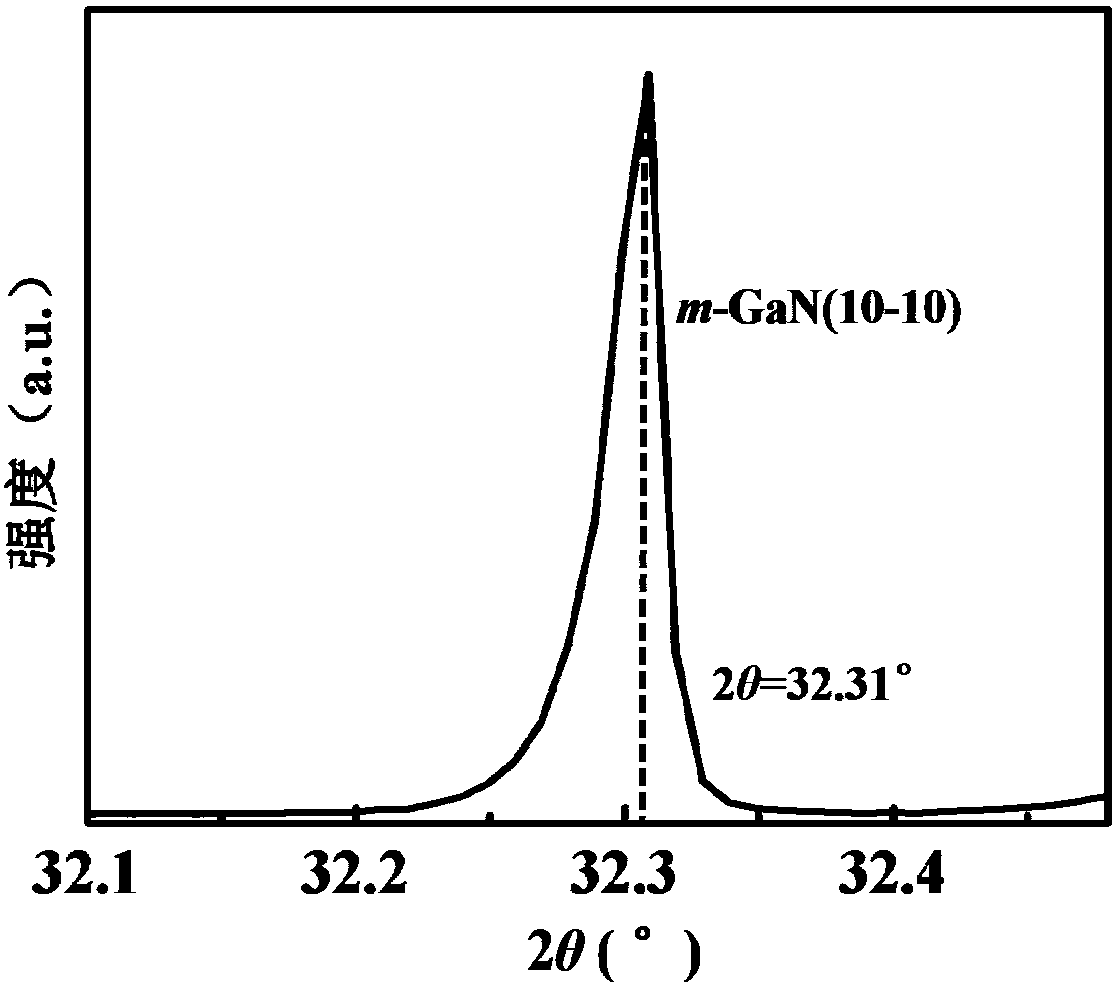
Patents
Literature
41results about How to "Reduce the difficulty of growing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Double-sided bonding long-wavelength vertical cavity surface emitting laser and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101667716AReduce the difficulty of growingNo secondary epitaxial processLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserCurrent limiting
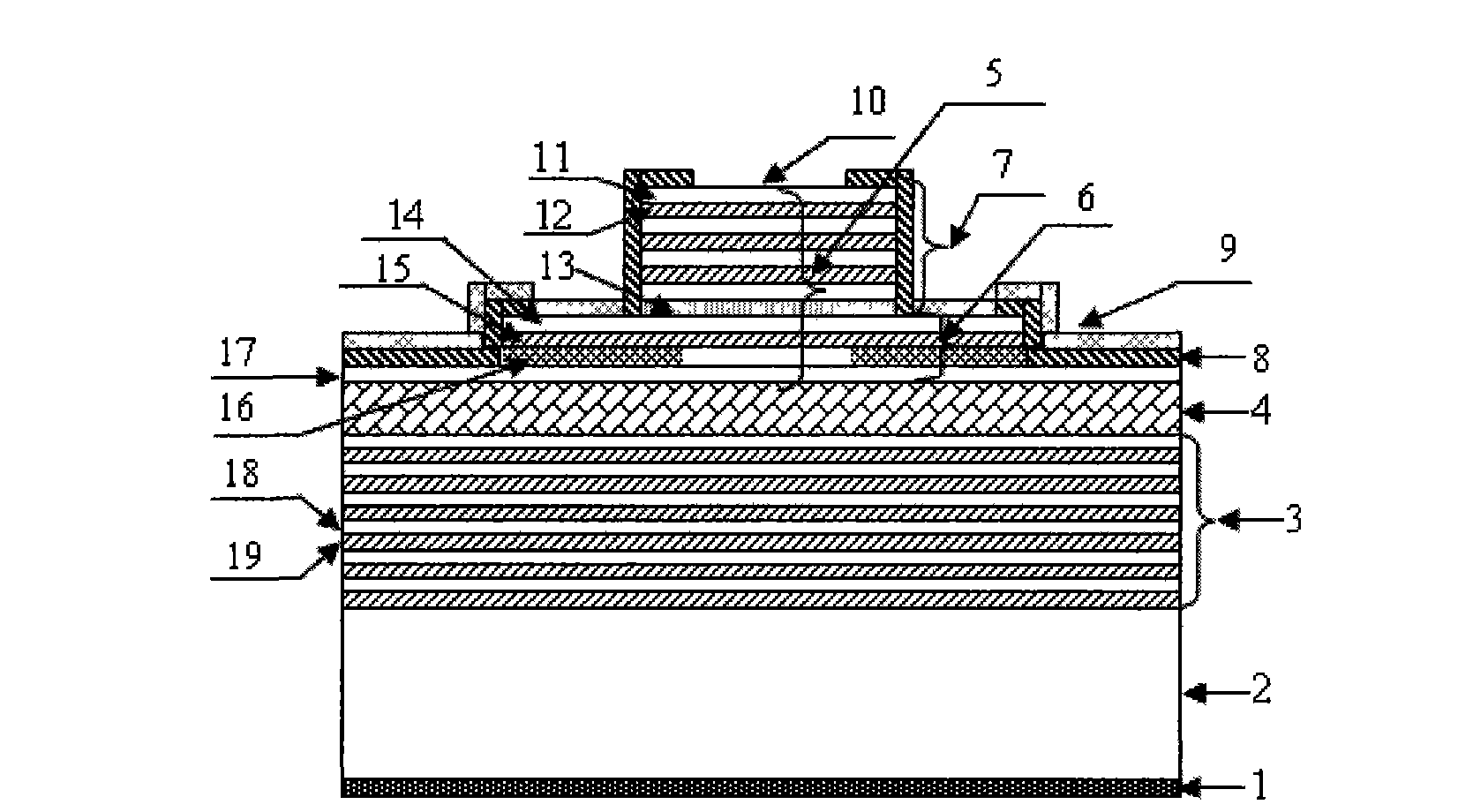
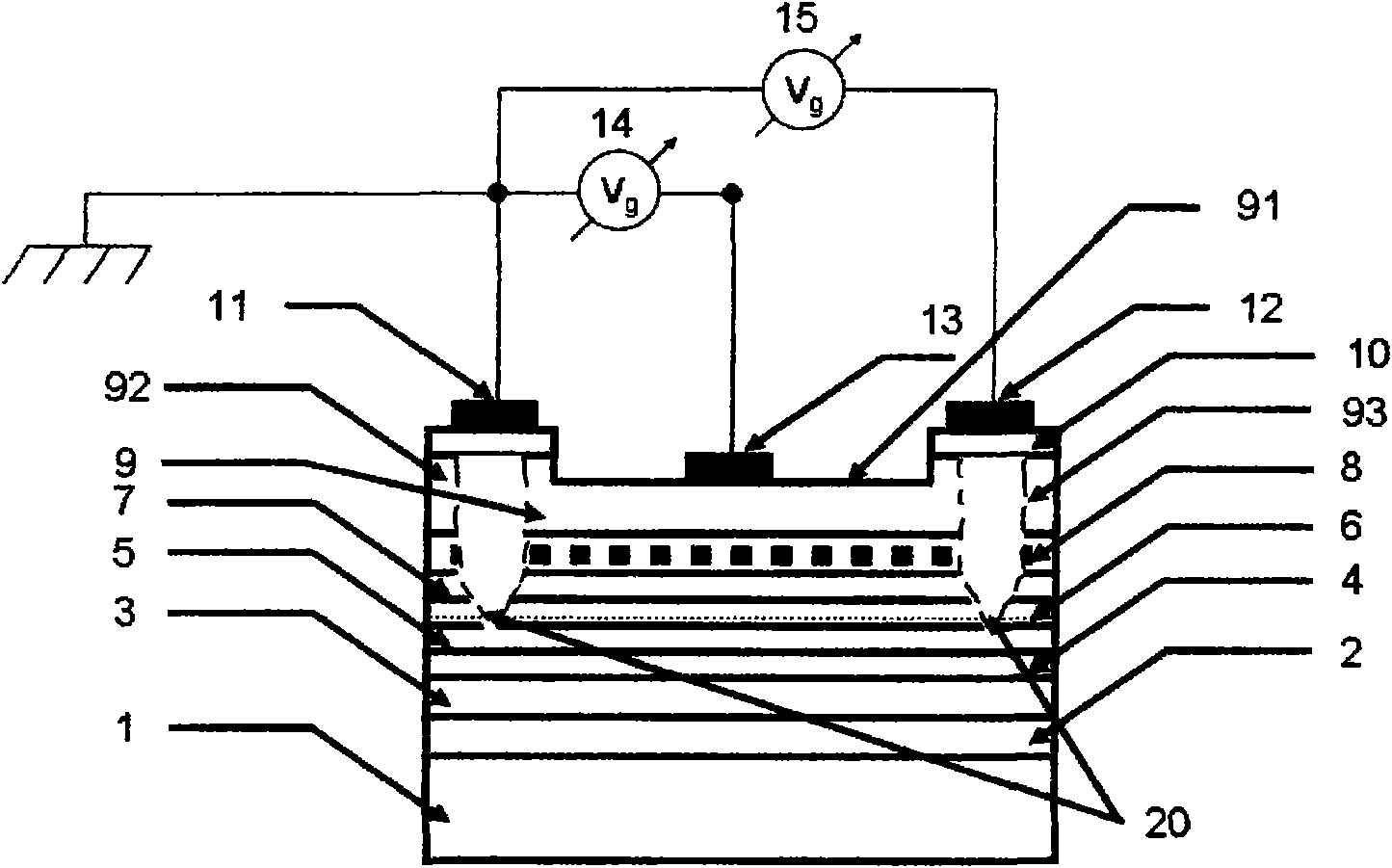
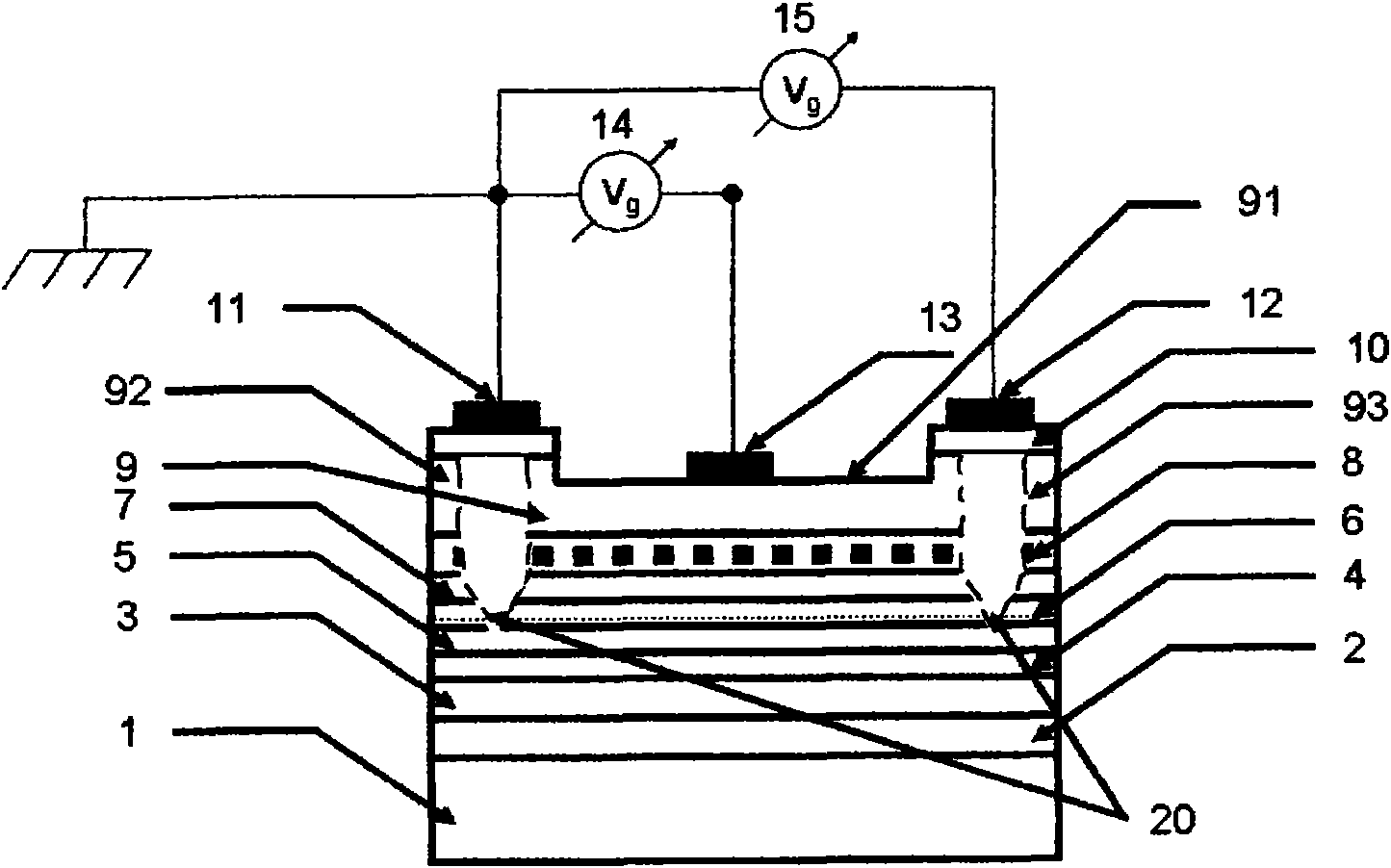
The invention relates to a double-sided bonding long-wavelength vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) and a manufacturing method thereof. The laser comprises an N electrode (1), an N-type GaAs substrate (2), an N-type GaAs / AlGaAs material series lower distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) (3), an InP based strained quantum well active area (4), a GaAs / AlGaAs material series upper DBR (5), a SiO2 mask (8), a P electrode (9) and a light-exiting window (10), wherein the upper DBR (5) consists of a P-type DBR (6) and an intrinsic DBR (7). The structure and the method overcome the defects of smaller refractive index difference, poor thermal conductivity and poor electrical conductivity of DBR materials of the conventional VCSEL, not only can realize good current limit, but also can reducethe absorption consumption and the growth difficulty of the materials and omit the step of secondary epitaxial process.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Epitaxial growth method of purple-light LED
InactiveCN103887380AReduce the difficulty of growingIncreased Radiation PowerSemiconductor devicesWavelength rangeCharge carrier
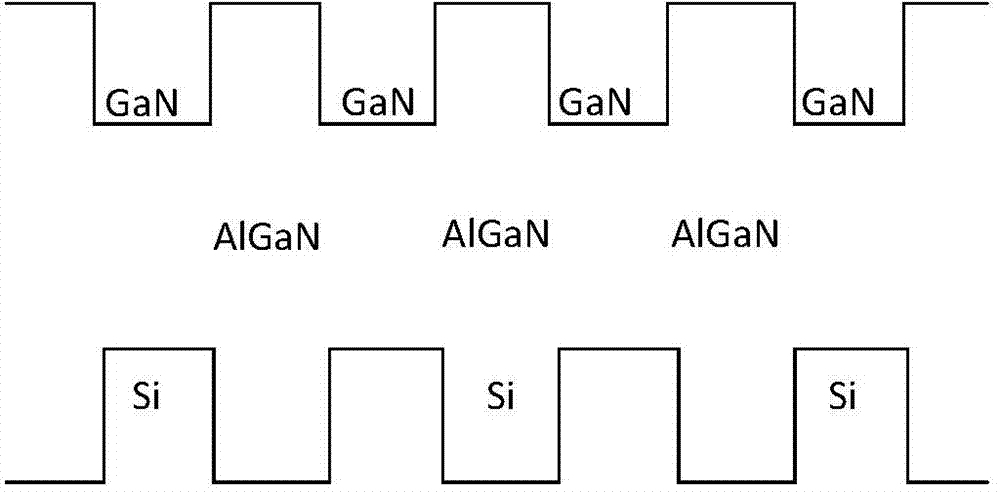
The invention provides an epitaxial growth method of a purple-light LED. The suitable wavelength range of the method is 365-420 nm, the growth difficulty of the purple-light LED can be greatly lowered, meanwhile, the radiation power of the purple-light LED can be increased and the reliability of purple-light LED devices is effectively improved. In the epitaxial growth method, an n-type AlGaN / GaN super lattice structure is adopted, potential-barrier-layer AlGaN and potential-well-layer GaN are doped alternately periodically, and therefore concentration of n-type carriers can be concentrated; the concentration of different layers change periodically, and periodic conductance changes enable currents to be diffused better; meanwhile, the conductance changing area is widened, so that the transmitting effect of an electric leakage channel with linear defects is weakened, forward voltage can be lowered, and ESD can be improved.
Owner:西安利科光电科技有限公司
High-mobility quantum-dot field effect transistor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101997029AReduce the difficulty of growingImprove yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesQuantum dotField-effect transistor
The invention discloses a high-mobility quantum-dot field effect transistor which comprises a substrate, a first stress buffer layer, a second stress buffer layer, a doping layer, a spacer layer, a channel layer, a lower potential barrier layer, a quantum-dot layer, an upper potential barrier layer, two cap layers, a first electrode, a second electrode and a third electrode, wherein the first stress buffer layer is manufactured on the substrate; the second stress buffer layer is manufactured on the first stress buffer layer; the doping layer is manufactured on the second stress buffer layer; the spacer layer is manufactured on the doping layer; the channel layer is manufactured on the spacer layer; the lower potential barrier layer is manufactured on the channel layer; the quantum-dot layer is manufactured on the lower potential barrier layer; the upper potential barrier layer is manufactured on the quantum-dot layer, a concave mesa is arranged on the middle of the top of the upper potential barrier layer, one side of the concave mesa is provided with a source region, and the other side of the concave mesa is provided with a drain region; the two cap layers are respectively manufactured on the source region and the drain region which are at the two sides of the upper potential barrier layer; the first electrode is manufactured on the top of one cap layer; the second electrode is manufactured on the top of the other cap layer; and the third electrode is manufactured on the concave mesa on the top of the upper potential barrier layer.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
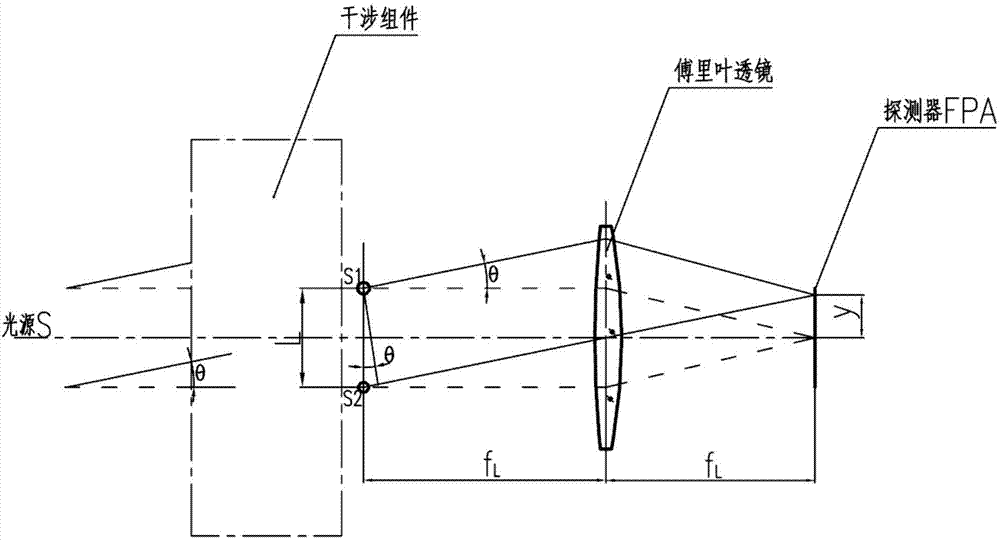
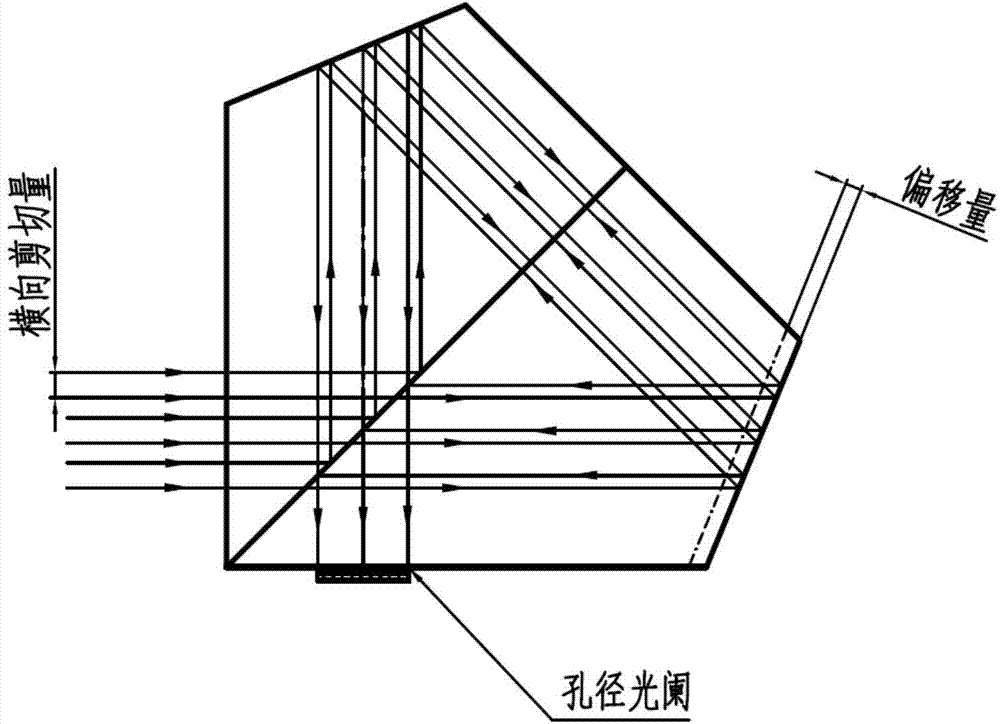
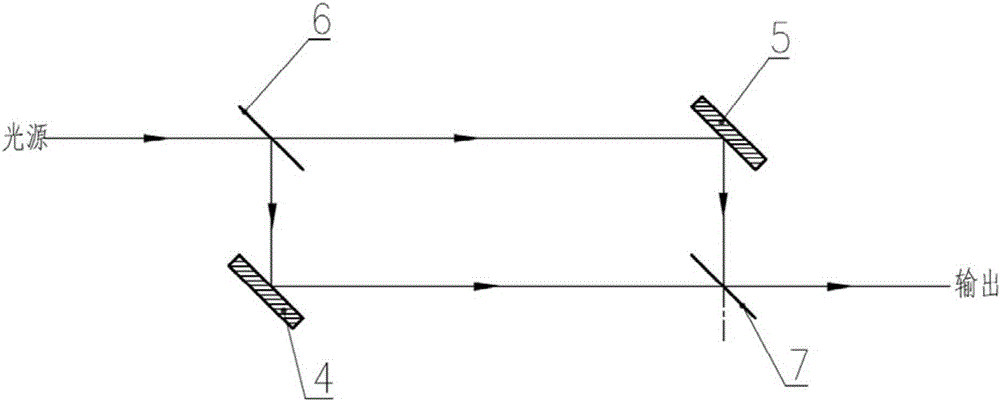
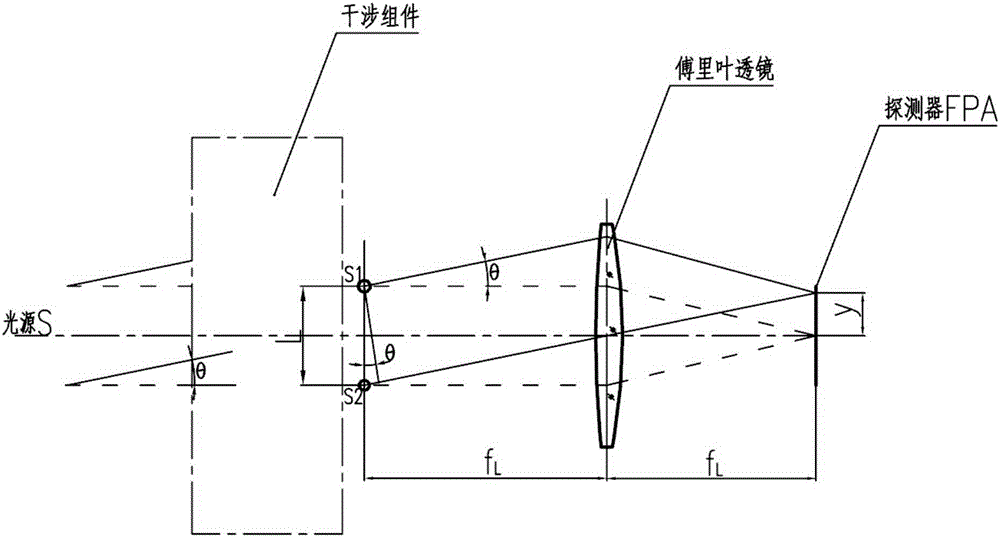
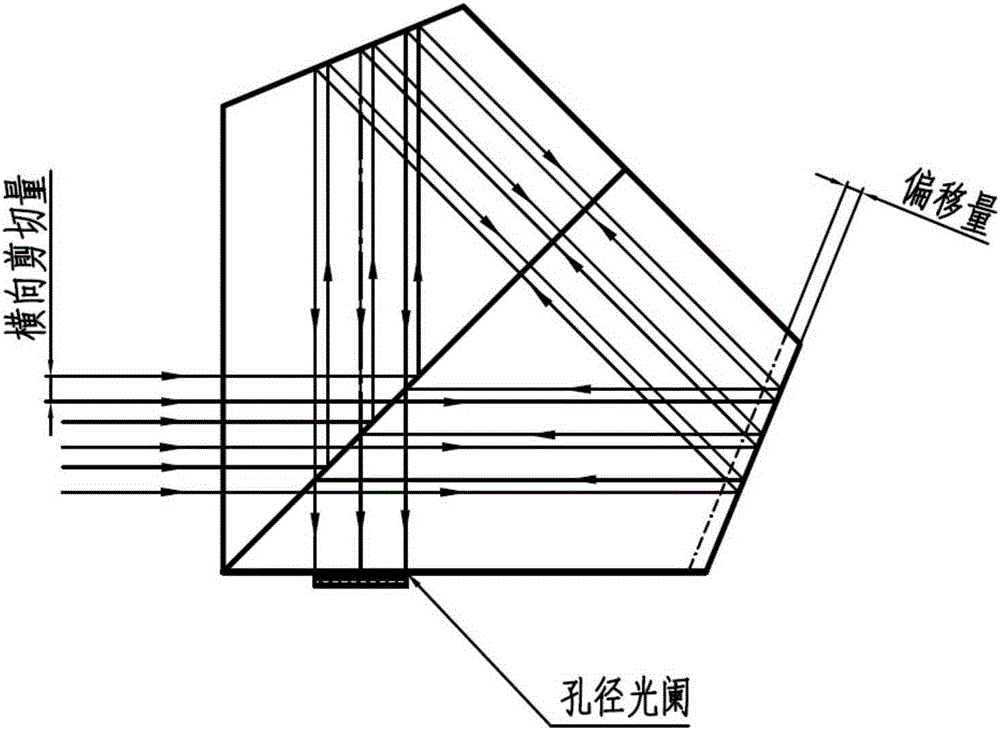
Long-wave infrared space modulation interference miniaturizing method
ActiveCN103674243ASmall sizeReduce the difficulty of growingSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionOptical axisMiniaturization
The invention relates to a long-wave infrared space modulation interference miniaturizing method. The method is characterized in that an interference assembly is composed of a spectroscope, a pyramid reflector I, a pyramid reflector II and two aperture diaphragms; an included angle between the spectroscope and parallel incident light is 135degree; from the optical axis position of reflected light, the top position of the pyramid reflector I starts to move anticlockwise for 1 / 4 transverse shear amount along the direction vertical to the optical axis of the reflected light; from the optical axis position of transmitted light, the top position of the pyramid reflector II starts to move anticlockwise for 1 / 4 transverse shear amount along the direction vertical to the optical axis of the transmitted light; and the two aperture diaphragms are respectively arranged at the top positions of the two pyramid reflectors, and are respectively placed vertical to the optical axes of the reflected light and the transmitted light. Under the condition that optical parameters are consistent, the size of the spectroscope is decreased, the sizes of the interference assembly and a spectrometer are effectively controlled, the difficulties in material growing and processing are reduced, and the cost is saved.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
Quadruple-junction cascading solar battery and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN102651419AReduce the difficulty of growingSimple processFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationGradual transitionEngineering
The invention provides a quadruple-junction cascading solar battery which comprises an InP substrate layer, and an InGaAs sub-battery, a first tunnel junction, an InGaAsP sub-battery, a second tunnel junction, a gradual transition layer, a GaAs sub-battery, a third tunnel junction, a GaInP sub-battery and a GaAs contact layer that are arranged on the substrate layer sequentially. The invention further provides a fabrication method of the quadruple-junction cascading solar battery, which comprises the step of allowing the InGaAs sub-battery, the first tunnel junction, the InGaAsP sub-battery, the second tunnel junction, the gradual transition layer, the GaAs sub-battery, the third tunnel junction, the GaInP sub-battery and the GaAs contact layer to be grown on the InP substrate layer.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Epitaxial growth method with p-layer special doped structure
InactiveCN103854976AImprove luminous efficiencyImprove mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSilanesSelf compensation
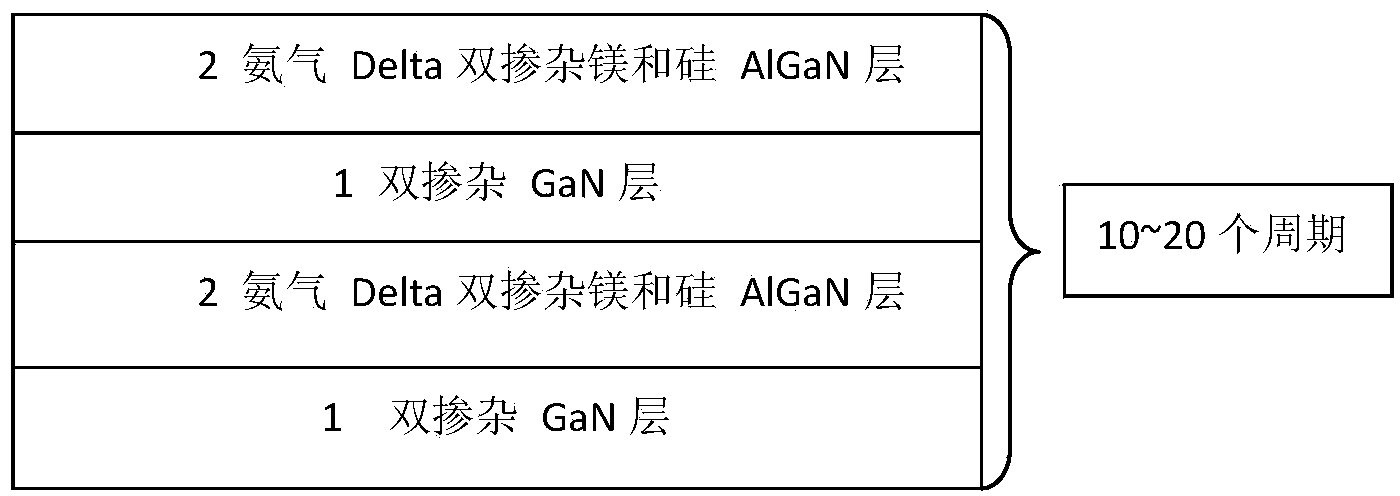
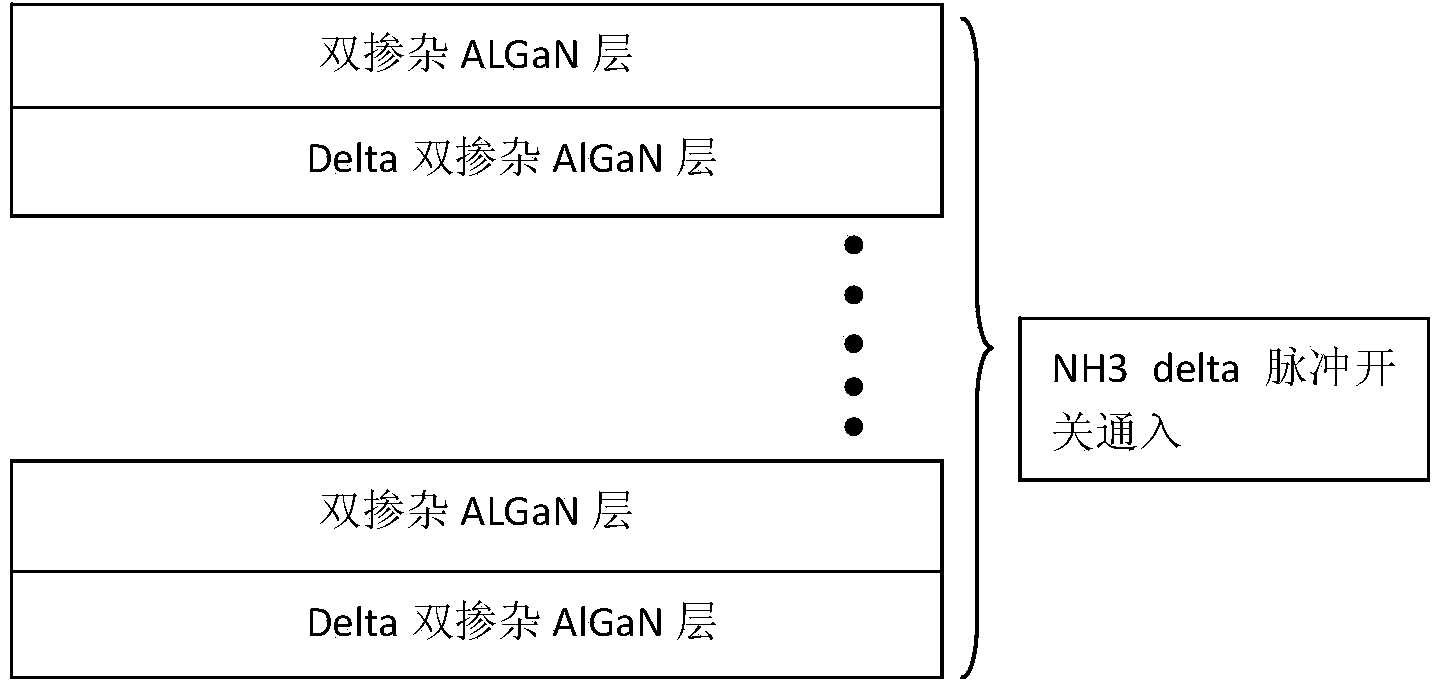
The invention discloses an epitaxial growth method with a p-layer special doped structure. According to the method, when a p-type layer of an LED (Light Emitting Diode) is grown, double-element doping of a GaN / AlGaN superlattice structure is adopted, that is, a small amount of silane is doped when doping magnesium. The silane is doped as a donor, however, due to the small amount of the doped silane, the lattice imperfection caused by the doped magnesium can be remarkably improved, a self-compensation effect is reduced, the crystal quality is improved, non-composite imperfection centers are reduced, a small number of scattering centers are caused, the carrier mobility and the ionization efficiency of an accepter are improved, and in addition, as the growing temperature of AlGaN is high, such doping is beneficial for improving the doping concentration of magnesium, the doping effect of the p-layer is improved, and the overall lighting efficiency of the LED is greatly improved. Due to improvement of the crystal quality and the improvement of barrier layer conductivity, the current expansion capability is improved, and the reliability of the LED device is also improved.
Owner:西安利科光电科技有限公司
Preparation method of rare earth substituted yttrium iron garnet crystal
InactiveCN110904506APromotes growth and growthReduce growing difficulty and energy costPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsYttrium iron garnetBoule
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rare earth substituted yttrium iron garnet crystal. The method includes the steps of: respectively weighing Y2O3, Re2O3 and Fe2O3 in molar ratio according to Y(3-x)RexFe5O12, conducting grinding and briquetting, and then carrying out solid-phase reaction to obtain a polycrystalline material block; crushing and grinding the polycrystalline materialblock, and adding a fluxing agent to obtain a mixed material; putting the mixed material into a crucible, putting the crucible into a crystal growth furnace, performing heating to a set temperature, and conducting heat preservation to obtain a high-temperature solution; then changing the relative positions of the crucible and a heating coil to enable the crucible to gradually move to a low-temperature area until the high-temperature solution is completely crystallized, stopping moving, and performing cooling to room temperature to obtain a crystal ingot; and removing the fluxing agent by adopting mechanical stripping or solution corrosion method to obtain the crystal. By means of the fluxing agent, the method provided by the invention effectively lowers the crystal growth temperature and reduces energy consumption, provides a driving force for crystal growth through vertical movement, promotes the growth of crystals, and can acquire the large-size blocky crystal.
Owner:SHANGHAI APPLIED TECHNOLOGIES COLLEGE
Transmissive AlGaN ultraviolet photocathode preparation method based on substrate stripping
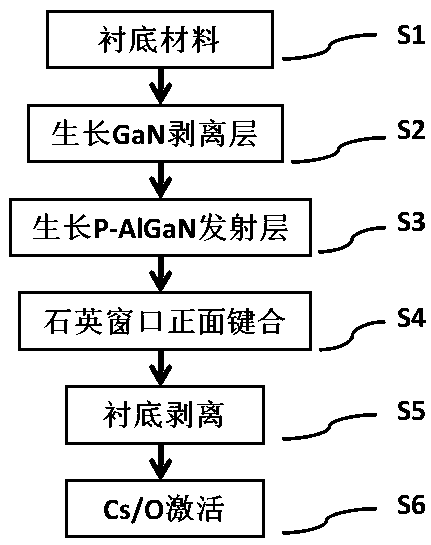
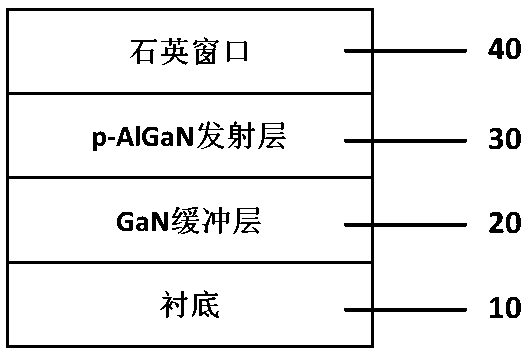
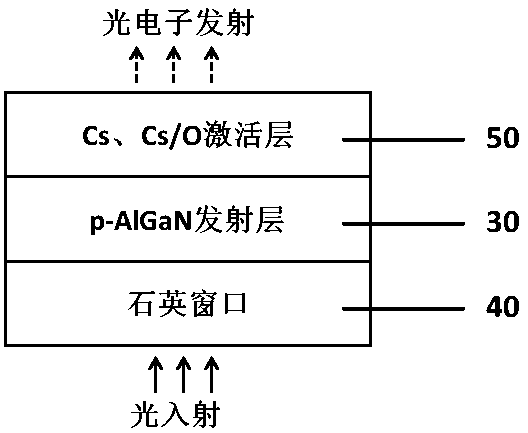
ActiveCN109256305AHigh sensitivityReduce the difficulty of growingPhoto-emissive cathodesPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureCooking & bakingPhotocathode
The invention relates to a method for preparing a transmissive AlGaN ultraviolet photocathode based on substrate peeling, comprising the following steps: 1) preparing a material; 2) sequentially carryout high-temperature baking, nucleate layer growth and high-quality GaN release layer growth; 3) growing a p-type Mg doped AlGaN photoemissive layer with high aluminum content; 4) bon that quartz window material on the surface of the AlGaN; 5) that GaN lay is thoroughly decomposed by use a laser decomposition technology, and the substrate is stripped; 6) activating surface of the AlGaN by Cs or Cs / O layer. 1) GaNis taken as that buffer lay of the ultraviolet photoelectric cathode instead of AlN, so that the growth difficulty of the buffer layer is reduce, the crystal quality of the p-type AlGaN emitting layer is improved, and the photocathode with higher sensitivity is prepared; 2) that lase decomposition technology of the buffer lay is adopted to fully decompose the GaN layer and realizethe substrate peeling off, thereby avoiding the absorption of the ultraviolet incident light by the substrate and the buff layer and ensuring the efficient detection of the ultraviolet light by the photoemission layer; 3) the substrate peeled off by the laser can be used repeatedly and economically.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
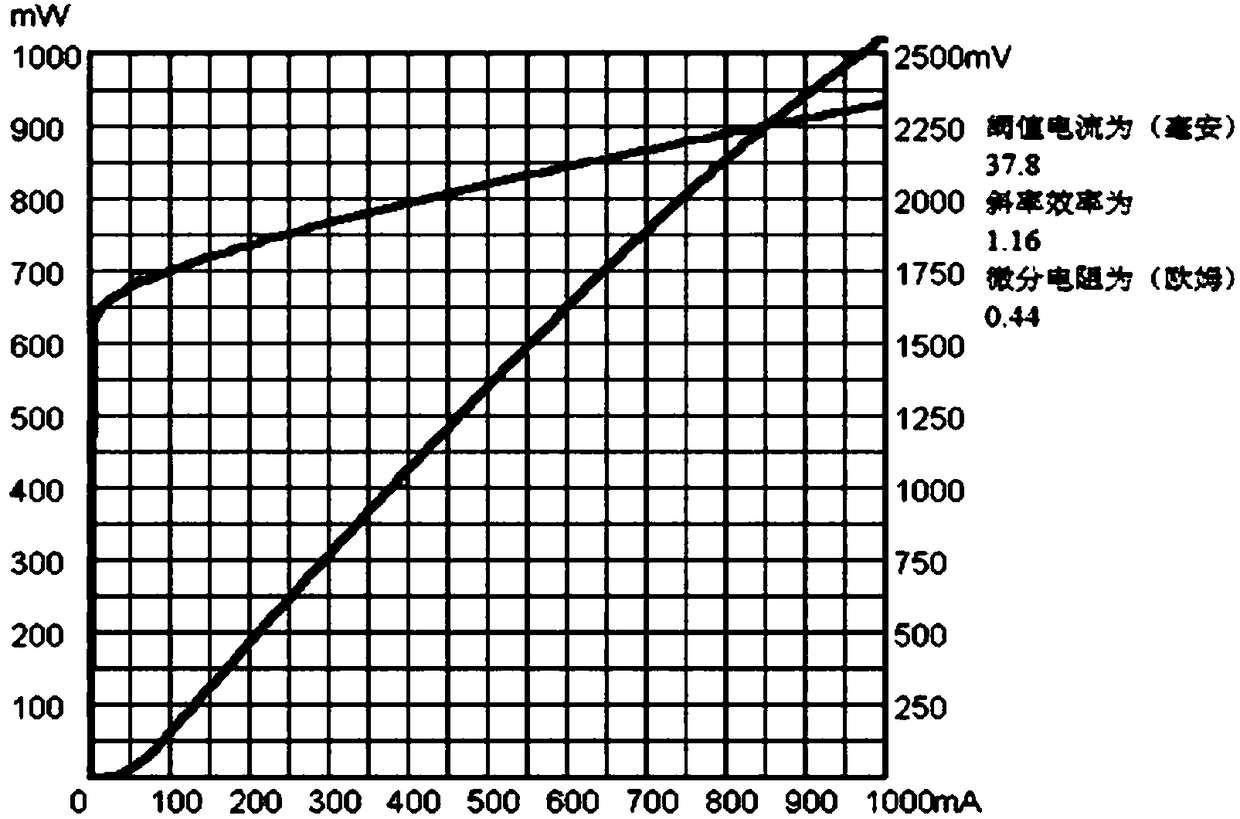
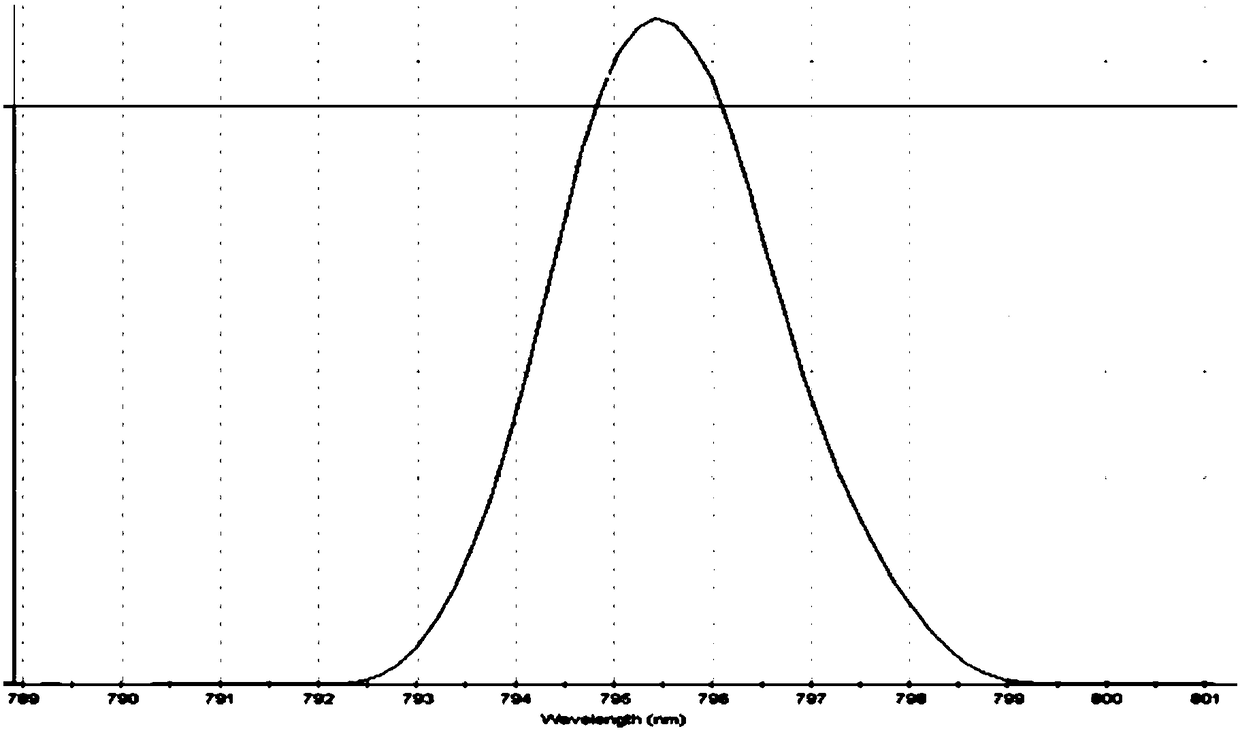
795nm quantum well laser based on AlGaAs/GaInP active region
ActiveCN108346973AReduce the difficulty of growingImprove lattice matchingLaser detailsLaser active region structureElectric fieldAluminium
The present invention provides a 795nm quantum well laser based on an AlGaAs / GaInP active region. The epitaxial structure comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, an N-type lower limit layer, a lower waveguide layer, a quantum well layer, an upper waveguide layer, and P-type upper limit layer and an ohmic contact layer from the bottom to the top. The upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer are made of an aluminum-free material gallium indium phosphate, the quantum well layer is made of an aluminum gallium arsenide material, and a wide waveguide semi-aluminum-free active region is formed by the waveguide layers and the quantum well layer. According to the 795nm quantum well laser, the special requirements of a pump laser with the application of a small and simplified self-doubledlaser crystal can be satisfied, at the same time, the influence of the roughness of a growth interface and an episodic field at a cavity surface on the service and reliability of the laser can be reduced effectively by an optimized laser structure.
Owner:Shandong Huaguang Optoelectronics Co. Ltd.
Method for growing yttrium iron garnet crystals by adopting composite fluxing agent
InactiveCN112267146ALow melting pointGrowth restrictionPolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsSingle crystalMixed materials
The invention discloses a method for growing yttrium iron garnet crystals by adopting a composite fluxing agent. The yttrium iron garnet (Y3Fe5O12, YIG for short) crystal is an important magneto-optical material and is prepared by the following steps: accurately weighing, mixing, grinding and sintering raw materials to obtain a polycrystal material, crushing the polycrystal material, adding the composite fluxing agent, carrying out ball milling to obtain a mixed material, filling a crucible with the mixed material, heating the crucible filled with the material to a set temperature, keeping thematerial at the temperature to obtain high-temperature molten crystal solution, then carrying out slow cooling until the solution in the crucible is completely cooled and crystallized, conducting cooling to room temperature to obtain a crystal ingot, and removing the fluxing agent by adopting a mechanical stripping and chemical corrosion method to finally obtain the crystal. According to the invention, through the lead-free composite fluxing agent, environmental pollution caused by lead and the corrosion to a platinum crucible are greatly reduced, the growth temperature of the crystal is effectively reduced, and the bulk single crystal with a larger size can be obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
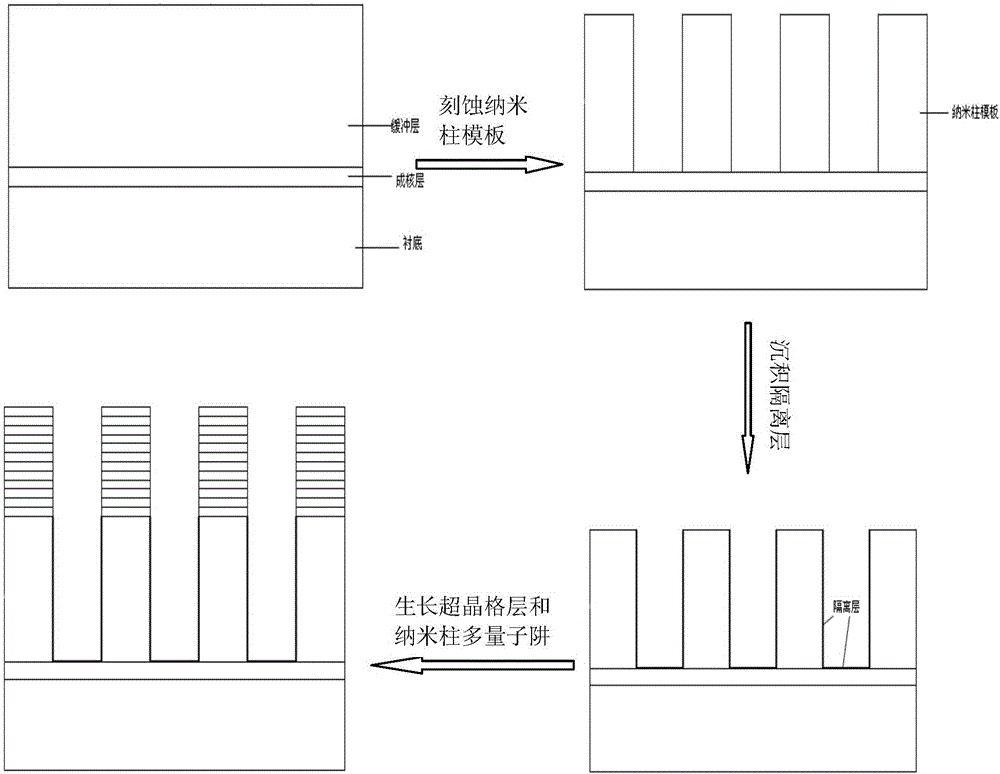
InGaN/GaN nano-pillar multiple quantum well grown on strontium tantalum lanthanum aluminate substrate and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of multiple quantum wells of nanometer arrays, and discloses an InGaN / GaN nano-pillar multiple quantum well grown on a strontium tantalum lanthanum aluminate substrate and a preparation method thereof. The InGaN / GaN nano-pillar multiple quantum well grown on a strontium tantalum lanthanum aluminate substrate comprises an AlN nucleation layer grown on a La<0.3> Sr<1.7>AlTaO<6> substrate, a GaN nano-pillar template grown on the AlN nucleation layer, an AlN / GaN super lattice layer grown on the nano-pillar template, and an InGaN / GaN nano-pillar multiple quantum well grown on the AlN / GaN super lattice layer. A nano-pillar array prepared is size-controllable and of uniform orientation. The obtained multiple quantum well has low defect density and excellent electrical and optical properties.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
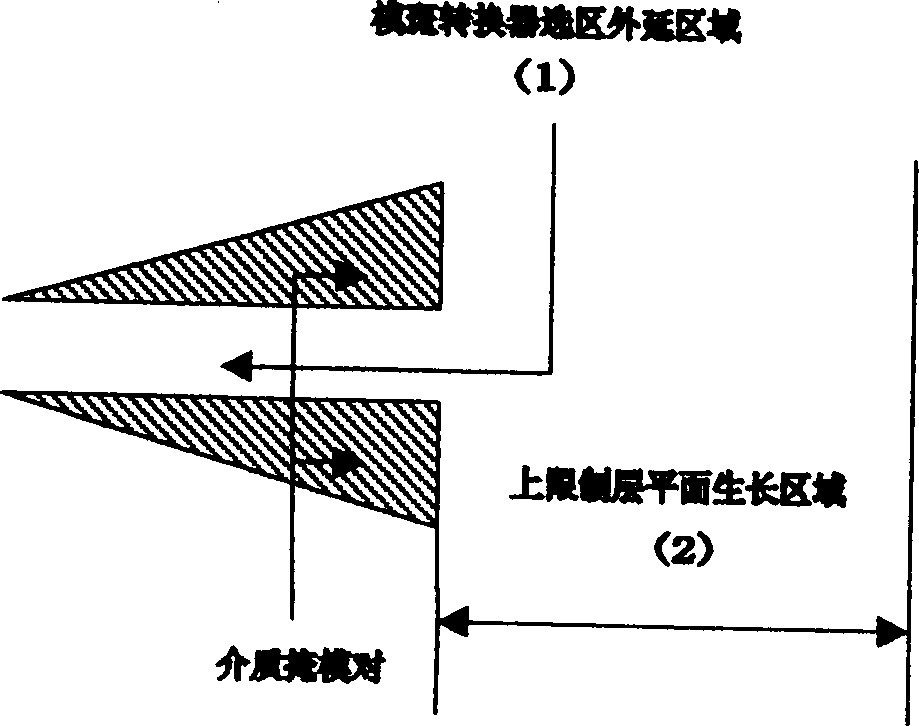
Optoelectronic device and selection district epitaxial method of autocollimation model spot inverter integration
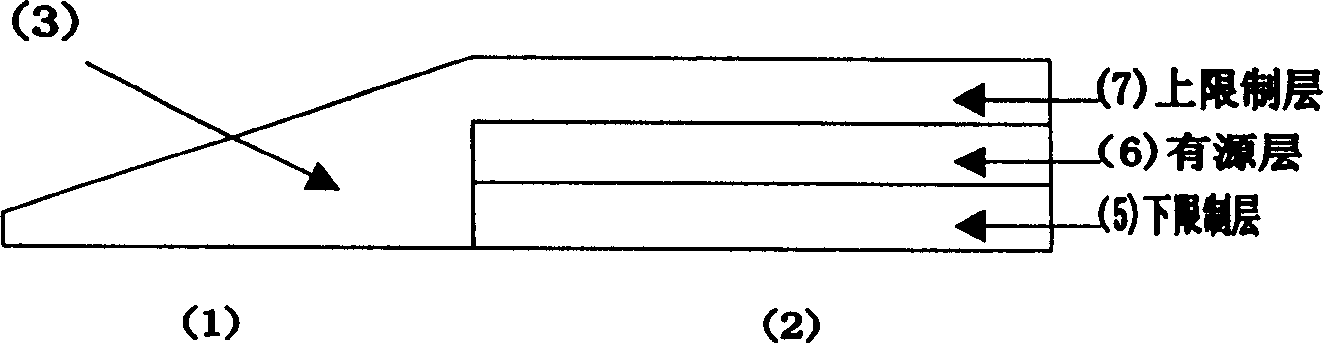
InactiveCN1430313AReduce absorption lossReduce the difficulty of growingLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutocollimationContact layer
A selective epitaxial method for integrated photoelectric device and self-aligned template converter includes such steps as growing buffering layer, lower limitting layer and active layer on the surface of substrate, selectively growing upper limitting layer and vertical wedge waveguide by SiO2 mask, preparing ridge waveguide or burried waveguide as required, and epitaxial growth of indium phosphide layer and ohm contact layer, and preparing p / n electrodes.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing large size lithium tetraborate piezoelectric crystal
InactiveCN101377014AIncrease growth rateLow costPolycrystalline material growthLithium compoundsLithiumCrucible
The invention relates to a preparation method of lithium tetraborate piezoelectric crystal, in particular to a preparation method of large-size lithium tetraborate piezoelectric crystal. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a synthetized lithium tetraborate polycrystal material is pressed into compact cylindrical blocks; the blocks are put into a Pt crucible in which seed crystal is put in earlier and into an oven; the oven temperature is controlled to be 950 DEG C to 1000 DEG C, the descending speed of the crucible is 0.1mm / h to 0.6mm / h, and high-grade large monocrystal with thickness of 30mm to 80mm, width more than 120mm and length more than 150mm can be grown; the large monocrystal is processed in the side direction, i.e. the direct along the side with larger size serves as the axial direction of a crystal bar and the side with smaller size serves as the thickness direction of the crystal bar, and a large-size lithium tetraborate piezoelectric crystal profile is obtained. Compared with traditional descending methods, the method solves the technical bottlenecks of difficulty in inoculation, easily leaking crucible, easy cracking of the crystal and the like in the growth of large-size lithium tetraborate piezoelectric crystal through traditional descending methods, adopts sideward growth and flat crucible design, can improve the growth speed of the crystal, thereby reducing the growth difficulty of the crystal and helping to realize the industrialized growth of the large-size lithium tetraborate piezoelectric crystal.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Si-based vertical cavity surface emitting chip
ActiveCN107749565AEasy to getEase of mass productionLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersDistributed Bragg reflectorRare earth
The invention discloses a Si-based vertical cavity surface emitting chip. The structure consists from bottom to top of an n-type electrode, a substrate, a buffer layer, a lower distributed Bragg reflector located on the substrate, active area located on the lower distributed Bragg reflector, an upper distributed Bragg reflector located on the active area, a p-type electrode located on the upper distributed Bragg reflector, and a SiO2 confinement layer located around a cylindrical mesa. In the invention, a silicon-doped (AlxGa1-x)2O3, (AlyGa1-y)2O3 stacked structure is prepared on an n-type silicon substrate as the lower distributed Bragg reflector, rare earth-doped Ga2O3 is used as an n-type luminous material, and a GaAs, AlGaAs or InP, InGaAsP stacked structure is used as the upper distributed Bragg reflector. As a silicon-based vertical cavity surface emitting light source according to the invention, the characteristics of high thermal stability, high chemical stability, simple preparation method and high reliability are gained.
Owner:张子旸
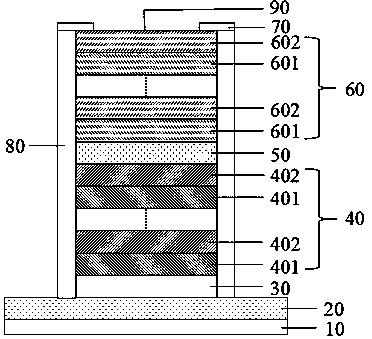
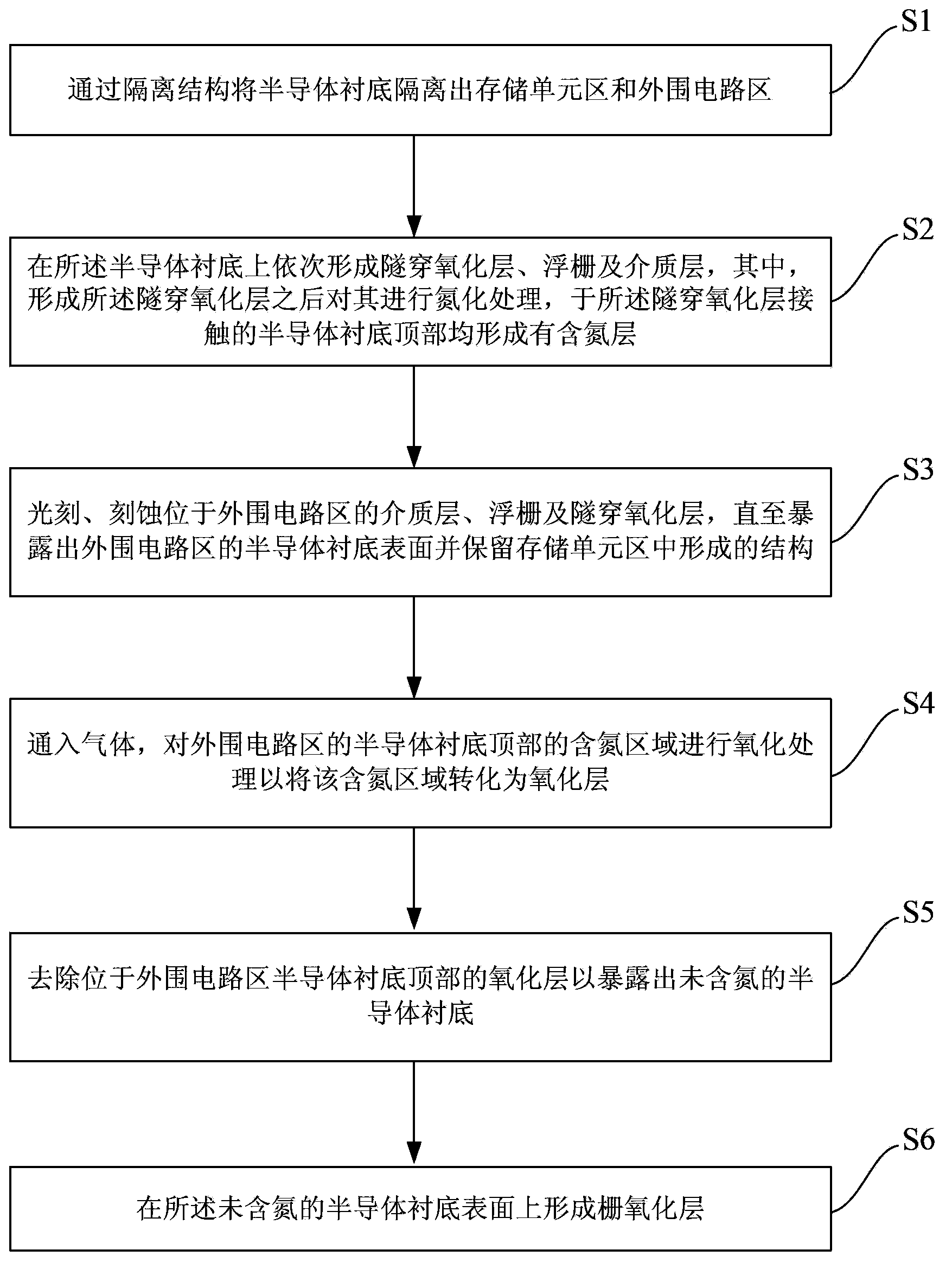
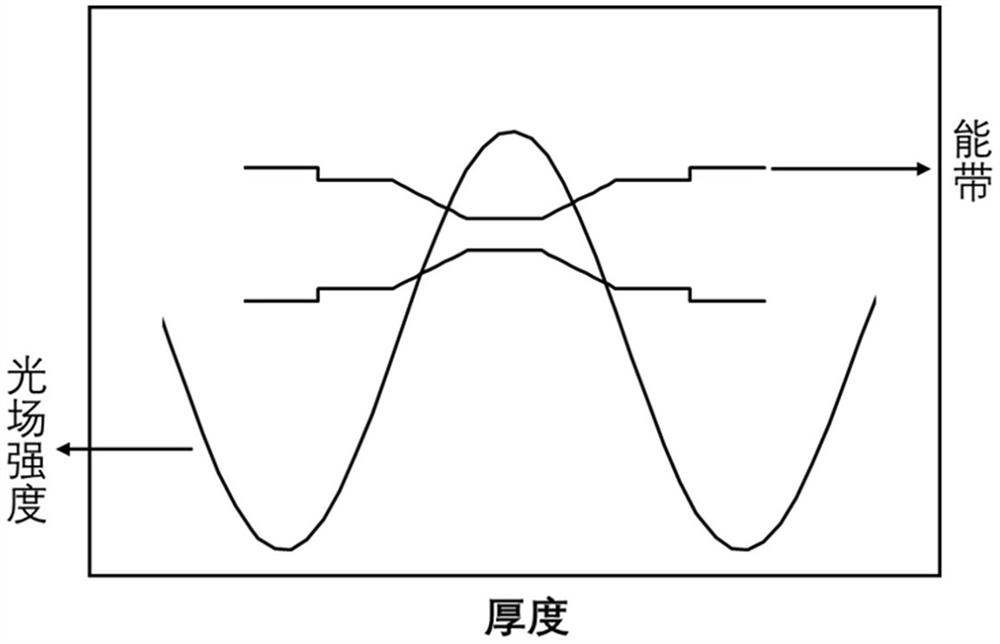
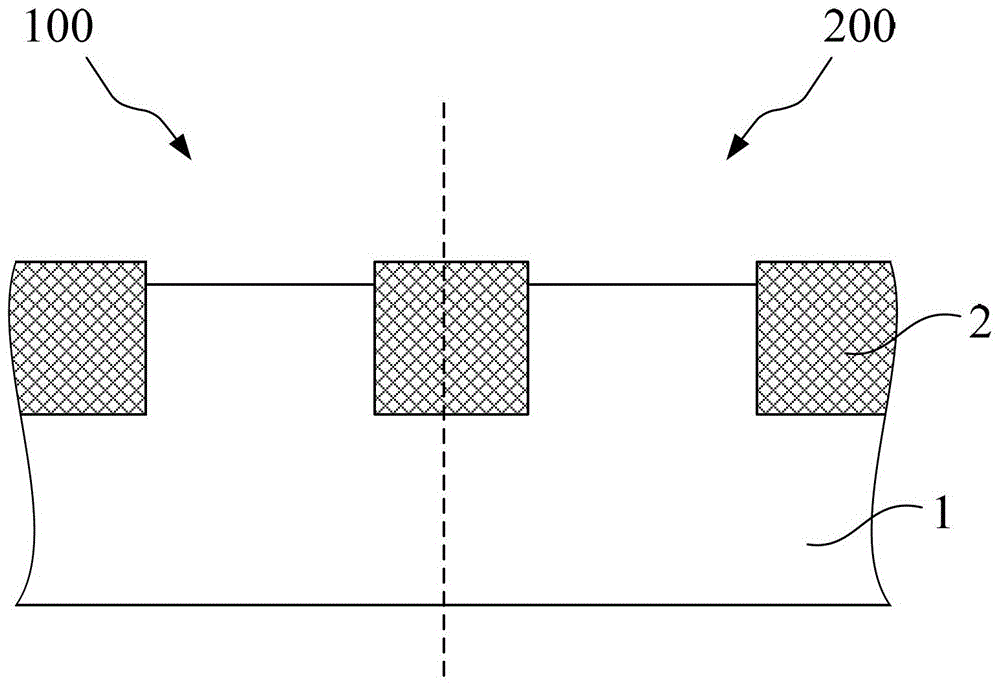
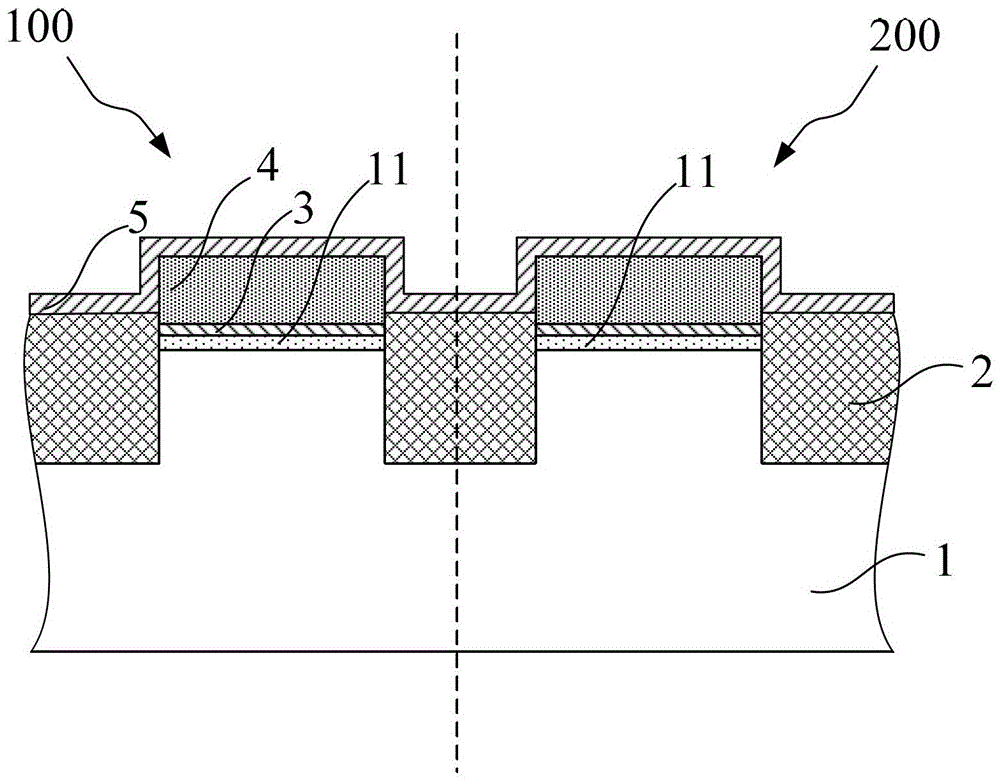
Method for improving reliability of gate oxide layer of peripheral circuit area of flash memory
ActiveCN104112656AImprove reliabilityReduce the difficulty of growingSemiconductor devicesPhysicsPeripheral
The invention provides a method for improving the reliability of a gate oxide layer of a peripheral circuit area of a flash memory. The method includes the following steps that: oxidation treatment is performed on a nitrogen containing region of the top of a semiconductor substrate at the peripheral circuit area; and the nitrogen containing region is converted into an oxide layer, and the oxide layer is removed, and therefore, a nitrogen-free semiconductor substrate surface of the peripheral circuit area is exposed; and a gate oxide layer is grown on the nitrogen-free semiconductor substrate surface. With the method adopted, when an MOS device is manufactured in the peripheral circuit area in a subsequent process, the nitrogen containing region of the top of the semiconductor substrate is removed, and therefore, the growth difficulty of the gate oxide layer on the surface of the semiconductor substrate can be lowered, and especially, the growth capacity of the gate oxide layer on the semiconductor substrate at corners of an isolation structure can be improved, and the integrity and uniformity of gate oxide layer growth can be increased, and the reliability of the gate oxide layer of the MOS device can be improved; and the oxidation treatment mentioned in the invention is performed at room temperature or low temperature, and therefore, thermal budget in the prior art can be decreased, and device doping profile shift can be avoided. The method is advantageous in convenient implementation and simple operation.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Al-doped CsLiB6O10 crystal growth fluxing agent and crystal growth method
PendingCN107059109ALow growth temperatureReal-time observation of growth statusPolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsViscosityCrystal growth
The invention belongs to the field of optical materials and provides an Al-doped CsLiB6O10 crystal growth fluxing agent. The Al-doped CsLiB6O10 crystal growth fluxing agent is characterized in that the Al-doped CsLiB6O10 crystal growth fluxing agent is a fluxing agent of a Cs2O-Li2O-MoO3 system; the mol ratio of Cs2O to Li2O to MoO3 in the system is 1 to (0.8 to 1.2) to (1.6 to 2.0). The invention further provides an Al-doped CsLiB6O10 crystal growth method utilizing the fluxing agent. According to a novel fluxing agent system provided by the invention, the growth temperature of a crystal can be effectively reduced and a temperature range is 800 DEG C to 820 DEG C; a growth solution is clear and transparent and a crystal growth condition is easy to observe in real time. The volatility of the system can be remarkably reduced and the stability of a growth system is improved; a floating crystal is prevented from forming and the crystal growth success rate is improved. The viscosity of the solution is remarkably reduced and solute transportation is facilitated; the crystal is easy to grow and almost no inclusions are generated.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Type-II superlattice structure based on indium arsenide and preparation method
InactiveCN105789355AIncrease growth temperatureIncrease the diffusion lengthFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesMaterial defectAluminium arsenide
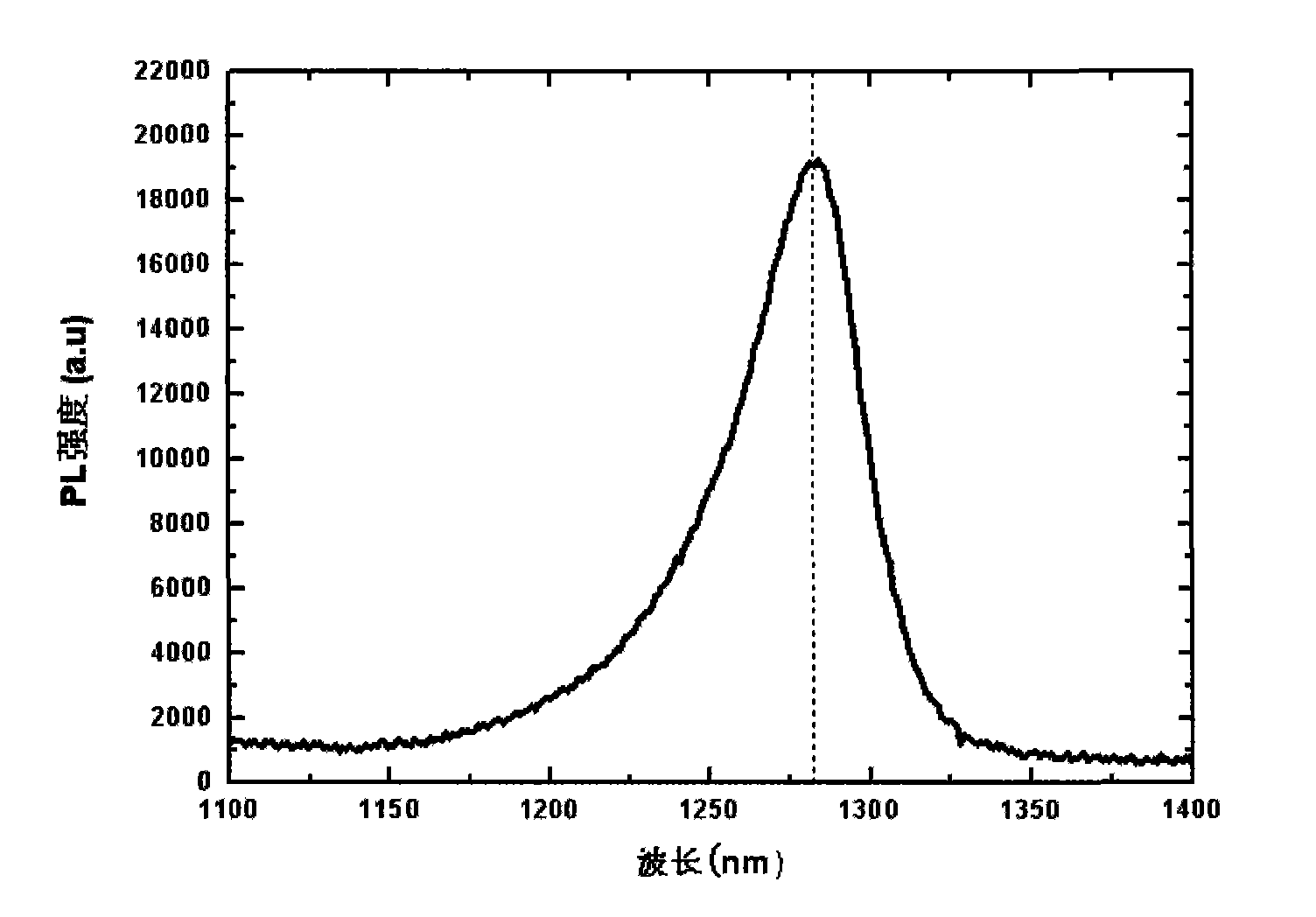
The invention discloses a type-II superlattice structure based on indium arsenide and a preparation method. The type-II superlattice structure based on indium arsenide comprises an InAs layer, a GaAs layer, a GaAsxSb1-xlayer and a GaAs layer from bottom to top, and is characterized in that: (1) an original GaSb substrate is replaced with an InAs substrate, so that the growth temperature of superlattices is substantially increased, and the increasement of the growth temperature is conductive to increasing a diffusion length of surface atoms, thereby being more conductive to the two-dimensional growth of materials and the reduction of material defect density; (2) an As valve is always in an open state during the whole growth process of type-II superlattices, so that a GaAsSb ternary compound is formed due to the outflow of partial As when growing a GaSb layer, growth temperature of the layers tends to be uniform due to the existence of the common element As in the layers, and the counterdiffusion at interfaces is reduced; (3) variation of thickness of the InAs layer has small influence on mismatching of the InAs-based type-II superlattices, the growth difficulty of long waves materials, particularly extremely-long-wave materials, is extremely reduced, and the performance and quality of the materials can be more easily improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite substrate based on aluminum nitride ceramic material and preparation method and application of composite substrate
PendingCN113838955AAchieve growthReduce dislocation densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGraphicsComposite substrate
The invention provides a composite substrate based on an aluminum nitride ceramic material. The composite substrate comprises (a) an aluminum nitride ceramic substrate; (b) a graphic structure layer which comprises graphic structures located on the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate, and the graphic structures are periodically distributed on the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate at intervals; and (c) a polycrystalline coating layer, wherein the polycrystalline coating layer is a continuous layer which covers the graphic structure layer and the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate which is not covered by the graphic structure layer. The composite substrate based on the AlN ceramic material provided by the invention is used for growing a GaN or AlN single crystal material, and the cost of the substrate material is reduced while thermal mismatch and dislocation are avoided.
Owner:SINO INNOV SEMICON (PKU) CO LTD
Multi-wavelength semiconductor laser based on annular resonant cavity
ActiveCN102570310BAvoid stackingReduce the difficulty of growingOptical wave guidanceSemiconductor laser arrangementsRidge waveguidesWaveguide
The invention discloses a multi-wavelength semiconductor laser based on an annular resonant cavity and belongs to the field of semiconductor lasers. The multi-wavelength semiconductor laser comprises a substrate layer, a buffer layer, a lower cladding, an active layer, an upper cladding and an ohmic contact layer which are arranged from bottom to top, wherein the laser is provided with more than one annular ridge waveguide and a coupled waveguide, each annular ridge waveguide is formed by at least the ohmic contact layer and part of the upper cladding or the whole upper cladding and can generate laser beams under forward bias, and the coupled waveguide can amplify the optical power of the laser beams under forward bias; the annular ridge waveguide and the active layer form the annular resonant cavity; the circumferences of the annular ridge waveguides are not equal; and the coupled waveguide is arranged adjacent to the annular ridge waveguides. The multi-wavelength semiconductor laser based on the annular resonant cavity has the advantages that the multi-wavelength semiconductor laser is simple and compact in structure and is easy in integration with other devices; the process is simplified, and the cost is lowered; the superposition of active layers of a plurality of single longitudinal-mode lasers is avoided, and the difficulty in the growth of materials is reduced; and the output paths of the laser beams are flexible and adjustable, and the large-scale integration of lasers is easily implemented.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
Preparation method of zirconium oxide crystal
PendingCN112695375ANo pollution in the processPromote growthPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsReduction treatmentCrucible
The invention discloses a preparation method of zirconium oxide crystal, and belongs to the field of preparation of metal oxide functional materials. Yttrium oxide and zirconium oxide are mixed in proportion and ground into uniform powder, the cubic zirconium oxide crystal is prepared through a cold crucible method, then reduction treatment is conducted, and the black cubic zirconium oxide crystal can be obtained. The material can realize large-size rapid crystallization growth and is suitable for large-scale production, the crucible material can be recycled as a raw material and the cost is saved, and the obtained crystal has a large crystal size and a high crystallinity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
A kind of epitaxial growth method with p-layer special doping structure
InactiveCN103854976BImprove luminous efficiencyImprove mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower flowCharge carrier mobility
The invention discloses an epitaxial growth method with a p-layer special doped structure. According to the method, when a p-type layer of an LED (Light Emitting Diode) is grown, double-element doping of a GaN / AlGaN superlattice structure is adopted, that is, a small amount of silane is doped when doping magnesium. The silane is doped as a donor, however, due to the small amount of the doped silane, the lattice imperfection caused by the doped magnesium can be remarkably improved, a self-compensation effect is reduced, the crystal quality is improved, non-composite imperfection centers are reduced, a small number of scattering centers are caused, the carrier mobility and the ionization efficiency of an accepter are improved, and in addition, as the growing temperature of AlGaN is high, such doping is beneficial for improving the doping concentration of magnesium, the doping effect of the p-layer is improved, and the overall lighting efficiency of the LED is greatly improved. Due to improvement of the crystal quality and the improvement of barrier layer conductivity, the current expansion capability is improved, and the reliability of the LED device is also improved.
Owner:西安利科光电科技有限公司
Si-based vertical cavity surface emitting chip
ActiveCN107749565BImprove conversion efficiencyImprove thermal stabilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersDistributed Bragg reflectorEngineering
The invention discloses a Si-based vertical cavity surface emitting chip. The structure consists from bottom to top of an n-type electrode, a substrate, a buffer layer, a lower distributed Bragg reflector located on the substrate, active area located on the lower distributed Bragg reflector, an upper distributed Bragg reflector located on the active area, a p-type electrode located on the upper distributed Bragg reflector, and a SiO2 confinement layer located around a cylindrical mesa. In the invention, a silicon-doped (AlxGa1-x)2O3, (AlyGa1-y)2O3 stacked structure is prepared on an n-type silicon substrate as the lower distributed Bragg reflector, rare earth-doped Ga2O3 is used as an n-type luminous material, and a GaAs, AlGaAs or InP, InGaAsP stacked structure is used as the upper distributed Bragg reflector. As a silicon-based vertical cavity surface emitting light source according to the invention, the characteristics of high thermal stability, high chemical stability, simple preparation method and high reliability are gained.
Owner:张子旸
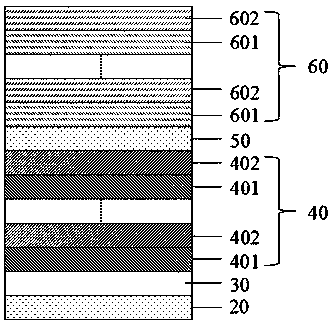
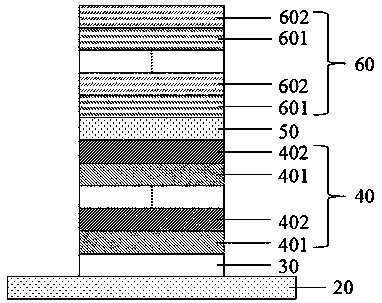
Semiconductor epitaxial structure, vcsel and manufacturing method based on flexible substrate
ActiveCN110739604BTaking into account the temperature requirementsEnhanced interactionLaser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsDevice materialCondensed matter physics
The invention provides a semiconductor epitaxial structure, VCSEL and manufacturing method based on a flexible substrate. Fluorphlogopite mica is used as the substrate, which not only solves the problem that the existing semiconductor substrate cannot be bent and is not easy to peel off, but also takes into account the cost of the semiconductor device. temperature requirements. For the buffer layer, the multi-layer first GaInP buffer layer is gradually changed layer by layer, showing a step gradient trend. By inserting the second layer of the In composition gradient opposite to the direction of the In composition gradient between two adjacent first GaInP buffer layers. The GaInP buffer layer forms a structure with fluctuating and gradual changes in the In composition, thereby introducing compressive stress in the buffer layer, increasing the interaction of dislocations, making the surface smoother, and further reducing threading dislocations, improving the performance of fluorine phlogopite. The quality of the epitaxial layer on the substrate realizes the application of fluorophlogopite substrate in semiconductor devices. VCSEL has the advantages of being bendable, easy to peel off, good epitaxial layer quality, and high light extraction efficiency.
Owner:XIAMEN QIANZHAO SEMICON TECH CO LTD
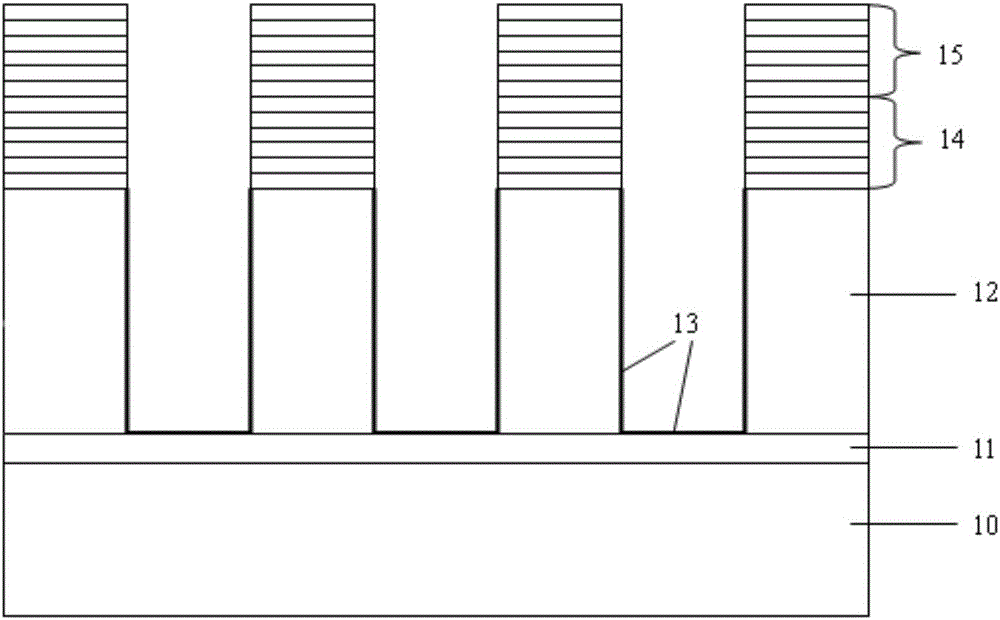
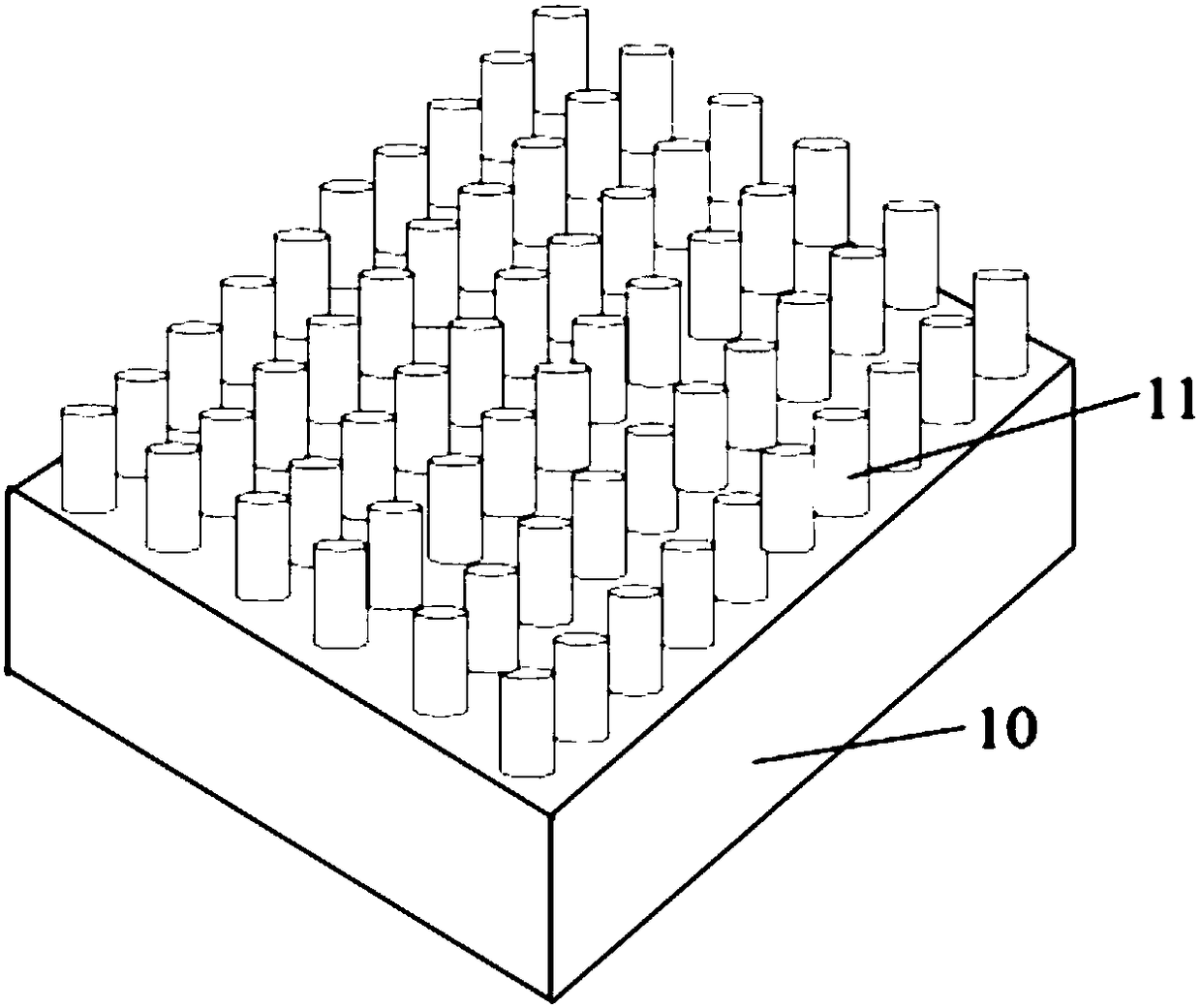
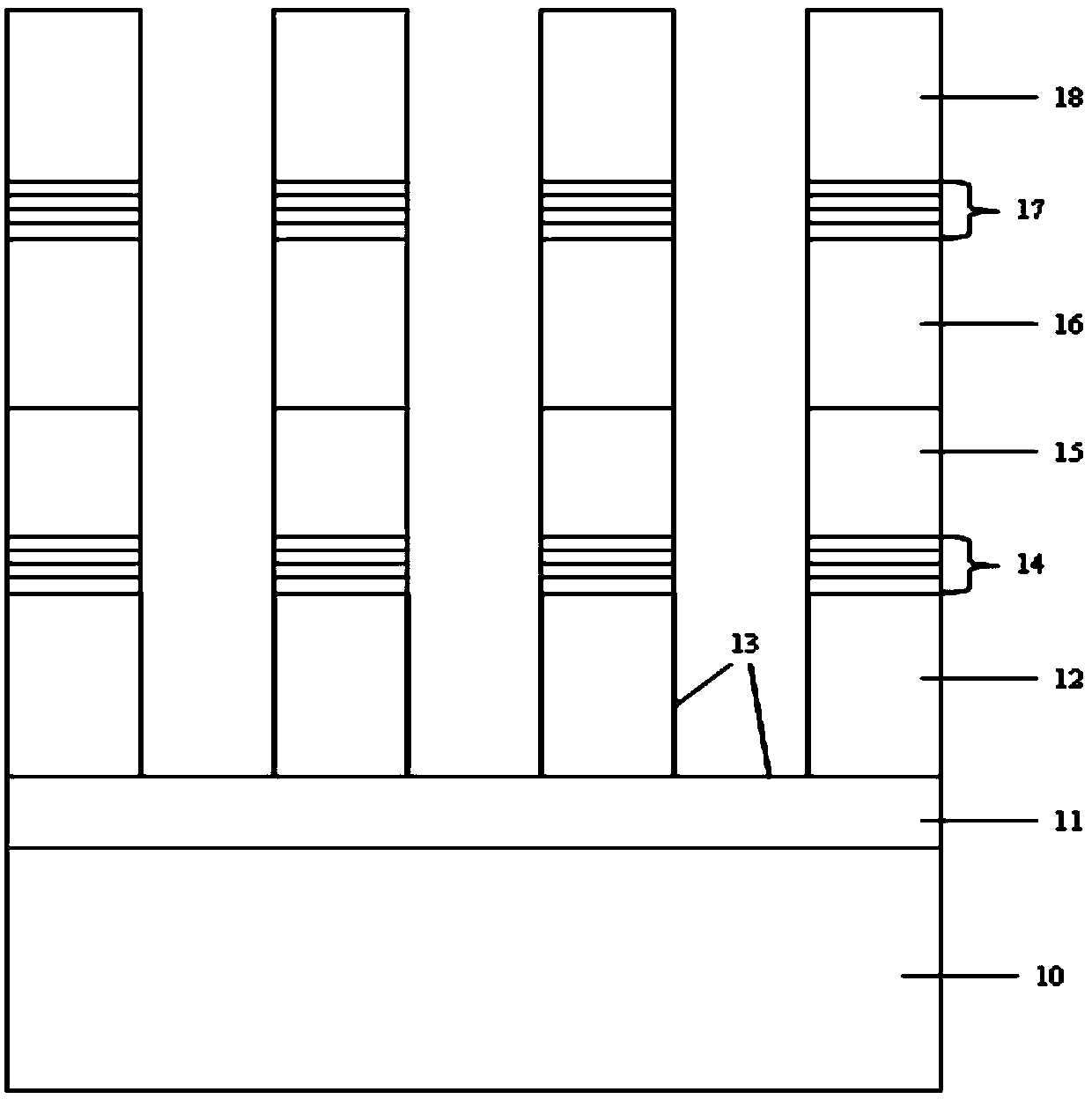
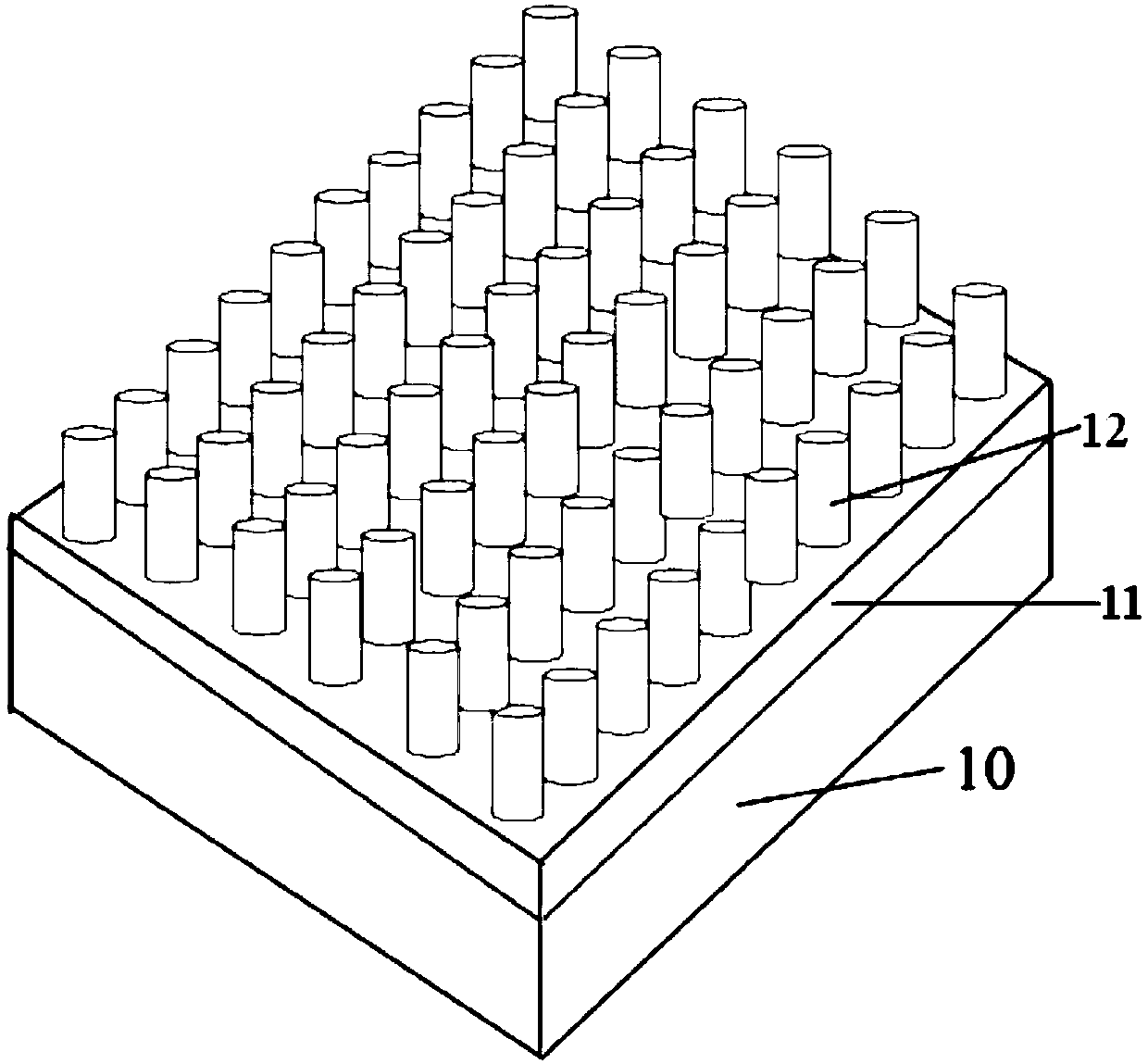
Nonpolar nanocolumn LED grown on lithium gallate substrate and its preparation method
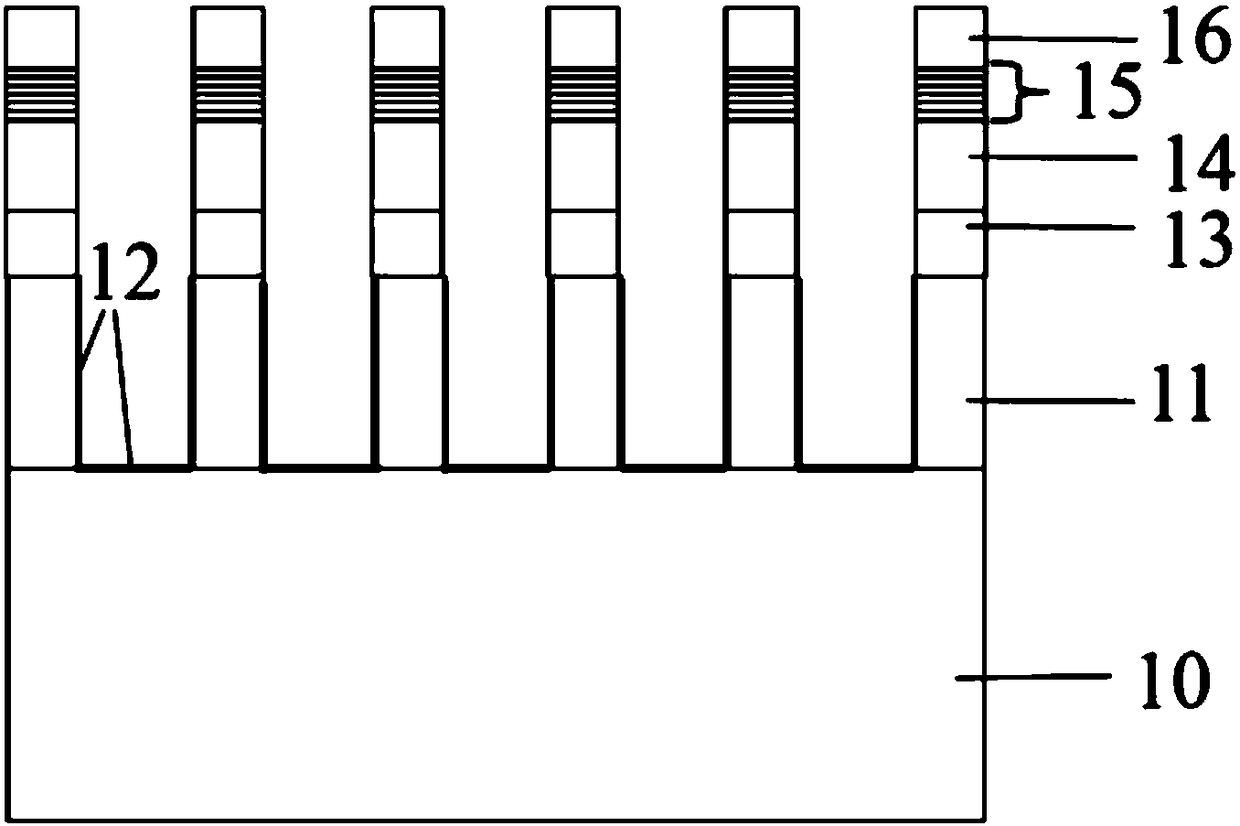
Disclosed are a nanorod LED grown on a lithium gallate substrate and a preparation method therefor. The nonpolar nanorod LED grown on the lithium gallate substrate comprises an LiGaO2 substrate (10), a GaN nanorod array (11) grown on the LiGaO2 substrate, a non-doped GaN layer (13) grown on the GaN nanorod array, an n-type doped GaN layer (14) grown on the non-doped GaN layer, an InGaN / GaN quantum well (15) grown on the n-type doped GaN layer, and a p-type doped GaN layer (16) grown on the InGaN / GaN quantum well, wherein the GaN nanorod array is a nonpolar GaN nanorod array. The selected lithium gallate substrate is low in material cost; the prepared nanorod array is controllable in dimensions and uniform in orientation; and the resulting nonpolar nanorod LED has a low defect density, and excellent electrical and optical properties.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
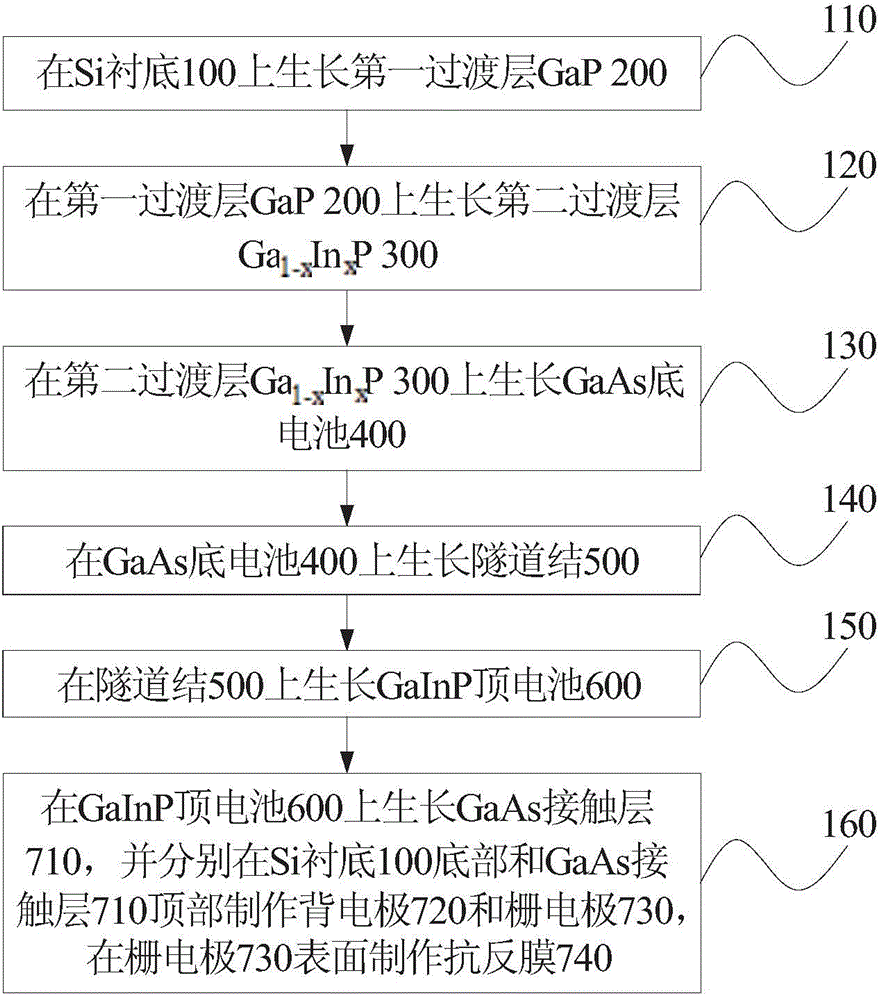
Preparation method for GaInP/GaAs dual-junction solar cell
InactiveCN106033785ALow costHigh mechanical strengthFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIndiumSolar cell
The invention discloses a preparation method for a GaInP / GaAs dual-junction solar cell. The preparation method comprises: step A, a first transition layer GaP grows on a substrate; step B, a second transition layer Ga(1-x)InxP grows on the first transition layer GaP; step C, a GaAs bottom cell grows on the second transition layer Ga(1-x)InxP; and step D, a GaInP top cell grows on the GaAs bottom cell, wherein the content of indium in the second transition layer Ga(1-x)InxP is adjusted to realize matching of the lattice constant of the second transition layer Ga(1-x)InxP with the lattice constant of the GaAs bottom cell. According to the preparation method, the GaP and the Ga(1-x)InxP are used as transition layers and transition of the lattice constant of the second transition layer Ga(1-x)InxP to the lattice constant of the GaAs bottom cell is realized, so that lattice constant matching is realized and thus an objective of growing and preparing a GaInP / GaAs dual-junction solar cell is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Miniaturization method of long-wave infrared spatial modulation interferometry
ActiveCN103674243BSmall sizeReduce the difficulty of growingSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionOptical axisMiniaturization
The invention relates to a long-wave infrared space modulation interference miniaturizing method. The method is characterized in that an interference assembly is composed of a spectroscope, a pyramid reflector I, a pyramid reflector II and two aperture diaphragms; an included angle between the spectroscope and parallel incident light is 135degree; from the optical axis position of reflected light, the top position of the pyramid reflector I starts to move anticlockwise for 1 / 4 transverse shear amount along the direction vertical to the optical axis of the reflected light; from the optical axis position of transmitted light, the top position of the pyramid reflector II starts to move anticlockwise for 1 / 4 transverse shear amount along the direction vertical to the optical axis of the transmitted light; and the two aperture diaphragms are respectively arranged at the top positions of the two pyramid reflectors, and are respectively placed vertical to the optical axes of the reflected light and the transmitted light. Under the condition that optical parameters are consistent, the size of the spectroscope is decreased, the sizes of the interference assembly and a spectrometer are effectively controlled, the difficulties in material growing and processing are reduced, and the cost is saved.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
Method for growing uranium dioxide crystals by using borate fluxing agent
InactiveCN111394781ALow growth temperatureEasy to industrializePolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsMolten stateUranium oxide
The invention belongs to the technical field of crystal preparation, and particularly discloses a method for growing uranium dioxide crystals by using a borate fluxing agent, which comprises the following steps: (1) mixing and grinding a fluxing agent Li5U (BO3)3 with Li2CO3, H3BO3 and UO2 powder in a stoichiometric ratio for 3 hours; (2) putting the mixed powder in the step (1) into a platinum crucible, and sintering at a three-stage temperature; (3) mixing fluxing agents Li5U (BO3) 3 and UO2 according to the molar ratio of 83 mol%: 1; preparing 17mol% of raw materials, fully mixing and grinding, loading into a platinum crucible, introducing Ar / 5% H2, putting into a tubular resistance furnace, heating to 1235 DEG C, dissolving UO2 by using a Li5U(BO3) 3 fluxing agent, enabling the systemto reach a molten state, and slowly cooling to reach supersaturation to drive the crystal to grow, thereby obtaining the UO2 crystal. The scheme is mainly used for preparing the uranium dioxide crystal, and the problem that the ultrahigh-melting-point uranium dioxide crystal is difficult to grow by an existing melt method is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
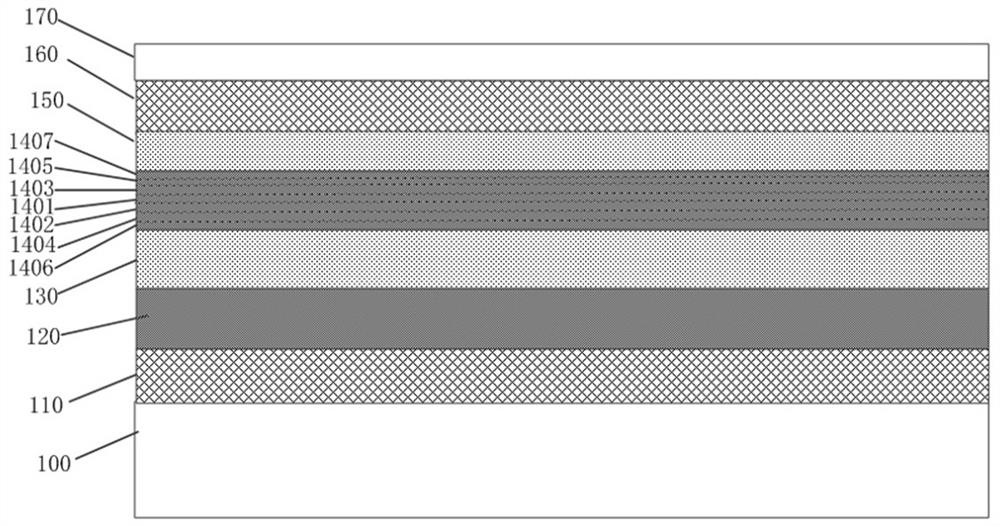
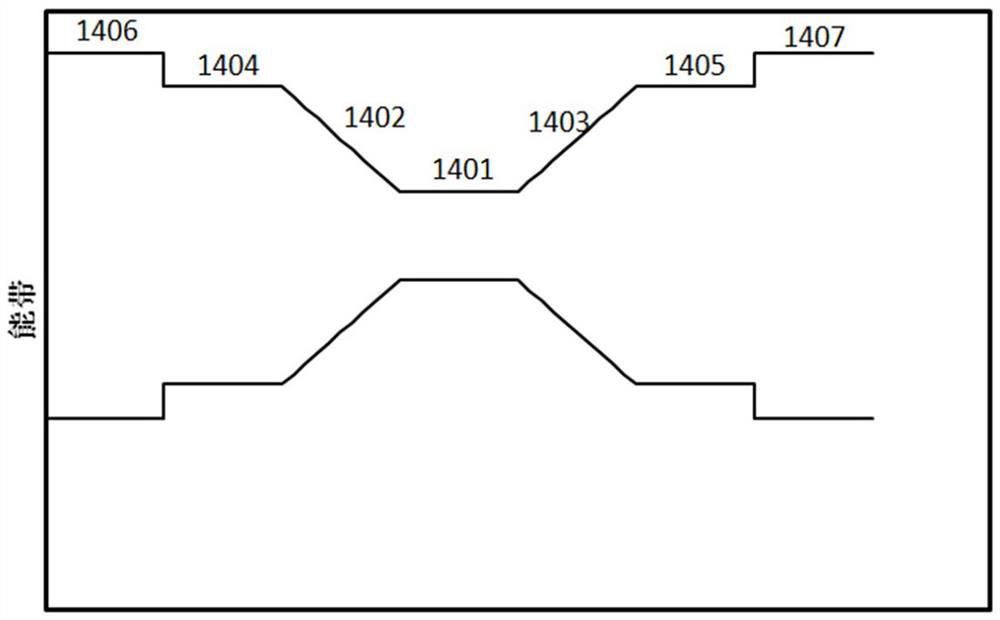
High-strain semiconductor structure and preparation method thereof
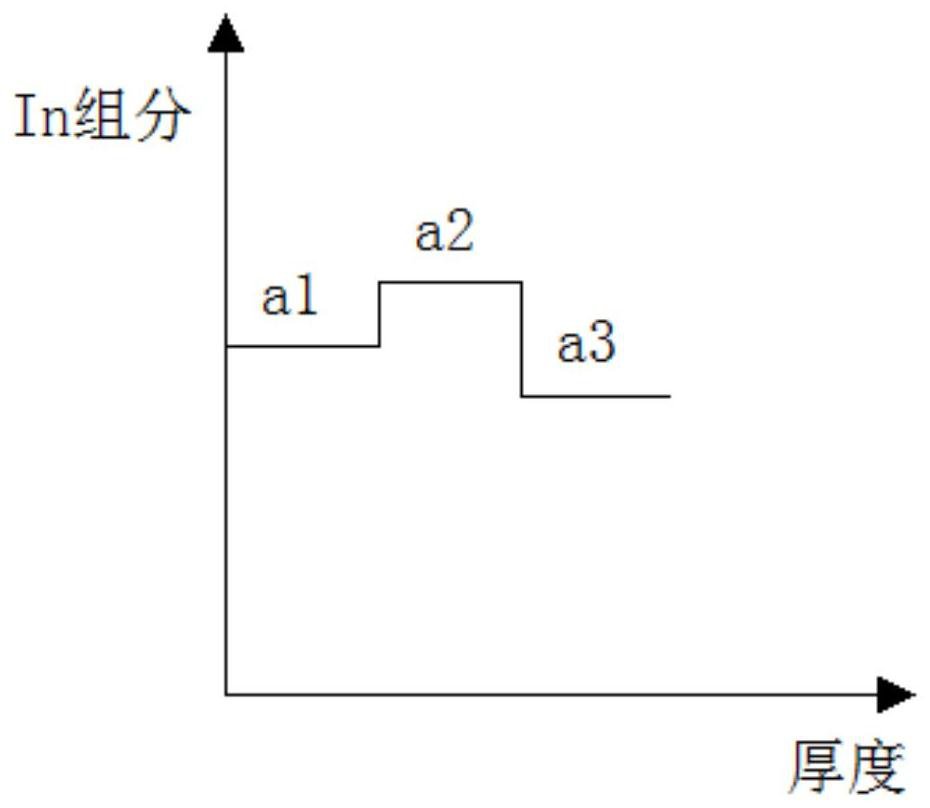
ActiveCN114094443AIncreasing the thicknessIncrease widthLaser detailsLaser active region structureIndiumSemiconductor structure
The invention provides a high-strain semiconductor structure and a preparation method thereof, and in a composite active layer of the high-strain semiconductor structure, the indium content in a first component gradient layer is smaller than the indium content in a quantum well layer and larger than the indium content in a first barrier layer. The indium content in the second component gradient layer is smaller than the indium content in the quantum well layer and larger than the indium content in the second barrier layer; the indium component content in a plurality of first sub-gradient layers in the first component gradient layer meets a progressive increase area of a Gaussian function along with the increase of the number of the first sub-gradient layers, and the indium component content in a plurality of second sub-gradient layers in the second component gradient layer meets a progressive decrease area of the Gaussian function along with the increase of the number of the second sub-gradient layers; the content of indium in the first stress compensation layer and the second stress compensation layer is zero; and the quantum well layer, the first component gradient layer and the second component gradient layer are used for laser light. The process difficulty and complexity of the high-strain semiconductor structure are reduced, and the growth quality is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU EVERBRIGHT PHOTONICS CO LTD +1
A method for improving the reliability of gate oxide layer in peripheral circuit region of flash memory
ActiveCN104112656BAvoid shifting doping profilesAvoid offsetSemiconductor devicesState of artRoom temperature
The invention provides a method for improving the reliability of a gate oxide layer of a peripheral circuit area of a flash memory. The method includes the following steps that: oxidation treatment is performed on a nitrogen containing region of the top of a semiconductor substrate at the peripheral circuit area; and the nitrogen containing region is converted into an oxide layer, and the oxide layer is removed, and therefore, a nitrogen-free semiconductor substrate surface of the peripheral circuit area is exposed; and a gate oxide layer is grown on the nitrogen-free semiconductor substrate surface. With the method adopted, when an MOS device is manufactured in the peripheral circuit area in a subsequent process, the nitrogen containing region of the top of the semiconductor substrate is removed, and therefore, the growth difficulty of the gate oxide layer on the surface of the semiconductor substrate can be lowered, and especially, the growth capacity of the gate oxide layer on the semiconductor substrate at corners of an isolation structure can be improved, and the integrity and uniformity of gate oxide layer growth can be increased, and the reliability of the gate oxide layer of the MOS device can be improved; and the oxidation treatment mentioned in the invention is performed at room temperature or low temperature, and therefore, thermal budget in the prior art can be decreased, and device doping profile shift can be avoided. The method is advantageous in convenient implementation and simple operation.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Nanocolumn led grown on strontium aluminate tantalum lanthanum substrate and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano-pillar LED preparation, and discloses a nano-pillar LED grown on a strontium tantalum lanthanum aluminate substrate and a preparation method thereof. The nano-pillar LED grown on a strontium tantalum lanthanum aluminate substrate comprises a strontium tantalum lanthanum aluminate substrate, an AlN nucleation layer grown on the strontium tantalum lanthanum aluminate substrate, a GaN nano-pillar template grown on the AlN nucleation layer, an AlN / GaN super lattice layer grown on the GaN nano-pillar template, a non-doped GaN layer grown on the AlN / GaN super lattice layer, an n-type doped GaN layer grown on the non-doped GaN layer, an InGaN / GaN quantum well grown on the n-type doped GaN layer, and a p-type doped GaN layer grown on the InGaN / GaN quantum well. The substrate material is of low cost. A nano-pillar array prepared is size-controllable and of uniform orientation. The obtained nano-pillar LED has low defect density and excellent electrical and optical properties.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com