Patents
Literature
188results about How to "Suppress luminescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
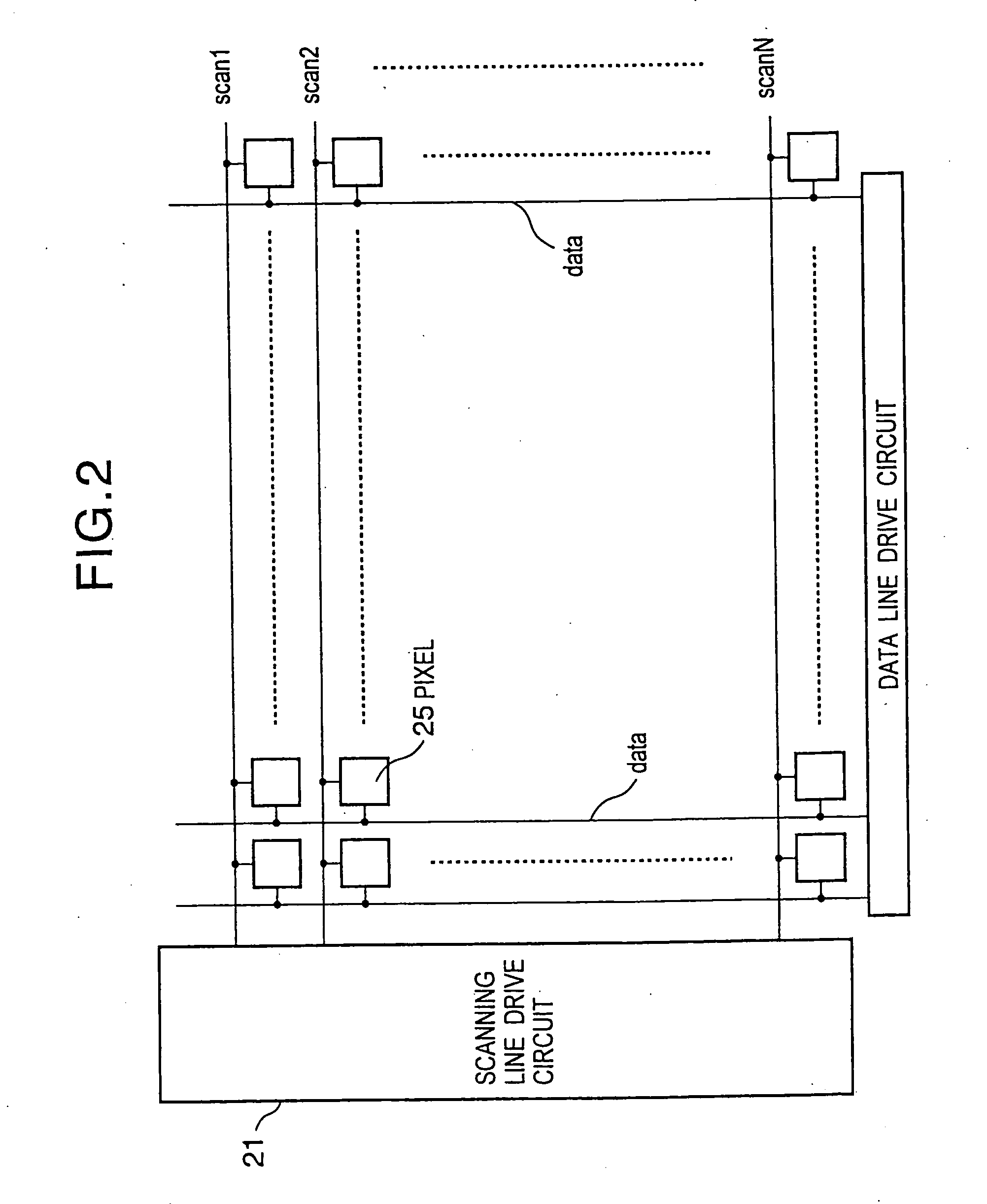
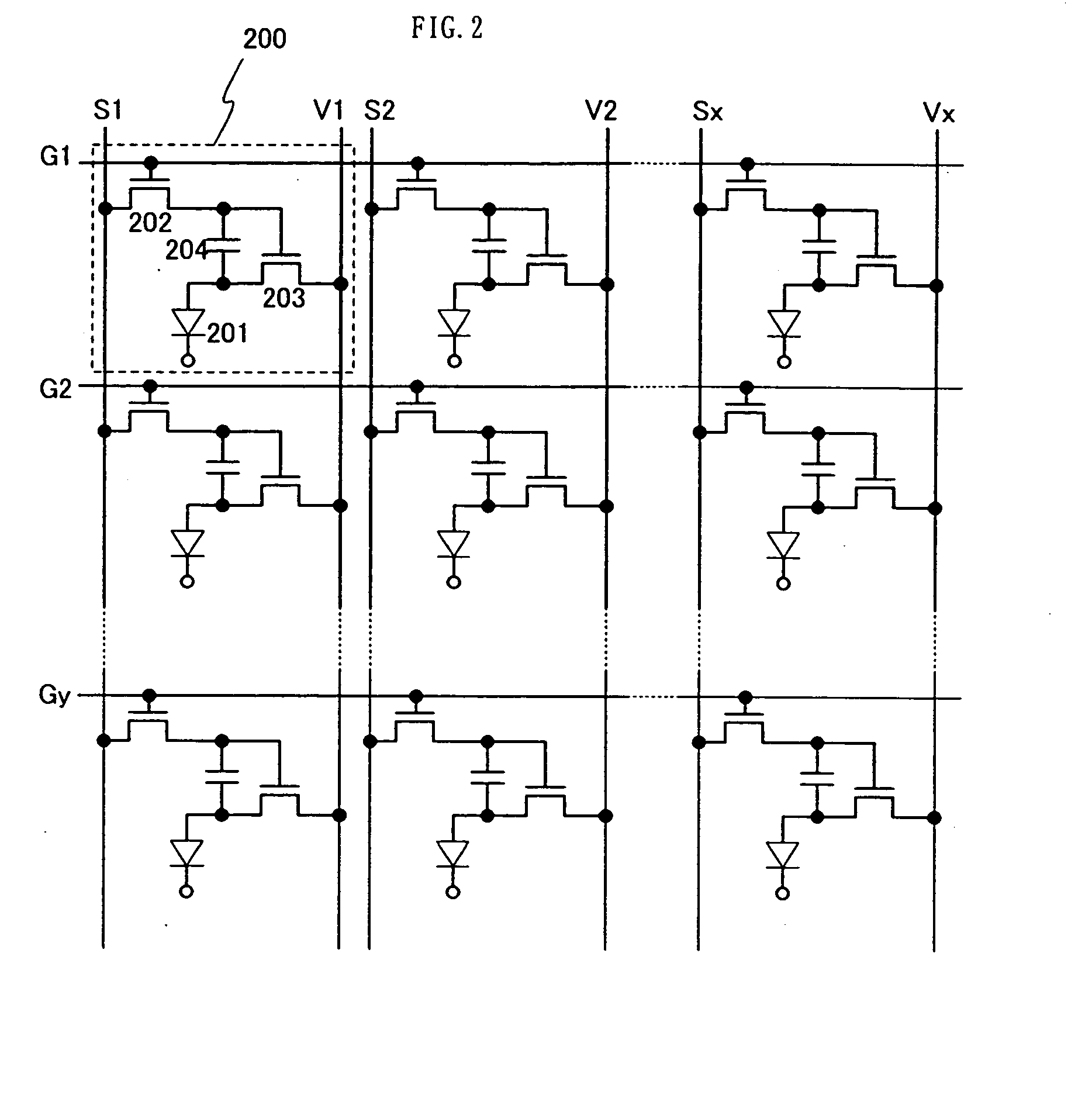
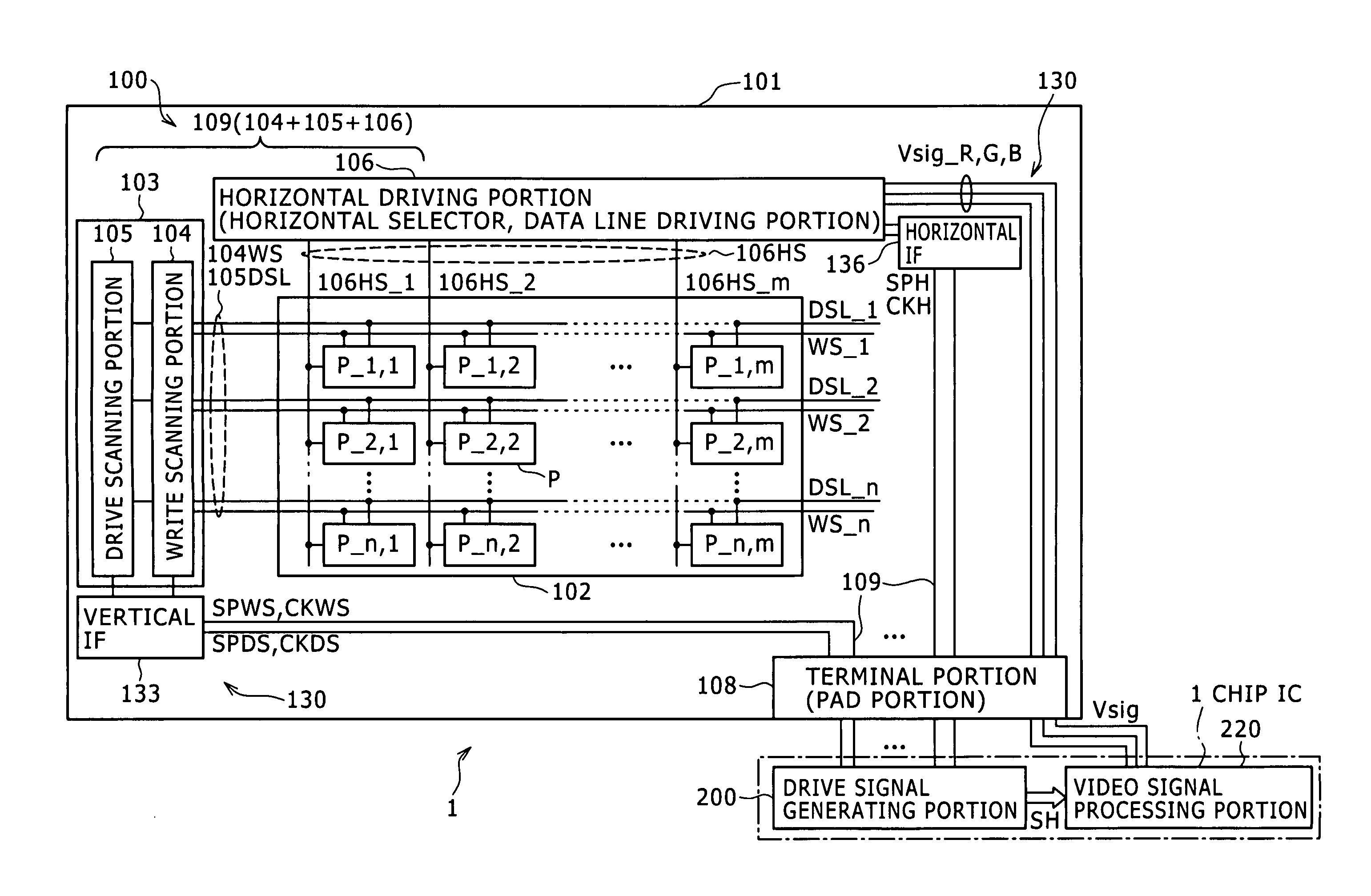
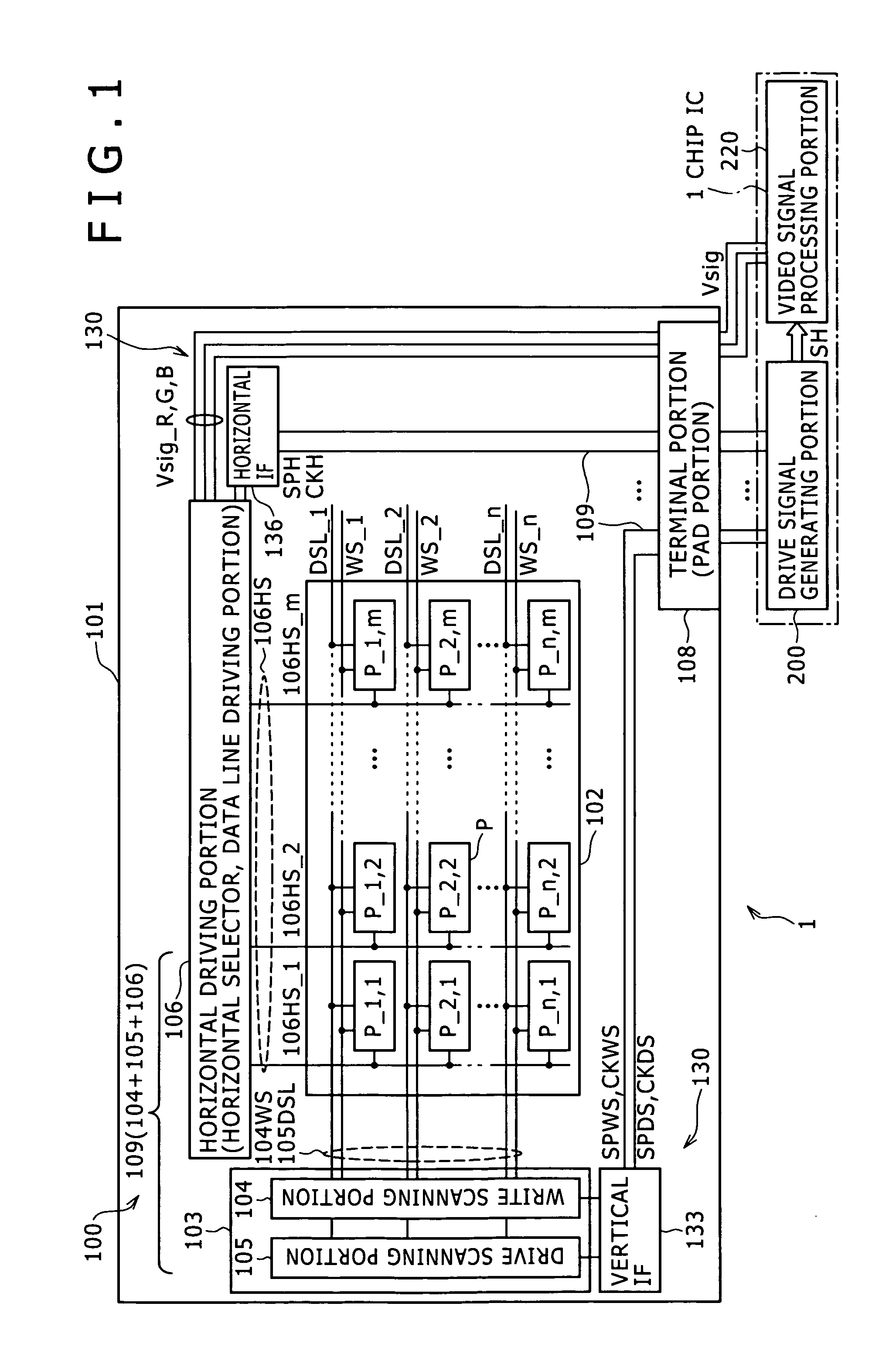
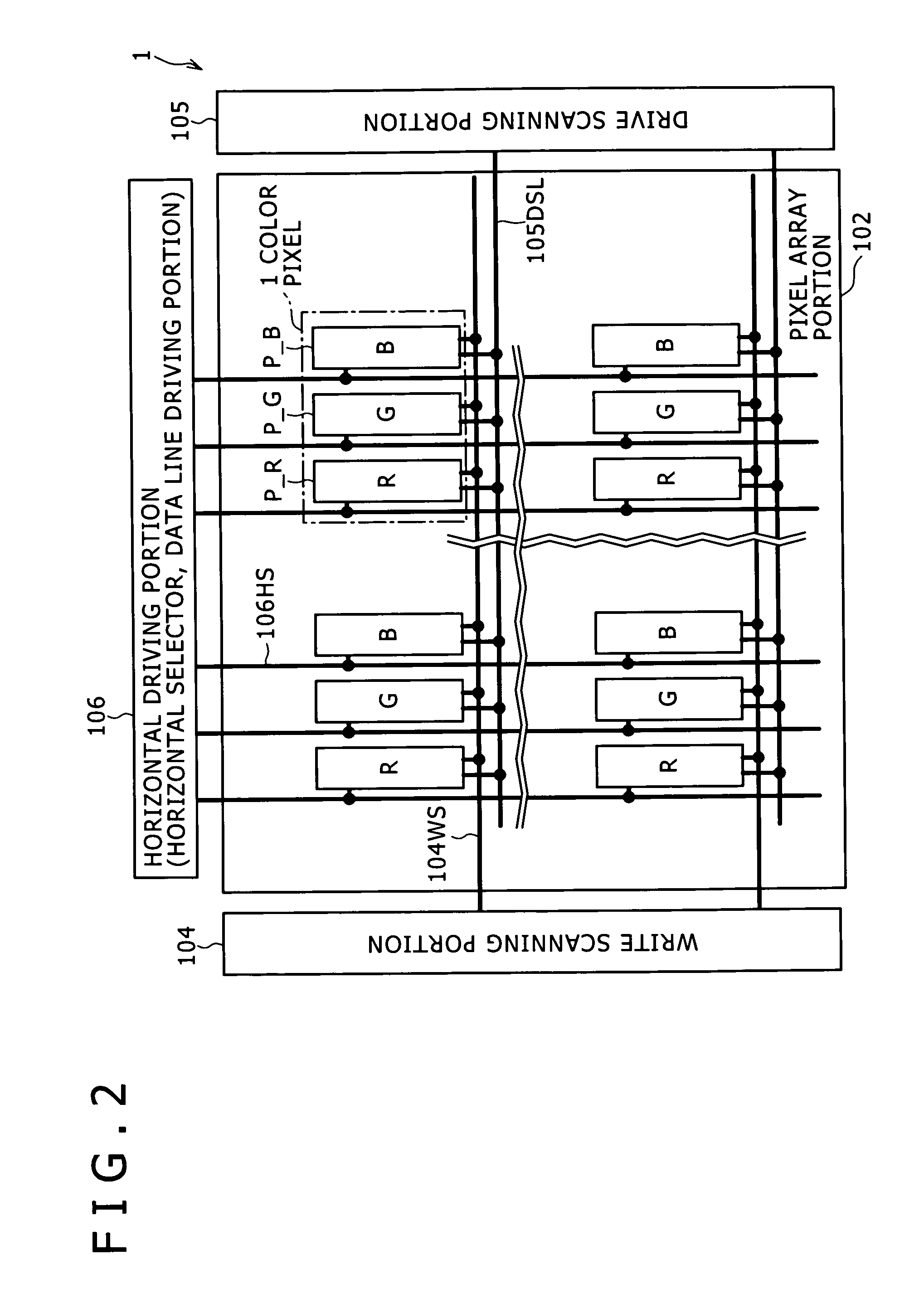
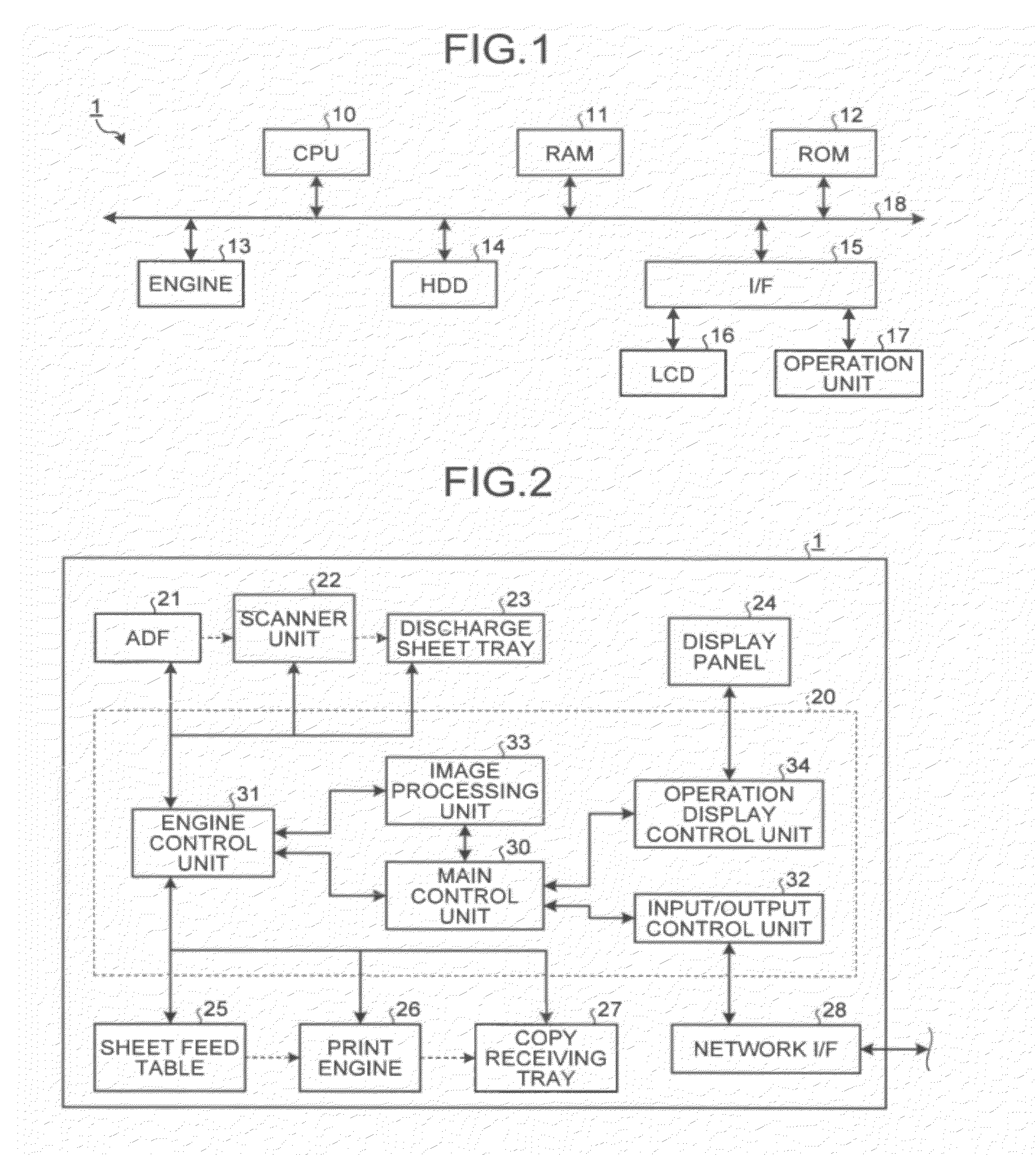
Current drive circuit and display device using the same, pixel circuit, and drive method
InactiveUS6859193B1Stably and accurately supplyingHigh quality imagingSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriving currentDisplay device
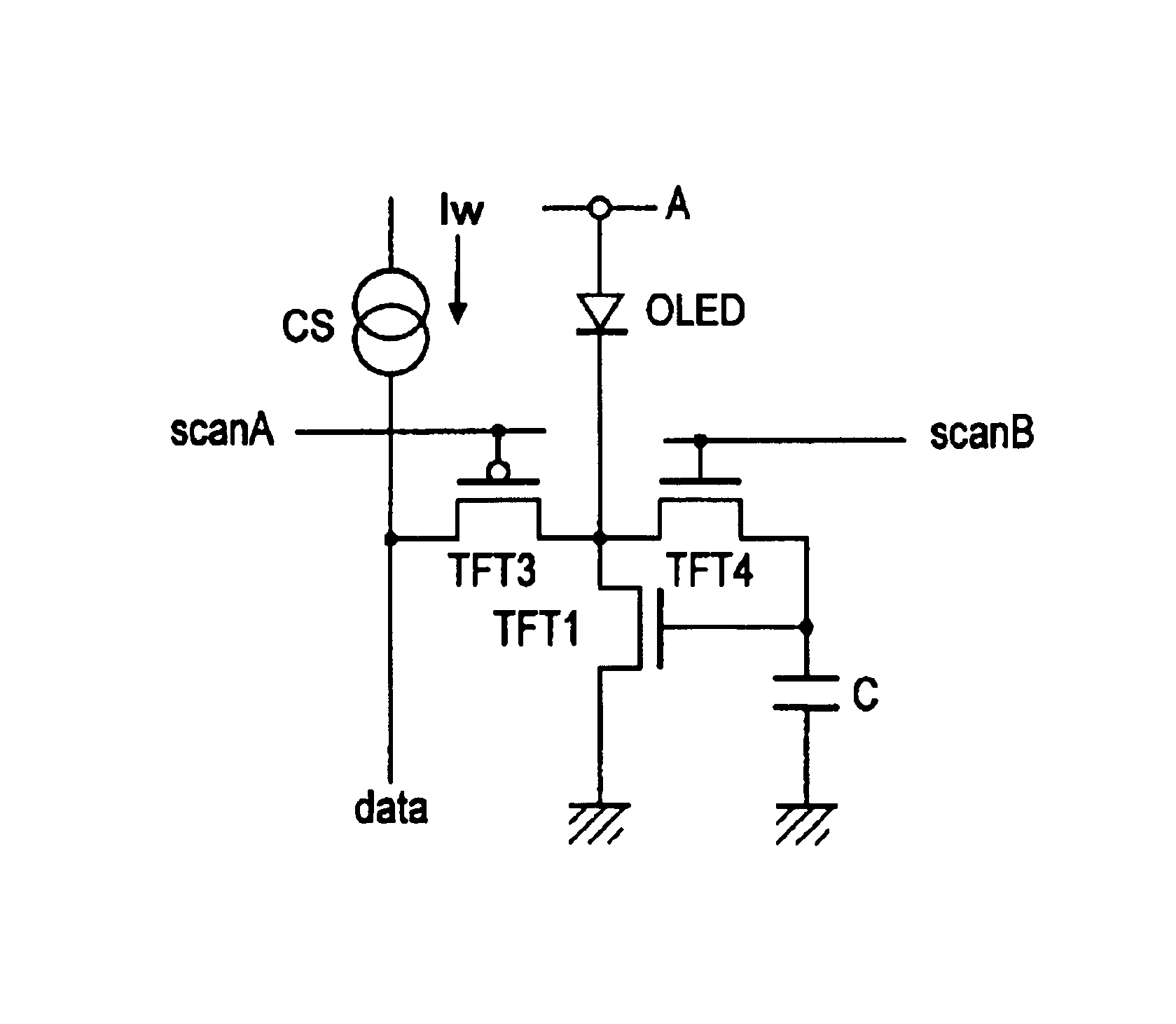
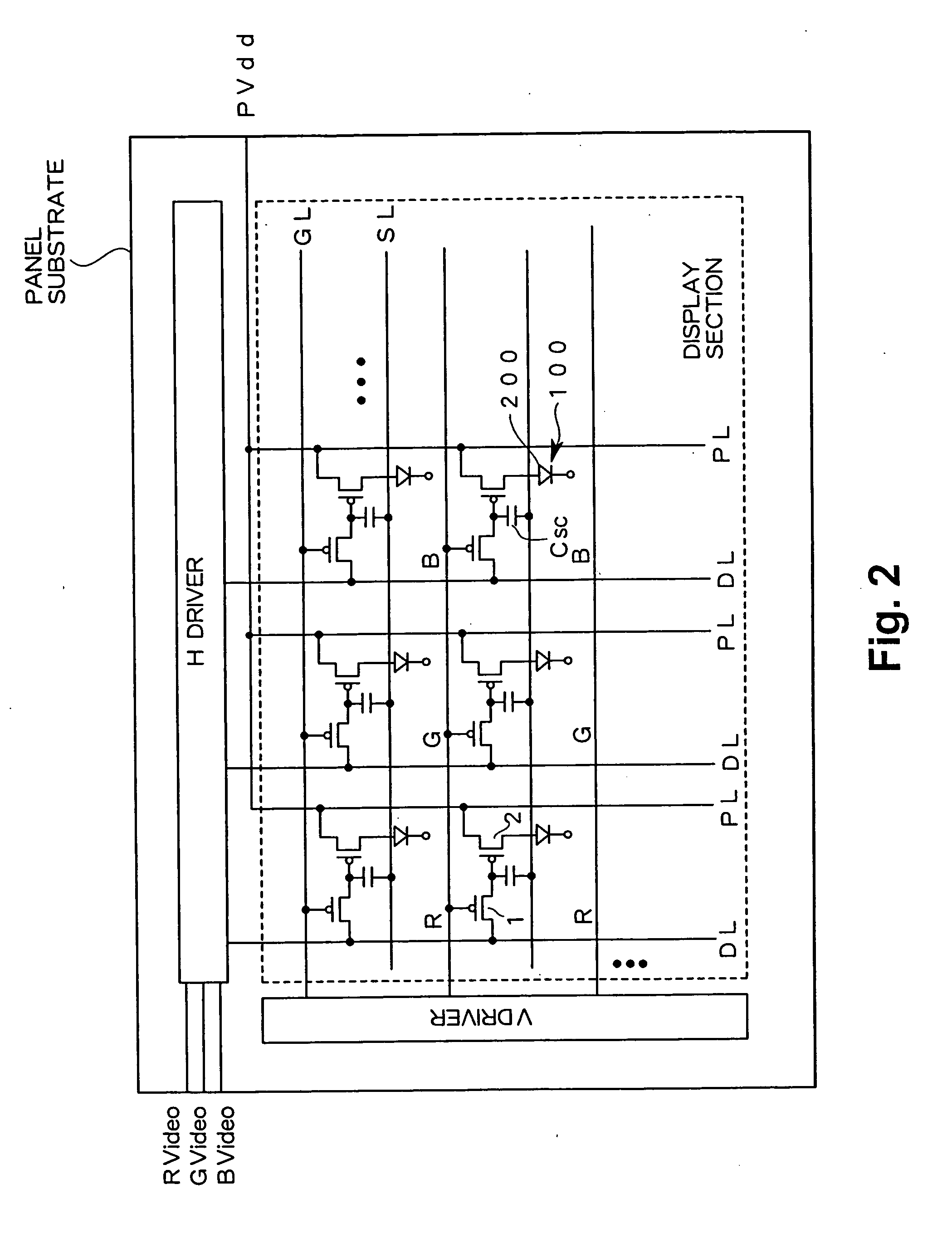
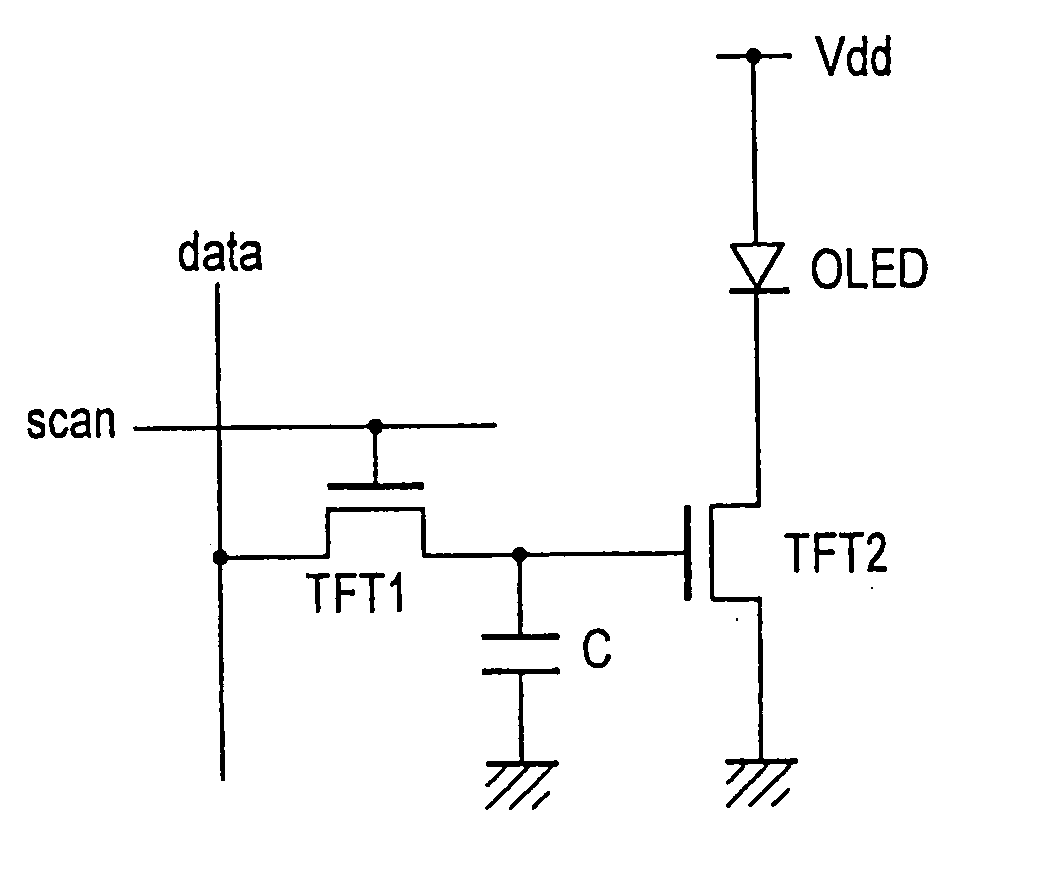
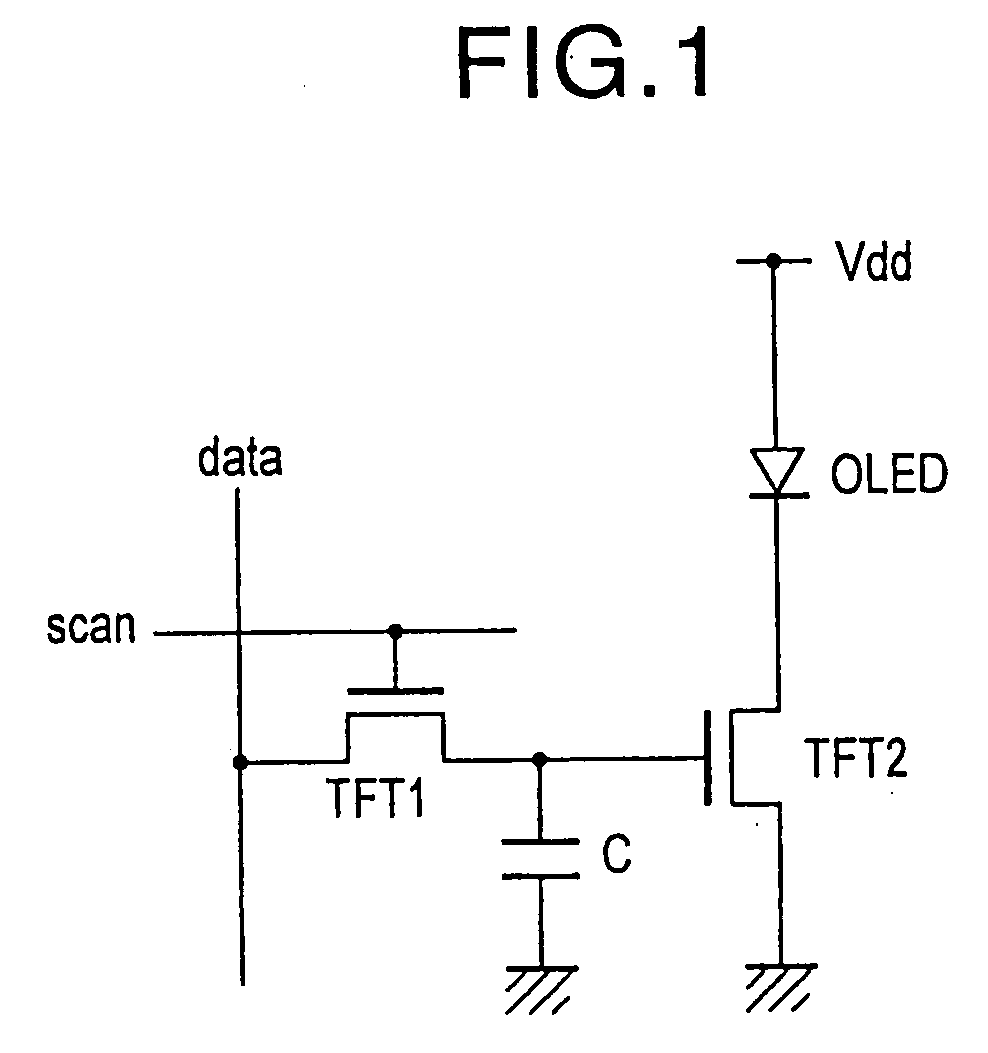
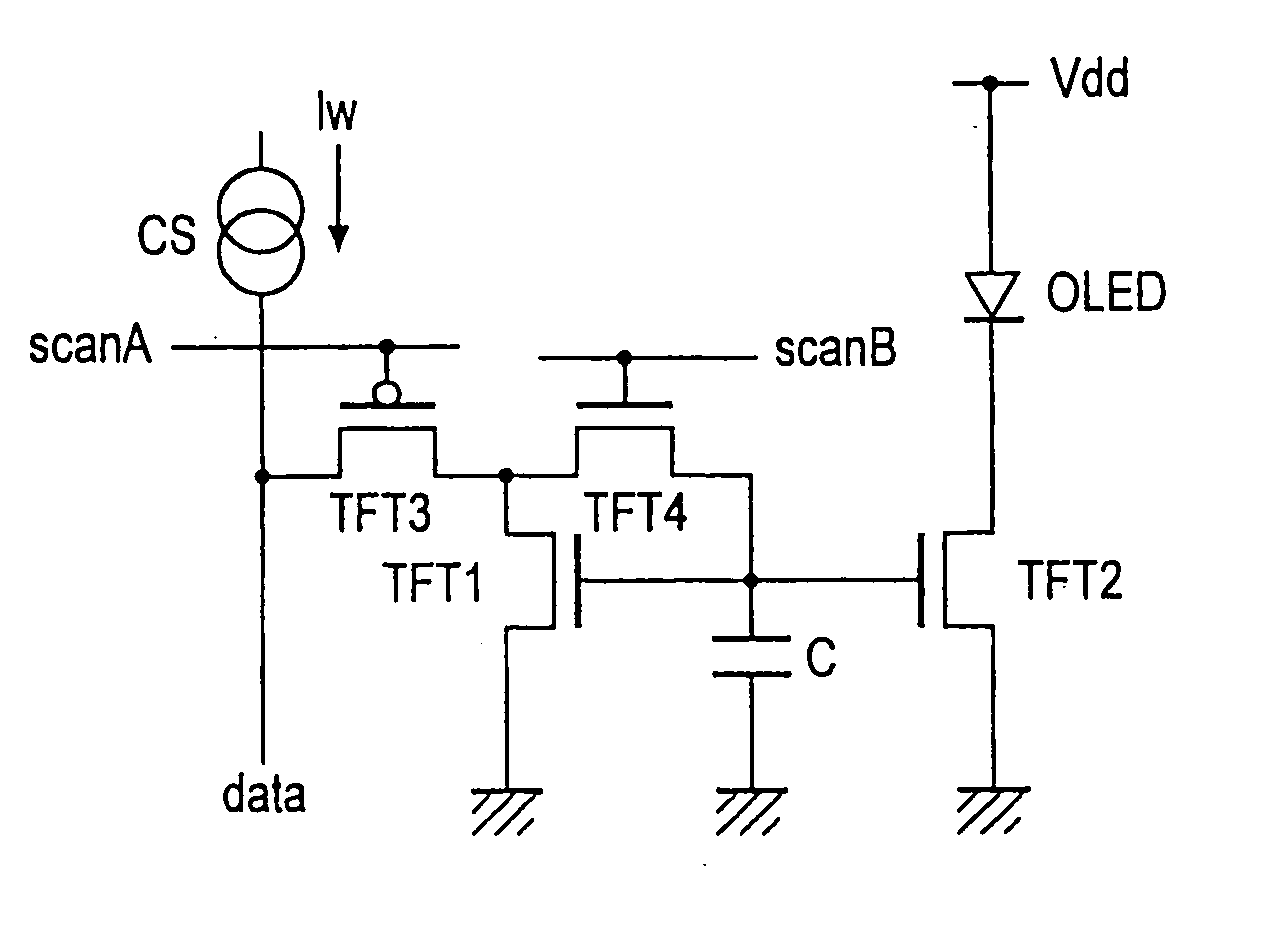
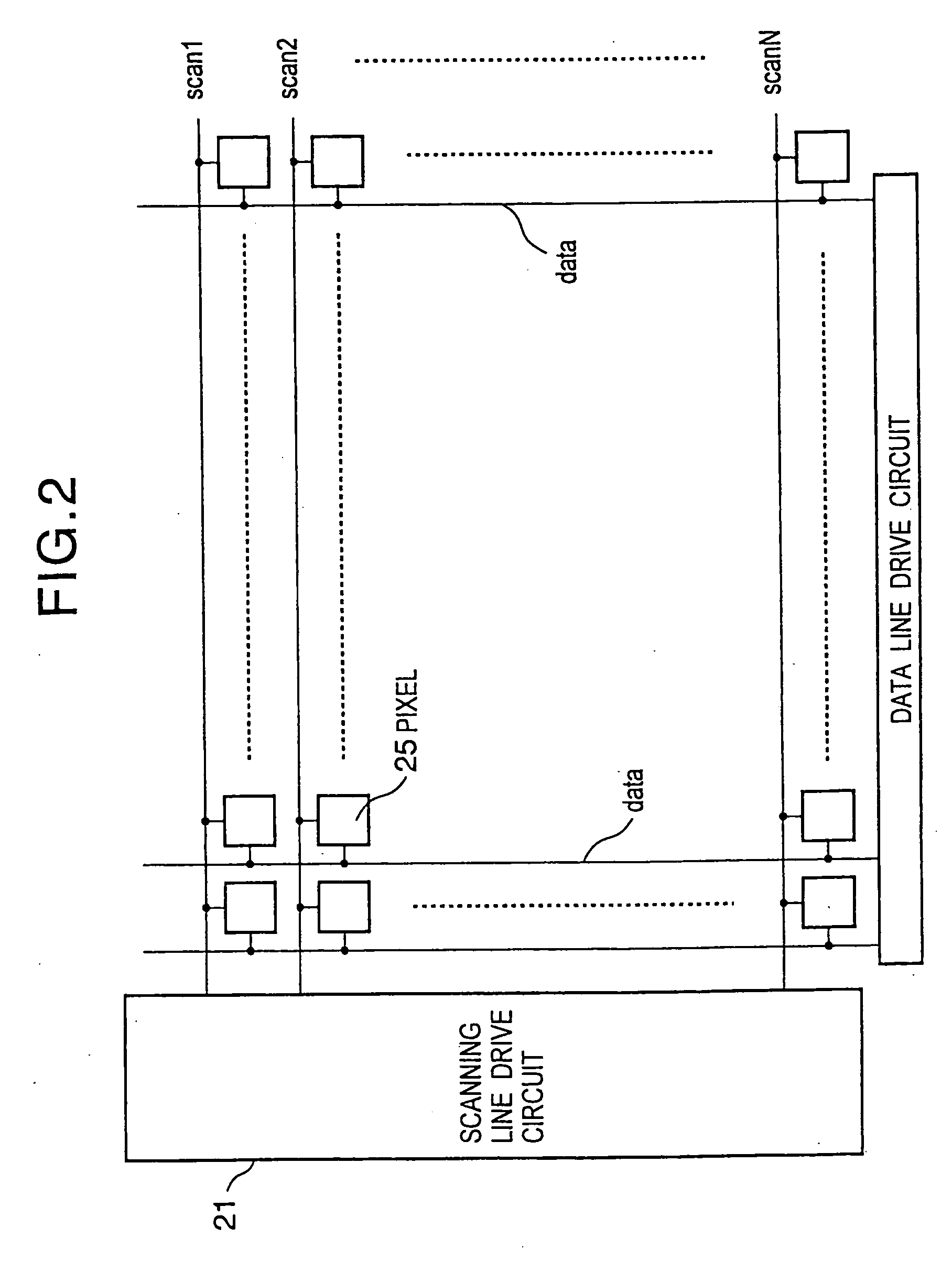
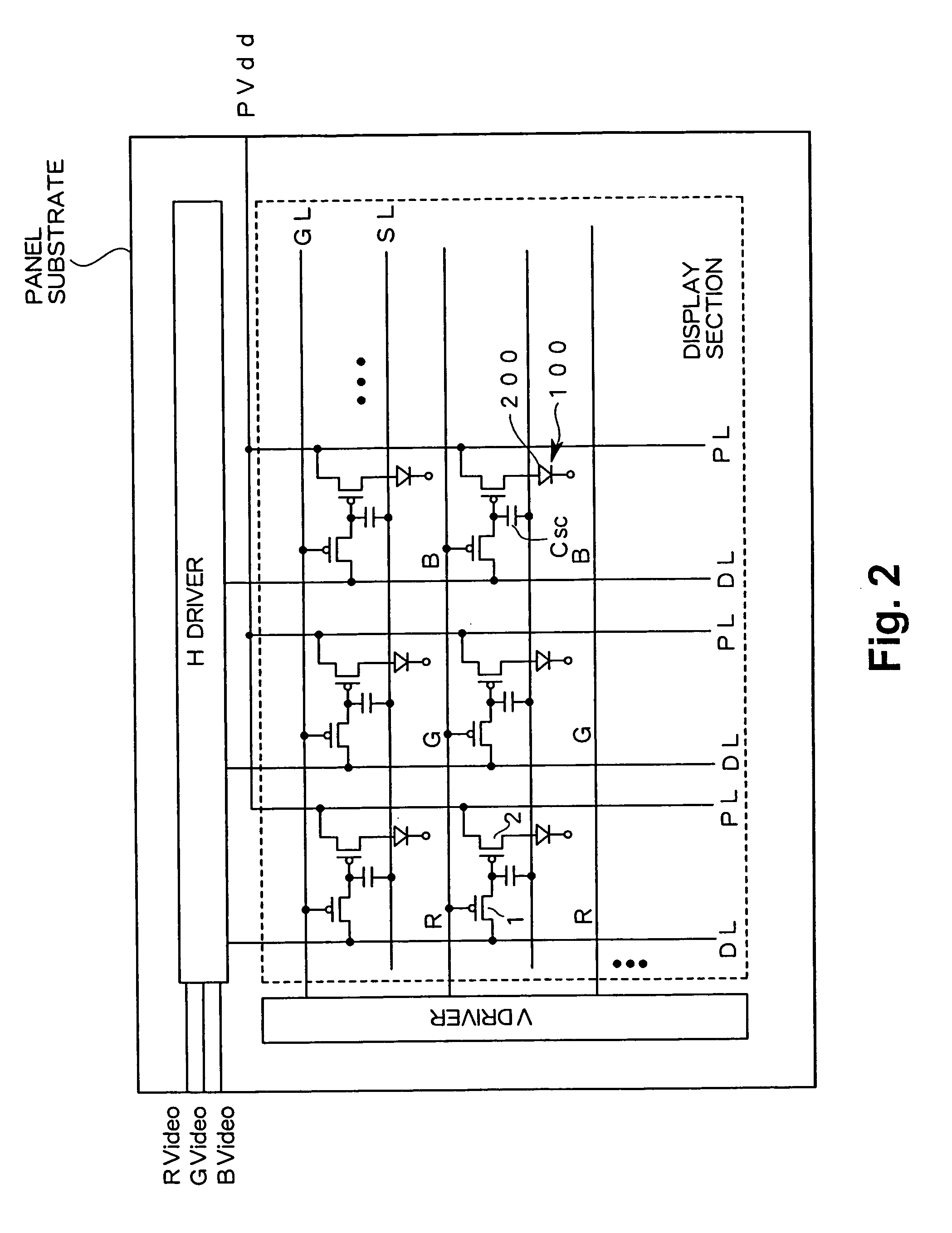
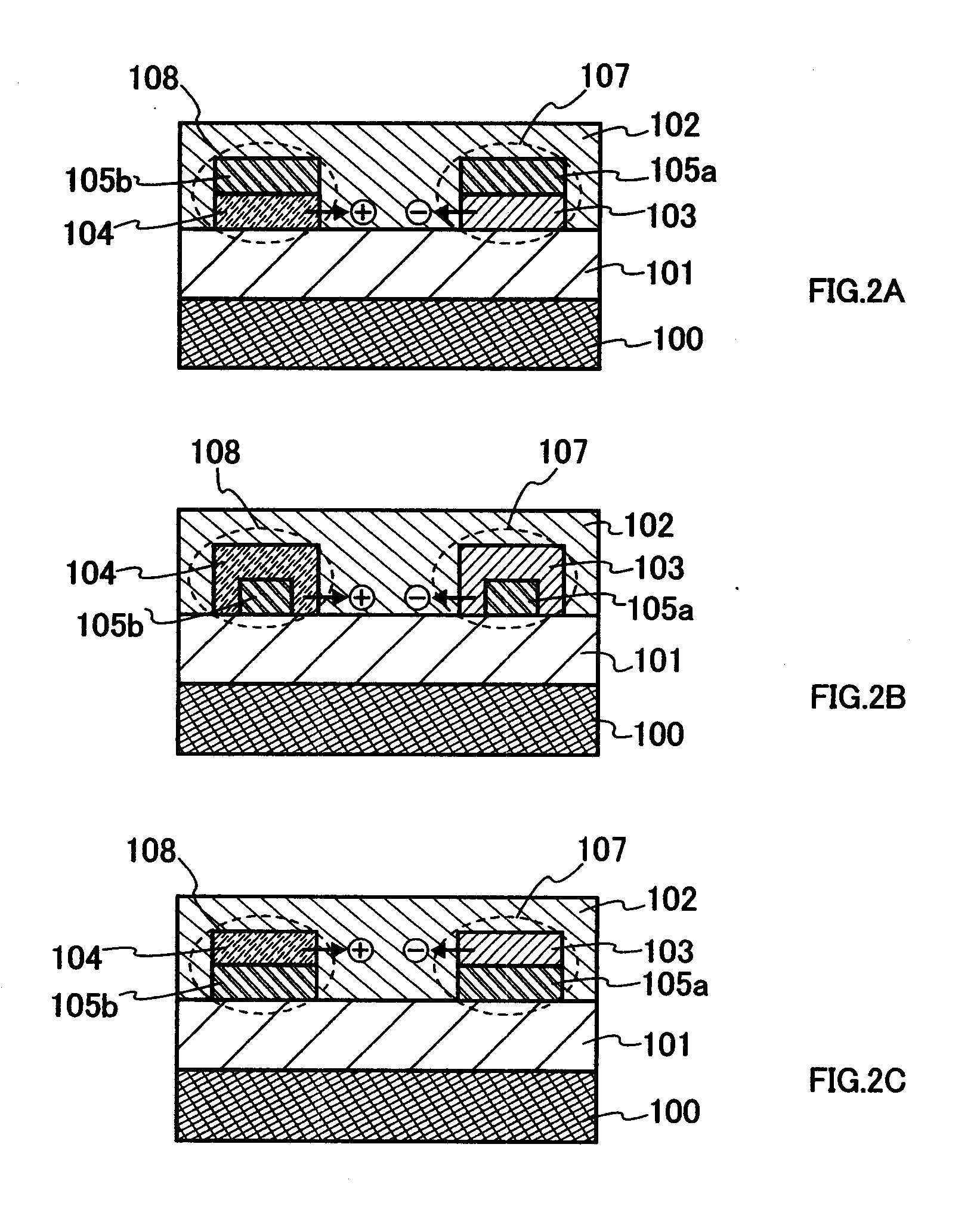
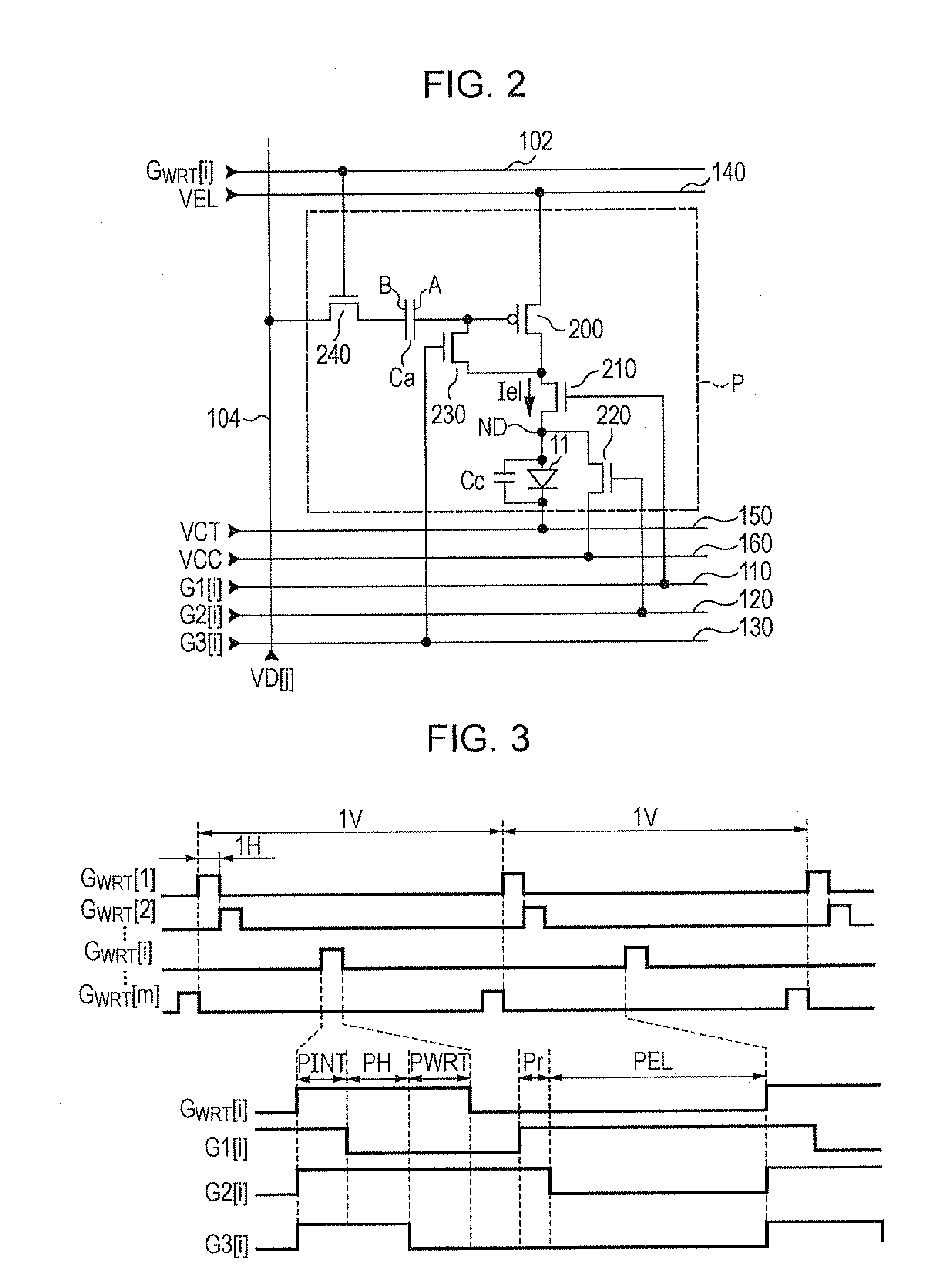
A display including a current drive circuit capable of supplying a desired current to a light-emitting element in each pixel stably and accurately irrespective of the characteristic variations of active elements in the pixel, thereby providing a high-definition image. Each pixel is composed of a receiving transistor (TFT3) for receiving a signal current (1w) from a data ine (data) when a scanning line (scanA) is selected, a converting transistor (TFT1) for converting the current level of the received signal current (1w) to a voltage level and holding the voltage level, and a driving transistor (TFT3) for allowing a drive current having a current level corresponding to the held voltage level to flow through light-emitting element (OLED). The converting thin film transistor (TFT1) generates the converted voltage level at its gate by allowing the signal current (Iw) through its channel, and a capacitor (C) holds the voltage level at the gate of the transistor (TFT1). The transistor (TFT2) allows the drive current having a current level corresponding to the voltage level held by the capacitor (C) to flow through the light-emitting element (OLED).
Owner:SONY CORP
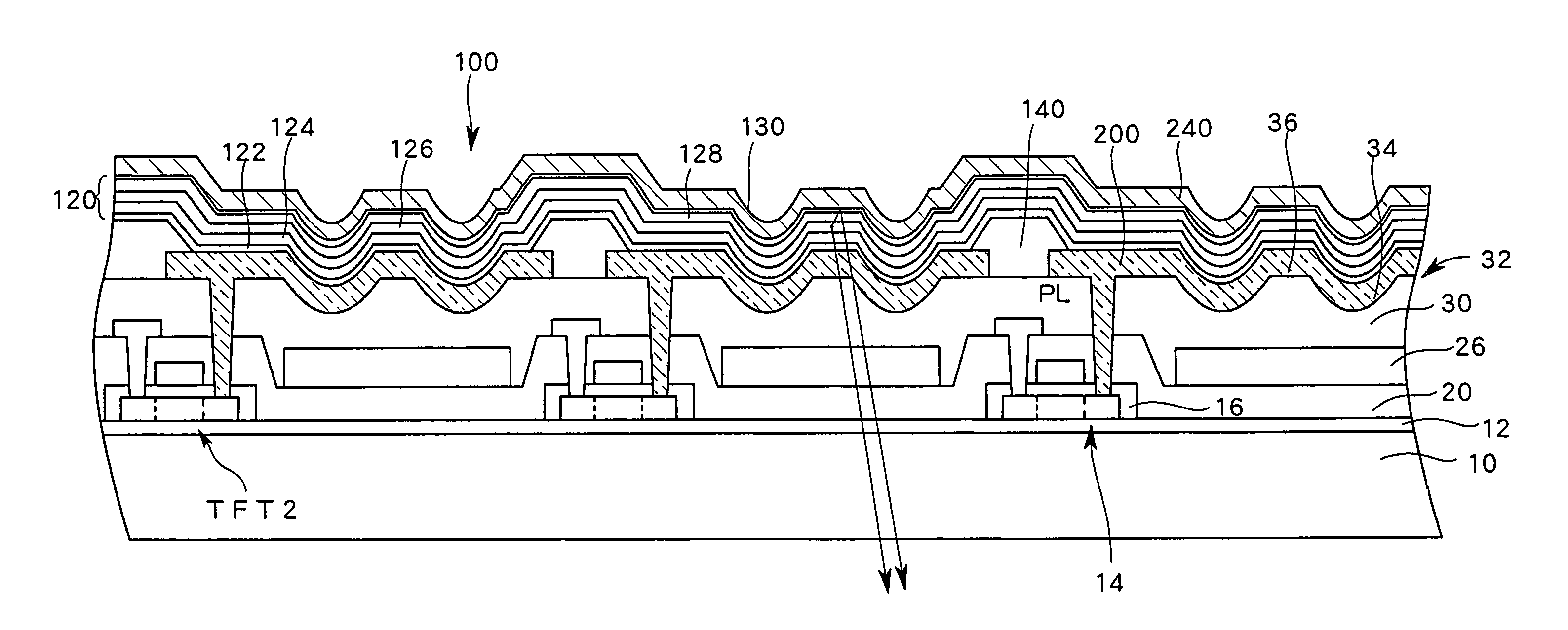
Light-Emitting Display
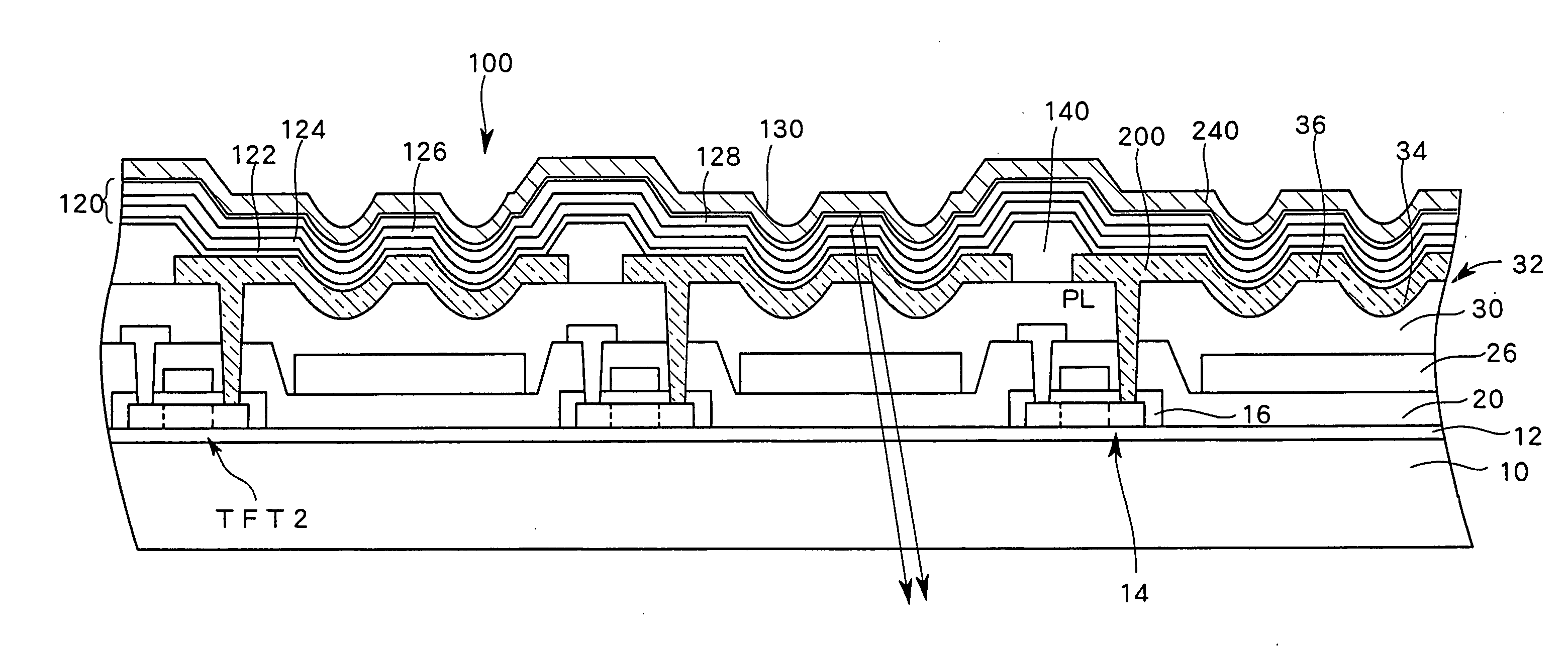
ActiveUS20080024402A1Improve efficiencyHighly accurate adjustmentStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringOptical path length
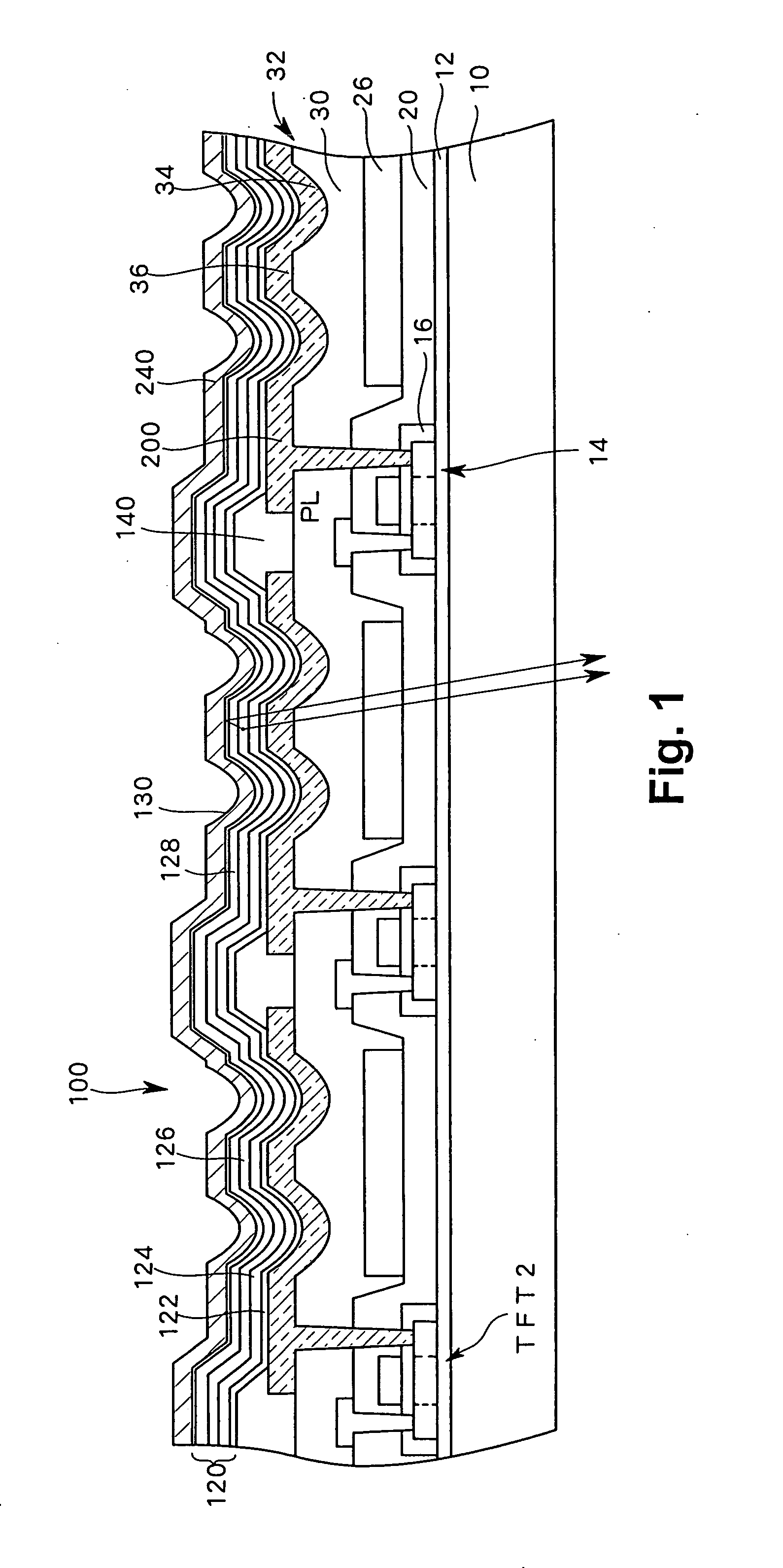
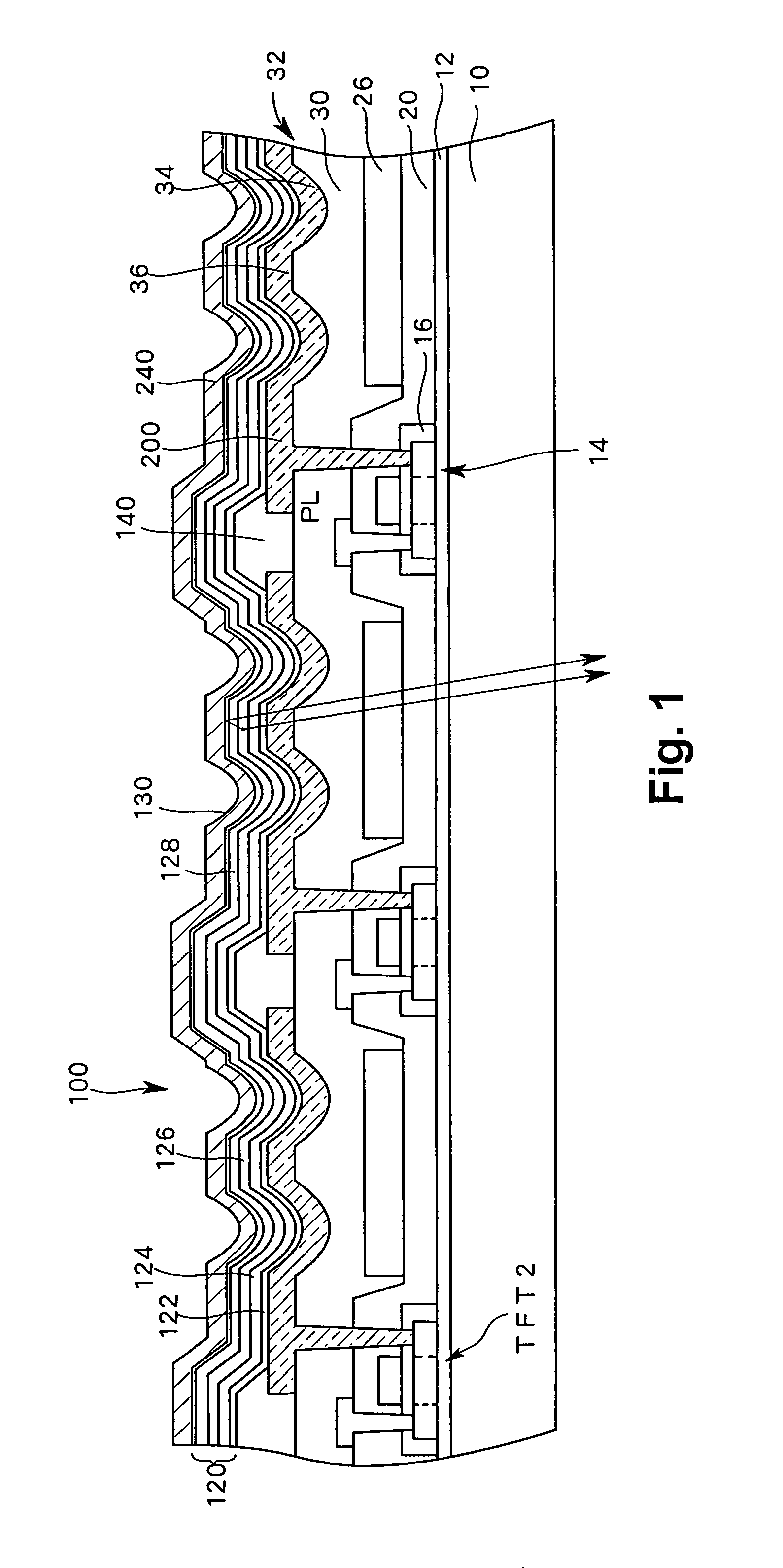
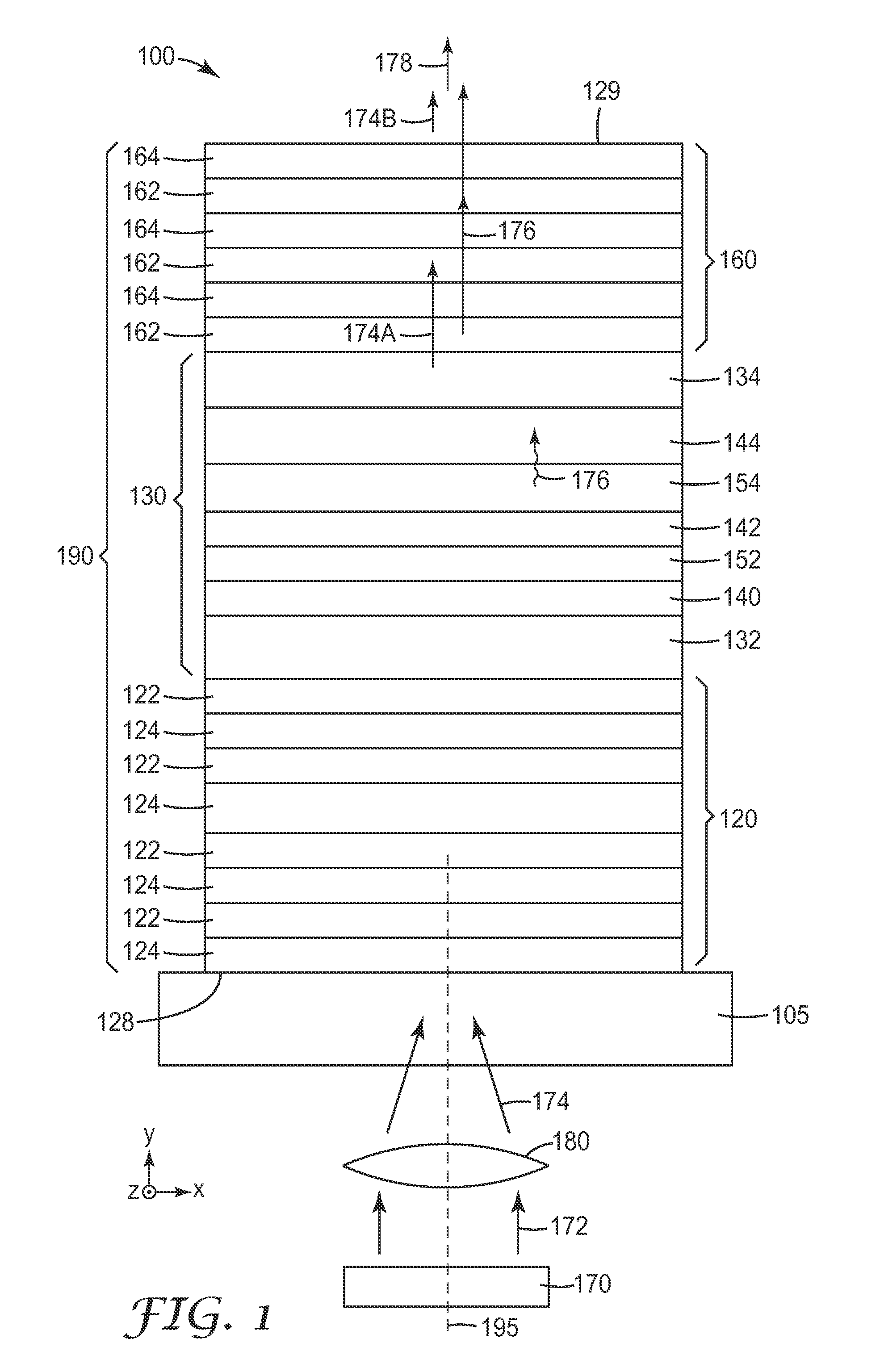
Disclosed is a light-emitting display having a plurality of pixels wherein each pixel comprises a light-emitting device (100) having a light-emitting element layer which is formed between a first electrode and a second electrode and contains at least a light-emitting layer. An insulating layer (30) is formed between the light-emitting device (100) and a surface of a first or second substrate on the viewing side of the display, and the insulating layer (30) is provided with recesses and projections in at least one or more pixel regions, thereby forming an optical path length adjusting portion (32). By forming such an optical path length adjusting portion (32) in a pixel region, there is an increase in the interference conditions for the light emitted from the light-emitting device (100) to the outside, thereby averaging the interference.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Current drive circuit and display device using same, pixel circuit, and drive method
InactiveUS20050190177A1Easy to replaceAdjustment of color balance is also easySolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriving currentDisplay device
A display device including a current drive circuit capable of stably and correctly supplying an intended current to a light emitting element of each pixel without being affected by variations in characteristics of an active element inside the pixel and as a result capable of displaying a high quality image, wherein each pixel comprises a receiving use transistor TFT3 for fetching a signal current Iw from a data line DATA when a scanning line SCAN-A is selected, a conversion use transistor TFT1 for once converting a current level of a fetched signal current Iw to a voltage level and holding the same, and a drive use transistor TFT2 for passing a drive current having a current level in accordance with the held voltage level through a light emitting element OLED. The conversion use thin film transistor TFT1 generates a converted voltage level at its own gate by passing the signal current Iw fetched by the TFT3 through its own channel. A capacitor C holds the voltage level created at the gate of the TFT1. The TFT2 passes the drive current having a current level in accordance with the held voltage level through the light emitting element OLED.
Owner:SONY CORP
Current drive circuit and display device using same, pixel circuit, and drive method
InactiveUS20050200300A1Stably and accurately supplyingHigh quality imagingSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriving currentDisplay device
A display device including a current drive circuit capable of stably and correctly supplying an intended current to a light emitting element of each pixel without being affected by variations in characteristics of an active element inside the pixel and as a result capable of displaying a high quality image, wherein each pixel comprises a receiving use transistor TFT3 for fetching a signal current Iw from a data line DATA when a scanning line SCAN-A is selected, a conversion use transistor TFT1 for once converting a current level of a fetched signal current Iw to a voltage level and holding the same, and a drive use transistor TFT2 for passing a drive current having a current level in accordance with the held voltage level through a light emitting element OLED. The conversion use thin film transistor TFT1 generates a converted voltage level at its own gate by passing the signal current Iw fetched by the TFT3 through its own channel. A capacitor C holds the voltage level created at the gate of the TFT1. The TFT2 passes the drive current having a current level in accordance with the held voltage level through the light emitting element OLED.
Owner:SONY CORP
Liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS7113163B2Increase the number ofIncrease probabilityStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
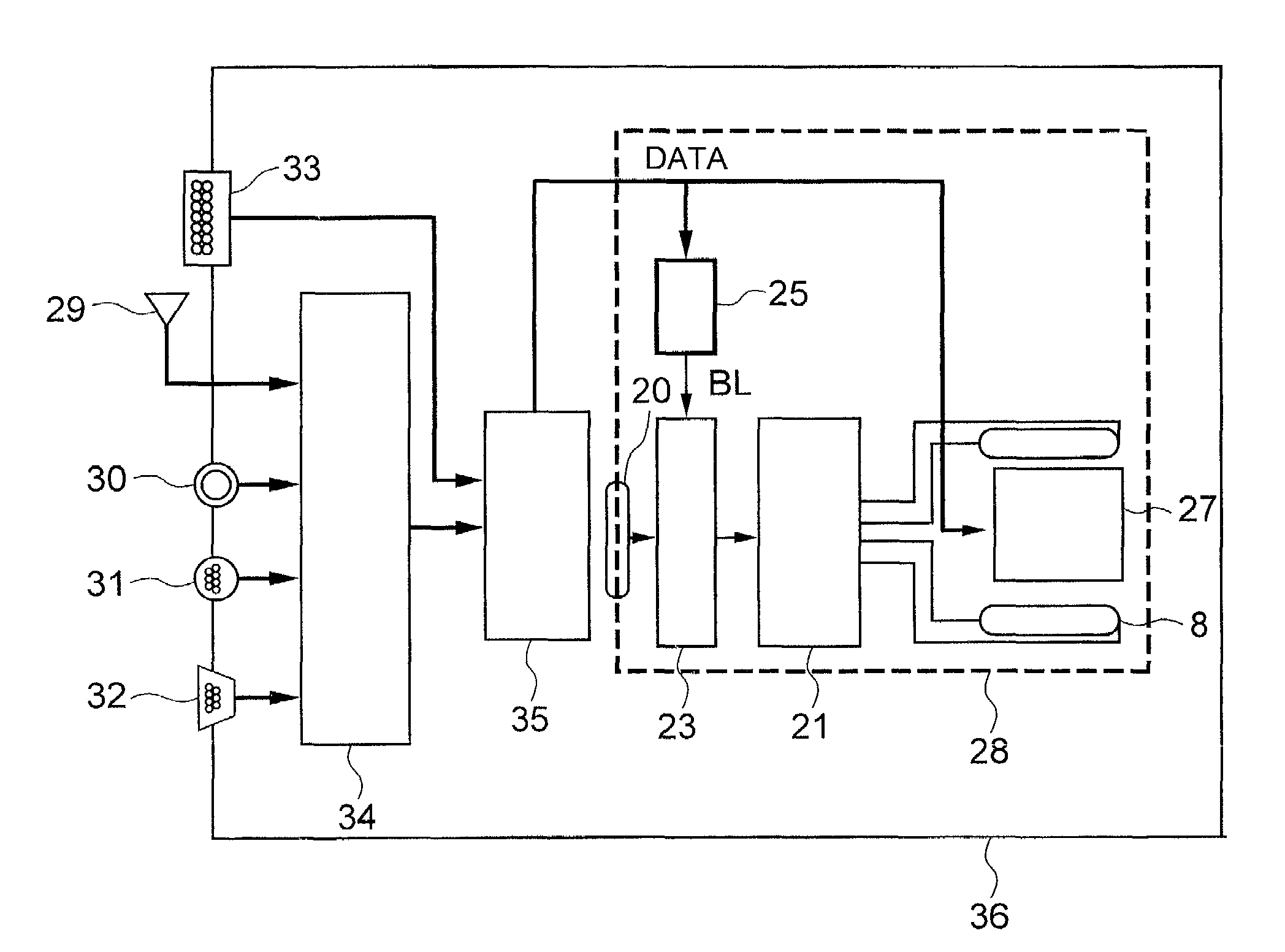
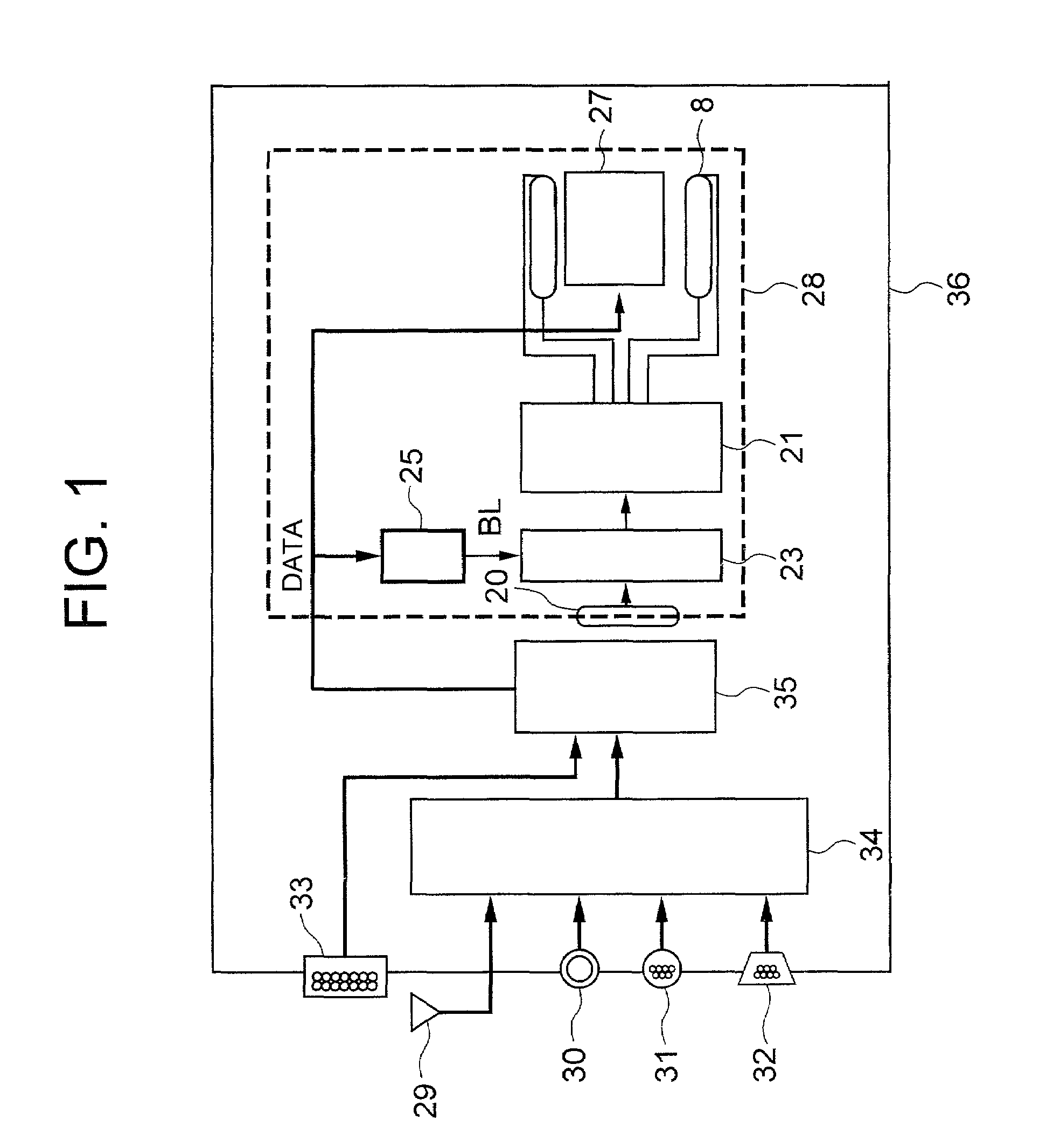
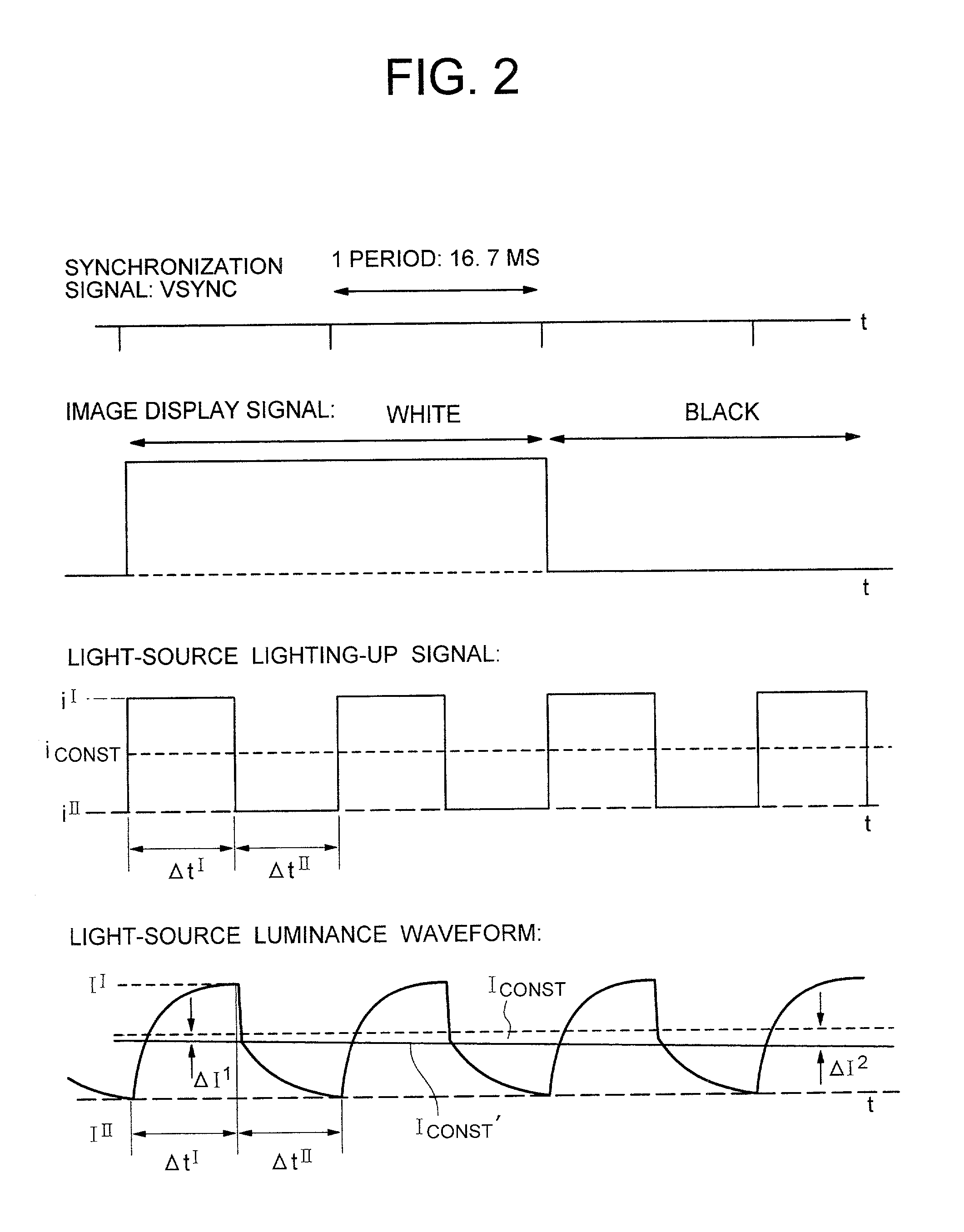
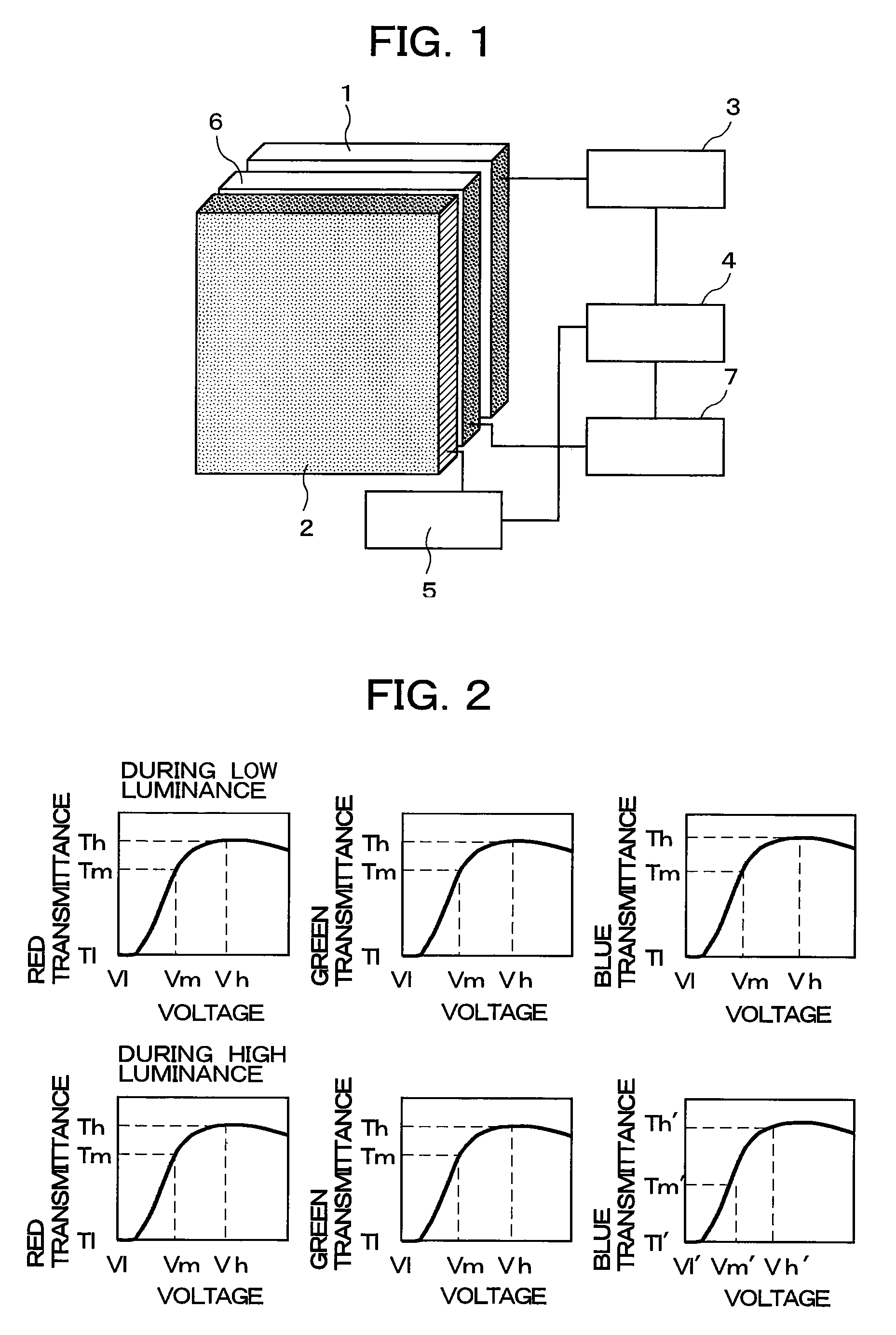
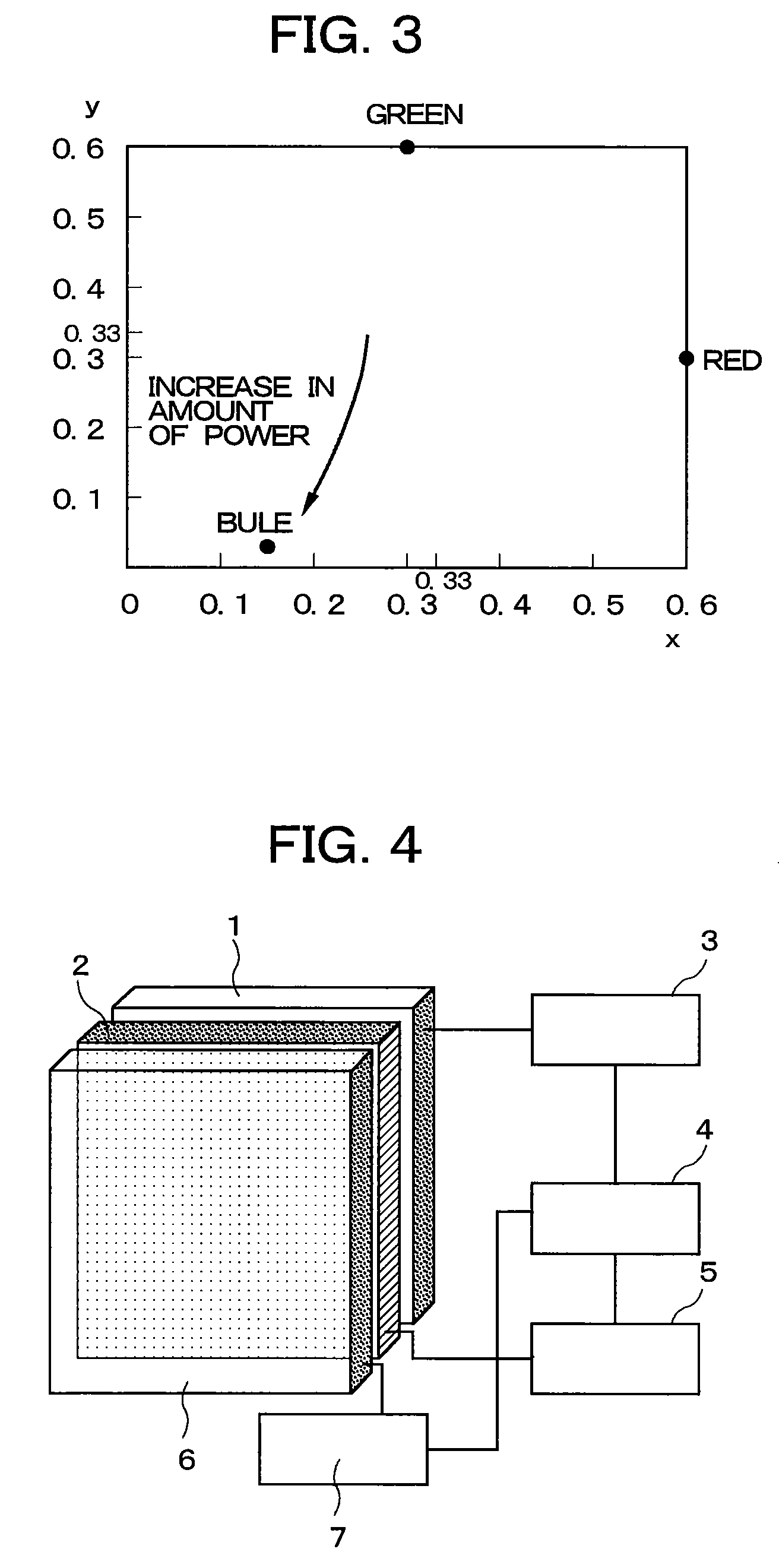
The present invention includes a panel on which a plurality of pixels are located, a light-source for visualizing an image displayed on the plurality of pixels, a controlling circuit for controlling the light-source, and an image-signal tone characteristic controlling circuit. Moreover, the light-source controlling circuit has a function of repeating a period. Here, the period includes a 1st time-period during which an electric current having a 1st intensity is fed to the light-source, and a 2nd time-period during which an electric current having a 2nd intensity differing from the 1st intensity is fed to the light-source. The light-source controlling circuit controls the 1st time-period and the 2nd time-period in accordance with display information. Also, in accordance with the display information as well, the tone characteristic controlling circuit is controlled so that the excellent contrast will be always available.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS +1
Display device, method, and terminal device having switchable viewing angle
InactiveUS20070030240A1Suppress mutationSuppress in of imageStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsScattered lightLight source
After light from a planar light source is switched to scattered light or collimated light by a switching element, the light is incident on a display panel, and an image is displayed. At this time, the luminance of the planar light source is adjusted, the contrast voltage of the display panel is reset, and adjustment is performed so that the luminance and hue of the frontal image does not vary before and after switching.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
Organic Electroluminescence Element Material, Organic Electroluminescence Element, Display Device and Lighting Apparatus
ActiveUS20090302745A1High light emit efficiencyLong light emission lifeIndium organic compoundsDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic electroluminescenceEmission efficiency
Provided is an organic EL element, which has a controlled emission wavelength, a high emission efficiency and a long emission life. An organic EL element material for such organic EL element, a lighting device, and a display device using such organic EL element are also provided.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Organic electroluminescent element and lighting device using same
InactiveUS20120193619A1Reducing luminescence unevennessReducing thickness fluctuationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron holeEngineering
An organic EL element having a high productivity and a multi-unit structure is produced by using an organic EL material which can meet the demands of an increased area and high productivity, uses a high-speed process at atmospheric pressure, that is, the non-discharge type coating process, and which has a high process adaptability. An organic electroluminescent element is provided, between a plurality of light-emitting units, with a charge generating layer which generates a hole and an electron by applying an electric field, wherein the charge generating layer comprises one or more layers, at least one layer of which is formed by means of the non-discharge type solution coating process, and the plurality of light-emitting units are formed by means of the non-discharge type solution coating process.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
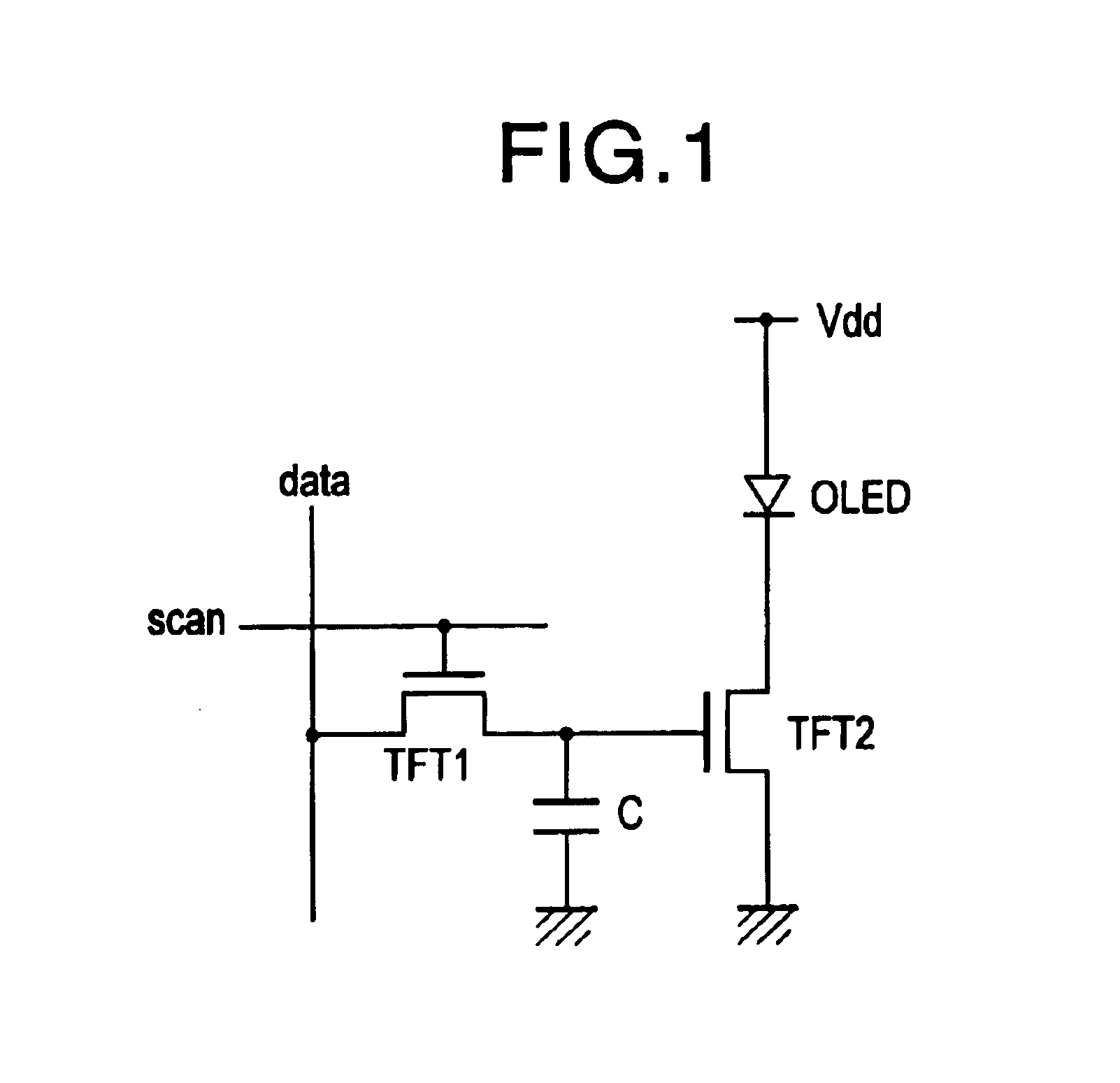
EL display device and driving method thereof
InactiveUS6351077B1Uniform processGood white balanceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDigital dataComputer graphics (images)
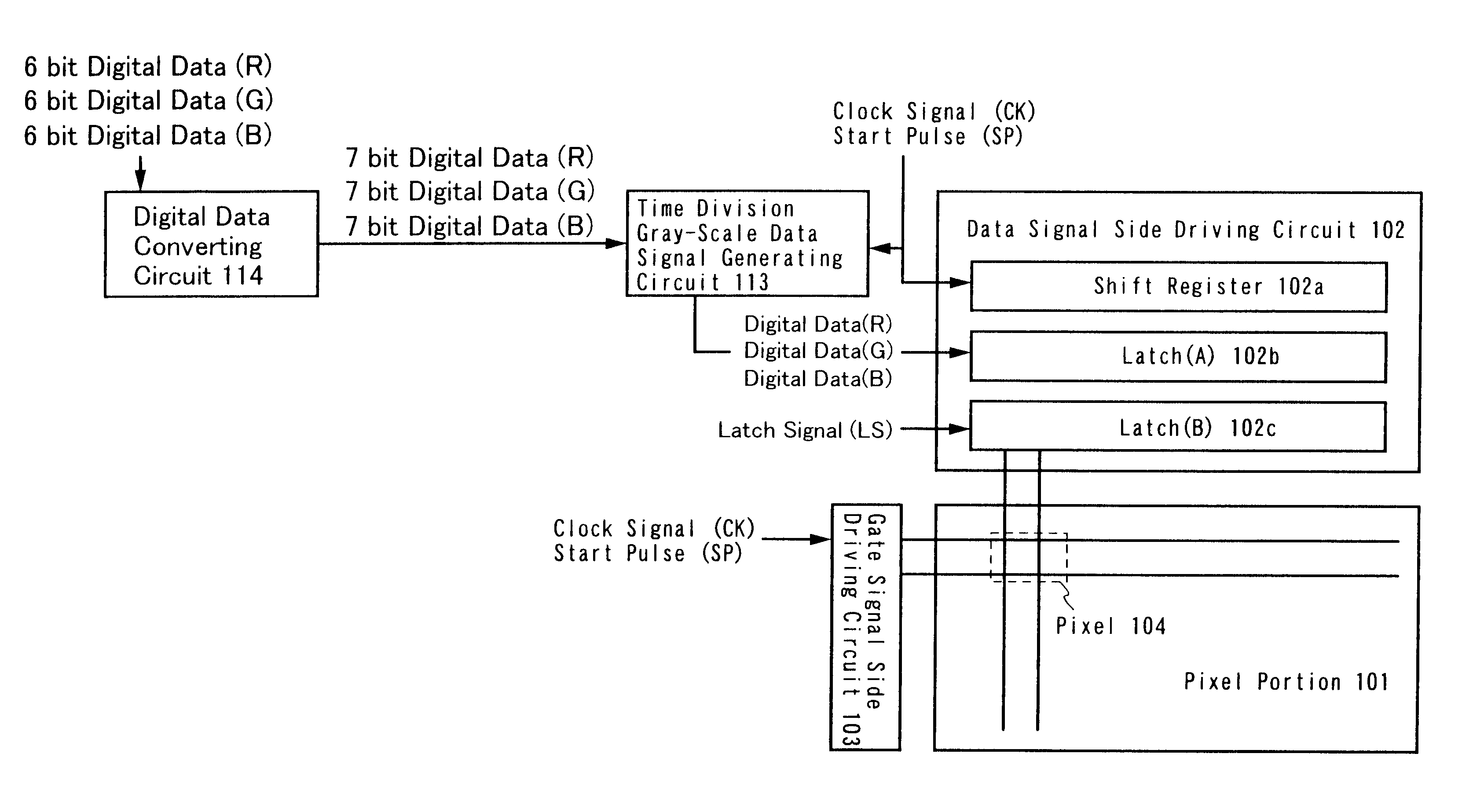
The present invention is characterized by adding a bit having the value of one below the least significant bit of n bit digital data having red image information inputted from the external, adding a bit having the value of zero above the most significant bit of n bit digital data having green image information inputted from the external, and adding a bit having the value of zero above the most significant bit of n bit digital data having blue image information inputted from the external, whereby producing (n+1) bit digital data having red image information, (n+1) bit digital data having green image information, and (n+1) bit digital data having blue image information, respectively, for displaying an image.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Display device
InactiveUS20120112988A1Avoid uneven brightnessReduce sizeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceComputer engineering
Luminance ununiformity and color shading are prevented in a display area of an irregular hexagonal shape formed by cutting-off a corner from a rectangular shape.Sub-pixels are formed in each of regions surrounded by scanning lines and video signal lines and a set of sub-pixels by the number of three define one pixel. The display area is an irregular hexagonal shape containing a display area sloping portion of a shape formed by cutting-off a corner from a rectangular shape. In the display area sloping portion, the number of sub-pixels in the extending direction of the scanning lines changes uniformly for every sub-pixels by the number of three or by the number of a multiple thereof on each side of the display area for one scanning line. The magnitude of the video signal in the source driver can be controlled easily by uniformly changing the number of the sub-pixels.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS
Optical member, backlight unit and display apparatus
ActiveUS20080291359A1Inhibited DiffusionSuppress luminescenceProjectorsNon-linear opticsVisibilityEngineering
An optical member enables a display apparatus to be improved in visibility of its display screen as viewed from a plurality of predetermined directions other than the directly forward direction. The optical member includes a lenticular lens member (3) having a plurality of convex lenses (2) and a light-reflecting layer (5) disposed on the back surface of the lenticular lens member. The light-reflecting layer (5) is provided with optical windows (6) each at a position corresponding to a midpoint between the apexes of mutually adjacent convex lenses. Light emitted from a planar light source, passed through each optical window (6), and configured to enter the mutually adjacent convex lenses (2) corresponding to the optical window is directed in mutually different directions by the mutually adjacent convex lenses, respectively.
Owner:CITIZEN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
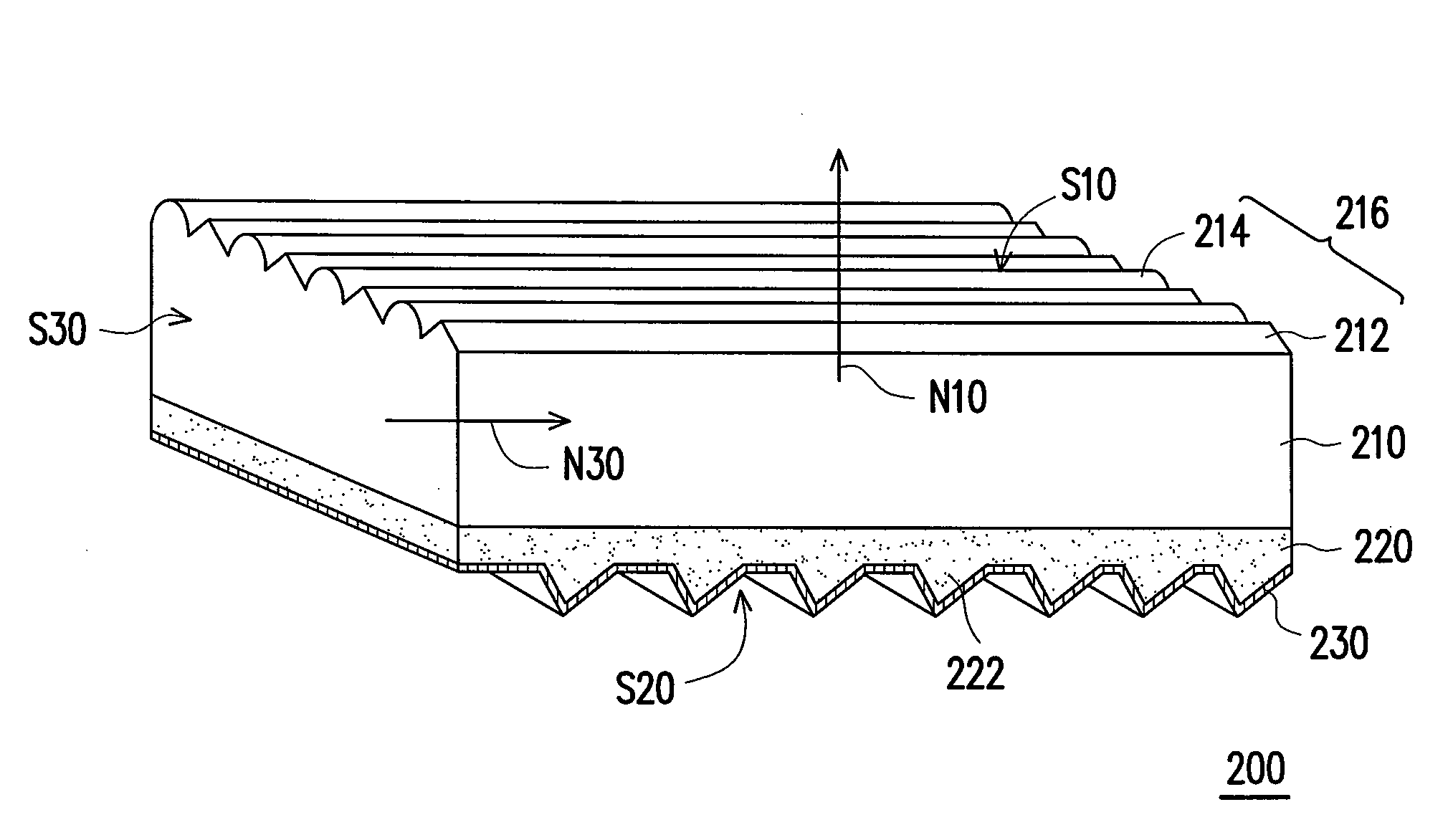
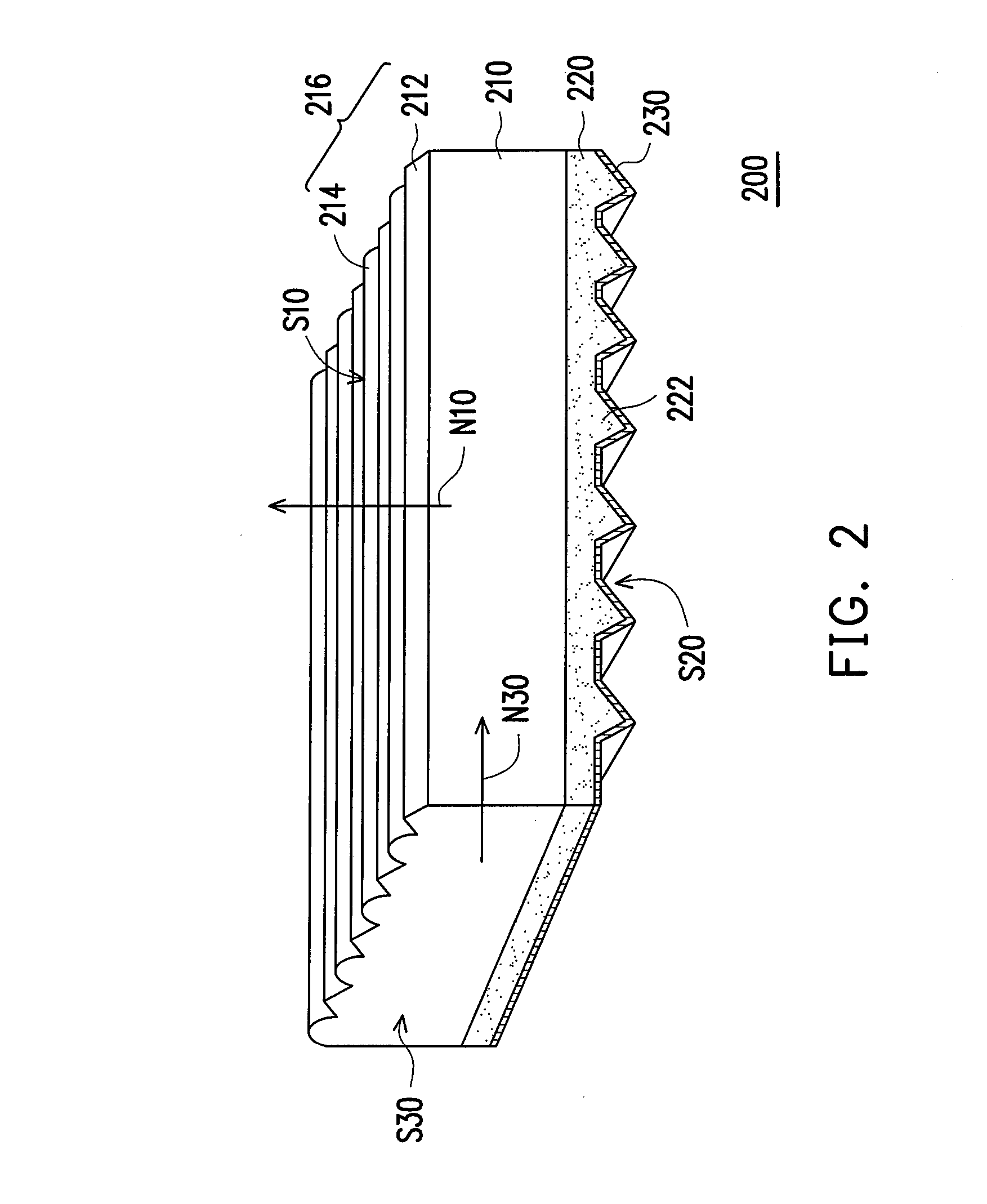
Light guide plate
InactiveUS20080158912A1Excellent light convergencyExcellent uniformityOptical light guidesReflectorsOptoelectronicsLight guide
A light guide plate with a light emitting surface, a bottom surface and at least one light incident surface being connected with the light emitting surface and the bottom surface is provided. The light guide plate is a superposition of a plurality of layers substantially parallel to the light emitting surface. A plurality of stripe-shaped light-controlling structures are formed on the light emitting surface and a plurality of light-reflecting structures are formed on the bottom surface. The light guide plate provides a surface light source with high brightness and excellent uniformity in a direction perpendicular to the light emitting surface.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Driving method of light emitting device and light emitting device
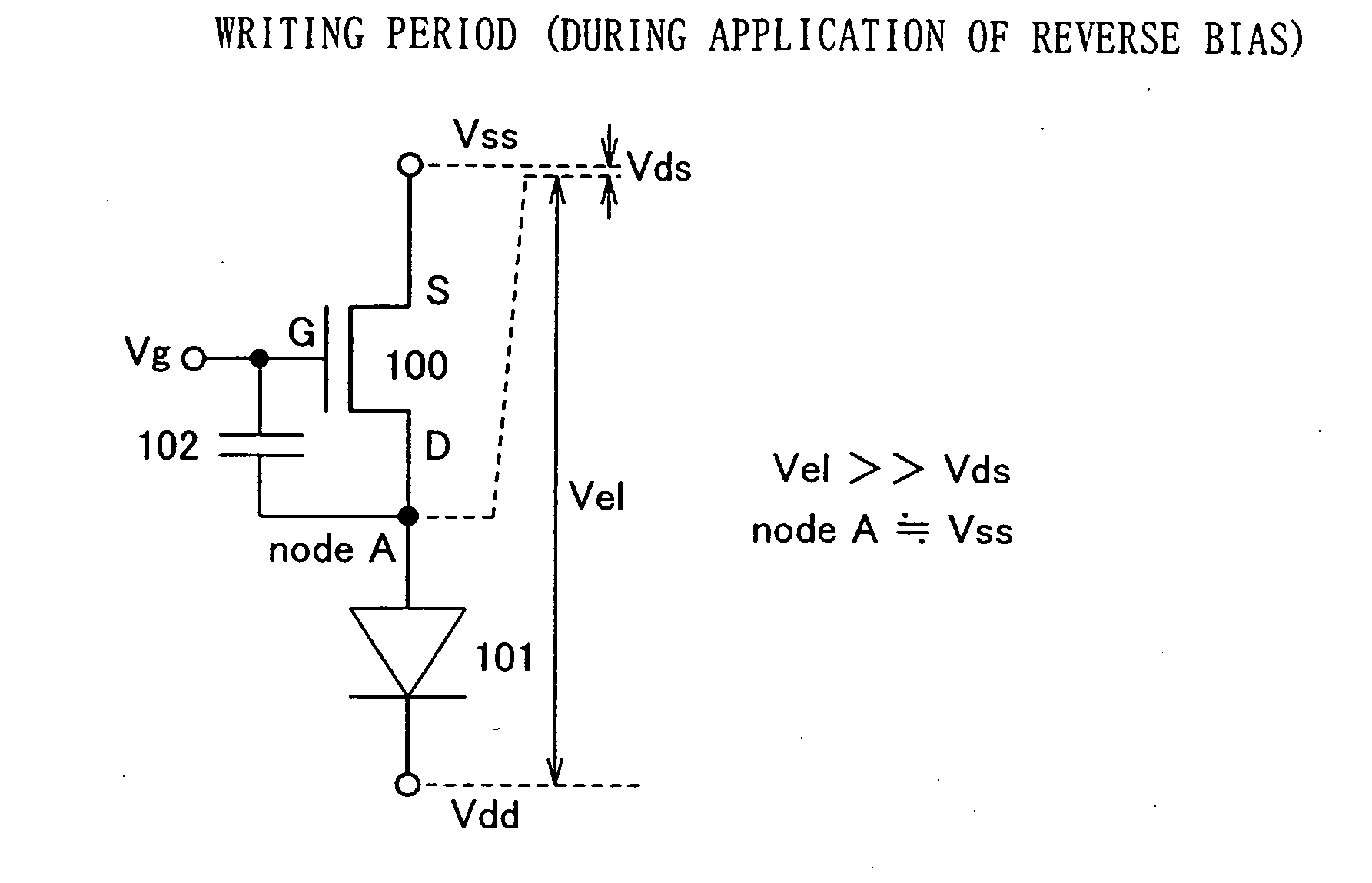
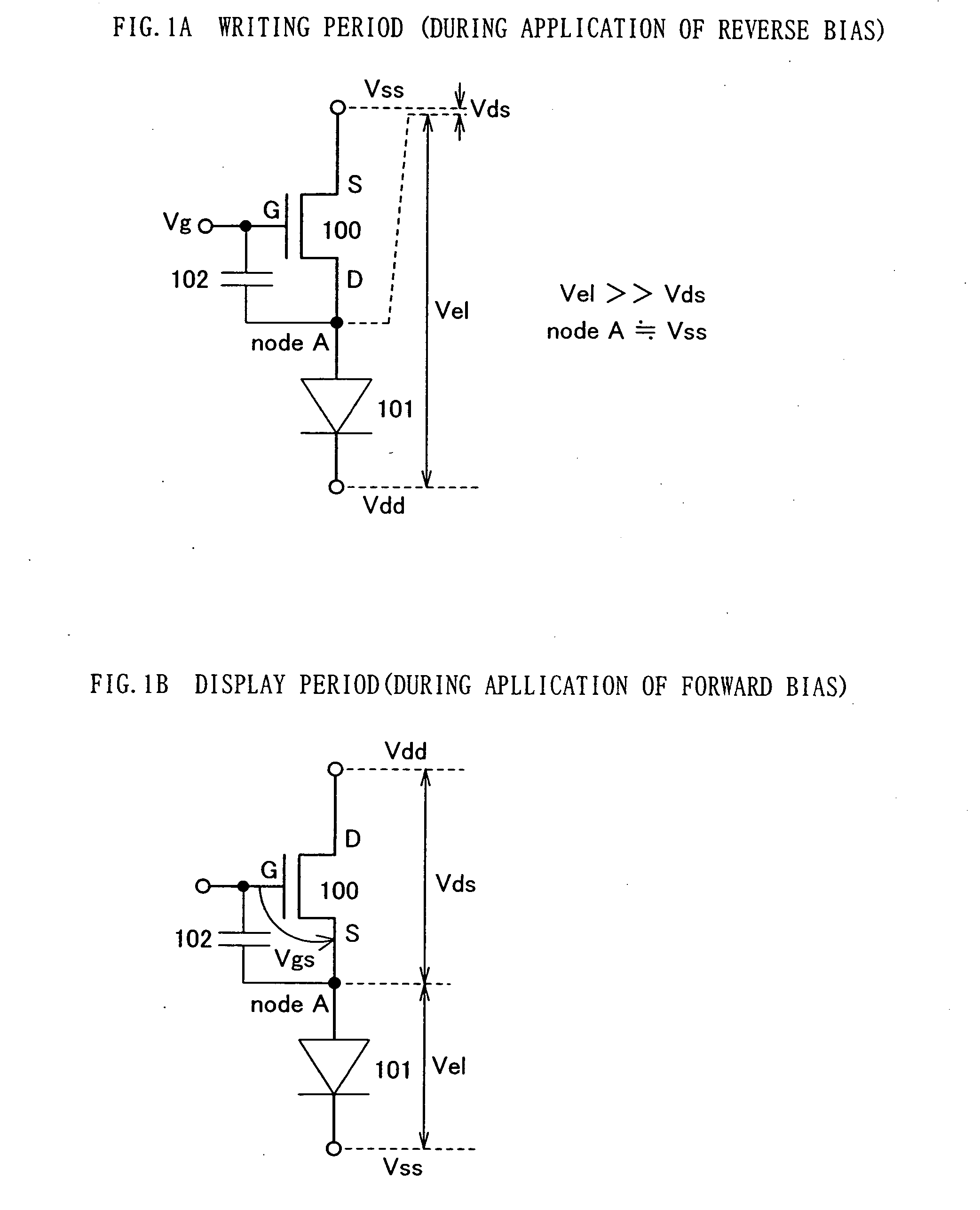
InactiveUS20050030265A1Suppress luminance decay luminanceSuppress variationStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesEngineeringReverse bias
A driving method of a light emitting device, in which when an N-type driving TFT is connected to an anode of a light emitting element or a P-type driving TFT is connected to a cathode thereof, the driving TFT operates in a saturation region and an image can be displayed with a desired gray scale level depending on a video signal. In addition, a light emitting device adopting the driving method is provided. According to the invention, when a potential having image data is supplied to a gate of a driving TFT depending on a video signal, a reverse bias voltage is applied to the driving TFT and a light emitting element which are connected in series with each other. Meanwhile, when a pixel displays an image depending on the video signal, a forward bias voltage is applied to the driving TFT and the light emitting element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
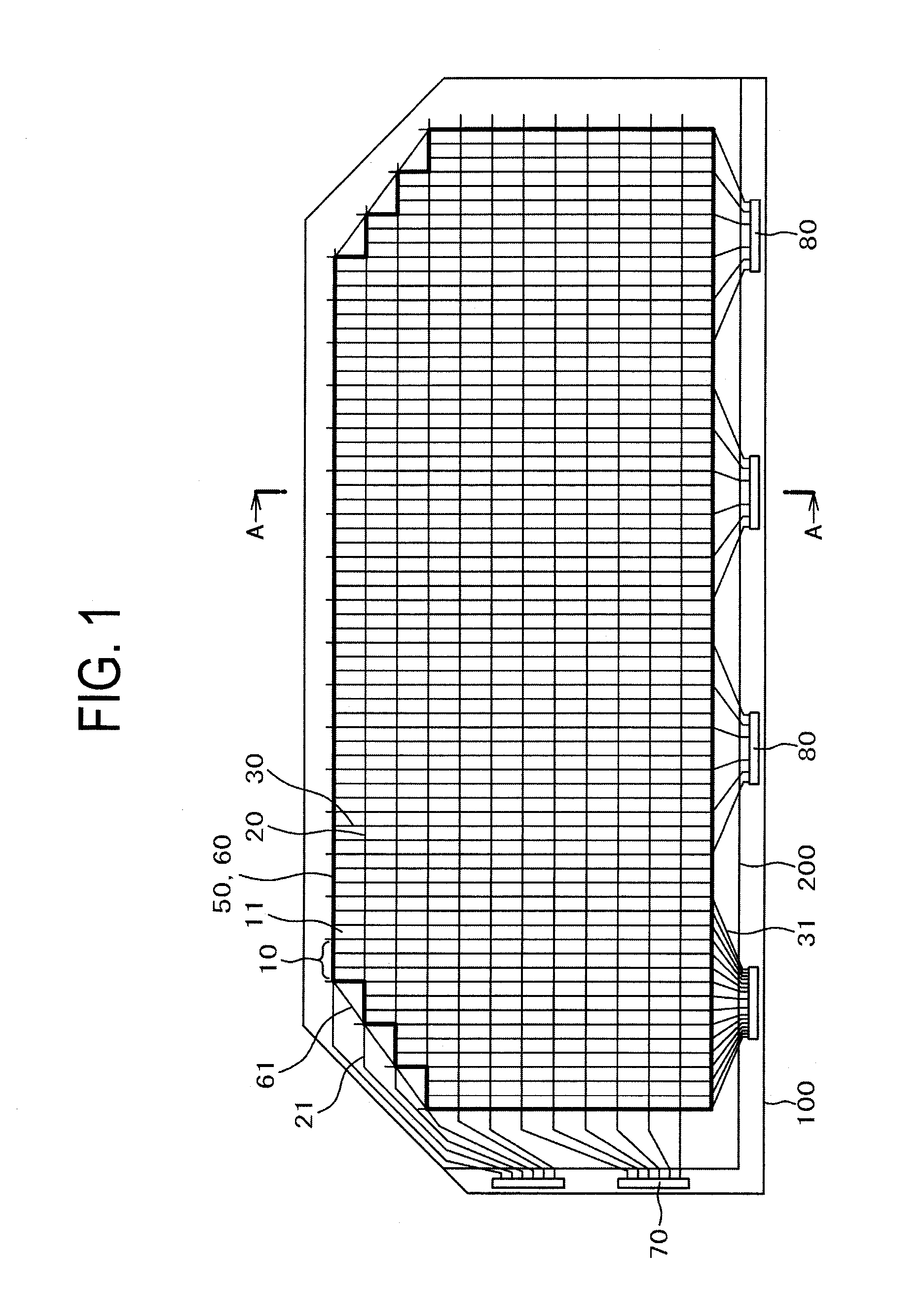
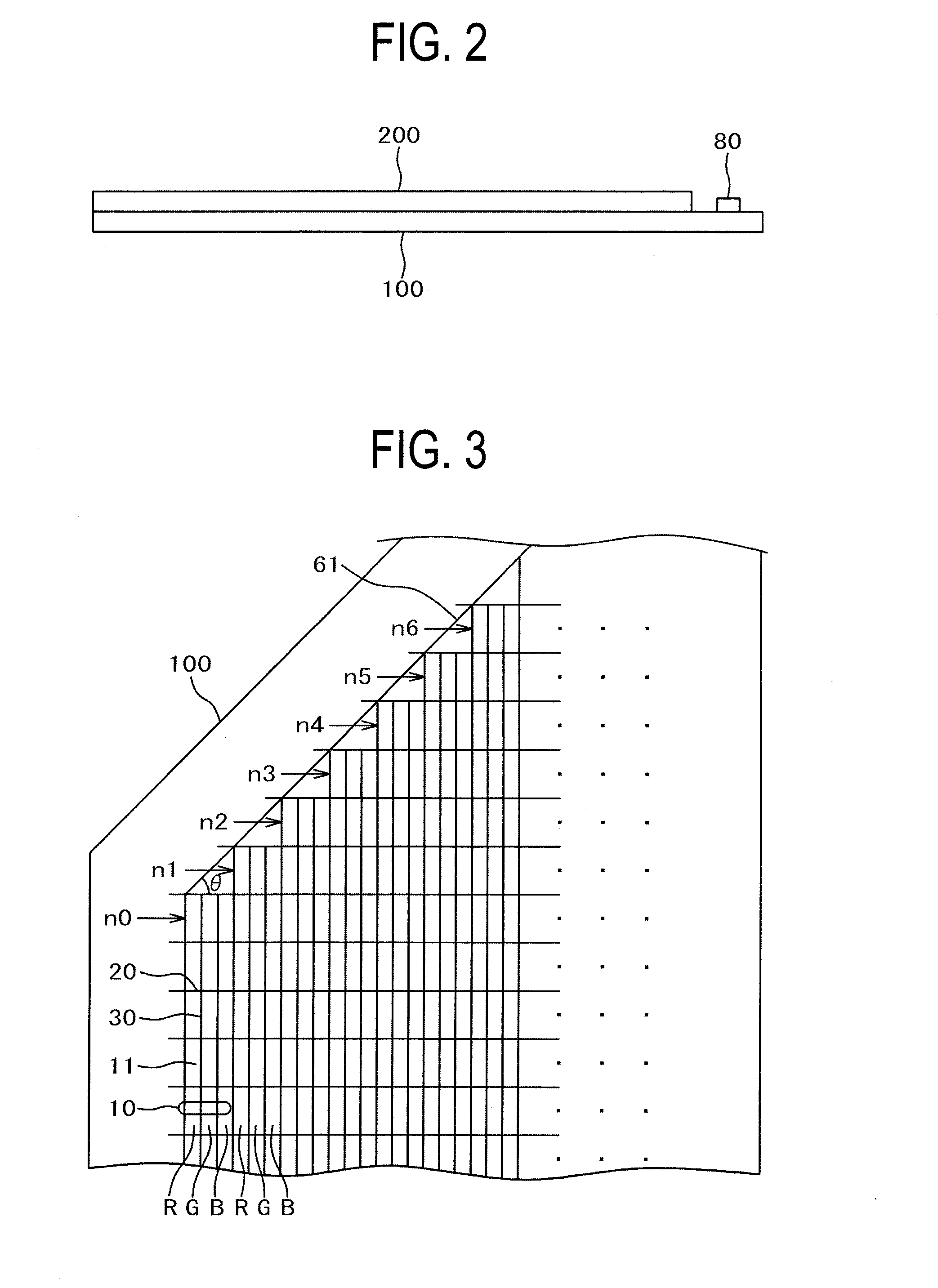
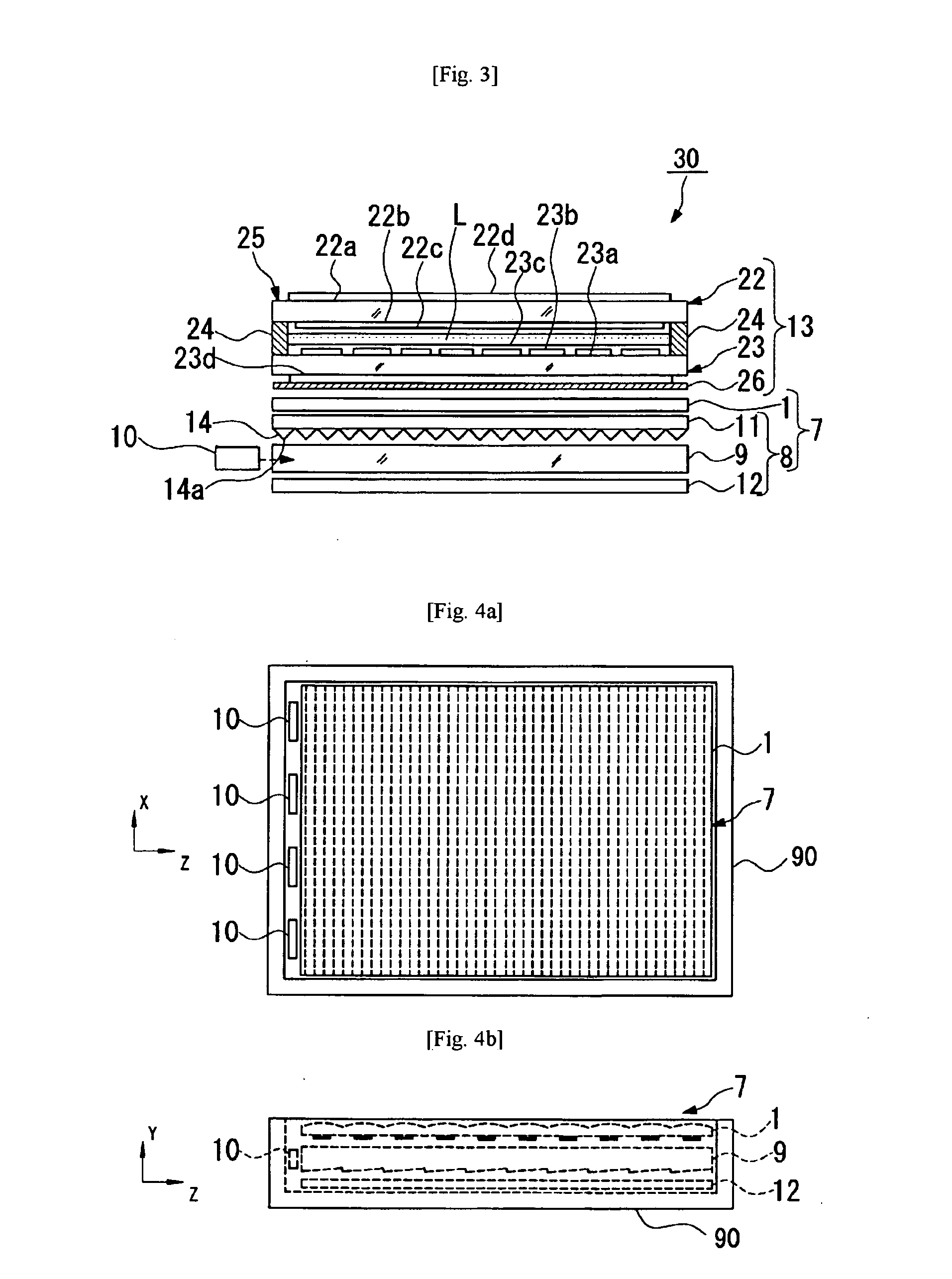
Light-emitting display
ActiveUS7903055B2Reduce above-described variation color and luminanceVariation in colorDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceEngineering
Disclosed is a light-emitting display having a plurality of pixels wherein each pixel comprises a light-emitting device (100) having a light-emitting element layer which is formed between a first electrode and a second electrode and contains at least a light-emitting layer. An insulating layer (30) is formed between the light-emitting device (100) and a surface of a first or second substrate on the viewing side of the display, and the insulating layer (30) is provided with recesses and projections in at least one or more pixel regions, thereby forming an optical path length adjusting portion (32). By forming such an optical path length adjusting portion (32) in a pixel region, there is an increase in the interference conditions for the light emitted from the light-emitting device (100) to the outside, thereby averaging the interference.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor element, organic transistor, light-emitting device, and electronic device
InactiveUS20060237731A1Low driving voltageManufacture simply and easilySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPhysicsOrganic crystal
It is an object of the present invention to provide an organic transistor having a low drive voltage. It is also another object of the present invention to provide an organic transistor, in which light emission can be obtained, which can be manufactured simply and easily. According to an organic light-emitting transistor, a composite layer containing an organic compound having a hole-transporting property and a metal oxide is used as part of the electrode that injects holes among source and drain electrodes, and a composite layer containing an organic compound having an electron-transporting property and an alkaline metal or an alkaline earth metal is used as part of the electrode that injects electrons, where either composite layer has a structure of being in contact with an organic semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
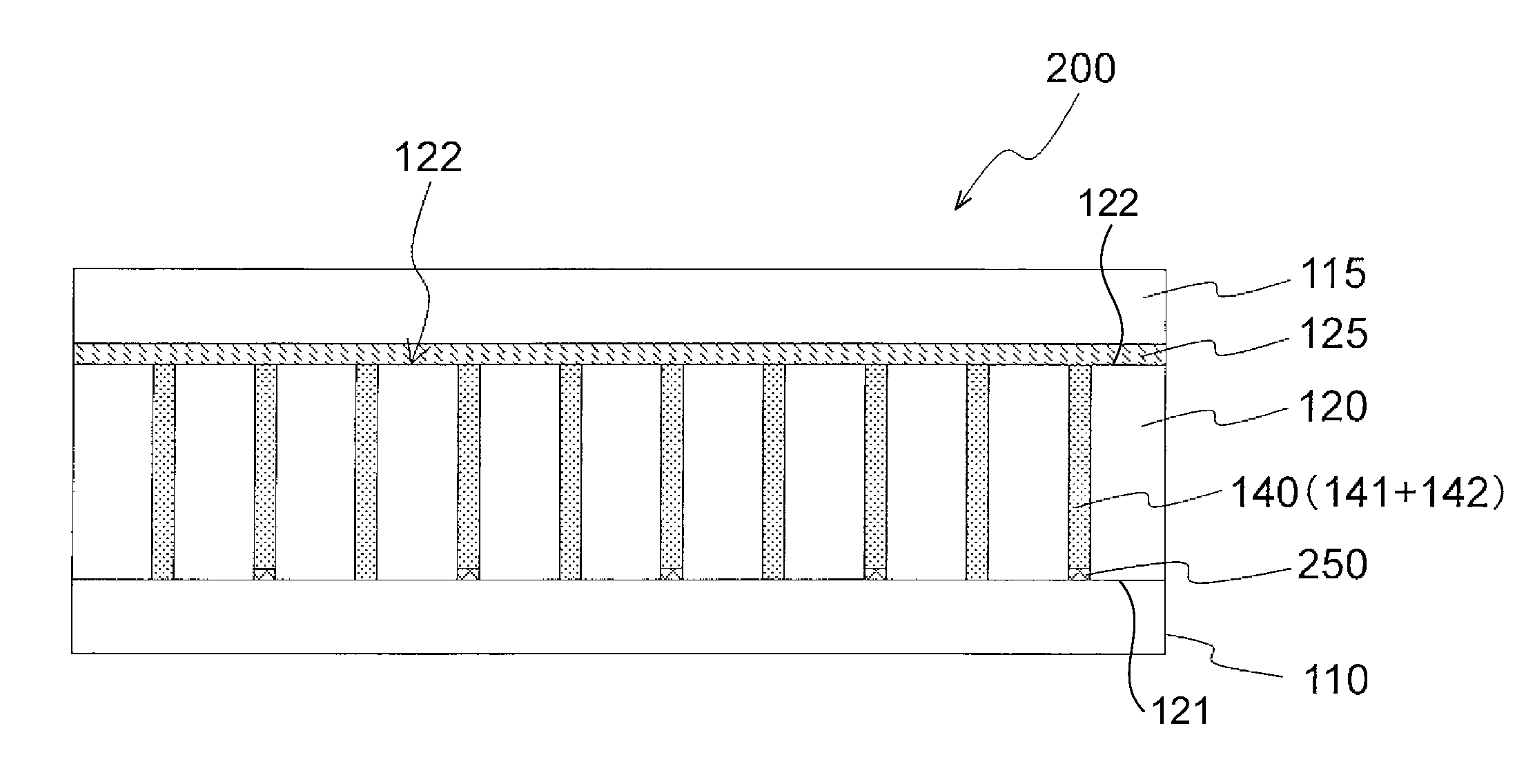
Organic electroluminescent element
InactiveUS20120248424A1Good emission balanceImprove emission efficiencyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesOrganic electroluminescenceFluorescent light
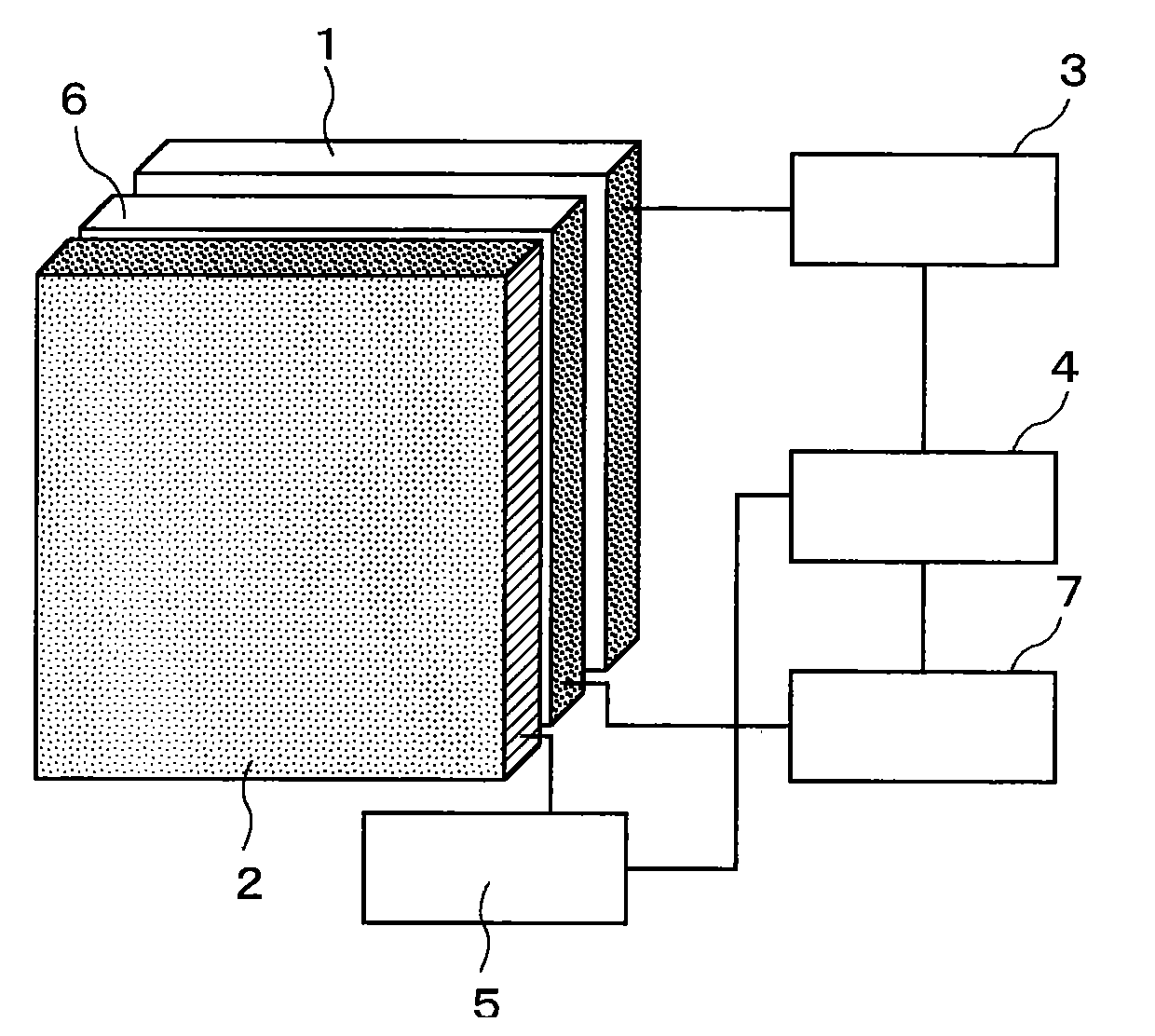
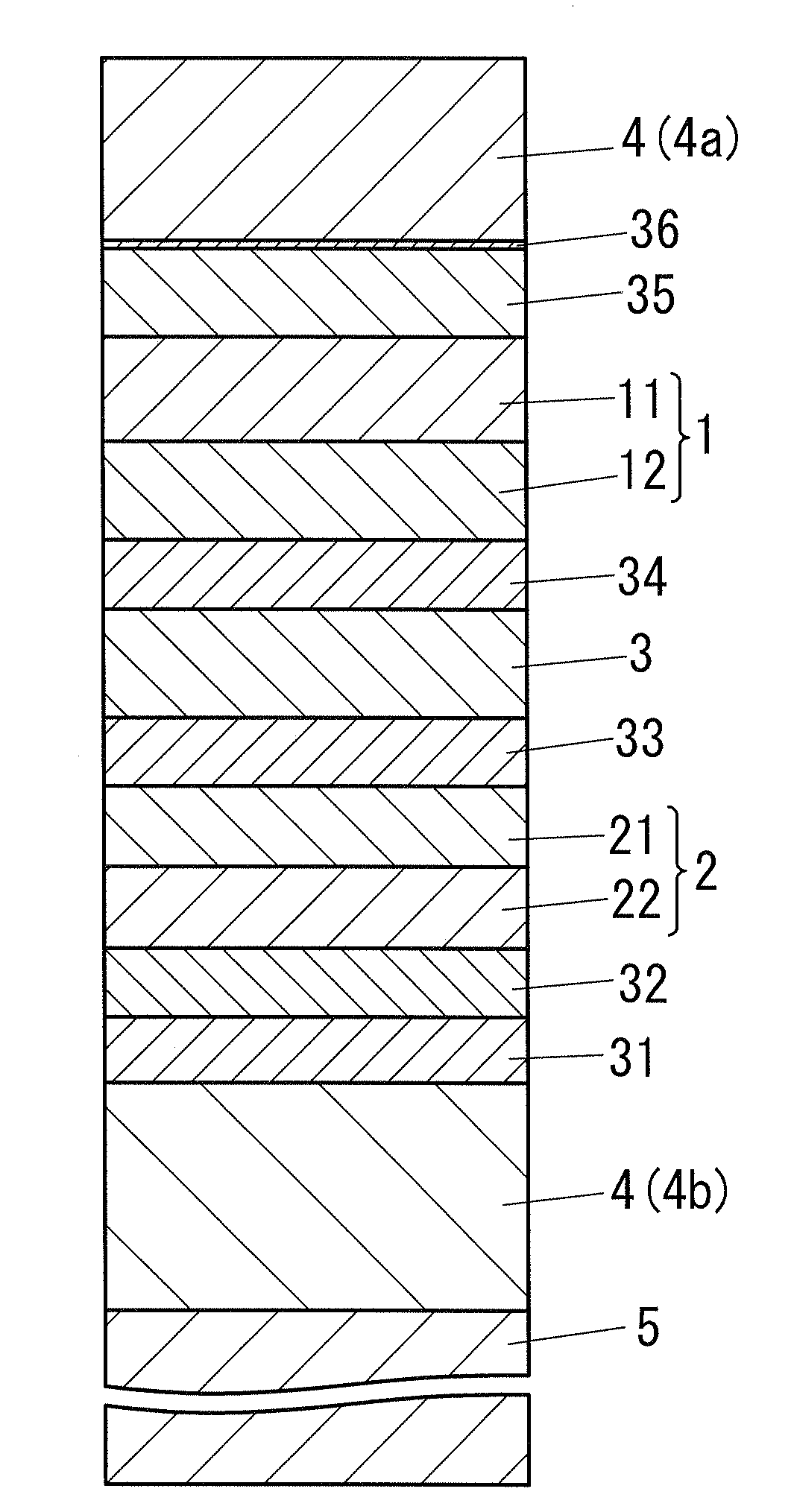
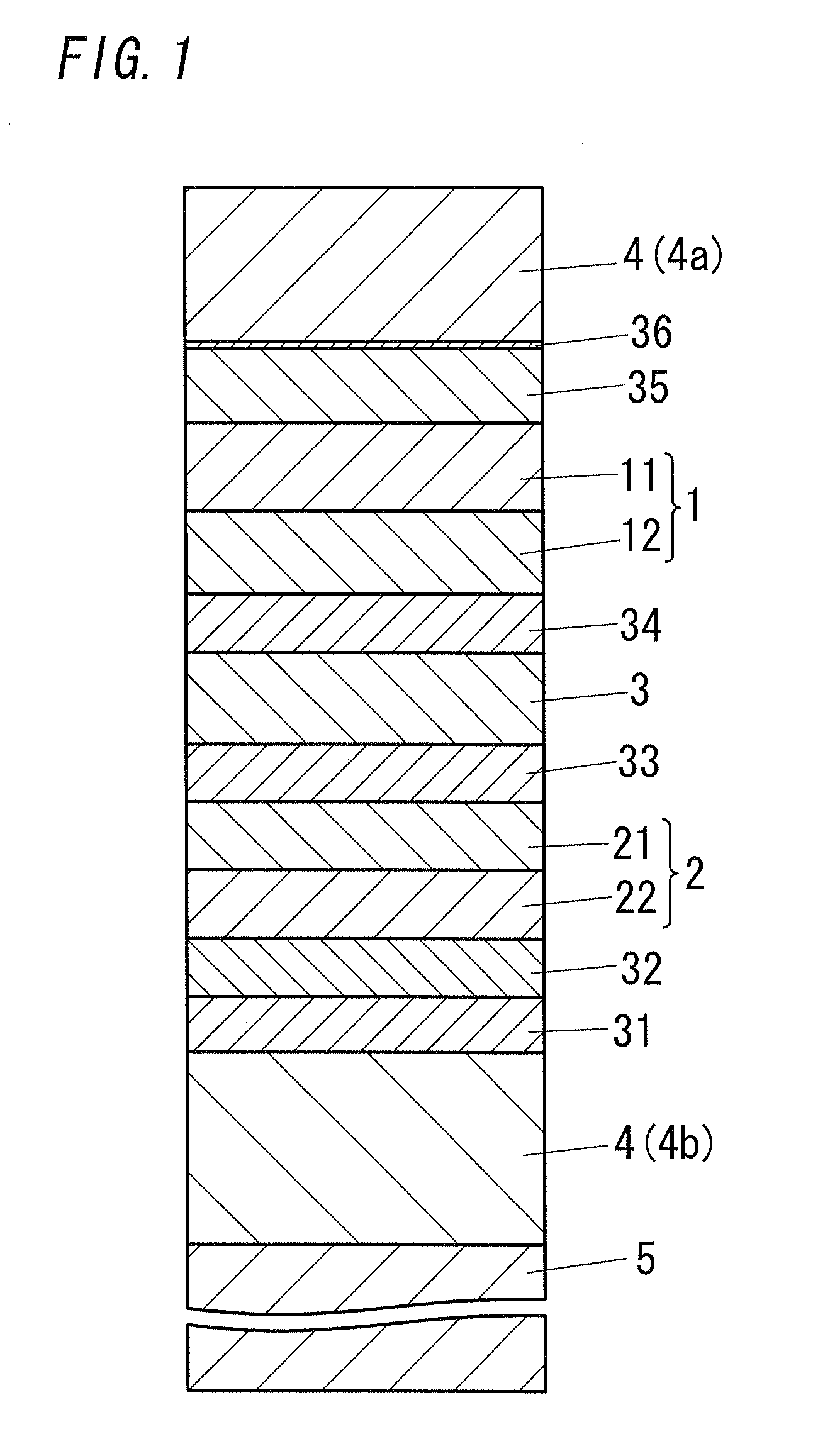
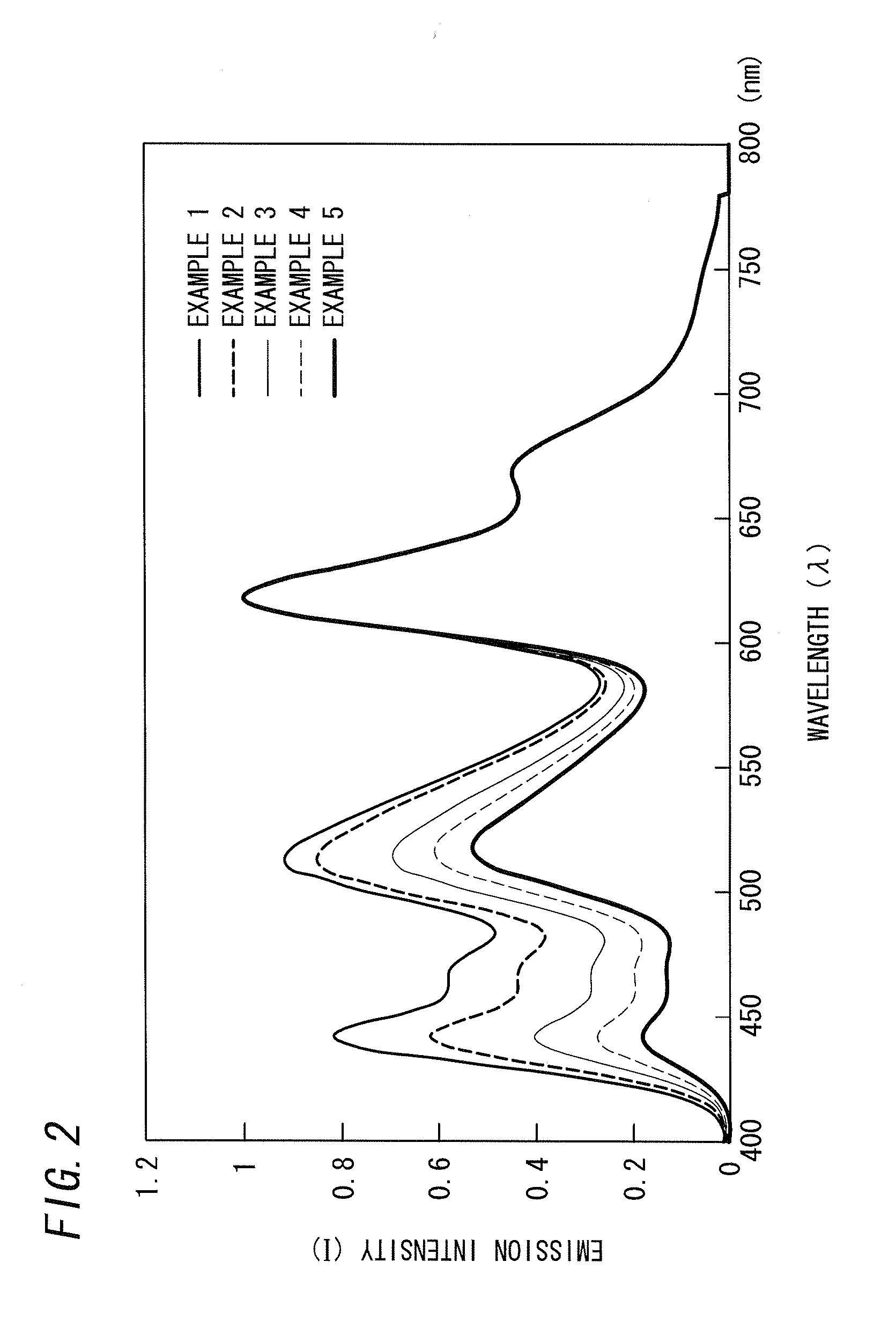
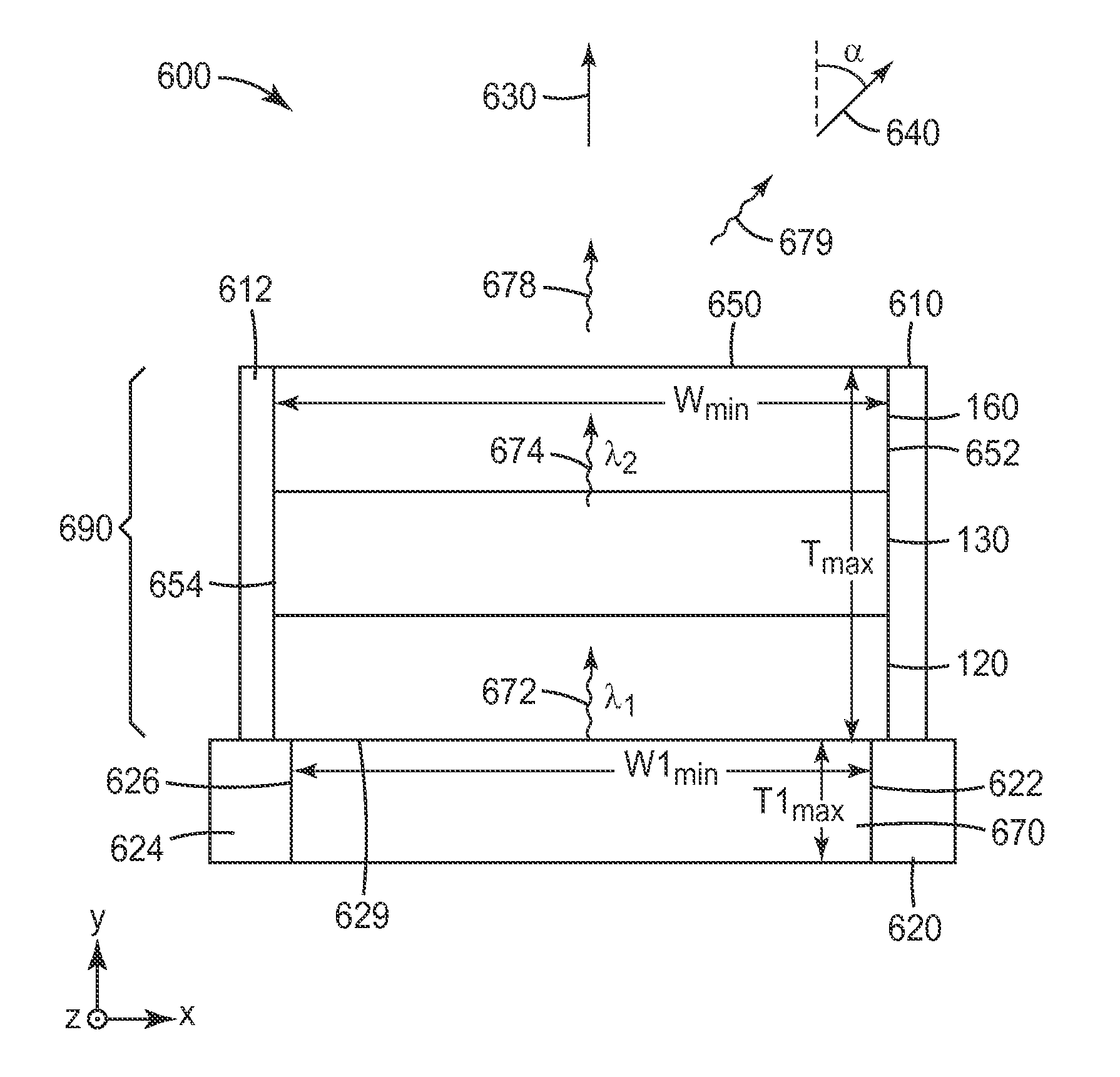
Disclosed is a high-efficiency, long-life white-emission organic electroluminescent element, in particular, a white-emission organic electroluminescent element. The organic electroluminescent element of the present invention has a red phosphorescent light emitting-layer 12; a green phosphorescent light emitting-layer 11; a blue fluorescent light-emitting layer 22 and a green fluorescent light-emitting layer 21. A phosphorescent light unit 1 is formed by the red phosphorescent light emitting-layer 12 and the green phosphorescent light emitting-layer 11. A fluorescent light unit 2 is formed by the blue fluorescent light-emitting layer 22 and the green fluorescent light-emitting layer 21. The phosphorescent light unit 1 and the fluorescent light unit 2 are connected via an interlayer 3. Preferably, the phosphorescent light unit 1 is disposed further towards a cathode 4a side than the fluorescent light unit 2. Preferably, the emission color is any of a W color, a WW color and an L color.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Display device, and data processing method in display device
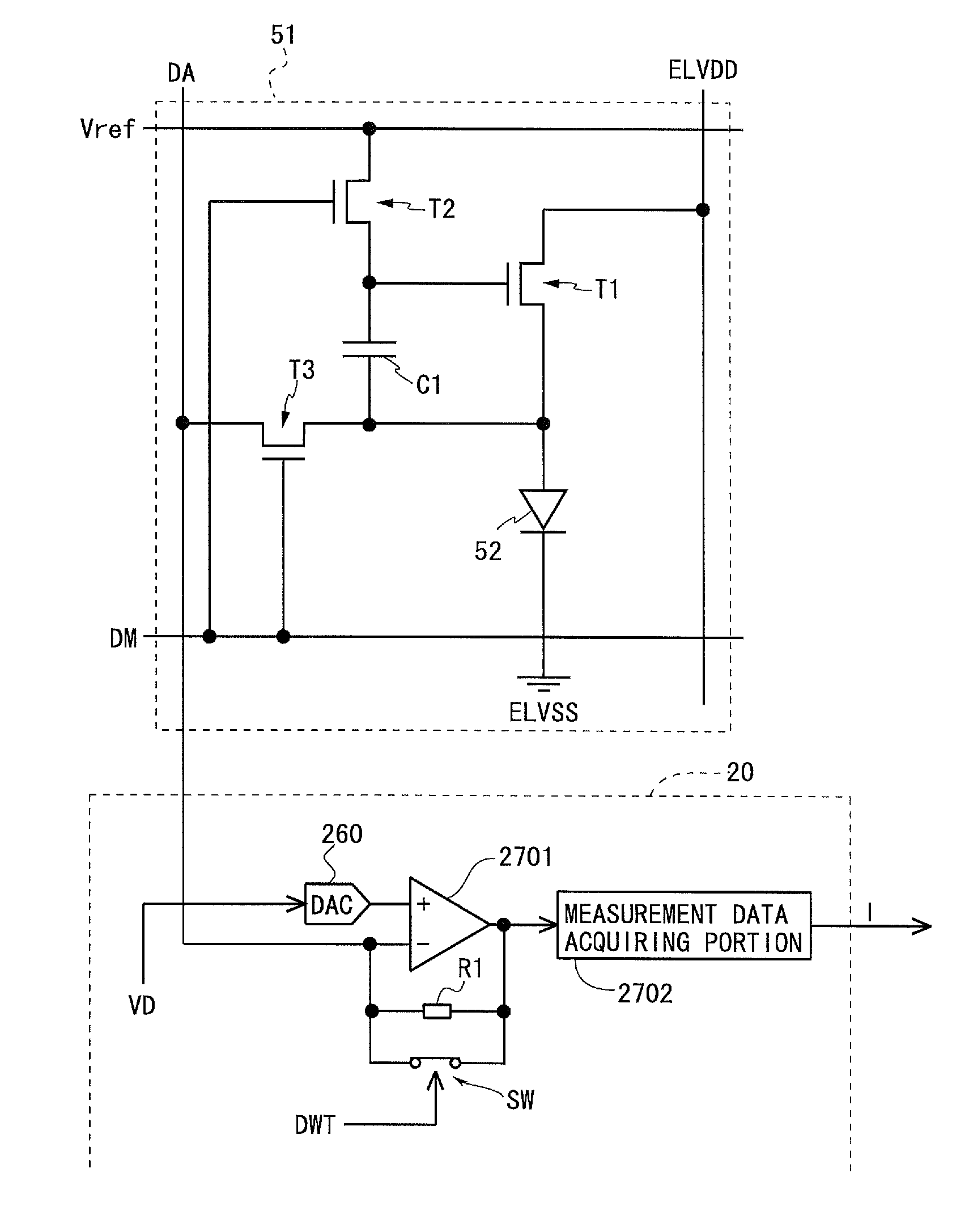
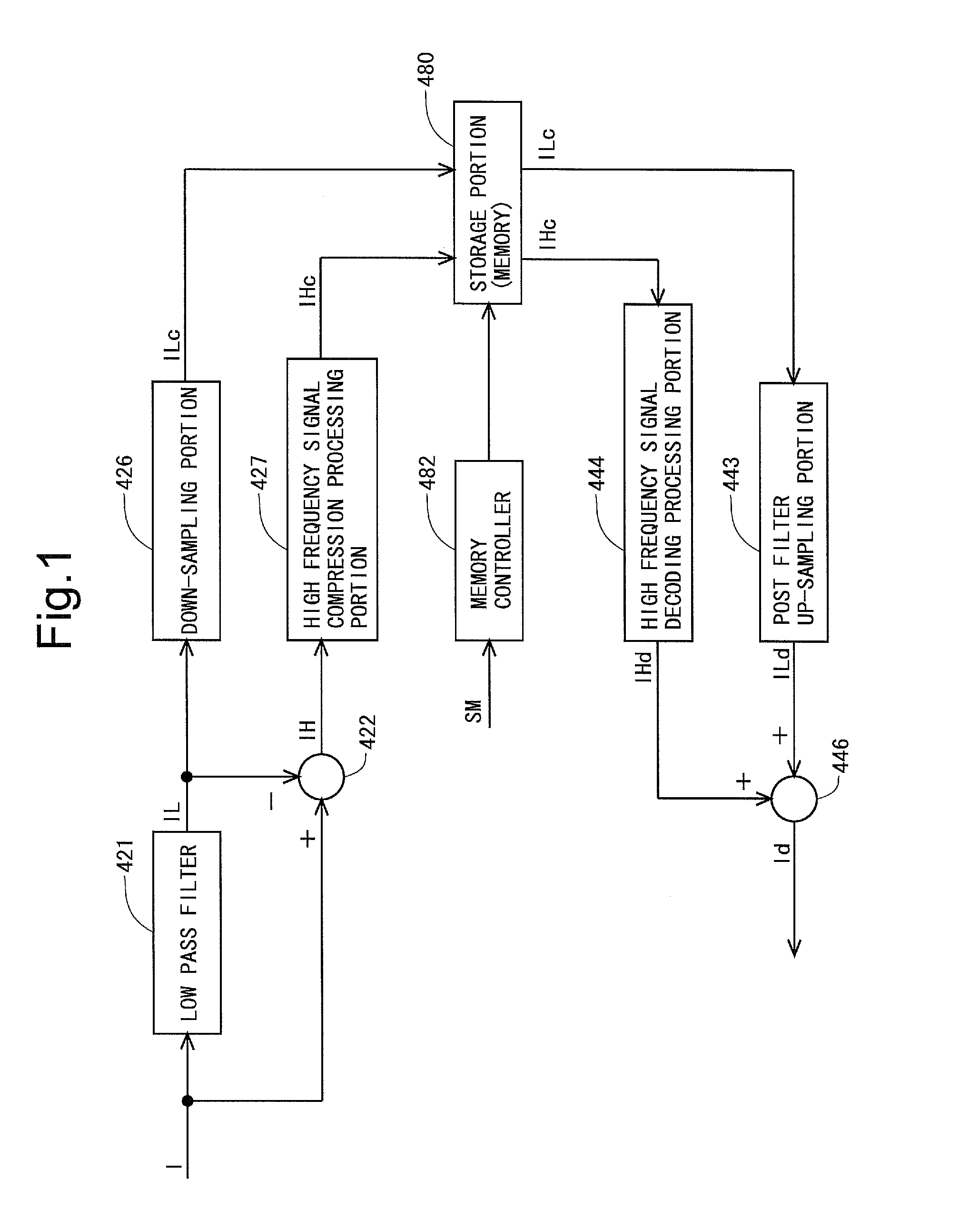
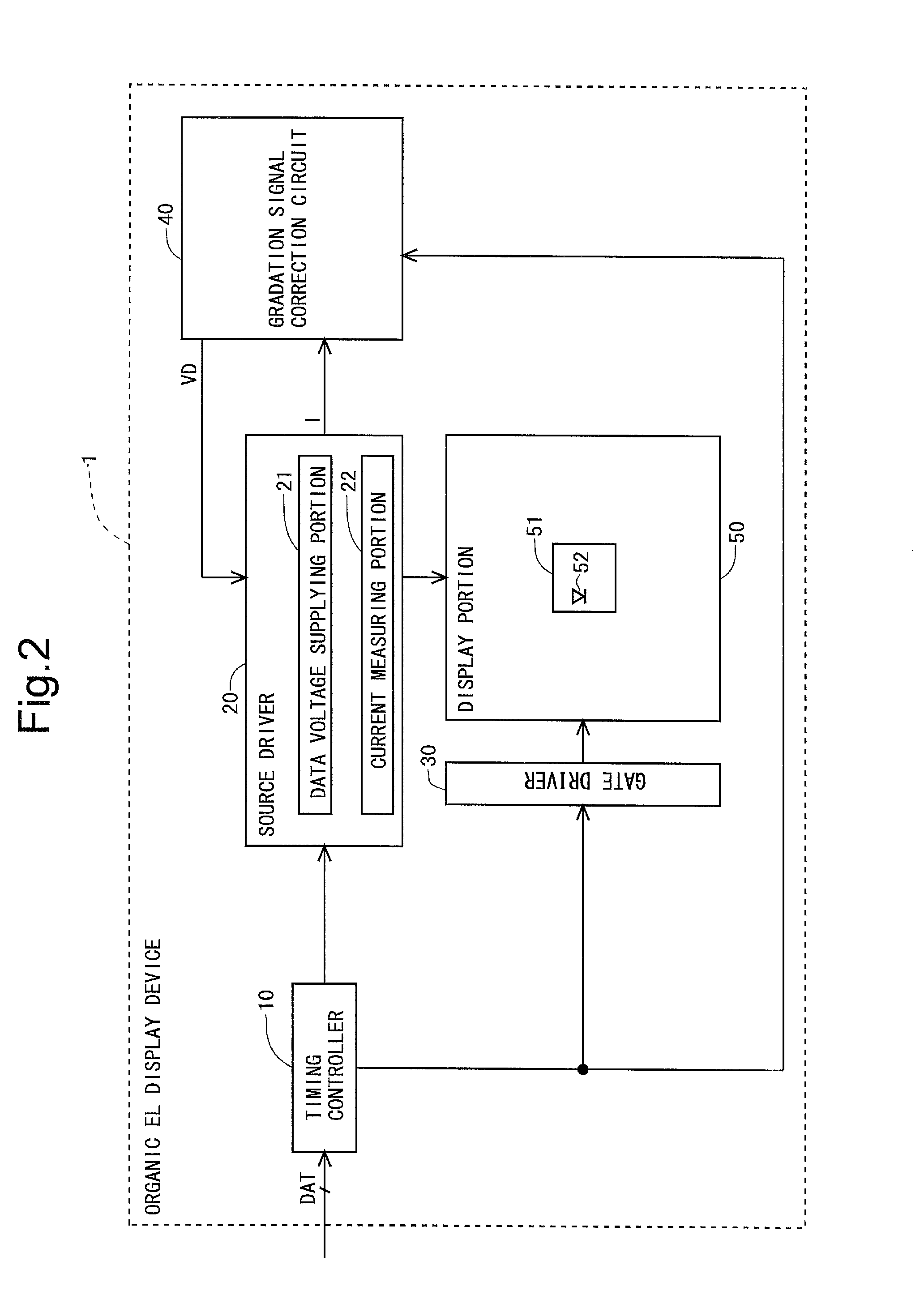
ActiveUS20150356899A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce storage capacityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLow-pass filterDisplay device
An embodiment of the present invention is directed to reducing a memory capacity required for saving compensating data (data used for compensating variations and the like in characteristic of a drive transistor) compared to conventional examples, in a display device. An organic EL display device using an oxide TFT for a drive transistor is provided with: a low pass filter for extracting low frequency component data from pixel current data as data of a drive current of the drive transistor; a first computing portion for obtaining high frequency component data by obtaining a difference between the pixel current data and the low frequency component data; a down-sampling portion for extracting data from the low frequency component data at predetermined sampling intervals; and a high frequency signal compression processing portion for extracting only high amplitude data out of the high frequency component data.
Owner:SHARP KK
Lighting device and display device
InactiveUS20150301266A1Suppresses uneven luminanceSuppress luminescenceMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideDisplay device
An illumination device of the present invention is provided with: a light source; a light guide plate having a light-receiving face that faces the light source and on which light that has been generated from the light source is incident, an opposite surface that is on the opposite side to the light-receiving face, and a light-exiting surface from which light that has entered the light guide plate from the light-receiving face exits; a first wall disposed along the front-back direction of the light guide plate and having a light absorbing surface that faces the opposite surface and absorbs light that has leaked out from the light guide plate; and a first light absorbing member that extends between a front periphery adjacent to the opposite surface on the light-exiting surface and a front end of the first wall, and absorbs light that has leaked out from the light guide plate.
Owner:SHARP KK
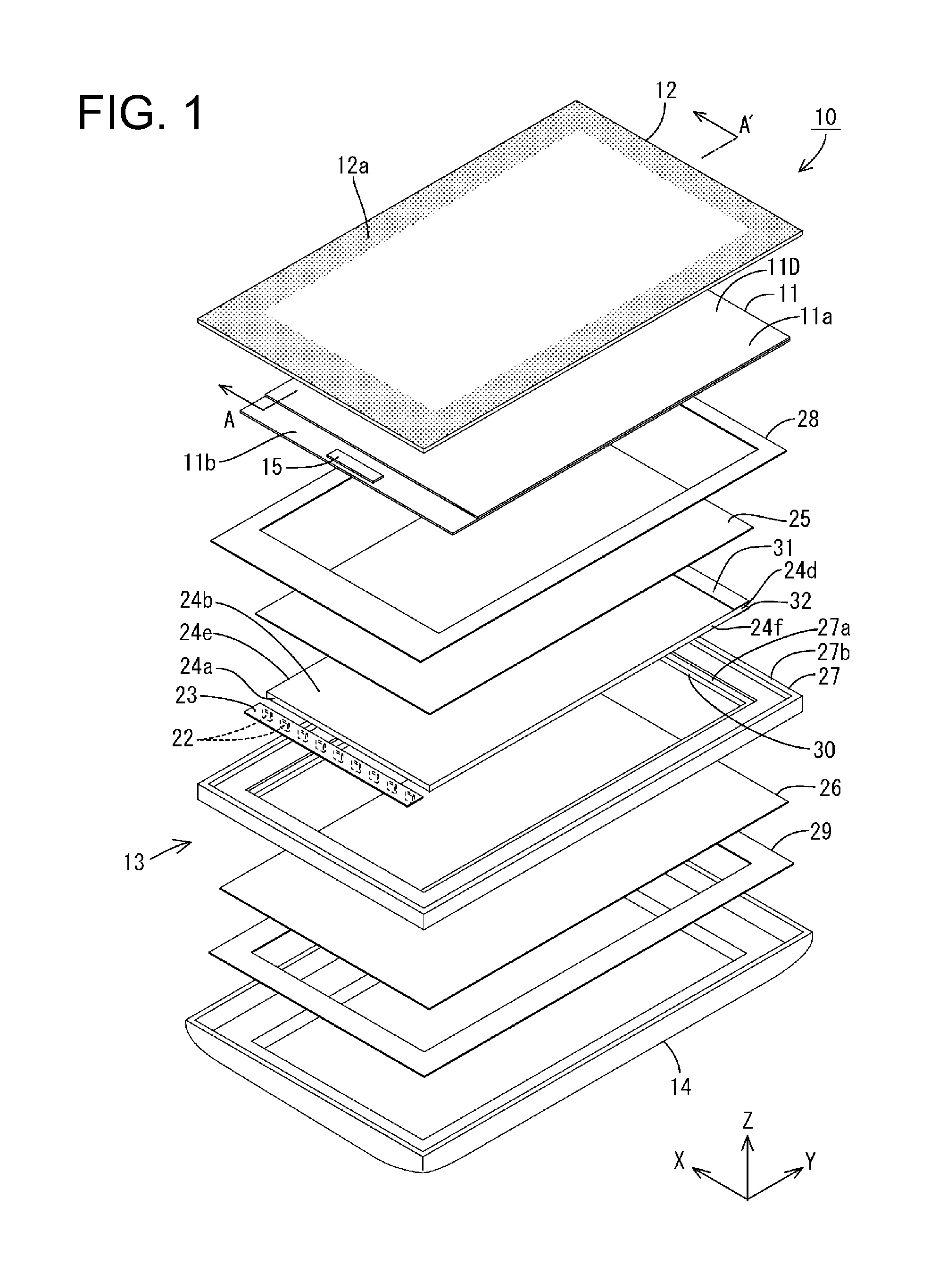
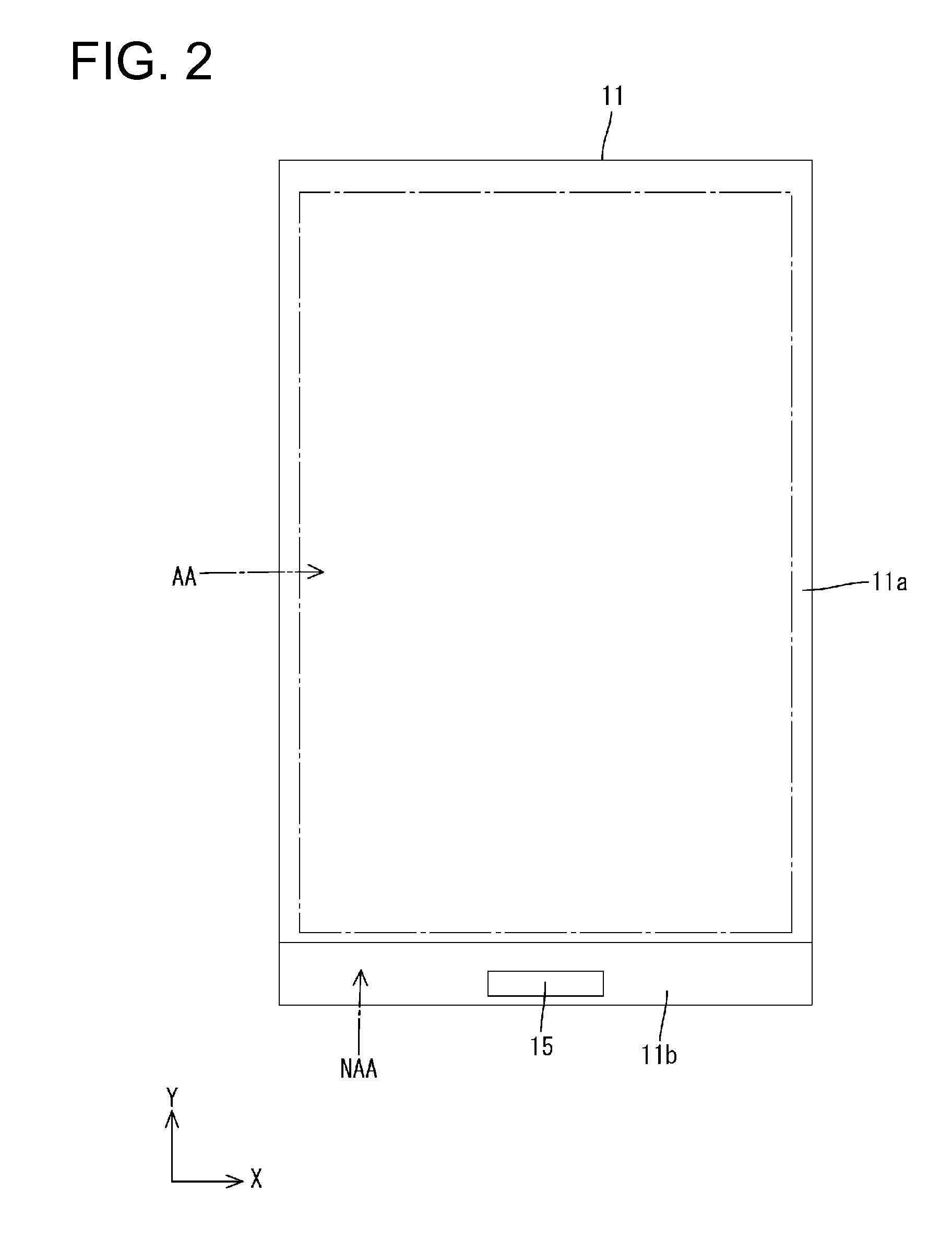
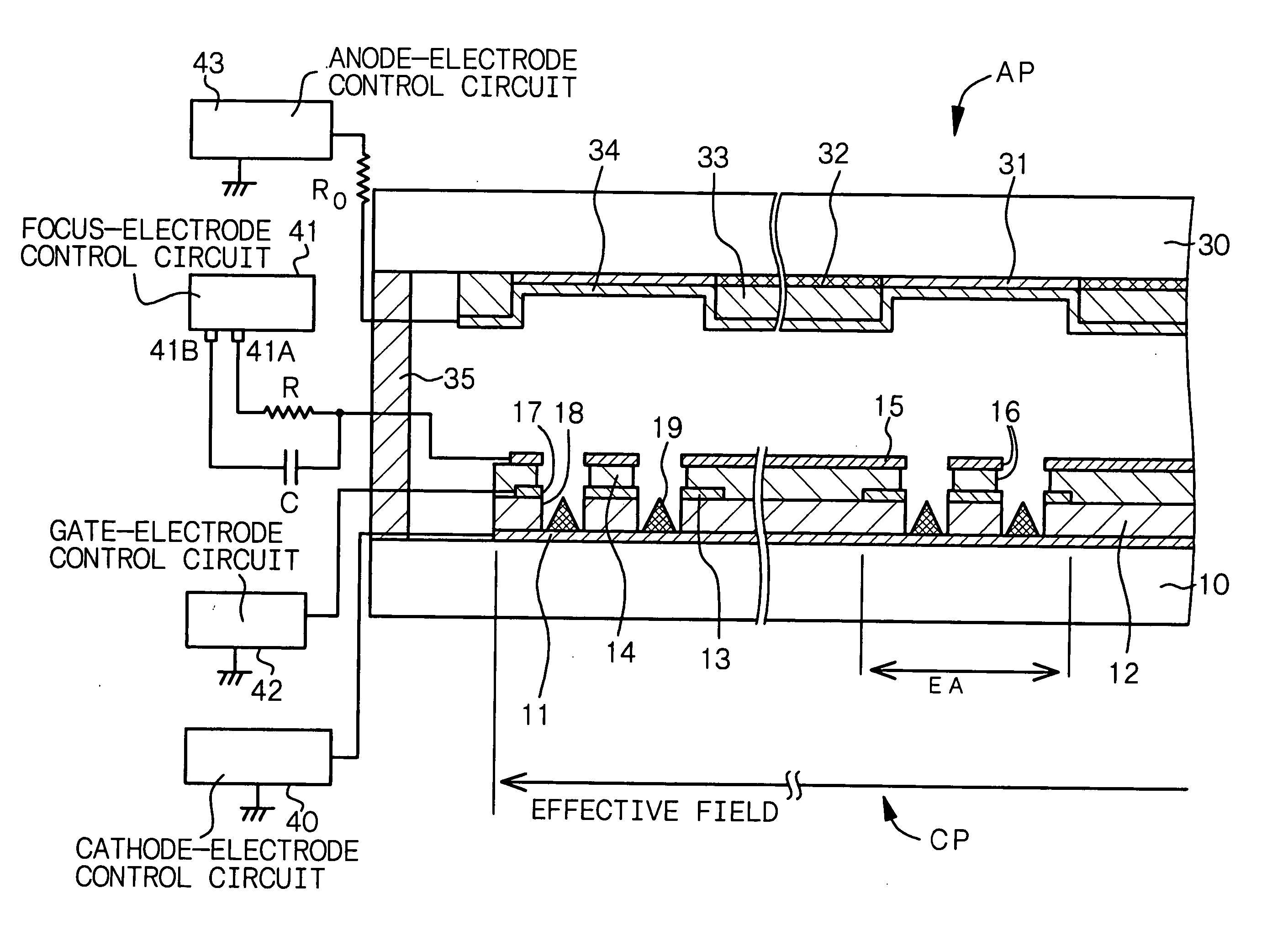
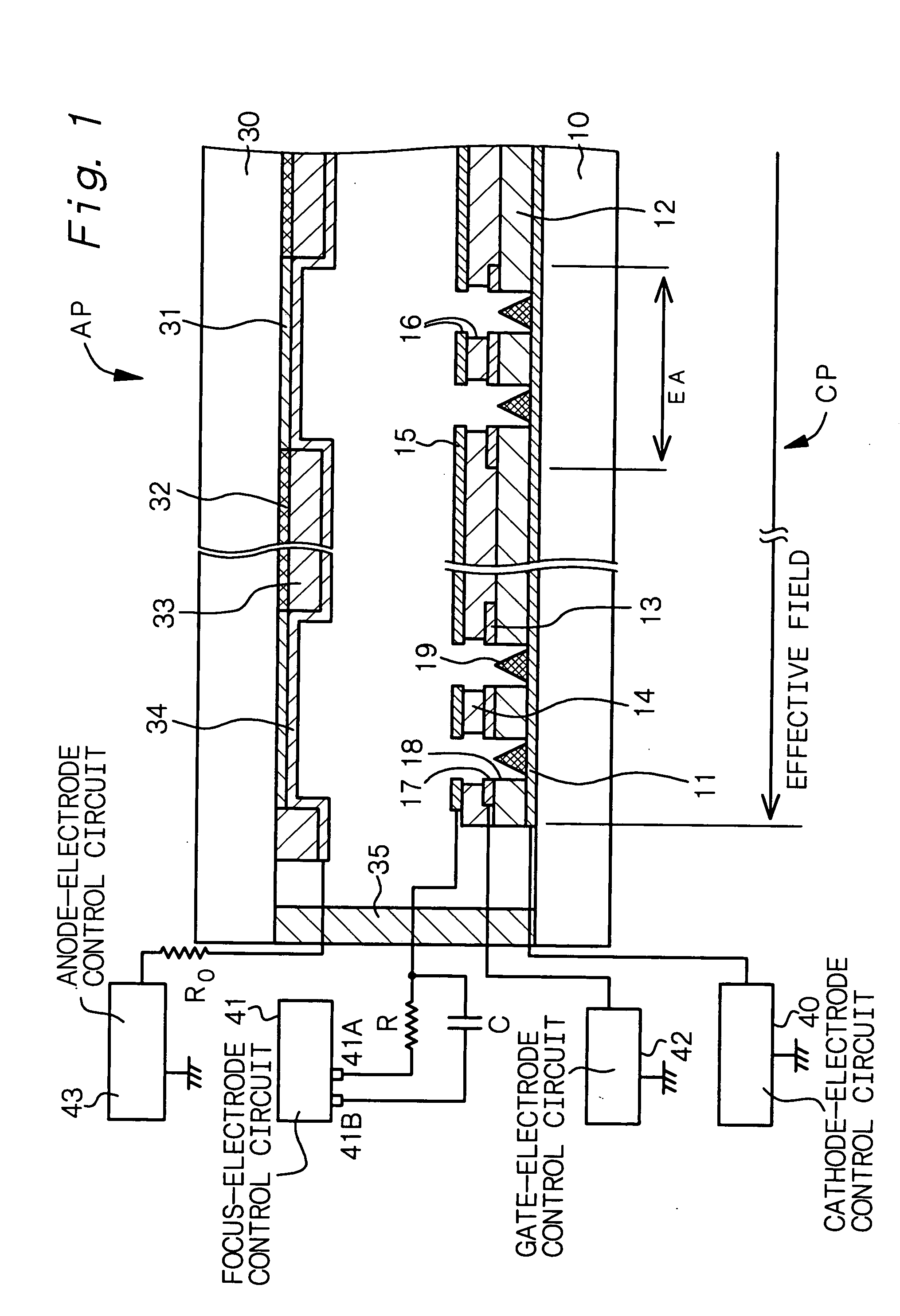
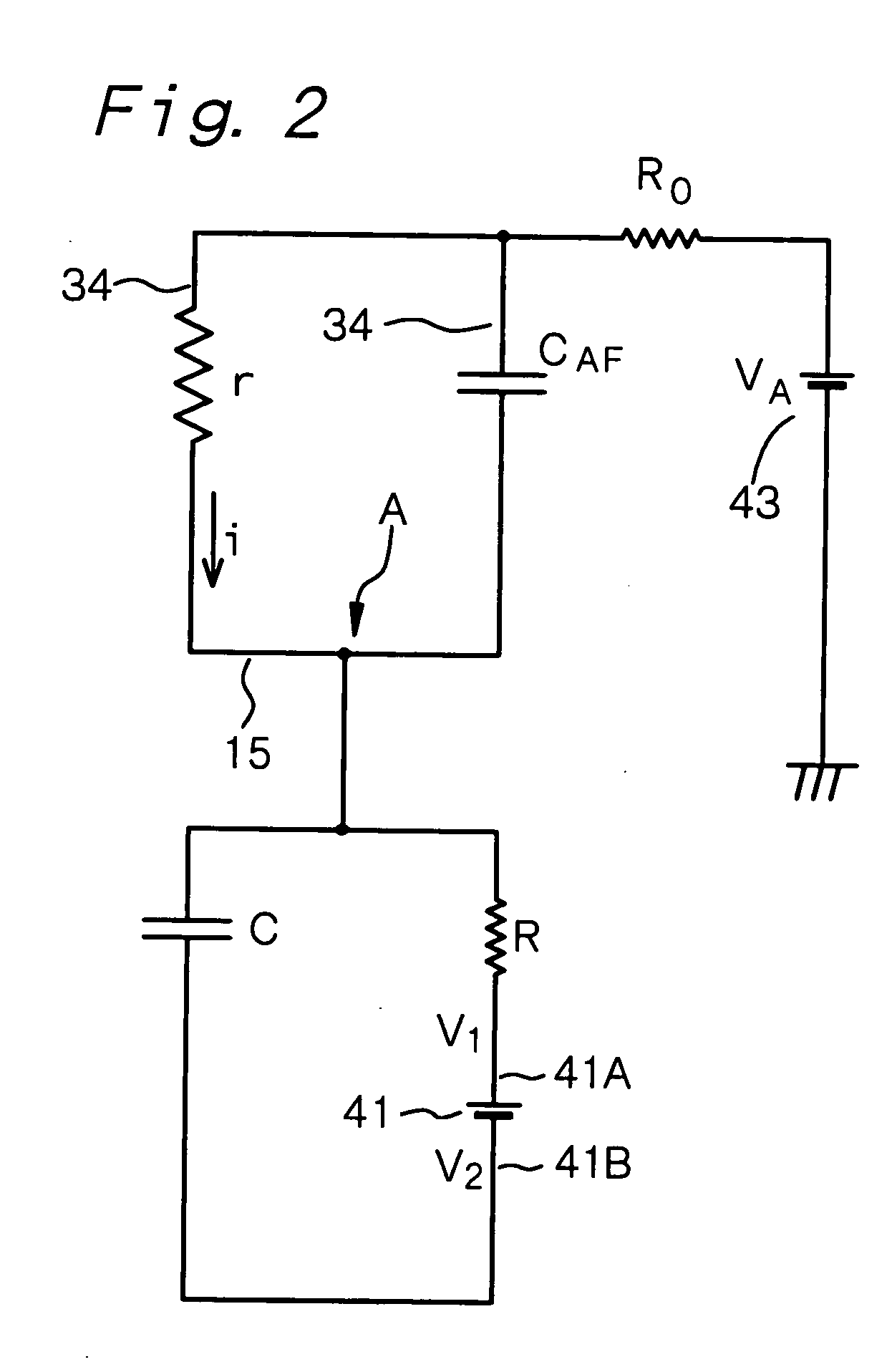
Cold cathode electric field electron emission display device
InactiveUS20050082964A1Increase display contrastAvoid collisionDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesCapacitancePhosphor
A cold cathode field emission display comprising at least (A) a display panel having a cathode panel CP provided with a plurality of electron-emitting regions EA and an anode panel AP provided with a phosphor layer 31 and an anode electrode 34, said cathode panel and said anode panel being bonded to each other in their circumferential regions, (B) a focus-electrode control circuit 41, (C) a resistance element R, and (D) a capacitor C, in which the focus electrode 15 formed in the electron-emitting region EA is connected to a first voltage-output portion 41A of the focus-electrode control circuit 41 through the resistance element R, and the focus electrode 15 is further connected to a second voltage-output portion 41B of the focus-electrode control circuit 41 through the capacitor C.
Owner:SONY CORP
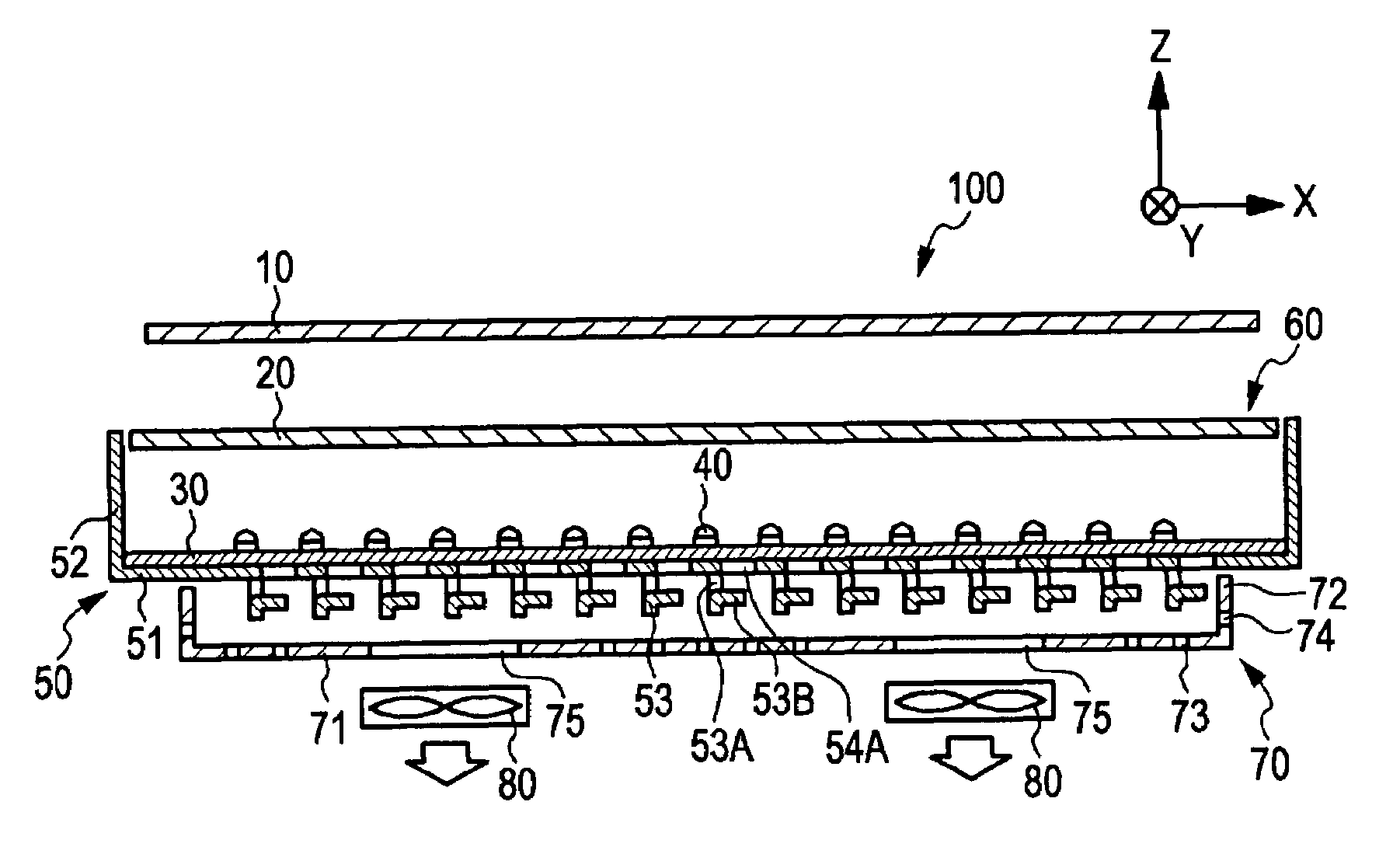
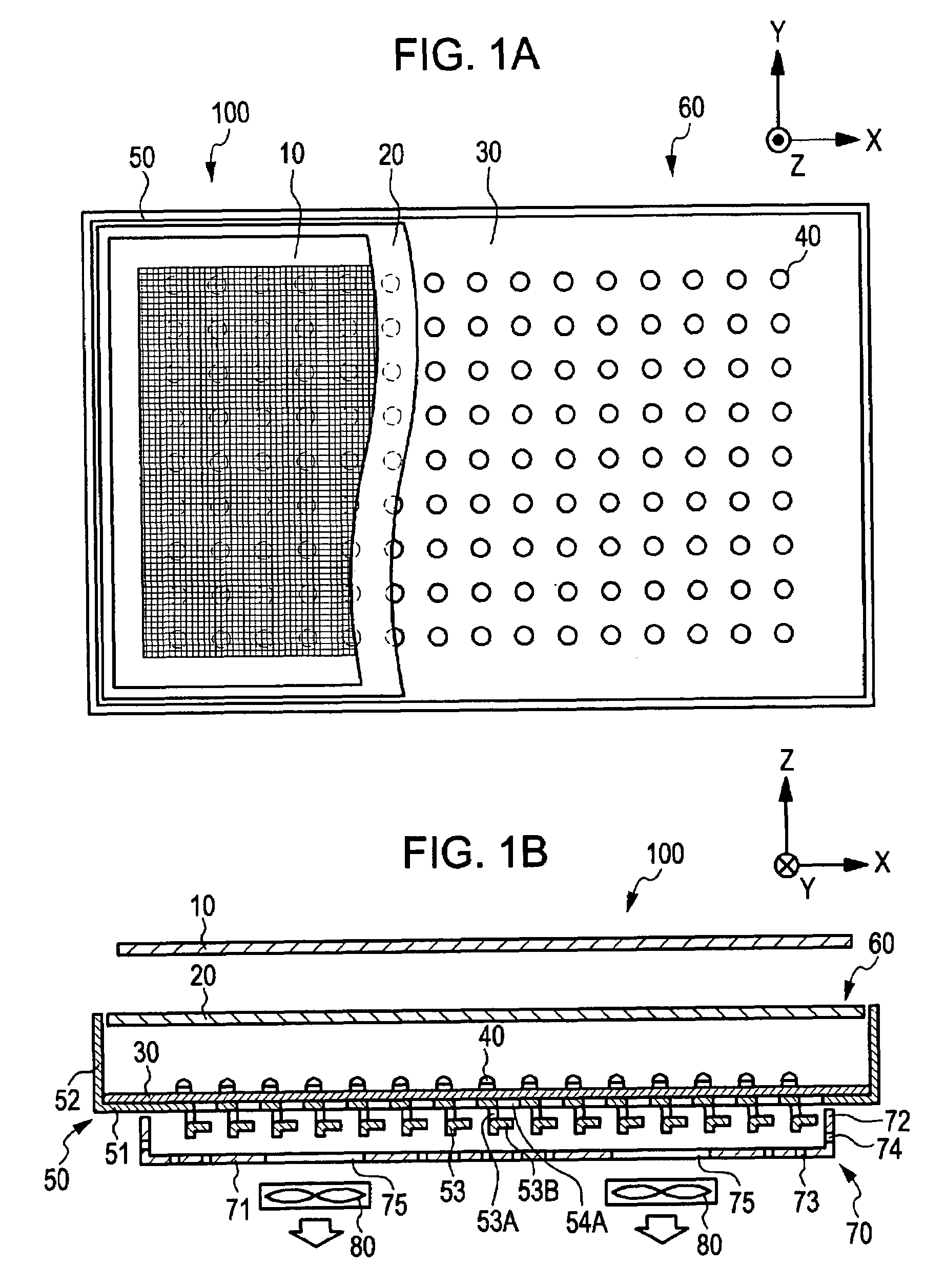
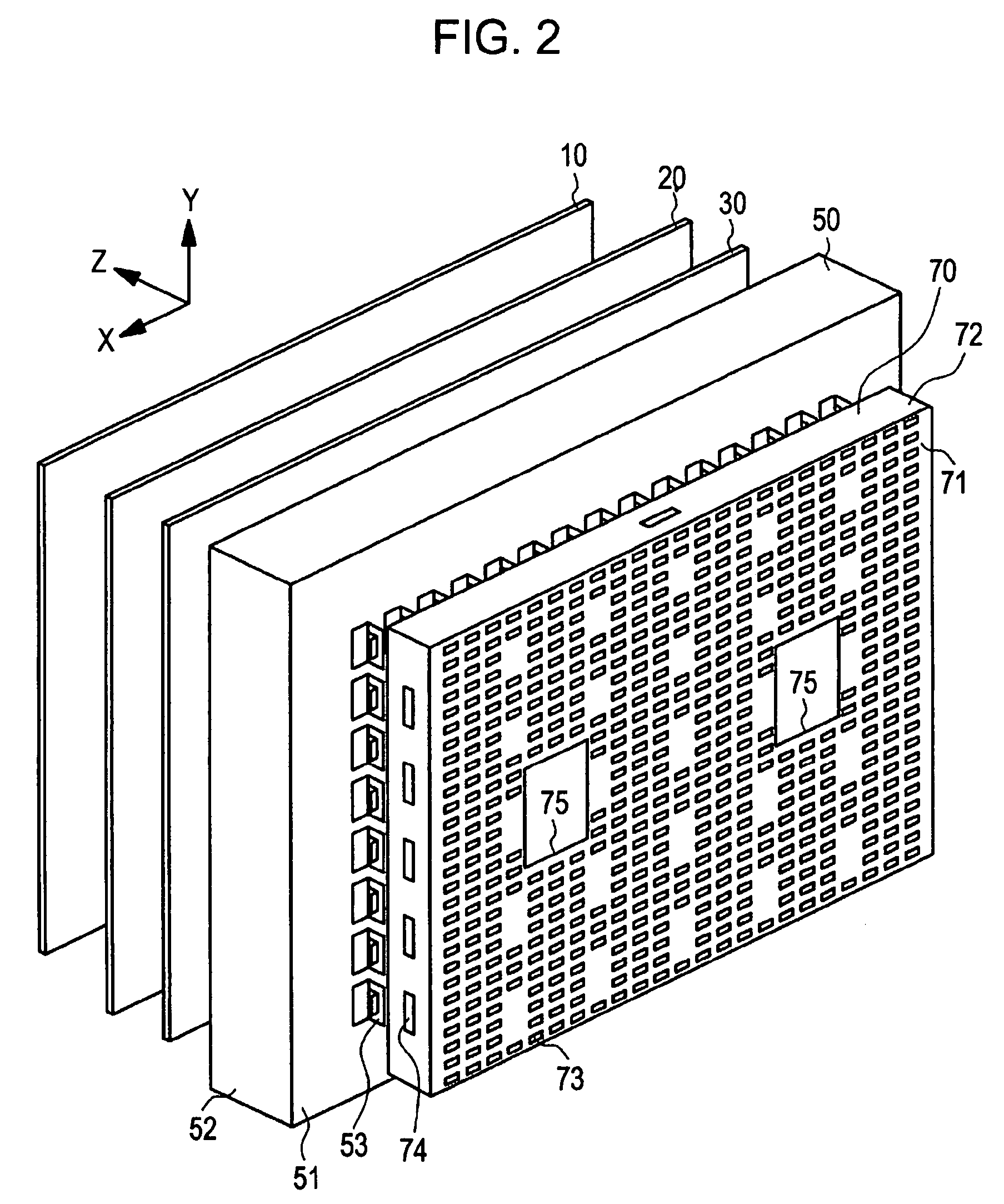
Display Device
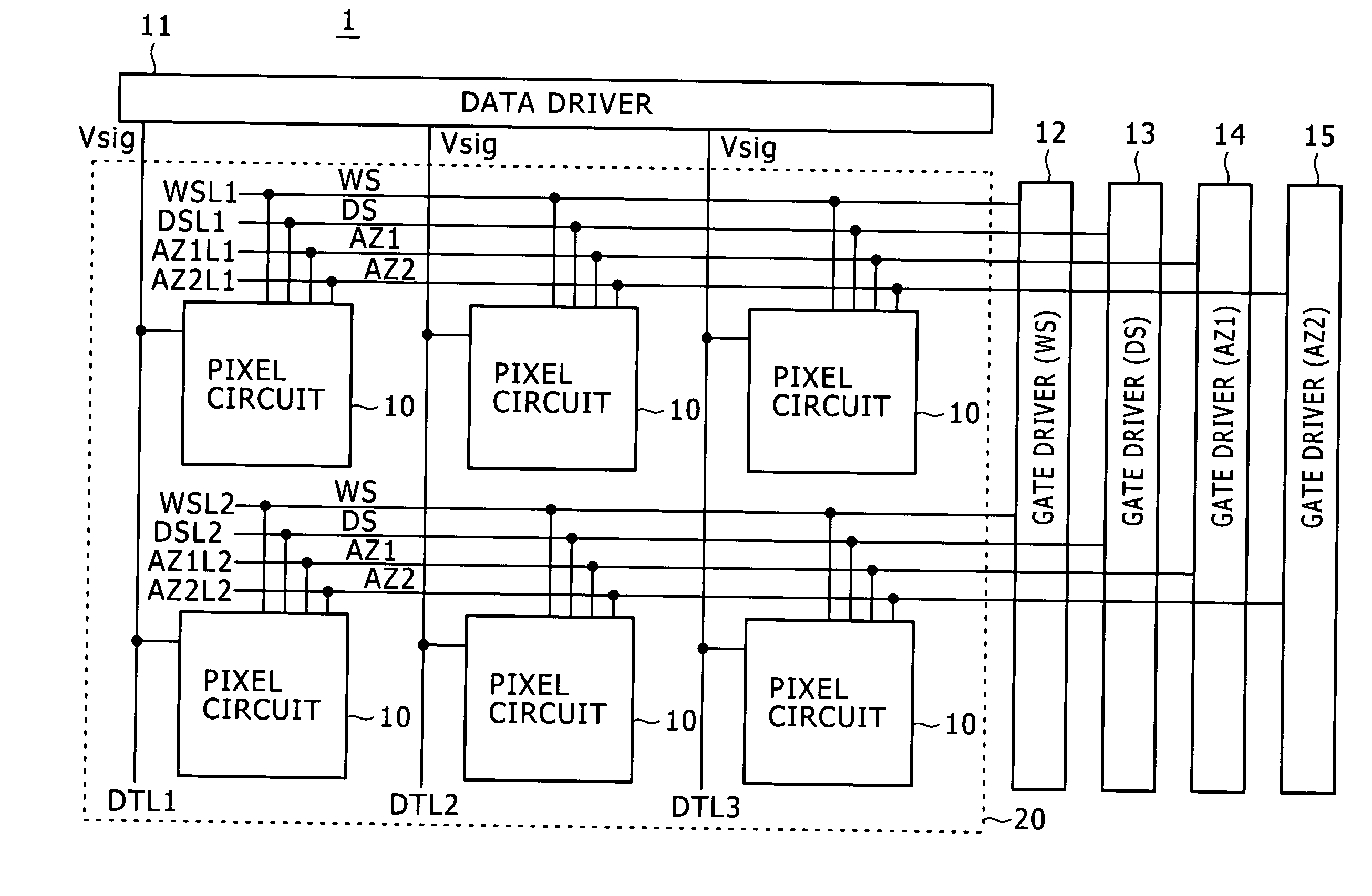
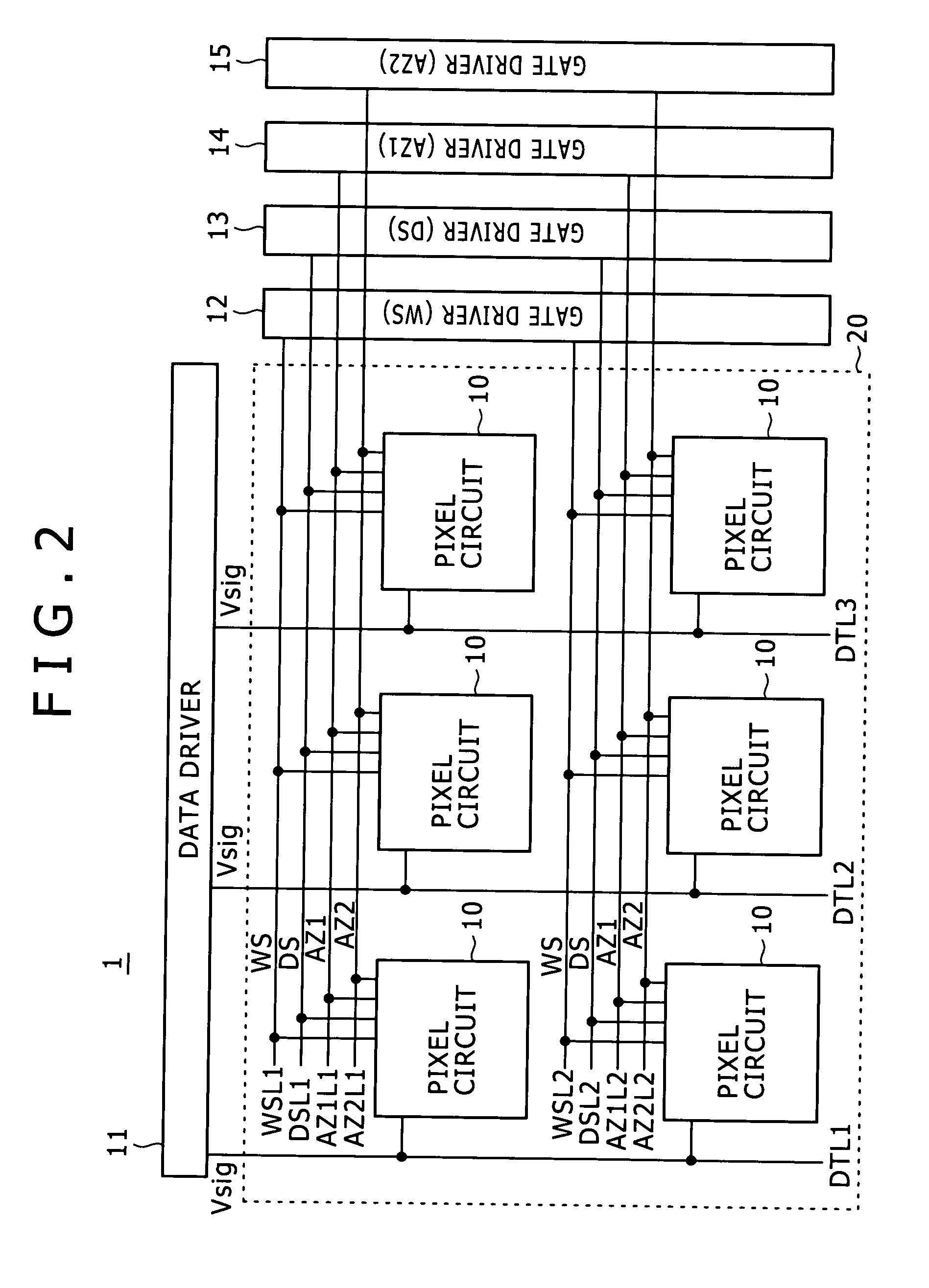
Any one of a write scanning line, a power source supply line, and a video signal line is structured as a subsidiary wiring disposed in the same layer as that having a lower electrode disposed therein. The subsidiary wiring is used in the power source supply line through which a power source drive pulse to be pulse-driven is transmitted, or other wirings (such as the write scanning line and the video signal line).
Owner:SONY CORP
Surface light source device and liquid crystal display assembly
ActiveUS7438450B2Improve image qualityLow costShow cabinetsImpedence networksLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A liquid crystal display assembly includes a liquid crystal display, and a surface light source device that illuminates the liquid crystal display from a back surface. The surface light source device includes a housing including a bottom plate, a light source that is arranged on the bottom plate and illuminates the liquid crystal display, and a plurality of radiator fins arranged at a spacing from each other. Each of the radiator fins includes a first fin portion formed by bending a part of the bottom plate in a direction away from the liquid crystal display, the first fin portion extending substantially perpendicularly to the bottom plate, and a second fin portion formed by bending a part of the first fin portion in a direction away from the liquid crystal display, the second fin portion extending substantially parallel to the bottom plate.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Optical element, and display device, electronic apparatus, lighting device using the same
ActiveUS20160077363A1Improve transmittanceHigh light transmittanceStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsPhysicsHigh transmittance
There is such an issue with the well-known optical element that it is difficult to achieve a high transmittance since the transmittance is determined according to the pattern size of the light transmission regions, so that the luminance of the display device to which such optical element is mounted is deteriorated. Provided is an optical element which employs a structure in which the shape of a conductive pattern where electrophoretic particles cohere in a wide viewing field mode is formed in a comb-like shape and plural stages and plural rows of light transmission regions are disposed in the spaces between the comb teeth. This makes it possible to exclude the electrophoretic particles from the regions other than the comb-like electrode for allowing the light to transmit that part.
Owner:TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light emitting apparatus, electronic equipment and method of driving pixel circuit
ActiveUS20100253666A1Suppress luminescenceEliminate chargeElectrical apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriving currentHemt circuits
A light emitting apparatus includes a pixel circuit and a driving circuit which drives the pixel circuit. The pixel circuit includes: a driving transistor which generates a driving current; a light emitting device that determines gradation depending on the driving current; a light emission control transistor; a discharge transistor; a capacitor device; and a first switching device interposed between a gate and a drain of the driving transistor.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Monochromatic light source
InactiveUS20110150019A1Enhance light emissionSuppress light emissionLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPhysicsLight source
Light emitting systems are disclosed. The light emitting system includes an electroluminescent device that emits light at a first wavelength. The light emitting system further includes an optical cavity that enhances emission of light from a top surface of the light emitting system and suppresses emission of light from one or more sides of the light emitting system. The optical cavity includes a semiconductor multilayer stack that receives the emitted first wavelength light and converts at least a portion of the received light to light of a second wavelength. The semiconductor multilayer stack includes a II-VI potential well. The integrated emission intensity of all light at the second wavelength that exit the light emitting system is at least 10 times the integrated emission intensity of all light at the first wavelength that exit the light emitting system.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Light emitting device
ActiveUS20090114936A1Reduce brightness unevennessSuppress luminescenceSolid-state devicesPlanar/plate-like light guidesShaped beamBand shape
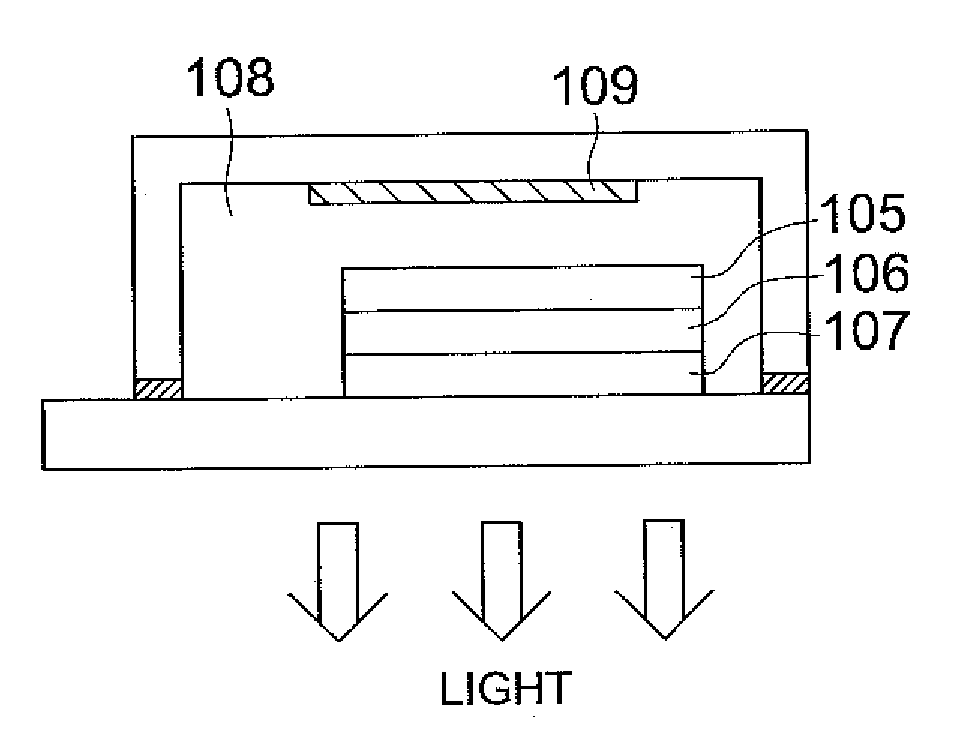
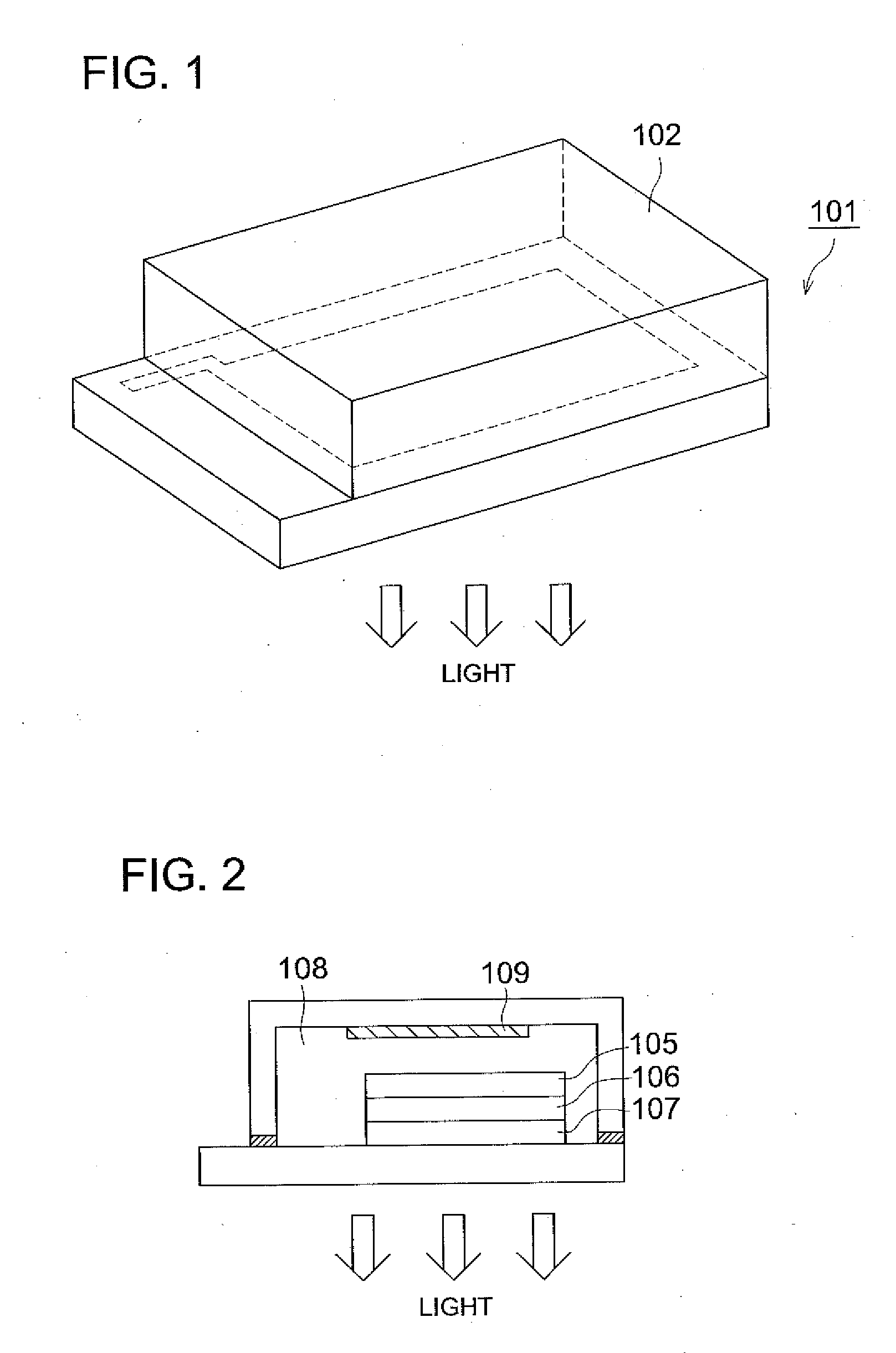
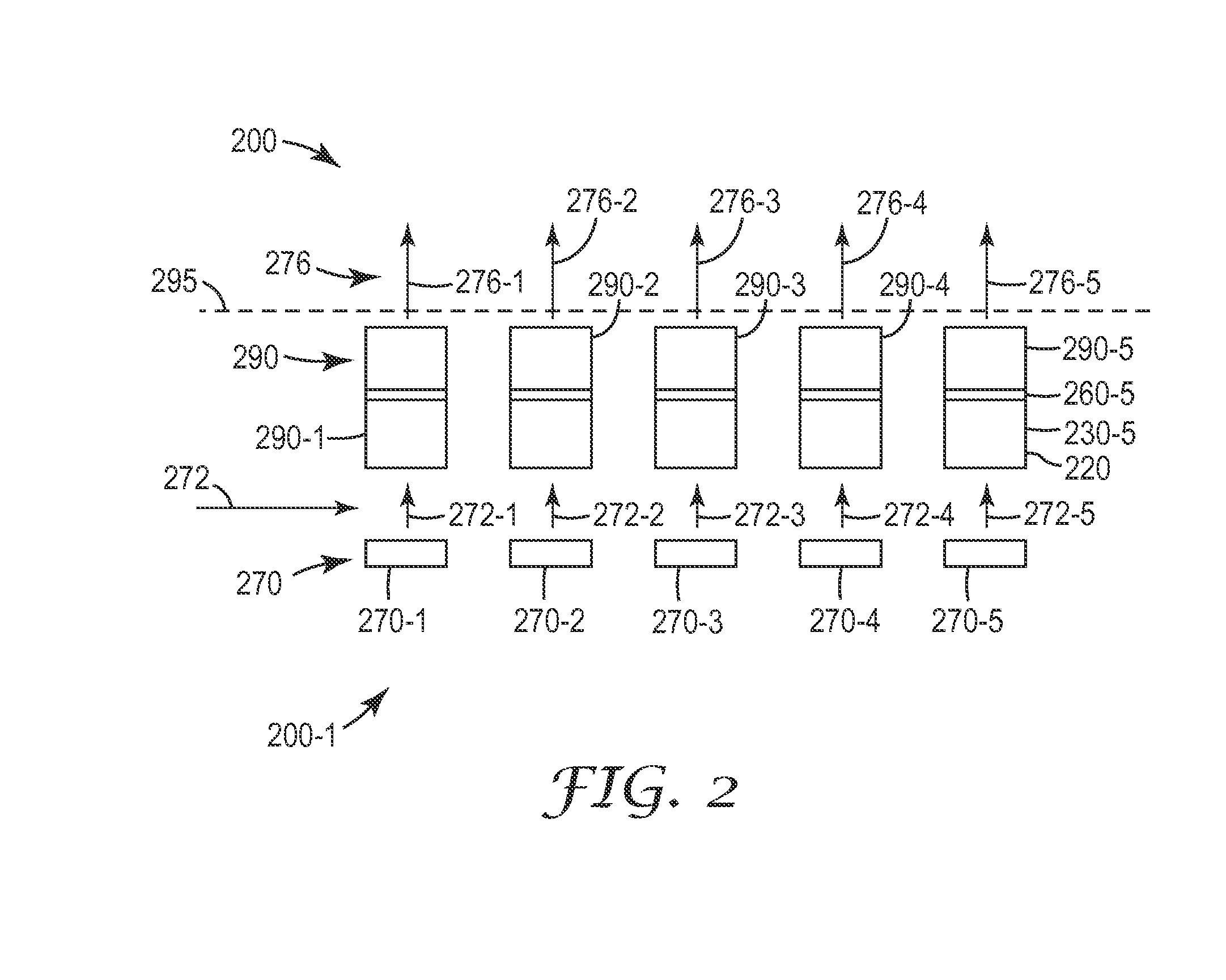
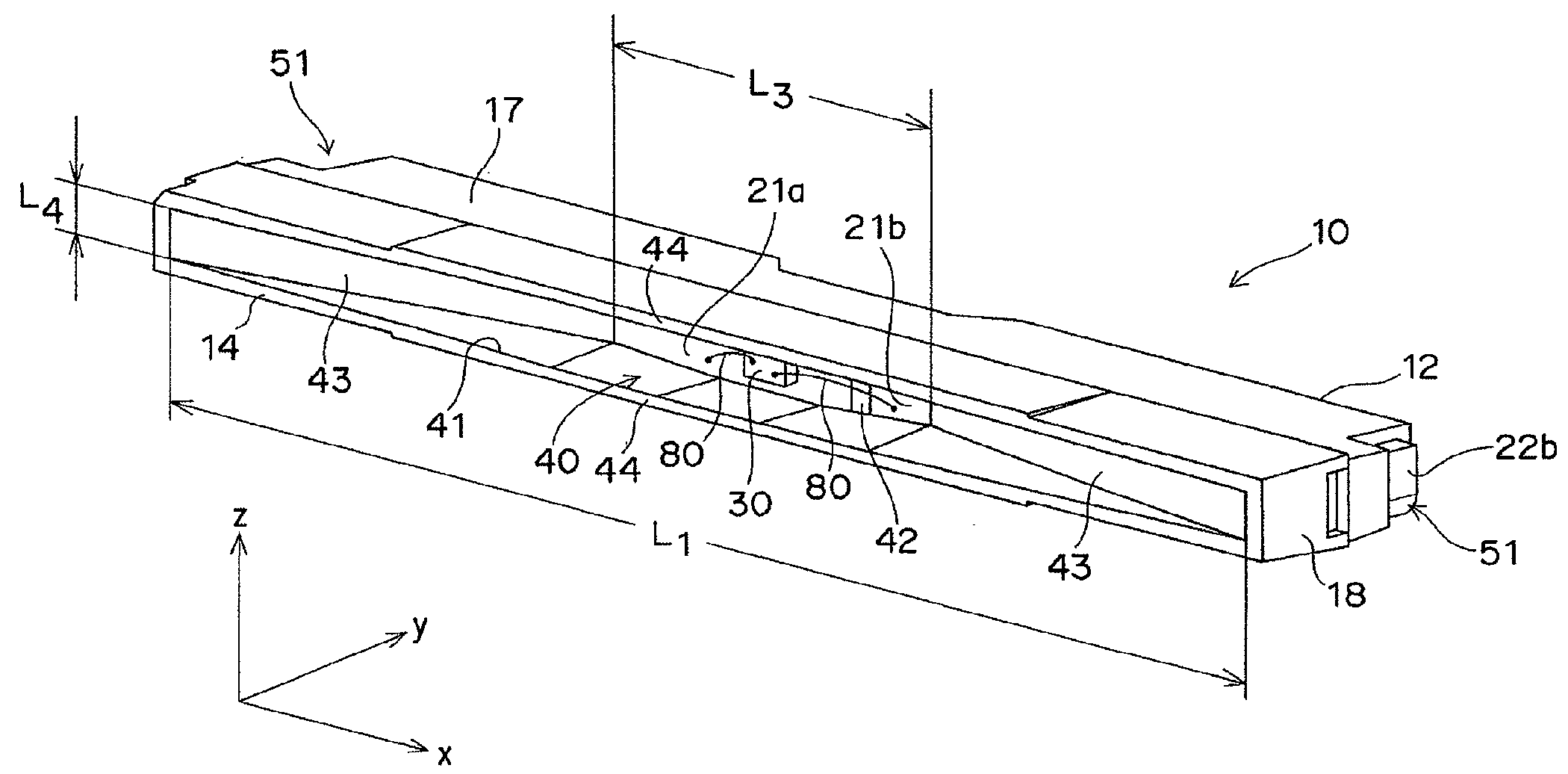
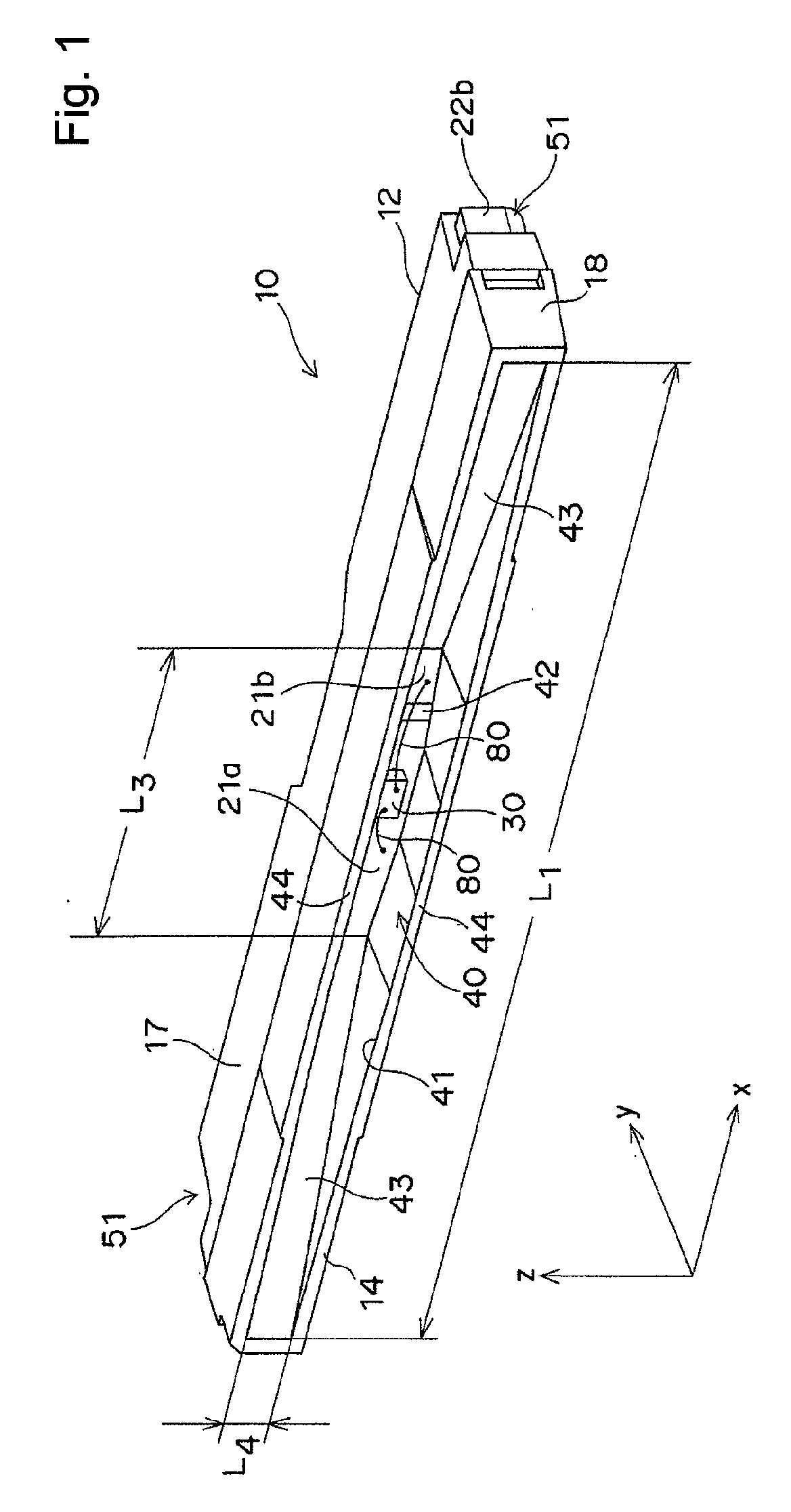
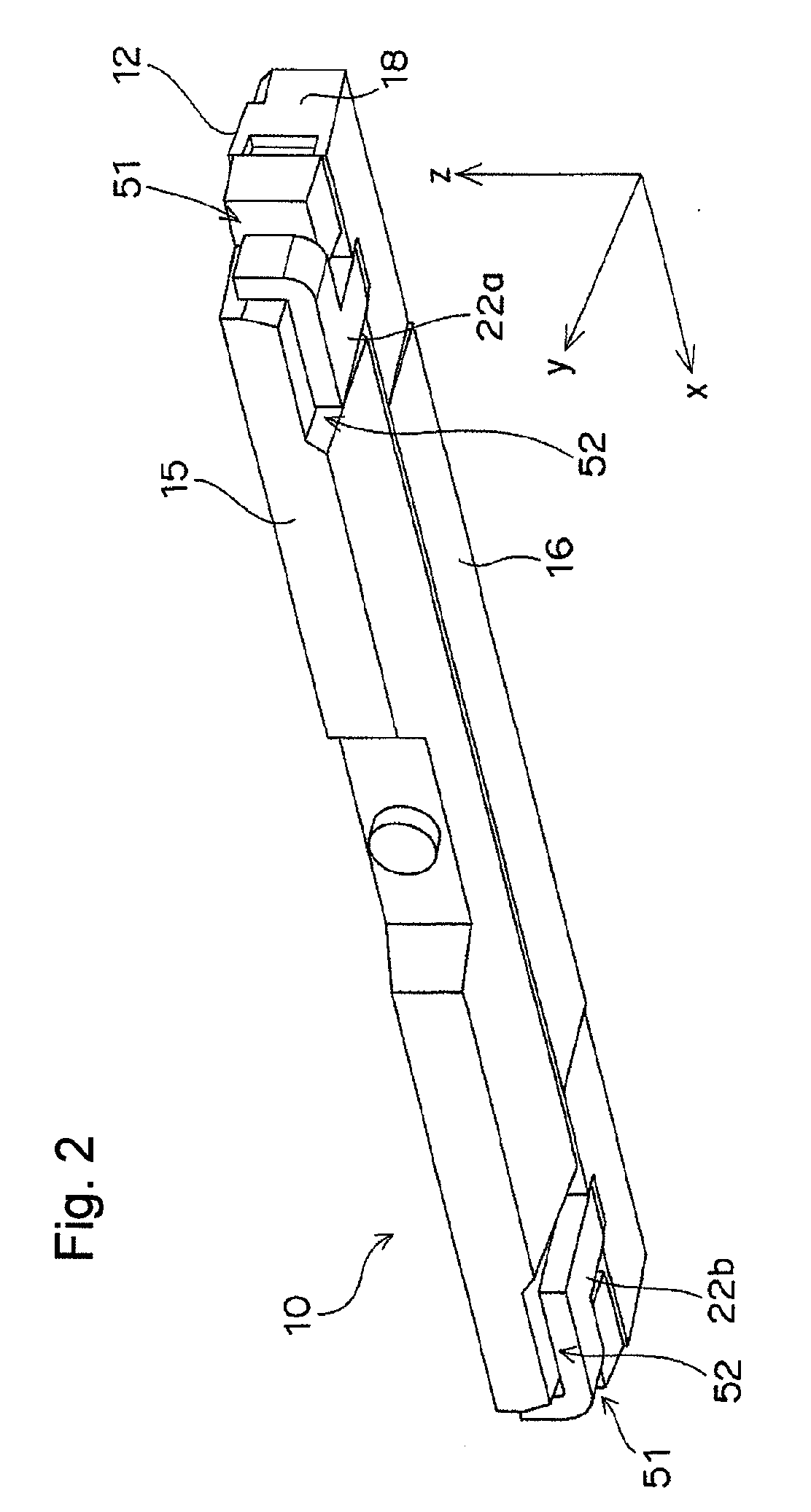
To provide a light emitting device that makes it possible to form a surface light emitting apparatus of less unevenness in luminance.The light emitting device 10 of the present invention comprises a light emitting element 30, connecting terminals 21a, 21b connected with the light emitting element30, a package 12 which has a recess 40 wherein the light emitting element 30 is mounted and from which a part of each connecting terminal 21a, 21b is projected outward, an opening 41 of the recess 40 being elongated in one direction, wherein both side walls of the recess 40 positioned in the longitudinal direction of the recess 40 are inclined surface 43, an angle θ between both the inclined surfaces 43 being 90 degrees or more. In the light emitting device 10 of the present invention, light emitted by the light emitting element 30 is spread sufficiently in the longitudinal direction of the opening 41 so as to produce a band-shaped beam. As a result, when a plurality of light emitting devices 10 are disposed along the longitudinal direction of the light receiving surface 72 of the light guide plate 71 for constituting the surface light emitting apparatus 70, unevenness in luminance can be suppressed from occurring as dark portions are less likely to be generated between adjacent light emitting devices 10.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
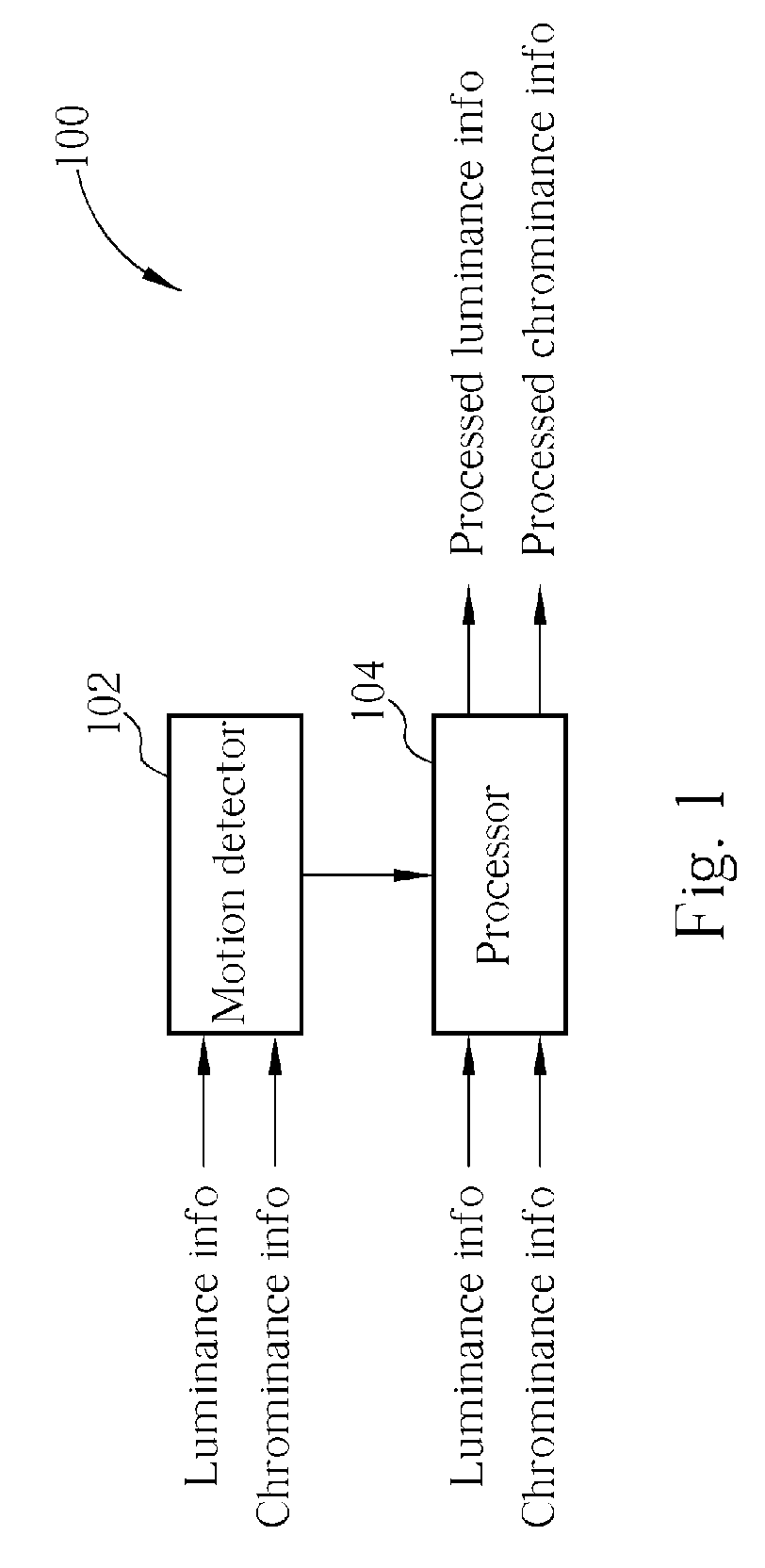
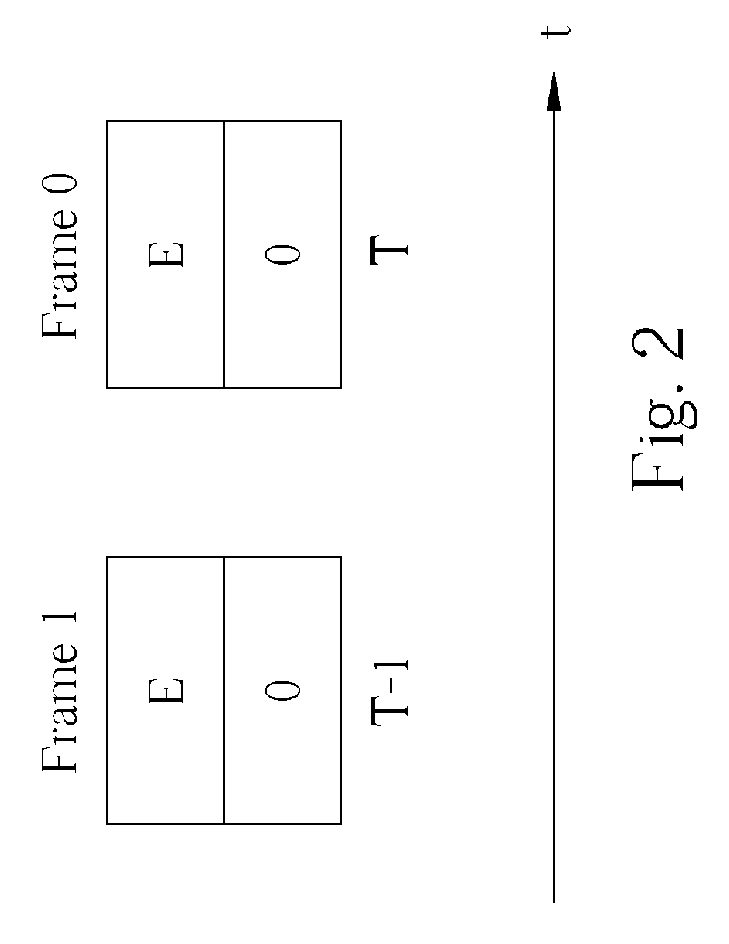
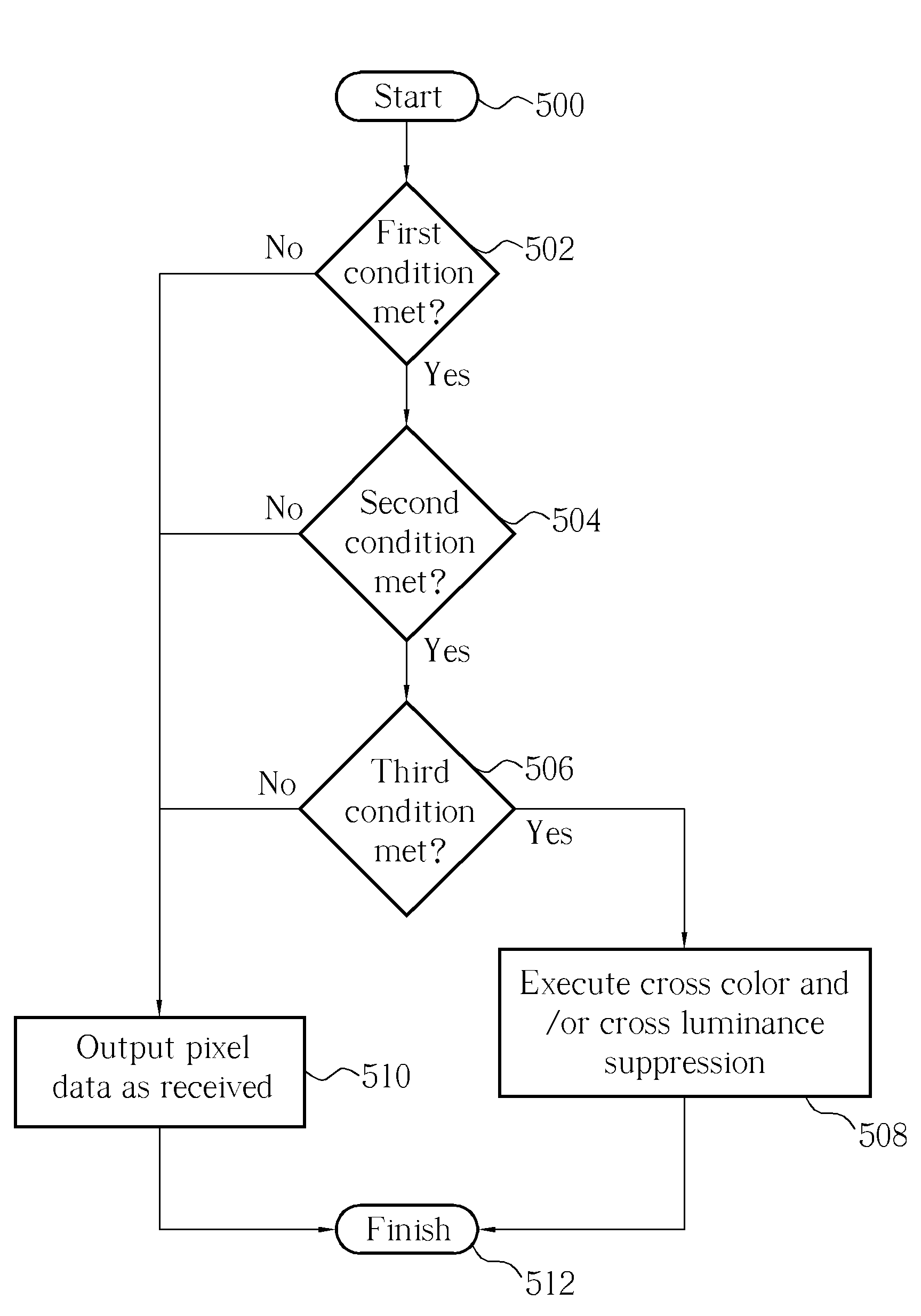
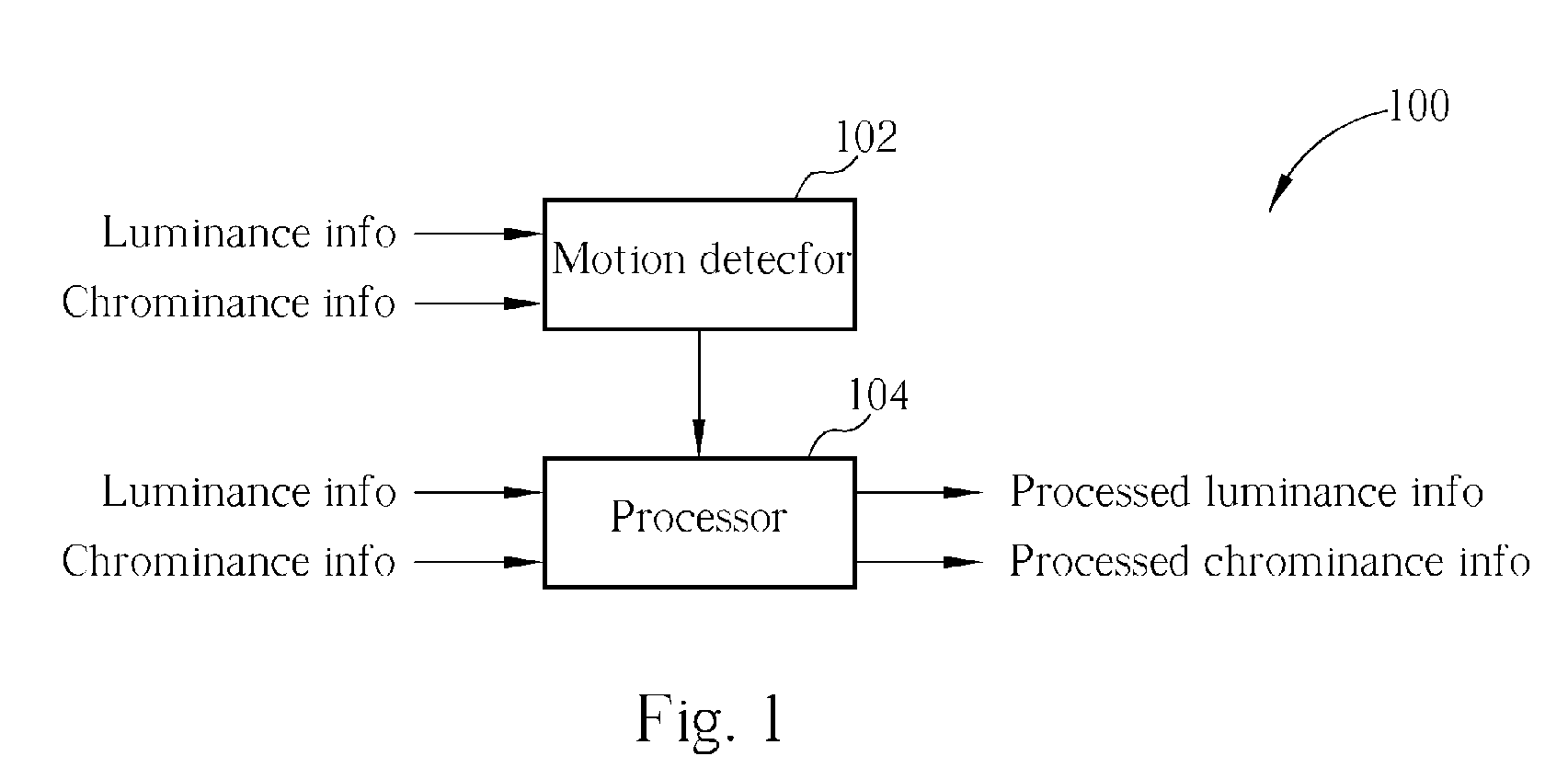
Method and apparatus for cross color/cross luminance suppression
ActiveUS7271850B2Suppress luminescenceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLightnessComputer science
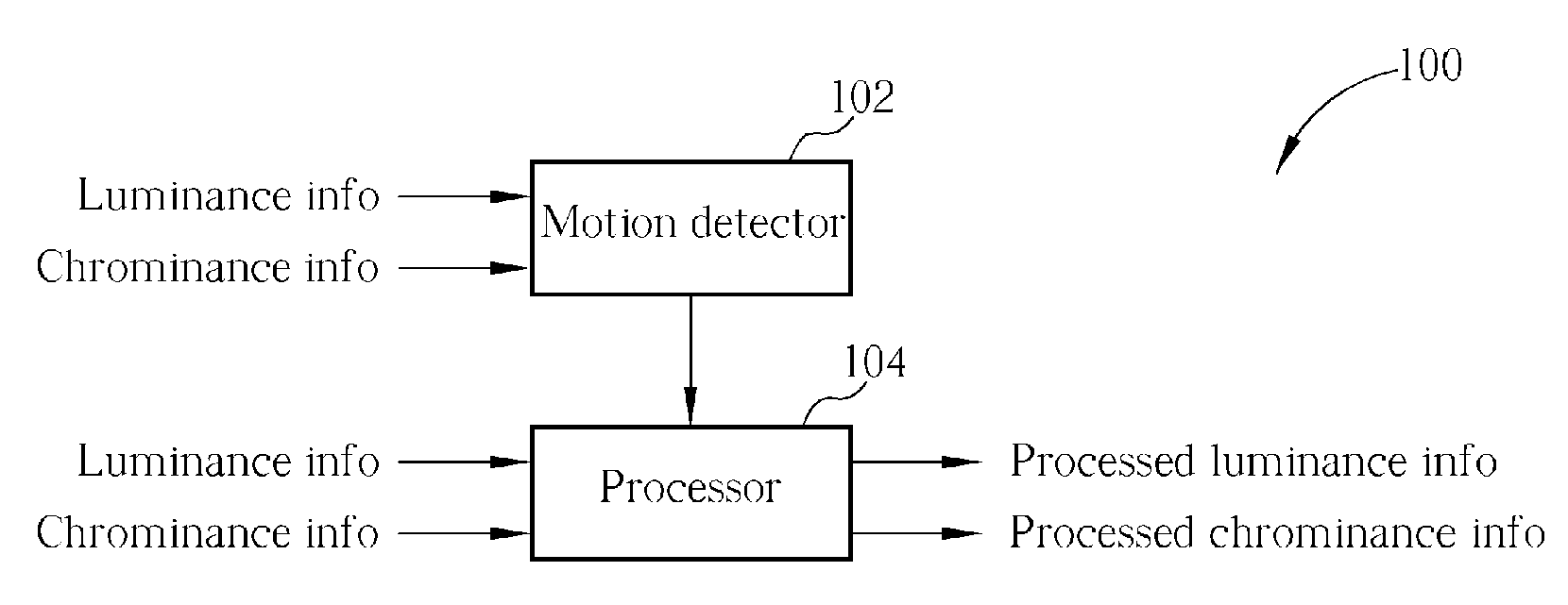
According to embodiments of the present invention, a method for processing an image in a video data is disclosed. The video data comprises at least a first frame and a second frame. The first frame is composed of a first even field and a first odd field, while the second frame is composed of a second even field and a second odd field. The method comprises obtaining a first difference set between pixel information of the first frame and pixel information of the second frame, wherein the first frame and the second frame are adjacent to each other; examining a first criterion with the first difference set; and performing cross color suppressing operation on pixel information of the second frame according to a set of stationary image judgment information comprising the result of the first criterion examination.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Method and apparatus for cross color and/or cross luminance suppression
ActiveUS7280159B2Suppressing colorSuppress luminescenceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionConsecutive frame
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Display device and display driving method
InactiveUS20090079678A1Increase contrastIncrease brightnessStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceData signal
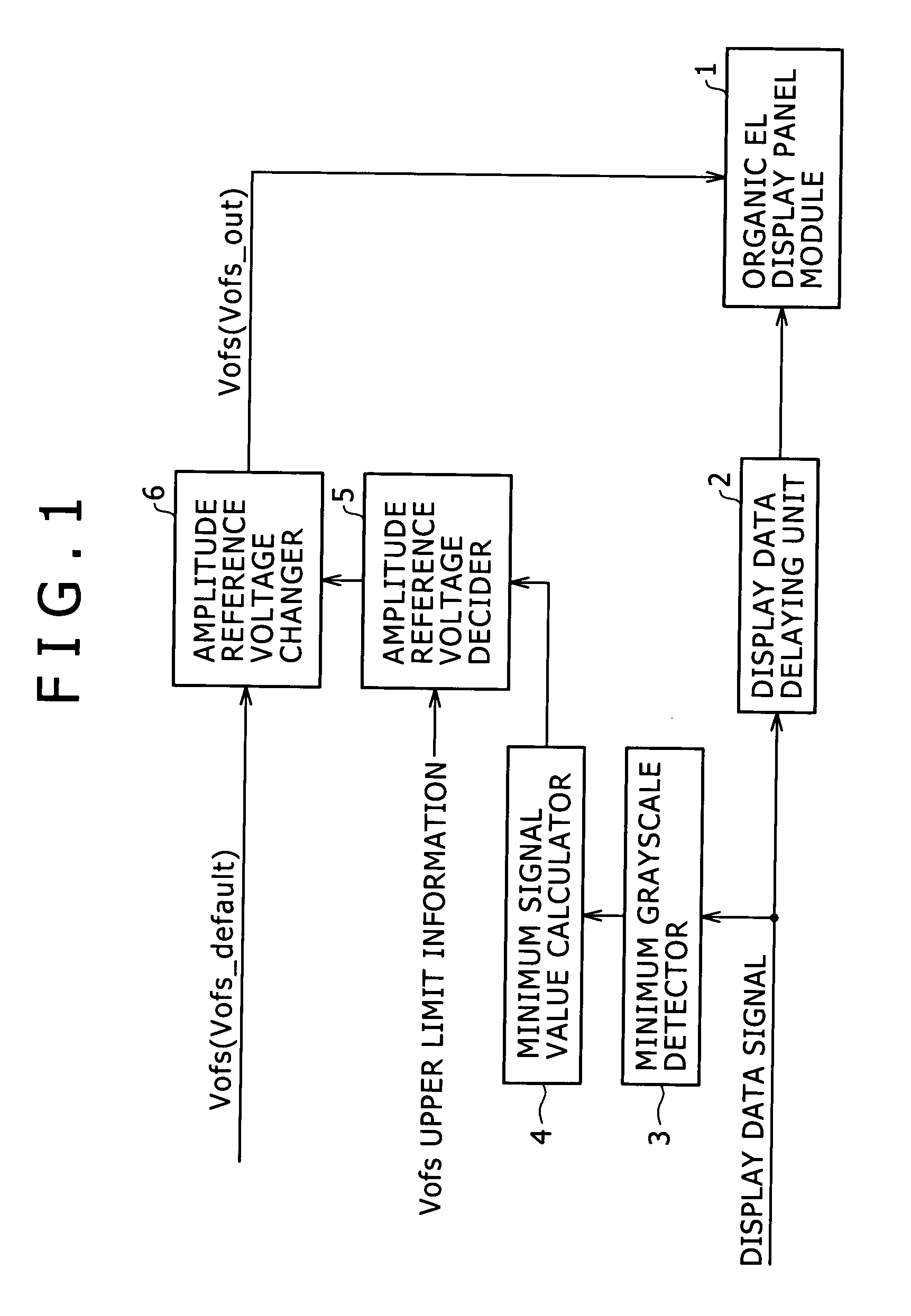
A display device includes a display panel unit configured to include pixel circuits in each of which an organic electroluminescence device is used as a light emitting device and is driven to emit light with luminance dependent upon a voltage difference between a signal value voltage of an input display data signal and a signal amplitude reference voltage. The display device further includes: a voltage controller configured to carry out grayscale value detection for a display data signal to be supplied to the display panel unit in every predetermined period, and create voltage control information of the signal amplitude reference voltage by using a detected grayscale value; and a signal amplitude reference voltage changer configured to change a voltage value of the signal amplitude reference voltage to be supplied to the pixel circuits of the display panel unit, based on voltage control information created by the voltage controller.
Owner:SONY CORP
Screen Device for Three-Dimensional Display with Full Viewing-Field
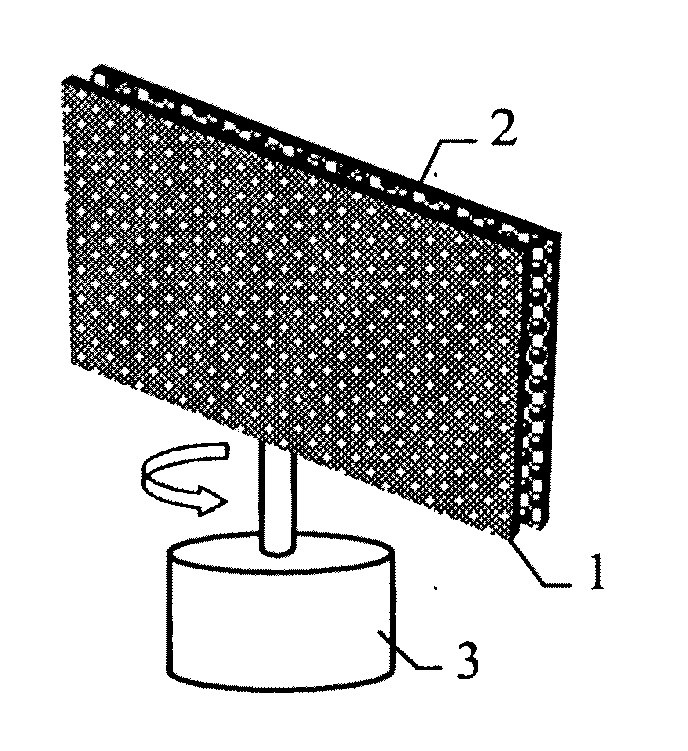
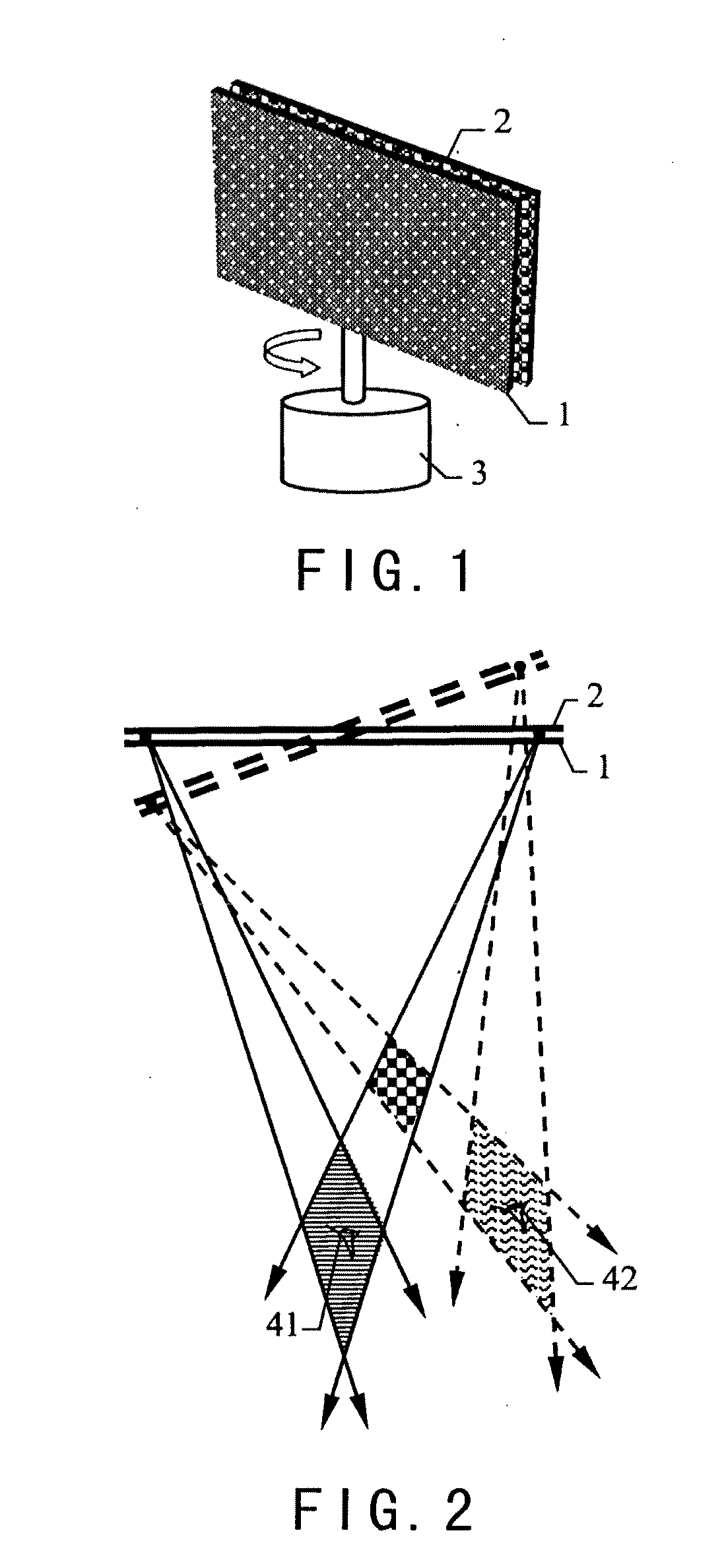
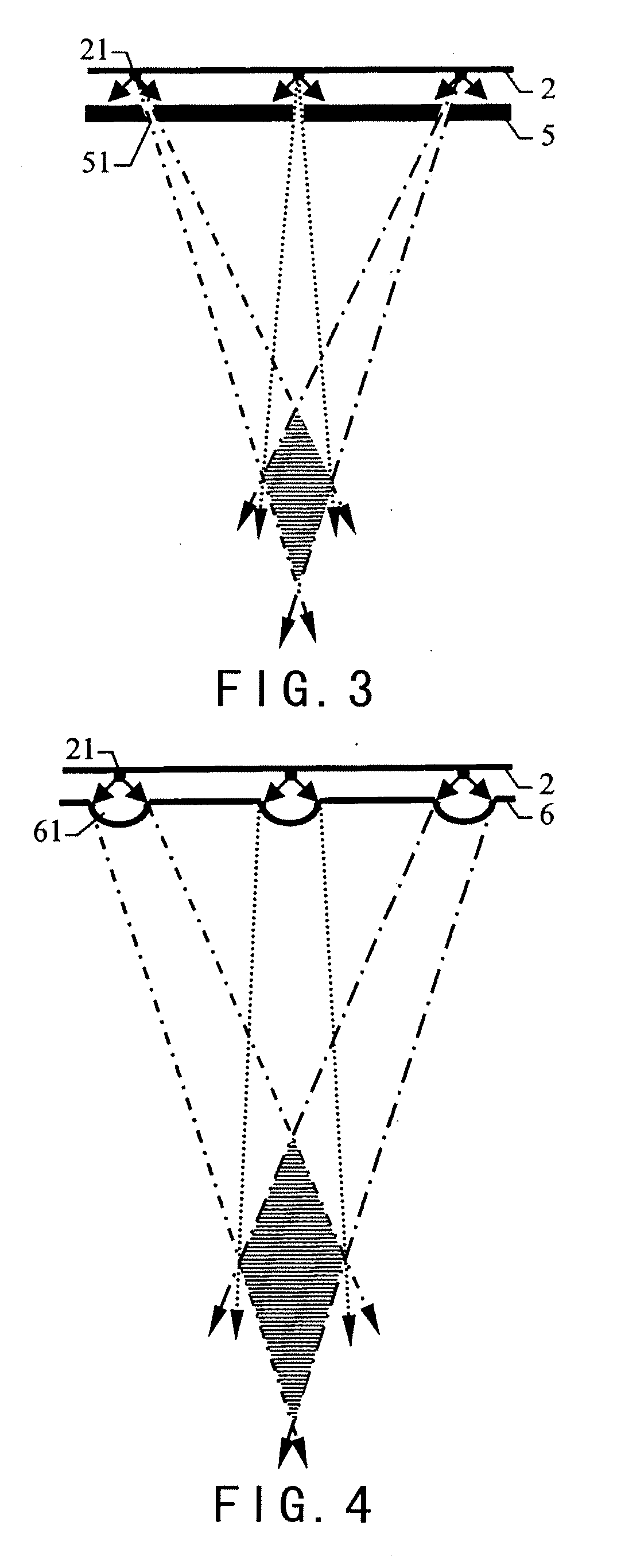
InactiveUS20110199373A1Suppress luminescenceEmission controlSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingLenticular lensEngineering
A screen device for three-dimensional display with full viewing-field comprises a display screen (2), a rotation device (3) for the display screen, and an optical device (1) disposed in front side of the display screen (2). The optical device (1) may be a two dimensional diaphragm array (5) with inclined openings, a vertical lenticular lens array (6), a combination of a two dimensional diaphragm array (7) with vertical openings and a lens (8), or a combination of a two dimensional micro-lens array (9), a vertical diffusion screen (10) and a cylindrical lens (11).
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optical writing device, image forming apparatus, and method and program product for controlling optical writing device
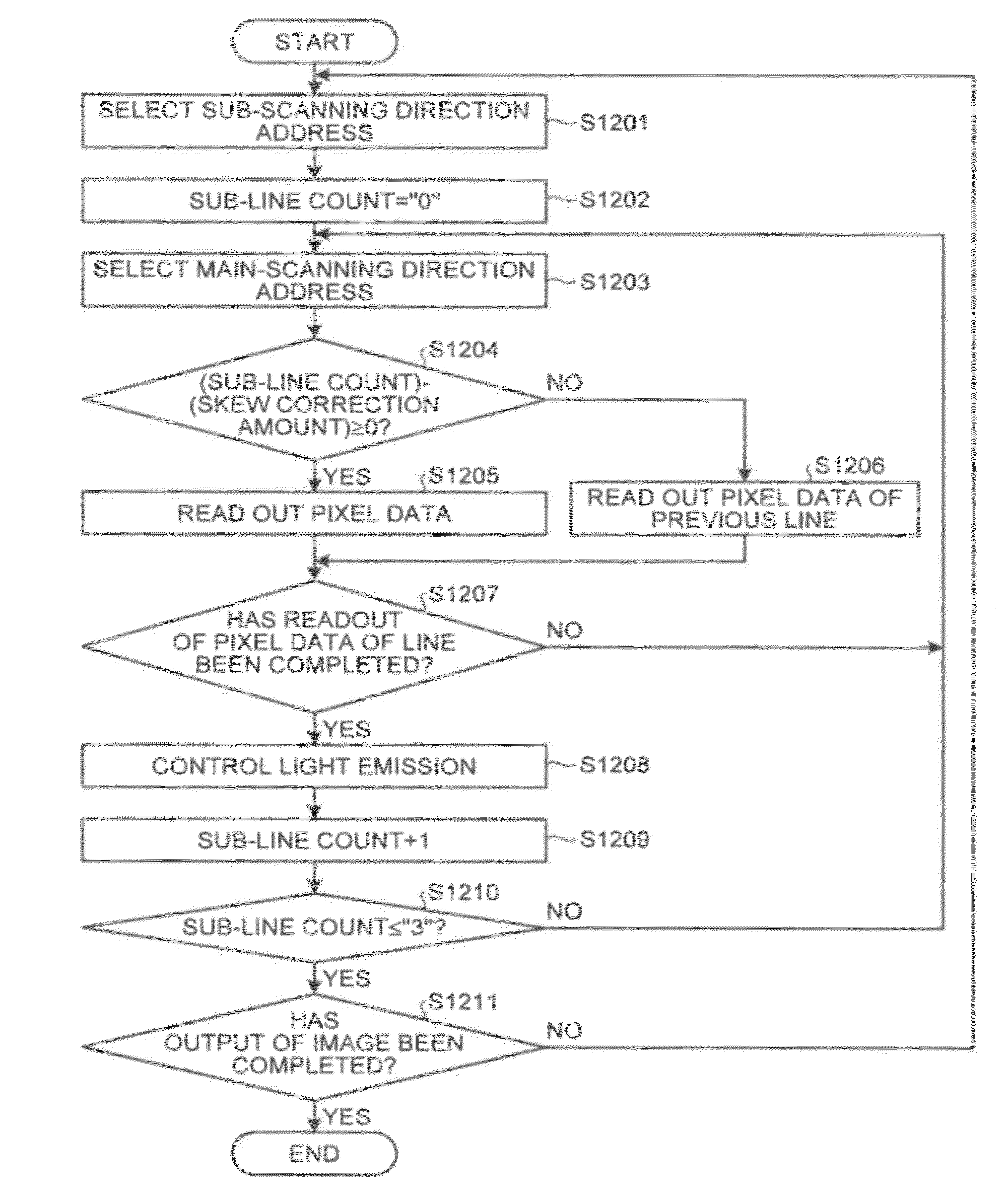
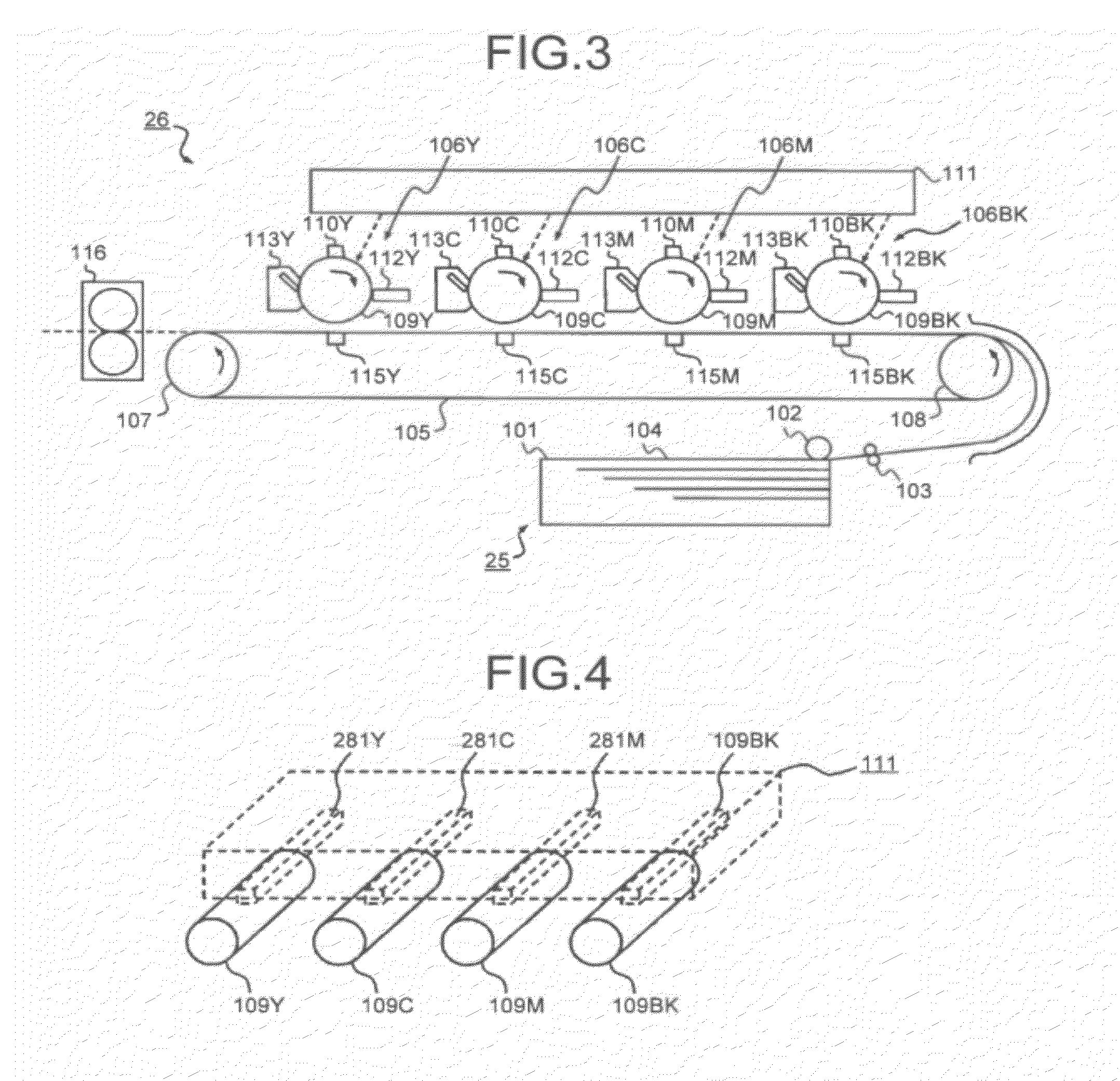
InactiveUS20120062681A1Solve problemsSuppress luminescenceRecording apparatusElectrode and associated part arrangementsImage resolutionLatent image
An optical writing device that forms an electrostatic latent image on a photoreceptor. The device includes a pixel-information acquiring unit, a line-pixel-information storage unit that stores the acquired pixel information corresponding to a plurality of lines for each main scanning line, a light source device that exposes the photoreceptor with a period corresponding to an N-fold sub-scanning direction resolution of the pixel information, a positional-shift-information storage unit that stores a positional shift information, a sub-line counting unit that counts a sub-line period, a reading-line selecting unit that performs N times of selection that determines which main scanning line is selected as the line from which the pixel information is read out, on the basis of a calculated value from the counted value of the sub-line period and the positional shift information, and a pixel-information reading unit.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com