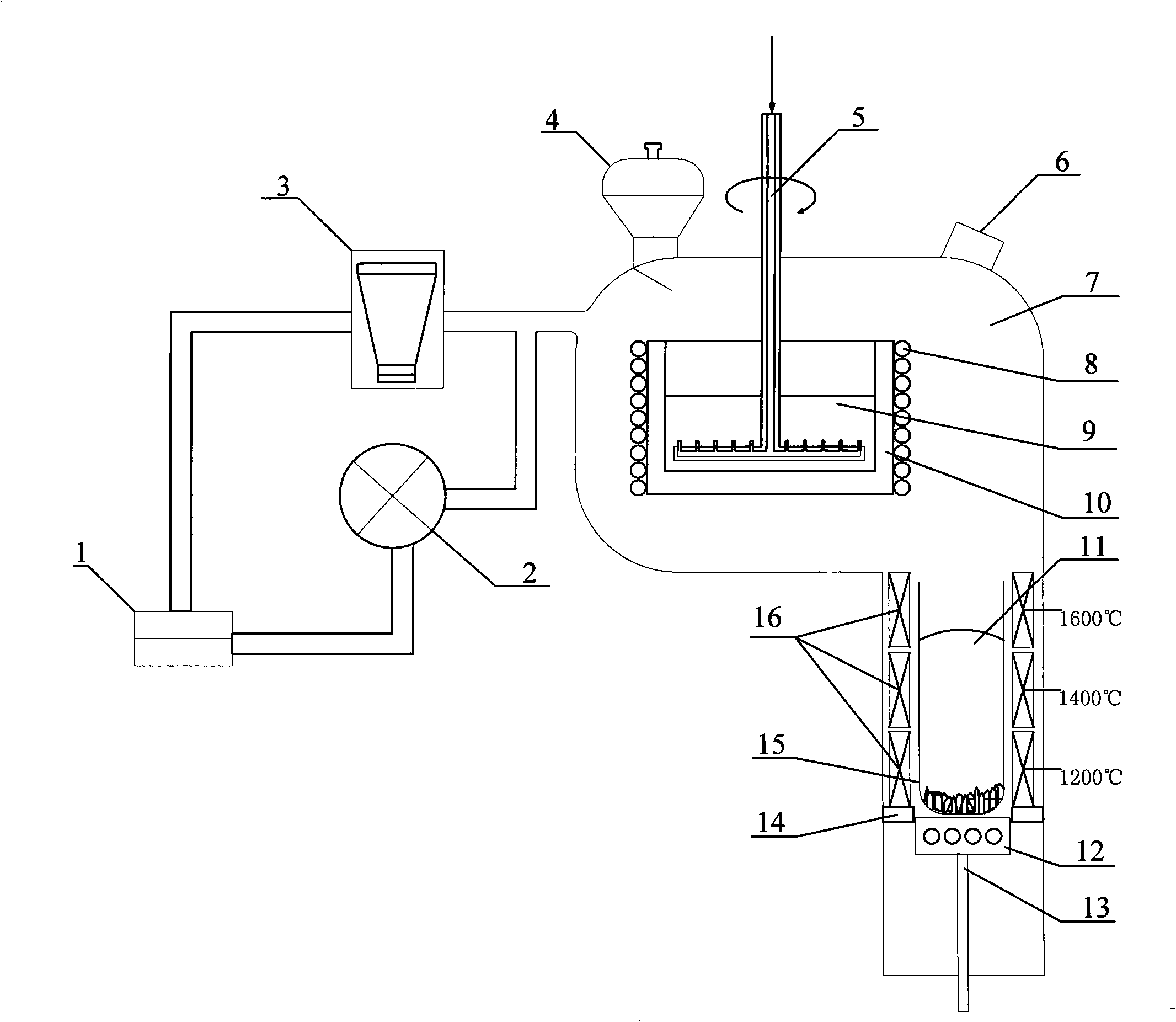
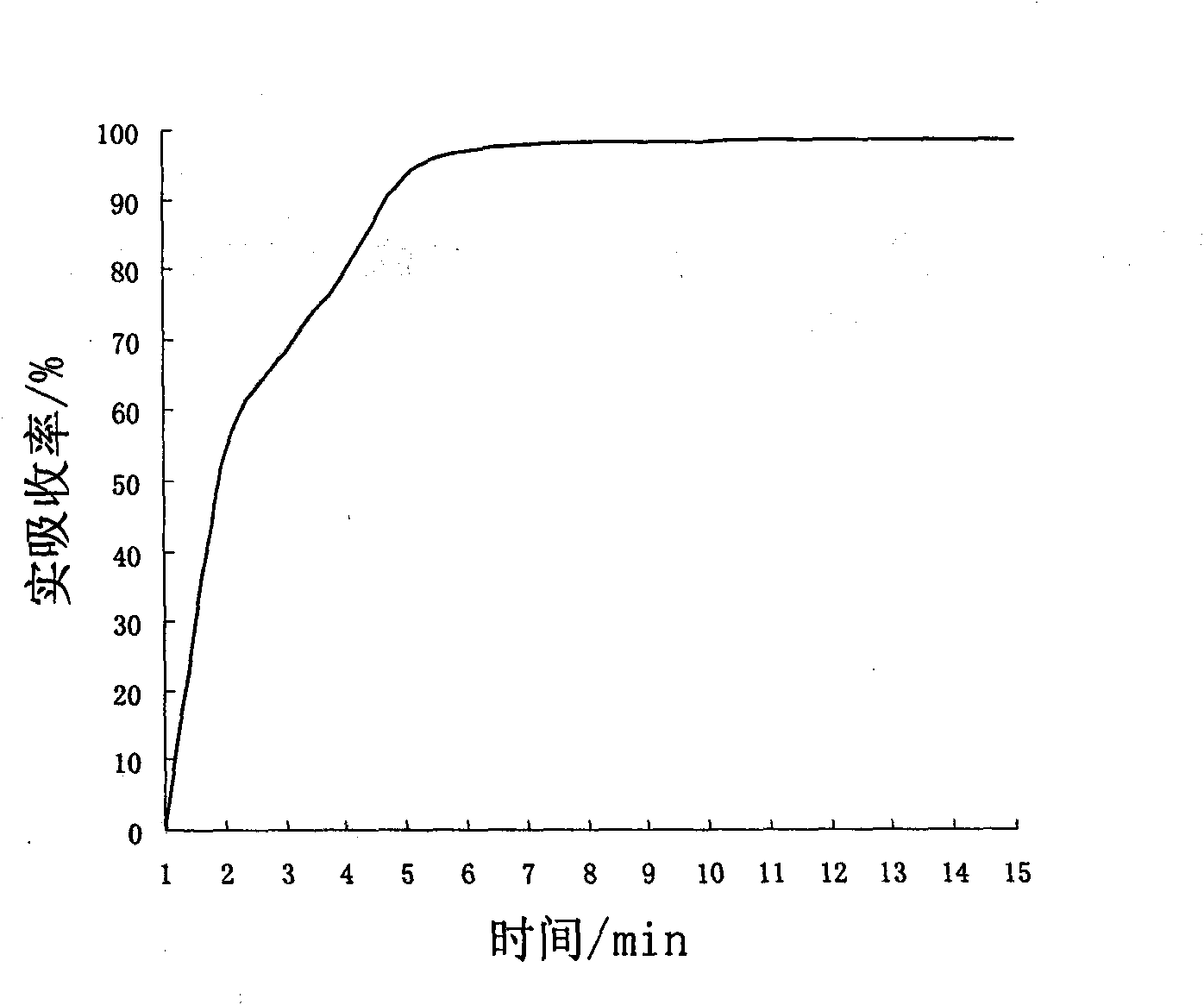
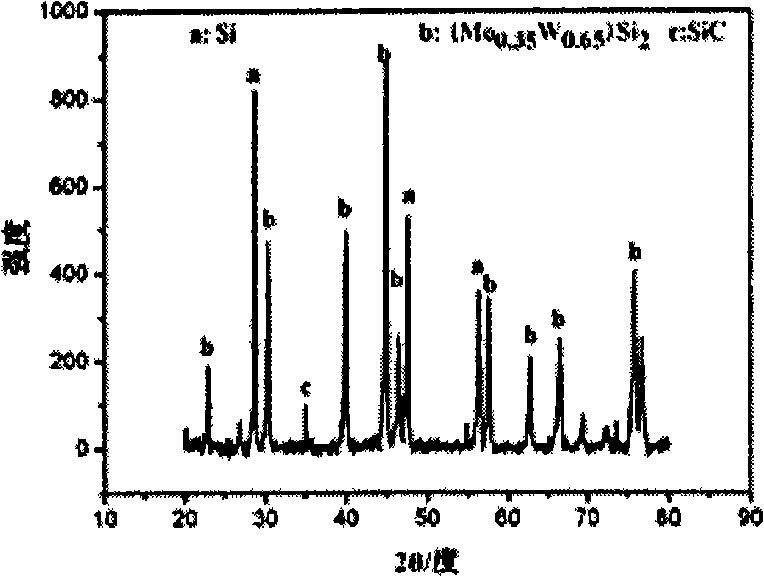
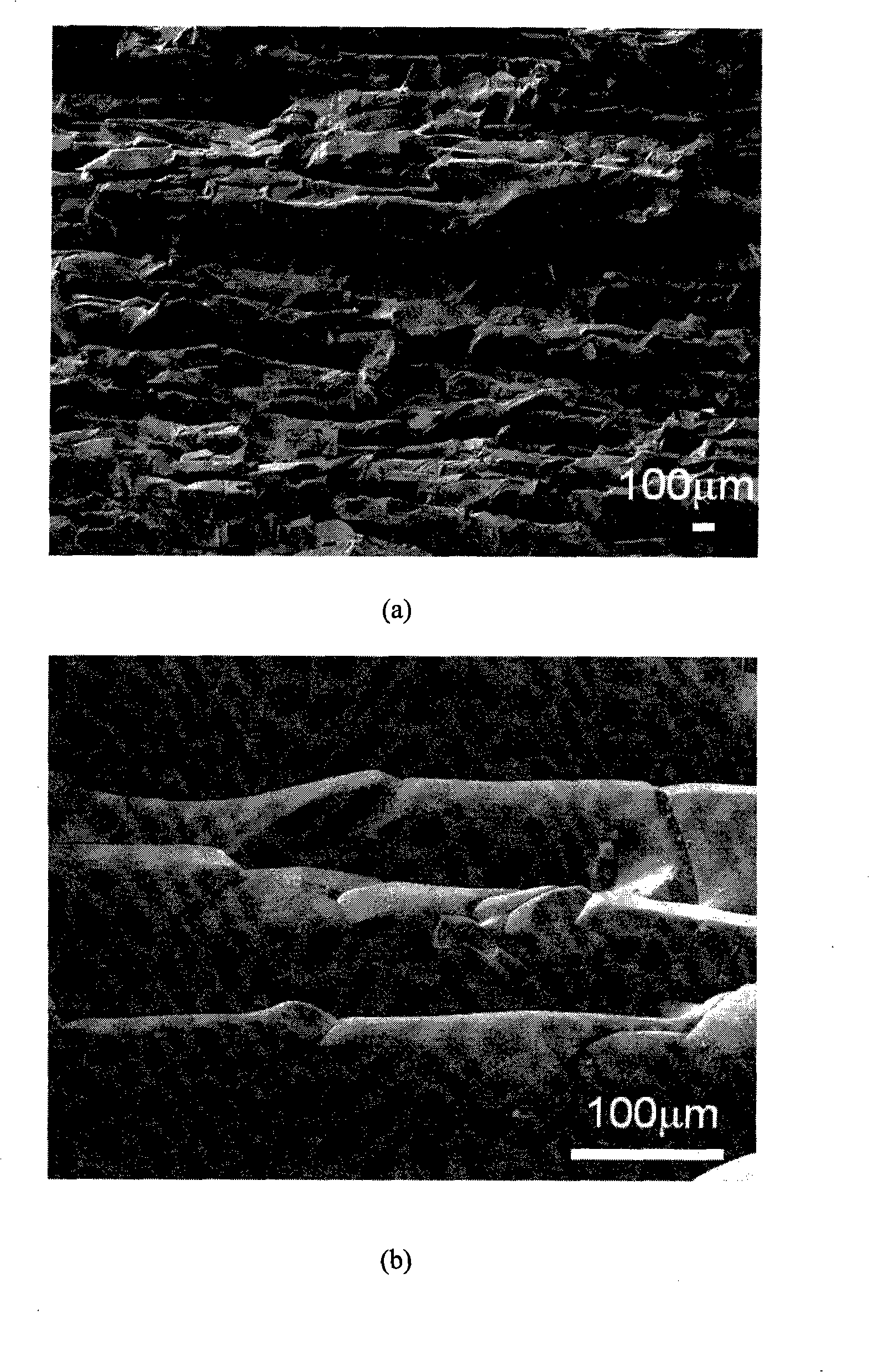
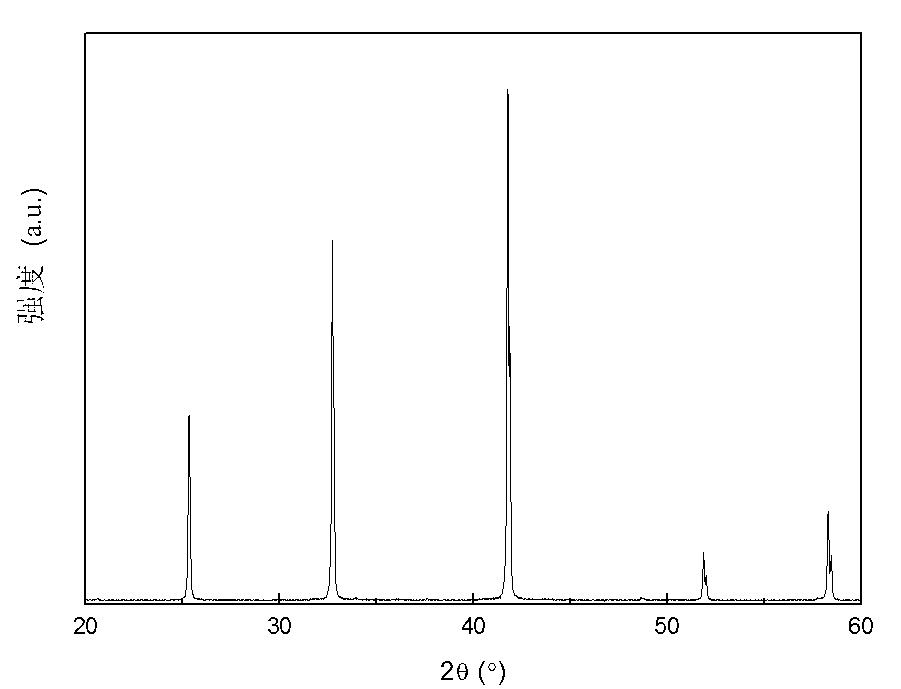
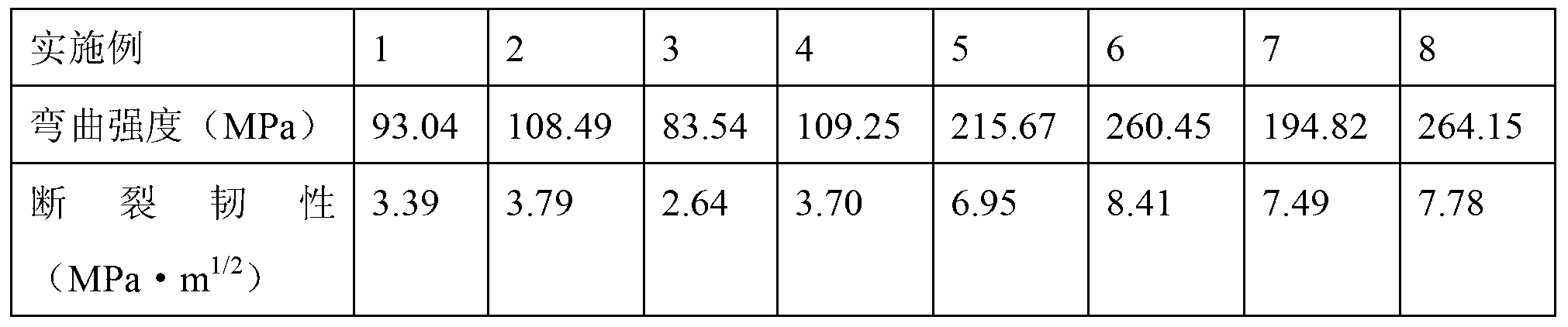Patents
Literature
1931 results about "Graphite crucible" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation method for fiber reinforced carbon-silicon carbide-zirconium carbide-based composite material
The invention discloses a preparation method for a fiber reinforced carbon-silicon carbide-zirconium carbide-based (C / C-SiC-ZrC) composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (a) evenly dispersing ZrC nanopowder in absolute ethyl alcohol; (b) mixing phenolic resin and ZrC dispersion liquid to form slurry; (c) immersing a two-dimensional carbon fiber sheet into the slurry for dipping and drying, then carrying out continuous superposition paving on the two-dimensional carbon fiber sheet, and carrying out curing and post-curing treatment to prepare a fiber-reinforced sintered body; (d) cracking the fiber-reinforced sintered body to obtain a porous C / C prefabricate; (e) placing silicon powder into a graphite crucible, burying the porous C / C prefabricate into the silicon powder, heating to 1,500-1,650 DEG C, and preserving heat for preset time so as to carry out liquid silicon permeation. The method can be used for improving the high-temperature oxidizing property and ablation property of the carbon fiber reinforced ceramic (C / C-SiC) composite material.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Purification apparatus and method for solar energy level polysilicon
Disclosed are a purification device as well as a purification method of solar-grade polysilicon, relating to a polysilicon, which provides a purification device and a purification method of solar-grade polysilicon characterized by low cost, high purity, simple process, easy operation and suitability for large-scale production. The purification device is equipped with a vacuum system, a melting system and a directional solidification system; wherein the vacuum system is provided with a mechanical rotary vane pump, a lobed element pump and an oil diffusion pump, and the melting system is provided with a vacuum chamber, a secondary feeder, an observation window, a rotary ventilation device which can be raised and lowered, an induction coil and a graphite crucible; and the directional solidification system is disposed at the lower part of the vacuum chamber and is equipped with an electric resistance-wire heating and holding furnace, a graphite mold, a holding furnace frame, a water-cooled copper tray and an elevating lever which can control speed. The metal silicon is treated by induction heating to be molten, the oxidizing gas is fed under conditions of low vacuum and high temperature to remove boron, and then under conditions of high temperature and high vacuum to remove phosphorus, and finally the molten silicon solution is poured into a directional mold to strictly conduct directional solidification to remove metal impurities.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
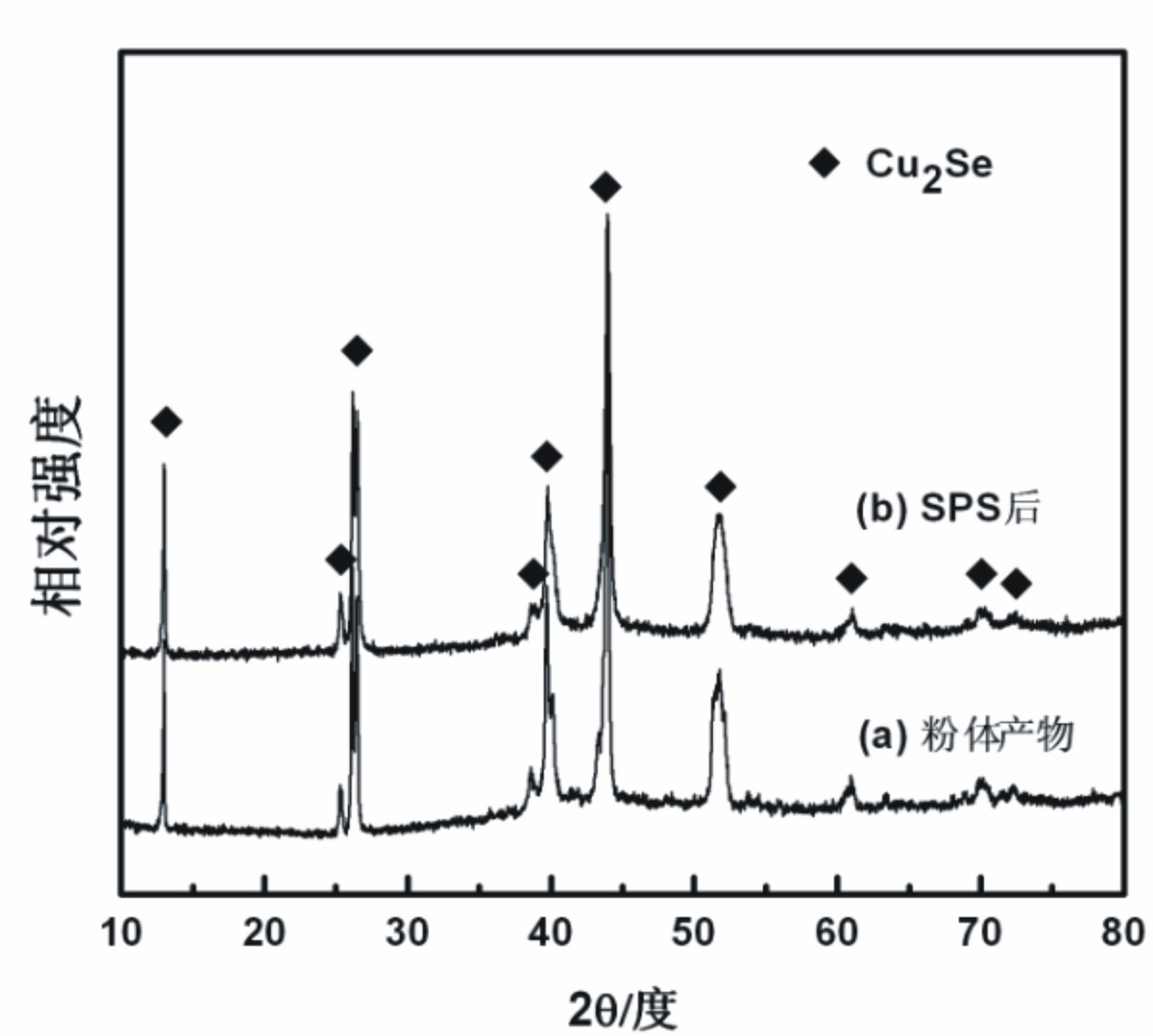
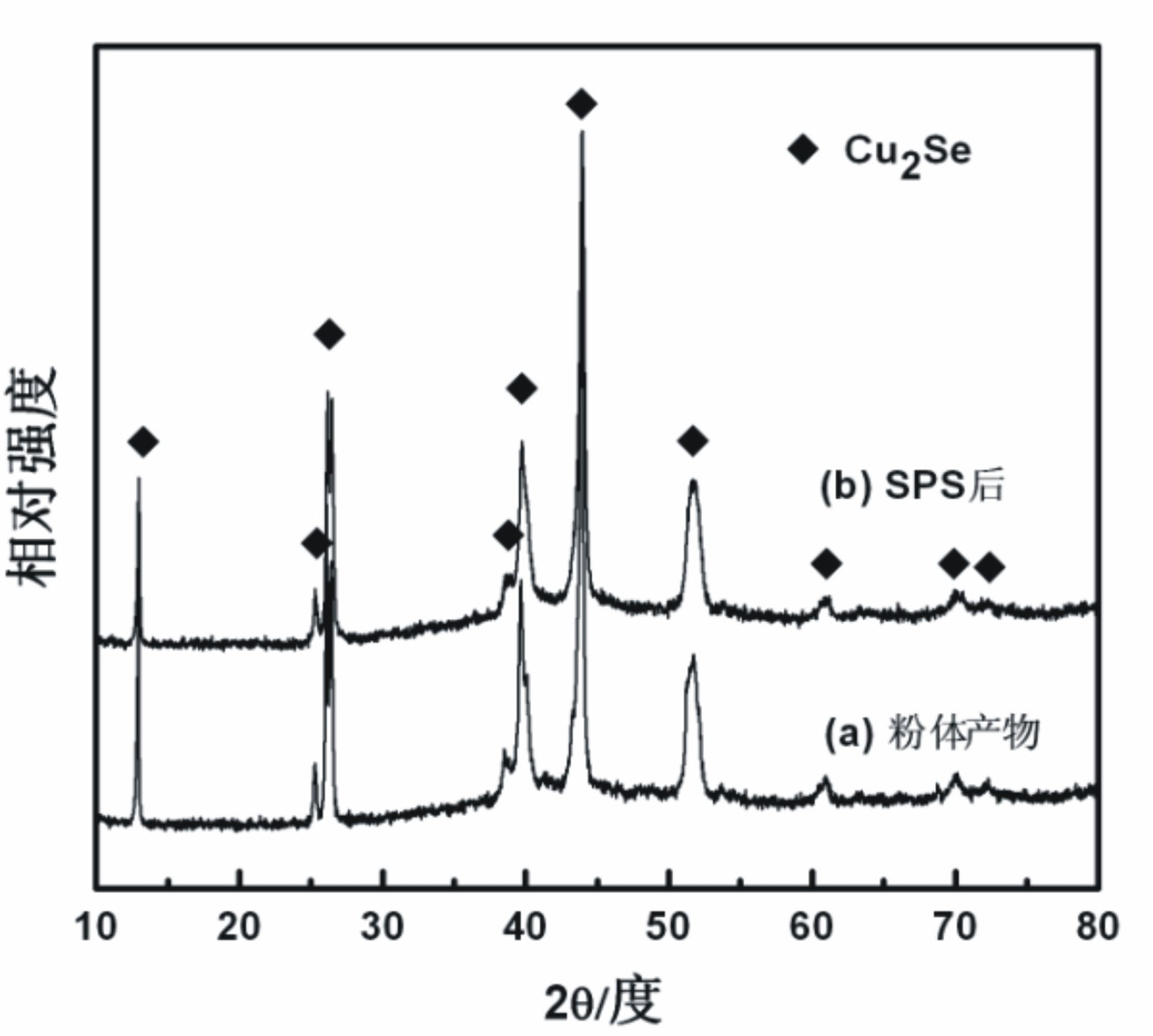
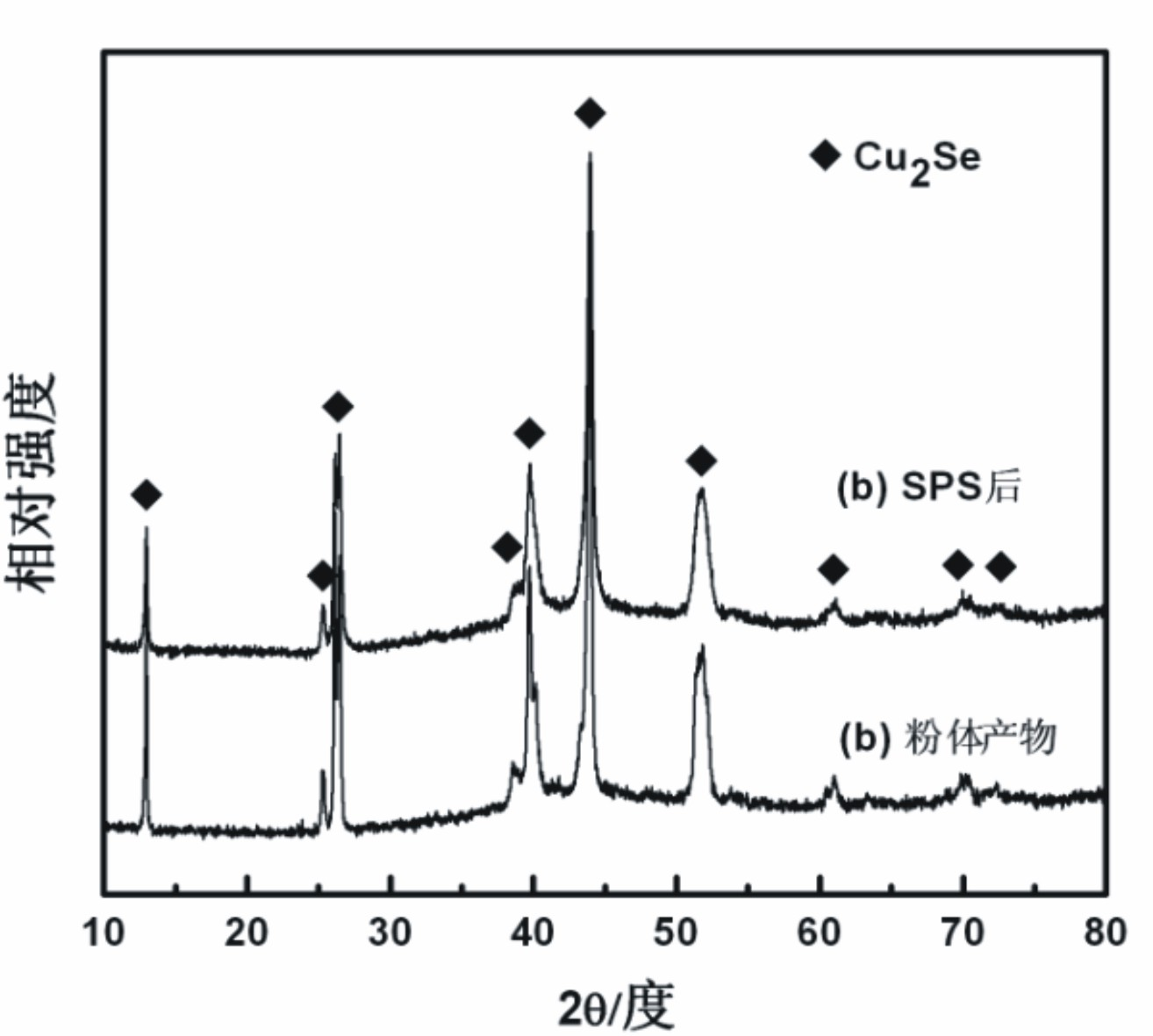
Method for preparing Cu2Se thermoelectric material by low-temperature solid-phase reaction
InactiveCN102674270ALow costControl compositionChemical industryBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsThermoelectric materialsMuffle furnace
The invention relates to a method for preparing a Cu2Se thermoelectric material. The method for preparing the Cu2Se thermoelectric material by the low-temperature solid-phase reaction is characterized by comprising the following step: 1) weighing Cu powder and Se powder according to the molar ratio of 2:1 and mixing the Cu powder and the Se powder uniformly to obtain mixed powder, wherein the Cu powder and the Se powder serve as raw materials; 2) pressing the mixed powder into a block body by using tablet press, placing the block body into a graphite crucible, vacuumizing, sealing into a quartz glass tube, placing into a muffle furnace, performing solid-phase reaction at the temperature of between 650 and 750 DEG C for 12 to 24 hours, and grinding the obtained product into powder; and 3) performing spark plasma sintering on the powder obtained in the step 2) to obtain a compact block body, namely the Cu2Se thermoelectric material. By the method, the raw materials have low cost; the reaction temperature is low; energy is saved; and the materials are fed according to the stoichiometric ratio of the Cu2Se, so the product composition can be controlled precisely; and the repeatability is high.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
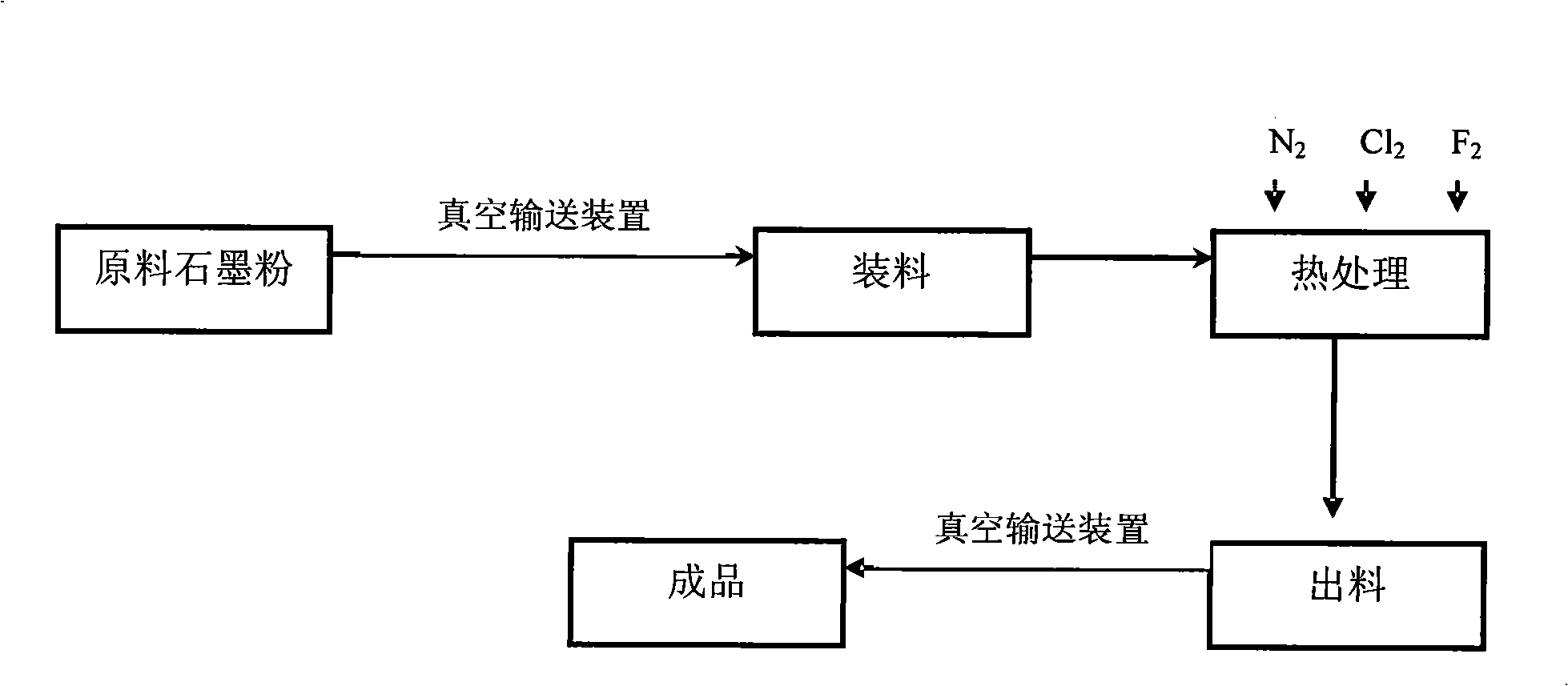
Process and equipment for producing graphite dust
ActiveCN101318648AReduce entryImprove graphitization heat treatment efficiencyCell electrodesChemical industryState of artVacuum delivery
The invention discloses a method for preparing graphite powder and the equipment thereof and aims at solving the technical problems of improving the purity of graphite powder and reducing cost. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: the raw micro powder is delivered to a graphite crucible under vacuum state and put into a graphitizing furnace; and a graphite powder product is obtained after heat treatment and cooling. The preparation equipment of graphite powder is composed of a vacuum delivery device, a graphitizing furnace and a vacuum discharging device sequentially connected; the graphitizing furnace is equipped with a graphite crucible and connected with a gas filling system. Compared with the prior art, the method and the equipment of the invention are characterized in that the raw micro power is put into the graphite crucible after vacuum delivery, thus the entry of impurities is reduced in the treatment process, the product purity is greatly improved after heat treatment, graphitization is even, the consistency of the product is good, the graphitization and heat treatment efficiency of the powder material is improved, the technique is simple and the cost is low.
Owner:BTR NEW MATERIAL GRP CO LTD
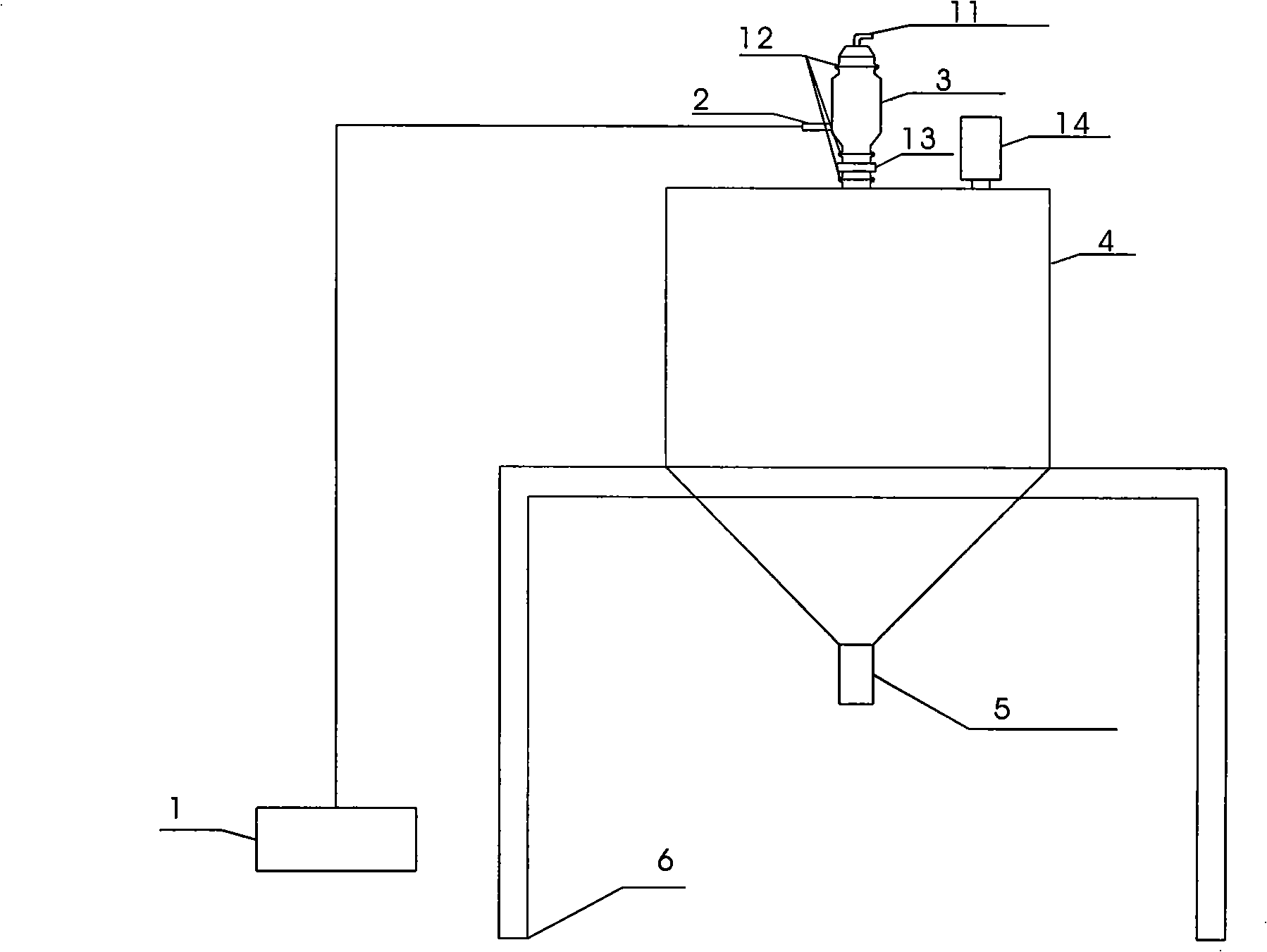
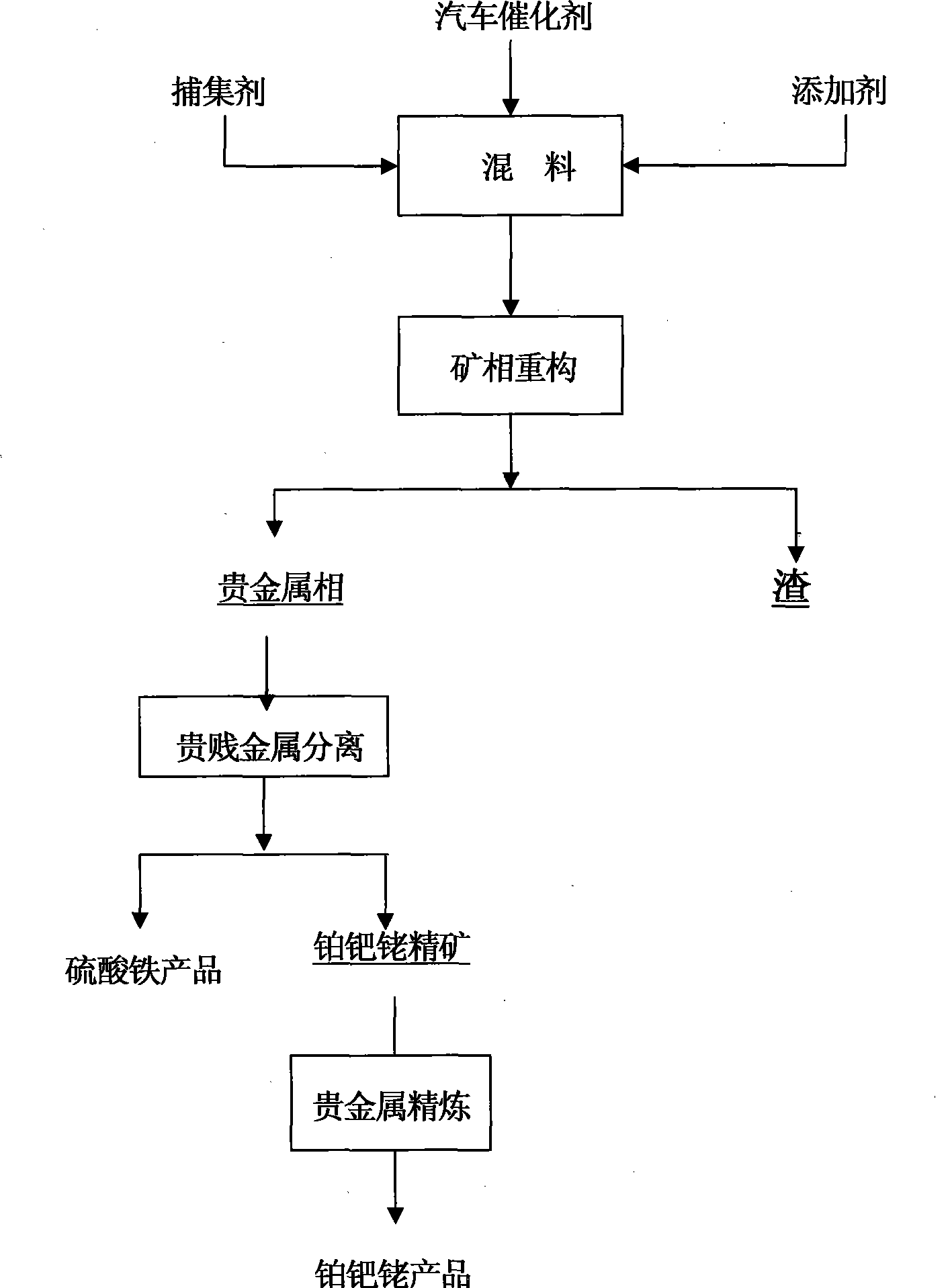
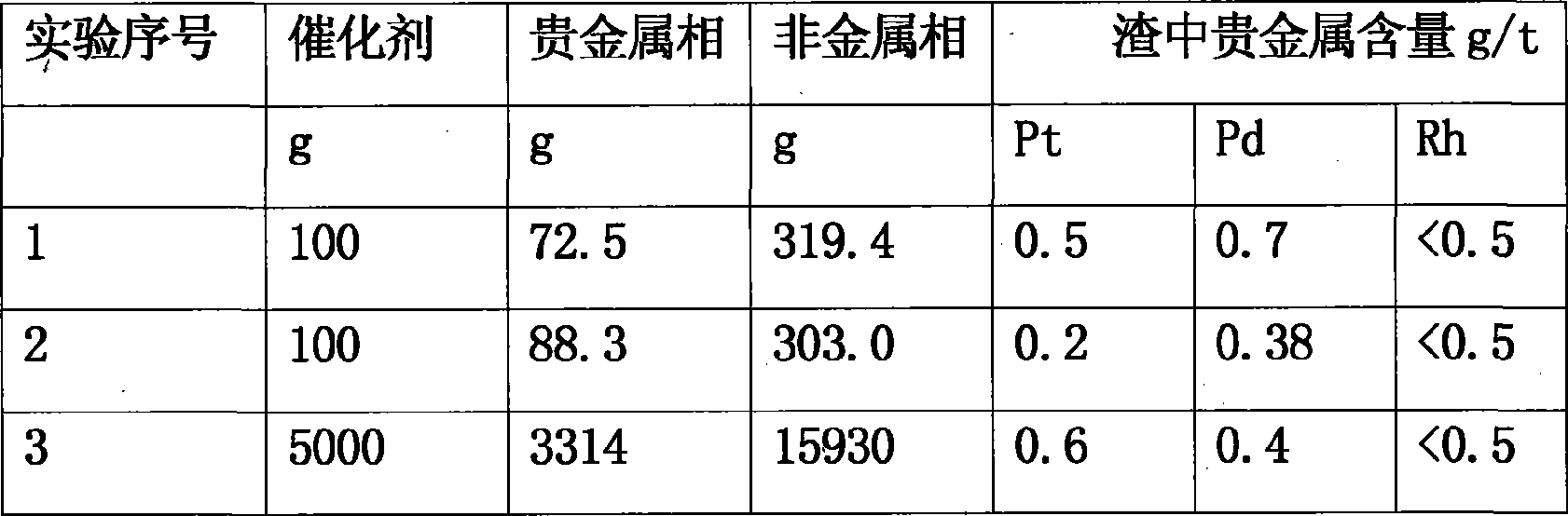
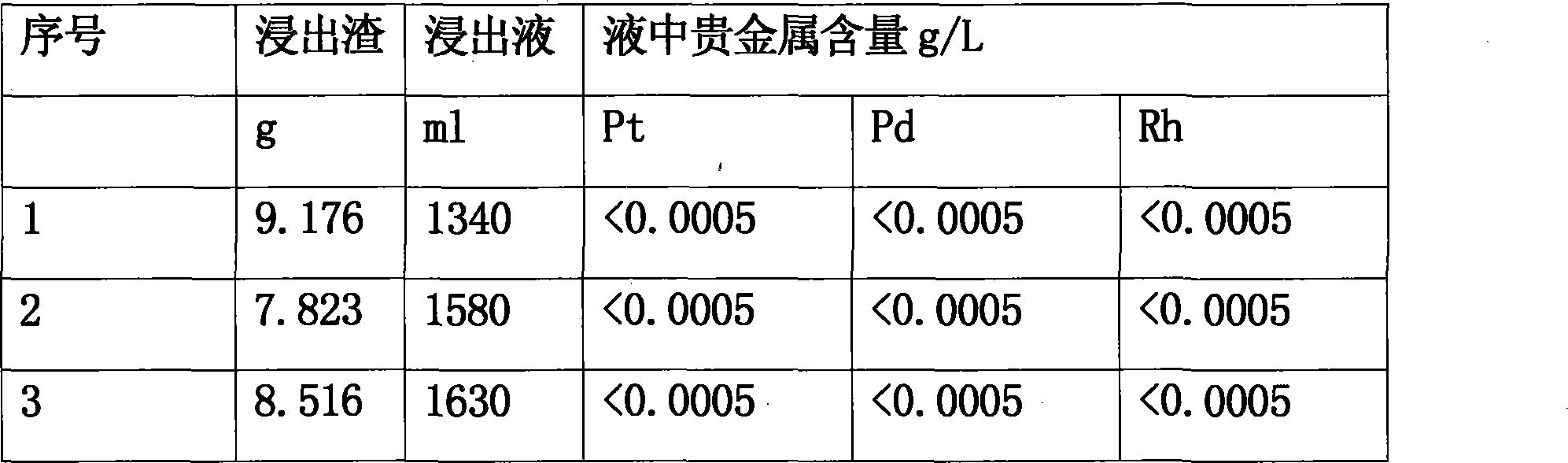
Method for extracting platinum, palladium, rhodium from automotive catalyst of ore phase reconstruction
InactiveCN101509077AEfficient captureReduce corrosionProcess efficiency improvementElectric arc furnaceSlag
The invention relates to a method for recovering noble metals from spent automotive exhaust catalysts, comprising the following processes: 1. mixing the spent automotive exhaust catalyst with a reducing agent, an additive and a trapping agent; 2. putting the mixed materials into a clay graphite crucible, and putting the clay graphite crucible into an electric furnace or an electric arc furnace for smelting, thus obtaining a noble metal phase; 3. selectively leaching base metals from the noble metal phase, thus obtaining the enrichment of the noble metal, refining the enrichment of the noble metal to produce platinum, palladium and rhodium products. The method is characterized by simple process flow and high recovery rates of noble metals. The platinum, palladium and rhodium in the waste slag are less than 1g / t and the product purity is 99.95%.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Aluminum-silicon based aluminum section and preparation technology thereof
The invention discloses an aluminum-silicon based aluminum section. The aluminum section is composed of, by weight, 5.0-14.0% of silicon, 0.2-0.7% of magnesium, less than 0.03% of boron, less than 0.06% of strontium, 0.1-6.55% of strengthening elements, less than 0.25% impurity elements, and the balance aluminum. The aluminum-silicon based aluminium section has the advantages of high strength, high hardness, good wear resistance, etc. the invention also discloses a preparation technology for the aluminum-silicon based aluminum section, which comprises a first step of adding aluminum-silicon alloy to a graphite crucible and heating the alloy to form melt; a second step of adding the magnesium, the silicon and the strengthening elements; a third step of adding hexachloroethane for refinement; a forth step of adding the strontium for deterioration, casting to a cast iron die to form an ingot casting; and a fifth step of hot extruding, hot rolling for deformation, solid solution treating and aging treating in sequence after annealing the ingot casting, thereby obtaining the aluminum-silicon based aluminum section. The preparation technology is simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Electric locomotive pantograph copper-soaking carbon contact strip producing method
ActiveCN104774012AImprove conductivityHigh mechanical strengthPower current collectorsShock resistanceNitrogen gas
The invention discloses an electric locomotive pantograph copper-impregnated carbon contact strip producing method. The method comprises the steps that 1, pitch coke powder, graphite powder, siliconized graphite powder and high temperature pitch are mixed according to the proportion to be ground into powder; the mixed powder is prepressed into a stage stock column, and then the stage stock column is solidified and squeezed to be molded and roasted, so that a composite carbon contact strip is obtained; 2, the composite carbon contact strip is cleaned and dried, then is cooled and placed into a graphite crucible, and is placed in an electric furnace at temperature of 1300-1400 DEG C to be preheated; copper liquid is poured into the crucible to soak the composite carbon contact strip, then the crucible is placed in an oil press cover, nitrogen is led in, heat preservation is kept for 3-5 min under the specific intensity of pressure, and finally cooling is carried after pressure releasing. According to the electric locomotive pantograph copper-impregnated carbon contact strip producing method, the electroconductibility of the copper-impregnated carbon contact strip is improved, the electrical resistivity is lowered, the mechanical strength of the carbon contact strip and copper impregnated angle can be increased, then the carbon contact strip abrasive resistance and self-lubrication are improved, the copper-impregnated carbon contact strip is more resistant to abrasion, main line damage and block dropping are avoided, the shock resistance is high, and the service life of the copper-impregnated carbon contact strip is prolonged.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
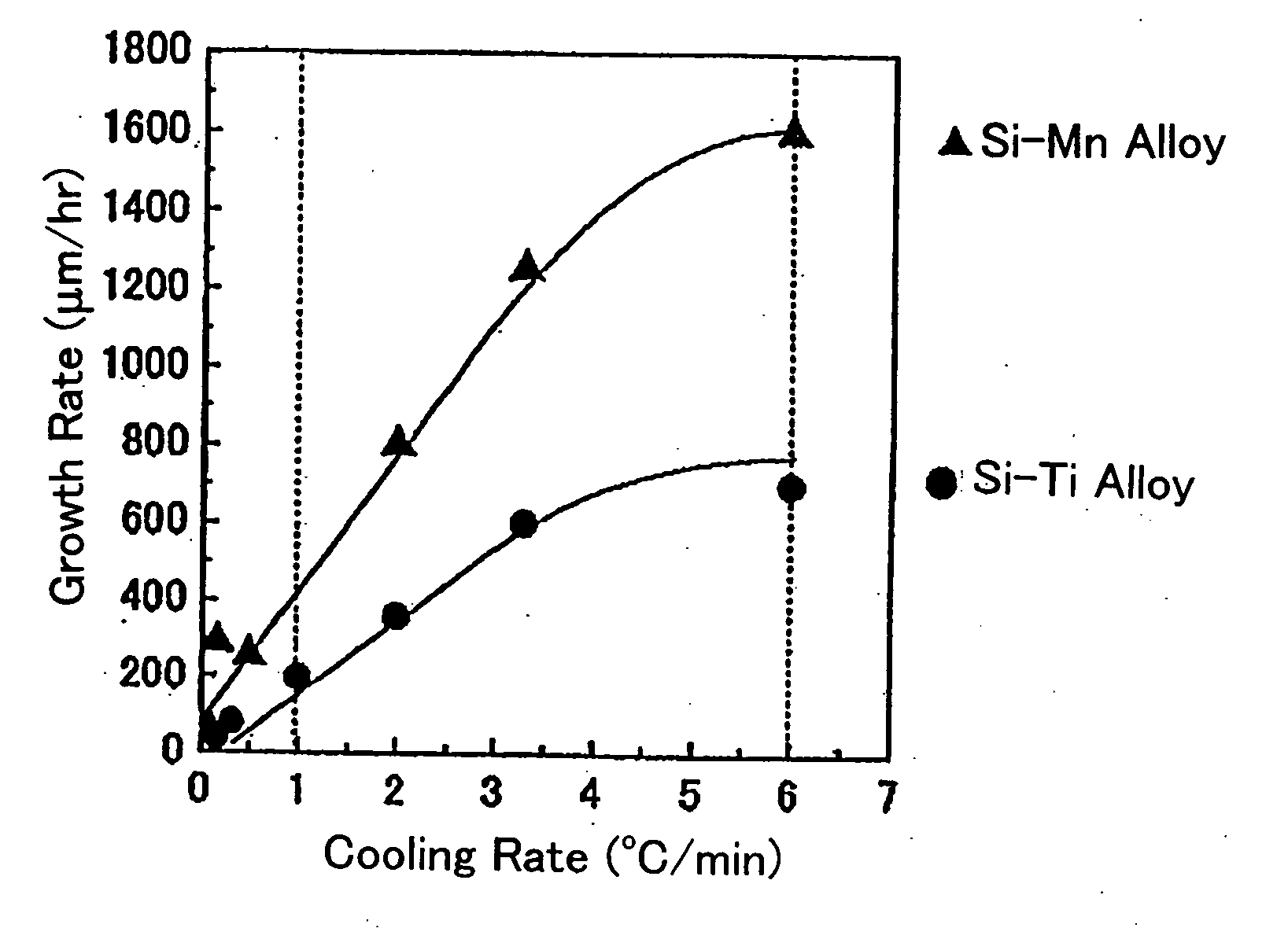
Silicon carbide single crystal and a method for its production
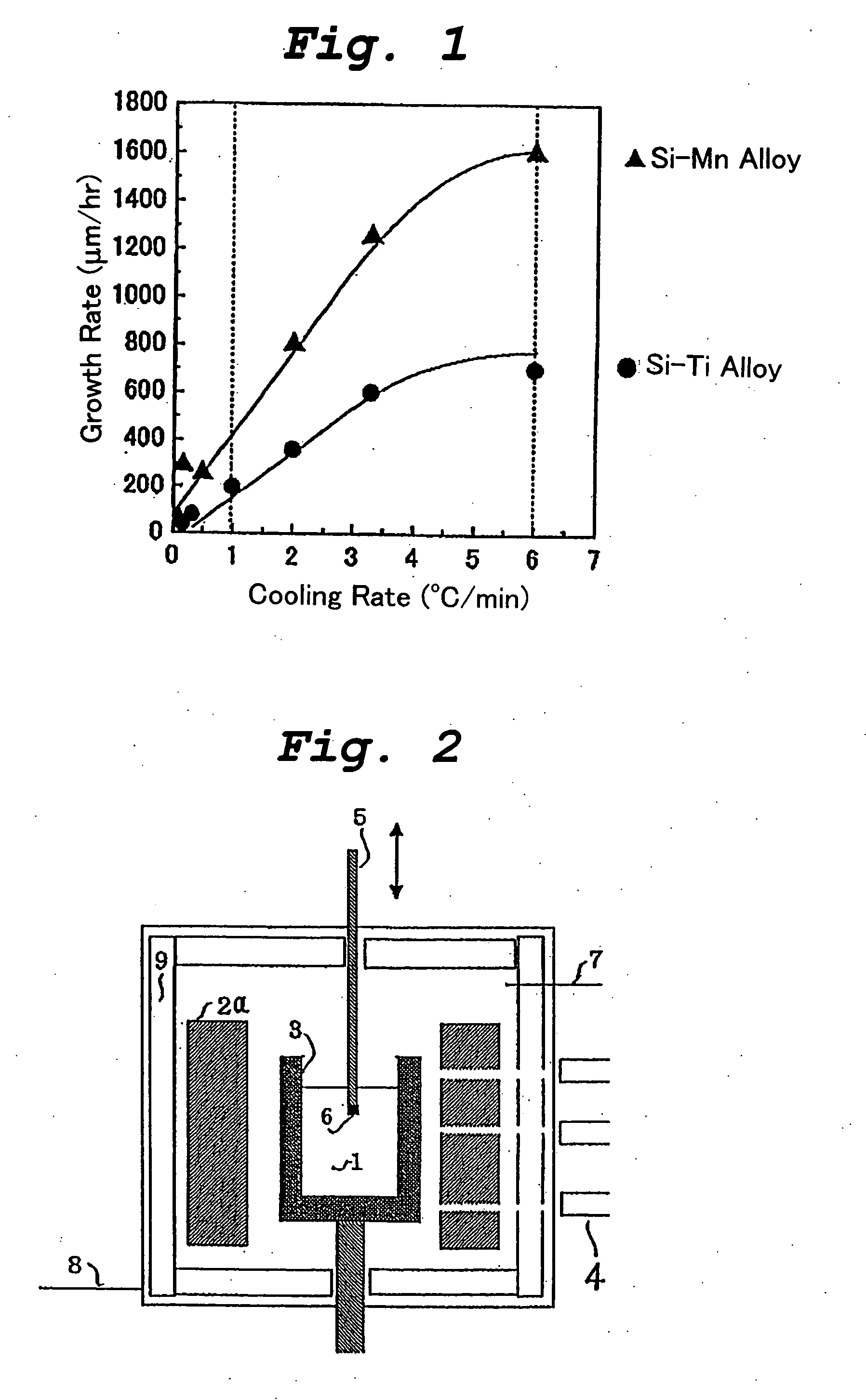
InactiveUS20050183657A1Easy to handleStable productionFrom gel statePolycrystalline material growthAlloyDissolution
A bulk silicon carbide single crystal of good crystalline quality which includes a minimized number of structural defects and is free from micropipe defects can be produced by crystal growth in a melt of an alloy comprising Si, C, and M (wherein M is either Mn or Ti) and having an atomic ratio between Si and M in which the value of x, when express as Si1-xMx, is 0.1≦×≦0.7 in the case where M is Mn or 0.1≦×≦0.25 in the case where M is Ti at a temperature of the melt which is below 2000° C. The C component is preferably supplied into the melt by dissolution of a graphite crucible which contains the melt such that the melt is free from undissolved C. One method of crystal growth is performed by cooling the melt after a seed substrate is immersed in the melt.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Device and method for growng large diameter 6H-SiC monocrystal with semiconductor property
ActiveCN1554808ALarge crystalsFor the purpose of dopingPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsEngineeringSingle crystal
The present invention relates to apparatus and method of growing great diameter 6H-SiC monocrystal with semiconductor characteristic and belongs to the field of crystal growing technology. The apparatus includes growing chamber, water cooler on the side wall of the growing chamber, graphite crucible, heat insulating material, induction heating system, cylindrical vapor guiding plate of Ta inside the crucible, and cylinder. Regulating the position of the crucible relative to the inducing coil can minimize the temperature at the crystal seed inside the crucible and increase the temperature field distribution in the growing direction. Altering the atmosphere composition or material compounding can obtain great diameter SiC monocrystal with n-type, p-type or semi-insulating type semiconductor characteristic. By means of selecting the Si plane of the crystal seed and growing temperature, the crystal form may be controlled and 6H-SiC may be obtained.
Owner:SICC CO LTD
Graphite crucible for growing large-size silicon carbide single crystal by physical vapor deposition method and application thereof
InactiveCN102534763AReduce corrosionImprove stabilityPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsCarbonizationSingle crystal
Owner:SICC CO LTD
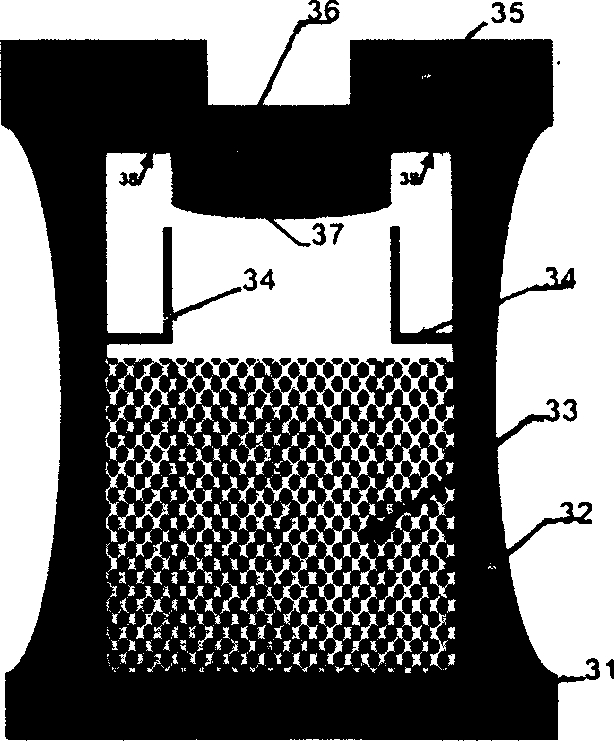
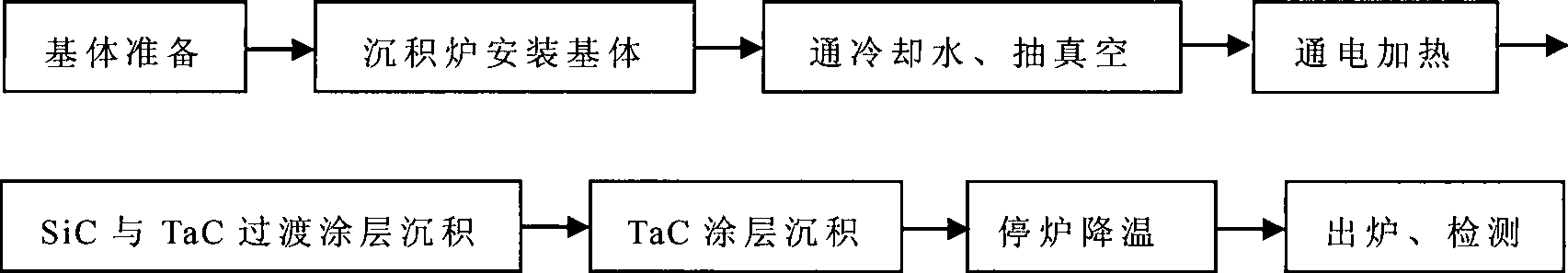
Graphite matrix flawless TaC coating and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101445392AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove diffusion resistanceGraphite substrateThermal stability
The invention discloses a graphite matrix flawless TaC coating and a manufacturing method thereof. A tie coat is deposited on a graphite matrix. A TaC main coating is deposited on the outer layer of the tie coat. The tie coat is composed of a SiC-TaC codeposition coating or compounded by two transition layers of the SiC-TaC codeposition coating and a SiC-TaC laminated coating. When the tie coat is compounded by two transition layers of the SiC-TaC codeposition coating and the SiC-TaC laminated coating, the SiC-TaC codeposition coating serves as a first transition layer, and the SiC-TaC laminated coating serves as a second transition layer; and then the deposition of the tie coat is ended; or the SiC-TaC codeposition coating and the SiC-TaC laminated coating are alternatively deposited many times. Good TaC coating which has small heat stress, no macroscopic cracking, corrosion-resistance, and good thermal stability is deposited out of the surface of the graphite material. The method is suitable for preparing graphite substrate, graphite crucible, graphite windpipe, graphite guide shell coating in the crystal and semiconductor production, protecting and cleaning coating such as antisepsis, anti-pollution, anti-infiltration, anti-oxidation of graphite parts in other various hot environments.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Additive for smelting aluminium alloy and preparation method and application method thereof
The invention relates to an additive for smelting aluminium alloy and a preparation method and an application method thereof, relating to the technical field of nonferrous alloy manufacturing with a special additive. The additive is composed of metal powder, cosolvent, heat-generating agent, detonating agent and moisture proof agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: raw materials comprising the following by mass percentage, 70-81.5% of metal powder, 15-20% of cosolvent, 2-5% of heat-generating agent, 1-3% of detonating agent and 0.5-2% of moisture proof agent, are fully mixed evenly into compound powder with a ball mill, and the mixture is put into a mould, and is performed with cold pressing by a hydraulic pressure machine so as to obtain the additive for smelting aluminium alloy. The application method of the invention comprises the following steps: a graphite crucible filled with a pure aluminium pig is arranged in a resistance furnace to be heated until the aluminium pig is melted into aluminium liquid, and then the additive is added to react with the aluminium liquid so as to obtain aluminium alloy. Under the condition that the quality of aluminium alloy is not lowered, the additive solves the problems of high dissolving temperature, low absorptivity and unstable absorptivity of the additive.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing inoxidzable coating at high-temperature on carbon/carbon composite material surface
The invention provides a preparation method of a high temperature oxidation-resistant coating on the surface of a carbon / carbon composite material. The preparation method comprises placing Si powder, C powder, and Al2O3 into an agate ball milling tank, adding distilled water, mixing and ball milling, taking out the mixed solution, and drying to form inner layer embedded powder; placing the treated C / C composite material into the powder in a graphite crucible; placing into a vertical type vacuum furnace with graphite being the heating body for preparing an undercoat; mixing the Si powder, Mo powder, W powder and C powder with absolute ethanol and silica sol to obtain slurry; and uniformly brush coating surface of the SiC inner layer of the C / C composite material I with the slurry, drying, and placing into an alumina crucible for preparing a top coating. The antioxidant protective time of the C / C composite material is increased from 100 hours in prior art to 200-252 hours in 1500 DEG C air using high temperature oxidation resistance of MoSi2 and WSi2 via combination of the undercoat and the top coating.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Preparation of oriented hole silicon carbide porous ceramic
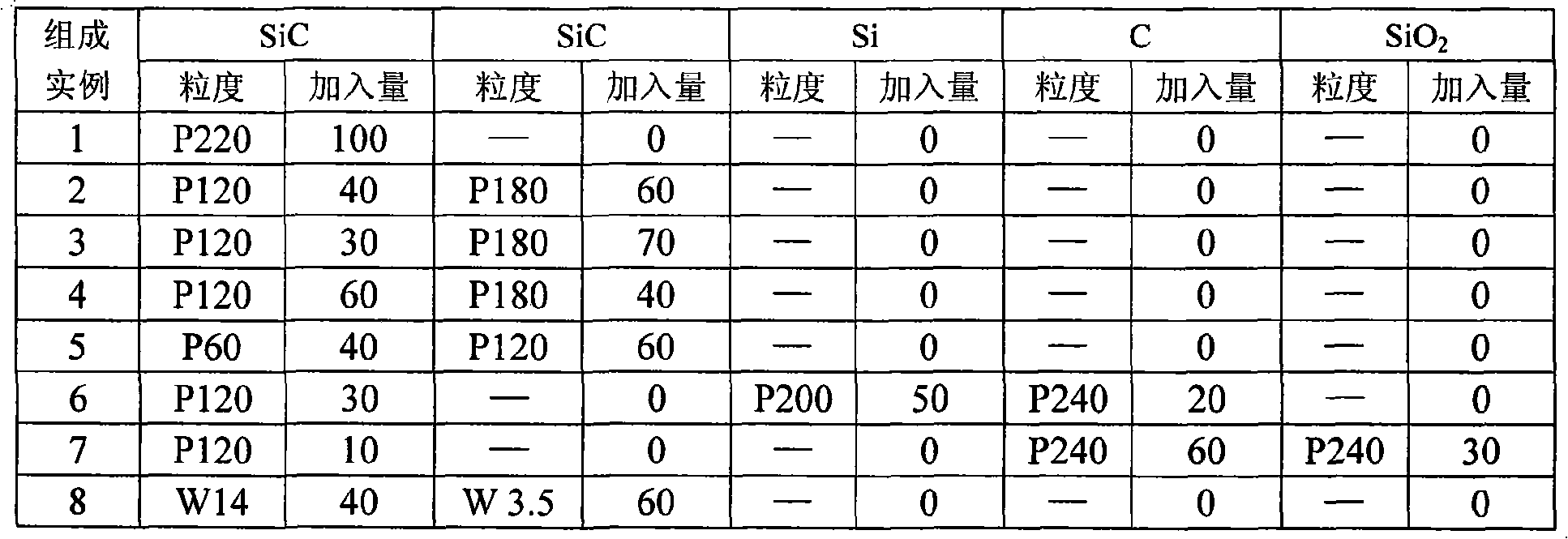
InactiveCN101323524AControl evaporation-condensation directionAdjust evaporation-condensation rateCeramicwareGranularitySaggar
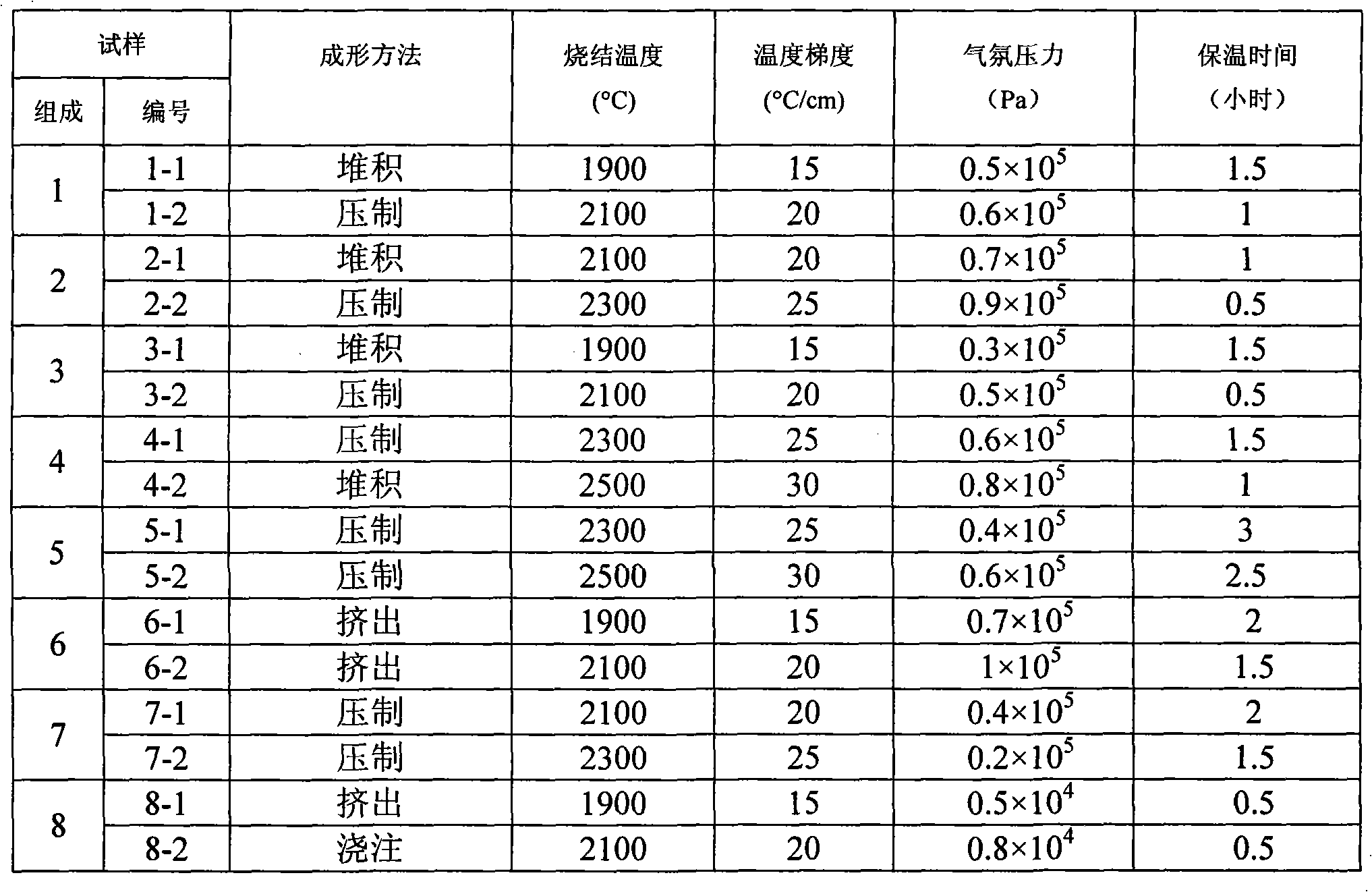
The invention discloses a preparation method of a porous silicon-carbide ceramic provided with oriented pores. Firstly, according to weight percentage, 0 to 30 percent of carbon powder, 0 to 50 percent of silicon powder and 0 to 60 percent of silica are added into the 10 to 100 percent of the basic material of silicon-carbide; wherein, the granularity of the silicon-carbide is W3.5 to P220, and one granularity or two granularities are adopted for graduation; then the equally mixed materials are processed through powder accumulation or normal ceramic forming process to obtain a green compact which is put into a graphite crucible or a saggar; the graphite crucible or saggar is placed into a vacuum sintering furnace provided with a temperature field with a temperature grade from 15 to 30 DEG C / cm, and then the temperature is raised to 1900 to 2500 DEG C in an argon environment and with pressure of 0.2 to 1 multipliedby 10 <5>Pa, and the insulation work for the graphite crucible or saggar is preserved for 0.5 to 3 hours; finally the temperature naturally falls down under air protection and the sintered body is taken out, namely, the recrystallization porous silicon-carbide ceramic provided with oriented pores is obtained.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for quickly growing large-size SiC (Silicon Carbide) single crystal
ActiveCN104805504AReduce investmentAvoid transmissionPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsSource materialLarge size
The invention relates to a method for quickly growing a large-size SiC (Silicon Carbide) single crystal. The method comprises the following steps: putting a mixture of silicon powder and carbon powder at the bottom of a graphite crucible, and placing a porous graphite flake on the surface; fixing a seed crystal to the top of the graphite crucible, vacuumizing a growth chamber, charging Ar gas or mixed gas of Ar and H2 into the growth chamber, heating the seed crystal until the temperature reaches 1,600-2,000 DEG C, and reacting for 2-5 hours under the pressure of 800-900mbar to obtain a SiC source material; raising the temperature to 2,200-2,500 DEG C, continuously charging the Ar gas, reducing the pressure, sublimating powder at the bottom to the surface of the seed crystal, and growing the seed crystal for 30-50 hours to obtain the large-size SiC single crystal. According to the method, SiC powder can be synthesized at one time, the SiC single crystal can be grown in situ, the cost is low, and the process is simple.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
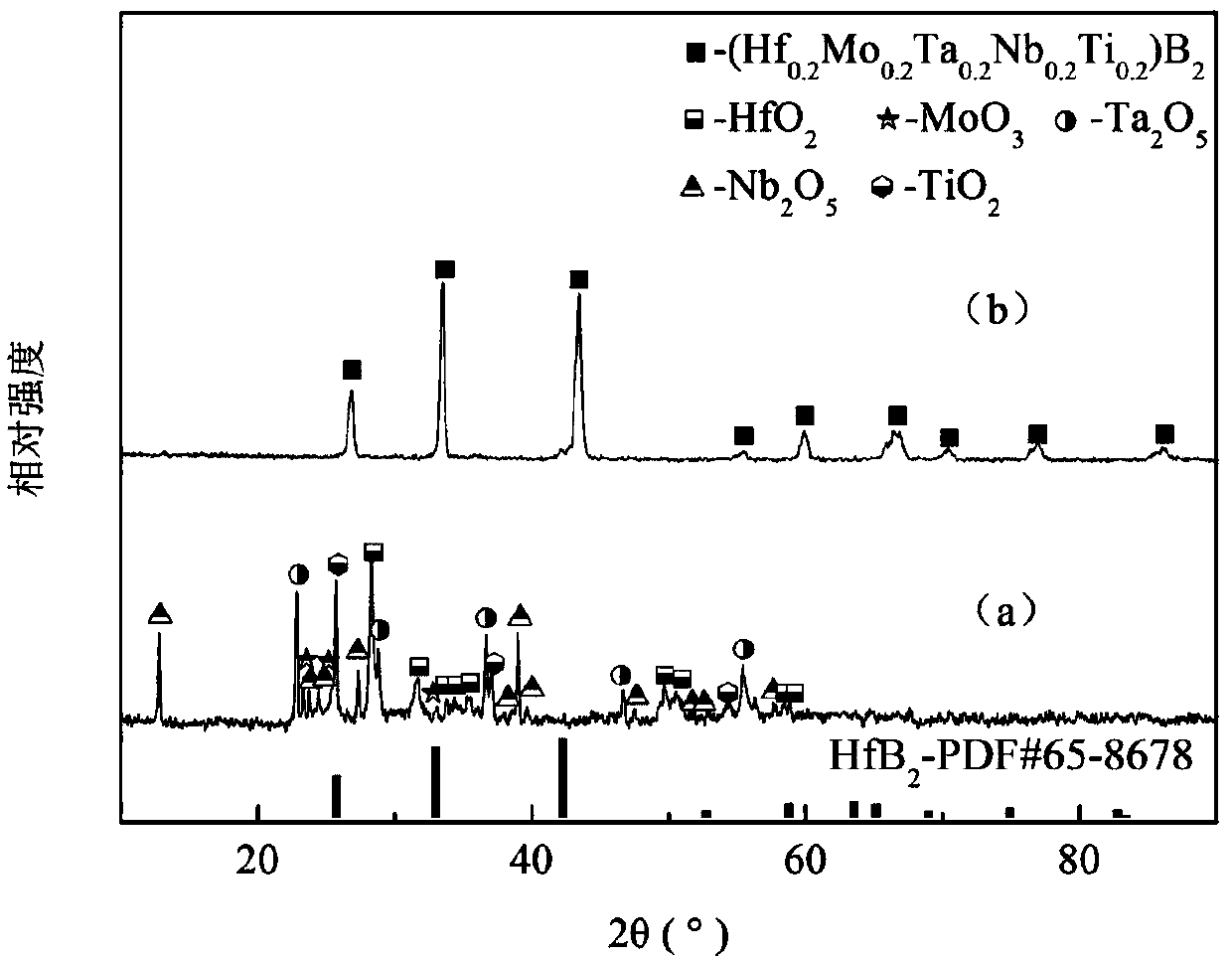
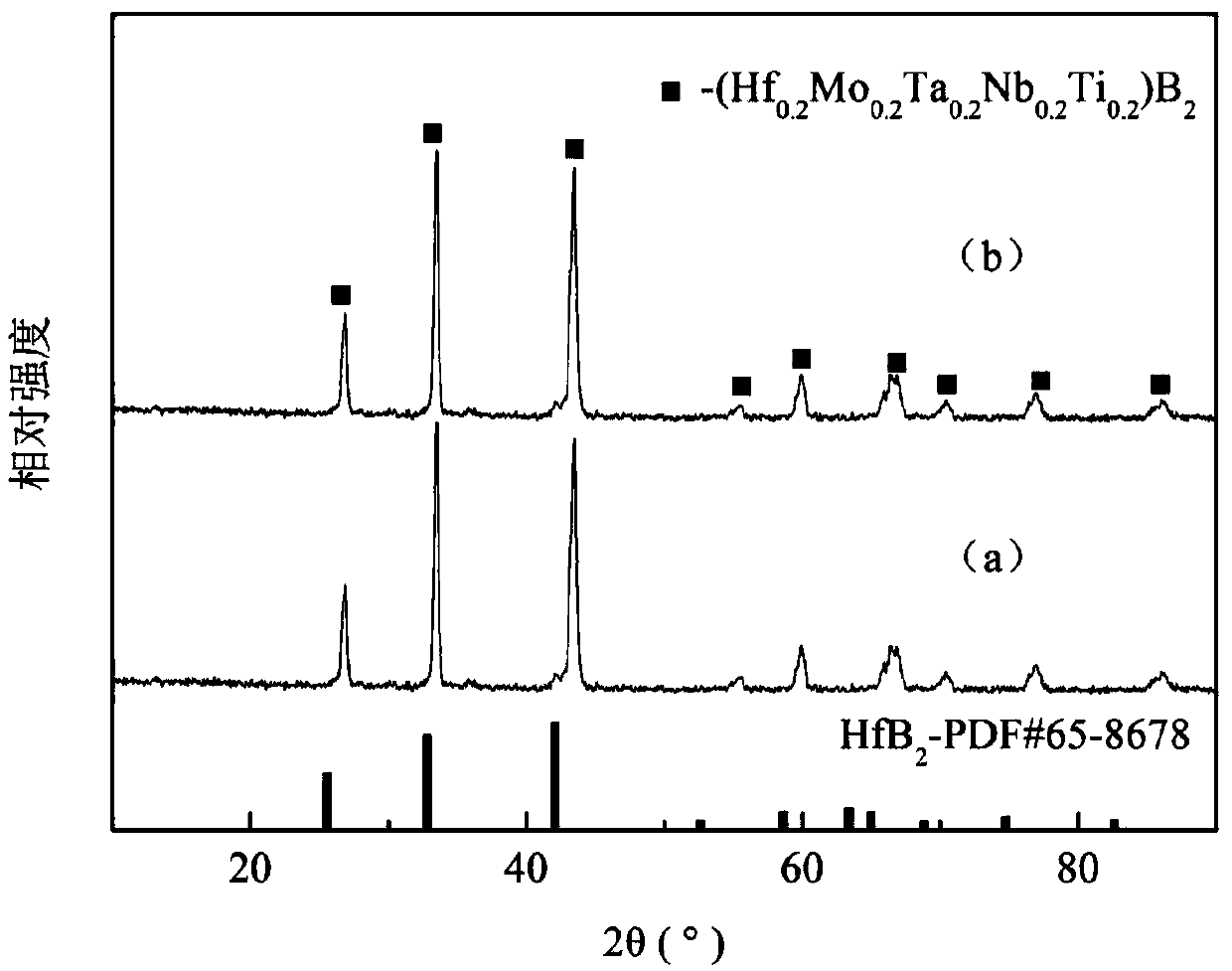
Ceramic with multi-element high entropy as well as preparation method and application of ceramic
The invention belongs to the technical field of ceramic materials and discloses a ceramic with multi-element high entropy as well as a preparation method and application of the ceramic. The ceramic isprepared by the following steps: taking an oxide of Me1, an oxide of Me2, an oxide of Me3, an oxide of Me4, an oxide of Me5 and amorphous boron powder as raw materials, performing ball milling, mixing and pressing into a green body; adding the green body into a graphite crucible, and performing vacuum heat treatment to obtain (Me1xMe2yMe3zMe4nMe5m)B2 solid solution powder; raising the temperatureof the solid solution powder to 1000-1400 DEG C by adopting spark plasma sintering, filling a protective atmosphere, and raising to a temperature of 1800-2200 DEG C for calcining, thereby obtaining the product. The prepared multi-element high-entropy ceramic has the relative density of more than 95%, the hardness of 25-35GPa, the breaking tenacity of 2-8MPa*m1 / 2 and the grain size of 0.1-1.1 microns, and after the heat treatment of 1000-1500 DEG C, the weight change rate is 0.3-1%.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of low-stress and high-purity semi-insulating SiC single crystal
ActiveCN105821471AReduce stressQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsGas phaseSeed crystal
The invention relates to a preparation method of a low-stress and high-purity semi-insulating SiC single crystal. The method includes the steps that synthesis of high-purity SiC powder is carried out, crystal growth is carried out with a physical vapor transport method, the concentration of shallow energy level impurities is reduced in the synthesis and crystal growth processes, a heat insulation material is subjected to high-temperature pretreatment, and boron impurities are prevented from being blended in; a silicon powder raw material and a carbon powder raw material are put into a graphite crucible with a coating for SiC synthesis; the obtained high-purity SiC powder is pretreated, seed crystals are fed, vacuumizing is carried out, high-purity argon or mixed gas of argon and hydrogen is introduced in to carry out crystal growth, then the temperature is rapidly lowered to enlarge point defects, and then the temperature is slowly lowered to the room temperature to eliminate stress. SiC crystal growth is carried out in an equilibrium state, so that the obtained crystal is small in stress, low in microtubule density and good in quality, and the resistivity on the area of the whole crystal is 108 ohm.cm or above. The method is small in preparation investment, high in safety and free of pollution.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Al-Si-Cu-Zn-Sn-Ni aluminum-based brazing filler metal and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102319963AReduce brittlenessImprove surface activityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSlagAlloy
The invention relates to an Al-Si-Cu-Zn-Sn-Ni aluminum-based brazing filler metal and a preparation method thereof. The components of the aluminum-based brazing filler metal are 7 to 13 percent by weight of Si, 5 to 11 percent by weight of Cu, 4 to 11 percent by weight of Zn, 1 to 6 percent by weight of Sn, 1 to 3 percent by weight of Ni, 0.02 to 0.3 percent by weight of Ce, 0.01 to 0.1 percent by weight of Sr, 0.01 to 0.2 percent by weight of Zr and the balance of Al. The process flow for preparing the aluminum-based brazing filler metal is that: pure aluminum is added into a graphite crucible and covered by flux for aluminum under the condition of 800 DEG C to 900 DEG C, and slag is removed after melting; the aluminum-based intermediate alloy of high-melting point elements and flux for aluminum are added at the same time, and melting, stirring and slag removal are carried out; the aluminum-based intermediate alloy of low-melting point elements is added under the protection of nitrogen, and melting and stirring are carried out; the mixture of argon and hexachloroethane is added to carry out refining, and standing and slag removal are carried out; the intermediate alloy of trace elements is added, and melting and stirring are carried out; secondary refining and slag removal are carried out; and under the protection of nitrogen, casting formation is carried out. The Al-Si-Cu-Zn-Sn-Ni aluminum-based brazing filler metal has the advantages of low melting point, high strength, high toughness, high corrosion-resistant property and good wetting property and spreadability.
Owner:GUILIN QINGTONG NON FERROUS METAL ARTS & CRAFTS MATERIAL DEV CO LTD
Purification and graphitization method of graphite material
ActiveCN102126721AImprove product qualityLow costChemical industryBromineElectrical energy consumption
The invention discloses a purification and graphitization method of a graphite material, aiming at solving the technical problems of improving the quality of the graphite material, saving energy and reducing cost. The method comprises the following steps: putting a graphite product or a carbon product in a graphite crucible in a furnace body; heating to 900-1700 DEG C, and then introducing nitrogen or argon; continuing to heat to 1000-1950 DEG C, introducing chlorine and then continuing to rising the temperature to 1400-2300 DEG C; simultaneously, introducing bromine or a fluorine-containing gas, heating to 1800-3300 DEG C and then stopping heating; introducing the chlorine until the temperature is reduced to below 1000-2000 DEG C; and feeding nitrogen or argon lasting for more than 0-15 hours. Compared with the prior art, the ash content of the obtained graphite product is less than 0.00011%; electrical energy consumption is reduced; and the method has the advantages that the processis simple, the cost is low, the quality of the graphite product is stable, and energy is saved.
Owner:BTR NEW MATERIAL GRP CO LTD
Preparation method of continuous high-performance intermediate-phase asphalt-based carbon fiber
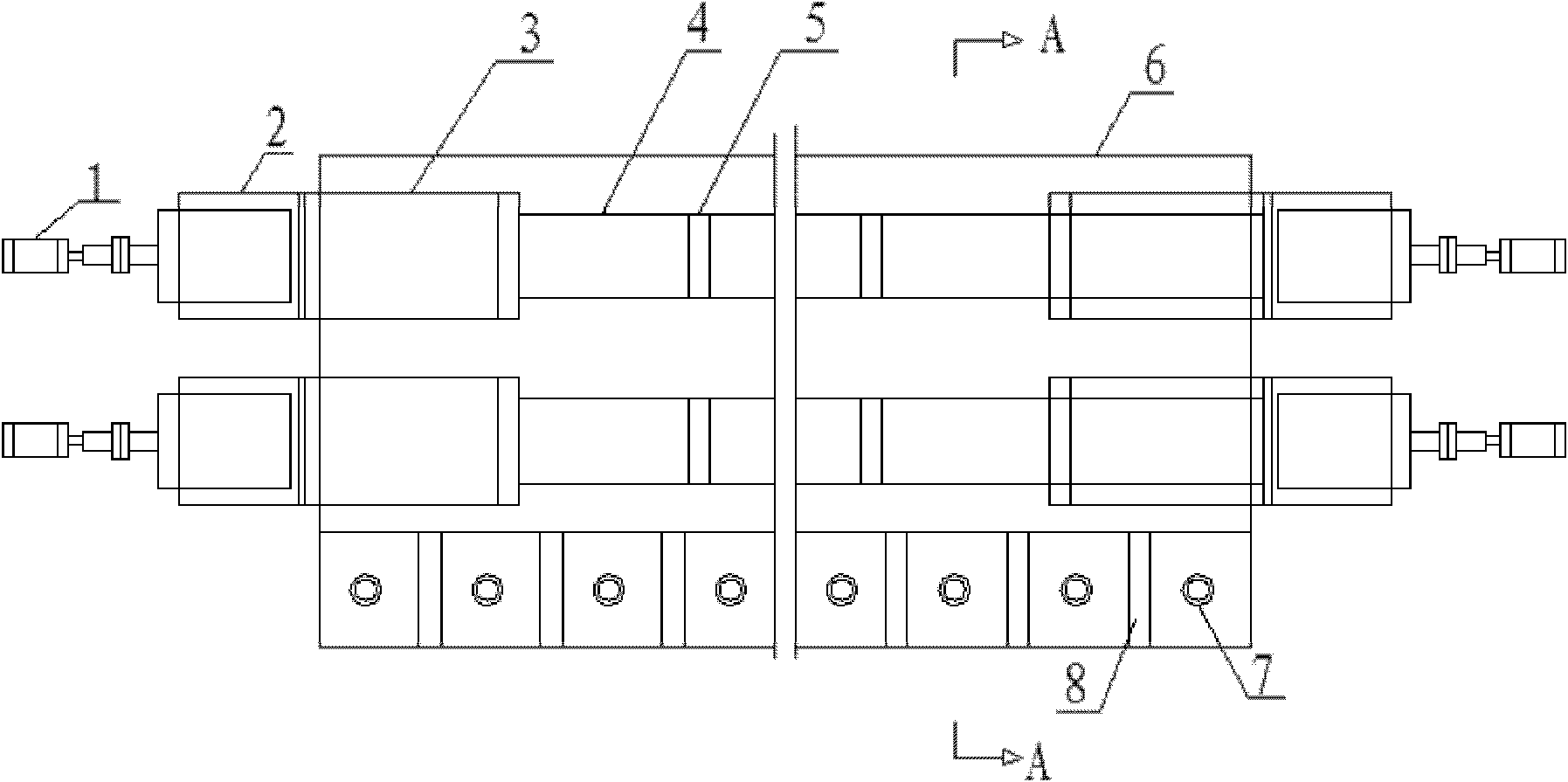
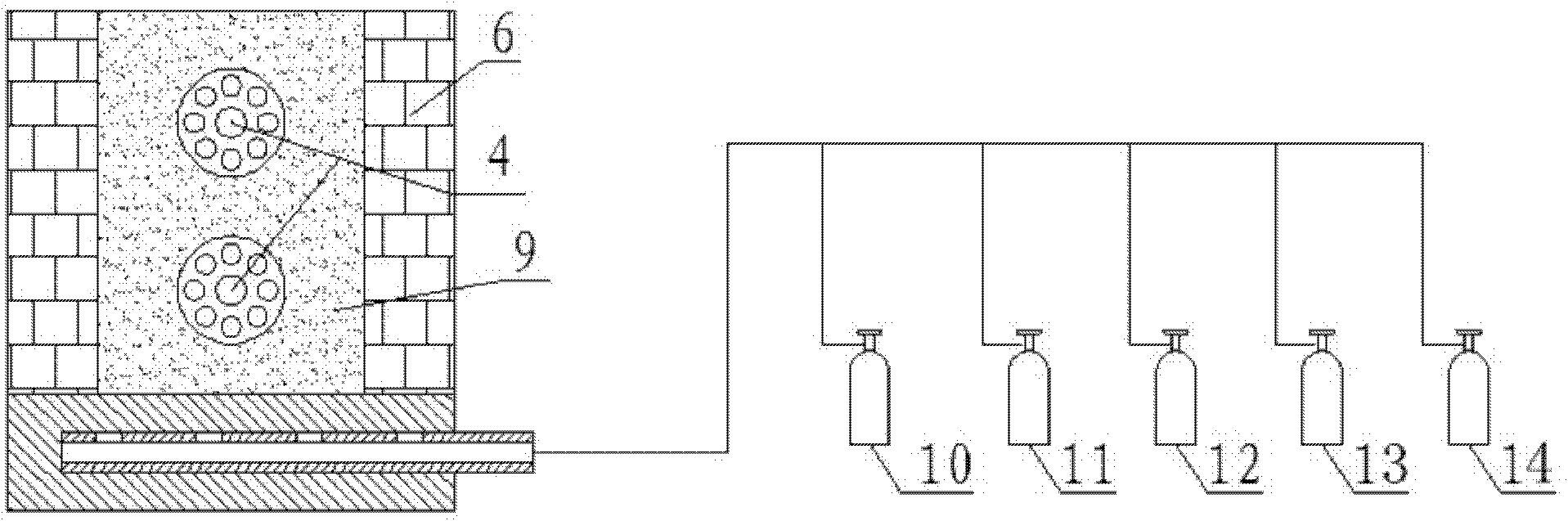
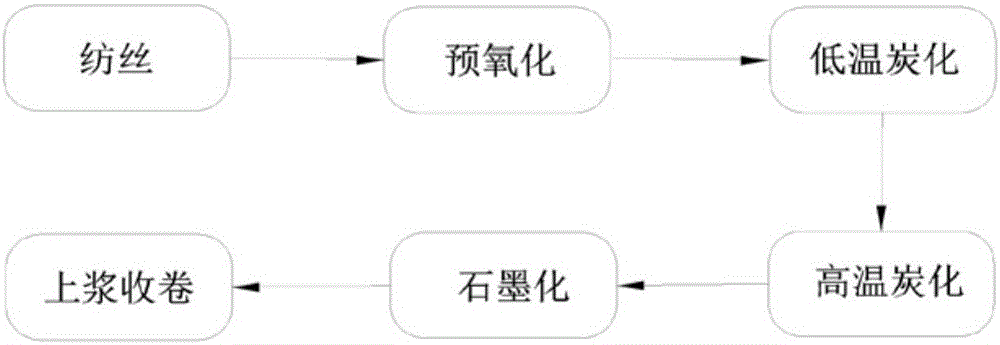
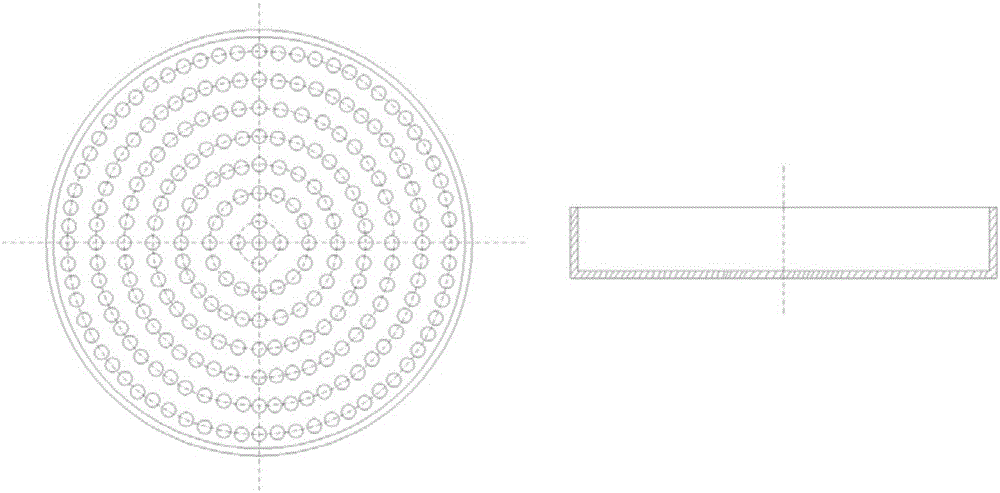
The invention discloses a preparation method of continuous high-performance intermediate-phase asphalt-based carbon fiber. The preparation method includes: winding spun carbon fiber precursor into a microporous graphite crucible through a garnett, disposing the graphite crucible in a pre-oxidation furnace, and feeding air to pre-oxidize the carbon fiber precursor in the pre-oxidation furnace; after pre-oxidation is finished, feeding inert gas, and performing low-temperature carbonization and high-temperature carbonization on pre-oxidized carbon fiber; cooling the pre-oxidation furnace to normal temperature, taking out the graphite crucible, and disposing the same in an intermittent high-temperature graphitizing furnace for graphitizing to obtain continuous high-strength high-modulus high-heat-conductivity asphalt-based carbon fiber. The preparation method is simple and high in controllability and yield, and the defect that a domestic continuous graphitizing furnace cannot be heated to higher than 2800 DEG C is overcome; tensile strength of the high-performance intermediate-phase asphalt-based carbon fiber is 2.2-3.5GPa, modulus of elasticity is 650-750GPa, and heat conductivity is 900-1050 W / m*K.
Owner:湖南东映碳材料科技股份有限公司
Preparation method of SiC nanowire with expandable graphite as carbon source
ActiveCN102730687AReduce consumptionLow costMaterial nanotechnologySilicon carbideNanowireShielding gas
The invention discloses a preparation method of SiC nanowire with expandable graphite as a carbon source. The expandable graphite is used as the carbon source, silicon powder and silica powder are used as a silicon source, or TEOS (tetraethoxysilane) is used as the silicon source. The TEOS is dissolved in absolute ethanol. And oxalic acid is added to accelerate the hydrolysis of TEOS. After drying, the carbon source and silicon source are mixed and grinded evenly, to be placed in a graphite crucible and then placed in a high-temperature-atmosphere box-type furnace and evacuated and filled with protective gas. The temperature is heated to 1300-1800 DEG C and the mixture is subjected to heat preservation and sintering for 2 hours. The pressure of the furnace is lower than 1MPa during the whole preparation process. After natural cooling is carried out on the furnace to the room temperature, the SiC nanowire is obtained. Themethod provided by the invention has characteristics of being cheap in raw material, simple in process, free of harmful gas polluting the environment, no requirement of any catalyst and large scale and high yield, which is suitable for industrial production of SiC nanowire.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Device and method for preparing large-size high-quality graphene single crystal
ActiveCN104695012AFast heating and cooling rateIncrease working temperaturePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesIntermediate frequencySingle crystal
The invention relates to a device and method for preparing a large-size high-quality graphene single crystal. The device comprises a shell and a top cover. The top cover is internally provided with a gas spray head with a gas distributing pipe so that inlet high-purity gas can enter a reaction cavity in an evenly-distributed mode. The reaction cavity is composed of sealed silica pipes, a graphite heating element connected between the two sealed silica pipes in an inserted mode and a graphite crucible placed in the graphite heating element. The graphite crucible is used for containing a SiC wafer substrate. A cooling water system and an intermediate frequency coil are arranged outside the graphite heating element. A gas outlet is formed in the bottom of the shell. The invention further provides the method for preparing the large-size high-quality graphene single crystal on the SiC substrate. By means of the device and method, the migration rate of the high-quality graphene crystal prepared on the SiC substrate is higher than that of graphene prepared through a SiC high-temperature pyrolysis method by 1-2 orders of magnitudes.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Silicon carbide based reinforced composite ceramic and preparation
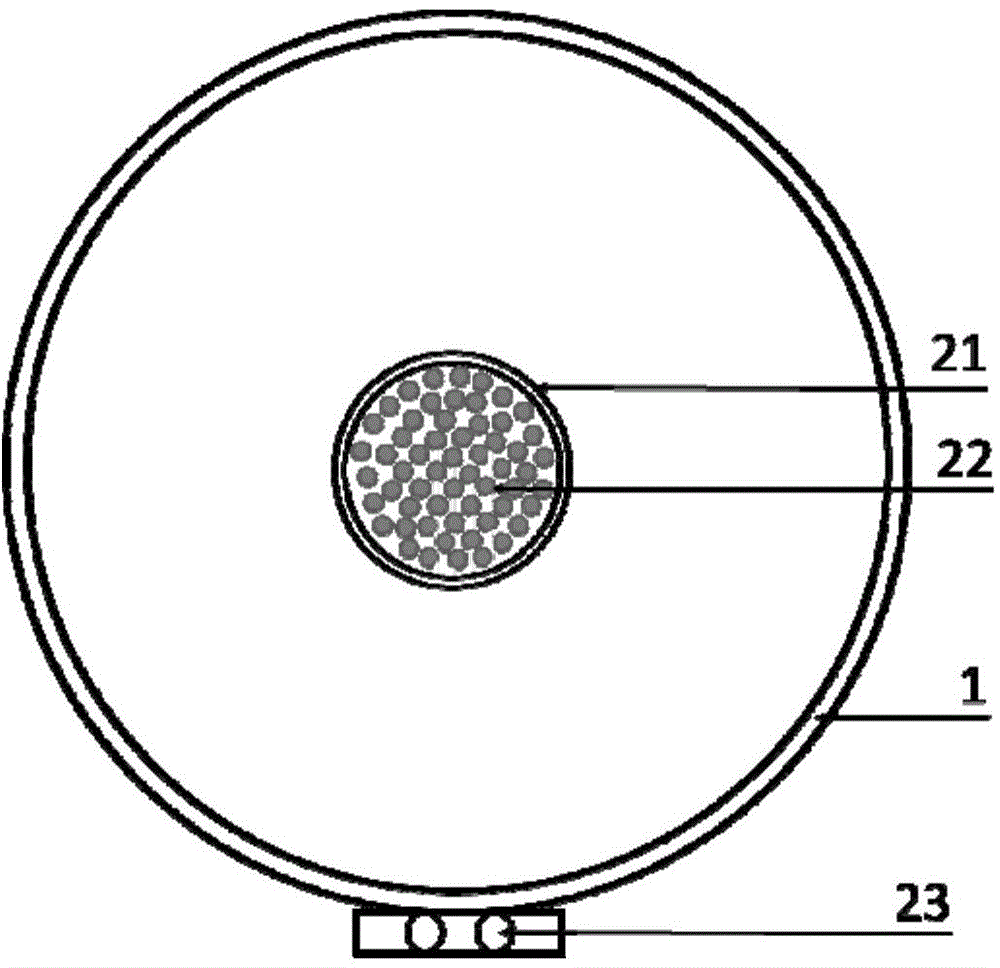
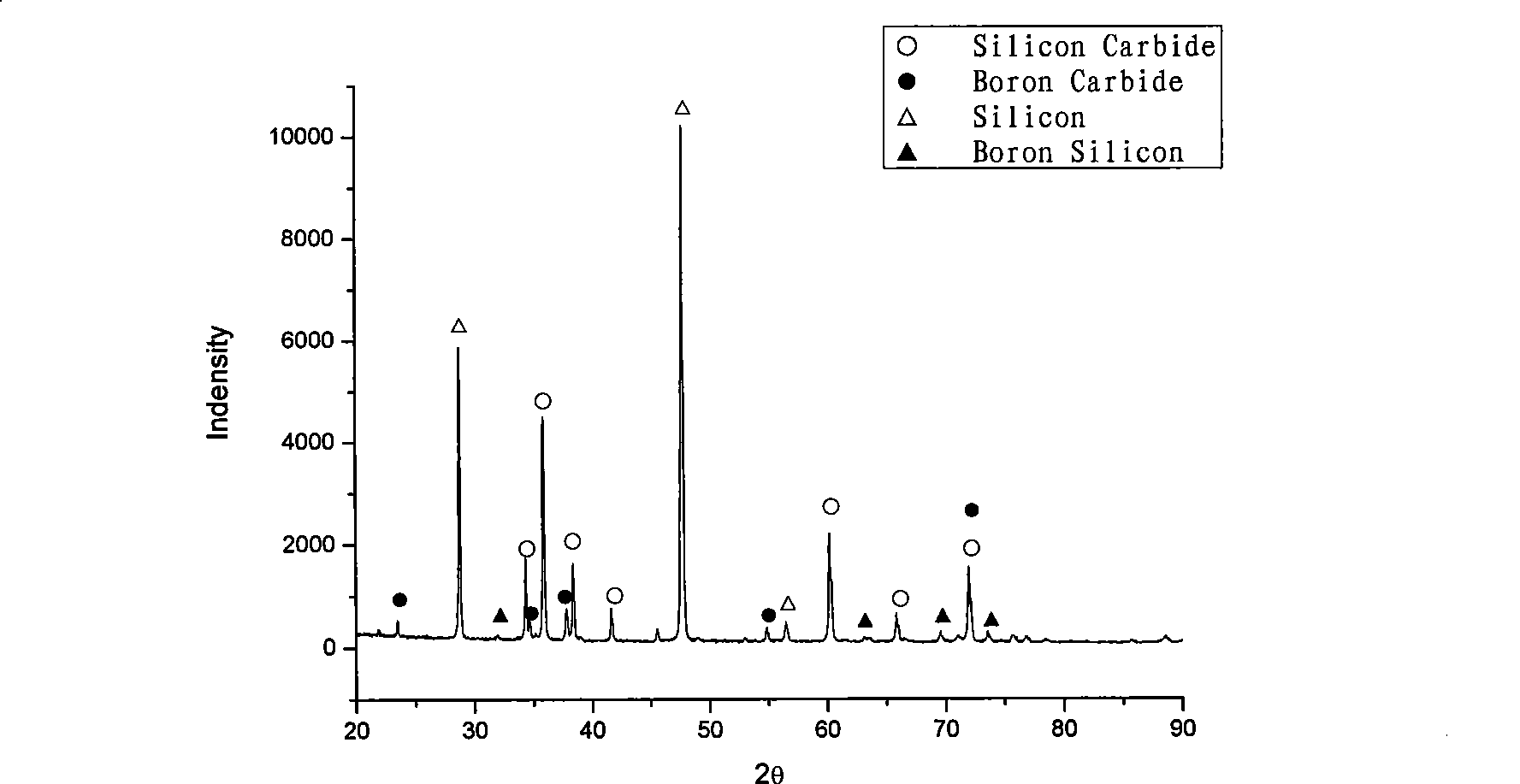
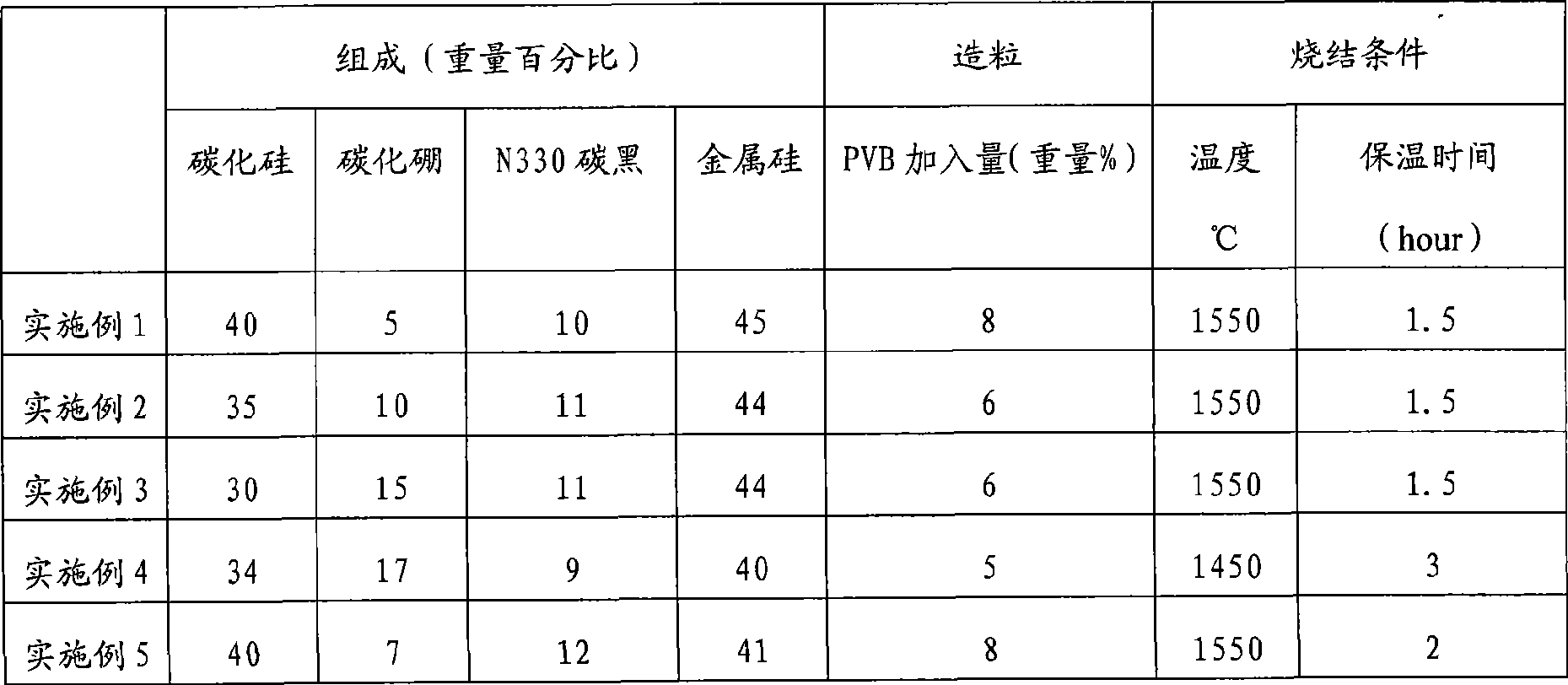
The invention discloses a reinforced silicon carbide-based composite ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The composite ceramic is characterized by comprising the following components based on weight percentages: 30%-40% of silicon carbide powder, 5%-17% of boron carbide powder, 9%-12% of nano carbon black and 40%-50% of silicon metal. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, ball milling and wet mixing are performed on the silicon carbide powder, the carbon black and the boron carbide powder to obtain mixed powder, and a bonding agent PVB is added for granulation, die pressing is performed for forming; then the formed green compact is dried and put in an air furnace for binder removal; and finally, the obtained green compact is put into a graphite crucible with silicon powder, and siliconizing and sintering are completed after 1-3h heat preservation at 1450-1550 DEG C under a vacuum environment, thus obtaining a sintering body. The boron carbide particle reinforced reaction sintered silicon carbide composite ceramic prepared by the method can be widely used as a structural material under high-temperature atmosphere and corrosive atmosphere, a frictional wear material and the like; and as the composite ceramic has better obdurability and hardness, the ceramic can be used as a substitute material of the traditional reaction sintered silicon carbide.
Owner:珠海亿特立新材料有限公司
Preparation technology of carbon/carbon composite material crucible for monocrystalline silicon furnace
InactiveCN102660768AExtended temperature rangeHigh densityBy pulling from meltCarbon compositesDifferential pressure
The invention discloses a preparation technology of a carbon / carbon composite material crucible for a monocrystalline silicon furnace, and the preparation technology comprises the following steps of: adopting a polyacrylonitrile nitrile base carbon fiber-woven performing body, taking mixed gas of natural gas, propylene, liquefied petroleum as a carbon source and nitrogen or argon as carrier gas, in a uniform temperature thermal field formed by a vertical pot type deposition furnace, timely switching the upper gas charging and lower gas charging of a pipeline, due to the pressure difference of the gas inside and outside the crucible, and in combination with a uniform temperature method, a differential-pressure method and a compulsive gas current method, realizing the quick densifying of the whole crucible blank body, wherein after 300-350 hours, the intensity of the crucible can reach to more than 1.6g / cm<3>, compared with the conventional free deposition technology, the preparation technology can be used for greatly shortening the deposition time, and reduces the production cost. After being mechanically machined, the crucible is used for a thermal field of the monocrystalline silicon furnace, compared with the hot isostatic pressure graphite crucible, the carbon / carbon composite material crucible has the advantages that the service life is prolonged by 3-5 times, the cost performance is obviously better than that of the graphite crucible, and the production cost and labor intensity of the monocrystalline silicon are greatly reduced.
Owner:保定顺天新材料股份有限公司
Seed crystal for growth of silicon carbide single crystal, process for producing the same, and silicone carbide single crystal and process for producing the same
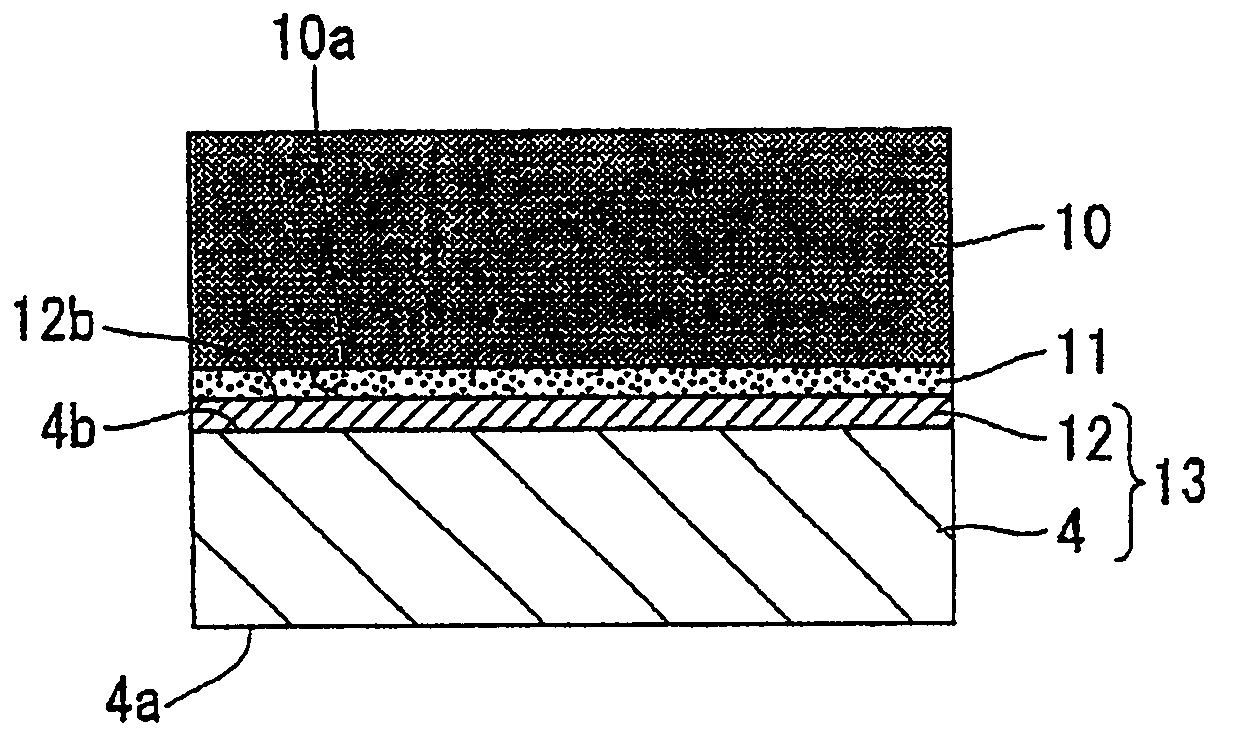
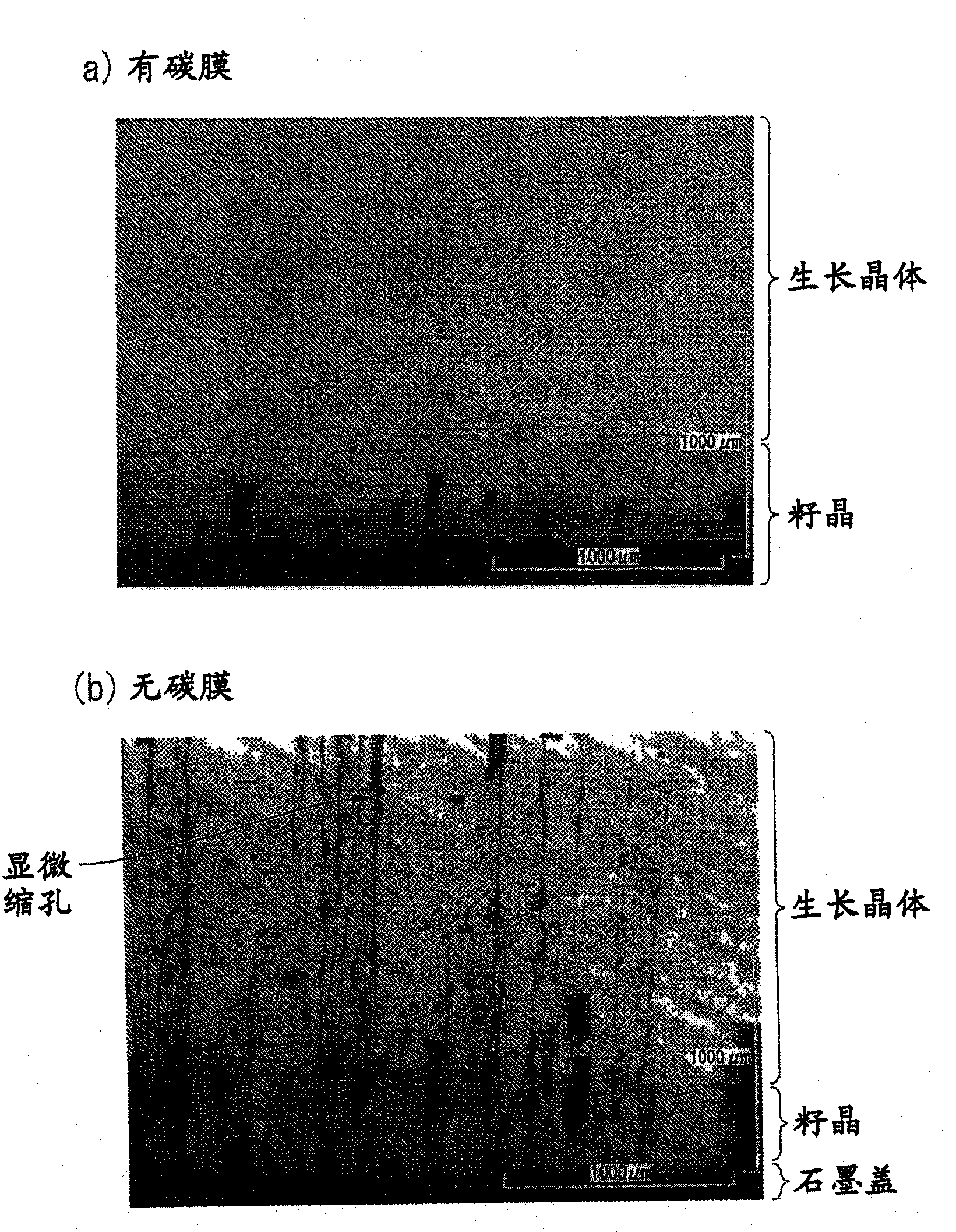
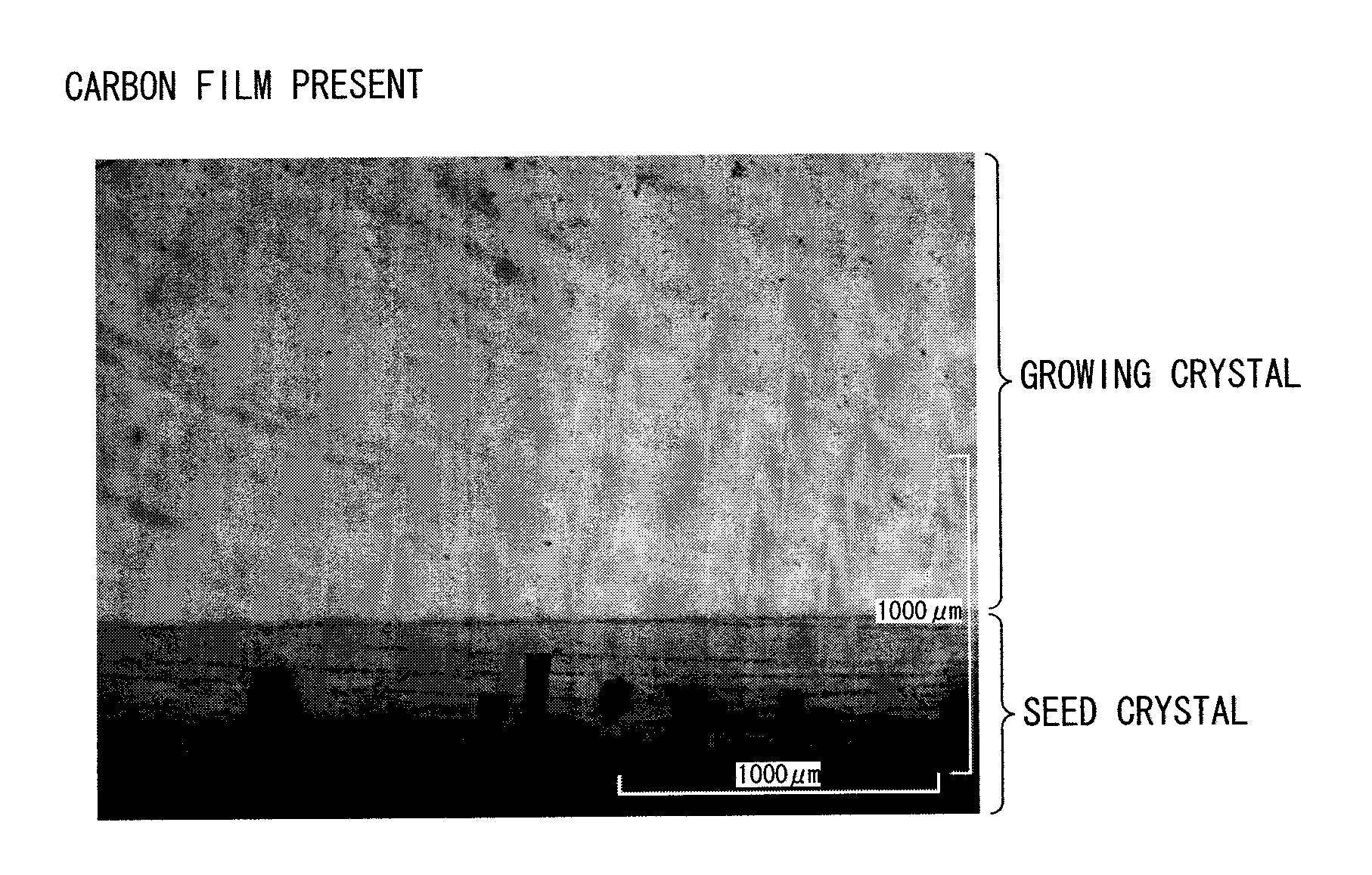
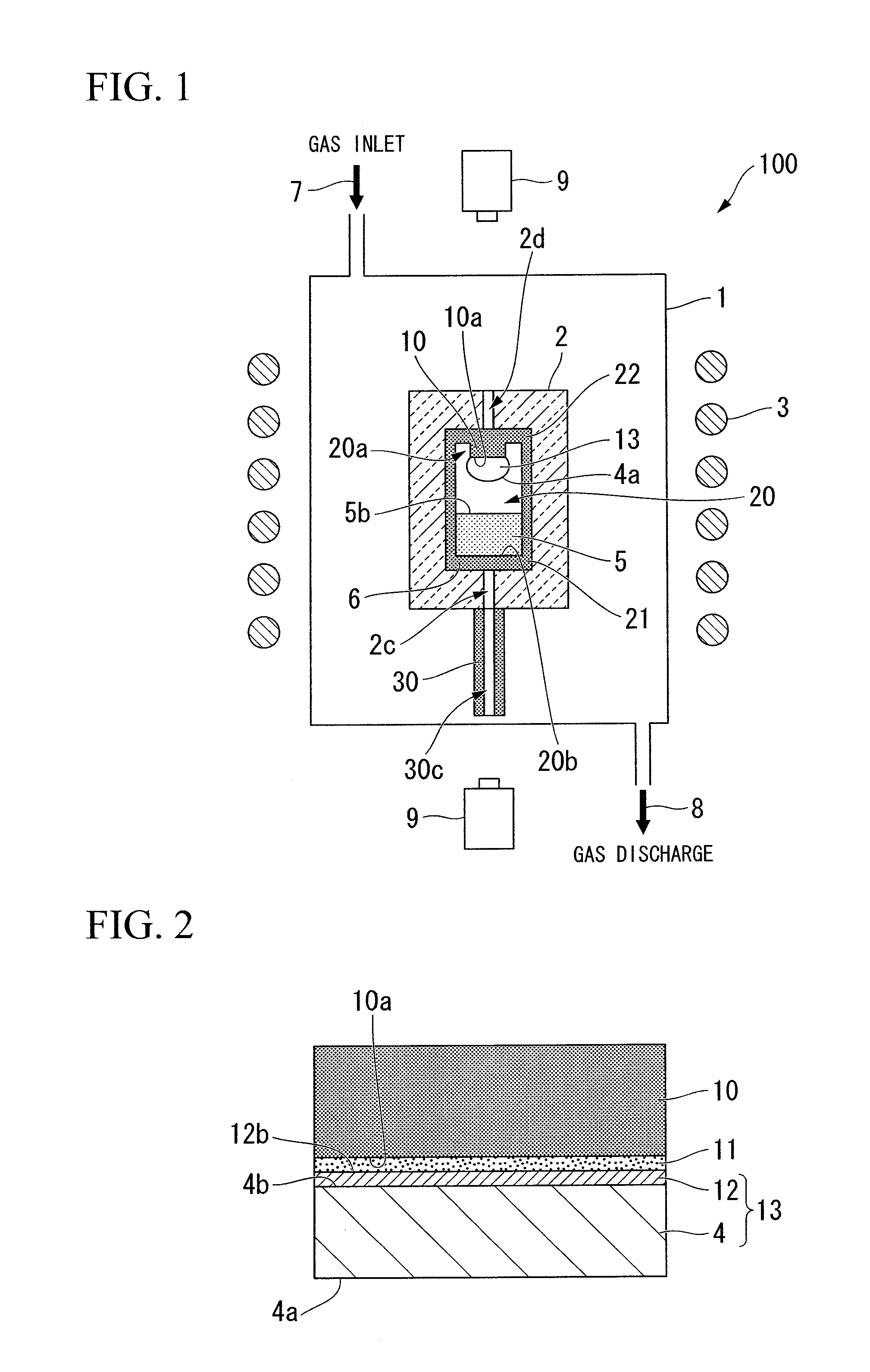
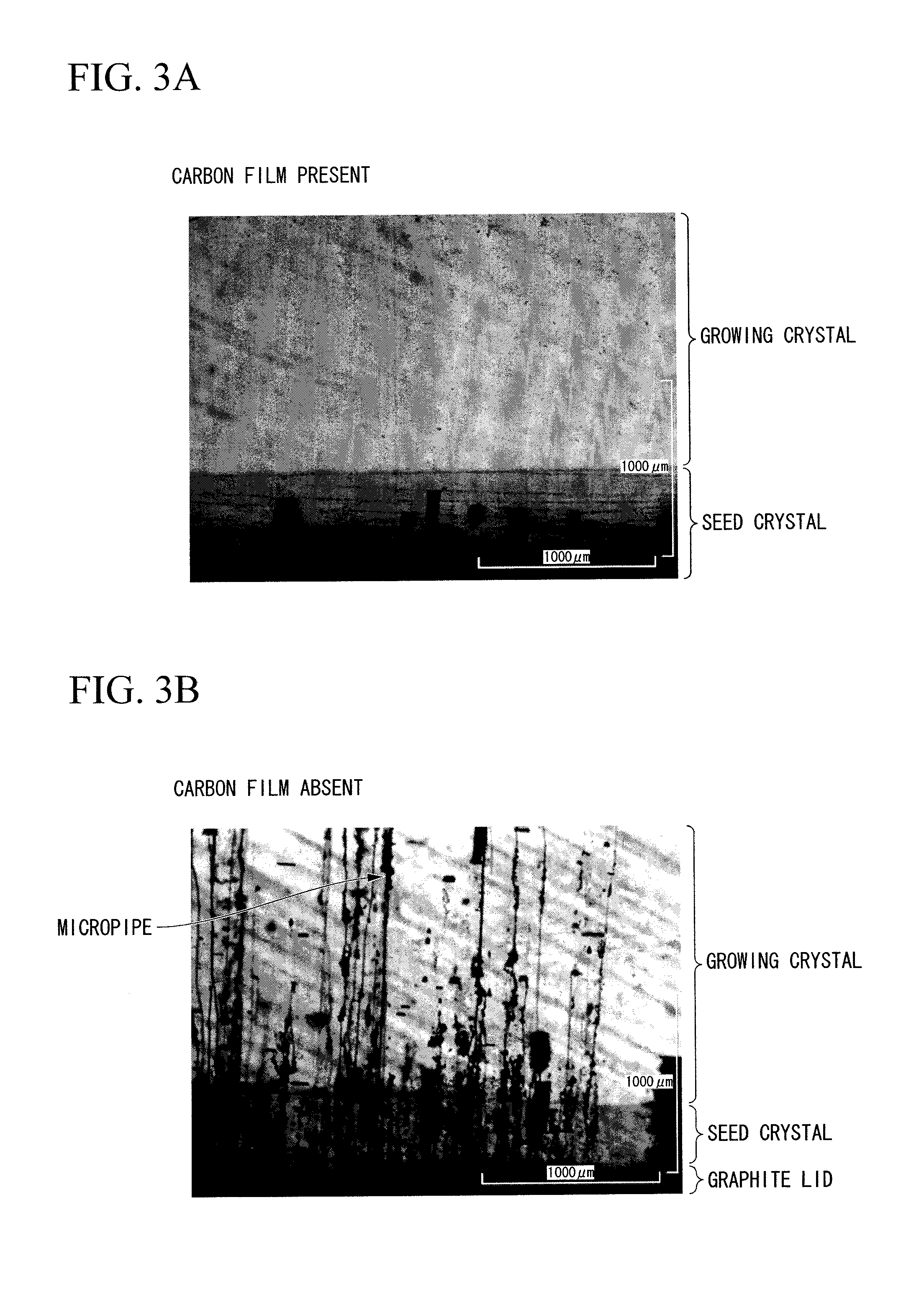
ActiveCN102057084ASuppression of crystal defectsHigh strengthPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsCarbon filmCarbide
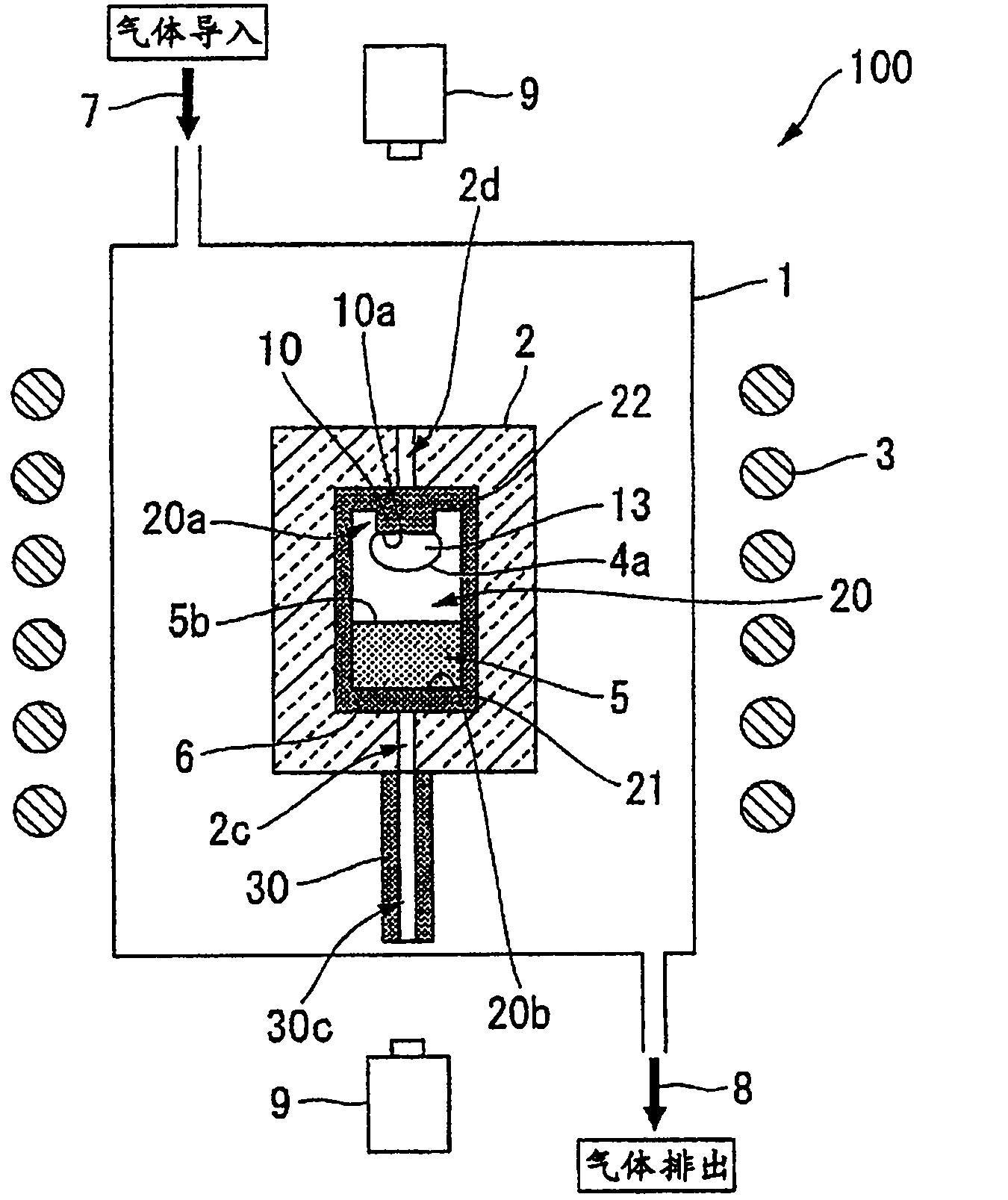
A seed crystal for the growth of a silicon carbide single crystal is provided which inhibits crystal defects from generating at the interface between the seed crystal and graphite and with which a high-quality silicon carbide single crystal having a low crystal defect density can be produced with satisfactory reproducibility. The seed crystal for the growth of a silicon carbide single crystal is a seed crystal (13) for silicon carbide single-crystal growth which is to be attached to the lid of a graphite crucible filled with a raw silicon carbide powder. The seed crystal (13) comprises: a seed crystal (4) which is constituted of silicon carbide and one side of which is a growth surface (4a) where a silicon carbide single crystal is to be grown by the sublimation method; and a carbon film (12) formed on the side (4b) opposite to the growth surface of the seed crystal (4), the carbon film (12) having a density of 1.2-3.3 g / cm3.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Seed crystal for silicon carbide single crystal growth, method for producing the seed crystal, silicon carbide single crystal, and method for producing the single crystal
InactiveUS20110111171A1Good reproducibilityQuality improvementVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCarbon filmOptoelectronics
A seed crystal for silicon carbide single crystal growth (13) which is attached to the lid of a graphite crucible charged with a raw material silicon carbide powder. The seed crystal includes a seed crystal (4) formed of silicon carbide having one surface defined as a growth surface (4a) for growing a silicon carbide single crystal by a sublimation method, and a carbon film (12) formed on the surface (4b) opposite to the growth surface of the seed crystal (4). Further, the film density of the carbon film (12) is 1.2 g / cm3 to 3.3 g / cm3.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Czochralski silicon monocrystal growth furnace and method for filling silicon melts continuously
InactiveCN102418140AReduce consumptionReduce energy consumptionPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltSingle crystalOxygen content
The invention discloses a czochralski silicon monocrystal growth furnace and a method for filling silicon melts continuously. In the czochralski silicon monocrystal growth furnace, a monocrystal lifting part comprises a lifting head, a slave furnace chamber, an isolating valve, a furnace body, an upper part heat-preserving cover, a heater, a crucible lifting rotary mechanism, a graphite crucible, a crucible, a steel wire rope, a chuck and the like; a melt continuously-filled part comprises a small furnace cylinder, a charging bin, the isolating valve, a charging and weighing device, a continuously-melted tube, a heat-insulating body, the heater, a melt temperature stabilizing tube and the like; and by the czochralski silicon monocrystal growth furnace, the continuous melting of polycrystalline silicon and the continuous growth of silicon monocrystal are realized. In the czochralski silicon monocrystal growth furnace, a spacing interval of opening a mono-crystal furnace for two times adjacently can be prolonged by over 30 days, the size of the crucible can be reduced effectively, the consumption and oxygen content of the czochralski silicon monocrystal growth method can be reduced effectively, and the production efficiency can be improved.
Owner:曾泽斌
Preparation method of zirconium diboride ceramic with in-situ-introduced boron as additive
InactiveCN103011827AAvoid introducingGood for maintaining excellent performanceArgon atmosphereZirconium dioxide
The invention relates to the field of structural ceramic manufacturing, in particular to a preparation method of zirconium diboride ceramic with in-situ-introduced boron as an additive. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing ball milling and mixing zirconium dioxide and elemental boron in a mol ratio of (1: 3.5)-(1: 4.5), and drying to obtain ZrO2 / B mixed powder; secondly, putting the ZrO2 / B mixed powder into a graphite crucible, and performing high-heat treatment at the air pressure of below 200Pa to obtain ZrB2 / B powder; and finally, sieving the obtained ZrB2 / B powder, performing isostatic pressing, putting the ZrB2 / B powder into the graphite crucible, performing pressureless sintering in an argon atmosphere, controlling the sintering temperature at 1800 -2100 DEG C, the heat-preserving time at 1-3 hours and the heating rate at 10-50 DEG C / min, and preserving heat for 0.5 hours at 1500-1700 DEG C to obtain the compact zirconium diboride ceramic. By the preparation method, a ball milling medium is not introduced, the impurity content is reduced, excellent performance of the zirconium diboride ceramic can be maintained easily, and the sintering compactness of the zirconium diboride ceramic is realized at a relatively low temperature (2000 DEG C).
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com