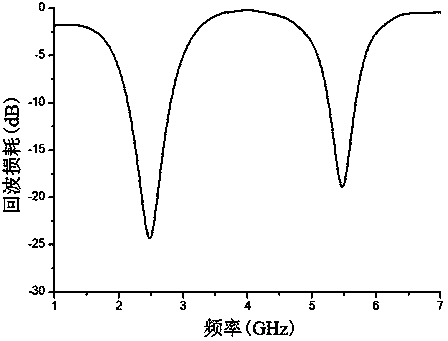
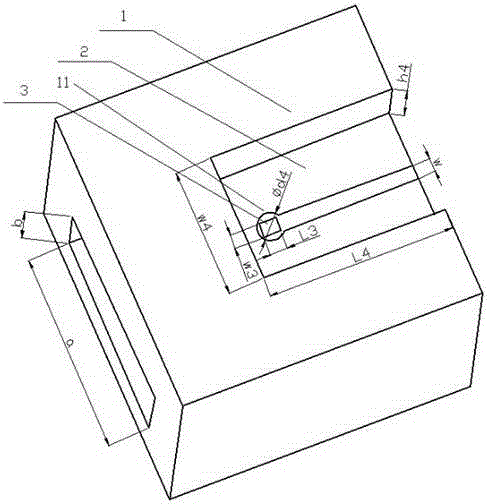
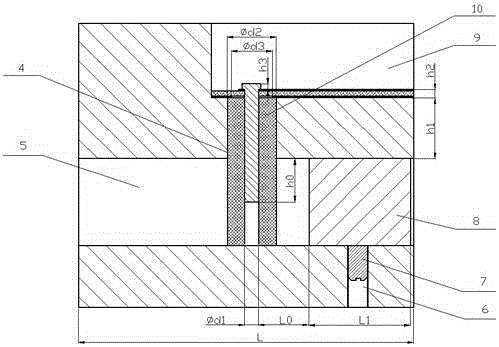
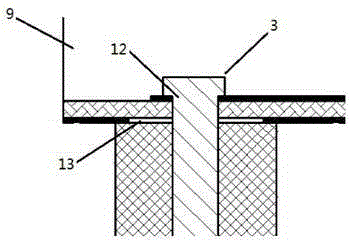
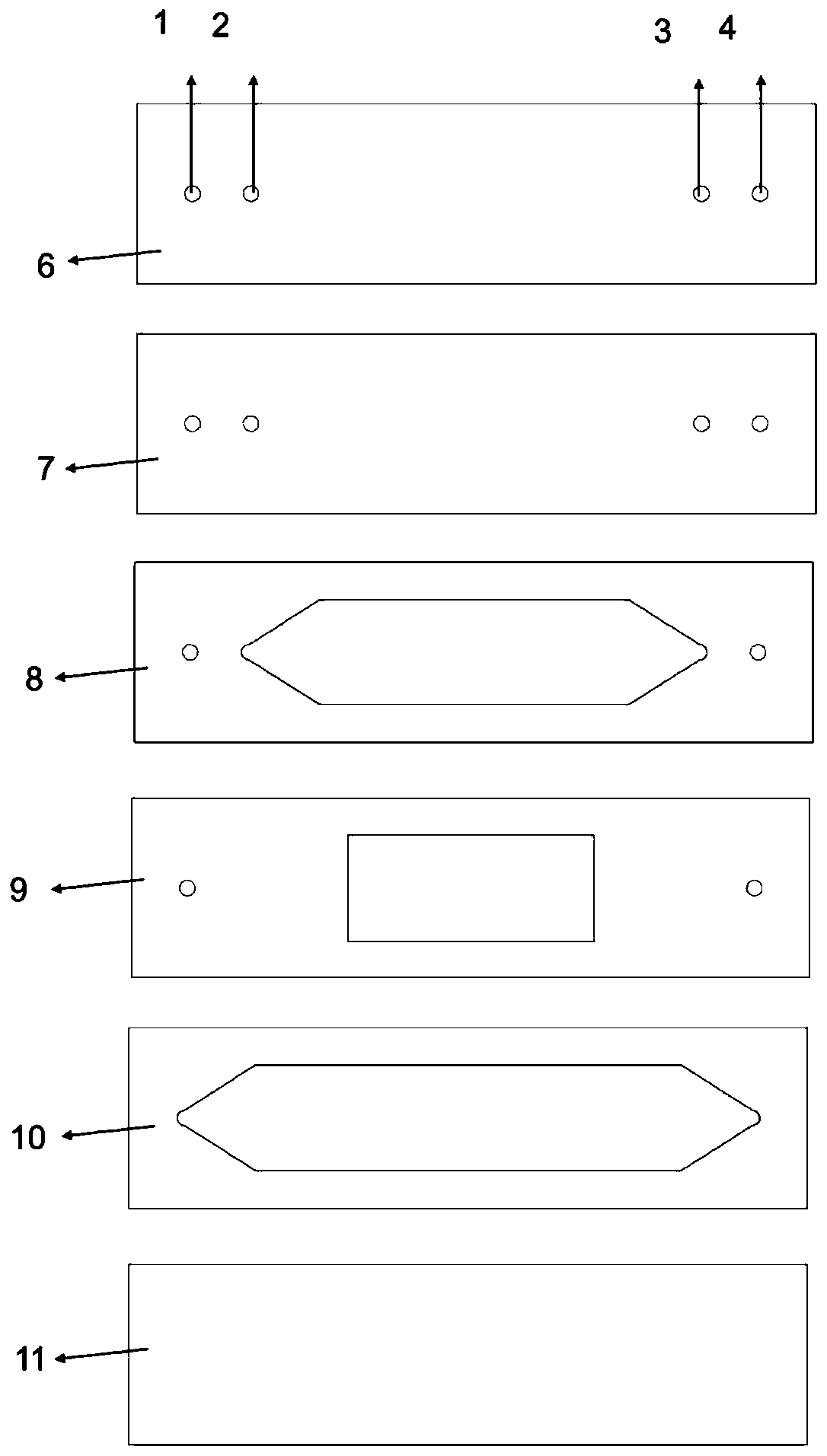
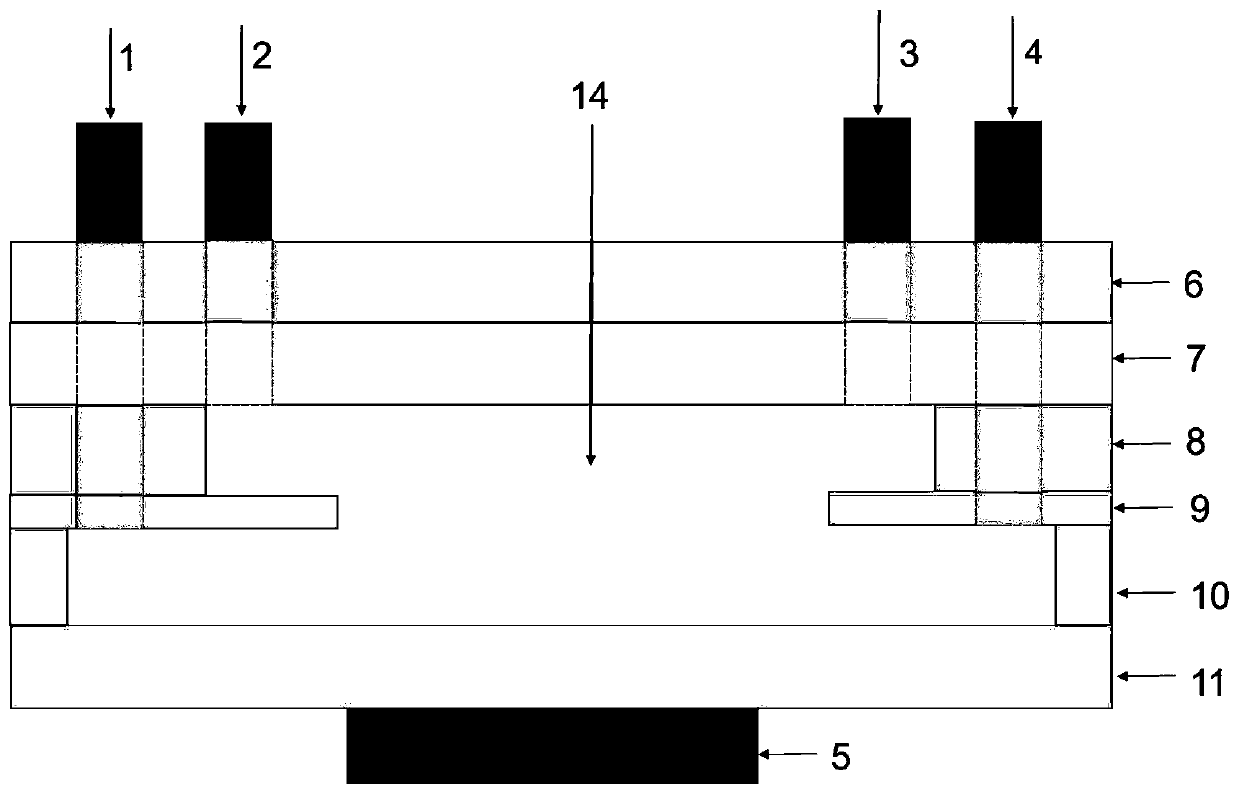
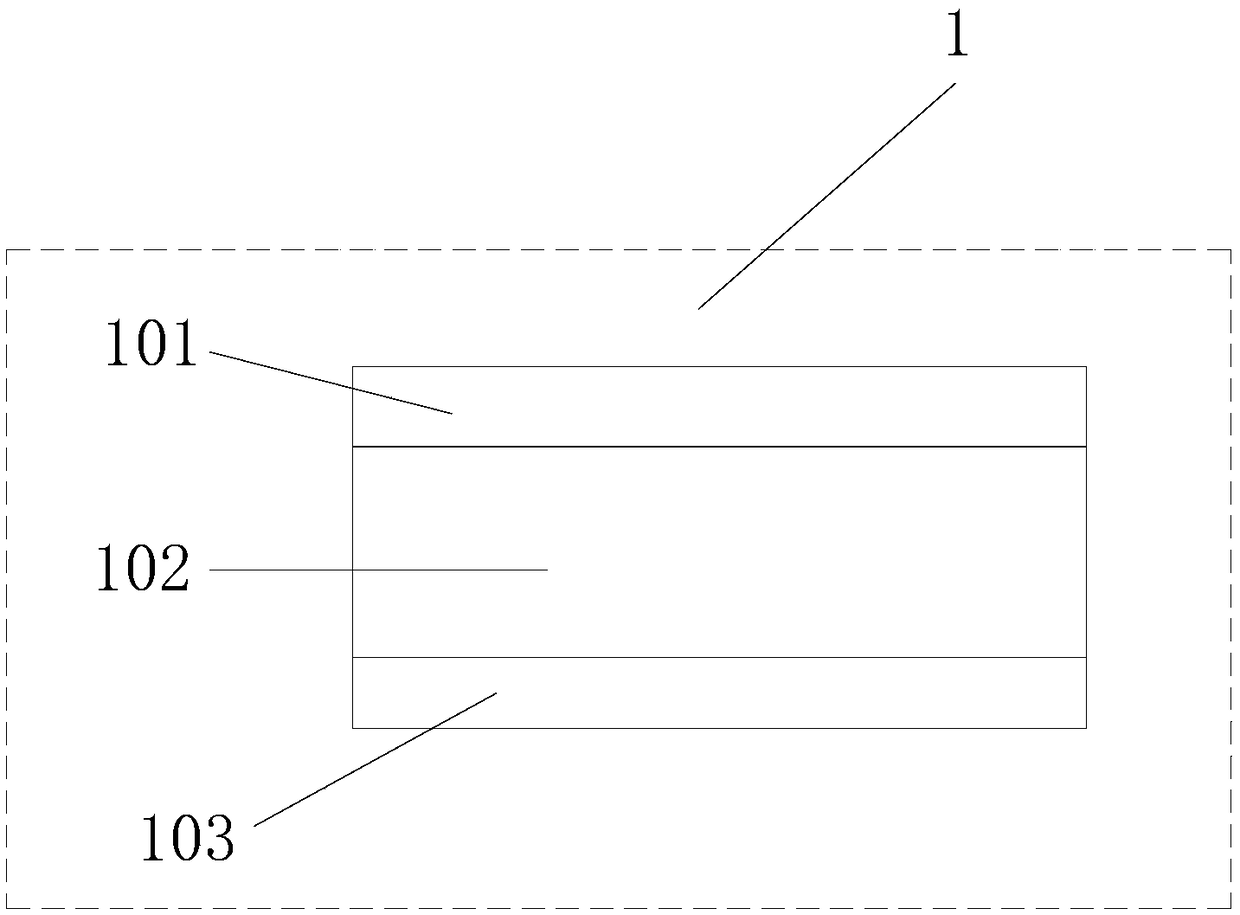
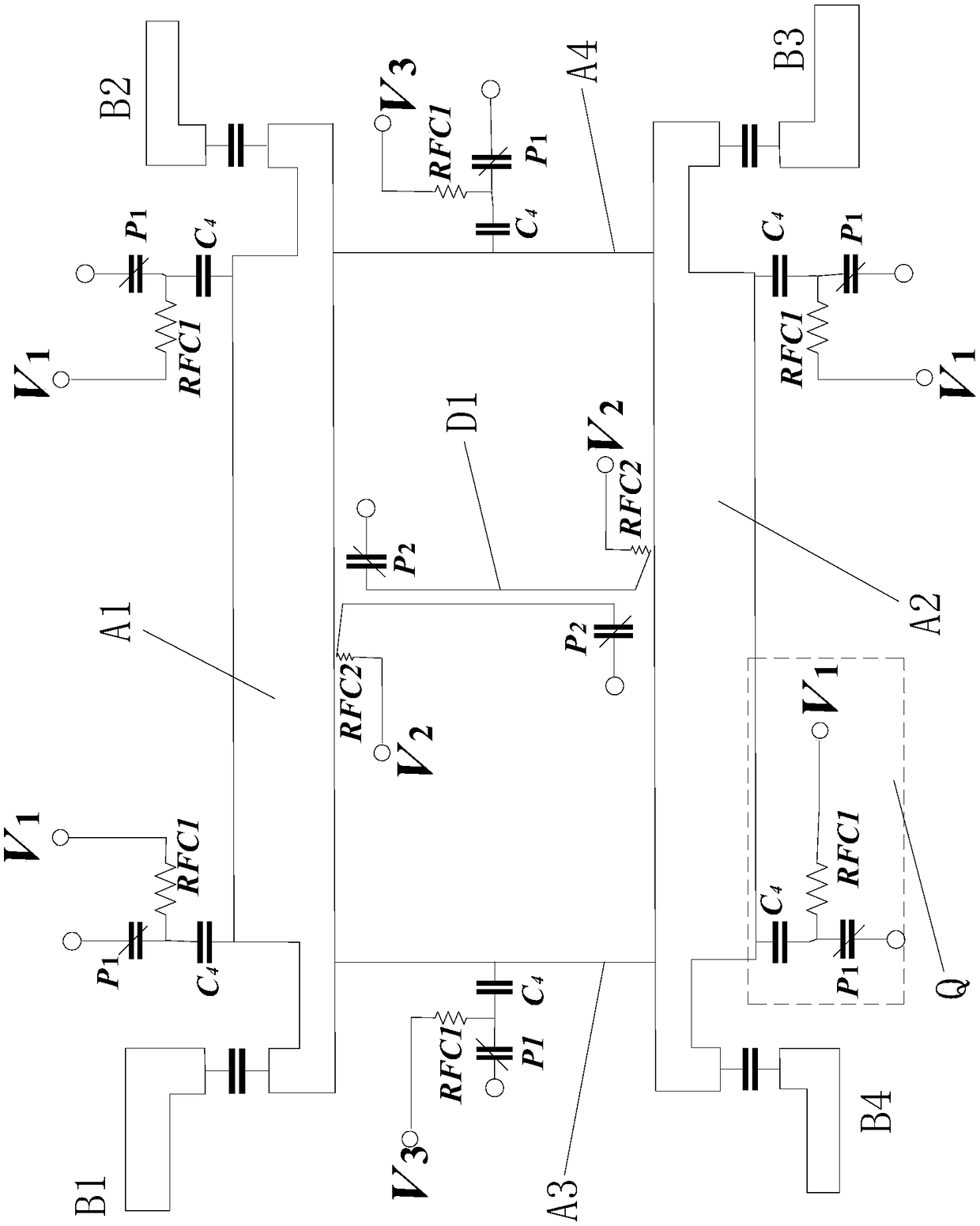
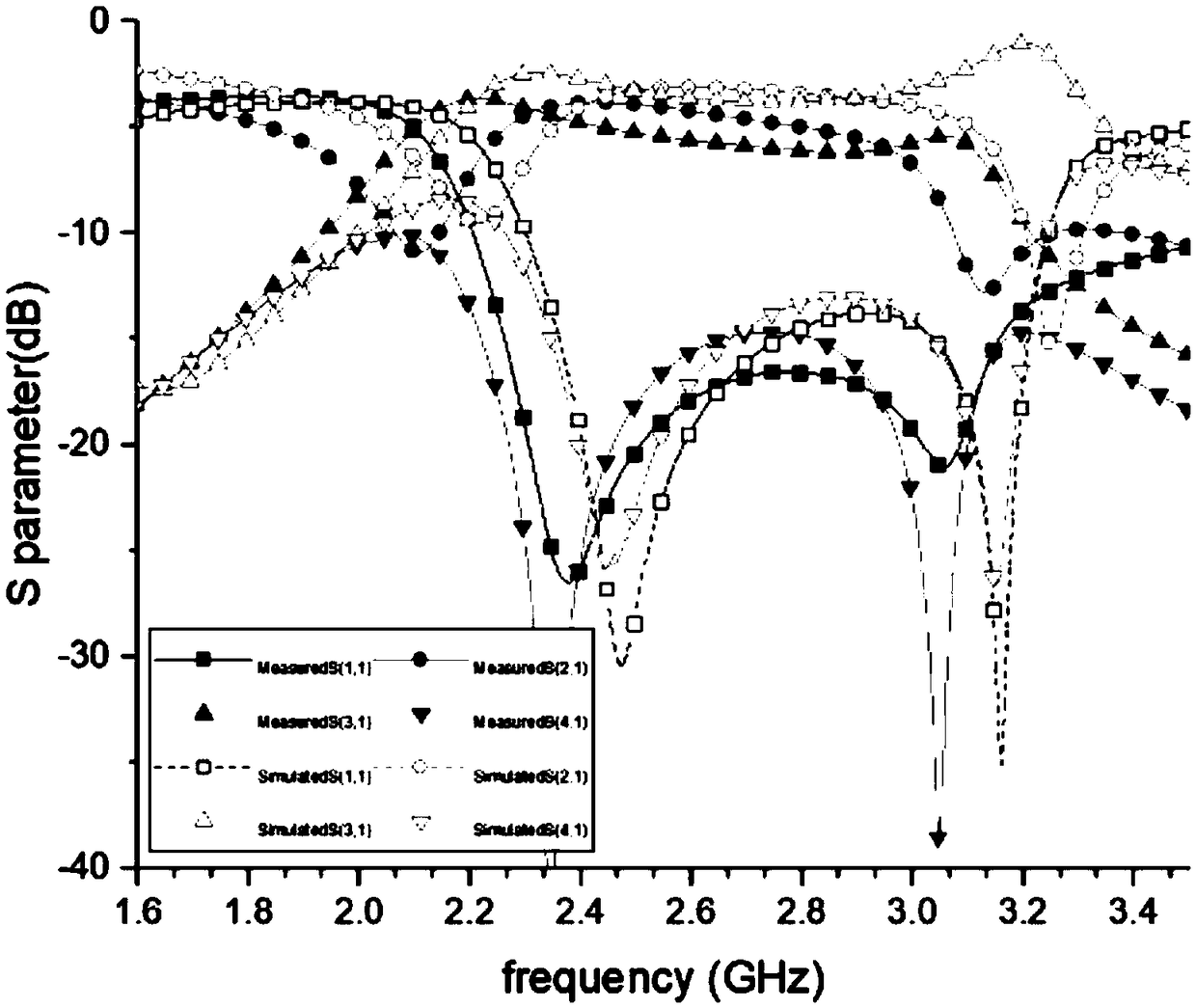
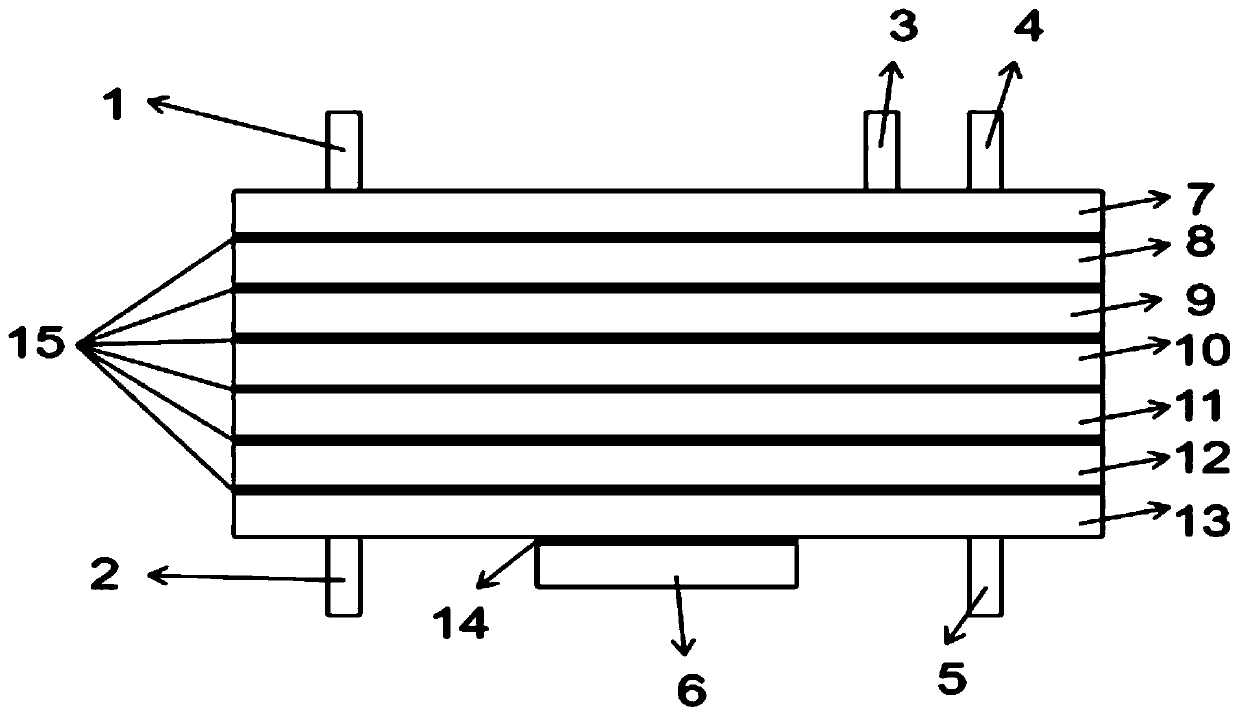
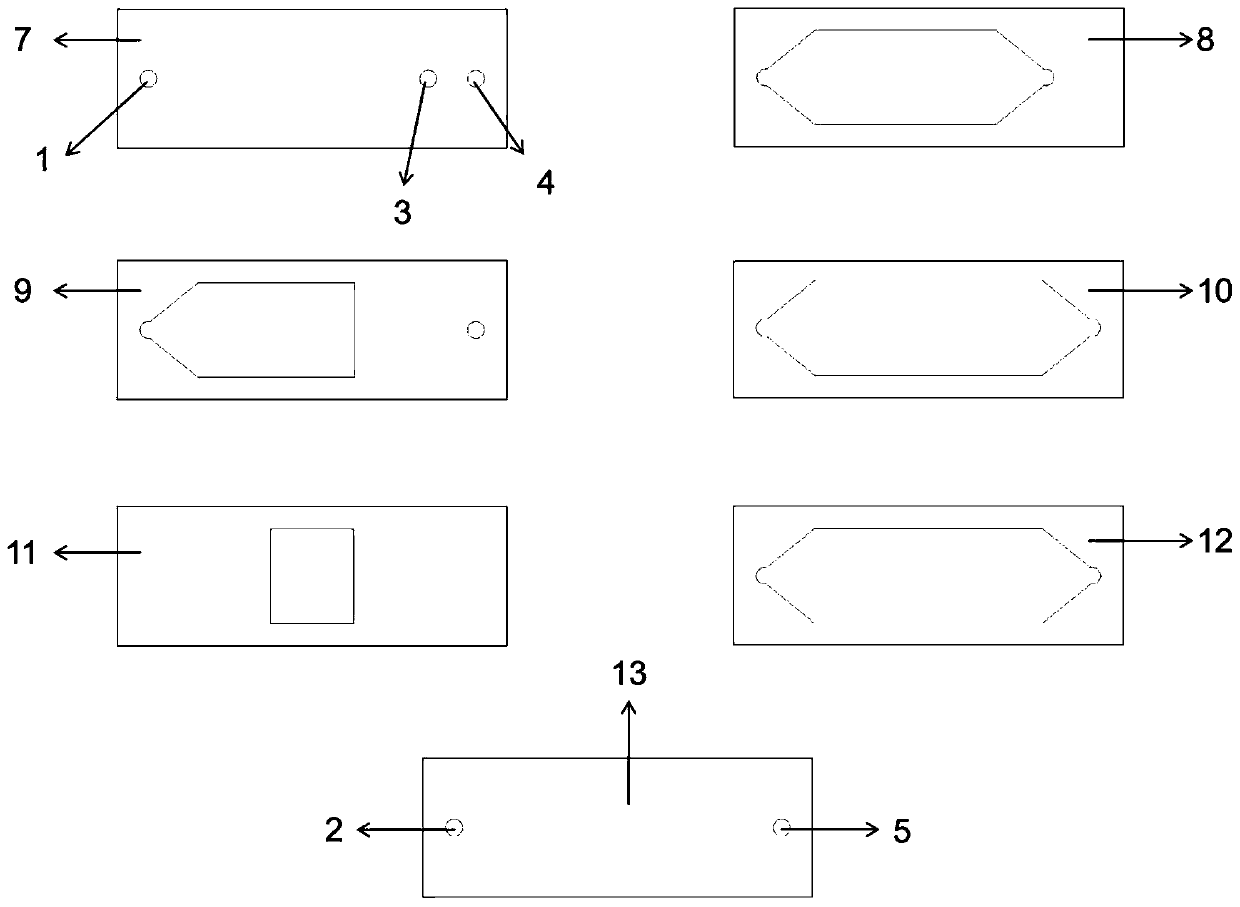
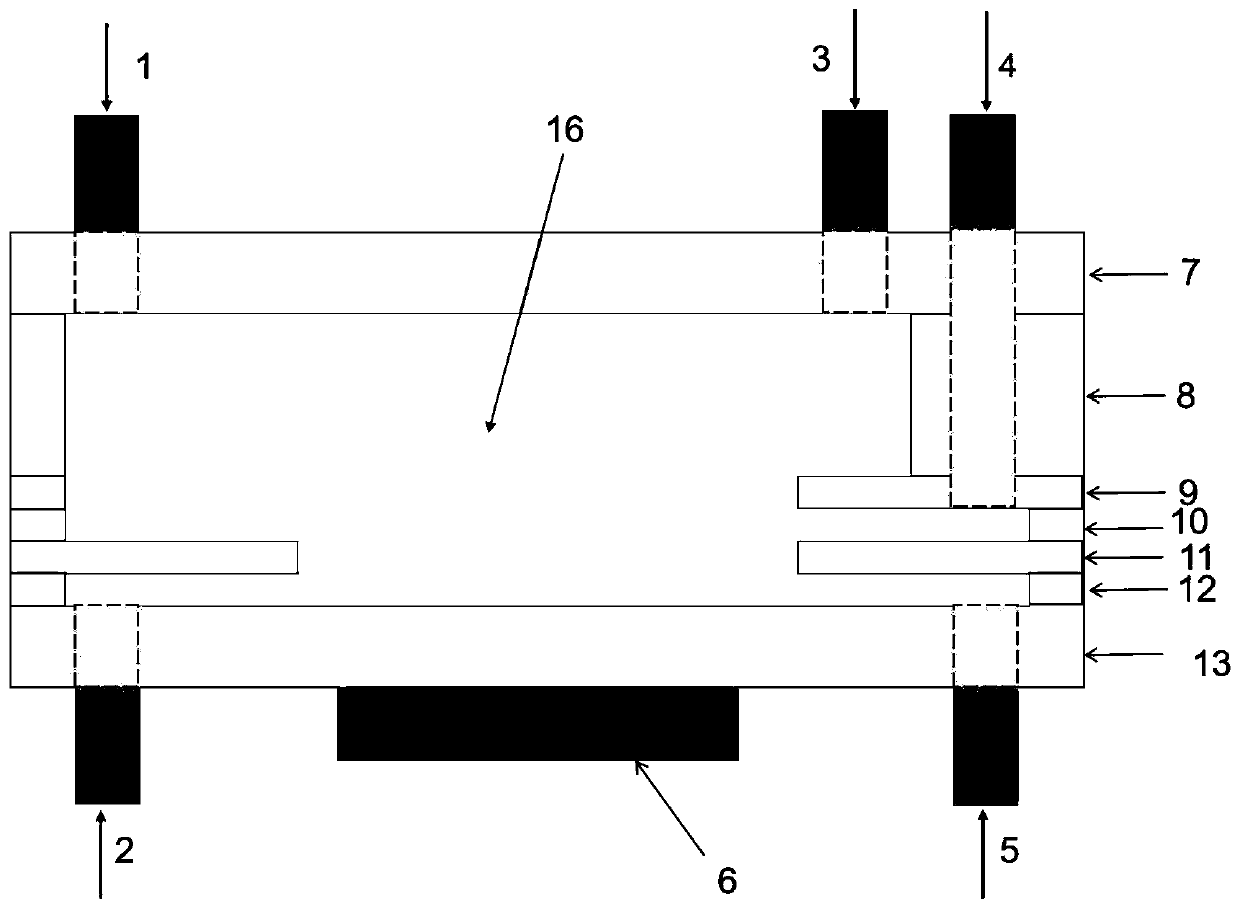
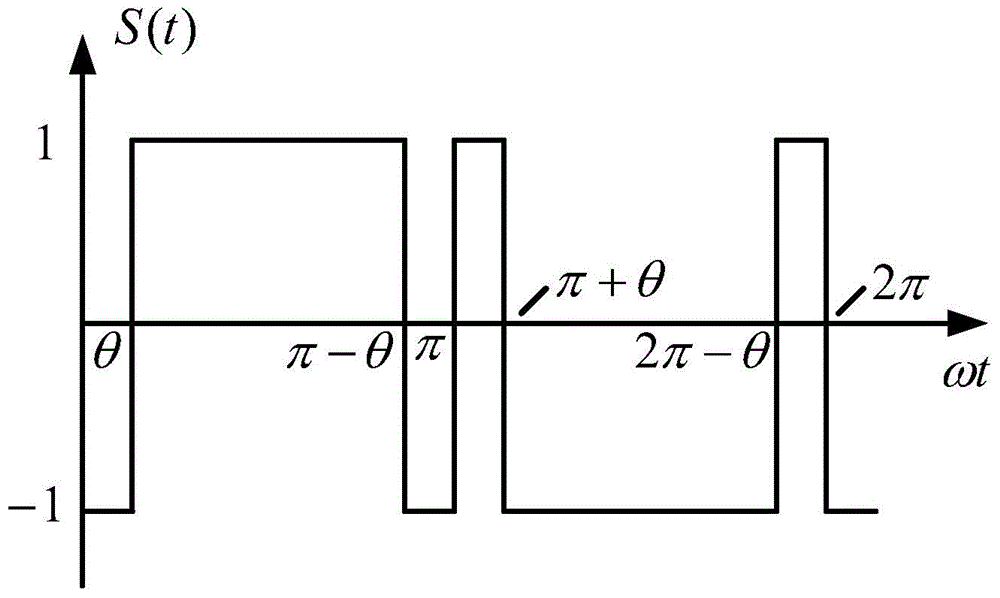Patents
Literature
59results about How to "Adjustable working frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
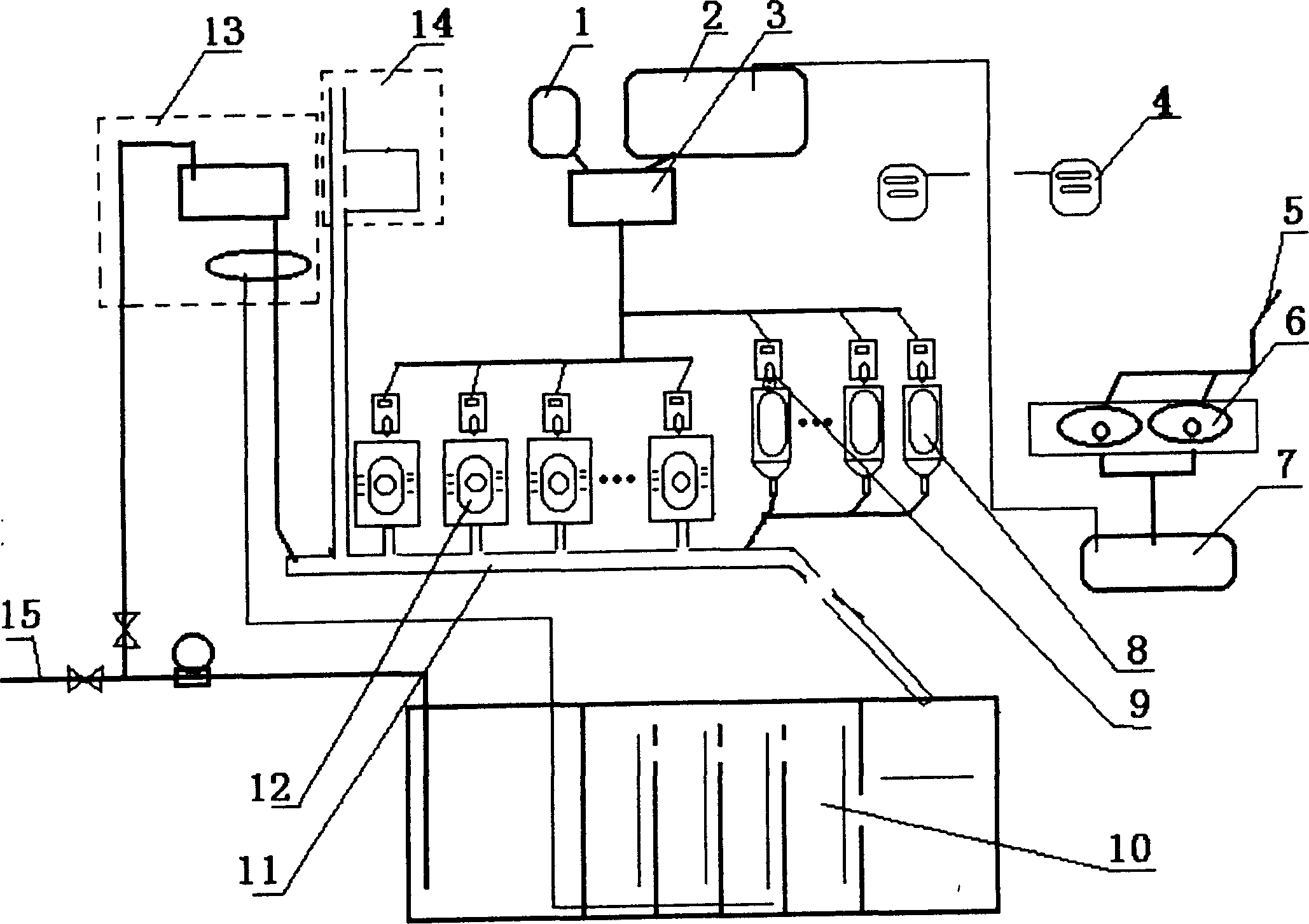
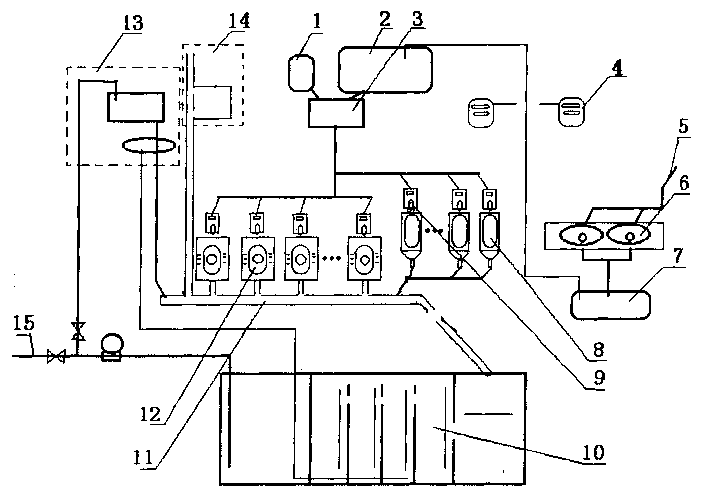
Magnetic coupling resonant wireless electric energy transmission device based on low frequency PWM rectifier
ActiveCN104821667AResonant realizationOvercome the tuning problem caused by the inability to adjust continuouslyElectromagnetic wave systemEfficient power electronics conversionResonant filterAnalog-to-digital converter
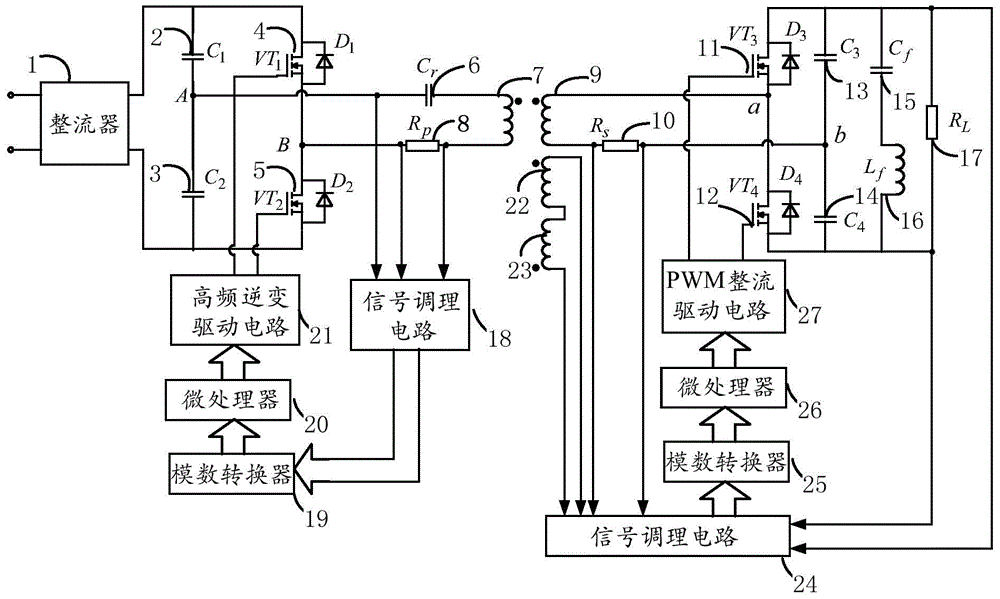
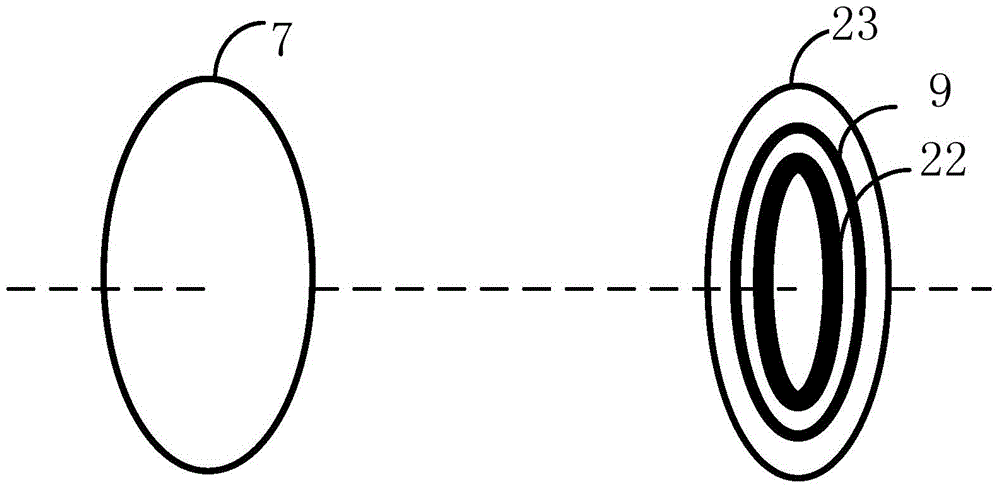
The invention discloses a magnetic coupling resonant wireless electric energy transmission device based on a low frequency PWM rectifier. The device comprises a rectifier, a voltage stabilizing capacitor, an inverter power switch, an emission circuit resonant capacitor, an emission circuit resonant coil, an emission circuit current sampling resistor, a receiving circuit resonant coil, a receiving circuit current sampling resistor, a rectifier power switch, a resonant filter capacitor, a resonant filter inductor, a load resistor, a transmitting end signal conditioning circuit, a transmitting end analog to digital converter, a transmitting end microprocessor, a transmitting end high frequency inverter driving circuit, an induction voltage detection coil, a receiving end signal conditioning circuit, a receiving end analog to digital converter, a receiving end microprocessor and a PWM rectifier driving circuit. According to the device, the resonance of an emission loop is ensured, the tracking of transmitting end working frequency, the resonance of a receiving circuit and the constant output of load voltage are realized, the requirement of working frequency by a power switch device is greatly reduced, and a space is provided for the device to raise power supply working frequency.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Novel multi-stable ultrasonic detection sensor
ActiveCN106198724AReduce volumeEasy to integrateAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSolid phasesImage resolution
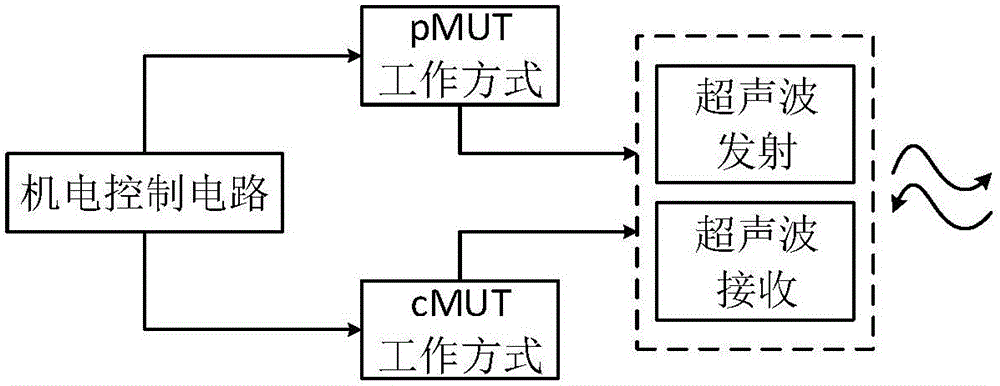
The invention relates to a novel multi-stable ultrasonic detection sensor which is used in the field of ultrasonic detection and includes: an acoustic resistance matching layer, a metal electrode, a piezoelectric film, a high-voltage-resistant insulating layer, a hollow chamber sealing layer, a back lining layer, and an electromechanical control circuit board. The ultrasonic detection sensor can achieve a multi-stable working mode of combination of piezoelectric ultrasonic sensing and capacitive ultrasonic sensing on one ultrasonic transducer unit through the electromechanical control circuit board, wherein each stable working mode can be designed according to optional ultrasonic frequencies, for example, a design scheme of capacitive low frequency ultrasonic sensing and piezoelectric high frequency ultrasonic sensing, thus considering both the depth and resolution of ultrasonic detection. The multi-stable ultrasonic detection sensor can be flexibly applied in ultrasonic detection on gas-phase, liquid-phase and solid-phase mediums, is simple in resistance matching, is small in size and is easy to integrate, can be produced in large scale and is low in cost, and has application prospects in the fields of underwater acoustic detection, bio-medical imaging, industrial ultrasonic non-destructive testing, etc.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
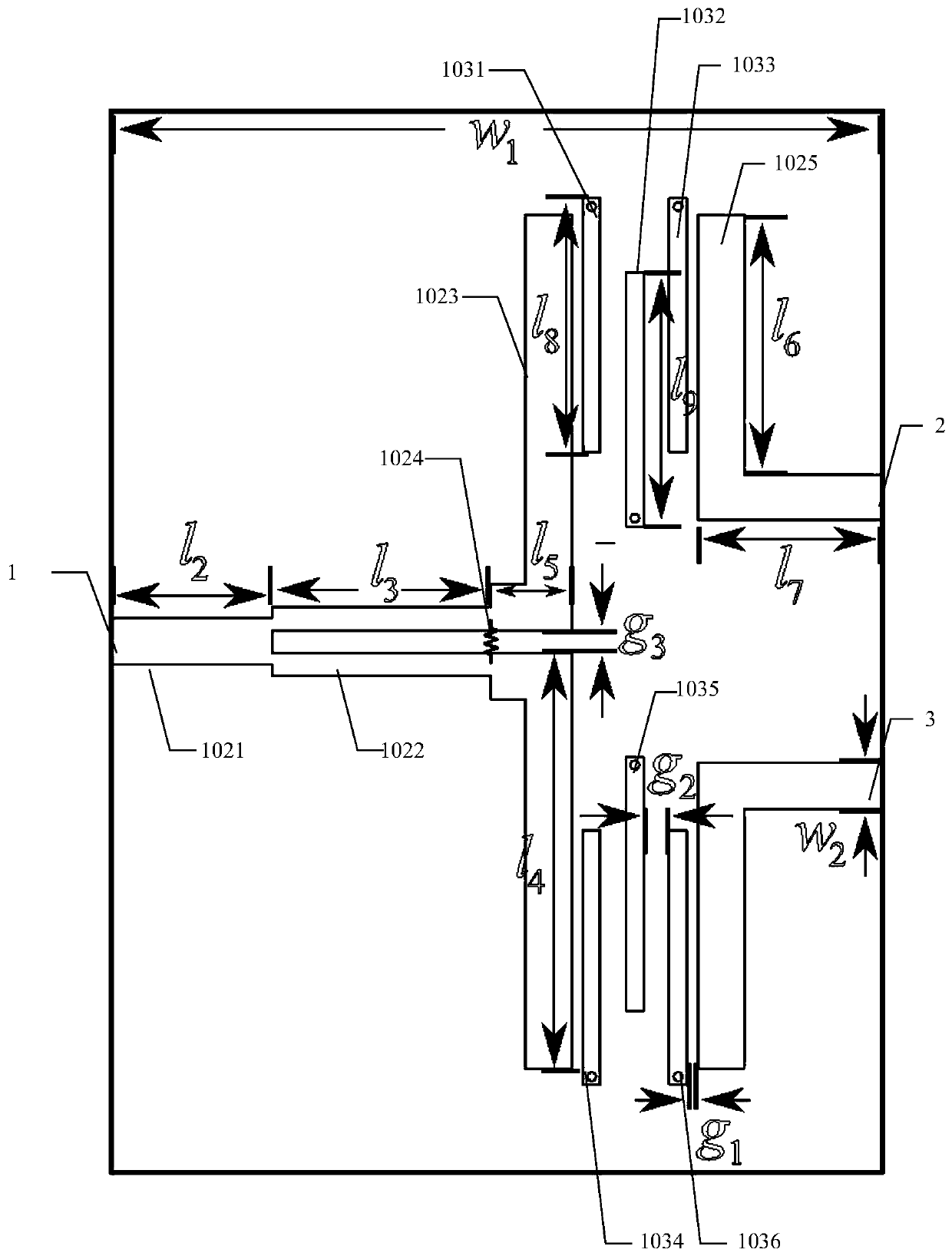
Electric adjusting power divider with filter function
ActiveCN104466335AEasy to integrate applicationsAchieve powerCoupling devicesBandpass filteringWavelength
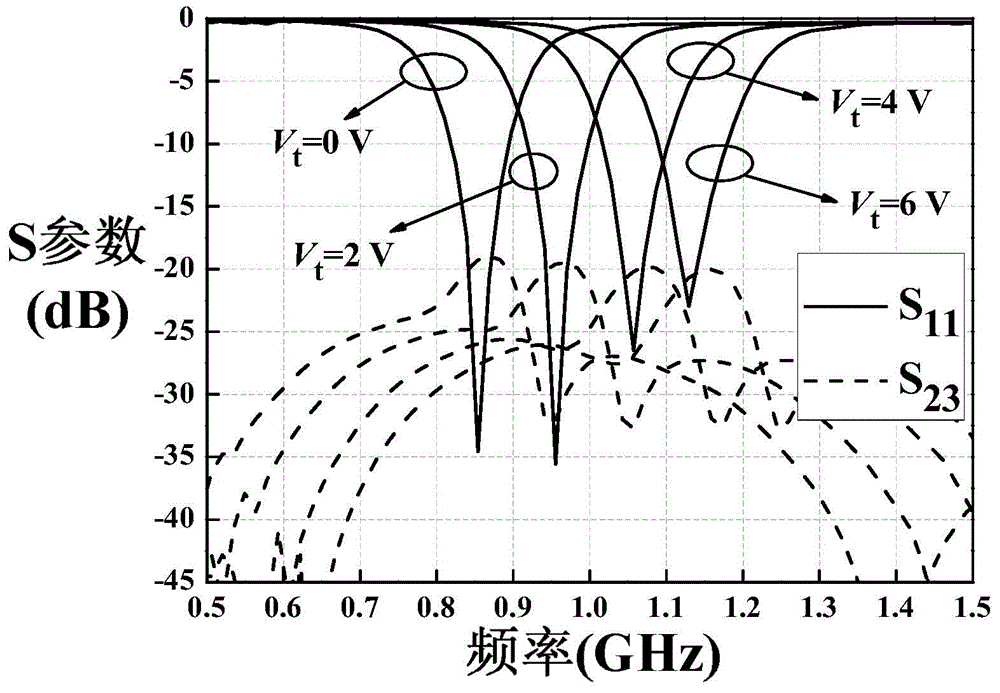
The invention provides an electric adjusting power divider with a filter function. The entire circuit structure of the electric adjusting power divider is symmetric, and the power dividing ratio is 1:1. Two pairs of quarter-wave resonators which are coupled with each other form two filter networks, and the characteristic of band-pass filtering is achieved. The matching of three ports of a circuit and the isolating of two output ports of the circuit are achieved by resistors. According to an on-load variable capacitance diode, the electrical length of the resonators and the electrical length of a feeder line are adjusted by changing the on-load voltage of the on-load variable capacitance diode, and the purpose that the center frequency is adjustable is achieved. In addition, three transmission zeros are introduced by source load coupling, so that the electric adjusting power divider has high selectivity and is also good in stopband suppression effect.
Owner:深圳锦峰信息技术有限公司
Vibration stick
ActiveCN103110505AEasy to useAdjustable working frequencyVibration massageGenitals massagePhysical medicine and rehabilitationMassage
The invention belongs to the technical field of adult appliances, and particularly relates to a vibration stick. The vibration stick comprises a shell body, wherein the interior of the shell body forms a containing space, a massage end is arranged at one end of the shell body, the containing space comprises a massage space corresponding to the massage end, a vibration motor is arranged in the massage space, and a control circuit is arranged in the containing space. The massage end is provided with a pressure sensing unit, and the pressure sensing unit and a vibration motor are connected with the control circuit. The vibration motor and the pressure sensing unit which is used for adjusting the vibration motor are arranged at the massage end, so that in the process of use, a working state of the vibration motor can be adjusted through pressure, working frequency of the vibration motor is adjusted, simultaneously, a middle soft sleeve pipe segment is arranged in the middle of the shell body, and the shape of the shell body is adjustable. The vibration stick is convenient to use and applied to requirements of different people.
Owner:GIZMOSPRING COM DONGGUAN
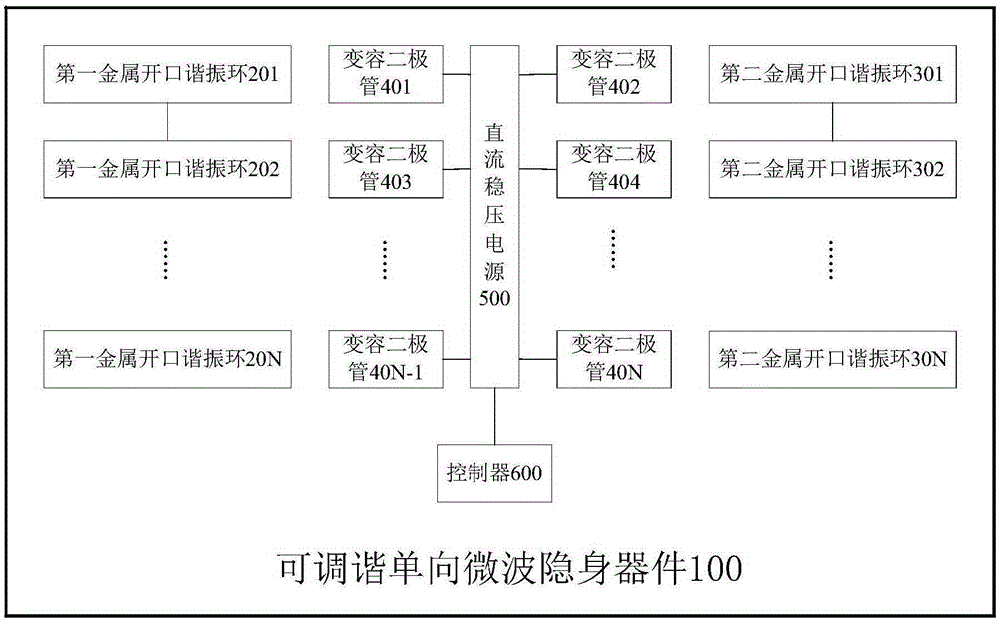
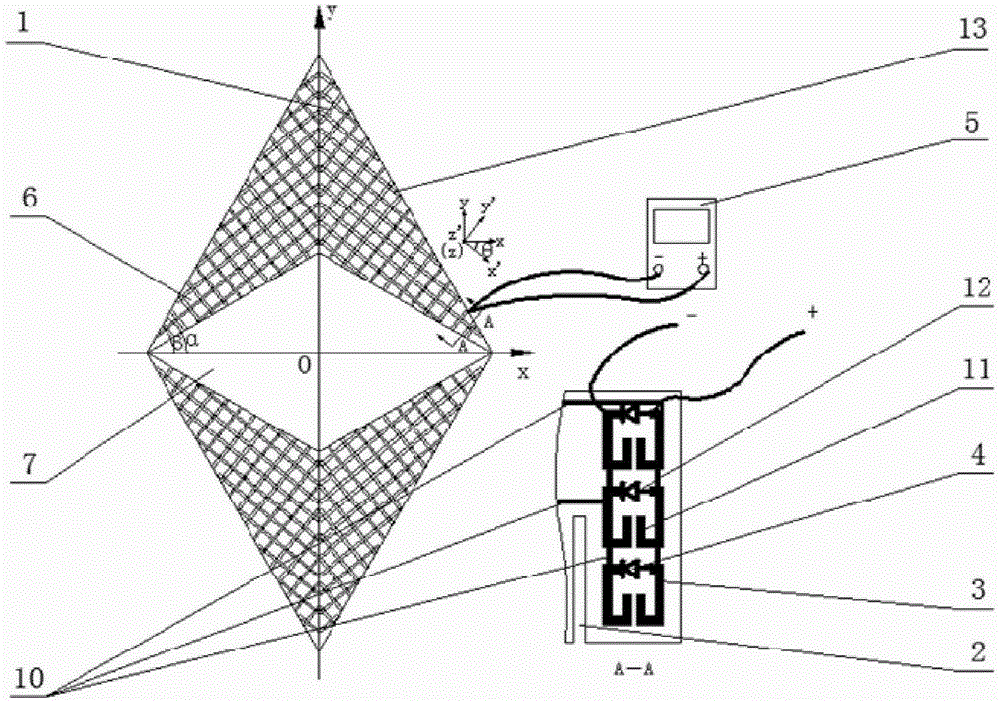
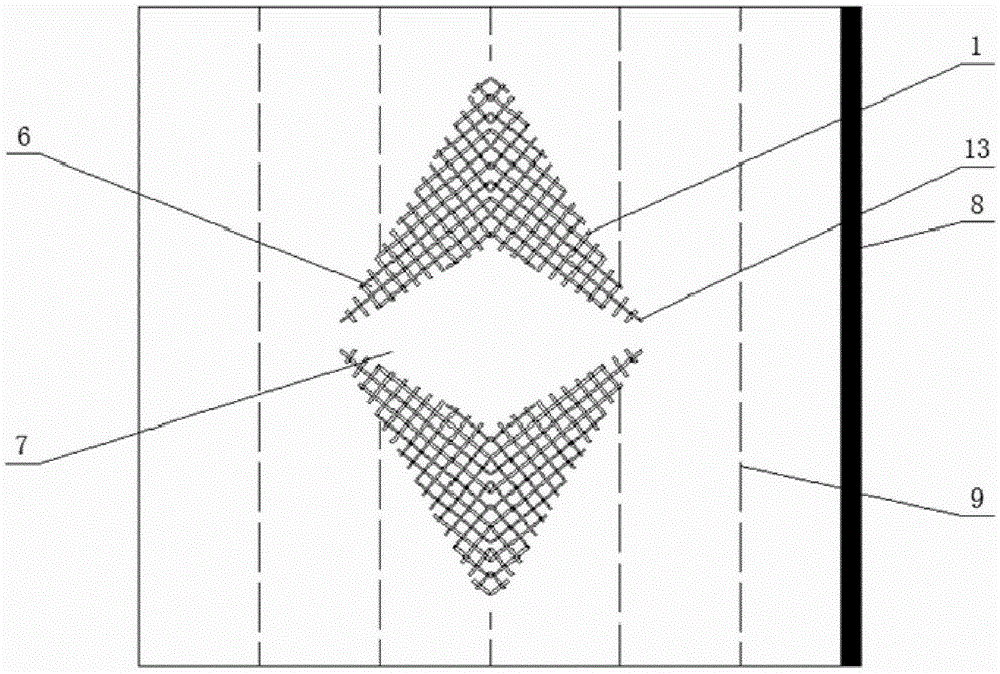
Tunable unidirectional microwave cloaking device
ActiveCN105244627AStealth implementationEasy to controlAntennasMicrowaveElectromagnetic wave transmission
The invention discloses a tunable unidirectional microwave cloaking device. The tunable unidirectional microwave cloaking device includes a first metal opening resonance ring array, a second metal opening resonance ring array, a plurality of variable capacitance diodes which correspondingly are arranged at the opening of each first metal opening resonance ring in the first metal opening resonance ring array and at the opening of each second metal opening resonance ring in the second metal opening resonance ring array, a direct-current voltage-stabilized power supply, and a controller, wherein the controller is used for controlling the output voltage of the direct-current voltage-stabilized power supply to regulate end voltage at two ends of each variable capacitance diode so as to change the capacitance values of the variable capacitance diodes, so that a frequency characteristic curve can be shifted. According to the cloaking device provided by the embodiment of the invention, control on electromagnetic wave transmission paths and phases can be realized through the resonance effects of the metal resonance rings, and obstacles in a cloaking region can be cloaked, and the frequency characteristic curve of the device can be shifted, so that the cloaking of electromagnetic wave waves in different frequency bands can be realized. The tunable unidirectional microwave cloaking device has the advantages of simple structure and easiness in control.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Electric power circuit and LCD
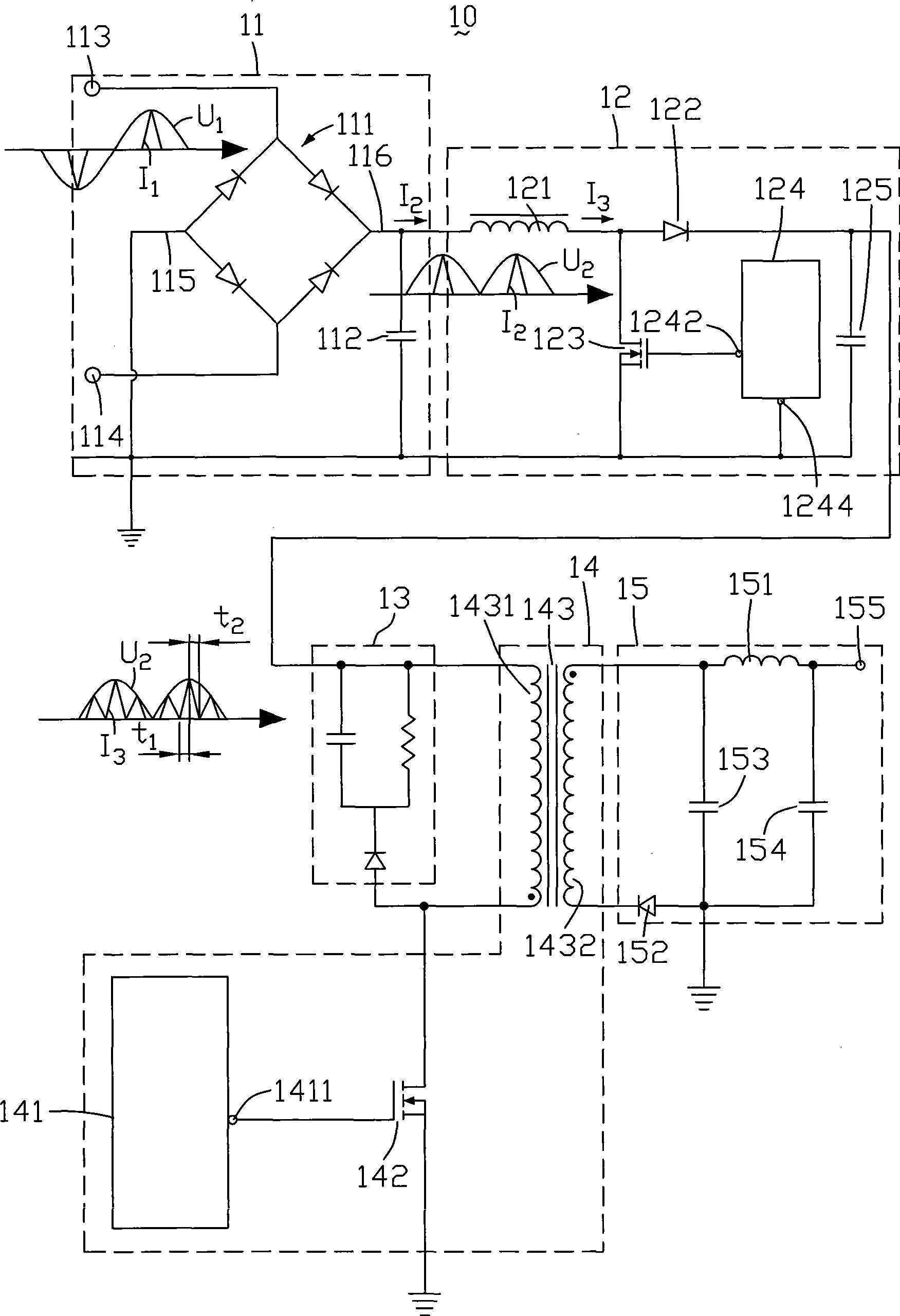
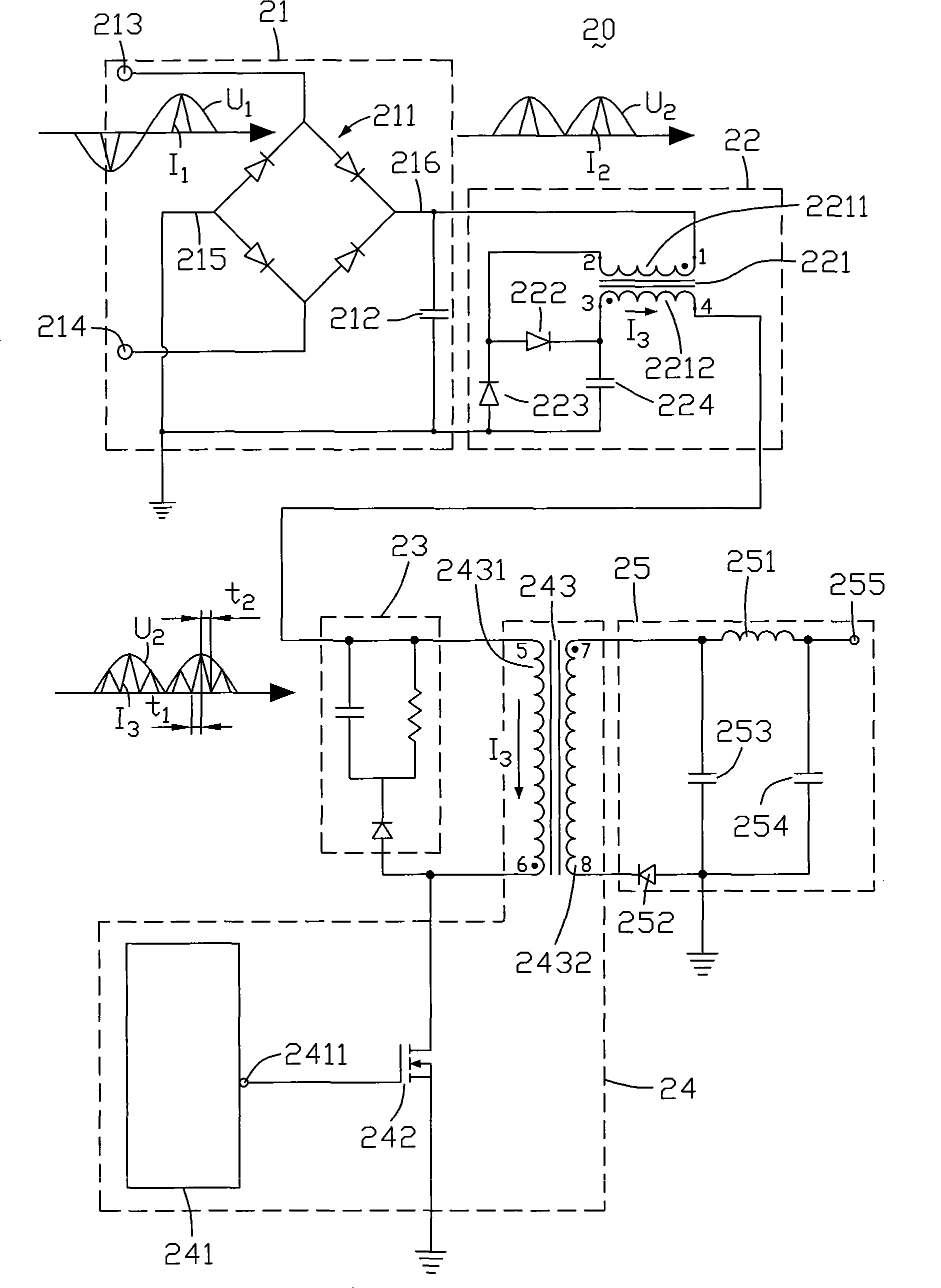
InactiveCN101398548AAdjustable working frequencyAvoid loud noisesEfficient power electronics conversionStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceTransformer
The invention relates to a power circuit and a liquid crystal display; the power circuit comprises a first rectifier filter circuit, a power factor correction circuit, a switch control circuit and a second rectifier filter circuit; the power factor correction circuit comprises a first transformer, a first LED and a first energy storage capacitor; the switch control circuit comprises a transistor and a second transformer; the first rectifier filter circuit converts an AC voltage into a DC voltage; when the transistor is conducted, the first rectifier filter circuit provides the DC voltage for the second transformer through the primary coil of the first transformer, the first LED and the secondary coil of the first transformer; the first energy storage capacitor keeps the DC voltage supplied to the second transformer; when the transistor is intercepted, the second transformer provides voltage for the load through the second rectifier filter circuit. The power circuit has small noise.
Owner:INNOCOM TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Adjustable multi-frequency slot antenna
InactiveCN104022362ASmall sizeAdjustable working frequencySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringImpedance matching
The invention discloses an adjustable multi-frequency slot antenna which comprises a substrate, a slot type rectangular earth plate and an impedance matching input transmission line. The slot type rectangular earth plate and the impedance matching input transmission line are arranged on the upper surface of the substrate, the slot type rectangular earth plate is provided with a middle rectangular slot, a left large rectangular slot, a right large rectangular slot, a first left adjustable rectangular slot, a second left adjustable rectangular slot, a third left adjustable rectangular slot, a first right adjustable rectangular slot, a second right adjustable rectangular slot and a third right adjustable rectangular slot, the first left adjustable rectangular slot and the first right adjustable rectangular slot are respectively provided with a first switch, the second left adjustable rectangular slot and the second right adjustable rectangular slot are respectively provided with a second switch, and the third left adjustable rectangular slot and the third right adjustable rectangular slot are respectively provided with a third switch. The adjustable multi-frequency slot antenna has the advantages of being small in size, adjustable in frequency, easy to manufacture and the like.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Waveguide and microwave transition circuit with adjustable working frequency
ActiveCN105261815ALarge size toleranceReduce the difficulty of buildingCoupling devicesHemt circuitsEngineering
The invention relates to a waveguide and microwave transition circuit with adjustable working frequency. The problem in the prior art that the dimensional tolerance of the waveguide and microwave transition circuit is small and the working frequency thereof is not adjustable is solved. A polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sleeve is inserted into a metal cylindrical channel. One end of the PTFE sleeve completely contacts the lower surface of a micro-strip circuit, and the other end of the PTFE sleeve completely contacts the lower surface of a waveguide through hole. The centers of a circular through hole, an insulating through hole and the PTFE sleeve correspond to one another in the vertical direction. The front end of a metal probe is inserted into the PTFE sleeve through the circular through hole of a circular metal bonding pad, and the tail end of the metal probe is fixedly installed on the micro-strip circuit. A rectangular metal block is movably installed at the tail end of the output of the waveguide through hole, and the cross section of the rectangular metal block is of the same shape and size as that of the waveguide through hole. According to the invention, microwave signals in different frequency bands can be transmitted between a rectangular waveguide and a micro-strip transmission line. The waveguide and microwave transition circuit has the characteristics of large circuit dimension tolerance and adjustable working frequency.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP NO 16 INST
Controllable surface type small four-element four-arm helical antenna array
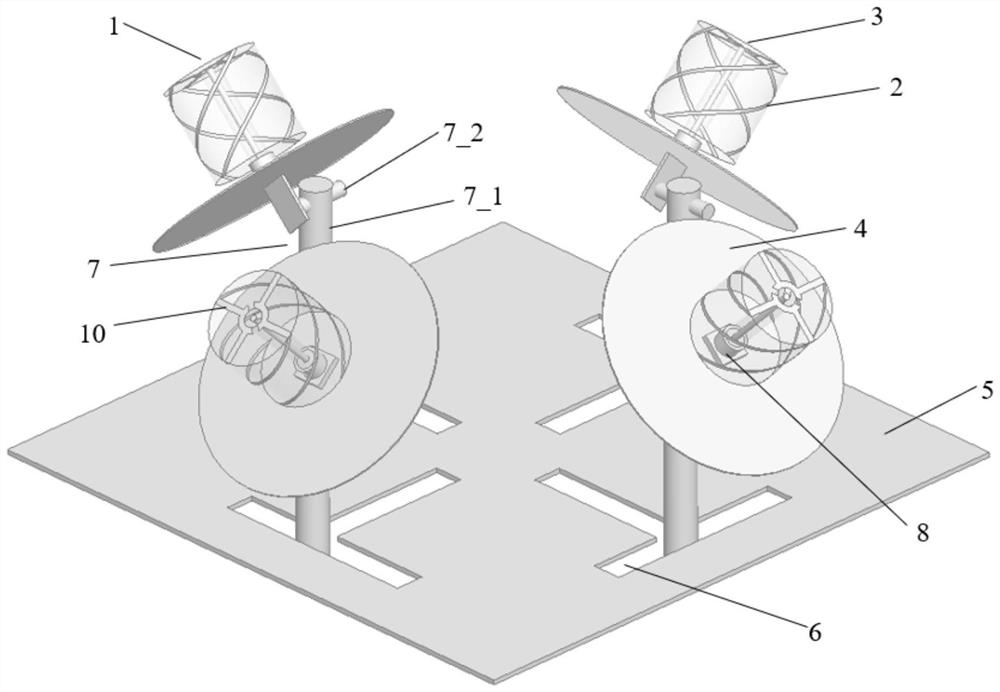
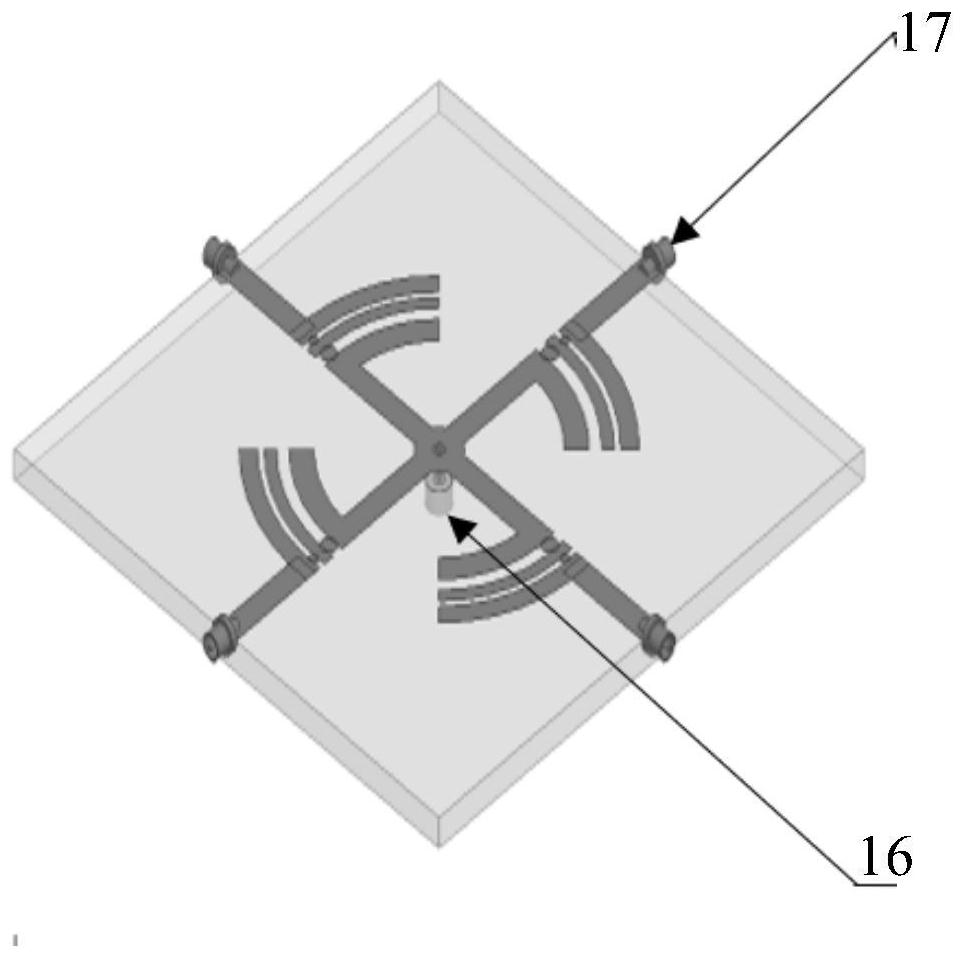
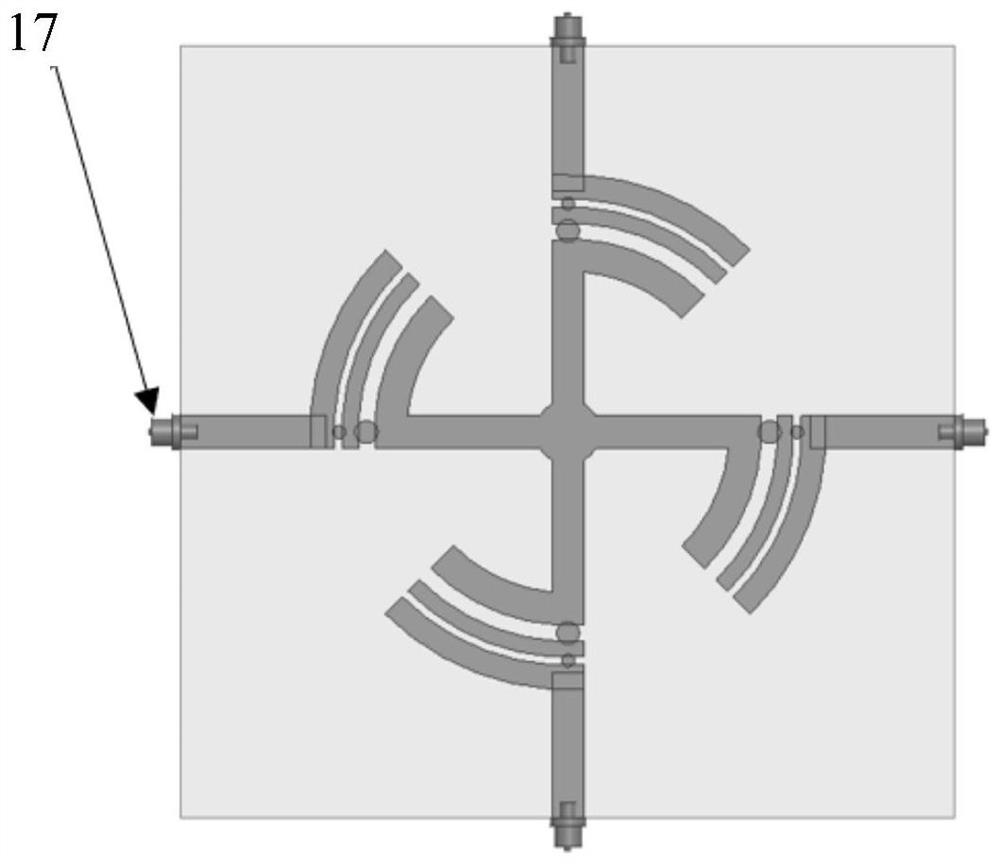
PendingCN113422213ABandwidthFacilitate communicationAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsImpedance ConverterCoaxial line
The invention discloses a controllable surface type small four-element four-arm helical antenna array, which comprises a four-arm helical antenna array for transmitting and receiving signals, a controllable reflecting surface bracket assembly and four controllable power division feed networks, whereinthe four-arm helical antenna array comprises four self-phase-shifting four-arm helical antennas, and each four-arm helical antenna comprises an adjustable slotted balun with an adjustable slotted length as an antenna outer conductor and an adjustable impedance converter with a movable slip ring as an antenna inner conductor; the controllable reflecting surface bracket assembly comprises four reflecting surfaces, and the four four-arm helical antennas are respectively mounted on the reflecting surfaces; and each controllable power division feed network is respectively connected with each four-arm helical antenna through a coaxial line. The antenna array has the advantages that the antenna array elements are combined with the controllable reflecting surface bracket, the controllable power division feed network and the like, parameters such as array element spacing, array element working quantity, array element direction, phase difference between array elements and the like can be adjusted according to different requirements, and then characteristic parameters such as impedance, frequency band, size, directional diagram, polarization and the like of the antenna array are adjusted.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Microfluid-controlled frequency adjustable microstrip patch antenna
InactiveCN106910993AIncrease the effective dielectric constantAdjustable working frequencyRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationElectric fieldMicrofluidic channel
The invention relates to a microfluid-controlled frequency adjustable microstrip patch antenna. The antenna comprises two oppositely-disposed substrates and microfluid channels into which a microfluid can be injected; one of the substrates is provided with a radiating unit in the form of a patch; clad copper arranged on the other substrate is adopted as reflection ground; a feed structure vertically passes through the two substrates and feeds electricity to the radiation unit; and the microfluid channels are arranged between the two substrates and are located in an electric field distribution area corresponding to the radiating unit; and the microfluid channels are perpendicular to the centering surface of the radiating unit where the feed structure is located. According to the microfluid-controlled frequency adjustable microstrip patch antenna of the invention, the microfluid is injected into the microfluid channels, so that an effective dielectric constant between the radiating unit and the reflection ground can be increased, and therefore, the operating frequency of the antenna can be adjusted so as to be lowered; and the adjustable frequency range of the antenna can be controlled through loading the locations of the microfluid channels; and the reversibility of such adjustment can be realized through exhausting the microfluid channels. According to the microfluid-controlled frequency adjustable microstrip patch antenna, the adjustability of the frequency of the antenna can be realized safely and effectively at low cost, and the size of the antenna is not increased, and the integrity of the patch of the antenna is not damaged.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY +1
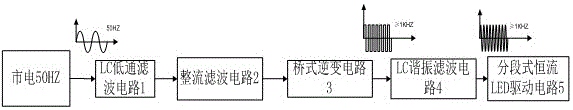
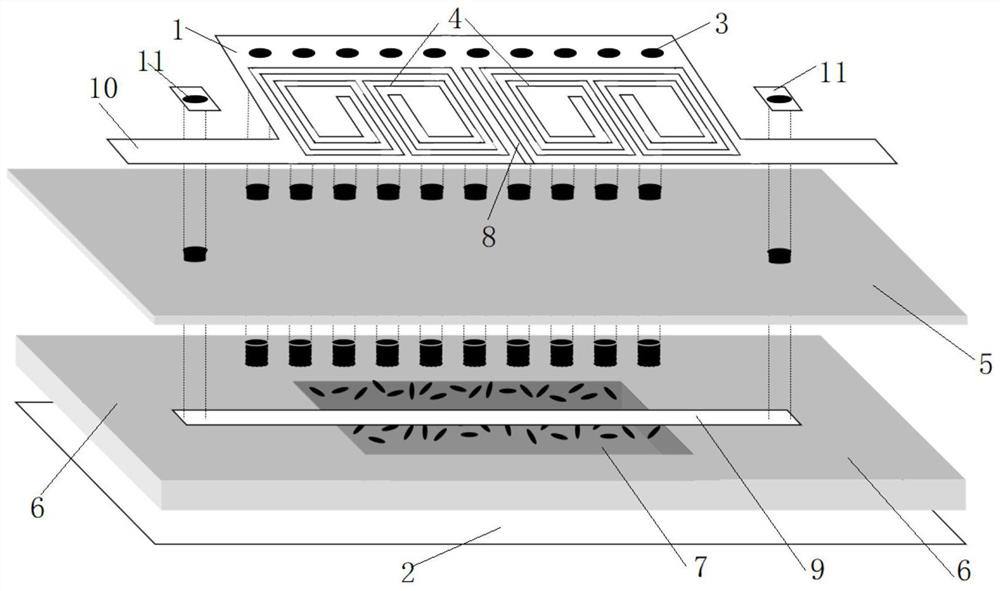
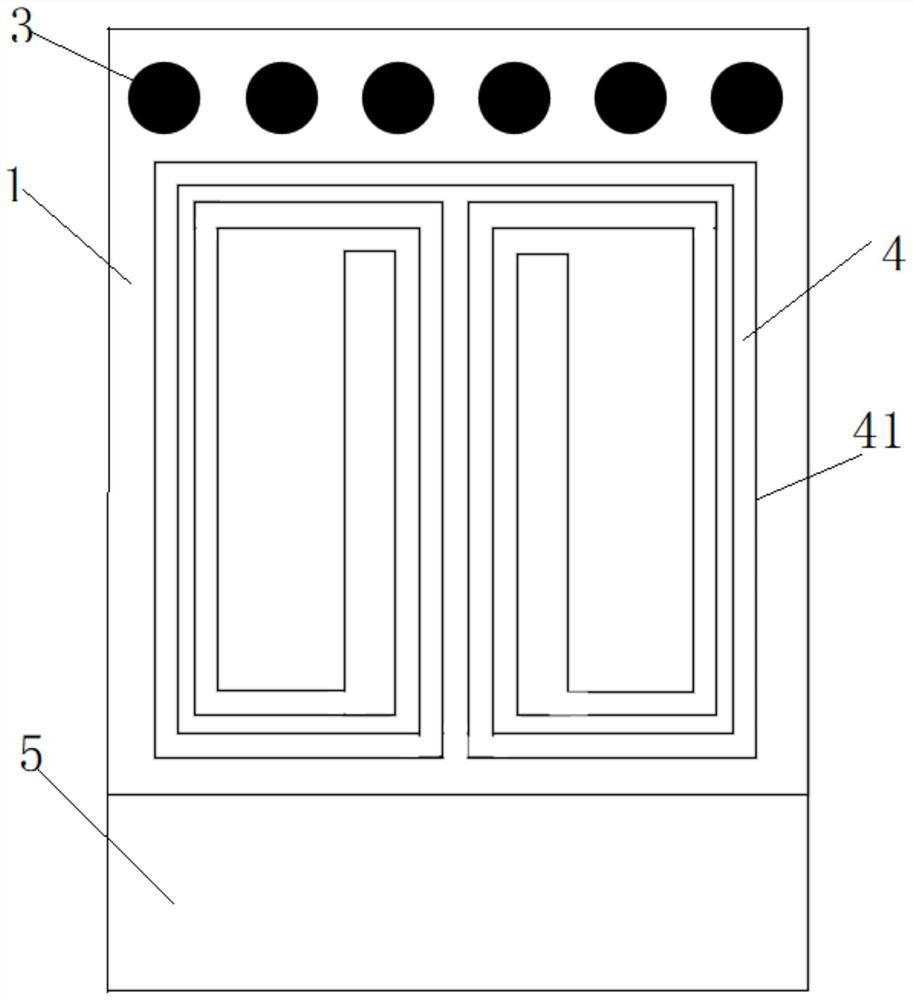
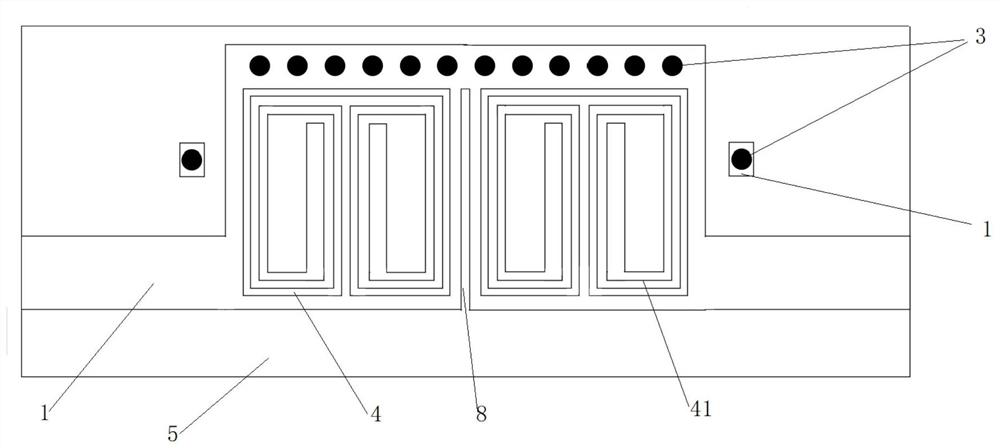
Stroboflash-free sectional type constant-current LED driving circuit
InactiveCN105764178AImprove filter characteristicsImprove system stabilityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringControl theory
The invention relates to a stroboflash-free sectional type constant-current LED driving circuit. The stroboflash-free sectional type constant-current LED driving circuit comprises an LC low-pass filtering circuit, a rectification filtering circuit, a bridge inversion circuit, an LC resonance filtering circuit and a sectional type constant-current LED driving circuit. The sectional type constant-current LED driving circuit is enabled to have quite high versatility and adaptability, and the application scope of a sectional type driving scheme in the field of LED illumination is expanded.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Half-mode substrate integrated waveguide liquid crystal adjustable filter with embedded coupling metal wires
ActiveCN113097670ALimit transmissionReconfigurableWaveguide type devicesWave structureDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a half-mode substrate integrated waveguide liquid crystal adjustable filter with embedded coupling metal wires. The filter comprises a half-mode substrate integrated waveguide, the half-mode substrate integrated waveguide comprises a dielectric substrate assembly, the dielectric substrate assembly comprises a first metal layer and a second metal layer arranged opposite to the first metal layer, the first metal layer and the second metal layer are connected through a plurality of metal through holes, the plurality of metal through holes form a through hole array to form a substrate integrated guided electromagnetic wave structure in the dielectric substrate assembly, a double-internal rotation type open-loop resonance structure is etched on the first metal layer, the double-internal rotation type open-loop resonance structure comprises two end points which are symmetrically arranged, and the two end points spirally extend towards the interior of the ring at the same time, so that each edge part of the double internal rotation type open-loop resonance structure at least comprises two etching lines. According to the half-mode substrate integrated waveguide liquid crystal adjustable filter with the embedded coupling metal wires, miniaturization of an existing filter can be achieved, and meanwhile the problem that the working frequency of the filter is fixed and cannot be adjusted is solved.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
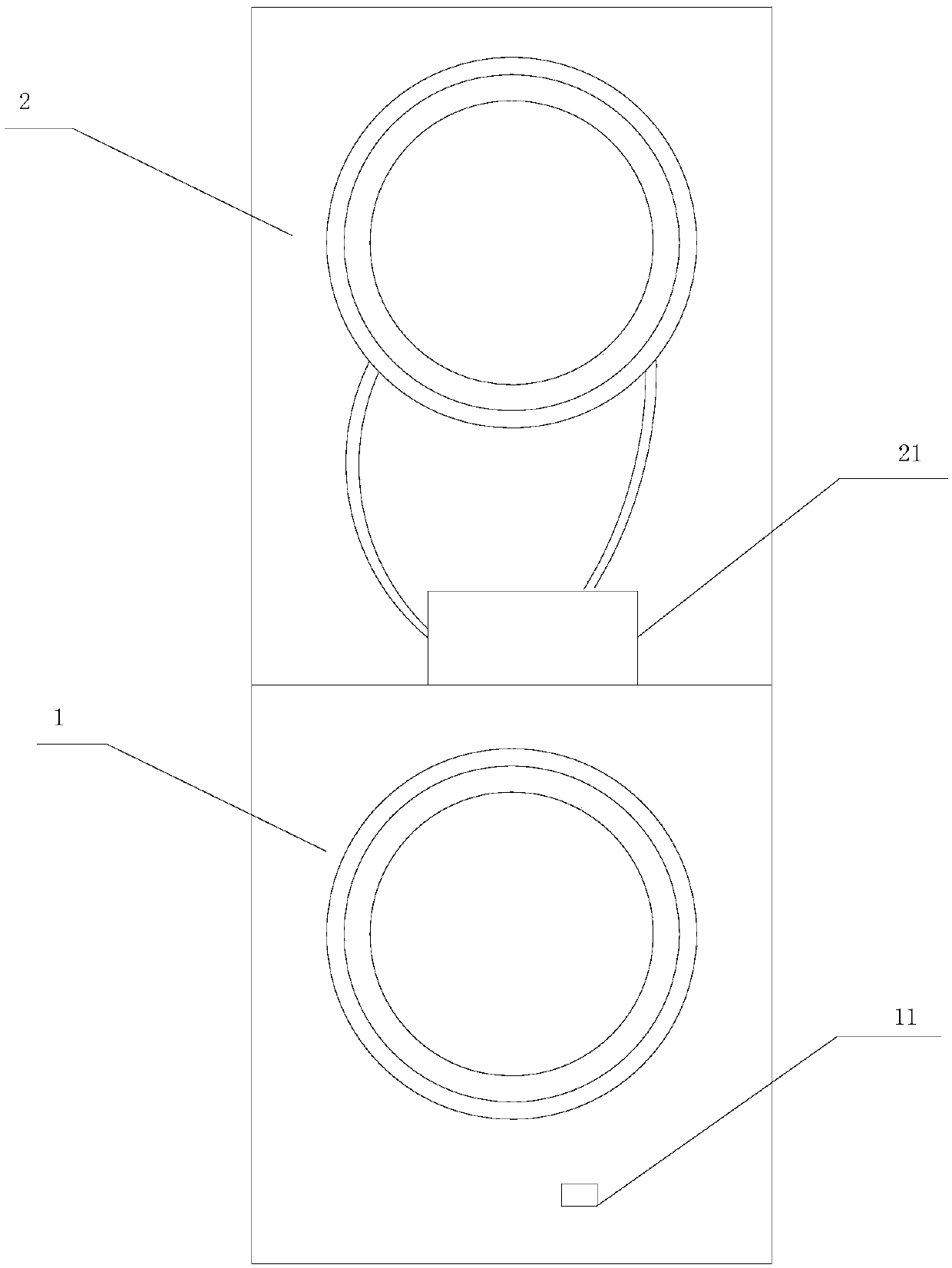
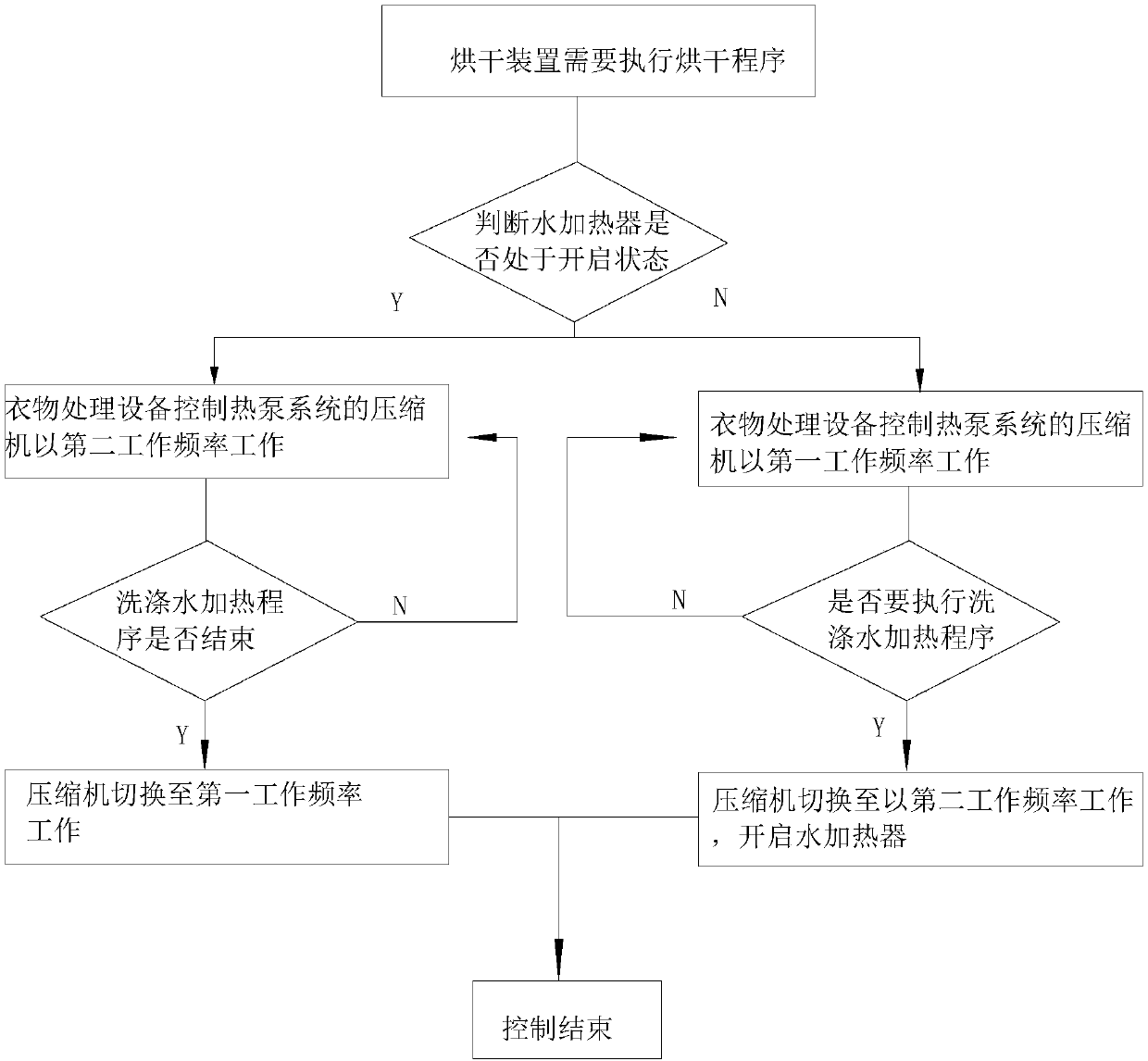
Clothes processing equipment and control method thereof
ActiveCN110130043AMeet the power requirements of the whole machineEnsure safe workOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusAutomatic controlProcess engineering
The invention discloses clothes treatment equipment and a control method thereof. The clothes treatment equipment comprises a washing device and a drying device, wherein the washing device comprises awater heater for heating washing water, and the drying device comprises a heat pump system for heating drying air. When the washing water heating program and the drying program need to be executed simultaneously, the clothes treatment equipment controls the water heater and the heat pump system to work asynchronously, or adjusts power of the water heater and / or the heat pump system to enable thewater heater and the heat pump system to work simultaneously. By adopting the technical scheme, a user can simultaneously issue and additionally issue different heating control instructions at any time, and washing processing equipment automatically controls and executes the control instructions issued by the user, safe operation of the clothes treatment equipment within the rated power is guaranteed, and safety of the user is guaranteed.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER WASHING ELECTRIC APPLIANCES CO LTD +1
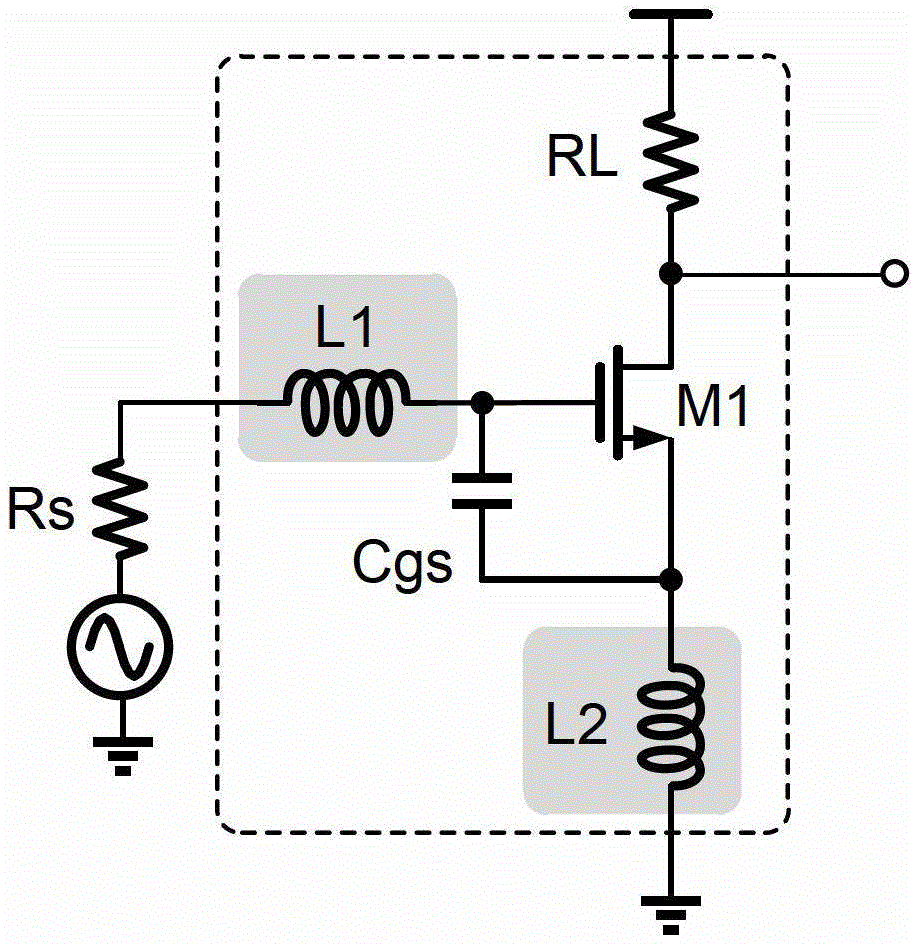
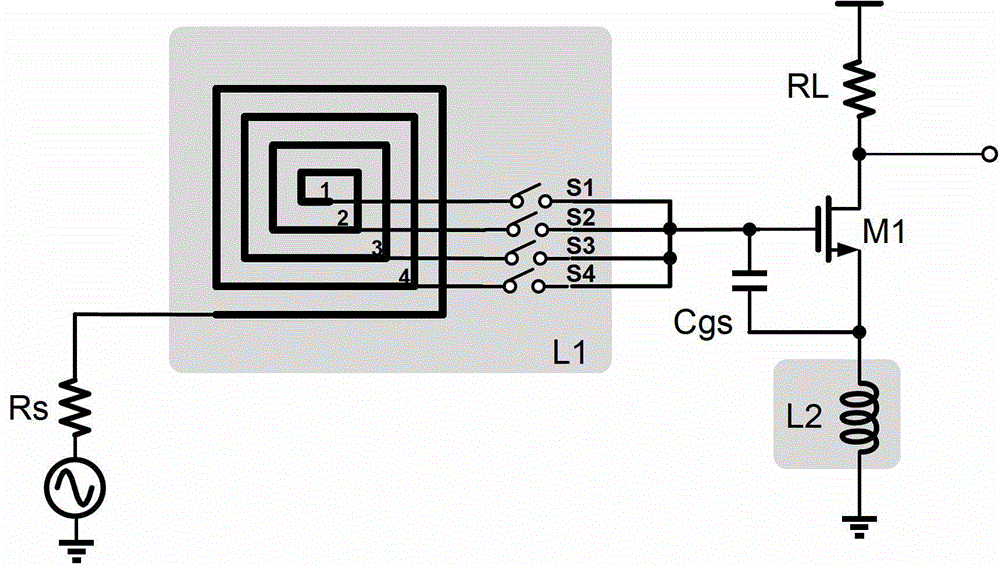
Low-noise amplifier
InactiveCN102983818AAdjustable working frequencyIncrease working frequencyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier input/output impedence modificationAudio power amplifierControl signal
The invention discloses a low-noise amplifier, which comprises at least one spiral coil, a plurality of control switches and an amplifier tube, wherein the spiral coil is formed by a conducting wire in a winding way, the different positions of the conducting wire are provided with a plurality of leading-out end points, one end of the conducting wire is used as the input end of an input matching inductor and the leading-out end points are used as the output ends of the input matching inductor; the control switches are correspondingly connected with the leading-out end points and are turned on or off according to control signals to lead out the leading-out end points at different positions of the input matching inductor, so as to switch the inductance of the input matching inductor; and the amplifier tube is connected with the output ends of the control switches. By adopting the technical scheme, the low-noise amplifier can work at different frequencies.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
Low-noise amplifier with adjustable working frequency in UHF (ultra-high-frequency) RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) reader
InactiveCN101895261AAdjustable working frequencySimple structureAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceLow voltage
The invention relates to a low-noise amplifier with an adjustable working frequency in a UHF (ultra-high-frequency) RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) reader, improving linearity by adopting a second-order intermodulation current injection structure at an input terminal and realizing an adjustable central working frequency by adopting a switched capacitor structure at an output terminal. The second-order intermodulation current injection structure acquires an injection current value when a third-order intermodulation current value is zero by analyzing the nonlinearity characteristic of a MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube; and a switched capacitor is formed by connecting the MOS tube and a capacitor at the output terminal. The capacitor is switched on when the MOS tube is conducted, and the capacitor is switched off when the MOS is cut off, i.e. the capacitor value is changed at the output terminal by conducting or cutting off the MOS. According to the known, when an inductor value L is unchanged, and a capacitor value C is changed, the central working frequency can vary with the capacitor value C so as to adjust the central working frequency of the low-noise amplifier. A frequency mixer proposed by the invention has a working voltage of 1.2 V and low power, accords with the requirements for low voltage and low power consumption and has great instruction meanings in aspects of simplifying a circuit structure, lowering the power consumption, expanding a central working frequency point, and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Non-resonant vibration auxiliary magneto-rheological polishing device and method for machining optical element
The invention relates to a non-resonant vibration auxiliary magneto-rheological polishing device and method for machining an optical element, and belongs to the field of ultra-precision machining. AnX-direction air floatation guide rail and a Y-direction air floatation guide rail are installed on a machine tool frame and drive an element to move in the X-direction and the Y-direction; an Z-direction air floatation guide rail and the Y-direction air floatation guide rail are connected through screws, so that a polishing tool bit moving platform fixed at the bottom end of the Z-direction air floatation guide rail moves in the Z direction; a magnet rotating table is fixed to the machine tool frame, and a generated dynamic magnetic field enables magnetorheological fluid to be subjected to a magnetization reaction to form a magnetic cluster; and a vibration device is installed on the magnet rotating table and drives the element to vibrate in a two-dimensional mode. According to the non-resonant vibration auxiliary magneto-rheological polishing method provided by the invention,a rotary magnetic brush is combined with two-dimensional vibration, so that an abrasive material makes full contact with a surface microstructure of the element, the abrasive material effectively removes scratches, burrs and cracks on the surface of the element through composite motion of the rotary magnetic brush and the two-dimensional vibration, and the polishing efficiency is improved, and the shape precision of the element is better reserved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Vertical channel tunable high-flux acoustic fluidic sorting chip and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111389473AEasy to separateIncrease fluid fluxLaboratory glasswaresFluid controllersMicron scaleEngineering
The invention discloses a vertical channel tunable high-flux acoustic fluidic sorting chip and a preparation method thereof. The vertical channel tunable high-flux acoustic fluidic sorting chip comprises a glass sheet with a standing wave resonant cavity, a piezoelectric ceramic sheet and a PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) film. The standing wave resonant cavity is formed by sequentially laminating andpackaging a glass bottom sheet, a glass gasket I, a glass spacer I, a glass gasket II, a PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) film and a glass top sheet from bottom to top, and the resonant cavity comprises two cavities and is provided with a sample inlet and a sample outlet. The height of the resonant cavity is micron-sized, and the width of the resonant cavity is centimeter-sized, so that high-flux fluid flow is realized. The piezoelectric ceramic sheet is adhered to the bottom of the resonant cavity, and two wires are led out from two poles. The piezoelectric ceramic is driven by an external electric signal to generate a standing wave field in the vertical direction in a channel, and different particles are sorted in the vertical direction. The preparation process is simple, the channel heightis adjustable, the cost is low, the controllability is high, and the vertical channel tunable high-flux acoustic fluidic sorting chip is convenient and suitable for large-flux aggregation, separationand control of biological samples such as cells.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A hybrid branch-line coupler for simultaneous reconstruction of frequency and power fraction
The invention discloses a hybrid branched line coupler which simultaneously realizes frequency and power division ratio reconstruction, realizes frequency and power division ratio reconfiguration based on the branched line structure, not only realizes the function of the power divider but also realizes the adjustable working frequency, which is very suitable for the application of modern wirelesscommunication system. Compared with the prior art, by loading a varactor diode on a branch line coupler, arbitrary power dividing ratio and arbitrary center frequency output can be realized, and the whole structure is simple, miniaturized and easy to integrate. In addition, because the planar microstrip structure is used, the manufacturing process is simple and the cost is low; Because the outputfrequency is adjustable, it is possible to communicate over a wide bandwidth. Therefore, the invention is reasonable in design and simple in structure, can meet the requirement of output power variation of an output signal, can work in a plurality of communication bands, and is conducive to improving the overall performance of a communication system.
Owner:FOSHAN SHUNDE SUN YAT SEN UNIV RES INST +2
High-flux microfluidic body-wave sorting chip and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-flux microfluidic body-wave sorting chip and a preparation method thereof. The high-flux microfluidic body-wave sorting chip is composed of glass sheets with a standingwave reaction cavity and a piezoelectric ceramic piece. The standing wave reaction cavity of the glass sheets is composed of channels and sample inlets and sample outlets, wherein the channels are formed among the glass sheets by sequentially packing a glass substrate, a glass gasket I, a glass spacer I, a glass gasket II, a glass spacer II and a glass top sheet from bottom to top by using an ultraviolet curing adhesive through lamination, the sample inlets and the sample outlets are formed in the channels, the width of the channels is of a centimeter level, and the height of the channels is of a micron level; so that high-flux liquid can be introduced. The piezoelectric ceramic piece is adhered to the bottom of the glass substrate, and two wires are led out of two poles. Under the drivingof an additional electric signal, the piezoelectric ceramic generates a standing wave field in the vertical direction of the channels, and different particles are sorted from the vertical direction.The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple in preparation process, low in cost and strong in controllability, and is conveniently suitable for high-flux gathering, separating and controlling of biological samples such as cells and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
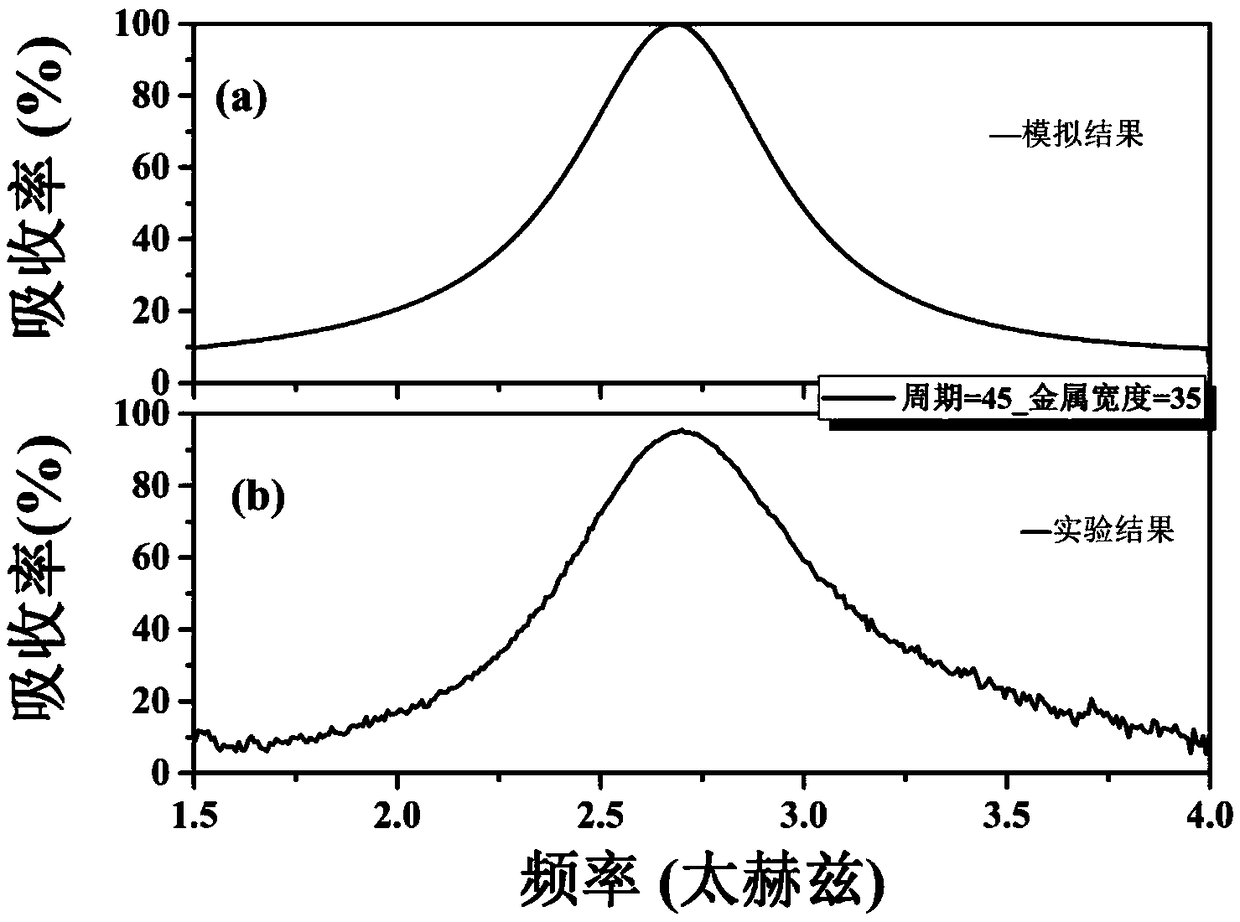
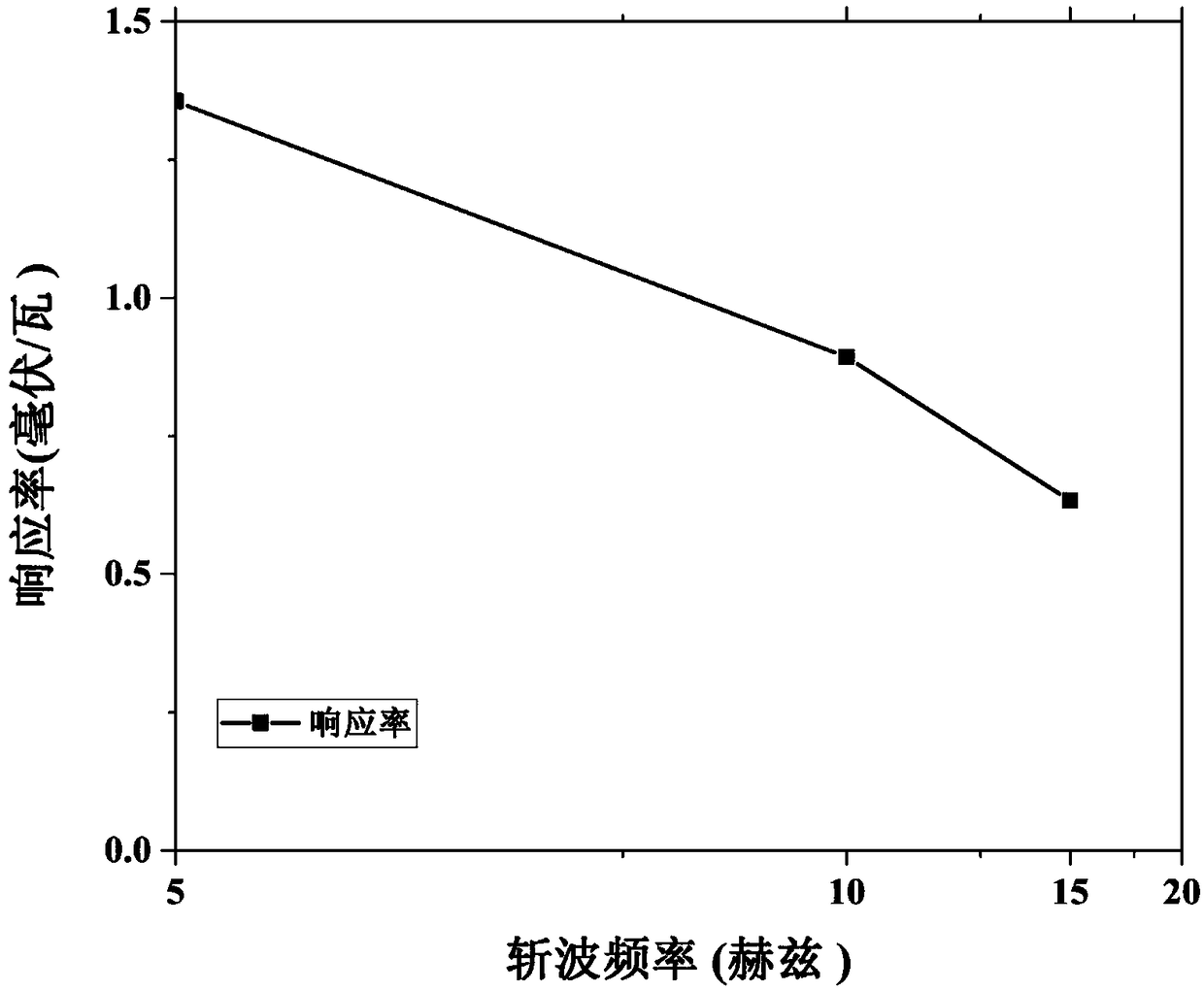
Non-refrigeration terahertz detector with adjustable working frequency
InactiveCN108831988ASimple structureGood insulation performanceThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changeLength waveRefrigeration
The invention discloses a non-refrigeration terahertz detector with an adjustable working frequency. The terahertz detector is composed of a metal-medium-metal structure and a substrate, and comprisesa metal microstructure, a medium cavity layer, a metal thin film layer, a matching layer and a flexible substrate layer from the top to bottom. The thickness of the medium cavity layer and the size and shape of the metal microstructure can adjust the detection frequency of the terahertz detector. The terahertz detector does not need an extra absorption material, and does not need refrigeration and has the prominent advantages of heat insulation performance, polarization selection and the like; and the terahertz detector has a series of advantages of simple structure, easy realization of large-area preparation, wavelength adjustability, flexible and bendable properties and the like, and has a high application prospect in terahertz signal detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microfluid frequency reconfigurable quasi-yagi antenna based on dielectric resonator
ActiveCN111786116AAdjustable working frequencyNon-resonant long antennasRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateEngineering
The invention relates to a microfluid frequency reconfigurable quasi-yagi antenna based on a dielectric resonator. The antenna comprises a dielectric substrate, a reflector, a driving unit, a differential feed network, and insulating tubes which are symmetrically arranged based on the center line of the antenna and vertically penetrate through the driving unit and the dielectric substrate, the working frequency of the antenna is adjusted by injecting liquid into the insulating tubes, the liquid injection states of the symmetrical insulating tubes are consistent, and the liquid injection statesinclude a full liquid injection state and a non-liquid injection state. The invention provides a frequency reconfigurable quasi-yagi antenna adopting a dielectric resonator working in a high-order TE3[delta]1 mode for the first time. According to the electric field distribution of a TE3[delta]1 mode, a place with a relatively strong electric field is selected as a position of four air holes penetrating through the dielectric resonator to load the insulating tubes so as to obtain a relatively large frequency tuning range. The working frequency of the antenna can be effectively adjusted by injecting purified water into the symmetrical insulating tubes in sequence.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate) thin plate bending vibration-based elastic SV-wave filter and filtering method
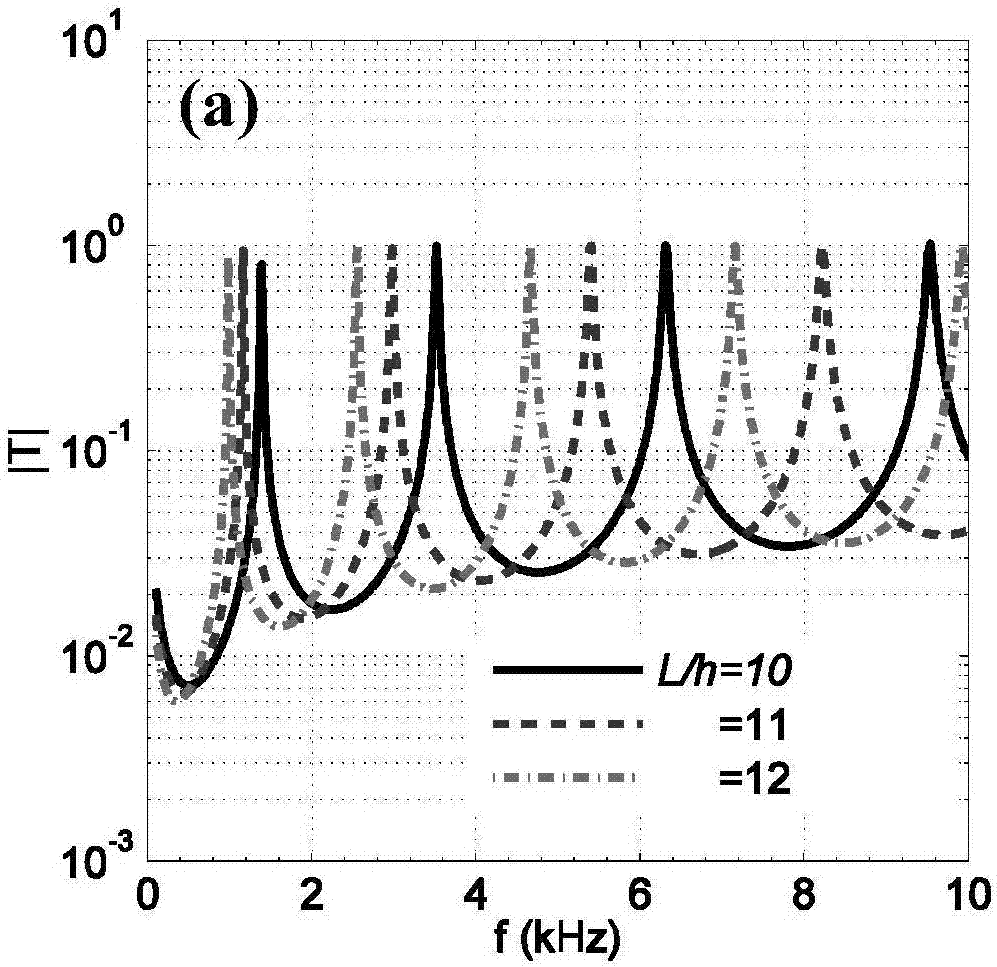
ActiveCN107229926ASimple configurationReduce manufacturing costFlexible AC transmissionCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringOperating frequency
The present invention discloses a PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate) thin plate bending vibration-based elastic SV-wave filter and a filtering method. The PMMA thin plate bending vibration-based elastic SV-wave filter comprises at least two base bodies which are arranged at intervals and polymethyl methacrylate thin plates which are connected between two adjacent base bodies; a plurality of polymethyl methacrylate thin plates are arranged equidistantly along the thickness direction of the polymethyl methacrylate thin plates; each of the polymethyl methacrylate thin plates is perpendicular to the connection surfaces of the base bodies; and the thickness of each of the polymethyl methacrylate thin plates is h; the length of the polymethyl methacrylate thin plates is a distance L between the corresponding two adjacent base bodies; and L / h is greater than or equal to 5. The PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate) thin plate bending vibration-based elastic SV-wave filter of the invention has the advantages of simple configuration, low manufacturing cost and adjustable operation frequency. The filtering method of the invention can be applied to narrow-pass band elastic SV-waves.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
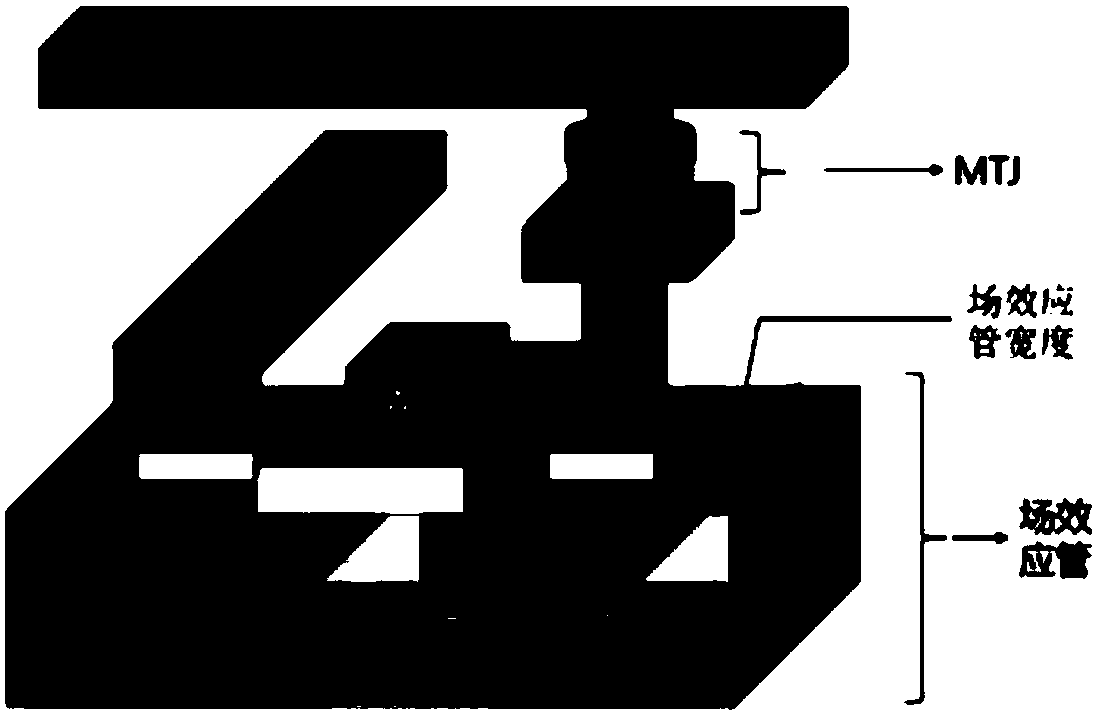
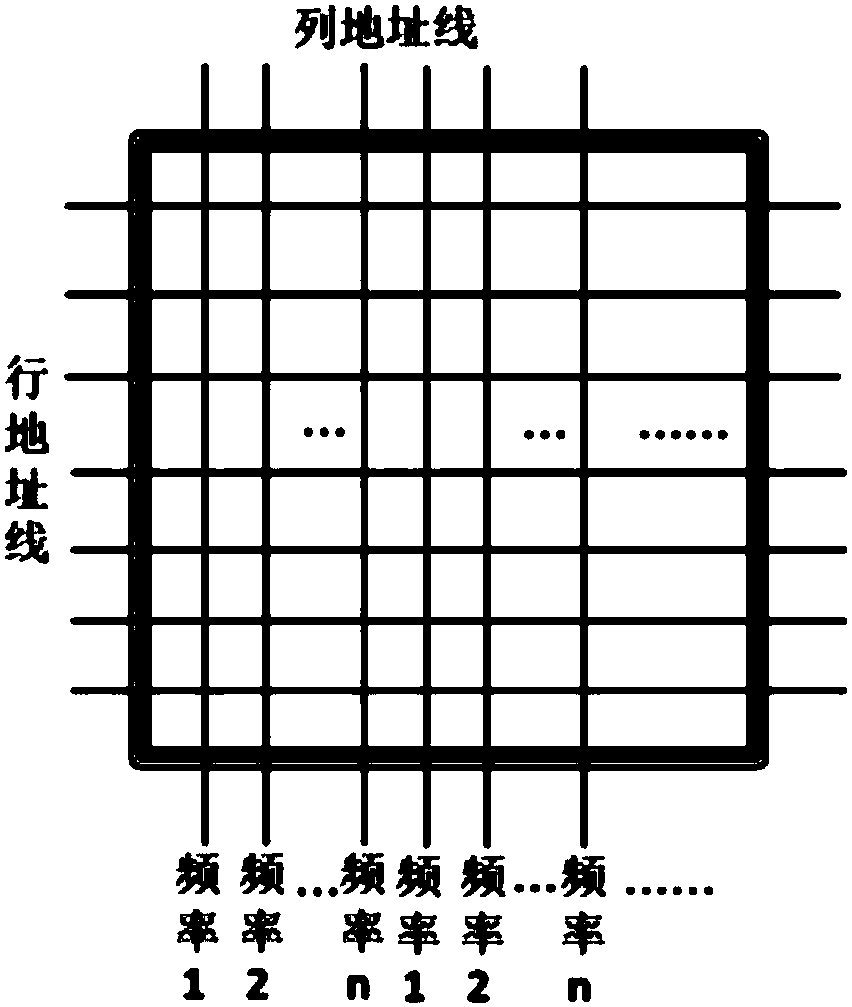
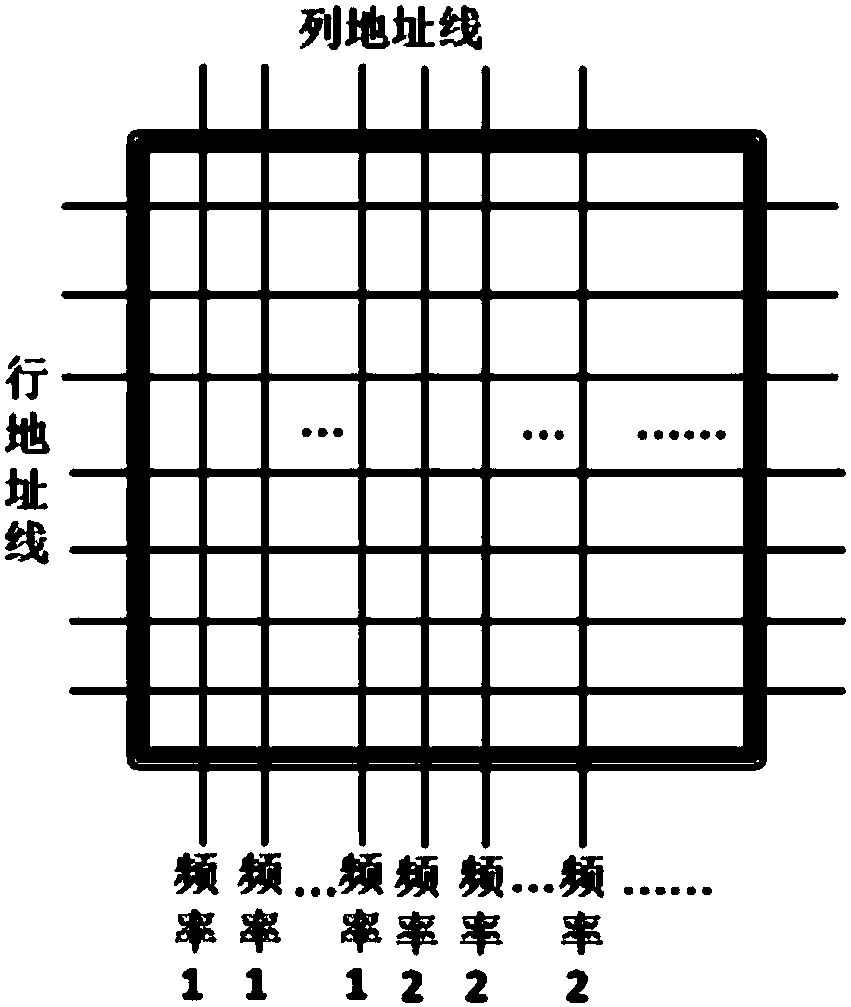
Magnetic random access memory
InactiveCN107767906AMeet the needs of different operating frequenciesExtended service lifeDigital storageStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
The invention discloses a magnetic random access memory. The magnetic random access memory comprises storage bits with at least two working frequencies; each storage bit comprises a magnetic tunnel junction, a metal wire and a field effect transistor; and the storage bits with the different working frequencies are same in magnetic tunnel junction diameter but different in field effect transistor width, or the storage bits with the different working frequencies are different in magnetic tunnel junction diameter but same in field effect transistor width. According to the magnetic random access memory, the storage bits with the different frequencies are located on a same chip, and the working frequency of the memory can be increased along with the increment of the calculation speed of a processor and the data throughput, so that the overall working performance of a system is improved; and the working frequency of the memory can be reduced according to an actual demand when the processor is relatively idle, so that the overall voltage, heating and working energy consumption of the system can be reduced and the service life and reliability of the memory are improved.
Owner:CETHIK GRP
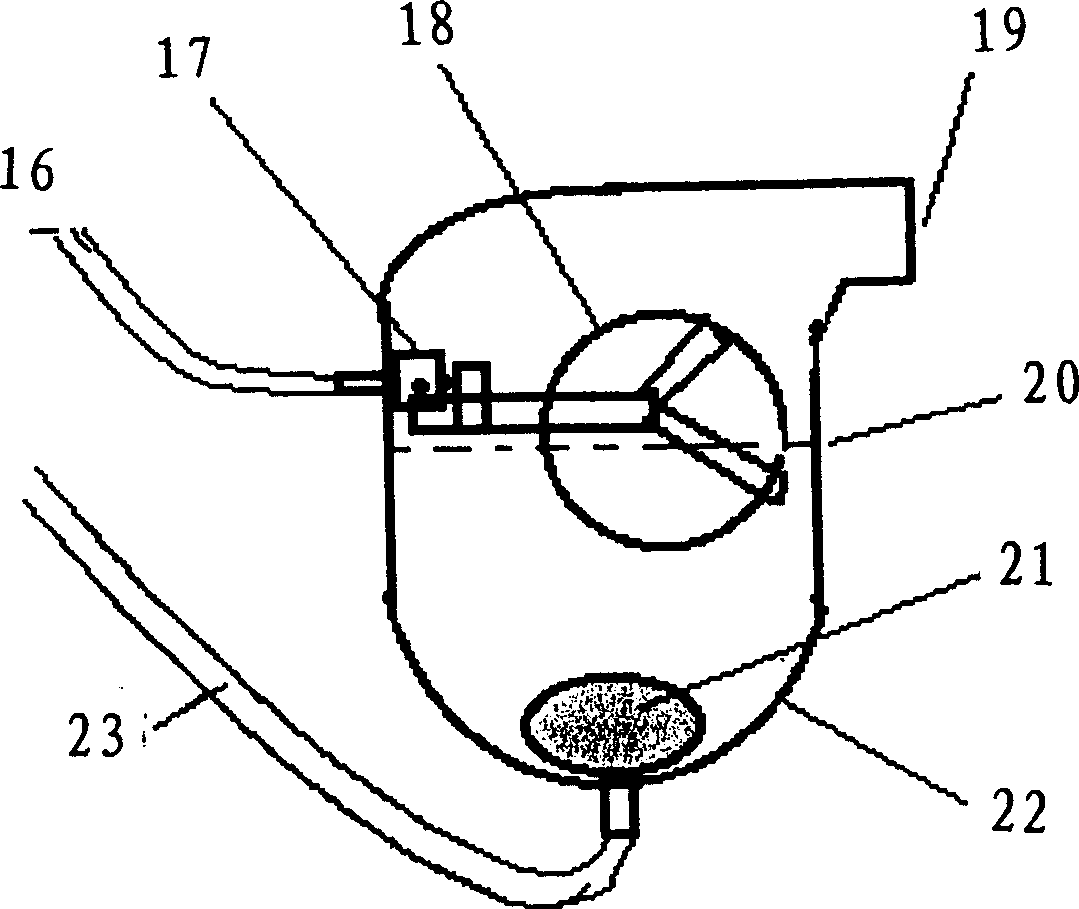
Water-saving ecological closet
InactiveCN1175782CGood water saving effectSolve the smoker's puzzleBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationWater savingEngineering
The present invention discloses a water-saving ecological closet. It includes foaming system, internal circulation system, deodorization system, fecal treatment system and eastern closet with check valve. The foaming cylinder and eastern closet with check valve are combined into one body so as to ensure that the closet can be covered stably and uniformly with foam, so that its water-saving and deodorization effect is obvious. In the anaerobic pool of fecal treatment system several flow-guiding conduct pipes are set, and between anaerobic pool and liquid fertilizer pool a liquid-discharge conduct pipe is set, under the action of flow-guiding conduct pipe and back-flushing stirring pipe the fecal sewage can form automatic flow-lift stirring in the anaerobic pool so as to ensure that the anaerobic treatment is full and effective.
Owner:陈云祖
Nonreciprocal power divider and electromagnetic wave transmission device
PendingCN111261989ALow costAdjustable working frequencyCoupling devicesRadio frequencyDielectric substrate
The invention provides a nonreciprocal power divider and an electromagnetic wave transmission device. The nonreciprocal power divider comprises a dielectric substrate and at least one Wilkinson powerdivider, wherein a port of the Wilkinson power divider is used as a radio frequency port of the nonreciprocal power divider; the Wilkinson power divider is arranged on the top surface of the dielectric substrate, each branch of the Wilkinson power divider comprises a filter, and each filter is composed of at least two resonators; the back surface of the dielectric substrate is provided with a plurality of variable capacitance diodes, a plurality of signal feed-in circuits, a plurality of metallized through holes and a plurality of modulation ports; the modulation ports are used for receiving modulation signals, each modulation port is connected to one metallized through hole through the signal feed-in circuit, one end of each variable capacitance diode is connected to one end of a resonator through the metallized through hole, and the other end of each variable capacitance diode is grounded. The non-reciprocal power divider is realized without bias of any magnetic material, and has theadvantages of integration with a circuit and the like.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF INFORMATION & COMM
High-efficiency mine tailing metal concentrating machine
InactiveCN103406276ASimple mechanical structureEasy to install and maintainGradingMining engineeringMachine
The invention relates to a mine tailing concentrating recovery device, in particular to a high-efficiency mine tailing metal concentrating machine. The high-efficiency mine tailing metal concentrating machine comprises a machine shell, a machine frame, a distribution hopper and a concentrating device, wherein the machine frame is fixed at the bottom of the machine shell, the machine shell is cylindrical, an annular waste sand groove is formed in the machine shell and provided with a water adding pipe and a water draining pipe, the distribution hoper is communicated with an ore inlet pipe, the bottom of the distribution hopper is connected with the concentrating device, and the concentrating device is of a vibration type or a rotary type. According to the high-efficiency mine tailing metal concentrating machine, different concentrating rates can be achieved by regulating the working frequency of the concentrating device according to requirements. Besides, the high-efficiency mine tailing metal concentrating machine is simple in structure, not prone to being damaged, and beneficial to improving mine tailing concentrating efficiency and quality.
Owner:彭建家
Method for inhibiting electromagnetic interference and electromagnetic interference filter
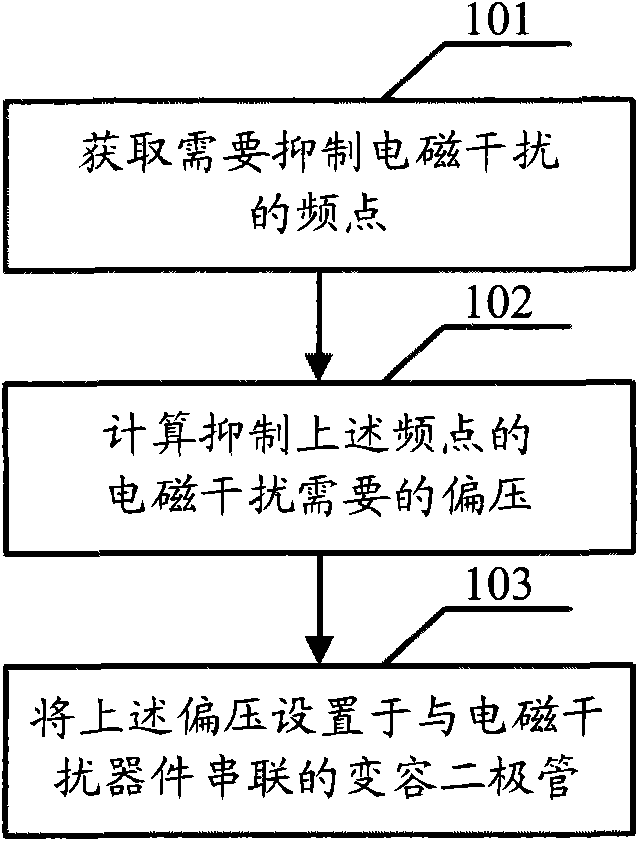
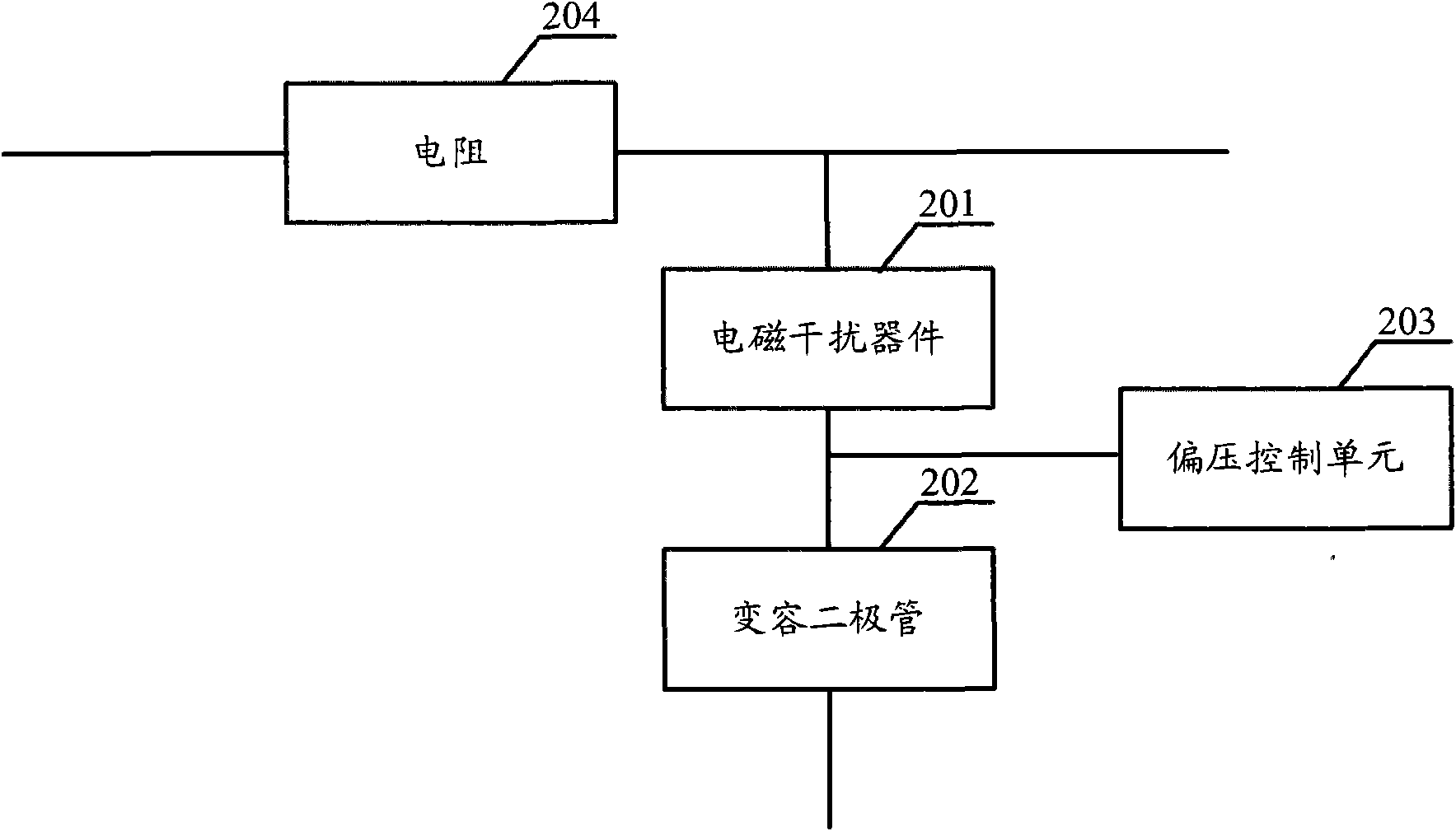
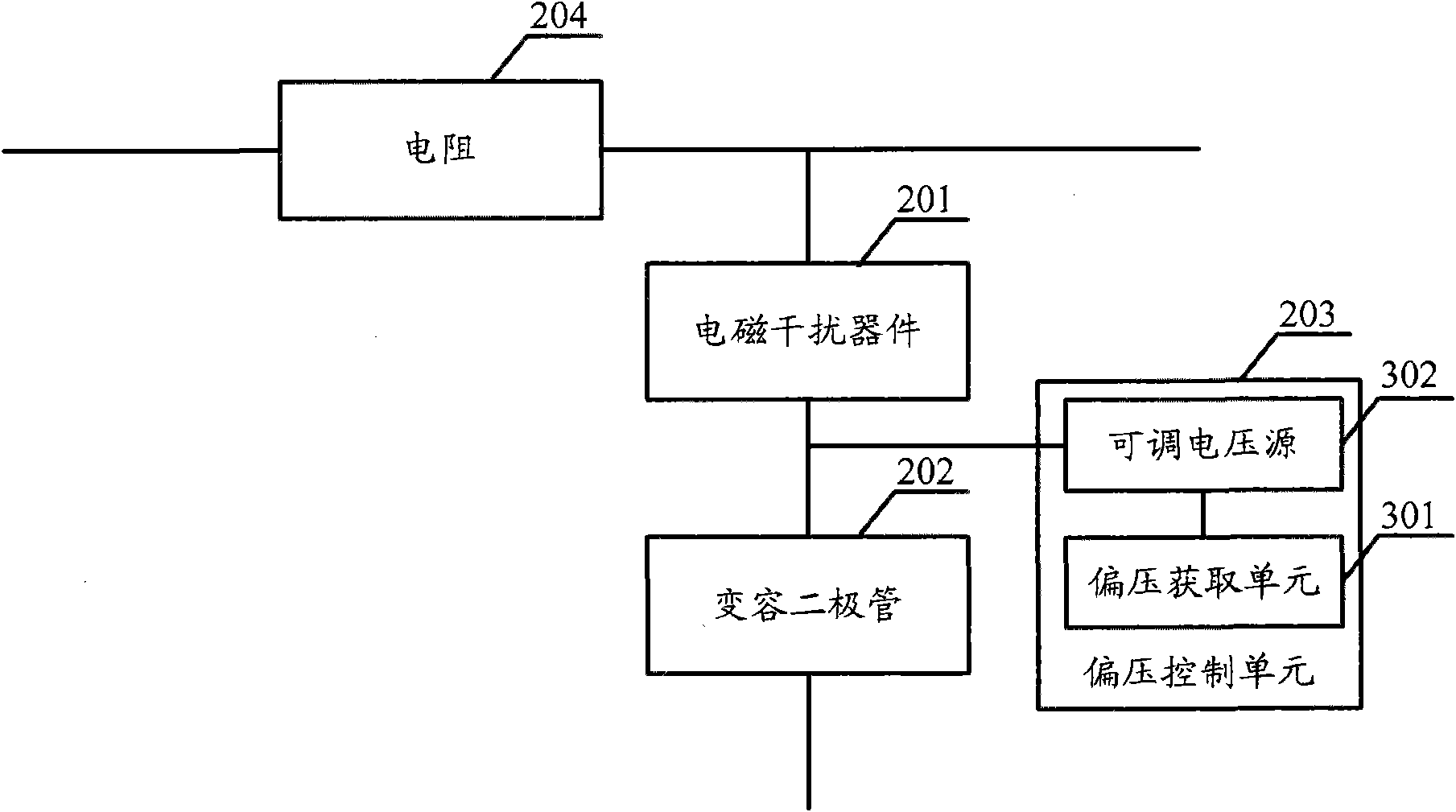
ActiveCN101667817AAdjustable working frequencyReal-time adjustment of working frequencyMultiple-port networksFrequency selective two-port networksVaricapMultiple frequency
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for inhibiting EMI and an EMI filter. The realization of the method comprises the following steps: obtaining the frequency points needing to inhibit the EMI, calculating the biasing voltage required by the EMI of the frequency points, arranging the biasing voltage at a variable capacitance diode connected in series with the EMI device (one end ofthe variable capacitance diode is connected with the EMI device and the other end thereof is grounded.), and utilizing the EMI device and the variable capacitance diode to inhibit the EMI of the frequency points. By increasing the variable capacitance diodes connected in series with the EMI device and changing the biasing voltage of the variable capacitance diodes, the EMI filter can work at different working frequencies so that the working frequency of the EMI filter is adjustable and the purpose of inhibiting the EMI at multiple frequency points can be realized. With realizing the purpose of inhibiting the EMI of multiple frequency points, the circuit is simplified and the cost is saved.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
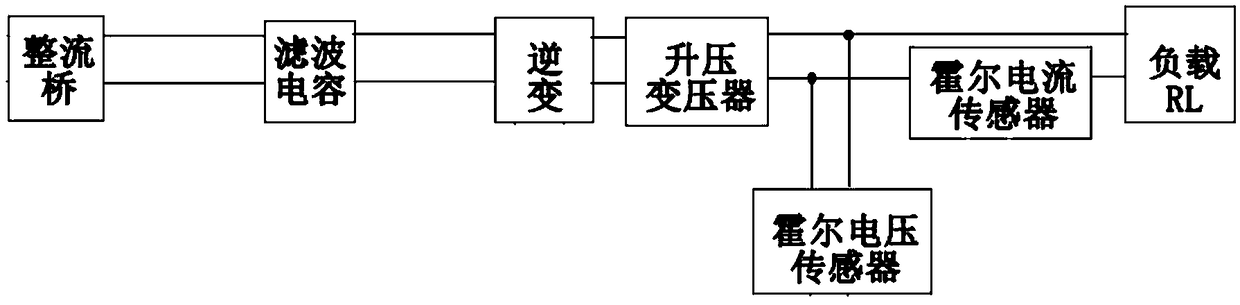
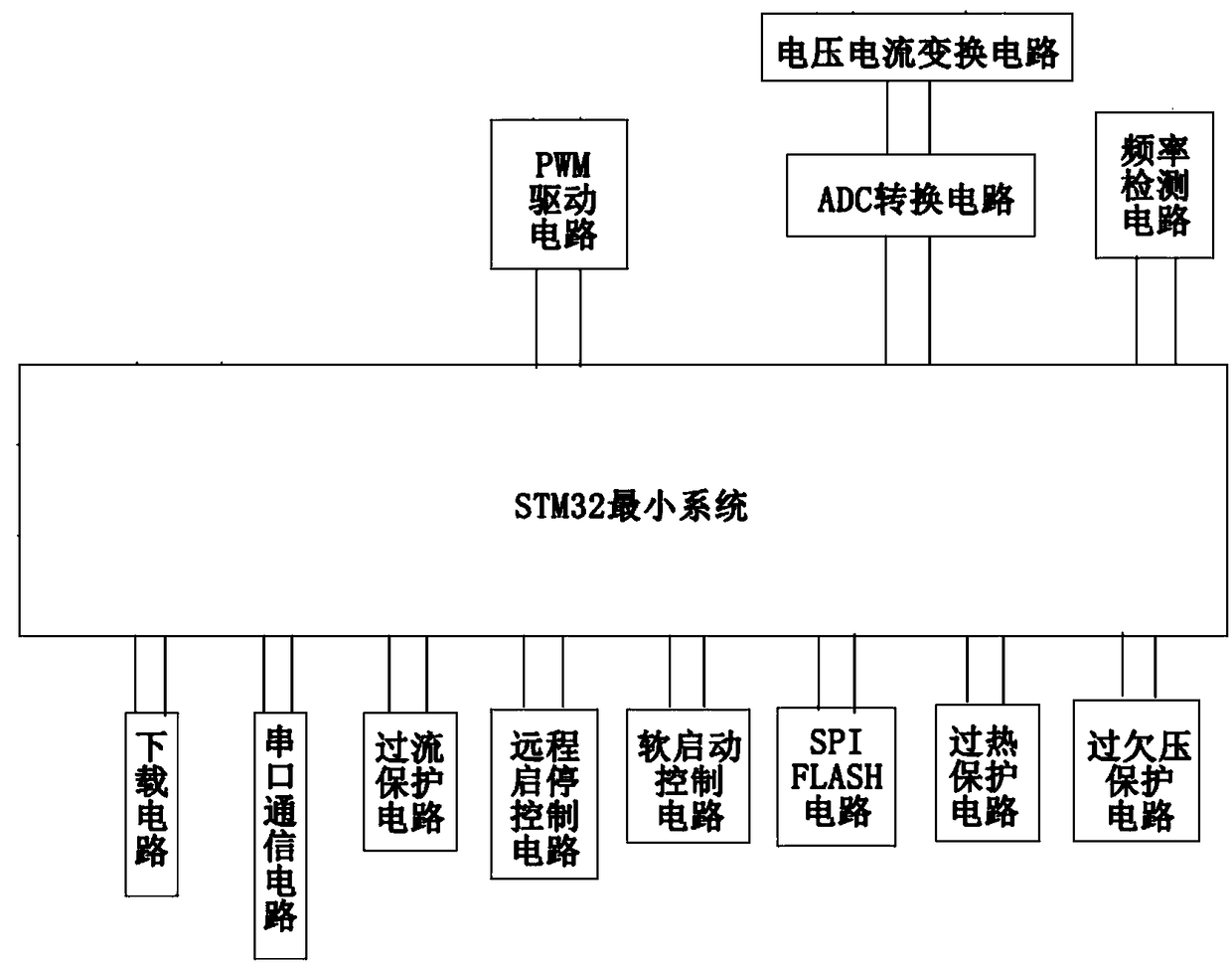
A high-voltage plasma discharge power supply device based on STM32 adjustable voltage
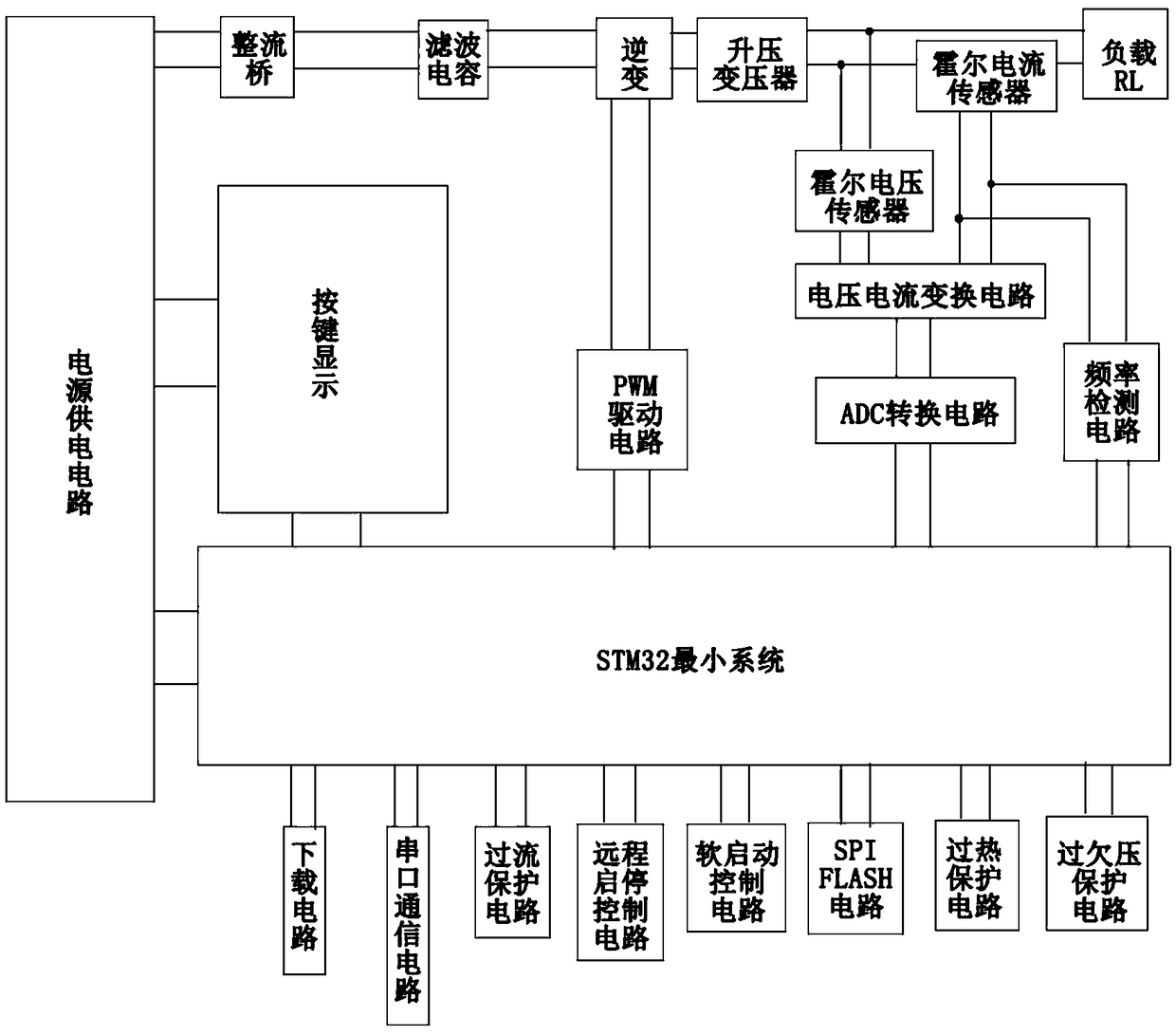
PendingCN109217686AIncrease productivityImprove reliabilityAc-dc conversion without reversalEmergency protective circuit arrangementsVoltage sensorEngineering
The invention discloses a high-voltage plasma discharge power supply device based on STM32 adjustable voltage, include the main circuit, Button and display circuit, A control circuit and a power supply circuit, the main circuit includes a rectifier bridge, Filter capacitor, inverter circuit, Hall voltage sensor, Hall current sensor and boost transformer, A control circuit includes a STM 32 minimumsystem, download circuit, serial communication circuit, An overcurrent protection circuit, a remote start-stop control circuit, a soft start control circuit, a SPI FLASH circuit, an overheat protection circuit, an undervoltage protection circuit, a PWM driving circuit, an ADC conversion circuit, a voltage-current conversion circuit and a frequency detection circuit, and a key and display circuitcomprise a key, an indicator light and an LCD display screen; The invention can improve the production efficiency, the processing quality and the production safety, meanwhile, the circuit of the invention adds a plurality of protective circuits to increase the reliability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A Hybrid Branch Line Coupler Realizing Frequency and Power Ratio Reconfiguration Simultaneously
The invention discloses a hybrid branch line coupler capable of realizing frequency and power division ratio reconstruction at the same time. Based on the branch line structure, the frequency and power division ratio can be reconfigured, which not only realizes the function of the power divider but also realizes the working frequency Adjustable, very suitable for the application of modern wireless communication systems; compared with the existing technology, by loading a varactor diode on the branch line coupler, any power ratio and any center frequency output can be realized, and the overall structure is simple, It can realize miniaturization and is easy to integrate; in addition, because it uses a planar microstrip structure, it is easy to manufacture and low in cost; because the output frequency is adjustable, it can realize communication in a wider broadband range. Therefore, the present invention is reasonable in design and simple in structure, can meet the requirements for output power variation of output signals, and can work in multiple communication frequency bands, which is beneficial to improving the overall performance of the communication system.
Owner:FOSHAN SHUNDE SUN YAT SEN UNIV RES INST +2
A vertical channel tunable high-throughput acoustofluidic sorting chip and its preparation method
ActiveCN111389473BEasy to separateIncrease fluid fluxLaboratory glasswaresFluid controllersResonant cavityGlass chip
The invention discloses a vertical channel tunable high-flux acoustofluidic sorting chip and a preparation method thereof. The device is composed of a glass sheet with a standing wave resonant cavity, a piezoelectric ceramic sheet and a PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) film. The standing wave resonant cavity is composed of a glass bottom plate, a glass spacer I, a glass spacer I, a glass spacer II, a PDMS film and a glass top plate, which are laminated and packaged sequentially from bottom to top. The resonant cavity consists of two chambers. There is a sample inlet and a sample outlet. The height of the resonant cavity is on the order of micrometers and the width is on the order of centimeters, so as to realize the fluid flow of large flux. The piezoelectric ceramic sheet is glued to the bottom of the resonant cavity and two wires are drawn out at the two poles. Driven by an external electrical signal, the piezoelectric ceramic generates a standing wave field in the vertical direction of the channel, and separates different particles from the vertical direction. The preparation process of the present invention is simple, the height of the channel is adjustable, the cost is low, the controllability is strong, and it is convenient and suitable for the aggregation, separation and manipulation of large flux of biological samples such as cells.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com