Starved source diffusion for avalanche photodiode
a photodiode and starved source technology, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve the problem of reducing the responsivity of the edge, and achieve the effect of reducing the edge gain, and improving the reliability of the method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
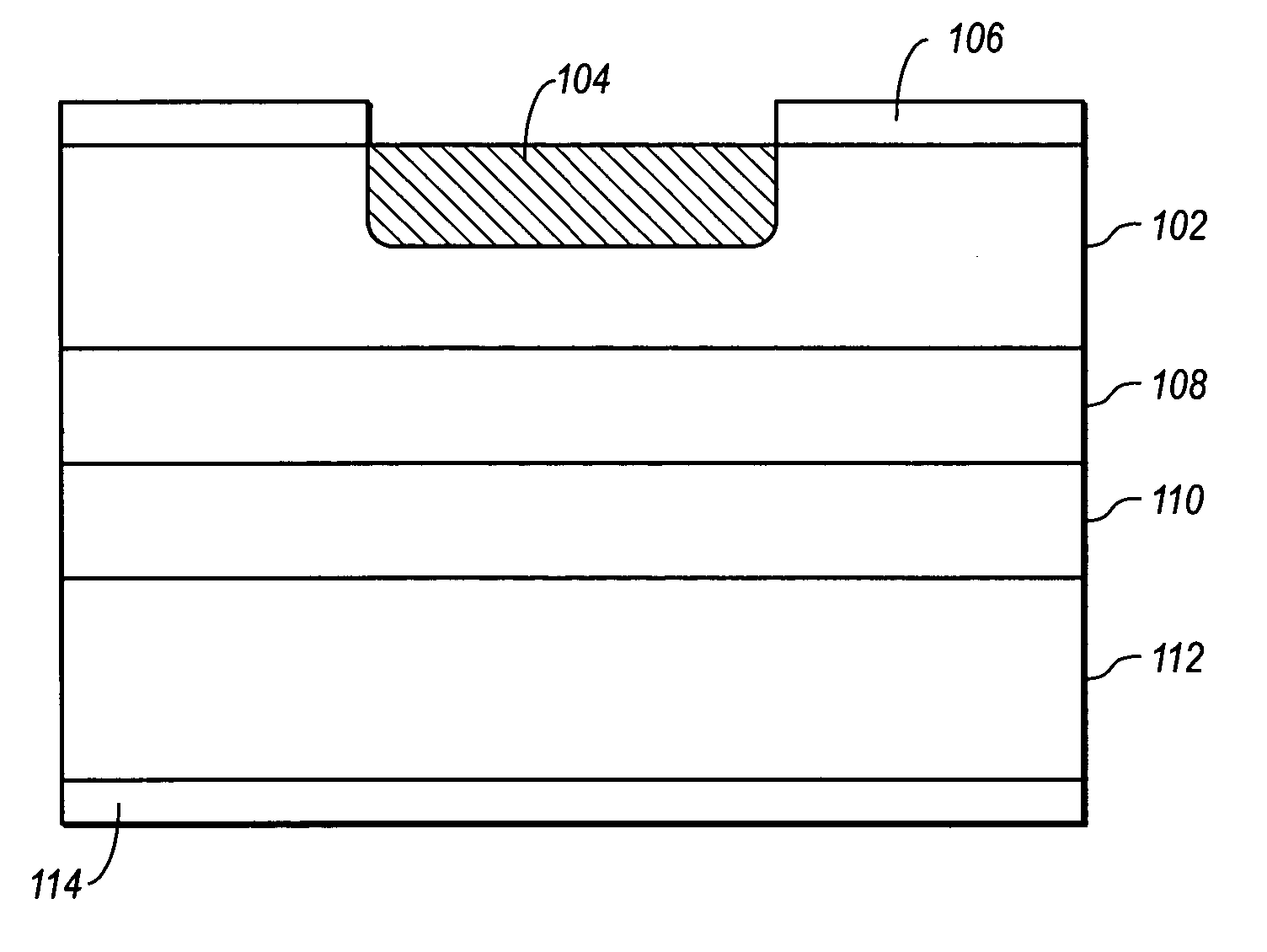
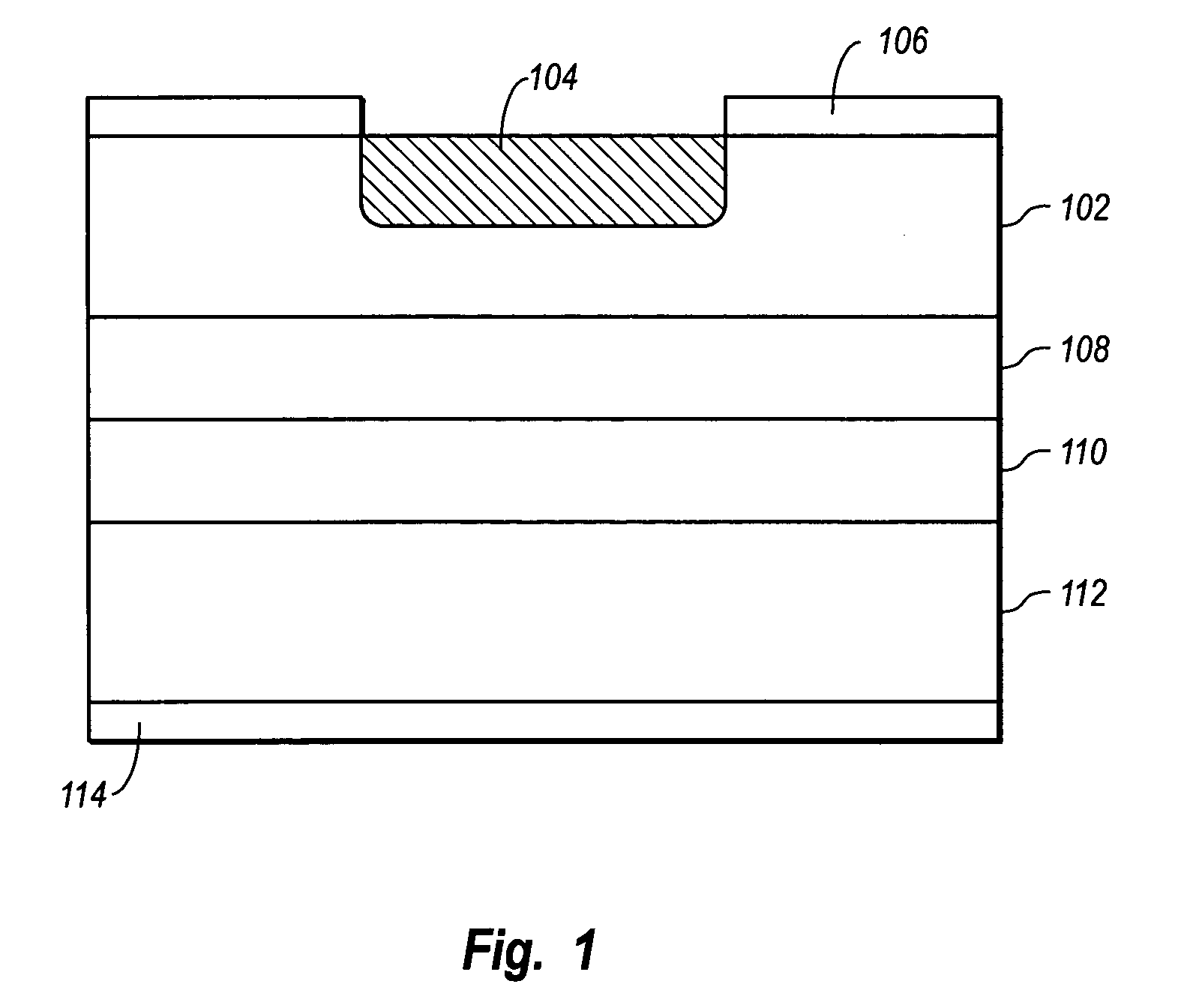
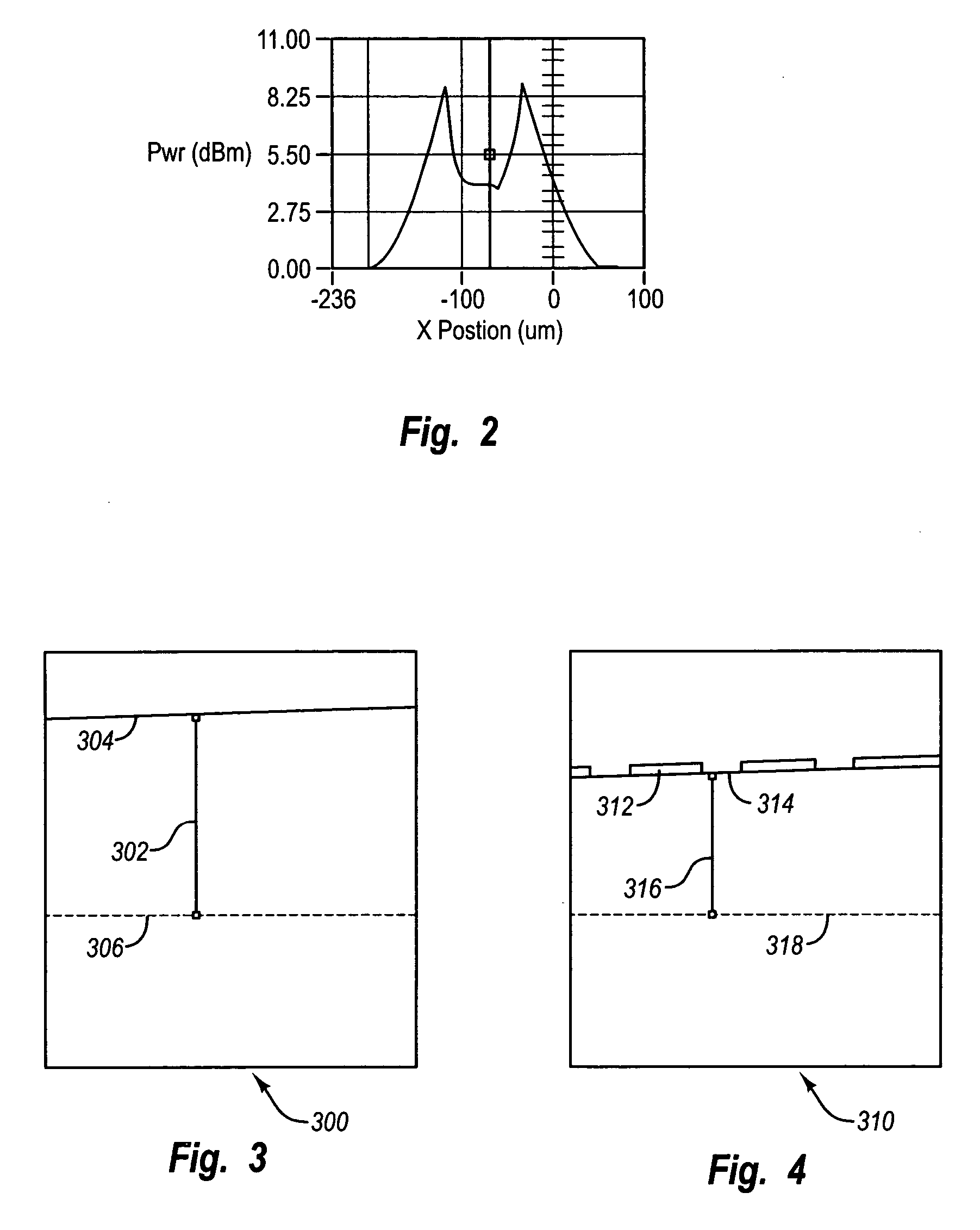
[0031] The present invention relates to starved source diffusion methods for controlling the edge effect in avalanche photodiodes (APDs). As noted in the Background Section above, edge effect is a phenomenon where the edges of a diffusion region in the active region of an APD have a higher responsivity, or ratio of current output to light input, than the center of the APD. As a result, a user or automated process aligning an APD to an optical fiber often misaligns the APD, mistaking the edge of the APD for the center.
[0032] According to the invention, the edge effect is controlled by reducing edge gain near the edges of the active region. This is accomplished by creating a sloped diffusion front near the edges of the active region such that the distance between a diffusion region and the charge layer below it is increased. In other words, a thicker avalanche layer is created, increasing the edge gain and reducing the responsivity of the edge.
[0033] The sloped diffusion front is ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com