Patents
Literature
237results about How to "Reduce interface defects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
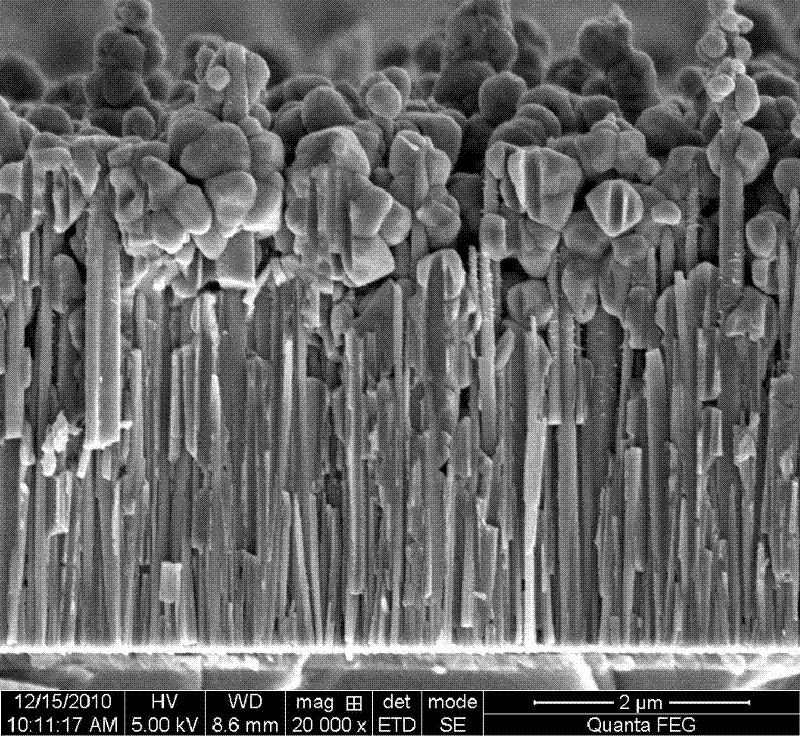
Carbon nano-tube connecting carbon fiber multi-scale reinforcing body and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101173386ATake full advantage of mechanical propertiesRealize chemical bond connectionFibre treatmentArtificial filament chemical after-treatmentFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a multi-scale reinforcement body that carbon nano-tube is connected with carbon fiber and a preparation method aiming at solving the drawbacks of increasing rigidity at the interface, lowering toughness of material and not improving performance of resin base between the fibers and between carbon fiber plywoods after prior carbon fiber treatment is made. The multi-scale reinforcement body of carbon nano-tube connecting carbon fiber is made through combining between a carbon nano-tube decorated by 1, 6 hexamethylenediamine and carbon fiber with acyl chloride functional group on the surface. The preparation method comprises: the carbon nano-tube decorated by 1, 6 hexamethylenediamine and the carbon fiber with acyl chloride functional group on the surface are prepared before put into N,N-dimethylformamide for reaction, thereby getting the multi-scale reinforcement body of carbon nano-tube connecting carbon fiber. The invention has the advantages of big activity on the surface, a plurality of chemical activated functional groups, strong reactive activity, good cohesiveness with the base, improving shearing intensity at the interface for composite material by 127.5% to 144.7% and improving toughness for the base by 34.43% to 48.67%.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
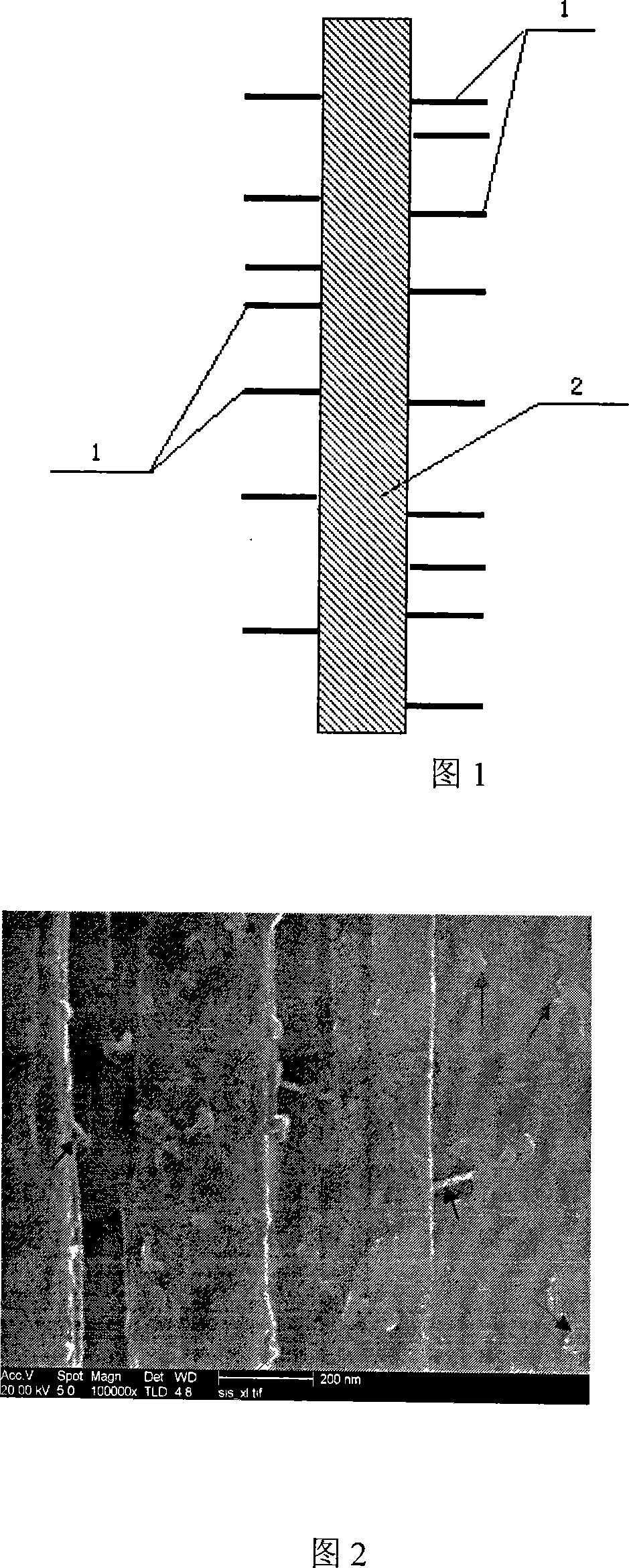
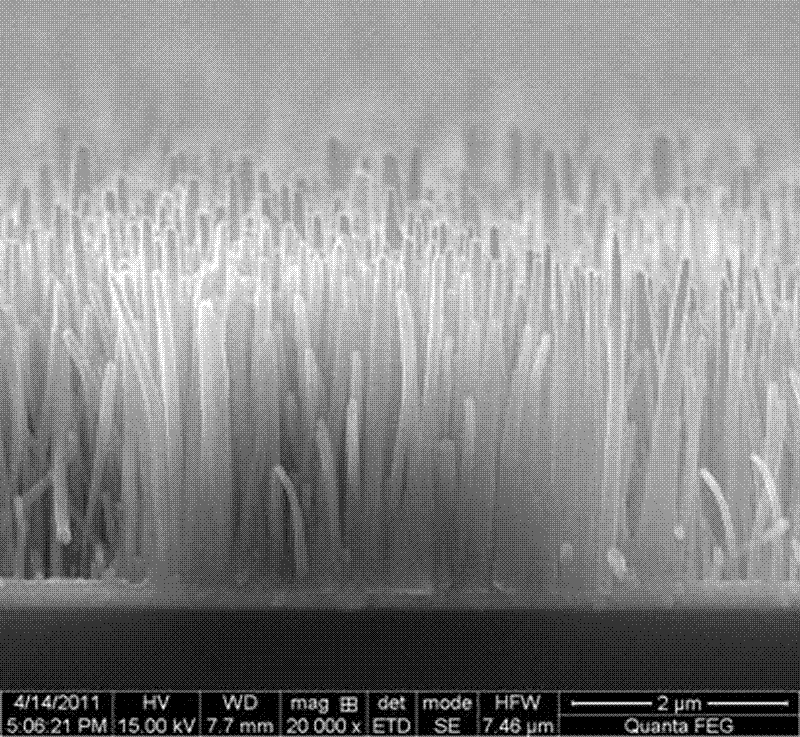
Method for preparing zno/cu2o heterojunction material and zno/cu2o three-dimensional structure heterojunction solar cell
InactiveCN102268706AReduce chance of recombinationImprove coverage uniformityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionElectrolytic agent
The invention discloses a method for preparing a ZnO / Cu2O heterojunction material and a ZnO / Cu2O three-dimensional structure heterojunction solar cell. The preparation method of the heterojunction material includes growing an n-type ZnO nanorod array on a substrate by a liquid phase growth method. Thin film, use alkaline copper salt solution as electrolyte, deposit at a deposition potential of -0.4~-0.6V for 60-150s, electrochemically deposit p-type Cu2O on the surface of ZnO nanorods to form a Cu2O seed layer; use alkaline copper The salt solution is a deposition solution, and the electrochemical deposition method is again used at a deposition potential of -0.05 to -0.3V to fully fill Cu2O from bottom to top into the gaps of the nanorod array to form a ZnO / Cu2O three-dimensional structure heterojunction material. The filling depth and density of the Cu2O semiconductor film of the present invention are increased, interface defects are reduced, and the heterojunction battery produced has high battery efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
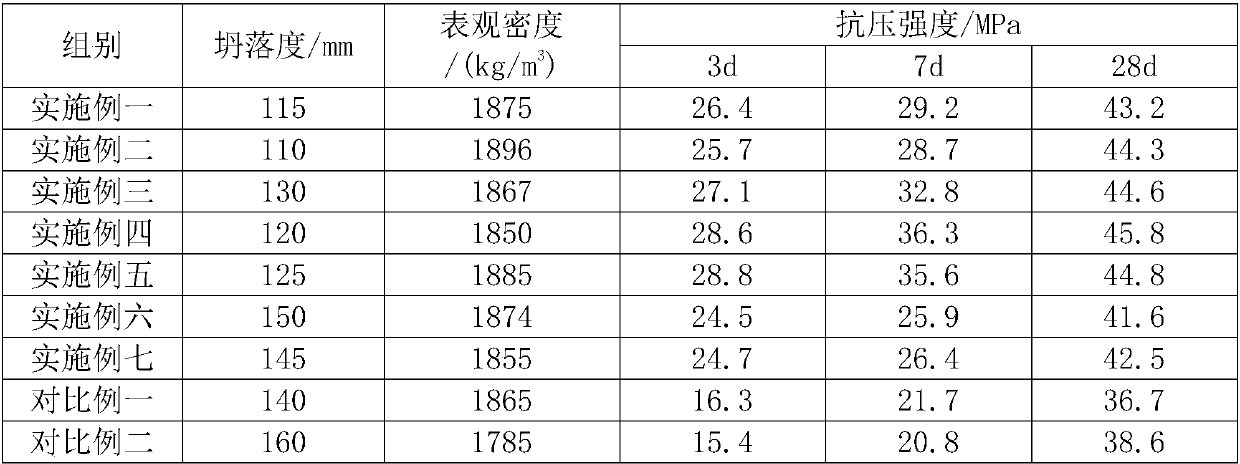
High-strength lightweight aggregate concrete and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to high-strength lightweight aggregate concrete and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of building material concrete. The lightweight aggregate concrete is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 105-118 parts of cement, 180-185 parts of light coarse aggregate, 120-125 parts of fine aggregate, 65-70 parts of mineral admixtures, 9-24 parts of modified polypropylene fiber, 3.4-3.8 parts of concrete admixtures and 65-70 parts of water. The preparation method comprises the following steps that the raw materials are weighed according to the formula ratio, the light coarse aggregate is added into water accounting for one half of the total water amount for pre-wetting for 45-60 minutes, then the fine aggregate is added, stirring is carried out for 1-2 minutes, the cement, the mineral admixtures and the modified polypropylene fiber are continuously added, uniform stirring is carried out, then the concrete admixtures andthe rest water are added, and uniform stirring is carried out so as to obtain the high-strength lightweight aggregate concrete. The high-strength lightweight aggregate concrete and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that the strength is high, and the quality is stable.
Owner:武汉中阳明建材有限公司
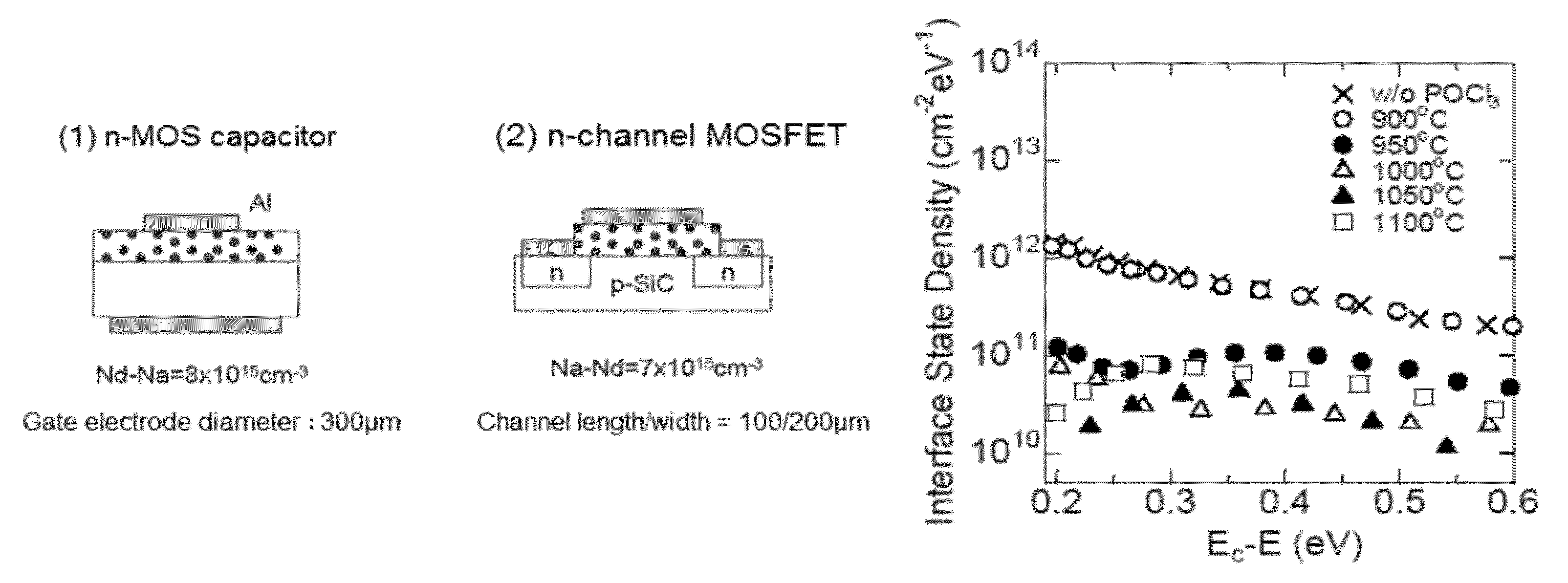
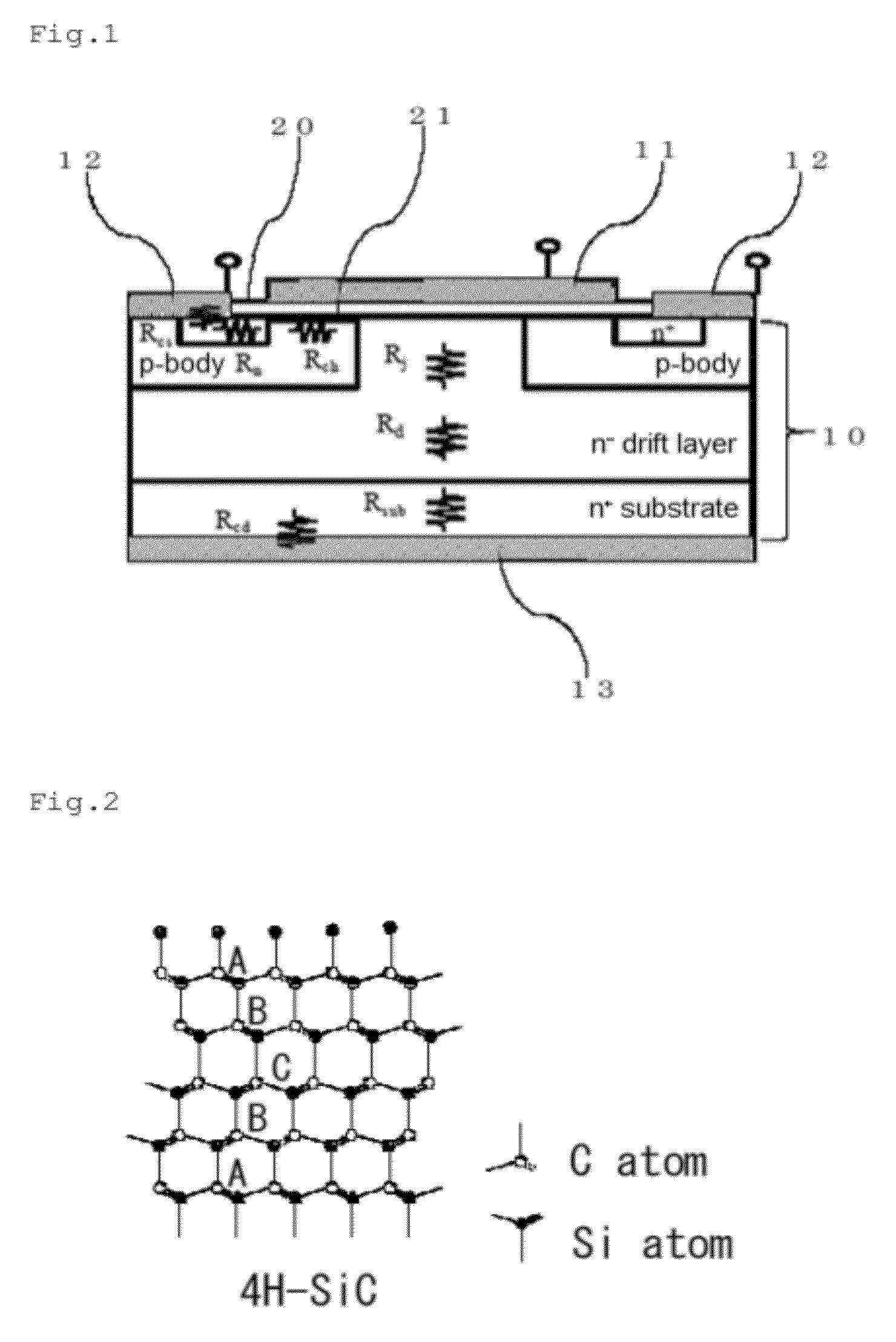
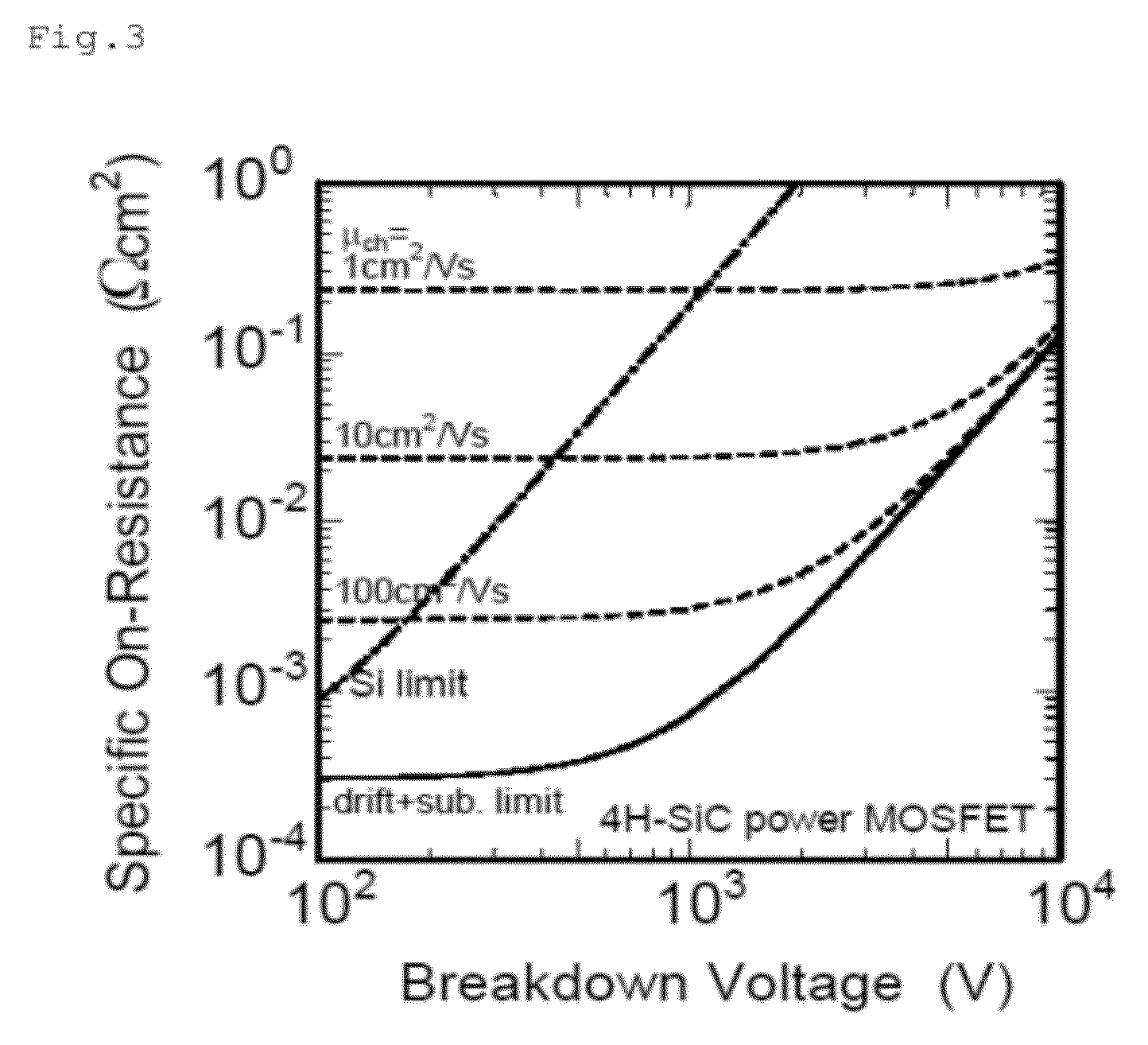
Sic semiconductor element and manufacturing method for same
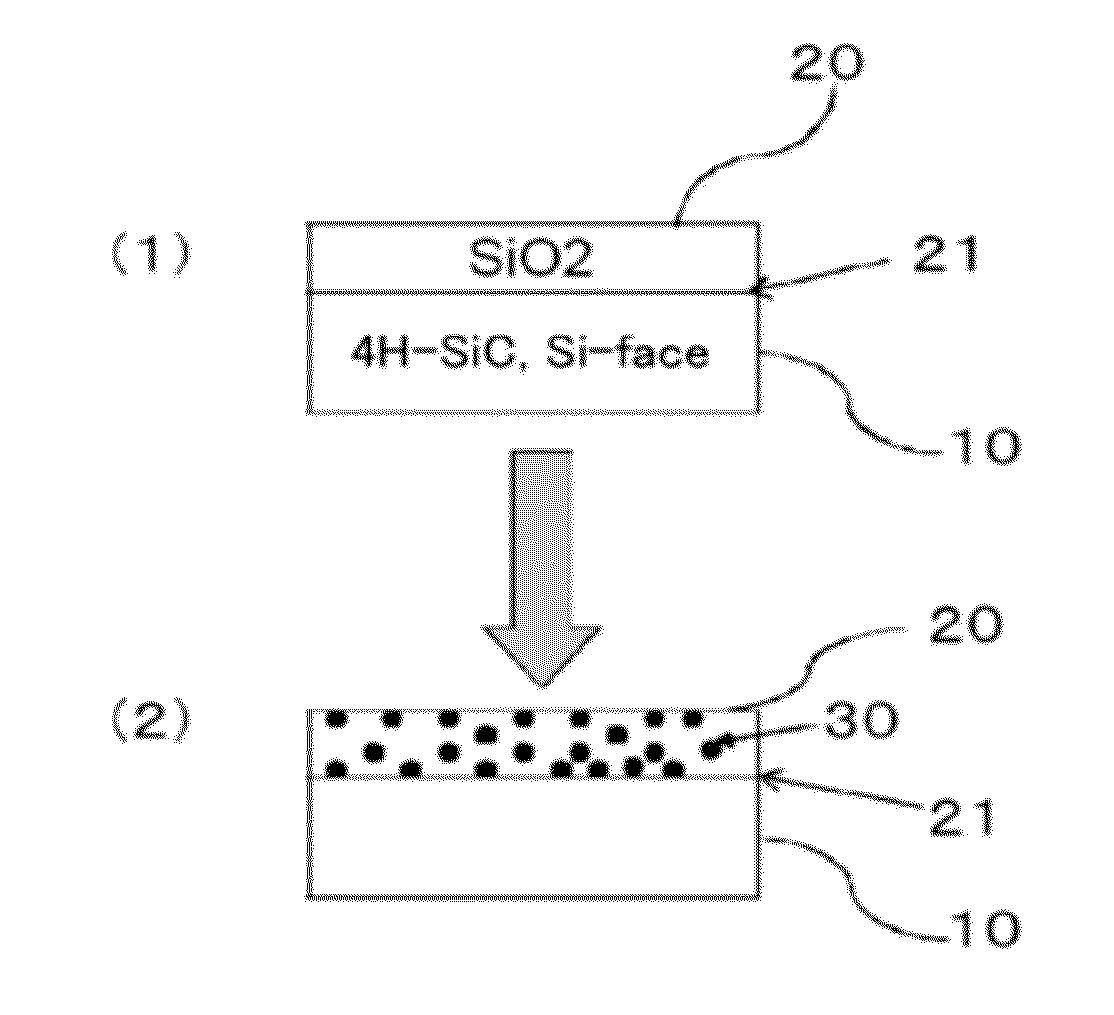
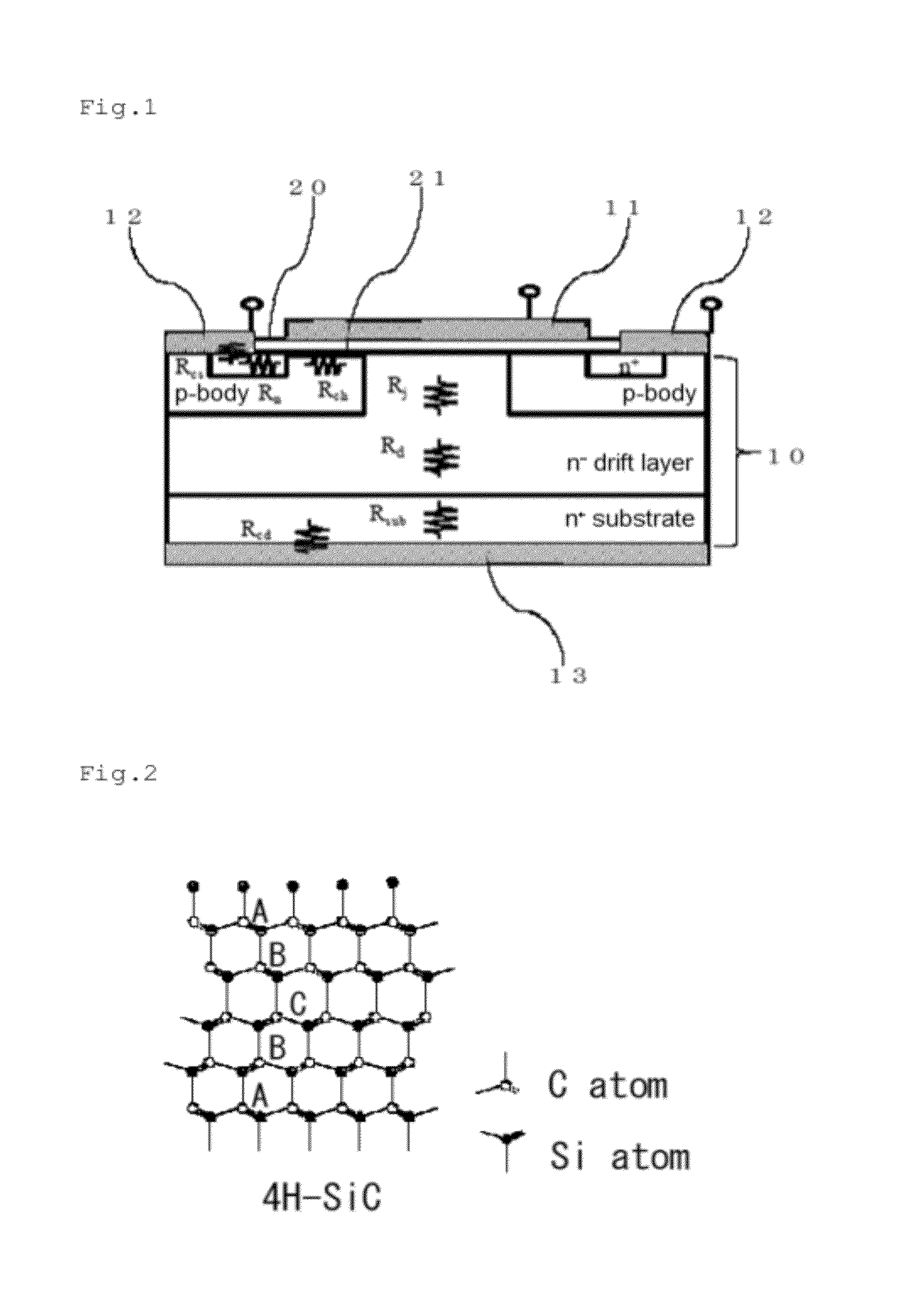
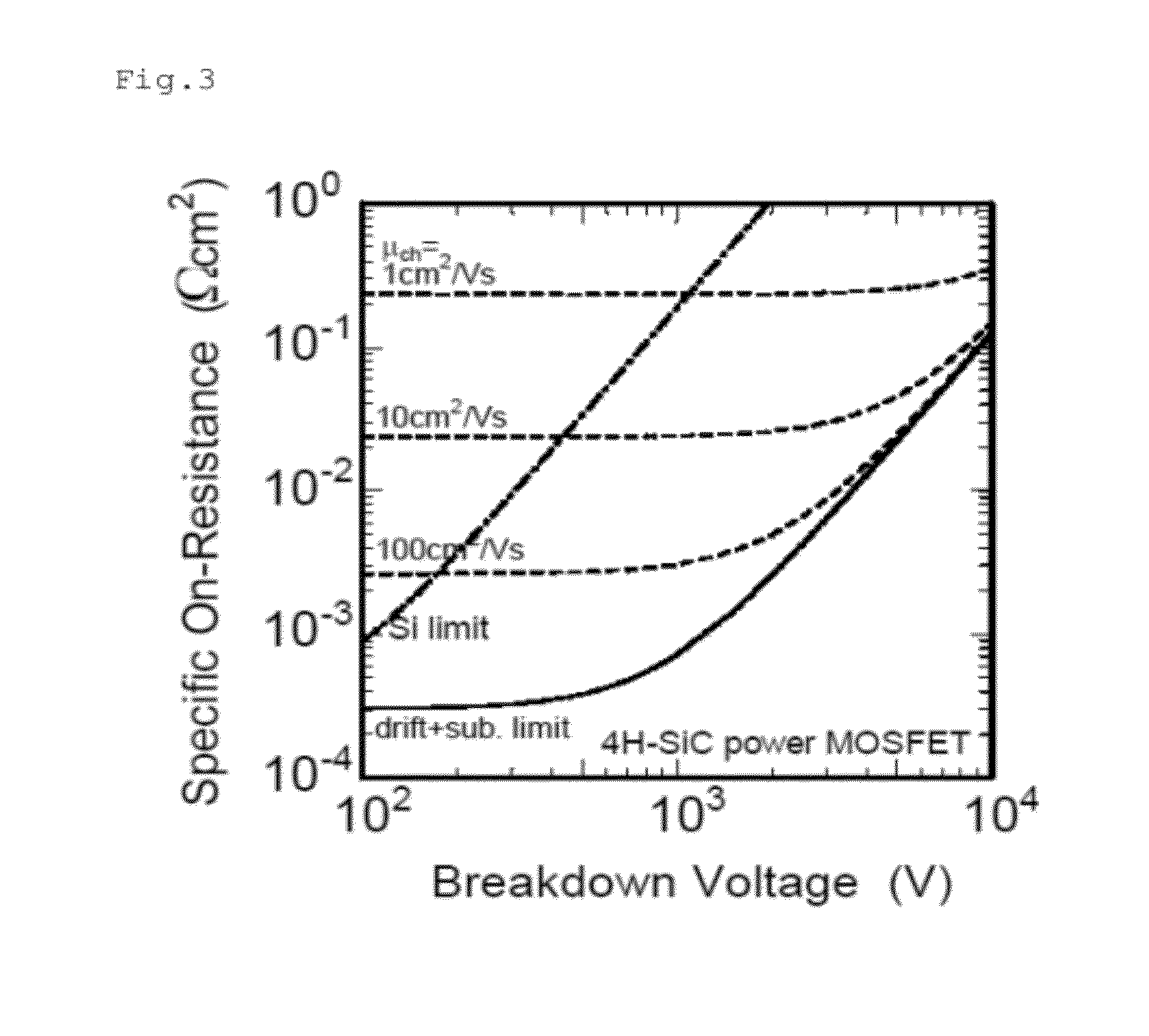
ActiveUS20120241767A1Reduce interface defectsReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesState densityThreshold voltage
Disclosed are an SiC semiconductor element and manufacturing method for an SiC semiconductor element in which the interface state density of the interface of the insulating film and the SiC is reduced, and channel mobility is improved. Phosphorus (30) is added to an insulating film (20) formed on an SiC semiconductor (10) substrate in a semiconductor element. The addition of phosphorous to the insulating film makes it possible to significantly reduce the defects (interface state density) in the interface (21) of the insulating film and the SiC, and to dramatically improve the channel mobility when compared with conventional SiC semiconductor elements. The addition of phosphorus to the insulating film is carried out by heat treatment. The use of heat treatment to add phosphorous to the insulating film makes it possible to maintain the reliability of the insulating film, and to avoid variation in channel mobility and threshold voltage.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
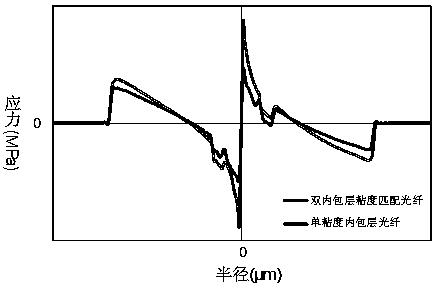
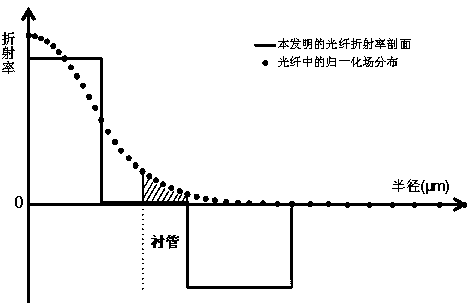
Low-attenuation bending insensitive single mode fiber
InactiveCN104316994AGood attenuation performanceDelay decayOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideUltrasound attenuationMicrometer
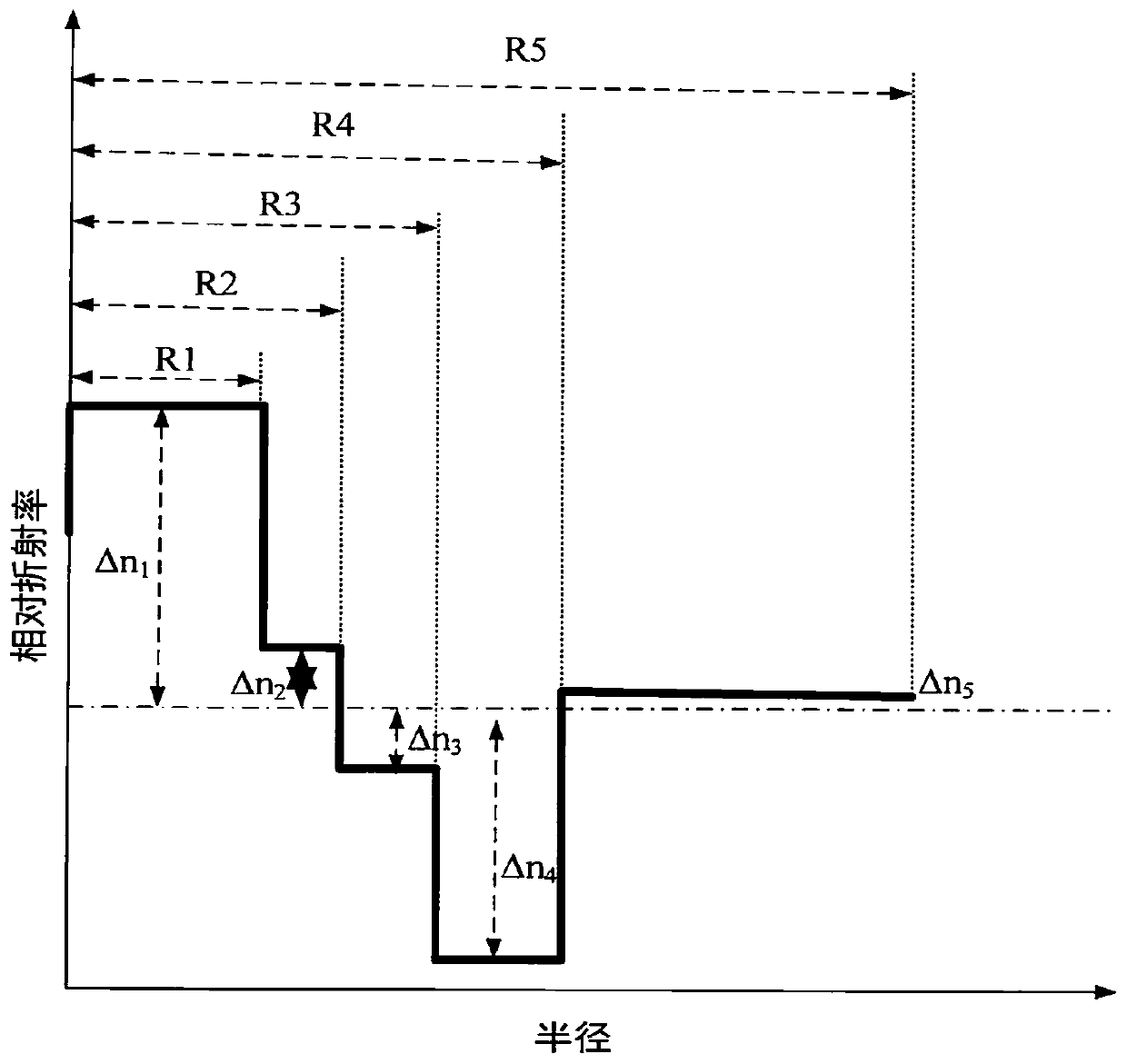
The invention relates to a low-attenuation bending insensitive single mode fiber which comprises a core layer and wrapping layers. The low-attenuation bending insensitive single mode fiber is characterized in that the relative refractive index difference delta1 of the core layer ranges from 0.30% to 0.38%, the radius R1 of the core layer ranges from 3.5 micrometers to 4.5 micrometers, the four wrapping layers are arranged outside the core layer, the first wrapping layer is a first inner wrapping layer tightly surrounding the core layer, the relative refractive index difference delta2 of the first wrapping layer ranges from -0.02% to 0.02%, the radius R2 of the first wrapping layer ranges from 6.5 micrometers to 8.5 micrometers, the second wrapping layer is a second inner wrapping layer tightly surrounding the first inner wrapping layer, the relative refractive index difference delta3 of the second wrapping layer ranges from -0.02% to 0.02%, the radius R3 of the second wrapping layer ranges from 8 micrometers to 11 micrometers, the third wrapping layer is a downwards-concave wrapping layer tightly surrounding the second inner wrapping layer, the relative refractive index difference delta4 of the third wrapping layer ranges from -0.5% to -0.2%, the radius R4 of the third wrapping layer ranges from 12 micrometers to 20 micrometers, and the fourth wrapping layer is an outer wrapping layer tightly surrounding the downwards-concave wrapping layer and is a pure quartz glass layer. The low-attenuation bending insensitive single mode fiber can be completely matched with a G.652.D optical fiber, and therefore the low attenuation, the large effective area and the bending resistance can be better unified.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Method for preparing organic-inorganic hybrid evaporation alcohol permselective membrane
ActiveCN101518719AEasy to separateEnhanced interactionDistillationHydroxy compound separation/purificationMolecular sieveAlcohol
The invention relates to a method for preparing an organic-inorganic hybrid evaporation alcohol permselective membrane used for the separation of alcohol / water system. Micropore molecular sieves are modified chemically, organic functional groups are led in the structure and the modified micropore molecular sieves and silicone rubber are mixed and coated to prepare the organic-inorganic hybrid evaporation alcohol permselective membrane. The method is characterized in that: the organic functional groups in the modified micropore molecular sieves can enhance the interaction force between the modified micropore molecular sieves and the silicone rubber, or form stable compound bond phase between the two substances, thus weakening the boundary defect between the inorganic and organic phases, improving the separation performance of the membrane and avoiding the defects of the deterioration of boundary defect between the inorganic and organic phases and unstability of the membrane due to compression during the use process of the membrane.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
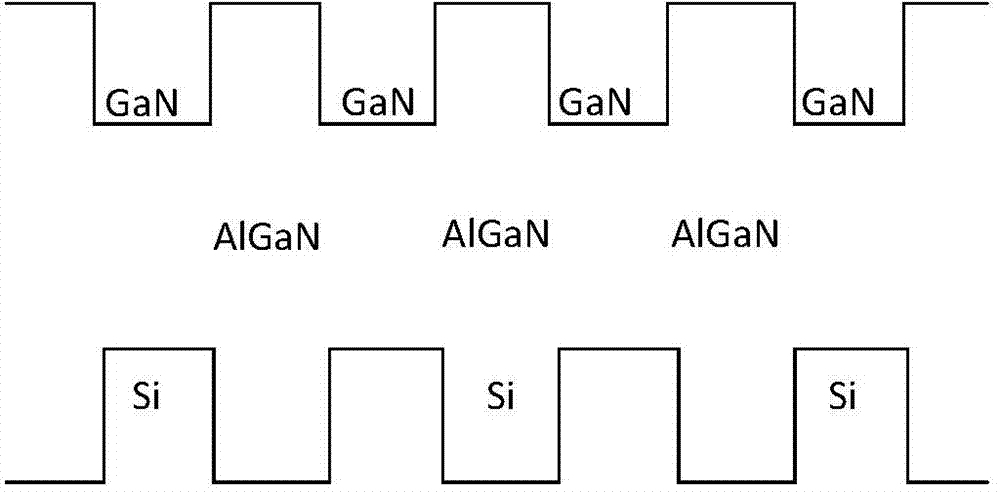
Epitaxial growth method of purple-light LED
InactiveCN103887380AReduce the difficulty of growingIncreased Radiation PowerSemiconductor devicesWavelength rangeCharge carrier
The invention provides an epitaxial growth method of a purple-light LED. The suitable wavelength range of the method is 365-420 nm, the growth difficulty of the purple-light LED can be greatly lowered, meanwhile, the radiation power of the purple-light LED can be increased and the reliability of purple-light LED devices is effectively improved. In the epitaxial growth method, an n-type AlGaN / GaN super lattice structure is adopted, potential-barrier-layer AlGaN and potential-well-layer GaN are doped alternately periodically, and therefore concentration of n-type carriers can be concentrated; the concentration of different layers change periodically, and periodic conductance changes enable currents to be diffused better; meanwhile, the conductance changing area is widened, so that the transmitting effect of an electric leakage channel with linear defects is weakened, forward voltage can be lowered, and ESD can be improved.
Owner:西安利科光电科技有限公司
Preparation method of acrylic polymer grafted carbon fiber multi-scale reinforcement
InactiveCN103275282AThe surface is inertSmall specific surface areaPhysical treatmentInterlaminar shearResin matrix
The invention discloses a preparation method of an acrylic polymer grafted carbon fiber multi-scale reinforcement, relating to a carbon fiber reinforcement and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1) performing oxidation treatment on a carbon fiber surface; 2) grafting a silane coupling agent to the carbon fiber surface after the oxidation treatment; 3) obtaining chain transfer agent grafted carbon fiber through a reaction between the carbon fiber surface grafted silane coupling agent and a chain transfer agent; and 4) initiating acrylic monomer grafting polymerization on the surface of the chain transfer agent grafted carbon fiber to finally obtain an acrylic polymer grafted carbon fiber multi-scale reinforcement. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the roughness of the carbon fiber surface can be greatly improved, a great quantity of active functional groups can be introduced, the reaction activity of the carbon fiber surface is improved, the wettability and cohesiveness between the carbon fiber and a resin matrix are improved, and the interlaminar shear strength of an epoxy composite material is enhanced by 40-50%.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Semiconductor structure and forming method thereof
ActiveCN105336620ALower Schottky BarrierAlleviate the Fermi level pinning effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMetallic materialsOxide
The invention discloses a semiconductor structure and a forming method thereof. The forming method of the semiconductor structure comprises the steps as follows: a semiconductor substrate is provided; a gate structure which covers partial surface of the semiconductor substrate is formed; a source and a drain are respectively formed in the semiconductor substrate at two sides of the gate structure; a dielectric layer is formed on the semiconductor substrate; the surface of the dielectric layer is higher than the top surface of the gate structure; a through hole is formed in the dielectric layer and exposes the surfaces of the source and the drain; an oxidation layer is formed on the surfaces of the source and the drain at the bottom of the through hole; a metal material layer is formed on the surface of the oxidation layer; an annealing treatment is carried out; the metal material layer reacts with the oxidation layer to form a metal oxide layer and a metal semiconductor compound layer; and the metal semiconductor compound layer is located on the surface of the metal oxide layer. The contact resistance between the source and the drain of the semiconductor structure formed by the method and the metal semiconductor compound layer is relatively small.
Owner:SMIC INT NEW TECH DEV SHANGHAI CO LTD
Planar structure perovskite photovoltaic cell with CrOx thin film prepared by solution method as anode interface layer and preparation method of planar structure perovskite photovoltaic cell
InactiveCN104485423AReduce manufacturing costReduce interface defectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChlorobenzeneSolvent
The invention belongs to the fields of thin film material and device, and in particular relates to a perovskite photovoltaic cell and a preparation method of the planar structure perovskite photovoltaic cell. The perovskite photovoltaic cell comprises a transparent conductive substrate, a CrOx thin film anode interface layer, a perovskite photosensitive active layer, a cathode interface layer and a metal electrode, wherein the CrOx thin film is prepared by the solution method comprising following steps: with chromium acetylacetonate as solute and chlorobenzene as solvent, preparing a chromium acetylacetonate solution, preparing a chromium acetylacetonate thin film on a substrate by a spin-coating method and annealing at low temperature; enabling the low-temperature annealed chromium acetylacetonate thin film to be subjected to high-temperature thermal annealing treatment or ultraviolet ozone treatment to obtain the CrOx thin film after the chromium acetylacetonate thin film is oxidized. The CrOx thin film disclosed in the invention is prepared by the solution method, and has small interface defect and good thermal stability, and the perovskite photovoltaic cell with the thin film has excellent photoelectric property; the preparation method is simple, and the preparation cost of the cell can be reduced greatly.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
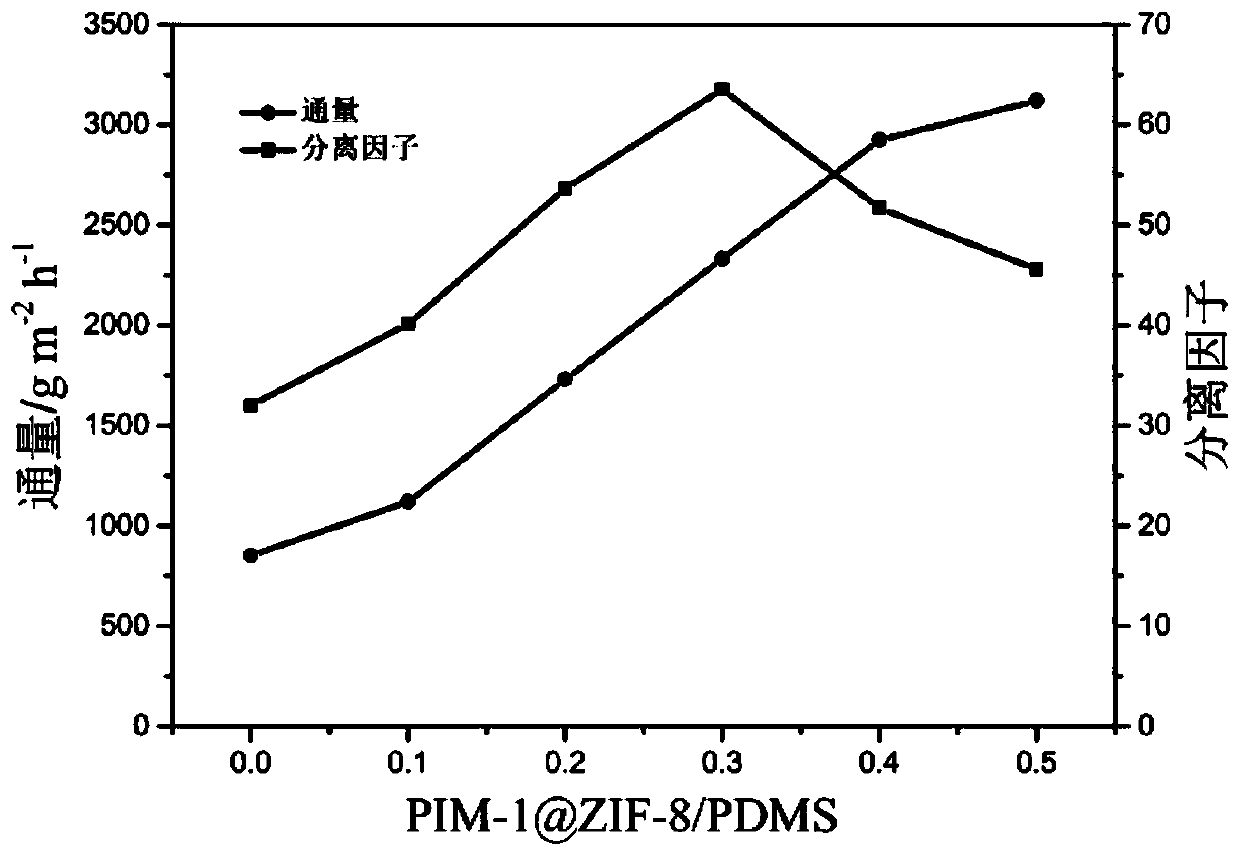
Preparation method of PIM-1@MOFs/polymer composite pervaporation membrane
ActiveCN110026097AReduce interface defectsReduce manufacturing costMembranesDistillationUltrafiltrationZinc nitrate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a PIM-1@MOFs / polymer defect-free composite pervaporation membrane, which comprises the following steps: respectively dissolving zinc nitrate hexahydrateand 2-methylimidazole serving as raw materials into methanol, mixing the obtained solutions, and reacting at 120-150 DEG C for 3-8 hours to obtain MOF powder; immersing the MOF powder into a polymersolution with micropores, and carrying out centrifugal separation to obtain treated MOF powder; dissolving a high molecular weight polymer in an organic solvent B, and adding a cross-linking agent, acatalyst and the treated MOF powder to obtain a PIM-1@MOF / polymer mixed solution; taking an ultrafiltration porous membrane of a high-molecular polymer as a bottom membrane, and uniformly dipping andcoating the bottom membrane with the obtained PIM-1@MOF / polymer mixed solution to obtain the PIM-1@MOF / polymer composite membrane. According to the prepared membrane, the hydrophobicity of an originalmembrane can be improved, and the interface defects between MOFs and polymers can be reduced, so that the permeation flux and the separation effect of the membrane are improved. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and feasible, low in price and wide in application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Organic insulating layer-based gradient-doped IGZO thin-film transistor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107123671AAvoid damageReduce defectsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsElectron
The present invention provides an organic insulating layer-based gradient-doped IGZO thin-film transistor and relates to the technical field of electronics. The organic insulating layer-based gradient-doped IGZO thin-film transistor comprises a substrate, a gate electrode, an organic insulating layer and a gradient-doped IGZO semiconductor layer, wherein the substrate, the gate electrode, the organic insulating layer and the gradient-doped IGZO semiconductor layer are sequentially arranged from bottom to top. On the gradient-doped IGZO semiconductor layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode are arranged in parallel. The gradient-doped IGZO semiconductor layer comprises a lowermost IGZO thin-film layer, an uppermost IGZO thin-film layer, and an intermediate IGZO thin-film layer, wherein the concentrations of the lowermost IGZO thin-film layer, the uppermost IGZO thin-film layer, and the intermediate IGZO thin-film layer are sequentially increased. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the problem that the IGZO semiconductor and the organic insulating layer are not matched in lattice so as to cause the damage of the subsequent DC magnetron sputtering to the organic insulating layer and the formation of a large leakage current can be solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Manufacturing method of thin film transistor
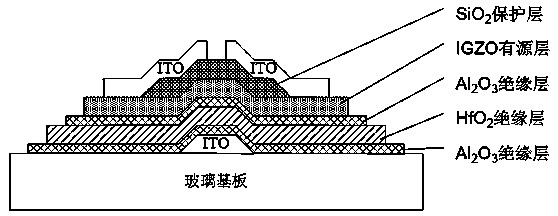
InactiveCN103474355AHighlight substantiveImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSputteringEngineering
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a thin film transistor. The thin film transistor is of a bottom grid structure and comprises a grid electrode, three insulating layers, an IGZO active layer, a SiO2 protection layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode, wherein the bottom is a glass substrate, the grid electrode ITO is deposited on the upper portion center area of the substrate with a magnetron sputtering method, the three insulating layers cover the grid electrode, the HfO2 insulating layer is in the middle, the Al2O3 insulating layers are on the two sides, a sandwich structure is formed by the HfO2 insulating layer and the Al2O3 insulating layers, Al2O3 and HfO2 are respectively prepared with the DC magnetron sputtering method and the sol gel method, the IGZO active layer and the SiO2 protection layer are sequentially arranged on the upper portion of the insulating layers, and the two ends of the source electrode and the two ends of the drain electrode are respectively located on the protection layer and the active layer.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Making method of OLED backplane
ActiveCN107611085AImprove conductivityImprove stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsOxygen content
The invention provides a making method of an OLED backplane, which is characterized in that an active layer of a film transistor is made by successively depositing a first oxide semiconductor layer, asecond oxide semiconductor layer, and a third oxide semiconductor layer; a flow ratio of argon and oxide input when the first oxide semiconductor layer and the third oxide semiconductor layer depositis larger than a flow ratio of argon and oxide input when the second oxide semiconductor layer deposits; an oxygen content of the first oxide semiconductor layer and the third oxide semiconductor layer is larger than an oxygen content of the second oxide semiconductor layer; thereby conductivity of the active layer of the film transistor device is increased, the interface defects are reduced, andstability of the film transistor device is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
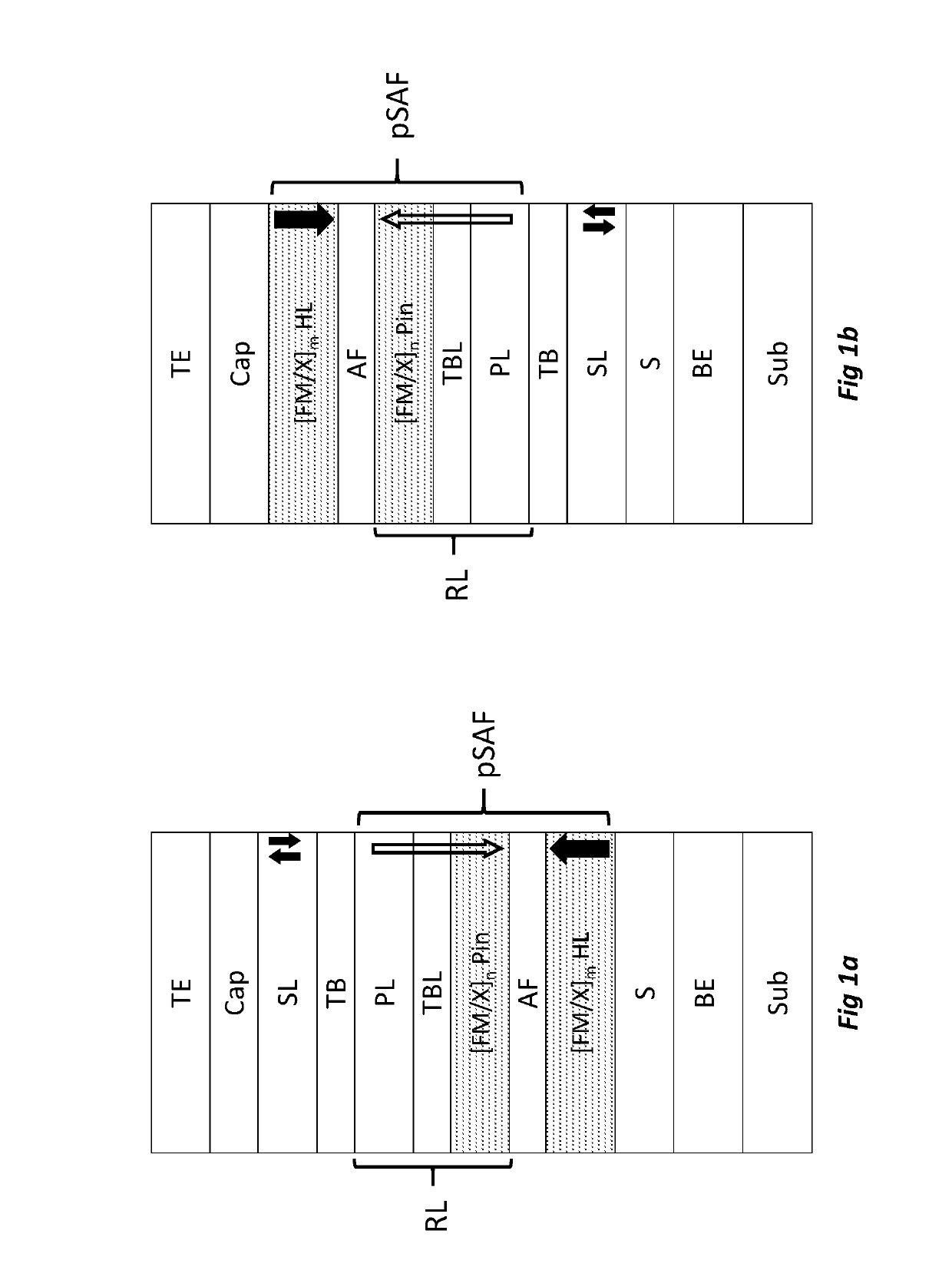
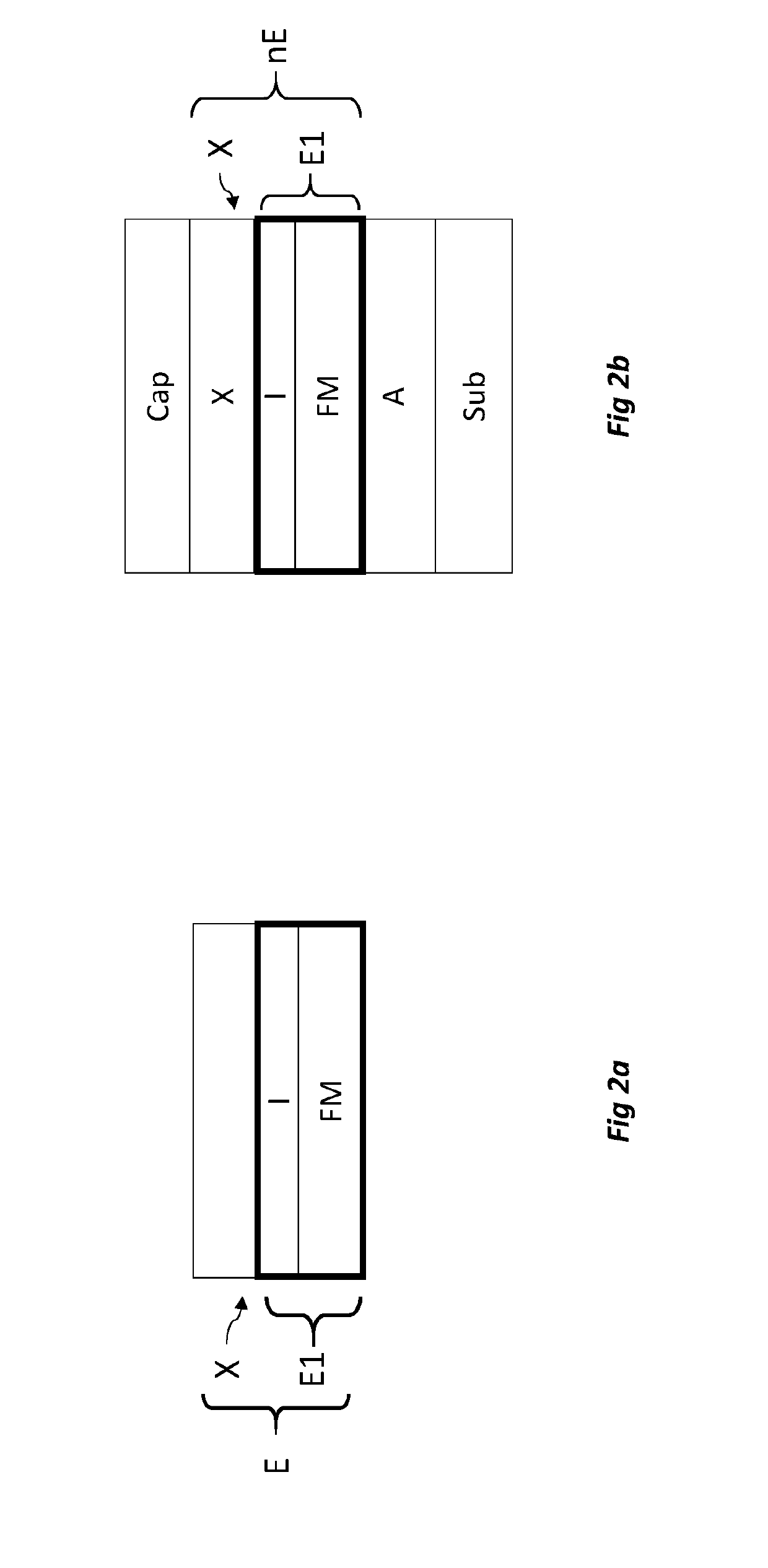
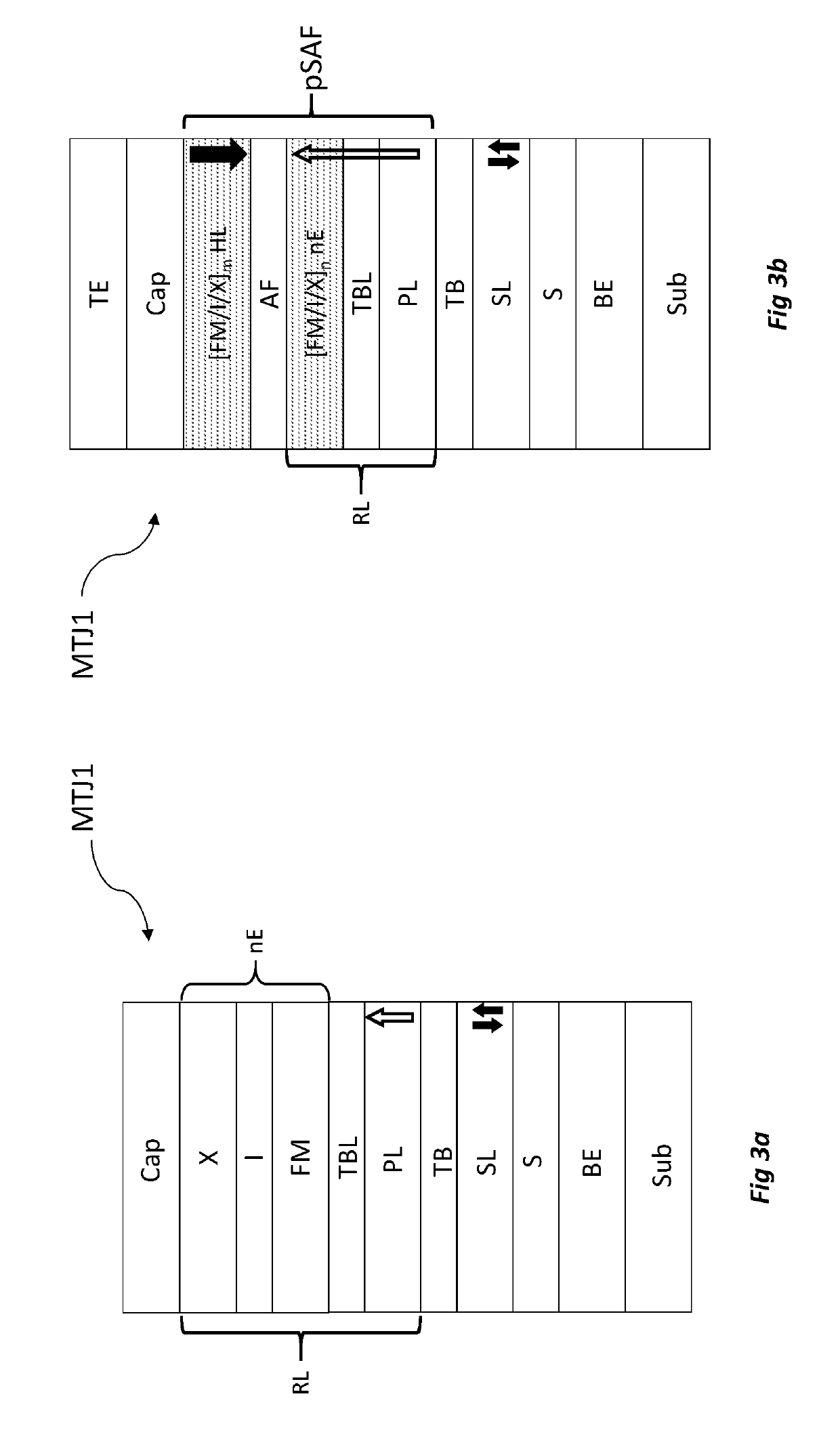
Magnetic stack, junction tunnel, memory point and sensor comprising such a stack
ActiveUS20190252601A1Higher perpendicular magnetic anisotropyHigh melting temperatureMagnetic measurementsSolid-state devicesMagnetic anisotropyAtomic physics
A magnetic stack includes a first element including a ferromagnetic layer; a second element including a metal layer able to confer on the assembly formed by the first and the second elements a magnetic anisotropy perpendicular to the plane of the layers. The first element further includes a refractory metal material, the second element being arranged on the first element.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +2
Polycrystalline-ferroelectric-film-based ferroelectric resistive random access memory
ActiveCN104009156AImprove data retentionImprove fatigue resistanceElectrical apparatusDielectricControl layer
The invention relates to a polycrystalline-ferroelectric-film-based ferroelectric resistive random access memory. Defect regulation and control layers are contained between a lower electrode layer and a polycrystalline ferroelectric film layer and / or between the polycrystalline ferroelectric film layer and an upper electrode layer. The relative dielectric constant of material of the defect regulation and control layers is no smaller than 5 and no larger than the relative dielectric constant of ferroelectric material, the thickness of each defect regulation and control layer ranges from 1 nm to 20 nm, and the ratio of the thickness of each defect regulation and control layer to the thickness of the polycrystalline ferroelectric film layer ranges from 0.001 to 0.2. The energy band gap of the material of the defect regulation and control layers is larger than 3eV, and the lattice mismatch of the material of the defect regulation and control layers with the polycrystalline ferroelectric film is smaller than 0.1. Because the defect regulation and control layers are implanted between the lower electrode layer and the polycrystalline ferroelectric film layer and / or between the polycrystalline ferroelectric film layer and the upper electrode layer, defects in the memory unit and the control difficulty of the defects are reduced, unfavorable influences of the defects on the resistance random access behavior are reduced, and thus the data retentivity and the anti-fatigue property of the memory are remarkably improved, the high-low resistance ratio of the memory is remarkably increased, and data volatility is reduced.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Carbon nano-tube film composite material preparation method
InactiveCN104943326AImprove interface performanceImprove performanceCarbon compoundsLaminationMaterials preparationCarbon nanotube
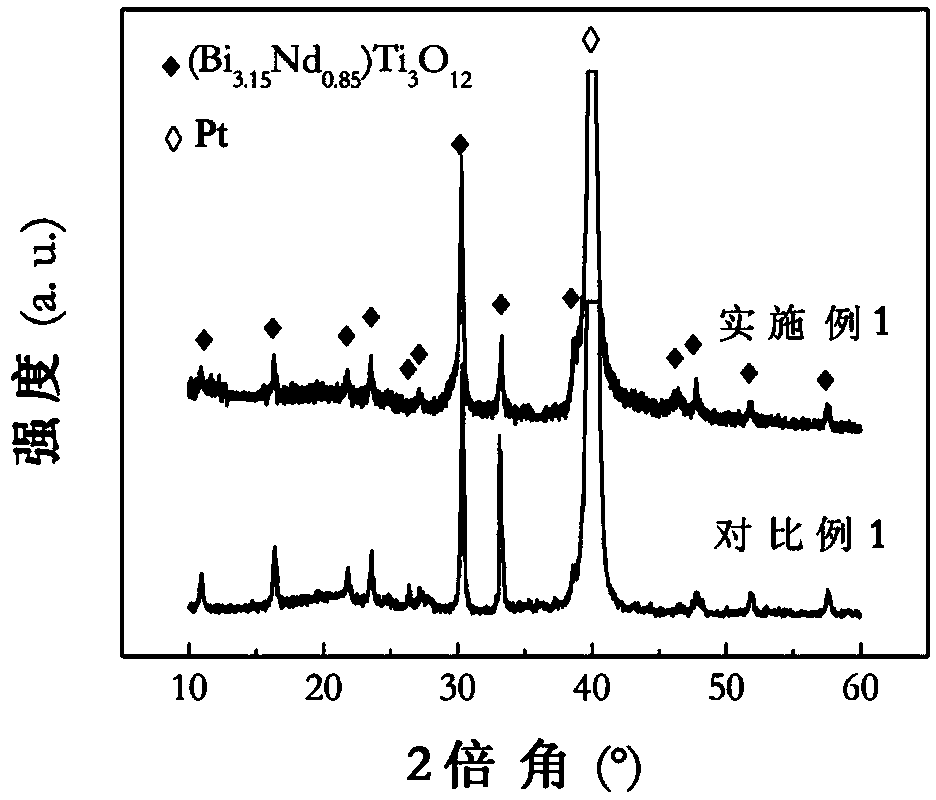
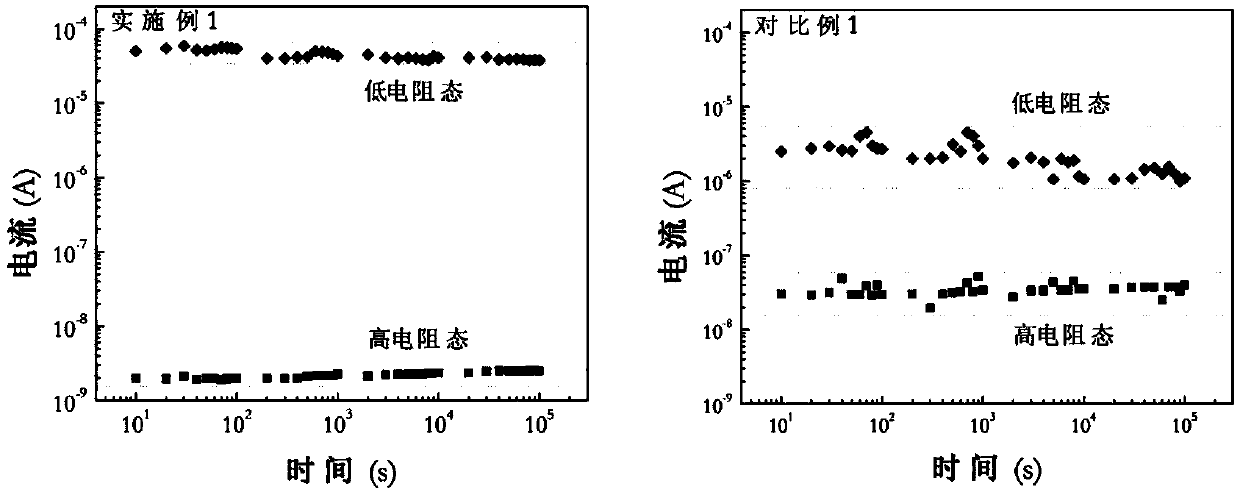
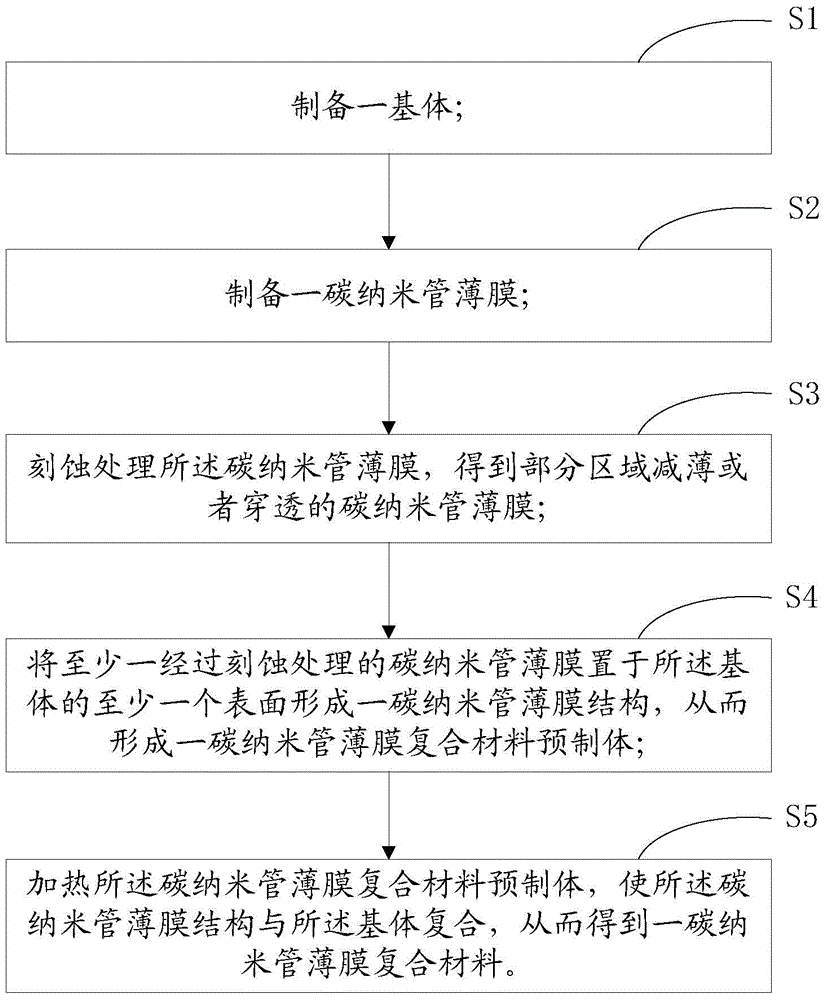
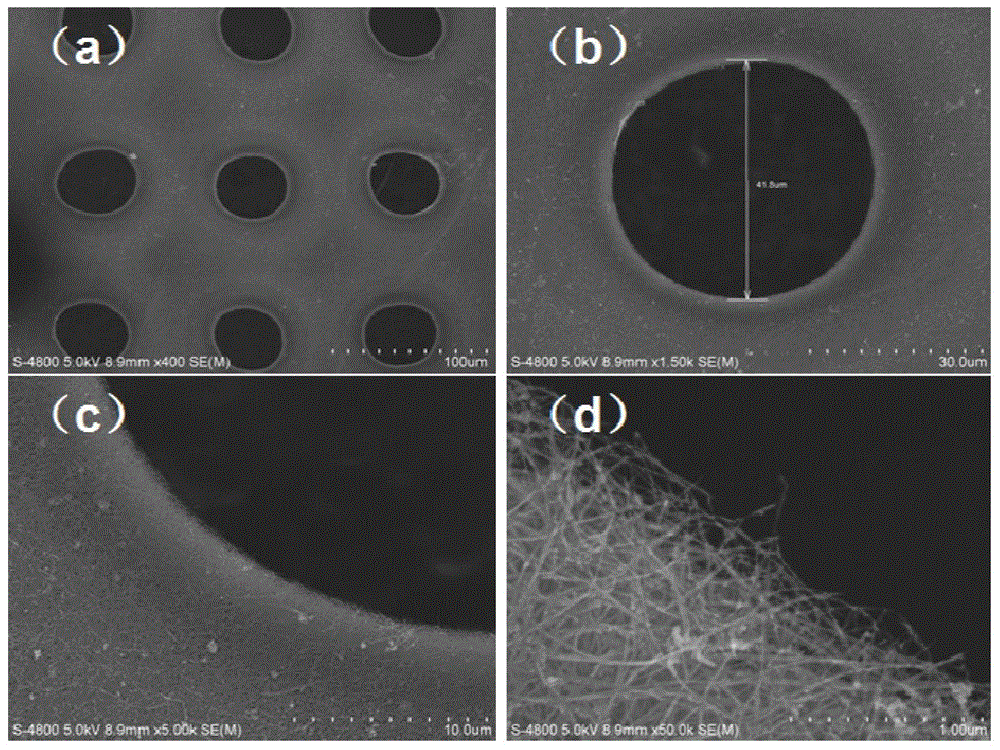
The present invention discloses a carbon nano-tube film composite material preparation method, which comprises: preparing a substrate; preparing a carbon nano-tube film; etching the carbon nano-tube film; placing the etched carbon nano-tube film on at least a surface of the substrate to form a carbon nano-tube structure so as to form a carbon nano-tube film composite material preform; and heating the carbon nano-tube film composite material preform to make the carbon nano-tube film structure and the substrate be compounded so as to obtain the carbon nano-tube film composite material. Compared with the method in the prior art, the method of the present invention has the following characteristics that: the carbon nano-tube film is etched before the carbon nano-tube film and the substrate are compounded to obtain the carbon nano-tube film with the partial thinned area or penetrating carbon nano-tube film so as to improve the interface performance of the carbon nano-tube composite material and reduce the interface defects, the obtained carbon nano-tube film composite material exhibits the excellent comprehensive performance and shows the application potential in a plurality of future fields.
Owner:SUZHOU CREATIVE CARBON NANOTECH
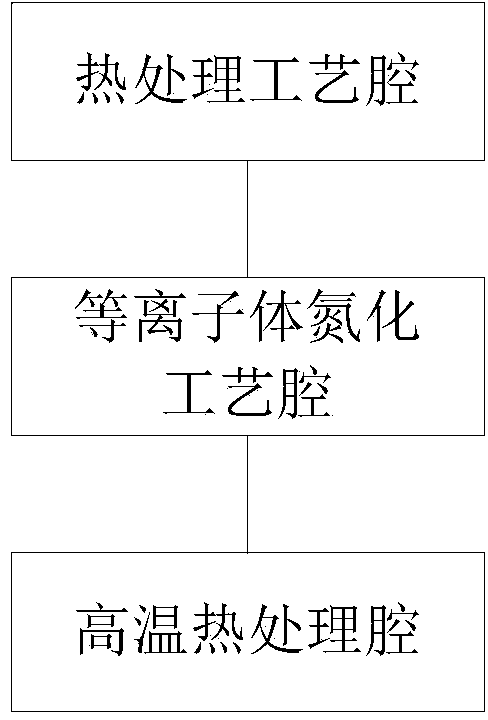
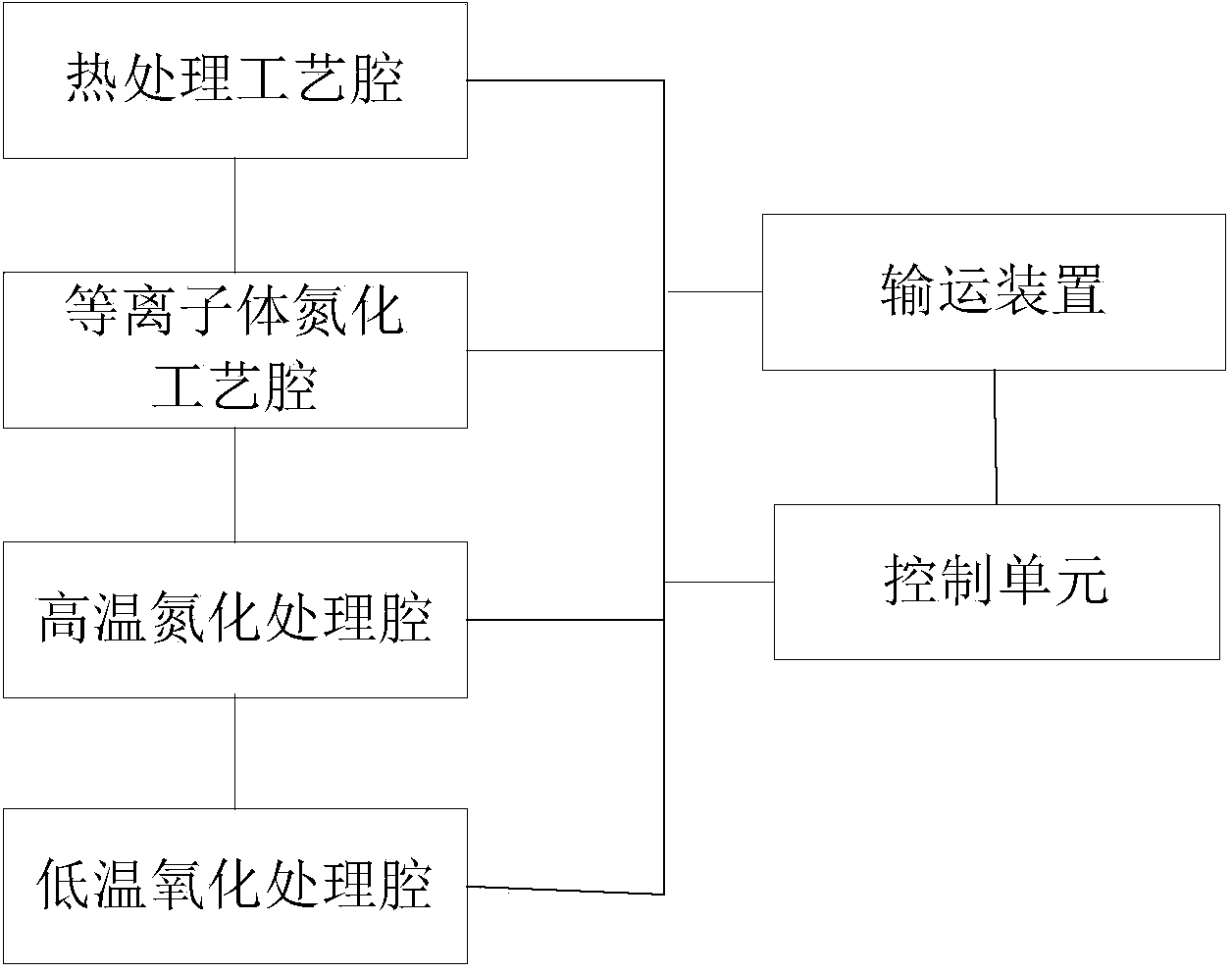
Equipment for preparing gate dielectric layer
InactiveCN103855035AHigh dielectric constantAvoid missingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricNitrogen
The invention provides equipment for preparing a gate dielectric layer. The equipment comprises a thermal treatment process cavity used for growing a SiO2 gate dielectric layer, a plasma nitriding process cavity used for performing plasma nitrogen injection on the gate dielectric layer to form a Si-N bond, a high-temperature nitriding cavity used for repairing lattice damage in the gate dielectric layer and stabilizing the Si-N bond, a low-temperature oxidizing cavity used for repairing a gate dielectric layer / channel interface, a control unit used for controlling conversion of a semiconductor substrate among all the process cavities and opening / closing of all the process cavities, and a conveying device used for conveying the semiconductor substrate among all the process cavities. By adopting a process for preparing the gate dielectric layer in the equipment provided by the invention, the Si-N bond tends to be stable to prevent the volatilization of N atoms, the N concentration in a SiON gate dielectric is stabilized, the dielectric constant of the SiON gate dielectric is increased, reduction of a carrier mobility caused by interface defect is avoided, and the interface quality and the performance of a device are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
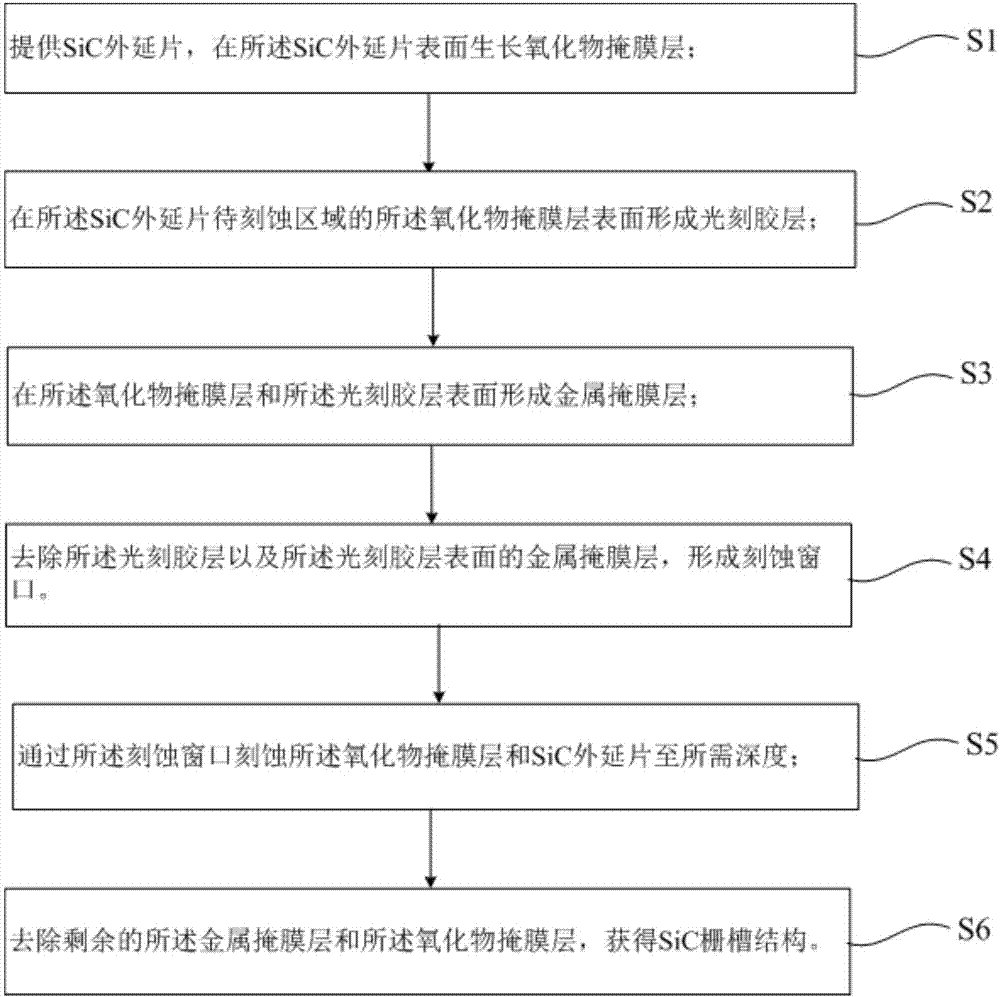
Method for etching SiC through metal/oxide double-layer mask structure
InactiveCN107275196AAvoid pollutionImprove pressure resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotoresistBlocking layer
The invention provides a method for etching SiC through a metal / oxide double-layer mask structure, and the method at least comprises the steps: 1), providing an SiC epitaxial wafer, and growing an oxide mask layer on the surface of the SiC epitaxial wafer; 2), forming a photoresist layer on the surface of the oxide mask layer of a to-be-etched region of the SiC epitaxial wafer; 3), forming metal mask layers on the oxide mask layer and the surface of the photoresist layer; 4), removing the photoresist layer and the metal mask layer on the surface of the photoresist layer, and forming an etching window; 5), etching the oxide mask layer and the SiC epitaxial wafer to a needed depth through the etching window; 6), removing the residual metal mask layer and oxide mask layer, and obtaining an SiC gate groove structure. According to the invention, the oxide mask layer is taken as a blocking layer, thereby preventing the metal elements from diffusing towards the SiC epitaxial wafer and the substrate, and solving a problem of element pollution. In addition, the method can obtain a high-etching-rate gate and high-anisotropism groove structure with the smooth etching surface.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
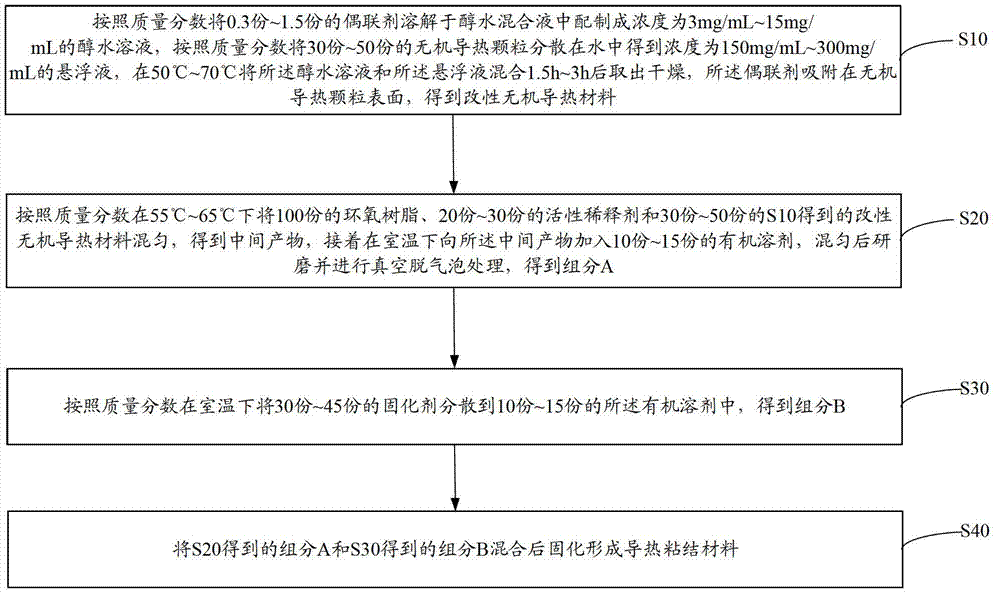
Heat-conduction binding material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102876272AImprove bindingImprove mechanical propertiesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesEpoxy resin adhesivesOrganic solventInorganic particle
The invention discloses a heat-conduction binding material. The heat-conduction binding material is formed by mixing components A and components B, wherein the components A include 100 parts of epoxy resin, 20-30 parts of reactive diluent, 30-50 parts of modified inorganic heat-conduction materials and 10-15 parts of organic solvent according to mass ratio and the modified inorganic heat-conduction materials are formed by coupling agents adsorbing on surfaces of inorganic heat-conduction particles. The components B include curing agents and organic solvents. The coupling agents are adsorbed on the inorganic heat-conduction particles to form the modified inorganic heat-conduction materials, so that compatibility of the inorganic particles in the organic resin can be improved, boundary defects and boundary stress between inorganic materials and organic materials after curing are reduced, organic layers among the inorganic heat-conduction particles can be reserved on the condition of adding a great quantity of modified inorganic heat-conduction materials, binding force of the heat-conduction binding material is improved, and accordingly, the heat-conduction binding material is better in mechanical performance. The invention further provides a preparation method of the heat-conduction binding material.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
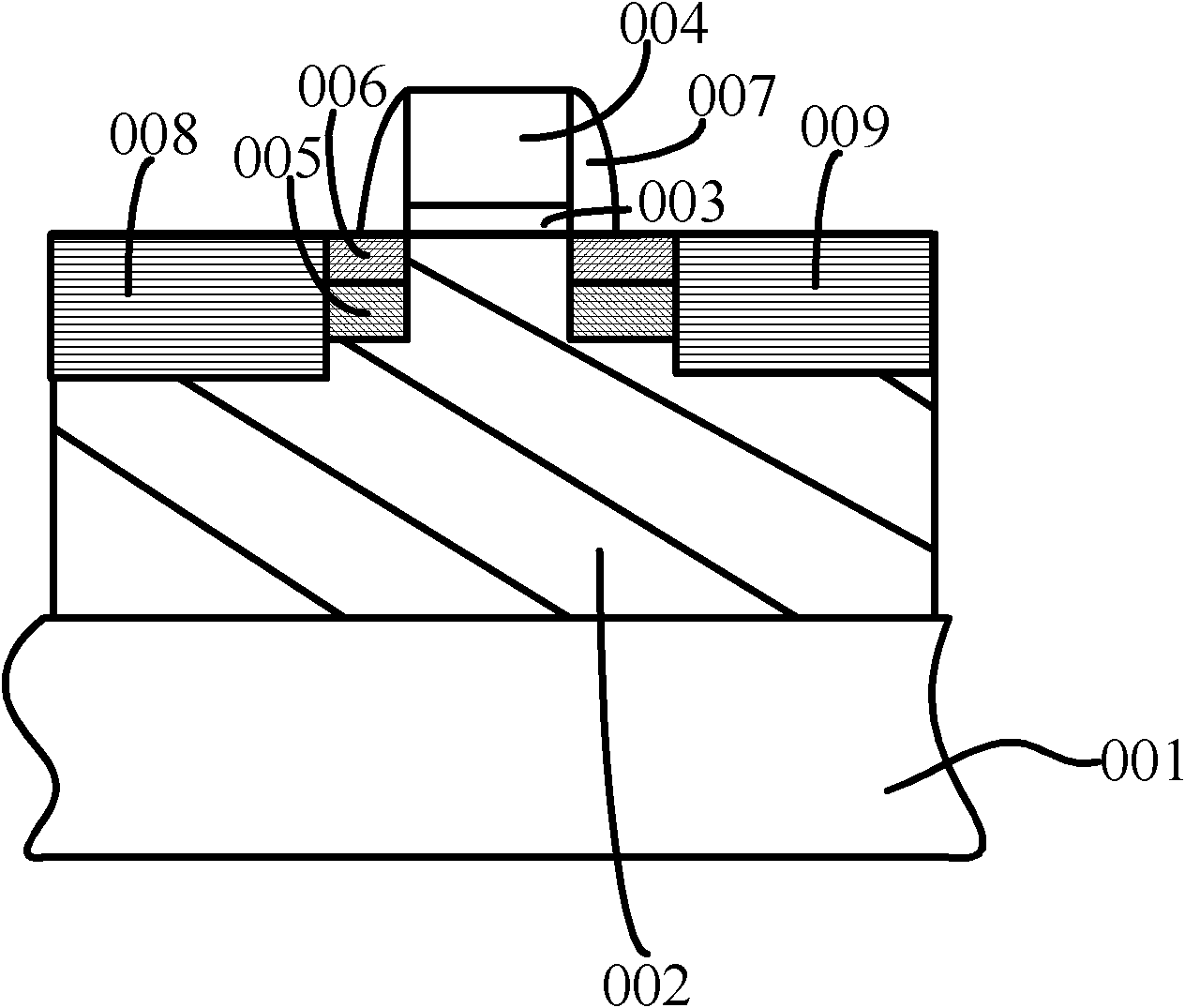
Method for forming semiconductor structure
InactiveCN102487047AReduce interface defectsSilicon dangling bond reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHot electronDeuterium
The invention provides a method for forming a semiconductor structure, comprising the following steps of: providing a substrate, wherein the substrate is provided with a grid structure, a source region and a drain region positioned in the substrate at the two sides of the grid structure; forming metal layers on the surfaces of the source region and the drain region; and carrying out annealing process on the source region and the drain region forming the metal layers on the surfaces, and forming metal silicide in the source region and the drain region, wherein annealing gas at least comprises one or combination of hydrogen and deuterium. According to the method, by adding one or combination of the hydrogen and the deuterium into the annealing gas, silicon dangling bonds in the substrate are bonded with one or combination of the hydrogen and the deuterium, the silicon dangling bonds in the substrate are reduced, the interface defects nearby the substrate are reduced, and silicon-hydrogen bonds and silicon-deuterium bonds are stronger respectively, the cracking probability of the silicon-hydrogen bonds and the silicon-deuterium bonds is reduced under the external stress of the process environment, the interface defects nearby the substrate are further reduced, and the hot electron effect is restrained.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP
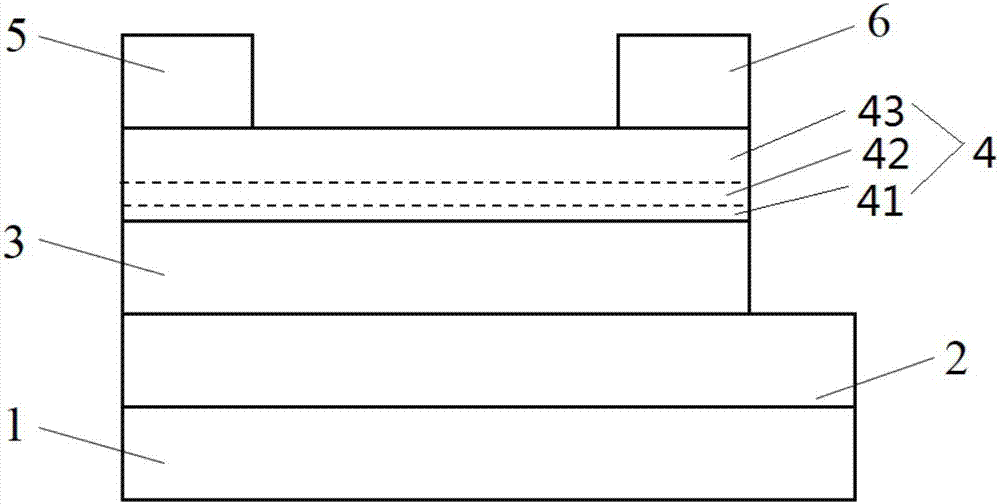
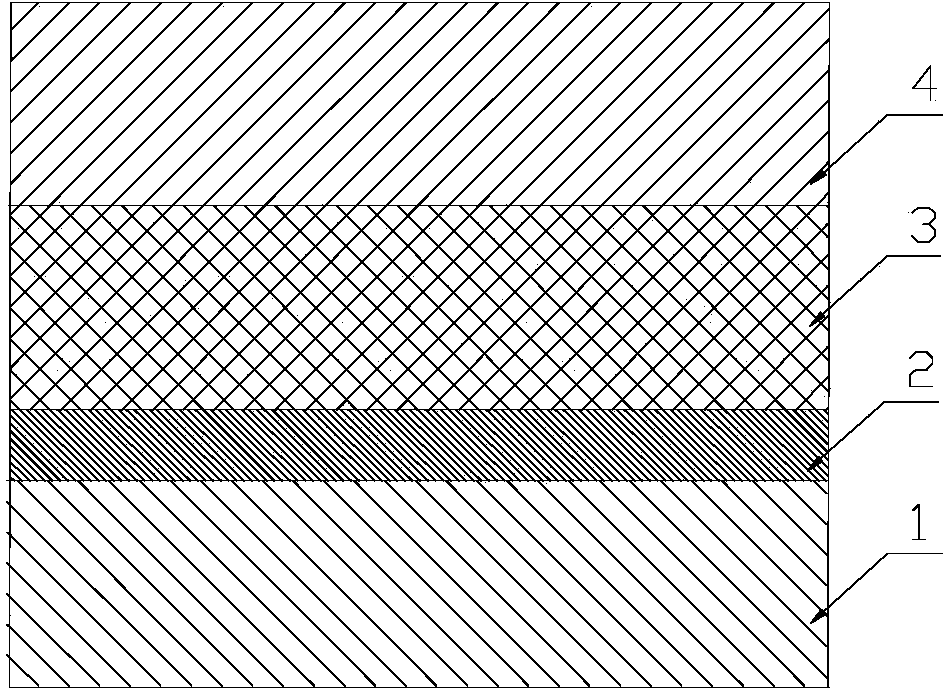
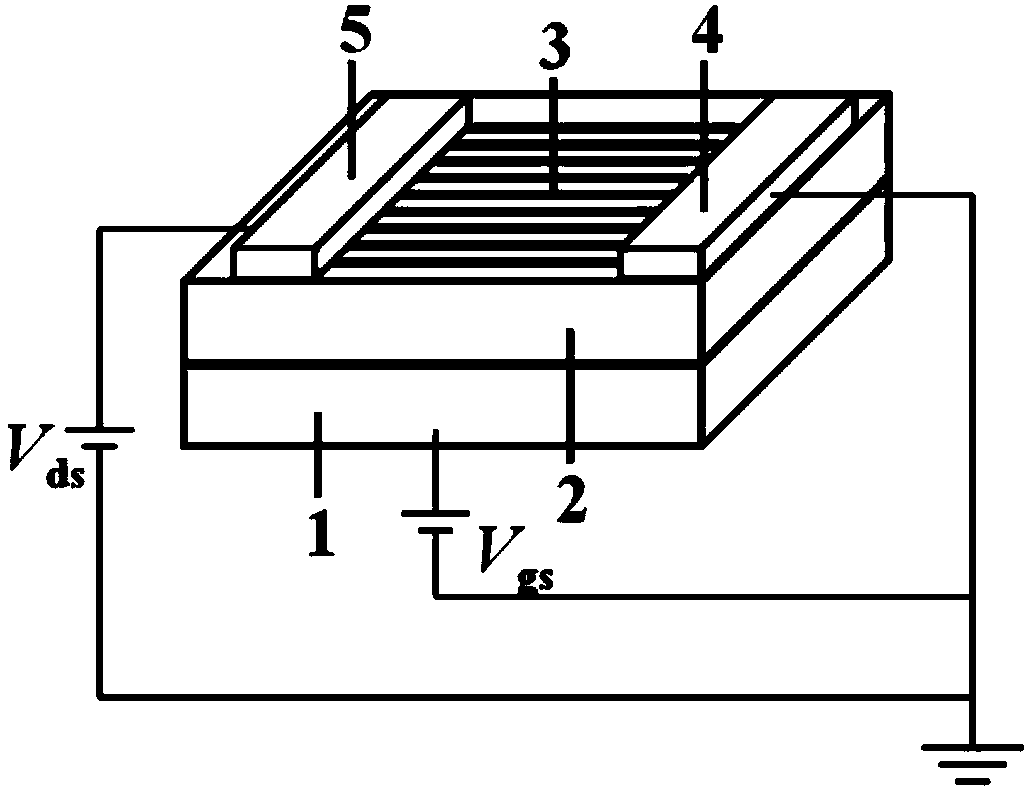
Ferro-electric field effect transistor based on structured carbon nano tube striped array and manufacturing method thereof
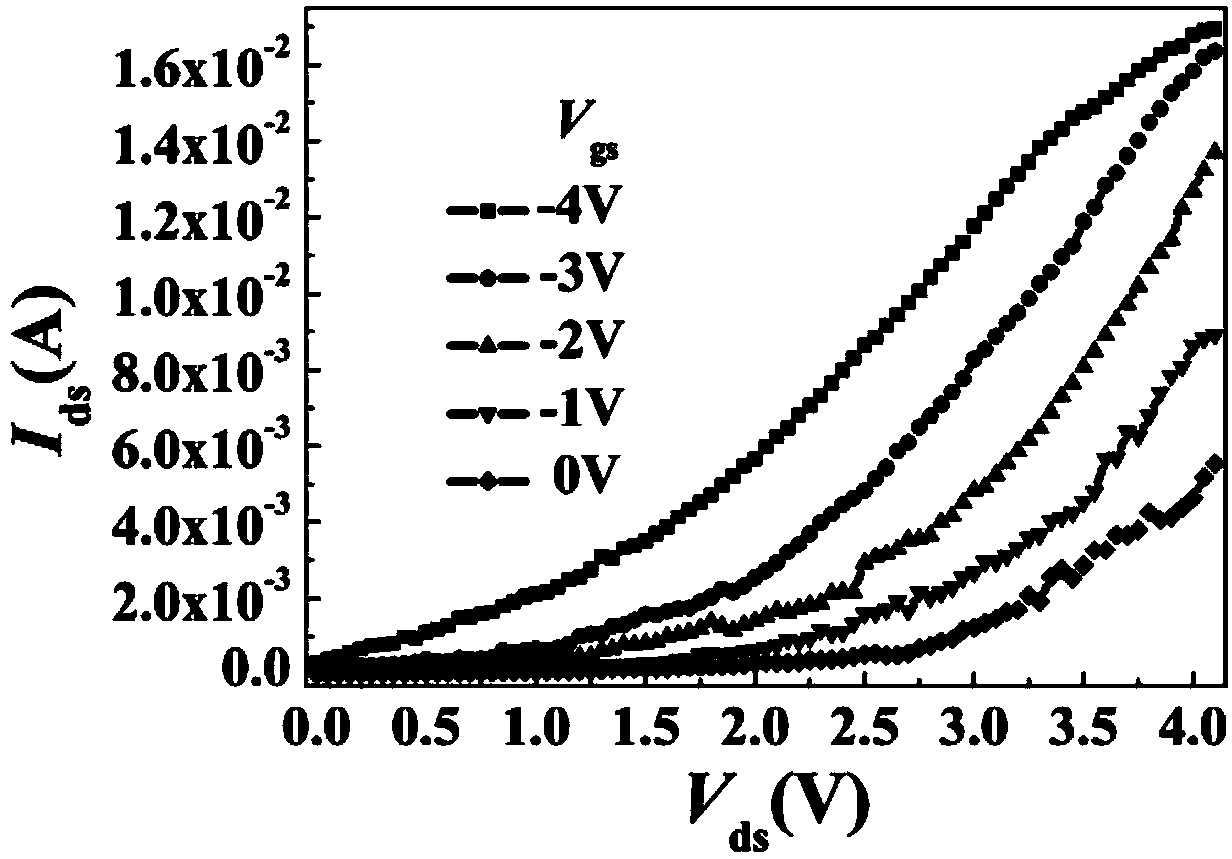
InactiveCN104009091AIncrease the on-state currentHigh switching ratioNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic field-effect transistorCharge carrier mobility
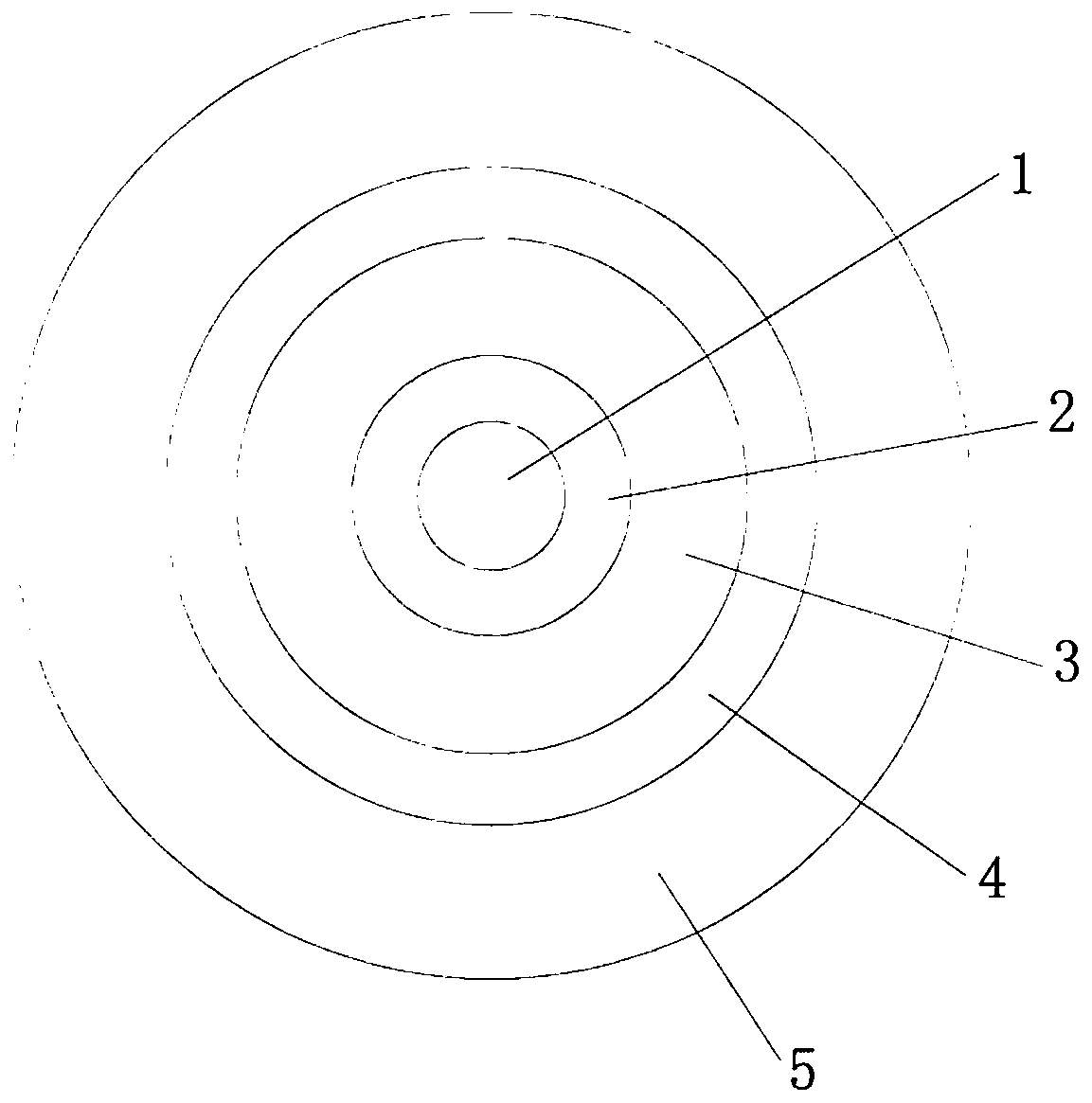
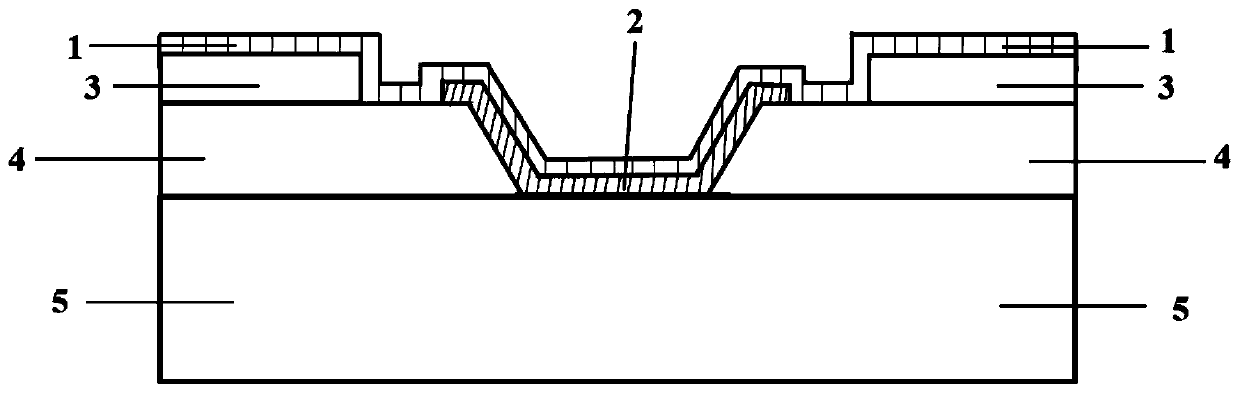
The invention discloses a ferro-electric field effect transistor based on a structured carbon nano tube striped array and a manufacturing method of the ferro-electric field effect transistor. According to the unit structure of the transistor, a bottom electrode layer (1) is arranged on the bottom layer, a ferro-electric film insulated gate layer (2) and a structured carbon nano tube striped array channel layer (3) are sequentially arranged on the middle layer, and a top layer is arranged on the structured carbon nano tube striped array channel layer (3) and comprises a transistor source electrode (4) and a transistor drain electrode (5); carbon nano tubes are single-walled carbon nano tubes, or double-walled carbon nano tubes or multi-walled carbon nano tubes. According to the ferro-electric field effect transistor, the on-state current and the switch ratio are large, carrier mobility is high, the starting voltage is small, the storage window is wide, and meanwhile the ferro-electric field effect transistor has the advantages of being simple in structure and a buffering layer is not needed, interface contact between a ferro-electric layer and a semiconductor layer is good, and large-area soft devices are easy to obtain. The manufacturing method is simple in technology, convenient to operate and low in cost and dispense with expensive equipment, and large-area and large-scale industrial production is easy to realize.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Single-mode fiber and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN110794509ALow loss and large effective areaBending Loss ImprovementsGlass optical fibreGlass making apparatusPhysicsChemistry
The invention relates to a single-mode fiber and a fabrication method thereof. A bare fiber comprises a core layer and a wrapping layer, wherein the core layer comprises a first core layer, a second core layer and an inner wrapping layer, the relative refractivity difference Delta 1 of the first core layer is more than 0.2% but less than 0.35%, the relative refractivity difference Delta 2 of the second core layer is more than or equal to 0.15% but less than or equal to 0.25%, the refractivity radius of the inner wrapping layer is 24-36 micrometers, the relative refractivity difference Delta 3of the inner wrapping layer is more than or equal to -0.12% but less than or equal to 0%, the wrapping layer comprises a sunken wrapping layer and an external wrapping layer, the relative refractivitydifference Delta 4 of the sunken wrapping layer is more than or equal to -0.40% but less than or equal to -0.28%, and the external wrapping layer is a high-hardness pure quartz sleeve. With the adoption of a method for on-line assembly and drawbenching by two sleeves and a core rod, fiber annealing for many times is performed during the drawbenching process, a coating layer with low modulus is coated in a surface of the fiber, a coating layer with high modulus is coated outside the surface of the fiber, and the fiber with low loss, large effective area and high strength is fabricated. The method is simple, the viscosity of the cord rod can be adjusted according to a demand, the fiber attenuation is reduced without employing a pure silicon core scheme, and production on a large scale is facilitated.
Owner:FASTEN HONGSHENG GRP CO LTD +1
Graphene/palladium diselenide/silicon heterojunction self-driven photoelectric detector
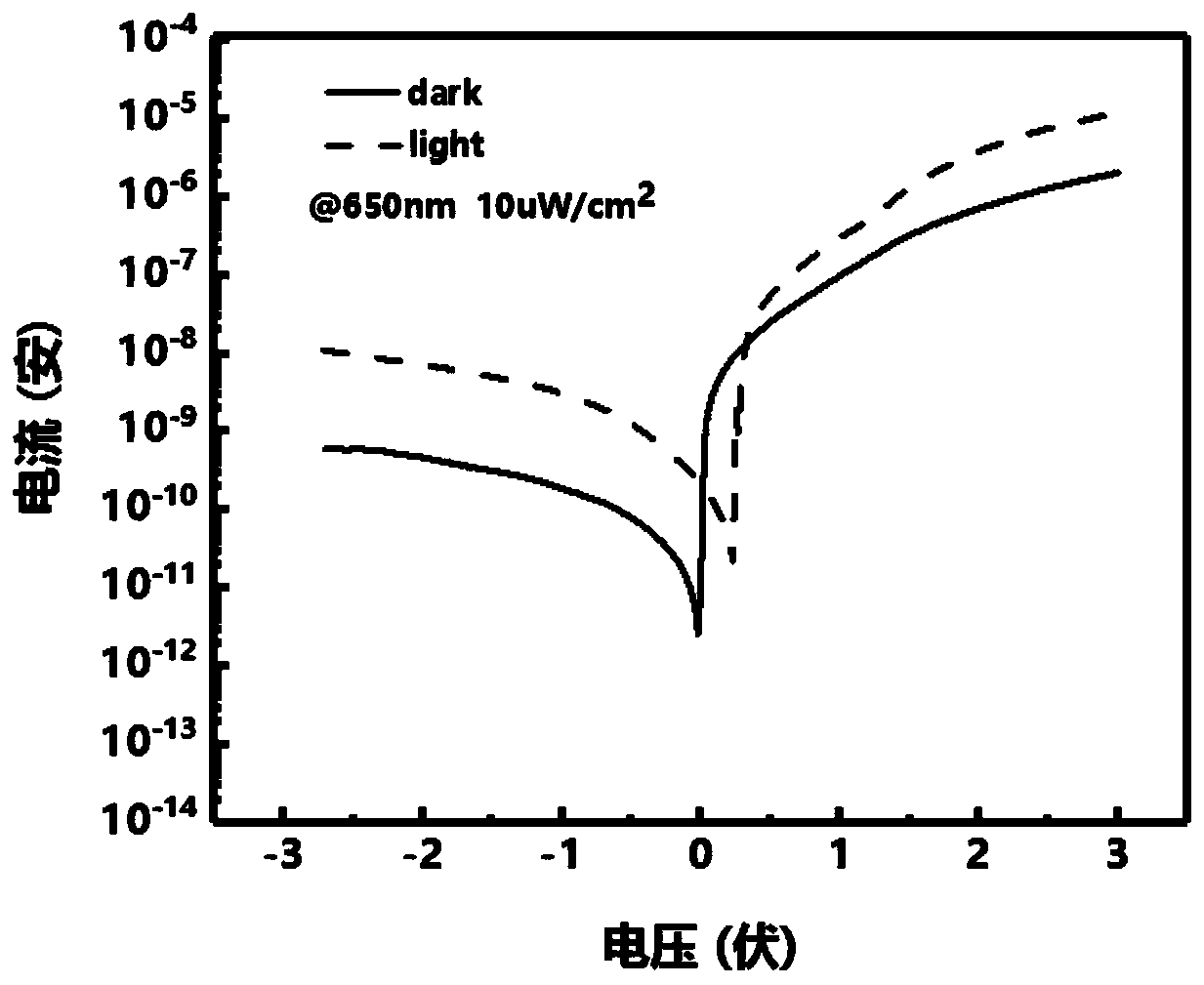
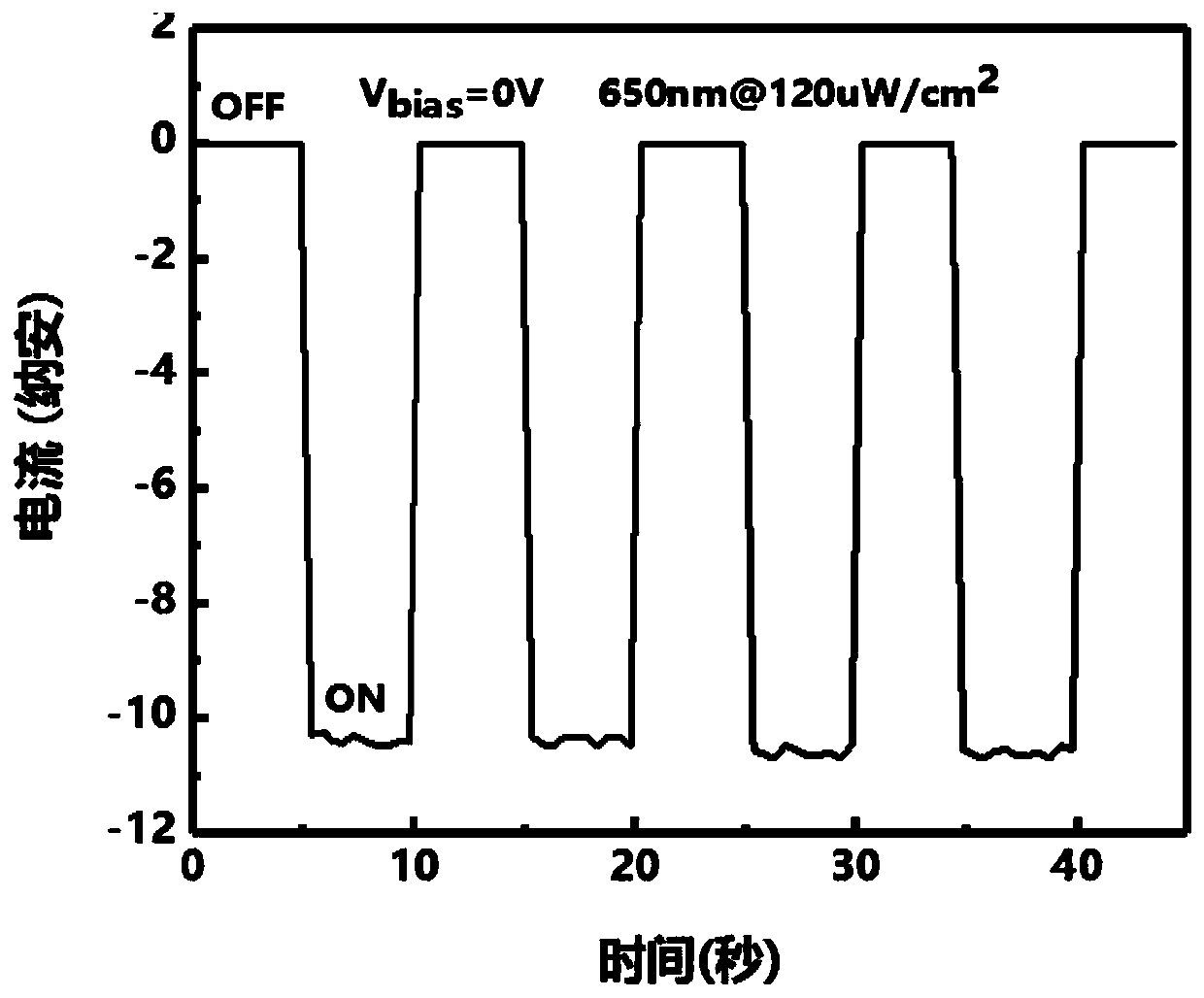
ActiveCN111341875ASelf-driving performanceImprove responsivenessFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionIndium
The invention discloses a graphene / palladium diselenide / silicon heterojunction self-driven photoelectric detector, which is applied to the technical field of photoelectric detection. In view of the problem that the existing photoelectric detector is limited by weak light absorption performance of graphene and low in responsivity, a technical scheme as follows is adopted: firstly, an n-type siliconwindow is exposed on an n-type silicon dioxide / silicon substrate through dry etching; a gold / indium electrode is plated near the silicon window, a palladium diselenide microchip is prepared by adopting mechanical stripping, and palladium diselenide is transferred to the silicon window by utilizing a positioning dry method; and finally, graphene is transferred in a wet transfer mode and covers thesurfaces of palladium diselenide and the electrode, palladium diselenide serves as an interface modification layer between graphene and silicon, and a graphene / palladium diselenide / silicon heterojunction is formed by the graphene layer, the palladium diselenide layer and the n-type silicon substrate corresponding to the single silicon window. The device provided by the invention is simple in preparation process, has self-driving performance, and has excellent performances such as relatively high responsivity in a visible-near-infrared light band.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Ultralow-attenuation and large-effective-area single-mode fiber
InactiveCN106997073AIncreased chlorine doping contentAccelerated structural relaxationOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideUltrasound attenuationFiber strain
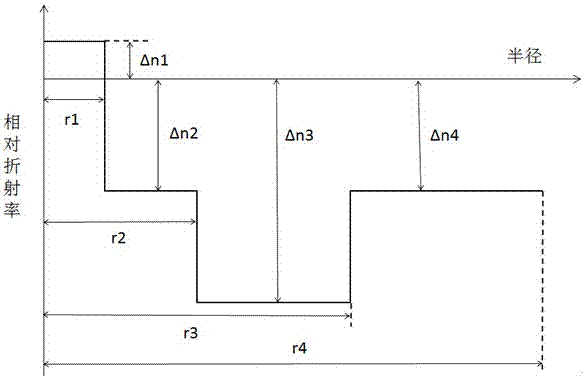
The invention relates to an ultralow-attenuation and large-effective-area single-mode fiber comprising a core layer and wrapping layers. The ultralow-attenuation and large-effective-area single-mode fiber is characterized in that the radius r1 of the core layer is 5-8 microns, the relative refractive index deltan1 of the core layer is 0-0.20%, and the core layer wraps an internal wrapping layer, a recessed internal wrapping layer and an external wrapping layer from inside to outside in turn. The radius r2 of the internal wrapping layer is 8.5-12 microns, and the relative refractive index deltan2 is -0.20--0.45%. The radius r3 of the recessed internal wrapping layer is 12.5-30 microns, and the relative refractive index deltan3 is -0.40--0.65%. The external wrapping layer is a fully fluoridated silicon dioxide glass layer, and the relative refractive index deltan4 is -0.22--0.53%. The ultralow-attenuation and large-effective-area single-mode fiber has the specific viscosity matching design: the core layer is not the pure silicon core and has the characteristics of co-doping of germanium and fluorine, and the chlorine doping technology is also performed so that the fiber viscosity can be reduced and the structural relaxation of glass can be accelerated; and the core layer viscosity matching is optimized by controlling the doping concentration, and the viscosity of each part of the fiber and the fiber strain are optimized so that ultralow-attenuation performance of the single-mode fiber can be realized.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
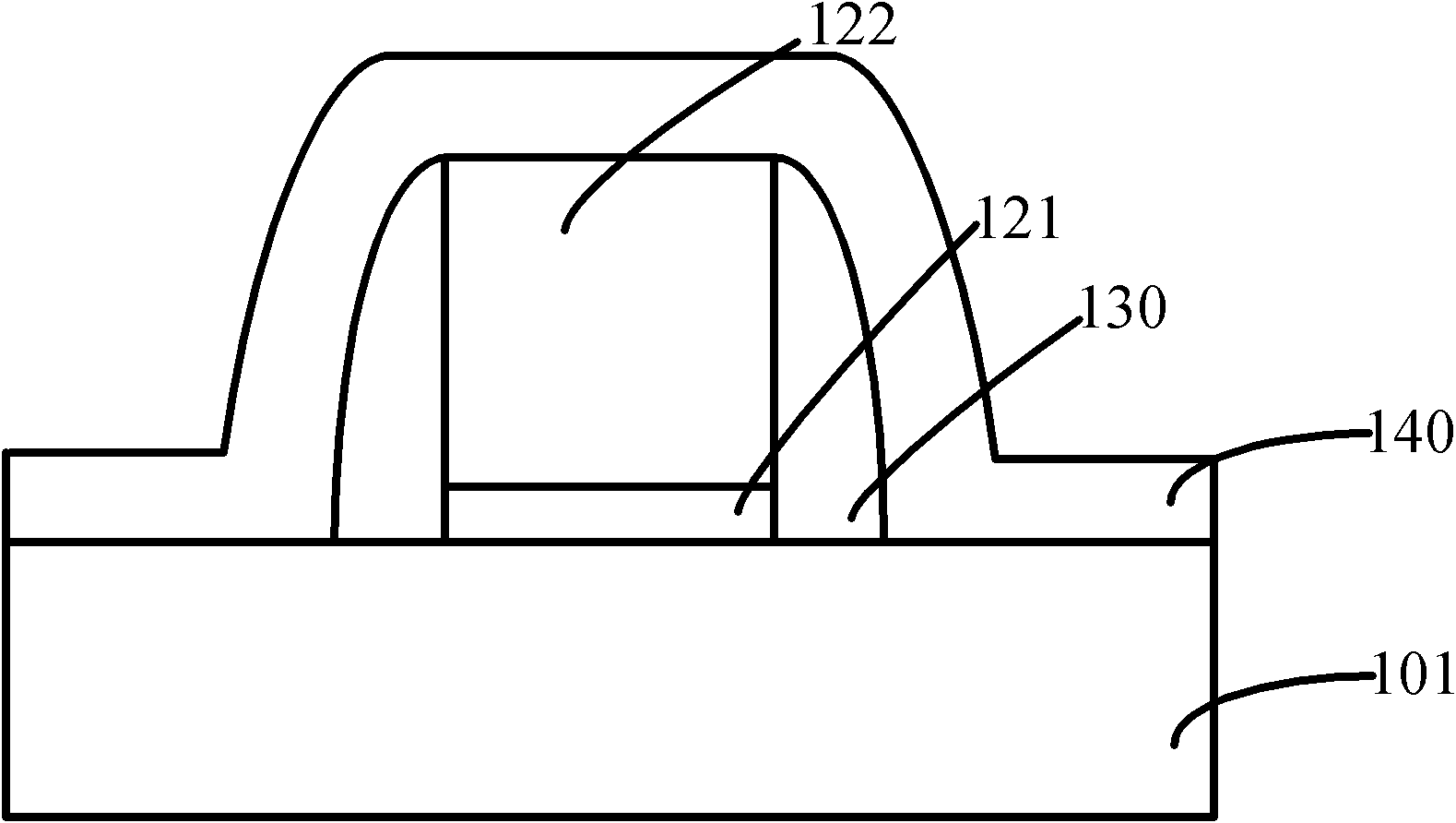
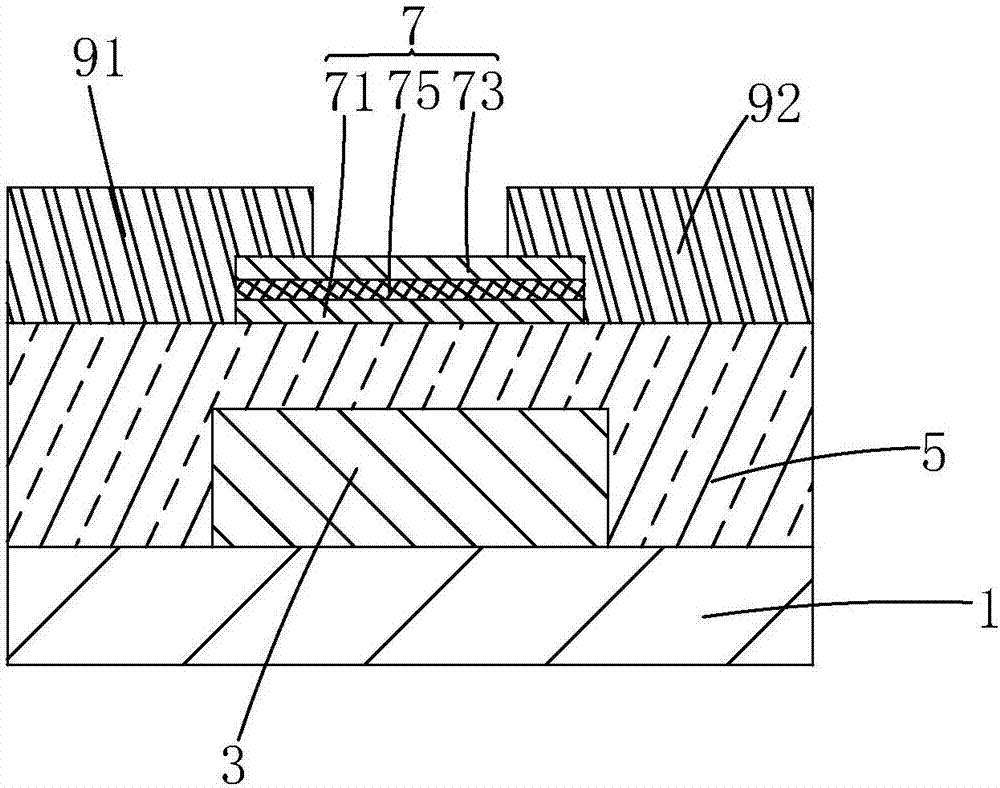
Metal oxide thin film transistor (TFT) device and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN107104150AHigh electron mobilityImprove mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerIndium
The invention provides a metal oxide thin film transistor (TFT) device and a fabrication method thereof. An active layer (7) of the metal oxide TFT device employs a structure similar to a sandwich and comprises a low-layer indium gallium zinc oxide thin film (71), an upper-layer indium gallium zinc oxide thin film (73) and an intermediate conductive layer (75), wherein the upper-layer indium gallium zinc oxide thin film (73) is arranged opposite to the low-layer indium gallium zinc oxide thin film (71), the intermediate conductive layer (75) is sandwiched between the low-layer indium gallium zinc oxide thin film (71) and the upper-layer indium gallium zinc oxide thin film (73), and a material of the intermediate conductive layer (75) is a metal oxide highly containing indium or a metal oxide highly containing zinc. By the metal oxide TFT device, the electron mobility can be further improved, the interface defect of the active layer (7) and a grid insulation layer (5) is reduced, and the electrical property of the TFT device is improved.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
SiC semiconductor element and manufacturing method for same
ActiveUS8546815B2Reduce interface defectsReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringState density
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Hydroxyl group termination for nucleation of a dielectric metallic oxide
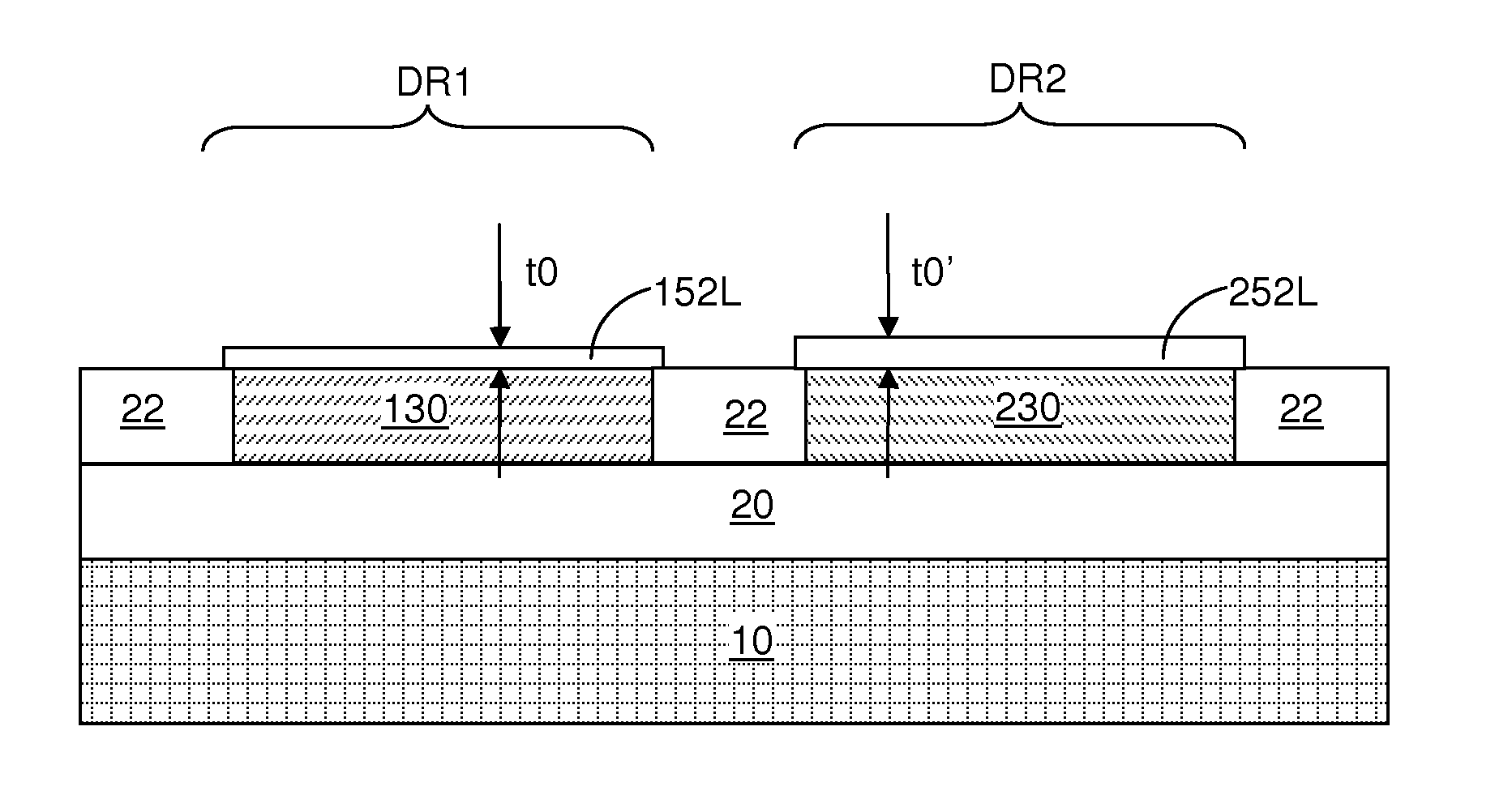
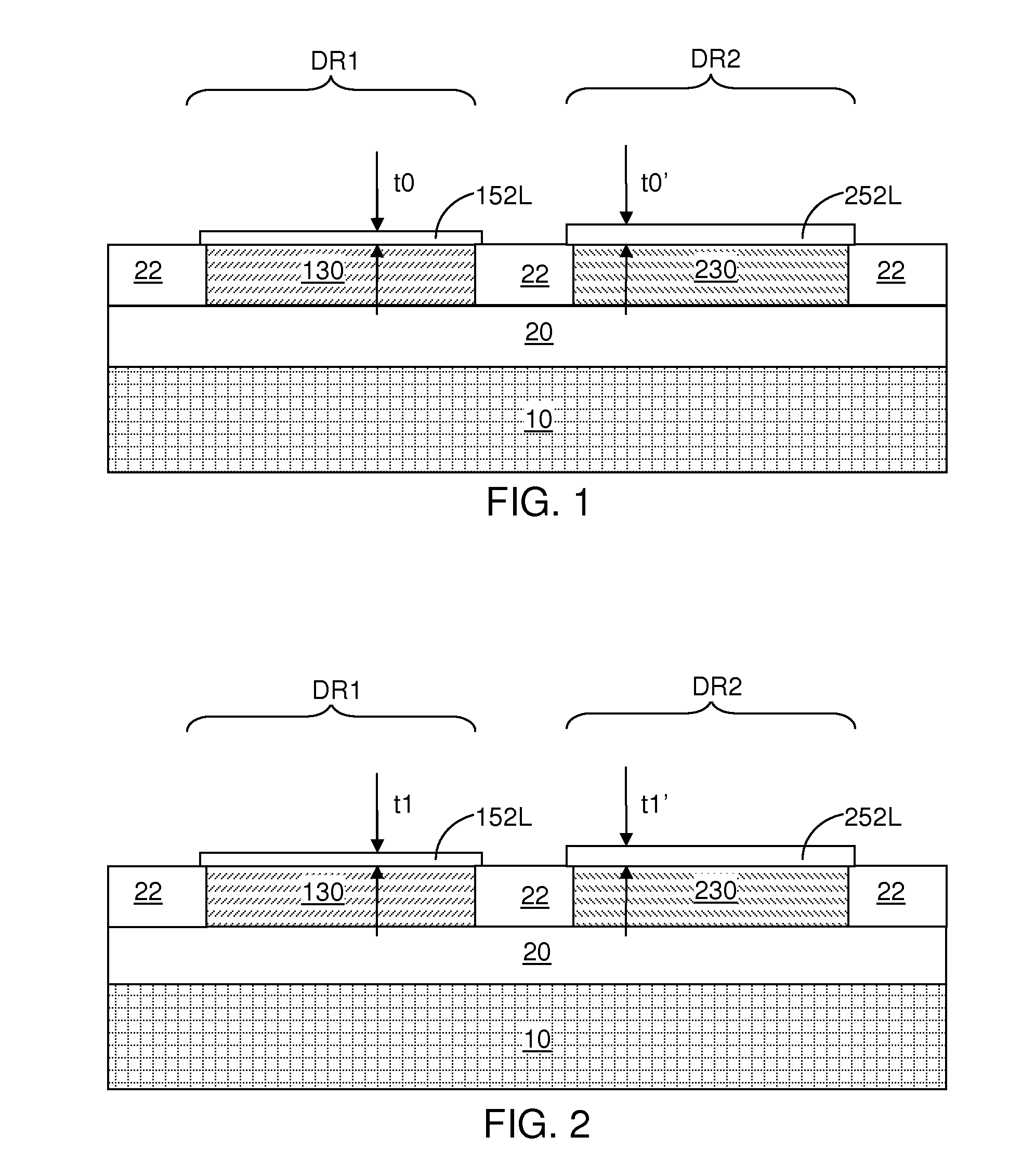
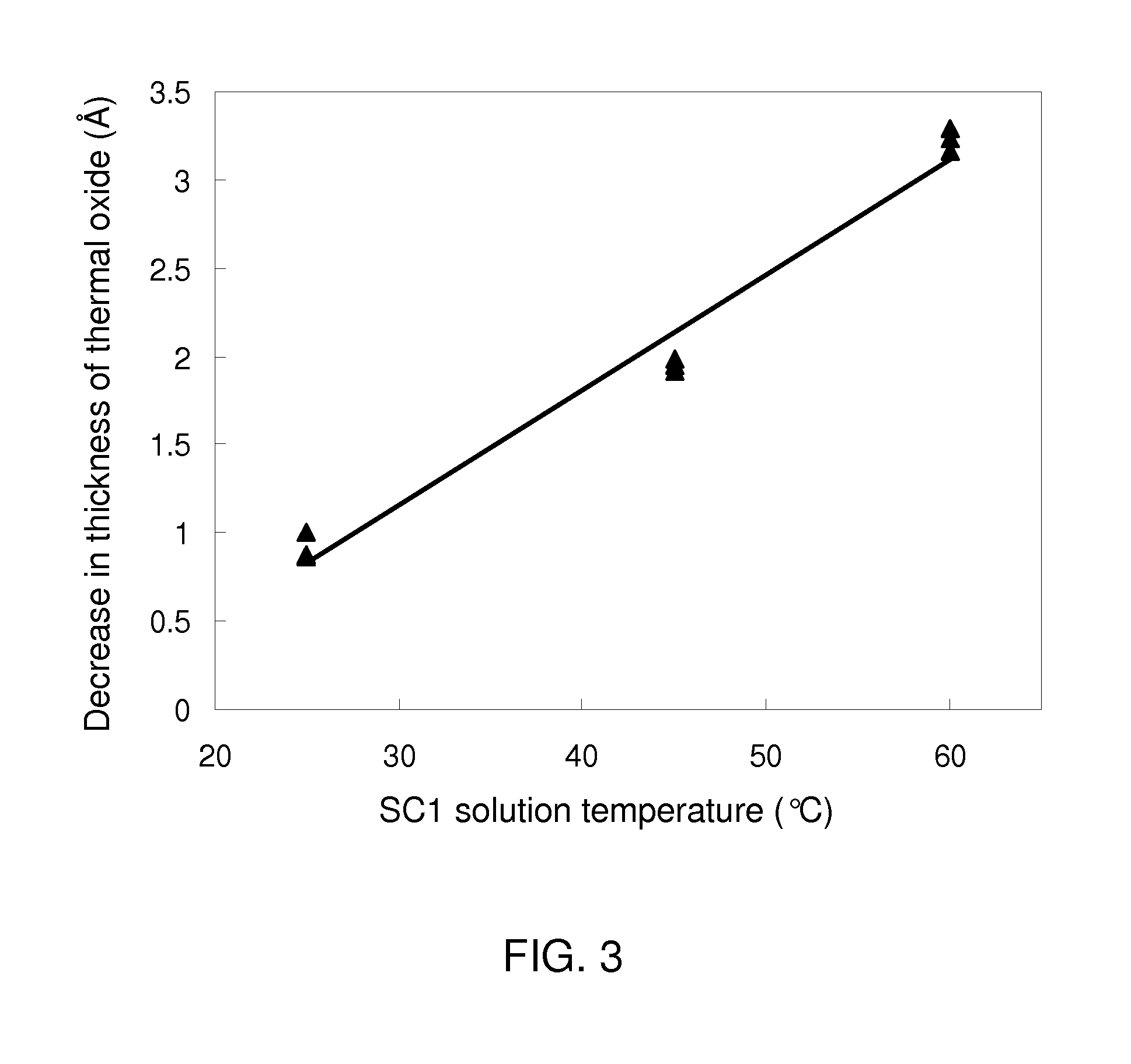
ActiveUS20140308821A1Facilitates nucleation and depositionReduce interface defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingAlloyAtomic layer deposition
A surface of a semiconductor-containing dielectric material / oxynitride / nitride is treated with a basic solution in order to provide hydroxyl group termination of the surface. A dielectric metal oxide is subsequently deposited by atomic layer deposition. The hydroxyl group termination provides a uniform surface condition that facilitates nucleation and deposition of the dielectric metal oxide, and reduces interfacial defects between the oxide and the dielectric metal oxide. Further, treatment with the basic solution removes more oxide from a surface of a silicon germanium alloy with a greater atomic concentration of germanium, thereby reducing a differential in the total thickness of the combination of the oxide and the dielectric metal oxide across surfaces with different germanium concentrations.
Owner:IBM CORP
Forming method of CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) transistor
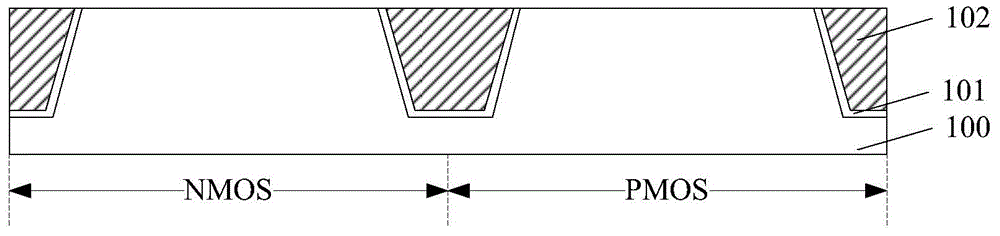
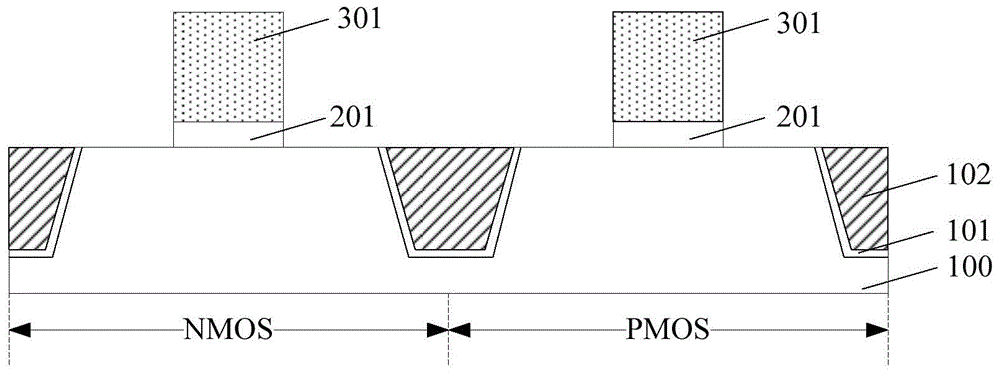
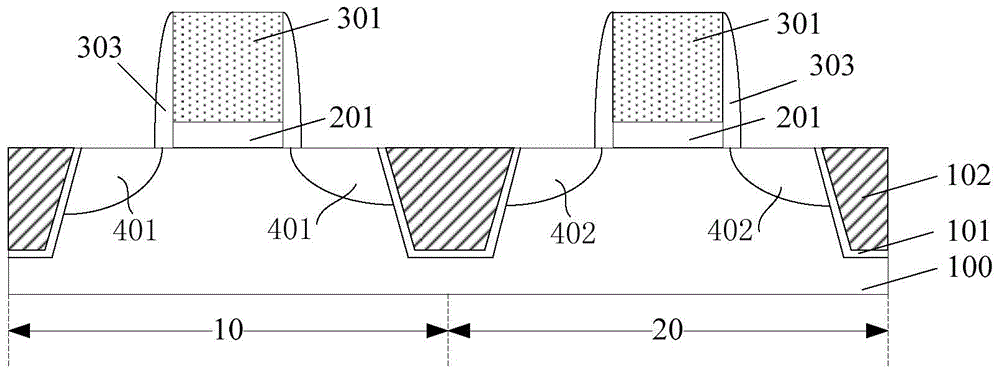
InactiveCN104681490AImprove performancePerformance impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSEngineering
The invention provides a forming method of a CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) transistor. The forming method comprises the following steps that a semiconductor substrate is provided, the semiconductor substrate comprises an NMOS (N-channel metal oxide semiconductor) region and a PMOS (P-channel metal oxide semiconductor) region, and a shallow groove isolation structure is also formed in the semiconductor substrate; a pseudo grid structure is respectively formed on the surfaces of the NMOS region and the PMOS region; a dielectric layer is respectively formed on the semiconductor substrate and the surface of the shallow groove isolation region; the pseudo grid structure is removed, a first groove is formed in the surface of the NMOS region, and a second groove is formed in the surface of the PMOS region; a high-K grid dielectric material layer is formed, and displacement ions are doped in the high-K grid dielectric material layer, and can overcome defects in the high-K grid dielectric material layer; the high-K grid dielectric material layer is subjected to annealing processing, and the defects in the high-K grid dielectric material layer are further eliminated; a first grid electrode and a second grid electrode are formed. The forming method of the CMOS transistor has the advantage that the quality of the high-K grid dielectric material layer can be improved.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
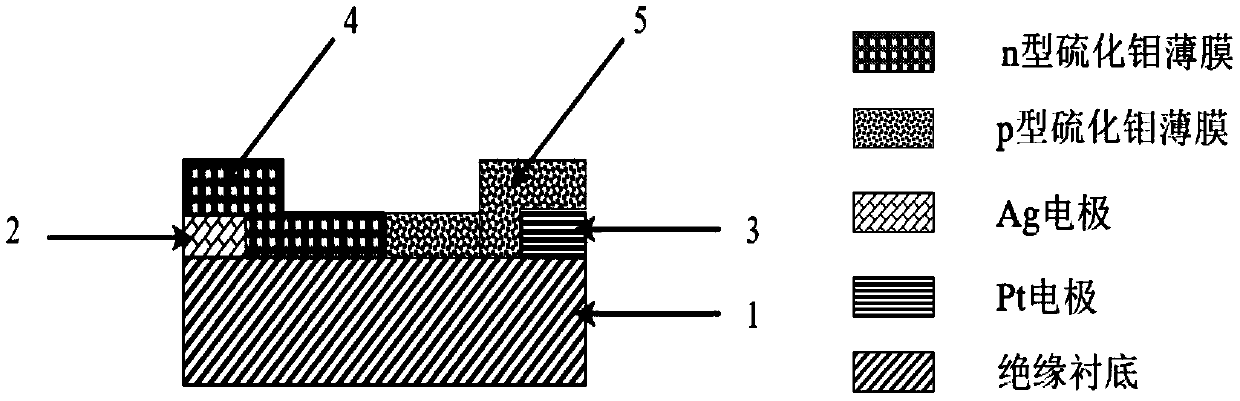
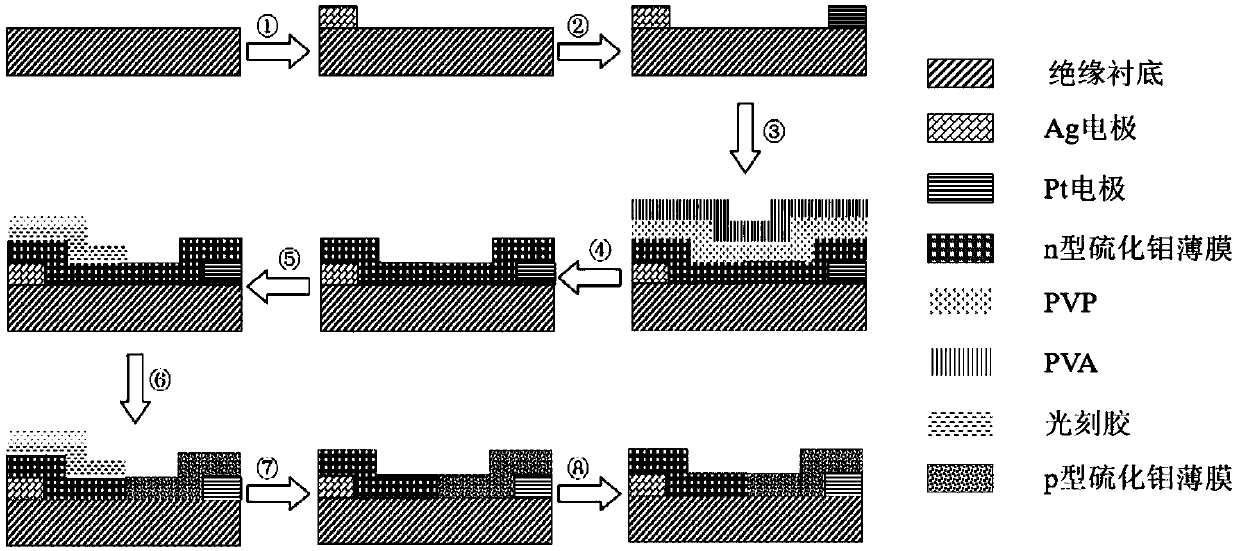
Transition metal chalcogenide compound horizontal homogeneous junction solar cell and preparation method thereof
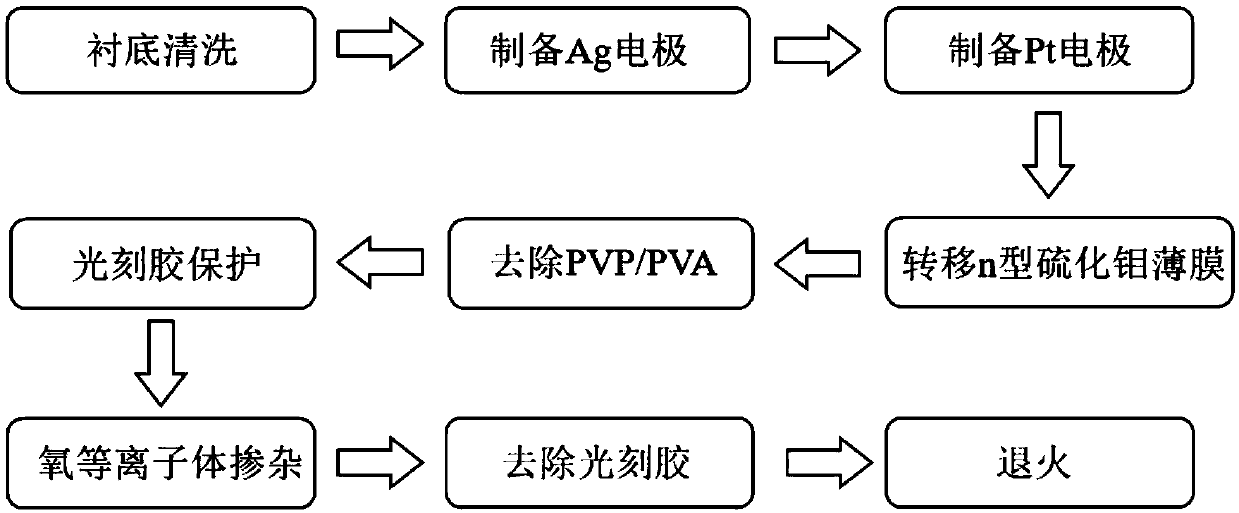
InactiveCN109616541AReduce the lattice mismatch rateReduce interface defectsFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsLattice mismatch
The invention discloses a transition metal chalcogenide compound horizontal homogeneous junction solar cell and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of semiconductor materials. The solar cell comprises an insulating substrate, an electrode A, an electrode B, an n-type transition metal chalcogenide compound film and a p-type transition metal chalcogenide compound film; the electrode A and the electrode B are located at the two ends of the insulating substrate respectively; and the n-type transition metal chalcogenide compound film and the p-type transition metal chalcogenide compound film are composed of the same compound, and are transversely connected to form a p-n junction. The method adopts a laser synthesis method to prepare the n-type transition metal chalcogenide compound film, and by virtue of the horizontal homogeneous p-n junction, the lattice mismatch rate of p-n junction is effectively lowered, and the interface defects are reduced; the electrodes are matched with a thin film work function to form high ohmic contact; and the electrodes and the thin films are combined by van der waals force, so that damage of an electrode preparation process to the thinfilms can be effectively avoided, the caused problems of stress, metal diffusion and the like are solved, and the conversion efficiency of the solar cell applying the thin films is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com