Identification method of ground fault phases in three-phase ungrounded system and identification device thereof
A grounding fault and grounding system technology, applied in the fault location, measuring device, phase angle between voltage and current, etc., can solve the problem of finding equal faults, and achieve the effect of ensuring safe operation and reducing troubleshooting time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, illustrate in detail the specific content of the present invention:
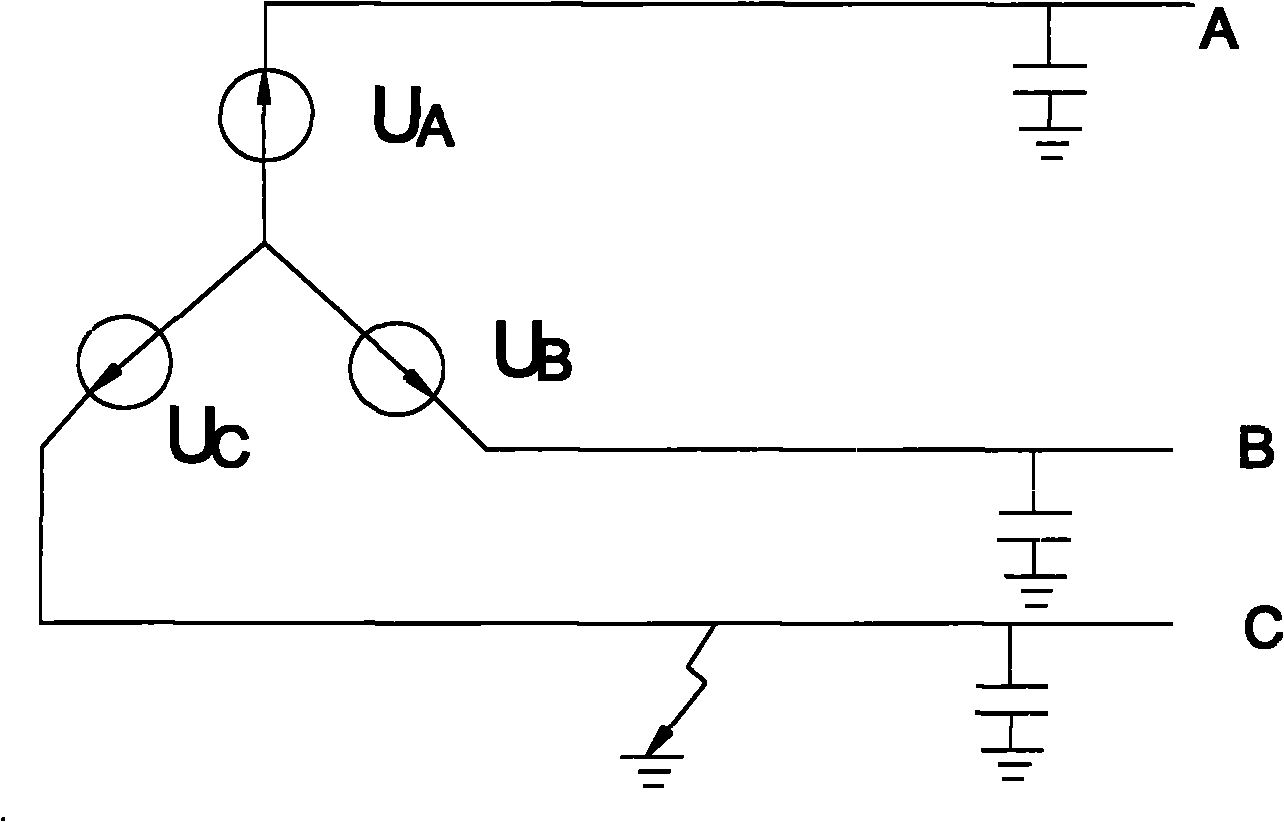
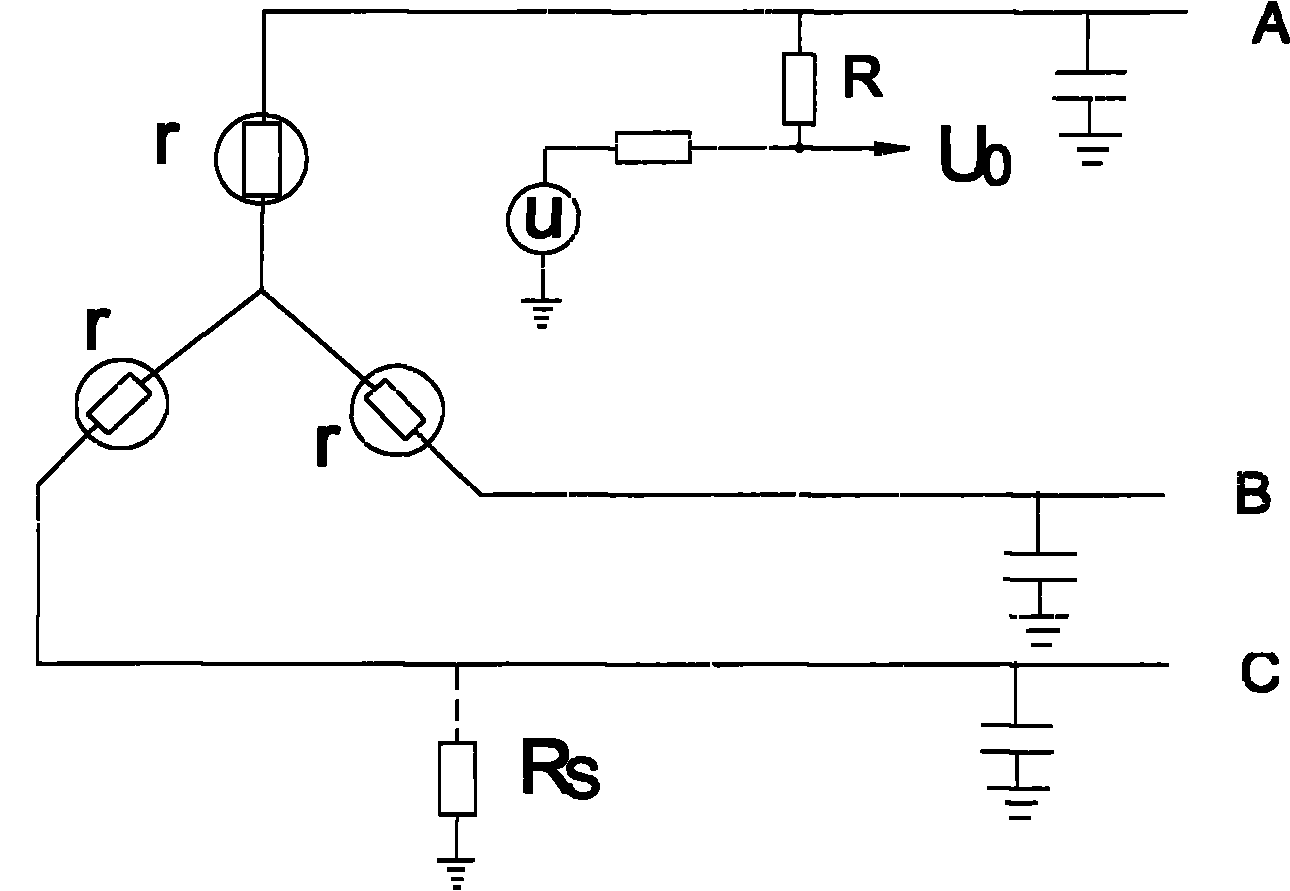
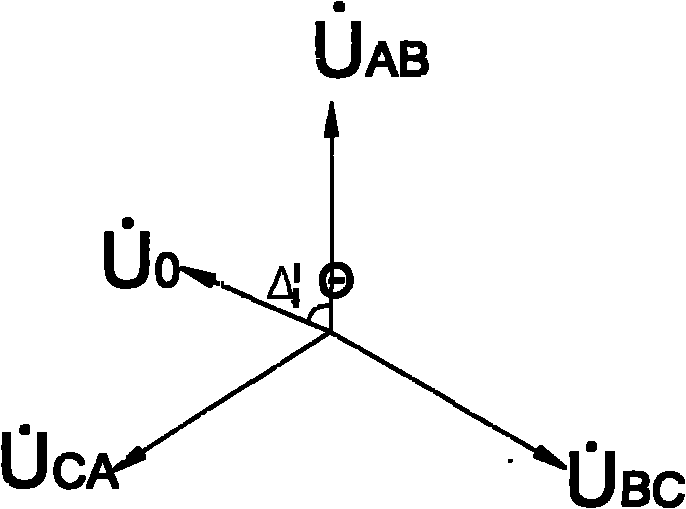
[0029] figure 1 The figure shows three phases A, B, and C drawn out by cables in the three-phase ungrounded system. When a ground fault occurs in one phase, a grounding resistance R is formed between the faulty phase and the ground. S , as shown in the figure, phase A is grounded. We lead a zero-sequence voltage sampling circuit from three phases A, B, and C. Specifically, resistor R1 is connected to phase A, resistor R2 is connected to phase B, and resistor R3 is connected to phase A. Connect with C, and then connect the sampling resistor R0 with the resistors R1, R2, and R3, so that the voltage on the sampling resistor R0 is the zero-sequence voltage. When the three-phase voltage is balanced and the insulation of A, B, and C is good, the grounding resistance Rs=∞, and the zero-sequence voltage U0=0. When any one phase fails, the grounding resistance ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com