Patents
Literature
206 results about "Boule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
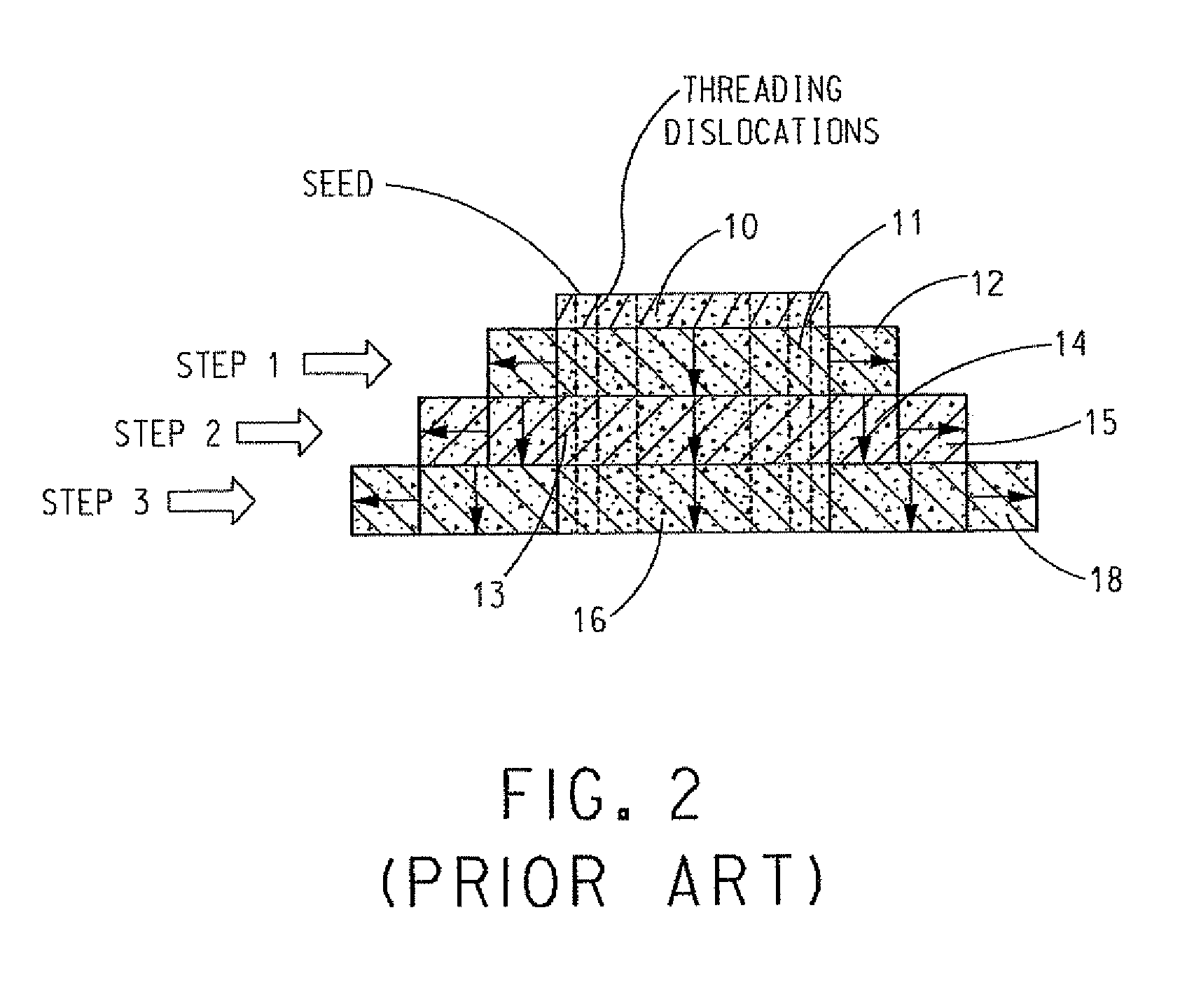
A boule is a single crystal ingot produced by synthetic means. A boule of silicon is the starting material for most of the integrated circuits used today. In the semiconductor industry synthetic boules can be made by a number of methods, such as the Bridgman technique and the Czochralski process, which result in a cylindrical rod of material.
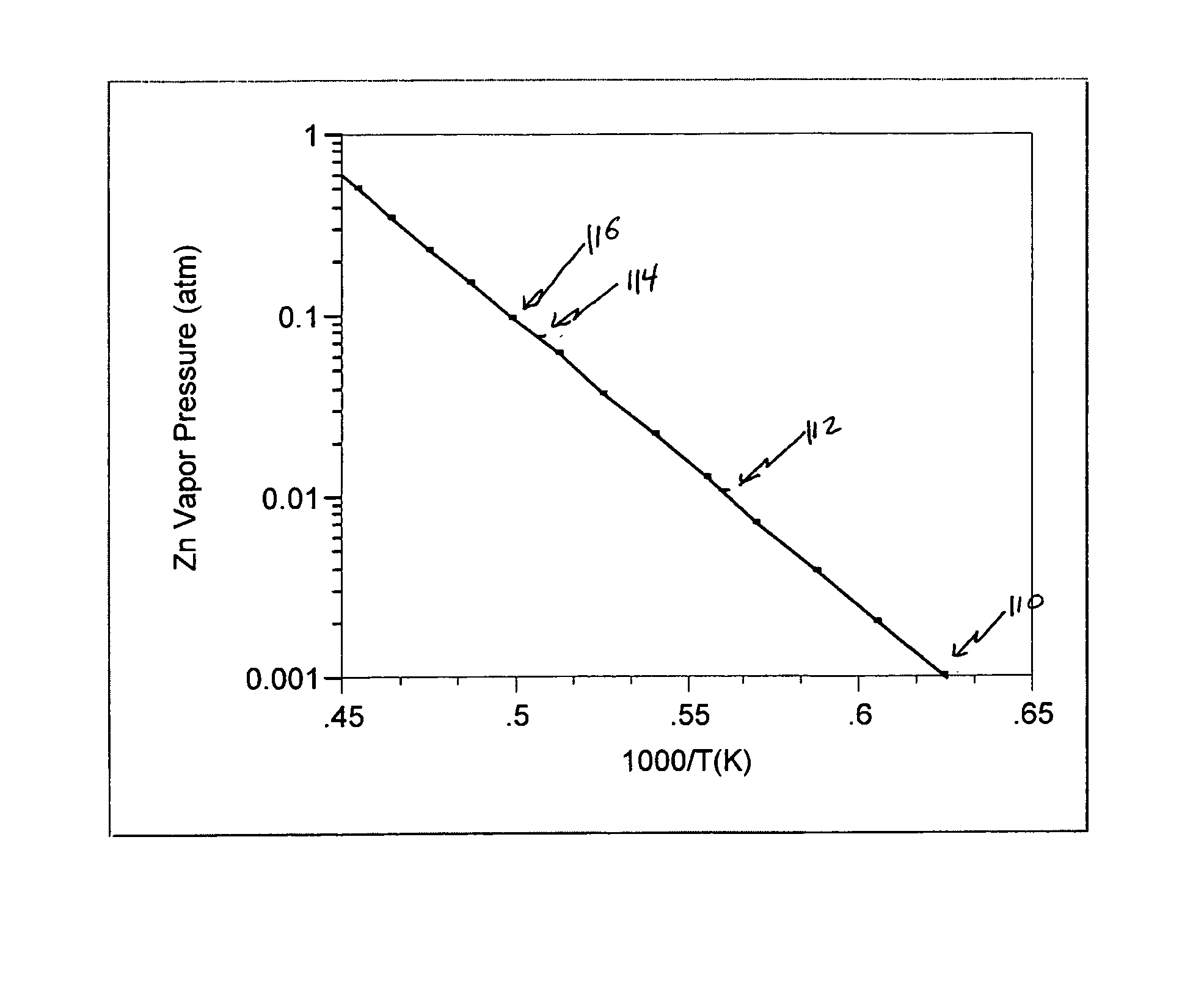
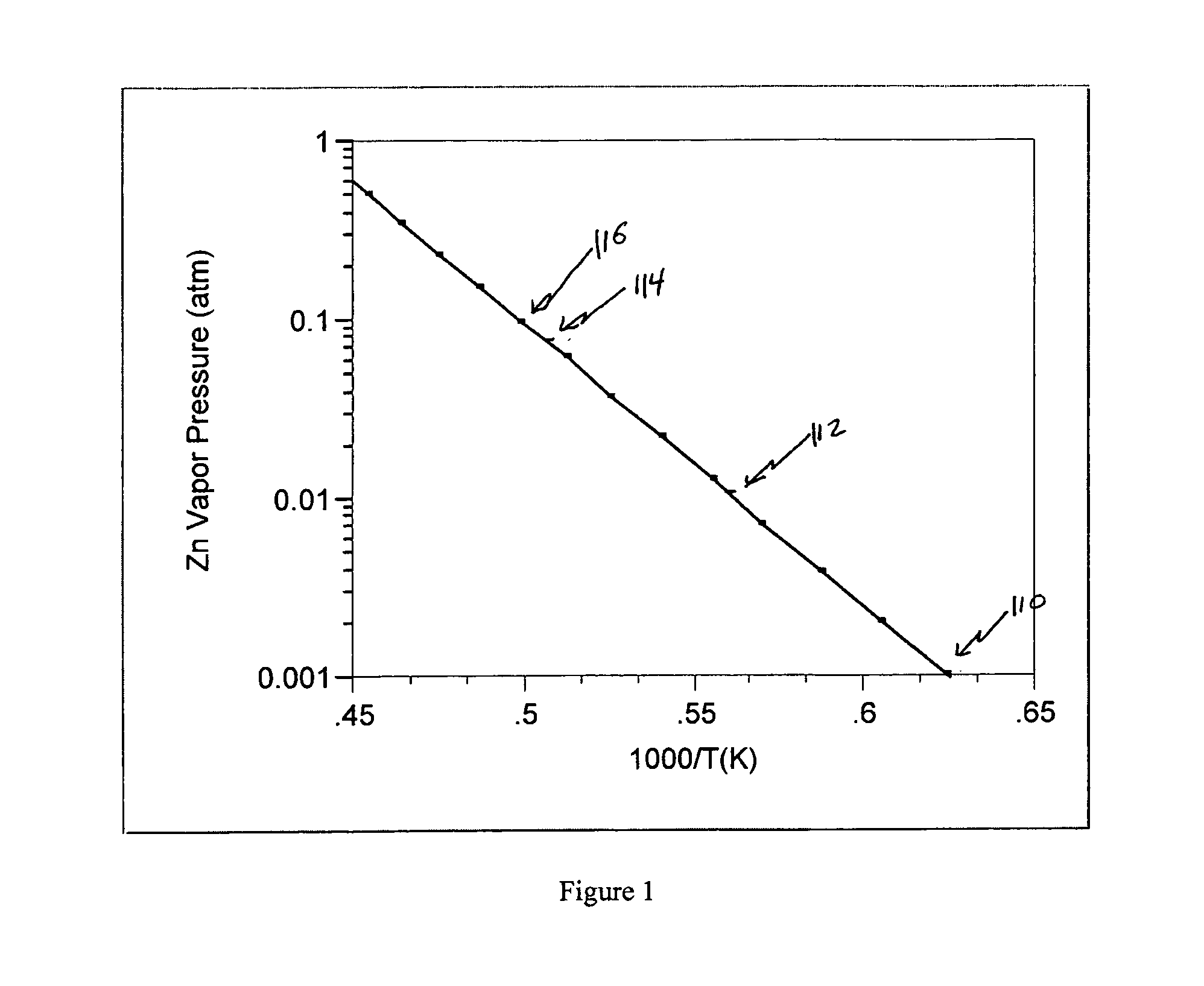
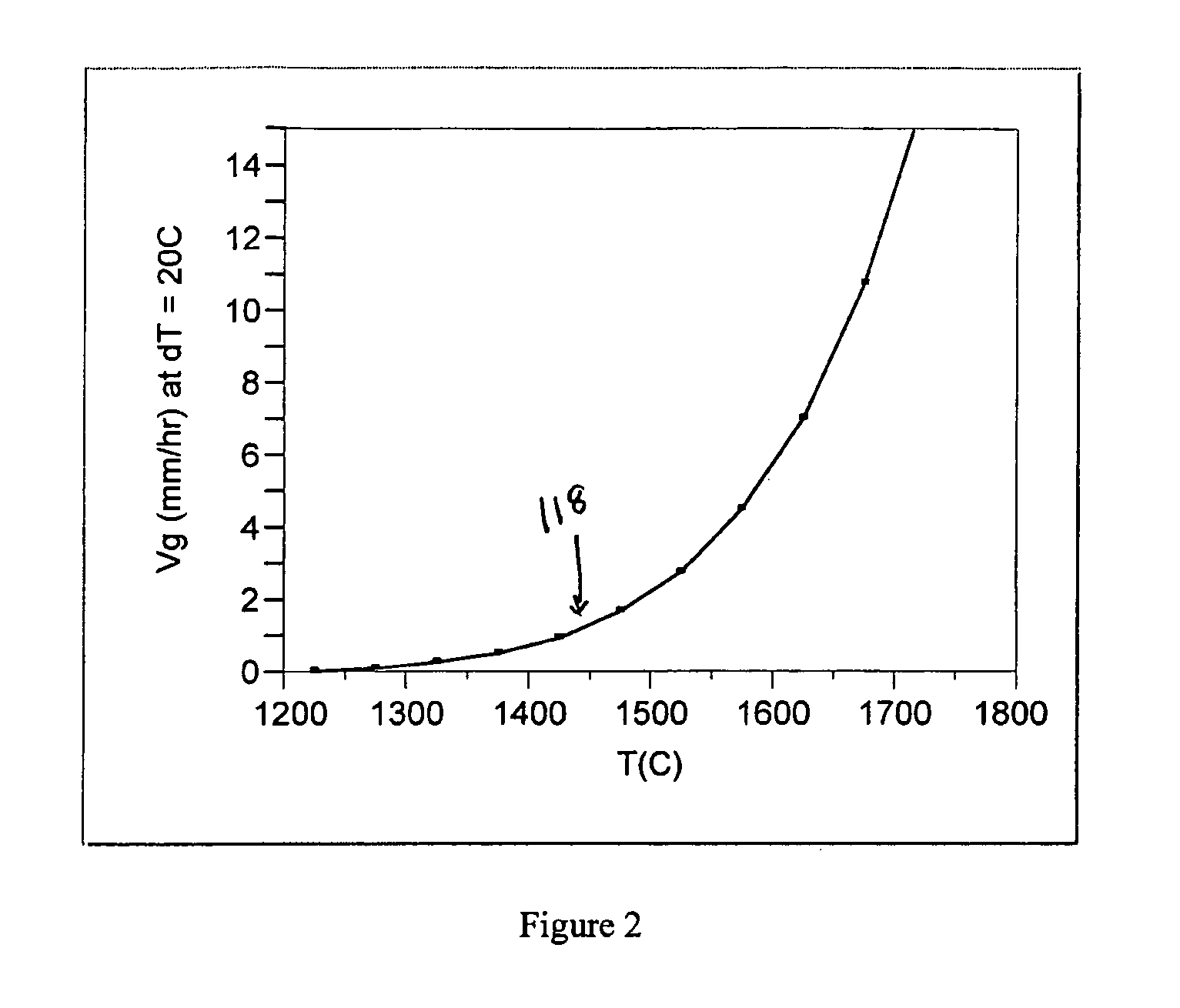
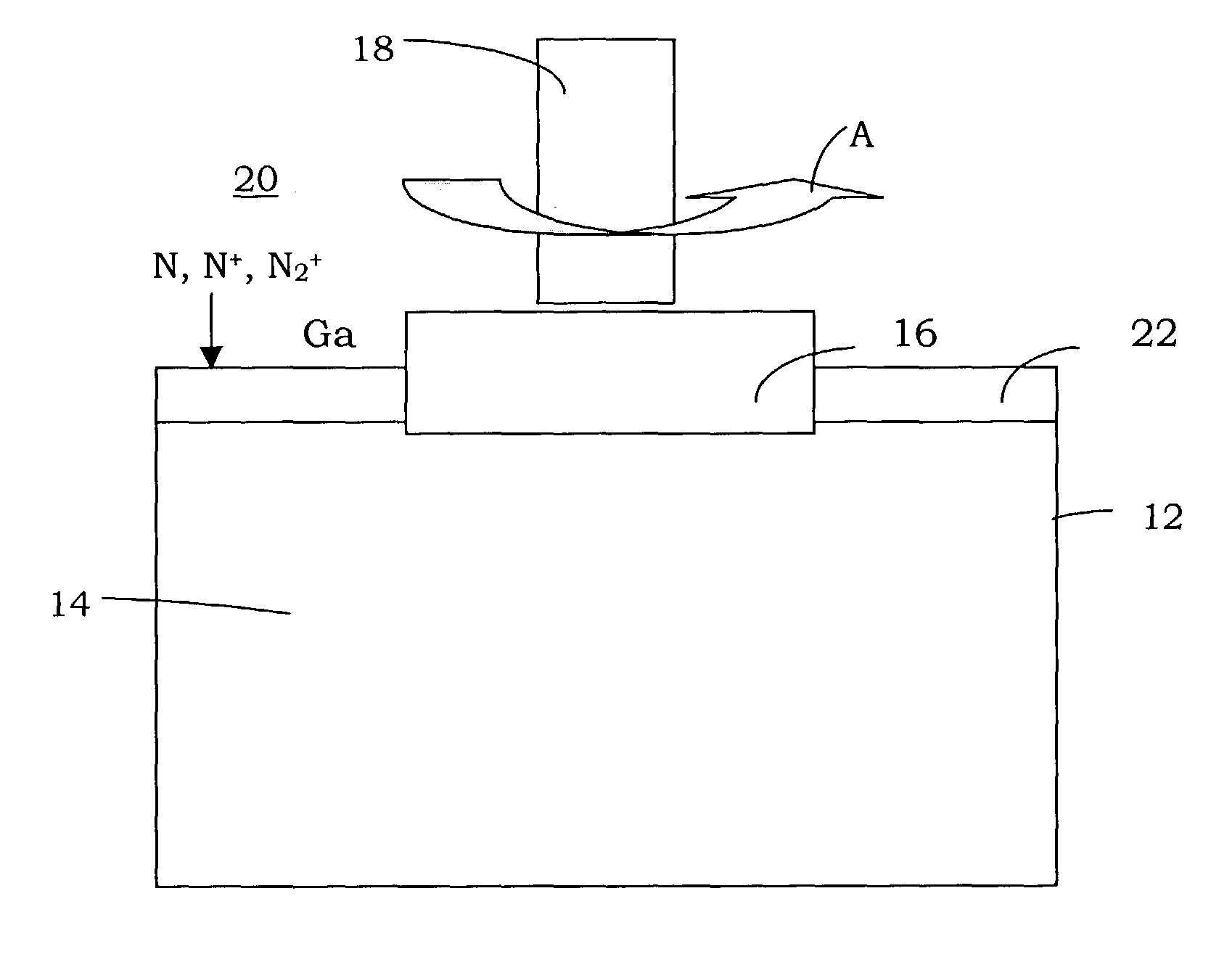
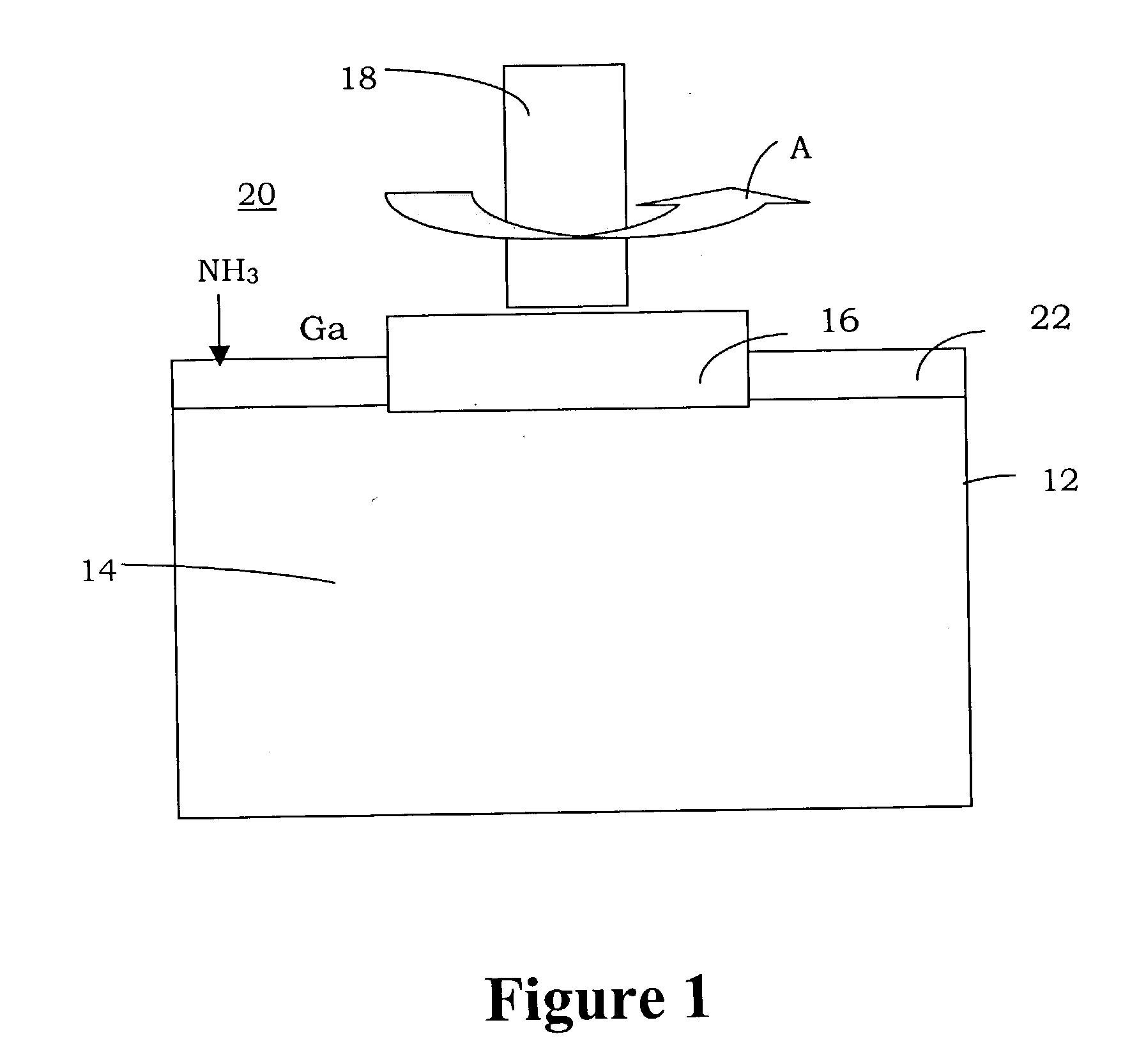
Method and apparatus for zinc oxide single crystal boule growth
ActiveUS7279040B1After-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthSeed crystalSource material
There is provided a method for growing one or more single crystal ZnO boules within a physical vapor transport furnace system. This method includes the steps of: (a.) placing a source material at a first end of an interior crucible enclosure and placing one or more seed crystals at an opposing second end of the interior crucible enclosure with the seed crystal and the source material separated by a predetermined distance; (b.) heating the crucible, the one or more seed crystals and the source material to predetermined temperatures in such way that the temperature of the source material is higher than the temperature of the seed crystal; (c.) maintaining a pressure within the interior crucible enclosure through flowing a gas mixture; and (d) maintaining a temperature distribution within the crucible enclosure thereby causing a ZnO boule growth on each one of the one or more seed crystals. The ZnO may be doped with desired additional elements. In alternative embodiments, that other boules, both doped and un-doped, such as ZnSe and ZnS may also be formed.
Owner:FAIRFIELD CRYSTAL TECH
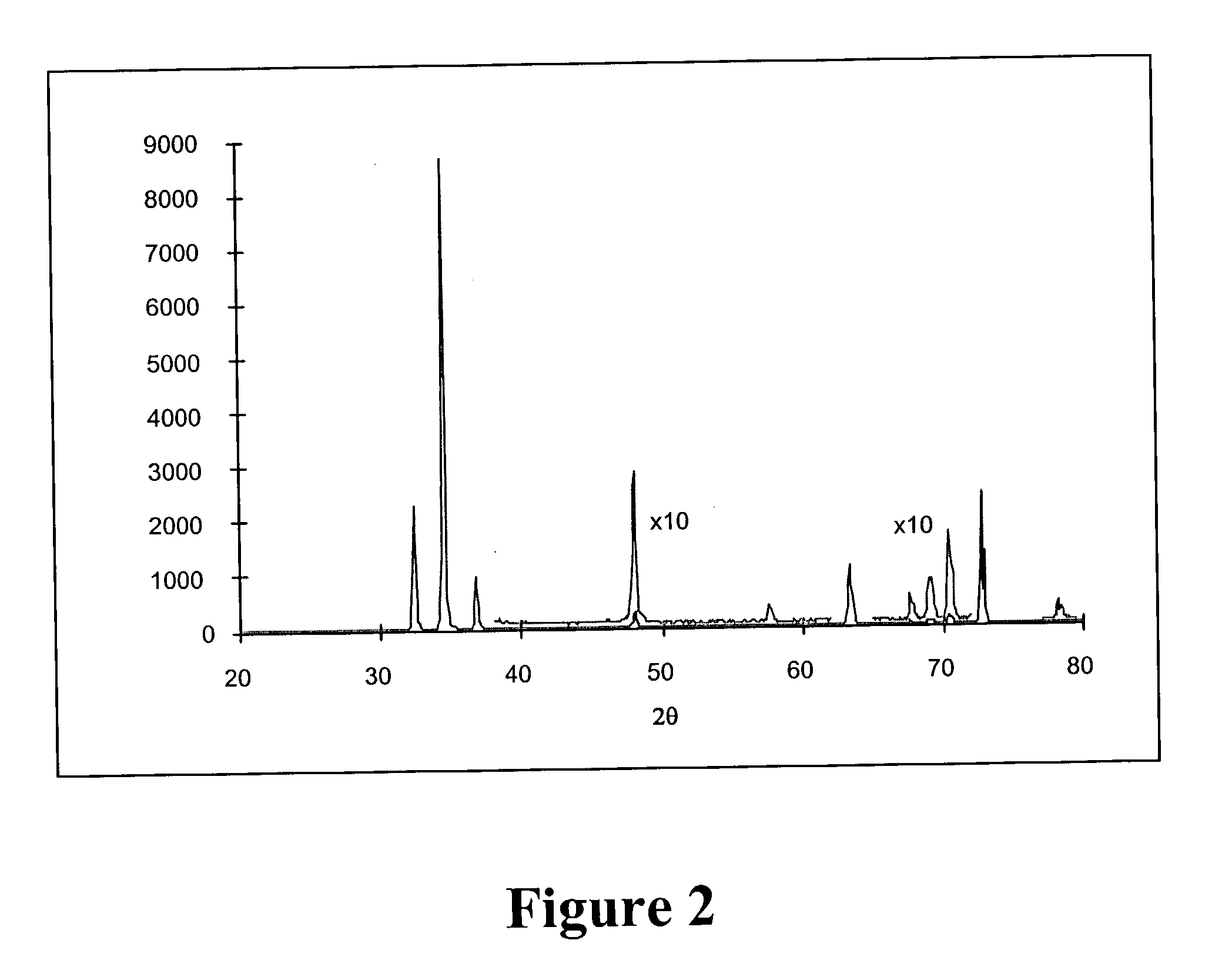
GaN boule grown from liquid melt using GaN seed wafers
ActiveUS20040003495A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBy pulling from meltWaferingMetallurgy
A method of making a single crystal GaN boule, comprising contacting a GaN seed wafer with a GaN source environment under process conditions including a thermal gradient in the GaN source environment producing growth of gallium nitride on the GaN seed wafer, thereby forming the GaN boule. The GaN source environment in various implementations includes gallium melt in an ambient atmosphere of nitrogen or ammonia, or alternatively, supercritical ammonia containing solubilized GaN. The method produces single crystal GaN boules >10 millimeters in diameter, of device quality suitable for production of GaN wafers useful in the fabrication of microelectronic, optoelectronic and microelectromechanical devices and device precursor structures therefor.
Owner:CREE INC
Vicinal gallium nitride substrate for high quality homoepitaxy
ActiveUS7118813B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingRms roughness
A III–V nitride, e.g., GaN, substrate including a (0001) surface offcut from the <0001> direction predominantly toward a direction selected from the group consisting of <10-10> and <11-20> directions, at an offcut angle in a range that is from about 0.2 to about 10 degrees, wherein the surface has a RMS roughness measured by 50×50 μm2 AFM scan that is less than 1 nm, and a dislocation density that is less than 3E6 cm−2. The substrate may be formed by offcut slicing of a corresponding boule or wafer blank, by offcut lapping or growth of the substrate body on a corresponding vicinal heteroepitaxial substrate, e.g., of offcut sapphire. The substrate is usefully employed for homoepitaxial deposition in the fabrication of III–V nitride-based microelectronic and opto-electronic devices.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
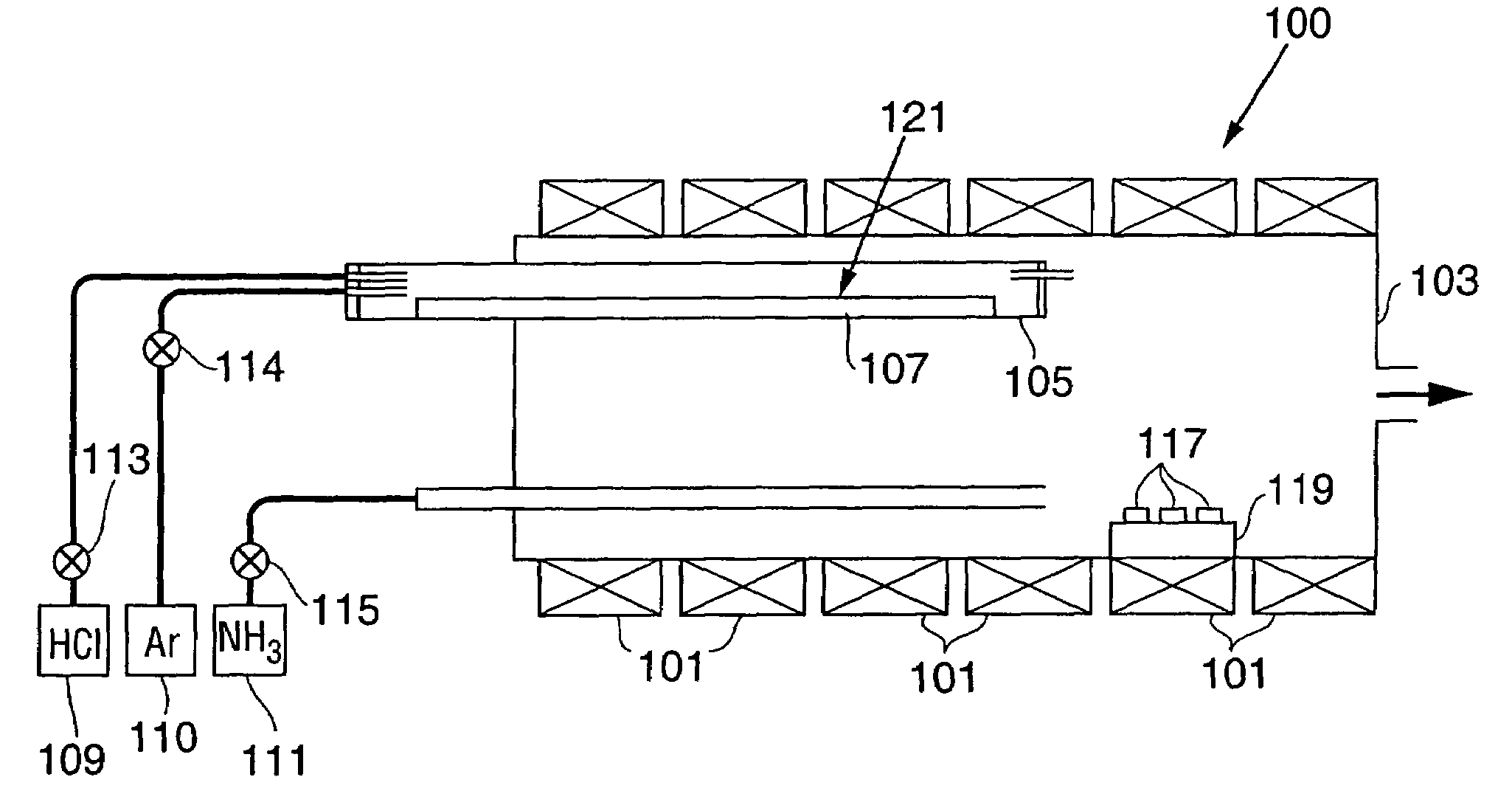
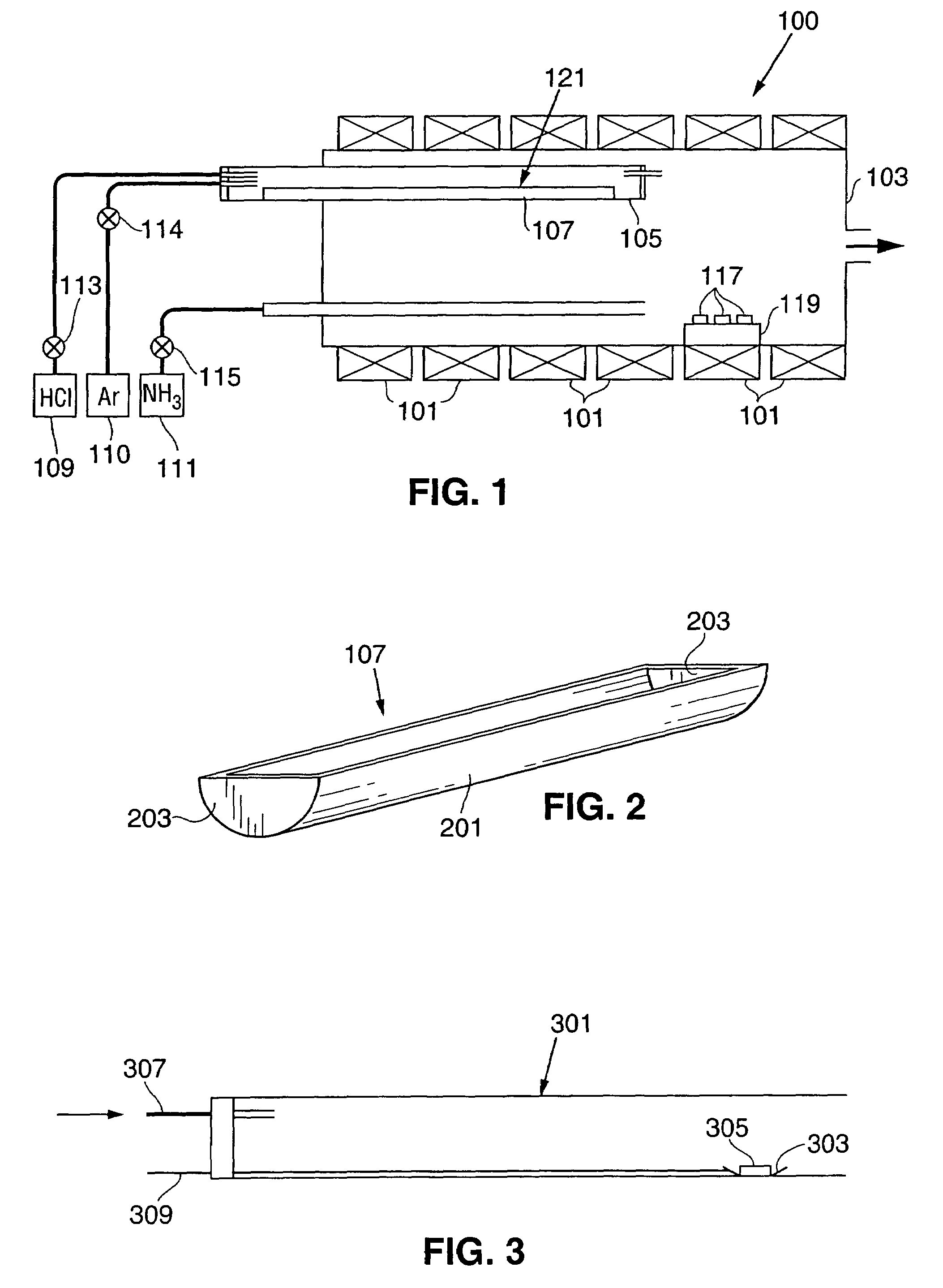
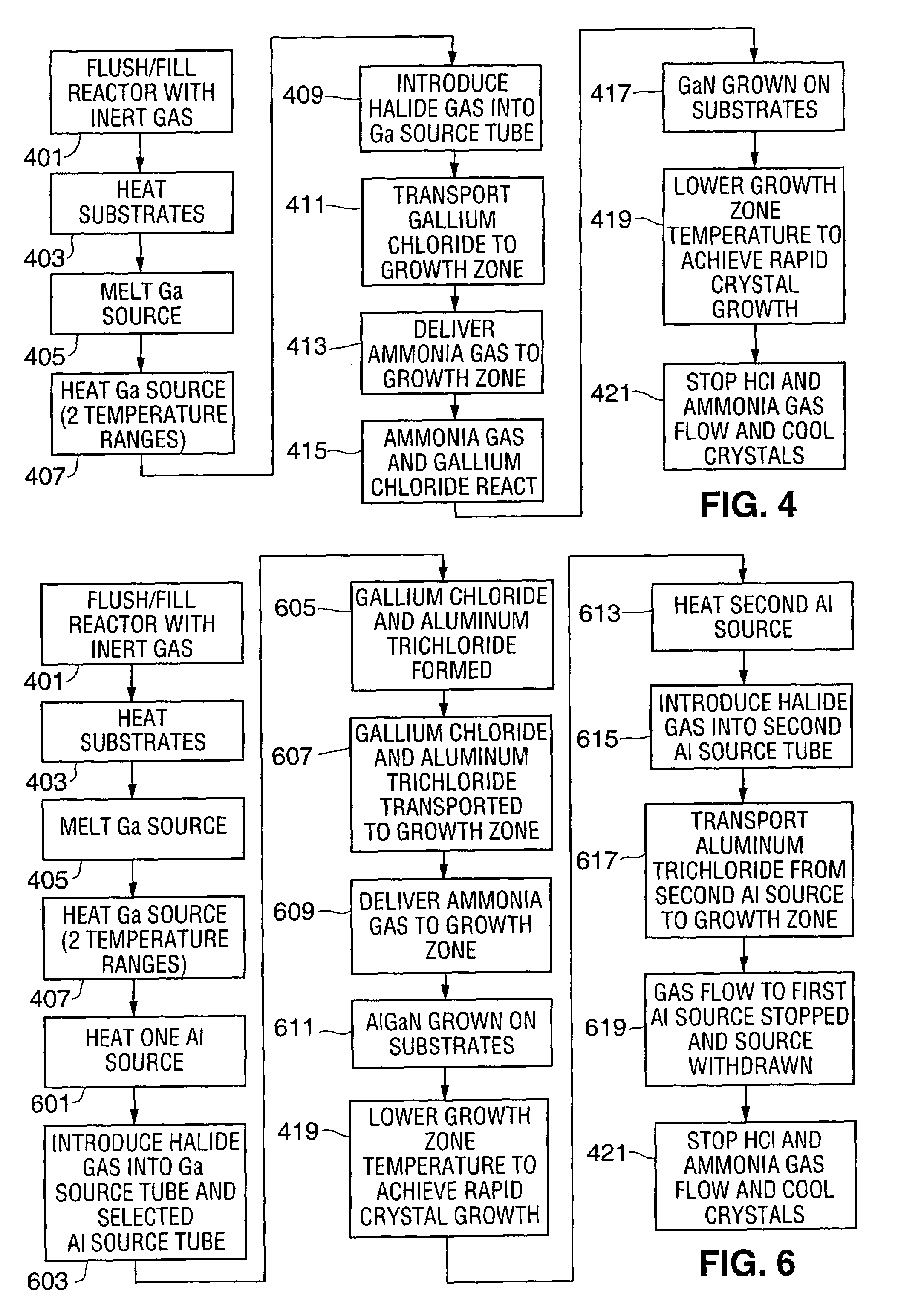
Reactor for extended duration growth of gallium containing single crystals
InactiveUS7279047B2Limited amountExtended growth cycleAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthCrystal structureNucleation
An apparatus for growing bulk GaN and AlGaN single crystal boules, preferably using a modified HVPE process, is provided. The single crystal boules typically have a volume in excess of 4 cubic centimeters with a minimum dimension of approximately 1 centimeter. If desired, the bulk material can be doped during growth to achieve n-, i-, or p-type conductivity. In order to have growth cycles of sufficient duration, preferably an extended Ga source is used in which a portion of the Ga source is maintained at a relatively high temperature while most of the Ga source is maintained at a temperature close to, and just above, the melting temperature of Ga. To grow large boules of AlGaN, preferably multiple Al sources are used, the Al sources being sequentially activated to avoid Al source depletion and excessive degradation. In order to achieve high growth rates, preferably a dual growth zone reactor is used in which a first, high temperature zone is used for crystal nucleation and a second, low temperature zone is used for rapid crystal growth. Although the process can be used to grow crystals in which the as-grown material and the seed crystal are of different composition, preferably the two crystalline structures have the same composition, thus yielding improved crystal quality.
Owner:OSTENDO TECH INC
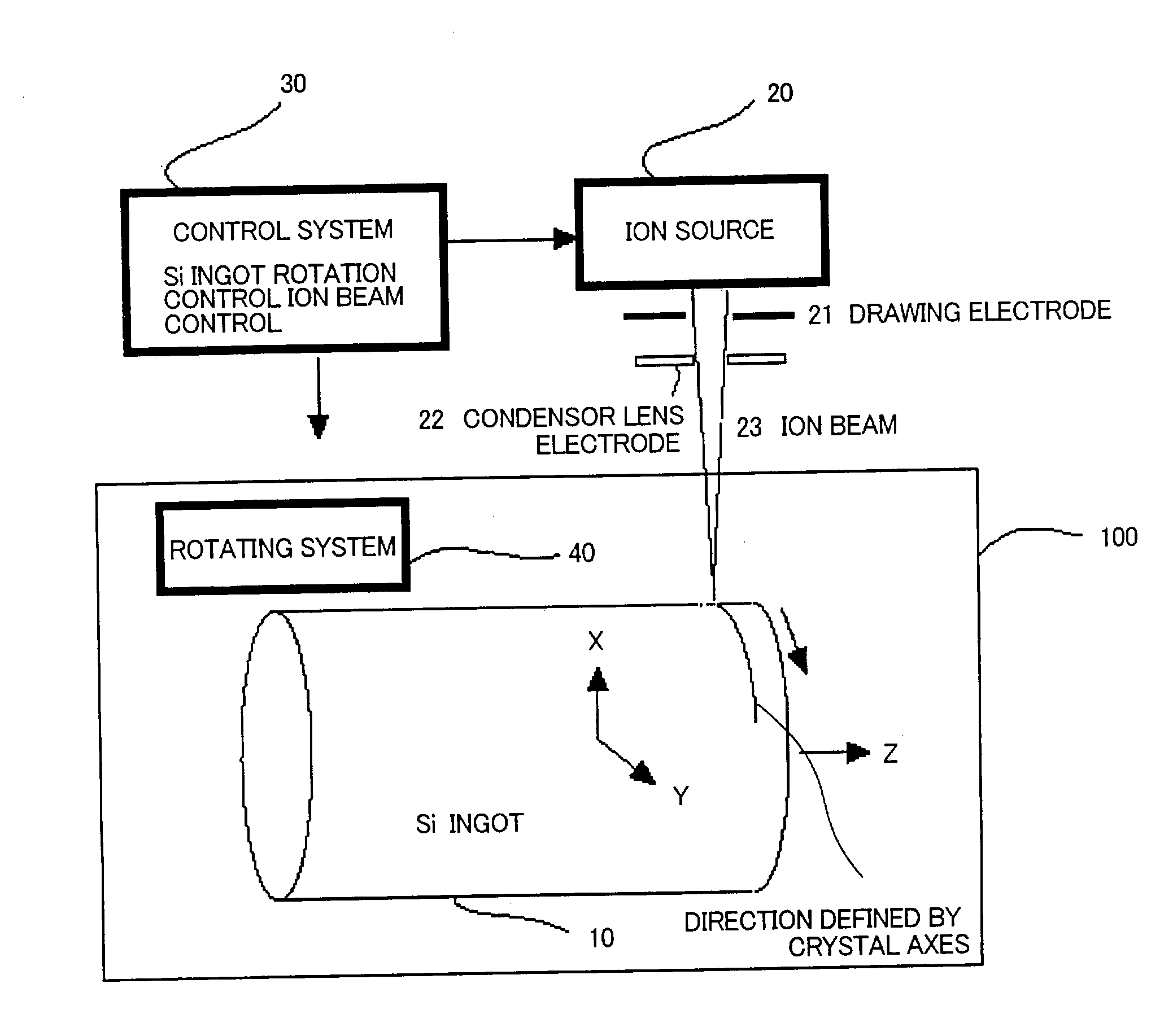
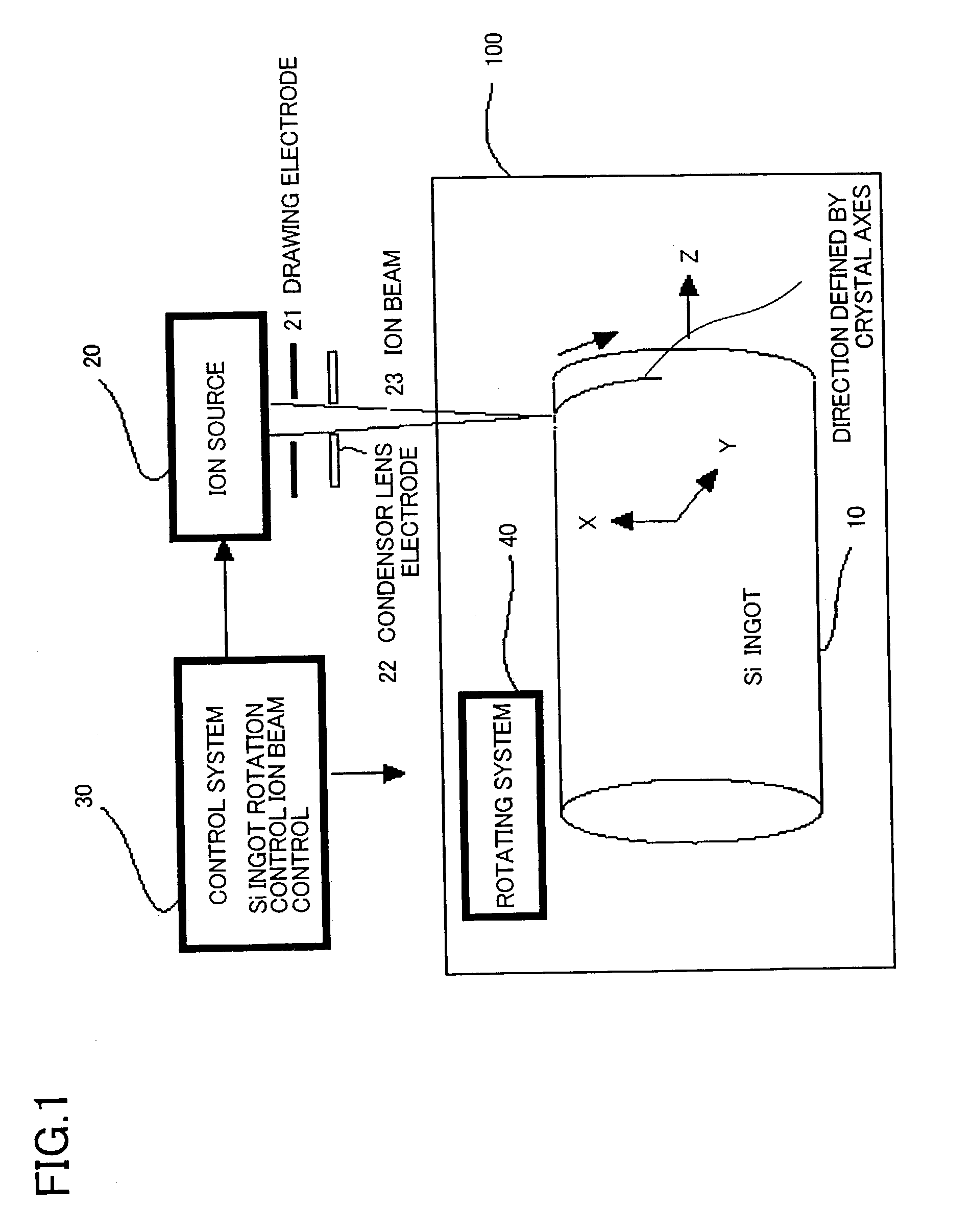
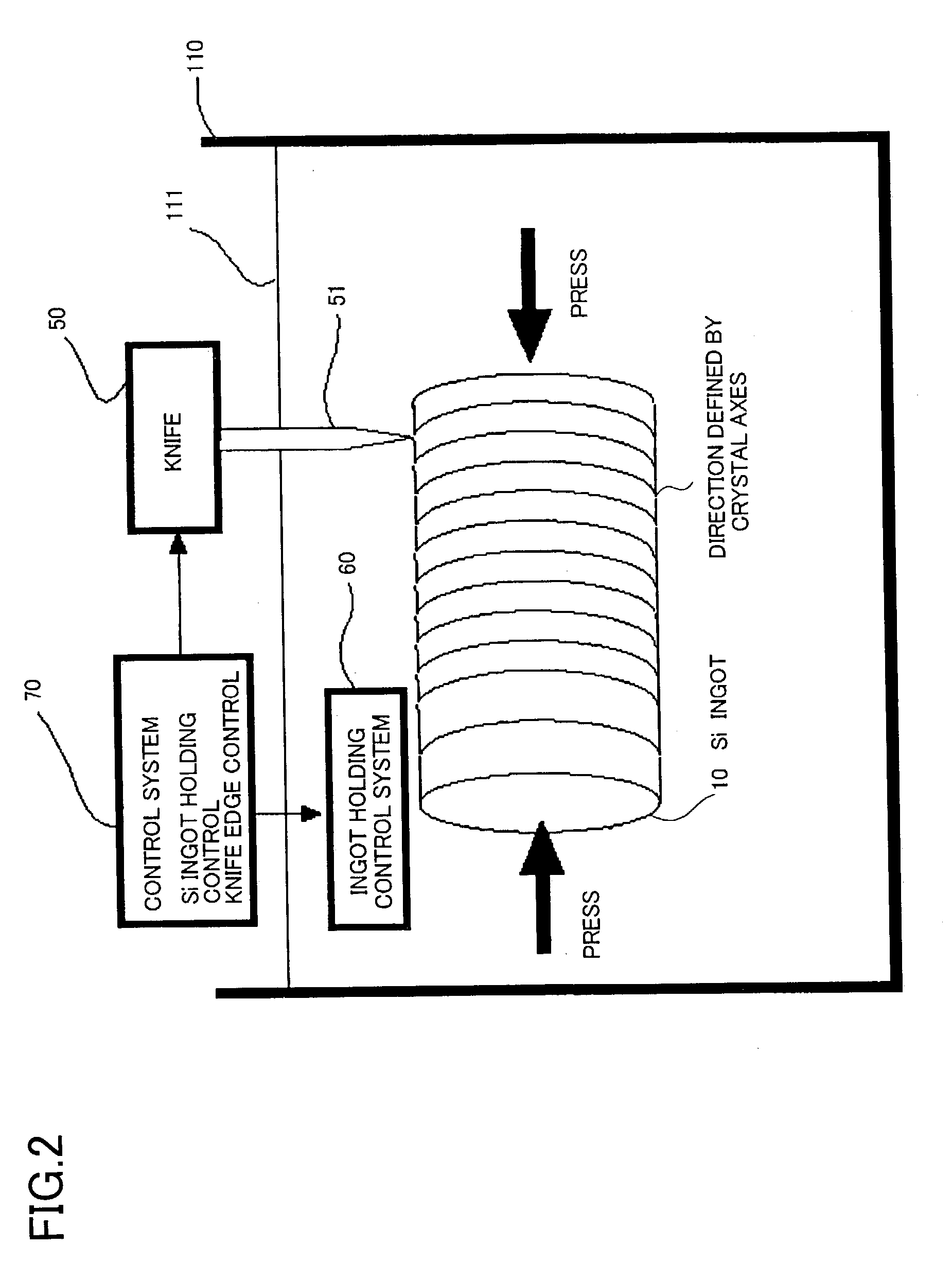
Cutting method and apparatus for ingot, wafer, and manufacturing method of solar cell
InactiveUS20040055634A1Shorten the timeProduce more and thinPolycrystalline material growthFinal product manufactureLattice defectsIon beam
Cutting method of ingot into wafers along cleavage plane. Onto surface of single crystal ingot 10 is implanted ion beam 23 to generate lattice defects in a direction defined by the crystal axes that corresponds to the cleavage plane. Cleavage is generated by applying a shock by a knife edge to the position of the lattice having a cutting face as a cleavage plane. Production time of waters is reduced with a more numbers of sliced wafers from one ingot.
Owner:Y Y L
Alkaline computer hard disk polishing liquid and producing method thereof
InactiveCN101016438AImprove polishing efficiencyPolishing machinesPolishing compositions with abrasivesAbrasive agentChemical preparation
The invention discloses a preparing method of alkality computer hard disk polishing liquid in chemical preparation domain, which comprises the following steps: setting pH value of polishing liquid at 7-10; making the mass percent of oxidant, organic complexing agent and grinding agent at 0.1%-5%, 0.1%-5% and 0.5%-20% separately; composing ingredient A with diamond pyramid hardness bigger than 7 and ingredient B with diamond pyramid hardness bigger than 5; getting grinding agent; forming oxidant, organic metal chelating agent, high hardness and low hardness rubbing agent in neutral and alkality agent; adopting soft and hard merging multiple polished rubbing particle method; decreasing grievous fish tail caused by big particle boule aluminum oxide; increasing graduation efficiency; This invention adopts alkality polishing agent, which decreases the polishing loss of hard disk edge.
Owner:孙韬
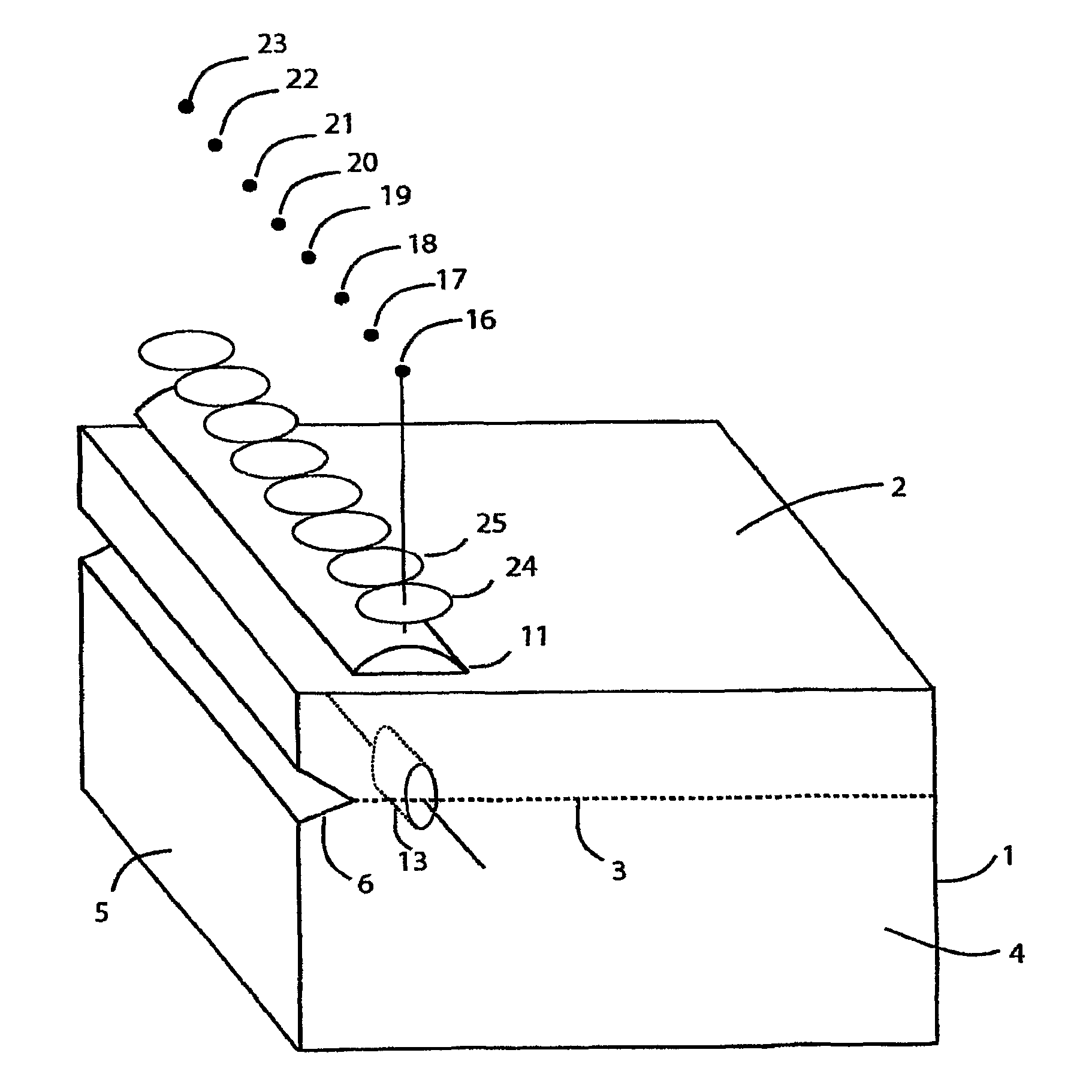
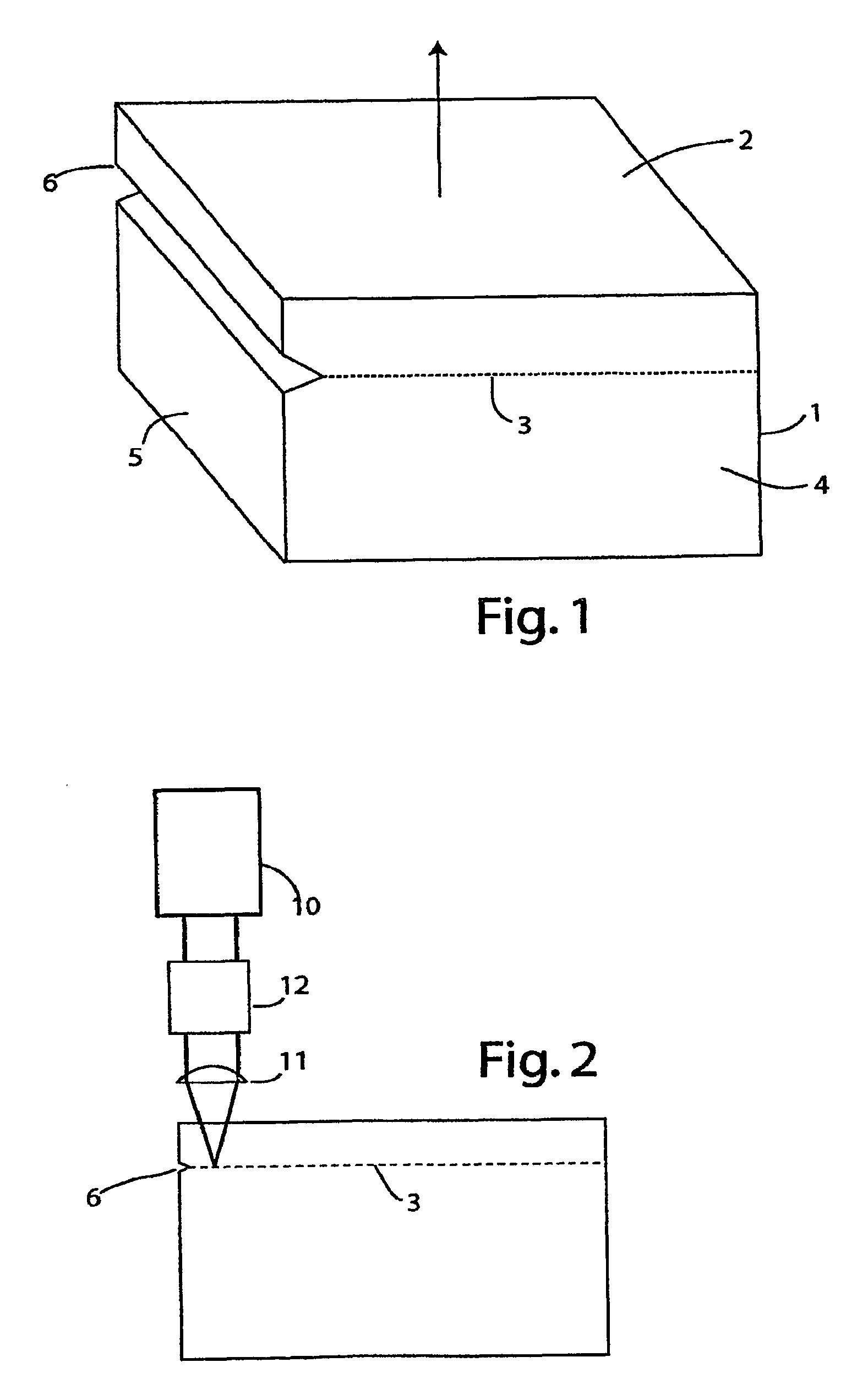
Cleaving wafers from silicon crystals
ActiveUS8835802B2Increase the areaEconomical to usePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsShortest distanceLight beam
A method of creating thin wafers of single crystal silicon wherein an ingot of single-crystal silicon with a (111) axis is flattened and polished at one end normal to the axis, and a notch with a vertex in the (111) plane is produced on a side or edge of the ingot, such that the distance between this vertex and said end is the desired thickness of a wafer to be cleaved from the ingot and such this vertex is in the desired plane of cleavage. Light of a wavelength able to penetrate into the silicon crystal without significant absorption, when the intensity of the beam is low, but is efficiently absorbed and converted to heat when the intensity of the beam is high, is focused to an elongated volume with an axis of elongation in the desired cleavage plane, parallel to and a short distance from said notch edge. Heating and the resulting transient local expansion of the silicon in this illuminated volume causes tensile stress at the vertex of said notch, substantially normal to the desired cleavage plane, thereby causing fracture of the crystal in the chosen cleavage plane. Movement of the illuminated volume relative to the ingot allows the fracture to propagate across the desired cleavage plane, thereby completely severing the wafer from the rest of the ingot.
Owner:BAER
Method for producing a high resolution detector array
InactiveUS20050016950A1The preparation method is simple and easyOptical articlesMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionDetector array
A method for producing a high resolution detector array so as to provide very high packing fraction, i.e., the distance between scintillator elements is minimized so the detector efficiency will be higher than is currently achievable. In the preferred embodiment of the present invention, the fabrication methodology is enhanced by handling LSO bars rather than single crystals when gluing on the Lumirror® as well as etching the LSO. Namely, an LSO boule is cut into wide bars of a selected dimension, for example 30 mm, which are then acid etched or mechanically polished. A selected number, N, of these LSO bars can then be glued together with Lumirror® sheets between each bar (coating the LSO disks and Lumirror® sheets with Epotek 301-2). The glued bar block is then cut again into bars in a perpendicular direction, and these new LSO-Lumirror® bars are etched. Finally, a selected number, M, of these LSO-Lumirror® bars are glued together with Lumirror® sheets between each bar; thus creating an etched N×M LSO-Lumirror® array, (where M may or may not be equal to N), without having to handle individual LSO crystals or small Lumirror® pieces.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
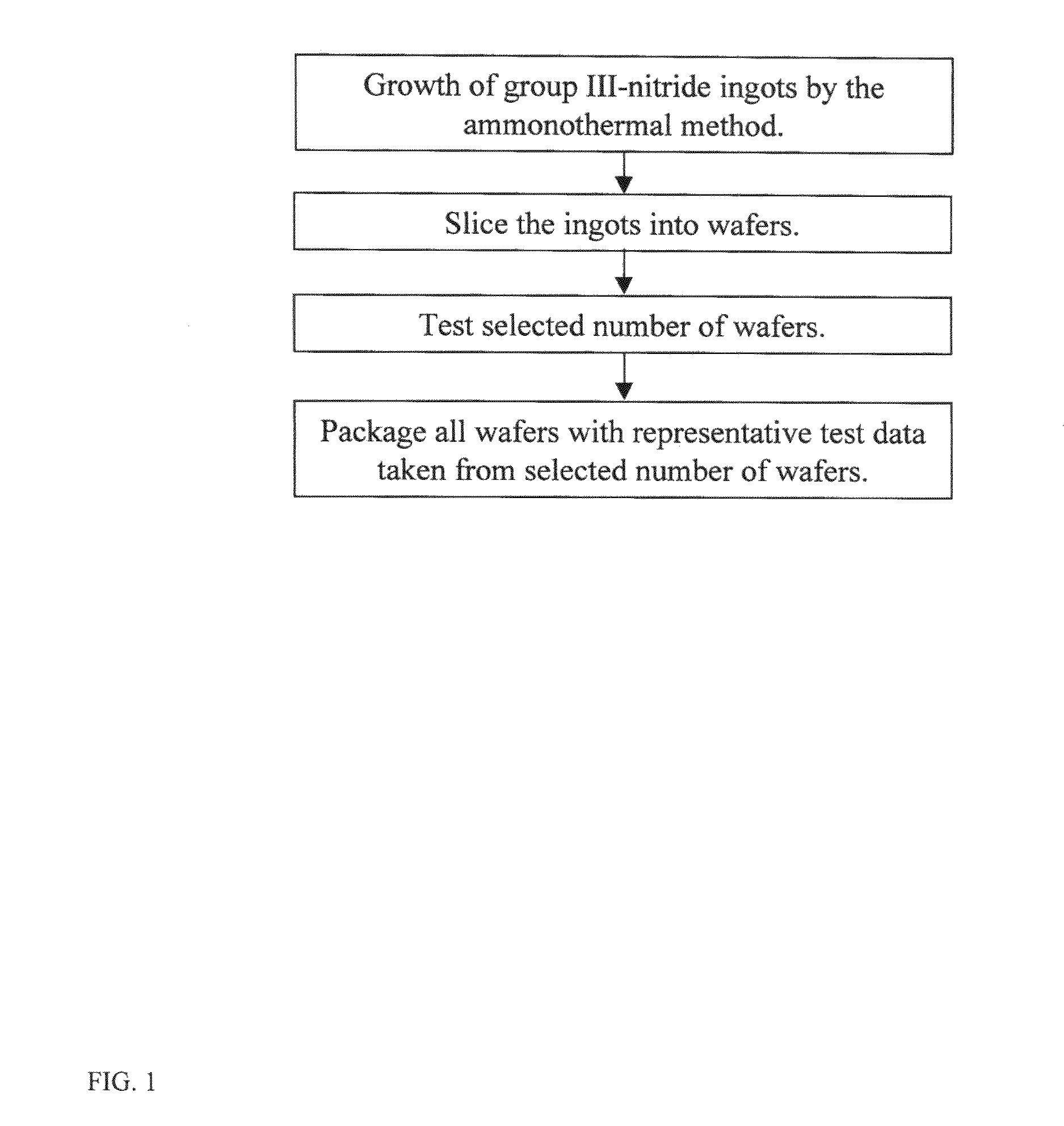
Method for testing group III-nitride wafers and group III-nitride wafers with test data
ActiveUS20090315151A1Low costReduce laborPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsWaferingQuality control
The present invention discloses a new testing method of group III-nitride wafers. By utilizing the ammonothermal method, GaN or other Group III-nitride wafers can be obtained by slicing the bulk GaN ingots. Since these wafers originate from the same ingot, these wafers have similar properties / qualities. Therefore, properties of wafers sliced from an ingot can be estimated from measurement data obtained from selected number of wafers sliced from the same ingot or an ingot before slicing. These estimated properties can be used for product certificate of untested wafers. This scheme can reduce a significant amount of time, labor and cost related to quality control.
Owner:SIXPOINT MATERIALS
Method for manufacturing silicon carbide substrate
InactiveUS20120325196A1InhibitionOccurrence is suppressedPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsCarbideSingle crystal
A method for manufacturing a silicon carbide substrate includes the steps of preparing an ingot of single crystal silicon carbide, obtaining a silicon carbide substrate by cutting the ingot, and forming a chamfer portion in a region including an outer peripheral surface of the silicon carbide substrate. In the step of obtaining the silicon carbide substrate, the ingot is cut such that a main surface of the silicon carbide substrate forms an angle of not less than 10° with respect to a {0001} plane.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
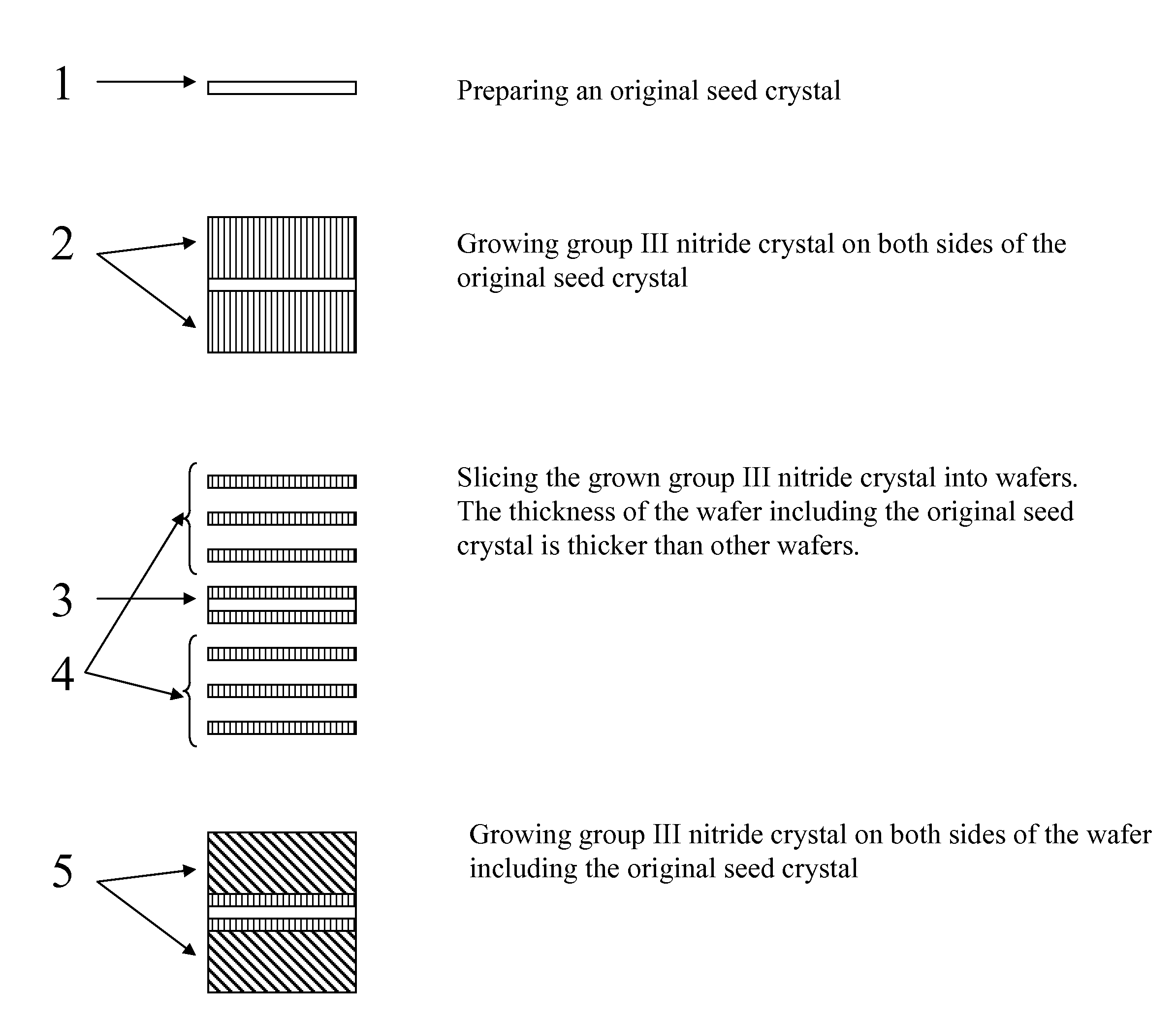
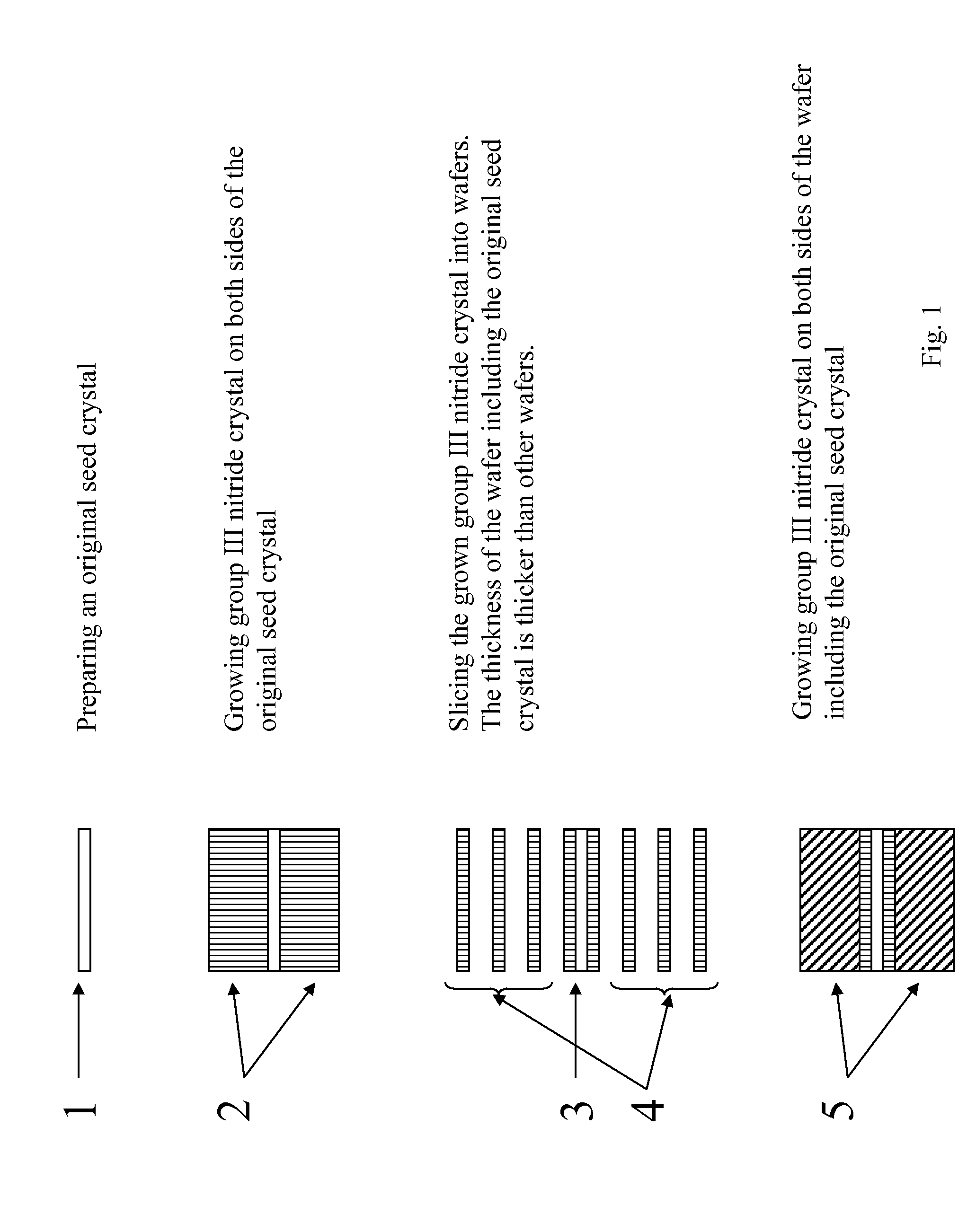
Method of growing group iii nitride crystals
ActiveUS20140087113A1Increase in sizeFrom normal temperature solutionsLayered productsWaferingFirst generation
The present invention provides a method of growing an ingot of group III nitride. Group III nitride crystals such as GaN are grown by the ammonothermal method on both sides of a seed to form an ingot and the ingot is sliced into wafers. The wafer including the first-generation seed is sliced thicker than the other wafers so that the wafer including the first-generation seed does not break. The wafer including the first-generation seed crystal can be used as a seed for the next ammonothermal growth.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Flow guide cylinder for monocrystal silicon growth furnace and application thereof
InactiveCN105239150AIncrease growth rateReduce oxygen contentPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltInsulation layerCarbon felt
The invention provides a flow guide cylinder for a monocrystal silicon growth furnace, which includes a tapered flow guide inner cylinder and a tapered flow guide outer cylinder, a heat preservation layer filled with heat preservation carbon felt is disposed therebetween. A heat insulation layer made from metal molybdenum or tungsten is disposed between the outer cylinder and the heat preservation layer. The tapered inner cylinder is used for absorbing radiation heat from a crystal ingot and then cooling the crystal ingot by means of gas rectifying to increase axial temperature gradient of the crystal ingot. Meanwhile, by means of the flow guide cylinder to rectify the gas, the flow speed of the gas is increased to reduce the partial pressure of SiO at liquid level of the melt, thereby reducing oxygen content in the melt. The flow guide cylinder can improve the quality of the crystal ingot, can accelerate growth of the crystal and can reduce production cost. The invention also provides an application method of eliminating polycrystal particles in quartz crucible walls by means of the flow guide cylinder.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED SILICON TECH CO LTD
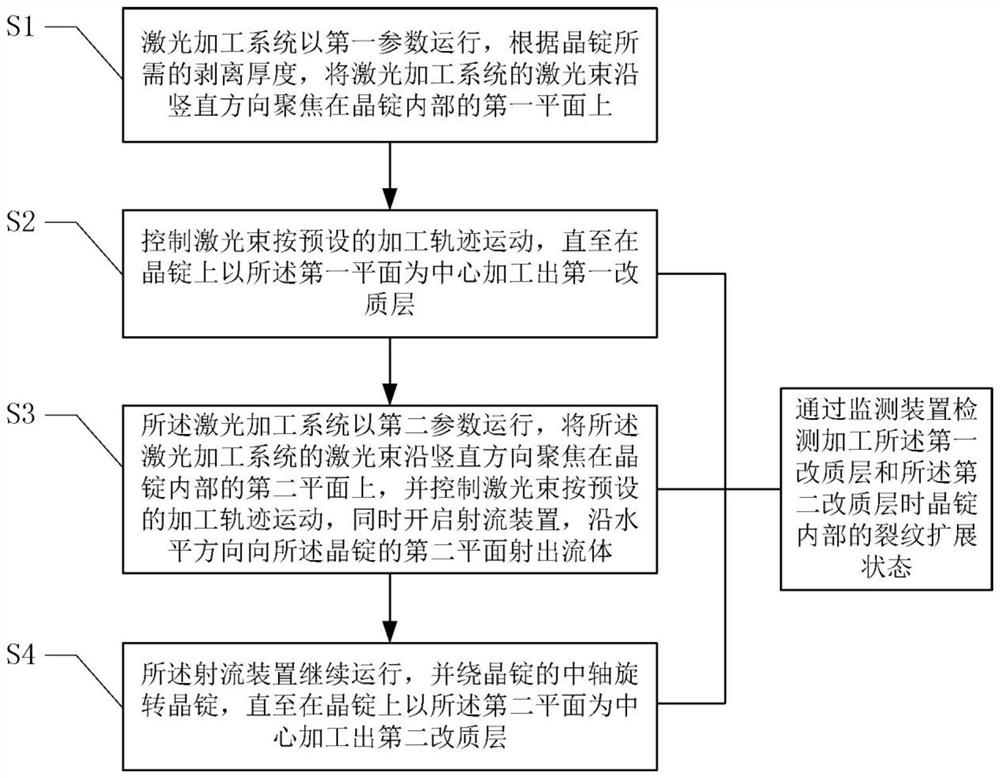
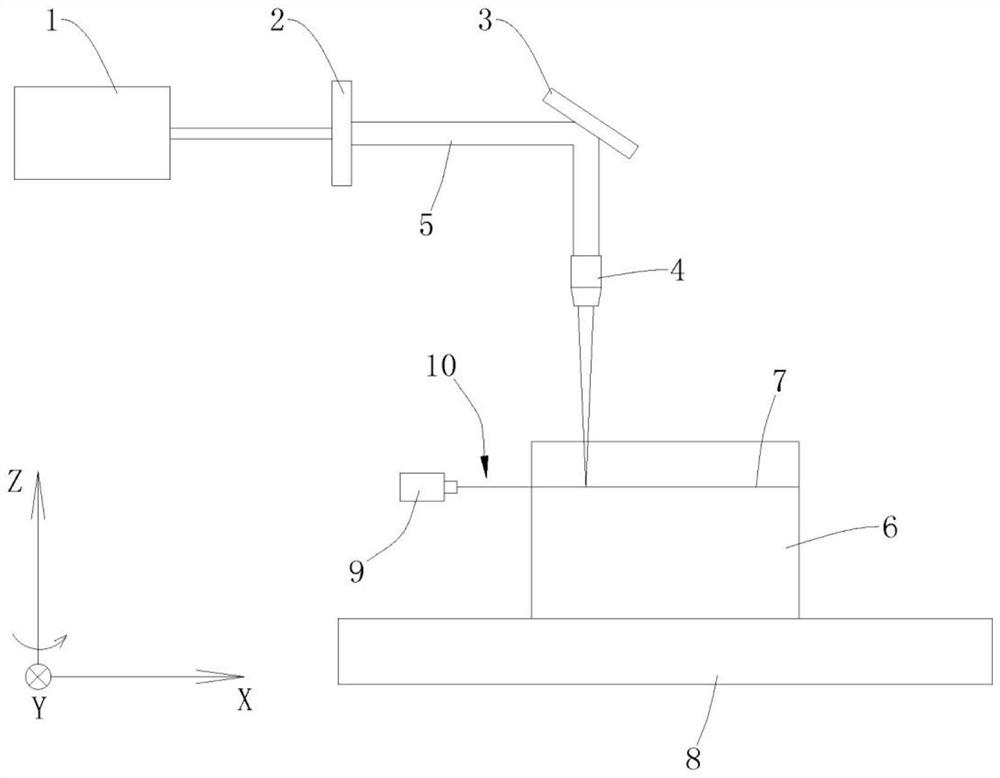
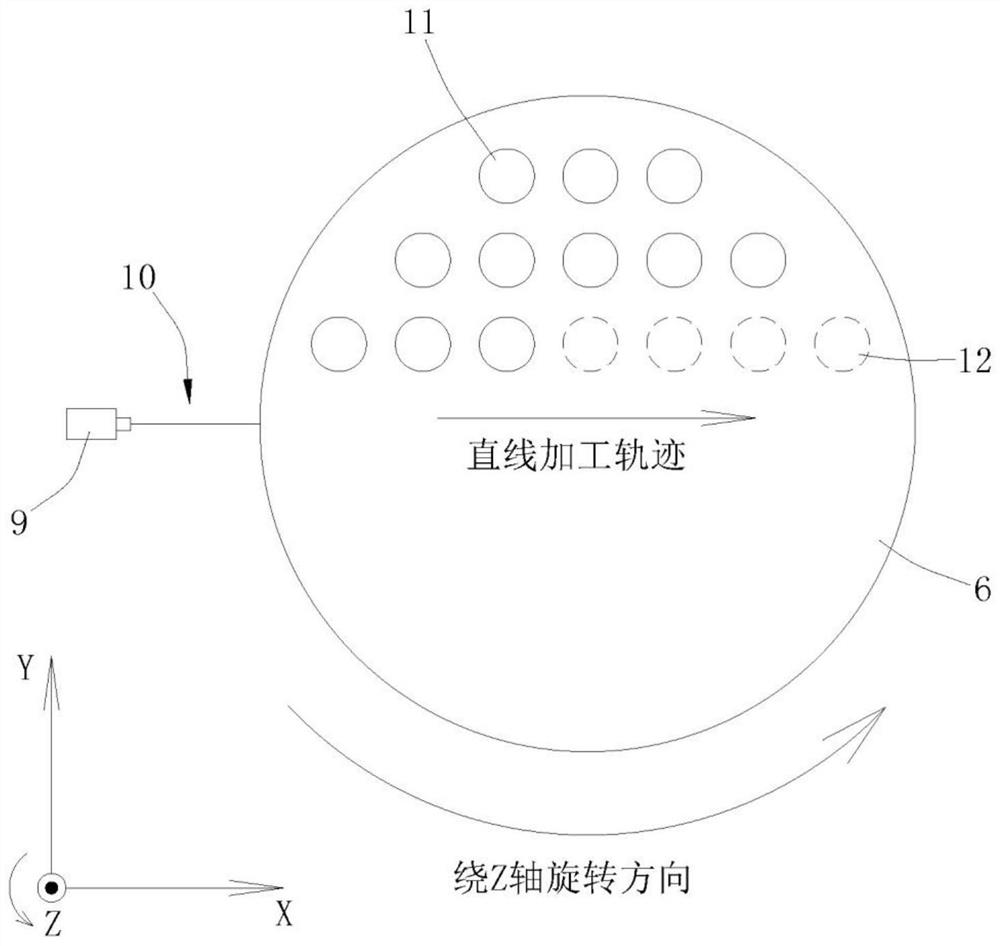
Jet-assisted multi-pulse-width laser peeling method for crystal ingot
InactiveCN111889895AImprove processing efficiencyContinuous processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingMachining system
The invention discloses a jet-assisted multi-pulse-width laser peeling method for a crystal ingot. The jet-assisted multi-pulse-width laser peeling method for the crystal ingot comprises the followingsteps: a laser machining system runs according to a first parameter, and a laser beam of the laser machining system is focused onto a first plane in a crystal ingot in the vertical direction; the laser beam is controlled to move according to a preset processing track until a first modified layer is machined on the crystal ingot by taking the first plane as a center; the laser machining system runs according to a second parameter, and the laser beam of the laser machining system is focused onto a second plane in the crystal ingot in the vertical direction, the laser beam is controlled to moveaccording to a preset processing track, a jet device is started simultaneously, and a fluid is jetted to the second plane of the crystal ingot in the horizontal direction; and the jet device continuesto run, and the crystal ingot is rotated around the central axis of the crystal ingot until a second modified layer is machined on the crystal ingot by taking the second plane as a center. The jet-assisted multi-pulse-width laser peeling method for the crystal ingot mainly solves the problem of dispersion of a crystal ingot peeling procedure; and the machining process is continuous, so that the machining efficiency of crystal ingot peeling is increased.
Owner:SONGSHAN LAKE MATERIALS LAB +1
2-dimensional line-defects controlled silicon ingot, wafer and epitaxial wafer, and manufacturing process and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS20090169460A1Reduce newly discovered crystal defectsHinders its propagationAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthLine defectsWafering
The present invention reports a defect that has not been reported, and discloses a defect-controlled silicon ingot, a defect-controlled wafer, and a process and apparatus for manufacturing the same. The new defect is a crystal defect generated when a screw dislocation caused by a HMCZ (Horizontal Magnetic Czochralski) method applying a strong horizontal magnetic field develops into a jogged screw dislocation and propagates to form a cross slip during thermal process wherein a crystal is cooled. The present invention changes the shape and structure of an upper heat shield structure arranged between a heater and an ingot above a silicon melt, and controls initial conditions or operation conditions of a silicon single crystalline ingot growth process to reduce a screw dislocation caused by a strong horizontal magnetic field and prevent the screw dislocation from propagating into a cross slip.
Owner:LG SILTRON
Polycrystalline silicon material screening and crucible filling method
ActiveCN105887192ASave operating timeIncrease productivitySievingPolycrystalline material growthIngotCrystal growth
The invention provides a polycrystalline silicon material screening and crucible filling method. The method is characterized in that a vibration screen is utilized for carrying out multi-layer screening on a polycrystalline silicon material, the screened-out polycrystalline silicon material is directly added into a quartz crucible according to specifications and dimensions, in-situ quartz crucible filling is achieved, operation time is shortened, working efficiency is improved, the dimension range of the polycrystalline silicon material can be precisely controlled, the crucible filling density is improved, influences caused by gas and pinholes on crystal ingot quality in the crystal growth process are reduced, and crystal ingot quality is improved; in addition, the problem that crystal ingot quality is affected by pollution caused by hand charging can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED SILICON TECH CO LTD
Mini lamp bead, manufacturing method, backlight source and display equipment
The invention discloses a mini lamp bead, a manufacturing method, a backlight source and display equipment, and relates to the technical field of display. The mini lamp bead comprises a light-emittingsource and a micro lens covering the light-emitting source. The micro lens is provided with a first light-emitting surface for realizing upward transmission of light and a second light-emitting surface for realizing lateral transmission of light. The backlight source comprises a substrate, and mini lamp beads are arranged on the substrate in an array mode. The display equipment comprises the backlight source. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of manufacturing a crystal ingot; cutting the crystal ingot into a wafer; generating an epitaxial layer on the wafer; manufacturing an electrode on the epitaxial layer to form an LED chip; and a base and a micro lens are additionally arranged on the LED chip. Lateral light emitting of the mini lamp beads can be achieved, the density of themini lamp beads on the backlight source is reduced, and then cost and power consumption are reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN SKYWORTH RGB ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Graphite crucible device for silicon carbide crystal growth and single crystal growth method thereof
InactiveCN111411395AReduce temperature gradientReduce stressPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsCarbon filmCarbide silicon
The invention discloses a graphite crucible device for silicon carbide crystal growth and a silicon carbide single crystal growth method thereof. The structure of the graphite crucible cover is changed, the graphite crucible cover is changed into a two-section type structure, furthermore, a seed crystal fixing mode is changed into a mechanical fixing mode from a traditional gluing mode; a carbon film is plated on the back of the seed crystal; the two-section type graphite crucible cover is screwed and fixed; a heat preservation graphite felt can be placed between the seed crystal and the upperlayer of the graphite crucible cover according to the thickness difference; high-purity silicon carbide powder is put into the graphite crucible; the sealed graphite crucible is put into a crystal growth furnace; a silicon carbide crystal is grown by adopting a physical vapor transport method; wherein the crystal growth temperature is 1950-2550 DEG C, the substrate temperature is 2200 DEG C or below, the raw material temperature is larger than 2350 DEG C, inert gas serves as carrier gas, the air pressure in the reaction chamber is 1-5 kPa, the growth time is 70 hours or longer, and the low-stress silicon carbide crystal ingot can be obtained.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
SiC single crystal growth device and liquid phase epitaxy SiC single crystal growth method
ActiveCN113322510AAvoid chippingImprove solubilityPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsArgon atmosphereSingle crystal growth
The invention relates to a SiC single crystal growth device and a liquid phase epitaxy SiC single crystal growth method. According to the SiC single crystal growth device, the top and the bottom of a furnace body of a high-temperature induction heating furnace are correspondingly and coaxially provided with a seed crystal shaft and a rotating shaft which can rotate oppositely and reversely, and the first end of the rotating shaft is fixed to the bottom of a graphite crucible; a first non-carbon crucible is arranged in the graphite crucible, and a second non-carbon crucible is fixed at the first end of the seed crystal shaft; a SiC crystal ingot and Fe powder serving as a cosolvent are respectively accommodated in the first non-carbon crucible from bottom to top; SiC seed crystals are accommodated in the second non-carbon crucible; the temperature of the high-temperature induction heating furnace is raised, argon is loaded when the temperature is raised to 800-1000 DEG C, and then SiC grows in the argon atmosphere of 1500-1700 DEG C; and along with the rise of the temperature, the crystal ingot SiC is dissolved in the molten Fe solvent to form a Fe solution, and then the Fe solution is transmitted to the SiC seed crystal. According to the SiC single crystal growth device provided by the invention, the growth structure and the thermal field distribution can be improved, and the problems of crystal position dislocation and crucible fragmentation are avoided.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
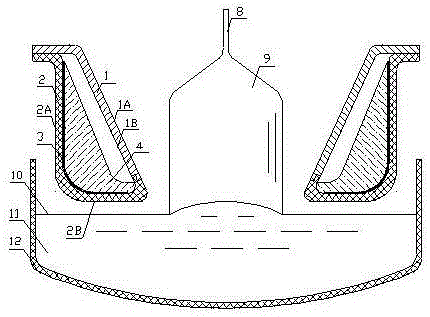
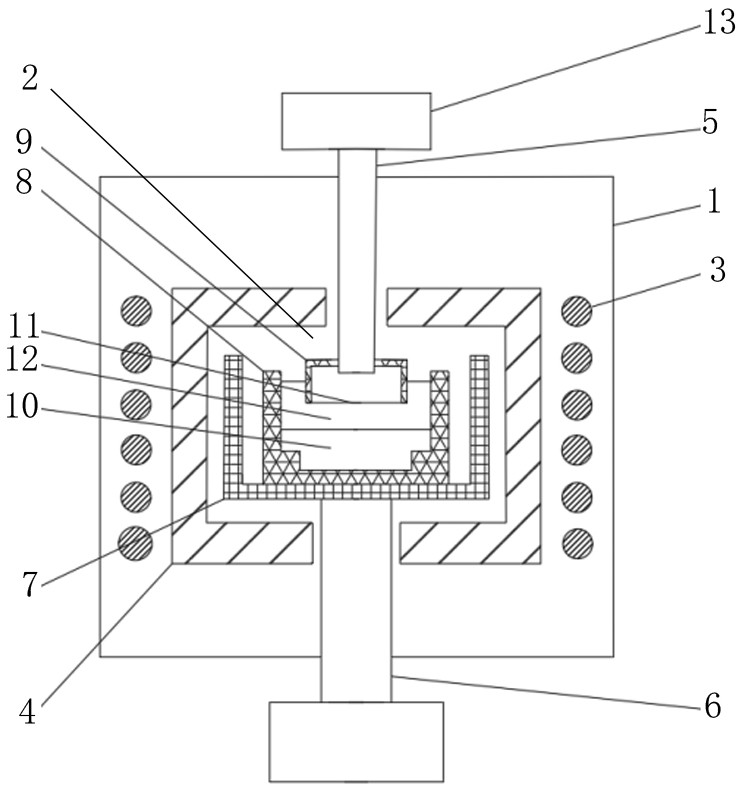
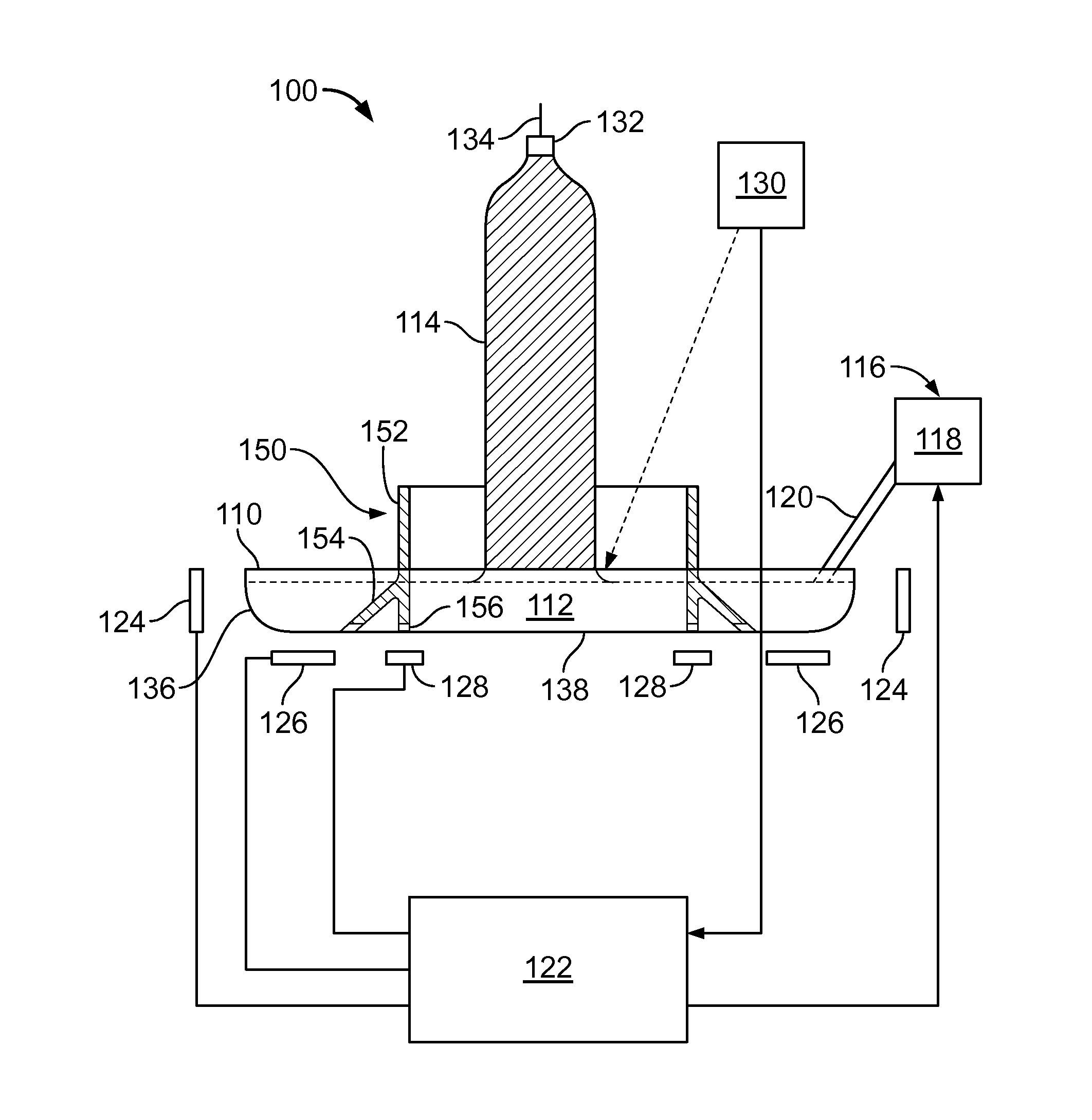
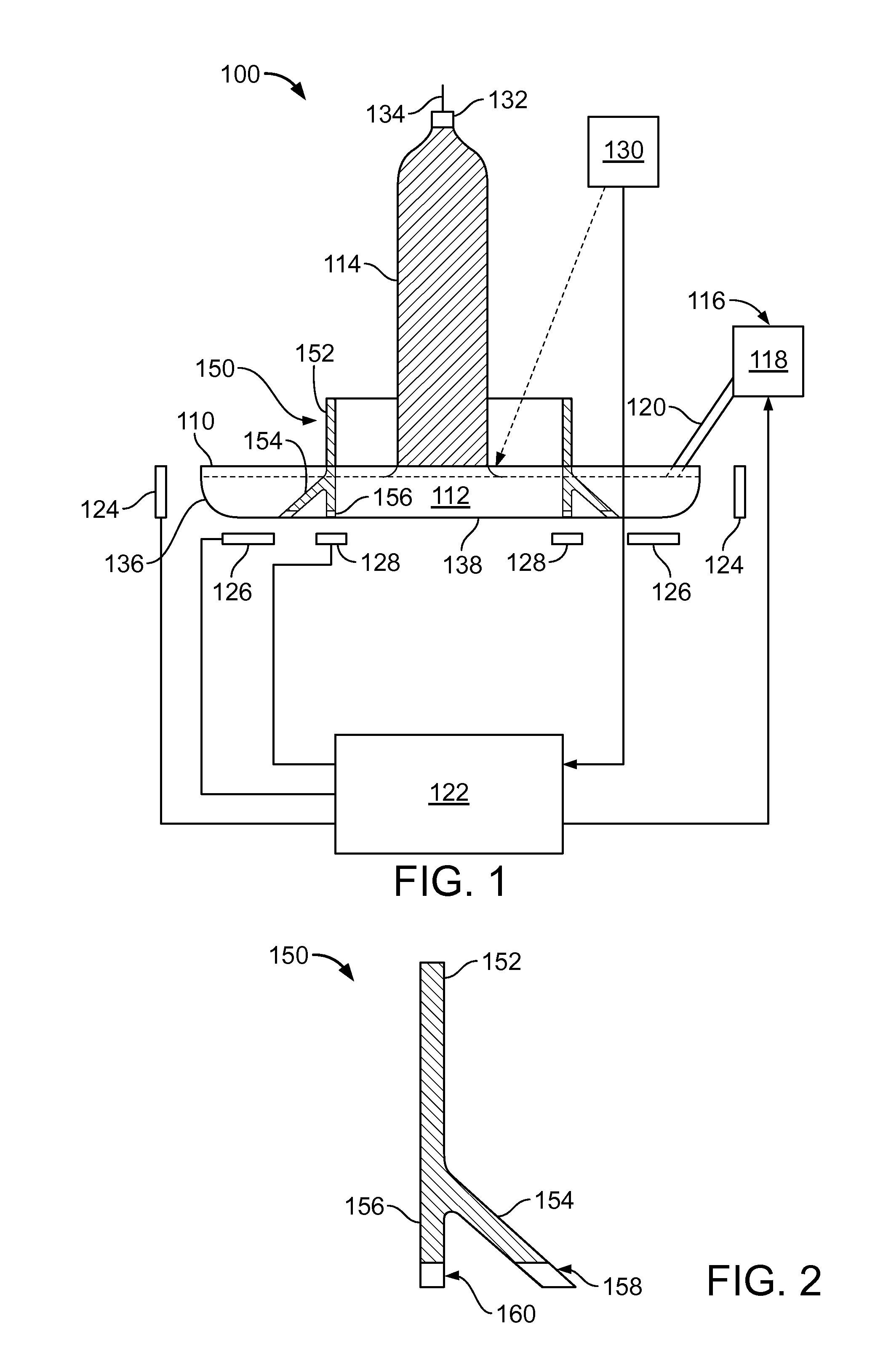
Weir for inhibiting melt flow in a crucible
A system for growing a crystal ingot includes a crucible and a weir. The crucible has a base and a sidewall for the containment of a silicon melt therein. The weir is located along the base of the crucible inward from the sidewall of the crucible. The weir has a body connected with at least a pair of legs disposed to inhibit movement of the silicon melt therebetween.
Owner:CORNER STAR LTD
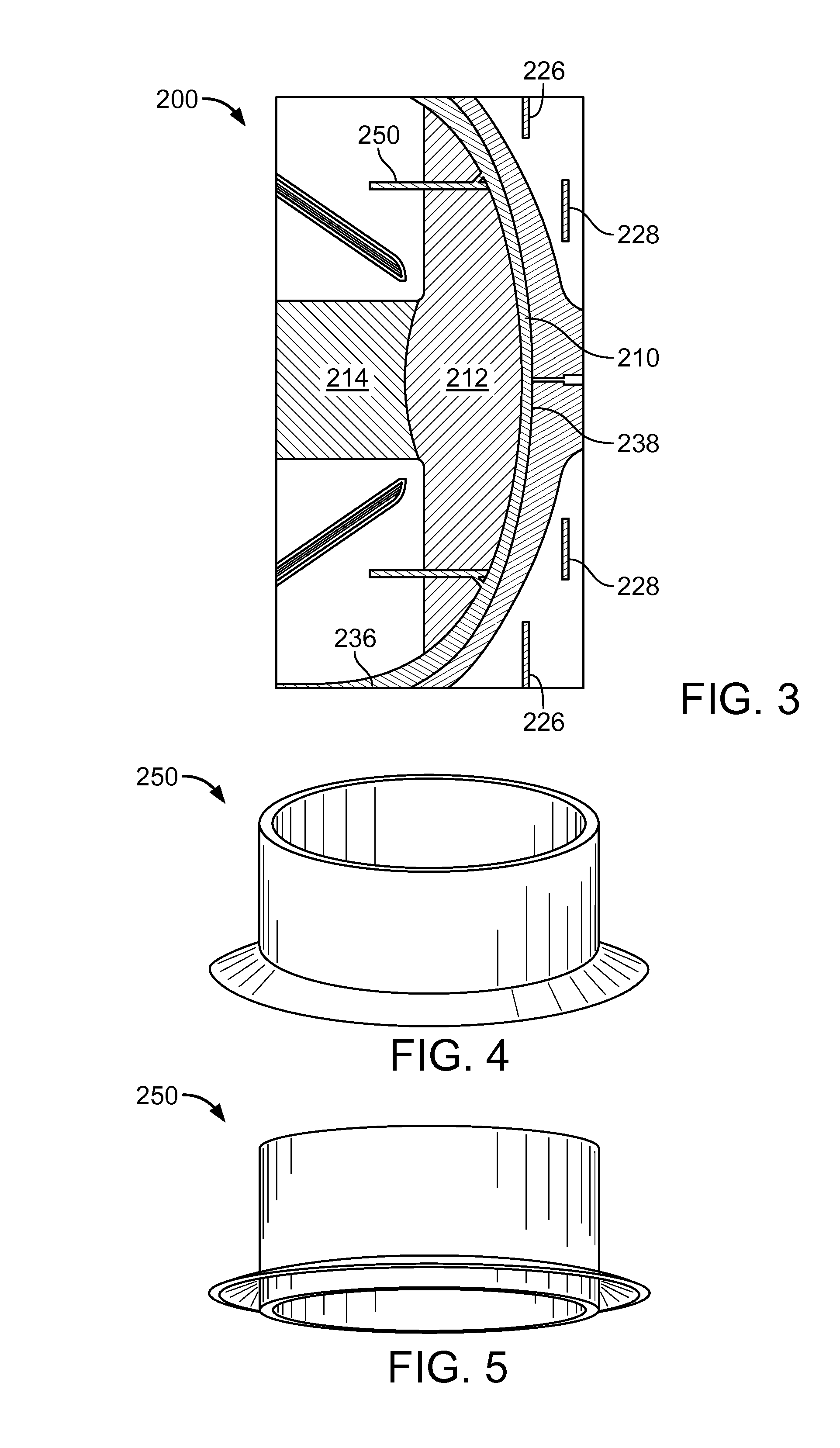
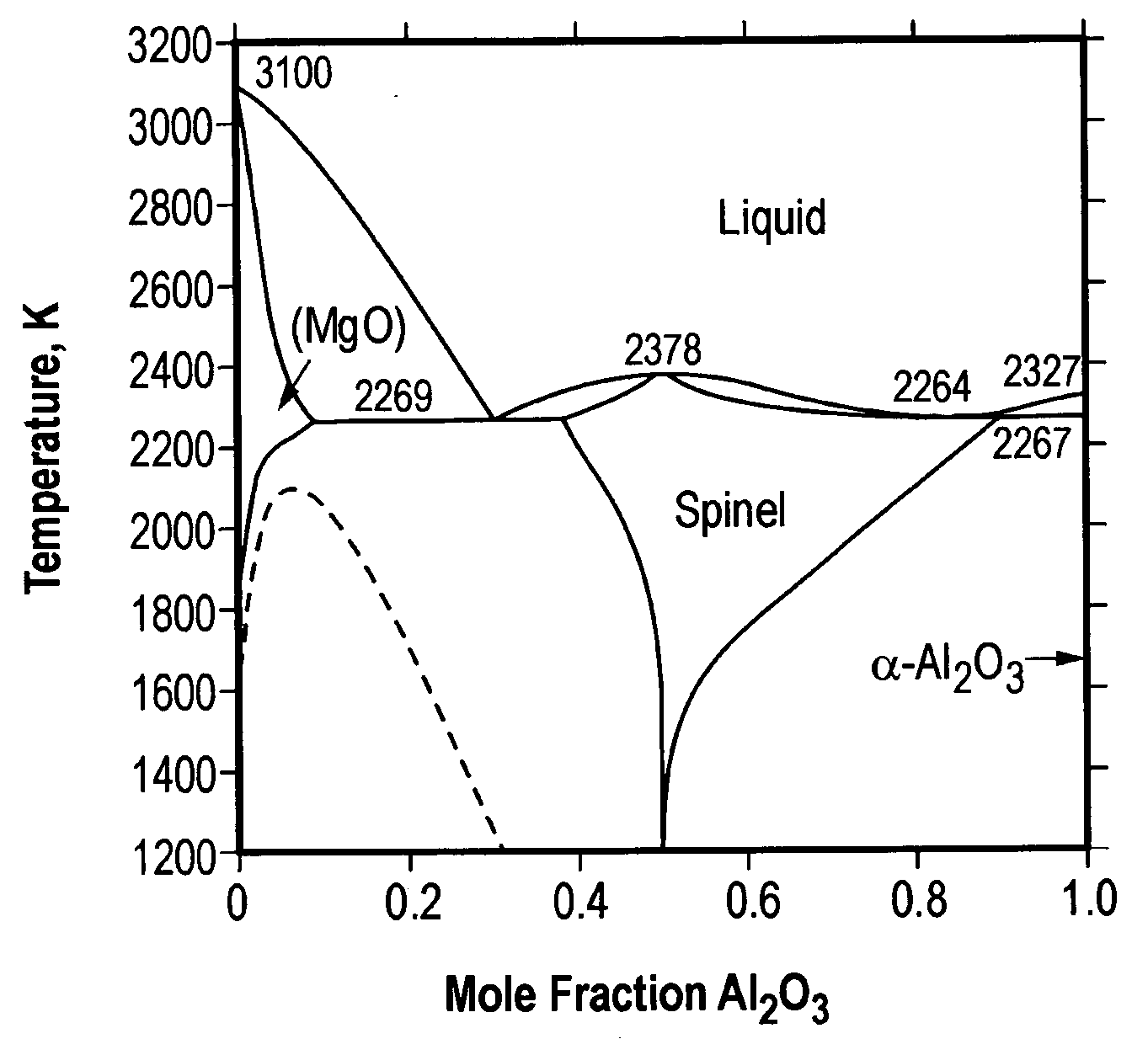
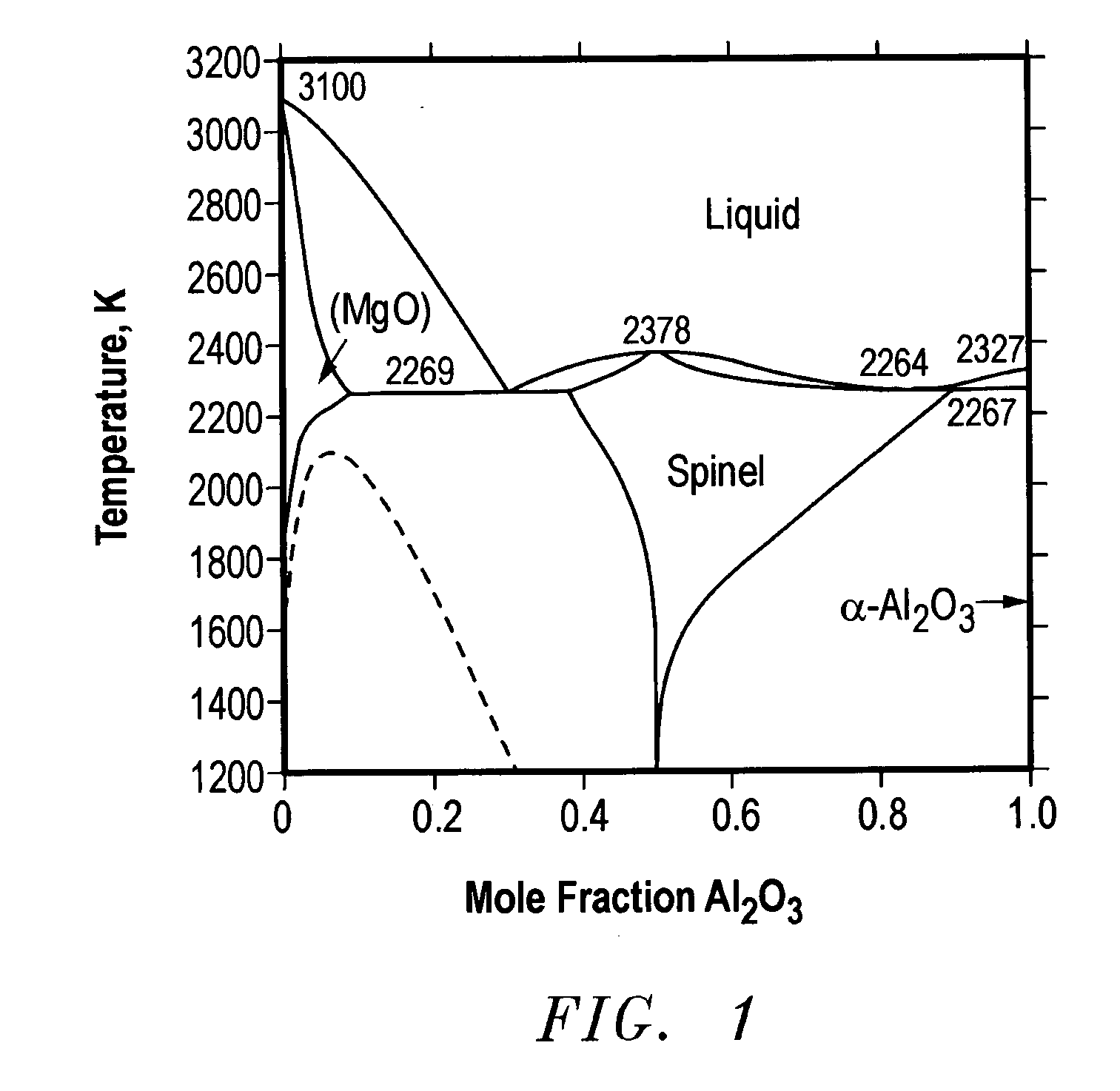
Spinel boules, wafers, and methods for fabricating same
A single crystal spinel wafer is disclosed, including a front face and a back face; and an outer periphery having first and second flats. In certain embodiments, the single crystal wafer has a specific crystallographic orientation, and the flats are provided to extend along desired plane sets. The flats may advantageously identify orientation of cleavage planes, and direction of cleavage of cleavage planes.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CERAMICS & PLASTICS INC
Single crystal furnace having auxiliary material adding mechanism and application thereof
ActiveCN105239153AReduce the magnitude of axial resistivity fluctuationsImprove uniformityBy pulling from meltMetallurgyPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a single crystal furnace having an auxiliary material adding mechanism and an application thereof. The auxiliary material adding mechanism is installed in the single crystal silicon growth furnace and is provided with an individual weighing device, so that the addition amount of auxiliary materials can be monitored and controlled in real time during auxiliary material addition, thereby achieving accurate control of doping concentration of the single crystal silicon. The single crystal furnace can stabilize axial resistivity of the single crystal silicon and can satisfy crystal ingot growth of the single crystal furnace with special doping requirement.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED SILICON TECH CO LTD
Spinel articles and methods for forming same
InactiveUS20050061230A1Reduce mechanical stressHigh yield ratePolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateSpinelSingle crystal
Single crystal spinel boules, wafers, substrates and active devices including same are disclosed. In one embodiment, such articles have reduced mechanical stress and / or strain represented by improved yield rates.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CERAMICS & PLASTICS INC
Silicon wafer slicing device using wire discharge machining
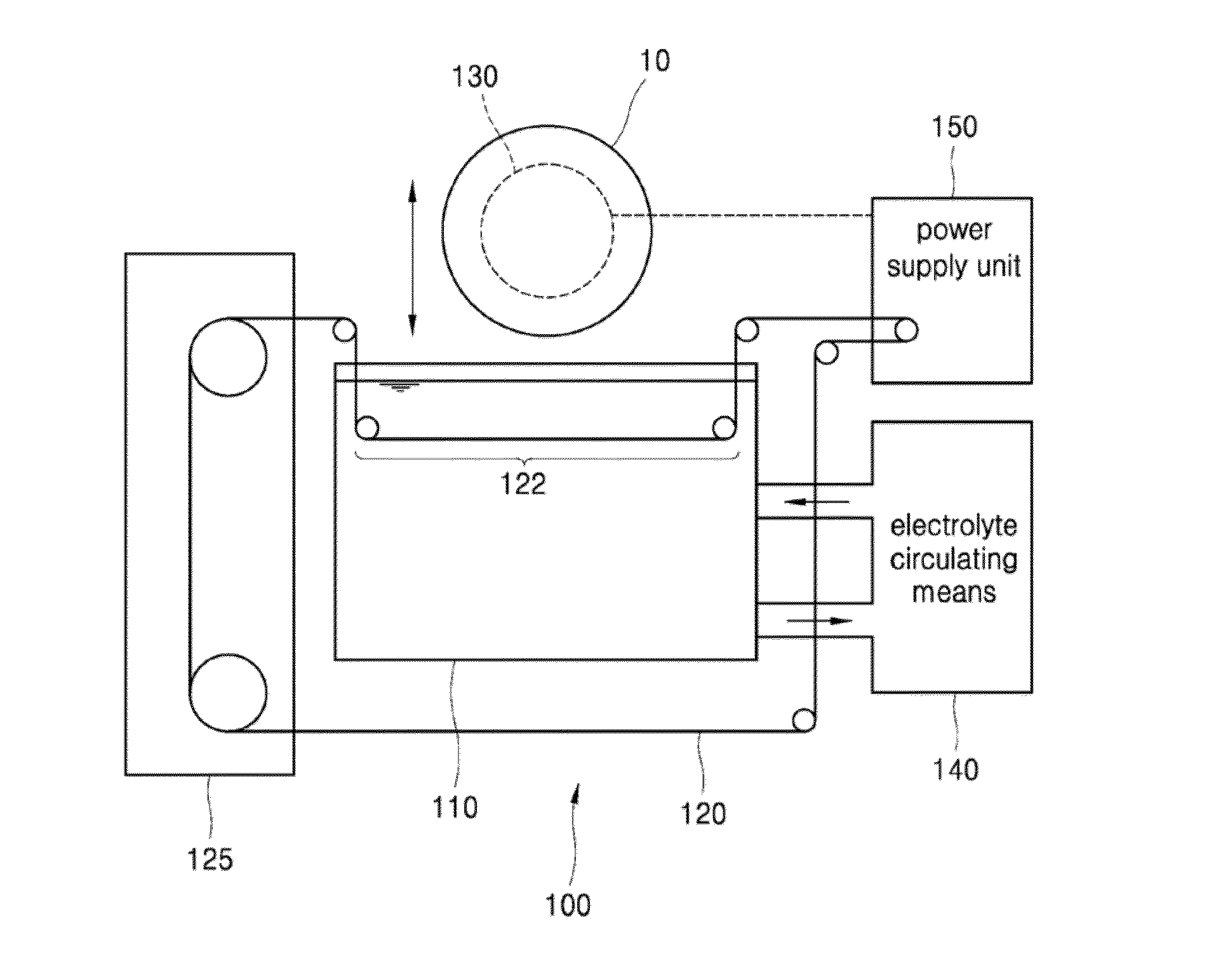
ActiveUS20160016243A1Improve surface roughnessIncrease volumeElectrolysis componentsElectrical-based machining electrodesWaferingWafer dicing
Disclosed is a wafer slicing apparatus which cuts a silicon ingot to fabricate a silicon wafer, and more specifically, a silicon wafer slicing apparatus cutting the silicon ingot using wire discharge machining is disclosed. The present invention provides a silicon wafer slicing apparatus using wire discharge machining comprising: a water tank which contains an electrolyte; a cutting wire which has a cutting section dipped into the water tank and is transferred by a wire driving means; an ingot transferring unit which includes an electrode on which a silicon ingot, an object to be cut, is fixed, and moves the silicon ingot up and down within the cutting section of the cutting wire; an electrolyte circulating means which circulates and refines the electrolyte stored in the water tank; and a power supply unit which supplies a source voltage to the electrode of the ingot transferring unit and the cutting wire.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
Production of mono-crystalline silicon
InactiveUS20150203986A1Easy alignmentAvoid misalignmentBy pulling from meltFrom melt solutionsCrucibleCrystal structure
A crystalline silicon ingot is produced using a directional solidification process. In particular, a crucible is loaded with silicon feedstock above a seed layer of uniform crystalline orientation. The silicon feedstock and an upper part of the seed layer are melted forming molten material in the crucible. This molten material is then solidified, during which process a crystalline structure based on that of the seed layer is formed in a silicon ingot. The seed layer is arranged such that a {110} crystallographic plane is normal to the direction of solidification. It is found that offers a substantial improvement in the proportion of mono-crystalline silicon formed in the ingot as compared to alternative crystallographic orientations and leads to highly uniform solar cells after an isotropic texture.
Owner:REC SOLAR
Guided diameter SiC sublimation growth with multi-layer growth guide
ActiveUS8313720B2Improve thermal conductivityLow thermal conductivityAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthCrucibleSource material
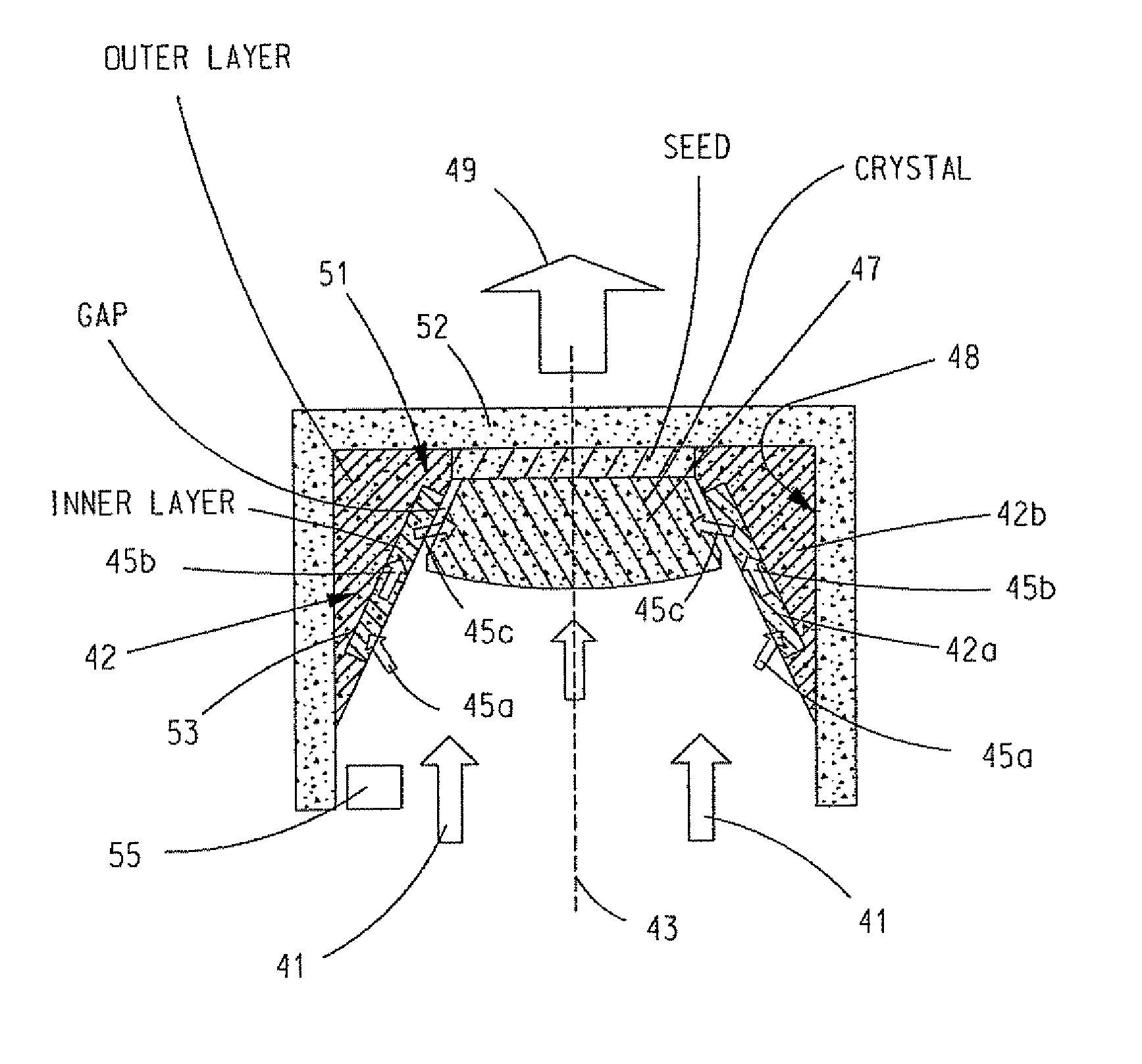
In the growth of a SiC boule, a growth guide is provided inside of a growth crucible that is charged with SiC source material at a bottom of the crucible and a SiC seed crystal at a top of the crucible. The growth guide has an inner layer that defines at least part of an opening in the growth guide and an outer layer that supports the inner layer in the crucible. The opening faces the source material with the seed crystal positioned at an end of the opening opposite the source material. The inner layer is formed from a first material having a higher thermal conductivity than the second, different material forming the outer layer. The source material is sublimation grown on the seed crystal in the growth crucible via the opening in the growth guide to thereby form the SiC boule on the seed crystal.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Laser wafer lift-off device and laser wafer lift-off method
The invention provides a laser wafer lift-off device and a laser wafer lift-off method, and relates to the field of semiconductor machining. The laser wafer lift-off device comprises an installing platform for installing a crystal ingot, a laser transmitter, a condensing lens assembly, a magnet for providing a magnetic field and a control system. The laser transmitter and the condensing lens assembly are matched to focus laser beams into the crystal ingot so as to induce the crystal ingot to generate a plasma body. The crystal ingot is located in the magnetic field so that the magnetic field can control the motion state of the plasma body. The control system is connected with the magnet. The control system can obtain characteristic parameters of the plasma body in real time and control themagnetic field where the crystal ingot is located in real time according to the characteristic parameters. According to the laser wafer lift-off device and the laser wafer lift-off method, the plasmabody induced by laser is controlled through the magnetic field, the motion process of the plasma body inside the crystal ingot can be changed in real time to perform secondary machining on a modification layer, secondary machining of the machining surface of the wafer is achieved, and the wafer lift-off machining quality and efficiency from the crystal ingot are greatly improved.
Owner:SONGSHAN LAKE MATERIALS LAB +1
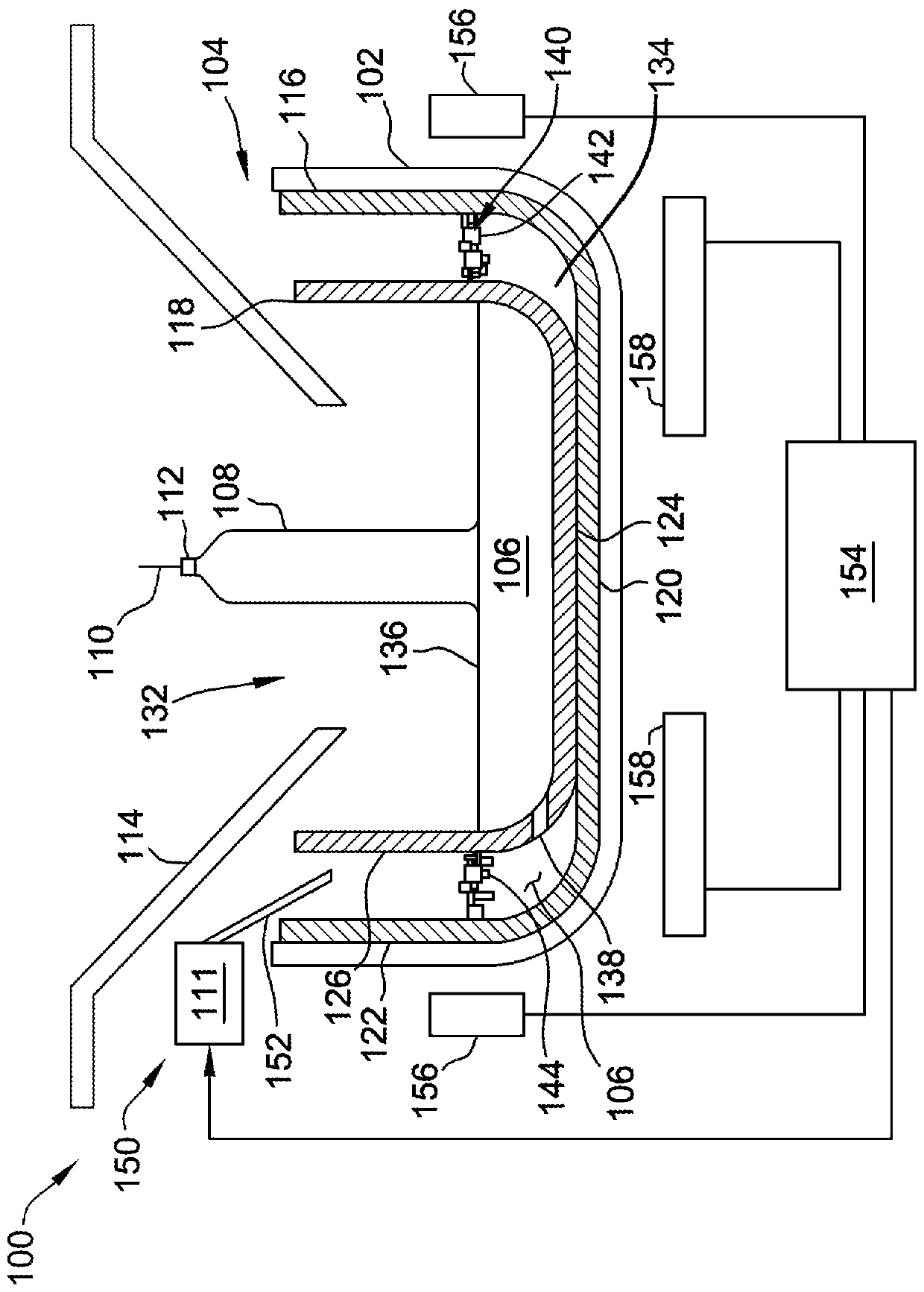
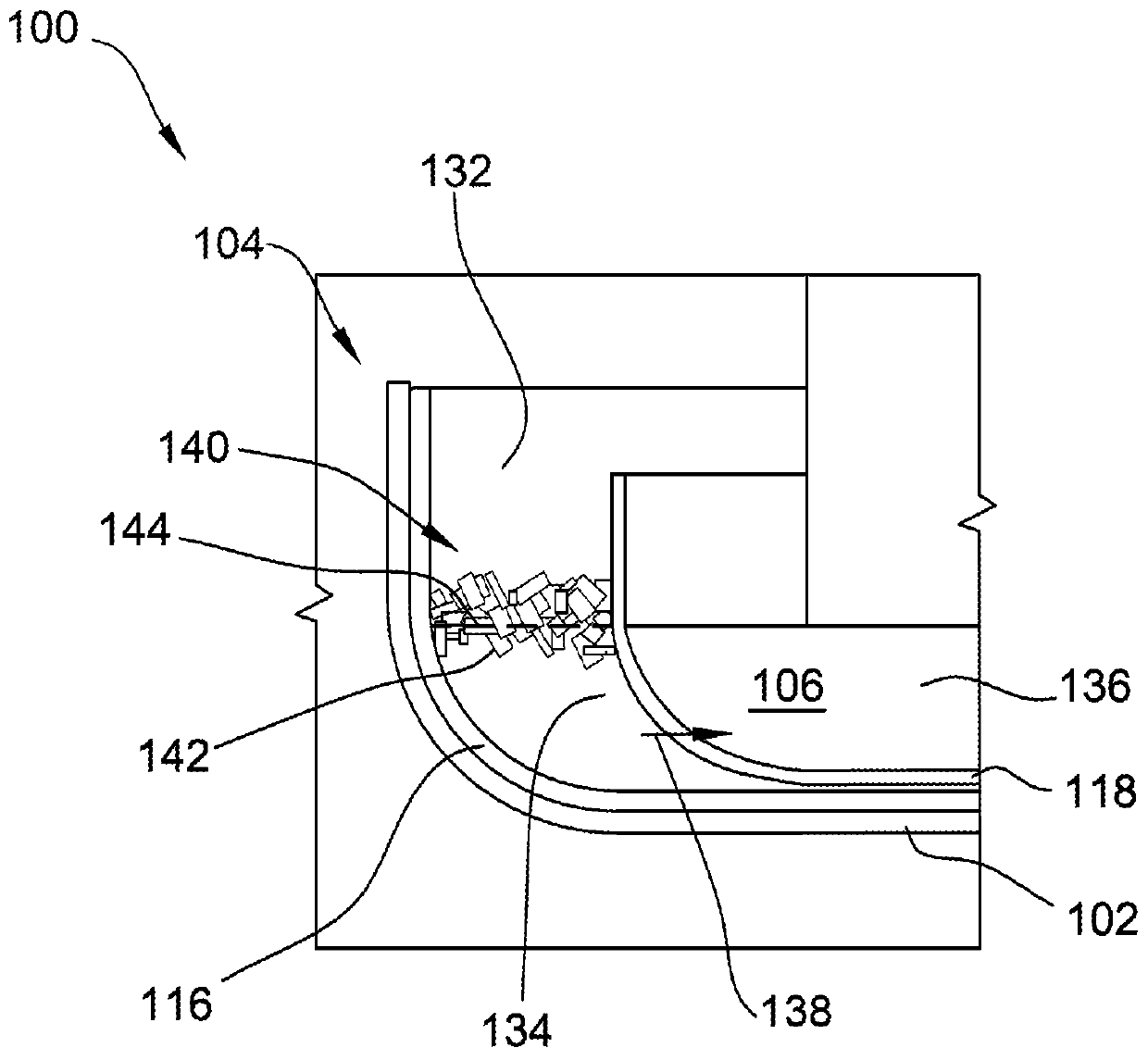
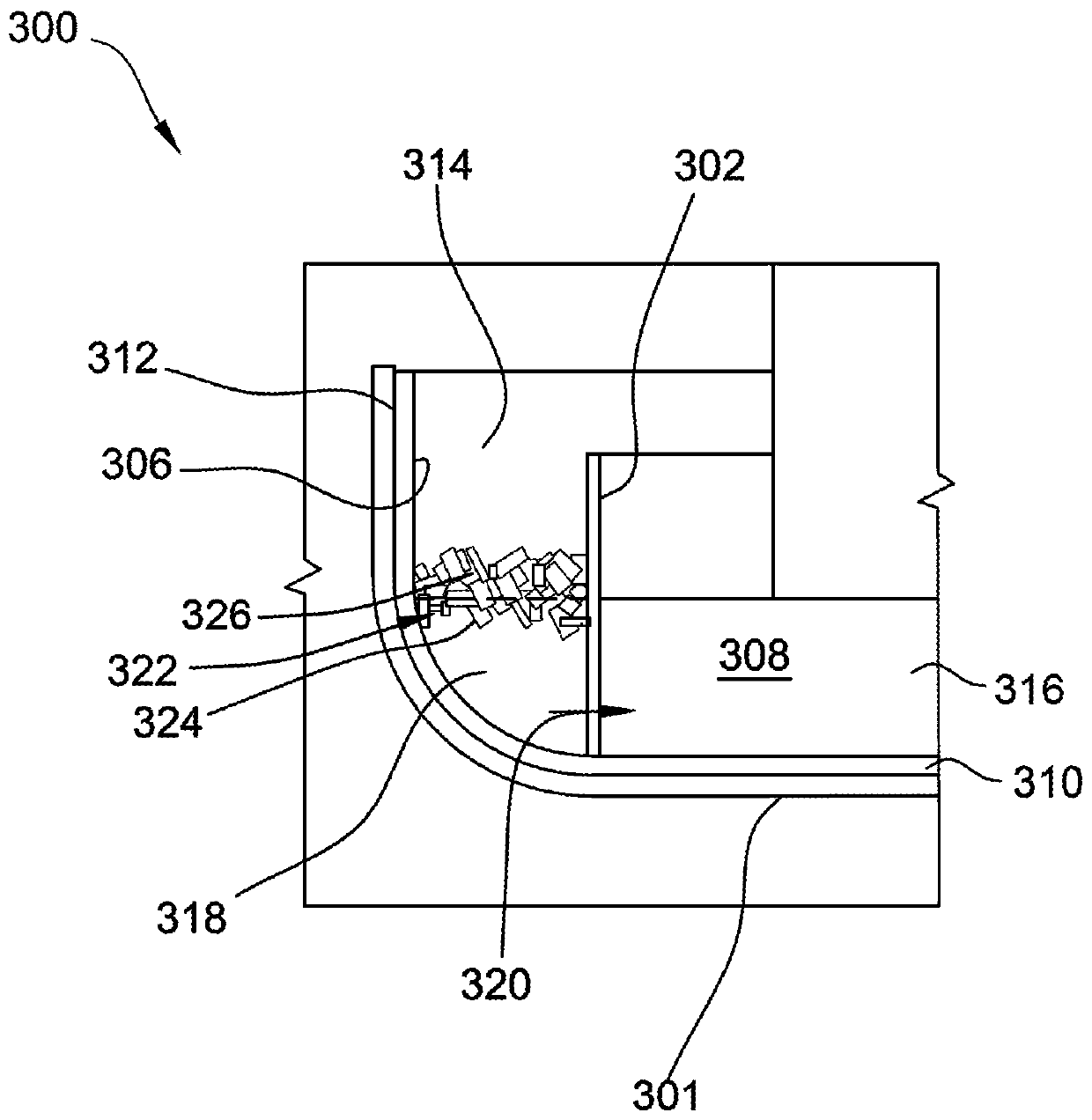
Crystal pulling system and method including crucible and barrier
A system for forming an ingot from a melt includes a first crucible defining a cavity for receiving the melt and a second crucible in the cavity. The second crucible separates an outer zone from an inner zone. The second crucible includes a passageway therethrough to allow the melt located within the outer zone to move into the inner zone. The inner zone defines a growth area for the ingot. The system also includes a barrier located within the outer zone to limit movement of the melt through the outer zone. The barrier includes members that are arranged to define a labyrinth for melt flow.
Owner:GCL NEW (SHANGHAI) PHOTOVOLTAIC TECH CO LTD
System and method of growing silicon ingots from seeds in a crucible and manufacture of seeds used therein
InactiveCN104769166AReduce manufacturing costAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthCrucibleIngot
Systems and methods that reduce the overall cost of producing a silicon ingot are provided herein. More specifically, one or more surface pieces may be sliced from a silicon boule in relation to a plurality of nodes at a particular orientation. These one or more surface pieces may then be formed into one or more seeds having a specific length, width and thickness usable in a silicon ingot growth process. By utilizing these pieces to form one or more seeds, pieces of a boule which would have been previously discarded may now be used to form high quality seeds for use in a silicon ingot grow process.
Owner:GTAT CORPORATION
Multi-crucible silicon carbide crystal synchronous growth method and equipment
ActiveCN114000198AAdjustable temperatureFast growthPolycrystalline material growthFinal product manufactureCarbide siliconInsulation layer
The invention provides a multi-crucible silicon carbide crystal synchronous growth method and equipment, the growth equipment comprises a cavity and a thermal insulation layer assembly arranged close to the inner wall of the cavity, the thermal insulation layer assembly divides the cavity into a plurality of growth cavities, and each growth cavity is internally provided with an independent growth assembly; the independent growth assembly comprises a graphite crucible, a seed crystal tray arranged at the top of the graphite crucible, a heating device arranged on the periphery of the graphite crucible and a driving assembly arranged at the bottom of the graphite crucible. According to the multi-crucible silicon carbide crystal synchronous growth equipment, a multi-section independently controlled graphite heater is adopted for heating, a traditional induction heating mode is replaced, the radial and longitudinal temperature gradients of the crucibles can be adjusted more accurately, particularly, the growth cost of the silicon carbide crystals can be greatly reduced, and the internal quality of a single crystal ingot can be ensured.
Owner:SUZHOU UKING PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Wafer producing apparatus
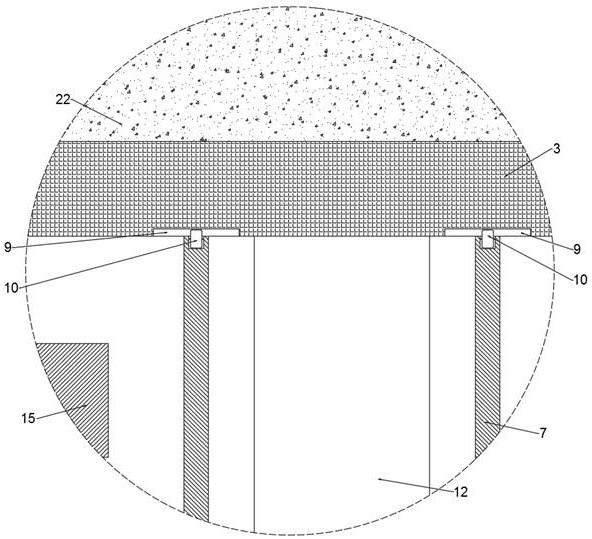
ActiveUS10840116B2Automatic productionIncrease productivityAbrasion apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingIngot
A wafer producing apparatus includes an ingot grinding unit that grinds the upper surface of an ingot to planarize the upper surface, a laser irradiation unit that positions the focal point of a laser beam with such a wavelength as to be transmitted through the ingot to a depth corresponding to the thickness of a wafer to be produced from the upper surface of the ingot and irradiates the ingot with the laser beam to form a separation layer, a wafer separating unit that separates the wafer from the ingot, and a tray having a support part that supports the separated wafer.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com