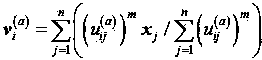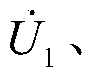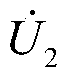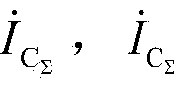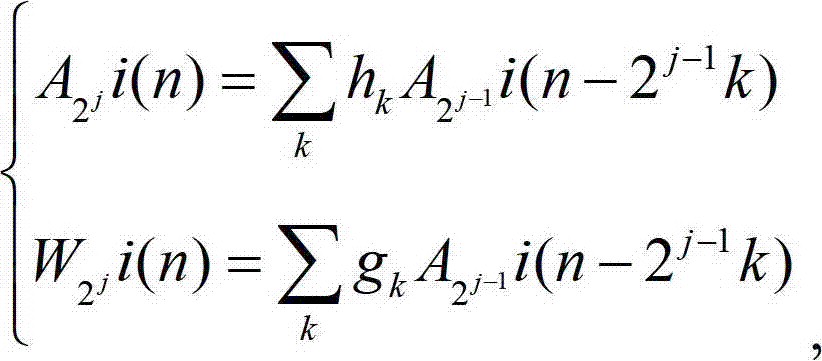Patents
Literature
979 results about "Earthing system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
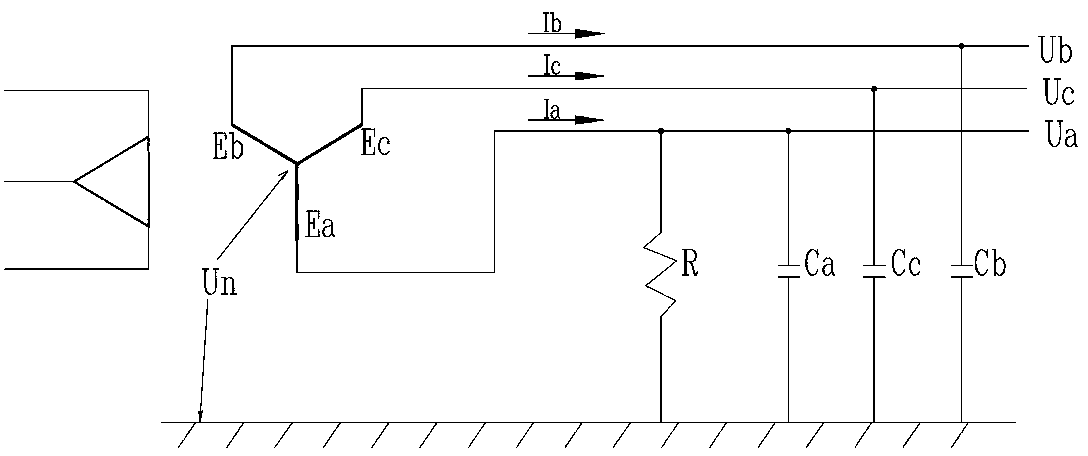
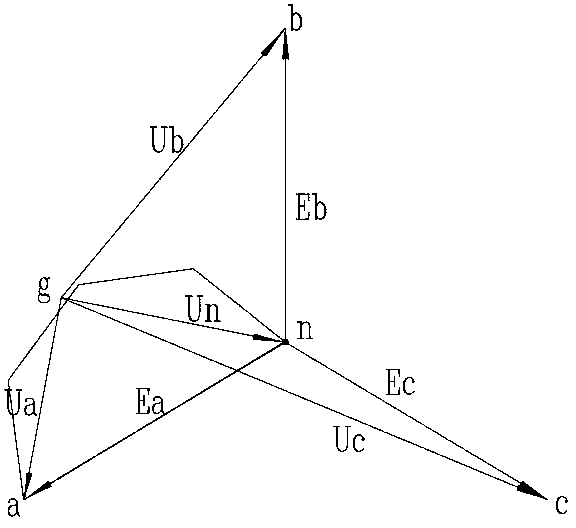
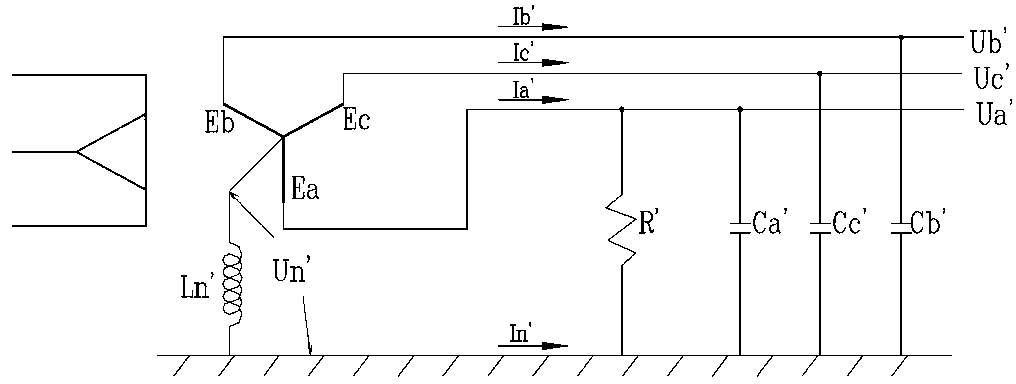
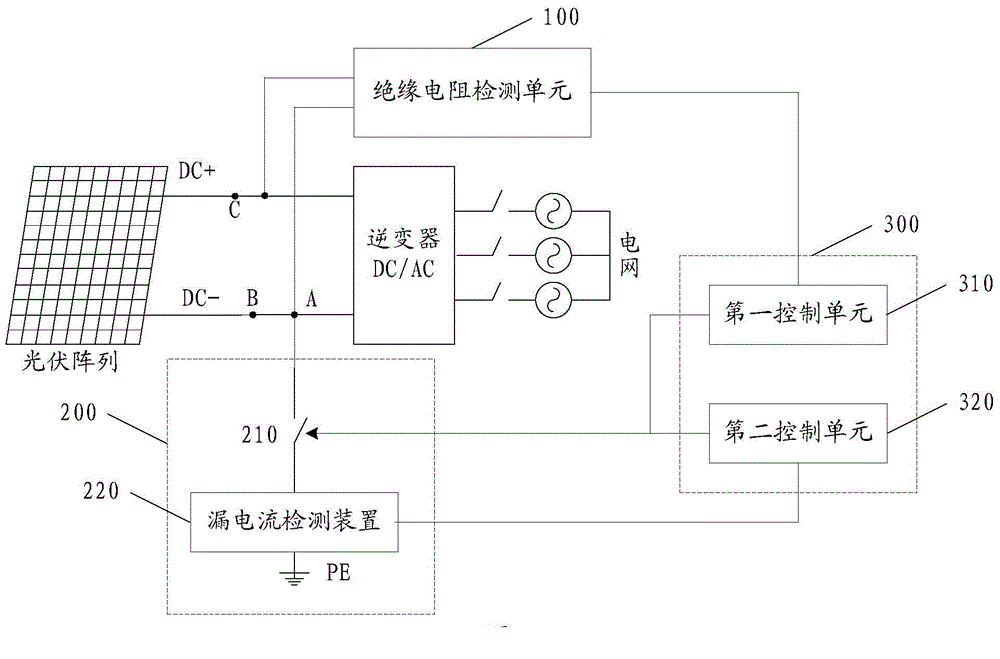
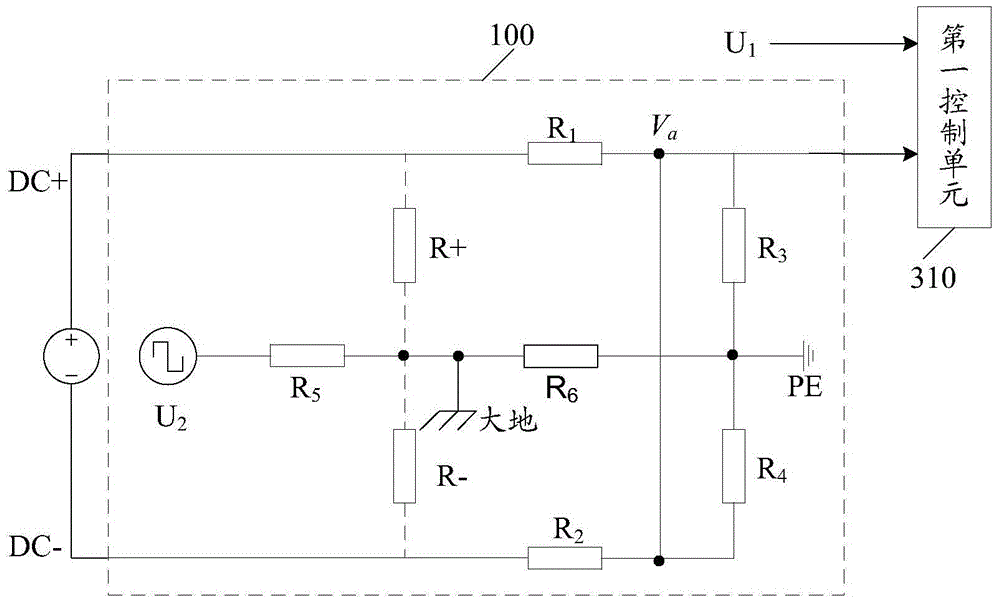
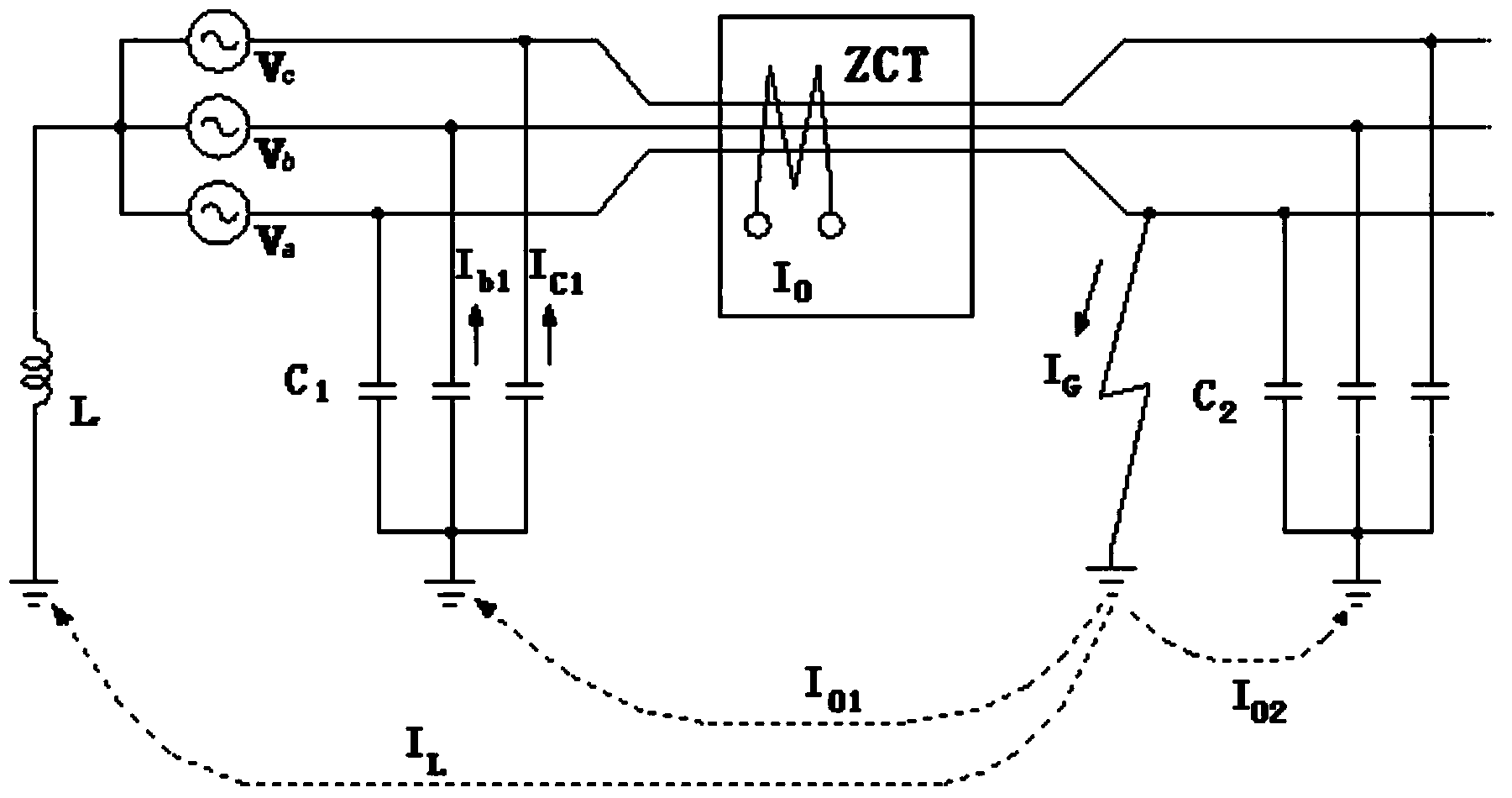
In an electrical installation, an earthing system or grounding system connects specific parts of that installation with the Earth's conductive surface for safety and functional purposes. The point of reference is the Earth's conductive surface. The choice of earthing system can affect the safety and electromagnetic compatibility of the installation. Regulations for earthing systems vary considerably among countries, though most follow the recommendations of the International Electrotechnical Commission. Regulations may identify special cases for earthing in mines, in patient care areas, or in hazardous areas of industrial plants.
Variable diameter wind turbine rotor blades
A system and method for changing wind turbine rotor diameters to meet changing wind speeds and control system loads is disclosed. The rotor blades on the wind turbine are able to adjust length by extensions nested within or containing the base blade. The blades can have more than one extension in a variety of configurations. A cable winching system, a hydraulic system, a pneumatic system, inflatable or elastic extensions, and a spring-loaded jack knife deployment are some of the methods of adjustment. The extension is also protected from lightning by a grounding system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
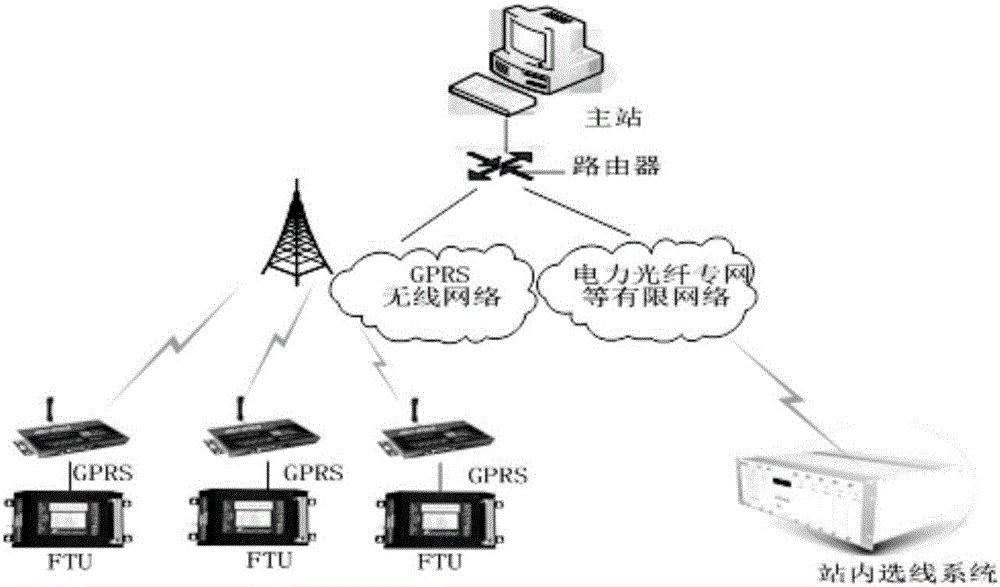
Distribution line breakage monitoring method and device based on voltage and current vectors
The invention discloses a distribution line breakage monitoring method and device based on voltage and current vectors. The method and device are applied in a three-phase three-wire power grid system with a neutral point not grounded or not directly grounded. The line breakage monitoring device is installed on a monitoring point of a line. The line leakage monitoring device works out the effective value and the phase angle of the three-phase line voltage and three-phase current at the same moment through the three-phase line voltage waveform and three-phase current waveform of a periodic three-phase synchronous sampling distribution line; whether a single-phase line breakage fault occurs on an upper-side line of the monitoring point or not is judged by computing and comparing the proportional relation of the sum of the largest voltage, the smallest voltage and the second smallest voltage in the effective value of the three-phase line voltage and the phase difference value relation of the smallest voltage and the second smallest voltage; whether a single-phase line breakage fault occurs on an upper-side or lower-side line of the monitoring point by comparing the proportional relation between the negative-sequence current and the positive-sequence current; whether a single-phase ground fault occurs on a lower-side line of the monitoring point by calculating the zero sequence current value.
Owner:福建省银邦电力工程有限公司
Sectional detection method of small current earthing fault of power system
InactiveCN1421704AIncrease amplitudeHigh detection sensitivityFault locationTransient stateElectric power system
The sectional detection method of small current earthing fault of power system, especially single phase long distance system, is suitable for system with several detection units in different sectionsof the line. Each unit variance in zero-sequence voltage or current is used as fault starting condition, the transient zero-sequence current amplitude and initial polarity are calculated, and the main station determines the fault section based on the fault information the detectors report. The basic criterion is that the transient zero-sequence currents on two sides of the fault point have opposite polarity and that each transient zero-sequence current amplitude is proportional inversely to the distance to the fault point. The said method is suitable for system with unearthed neutral point, earthed arc extinguishing coil or high earthing resistance as well as system with reactive load.
Owner:SHANDONG KEHUI POWER AUTOMATION
Flexible grounding device single-phase grounding fault line selection and arc extinguishing method for power distribution network
InactiveCN107064733AImprove power supply reliabilityReduce protection misoperation rateFault location by conductor typesEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentFeeder lineControl engineering
The invention discloses a flexible grounding device single-phase grounding fault line selection and arc extinguishing method for a power distribution network. The method mainly comprises the steps: employing a virtual resistor control mode when a single-phase grounding fault happens to the power distribution network, controlling a flexible grounding device to inject a resistive current with the controllable amplitude value into a neutral point, enabling a system to operate in a small-resistance grounding mode, and judging a fault feed line through the measurement and comparison of the zero sequence currents of all feed lines, and giving the feedback to a relay protection device; employing a virtual inductance control method, controlling the flexible grounding device to inject an arc-extinguishing compensation current into the neutral point, enabling the system to operate in a resonant grounding mode, and achieving a purpose of single-phase grounding fault arc extinguishing. Through the switching of control modes, the method can solve problems that a resonant grounding system cannot accurately judge the fault feed line, a small-resistance grounding system is high in fault trip-out rate and a fault of a conventional flexible grounding device control method is difficult to detect during high-resistance grounding. The method can reduce the maloperation rate of protection, improves the fault arc extinguishing success rate, and improves the power supply reliability of the power distribution network.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Power distribution network fault circuit selection method based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristic vectors
ActiveCN103245883AThe principle is simpleImprove timelinessFault locationElectric power systemTransient current
The invention relates to a power distribution network fault circuit selection method based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristic vectors, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. When a power distribution network runs into a single-phase earth fault via an arc suppression coil grounding system, a transient zero-sequence current component detected by a measuring end is a nonlinear non-stationary signal formed by different frequency components. By taking the fault component as a study object, time-frequency characteristics of a fault transient current of the fault component are analyzed by utilizing the wavelet packet theory, time-frequency distribution regularities among all feeder lines under different fault conditions are described according to similarity of the time-frequency characteristics, and consequently line selection criteria based on transient zero-sequence current time-frequency characteristics can be obtained. The method is simple in principle, only utilizes short-time window zero-sequence current data of 5ms after the fault, can identify faulty feeders under the conditions of small fault angle and high resistance ground fault, has excellent timeliness and robustness, is free from influence of an arc fault or a resistance ground fault, requires a low sampling rate for hardware, and is highly practical.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Adaptive fault type fault line detection method for non-effectively earthed system
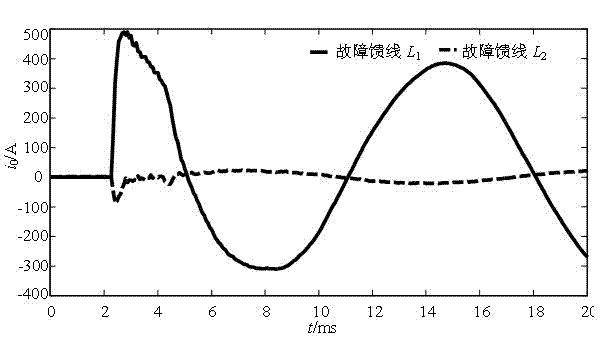
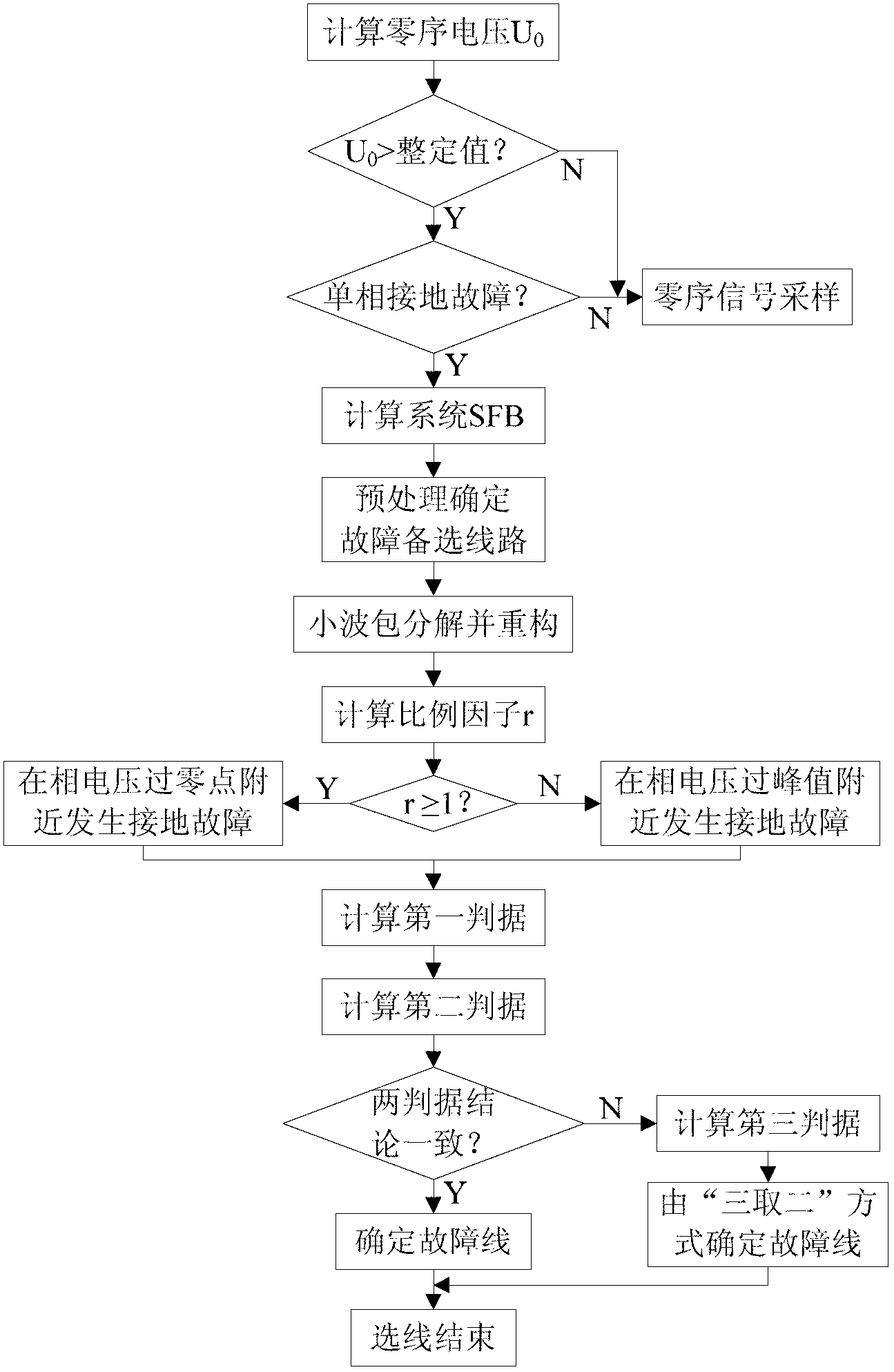
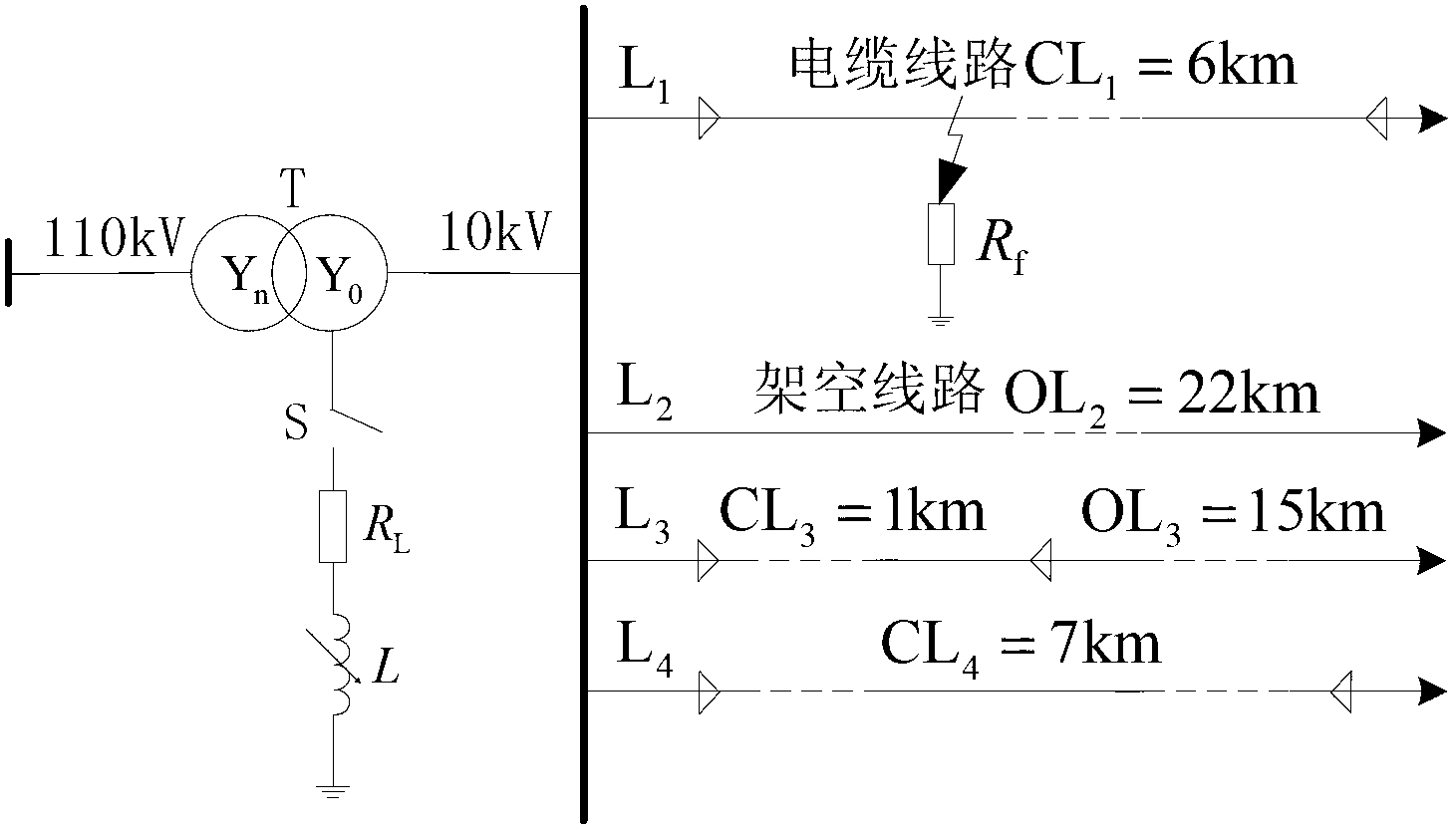
The invention discloses an adaptive transient characteristic fault line detection algorithm for a non-effectively earthed system by utilizing wavelet packet frequency division characteristics. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) monitoring a waveform of a bus zero sequence voltage, and when an instantaneous value of the bus zero sequence voltage exceeds a setting value, starting a fault line detection device and recording, and acquiring transient zero sequence current of each line; (2) calculating the selected frequency band of the system according to the grid structure and line parameters of a power distribution network; (3) decomposing and reconstructing the zero sequence current of the line by employing a wavelet packet, and taking three lines with the highest zero sequence current envelope line area as alternative fault lines; (4) calculating a scaling factor r and a transient factor h, and judging the earthing fault generation type; and (5) calculating a first amplitude value comparison criterion and a second polarity comparison criterion according to the earthing fault type, introducing a third criterion when the two criterion results are inconsistent, and selecting the earthing line. The method is accurate in line selection, and the earth line selection reliability of the power distribution network can be improved.
Owner:STATE GRID FUJIAN ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD +3
Single-phase ground wire selecting equipment and method of neutral-point uneffect earthed system
InactiveCN1912642AAmplitude controllableHigh strengthFault locationArrangements responsive to excess currentVoltage polarityElectrical polarity
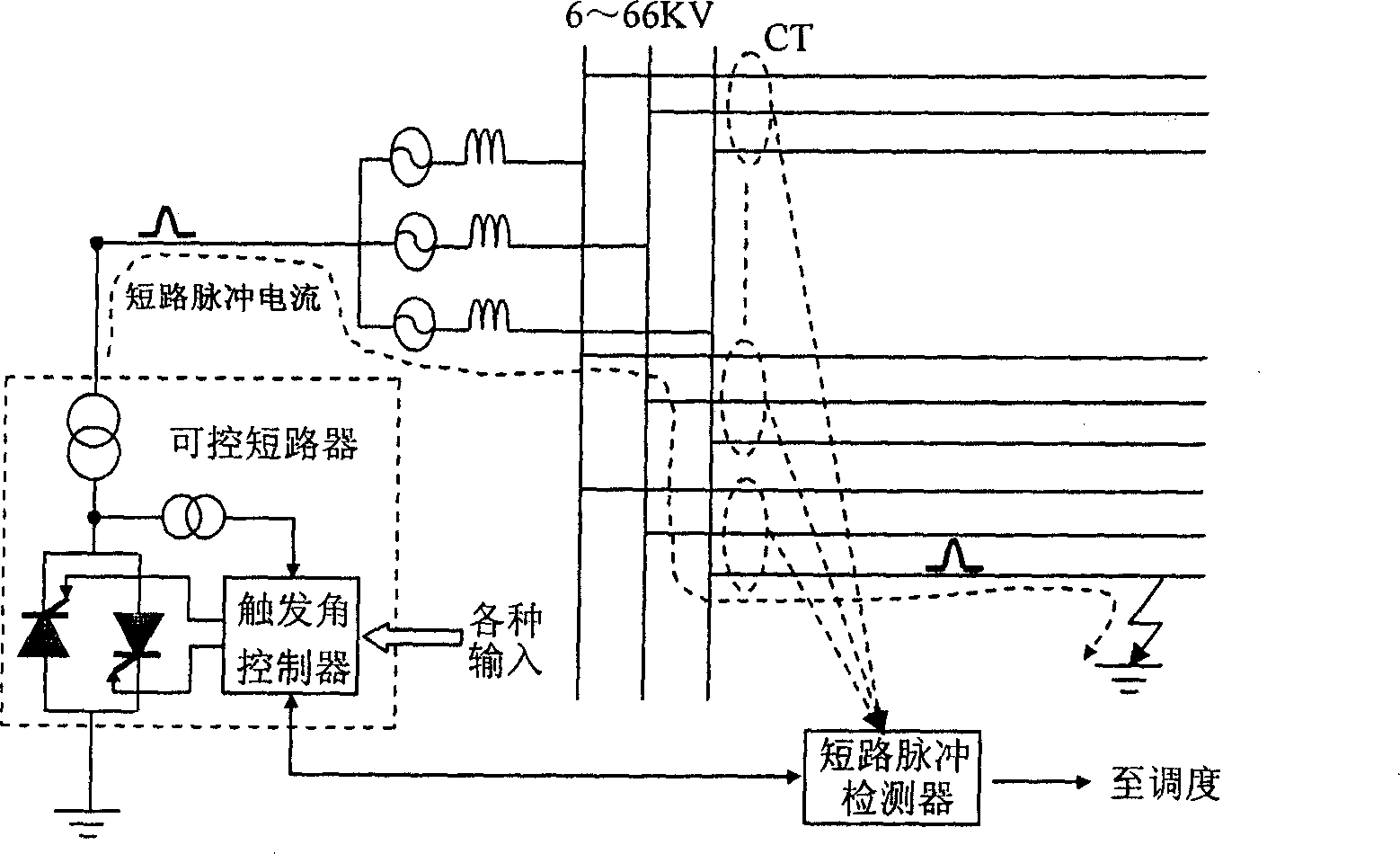
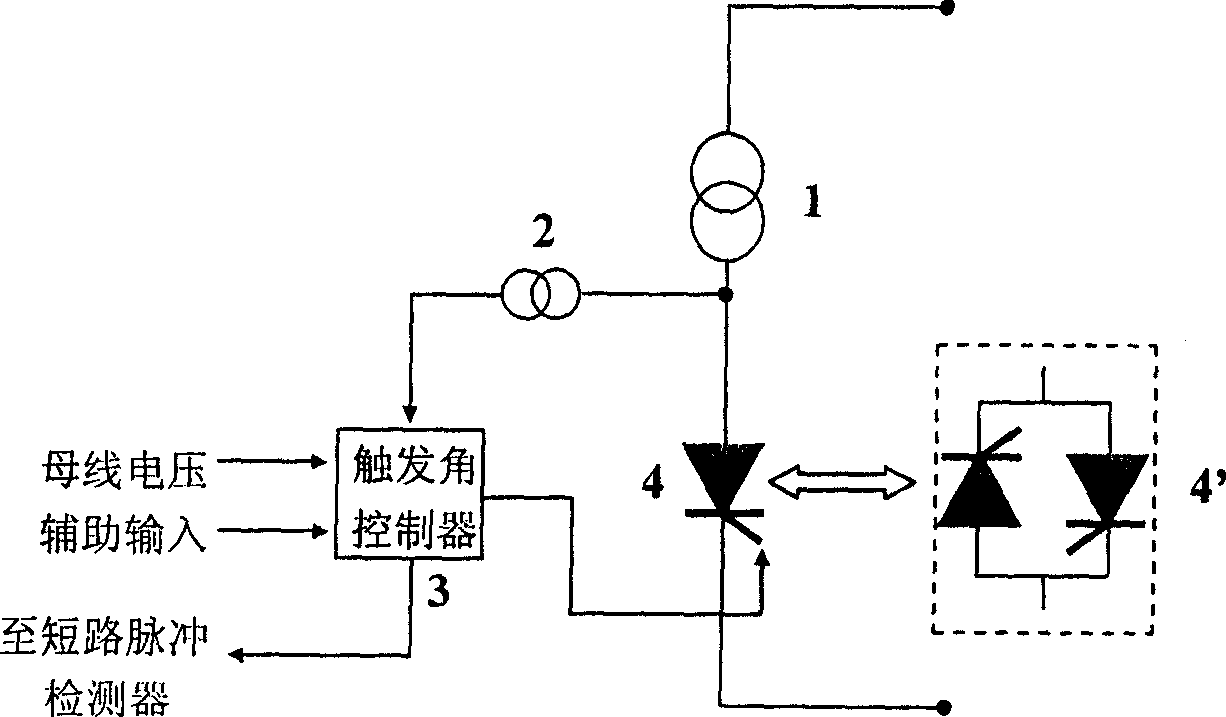
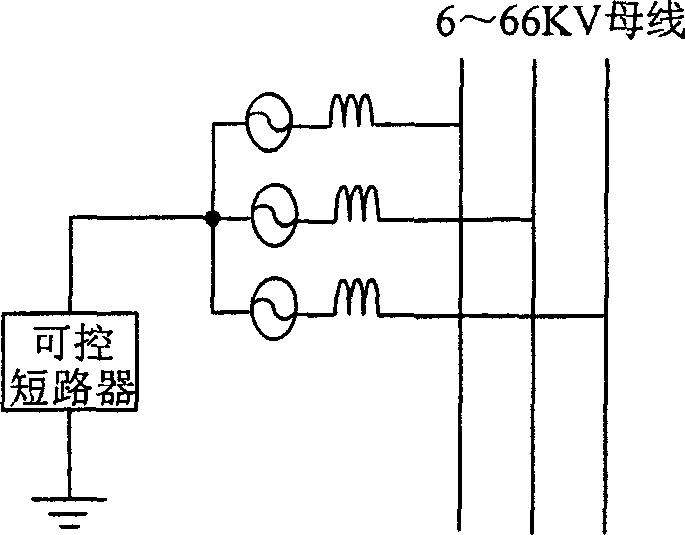
A method for selecting wire of single phase earthing in neutral point noneffective earthing system includes making instant short circuit between neutral point and ground at position near two ends voltage polarity from positive to negative over zero by short circuiter set between neutral point and ground when single phase earthing is occurred in neutral point noneffective earthing system and state is stabilized in order to generate a short circuit pulse current being used to judge earthing line through short circuit detector. The device for realizing said method is also disclosed.
Owner:徐文远 +1
Magnetizing inrush current suppression device for transformer and control method of same
ActiveUS20100039737A1Accurate calculationEnlarge the circuit breakerBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionResidual fluxElectrical polarity
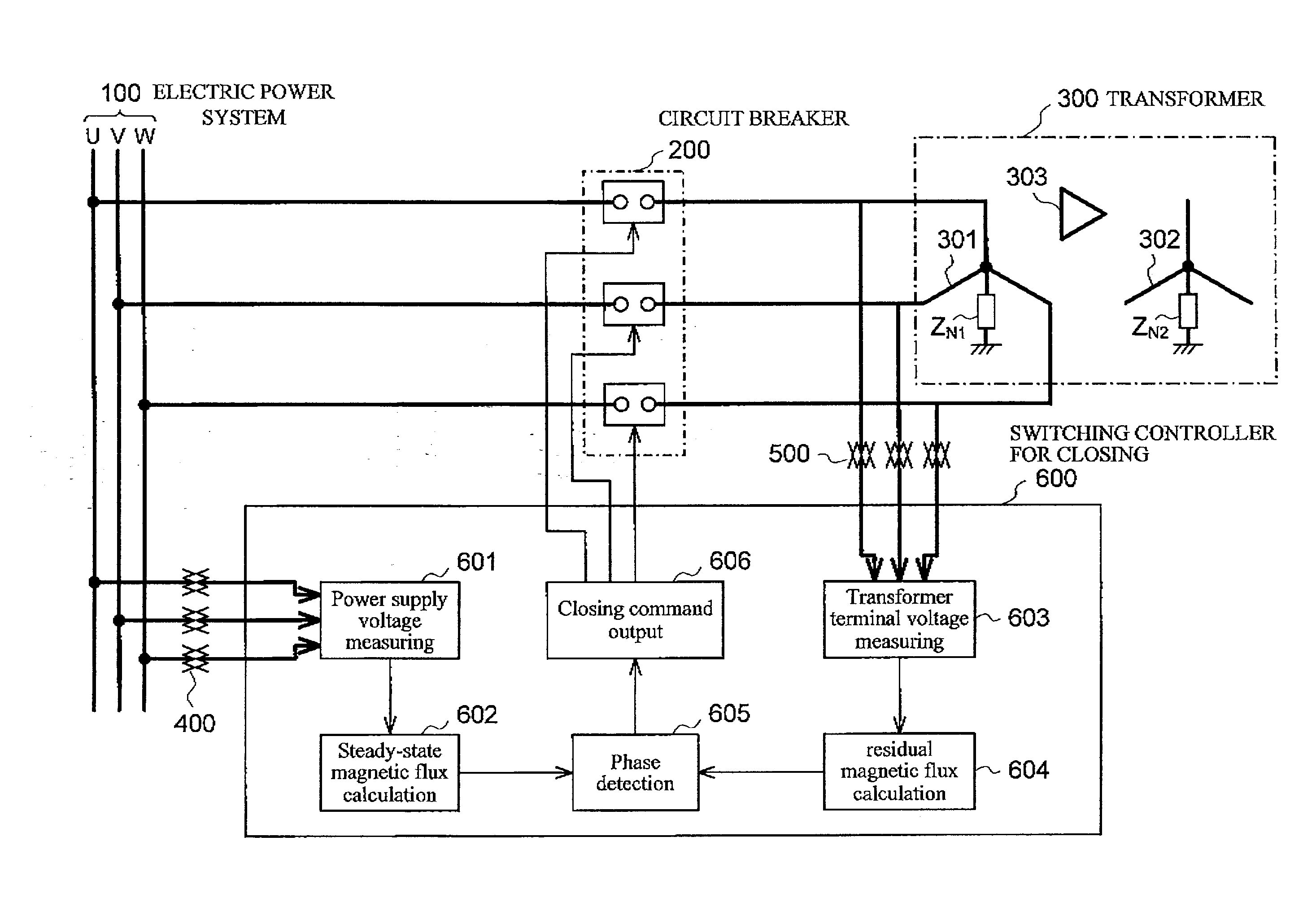
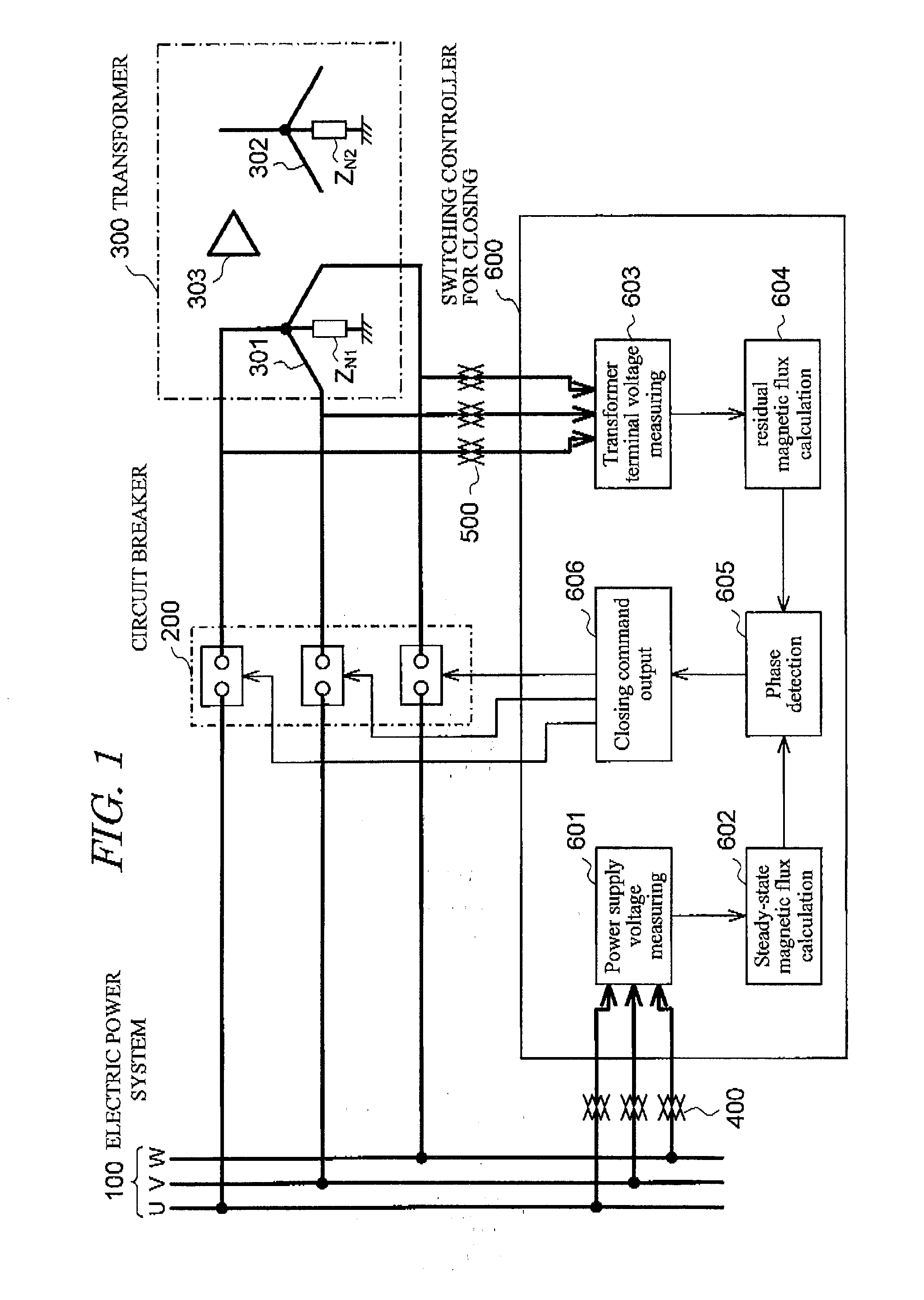
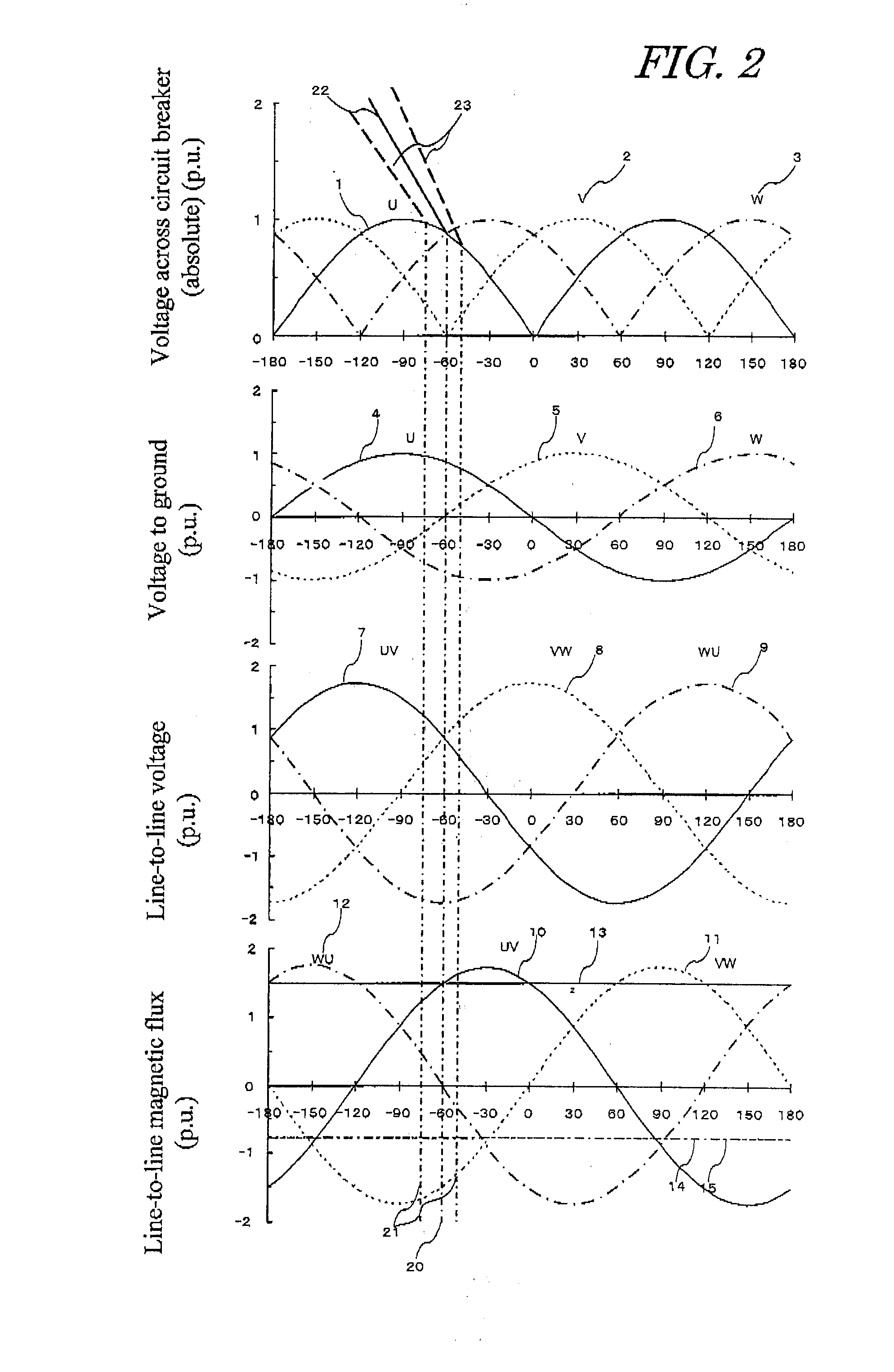
To provide a magnetizing inrush current suppression device for transformer and control method of same, which accurately calculates the residual magnetic flux when a transformer installed in a non-solidly earthed system, is interrupted by circuit breakers, and which enables suppression of the magnetizing inrush current occurring when three single-phase circuit breakers or single-phase circuit breakers are used for simultaneously supplying power to three phases of the transformer, without providing a circuit breaker with a resistor or other equipment to enlarge the circuit breaker. The device has steady-state magnetic flux calculation means for calculating the line-to-line steady-state magnetic flux of three-phase power supplies, residual magnetic flux calculation means for calculating the primary line-to-line residual magnetic flux of the transformer when the circuit breakers interrupt the transformer, phase detection means for detecting a phase at which the polarity and magnitude of the calculated steady-state magnetic flux and residual magnetic flux coincide for each line-to-line. Closing control means firstly causes only two-phase of the circuit breakers, which are connected with the line-to-line, to close at the detected phase, and then causes the remaining one-phase circuit breaker to close.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for achieving single-phase earth fault line selection of small current grounding system
InactiveCN103592571AHigh sensitivityGuaranteed reliabilityFault locationHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
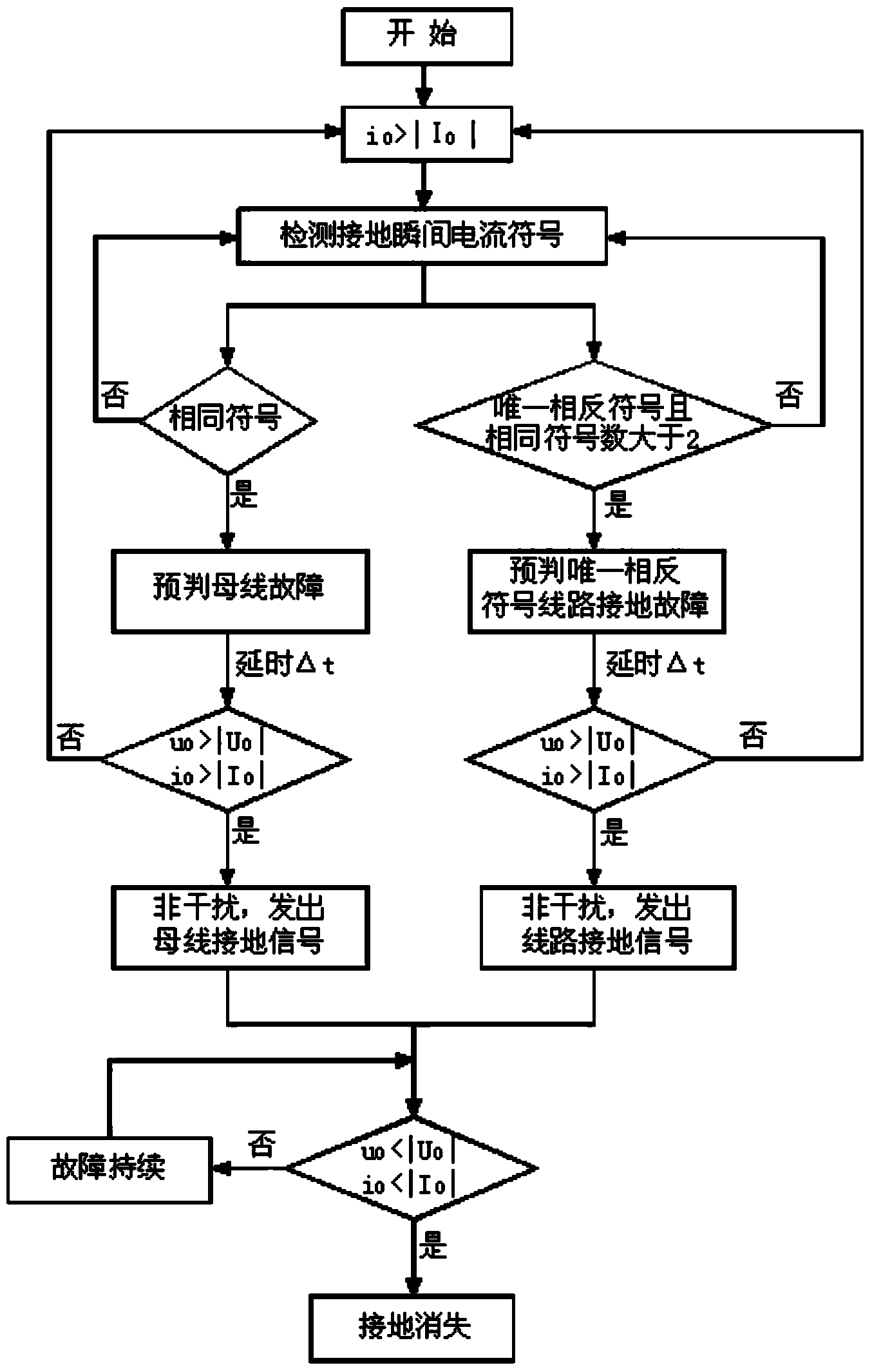
A method for achieving single-phase earth fault line selection of a small current grounding system is characterized in that a high-precision zero-sequence current transformer is adopted by each feeder line; a single-phase earth fault of the system is confirmed when the instantaneous value of the zero-sequence current i0 of any one feeder line exceeds a set threshold / I0 / ; comparison is conducted on symbols of all loop circuits at the moment of threshold triggering, and data after the triggering do not participate in judgment; the symbol of a faulty line current is unique and opposite to the symbols of non-faulty line currents, and the number of non-faulty lines is larger than or equal to 2; when the symbols of all the currents are identical, a bus earth fault is confirmed. The method for achieving single-phase earth fault line selection of the small current grounding system is adaptable to three grounding modes, namely neutral non-grounding, arc suppression coil grounding and neutral point high resistance grounding, of the small current grounding system and is not affected by a grounding moment phase angle, system unreal grounding and TV disconnection, and correction operation can still be achieved when the zero-sequence voltage of a bus is reduced to be 10% of a phase voltage by a transition resistor.
Owner:珠海威瀚科技发展有限公司
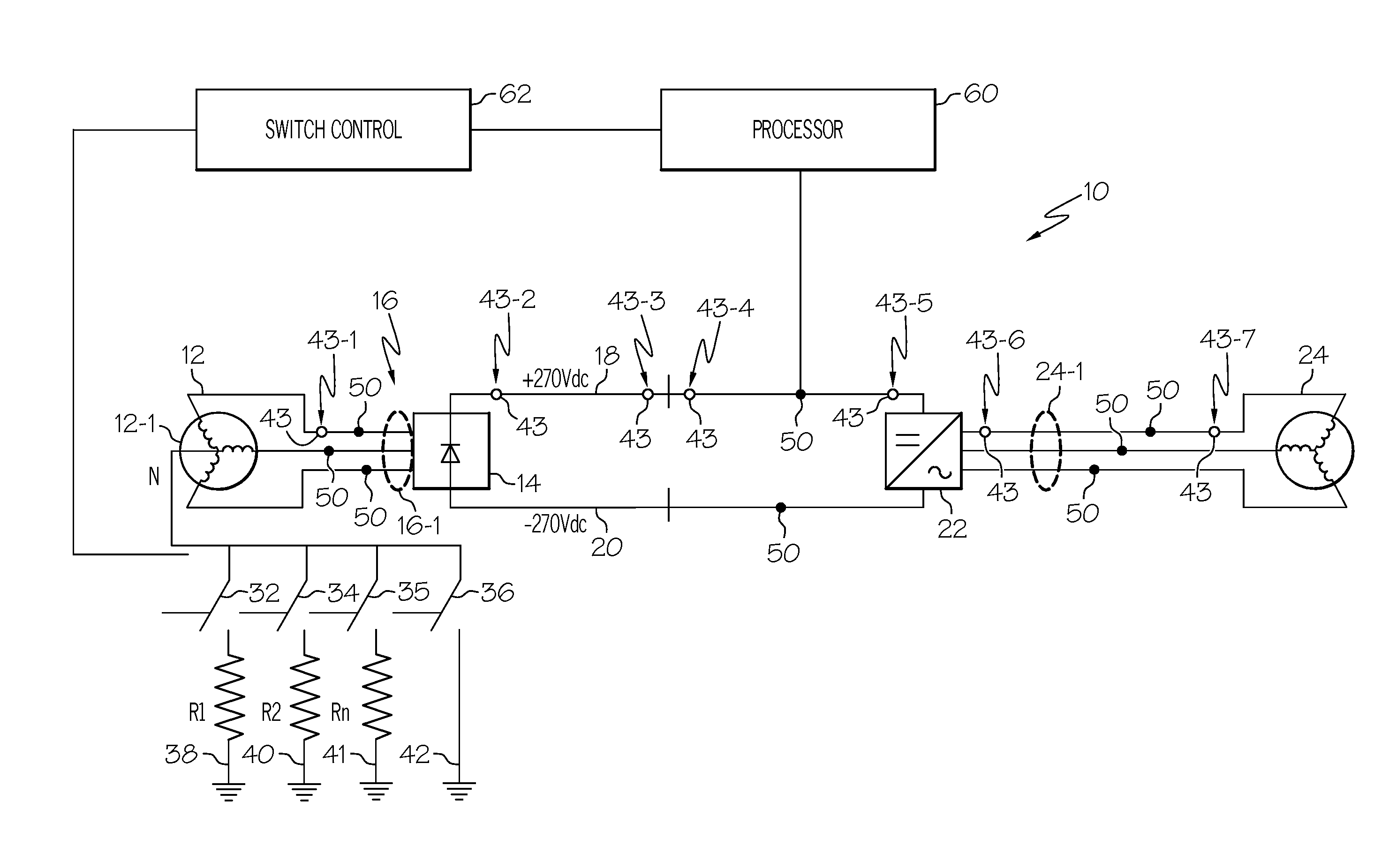
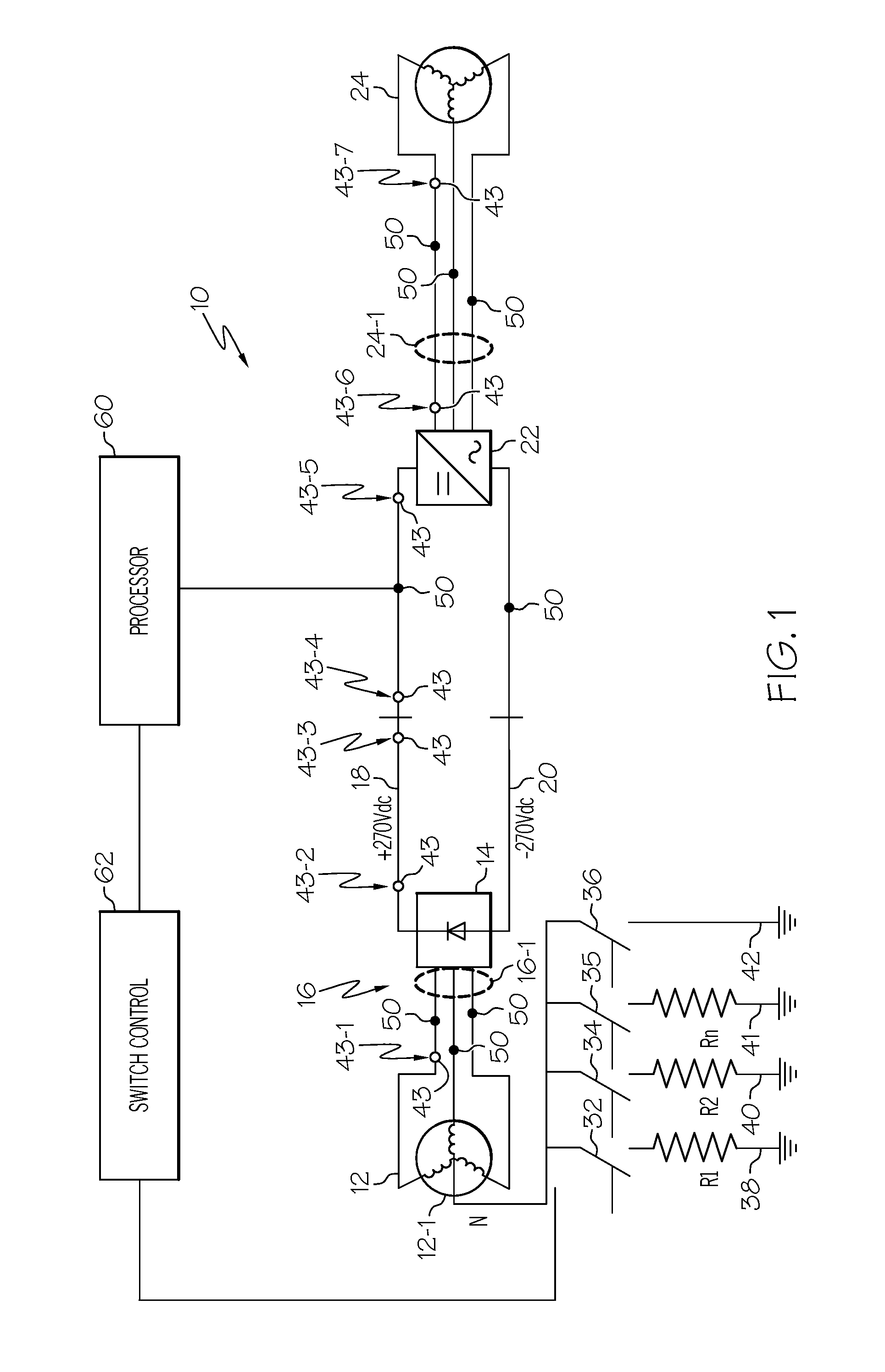
Continuous uninterruptable AC grounding system for power system protection
ActiveUS8878396B2Electric signal transmission systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsTransformerDc current
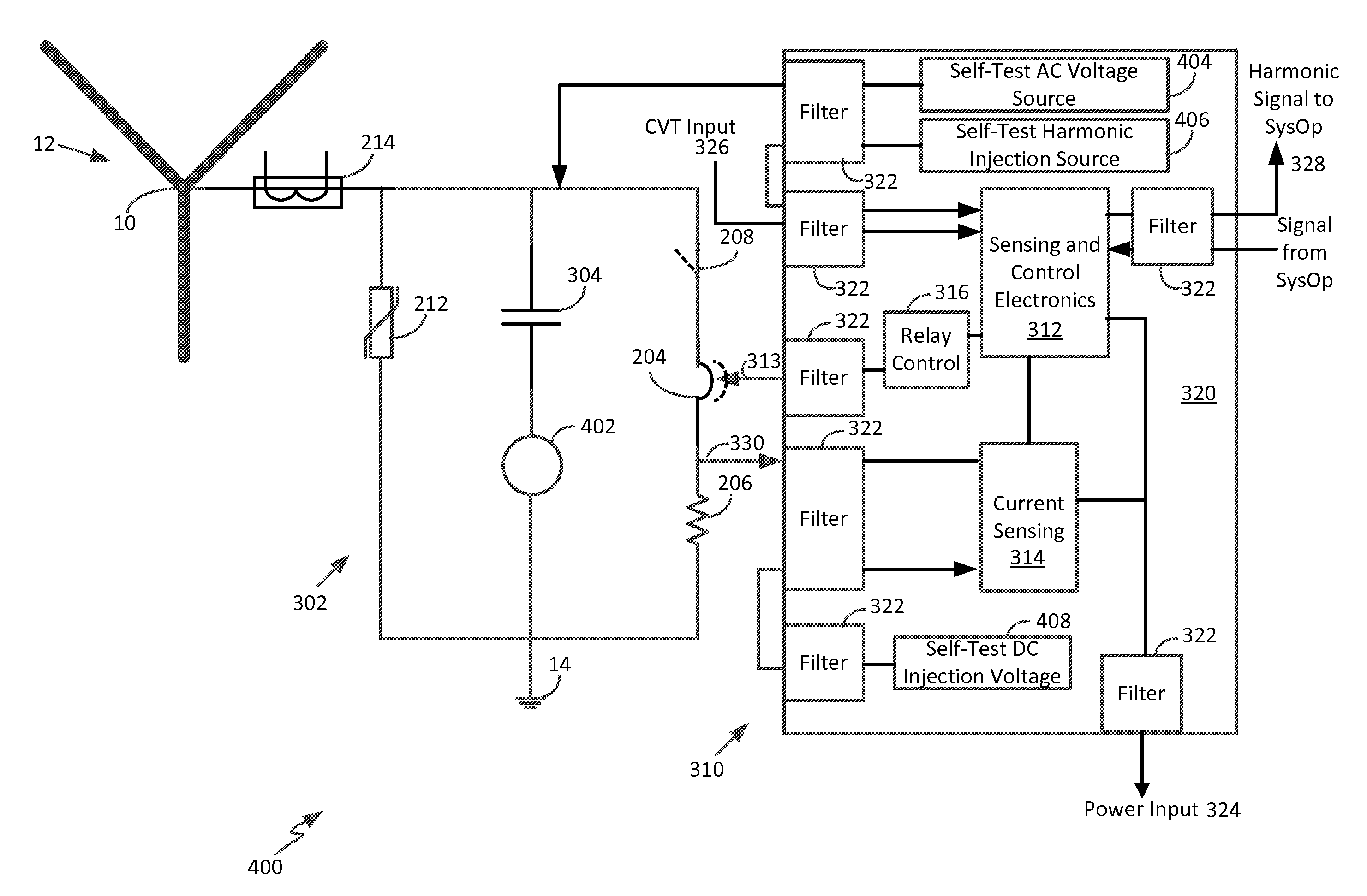
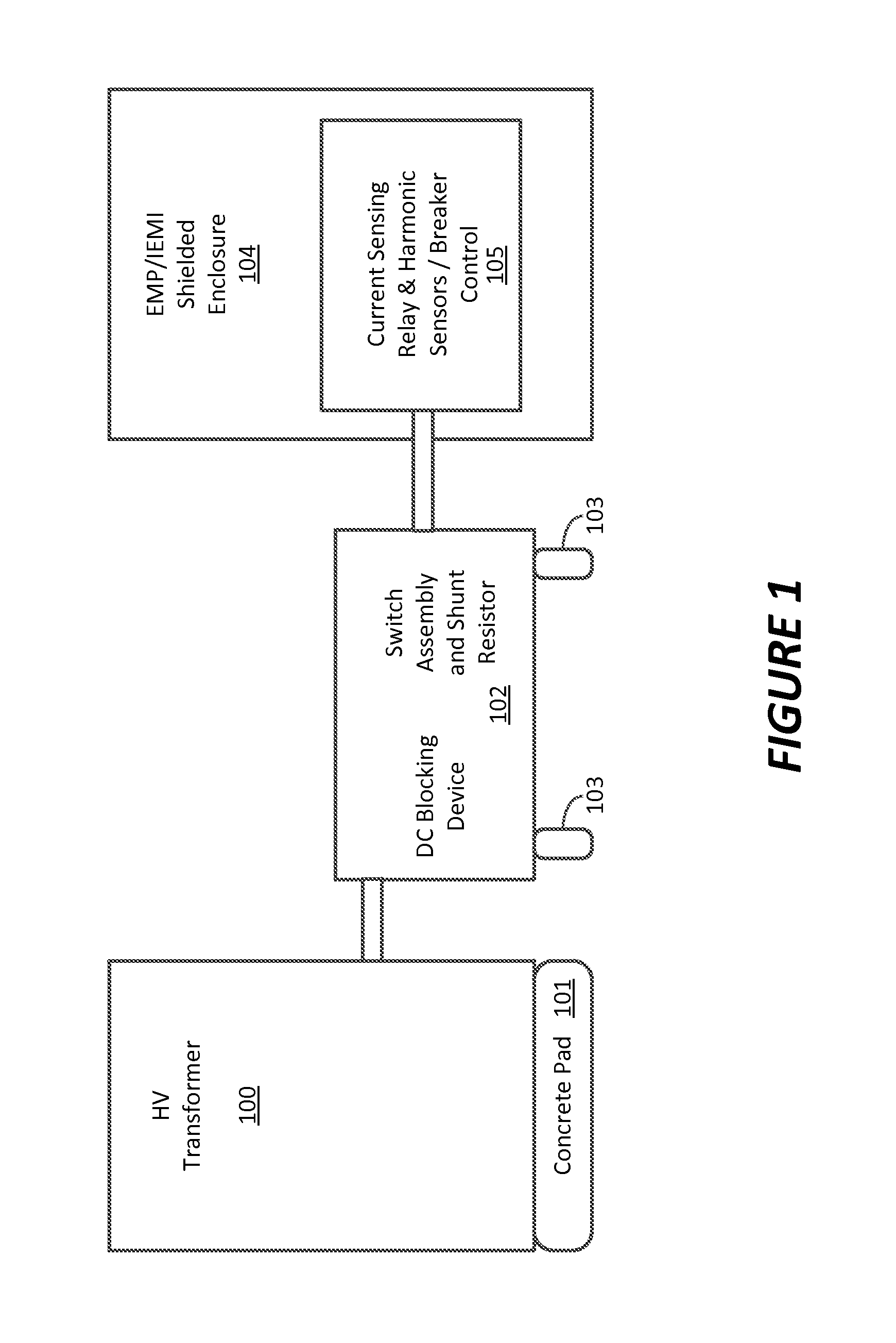
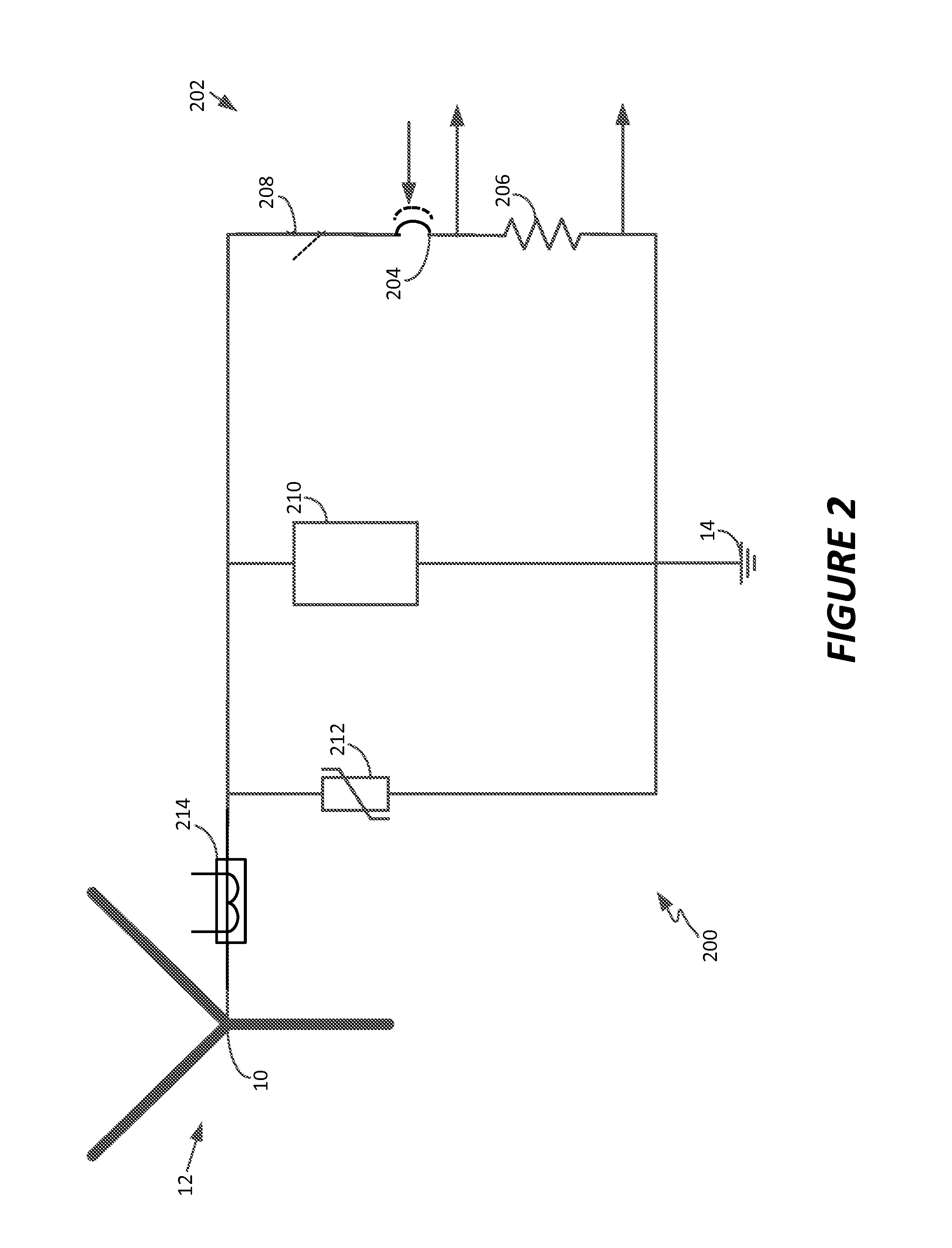
A continuous grounding system for use in an alternating current system including a transformer is disclosed. The system includes a switch assembly connected between a transformer neutral of a transformer and a ground, the switch assembly having an open position and a closed position, the open position disrupting the path through the switch assembly between the electrical connection and the transformer neutral, and the closed position establishing a path connecting the electrical connection to the transformer neutral through the switch assembly, wherein in normal operation of the alternating current electrical device the switch assembly remains in a closed position. The system also includes a DC blocking component positioned in parallel with the switch assembly and connected between the transformer neutral and the ground. The system further includes a control circuit configured to control the switch assembly, the control circuit including a sensor configured to actuate the switch assembly to an open position upon detection of a predetermined harmonic signal threshold at one of the transformer phases or a predetermined threshold of DC current between the transformer neutral and ground.
Owner:TECHHOLD LLC
Neutral point non-effective earthing system single-phase earthing fault identification method
ActiveCN102955098AEfficiently reflects mutationsGuaranteed reliabilityFault locationThree-phaseEngineering
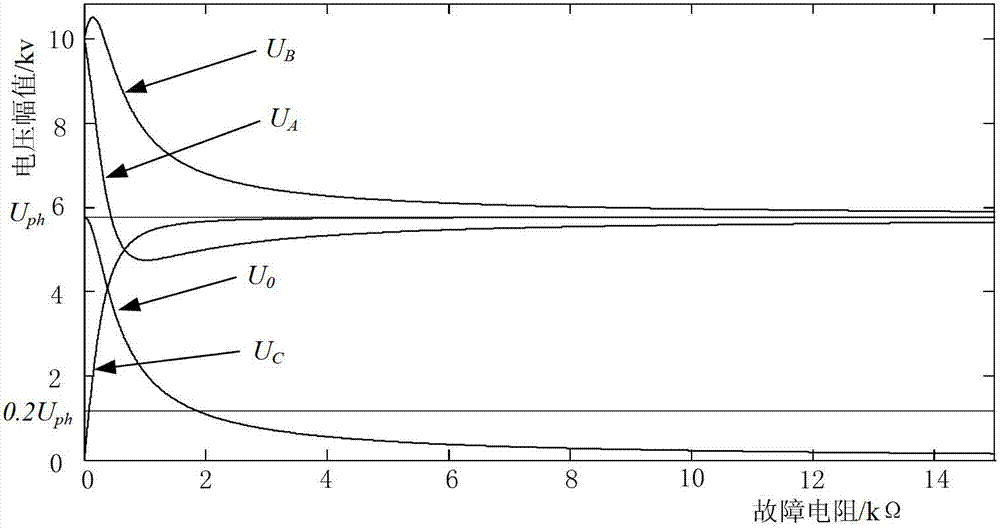
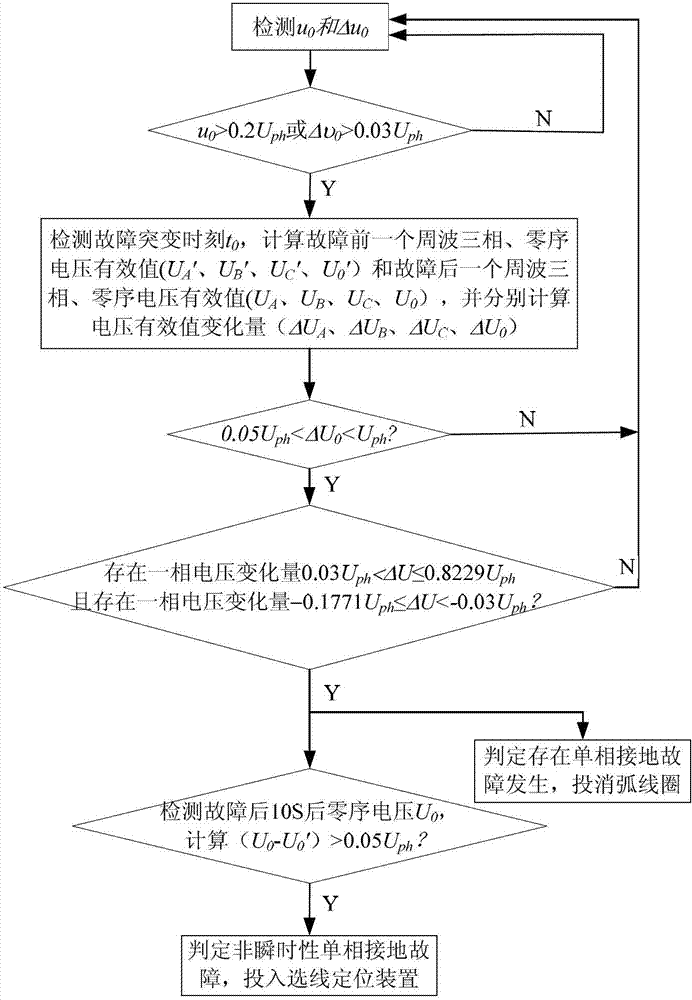
The invention discloses a neutral point non-effective earthing system single-phase earthing fault identification method which includes the steps that a zero sequence voltage instantaneous value and a instantaneous saltation value are taken as the startup criteria of an identification scheme; when any of the above values is out of the limit, an identification process is started, a saltation moment is determined according to a signal saltation point, and the effective values of the zero sequence voltages and the three-phase voltages in cycles before and after the signal saltation point and the variations of the effective values are calculated; and a single-phase earthing fault is judged to have happened only when the variation of the zero sequence voltage and the variations of all phases of voltage all satisfy all the criteria. The method takes voltage variation for identification, and the saltation of the state of the system can be reflected; a low threshold value scheme is adopted in the method, so the system can be started sensitively under a high impedance fault; and the multiple criteria scheme of zero sequence voltage and three-phase voltage are adopted, so the method has high reliability. The method is simple and easy to realize.
Owner:ZIYANG POWER SUPPLY COMPANY STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER +2
Resonant earthed system fault line selection method utilizing fuzzy K-means clustering
The invention relates to a resonant earthed system fault line selection method utilizing fuzzy K-means clustering. The resonant earthed system fault line selection method comprises the following steps of 1 performing stretching transformation treatment on transient-state zero-sequence current of each line to improve similarities of transient-state zero-sequence currents of non-fault lines; 2 dividing the transient-state zero-sequence currents of all of lines according to a certain time period, performing subsection phase plane transformation to obtain Euclidean distances from all of phase points of the transient-state zero-sequence current of each section to determinacy points x and y on a phase plane so as to extract local features of the transient-state zero-sequence currents of all of subsections and obtain feature matrixes of global features of all of lines; 3 performing normalization processing on elements in the feature matrixes to improve comparability; 4 utilizing a fuzzy K-means clustering method to perform clustering on the normalized feature matrixes, dividing the transient-state zero-sequence currents of all of lines into two categories and the lines independently included in one category are fault line. The method improves the automation degree and line selection margin.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Power distribution network one-phase grounding fault location method based on zero sequence voltage
ActiveCN103792465AOvercome the problem of large errorsEasy to implementFault locationLow voltageDistributed parameter model
A power distribution network one-phase grounding fault location method based on a zero sequence voltage belongs to a power distribution network grounding fault location method. The fault location method starts from an overall zero sequence parameter of a single-end radial medium voltage power distribution network, analyzes a one-phase grounding fault while taking a distributed parameter model influence into consideration, measures a steady-state zero sequence voltage value and a zero sequence current of each feeder line at a bus position and at a tail end of each outlet line, and finds zero sequence voltage variation characteristics of a fault feeder line and non-fault feeder line. According to the invention, a large number of existing devices are used, the data sampling requirement is low in terms of being real-time, and the method of the invention is easy to realize; the simulation model analysis is established according to the actual parameters, so that the fault location can be realized in the system in which the neutral point is not grounded or the neutral point is grounded through an arc suppression coil; the precision is quite high; and the location method of the invention can be applied to the medium and low voltage power distribution network.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method capable of realizing low-current route selection and fault location
ActiveCN102798795AChange compensationChange ground capacitanceFault locationInformation technology support systemCapacitanceTransformer
The invention discloses a method capable of realizing low-current route selection and fault location and discloses a novel method capable of realizing single-phase grounding route selection and fault location. The method comprises the following steps: detecting the zero sequence voltage value of a system and the zero sequence current value of each branch line at the first time of the single-phase grounding fault; at the second time, changing the capacitance value or the inductance value of the whole power distribution network on the ground for a neutral point ungrounded system, changing the compensation degree of an arc suppression coil or changing the capacitance value or the inductance value of the whole power distribution network on the ground for an arc suppression coil grounding system, and detecting the zero sequence voltage value of the system and the zero sequence current value of each branch line at the second time after adjusting; and after determining the branch line of the single-phase grounding fault, uploading the detected zero sequence current value of the branch line, dividing the zero sequence voltage of the system by the detected zero sequence current value and judging to determine the position of the fault point. When the zero sequence current change of a voltage transformer on a bus influences the fault route selection and location, the zero sequence loop of the voltage transformer can be cut off, so that the detection precision is improved.
Owner:DALIAN ELECTRIC POWER SURVEY & DESIGN INST
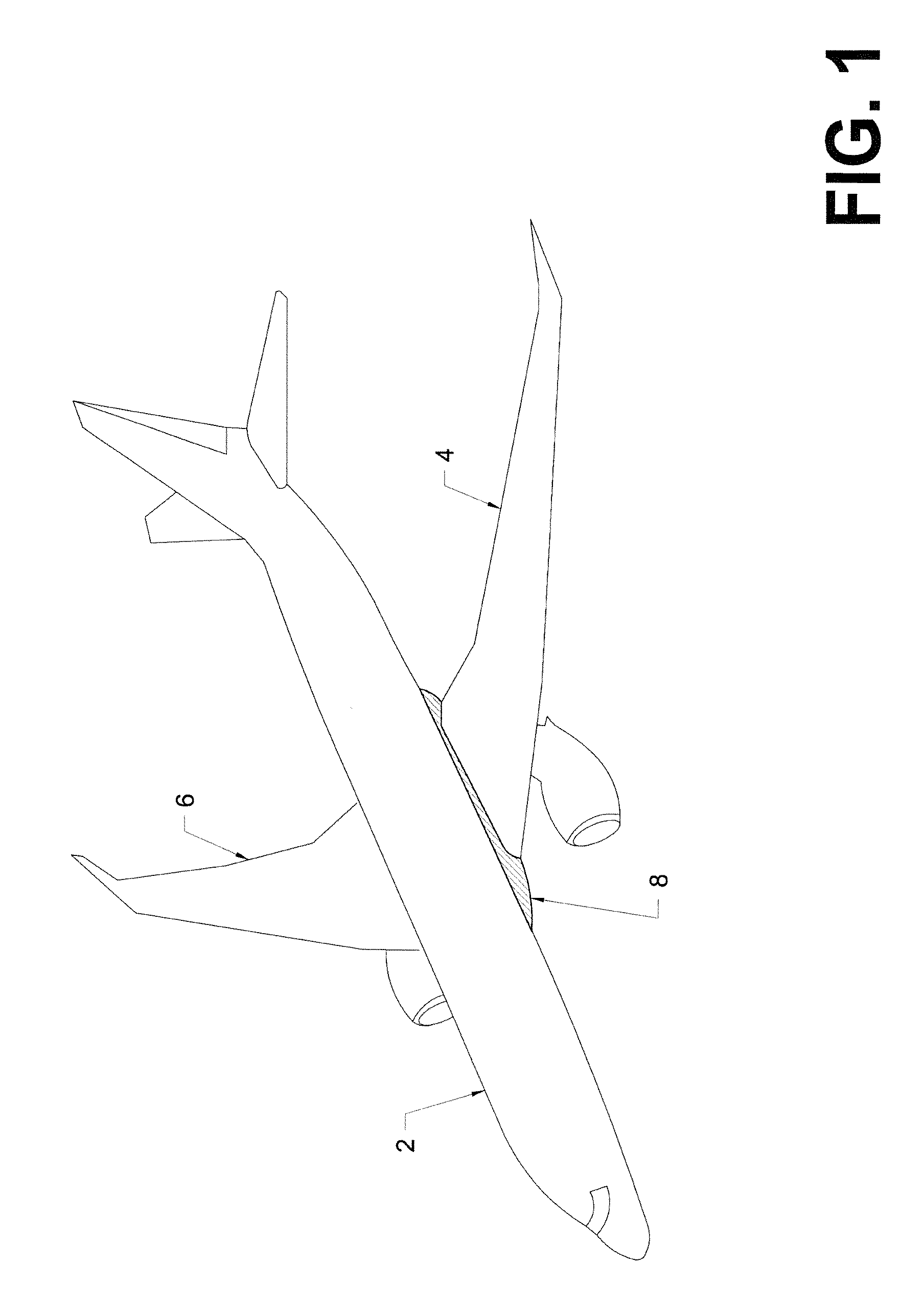
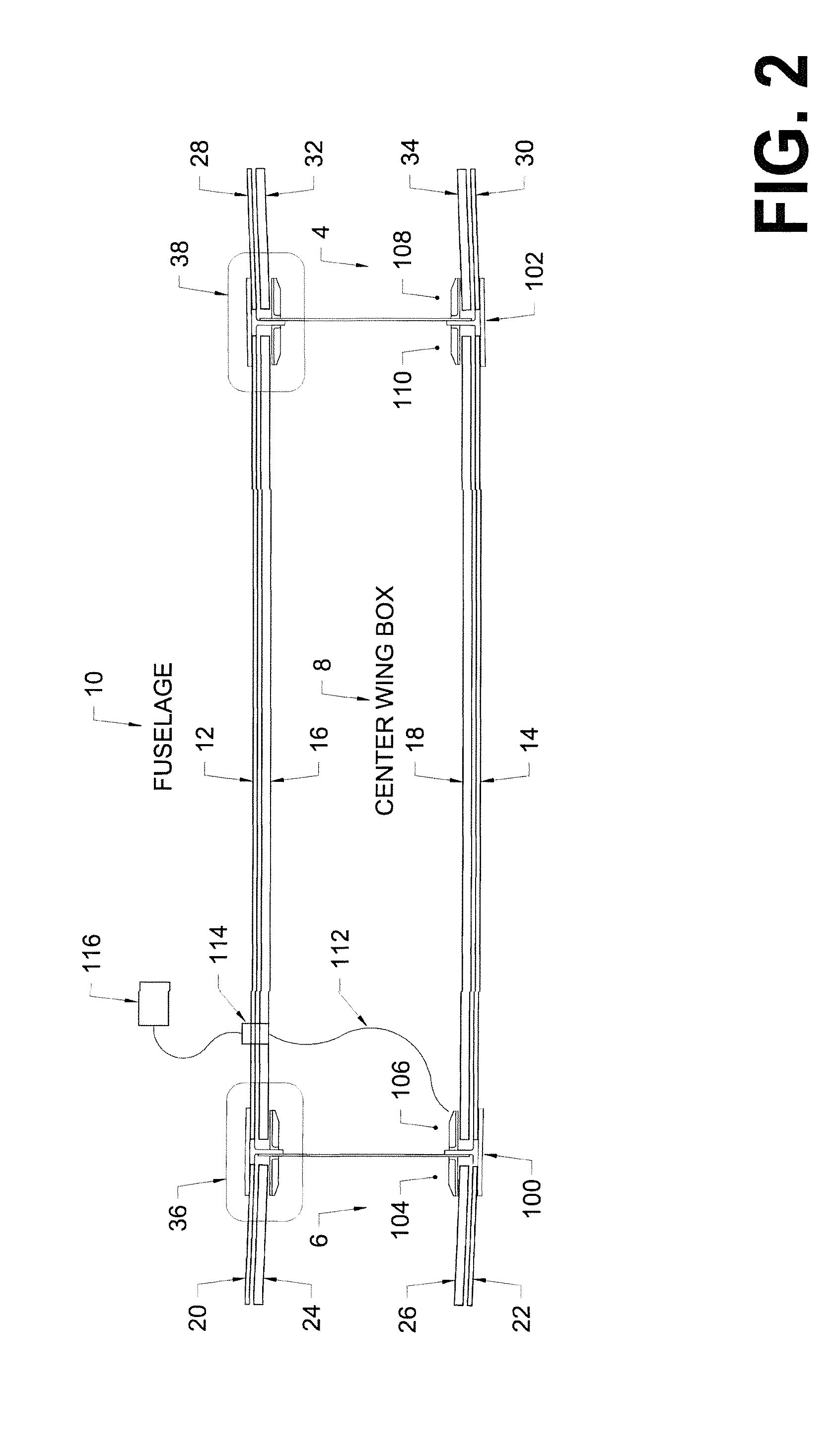
Stable grounding system to avoid catastrophic electrical failures in fiber-reinforced composite aircraft
InactiveUS20150344156A1Avoid catastrophic failureVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesElectrical FailurePower flow
Methods and apparatus are described to detect, measure, and determine the presence of unknown Groundloop currents flowing through unidentified circuit pathways within the wiring system distributed within a portion of a fuselage of an airplane substantially made from fiber-reinforced composite materials to avoid catastrophic failures of the electrical system within such an airplane.
Owner:SMART DRILLING & COMPLETION
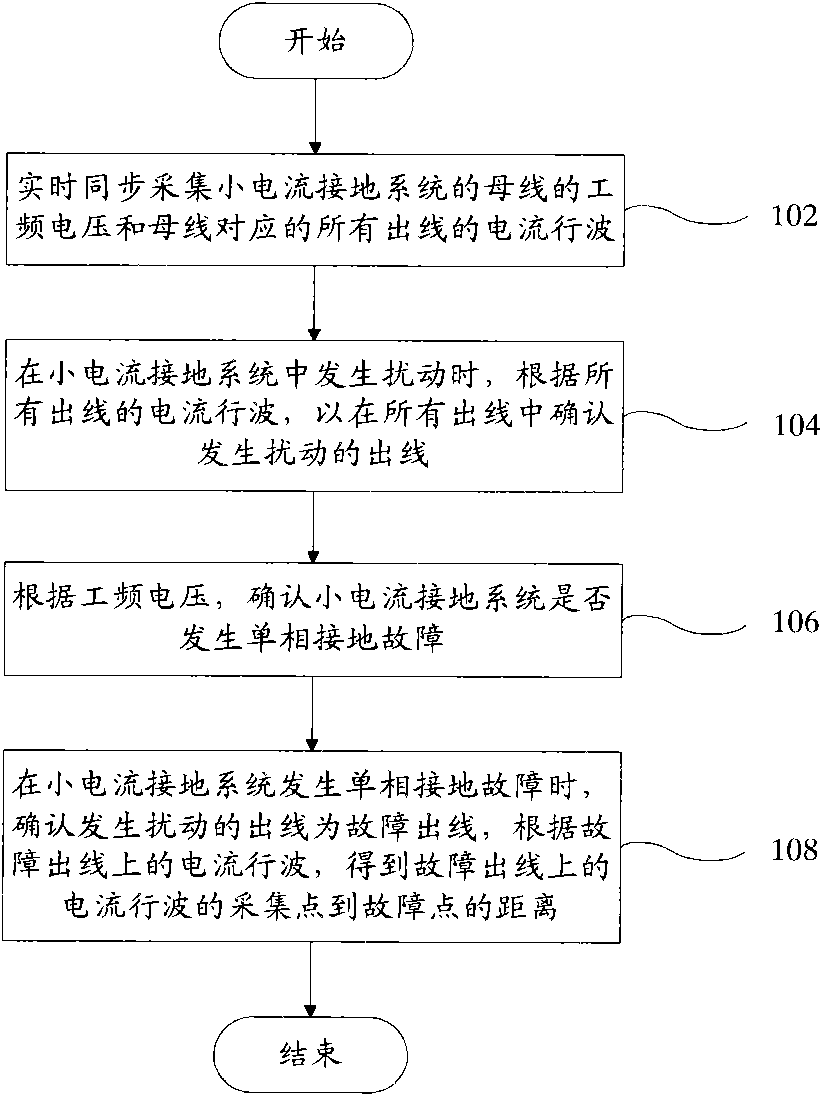
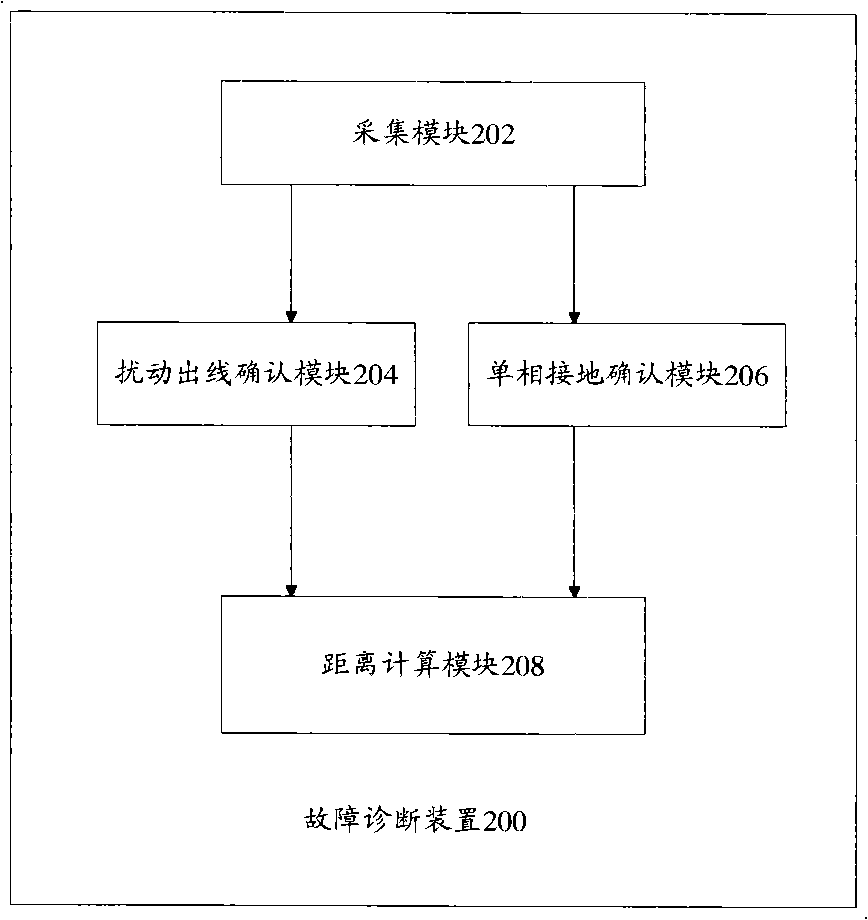
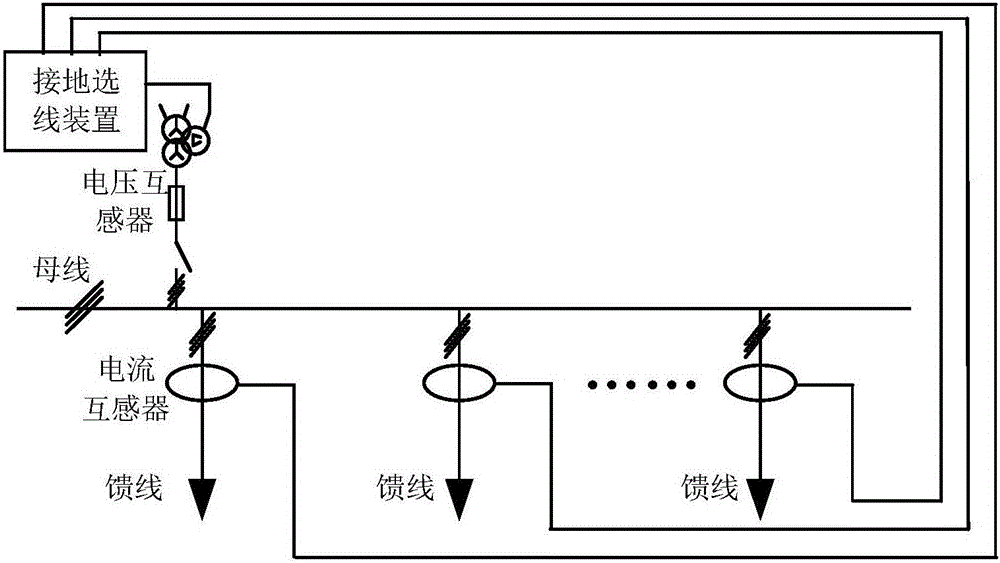
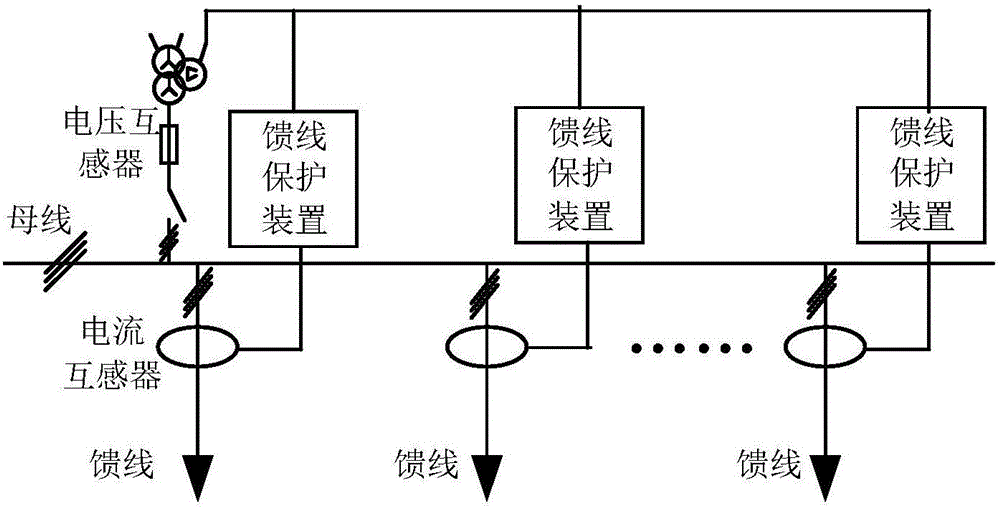
Single-phase earth fault diagnosis method and device
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis method which is used for determining whether a single-phase earth fault occurs in a low current earth system and determining the position of a fault point. The method comprises the following steps of: (102) synchronously acquiring the power frequency voltage of a busbar of the low current earth system and the current traveling wave of all outgoing lines in real time; (104) determining an outgoing line with turbulence in all the outgoing lines when the turbulence occurs in the low current earth system; (106) determining whether the single-phase earth fault occurred in the low current earth system according to the power frequency voltage; and (108) determining the outgoing line with the turbulence as a faulty outgoing line to obtain the distance between the acquisition point and the fault point on the current traveling wave of the faulty outgoing line when the single-phase earth fault occurred in the low current earth system. The invention discloses a fault diagnosis device. The single-phase earth fault of the low current earth system can be detected according to the fault diagnosis method and device.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
One-phase grounding clustering line selection method of resonant grounding system
ActiveCN103454562AAvoid artificial experience selection thresholdStable algebraic featuresFault locationSingular value decompositionCapacitance
The invention relates to a resonant grounding system fault line selection method with clustering achieved by means of time-frequency matrix singular values. The resonant grounding system fault line selection method comprises the steps that empirical mode decomposition is carried out on the transient-state zero-sequence current waveform of each circuit and the transient-state zero-sequence current waveform of a bus after a fault occurs to obtain a plurality of IMF components; Hilbert conversion is carried out on the IMF components to obtain a two-dimensional Hilbert gray-scale time-frequency spectrogram of transient-state zero-sequence currents; a time-frequency matrix of the transient-state zero-sequence current waveforms is constructed by means of HHT band-pass filtering; singular value decomposition is carried out on the time-frequency matrix to obtain a series of singular values which can reflect time-frequency characteristics of the waveforms, and the singular values serve as the characteristic quantity of transient-state zero-sequence currents of each circuit and the bus; vague C mean value clustering is carried out on the singular values to select a fault line. According to the resonant grounding system fault line selection method, influence of distributed capacitance and currents of a sound long line is avoided when a short line breaks down, and accurate line selection can be achieved under the conditions of high resistance grounding, noise interference, arc faults and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
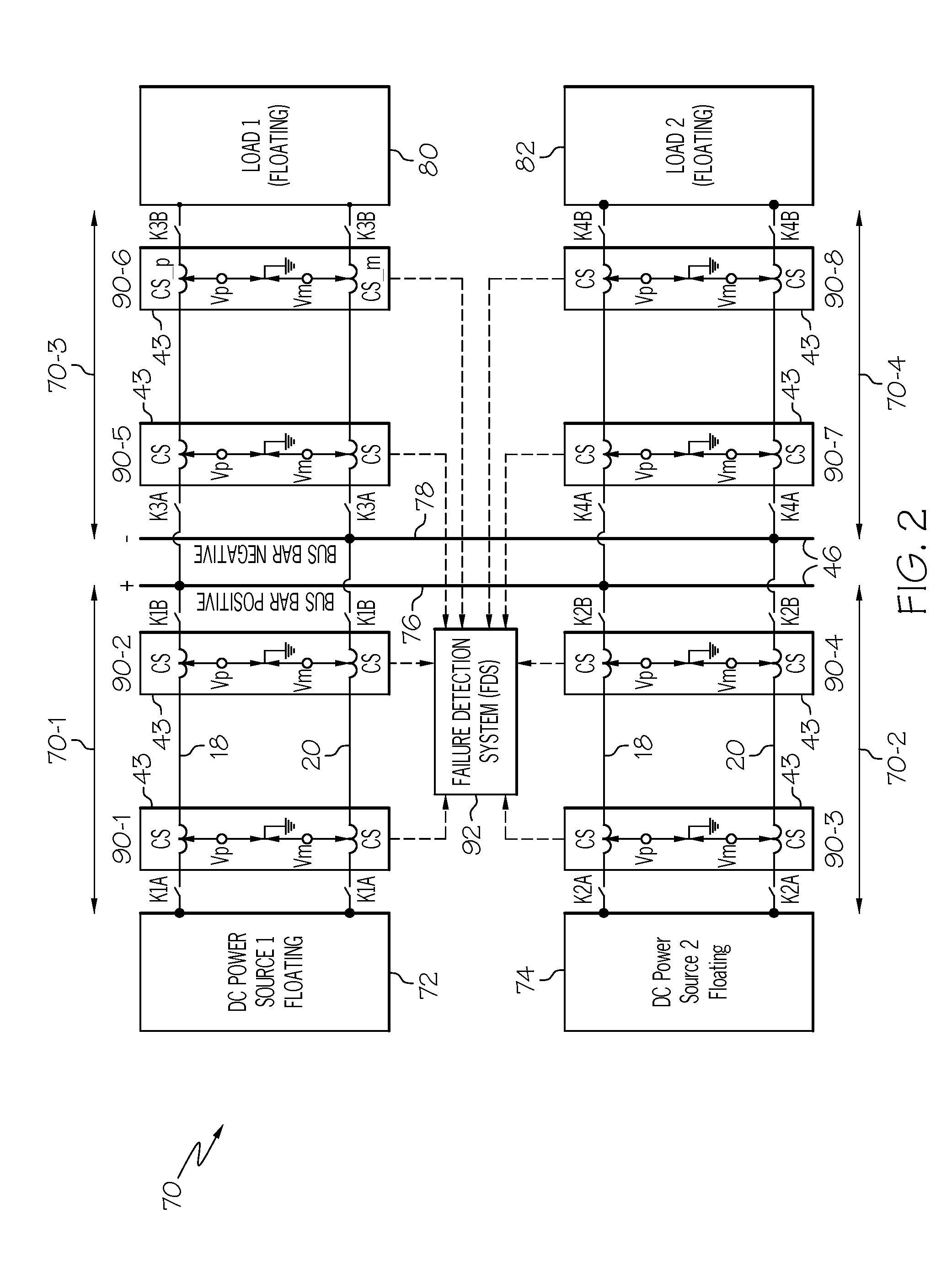
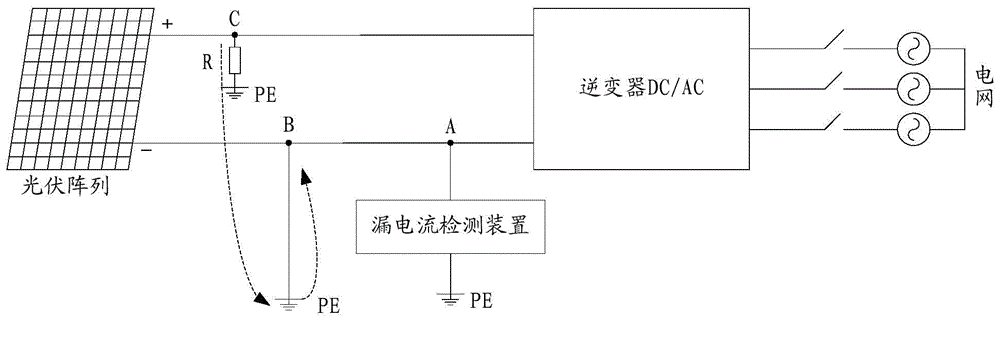
Ground fault detection and localization in an ungrounded or floating DC electrical system
InactiveUS20090147415A1Short-circuit testingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionDistribution power systemCapacitive current
An ungrounded or floating DC electrical power distribution system may experience a single line to ground fault. Such a fault may not disrupt operation of the system, but its presence may raise a risk of additional problems if left uncorrected. A system for progressively grounding the ungrounded system may be initiated when a line to ground fault is suspected based on the voltage difference measured to a common chassis point. As grounding through successively lower impedance proceeds, fault current may increase and detection of severity of the line to ground fault may be more readily achieved, thus facilitating localization of the fault. Localization may be achieved through an analysis of direction of capacitive currents in isolatable zones of the system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Single pole grounding system and fault detection device and method thereof
ActiveCN103558496ARealize multi-point ground faultImplement pre-detectionElectrical testingArrangements resposive to fault currentDrain currentDirect current
The invention discloses a single pole grounding system and a fault detection device and method. According to the single pole grounding system and the fault detection device and method, before the grounding of a normal grounding point, the direct current bus voltages of a system and impedance sampling signals are obtained to calculate the earth impedance of the positive / negative pole of the single pole grounding system, then whether fault grounding points exist is judged, pre-detection before system operation is achieved, and no faults exist before the operation of the system; after the normal grounding points are grounded, whether a grounding fault exists is judged by detecting leaked currents; the grounding pole multipoint grounding fault and non-grounding pole grounding fault which occur during the operation process can be detected when the system is down or the normal grounding points are not grounded through calculating the earth impedance of the positive / negative pole of the single pole grounding system again. Thus, the single pole grounding system and the fault detection device and method achieve the detection on the multipoint grounding fault of the single pole grounding system and the non-grounding pole grounding fault which may occur at the same time.
Owner:SUNGROW POWER SUPPLY CO LTD
Single-phase earth fault direction judgment and processing method of small current grounding system
ActiveCN103760465AGuaranteed power supplyImprove power supply reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationSingle phaseFeed line
The invention relates to a single-phase earth fault direction judgment and processing method of a small current grounding system. In terms of a fault direction judgment method, the session which a single-phase fault point belongs to on a main line is judged according to zero-sequence currents, zero-sequence voltage and the included angle relation between the zero-sequence currents and the zero-sequence voltage tested through a section switch on the main line where a single-phase earth fault occurs, the fault session is isolated according to the judgment result, and normal power supply of a non-fault session line is guaranteed to the largest extent. According to the judgment and processing method, the single-phase earth fault session of the main line can be automatically isolated, and power supply reliability of a power distribution network is improved; additionally, according to the single-phase grounding direction judgment method, a main line boundary function is embedded in the section switch of a 10kV feeder line, the range in power failure caused by the single-phase earth fault can be shortened to the largest extent, and accordingly reliability and safety of power supply are improved.
Owner:泉州维盾电气有限公司
Circuit fault directional detecting and protecting method for power supply system
InactiveCN1614435AGuaranteed Protection SensitivityGuaranteed protection reliabilityEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionFault locationTransient stateElectric power system
A method for detecting line fault direction judges the fault direction by calculating instant idle power or specific frequency component idle power of transient state voltage current generated by the fault. The fault direction can be detected out quickly within 5 ms and tripping command is followed immediately to separate the fault line out for protection.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNYOUTH ELECTRIC TECH GRP CO LTD
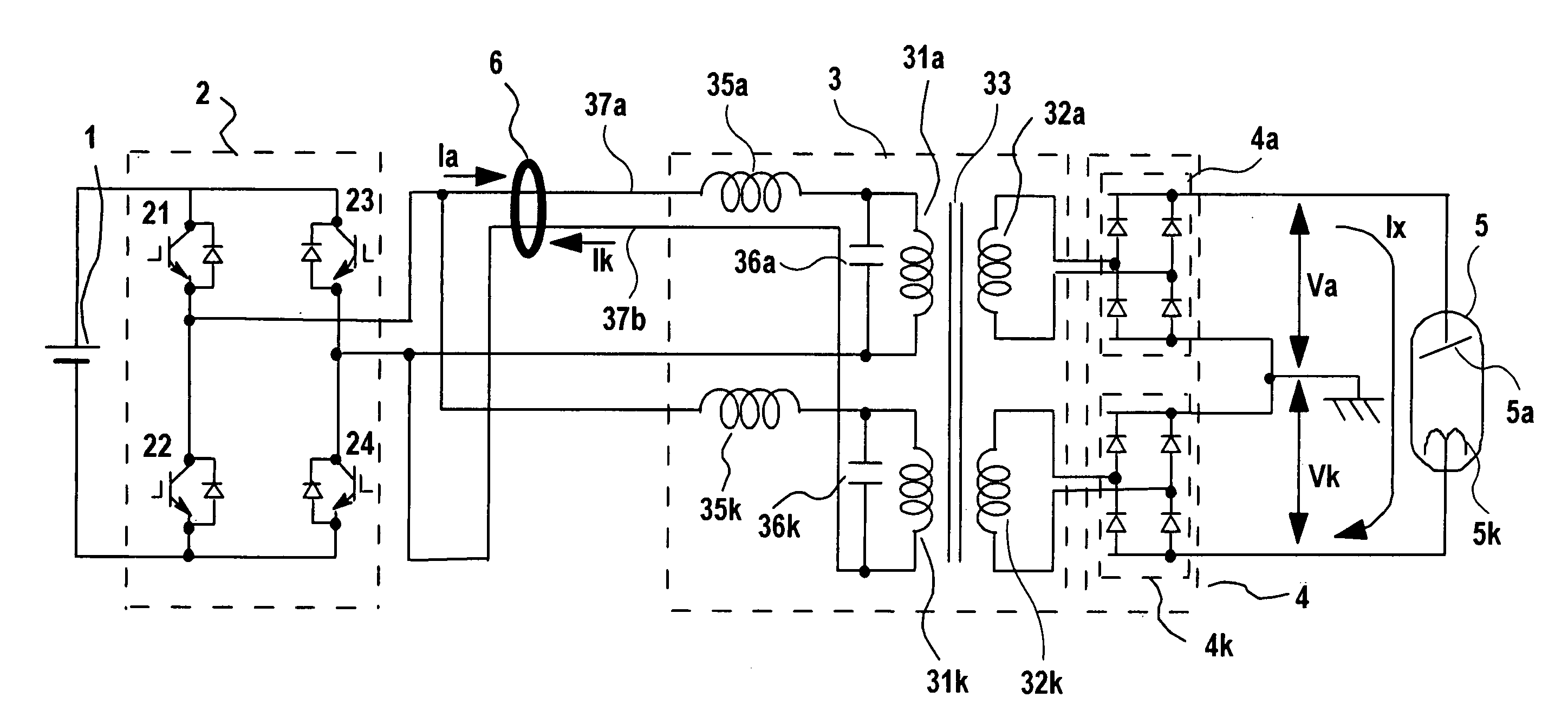
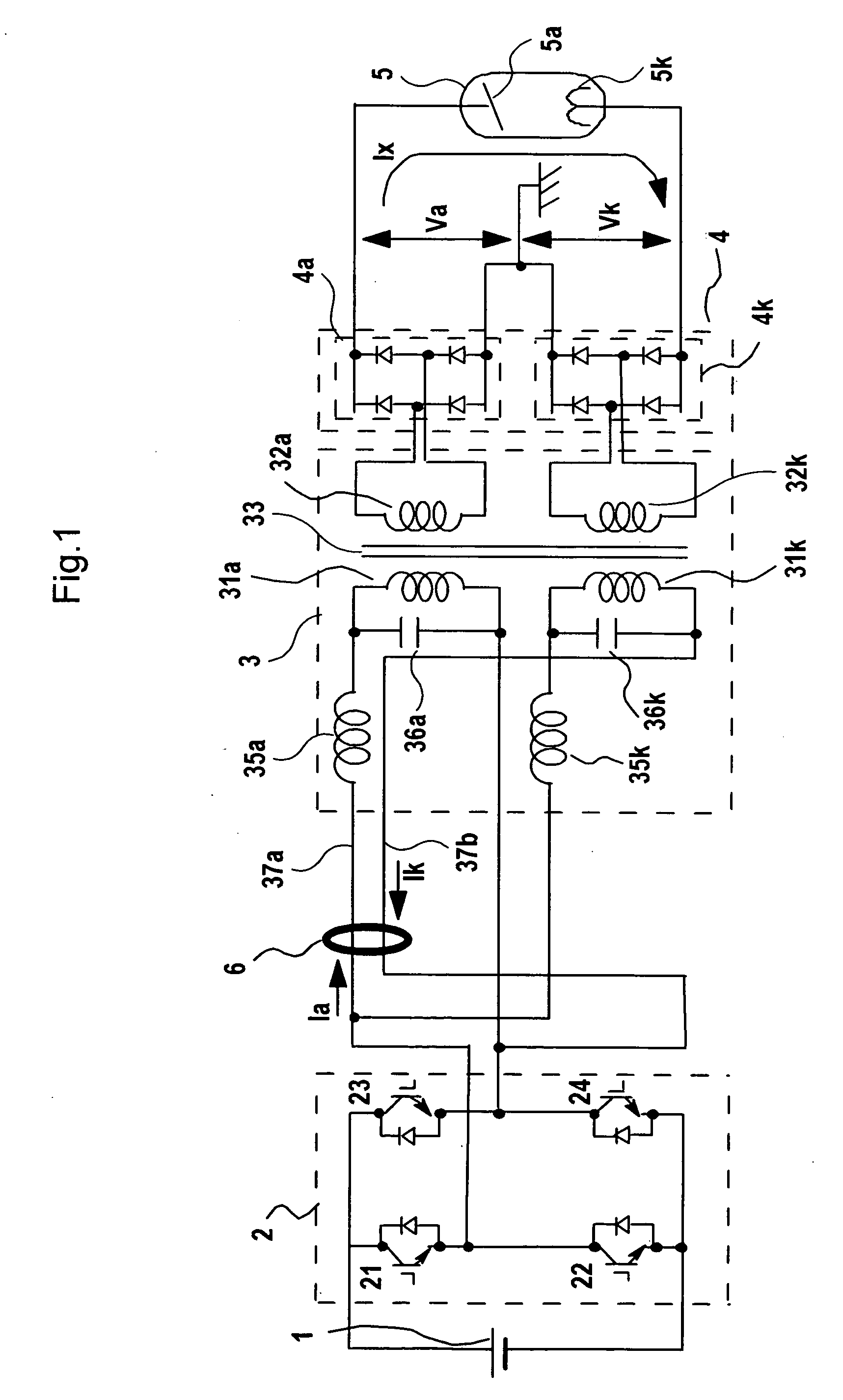
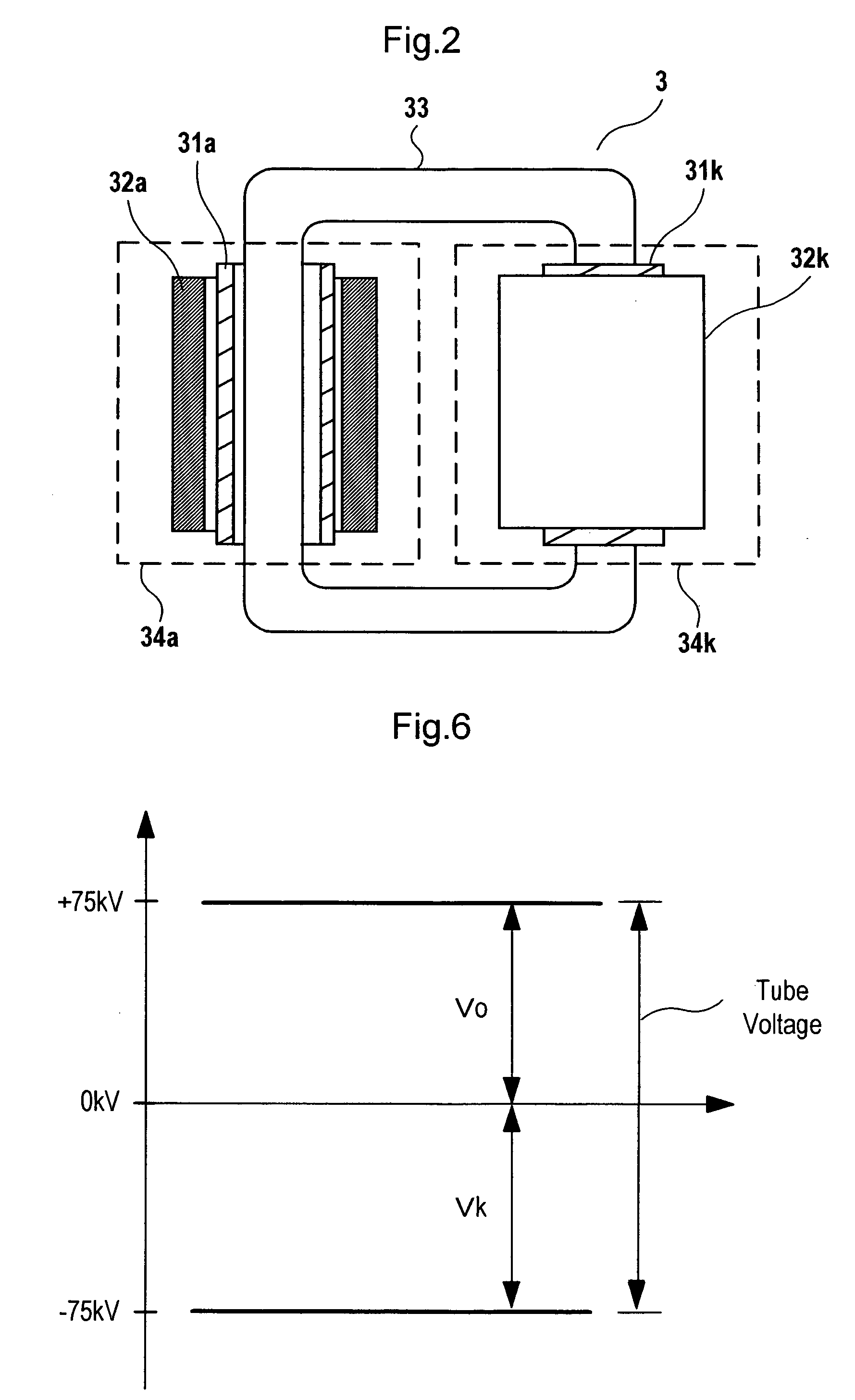
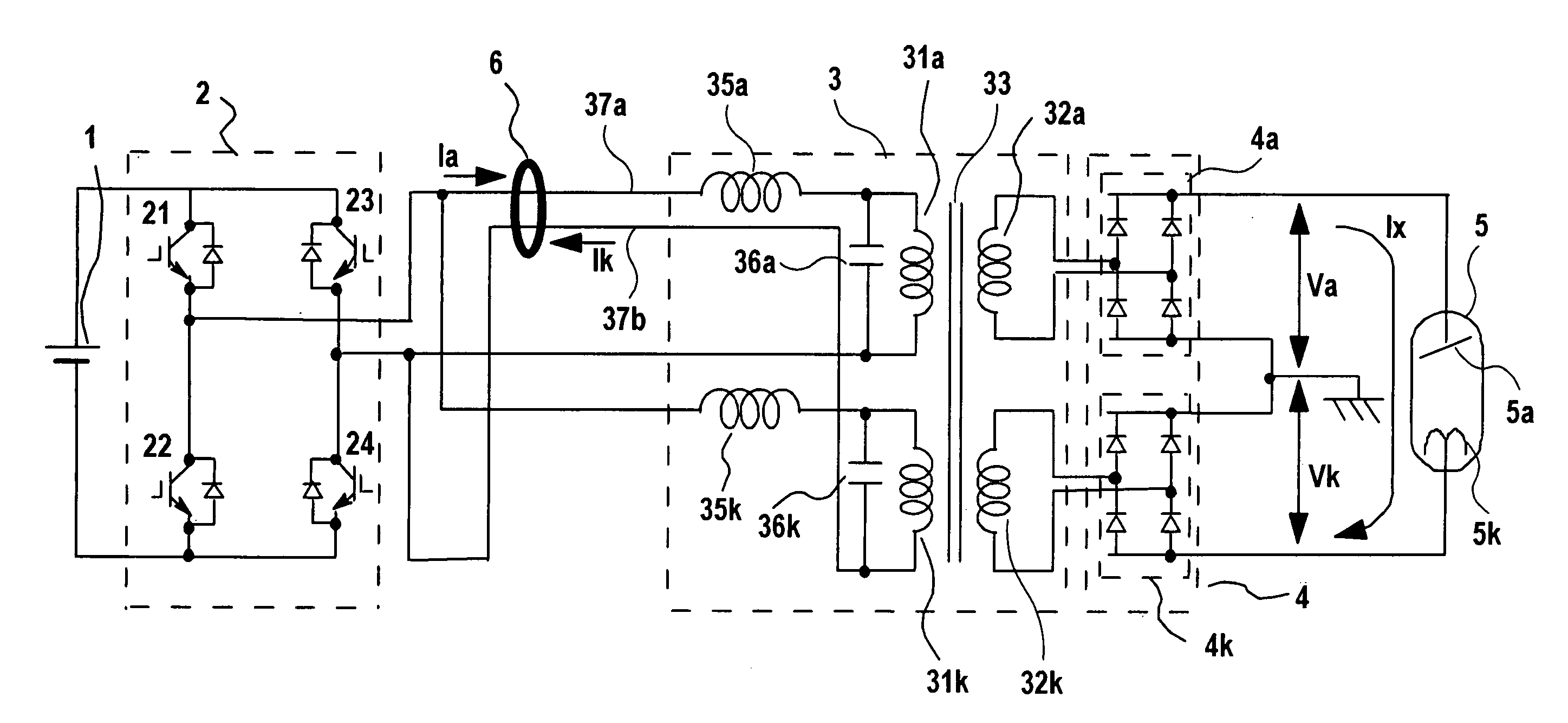
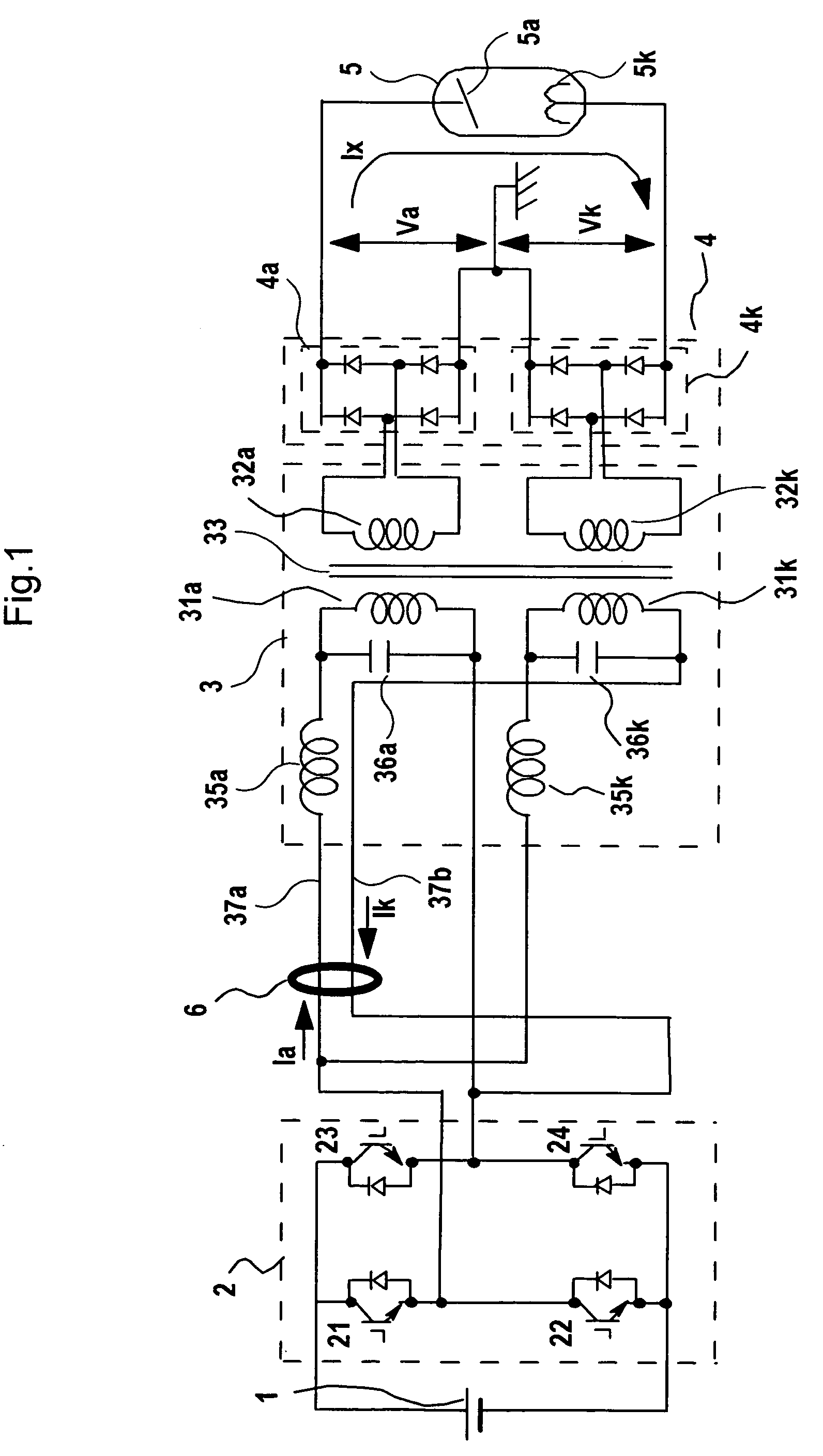
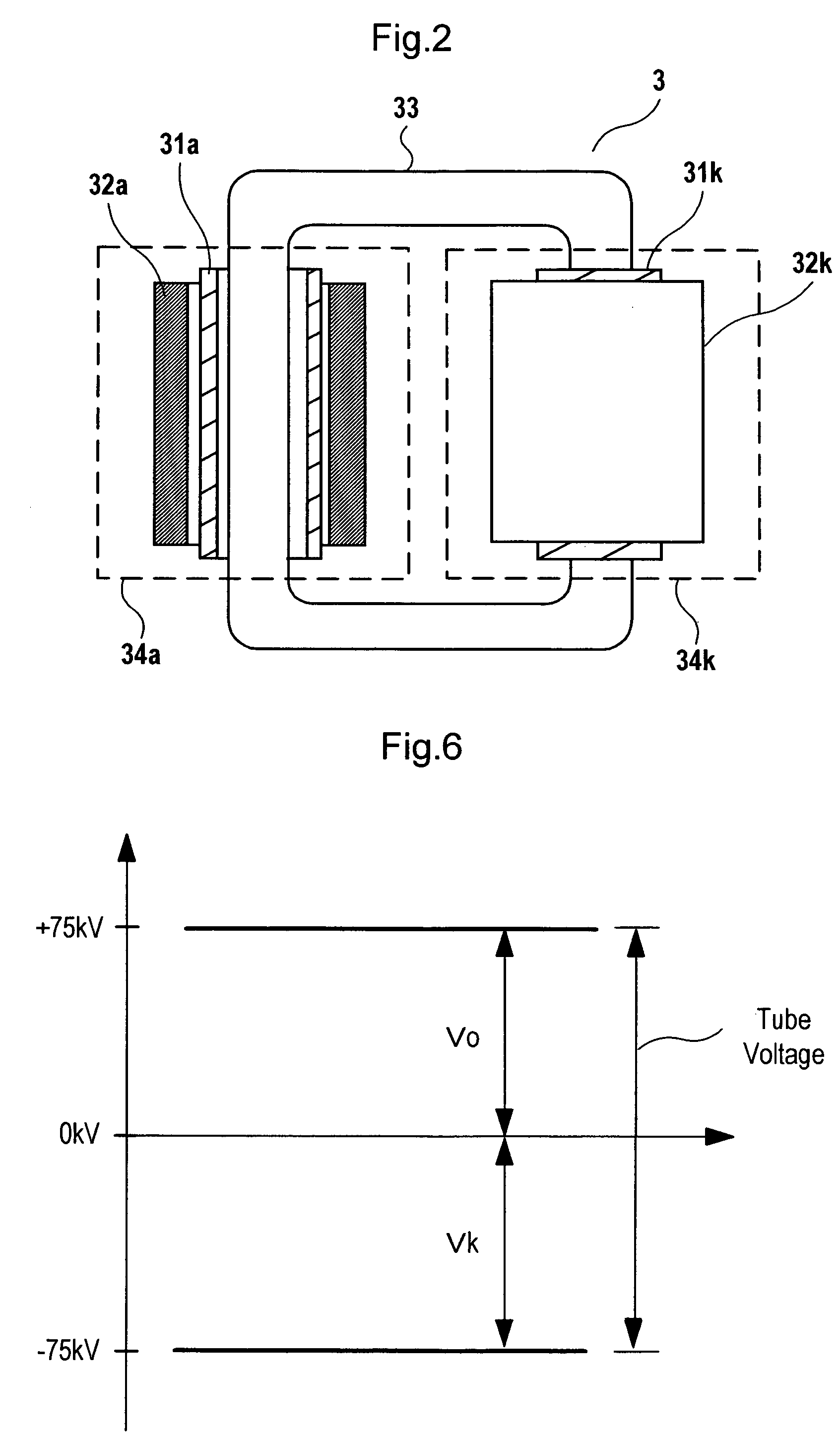
X-ray generator and x-ray ct apparatus comprising same
InactiveUS20060165220A1Reduce unbalance voltageImprove reducibilityX-ray apparatusToroidal coilElectrical impedance
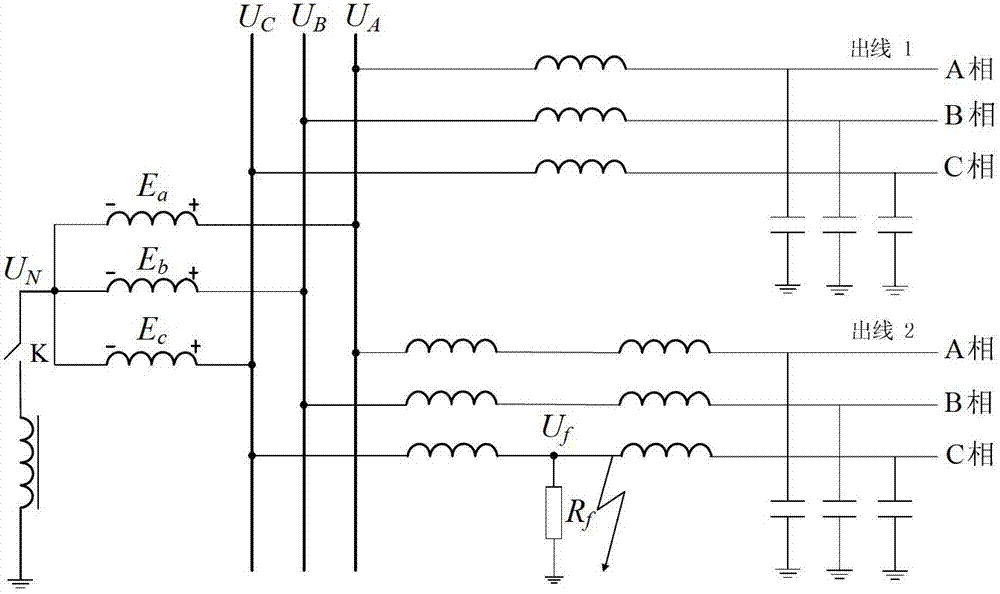
In an X-ray generating device of the neutral grounding system, to remove an unbalance voltage generated due to difference in impedance of parallel transformer coils of the high voltage transformer and particularly an unbalance voltage involved with difference in impedance above and below the neutral points generated in a metal X-ray tube, a plurality of currents flowing in opposite directions through primary windings of the parallel transformer coils in the high voltage transformer are passed through by or wound around a common toroidal coil or wound around an outer circumference of the toroidal coil at a predetermined ratio of winding number, and the unbalance voltage occurring to the secondary side is cancelled by changing primary current with magnetic behavior.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
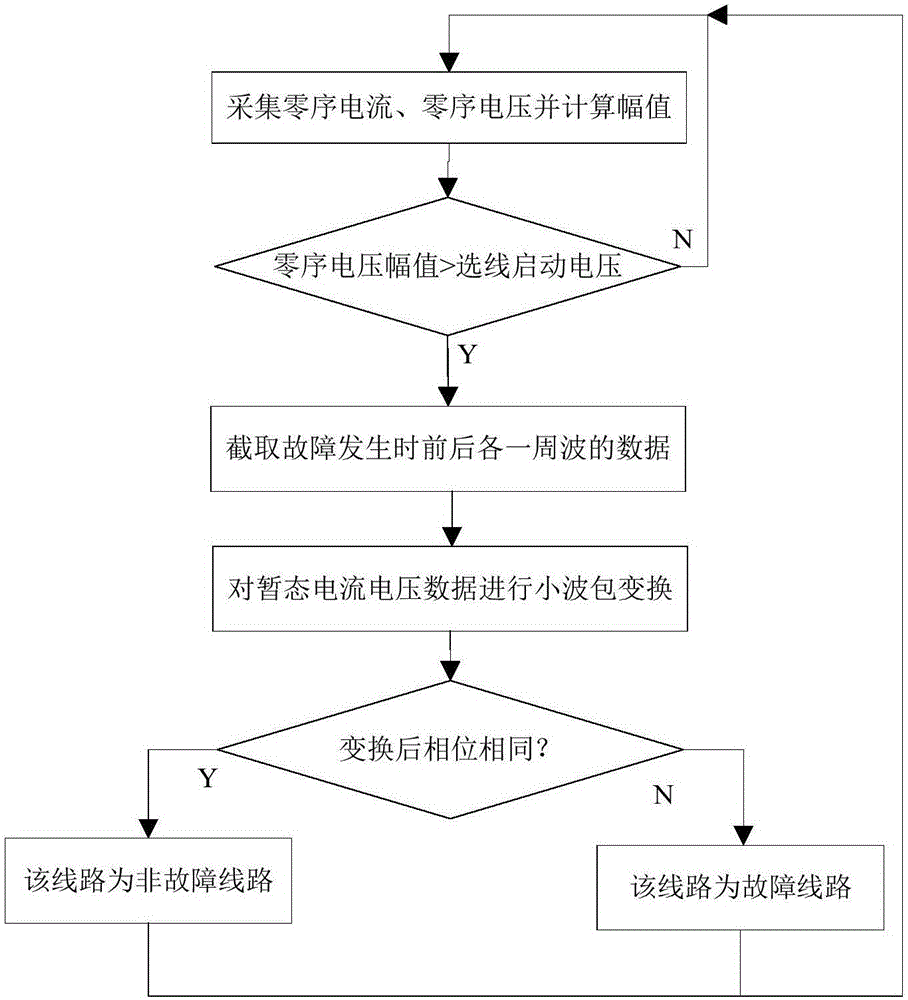
Single-phase grounding line selection method for small-current grounding system
InactiveCN106324432ARich in transient componentsSolve the problem of inaccurate line selectionFault location by conductor typesTransient stateEngineering
The invention discloses a single-phase grounding line selection method for a small-current grounding system, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, collecting the zero sequence voltage of a bus or an outgoing line and the zero sequence current of the outgoing line, and calculating the amplitude of the zero sequence voltage in real time; 2, determining that the bus or the outgoing line has a single-phase grounding fault when the amplitude of the zero sequence voltage is greater than the amplitude of a line selection start voltage, and switching to step 3; 3, extracting the data of zero sequence current and voltage of a cycle before a moment when a fault happens and a cycle after the moment of the fault happens, and carrying out the wavelet packet transformation of the data of transient zero sequence voltage and current; 4, comparing the phases of the transient zero sequence current and voltage after the wavelet packet transformation: determining that a line is not a fault line if the phases are the same, and determining that the line is a fault line if the phases are opposite, thereby completing the grounding line section. The method solves a problem of a higher line selection misjudgment rate caused by that the phases and amplitudes of the zero sequence currents of the fault line and the non-fault line when a conventional arc suppression coil grounding system has a single-phase grounding fault.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
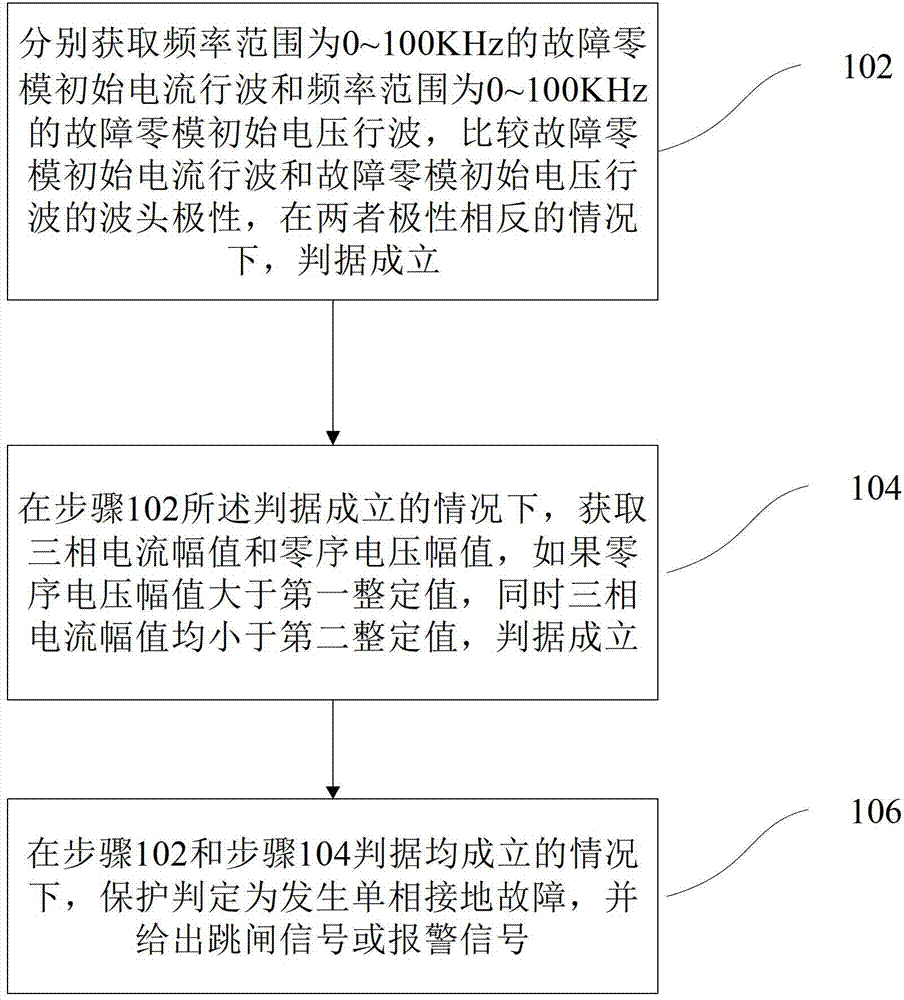
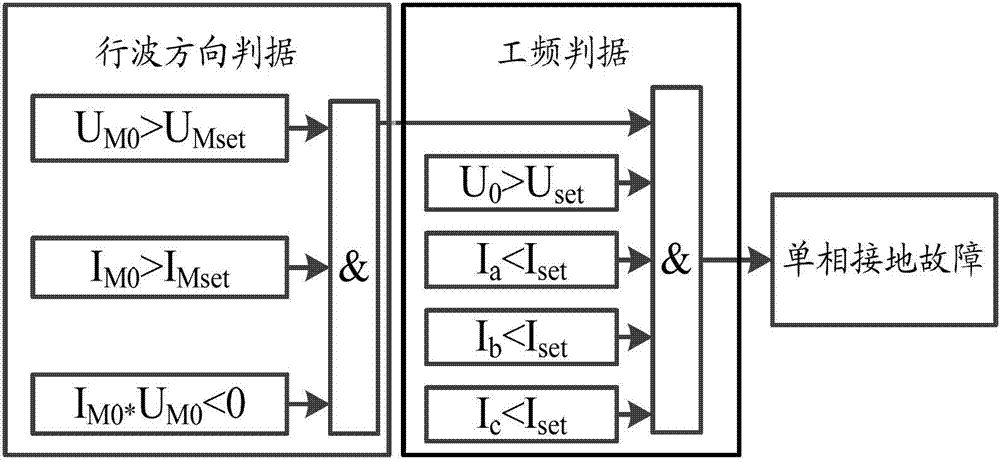
Distribution line single-phase grounding traveling wave protection method
ActiveCN102780211AOvercome insensitivityOvercomer's failureEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationElectrical polarityEngineering
The invention provides a distribution line single-phase grounding traveling wave protection method. The method includes: step 102, respectively acquiring fault zero modal initial current traveling wave within a frequency range of 0-100KHz and fault zero modal initial voltage traveling wave within a frequency range of 0-100KHz, comparing wavefront polarity of the fault zero modal initial current traveling wave with that of the fault zero modal initial voltage traveling wave, and enabling a first criterion to be established when the polarity of the fault zero modal initial current traveling wave and the polarity of the fault zero modal initial voltage traveling wave are opposite; step 104, acquiring three-phase current magnitude and zero-sequence voltage magnitude under the condition that the first criterion is established, and enabling a second criterion to be established if the zero-sequence voltage magnitude is larger than a first setting value and the three-phase current magnitude is smaller than a second setting value; and step 106, judging to determine that a single-phase grounding fault occurs and giving out a trip signal or an alarm signal when the first criterion and the second criterion are both established. By the technical scheme, when the single-phase grounding fault occurs in a distribution line neutral point ineffective grounding system, the fault can be detected quickly and accurately, and reliable protection actions can be taken.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Identification method of ground fault phases in three-phase ungrounded system and identification device thereof
ActiveCN101915884AReduce troubleshooting timeGuaranteed safe operationVoltage-current phase angleFault locationPhase differenceThree-phase
The invention relates to an identification method of ground fault phases in a three-phase ungrounded system and an identification device thereof. The identification method comprises the following steps: firstly selecting any line voltage in the three-phase ungrounded system as reference voltage, determining value domains of phase difference between theoretical zero-sequence voltage of the fault phases and the reference voltage when a ground fault occurs on each phase aiming at the reference voltage, and carrying out real-time online acquisition of the actually measured zero-sequence voltage; if the actually measured zero-sequence voltage is zero, judging no ground fault occurs; and if the actually measured zero-sequence voltage is not zero, calculating the phase difference between the actually measured zero-sequence voltage and the reference voltage, and judging which value domain the phase difference falls into so as to judge that the ground fault occurs on the phase corresponding to the value domain. The identification method can rapidly judge the ground fault occurs on A phase or B phase or C phase in the three-phase ungrounded system and directly point out the ground fault phases while finding out the fault, thus reducing troubleshooting time, being beneficial to eliminate faults timely, and guaranteeing safe operation of the system.
Owner:苏州市电通电力电子有限公司
X-ray generator and X-ray CT apparatus comprising same
In an X-ray generating device of the neutral grounding system, to remove an unbalance voltage generated due to difference in impedance of parallel transformer coils of the high voltage transformer and particularly an unbalance voltage involved with difference in impedance above and below the neutral points generated in a metal X-ray tube, a plurality of currents flowing in opposite directions through primary windings of the parallel transformer coils in the high voltage transformer are passed through by or wound around a common toroidal coil or wound around an outer circumference of the toroidal coil at a predetermined ratio of winding number, and the unbalance voltage occurring to the secondary side is cancelled by changing primary current with magnetic behavior.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Electric animal deterrent for contact with underlying ground system
InactiveUS6948452B2Lower Level RequirementsLimiting energy deliveredElectric shock equipmentsPasturing equipmentElectrical conductorEngineering
The present invention provides a high voltage pulse generator used for deterring animals where the high voltage pulses are delivered to the animal through an electrical conductor that lays directly on the ground and is not insulated from the underlying ground system. The invention's high voltage pulse generator has a predetermined output impedance that is significantly lower than the impedance of an animal that may contact either the device's output or a conductor laying on the ground that is connected to the devices output. The invention's high voltage pulse generator also has a predetermined output impedance that is lower than the impedance of the conductor in contact with the underlying ground system. This significantly low output impedance allows the device to deliver maximum output energy to the conductor in contact with the underlying ground system while maintaining high voltage and adequate energy levels to deliver an effective shock for deterring animals. This significantly low output impedance also allows the device to limit the energy delivered to an animal to a small percentage of the devices maximum output such that the shock intensity felt by the animal is at a mild or annoying level for lengths of conductors in contact with the underlying ground system that vary from zero to hundreds or thousands of feet in length or more.
Owner:WOLFGRAM INDS
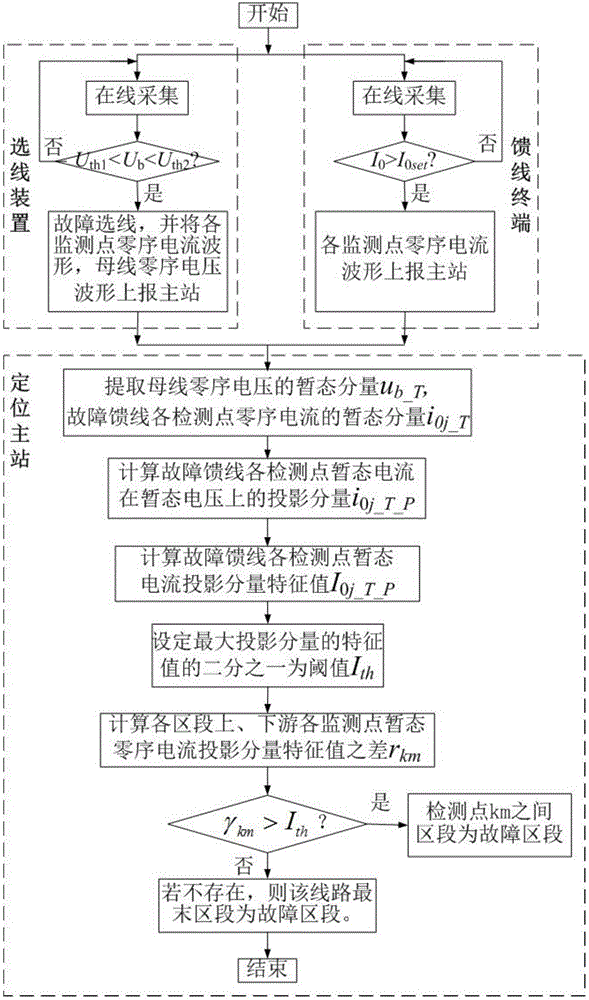
Small-current grounding system high-resistance grounding fault positioning method based on transient current projection component amplitude comparison
InactiveCN106526410ASolve the problem of fault locationFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemTransient stateHigh resistance
A small-current grounding system high-resistance grounding fault positioning method based on transient current projection component amplitude comparison belongs to the field of power distribution network fault detection. The method settles a problem of small-current grounding system high-resistance grounding fault positioning and is a positioning method which utilizes projection component amplitude comparison of transient zero-sequence current of each monitoring point at upstream and downstream of each segment on bus transient zero-sequence voltage. According to a fault line selecting result, the projection components of the transient zero-sequence current at upstream and downstream of each segment in a faulted line on the bus transient zero-sequence voltage are calculated. A characteristic value which comprises projection component polarity and amplitude information of each monitoring point is compared. One second value of the characteristic value of a largest projection component is set as a threshold. The segment in which the difference between the characteristic values of the projection components of the transient zero-sequence current at upstream and downstream of the segment is larger than the threshold is selected as the faulted segment. If the difference between the characteristic values of the projection components of the transient zero-sequence current at upstream and downstream of each segment is lower than the threshold, a line end fault is determined. The small-current grounding system high-resistance grounding fault positioning method settles a problem of positioning the high-resistance grounding fault in the small-current grounding system and furthermore has high practical application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Small current grounding system single-phase earth fault direction detecting method utilizing linearity between line zero sequence current and voltage derivative
ActiveCN109683063ASolve low resistanceResolve detectionFault location by conductor typesHigh resistanceLinearity
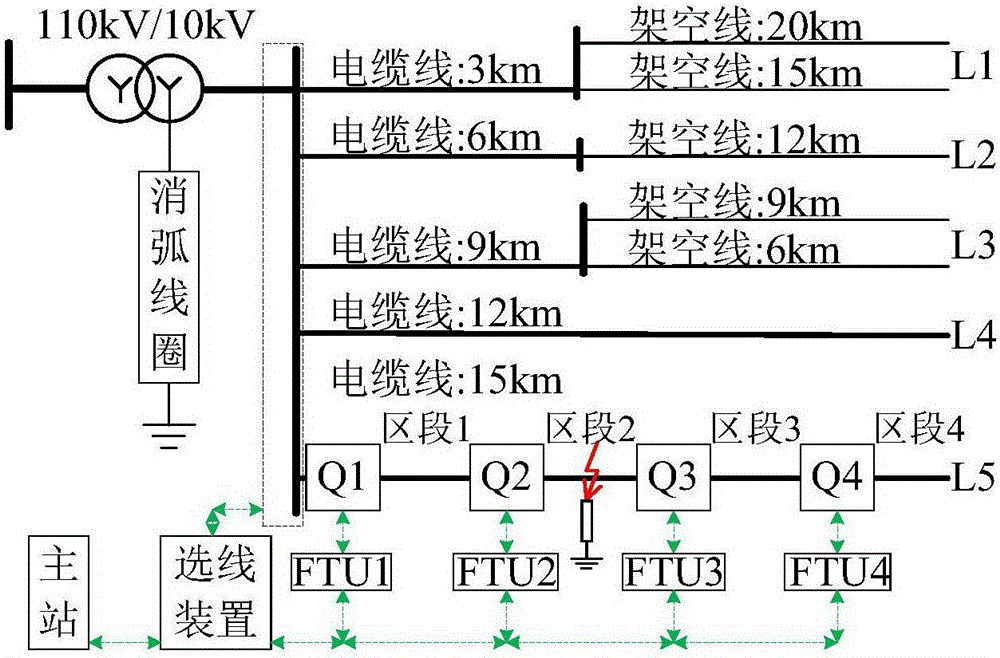
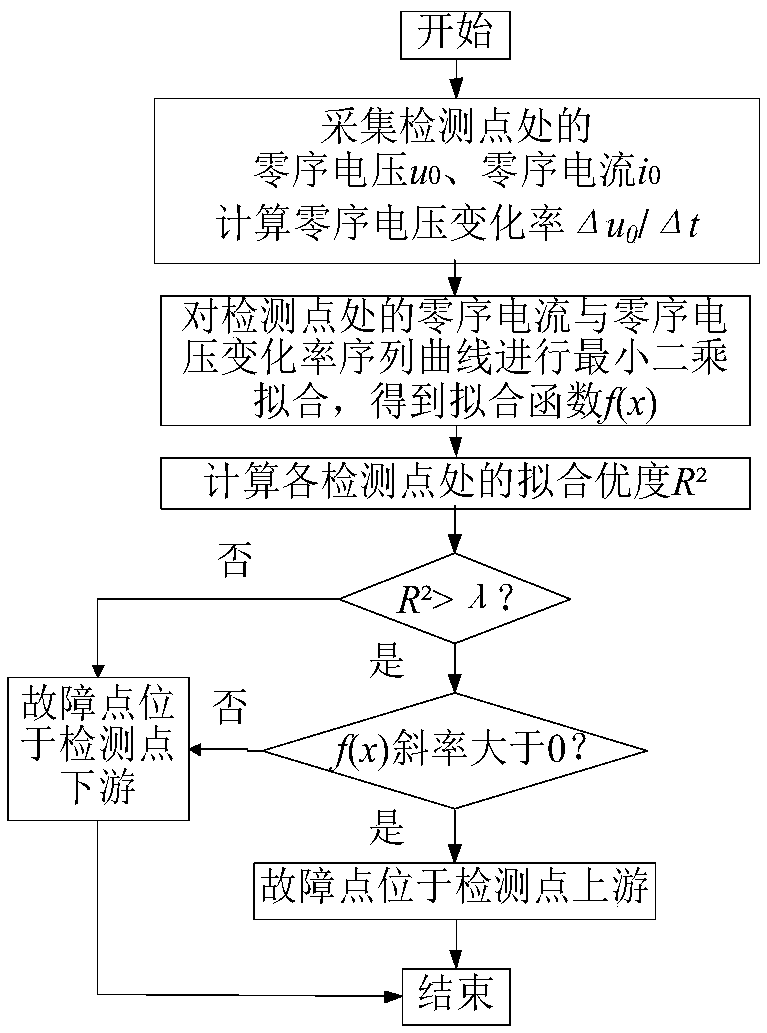
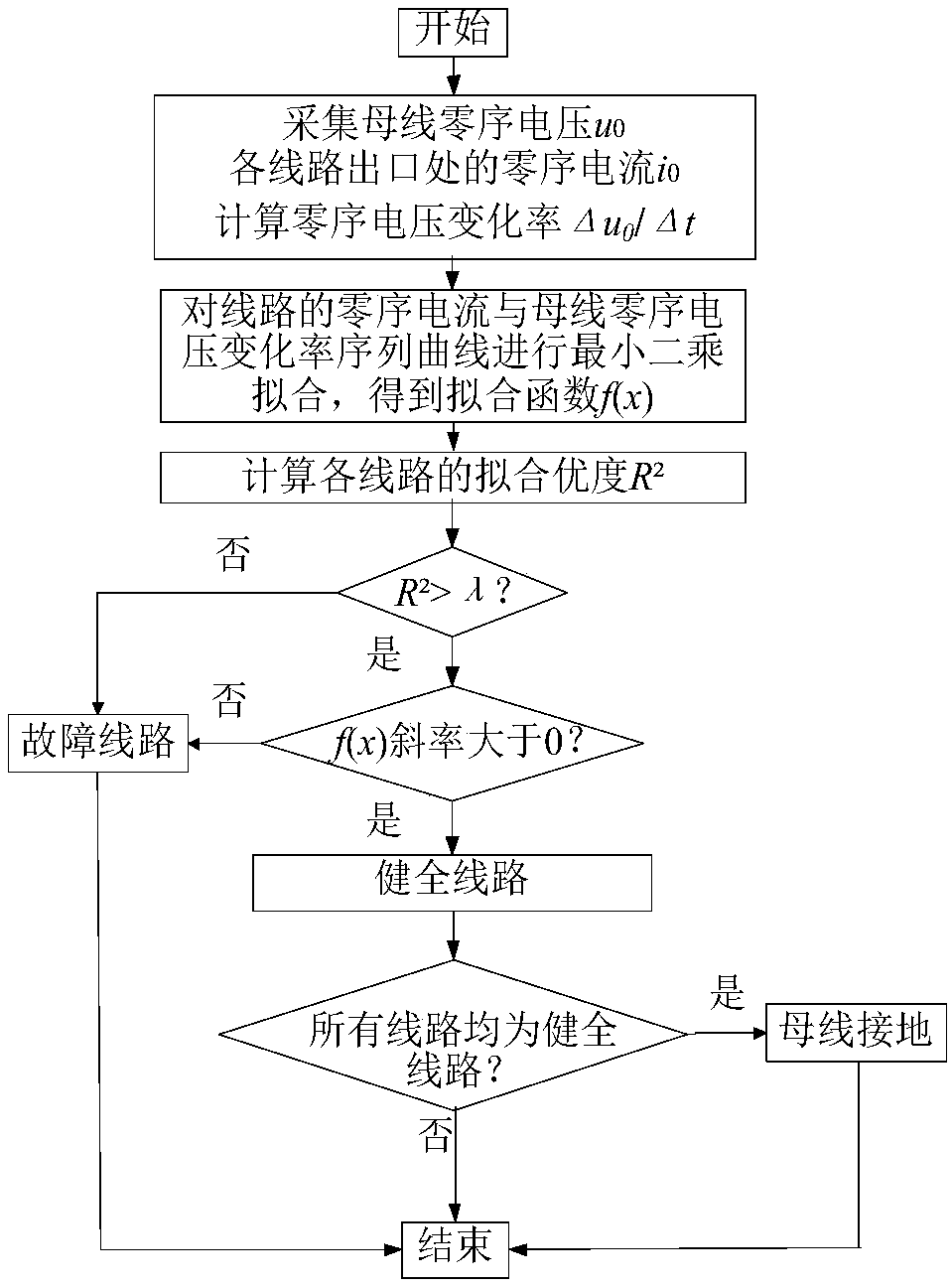
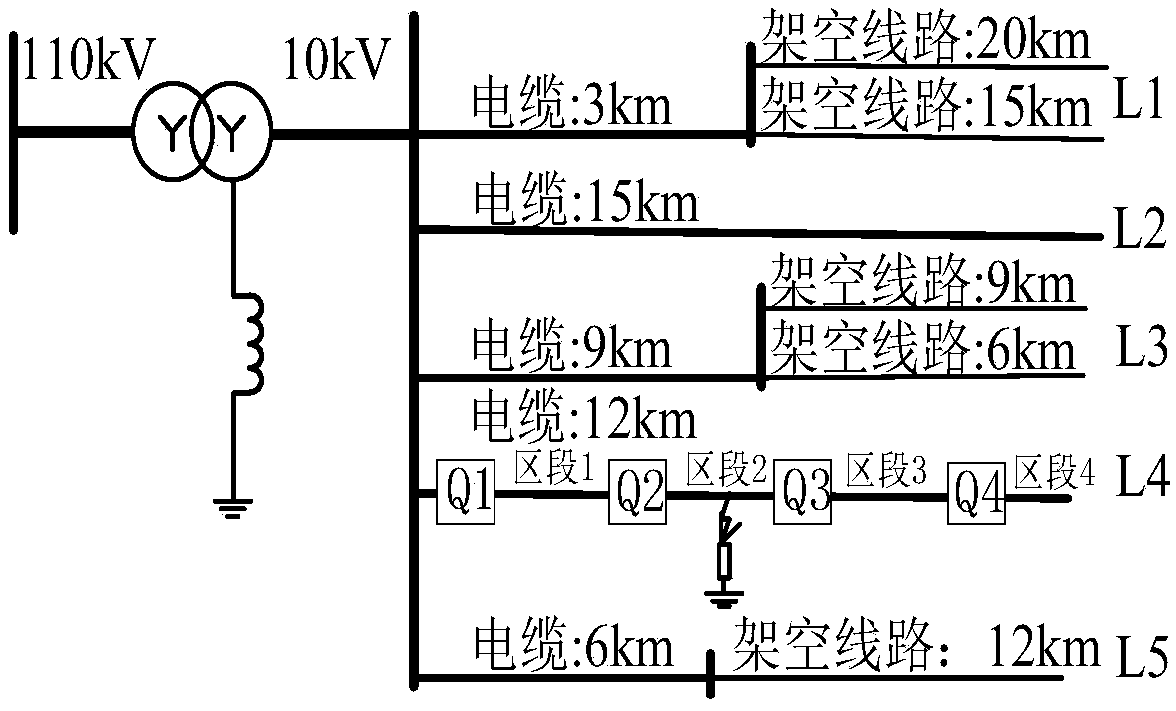
The invention provides a small current grounding system single-phase earth fault direction detecting method utilizing the linearity relation between a line zero sequence current and a voltage derivative and belongs to the field of relay protection of power distribution networks. The linearity relation between upstream and downstream voltages and currents of a fault point is analyzed when a single-phase earth fault occurs in an unearthed and arc suppression coil grounded system, a method for fault direction detection by utilizing the linearity relation between the line zero sequence current andthe voltage derivative at a detection point is provided. The zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current at each detection point are acquired, linear fitting is conducted on a zero-sequence current sample value sequence and a corresponding zero-sequence voltage difference value sequence, it is judged whether the detection points having the fit goodness greater than a threshold value and the fitting function slope greater than 0 are located at the downstream of fault points or not, if not, the detection points are located at the upstream of the fault points. The method can be simultaneously suitable for low-resistance and high-resistance earth faults of a small current grounding system, improves the adaptability of a fault direction detection algorithm and has a wide actual applicationvalue.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Grounding and line selection method for low current grounding system
ActiveCN101436776AEliminate the effects ofRealize online measurementFault locationEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentMicrocomputerGround line
The invention discloses a ground line selection method for a small current grounding system. The method solves the problem that the prior line selection method is low in sensitivity and generates errors in line selection. The method comprises the following steps: 1, single-circuit lines and double-circuit lines are numbered and placed in a microcomputer; 2, the microcomputer judges whether the system is grounded or not and identifies a grounding phrase of the system; 3, according to the number of the single-circuit lines and the double-circuit lines, the microcomputer calculates a grounding transfer characteristic formula with zero sequence current which is measured during the normal operation of the system, zero sequence current of the single-circuit lines, zero sequence voltage of a bus and zero sequence current of the double-circuit lines which are measured when the system is grounded, and zero sequence voltage of a bus, zero sequence current of the double-circuit lines and zero sequence current of the single-circuit lines which are measured during grounding transfer of the system; the result of the calculation is compared with grounding current IJ passing through a split phase switch of the grounding phase during grounding transfer to determine a fault line. The method has the advantages of the characteristics of high sensitivity and accurate line selection and great significance on accurate identification of grounding circuit, grasp of grounding and arc-suppression coil conditions of the system, and promotion and improvement of safe and reliable operation of the system.
Owner:JINZHOU ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com