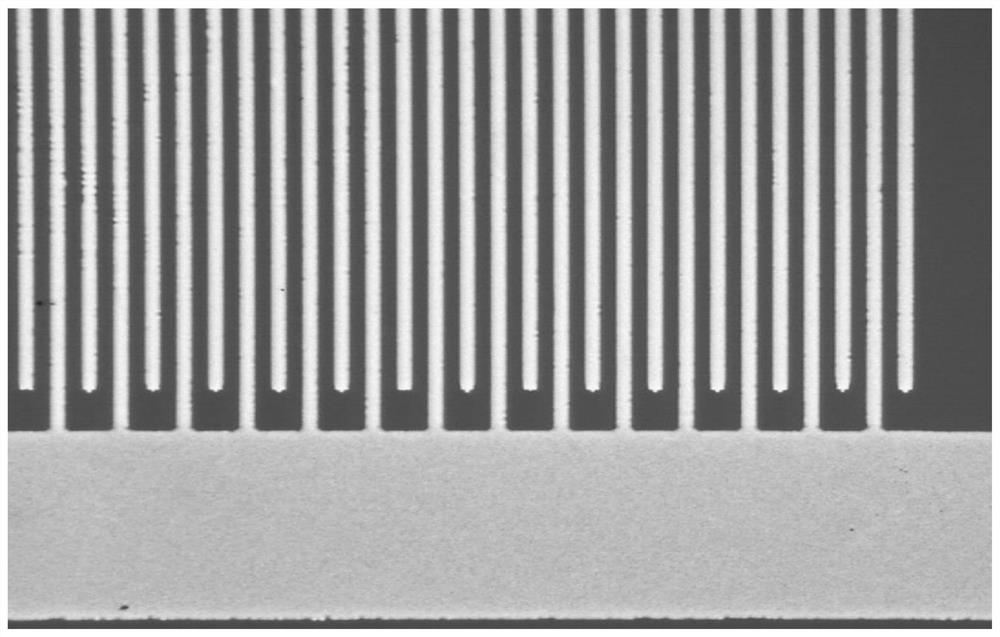
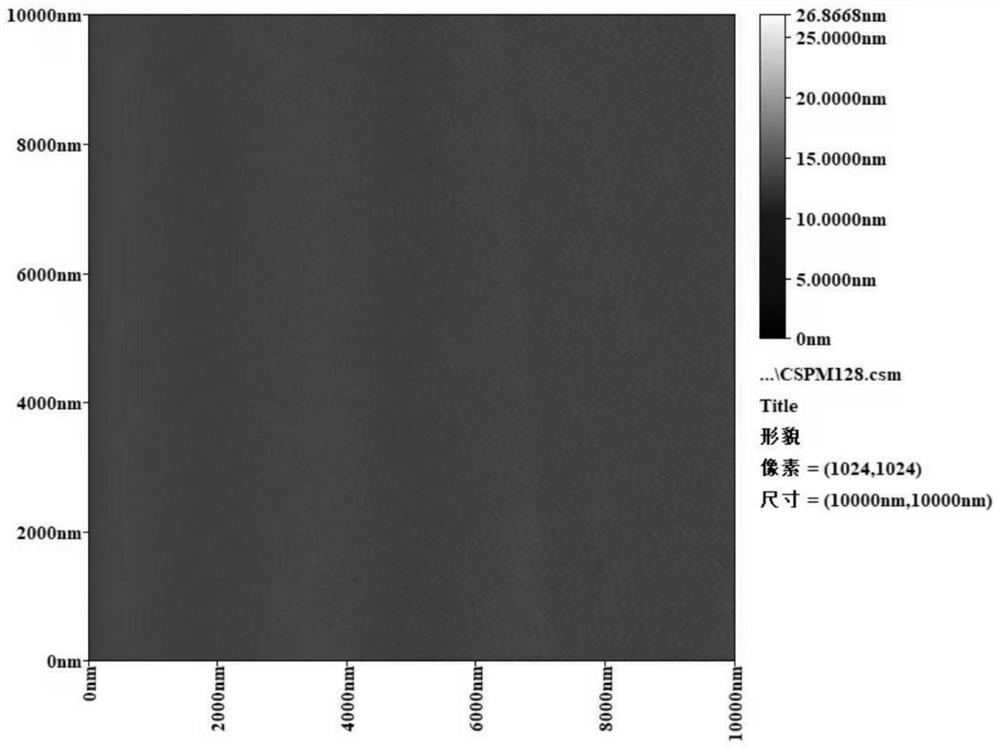
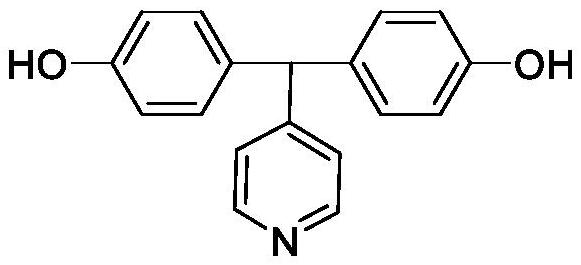
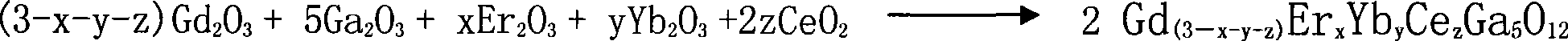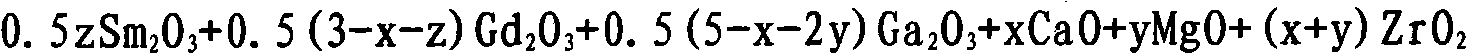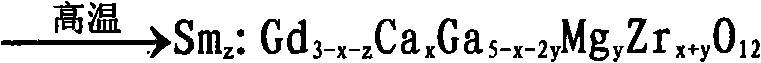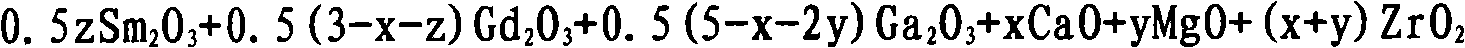Patents
Literature
64 results about "Gadolinium gallium garnet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
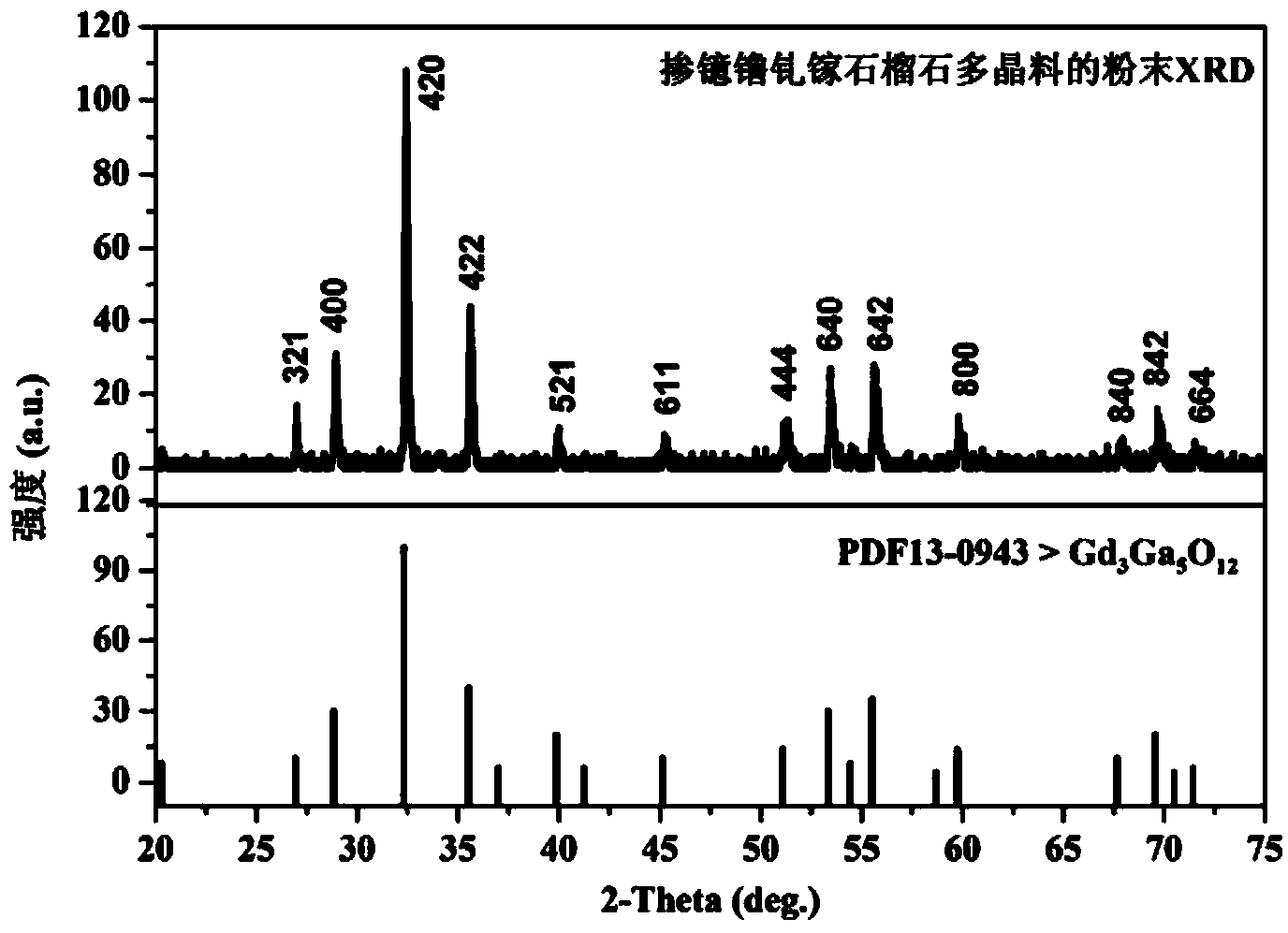
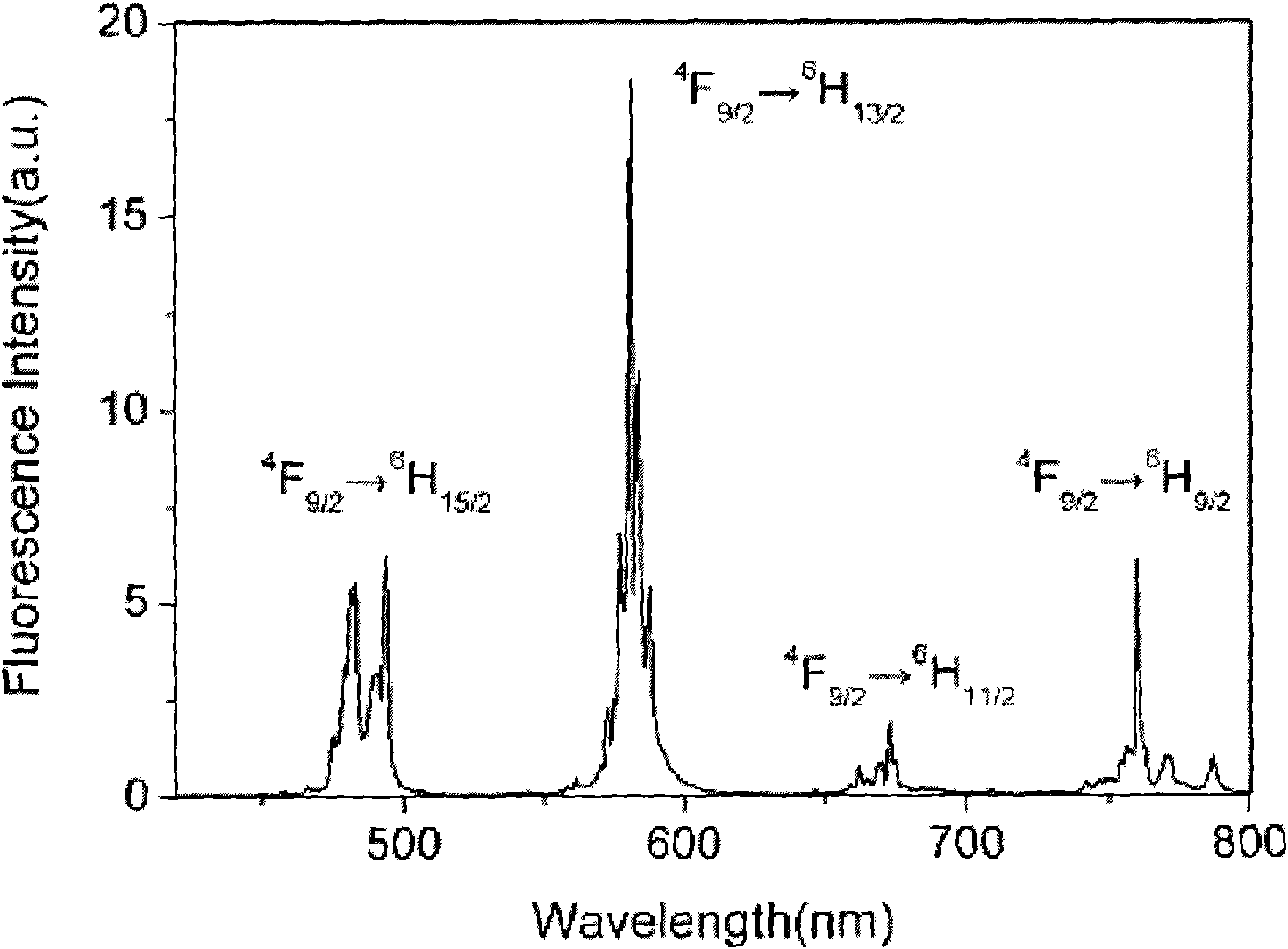
Gadolinium Gallium Garnet (GGG, Gd₃Ga₅O₁₂) is a synthetic crystalline material of the garnet group, with good mechanical, thermal, and optical properties. It is typically colorless. It has a cubic lattice, a density of 7.08 g/cm³ and its Mohs hardness is variously noted as 6.5 and 7.5. Its crystals are produced with the Czochralski method. During production, various dopants can be added for colour modification. The material is also used in fabrication of various optical components and as a substrate material for magneto–optical films (magnetic bubble memory). It also finds use in jewelry as a diamond simulant. GGG can also be used as a seed substrate for the growth of other garnets such as YIG.
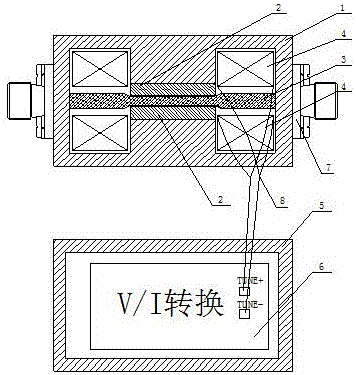
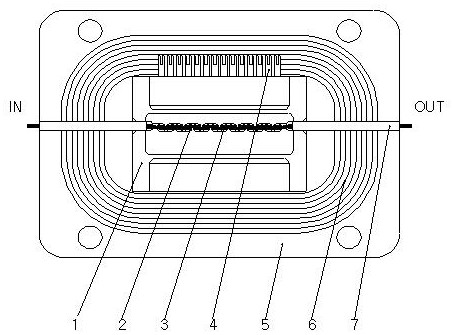
YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) band rejection filter based on planar resonant coupling structure and fabrication method of YIG band rejection filter
ActiveCN106252802ACompact designImproved tuning sensitivityWaveguide type devicesSputteringGadolinium gallium garnet
The invention discloses a YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) band rejection filter based on a planar resonant coupling structure and a fabrication method of the YIG band rejection filter. The filter comprises a YIG band rejection filter and a driver, wherein the YIG band rejection filter comprises a resonant cavity, a planar resonant coupling structure, a permanent-magnet biasing magnetic path and an excitation coil, the planar resonant coupling structure is arranged in the resonant cavity, and the permanent-magnet biasing magnetic path provides a stable magnetic field for the resonant cavity. With the adoption of a mode of arranging a YIG thin film on a front surface of GGG (Gadolinium gallium garnet) glass and photoetching a coplanar waveguide circuit on the YIG thin film by sputtering, the planar resonant coupling structure is formed, a traditional spherical three-dimensional coupling structured YIG band rejection resonant coupling structure is substituted, and the technical defect existing in the traditional structure is also overcome. In the processing technology, The YIG thin film is first photoetched to a required shape according to a product shape needed to fabricate, and then the GGG glass is cut along appearance; and the defect of edge breakage or damage of the YIG thin film easily caused by directly cutting the YIG thin film based on a GGG substrate is overcome.
Owner:SOUTHWEST INST OF APPLIED MAGNETICS
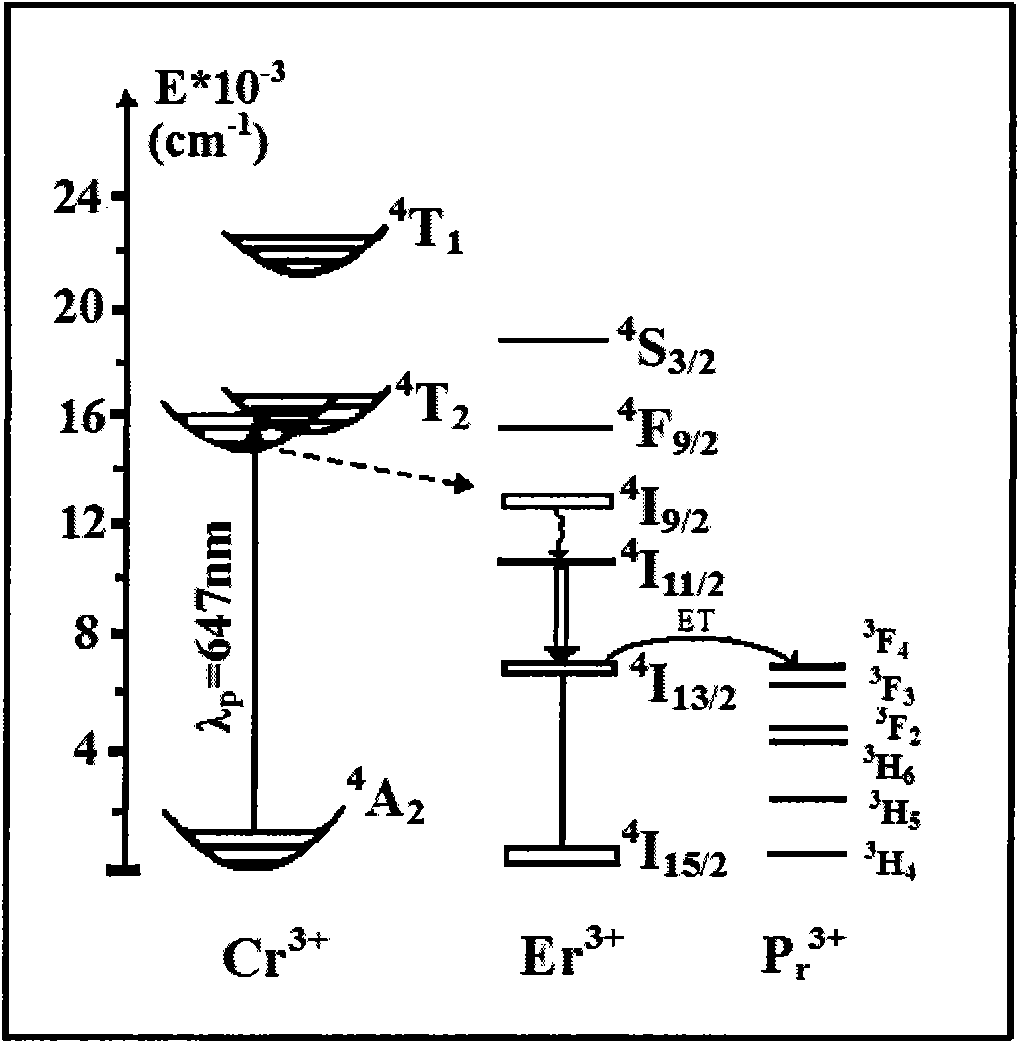
Chromium and praseodymium sensitized ions co-doped gadolinium gallium garnet novel laser crystal activated by erbium ions
InactiveCN101619492ATunable laser outputPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltGadolinium gallium garnetNitrogen atmosphere
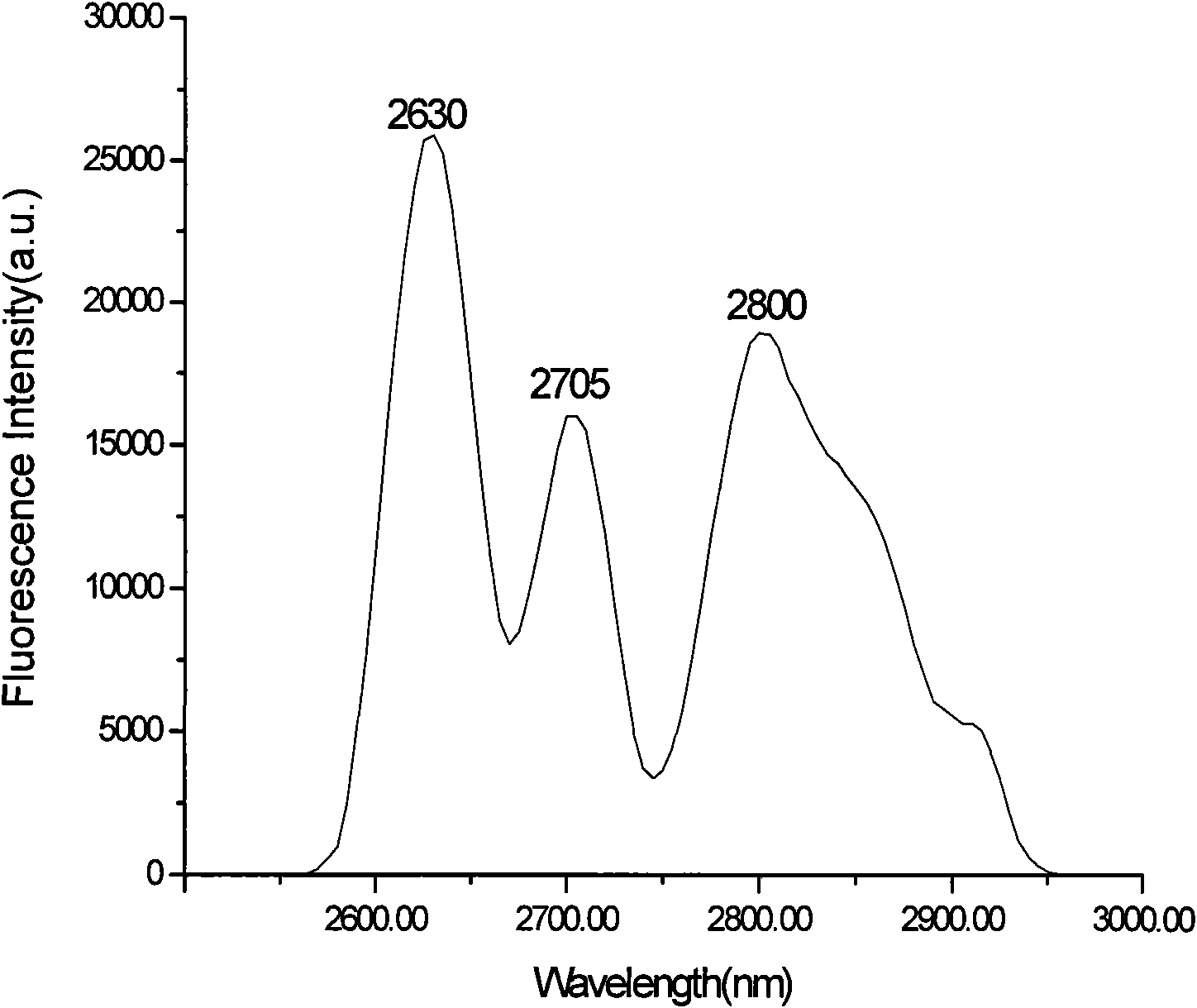
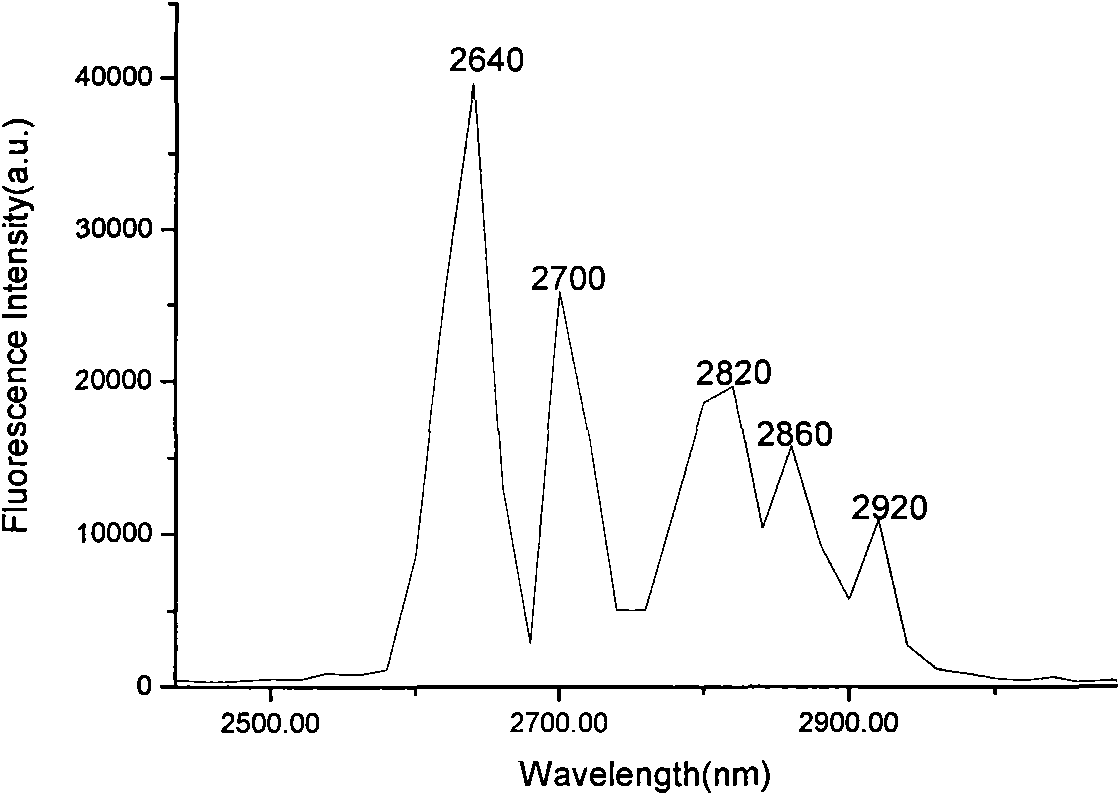
The invention relates to a chromium and praseodymium sensitized ions co-doped gadolinium gallium garnet novel laser crystal activated by erbium ions. The crystal material has a chemical formula of Cr:Er:Pr:Gd3Ga5O12. Gd2O3, Ga2O3, Er2O3, Cr2O3 and Pr2O3 of 4N are used as raw materials which are subjected to high-temperature solid-phase reaction to obtain Cr:Er:Pr:Gd3Ga5O12 raw material and used to grow the crystal by a crystal pulling method under the condition of nitrogen atmosphere. The material is used for achieving tunable laser output of 2,600 to 3,000nm waveband.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for controlling gallium content in gadolinium-gallium garnet scintillators
InactiveCN106978629APolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsRare-earth elementLutetium
Disclosed herein is a method including manufacturing a powder having a composition of formula (1), M1aM2bM3cM4dO12 (1) where O represents oxygen, M1, M2, M3, and M4 represents a first, second, third, and fourth metal that are different from each other, where the sum of a + b + c+ d is about 8, where 'a' has a value of about 2 to about 3.5, 'b' has a value of 0 to about 5, 'c' has a value of 0 to about 5, 'd' has a value of 0 to about 1, where 'b' and 'c', 'b' and 'd', or 'c' and 'd' cannot both be equal to zero simultaneously, where M1 is a rare earth element comprising gadolinium, yttrium, lutetium, scandium, or a combination of thereof, M2 is aluminum or boron, M3 is gallium, and M4 is a codopant; and heating the powder to a temperature of 500 to 1700 degrees centigrade in an oxygen containing atmosphere to manufacture a crystalline scintillator.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Frequency source with improved phase noise
ActiveUS20160164528A1Improve phase noiseSuppress phase noiseMultiple-port networksPulse automatic controlGadolinium gallium garnetPhase noise
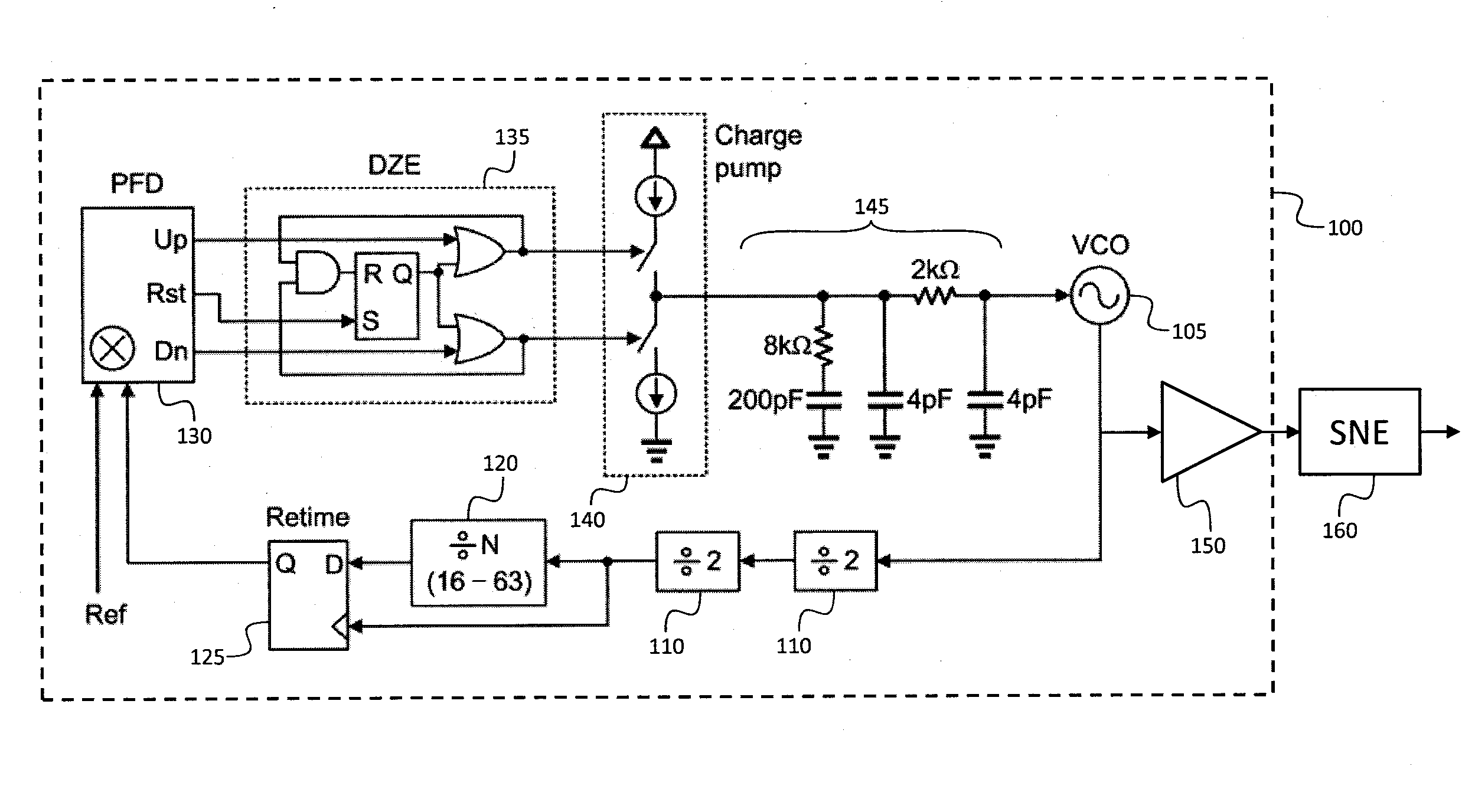
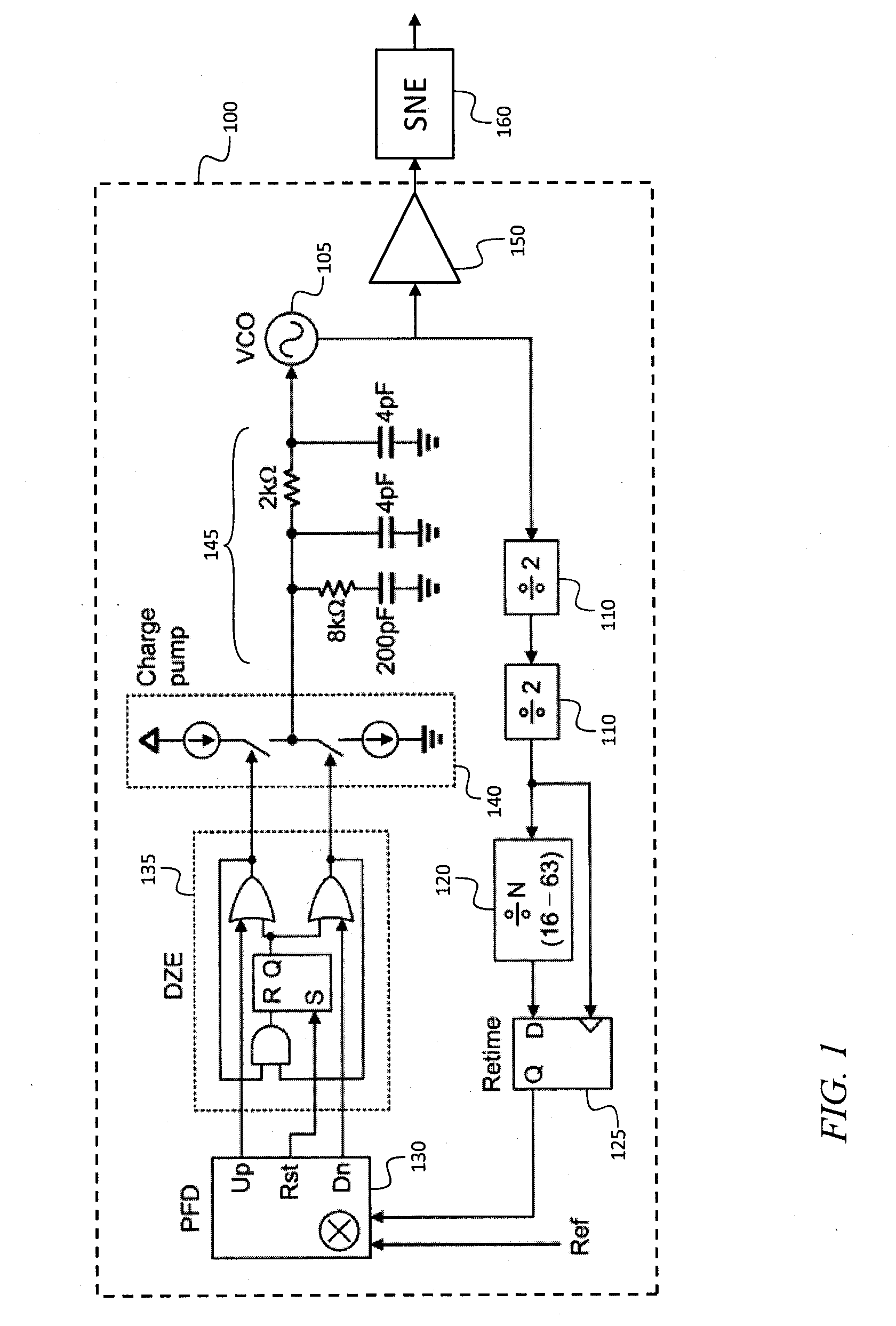
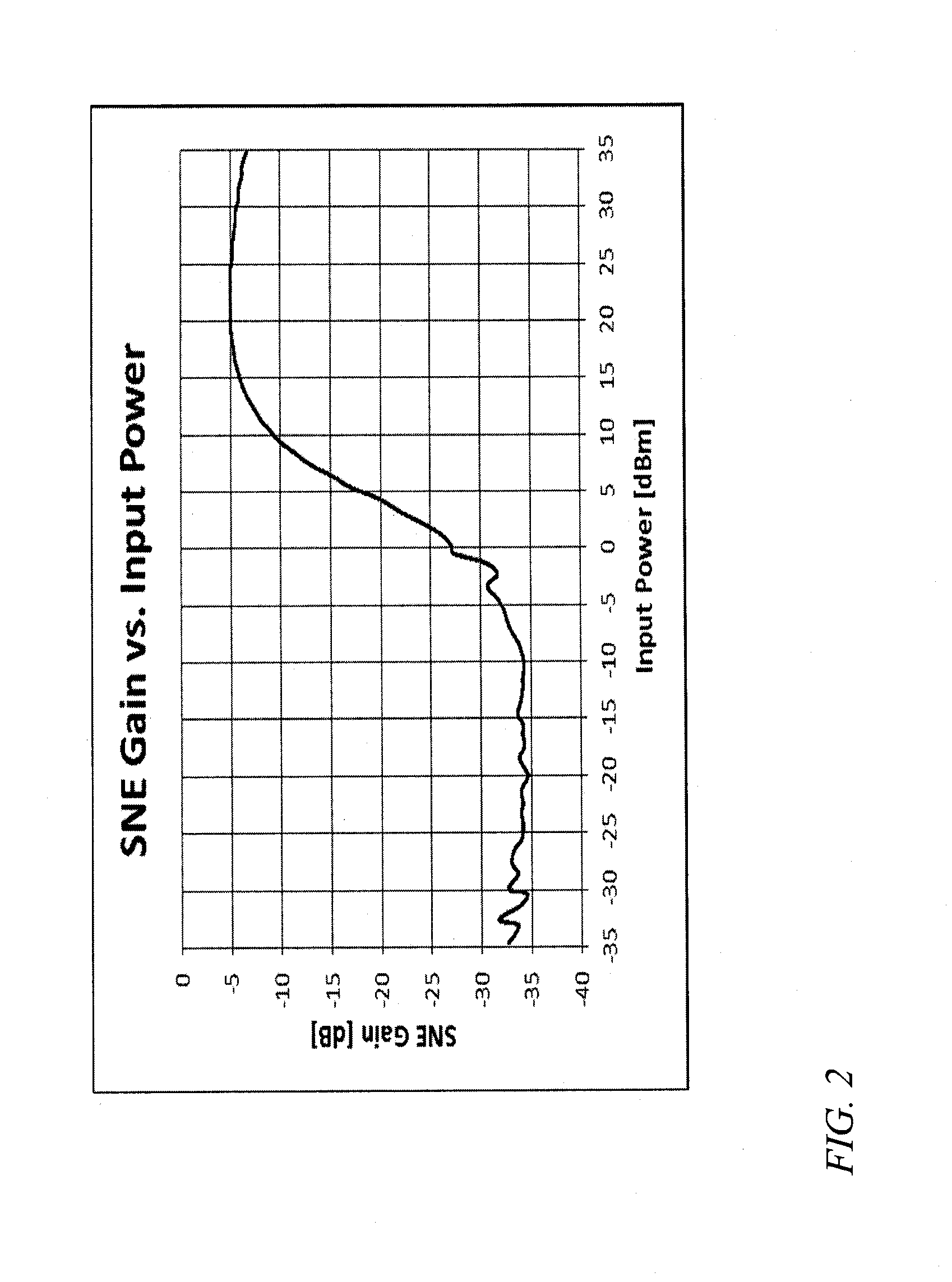
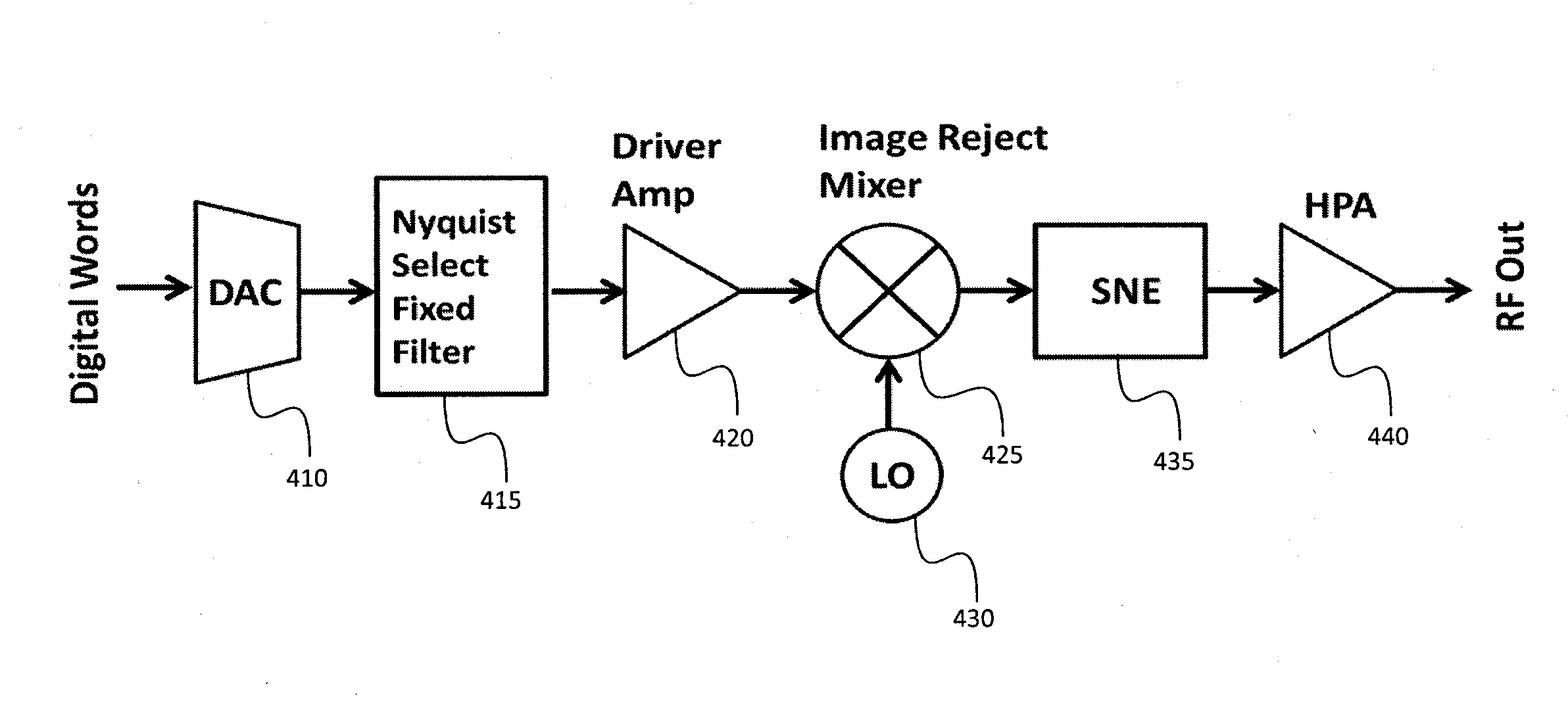
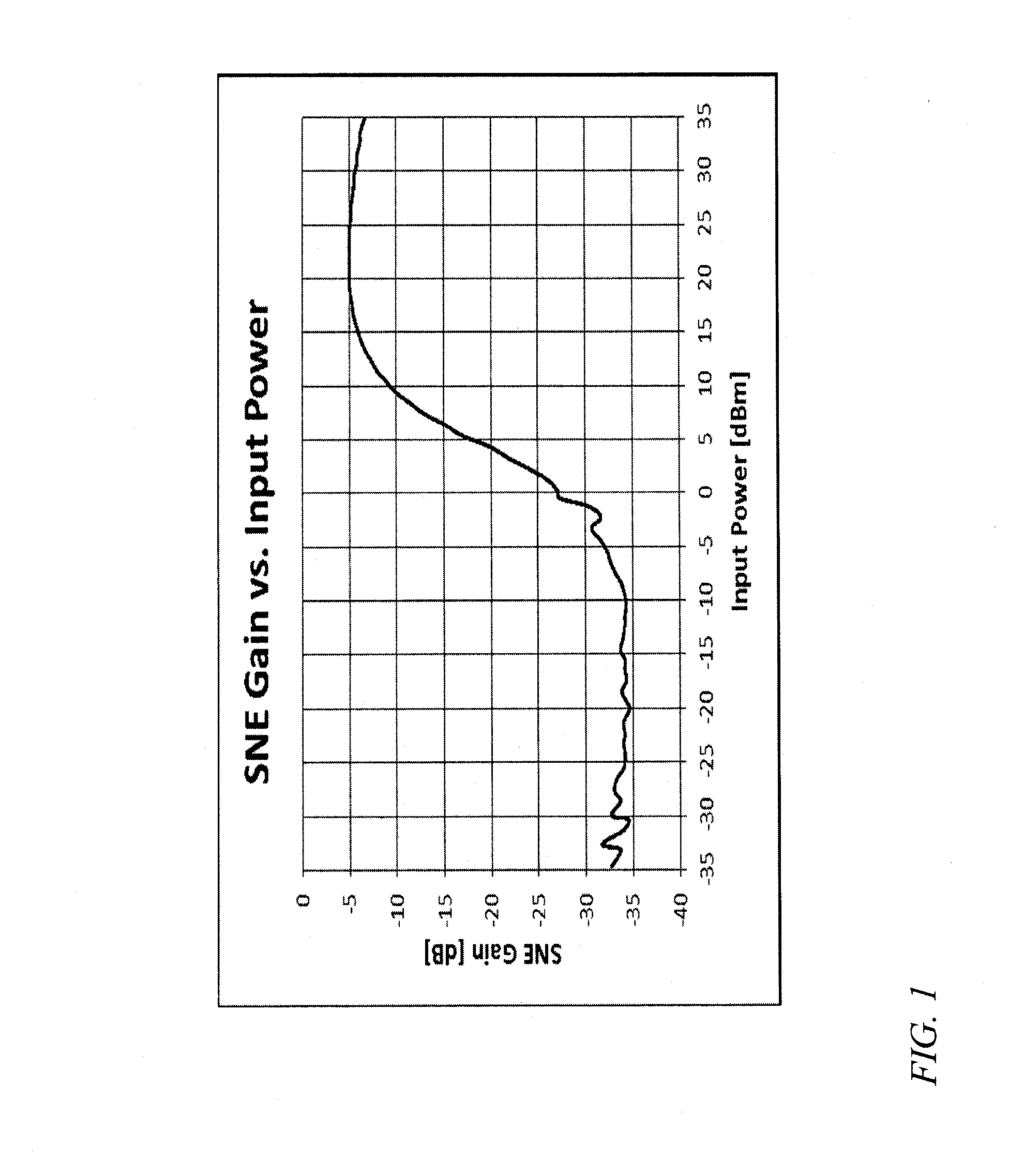
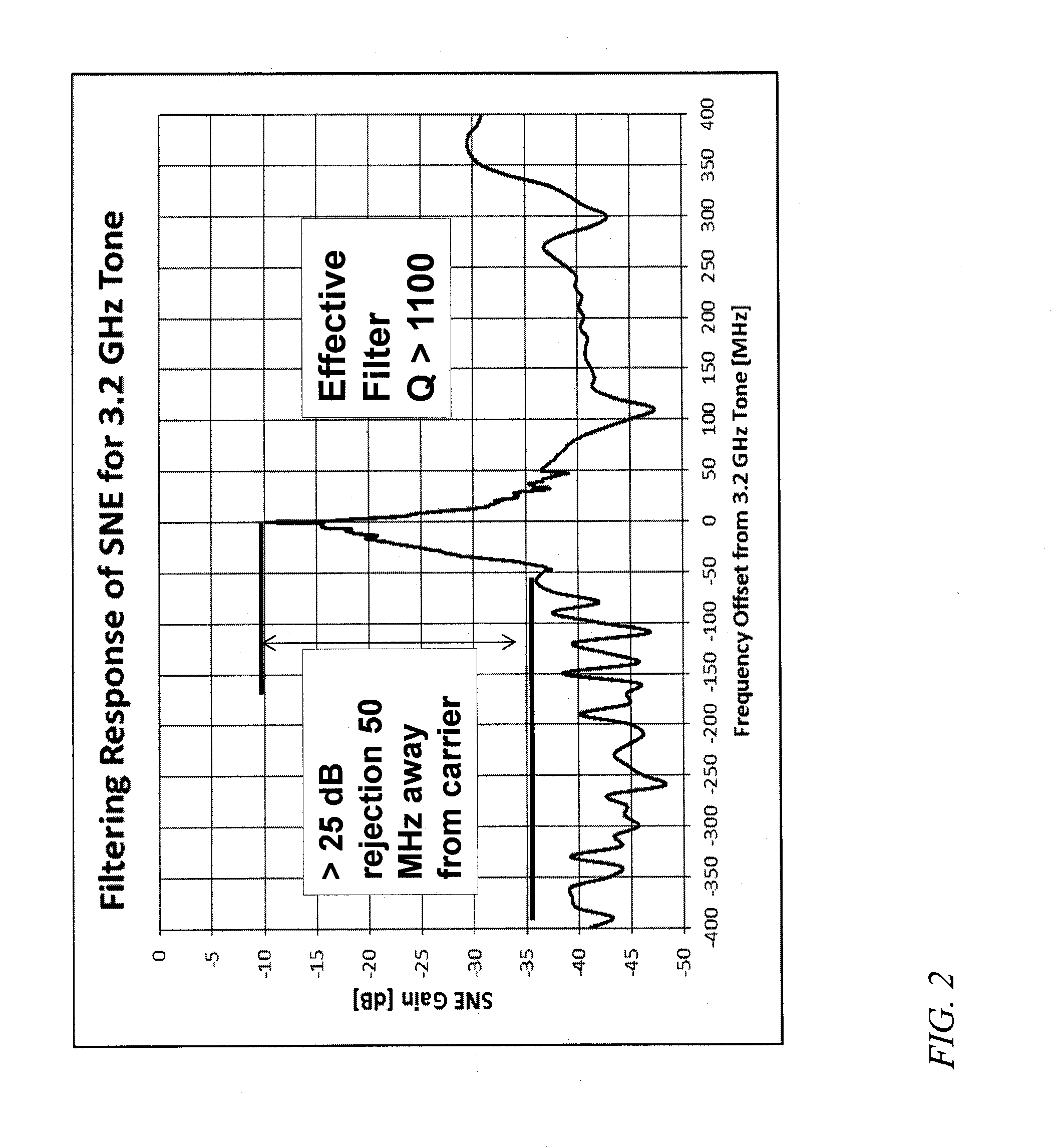
A frequency source with improved phase noise. In one embodiment a phase-locked loop is used as a component of a frequency source and a signal to noise enhancer (SNE) is used to suppress phase noise produced by the phase-locked loop. The signal to noise enhancer is a nonlinear passive device that attenuates low-power signals while transmitting high power signals with little loss. The signal to noise enhancer may be fabricated as a thin film of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) epitaxially grown on a gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG) substrate, the GGG substrate being secured to a microwave transmission line from the input to the output of the signal to noise enhancer, such that the thin film of yttrium iron garnet is close to the transmission line.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
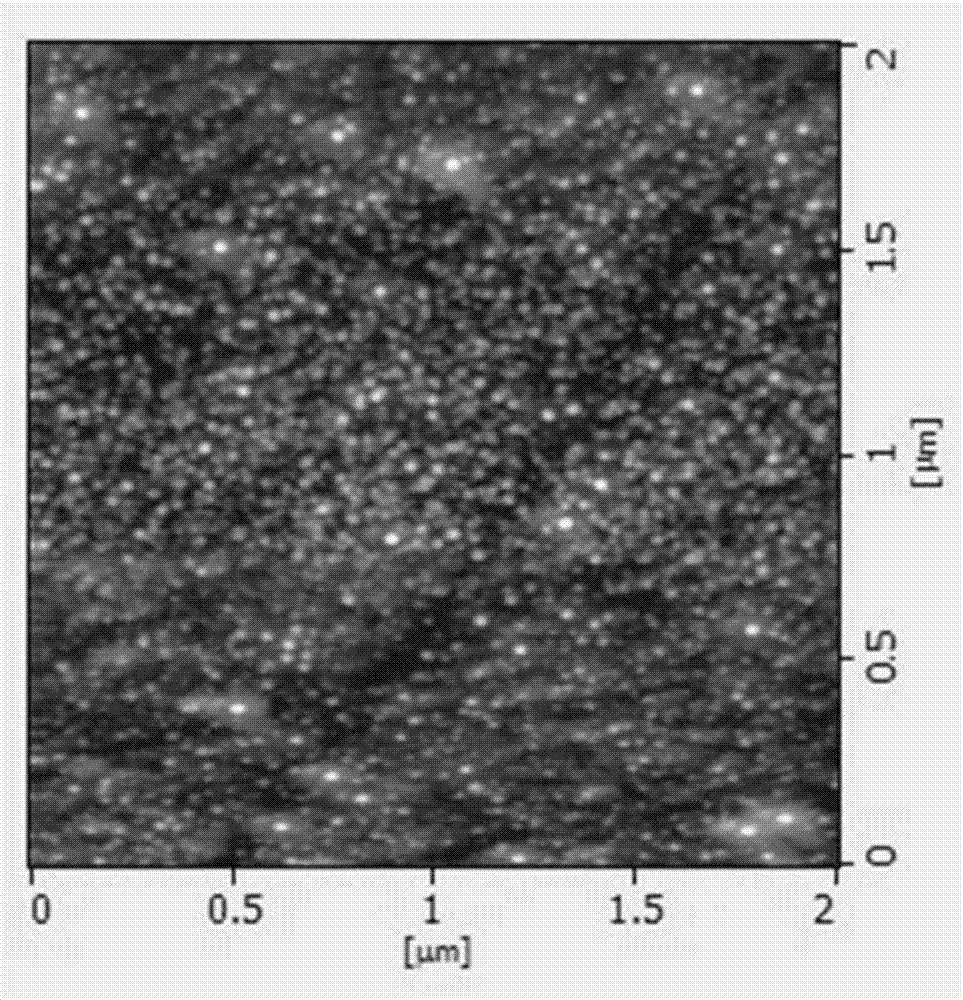
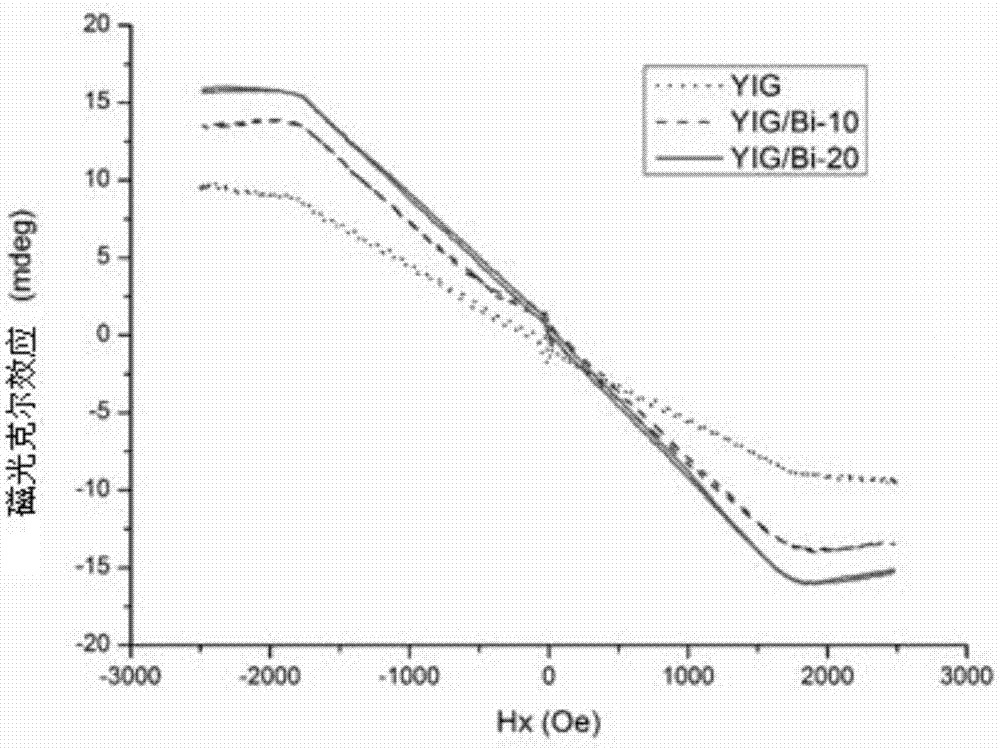
YIG/bismuth heterogenous thin film with giant magnetooptical effect and preparation method of YIG/bismuth heterogenous thin film
ActiveCN107146761AIncreased magneto-optical rotationIncreased magneto-optic Kerr angleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionGadolinium gallium garnet
The invention discloses a YIG / bismuth heterogenous thin film with a giant magnetooptical effect and a preparation method of the YIG / bismuth heterogenous thin film. The method comprises the steps of growing high-quality single-crystal YIG used as a substrate on gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG) in a crystal direction [111] by liquid phase epitaxy, and growing a thin layer of bismuth on the YIG substrate by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) to obtain the YIG / bismuth heterogenous thin film. The method is simple and practical, the magneto-optical kerr corner of the obtained YIG / bismuth heterogenous thin film is remarkably increased compared with YIG of a bismuth-free thin film; and compared with replacement doping of bismuth in YIG, the preparation process is simple, a new method is provided for preparation and research of a heterojunction magnetooptical material and has wide application in various fields of optical communication, magnetooptical storage and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
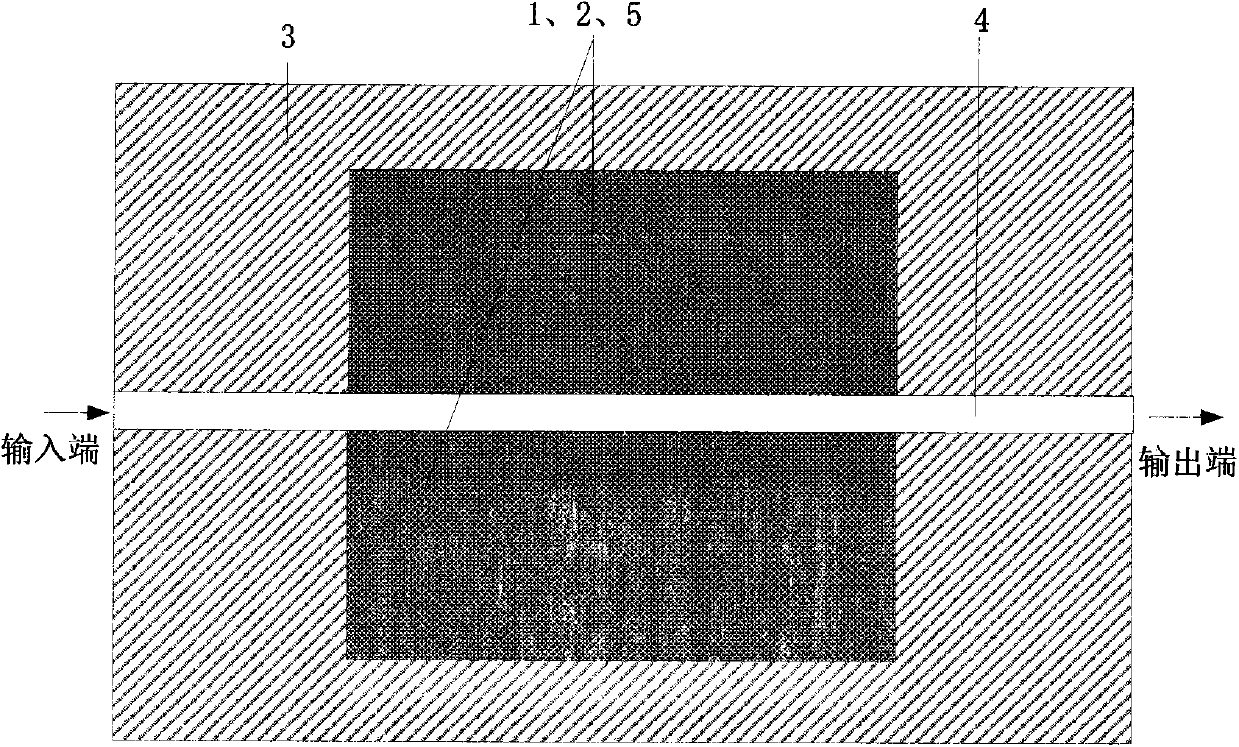
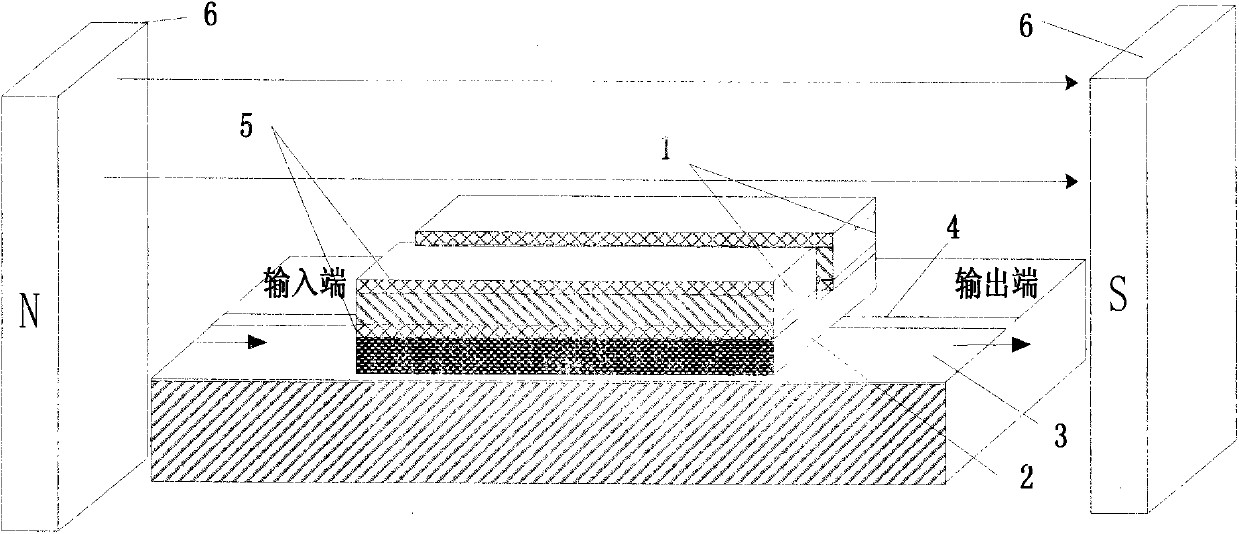
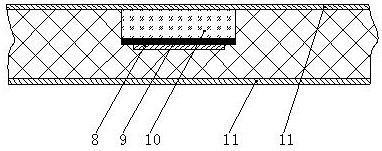
Micro-strip line filter sharing substrate with YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) thin film material, and regulation method thereof
InactiveCN103401047AReduce volumeSimple structureWaveguide type devicesAntennasElectricityGadolinium gallium garnet
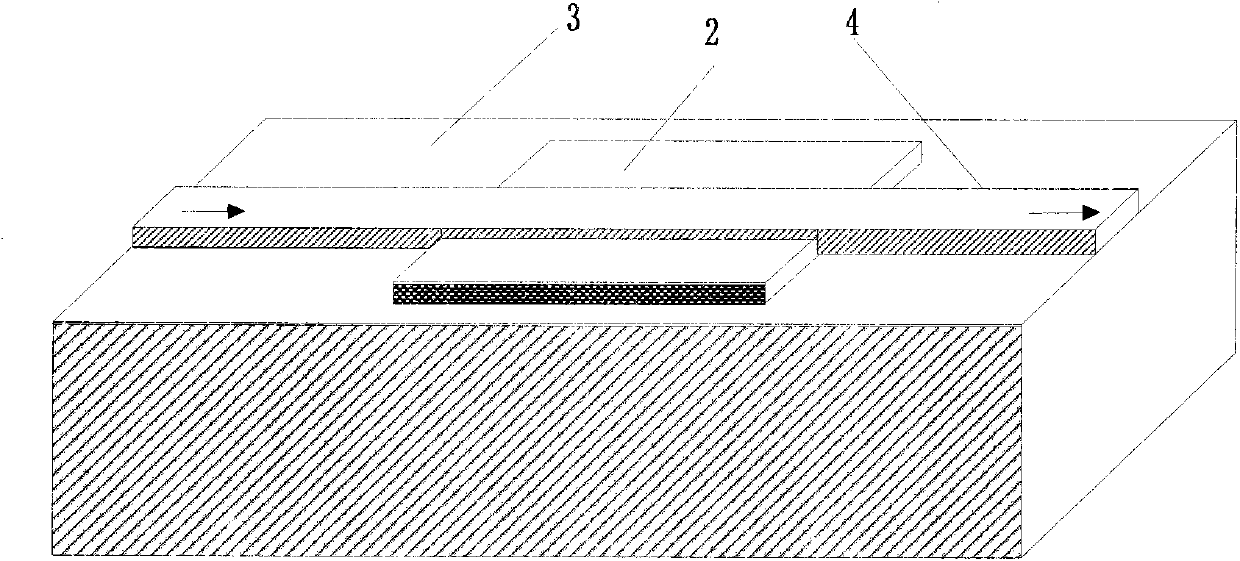
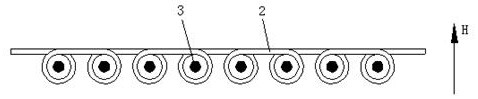
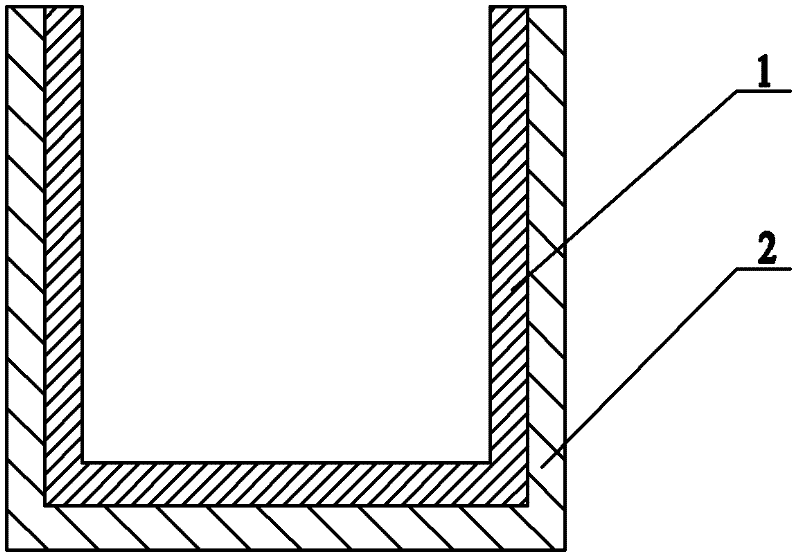
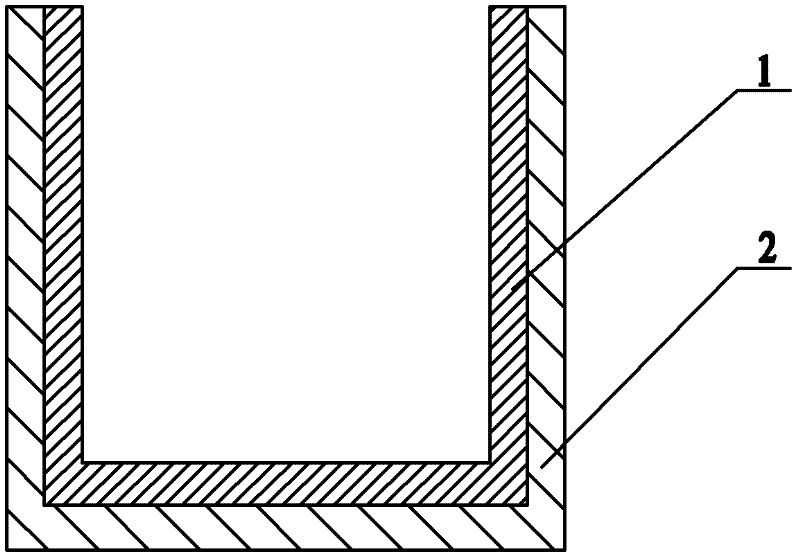
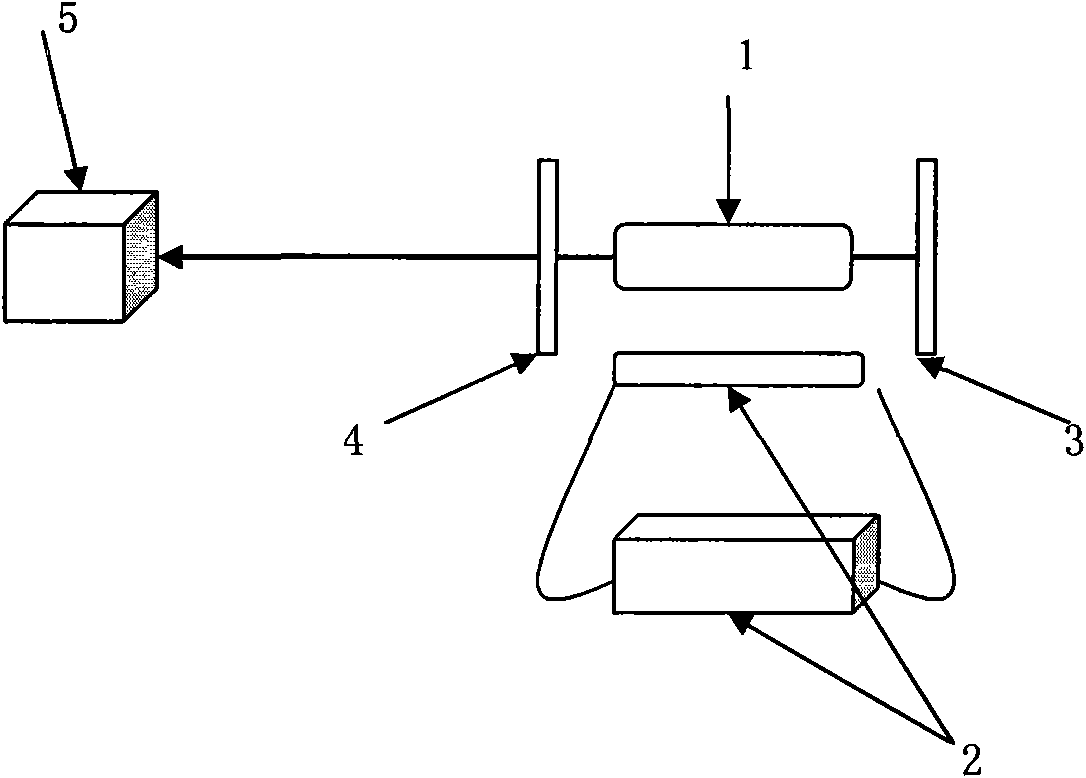
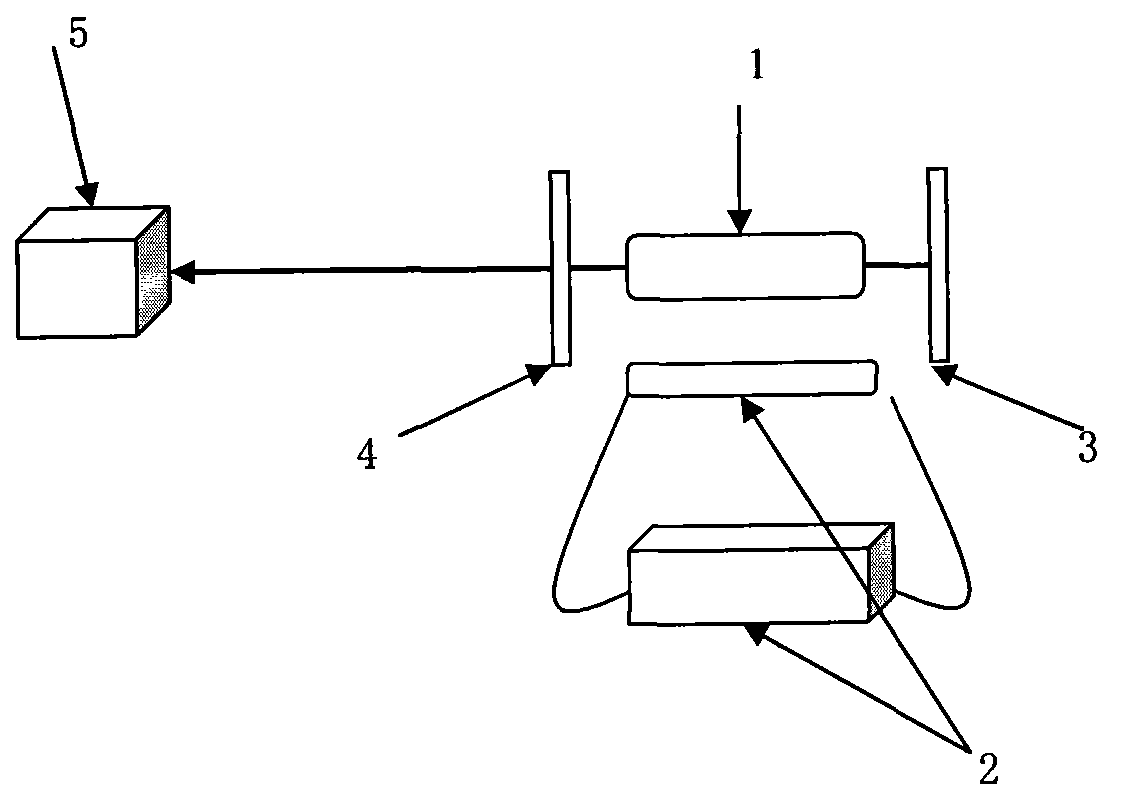
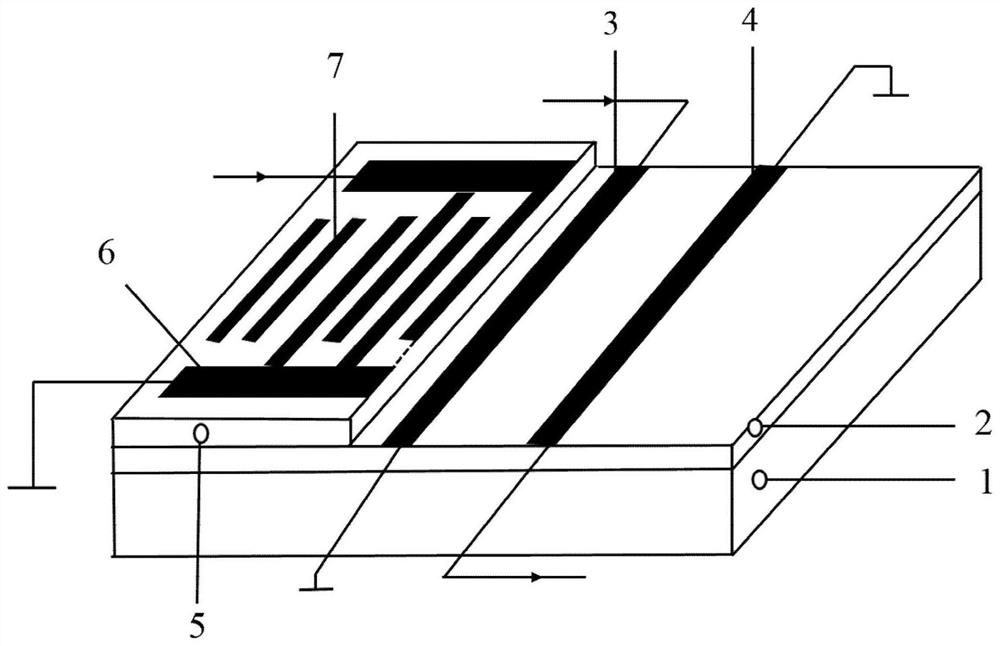
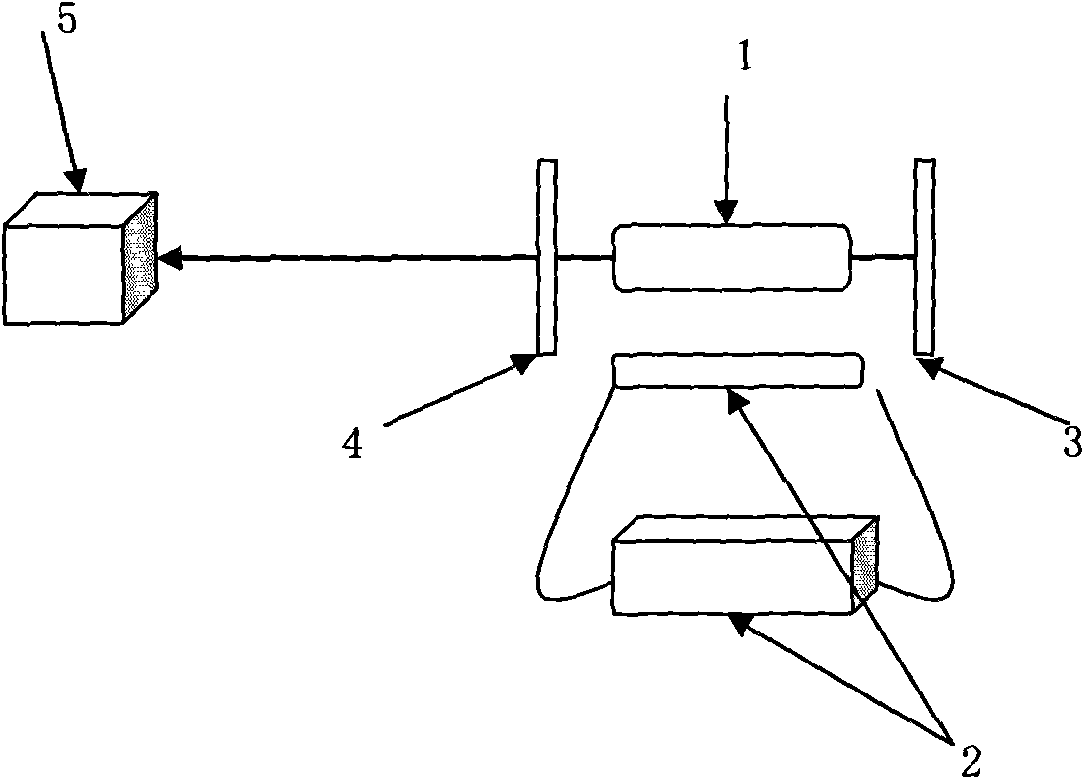
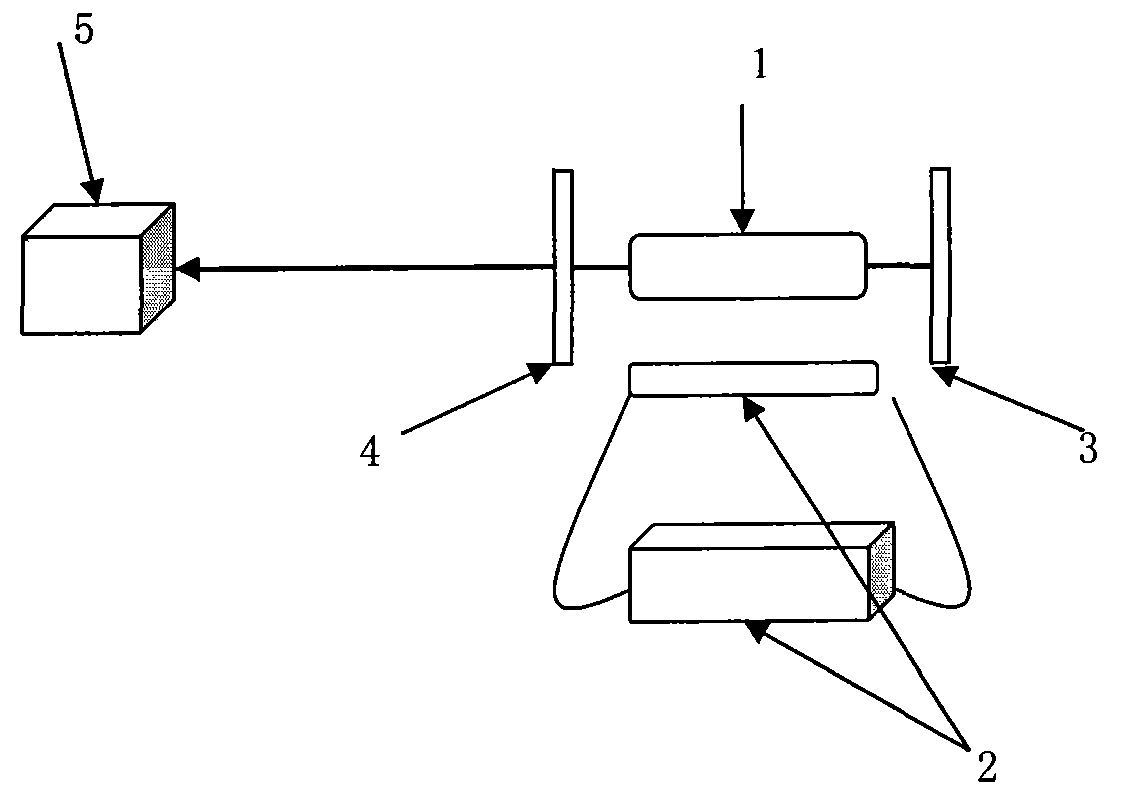
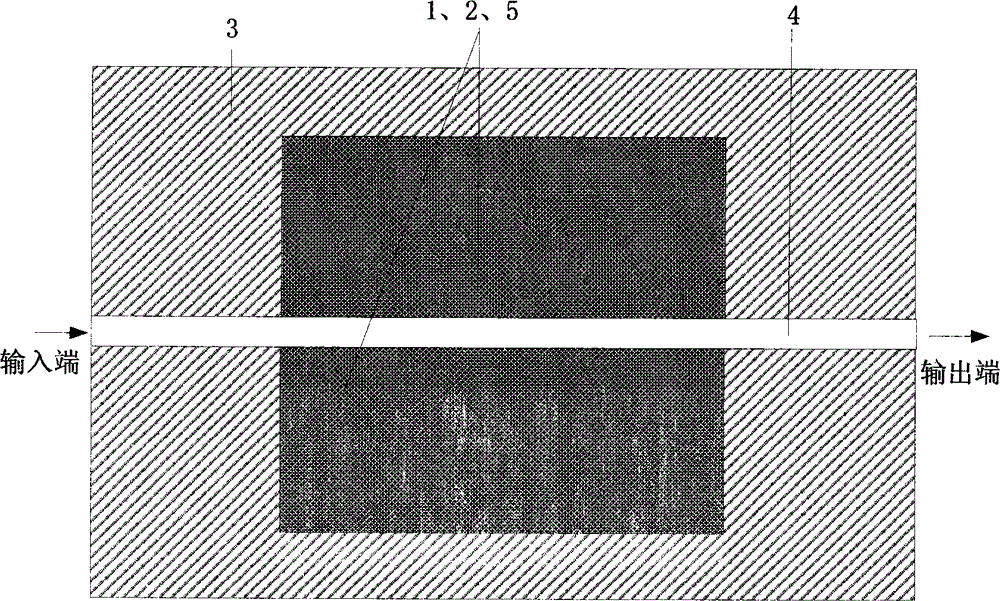
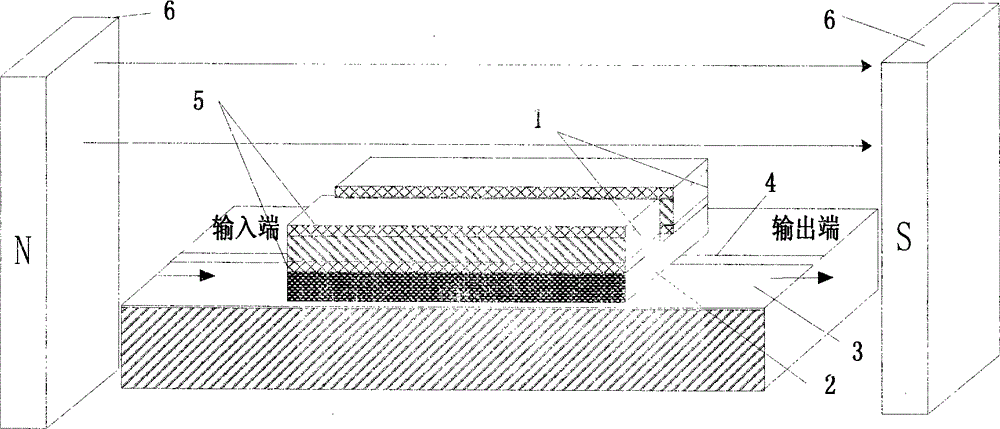
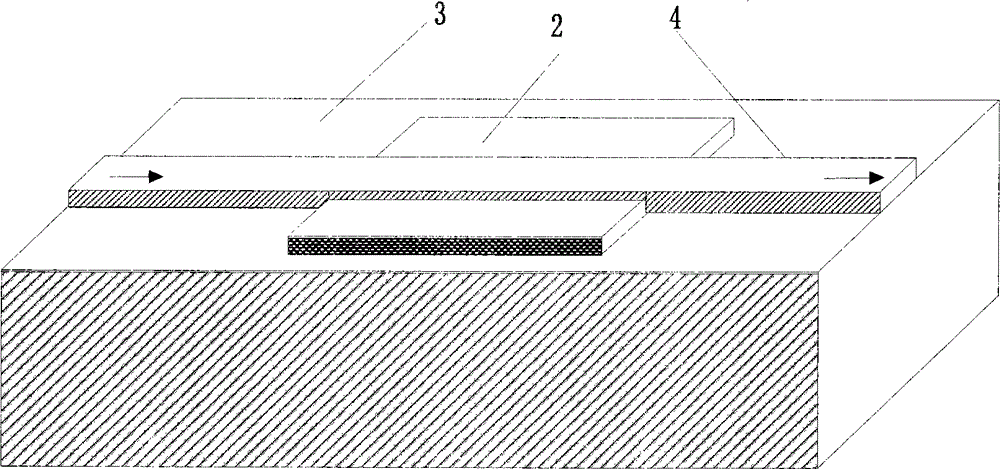
The invention discloses a micro-strip line filter sharing a substrate with YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) thin film material, and a regulation method thereof. The micro-strip line filter comprises two piezoelectric layers (1), one YIG layer (2), GGG (Gadolinium Gallium Garnet) substrate material (3) and a metal micro-strip line (4); the micro-strip line filter takes the GGG substrate material (3), needed for the growth of the YIG layer (2), as a substrate; a layer of metal micro-strip line (4) in single conduction band is printed on the upper surface of the GGG substrate material (3), on which the YIG layer (2) is grown, along a central axis in a length direction; the two piezoelectric layers (1) are respectively arranged at two sides of the metal micro-strip line. Compared with a traditional micro-strip line filter, the miniaturization of the micro-strip line filter can be realized due to the advantages of high dielectric constant (epsilon is greater than 10) and high magnetic permeability (mu is greater than 10) of YIG material and piezoelectric material. According to the micro-strip line filter disclosed by the invention, the GGG substrate material of which the length-width size is the same as that of a YIG thin film is selected, and thus the selecting difficulty on size of the YIG material is reduced.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Gadolinium illinium scandium gallium garnet crystal GYSGG and its smelt method crystal growth method
The invention discloses a gadolinium yttrium scandium gallium garnet crystal (GYSGG) and a crystal growth method by a melt method thereof. The molecular formula of the crystal can be expressed as Gd3xY3(1-x)Sc2Ga3(1+delta)O12 (the x is equal to between 0 and 1 or between -0.2 and 0.2); Gd2O3, Y2O3, Sc2O3 and Ga2O3, or corresponding other compounds of gadolinium, yttrium, scandium, and gallium canbe used to perform the material mixing, and the premise is that the Gd3xY3(1-x)Sc2Ga3(1+delta)O12 is produced; prepared raw materials are subject to the perfect mixing, press forming and high temperature sintering, and then become an initial raw material of crystal growth; the initial raw material of the growth is placed into a crucible, is heated to fully melt down, and then becomes an initial melt of the growth by the melt method, and then melt methods such as a pulling method, a crucible descending method or a temperature gradient method as well as other melt methods can be used for the growth; for the melt method which needs seed crystals to directionally grow, the seed crystals are GYSGG monocrystals or yttrium scandium gallium garnet (YSGG) monocrystals or gadolinium scandium gallium garnet (GSGG) monocrystals. The GYSGG monocrystals can be used as a substrate material of a Bi3+-doped yttrium iron garnet epitaxial film.
Owner:ZHONGKE JIUYAO TECH CO LTD
Nonreciprocal spin-wave heterojunction waveguide material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107190321ASignificant nonreciprocityPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthGadolinium gallium garnetHeterojunction
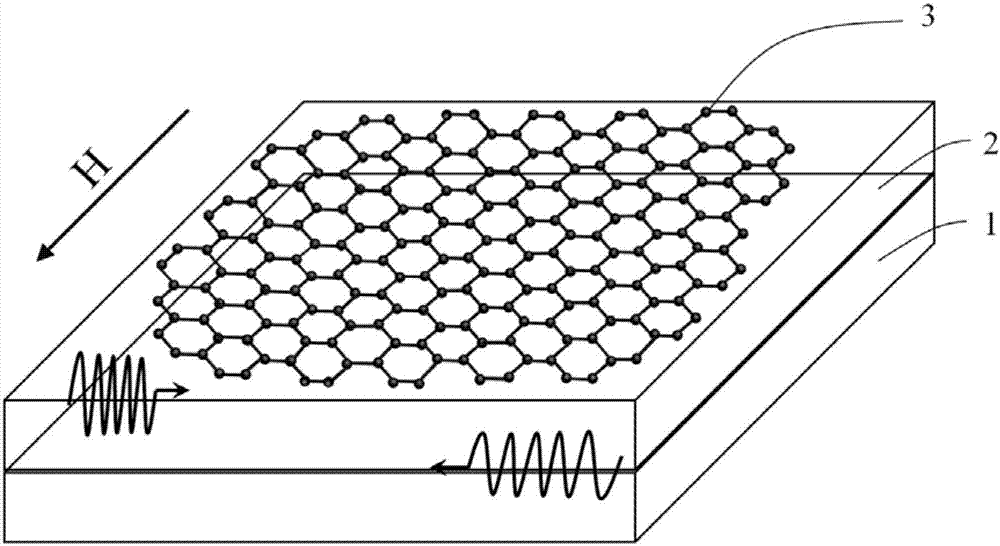
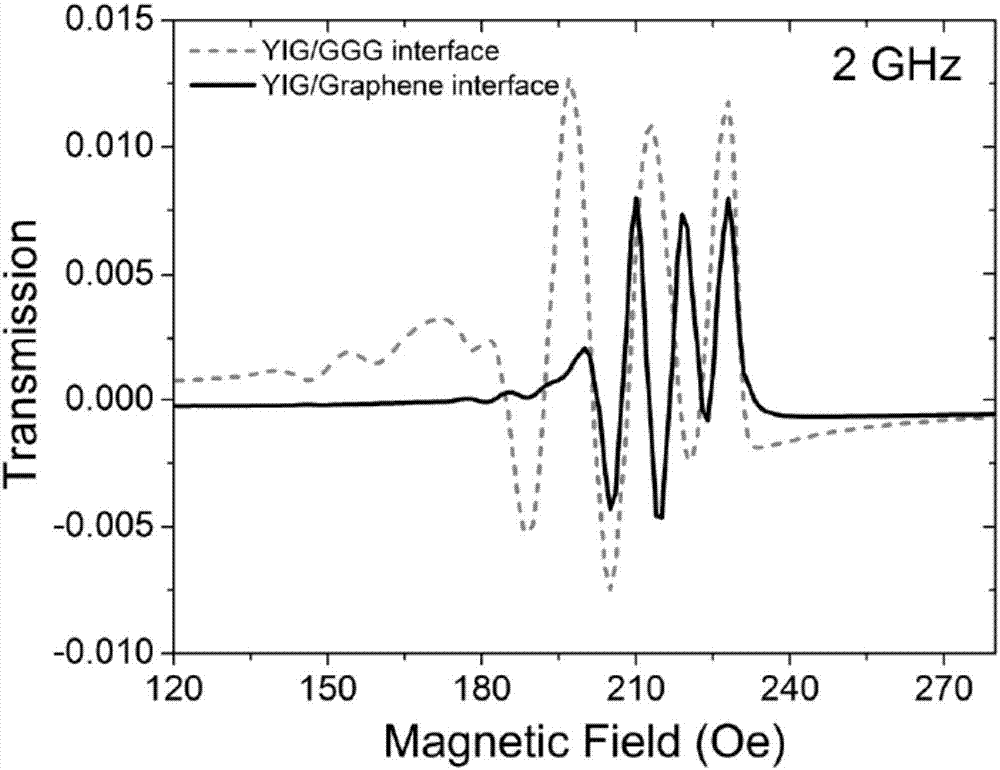
A nonreciprocal spin-wave heterojunction waveguide material comprises a GGG (gadolinium gallium garnet) monocrystalline substrate and a YIG (yttrium iron garnet) / graphene heterojunction material; the YIG / graphene heterojunction material is formed by growing YIG film on the surface of the GGG monocrystalline substrate, transferring single-layer graphene to the YIG film, and drying. The invention also provides a preparation method and application of the nonreciprocal spin-wave heterojunction waveguide material. Compared with single YIG film, the YIG / graphene heterojunction film prepared herein has the advantage that spin waves propagated on the upper and lower surfaces are of significant nonreciprocity, namely both amplitude and peaks of the spin waves propagated on the upper and lower surfaces of the YIG / graphene heterojunction material experience significant changes.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Ytterbium, lutecium, gadolinium and gallium doped garnet laser crystal, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103397385AQuality improvementImprove performancePolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltCzochralski methodDodecahedron
The invention provides an ytterbium, lutecium, gadolinium and gallium doped garnet laser crystal, a preparation method and applications thereof. The formula of the crystal is (Yb<y>Lu<x>Gd<1-x-y>)3Ga5O12, wherein the x is larger than 0 and smaller than 1, the y is not smaller than 0.01 and not larger than 0.5, and the sum of x and y is not larger than 1. Yb3+ is taken as the activated ion and can achieve continuous and impulse laser output near 1 [mu]m under the pumping of laser diode (LD) or other lasers. The crystal Yb(Lu<x>Gd<1-x>)3Ga5O12 is prepared by adopting the Czochralski method. Yb:LGGG crystal is obtained by mixing part Lu3+ into the dodecahedron cases of the Yb:GGG crystal. The crystal has the advantages of stable growth interface and high crystalline quality, and can be applied to the production of laser crystal, which can generate continuous laser output, Q-switch laser and mode-locked laser.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Rare-earth ion doped gadolinium gallium garnet porous nano-belt and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a rare-earth ion doped gadolinium gallium garnet porous nano-belt and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of nanometer material preparation. The method comprises three steps: (1) spinning solution preparation, in which, mass percentage of nitrate is between 6 and 10 percent, mass percentage of PVP is between 26 and 30 percent, and the balance is solvent DMF; (2) PVP / [Gd(NO3)3+Ga(NO3)3+RE(NO3)3] composite nano-belt preparation, in which, static spinning technology is adopted, and the technical parameters are that voltage is between 15 and 18 kV, and the solidification distance is between 10 and 15cm; the inner diameter of a needle nozzle of a syringe is 1.2mm, a vertical spraying mode is adopted, the indoor temperature is between 20 and 30 DEG C, and relative humidity is between 40 and 50 percent; and (3) GGG preparation, wherein heat treatment is performed on the obtained PVP / [Gd(NO3)3+Ga(NO3)3+RE(NO3)3] composite nano-belt by RE3+porous nano-belt to obtain GGG: RE3+porous nano-belt.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel 1.54 mu m waveband rare earth ion activated gadolinium gallium garnet laser crystal
InactiveCN101377015ALow laser efficiencyImprove laser efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltNitrogen gasMaterials science
The invention relates to novel gadolinium gallium garnet laser crystal activated by 1.54mu m wave-band rare earth ion, which belongs to the field of laser crystal materials. The chemical formula of the laser crystal material is Yb: Er: Ce: Gd3Ga5O12. Super-fine powders of Ga2O3, Gd2O3, Er2O3, Yb2O3 and CeO2 serve as the raw material, and the Yb: Er: Ce: Gd3Ga5O12 raw material is obtained through a high-temperature solid phase reaction in reducing atmosphere like nitrogen; the crystal is grown through a pulling method in the reducing atmosphere like nitrogen. The material is used to output the 1.54mu m wave-band laser.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gel burning synthetic method for preparing reodymium doped gadolinium-gallium garnet nano powder
The gel burning synthesis process of preparing neodymium doped gadolinium-gallium garnet includes the following steps: mixing Nd compound, Gd compound and Ga compound in the molar ratio of Nd, Gd and Ga in X to 3-X to 5, where X is 0-0.3 to form mixture solution; adding organic fuel citric acid, amino acid, urea, tartaric acid and / or hydrazine carbonate to the mixture solution; evaporating to dewater the solution at 60-80 deg.c in a water bath to obtain viscose gel; burning the viscose gel to produce exothermal reaction at 160-220 deg.c and normal pressure to obtain black puffy precursor; grinding; and calcining at 900-1100 deg.c to obtain the neodymium doped gadolinium-gallium garnet powder. The present invention has the advantages of ion level homogeneous mixing, short preparing process, low temperature, superfine product granularity, homogeneous dispersivity and homogeneous chemical components.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cleaning method of gadolinium-gallium-garnet single-crystal substrate for liquid-phase epitaxy
InactiveCN104831358AEfficient removalGood adhesionPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthSingle crystalCleaning methods
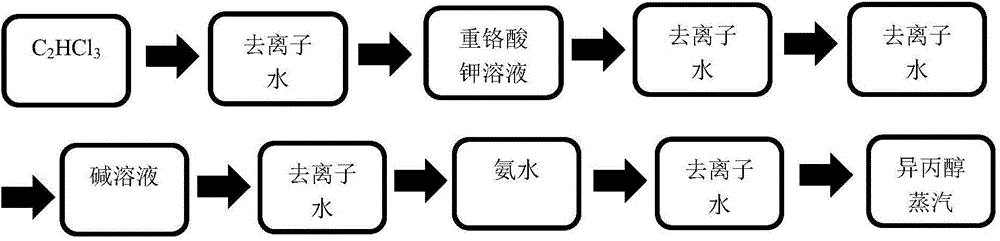
The present invention provides a cleaning method of a gadolinium-gallium-garnet single-crystal substrate for liquid-phase epitaxy. The cleaning method comprises: carrying out soaking cleaning on a substrate sequentially in trichlorethylene with a temperature of 70-80 DEG C and deionized water with a temperature of 70-80 DEG C; carrying out dipping cleaning in a 70-80 DEG C mixed solution of potassium dichromate, concentrated sulfuric acid and water 10-15 times, wherein each dipping cleaning time is 1-2 s; taking out, and respectively carrying out soaking cleaning 2 times in deionized water with a temperature of 70-80 DEG C; sequentially and respectively carrying out soaking cleaning in an alkali solution with a temperature of 70-80 DEG C and deionized water with a temperature of 70-80 DEG C; sequentially and respectively carrying out soaking cleaning in a weak alkali and deionized water; and finally cleaning in isopropyl alcohol steam. With the cleaning method of the present invention, the impurity stains on the substrate surface can be effectively removed, such that the substrate can present the mirror surface effect; with the slight corrosion of the cleaning liquid on the substrate surface, the substrate wafer bond is opened, the surface is activated, the adhering and the growth of various film forming raw materials are easily achieved, and the film forming rate and the film quality are improved; and the soaking cleaning is used, such that the large substrate stress problem produced by ultrasonic cleaning is avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Strip line resonator structure and magnetic tuning wave trap composed of resonator structure
PendingCN111613863AInhibition Excitation ModeIncreased Stop Band DepthResonatorsGadolinium gallium garnetElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a strip line resonator structure and a magnetic tuning wave trap composed of the resonator structure, and belongs to the technical field of electronic components. The strip line resonator structure is composed of a strip line central conductor, a strip line outer conductor, a gadolinium gallium garnet crystal and a YIG single crystal film, and the strip line central conductor, the YIG single crystal film and the gadolinium gallium garnet crystal are sequentially arranged in the strip line outer conductor; according to the invention, the resonator planarization of the magnetic tuning wave trap is realized, and the structural design of the strip line resonance circuit is simplified; a strip line transmission mode is adopted, so that the passband working frequency of the magnetic tuning wave trap is expanded; a plurality of strip line resonance circuits can be arranged on the same plane, so that the integration of the multi-channel wave trap is facilitated; the resonance circuit adopts a plurality of single crystal thin film blocks to form resonator cascade connection, so that a plurality of excitation modes of the single crystal thin films are effectively suppressed, the stop band depth of the wave trap is increased, and the performance of the wave trap is improved.
Owner:中国电子科技集团公司第九研究所
Preparation method of in-plane anisotropy Bi-substituted garnet magneto-optic single crystal thin film
InactiveCN104818518AImprove stabilityLower melting temperaturePolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsIn planeGadolinium gallium garnet
The invention aims to provide a preparation method of an in-plane anisotropy Bi-substituted garnet magneto-optic single crystal thin film. The method is used for application of a TE-TM (Transverse Electric-Transverse Magnetic) light mode conversion modulator. A liquid-phase epitaxial process is adopted to realize growth of Bi ion and Lu ion codoped single crystal garnet (BiLuIG) on a gadolinium gallium garnet substrate (orientation of being <111>), a melt reaches the growth temperature of the thin film through a mixing, temperature rising-thermal insulation-triple cooling method, and the growth process of the thin film is controlled to finally prepare the in-plane anisotropy Bi-substituted garnet magneto-optic single crystal thin film. For the growth of the thin film, the three-step cooling mode can achieve good temperature stability and melt state stability. The in-plane anisotropy Bi-substituted garnet magneto-optic single crystal thin film is prepared, the preparation process is simple, and the stability is high.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation method of gadolinium gallium garnet planar interface crystal
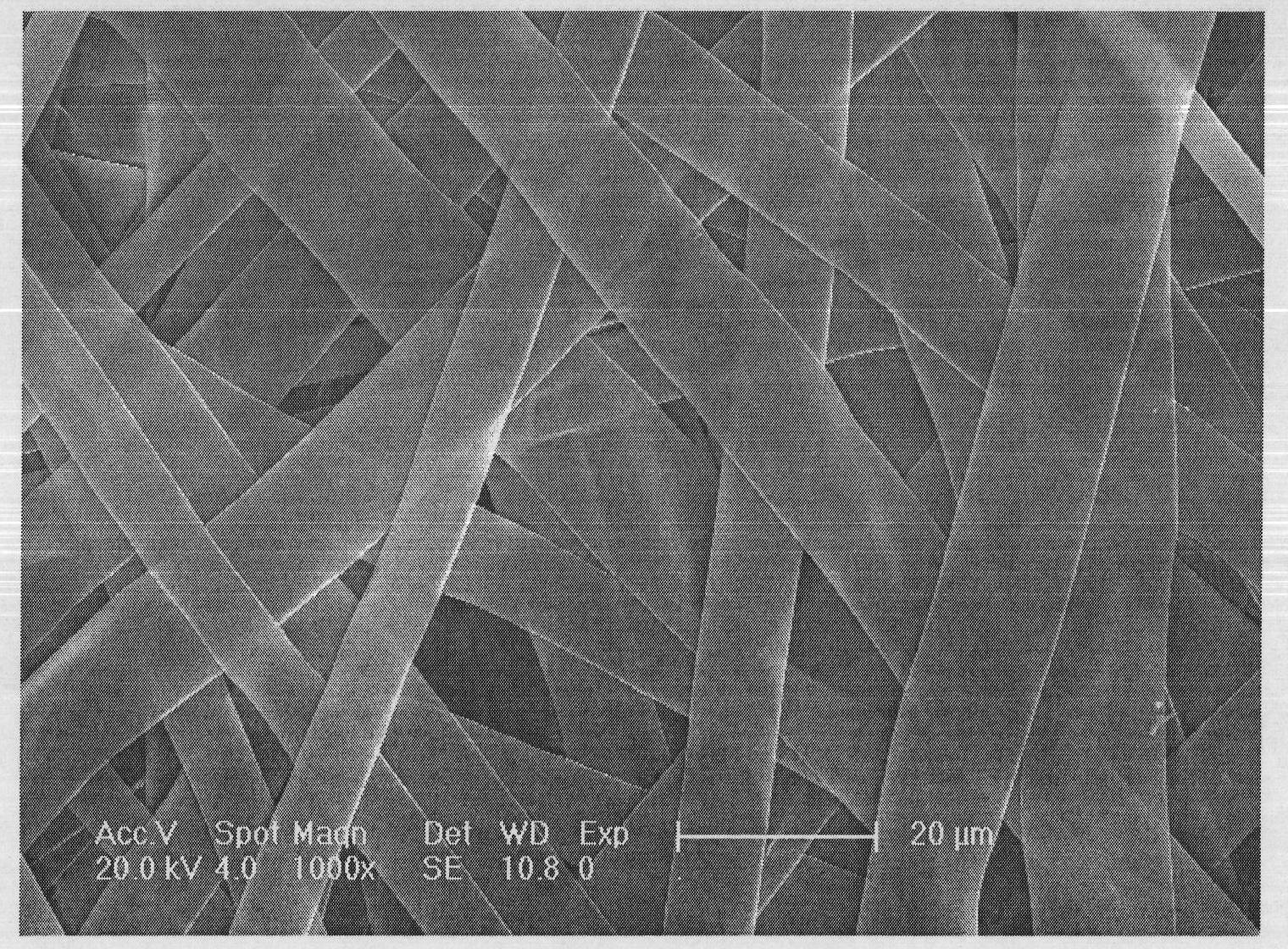
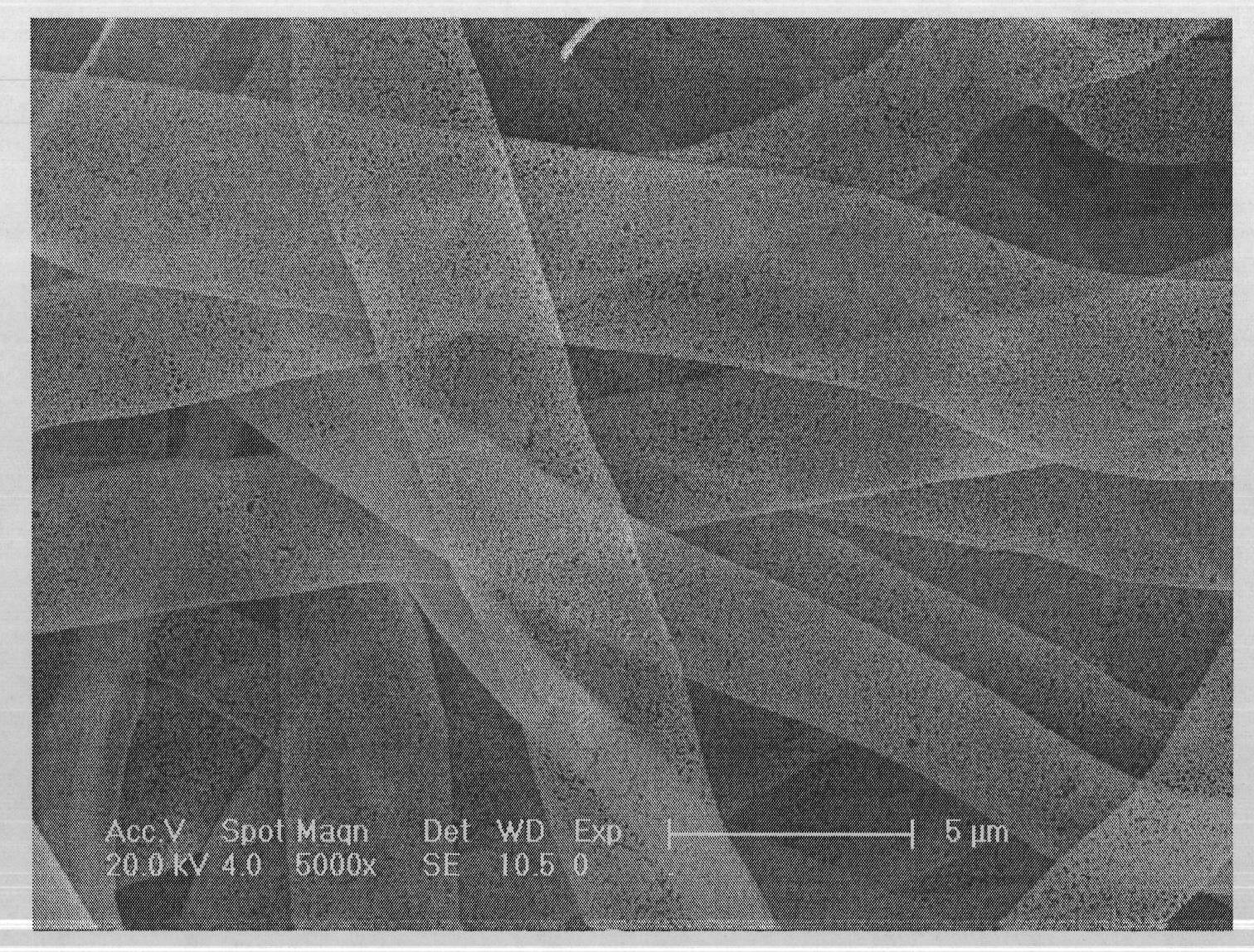
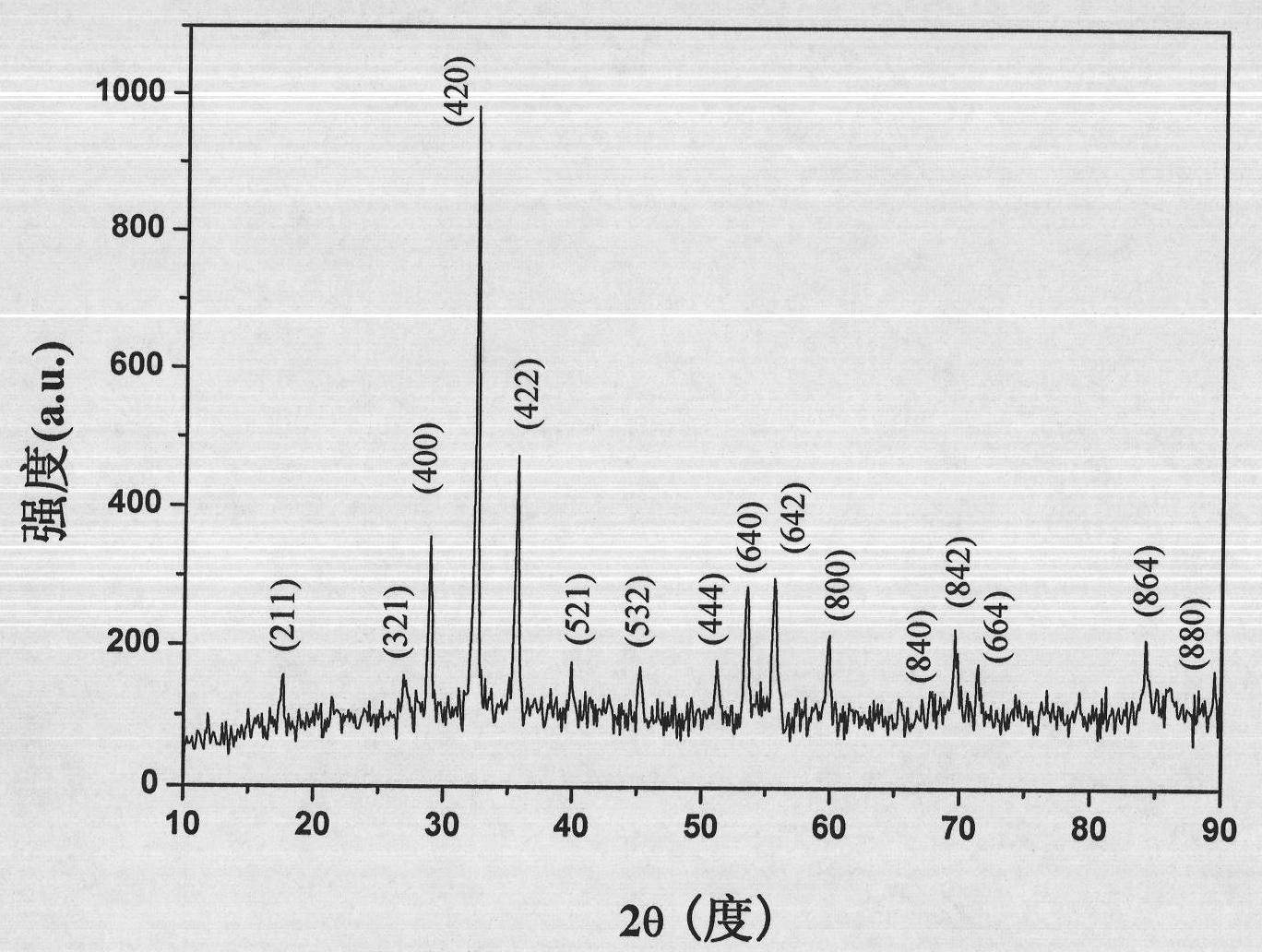
ActiveCN101319389ACrystal internal quality is goodUniform stressPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltGadolinium gallium garnetLattice constant
The invention discloses a method for preparing a gadolinium gallium garnet(GGG)planar interface crystal, belonging to the optical crystal technical field. The method comprises the following steps that: CaO and / or MgO and ZrO2 are doped in a raw material formula of the GGG crystal and a manual control interface converting technology method is used so that the planar interface doped large lattice parameter GGG crystal with good stress and internal quality is grown, The calcium-magnesium-zirconium doped large lattice parameter GGG planar interface crystal with a diameter more than 2 inches and a length more than 120 millimeters is grown by the method. The crystal has good internal quality, even stress, and zero dislocation, does not observe any scattering particle under the He-Ne light, has a lattice parameter of between 12.383 and 12.620, and the change in the crystal head and tail lattice parameters is within 10<-2>. The method is particularly suitable for the large lattice parameter (Ca, Mg and Zr):GGG crystal growth field of an epitaxial substrate.
Owner:成都东骏激光股份有限公司
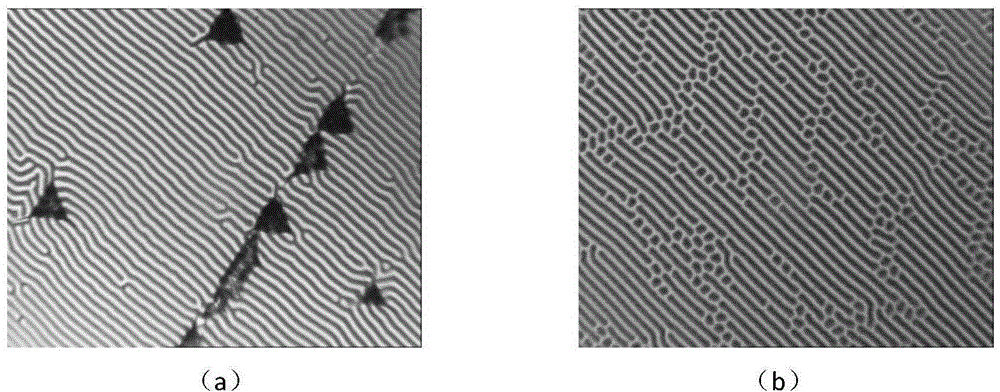
Ca, Mg, Zr, Gd and Ga garnet doped with Sm and melt method crystal growth method thereof
InactiveCN101671844AImprove performanceUniform optical qualityPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltFlux growthLarge screen
The invention discloses a Ca, Mg, Zr, Gd and Ga garnet doped with Sm and a melt method crystal growth method thereof, the molecular formula thereof is Smz: Gd(3-x-z)CaxGa(5-x-2y)MgyZr(x+y)O12 (0<x<3,0<y<2.5, 0<z<3, 0<x+2y<5, 0<x+z<3), and the method comprises the following steps: the well-prepared raw materials are mixed fully, pressed and shaped, calcined in high temperature to obtain the starting raw material for crystal growth; the starting raw material is placed into a pot, heated and fully melt to obtain the initial melt of the melt method crystal growth, and is subjected to directionalor nondirectional growth on crystals by a melt method such as a traditional pulling method, a Bridgman-Stockbarge method, a flux growth method and the like to obtain solid laser working substances ofblue light pumping. By the invention, laser crystal with large size, even optical quality and fine performance can be obtained, which also can be used as solid laser working substances of blue light pumping and has the possibility of being used in fields such as medical diagnosis, material treatment, high density information reading and writing, monitoring and controlling, large screen color display, high definition color televisions and the like.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sapphire crucible for growing garnet type single crystal
InactiveCN102363898AEliminate the promoting effect of decomposition and volatilizationAffect internal qualityPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltTerbium gallium garnetGadolinium gallium garnet
The invention relates to a sapphire crucible for preparing a garnet type single crystal of gadolinium gallium garnet and terbium gallium garnet and the like containing Ga2O3 component. The sapphire crucible for growing the garnet type single crystal comprises an outer crucible sleeved outside an inner crucible, the inner crucible is flush with the top end face of the outer crucible, the inner crucible is matched with the section shape of the outer crucible, and the inner crucible is made of sapphire. By adopting the sapphire crucible device of the technical scheme, iraurite grown by reaction of an iraurite oxide and the Ga2O3 component when an iraurite crucible is used can be prevented from floating on the surface of the melt to affect the internal quality of the crystal, and meanwhile, the promoting effect of the iraurite oxide on decomposition and volatilization of the Ga2O3 component is eliminated.
Owner:UNIONLIGHT TECH
Method for increasing diffusion length of magnon
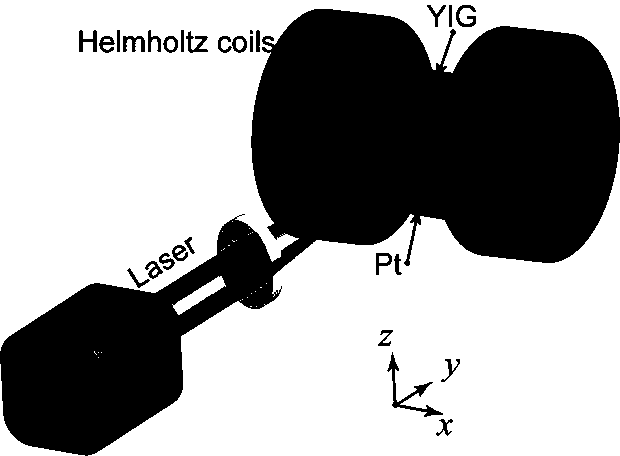
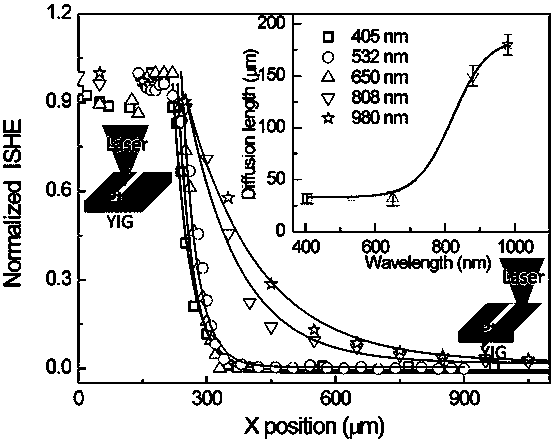
InactiveCN108123030AChanging the dispersion relationIncrease the diffusion lengthUsing electrical meansGalvano-magnetic device manufacture/treatmentLight spotLaser beams
The invention discloses a method for increasing the diffusion length of a magnon. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, 40 nm YIG (Y3Fe5O12) is grown on a gadolinium gallium garnet substrate by a pulsed laser deposition method, and after that, a strip-shaped Pt electrode is prepared on YIG by a magnetron sputtering method; the surface of a sample is irradiated by a focused laser beam,and a temperature gradient perpendicular to the surface of the sample is formed on an irradiated part; an unbalanced magnon is generated by parameters of a spin Seebeck effect, the unbalanced magnonperforms in-plane diffusion, a reverse spin Seebeck effect is generated in the Pt electrode when the unbalanced magnon reaches the Pt electrode, and voltage is further generated. The position of a light spot is changed to detect the voltage in Pt, so that the diffusion length of the magnon can be detected. The diffusion length of the YIG magnon is greatly increased.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
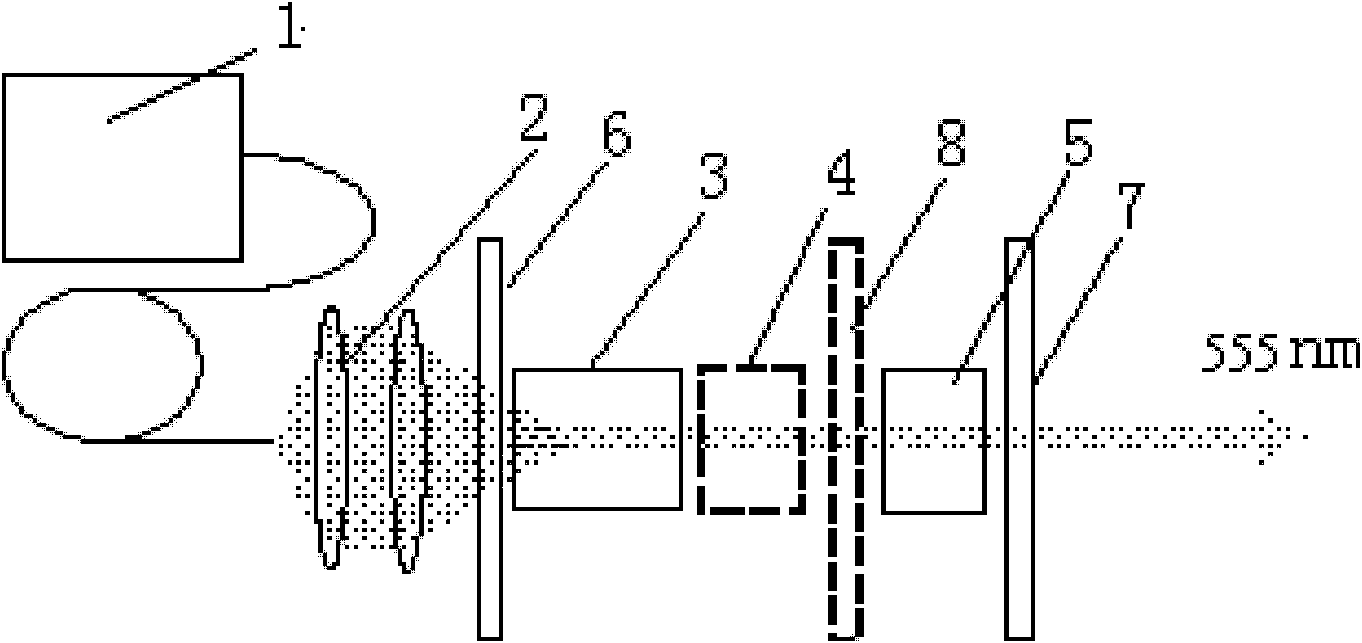
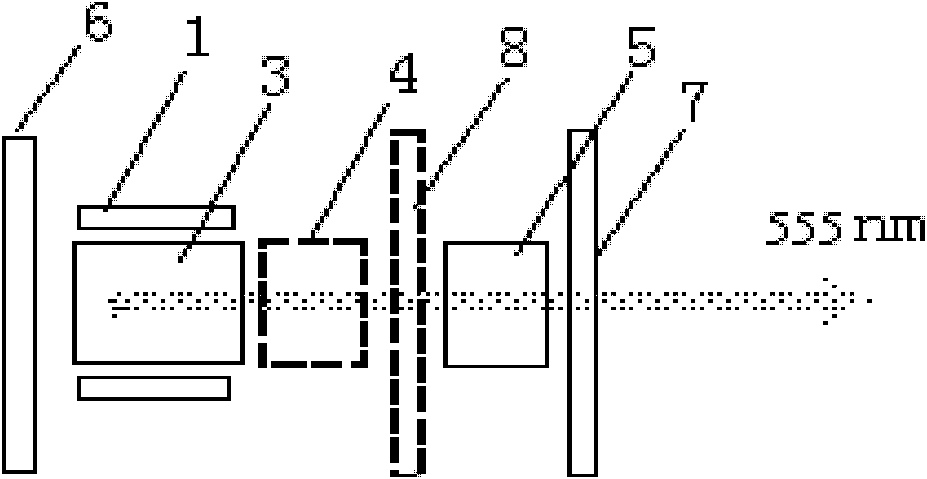
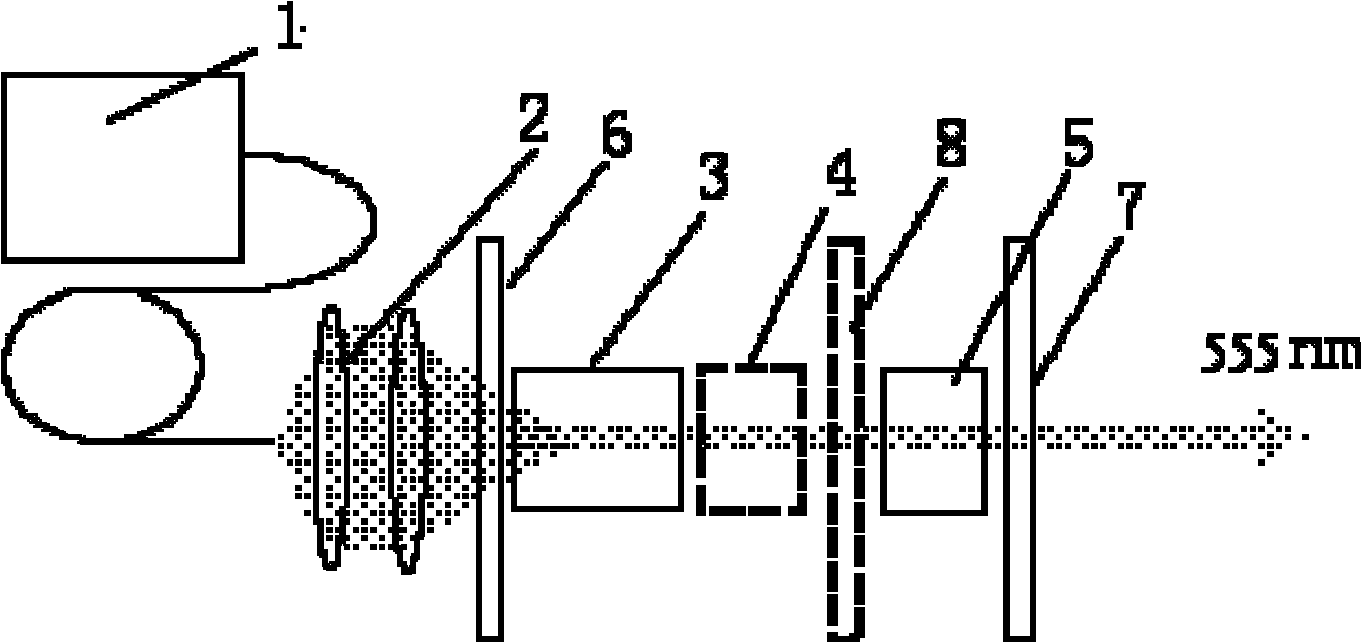
555-nanometer laser all-solid-state laser
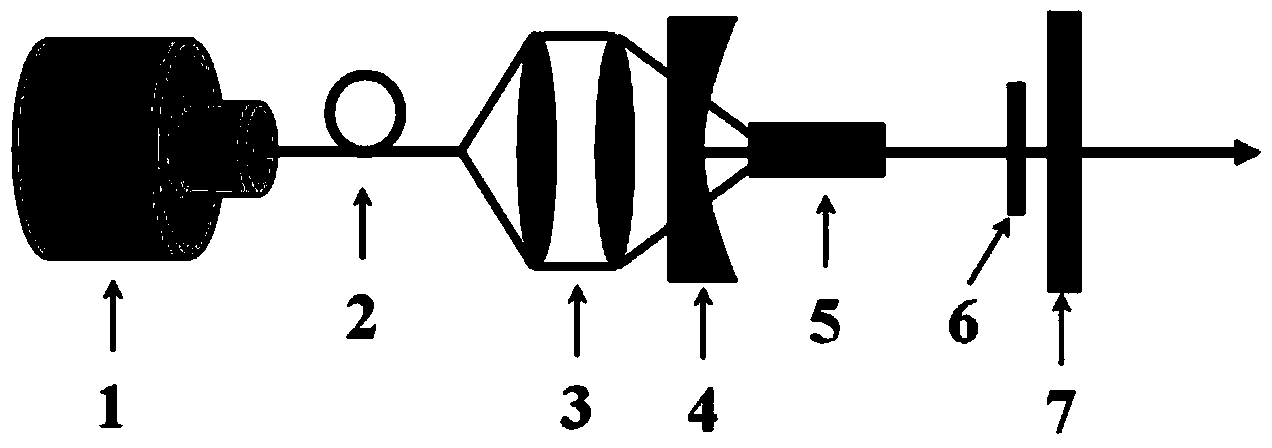
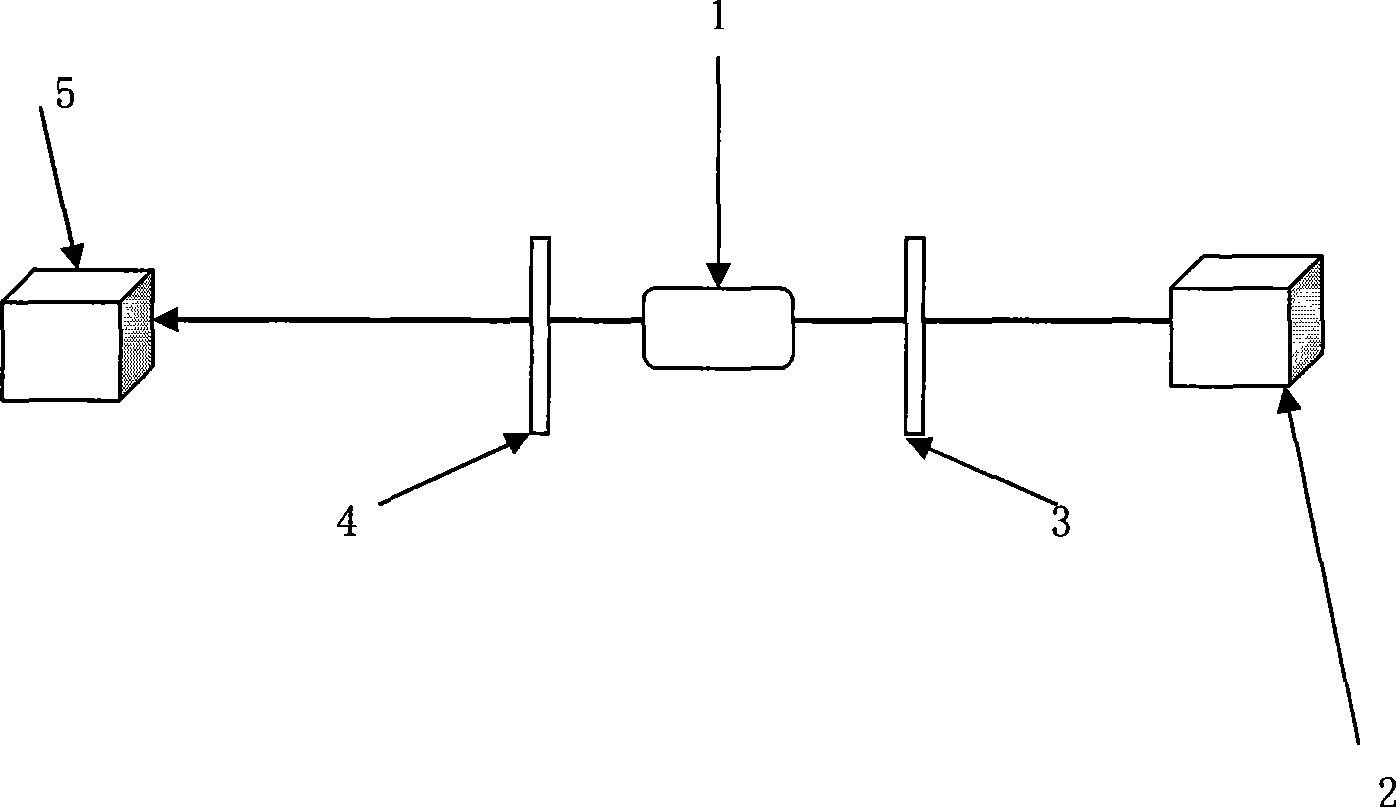
The invention discloses a 555-nanometer laser all-solid-state laser, belonging to the technical field of solid lasers. The laser comprises a pumping source, a coupled lens group, a coupled cavity and the like, wherein a laser crystal, a Q-switched device and a doubling frequency crystal are arranged in the coupled cavity; and the temperatures of the crystals and the device are kept constant by a temperature control system. The laser is characterized in that: a new wavelength is produced by using a specific gain spectrum line of a Nd:GGG (Gadolinium Gallium Garnet doped with Neodymium) crystal; and medium films which have transmission rates or reflection rates of not less than 99 percent on light of corresponding wavelengths are coated on the end faces of an input lens M1, an endoscopy M2, an output lens M3, the laser crystal and the doubling frequency crystal respectively. The laser has a compact and reliable frame and large output power which can be up to dozens of watts. The laser generates 555-anometer laser light which is most sensitive to human eyes, has wide and important application in the fields of laser display, construction and military affairs, and can be applied in the fields of biology, medicines, astronomy and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Chromium and ytterbium sensitized ions co-doped holmium ion activated gadolinium gallium garnet novel laser crystal
InactiveCN102134750APolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsGadolinium gallium garnetHolmium
The invention discloses a chromium and ytterbium sensitized ions co-doped holmium ion activated gadolinium gallium garnet novel laser crystal, and relates to the field of laser crystal materials. The crystal material has the chemical formula of Cr:Yb:Ho:Gd3Ga5O12. Gd2O3, Ga2O3, Cr2O3, Yb2O3 and Ho2O3 of 4N are adopted as raw materials, a Cr:Yb:Ho:Gd3Ga5O12 raw material is obtained through high temperature solid-phase reaction, and crystals are grown through a Czochralski method. The material is used for realizing output of laser in a wave band of 2.6-3.1 mu m.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Growing method of chromium and neodymium double doped gadolinium-gallium garnet self Q switching laser crystal
InactiveCN1648288AQuality improvementEvenly dopedPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltNitrogen gasOxygen
The present invention is growth process of chromium and neodymium double doped gadolinium-gallium garnet as self Q switching laser crystal. The present invention features that the crystal of structure expression of Ca3z / 2Nd3yGd3(1-y-z / 2)Ga5-xCrxO12 is prepared with gadolinium oxide, gallium oxide, neodymium oxide, crhromium oxide and calcium oxide as main material and through solid synthesis to form crystal material and subsequent crystal growth in 98 % nitrogen +2 % oxygen condition in Czochralski process. The chromium and neodymium double doped gadolinium-gallium garnet as self Q switching laser crystal of the present invention has the features of ion concentration difference within 1 % in the plane perpendicular to the crystal growth direction, great size and high quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Frequency conversion system with improved spurious response and frequency agility
ActiveUS20160164569A1Improve performanceSmall lossSecret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksLocal oscillator signalEngineering
A frequency conversion system with improved performance. In one embodiment an image reject mixer is used to perform frequency conversion providing an initial degree of suppression of the image and local oscillator leakage signals, and a signal to noise enhancer (SNE) is used to further suppress the image and local oscillator signals, the signal to noise enhancer being a nonlinear passive device that attenuates low-power signals while transmitting high power signals with little loss. The signal to noise enhancer may be fabricated as a thin film of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) epitaxially grown on a gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG) substrate, the GGG substrate secured to a microwave transmission line from the input to the output of the signal to noise enhancer, such that the thin film of yttrium iron garnet is close to the transmission line.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Growth method of neodymium-doped gadolinium gallium garnet laser crystal
InactiveCN1621576AReduce dislocation densityImprove radiation resistancePolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltGadolinium gallium garnetNitrogen gas
The Nd doped gadolinium gallium garnet laser (Nd:GGG) crystal has the material including gadolinium oxide, gallium oxide, neodymium oxide and cerium oxide in certain proportion prepared in two-step composing process. The Nd doped gadolinium gallium garnet laser crystal is grown in a Czochrolski process under the 98 % N2+2% O2 condition. The present invention solves the problem of doping Nd2O3 to cause lattice deformation, and the Nd:GGG crystal has raised radiation resistance and improved spectral and laser performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of magnon crystal magnetic sensor and its preparation method
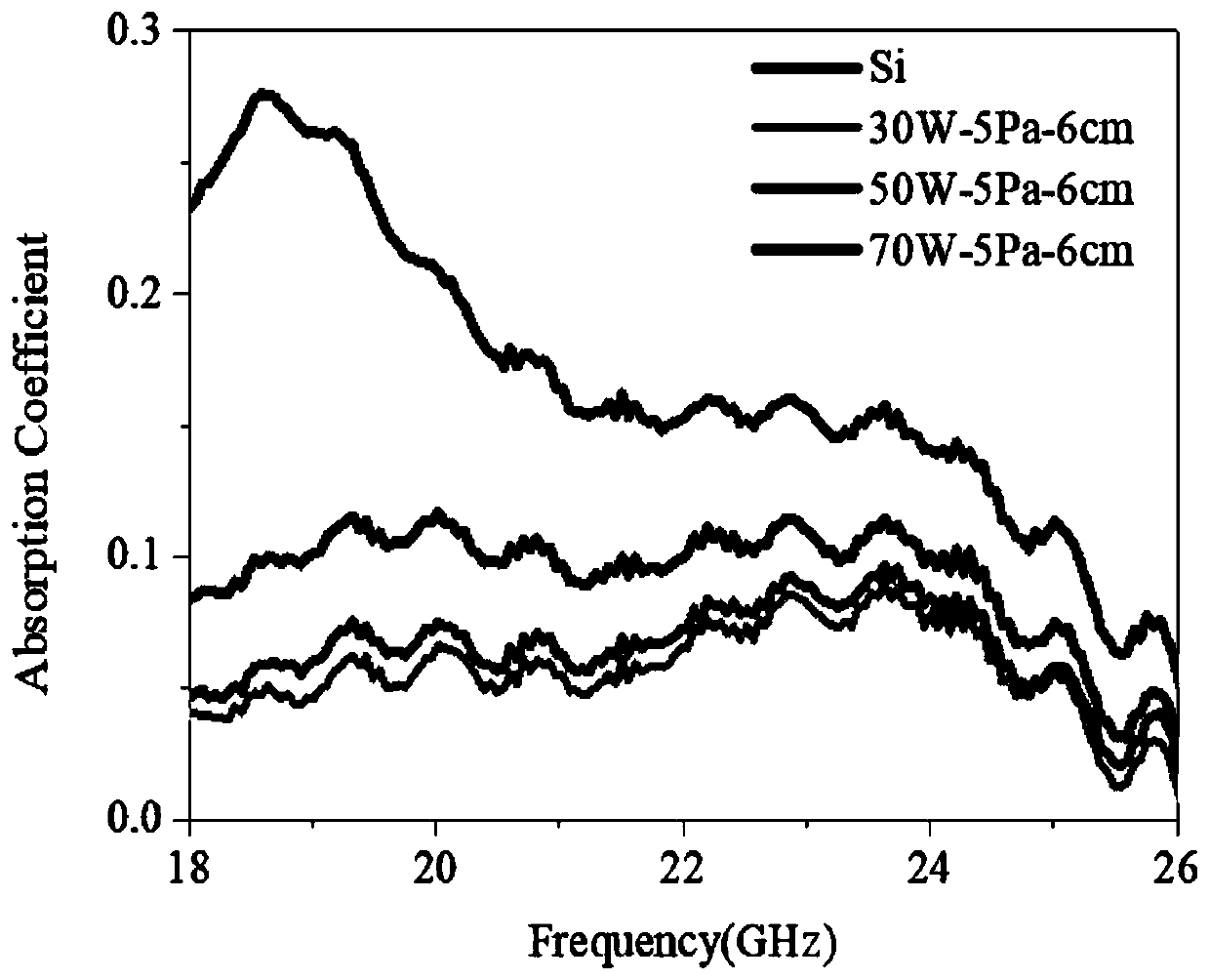
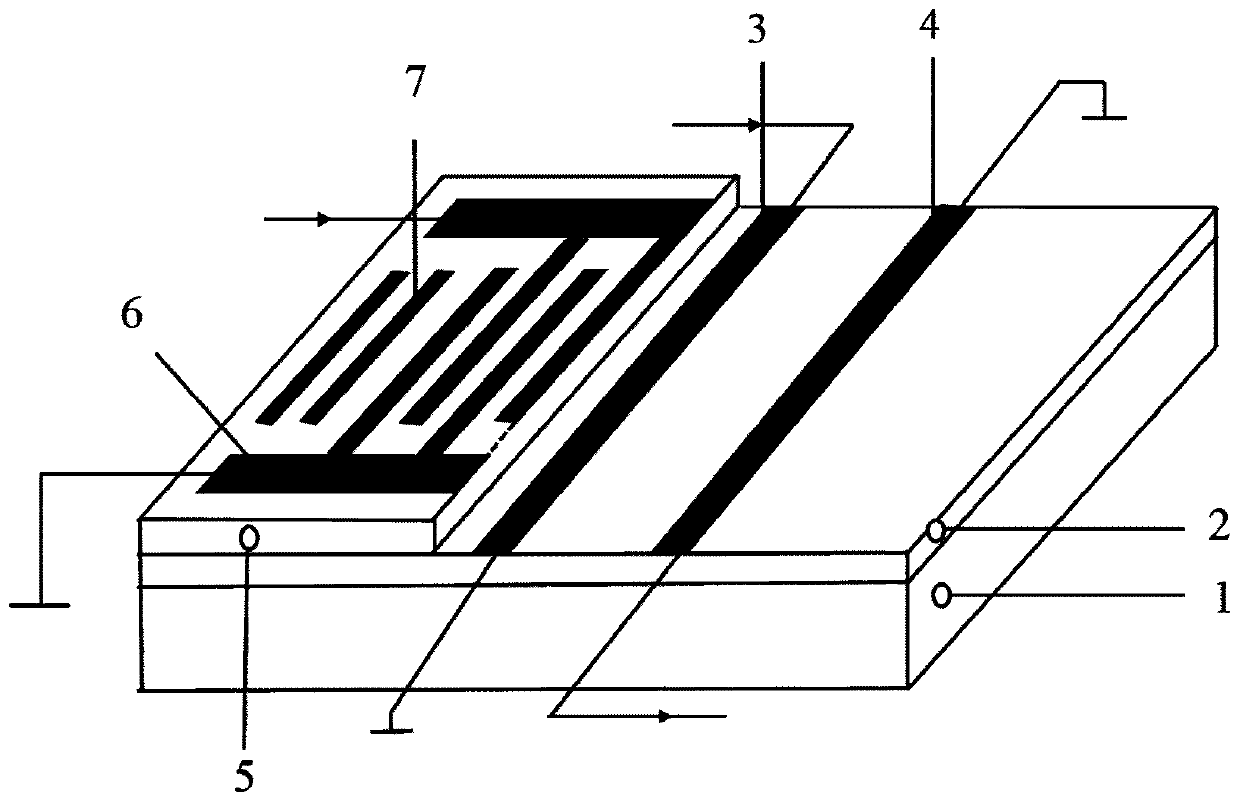
ActiveCN109811325BSimple preparation processImprove temperature stabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGadolinium gallium garnetMagnetostatic surface waves
A magnon crystal magnetic sensor and a preparation method thereof belong to the technical field of magnetic sensing. The magnetic sensor includes a gadolinium gallium garnet substrate, a yttrium iron garnet film on the gadolinium gallium garnet substrate, a magnetostatic surface wave excitation antenna and a receiving antenna on the YIG, a zinc oxide film on the YIG and Equidistant interdigitated electrodes with reflective grids on top of ZnO film. The magnon crystal magnetic sensor provided by the present invention realizes magnetic detection by using the linear relationship between the slight change of the external magnetic field and the offset of the absorption peak of SMSW propagating in the magnon crystal. The SAW frequency obtained by the method of the invention is relatively high, which can effectively improve the temperature stability of the magnon bandgap structure, and further improve the temperature stability of the magnetic sensor.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Processing method of ion-doped gadolinium gallium garnet wafer
InactiveCN114083429AAvoid deformationAvoid breakingLapping machinesGrinding feed controlGadolinium gallium garnetWafering
The invention relates to a processing method of an ion-doped gadolinium gallium garnet wafer, and belongs to the technical field of precision processing of gadolinium gallium garnet wafers. The processing method comprises the following steps of: 1, carrying out mechanical grinding at room temperature to obtain a roughly ground GGG wafer; 2, carrying out mechanical polishing to obtain a mechanically polished GGG wafer; and 3, carrying out chemical and mechanical polishing: adopting a silica sol polishing solution as a chemical and mechanical polishing solution to chemically and mechanically polish the mechanically polished GGG wafer at room temperature. The GGG wafer is processed by adopting the process steps of mechanical grinding, mechanical polishing and chemical mechanical polishing, and the obtained GGG wafer has lower surface roughness and high planeness through the combination of the process parameters of the stages. An auxiliary agent is introduced into the silica sol polishing solution, and the auxiliary agent plays a role in adjusting the corrosion speed of the silica sol polishing solution to the surface of the GGG wafer, so that the orange peel phenomenon is avoided.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Dysprosium ion activated gadolinium gallium garnet novel laser crystal
InactiveCN102134749APolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltGadolinium gallium garnetCzochralski method
The invention discloses a dysprosium ion activated gadolinium gallium garnet novel laser crystal, and relates to the field of laser crystal materials. The crystal material has the chemical formula of Dy:Gd3Ga5O12. Gd2O3, Ga2O3 and Dy2O3 of 4N are adopted as raw materials, a Dy:Gd3Ga5O12 raw material is obtained through high temperature solid-phase reaction, and crystals are grown through a Czochralski method. The material is used for realizing yellow laser output.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microwave absorbing body based on YIG thin film material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110846629AExtended Build SchemeEasy to prepareVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingRadio frequency magnetron sputteringSingle crystal
The invention belongs to the field of electromagnetic wave absorbing materials, in particular to a microwave absorbing body based on a YIG thin film material and a preparation method thereof. The coating methods involved comprise radio frequency magnetron sputtering, chemical vapour deposition, liquid phase epitaxy, pulsed laser deposition and the like; and the wave absorbing body involved is a thin film material deposited on the surface of a substrate. The substrate is one of a silicon substrate, an yttrium iron garnet substrate, a glass substrate and a magnesium oxide substrate; and the thinfilm can be one of a YIG single crystal thin film, a doped YIG thin film and a Gd:Ga:YIG thin film with a movable magnetic domain. According to the microwave absorbing body based on the YIG thin filmmaterial and the preparation method thereof, the YIG thin film is deposited on the substrate by mainly utilizing a YIG target material; and the prepared YIG thin film has the advantages of wide waveabsorbing frequency band, good wave absorbing performance and the like, and can be widely applied to the field of wave absorbing materials.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Magnon crystal magnetic sensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109811325AImprove temperature stabilitySimple methodVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGratingMagnetostatic surface waves
The invention discloses a magnon crystal magnetic sensor and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of magnetic sensing. The magnetic sensor comprises a gadolinium gallium garnet substrate, a gadolinium gallium garnet film positioned on the gadolinium gallium garnet substrate, a magnetostatic surface wave excitation antenna and a receiving antenna positioned on a YIG, a zinc oxide film positioned on the YIG, and equal-distance interdigital electrodes with reflecting gratings and positioned above the zinc oxide film. The magnon crystal magnetic sensor realizes magneticdetection by using the linear relation between tiny change of an external magnetic field and deviation of absorption waves of SMSW propagated in magnon crystals. The SAW frequency obtained by the method is higher, and the temperature stability of a magnon band gap structure can be effectively improved, so that the temperature stability of the magnetic sensor is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Micro-strip line filter sharing substrate with YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) thin film material, and regulation method thereof
InactiveCN103401047BMiniaturizationPrecise adjustment of working frequencyWaveguide type devicesAntennasGadolinium gallium garnetMiniaturization
The invention discloses a micro-strip line filter sharing a substrate with YIG (Yttrium Iron Garnet) thin film material, and a regulation method thereof. The micro-strip line filter comprises two piezoelectric layers (1), one YIG layer (2), GGG (Gadolinium Gallium Garnet) substrate material (3) and a metal micro-strip line (4); the micro-strip line filter takes the GGG substrate material (3), needed for the growth of the YIG layer (2), as a substrate; a layer of metal micro-strip line (4) in single conduction band is printed on the upper surface of the GGG substrate material (3), on which the YIG layer (2) is grown, along a central axis in a length direction; the two piezoelectric layers (1) are respectively arranged at two sides of the metal micro-strip line. Compared with a traditional micro-strip line filter, the miniaturization of the micro-strip line filter can be realized due to the advantages of high dielectric constant (epsilon is greater than 10) and high magnetic permeability (mu is greater than 10) of YIG material and piezoelectric material. According to the micro-strip line filter disclosed by the invention, the GGG substrate material of which the length-width size is the same as that of a YIG thin film is selected, and thus the selecting difficulty on size of the YIG material is reduced.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com