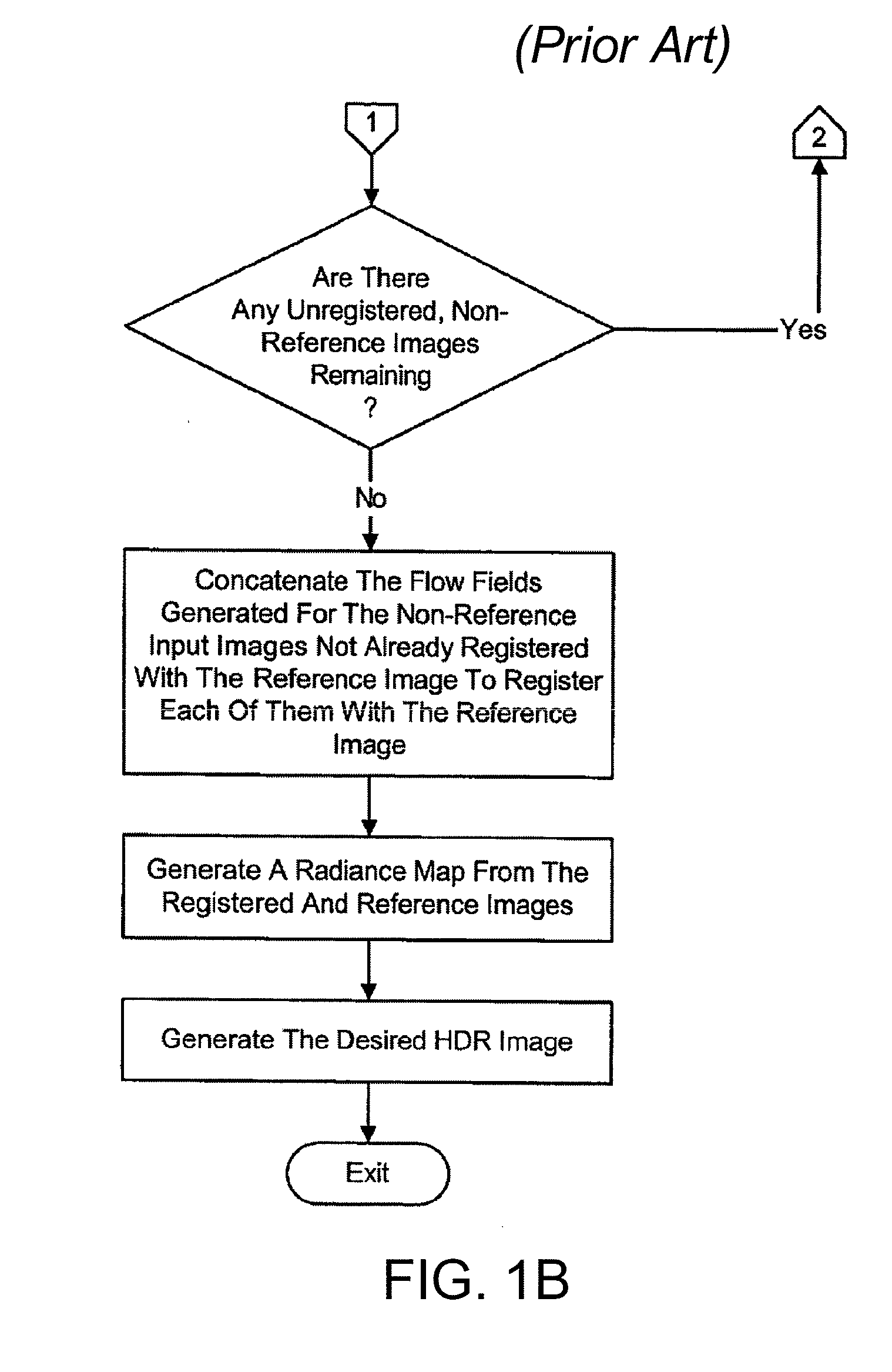
Patents
Literature
222 results about "Temporal filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Temporal filters are often used to remove signal drift in brain imaging (brain scans become brighter or darker gradually during scannning) or external noise in electrophysiological data (e.g. 50-60Hz noise due to electrical signals).
Augmented surgical reality environment
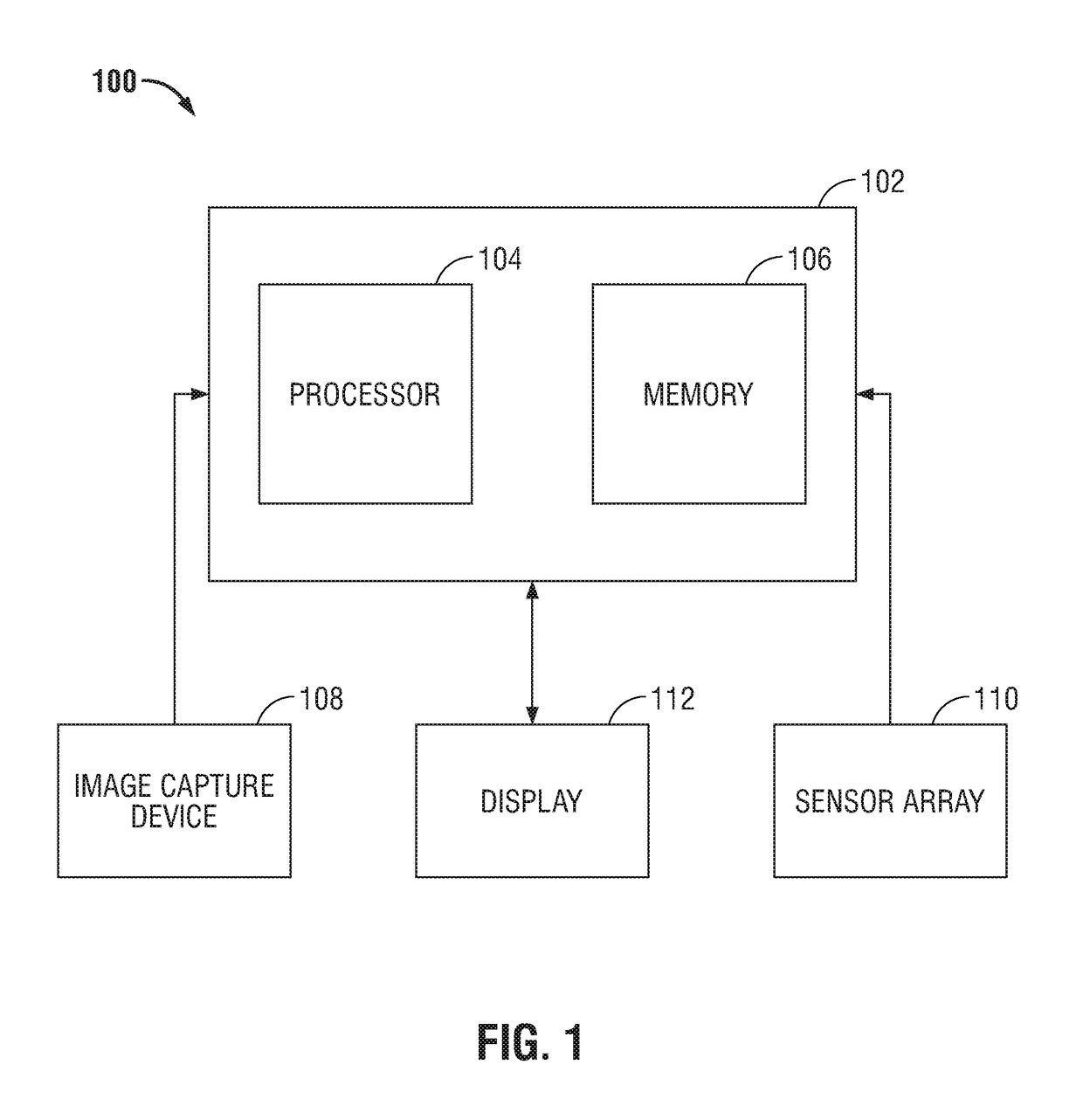
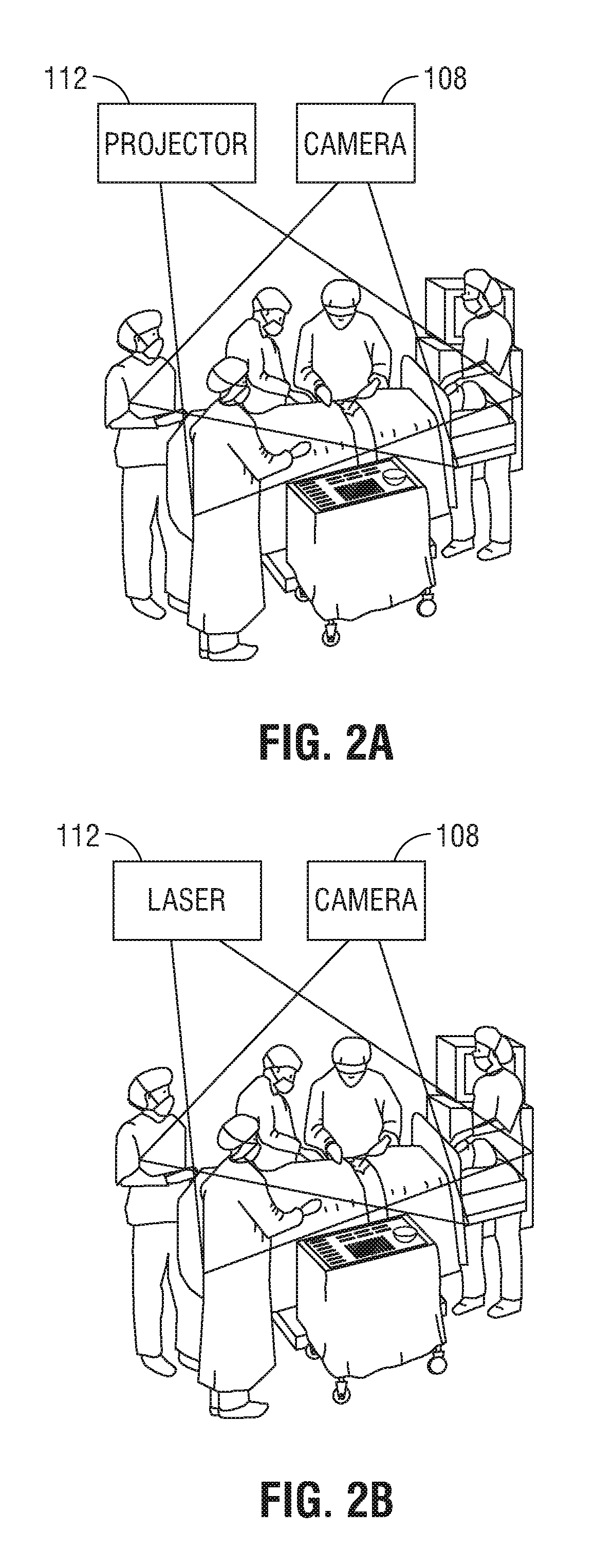
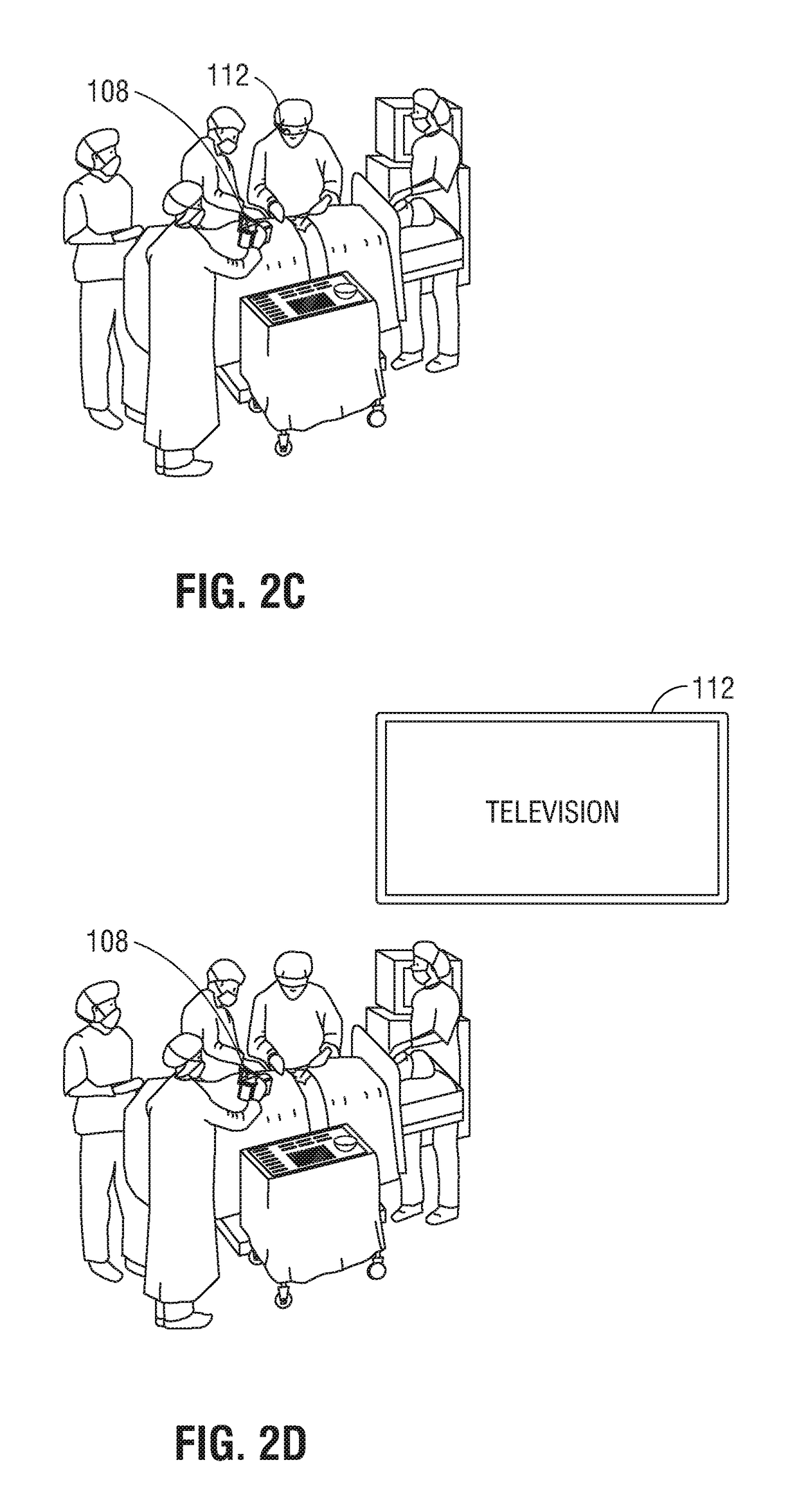
The present disclosure is directed to an augmented reality surgical system for viewing an augmented image of a region of interest during a surgical procedure. The system includes an image capture device that captures an image of the region of interest. A controller receives the image and applies at least one image processing filter to the image. The image processing filter includes a spatial decomposition filter that decomposes the image into spatial frequency bands. A temporal filter is applied to the spatial frequency bands to generate temporally filtered bands. An adder adds each band spatial frequency band to a corresponding temporally filtered band to generate augmented bands. A reconstruction filter generates an augmented image by collapsing the augmented bands. A display displays the augmented image to a user.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
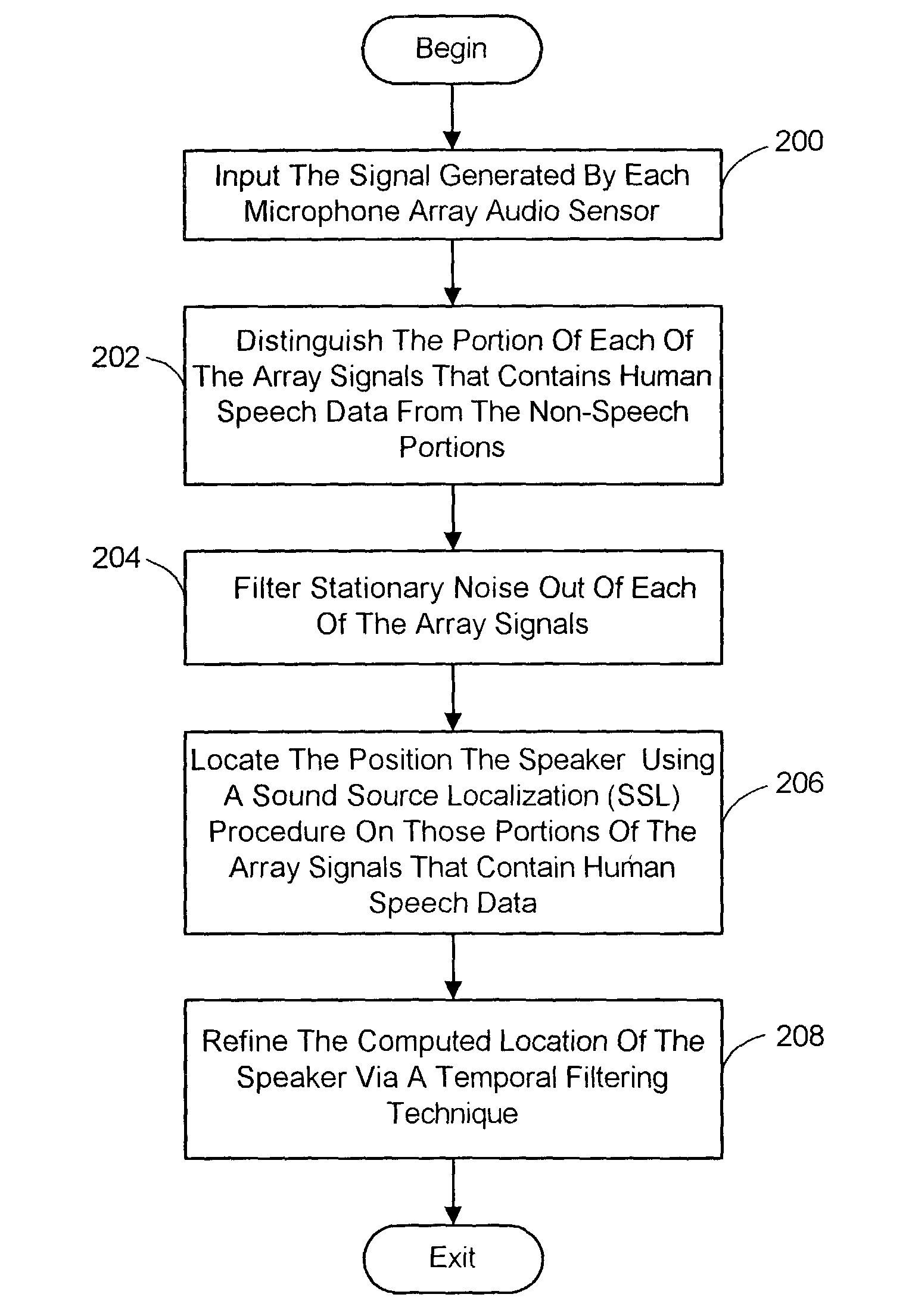
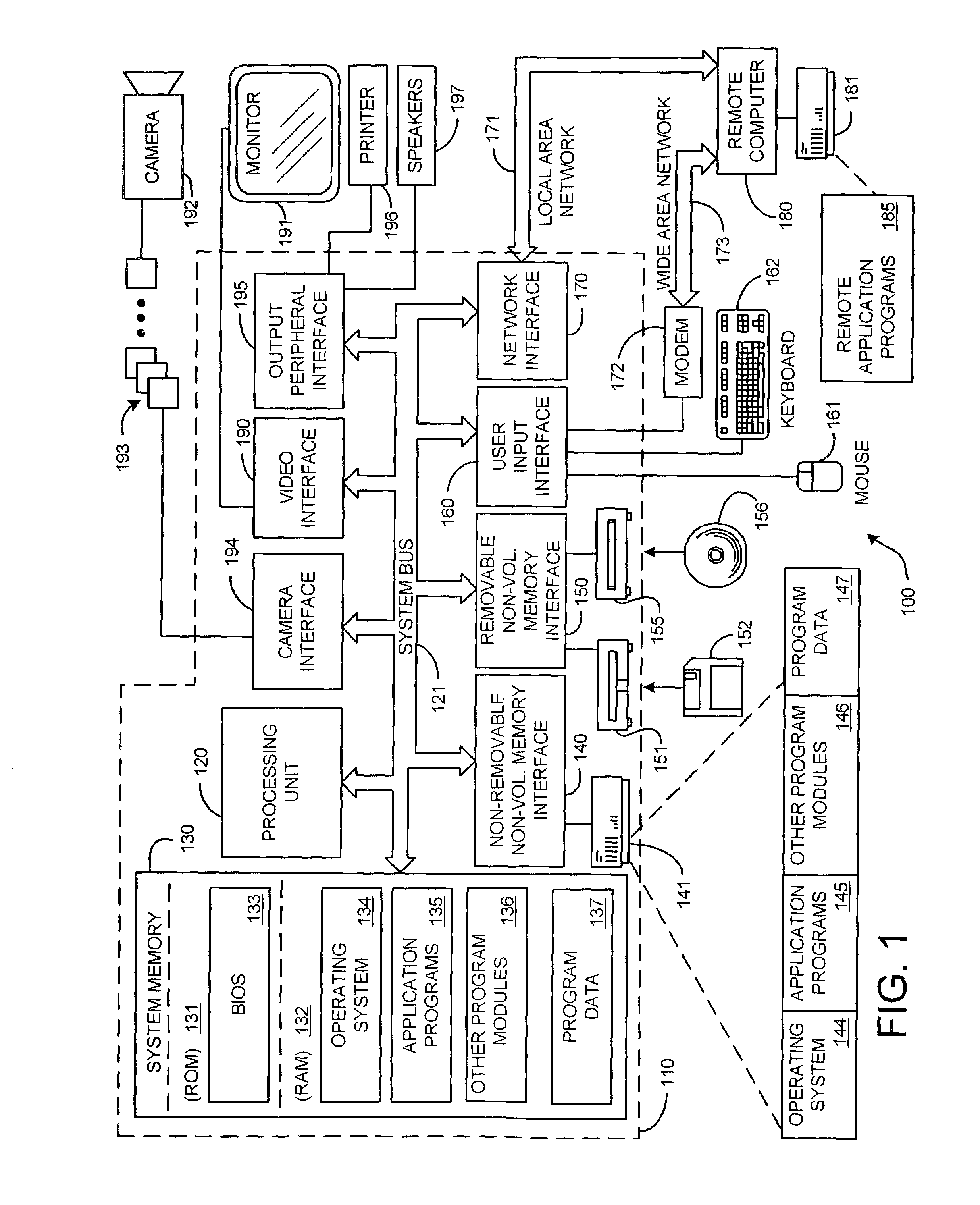
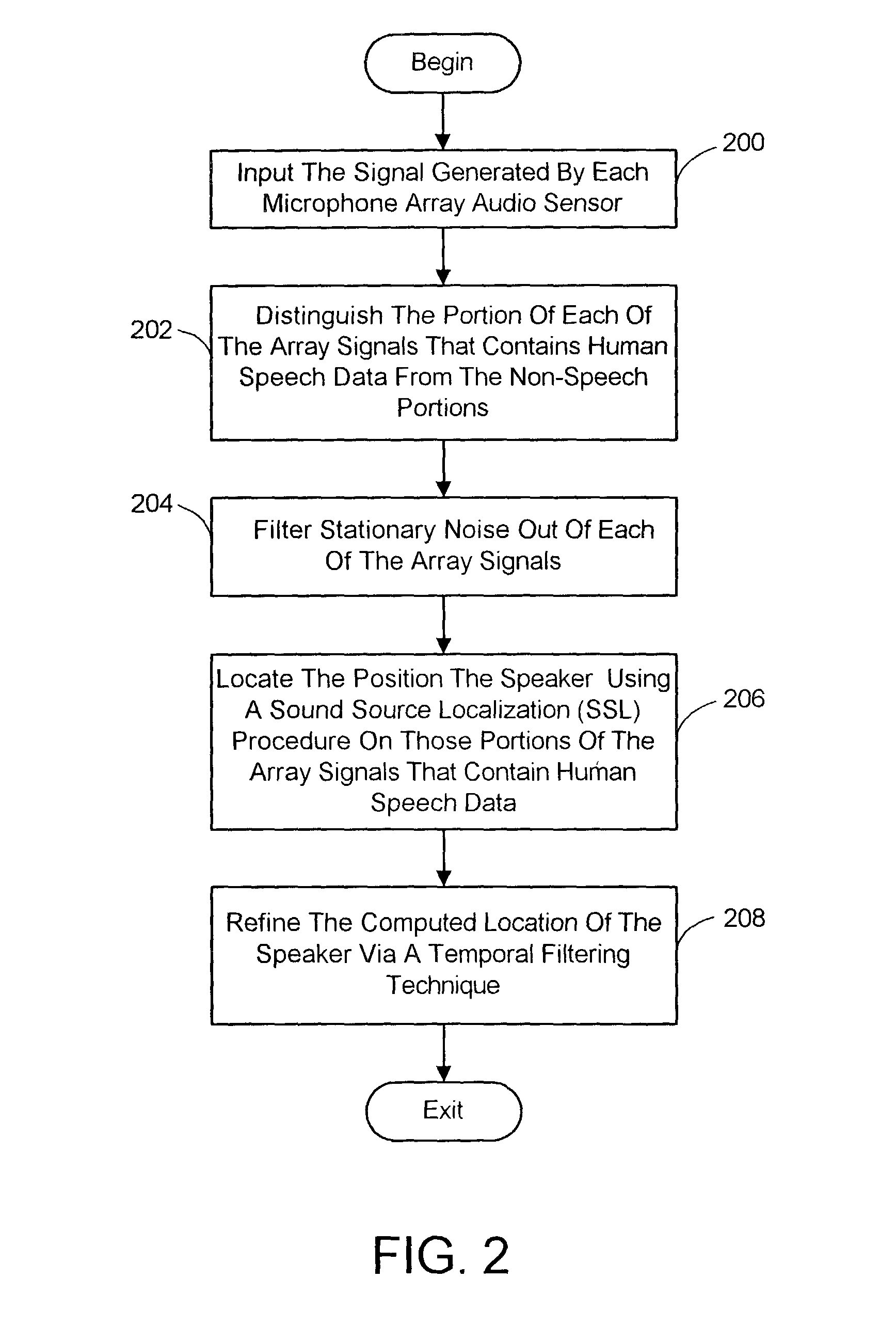
System and process for locating a speaker using 360 degree sound source localization
InactiveUS7039199B2Accurate and robust capabilityEasy procedureTelevision system detailsMicrophonesSound sourcesSituated computing
A system and process is described for estimating the location of a speaker using signals output by a microphone array characterized by multiple pairs of audio sensors. The location of a speaker is estimated by first determining whether the signal data contains human speech components and filtering out noise attributable to stationary sources. The location of the person speaking is then estimated using a time-delay-of-arrival based SSL technique on those parts of the data determined to contain human speech components. A consensus location for the speaker is computed from the individual location estimates associated with each pair of microphone array audio sensors taking into consideration the uncertainty of each estimate. A final consensus location is also computed from the individual consensus locations computed over a prescribed number of sampling periods using a temporal filtering technique.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and method for adaptive 3D artifact reducing for encoded image signal
InactiveUS20060050783A1Efficient reductionReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementRandom noiseNoise reduction
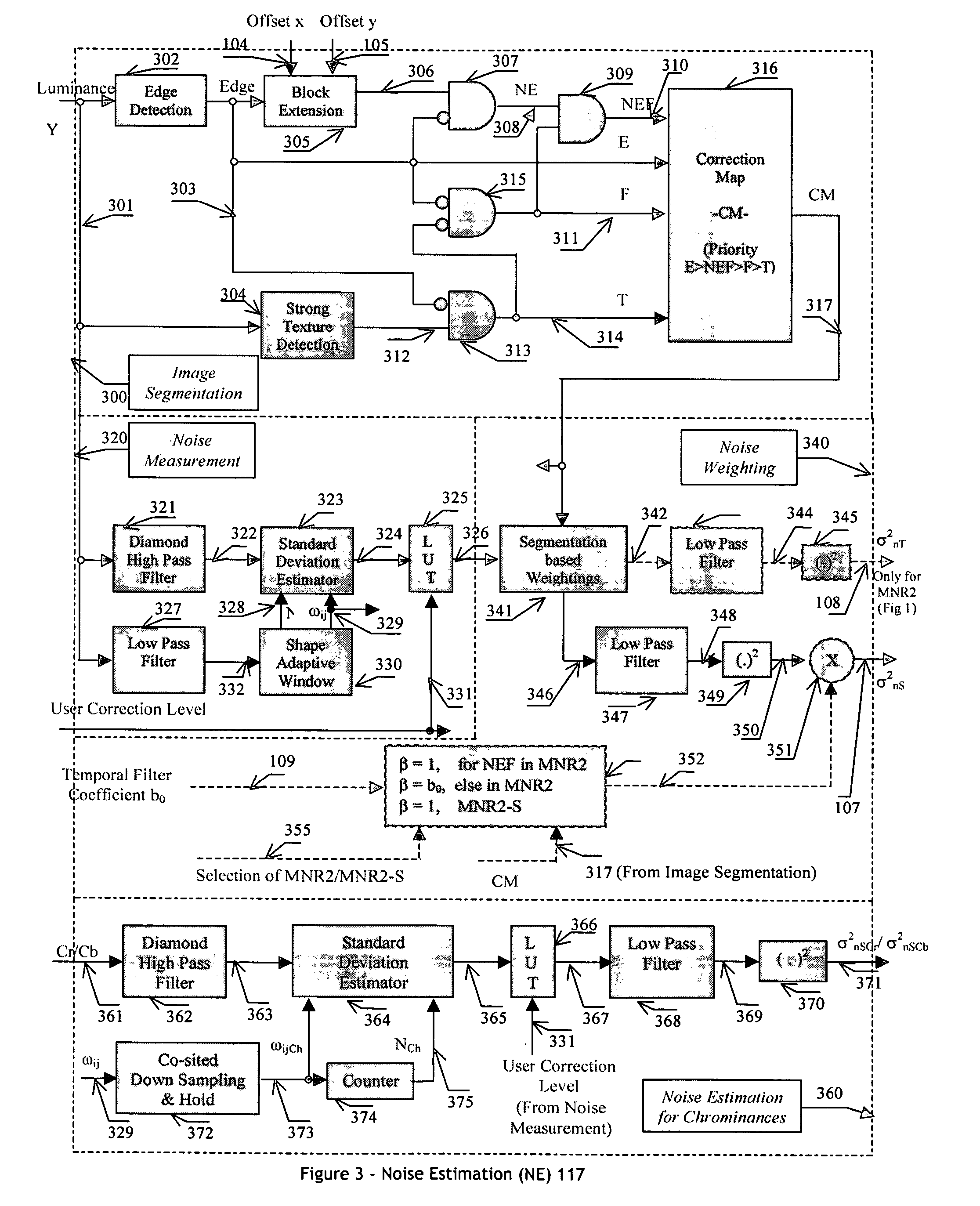
An efficient and non-iterative 3D post processing method and system is proposed for mosquito noise reduction, block localization and correction in DCT block-based decoded images. The 3D post processing is based on a simple classification that segments a picture in multiple regions such as Edge, Near Edge, Flat, Near Flat and Texture regions. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient and shape adaptive local power estimation for equivalent additive noise and provides simple noise power weighting for each above cited region. Temporal filtering configurations using Minimum Noise Variance Criterion are proposed for reducing temporally varying coding artifacts. A Minimum Mean Square Error or Minimum Mean Square Error-like noise reduction with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing is utilized for smoothing mosquito and / or random noise for the whole image, particularly for Edge regions. The proposed technique comprises also signal domain histogram analysis based Block Localization and adaptive edge based Block artifact correction. Finally, is also proposed an optional adaptive detail enhancer which can enhances the luminance signal in eight directions differently.
Owner:SENSIO TECHNOLOGIES
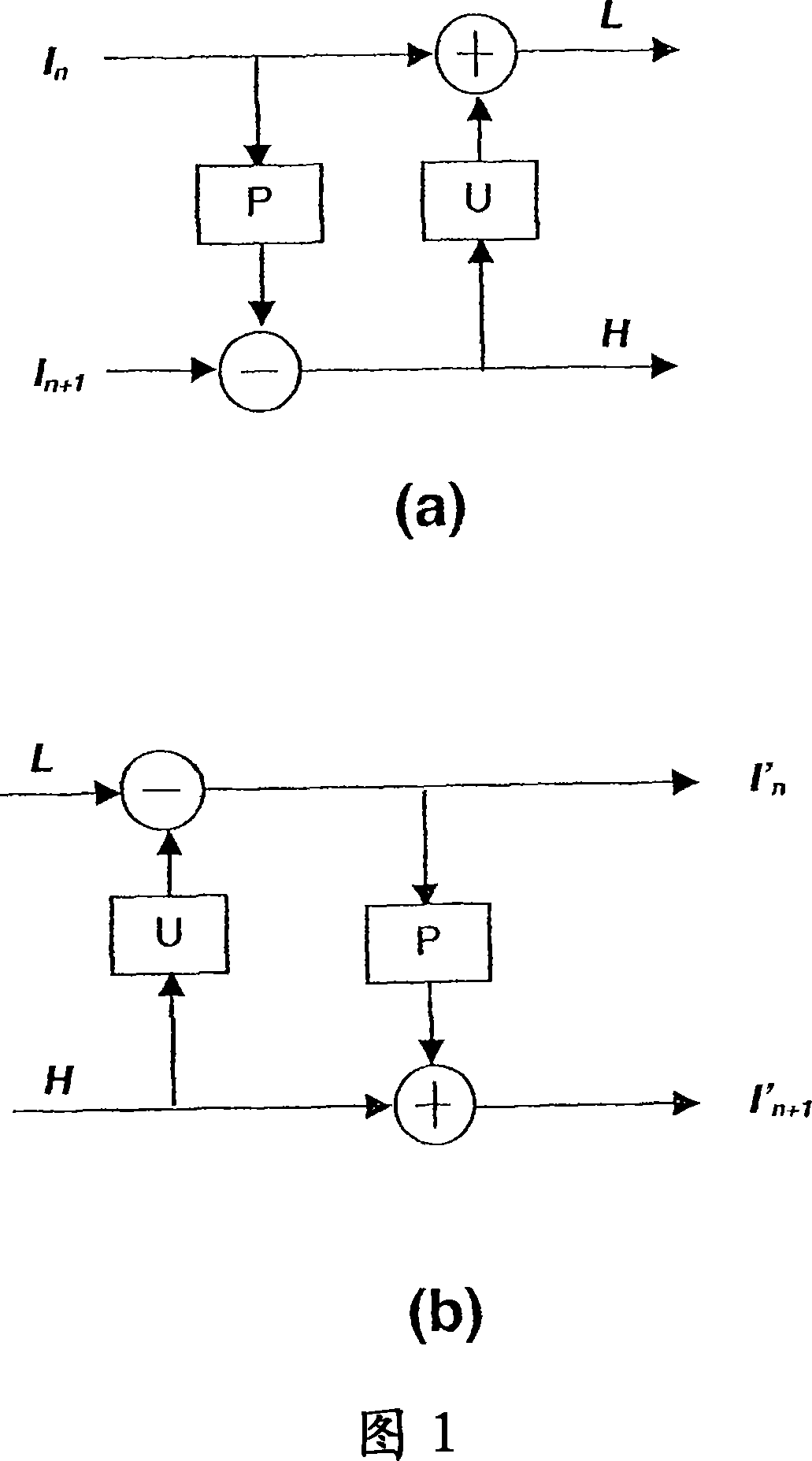
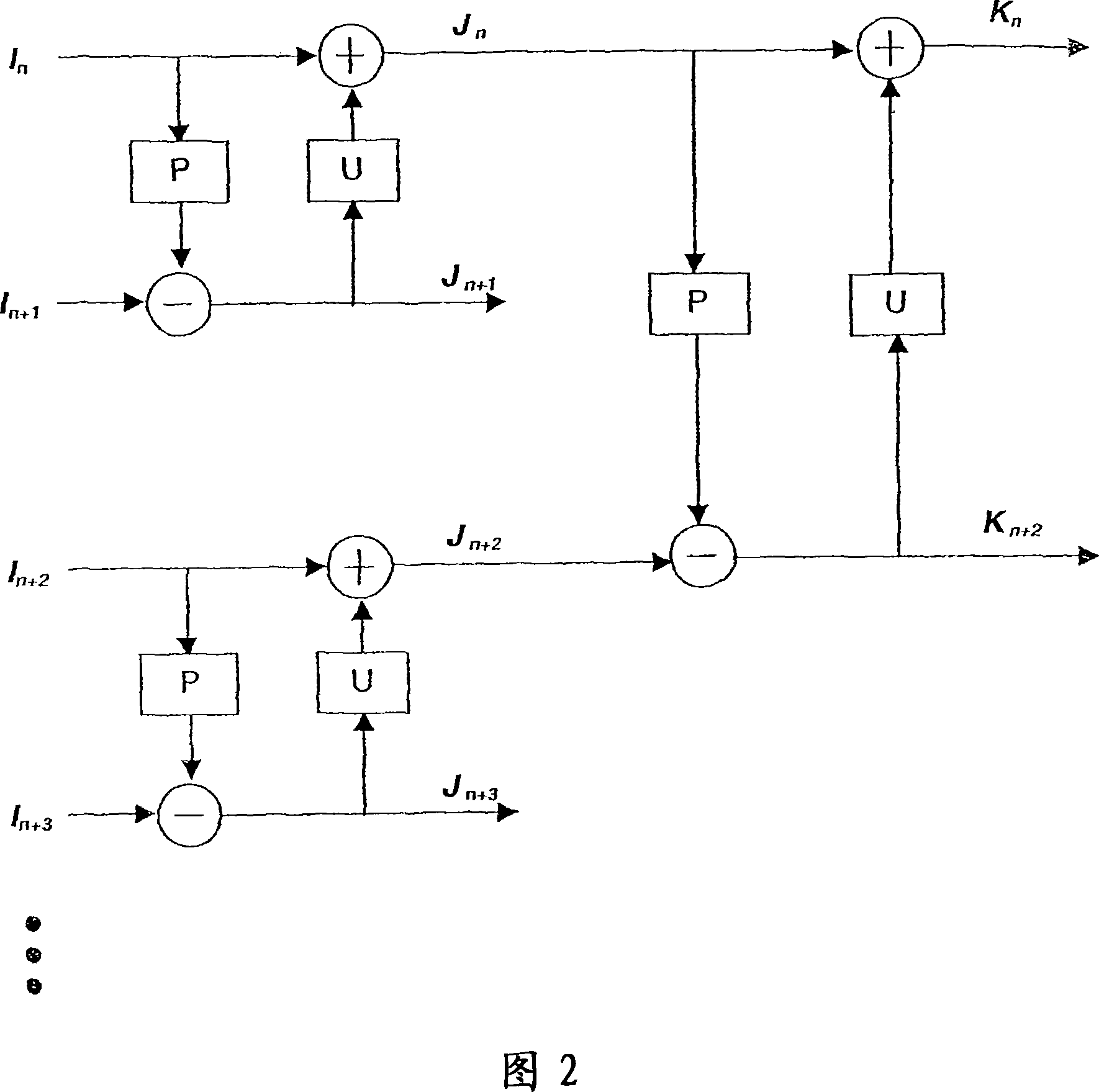
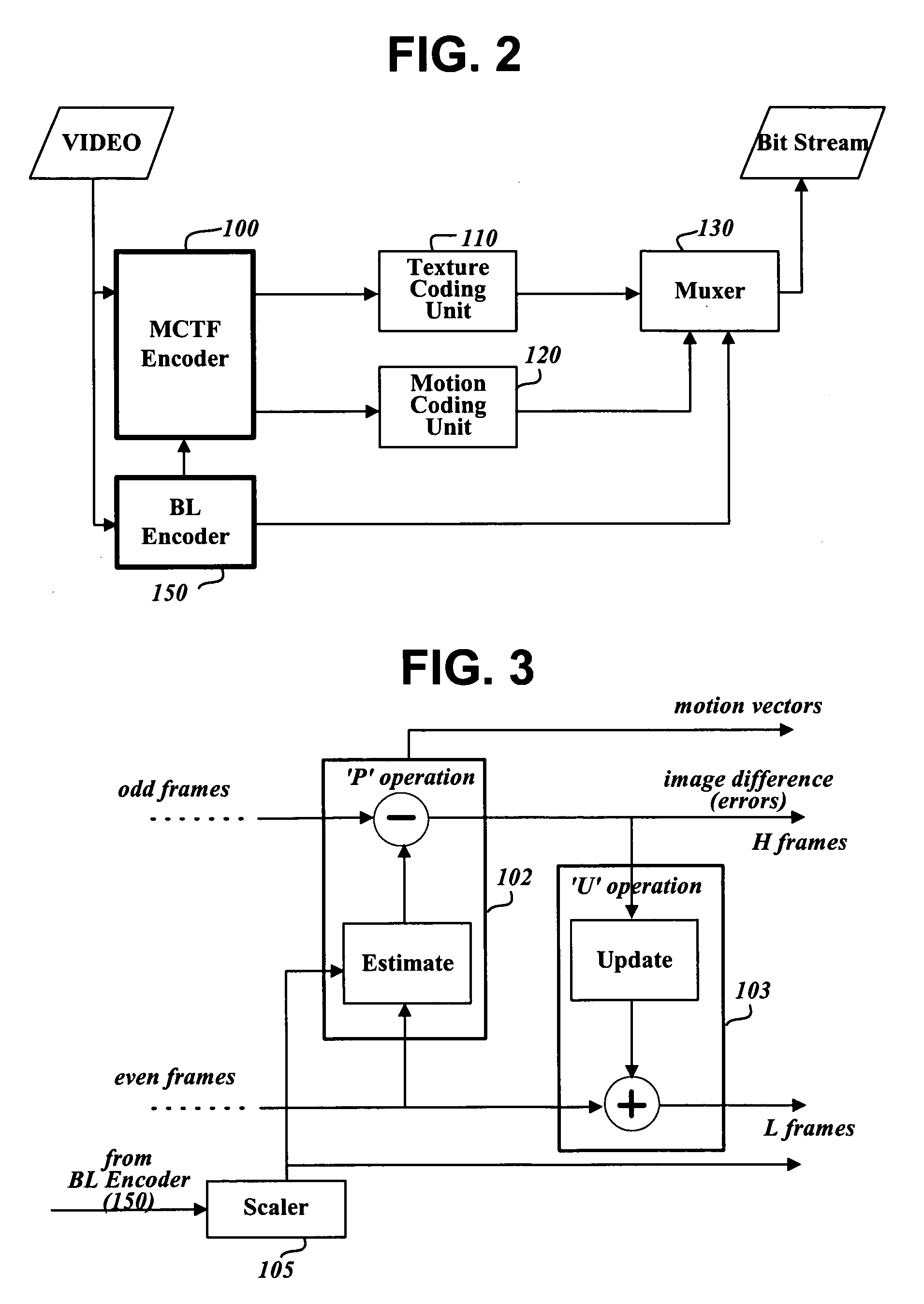
Method and apparatus for update step in video coding using motion compensated temporal filtering
InactiveCN101213842ASimplify the interpolation processEliminate the need to update the motion vector derivation processTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationCoding blockTime domain
The present invention provides a method and module for performing the update operation in motion compensated temporal filtering for video coding. The update operation is performed according to coding blocks in the prediction residue frame. Depending on macroblock mode in the prediction step, a coding block can have different sizes. Macroblock modes are used to specify how a macroblock is segmented into blocks. In the prediction step, the reverse direction of the motion vectors is used directly as an update motion vector and therefore no motion vector derivation process is performed. Motion vectors that significantly deviate from their neighboring motion vectors are considered not reliable and excluded from the update step. An adaptive filter is used in interpolating the prediction residue block for the update operation. The adaptive filter is an adaptive combination of a short filter and a long filter.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Apparatus and method for adaptive 3D noise reduction
InactiveUS20060056724A1Reduce noiseType of reductionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSpatial noise
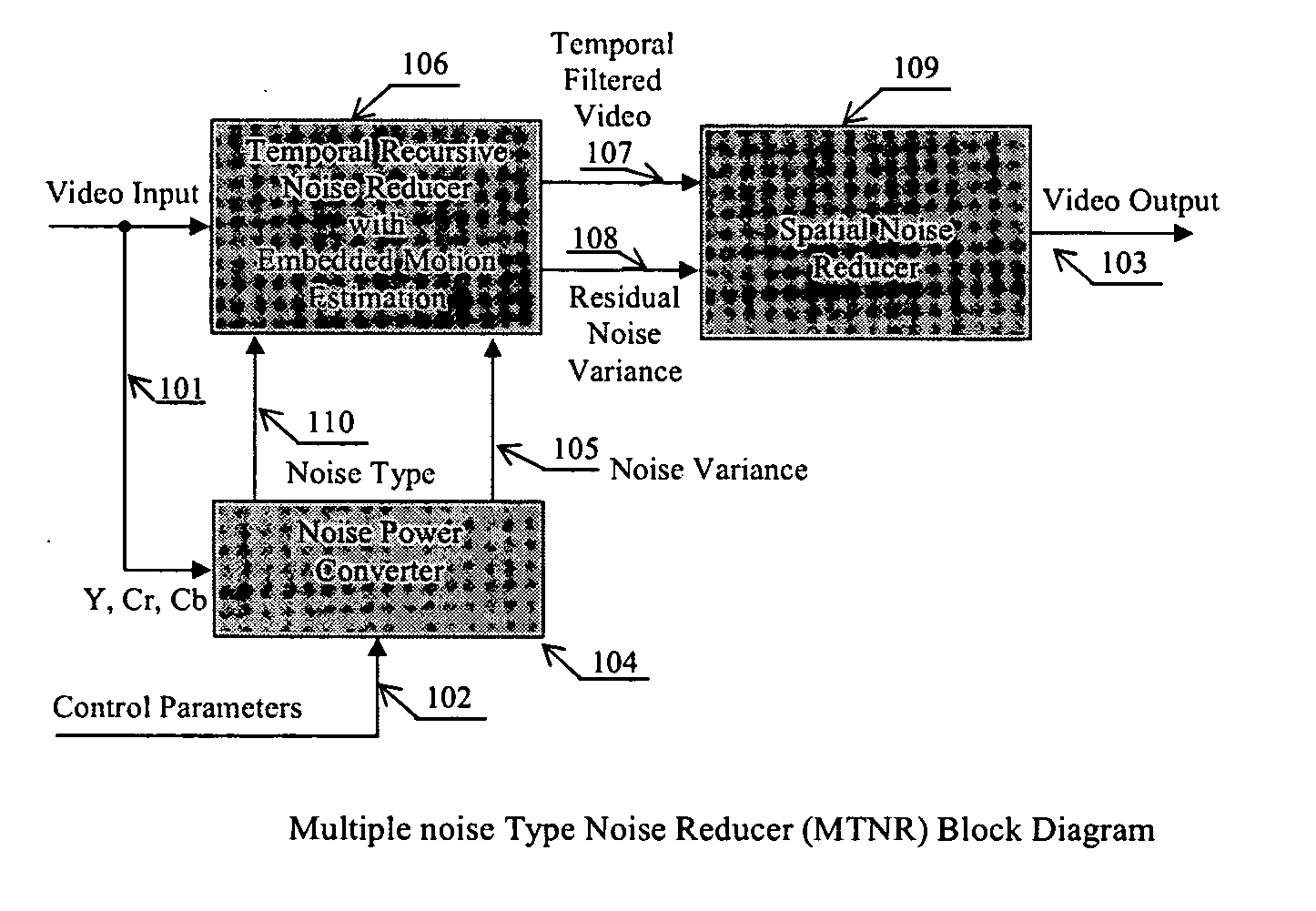
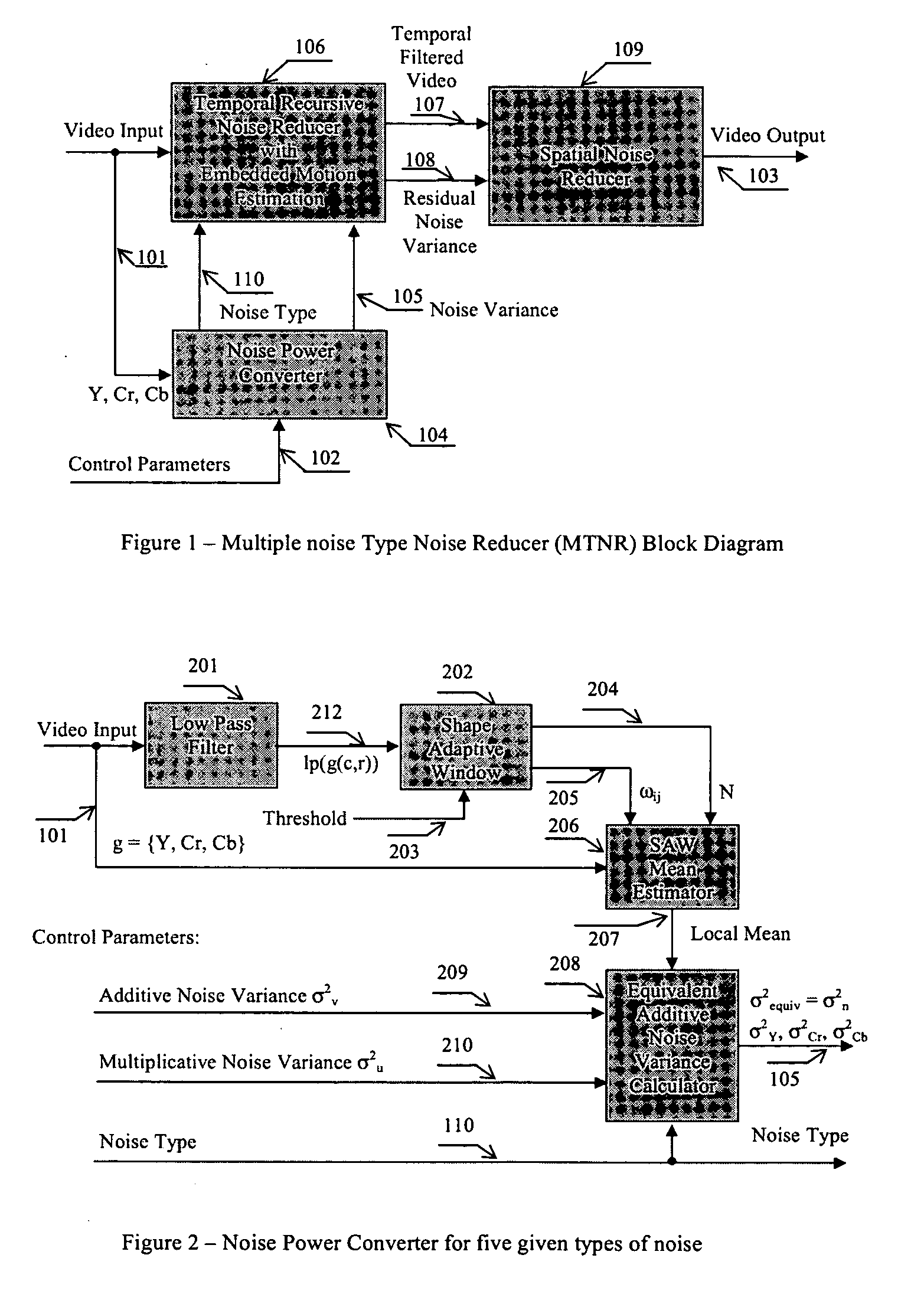
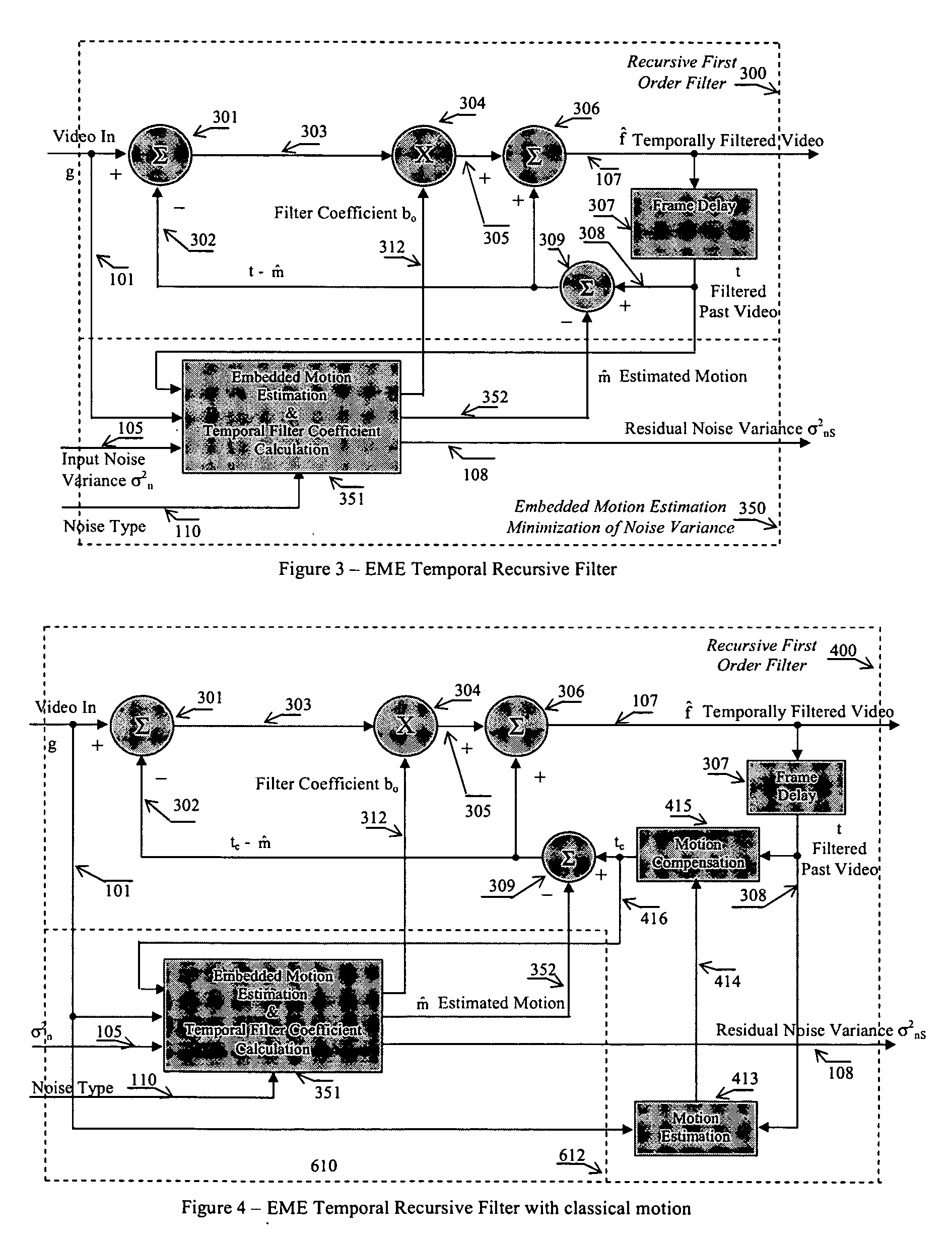
A non-iterative 3D processing method and system is disclosed for generic noise reduction. The 3D noise reducer is based on a simple conversion of the five types of noise to equivalent additive noise of varying statistics. The proposed technique comprises also an efficient temporal filtering technique which combines Minimization of Output Noise Variance (MNV) and Embedded Motion Estimation (EME). The proposed temporal filtering technique may be furthermore combined with classical motion estimation and motion compensation for more efficient noise reducer. The proposed technique comprises also a spatial noise reducer which combines Minimum Mean Squared Error (MMSE) with robust and effective shape adaptive windowing (SAW) is utilized for smoothing random noise in the whole image, particularly for edge regions. Another modification to MMSE is also introduced for handling banding effect for eventual excessive filtering in slowly varying regions.
Owner:SENSIO TECHNOLOGIES
Method of removing noise from digital moving picture data
ActiveUS20050128355A1Cancel noiseMinimize the numberImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionYcbcr color space
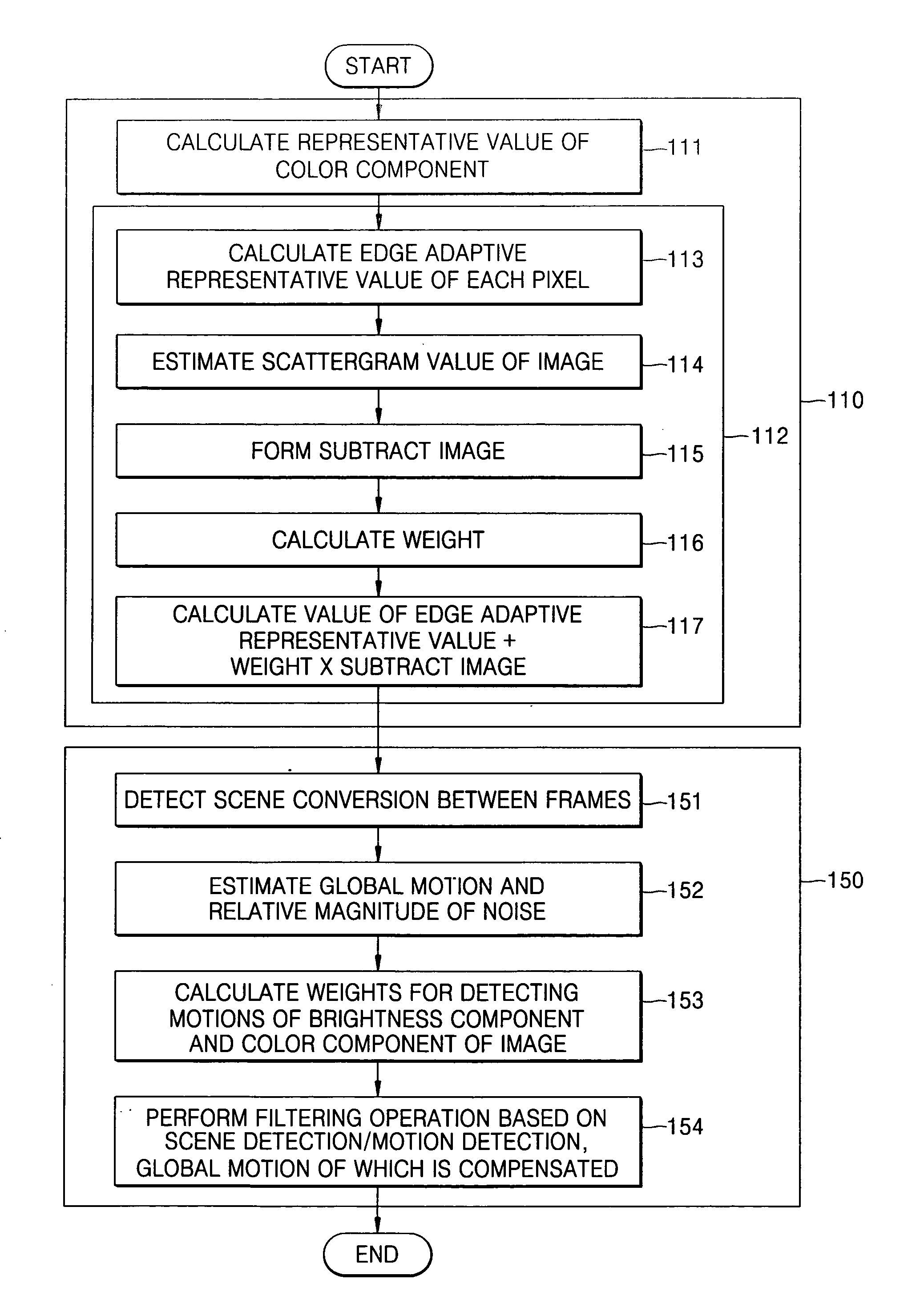
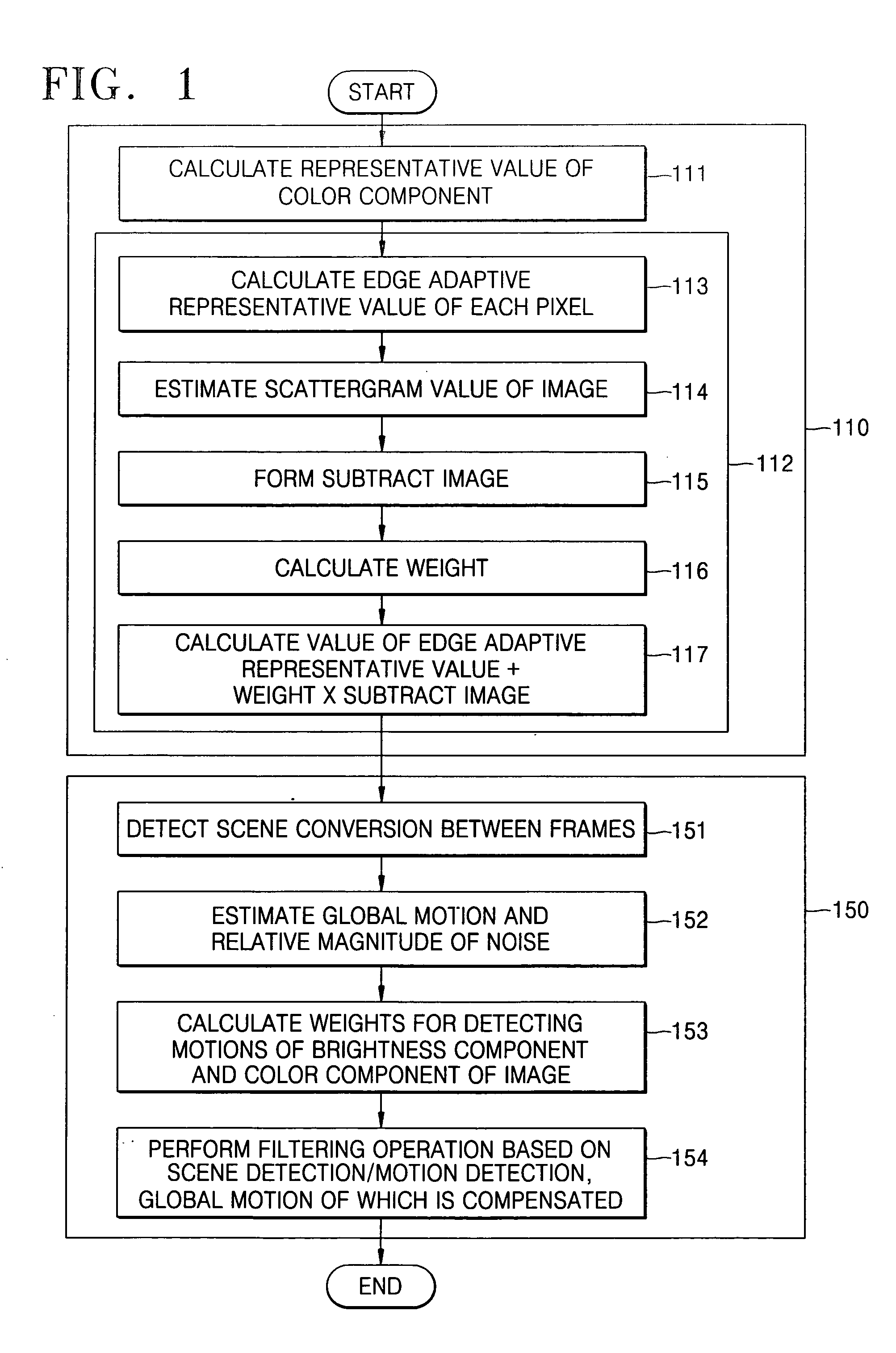
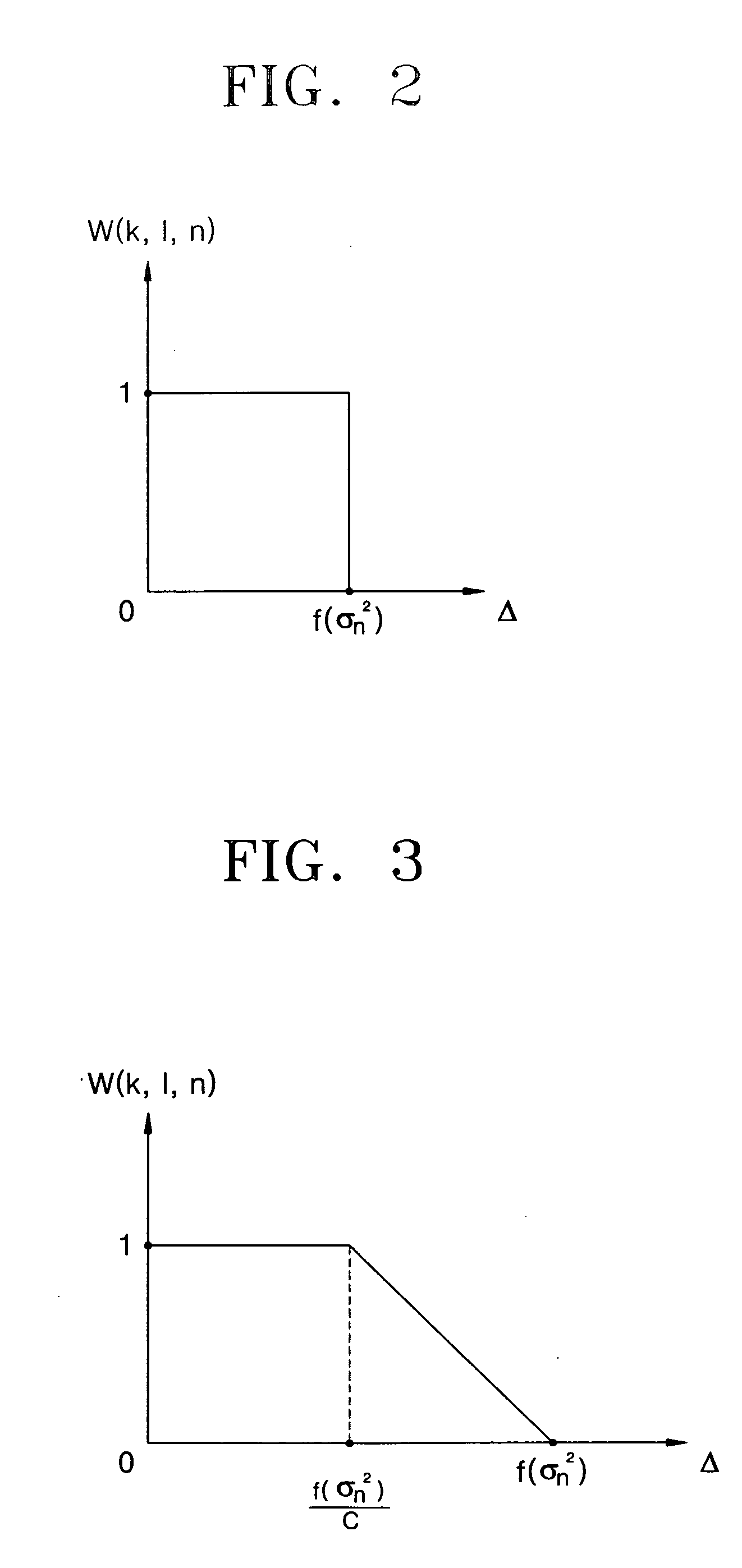
Provided is a method of removing noise from digital moving picture data reducing the number of frames used in a temporal filtering operation and able to detect motion between frames easily. The method comprises a method of spatial filtering, a method of temporal filtering, and a method of performing the spatial filtering and the temporal filtering sequentially. The spatial filtering method applies a spatial filtering in a YCbCr color space, preserving a contour / edge in the image in the spatial domain, and generating a weight that is adaptive to the noise for discriminating the contour / edge in the temporal filtering operation. The temporal filtering method applies temporal filtering based on motion detection and scene change detection, compensating for global motion, the motion detection considering the brightness difference and color difference of the pixels compared between frames in the temporal filtering operation, and a weight that is adaptive to the noise for detecting the motion in the temporal filtering operation. The spatial filtering method is preferably performed first, and the temporal filtering method is performed with the result of the spatial filtering.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
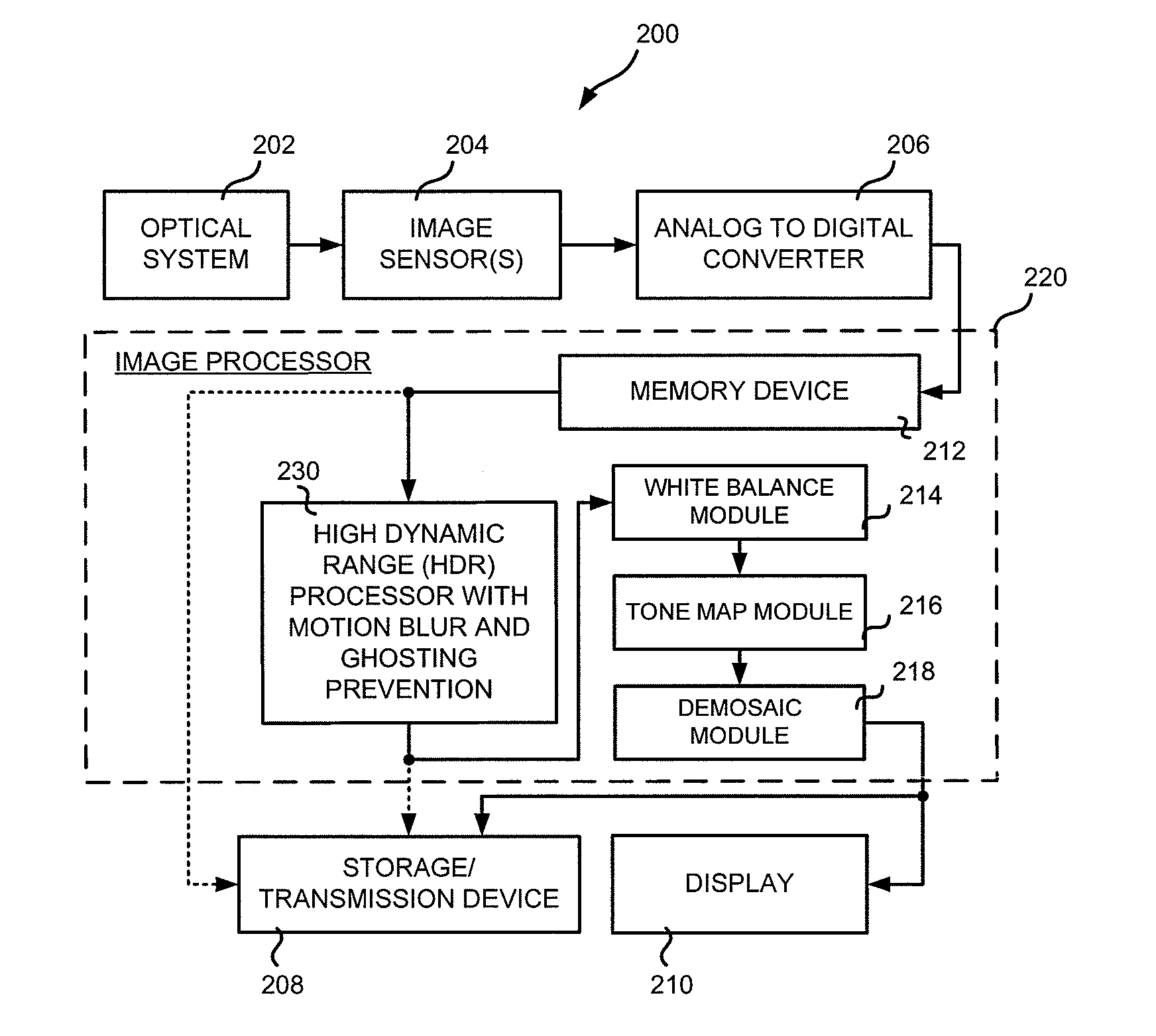
Method and apparatus for motion blur and ghosting prevention in imaging system
InactiveUS20110058050A1Noise robustPromote differentiationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAlong edgeImage pair
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Spatio-temporal video noise reduction system
InactiveUS7145607B1Maximise noise reductionMinimize artefactTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionDigital video
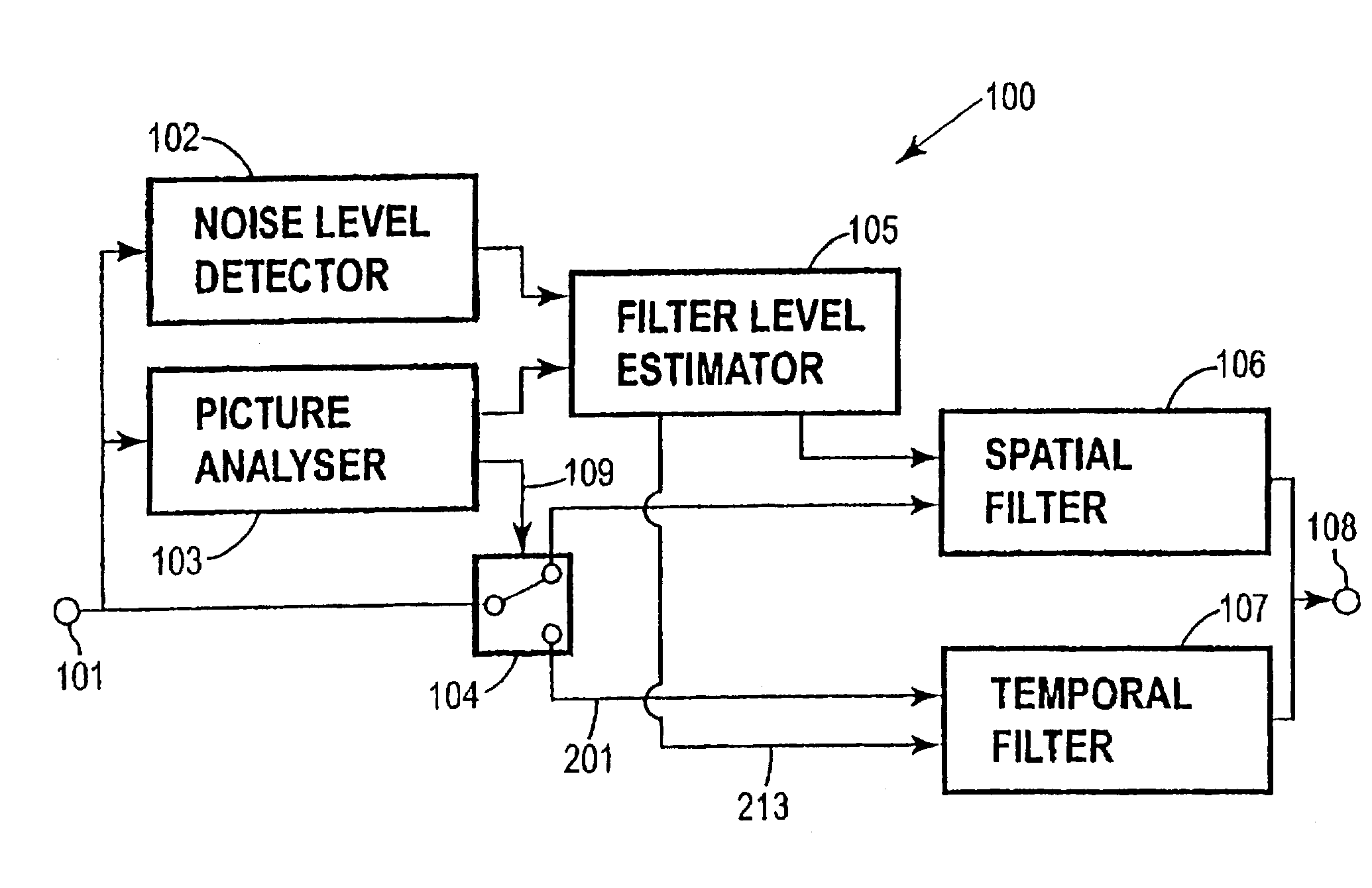
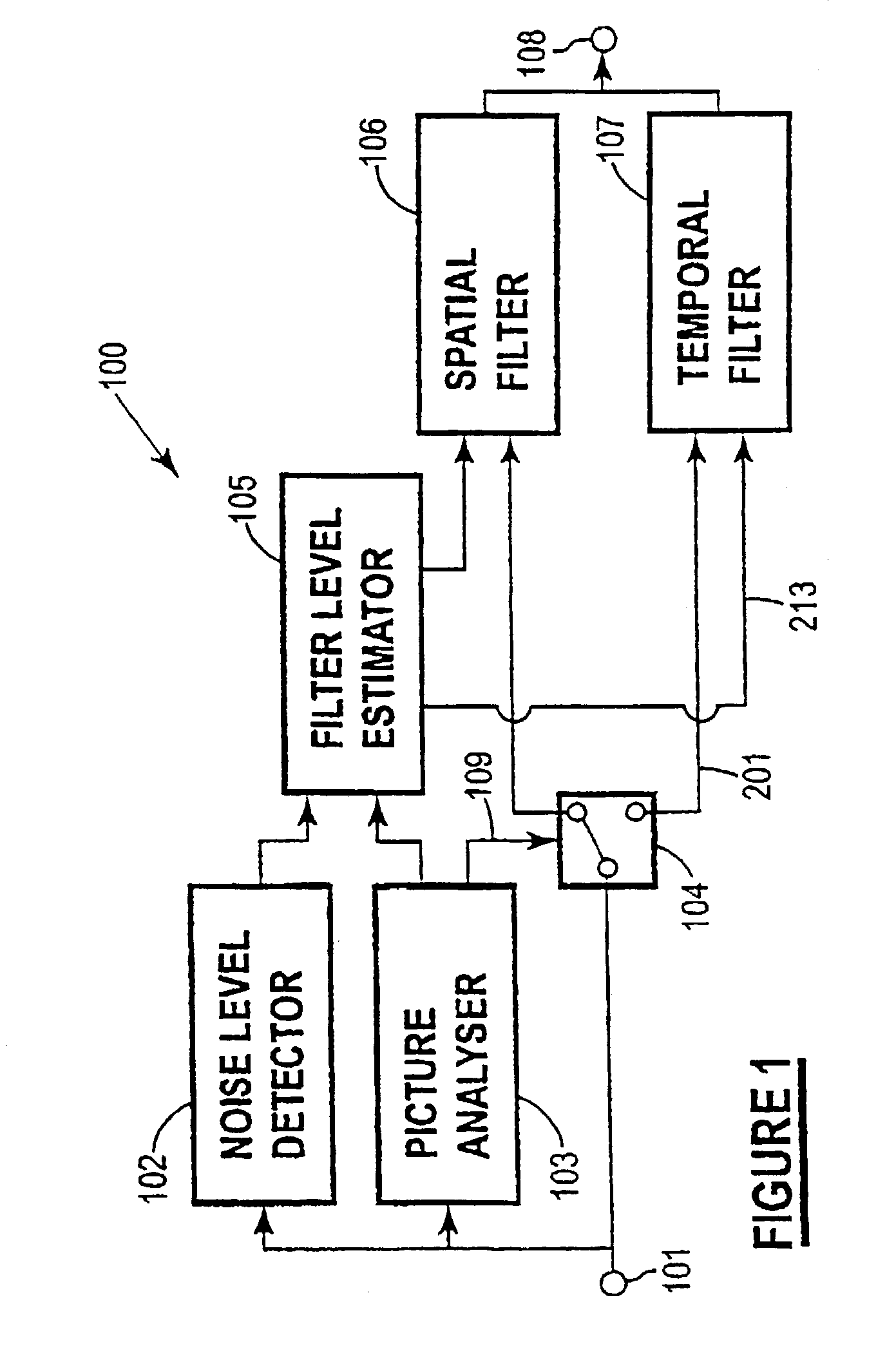
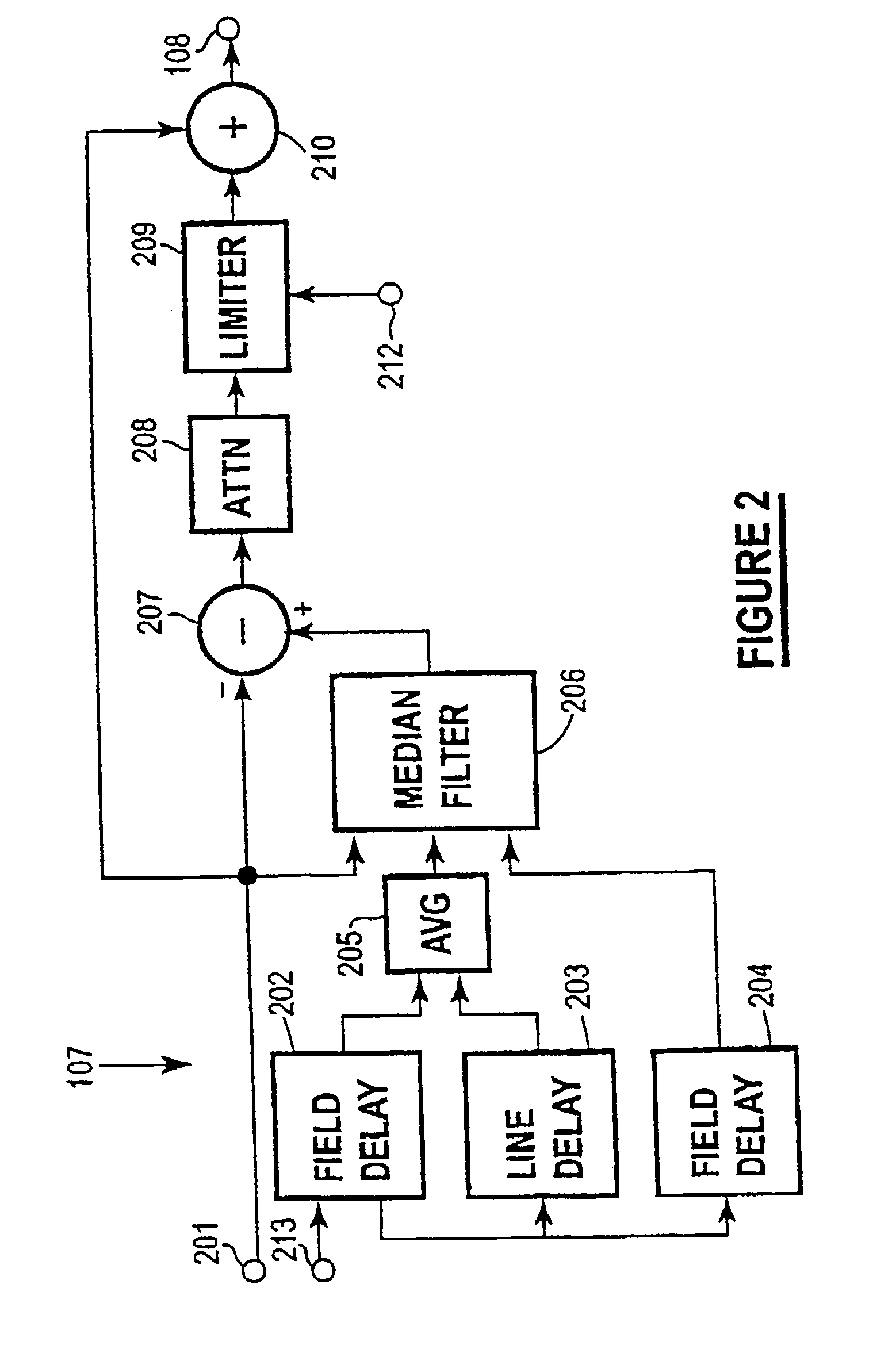
A method and system for digital video noise reduction which includes a picture analyser (103) for analysing pictures in a video sequence to determine the amount of moving regions therein, a noise level detector (102) for estimating the noise level (N) in the video sequence, a filtering level estimator (105, 103) for determining a maximum filtering level (L) for each picture based on the amount of moving regions and the estimated noise level (N) and a spatial filter (106) and a temporal filter (107), the temporal filter being coupled to the filter level estimator for controlling the level of filtering of each picture in the sequence in accordance with the maximum filtering level.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
Motion adaptive noise reduction apparatus and method for video signals
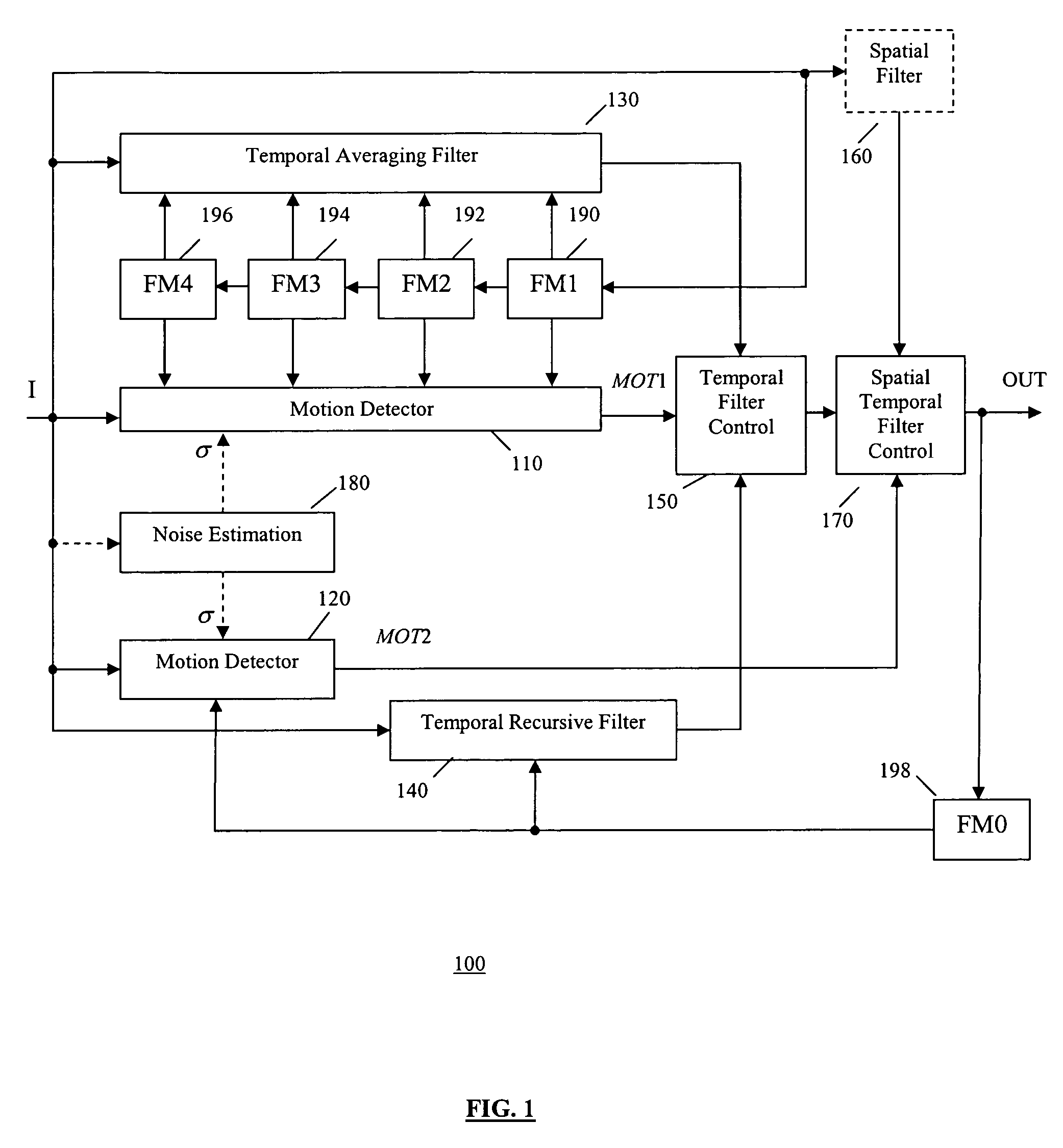
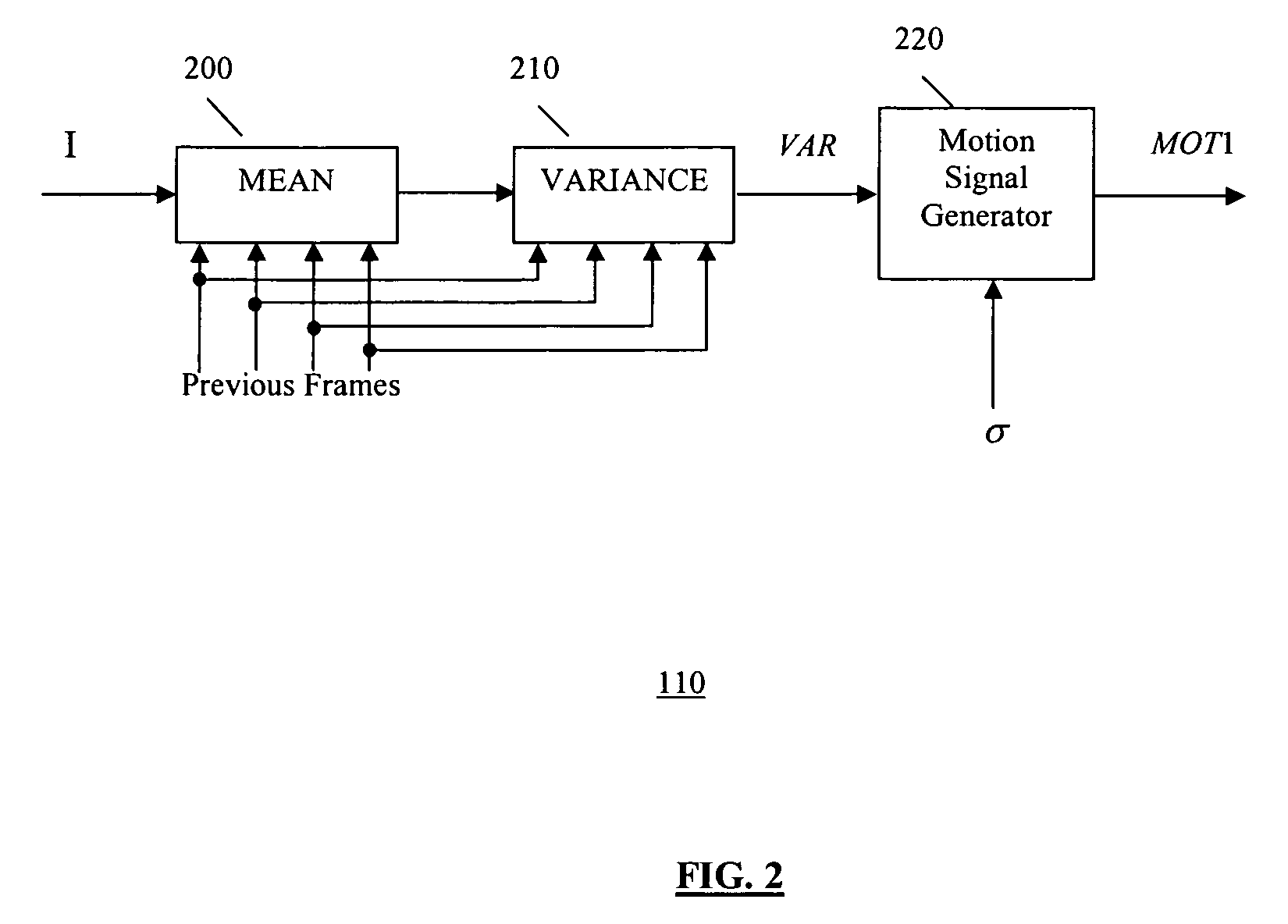
InactiveUS20050280739A1Optimal noise reductionIncrease the areaTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionSoft switching
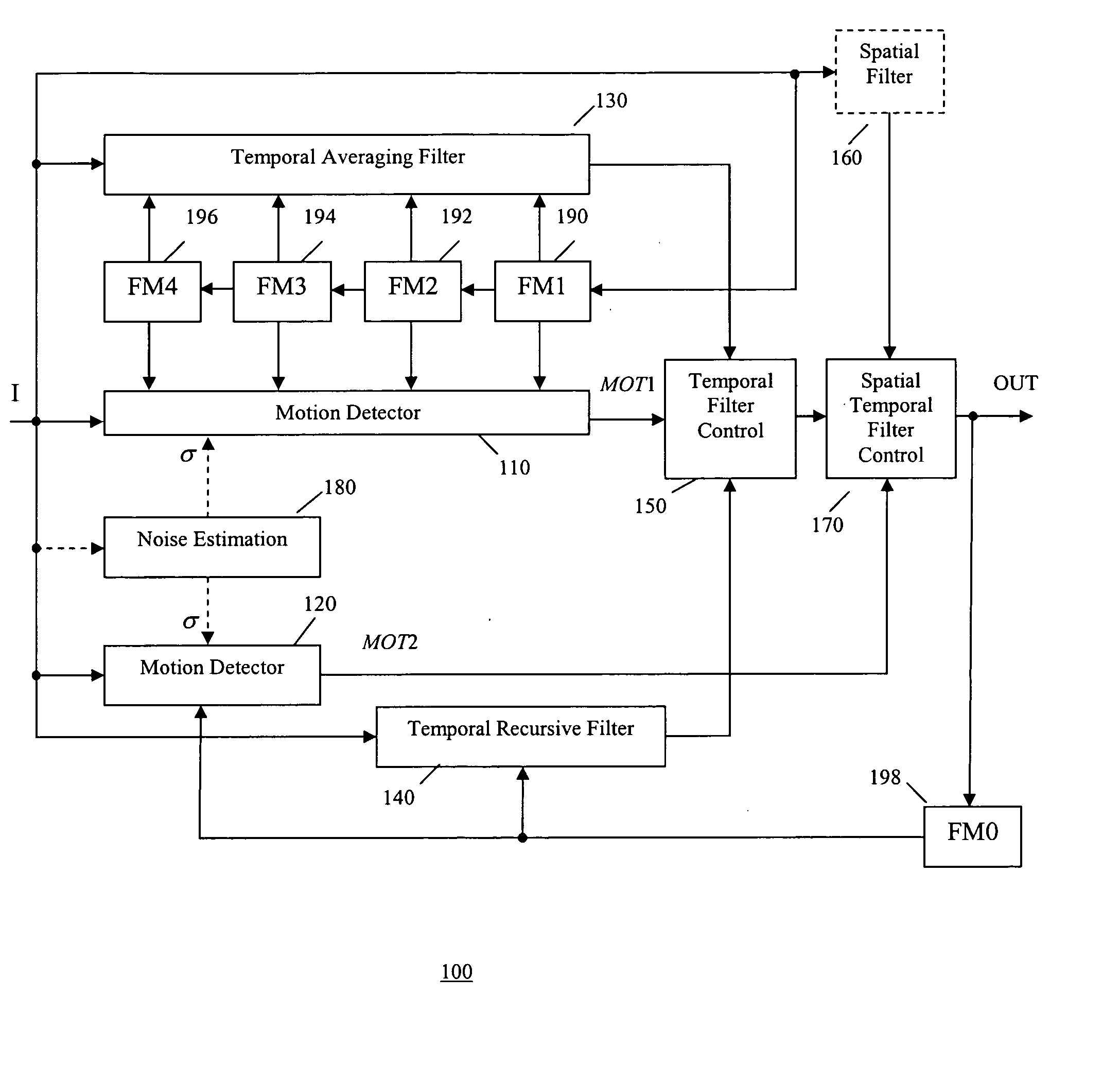
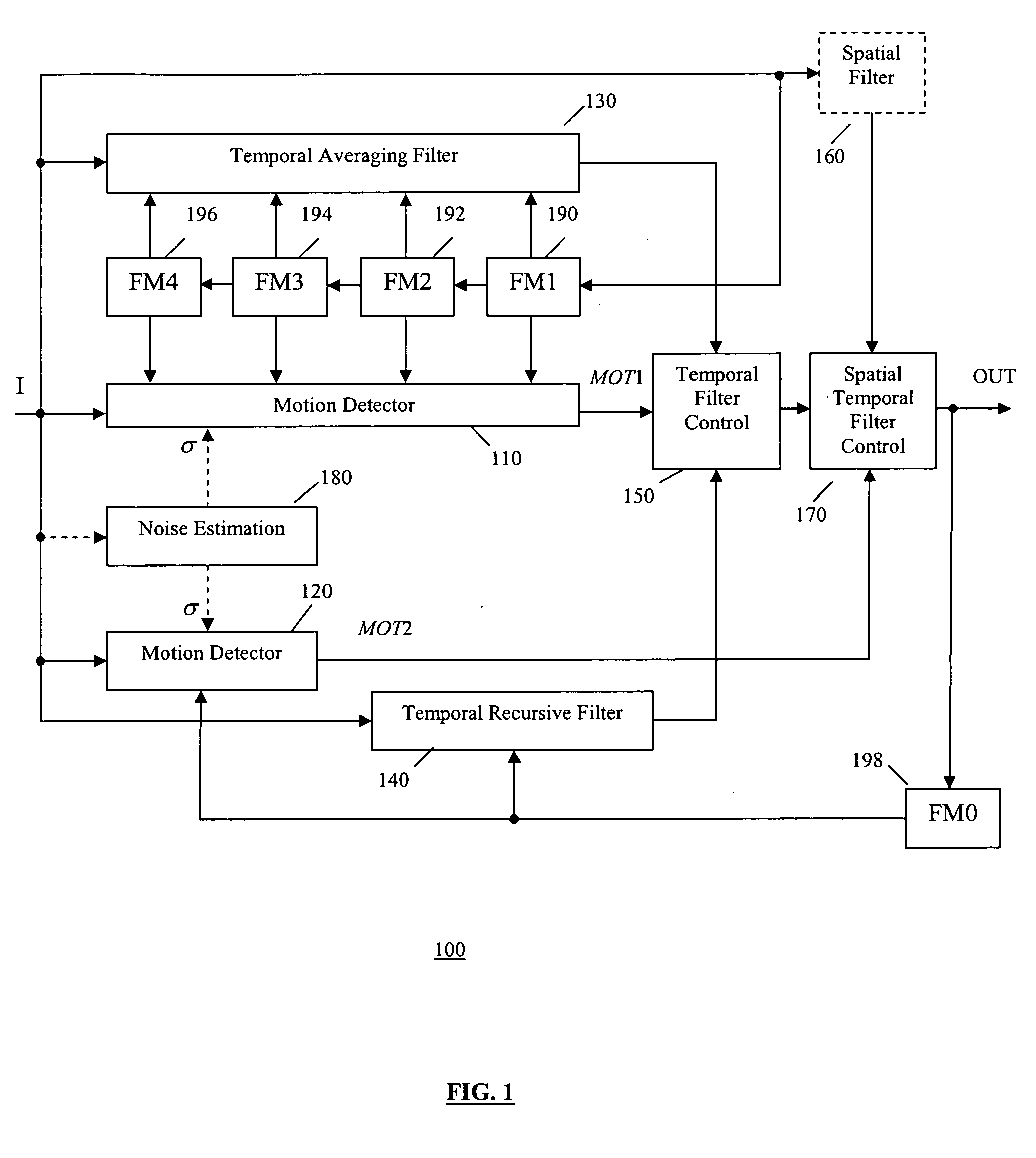
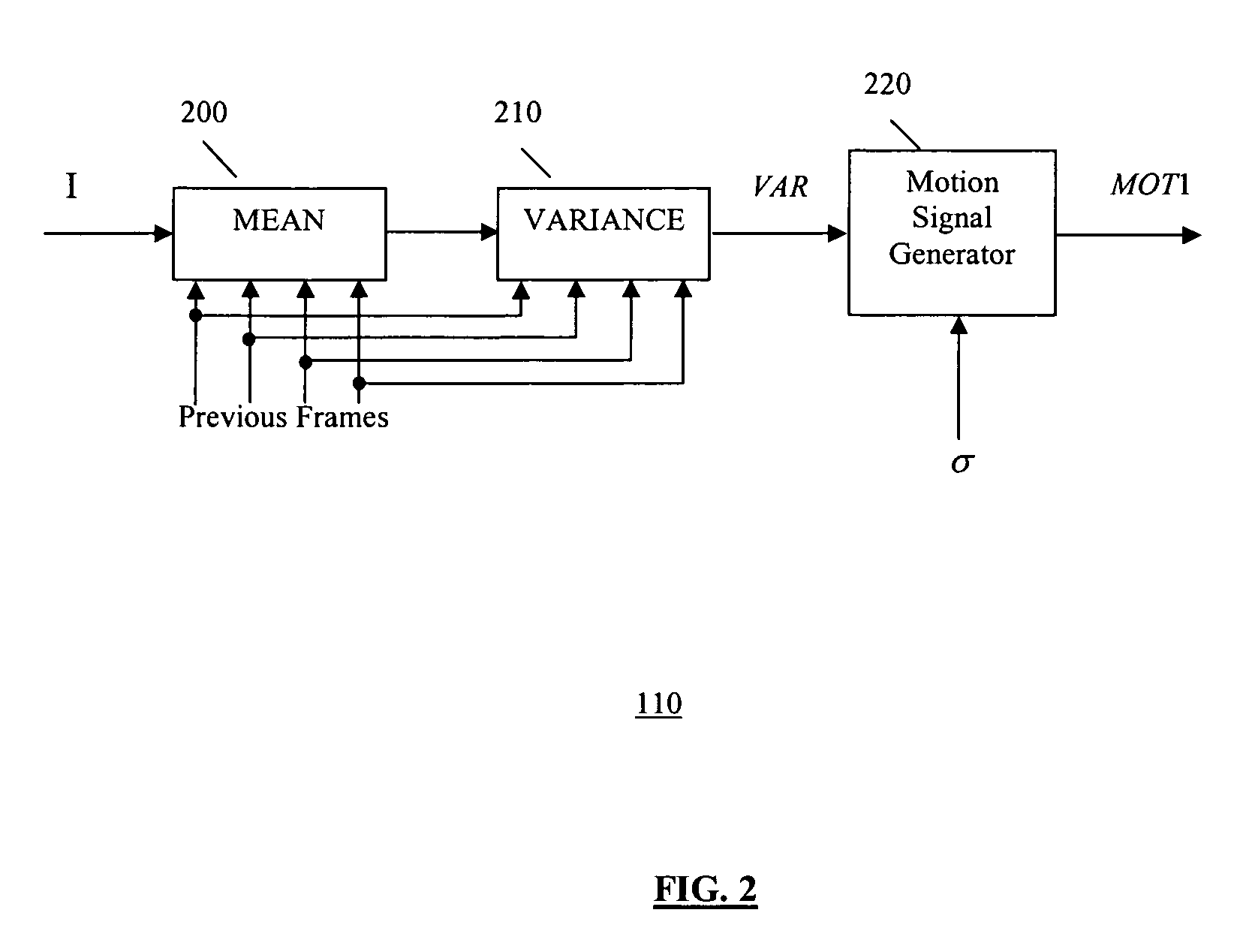
A video noise reduction system for a set of video frames that computes a first motion signal using a current frame and multiple consecutive previous frames, computes a second motion signal using the current frame and the processed preceding frame; computes the multi-frame temporal average of the current frame and multiple consecutive previous frames; computes the recursive average of the current frame and the processed preceding frame; generates a temporal filtered signal by soft switching between the multi-frame temporal average and the recursive average based on the first motion signal; applies a spatial filter to the current frame to generate a spatial filtered signal; and combines the temporal filtered signal and the spatial filtered signal based on the second motion signal to generate a final noise reduced video output signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
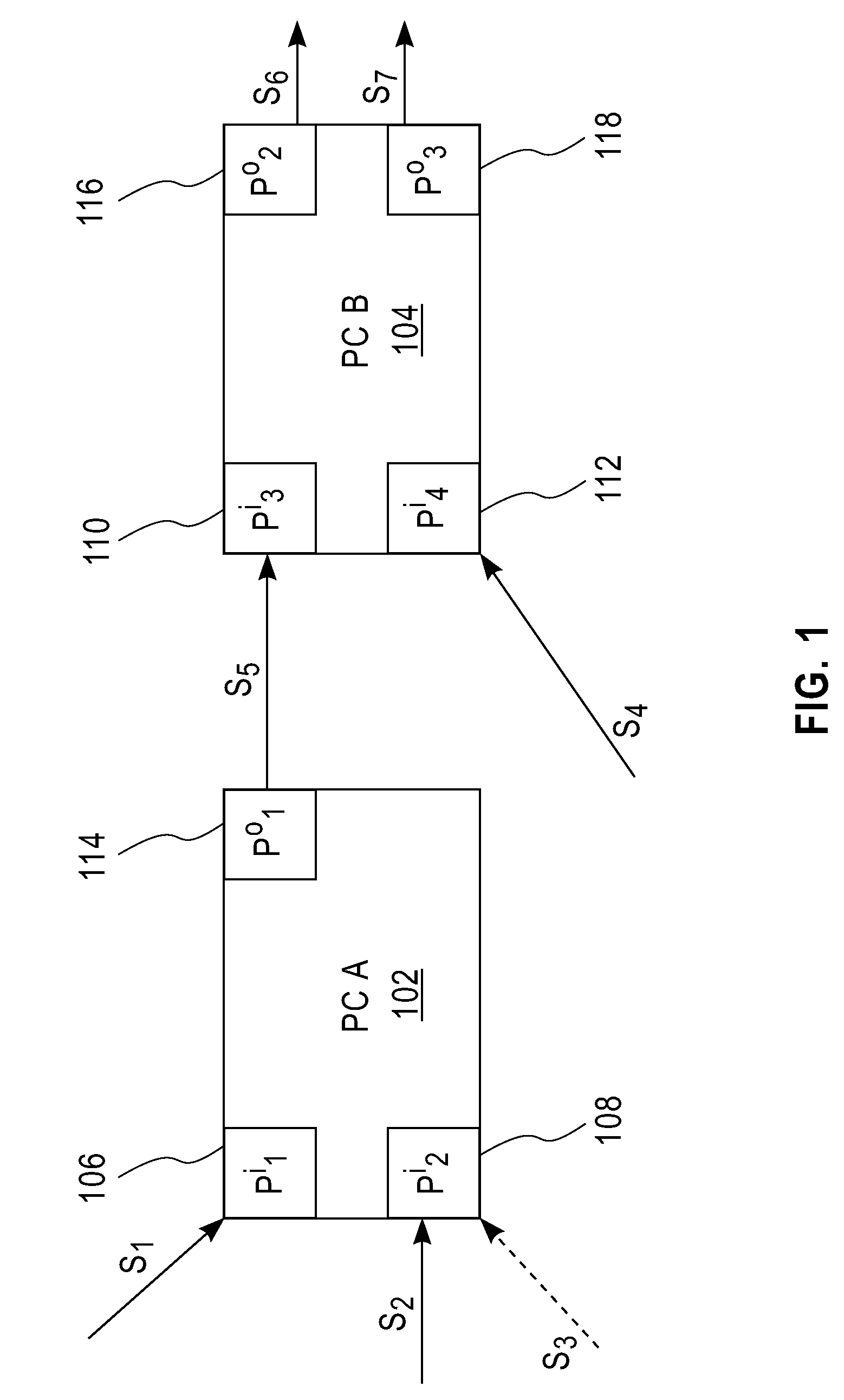
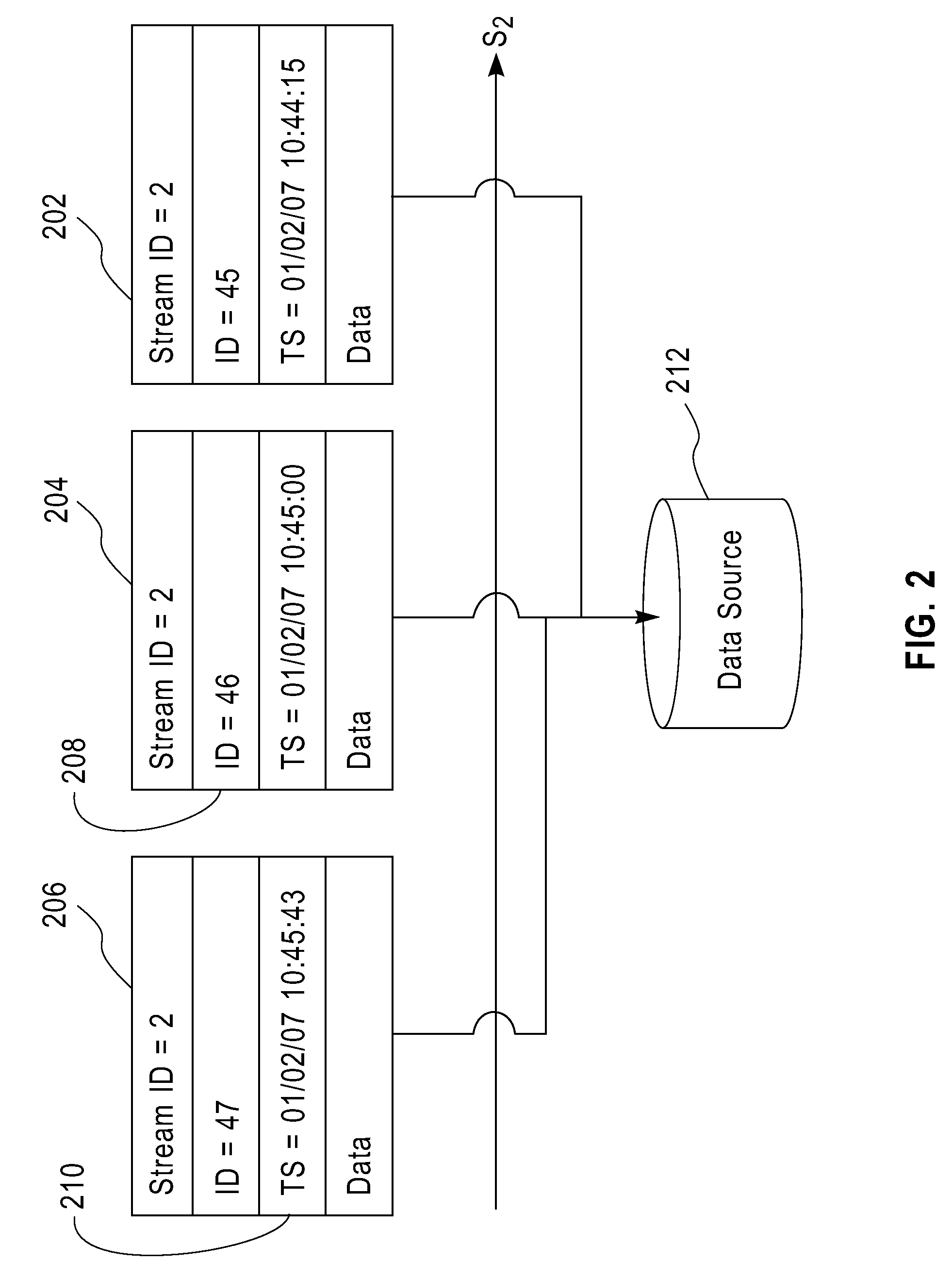
Methods and Apparatus for Functional Model-Based Data Provenance in Stream Processing Environments
InactiveUS20080307104A1Ability to useDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsData sourceTheoretical computer science
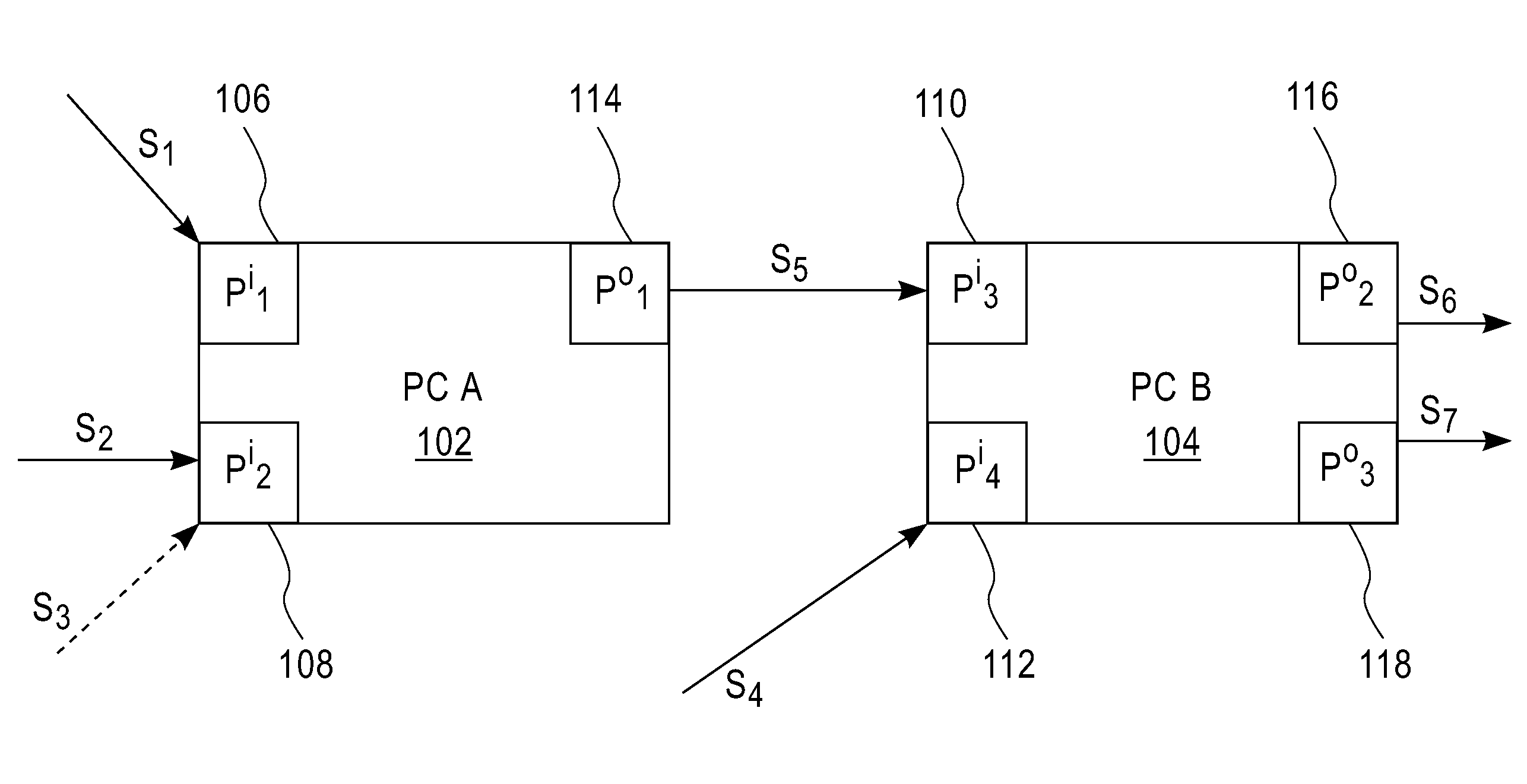
Techniques for deriving a provenance of one or more of a plurality of output data elements generated from a given output port of a PC are provided. At least one dependency function is created that relates the one or more output data elements to a set of one or more input ports of the PC and a corresponding plurality of input data elements. The dependency function comprises an encoding of at least one of one or more temporal filters and one or more sequence filters relating to the plurality of input data elements. The at least one dependency function is stored. A history of stream-level bindings of one or more input streams to one or more input ports of the processing component and one or more output streams from one or more output ports of the processing component is stored. The plurality of input data elements belonging to the one or more input streams and the plurality of output data elements belonging to the one or more output streams are stored. The set of one or more input data elements from the plurality of input data elements are determined that relate to the one or more output data elements in accordance with at least one dependency function and the history of stream-level bindings.
Owner:IBM CORP
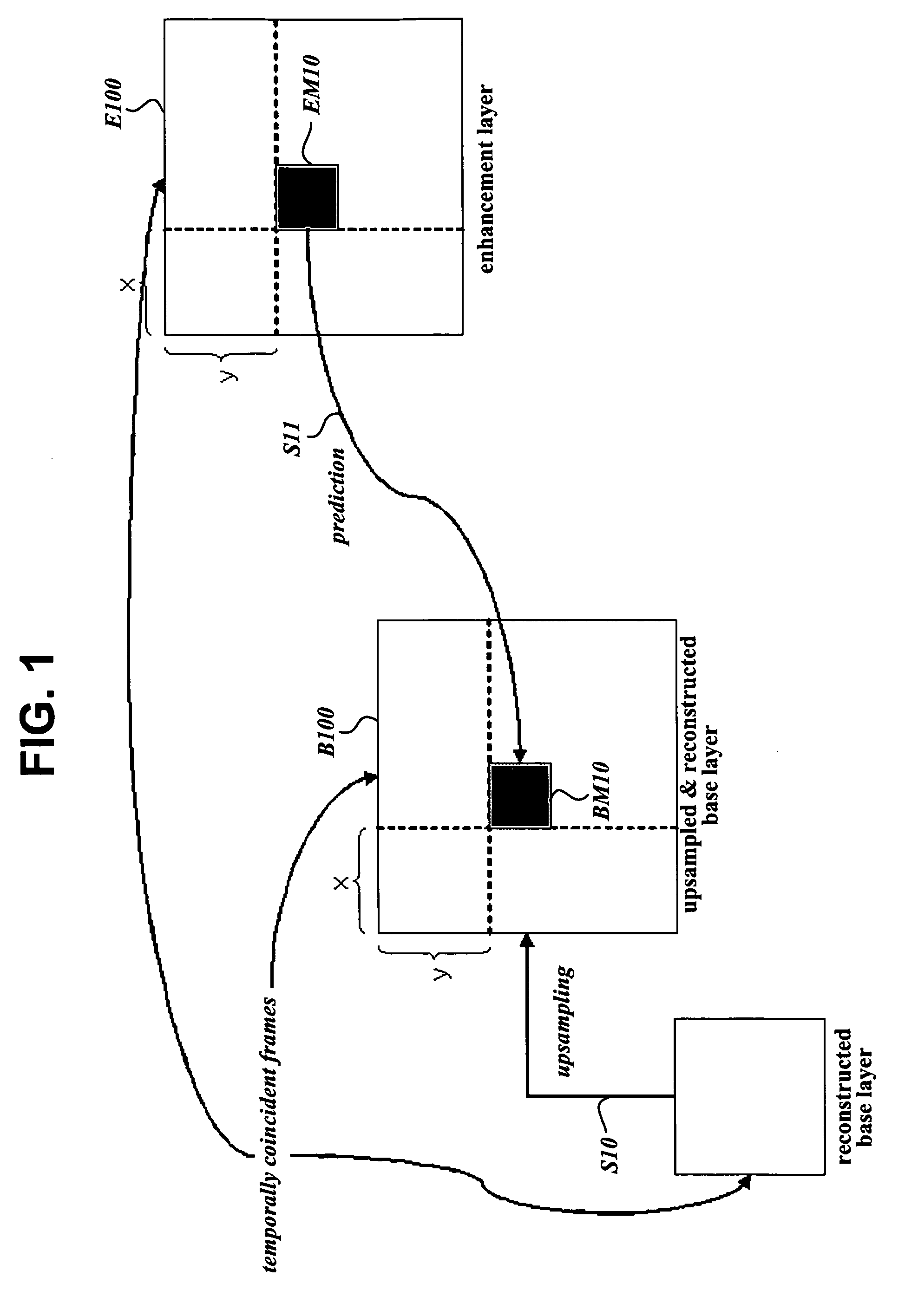
Method for encoding and decoding video signals
InactiveUS20060093036A1MouldsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionFrame sequence
A method for encoding video signals by inverse motion compensated temporal filtering where video frames of a base layer are used to encode video frames of an enhanced layer into predicted images. For each image block in an arbitrary frame in an enhanced layer frame sequence, an area including a block, which is present in a base layer frame temporally coincident with the arbitrary frame and is at the same position as the image block, is enlarged according to the ratio between screen sizes of the two layers. A reference block most highly correlated with the image block is searched for in the enlarged area in the temporally coincident base layer frame through motion estimation and is used to obtain pixel difference values and a motion vector of the image block for encoding the image block into a predicted image, thereby improving coding efficiency.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
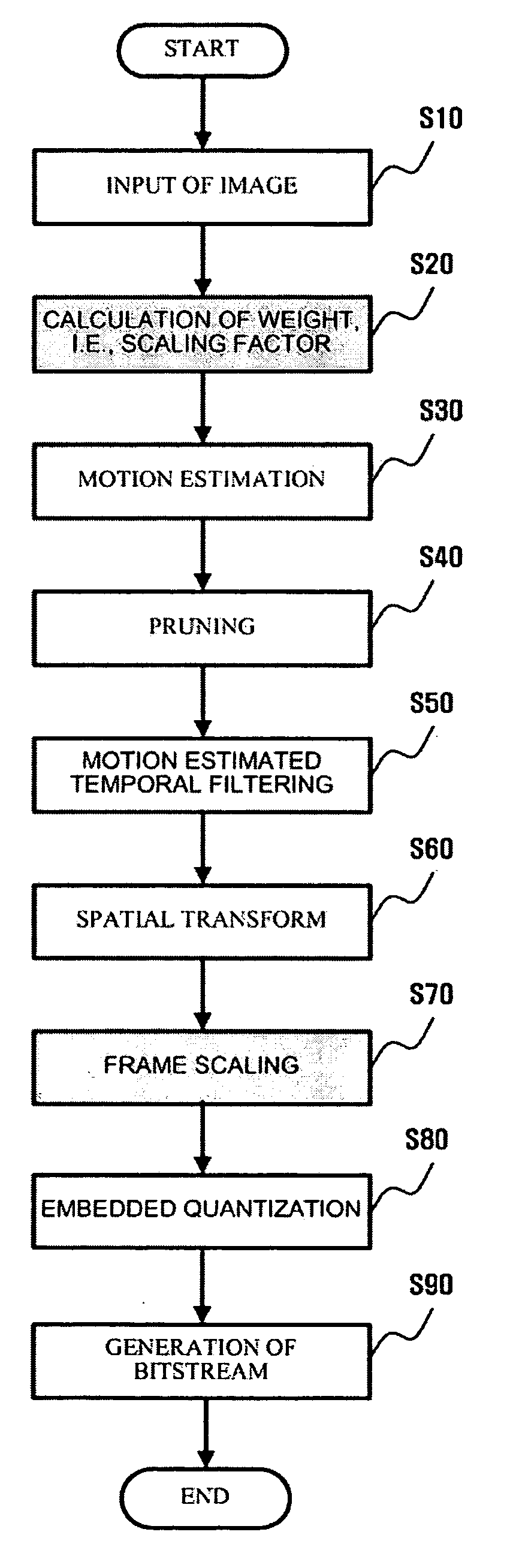
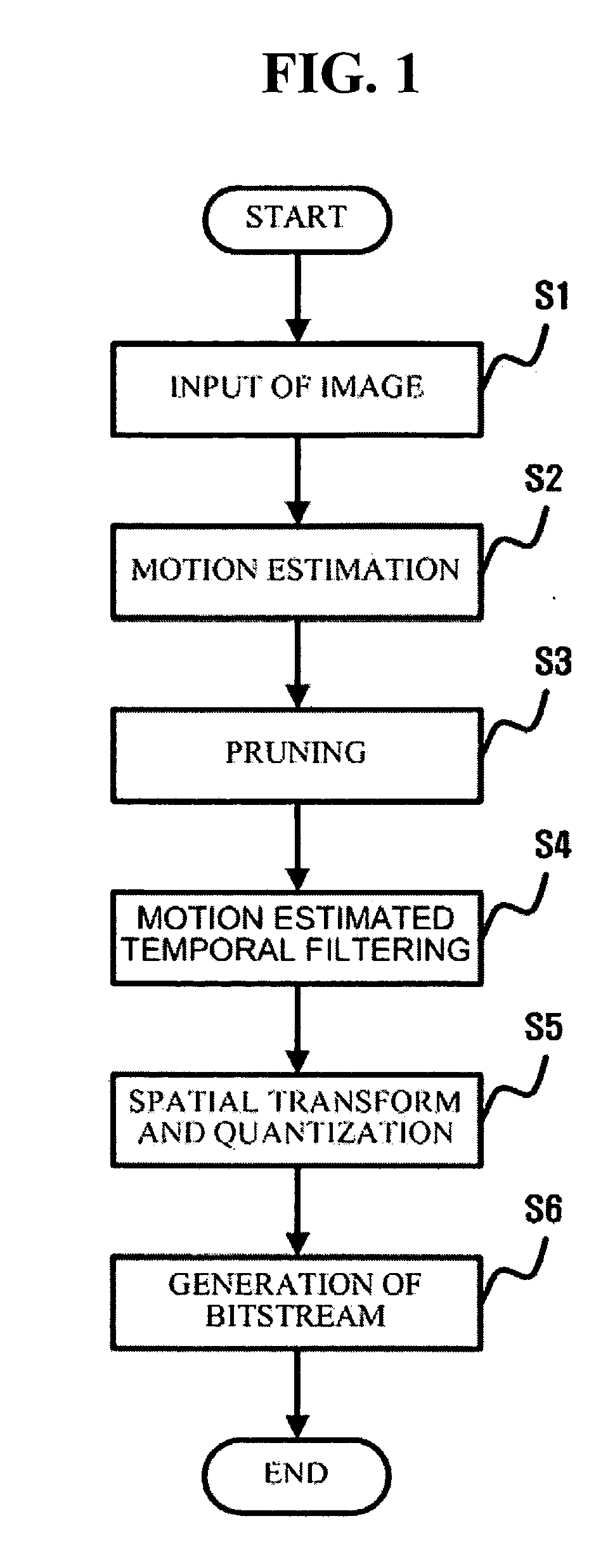
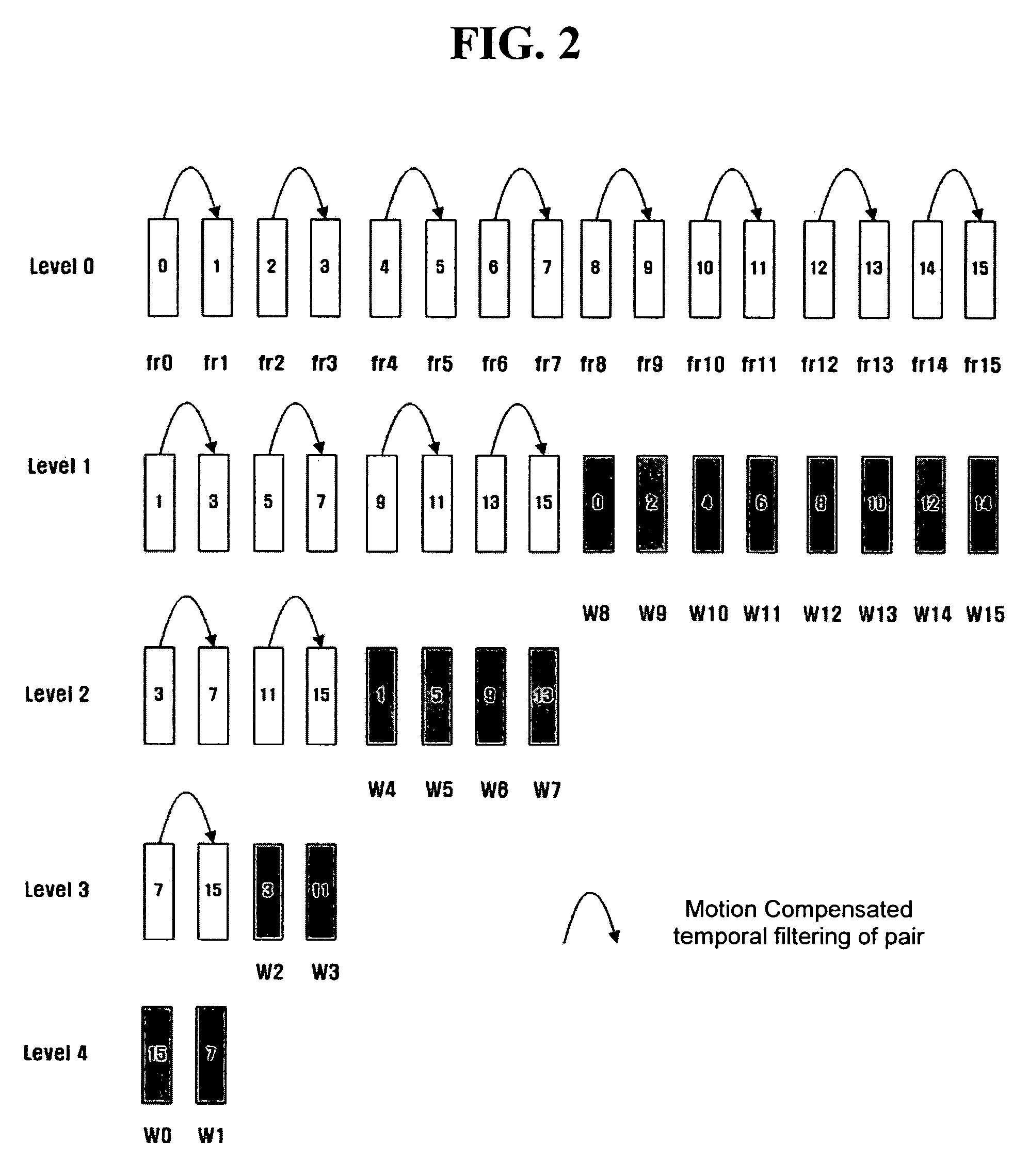
Scalable video coding and decoding methods, and scalable video encoder and decoder
InactiveUS20050047509A1Slow changeEliminate spaceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureGroup of pictures
Scalable video coding and decoding methods, a scalable video encoder, and a scalable video decoder. The scalable video coding method includes receiving a GOP, performing temporal filtering and spatial transformation thereon, quantizing and generating a bitstream. The scalable video encoder for performing the scalable video coding method includes a weight determination block which determines a weight for scaling. The scalable video decoding method includes dequantizing the coded image information obtained from a received bitstream, performing descaling, inverse spatial transformation, and inverse temporal filtering on the scaled transform coefficients, thereby recovering video frames. The scalable video decoder for performing the scalable video decoding method includes an inverse weighting block. The standard deviation of Peak Signal to Noise Ratios (PSNRs) of frames included in a group of pictures (GOP) is reduced so that video coding performance can be increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
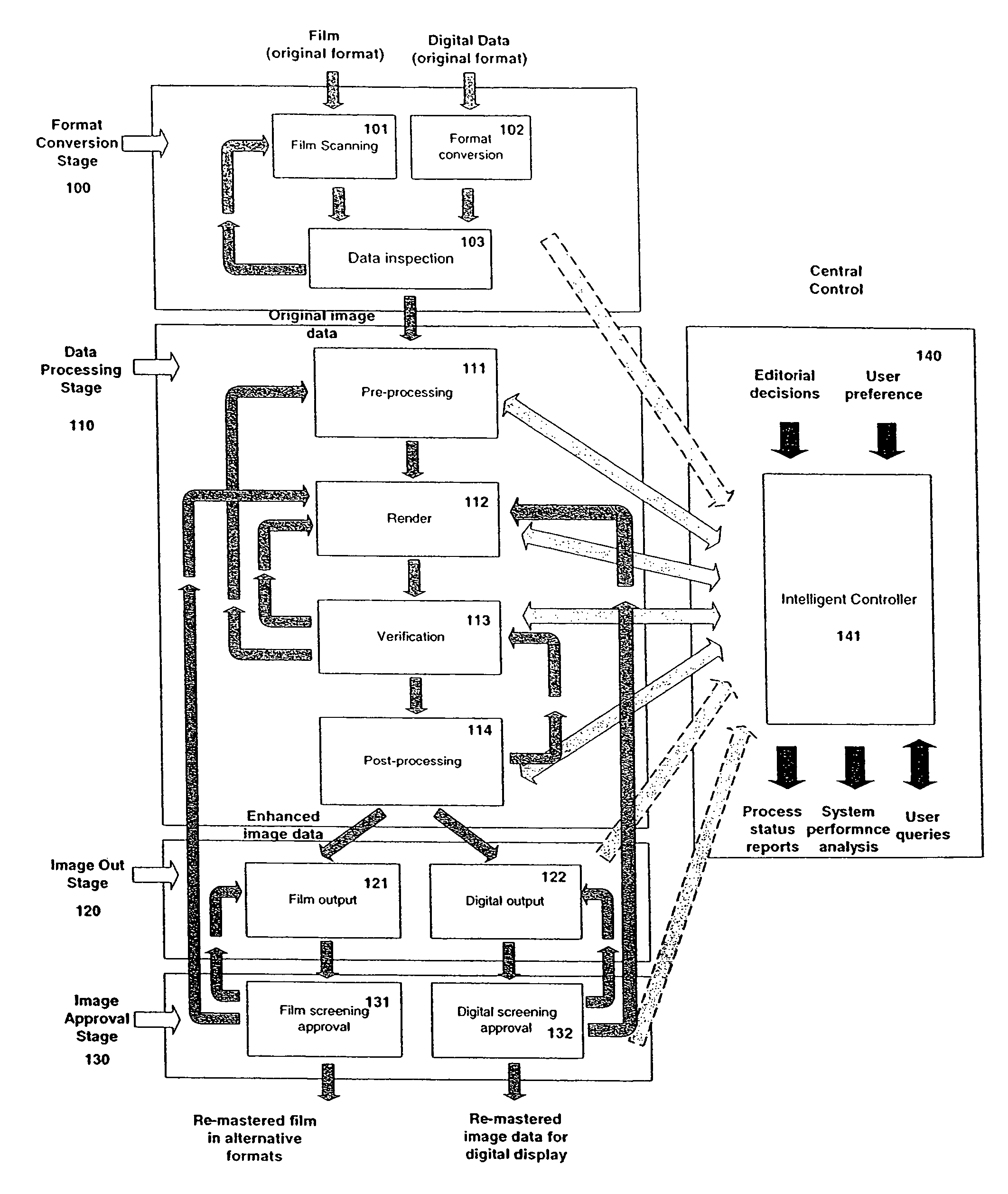
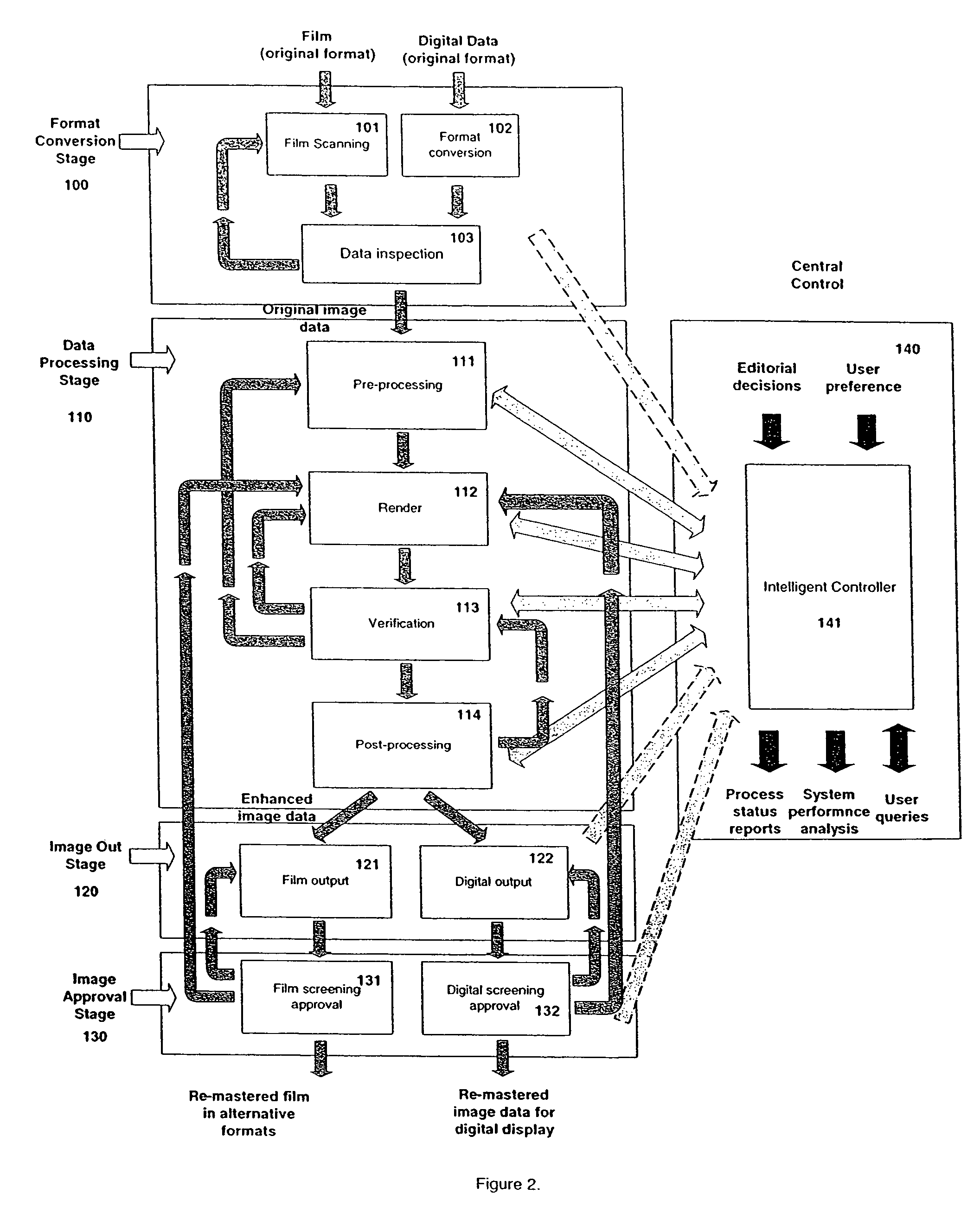
Systems and methods for digitally re-mastering or otherwise modifying motion pictures or other image sequences data
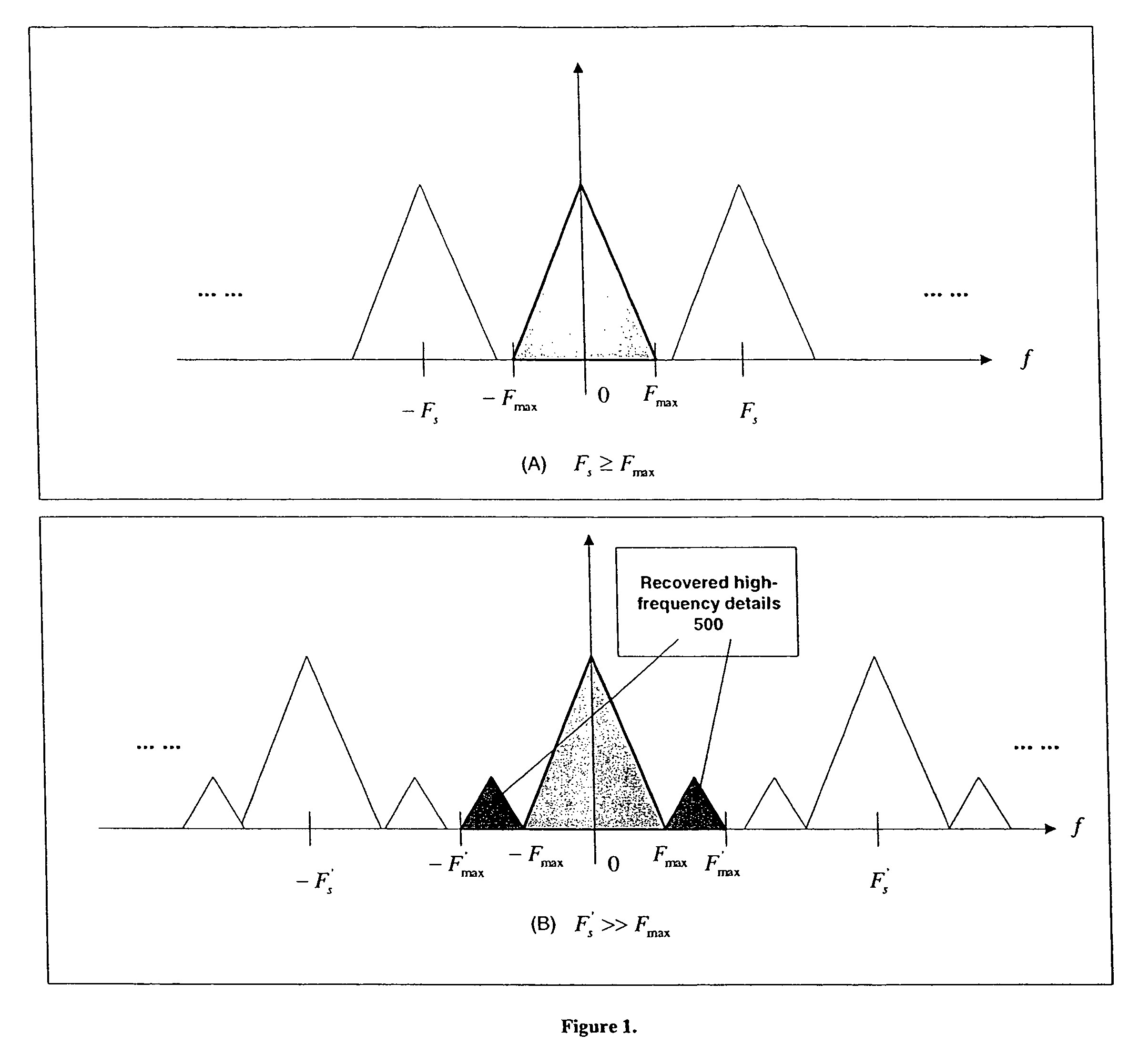
ActiveUS7856055B2Improve spatial resolutionExpands image frequency spectrumTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesImage resolutionStatistical quality
A process and methods of digital enhancement of motion pictures and other moving image sequences for the purpose of being exhibited in an alternative display format including a large format cinema are disclosed. The invention efficiently enhances image resolution and quality through a temporal filtering process and achieves high performance using automated or interactive statistical quality evaluation methods. A system specially designed for efficient temporal computing with a parallel and distributed computing configuration equipped with a variety of optimization schemes is also disclosed. The performance of the process and the system is optimized through an intelligent controller and is scalable to support any throughput requirements demanded for concurrent motion picture releases in the original format as well as in any alternative format.
Owner:IMAX CORP
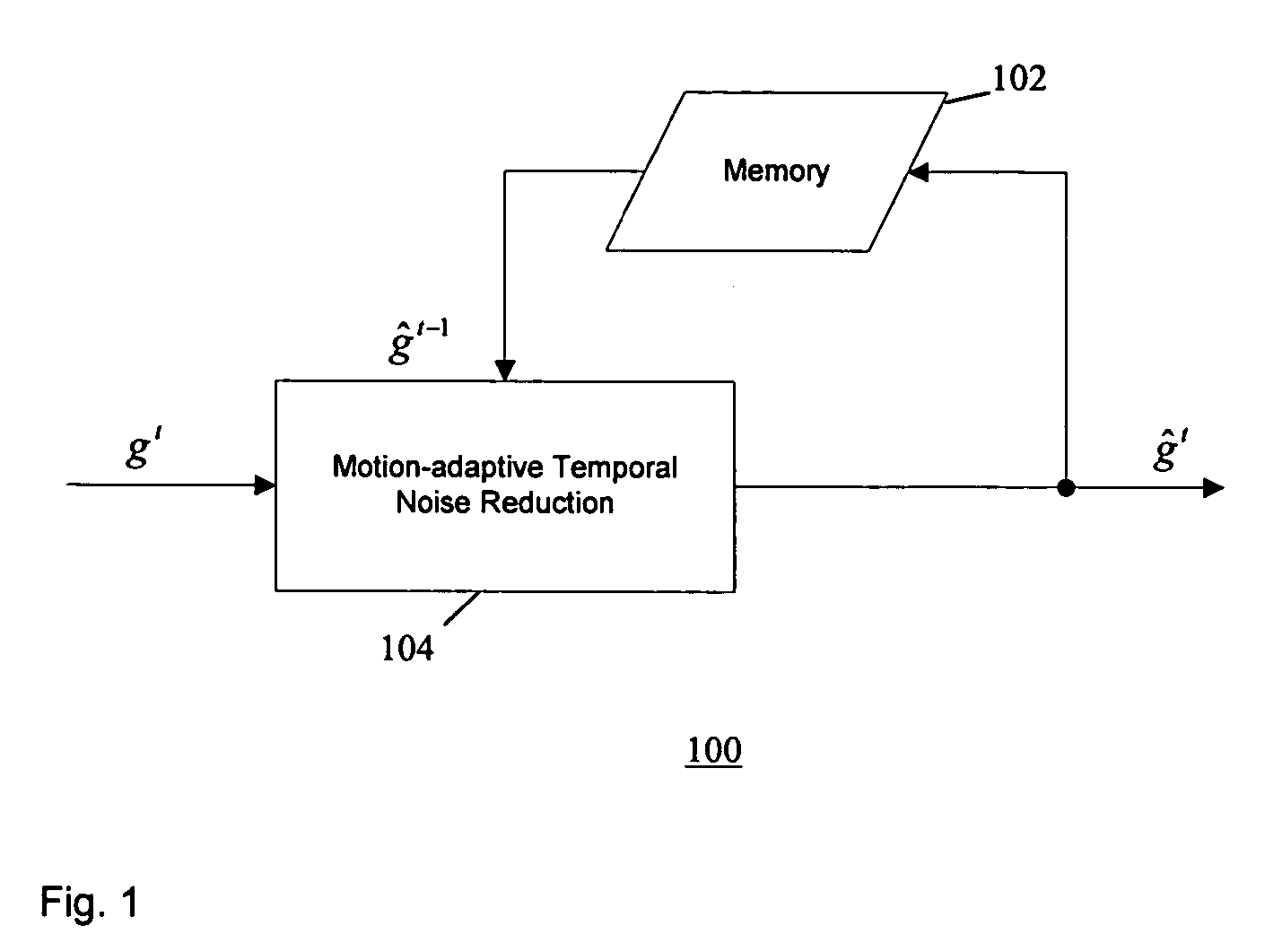
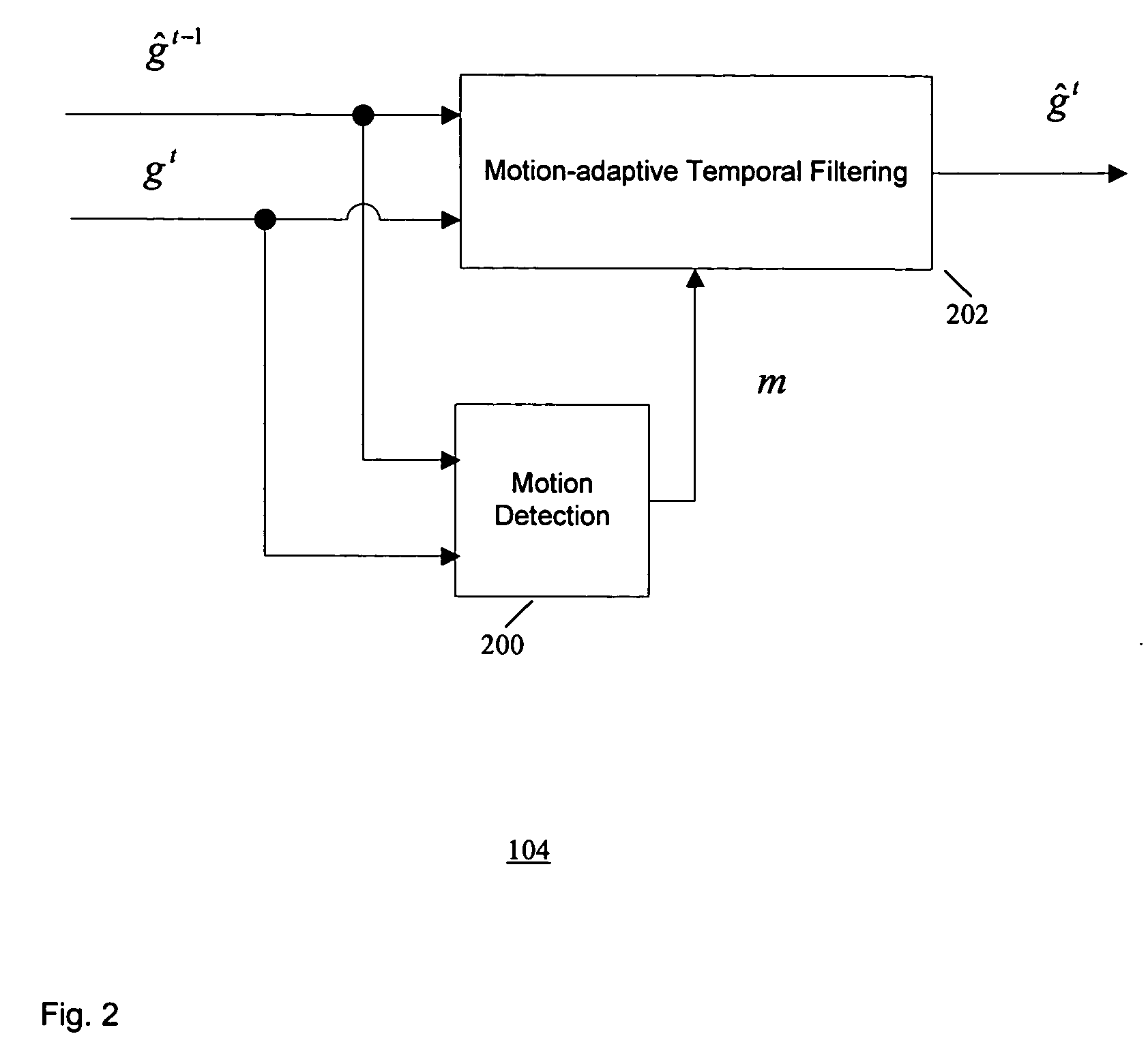
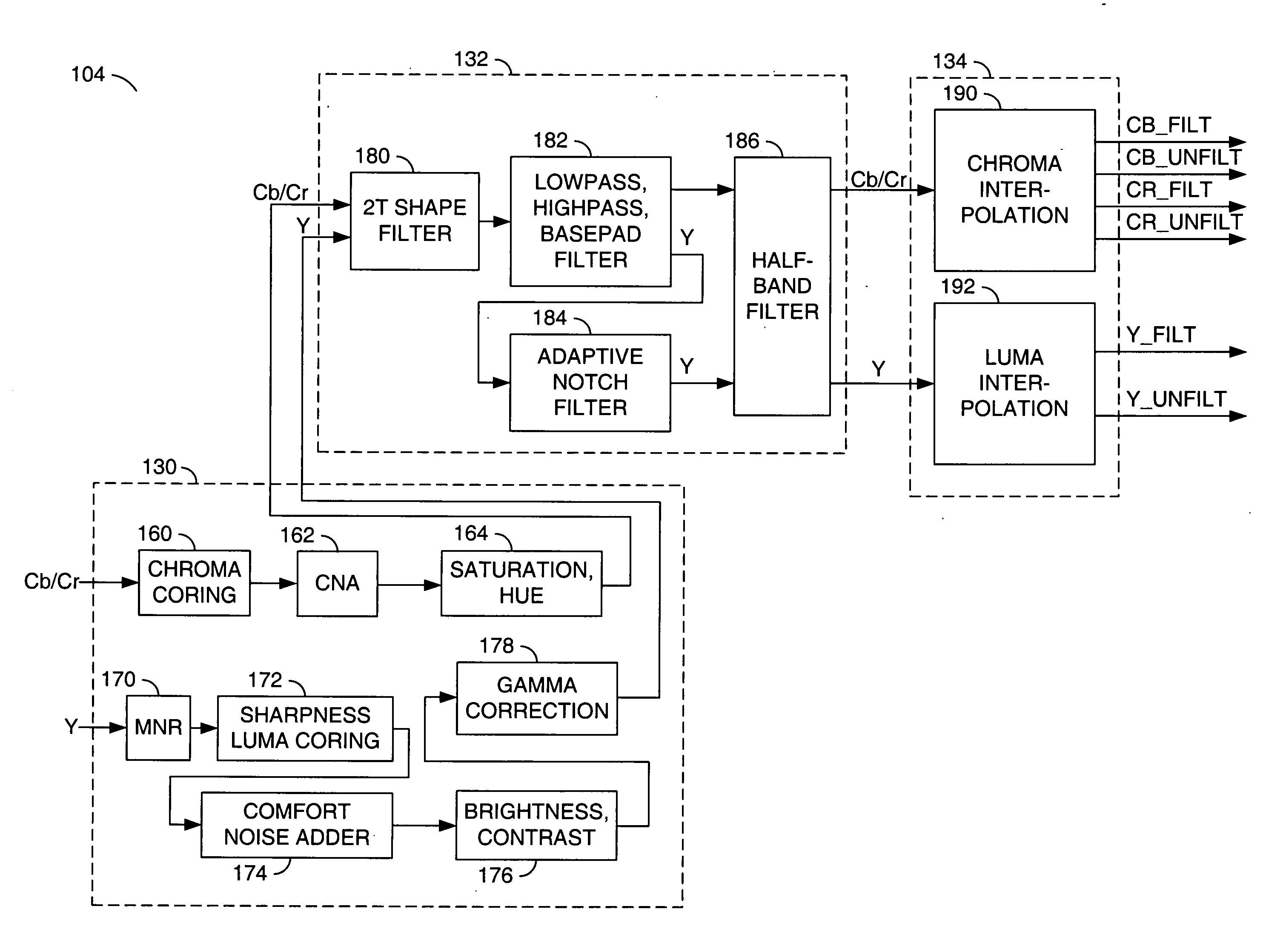
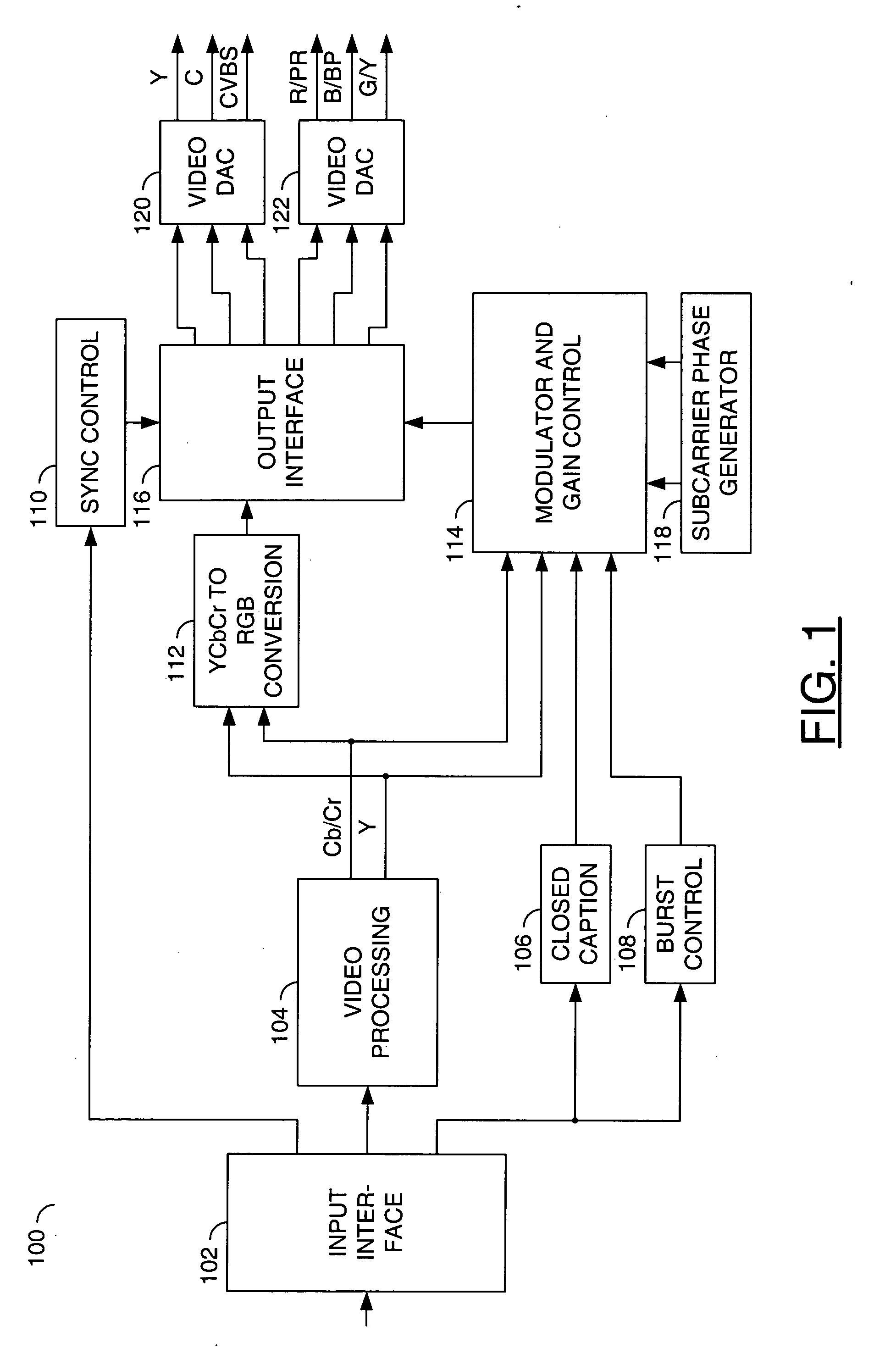
Method of temporal noise reduction in video sequences
InactiveUS20060139494A1LessMaintain performanceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionVideo sequence
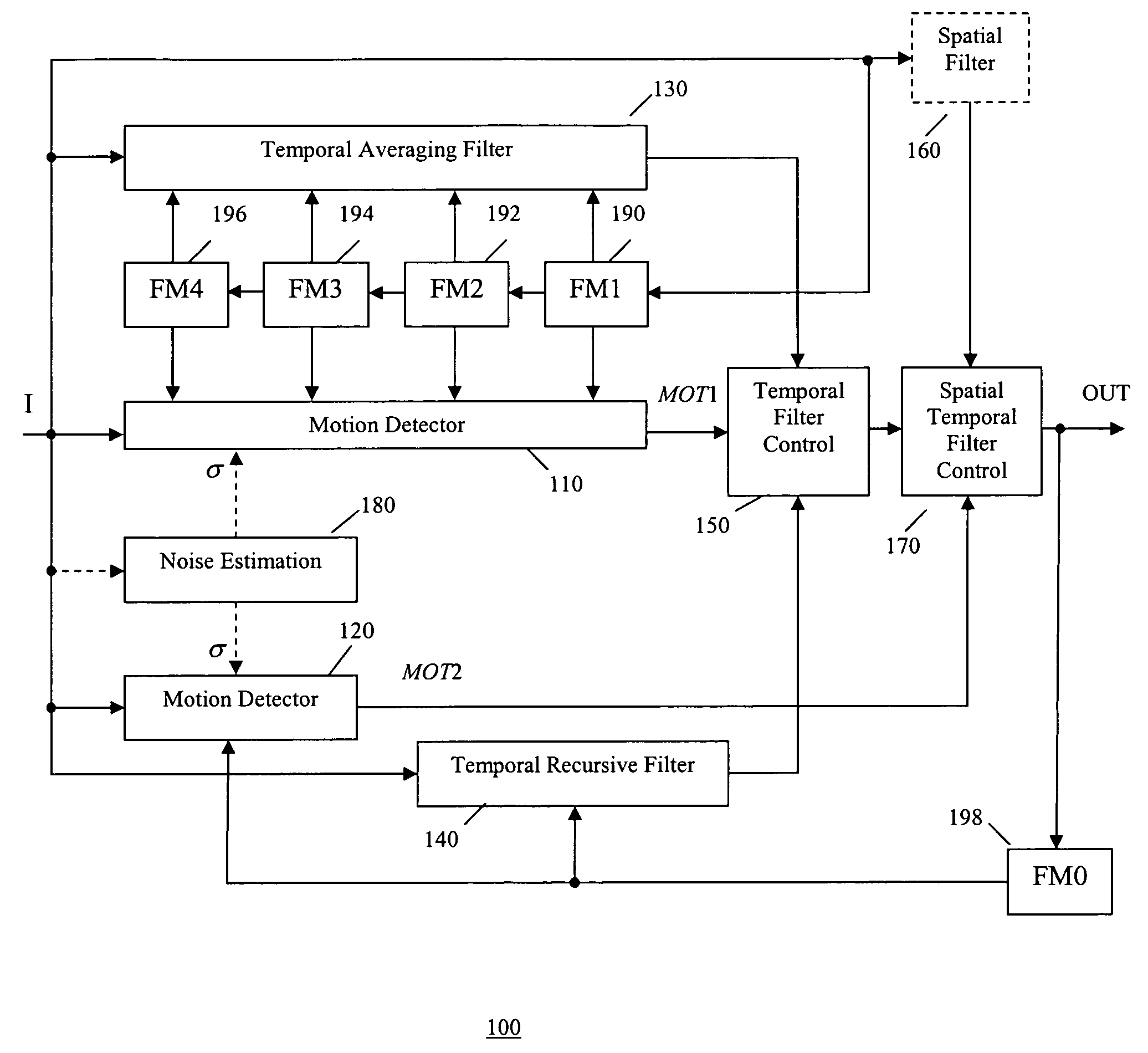
A motion-adaptive temporal noise reducing method and system for reducing noise in a sequence of video frames is provided. Temporal noise reduction is applied to two video frames, wherein one video frame is the current input noisy frame, and the other video frame is a previous filtered frame stored in memory. Once the current frame is filtered, it is saved into memory for filtering the next incoming frame. A motion-adaptive temporal filtering method is applied for noise reduction. Pixel-wise motion information between the current frame and the previous (filtered) frame in memory is examined. Then the pixels in the current frame are classified into motion region and non-motion region relative to the previous (filtered) frame. In a non-motion region, pixels in the current frame are filtered along the temporal axis. In a motion region, the temporal filter is switched off to avoid motion blurring.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for masking of video artifacts and/or insertion of film grain in a video decoder
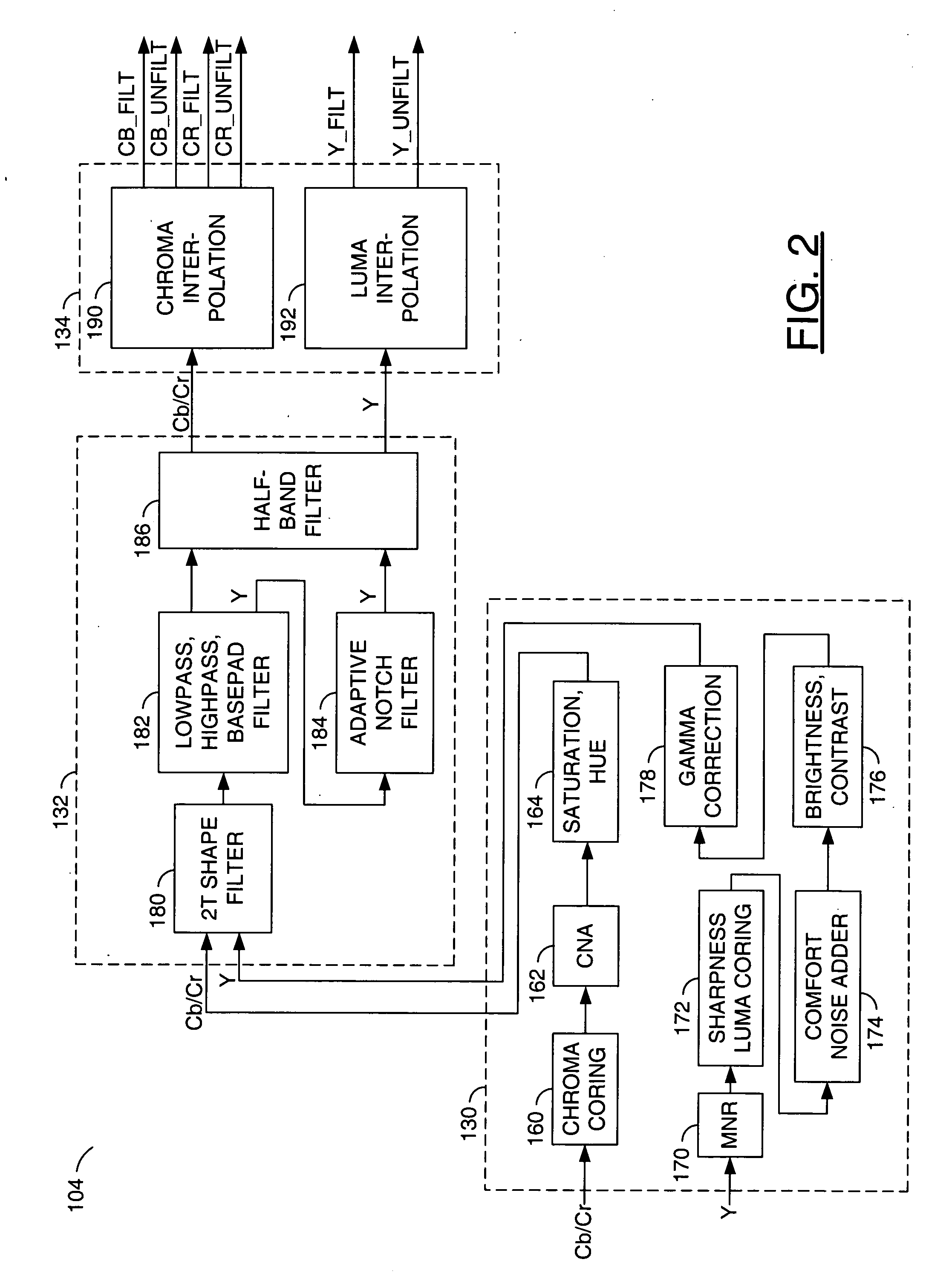
A video decoder comprising (i) a post-processing filter block, (ii) a comfort noise addition block and (iii) a video value / range adjustment block, where the comfort noise addition block is integrated into a video output path of the video decoder. The post-processing filter block may be configured to perform one or more of noise reduction, spatial filtering and temporal filtering on luminance data. The comfort noise addition block may be configured to add comfort noise to the luminance data. The video value / range adjustment block may be configured to adjust one or both of a value and a range of the luminance data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Service Provider Analytics
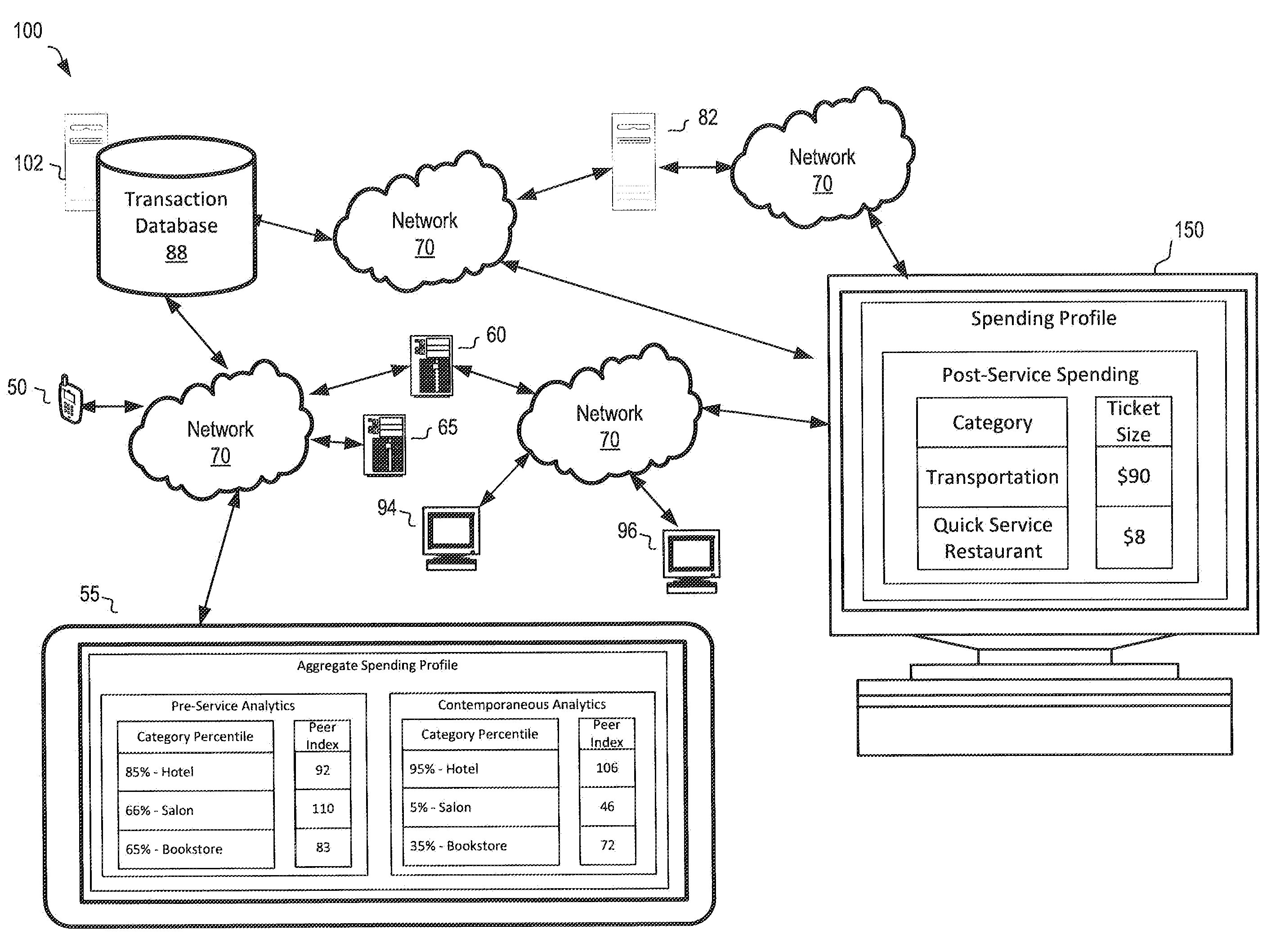
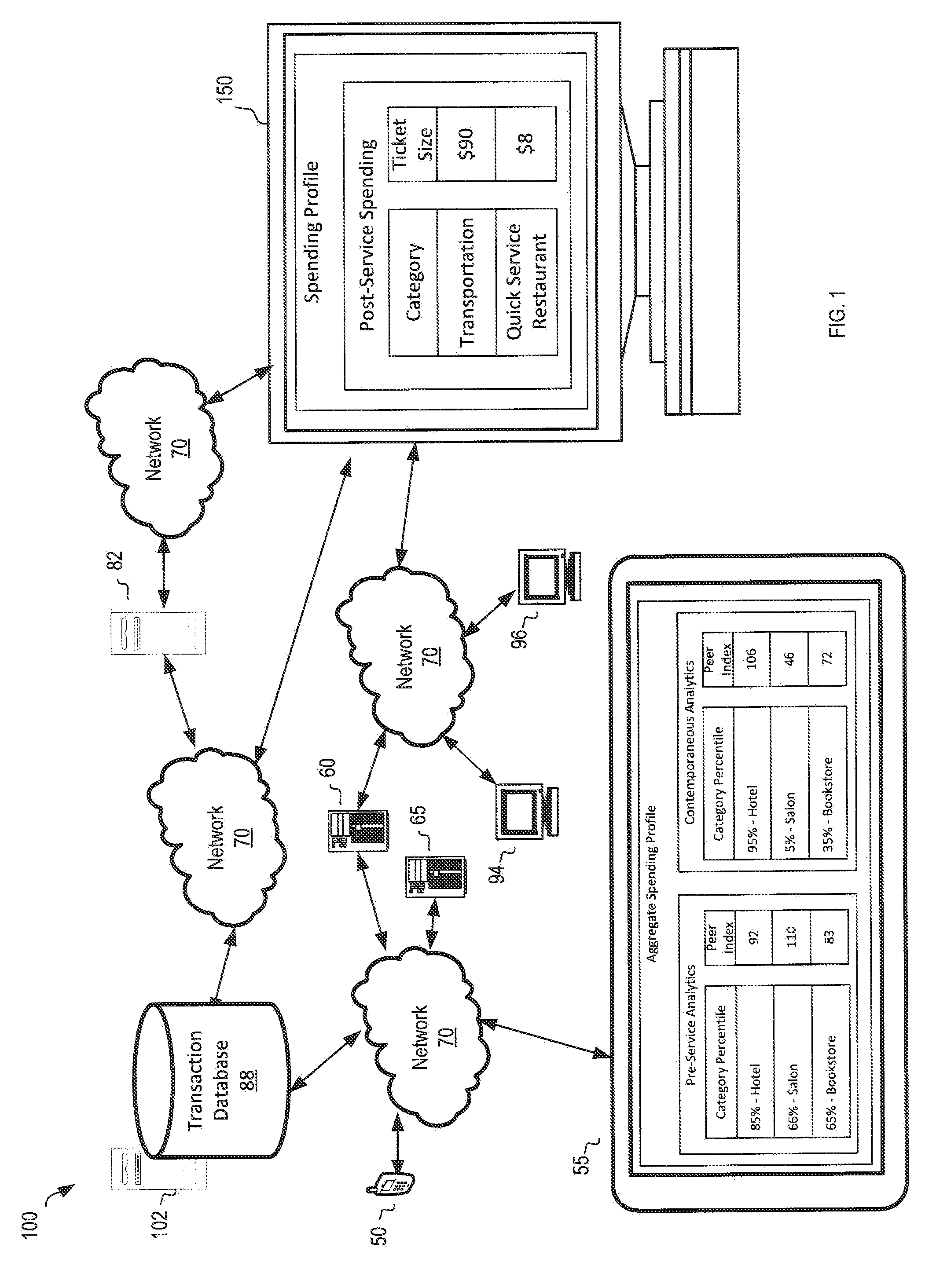
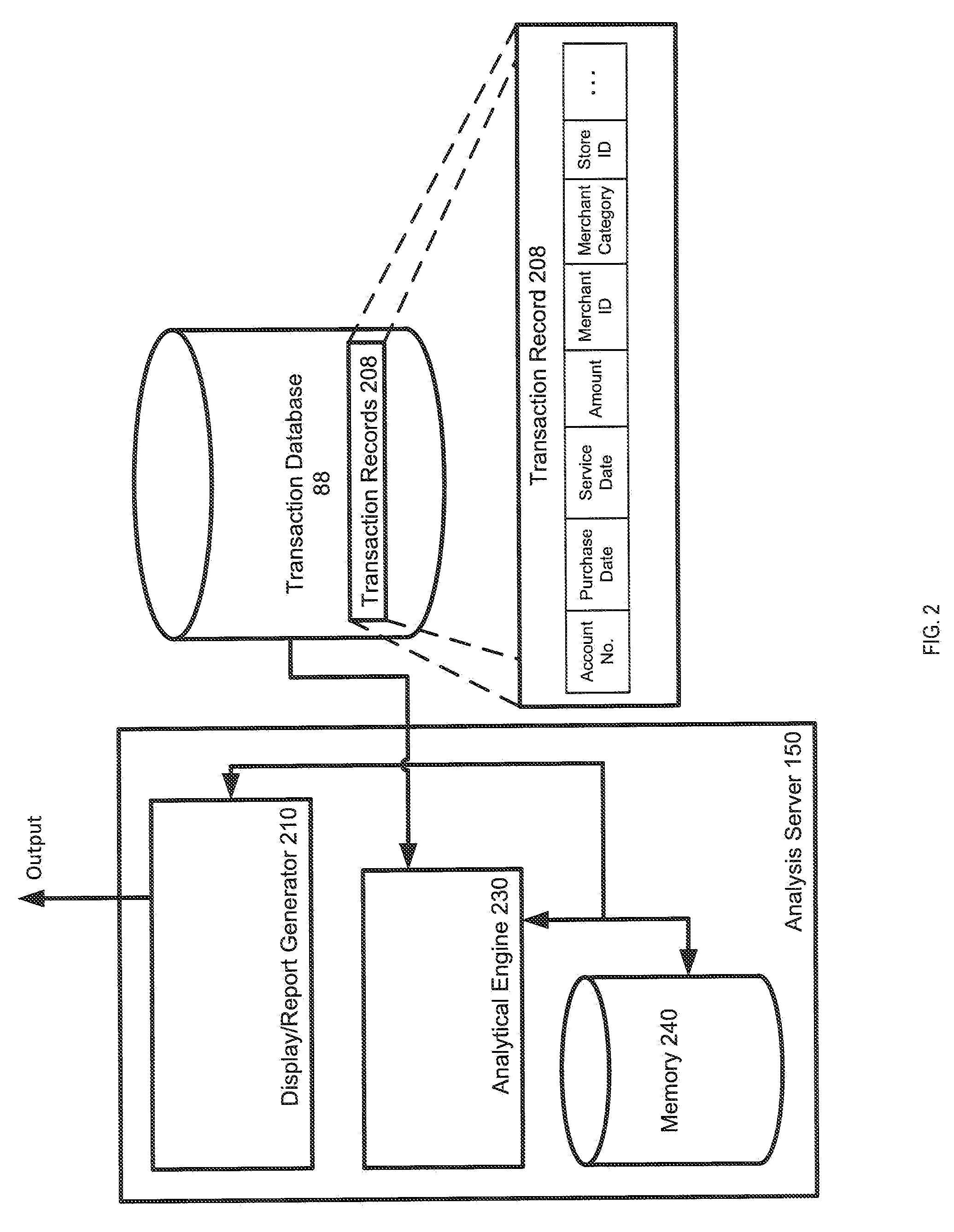
A system, apparatus, computer readable media, and method are disclosed for generating analytics on customers of service provider merchants. In an example, a transaction record associated with an account identifier of a customer that purchased a first service from a first merchant may be processed and a service date for the first service may be determined. Other transaction records comprising the account identifier and that satisfy a temporal filter may be identified. Each of the other transaction records may include transaction data associated with at least one of: (1) purchase of another service to be provided within a first predetermined amount of time of the service date, and (2) purchase of a product within a second predetermined amount of time of the service date. A spending profile including information on the first service, the service date, and the transaction data for each of the other transaction records may be generated.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Temporal filtering techniques for image signal processing
Various techniques for temporally filtering raw image data acquired by an image sensor are provided. In one embodiment, a temporal filter determines a spatial location of a current pixel and identifies at least one collocated reference pixel from a previous frame. A motion delta value is determined based at least partially upon the current pixel and its collocated reference pixel. Next, an index is determined based upon the motion delta value and a motion history value corresponding to the spatial location of the current pixel, but from the previous frame. Using the index, a first filtering coefficient may be selected from a motion table. After selecting the first filtering coefficient, an attenuation factor may be selected from a luma table based upon the value of the current pixel, and a second filtering coefficient may subsequently be determined based upon the selected attenuation factor and the first filtering coefficient. The temporally filtered output value corresponding to the current pixel may then be calculated based upon the second filtering coefficient, the current pixel, and the collocated reference pixel.
Owner:APPLE INC
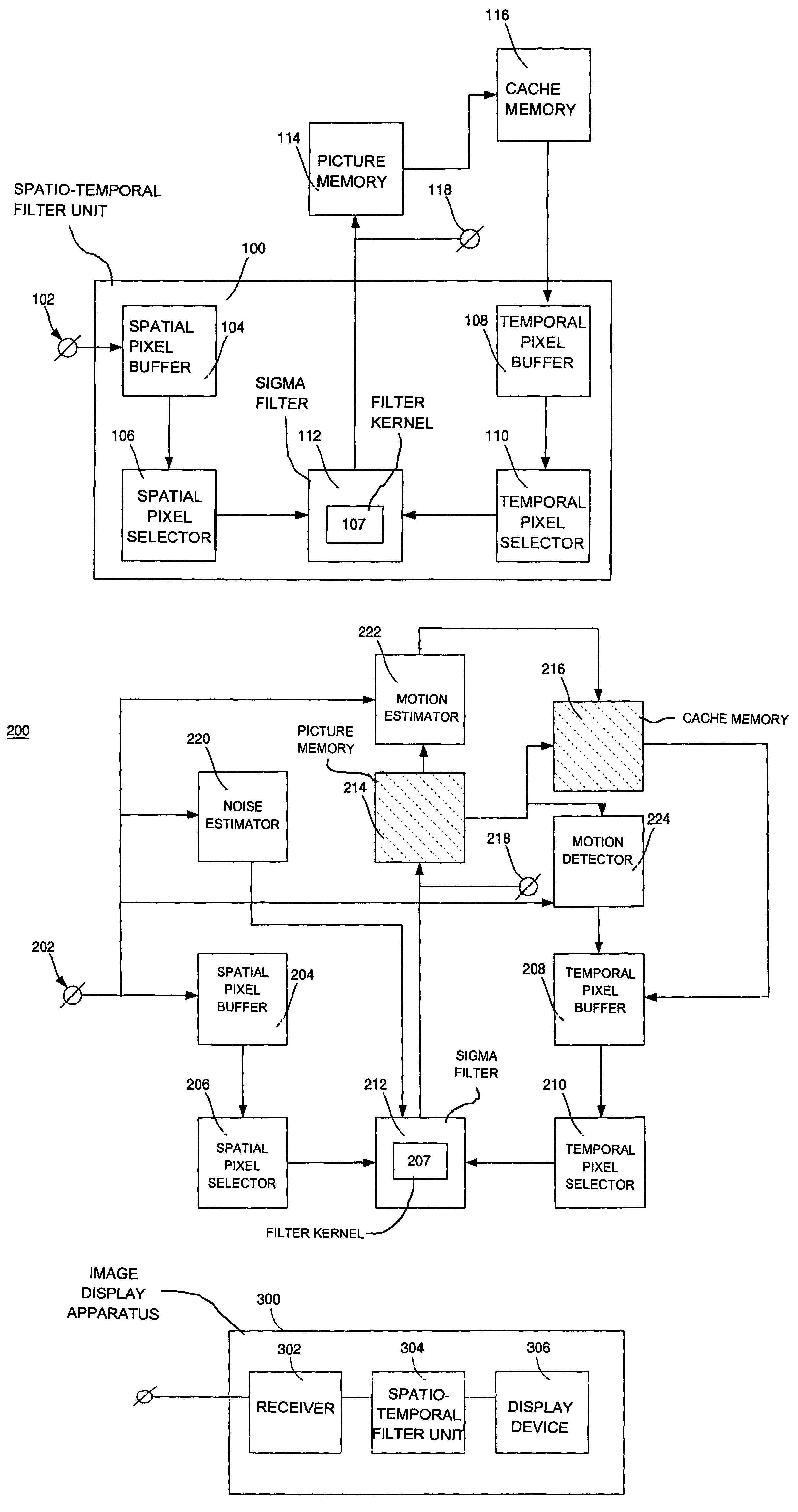
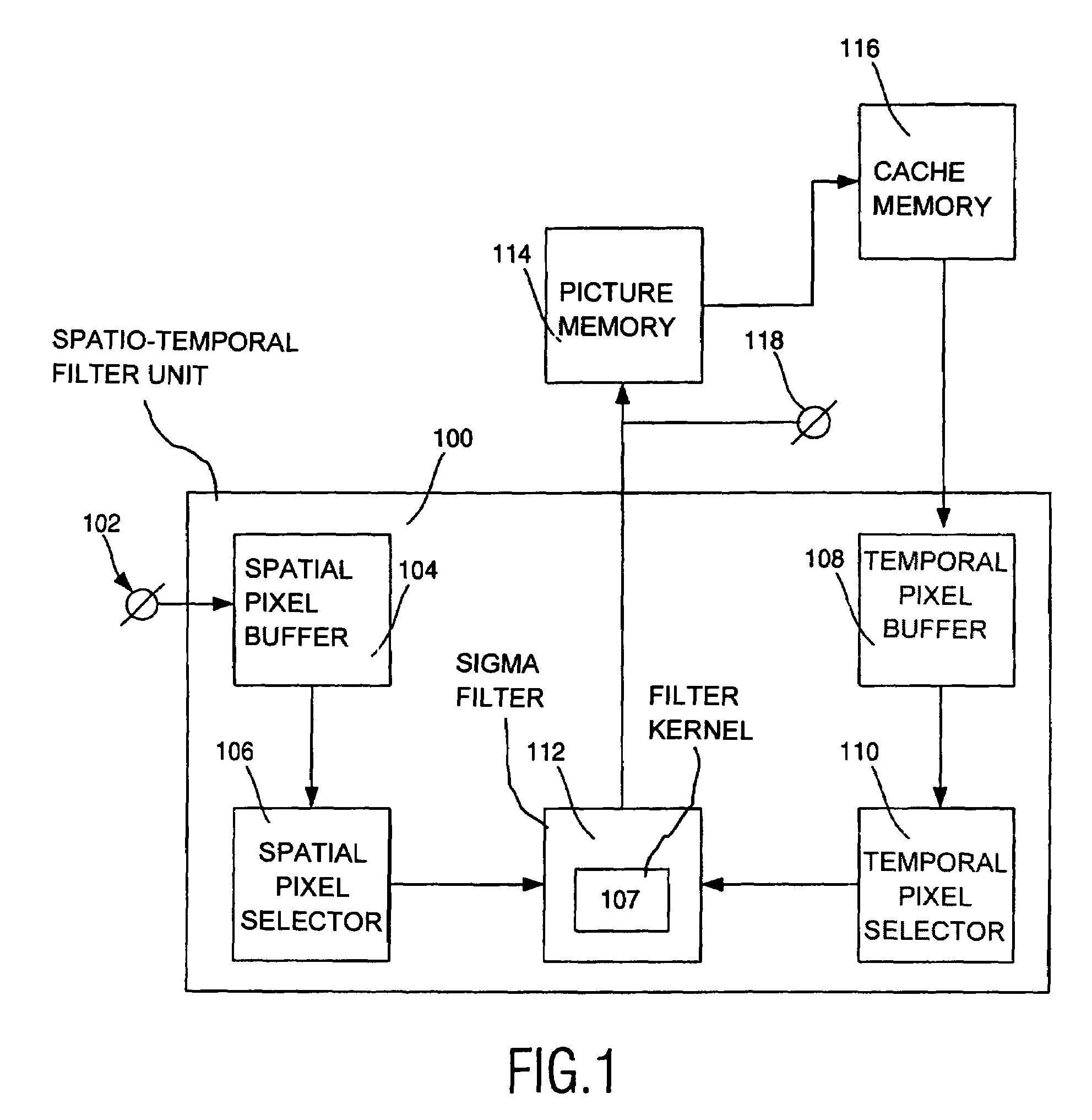
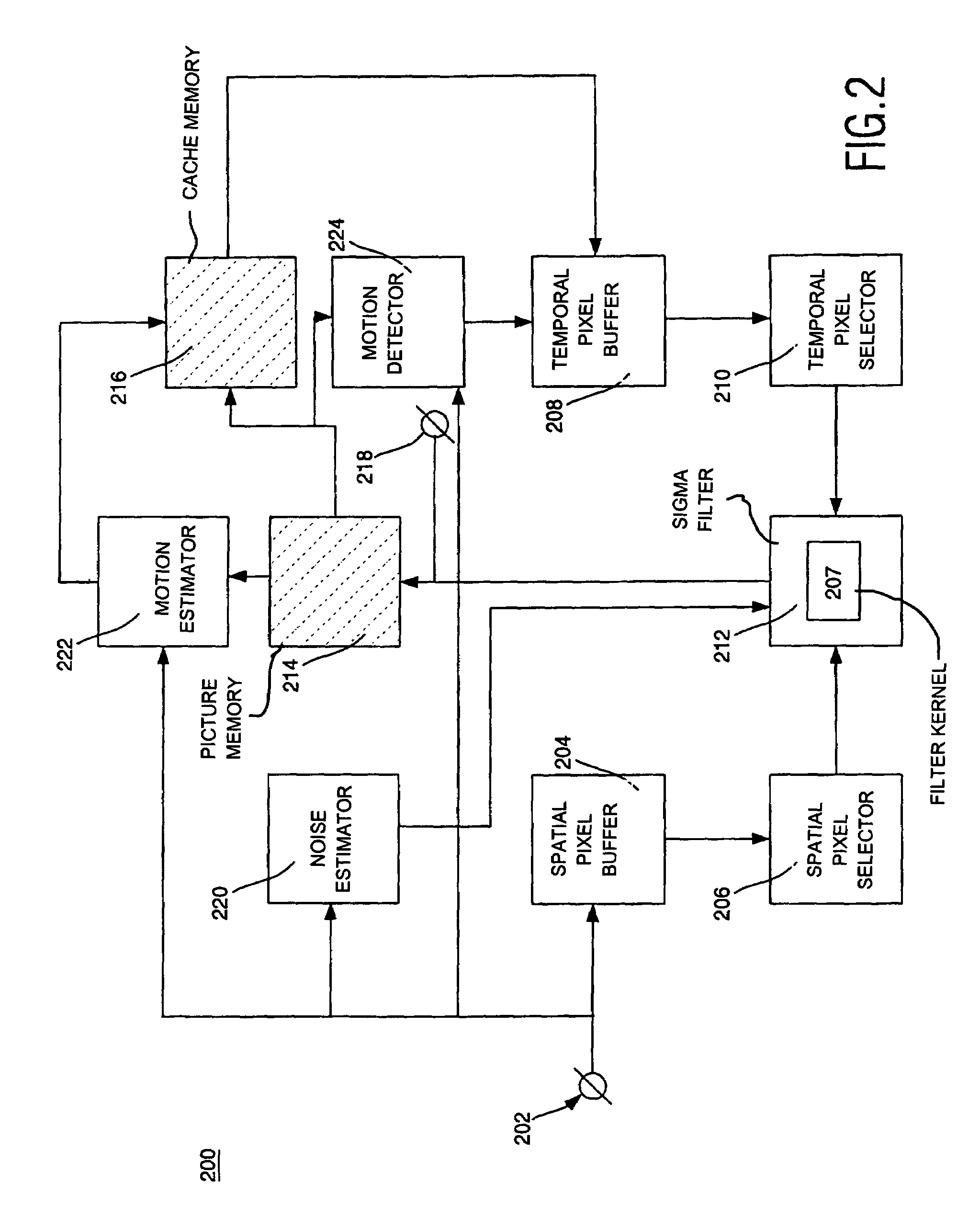
Spatio-temporal filter unit and image display apparatus comprising such a spatio-temporal filter unit
InactiveUS7034892B2Easy to optimizeLow implementation costImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMotion detectorMotion vector
Noise reduction is an important feature in consumer television. This is realized by spatial, temporal or spatio-temporal filters. Spatial filters require pixels from within one image, while temporal filters require samples from two or more successive images. The spatio-temporal filter unit (100) integrates spatial and implicit motion-compensated temporal noise reduction in one filter. For the motion compensation, no motion vectors are required. The spatio-temporal filter unit (100) is provided with a sigma filter (112) having one filter kernel (107) designed to operate on the pixels from both a current image and from the output of the spatio-temporal filter unit, being a temporally recursive filtered image. The operation of the spatio-temporal filter unit (100) can be adjusted by varying the thresholds of the sigma filter (112) and the selection of pixels. The adjustments can be controlled by a motion estimator (222), a motion detector (224) and a noise estimator (220).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
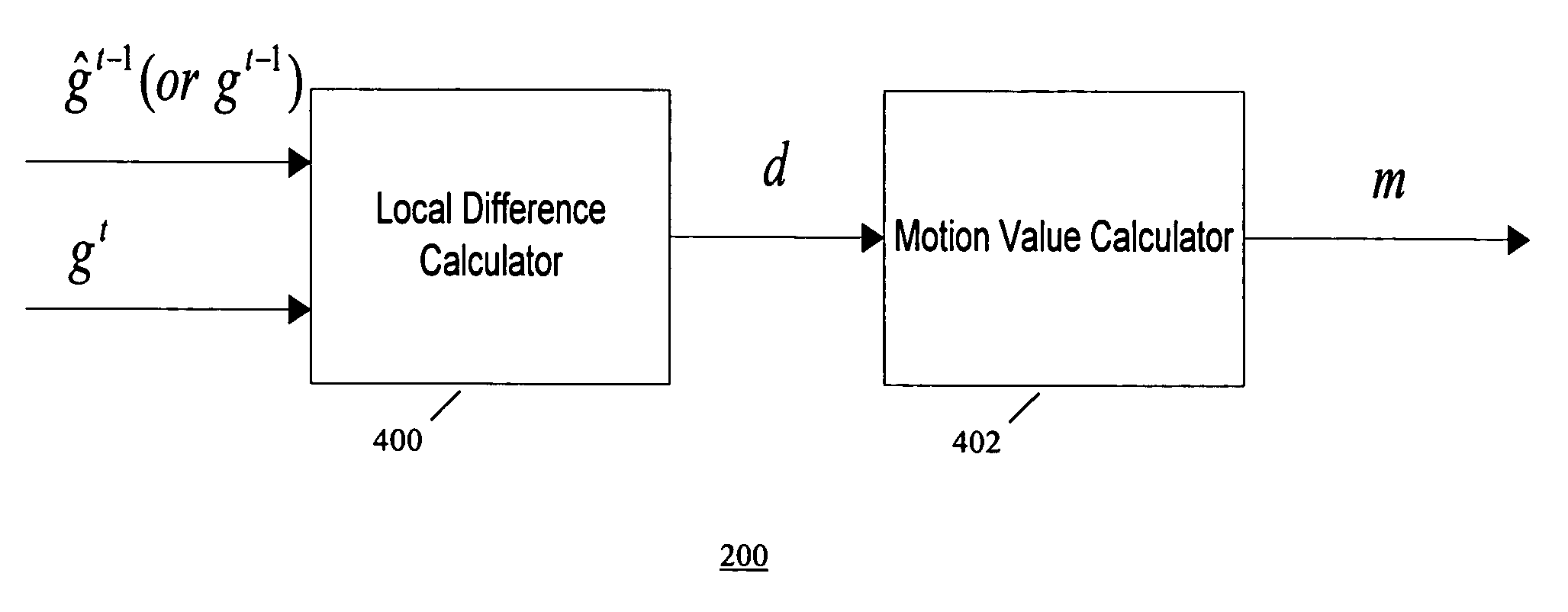
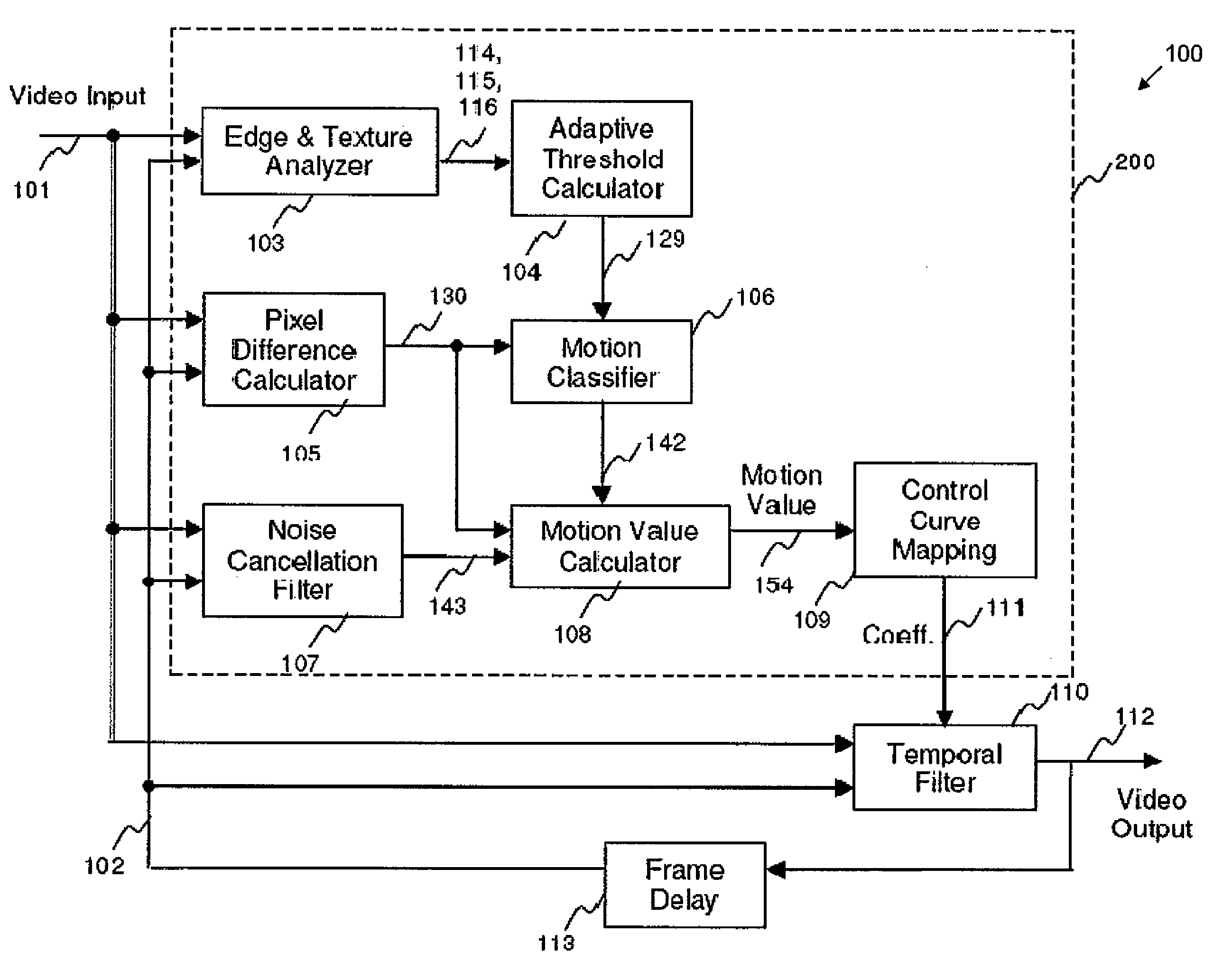
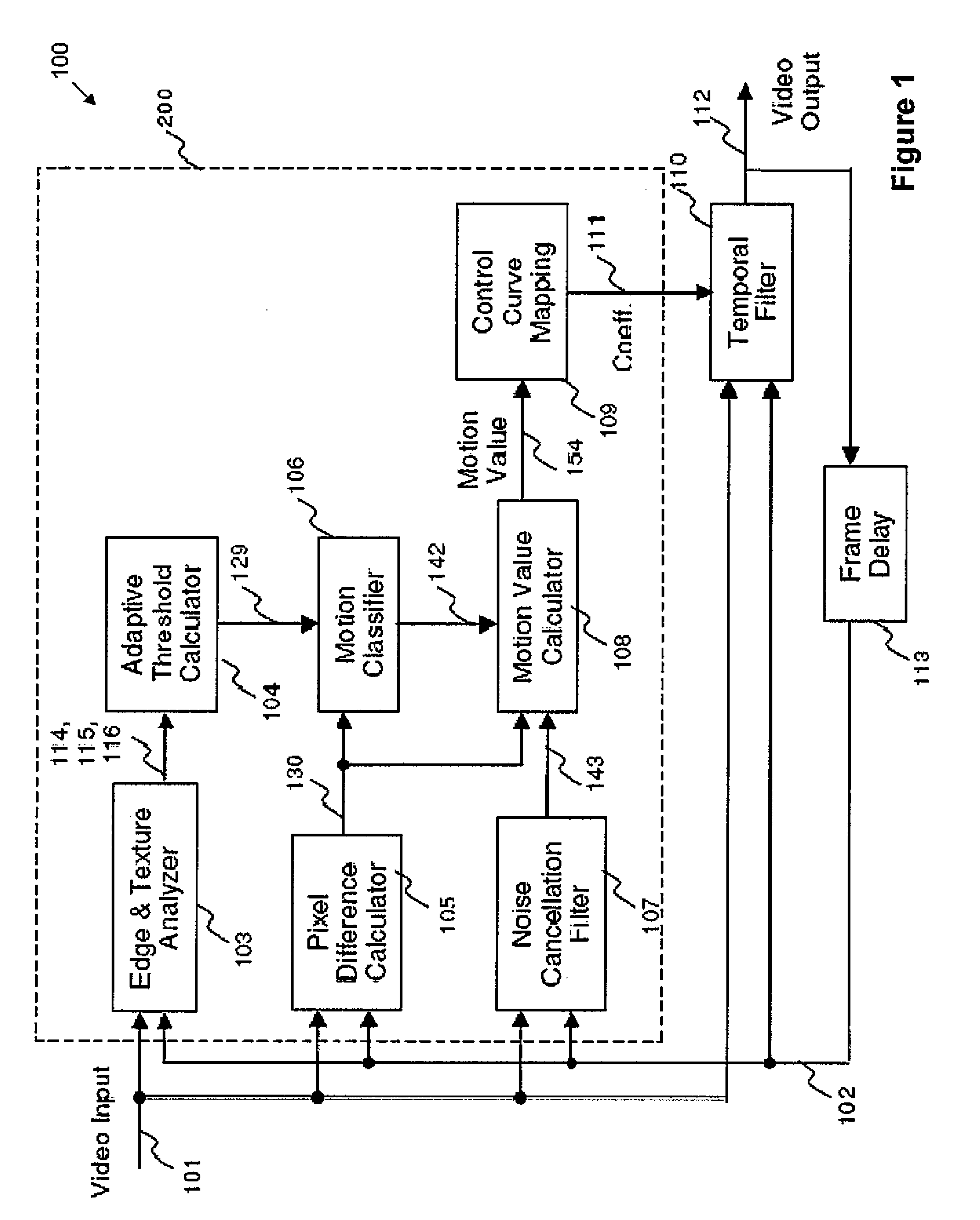
Apparatus and method of motion detection for temporal mosquito noise reduction in video sequences
ActiveUS20100165207A1Improve robustnessReduce noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoVideo sequence
Apparatus and methods of motion detection for mosquito noise reduction in video sequences are provided. In one aspect, a method of motion detection in a sequence of digital images classifies a pixel of a plurality of pixels of a current image frame represented by a digital video input signal as a motion or non-motion pixel. A motion value for the pixel is calculated based on the classification of the pixel. The motion value is mapped to a coefficient of a temporal filter based on a control curve. A digital video output signal is generated based on the coefficient.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
Video encoding/decoding method and apparatus
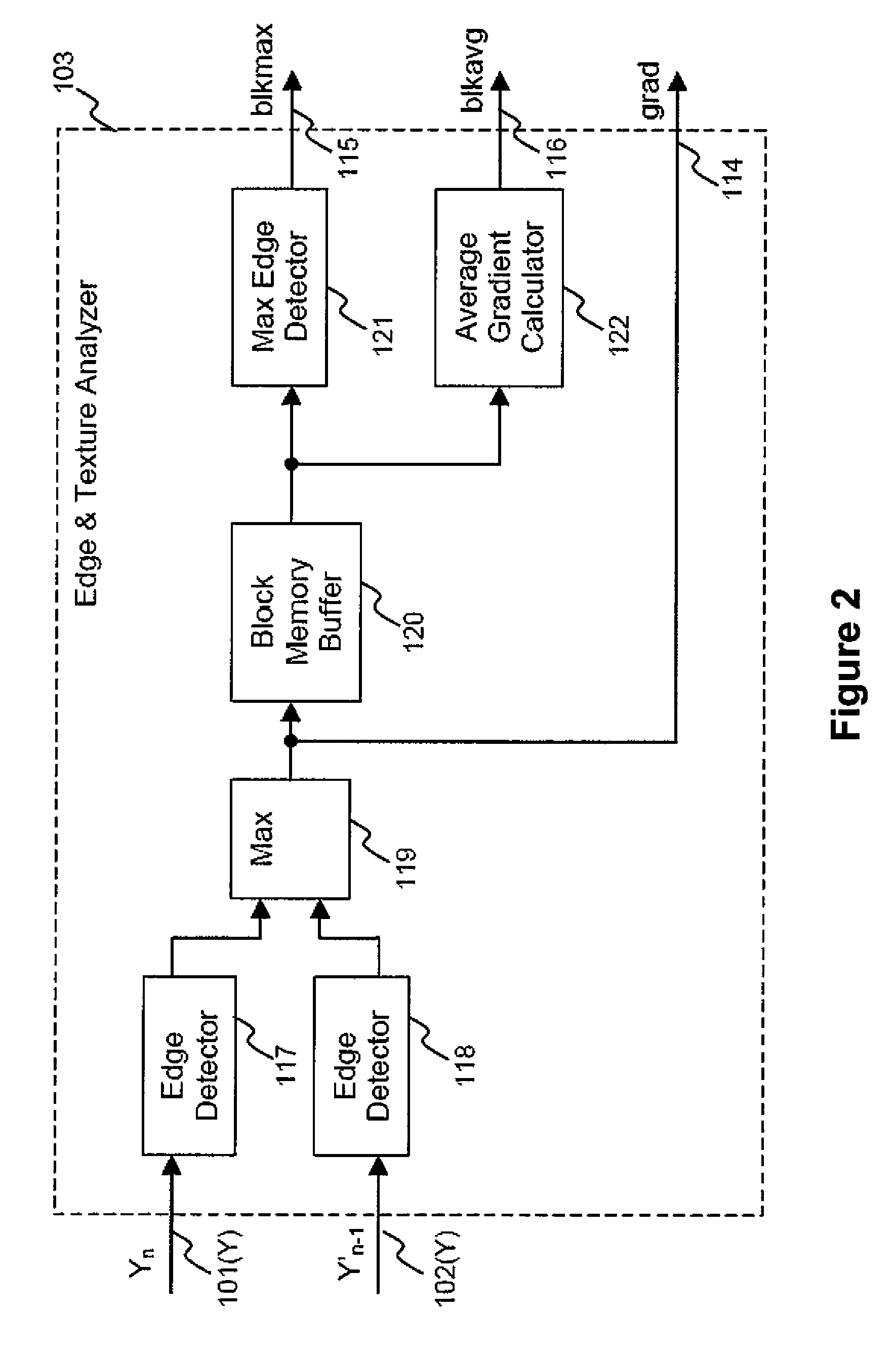
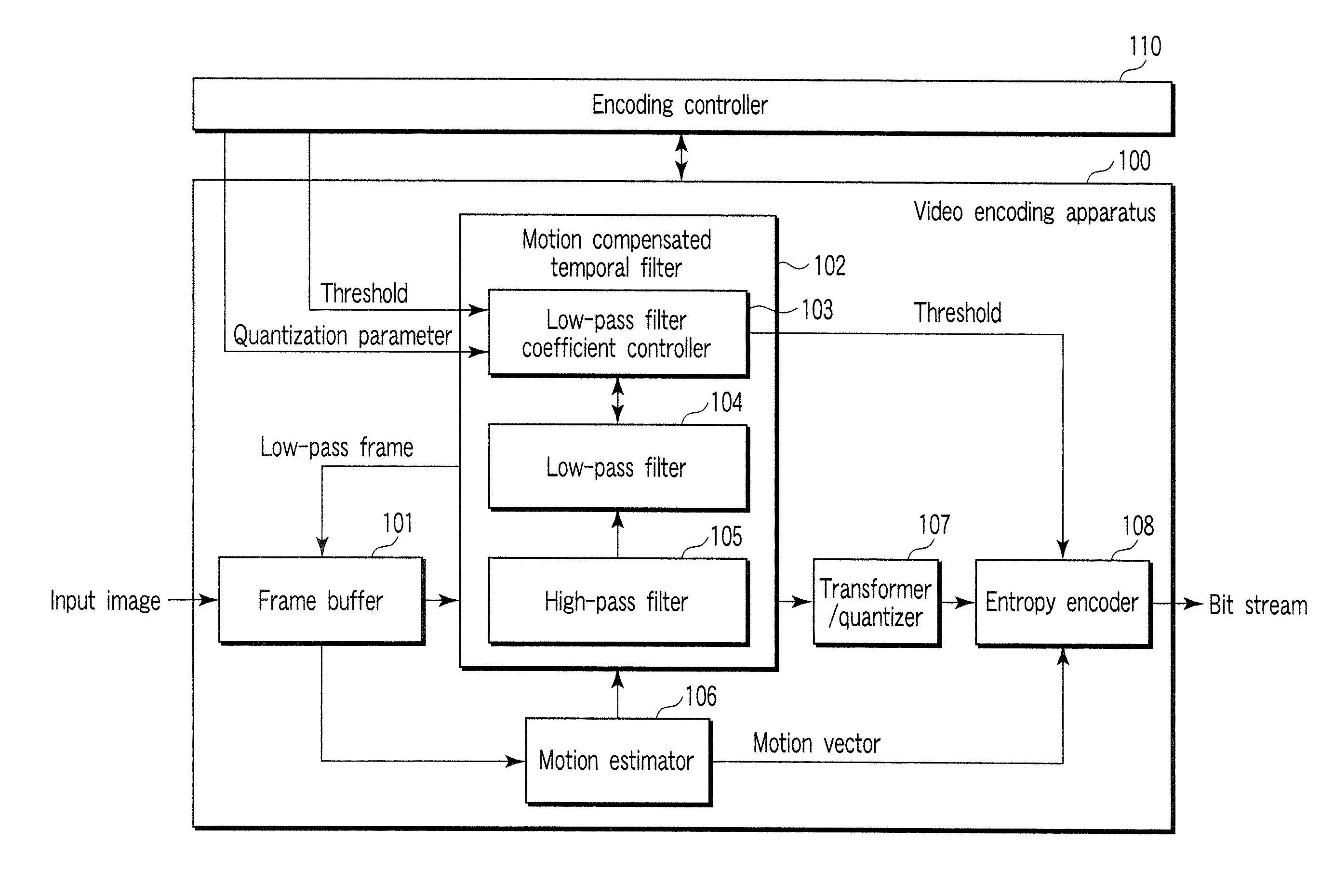
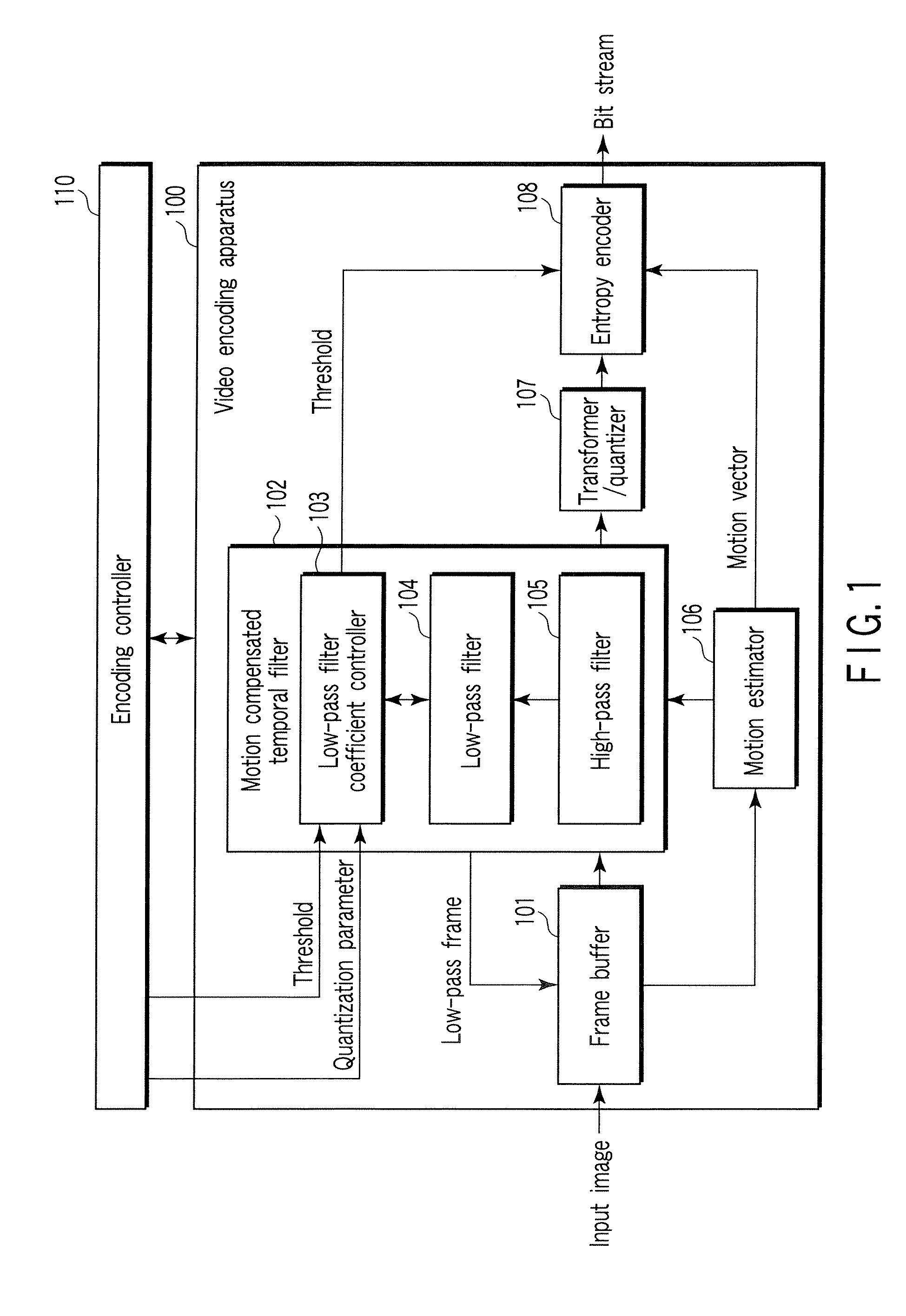
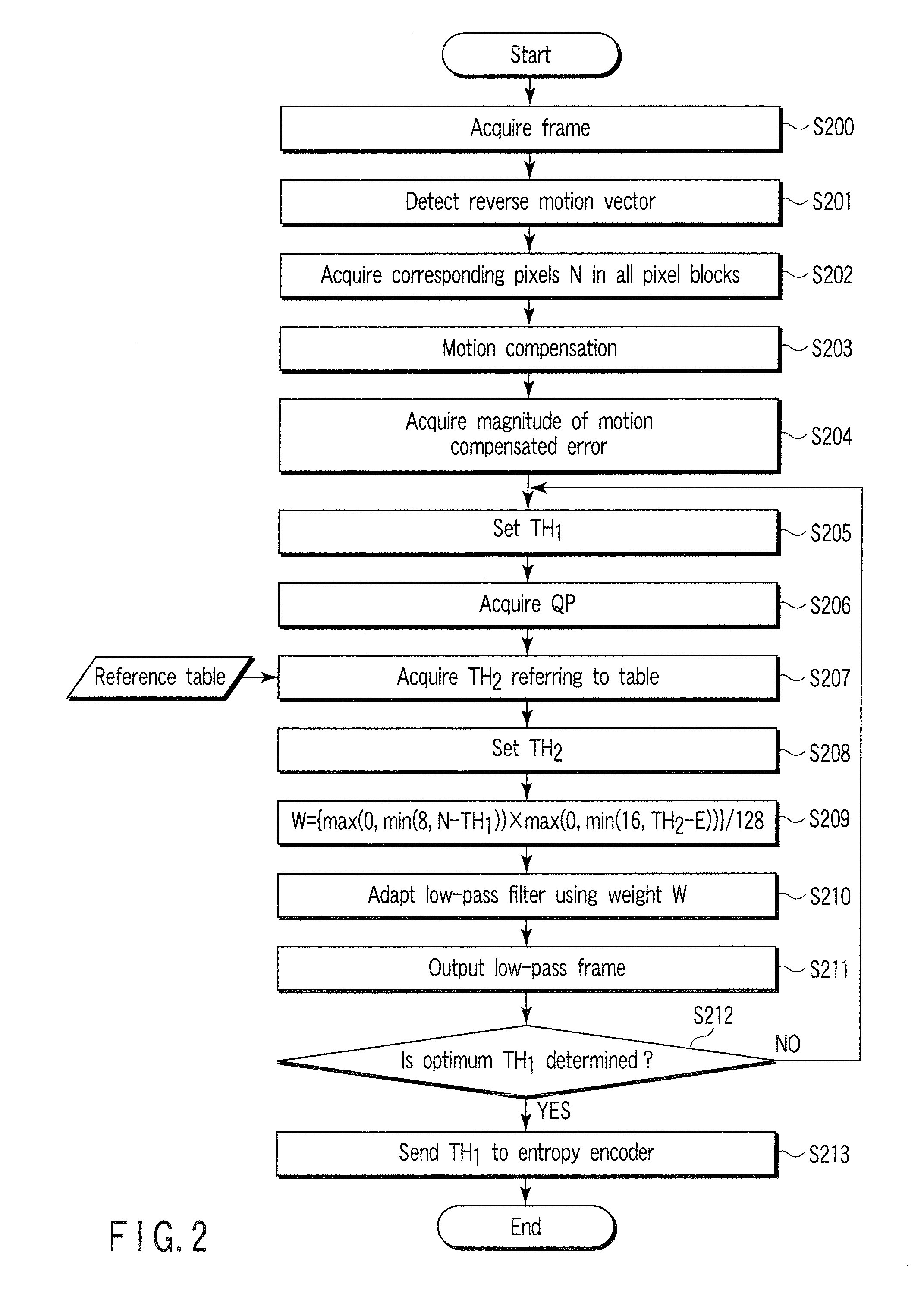
InactiveUS20070116125A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingLow-pass filter
A video encoding method includes subjecting an input video image to motion compensated temporal filtering using a motion compensated temporal filter to produce a low-pass filtered image, quantizing a transform coefficient of the low-pass filtered image, encoding a quantized transform coefficient, calculating a weight to be given to a low-pass filter coefficient of a low-pass filter of the motion compensated temporal filter according to coarseness of quantization and a magnitude of a motion compensated error, and controlling a high band stopping characteristic of the low-pass filter according to the low-pass filter coefficient weighted by the weight, wherein the controlling controls the high band stopping characteristic of the low-pass filter to provide a positive correlation with respect to the quantization parameter and provide a negative correlation with respect to the magnitude of the motion compensated error.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Adaptive spatio-temporal filter for human vision system models
InactiveUS6907143B2Image enhancementTelevision system detailsHuman visual system modelLow-pass filter
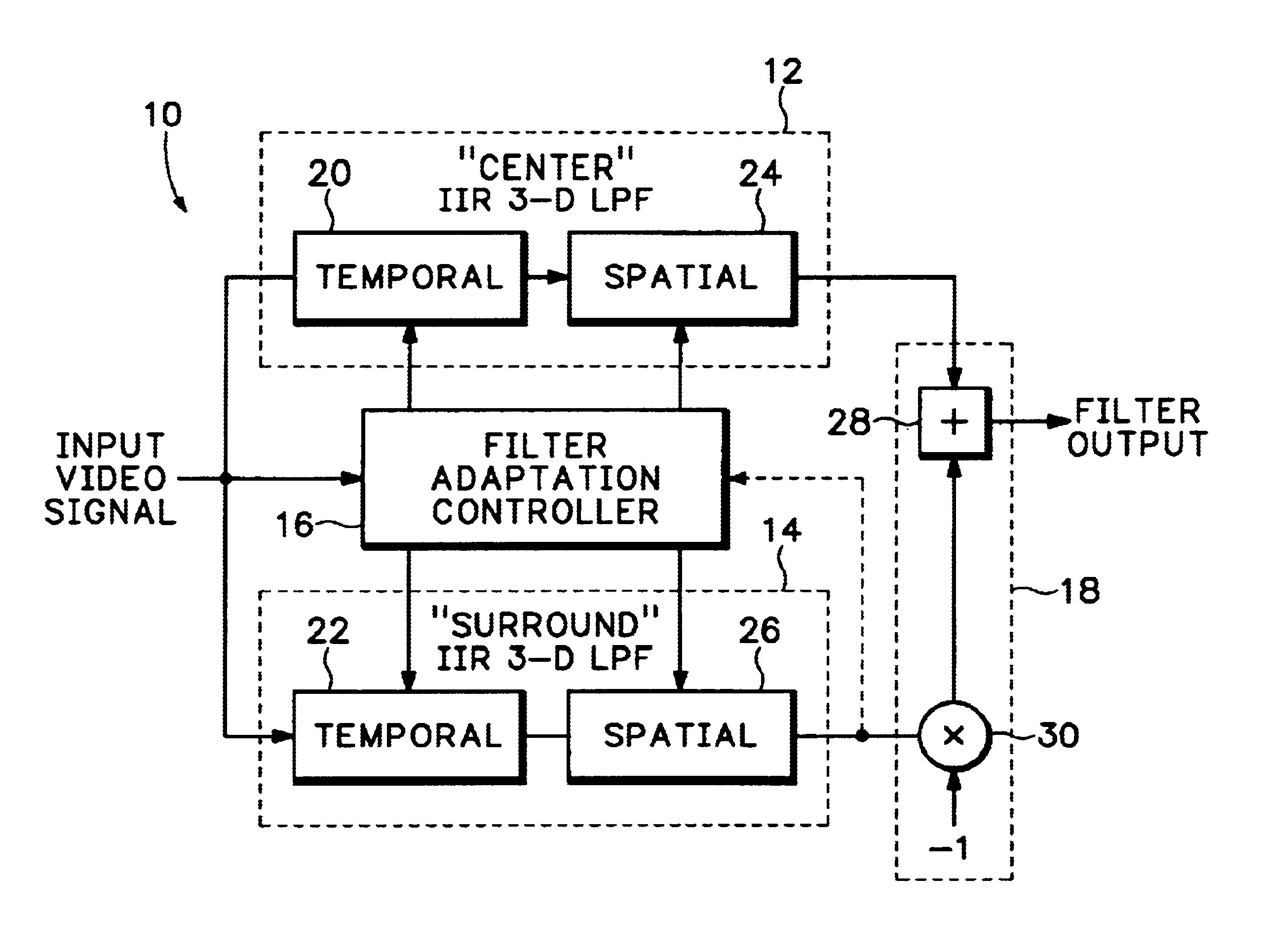
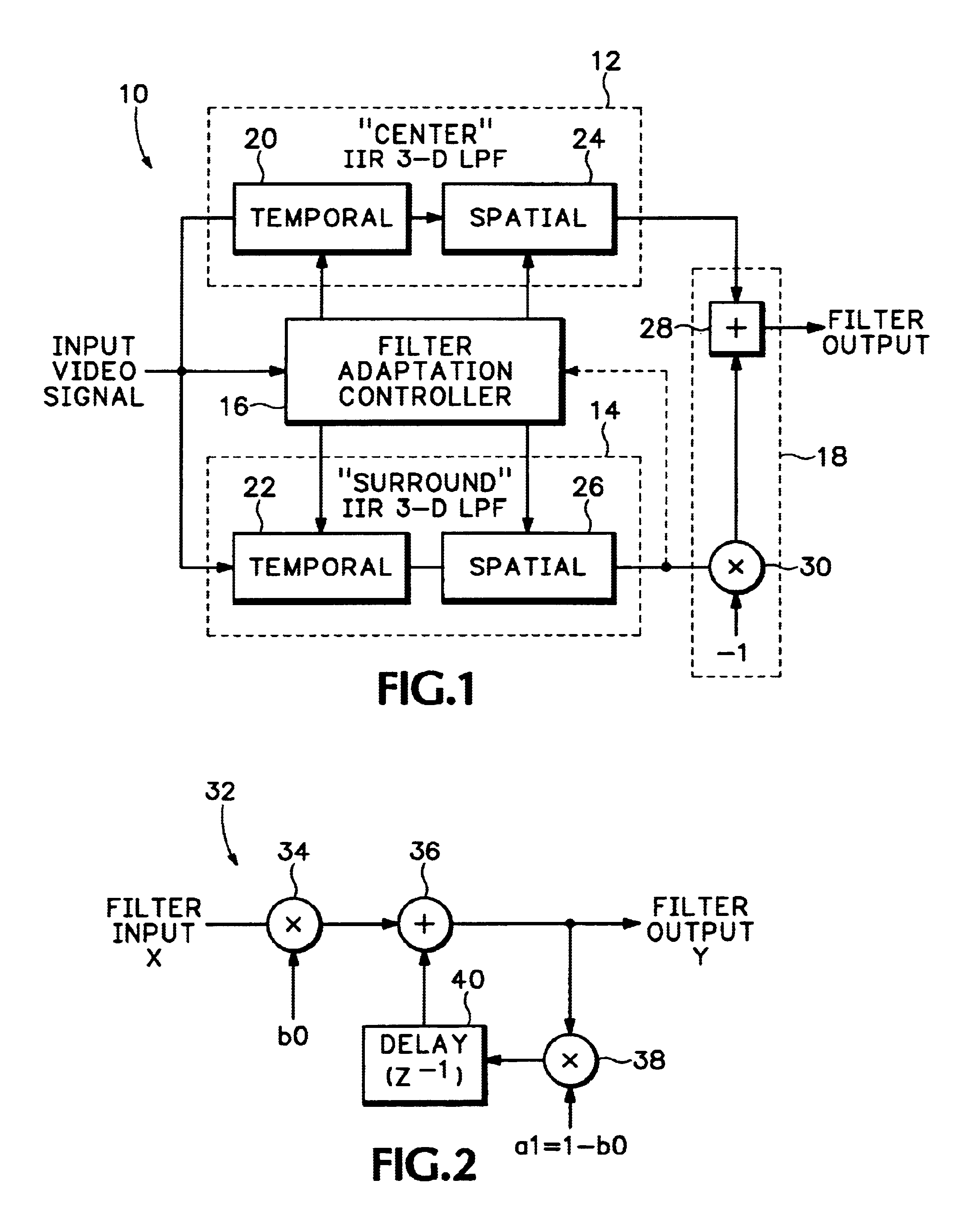
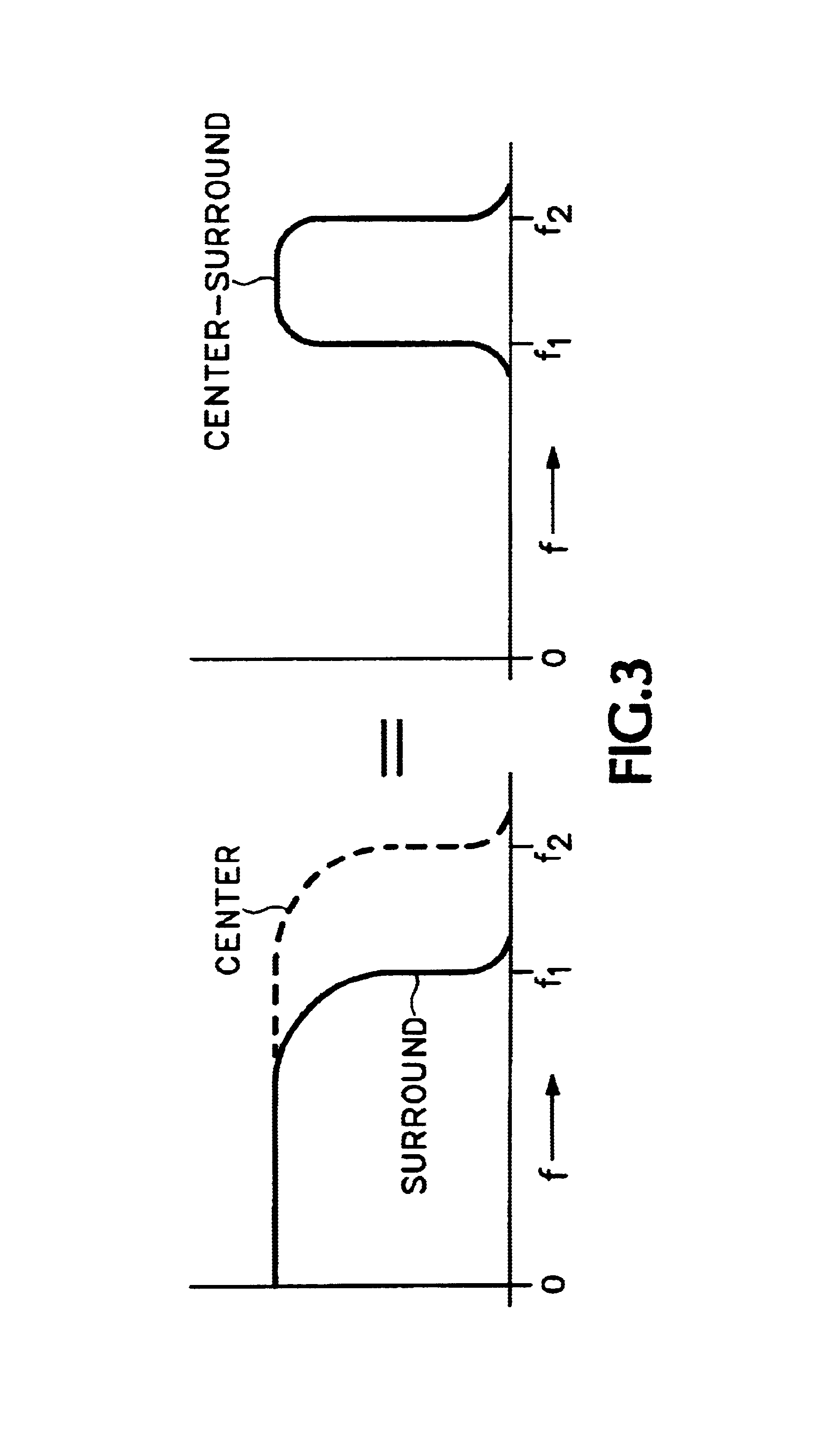
An adaptive spatio-temporal filter for use in video quality of service instruments based on human vision system models has a pair of parallel, lowpass, spatio-temporal filters receiving a common video input signal. The outputs from the pair of lowpass spatio-temporal filters are differenced to produce the output of the adaptive spatio-temporal filter, with the bandwidths of the pair being such as to produce an overall bandpass response. A filter adaptation controller generates adaptive filter coefficients for each pixel processed based on a perceptual parameter, such as the local average luminance, contrast, etc., of either the input video signal or the output of one of the pair of lowpass spatio-temporal filters. Each of the pair of lowpass spatio-temporal filters has a temporal IIR filter in cascade with a 2-D spatial IIR filter, and each individual filter is composed of a common building block,5 i.e., a first order, unity DC gain, tunable lowpass filter having a topology suitable for IC implementation. At least two of the building blocks make up each filter with the overall adaptive spatio-temporal filter response having a linear portion and a non-linear portion, the linear portion being dominant at low luminance levels and the non-linear portion being consistent with enhanced perceived brightness as the luminance level increases.
Owner:PROJECT GIANTS LLC
Motion adaptive noise reduction apparatus and method for video signals
InactiveUS7199838B2Optimal noise reductionIncrease the areaImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSoft switching
A video noise reduction system for a set of video frames that computes a first motion signal using a current frame and multiple consecutive previous frames, computes a second motion signal using the current frame and the processed preceding frame; computes the multi-frame temporal average of the current frame and multiple consecutive previous frames; computes the recursive average of the current frame and the processed preceding frame; generates a temporal filtered signal by soft switching between the multi-frame temporal average and the recursive average based on the first motion signal; applies a spatial filter to the current frame to generate a spatial filtered signal; and combines the temporal filtered signal and the spatial filtered signal based on the second motion signal to generate a final noise reduced video output signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
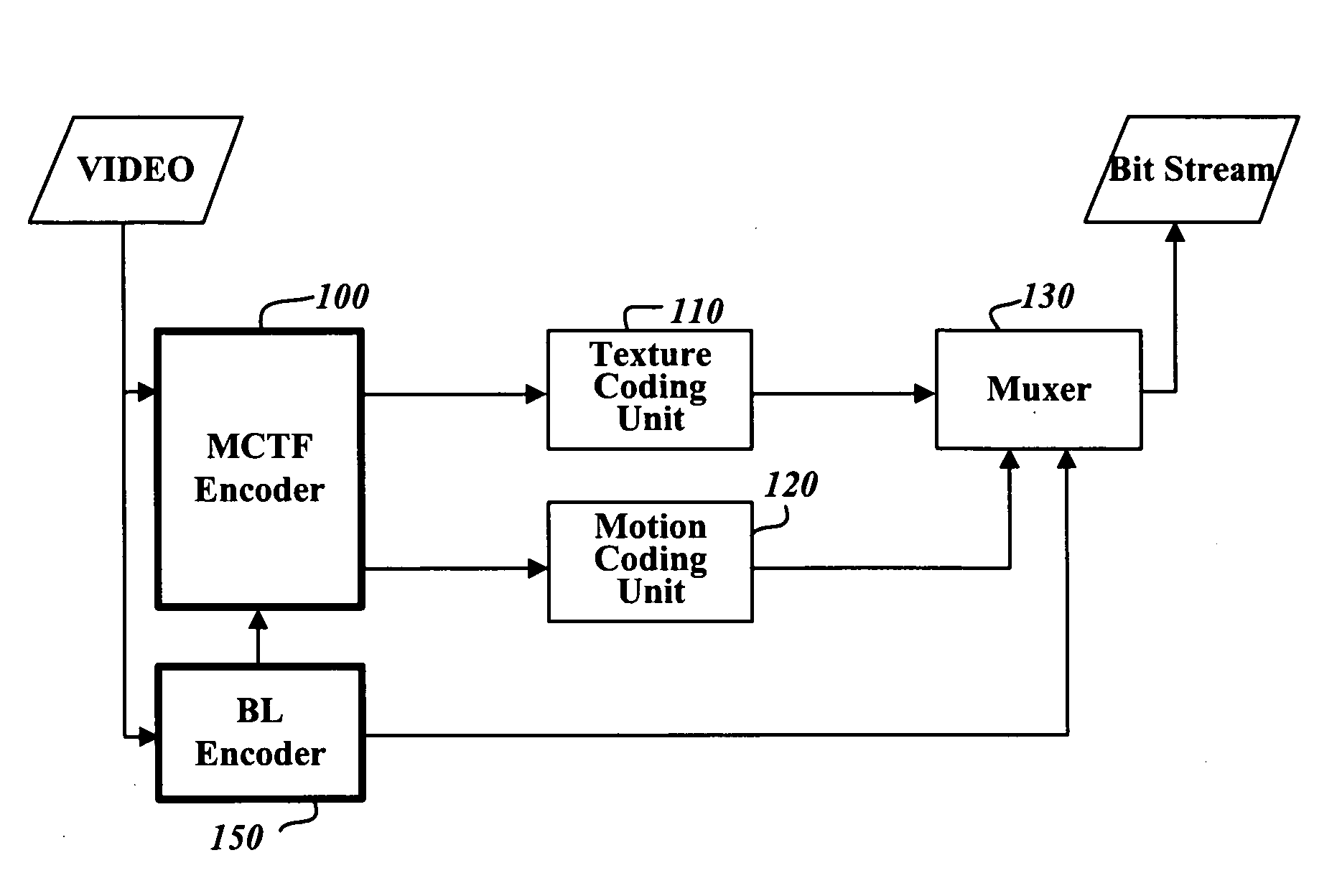
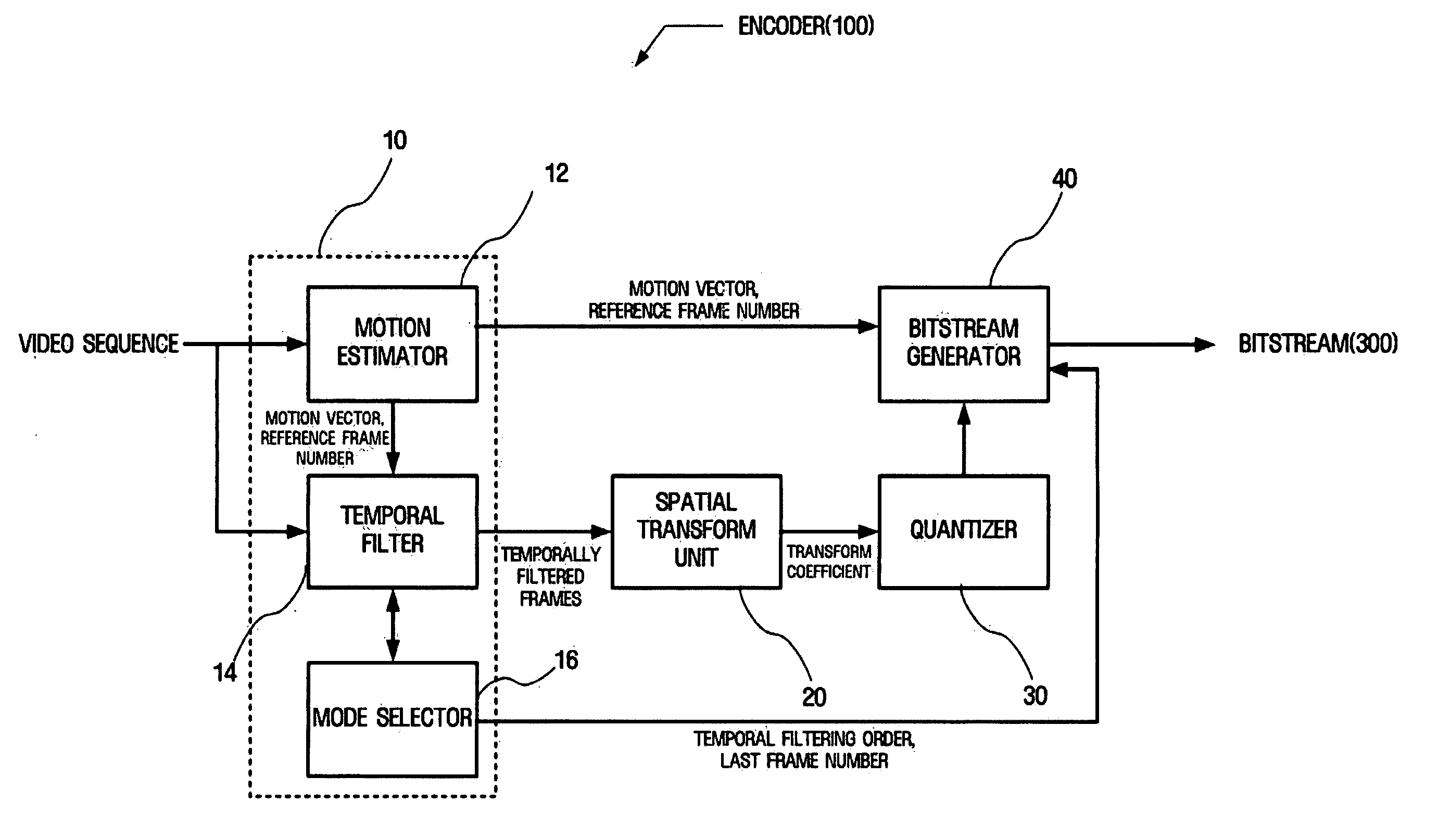
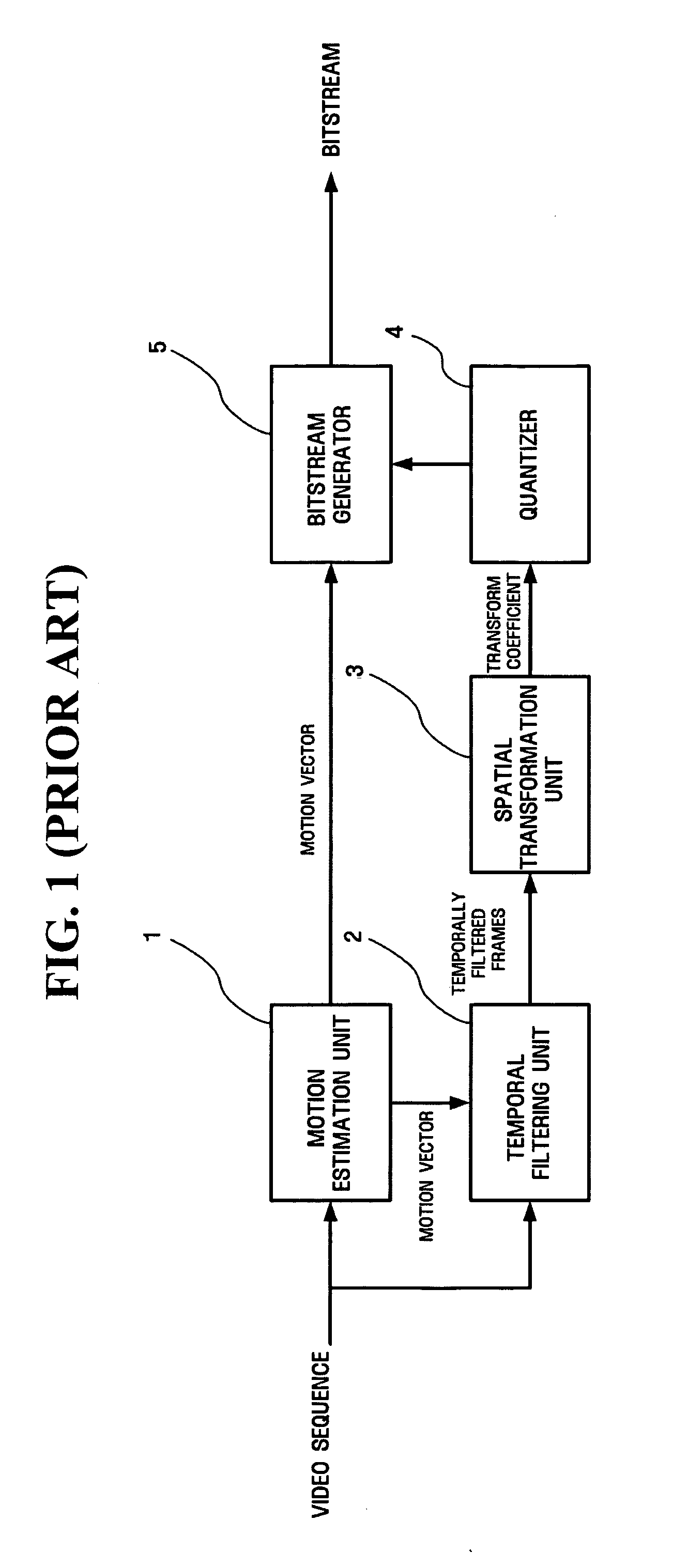
Apparatus and method for scalable video coding providing scalability in encoder part
InactiveUS20050169379A1Color television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionExtensibilityVideo encoding
A method and apparatus for scalable encoding providing scalability in an encoder. The scalable video encoding apparatus includes a mode selector that determines a temporal filtering order of a frame and a predetermined time limit as a condition for determining to which frame temporal filtering is to be performed, and a temporal filter which performs motion compensation and temporal filtering, according to the temporal filtering order determined in the mode selector, on frames that satisfy the above-described condition. According to the method and apparatus, since scalability is provided in the encoder, stability in the operation of real-time, bidirectional video streaming applications, such as video conferencing, can be ensured.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
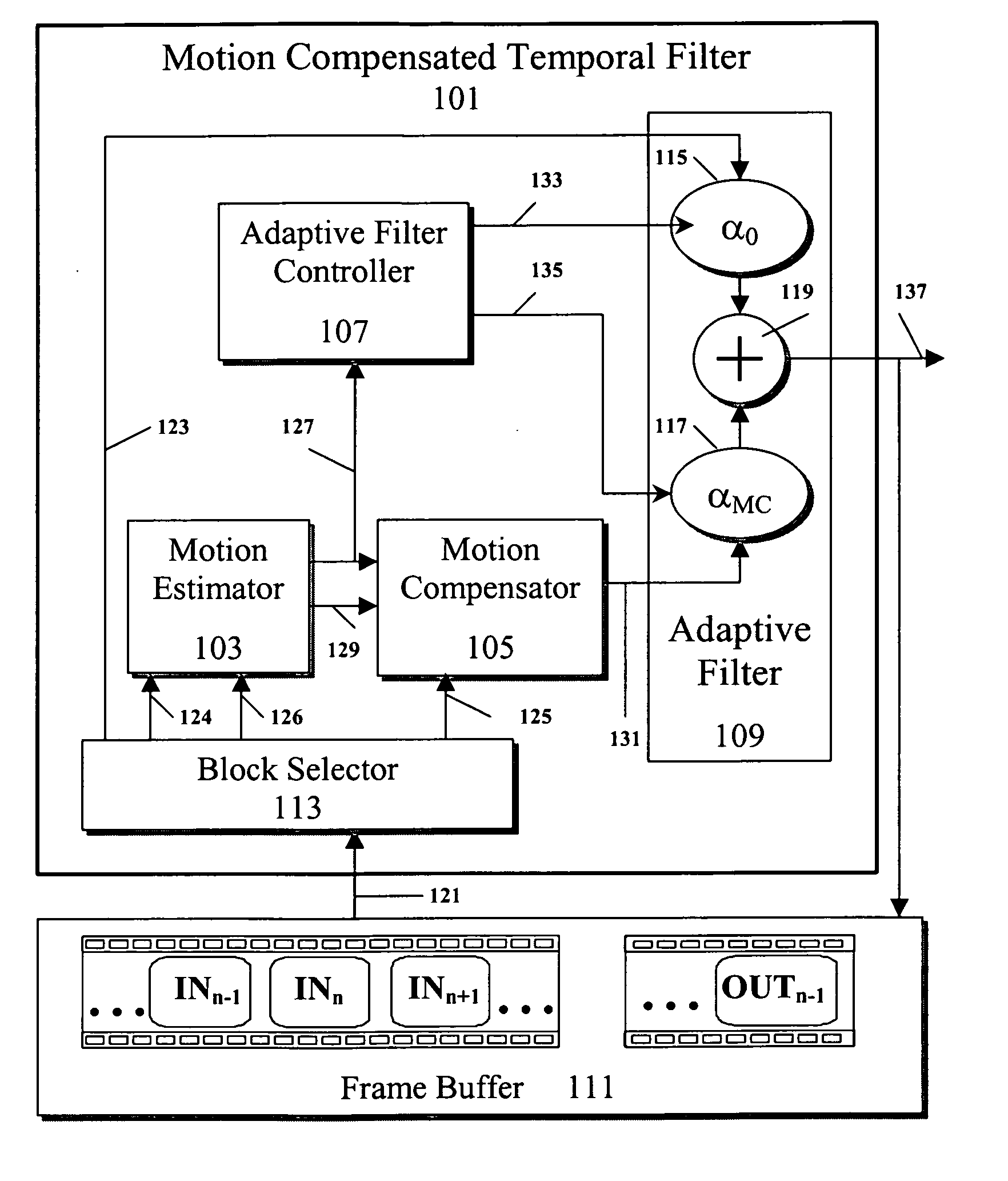
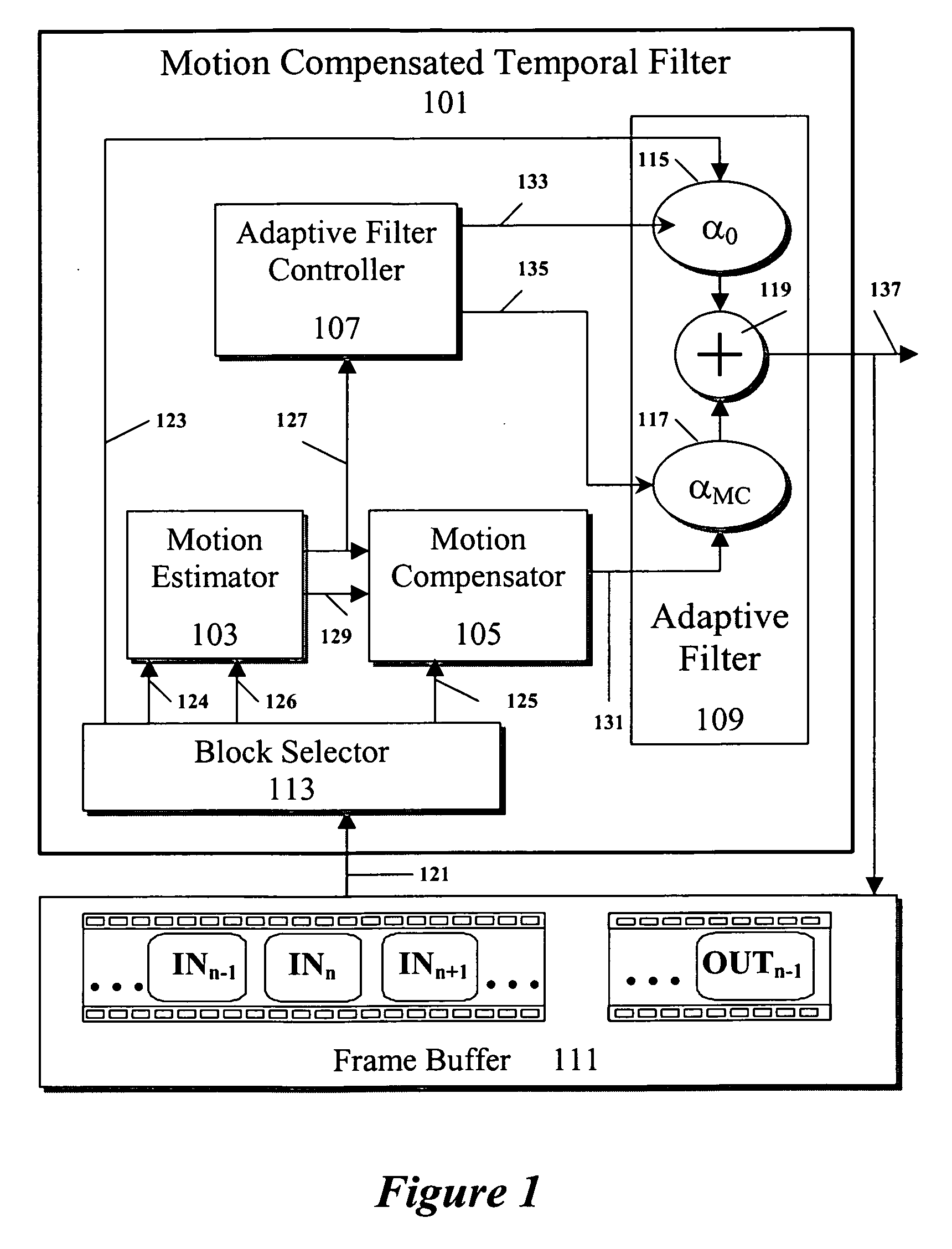
Method and system for noise reduction with a motion compensated temporal filter
ActiveUS20070014368A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationPattern recognitionTime domain
Described herein is a method and system for the reduction of noise in a video sequence. When motion is present in the video sequence, this system and method identifies motion data. With the motion data, a Motion Compensated Temporal Filter (MCTF) can apply motion compensation prior to filtering in the time domain. Temporal filtering can be performed to reduce visible noise and other detrimental artifacts.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
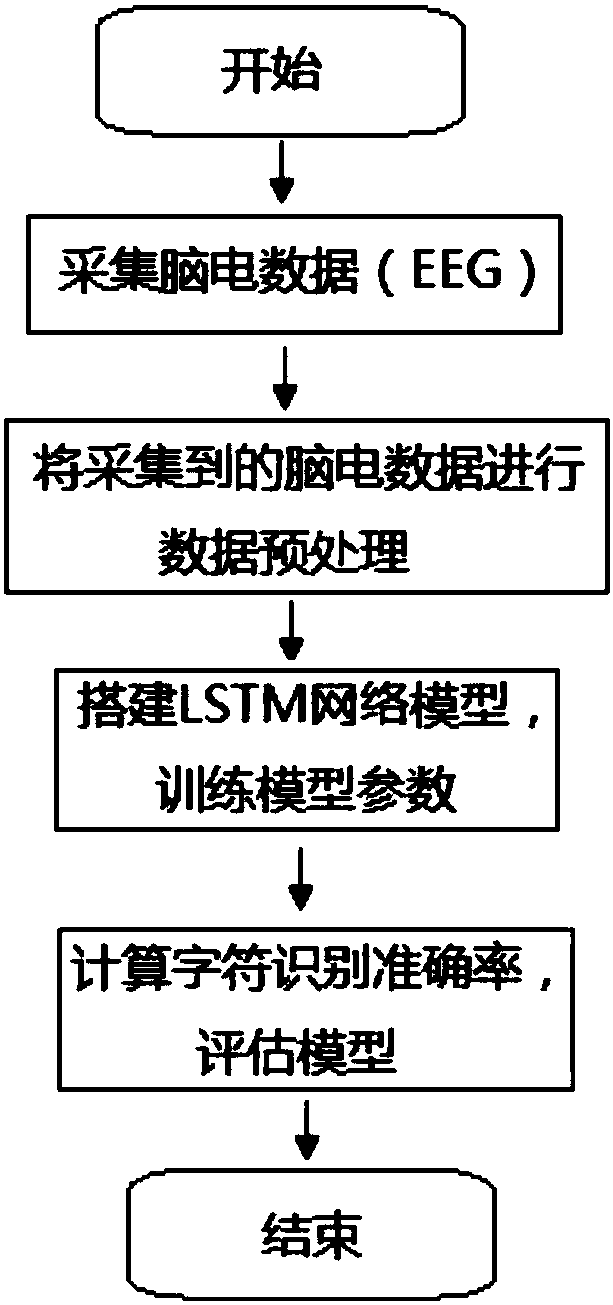
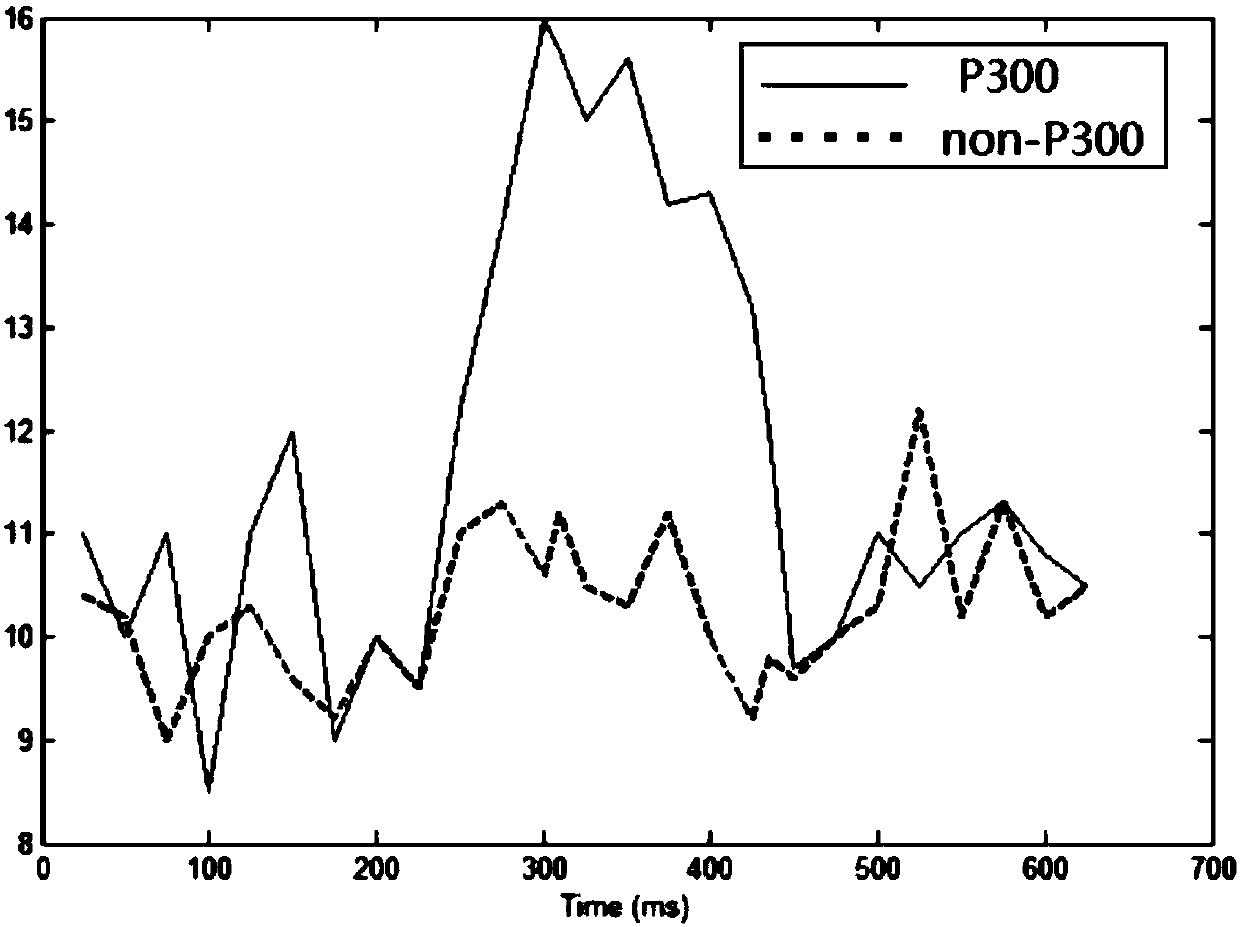
P300 signal detection method based on LSTM network
ActiveCN108304917AImprove recognition accuracyImprove generalization abilityInput/output for user-computer interactionNeural architecturesData setEeg data
The invention discloses a P300 signal detection method based on an LSTM network. The method comprises the following steps: step one, an experiment is carried out by using a P300 character speller andEEG signals are extracted to form a training set and a testing set; step two, preprocessing is carried out on the collected data and the processed data are used as an input data set of a model; step three, an LSTM layer is designed as a spatio-temporal filter of the EEG data set, an all-connection layer is added after a least time step of the LSTM layer, a Softmax layer is added to convert a network output value into a probability form, and then the network is trained and a model parameter is determined, wherein the Softmax layer is a generalized form of the logic function; and step four, a model evaluation index and a testing set character recognition rate are calculate to verify the performance of the model. The method has the following characteristics: no manual feature extraction is needed; the recognition performance is good; the generalization ability is high; and the good information conversion rate is realized. The P300 signal detection method is a good P300 classification algorithm.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GUANGDA INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for motion adaptive pre-filtering
A video filter includes a motion detector to detect motion between frames of a video for each pixel, a shape adaptive spatial filter and a weighted temporal filter. The spatial filter and the temporal filter are smoothly mixed together based on the amount of motion detected by the motion detector for each pixel. When the motion detected by the motion detector is low, the video filter tends to do more temporal filtering. When the motion detected by the motion detector is high, the video filter tends to do more spatial filtering.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
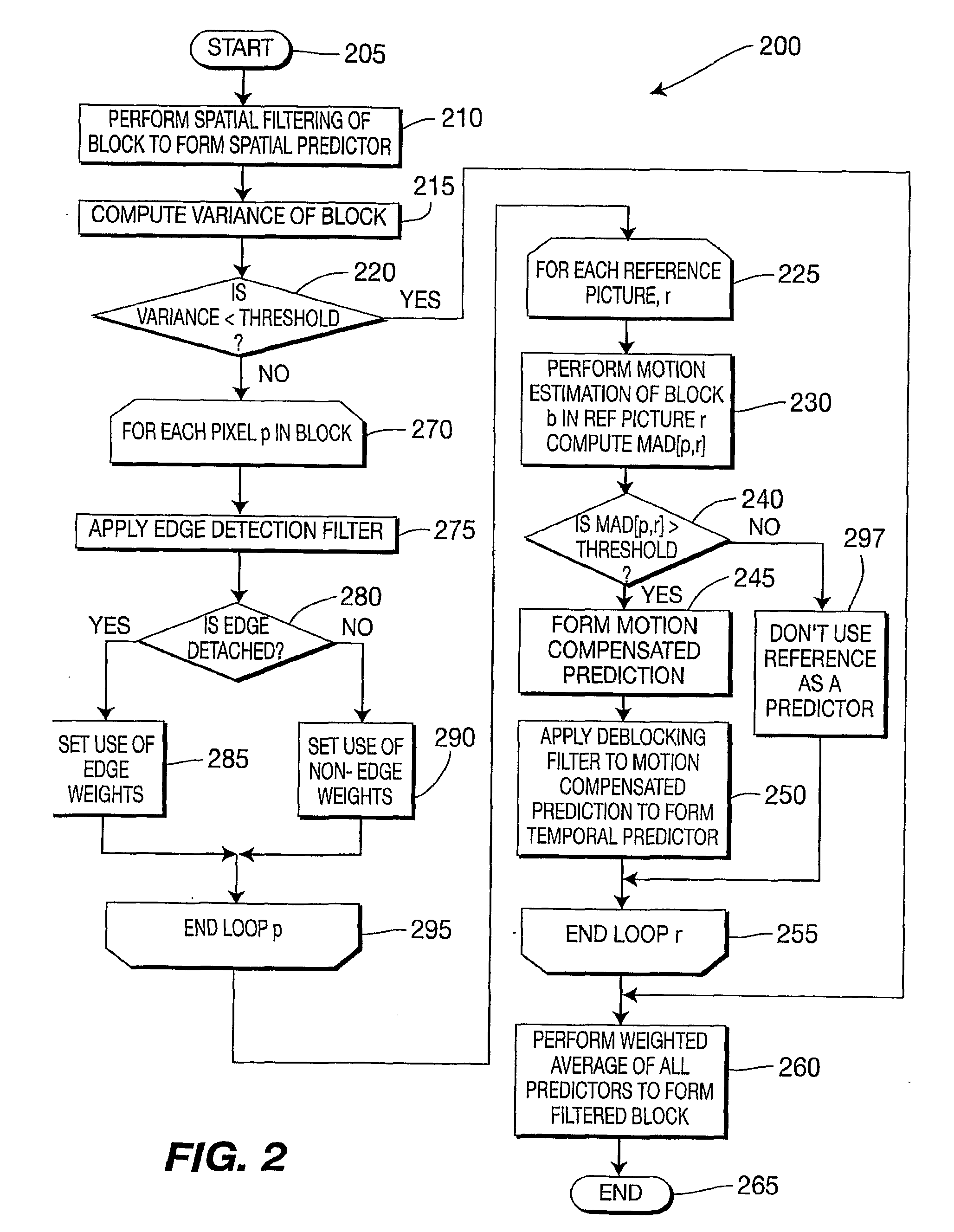
Method and Apparatus for Edge-Based Spatio-Temporal Filtering
ActiveUS20100220939A1Reduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
There are provided methods and apparatus for edge-based spatio-temporal filtering. An apparatus for filtering a sequence of pictures includes a spatial filter, a motion compensator, a deblocking filter, and a temporal filter. The spatial filter is for spatially filtering a picture in the sequence and at least one reference picture selected from among previous pictures and subsequent pictures in the sequence with respect to the picture. The motion compensator, in signal communication with the spatial filter, is for forming, subsequent to spatial filtering, multiple temporal predictions for the picture from the at least one reference picture. The deblocking filter, in signal communication with the motion compensator, is for deblock filtering the multiple temporal predictions. The temporal filter, in signal communication with the deblocking filter, is for temporally filtering the multiple temporal predictions and combining the multiple temporal predictions to generate a noise reduced version of the picture.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method and System for Adaptive Preprocessing for Video Encoder
InactiveUS20090074084A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNoise levelMotion vector
Certain aspects of a method and system for adaptive preprocessing for an encoder may comprise filtering received video data using one or more spatial and / or temporal filtering parameters. The spatial and / or temporal filtering parameters may be adaptively updated to achieve a targeted bitrate based on statistical analysis of received video data and encoder feedback. The statistical analysis of received video data may comprise analysis of statistical inputs such as an encoding standard of the received video data, an average quantization factor, an input noise level, an average picture luma level, a motion vectors histogram, and a content type detection of the received video data. The spatial filtering parameters may be adaptively updated during an I frame of the received video data and the temporal filtering parameters may be adaptively updated per frame of the received video data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
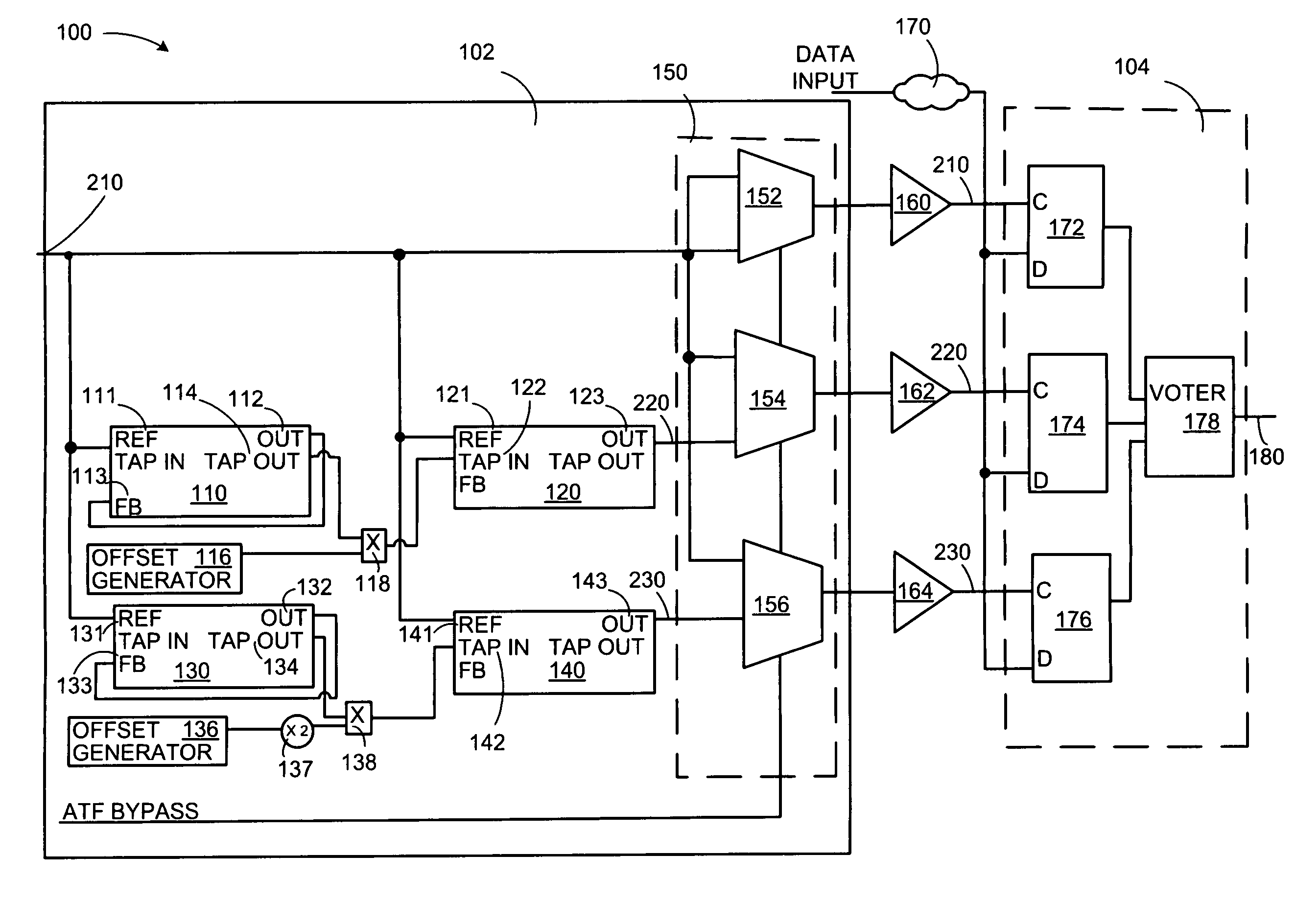
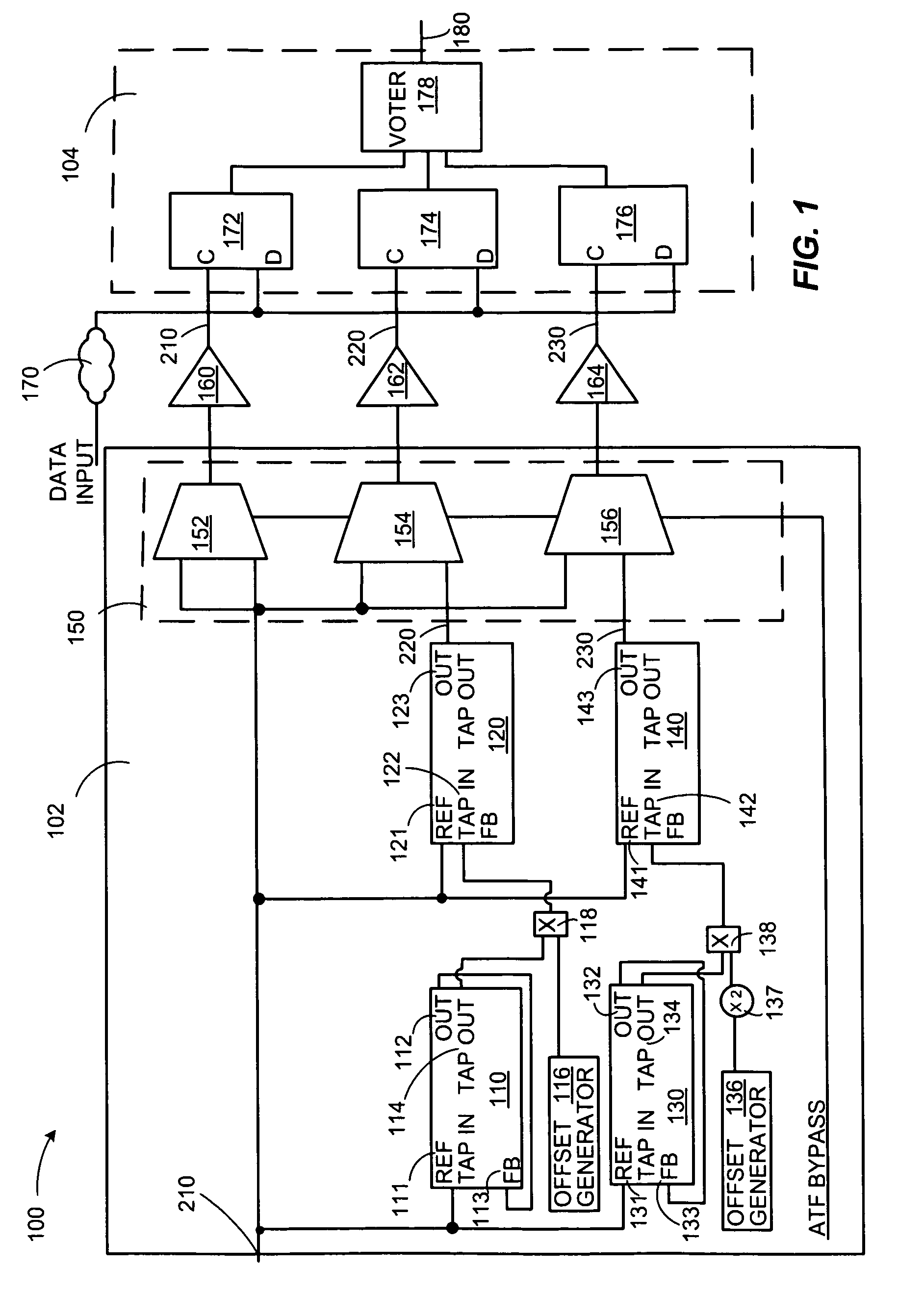
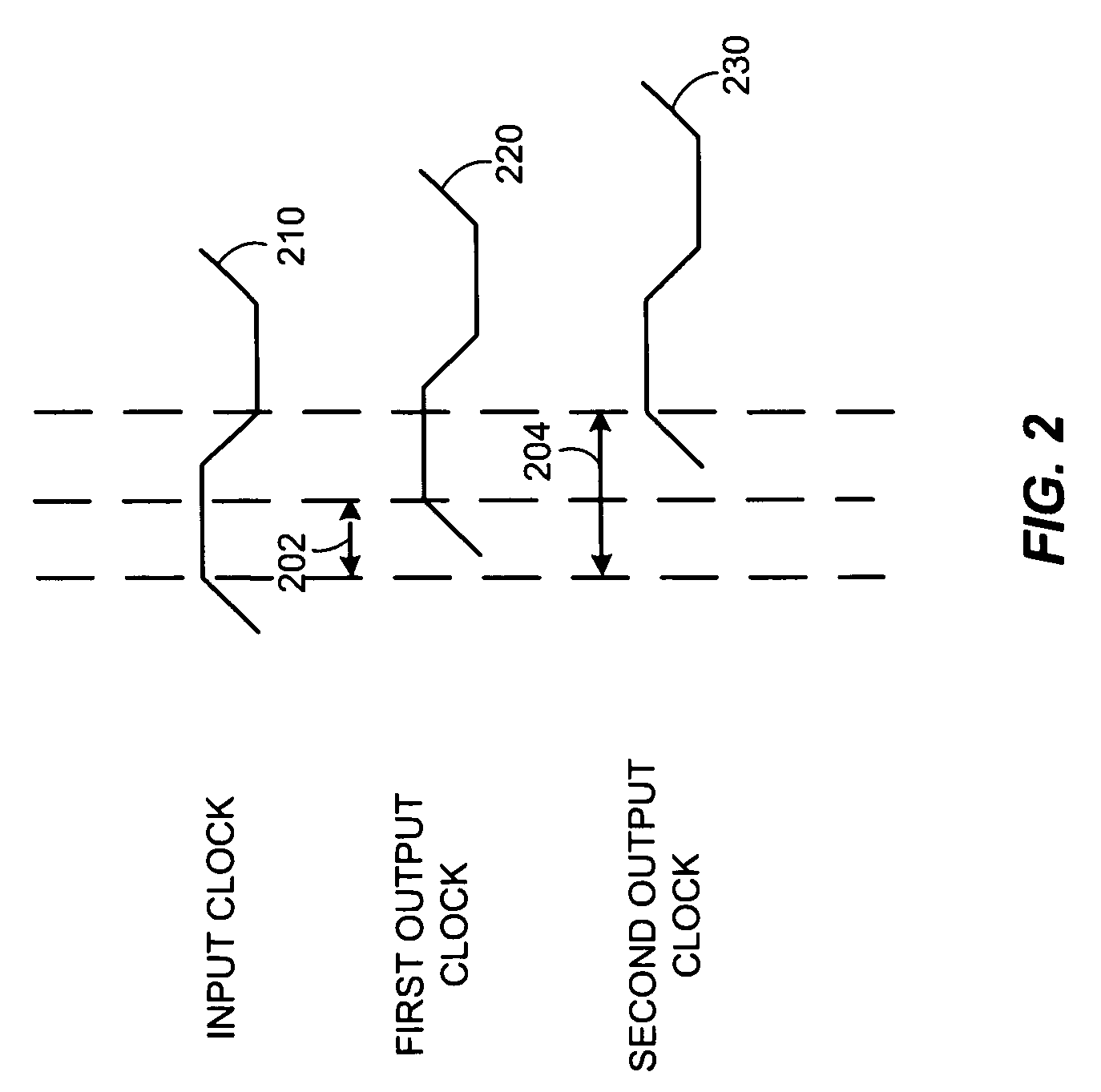
Adaptive temporal filtering of single event effects
Technologies are described herein for mitigating the effects of single event effects or upsets on digital semiconductor device data paths and clocks utilizing an adaptive temporal filter. The adaptive temporal filter includes a master delay line and a slave delay line to generate two output clock signals that remain unaffected by variations in process, voltage and temperature (PVT) conditions. The adaptive temporal filter supplies the three independent clock signals having a programmable phase relationship, to a triple voting register structure for storing and outputting an uncorrupted data value using a majority voter.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System, computer program product and associated methodology for video motion detection using spatio-temporal slice processing
ActiveUS8121424B2Accurate identificationMotion can be efficientImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo sequenceA* search algorithm
A system, computer program product and associated methodology for video motion detection combines a series of images of a video sequence into an image volume having vertices of X, Y and t. The image volume is sliced in either the (X,t) or (Y,t) planes, filtered with a spatio-temporal filter and thresholded to reduce the amount of information. Then a search algorithm searches along search lines in a subset of the video sequence to locate motion. Motion can be detected by identifying lines that are not parallel to any of the vertices. Stationary subjects and lighting changes appear as lines parallel to one of the vertices. Thus, true motion can be distinguished from lighting changes.
Owner:AXIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com