Small-current grounding system high-resistance grounding fault positioning method based on transient current projection component amplitude comparison
A transient current and projection technology, applied in fault location, measurement of electrical variables, information technology support systems, etc., can solve the problems of TV/TA transmission characteristics, inconspicuous, unsuitable for high-resistance grounding faults, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] To achieve the above object, the present invention intends to realize with the following technical solutions:
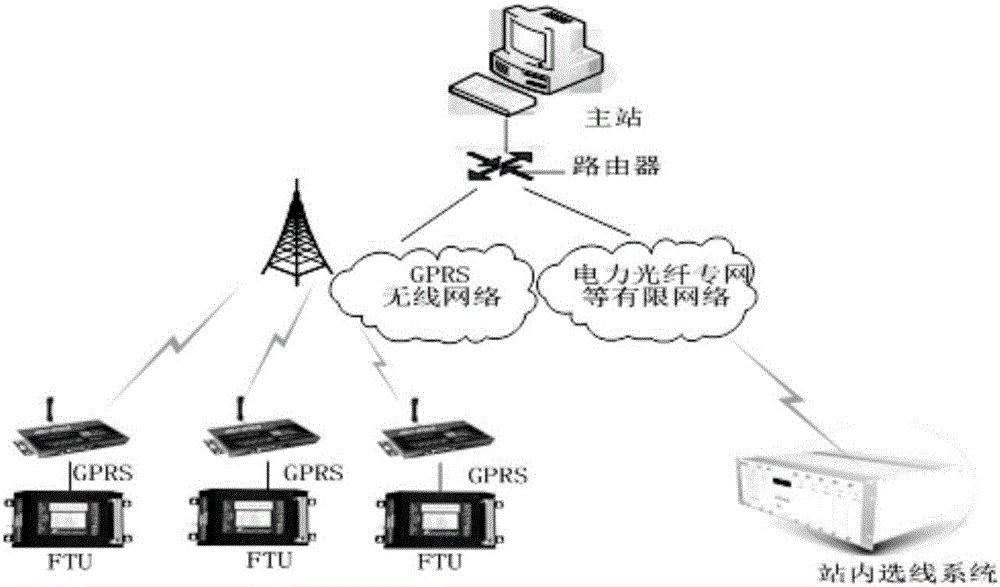
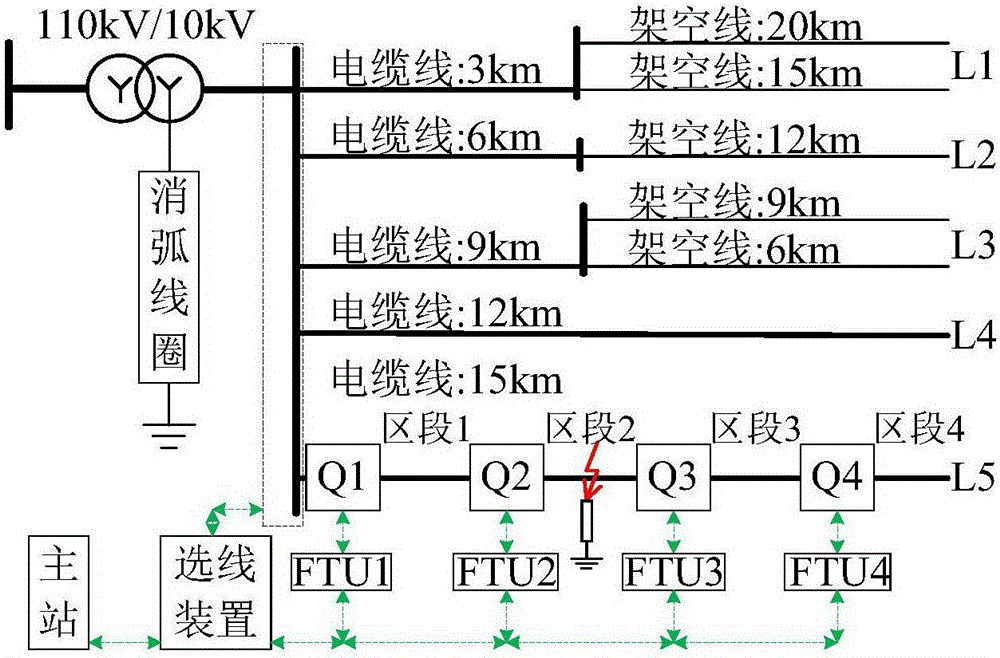
[0025] I. If attached figure 1 Shown is a small current ground fault location system based on the distribution network automation system platform. The main control room consists of a small current ground fault location master station and a communication network. The specific workflow of the positioning system is as follows:
[0026] 1) System workflow during normal operation
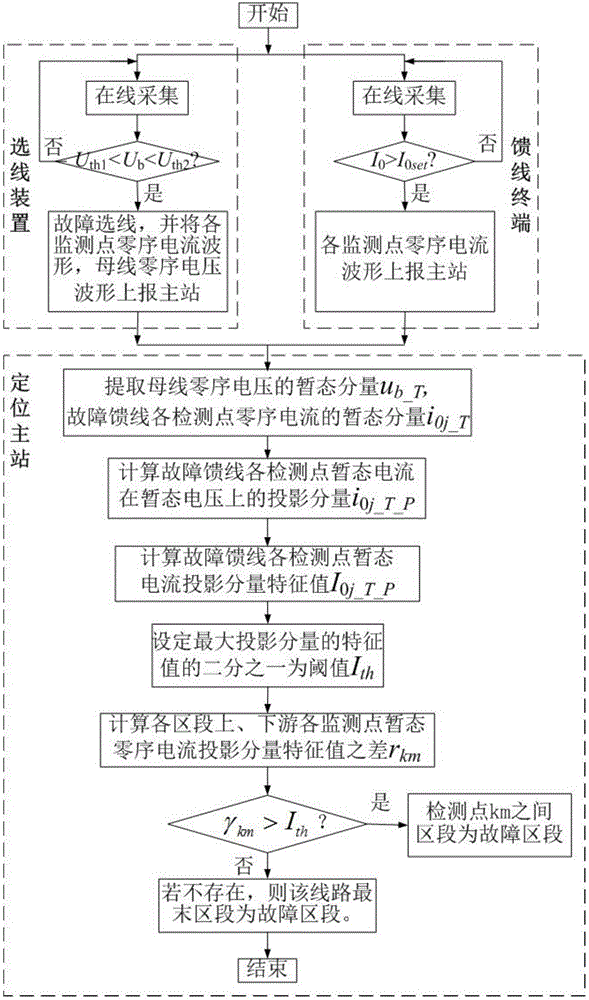
[0027] The feeder terminal in the line is always in the state of sampling the zero-sequence current and zero-sequence voltage (when conditions permit) signals at each monitoring point of the line, and compares the zero-sequence voltage sampling signal or zero-sequence current variation with the device startup threshold Judging whether the zero-sequence voltage amplitude of the bus is in U th1 b th2 when (normal U th1 =15V, U th2 =90V), to judge whether it meets the start-up conditi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com