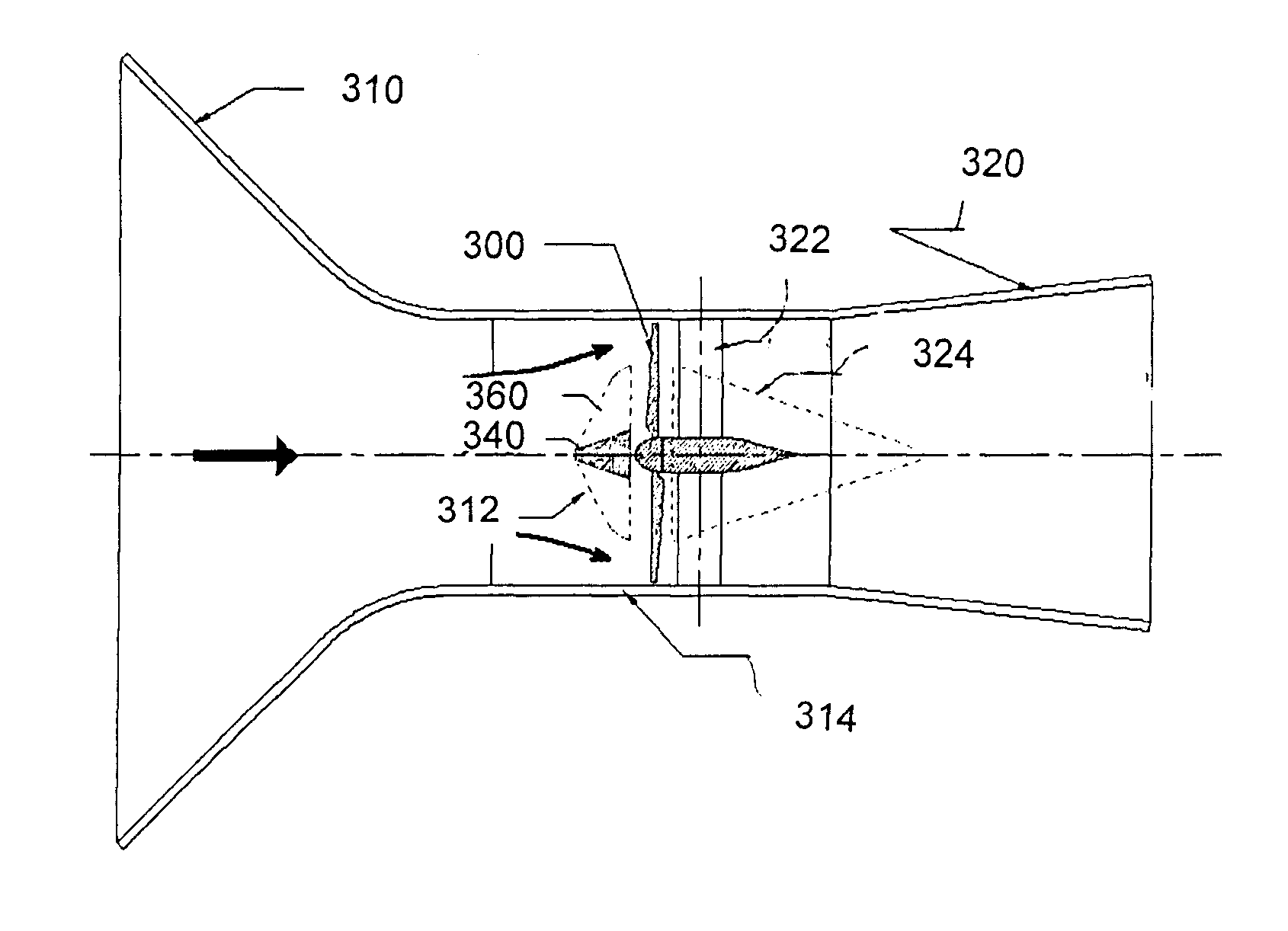
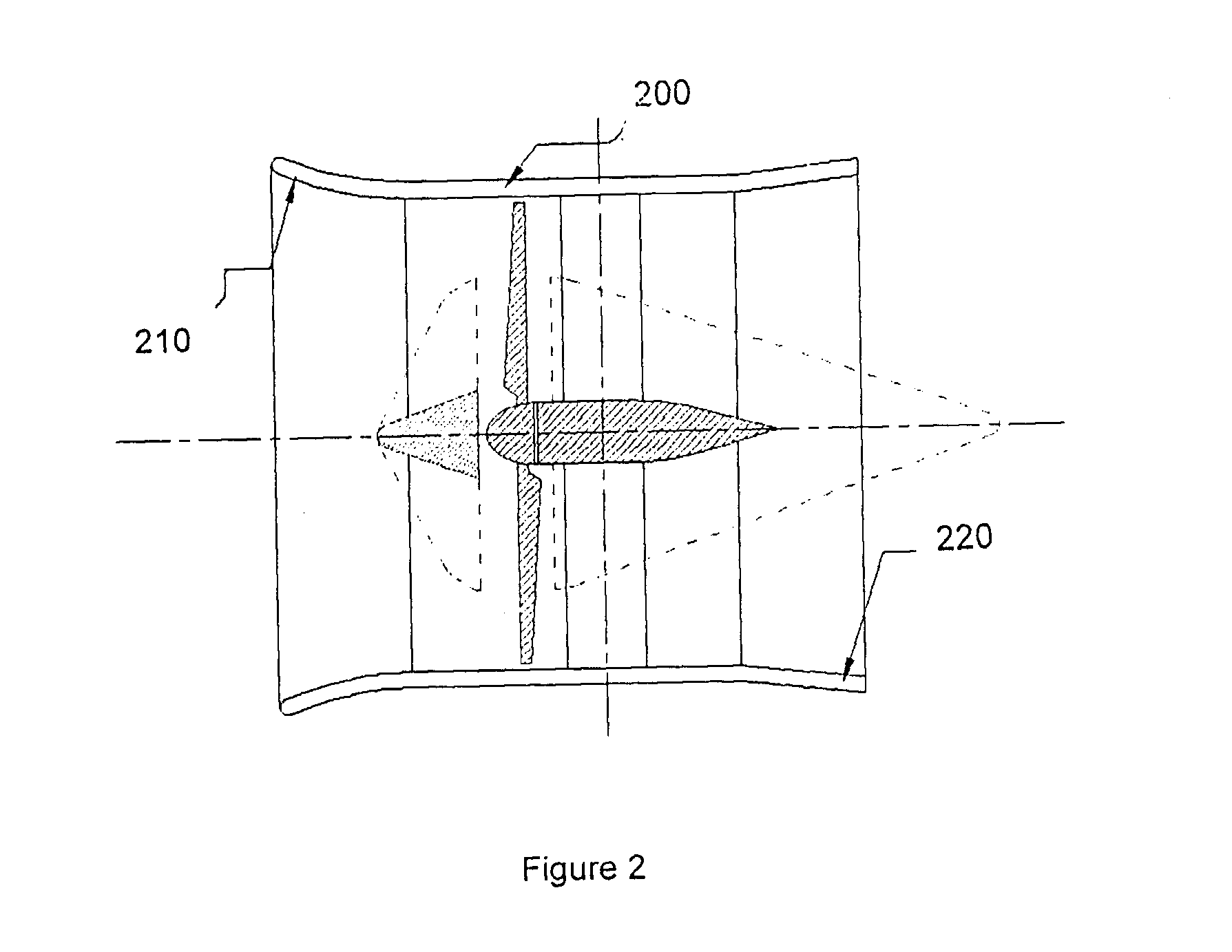
Fluid directing system for turbines
a technology of fluid directing system and turbine, which is applied in the direction of engine control parameters, working fluid for engines, motors, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the power generated by the blades once the rated velocity is exceeded, reducing the swept area of the rotor, and reducing the useful energy of the engine, so as to achieve the effect of increasing the fluid directing pressure over the high torque area, reducing the swept area of the rotor, and increasing the speed of the fluid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
A VAWT and Sectored Rotor at 4.0 m / s
[0178]At 4.0 m / s the sectoring ratio was varied between 1.0 and 0.67. The power produced increased from 10 to 35 kW or an increase of 3.5 fold.
example 2
A VAWT and Sectored Rotor at 7.0 m / s
[0179]At 7.0 m / s the sectoring ratio was varied between 1.0 and 0.67. The power produced increased from 50 to 120 kW or an increase of 2.5 fold.
example 3
A VAWT and Sectored Rotor at 12.0 m / s
[0180]At 12.0 m / s the sectoring ratio was varied between 1.0 and 0.67. The power produced increased from 200 to 625 kW or an increase of 3.1 fold.
[0181]The results obtained are shown as curves in FIG. 19.
[0182]As a person skilled in the art would understand a plurality of types of cross-flow or vertical axis turbines may be used with the device of the present invention. Also for each wind turbine different combinations may be used for example a different number and / or configuration of blades, the space between the wind section and the wind turbine, etc.
[0183]As a person skilled in the art would understand the parameters of the sectoring cone may differ from the examples shown in this document. Similarly the mechanism for adjusting the opening of the aperture or flow channel may differ based on the fluids, operating conditions and turbine apparatus.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com