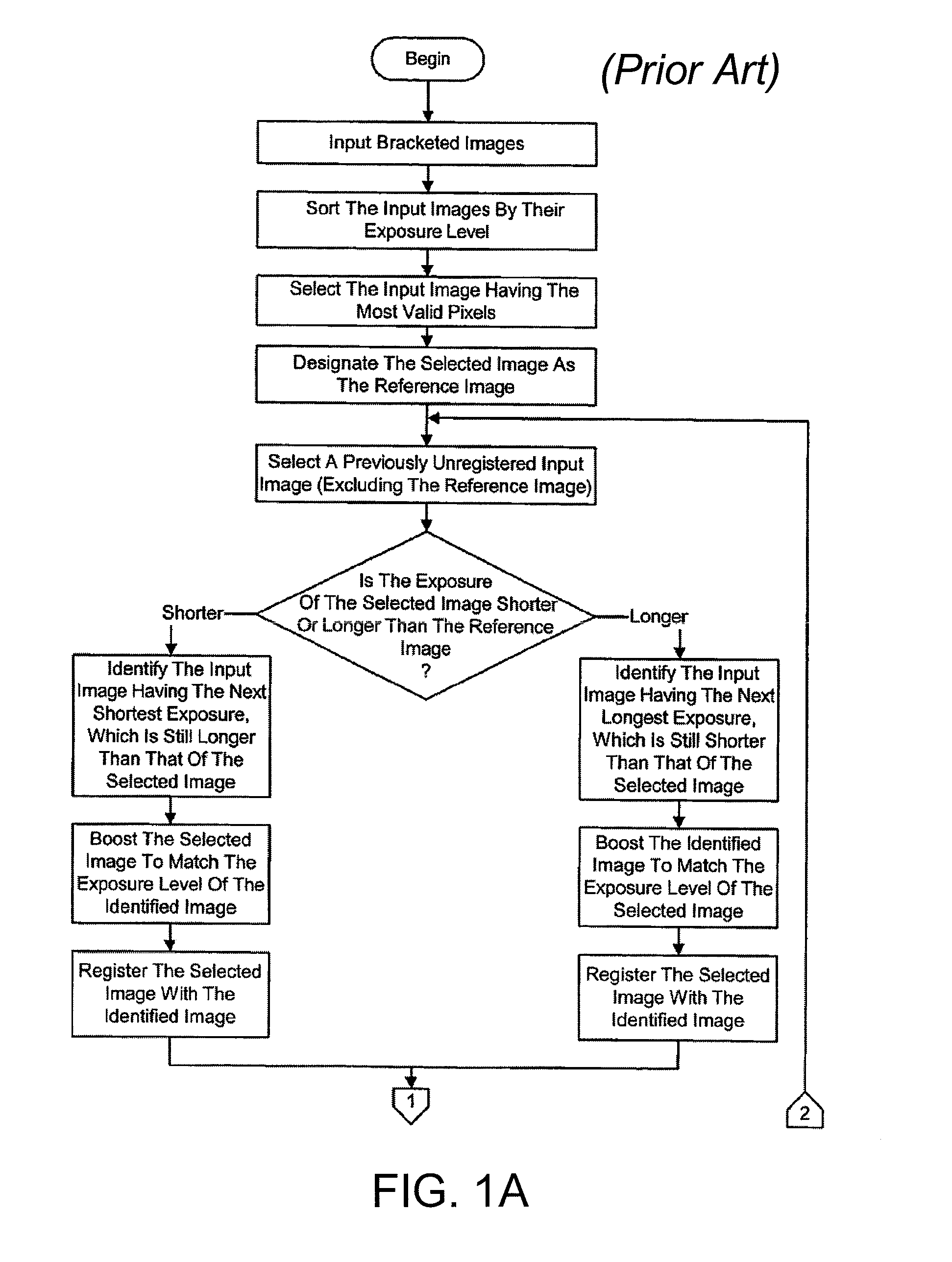
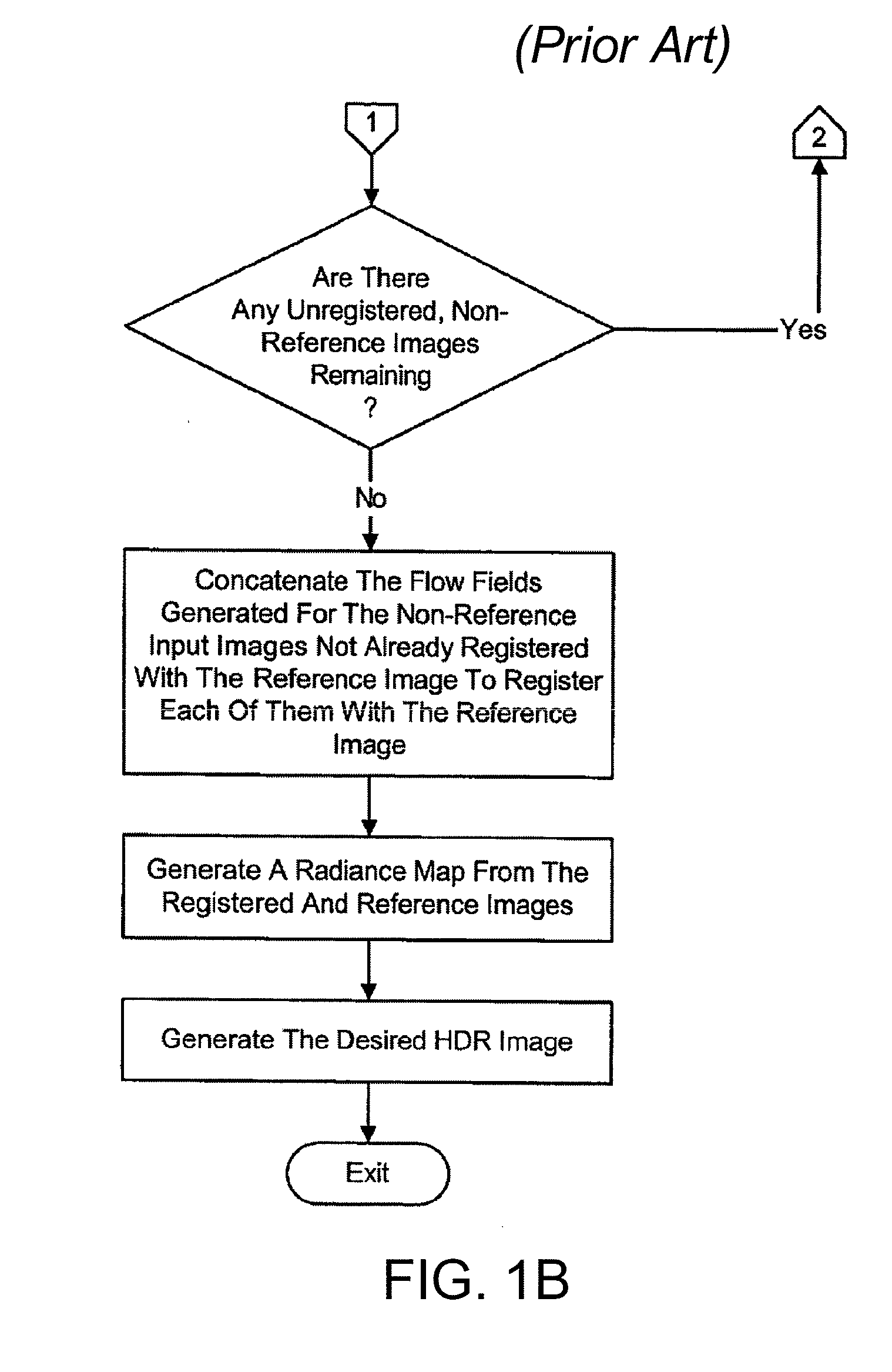
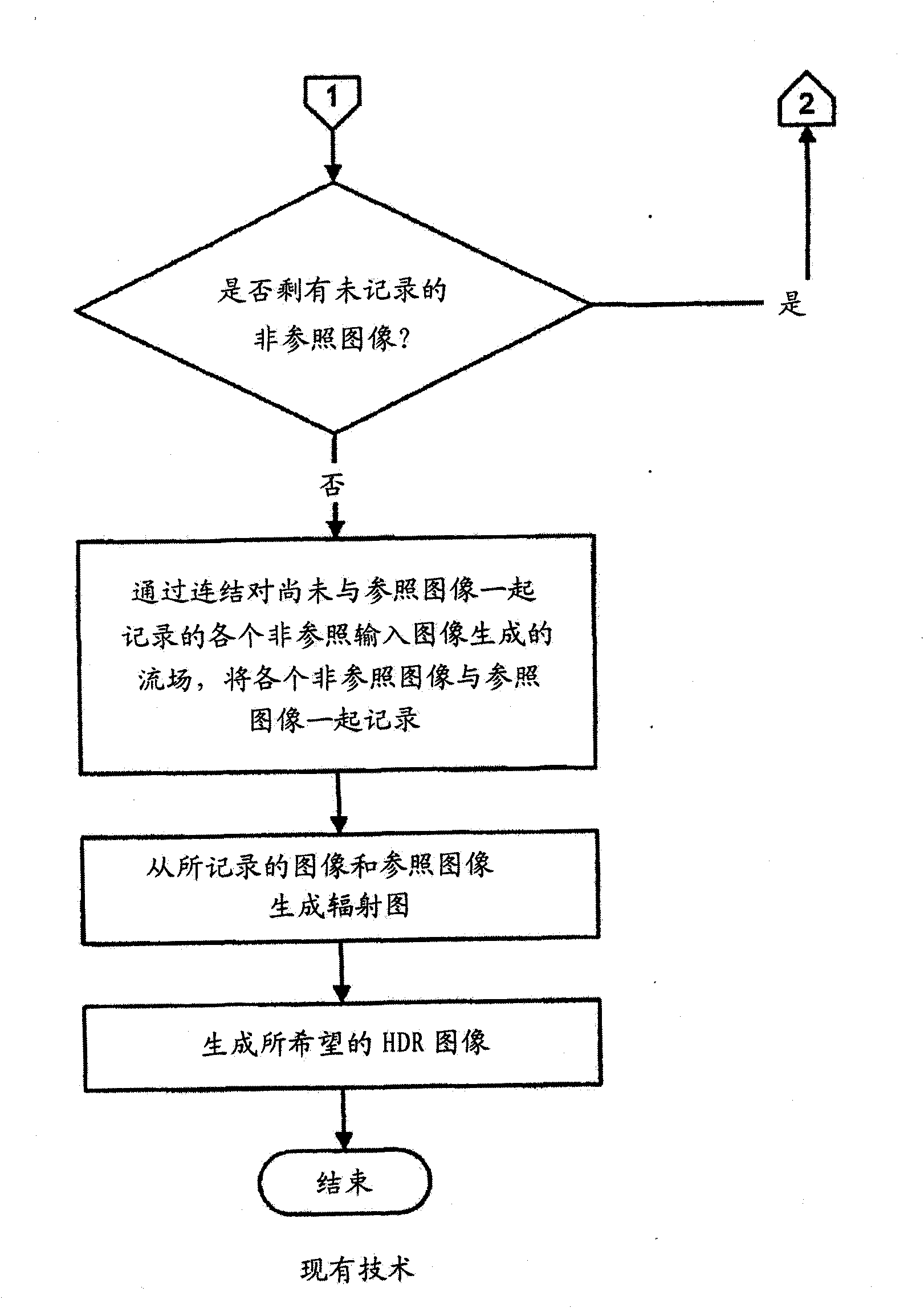
Method and apparatus for motion blur and ghosting prevention in imaging system
InactiveUS20110058050A1Noise robustPromote differentiationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAlong edgeImage pair
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Multi-image feature matching using multi-scale oriented patches
InactiveUS7382897B2Quick extractionEasy to liftConveyorsImage analysisPattern recognitionNear neighbor
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
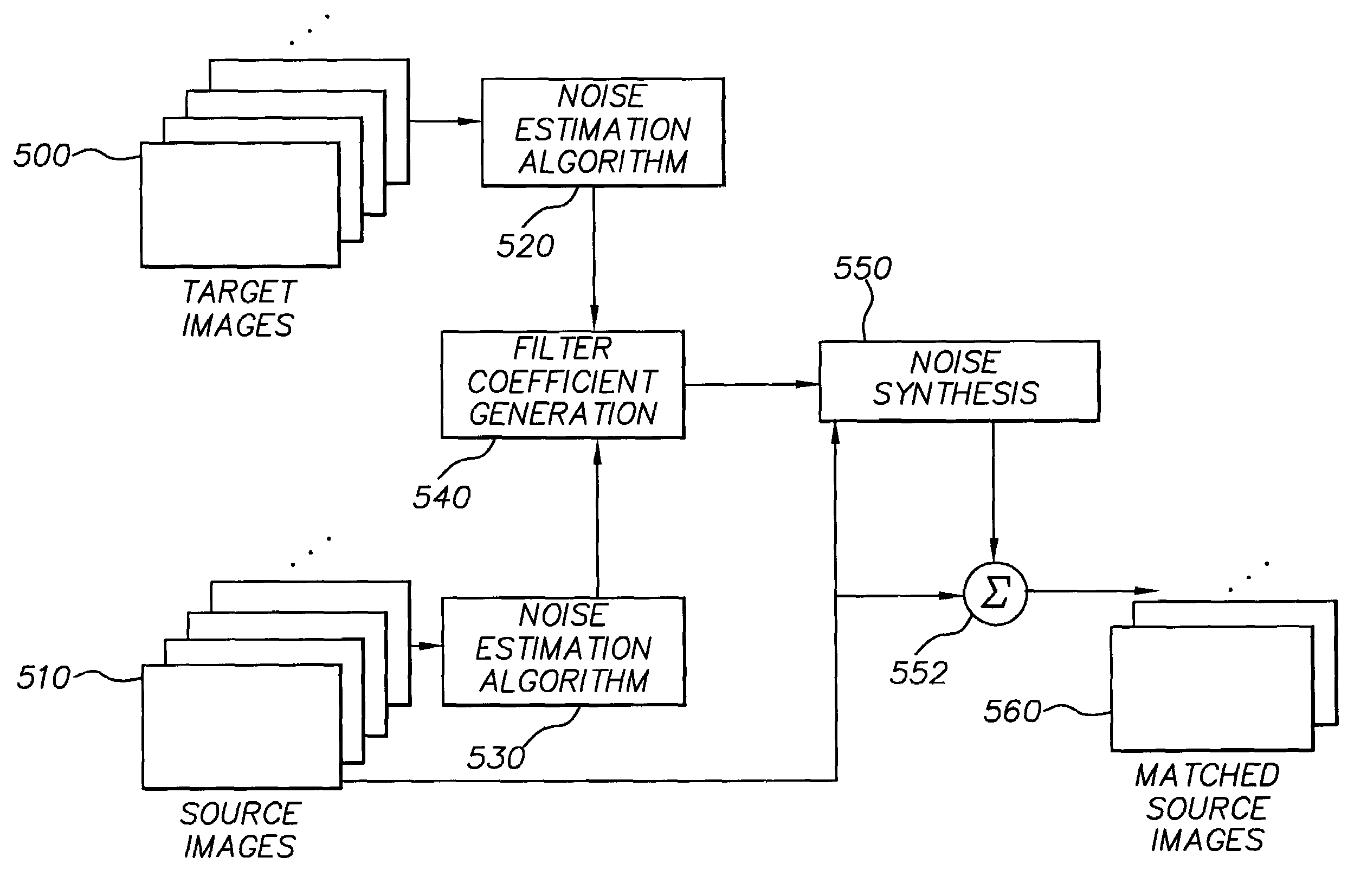
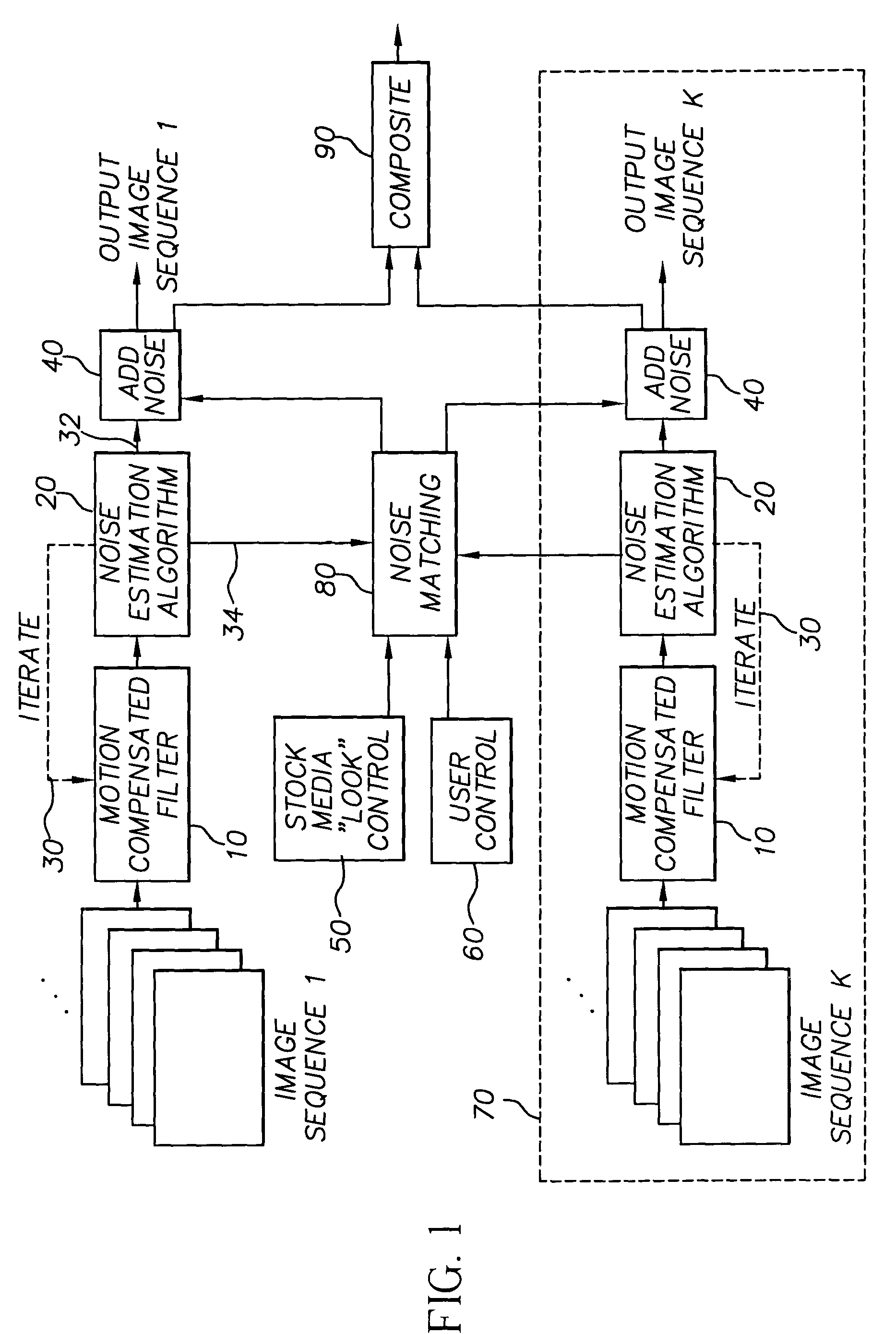
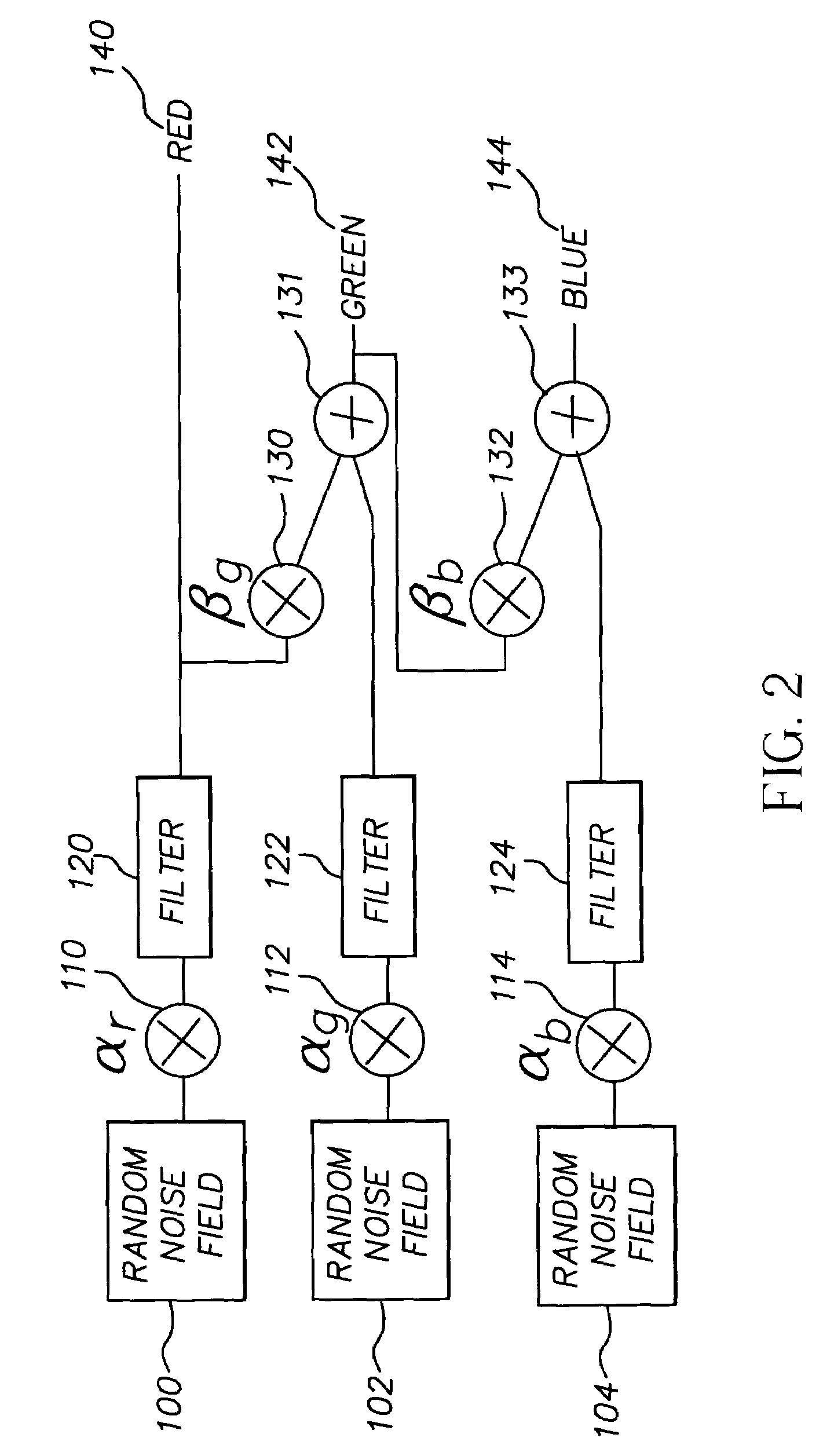
System and method for estimating, synthesizing and matching noise in digital images and image sequences
InactiveUS7245783B2Improve textureQuality improvementImage enhancementTelevision system detailsNoise fieldCorrelation coefficient
A method for synthesizing noise in a digital image comprises the steps of (a) estimating noise statistics based on a set of spatial autocorrelation coefficients and a set of spectral correlation coefficients that correspond to the color channels of the image, where at least one of the spatial autocorrelation coefficients is weighted by at least one of the spectral correlation coefficients, thereby providing a weighted set of autocorrelation coefficients, and where a set of filter coefficients is obtained from the weighted set of autocorrelation coefficients; and (b) synthesizing a synthetic texture by using the filter coefficients to filter a random noise field in each of the color channels, thereby producing output noise fields in each of the color channels that replicate a synthetic texture, e.g., a desired grain appearance, when combined into the digital image.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
Methods and systems for generating an inspection process for a wafer
ActiveUS8112241B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringNoise statistics
Methods and systems for generating an inspection process for a wafer are provided. One computer-implemented method includes separately determining a value of a local attribute for different locations within a design for a wafer based on a defect that can cause at least one type of fault mechanism at the different locations. The method also includes determining a sensitivity with which defects will be reported for different locations on the wafer corresponding to the different locations within the design based on the value of the local attribute. In addition, the method includes generating an inspection process for the wafer based on the determined sensitivity. Groups may be generated based on the value of the local attribute thereby assigning pixels that will have at least similar noise statistics to the same group, which can be important for defect detection algorithms. Better segmentation may lead to better noise statistics estimation.
Owner:KLA CORP
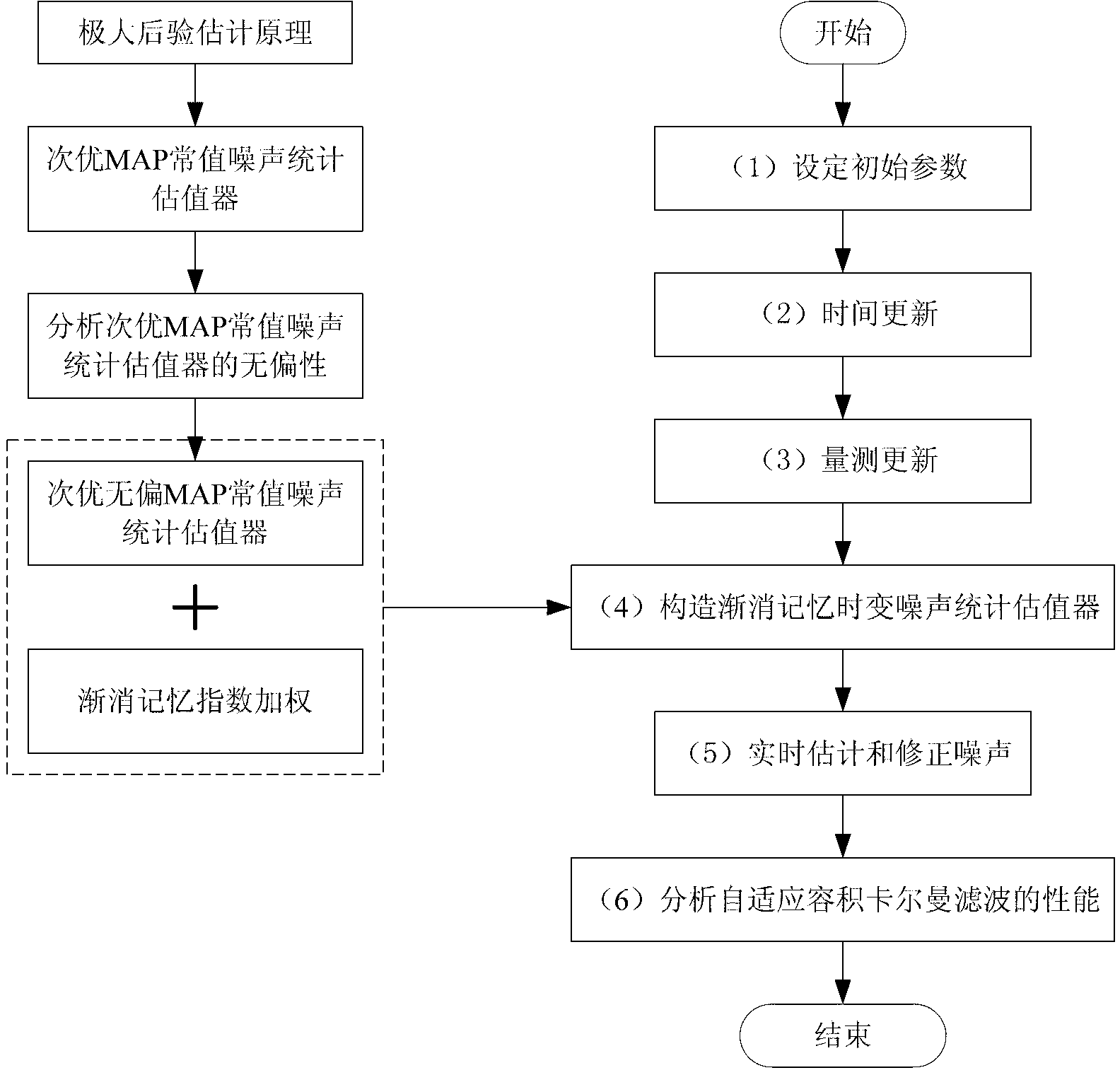
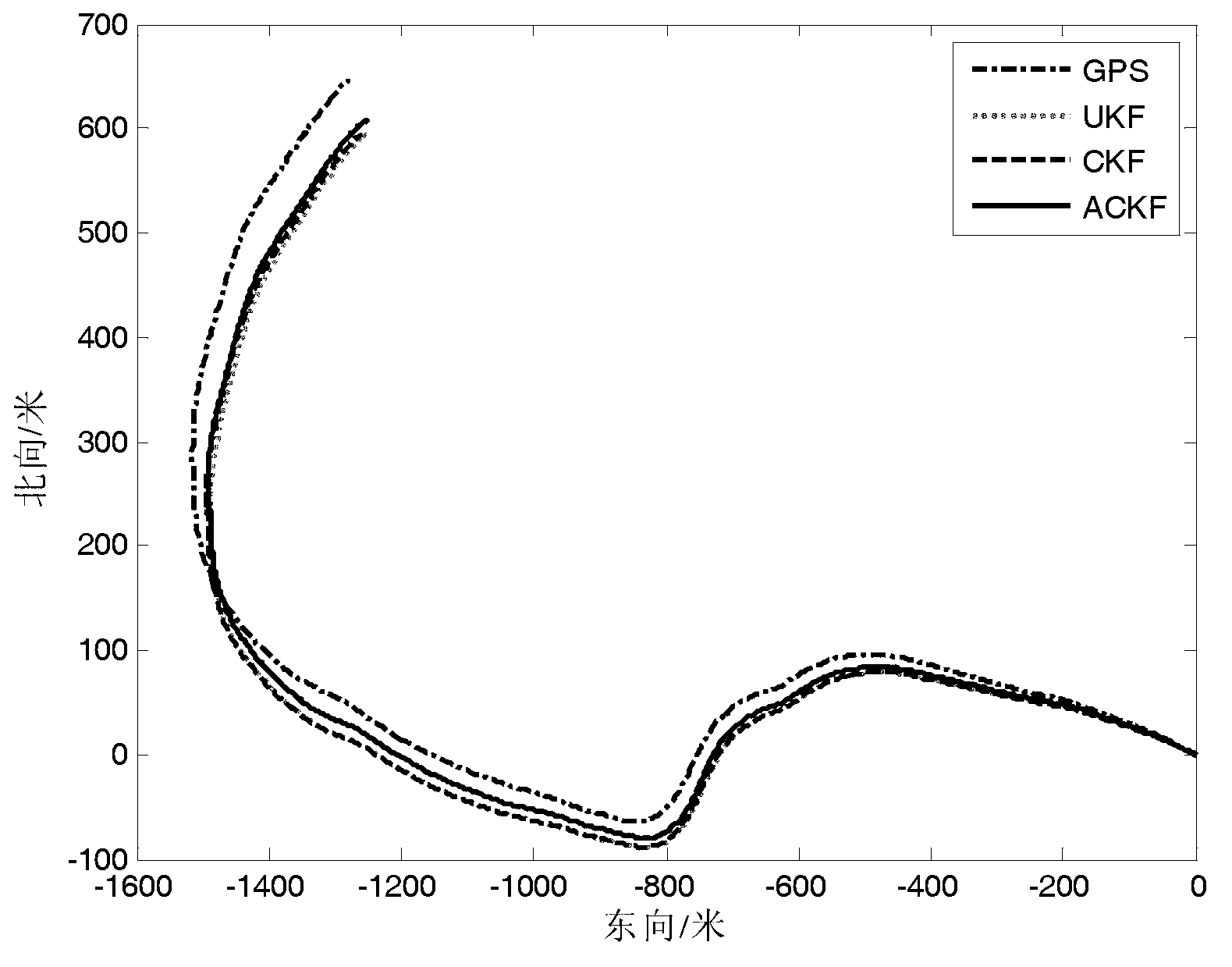
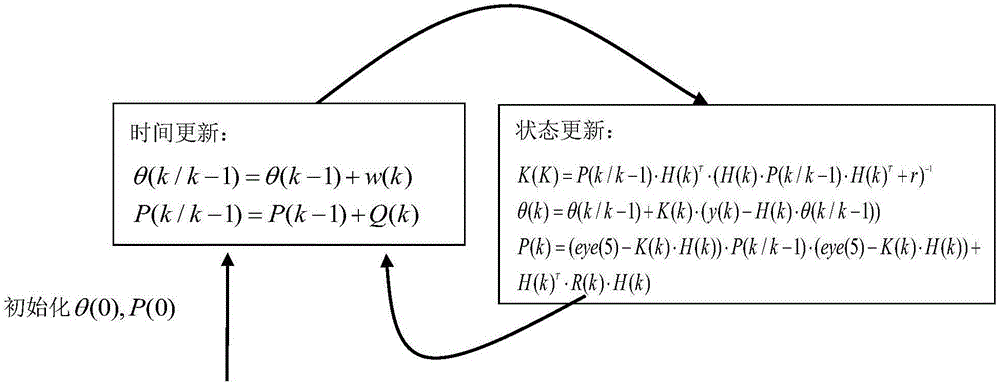
Self-adaptive volume Kalman filtering method
InactiveCN103217175AThe recursive formula is simpleAdaptableNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPattern recognitionTime changes
The invention relates to a self-adaptive volume Kalman filtering method, and in particular relates to a self-adaptive volume Kalman filtering method with a fading memory time-change noise statistic estimator. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) setting initial parameters; (2) updating the time; (3) updating the measurement; (4) constructing the fading memory time-change noise statistics estimator; and (5) estimating and modifying the noise in real time. Compared with a standard volume Kalman filtering method, the method does not demand to make the prior statistic characteristics of the known noise precise and has the self-adaptive capability to copy with the noise change; and moreover, the recursion formula of the noise statistic estimator is simple and easy to realize, and is unbiased to noise statistic estimation.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
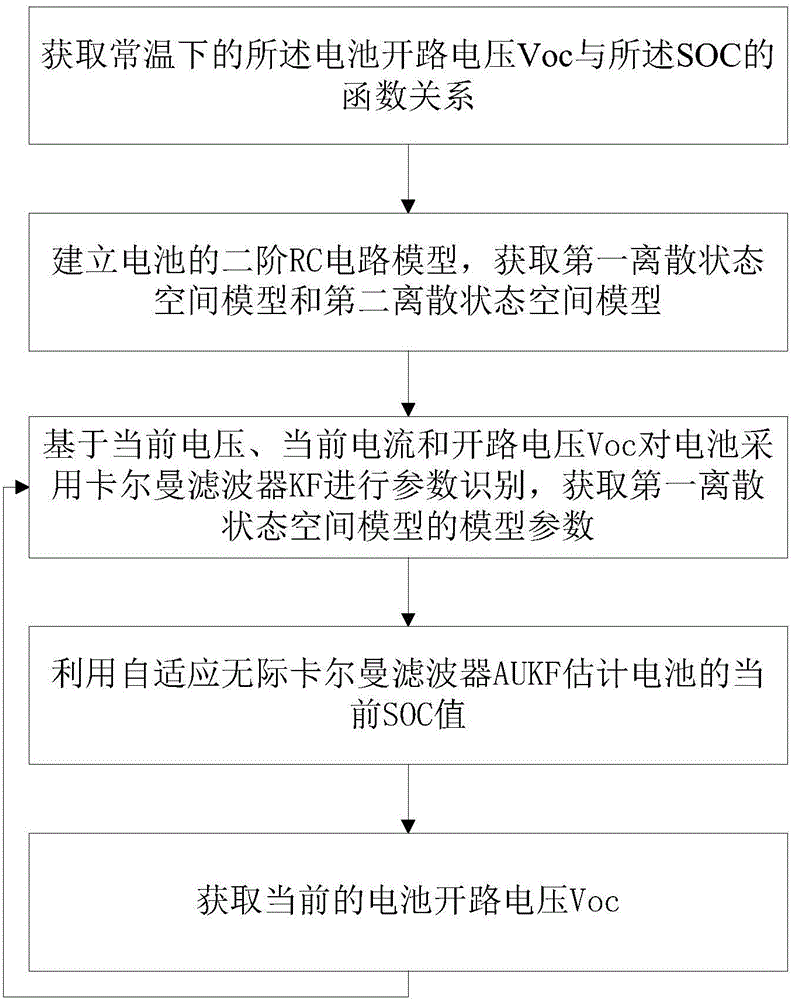
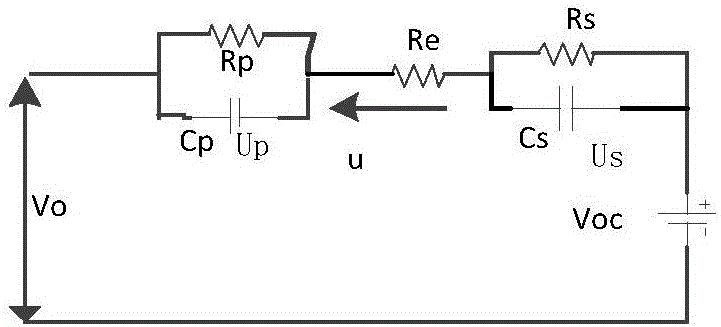
Lithium battery SOC estimation algorithm based on dual adaptive unscented Kalman filter
The invention provides a lithium battery SOC estimation algorithm based on dual adaptive unscented Kalman filter. The algorithm utilizes the advantages of a Kalman filter to track the accurate state value of SOC and is free of cumulative errors caused by a traditional time integration method. In particular, through the use of an adaptive unscented Kalman filter, the SOC value of a lithium battery can be estimated in real time; a covariance matrix of process noise and measurement noise can be estimated on-line; this avoids the filter estimation performance degradation of a traditional Kalman filter due to the only assumption that there exists Gaussian white noise in an estimation process and even the problem that filter divergence deviates from the true value, etc. The algorithm provided by the invention conducts filter calculations and utilizes a noise statistic estimator to perform on-line correction to the statistics of the unknown or inaccurate noise in real time so as to realize on-line estimation of a lithium battery SOC and to improve the precision and accuracy of SOC estimation. The convergence speed is greatly enhanced under the condition with erroneous initial SOC.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
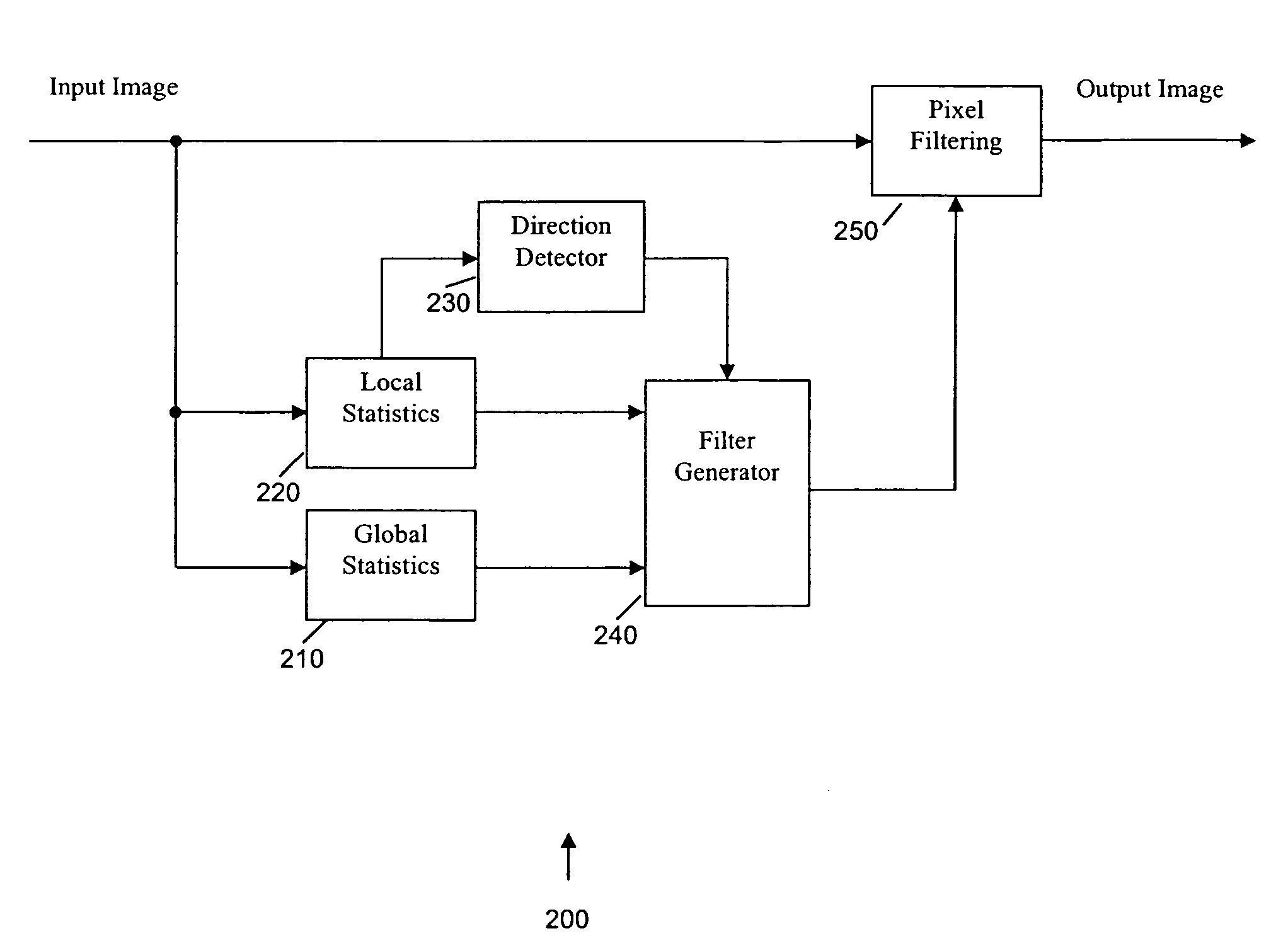
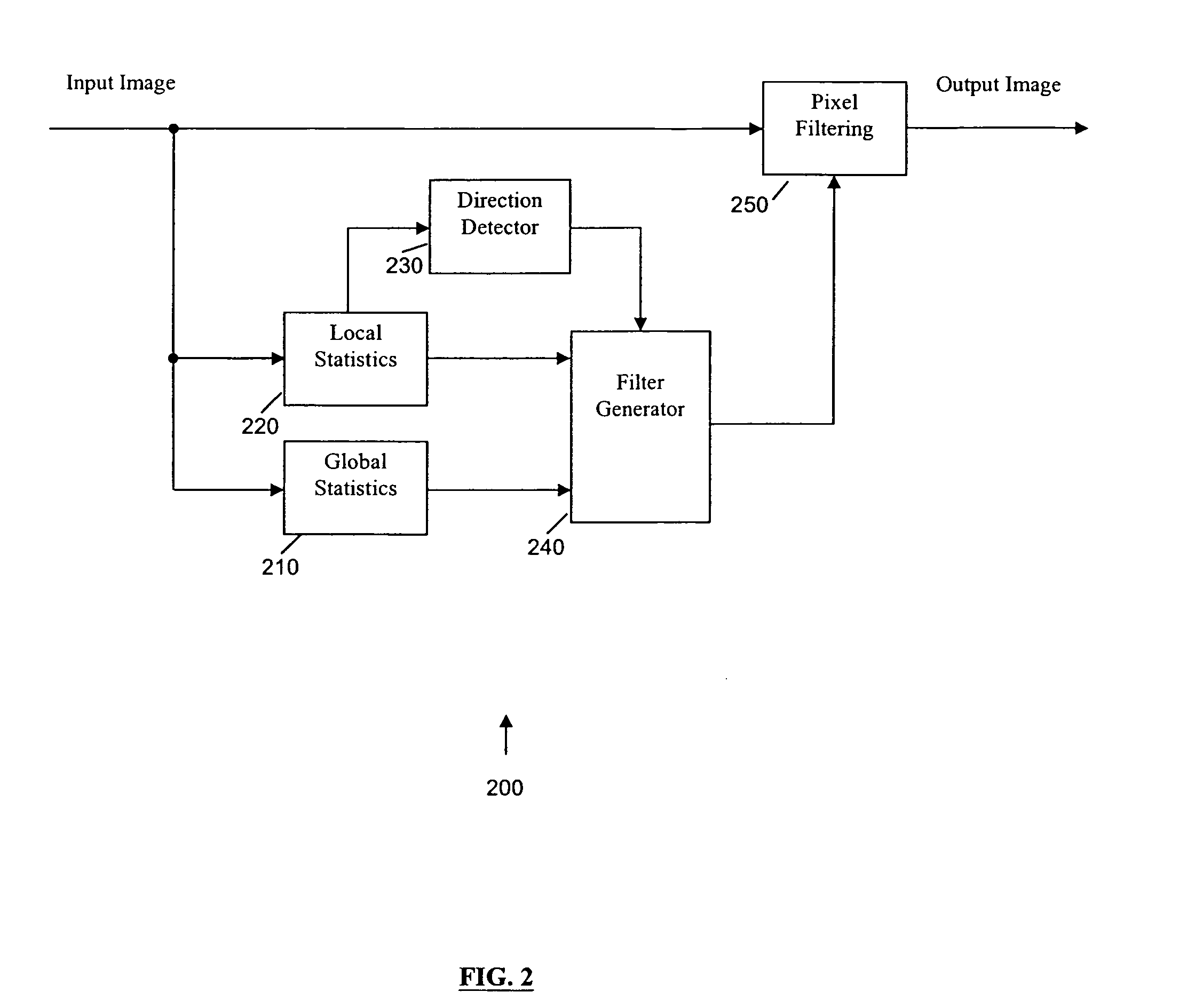
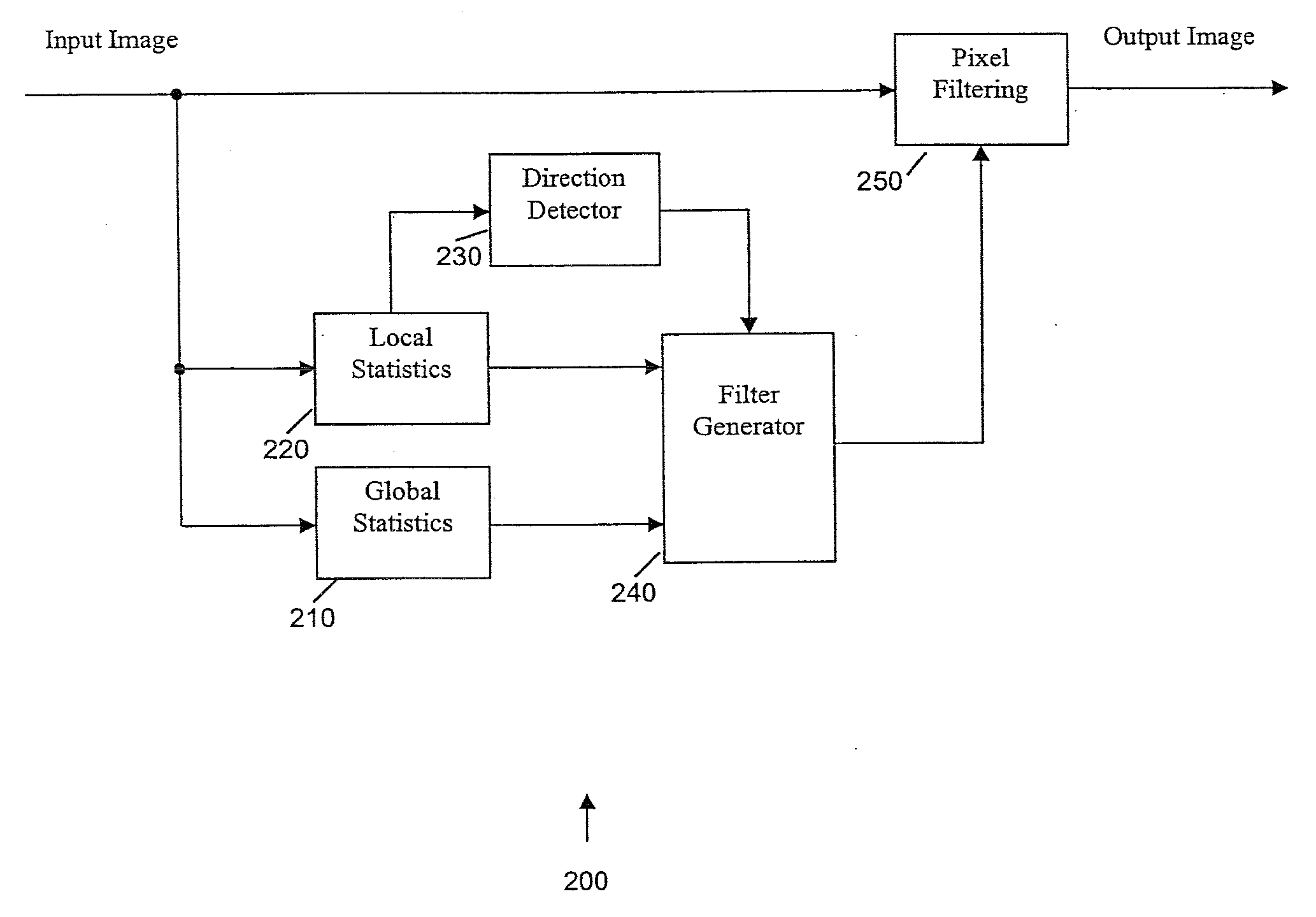
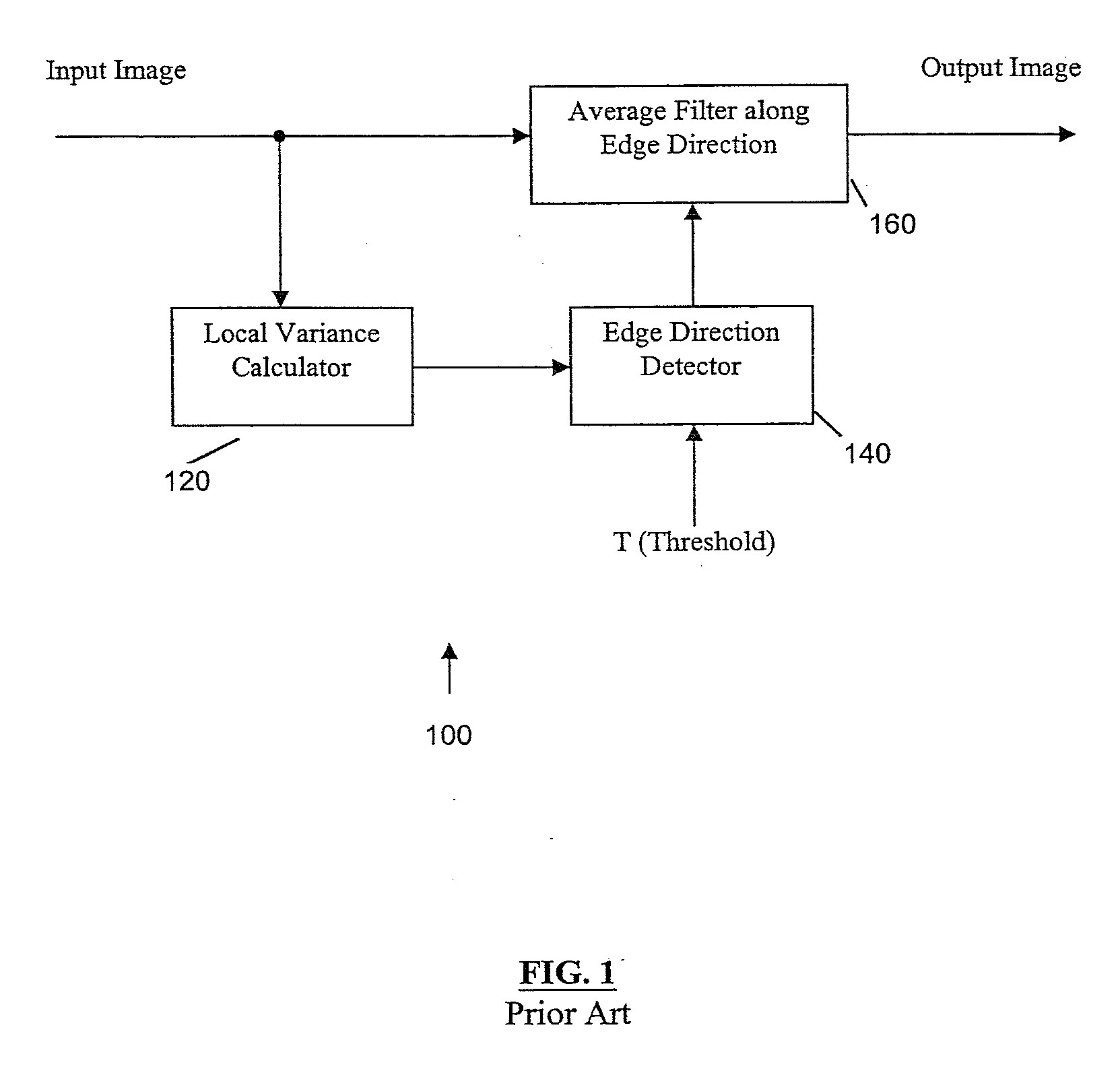
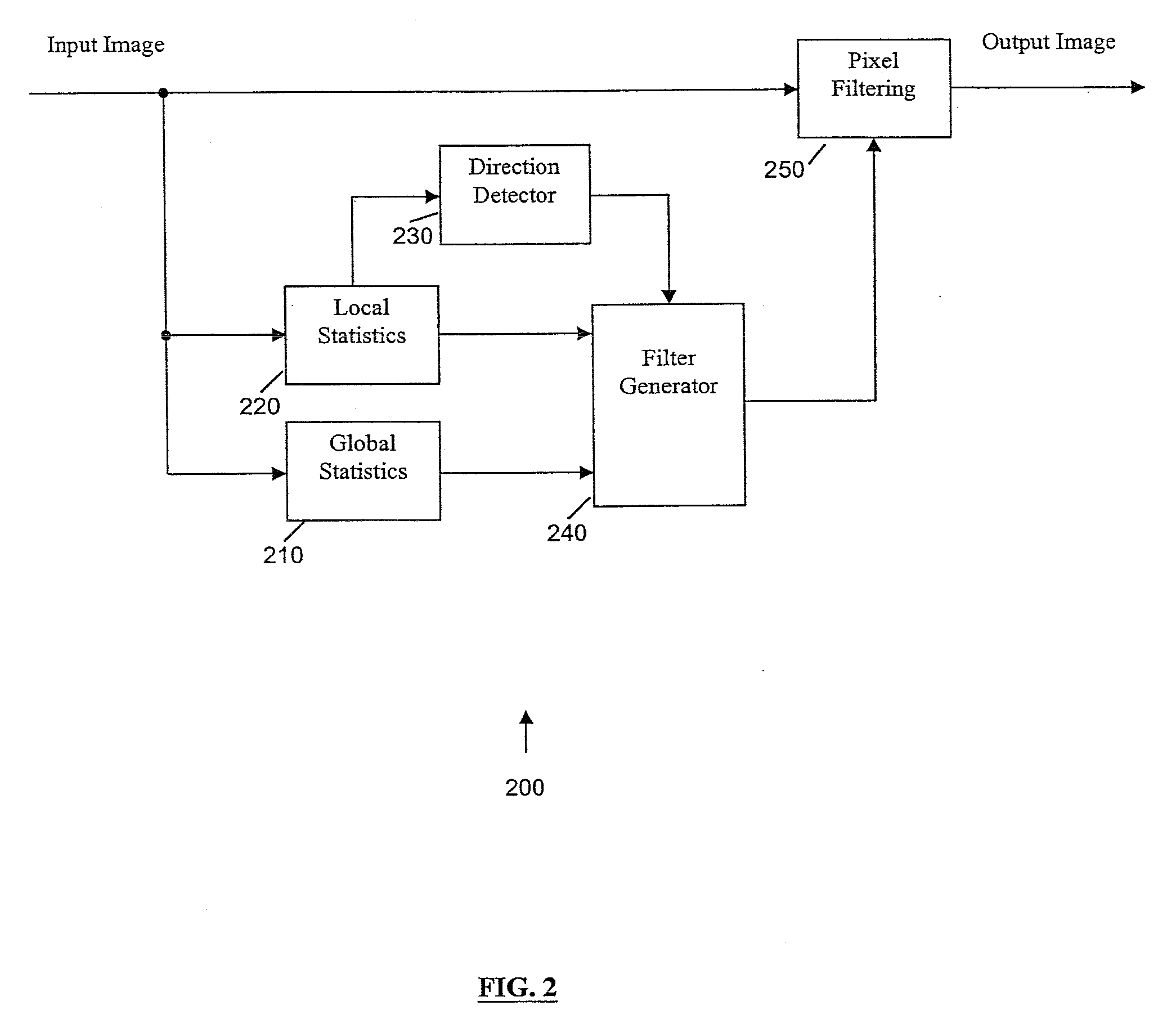
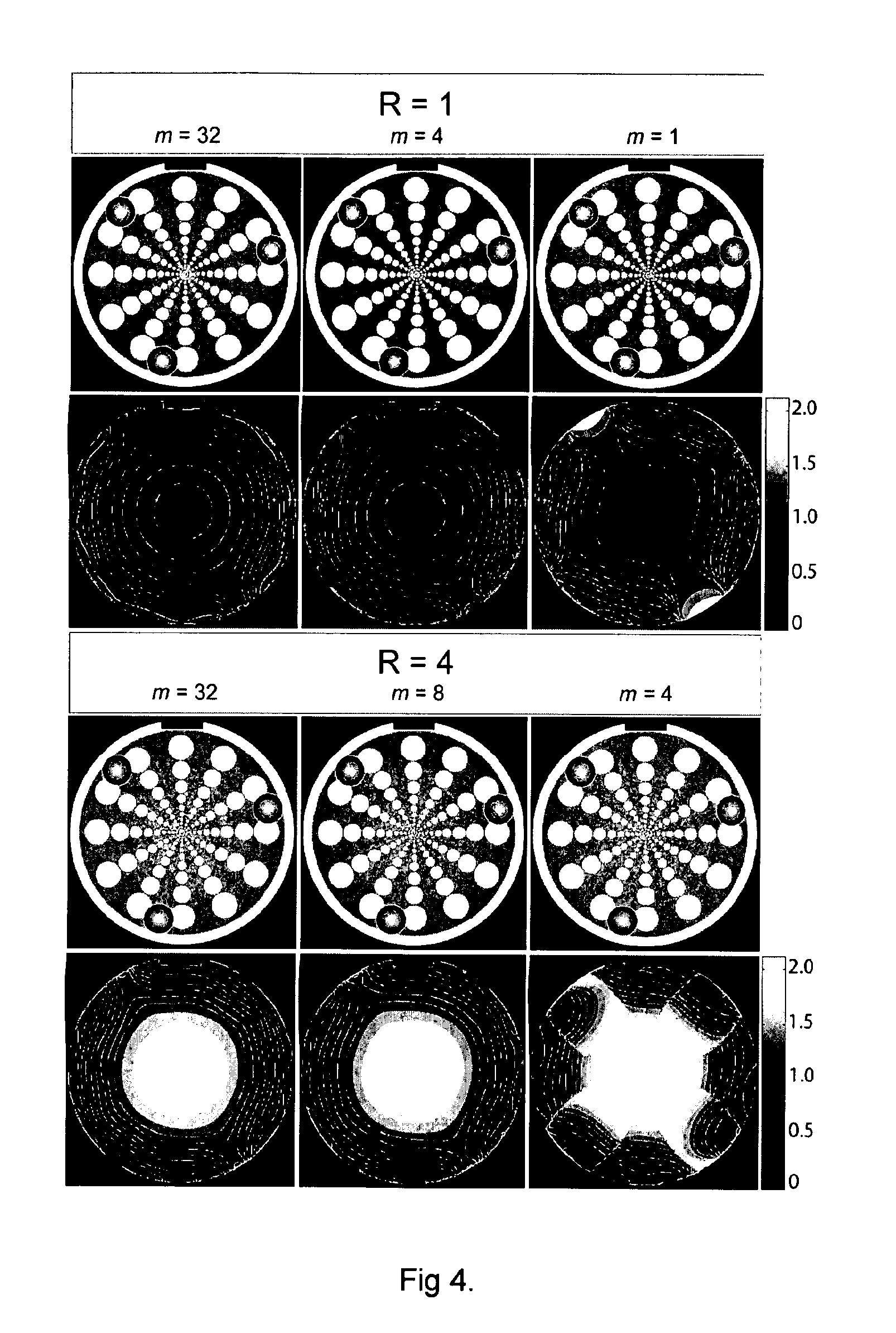
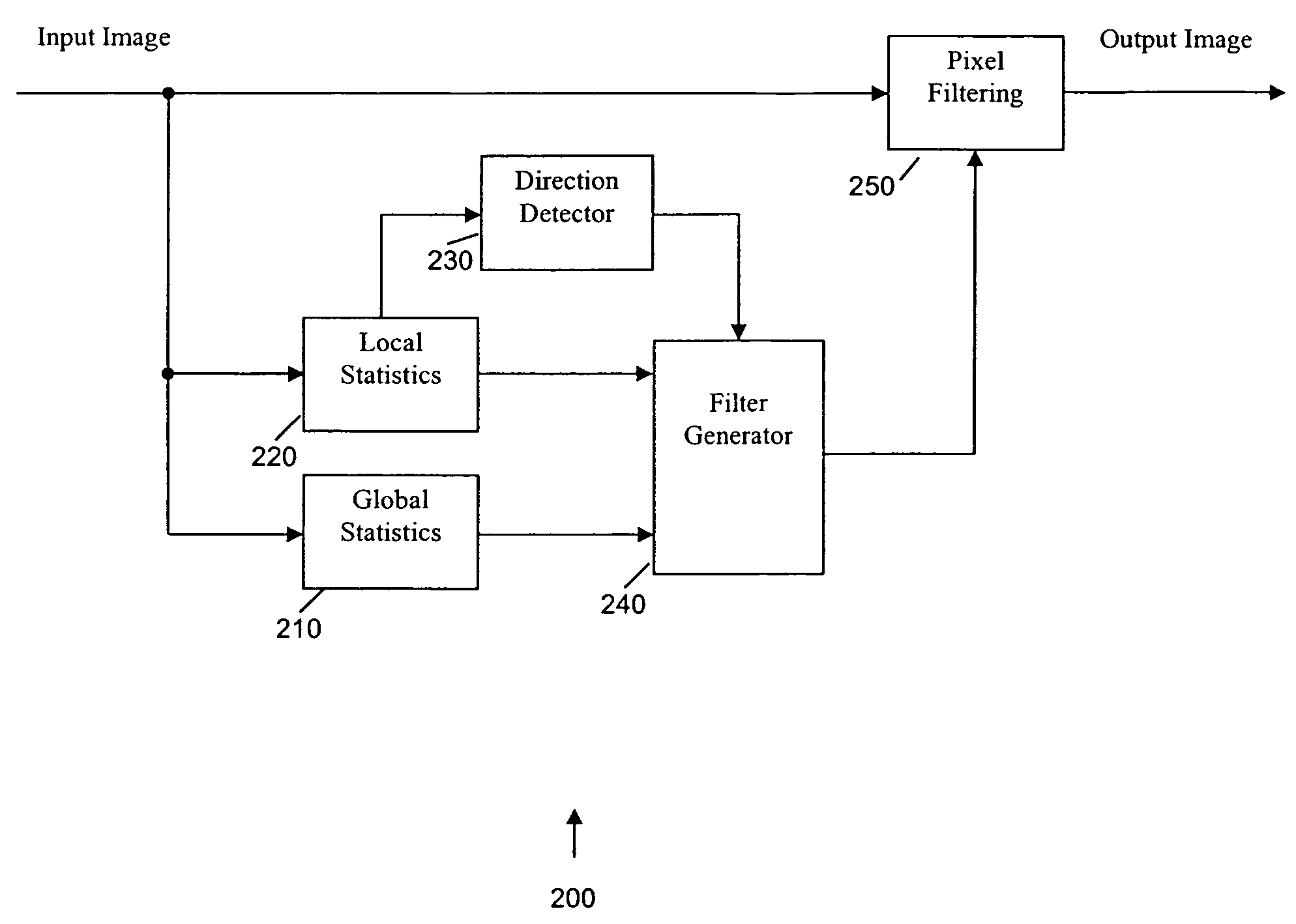
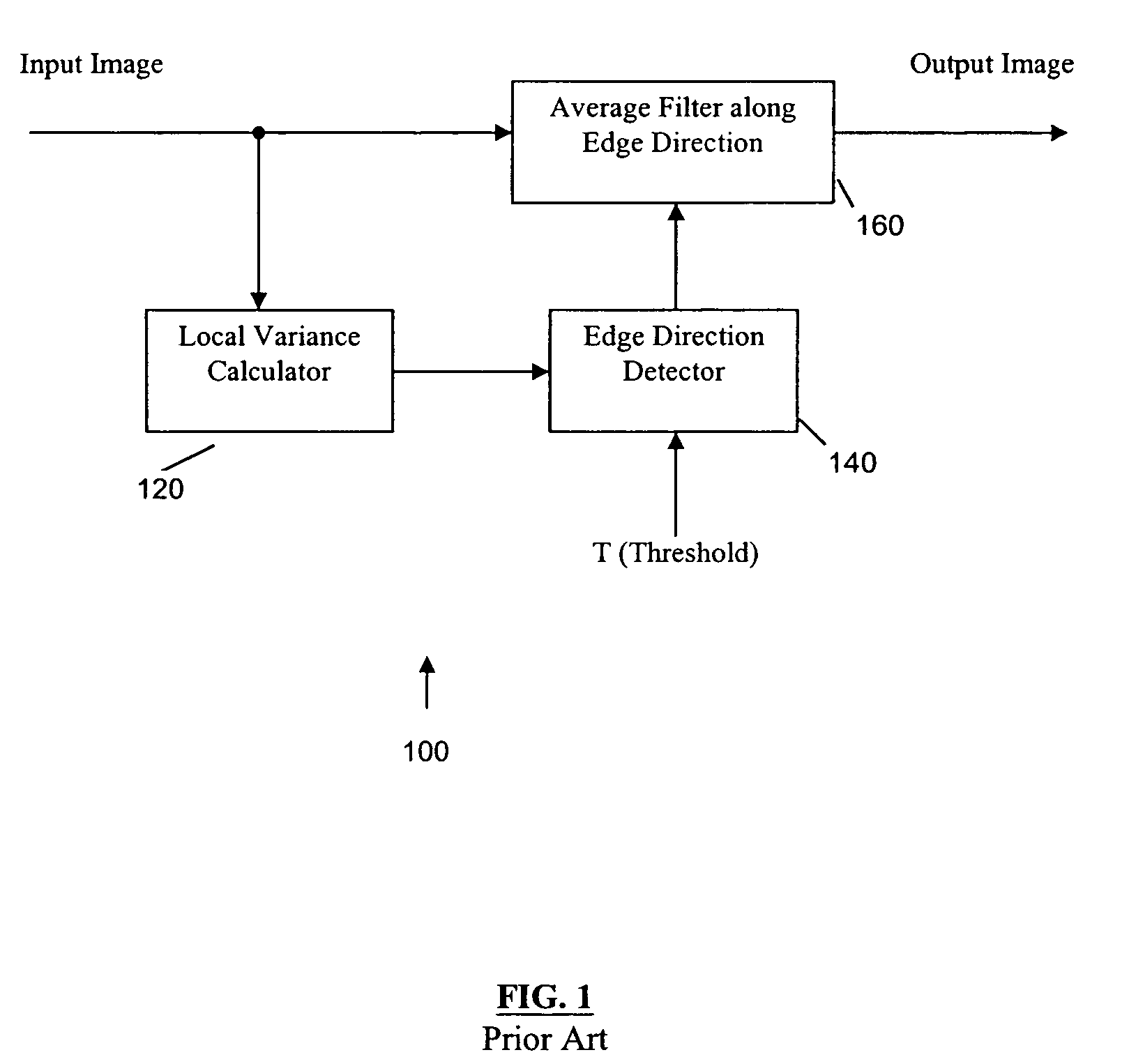
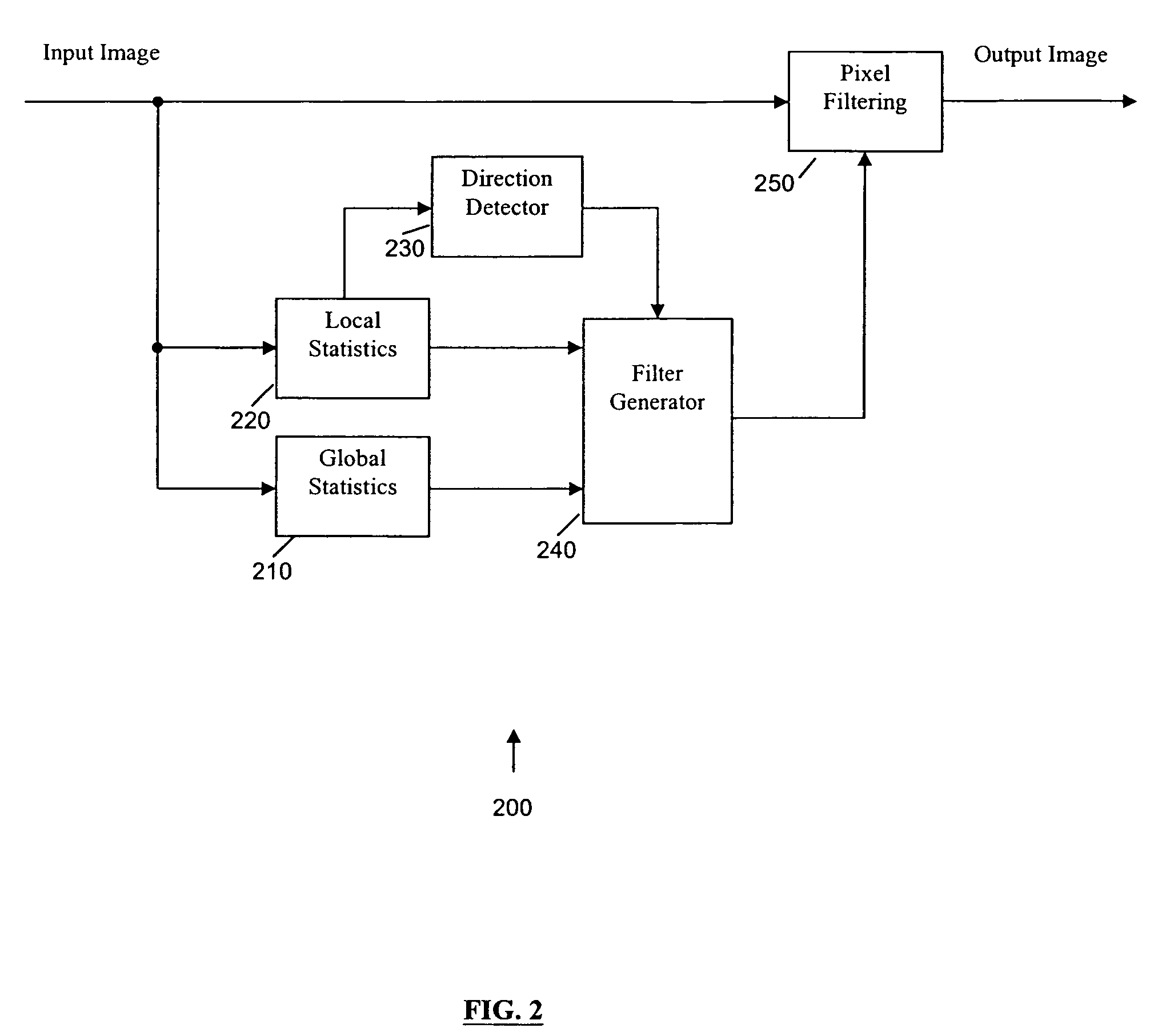
Global and local statistics controlled noise reduction system
InactiveUS20050094889A1Reliable global noise statisticAdapt effectivelyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage denoisingNoise level
A global and local statistics controlled noise reduction system in which the video image noise reduction processing is effectively adaptive to both image local structure and global noise level. A noise estimation method provides reliable global noise statistics to the noise reduction system. The noise reduction system dynamically / adaptively configures a local filter for processing each image pixel, and processes the pixel with that local filter. The filtering process of the noise reduction system is controlled by both global and local image statistics that are also computed by the system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
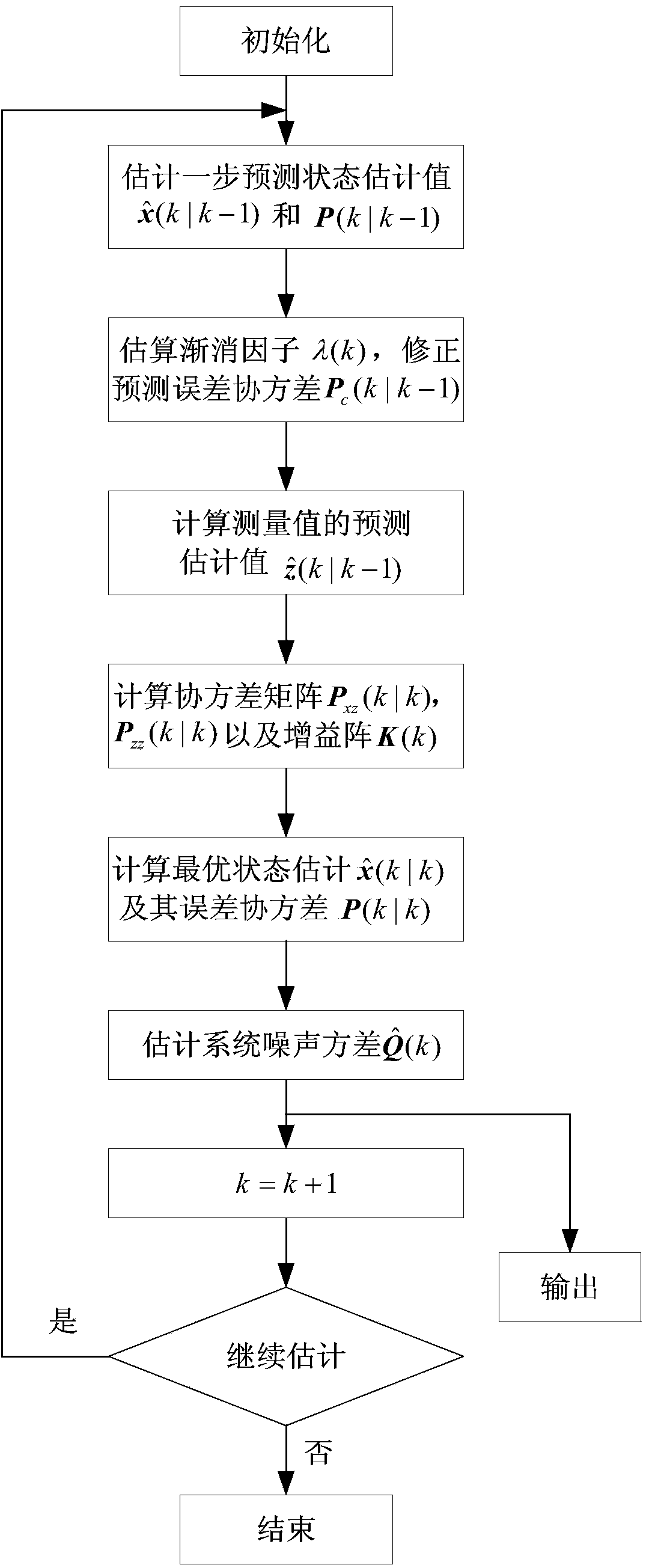
Self-adaptive high-order volume Kalman filtering method
InactiveCN103927436AImprove estimation accuracyStrong tracking abilityAdaptive networkSpecial data processing applicationsCovarianceHandling system
The invention relates to a self-adaptive high-order volume Kalman filtering method in the field of signal processing. The self-adaptive high-order volume Kalman filtering method includes: estimating the one-step predicted target state x (k / k-1) and a covariance matrix P (k / k-1) of the same; calculating fading factor h (k) and using the same to adjust the corrected covariance matrix Po (k / k-1); calculating optimal linear estimation x (k / k) and error covariance P (k / k) of the target state, and estimating the variance Q (k) of system noise in real time. The self-adaptive high-order volume Kalman filtering method has the estimation accuracy higher than that of unscented Kalman filter and volume Kalman filter. In addition, through real-time estimation of the variance of the system noise, filter errors caused by unknown time-varying of noise statistic properties are effectively restricted.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU COLLEGE OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY ENG
Combined DC restoration double detection and loops
InactiveUS8046666B2Reduce second error rateSimplify digital design processData representation error detection/correctionSignal processing for reducing noiseEngineeringNoise statistics
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
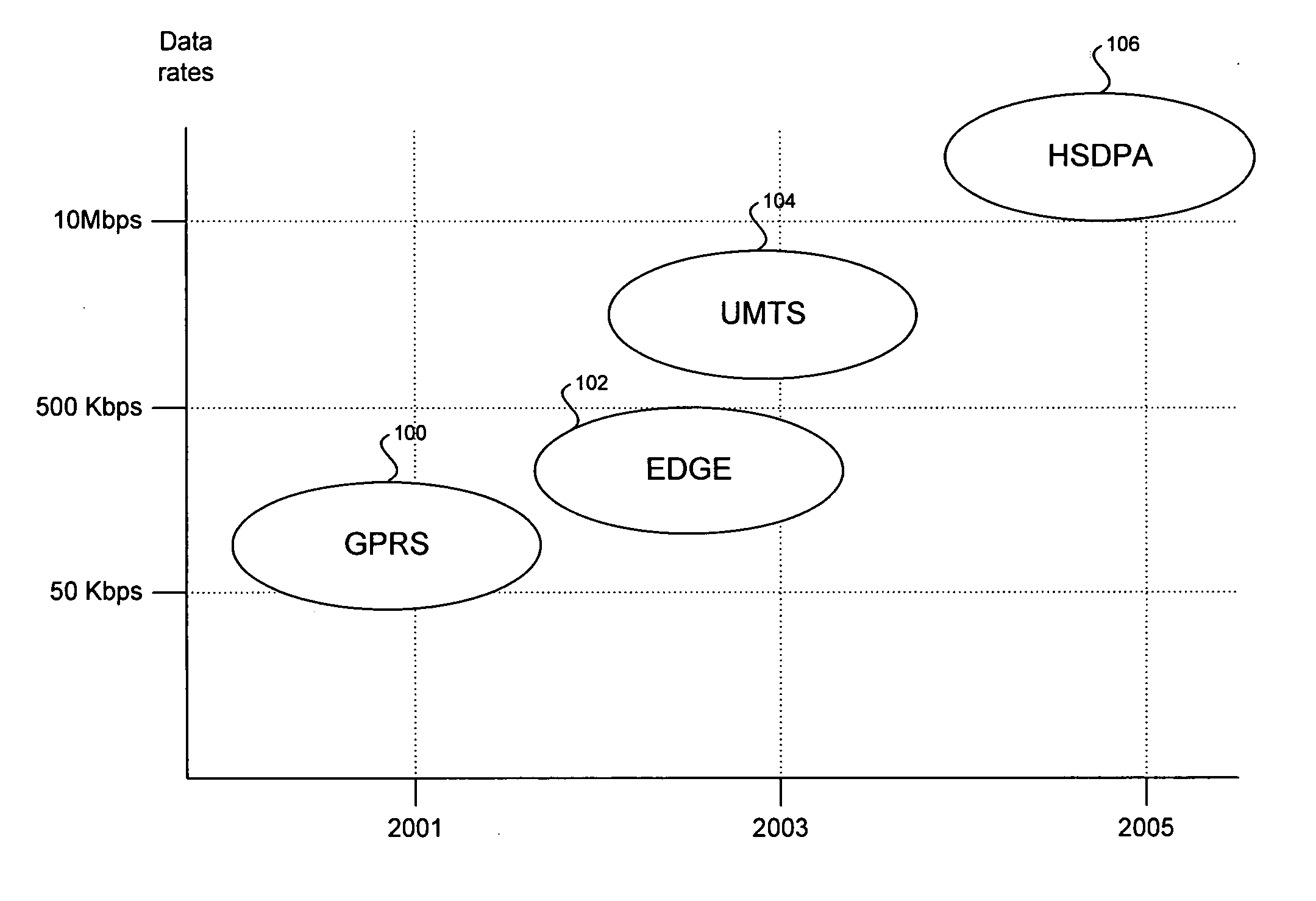
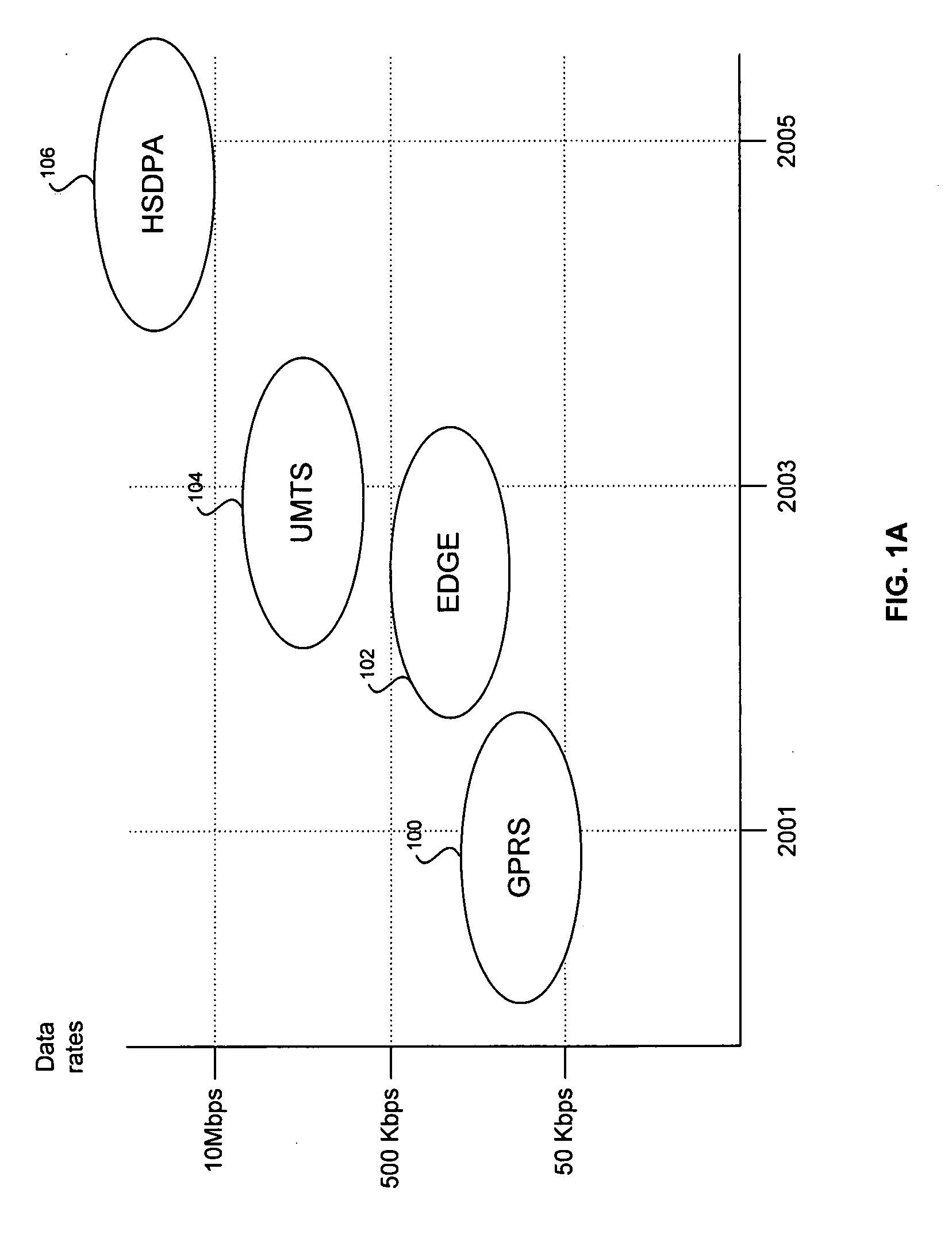
Method and system for weight determination in a single channel (SC) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system for WCDMA/HSDPA
ActiveUS20060074612A1Polarisation/directional diversityTime-division multiplexSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
In wireless systems, method and system for weight determination in a single channel (SC) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system for WCDMA / HSDPA are provided. Models of signals received in multiple receive antennas may be determined in a single weight baseband generator (SWBBG) from propagation channel estimates and noise statistics. The models may be utilized to determine combined signal and noise components. The combined signal and noise components may be utilized to determine a plurality of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) or signal-to-interference-and-noise ratio (SINR) values for various phase and / or amplitude factors. The SINR may be utilized when either single or multiple interfering signals are present. A highest of the SINR or SNR values may be selected to determine a channel weight to apply to the additional receive antennas.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
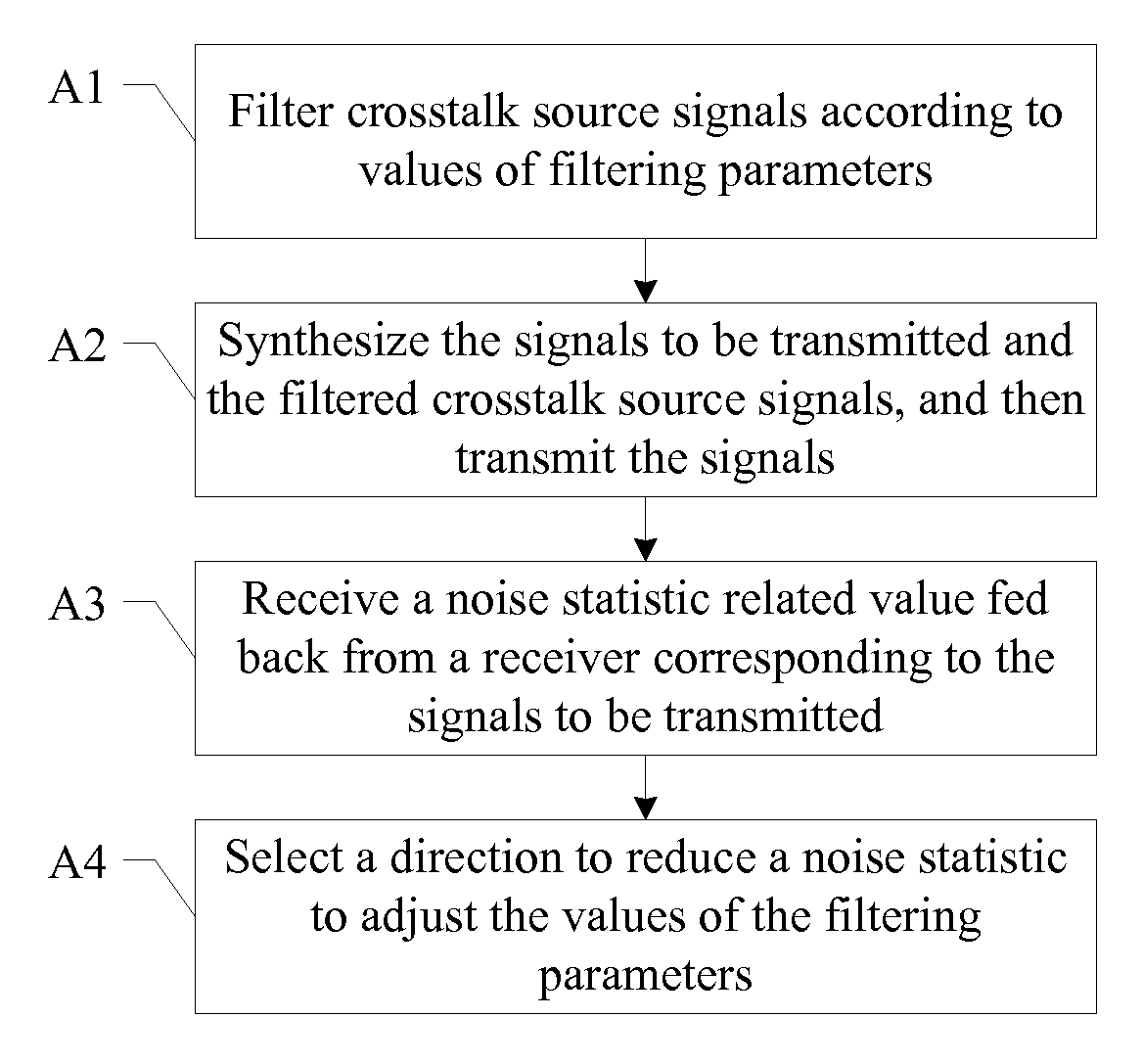
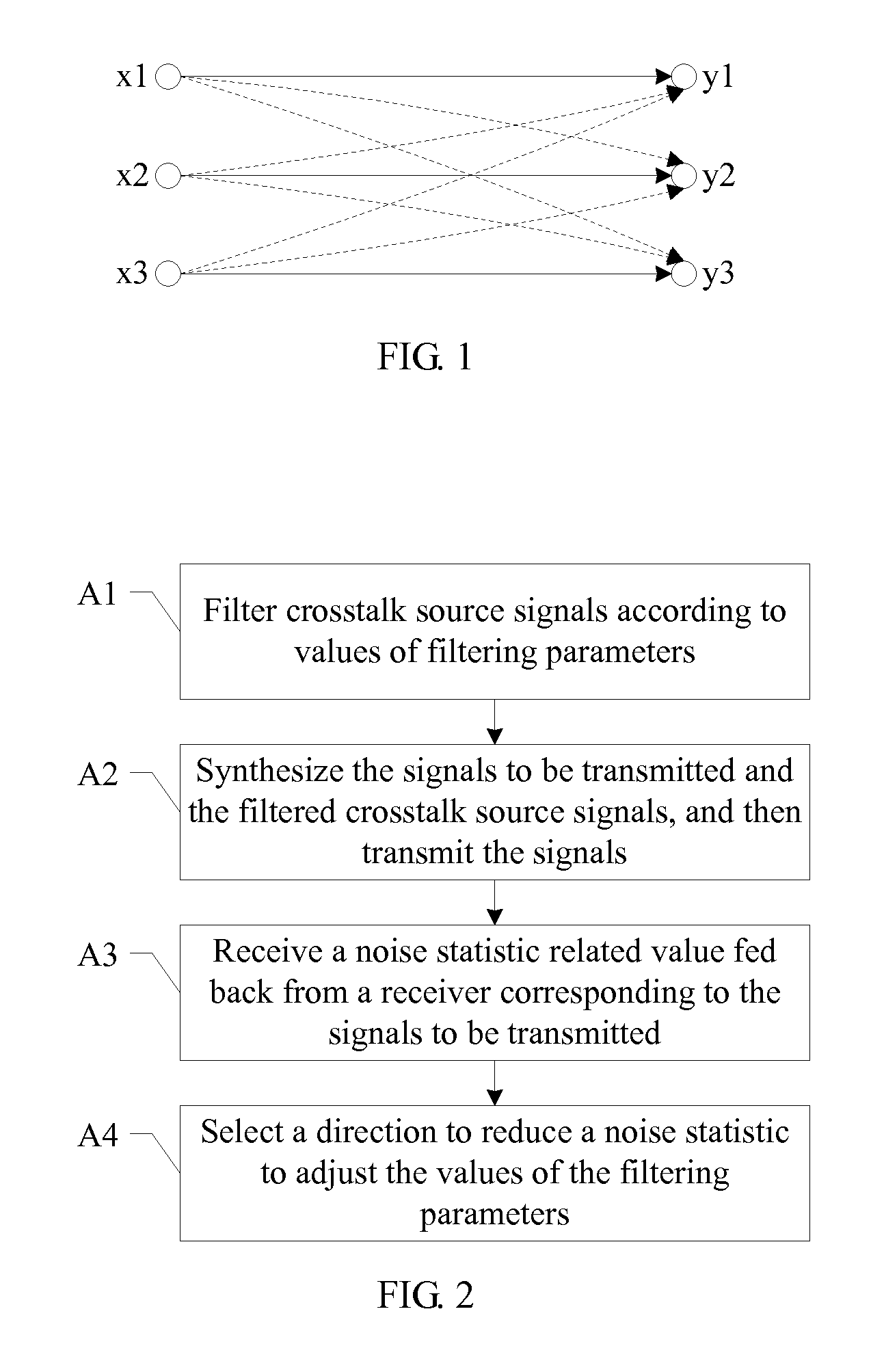
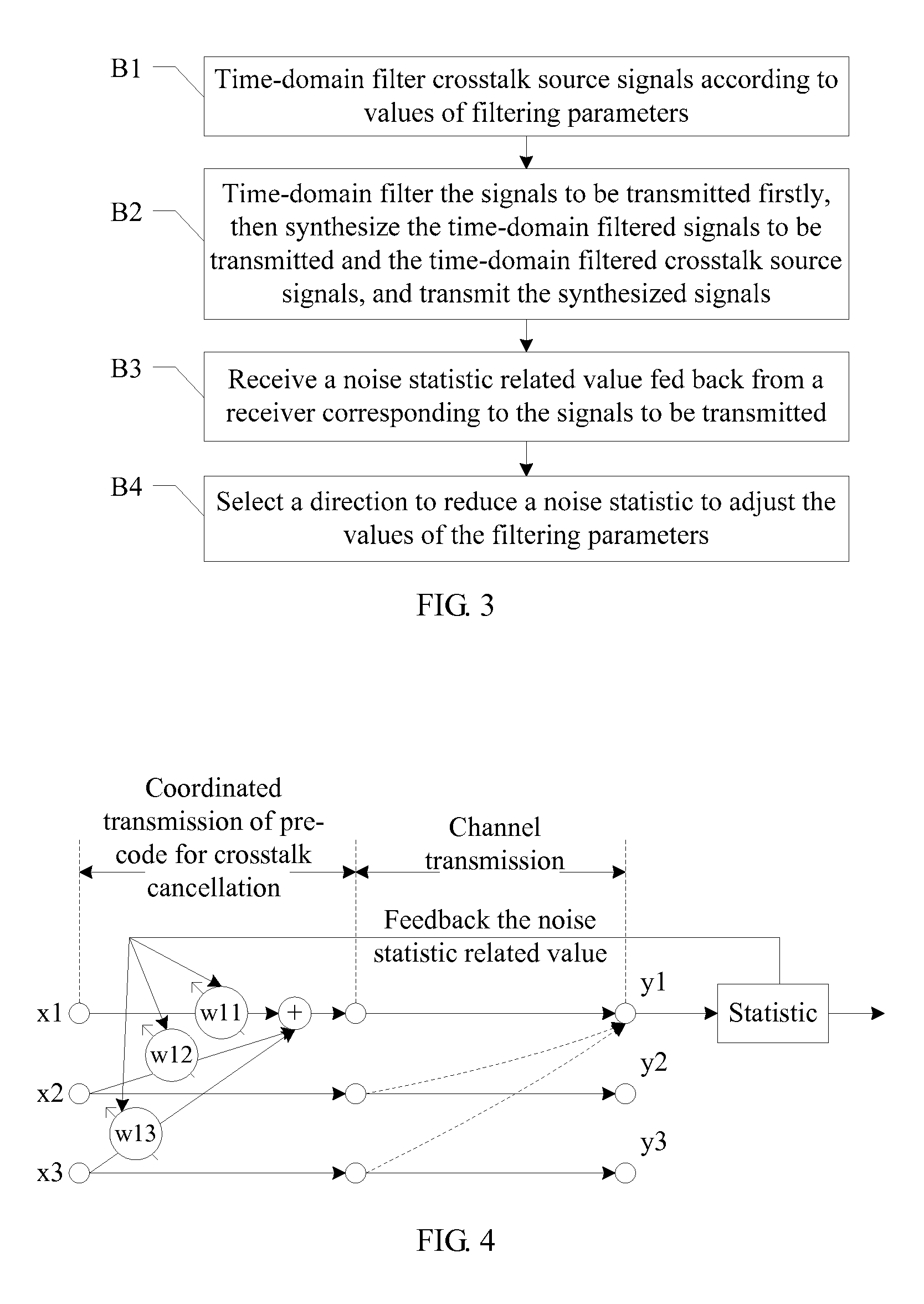
Far-end crosstalk canceling method and device, and signal processing system
ActiveUS20090245444A1Applies impactAccurate directionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCrosstalk cancellationTransmission matrix
A method for remote crosstalk cancellation, includes: the combination transmitting signal is performed a pre-coding of crosstalk cancellation in the manner of self-adapting filtering, the self-adapting changes of the values of filtering parameters are guided correctly with the influence of the crosstalk component in the received signals which is reflected indirectly by relevant values of the noise statistic reported by the receiver. A corresponding device and a signal processing system for remote crosstalk cancellation are provided. The self-adapting adjustment of the values of filtering parameters has a favorable astringency and an effect for crosstalk cancellation, avoiding the need to know the channel transmission matrix in advance, while absolutely avoiding the conflict to the existing transmission standard.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for producing random quantum number at high speed based on vacuum state quantum fluctuation
ActiveCN107220026AIncrease spawn rateIncreased entropy contentRandom number generatorsGeneration ratePhase space
The invention relates to a high-speed true random quantum number generating method, in particular to a method for producing random quantum number at high speed based on vacuum state quantum fluctuation. The problem that the production speed of an existing vacuum random quantum number generator is lower is solved. According to the specific scheme, the high-speed true random quantum number generating method mainly comprises the following steps that the translation effect of Gaussian distribution is firstly exerted to a vacuum state in a phase space, amplification of vacuum-state orthogonal amplitude component noise in the phase space is achieved, and the entropy content introduced by quantum noise in a system is increased; the true random bits which can be extracted in data postprocessing are increased; the background light of a homodyne detection system is strengthened, the sensitivity of the detection system to vacuum noise is improved, and a vacuum noise measurement value is amplified, so that the framing amount of vacuum noise statistics, namely sampling quantization bits are remarkably increased. By adopting the method, the vacuum random quantum number generating rate is effectively improved, and a new means is provided for manufacturing of high-speed random quantum number generators.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
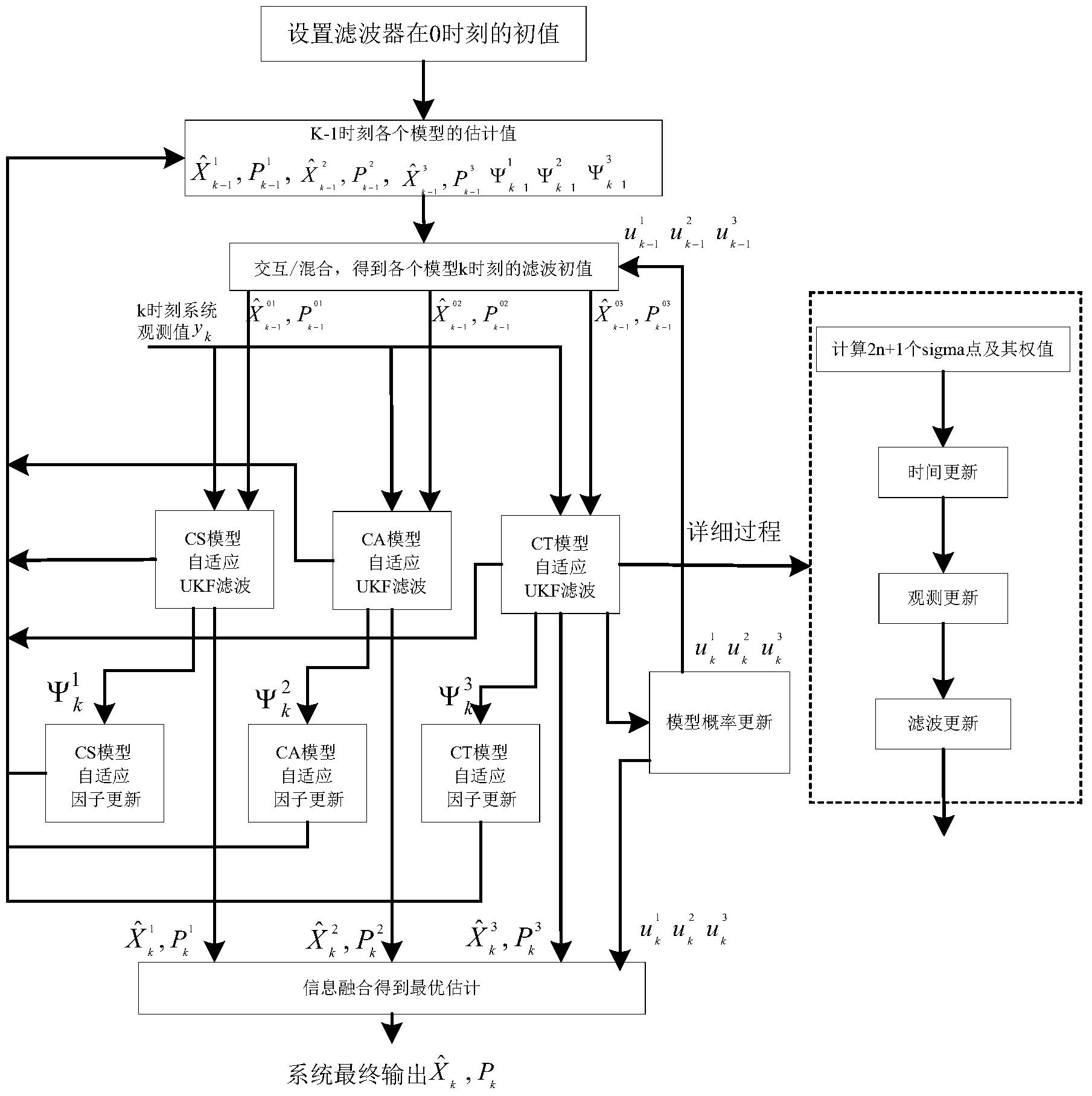
Satellite navigation method for interactive multi-model UKF with self-adapting factors
ActiveCN104020480AHigh positioning accuracyHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmMotor carrier
The invention relates to a satellite navigation method for an interactive multi-model UKF with self-adapting factors, and belongs to the field of navigation control. The method comprises the steps that firstly, an auto-covariance matrix of a residual sequence is used as a correcting value, and a smoothing filter is designed for fusing the correcting value with the old self-adapting factor to obtain the new self-adapting factor; secondly, a covariance matrix of process noise is adjusted in real time by utilizing the self-adapting factor, and therefore positioning errors, caused by unknown noise statistics properties, in a system are effectively reduced; afterwards, a model set M is set by the adoption of the interactive multi-model (IMM) algorithm; finally, soft handover between models is achieved by adjusting model probability in real time according to measurement residual errors, so that positioning errors caused by inaccurate system models are reduced. According to the method, the positioning accuracy of a complex motor carrier in a satellite navigation system is effectively improved with models and noise statistical properties unknown.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
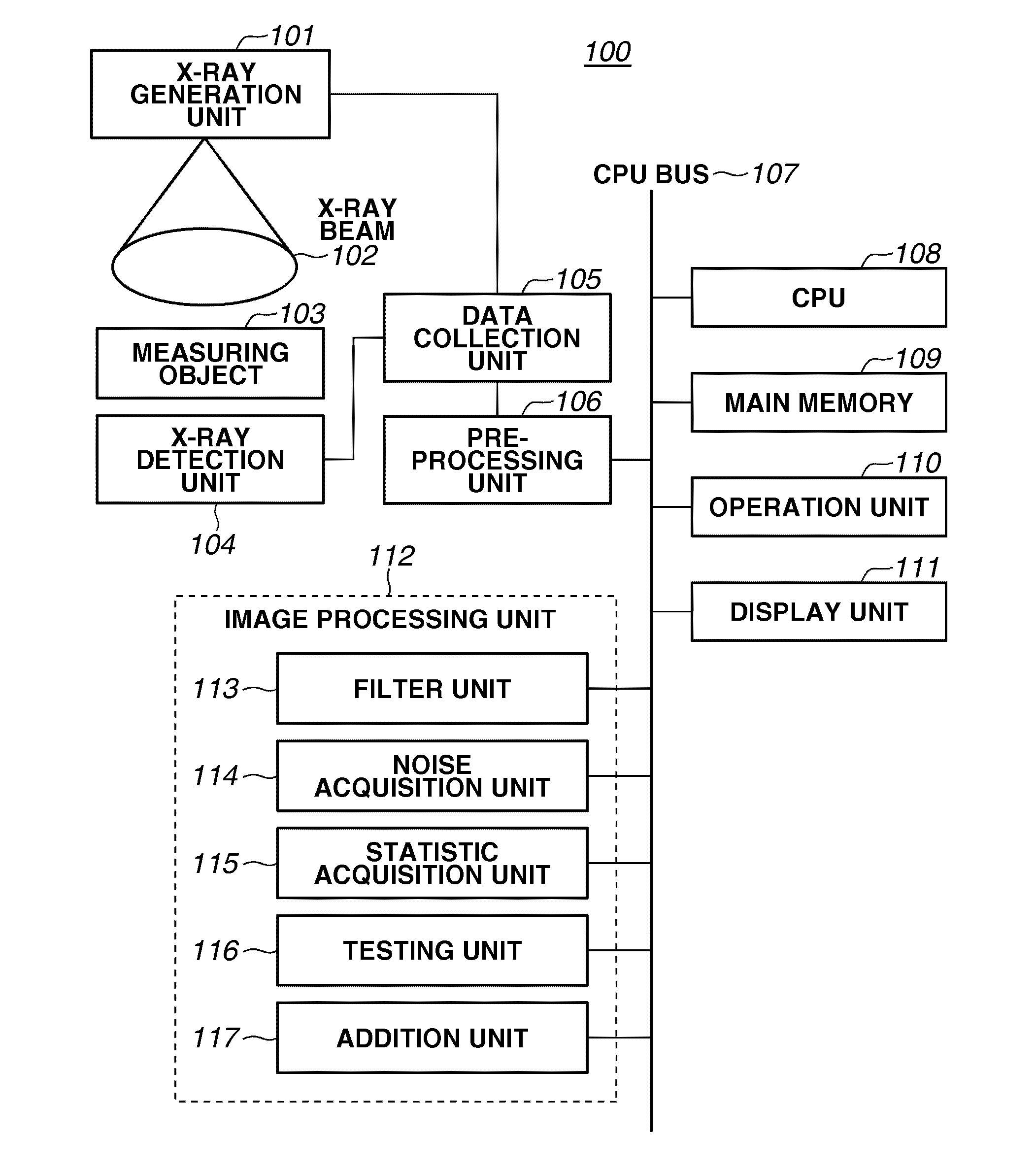
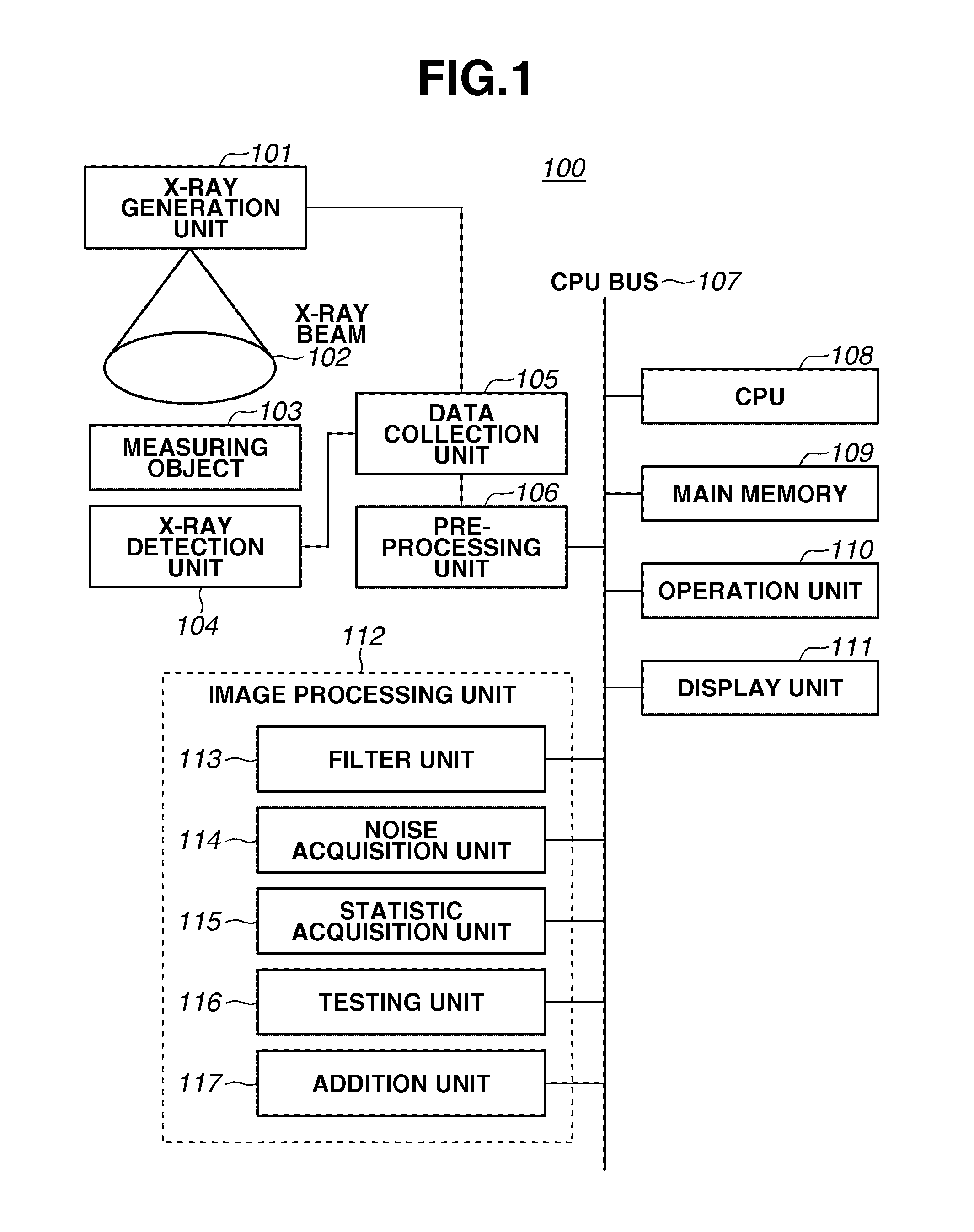
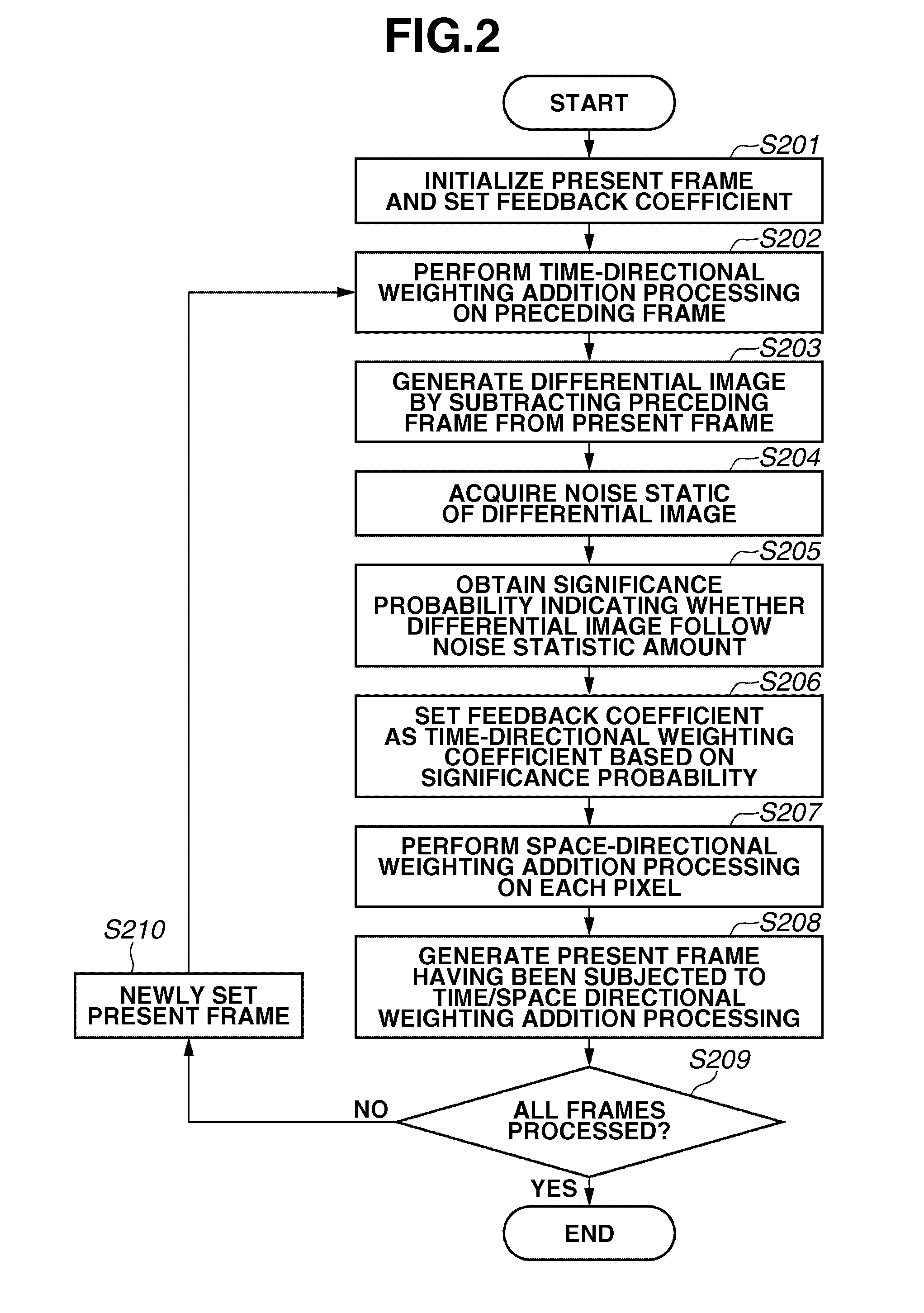
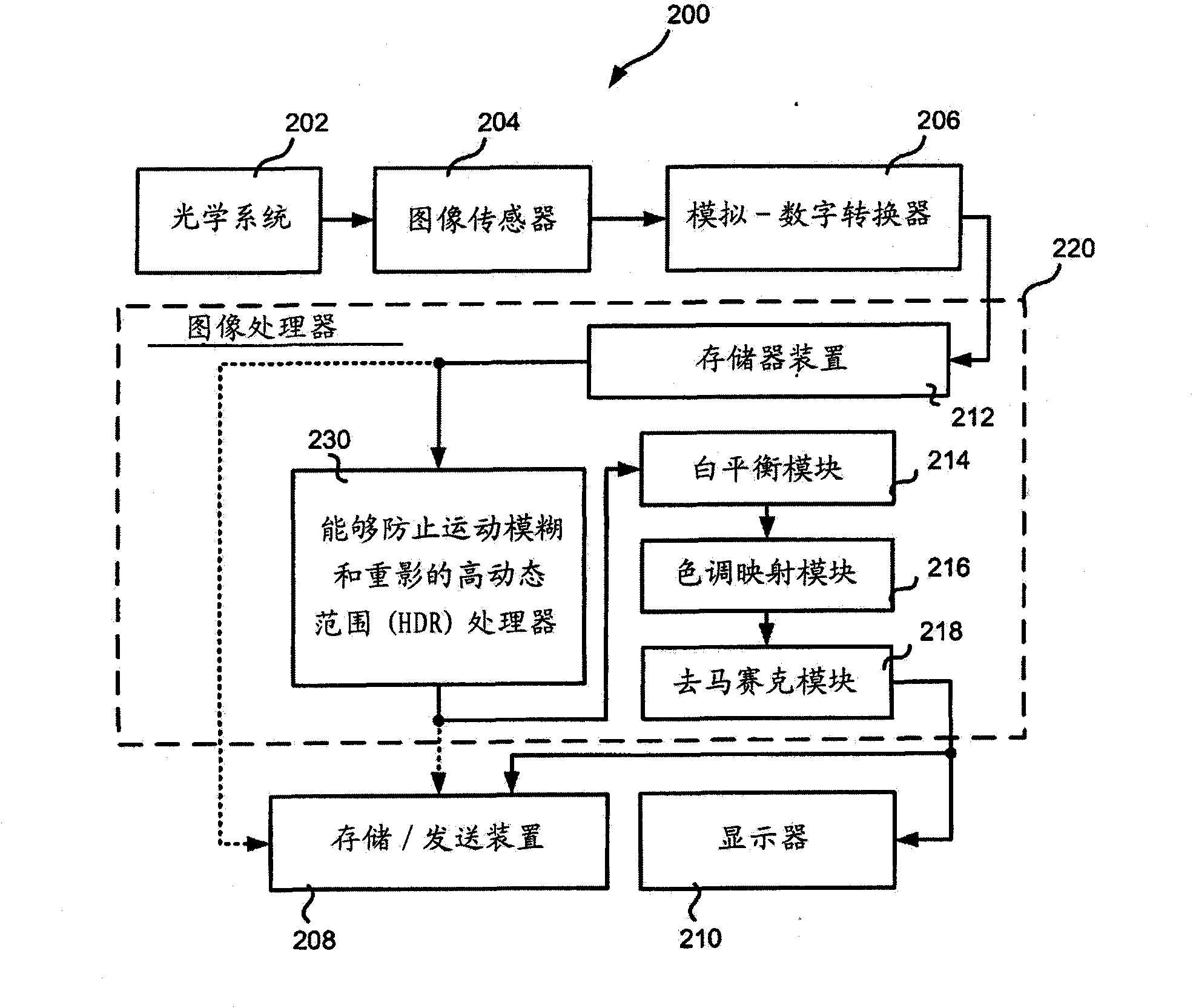
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and computer recording medium for reducing an amount of noise included in an image
ActiveUS20130051697A1Accurate extractionReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingFrame based
An image processing apparatus can perform time-sequential weighting addition processing on a moving image constituted by a plurality of frames includes a filter unit configured to obtain an image by performing recursive filter processing on a frame image that precedes a present target frame, which is one of the plurality of frames constituting the moving image, a coefficient acquisition unit configured to acquire a weighting coefficient for the present target frame based on a noise statistic of a differential image between an image of the present target frame and the image obtained by the filter unit, and an addition unit configured to perform addition processing on the moving image constituted by the plurality of frames based on weighting coefficients acquired by the coefficient acquisition unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Global and local statistics controlled noise reduction system
InactiveUS20080002902A1Reliable global noise statisticAdapt effectivelyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage denoisingNoise level
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
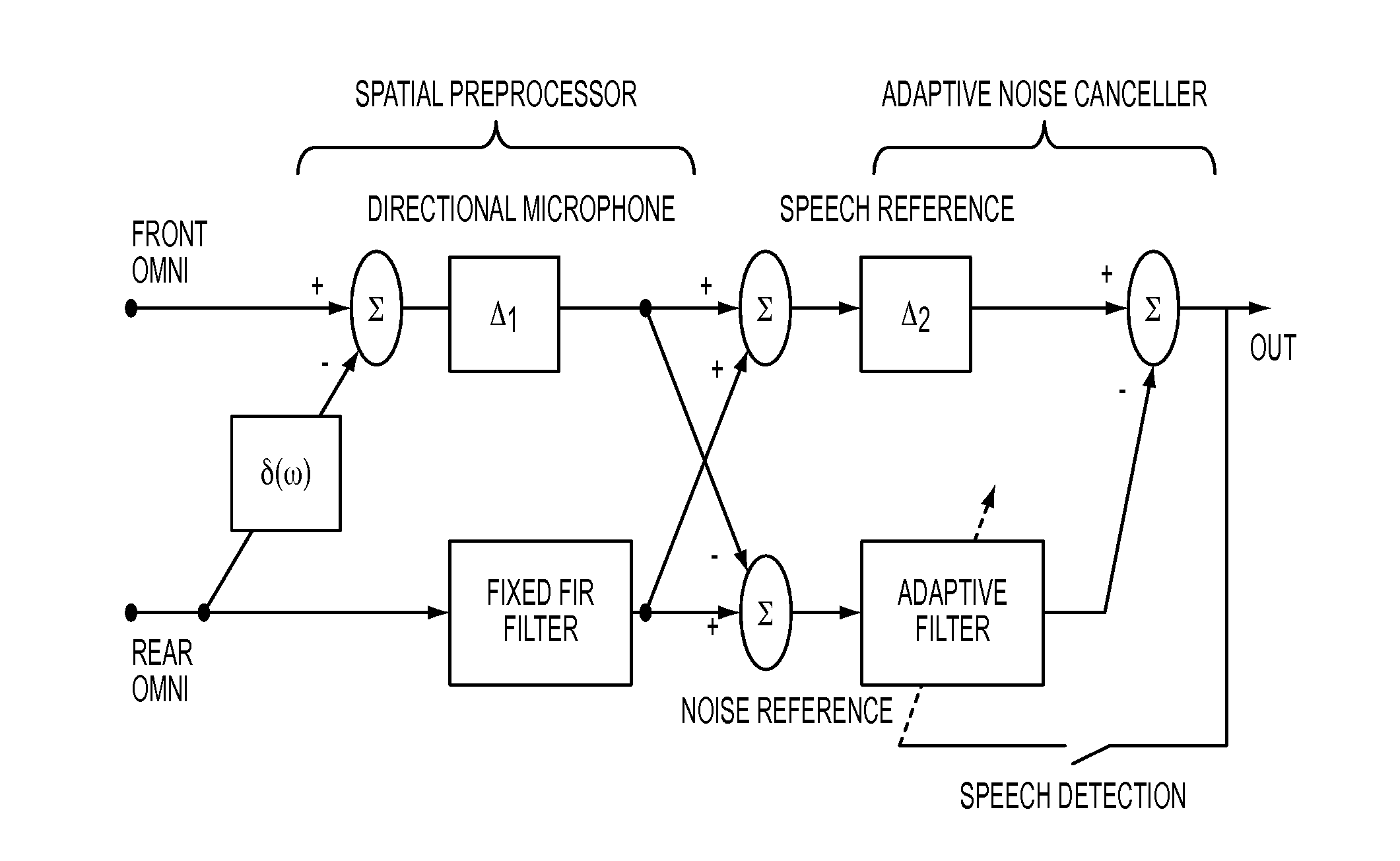
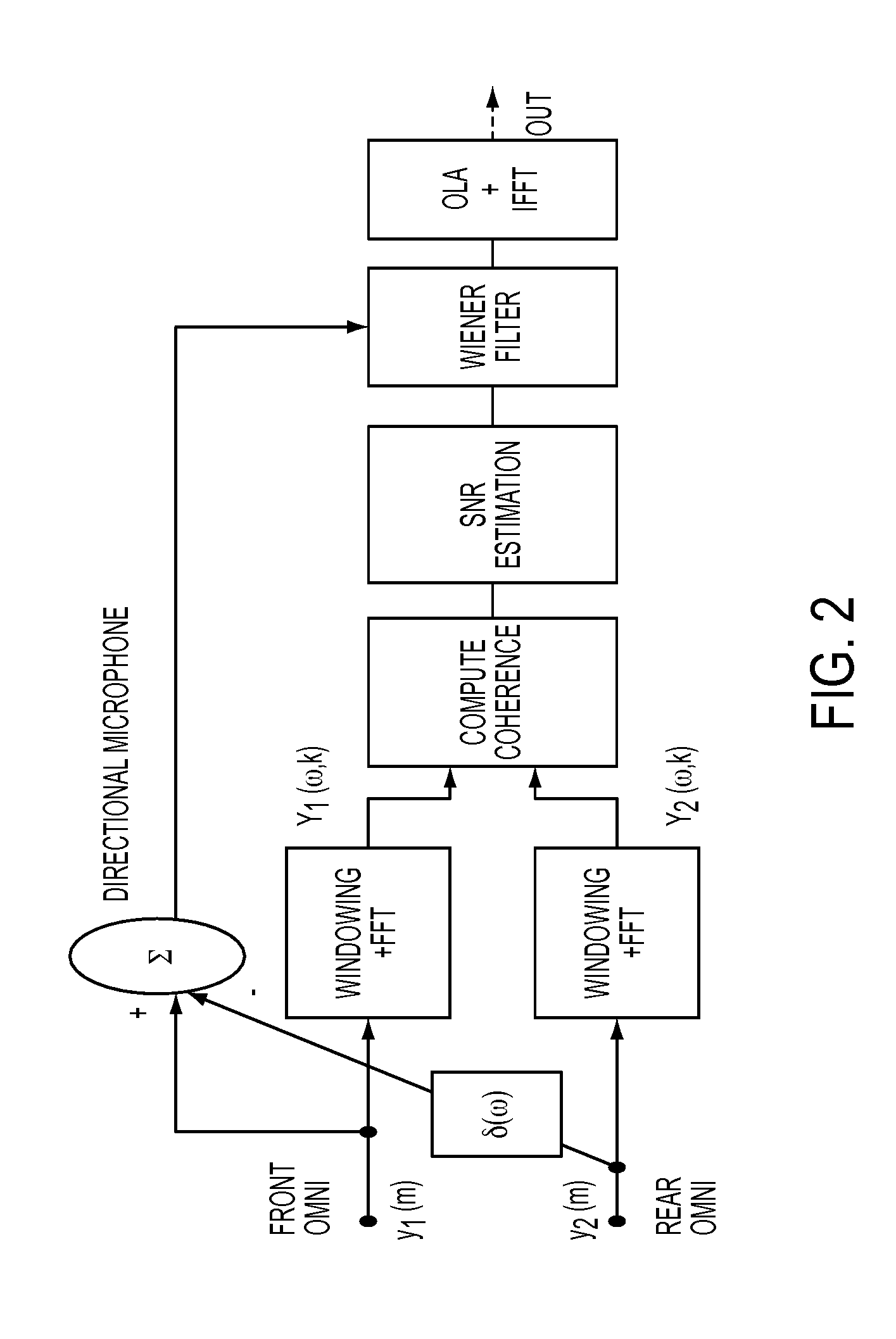
Method and system for enhancing the intelligibility of sounds relative to background noise
InactiveUS20140193009A1Reduce voice distortionLimit their maximum strengthSpeech analysisHearing aids signal processingNoise reductionBackground noise
A novel dual-microphone speech enhancement technique is proposed that utilizes the coherence function between input signals as a criterion for noise reduction. The technique is based on certain assumptions regarding the spatial properties of the target and noise signals and can be applied to arrays with closely spaced microphones, where noise captured by sensors is highly correlated (e.g., inside a mildly reverberant environment). The proposed algorithm is simple to implement and requires no estimation of noise statistics. In addition, it offers the advantage of coping with situations in which multiple interfering sources located at different azimuths might be present.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods and systems for generating an inspection process for a wafer
ActiveUS20100235134A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringNoise statistics
Methods and systems for generating an inspection process for a wafer are provided. One computer-implemented method includes separately determining a value of a local attribute for different locations within a design for a wafer based on a defect that can cause at least one type of fault mechanism at the different locations. The method also includes determining a sensitivity with which defects will be reported for different locations on the wafer corresponding to the different locations within the design based on the value of the local attribute. In addition, the method includes generating an inspection process for the wafer based on the determined sensitivity. Groups may be generated based on the value of the local attribute thereby assigning pixels that will have at least similar noise statistics to the same group, which can be important for defect detection algorithms. Better segmentation may lead to better noise statistics estimation.
Owner:KLA CORP
Method and apparatus for motion blur and ghosting prevention in imaging system
InactiveCN102077572AEasy to distinguishRobustTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage basedMotion blur
A method and apparatus for motion blur and ghosting prevention in imaging system is presented. A residue image is computed by performing spatial-temporal filter with a set of absolute image difference of image pairs from input images. A noise adaptive pixel threshold is computed for every pixel based on noise statistics of image sensor. The residue image and the noise adaptive pixel threshold are used to create a motion masking map. The motion masking map is used to represent motion and non-motion pixels in pixels merging. The pixels merging step is performed to generate an output image by considering the motion pixels where the motion pixels are performed separately. The resulting output image having no or less motion blur and ghosting artifacts can be obtained, even the input images having different degree of motion blur between each of the image, while the complexity is low. It is preferred that the current invention is applied in the Bayer raw domain. The benefit is reduced computation and memory because only 1 color component is processed for each pixel. Another benefit is higher signal fidelity because processing in the Bayer raw domain is unaffected by demosaicing artifacts, especially along edges. However, the current invention can also be applied in RGB domain.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
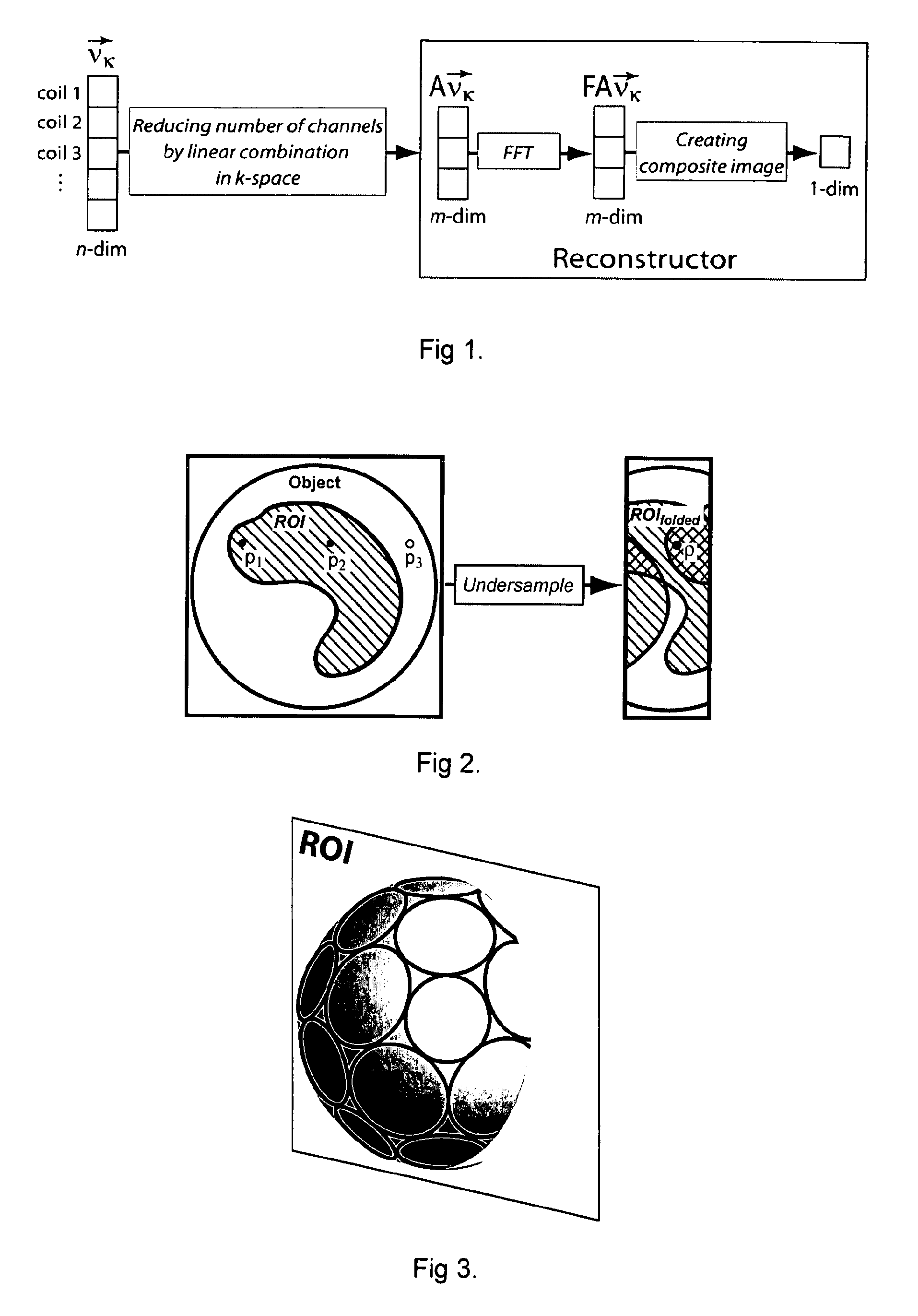
Method and apparatus for coil array compression
InactiveUS20100013472A1Improve accuracyImprove adaptabilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTime domainSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method of processing magnetic resonance imaging signals from a plurality of receiver coils of a magnetic resonance imaging system, comprises the steps of receiving from said plurality of receiver coils a corresponding plurality of original signals in the time-domain forming an n-dimensional signal vector νk wherein n is the number of receiver coils; linearly combining said original signals so as to obtain a plurality of transformed signals forming an m-dimensional transformed signal vector ν′k wherein m is smaller than n and wherein said step of linearly combining is represented by a linear transformation matrix A; and reconstructing an image from said plurality of transformed signals. Said transformation matrix A is determined for given sensitivity characteristics and noise statistics of said plurality of receiver coils so as to substantially maximize the signal-to-noise ratio in a preselected image region or volume which is preferably smaller than the imaging slice or volume selected by the magnetic resonance experiment.
Owner:EIDGENOSSISCHE TECHN HOCHSCHULE ETH +1
Global and local statistics controlled noise reduction system
InactiveUS7317842B2Reliable global noise statisticAdapt effectivelyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage denoisingNoise level
A global and local statistics controlled noise reduction system in which the video image noise reduction processing is effectively adaptive to both image local structure and global noise level. A noise estimation method provides reliable global noise statistics to the noise reduction system. The noise reduction system dynamically / adaptively configures a local filter for processing each image pixel, and processes the pixel with that local filter. The filtering process of the noise reduction system is controlled by both global and local image statistics that are also computed by the system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Noise plus interference power estimation method for OFDM systems
ActiveUS7688905B1Improve performanceNoise varianceError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionSignal qualitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
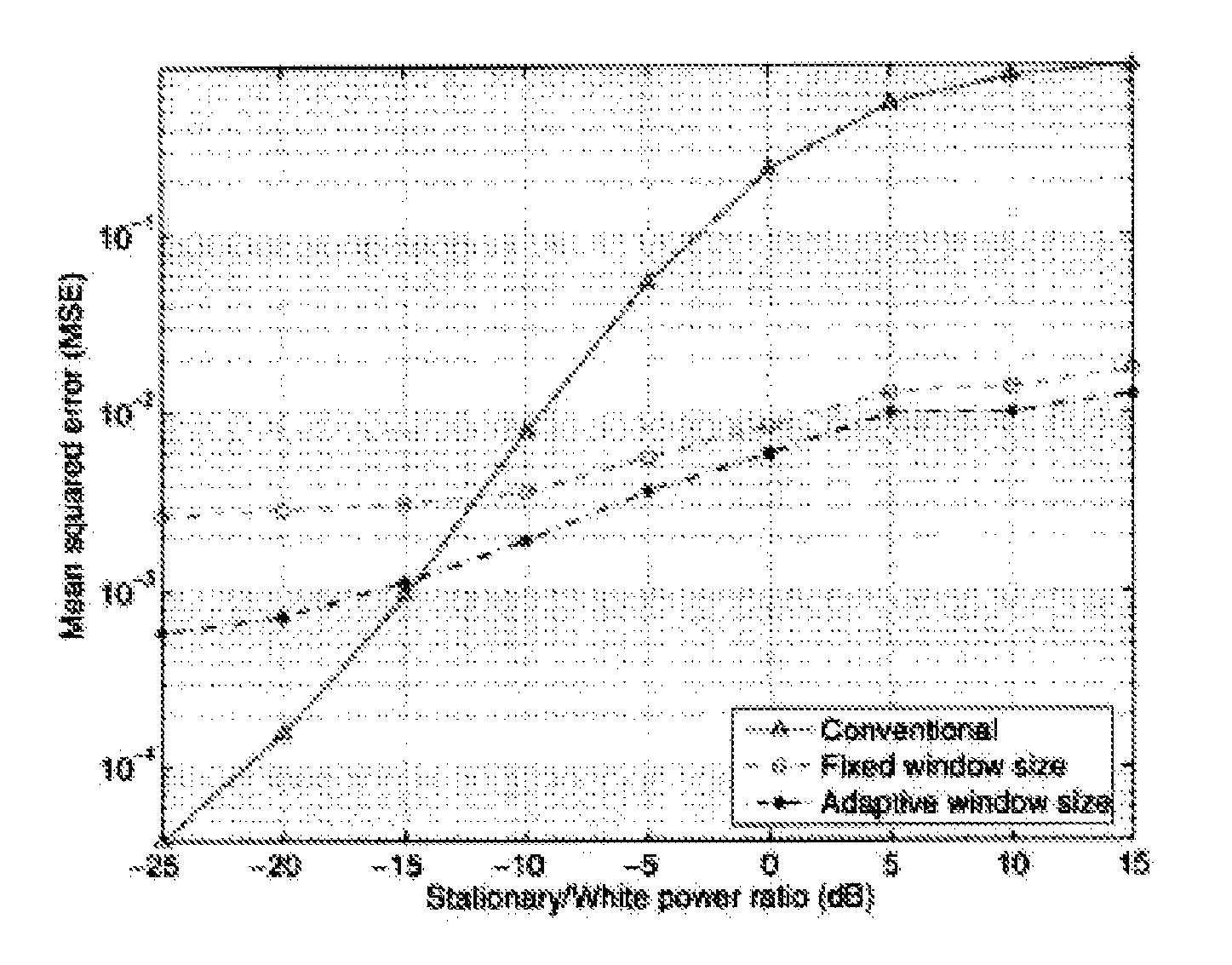
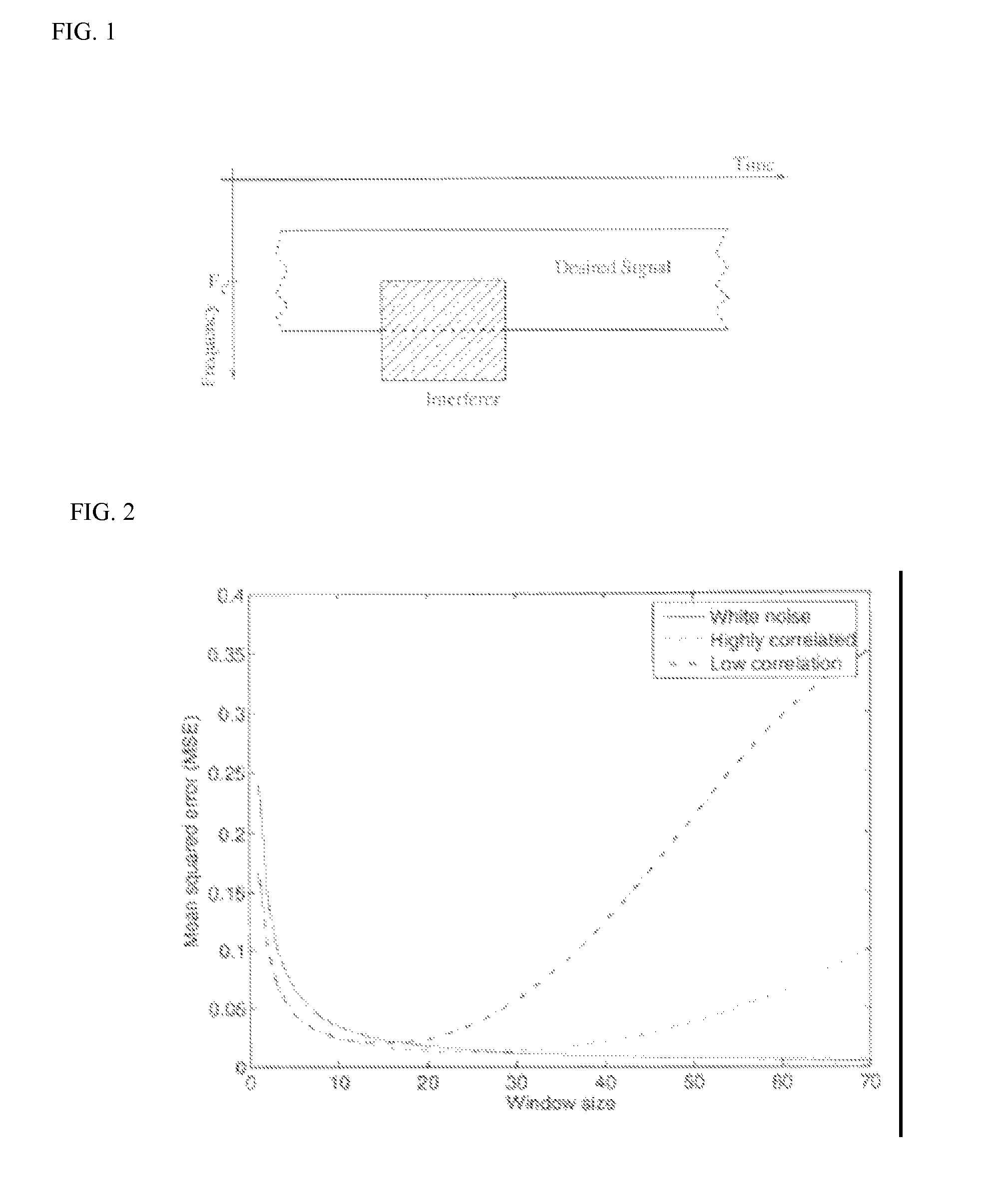
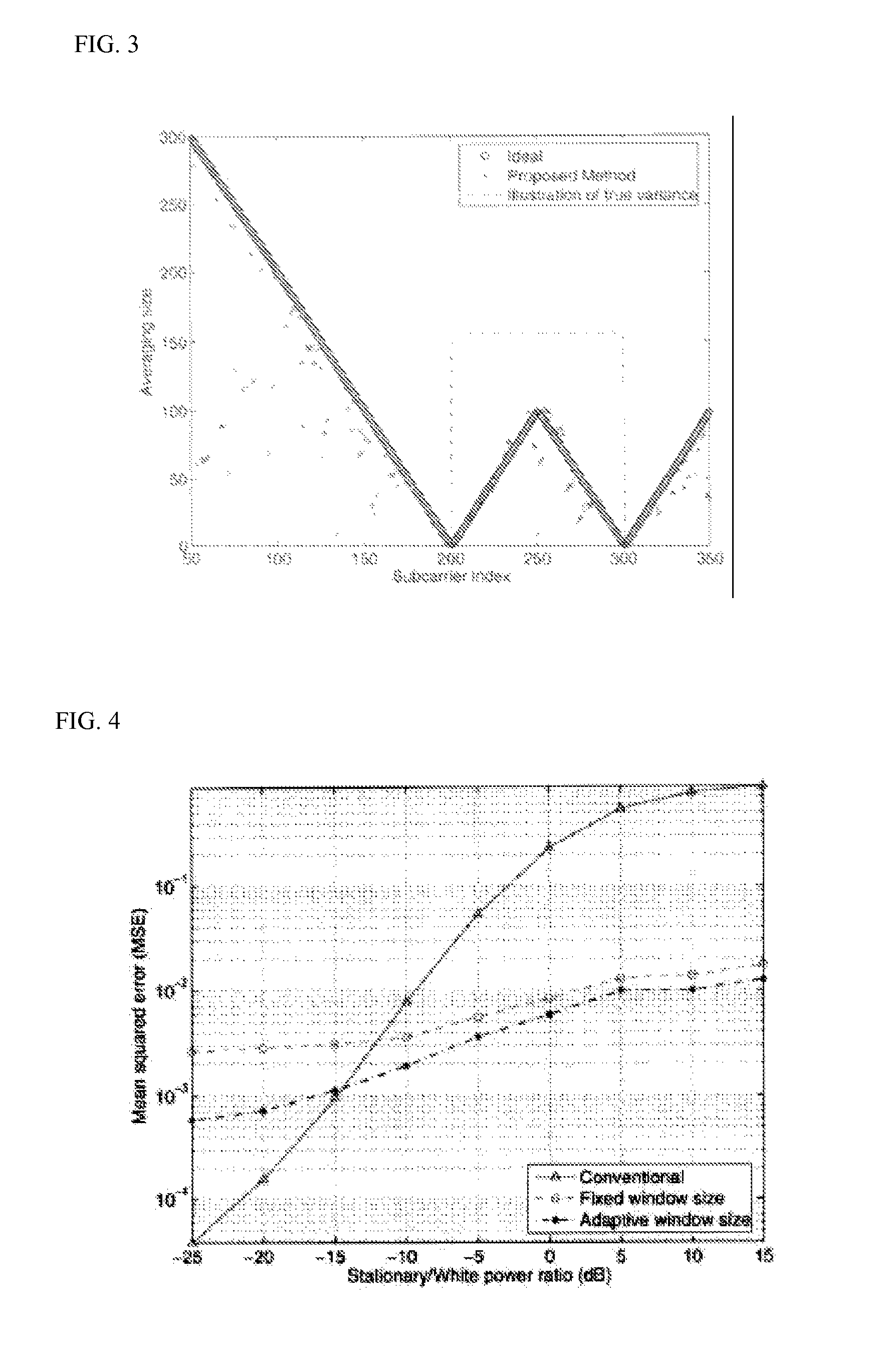
In accordance with the present invention, a method and apparatus for estimating the noise and interference over the transmission band for OFDM systems are provided. Noise variance and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) are important parameters for adaptive orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems since they serve as a standard measure of signal quality. Conventional algorithms assume that the noise statistics remain constant over the OFDM frequency band, and thereby average the instantaneous noise samples to get a single estimate. In reality, noise is often made up of white Gaussian noise along with correlated colored noise that affects the OFDM spectrum unevenly. Provided is an adaptive windowing technique to estimate the noise power that takes into account the variation of the noise statistics across the OFDM sub-carrier index as well as across OFDM symbols. The proposed method provides many local estimates, allowing tracking of the variation of the noise statistics in frequency and time. A mean-squared-error (MSE) expression in order to choose the optimal window dimensions for averaging in time and frequency is derived.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
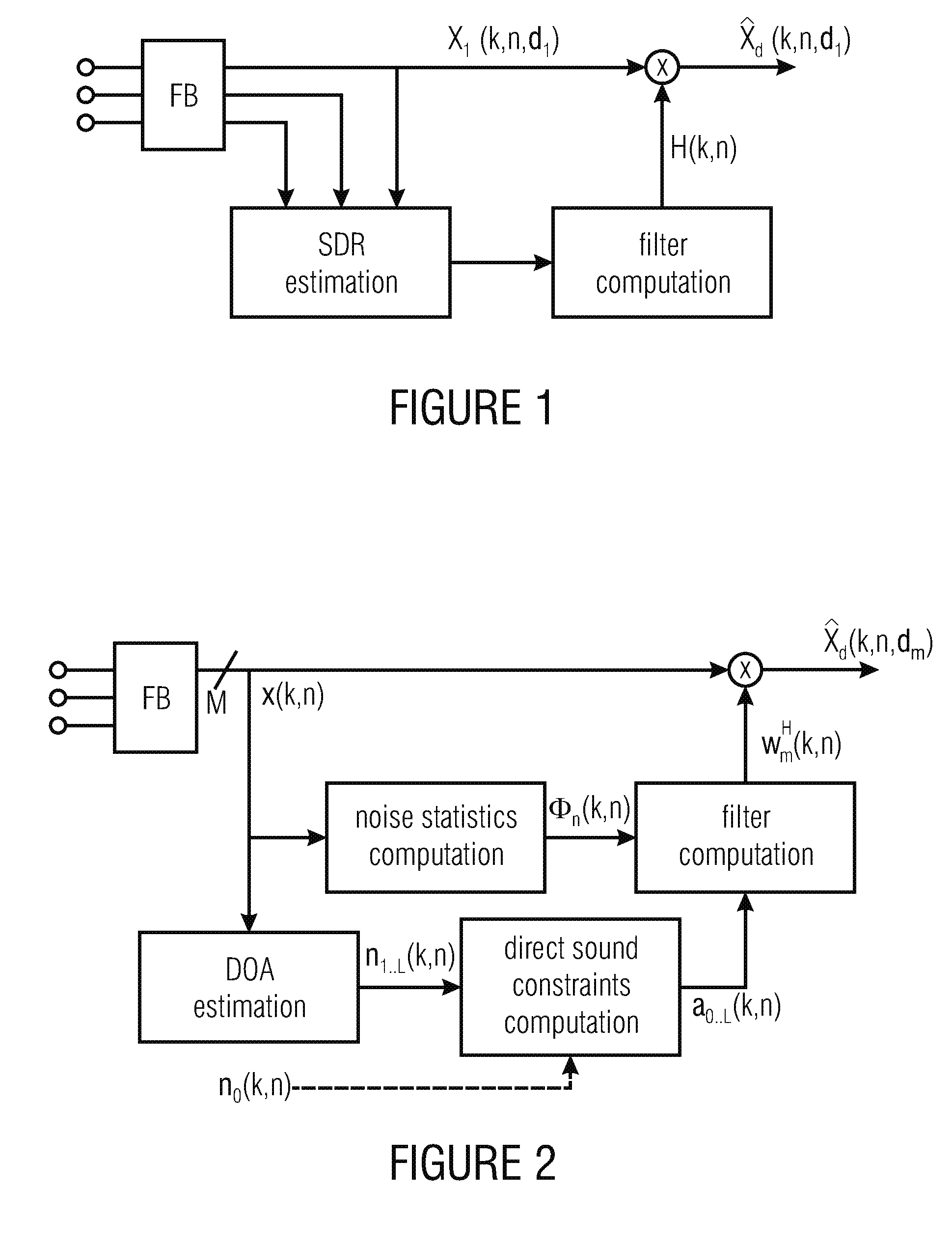
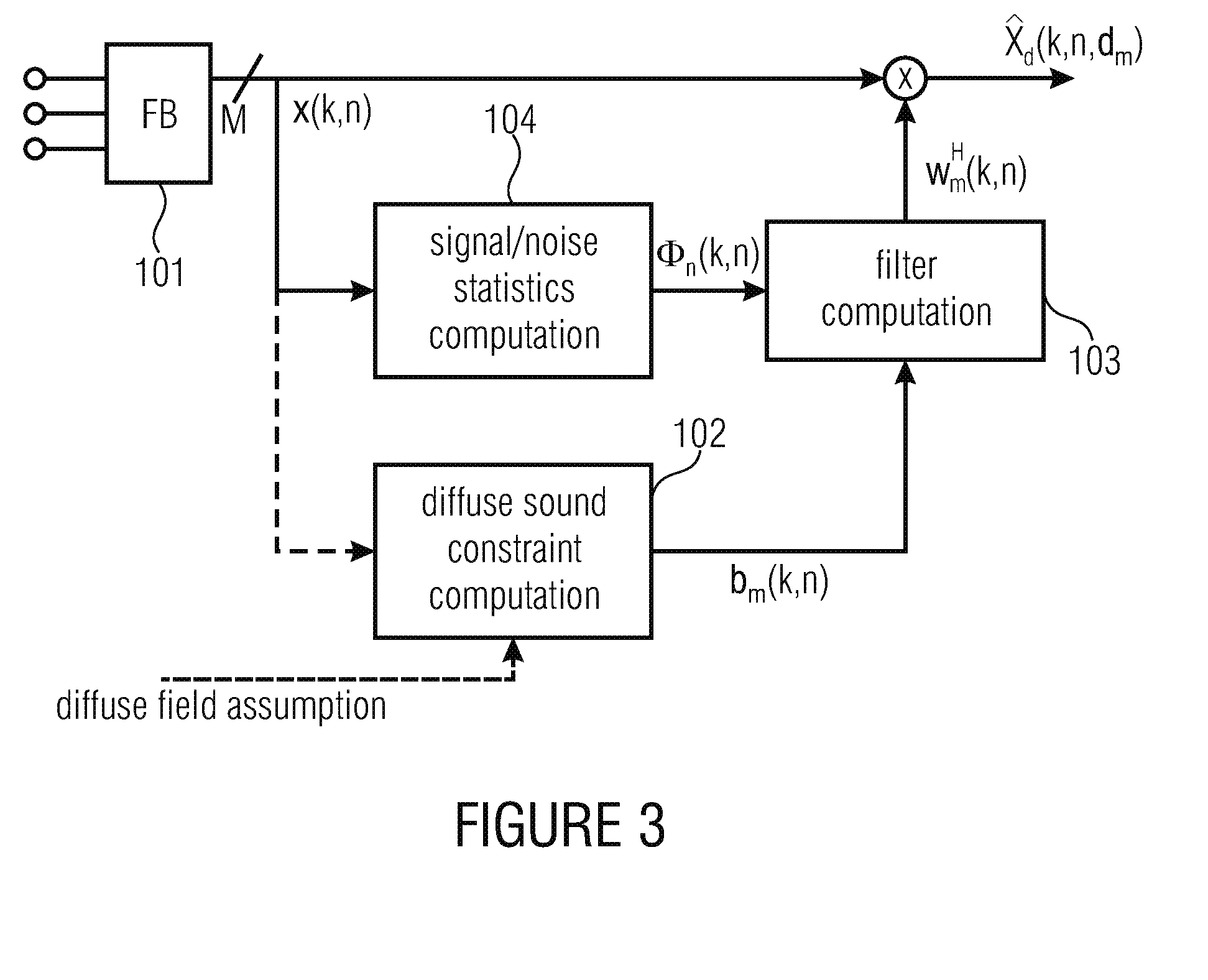
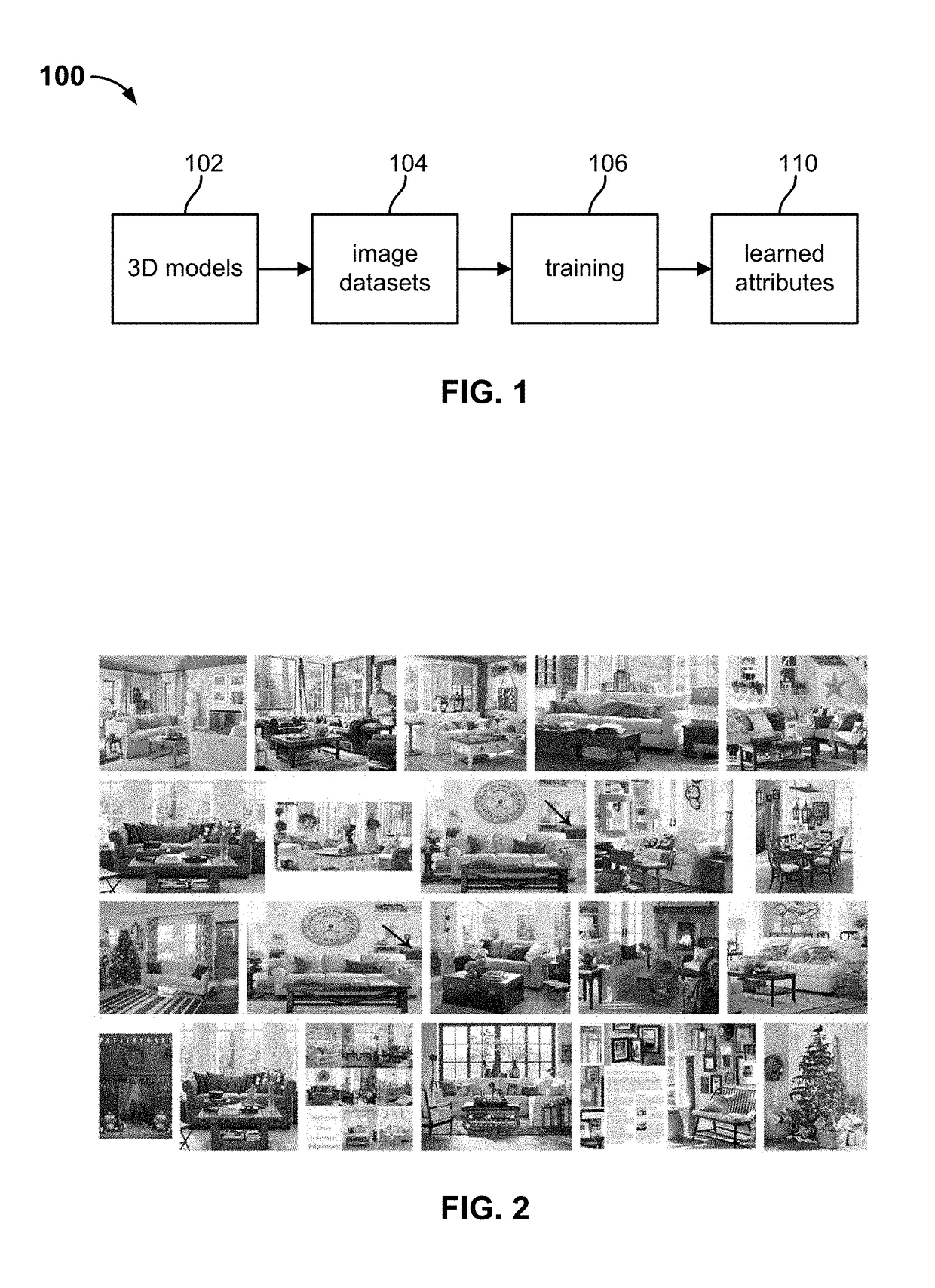
Extraction of reverberant sound using microphone arrays
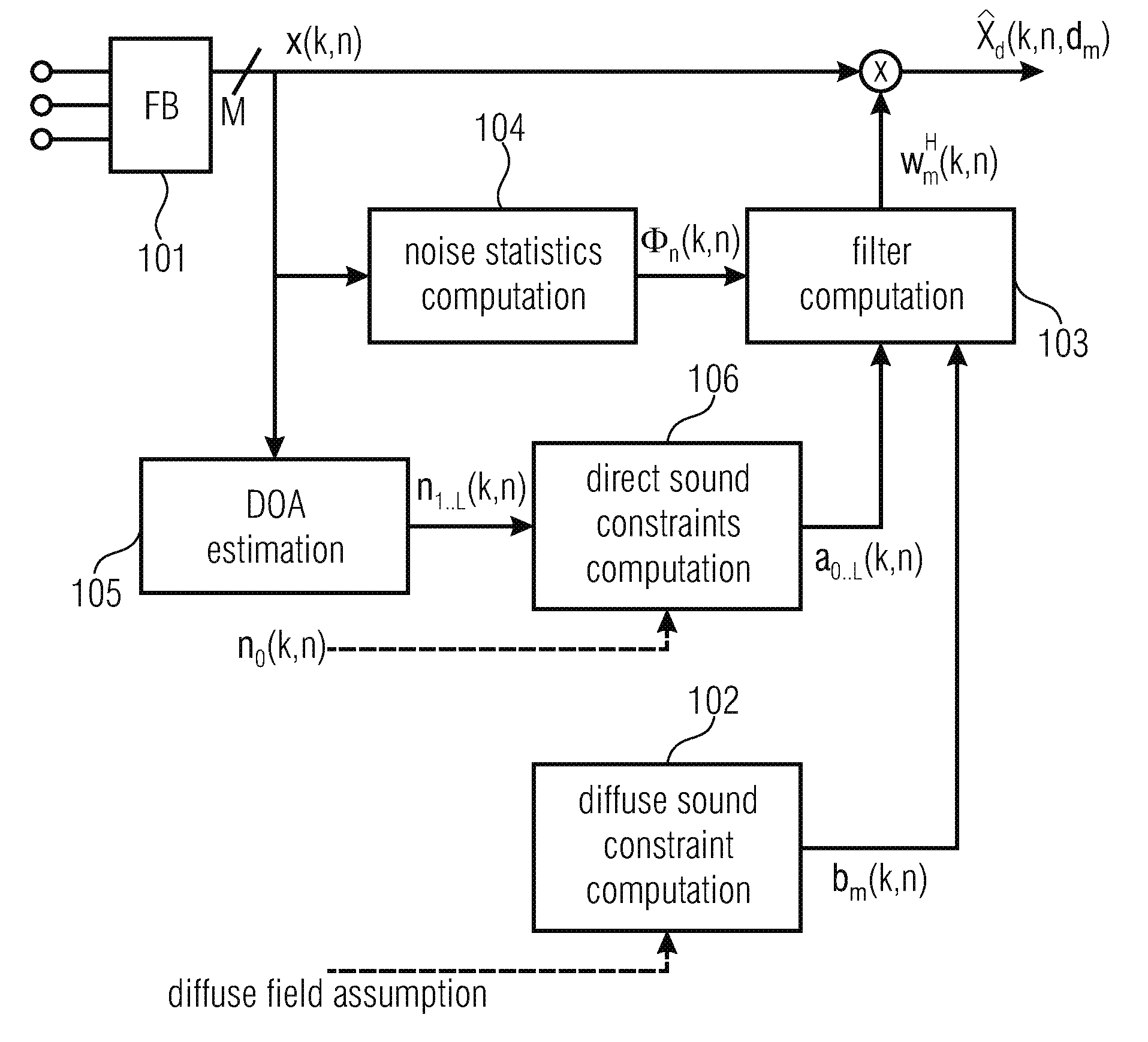
A method includes estimating a spatial coherence between a first diffuse sound portion in a first microphone signal and a second diffuse sound portion in a second microphone signal. The first microphone signal is captured by a first microphone and the second microphone signal is captured by a second microphone which is spaced apart from the first microphone in a known manner. The method further includes defining a linear constraint for filter coefficients of a diffuse sound filter, the linear constraint being based on the spatial coherence. The method also includes calculating at least one of signal statistics and noise statistics over the first microphone signal and the second microphone signal. The method also includes determining the filter coefficients of the diffuse sound filter by solving an optimization problem concerning at least one of the signal statistics and noise statistics while considering the linear constraint for the filter coefficients.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
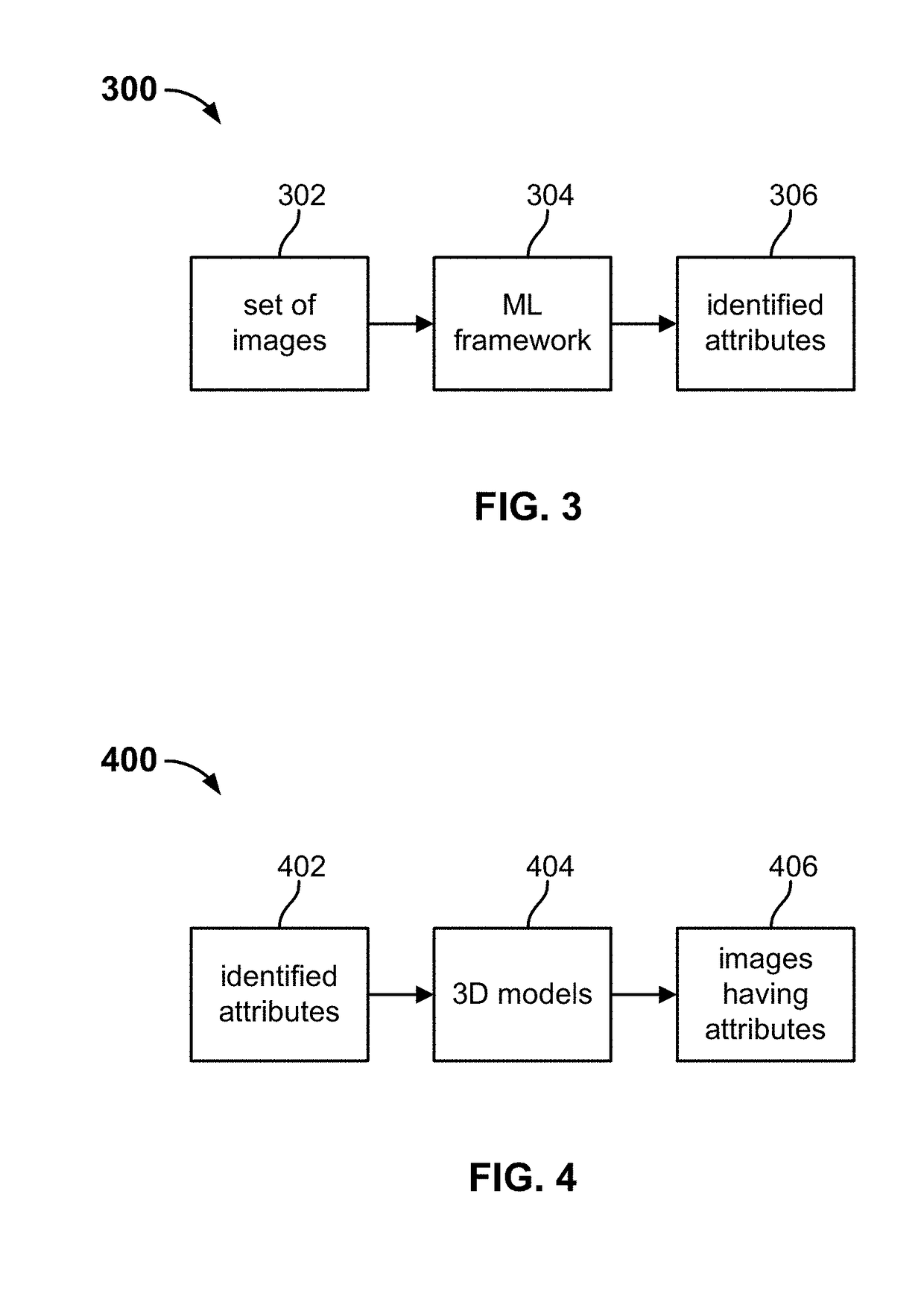
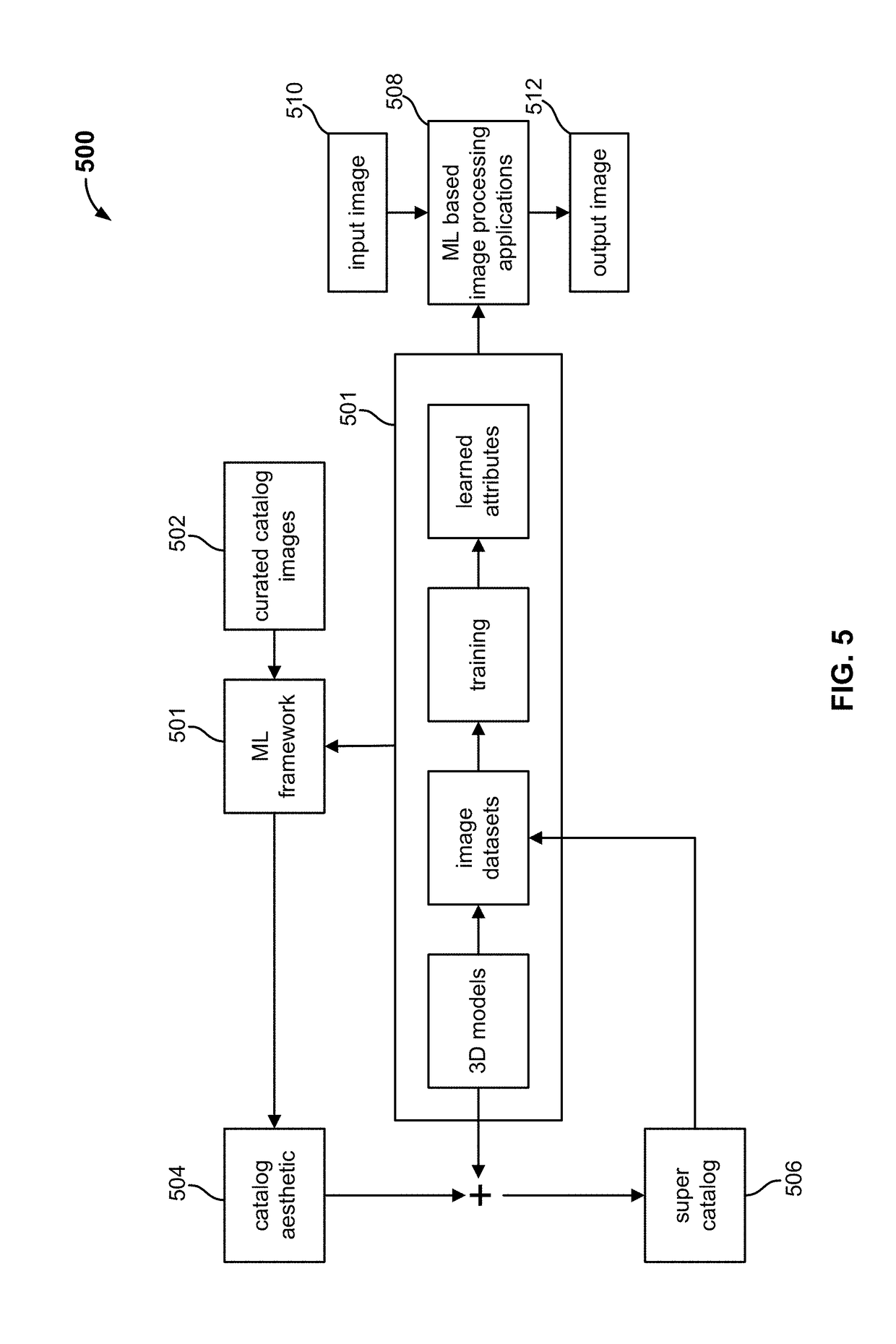
Machine learning based image processing techniques
A machine learning based image processing architecture and associated applications are disclosed herein. In some embodiments, a machine learning framework is trained to learn low level image attributes such as object / scene types, geometries, placements, materials and textures, camera characteristics, lighting characteristics, contrast, noise statistics, etc. Thereafter, the machine learning framework may be employed to detect such attributes in other images and process the images at the attribute level.
Owner:OUTWARD
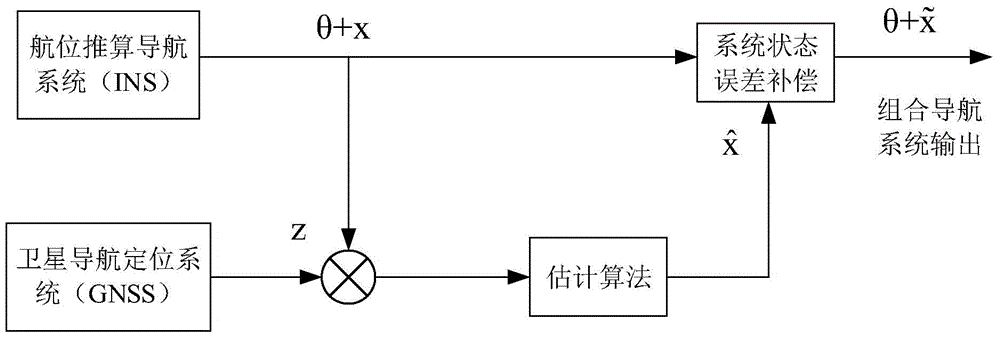
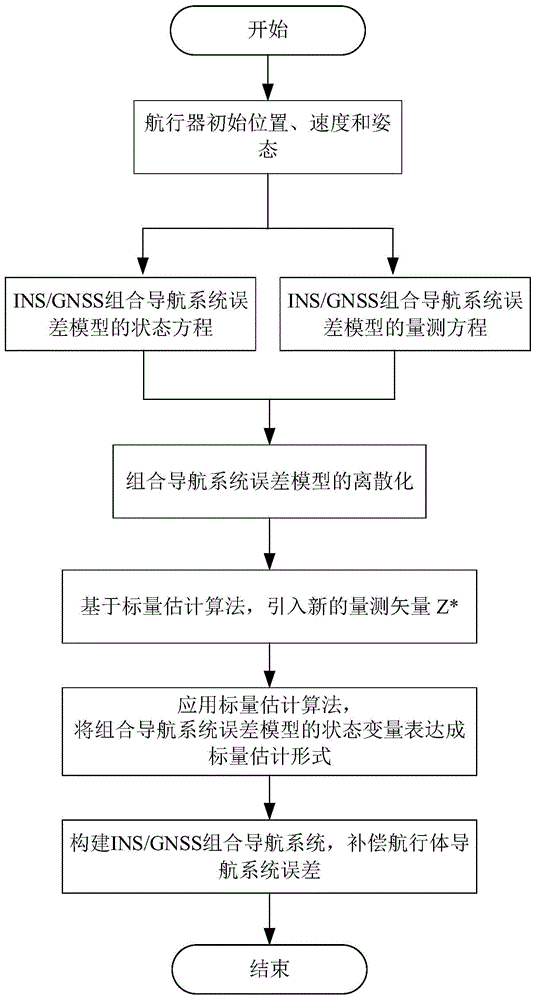
Scalar-estimation-algorithm-based INS/GNSS combined navigation method
InactiveCN105988129ASimple build structureLow priceSatellite radio beaconingState variableNavigation system
The invention discloses a scalar-estimation-algorithm-based INS / GNSS combined navigation method. According to different error dynamic characteristics of a dead reckoning technology and a satellite navigation positioning technology, the two kinds of navigation methods are combined based on a scalar estimation algorithm to construct an INS / GNSS combined navigation system. The method comprises: a discretized INS / GNSS combined navigation system error model is established; on the basis of a kalman filtering algorithm, a scalar estimation algorithm is constructed; on the basis of the scalar estimation algorithm, a new measurement vector Z* is introduced; a state variable of the combined navigation system error model is expressed into a scalar estimation mode by using the scalar estimation algorithm; and then on the basis of the scalar estimation mode, an INS / GNSS combined navigation system is constructed and thus a navigation body navigation system error is compensated. According to the invention, a filter divergence problem caused by inaccurate noise statistic characteristic determination of the traditional kalman filtering algorithm can be solved; reliability of the combined navigation system is improved; and the combined navigation system cost is reduced. A novel combined navigation method is provided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
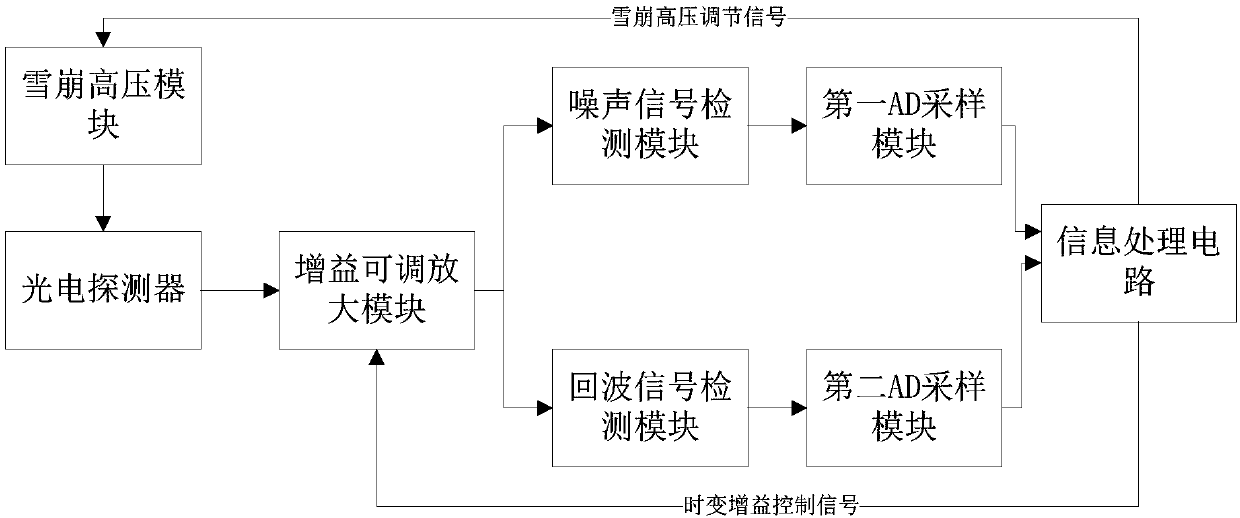
Full digital adjusting laser spacing system
InactiveCN107861112AWill not deformImprove detection accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationInformation processingControl signal
The invention relates to an all-digital adjustable laser ranging system, which includes an avalanche high-voltage module, a photoelectric detector, an adjustable gain amplifier module, a noise signal detection module, a first AD sampling module, an echo signal detection module, and a second AD sampling module. module, the information processing circuit is used to adjust the avalanche voltage provided by the avalanche high voltage module to the photodetector according to the number of noises counted by the first AD sampling module, and output a corresponding avalanche high voltage adjustment signal to the avalanche high voltage module; 2. The AD sampling module counts the number of echoes, adjusts the amplification gain of the gain-adjustable amplifying module, and outputs a corresponding time-varying gain control signal to the gain-adjustable amplifying module. The main function of this system is to complete the detection of target distance and target reflection intensity. The laser echo signal reflected by the target received by the photoelectric D detector, after automatic gain amplification and AD sampling, is used to time the flight time of the laser pulse and detect the amplitude width signal, so as to calculate the distance information and target reflection characteristics of the target.
Owner:成都心无界光电技术有限公司
Mixed interactive multi-model filtering method
InactiveCN110375731ASolve the problem of decreasing filtering accuracySuppress outlier interferenceNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingAlgorithmBayesian hypothesis testing
The invention discloses a mixed interactive multi-model filtering method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, building a system model and an observation model of an application object,building a total model set according to a change condition of noise statistic characteristics of external information, and describing current noise characteristics by adopting the adjacent three models; storing a robust filter real-time noise variance matrix in a historical sequence by adopting a sliding window, and adaptively selecting a proper model according to the smoothed noise statistic characteristics; setting an initial probability of each model and a mixed initial state and a covariance matrix of each filter, and according to the system model and the observation model, performing state estimation and covariance matrix updating processes, and performing model updating by adopting a Bayesian hypothesis testing method; and performing an output interactive process according to a weight, and outputting a final filtering result. By taking an inertia / Doppler combined navigation system as an example, the interference of noise sudden change type errors and outliers existing in Dopplerspeed measurement information can be effectively relieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for detecting emitted acoustic signals including signal to noise ratio enhancement
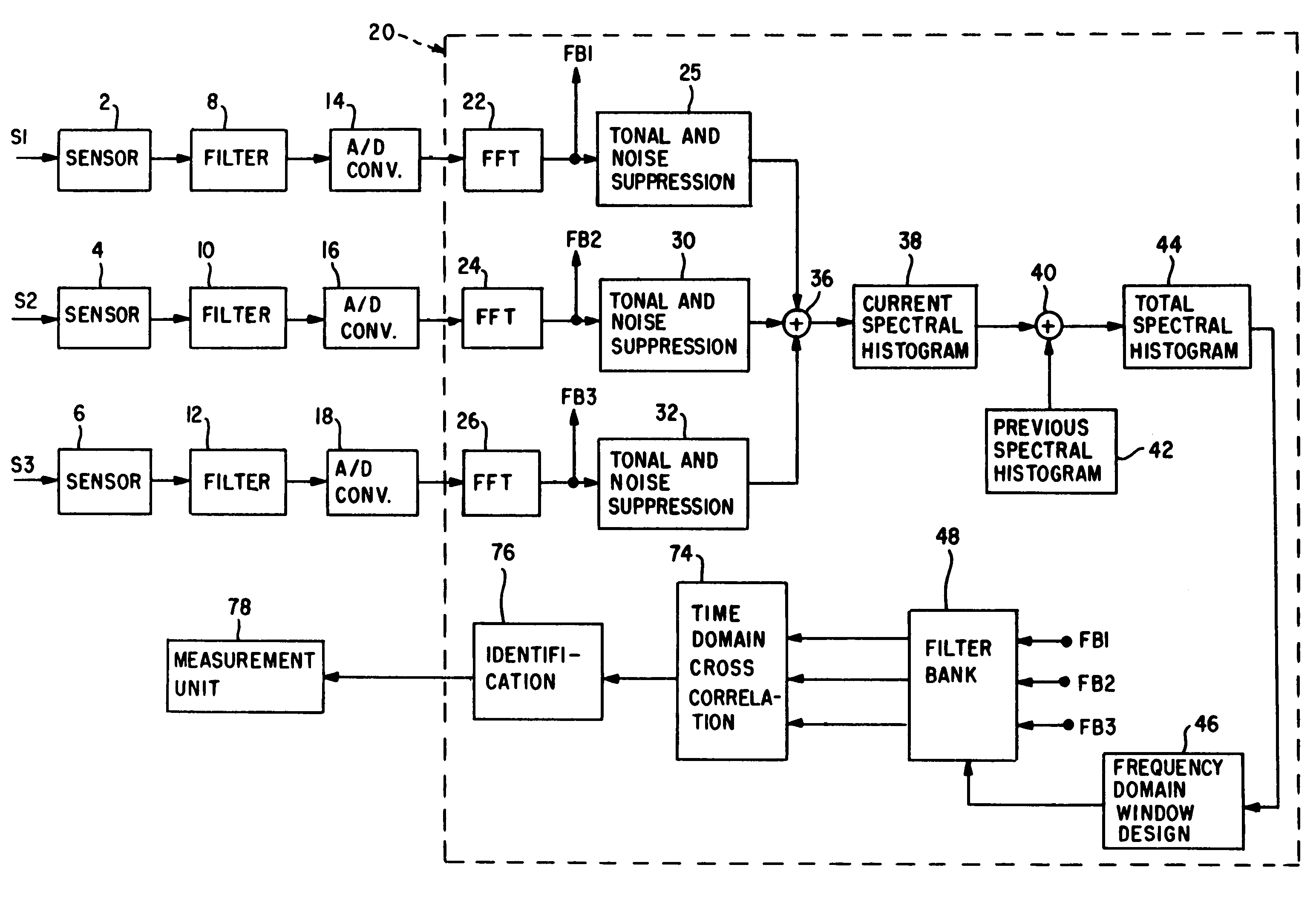
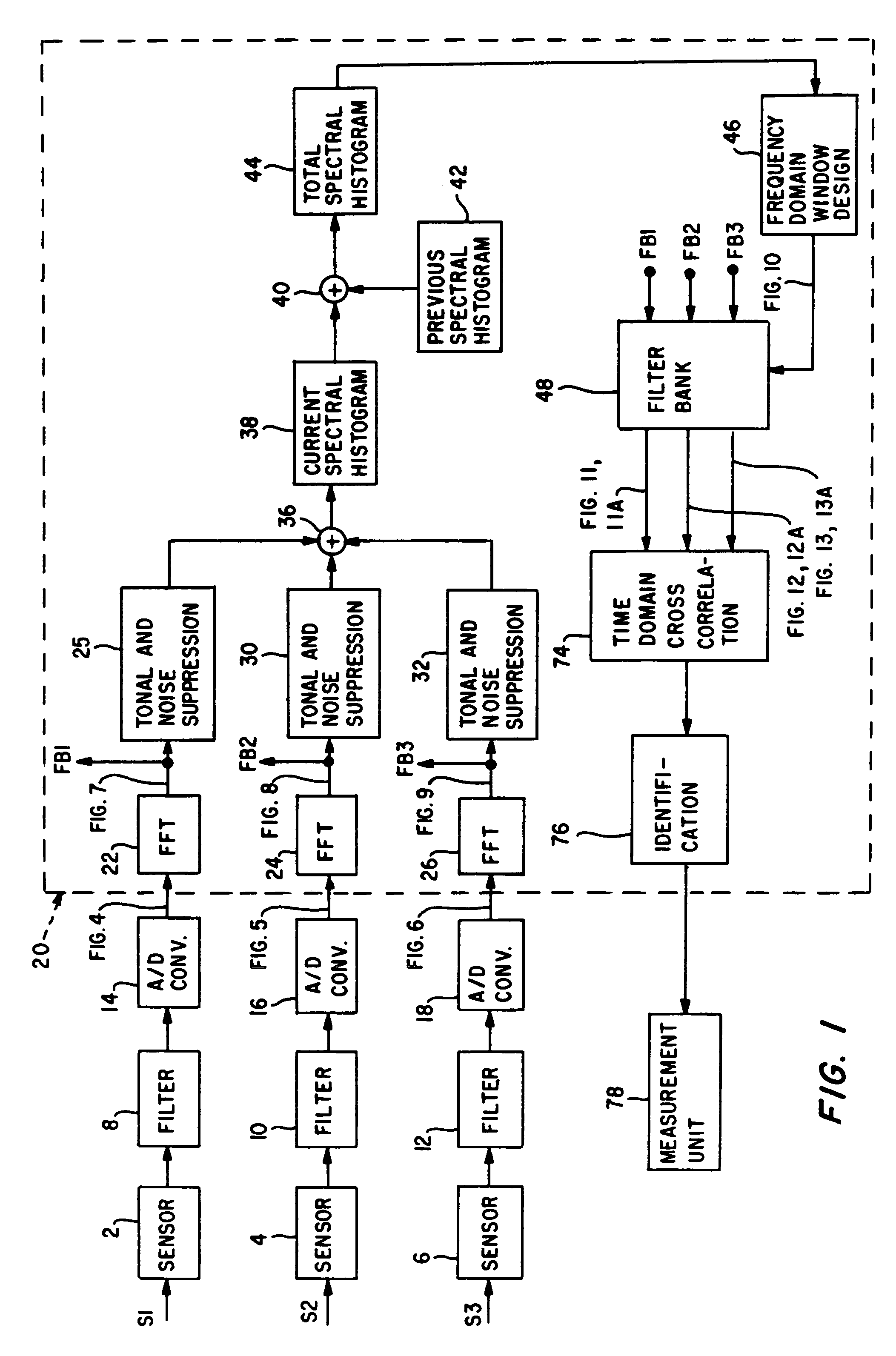
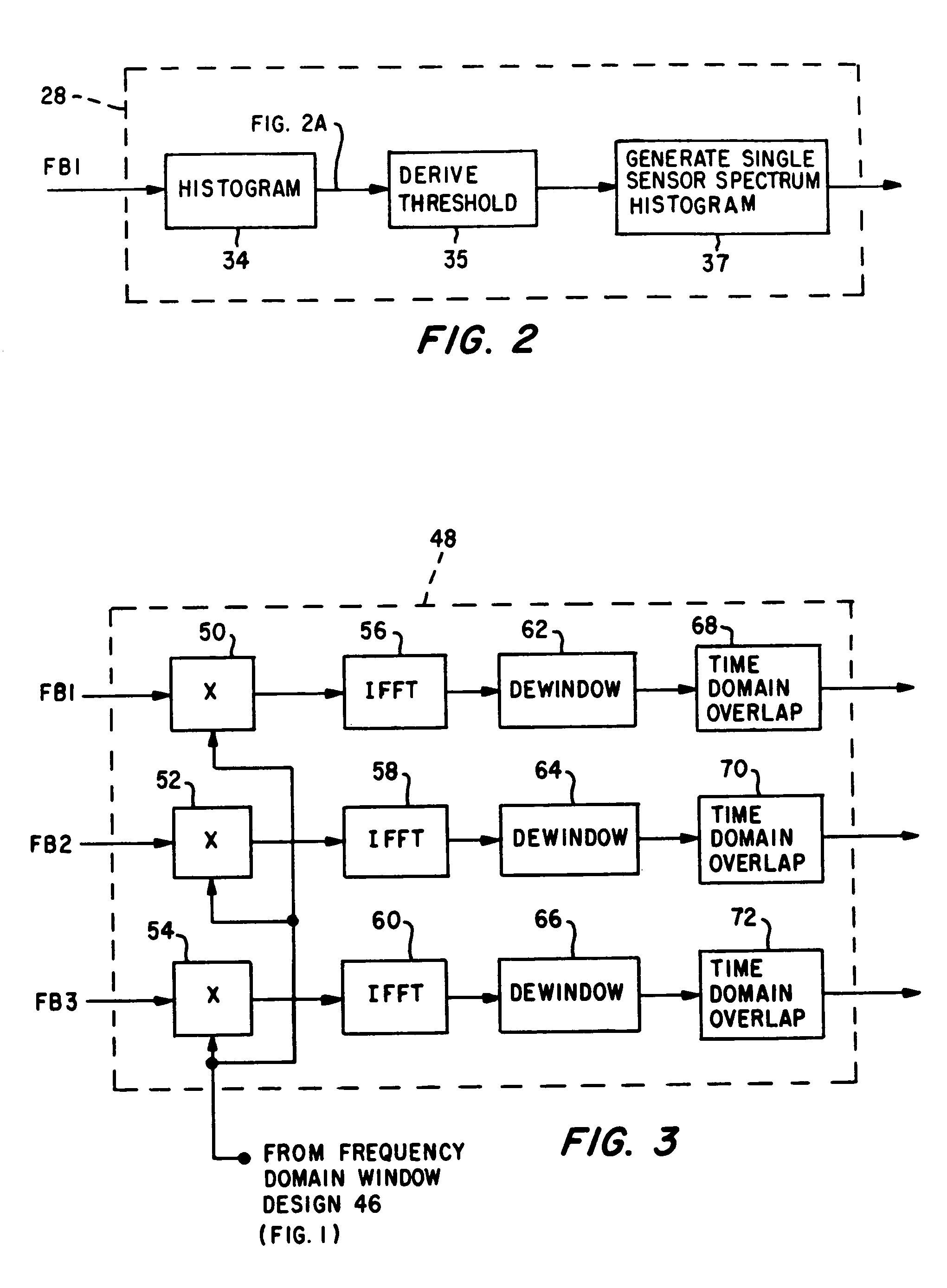
InactiveUS7012854B1Signal to noise ratioIncreased signal noiseSpeech analysisTransmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Time segment
A plurality of sensors and a digital adaptive tuning filter bank are used in extracting a desired emitted signal embedded in a noisy environment. By monitoring noise statistics of the sensor signals, the digital adaptive tuning filter bank automatically adjusts its upper (to eliminate strong tonals) and lower (to eliminate background noise) thresholds to obtain a discovery frequency band. The filter bank is designed by examining the discovery band across the sensors and over a predefined period of time. The method described significantly reduces the possibilities of matching self-noise transients (unwanted signals) and thus minimizes the false alarm rate in emitted signal recognition.
Owner:ALLIEDSIGNAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com