Small current grounding system single-phase earth fault direction detecting method utilizing linearity between line zero sequence current and voltage derivative
A small-current grounding and zero-sequence current technology, which is applied in the direction of fault detection, fault location, and electrical measurement according to conductor type, can solve the problems of increasing algorithm complexity, low detection speed, and difficulty in reliable detection of single-phase ground faults. High engineering application value and strong applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
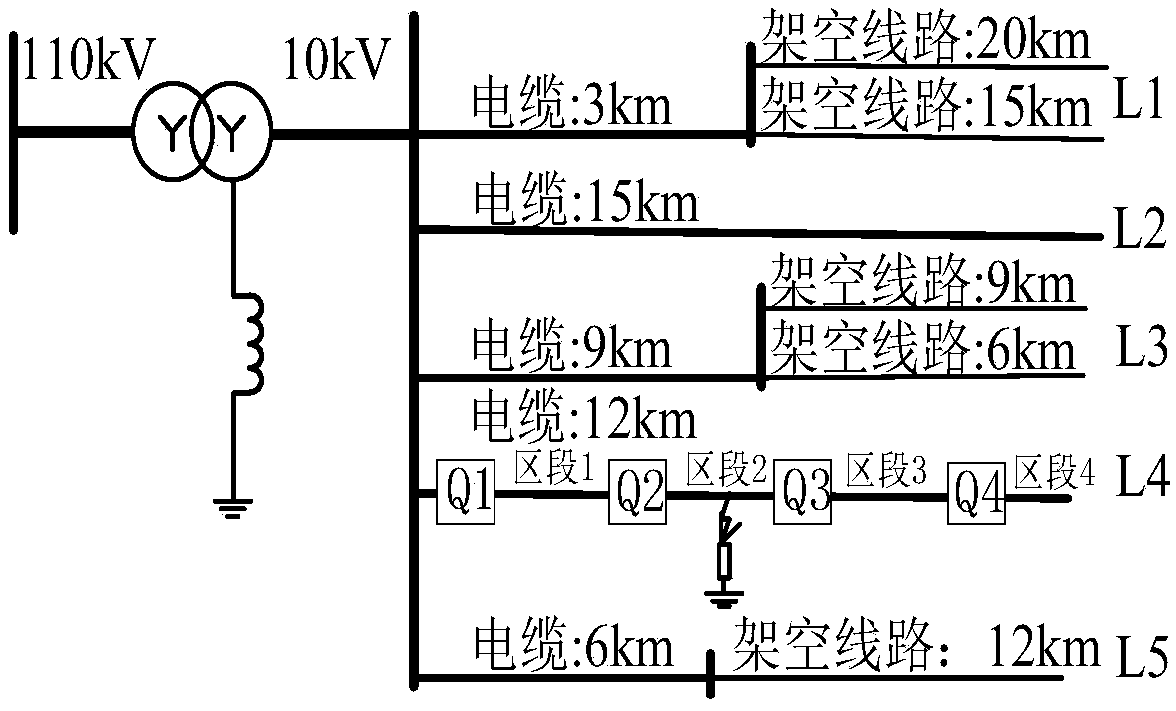
[0063] The power system line fault direction detection and protection method of the present invention can be applied in different small current grounding systems, and can be realized by various methods. It can be a protection device with a specific function, and can also share a software and hardware platform with other functions.
[0064] The following are respectively described:
[0065] 1. Using protective equipment to protect the method
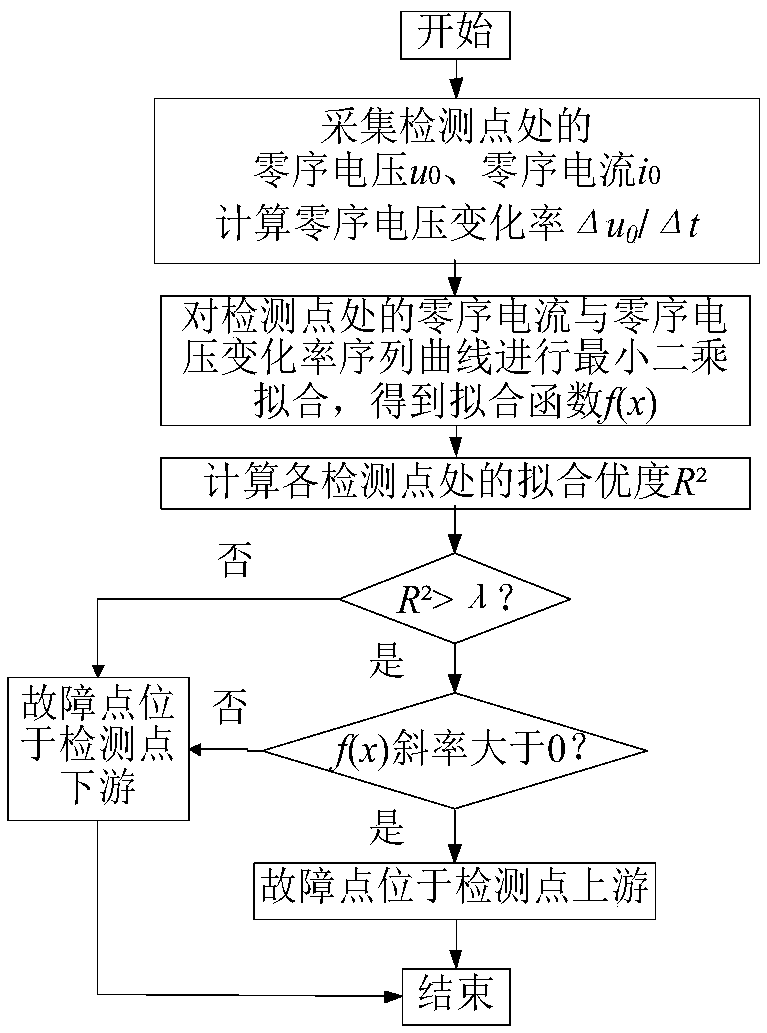
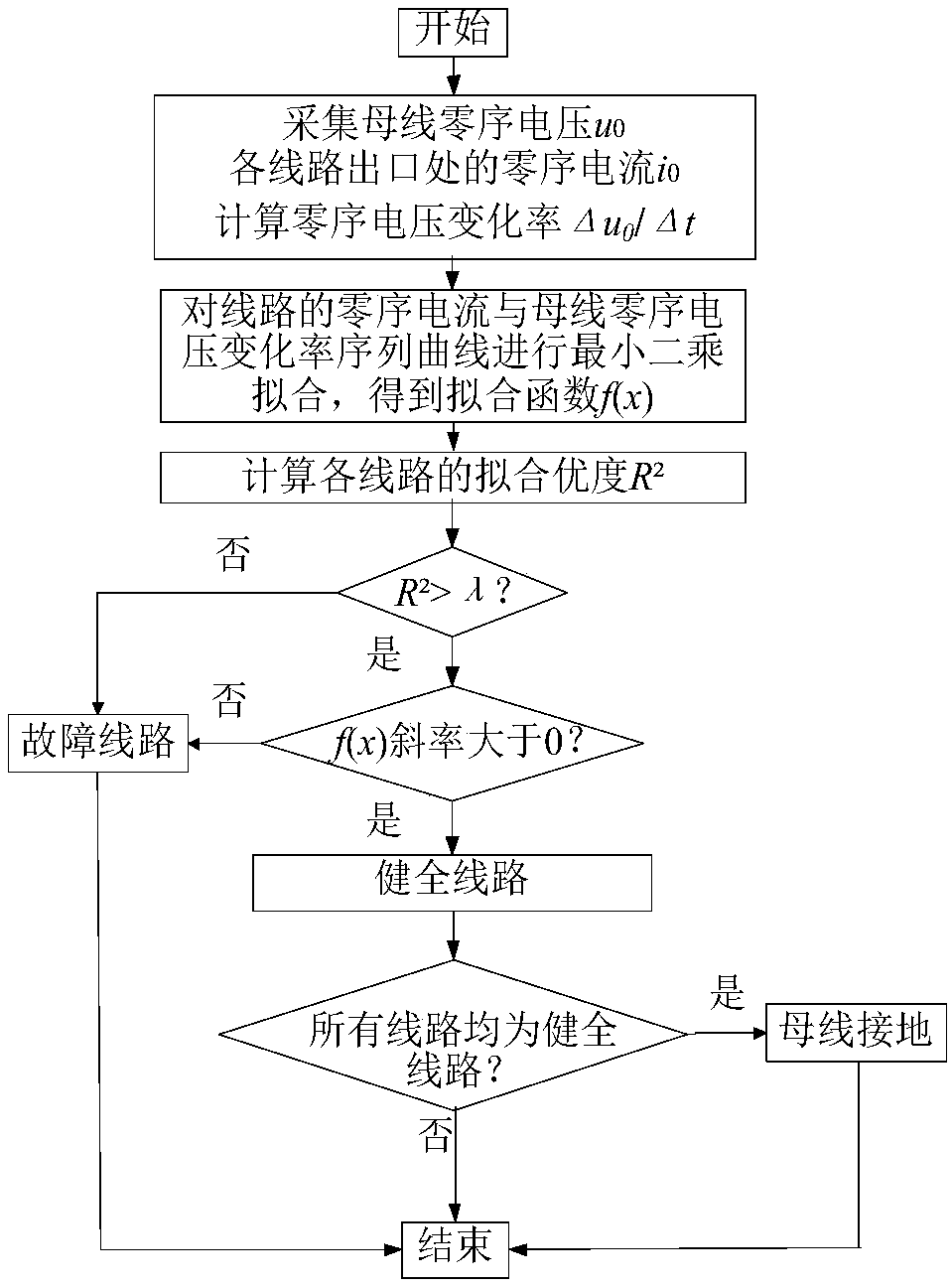
[0066] I. Using the present invention to determine the fault direction only needs the voltage and current signals of the detection point, and does not need fault information of other lines or detection points, which has its own characteristics. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0067] a. Taking the change of bus zero-sequence voltage as the fault start condition, record the zero-sequence current i at each detection point 0 , zero sequence voltage u 0 ;
[0068] b. Calculate the zero-sequence voltage change rate Δu at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com