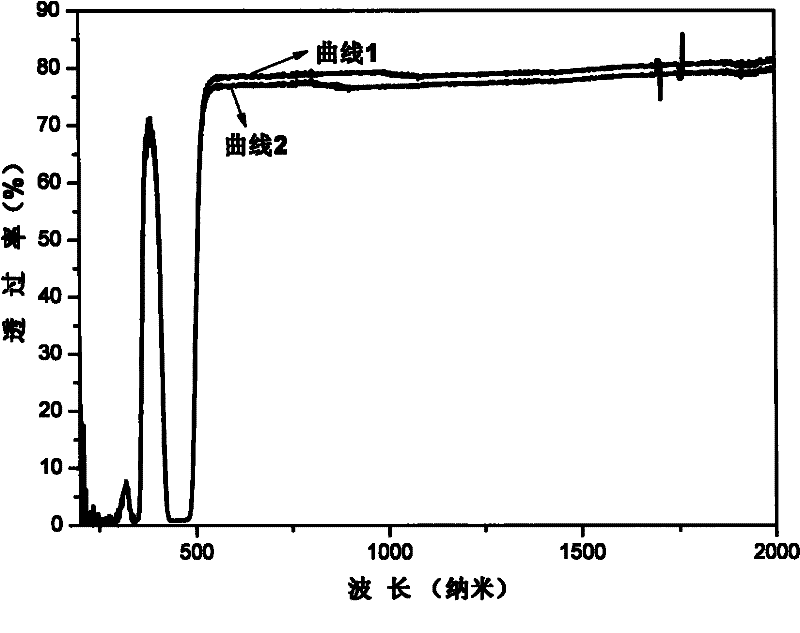
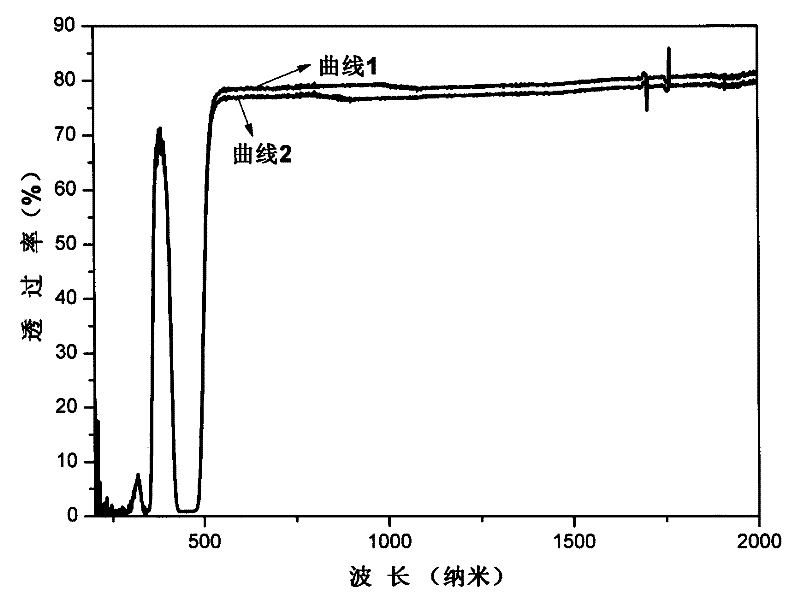
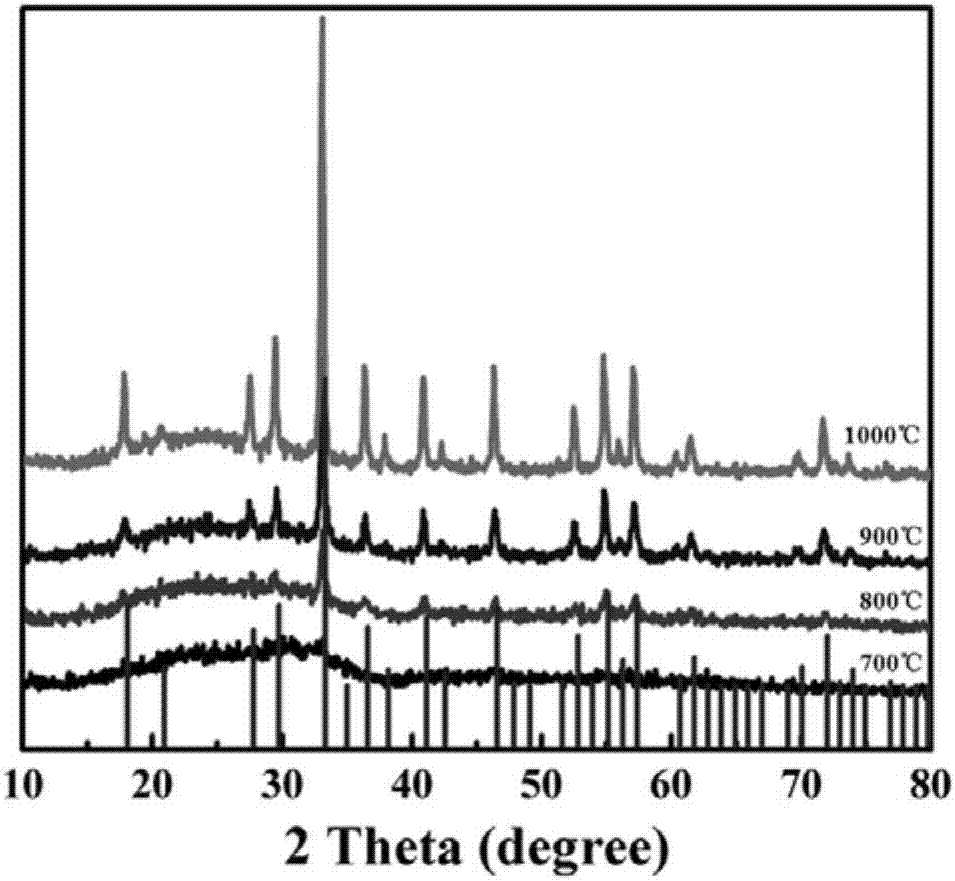
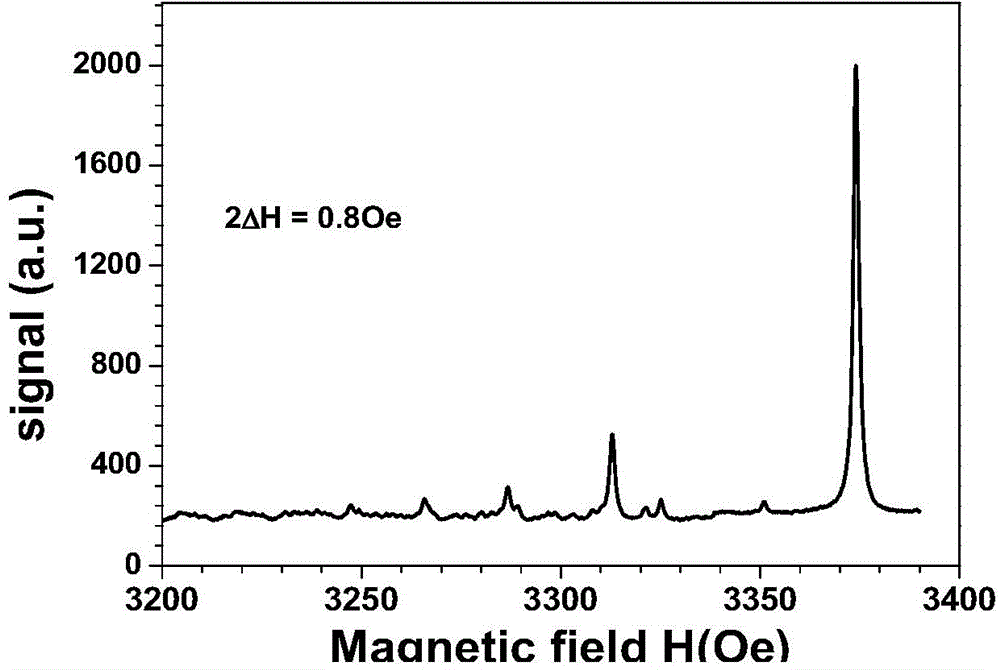
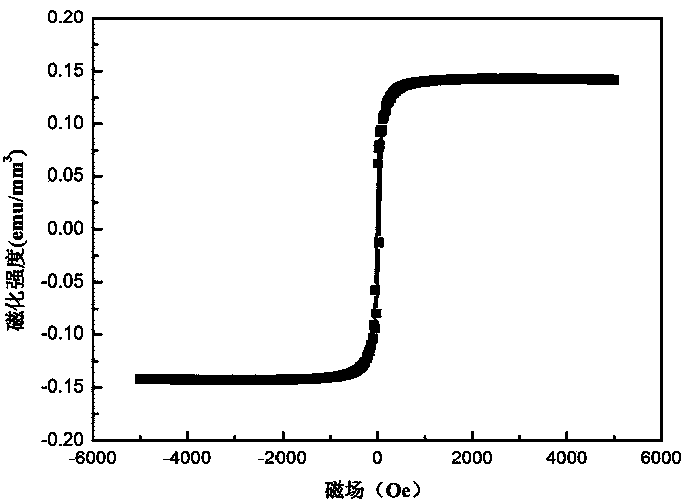
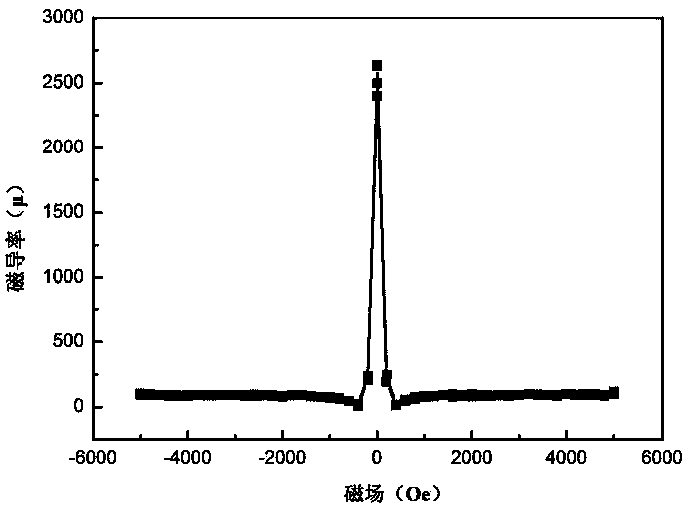
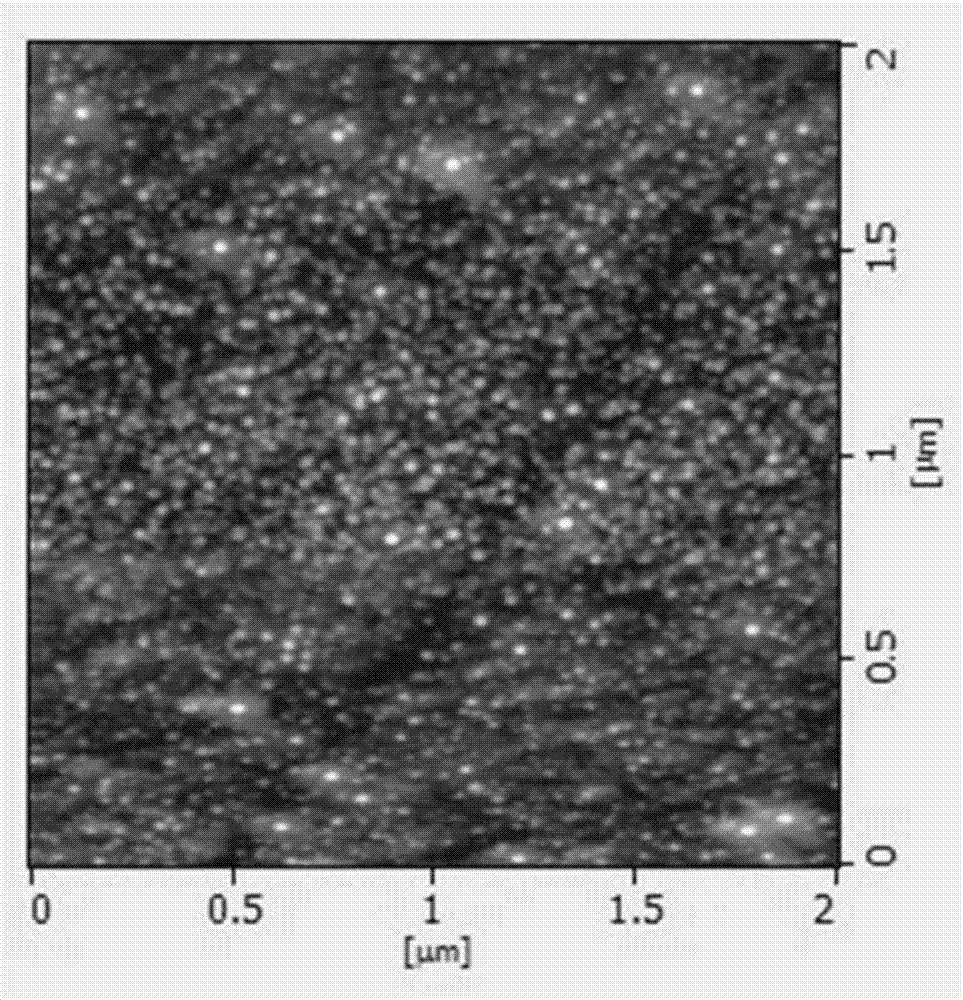
Patents
Literature
193 results about "Yttrium iron garnet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
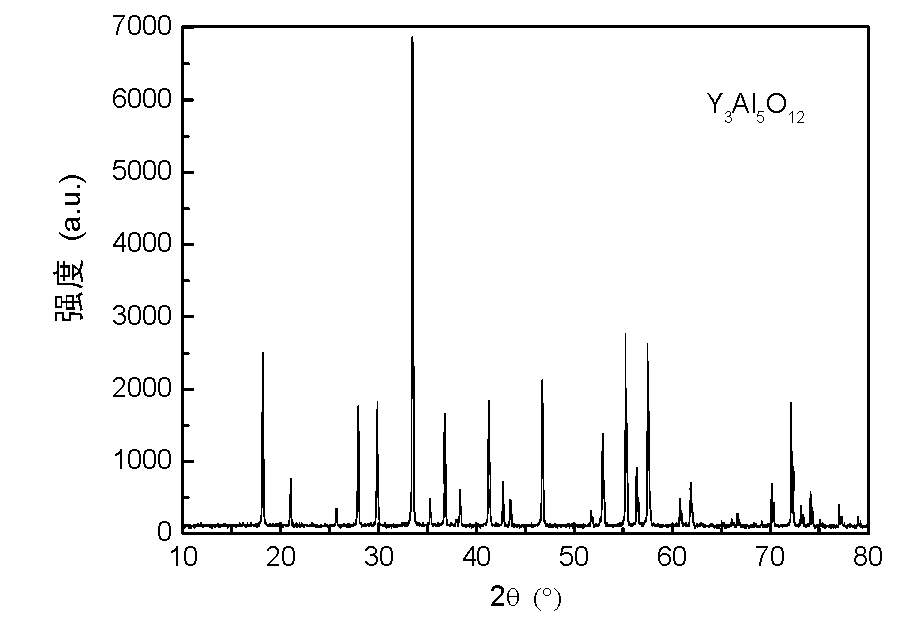
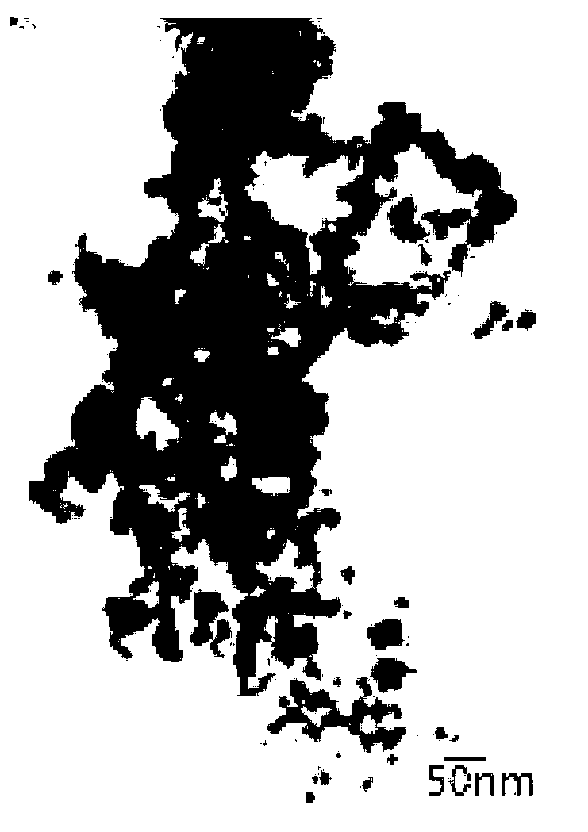
Yttrium iron garnet (YIG) is a kind of synthetic garnet, with chemical composition Y₃Fe₂(FeO₄)₃, or Y₃Fe₅O₁₂. It is a ferrimagnetic material with a Curie temperature of 560 K. YIG may also be known as yttrium ferrite garnet, or as iron yttrium oxide or yttrium iron oxide, the latter two names usually associated with powdered forms.
Composition for mobile phone case and method of manufacturing mobile phone case using the same
InactiveUS20100171234A1Low absorption rateReduce lossesCeramic shaping apparatusSolid electrolyte fuel cellsPolytetramethylene terephthalateAcrylic resin
There are provided a composition for mobile phone cases and a method of manufacturing a mobile phone case using the same. The composition comprises 70 to 97% by weight of a thermoplastic resin selected from the group consisting of polycarbonate (PC), acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), polybutyrene terephtalate (PBT), acrylic resin and combinations thereof; and 3 to 30% by weight of ferrite selected from the group consisting of nickel-zinc ferrite, manganese-magnesium ferrite, manganese-zinc ferrite, copper-zinc ferrite, manganese-magnesium-aluminum ferrite, yttrium iron garnet (YIG) ferrite and combinations thereof, wherein the composition is a pellet resin formed by extruding the thermoplastic resin and the ferrite at a high temperature of 160 to 290° C.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method for preparing rare earth ion-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Re: YAG) transparent laser ceramic by using hot-pressing post treatment
ActiveCN102924073AOvercoming low driving force for sinteringDegree of overcomingRare earth ionsControllability
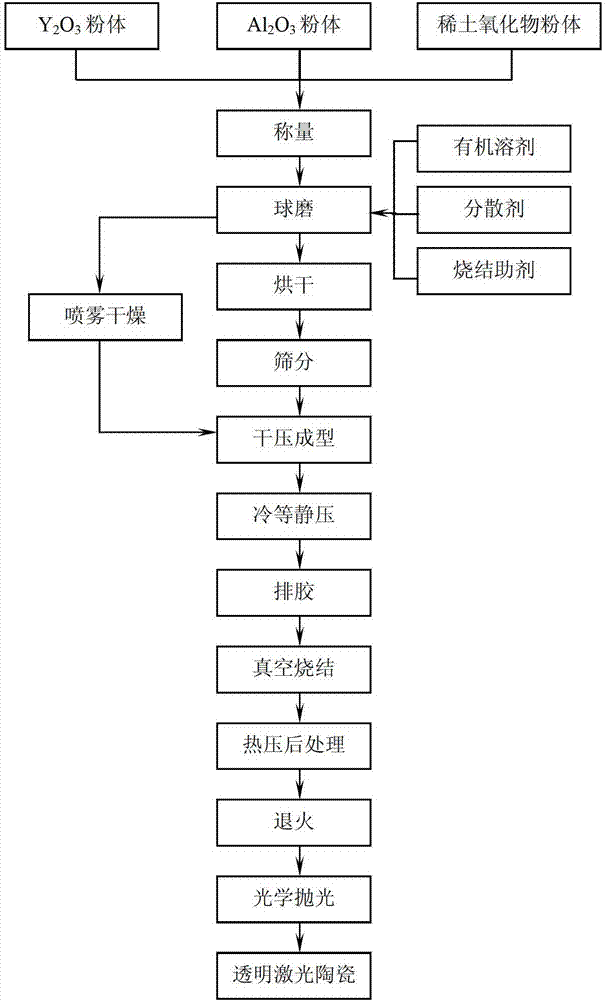
The invention discloses a method for preparing rare earth ion-doped yttrium-aluminum garnet (Re: YAG) transparent laser ceramic by using hot-pressing post treatment. The method comprises the steps of using oxide powder as a raw material, mixing with a ball mill, drying, forming, performing cold isotactic processing to obtain a ceramic biscuits, then dumping, and carrying out vacuum sintering to obtain the Re: YAG ceramic; and performing powder-embedded hot pressing, annealing and optically polishing on the Re: YAG ceramic to obtain the final Re: YAG transparent laser ceramic. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of strong controllability and repeatability, and low cost, and the Re: YAG transparent ceramic prepared by the method provided by the invention has high transmittance.
Owner:北京雷生强式科技有限责任公司
Microcrystalline glass containing rare earth mixing yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) phase and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses microcrystalline glass containing rare earth mixing yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) phase and a preparation method thereof. A glass matrix material uses SiO2, B2O3, Na2O, BaO, K2O, ZnO, CaO and Li2O as raw materials and is obtained by melting and fusing, a general form of yttrium aluminum pomegranate stone microcrystal materials containing the rare earth is (Y1-XLnX)3A15O12, Ln is Ce, Eu or Nd, X=0.03-0.08, and the glass matrix material and the yttrium aluminum pomegranate stone microcrystal materials containing the rare earth are melted and fused according to the weight ratio of 95:4-6. The microcrystalline glass containing the rare earth mixing the YAG phase is obtained by annealing. The microcrystalline glass is semi-transparent, the microcrystalline glass containing the rare earth mixing the YAG phase is small in crystal particle, the microcrystalline glass is good in dispersibility of rare earth mixed YAG phase crystal, rare earth ion basically enters YAG crystal lattices, and the rare earth ion is also good in dispersibility, so that the microcrystalline glass is excellent in optical property and strong in fluorescence, and can be obtained through a two-step fusion method, melting and fusing temperature is low and lower than 100 DEG C, requirements of a preparation process are low, production cost is low, and the microcrystal materials are good in uniformity.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) band rejection filter based on planar resonant coupling structure and fabrication method of YIG band rejection filter
ActiveCN106252802ACompact designImproved tuning sensitivityWaveguide type devicesSputteringGadolinium gallium garnet
The invention discloses a YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) band rejection filter based on a planar resonant coupling structure and a fabrication method of the YIG band rejection filter. The filter comprises a YIG band rejection filter and a driver, wherein the YIG band rejection filter comprises a resonant cavity, a planar resonant coupling structure, a permanent-magnet biasing magnetic path and an excitation coil, the planar resonant coupling structure is arranged in the resonant cavity, and the permanent-magnet biasing magnetic path provides a stable magnetic field for the resonant cavity. With the adoption of a mode of arranging a YIG thin film on a front surface of GGG (Gadolinium gallium garnet) glass and photoetching a coplanar waveguide circuit on the YIG thin film by sputtering, the planar resonant coupling structure is formed, a traditional spherical three-dimensional coupling structured YIG band rejection resonant coupling structure is substituted, and the technical defect existing in the traditional structure is also overcome. In the processing technology, The YIG thin film is first photoetched to a required shape according to a product shape needed to fabricate, and then the GGG glass is cut along appearance; and the defect of edge breakage or damage of the YIG thin film easily caused by directly cutting the YIG thin film based on a GGG substrate is overcome.
Owner:SOUTHWEST INST OF APPLIED MAGNETICS
Method for preparing yttrium aluminum garnet based transparent ceramic by slip casting
The invention discloses a method for preparing a yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) based transparent ceramic by slip casting. The method comprises the following steps: performing ball-milling and mixing on oxide ceramic powder, a sintering adjuvant, a nonaqueous solvent and a dispersant; adding an adhesive, a plasticizer and a defoaming agent; and preparing a nonaqueous based slurry through ball-milling and mixing, wherein the slurry consists of the following components in percentage by mass: 40 to 70 percent of oxide ceramic powder, 0.01 to 1 percent of sintering adjuvant, 0.005 to 2.5 percent of dispersant, 0.01 to 5 percent of adhesive, 0.01 to 3 percent of plasticizer, 0.005 to 0.5 percent of defoaming agent, and the balance of the nonaqueous solvent; and preparing a ceramic block from the slurry through slip casting, preparing a ceramic biscuit by adopting a two-step drying method, and preparing the transparent ceramic through vacuum sintering. The method adopts the slip casting, is particularly suitable for preparing the ceramic sample with complicated shape, large size and composite structure, and greatly widens the preparation means of the transparent ceramic.
Owner:中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所苏州研究院
Method for preparing yttrium iron garnet ferrite material
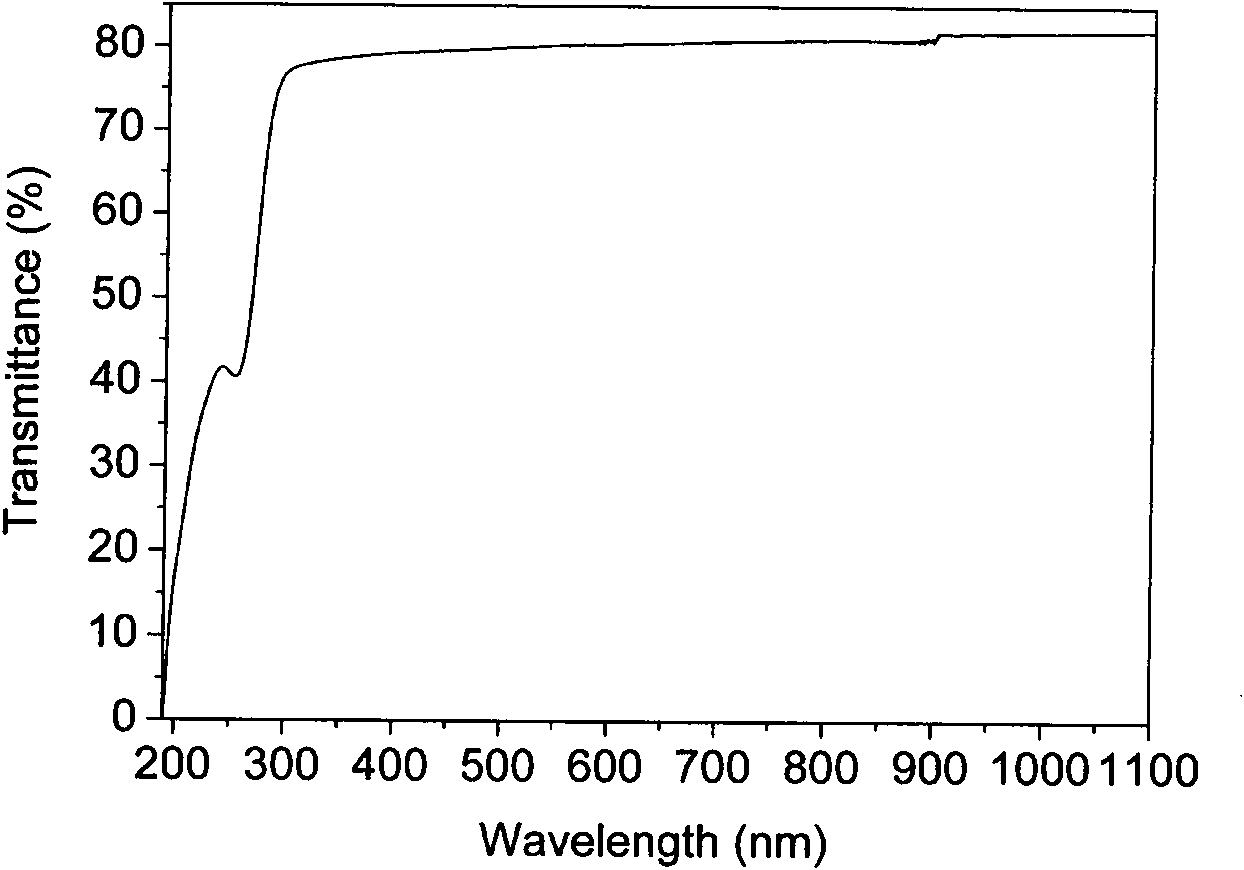
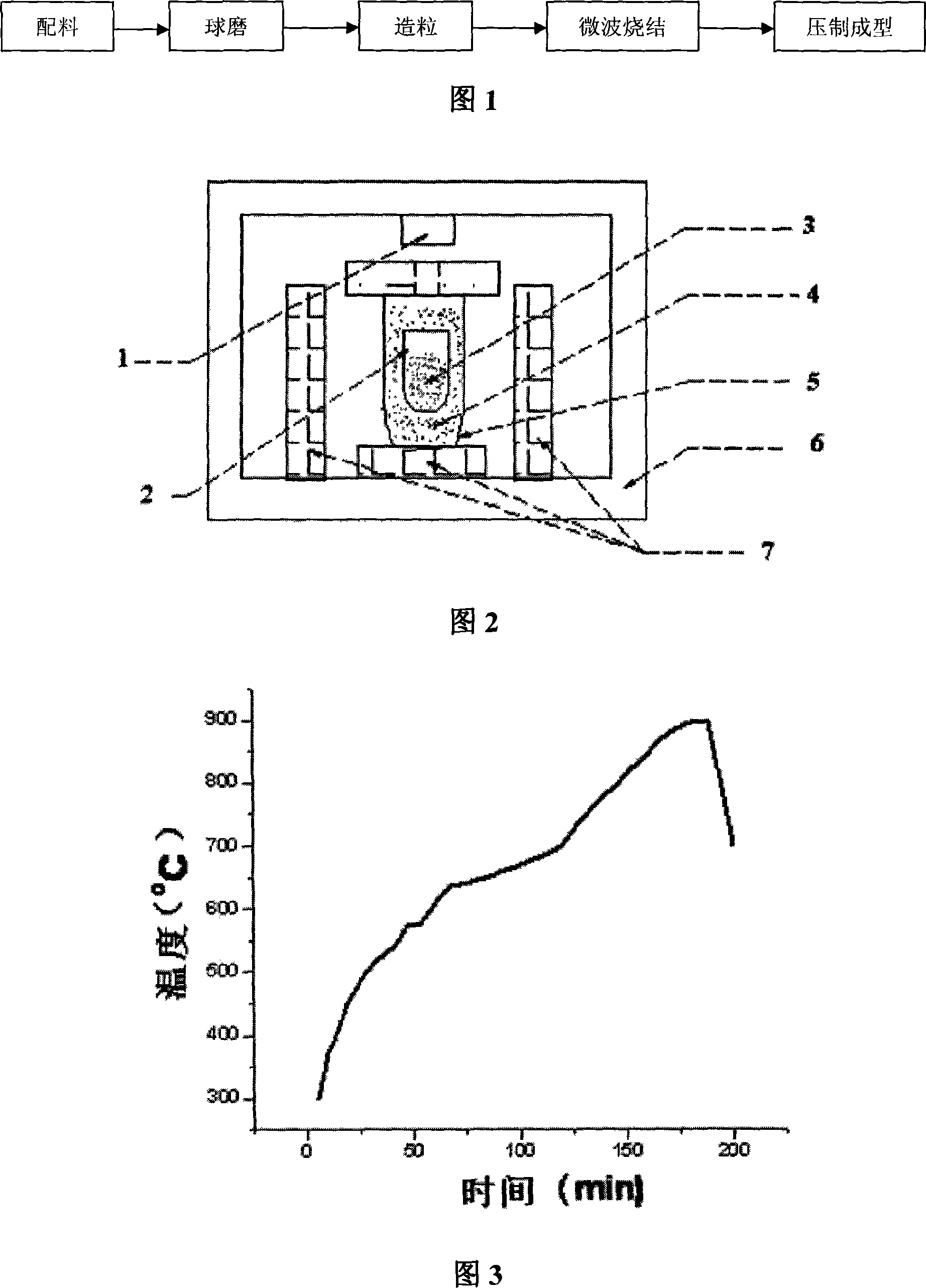
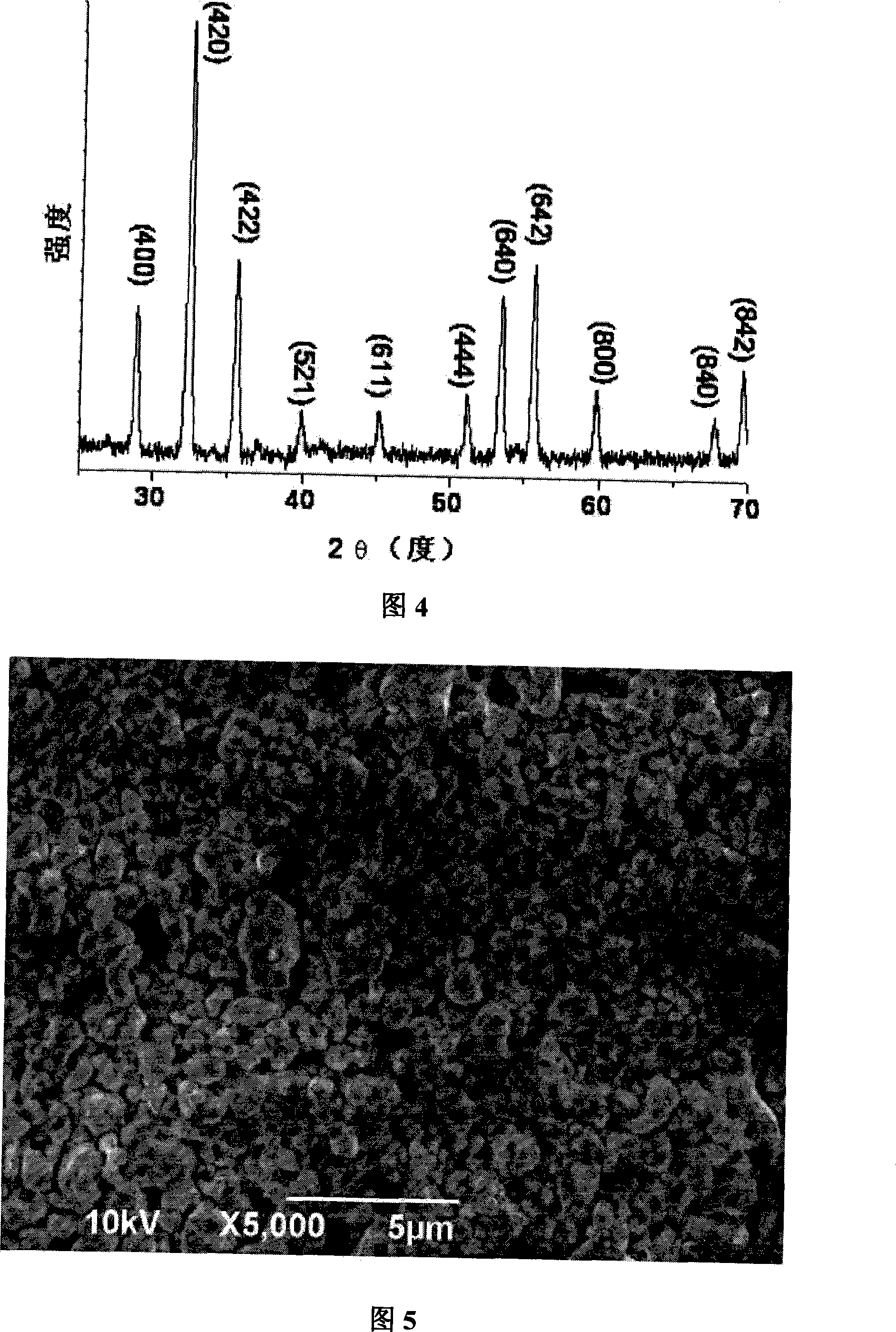
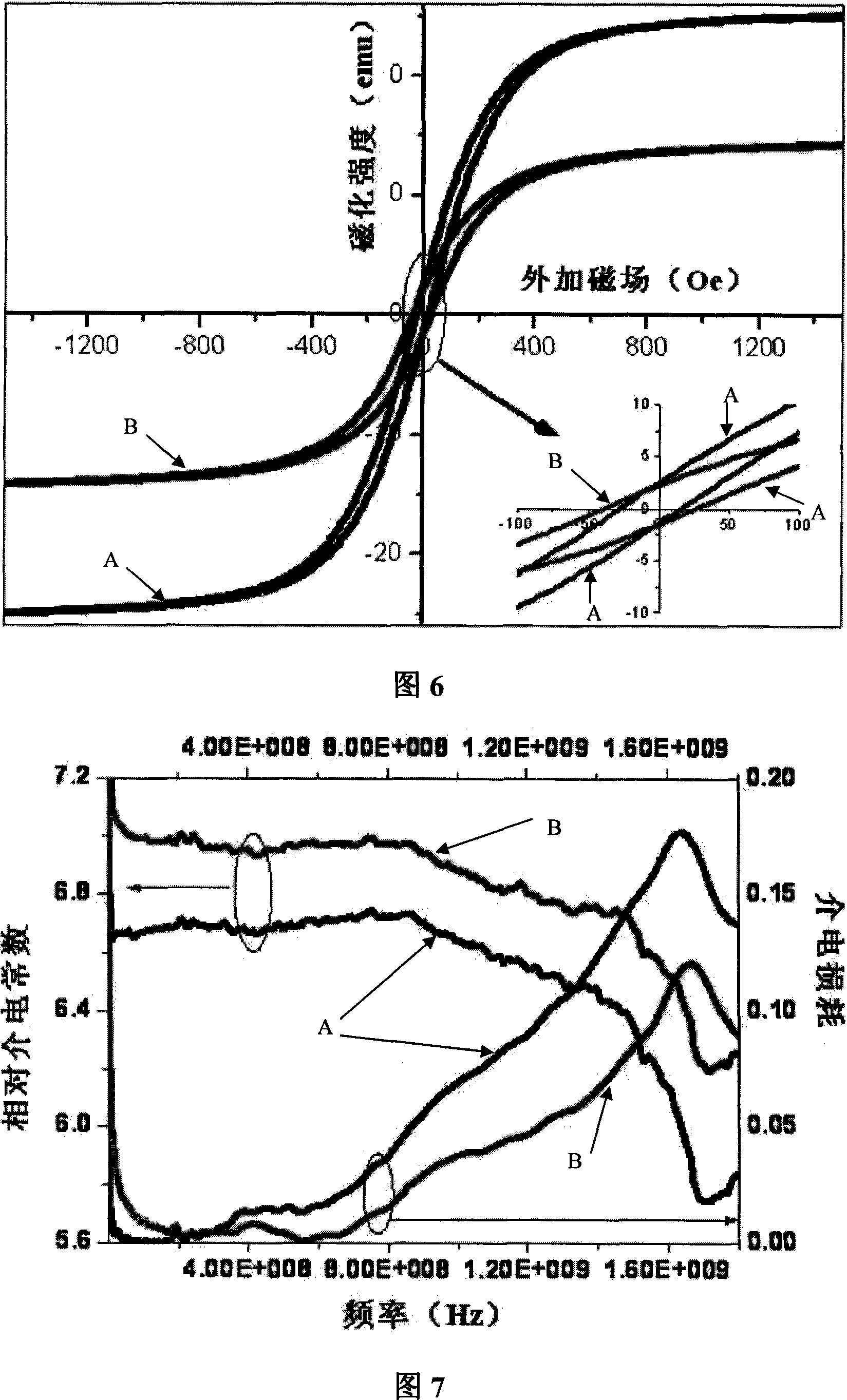
The invention relates to yttrium iron garnet ferrite preparation method, belonging to a field of electronic material. The invention comprises the following steps: 1 the proportion of the required materials Fe2O3 and Y2O3 is calculated according to the chemical formula Y3Fe5O12; 2. According to the proportion calculated in the step 1, the Fe2O3 and Y2O3 are mixed and milled; 3. Drying and crushing; 4, the dried and crushed powder is sintered by microwave; 5. Granulation; 6. Pressing formation. The invention has the advantages of: 1. Density structure; 2. excellent magnetic energy; 3 large dielectric constant and small dielectric loss; 4. Small electromagnetic loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
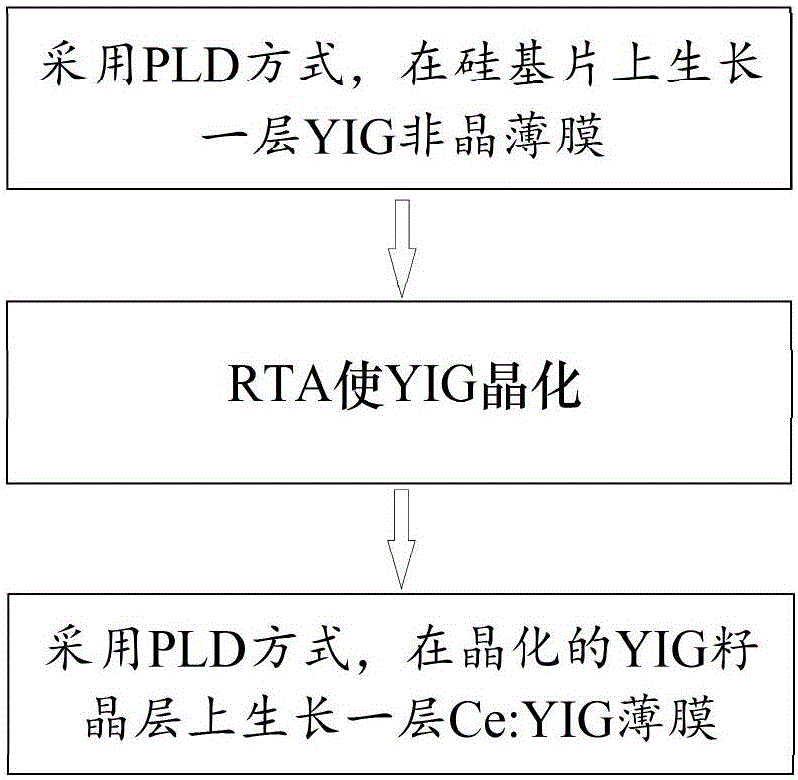
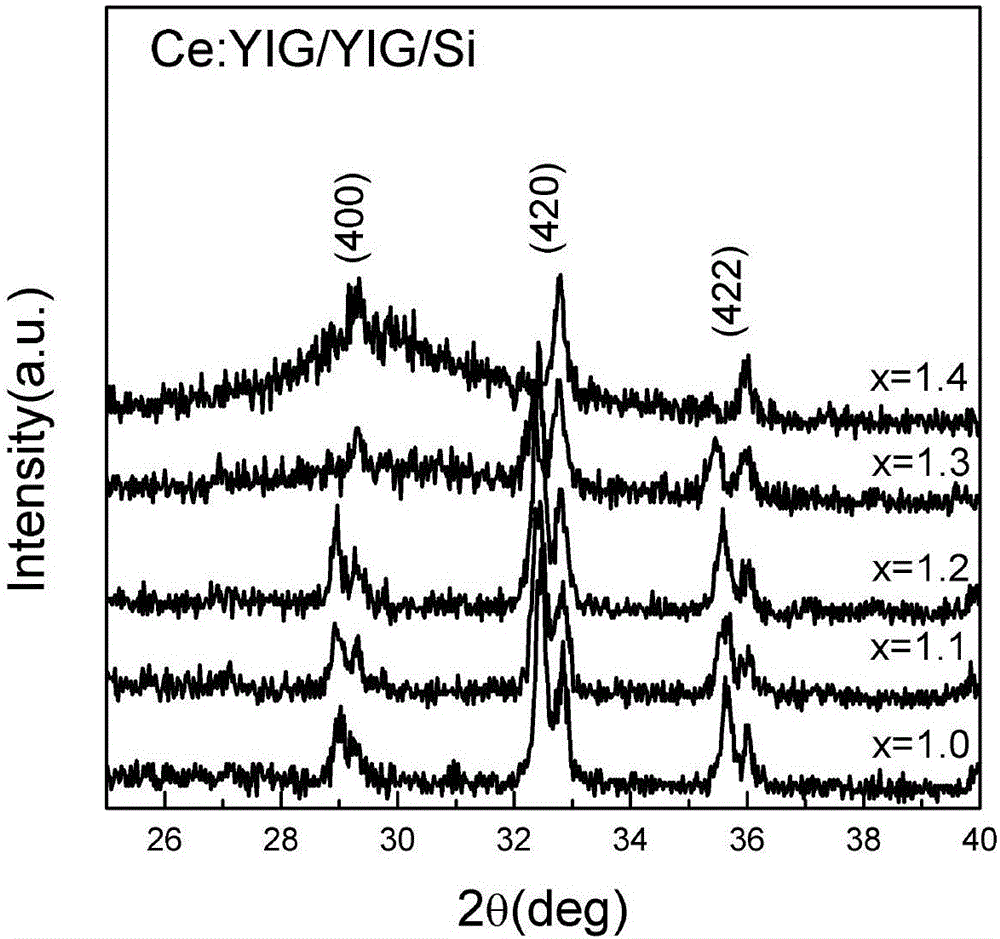
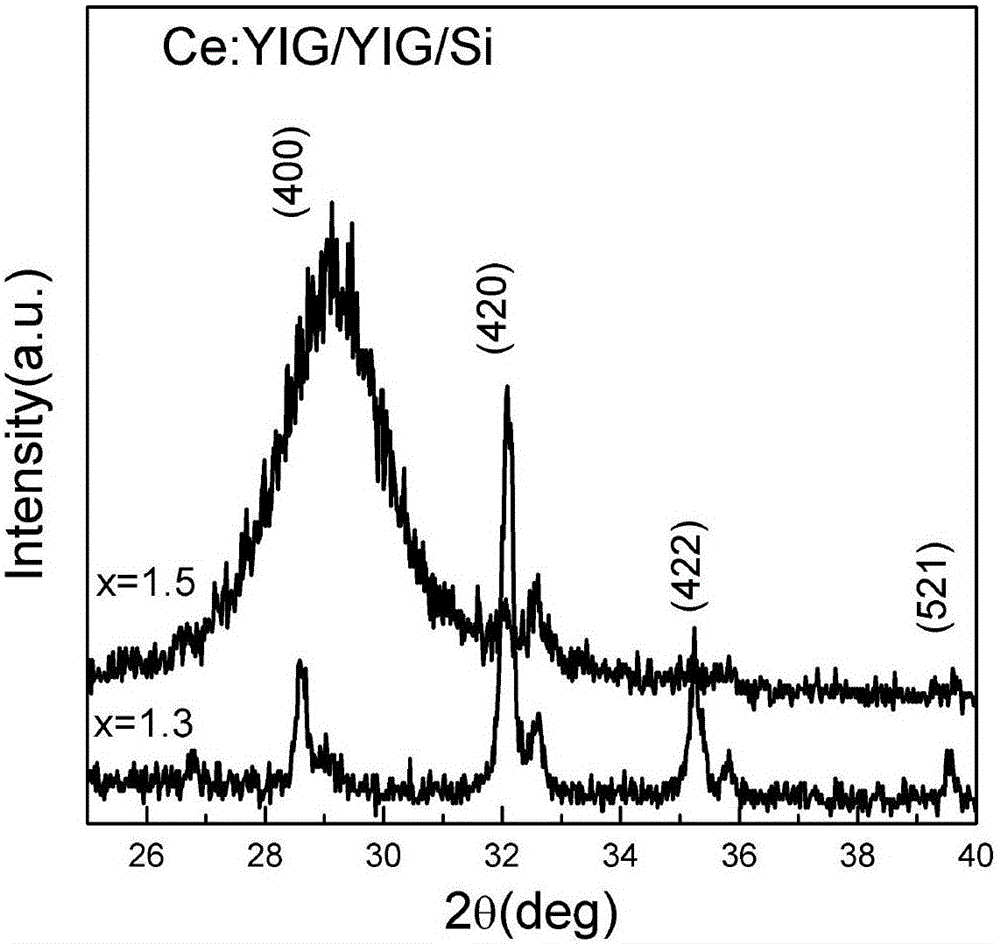
Preparation method for directly growing highly-doped yttrium iron garnet film on silicon
ActiveCN105714379AEnhanced magneto-optical performancePolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsDeposition temperatureRare earth
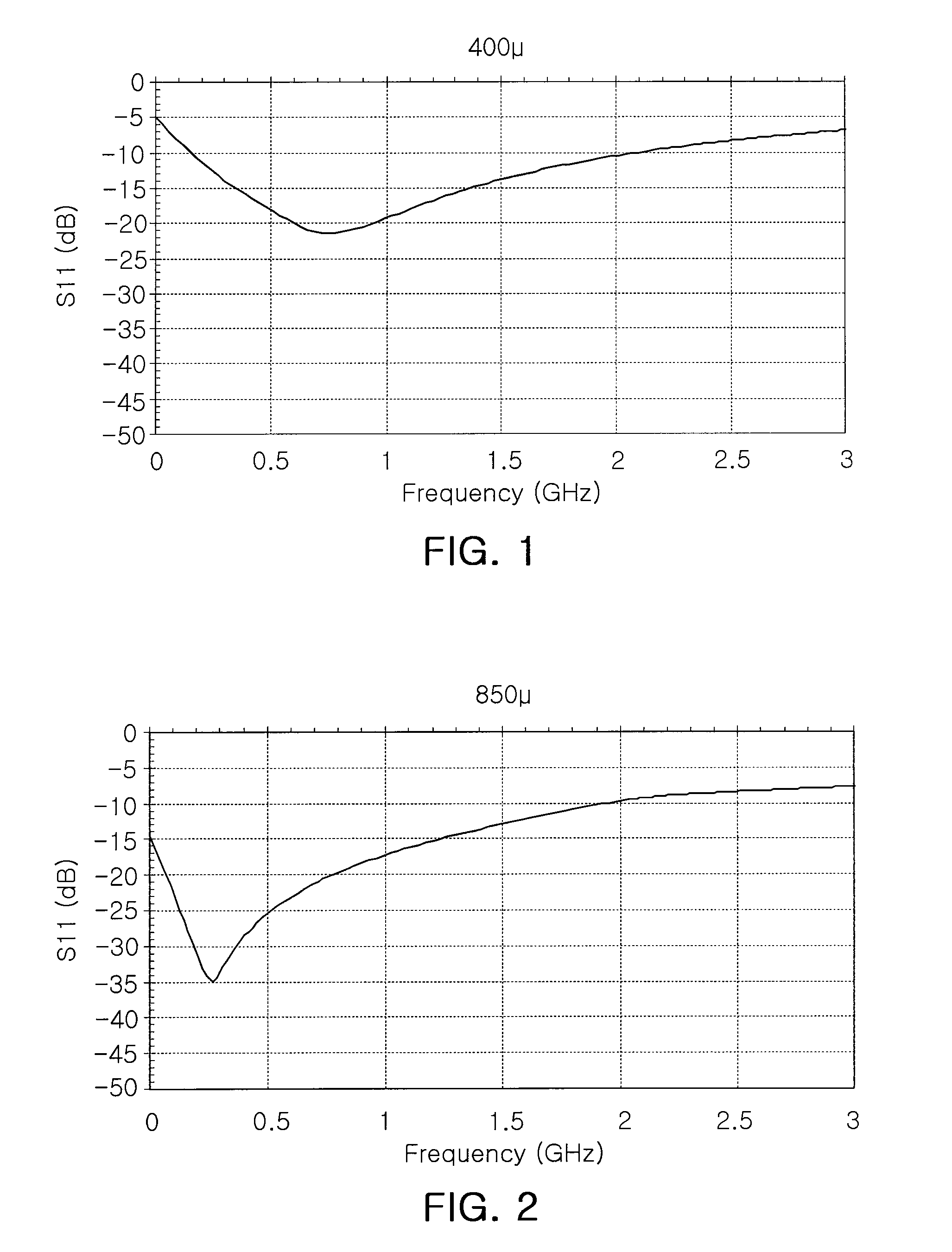
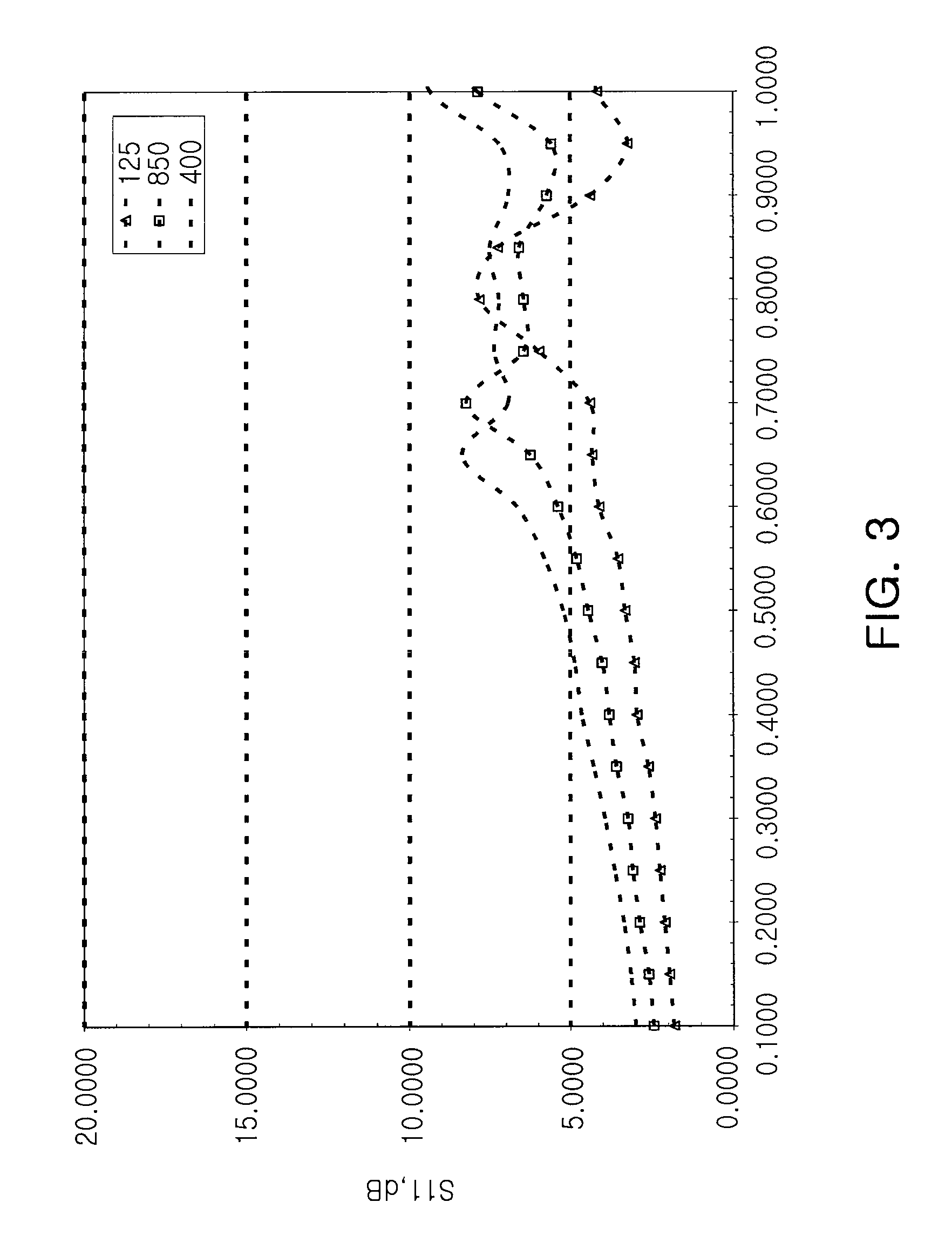
The invention belongs to the technical field of production of magnetic oxide films, and particularly relates to a preparation method for directly growing a highly-doped yttrium iron garnet film on silicon. The laser energy density in the growth process of a rare earth-doped yttrium iron garnet film is changed from 1.8 J / cm<2> to 4.0 J / cm<2>, the film deposition temperature is changed from 400 DEG C to 850 DEG C, and the film deposition air pressure is changed from 1 mTorr to 20 mTorr, so that the rare earth doping concentration in the yttrium iron garnet film growing on a silicon substrate is improved from 33% to 50%, the Faraday optical constant of the material in photo-communication 1550 nm wavelengths is improved from 2800 degrees / cm to 6000 degrees / cm, and the magneto-optical property of the material is greatly enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for preparing yttrium aluminum garnet-based transparent ceramic through aqueous tape casting
The invention provides a method for preparing yttrium aluminum garnet-based transparent ceramic through aqueous tape casting. The method comprises steps: preparing a slurry of the yttrium aluminum garnet-based transparent ceramic and a casting film by adopting water as a solvent through adopting an aqueous tape casting technology; processing the casting film to form diaphragms having different shapes as needed; carrying out lamination treatment of the diaphragms at a lamination temperature of 75-95DEG C under a lamination pressure of 40-120MPa to obtain a biscuit; and carrying out degumming treatment and cold isostatic pressing treatment of the biscuit, and sintering to obtain the yttrium aluminum garnet-based transparent ceramic. The method has a good environmental compatibility, and the transparent ceramic can be obtained through the method.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for preparing yttrium aluminum garnet-based continuous fibers through sol-gel method
InactiveCN102011215AAvoid growing upGrowth retardationArtificial filament washing/dryingFibre chemical featuresFiberYttrium
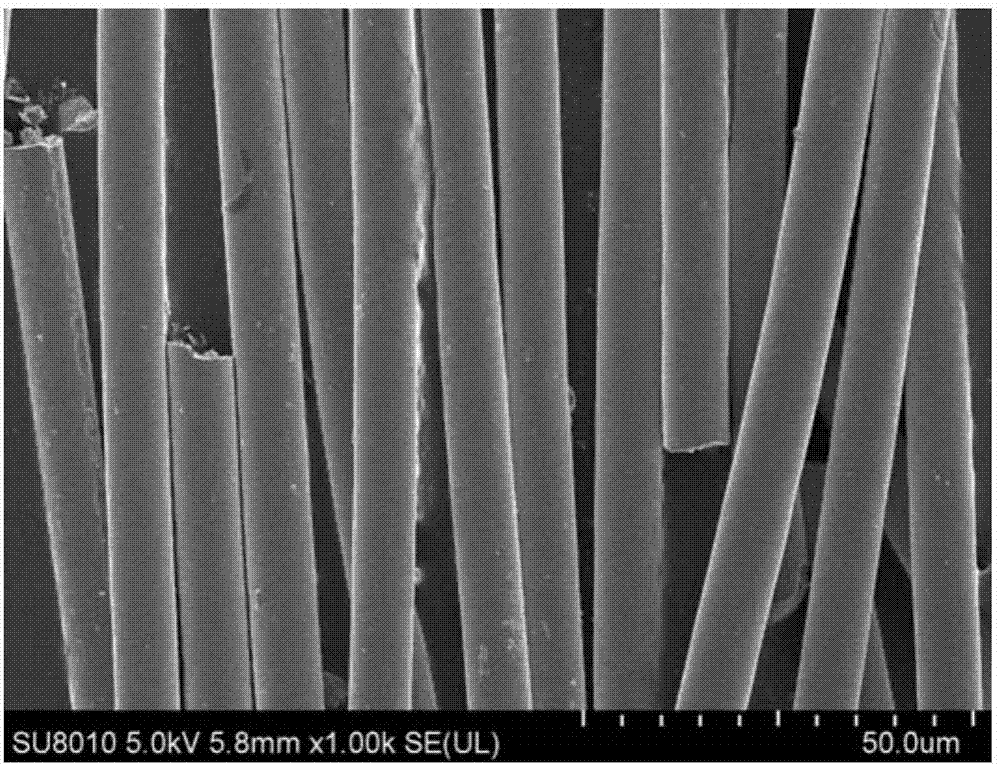
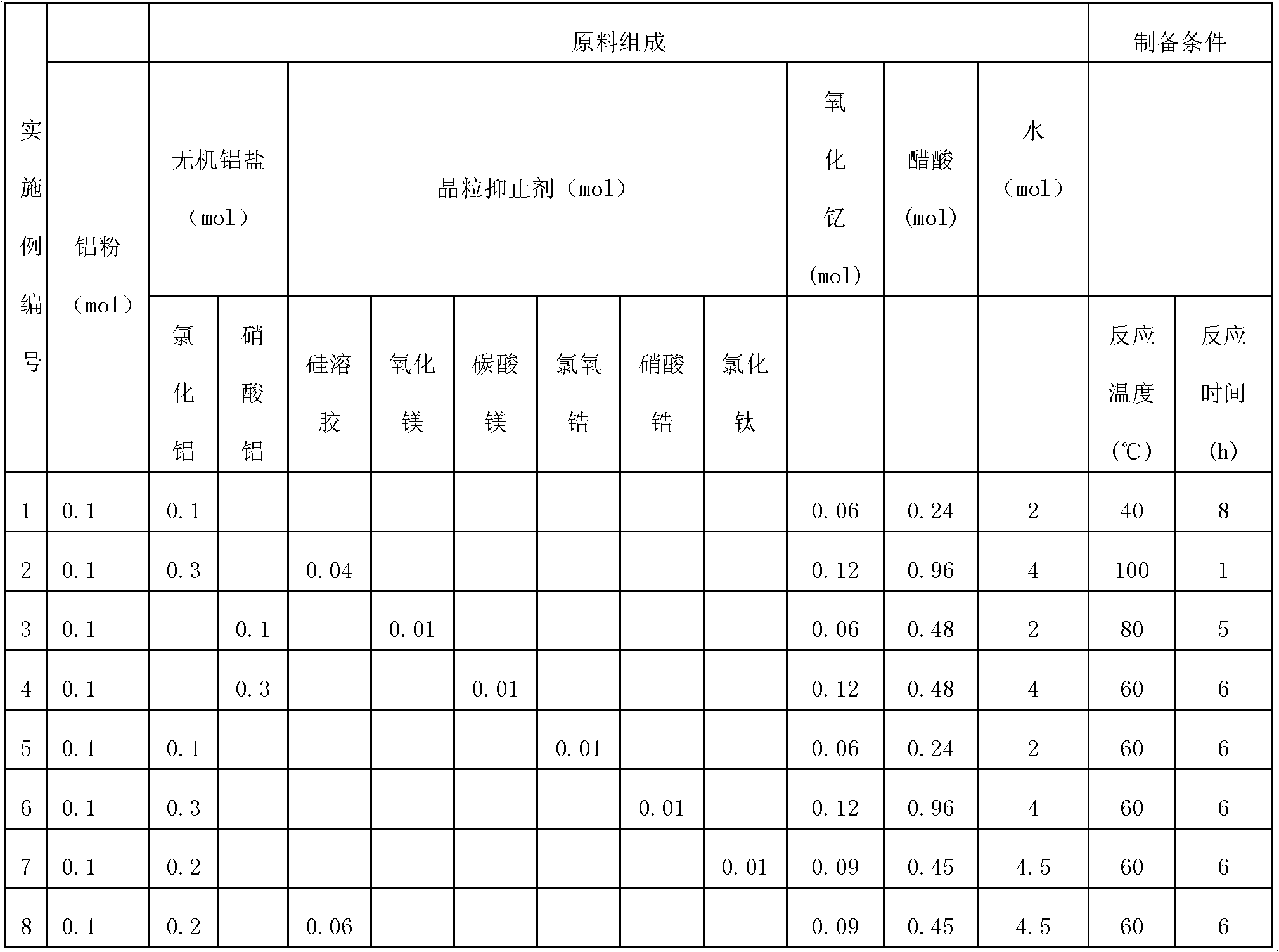
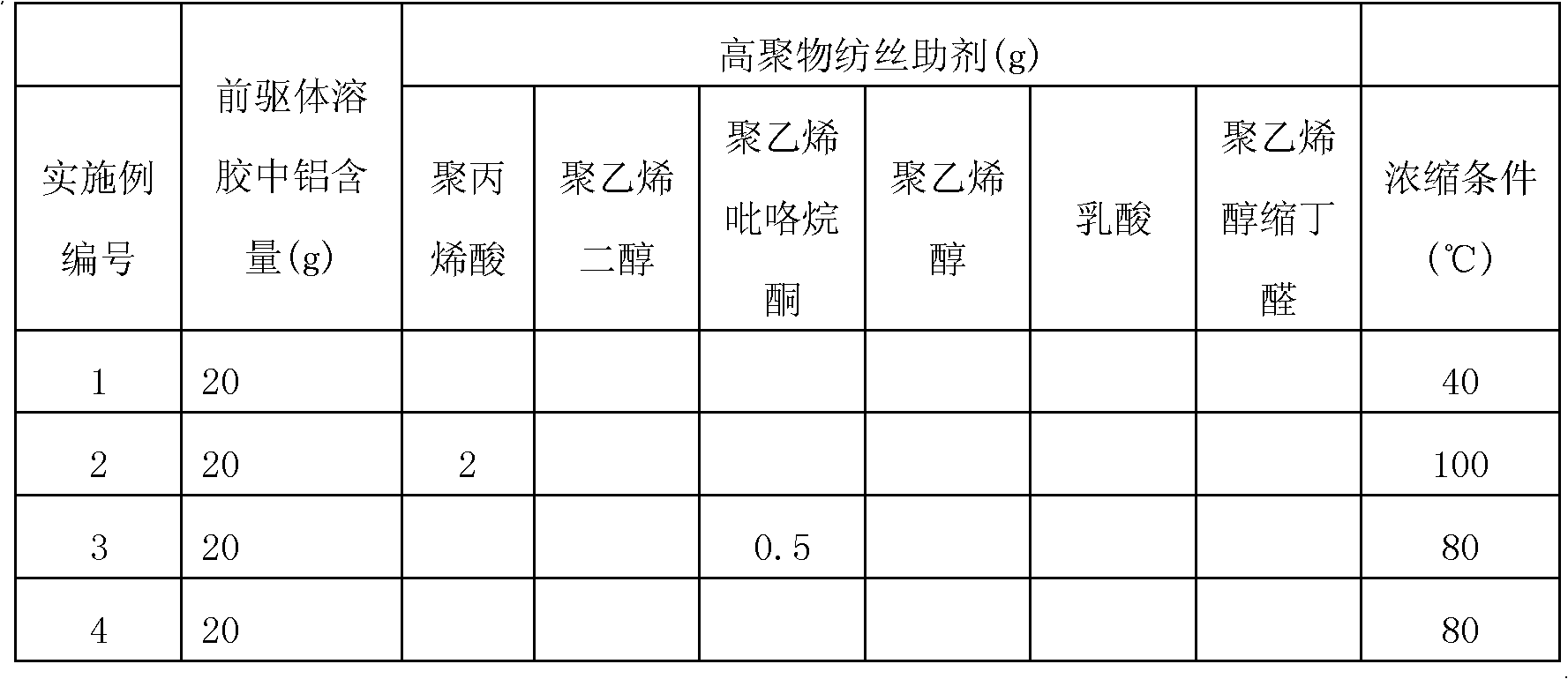
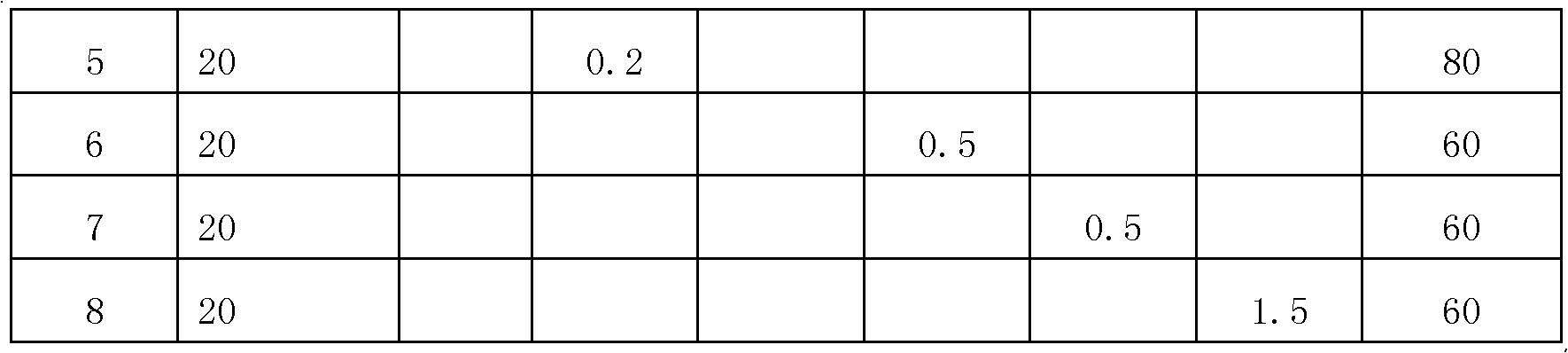
The invention discloses a process for preparing yttrium aluminum garnet-based continuous fibers through a sol-gel method. Yttrium aluminum garnet is taken as a main component, and a second component is added to serve as a grain inhibitor. The process comprises the following steps of: adding inorganic aluminum salt, yttrium oxide, the grain inhibitor, acetic acid and metal aluminum into distilled water, and reacting the mixture solution under the conditions of certain temperature, continuously stirring and condensing reflux so as to prepare grain inhibitor-containing yttrium aluminum garnet sol; adding a certain amount of spinning aid into the sol, and concentrating the solution so as to prepare spinnable fiber precursor sol; spinning to prepare precursors of organic matter-containing yttrium aluminum garnet-based continuous fibers by adopting a dry method or a wet method; and drying and sintering the precursors to prepare the yttrium aluminum garnet-based fibers. The prepared yttrium aluminum garnet-based continuous fibers can be used as reinforcement in a composite material to improve the strength, toughness and heat resistance of the material, and is widely applied in the fields of aerospace, automobiles and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF TECH
Sintering aid for yttrium aluminum garnet-based fluorescent transparent ceramic and using method thereof
The invention relates to a sintering aid for yttrium aluminum garnet-based fluorescent transparent ceramic and a using method thereof. The sintering aid particularly comprises tetraethoxysilane and magnesium oxide, wherein the using amount of the tetraethoxysilane with the silicon oxide content of not less than 28.4 percent is 0.3 to 0.7 weight percent of the garnet-based transparent ceramic fluorescent powder raw material; and the using amount of the magnesium oxide with the purity of not less than 99.9 percent is 0.01 to 0.8 weight percent of the garnet-based transparent ceramic fluorescent powder raw material. The garnet-based transparent ceramic fluorescent material prepared from the sintering aid has a compact microstructure and is uniform in crystallite dimension distribution.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet): Ce rare earth fluorescent powder
InactiveCN102391870ALower activation energyOvercome uniformity issuesLuminescent compositionsAcetic acidAlcohol
The invention relates to a preparation method of a YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet): Ce rare earth fluorescent powder, comprising the following steps of: weighing Y2O3 or Gd2O3 or mixture of the Y2O3 and the Gd2O3, Al2O3 or Ga2O3 or mixture of the Al2O3 and the Ga2O3, and CeO3 according to molar ratio as shown in the chemical formula of a target fluorescent powder; weighing a YAG seed crystal and a fluxing agent according to a certain proportion, and mixing the materials; adjusting the mixture into a flowing deformation phase by taking proper amount of water or alcohol or acetic acid, and stirring for 6-24 hours; putting the flowing deformation phase mixture into an oven with the temperature of 80-120 DEG C and insulating for 6-24 hours; putting an obtained product into a high temperature furnace with the temperature of 900-1600 DEG C, and roasting under reducing atmosphere for 2-6 hours; and performing the washing and the impurity removing to a roasted product so as to obtain the YAG: Ce rare earth fluorescent powder. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the preparation method is low in energy consumption and low in production cost, and the fluorescent powder is even in particle size and regular in shape.
Owner:宁波浩威尔新材料科技有限公司
Preparation method of continuous fiber of yttrium aluminum garnet
ActiveCN106927808AGood effectUniform diameterInorganic material artificial filamentsMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberPolymer science
The invention relates to a preparation method of a continuous fiber of a yttrium aluminum garnet. The method comprises the steps of preparing a spinnable precursor sol from aluminum oxide sol containing Al13 colloidal particles, a gamma-AlOOH nano dispersion liquid, yttrium oxide sol, glacial acetic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), preparing a gel continuous fiber by adopting a dry spinning technology and carrying out thermal treatment to obtain the continuous fiber of yttrium aluminum garnet, which is 6-12 microns in diameter. The precursor sol prepared by adopting a sol-gel method is uniform and stable, and can be stored for a long period of time. The length of the gel continuous fiber prepared with dry spinning can reach 3,000m, the fiber subjected to thermal treatment is smooth in surface, the internal structure is compact, the strength is high, and the fiber has very good flexibility, is small in high-temperature creep in a high-temperature using process, and can be widely applied to a composite material and a thermal protection material in the industries such as aerospace. The method is simple in process and short in production period, and industrialization is easy to implement.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104831357AFerromagnetic resonance linewidthThe ferromagnetic resonance linewidth is very narrowPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthSingle crystalElectronic materials
The present invention provides an yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film and a liquid-phase epitaxy preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of electronic materials. According to the present invention, the component of the yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film is La[x]Y[3-x]Fe5O12, wherein x is 0.01-0.05; 0.44% by mass of Y2O3, 10.31% by mass of Fe2O3, 0.06% by mass of La2O3, 87.44% by mass of PbO and 1.75% by mass of B2O3 are adopted as raw materials; the liquid-phase epitaxy method is used to grow the single-crystal film; the ferromagnetic resonance line width of the obtained yttrium-iron-garnet single-crystal film is narrow and achieves less than or equal to 1 Oe; and the roughness, the lattice matching, the film stress, the lead content, the impure phase and the like of the film are improved.
Owner:成都威频科技有限公司
Tunable microwave material with negative refractive index
InactiveCN101494310AAdjustable working frequencyImprove performanceLayered productsWaveguide type devicesSaturation intensityOperating frequency
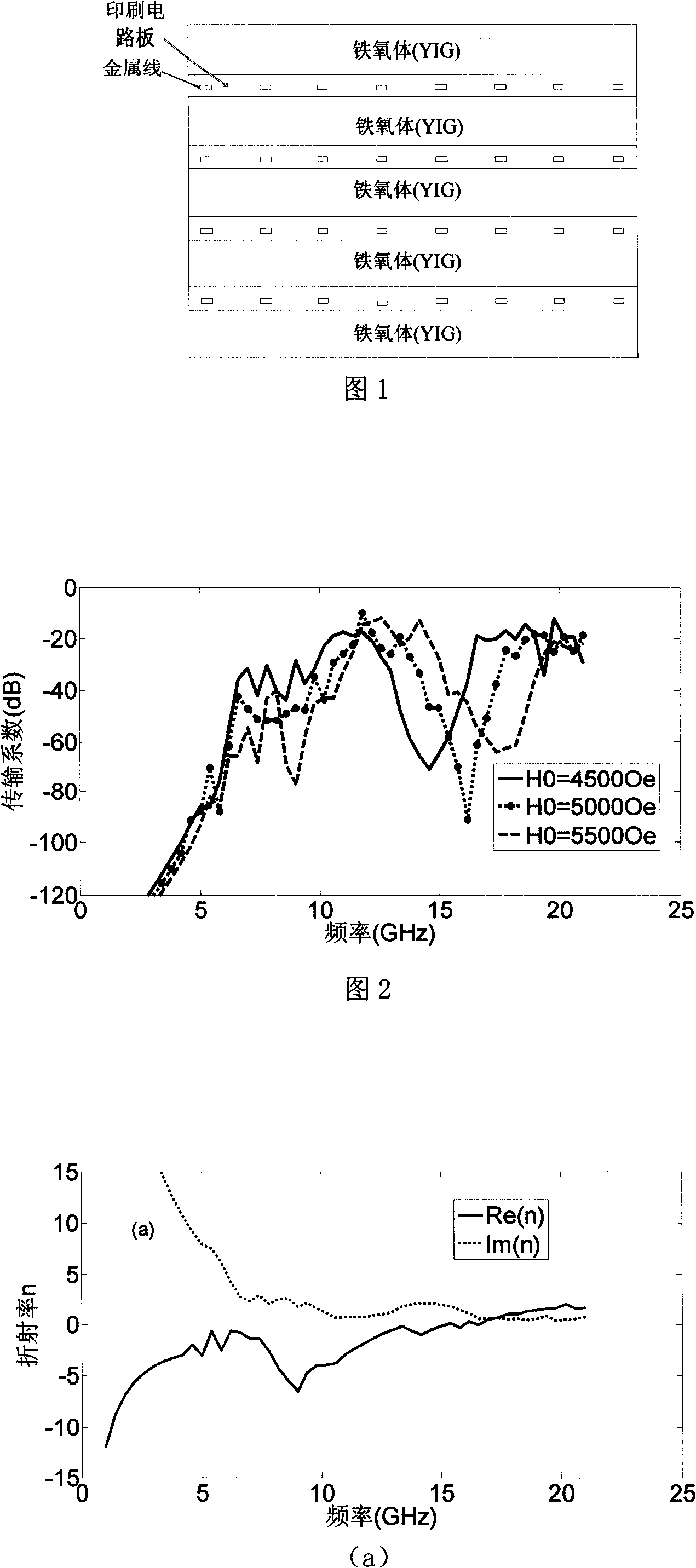
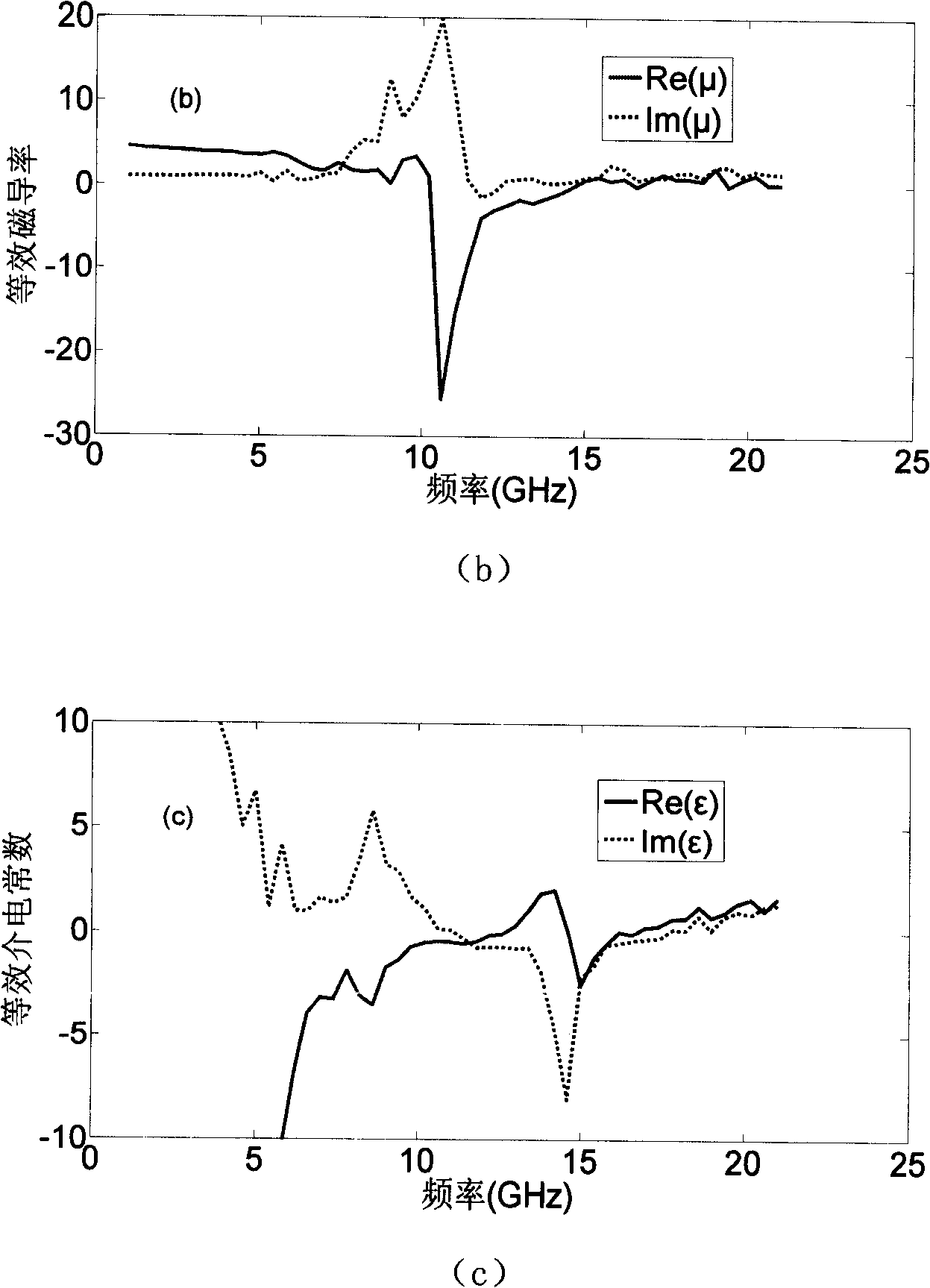
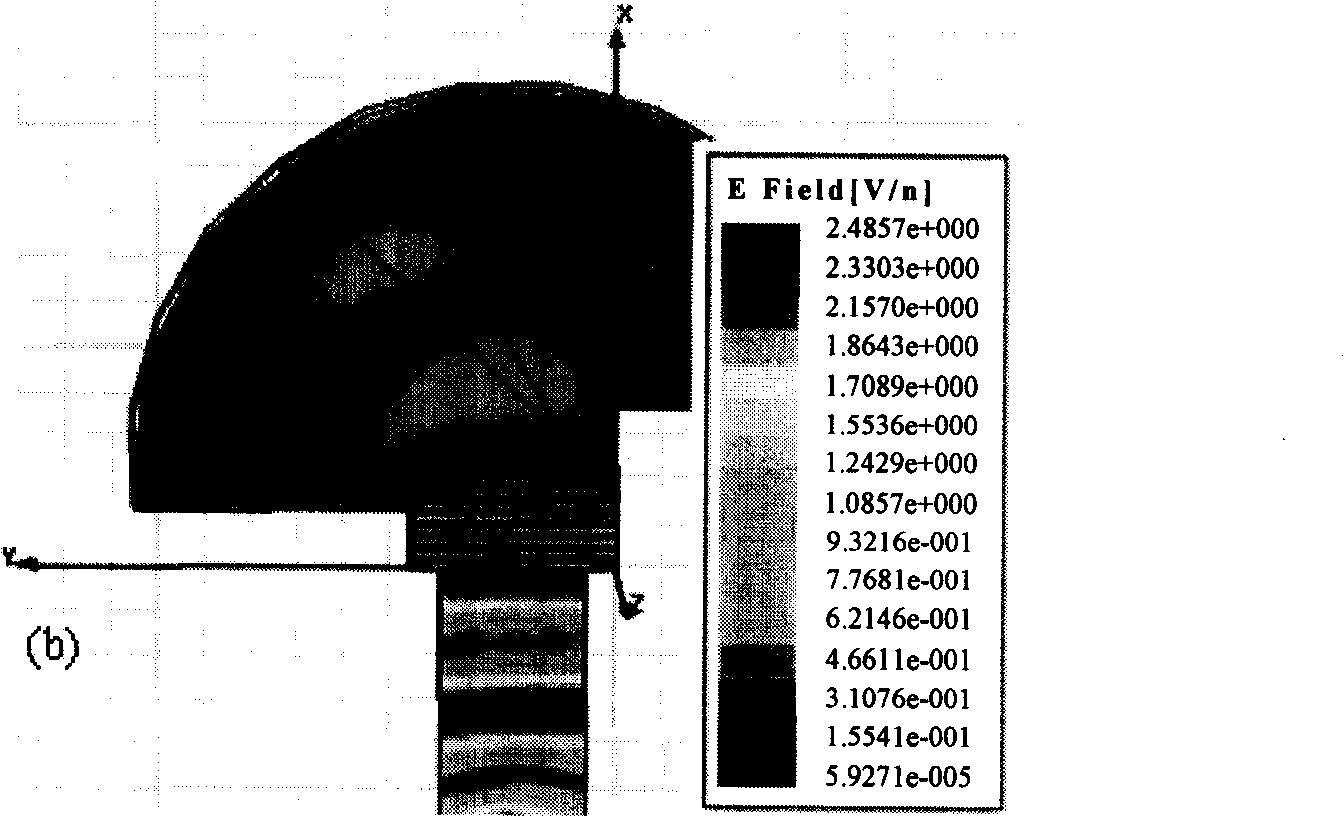
A material with a tunable negative refraction index belongs to the technique field of microwave materials. The material is formed by periodically stacking a sheeting-shaped isolation-typed ferrimagnetic material with an equivalent negative permeability and a sheeting-shaped material with an equivalent negative specific inductive capacity; the sheeting-shaped isolation-typed ferrimagnetic material is a ferrite garnet ferrimagnetic material with the specific inductive capacity being 13.8, the saturation intensity being 1830 Gs, the loss tangent being 0.0004, and the thickness being 1mm to 2mm; the sheeting-shaped material with the equivalent negative specific inductive capacity is a metal array formed by parallel metal lines sedimentated on a polytetrafluoroethylene glass fiber circuit substrate with the thickness being 0.254mm to 0.508mm; and for each metal line, the thickness is 0.018mm to 0.035mm, the width is 0.2mm, and the interval among the metal lines is 1.508mm to 2 mm. The material with the negative refraction index has wide operating frequency; the frequency band realizing negative refraction index can change along with the change of externally-applied magnetic field. The material with the tunable refraction index has wide application foreground in the fields such as stealth materials, antenna works, microwave devices and millimeter wave devices.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Manufacturing method of yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) fluorescent powder for white light LED
InactiveCN101787280AHigh absorption strengthHigh emission intensityLuminescent compositionsUltrasound attenuationMechanical crushing
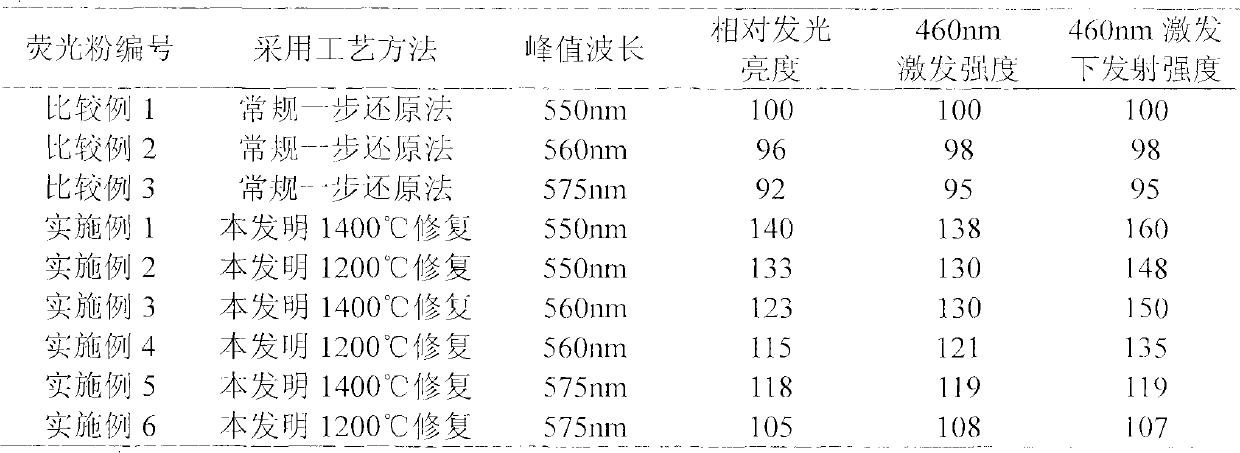
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) fluorescent powder for a white light LED with high brightness. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: adopting once high-temperature presintering, crushing and then entering into a secondary high-temperature reducing sintering, and then crushing, screening, ball-milling, wetly sieving and washing the dried fluorescent powder, wherein the lighting brightness of the fluorescent powder is reduced due to partial crystal defects caused by mechanical crushing, and the like; and in the invention, a 1200-1400 DEG C low-temperature reducing restoration process is then increased so that tetravalent cerium of the damaged crystal face is reduced into tervalent cerium, therefore, the brightness of the fluorescent powder is improved. The fluorescent powder for the white light LED has increased 450-460nm absorption intensity, high emission intensity and relative brightness, good thermal stability and less optical attenuation.
Owner:佛山市南海区朗达荧光材料有限公司
Preparation method of transforming yttrium aluminum garnet doped ceramic into single crystal
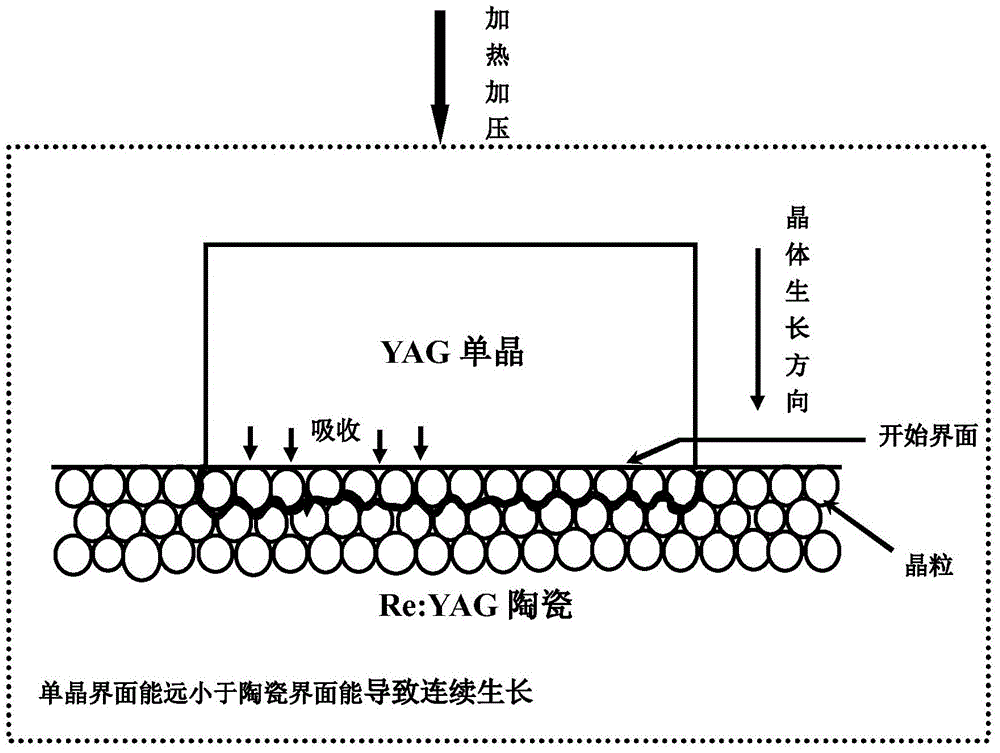
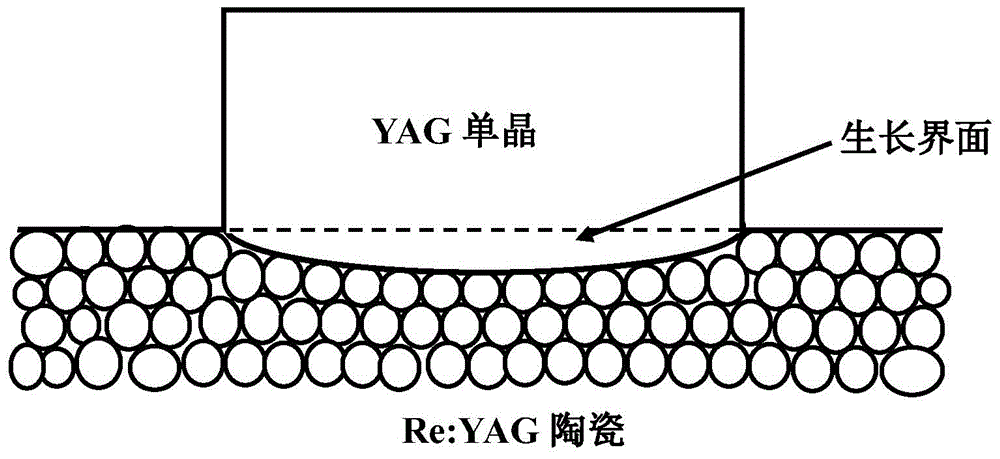
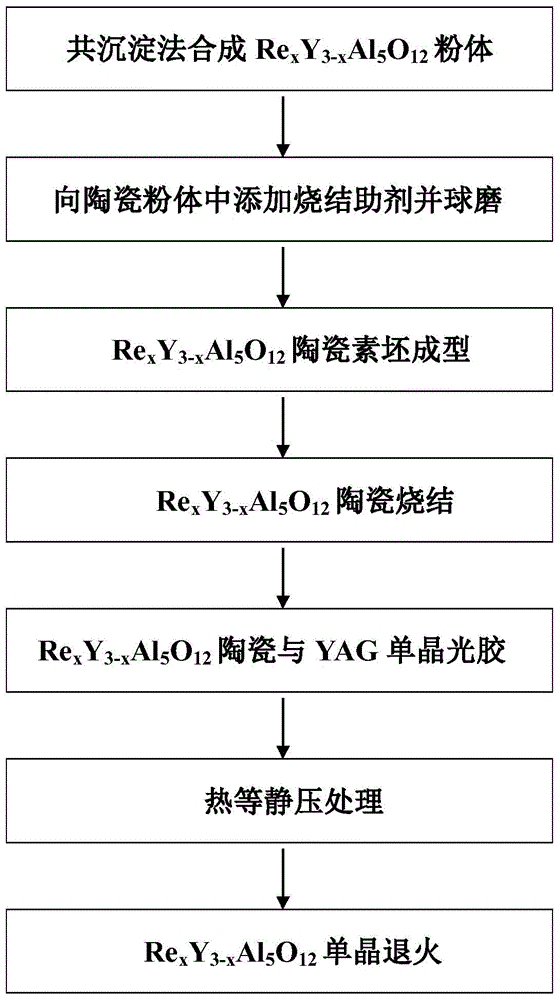
InactiveCN103820859APromote growthIncrease conversion ratePolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsAir atmosphereSingle crystal
The invention provides a preparation method for transforming yttrium aluminum garnet doped ceramic into a single crystal. The method aims at providing a solid-state crystal growth method with strong controllability and uniform yttrium aluminum garnet doped crystal components. The method is realized through the following technical scheme: at least one of silicon dioxide, magnesium oxide and lithium fluoride is added in nanometer yttrium aluminum garnet doped ceramic powder according to 0.2% to 1% of powder weight to serve as a sintering additive and then the sintering additive takes alcohol as a medium ball mill with an agate ball; heating is carried out under flow oxygen atmosphere at a temperature of 600 to 800 DEG C, the powder is placed into a stainless steel grinding tool again to form a ceramic biscuit in a dry-pressed manner, furthermore, cold isostatic pressing is carried out on the ceramic biscuit, and heat preservation is implemented under the vacuum degree higher than 10-3 Pa and the temperature being greater than 1550 DEG C to obtain the doped yttrium aluminum garnet ceramic; a yttrium aluminum garnet crystal and the doped yttrium aluminum garnet ceramic are in a light glue combination to form a complex, and an argon treatment is carried out for 20 hours at the temperature higher than 1600 DEG C and the high pressure of 0 to 300 MPa; the heat preservation is carried out on a yttrium aluminum garnet doped single crystal for 100 hours under hydrogen, oxygen or air atmosphere at a temperature higher than 1200 DEG C.
Owner:SOUTH WEST INST OF TECHN PHYSICS
Method for preparing small-particle-size cerium-activated yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) florescent powder
ActiveCN105062482AImprove luminous efficiencyCrystallization perfectEnergy efficient lightingLuminescent compositionsCeriumCrystallinity
The invention discloses a method for preparing small-particle-size cerium-activated yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) florescent powder. According to the method, first, in fused salt, a wrapping structure of nanometer yttrium oxide (cerium oxide) @ aluminum oxide particles is obtained through controlled synthesis, then the aggregate of small-particle YAG florescent powder particles is generated through reaction in high-temperature fused salt, and finally the small-particle-size YAG: Ce florescent powder is obtained through weak ball milling. It is avoided that in the reaction process, the aluminum oxide particles and intermediate-phase particles abnormally grow, and while the high crystallinity of the particles is kept, final YAG is effectively controlled; the particle size of the Ce florescent powder has important significance for improving light-color quality of white-light LEDs, lowering the complexity of a white-light LED packaging technology and increasing the yield.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
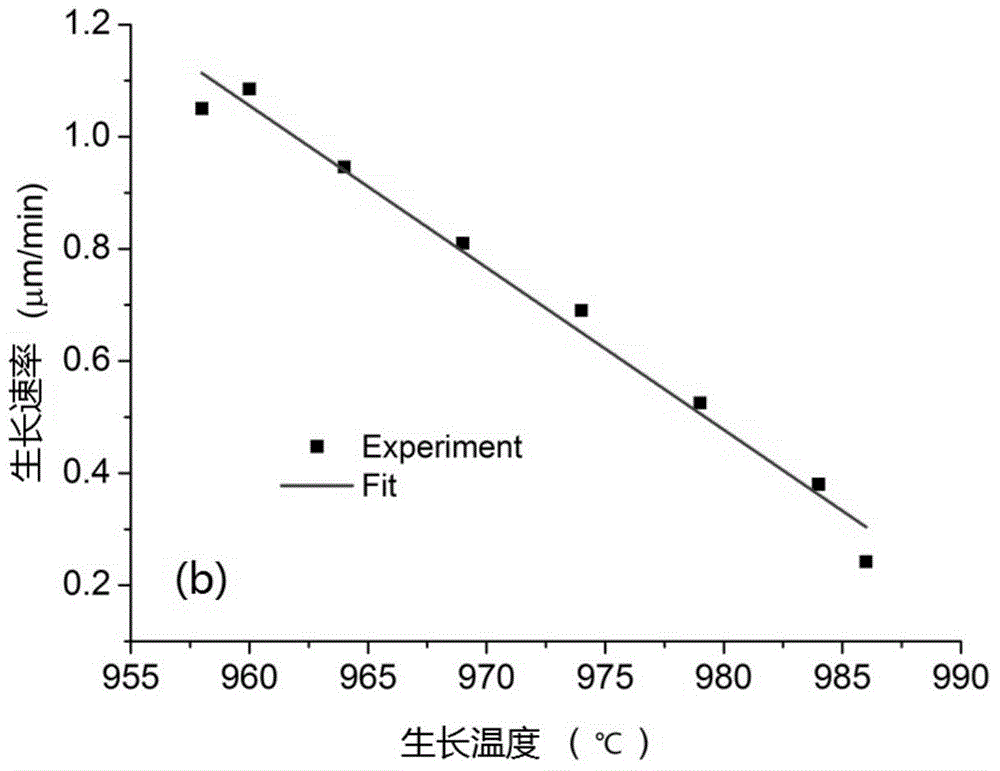
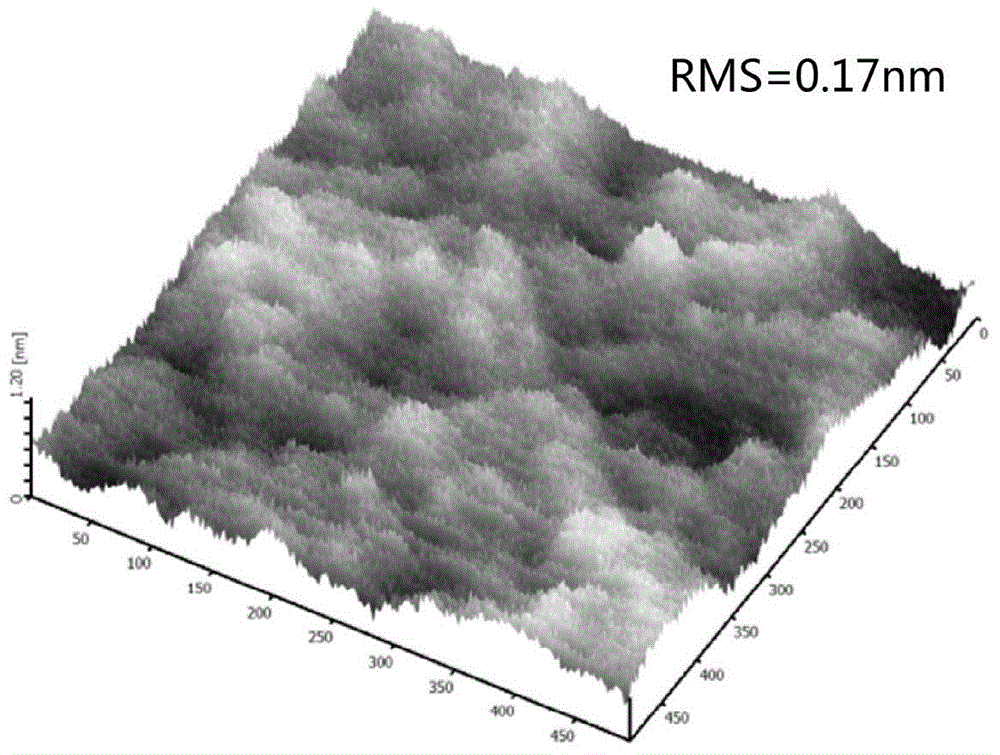
Submicron-scale low-loss single-crystal yttrium-iron-garnet film liquid-phase epitaxy preparation method
InactiveCN104831359ACompact structureFlat surfacePolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthSingle crystalThermal expansion
The present invention provides a submicron-scale low-loss single-crystal yttrium-iron-garnet film liquid-phase epitaxy preparation method, and belongs to the field of electronic materials. According to the present invention, a liquid-phase epitaxy method is used to grow the submicron-scale low-loss single-crystal yttrium-iron-garnet film at the lowest temperature point in the growth temperature range of the single-crystal yttrium-iron-garnet film under a high rotation speed; and the submicron-scale low-loss single-crystal yttrium-iron-garnet film prepared by using the low growth temperature and high rotation speed method has the following characteristics that: the lattice constant and thermal expansion coefficient matching degree with the substrate is good, the film is in the single crystal state, the film thickness is 100-1000 nm, the ferromagnetic resonance line width is narrow and is about less than or equal to 3 Oe, and the film has characteristics of compact structure and smooth surface, and is the good material capable of being used for spin-logic devices.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation method of yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) nano-powder
ActiveCN103214016ASmall granularityHigh sintering activityRare earth metal compoundsRare earth ionsFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a preparation method of yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) nano-powder. The preparation method comprises the steps of dissolving aluminum salt in isopropanol to prepare an aluminum solution, dissolving acetate of yttrium ions and / or other rare earth ions in deionized water to prepare a solution A, dropwise adding the aluminum solution to the solution A under the condition of vigorous stirring, executing the stages of collosol, gel, freeze drying and the like to form a precursor, and calcinating the precursor at a high temperature to form the YAG nano-powder. With the adoption of the preparation method, the YAG nano-powder which is small in particle size (30-110nm), high in sintering activity and uniform in doping can be prepared at lower cost and lower temperature (900-1100 DEG C).
Owner:SINOMA SYNTHETIC CRYSTALS CO LTD +1
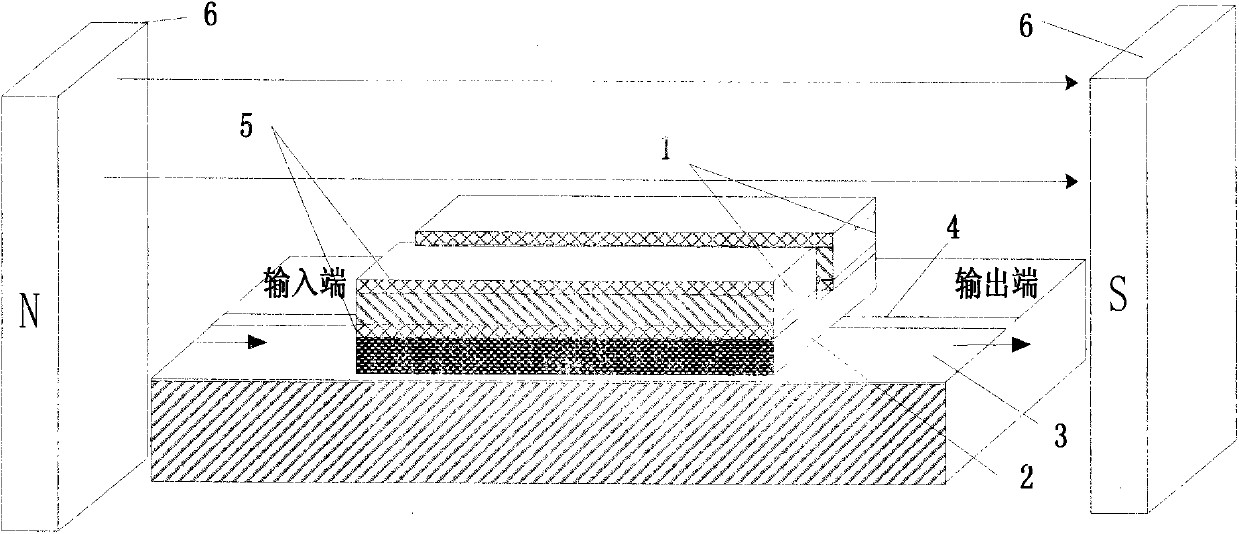
Hairpin-type magneto-electric double-tunable microwave filter and tuning method thereof
InactiveCN103117439AMiniaturizationPrecise adjustment of working frequencyWaveguide type devicesEpoxyZirconate
The invention discloses a hairpin-type magneto-electric double-tunable microwave filter and a tuning method thereof. The hairpin-type magneto-electric double-tunable microwave filter comprises an aluminum oxide substrate, an electromagnet, a microstrip line, and a magneto-electric laminating material structure. The magneto-electric laminating material structure includes a piezoelectric phase and a ferromagnetic phase from top to bottom. The piezoelectric phase and the ferromagnetic phase are adhered through epoxy resin. Two metal films Ag are plated on the upper and lower surfaces of the piezoelectric phase respectively to form electrodes. The piezoelectric phase is made of Pb-based lanthanum-doped zirconate titanate. The ferromagnetic phase is made of YIG (yttrium iron garnet). The metal microstrip line made on the upper surface of the aluminum oxide substrate by photoetching serves a signal transmission line. The metal microstrip line is hairpin-typed and is in axial symmetry with a lengthwise center line of the substrate as an axis of symmetry. The defects of tuning failure of the traditional filter in operating frequency, failure in precise adjustment of operating frequency and the like are overcome. The hairpin-type magneto-electric double-tunable microwave filter has the advantages of small size and magneto-electric double-tunability. The defects that the traditional magnetically-tunable microwave device is high in operation loss, long in response time and the like are overcome. The hairpin-type magneto-electric double-tunable microwave filter is widely applicable to wireless communication.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
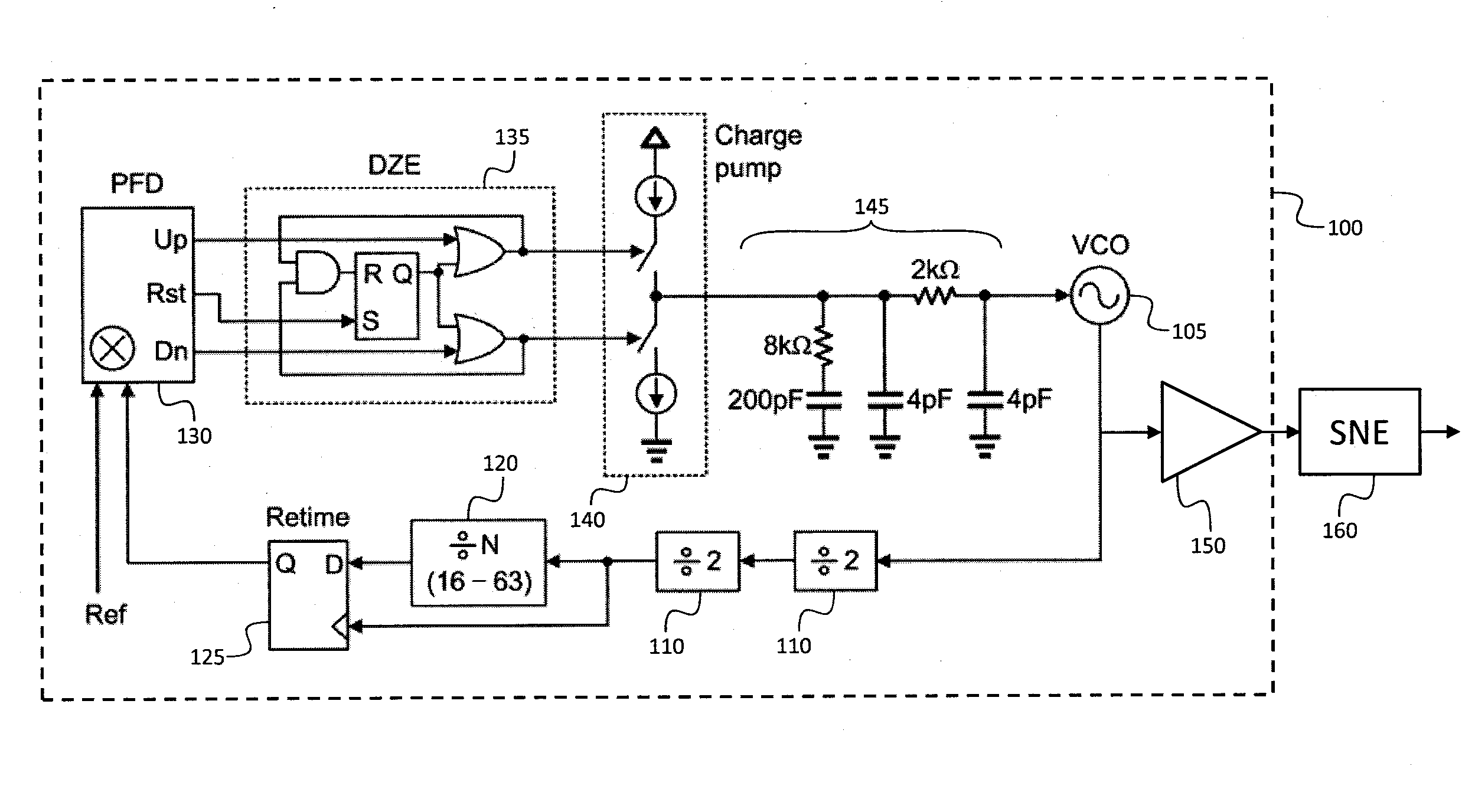
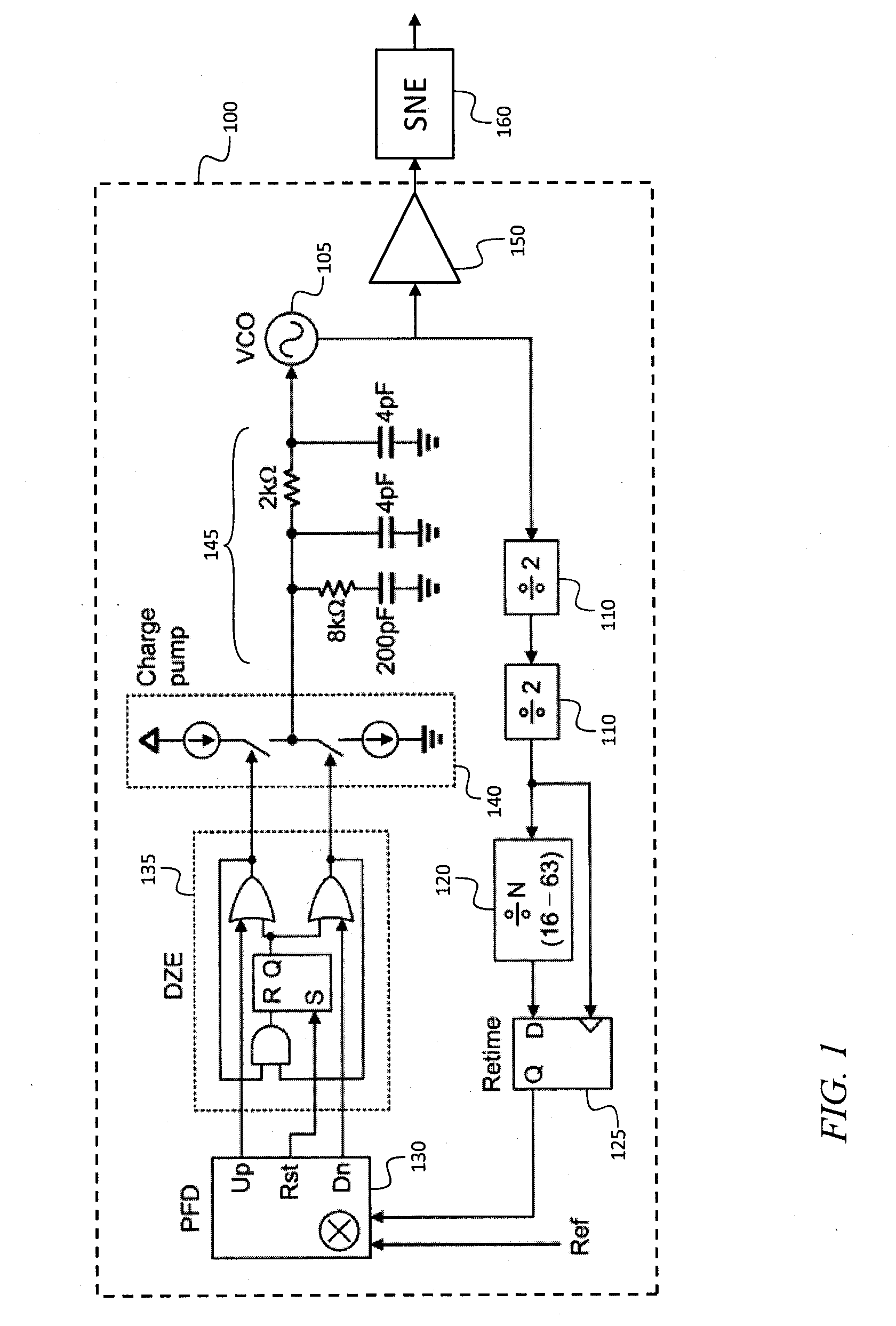
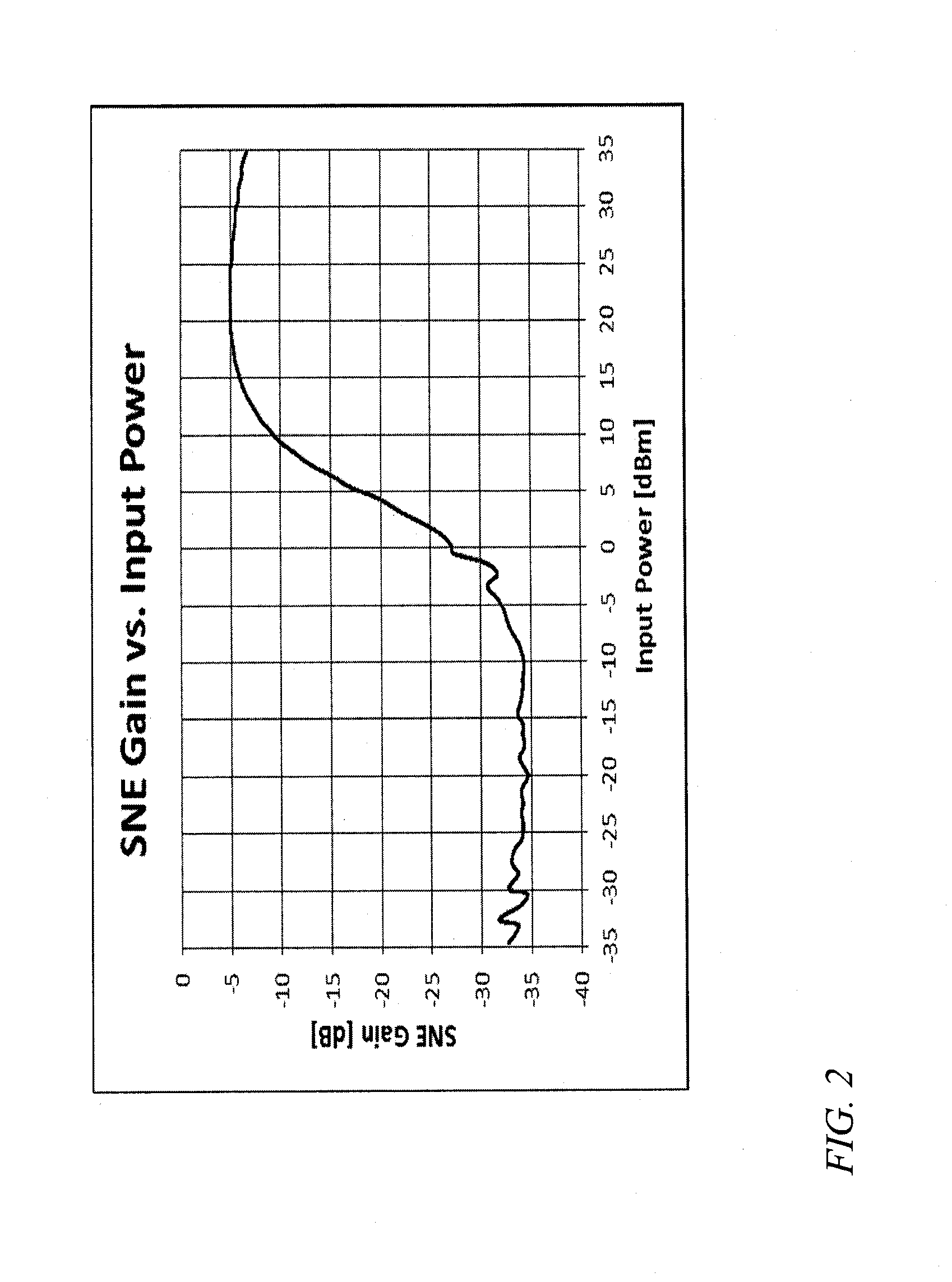
Frequency source with improved phase noise
ActiveUS20160164528A1Improve phase noiseSuppress phase noiseMultiple-port networksPulse automatic controlGadolinium gallium garnetPhase noise
A frequency source with improved phase noise. In one embodiment a phase-locked loop is used as a component of a frequency source and a signal to noise enhancer (SNE) is used to suppress phase noise produced by the phase-locked loop. The signal to noise enhancer is a nonlinear passive device that attenuates low-power signals while transmitting high power signals with little loss. The signal to noise enhancer may be fabricated as a thin film of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) epitaxially grown on a gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG) substrate, the GGG substrate being secured to a microwave transmission line from the input to the output of the signal to noise enhancer, such that the thin film of yttrium iron garnet is close to the transmission line.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
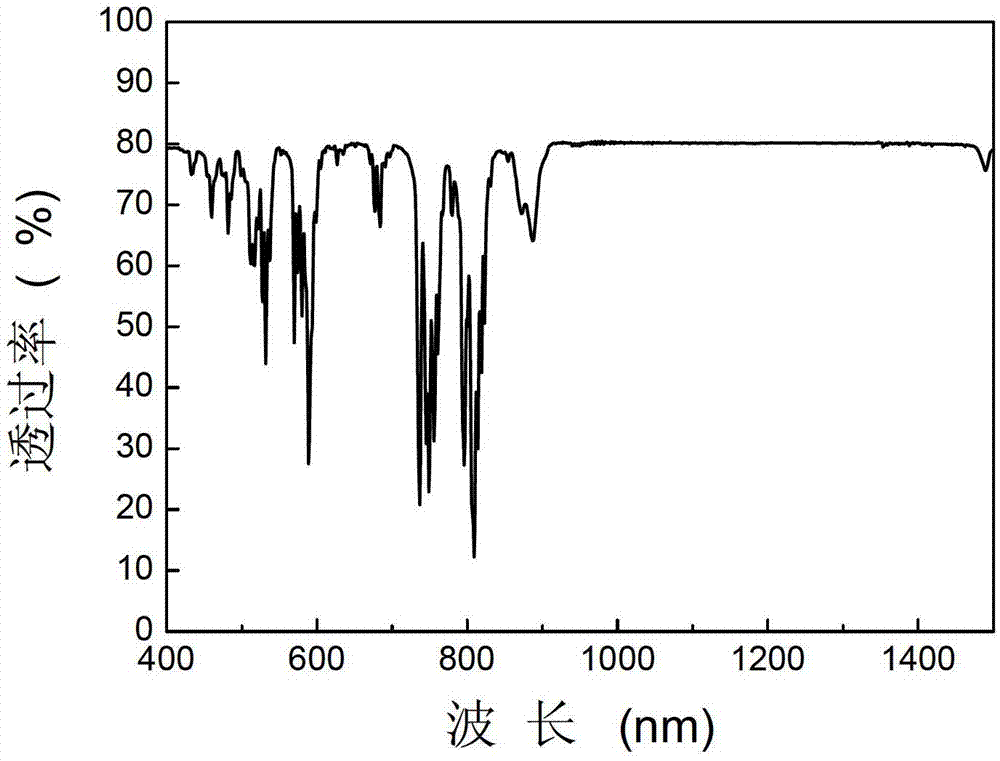
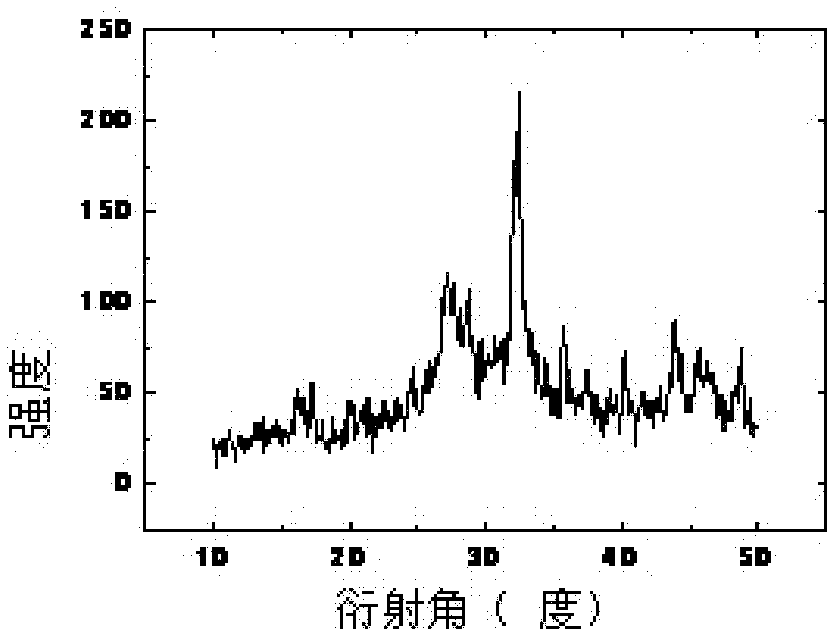
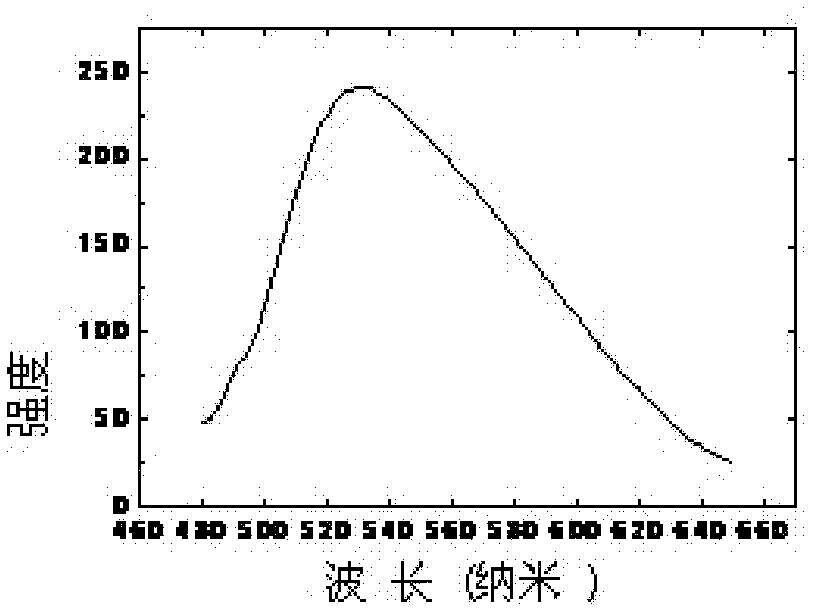
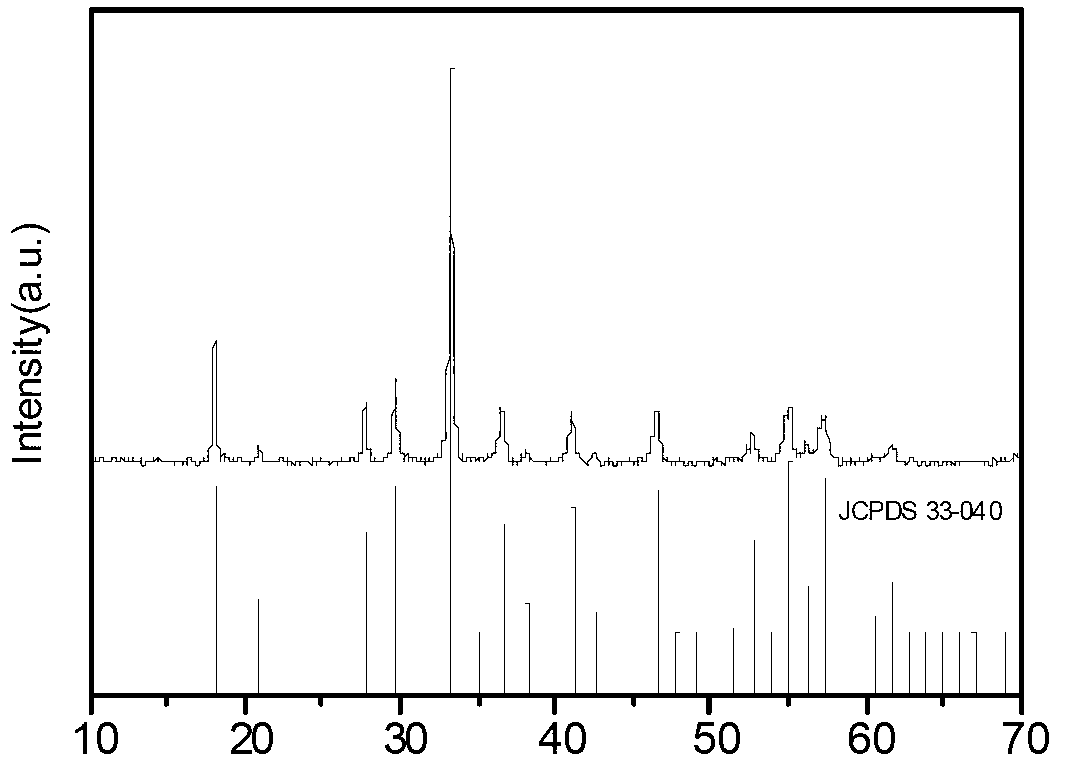
Yttrium iron garnet film and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a yttrium iron garnet film and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) dissolving yttrium oxide and ferric nitrate in a mixed solvent consisting of acetic acid and water to obtain a mixed solution; 2) adding acetylacetone into the mixed solution to react; 3) after standing the mixed solution, filtering out precipitates by virtue of a microfiltration membrane to obtain a yttrium iron garnet precursor solution; 4) dropwise adding the yttrium iron garnet precursor solution on a substrate to form a gel film; 5) firstly, preserving heat for the gel film and then carrying out pyrolysis treatment; and 6) annealing the gel film subjected to pyrolysis treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
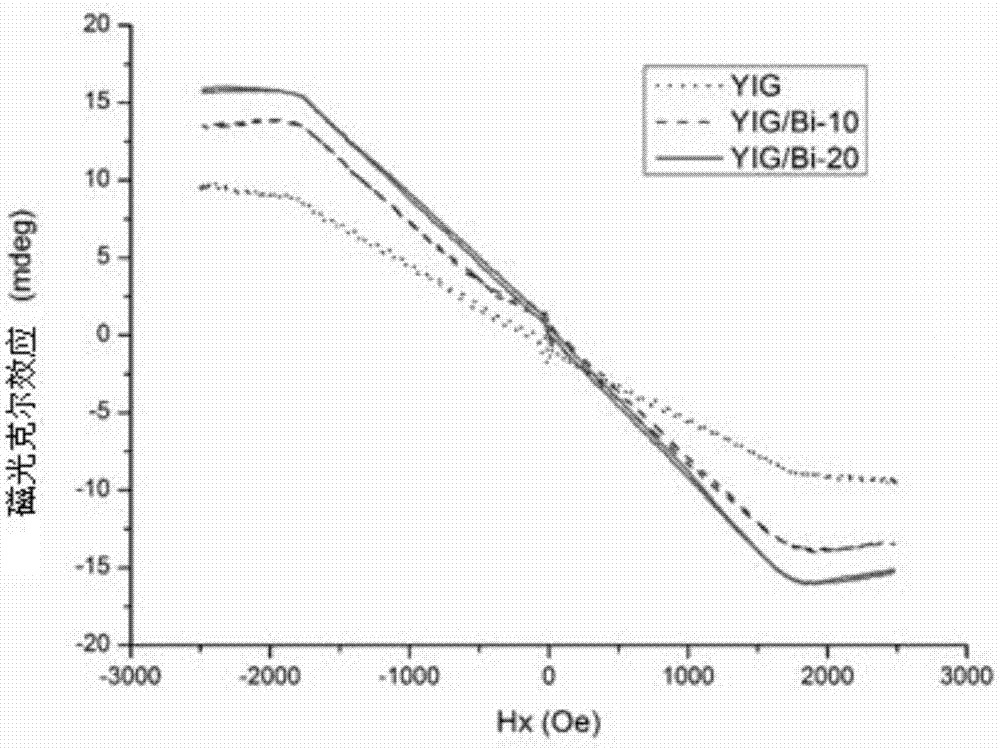
YIG/bismuth heterogenous thin film with giant magnetooptical effect and preparation method of YIG/bismuth heterogenous thin film
ActiveCN107146761AIncreased magneto-optical rotationIncreased magneto-optic Kerr angleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionGadolinium gallium garnet
The invention discloses a YIG / bismuth heterogenous thin film with a giant magnetooptical effect and a preparation method of the YIG / bismuth heterogenous thin film. The method comprises the steps of growing high-quality single-crystal YIG used as a substrate on gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG) in a crystal direction [111] by liquid phase epitaxy, and growing a thin layer of bismuth on the YIG substrate by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) to obtain the YIG / bismuth heterogenous thin film. The method is simple and practical, the magneto-optical kerr corner of the obtained YIG / bismuth heterogenous thin film is remarkably increased compared with YIG of a bismuth-free thin film; and compared with replacement doping of bismuth in YIG, the preparation process is simple, a new method is provided for preparation and research of a heterojunction magnetooptical material and has wide application in various fields of optical communication, magnetooptical storage and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
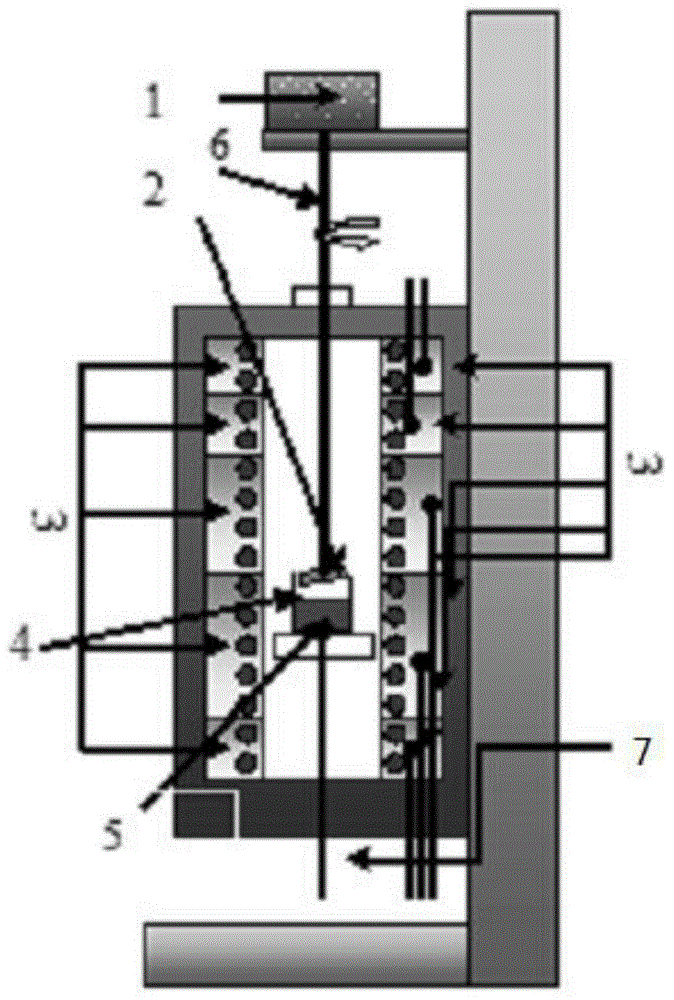
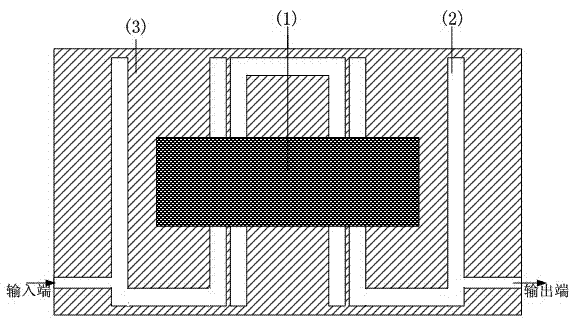
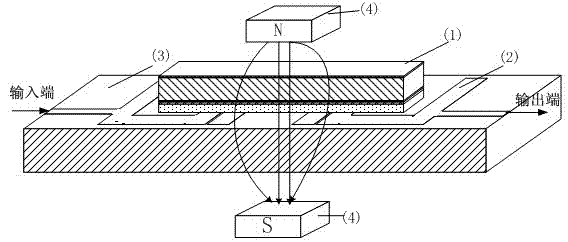
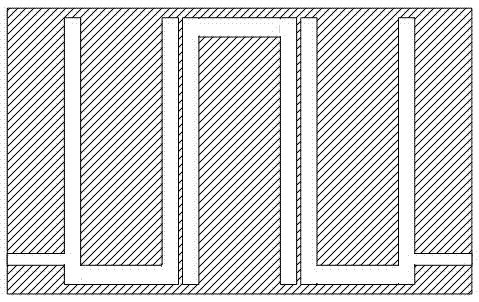
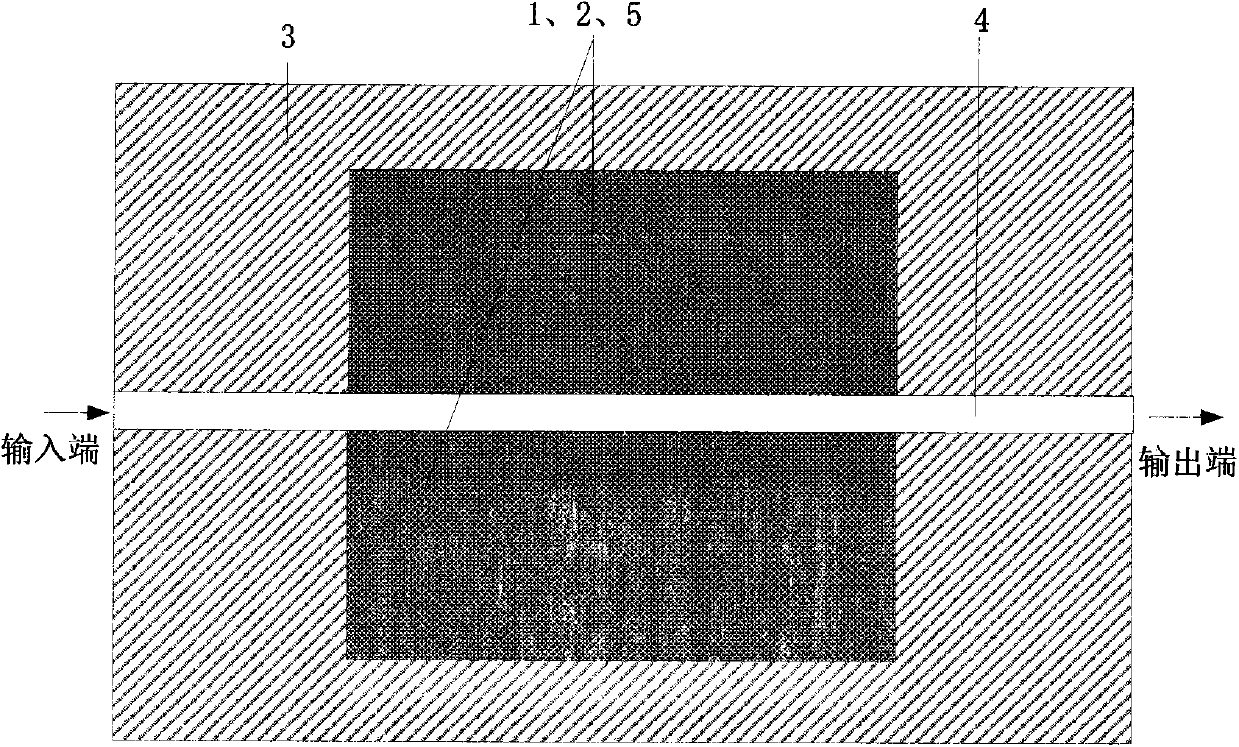
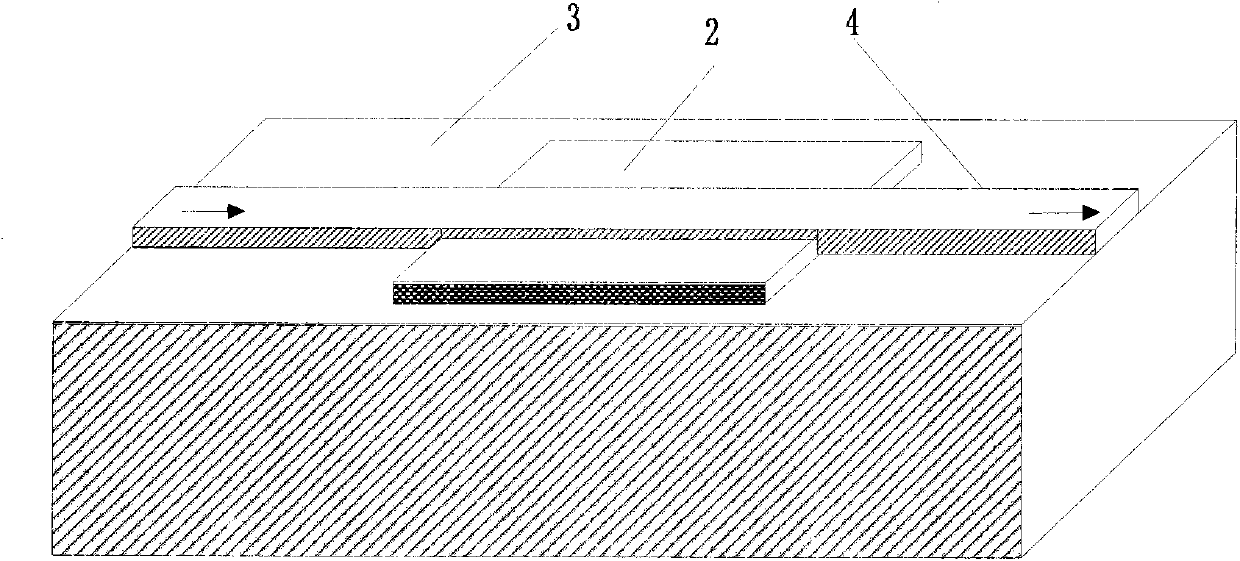
Micro-strip line filter sharing substrate with YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) thin film material, and regulation method thereof
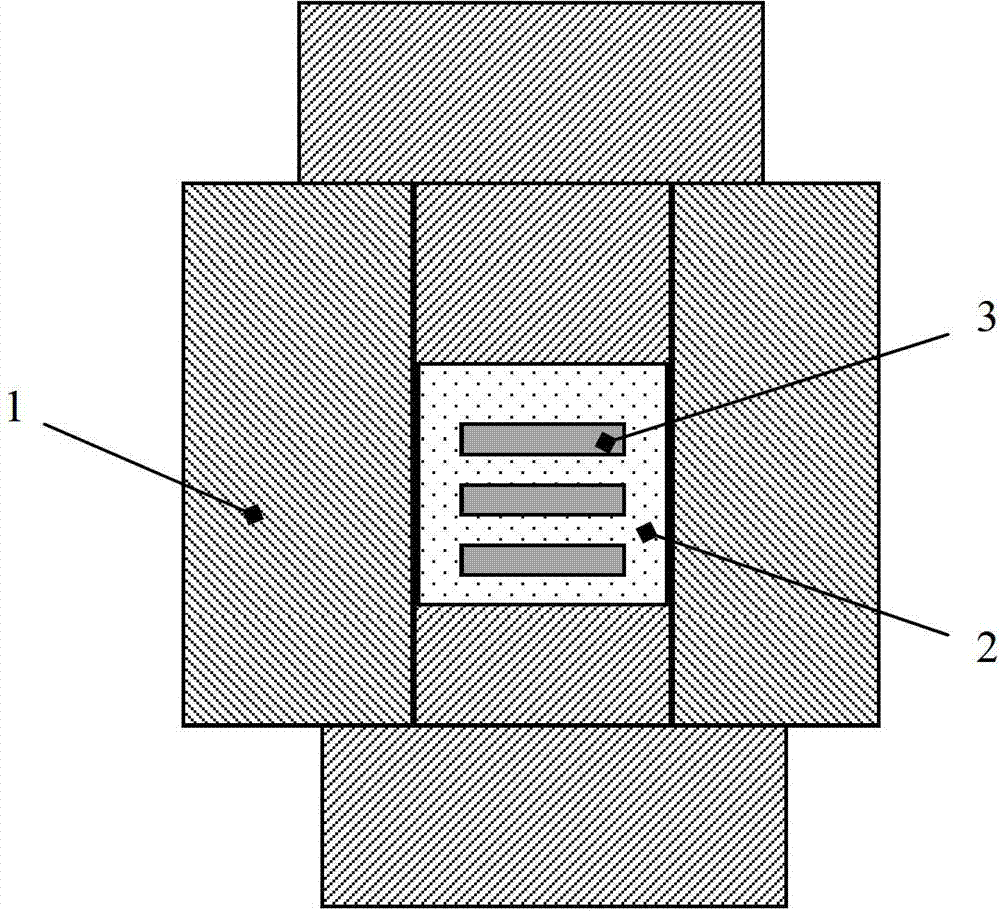
InactiveCN103401047AReduce volumeSimple structureWaveguide type devicesAntennasElectricityGadolinium gallium garnet
The invention discloses a micro-strip line filter sharing a substrate with YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) thin film material, and a regulation method thereof. The micro-strip line filter comprises two piezoelectric layers (1), one YIG layer (2), GGG (Gadolinium Gallium Garnet) substrate material (3) and a metal micro-strip line (4); the micro-strip line filter takes the GGG substrate material (3), needed for the growth of the YIG layer (2), as a substrate; a layer of metal micro-strip line (4) in single conduction band is printed on the upper surface of the GGG substrate material (3), on which the YIG layer (2) is grown, along a central axis in a length direction; the two piezoelectric layers (1) are respectively arranged at two sides of the metal micro-strip line. Compared with a traditional micro-strip line filter, the miniaturization of the micro-strip line filter can be realized due to the advantages of high dielectric constant (epsilon is greater than 10) and high magnetic permeability (mu is greater than 10) of YIG material and piezoelectric material. According to the micro-strip line filter disclosed by the invention, the GGG substrate material of which the length-width size is the same as that of a YIG thin film is selected, and thus the selecting difficulty on size of the YIG material is reduced.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
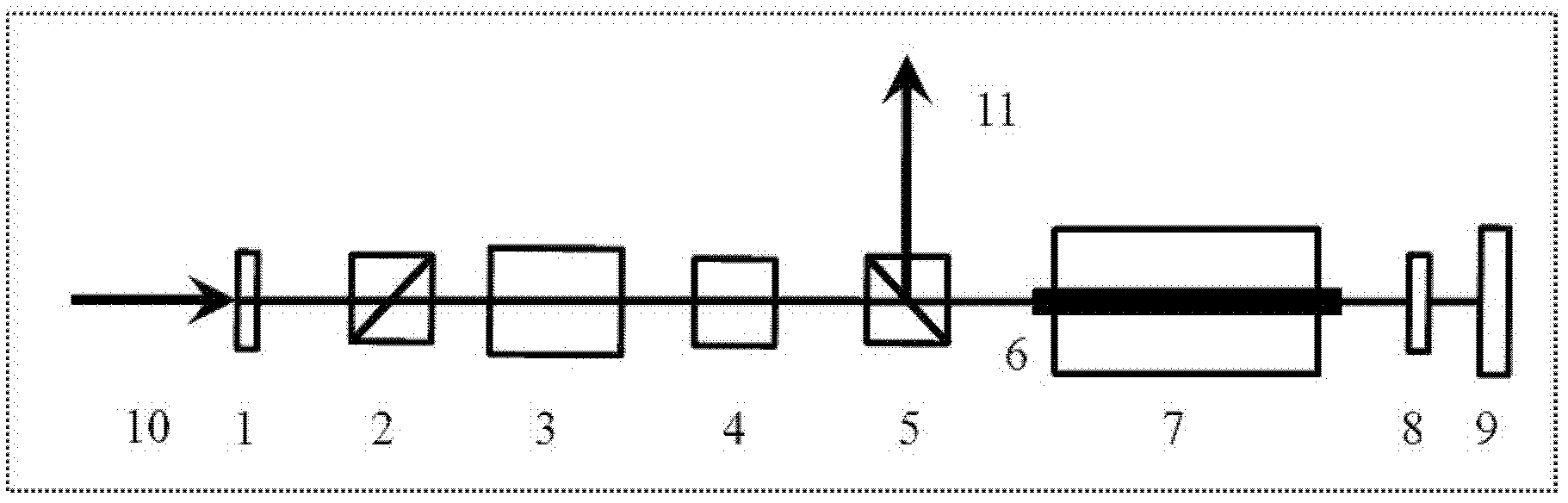
Amplifier and method for increasing multipass amplifying output power of bar-like Nd: YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet) laser
The invention relates to an amplifier and a method for increasing multipass amplifying output power of bar-like Nd: YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet) laser, belonging to the technical field of a laser device. A 1 / 2 wave plate, a polarized beam splitter a, a 45-degree faraday rotator, a 45-degree quartz rotator and a polarized beam splitter b are placed in sequence to form an opto-isolator, and a laser medium is installed in a semiconductor laser module. After seed light is injected, the seed light enters into the laser medium through the opto-isolator. The laser medium is an Nd: YAG crystal bar in a [100] cutting direction. After output, one-pass amplification is realized. The one-pass amplifying laser passes through a 1 / 4 wave plate and a total-reflecting mirror and then enters into the laser medium again, and two-pass amplifying laser is output through the polarized beam splitter b. When the laser enters into the laser medium, a direction in which the output power of linearly polarized light is a maximum value is selected as the direction of the crystal bar in the rotation range of 360 degrees. According to the amplifier and the method, the heat depolarization effect is obviously reduced, and additional loss brought by inserting a heat depolarization compensation device is avoided.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Gadolinium illinium scandium gallium garnet crystal GYSGG and its smelt method crystal growth method
The invention discloses a gadolinium yttrium scandium gallium garnet crystal (GYSGG) and a crystal growth method by a melt method thereof. The molecular formula of the crystal can be expressed as Gd3xY3(1-x)Sc2Ga3(1+delta)O12 (the x is equal to between 0 and 1 or between -0.2 and 0.2); Gd2O3, Y2O3, Sc2O3 and Ga2O3, or corresponding other compounds of gadolinium, yttrium, scandium, and gallium canbe used to perform the material mixing, and the premise is that the Gd3xY3(1-x)Sc2Ga3(1+delta)O12 is produced; prepared raw materials are subject to the perfect mixing, press forming and high temperature sintering, and then become an initial raw material of crystal growth; the initial raw material of the growth is placed into a crucible, is heated to fully melt down, and then becomes an initial melt of the growth by the melt method, and then melt methods such as a pulling method, a crucible descending method or a temperature gradient method as well as other melt methods can be used for the growth; for the melt method which needs seed crystals to directionally grow, the seed crystals are GYSGG monocrystals or yttrium scandium gallium garnet (YSGG) monocrystals or gadolinium scandium gallium garnet (GSGG) monocrystals. The GYSGG monocrystals can be used as a substrate material of a Bi3+-doped yttrium iron garnet epitaxial film.
Owner:ZHONGKE JIUYAO TECH CO LTD
Method for epitaxially growing yttrium iron garnet nanometer thin film with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy
ActiveCN106887329AOvercome the stress relaxation problemHigh quality epitaxyNanostructure applicationCathode sputtering applicationMicrowaveStress relaxation
The invention relates to a method for epitaxially growing an yttrium iron garnet nanometer thin film with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy. The method comprises the steps that a buffer layer is epitaxially grown on a substrate, and the yttrium iron garnet nanometer thin film is epitaxially grown on the buffer layer. The buffer layer is the material such as samarium gallium garnet, and the lattice constant of the material is between the substrate and yttrium iron garnet. The substrate can adopt doped and substituted samarium gallium garnet. A layer of material with the lattice constant larger than the yttrium iron garnet can be epitaxially grown on the yttrium iron garnet nanometer thin film so as to increase the strain degree in the perpendicular direction. Accordingly, by means of the buffer layer, the stress relaxation problem in the surface is solved, high induced magnetic anisotropy is obtained, and the high-quality epitaxial yttrium iron garnet nanometer thin film with the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy is finally obtained. The method has great significance for research and application of magneto-optical devices, microwave and spin electronic devices.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for preparing cerium doped yttrium aluminum garnet
InactiveCN101456570AImprove responseSolve pollutionLuminescent compositionsAluminium oxides/hydroxidesCerium nitratePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a method for preparing cerium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet powder in the technical field of luminescent materials, which comprises: weighing yttria according to the proportion of raw materials, and mixing the yttria and a concentrated nitric acid solution in a sealed reaction kettle; weighing aluminum nitrate and cerium nitrate, and dissolving the aluminum nitrate and the cerium nitrate into deionized water; mixing the two solutions to obtain a reaction precursor solution, adding urea which is 6 to 20 percent of the weight of the reaction precursor solution as an incendiary agent, and adding polyethylene glycol which is 0.5 to 2 percent of the weight of the reaction precursor solution as an organic dispersant; and placing the precursor solution into a sintering furnace, and obtaining a finished product. The method does not need ball milling and has no agglomeration phenomenon; samples have uniform particles and small particle diameter, and can be directly used for encapsulation; and the method gives full play to the optical performance of the samples to the maximum degree, and has simple and stable technology, low production cost and no environmental pollution.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG): Ce<3+> fluorescent powder using chlorides as fluxing agents
InactiveCN102863962AHigh light conversion efficiencyReduce the formation temperatureLuminescent compositionsChlorideCrystallinity
The invention relates to a preparation method of yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG): Ce<3+> fluorescent powder using chlorides as fluxing agents and belongs to the field of light-emitting materials. According to the preparation method, Y2O3 (99.99%), CeO2 (99.99%), Al2O3 (analytical pure, namely AR) and the fluxing agents which contain LiCl, NaCl, KCl and SrCl2 are weighted in the stoichiometric ratio according to fluorescent powder composition (Y0.98)3Al5O12:Ce0.06, wherein the fluxing agents account for 1%-13% of the total weight. By adding the fluxing agents, the light conversion efficiency of the YAG:Ce<3+> fluorescent powder can be increased and the formation temperature of the single-phase YAG can be reduced; improvement of the crystallinity and morphology of the YAG:Ce<3+> fluorescent powder is beneficial to absorption and emission of the light; and the preparation method adopts a high temperature solid state method, chlorides used as the fluxing agents, namely LiCl, NaCl, KCl and SrCl2 are added to prepare the YAG:Ce<3+> fluorescent powder and the obtained YAG:Ce<3+> fluorescent powder maintains the structure, regular morphology and narrow particle size distribution of YAG, thus the light conversion efficiency of the YAG:Ce<3+> fluorescent powder is greatly increased.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG)-based transparent ceramics in system taking Ca as auxiliary agent
The invention provides a method for preparing yttrium aluminum garnet (Y3Al5O12, YAG)-based transparent ceramics by means of vacuum sintering based on a system taking a small amount of Ca as a single-sintering auxiliary agent. According to the method, the small amount of Ca is used as the single-sintering auxiliary agent, and a single-step vacuum sintering method is adopted, so that the YAG-based transparent ceramics having good optical quality and fine crystalline grain size can be prepared under the condition of not adding post annealing treatment.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com