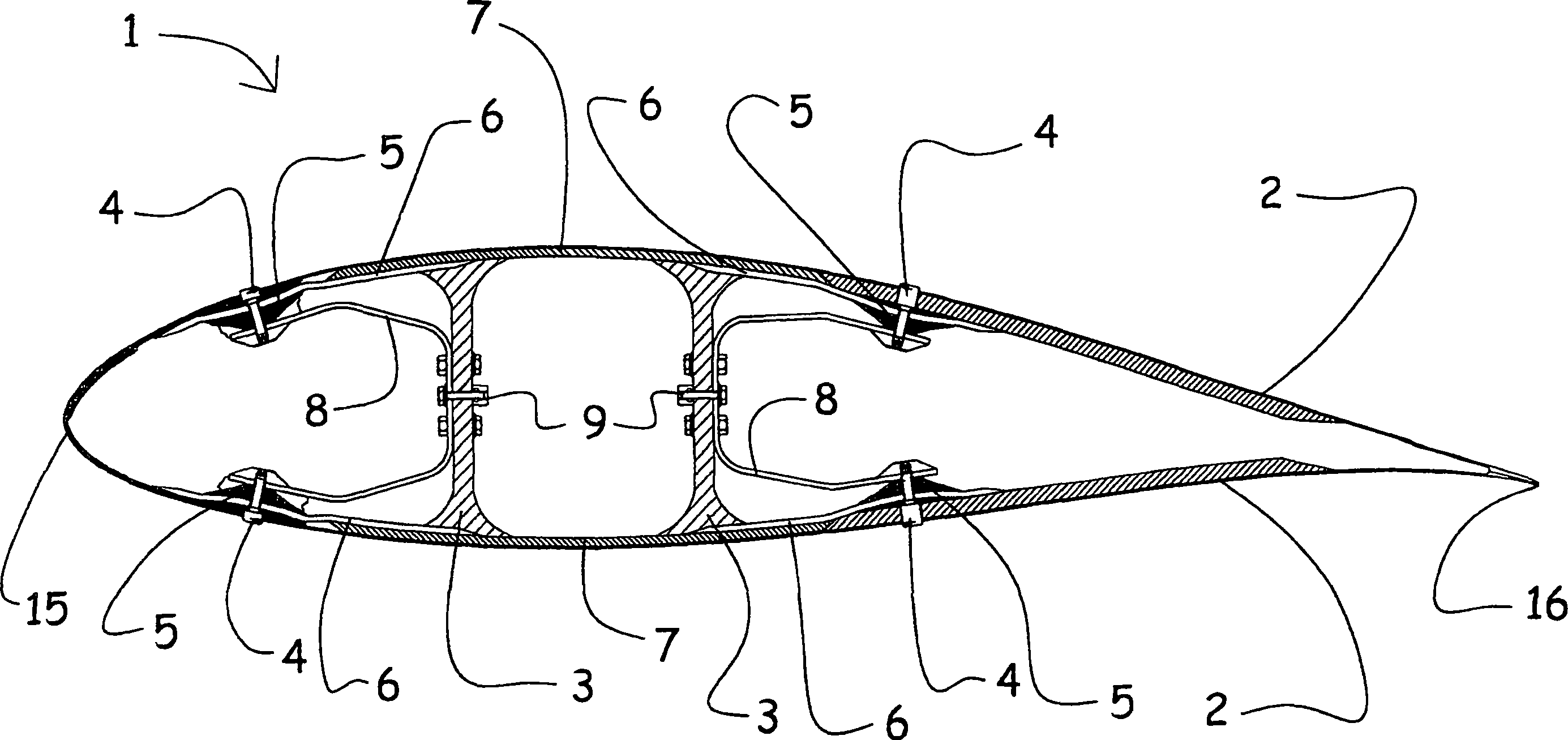
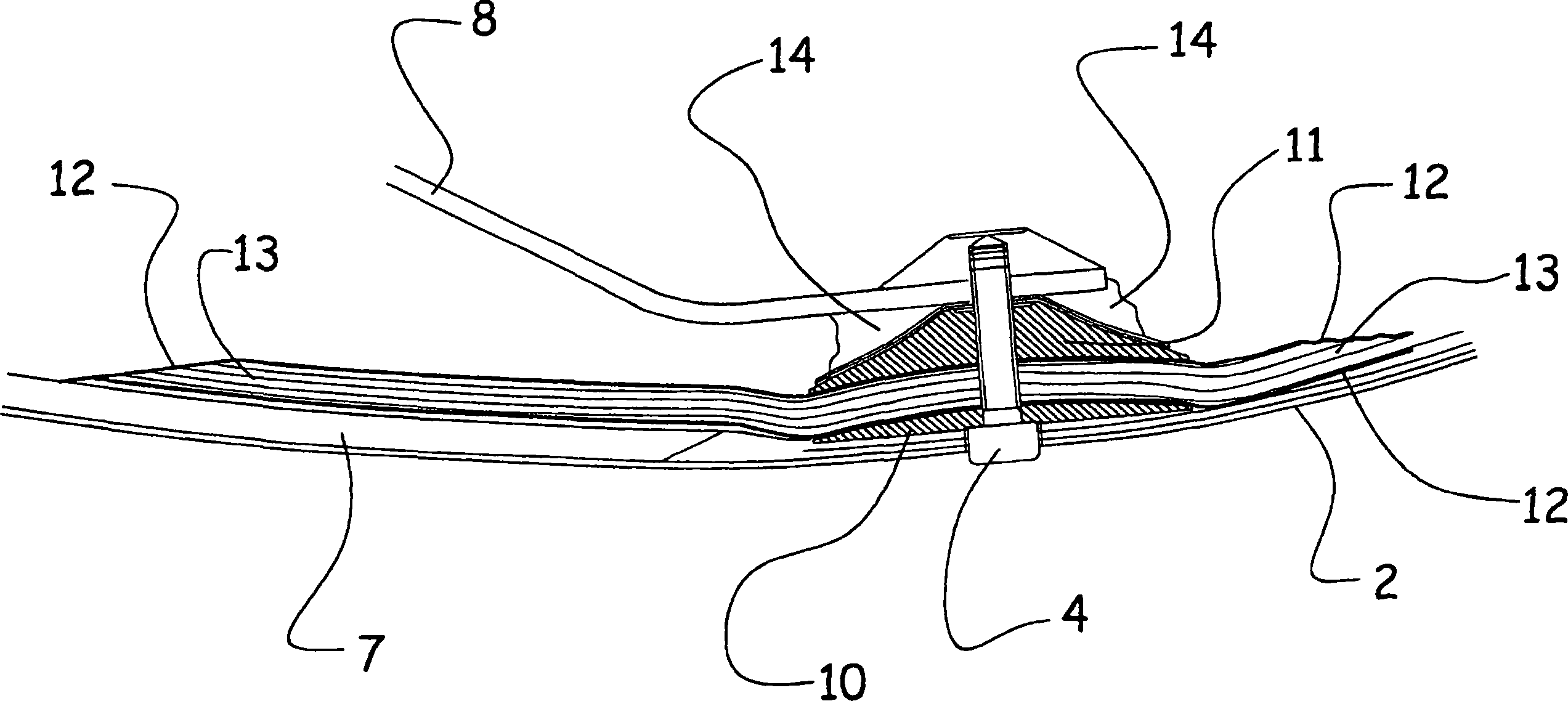
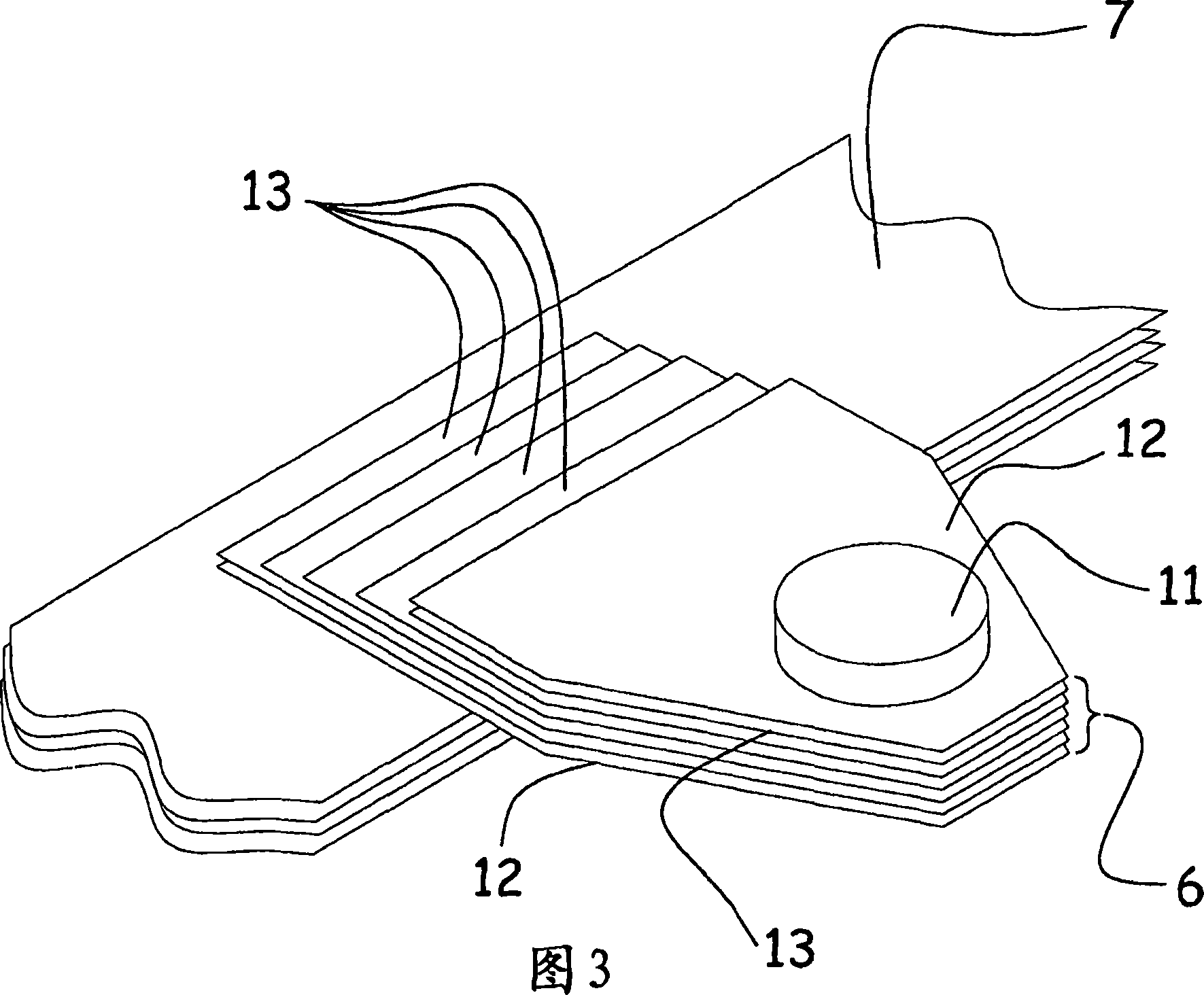
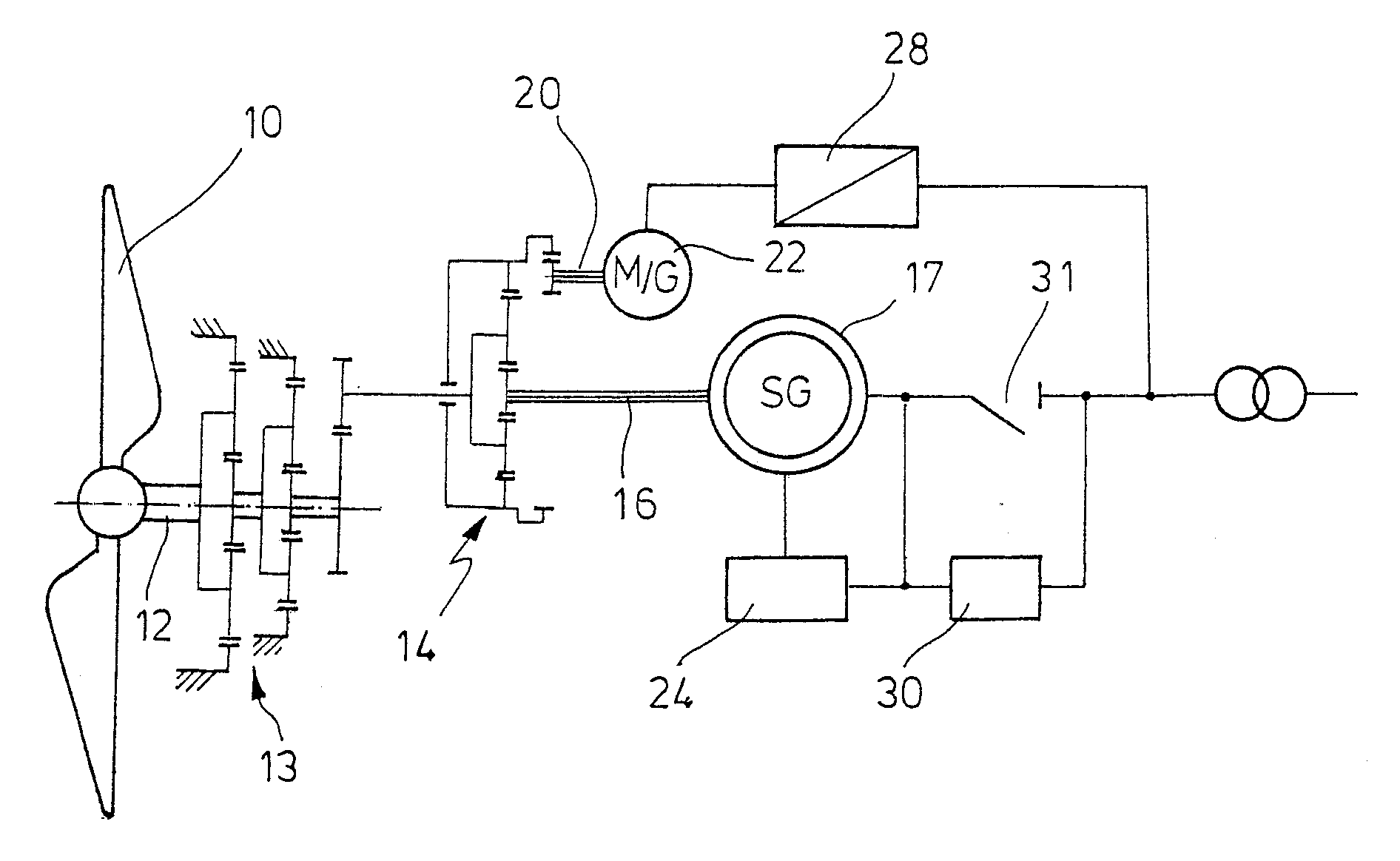
Patents
Literature
260 results about "Energy plant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Power Plants Defined The plant that produces electricity is called as power plant. The other names for the power plant are power station, power house, and generating plant. In power plants the chemical energy within the fuel is converted into electrical energy, which can be used for various domestic purposes.
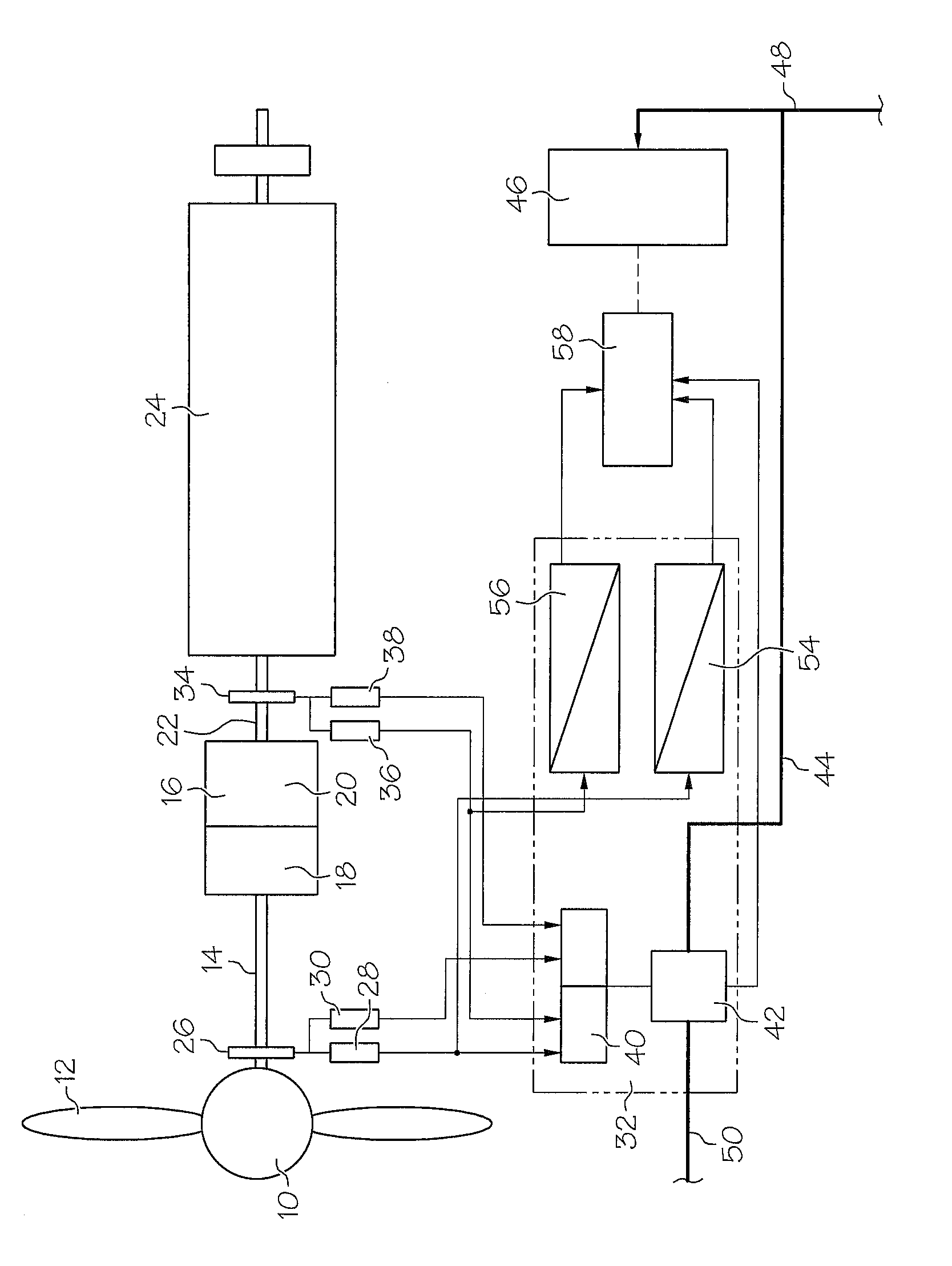
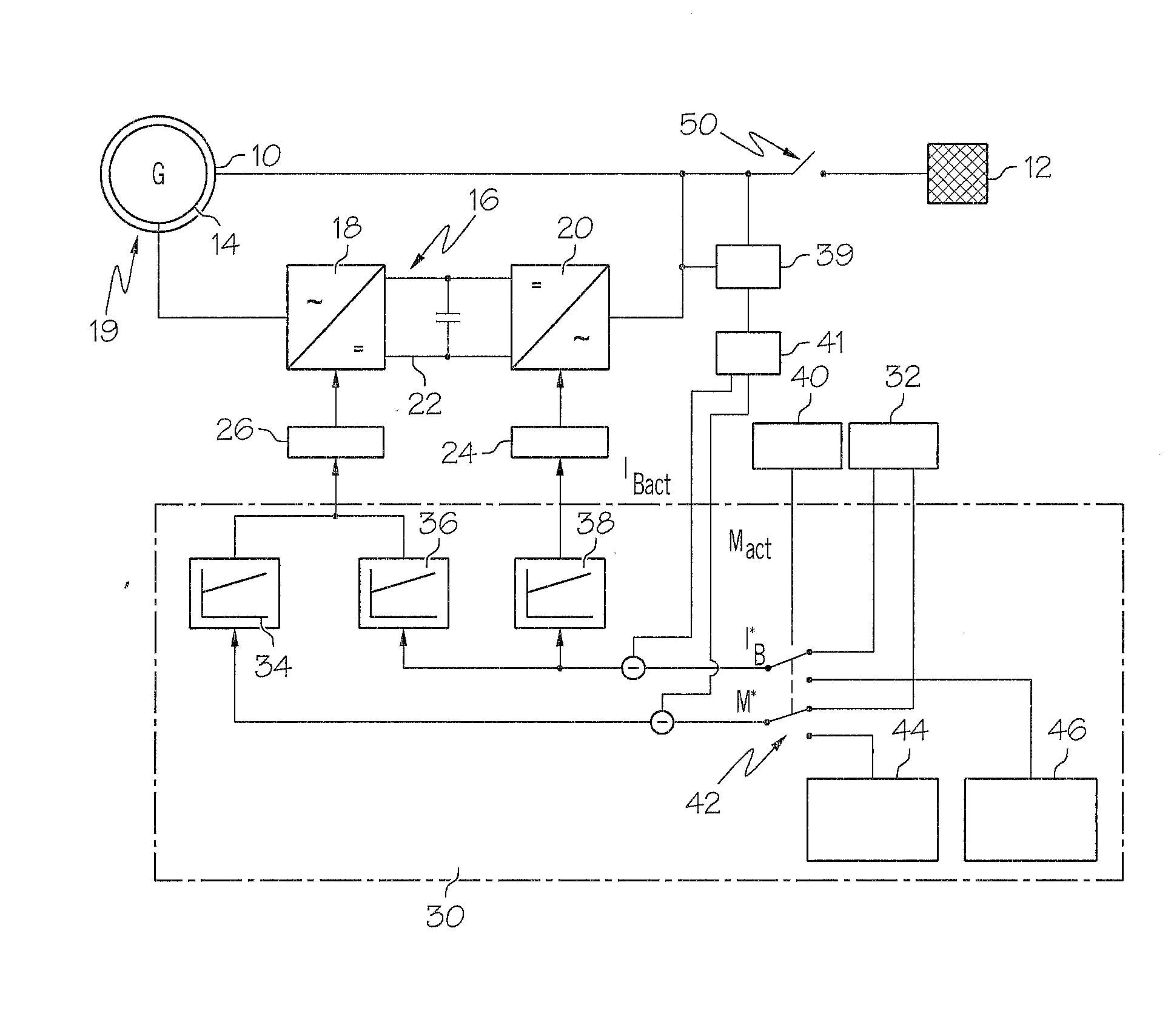
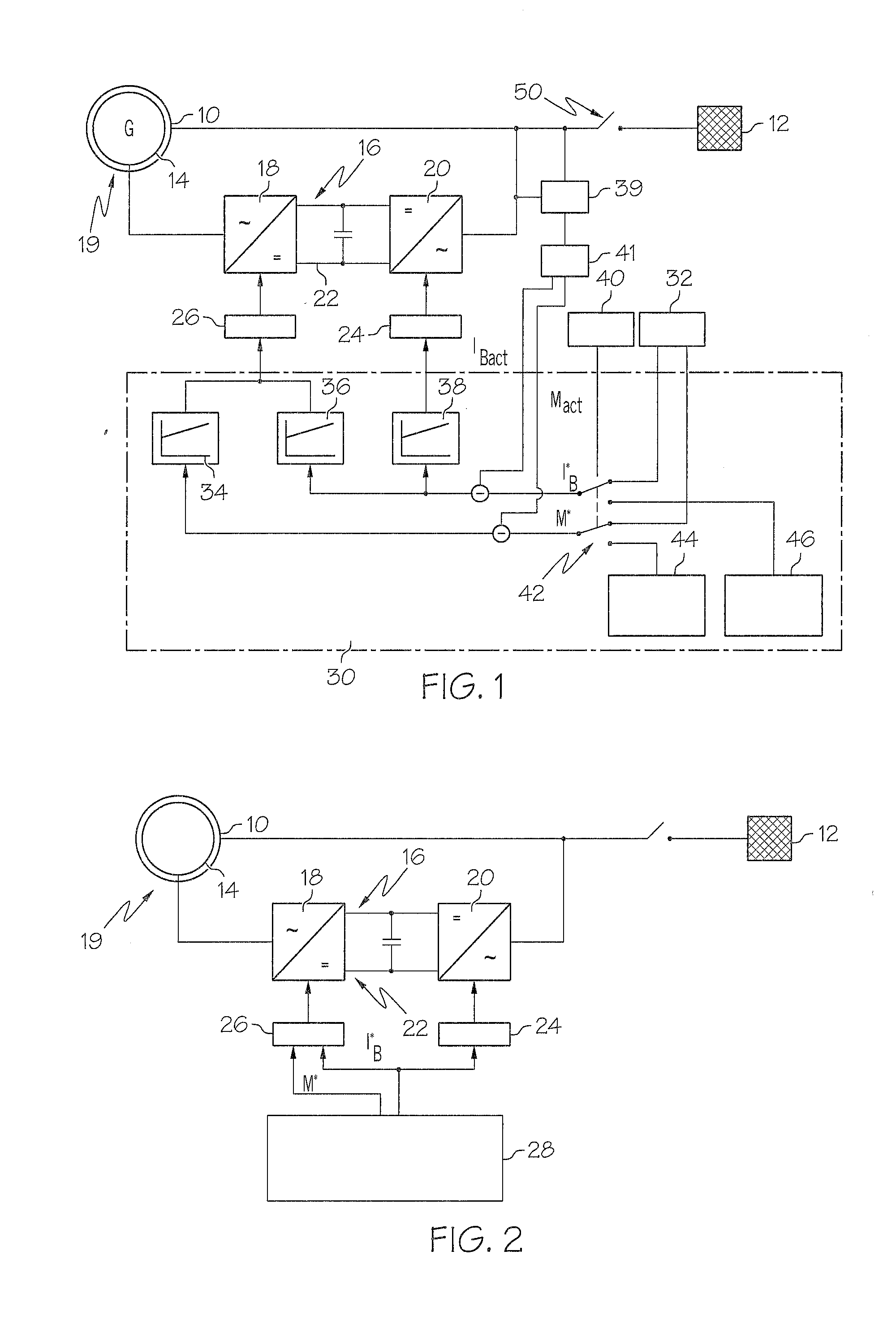
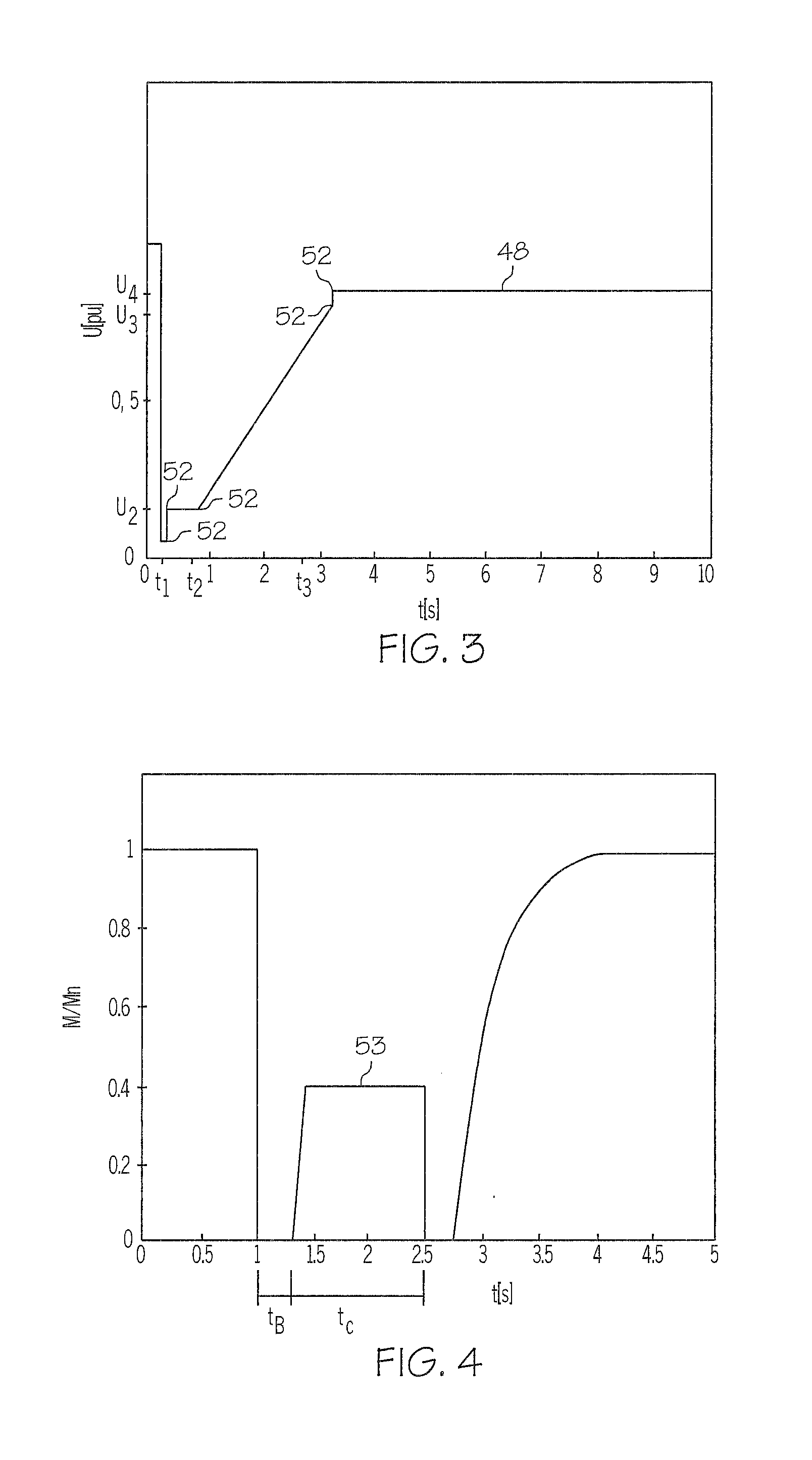
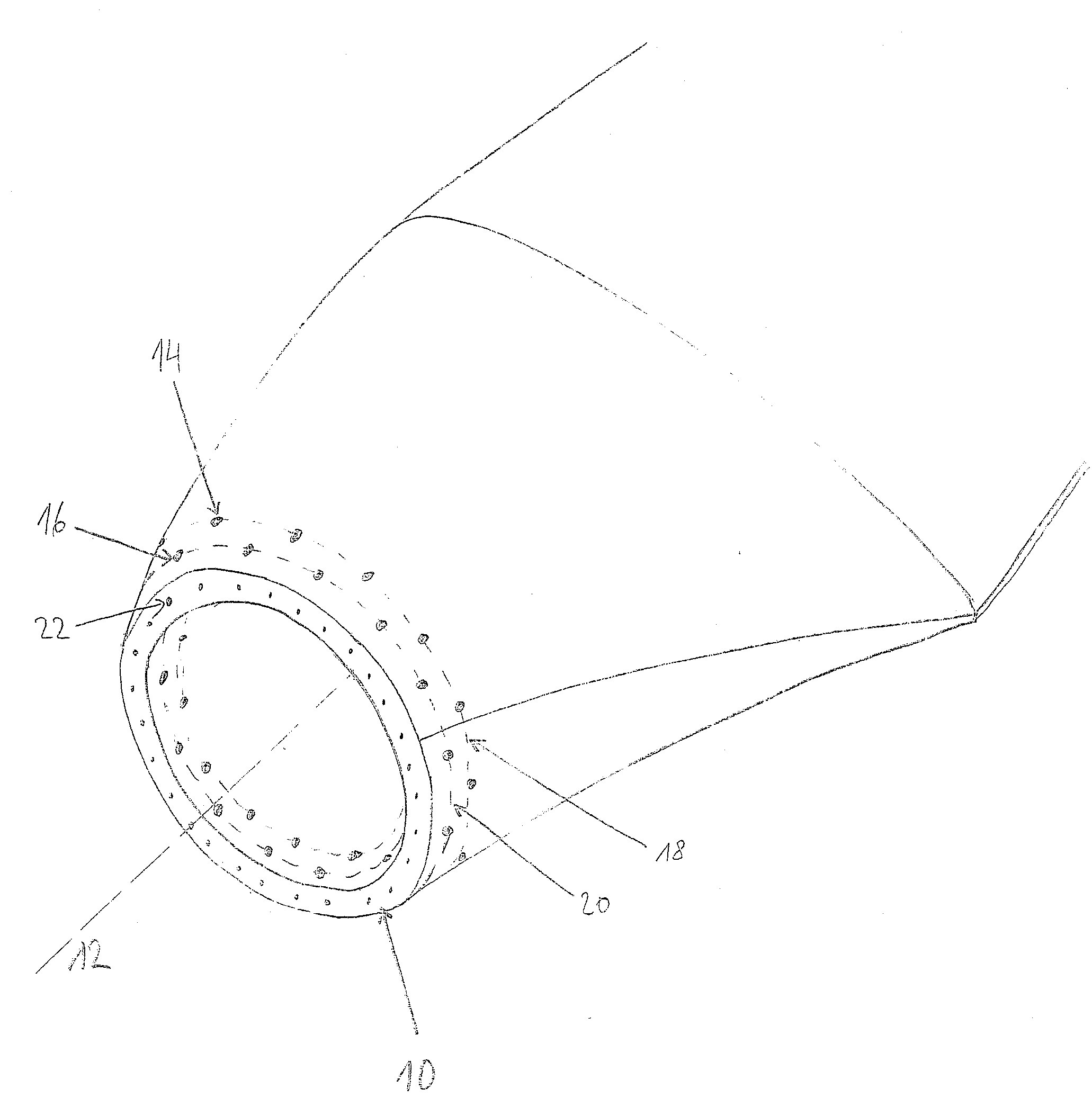
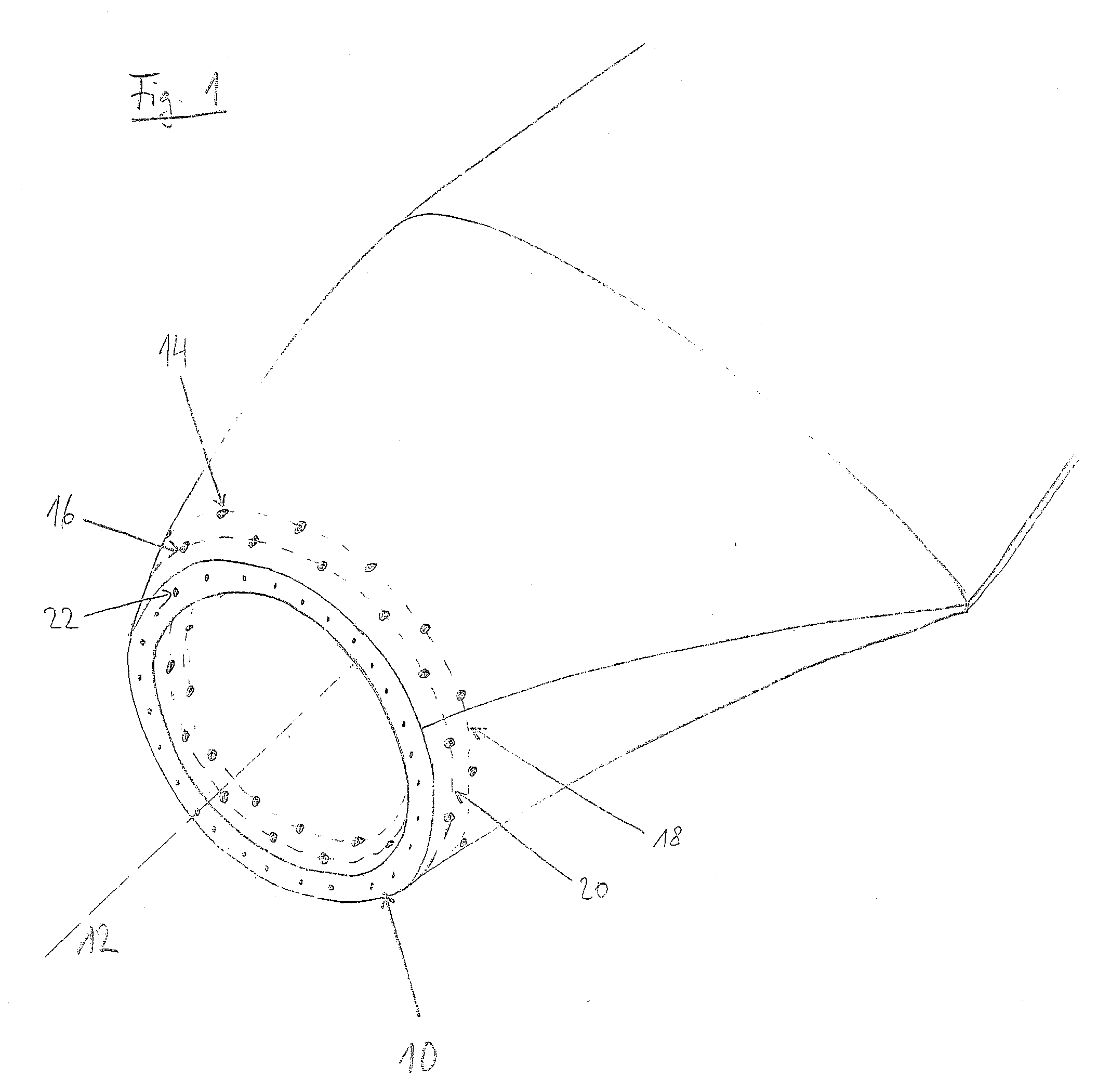
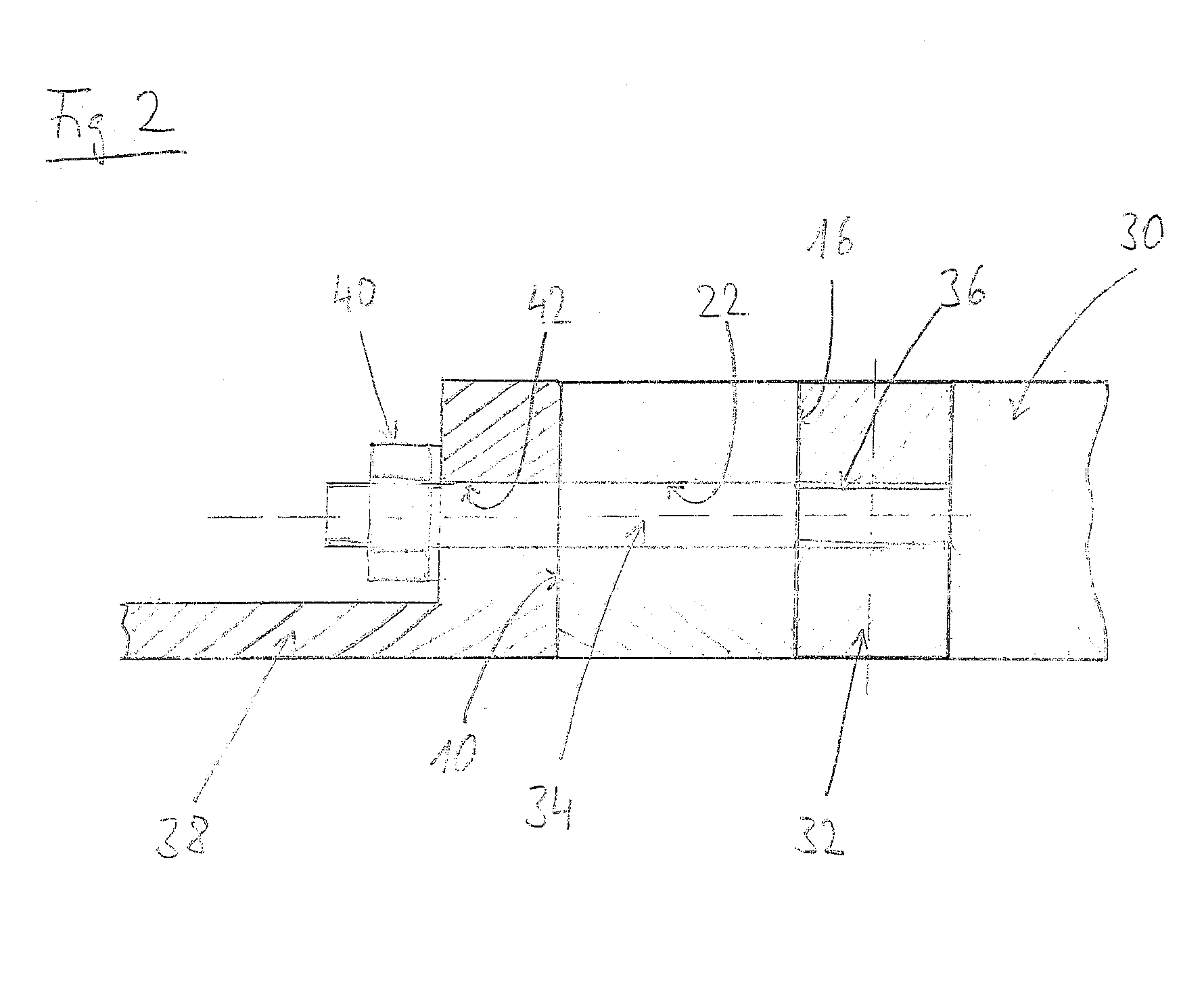
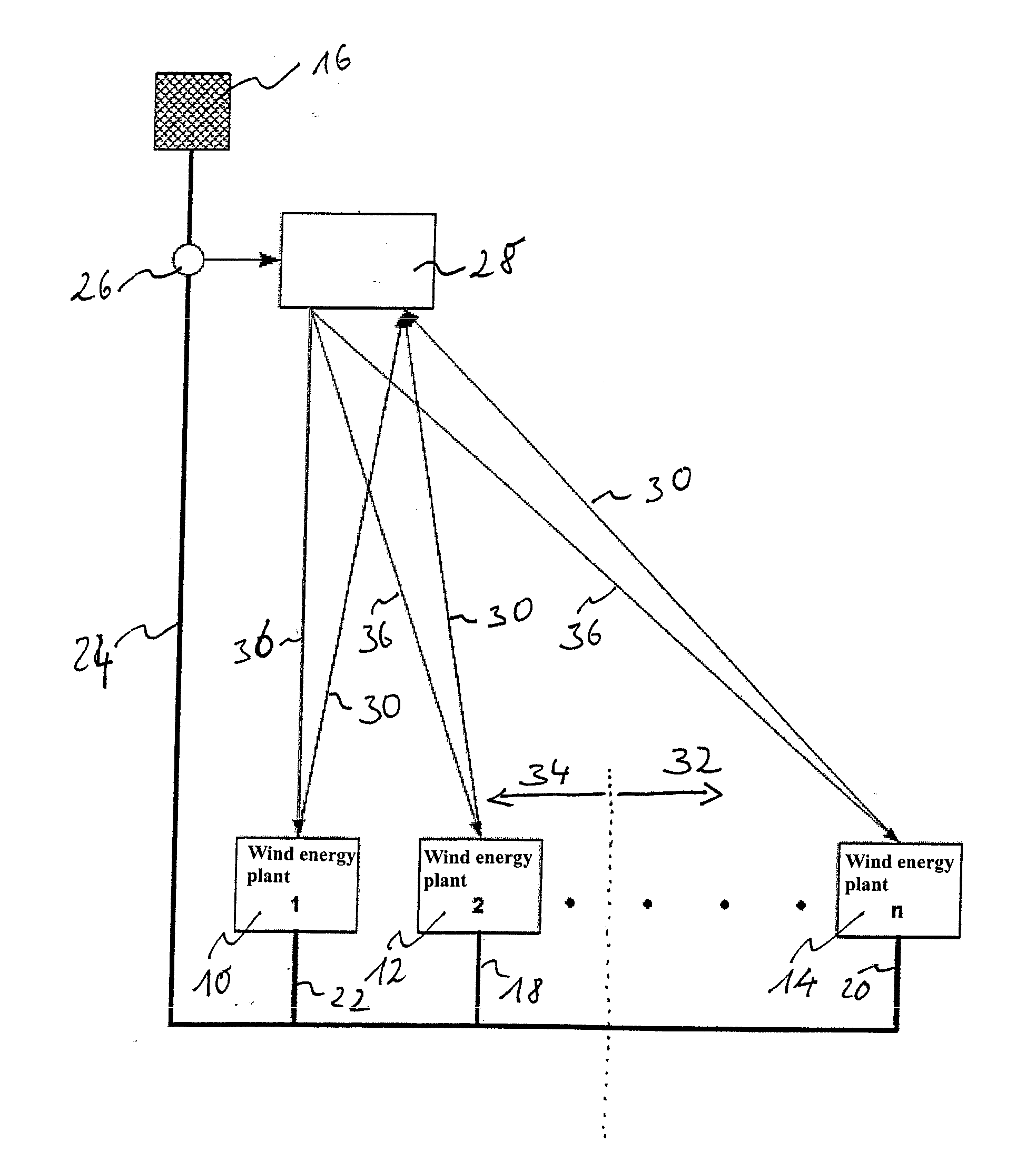
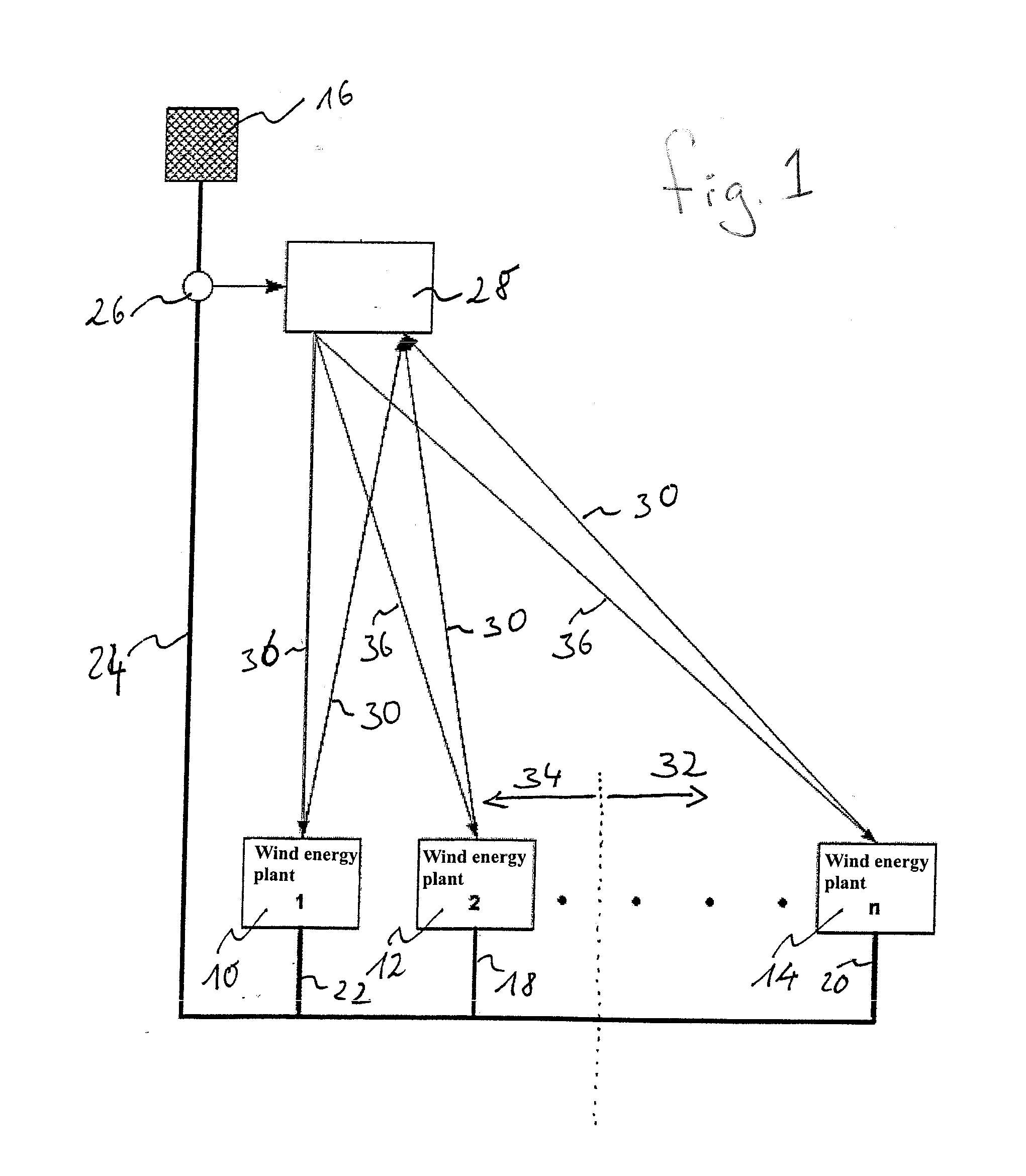
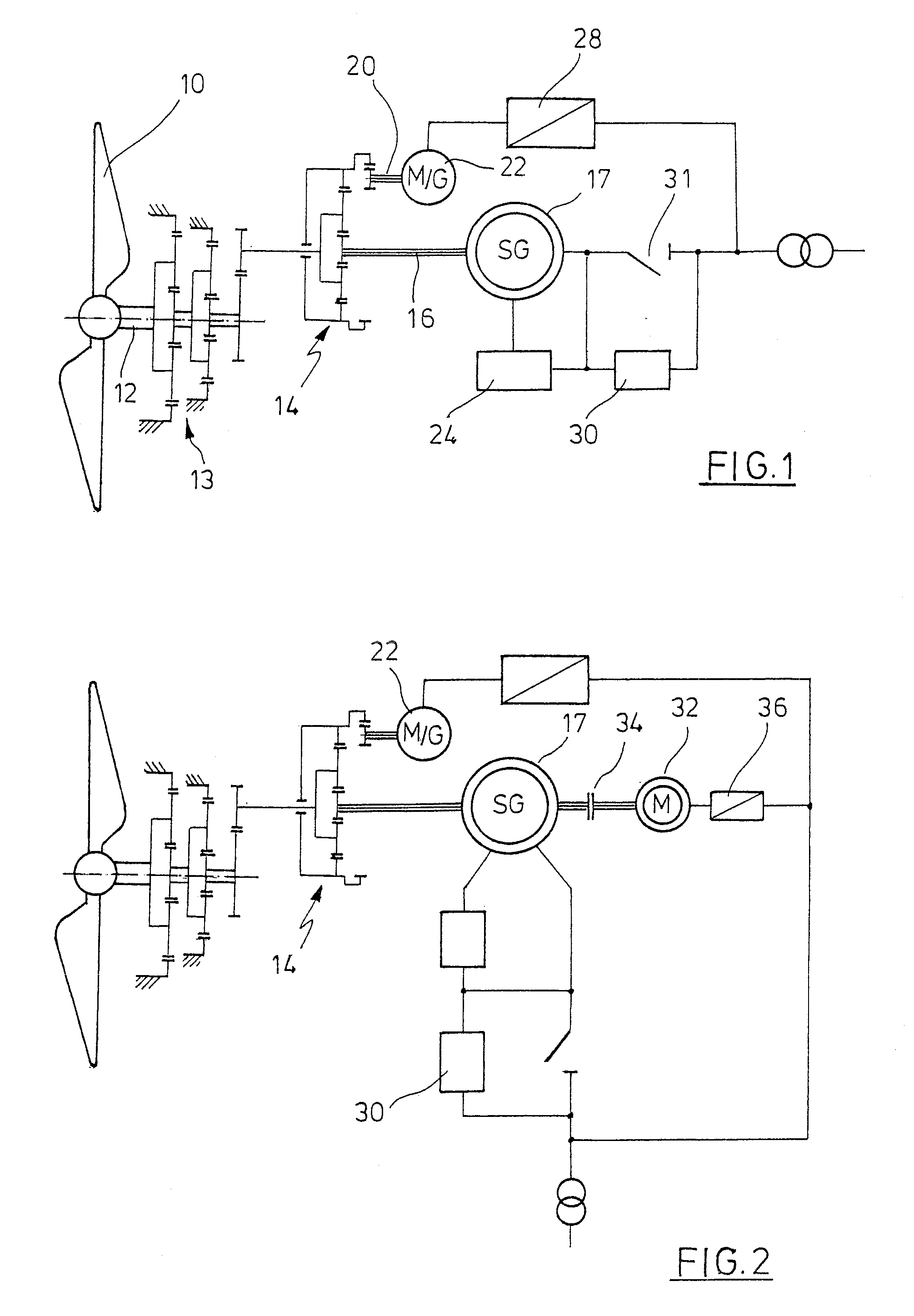
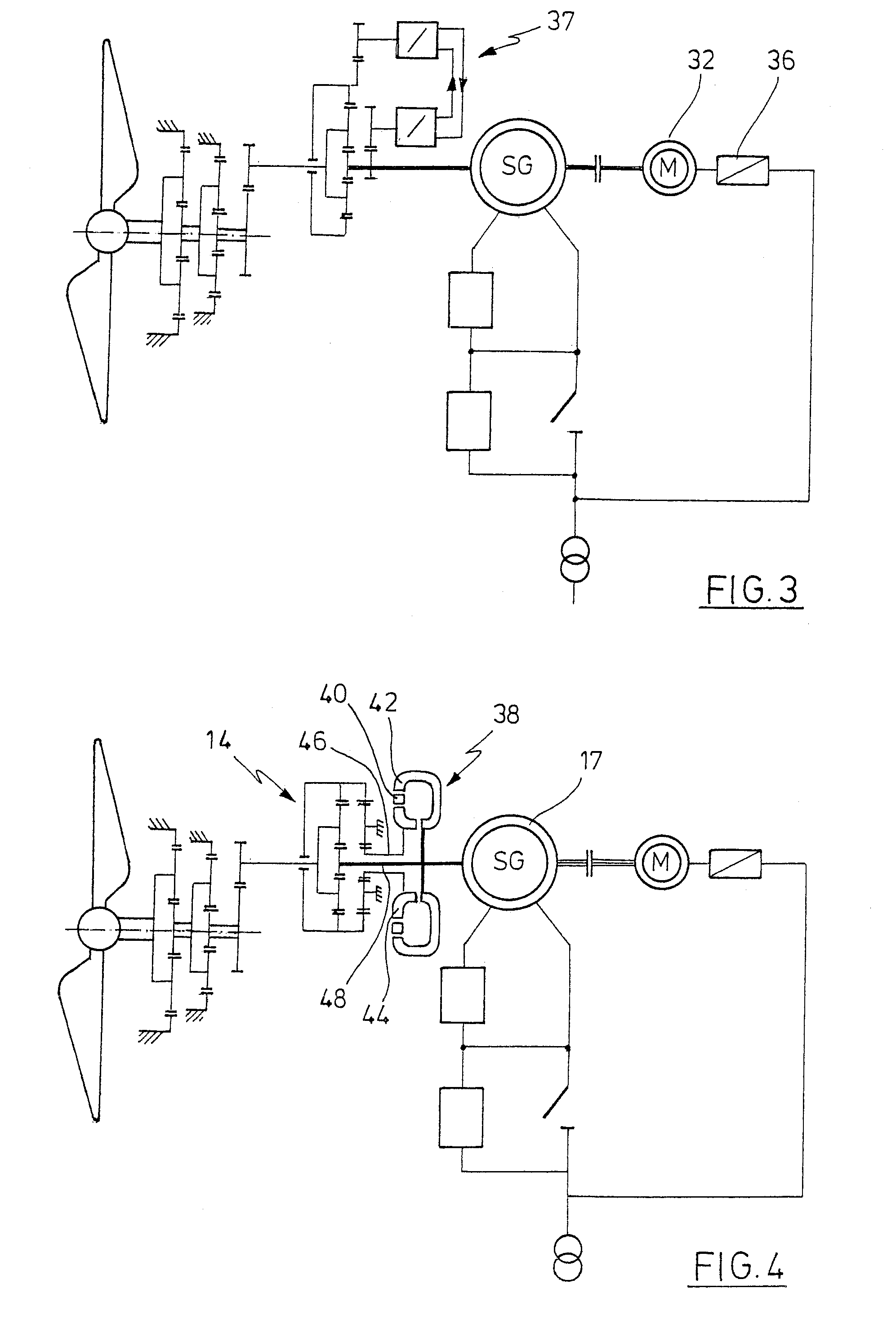
Island network and method for operation of an island network
InactiveUS20050225090A1Improve efficiencyNeed lessWind motor controlWorking fluid for enginesElectromagnetic couplingPower inverter
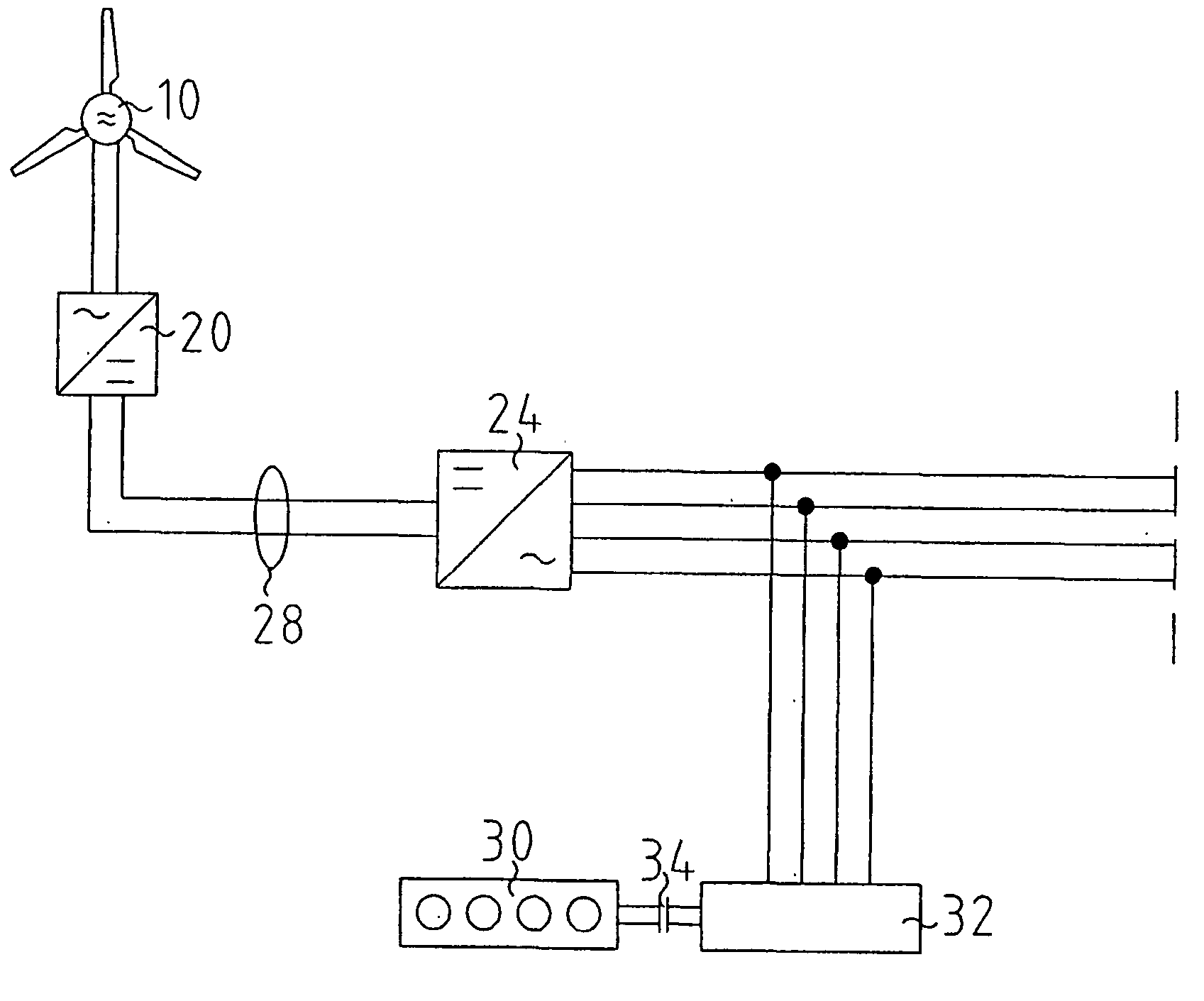
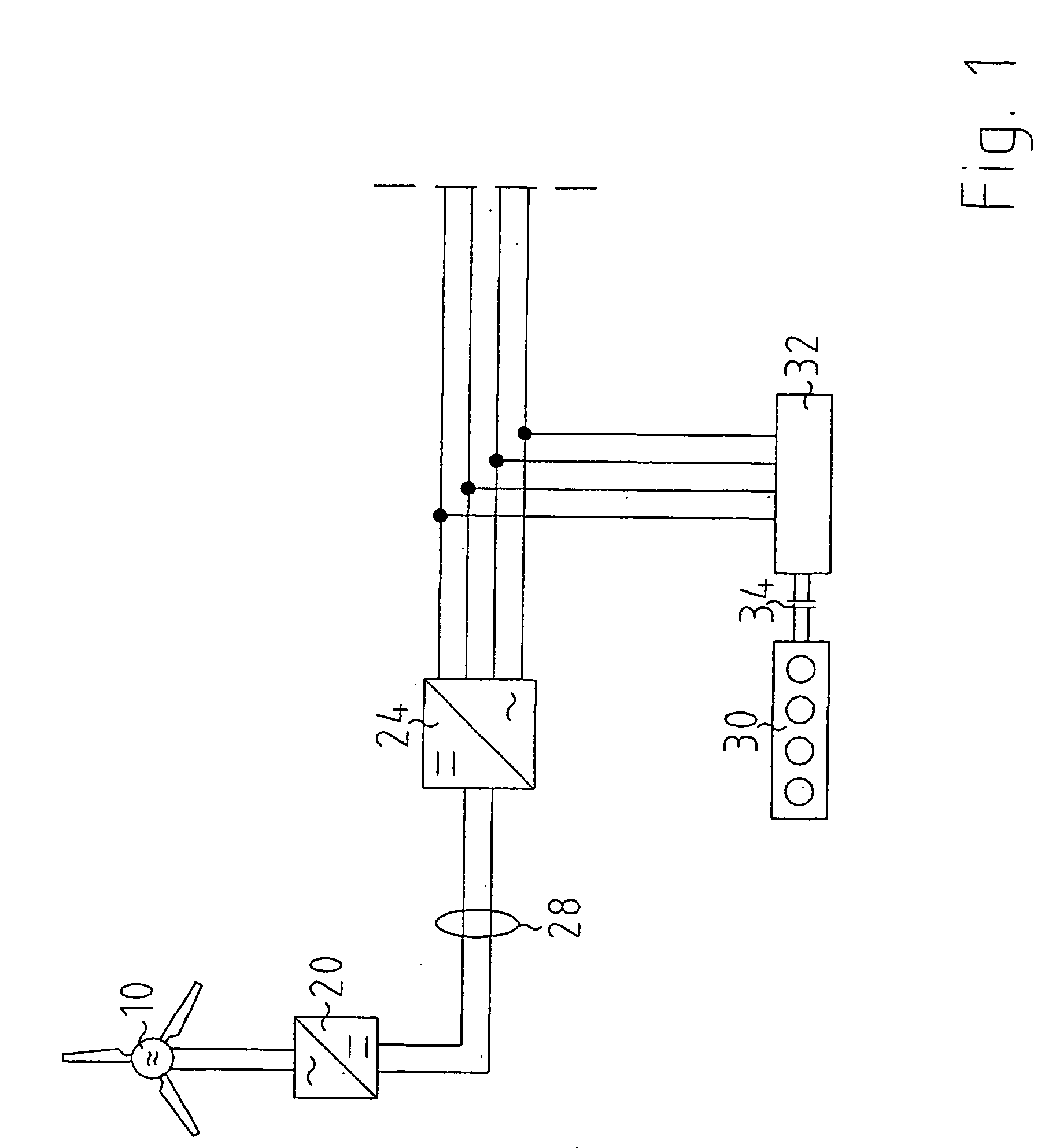
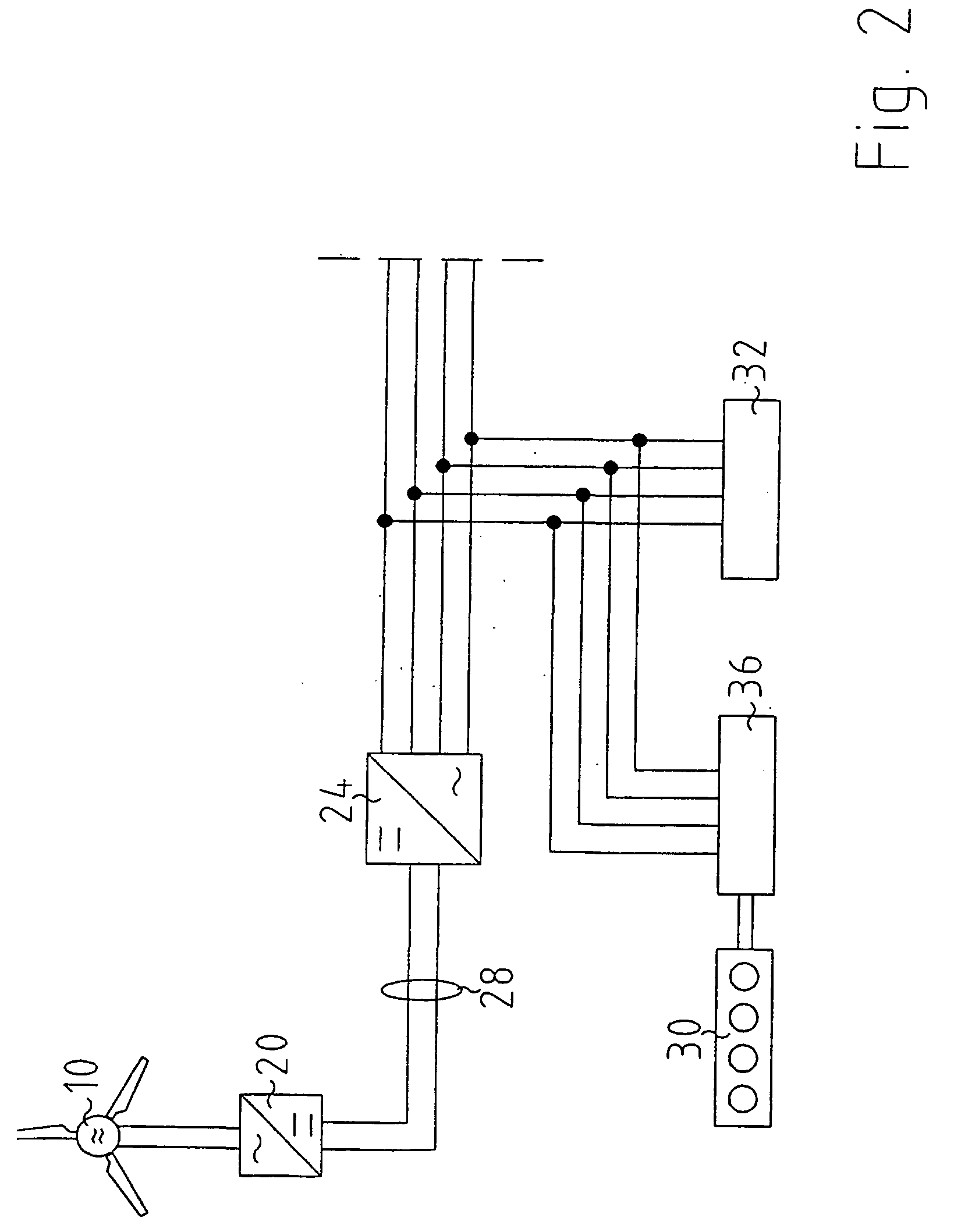
The invention relates to an island network with at least one energy generator, using regenerative energy sources, whereby the energy generator is preferably a wind energy plant with a first synchronous generator, a DC link, at least one first power rectifier and a power inverter, a second synchronous generator and an internal combustion engine which may be coupled with the second synchronous generator. A fully controllable wind energy unit (10) and an electromagnetic coupling (34) between the second synchronous generator (32) and the internal combustion engine (30) are provided in order to establish an island network in which the internal combustion engine can be switched off completely, so long as the wind energy unit is generating enough power for all connected users with an efficiency which is as high as possible.
Owner:WOBBEN ALOYS
Energy plant design and operation
InactiveUS8903554B2Low costEasy to operateSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlTime segmentNew energy
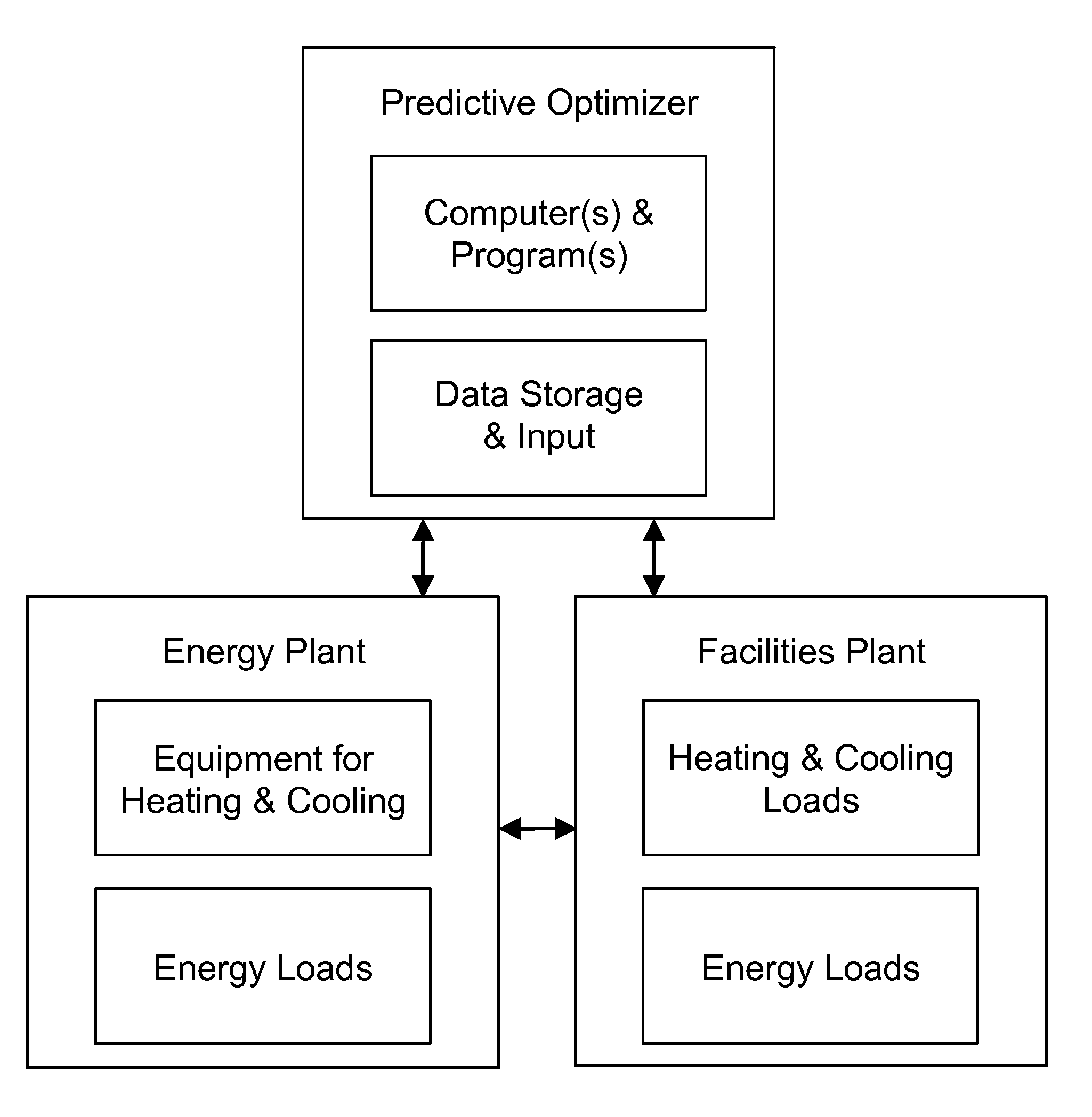
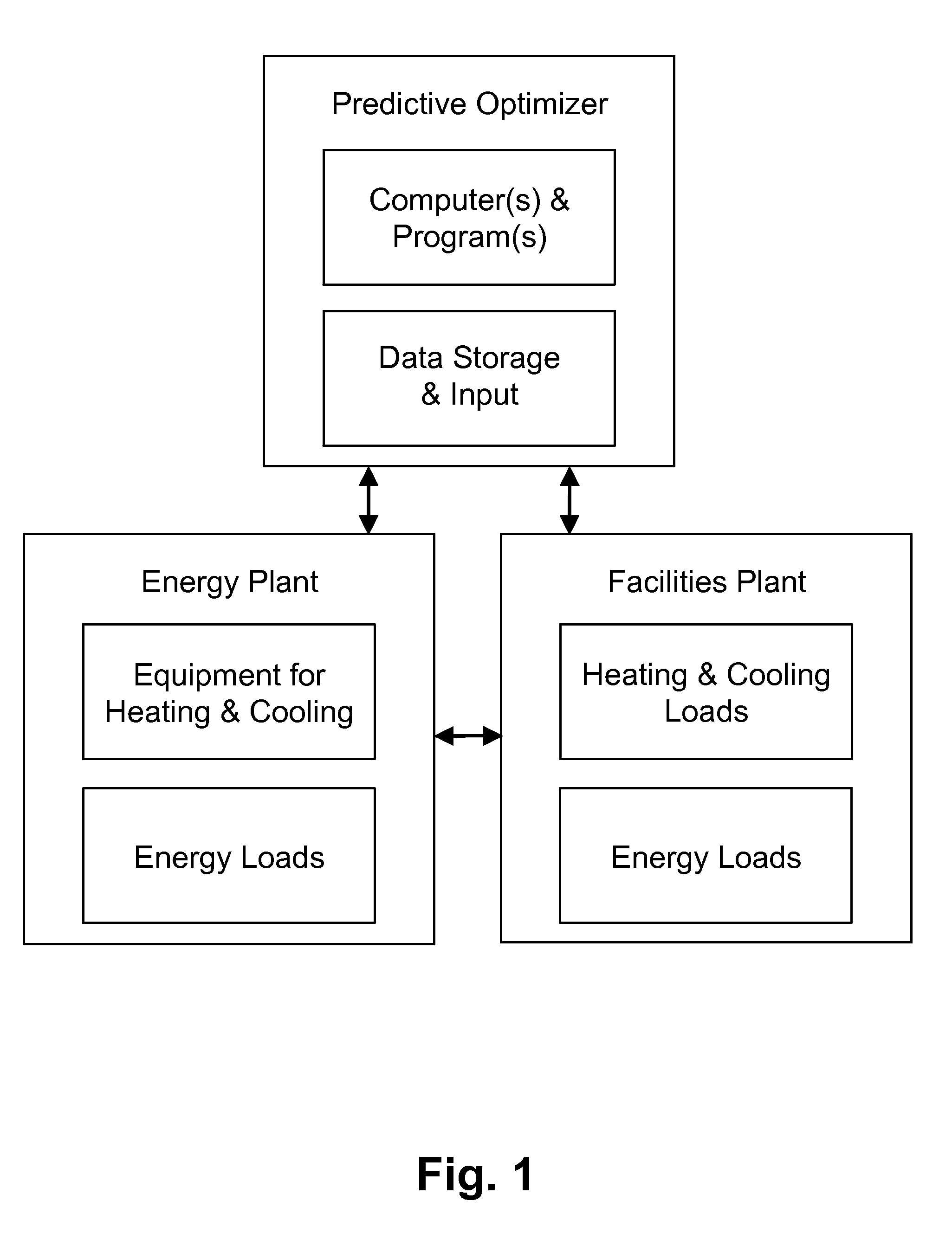
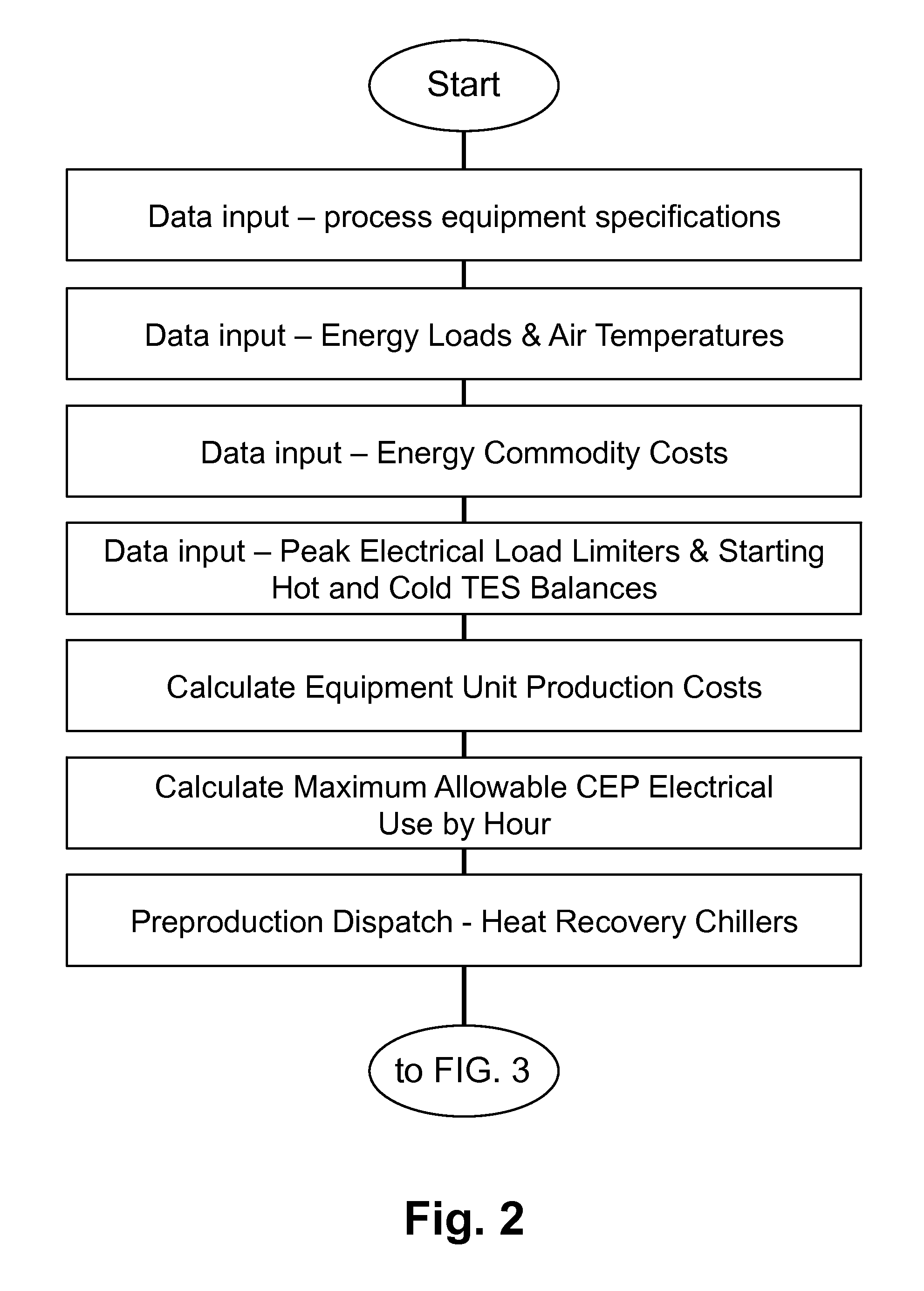
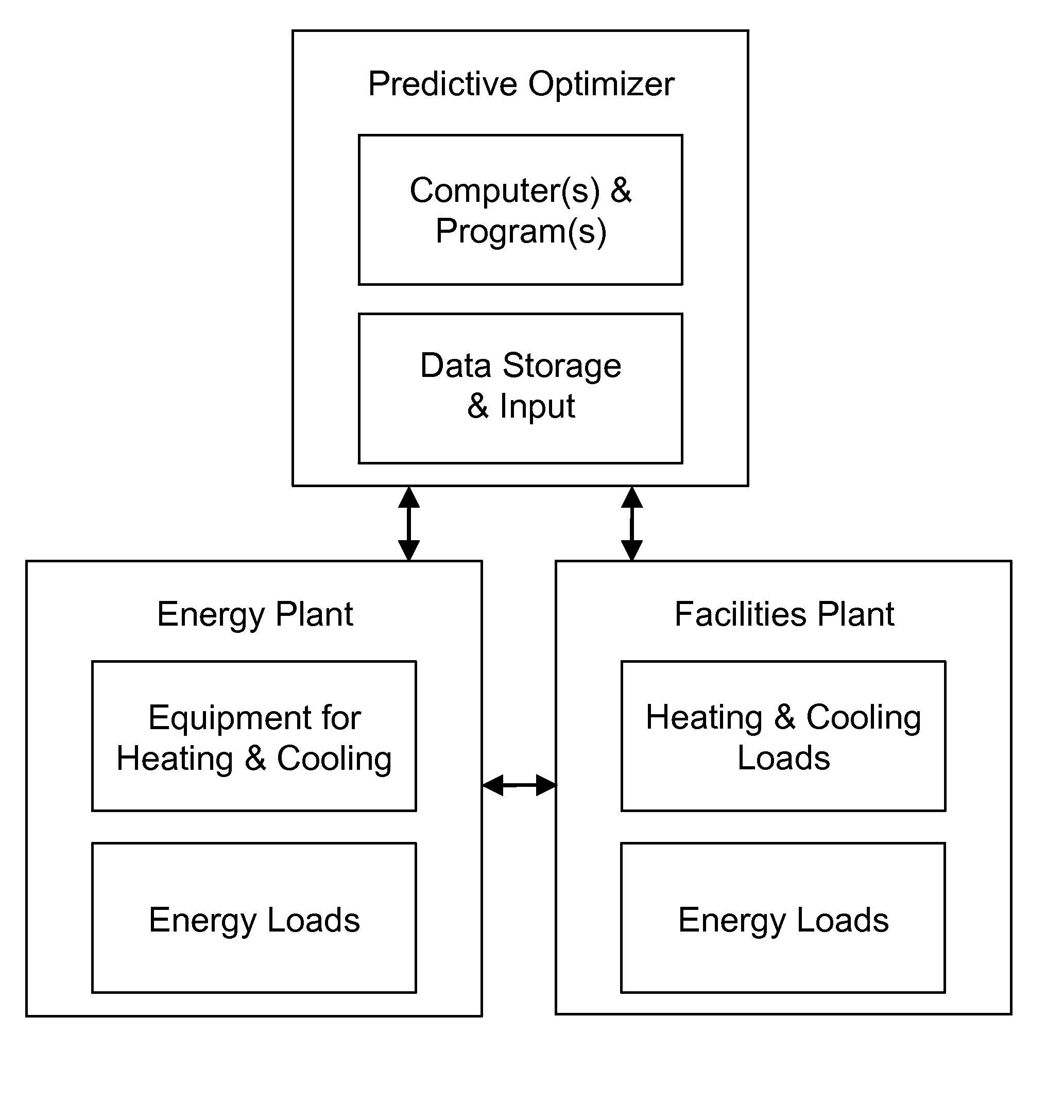
A forward-looking method and system is provided for determining an economically optimal energy dispatching schema to meet the combined demands of heating, cooling and electrical by an energy plant and a facilities plant. The optimal energy dispatching schema is determined for each of a plurality of incremental time segments defined in a forward-looking time period by optimizing these loads. The schema can be used for real time energy dispatching by the energy plant, in an existing energy plant optimization, and / or a new energy plant planning and design over the forward looking time period or any other forward-looking time period.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Wind energy plant with a steerable kite
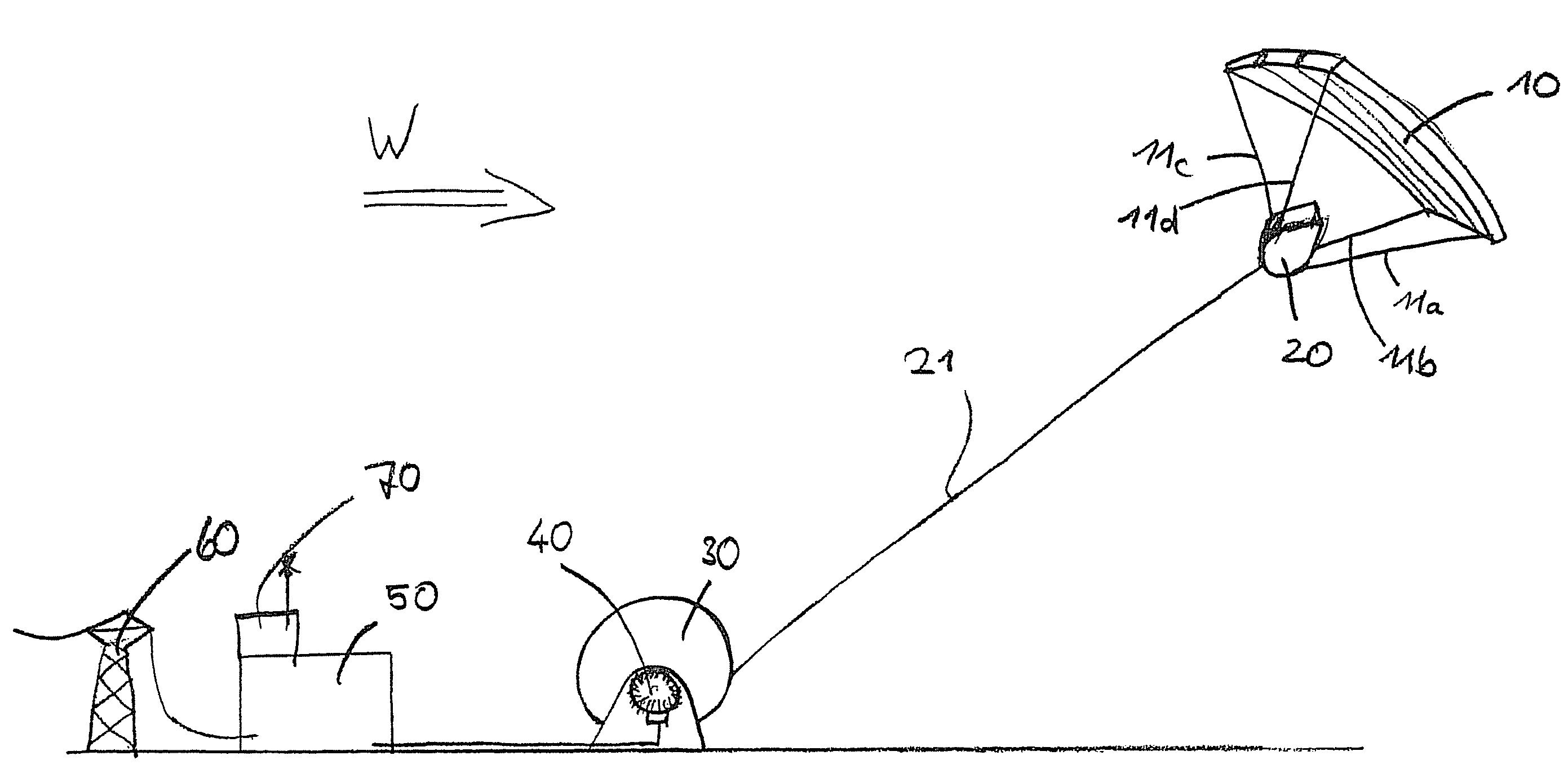
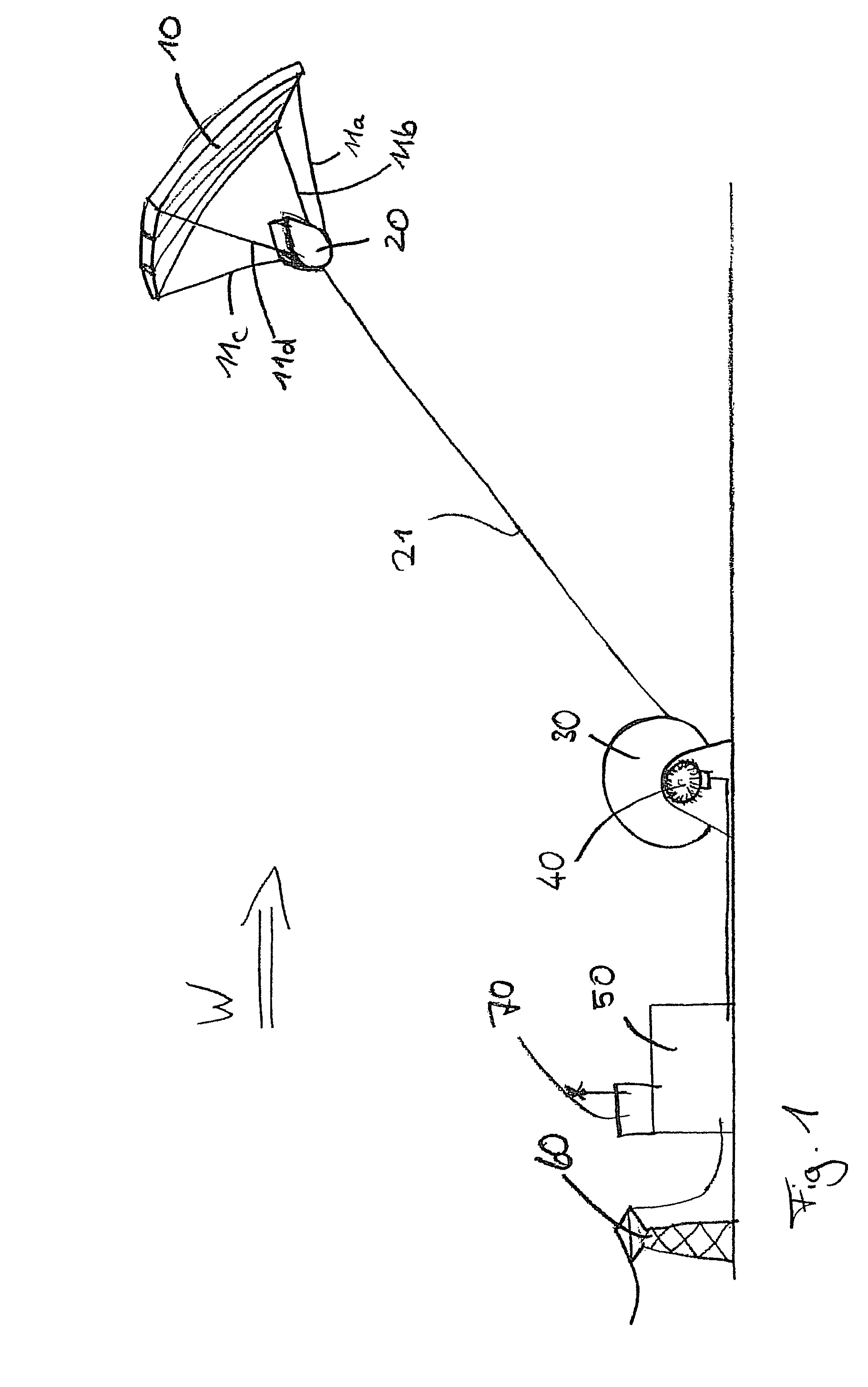
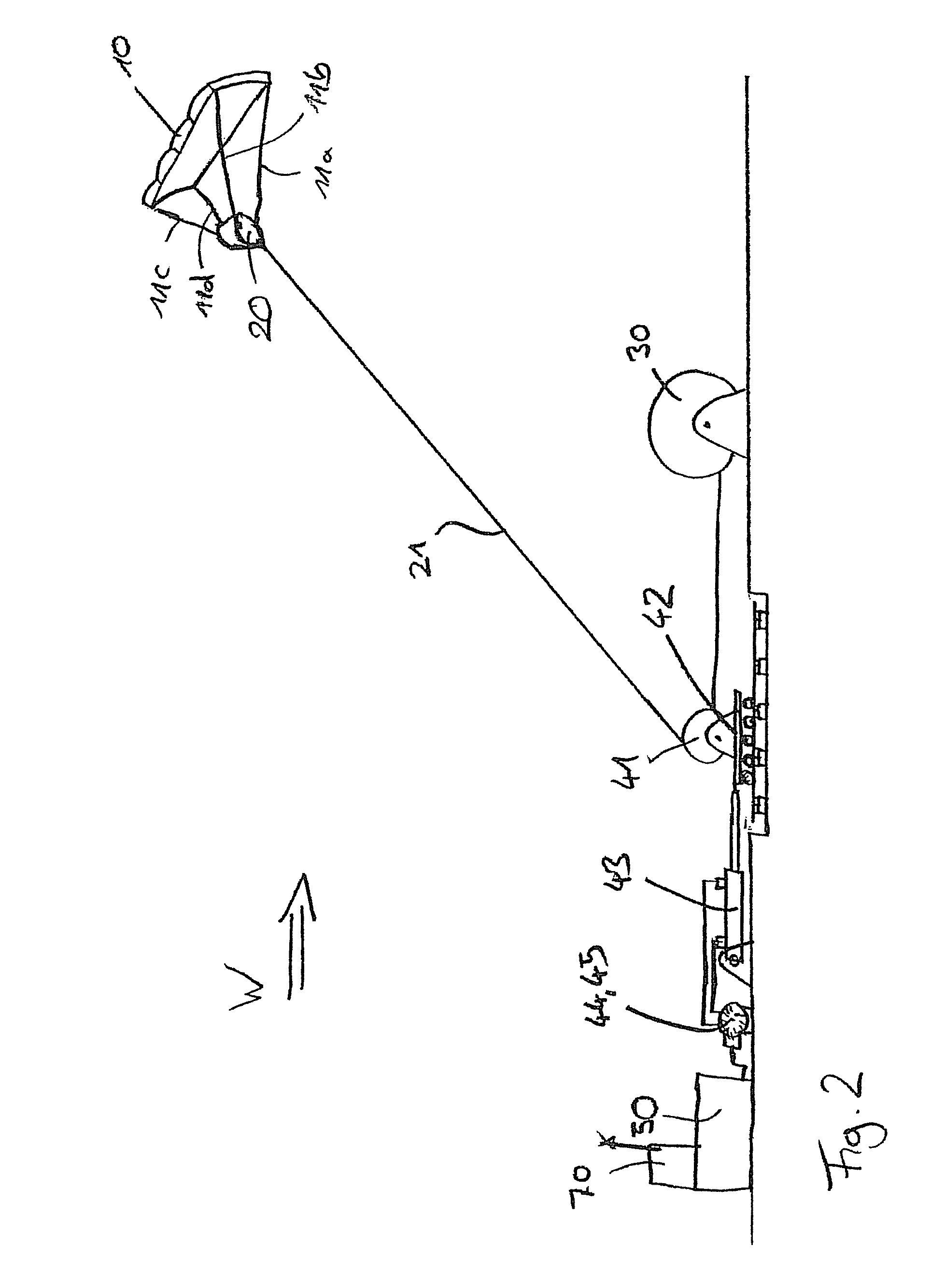
The present invention provides a device for converting wind flow energy into mechanical energy, comprising a wind-engaging member having an aerodynamic profile which generates an uplift force in the direction of a load cable when the airflow direction is perpendicular to the load cable, a steering mechanism configured to produce a steered movement about a first axis or in a first direction of the wind-engaging member and about a second axis or in a second direction that is different from the first direction or axis of the wind-engaging member, relative to the airflow direction, and a control unit configured to use the steering mechanism to move the wind-engaging member along a predetermined flight path in a flight plane perpendicular to the load cable. The present invention further provides a method for converting wind flow energy into mechanical energy and a docking station for use with the device.
Owner:SKYSAILS GMBH & CO KG
Wind energy installation comprising a concentric gearbox generator arrangement
A wind energy plant comprising a rotor, a rotor shaft, a gear, and a generator, the generator embodied as a ring concentrically embracing the gear.
Owner:AERODYN ENG GMBH
Drought-resistant energy plant seed pelleting agent, preparation method and using method thereof
InactiveCN101602632APriming hasPromote expansionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAdhesiveMonopotassium phosphate
The invention discloses a drought-resistant energy crop seed pelleting agent, a preparation method and a using method thereof. The seed pelleting agent comprises the following components: straw powder or overrotten organic matter, a plant growth regulating substance, a water absorbent resin, a filler, an adhesive, an insecticide, a bactericide, urea and monopotassium phosphate. The method for seed pelleting comprises the following steps of: 1) spraying an adhesive water solution on the surfaces of drought-resistant energy seeds evenly; 2) mixing the drought-resistant energy seeds of which the surfaces are the adhesive water solution and a pelleting agent for coating; and 3) repeating the step 1) and the step 2) until the diameters of the seeds meet the requirement. The invention breaks the traditional idea that the pelleting agent absorbs water in soil of a plough layer, establishes a theory of absorbing water before the sowing and sowing after the germination acceleration, and realizes the aim that the pelleting agent can absorb the water before the sowing after the coating, does not disperse after the water absorption, has good expansibility, ensures that the seeds germinate in the palleting agent and can adopt mechanized sowing by adding crop straw powder or the overrotten organic matter which is rich in water absorption expansibility into the components of the pelleting agent.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Wind energy installation comprising a concentric gearbox generator arrangement
A wind energy plant comprising a rotor, a rotor shaft, a gear, and a generator, the generator embodied as a ring concentrically embracing the gear.
Owner:AERODYN ENG GMBH
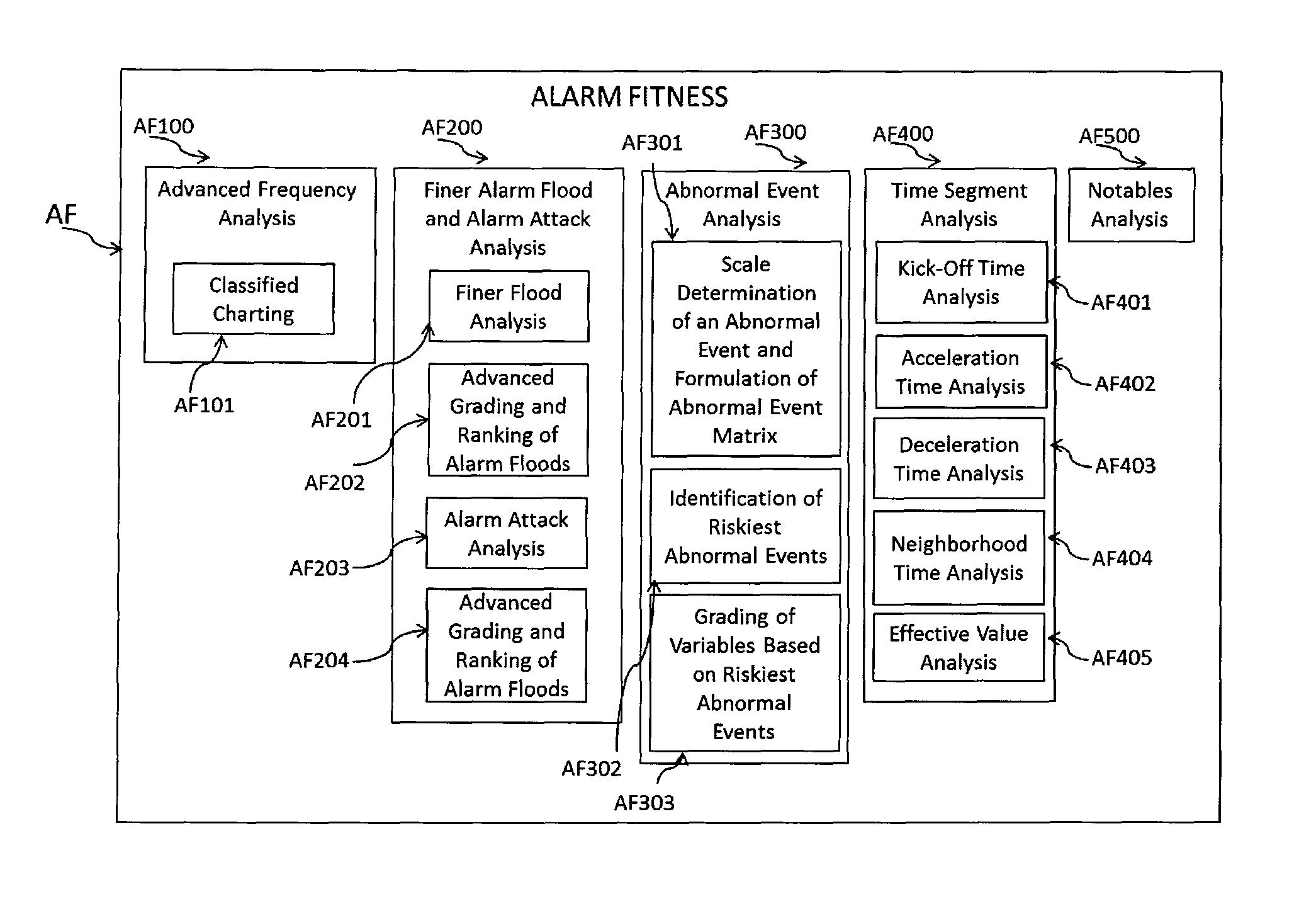
Dynamic prediction of risk levels for manufacturing operations through leading risk indicators
ActiveUS20130063264A1Raise the possibilityImprove securityTesting/monitoring control systemsAlarmsRisk levelDisposal waste
Provided are methodologies to properly assess and manage operational risks at operations sites, e.g., a manufacturing, production or processing facility, such as a refinery, chemical plant, fluid-catalytic-cracking units, or nuclear energy plant, or a biological or waste management facility, airport or even financial institutions, or at any facility in which operations are often accompanied by risk associated with many high-probability, low-consequence events, often resulting in near-misses. In some operations, processes are monitored by alarms, but the invention operates on either process data or alarm data. The methods are based upon measurement of one or more variables, and / or utilization and management of the concept of “hidden process near-miss(es)” to identify a change or escalation, if any, in probability of occurrence of an adverse incident. The methodologies combine a plurality of subsets (also useful independently) of dynamically calculated leading risk indicators for dynamic risk management.
Owner:NEAR MISS MANAGEMENT
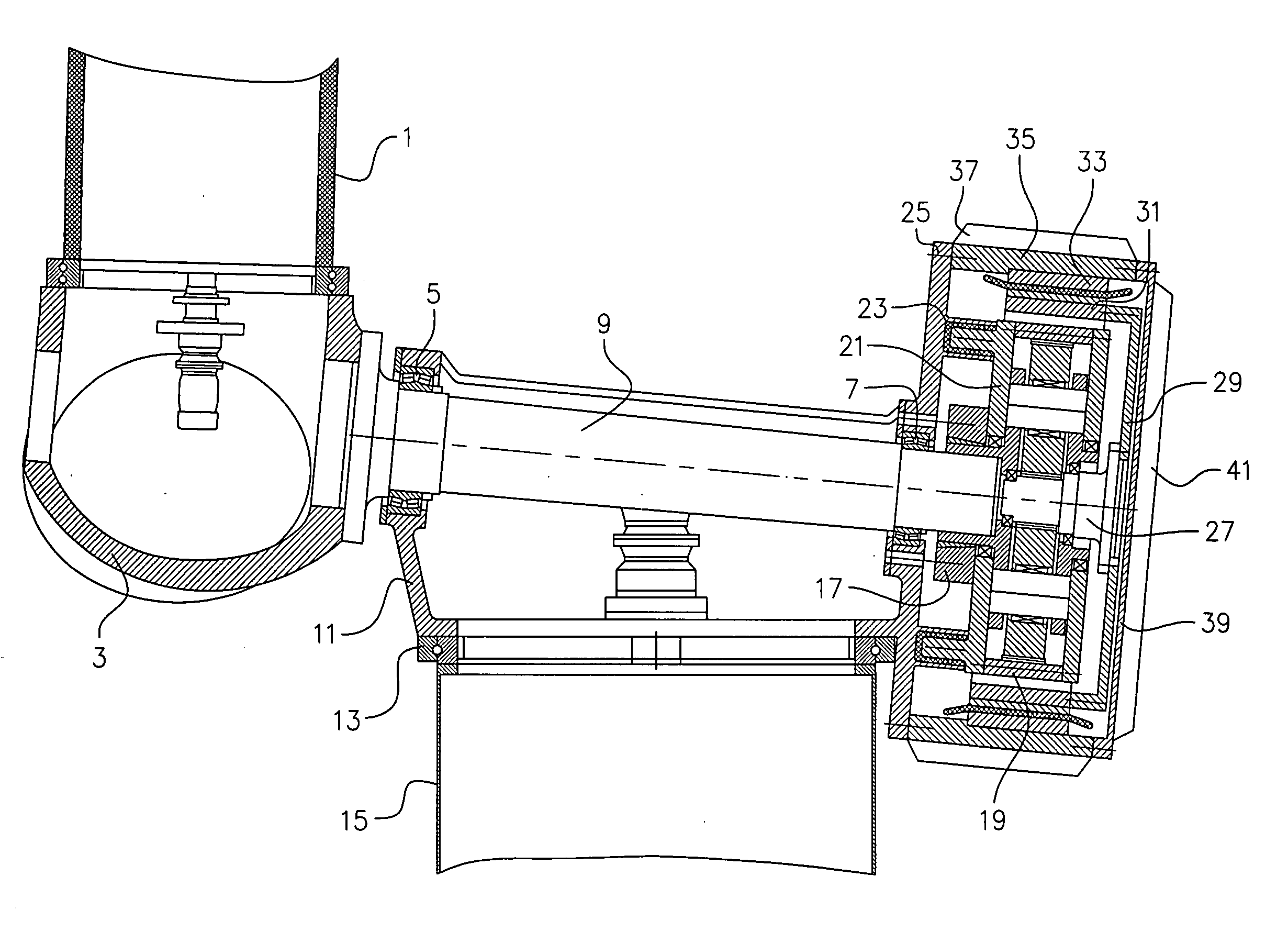
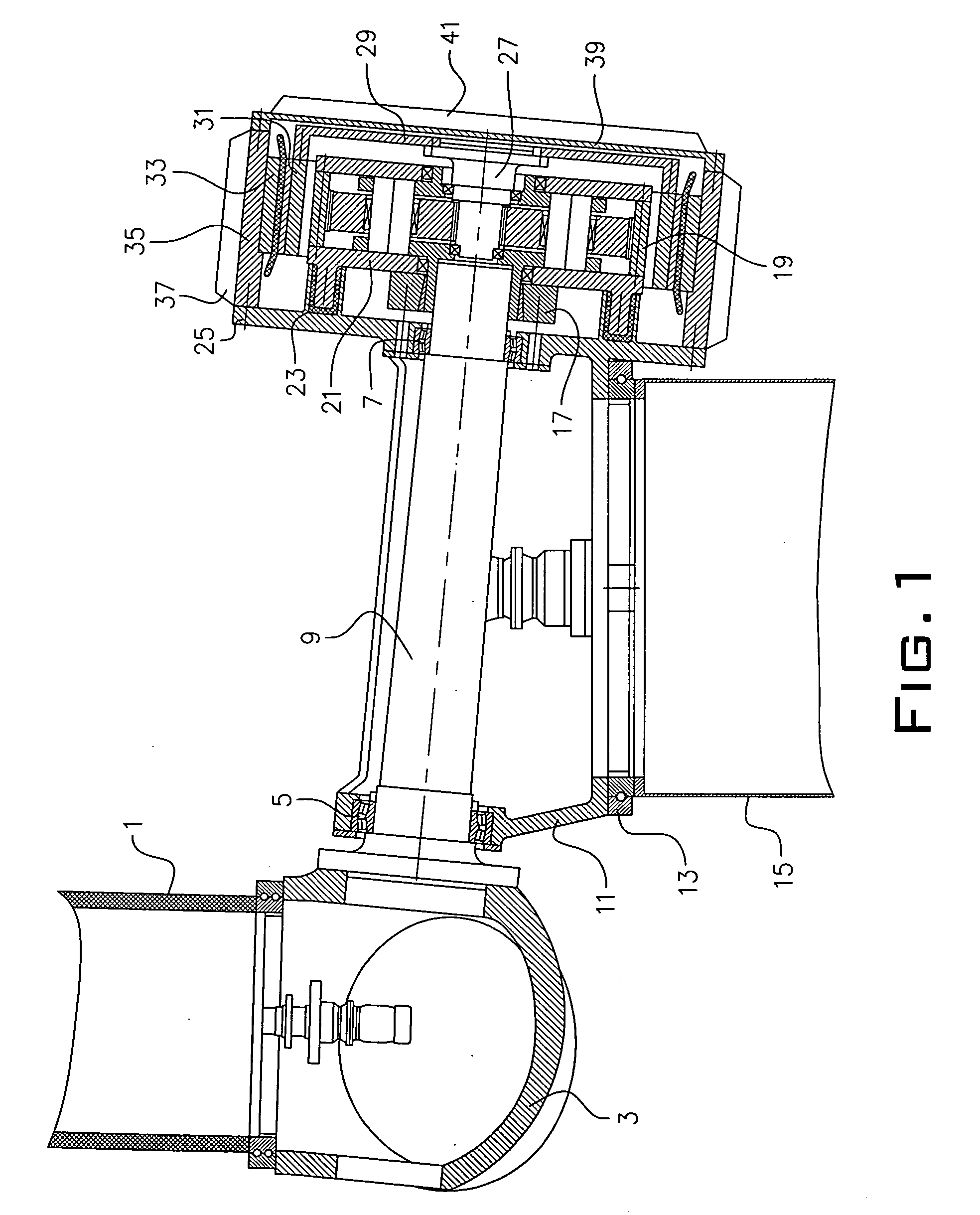
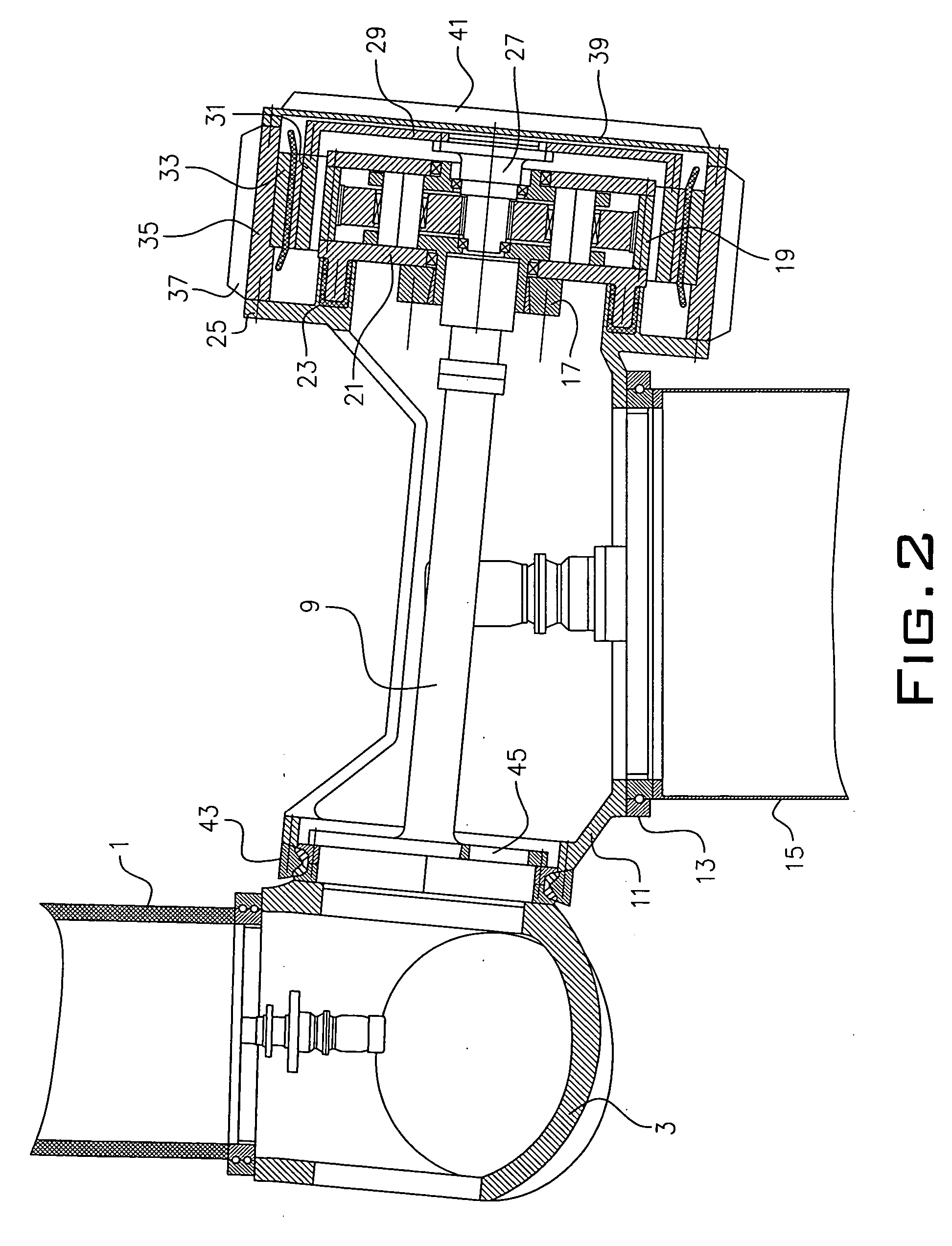
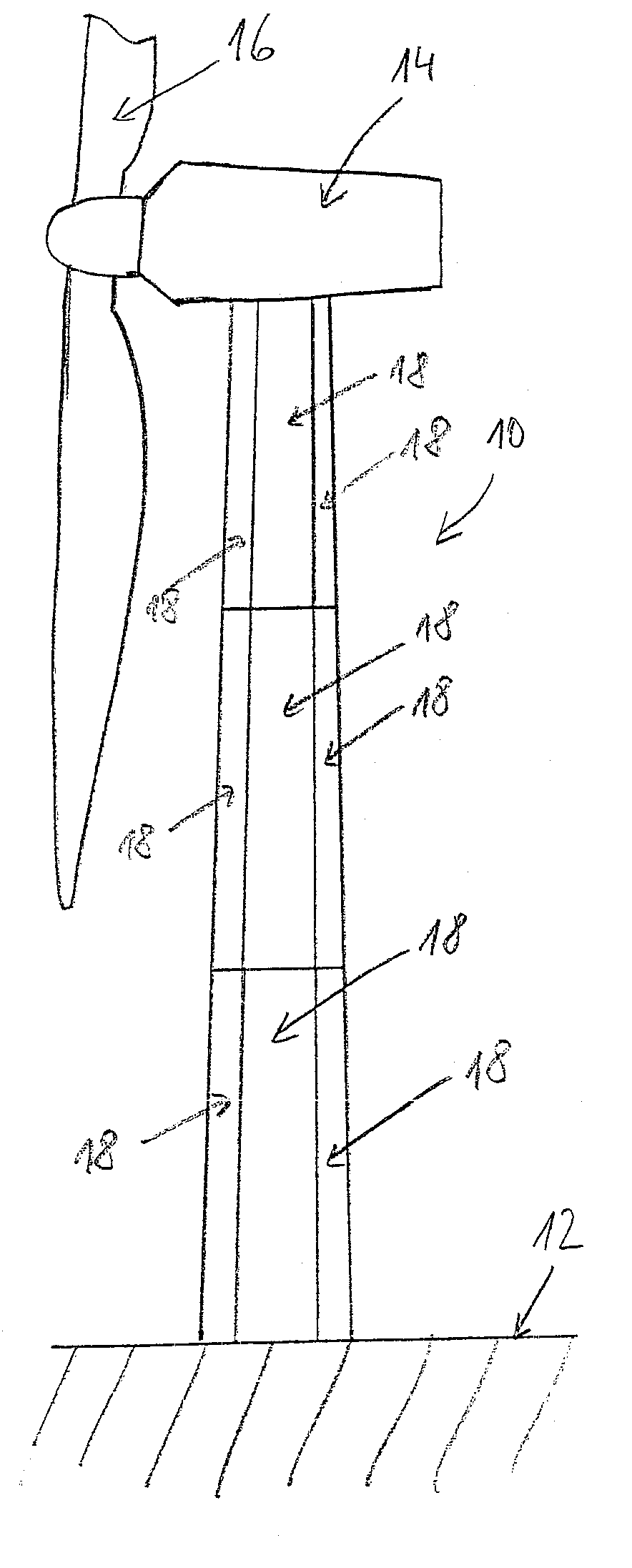
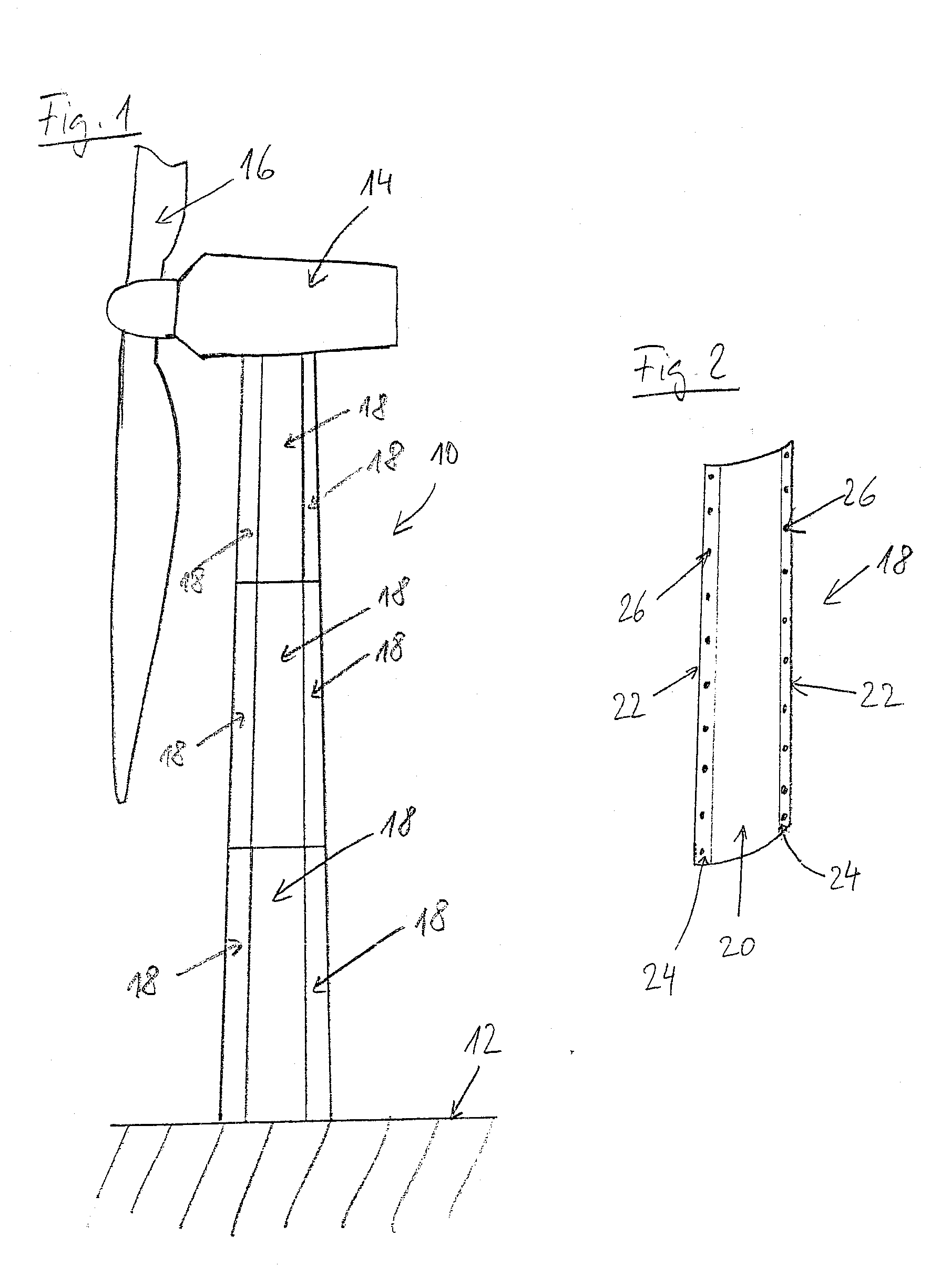
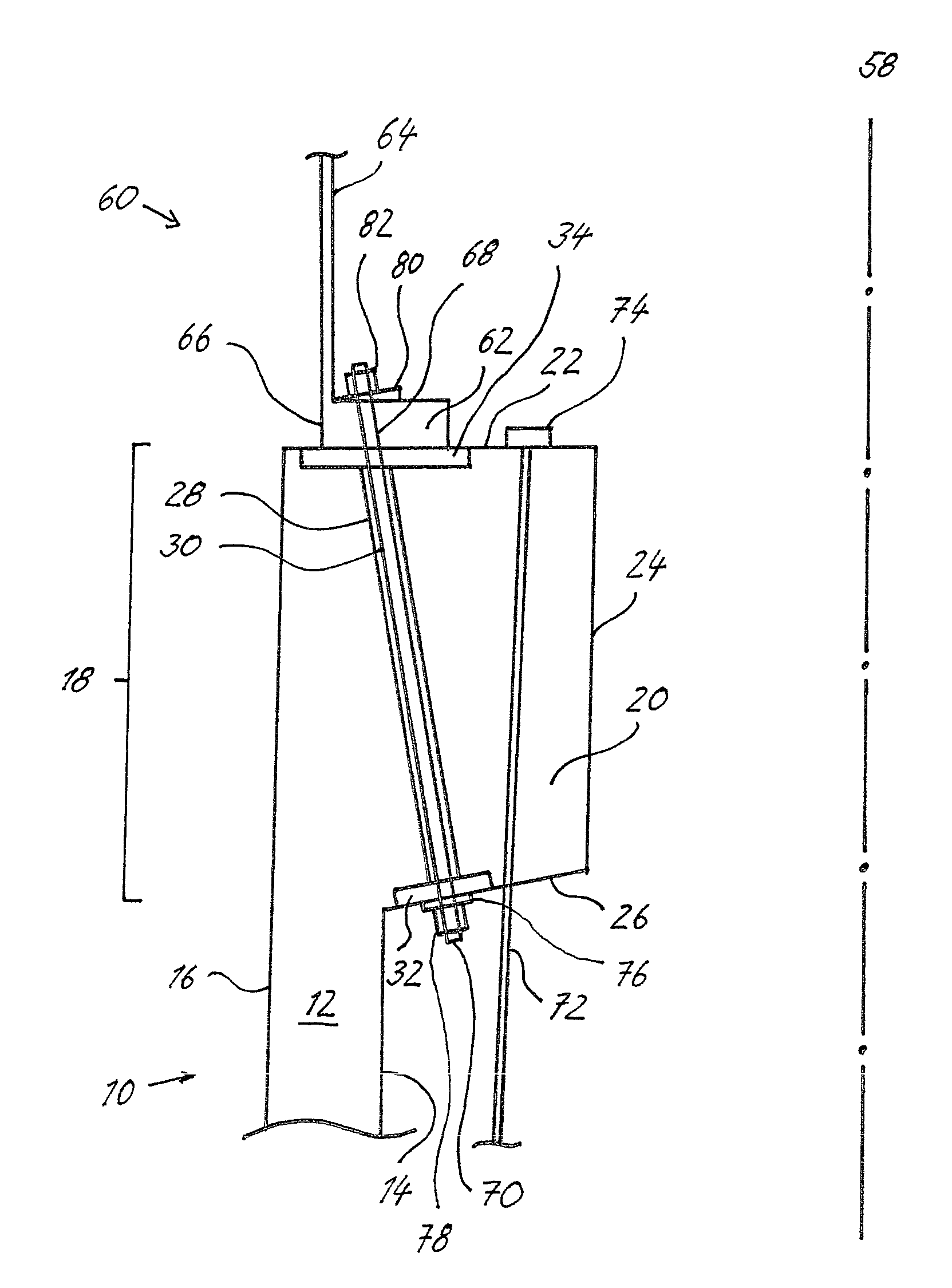
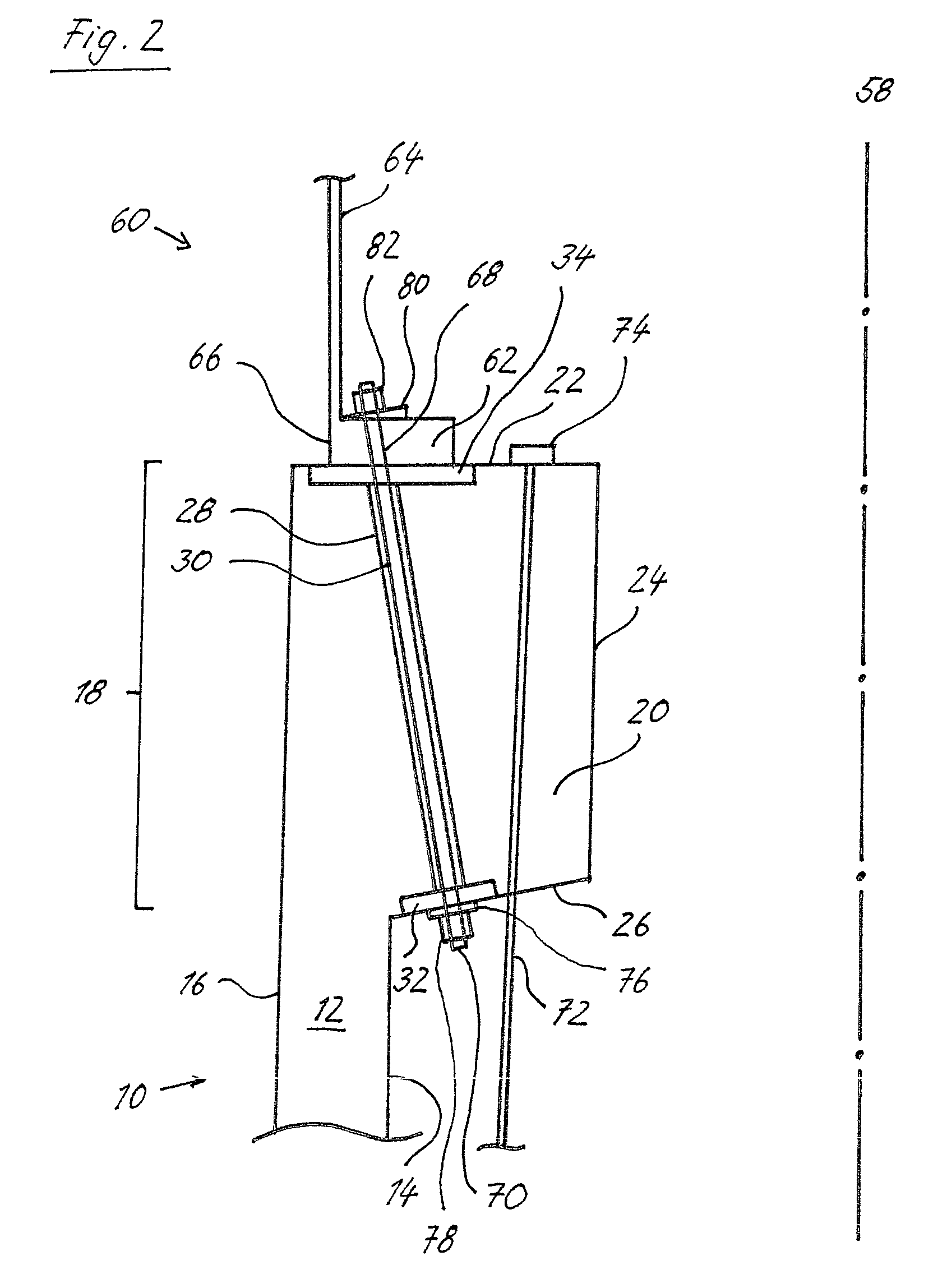
Method for establishing a foundation in particular for a tower of a wind energy plant
The invention relates to a method for building a foundation for a structure comprising a plurality of segments, in particular for a wind turbine tower, a foundation segment for use in such method, and a wind turbine. In order to create a stable foundation, a method comprising the following steps is proposed on the basis of experience gained:_excavating a foundation bed,_building a stable, substantially level and horizontal subbase in a foundation bed, setting down a foundation segment of the structure on the subbase, wherein at least three vertically adjustable support poles are fixedly attached to said foundation segment by means of a supporting bracket mounted at the end of the support poles in such a way that only the support poles are placed onto predetermined points of support on the subbase,_producing a reinforcement on the subbase,_filling the remainder of the foundation bed with foundation mass, in particular concrete, to a level above the bottom rim of the foundation segment.
Owner:WOBBEN ALOYS
Energy Plant Design and Operation
InactiveUS20120215362A1Low costEasy to operateSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlNew energyTime segment
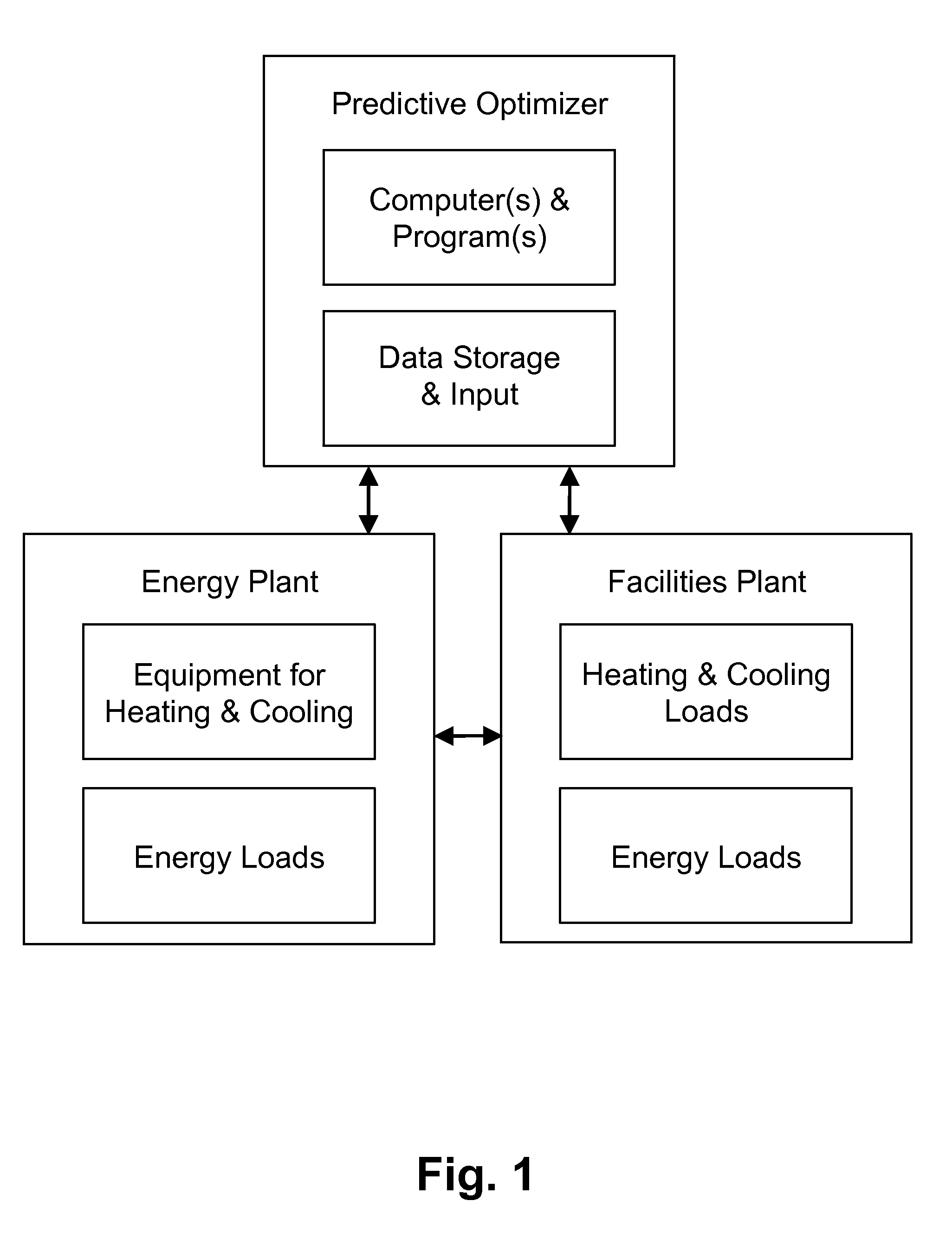
A forward-looking method and system is provided for determining an economically optimal energy dispatching schema to meet the combined demands of heating, cooling and electrical by an energy plant and a facilities plant. The optimal energy dispatching schema is determined for each of a plurality of incremental time segments defined in a forward-looking time period by optimizing these loads. The schema can be used for real time energy dispatching by the energy plant, in an existing energy plant optimization, and / or a new energy plant planning and design over the forward looking time period or any other forward-looking time period.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Wind energy plant tower
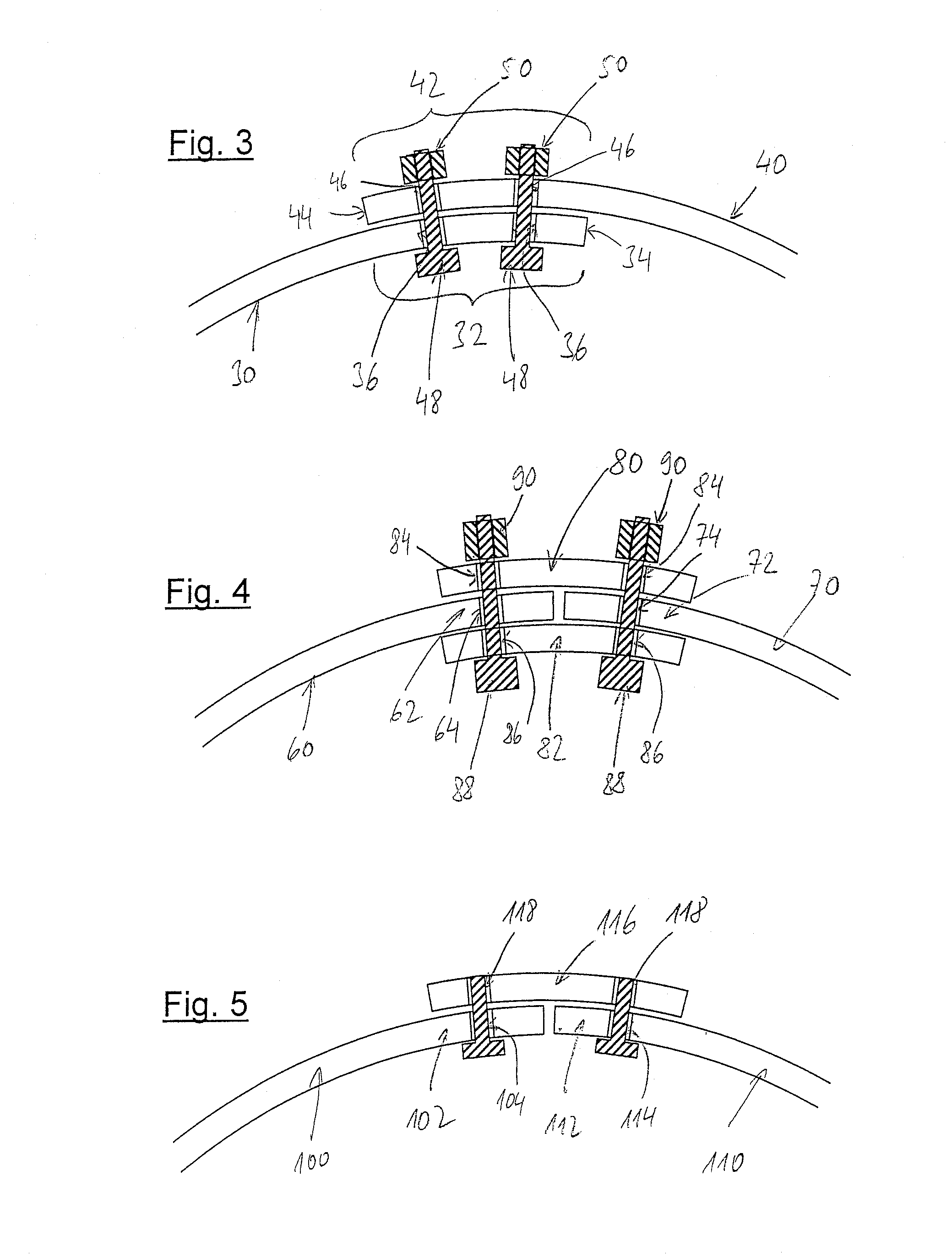
InactiveUS20080256892A1Simple sectionReduce riskWind motor supports/mountsMachines/enginesEngineeringTower
A wind energy plant tower with a load-bearing tower wall, which has a circulating outer periphery and consists of a plurality of wall sections, which each one have one centre section and two border sections running in the longitudinal direction of the tower, which are provided with a plurality of connection bores, wherein the surfaces defined by the border sections run along the outer periphery or in a constant distance to the same, and the connection bores are aligned transversely to the outer periphery.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
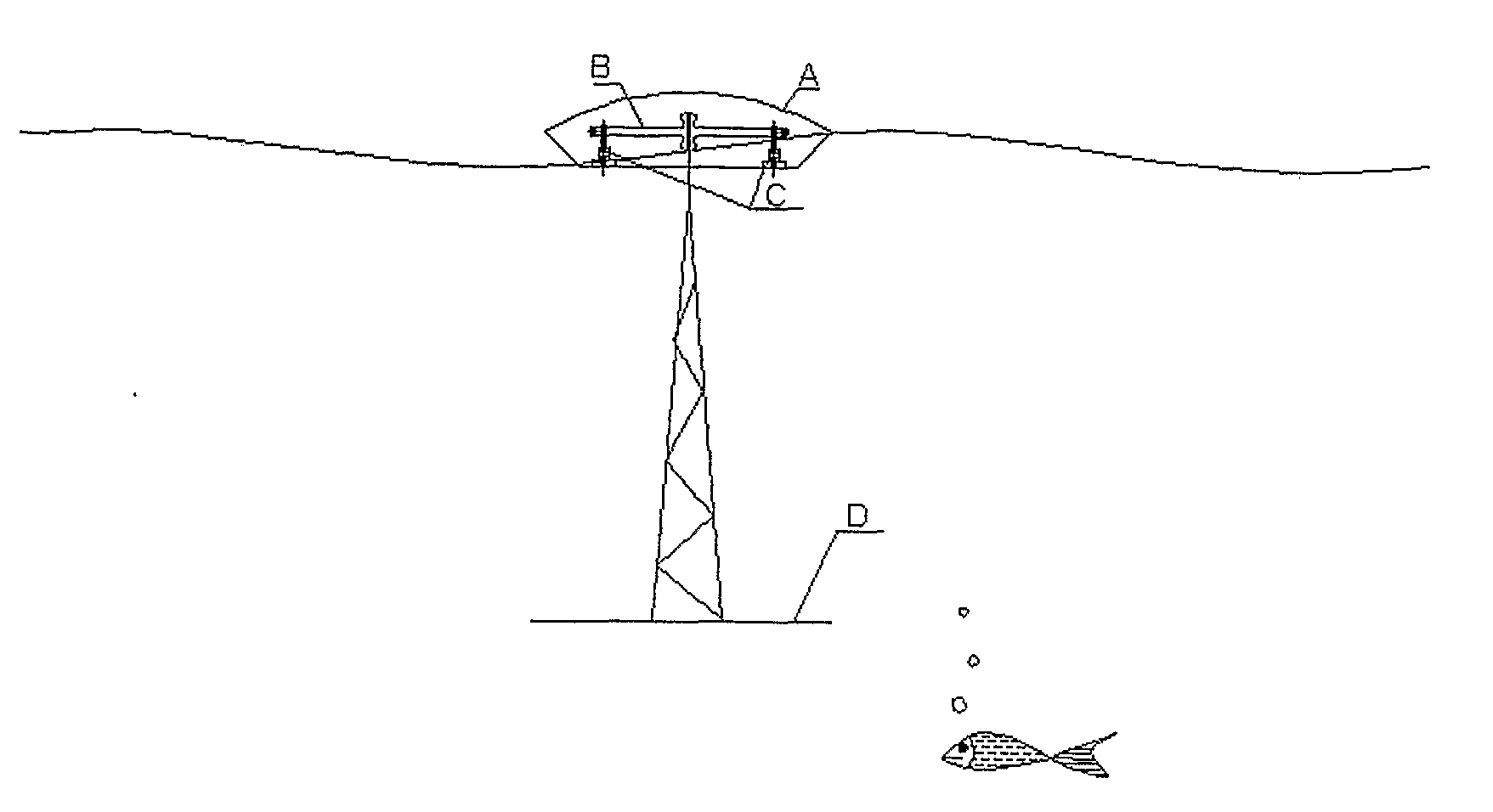
Hybrid wave energy plant for electricity generation
InactiveUS20100013229A1Constant the system pressure during operationGuaranteed levelFluid couplingsEngine fuctionsSea wavesHigh pressure
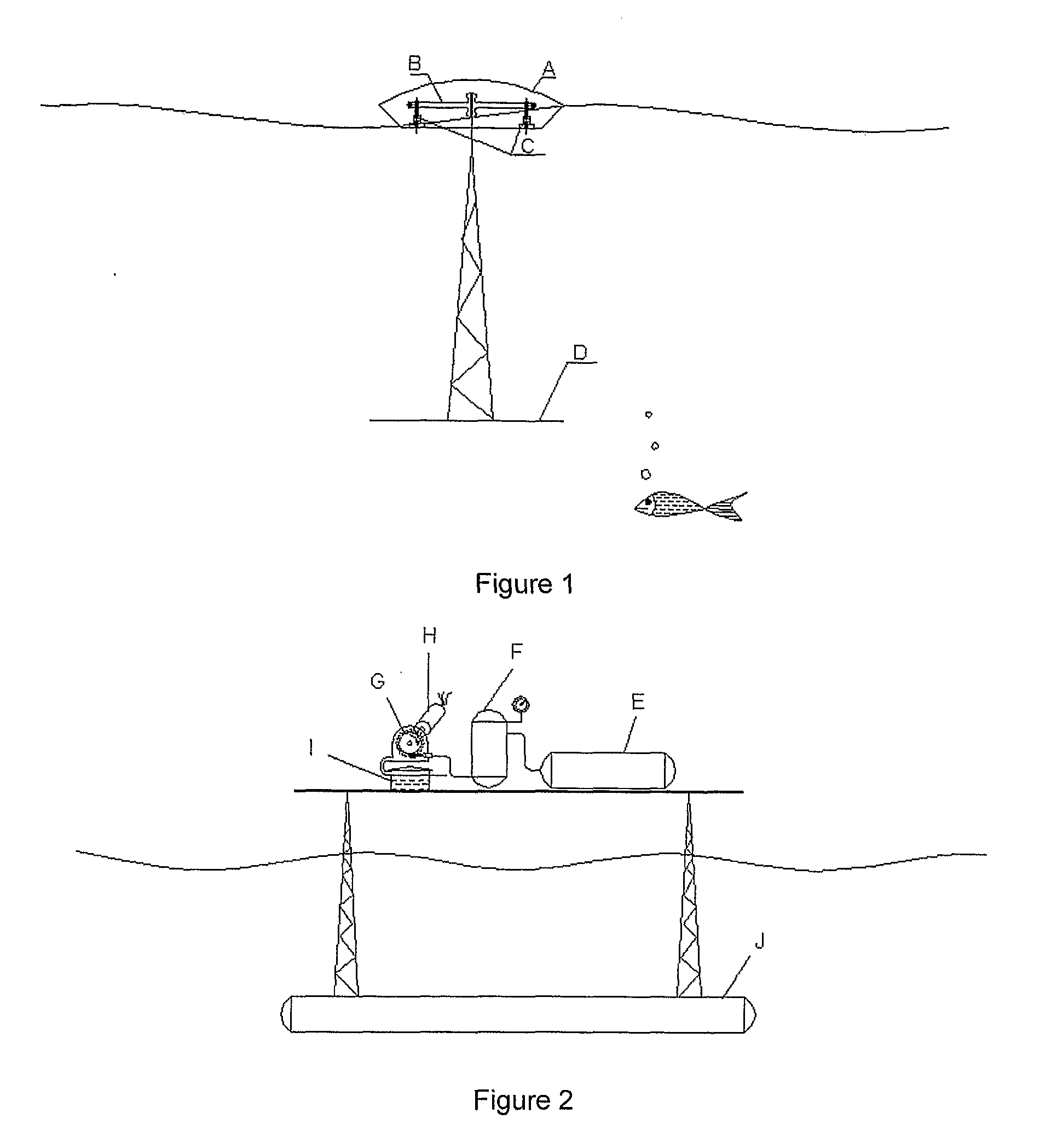
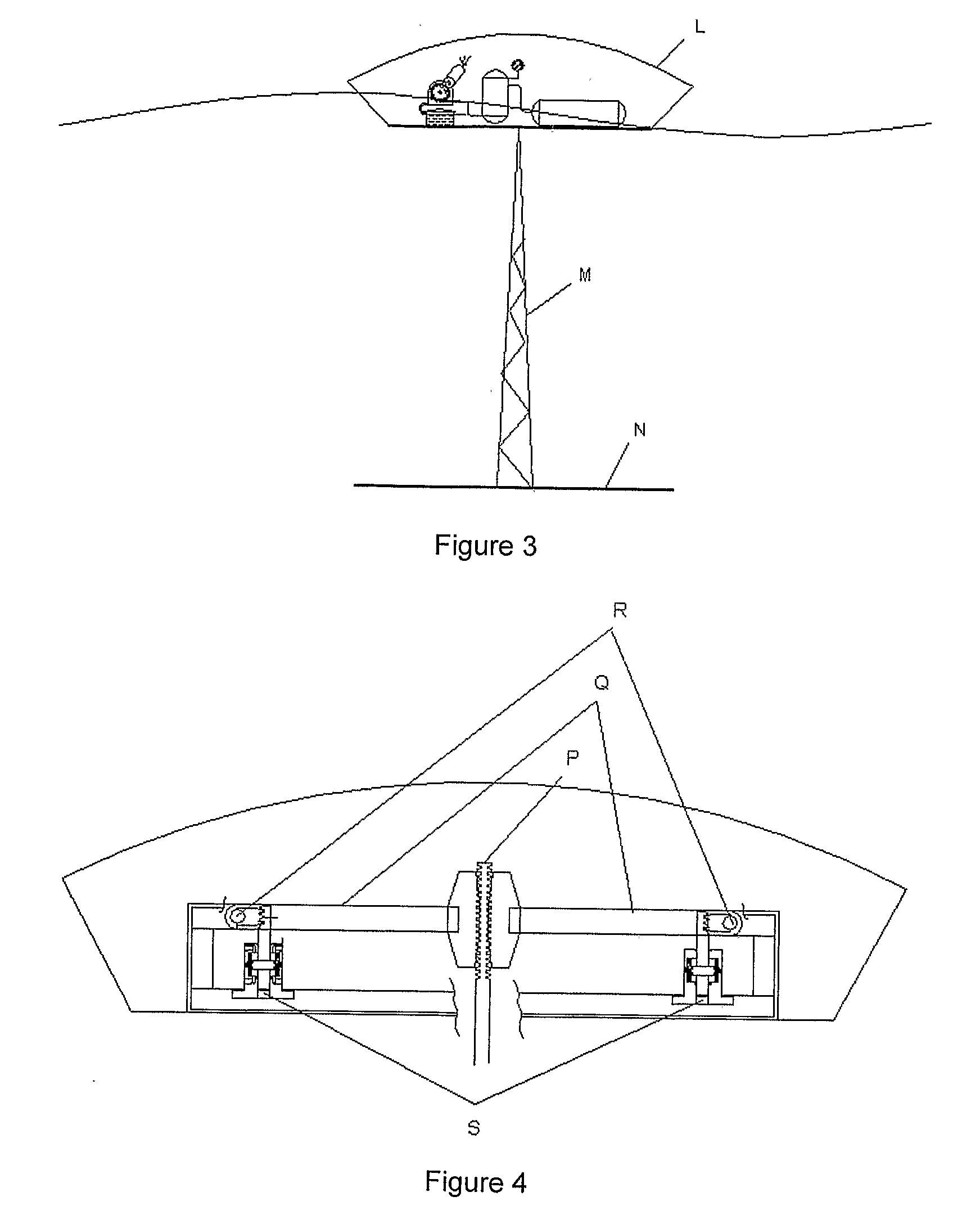
The innovation herein proposed describes a plant to produce electricity by the sea waves. The plant is designed to be installed on shore, near shore and offshore scenarios: on the coast line, in shallow waters and in deep waters. The plant is operated by action of the sea waves on a series of floaters (A). The resultant force on each floater (A) acts on a mechanical load amplifier (B) which moves two vertical high pressure piston pumps (C). These pumps (C) send pressurized fresh water to a hyperbaric system (E). The hyperbaric system (E) supplies an outflow water jet through a controlled valve that moves a conventional turbine (G). This turbine (G) connected to the electric generator (H) produce electricity.
Owner:SEAHORSE WAVE ENERGY ENERGIA DAS ONDAS
Method for controlling a wind energy plant
ActiveUS20090081041A1The method is simple and reliableReduce loadRotational speed controlPropellersNacelleRest position
The present invention is related to a method for controlling a wind energy plant, with a nacelle disposed on a tower and with a rotor with at least one rotor blade, the blade adjustment angle of which can be adjusted by means of a blade adjustment equipment. The objective to provide a reduction of the loads acting on the plant when there is a malfunction of the blade adjustment equipment is resolved according to the present invention in that the function of the blade adjustment equipment is monitored, and when an error of the blade adjustment equipment occurs, the nacelle is rotated from an operating position into a rest position, in which there is a flow of the wind against the surface extended by the at least one rotor blade (4) in a rotation of the rotor which is reduced with respect to the operating position.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY SE & CO KG
Method and apparatus for rotating a component of a wind energy plant
ActiveUS20090232652A1Increase stiffnessMinimizing total elasticityPropellersPump componentsWind powerElectric motor
The invention is related to a method for rotating a component of a wind energy plant by traversing an adjustment device, wherein the adjustment device comprises at least two adjustment drives, each one thereof having at least one electric motor, for traversing the adjustment device, and wherein during the traversing of the adjustment device, the electric motor of at least one of the at least two adjustment drives is operated at another rotational speed than the electric motor of at least one other of the at least two adjustment drives. Furthermore, the invention is related to a corresponding device.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY SE & CO KG
Apparatus for monitoring the rotational speed in a wind energy plant
ActiveUS20090193894A1Analysis is accurate and reliableImprove reliabilityTesting/calibration apparatusWind motor controlRotation velocityWind power
An apparatus for monitoring the rotational speed in a wind energy plant, with a rotor shaft which is driven by the rotor and runs out into a gear unit, and with a generator shaft, which connects an output shaft of the gear unit with a generator / converter unit, characterised by a first rotational speed detection unit on the rotor shaft and a second rotational speed detection unit on the generator shaft, wherein each rotational speed detection unit has at least two rotational speed sensors working independently from each other, an analysing unit for the rotational speed, to which the measured signals of the rotational speed detection units are applied and which generates an error signal for a rotational overspeed when a certain maximum value for the rotational speed is exceeded.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY SE & CO KG
Method for operating a wind energy plant with a doubly-fed asynchronous machine and wind energy plant with a doubly-fed asynchronous machine
ActiveUS20090250931A1Easy to adaptReduce changesGenerator control circuitsWind motor controlPower gridWind power
Method for operating a wind energy plant having a doubly-fed asynchronous machine, a grid-sided converter and a generator-sided converter both being controlled by a control means, the method comprising the following steps: in a regular operating mode the converters are controlled by the control means by means of command variables, in case of fault the converters are controlled by at least one control module which controls the torque and / or the active power and the reactive current and / or the reactive power by means of command variables such that a disconnection of the asynchronous machine from the grid will be performed only if the grid voltage falls below a predetermined voltage-time-characteristic curve, wherein the shape of the voltage-time-characteristic curve is configured by a plurality of pre-selectable parameters in the at least one control module.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY SE & CO KG
Rotor blade for wind energy plants
InactiveUS20070231146A1Firmly connectedAvoid attenuationPropellersRotary propellersEngineeringWind power
A rotor blade for wind energy plants with a multiplicity of cross bores running transversely to the longitudinal axis of the rotor blade in the region of the blade base, which are provided for the accommodation of cross pins, wherein for fastening the rotor blade on a rotor blade fixture, tensioning elements act upon the cross pins wherein at least one of the cross bores has a distance from the hub-side rotor blade edge which is different from the distance of a further cross bore from the rotor blade edge.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
Wind park and method for the operation of a wind park
ActiveUS20080048501A1Quick limitLonger constant productionBatteries circuit arrangementsWind motor controlElectricityEngineering
A wind park with a plurality of wind energy plants, which each have one plant control, which presets a desired value for the active power to its wind energy plant, and with a park control, which presets a desired value for the active power to be generated for each plant control and limits the active power fed by the wind park to a preset value, by shutting down a first group of wind energy plants and presetting a desired value for the active power to a second group of wind energy plants at a time, characterised in that the park control starts the wind energy plants of the first group again when the sum of the actual values of the active power of the wind energy plants of the second group has reached the preset desired value and / or a predetermined time duration has elapsed.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY SE & CO KG
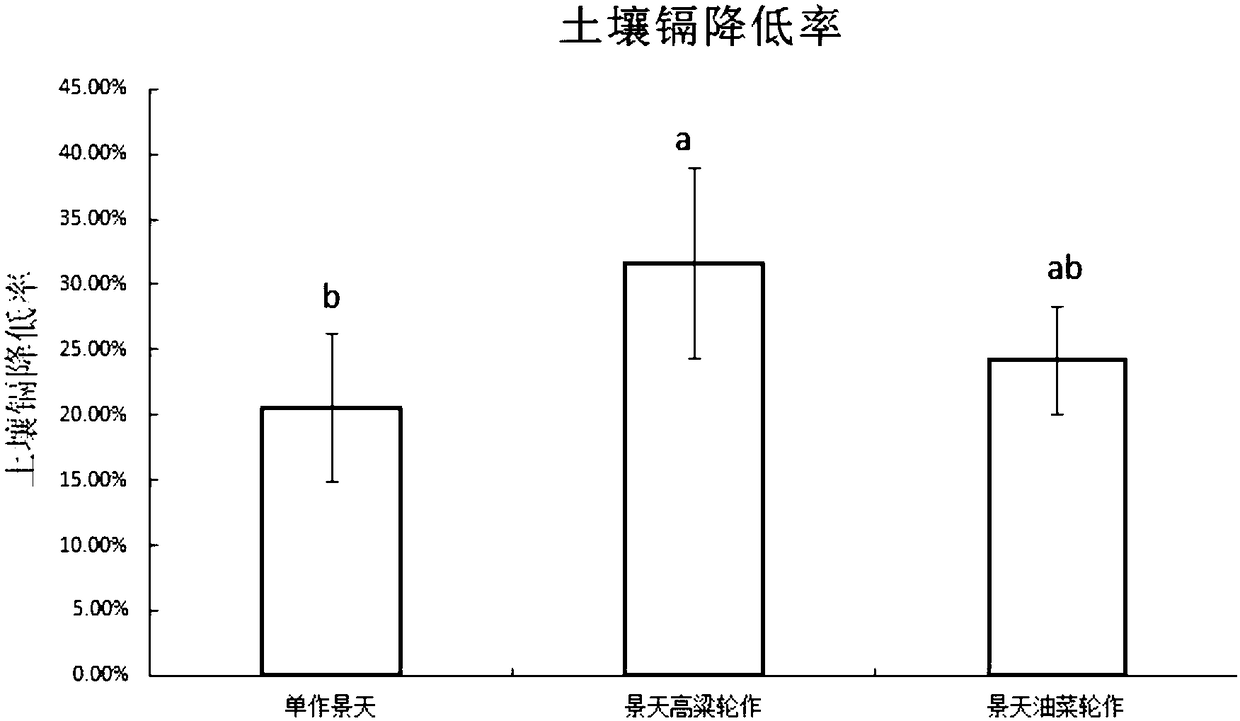
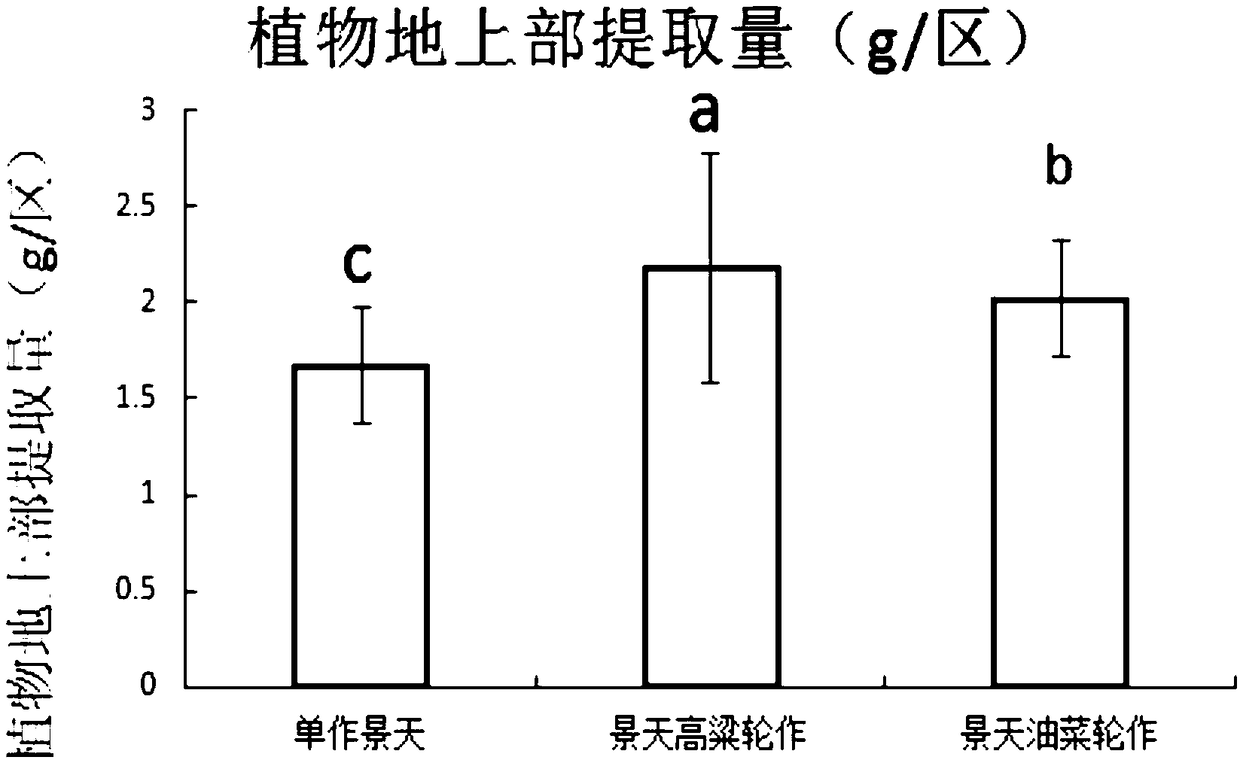
Method of quickly repairing cadmium polluted cultivated land by crop rotation of cadmium super-enriching plant and energy plant
InactiveCN108114977ASolve the problem of repair effectEfficient repairContaminated soil reclamationSoil remediationGrowing season
The invention discloses a method of quickly repairing a cadmium polluted cultivated land by crop rotation of a cadmium super-enriching plant and an energy plant. The method comprises the following step: planting the cadmium super-enriching plant and the energy plant in the cadmium polluted cultivated land in the natural growth periods thereof for conventional cultivation to achieve the purpose ofrepairing the cadmium polluted cultivated land by means of adsorbing and enriching abilities of the cadmium super-enriching plant and the energy plant, wherein the cadmium super-enriching plant is sedum plumbizincicola and the energy plant is sorghum or oilseed rape. The invention provides a planting mode which is not limited by growth seasons. Based on one year as the repair period, the soil repair efficiency of the polluted cultivated land is increased by means of a relatively long growth period in multi-cropping plantation, and the method is short in repair period, high in operability and low in cost, and repairs the land more thoroughly.
Owner:北京复天科技有限公司
Rotor blade and wind energy plant
InactiveUS20080112813A1Minimise undesired air vortexIncrease distancePropellersWind motor controlRotational axisEngineering
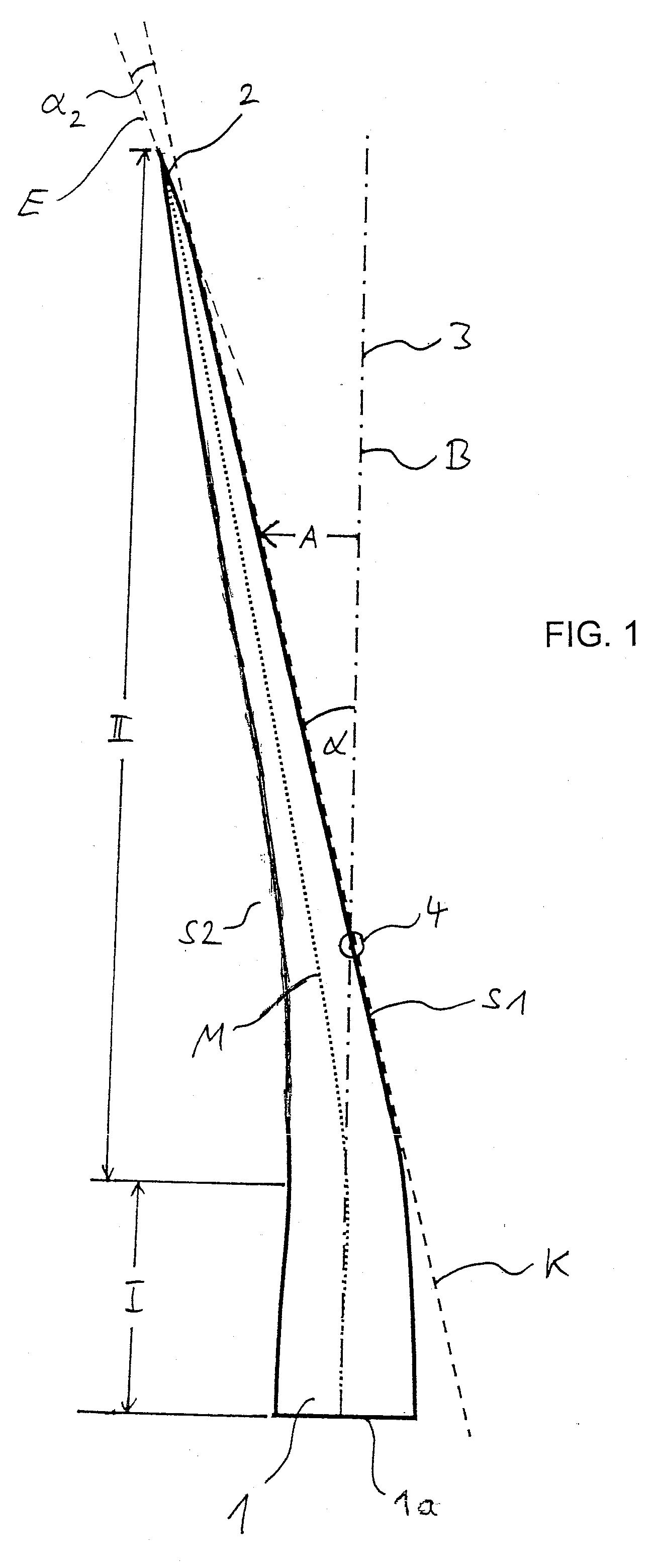
The present invention is related to rotor blade for a wind energy plant, with a blade root, with a first longitudinal portion starting from the blade root, with a second longitudinal portion, following up the first longitudinal portion and running into a blade tip, with a first surface, facing a tower of the wind energy plant in its assembled state, and a second surface, facing away from the tower of the wind energy plant in its assembled state, wherein an imaginary reference plane is spanned up by a rotation, taking place in the operation of the rotor blade, of the longitudinal axis of the first longitudinal portion around the rotational axis of a rotor of the wind energy plant carrying the rotor blade. The objective to provide a rotor blade which has a high efficiency even at safe prevention of collisions of the blade tip with the tower of the wind energy plant, and in which the moments around the longitudinal blade axis occurring in the operation are reduced, is resolved by the invention in that the first surface runs along an imaginary cone plane in the region of the second longitudinal portion, which is spanned up by a rotation, taking place in the operation, of the first surface in the region of the second longitudinal portion around the rotational axis of a rotor carrying the rotor blade, wherein the cone plane intersects the reference plane in an angle, and that the distance between the first surface and the reference plane along the second longitudinal portion increases linearly in the direction towards the blade tip, and that the second longitudinal portion is longer than the first longitudinal portion. In addition, the present invention is related to a wind energy plant.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
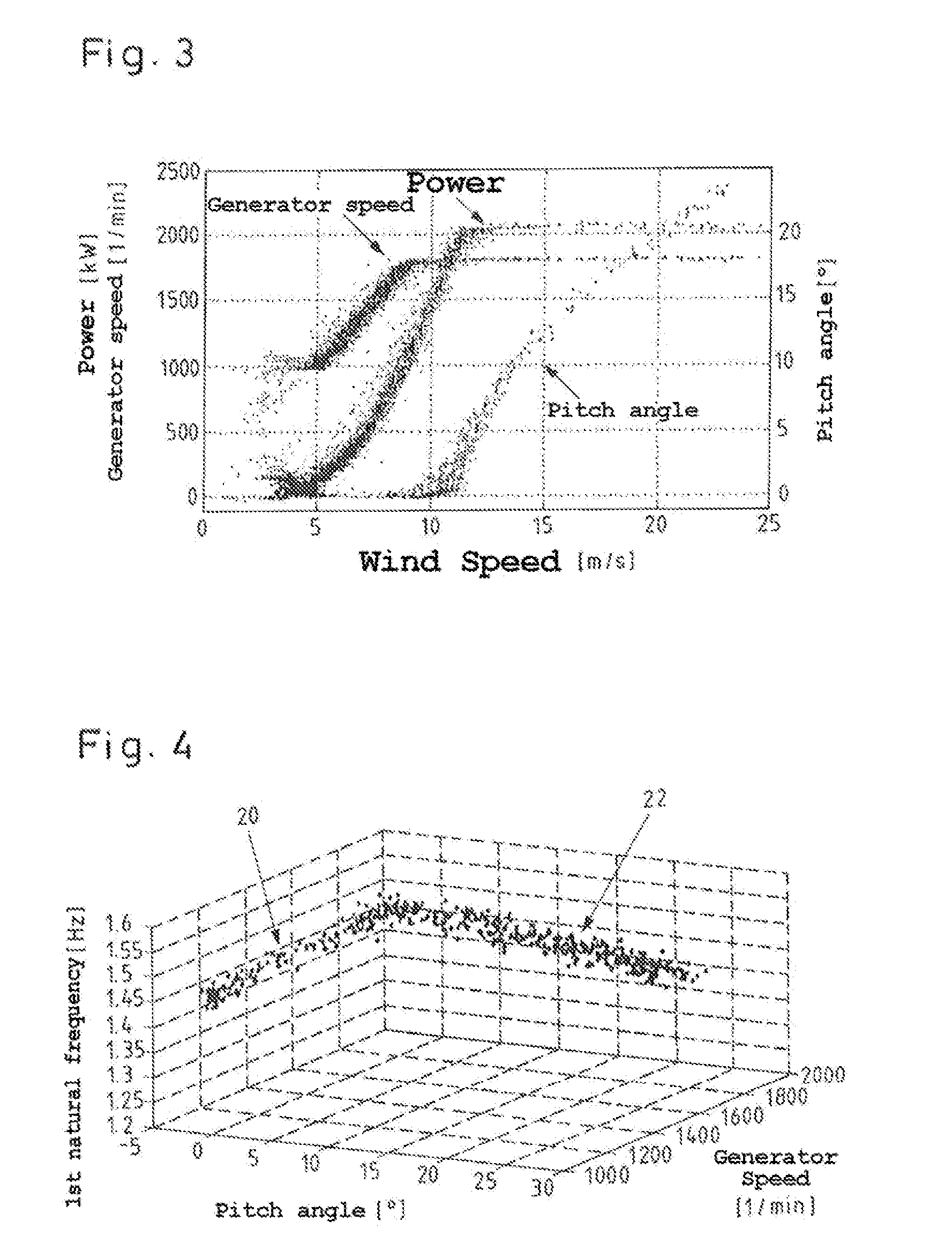
Method for monitoring the operation of a wind energy plant and wind energy plant
ActiveUS20150345467A1Function increaseConvenient statisticsWind motor controlEngine fuctionsEngineeringStatistical Confidence
A method for monitoring the operation of a wind energy plant having at least one blade angle adjustable rotor blade. Rotor blade vibrations are registered during operation by at least one measuring device, and at least one current natural frequency is established from the registered vibrations. At least one environmental parameter and / or at least one operational parameter, which influence the natural frequency of the rotor blade, is or are additionally registered. At least one natural frequency expected value dependent on the additionally registered parameter(s) and at least one confidence interval are calculated for the at least one established current natural frequency of the rotor blade, and whether the established current natural frequency lies within, or outside of, the confidence interval around the natural frequency expected value is monitored. Also disclosed is an operational control apparatus of a wind energy plant and a corresponding wind energy plant.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
Organic sewage constructed wetland processing and high-yield non-food energy plant cultivating technology
InactiveCN101805061AAvoid Fugitive EmissionsPromotes fast digestionWater contaminantsGas production bioreactorsConstructed wetlandNormal growth
The invention relates to an organic sewage constructed wetland processing and high-yield non-food energy plant cultivating technology, which is characterized in that the organic sewage is sent into a methane tank, an oxidation pond and a constructed wetland orderly to achieve the purpose of sewage purification, and simultaneously, the non-food energy plant is cultivated. The invention has the advantages that a buried type ABR system can be ensured to be in an intermediate-temperature fermentation state, the organic matter is digested quickly, and methane is produced with high yield; the methane is used for intensifying light, heating, increasing carbon dioxide fertilizer and enhancing photosynthesis for the system to produce the non-food energy plant with high yield; under the previous condition, plant seeds and energy plants on the oxidation pond (the stabilization pond) and the constructed wetland can grow quickly so as to obtain high yield and produce high-quality protein feed, and the normal growth and absorption of eutrophic substances in the sewage in winter can be ensured; simultaneously, purified reclaimed water is fully utilized; and the plants inside and outside the system grow quickly, a large amount of carbon dioxide is absorbed and utilized, and zero emission of sewage and methane is realized.
Owner:罗仕均
Wind park with a plurality of wind energy plants and method for the operation of the wind park
InactiveUS7756609B2Short timeMechanical power/torque controlOptimise machine performanceOrder controlEngineering
A method for the operation of a wind park with a plurality of wind energy plants, which each one have one control unit at a time, which can control and / or adjust the wind energy plant in response to a received desired value for an electric variable, the method having the following steps: a higher order control calculates and / or receives a currently permitted maximum value for the electric variable which the wind park is allowed to provide, the higher order control determines a desired value for the electric variable for each wind energy plant and forwards the same to the wind energy plants, characterized in that the higher order control determines the desired value for each one of the wind energy plants depending on the currently maximum and / or minimum available values of all the wind energy plants.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
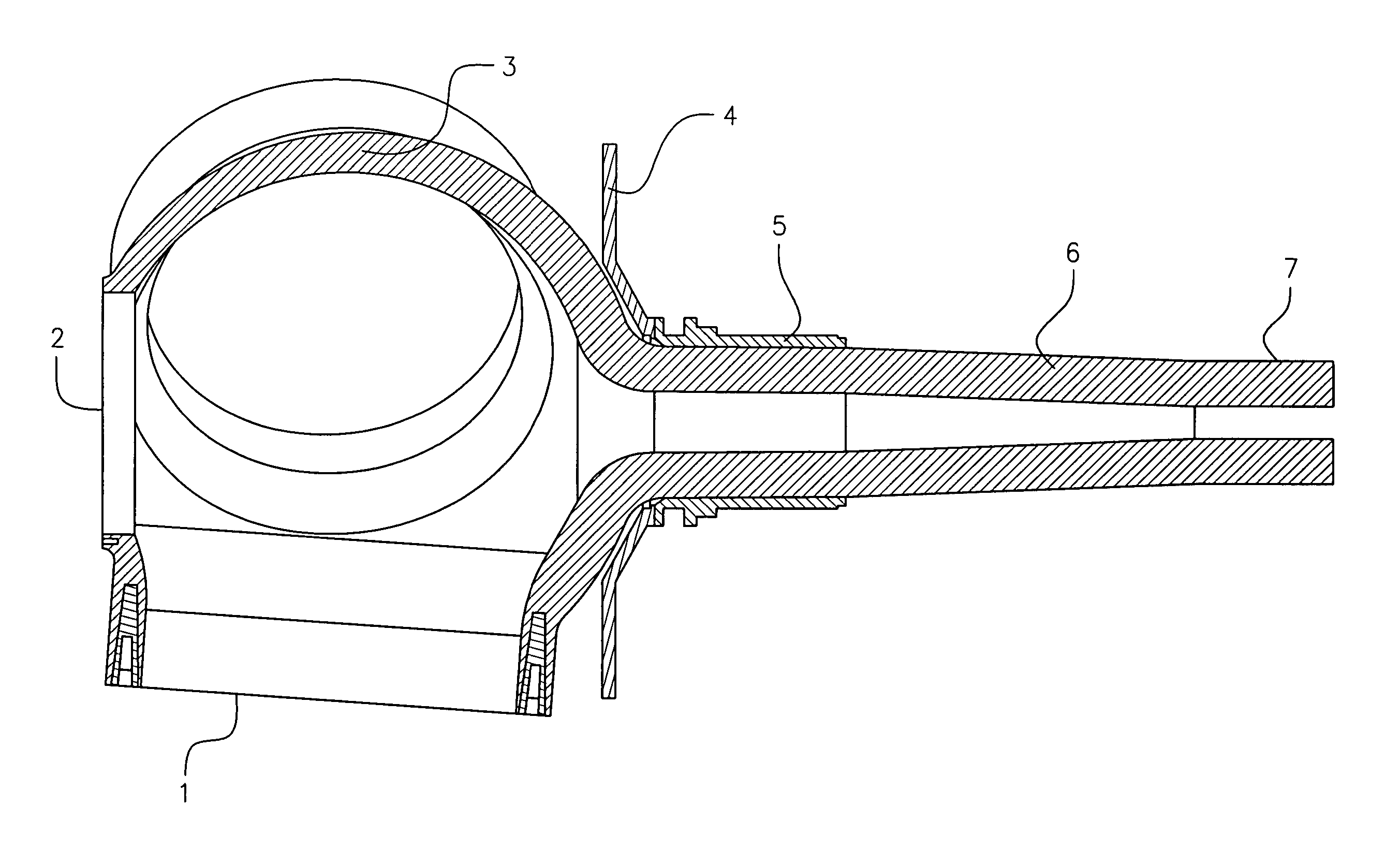
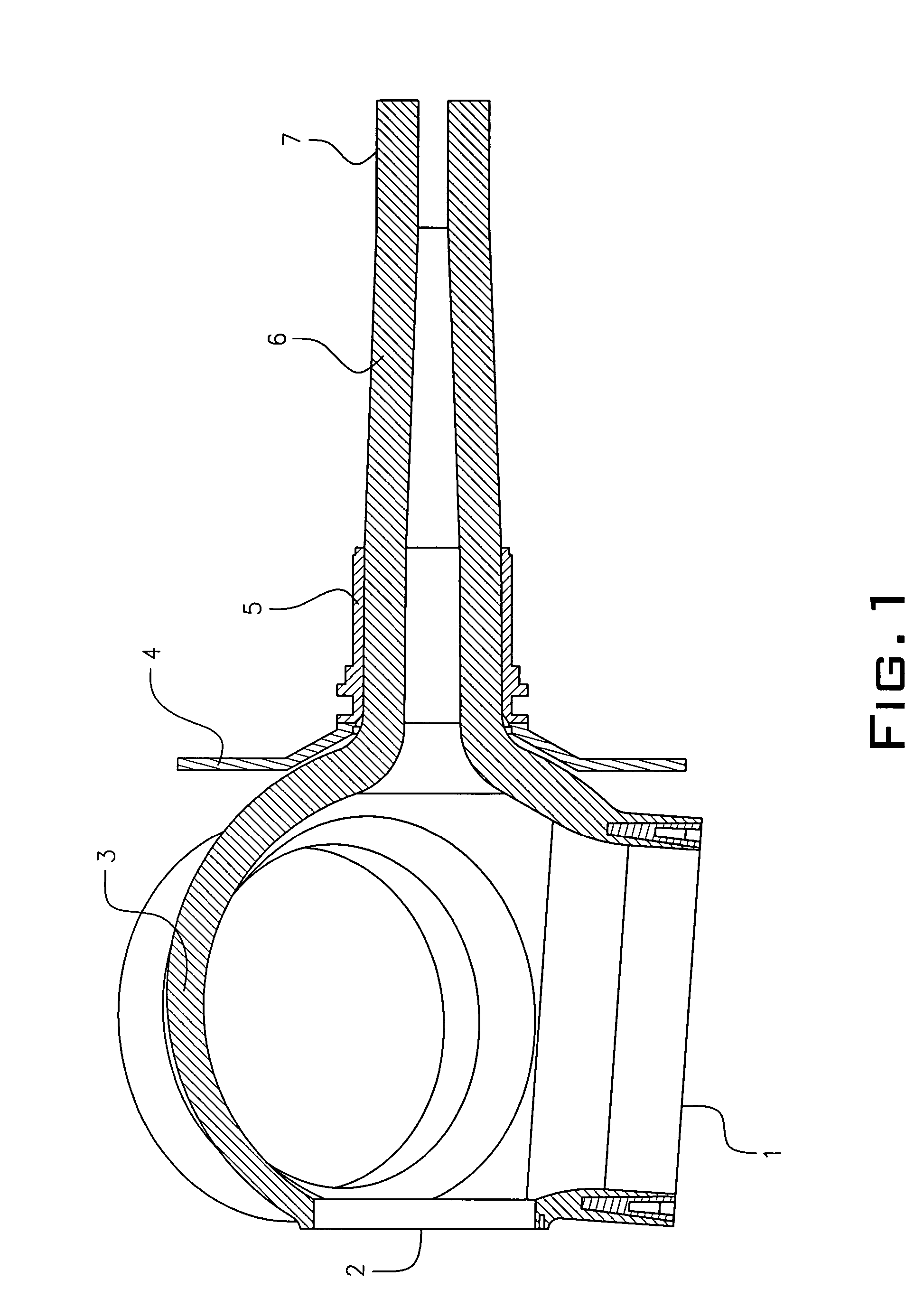
Method of lightning proofing a blade for a wind-energy plant
ActiveCN1867772AProper electrical connectionReliable electrical connectionConnection to earthDischarge by conduction/dissipationFiberElectricity
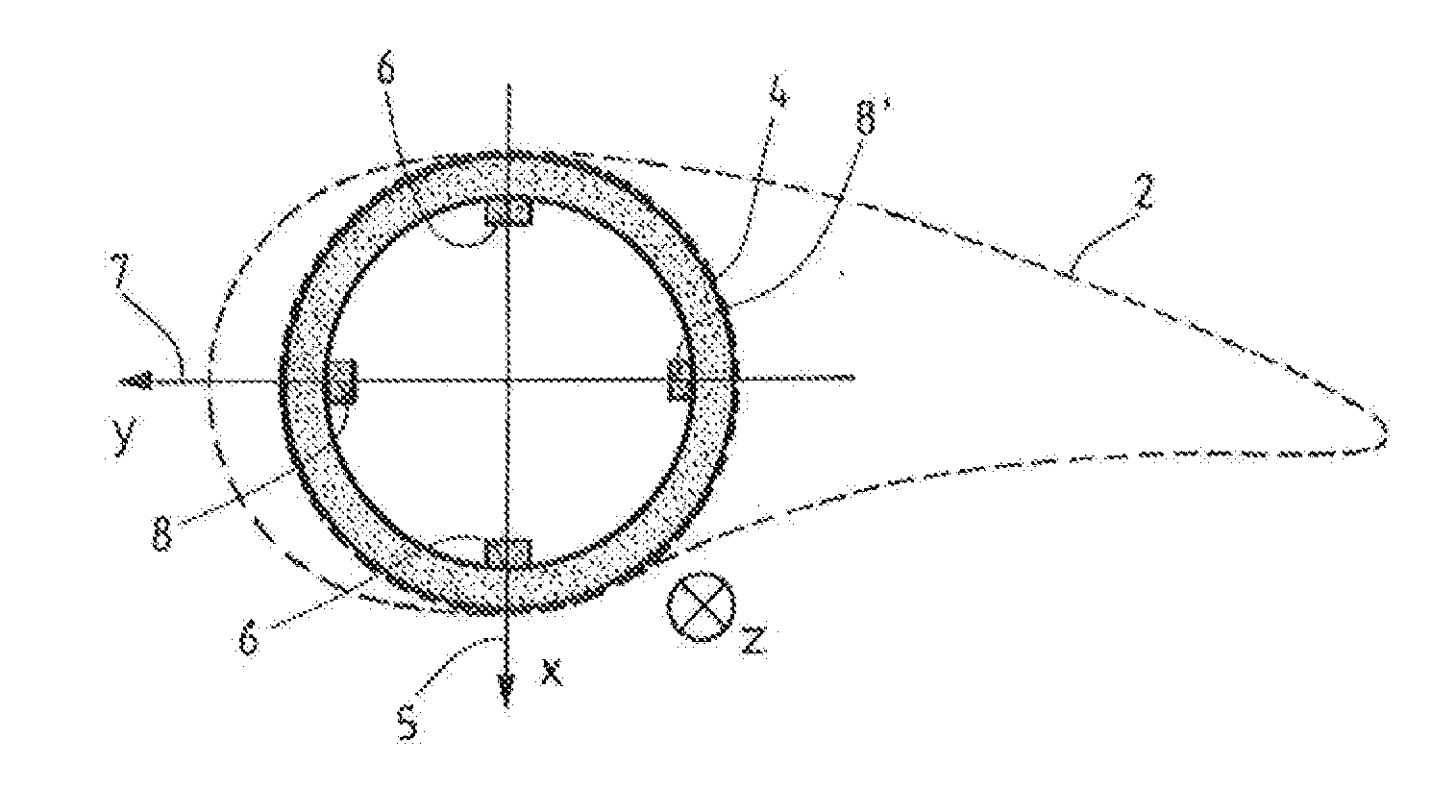
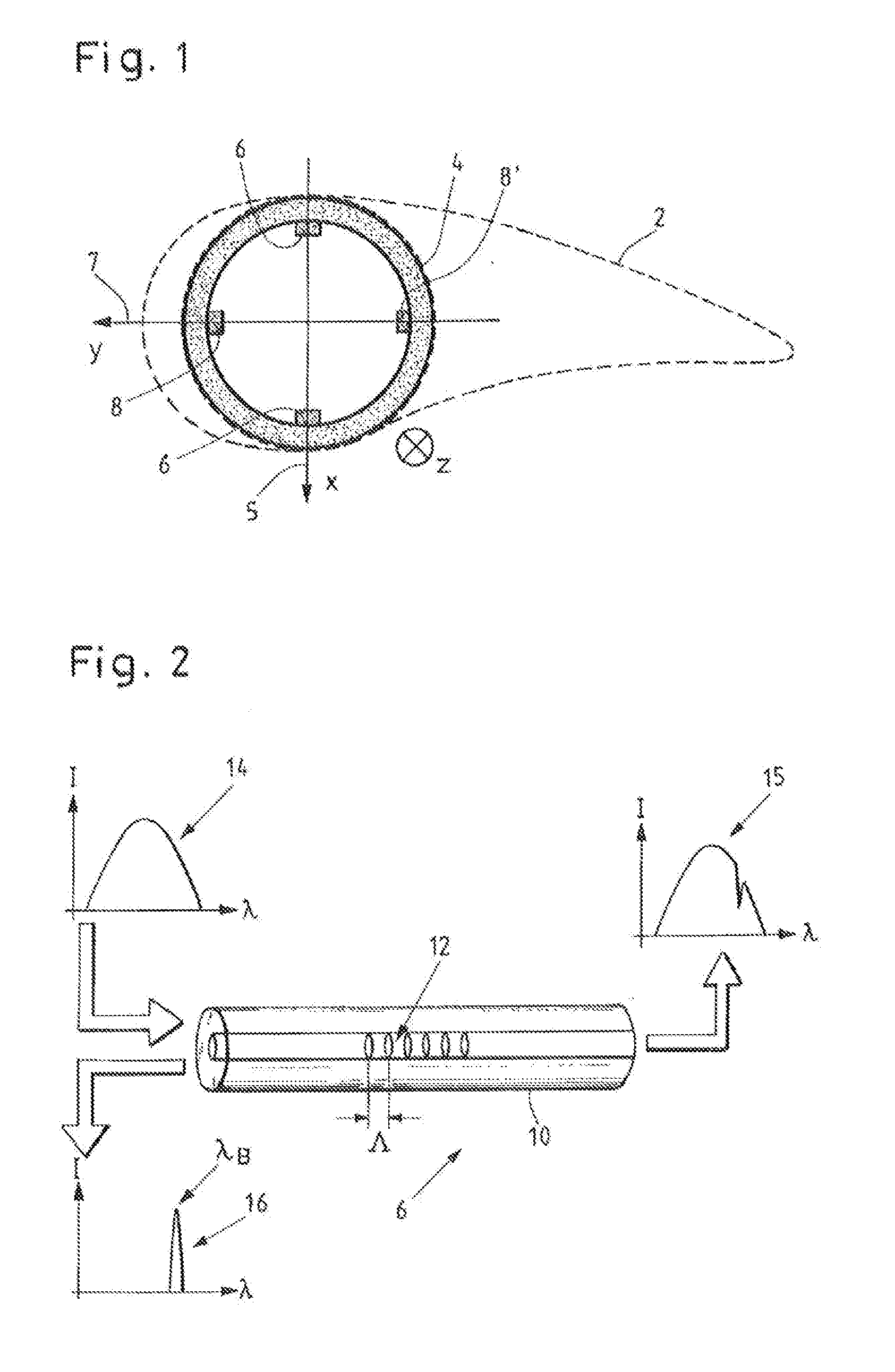
The invention relates to a method of lightning-proofing a blade (1) on a wind-energy plant, which blade comprises a blade shell (2) configured essentially as a fibre-reinforced laminate, which laminate comprises electrically conductive fibres, wherein the blade comprises at least one lightning arrester (9) configured for conducting lightning current, including preferably to ground. The method comprises that the electrically conductive fibres are connected to each other, and that at least one metallic receptor (4, 24, 25) is arranged for capturing lightning current at or in proximity of the external face of the blade; and that the receptor and the fibres are connected to the lightning arrester for equalising the difference in potential between the lightning arrester and the electrically conductive fibres. When the electrically conductive fibres are connected to each other, the fibres will cooperate on the conduction of a possible lightning current to prevent the current from running in individual fibres. Simultaneously the metallic receptor will serve as the primary lightning capturing device and reduce the risk of lightning striking the laminate. The receptor being connected to the lightning arrester, the current will predominately be conducted to ground, while the risk of transfer to the laminate is minimised in that a possible difference in potential between fibres and lightning arrester has been equalised.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
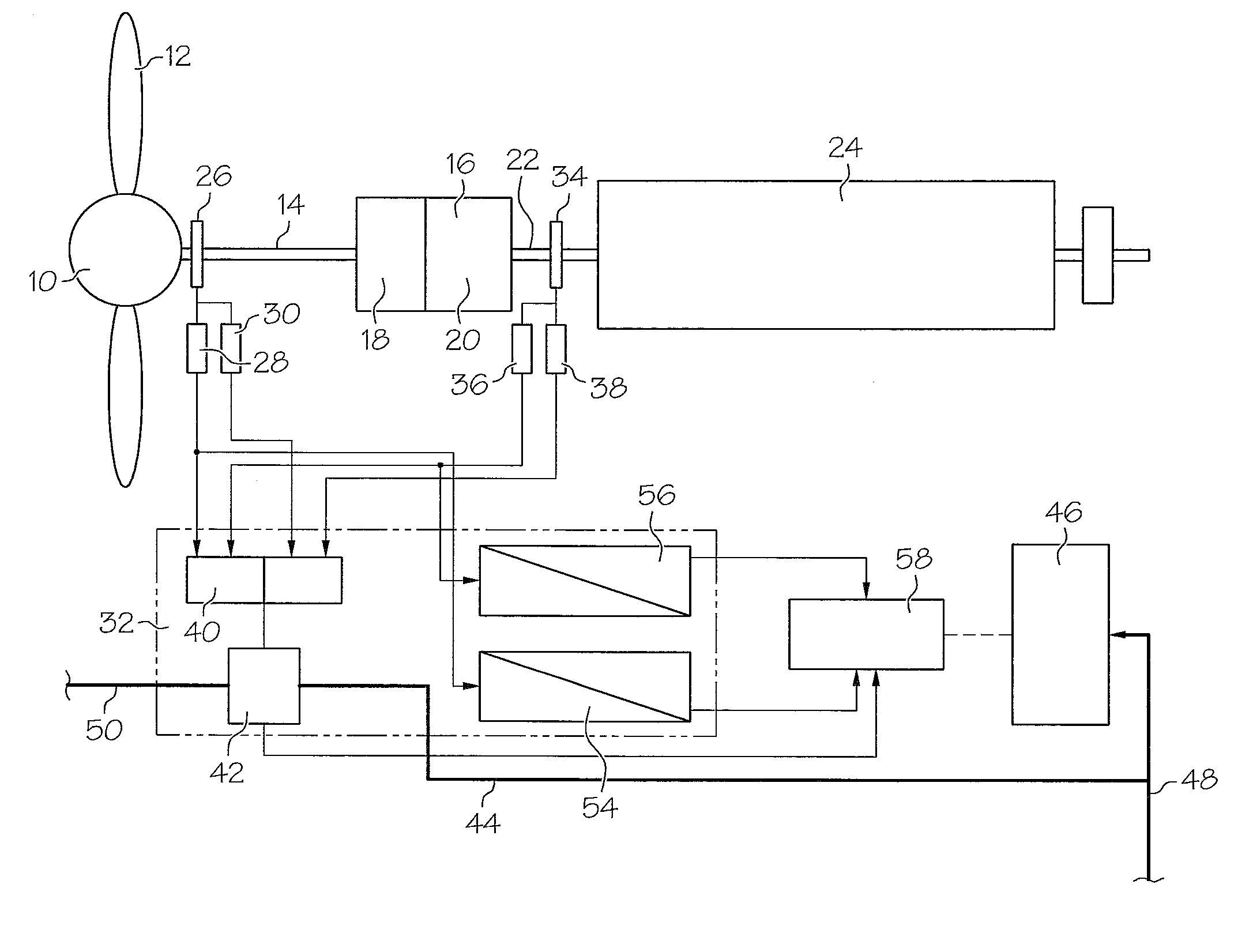
Method for the operation of a wind energy plant with a synchronous generator and a superimposition gearbox
InactiveUS20080054642A1Process stabilityStabilise electric supply gridsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlSuperimpositionPower grid
A method for the operation of a wind energy plant, with a synchronous generator and a superimposition gearbox, which is connected between rotor and generator, and the gear ratio of which is adjusted by a control unit, characterised in that a mode of operation is provided in which the generator is connected to the electric grid, and the generator shaft is uncoupled from the rotor shaft via the superimposition gearbox.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
Shaft/hub unit for wind turbine rotor
InactiveUS7011497B2Economic advantageHigh specific strengthPropellersRotary propellersFiberMechanical engineering
A rotor shaft / hub unit for a wind energy plant with a rotor shaft provided with a rotor bearing seat which is connected to a rotor hub provided with a blade or blade bearing connection, the rotor hub and rotor shaft are manufactured in one piece from bonded fiber fabrics.
Owner:AERODYN ENG GMBH
Method for producing L-lactic acid from lignocellulose through fermentation
InactiveCN106834368ASolve the problem of incineration pollutionIncrease incomeMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for producing L-lactic acid from lignocellulose through fermentation. The method comprises the following steps that 1, bacillus coagulans fermentation seed culturing is conducted; 2, crop straw or energy plants are pretreated through a steam explosion method; 3, L-lactic acid is produced by conducting saccharification and fermentation simultaneously, wherein fermentation medium ingredients are added into a fermentation tank, a bacillus coagulans fermentation seed solution cultured in the step 1 and the crop straw or energy plants pretreated through steam explosion in the step 2 are added, simultaneous saccharification and fermentation are conducted for 48 h-72 h, samples are taken regularly to measure the concentration of lactic acid in the fermentation liquid. The method has the comprehensive advantages of being simple in process, short in fermentation period, high in lactic acid optical purity, easy to purity, free of pollution in the whole production process and the like, the production cost is effective controlled, and industrialization is convenient to achieve.
Owner:JIANGSU DIYIN BIOTECH
Wind energy plant tower
InactiveUS7694473B2Promote quick completionEasy to set upEngine manufactureEngine fuctionsEngineeringTower
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
Wind turbine with current conducting means, which are pre-assembled in the tower
InactiveUS7199485B2Faster and cheapEasy erectionWind motor assemblyBus-bar installationPower flowEngineering
The present invention concerns a wind energy plant for generation of alternating current with a tower constructed of several tower segments, a generator arranged in the region of the top of the tower, a power module arranged in the region of the base of the tower, and current carrying means for transferred current from the generator to the power module. In order to enable faster, easier and thereby cheaper erection of the wind energy plant, it is provided in accordance with the present invention that the current carrying means be premounted in the tower segments in segmented form.
Owner:WOBBEN ALOYS
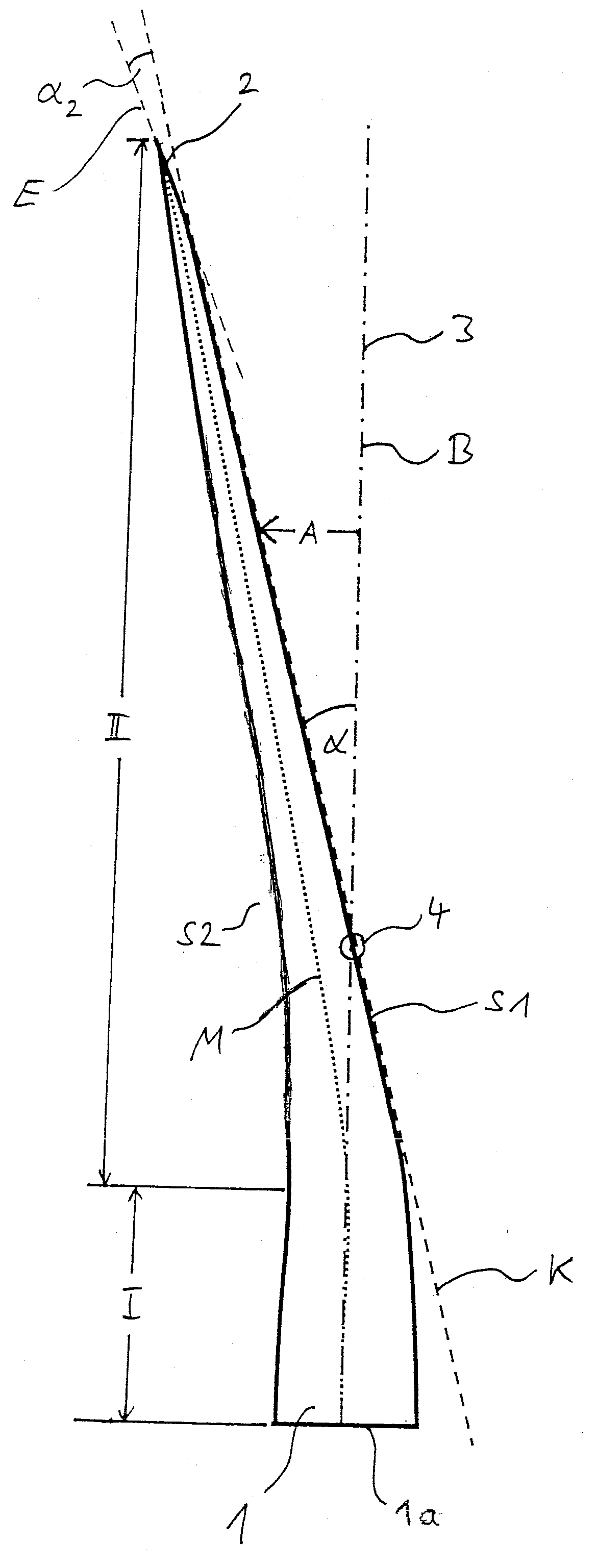
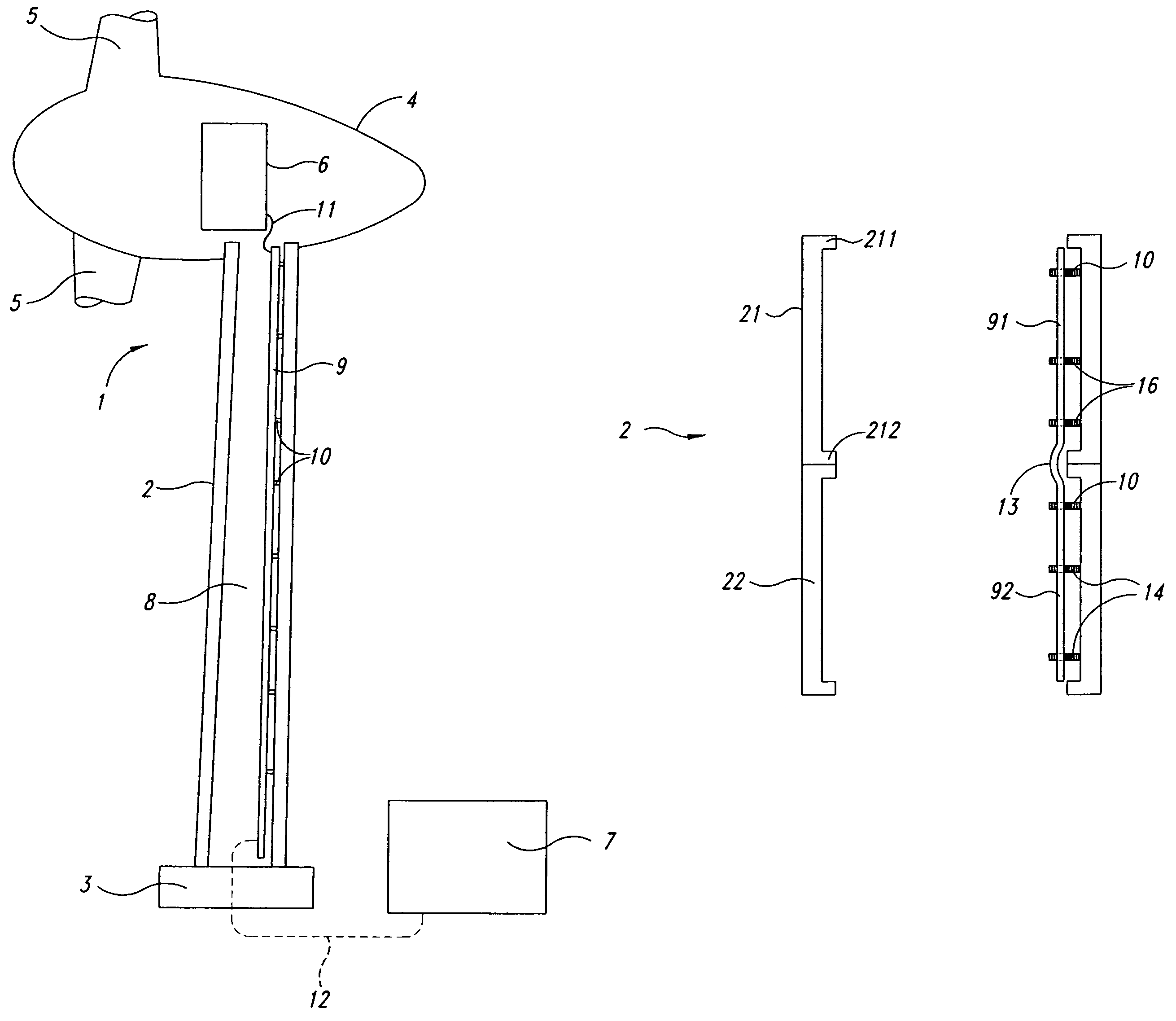
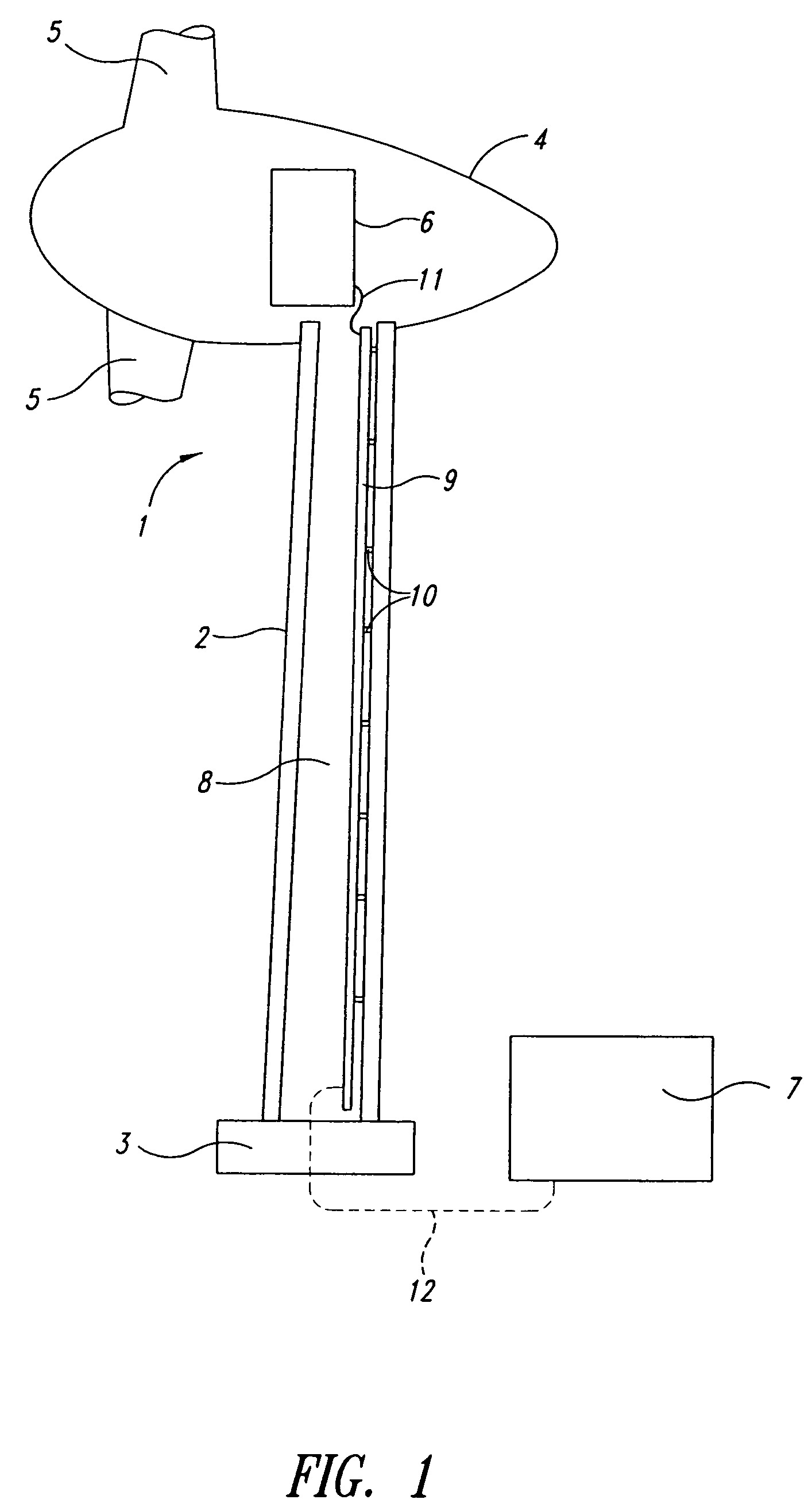
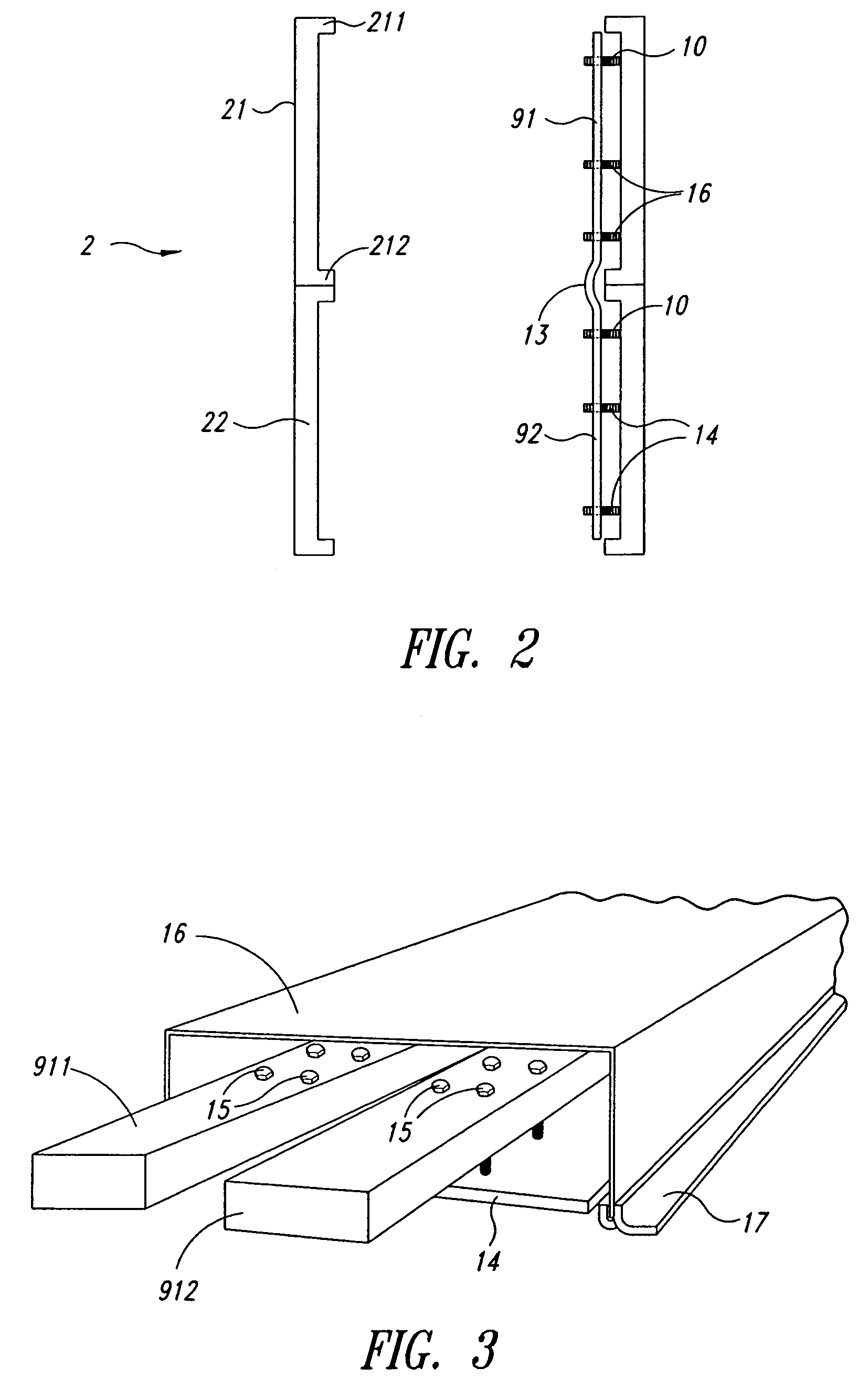
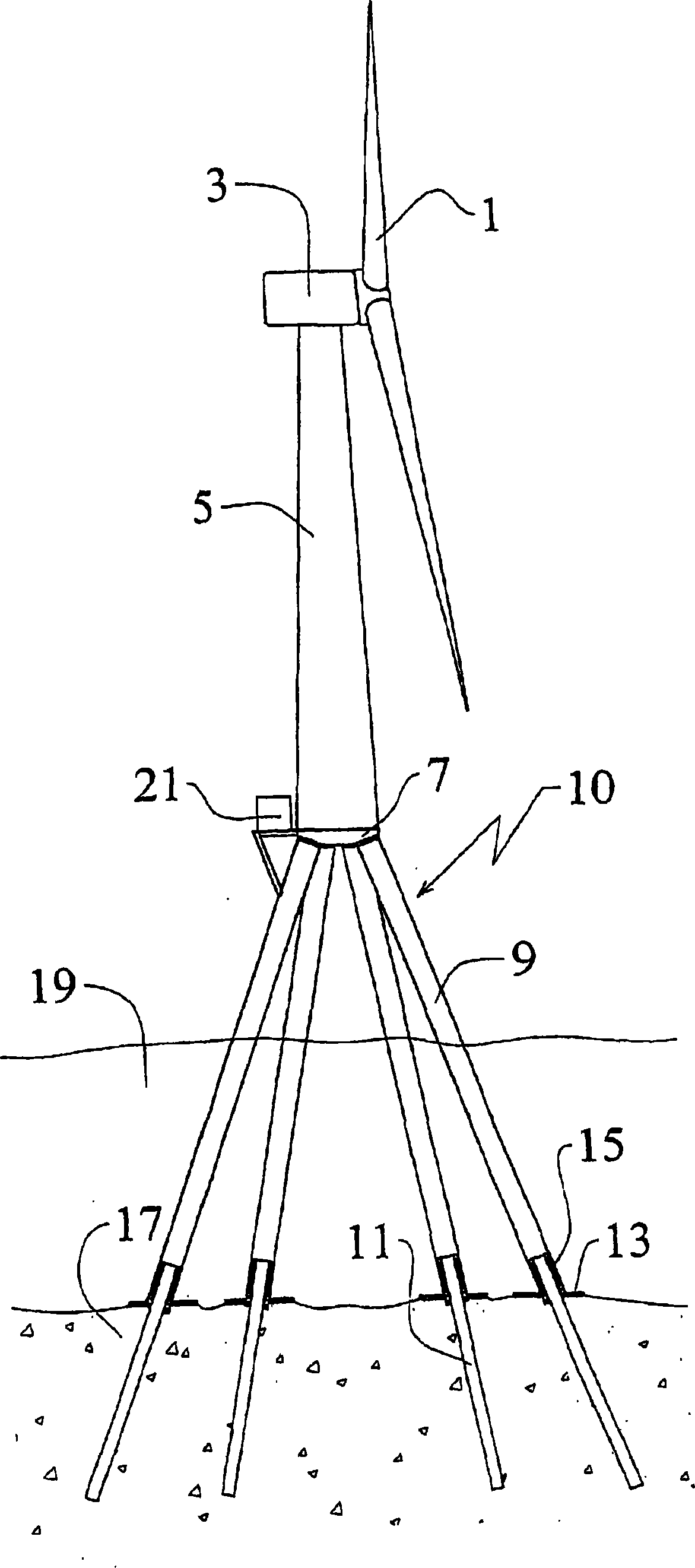
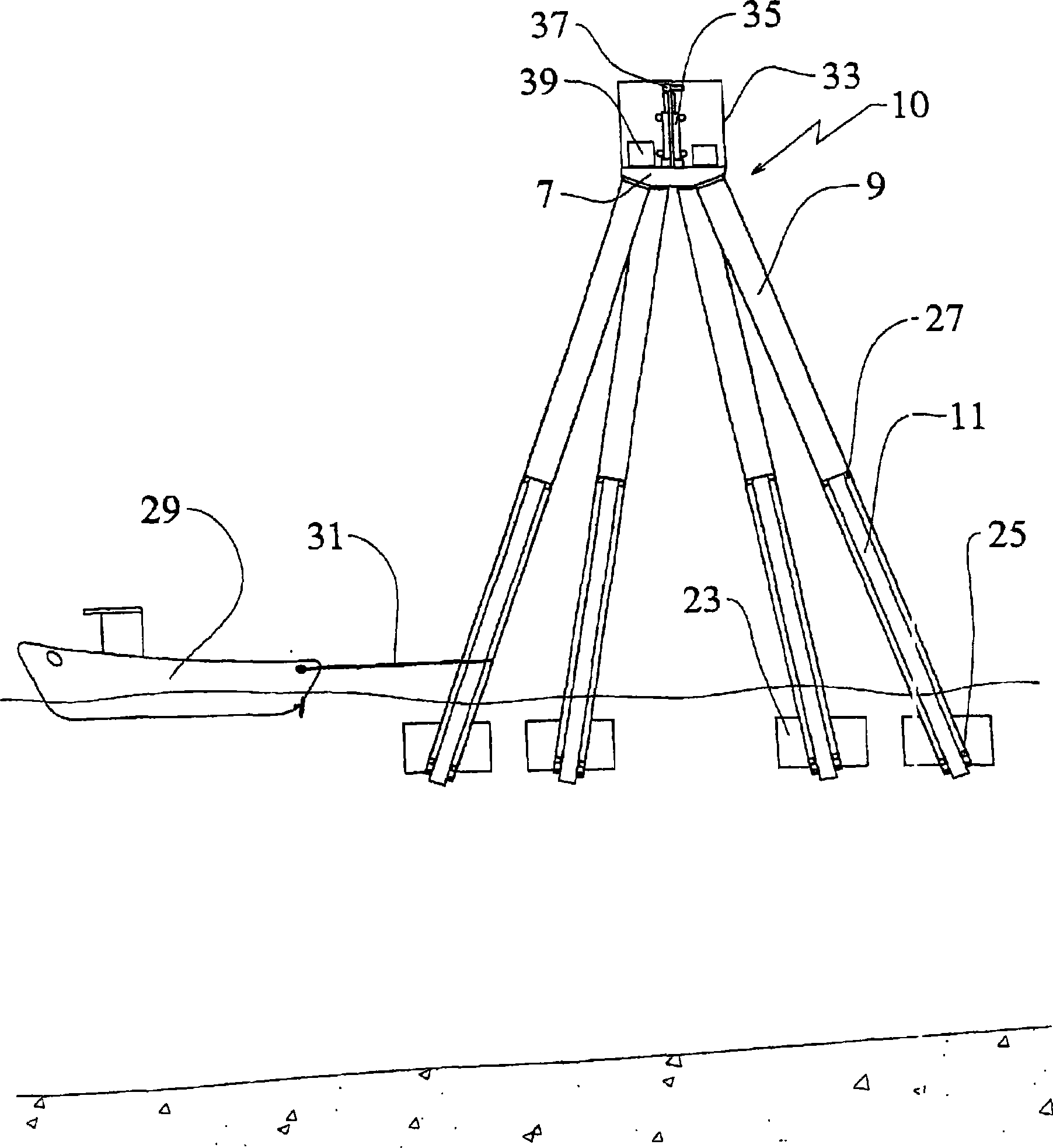
Foundation for an offshore wind energy plant
InactiveCN1867769AEasy to migrateHave the ability to floatArtificial islandsEngine fuctionsLoad distributionOffshore wind power
The invention relates to foundation for an offshore wind energy plant (WEA), comprising a load distribution element (7) supporting the tower (5) of the WEA provided with a gondola (3) and a rotor (1) and a plurality of foundation legs (9) which support the load distribution element (7) and which extend in an inclined manner towards the outside in relation to the vertical. The central axes (M) of the foundation legs (9) intersect with the circular surface (K) which is circumscribed by the external diameter of the tower (5) in the joining plane (V) of the load distribution element (7) and said tower (5).
Owner:AERODYN ENG GMBH
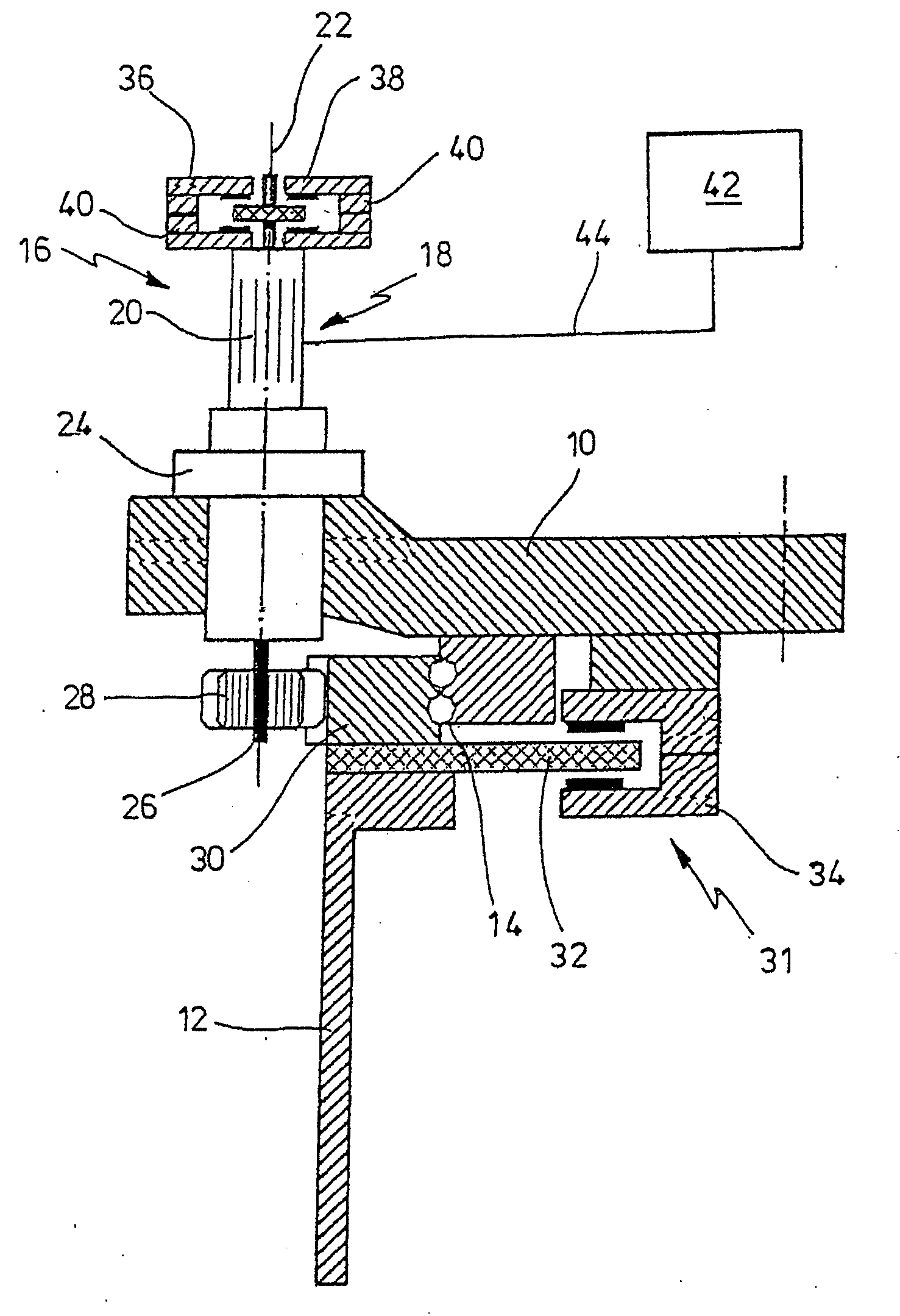
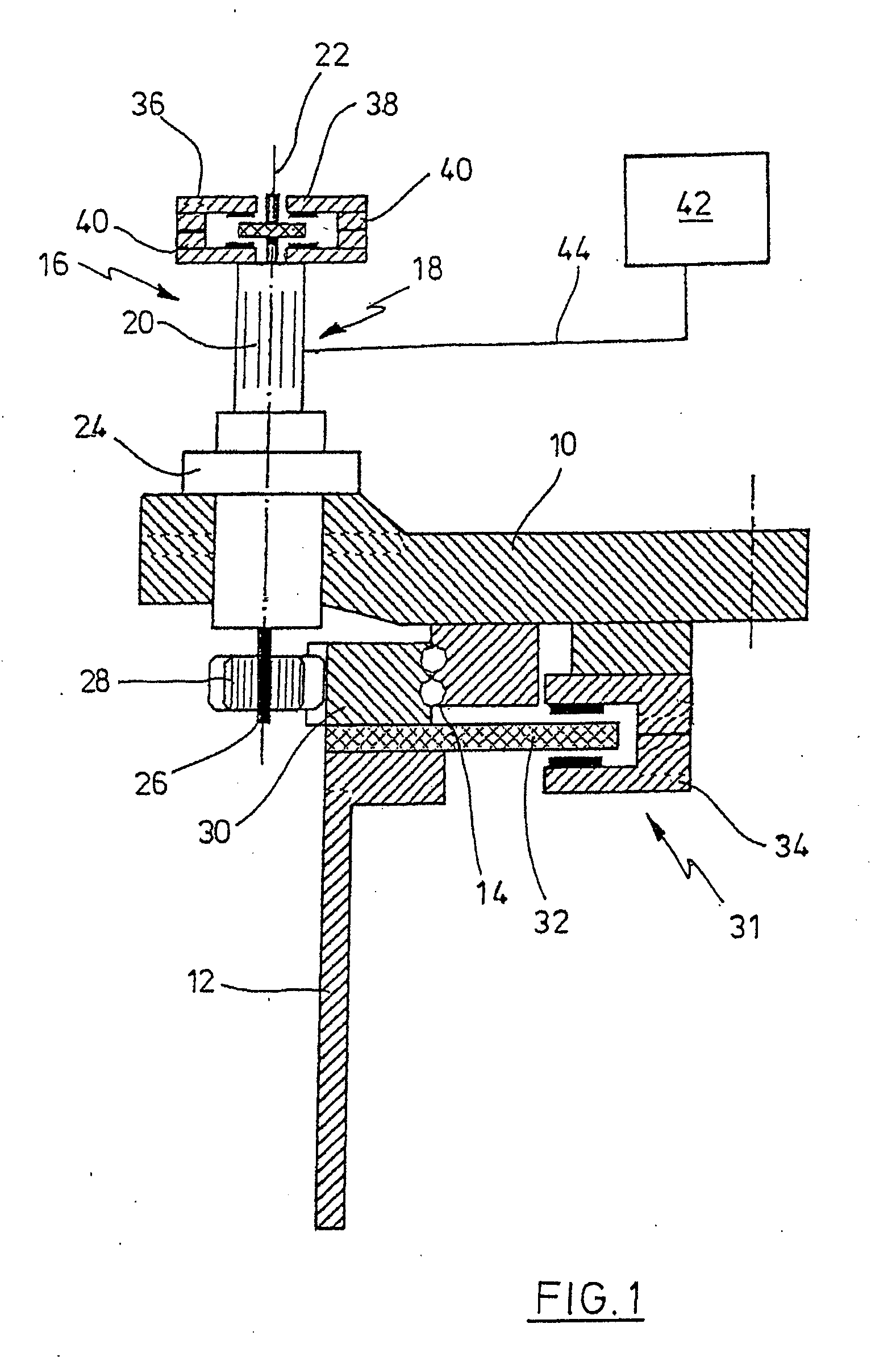
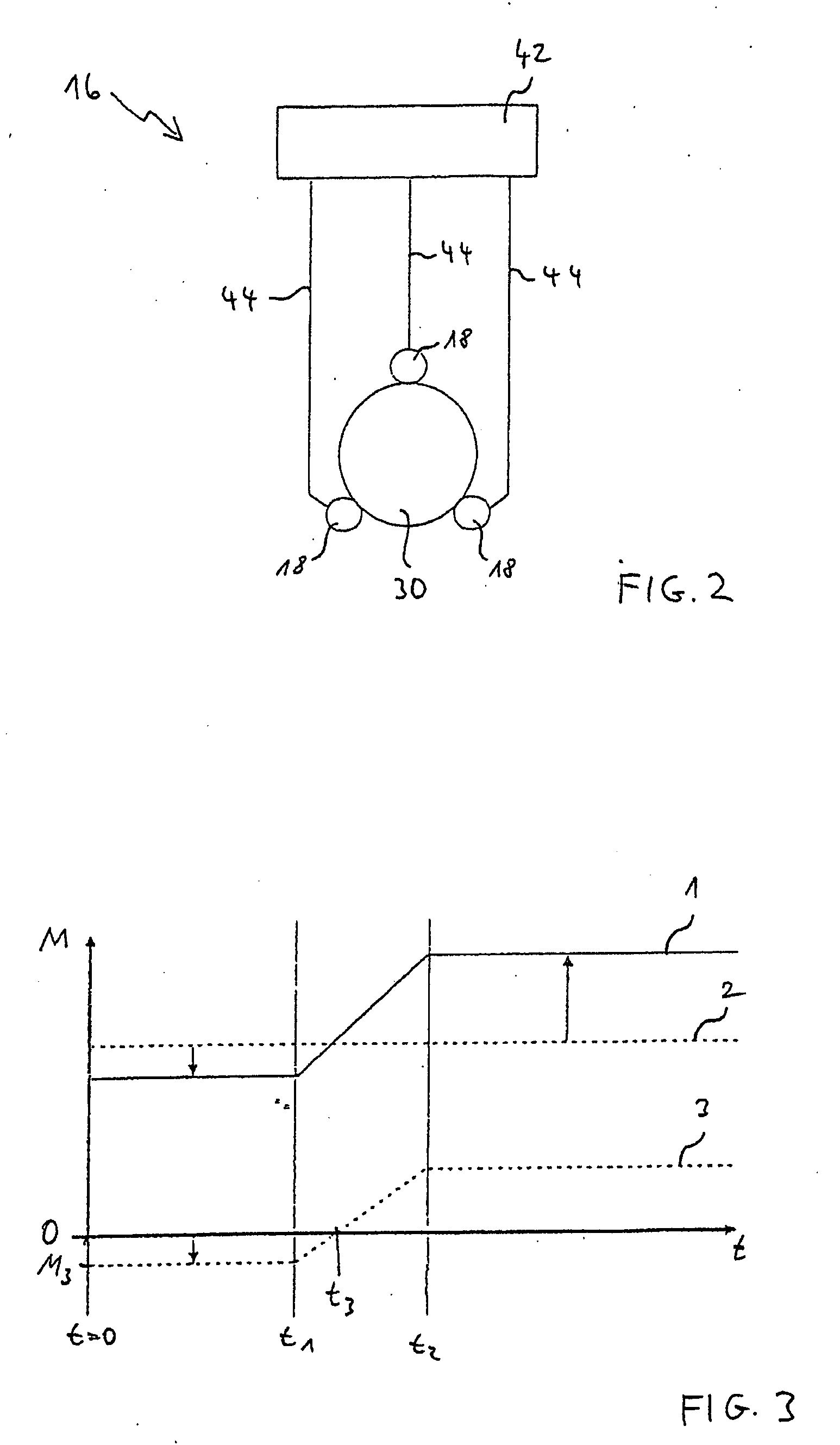
Hydraulic brake system for a wind energy plant
InactiveUS7357462B2Simple configurationReliable of componentWind motor controlBraking action transmissionWorking fluidEngineering
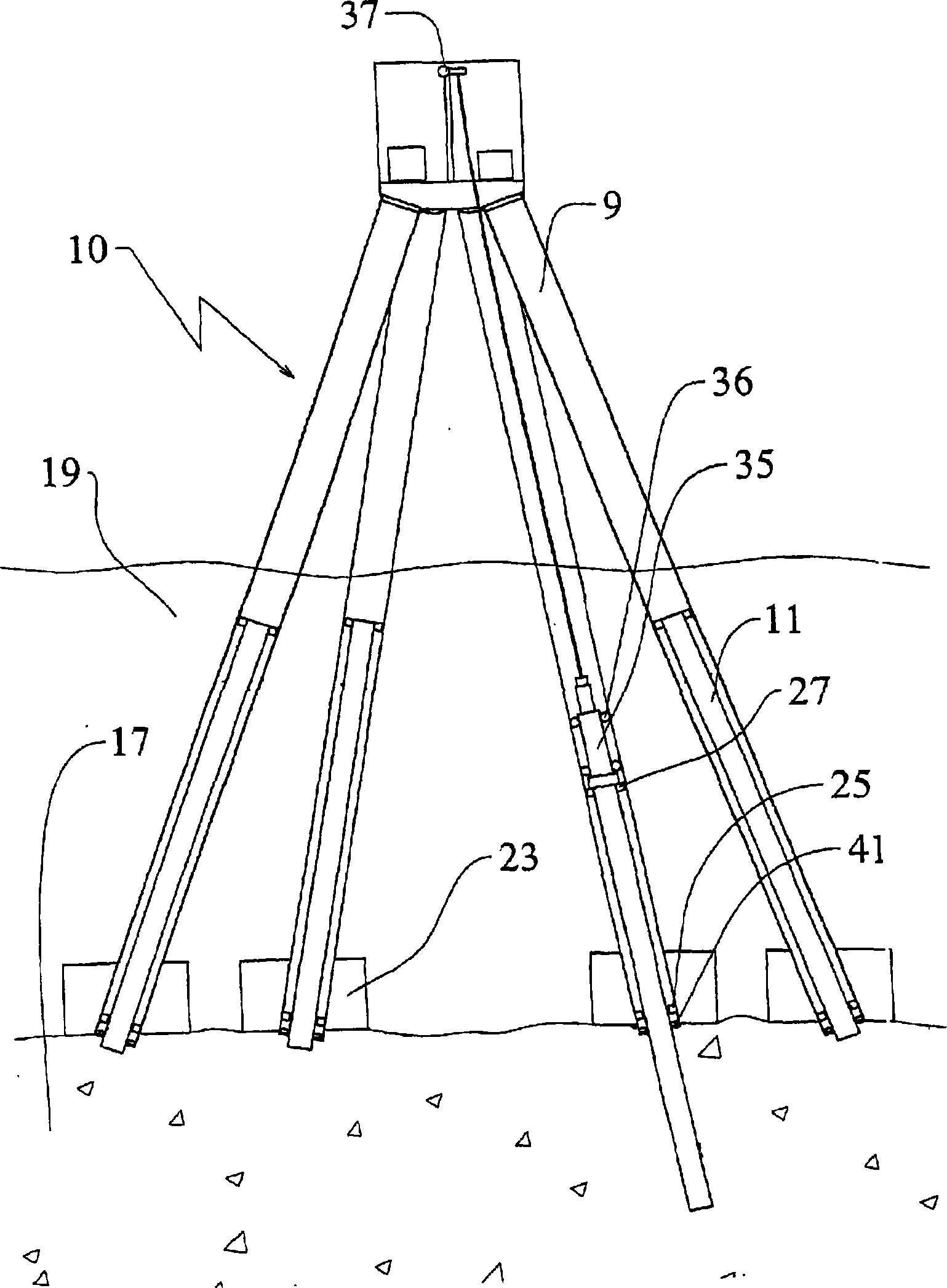
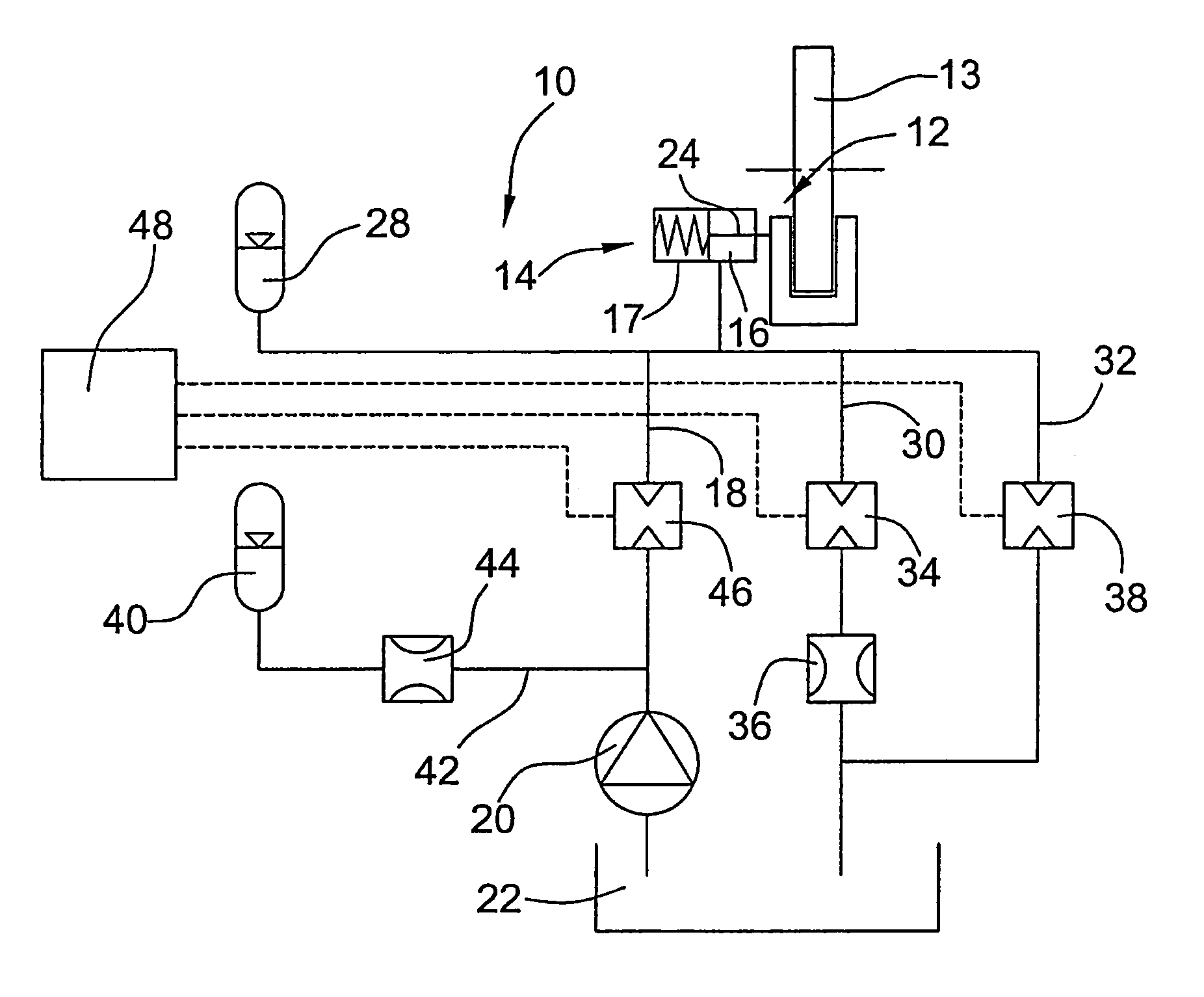
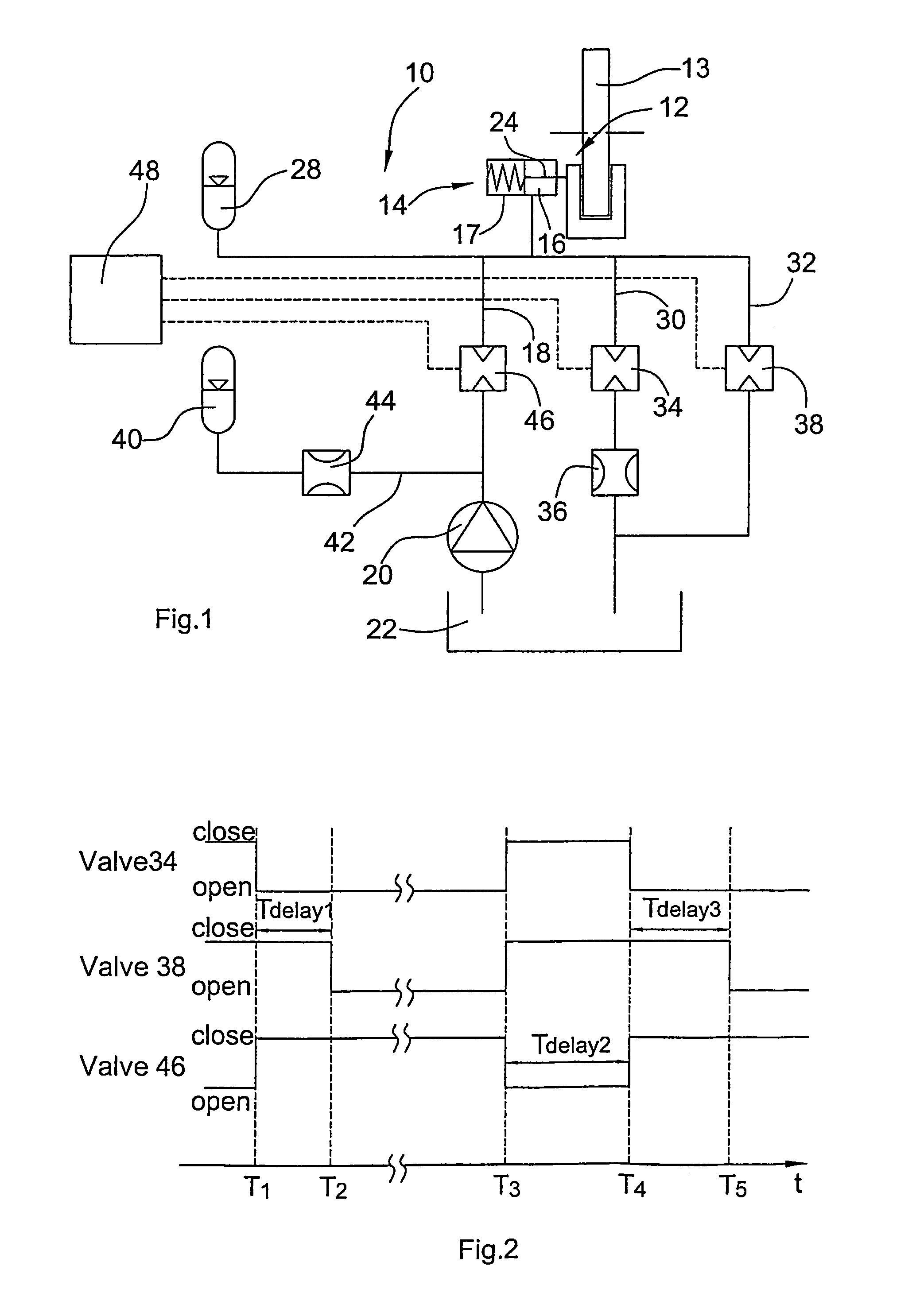
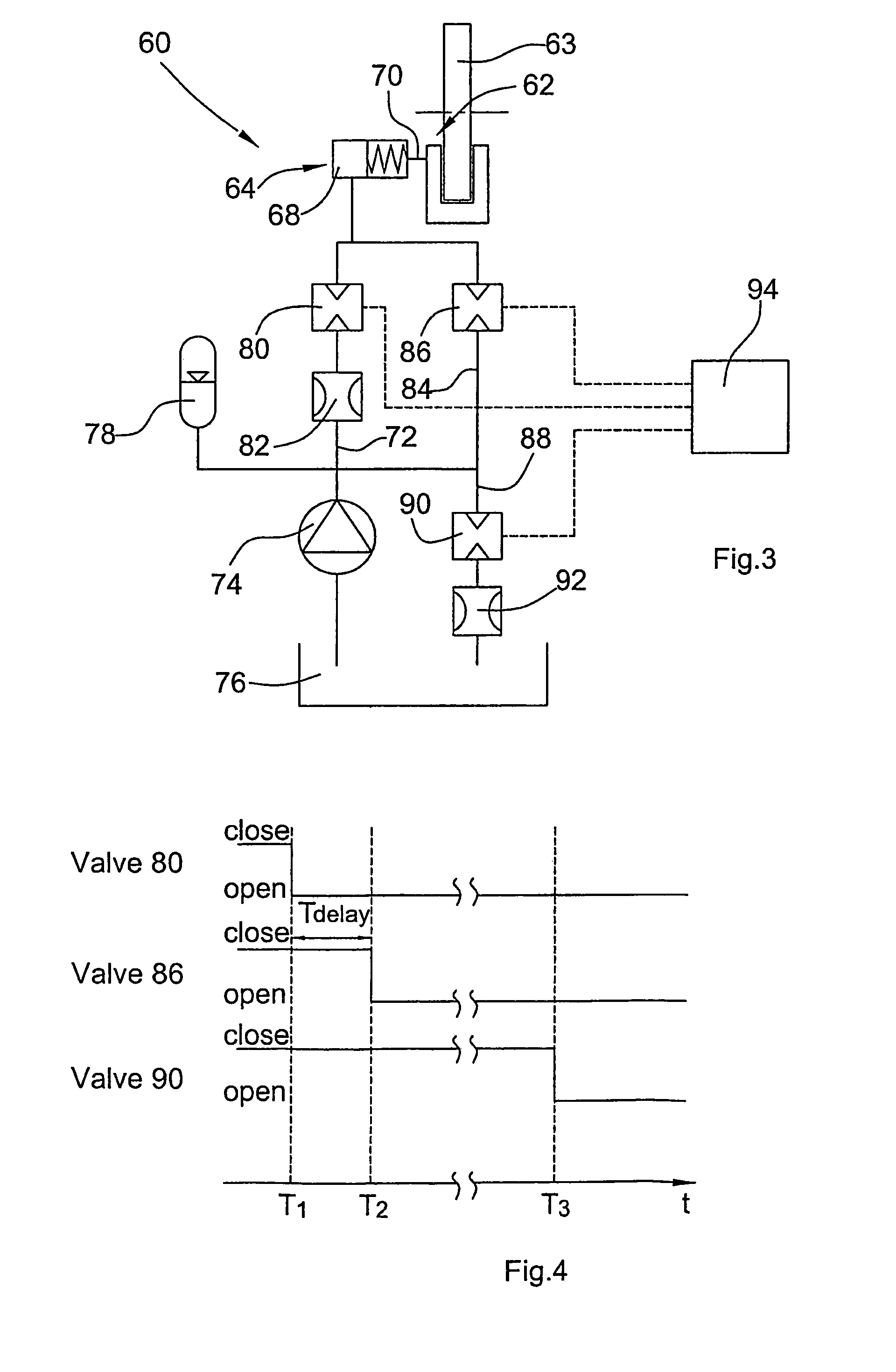
The hydraulic brake system comprises a piston / cylinder unit (14) for activating and releasing a brake (12), comprising a volume (16) adapted to have a pressurized working fluid supplied thereto for moving the piston (24) from a braking position into a release position for releasing the brake. Further, the hydraulic brake system comprises a supply line (18) for the supply of working fluid from a reservoir (22), a discharge line (30) for the discharge of working fluid from the volume (16) of the piston / cyliinder unit (14), a first valve (34) and an element (36) for determining the flow resistance, a bypass line (32) provided with a second ON / OFF valve (38) and arranged for a flow in parallel to the discharge line (30). At the start of a braking process, among the two ON / OFF valves (34,38) which in the released condition of the brake are in the closed condition, the first ON / OFF valve (34) is opened and, upon lapse of a presettable first time period (Tdelay1) from the opening of the first ON / OFF valve (34), the second ON / OFF valve (38) is opened.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com