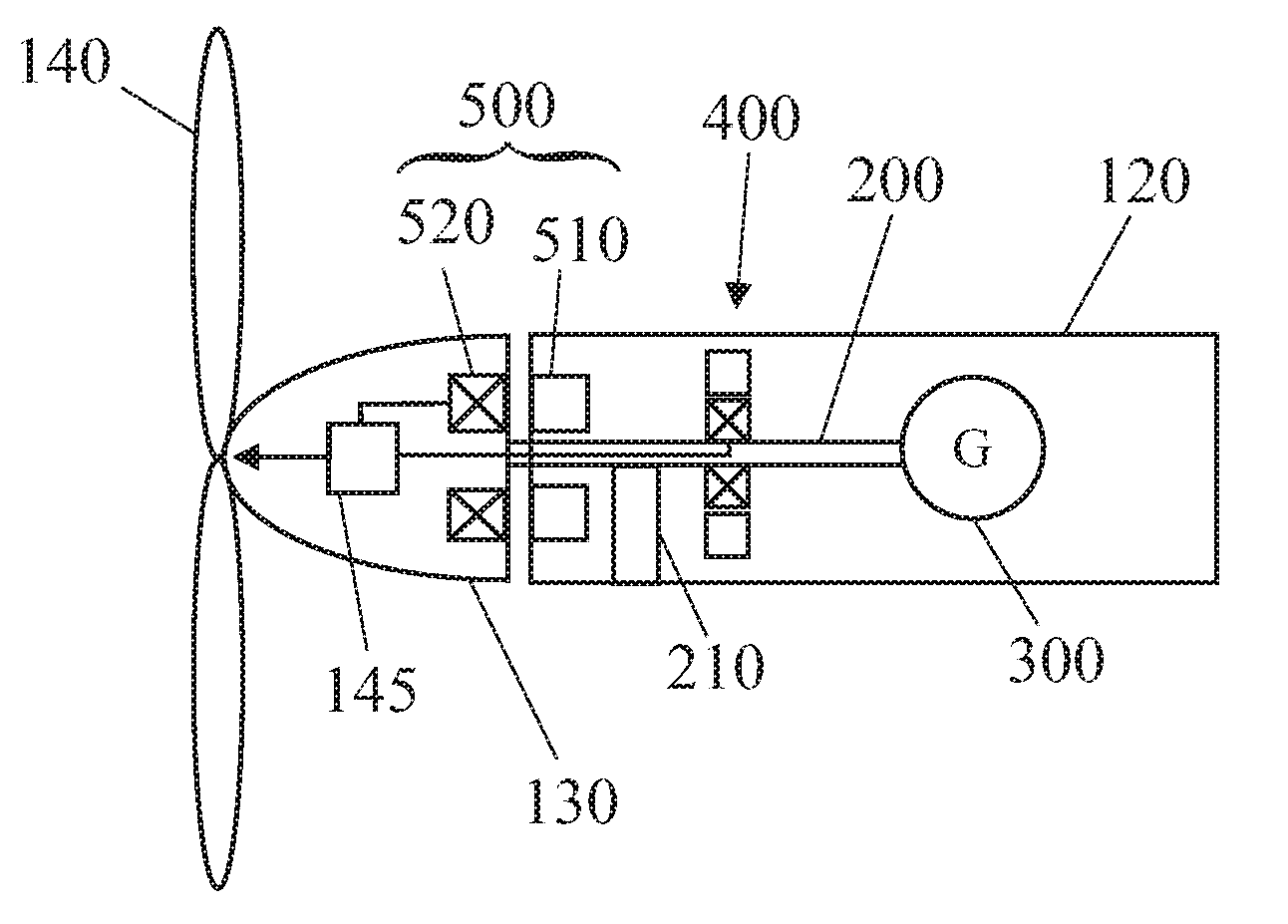
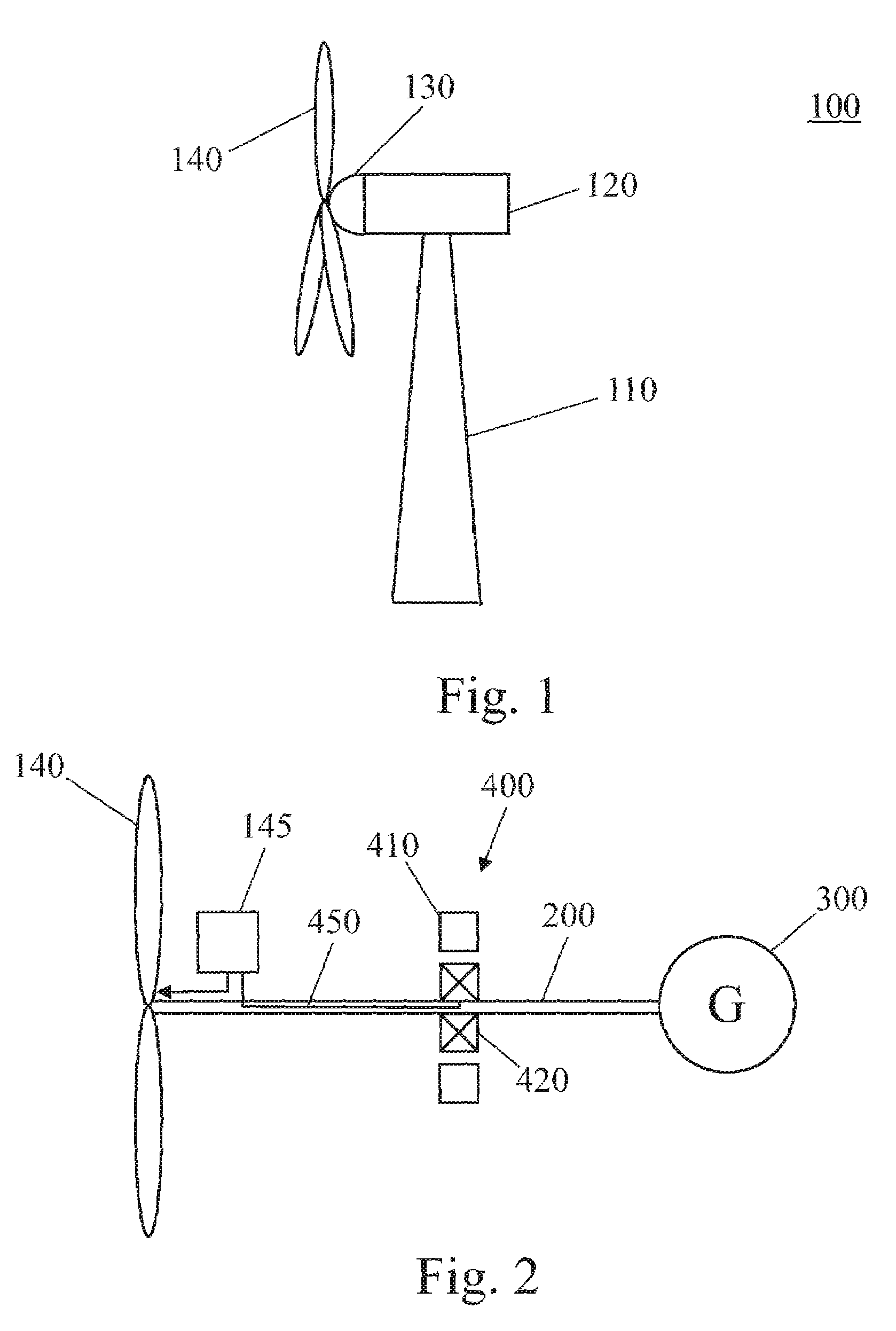
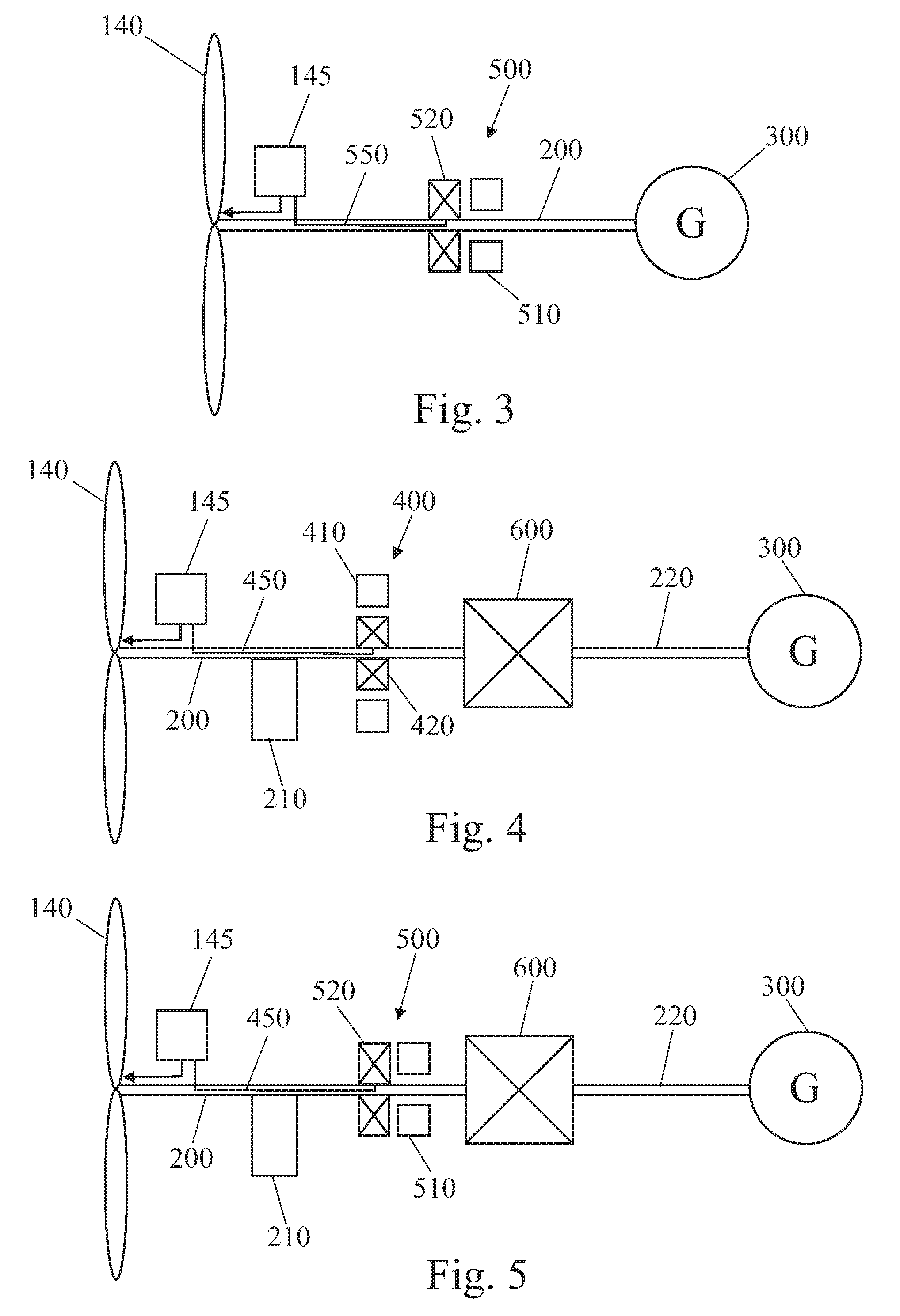
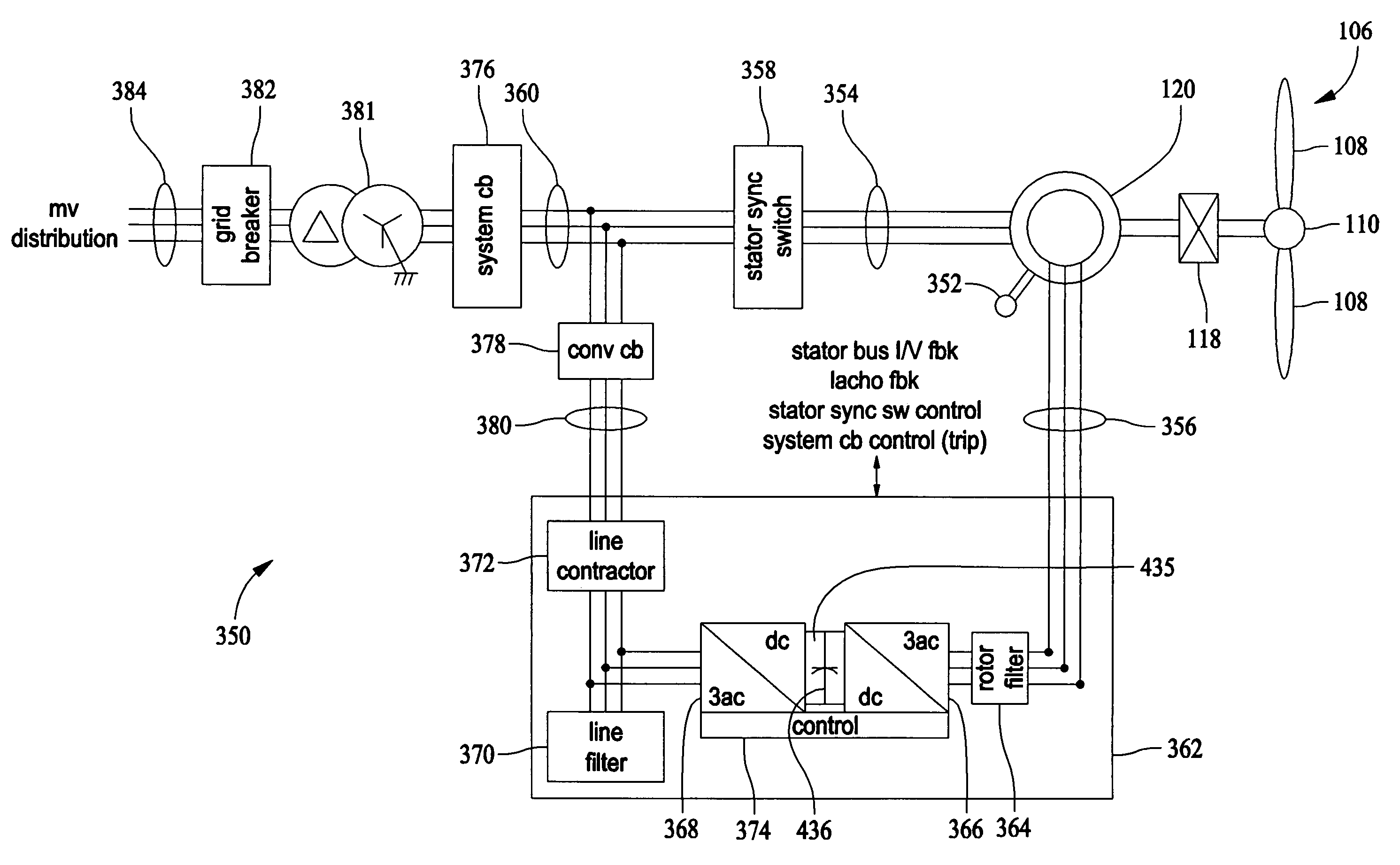
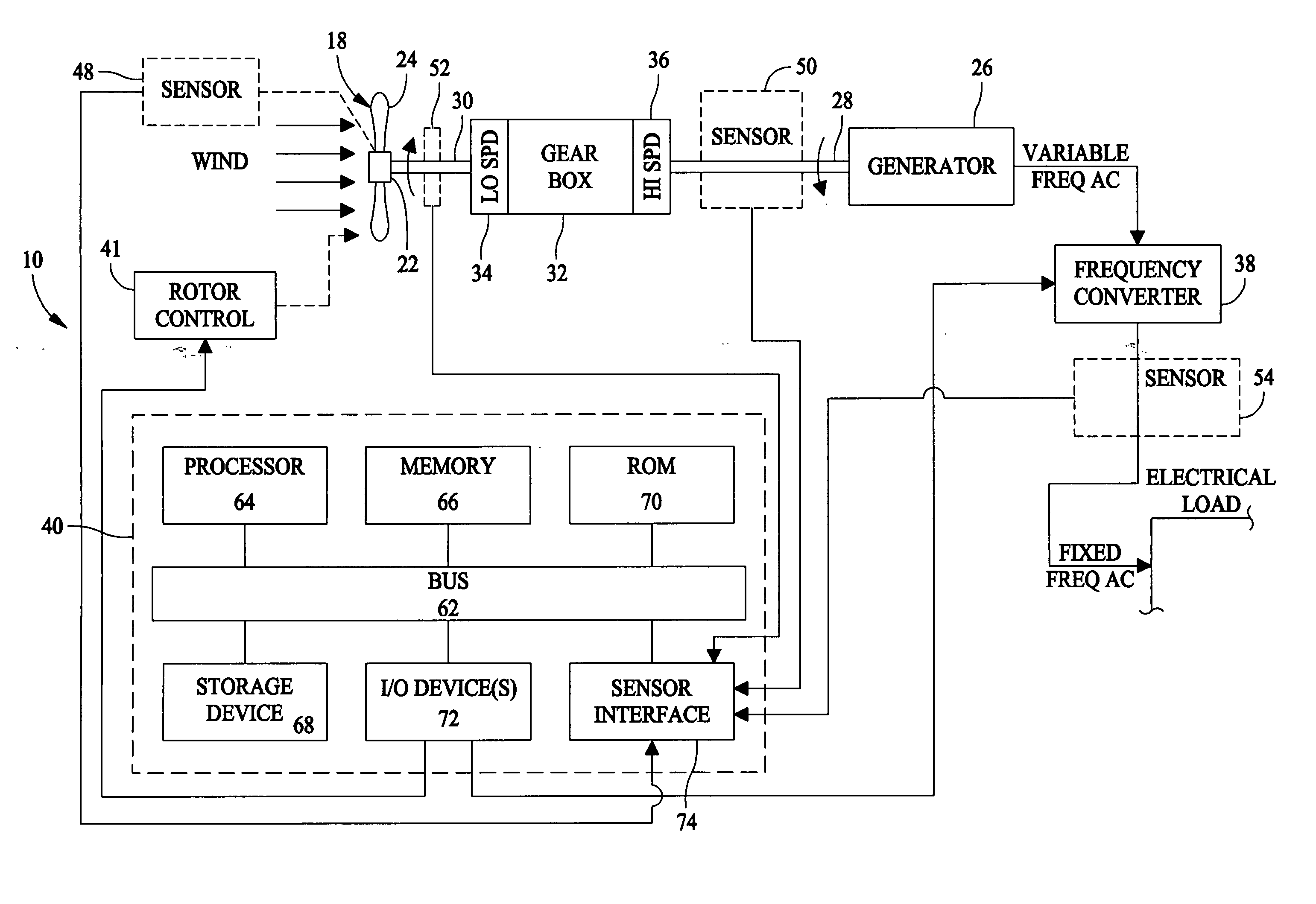
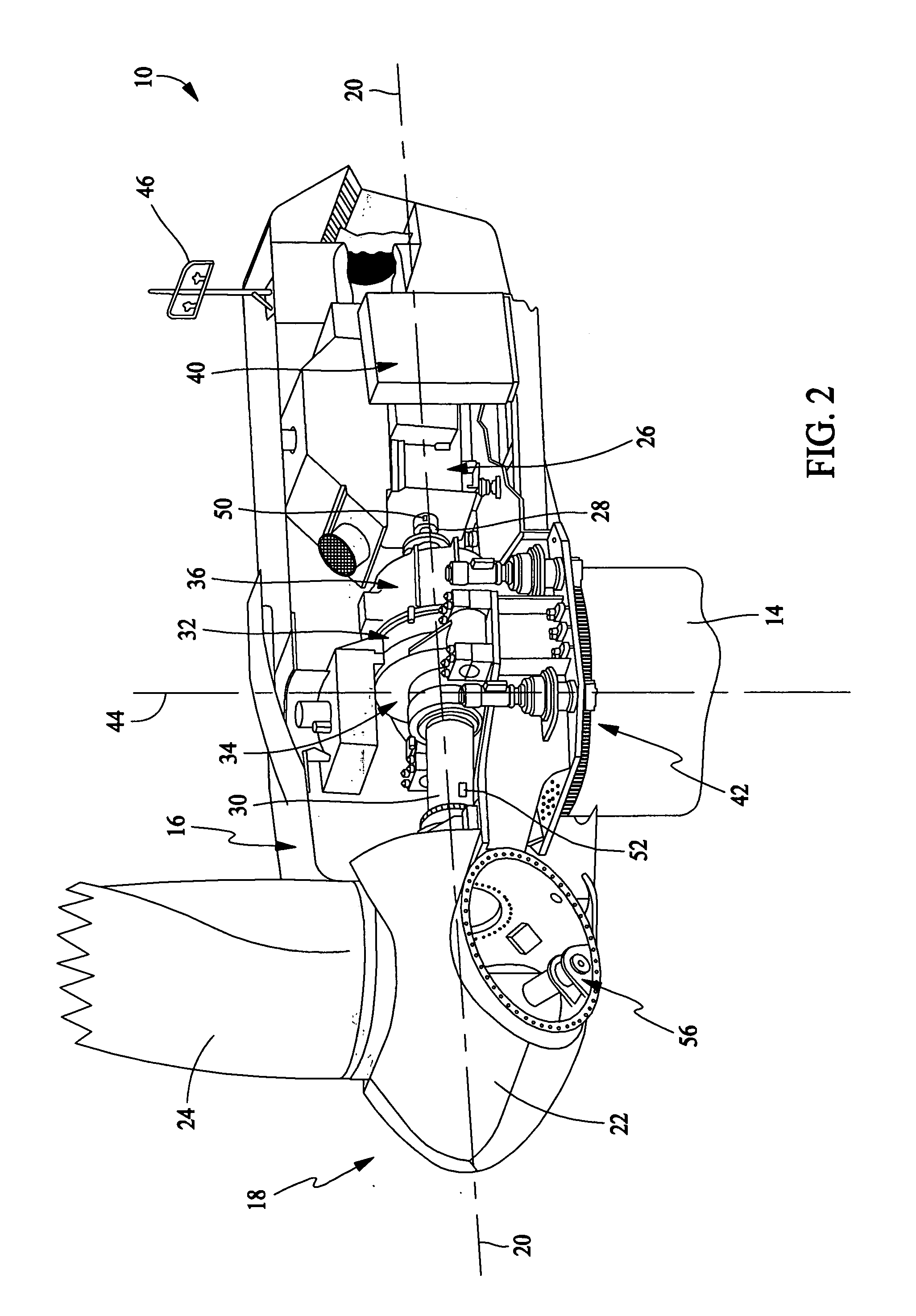
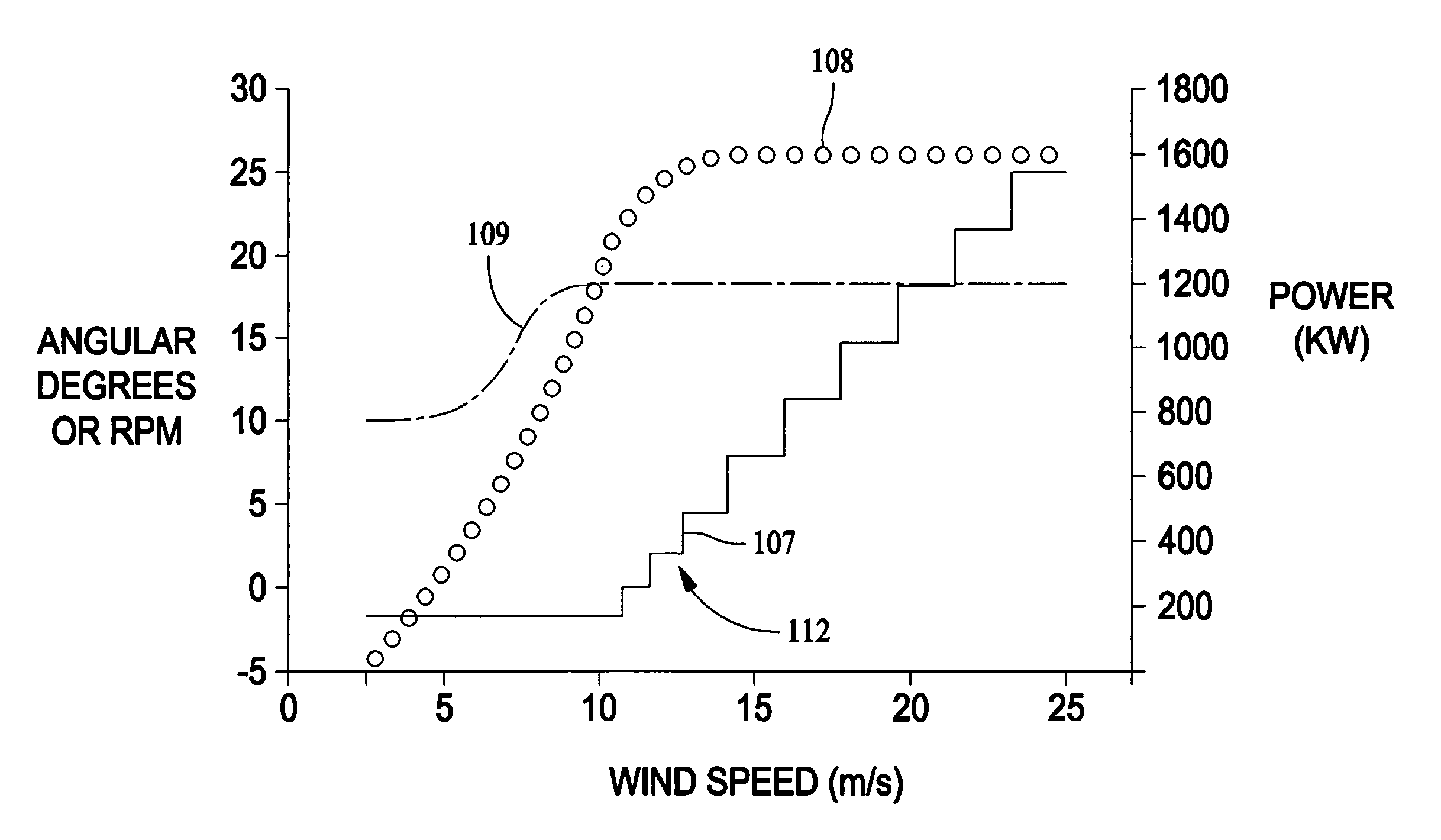
Patents
Literature
331results about "Rotational speed control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
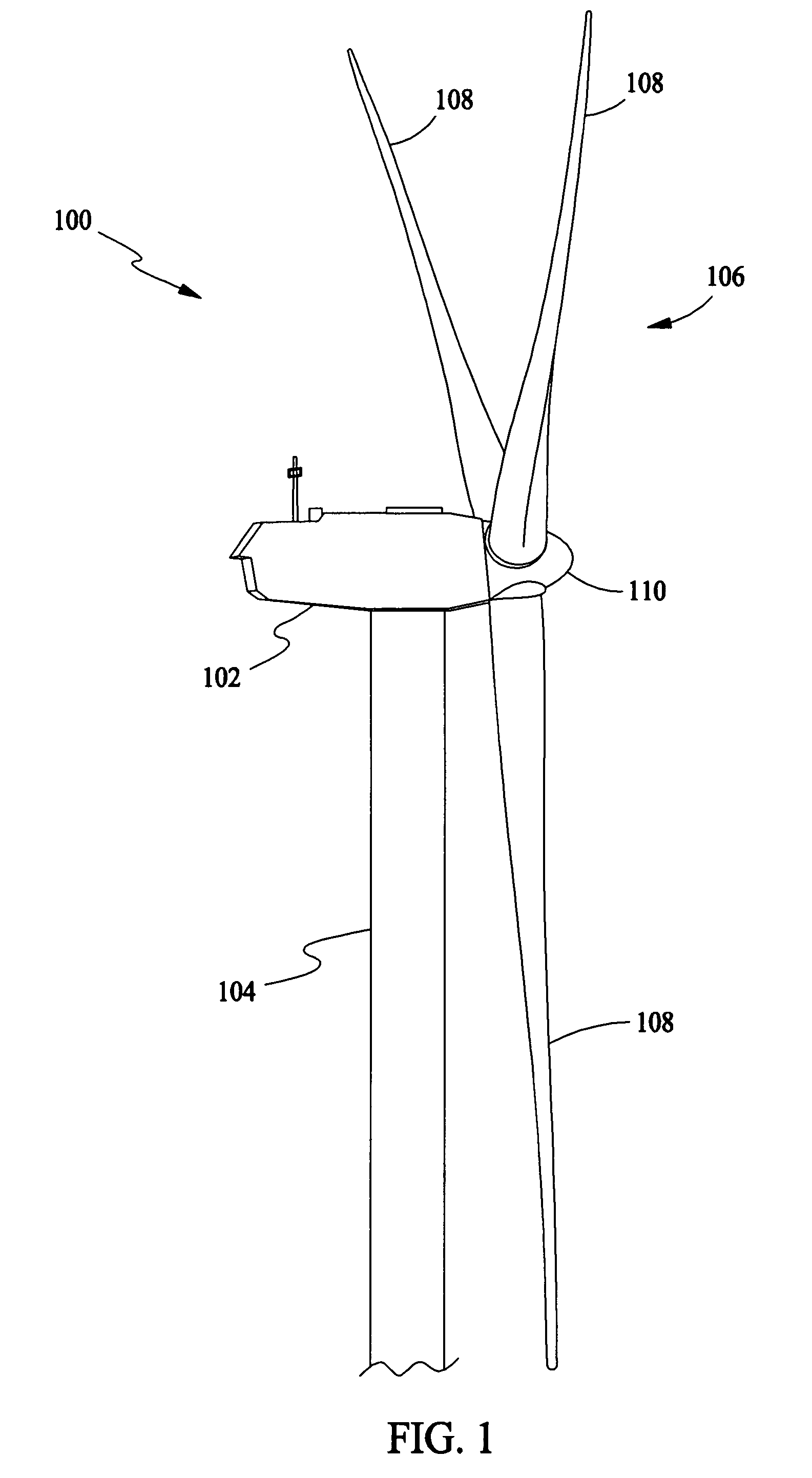
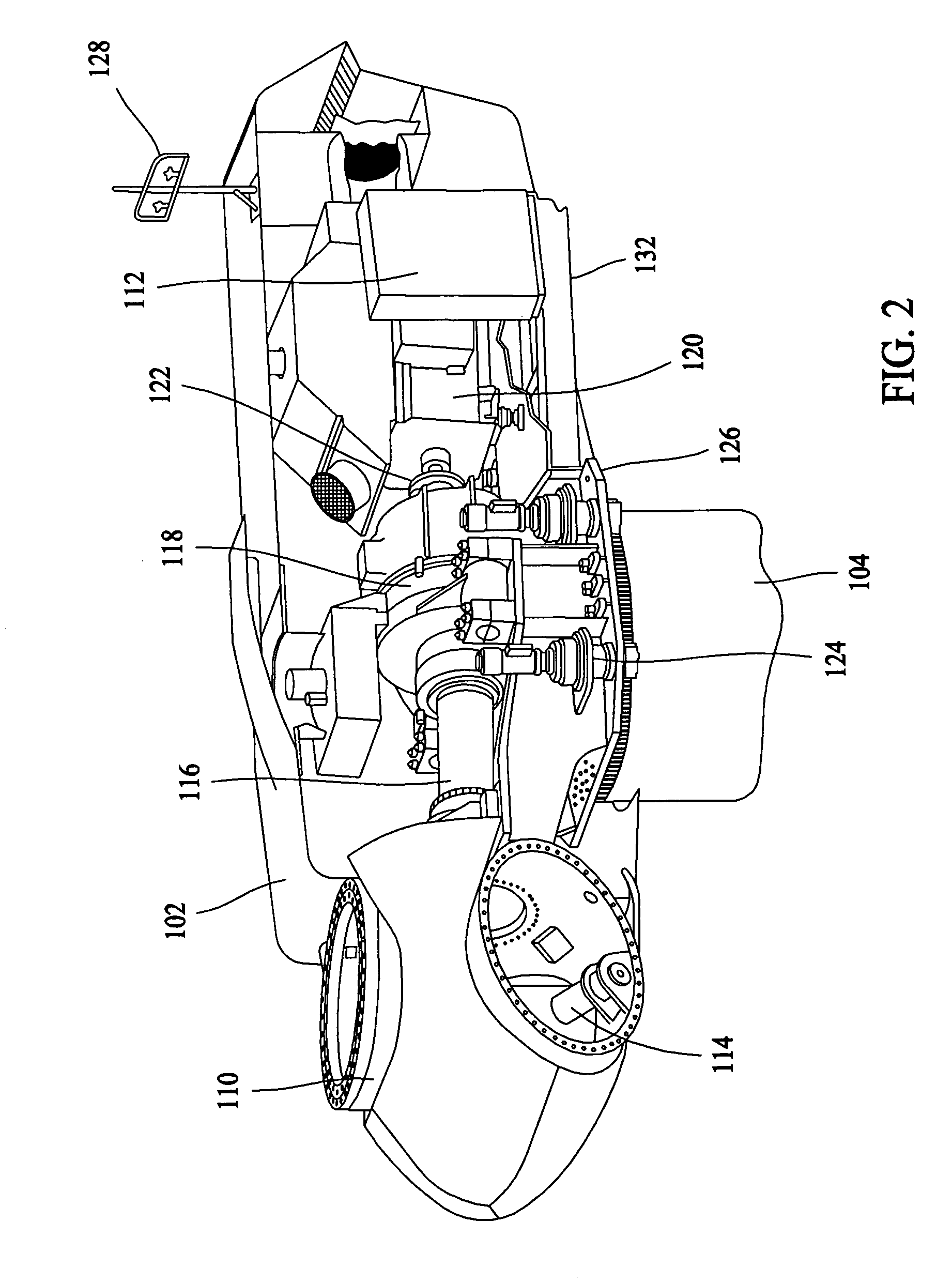
Emergency pitch drive power supply
InactiveUS7218012B1Improve usabilityLow costRotational speed controlWind motor controlDrive motorTurbine
An emergency pitch drive power supply is provided, the emergency pitch drive power supply comprising an auxiliary generator for producing electric power, wherein the auxiliary generator is a permanently excited multi-pole generator adapted to generate sufficient power for a pitch drive of a wind turbine when driven with wind rotor speed, and wherein the auxiliary generator is connected to at least one pitch drive motor of the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for power control in wind turbines
A system and method for power control in wind turbines are provided. The method includes switching a plurality of switching devices in a power conversion component of the wind turbine system in a normal switching mode to provide power flow through the power conversion component. The method further includes switching the plurality of switches devices in the power conversion component of the wind turbine system in a short circuit switching mode to prevent power flow through the power conversion component.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
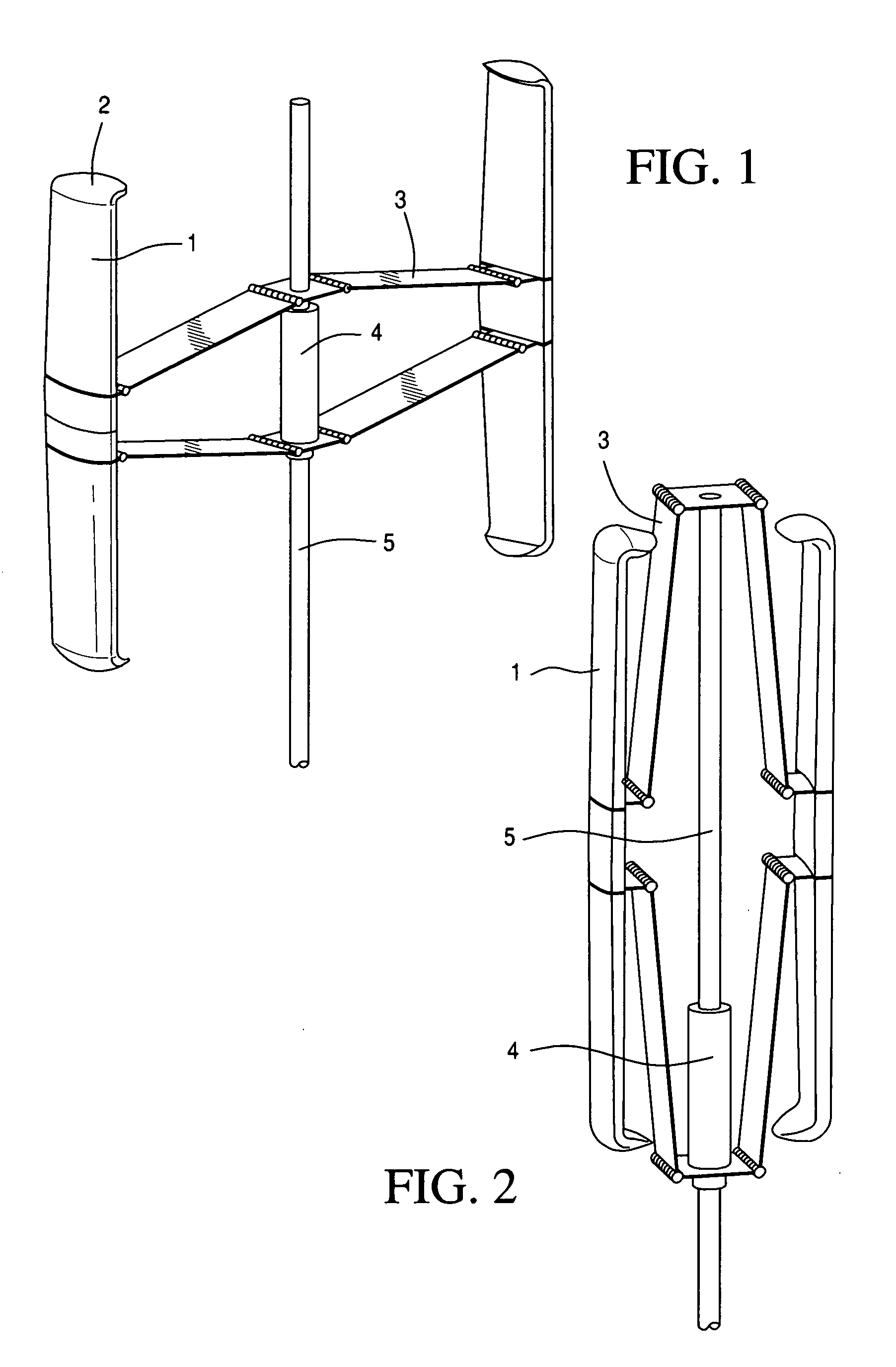
Vertical axis wind turbine
InactiveUS6242818B1Rotational speed controlWind motor controlVertical axis wind turbineGravitational force
A vertical axis wind turbine having a plurality of blades around its periphery and a pivotable door associated with each blade. Each door has a pivot axis that is inclined outwardly toward the bottom of the turbine so that gravitational forces will pull the doors toward an open position. The doors are designed to move toward a closed position to at least partially block wind forces from the blades when the rotor rotates at potentially damaging speeds. The turbine has mating coils on the rotor and the support column to generate electrical energy when the rotor rotates.
Owner:SMEDLEY RONALD H
System and method for power control in wind turbines
A system and method for power control in wind turbines are provided. The method includes switching a plurality of switching devices in a power conversion component of the wind turbine system in a normal switching mode to provide power flow through the power conversion component. The method further includes switching the plurality of switches devices in the power conversion component of the wind turbine system in a short circuit switching mode to prevent power flow through the power conversion component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for controlling rotational speed of a rotor
A method for controlling a rotational speed of a rotor having at least one rotor blade, a rotor shaft, and an electrical generator coupled thereto. The method includes controlling a torque of the rotor shaft by controlling a torque of the electrical generator, alternating between changing an angle of pitch of the at least one rotor blade and maintaining the angle of pitch of the at least one rotor blade substantially constant, and maintaining a substantially constant rotational speed of the rotor during variable wind speeds above a predetermined rated wind speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for controlling rotational speed of a rotor
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
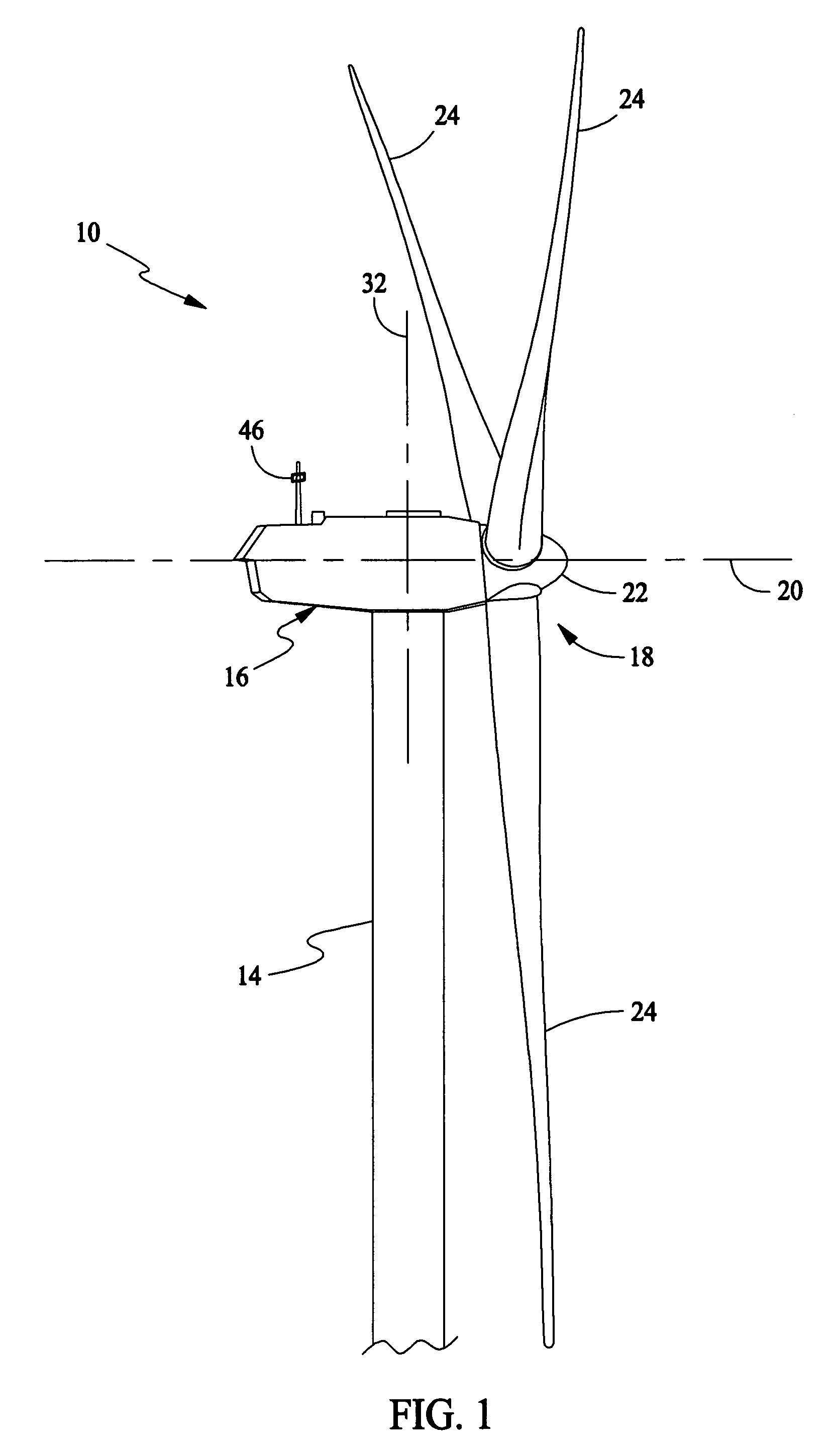
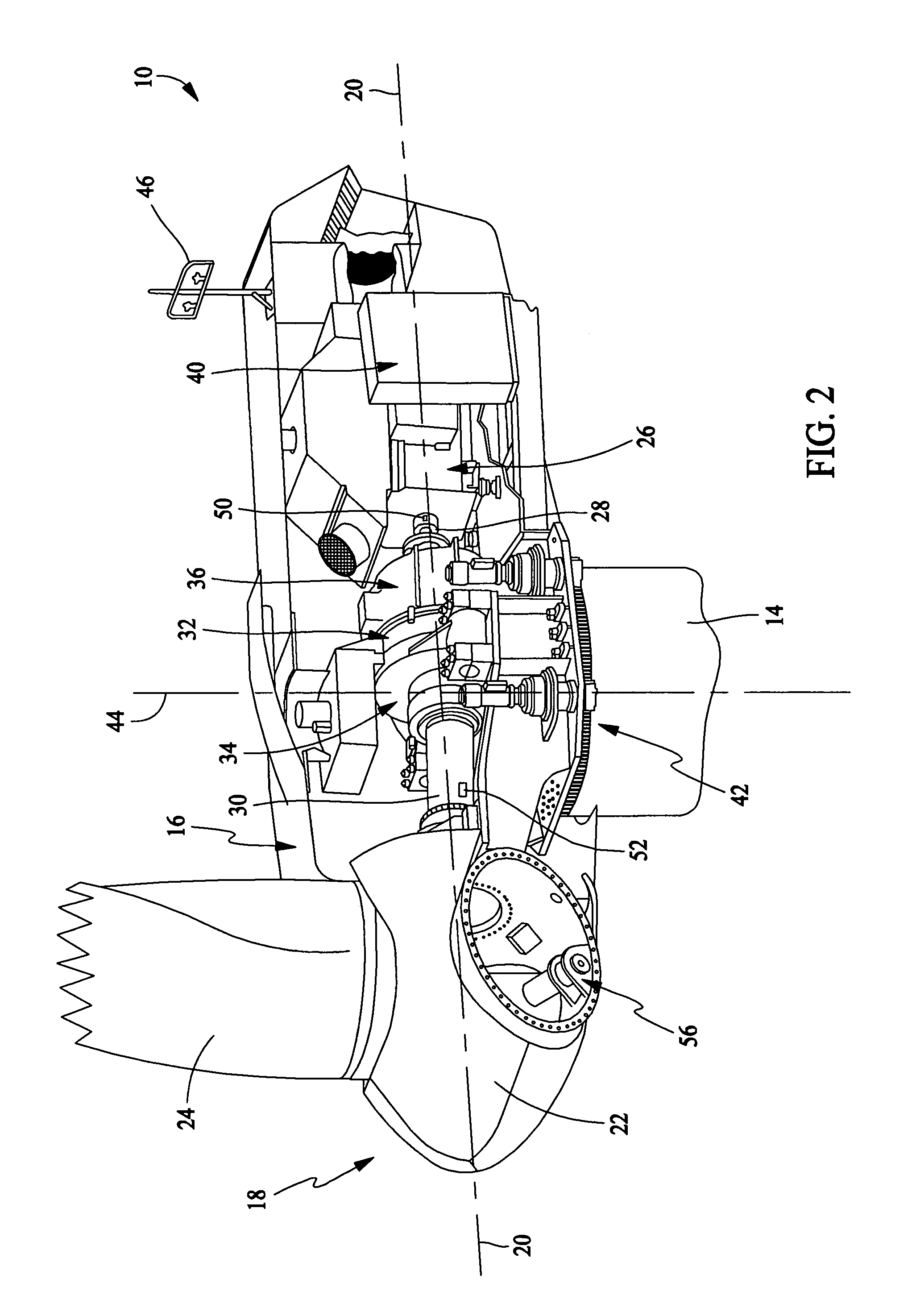
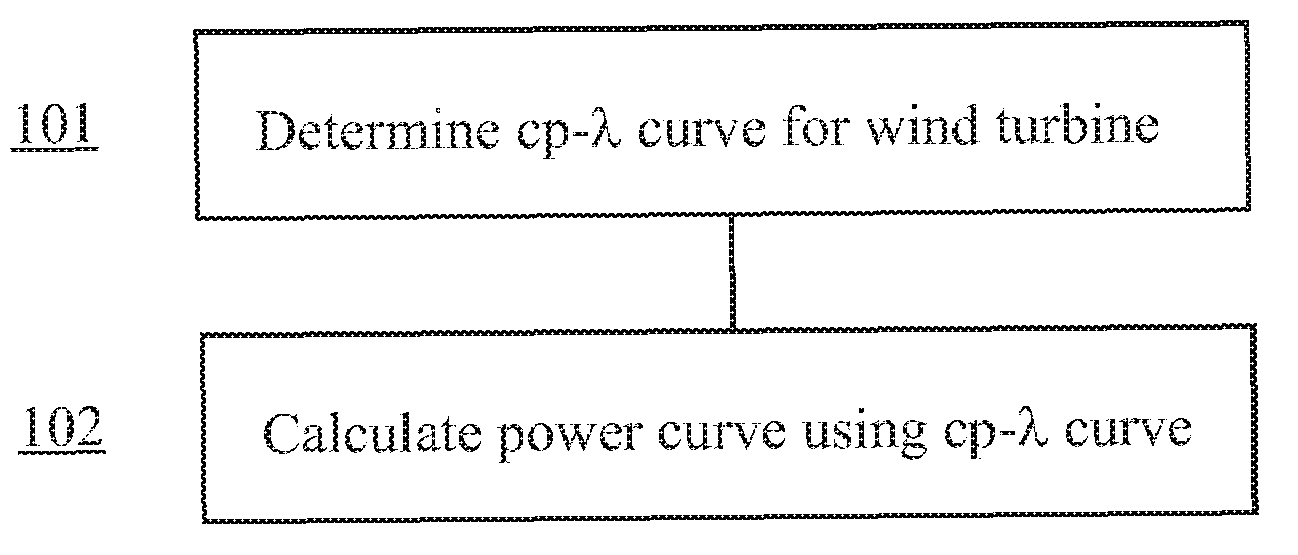
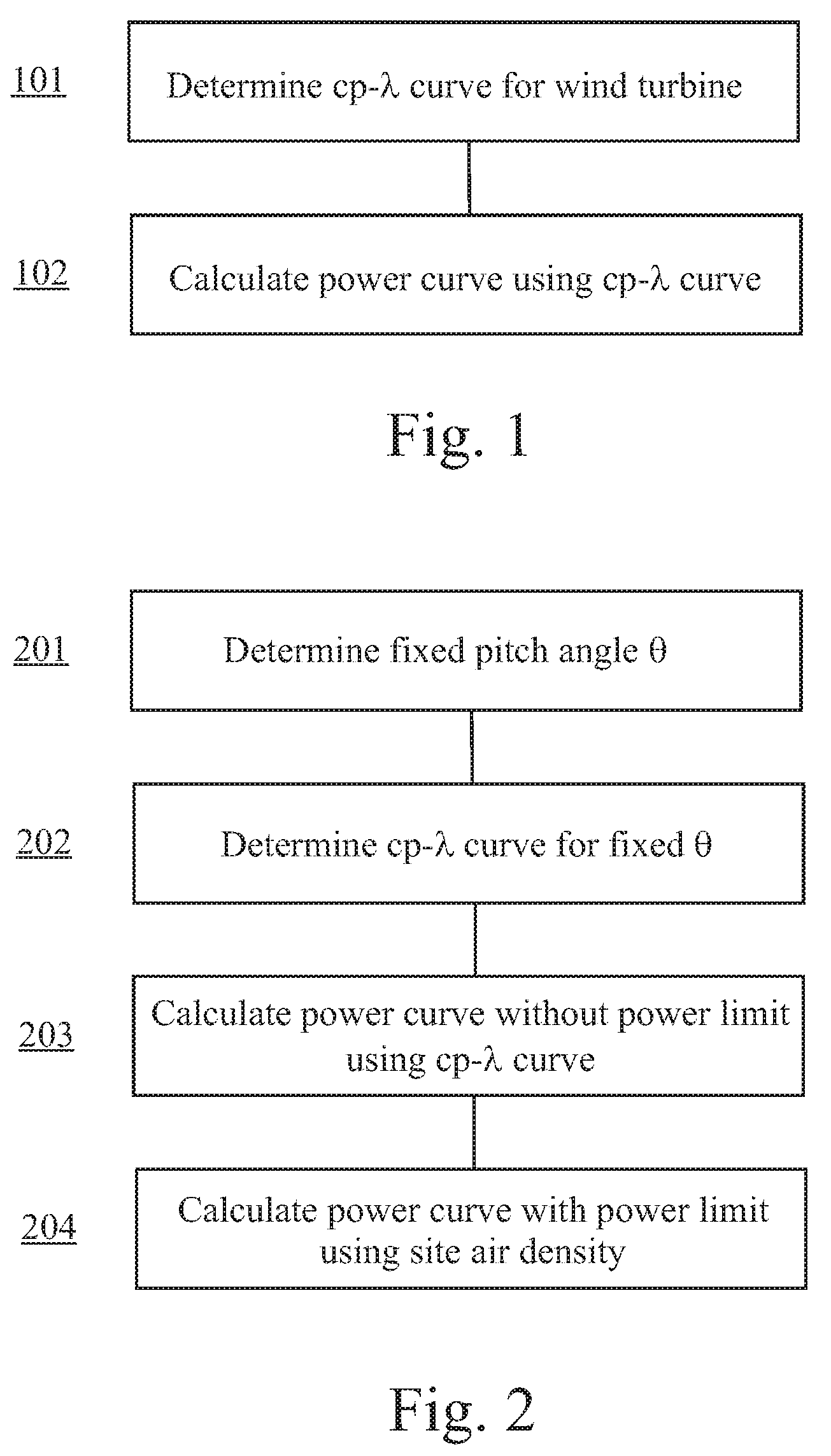
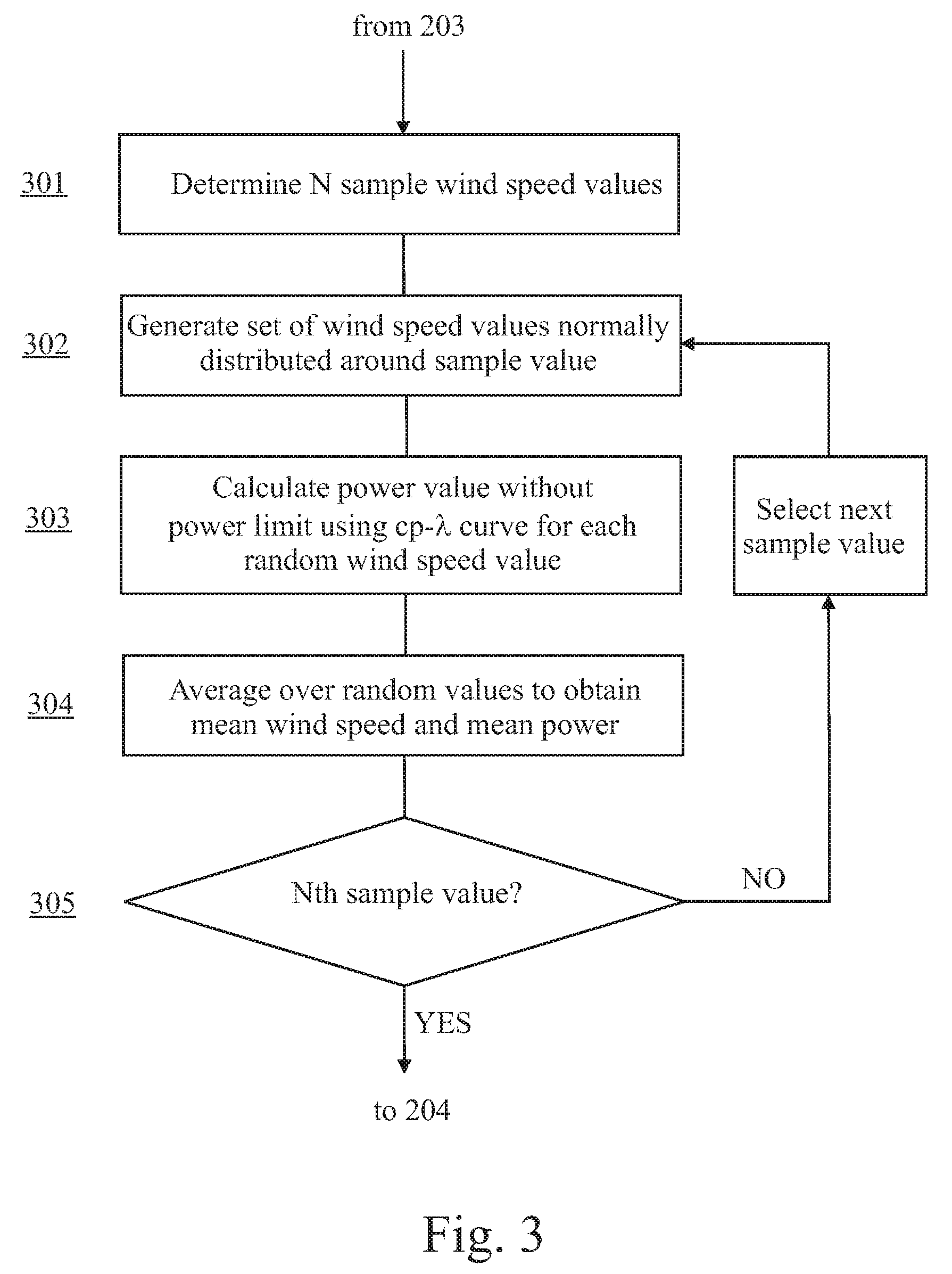
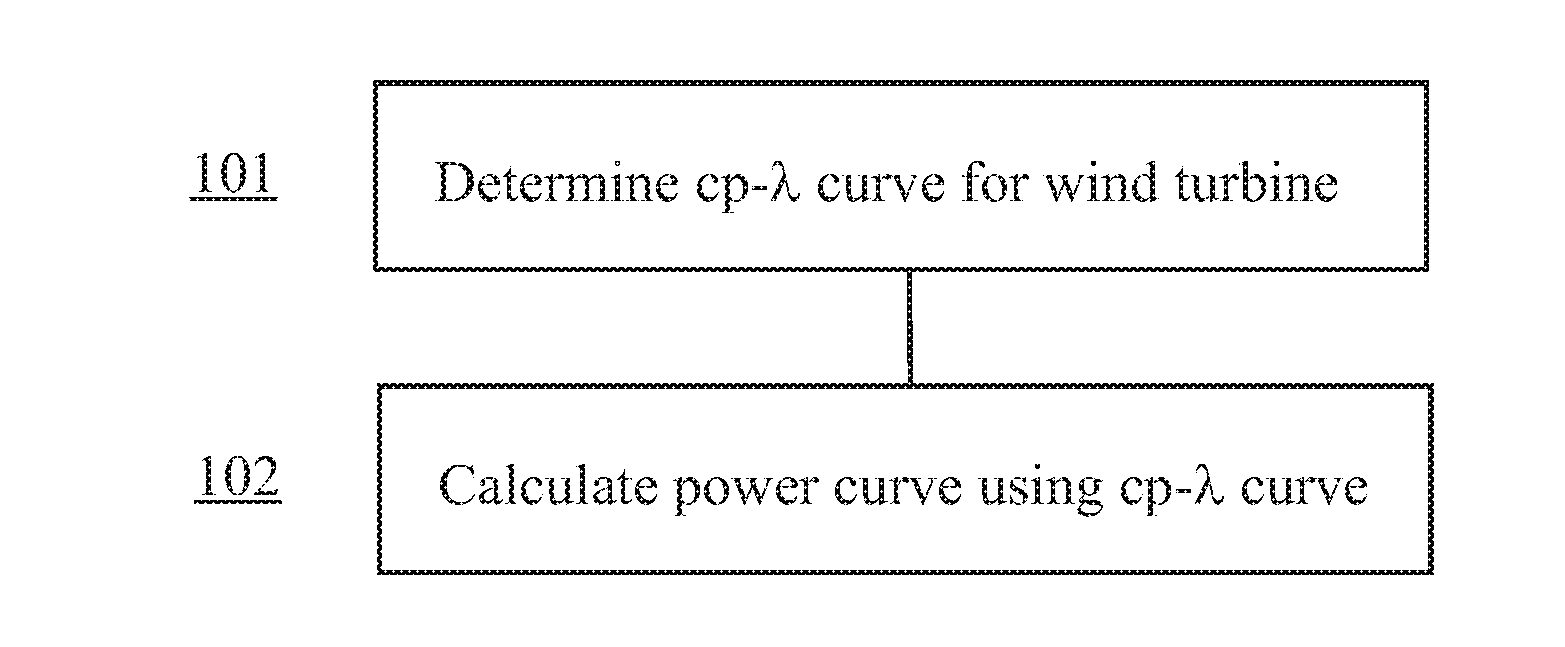
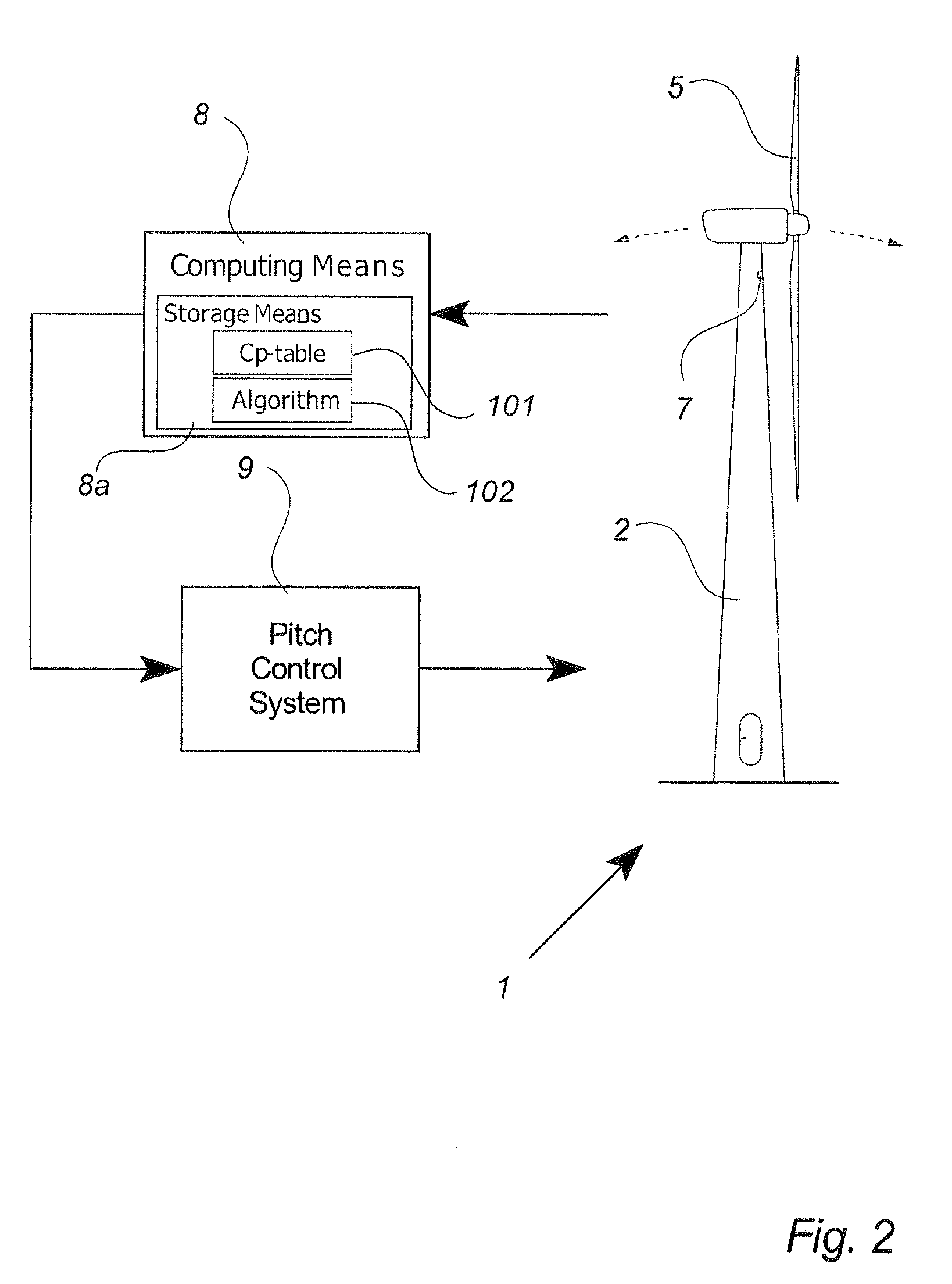
Method for predicting a power curve for a wind turbine
ActiveUS7420289B2Easy to controlQuality improvementRotational speed controlLevel controlEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
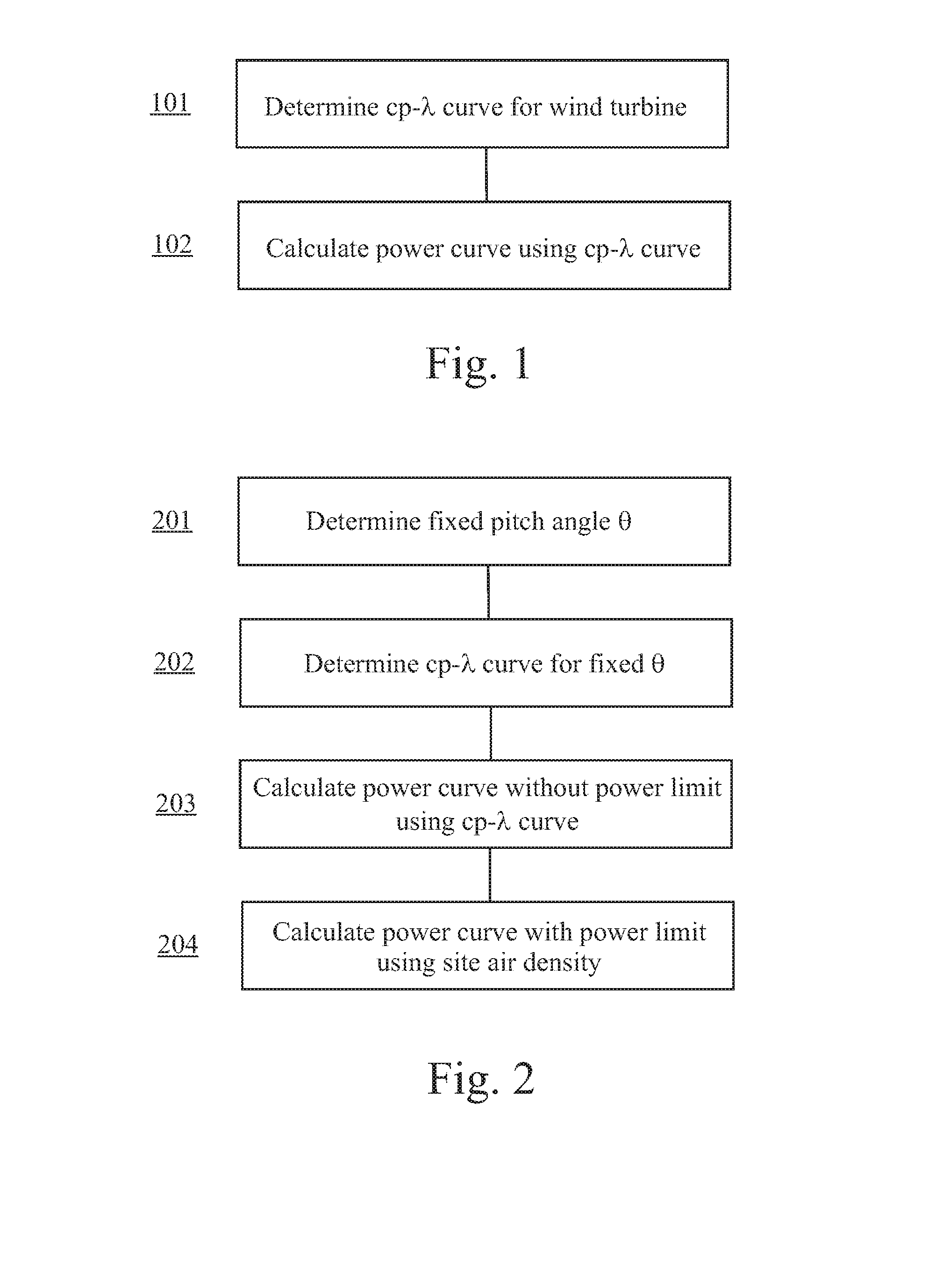
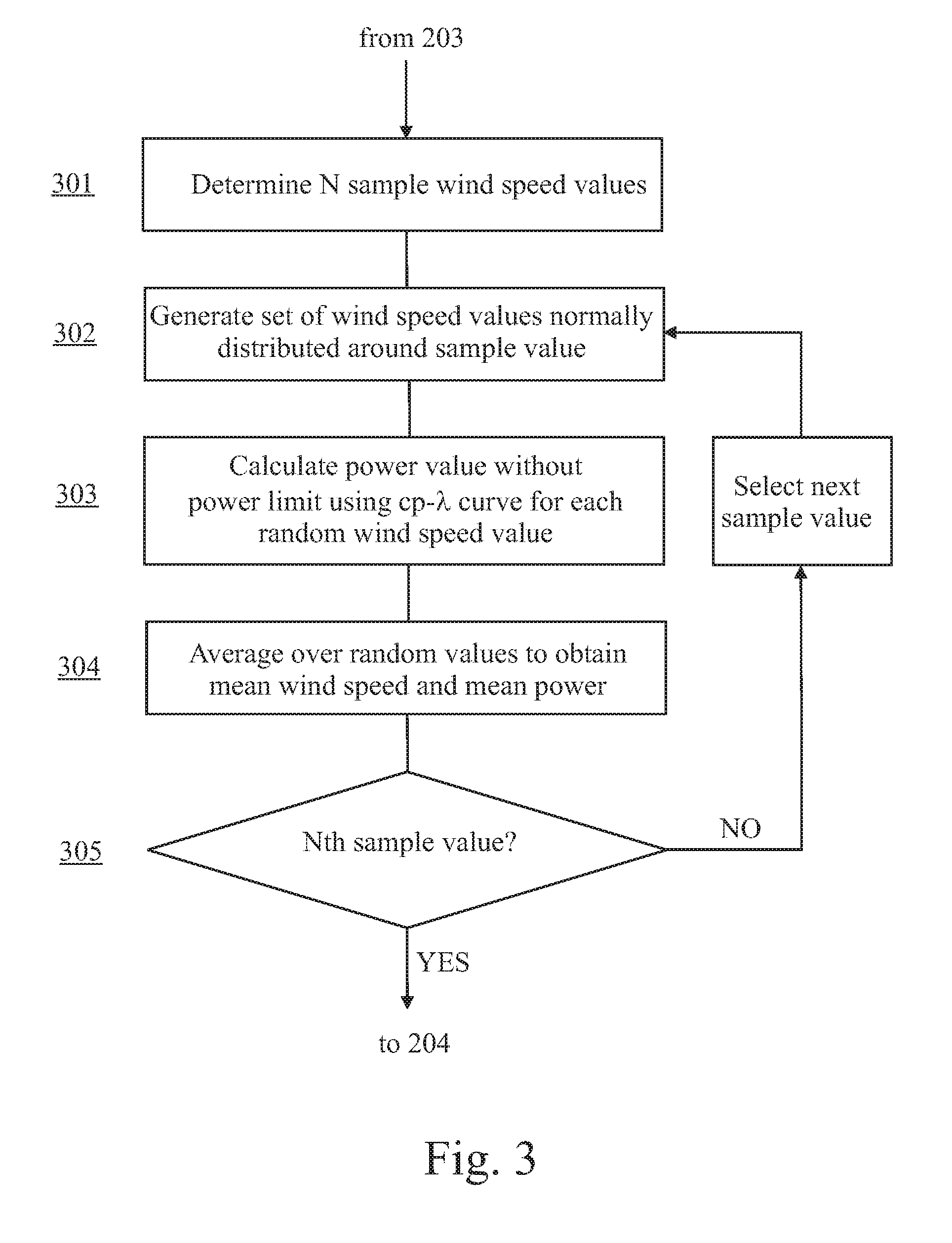
A method for calculating a high-altitude power curve for a wind turbine is provided, the method including the steps of determining a cp-λ curve for a predetermined blade pitch angle of said wind turbine; calculating a first power curve without power limit based on the cp-λ curve; and calculating the high-altitude power curve with power limit from said first power curve, thereby using a site air density.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Retractable wind turbines
InactiveUS20100172759A1Protection from damageGuaranteed normal operationRotational speed controlPropellersState of artTurbine blade
A wind turbine electrical generating device is described where the blades that comprise the airfoil are retractable during operation. This feature allows for a number of improvements over the current state of the art including damage protection and the ability to remain operational during high wind conditions. Further described is a computer feedback loop that controls the degree of retraction. In addition, lightweight airfoil turbine blades are described that are assembled from discrete segments.
Owner:SULLIVAN JOHN T
Wind turbine and operating method thereof
InactiveUS20080069692A1Prevent speedingControl moreRotational speed controlLevel controlClassical mechanicsControl theory
A pitch controller, uninterruptible power supply, and rotational speed detector are disposed in the rotor in a wind turbine. When a slip ring failure or wire breakage occurs, the pitch controller internally creates a pitch angle command so as to control the pitch angle.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
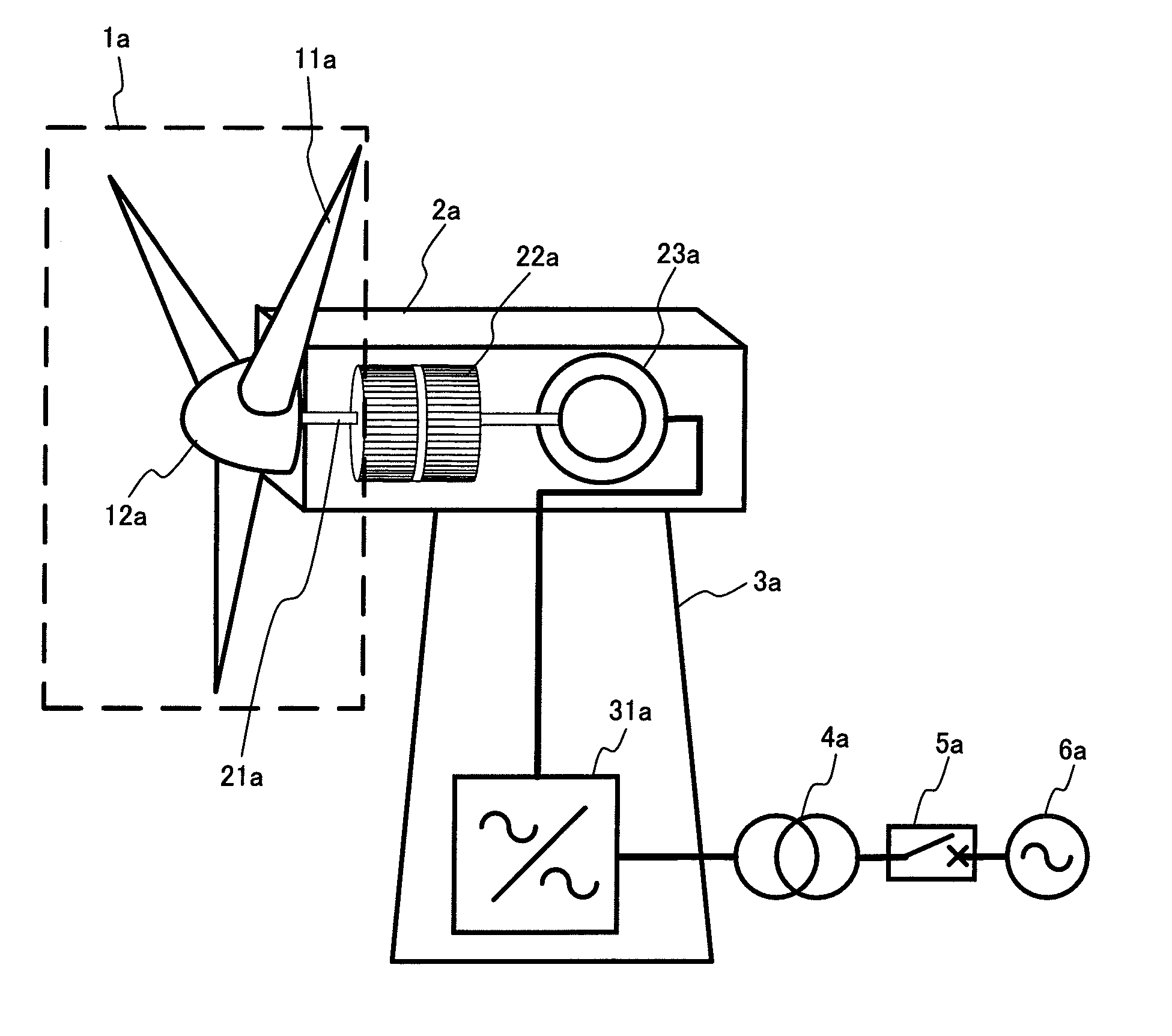
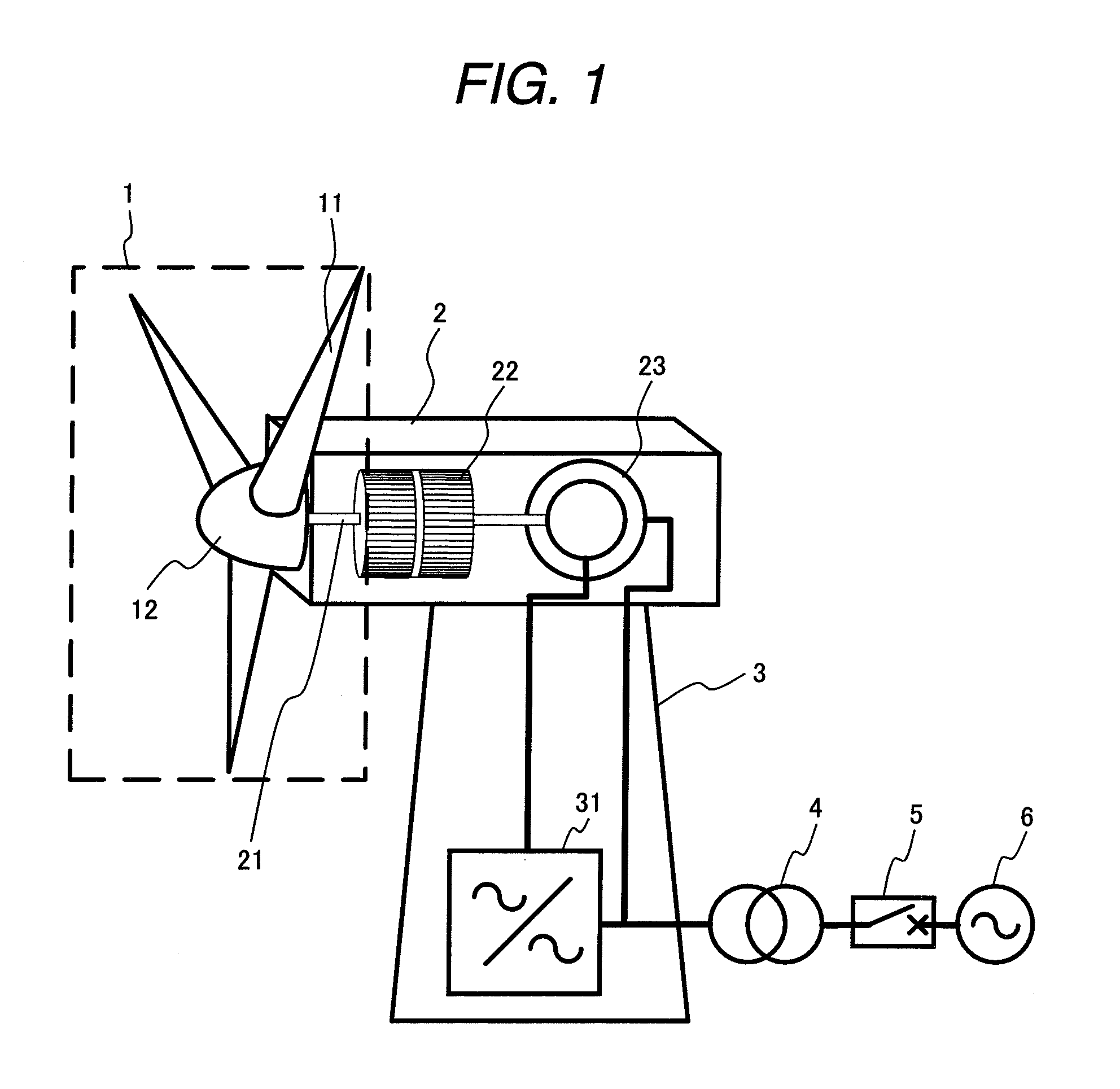
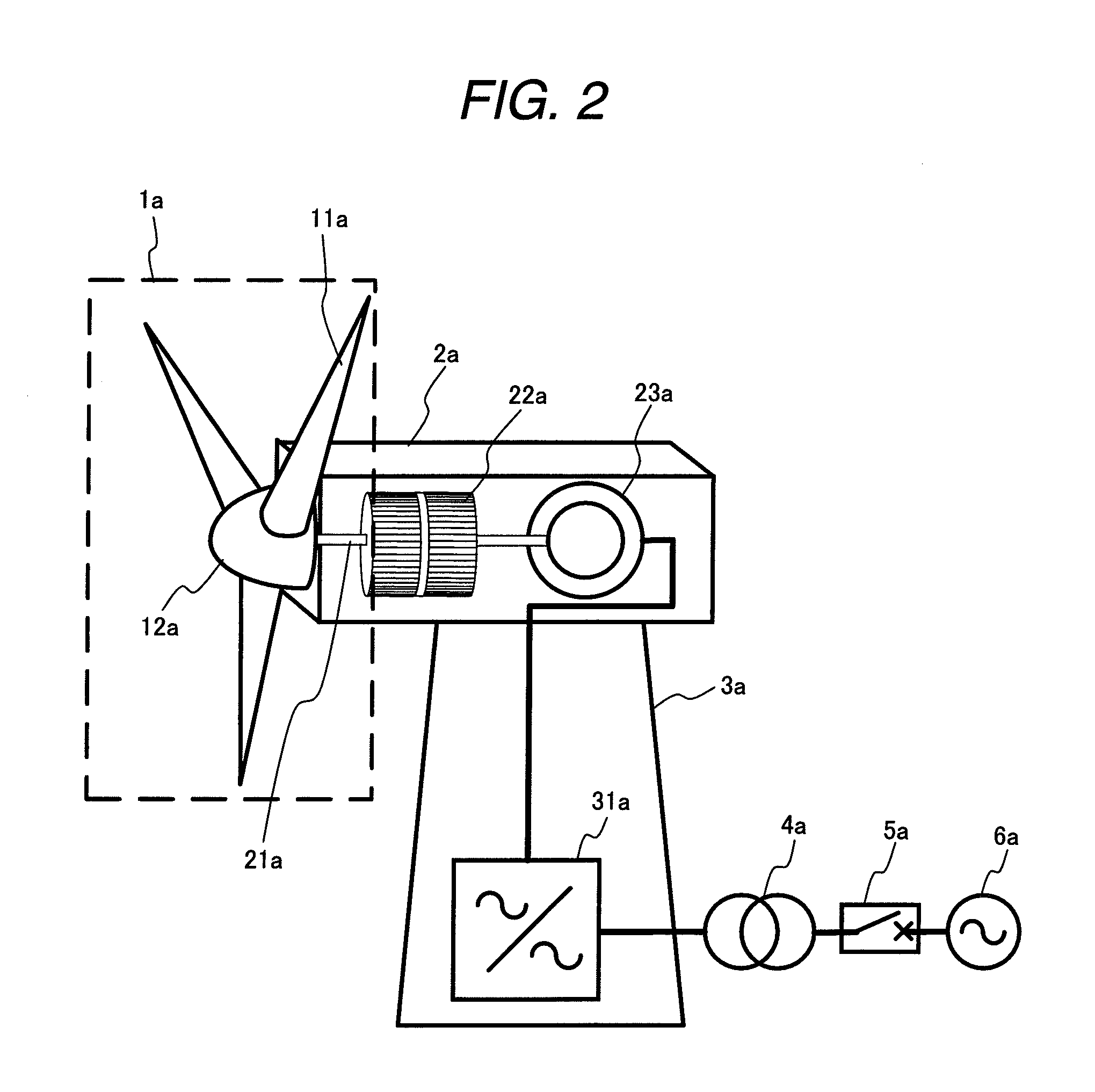
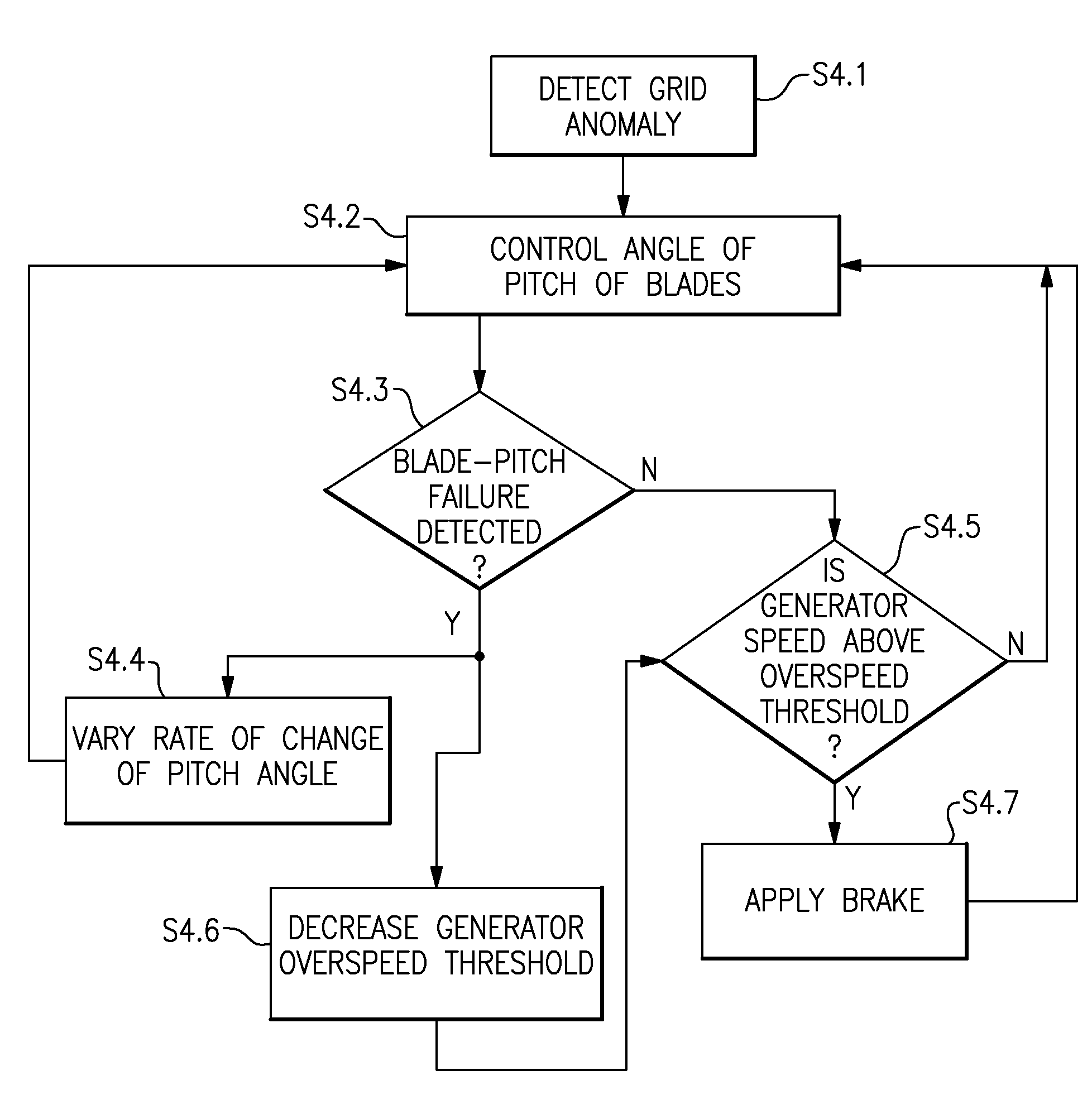
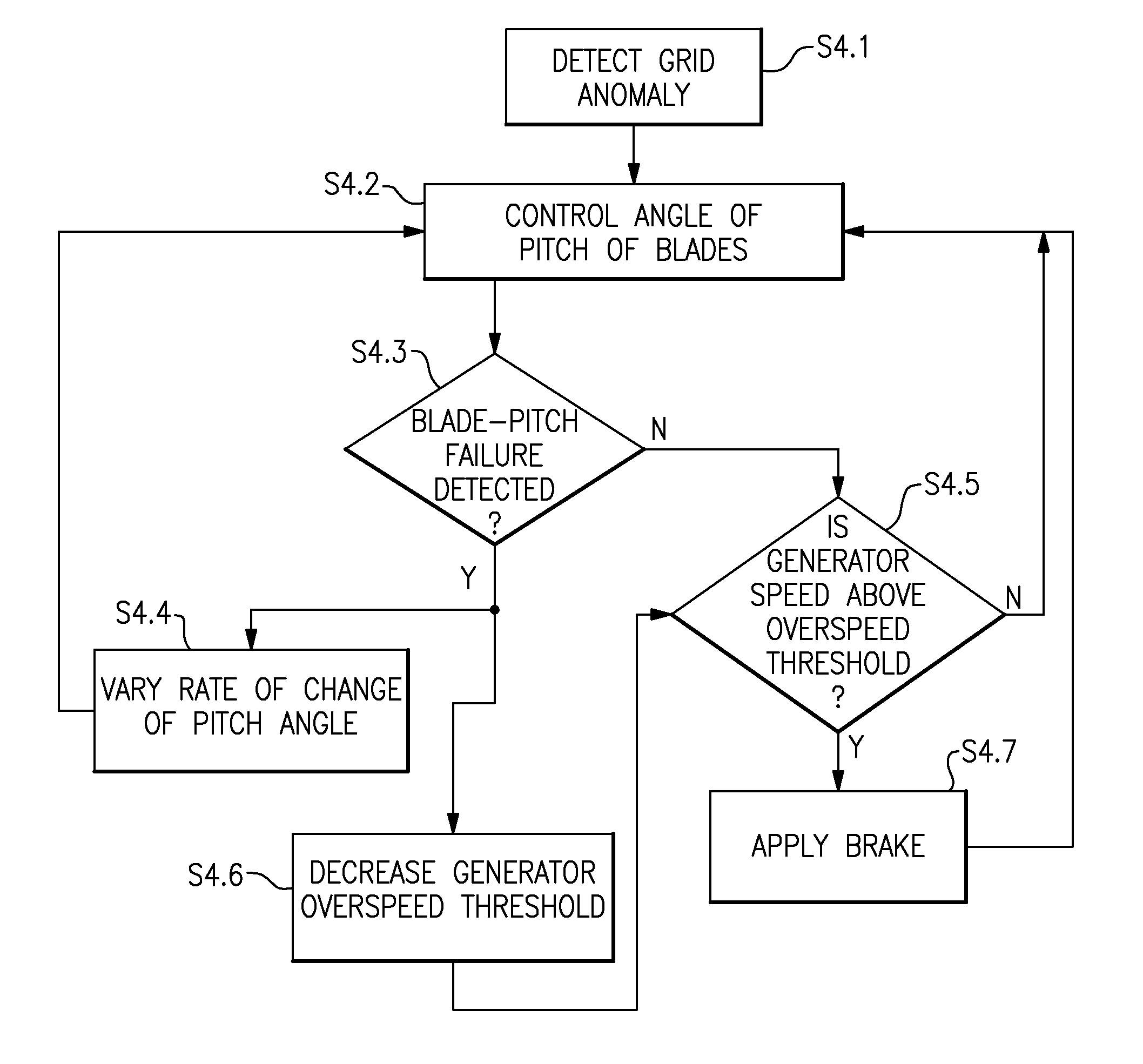
System and method for reducing rotor loads in a wind turbine upon detection of blade-pitch failure and loss of counter-torque
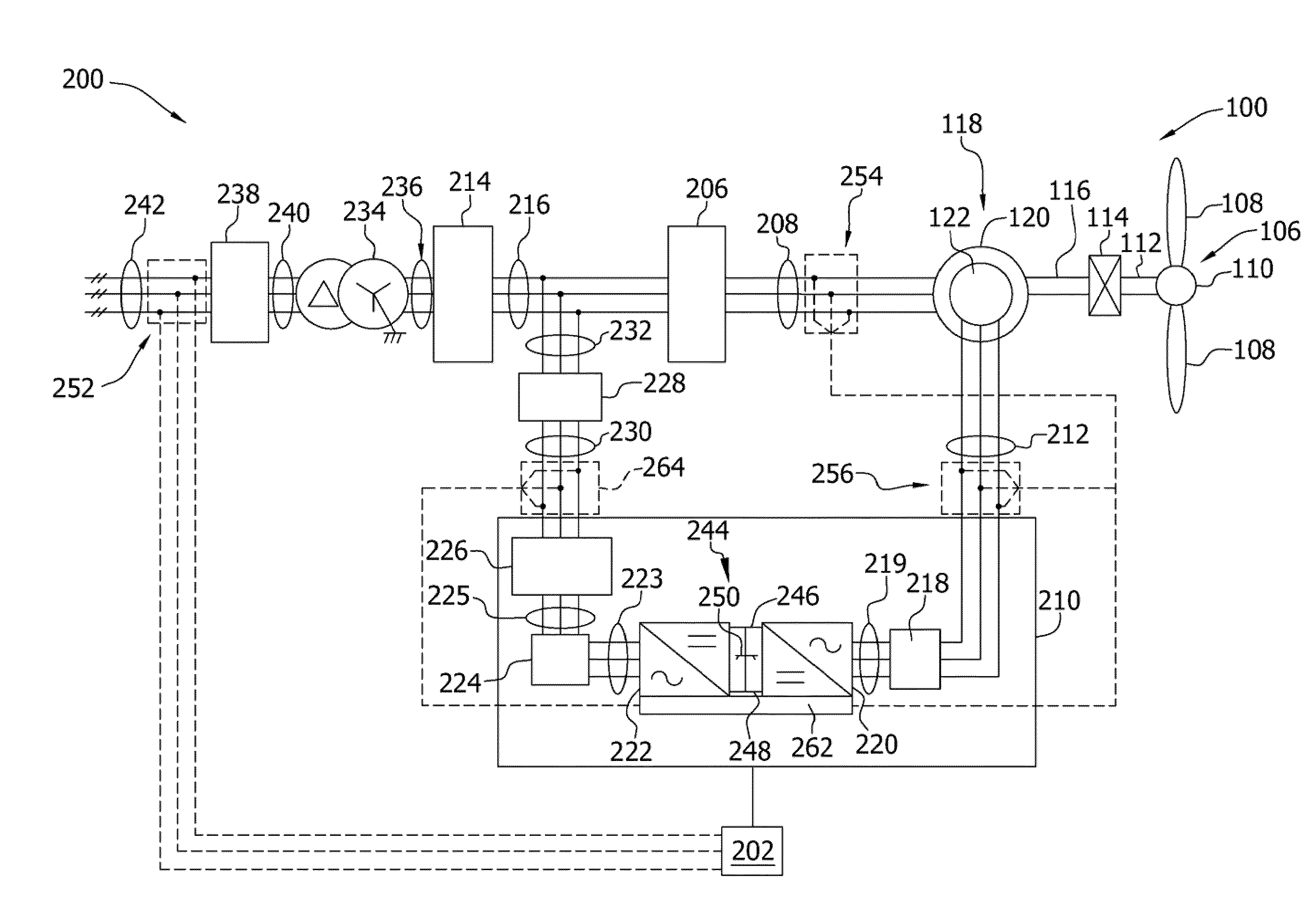
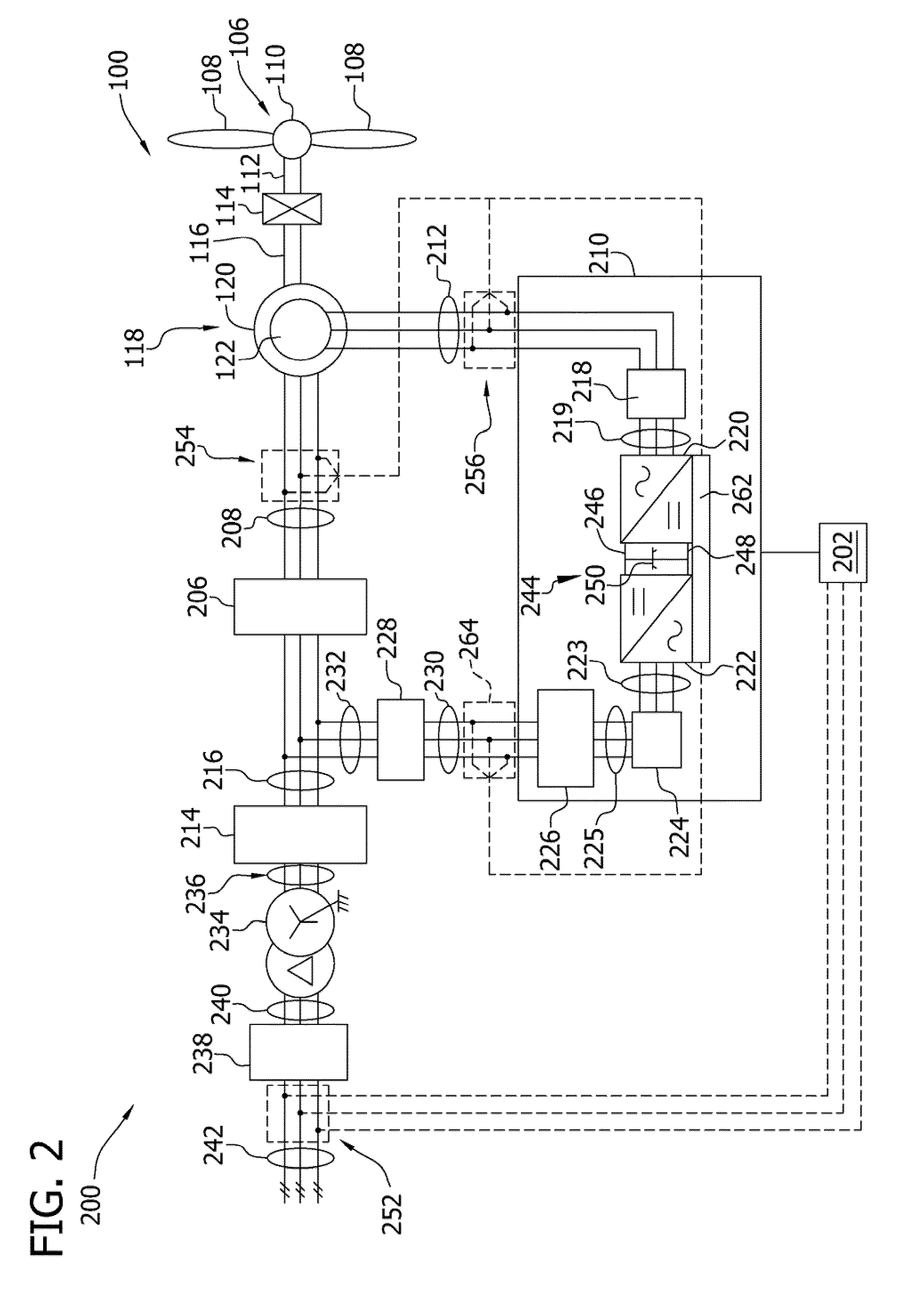
A system and method for reducing rotor loads in a wind turbine that includes a brake and one or more rotor blades coupled to a rotor. Upon detection of a loss of counter torque and a blade-pitch failure in at least one rotor blade, a processor reduces a generator overspeed threshold value by a predetermined amount and determines a brake-release threshold value. The brake is applied to slow the rotor if the generator / rotor speed exceeds the reduced generator / rotor overspeed threshold value. In addition, the brake is applied to slow the rotor until the generator / rotor speed is below the brake-release threshold value. The rate of change of the pitch angle of the rotor blade may be varied as the blade moves toward feather in response to the detected blade-pitch failure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
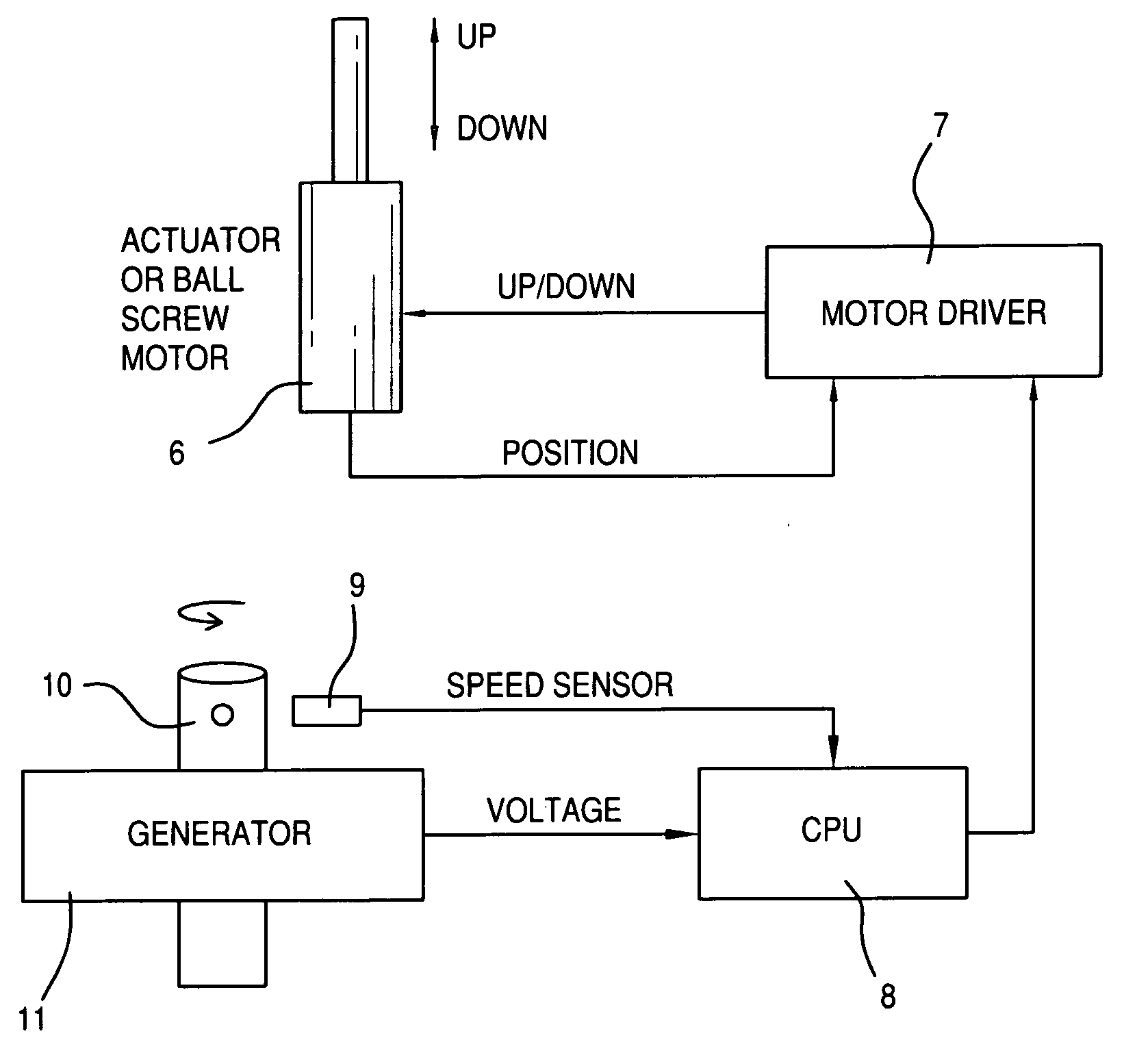
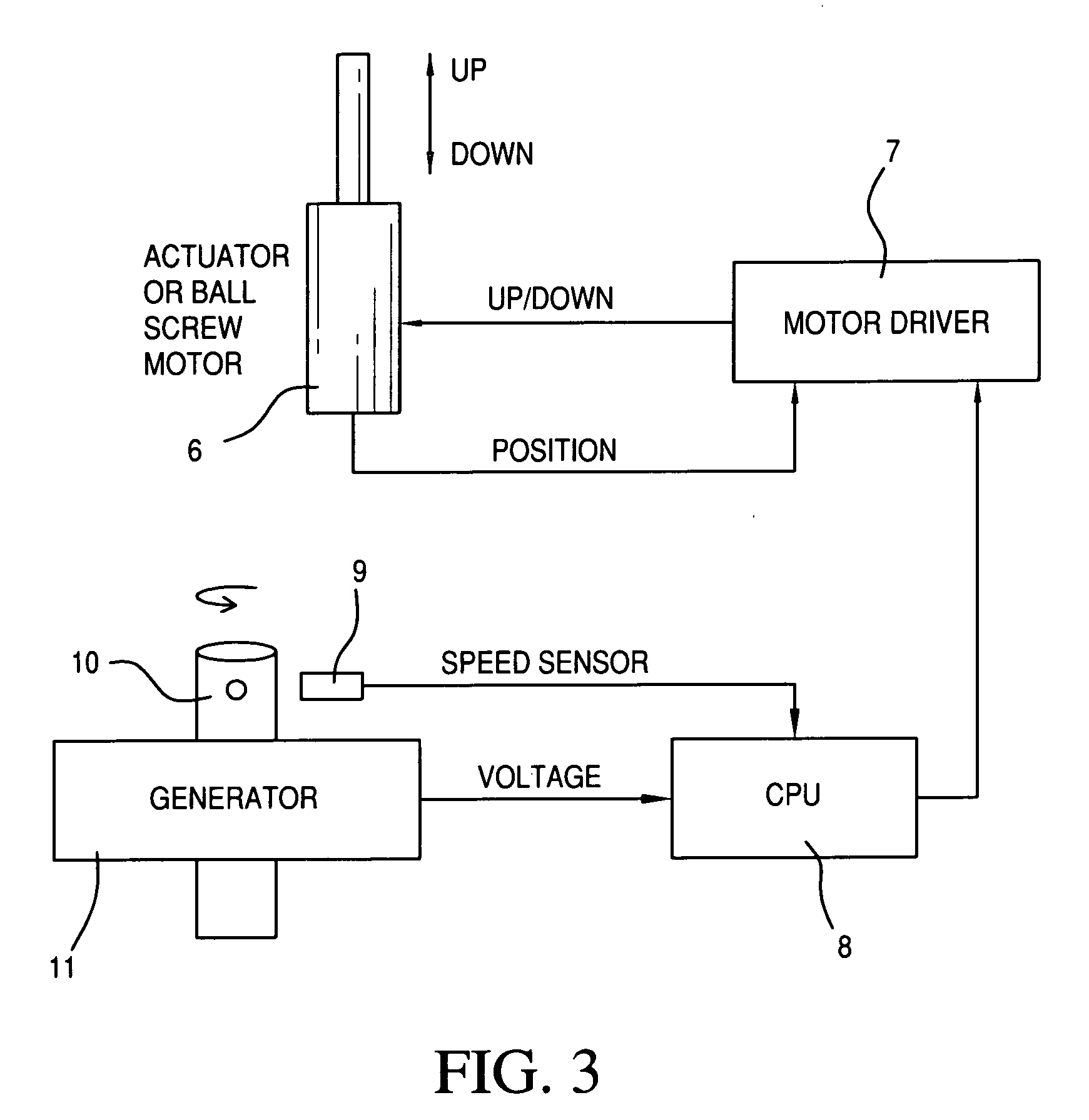
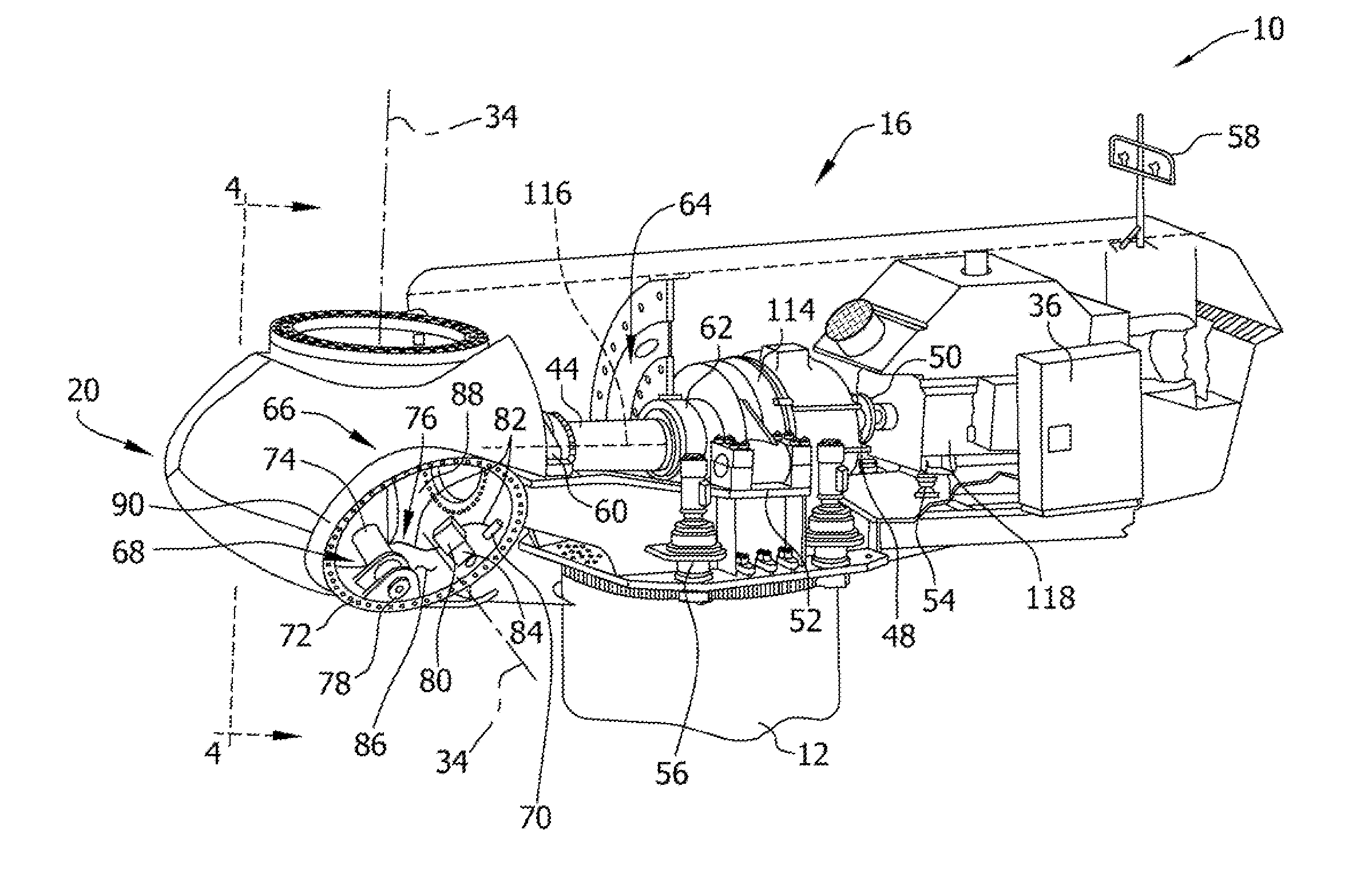
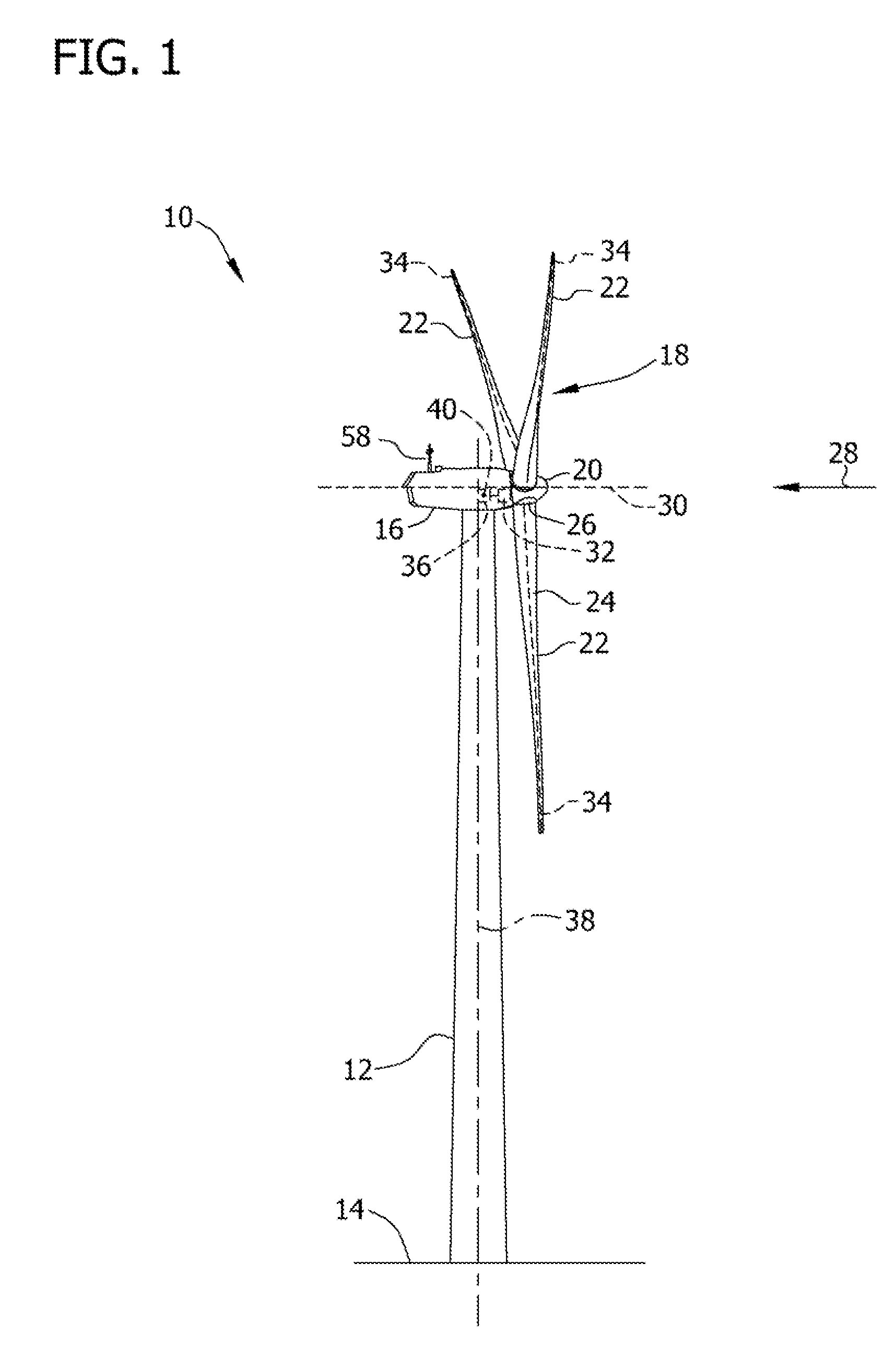
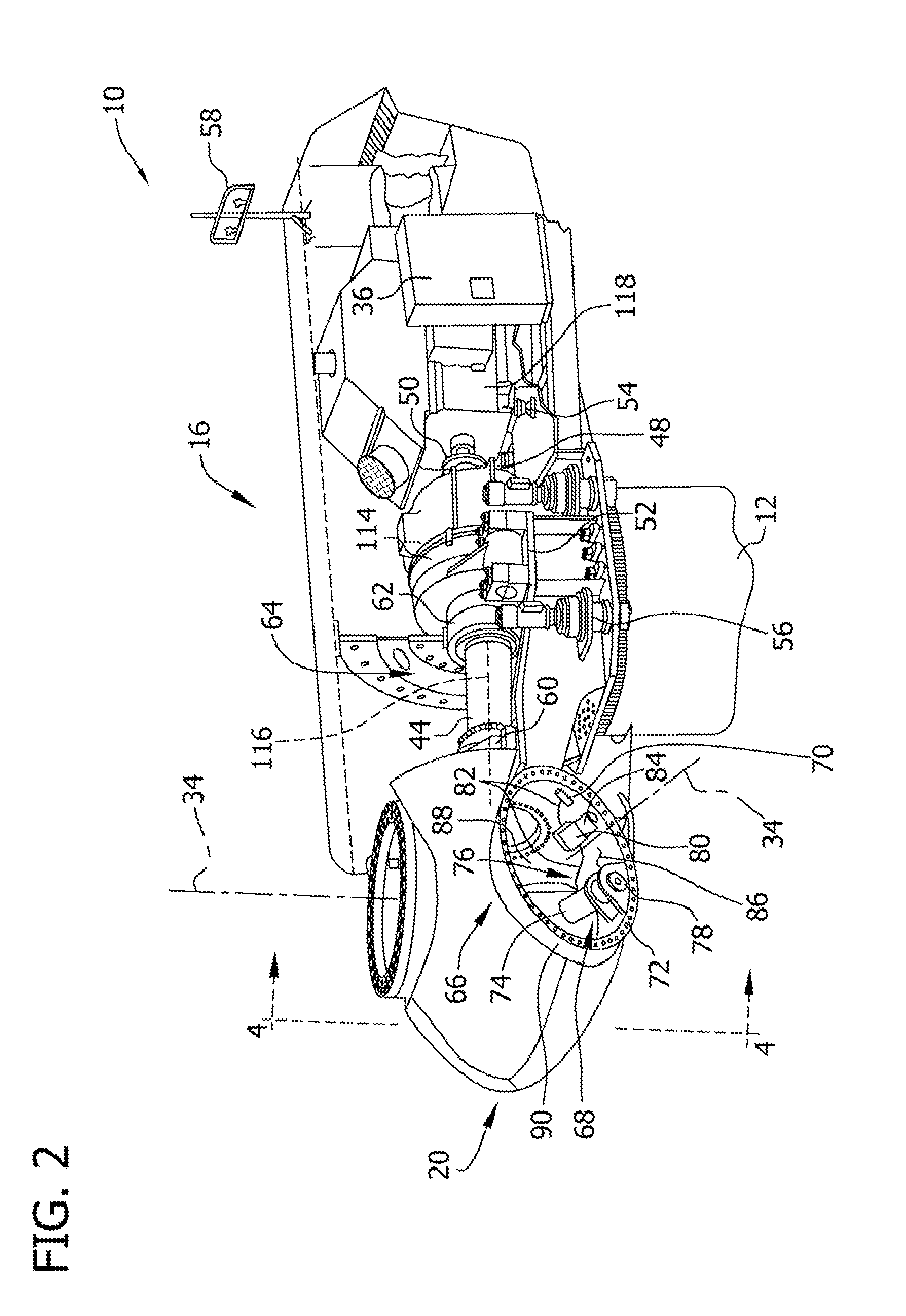
Wind turbine blade pitch control system
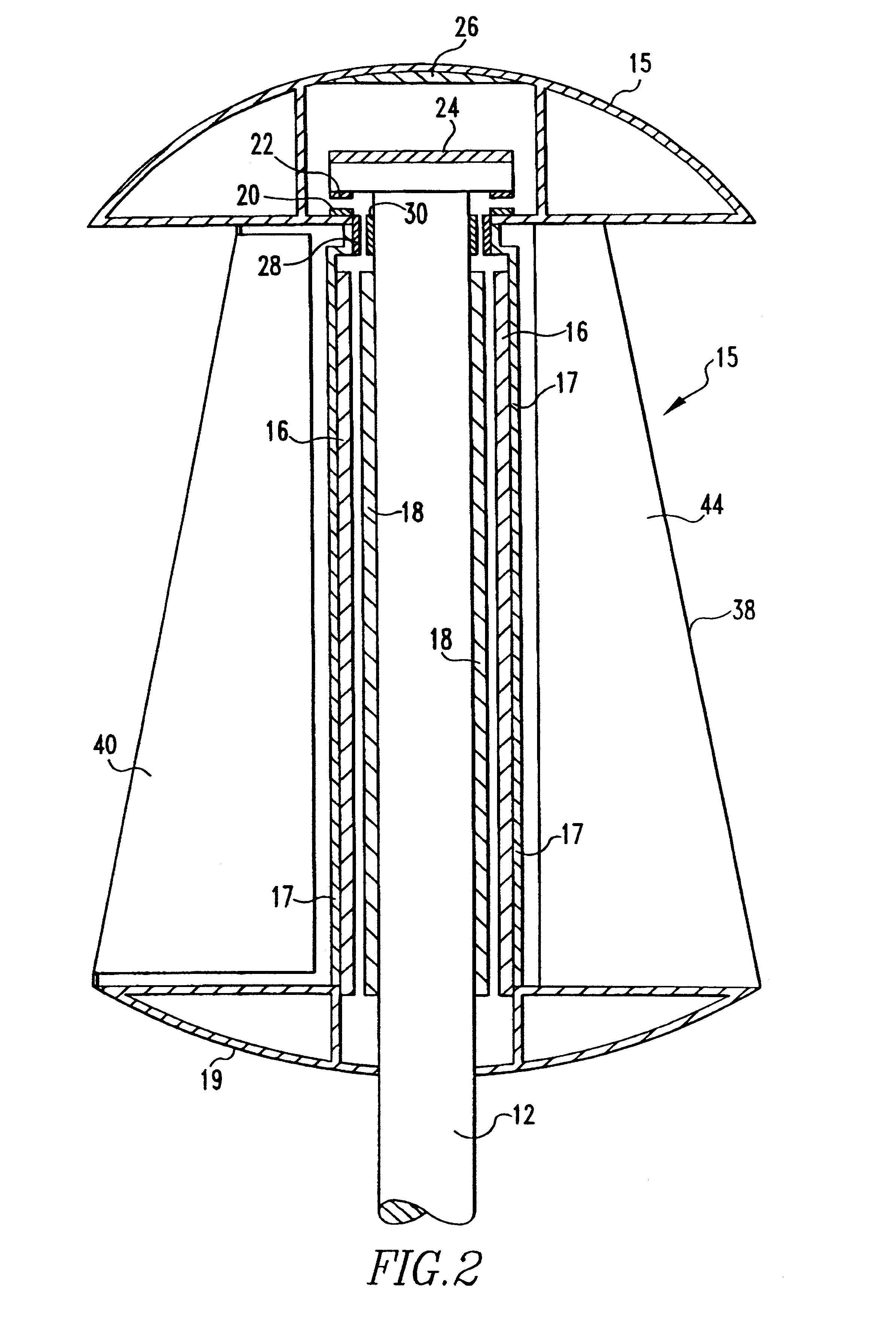
InactiveUS20100061852A1Reduce the total massLow costRotational speed controlPropellersWind forceNacelle
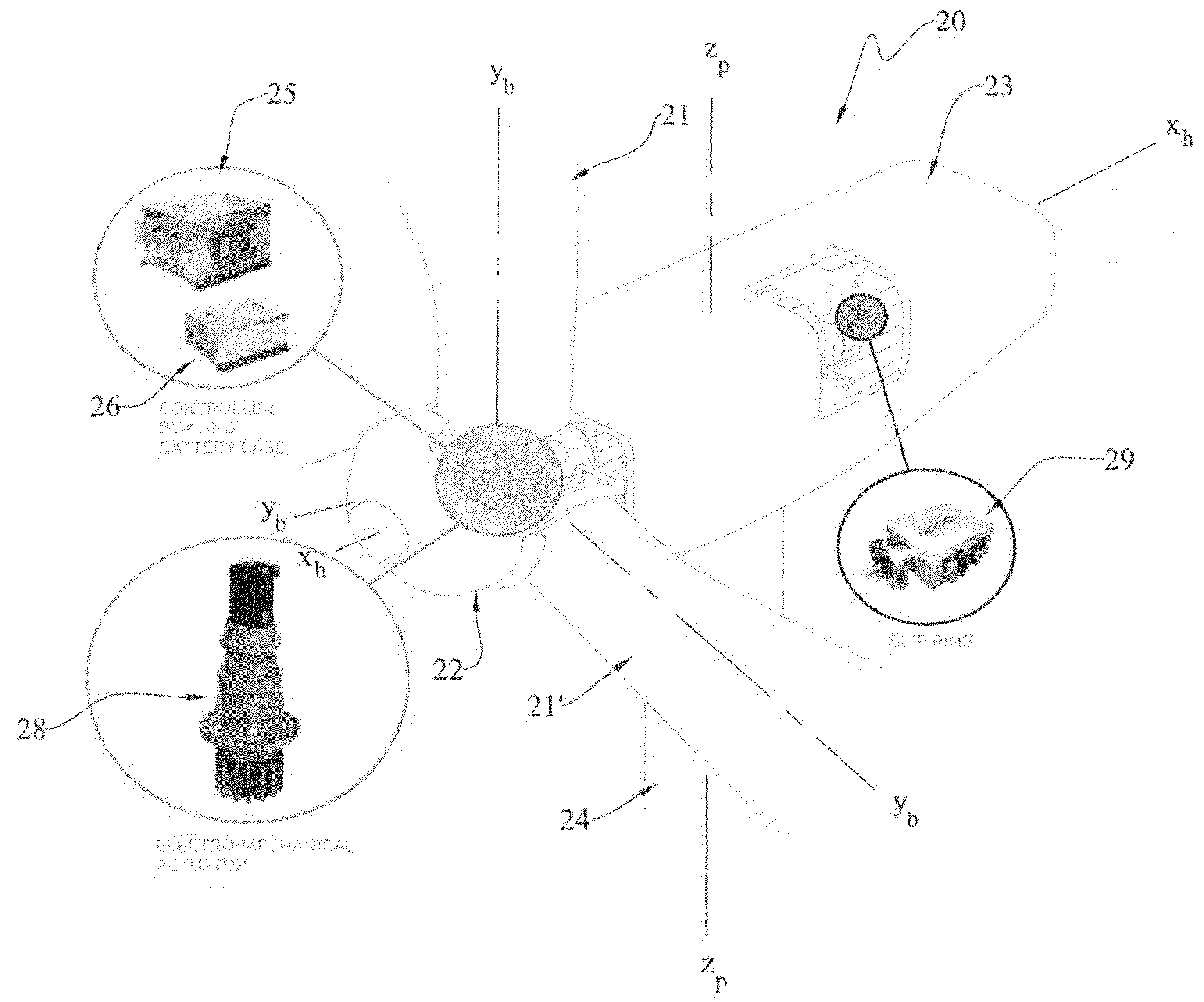
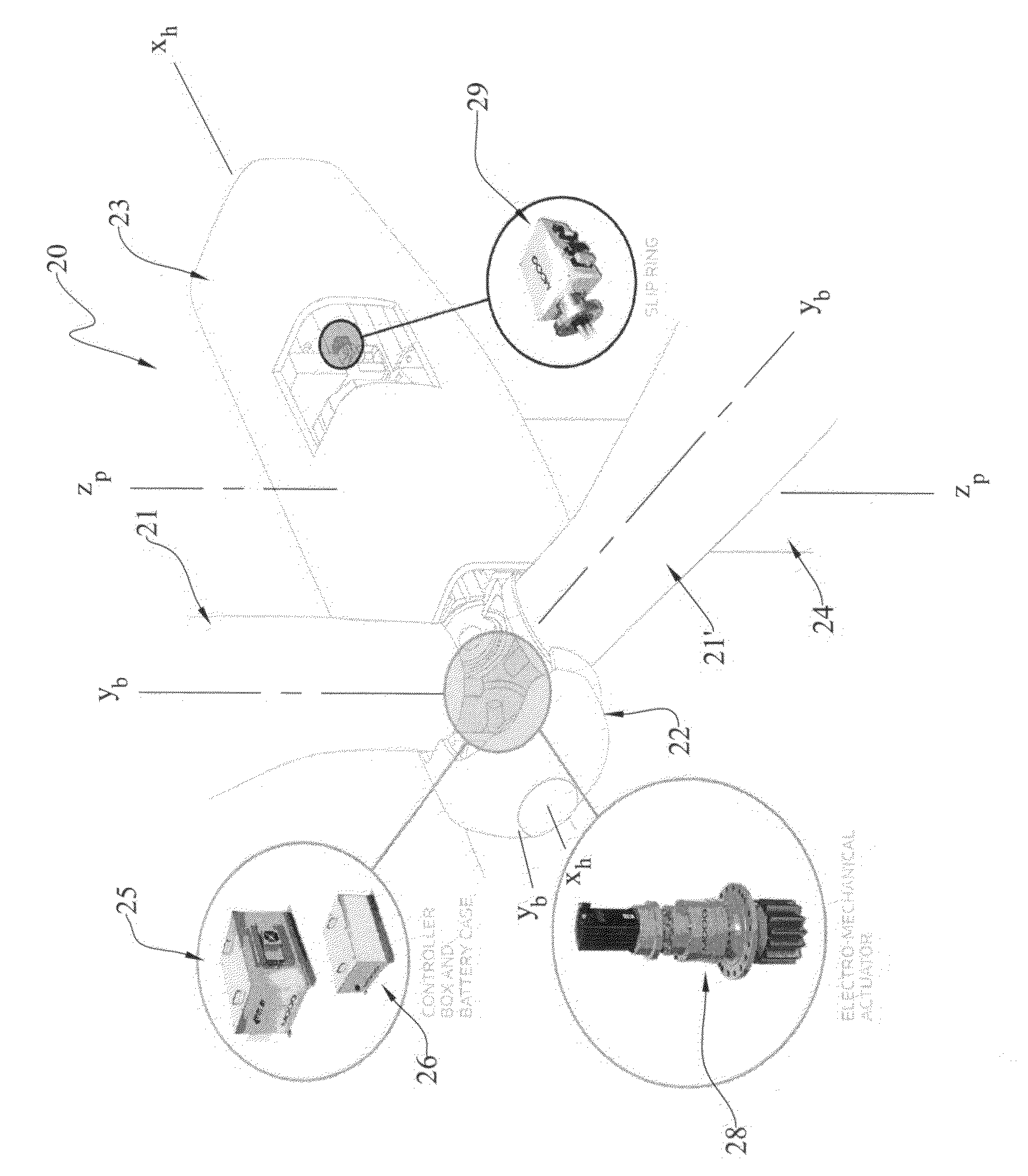
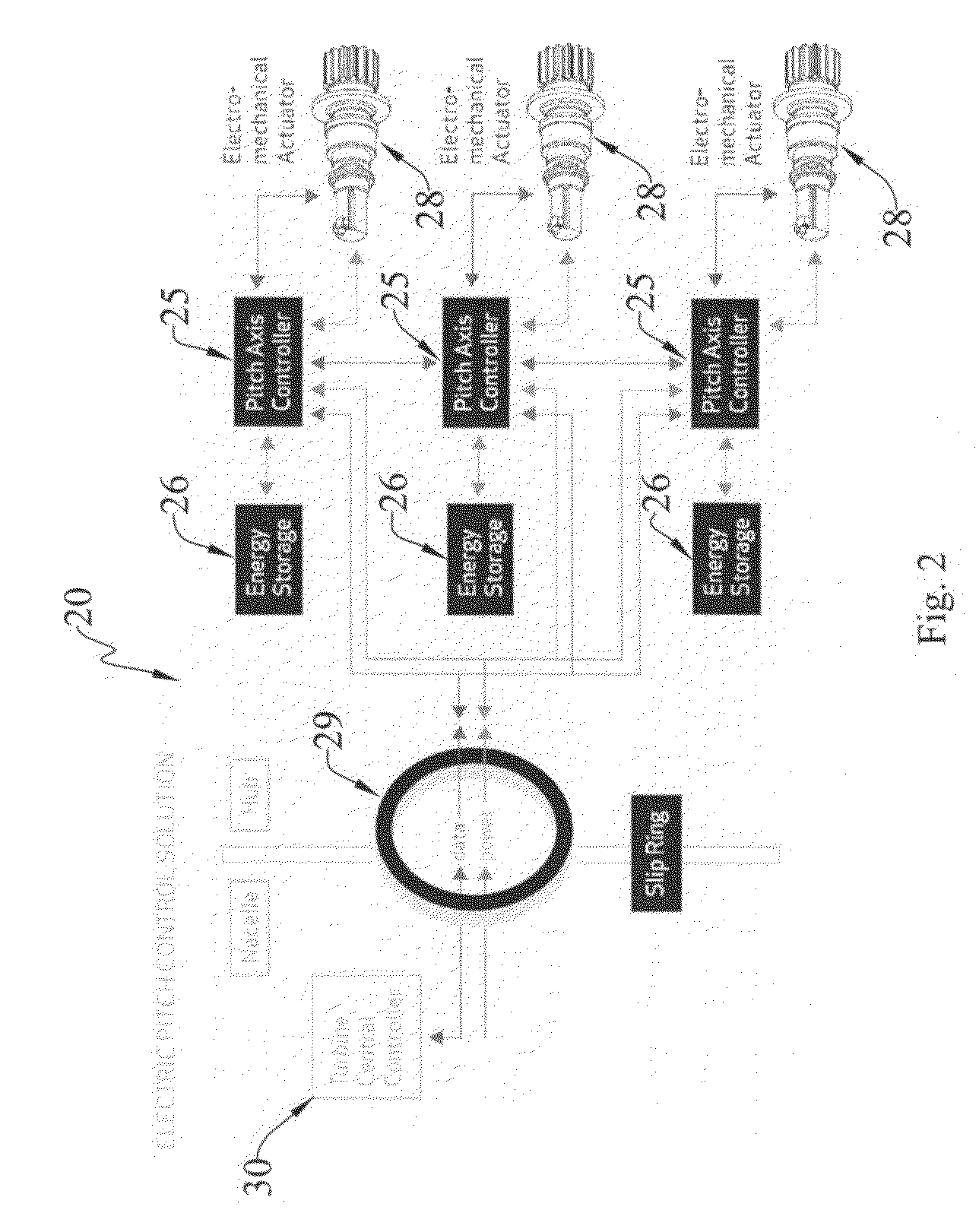
The present invention provides an improvement for a wind turbine (20) having at least one blade (21) mounted on a hub (22) for controlled rotation about a blade axis (yb-yb) to vary the pitch of the blade relative to an airstream. The hub is mounted on a nacelle (23) for rotation about a hub axis (xh-xh). The wind turbine includes a main pitch control system for selectively controlling the pitch of the blade, and / or a safety pitch control system for overriding the main blade pitch control system and for causing the blade to move toward a feathered position in the event of an overspeed or fault condition. The improvement includes: an energy storage device (26) mounted on the nacelle and associated with the blade; a pitch-axis controller (25) mounted on the nacelle and associated with the blade and with the energy storage device; an electro-mechanical actuator (28) mounted on the hub and associated with the blade; and at least one slip ring (29) operatively arranged to transmit power and / or data signals between the pitch-axis controller and the electro-mechanical actuator; whereby the mass on the rotating hub may be reduced.
Owner:MOOG JAPAN
Method for predicting a power curve for a wind turbine
ActiveUS20080140263A1Quality improvementEasy to controlRotational speed controlLevel controlDensity of airEngineering
A method for calculating a high-altitude power curve for a wind turbine is provided, the method including the steps of determining a cp-λ curve for a predetermined blade pitch angle of said wind turbine; calculating a first power curve without power limit based on the cp-λ curve; and calculating the high-altitude power curve with power limit from said first power curve, thereby using a site air density.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
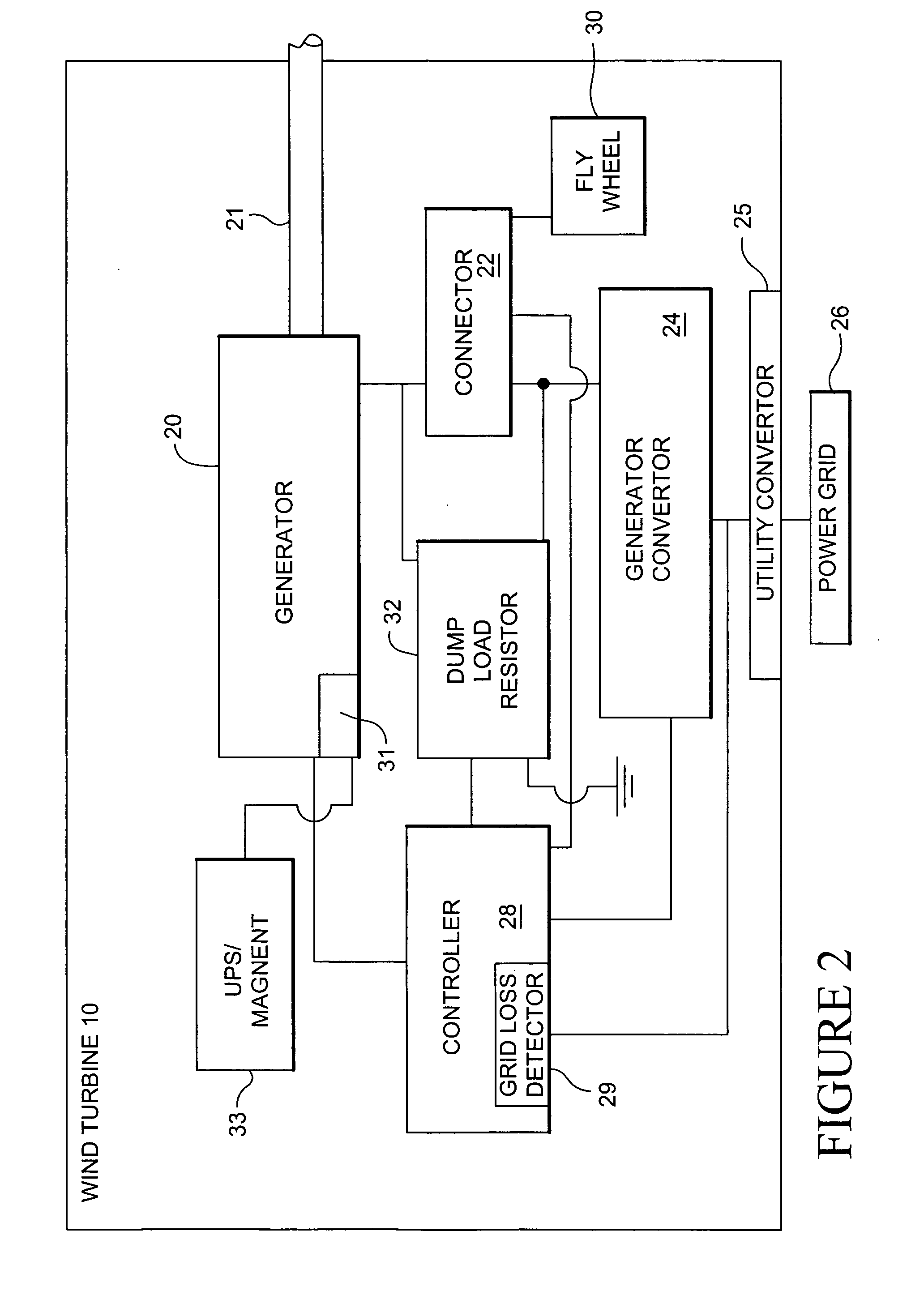
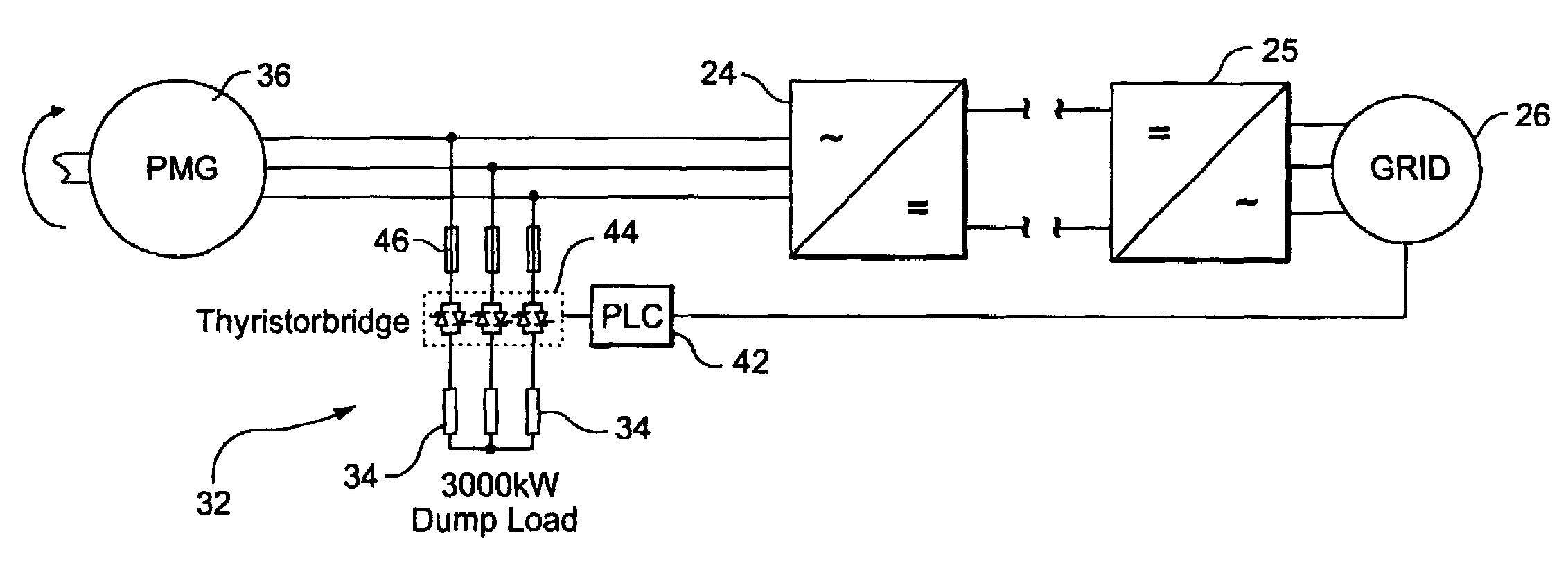
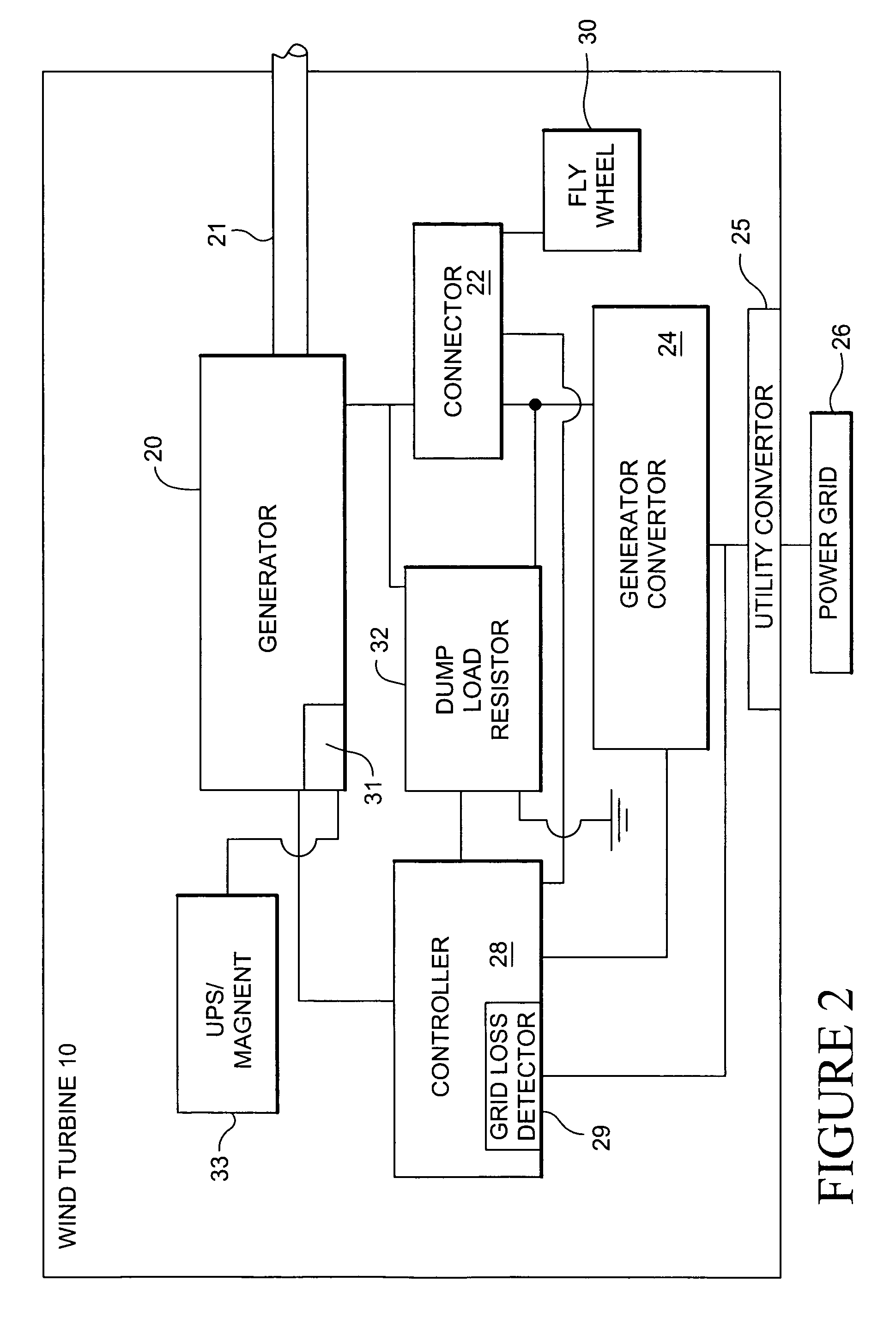
Wind turbine dump load system and method
ActiveUS20070164567A1Avoids excessively unloadingAvoids a heavy acceleration of the rotorRotational speed controlWind motor controlTurbine bladeControl system
A wind turbine braking system including: a wind turbine including turbine blades and a control system; a generator coupled to the turbine blades; a generator converter coupled to the generator and connectable to a utility power grid; at least one dump resistor coupled to the generator and generator converter, and if the utility power grid losses power, the dump resistor applying an electrical load to the generator converter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind turbine blade with lift-regulating means in form of slots or holes
ActiveUS20100014970A1Easy to adjustImprove propertiesRotational speed controlPropellersLeading edgeTurbine blade
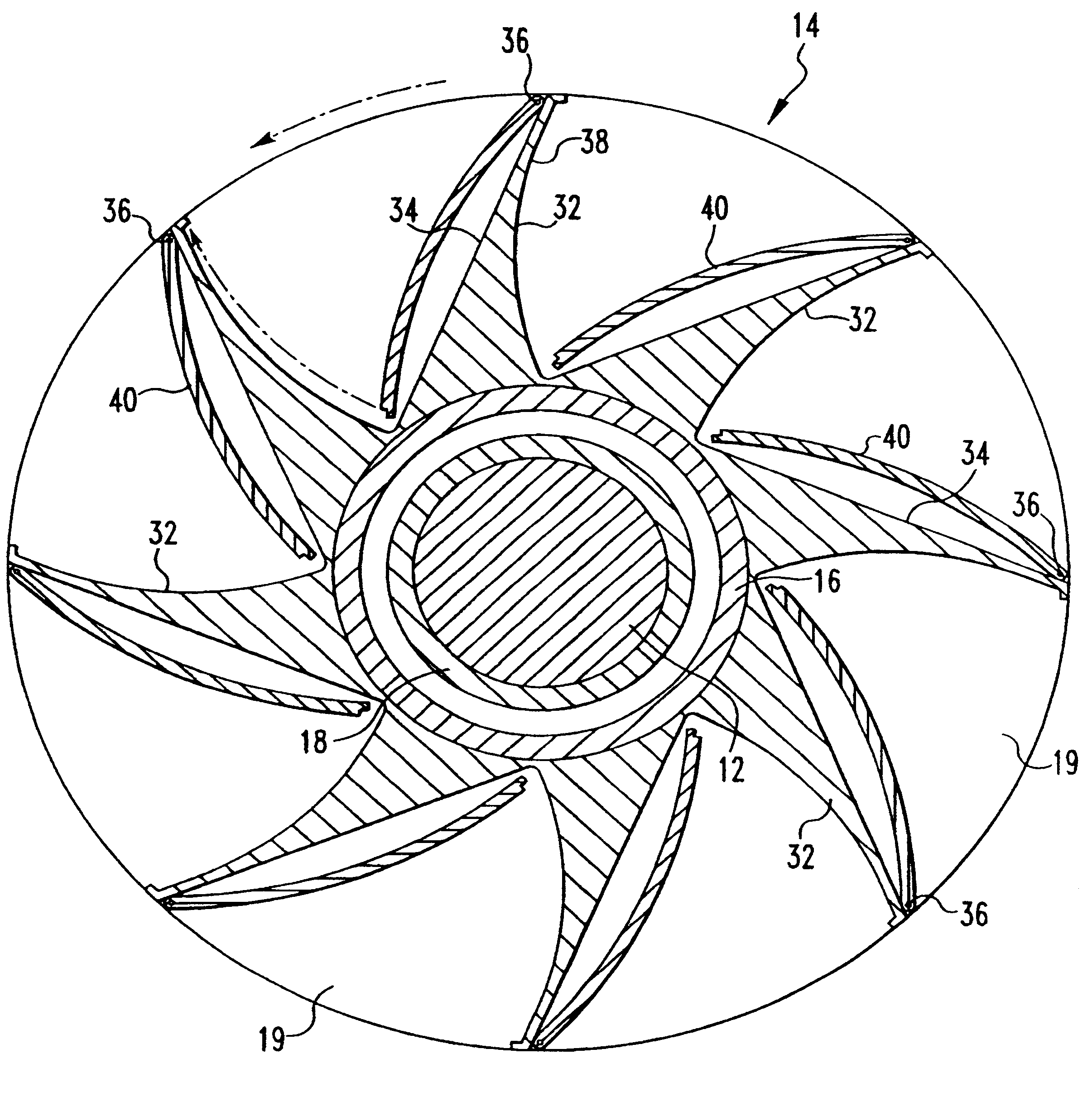
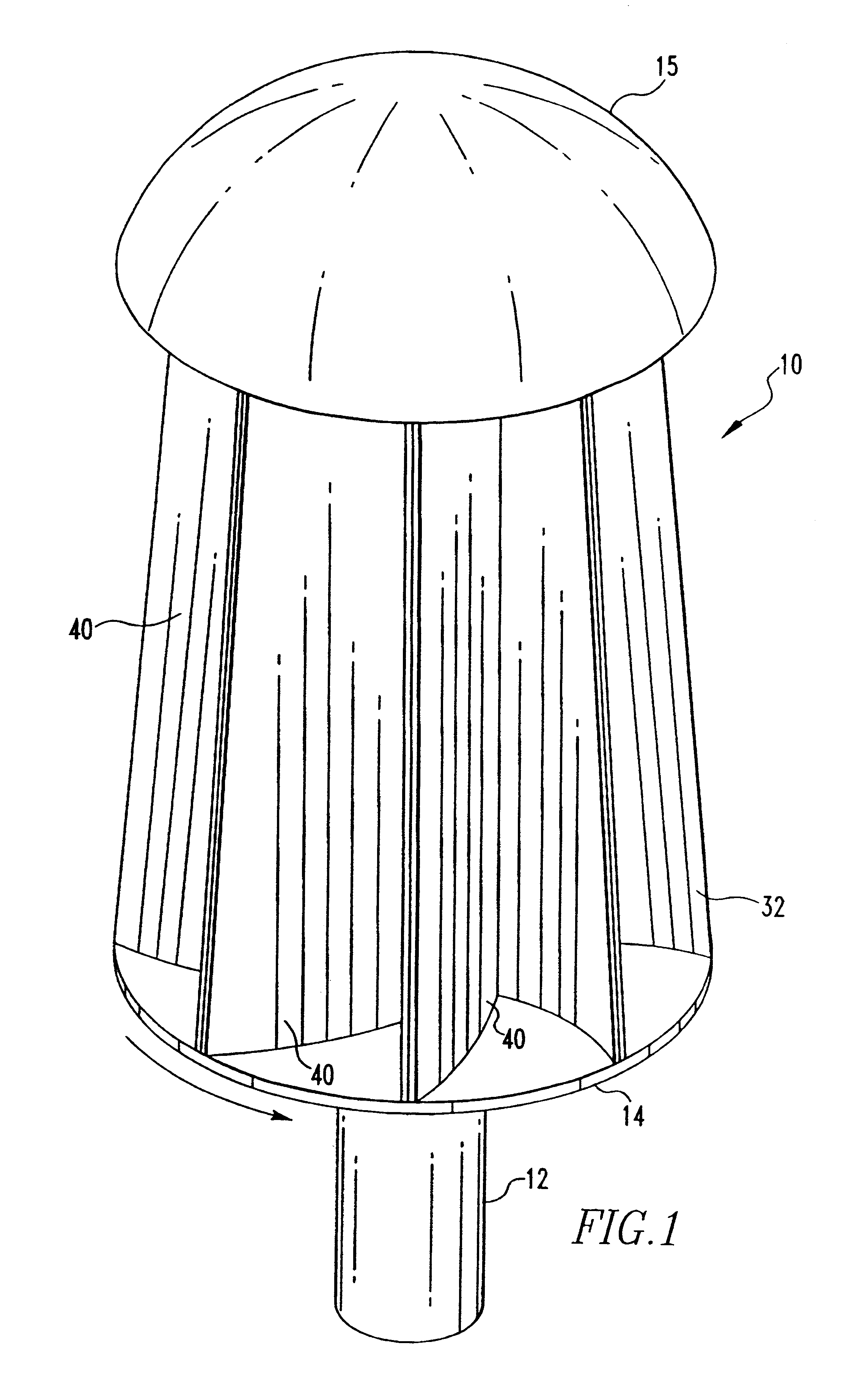
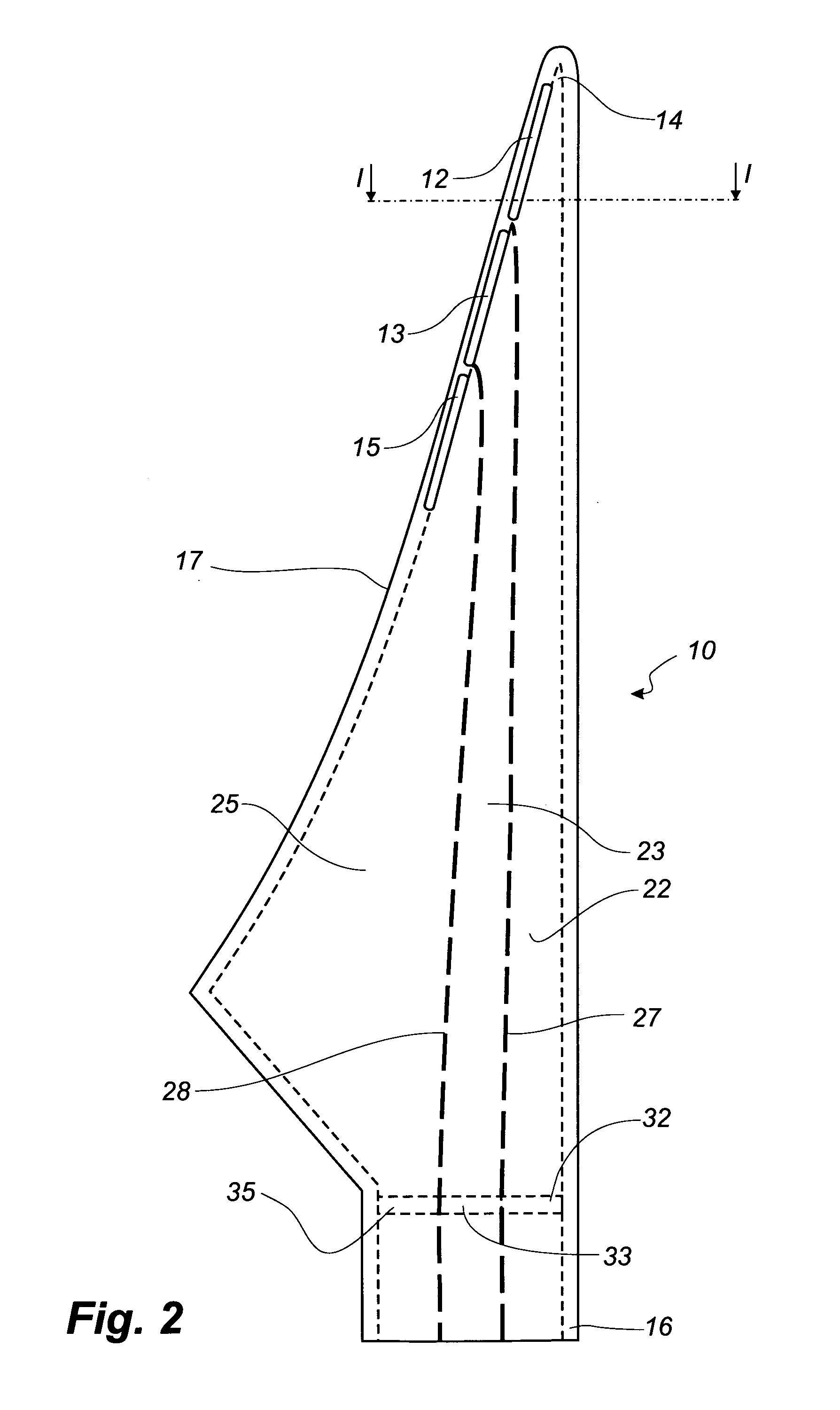
A blade (10) for a wind turbine rotor with a hub is described. The blade extends in a longitudinal direction along a longitudinal axis and having a root area (16) closest to the hub and a tip region furthest away from the hub. The blade (10) along at least a portion of the longitudinal direction of the blade has an envelope, which defines an airfoil profile having, in normal operation, a pressure side (20) and a suction side (19), and further having a leading edge (18) and a trailing edge (17), which edges define an airfoil chord line extending between them. The blade (10) comprises adjustable lift-regulating means extending in the longitudinal direction of the blade (10), and activating means by means of which the lift-regulating means can be adjusted and thus alter the aerodynamic properties of the blade (10). The lift-regulating means are adapted and arranged so that by activation of the activating means, the lift can be reduced in a zone extending in the longitudinal direction of the blade (10) from a first position in proximity to the blade tip (14) to a second position between the first position and the root area (16) and this second position being variable in the longitudinal direction of the blade. The lift-regulating means are formed of at least one slot (12, 13, 15) or a number of holes (42, 43, 45, 52, 53, 55) arranged in at least one longitudinally extending zone, thereby allowing an interior cavity (22, 23, 25) of the blade (10) to communicate with the exterior. The lift-regulating means are adjustable by means of one or more activating means to regulate the amount of air emitted from the interior cavity (22, 23, 25) to the exterior to alter the aerodynamic properties of the blade (10).
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
Wind turbine dump load system and method
ActiveUS7276807B2Avoids excessively unloadingAvoids a heavy acceleration of the rotorRotational speed controlWind motor controlTurbine bladeControl system
A wind turbine braking system including: a wind turbine including turbine blades and a control system; a generator coupled to the turbine blades; a generator converter coupled to the generator and connectable to a utility power grid; at least one dump resistor coupled to the generator and generator converter, and if the utility power grid losses power, the dump resistor applying an electrical load to the generator converter.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Method for controlling a wind energy plant
ActiveUS20090081041A1The method is simple and reliableReduce loadRotational speed controlPropellersNacelleRest position
The present invention is related to a method for controlling a wind energy plant, with a nacelle disposed on a tower and with a rotor with at least one rotor blade, the blade adjustment angle of which can be adjusted by means of a blade adjustment equipment. The objective to provide a reduction of the loads acting on the plant when there is a malfunction of the blade adjustment equipment is resolved according to the present invention in that the function of the blade adjustment equipment is monitored, and when an error of the blade adjustment equipment occurs, the nacelle is rotated from an operating position into a rest position, in which there is a flow of the wind against the surface extended by the at least one rotor blade (4) in a rotation of the rotor which is reduced with respect to the operating position.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY SE & CO KG
Method for preventing rotor overspeed of a wind turbine
ActiveUS20120134807A1Preventing possible overspeedRotational speed controlPropellersControl systemWind force
A method for preventing a possible overspeed of a wind turbine rotor with at least one rotor blade is provided. The method includes detecting a yaw misalignment of the rotor, and imposing a restriction on changes of a pitch angle towards a feathered position of the at least one rotor blade after detecting the yaw misalignment. Further, a wind turbine having a rotor and a control system configured to prevent a possible overspeed of the rotor is provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
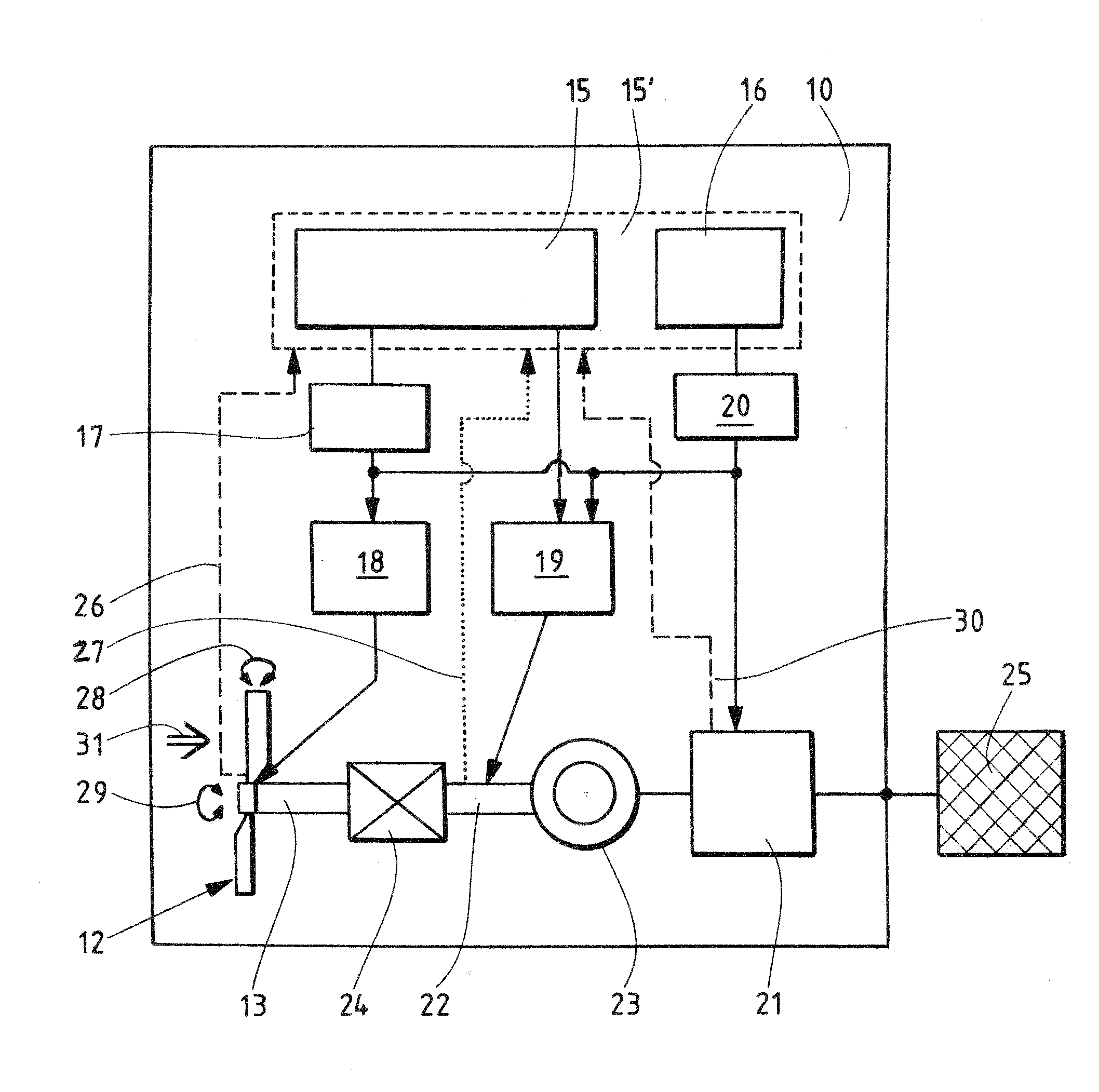
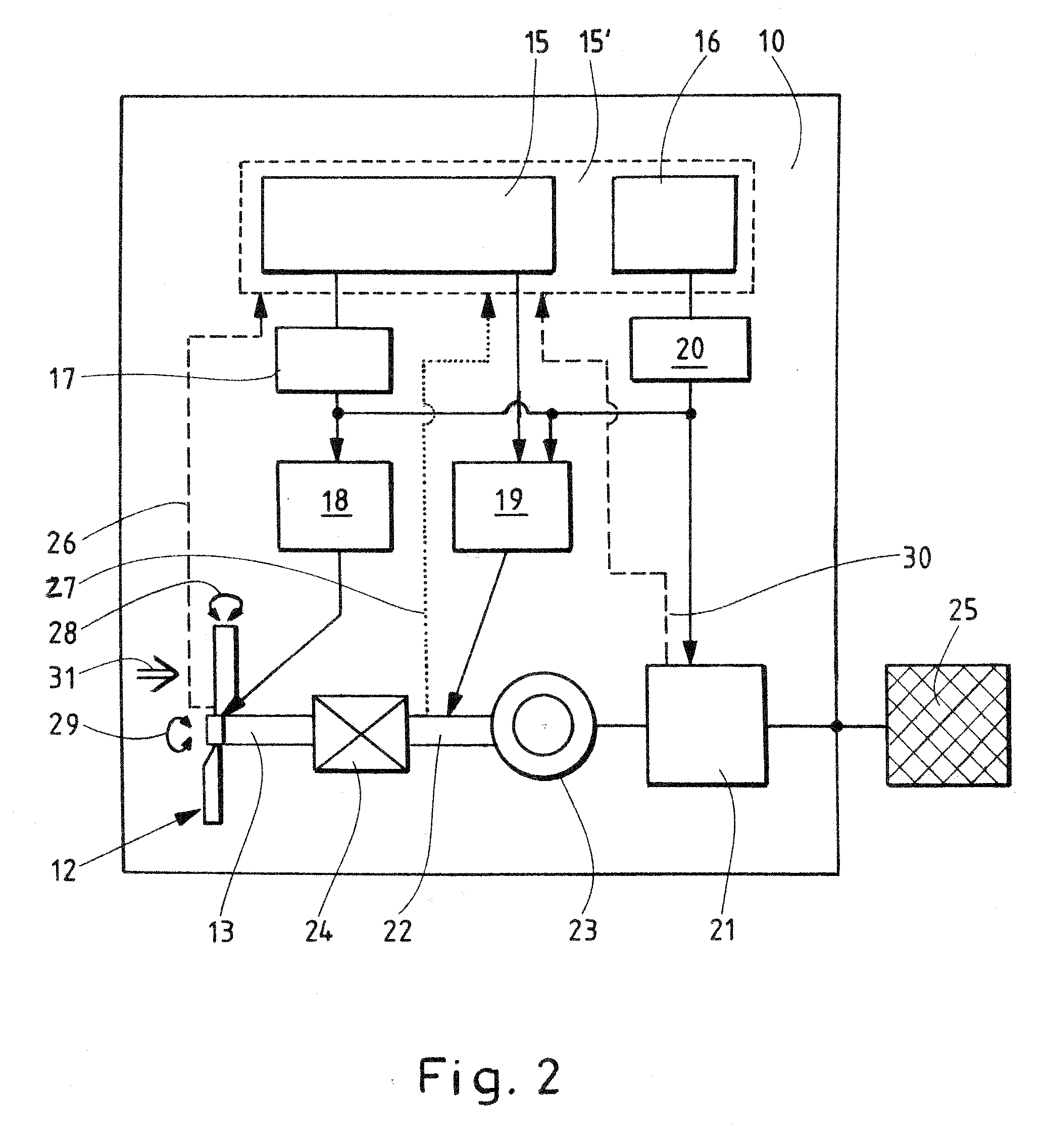
Method for operating a wind energy installation and a wind energy installation
InactiveUS20090295161A1Reduce speedExtreme loadRotational speed controlWind motor controlEngineeringWind power
The invention relates to a method for operating a wind energy installation (10), in which the wind energy installation (10) has a rotor (12, 13, 22), at least one rotor blade (14) with an adjustable angle, a mechanical brake device (19) for braking the rotor (14), an operational control device (15, 15′) and a safety system (16, 20). The invention also relates to a corresponding wind energy installation (10). The method according to the invention is defined by the following method steps: braking of the rotor (12, 13, 22) by means of an angular adjustment (28) with an average angular adjustment rate of less than 8.5° / s of the at least one rotor blade (14) after a fault signal (30) occurs, braking of the rotor (12, 13, 22) by means of the mechanical brake device (19) as soon as the rotational speed of the rotor (12, 13, 22) exceeds a predefinable first rotational speed limit, and triggering of the safety system (16, 20) as soon as the rotational speed of the rotor (12, 13, 22) exceeds a predefinable second rotational speed limit.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
Fluid directing system for turbines
InactiveUS20120099977A1Considerable powerGreat contributionRotational speed controlPump componentsTurbine bladeCross-flow turbine
A directing system for directing fluid entering an axial flow turbine along an inlet flow direction. The turbine includes a plurality of turbine blades. The directing system includes a base structure, a plurality of directing segments attached to the base structure, downstream of the base structure, and a directing segment adjustment system for adjustably positioning the directing segments between a retracted configuration and a deployed configuration. The directing segments, in the deployed configuration, extend beyond the base structure in a direction transversal to the inlet flow direction and deflect the fluid towards an outer circumference of the plurality of turbine blades corresponding to a higher torque area of the blades. A directing system for directing fluid entering a cross-flow turbine is also disclosed. In the cross-flow turbine, the fluid is directed towards a centerline of the rotor of the turbine, which is a high torque area of the turbine blades.
Owner:ORGANOWORLD
Method For Controlling A Wind Turbine Connected To The Utility Grid, Wind Turbine And Wind Park
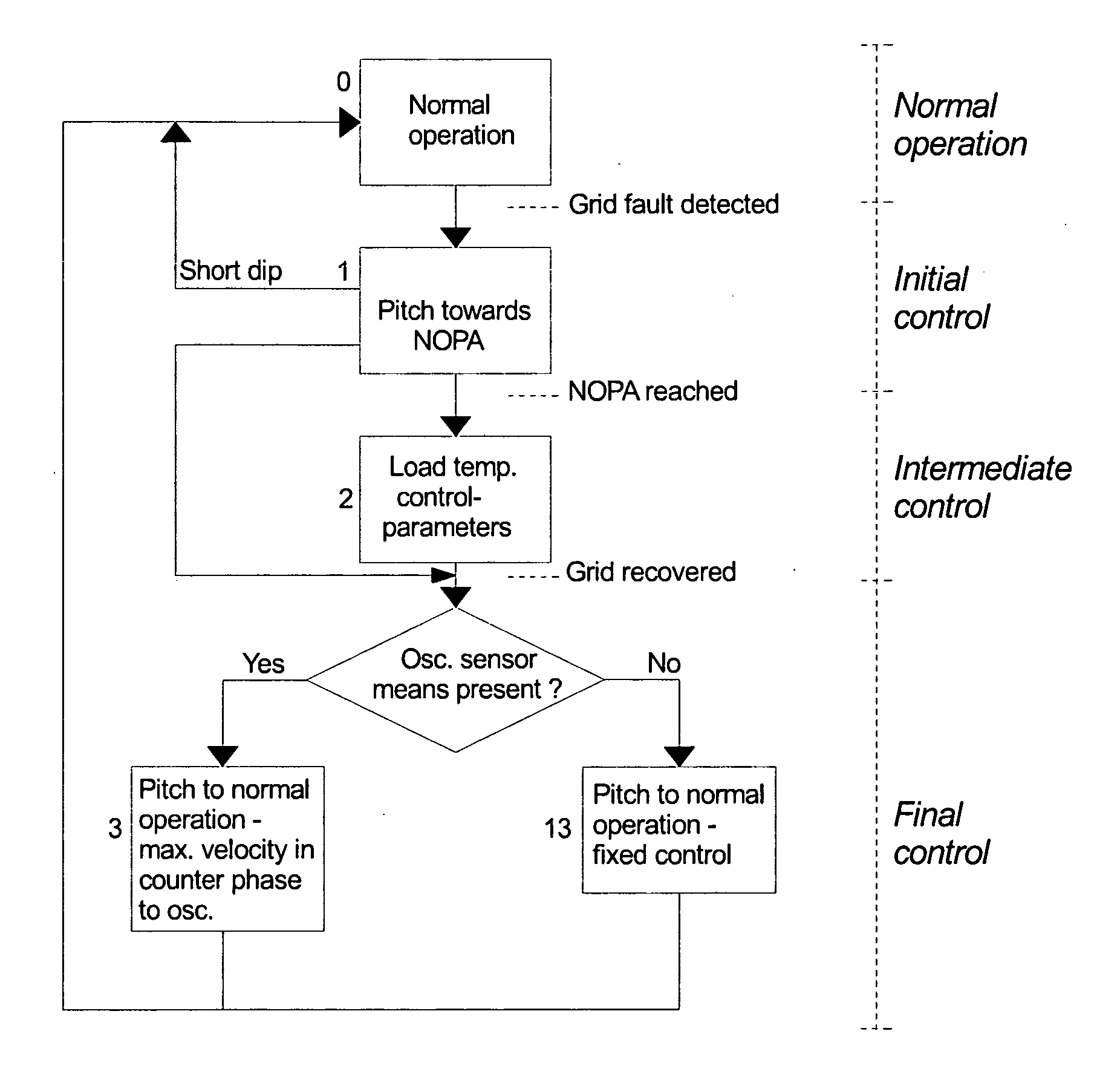
The invention relates to a method for controlling a wind turbine connected to the utility grid comprising steps of detecting a fault of the utility grid, and controlling one or more rotor blades in a fault mode wherein said one or more rotor blades are pitched in order to stabilize the rotor speed within an over speed range. The invention also relates to a wind turbine and a wind park comprising at least two wind turbines.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
System and method for controlling a wind turbine
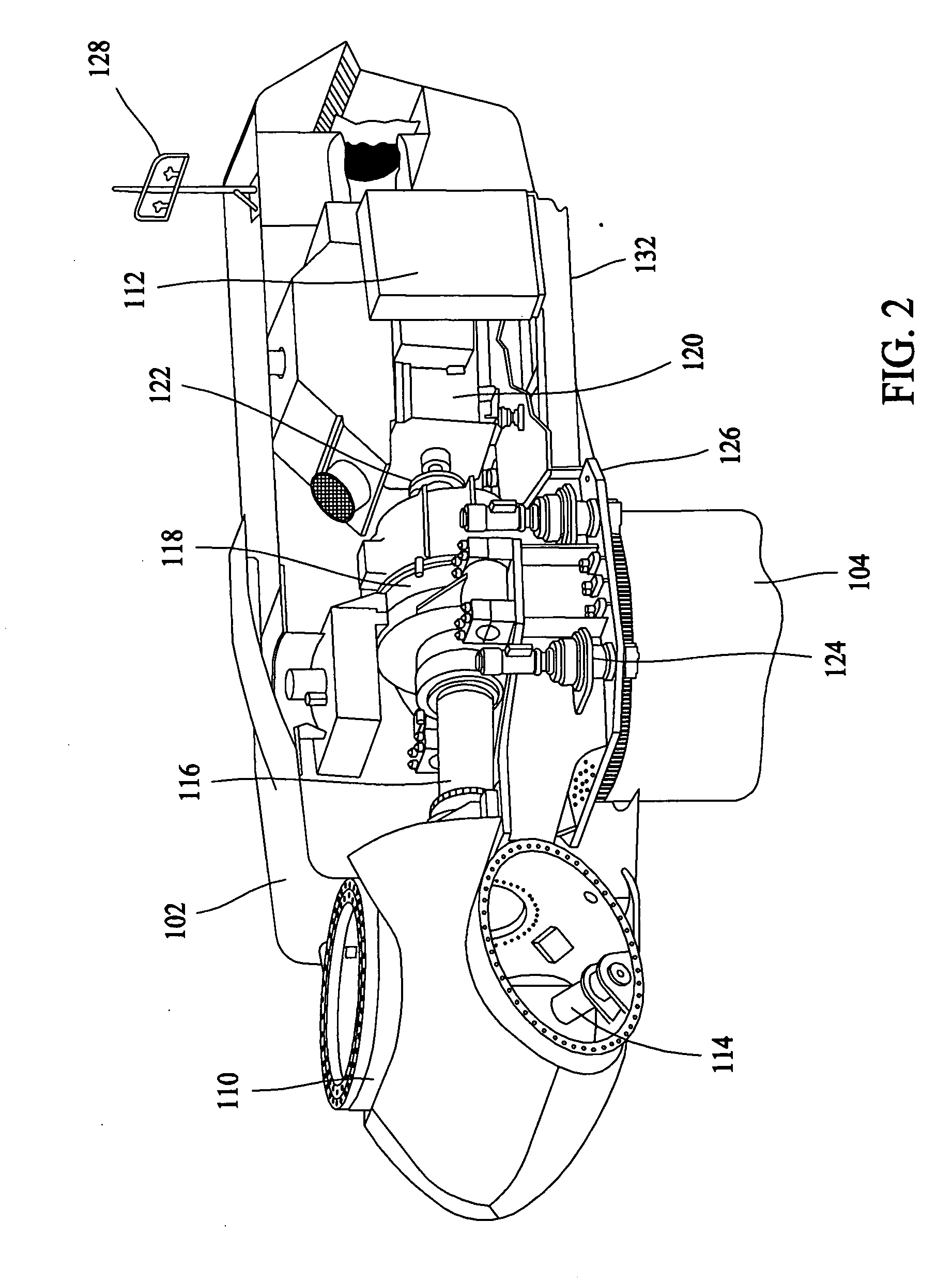
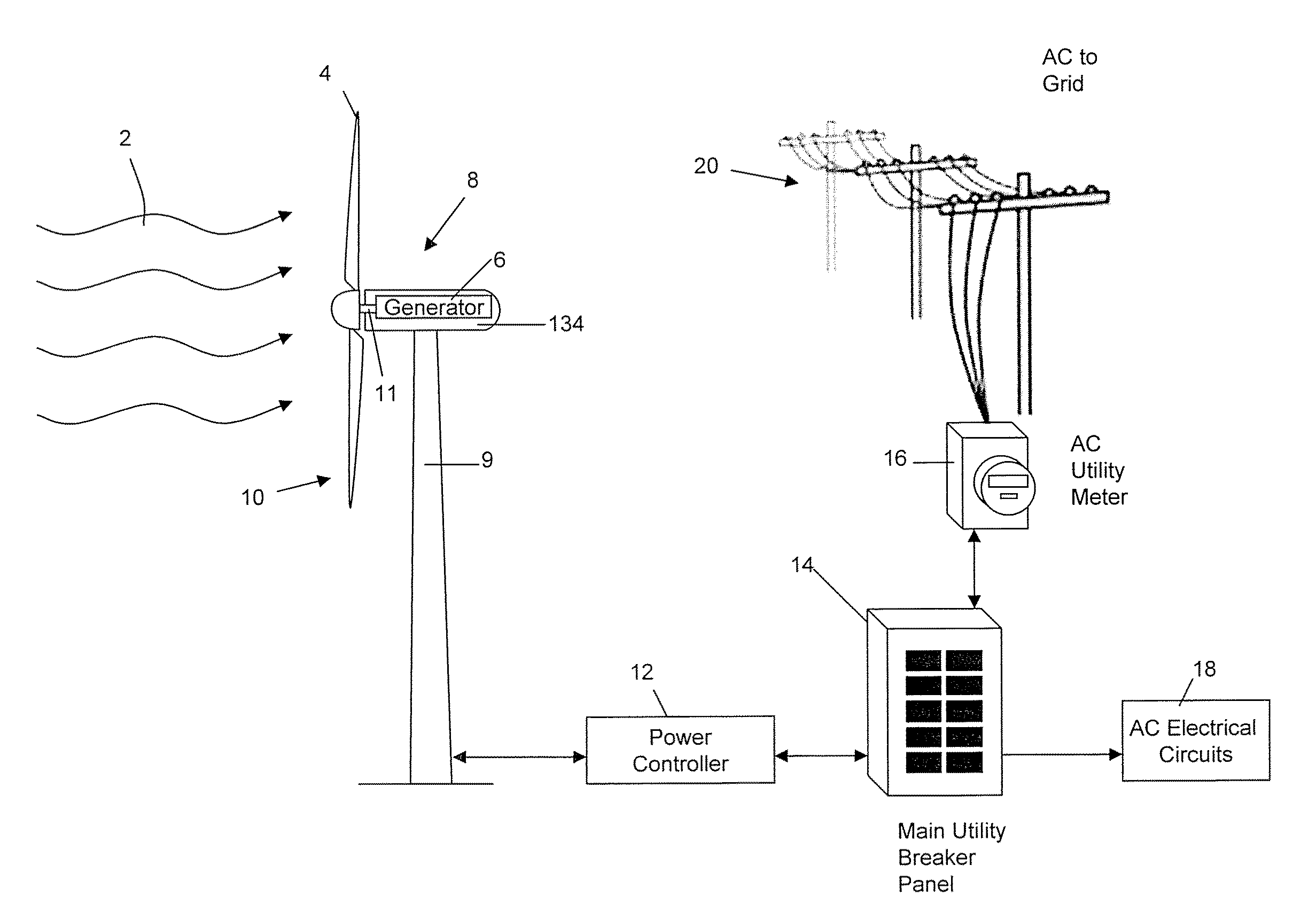
InactiveUS20100314875A1Shorten speedMore speedRotational speed controlWind motor controlNacelleTurbine blade
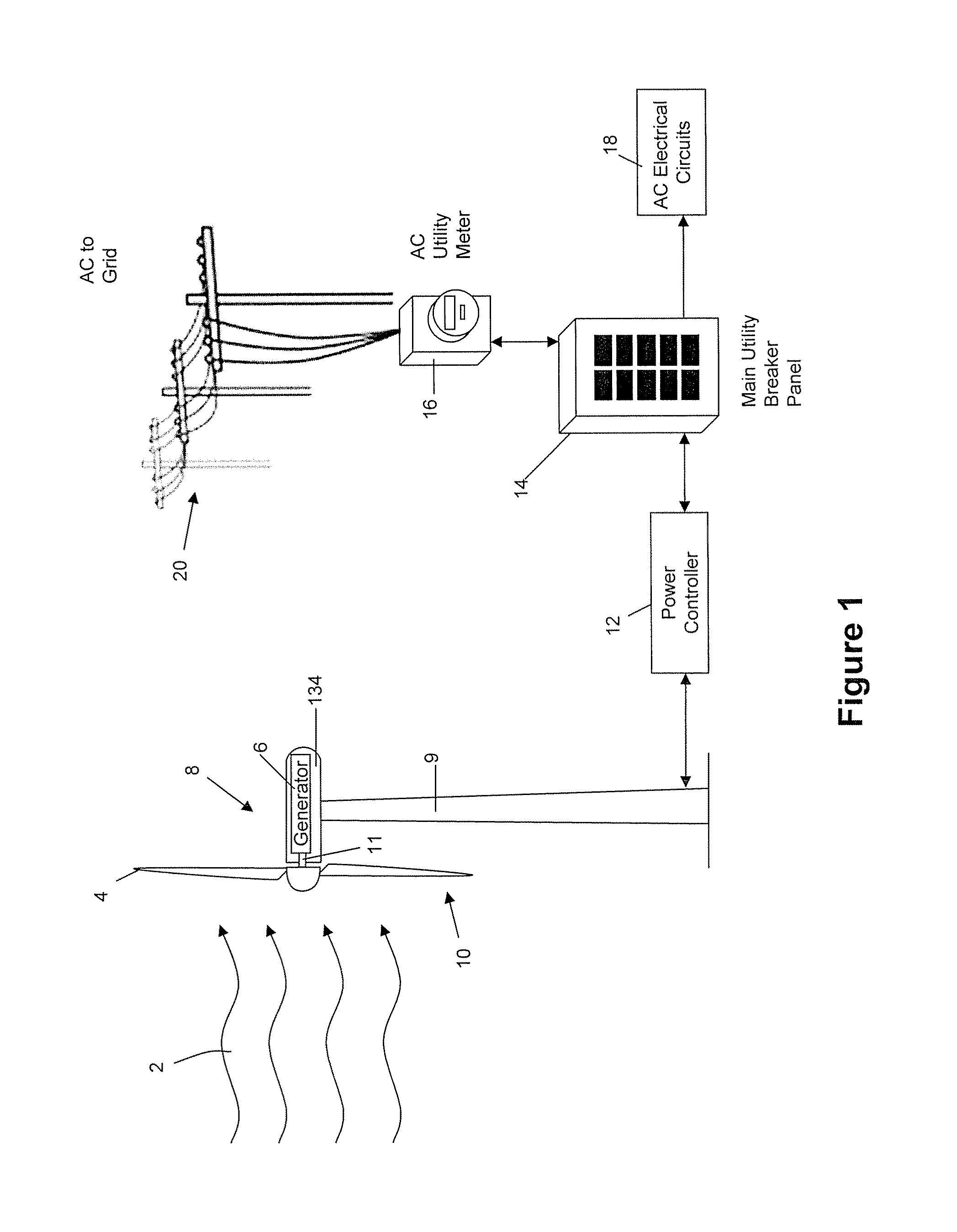
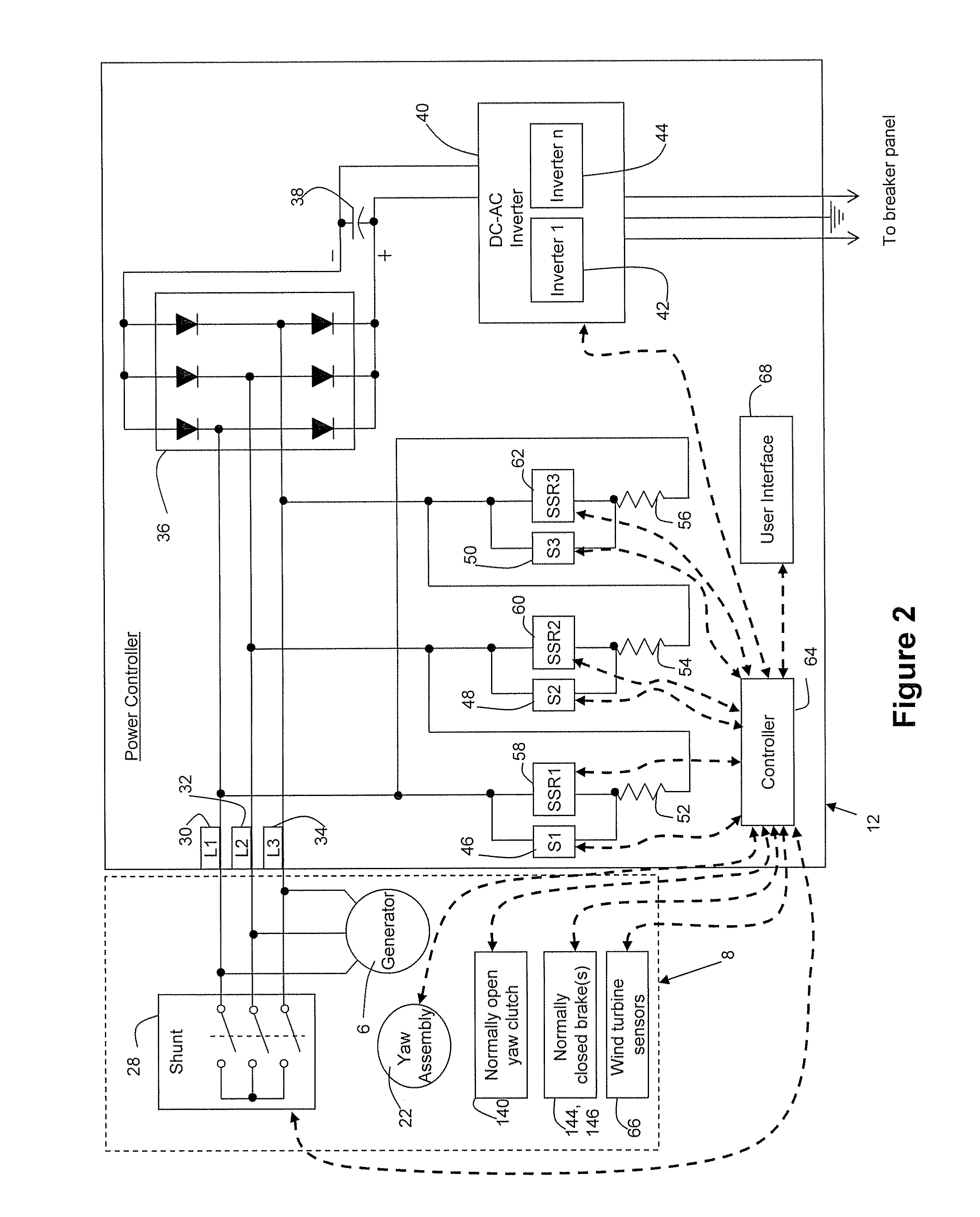
A system for controlling the RPM of a wind turbine comprising using inverters to draw current from the wind turbine, thereby slowing the rotational speed of the wind turbine blades. In another aspect, a resistor and a switching mechanism attached between the resistor and a phase line is provided to increase the load on the phase line. A yaw motor is also used to yaw the facing direction of the wind turbine out of the wind. Moreover, a normally closed switching mechanism can redirect current from a phase line through a resistor. A normally closed brake is also used to mechanically engage the turbine when the control system fails. A normally open yawing clutch when disengaged allows the nacelle of the wind turbine to rotate freely into the down wind direction. The system also comprises a switch that can create an electrical short between the phase lines of the turbine.
Owner:REDRIVEN POWER
Apparatus and method for operation of a wind turbine
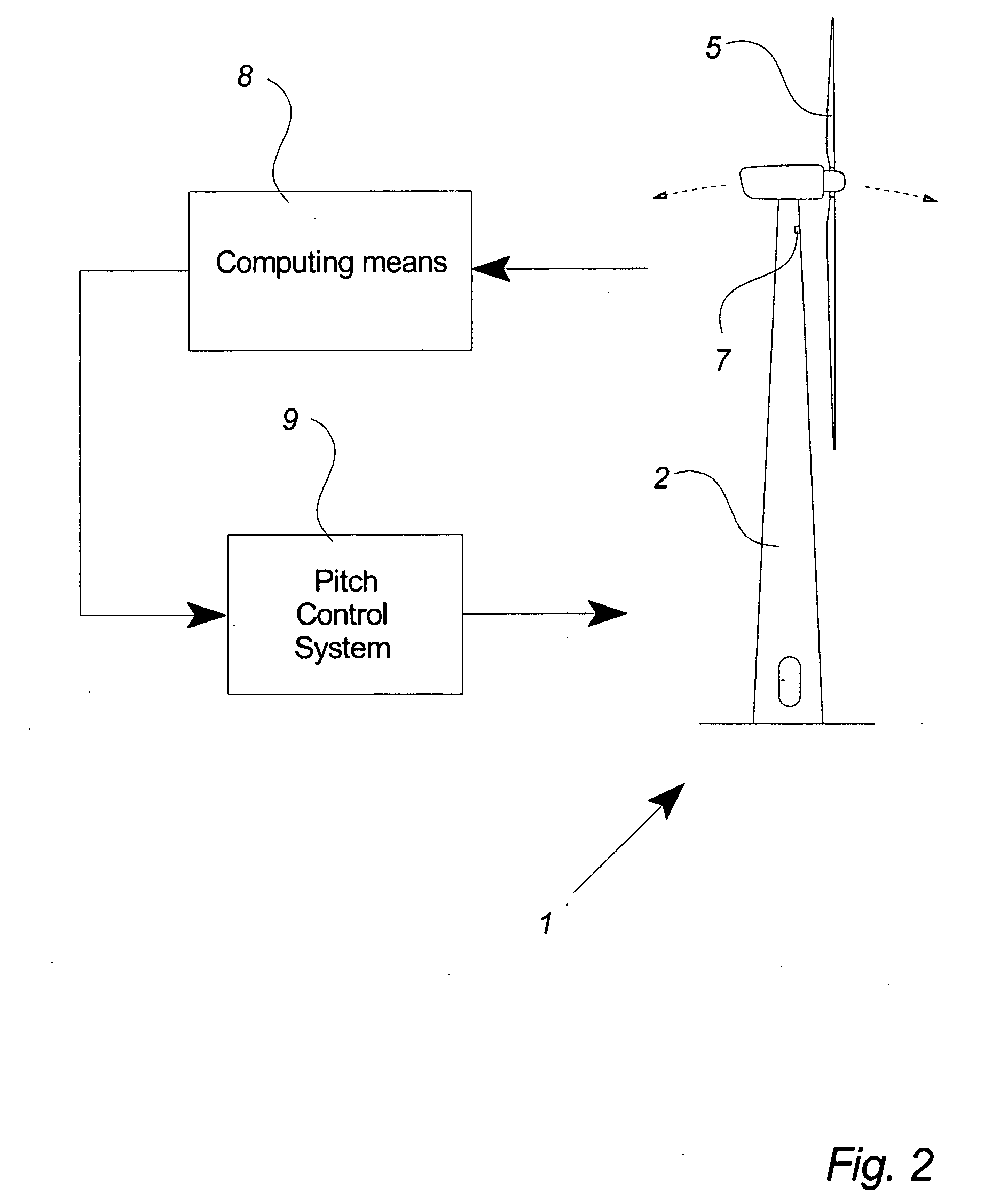
ActiveUS20110142620A1Reduce riskEasy to operateRotational speed controlPropellersAutomotive engineeringWind force
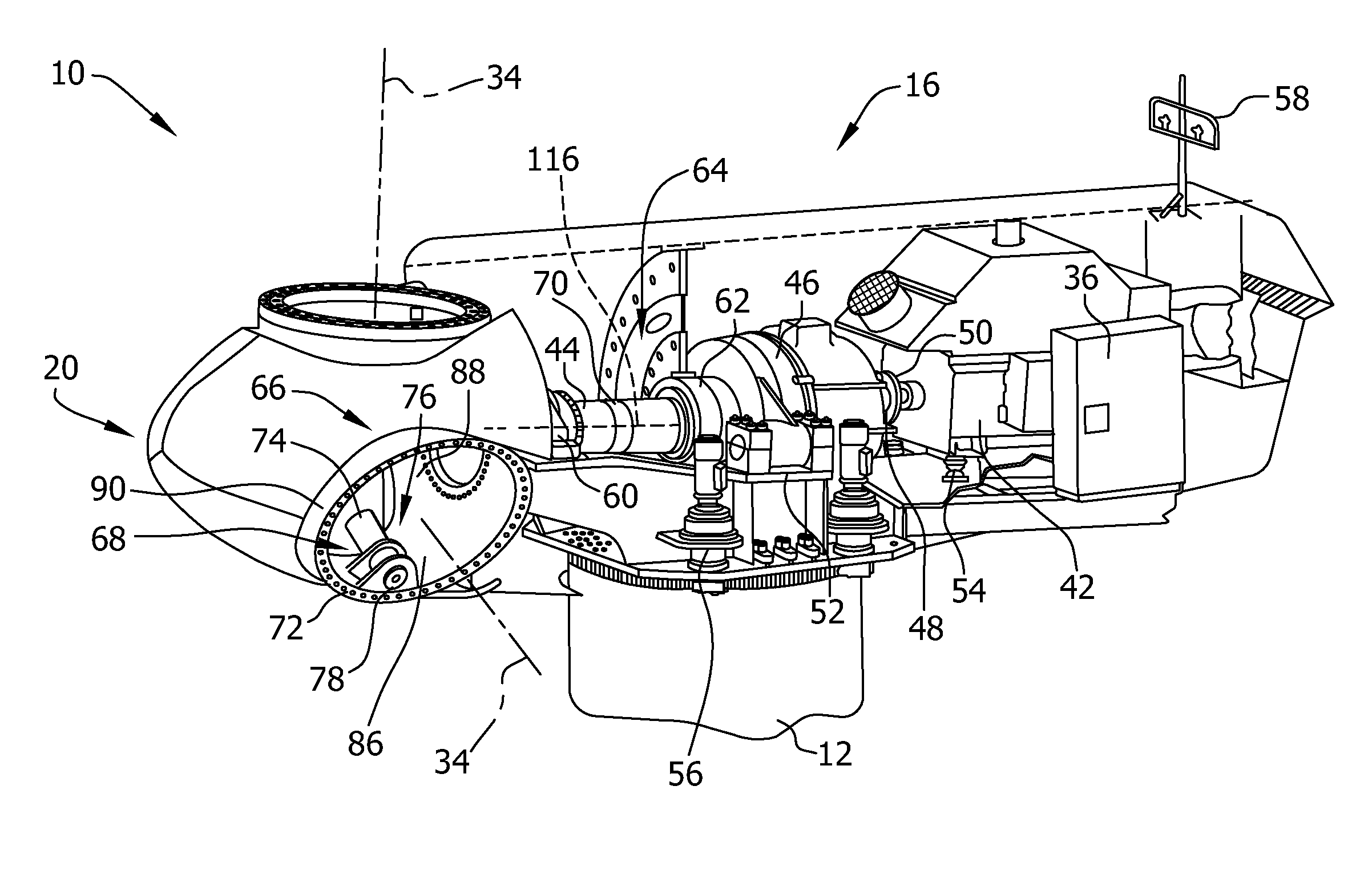
A method for operating a wind turbine is provided. The wind turbine includes a rotor including at least one rotor blade and a pitch drive system coupled to the at least one rotor blade. The pitch drive system is adapted for pitching the rotor blade. The method includes: determining an actual value of a first variable indicative of an overspeed state of the wind turbine; determining an actual value of a second variable of the wind turbine correlated to the rate of change over time of the first variable; and, estimating an occurrence of an overspeed state of the wind turbine from at least the determined actual values of the first and second variables. The pitch drive system pitches the rotor blade for aerodynamically braking the rotor based on the result of the estimation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Turbine speed stabilisation control system
InactiveUS20120161442A1Reduce variationImprove stabilityRotational speed controlWind motor controlClosed loopDisplacement control
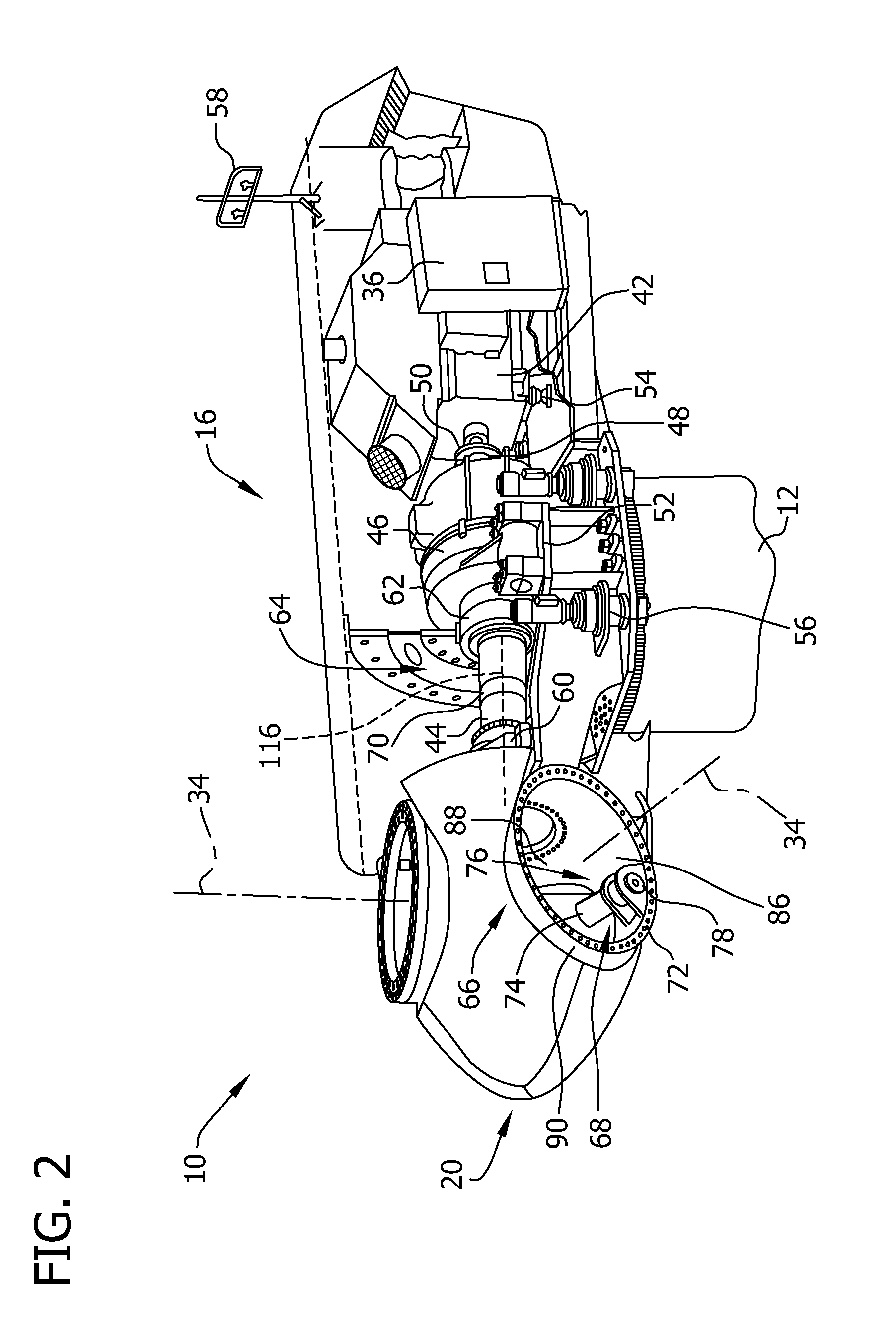
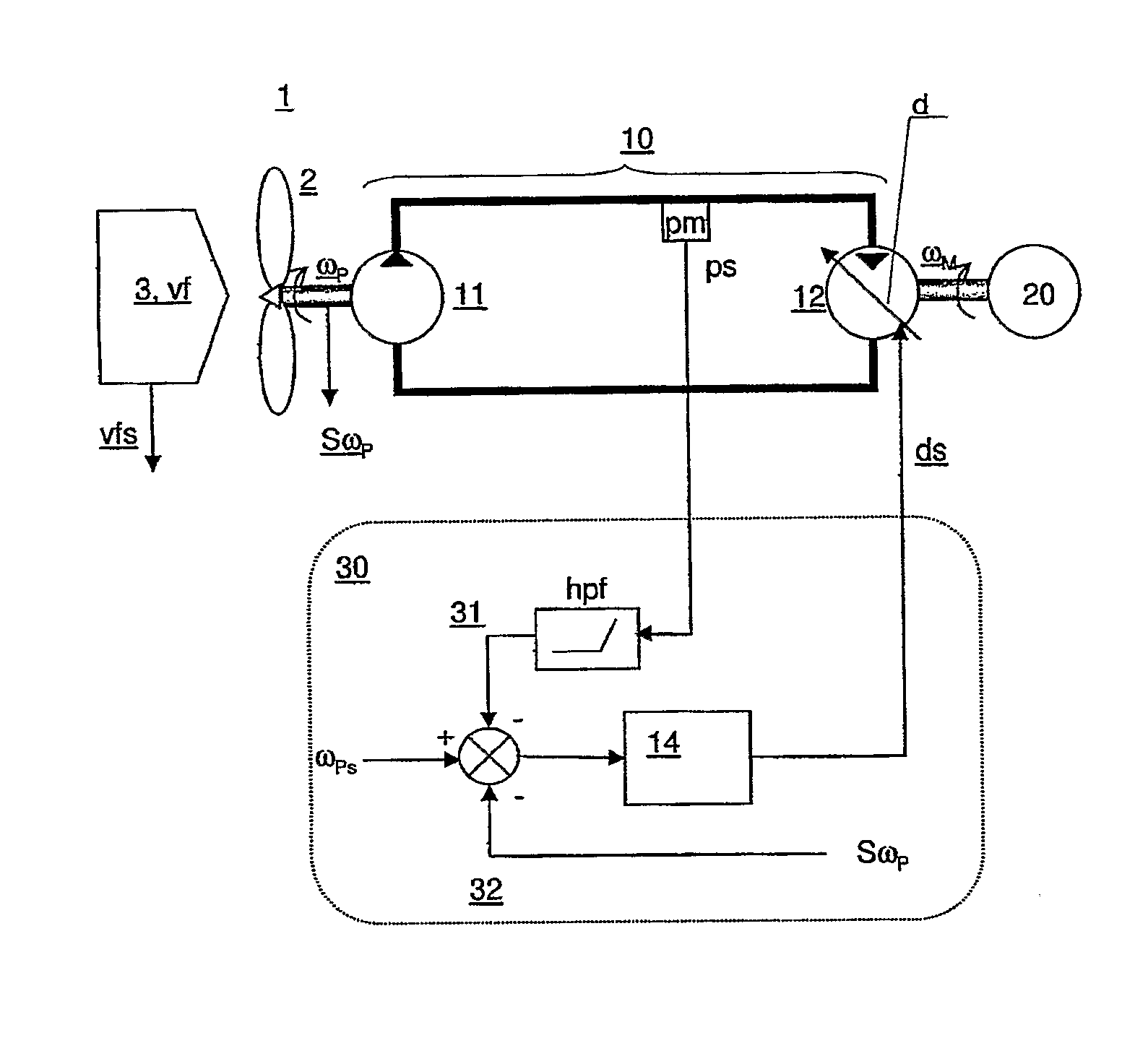
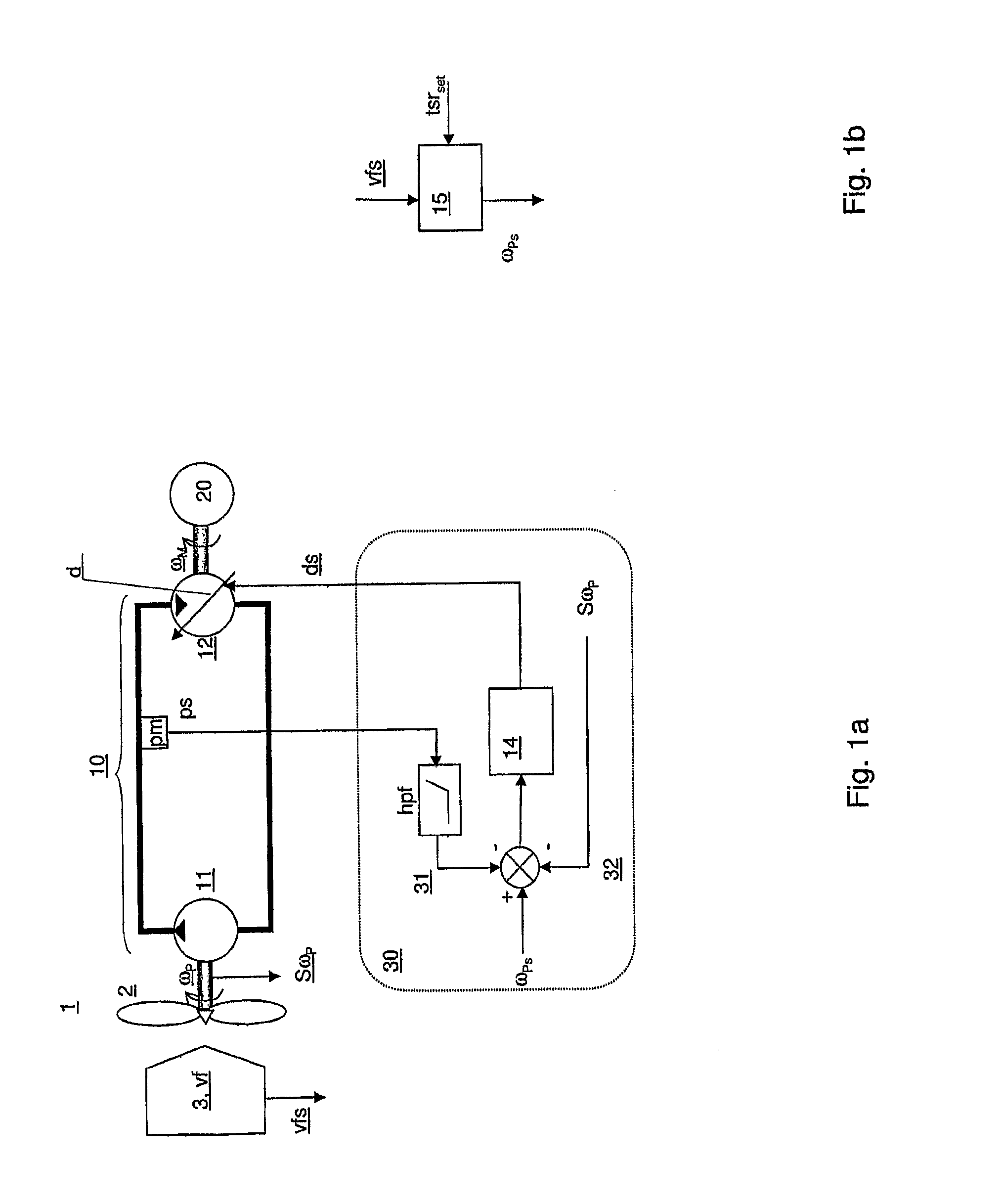
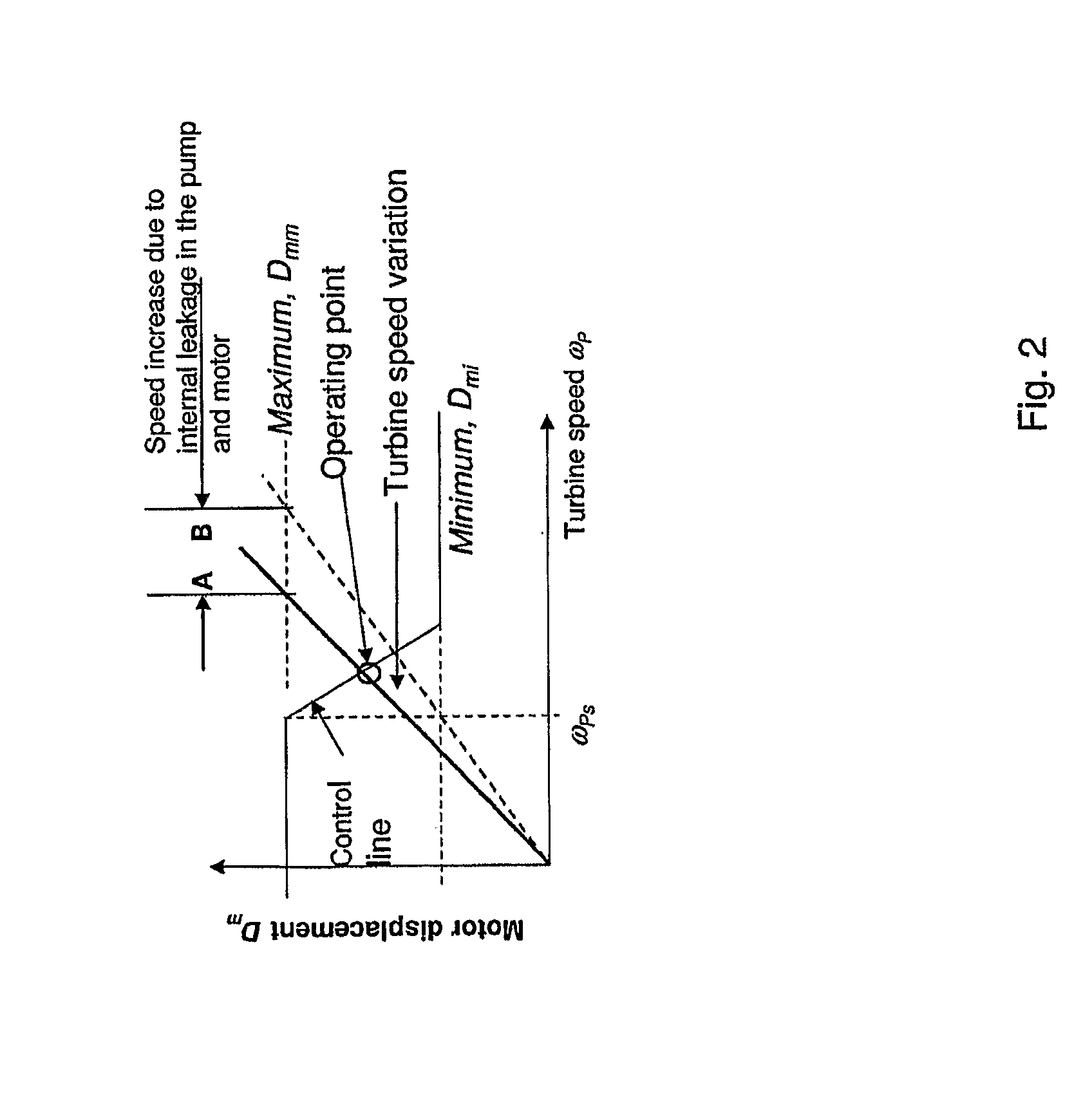
A closed loop turbine speed control system for a turbine power production system including a closed loop hydrostatic transmission system for the transfer of energy from a wind turbine rotor to a generator. A displacement actuator is arranged for receiving a displacement control signal from the control system and for controlling a displacement of the displacement motor. The control system includes a turbine rotor speed feedback control loop for calculating the displacement control signal based on deviations of a turbine rotor actual rotational speed from a turbine rotor set rotational speed. In addition a hydraulic pressure meter measures the hydraulic pressure of the hydrostatic system and provides a hydraulic pressure signal as an input to a pressure feedback control loop for stabilizing the displacement control signal based on the hydraulic pressure signal.
Owner:CHAPDRIVE AS
Overspeed protection system and method
InactiveUS20110142634A1Preventing overspeed conditionAvoid adjustmentRotational speed controlPropellersTurbineProtection system
An overspeed protection system for a wind turbine having a hub and at least one rotor blade mounted to the hub includes a rotation sensor adapted for measuring a rotor speed of said wind turbine; a comparator connected to the rotation sensor and adapted for comparing the measured rotor speed with a predetermined threshold value of the rotor speed wherein the comparator outputs a signal indicative of the comparison; and an auxiliary pitch drive controller connected to the comparator and adapted to receive the signal indicative of the comparison, the auxiliary pitch drive controller being further adapted for controlling a pitch drive unit of the wind turbine independently of a main turbine controller and, if the threshold value is exceeded, to adjust a pitch angle of the rotor blade of the wind turbine so that aerodynamic braking of the wind turbine is effected.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Eolic converter
InactiveUS20080203731A1Significant potencyRange of precisionRotational speed controlPropellersConvertersRotational axis
The present invention relates to an eolic converter endowed with a winds keeping system that allows an utilization of above 97% of the wind force to transform in mechanical rotational energy, at the same time that is added to this high efficiency the possibility to add several levels of plates without limit of size of the referred plates, what provides for an unique propeller shaft the use of gigantic areas of reception of the wind force where these shafts can be added in order to allow a great area of wind reception to rotate a shaft, even with low values of wind speed, this system doesn't need to be oriented for the wind direction, because traction independently of the moment wind direction, always rotating in the same direction that it was programmed to rotate.
Owner:DULCETTI FILHO FLAVIO FRANCISCO
Method for controlling a wind turbine connected to the utility grid, wind turbine and wind park
The invention relates to a method for controlling a wind turbine connected to the utility grid comprising steps of detecting a fault of the utility grid, and controlling one or more rotor blades in a fault mode wherein said one or more rotor blades are pitched in order to stabilize the rotor speed within an over speed range. The invention also relates to a wind turbine and a wind park comprising at least two wind turbines.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
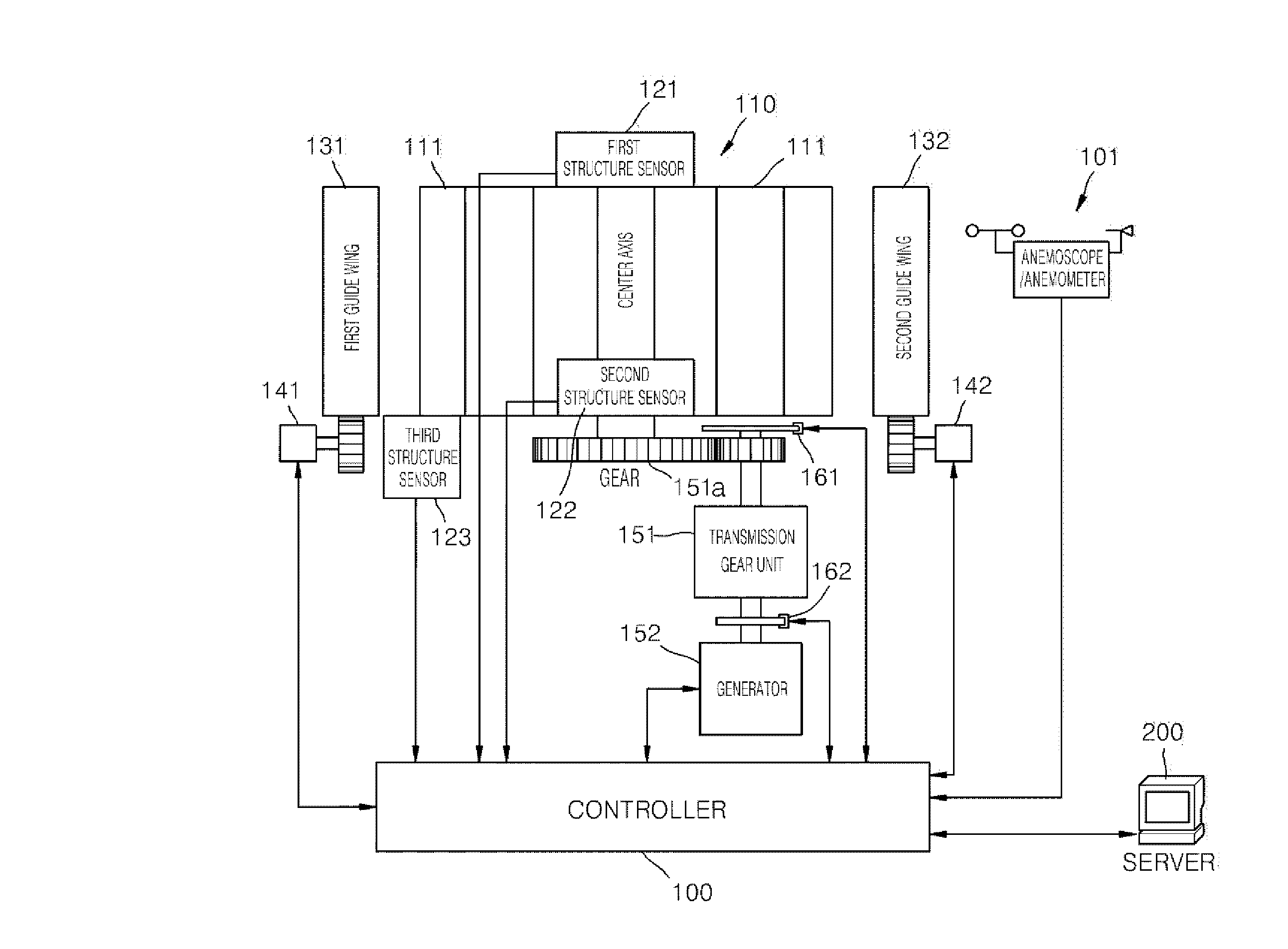
Method and apparatus for controlling vertical axis wind power generation system
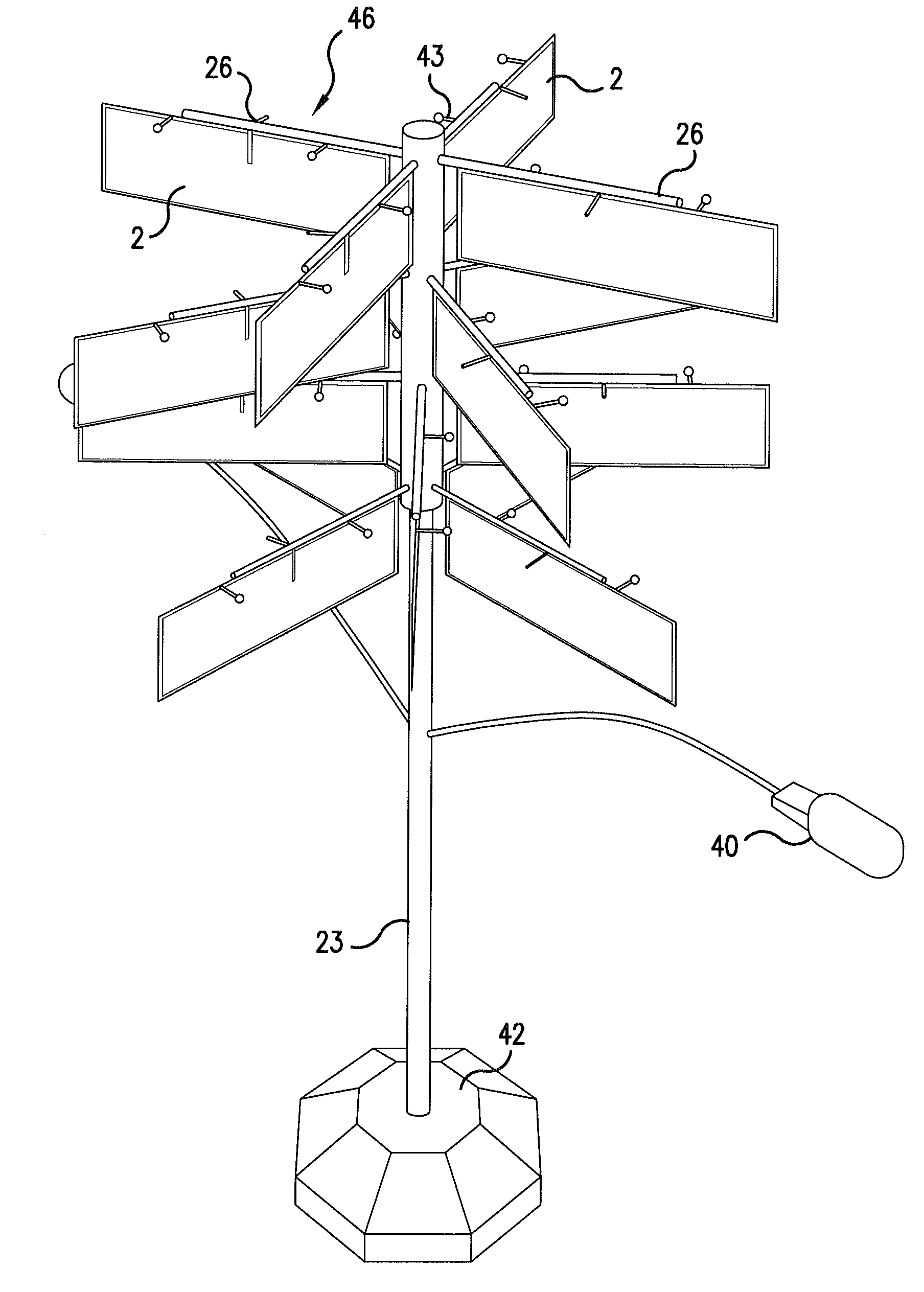
Provided are an apparatus and method for controlling a vertical axis wind power generation system that controls the rotation of guide vanes according to wind direction and speed, appropriately controls a direction of wind passing over an impeller, thereby maintaining a rotational speed generating the maximum power, maintains output power of a generator as rated power according to wind direction and speed, and stops the generator when a low or high wind speed outside a setting value range, an error in a structure, a fault in a braking unit, and / or a fault in guide vanes is detected.
Owner:KR
Fluid guidance systems for turbines
InactiveCN102272444AIncrease fluid velocityIncrease fluid pressureRotational speed controlWind motor controlTurbine bladeCross-flow turbine
A directing system for directing fluid entering an axial flow turbine along an inlet flow direction. The turbine includes a plurality of turbine blades. The directing system includes a base structure, a plurality of directing segments attached to the base structure, downstream of the base structure, and a directing segment adjustment system for adjustably positioning the directing segments between a retracted configuration and a deployed configuration. The directing segments, in the deployed configuration, extend beyond the base structure in a direction transversal to the inlet flow direction and deflect the fluid towards an outer circumference of the plurality of turbine blades corresponding to a higher torque area of the blades. A directing system for directing fluid entering a cross-flow turbine is also disclosed. In the cross-flow turbine, the fluid is directed towards a centerline of the rotor of the turbine, which is a high torque area of the turbine blades.
Owner:ORGANOWORLD
System and method for reducing rotor loads in a wind turbine upon detection of blade-pitch failure and loss of counter-torque
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
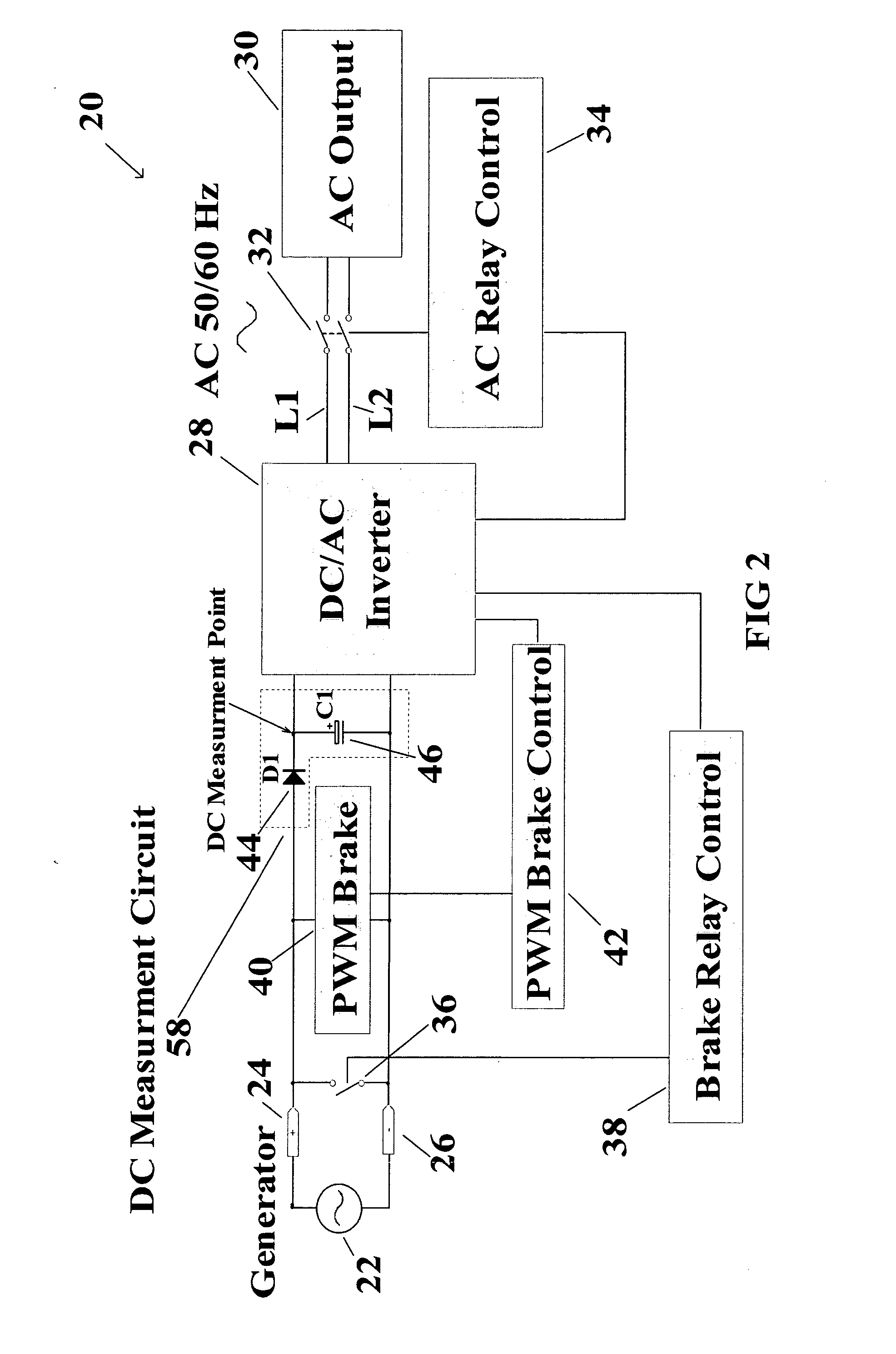
Over speed control circuit for a wind turbine generator which maximizes the power exported from the generator over time
InactiveUS20070216163A1Convenient timeMiniaturizationRotational speed controlWind motor controlEngineeringTurbine
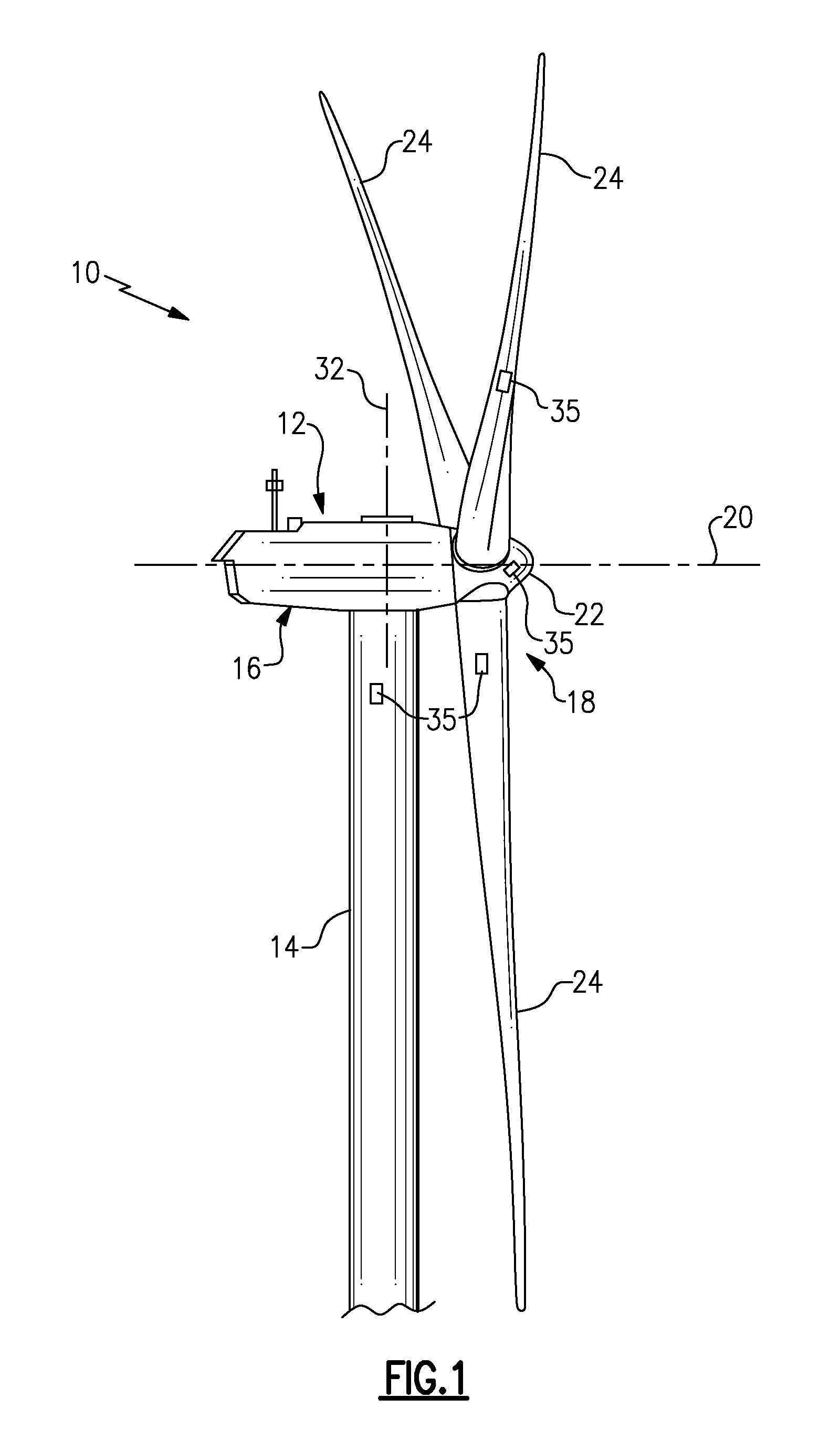
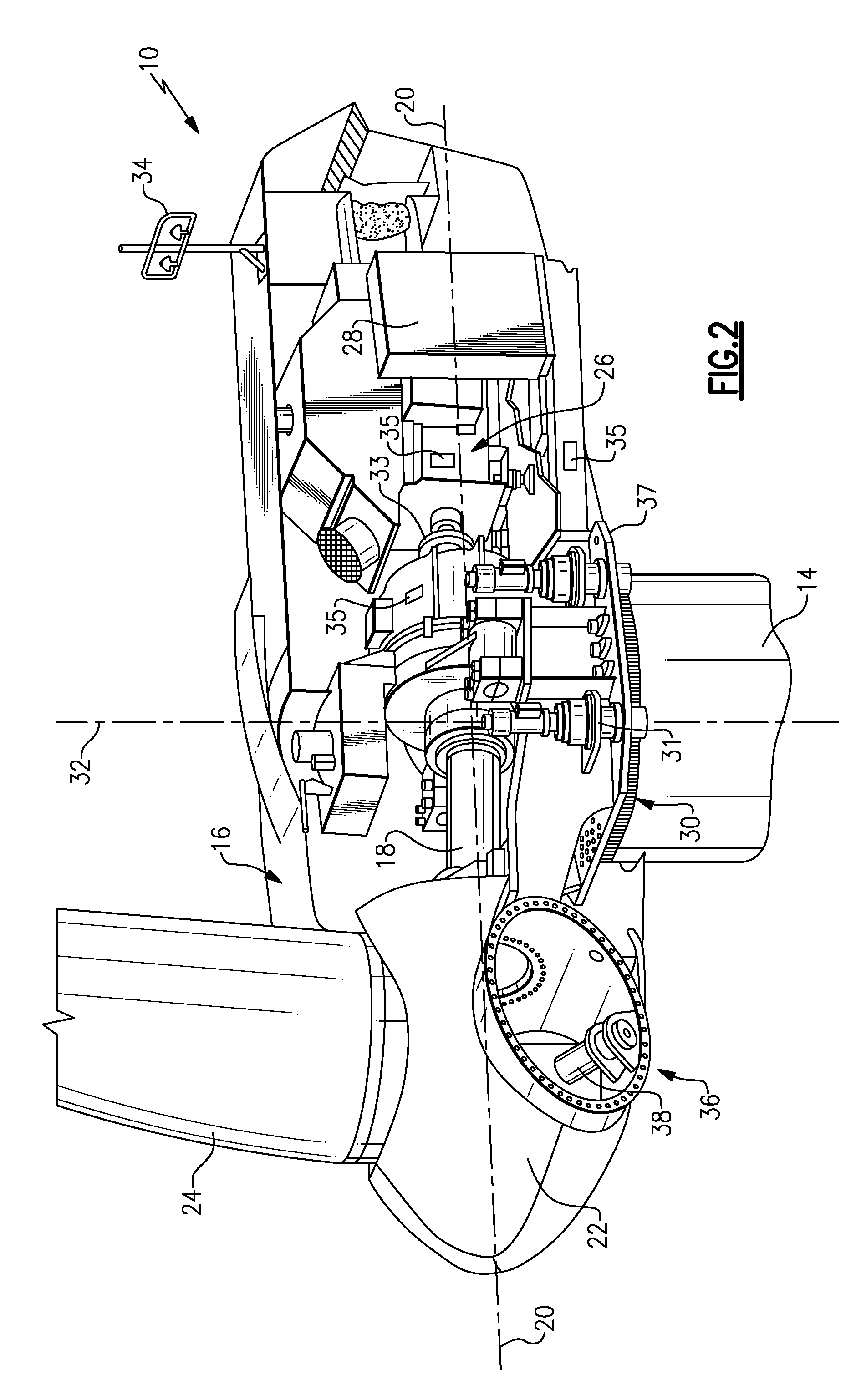
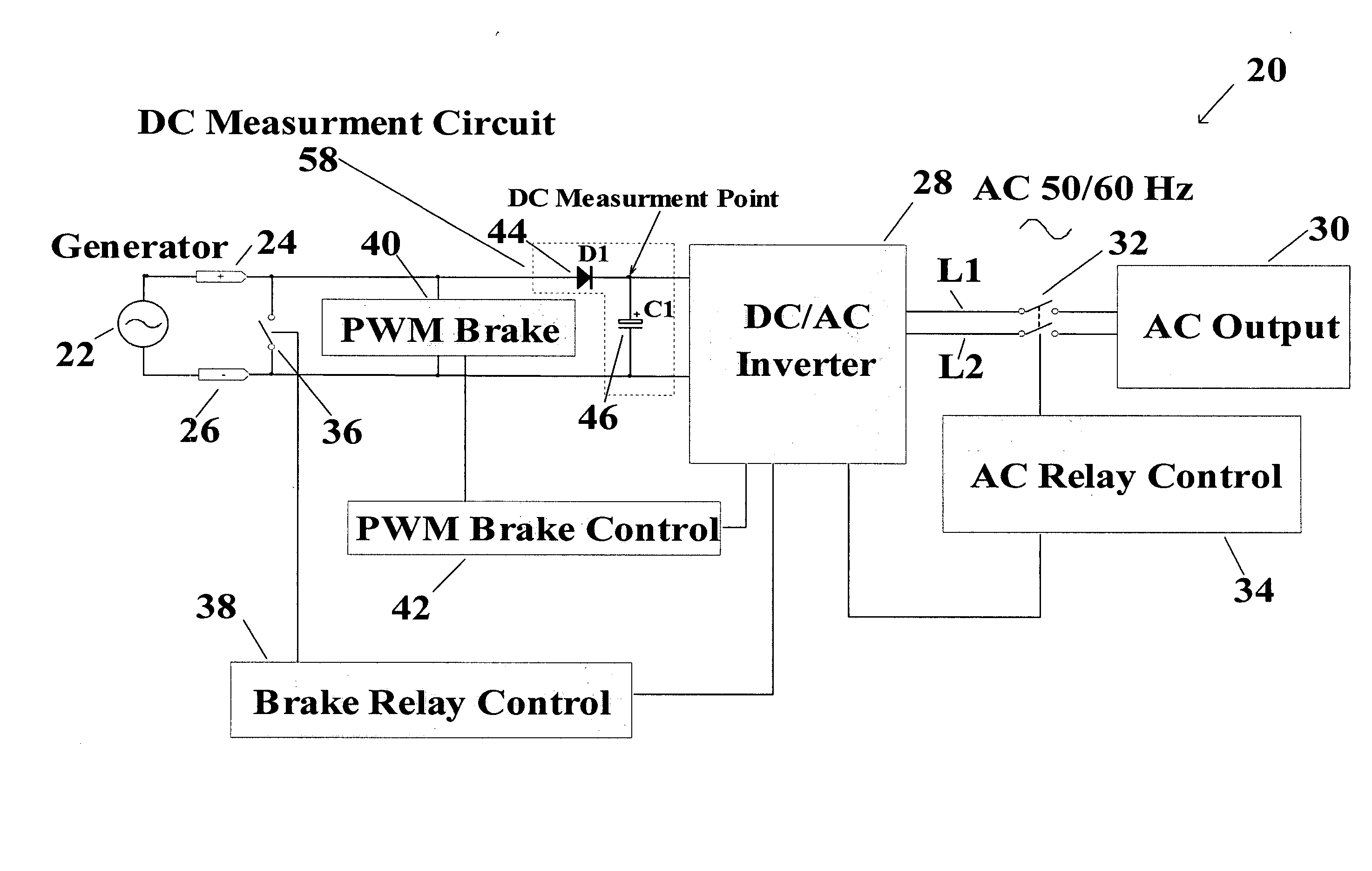
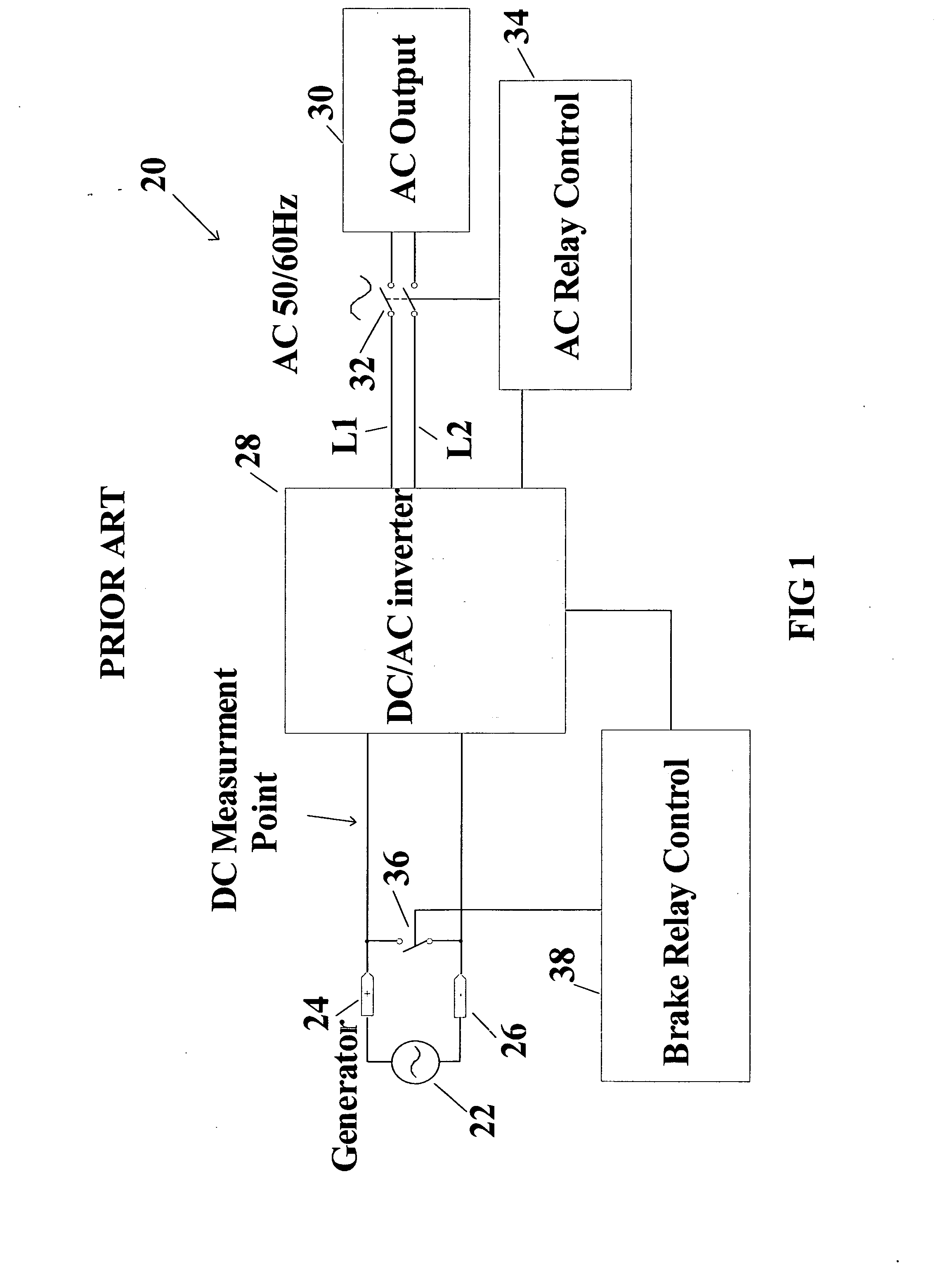
An over speed control circuit for a wind turbine generator is disclosed which optimizes the time that the wind turbine generator is operational and thus maximizes the power output over time. The over speed control circuit forms a closed feedback loop which periodically measures the output voltage of the wind turbine generator in order to regulate its speed by electronically controlling the load on the generator. The over speed control circuit in accordance with the present invention is adapted to work in conjunction with known over speed protection lock out relays. More particularly, the over speed control circuit causes a short circuit to be placed the generator terminals when the generator voltage reaches a threshold value, relatively less than the threshold value used to trigger the over speed lockout relay. As such, the over speed control circuit minimizes the operation of the lockout relay, thereby maximizing the power output of the generator over time making such wind turbine generator systems much more practical as a renewable energy source.
Owner:ICC NEXERGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com