Magnetic random access memory
A random access memory, magnetic technology, applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., can solve the problems of data stability and reliability, improve overall performance, increase heat generation and work energy consumption, and reduce voltage. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
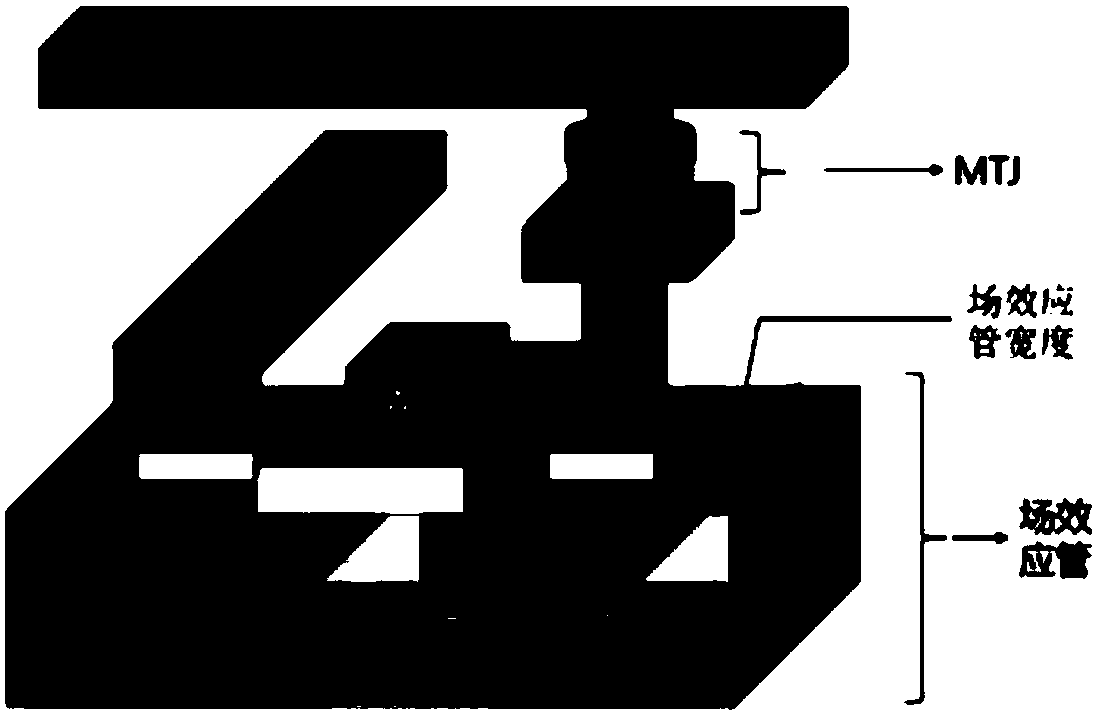
[0028] Embodiment 1: The magnetic storage bit contains one MTJ module and one field effect transistor.
[0029] The information of this embodiment is stored in the MTJ module, and the information of "1" and "0" is marked with the value of magnetoresistance; the resistance of the tunnel junction can be changed by the spin transfer torque effect of the current flowing through the MTJ tunnel junction. value, to realize the rewriting of stored information; the field effect transistor provides driving current for MTJ programming and is responsible for the selection and switching of information bits in reading and writing.
[0030] Because the critical write current value of the storage bit increases with the increase of the operating frequency, and the critical current increases with the increase of the field effect transistor width; on the other hand, the critical write current value increases with the shrinkage of the MTJ diameter abbreviation. Therefore, based on the above prin...
Embodiment 2
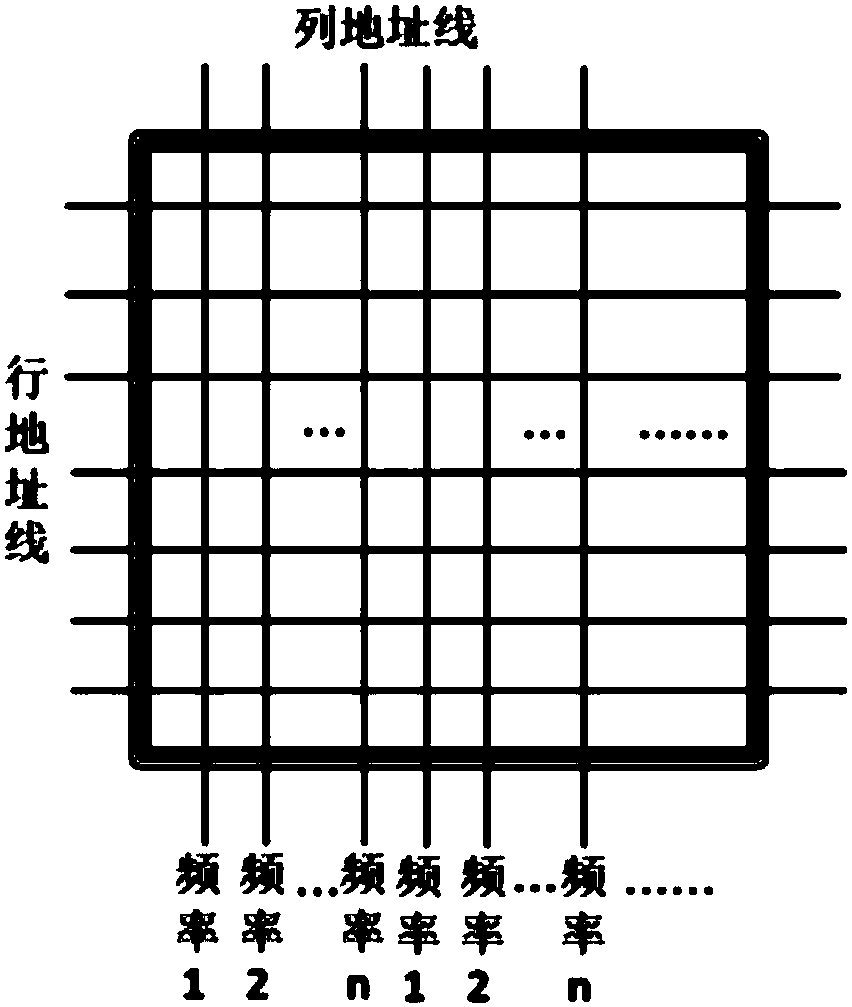
[0033] Embodiment 2: The magnetic storage bit contains one MTJ module and multiple field effect transistors.
[0034] The same information is stored in the MTJ module, and the information of "1" and "0" is marked with the value of the magnetoresistance value; the resistance value of the tunnel junction can be changed by the spin transfer torque effect of the current flowing through the MTJ tunnel junction, Realize the rewriting of stored information; the field effect transistor provides driving current for MTJ programming and is responsible for the selection and switching of information bits in reading and writing.
[0035] like image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, the magnetic storage bit includes one MTJ module and multiple field effect transistors. For example, a storage bit is implemented by n field effect transistors MOSFETs with different widths and one MTJ, and n field effect transistors share one MTJ. By changing the width of the MOSFET to change the value of the d...
Embodiment 3
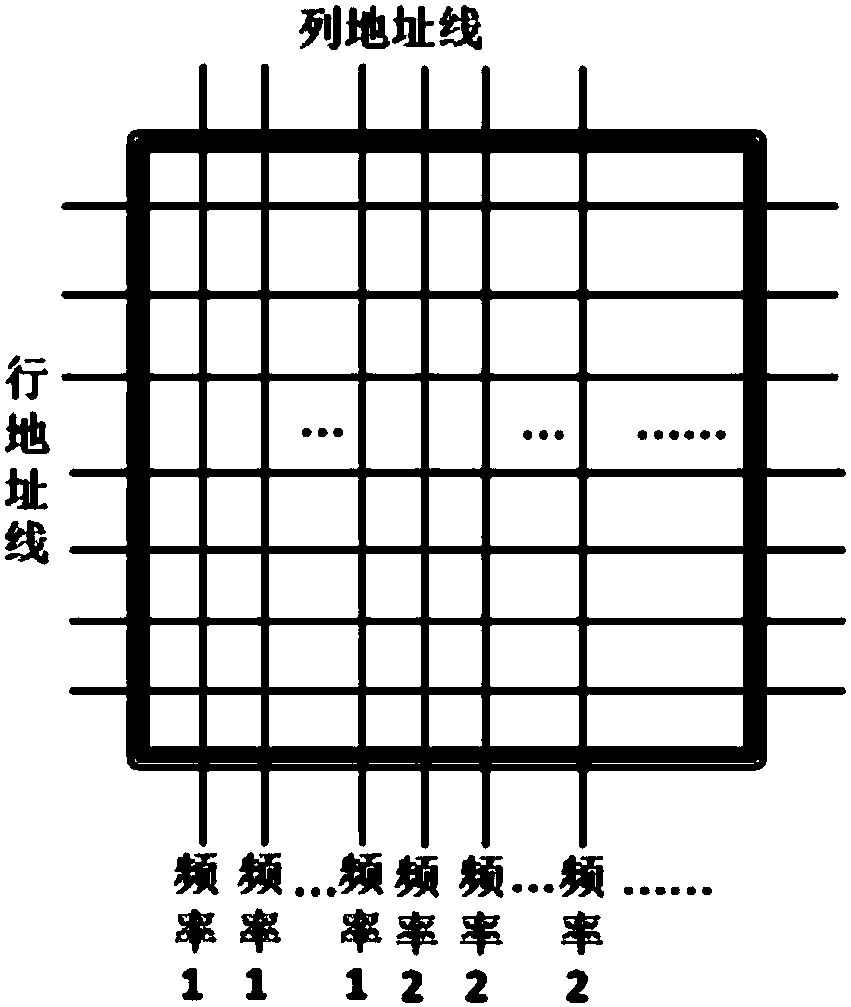
[0038] Embodiment 3: The magnetic storage bit contains multiple MTJ modules and one field effect transistor.
[0039] Similarly, the information is stored in the MTJ module, and the information of "1" and "0" is marked with the value of magnetoresistance; the resistance of the tunnel junction can be changed by the spin transfer torque effect of the current flowing through the MTJ tunnel junction. value, to realize the rewriting of stored information; the field effect transistor provides driving current for MTJ programming and is responsible for the selection and switching of information bits in reading and writing.
[0040] like Figure 4 As shown, in this embodiment, the magnetic storage bit includes n MTJs with different diameters and one field effect transistor, and the MTJs with different diameters share one field effect transistor MOSFET. By changing the diameter of the MTJ to change the critical driving current value, different operating frequencies of storage bits are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com