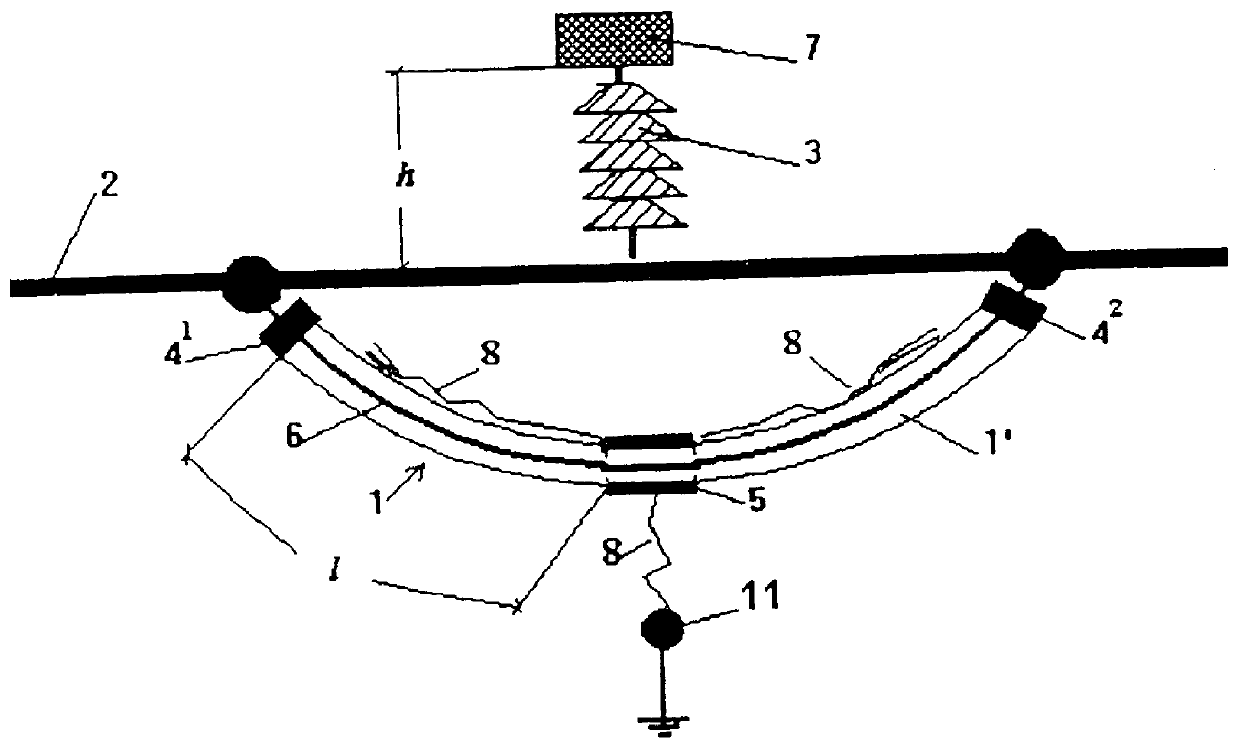
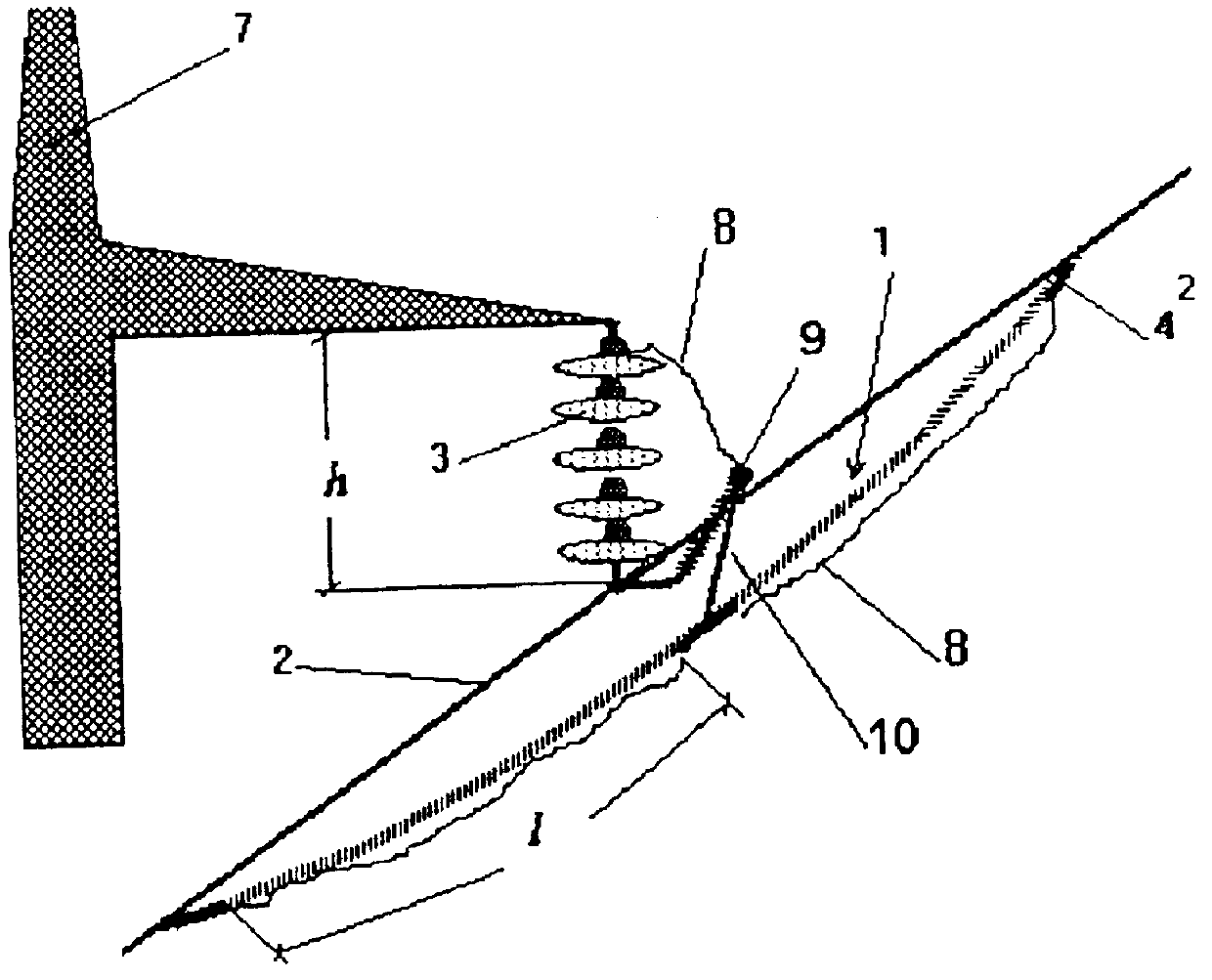
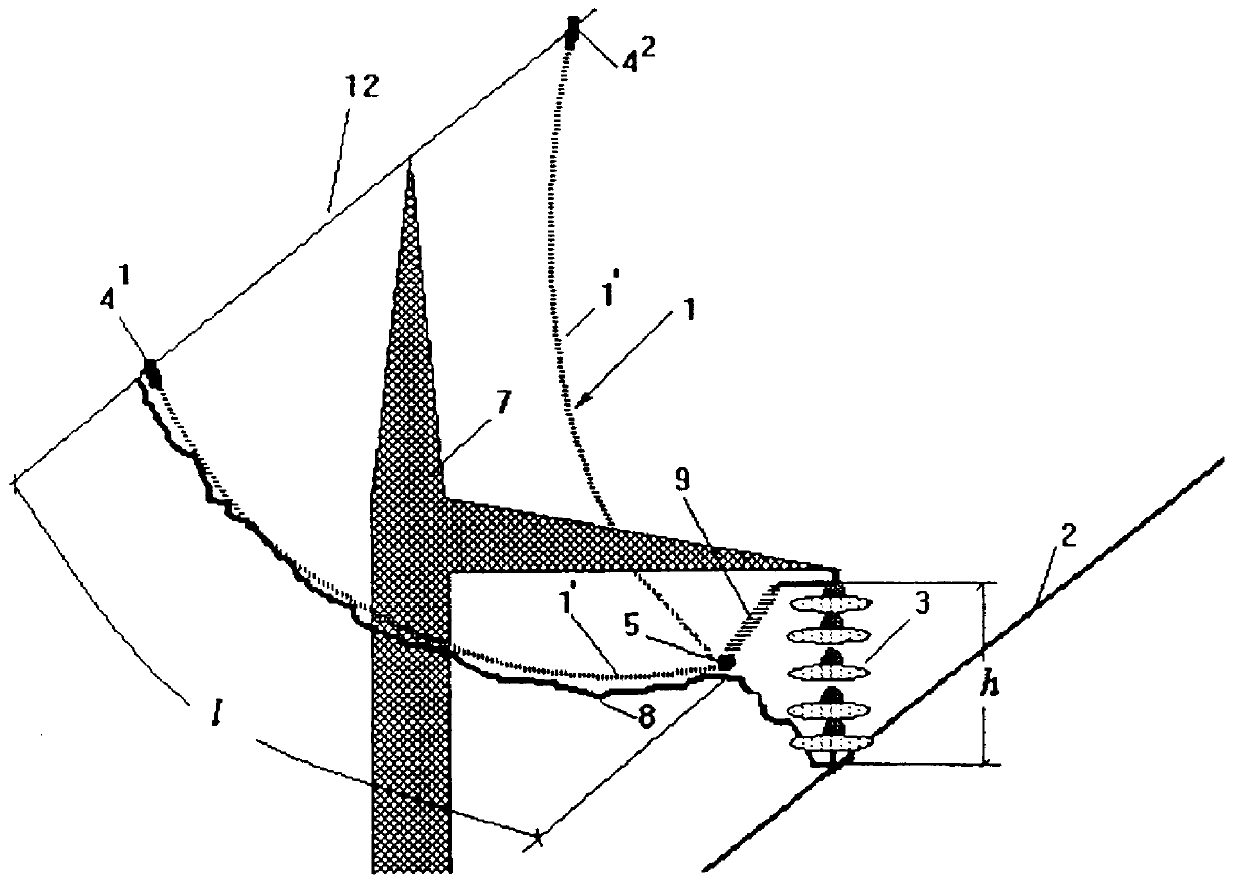
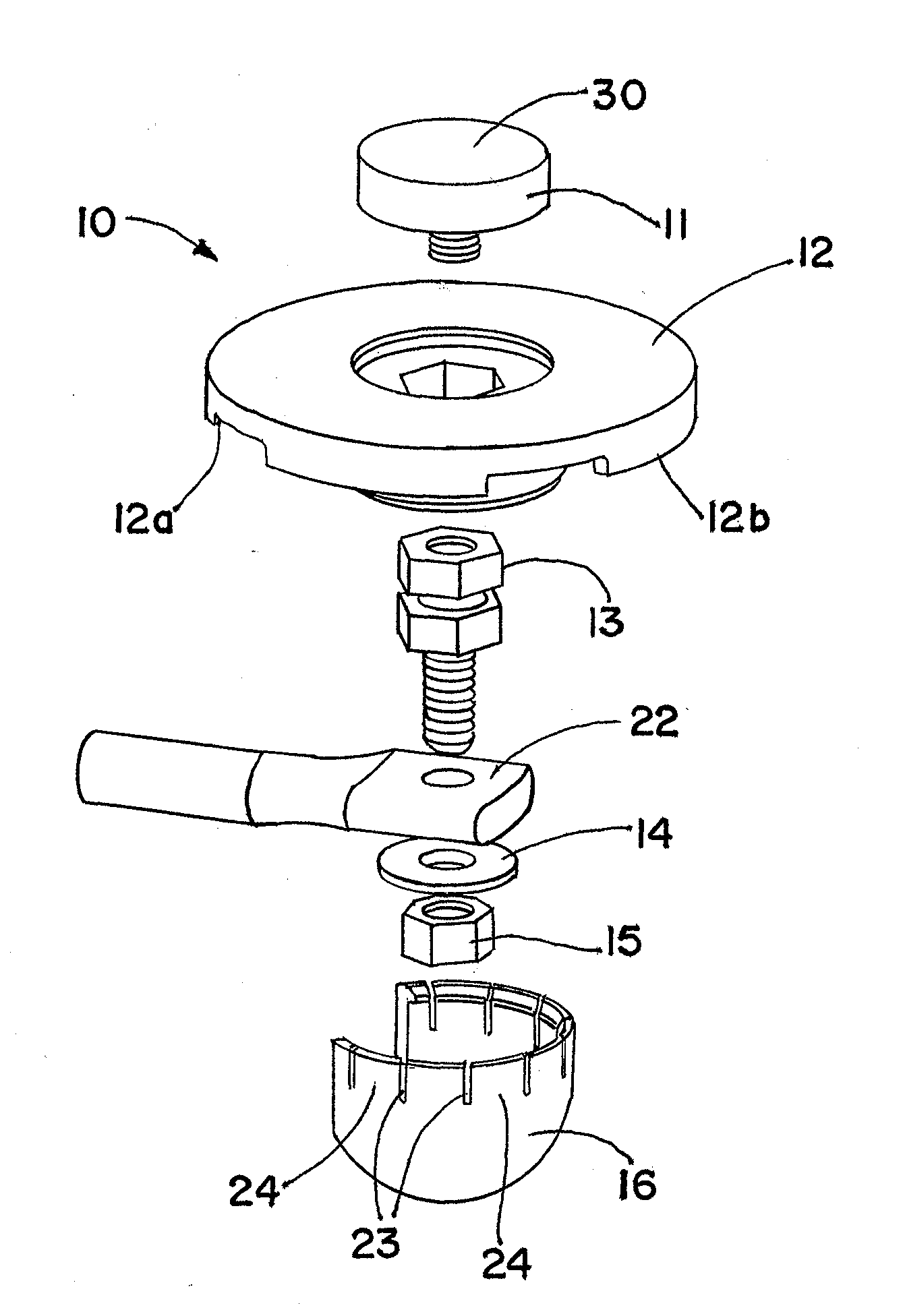
Patents
Literature
370results about "Connection to earth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
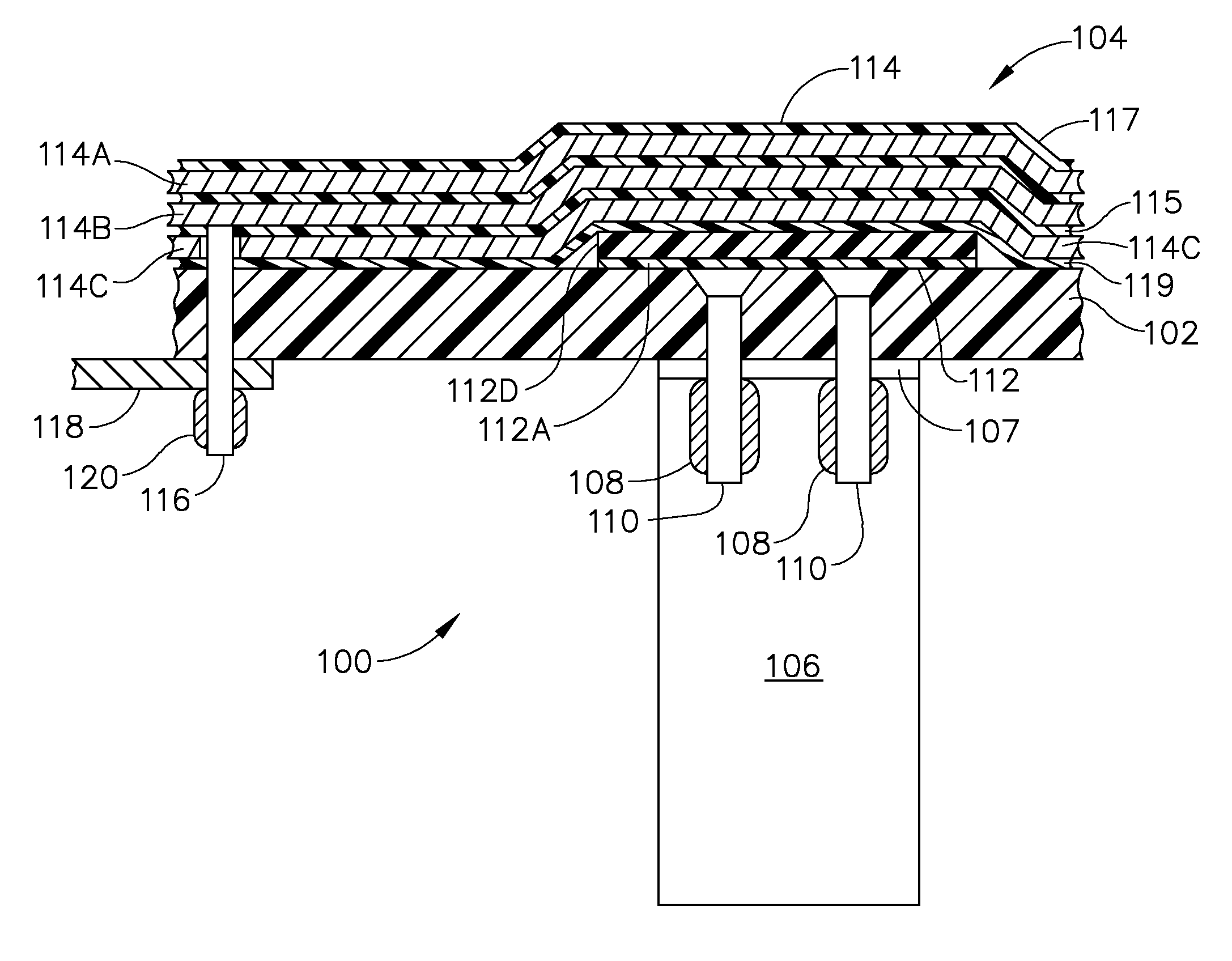
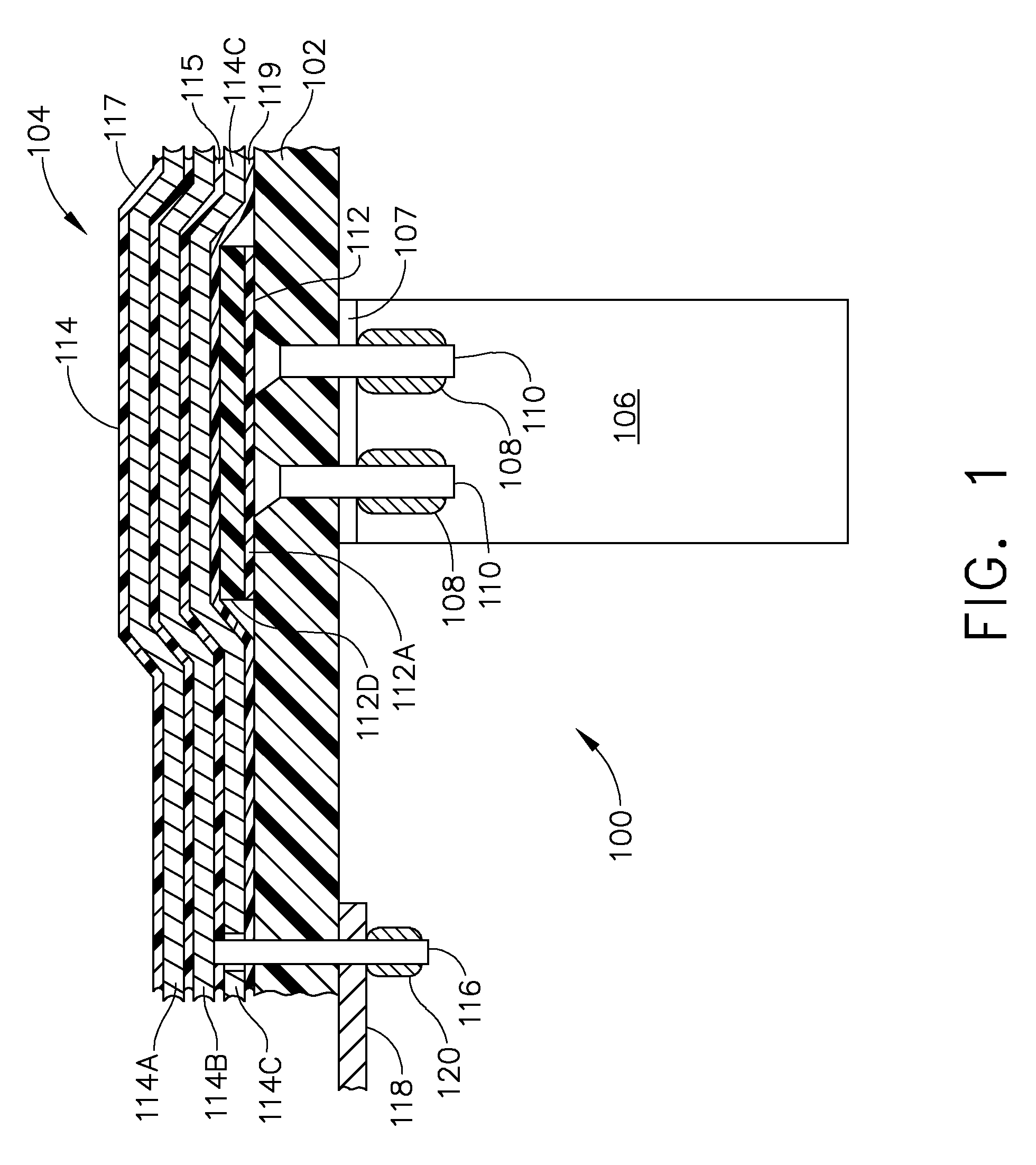
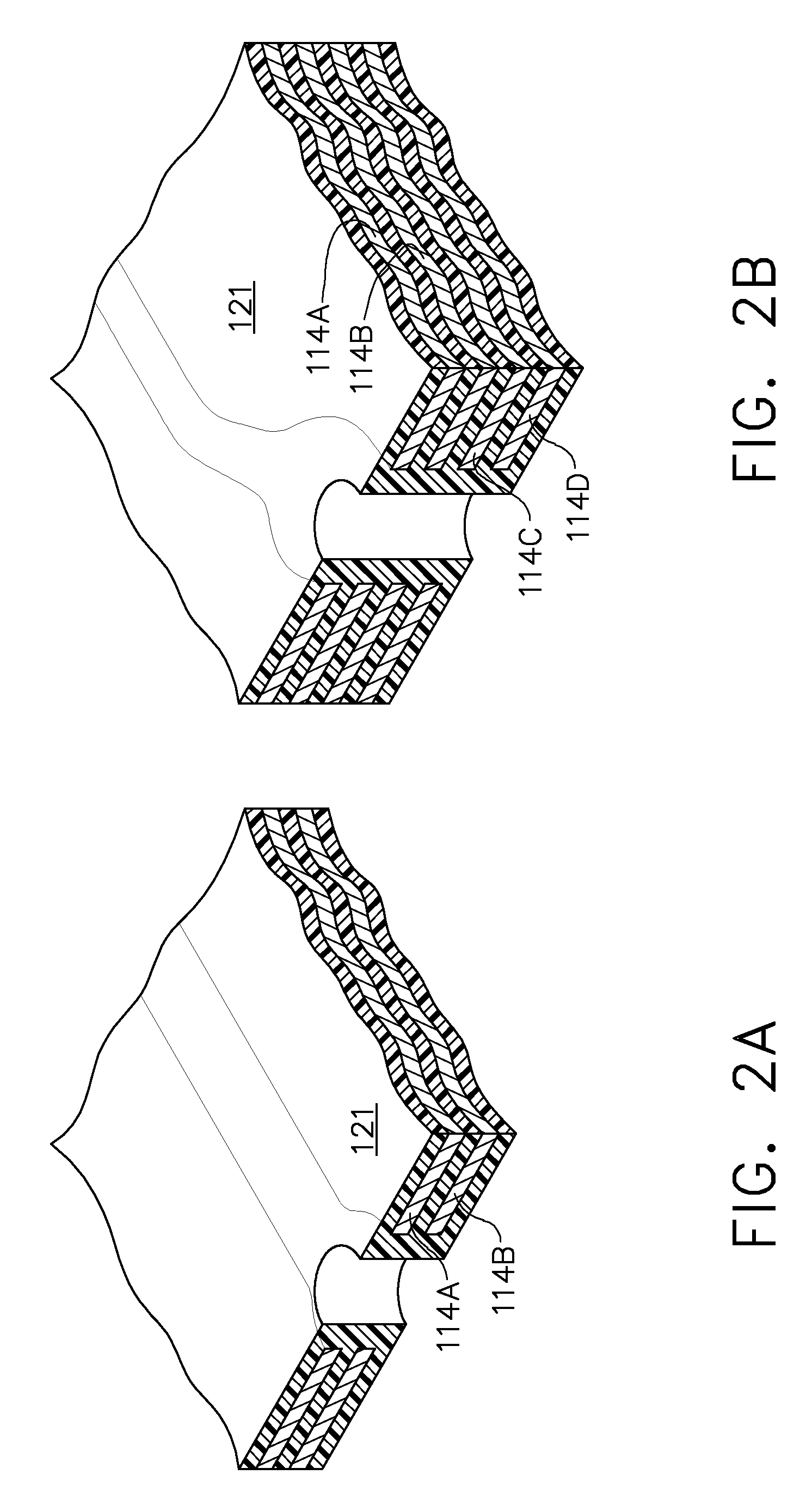
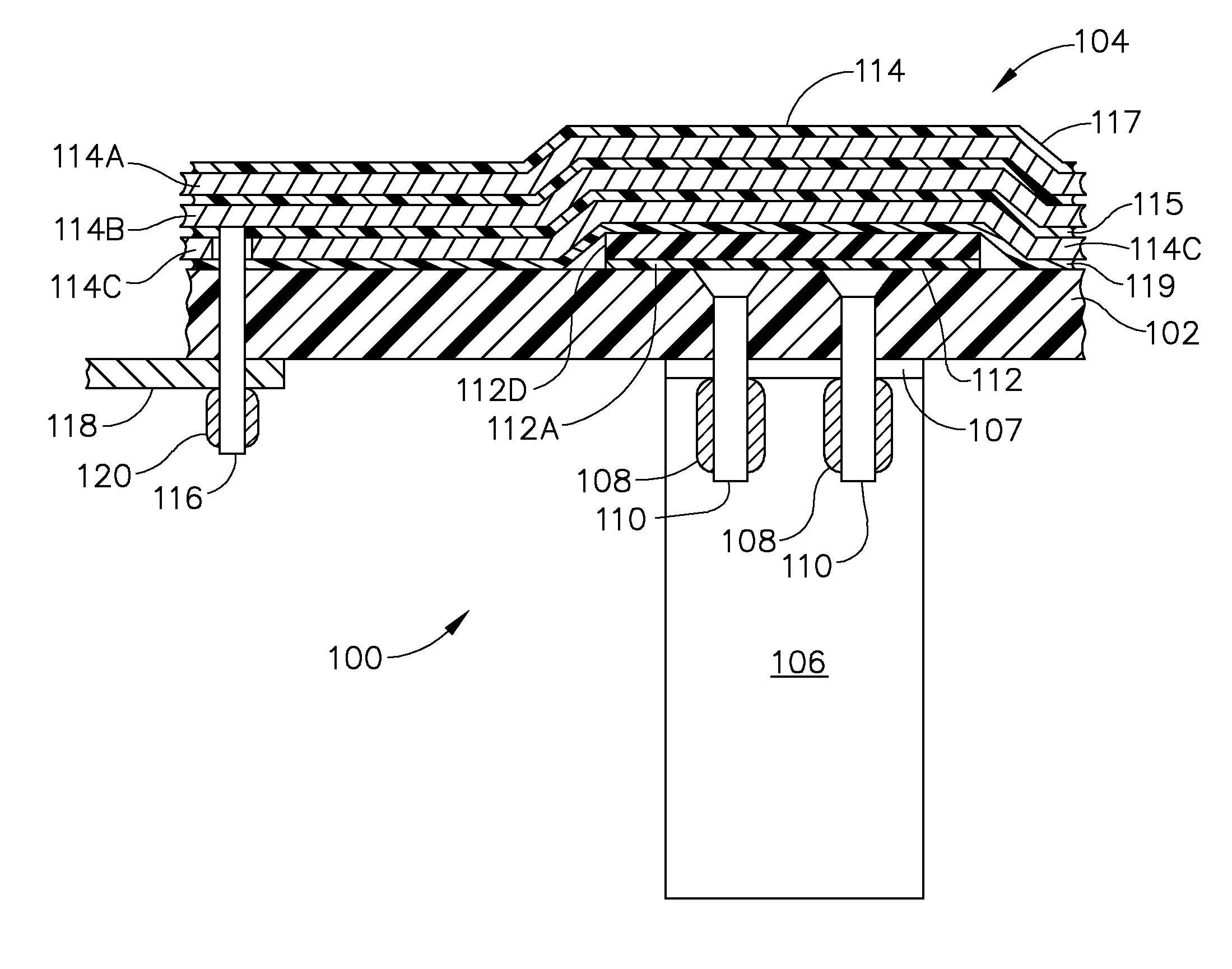
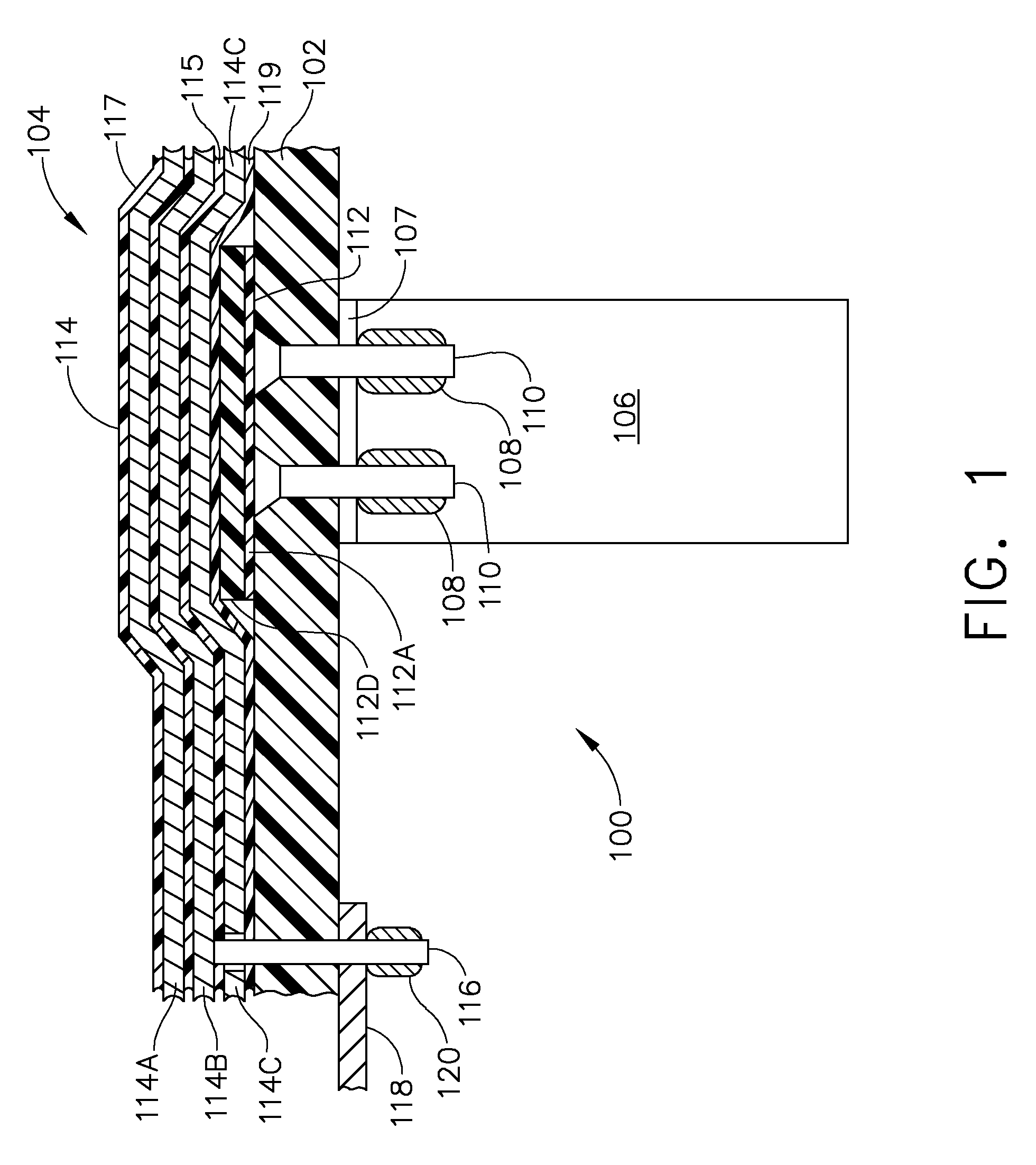
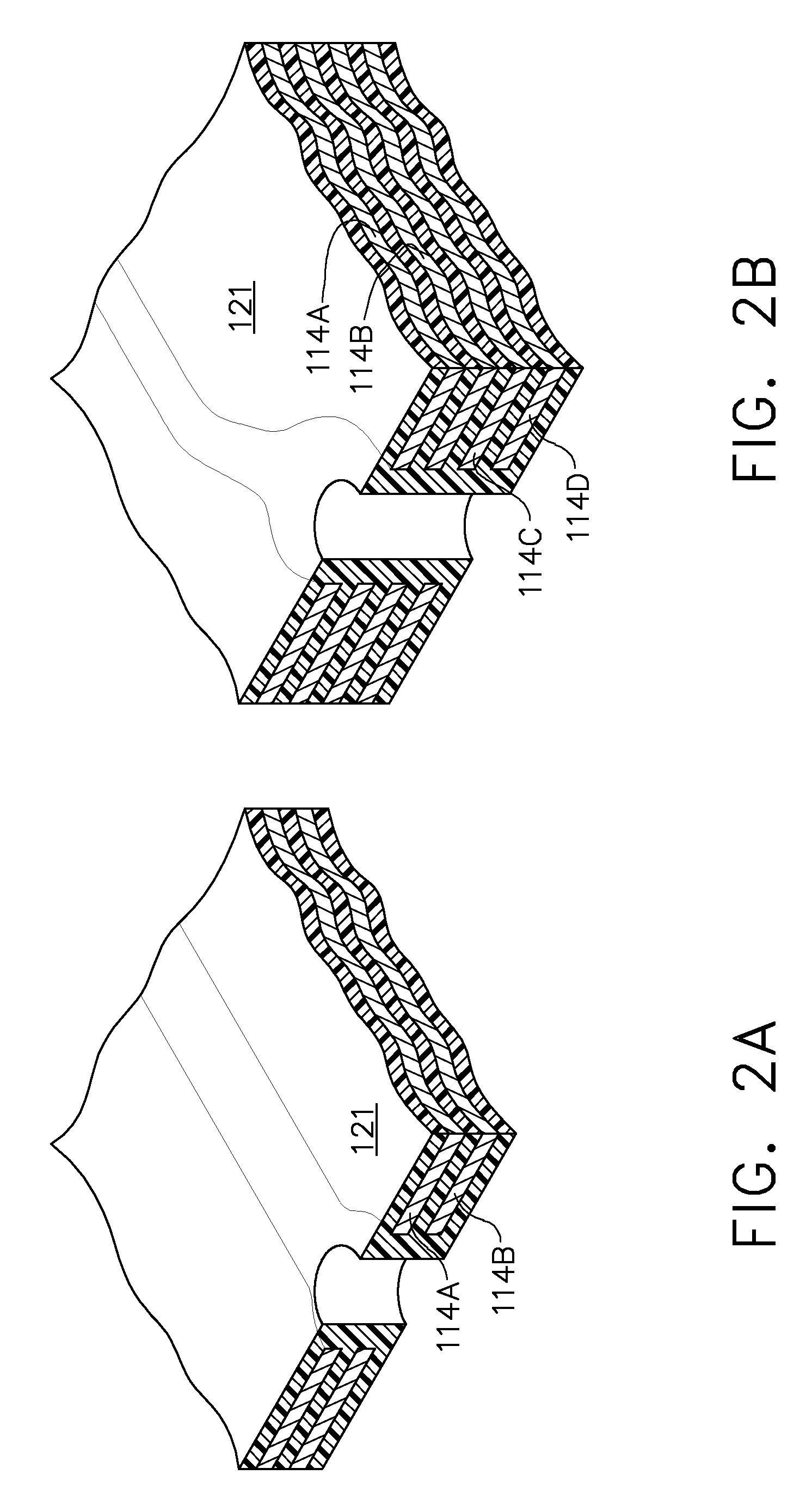
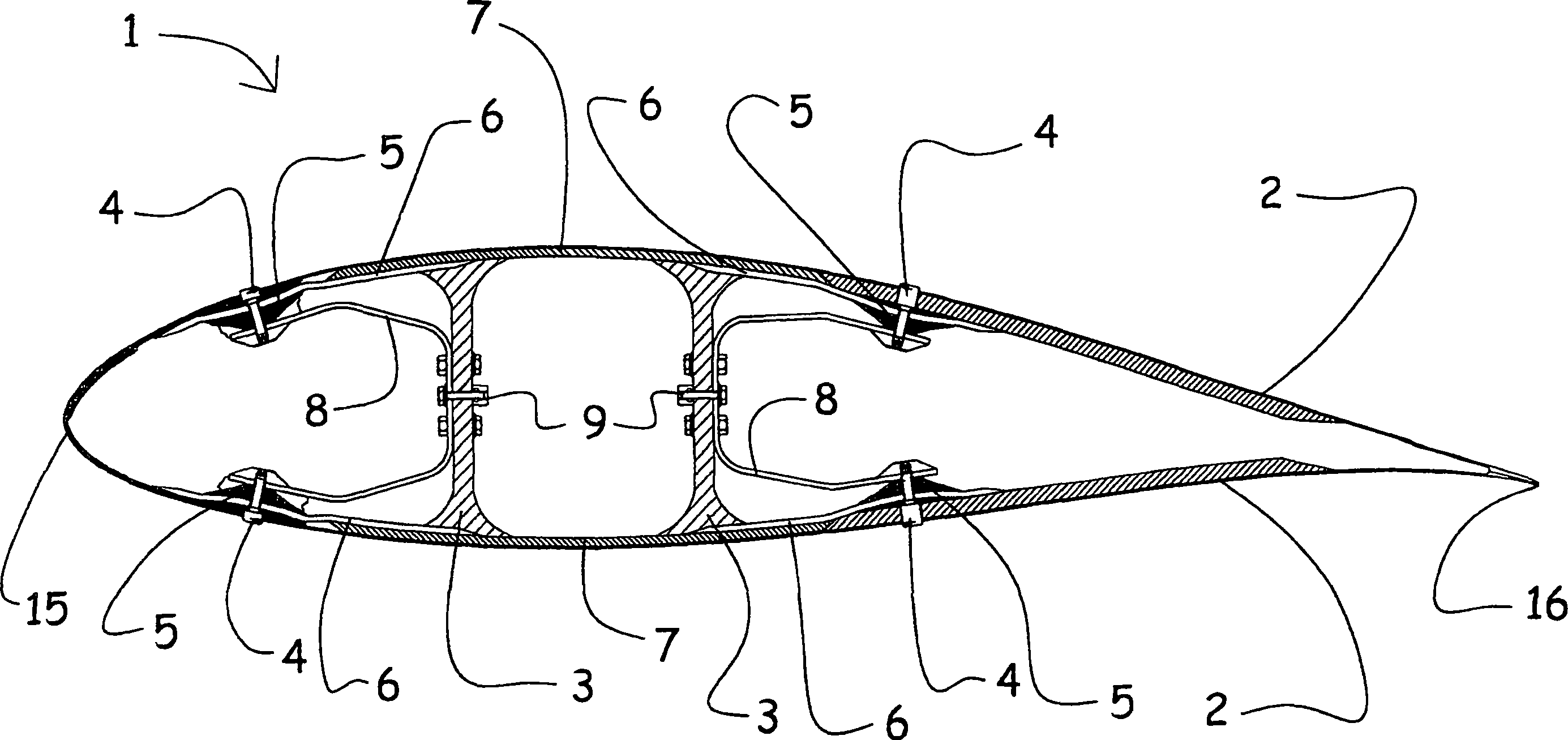
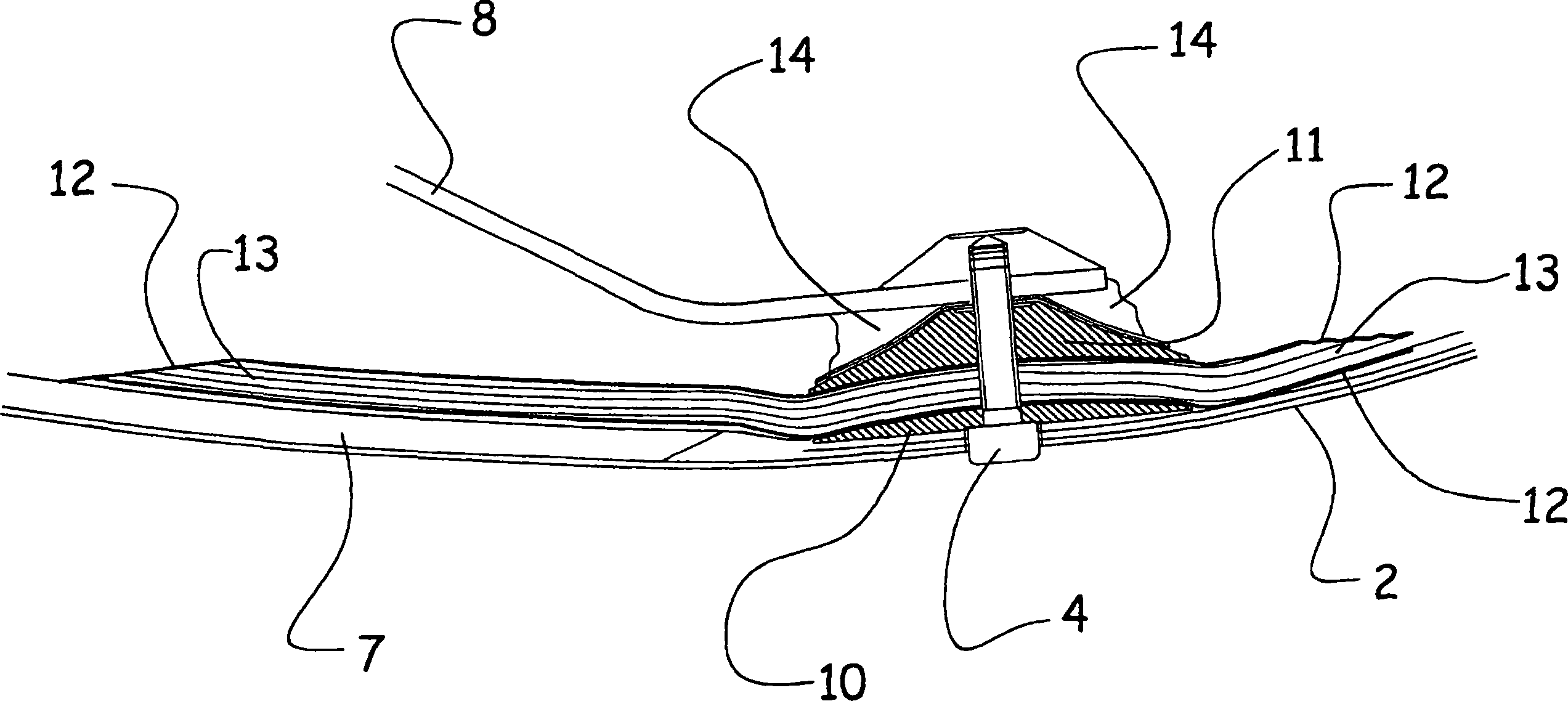
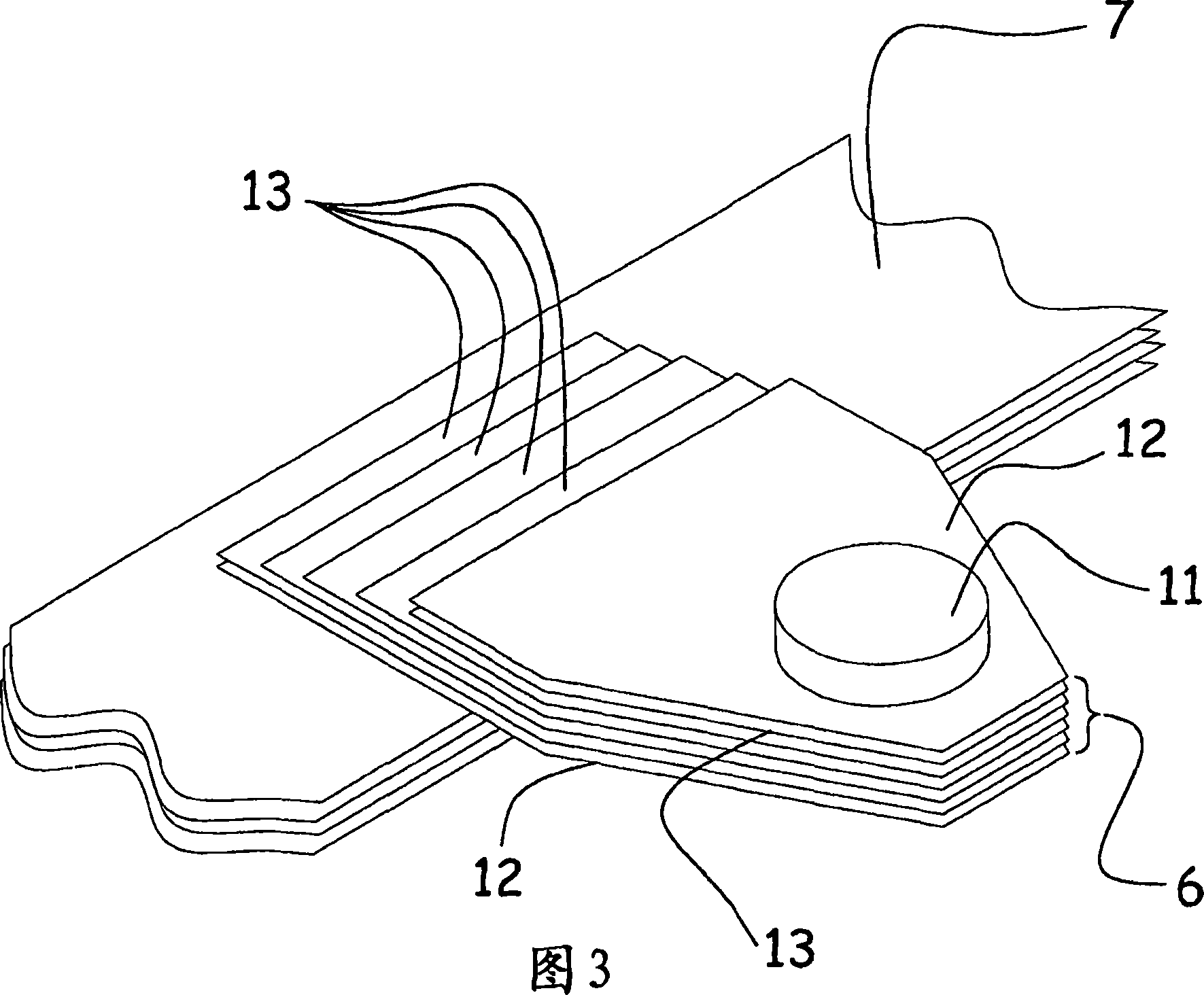
Flex circuit lightning protection applique system for skin fasteners in composite structures
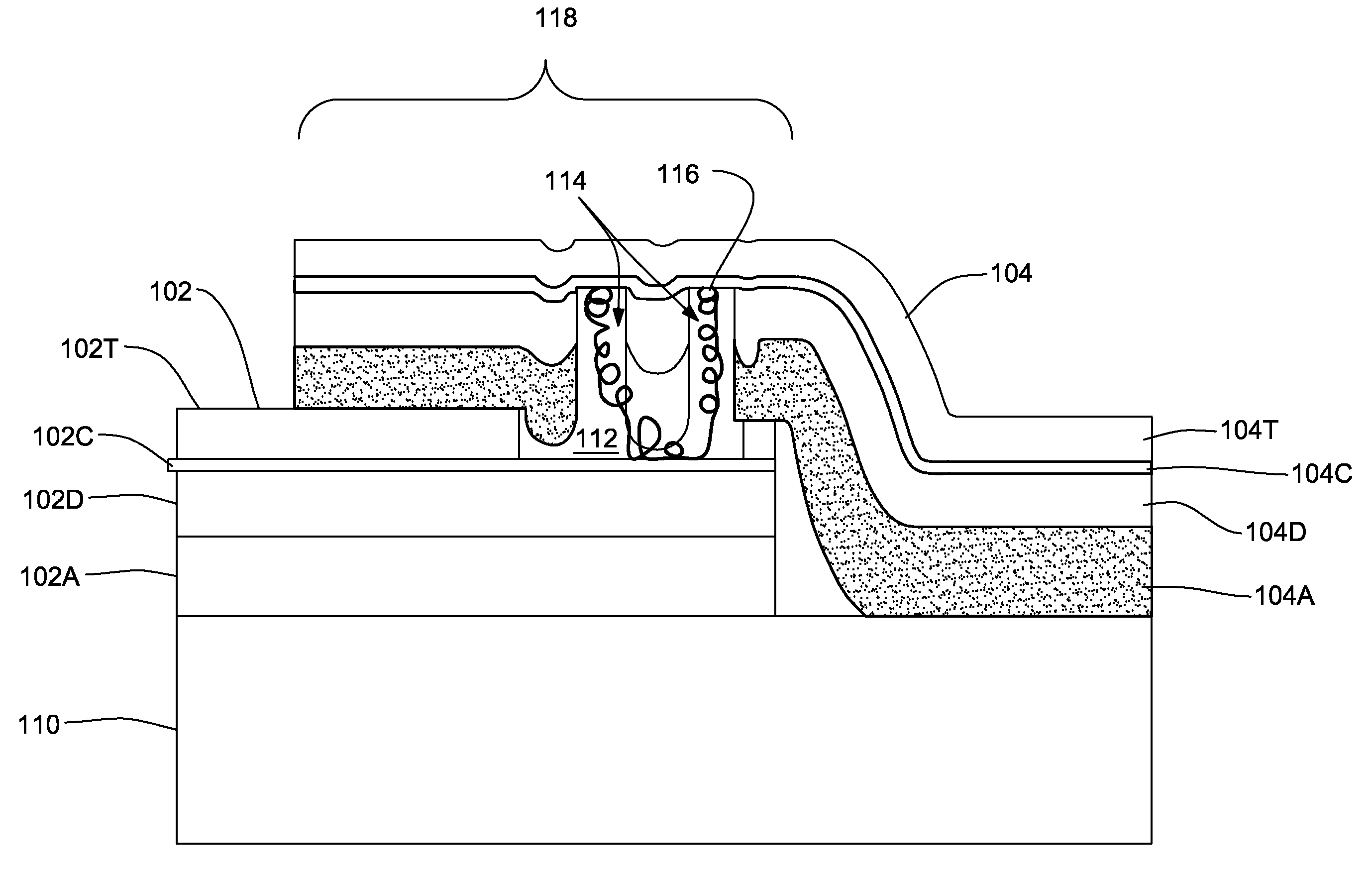
A lightning protection appliqué incorporates a plurality of conductive plies adhesively affixed to a composite surface, at least a first one of the plies providing conductive characteristics sufficient to divert electrical energy from a lightning strike and at least a second one of the plies comprising operational circuitry. A dielectric ply is fixed to the composite surface over and completely covering at least one metal surface feature between the plurality of conductive plies and the composite surface.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
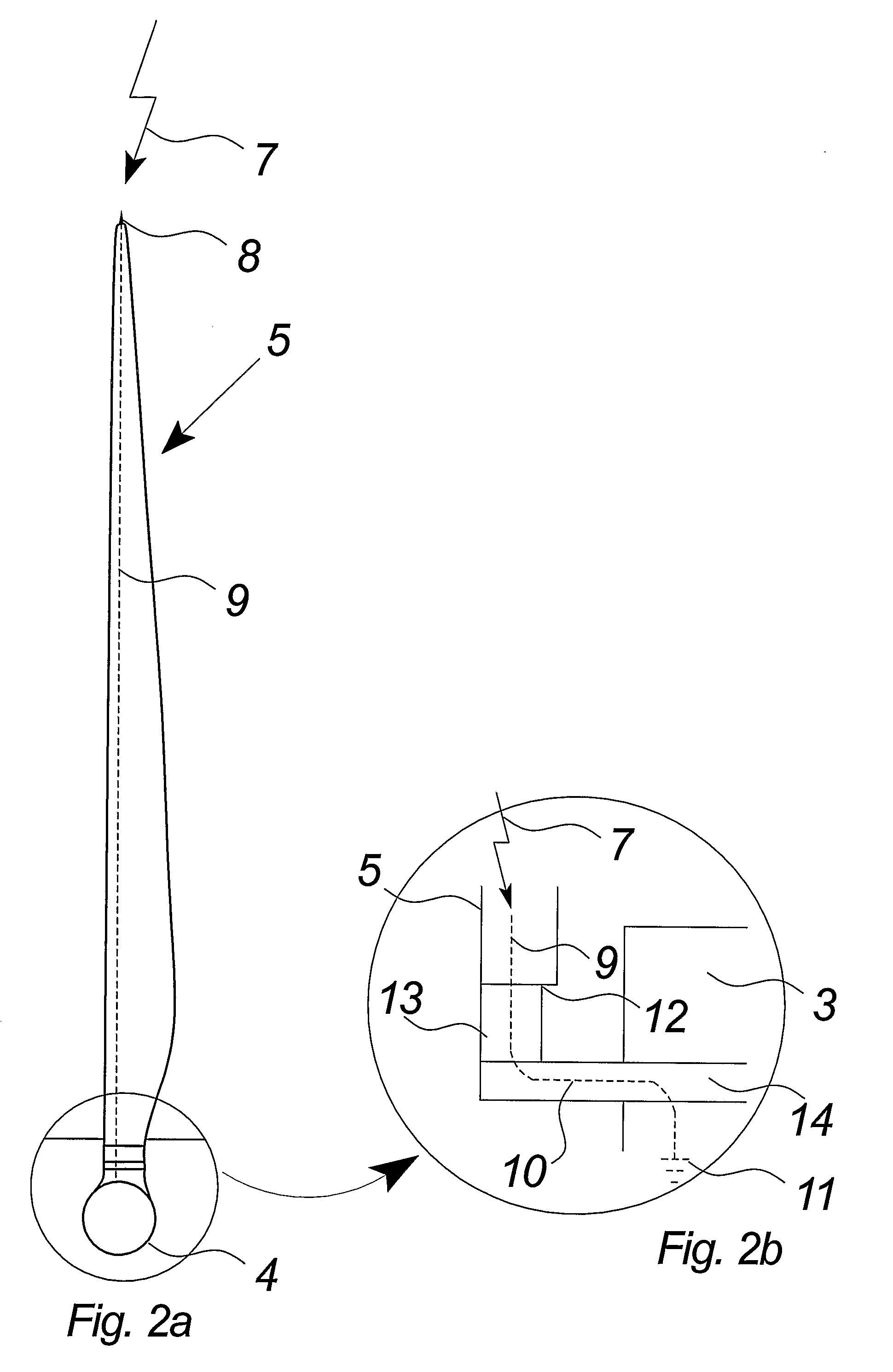
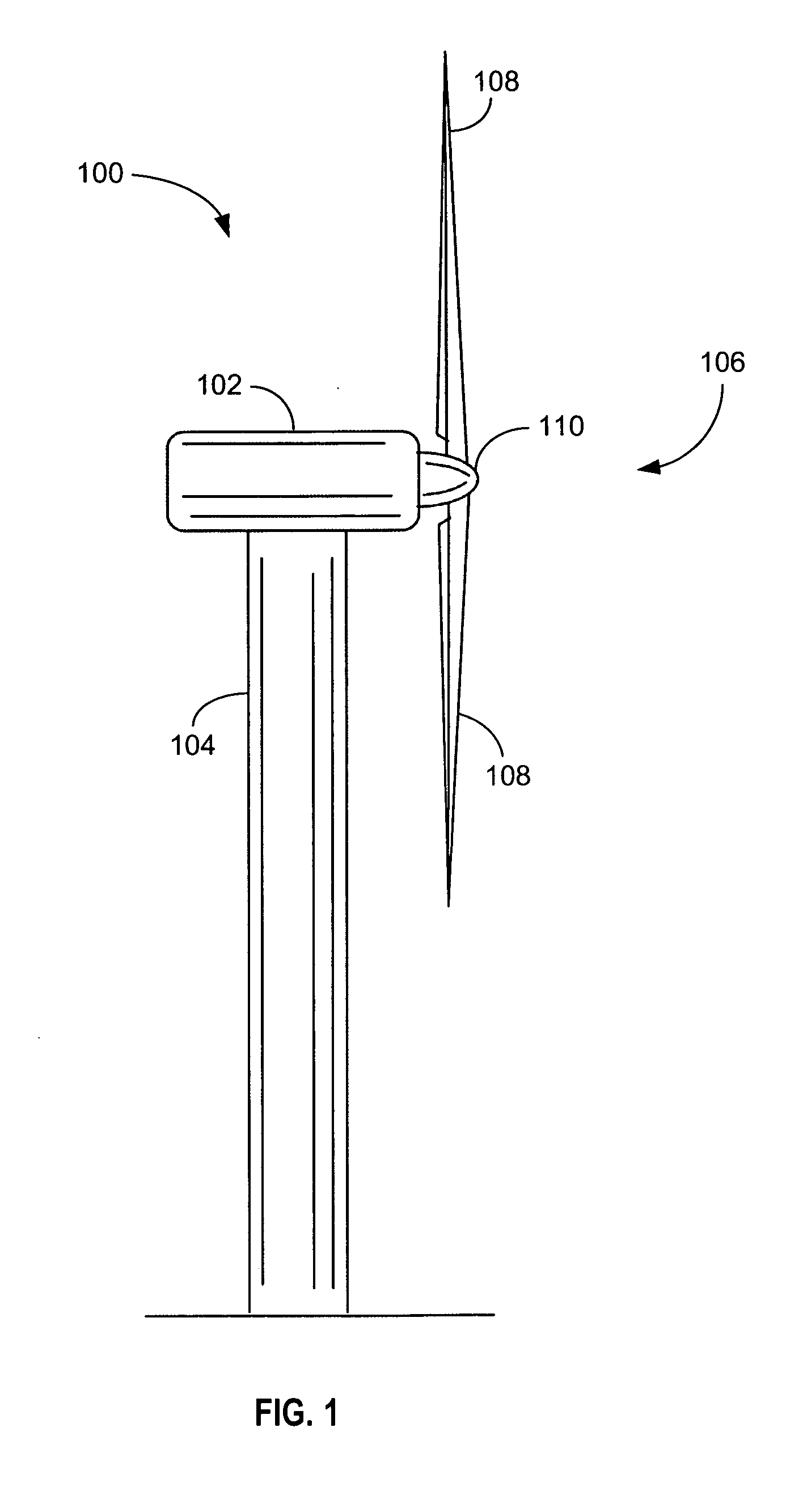
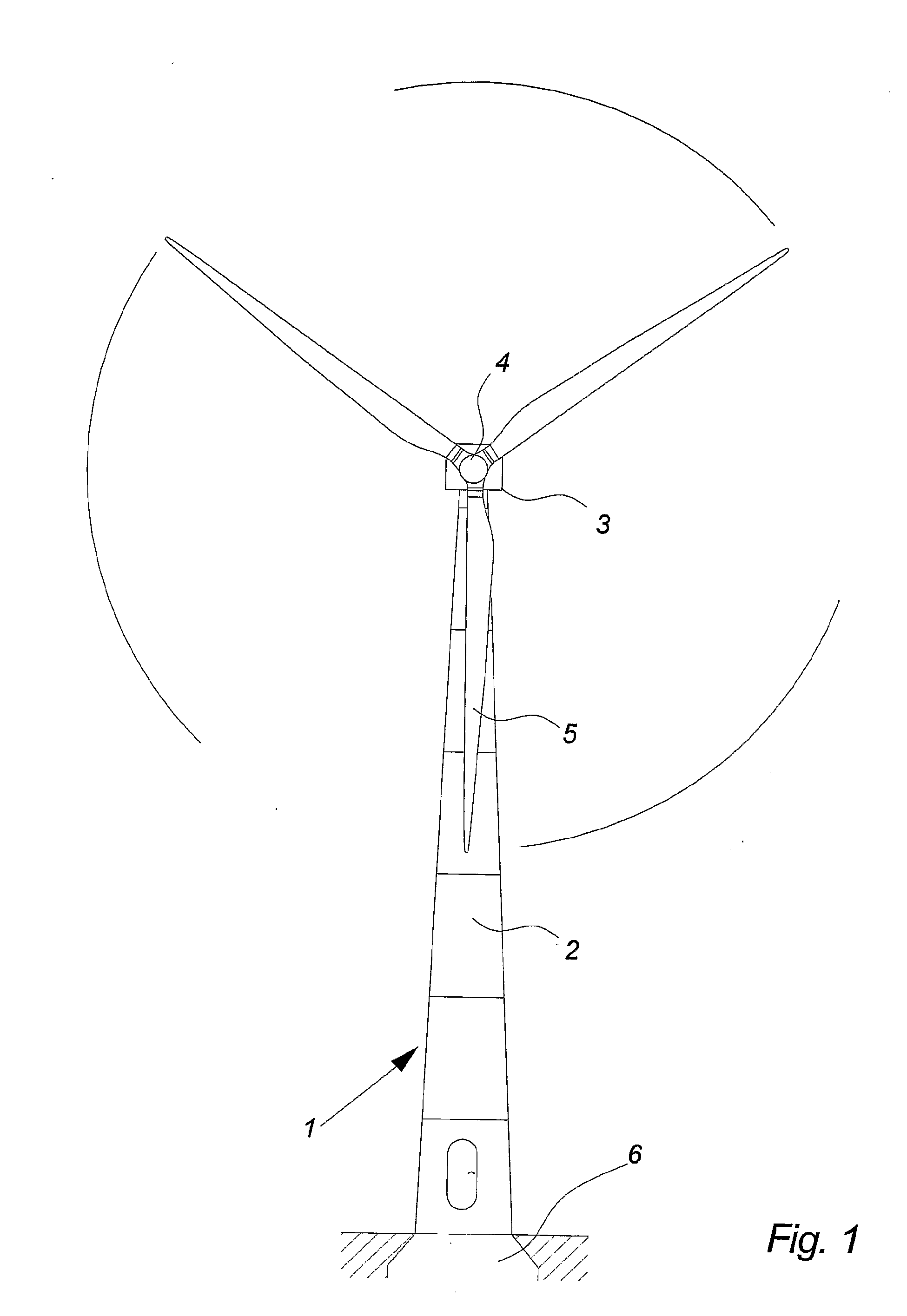
Wind power installation
The invention concerns a wind power installation. Such wind power installations of modern type, for example one of type E-40 or E-66 from Enercon are usually equipped with a lightning protection system which is known for example from DE 44 36 197.The present invention assists to minimise the number of interference with the electronic system by virtue of the flash-over effects at the spark path. A wind power installation comprising an arrangement for continuously discharging electrostatic charging of at least one rotor blade of a wind power installation.
Owner:WOBBEN ALOYS
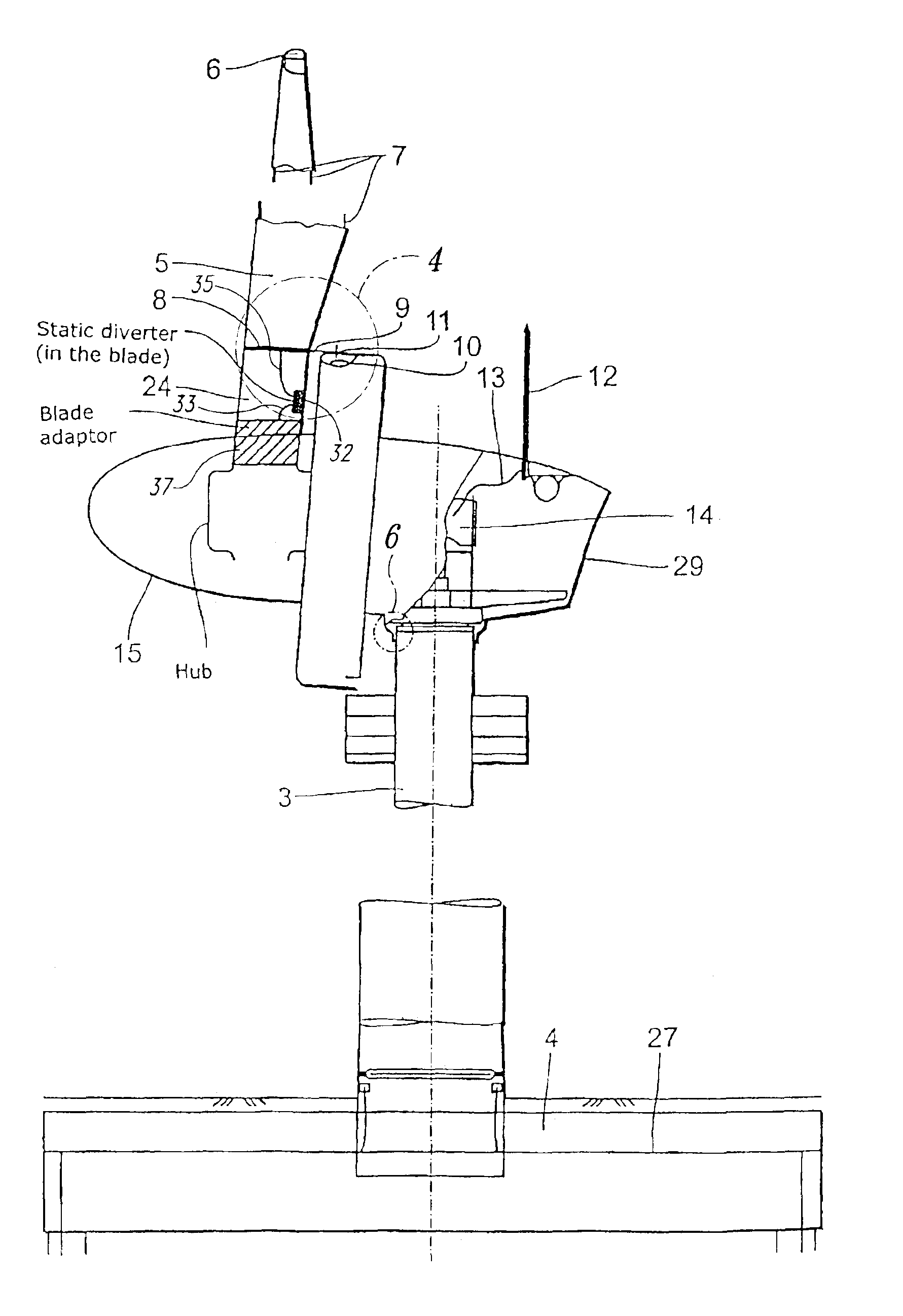
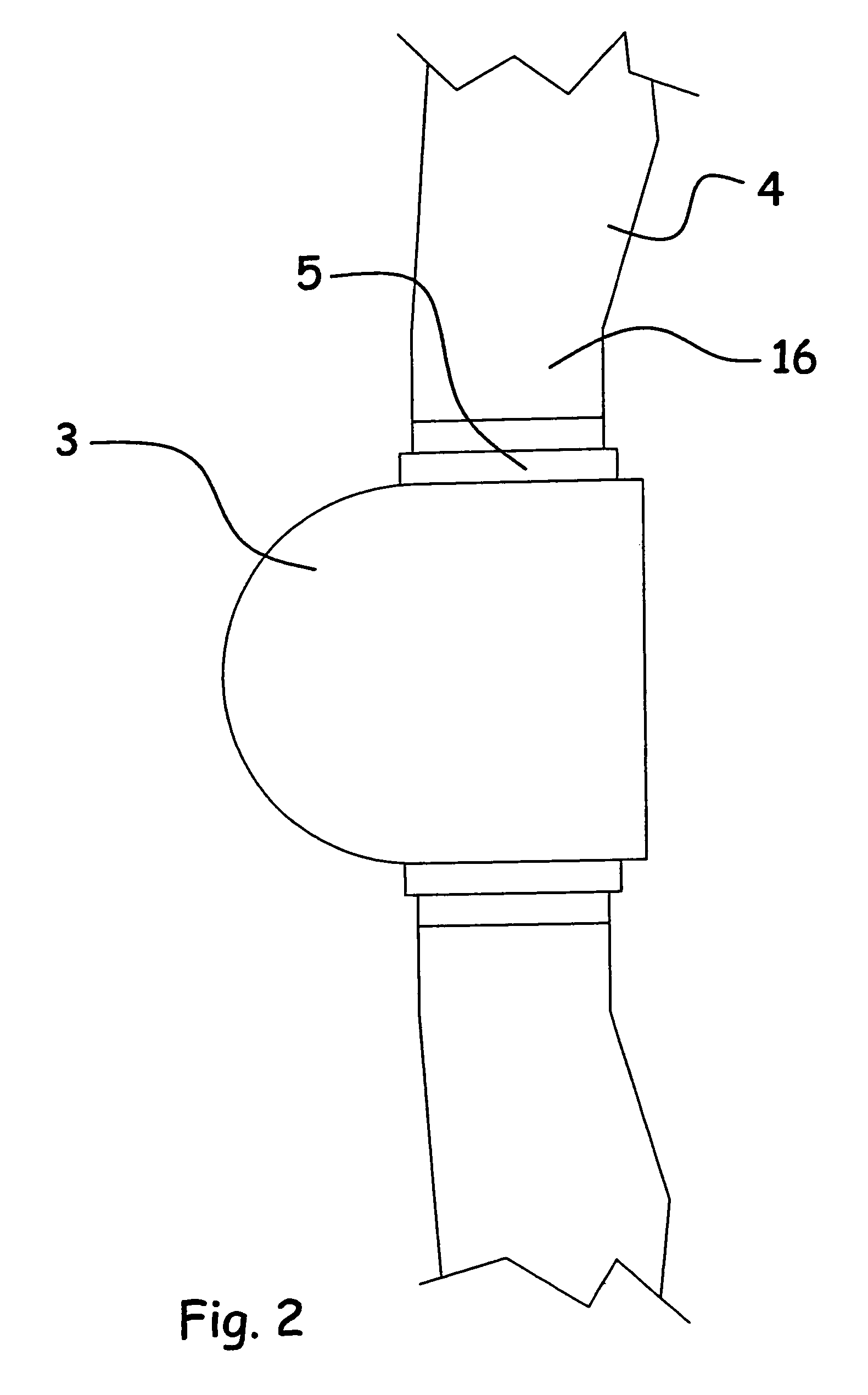
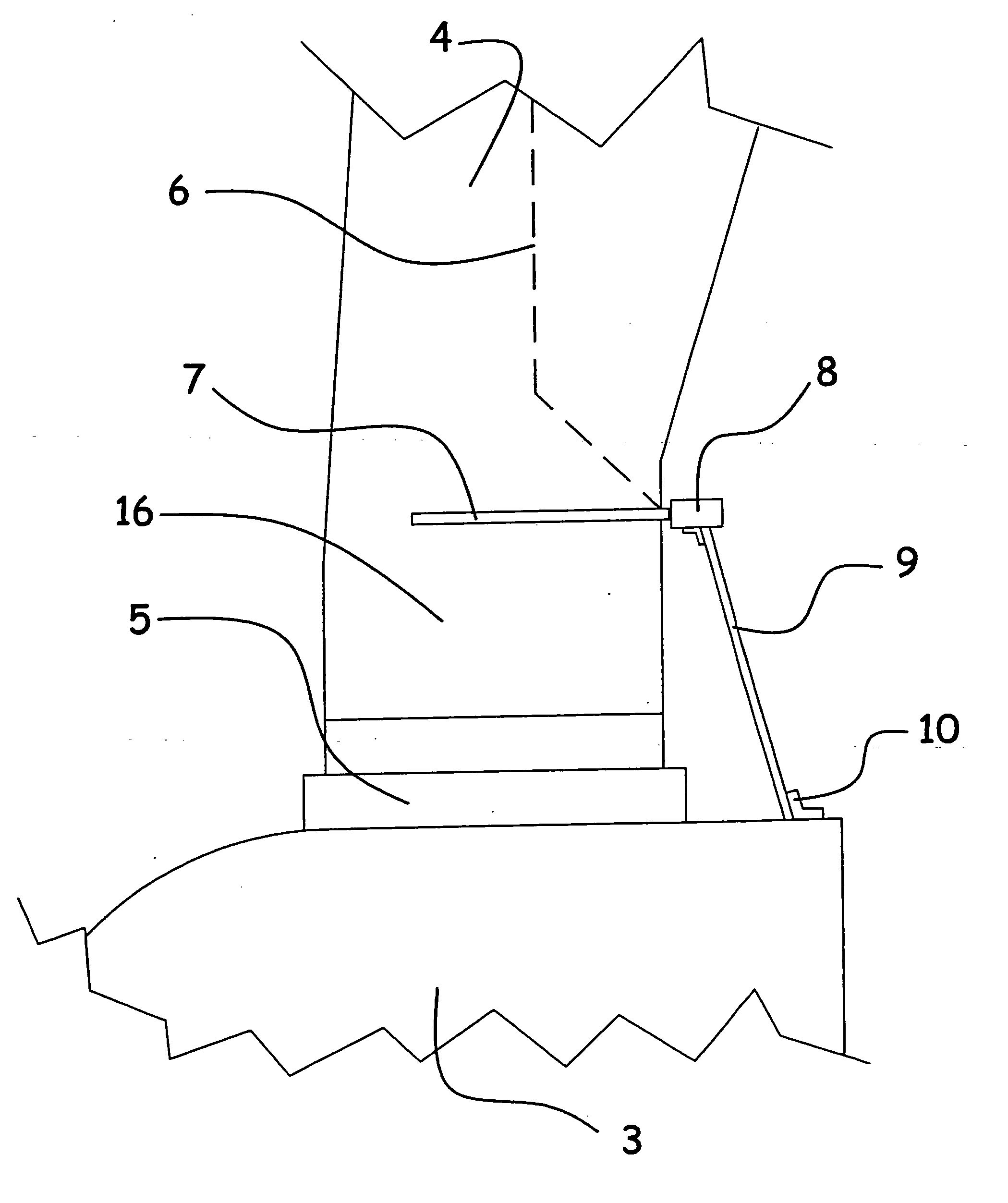
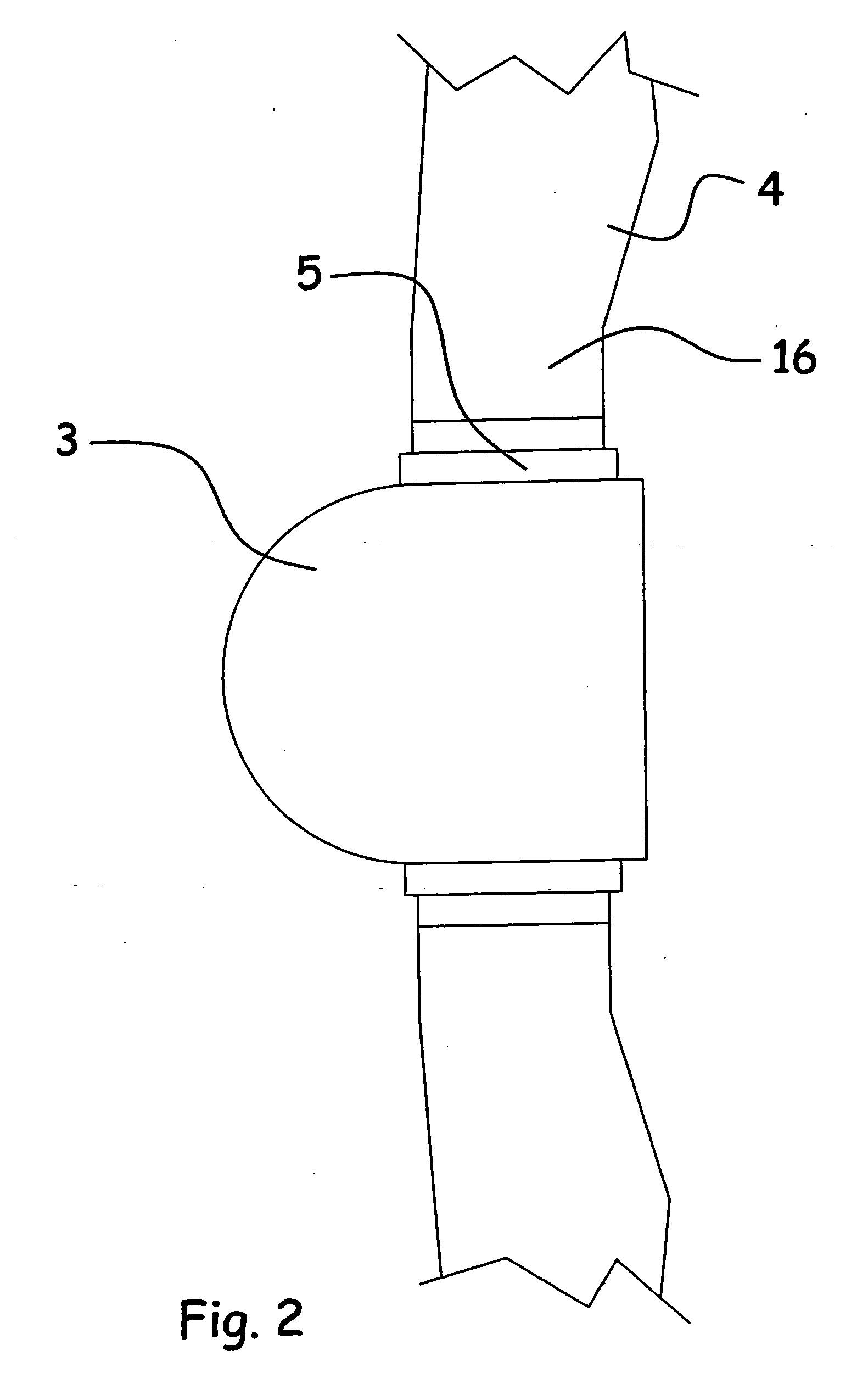
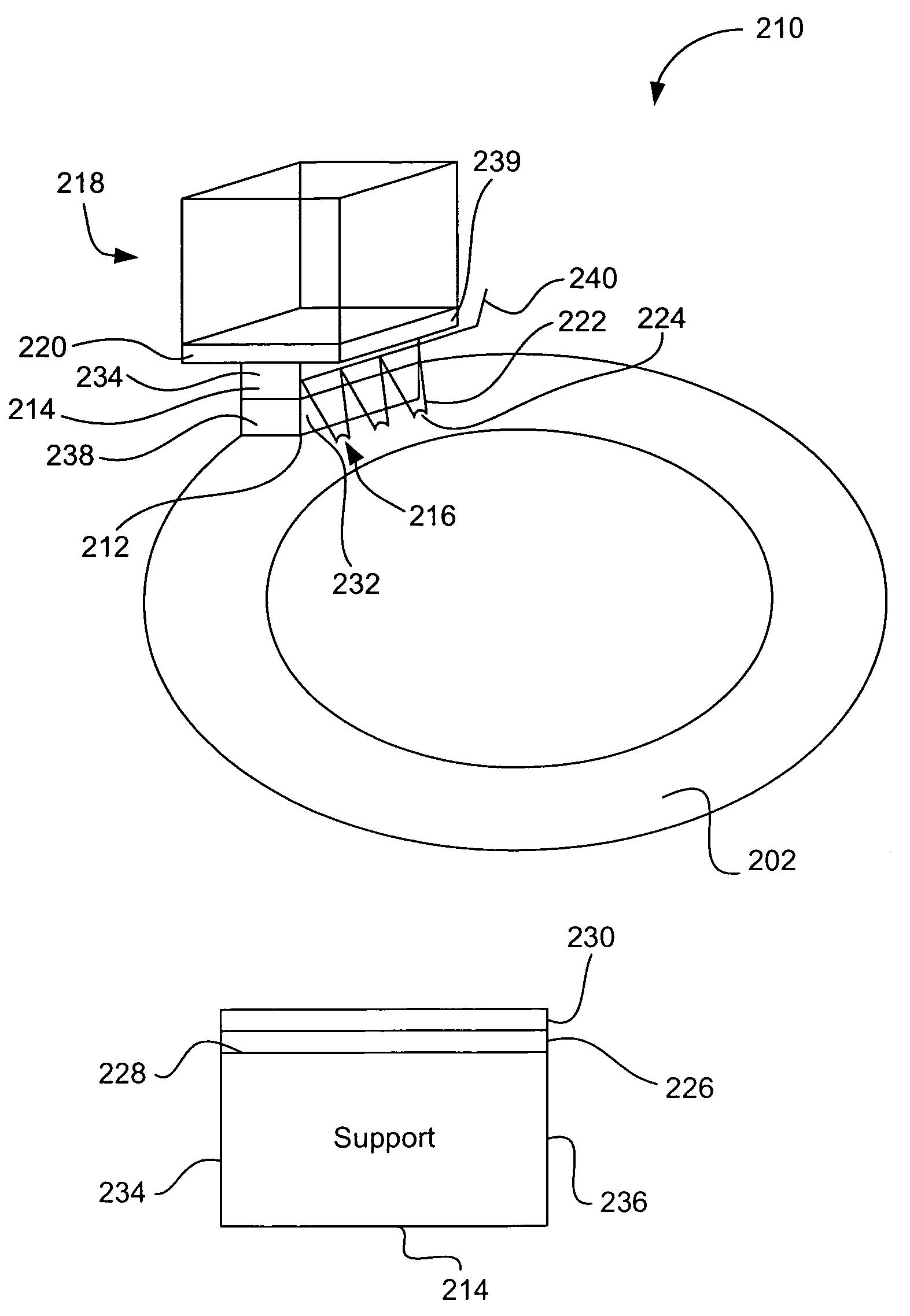
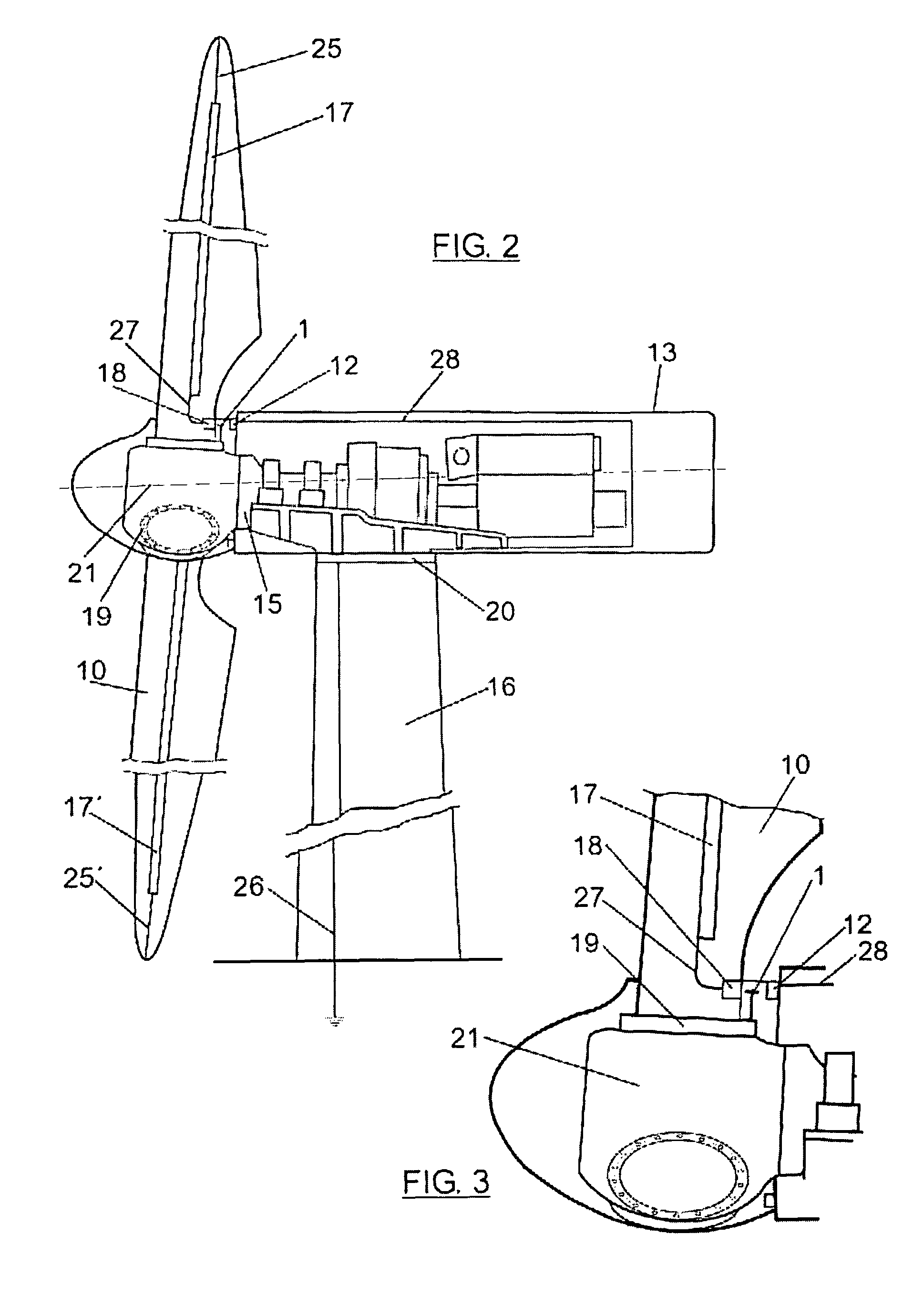
Lightning protection of a pitch-controlled wind turbine blade
ActiveUS7390169B2Current protectionReduce resistancePropellersPump componentsTurbine bladeBlade pitch
A wind turbine rotor including a rotor hub (3) and a plurality of blades (4), and where each blade root (16) is connected to said rotor hub through a pitch bearing (5) in such a manner that the pitch angle of the blade is adjustable by a turning of the blade about its longitudinal axis relative to the rotor hub. The blade is provided with at least one electrically conducting lightening down-conductor (6) extending in the longitudinal direction of the blade to the blade root and being electrically isolated from the pitch bearing (5). A spark gap (15) is provided between the lightning down-conductor and the rotor hub, said spark gap (15) being adapted to conduct a lightning current passing through the lightning down-conductor. A sliding contact connection (7, 12) is provided parallel to the spark gap (15) between the lightning down-conductor (6) and the rotor hub (3), said sliding contact connection ensuring electrical contact between said lightening down-conductor (6) and said rotor hub (3) irrespective of the pitch angle of the blade. The invention also relates to a wind turbine including such a rotor.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
Lightning protection of a pitch-controlied wind turbine blade
A wind turbine rotor including a rotor hub (3) and a plurality of blades (4), and where each blade root (16) is connected to said rotor hub through a pitch bearing (5) in such a manner that the pitch angle of the blade is adjustable by a turning of the blade about its longitudinal axis relative to the rotor hub. The blade is provided with at least one electrically conducting lightening down-conductor (6) extending in the longitudinal direction of the blade to the blade root and being electrically isolated from the pitch bearing (5). A spark gap (15) is provided between the lightning down-conductor and the rotor hub, said spark gap (15) being adapted to conduct a lightning current passing through the lightning down-conductor. A sliding contact connection (7, 12) is provided parallel to the spark gap (15) between the lightning down-conductor (6) and the rotor hub (3), said sliding contact connection ensuring electrical contact between said lightening down-conductor (6) and said rotor hub (3) irrespective of the pitch angle of the blade. The invention also relates to a wind turbine including such a rotor.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
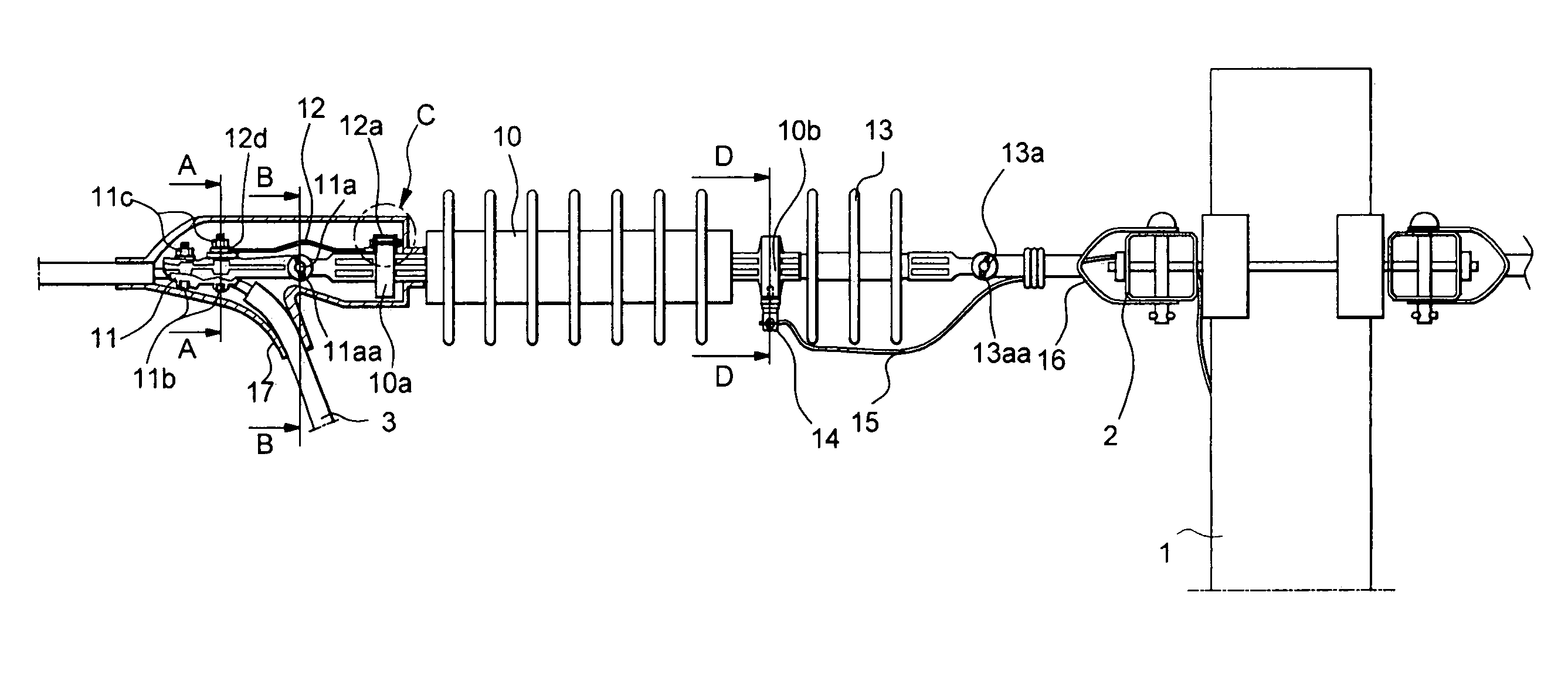
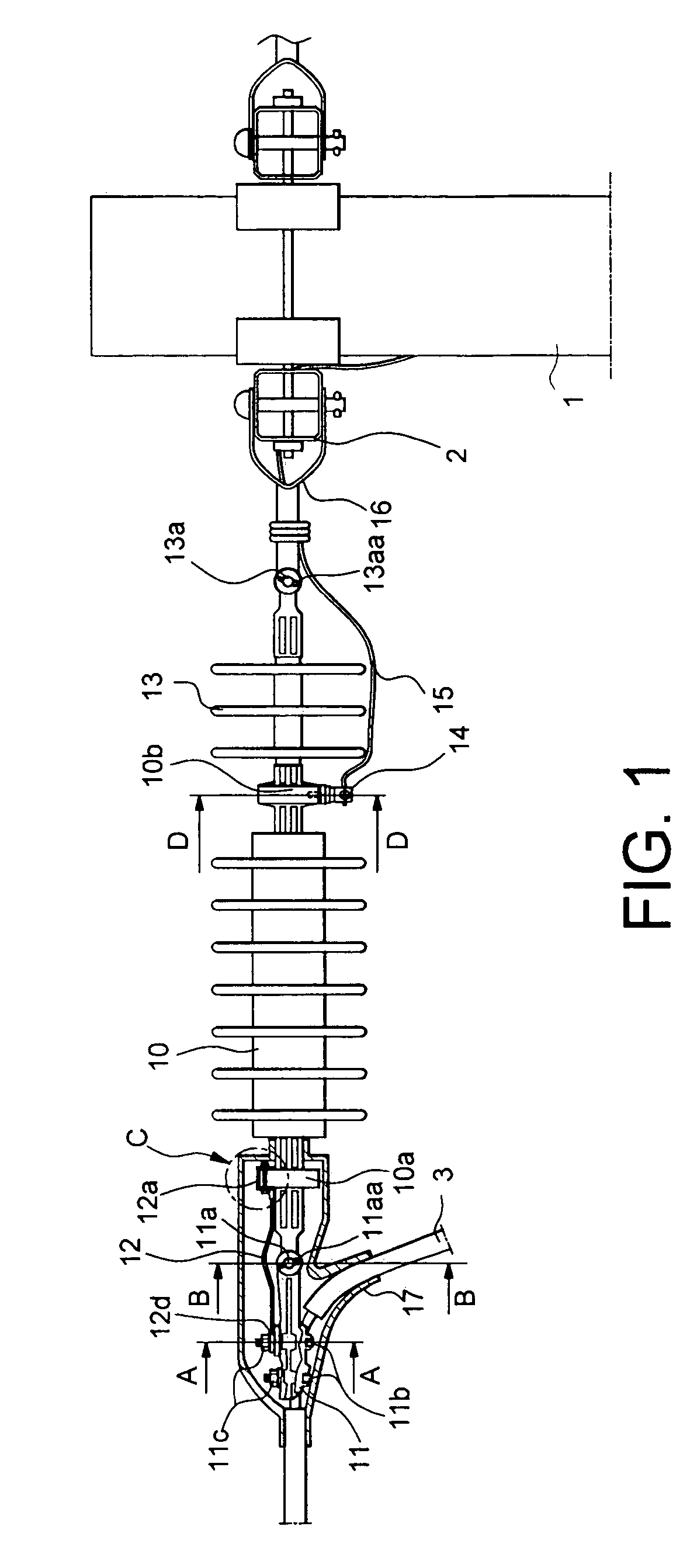
Electric power transmission line with protection devices against lightning overvoltages
InactiveUS6108187AImprove reliabilitySimplify the impulse lightning arresterOverhead installationEmergency protective arrangement detailsElectric power transmissionS function
PCT No. PCT / RU96 / 00251 Sec. 371 Date May 18, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date May 18, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 5, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 19456 PCT Pub. Date May 29, 1997An electric power transmission line with protection devices against lightening overvoltages in the form of a lighting arrester with a surface discharge. Having a relatively long discharge path, the impulse lightening flashover does not lap over a power arc of operational frequency and, after passing of the lightening overvoltage impulse current, the line will continue a trouble-free operation without being disconnected. Simple and reliable arrester designs are disclosed among which are fittings with dielectric covers and insulators, integrating their direct functions with the lightening arrester's functions.
Owner:OTKRYTOE AKTSIONERNOE OBSCHESTVO NPO STREAMER
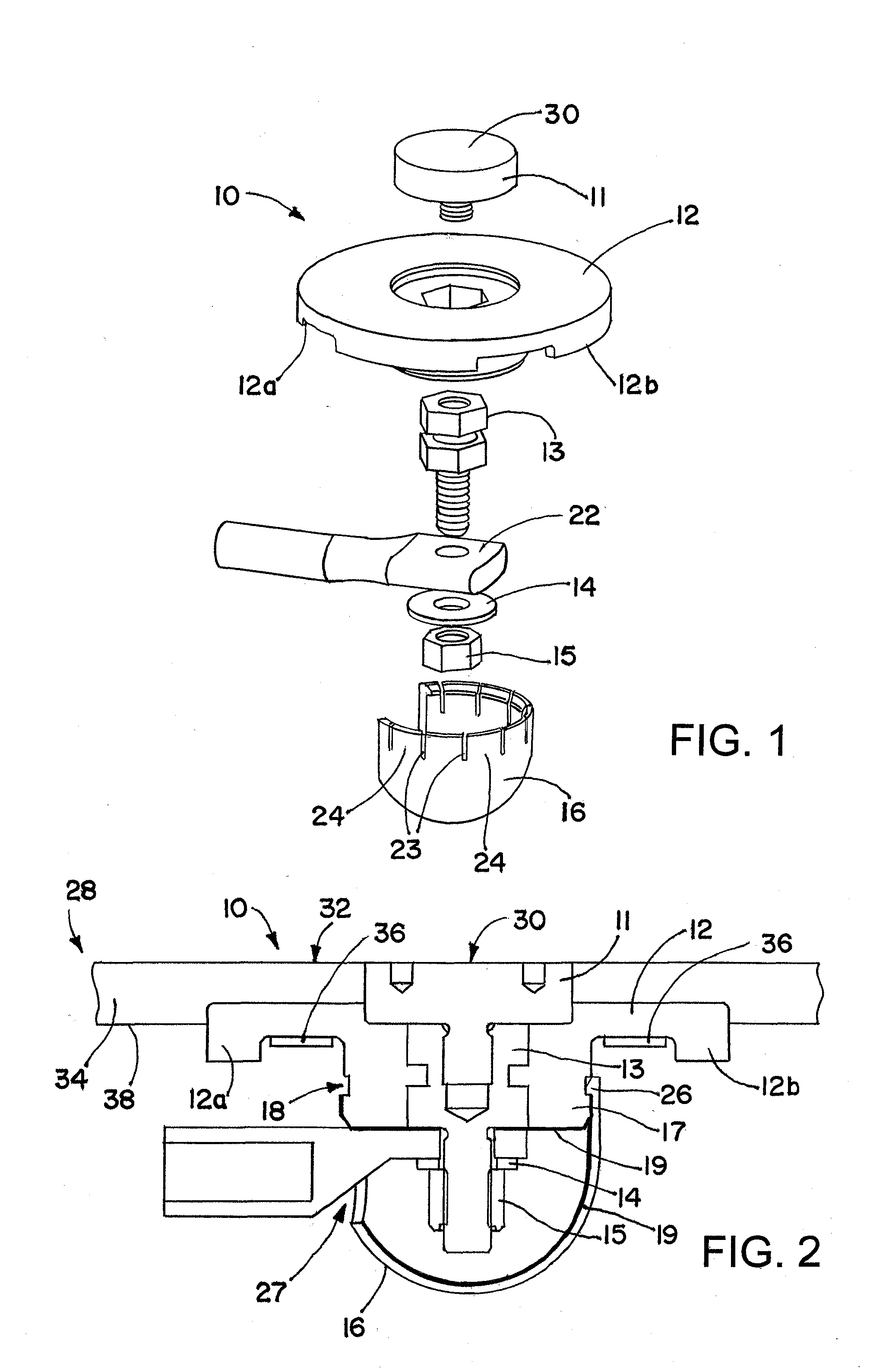
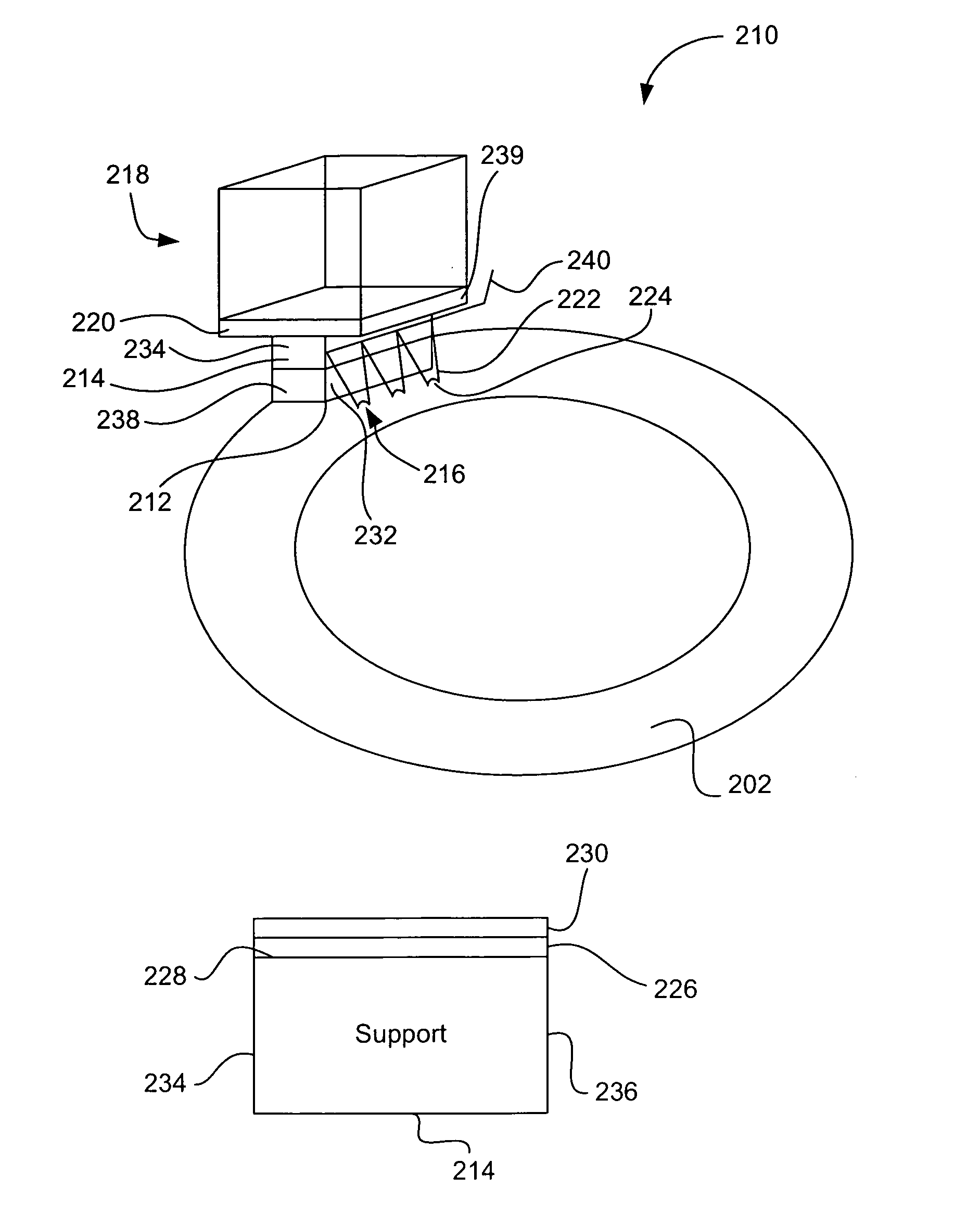
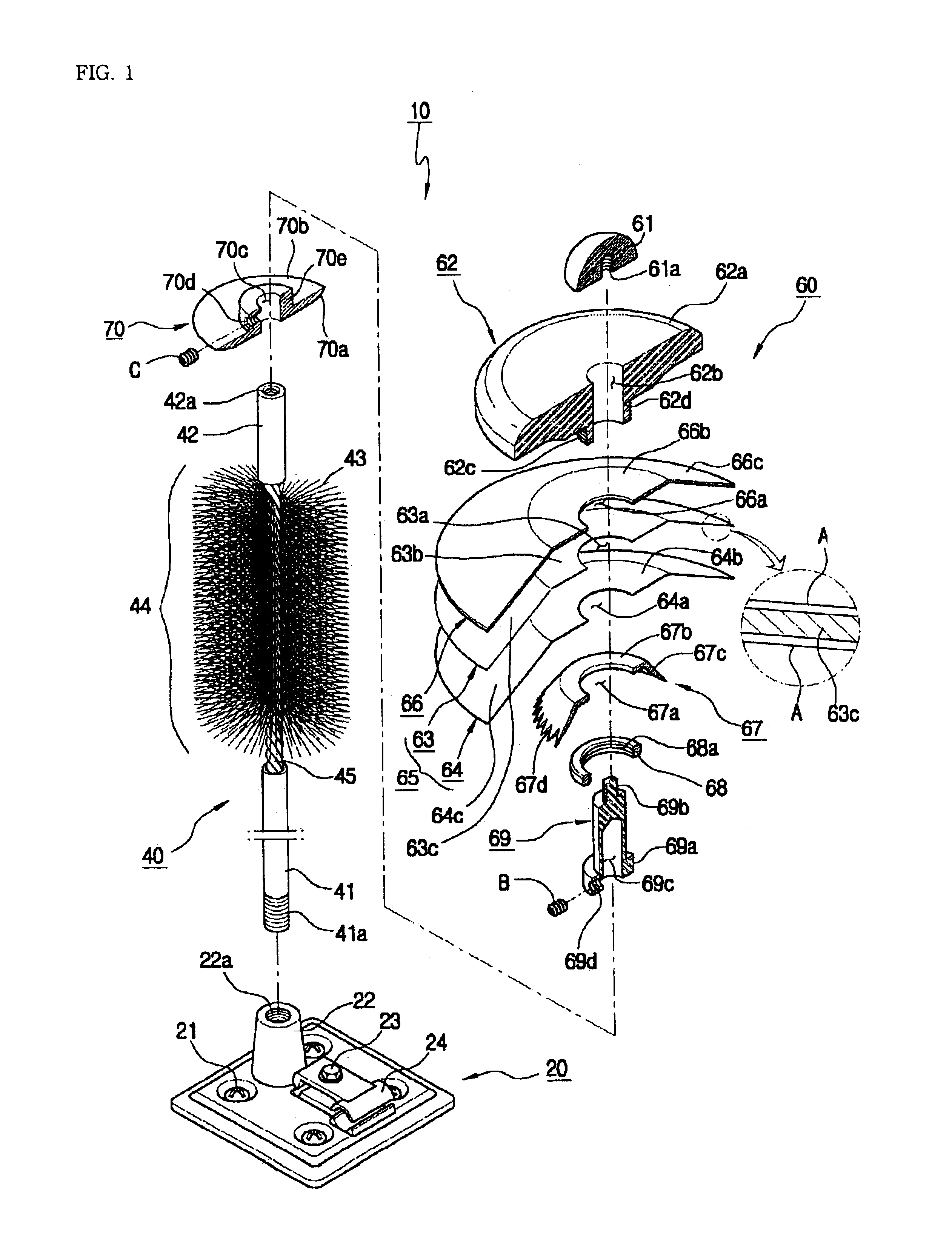
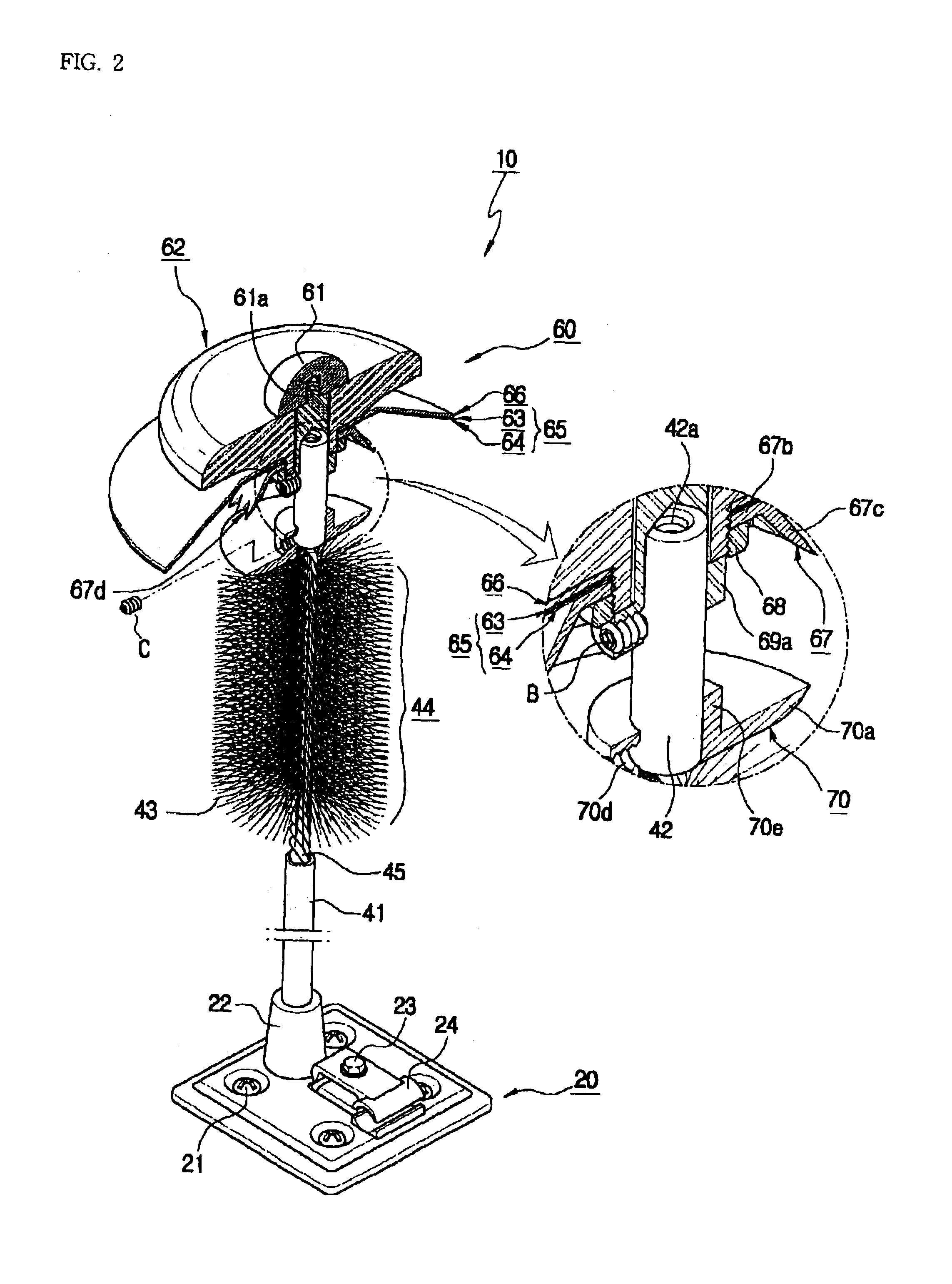
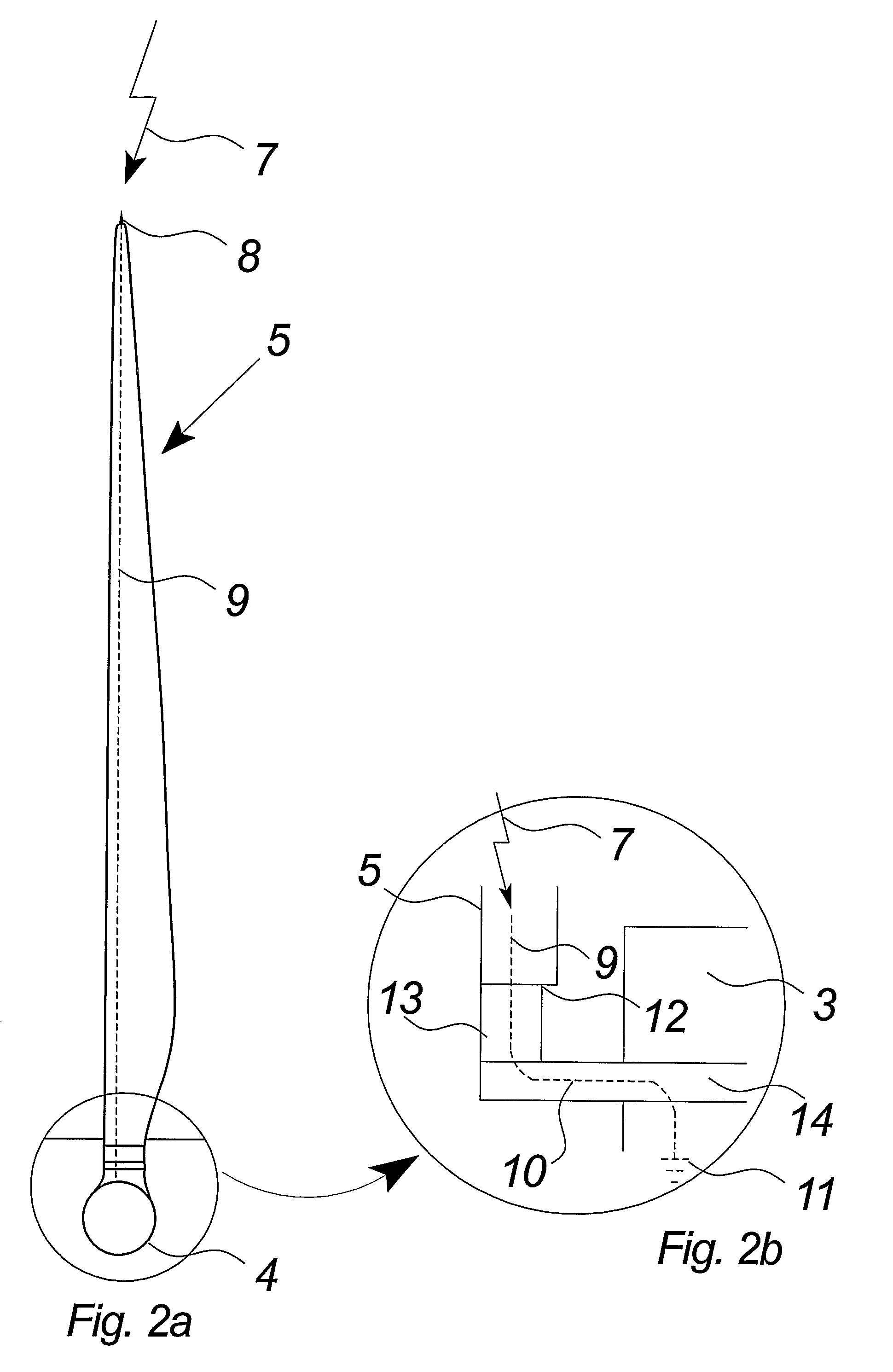
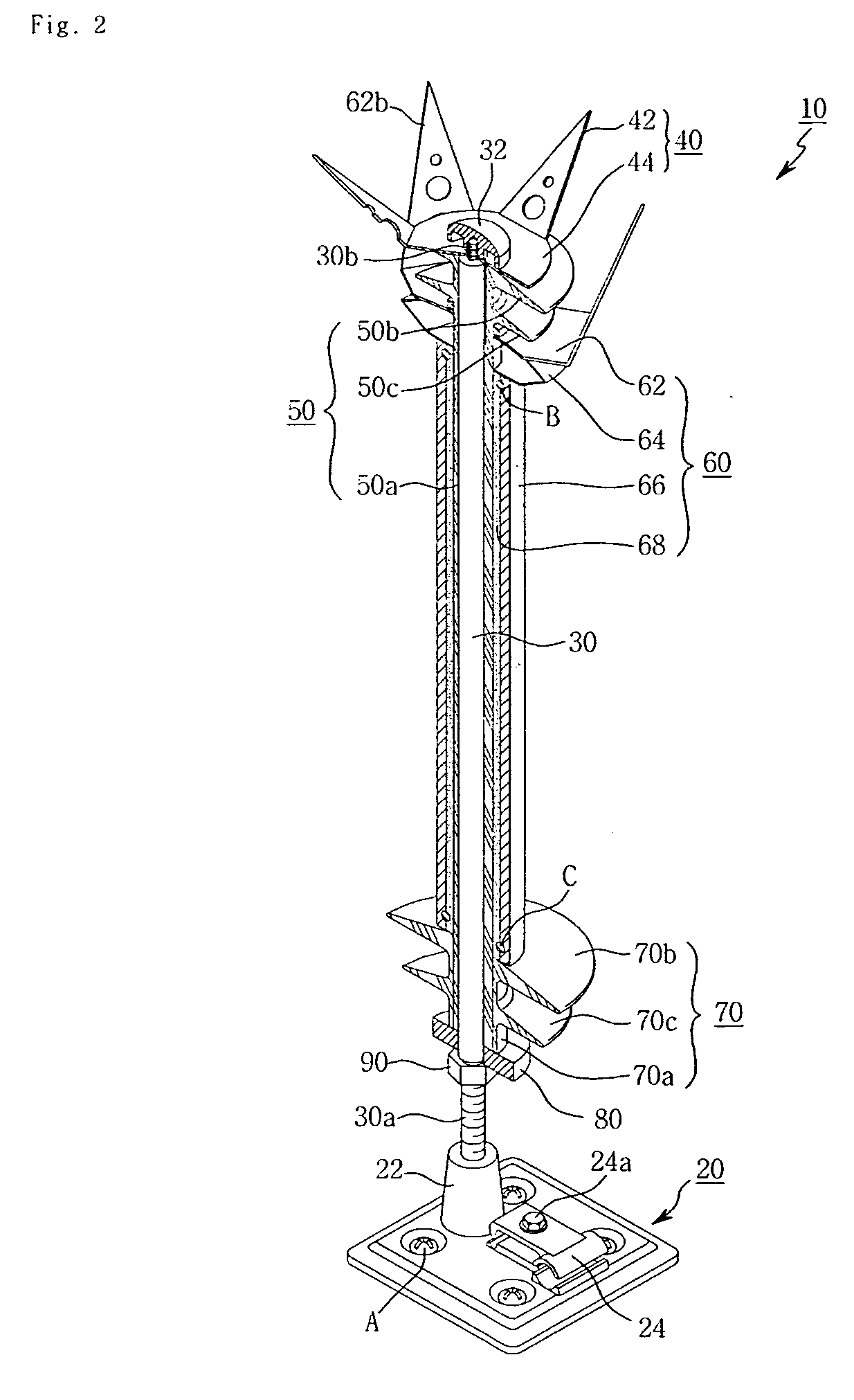
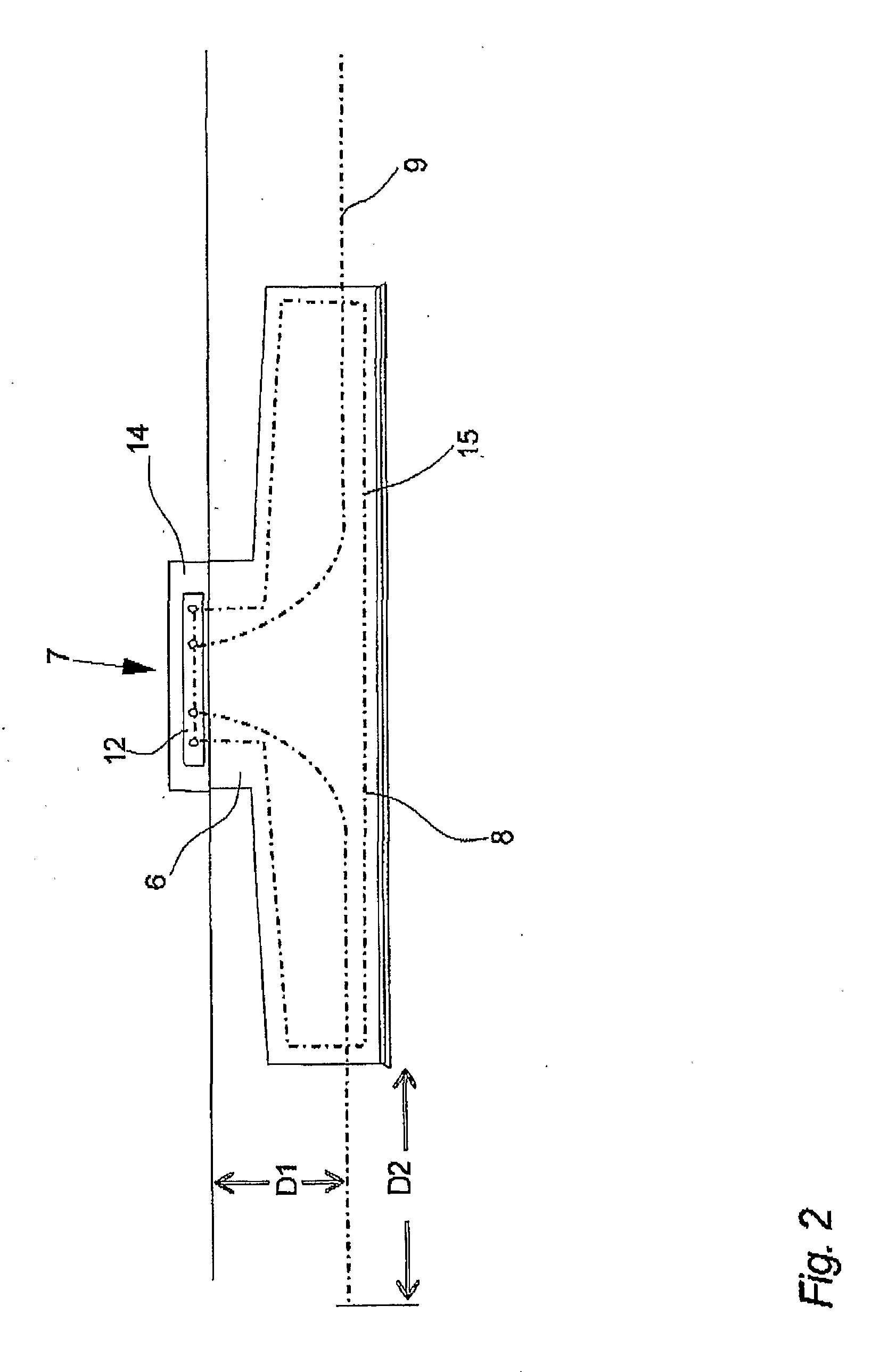
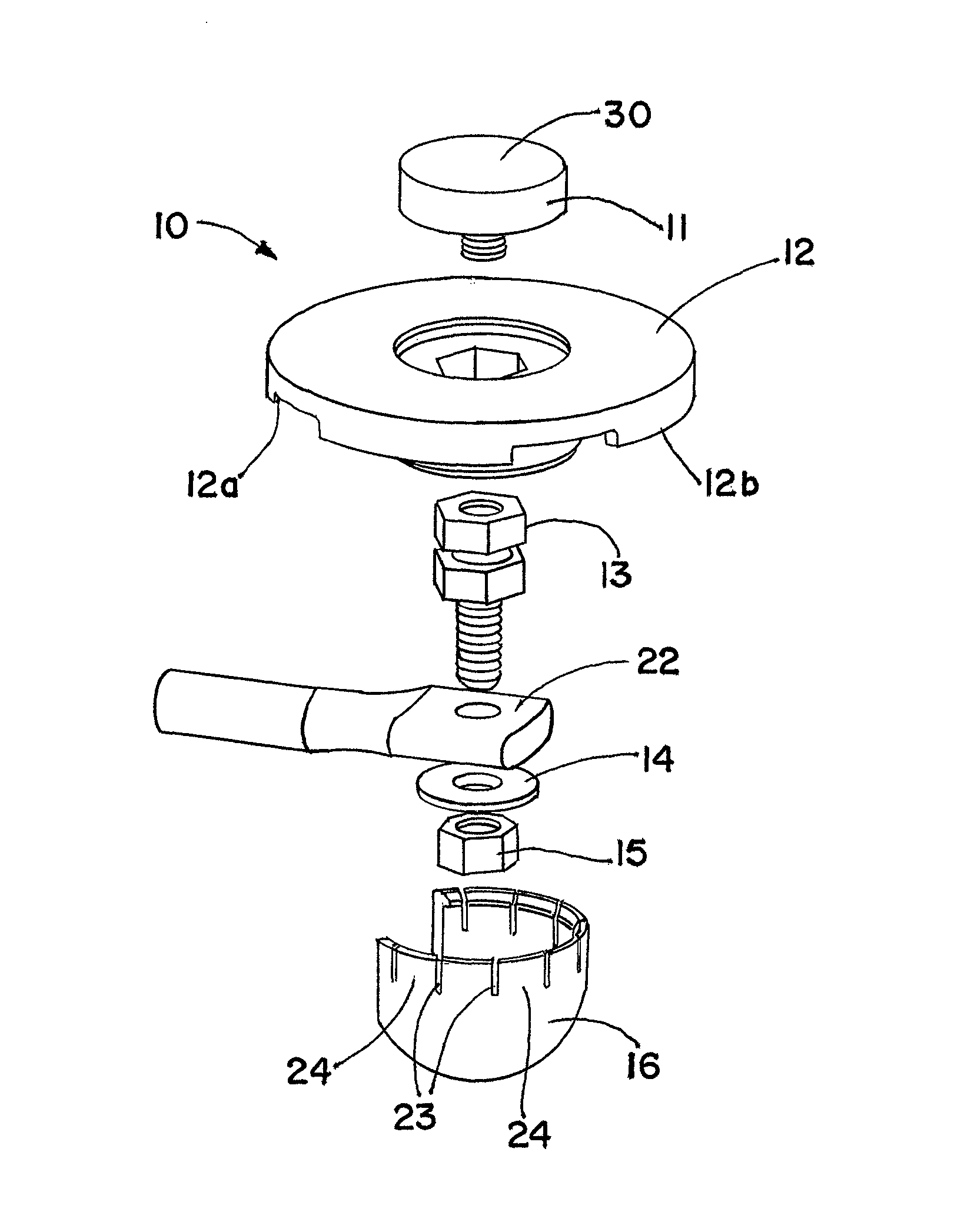
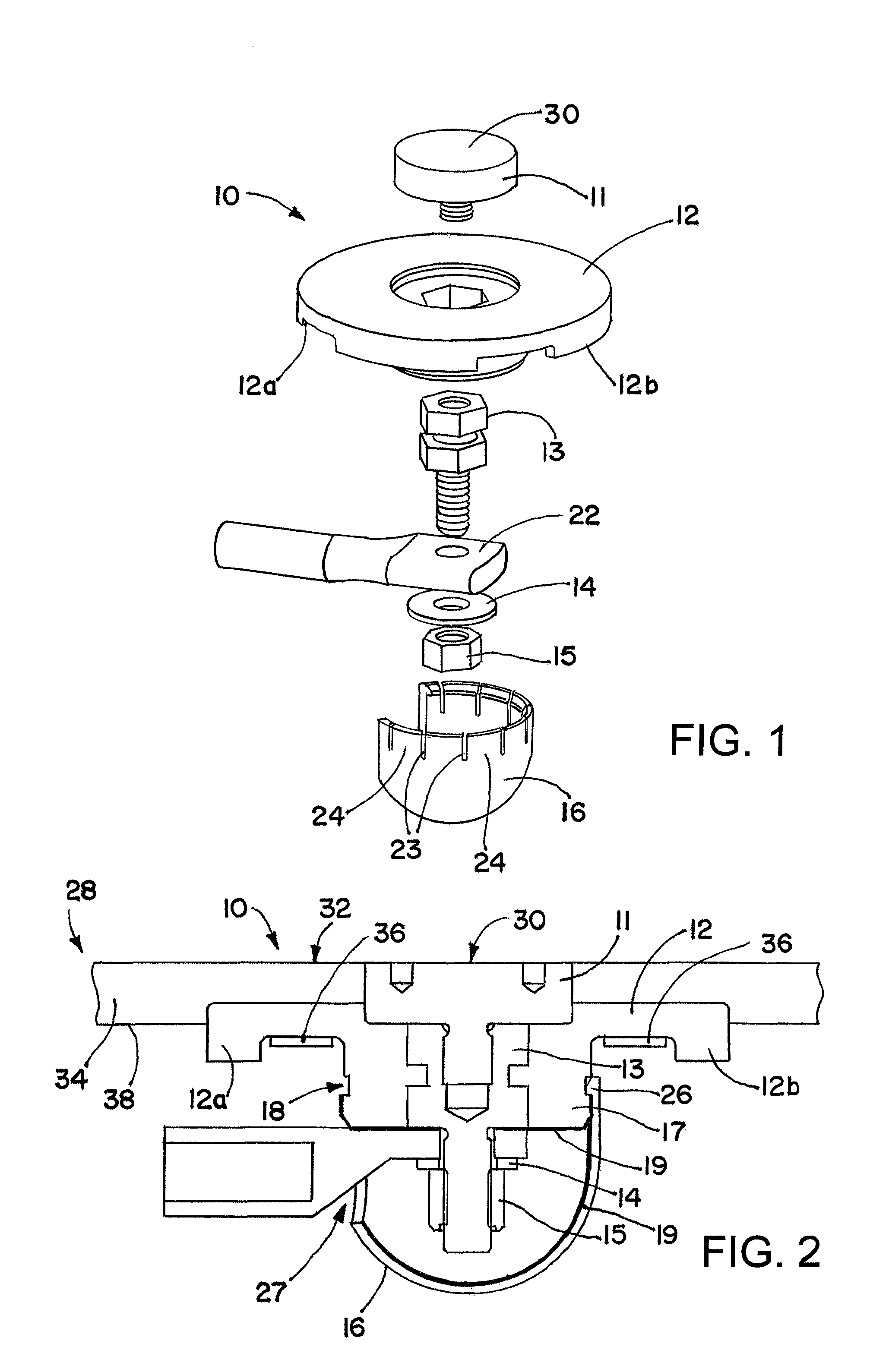
Receptor for wind turbine blade lightning protection
InactiveUS20120020791A1Reduce localized electrical field stressHigh dielectric strengthPropellersConnection to earthElectricityLightning strike
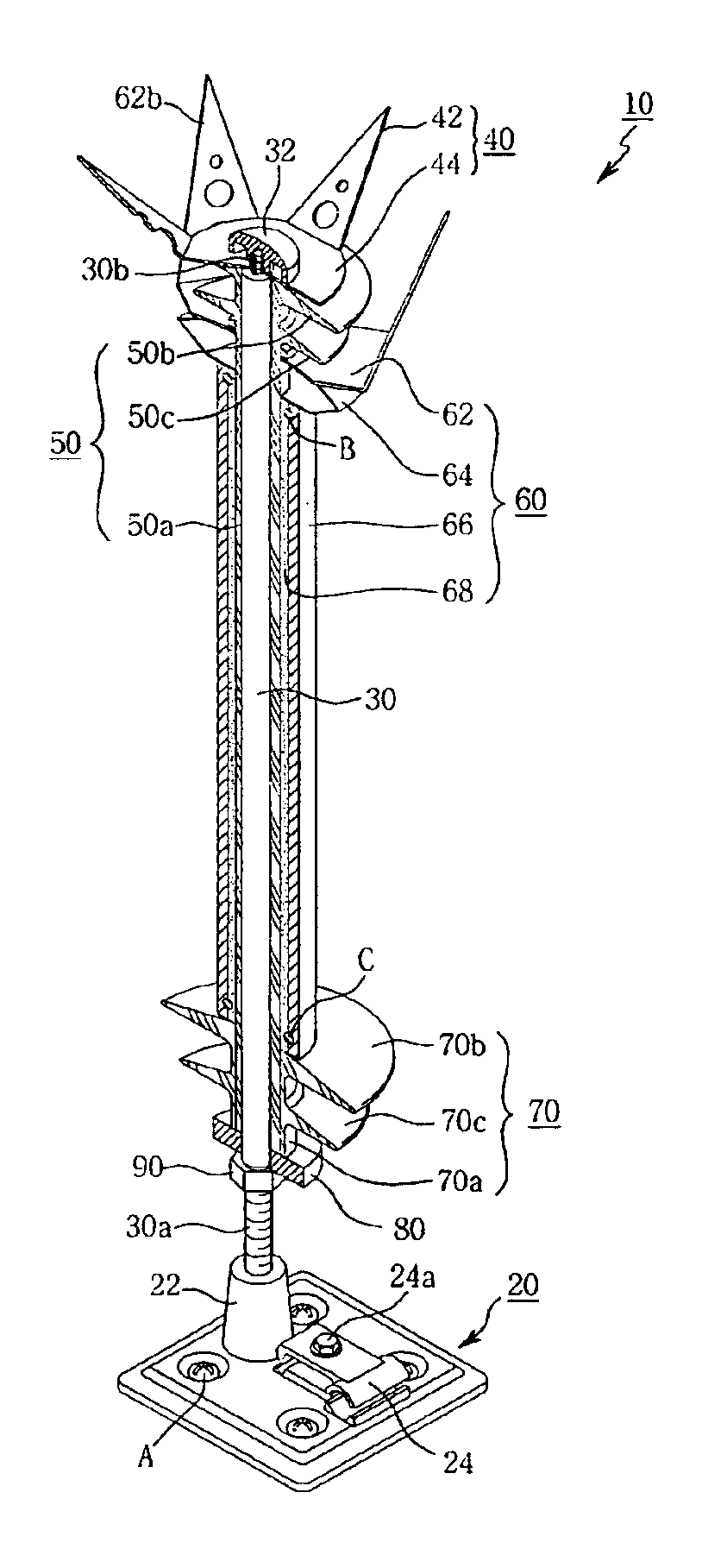
A receptor assembly for lightning protection of an object, such as a wind turbine blade, includes a receptor disk configured to be placed on a surface of the object, a receptor block insulator with an integral receptor block, a cover that engages the receptor block insulator, and a cap that engages the cover. The receptor disk and the receptor block may be made of electrically conductive materials, and the cover, and the cap, and the receptor block insulator may define a chamber among them that is lined with an electrically-conductive coating sandwiched between relatively high dielectric media to electrically isolate and shield internal parts of the receptor assembly from receiving a lightning strike directly.
Owner:ERICO INT
Flex circuit lightning protection applique system for skin fasteners in composite structures
A lightning protection appliqué incorporates a plurality of conductive plies adhesively affixed to a composite surface, at least a first one of the plies providing conductive characteristics sufficient to divert electrical energy from a lightning strike and at least a second one of the plies comprising operational circuitry. A dielectric ply is fixed to the composite surface over and completely covering at least one metal surface feature between the plurality of conductive plies and the composite surface.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
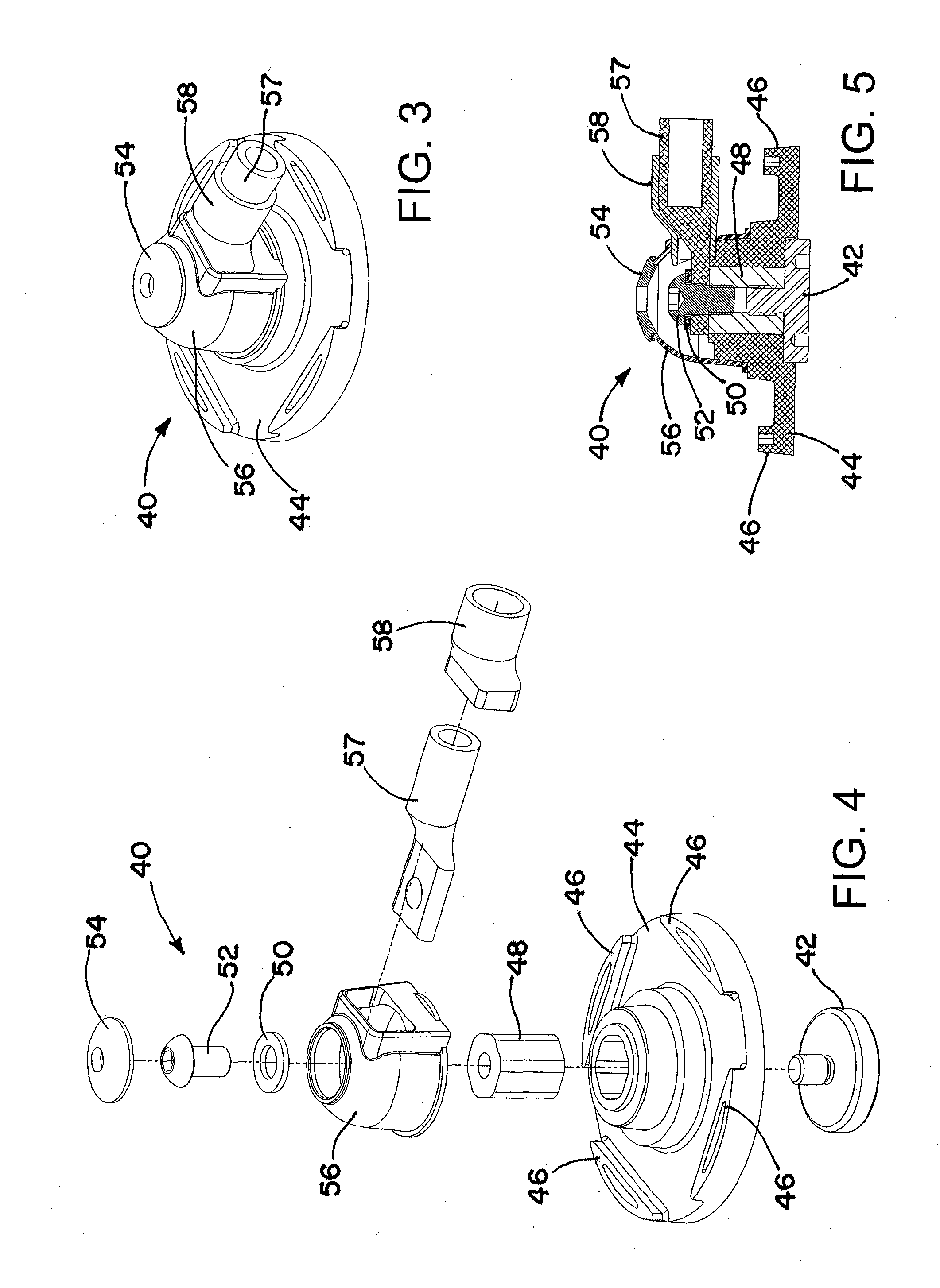
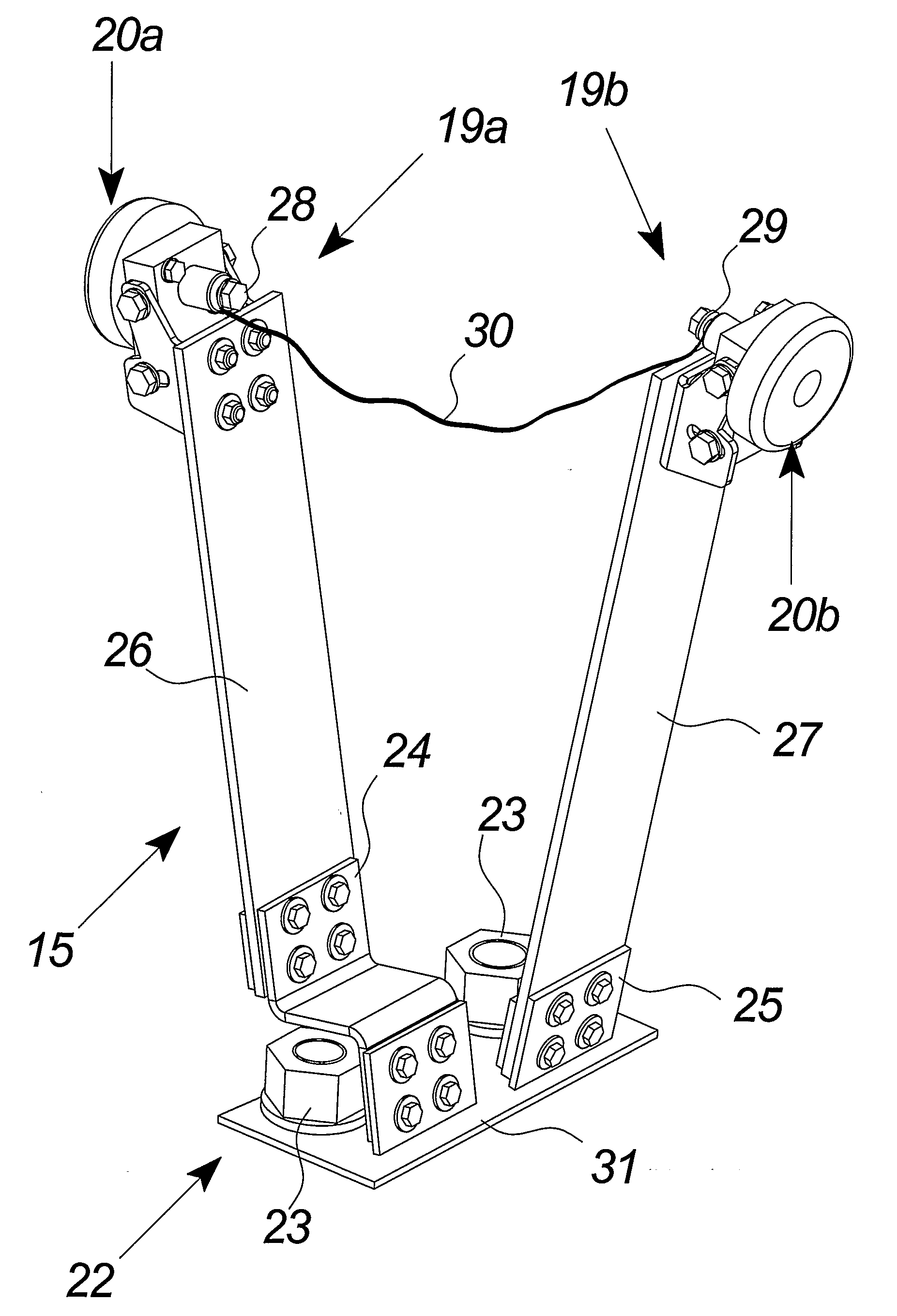
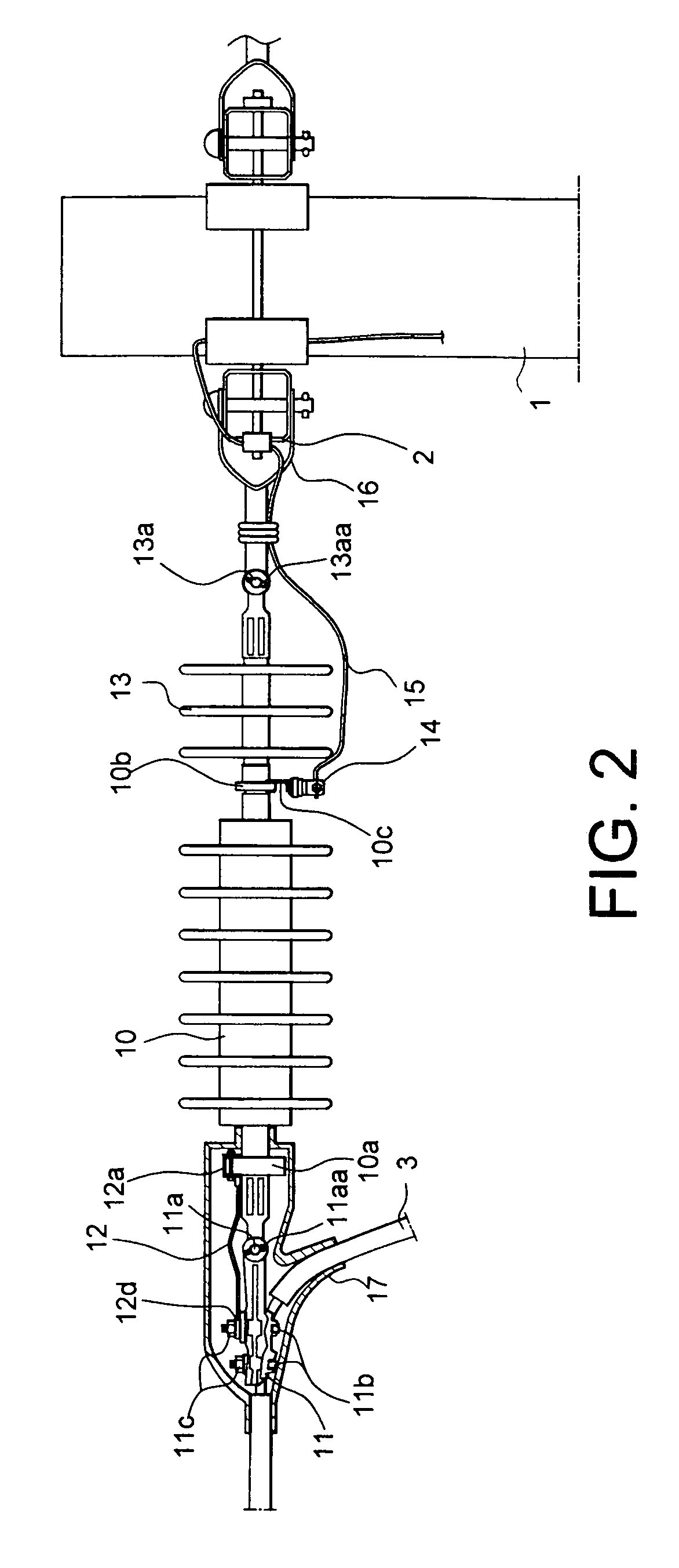
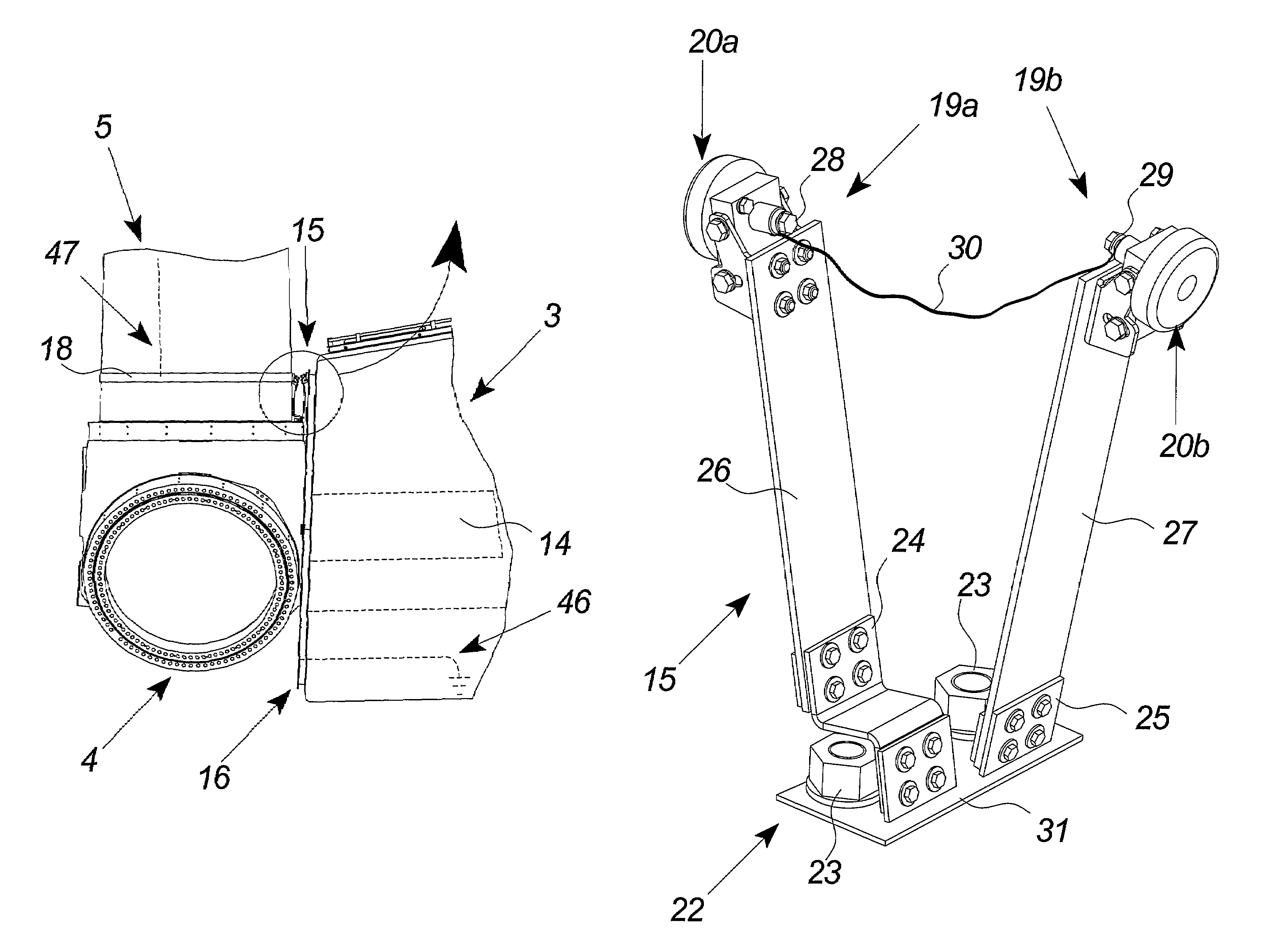
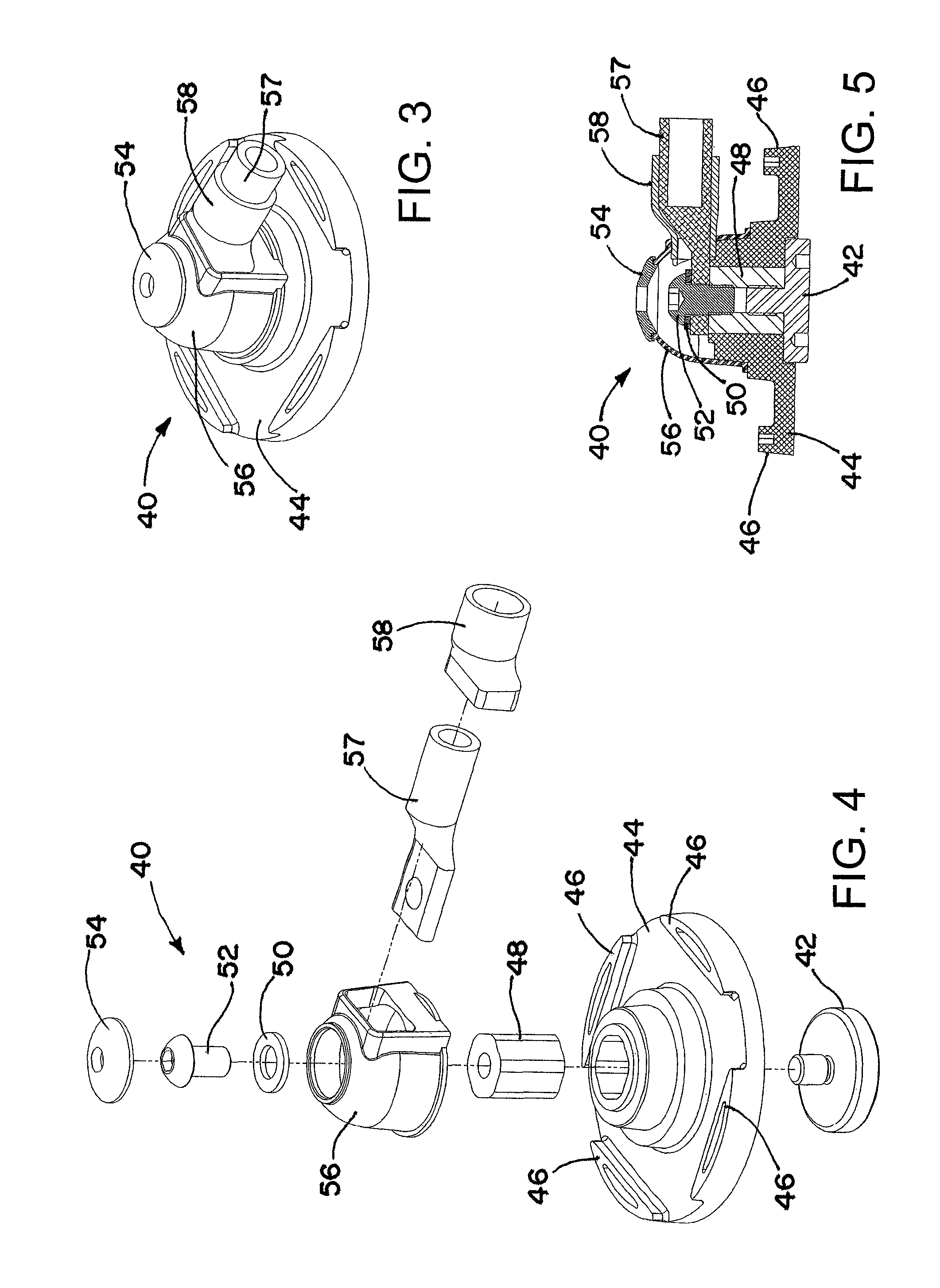
Wind Turbine Lightning Connection Means Method and Use Hereof
ActiveUS20090038819A1Simple mechanical structureReliable serviceConnection to earthDischarge by conduction/dissipationNacelleTurbine blade
The invention relates to a wind turbine (1) comprising stationary means such as a nacelle (3) and a tower (2) comprising stationary lightning protection means (46), and rotating means such as a rotor including at least one wind turbine blade (5) and shaft means (14), each of said at least one wind turbine blade (5) comprising rotating lightning protection means (47). The stationary and rotating lightning protection means (46, 47) comprise contact surfaces (17, 18) connected by lightning connection means (15). The lightning connection means (15) comprises at least two contact means (19, 19a, 19b) adapted for connecting said rotating and stationary lightning protection means (46, 47). Further, it comprises at least one electric conductor (30) establishing a dedicated connection between said at least two contact means (19, 19a, 19b) and force transferring means (26, 27) for said at least two contact means (19, 19a, 19b) establishing a continuous connection between said at least two contact means (19, 19a, 19b) and the contact surfaces (17, 18) of said stationary and rotating lightning protection means (46, 47). The invention also relates to lightning connection means (15) for a wind turbine (1), a method and use hereof.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
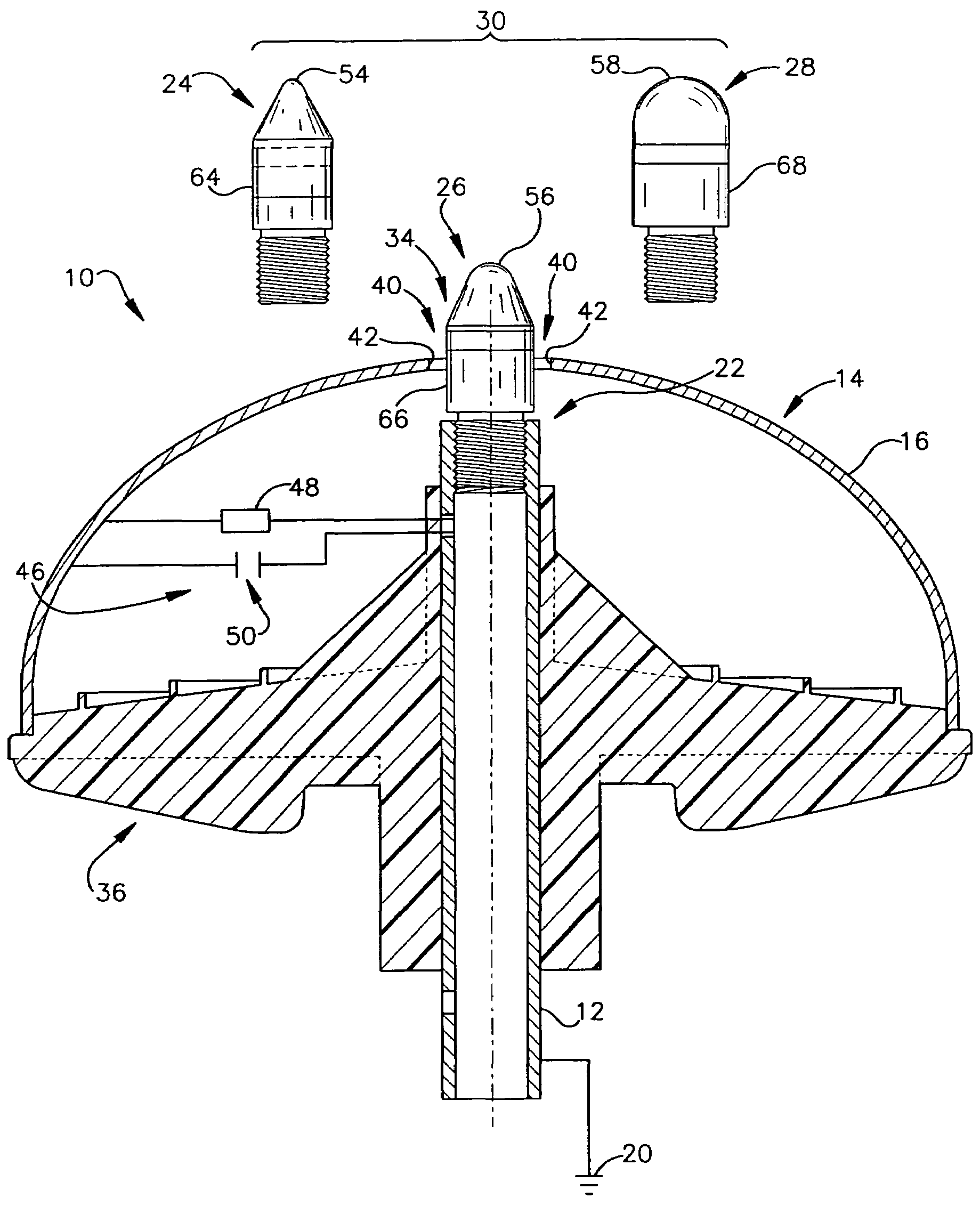
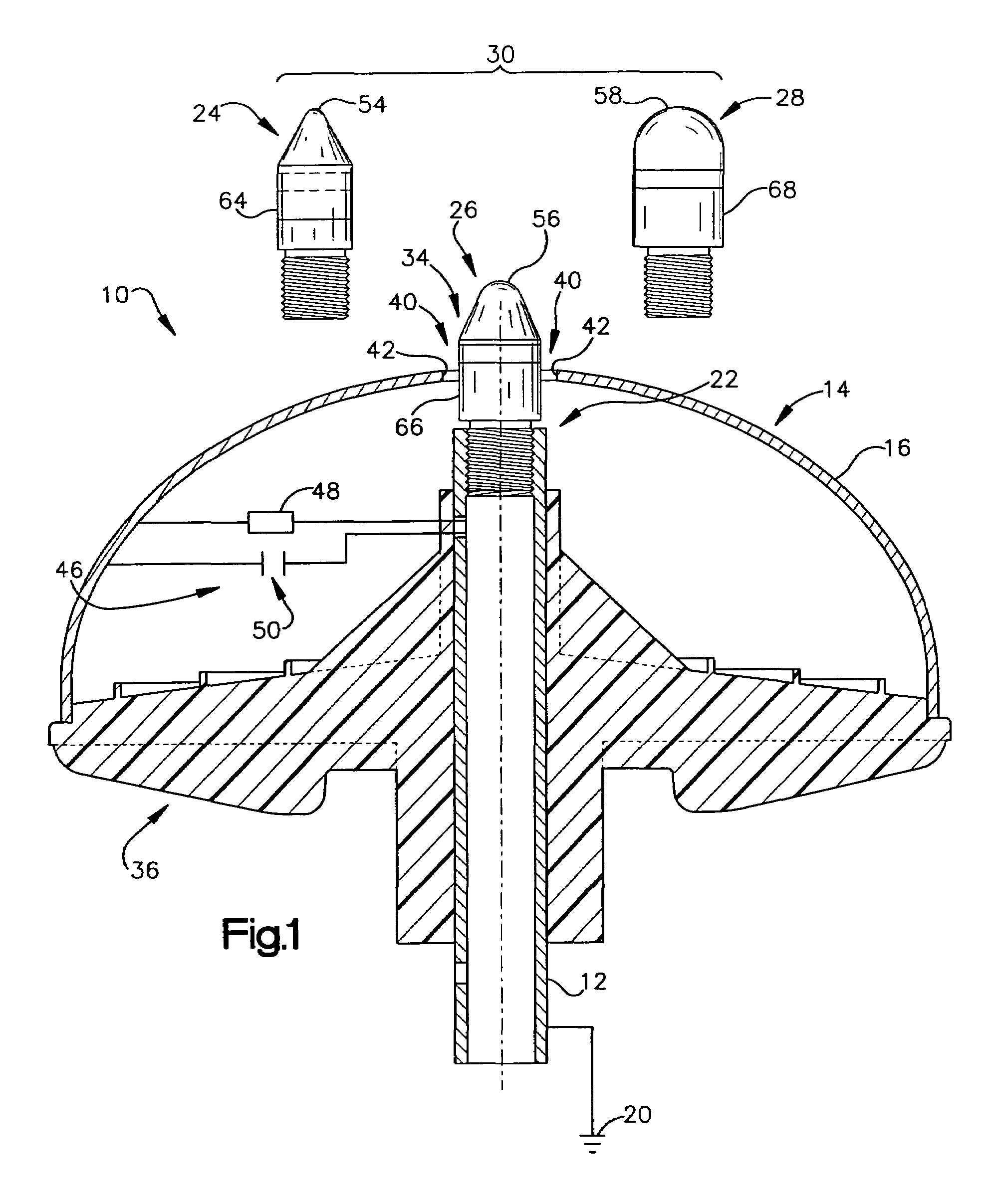
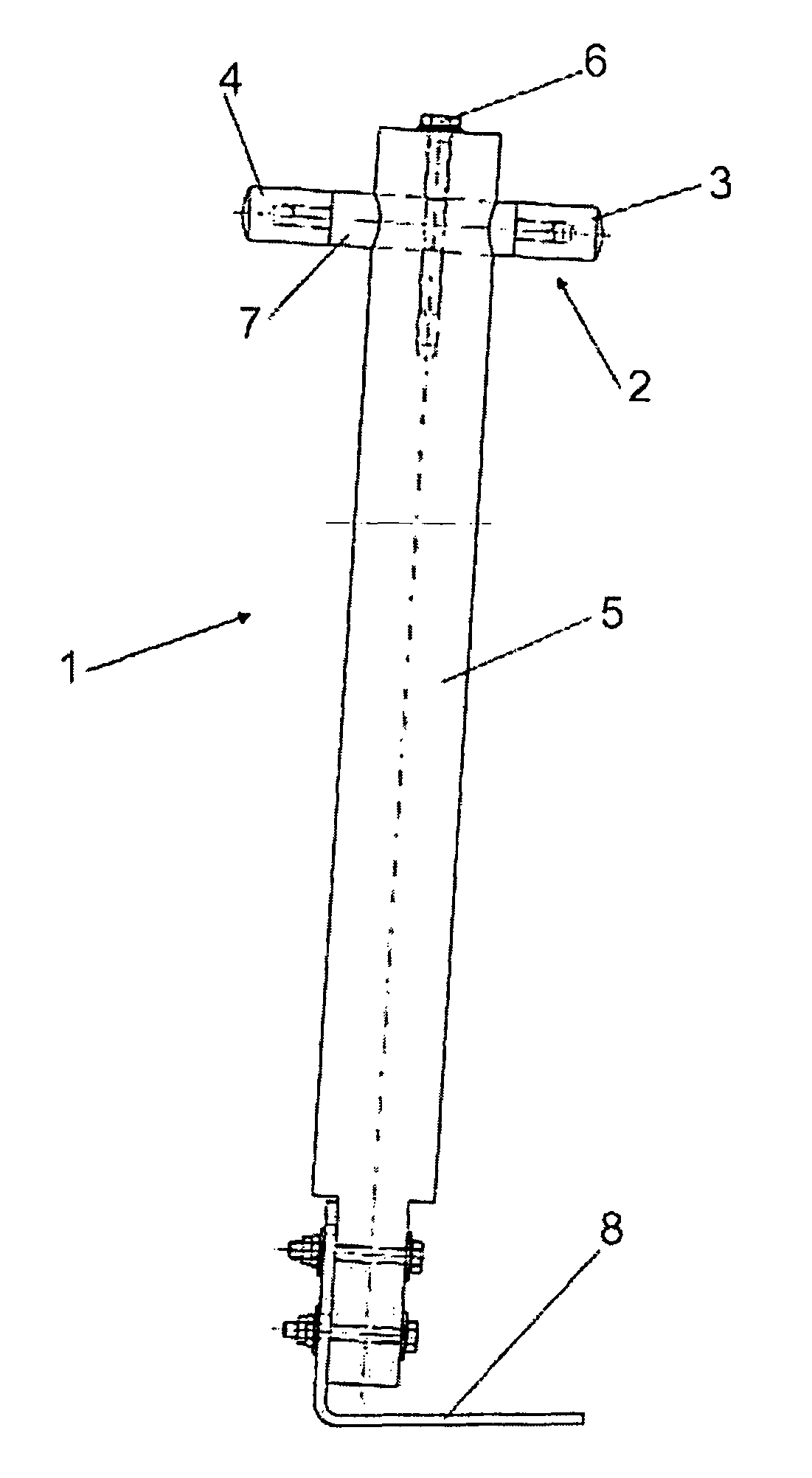
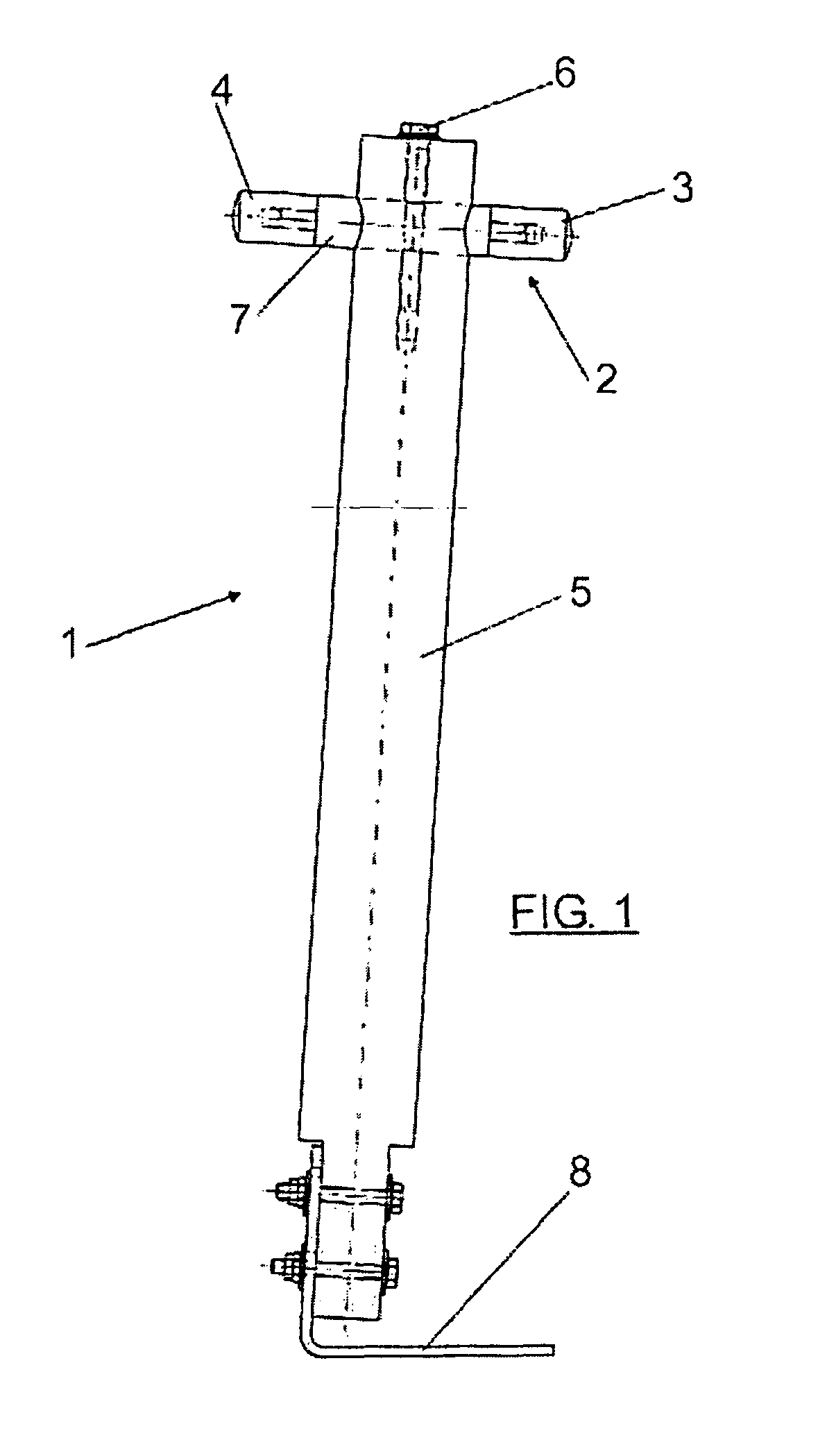
Lightning protection device and method
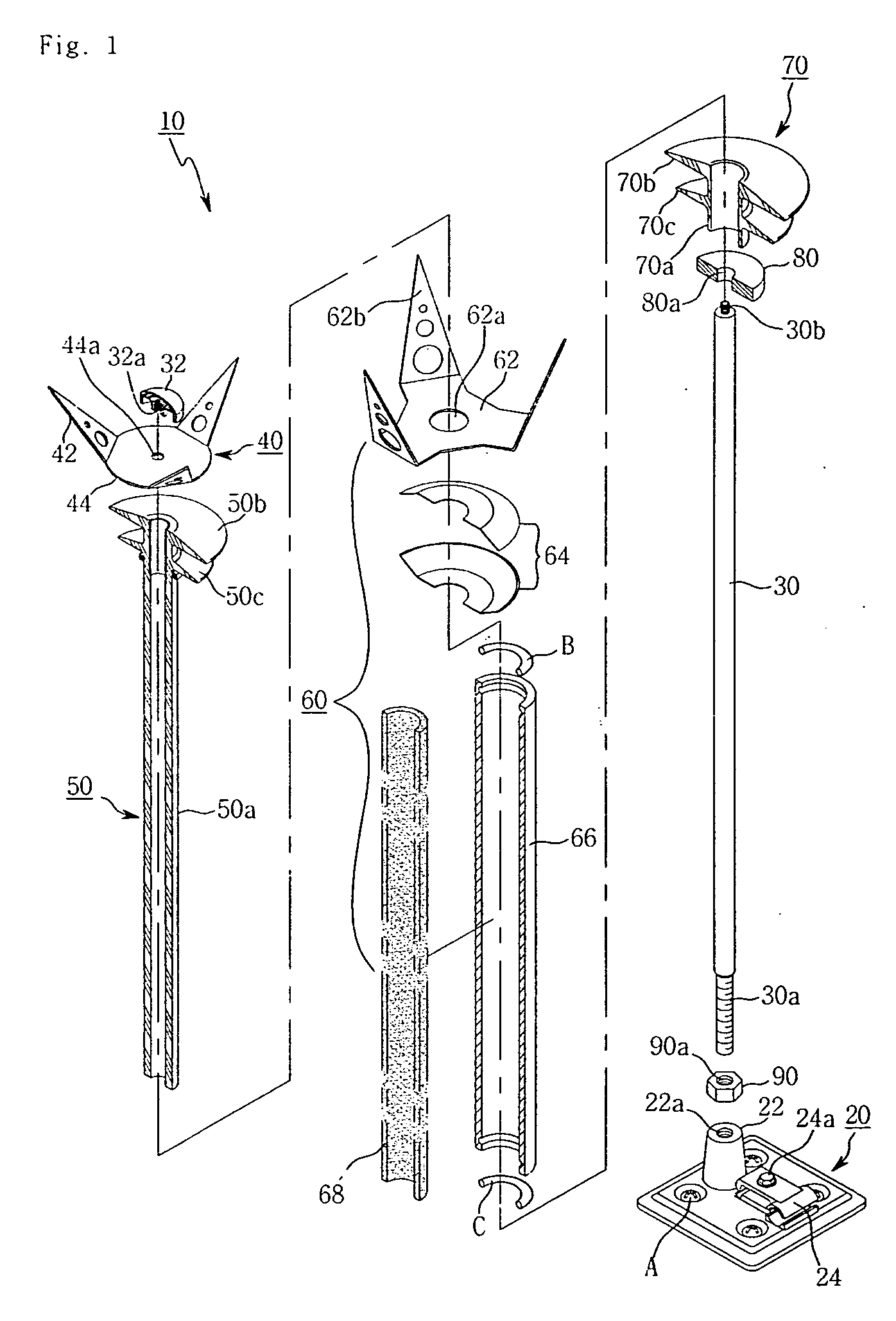
ActiveUS20050146832A1Emergency protective arrangement detailsConnection to earthElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical connection
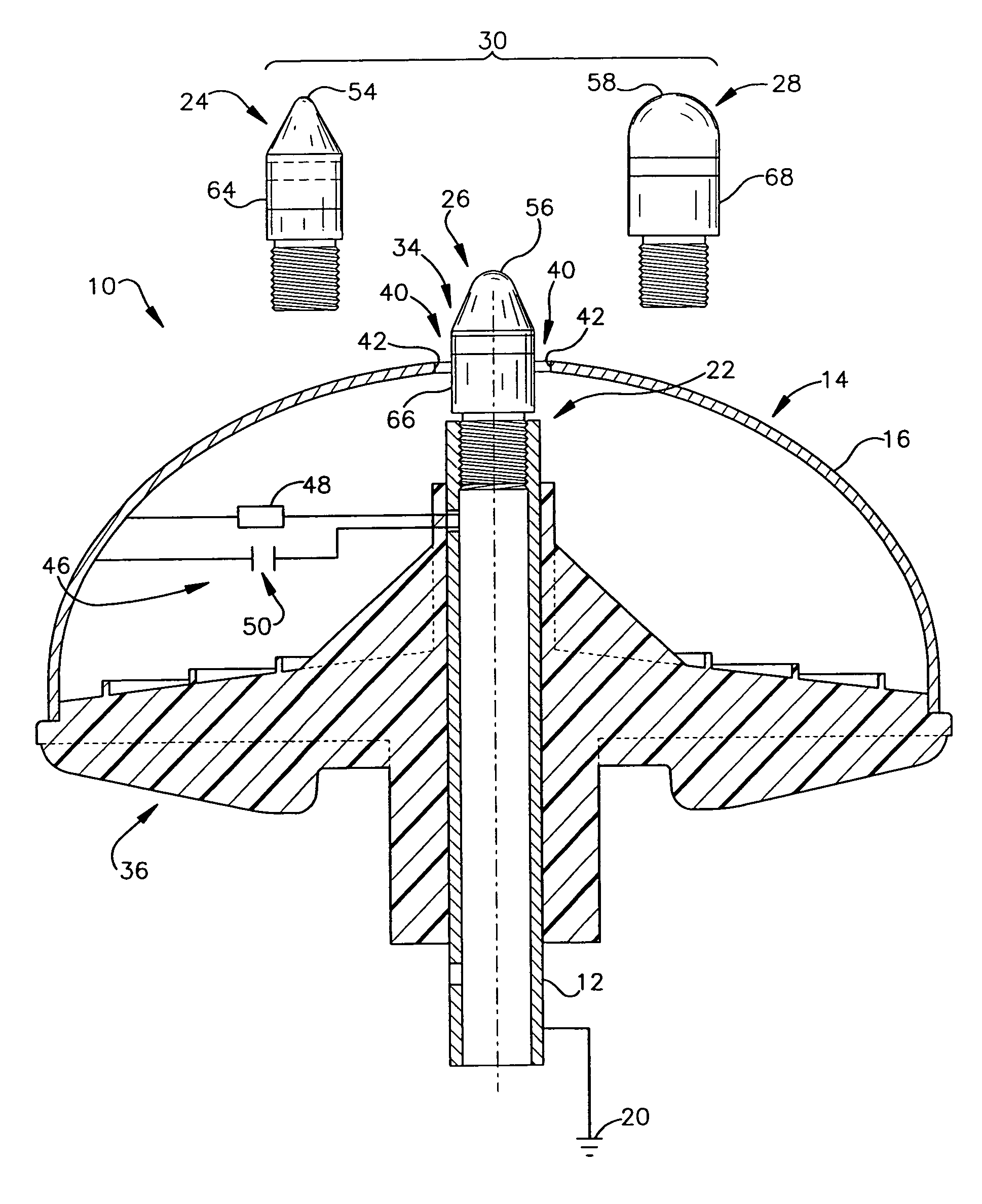
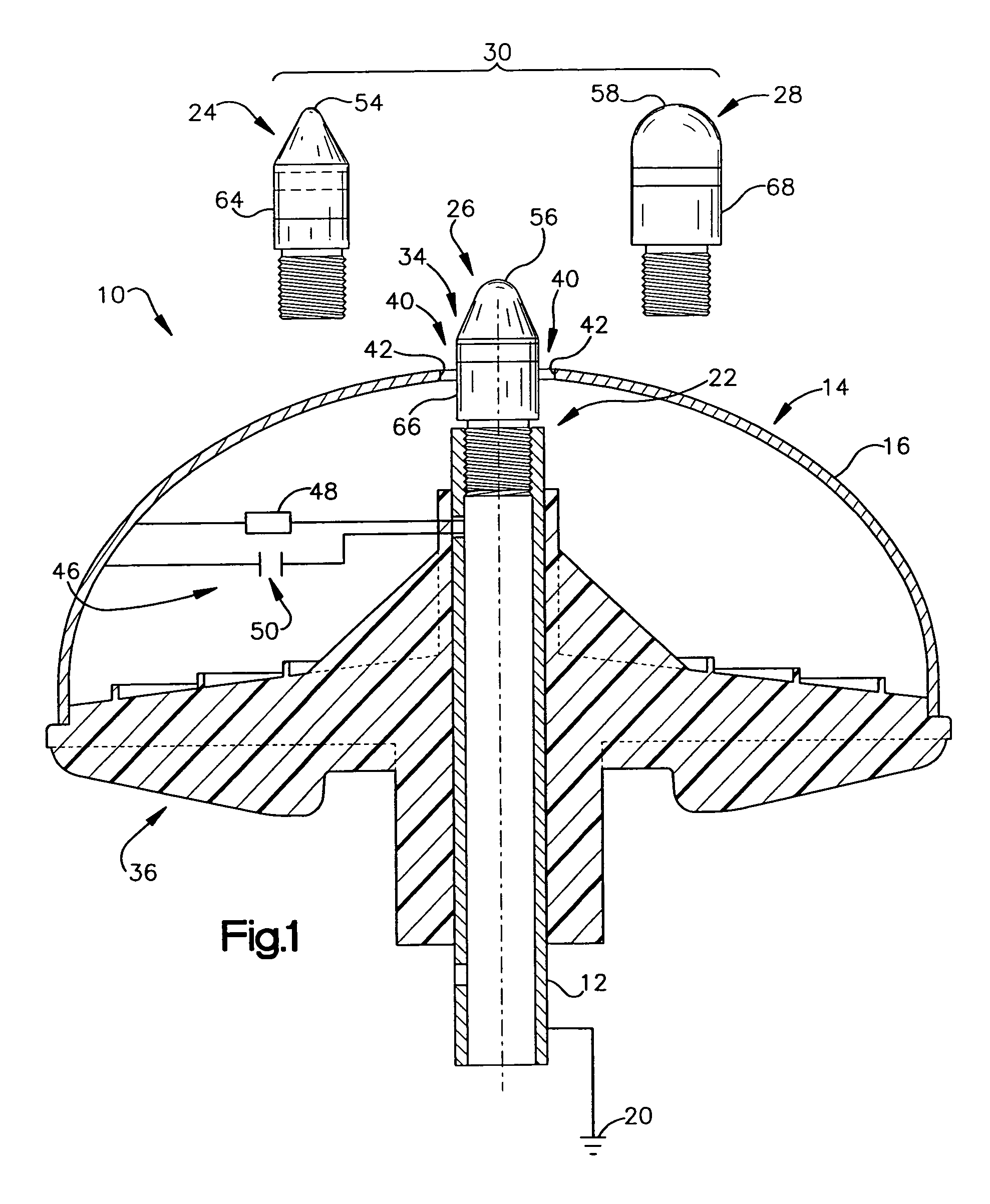
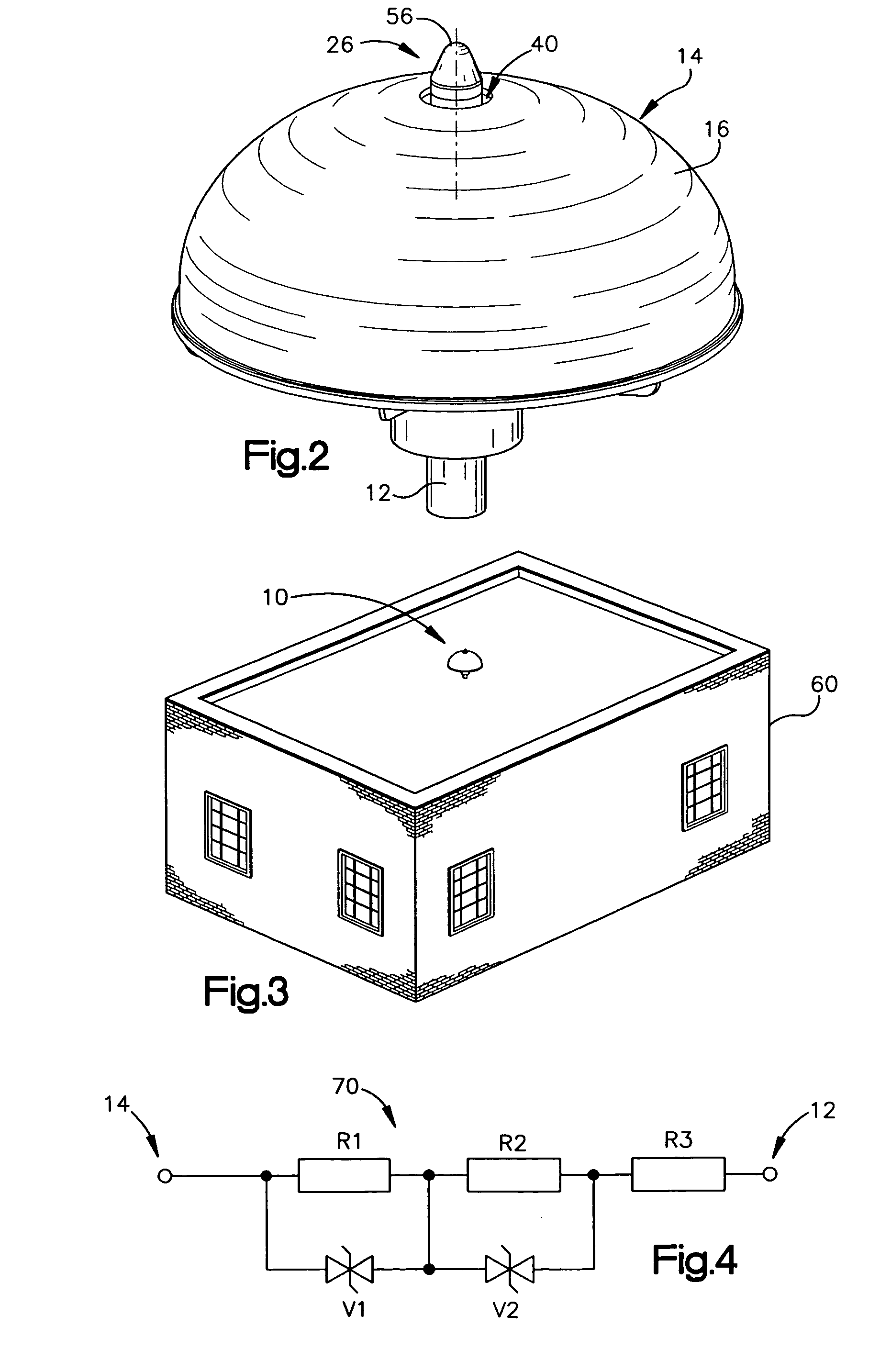
An air terminal for lightning protection includes a central rod and a curved conductive surface around the central rod. The central rod includes a tip mount for receiving a tip from a tip set that includes a plurality of tips that impart different electrical characteristics to the air terminal. For example, the tips of the tip set may have a variety of radii of curvature, and may provide different gap sizes between the various tips and the curved conductive surface. The curved conductive surface and the grounded central rod may be electrically coupled together via an electrical connection. The electrical connection may include a fixed impedance or resistance, or may include a variable impedance unit that automatically varies impedance based on a voltage difference between the curved conductive surface and the grounded central rod.
Owner:ERICO INT
Lightning arrester
InactiveUS6875915B1Improve reliabilityDischarge safetyTents/canopiesConnection to earthPolymer insulationEngineering
Disclosed is a lightning arrester. The lightning arrester safely discharges earth charge of a main electrode section and an auxiliary electrode section regardless of a variation of charge contained in air, so charge charged in a thundercloud is safely discharged into the earth even if the thundercloud is located far-remote from the earth. The lightning arrester has a fixing base fixedly installed on an object to be protected by grounding a lightning circuit connected to a ground electrode grounded to an earth, a fixing bar vertically installed at one side of an upper surface of the fixing base and made of conductive material, a main electrode section making contact with an upper portion of the fixing bar and made of conductive material, an upper polymer insulator including an elongated column member formed at a center thereof with a hollow section for receiving the fixing bar therein, and upper and lower disc-shaped plates integrally formed at an upper end of the elongated column member for ensuring an insulation distance, and an auxiliary electrode section aligned below the main electrode section without making contact with the main electrode section and made of conductive material. The elongated column member of the upper polymer insulator passes through a center of the auxiliary electrode section in order to fill space charge in the auxiliary electrode section.
Owner:LEE TECH KOREA CO LTD
Method of lightning proofing a blade for a wind-energy plant
ActiveCN1867772AProper electrical connectionReliable electrical connectionConnection to earthDischarge by conduction/dissipationFiberElectricity
The invention relates to a method of lightning-proofing a blade (1) on a wind-energy plant, which blade comprises a blade shell (2) configured essentially as a fibre-reinforced laminate, which laminate comprises electrically conductive fibres, wherein the blade comprises at least one lightning arrester (9) configured for conducting lightning current, including preferably to ground. The method comprises that the electrically conductive fibres are connected to each other, and that at least one metallic receptor (4, 24, 25) is arranged for capturing lightning current at or in proximity of the external face of the blade; and that the receptor and the fibres are connected to the lightning arrester for equalising the difference in potential between the lightning arrester and the electrically conductive fibres. When the electrically conductive fibres are connected to each other, the fibres will cooperate on the conduction of a possible lightning current to prevent the current from running in individual fibres. Simultaneously the metallic receptor will serve as the primary lightning capturing device and reduce the risk of lightning striking the laminate. The receptor being connected to the lightning arrester, the current will predominately be conducted to ground, while the risk of transfer to the laminate is minimised in that a possible difference in potential between fibres and lightning arrester has been equalised.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
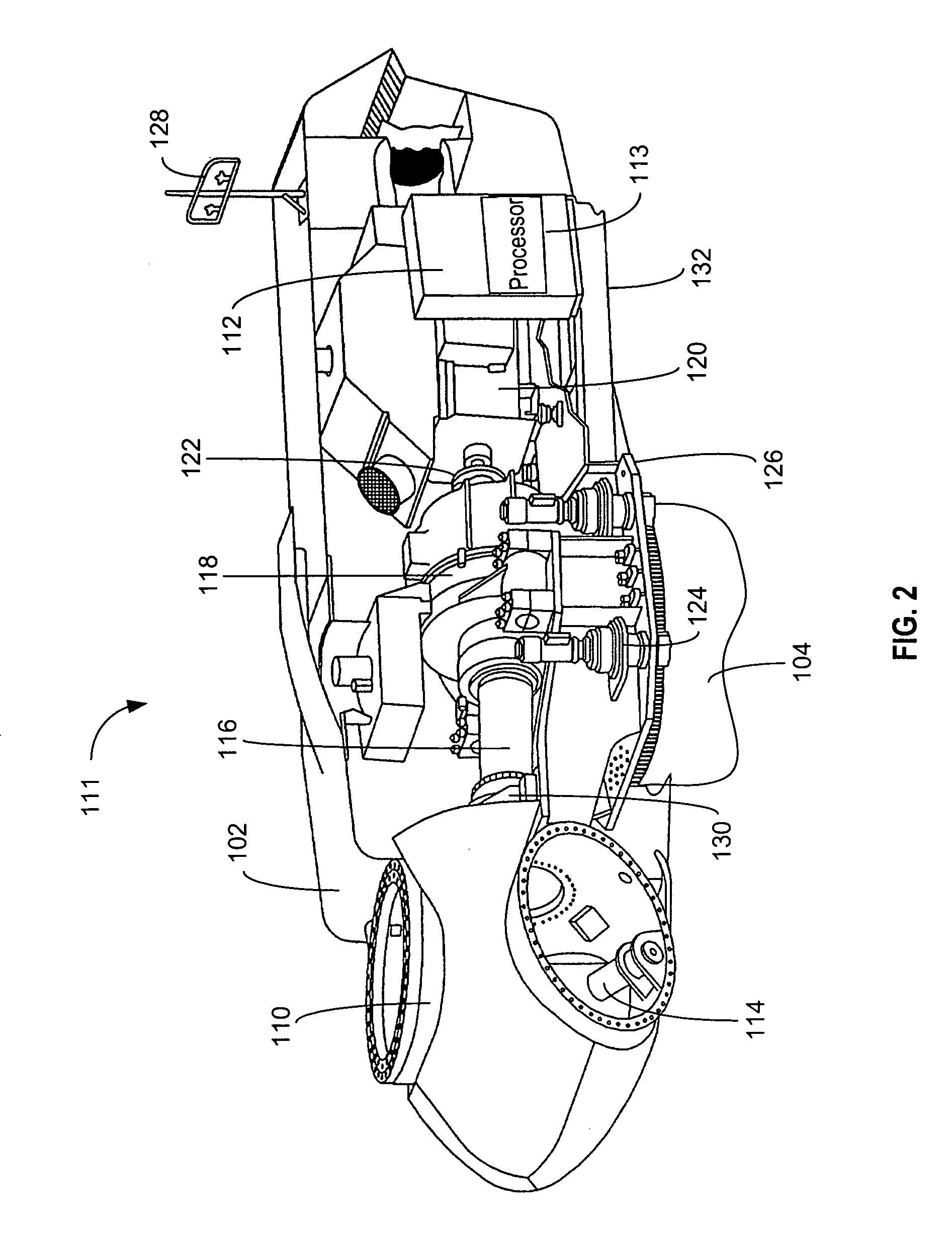
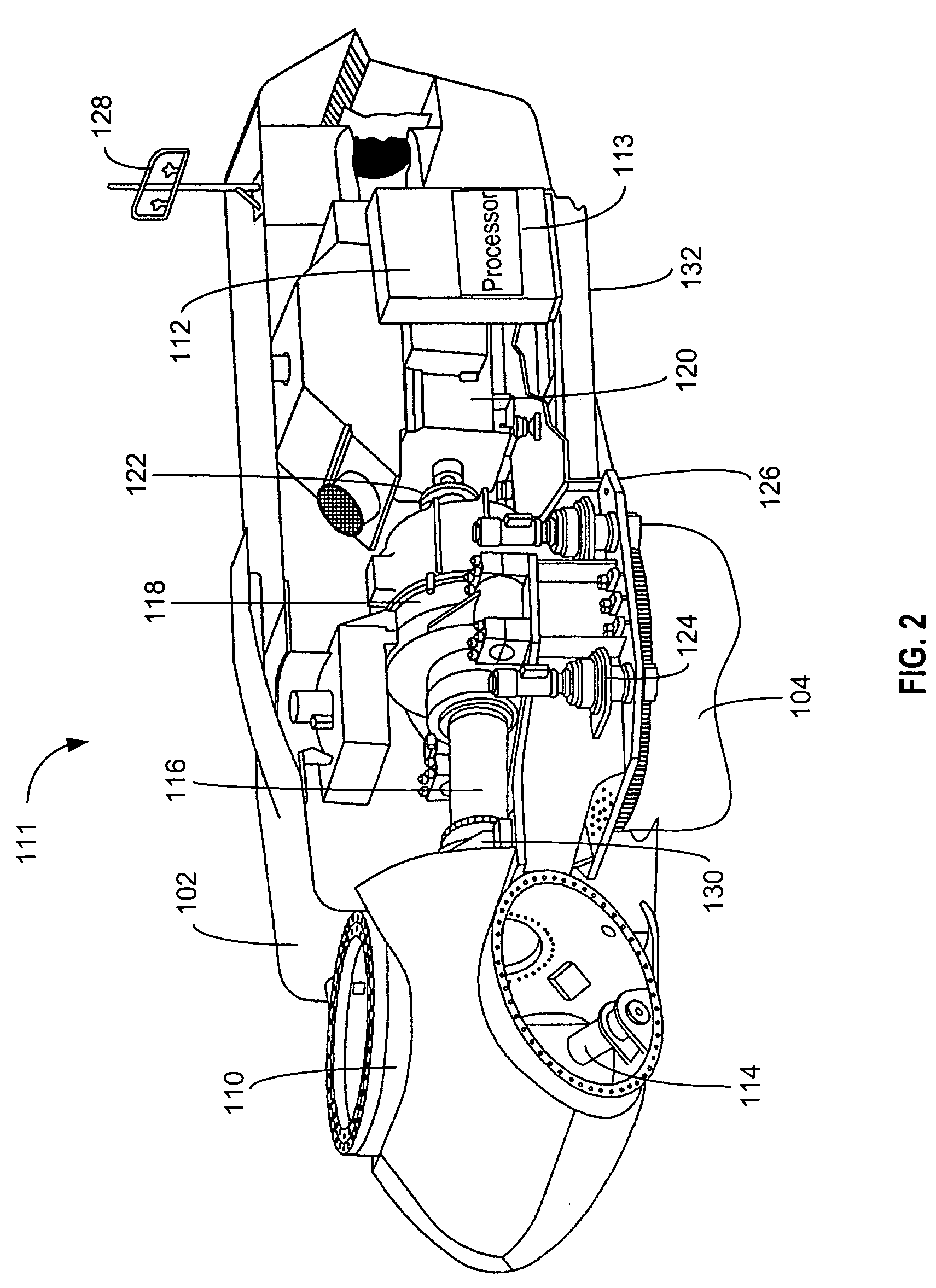
Systems and methods for directing a current
InactiveUS20070114797A1Connection to earthDischarge by conduction/dissipationLightning strikeEngineering
A method for directing a current generated by a lightning striking a wind turbine is described. The method includes directing the current from a main shaft of the wind turbine to a brake disc attached to the shaft, and directing the current from the brake disc to one of a spark gap and a roller mechanism coupled to a down-conductor at a ground voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electrical connects for charge distribution applique
A lightning strike protection system for protecting composite structures, an improved lightning strike appliqué (LSA) for such a lightning strike protection system, and a method of protecting composite structures, such as an aircraft fuselage. The LSA is electrically connected to adjacent conductive surfaces, e.g., by a fuzz button or a wire bond inserted in the bottom of the LSA. An adjacent conductive surface may be another LSA, a lightning diverter overlay, or a current return network. Charge, e.g., from a lightning strike to the LSA, flows to the conductive layer through the electrical connector.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Bipolar discharge-dissipation lightning air terminals
ActiveUS6943285B2Prevent fallingConnection to earthDischarge by conduction/dissipationCouplingEngineering
The present invention relates to a Bipolar Discharge-Dissipation Lightning Air-Terminals, and an object of the present invention is to disperse and discharge an earth charge following a thundercloud approach in a space according to electric dipole, bipolar and electric double layer principle. The above object of the present invention is achieved by providing the bipolar discharge-dissipation lightning air-terminals comprising: a base member fixed and installed in a top region of a protected object, including a coupling projection on whose inner periphery surface coupling screw grooves are formed, the coupling projection protruded and formed at a side of an upper surface of the base member, and a grounding piece formed at a side opposite to the coupling projection in order to earth a ground electrode and a grounded lightning wire; a discharge member coupled releasably to the base member, for focusing an earth charge following a thundercloud approach on the upper surface of the base member; and a potential modifying unit attached releasably on the discharge member so that the potential modifying unit is charged with different charges by electric dipole, bipolar and electric double layer principle according to the thundercloud approach to disperse and discharge the earth charge in a space separated from the discharge member.
Owner:LEE TECH KOREA CO LTD
Structure for installing lightning arrester for electric pole
InactiveUS20080310071A1Easy to useReduce in quantityOverhead installationProtective switch detailsShackleGround line
A structure for installing a lightning arrester between the cross arm mounted to the upper end of an electric pole and a power line is disclosed. A dead end clamp, the lightning arrester and an insulation reinforcing insulator are connected in series, an end of the insulation reinforcing insulator is connected to the cross arm by a shackle, a disconnector is connected to the voltage outlet portion of the lightning arrester, a grounding wire for diverting abnormal voltage to the ground is connected to the disconnector, and an insulation cover surrounds the dead end clamp and the voltage inlet portion of the lightning arrester.
Owner:JEON YOO CHEOR
Transformer substation lightning protection device convenient to detach, assemble and maintain
PendingCN108075432AAdjustment installation and removalConvenient angle adjustment, installation and disassemblyEarthing arrangementsConnection to earthLightning rodTransformer
The invention discloses a transformer substation lightning protection device convenient to detach, assemble and maintain. The transformer substation lightning protection device comprises a base, a supporting box body, an angle adjusting box body, a lightning protection ball and a lightning rod. A lifting plate is arranged in the supporting box body in a vertical sliding mode. The stands are symmetrically fixedly arranged on the upper surface of the middle of the lifting plate. The tops of the two stands are each provided with an inclined face. The ends of a telescopic rod on an electric push rod are each provided with a supporting column. The bottom end of each supporting column is provided with a guide slide wheel. The guide slide wheels are arranged on the inclined faces in a sliding mode. The bottom of the lifting plate is connected with an inner cavity bottom plate of the supporting box body through a plurality of springs. A hinge base is fixedly arranged on the right side wall ofan inner cavity of the angle adjusting box body. A supporting plate is rotationally arranged on the hinge base in a hinged mode. A guide column is fixedly installed on the outer end face of a rotatingplate. The supporting plate is arranged on the circumference of the guide column in a sliding and sleeving mode. The transformer substation lightning protection device is simple and reasonable in structure, convenient to move, convenient to detach, assemble and maintain, beneficial for angle adjustment, flexible to use and suitable for use and popularization.
Owner:宁夏中科天际防雷检测有限公司
Systems and methods for directing a current
InactiveUS7502215B2Connection to earthDischarge by conduction/dissipationLightning strikeEngineering
A method for directing a current generated by a lightning striking a wind turbine is described. The method includes directing the current from a main shaft of the wind turbine to a brake disc attached to the shaft, and directing the current from the brake disc to one of a spark gap and a roller mechanism coupled to a down-conductor at a ground voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
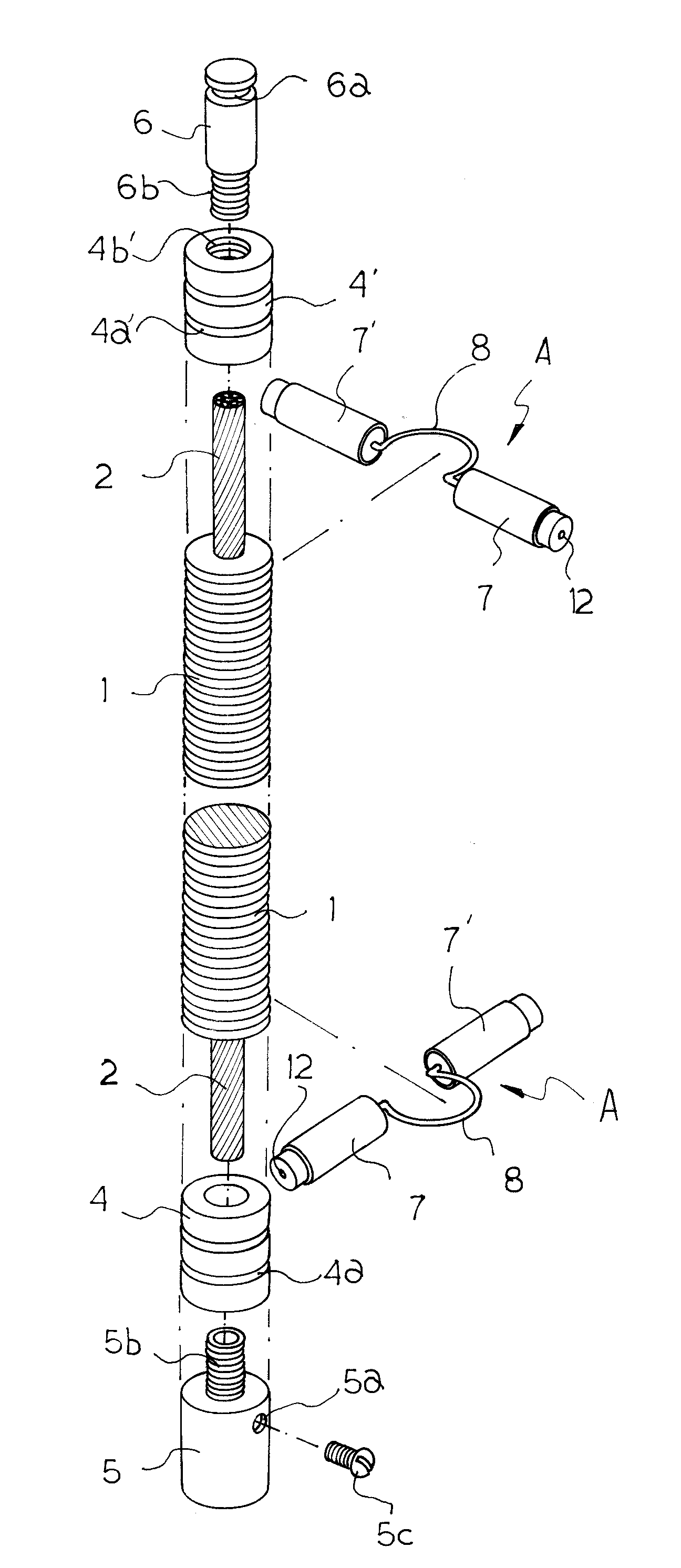
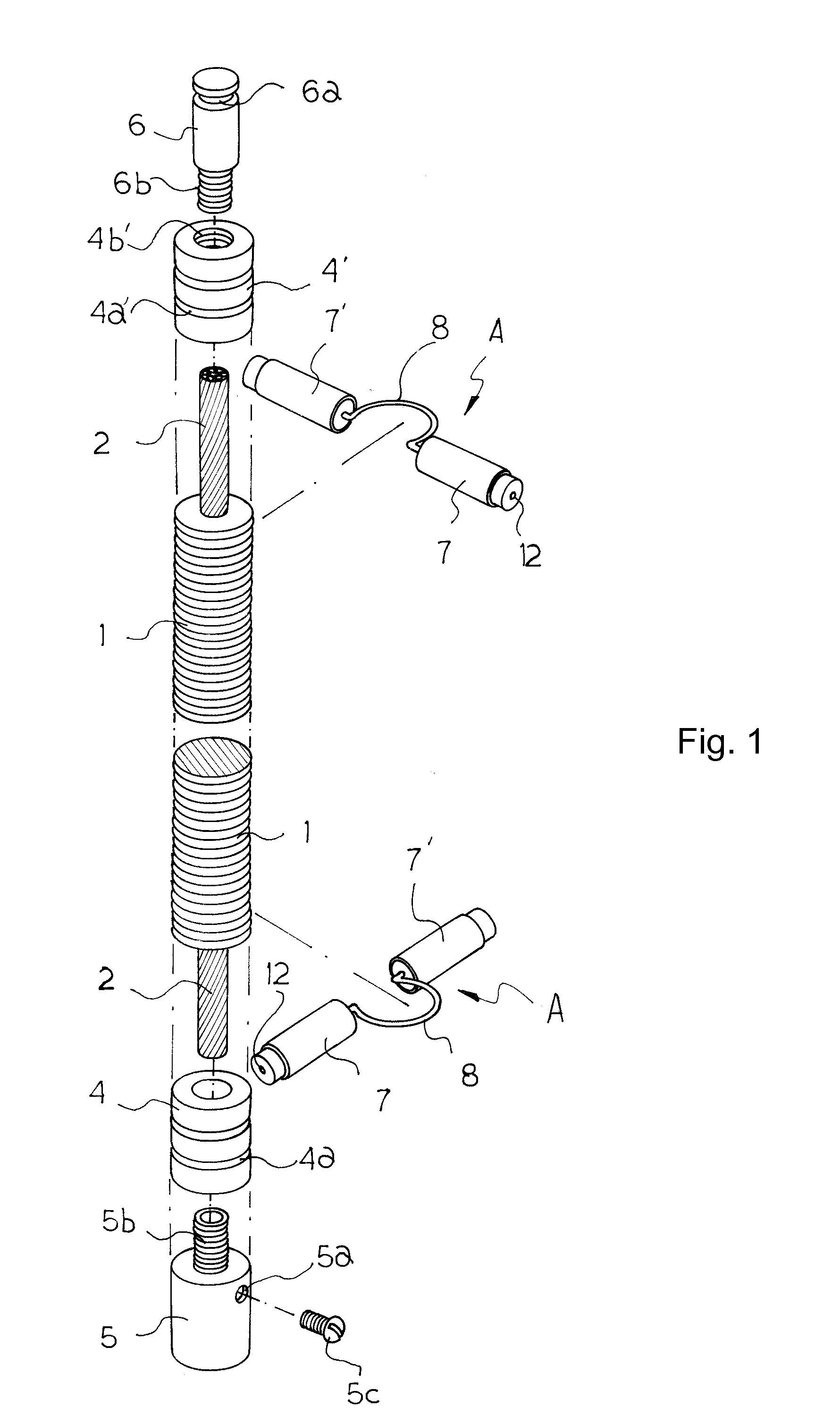
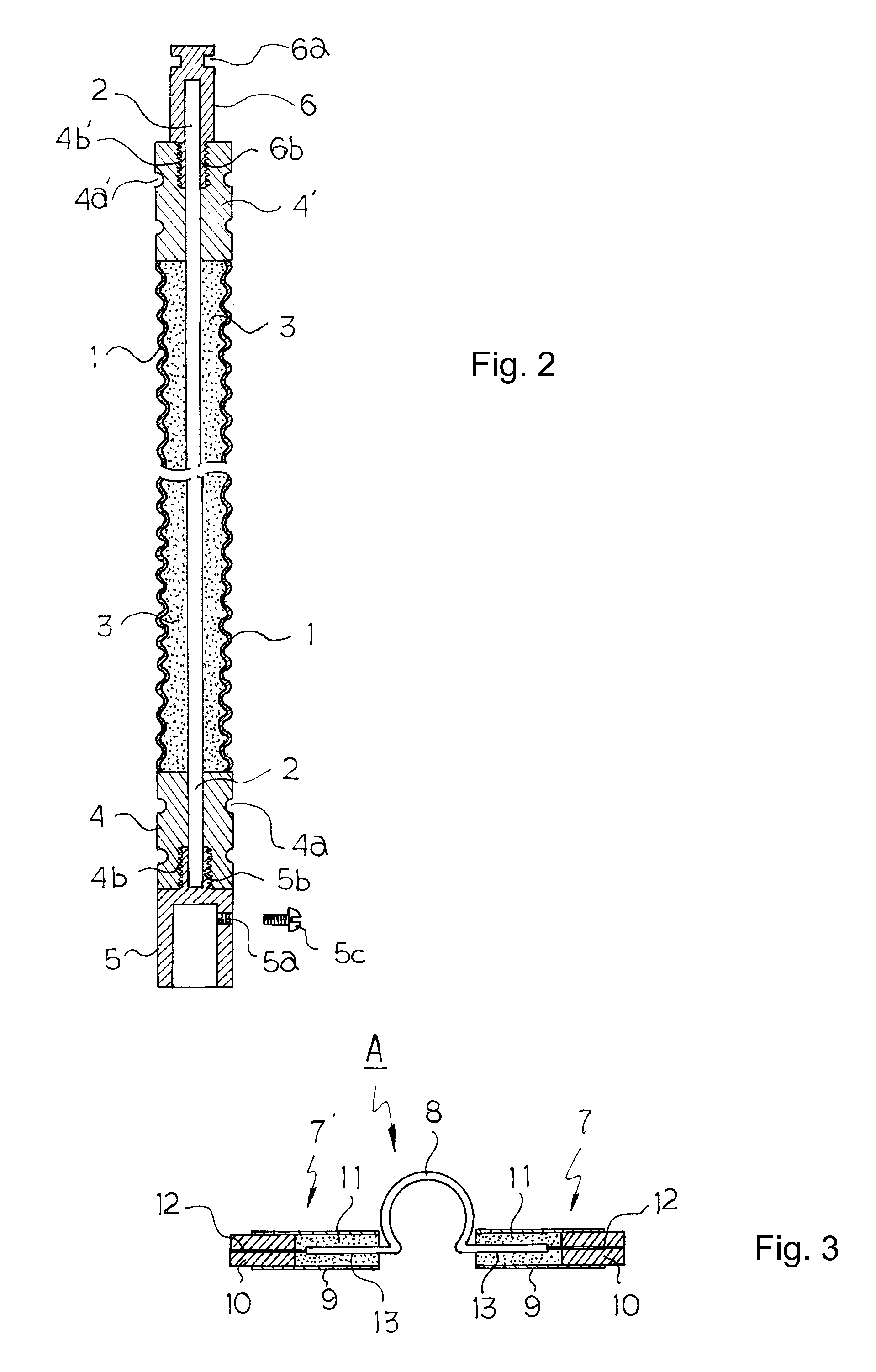
Grounding Wire Structure Having Stainless Steel Covering and Method of Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20080217041A1Prevent burstAvoid mistakesLine/current collector detailsRigid-tube cablesGraphiteGround line
The present invention provides a grounding wire structure having a stainless steel covering and a method of manufacturing the grounding wire structure. In the present invention, first and second hollow connection frames (4) and (4′), each of which has a compressing groove (4a), (4a′) and an internal thread (4b), (4b′), are coupled to respective opposite ends of a stainless steel pipe (1), in which a grounding wire (2) is provided, and which is filled with graphite (3). Corrugated grooves are formed in the outer surface of the stainless steel pipe (1). A connection socket (5) is coupled to the internal thread (4b) of the first connection frame (4). A connection rod (6) is coupled to the internal thread (4b′) of the second connection frame (4′). Discharge tip assemblies (A), each of which has discharge tip bodies (7) and (7′) connected to each other through a connection pin (8), are fitted over the corrugated grooves of the stainless steel covering pipe (1).
Owner:KIM KUI YEUN
Structure for installing lightning arrester for electric pole
InactiveUS7701688B2Reduce in quantityOverhead installationProtective switch detailsShackleGround line
Owner:JEON YOO CHEOR
Wind turbine lightning connection means method and use hereof
ActiveUS7654790B2Simple mechanical structureReliable servicePropellersPump componentsNacelleTurbine blade
The invention relates to a wind turbine (1) comprising stationary means such as a nacelle (3) and a tower (2) comprising stationary lightning protection means (46), and rotating means such as a rotor including at least one wind turbine blade (5) and shaft means (14), each of said at least one wind turbine blade (5) comprising rotating lightning protection means (47). The stationary and rotating lightning protection means (46, 47) comprise contact surfaces (17, 18) connected by lightning connection means (15). The lightning connection means (15) comprises at least two contact means (19, 19a, 19b) adapted for connecting said rotating and stationary lightning protection means (46, 47). Further, it comprises at least one electric conductor (30) establishing a dedicated connection between said at least two contact means (19, 19a, 19b) and force transferring means (26, 27) for said at least two contact means (19, 19a, 19b) establishing a continuous connection between said at least two contact means (19, 19a, 19b) and the contact surfaces (17, 18) of said stationary and rotating lightning protection means (46, 47). The invention also relates to lightning connection means (15) for a wind turbine (1), a method and use hereof.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
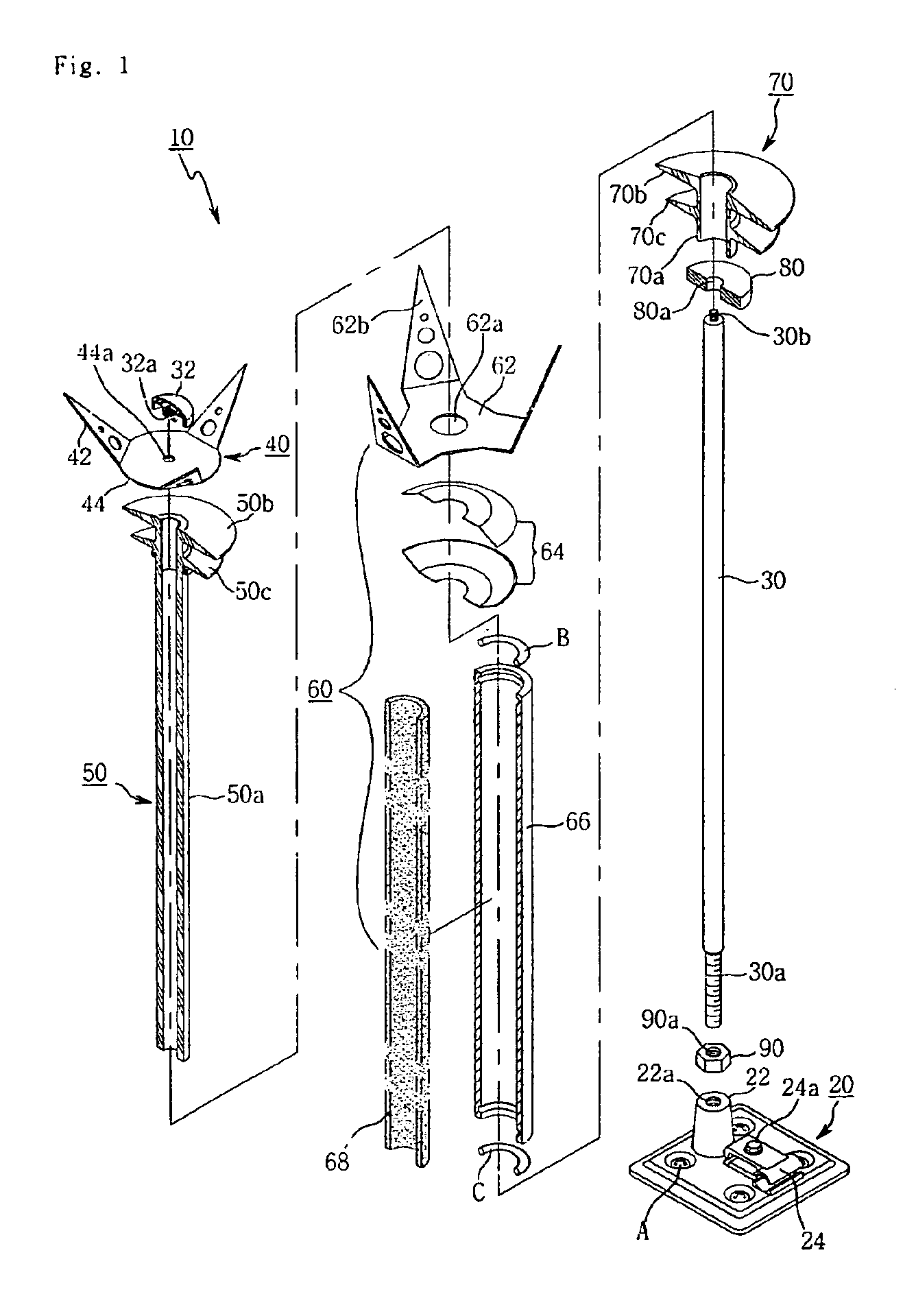
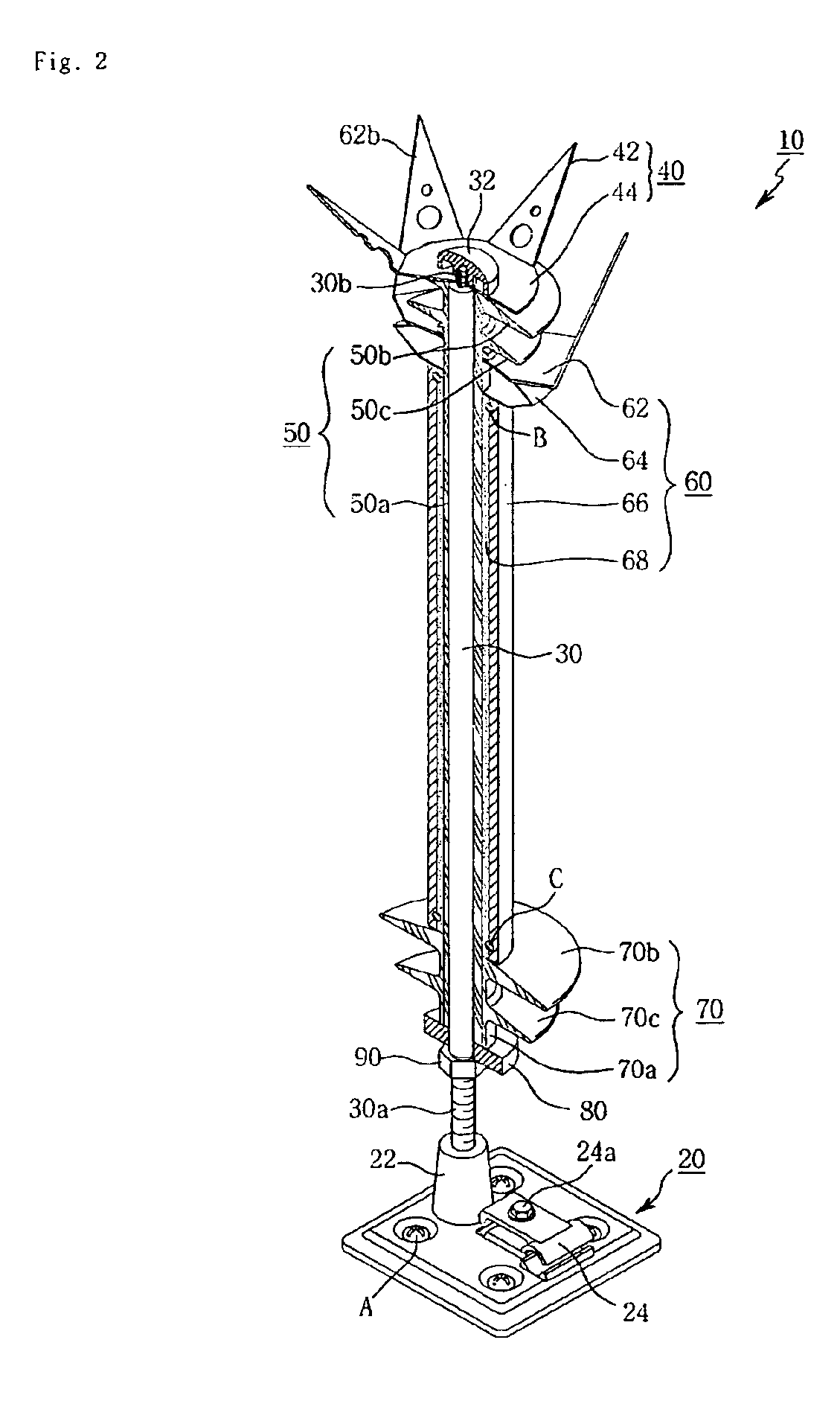
Lightning protection device of windmill blade
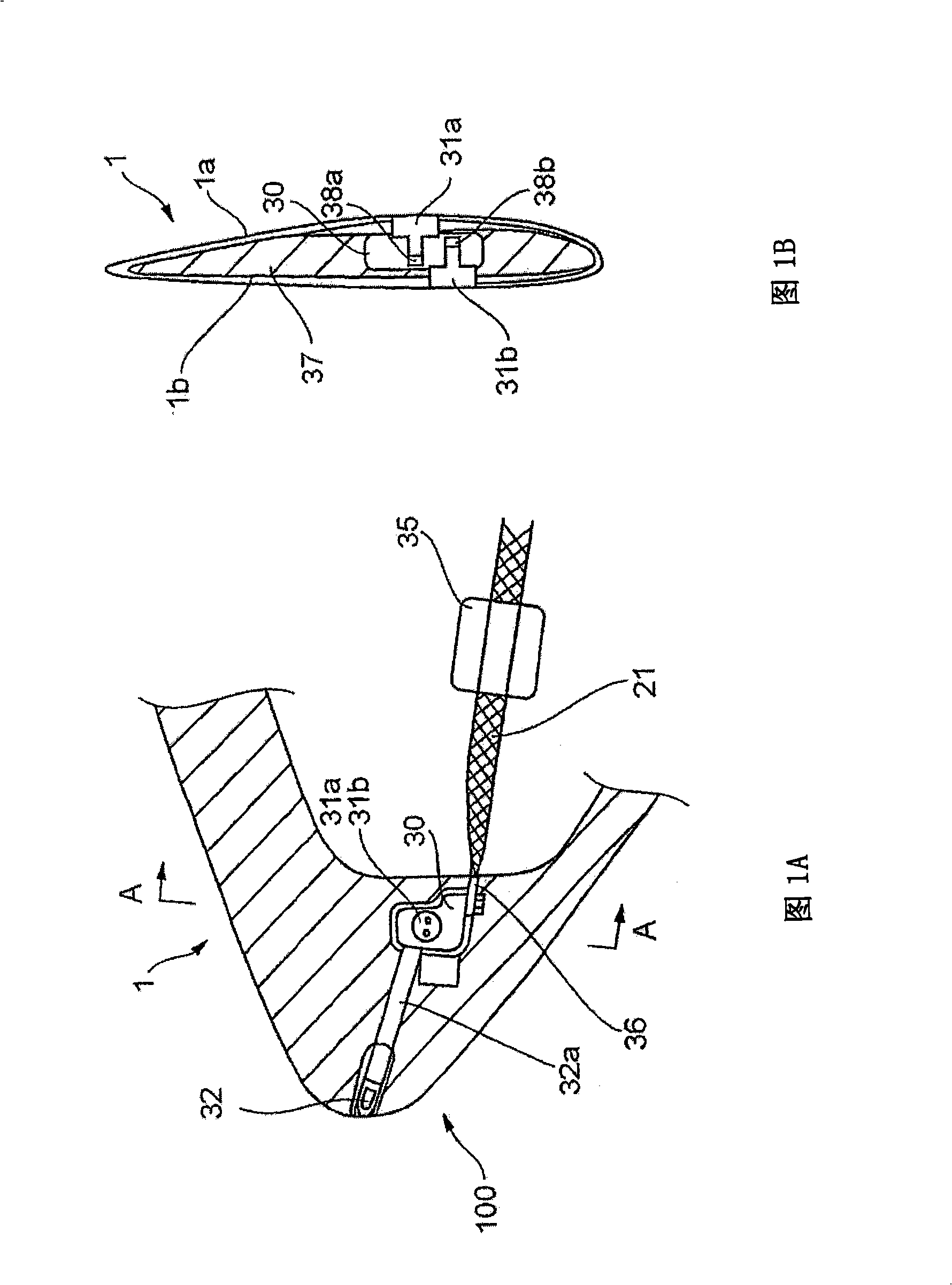
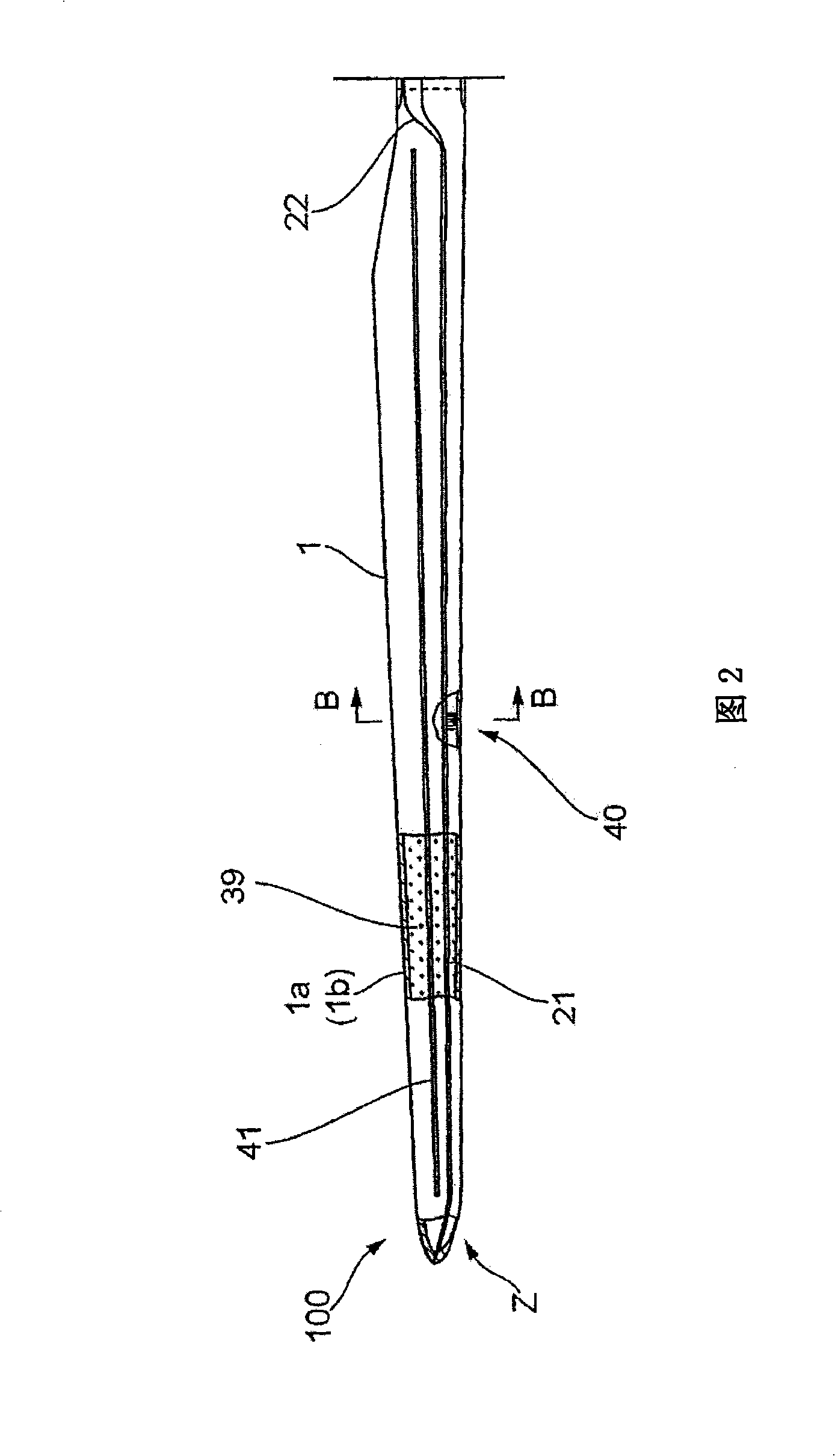
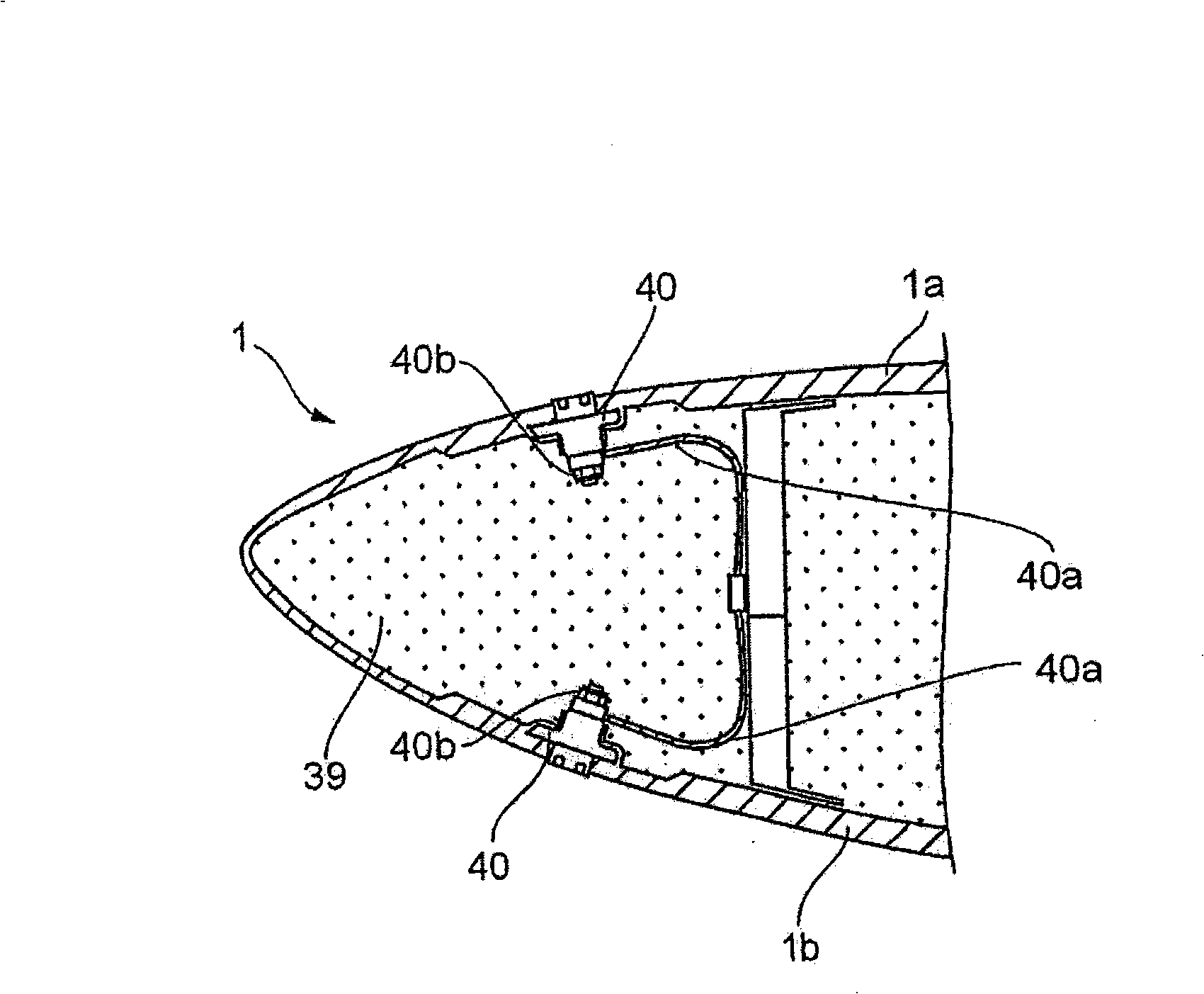
ActiveCN101341334ASimple structureEasy to operateConnection to earthDischarge by conduction/dissipationLightning strikeCountermeasure
The present invention proposes a lightning protection device of a windmill blade, comprising a tip receptor assembly having receptors which are mounted, in particular to, the tip end part of the blade where the blade profile becomes smaller, and having a simple structure so as to be readily assembled, and an intermediate receptor assembly having a receptor which is set at the outer surface of the blade so as to exhibit an effective countermeasure against increasing of the air pressure in the blade upon a lightning striking upon the blade, a lightening current being discharged to the ground from the receptors through connection equipment such as lead wires laid through the inside of the blade the windmill body and bypass brushes, characterized in that a base plate made of an electrically conductive material and connected thereto with the lead wires is embedded in the blade, and the receptors are secured and supported to the base plate, being exposed at the outer surface of the blade. Further, the present invention also proposes a method of assembling the lightning protection device.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
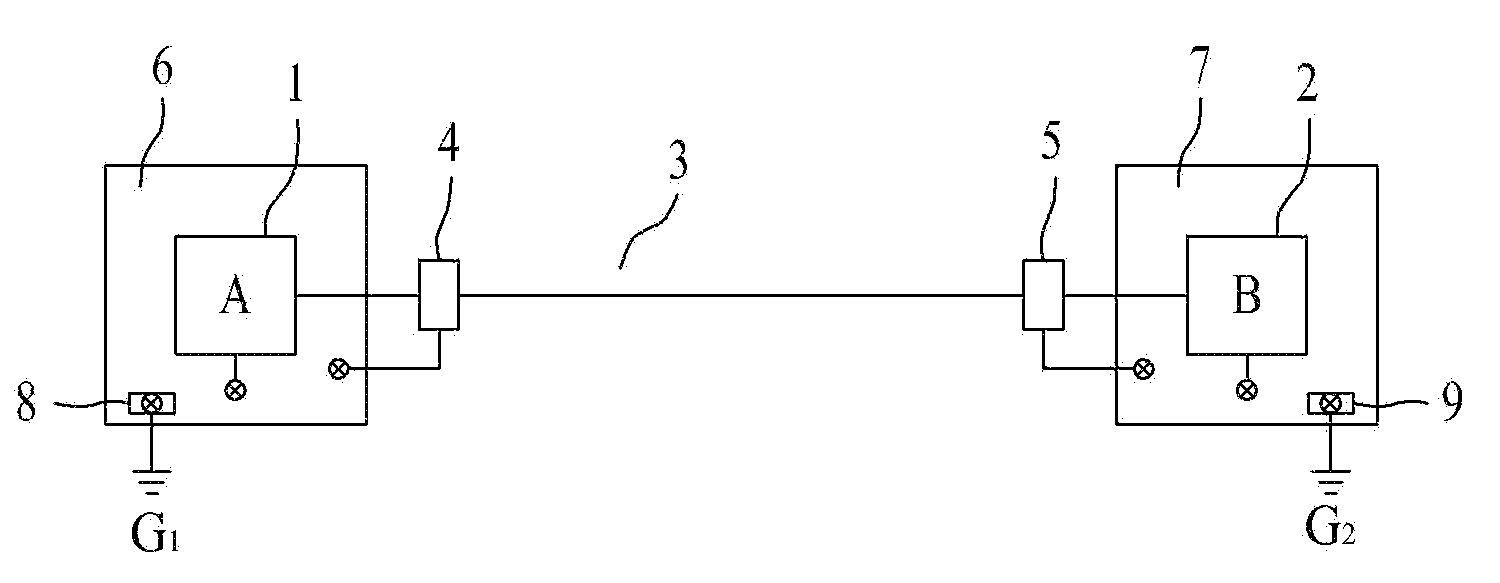
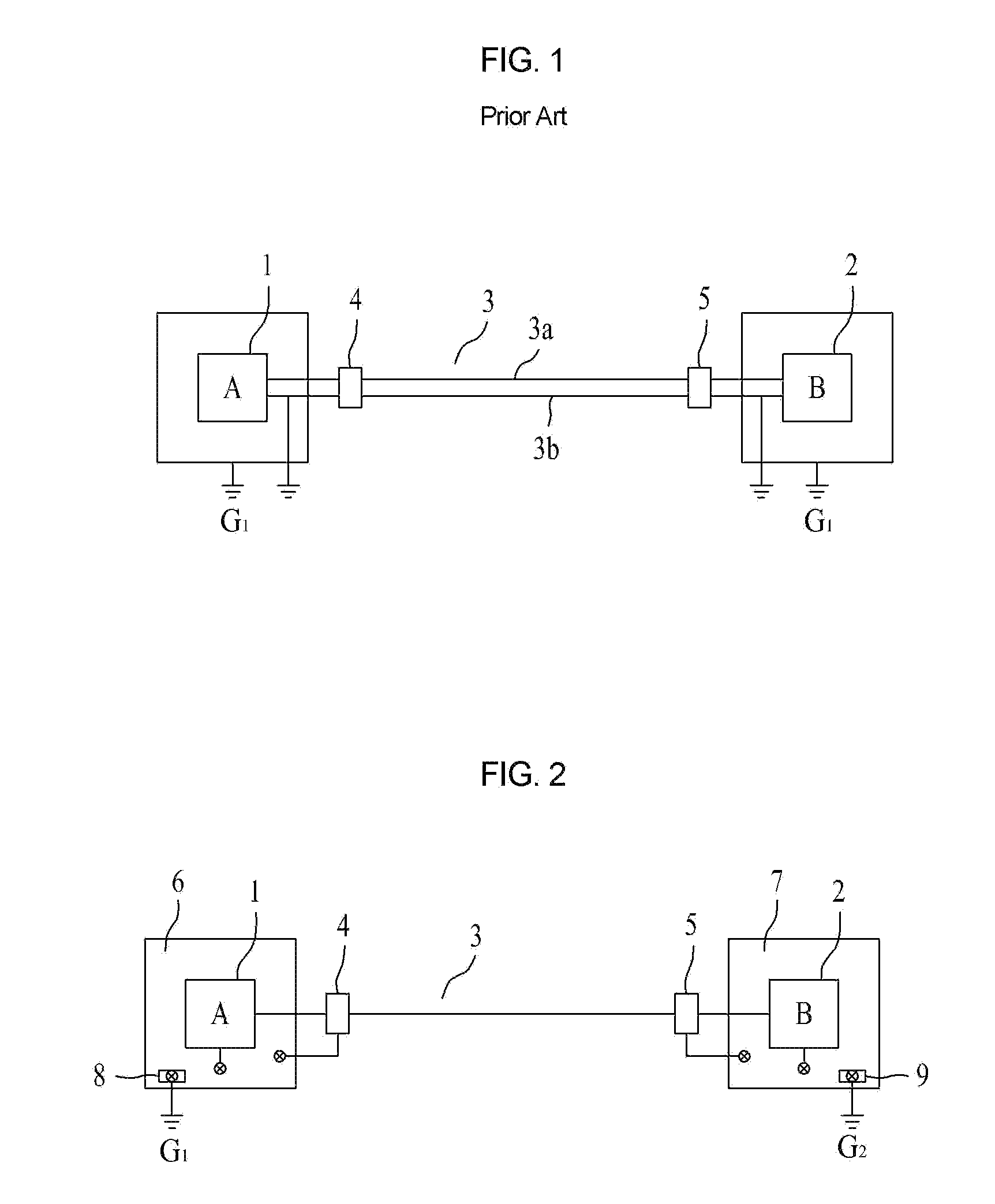
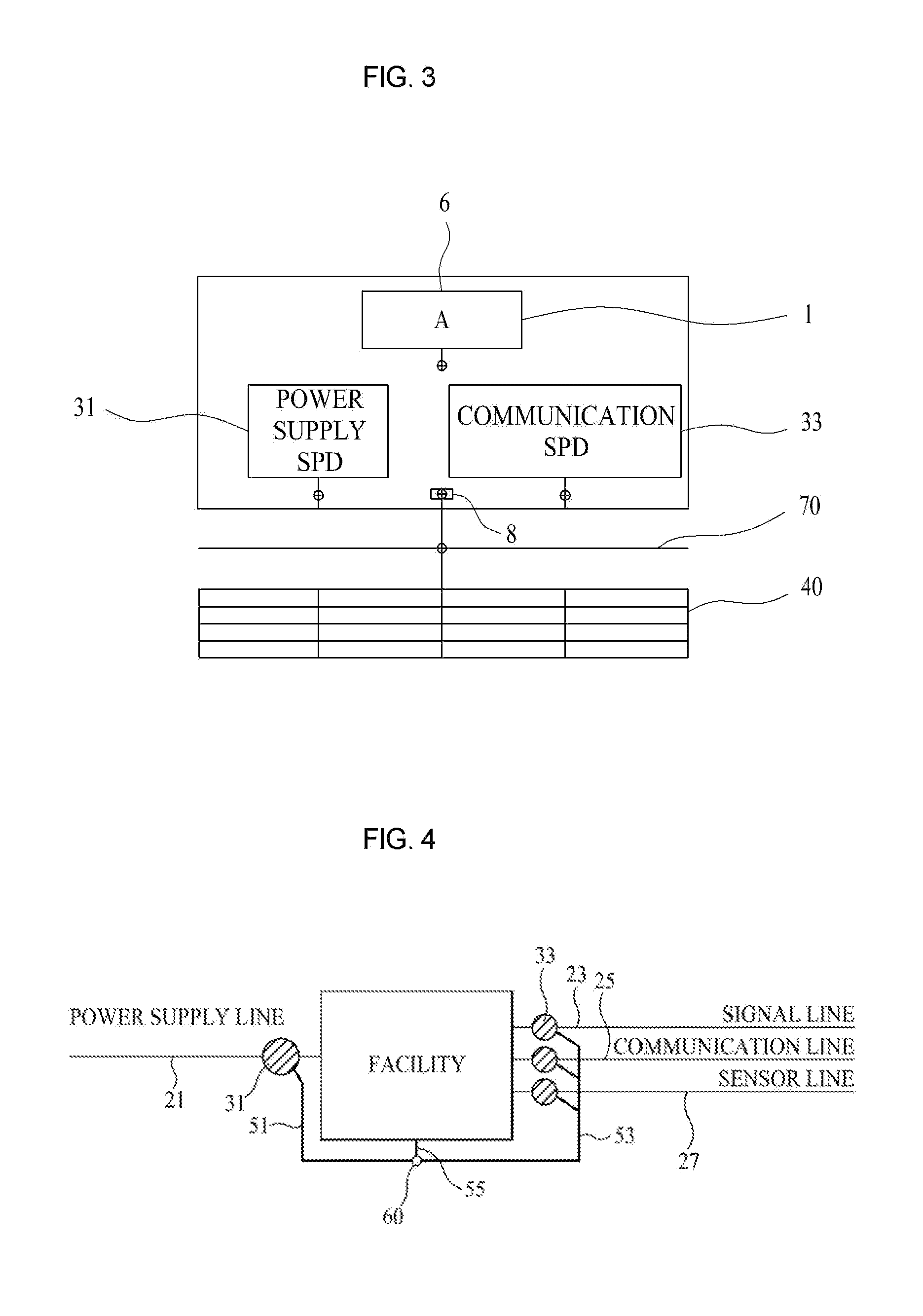
Smart ground bonding method for facilities
InactiveUS20120147511A1Avoid damageConnection to earthArrangements responsive to excess voltageEngineeringElectrical wiring
Disclosed is a smart ground bonding method for facilities, wherein an electric wire is connected between a first facility and a second facility, a first surge protection device is connected between the first facility and the electric wire, a second surge protection device is connected between the electric wire and the second facility, and wherein ground terminals of the first and second surge protection devices are bonded to metal boxes of the first and second facilities and sides of the bonded metal boxes are connected to the ground. The present invention can form potential differences between all lines of facilities such that they correspond to an equipotential to a ground, blocking a surge current passing through the facilities and basically preventing damage due to a lightning surge.
Owner:SURGELAB KOREA
Lightning arrester
InactiveUS20050061525A1Improve reliabilityDischarge safetyTents/canopiesConnection to earthPolymer insulationEngineering
Disclosed is a lightning arrester. The lightning arrester safely discharges earth charge of a main electrode section and an auxiliary electrode section regardless of a variation of charge contained in air, so charge charged in a thundercloud is safely discharged into the earth even if the thundercloud is located far-remote from the earth. The lightning arrester has a fixing base fixedly installed on an object to be protected by grounding a lightning circuit connected to a ground electrode grounded to an earth, a fixing bar vertically installed at one side of an upper surface of the fixing base and made of conductive material, a main electrode section making contact with an upper portion of the fixing bar and made of conductive material, an upper polymer insulator including an elongated column member formed at a center thereof with a hollow section for receiving the fixing bar therein, and upper and lower disc-shaped plates integrally formed at an upper end of the elongated column member for ensuring an insulation distance, and an auxiliary electrode section aligned below the main electrode section without making contact with the main electrode section and made of conductive material. The elongated column member of the upper polymer insulator passes through a center of the auxiliary electrode section in order to fill space charge in the auxiliary electrode section.
Owner:LEE TECH KOREA CO LTD
Lightning protection device and method
ActiveUS7265961B2Emergency protective arrangement detailsConnection to earthElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical connection
An air terminal for lightning protection includes a central rod and a curved conductive surface around the central rod. The central rod includes a tip mount for receiving a tip from a tip set that includes a plurality of tips that impart different electrical characteristics to the air terminal. For example, the tips of the tip set may have a variety of radii of curvature, and may provide different gap sizes between the various tips and the curved conductive surface. The curved conductive surface and the grounded central rod may be electrically coupled together via an electrical connection. The electrical connection may include a fixed impedance or resistance, or may include a variable impedance unit that automatically varies impedance based on a voltage difference between the curved conductive surface and the grounded central rod.
Owner:ERICO INT
Systems and methods for directing a current
A method for directing a current generated by a lightning striking a wind turbine (100) is described. The method includes directing the current from a main shaft (116) of the wind turbine to a brake disc (202) attached to the shaft, and directing the current from the brake disc to one of a spark gap (224) and a roller mechanism (302) coupled to a down-conductor at a ground voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC RENOVABLES ESPANA SL
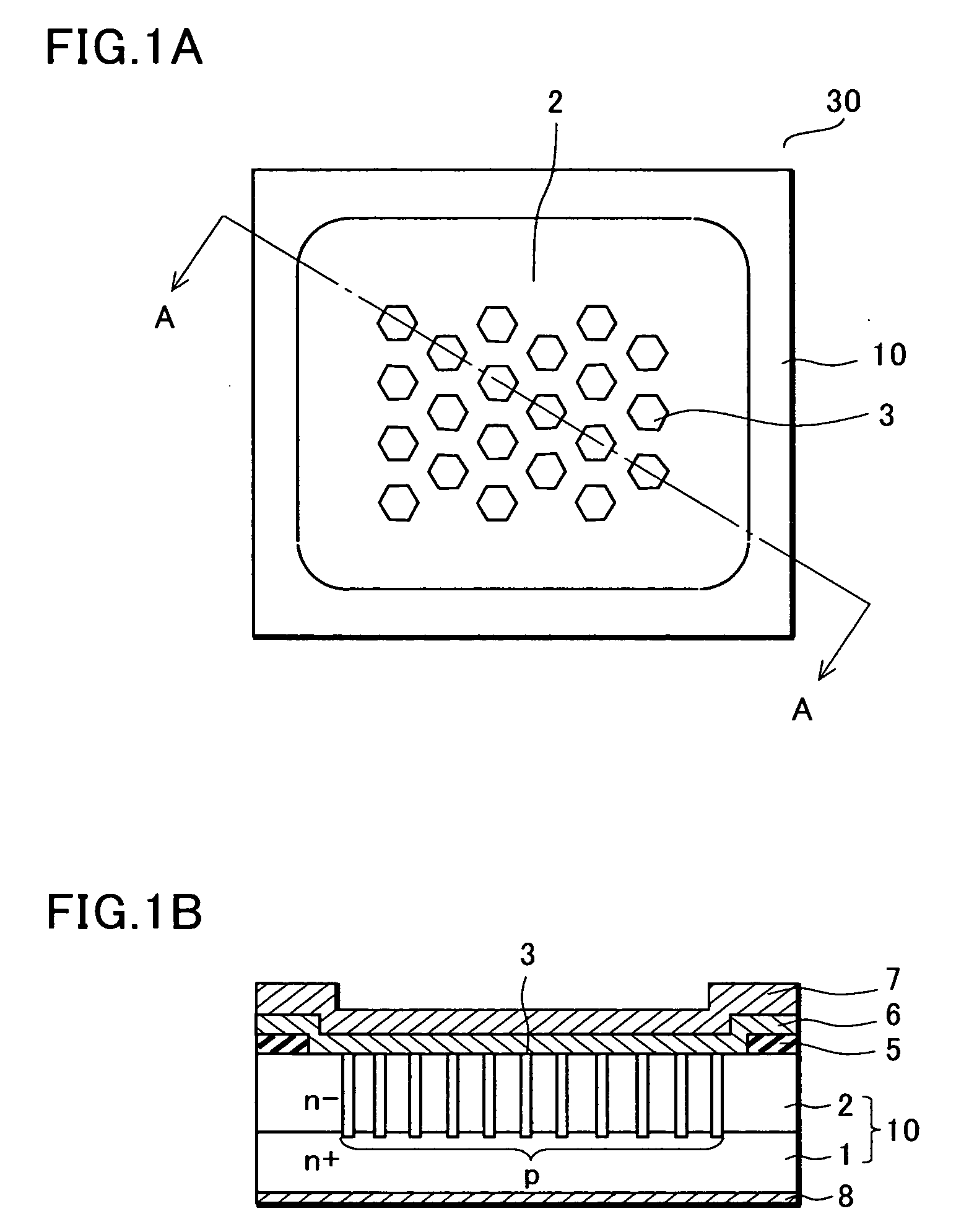
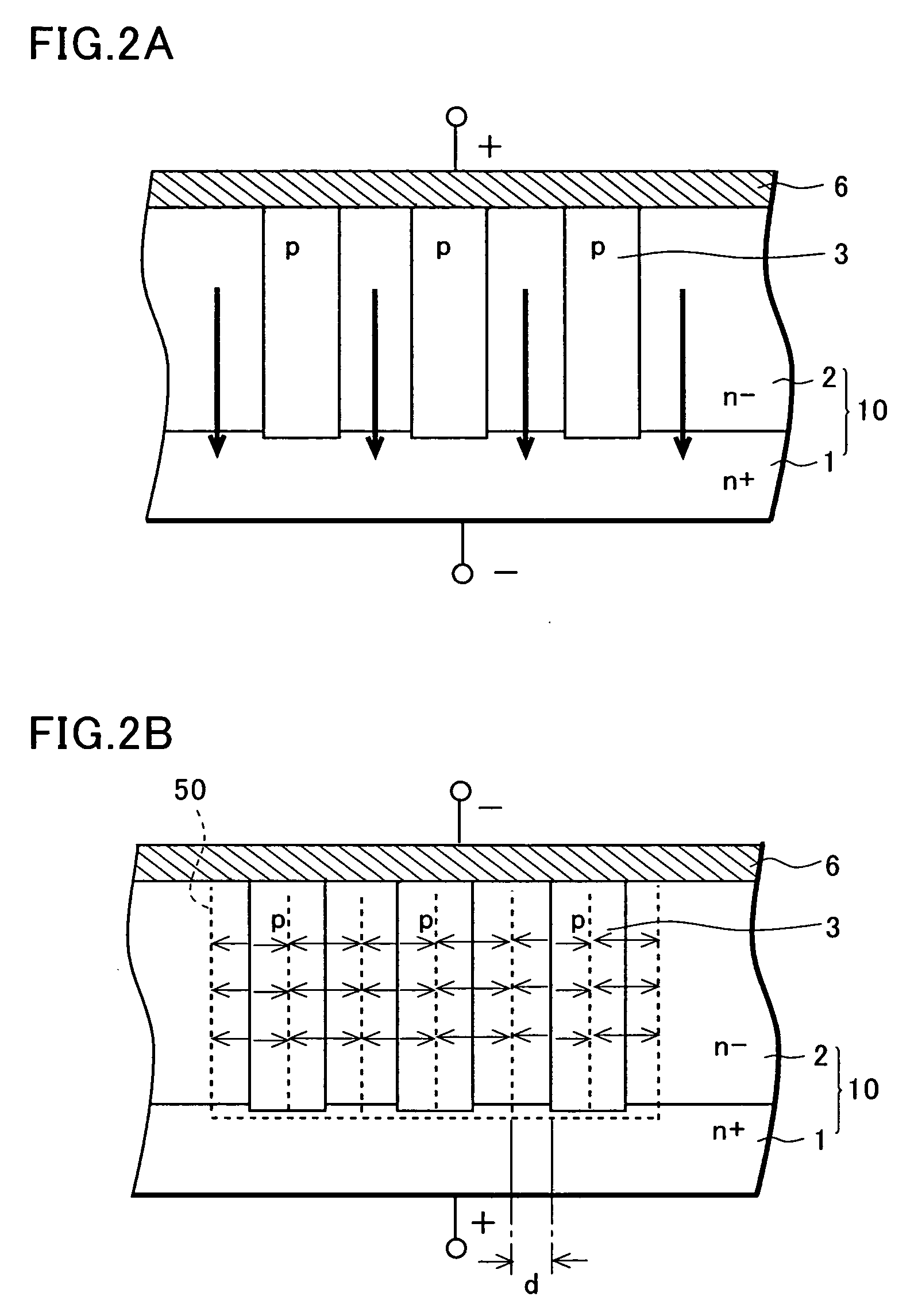
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050184406A1Improve breakdown voltageStay unifiedConnection to earthConnection contact member materialSchottky barrierDevice material
Conventionally, VF and IR characteristics of a Schottky barrier diode are in a tradeoff relation and there is a problem in that an increase in a leak current is unavoidable in order to realize a reduction in VF. To solve the problem, p type semiconductor regions of a pillar shape reaching an n+ type semiconductor substrate are provided in an n− type semiconductor layer. When a reverse voltage is applied, a depletion layer expanding in a substrate horizontal direction from the p type semiconductor regions fills the n− type semiconductor layer. Thus, it is possible to prevent the leak current generated on a Schottky junction interface from leaking to a cathode side. Since an impurity concentration of the n− type semiconductor layer can be increased to a degree at which the depletion layer expanding from the p type semiconductor regions adjacent to each other can be pinched off, it is possible to realize a reduction in VF and it is possible to secure a predetermined breakdown voltage if only the depletion layer is pinched off.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
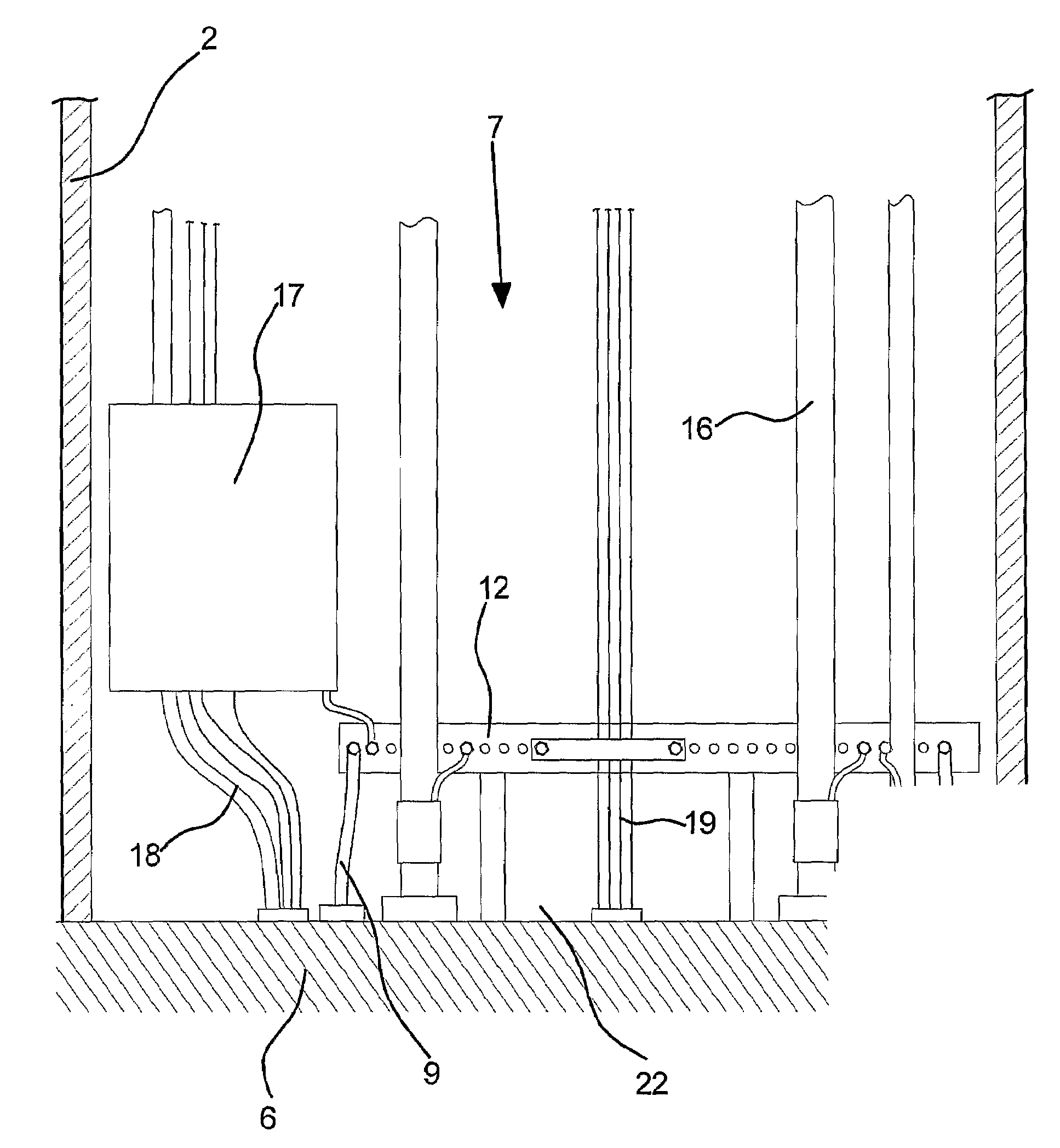
Earthing system for a wind turbine connected to a utility grid and for a wind turbine park
ActiveUS20090272557A1Simple and secure and efficientSecure and efficient connectionPropellersWind motor supports/mountsElectricityElectric power system
The invention relates to an earthing system for a wind turbine connected to a utility grid. The wind turbine comprises at least one electric system such as low or high voltage power systems and cables (16), at least one control system such as a SCADA system and control cables (18), and / or at least one safety system such as a lightning protection system, wherein a connection to an electrically earth potential is established from one defined place (12) within the wind turbine for said systems. In another embodiment, a wind turbine comprises at least two electric systems such as a lightning protection system and a low or high voltage power system, an electrically earth potential established by at least one foundation earthing (8) including at least one earthing wire embedded partly or totally in the wind turbine foundation (6), and at least one electric conducting means (9) extending radial from said wind turbine (1) into the ground, wherein a connection to said electrically earth potential is established from one defined place within the wind turbine (1) for said systems. Even further the invention relates to an earthing system
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Receptor for wind turbine blade lightning protection
InactiveUS8727723B2Reduce localized electrical field stressHigh dielectric strengthPropellersConnection to earthElectricityLightning strike
A receptor assembly for lightning protection of an object, such as a wind turbine blade, includes a receptor disk configured to be placed on a surface of the object, a receptor block insulator with an integral receptor block, a cover that engages the receptor block insulator, and a cap that engages the cover. The receptor disk and the receptor block may be made of electrically conductive materials, and the cover, and the cap, and the receptor block insulator may define a chamber among them that is lined with an electrically-conductive coating sandwiched between relatively high dielectric media to electrically isolate and shield internal parts of the receptor assembly from receiving a lightning strike directly.
Owner:ERICO INT
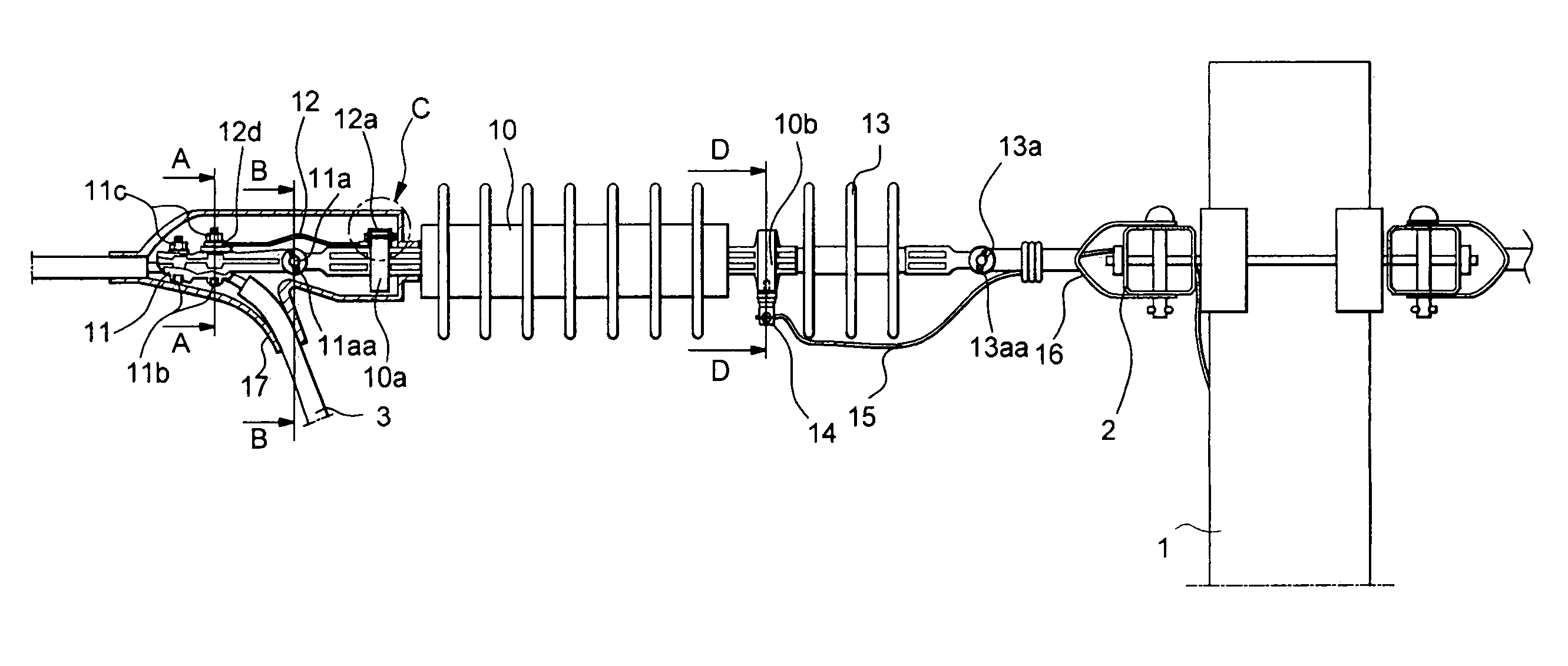
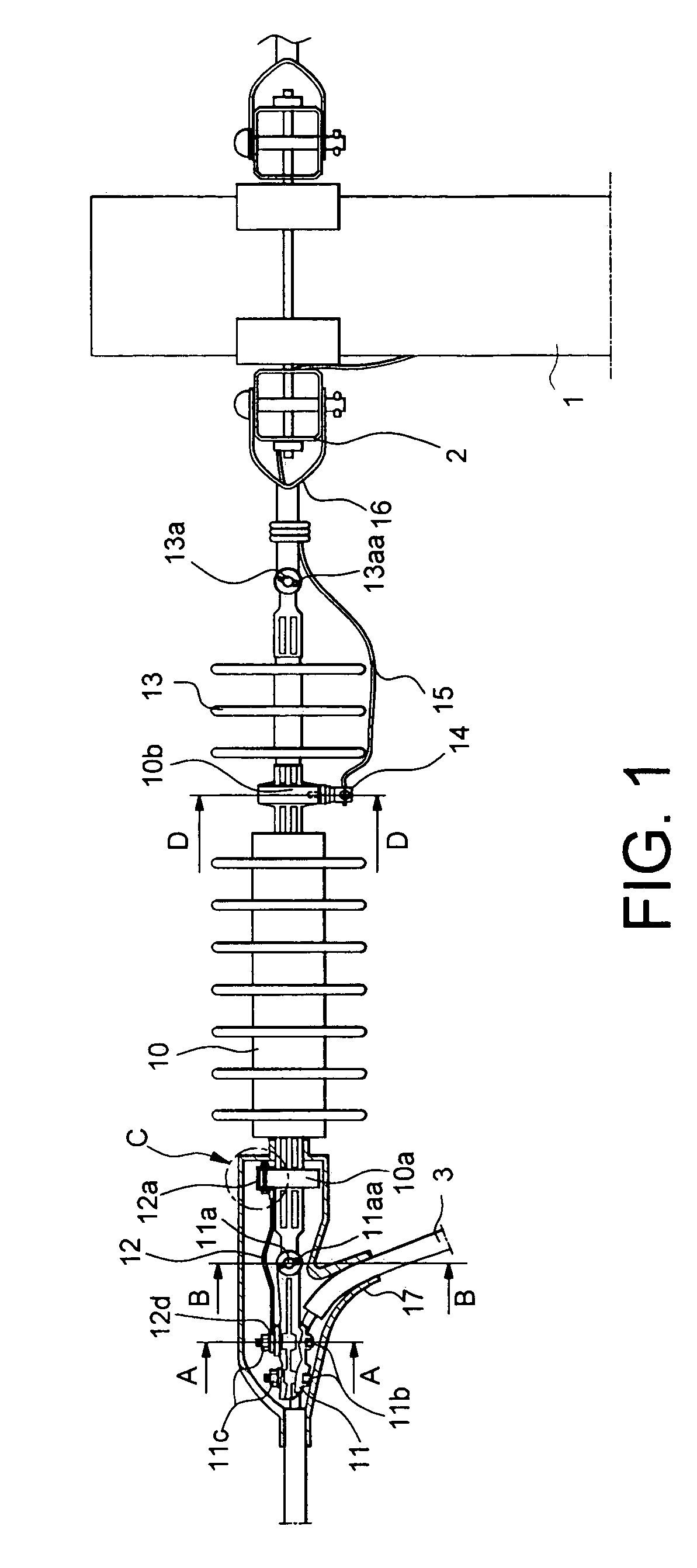
Lighting protection system for wind generators
ActiveUS8081414B2Easy maintenanceAvoid passingEmergency protective arrangement detailsConnection to earthMetal stripsElectrical conductor
The invention relates to a lightning transmission element (1) which is fixed to a hub (21) of a wind generator and which is formed by a first conductor bar (2) which is fixed to a second insulating bar (5). According to the invention, a first end (4) of the lightning transmission element (1) is positioned opposite a metal strip (18) that is disposed at the root of each blade (10) of the wind generator at a first distance which enables a flashover of incident lightning at a point on a blade (10) of the wind generator, while a second end (3) thereof is positioned opposite a gutter (12) of a nacelle (13) of the wind generator at a second distance which enables a lightning flashover. The lightning is conveyed from the point on the blade (10) at which it is incident thereon to the earth through a series of conduction means including the lightning transmission element (1), said means preventing the lightning from striking the sensitive parts of the wind generator.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Lightning protection and deicing device of ground wire on high voltage overhead power transmission line
ActiveCN106655055AReduce power consumptionQuickly dischargedOverhead installationInsulated cablesElectrical conductorElectric power system
The invention relates to a lightning protection and deicing device of a ground wire on a high voltage overhead power transmission line, and aims at comprehensively solving the problem occurring on the ground wire so that the overhead ground wire is enabled to have lightning protection and also have the functions of communication optical fibers, deicing and snow removing, energy conservation and loss reduction and field power taking. The technical scheme is the lightning protection and deicing device of the ground wire on the high voltage overhead power transmission line. The lightning protection and deicing device is provided with the ground wire erected on a tower. Insulators are connected between the tower and the ground wire. The ground wire is composed of an internal conductor, an insulting layer and an external conductor. The internal conductor is directly connected with the tower. The external conductor is connected with the tower through the insulators. The external conductor and the insulators are connected and installed on a lightning protection unit of the bottom part of the tower through a high voltage connecting cable. The other end of the lightning protection unit is grounded. The lightning protection unit is bridged between the insulators of the two sides of the tower, and an electric reactor is connected in parallel on the lightning protection unit. The lightning protection and deicing device is suitable for safety and energy conservation of power system line engineering.
Owner:张兴莲 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com