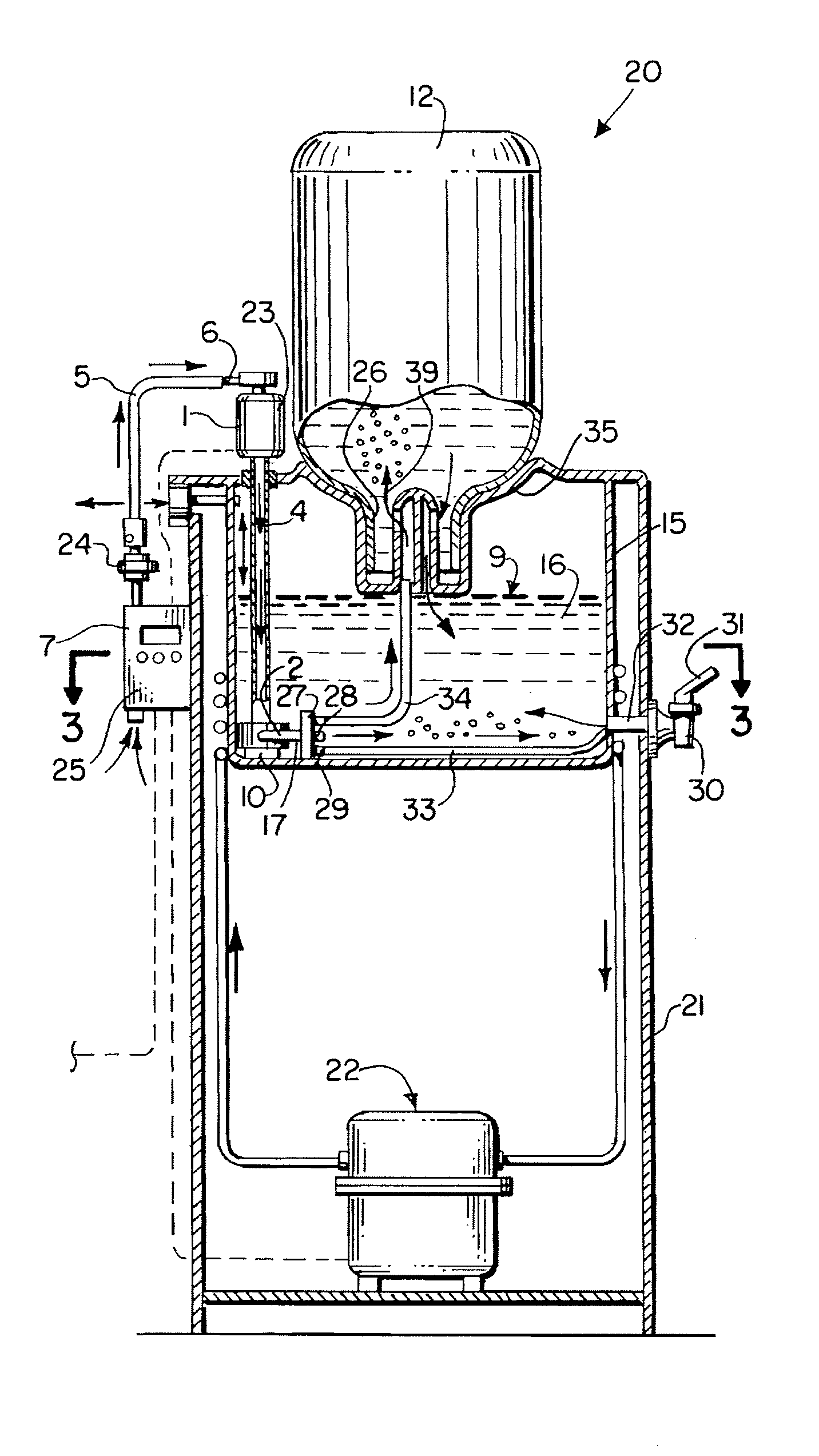
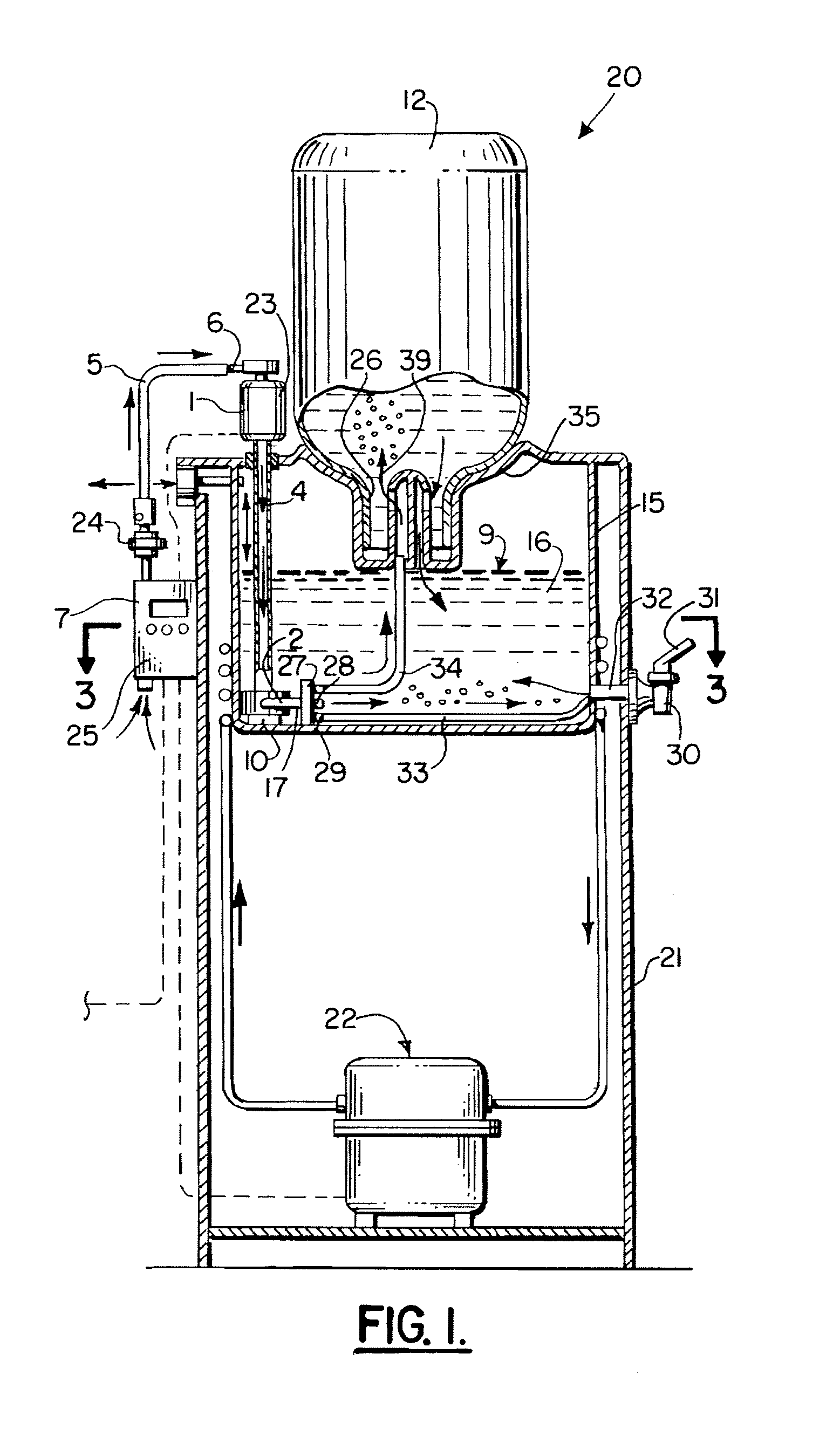
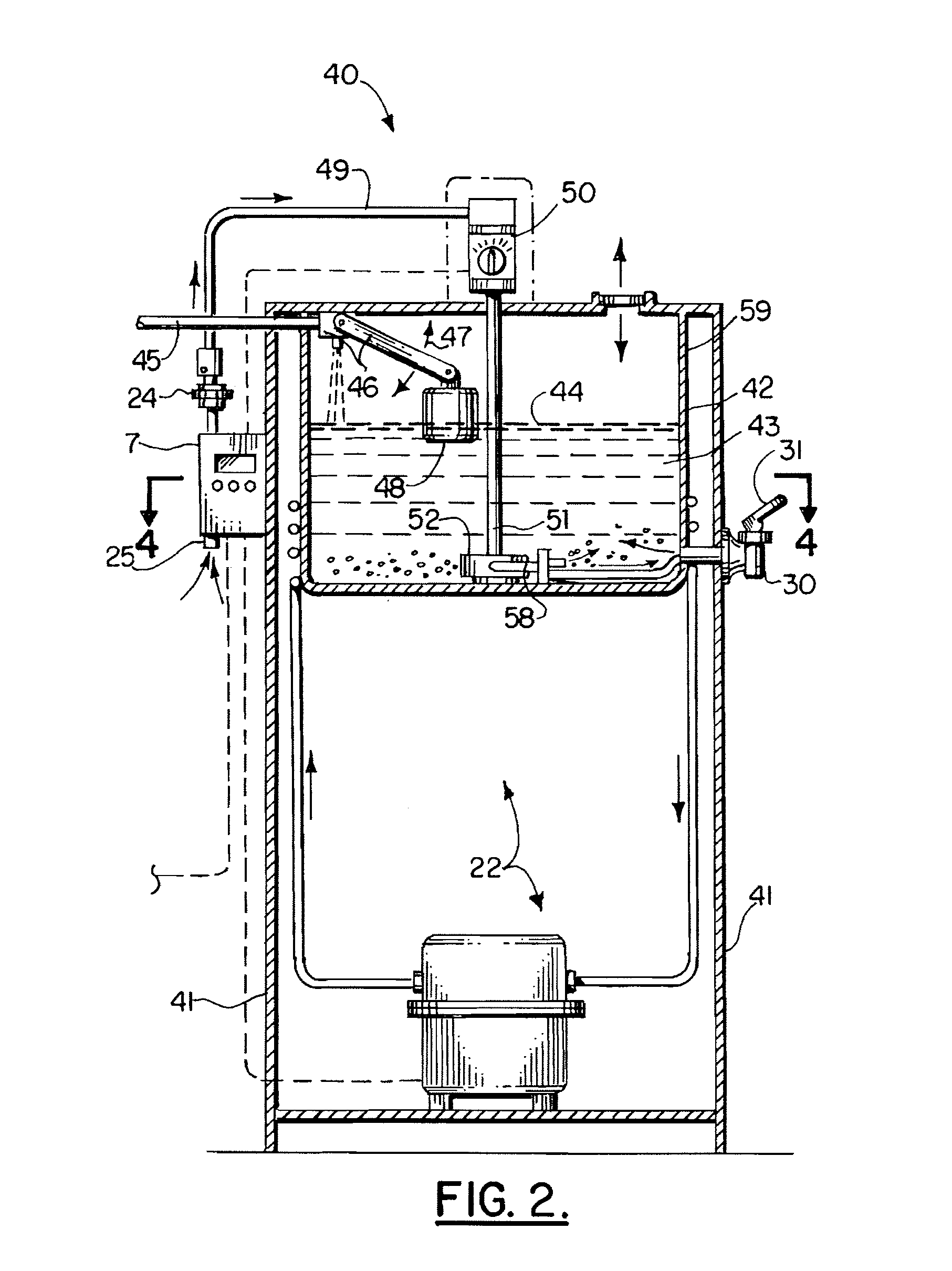
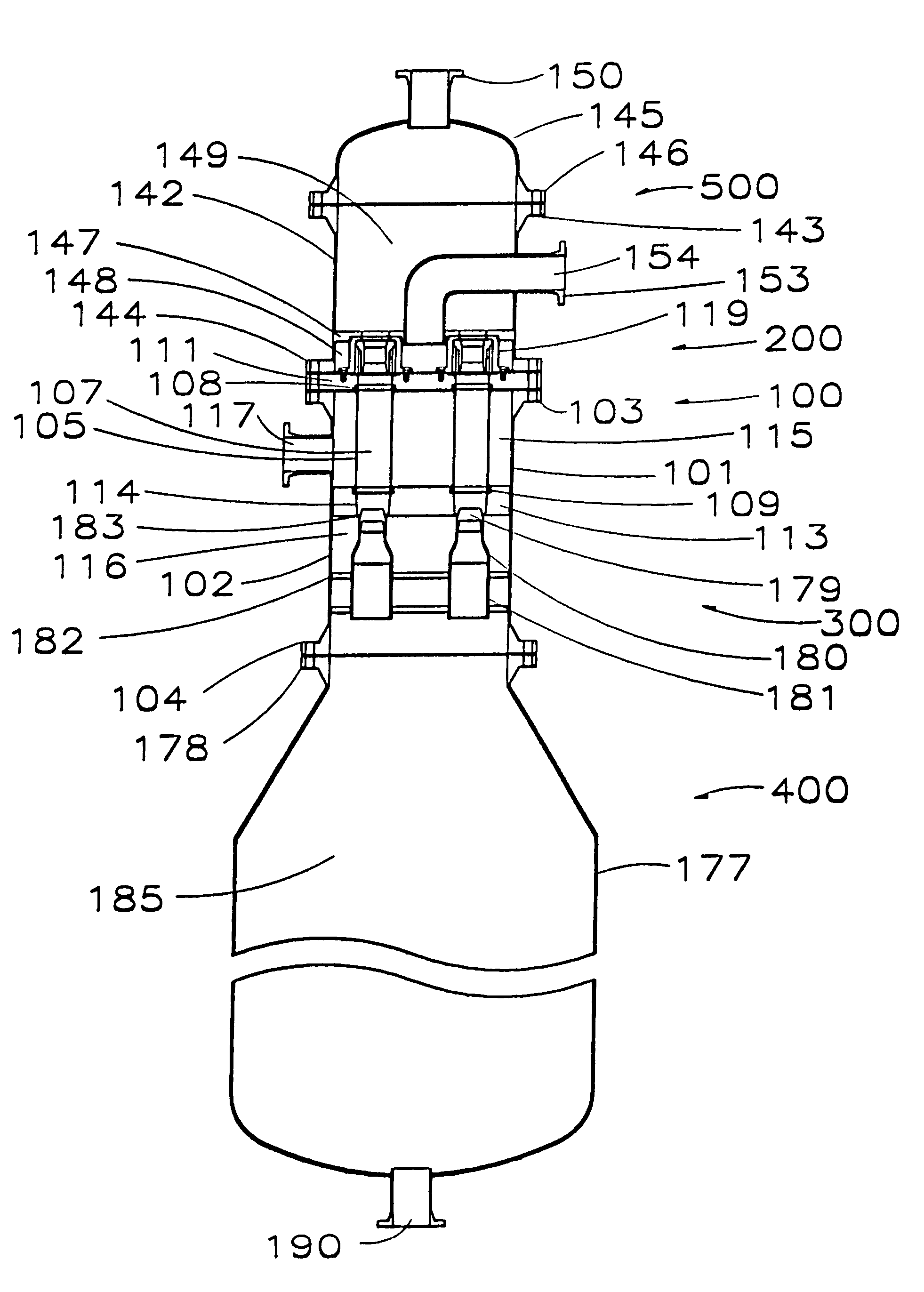
Patents
Literature
4543 results about "Gas bubble" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
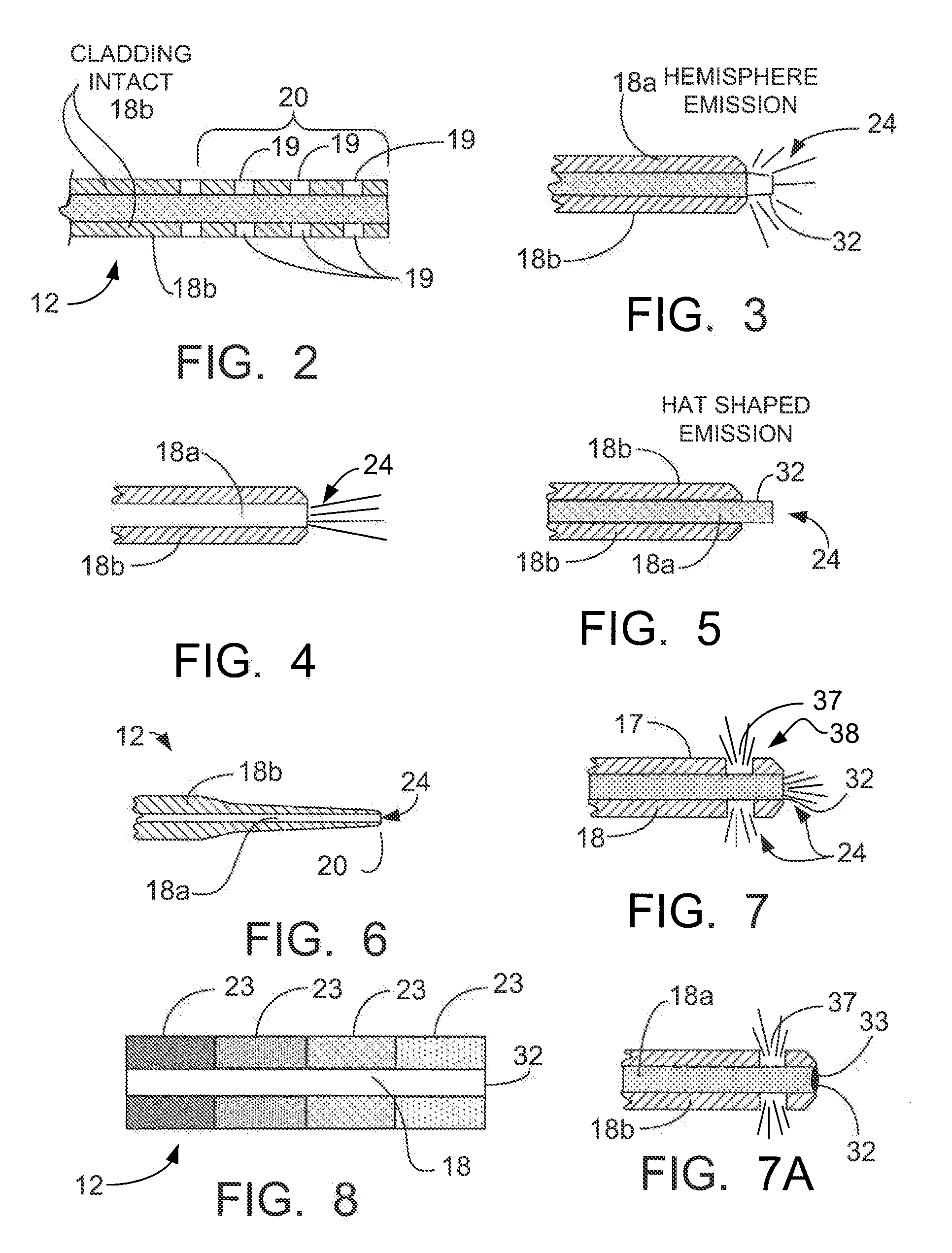
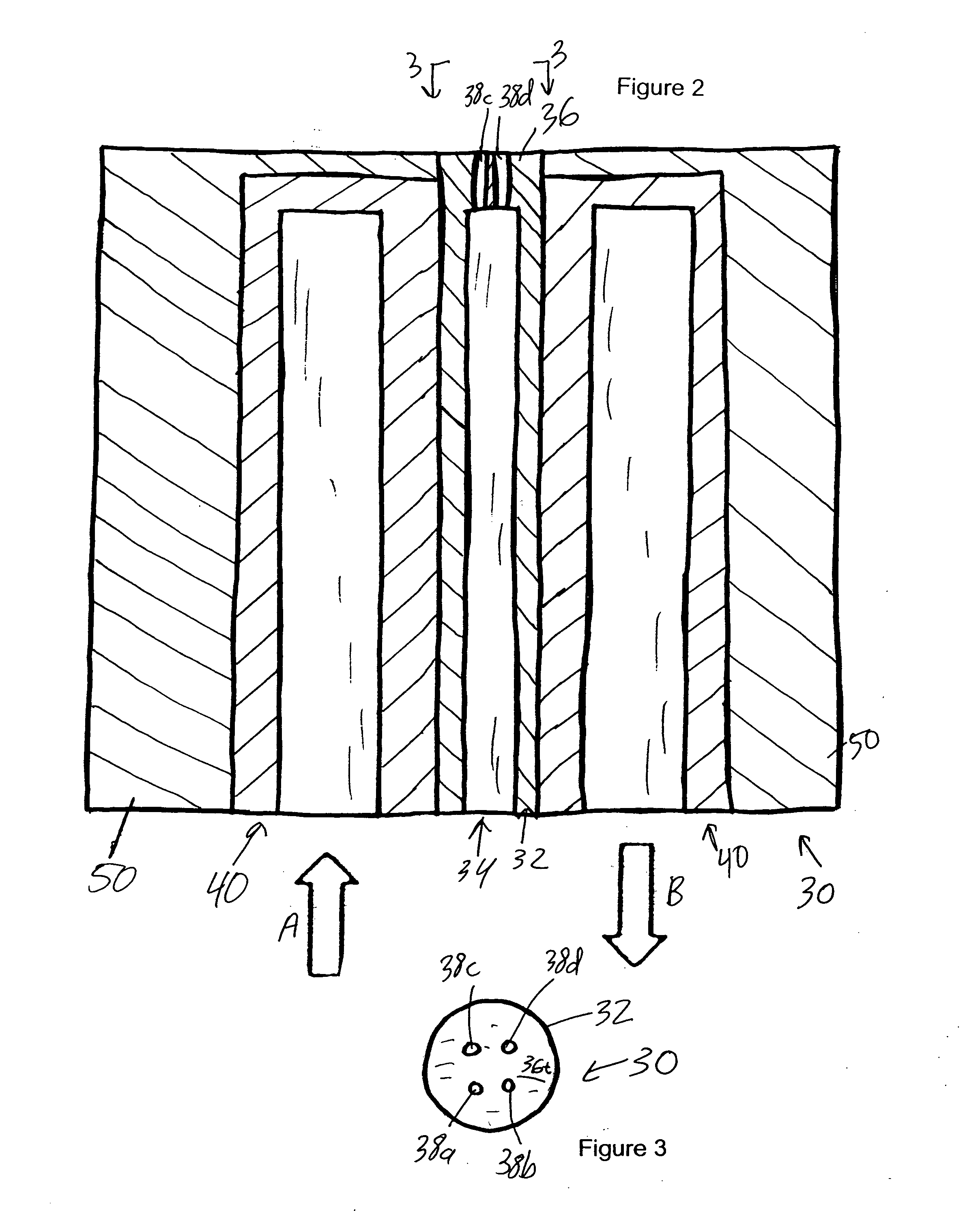
Endoscope having auto-insufflation and exsufflation
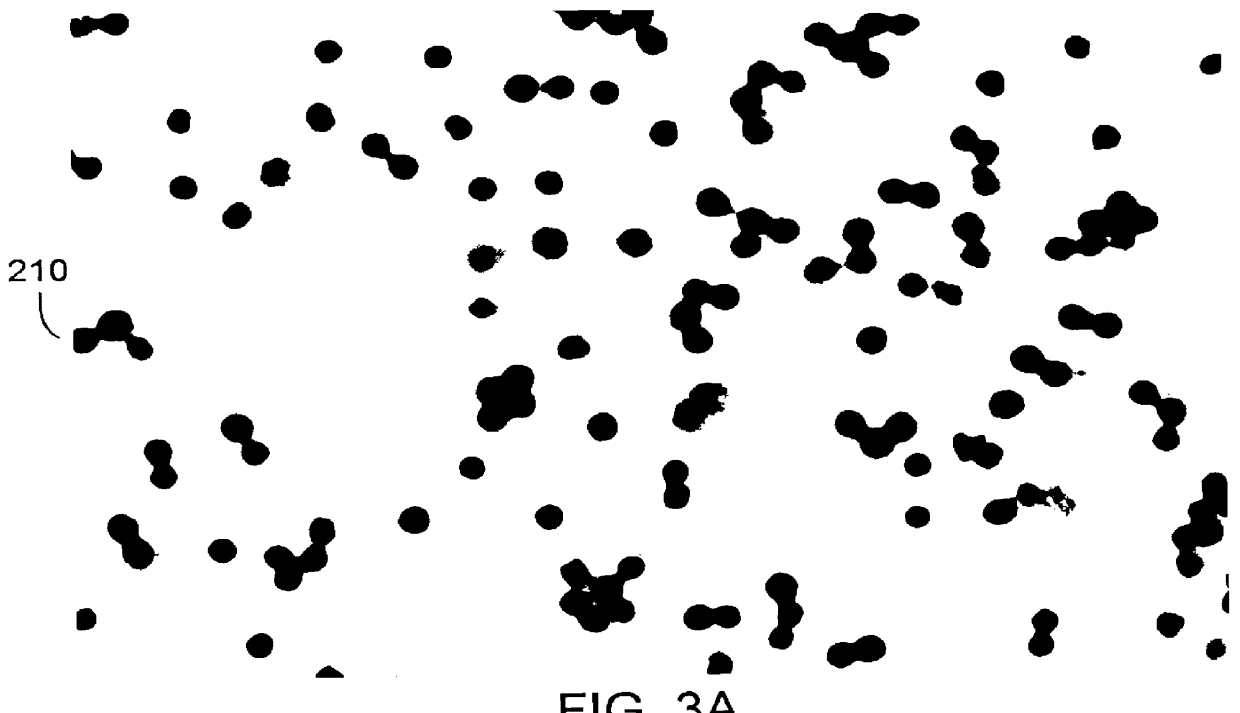
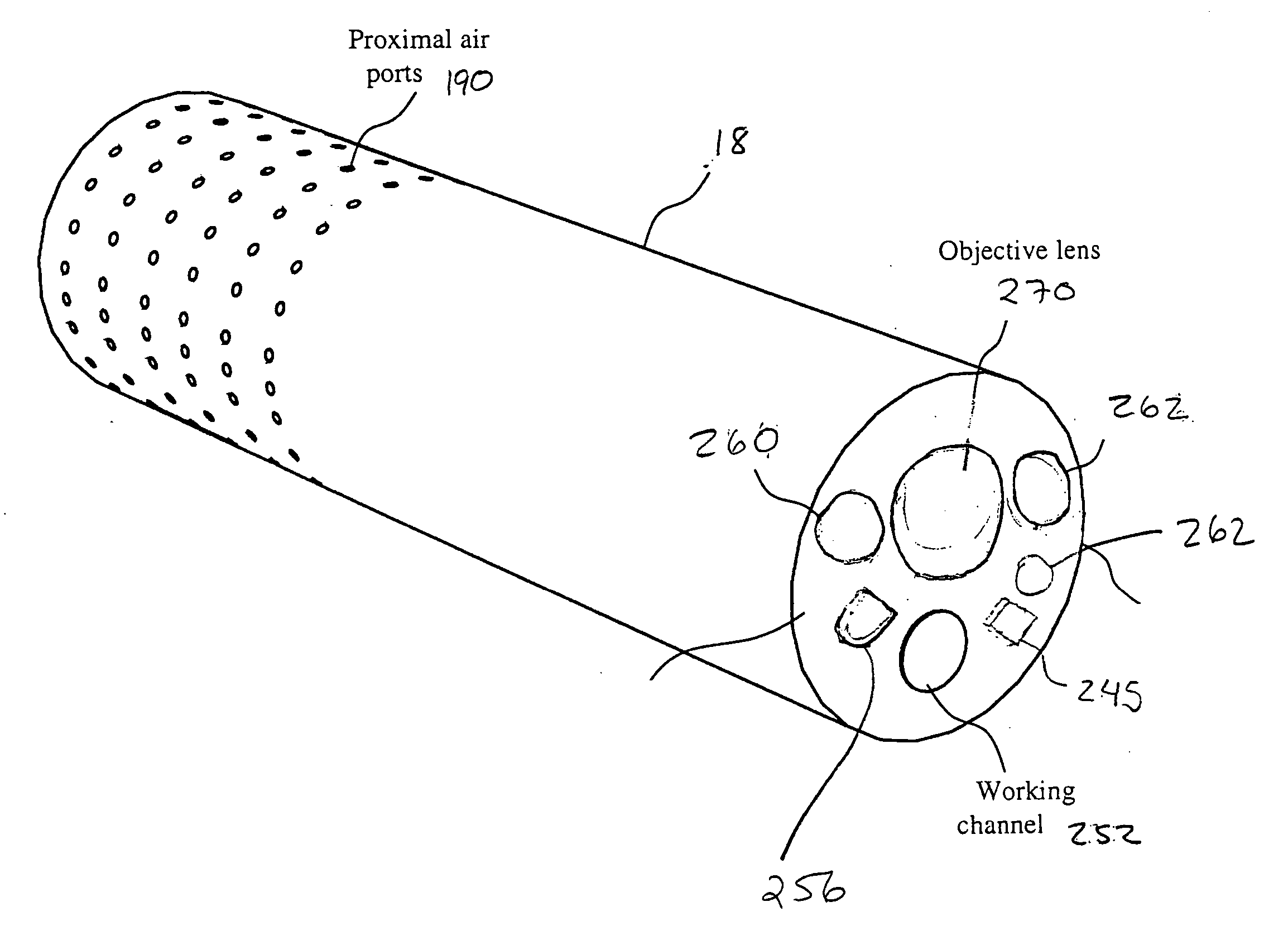
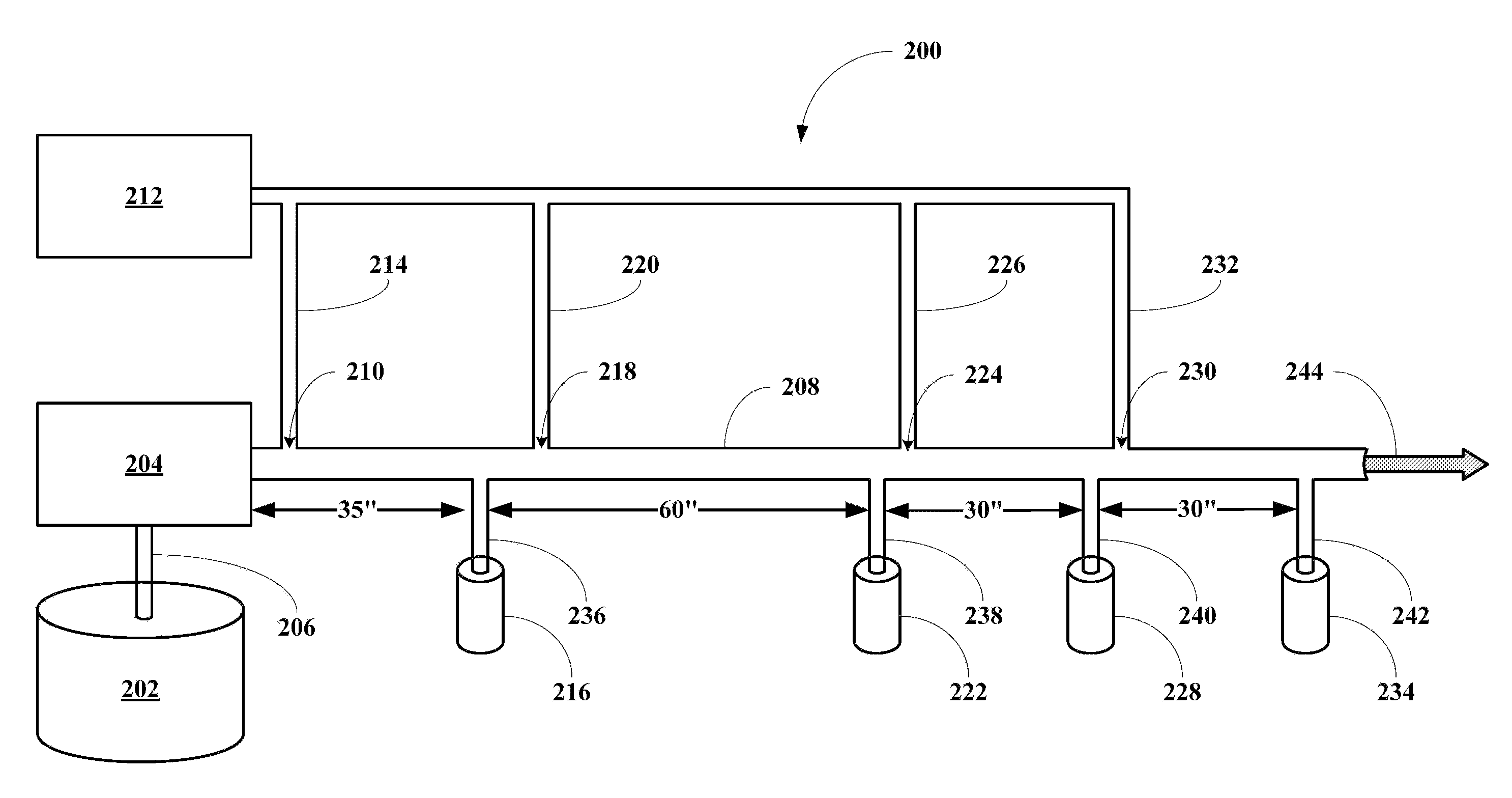
An endoscopic imaging system for examining a patient's body cavity includes an endoscope having a distal end, a proximal end and a number of lumens therein. One or more distal gas ports are disposed at or adjacent the distal end of the endoscope and one or more proximal gas ports are disposed proximal to the distal gas ports. Insufflation gas is delivered to the distal gas ports and withdrawn from the proximal gas ports or vice versa such that a gas bubble is formed in the body cavity and travels with the distal tip of the endoscope.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
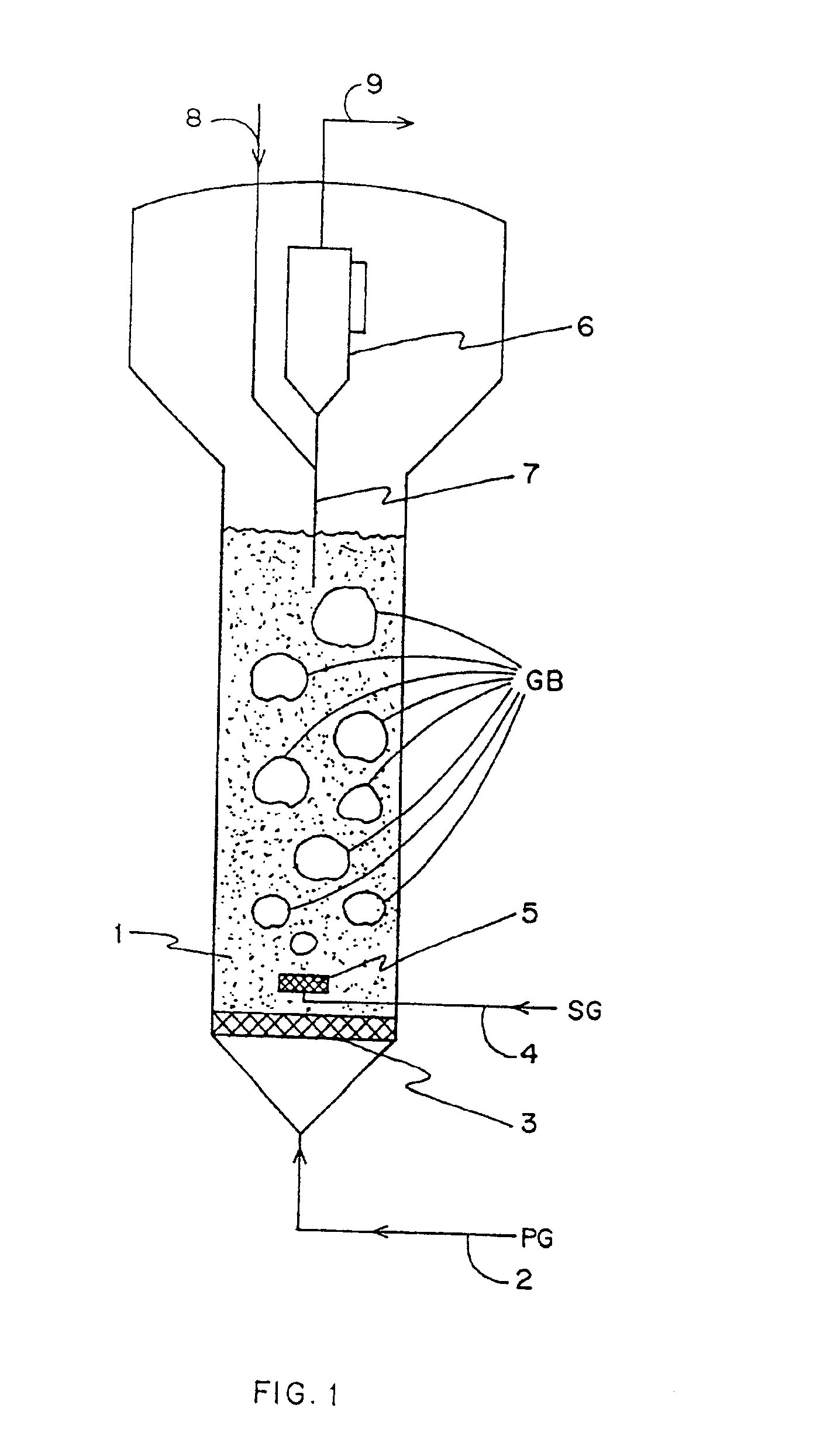
Method for gas-solid contacting in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor
InactiveUS6894183B2Eliminate and drastically reduce bypassEffective contactThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingForming gasSolid particle
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Use of state-change materials in reformable shapes, templates or tooling
Techniques for generating a stable, force-resisting positive or negative representation of a shape. A state-changeable mixture includes uniform, generally ordered, closely-spaced solid bodies and a liquid carrier medium, with the liquid filling any voids or interstices between the bodies and excluding air or gas bubbles from the mixture. Within the mixture, the solid bodies can be caused to transition from a near-liquid or fluent condition of mobility to a stable, force-resisting condition. To create mobility, a small excess quantity or transition liquid is introduced to create a fluent condition by providing a slight clearance between the bodies which permits the gently-forced introduction of at least two simultaneous slip planes between ordered bulk masses of the bodies at any point in the mixture. Transition to the stable condition is caused by extraction of the transition liquid, removing the clearance between bodies and causing them to make stable, consolidated contact.
Owner:TRAN BAO
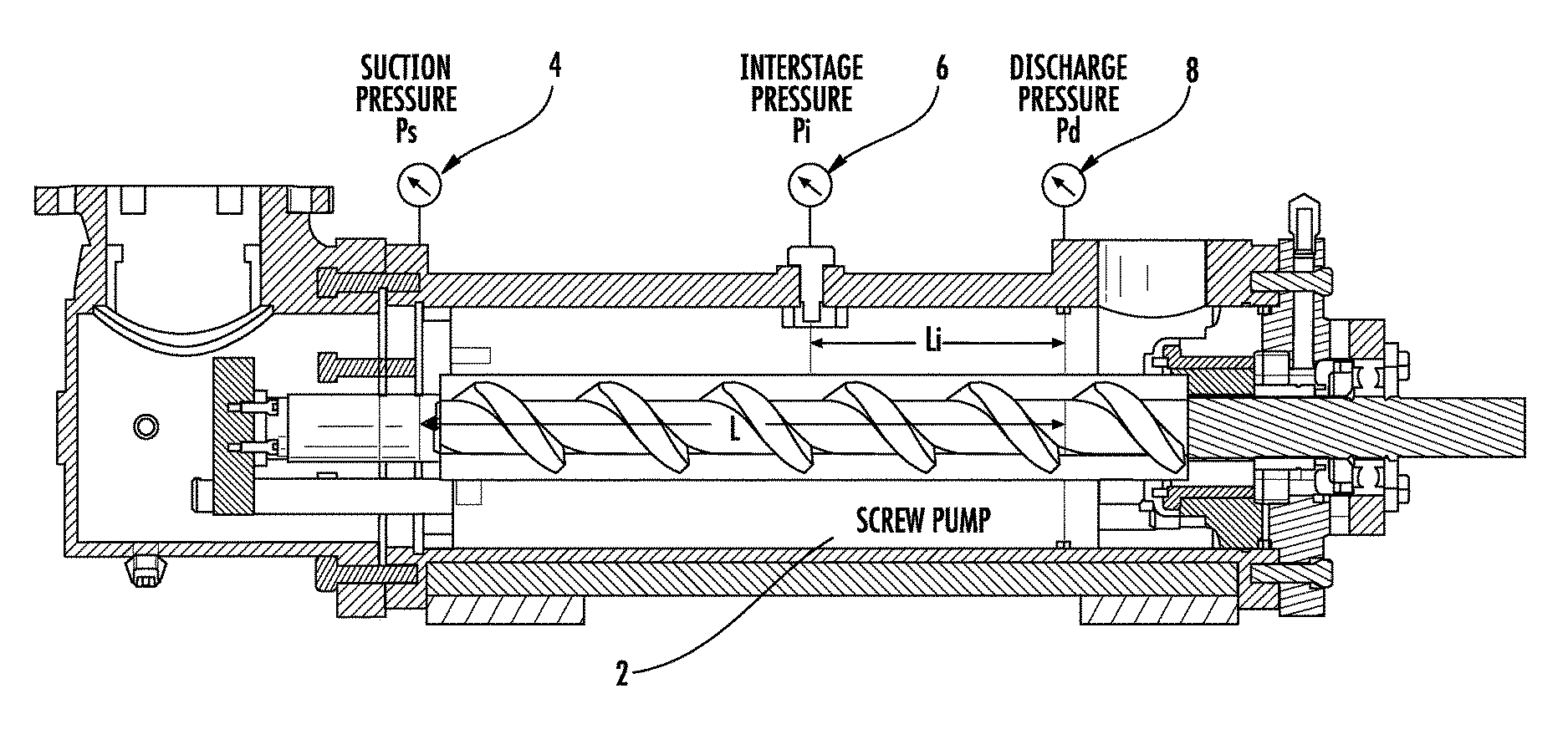
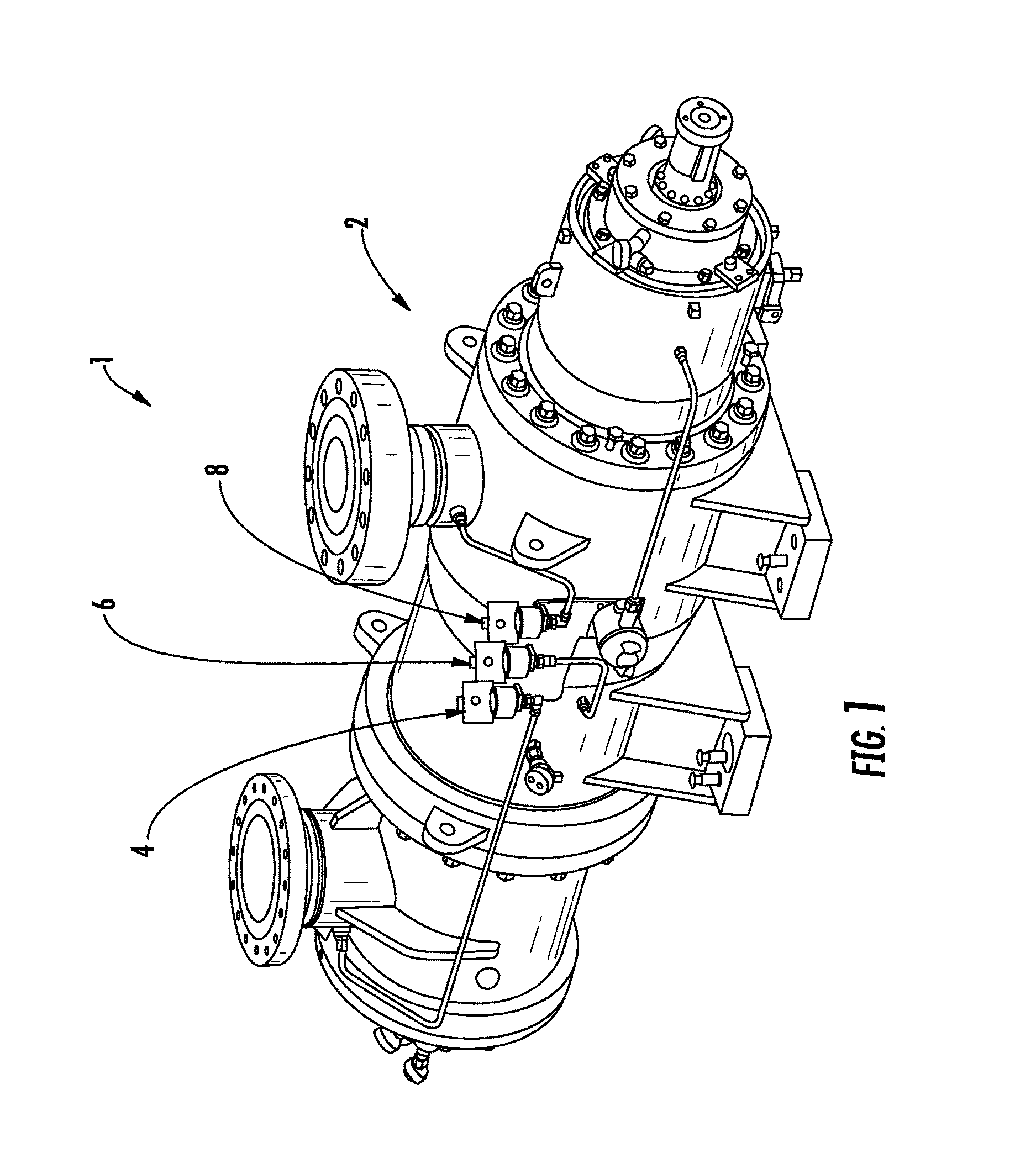
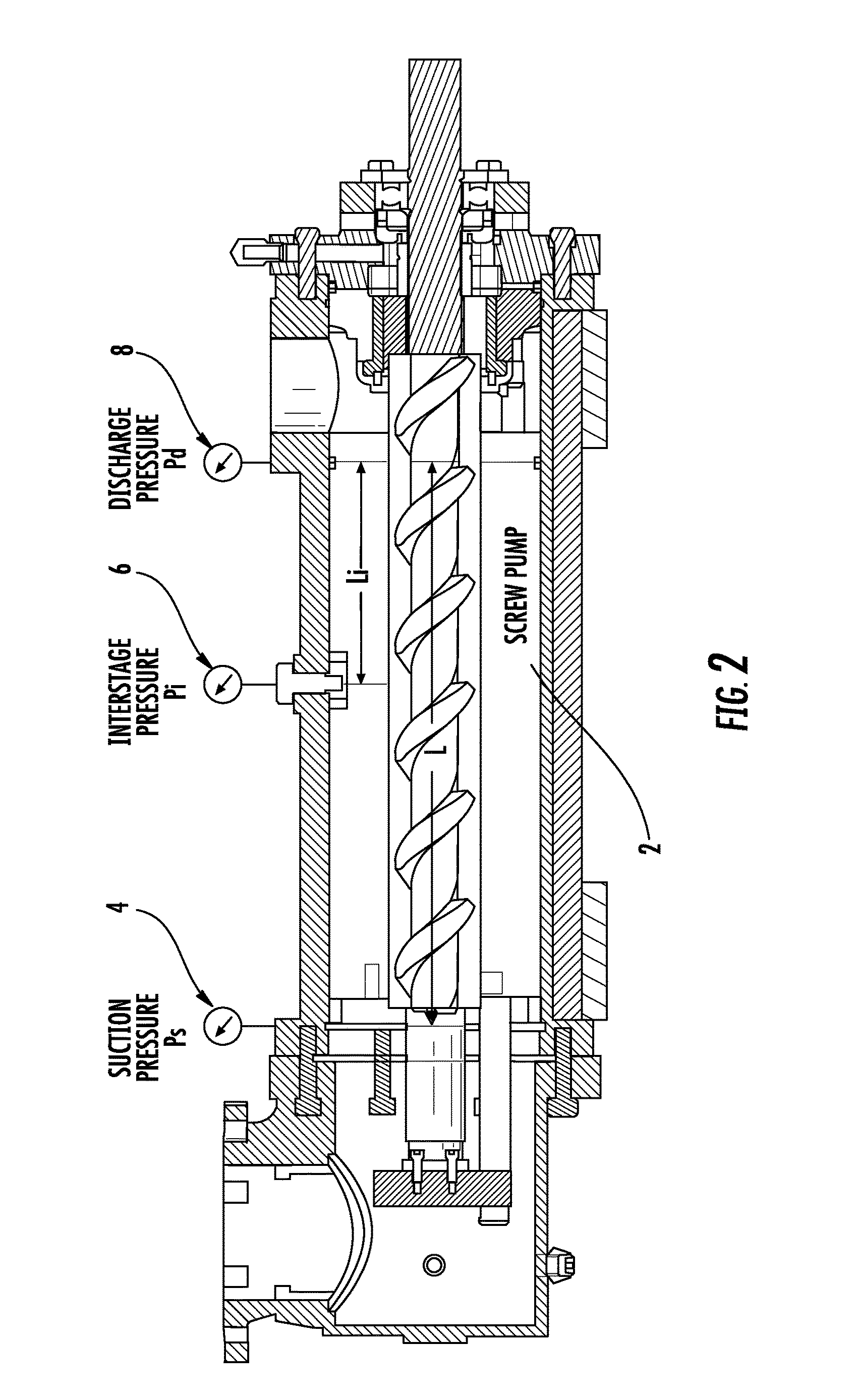
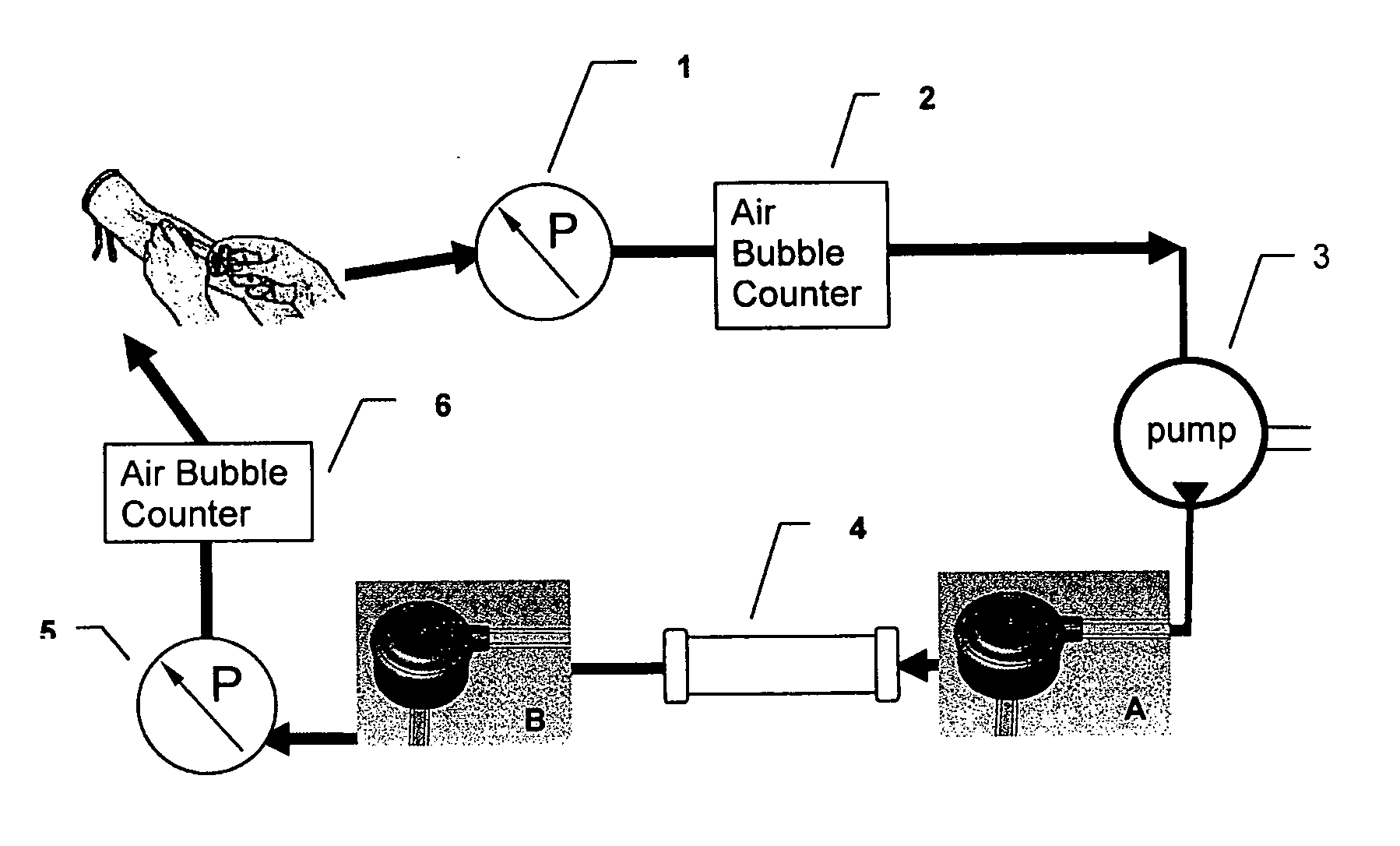
System and method for monitoring and control of cavitation in positive displacement pumps
A system and method are disclosed for monitoring and controlling a positive displacement pump using readings obtained from a plurality of pressure sensors. The pressure sensors may be mounted at the suction, discharge and interstage regions of the pump. Signals from the pressure sensors are compared to obtain a ratio that is used to predict whether a cavitation condition exists within the pump. The ratio can be compared to user provided limits to change an operating characteristic of the pump to reduce predicted cavitation. The pump may be stopped, or pump speed changed, when the ratio is less than a predetermined value. In some embodiments, historical information regarding the ratio may be used to obtain standard deviation information which may then be used to predict whether gas bubbles are passing through the pump. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:CIRCOR PUMPS NORTH AMERICA LLC
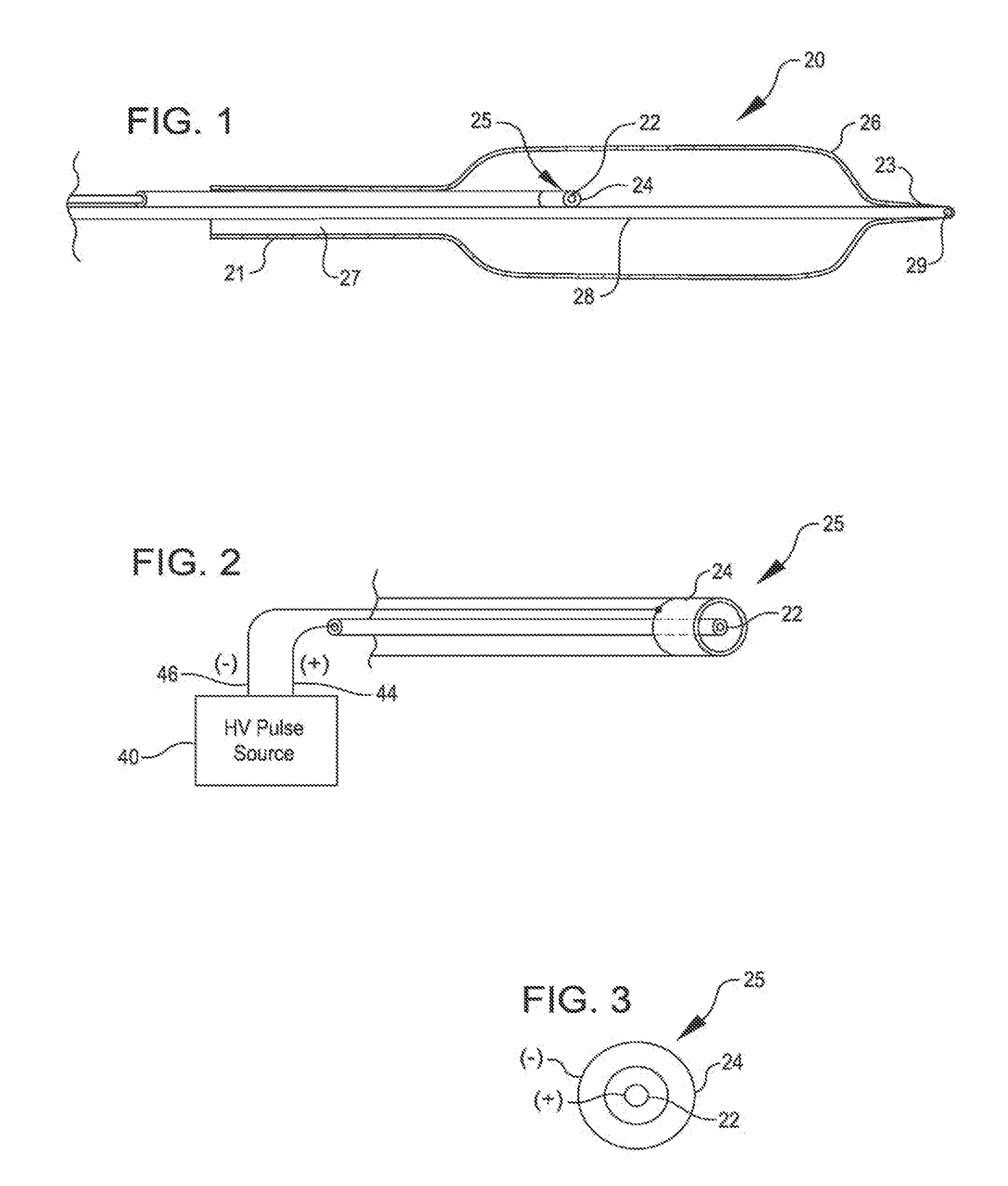
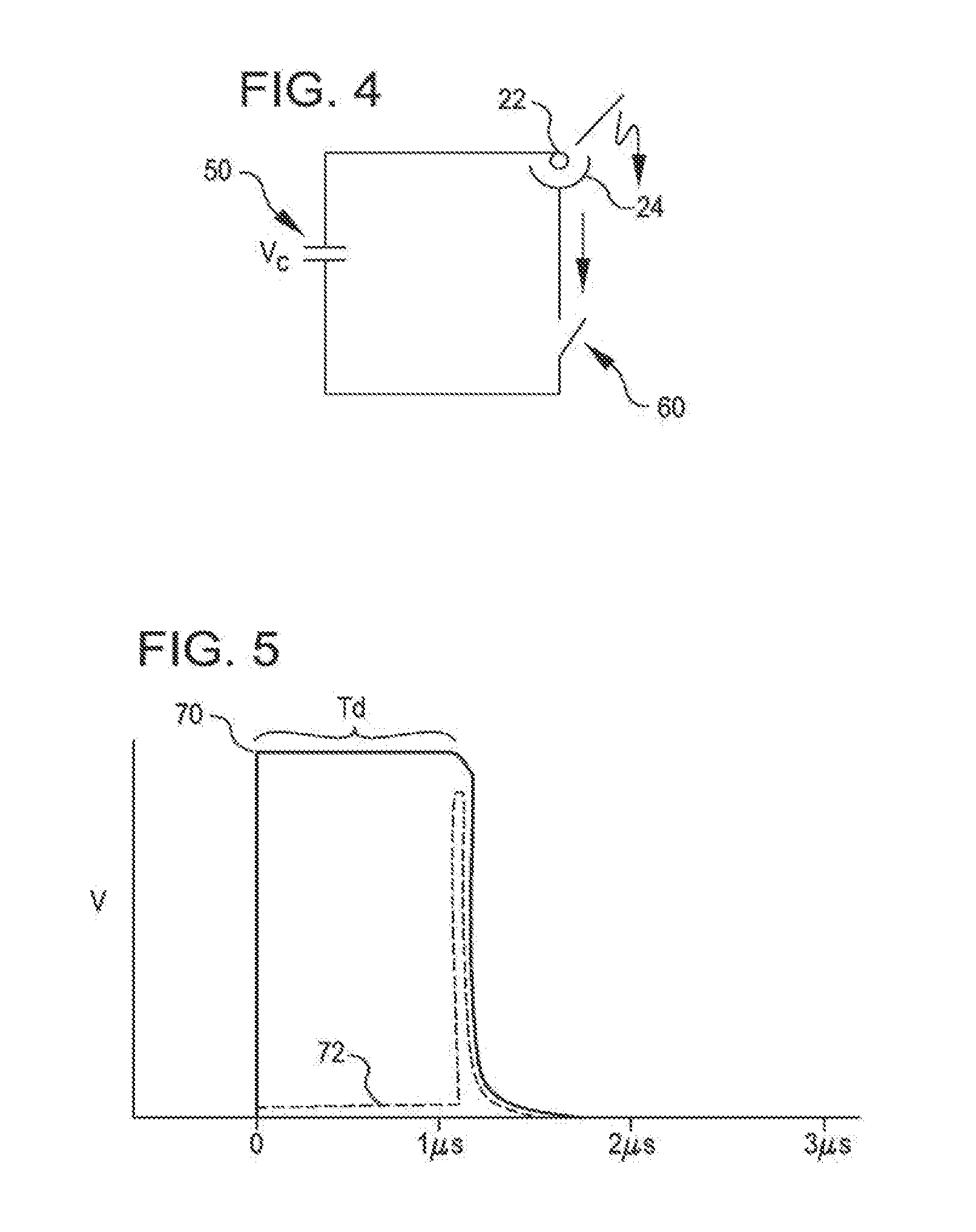
Shockwave catheter system with energy control
A system that breaks calcium in a liquid includes a catheter including first and second electrodes arranged to receive there-across a high electrical voltage at an initial low current. The high electrical voltage causes an electrical arc to form across the electrodes creating a gas bubble within the liquid, a high current to flow through the electrodes, and a mechanical shock wave. A power source provides the electrodes with the high electrical voltage at the initial current and terminates the high electrical voltage in response to the high current flow through the electrodes.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
Apparatus and method for cleaning membrane filtration modules
InactiveUS6841070B2Easy to cleanReduce concentrationSemi-permeable membranesMembranesFiltrationPorous membrane
A method and apparatus for cleaning a membrane module, the membrane module having a plurality of porous membranes, the membranes being arranged in close proximity to one another and mounted to prevent excessive movement therebetween and means for providing, from within the module, by means other than gas passing through the pores of the membranes, gas bubbles entrained in a liquid flow such that, in use, the liquid and bubbles entrained therein move past the surfaces of the membranes to dislodge fouling materials therefrom, the gas bubbles being entrained in the liquid by flowing the liquid past a source of gas to draw the gas into the liquid flow. The gas bubbles are preferably entrained into the liquid using a venturi type device. The membranes are preferably partitioned into discrete groups to assist cleaning while maintaining high packing density.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
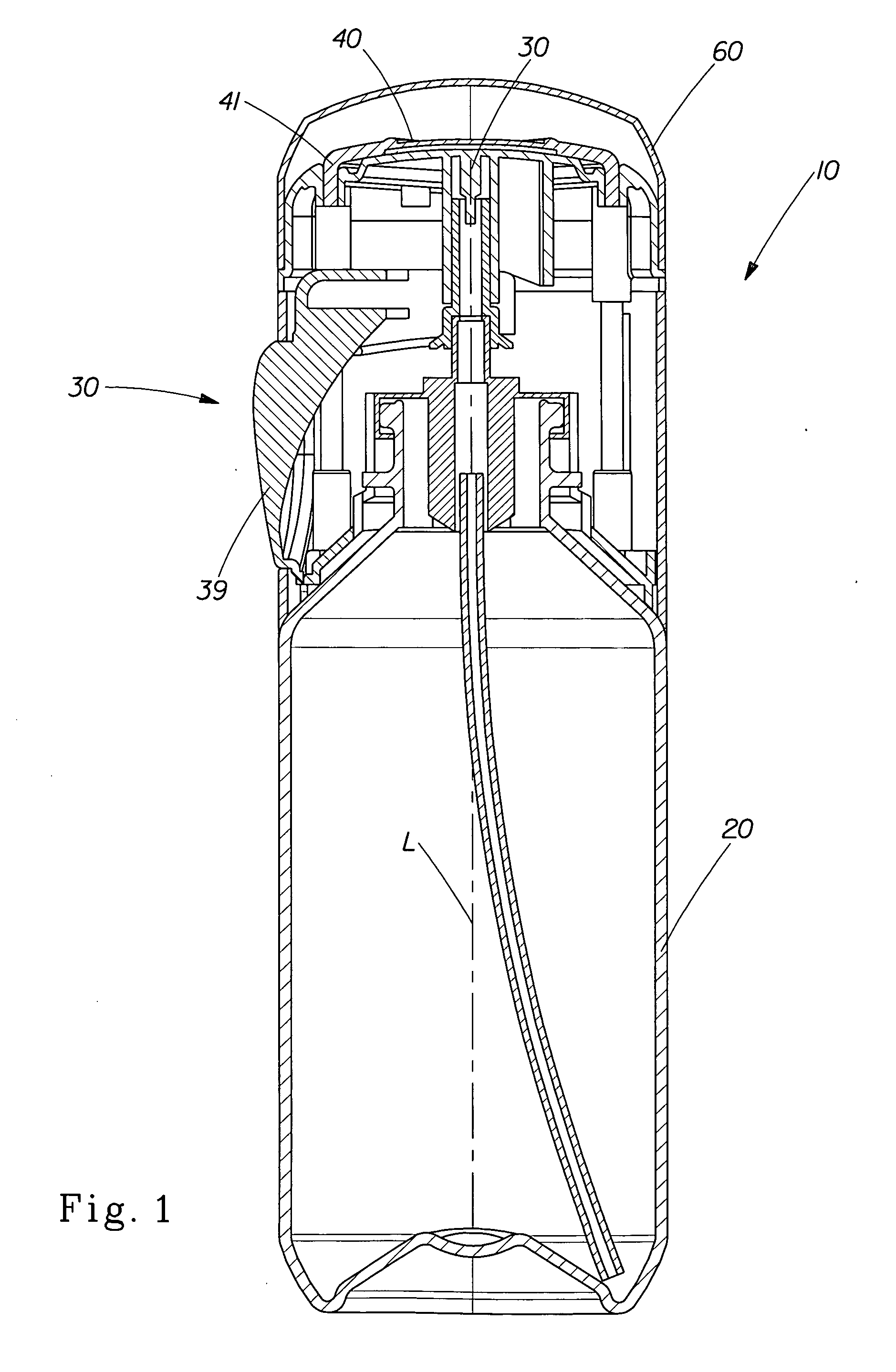
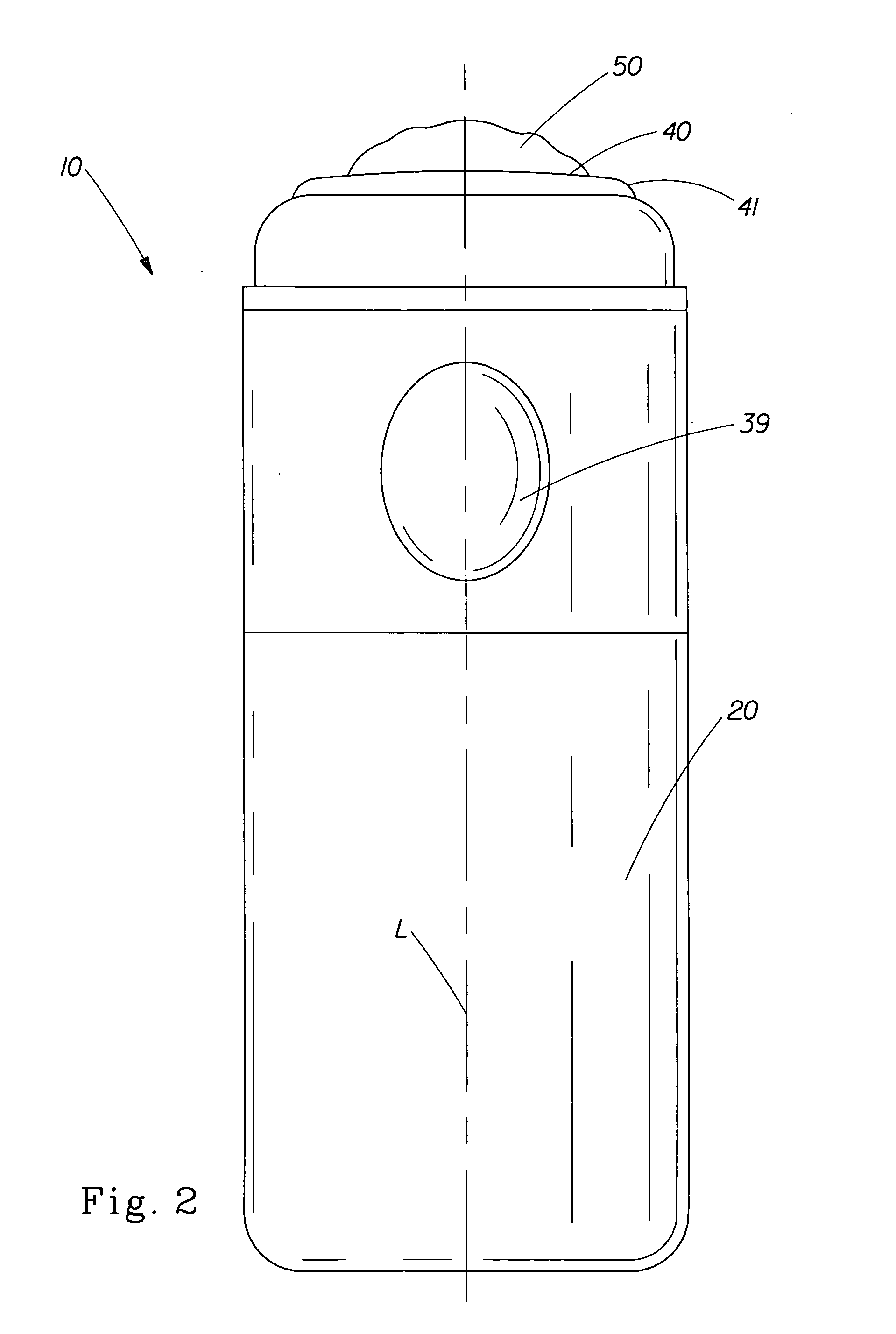
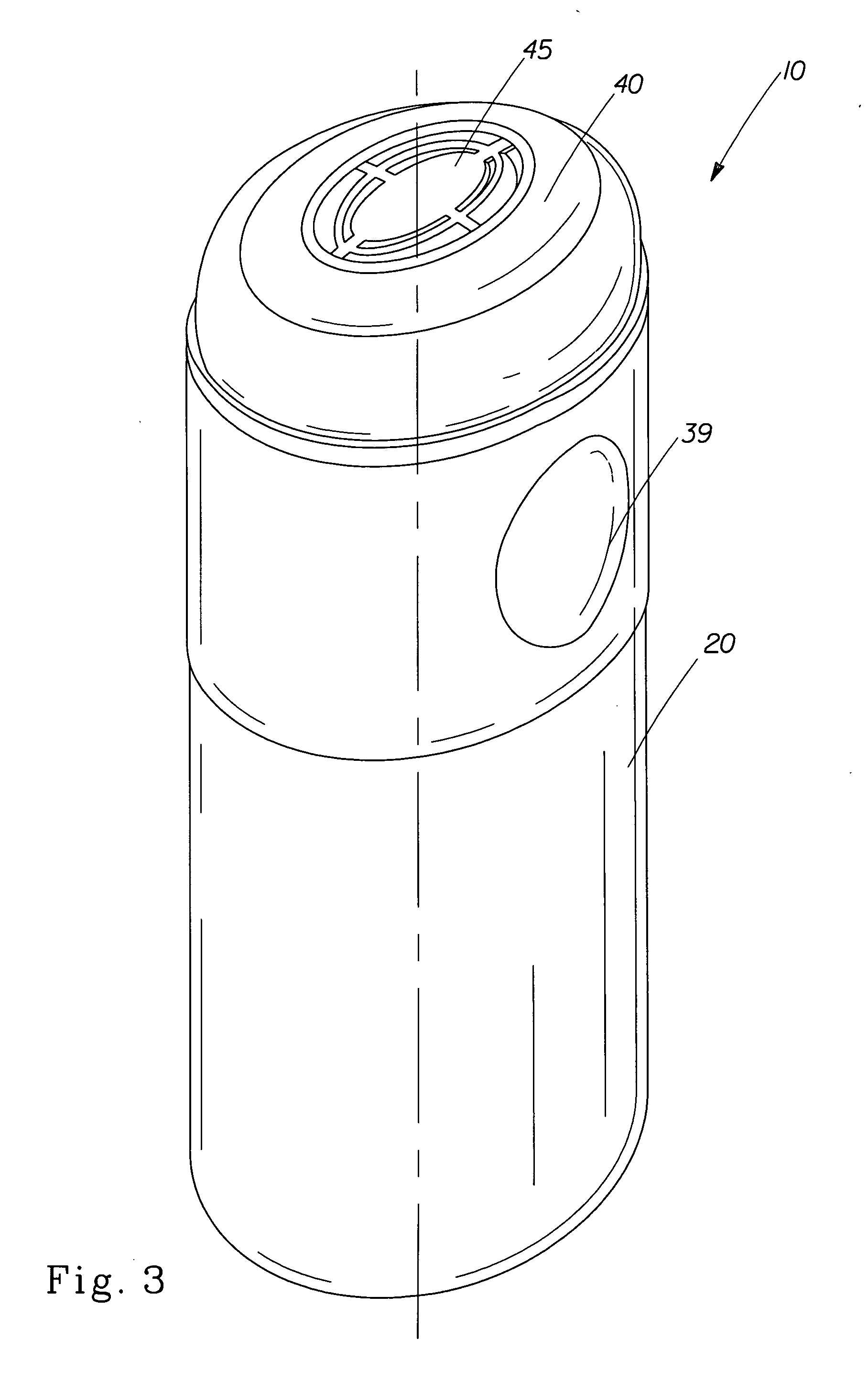
Antiperspirant composition and applicator therefor
An antiperspirant product comprising an antiperspirant composition and an applicator for storing and discharging the antiperspirant composition. The antiperspirant composition comprises an antiperspirant active. The applicator has a longitudinal axis and comprises a release system structured to facilitate discharge of the antiperspirant composition such that the antiperspirant composition discharges as a portion of a foam comprising a dispersion of gas bubbles in a continuous liquid medium comprising the antiperspirant active that is suspended or dissolved therein, and a skin-contacting surface structured to receive and retain the portion of the foam thereon such that the portion of the foam of 0.2 gram is retained on the skin-contacting surface for at least 2 seconds when the applicator is inclined so that the longitudinal axis of the applicator and a gravity force vector form an angle of about 15 degrees therebetween, the skin-contacting surface being configured to apply an effective amount of the foam directly to an underarm area of a consumer.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
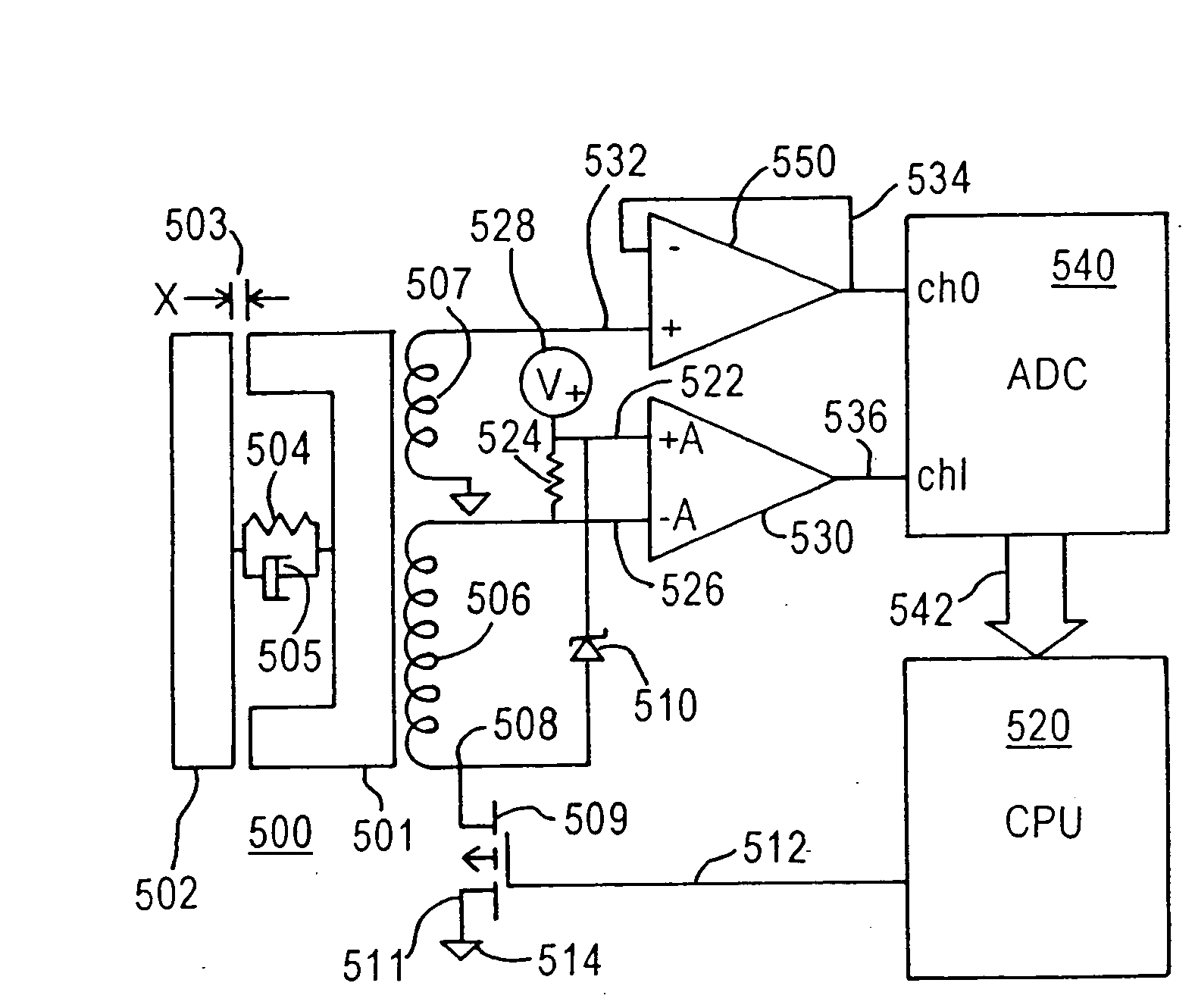
System and method for servo control of nonlinear electromagnetic actuators
InactiveUS20060171091A1Eliminate impactRemove noiseElectrical controlAC motor controlResonance measurementInstability
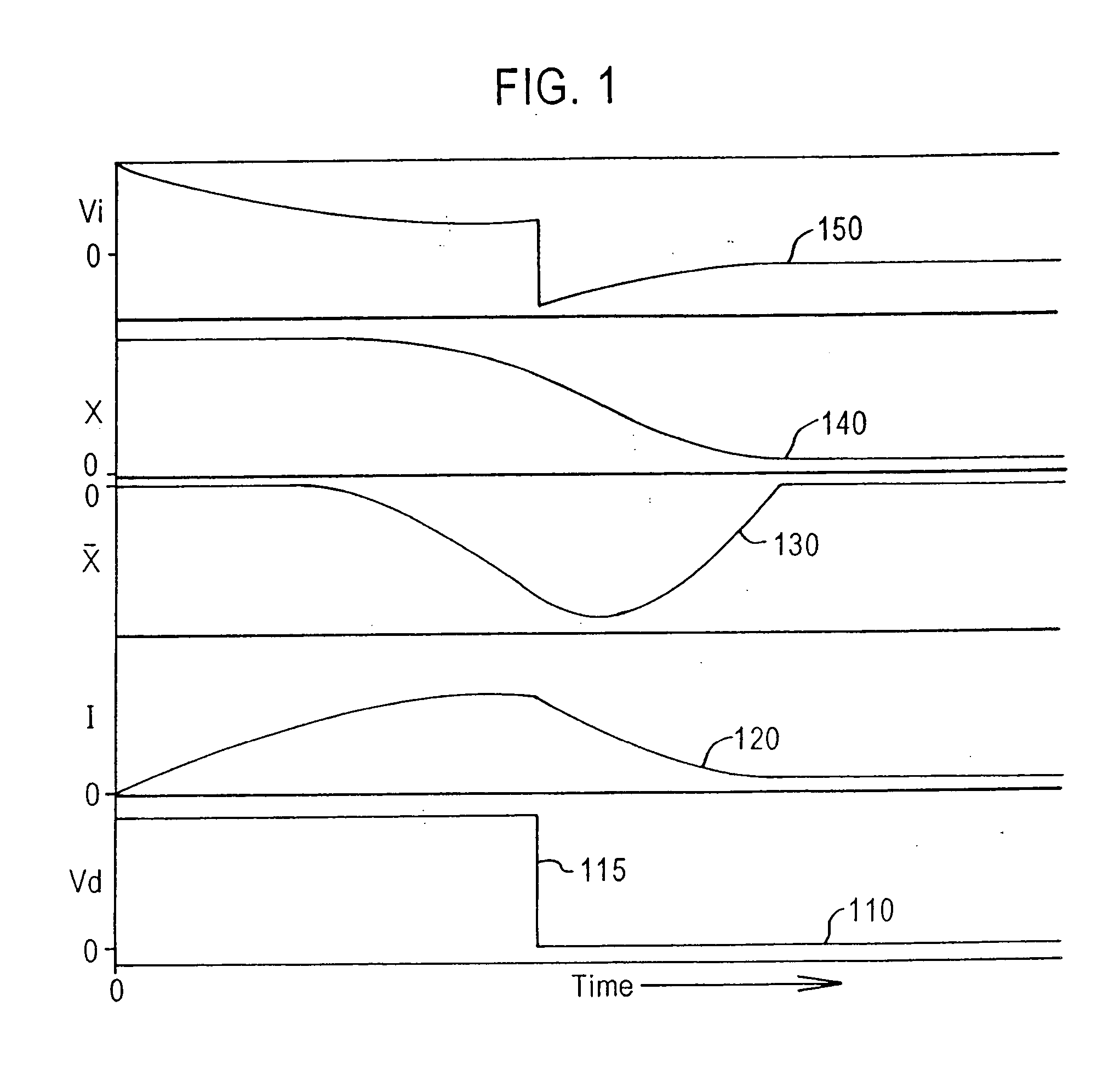
Servo control using ferromagnetic core material and electrical windings is based on monitoring of winding currents and voltages and inference of magnetic flux, a force indication; and magnetic gap, a position indication. Third order nonlinear servo control is split into nested control loops: a fast nonlinear first-order inner loop causing flux to track a target by varying a voltage output; and a slower almost linear second-order outer loop causing magnetic gap to track a target by controlling the flux target of the inner loop. The inner loop uses efficient switching regulation, preferably based on controlled feedback instabilities, to control voltage output. The outer loop achieves damping and accurate convergence using proportional, time-integral, and time-derivative gain terms. The time-integral feedback may be based on measured and target solenoid drive currents, adjusting the magnetic gap for force balance at the target current. Incorporation of permanent magnet material permits the target current to be zero, achieving levitation with low power, including for a monorail deriving propulsion from the levitation magnets. Linear magnetic approximations lead to the simplest controller, but nonlinear analog computation in the log domain yields a better controller with relatively few parts. When servo-controlled solenoids provide actuation of a pump piston and valves, electronic LC resonance measurements determine liquid volume and gas bubble volume.
Owner:SEALE JOSEPH B +1
Method and Apparatus for Disinfecting or Sterilizing a Root Canal System Using Lasers Targeting Water
InactiveUS20090130622A1Sufficient deliveryEnhanced light absorptionSurgical instrument detailsDental toolsDiseaseEnergy absorption
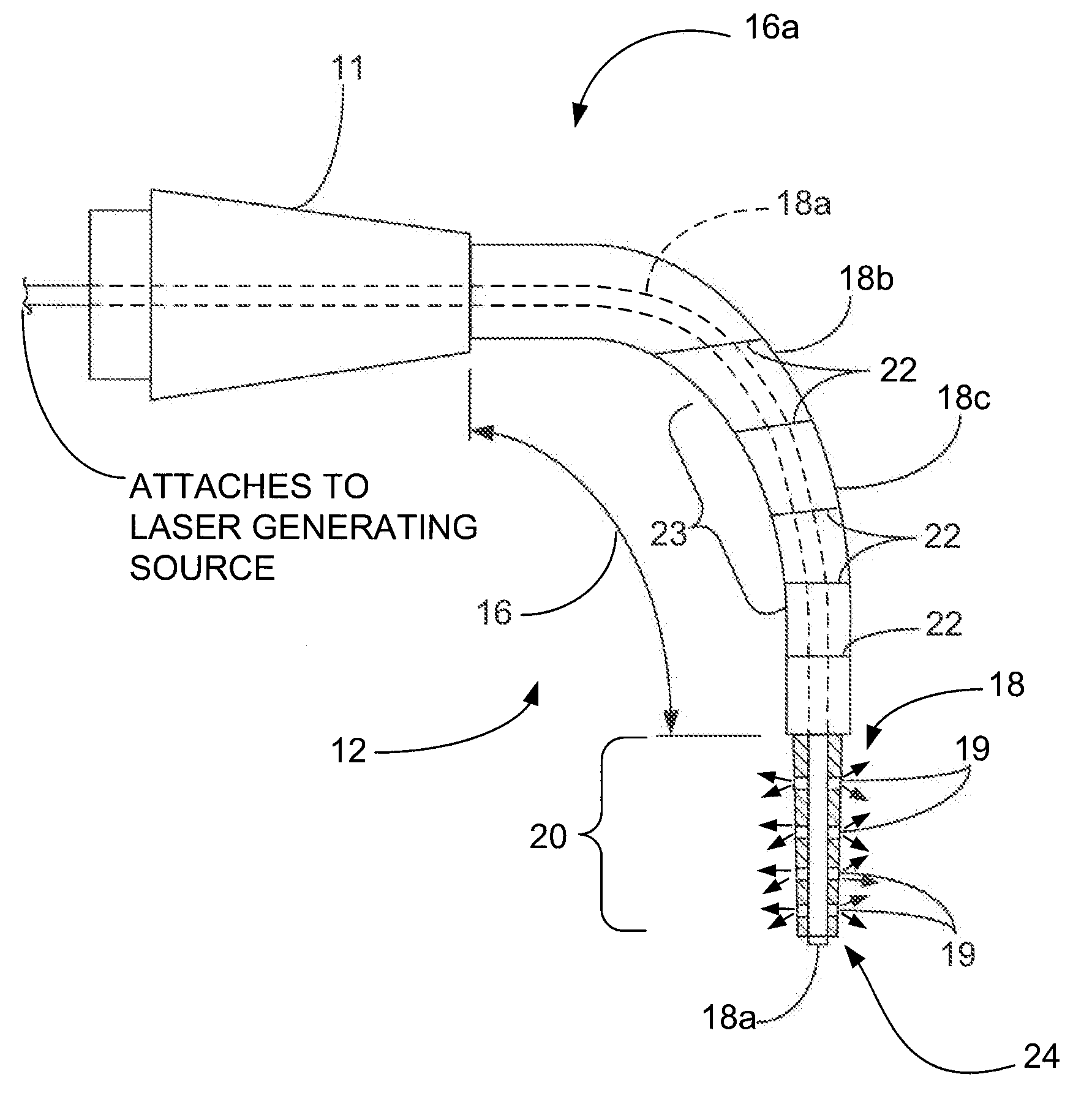
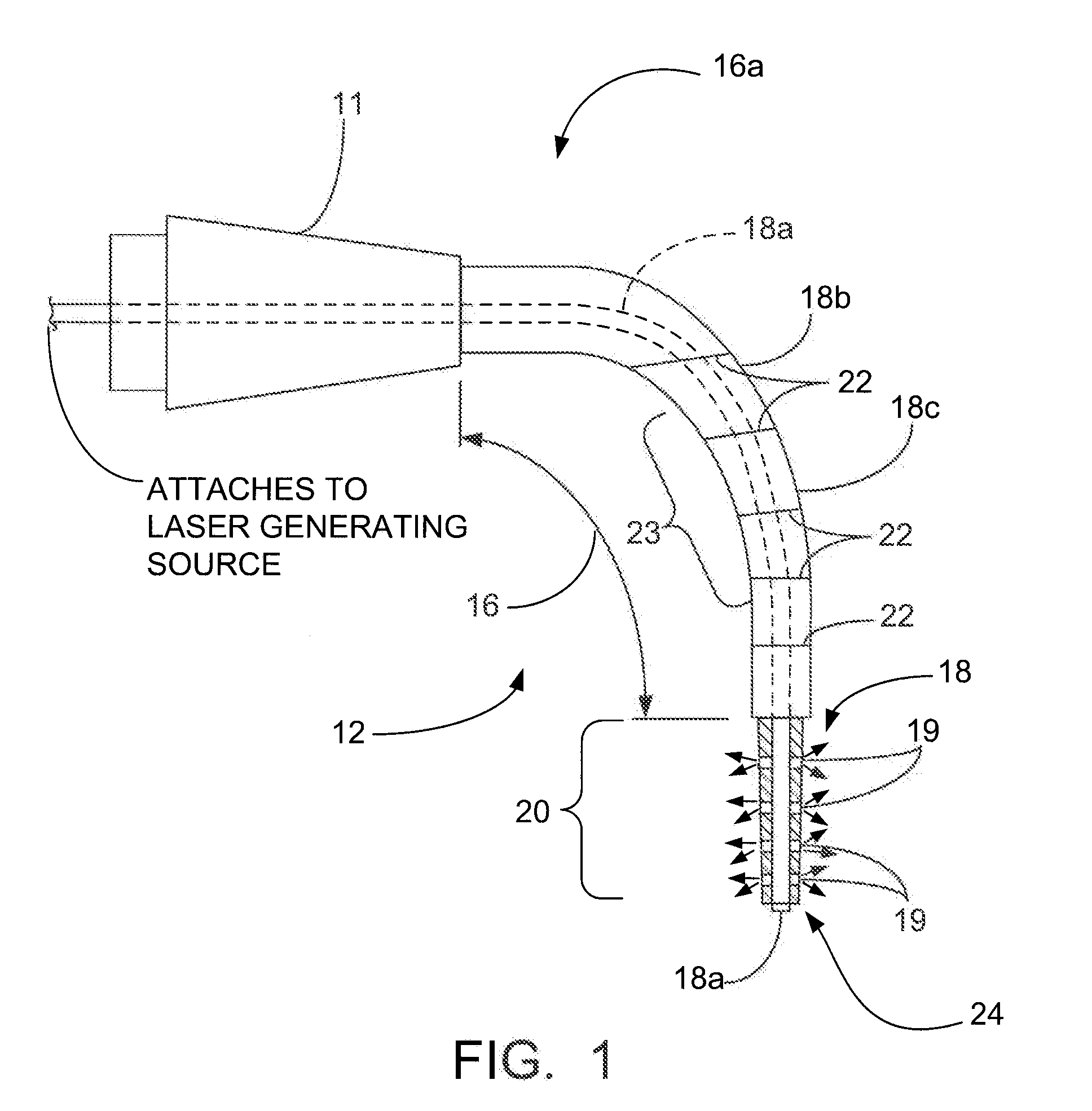
Method and apparatus for disinfecting and / or sterilizing a root canal system by targeting the water content of disease and debris in the canals. The laser technique of employs a frequency of the wavelength emissions between about 930 to about 1065 nanometers with an optimum of 980 nm. This range of wavelengths targets the water content of tissue cells and pathogens as well as any residual organic debris in water within the root canal system after its preparation while being poorly absorbed by the surrounding dentin. The selection of the optimum wavelength produces significant effects generating and advancing treatment to the targeted aqueous environments. This is due to the rapid energy absorption by the water and the subsequent creation of gas bubbles, liberation of heat and subsequent propulsion of waves of heat and gas that impact along the canal walls and ramifications resulting in an enhanced bacterial kill and cleaning of the canal walls and ramifications. No dyes or other additives are necessary to enhance the effectiveness of the laser kill of bacteria, etc.
Owner:BOLLINGER JAMES EDWIN +2
Degassing device
ActiveUS20110092875A1Maximize advantageReduced effectivenessDialysis systemsMedical devicesHaemodialysis machineEngineering
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Pneumatic control of formation and transport of small volume liquid samples
A process and system are provided for forming and transporting precise small volumes of liquid samples by means of controlled gas pressures. As the controlled gas pressures are changed at a multiplicity of control points in the fluid circuit, transitions take place involving the transport of small liquid samples. This transport is arrested by the geometry of the fluid circuit to produce a new state, which state remains stable until another transition is initiated by a change in the multiplicity of controlled gas pressures. Various combinations of control elements are described for effecting formation of fixed liquid volumes, transporting, mixing, and removing entrained bubbles from small liquid samples.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Scouring method
InactiveUS20020195390A1Avoid excessive movementAvoid enteringMembranesUltrafiltrationGas passingPorous membrane
A method and apparatus for removing fouling materials from the surface of a plurality of porous membranes (9) arranged in a membrane module (4) by providing, from within the module, by means (10) other than gas passing through the pores of said membranes, gas bubbles in a uniform distribution relative to the porous membrane array such that the bubbles move past the surfaces of the membranes (9) to dislodge fouling materials therefrom. The membranes (9) are arranged in close proximity to one another and mounted to prevent excessive movement therebetween. The bubbles also produce vibration and rubbing together of the membranes to further assist removal of fouling materials.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Scouring method
InactiveUS6969465B2The process is simple and effectiveAvoid excessive movementMembranesUltrafiltrationPorous membraneGas passing
A method and apparatus for removing fouling materials from the surface of a plurality of porous membranes (9) arranged in a membrane module (4) by providing, from within the module, by means (10) other than gas passing through the pores of said membranes, gas bubbles in a uniform distribution relative to the porous membrane array such that the bubbles move past the surfaces of the membranes (9) to dislodge fouling materials therefrom. The membranes (9) are arranged in close proximity to one another and mounted to prevent excessive movement therebetween. The bubbles also produce vibration and rubbing together of the membranes to further assist removal of fouling materials.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
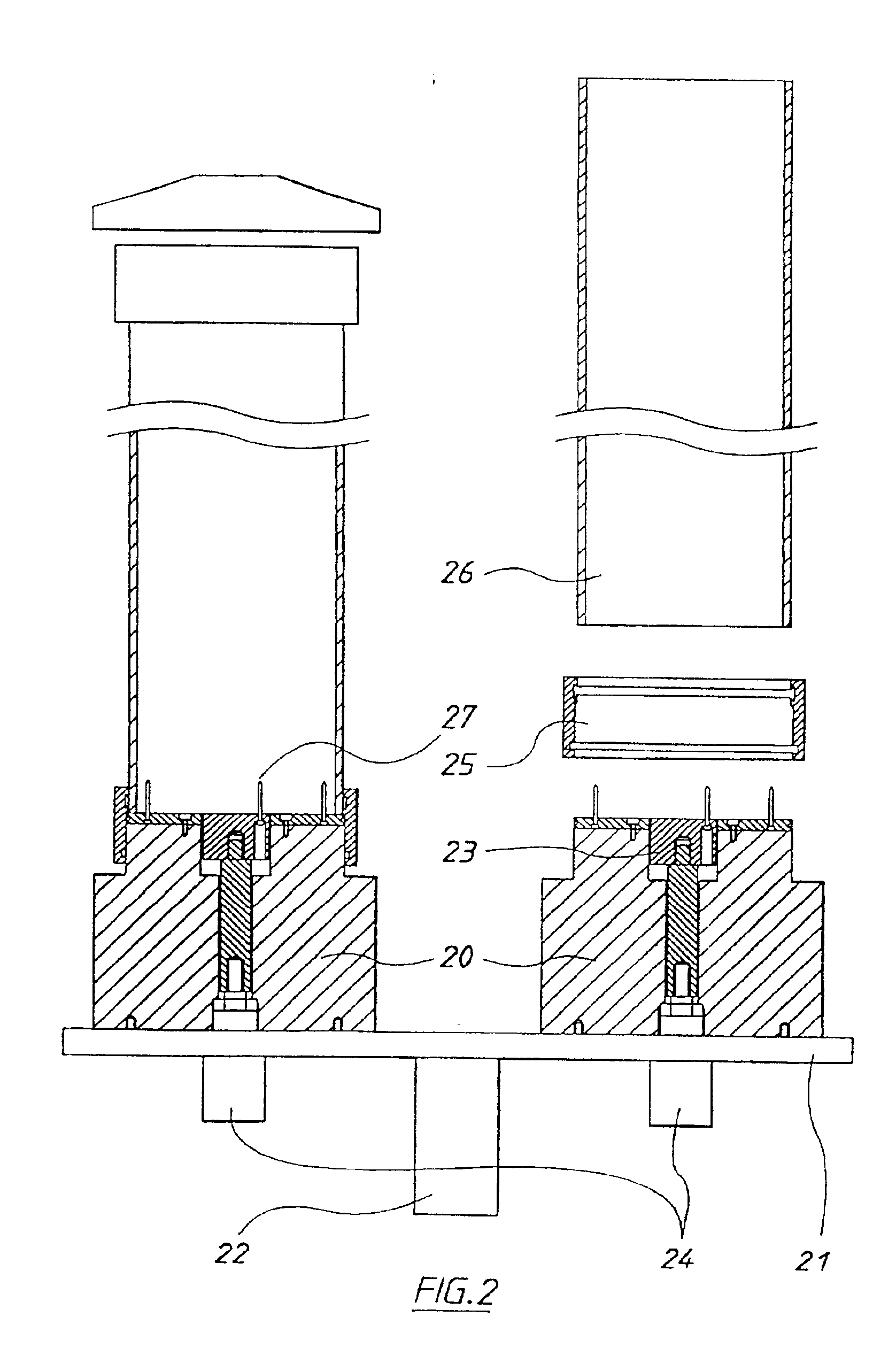
Needleless injector drug capsule and a method for filling thereof
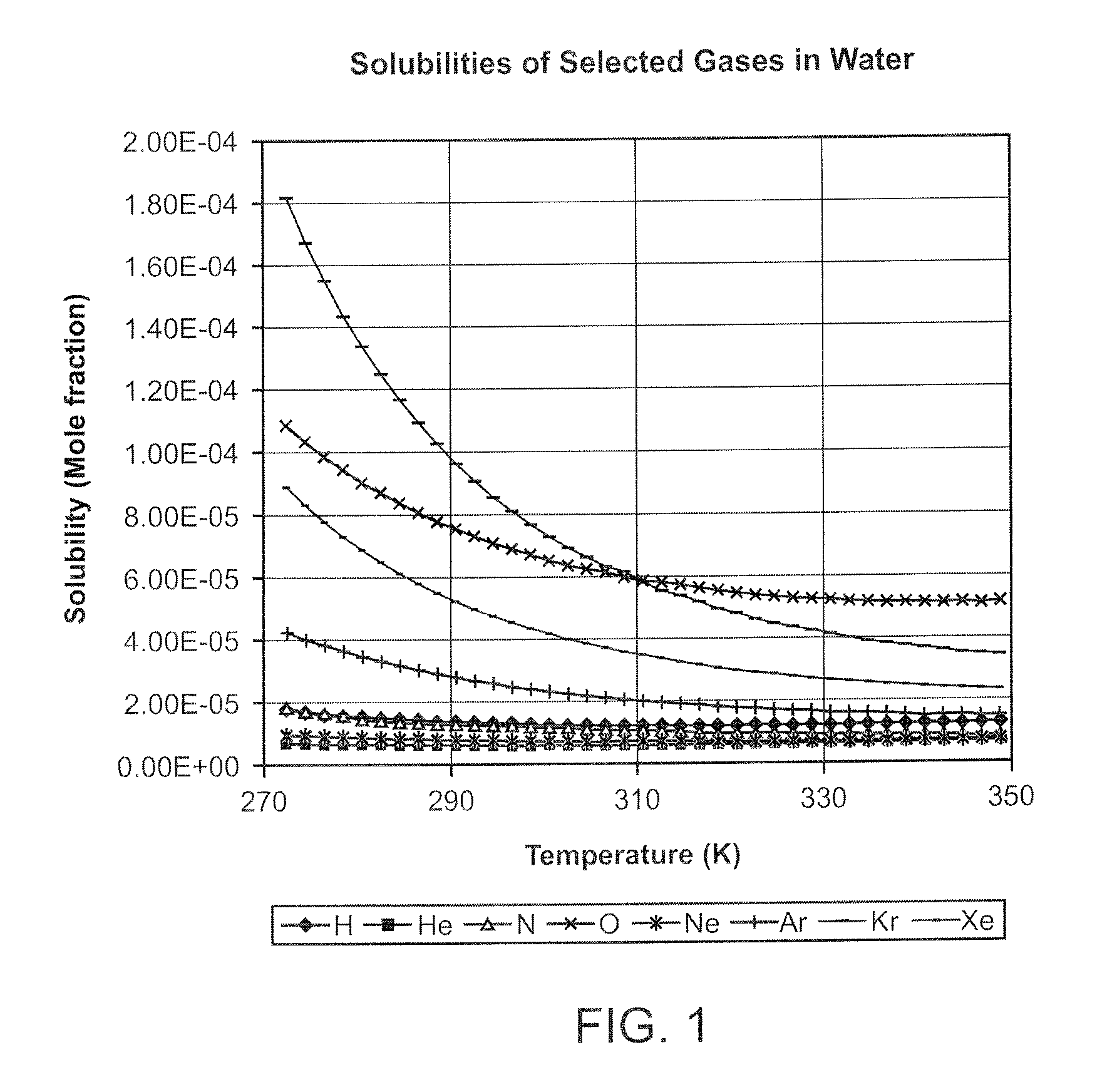
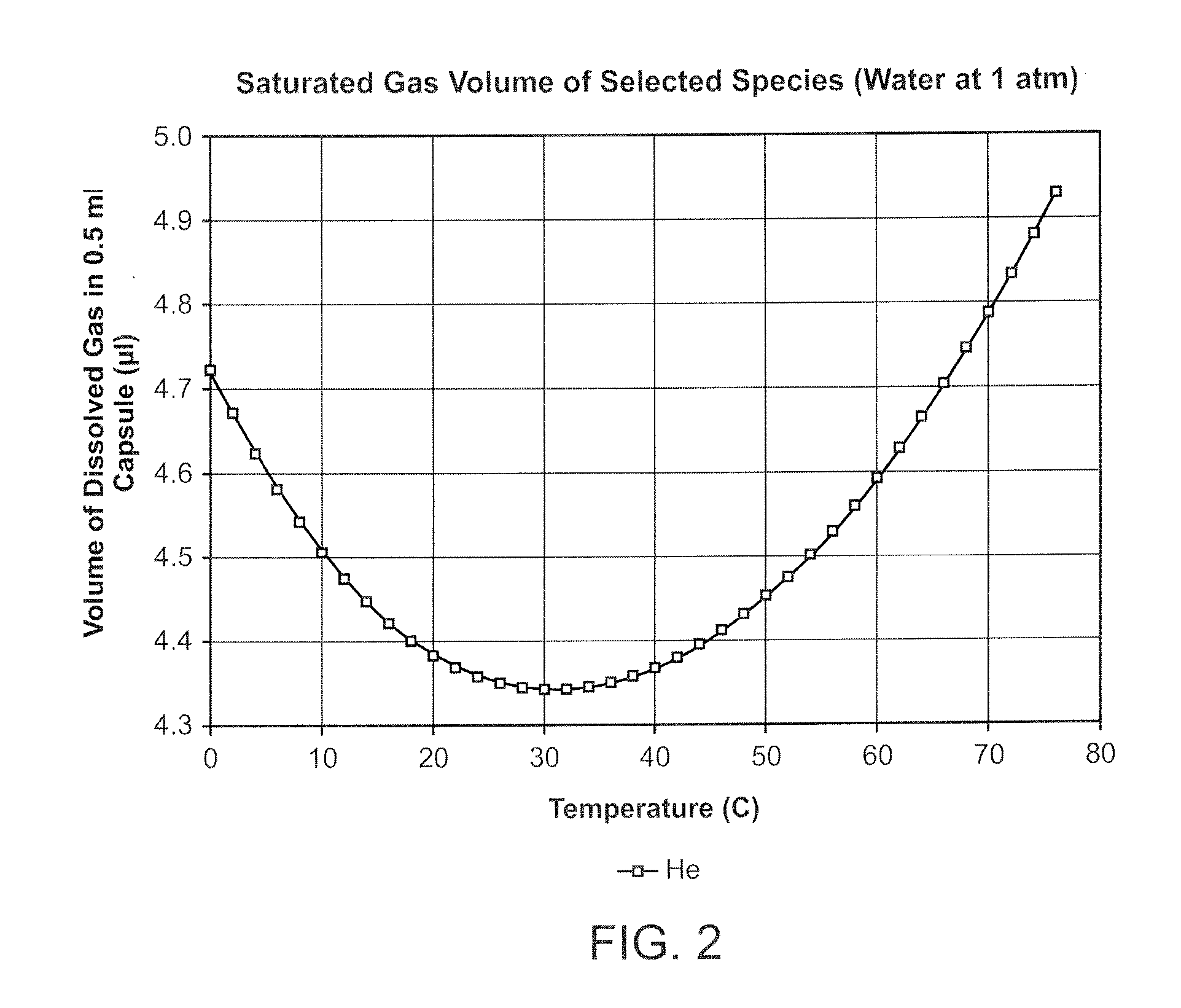
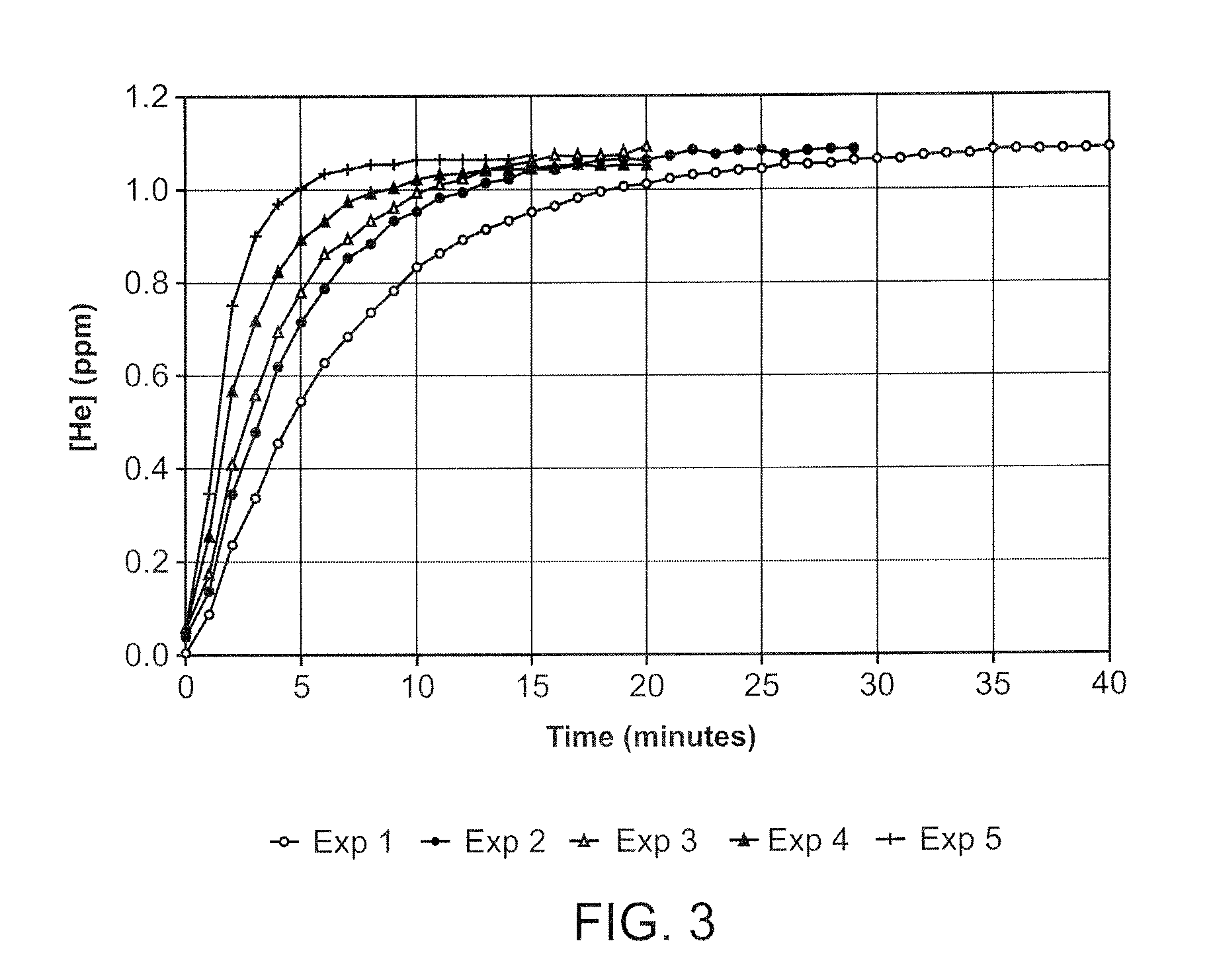
InactiveUS20080281260A1Reduce morbidityLiquid degasification with auxillary substancesJet injection syringesSolubilityDrug capsule
Owner:ZOGENIX INC
Low concentrations of gas bubbles to hinder proppant settling
InactiveUS20100252262A1Low densityReduce sedimentation rateFluid removalFlushingFracturing fluidBuoyancy
Owner:CLEARWATER INT LLC
Method and apparatus for removal of gas bubbles from blood
InactiveUS7488448B2Semi-permeable membranesReversed direction vortexAssisting proceduresAssisted procedure
A system for removing gas bubbles from blood during circulatory assist procedures. An active filter apparatus forces the bubbles to the center of the system where they are removed from the blood before the blood exits the filter.
Owner:INDIAN WELLS MEDICAL
Degassing of molten alloys with the assistance of ultrasonic vibration
InactiveUS20070235159A1Reduce gas contentReduce heat transferMelt-holding vesselsLiquid degasificationNitrogen gasCavitation bubble
An apparatus and method are disclosed in which ultrasonic vibration is used to assist the degassing of molten metals or metal alloys thereby reducing gas content in the molten metals or alloys. High-intensity ultrasonic vibration is applied to a radiator that creates cavitation bubbles, induces acoustic streaming in the melt, and breaks up purge gas (e.g., argon or nitrogen) which is intentionally introduced in a small amount into the melt in order to collect the cavitation bubbles and to make the cavitation bubbles survive in the melt. The molten metal or alloy in one version of the invention is an aluminum alloy. The ultrasonic vibrations create cavitation bubbles and break up the large purge gas bubbles into small bubbles and disperse the bubbles in the molten metal or alloy more uniformly, resulting in a fast and clean degassing.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
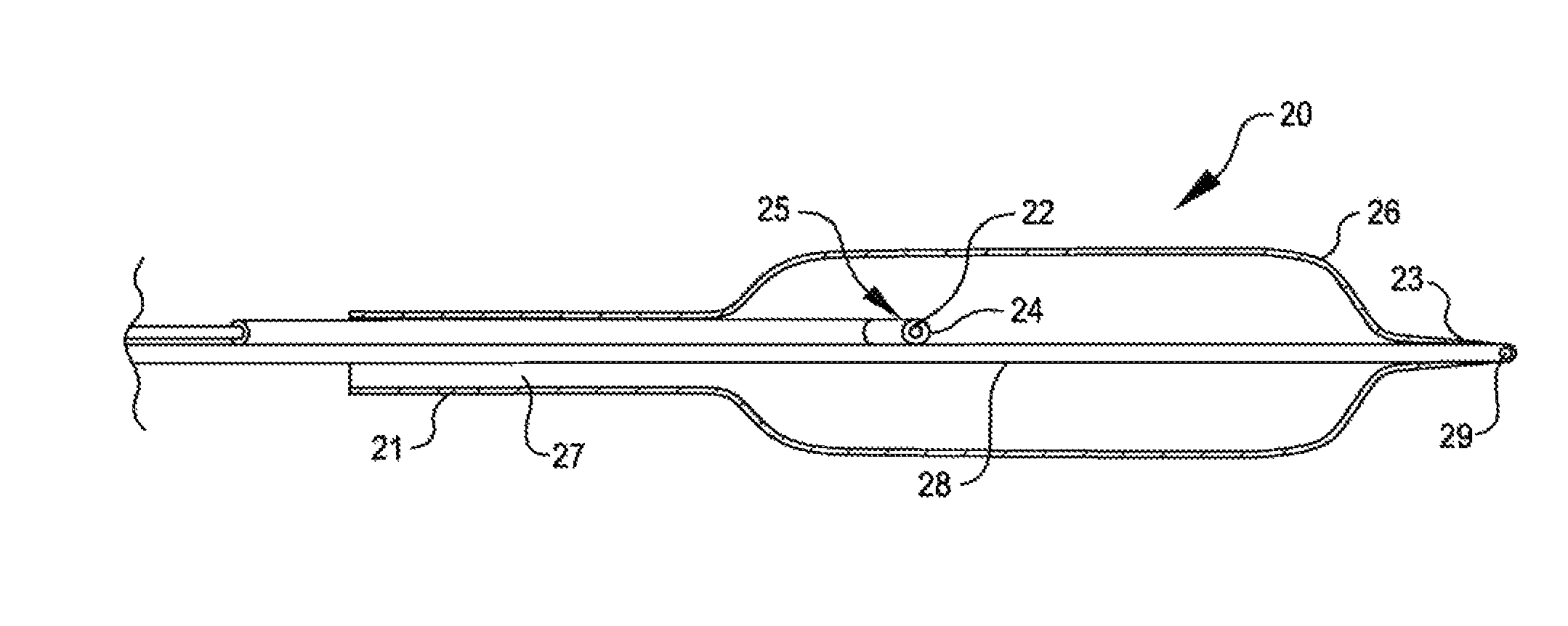
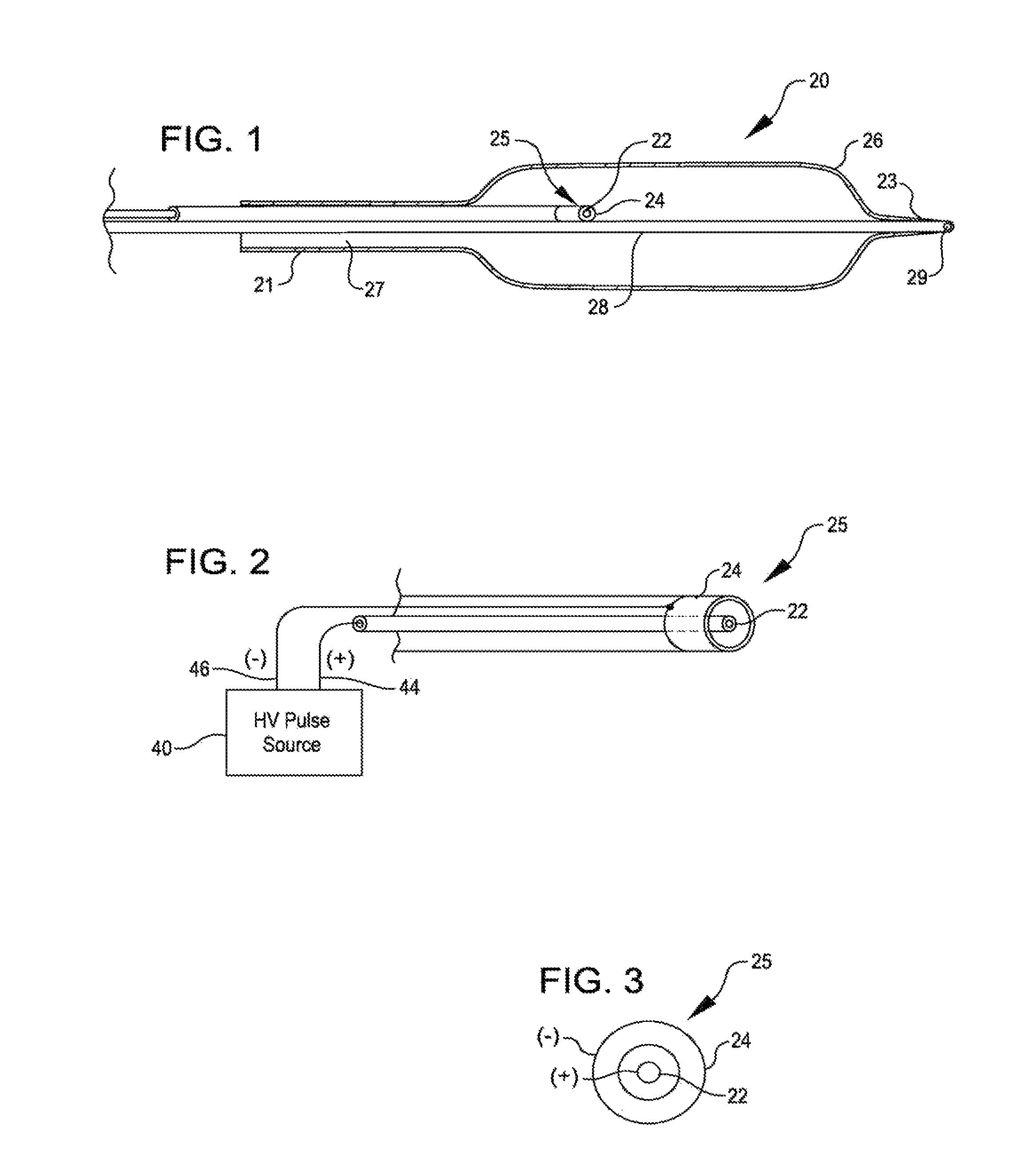
Systems and methods of identifying catheter malfunctions using pressure sensing
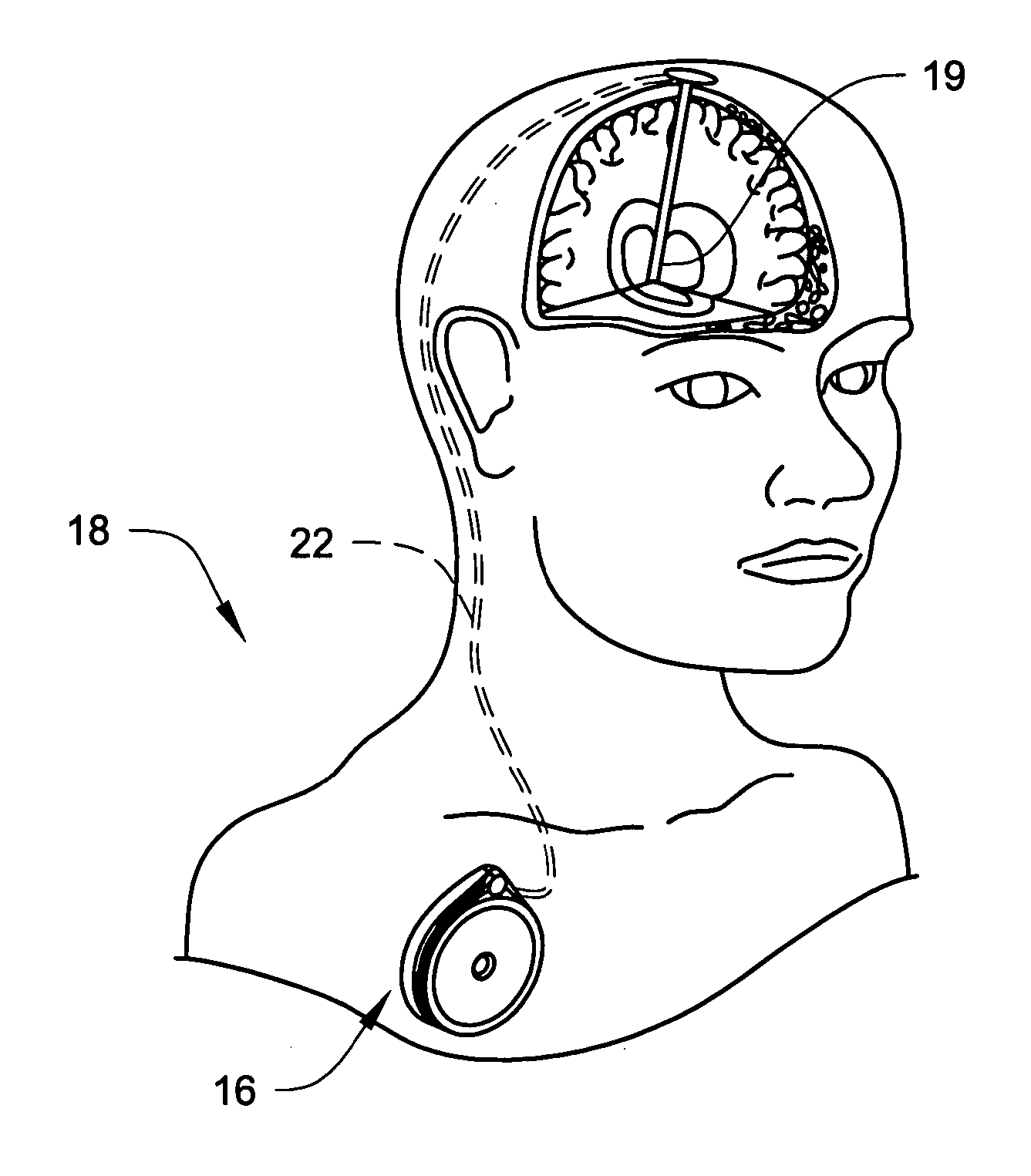
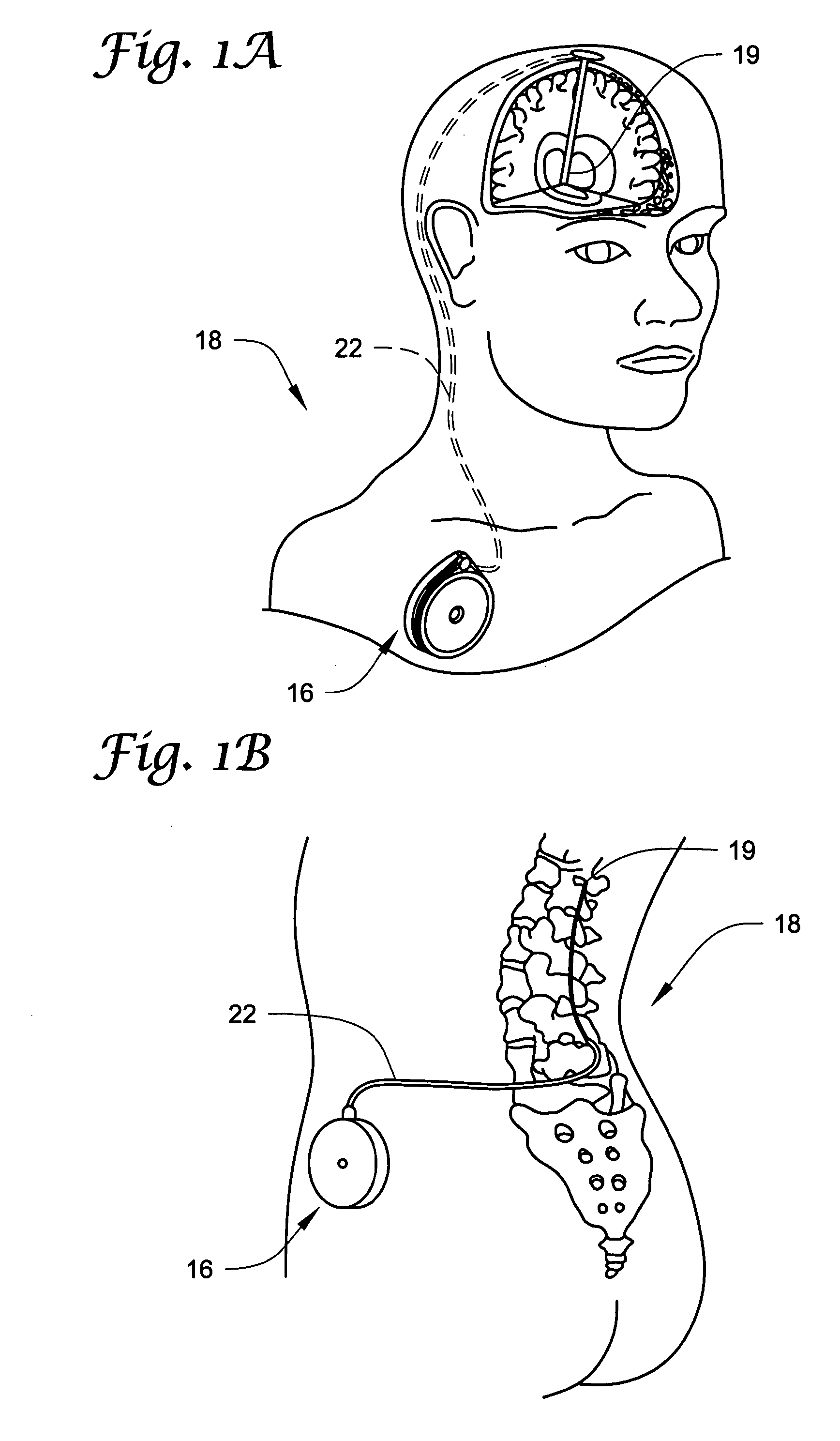
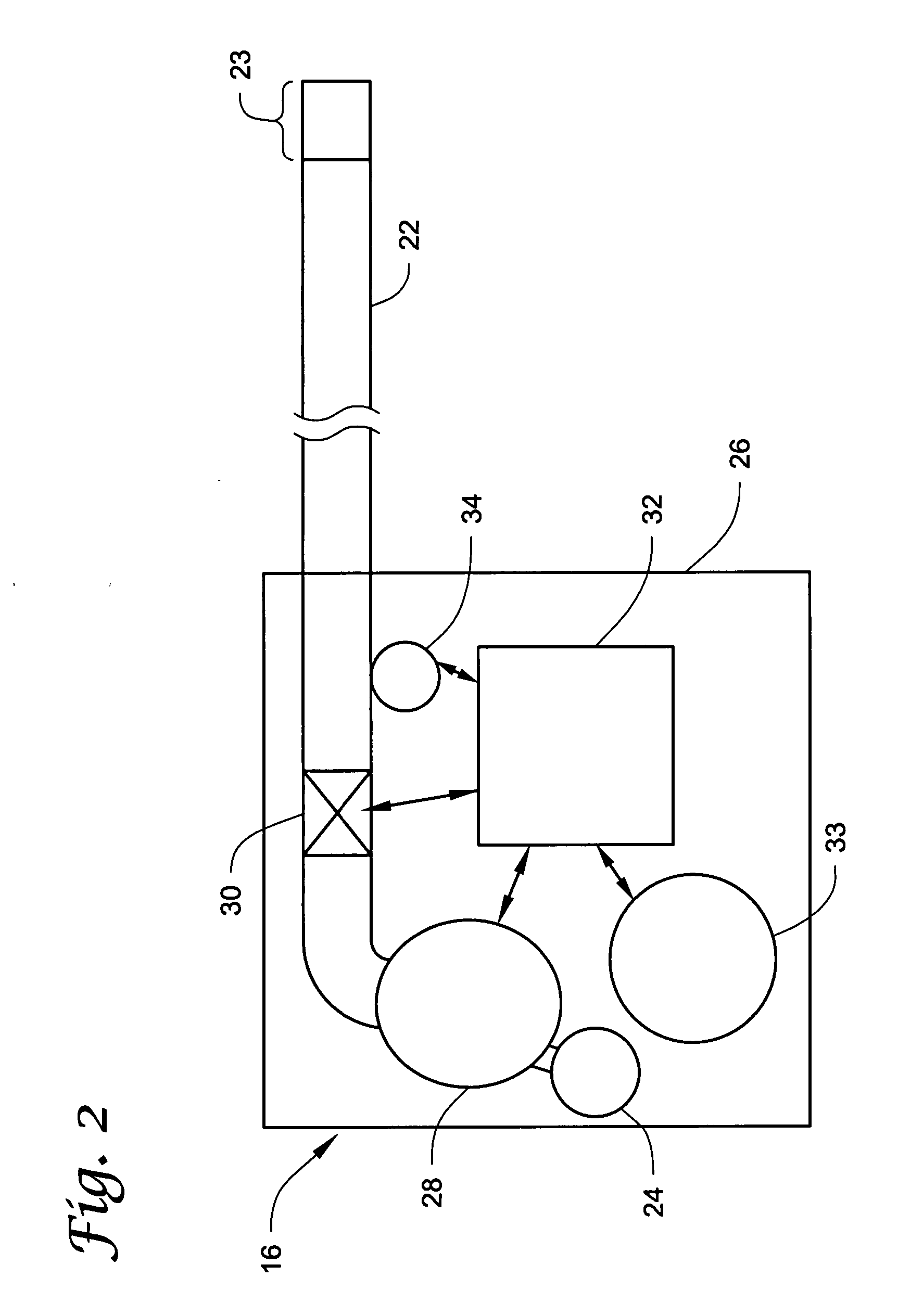
ActiveUS20070270782A1Complete understandingMedical devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismGas bubblePressure decay
Methods and systems for determining whether a catheter malfunction is present in a catheter by analyzing changes in the pressure of fluids being pumped through the delivery lumen of the catheter. The pressure changes that may be monitored may include, e.g., the peak pressure within the catheter and / or the pressure decay profile. The catheter malfunctions that may be determined using the methods and systems of the invention may include, e.g., leaks, blockages, the presence of gas bubbles, etc.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Two-phase flow digital particle image speed measurement method and device
InactiveCN1654962AGood monochromaticityHas a Gaussian distributionDevices using time traversedFluid speed measurementMeasurement deviceSpeed test
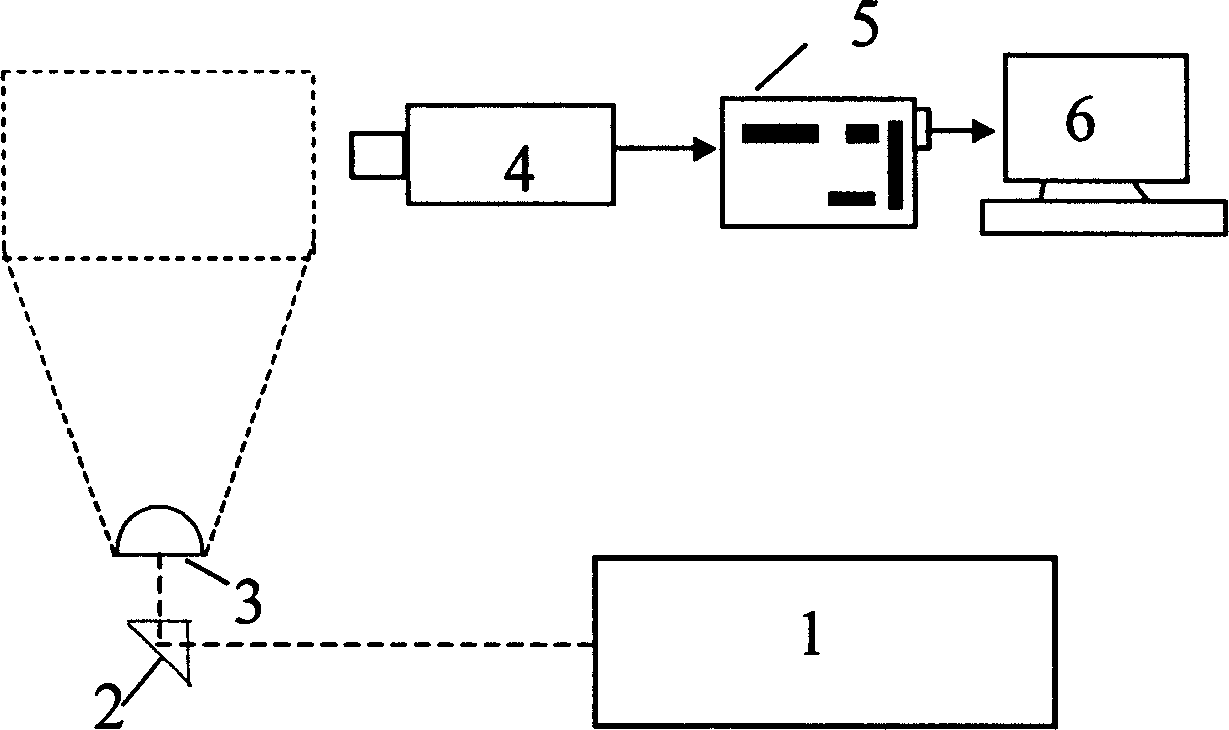
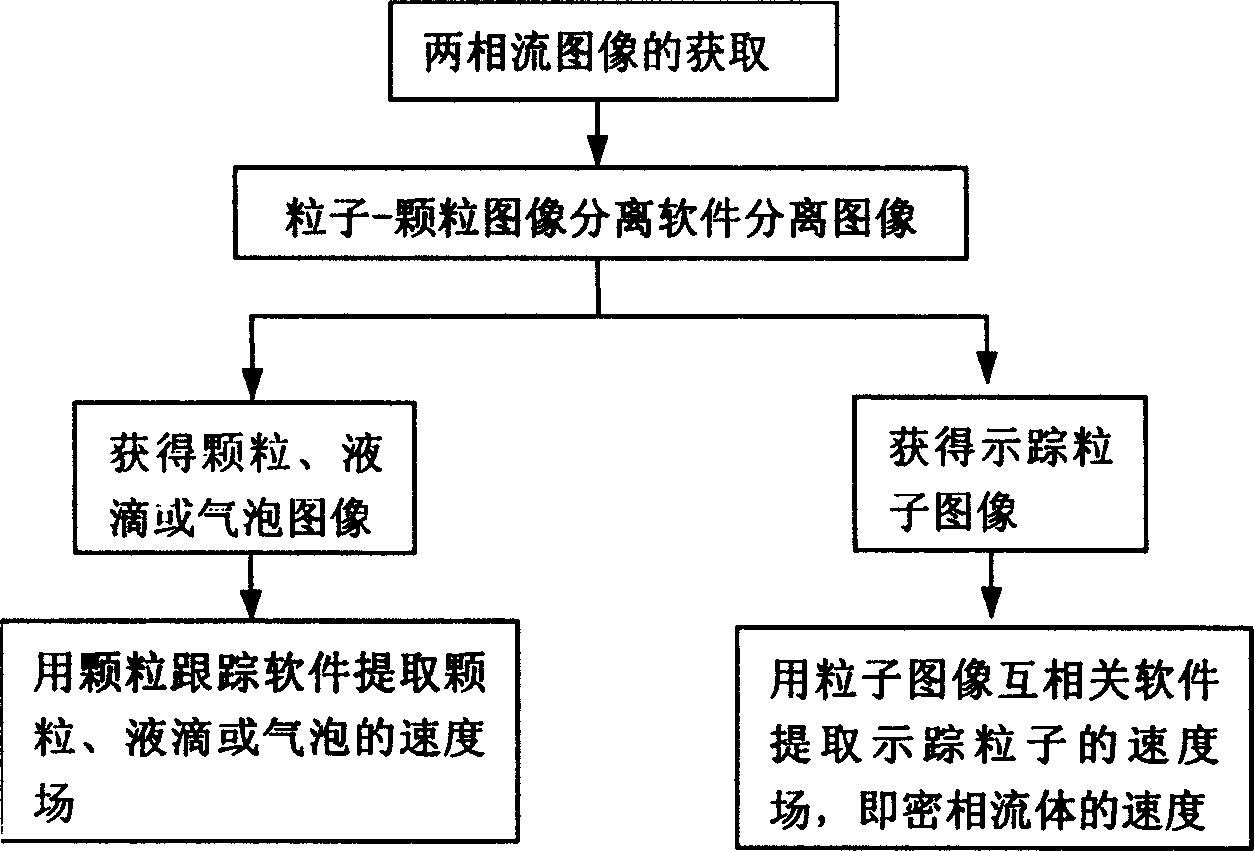
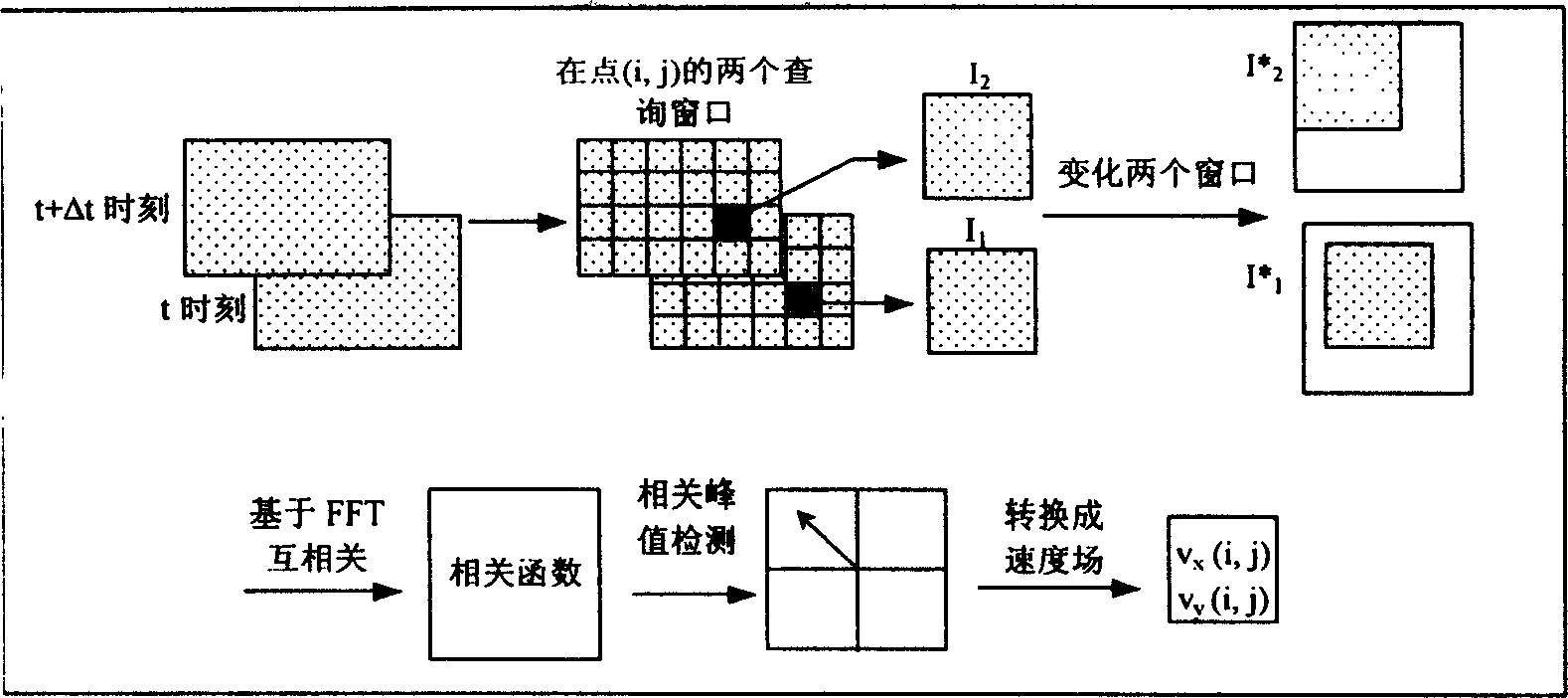
This invention discloses a two-phase flow digital particle image speed test method and its device, which uses suitable particles to trace flow of fluids and uses high speed CCD camera to register motion images for tracing particles, liquid drops or gas bubbles, applies an image process method to separate the images of scattered phase particles drops or bubbles from original images and extracts velocities of them from their images and applies an improved cross correlation technology based on quick Fourier transformation to extract the velocity field of the tracing particles to realize the synchronous measurement to the two phase flows with different phase velocity fields. The device includes a HeNe laser, a triple prism and a cylinder lens, a high speed CCD camera, an image collecting card and a control and image process computer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Shockwave catheter system with energy control
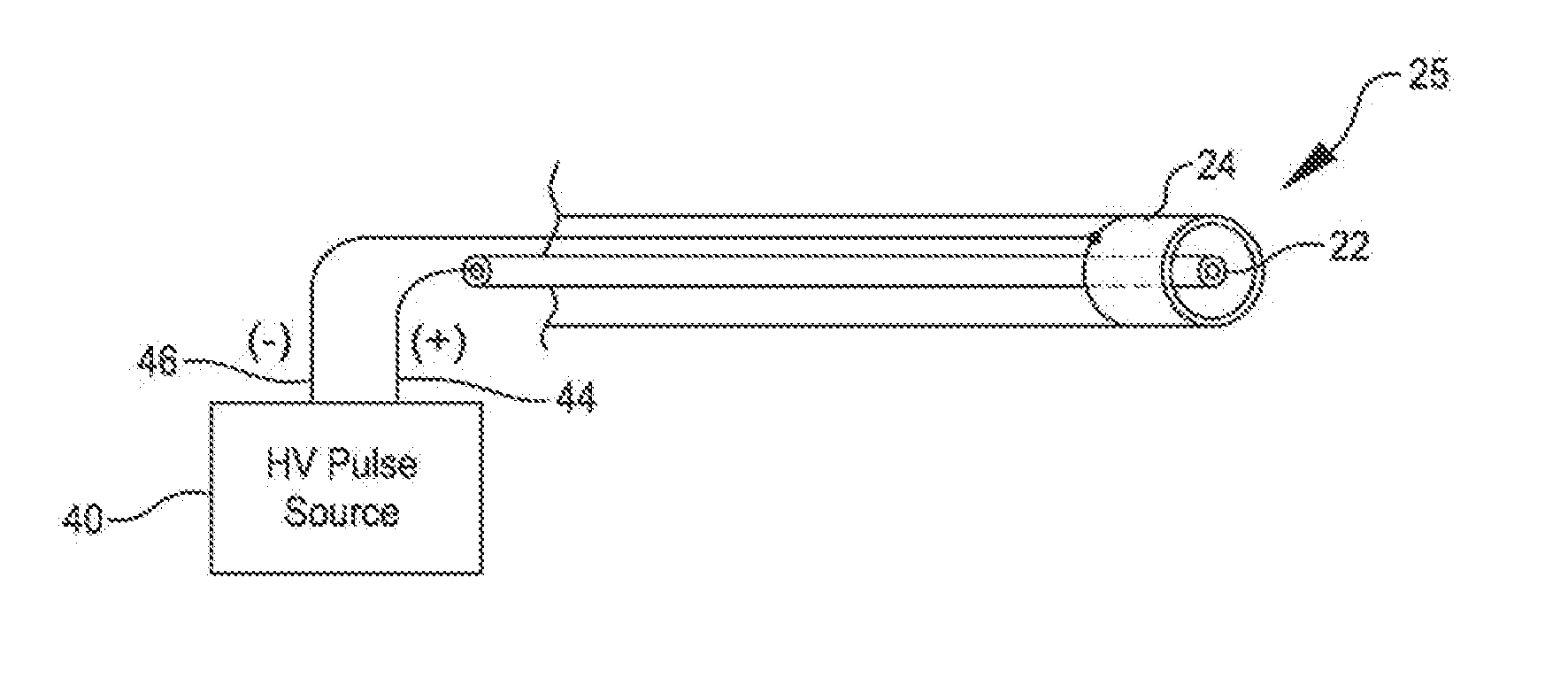
A system includes a catheter including an elongated carrier, a balloon about the carrier in sealed relation thereto, the balloon being arranged to receive a fluid therein that inflates the balloon, and first and second electrodes within the balloon arranged to carry a voltage there-across including an initial high electrical voltage at an initial low current. The initial high electrical voltage causes an electrical arc to form across the first and second electrodes within the balloon. The electrical arc causes a gas bubble within the liquid, a high current to flow through the first and second electrodes, a decrease in the initial high electrical voltage, and a mechanical shock wave within the balloon. The system further includes a power source that provides the first and second electrodes with a drive voltage that creates the initial high electrical voltage at the initial current and that terminates the drive voltage in response to the decrease in the initial high electrical voltage.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
System and method for diffusing gas bubbles into a body of water
InactiveUS6017020ATreatment using aerobic processesTransportation and packagingAbove groundWhole body
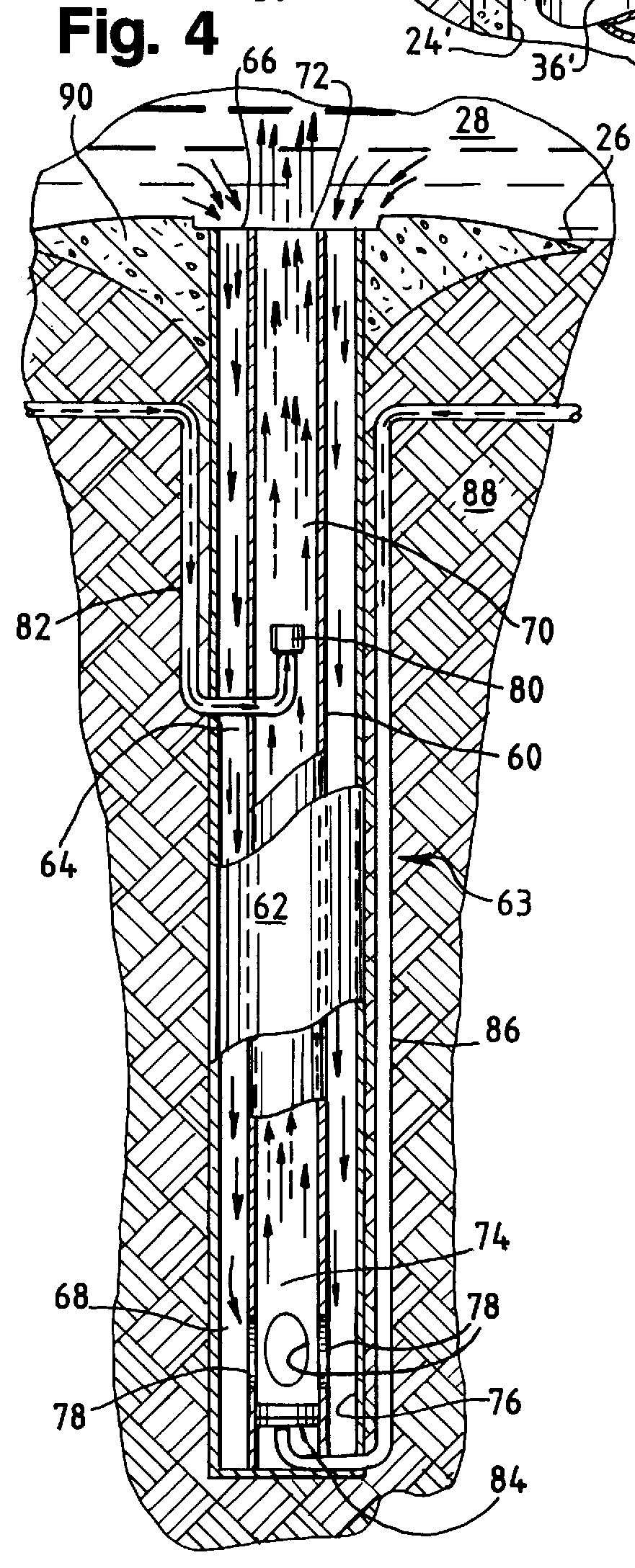
System and method for diffusing gas bubbles into a pond, lagoon or basin that is used for fish farming or other form of aquaculture. A small amount of water is continuously removed from the bottom of the body of water by one or more counterflow gas lift diffusers. This small amount of water is flowed down underground, has gas bubbles introduced into it, and is then returned to the body of water. The quantity of water removed and treated in this way is a small fraction of the total body of water in the pond, lagoon or basin. The ratio of (1) the total volume of the channels below ground through which the water flows downward, and then back up into the body of water, to (2) the volume of the body of water above ground is at all times less than about 1:100. In the broadest form of the invention, a gas diffuser introduces gas bubbles into the water in the return channel at a level at least about 2 feet below the bottom of the body of water, and no more then about 50 feet below the surface of the body of water being treated. The downflow and return channels and the space joining them at their bottom ends extend no more than about 50 feet below the surface of the water being treated.
Owner:BAUGHMAN MICHAEL L +1
Apparatus and method for cleaning membrane filtration modules
InactiveUS20050109692A1Easy to cleanLimit amplitudeSemi-permeable membranesMembranesFiltrationPorous membrane
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
Ferrographic method
InactiveUS6156208AAccelerated dissipationReduce adventitious depositionWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansMagnetic field gradientFree interface
A ferrographic apparatus and method incorporate a priming operation that moves a priming fluid, in a direction opposite to the flow direction subsequently followed by the sample fluid, through a fluid pathway including the flow chamber. The fluid pathway is configured to facilitate dissipation of any gas bubble introduced into it during the priming operation and to reduce adventitious deposition of specimen material at locations other than the substrate. Sample fluid to be analyzed is added to the reservoir so as to form a bubble-free interface with the priming fluid, and the direction of movement through the flow chamber is reversed. The resulting continuous fluid column is advanced through the fluid pathway so that the sample fluid enters the flow chamber through the inlet port and passes through the magnetic field gradient, exiting through an orifice at the opposite end of the flow chamber serving as the outlet port. The flow chamber of the ferrograph is preferably contained in a deposition cassette comprising the substrate, a gasket and a platen which incorporates an integral fluid reservoir in communication with the inlet port. A pump is preferably configured to move each liquid through the fluid pathway at a distinct flow rate and in a direction according to the function performed by the respective liquid.
Owner:INST GUILFOYLE
Method and apparatus for controlled transient cavitation
InactiveUS20060060991A1Rapid pressure dropMixing methodsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCavitationGas bubble
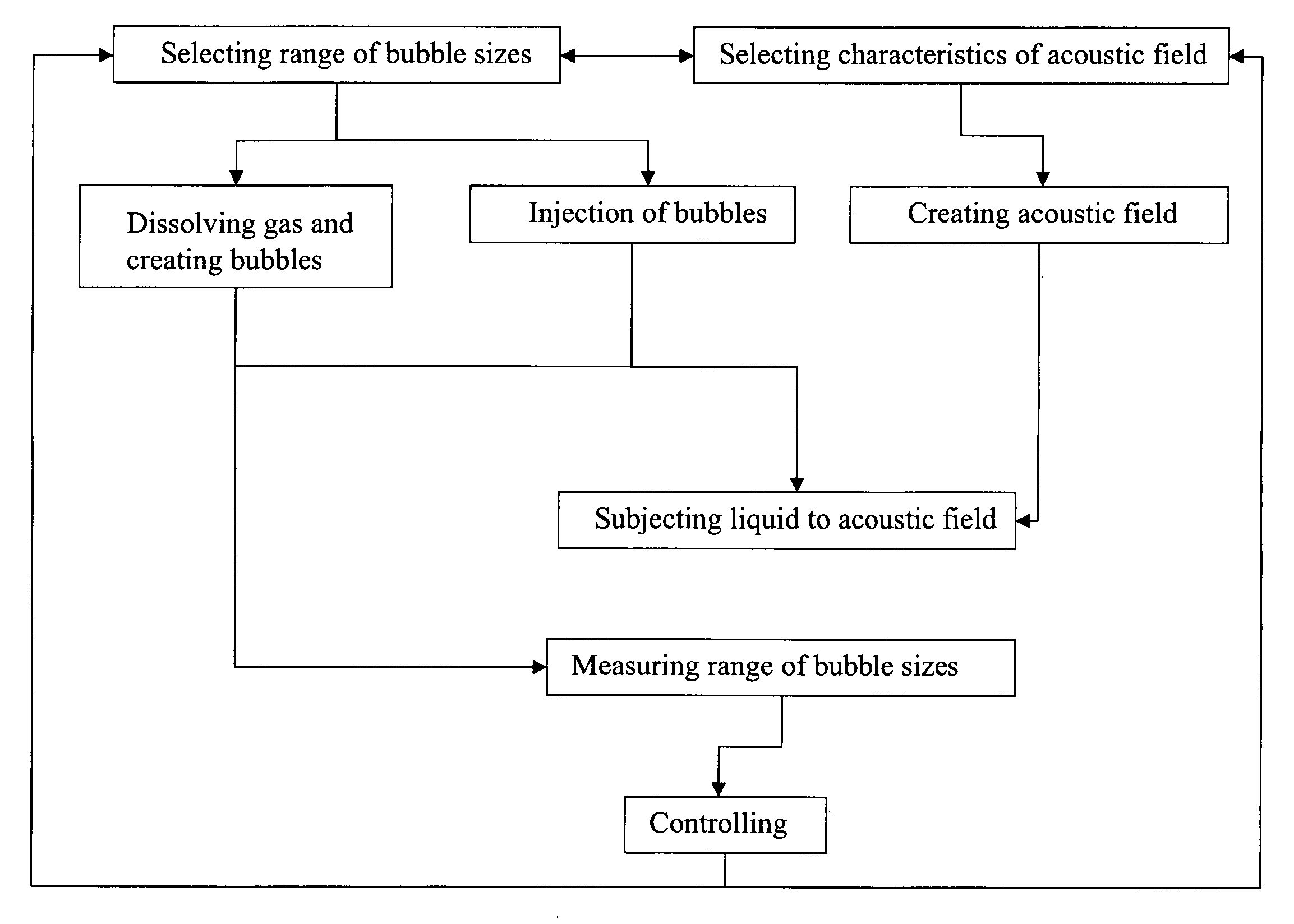
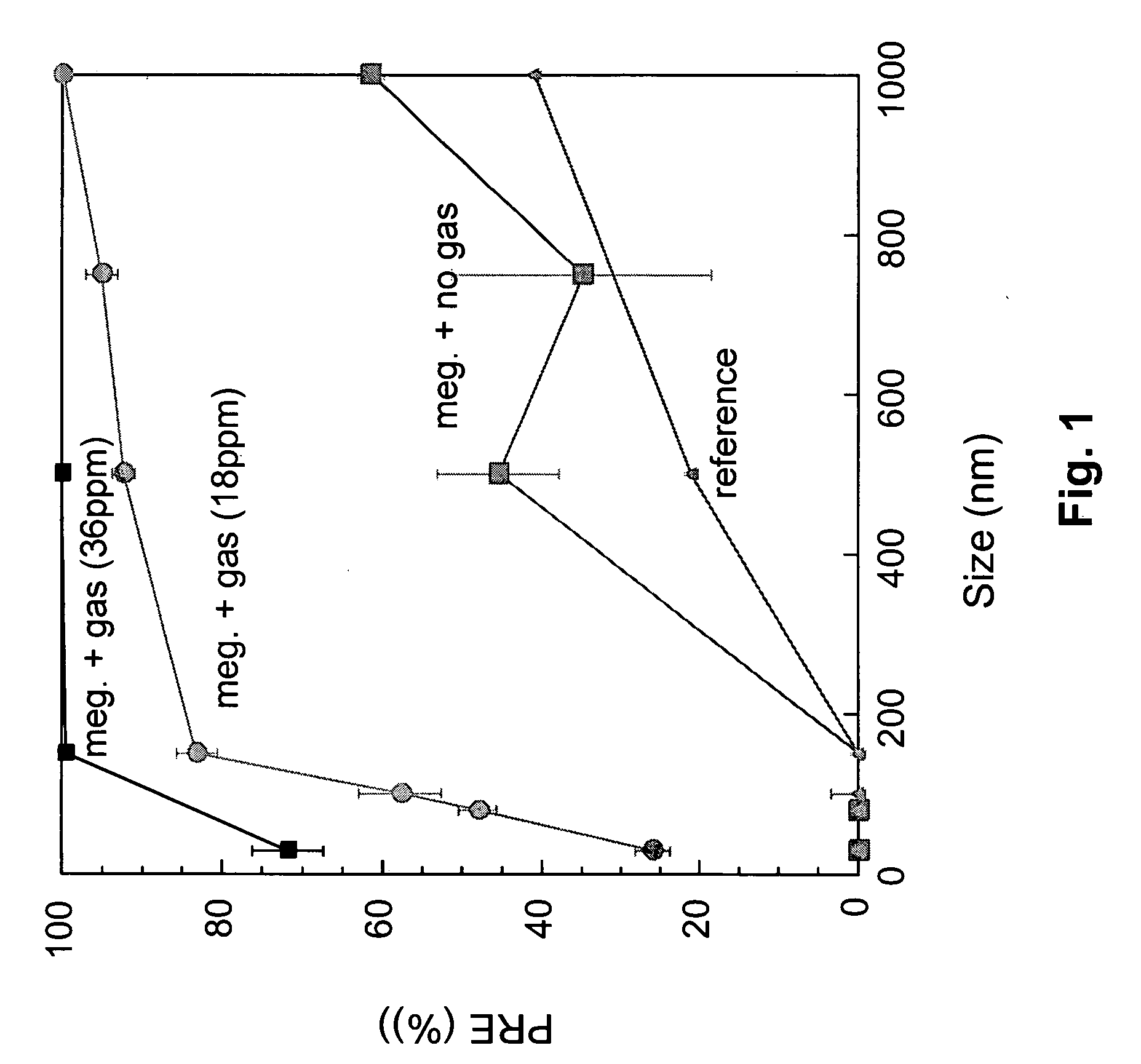
The invention relates to a method for creating transient cavitation comprising the steps of creating gas bubbles having a range of bubble sizes in a liquid, creating an acoustic field and subjecting the liquid to the acoustic field, characterized in that the range of bubble sizes and / or the characteristics of the acoustic field are selected to tune them to each other, thereby controlling transient cavitation in the selected range of bubble sizes. It also relates to an apparatus suitable for performing the method according to the invention.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Solenoid cassette pump with servo controlled volume detection
InactiveUS6942469B2Eliminate closure impactEliminate associated noiseAC motor controlElectrical controlResonance measurementDriving current
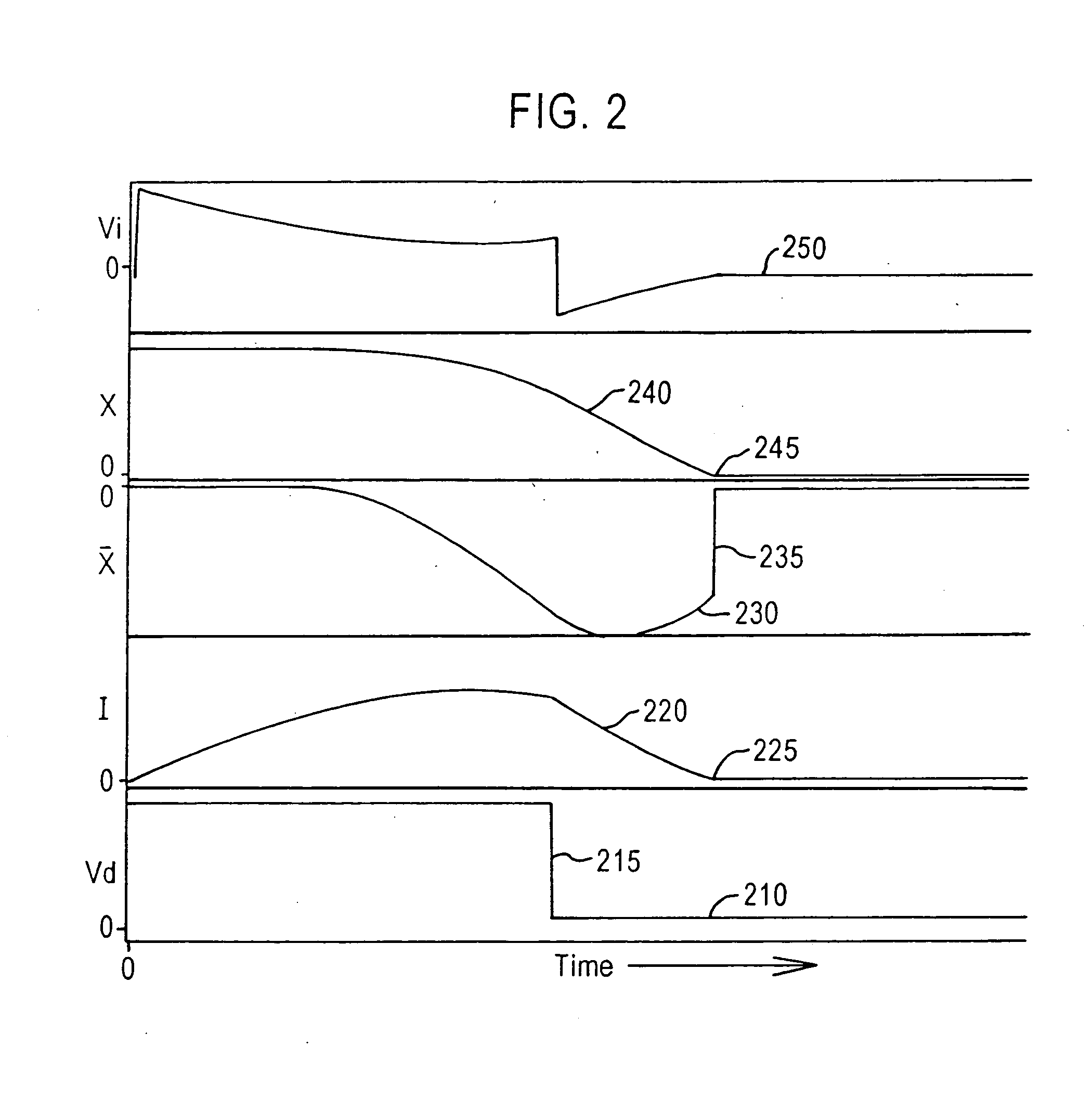
Servo controlled solenoids provide actuation of a pump piston and valves, and electronic LC resonance measurements to determine liquid volume and gas bubble volume. Third order nonlinear servo control is split into nested control loops: a fast nonlinear first-order inner loop causing flux to track a target by varying a voltage output, and a slower almost linear second-order outer loop causing magnetic gap to track a target by controlling the flux target or the inner loop. The inner loop uses efficient switching regulation, preferably based on controlled feedback instabilities, to control voltage output. The outer loop achieves damping and accurate convergence using proportional, time-integral, and time-derivative gain terms. The time-integral feedback may be based on measured and target solenoid drive currents, adjusting the magnetic gap for force balance at the target current.
Owner:THISTLE ADVISORS
Method and apparatus for sanitizing water dispensed from a water dispenser having a reservoir
ActiveUS7422684B1Space heating and ventilationUsing liquid separation agentEnvironmental engineeringGas bubble
A method and apparatus of sanitizing drinking water to be dispensed from a water dispenser having a reservoir includes the steps of providing the ozone gas generator that generates an ozone gas stream, transmitting the ozone gas stream from the generator to the water dispenser reservoir, mechanically breaking up the ozone gas stream inside the reservoir to produce ozone gas bubbles, and using the ozone gas bubbles to disinfect water in the reservoir. The ozone gas stream can be mechanically broken up using a pump such as, for example, an impeller type pump.
Owner:S I P TECH L L C
Method for contacting large volumes of gas and liquid across microscopic interfaces
InactiveUS6918949B1Improve efficiencyReduced spatial separationCarburetting airLiquid degasificationPorous mediumTransfer procedure
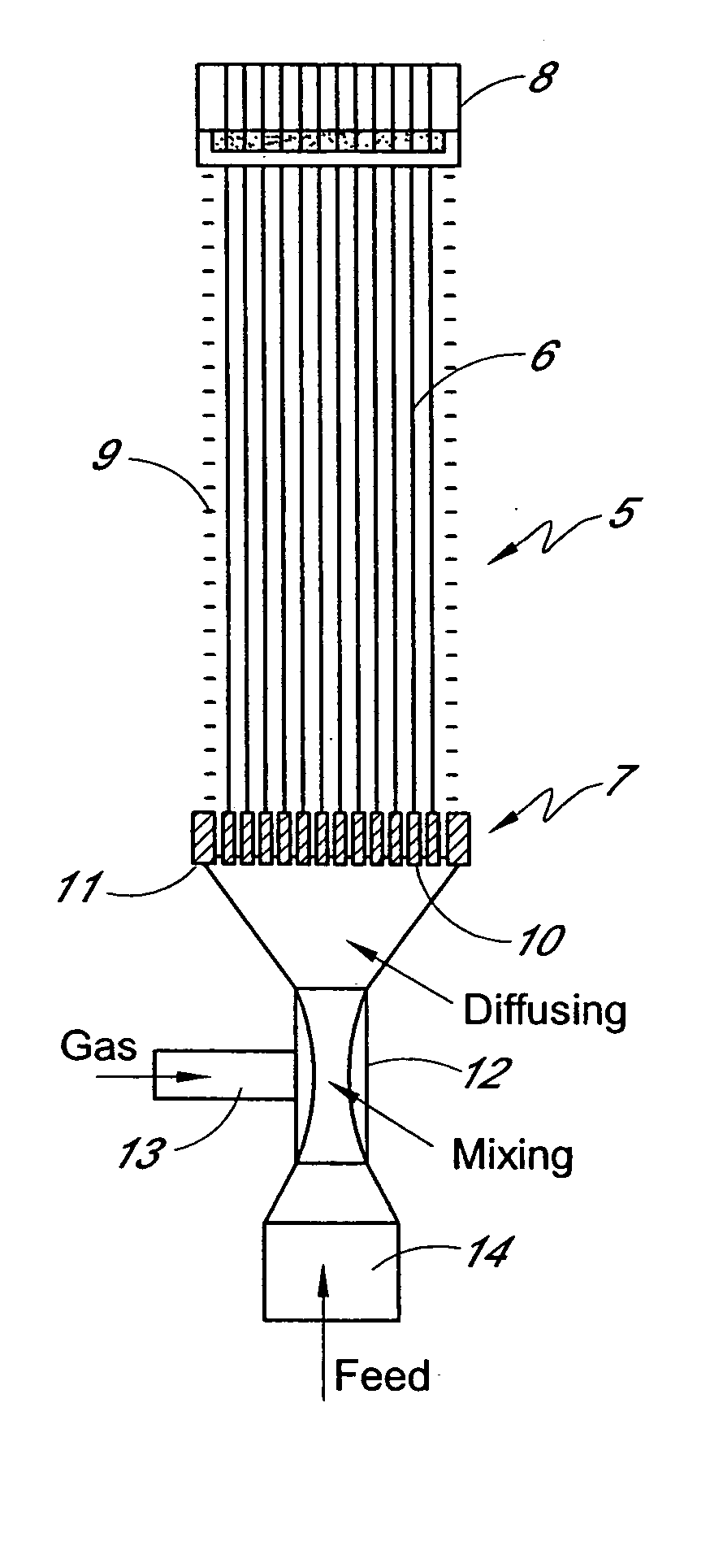
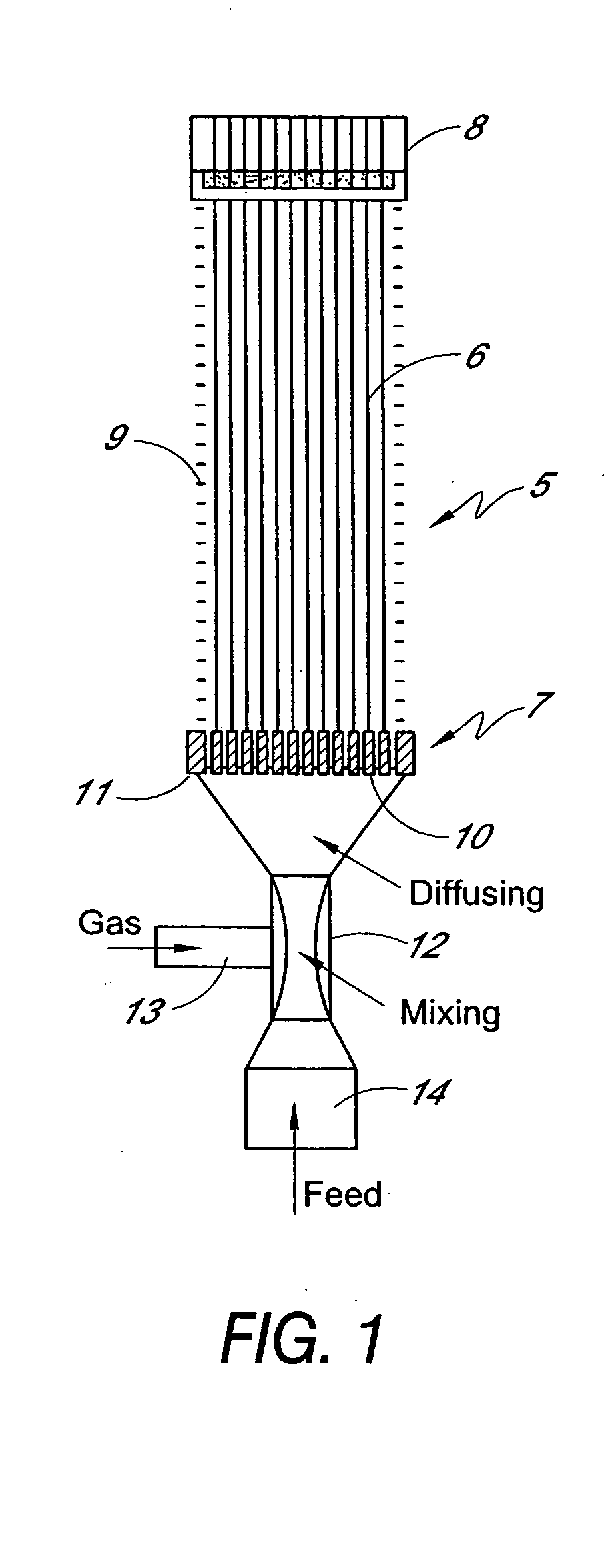
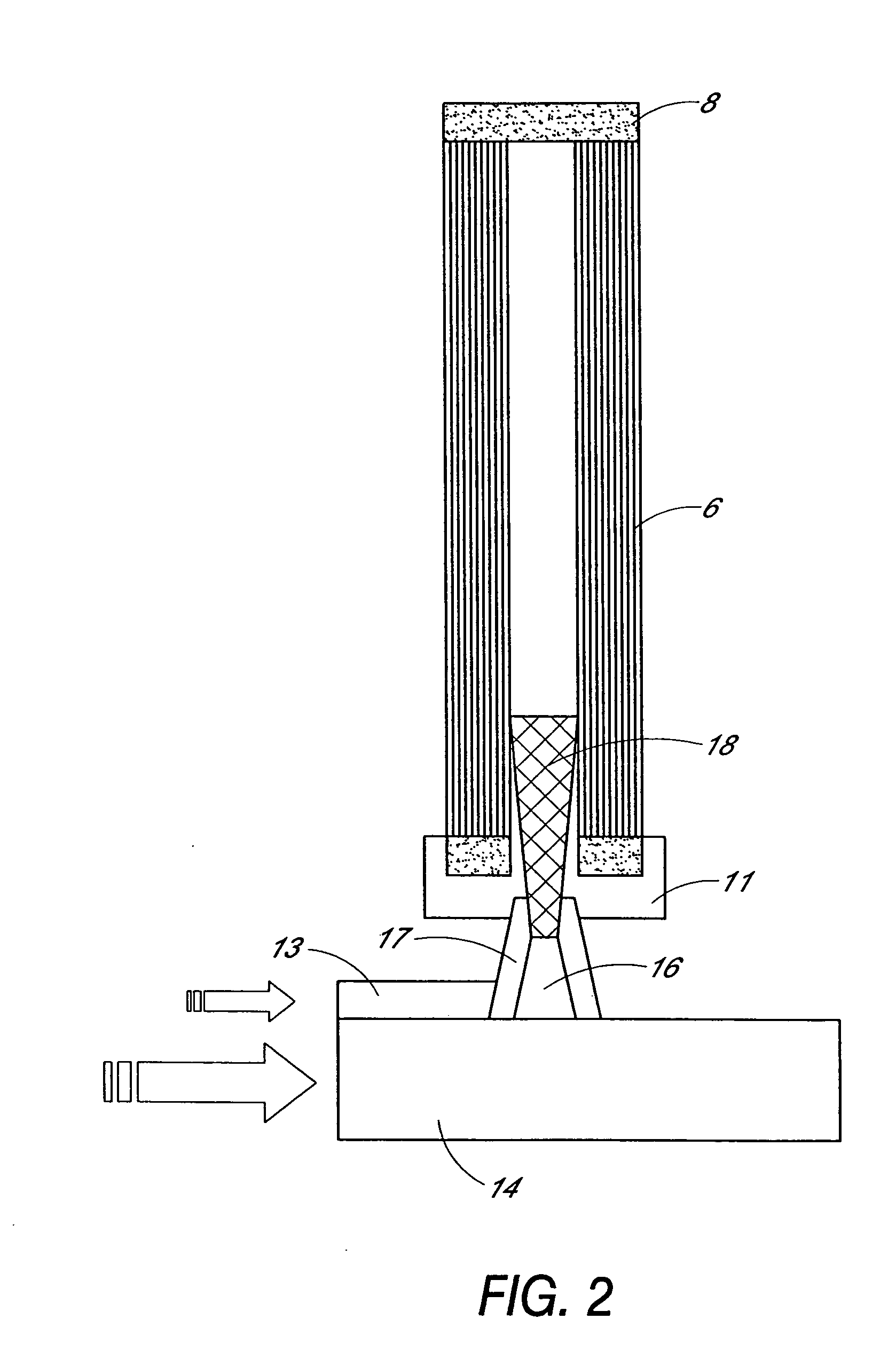
A method for contacting large volumes of gas and liquid together on a microscopic scale for mass transfer or transport processes wherein the contact between liquid and gas occurs at the interfaces of a multitude of gas bubbles. Multiple porous tubes assembled in a bundle inside a pressure vessel terminate at each end in a tube sheet. A thin film helical liquid flow is introduced into the inside of each porous tube around and along its inside wall. Gas is sparged into the porous media and the liquid film so that an annular two phase flow with a uniform distribution of tiny gas bubbles results. The gas flow is segregated from the liquid flow without first passing through the porous media and through the liquid film. Nozzles at the lower end of the tubes divert liquid flow to a vessel and redirect the gas flow in a countercurrent direction.
Owner:JAECO TECH
Optical members and devices employing the same
InactiveUS20120057100A1Light utilization efficiency can be improvedThe process is simple and fastProjectorsOptical articlesEngineeringMicro lens array
There are provided optical members having a microlens array structure that can be produced by a more simple process, as well as devices employing them. The optical members have on one main surface a microlens array formed using a replication process that employs a mold comprising a plurality of gas bubbles arranged on a replication surface. There are also provided devices that employ the optical members.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Removing bubbles in microfluidic systems
ActiveUS20150209783A1Avoid problemsReduce evaporation lossBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorous membraneEvaporation
A microfluidic system includes a microfluidic device connected to a bubble trap device whereby fluid flowing to the microfluidic device passes through the bubble trap device to remove gas bubbles prior to entering the microfluidic device. The bubble trap can include a separation chamber and an exhaust chamber separated by a hydrophobic porous membrane and gas bubbles in the fluid entering the separation chamber pass through the hydrophobic porous membrane into the exhaust chamber while the fluid remains in the separation chamber. The bubble trap can be formed by bonding a first body portion to a first side of the hydrophobic porous membrane and bonding a second body portion to a second side of the hydrophobic porous membrane. The exhaust chamber can be connected to an elongated exhaust channel that limits the evaporation losses of the fluid through the hydrophobic porous membrane.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
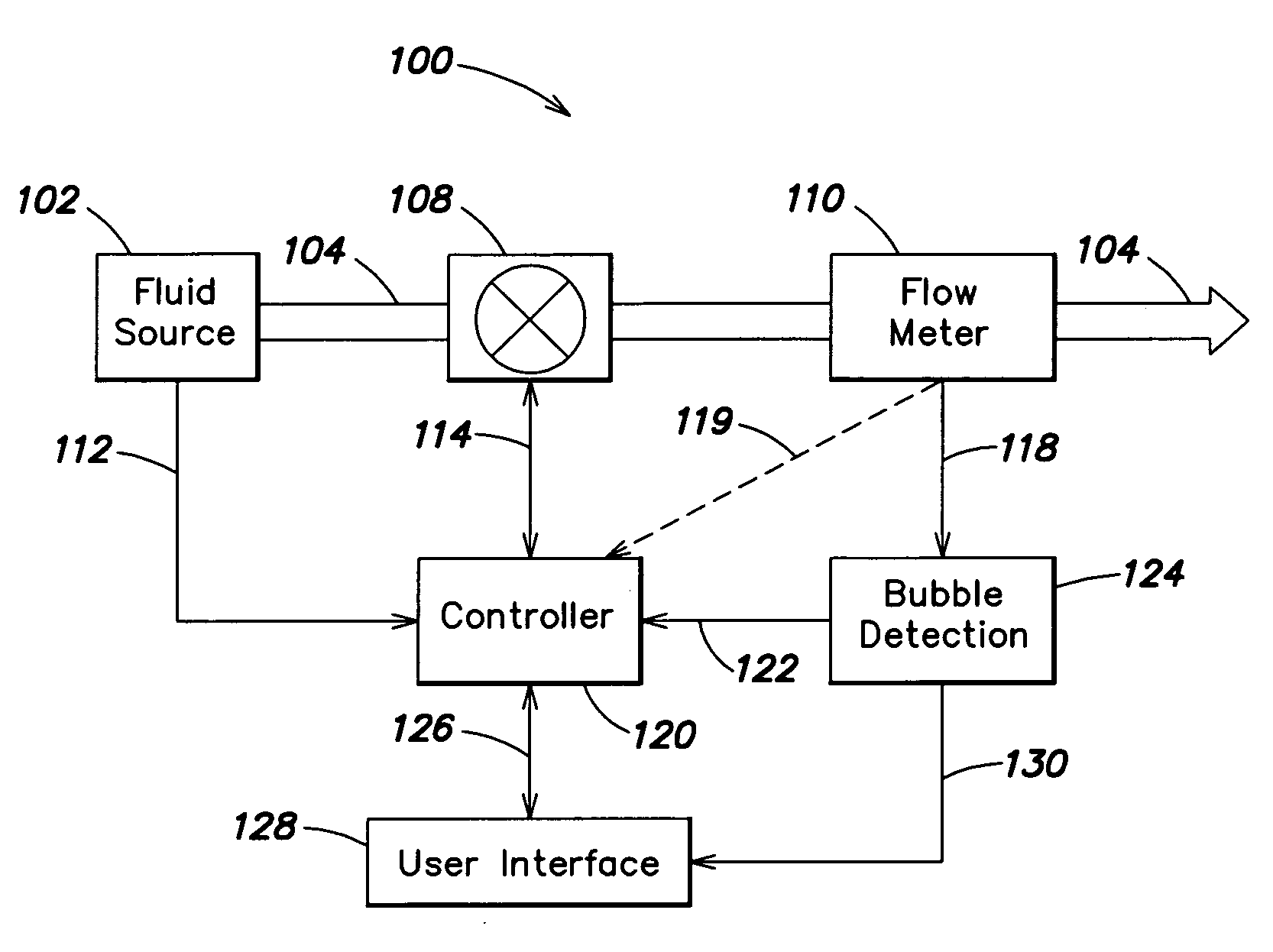
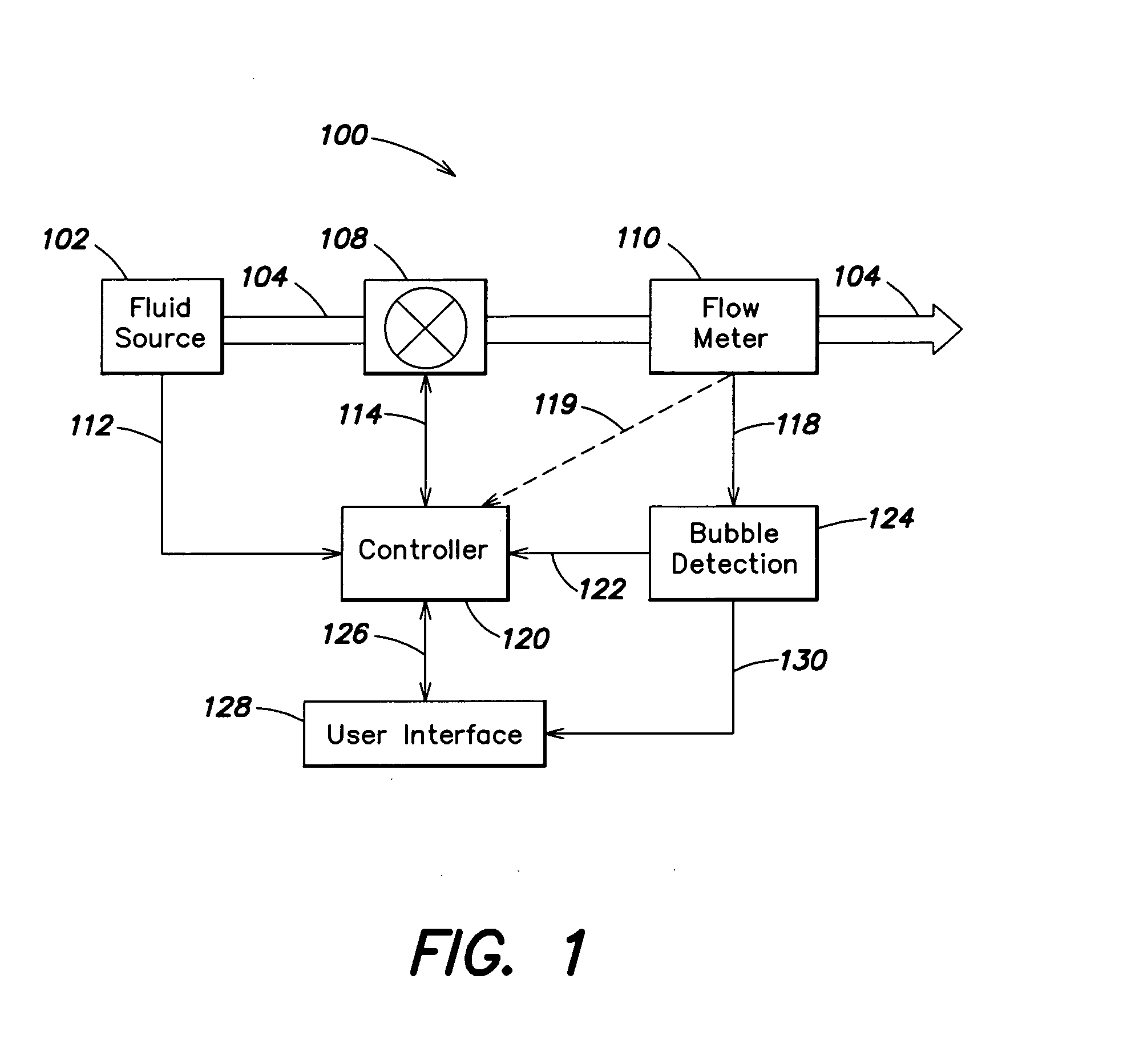
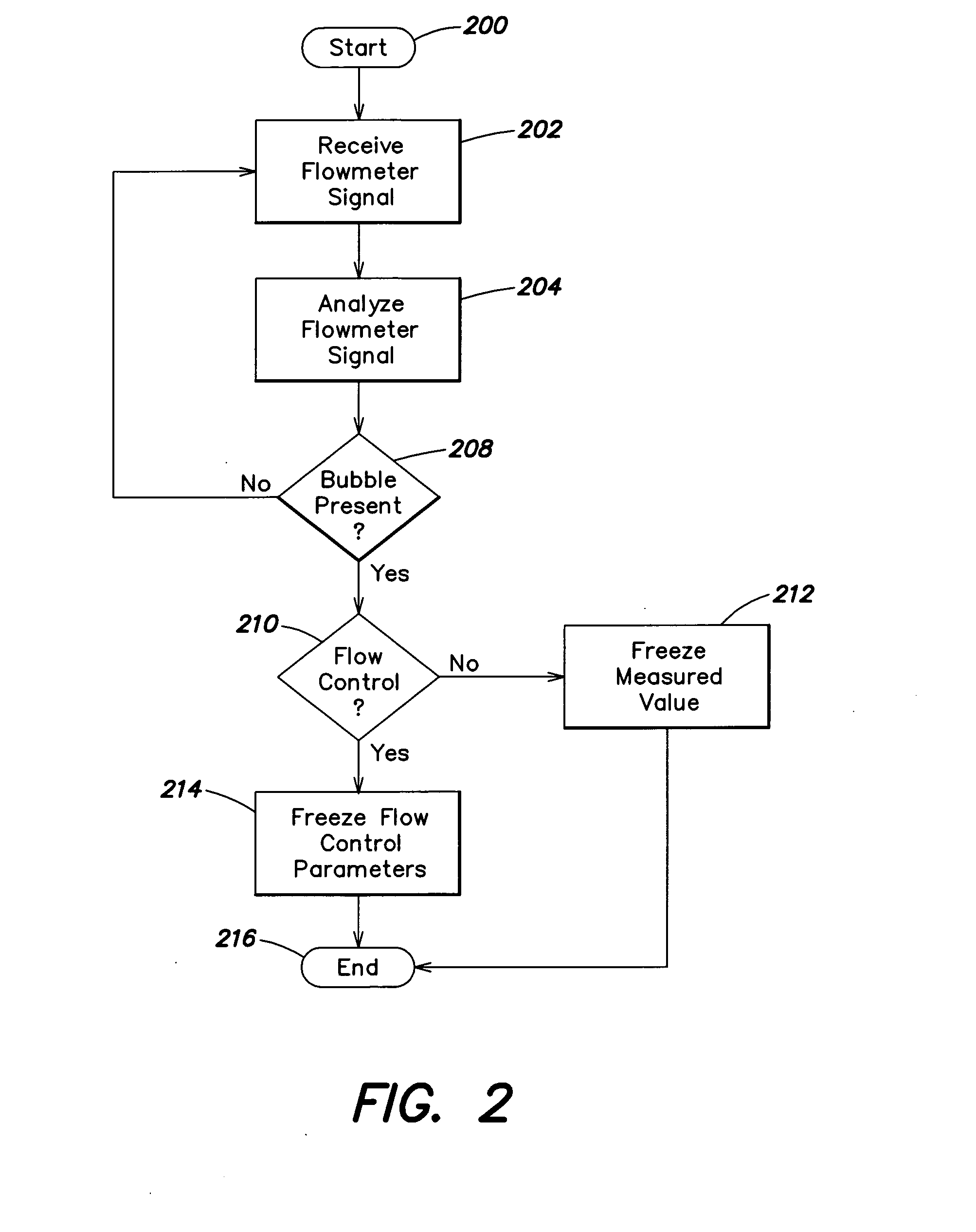
Flow measurement and control with bubble detection
InactiveUS20070191990A1Guaranteed uptimeMinimize impactVolume/mass flow measurementTesting/calibration for volume flowFlow transducerControl system
Systems and methods for liquid flow sensing and control for use with a variety of different types of liquid flow measurement and control systems. The liquid flow sensor system senses a flow signal indicative of the flow rate of the liquid flowing in a sensor conduit and analyzes the flow signal to determine, by detecting characteristic changes in the signal, whether a bubble is present in the sensor conduit. Where the system determines that a bubble is present, it may generate an alarm signal indicative of the presence of the bubble. A flow control system incorporating the flow sensor as a feedback source may respond to the detection of a bubble by temporarily freezing the flow control parameters until the bubble has exited the sensor conduit. The flow control system can implement procedures for clearing a bubble from the sensor conduit where the system detects that the bubble has become stuck.
Owner:CELERITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com