Patents
Literature
493 results about "Initial current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
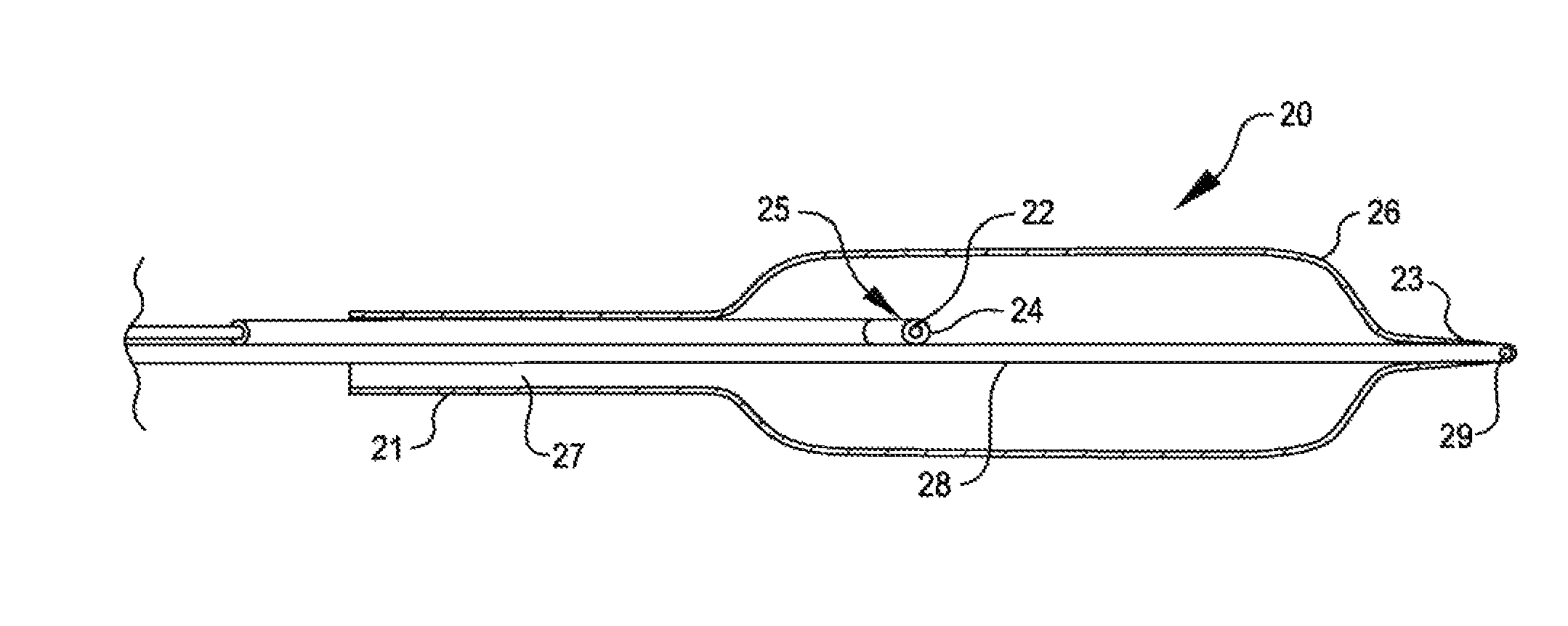
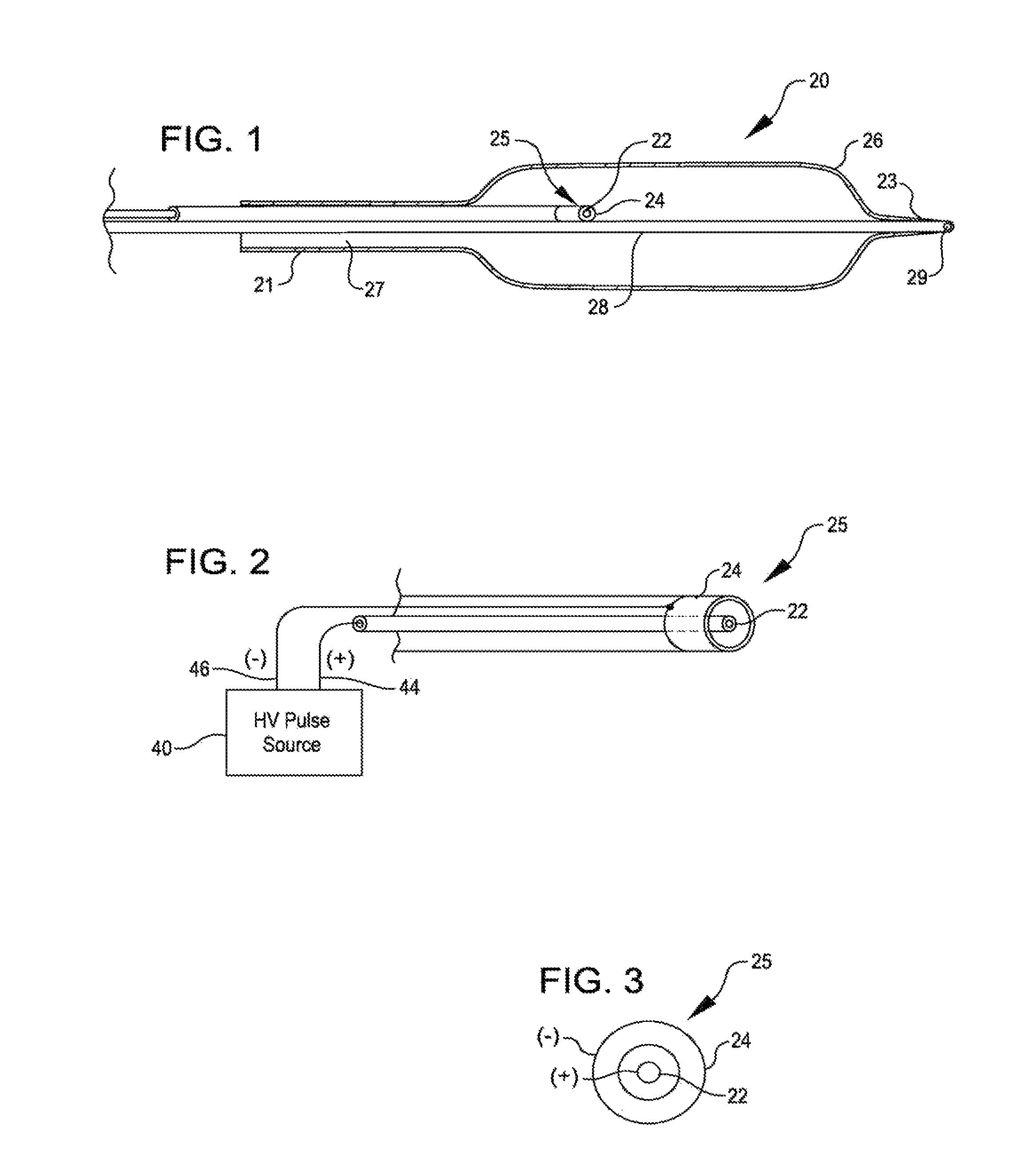
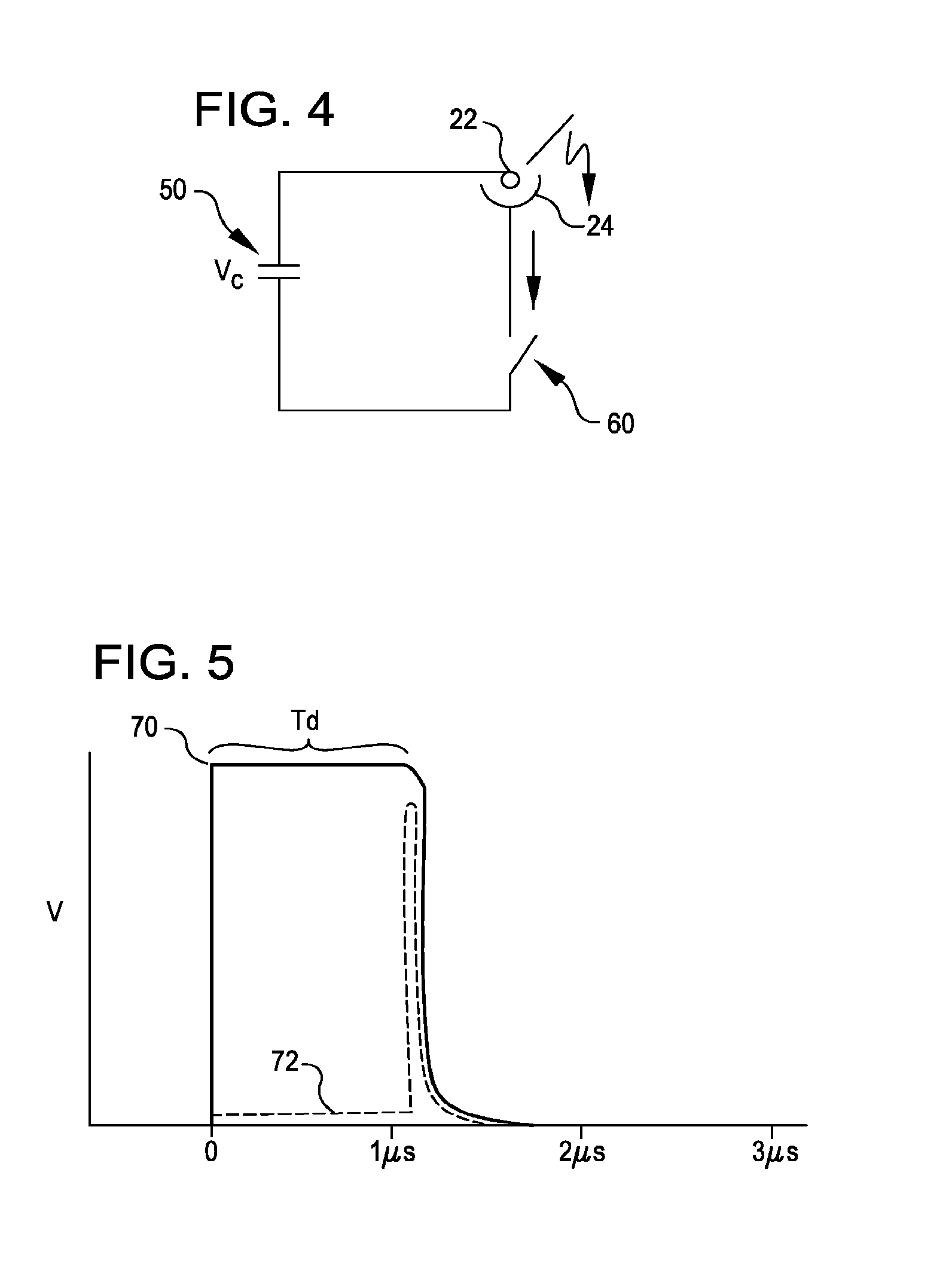
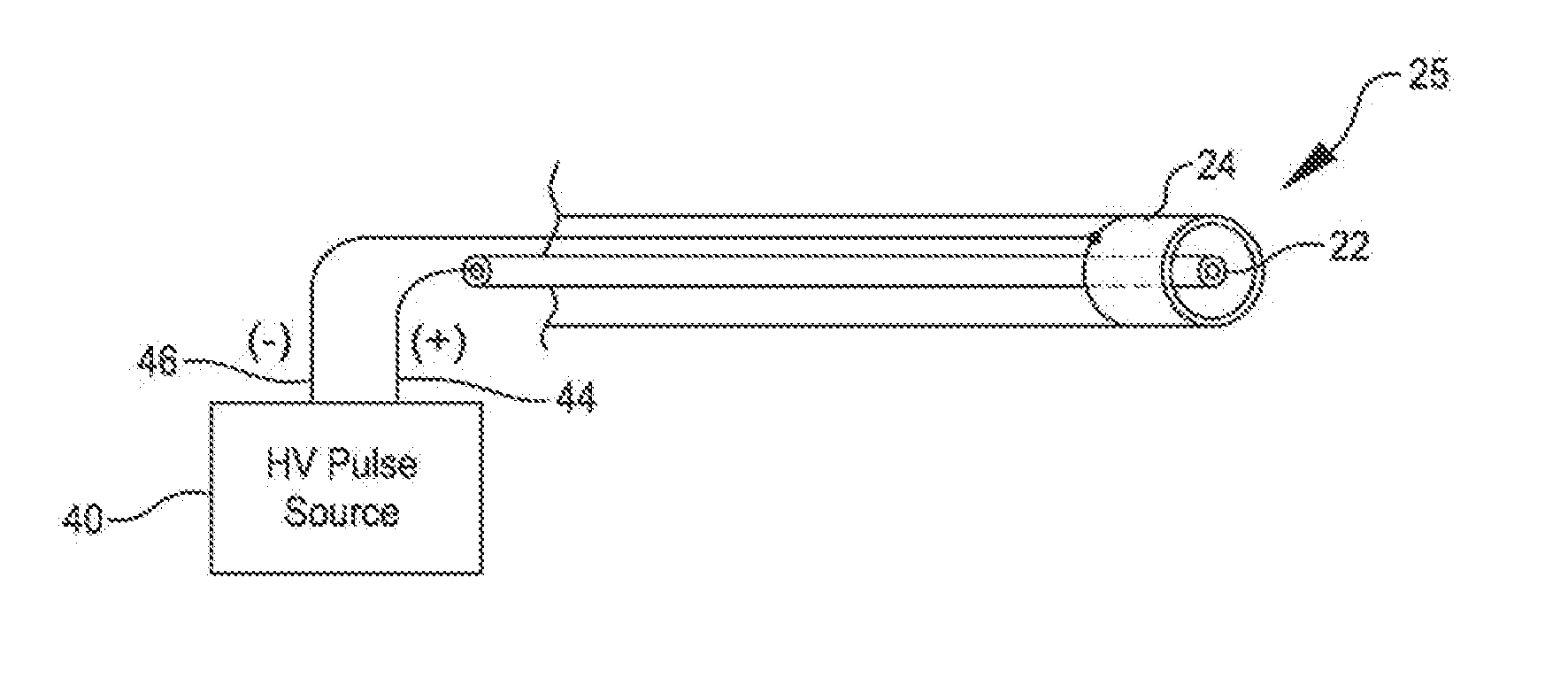
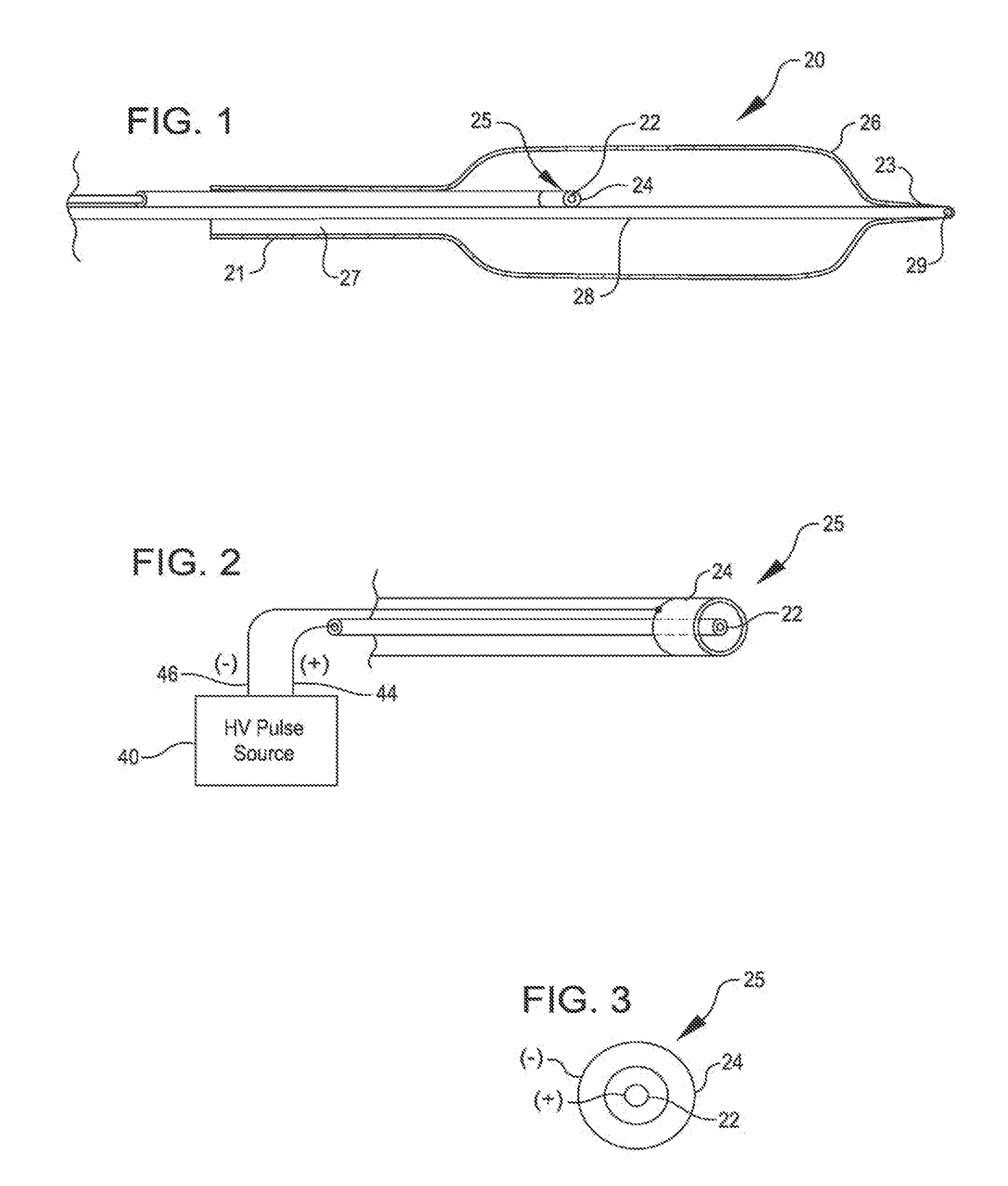
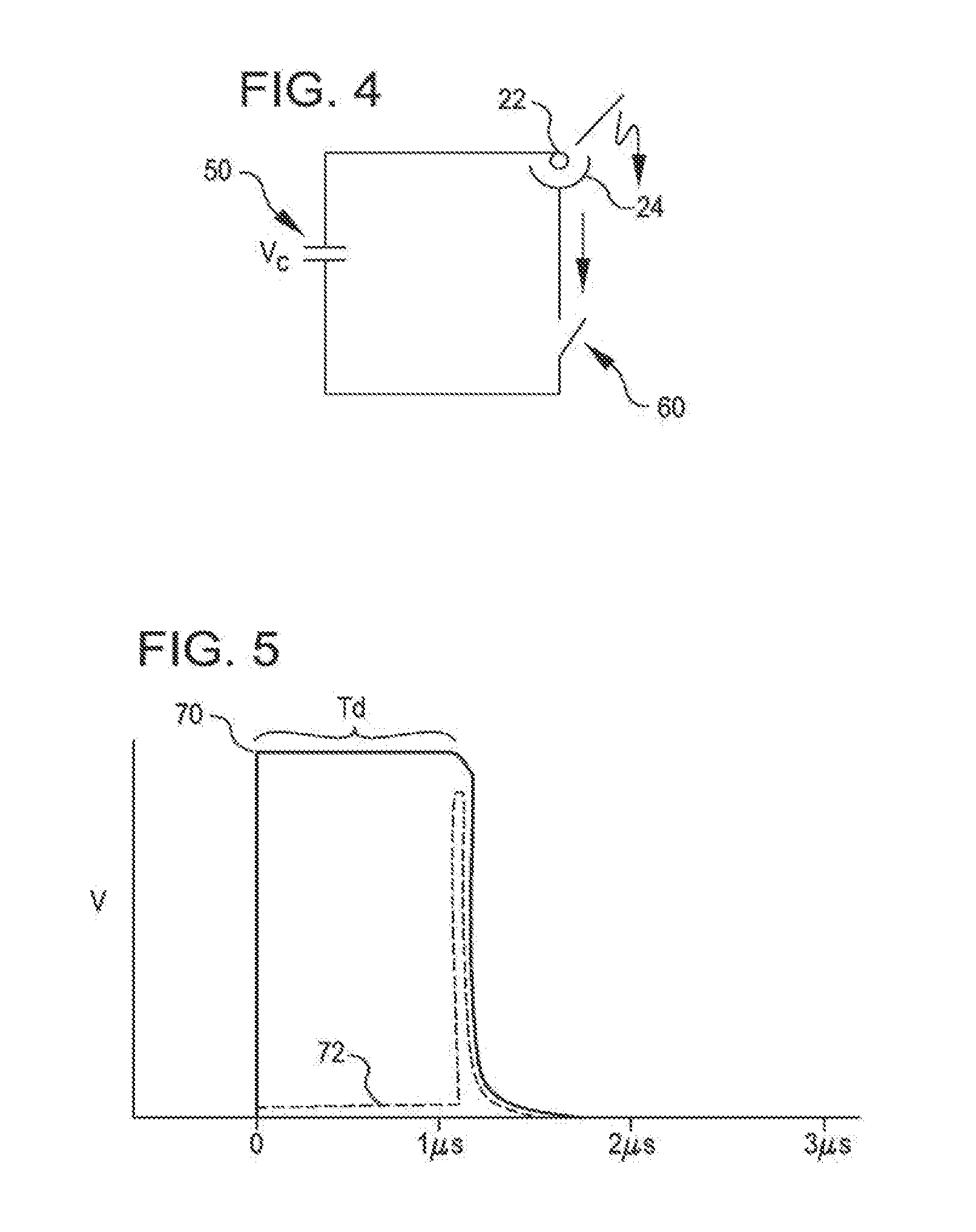
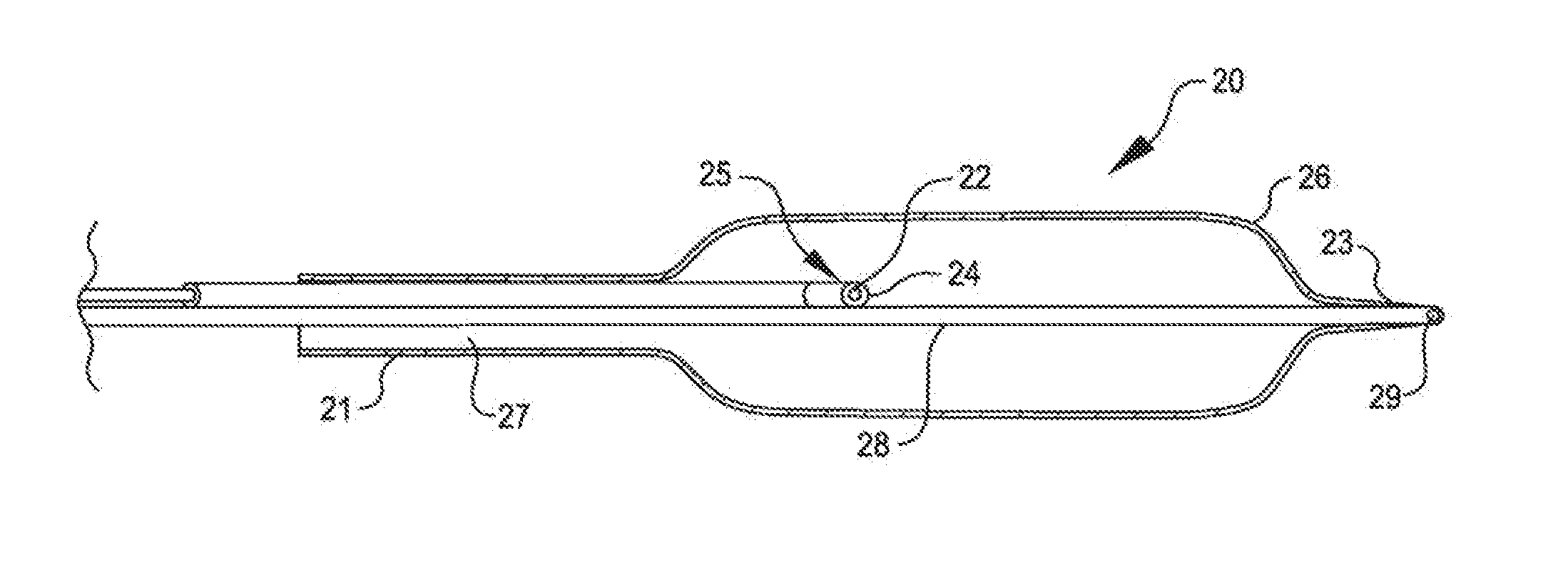
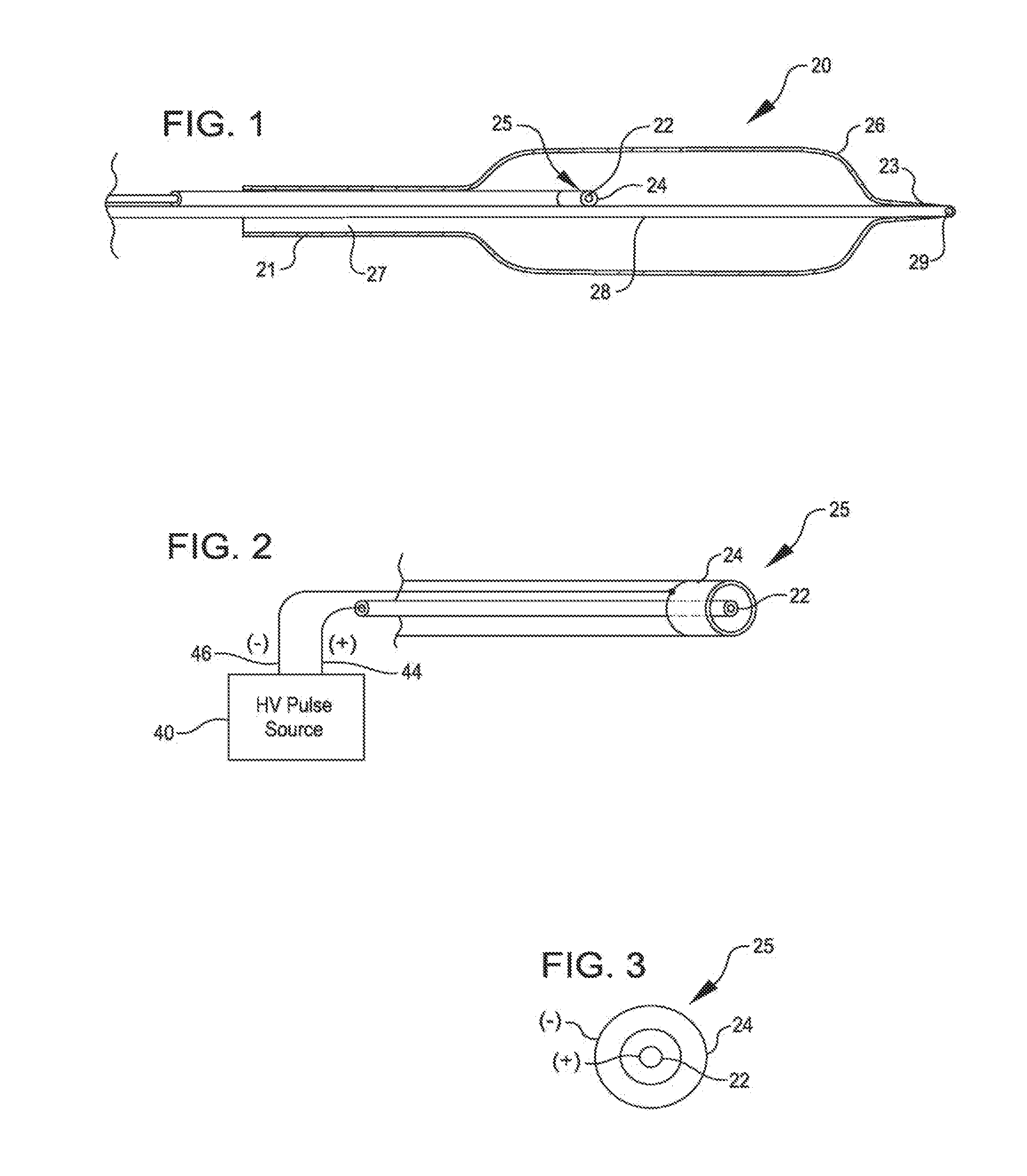
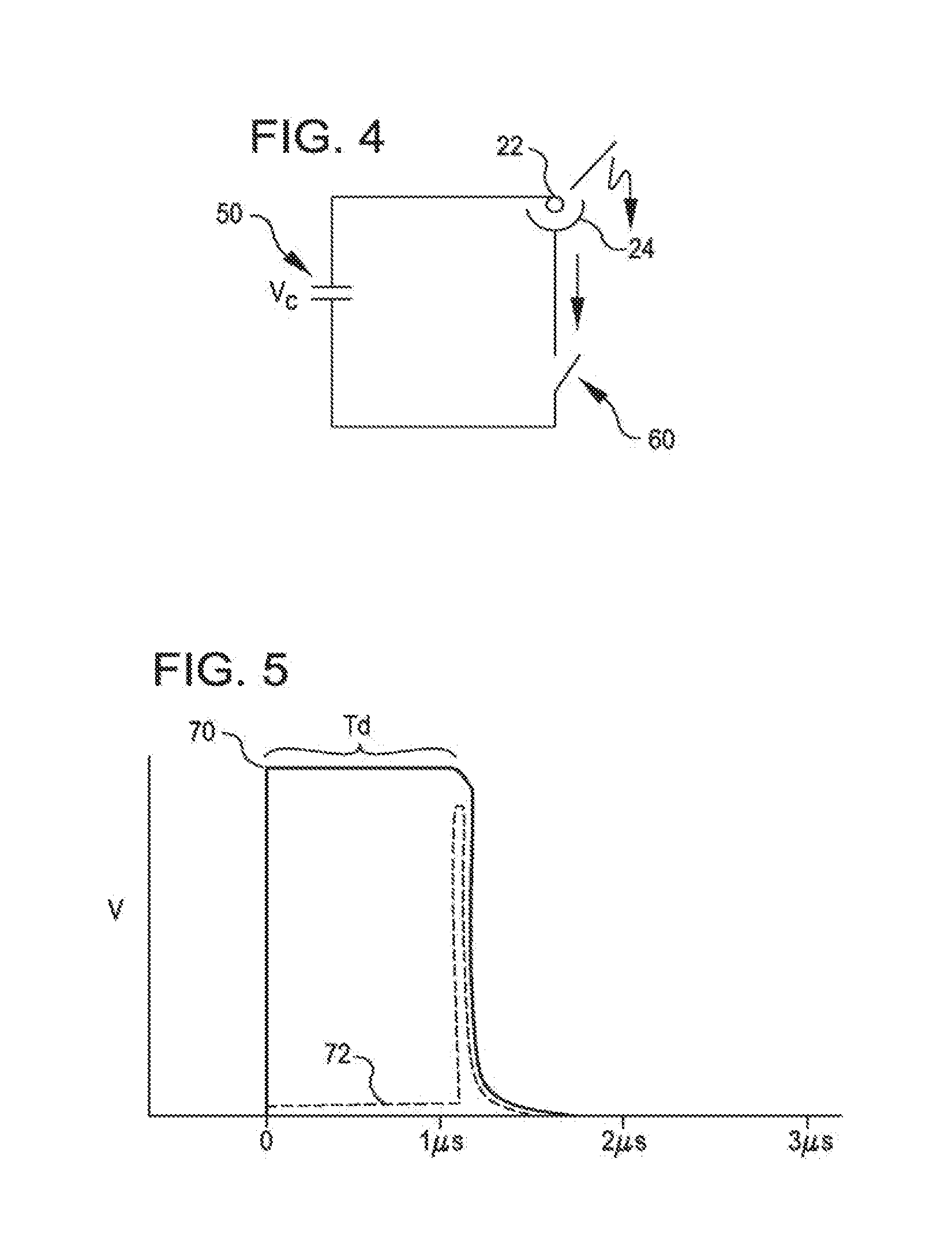
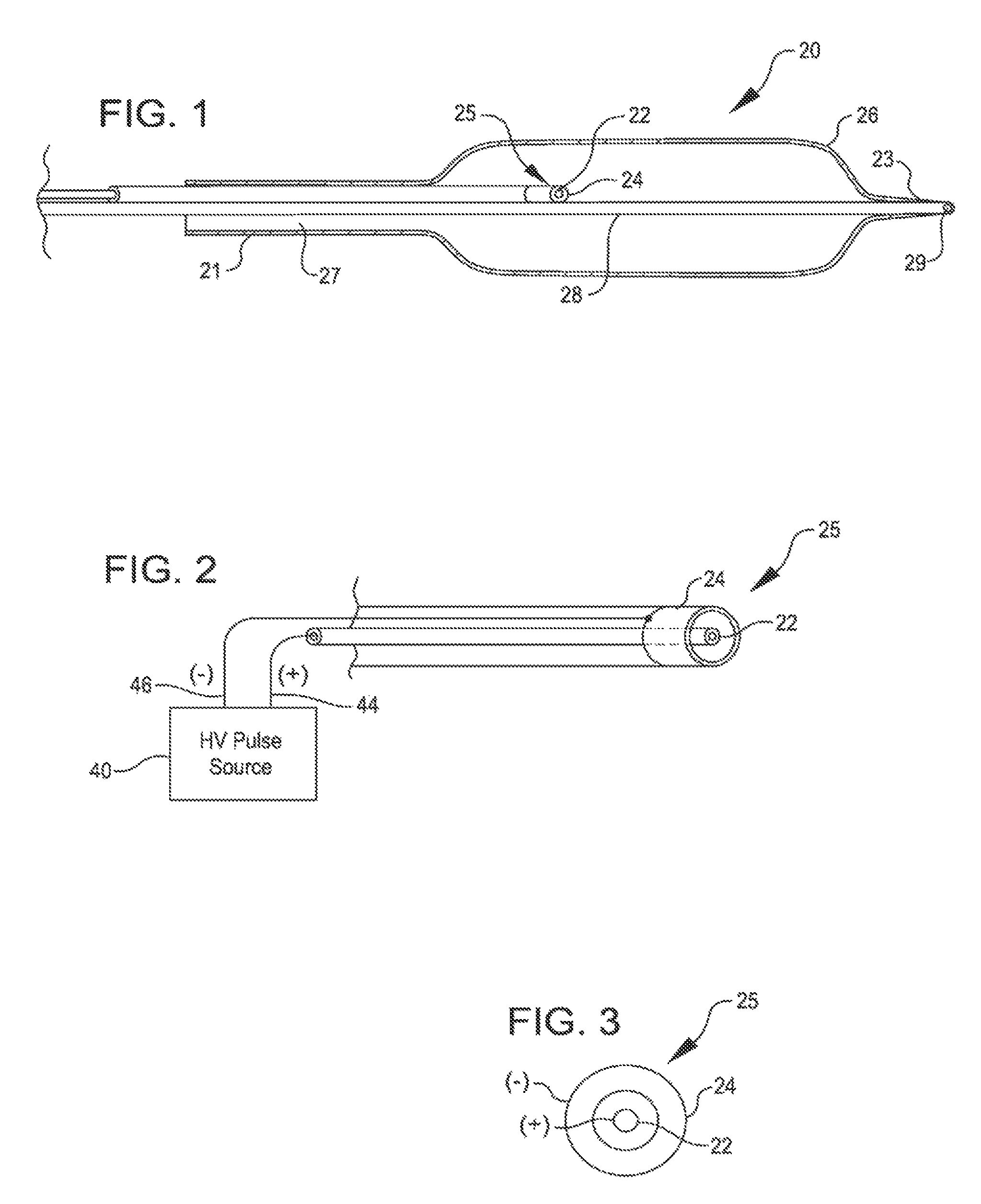
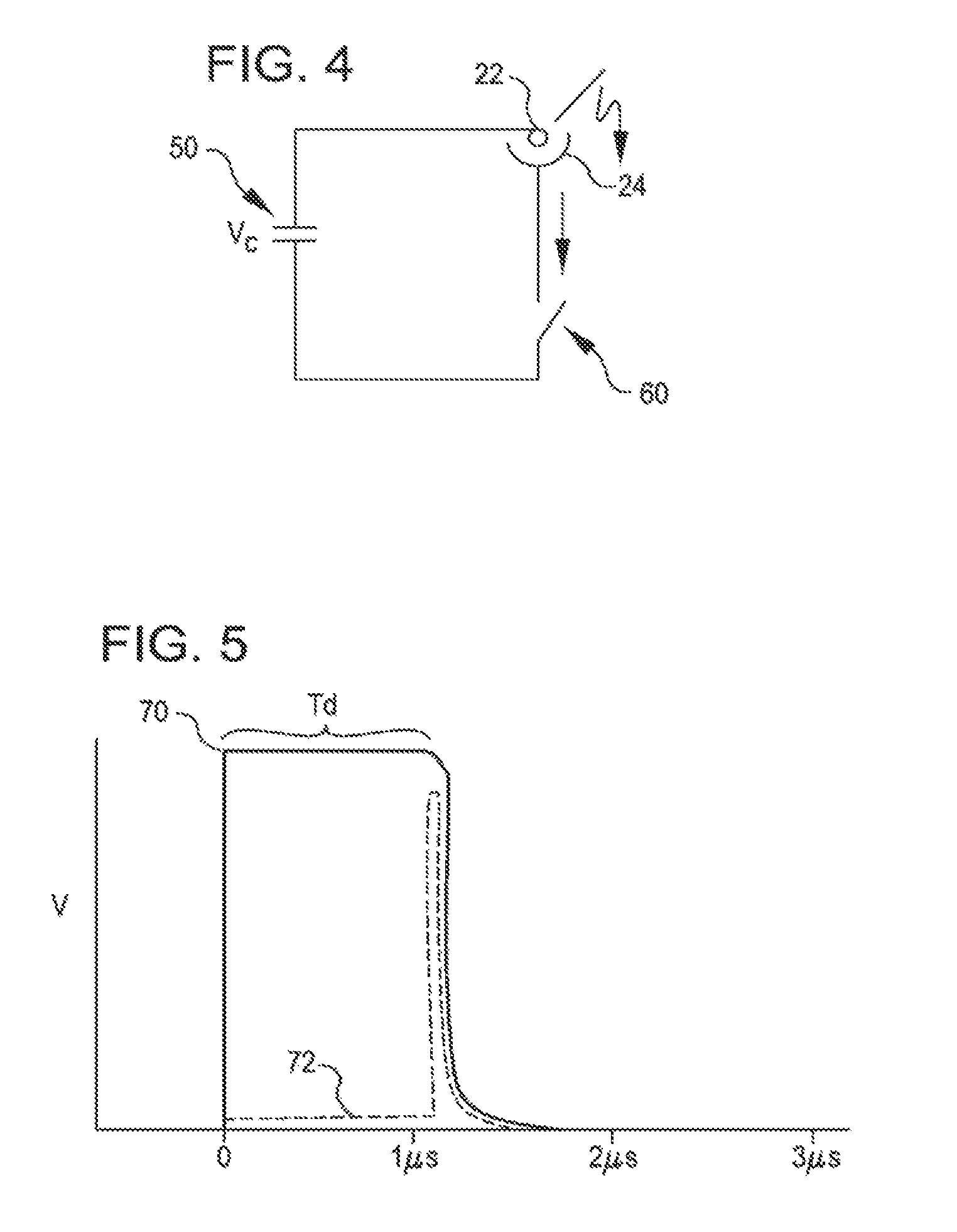
Shockwave catheter system with energy control
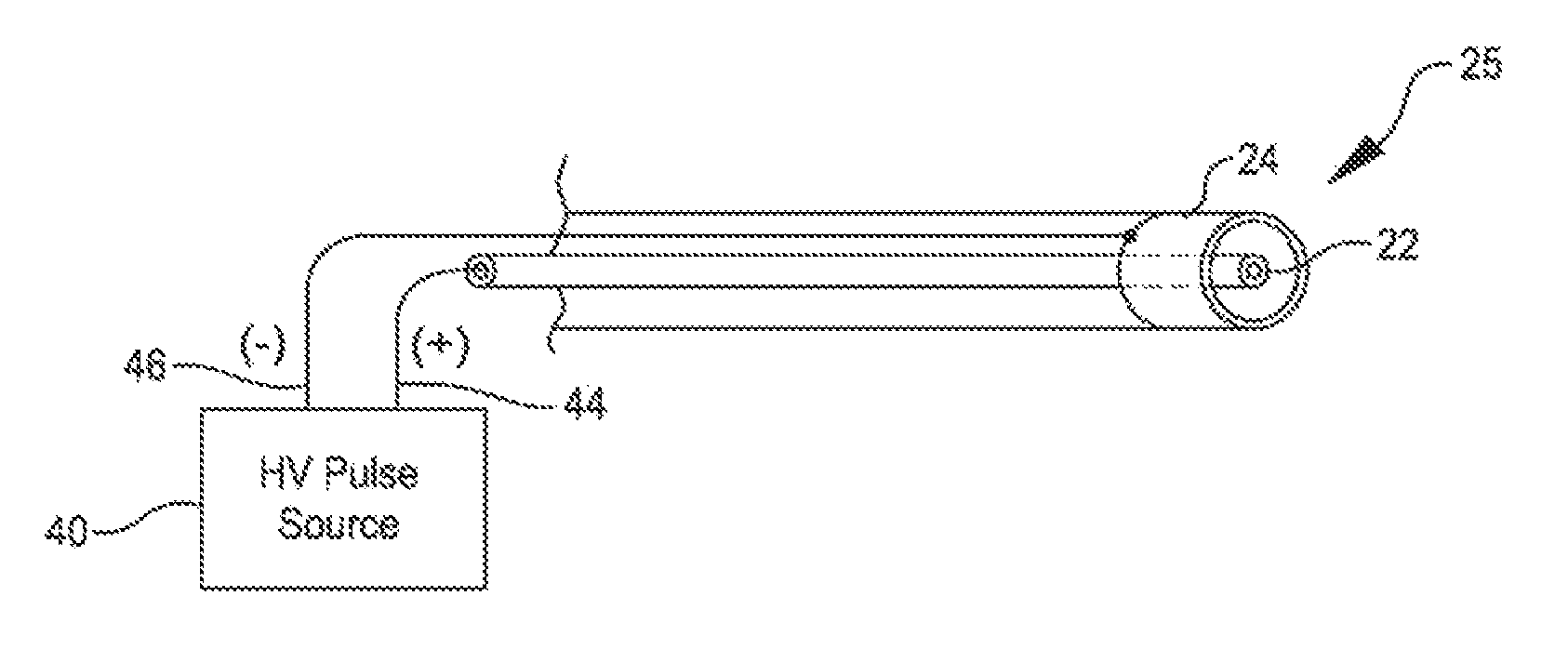
A system that breaks calcium in a liquid includes a catheter including first and second electrodes arranged to receive there-across a high electrical voltage at an initial low current. The high electrical voltage causes an electrical arc to form across the electrodes creating a gas bubble within the liquid, a high current to flow through the electrodes, and a mechanical shock wave. A power source provides the electrodes with the high electrical voltage at the initial current and terminates the high electrical voltage in response to the high current flow through the electrodes.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
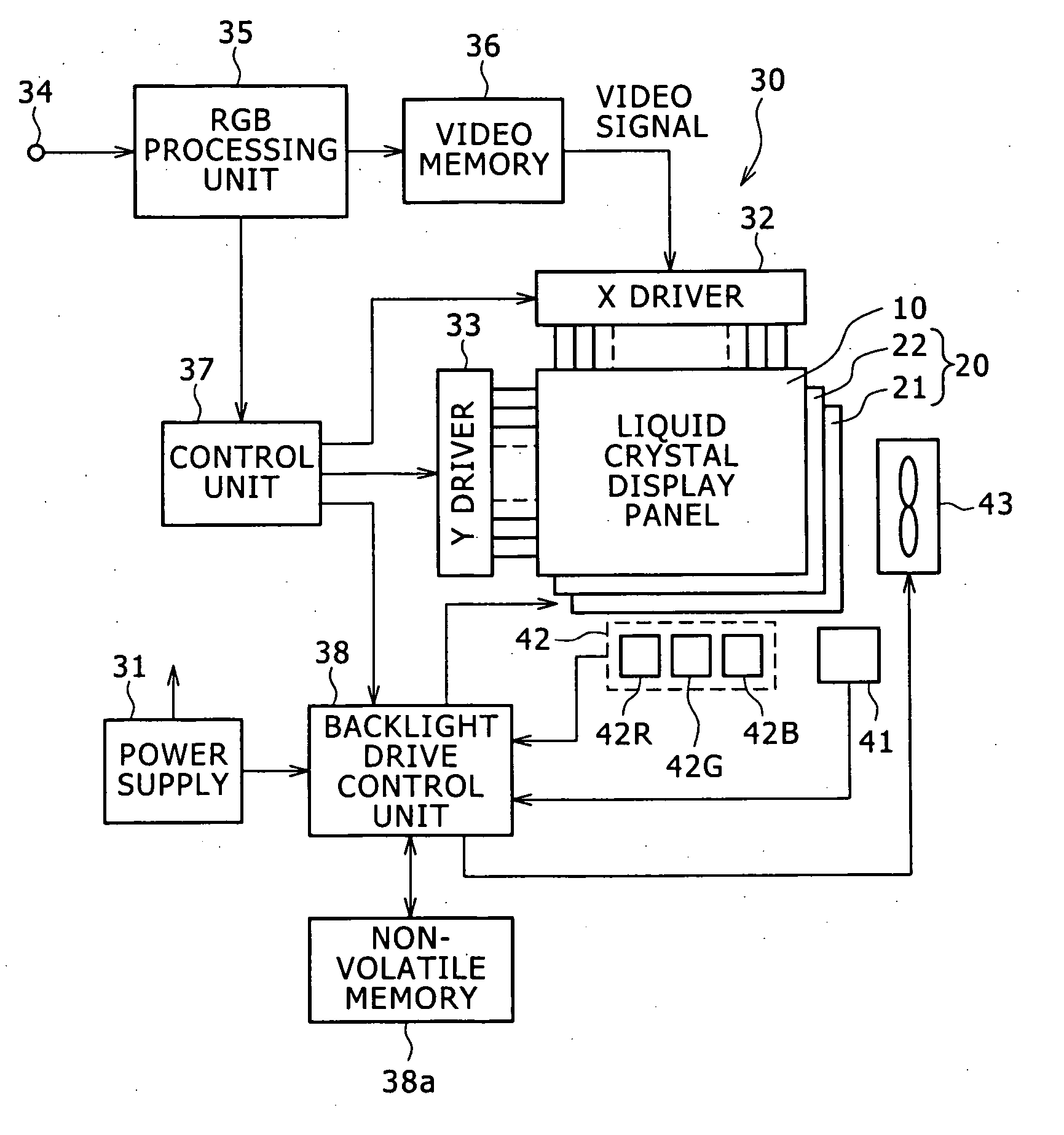
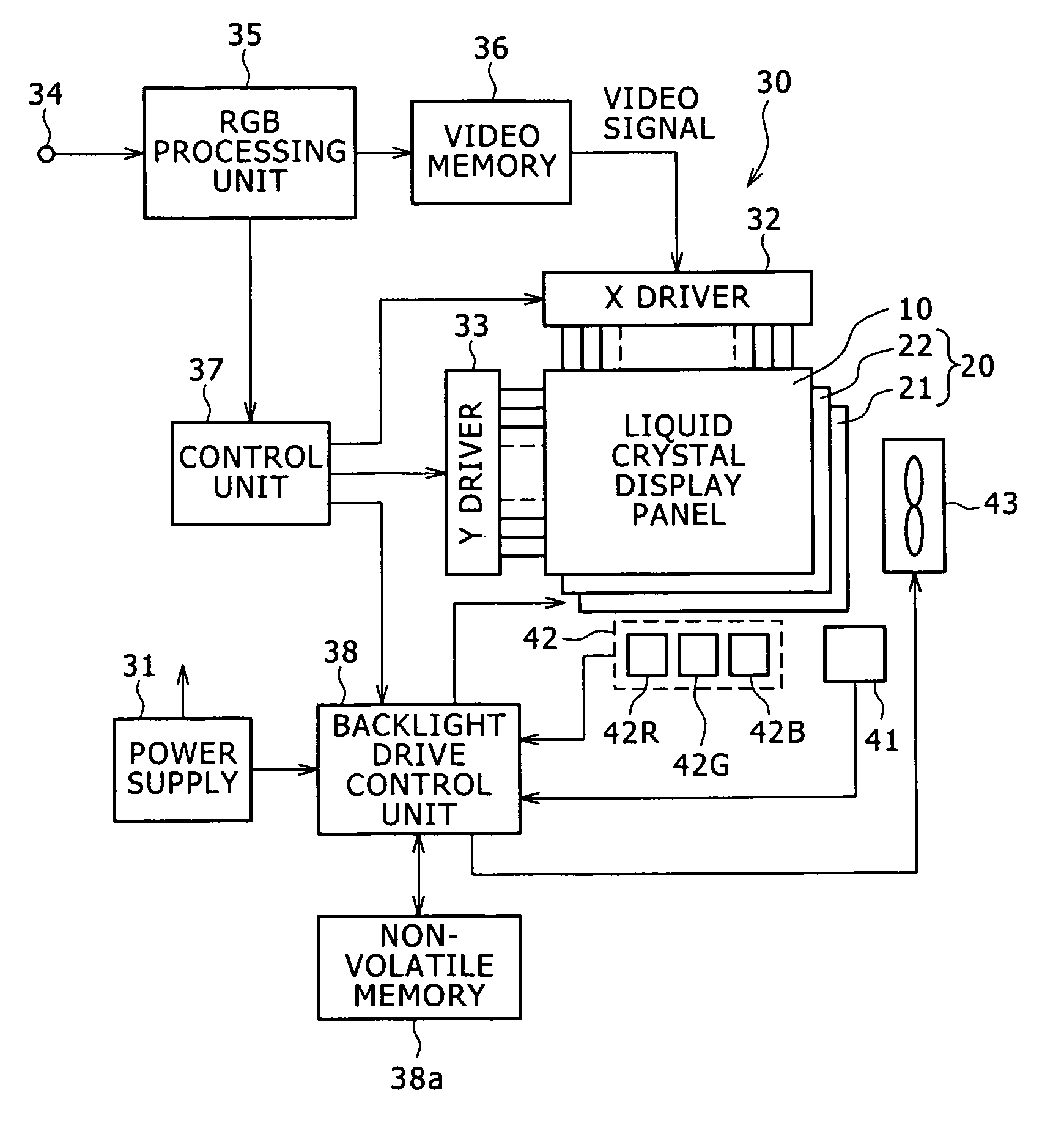
Backlight device, method of driving backlight and liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS20060125773A1Avoid elevationShorten the time periodCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric light circuit arrangementLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The present invention prevents extension of the time period from powering on a device to convergence of chromaticity of emitted white light on a certain chromaticity, irrespective of the temperature when the device is powered on. A color liquid crystal display apparatus includes a liquid crystal display unit, a backlight employing LEDs of red, green and blue as its light source, a drive unit for driving the LEDs of each color, a temperature sensor for sensing the temperature of the LEDs, and a chromaticity sensor for sensing the chromaticity of white light emitted from the LEDs. The drive unit supplies a current to the LEDs to drive them, and implements feedback control of the amount of current for the LEDs of each color based on a value sensed by the chromaticity sensor so that the white light has a certain chromaticity. Furthermore, upon powering on the backlight, the drive unit retrieves initial current values of the LEDs of each color from a non-volatile memory, and corrects the initial current values according to a value sensed by the temperature sensor to activate the LEDs of each color with the corrected value.
Owner:SONY CORP
Parametric fitting of a cochlear implant
ActiveUS20060235332A1Reduce the amount requiredMore recipient friendlyElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringPower flowEngineering
A method of fitting an auditory stimulation system to a recipient the system having a plurality of channels, and the method including the steps of establishing an initial current level profile representative of a current level setting spanning across at least some of the plurality of channels and adjusting parameters of the initial current level profile in the presence of a stimulation signal. There is further included a programming apparatus adapted to be interfaced with the auditory stimulation system to allow manipulation of threshold (T) and comfort (C) levels of the system. The apparatus includes a graphical display means adapted to display a graphical representation of the current profile of the channel array and means for adjusting a current level setting of the current pmfile of the array.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Automatic Determination of the Threshold of an Evoked Neural Response
Automatically analysing an evoked neural response. The method comprises: applying electrical stimulation to a target neural region at incrementally greater current levels beginning with an initial current level that is as close as possible to a typical threshold-NRT level; recording an NRT measurement of an auditory signal which generated by the target neural region in response to the stimulation; and utilizing a machine-learned expert system to predict whether the NRT measurement contains a neural response based on a plurality of features extracted from the auditory signal.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
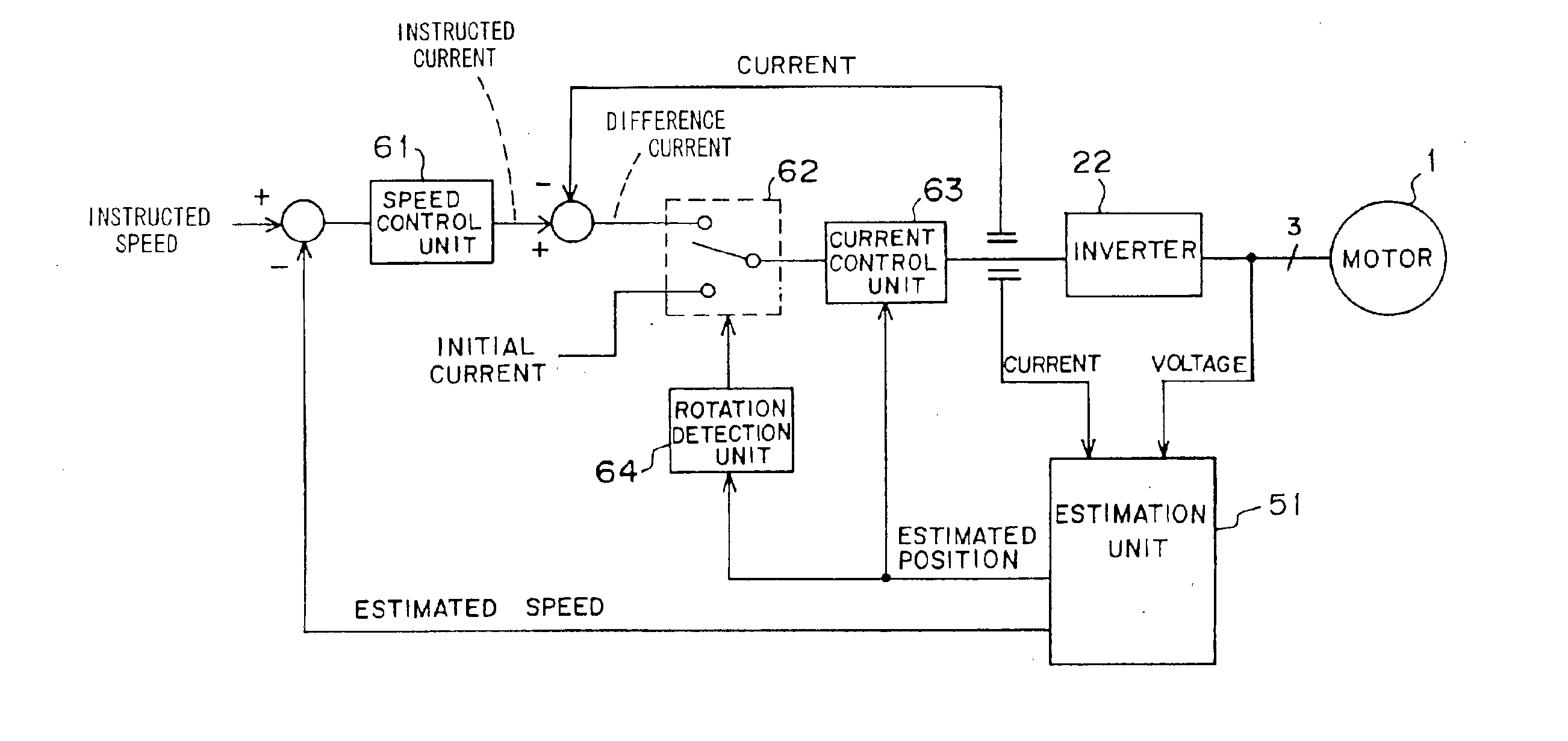
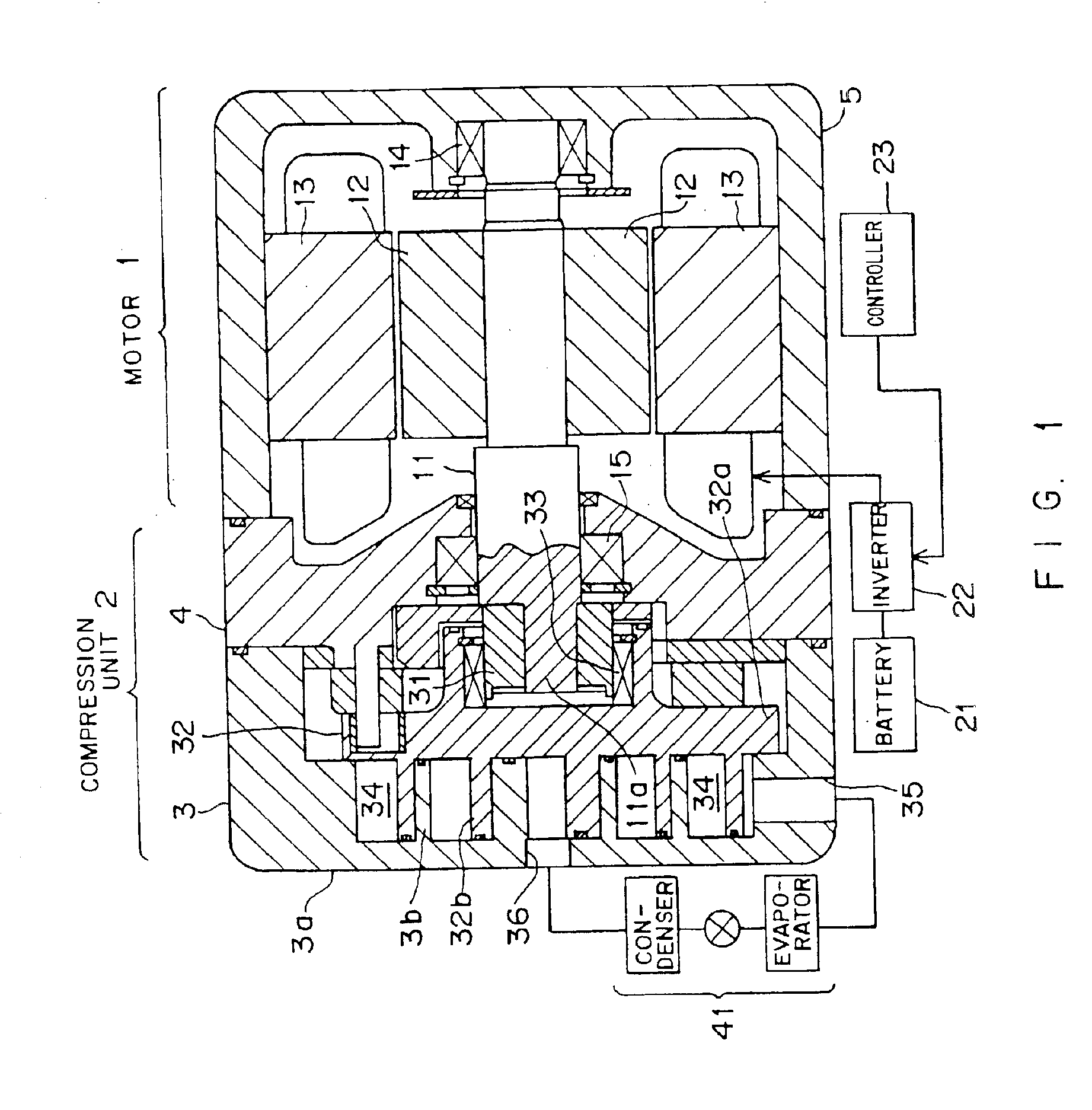
Electric compressor and control method therefor
InactiveUS6869272B2Efficient driveLight loadSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor parameterControl theoryInitial current
When an electric compressor is activated, initial current data is selected by a selector, and a motor is driven with the torque corresponding to the initial current data. When the motor is driven by a ½ turn, the selector selects current difference data. The current difference data corresponds to an instructed speed. After the switch of the selector, the motor is driven to rotate at the instructed speed.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP
High-voltage direct-current breaker
ActiveCN103618298AFast topology breakingAchieve zero arc breakingEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentPower flowHigh-voltage direct current
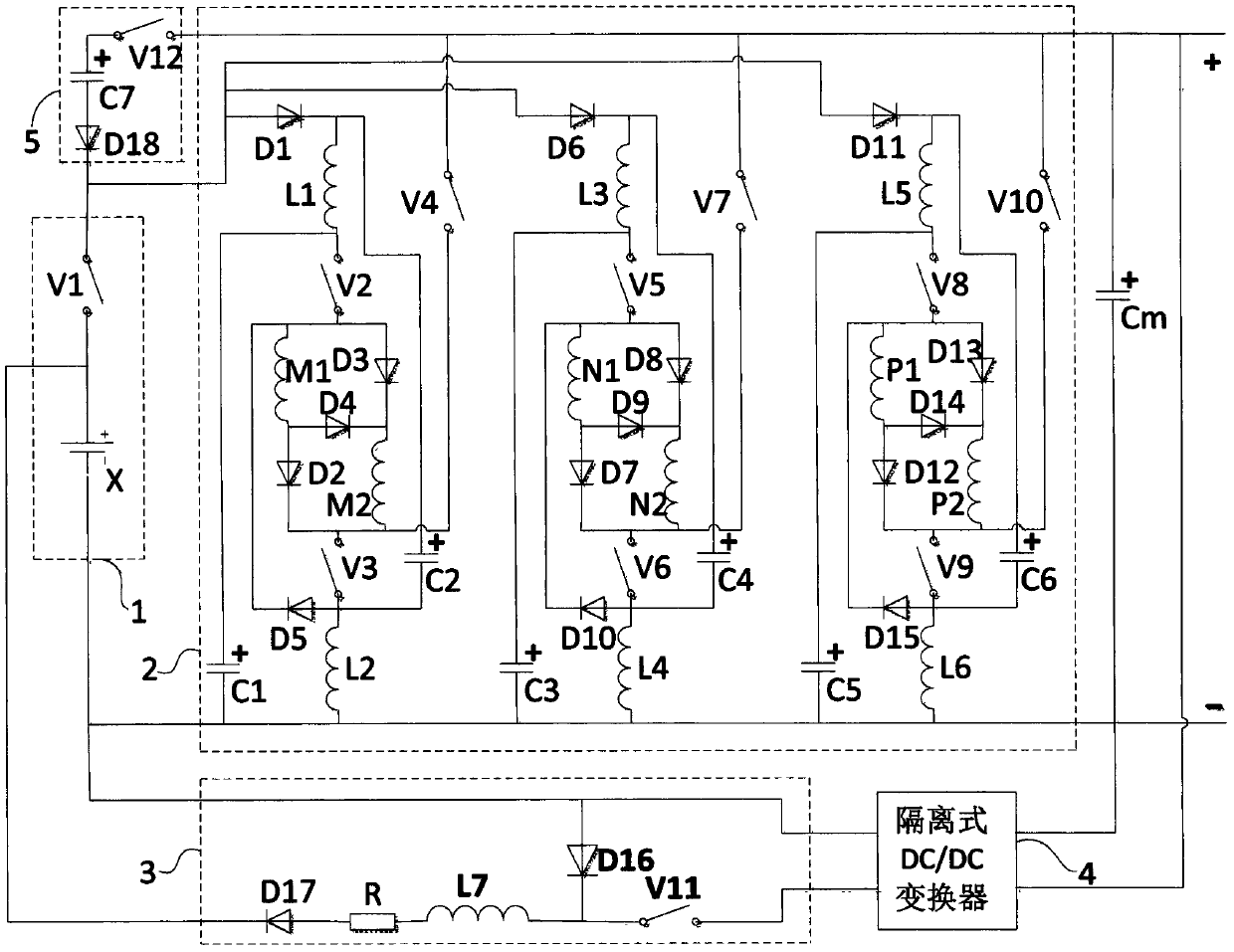
A high-voltage direct-current breaker is composed of an initial current path (1) and a fail current interdicting path (2). The initial current path (1) comprises at least one electric electronic switch module (3) and a mechanical switch (4), and the fail current interdicting path (2) comprises an initial capacitor (C) and a modular switching subunit series connection component (5). The modular switching subunit series connection component (5) is formed by connecting a plurality of sub units (6) in series. When a high-voltage direct-current electric transmission line fails, the opening and closing of a fail electric transmission line can be rapidly achieved.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
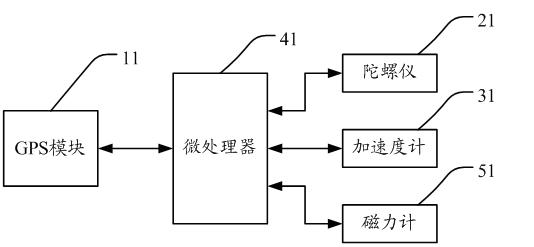
Mobile terminal having auxiliary positioning function and method
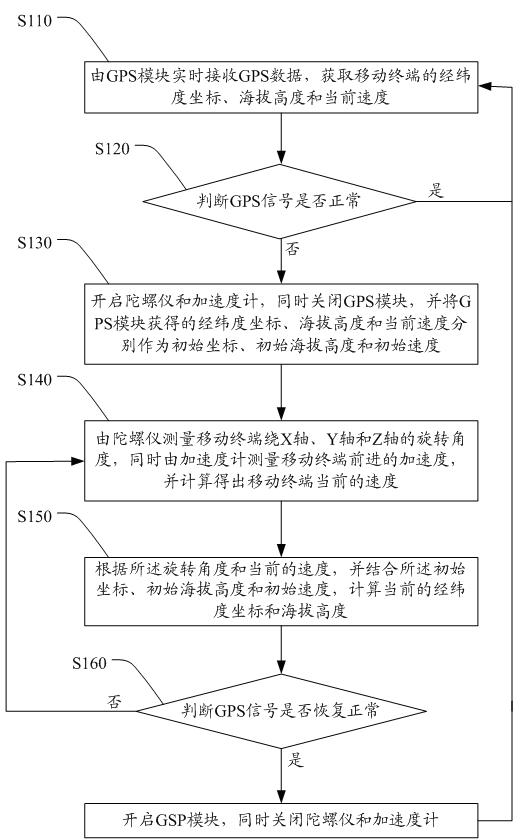
InactiveCN102243315AImprove experienceNo changes in app functionalitySatellite radio beaconingCurrent velocityGyroscope
The invention discloses a mobile terminal having an auxiliary positioning function and a method. The mobile terminal comprises a global positioning system (GPS) module, a gyroscope, an accelerometer and a microprocessor, wherein the GPS module, the gyroscope and the accelerometer are respectively connected with the microprocessor. By the mobile terminal having the auxiliary positioning function and the method provided by the invention, angular speeds and angles of the mobile terminal around an X axis, a Y axis and a Z axis are tested by using the gyroscope; the forward acceleration of the mobile terminal is measured by the accelerometer, and the current speed of the mobile terminal is calculated; and according to initial longitude and latitude coordinates, an initial altitude and an initial current speed, which are acquired by the GPS module, the final longitude and latitude, the final altitude and the final forward speed of the mobile terminal are calculated, so when a GPS signal is abnormal, the function of continuously positioning and navigating the mobile terminal is realized, a user cannot feel the change of GPS application functions completely, and a good use experience effect is achieved.
Owner:HUIZHOU TCL MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Shockwave catheter system with energy control
A system includes a catheter including an elongated carrier, a balloon about the carrier in sealed relation thereto, the balloon being arranged to receive a fluid therein that inflates the balloon, and first and second electrodes within the balloon arranged to carry a voltage there-across including an initial high electrical voltage at an initial low current. The initial high electrical voltage causes an electrical arc to form across the first and second electrodes within the balloon. The electrical arc causes a gas bubble within the liquid, a high current to flow through the first and second electrodes, a decrease in the initial high electrical voltage, and a mechanical shock wave within the balloon. The system further includes a power source that provides the first and second electrodes with a drive voltage that creates the initial high electrical voltage at the initial current and that terminates the drive voltage in response to the decrease in the initial high electrical voltage.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
Backlight device, method of driving backlight and liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS7982706B2Avoid elevationShorten the time periodCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric light circuit arrangementElectricityPower flow
The present invention prevents extension of the time period from powering on a device to convergence of chromaticity of emitted white light on a certain chromaticity, irrespective of the temperature when the device is powered on. A color liquid crystal display apparatus includes a liquid crystal display unit, a backlight employing LEDs of red, green and blue as its light source, a drive unit for driving the LEDs of each color, a temperature sensor for sensing the temperature of the LEDs, and a chromaticity sensor for sensing the chromaticity of white light emitted from the LEDs. The drive unit supplies a current to the LEDs to drive them, and implements feedback control of the amount of current for the LEDs of each color based on a value sensed by the chromaticity sensor so that the white light has a certain chromaticity. Furthermore, upon powering on the backlight, the drive unit retrieves initial current values of the LEDs of each color from a non-volatile memory, and corrects the initial current values according to a value sensed by the temperature sensor to activate the LEDs of each color with the corrected value.
Owner:SONY CORP
Overvoltage protection device, overvoltage protection method and electrolytic-capacitor-free motor driving system
ActiveCN104934943AAvoid damageTo achieve the purpose of overvoltage protectionAC motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceOvervoltage
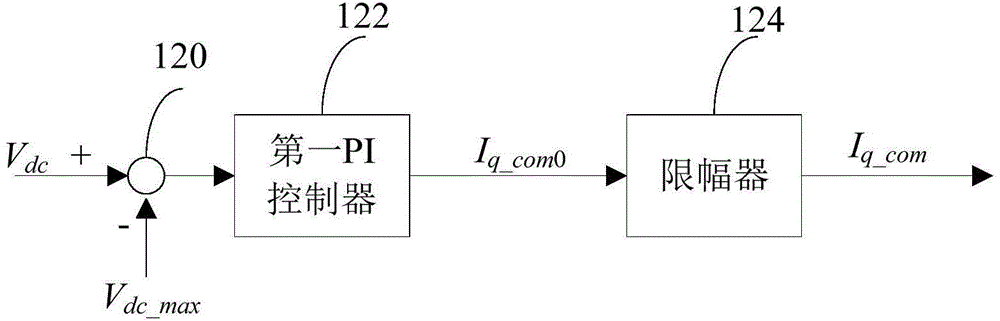
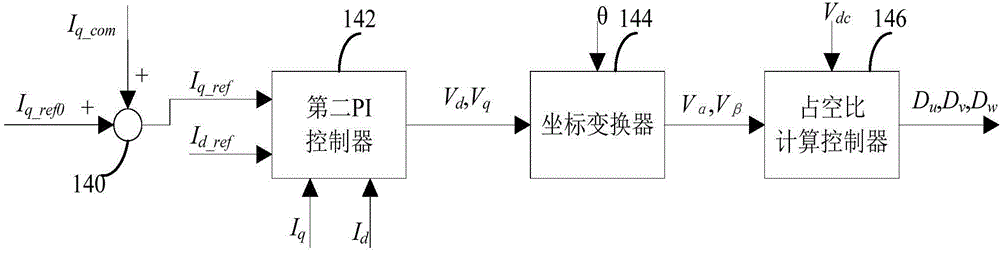
The invention relates to the field of motor control, and discloses an overvoltage protection device, an overvoltage protection method and an electrolytic-capacitor-free motor driving system. The overvoltage protection device comprises a voltage detection module for detecting direct-current bus voltage Vdc in real time, a current compensation dosage calculation module which is connected with the voltage detection module and is used for calculating a current compensation value according to the detected direct-current bus voltage Vdc and a preset safety voltage Vdc_max, and a current control module which is connected with the current compensation dosage calculation module and is used for generating a final current instruction value according to the calculated current compensation value and an initial current instruction value and adjusting three-phase current input into a motor by an inverter according to the final current instruction value in order to avoid overvoltage damage of the electrolytic-capacitor-free motor driving system. Through adoption of the voltage protection device and method and the electrolytic-capacitor-free motor driving system, the three-phase current of the motor can be adjusted according to the direct-current bus voltage detected in real time and the preset safety voltage, so that over high direct-current bus voltage is lowered, and the aim of overvoltage protection is fulfilled.
Owner:GD MIDEA AIR-CONDITIONING EQUIP CO LTD +1
Dual-closed-loop control-based active voltage arc extinction method and apparatus for power distribution network in fault
InactiveCN106655144ABest injection currentRealize fault arc suppressionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentClosed loopThree-phase
The invention discloses a dual-closed-loop control-based active voltage arc extinction method and apparatus for a power distribution network in fault. The arc extinction method comprises the following steps of collecting a three-phase voltage and a neutral point voltage of the power distribution network, and judging whether the power distribution network suffers from a single phase grounding fault or not; if the power distribution network suffers from the single phase grounding fault, determining a fault phase according to the value of the three-phase voltage; injecting an initial current to the power distribution network to obtain a phase voltage and a neutral point voltage of the fault phase, and determining an optimal injection current through a dual-closed-loop control method; and injecting the optimal injection current to the power distribution network to realize arc extinction on an instantaneous single phase grounding fault. According to the method and the apparatus disclosed by the embodiments, based on the dual-closed-loop control method, a current is injected to the neutral point of the active arc extinction apparatus when the power distribution network suffers from the single phase grounding fault; and the fault phase voltage is controlled to be zero, and the reactive current component, the active current component and the harmonic component of the fault phase are compensated, so as to realize rapid and high-precision complete arc extinction on the instantaneous single phase grounding fault.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
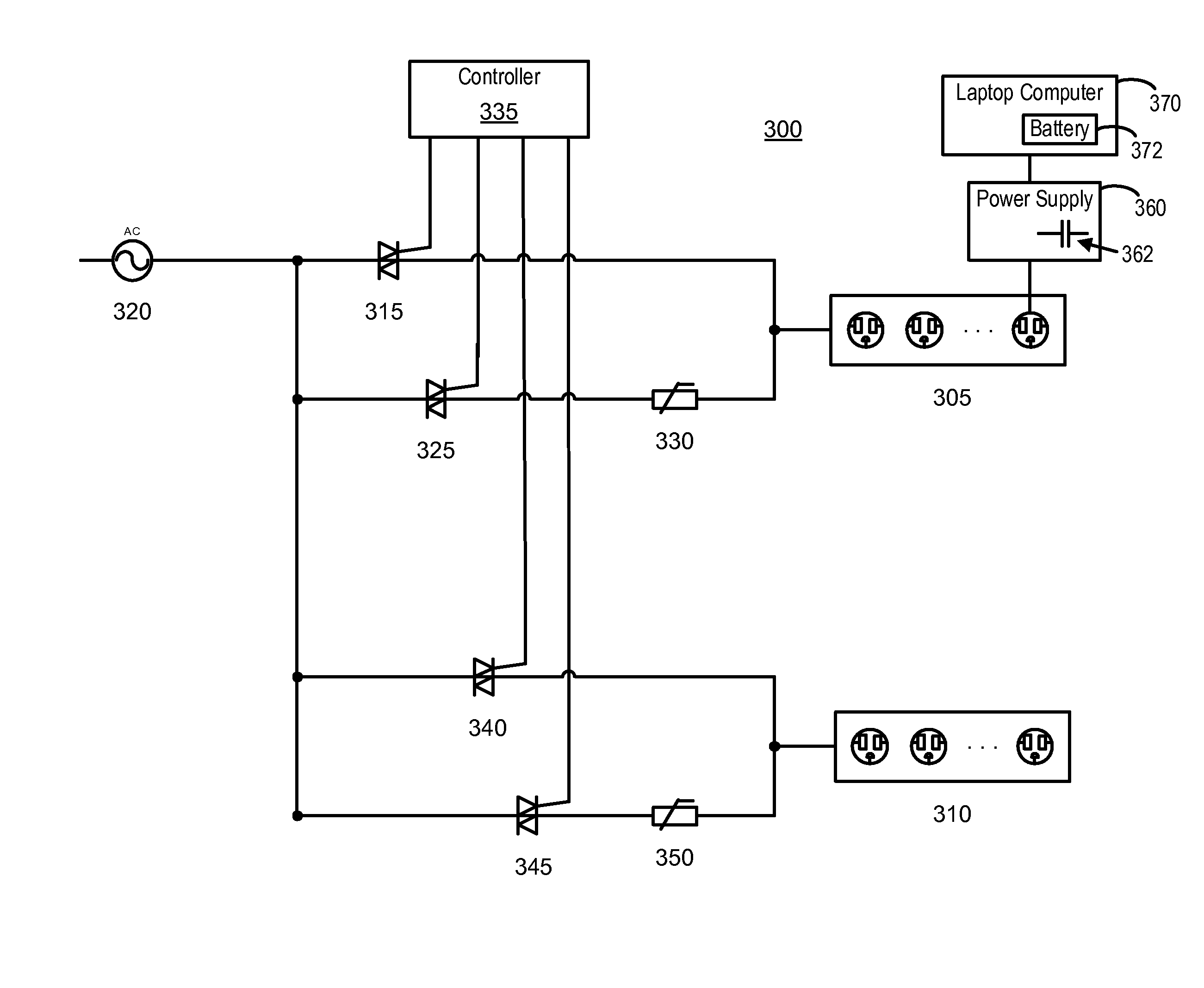
Laptop computer storage and battery charging systems and methods including transient current inrush limiter
A control system of a laptop computer storage system comprises a plurality of receptacles for charging one or more laptop computer batteries. A first switch may be provided for coupling the receptacles to a power source via a current limiter having an impedance that initially limits a current inrush and then decreases with temperature. A second switch may be provided for coupling the receptacles to the power source via a low impedance path. A controller may be provided and configured to activate the first switch to limit an initial current inrush while charging energy storing components associated with the laptop computer's power supply and then activate the second switch to allow each laptop coupled to the receptacles to at least partially charge its battery.
Owner:ERGOTRON
Constant pressure impulse quick charge method
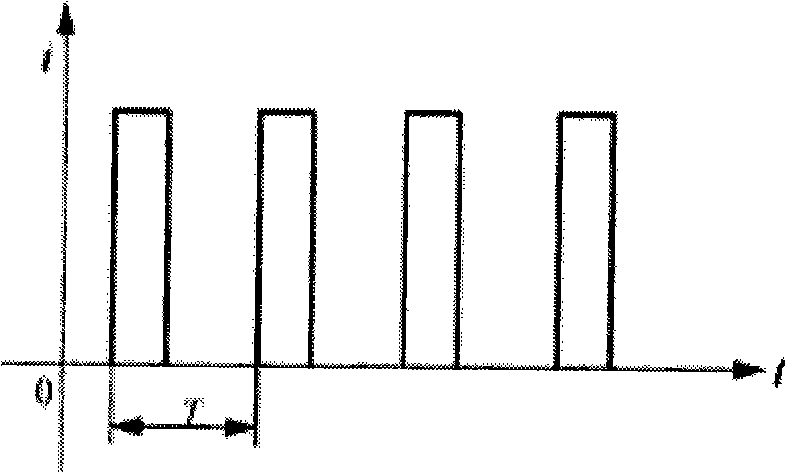
InactiveCN101404346AShort charging timeImprove charging efficiencySecondary cells charging/dischargingCharge currentCurrent amplitude
The invention discloses a constant voltage impulse rapid charging method which charges a storage battery by using constant charging voltage and charging impulse with constant cycle; the charge current curve in each charging cycle includes four stages which are positive impulse charge, zero impulse charge stop, negative impulsive discharge and zero impulse discharge stop, wherein, the initial current amplitude value of the positive impulse charge is 1C and takes on index movement along with the charge time, and the current amplitude of the negative impulsive discharge is 2C all the time. The constant voltage impulse rapid charging integrates the advantages of constant voltage charge and pulse current charge into a whole, charges by using heavy current with the constant voltage and adopts depolarized measures such as instant discharge, charge stop and the like to form periodical charging impulse to lead the storage battery to be close to the initial charging state; the method is characterized by short charge time, high charging efficiency, low temperature rise, little gassing, simple operation and the like, and is suitable for charging various types of lead acid storage batteries.
Owner:PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY ORDNANCE ENG COLLEGE
Charger for electronic device, electronic device, and charging method
InactiveUS20100164440A1Increase valueStable chargingBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerCharge currentVoltage drop
A charger for an electronic device that charges a rechargeable battery of the electronic device. The charger includes a detection unit, which detects connection of another electronic device to the electronic device through a communication cable including a power supply line. A charging unit charges the rechargeable battery with power supply voltage from the power supply line. A measurement unit acquires a measurement value indicating a degree of a voltage drop of the power supply voltage occurred when the charging unit performs charging. A control unit instructs a charging current value for charging the rechargeable battery with the charging unit. When the detection unit detects connection of the other electronic device, the control unit monitors the measurement value while instructing the charging unit to increase the charging current value from an initial current value and determines the charging current value based on the monitored measurement value.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Backlight device, method of driving backlight and liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveCN1776497AShorten the time intervalRegardless of temperatureStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The present invention can prevent the prolongation of the time interval from energizing the device to converging the chromaticity of emitted white light to a definite chromaticity regardless of the temperature at which the device is energized. A color liquid crystal display device comprises: a liquid crystal display unit; a backlight, which adopts red, green, and blue LEDs as its light source; a driving unit, which is used to drive the LEDs of each color; a temperature sensor, which is used to sense the temperature of the LEDs and a chromaticity sensor for sensing the chromaticity of the white light emitted from the LED. The driving unit supplies current to the LEDs to drive them, and performs feedback control of the current amount for each color of the LED based on the value sensed by the chromaticity sensor so that white light has a certain chromaticity. In addition, when the backlight is powered on, the drive unit retrieves the initial current value of each color LED from the nonvolatile memory, and corrects the initial current value according to the value sensed by the temperature sensor to activate each color LED using the corrected value. LED.
Owner:SONY CORP
LED driver device
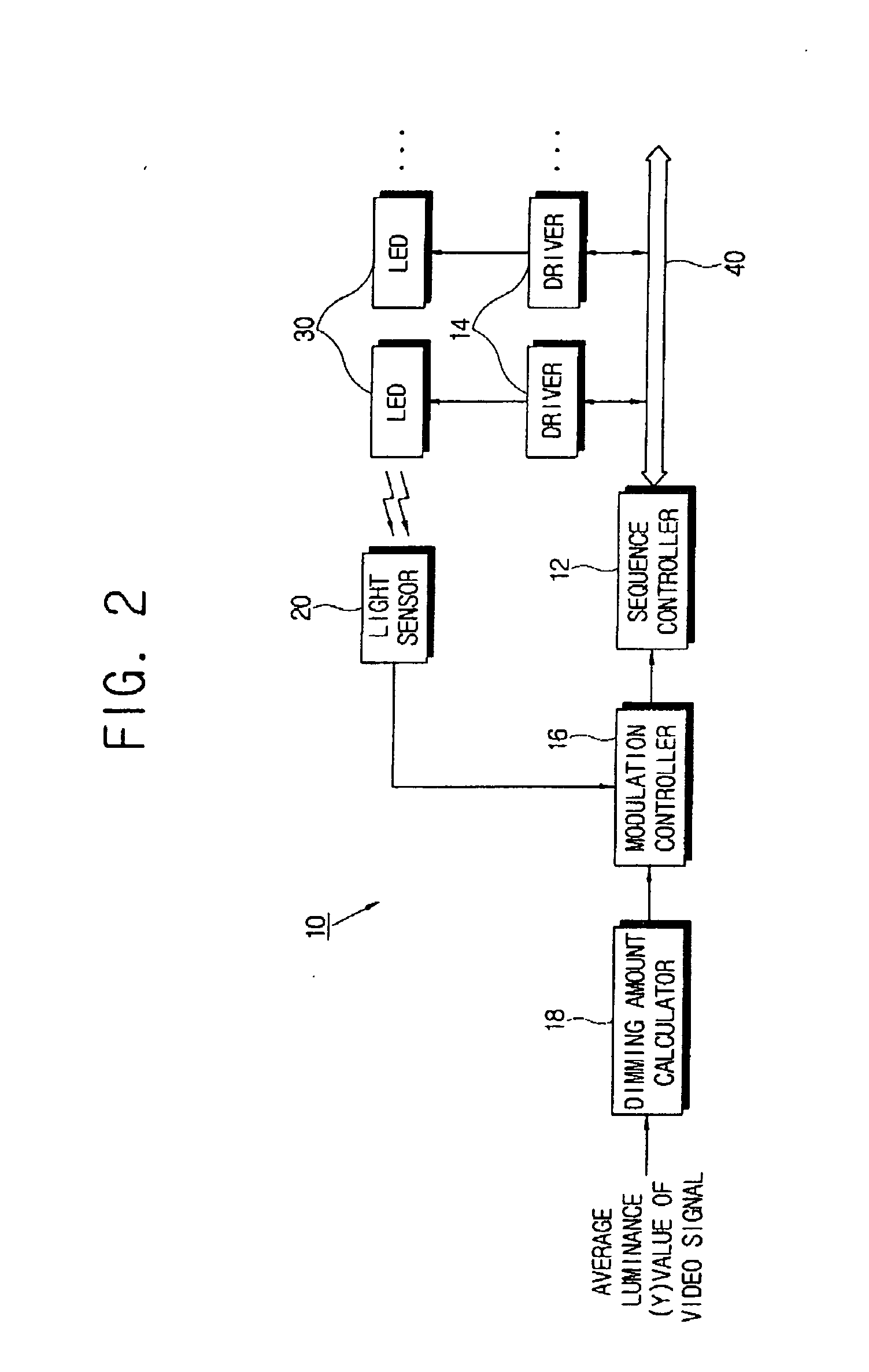
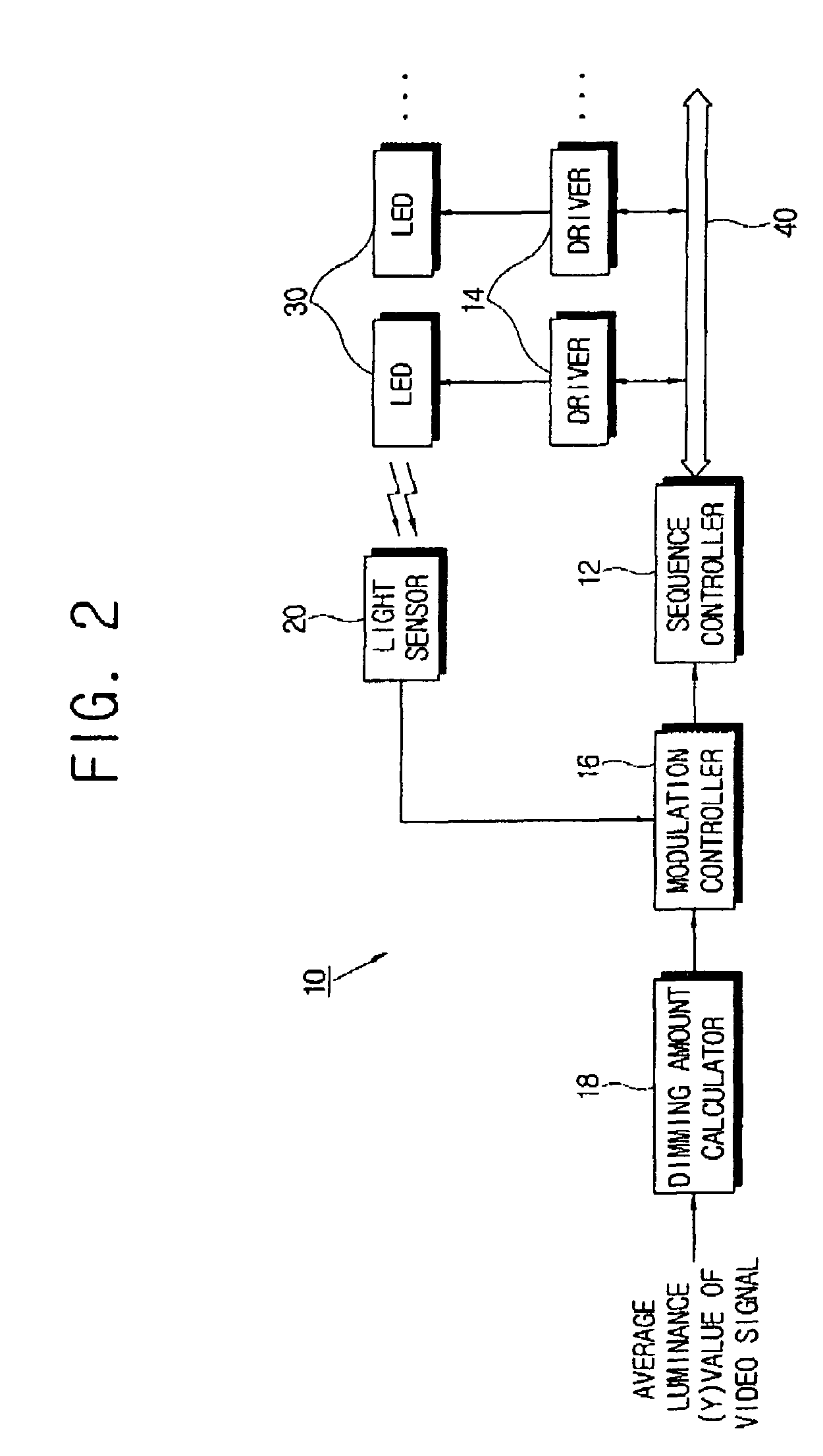
InactiveUS20060186820A1Easy to makeSmall sizeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesSequence controlDigital data
A light emitting diode (LED) driver drives a plurality of LEDs, and includes a plurality of LED drivers with inherent addresses thereof respectively driving the plurality of LEDs; a serial bus connected to the plurality of LED drivers; and a sequence controller serially transmitting a control signal for driving the plurality of LEDs and the inherent addresses, allowing the plurality of LED drivers to be sequentially driven, in the form of digital data through the serial bus. Thus, the LED driver accomplishes appropriate response speed corresponding to a human eye's recognition limit. Further, the LED driver provides easy fabrication, small size and lower production cost. The LED driver generates less noise while large current and high voltage fluctuate. Also, the LED driver automatically detects malfunction and automates initial current setting for production.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Charging system, charger, and battery pack
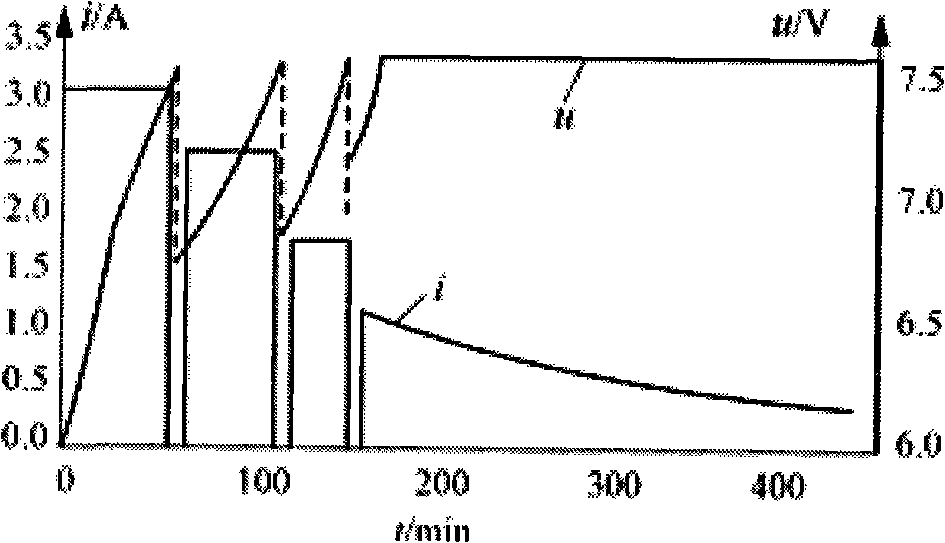
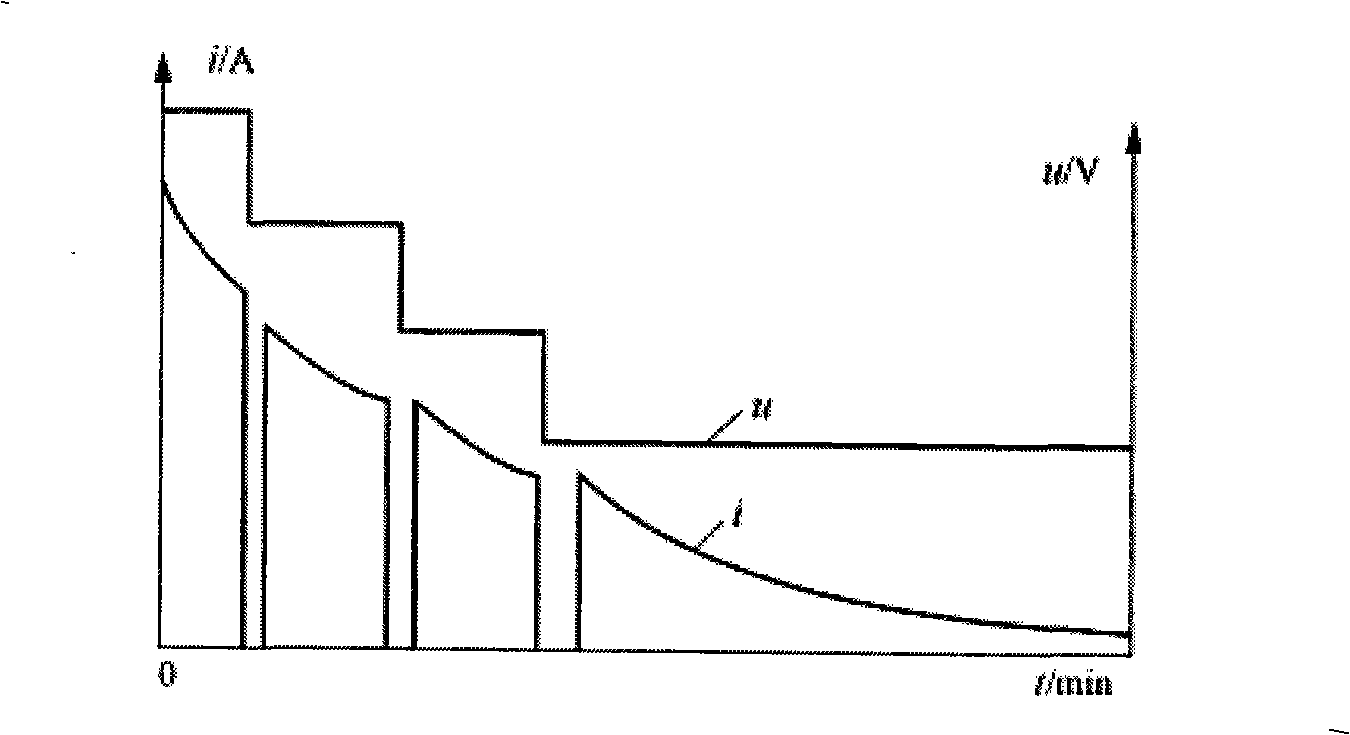
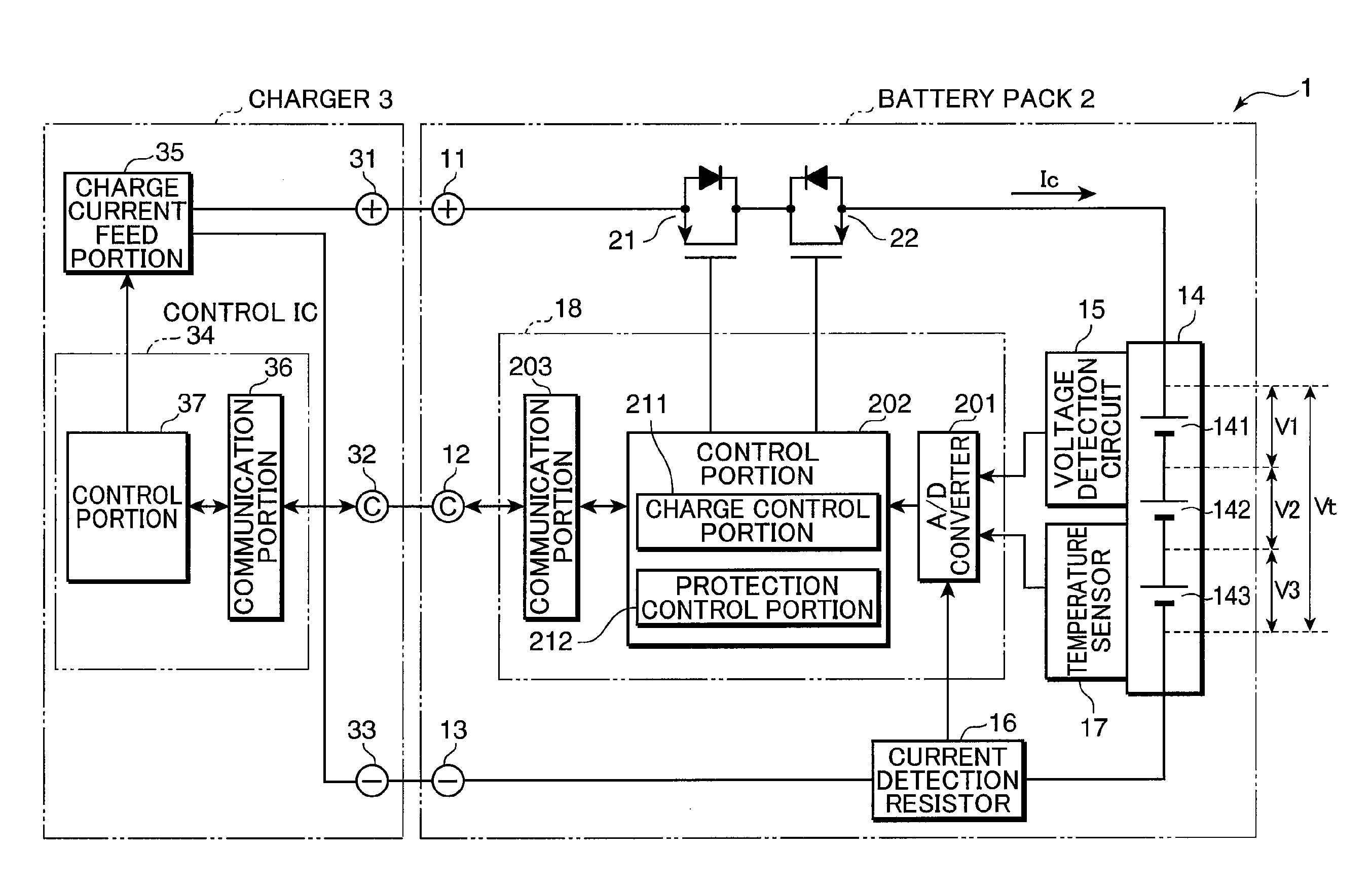
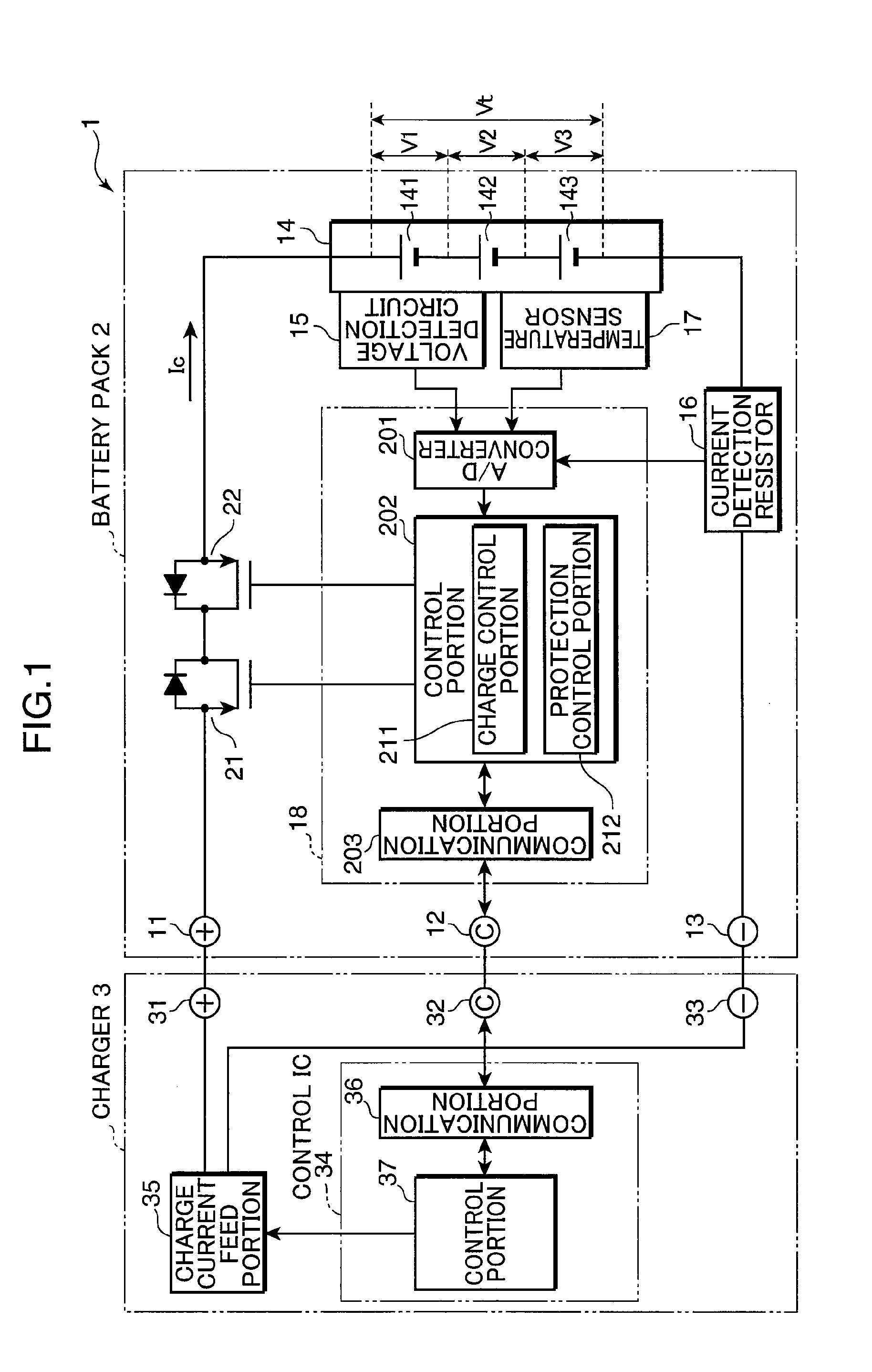
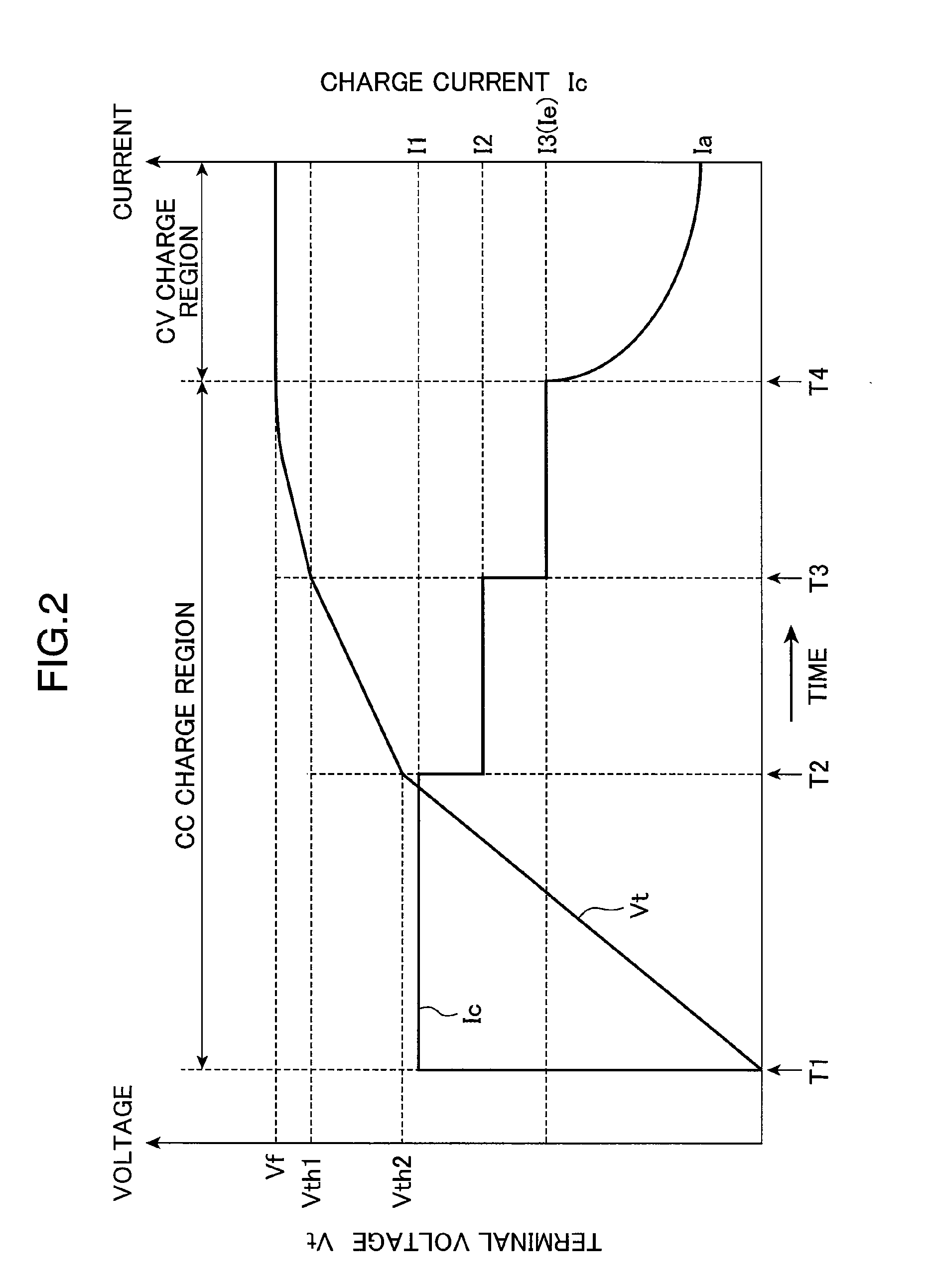
ActiveUS20100102778A1Reduce deteriorationShorten charging timeBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectrode potentialCharge current
After the initial current set processing is performed, by which a feed amount of a charge current Ic by a charge current feed portion 35 is set to a first current value I1 exceeding a reference current value Ie preset as a current value of the charge current at which the charge current is flown without causing substantially any deterioration in secondary batteries 141, 142, and 143 while negative electrode potential of the secondary batteries 141, 142, and 143 has dropped to substantially 0 V, the charge current is changed in such a manner that the current value keeps decreasing with an increase of a terminal voltage Vt detected by a voltage detection portion 15 until the terminal voltage Vt detected by the voltage detection portion 15 reaches an end voltage Vf, which is the terminal voltage across a set battery 14 when the negative electrode potentials of the secondary batteries 141, 142, and 143 have dropped to substantially 0 V.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Fixing device and image formation apparatus
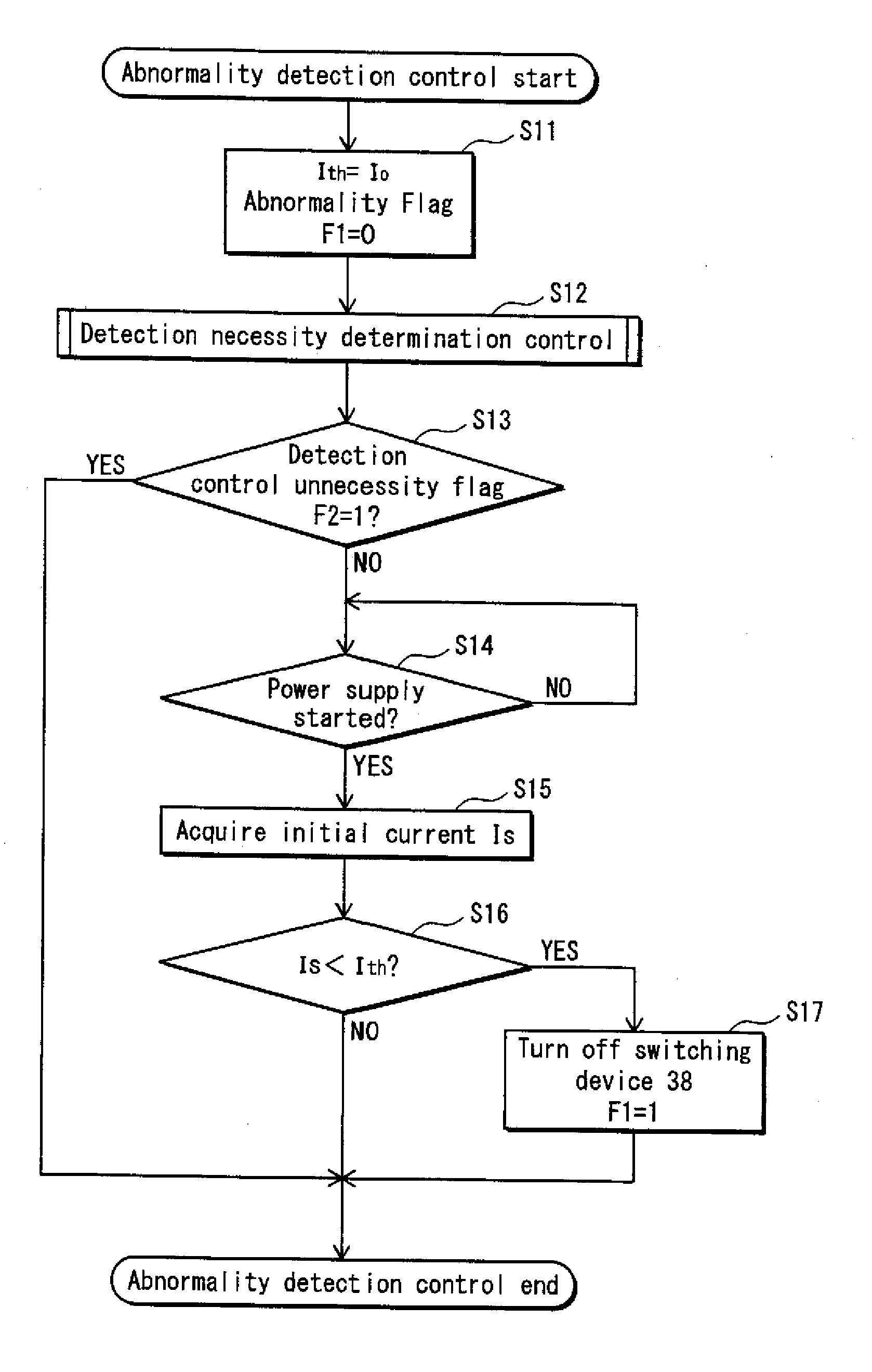
A fixing device for fixing an unfixed toner image on a recording sheet by passing the recording sheet through a fixing nip and applying heat and pressure to the recording sheet, the fixing device comprising: a heater including a resistance heater part and a supporting member, the resistance heater part having a positive resistance-temperature characteristic in a temperature range above a predetermined level, and the supporting member being insulative and supporting the resistance heater part such that the resistance heater part applies heat to the recording sheet; a current detector detecting a current supplied to the resistance heater part; and an abnormality determiner determining whether the resistance heater part has an abnormality, based on an initial current detected by the current detector at a predetermined time after a beginning of power supply to the resistance heater part and before the temperature of the resistance heater part reaches the predetermined level.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
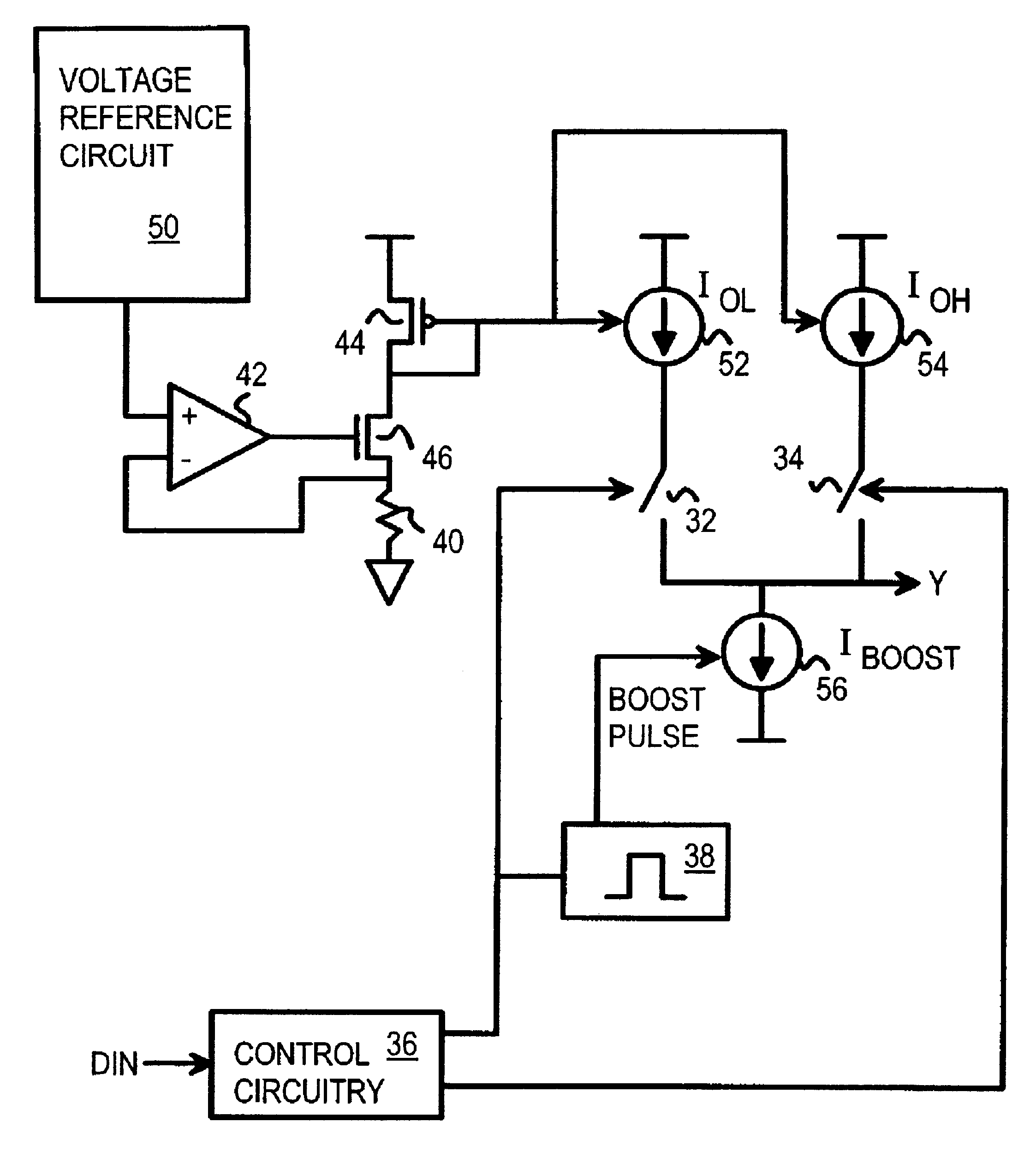
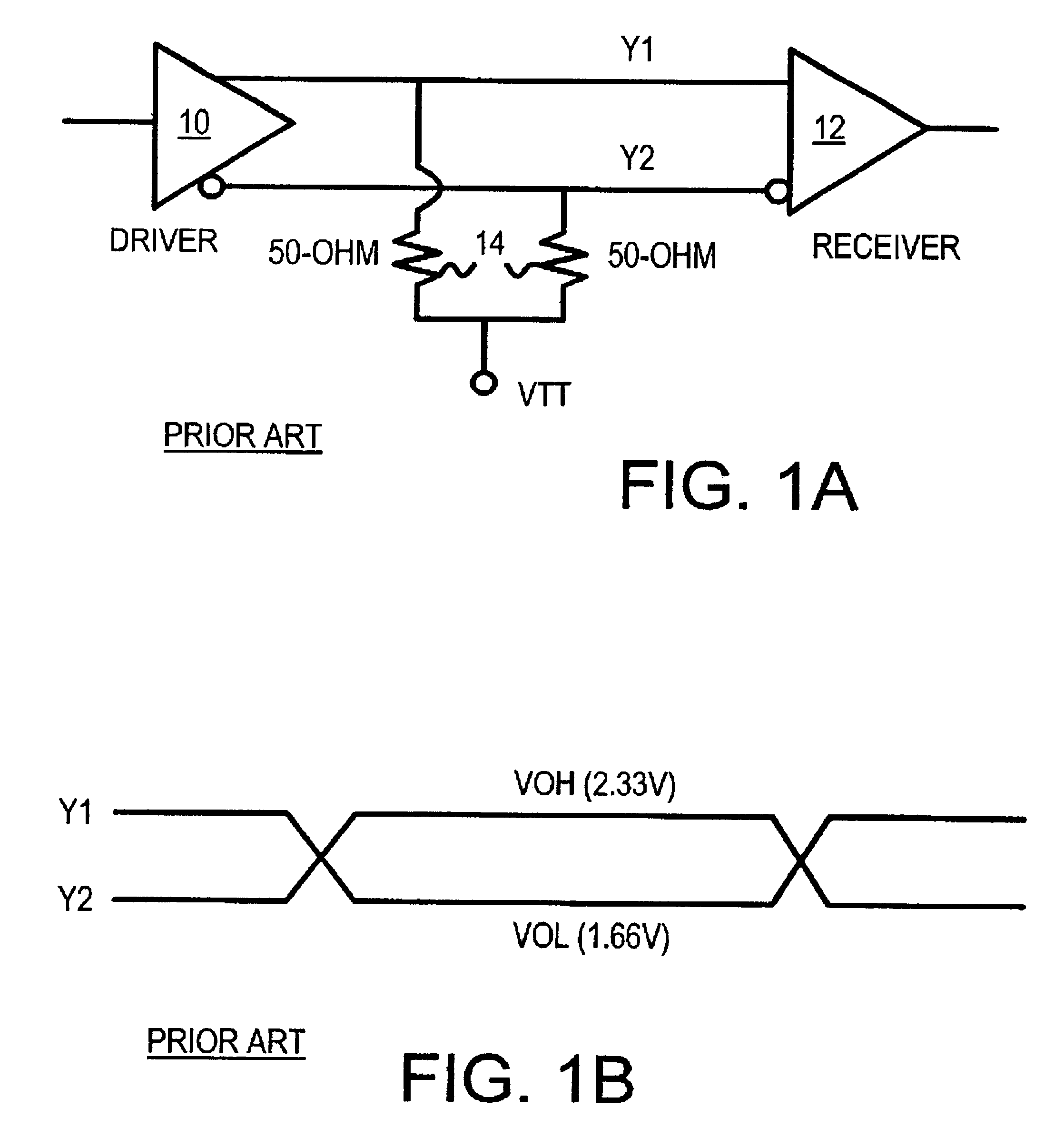
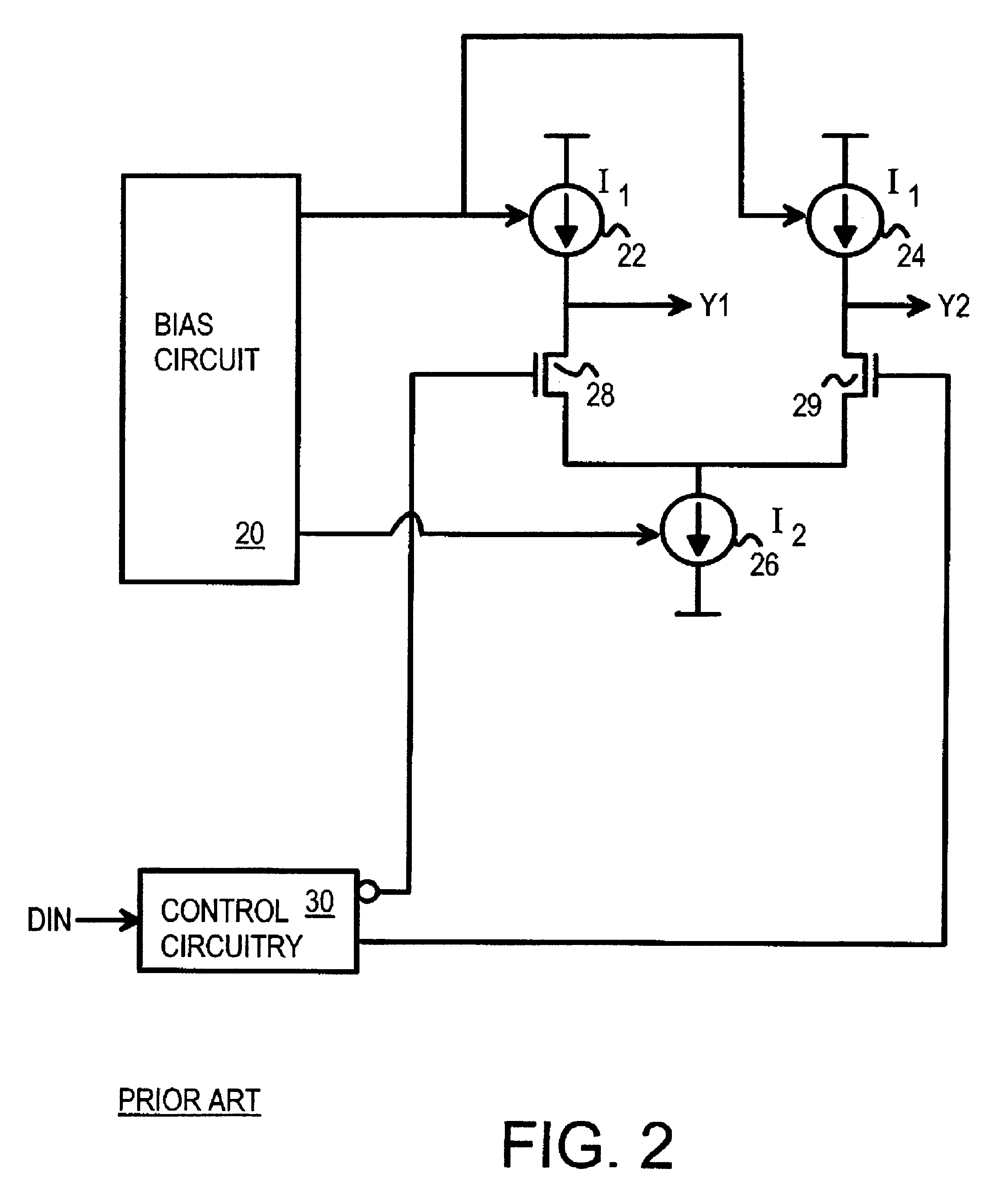
CMOS low-voltage PECL driver with initial current boost
InactiveUS6424217B1Power reduction by control/clock signalAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyElectricityCMOS
A differential amplifier has a boosted sink current that is turned on by a pulse generator when the output is driven low. This boosted sink current quickly lowers the output to the voltage-output-low VOL level. After the pulse ends, the sink current ends and power is reduced to a lower standby level. A differential pair of switches receives the true and complement data. One switch is closed when the data is true, connecting a current source that sets the standby voltage-output-high VOH level. The other switch is closed when the complement data is high, connecting another current source that sets the standby VOL level. A second differential amplifier with reversed true and complement data drives a complement output for a differential signaling transmitter, such as for a pseudo-emitter-coupled logic (PECL) driver.
Owner:DIODES INC
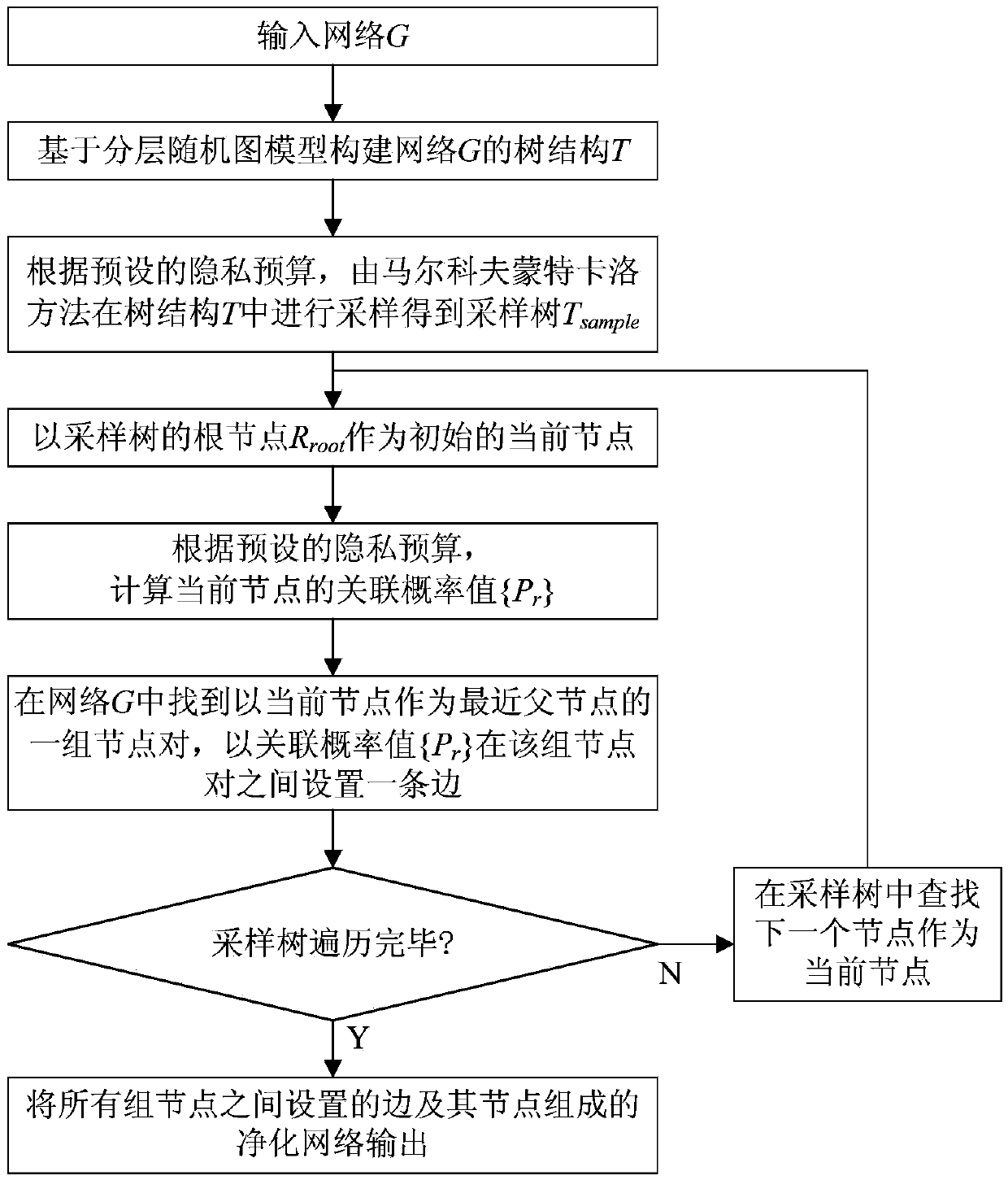
Differential privacy protection method for online social network based on stratified random graph
InactiveCN105376243ASolve the problem of privacy protectionGuaranteed availabilityTransmissionNODALRelationship - Father
The invention discloses a differential privacy protection method for an online social network based on a stratified random graph. The differential privacy protection method comprises the following steps: inputting a network; constructing a tree structure of the network based on a stratified random graph model; sampling in the network through a Markov chain Monte Carlo method according to a preset privacy budget so as to obtain a sampled tree; taking the root node of the sampled tree as an initial current node; calculating an associated probability value of the current node according to the preset privacy budget; finding out a set of node pairs by taking the current node as the nearest father node in the network, and setting an edge among the set of node pairs according to the associated probability value; judging whether traversal of the sampled tree is completed or not, and if not, continuously traversing the next node in the sampled tree; and otherwise, outputting a purified network composed of edges arranged among all the sets of nodes and nodes thereof. According to the invention, the privacy protection problem of sensitive structural data information in the social network can be solved; differential privacy protection requirements can be satisfied; and simultaneously, the good data availability is kept.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Shock wave catheter system with energy control
A system includes a catheter including an elongated carrier, a balloon about the carrier in sealed relation thereto, the balloon being arranged to receive a fluid therein that inflates the balloon, and first and second electrodes within the balloon arranged to carry a voltage there-across including an initial high electrical voltage at an initial low current. The initial high electrical voltage causes an electrical arc to form across the first and second electrodes within the balloon. The electrical arc causes a gas bubble within the liquid, a high current to flow through the first and second electrodes, a decrease in the initial high electrical voltage, and a mechanical shock wave within the balloon. The system further includes a power source that provides the first and second electrodes with a drive voltage that creates the initial high electrical voltage at the initial current and that terminates the drive voltage in response to the decrease in the initial high electrical voltage.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
Distribution line single-phase grounding traveling wave protection method
ActiveCN102780211AOvercome insensitivityOvercomer's failureEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationElectrical polarityEngineering
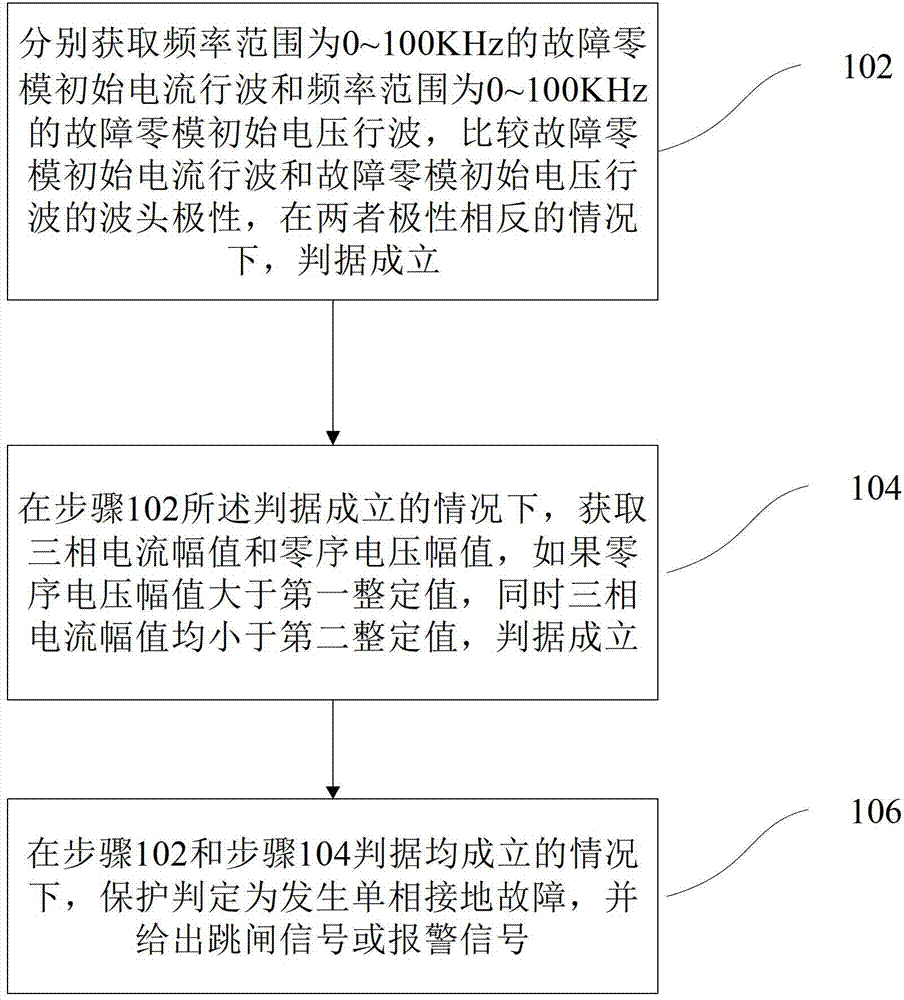
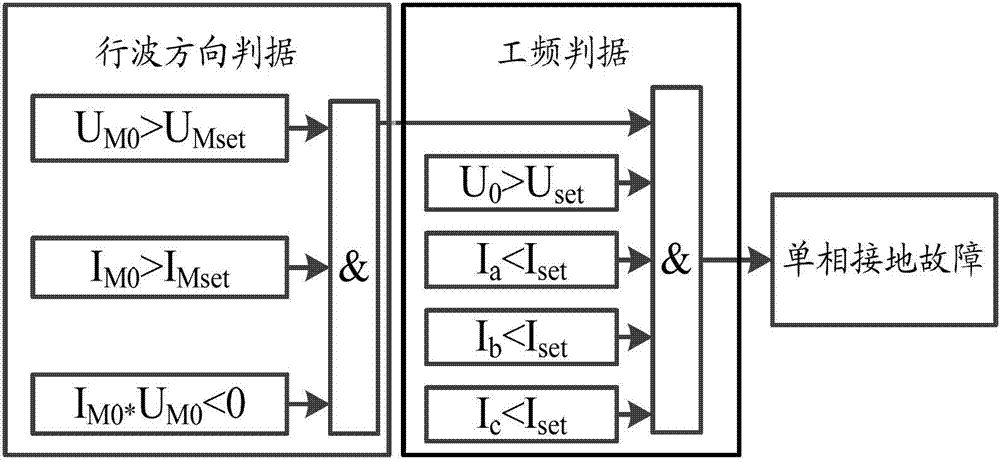
The invention provides a distribution line single-phase grounding traveling wave protection method. The method includes: step 102, respectively acquiring fault zero modal initial current traveling wave within a frequency range of 0-100KHz and fault zero modal initial voltage traveling wave within a frequency range of 0-100KHz, comparing wavefront polarity of the fault zero modal initial current traveling wave with that of the fault zero modal initial voltage traveling wave, and enabling a first criterion to be established when the polarity of the fault zero modal initial current traveling wave and the polarity of the fault zero modal initial voltage traveling wave are opposite; step 104, acquiring three-phase current magnitude and zero-sequence voltage magnitude under the condition that the first criterion is established, and enabling a second criterion to be established if the zero-sequence voltage magnitude is larger than a first setting value and the three-phase current magnitude is smaller than a second setting value; and step 106, judging to determine that a single-phase grounding fault occurs and giving out a trip signal or an alarm signal when the first criterion and the second criterion are both established. By the technical scheme, when the single-phase grounding fault occurs in a distribution line neutral point ineffective grounding system, the fault can be detected quickly and accurately, and reliable protection actions can be taken.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Shockwave catheter system with energy control
A system includes a catheter including an elongated carrier, a balloon about the carrier in sealed relation thereto, the balloon being arranged to receive a fluid therein that inflates the balloon, and first and second electrodes within the balloon arranged to carry a voltage there-across including an initial high electrical voltage at an initial low current. The initial high electrical voltage causes an electrical arc to form across the first and second electrodes within the balloon. The electrical arc causes a gas bubble within the liquid, a high current to flow through the first and second electrodes, a decrease in the initial high electrical voltage, and a mechanical shock wave within the balloon. The system further includes a power source that provides the first and second electrodes with a drive voltage that creates the initial high electrical voltage at the initial current and that terminates the drive voltage in response to the decrease in the initial high electrical voltage.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
Switched reluctance generator current transformer topology and control method thereof
InactiveCN107070334AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilitySynchronous generator controlGenerator control by field variationPower flowCapacitor
The invention relates to a switched reluctance generator current transformer topology and a control method thereof. The topology comprises an excitation power source, a main current transformer circuit, a bus capacitor, an isolated DC / DC converter and a discharging circuit, wherein the excitation power source supplies electric excitation for the main current transformer circuit. Through the main current transformer circuit structure and the control method thereof, the excitation effect can be enhanced, the charging circuit works when a storage cell of the excitation power source needs charging and enhancing power output capability and protection, power generation initial current capability is protected and properly enhanced through controlling the discharging circuit, whole system intelligence, high efficiency and high benefits are realized, a special excitation initiating power source is omitted, and the topology and the method are suitable for application in the small and medium switched reluctance generator current transformer field.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Dynamic adjustment method based on index avoidance
InactiveCN101267377AEvasion range shortenedReduced backoff timeEnergy efficient ICTData switching networksLow speedWireless lan
The invention discloses a dynamic adjustment method based on an IEEE802.15.4 retreated index, which belongs to a wireless LAN technology filed, a superframe or last time transmission state is judged, the initial value of current retreated index is dynamically adjusted, if a node has a successful data transmission in the last time of the superframe, or has a last time successful data transmission in the same superframe, a competition window size is minished through minishing an initial current retreated index when the next transmission is started; contrarily, if the node does not have the successful data transmission in the last time of the superframe, or does not have a last time successful data transmission in the same superframe, a competition window size is enlarged through adding the initial value of the retreat index when the next frame is started; if both of above are not established, the initial value of the retreat index is set the same as an energy saving mode2.The invention decreases consumption of a low speed wireless LAN, improved consumption is decreased about 40%, throughput performance of the network is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
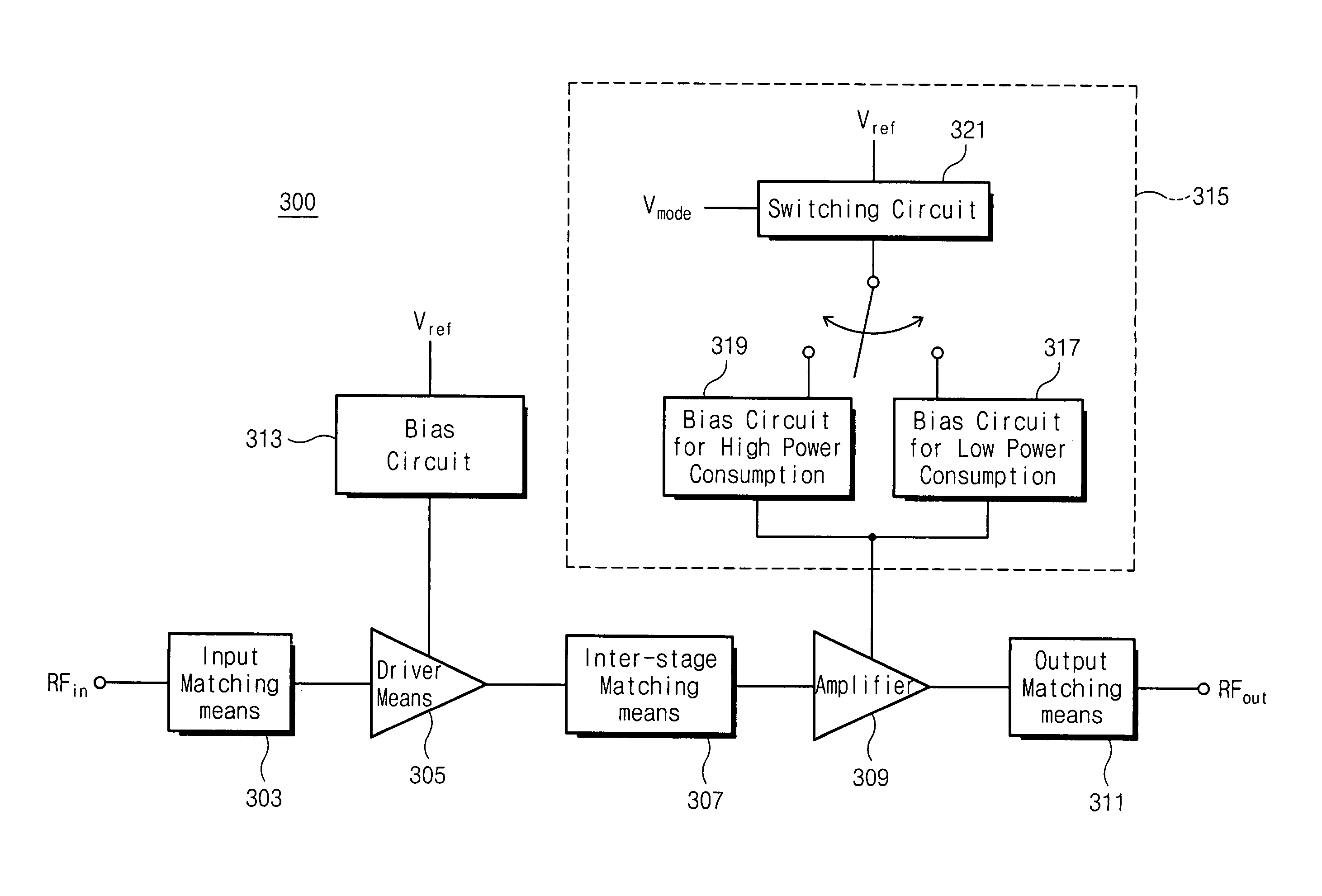
Bias circuit for smart power amplifier
ActiveUS7129786B2Reduce variationLow efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationGain controlPower modeAudio power amplifier
A bias circuit for a smart power amplifier includes a high power mode bias circuit and a low power mode bias circuit, and operates only one of the bias circuits selectively using a switching circuit according to an input signal. Therefore, the bias circuit of high power mode and the bias circuit of the low power mode are divided and can be optimized according to characteristics of the power. Accordingly, a gain difference with respect to each power can be minimized and the low power mode can be controlled with a small amount of current in a state of initial current with a low power and in a middle power, such that an efficiency of the power amplifier can be improved at low power.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICON KOREA INC
Method and device for determining the moisture content and conductivity in the ground and in bulk materials
InactiveUS20050212532A1Simple and accurate measurementDisturbances can be eliminatedResistance/reactance/impedenceEarth material testingEngineeringVoltage source
Owner:GSF FORSCHUNGSZENT FUR UMWELT & GESUNDHEIT
LED driver device
InactiveUS7294970B2Easy to makeSmall sizeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDigital dataSerial transfer
A light emitting diode (LED) driver drives a plurality of LEDs, and includes a plurality of LED drivers with inherent addresses thereof respectively driving the plurality of LEDs; a serial bus connected to the plurality of LED drivers; and a sequence controller serially transmitting a control signal for driving the plurality of LEDs and the inherent addresses, allowing the plurality of LED drivers to be sequentially driven, in the form of digital data through the serial bus. Thus, the LED driver accomplishes appropriate response speed corresponding to a human eye's recognition limit. Further, the LED driver provides easy fabrication, small size and lower production cost. The LED driver generates less noise while large current and high voltage fluctuate. Also, the LED driver automatically detects malfunction and automates initial current setting for production.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Arc start control method in consumable electrode arc welding
ActiveCN101204753AReduce contact resistance valueSuppresses instantaneous arcArc welding apparatusPower flowElectrical current
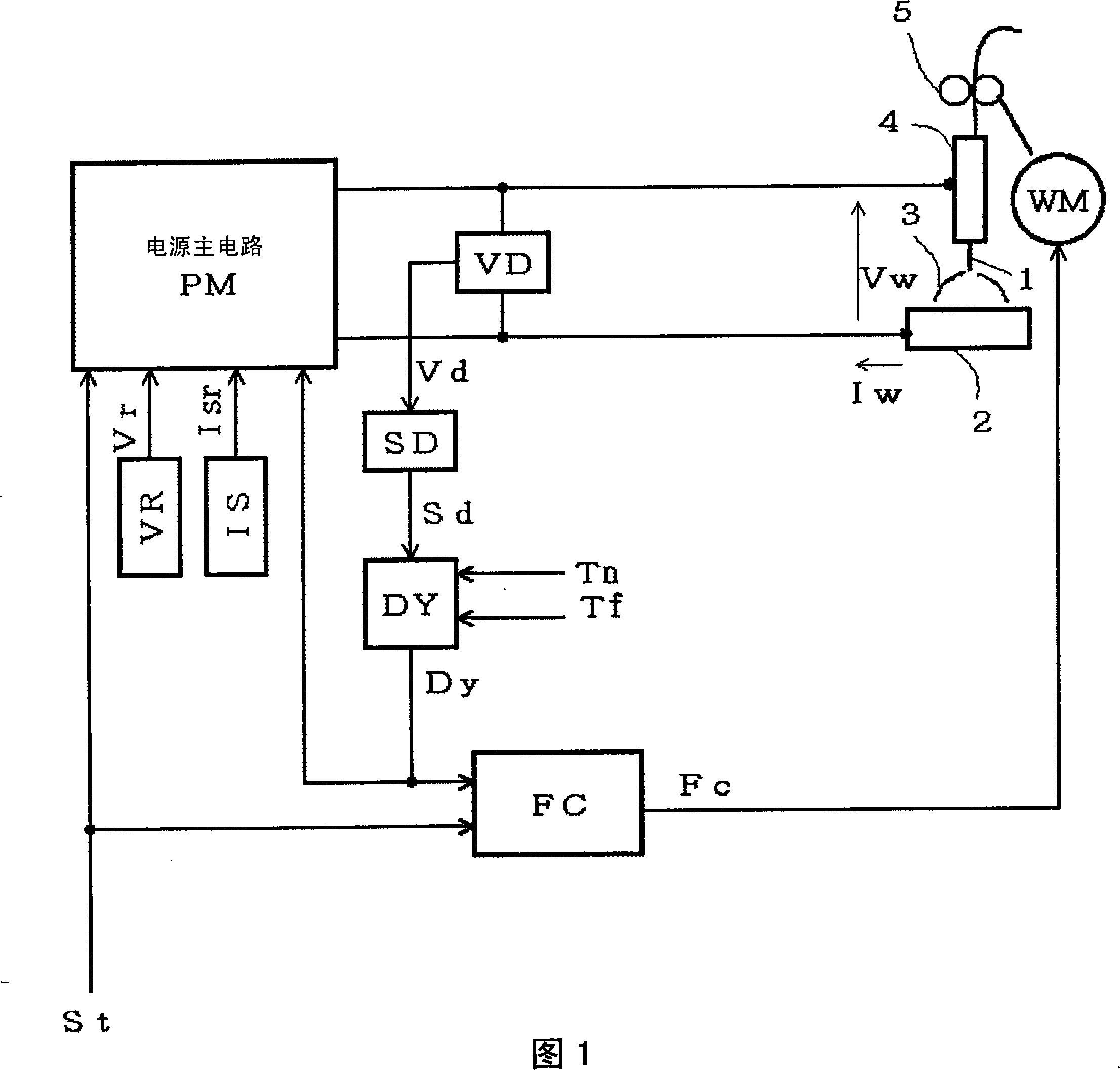
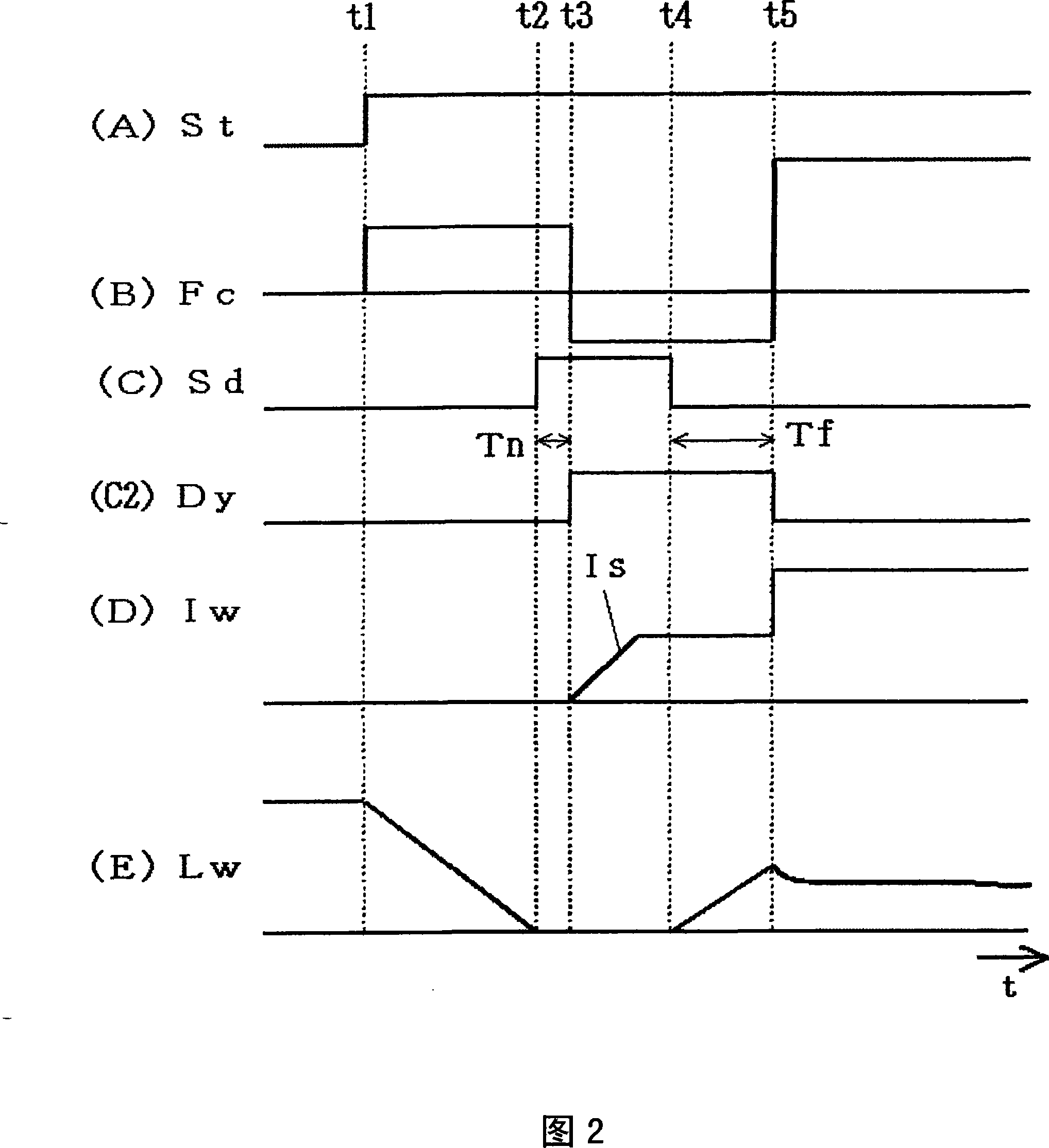
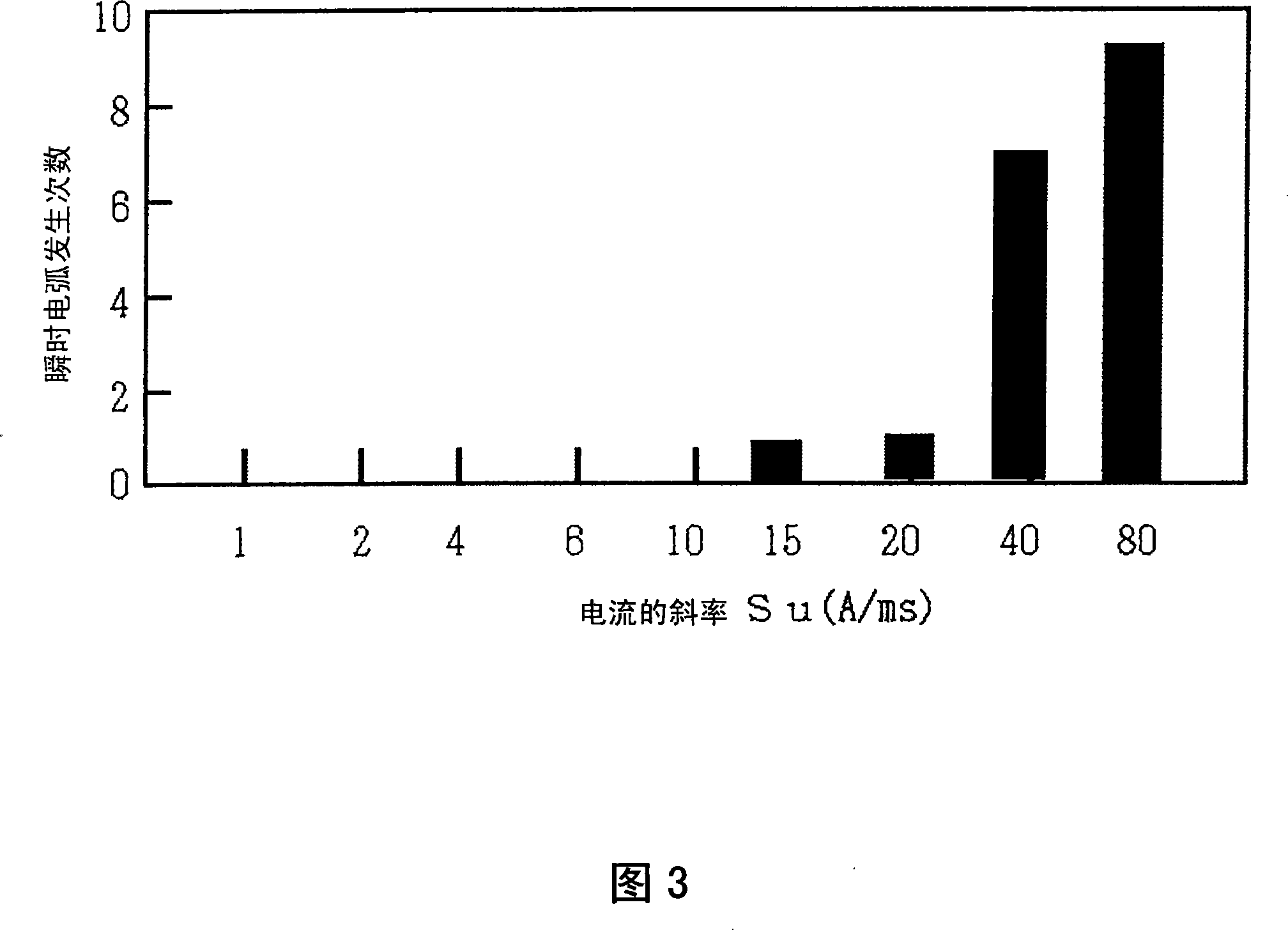
An arc start control method is provided for consumable electrode arc welding. According to this method, a welding wire (1), supplied through a welding torch (4), is brought into contact with a work (2) and an initial current is applied to the welding wire (1) (at time t2) and the work (2) that are held in contact with each other (at time t3). Then, an initial arc is generated by moving the welding wire (1) away from the work (2) with the application of the initial current maintained, and thereafter the initial arc is changed to a steady arc, wherein the initial current is increased gradually with a predetermined increase rate (at time t4). Thus when the welding starts, the welding wire (1) is temporarily contacted to the work (2) then separated from the same, in the contraction arc guide method generating arc to guide arc, arc guide badness on the work (20) to be welded coated by the welding wire (1) can be restrained.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Resistance change memory device and current trimming method thereof
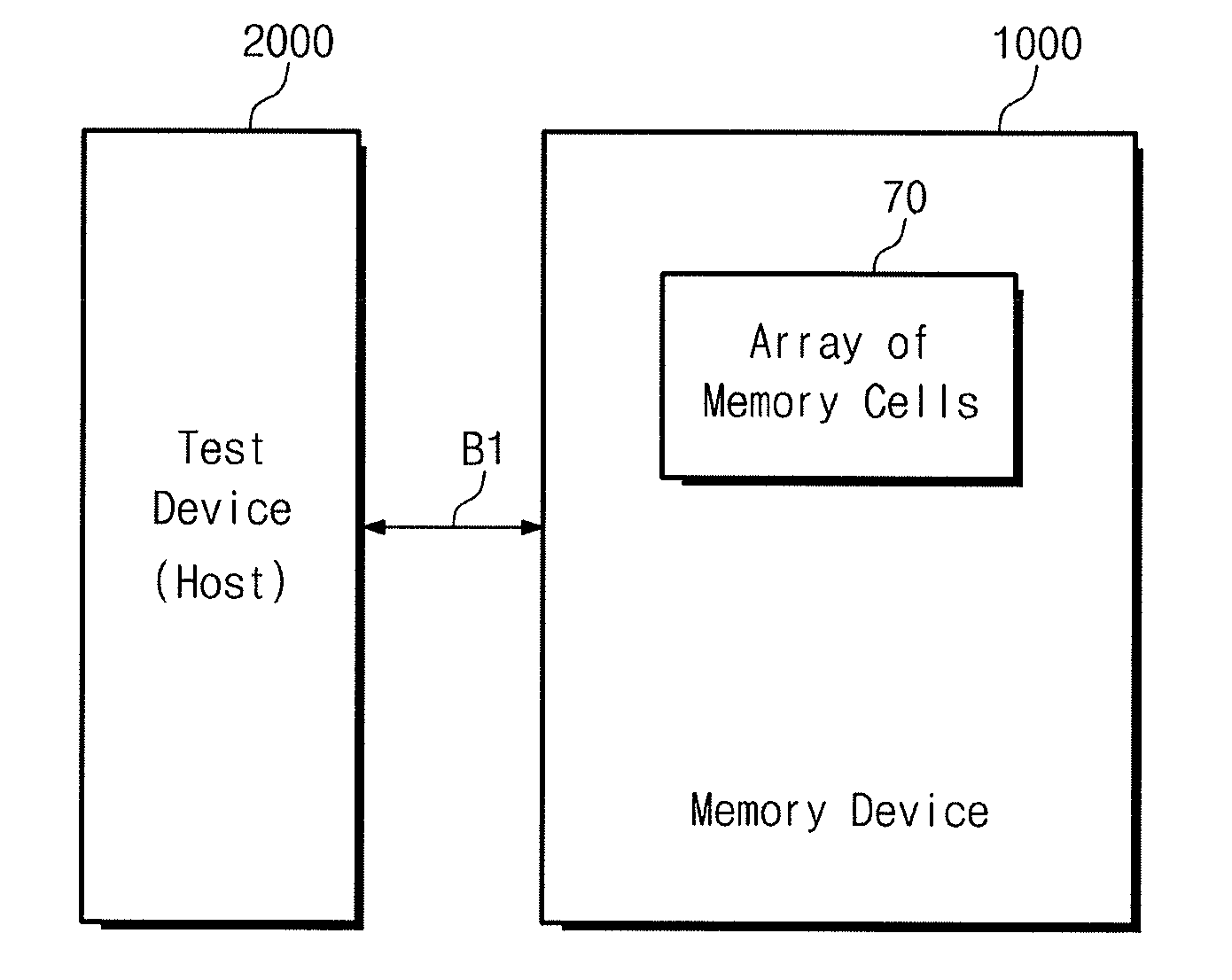
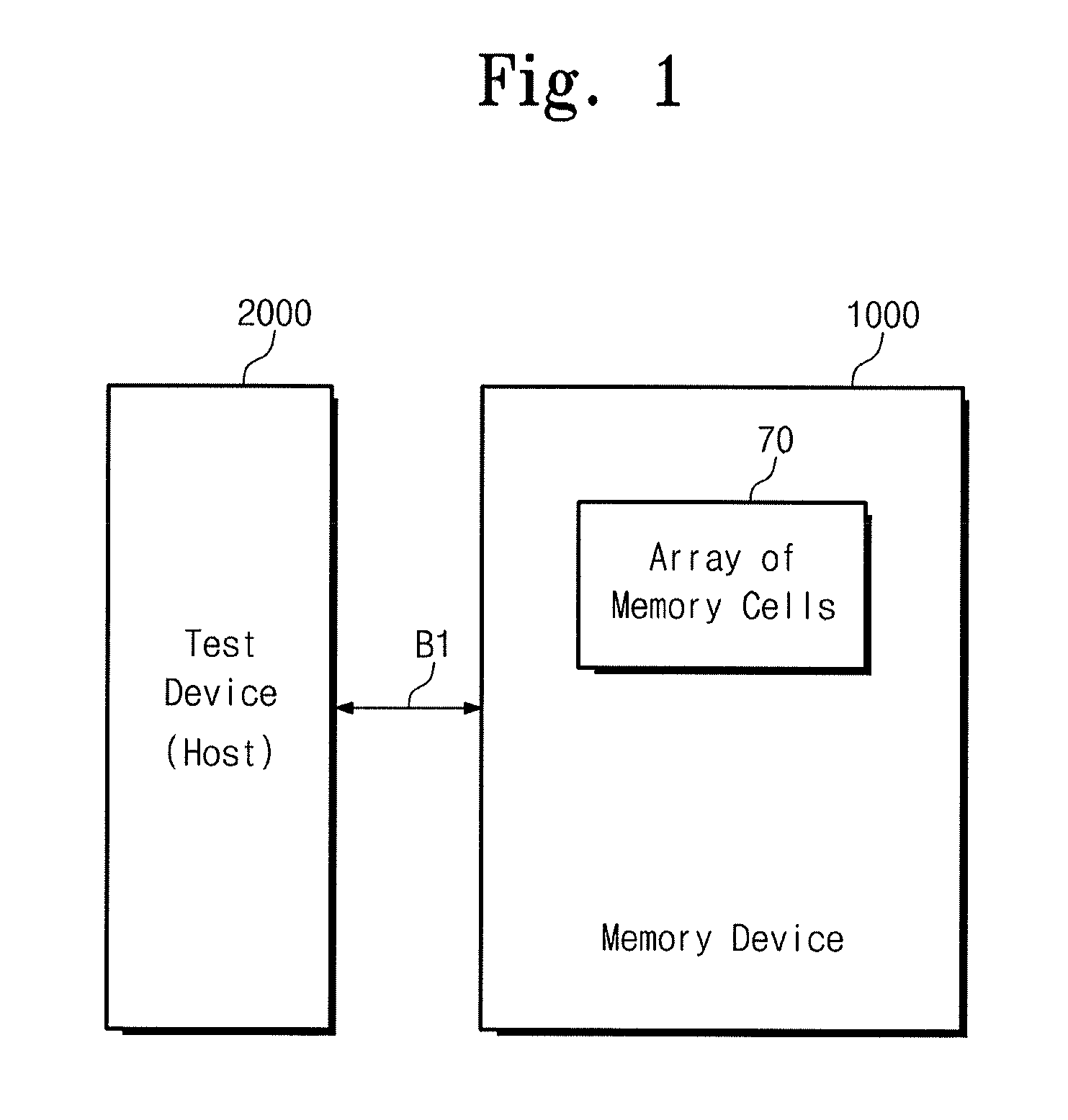
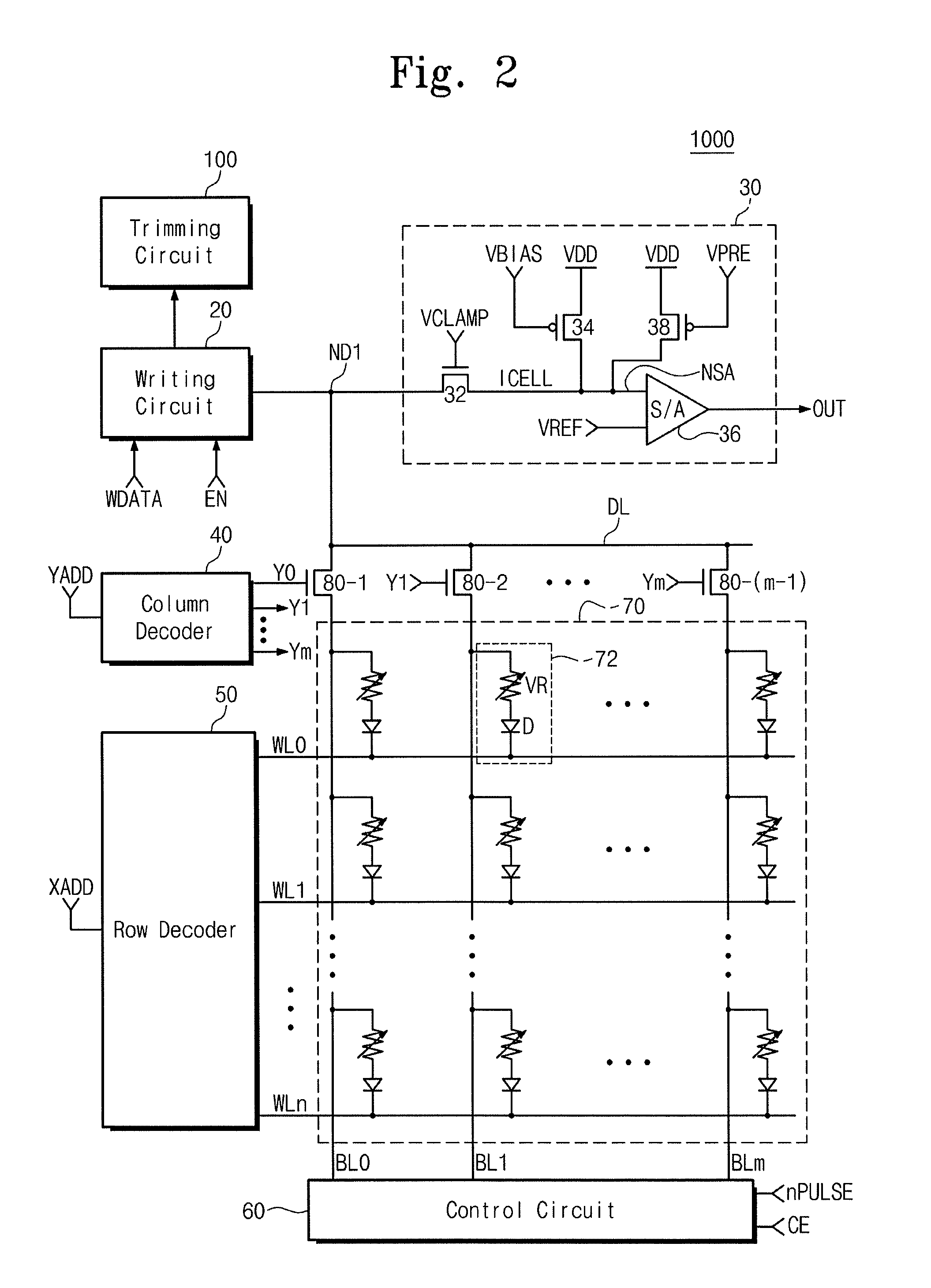
A resistance change memory device includes an array of resistance change memory cells, and a writing circuit configured to reset a selected memory cell to a high resistance state by supplying a RESET current to the selected memory cell in the array of resistance change memory cells in a program operation mode, wherein a level of the RESET current depends on a distribution of initial RESET currents for the array of resistance change memory cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com