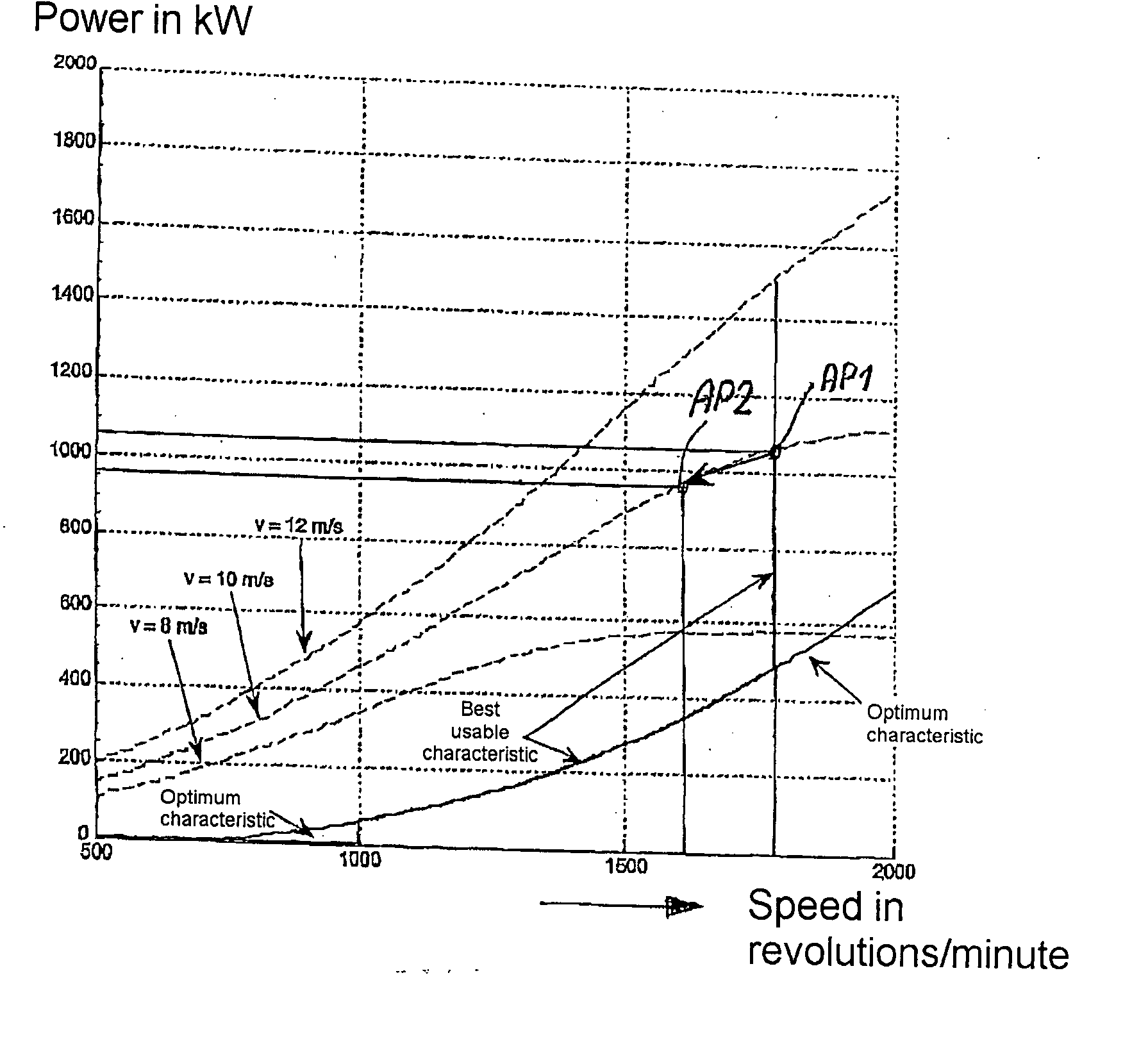
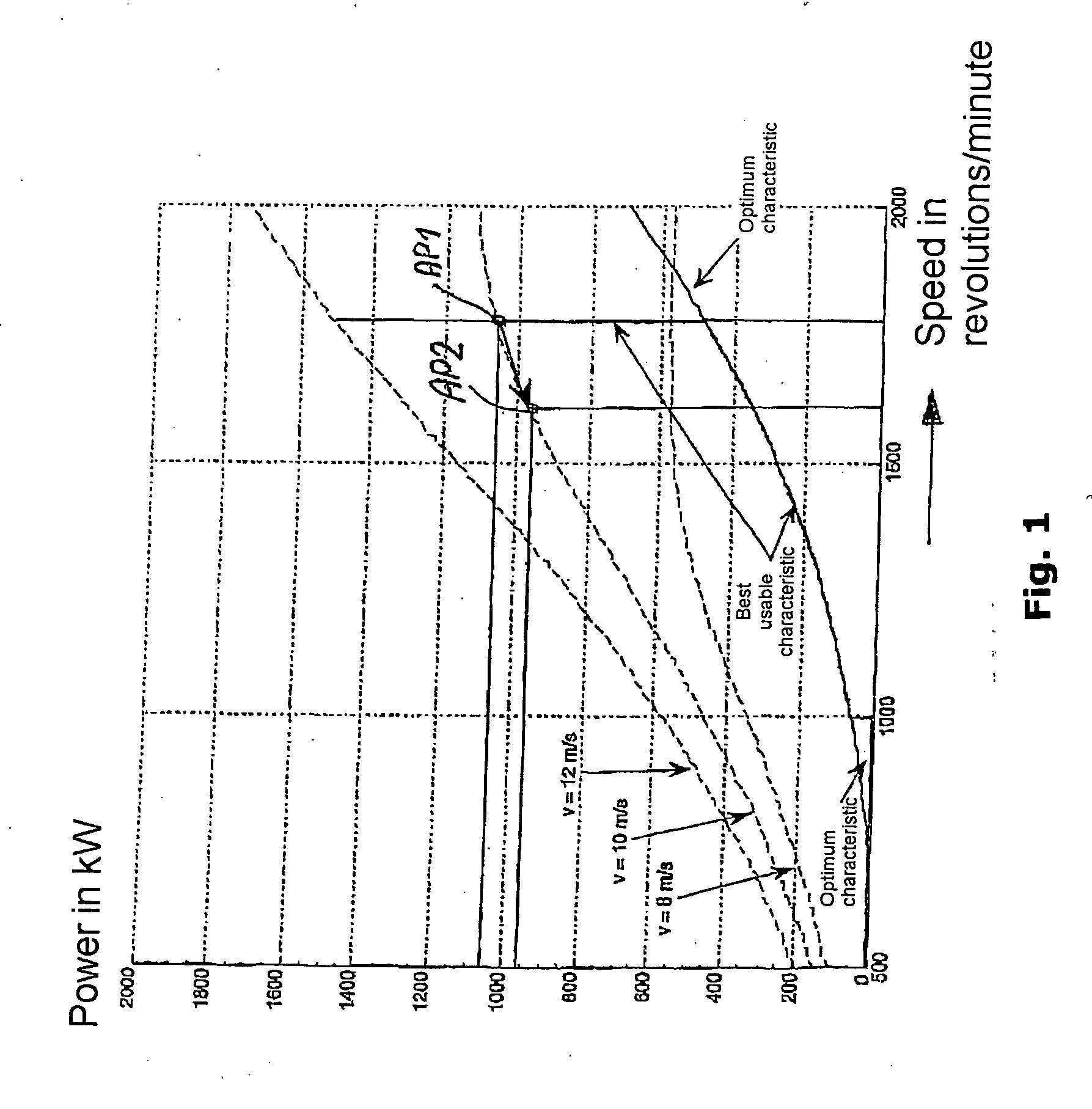
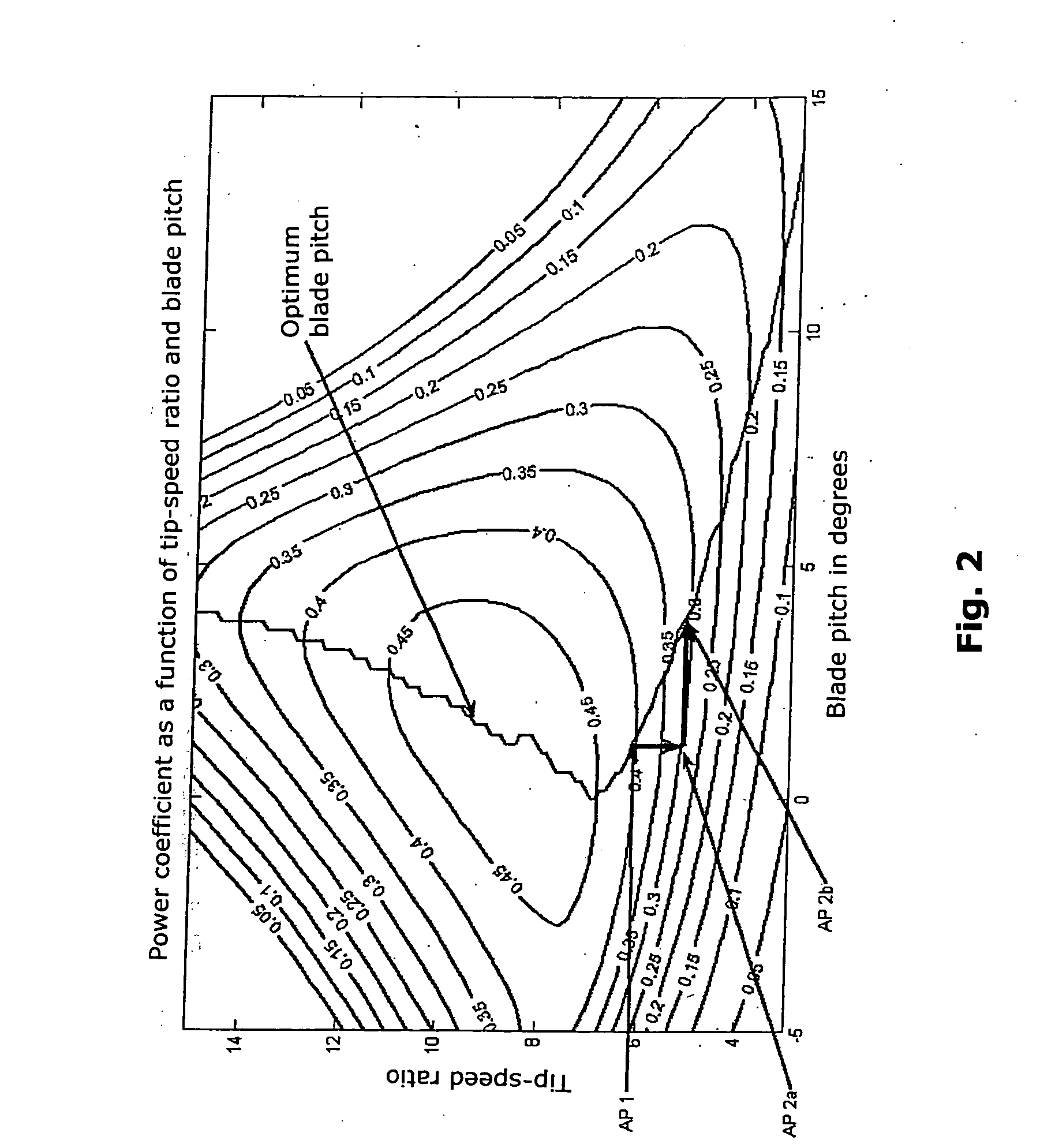
Patents
Literature
310results about "Control to cope with emergencies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
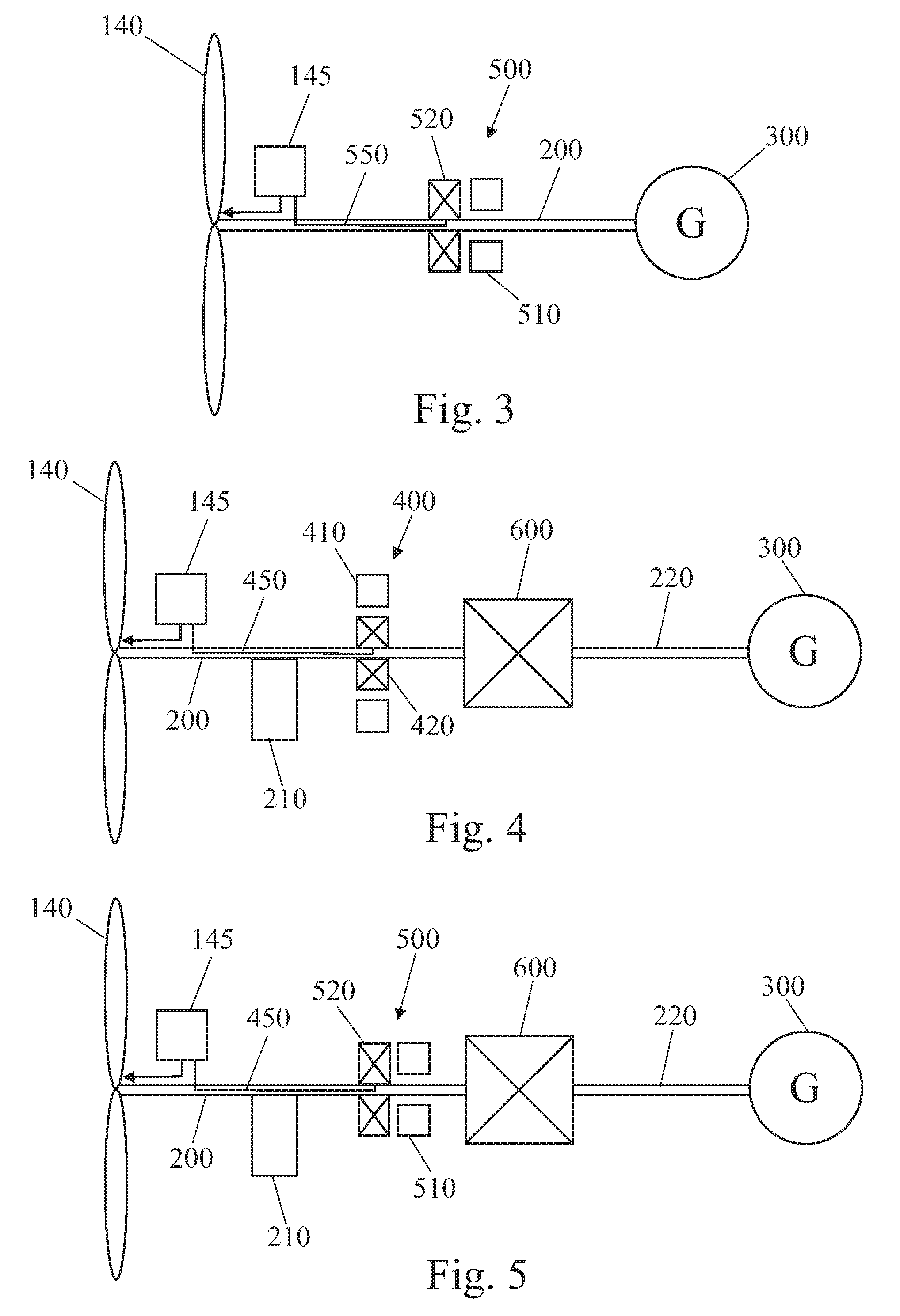
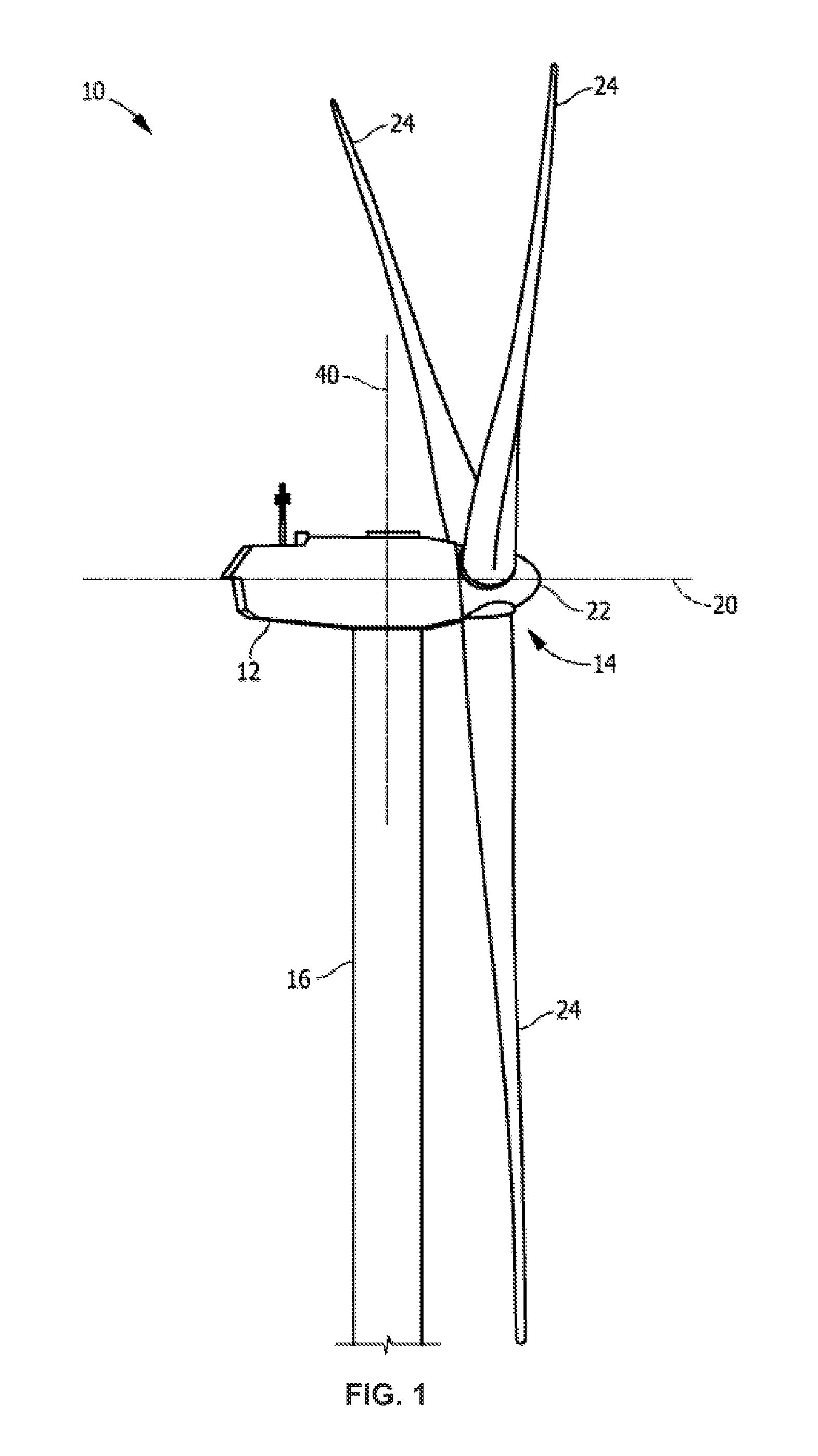
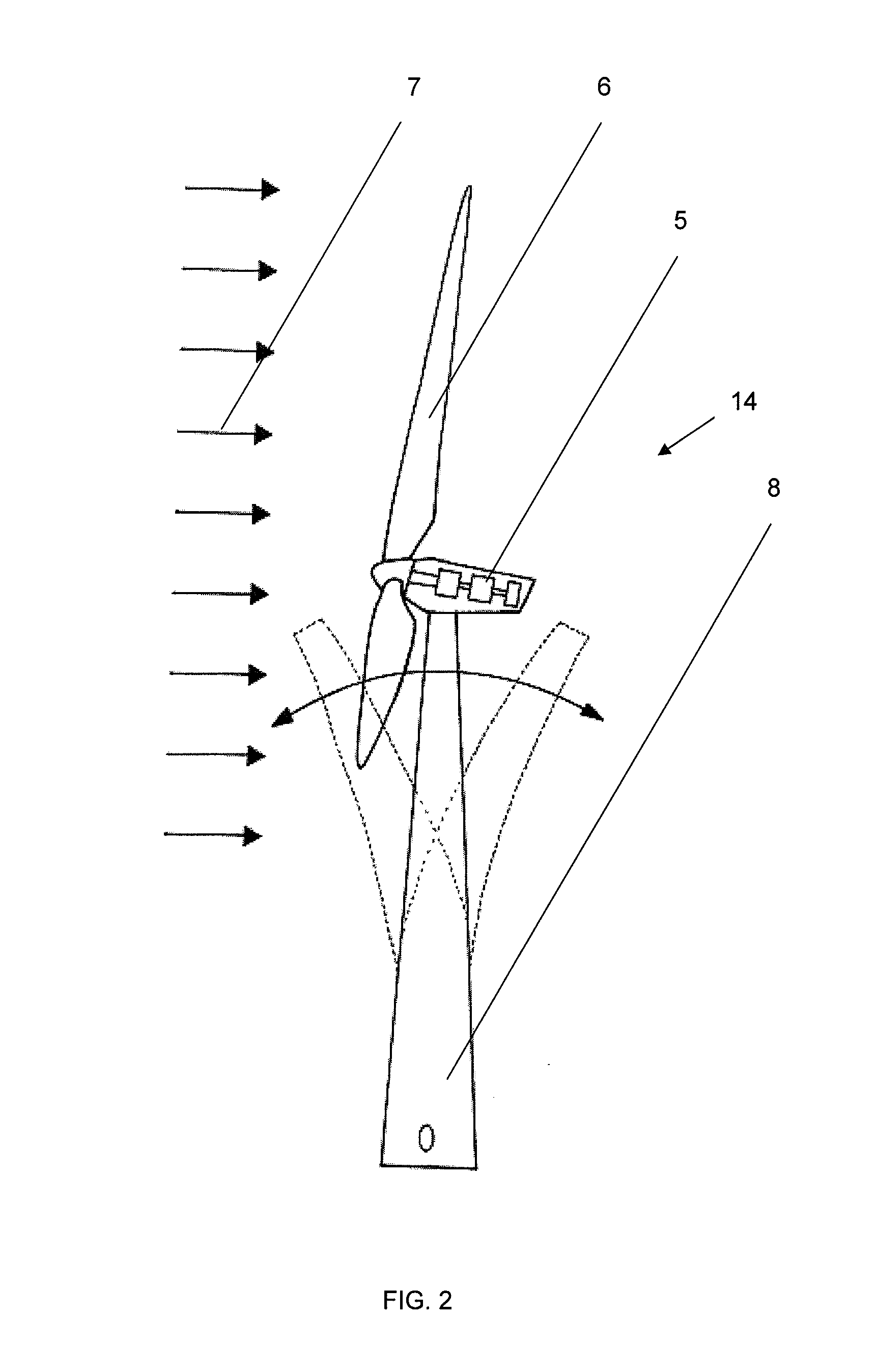
Method for operating or controlling a wind turbine and method for providing primary control power by means of wind turbines
ActiveUS20070085343A1Reduce yield lossImprove power transmissionWind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectric forcePower station
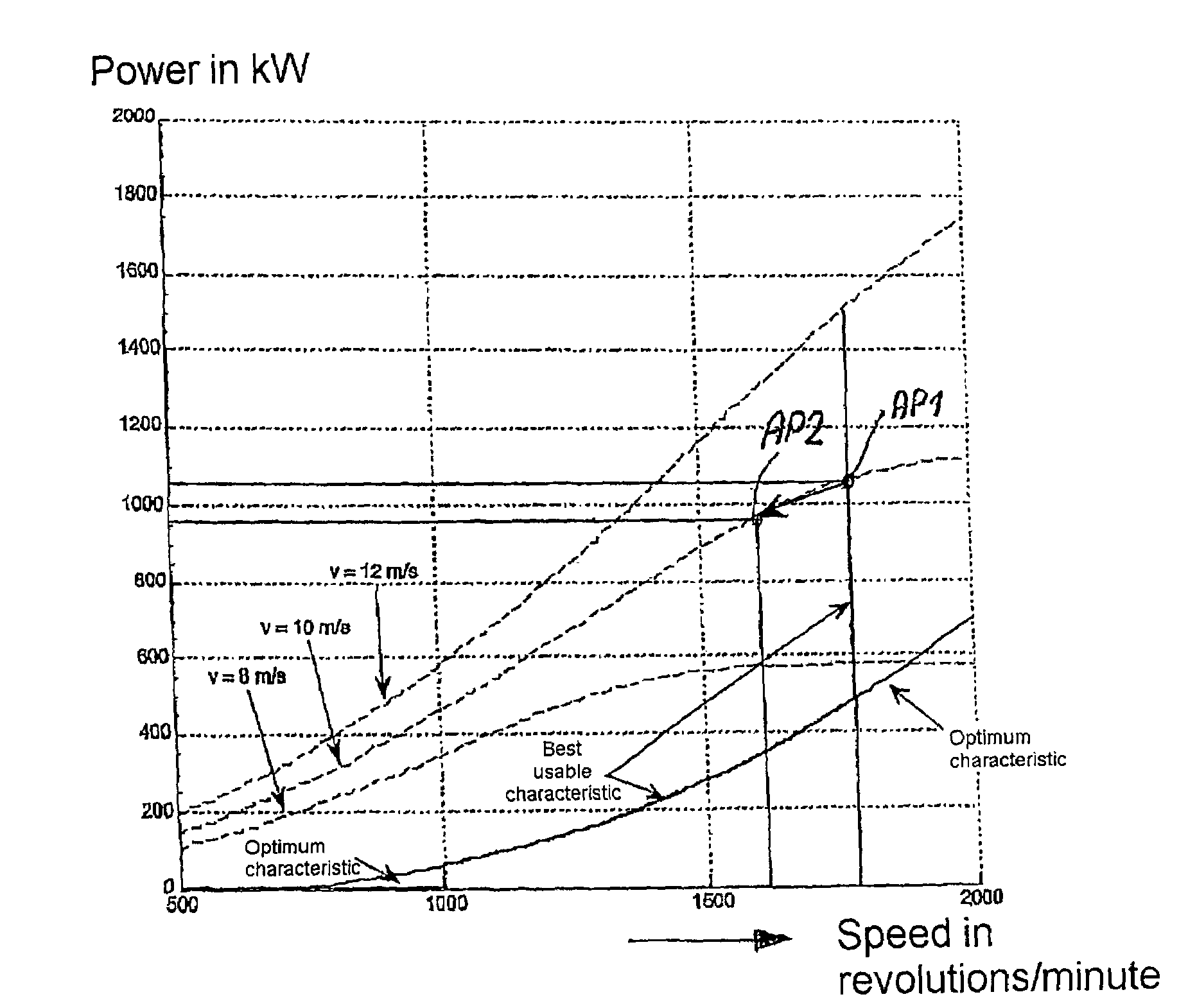
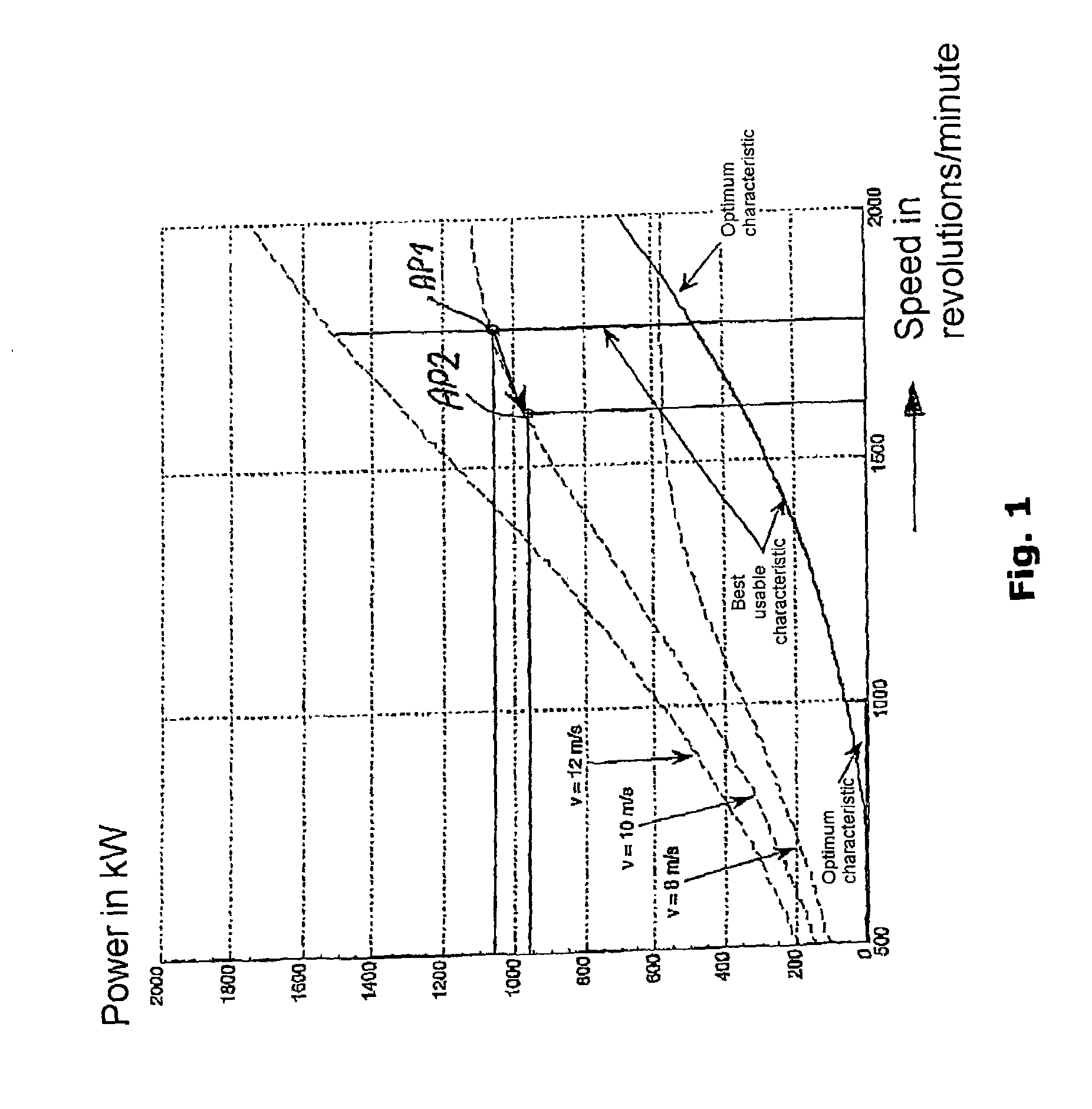
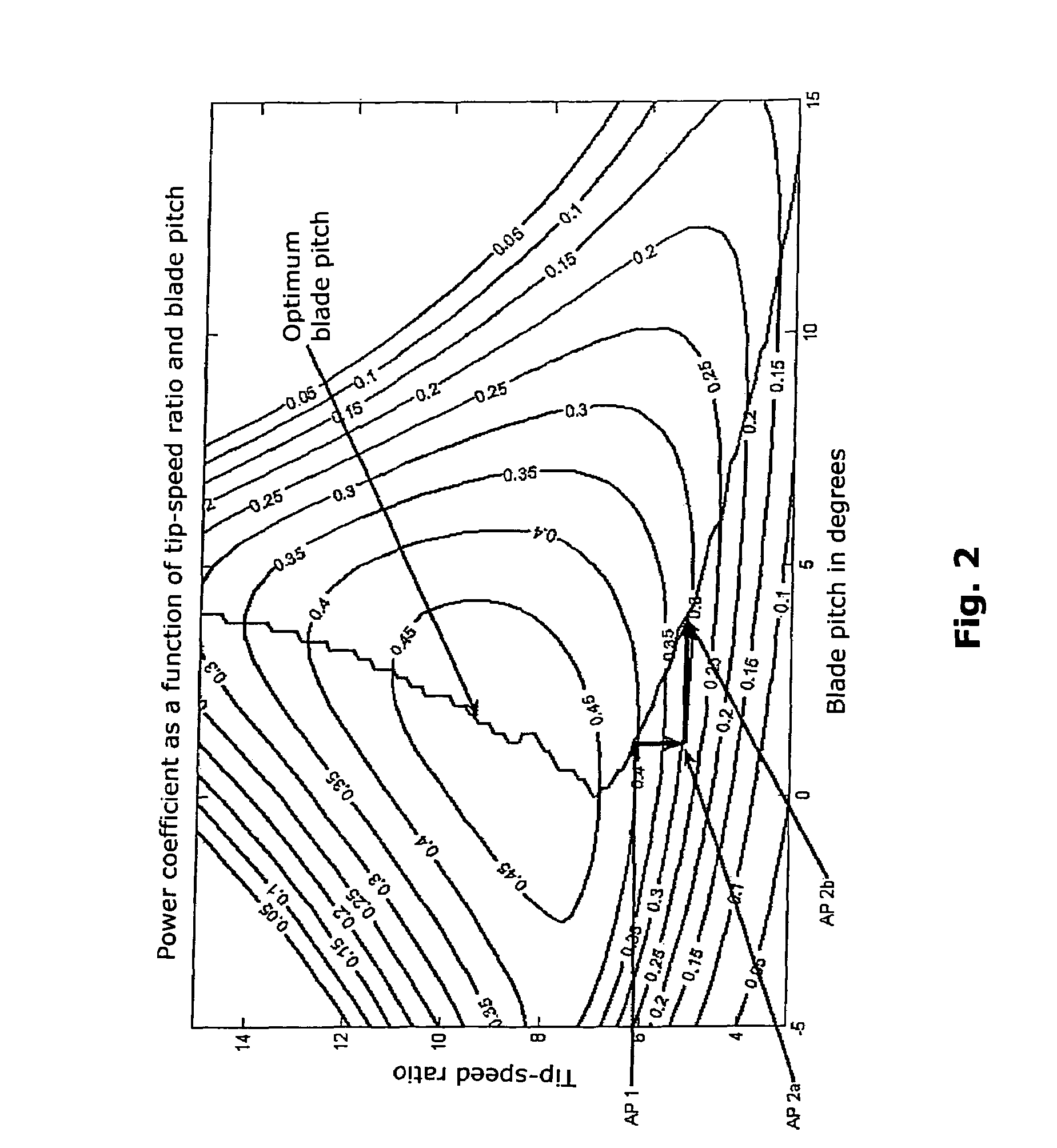
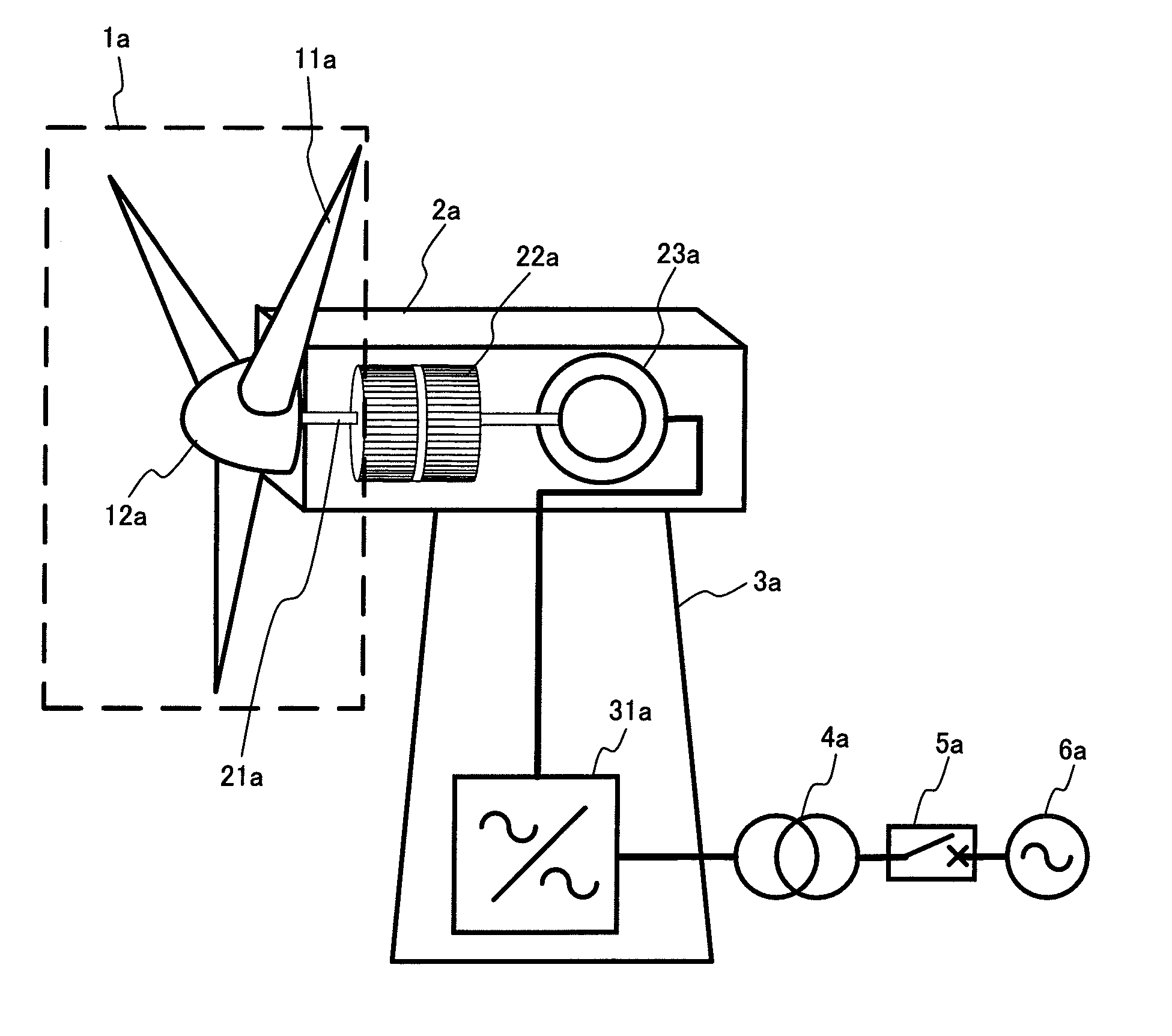
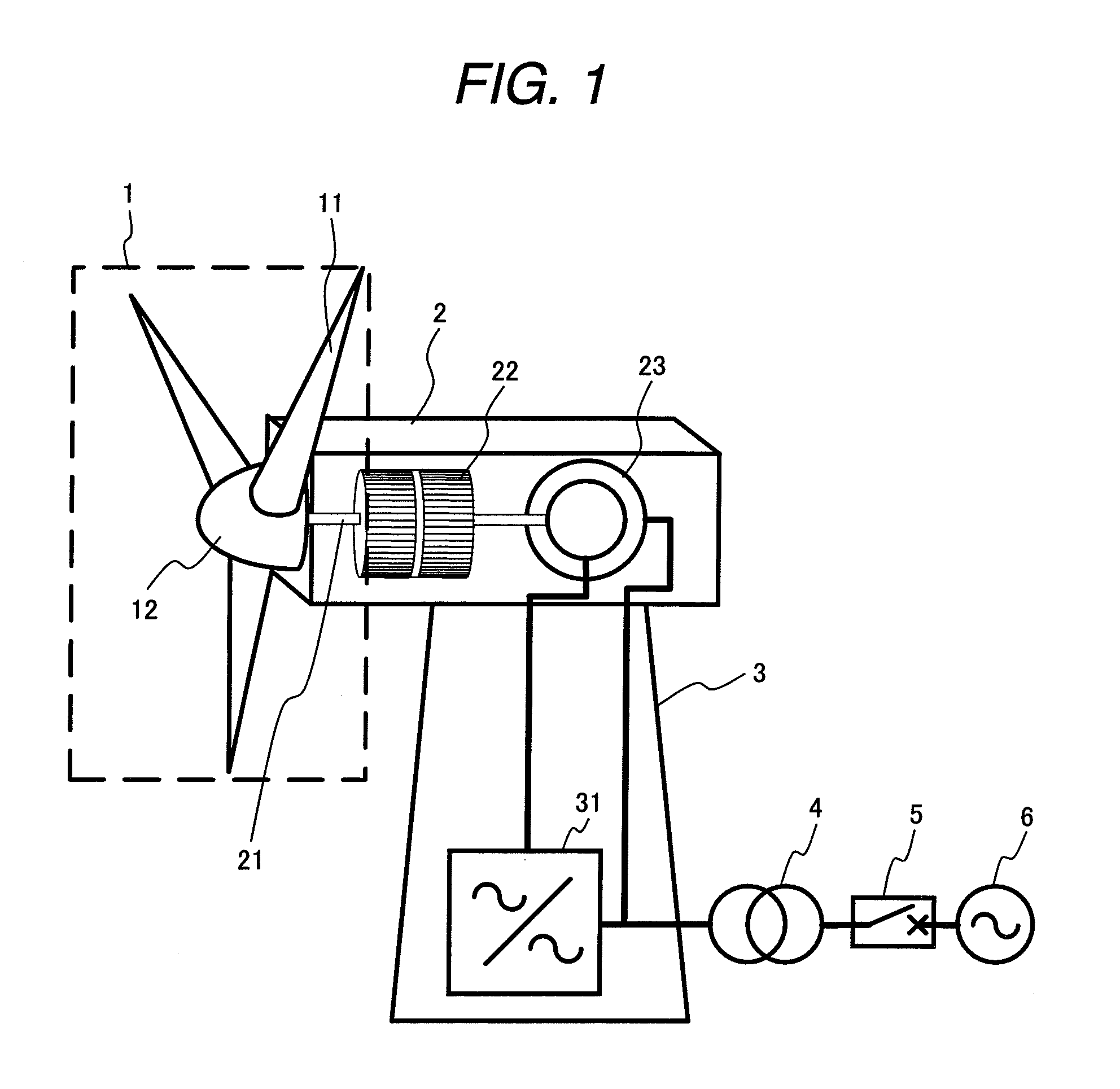
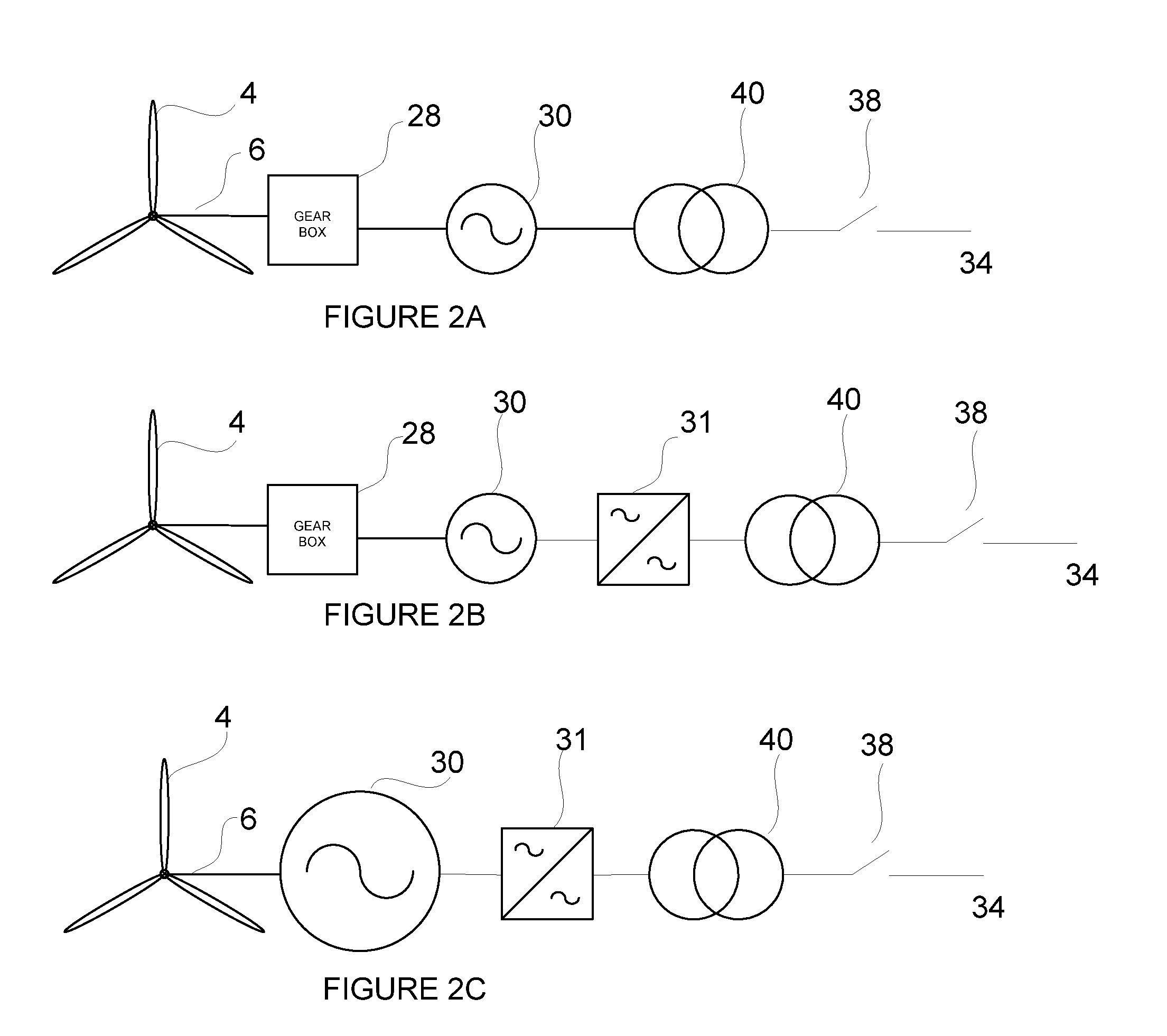
A method for operating at least one wind turbine with a rotor and an electric generator coupled to the rotor for delivering electrical power into an energy distribution system with the aid of a control device ensures that the wind turbine operates within its operating range. The wind turbine is controlled in response to the change of a system operating parameter and for a period of time, in such a manner that a higher power is fed into the system than belongs to the operating range of the steady-state operation. The same conditions also apply to a method for providing control power or primary control power for an electric energy generator and distributor system to which a multiplicity of power stations including wind turbines is connected, and to a wind turbine.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
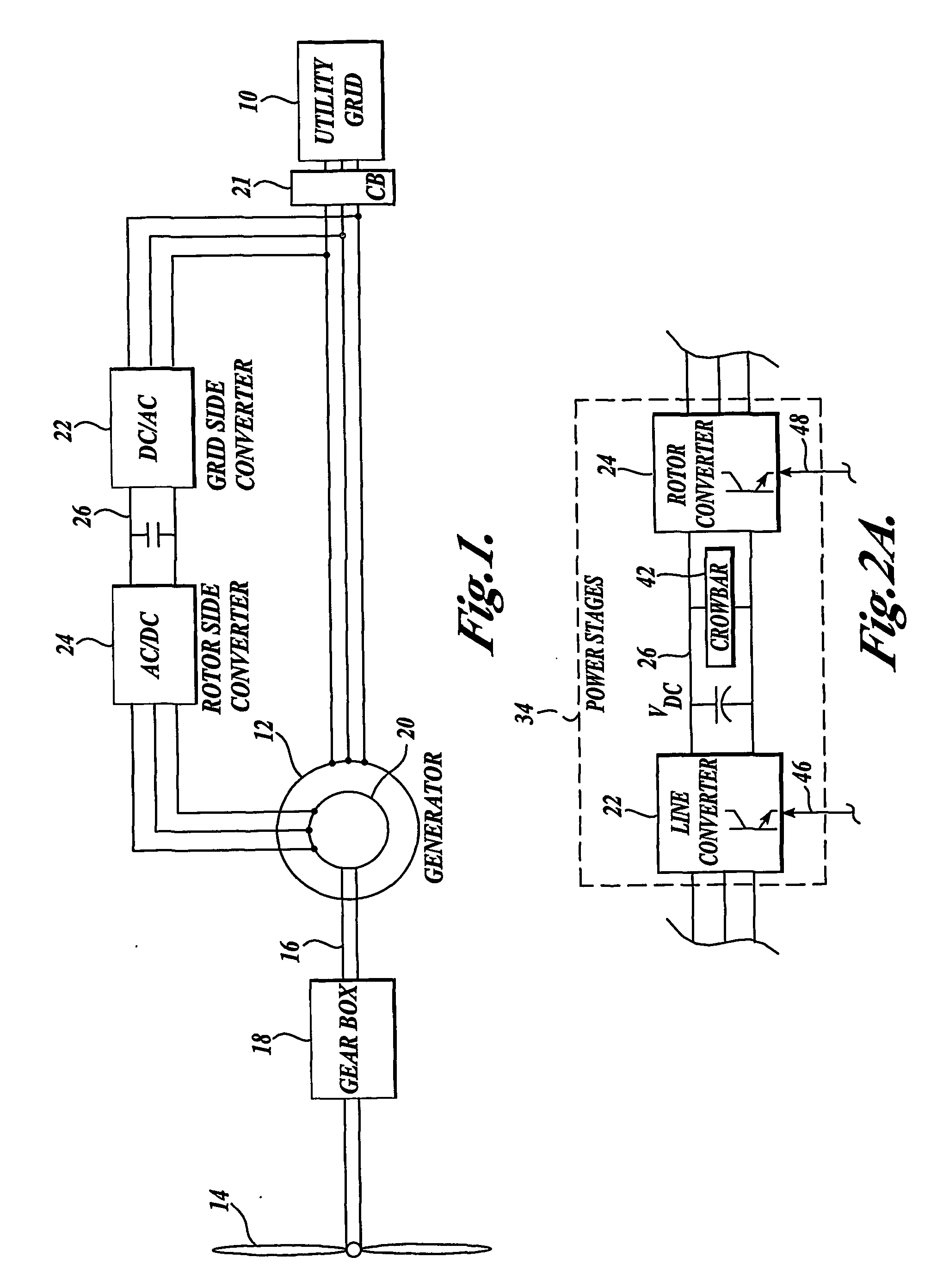
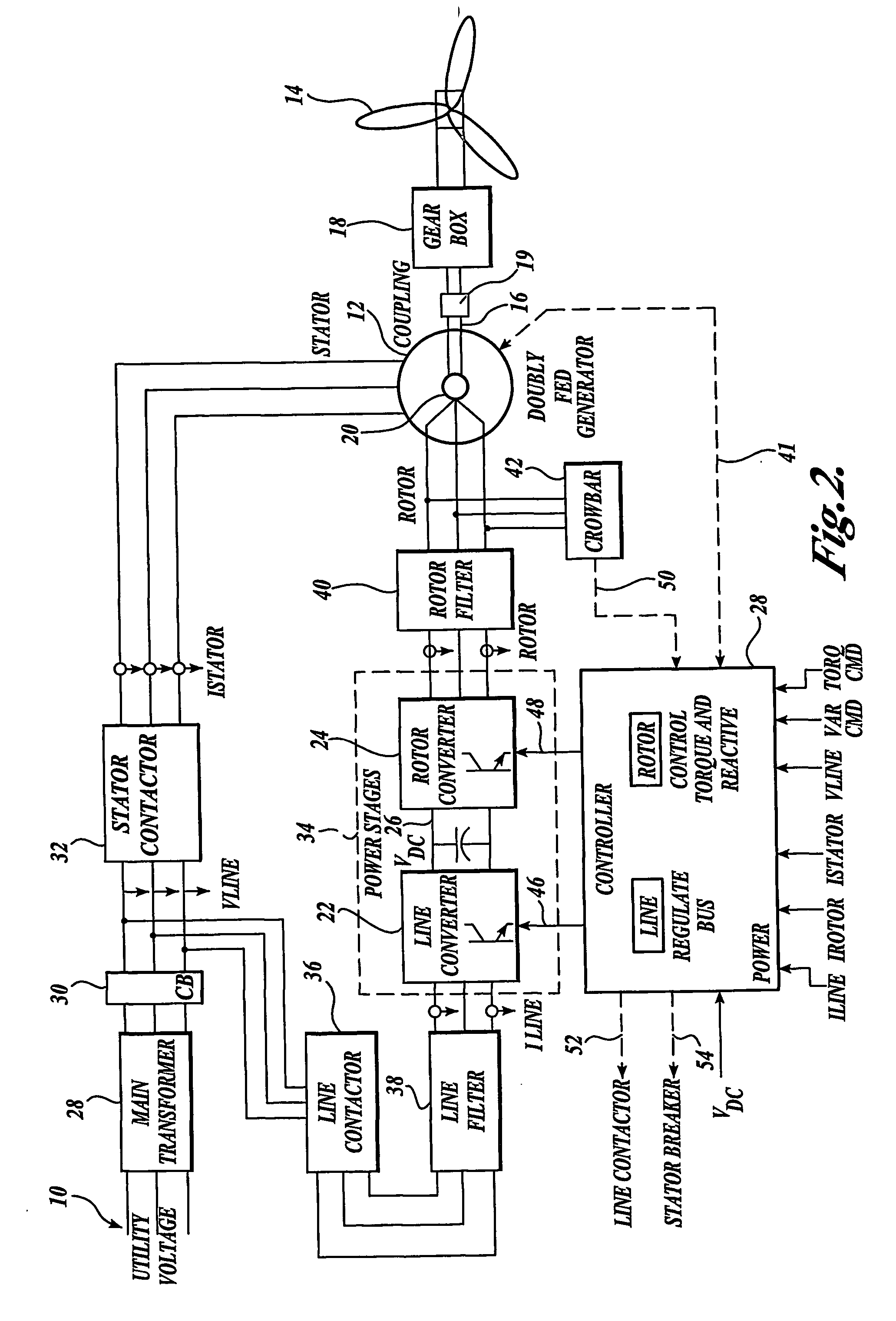
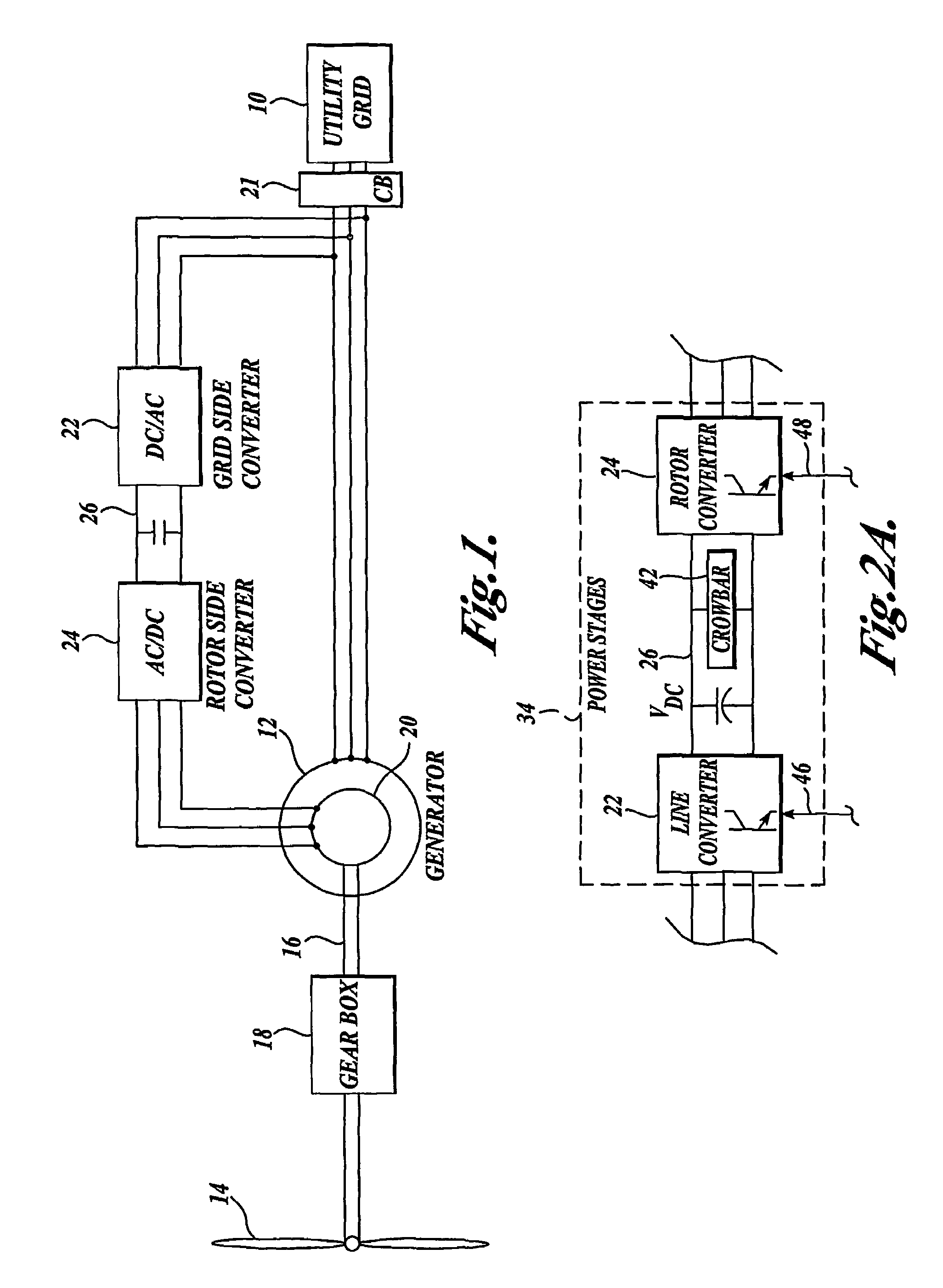
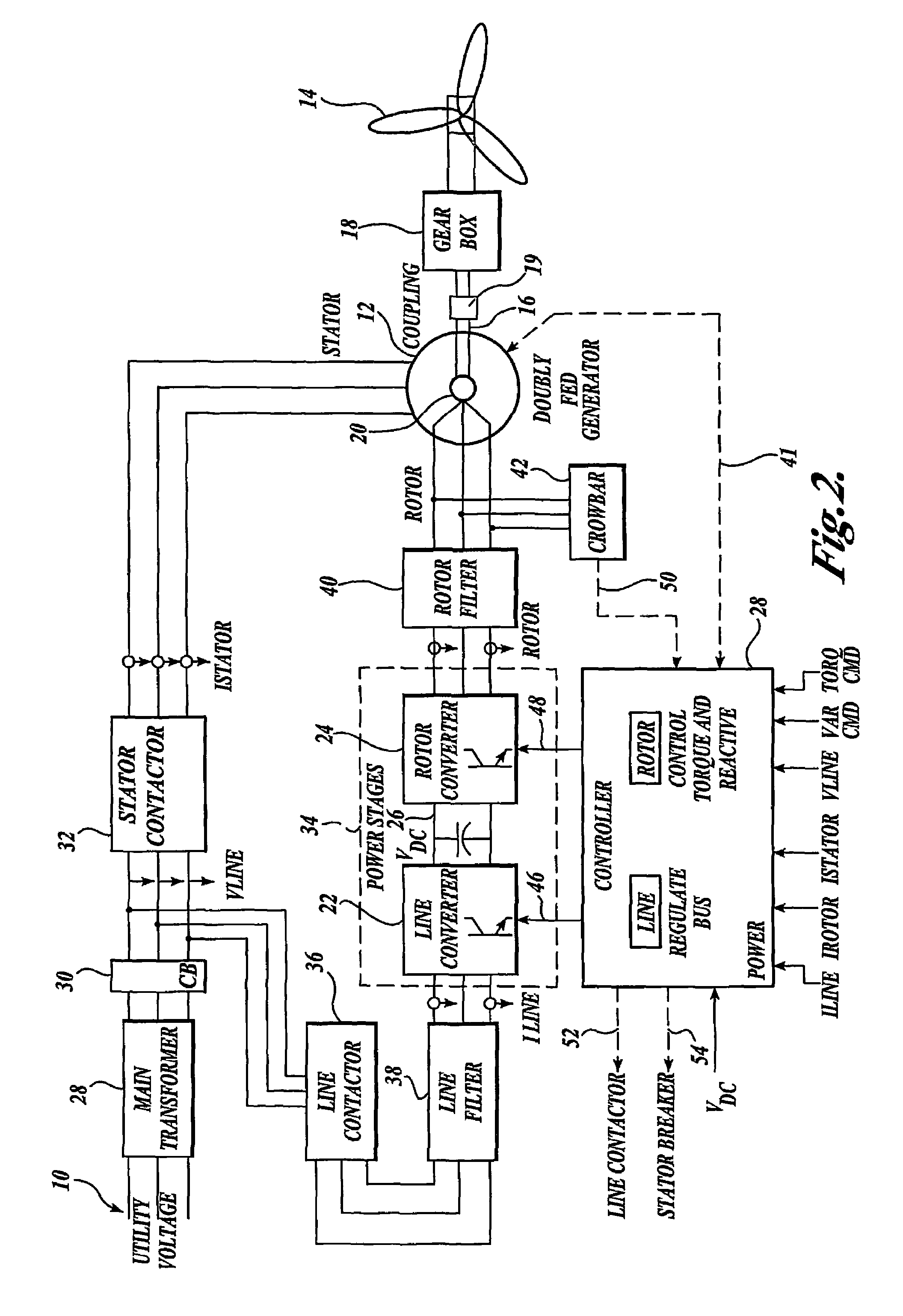
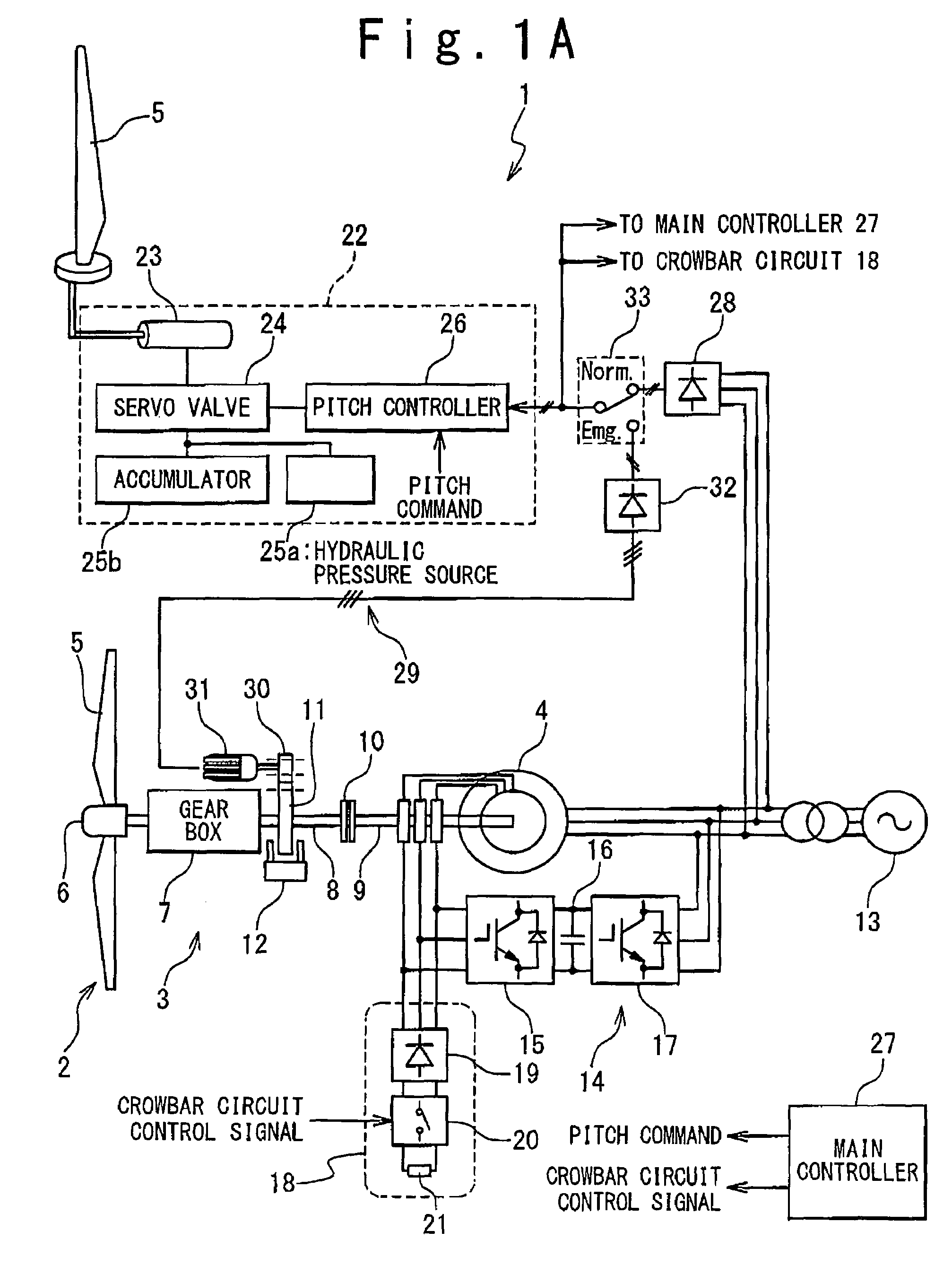
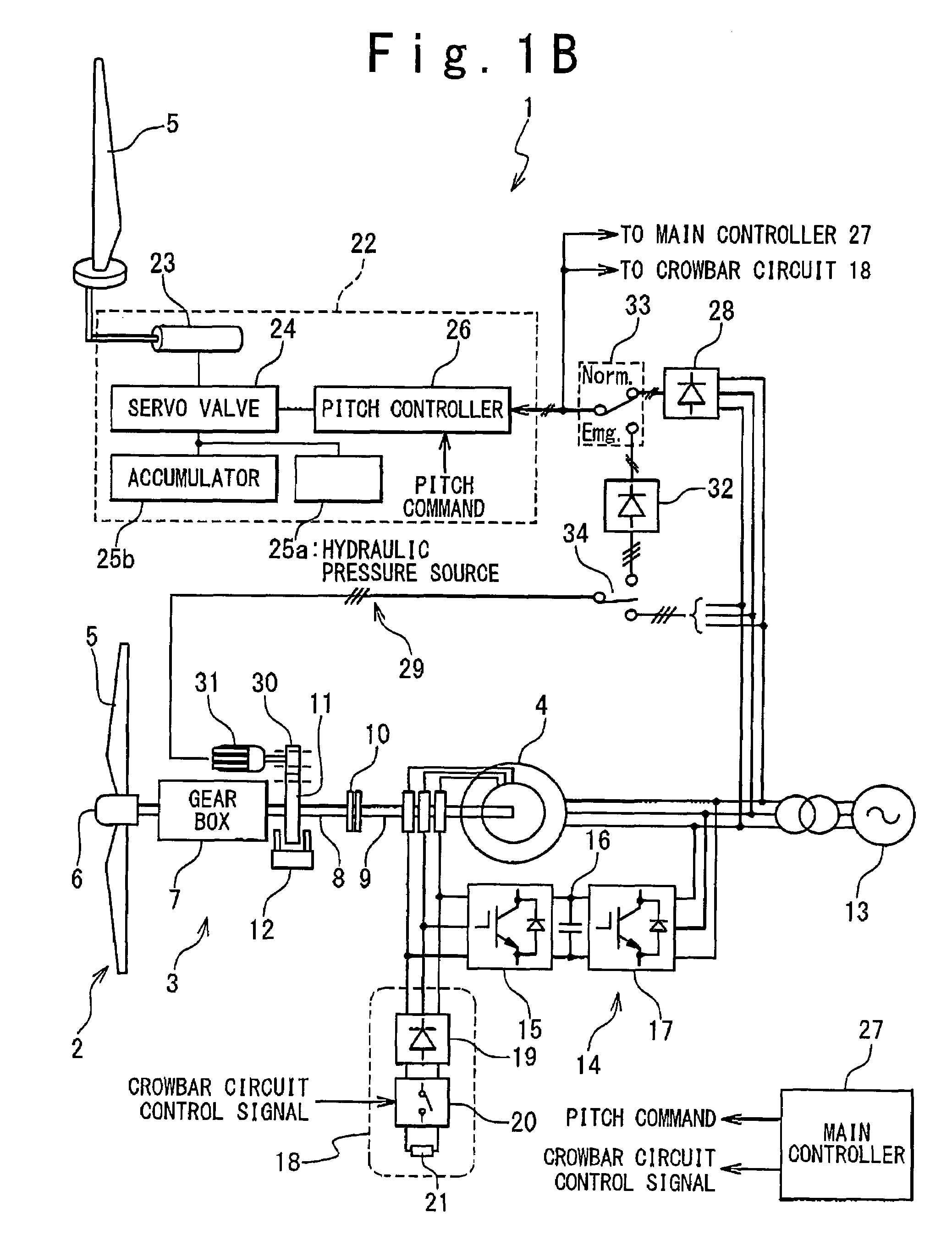
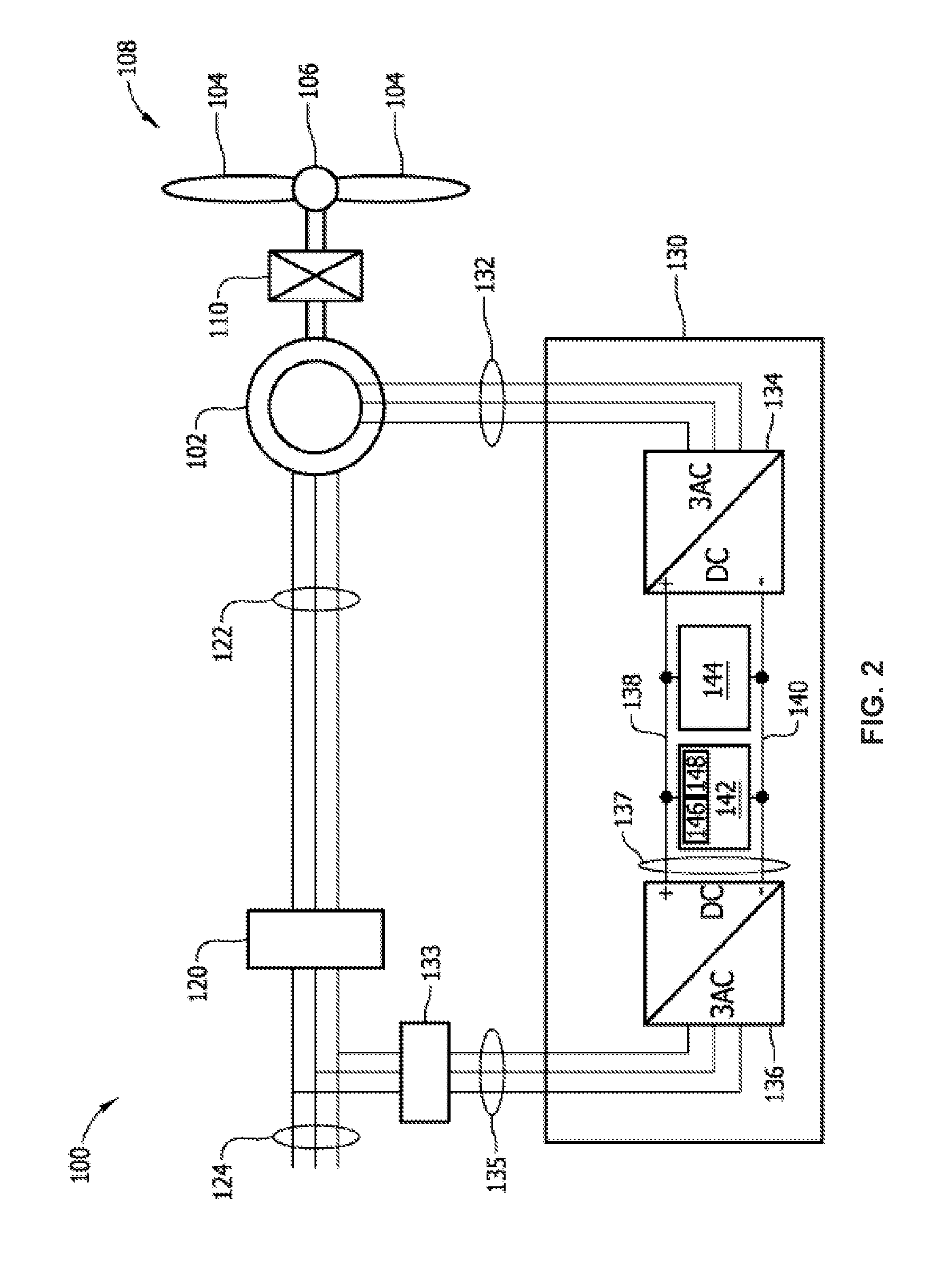
Control system for doubly fed induction generator
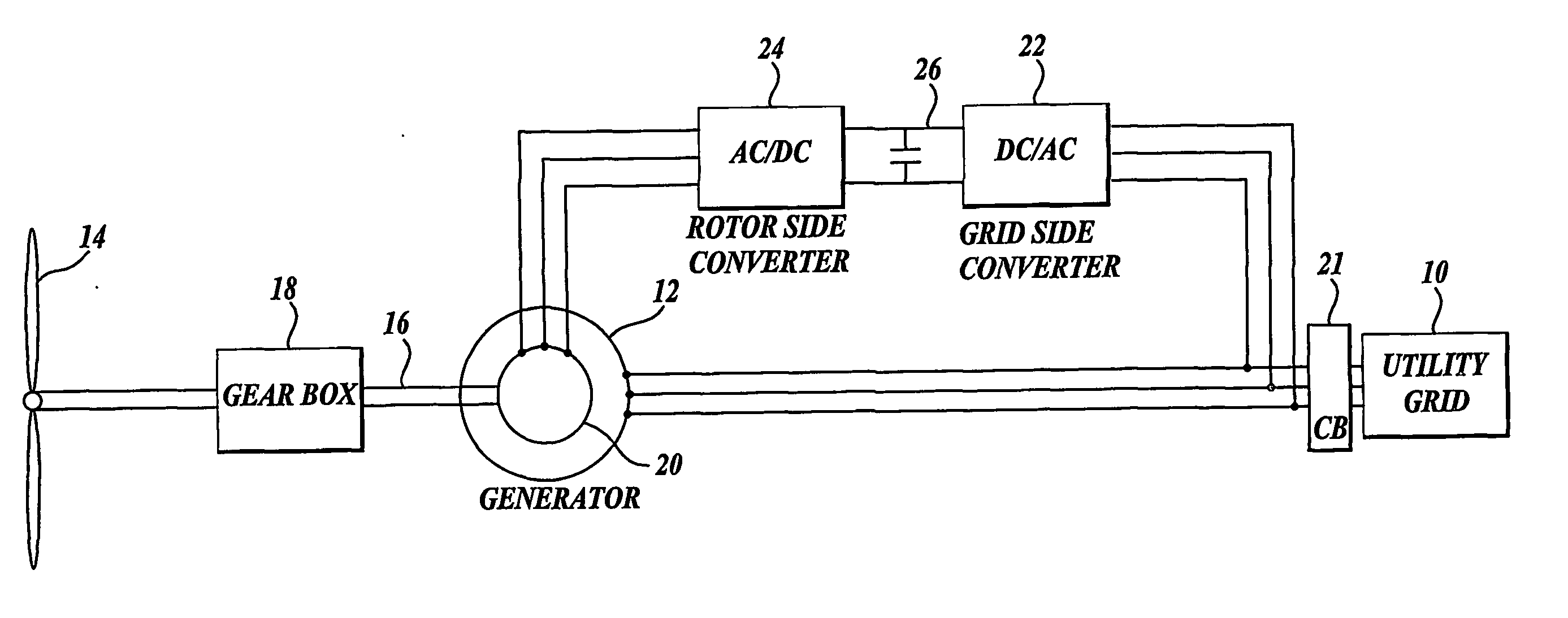
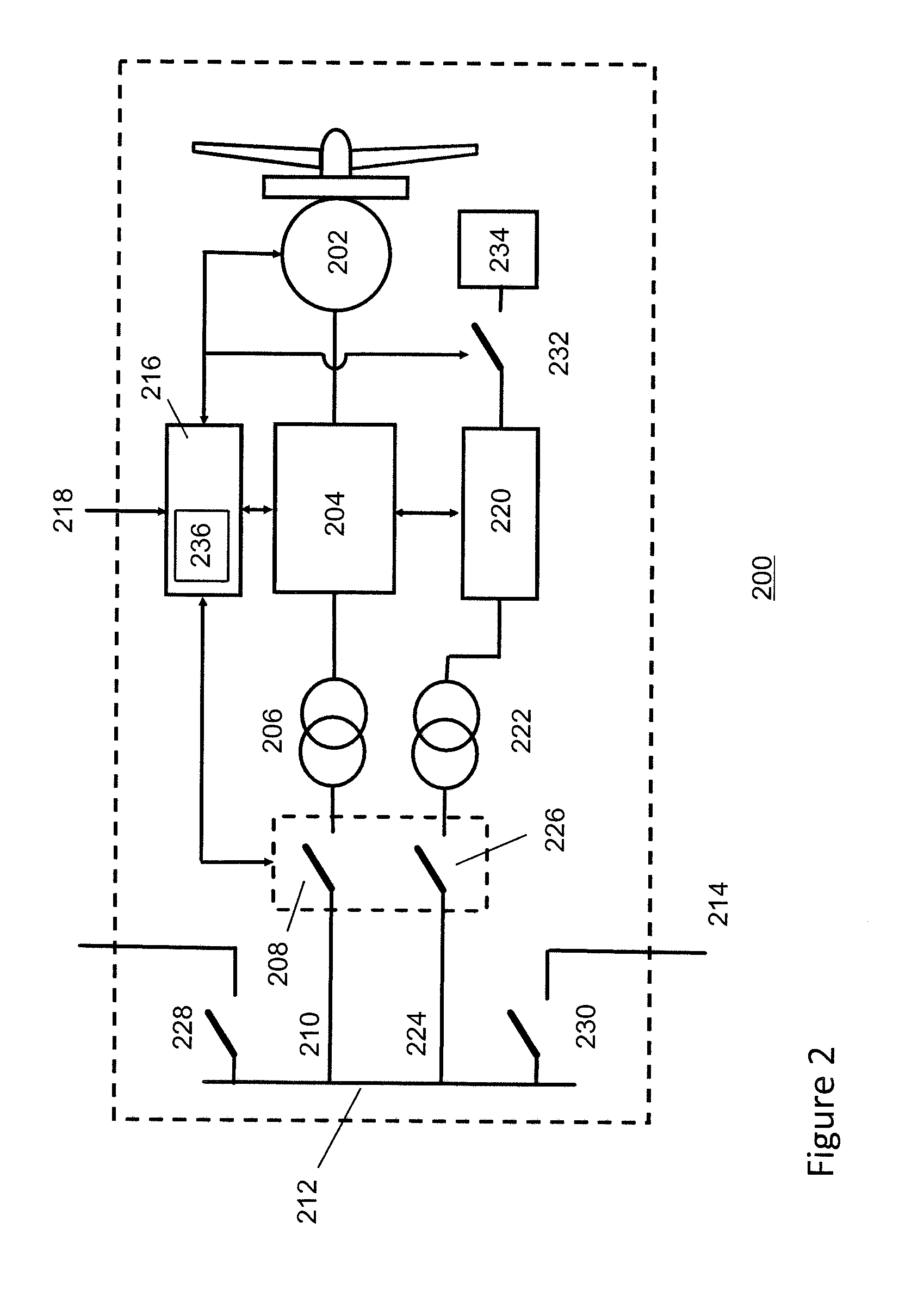
ActiveUS20070052244A1Reducing rotor currentMaintain balanceGenerator control circuitsAC motor controlControl systemControl signal
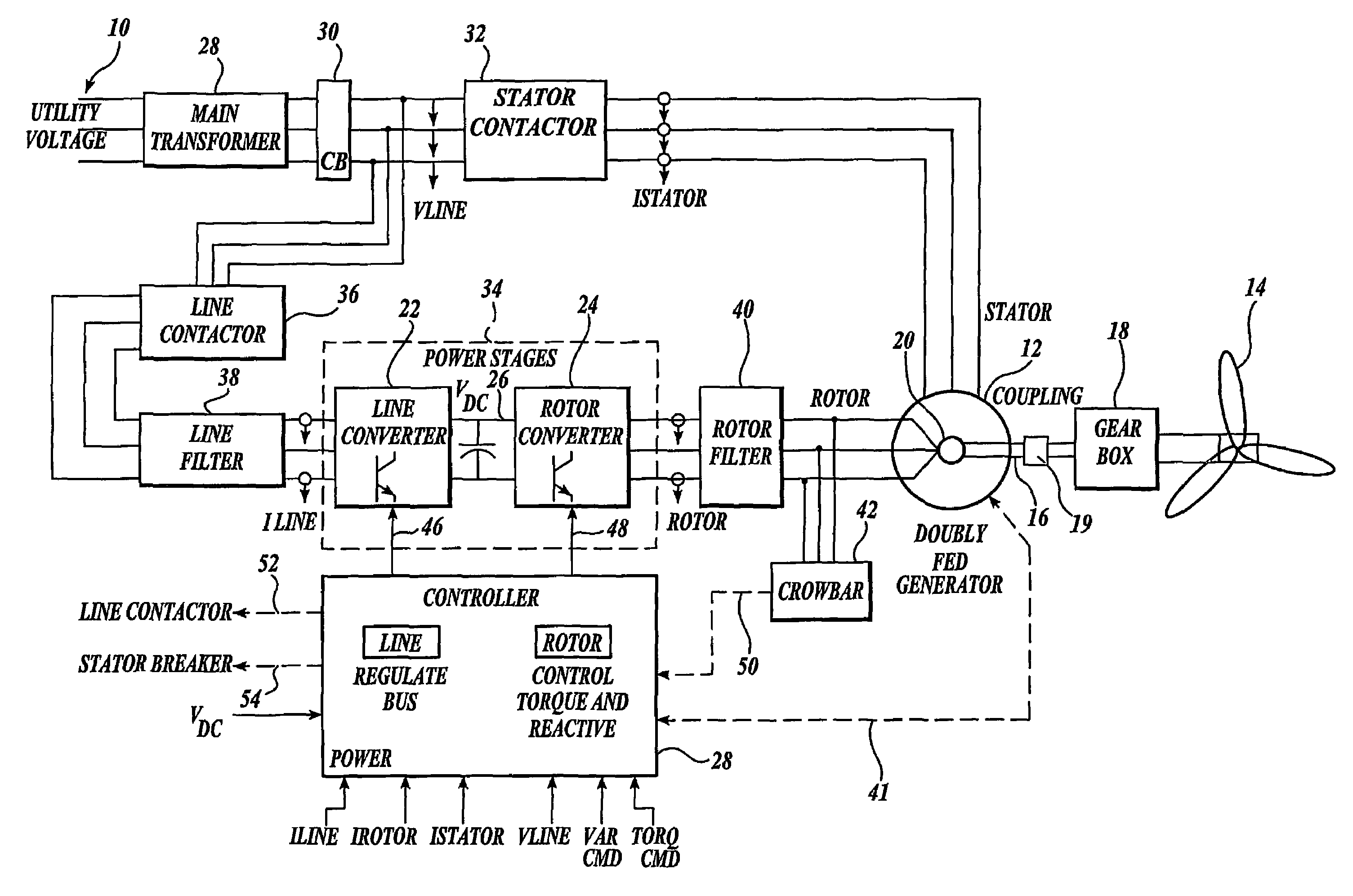
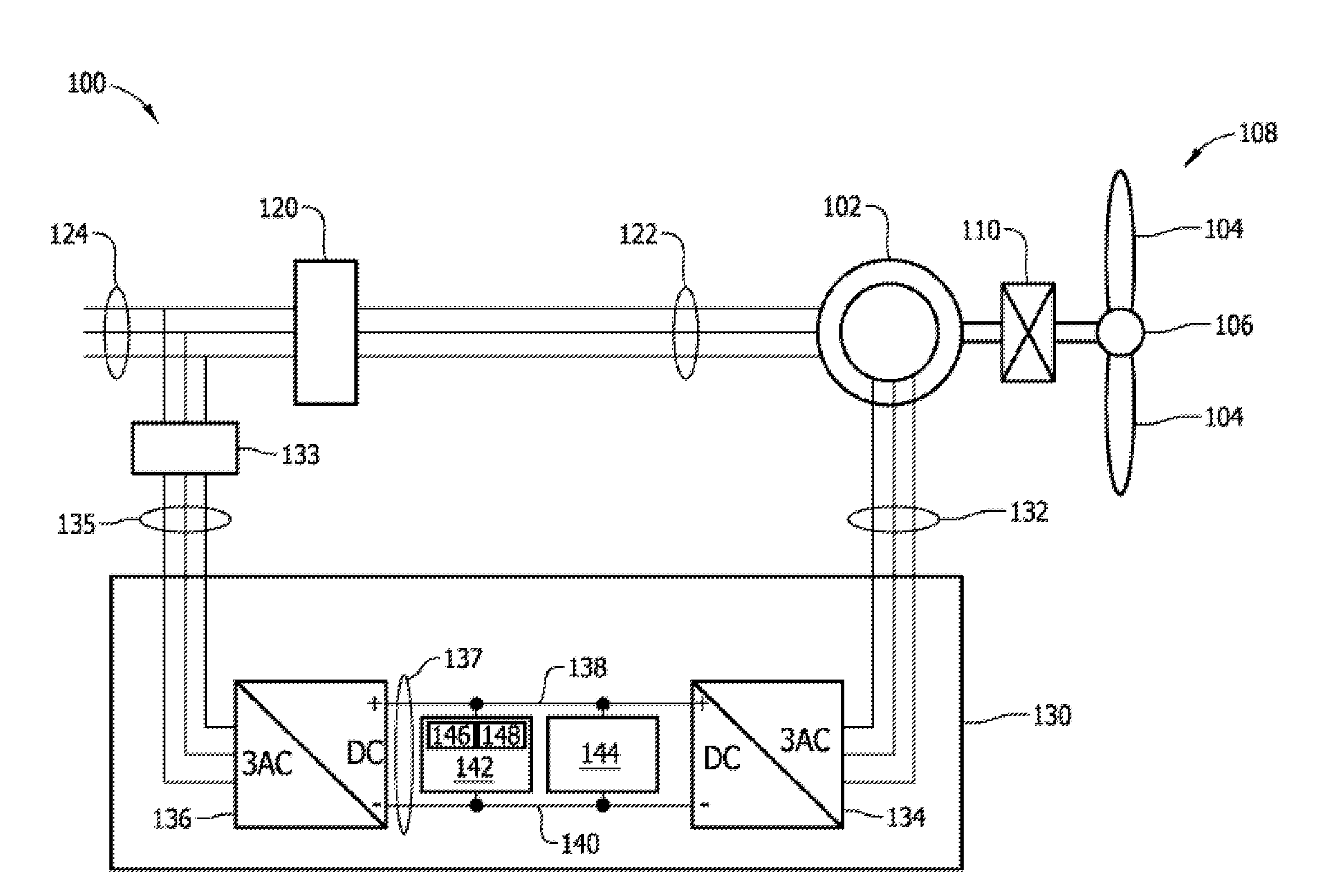
A controller (28) for a doubly fed induction generator (12,20) adjusts control signals to a rotor side converter (24) and line side converter (22) to adjust rotor current when a voltage transient on a utility grid (10) occurs, so that the doubly fed induction generator can ride through the transient. The controller can also turn off the transistors of the rotor side converter (24) to reduce rotor current and / or activate a crowbar (42) to reduce the voltage of the DC link (26) connecting the converters (22, 24) when significant voltage transients occur on the grid (10). This permits continued operation of the DFIG system without disconnecting from the grid.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOLAR INVERTERS USA
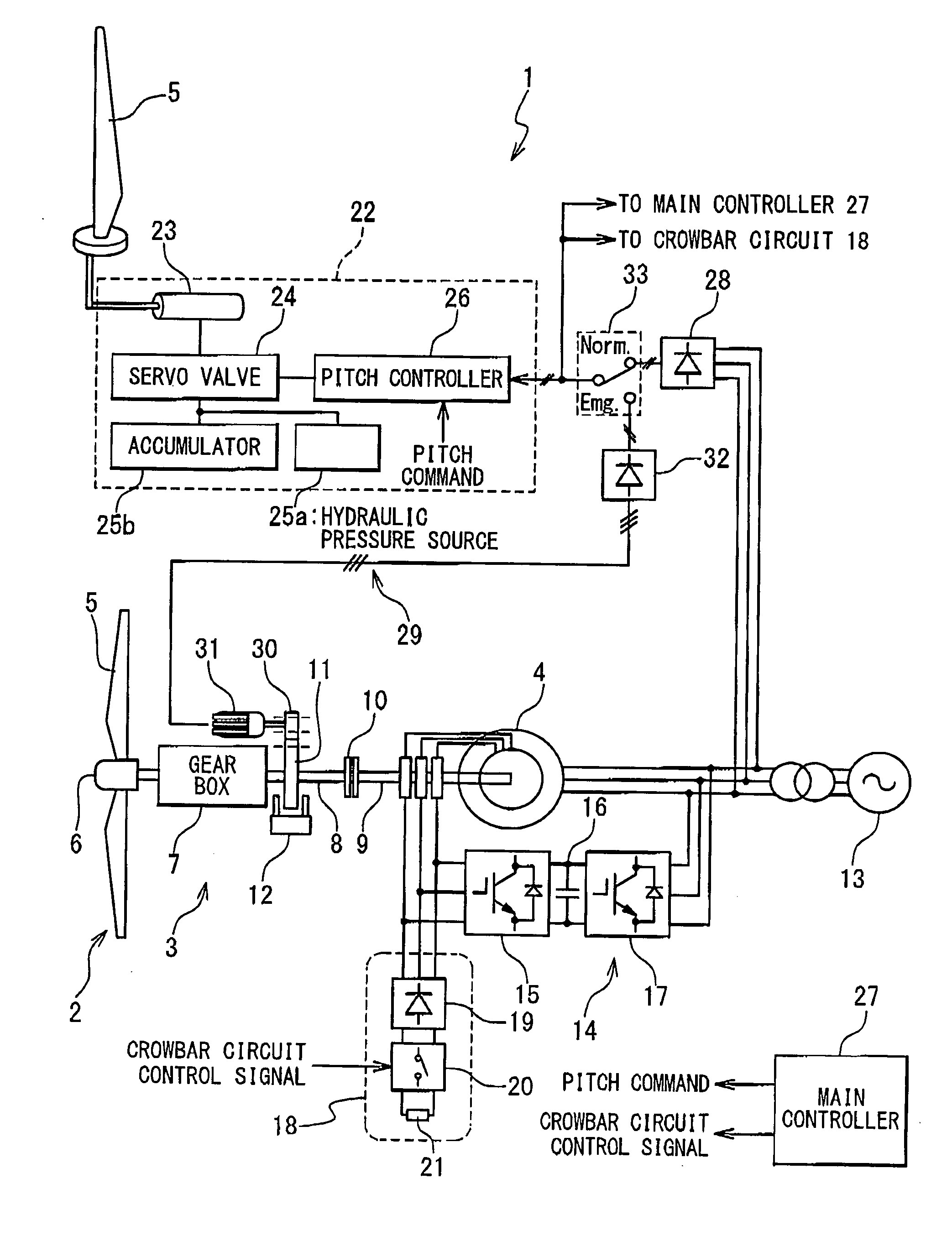
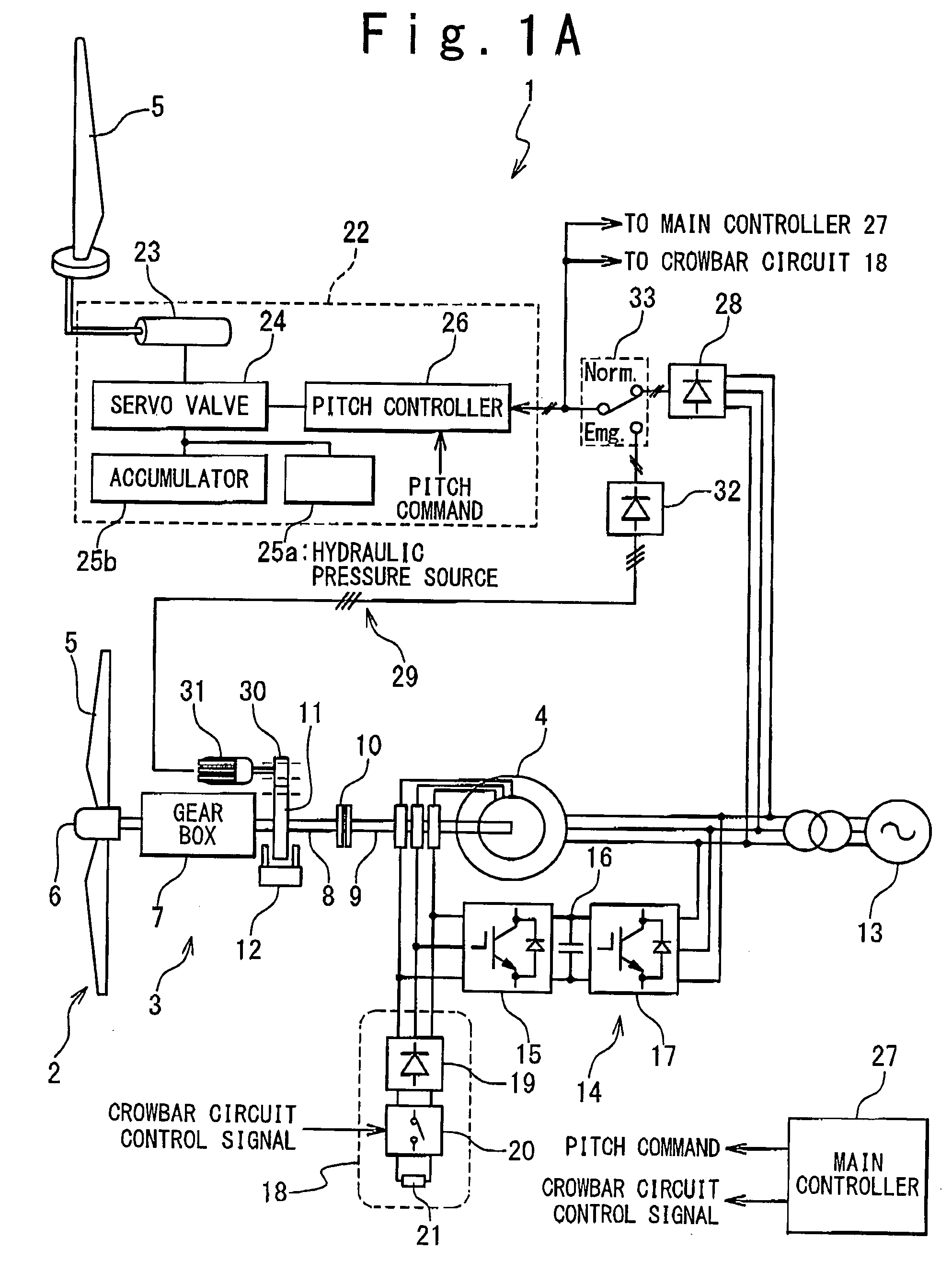
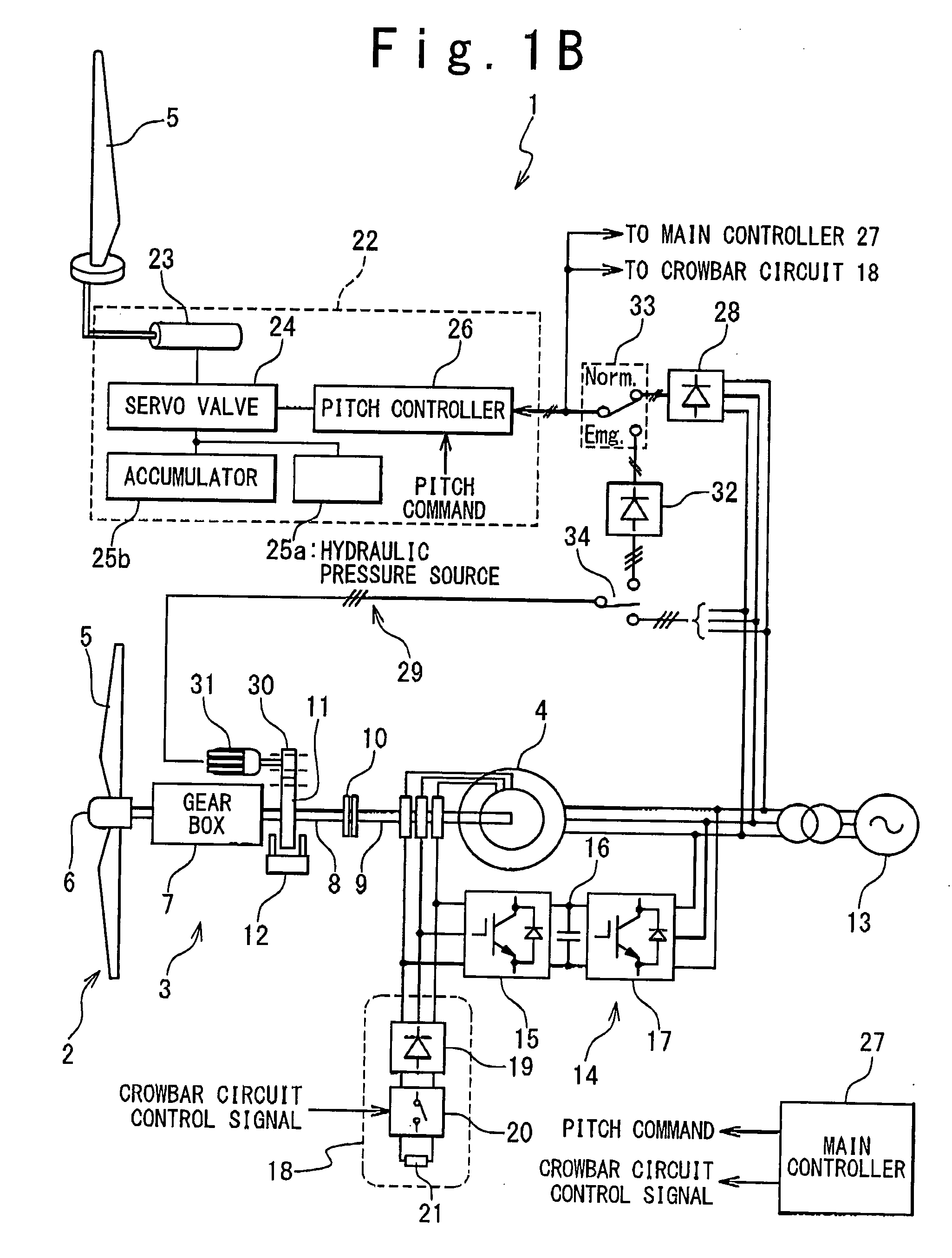
Emergency pitch drive power supply
InactiveUS7218012B1Improve usabilityLow costRotational speed controlWind motor controlDrive motorTurbine
An emergency pitch drive power supply is provided, the emergency pitch drive power supply comprising an auxiliary generator for producing electric power, wherein the auxiliary generator is a permanently excited multi-pole generator adapted to generate sufficient power for a pitch drive of a wind turbine when driven with wind rotor speed, and wherein the auxiliary generator is connected to at least one pitch drive motor of the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind turbine system for satisfying low-voltage ride through requirement
ActiveUS20090058086A1Reduce maintenanceReduce necessityPropellersWind motor controlPower gridBlade pitch
A wind turbine system is provided with a wind turbine rotor, a pitch control mechanism, and an emergency power supply mechanism. The wind turbine rotor includes a blade having a variable pitch angle. The pitch control mechanism drives the blade to control the pitch angle. The emergency power supply mechanism generates electric power from rotation of the wind turbine rotor and feeds the electric power to the pitch control mechanism, in response to occurrence of an accidental drop of a system voltage of a power grid.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Method for operating or controlling a wind turbine and method for providing primary control power by means of wind turbines
ActiveUS7528496B2Improve power transmissionHigh yieldWind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEngineeringDistributor
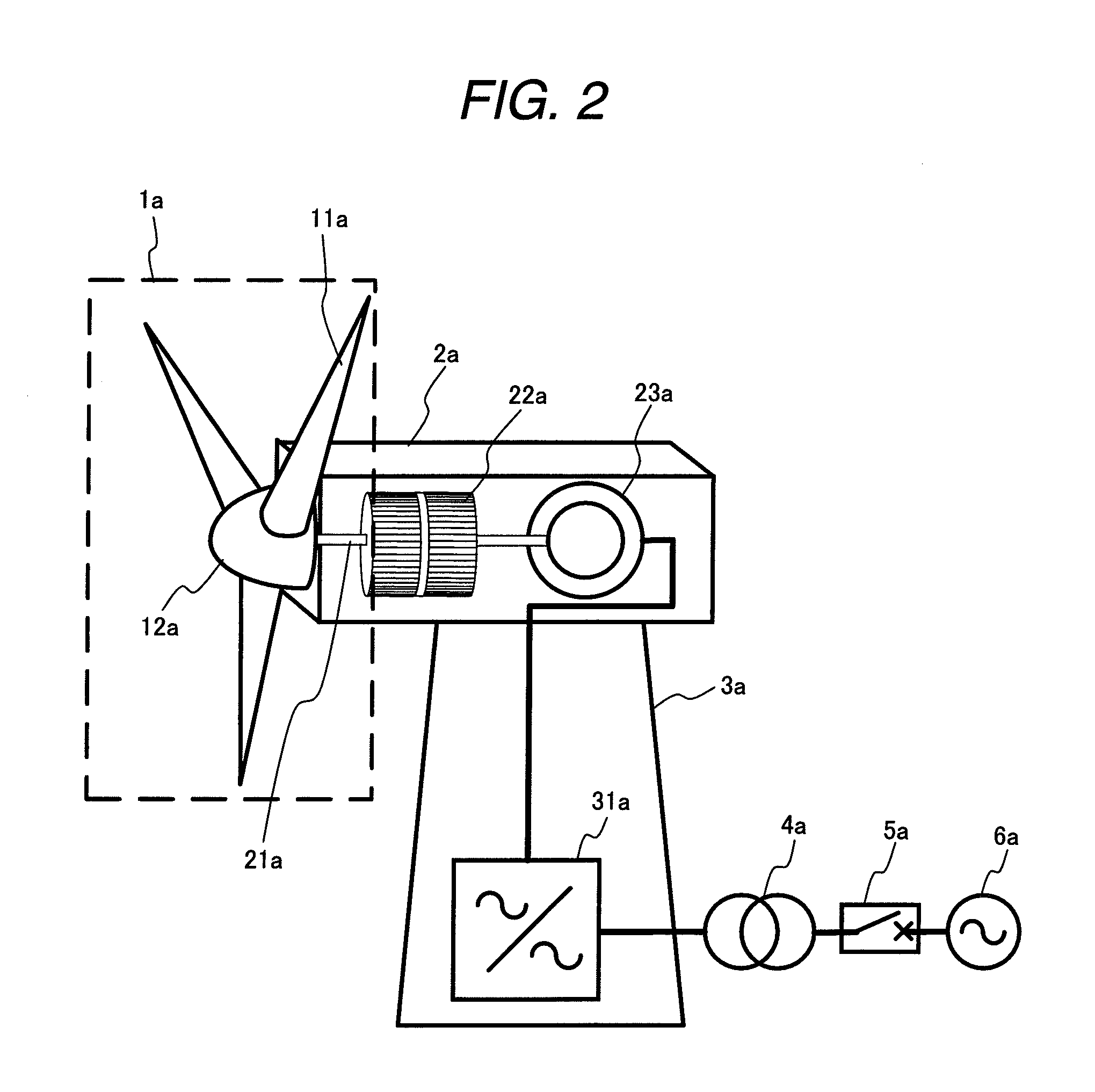
A method for operating at least one wind turbine with a rotor and an electric generator coupled to the rotor for delivering electrical power into an energy distribution system with the aid of a control device ensures that the wind turbine operates within its operating range. The wind turbine is controlled in response to the change of a system operating parameter and for a period of time, in such a manner that a higher power is fed into the system than belongs to the operating range of the steady-state operation. The same conditions also apply to a method for providing control power or primary control power for an electric energy generator and distributor system to which a multiplicity of power stations including wind turbines is connected, and to a wind turbine.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
Control system for doubly fed induction generator
ActiveUS7411309B2Total current dropGuaranteed uptimeGenerator control circuitsAC motor controlControl systemControl signal
A controller (28) for a doubly fed induction generator (12,20) adjusts control signals to a rotor side converter (24) and line side converter (22) to adjust rotor current when a voltage transient on a utility grid (10) occurs, so that the doubly fed induction generator can ride through the transient. The controller can also turn off the transistors of the rotor side converter (24) to reduce rotor current and / or activate a crowbar (42) to reduce the voltage of the DC link (26) connecting the converters (22, 24) when significant voltage transients occur on the grid (10). This permits continued operation of the DFIG system without disconnecting from the grid.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOLAR INVERTERS USA
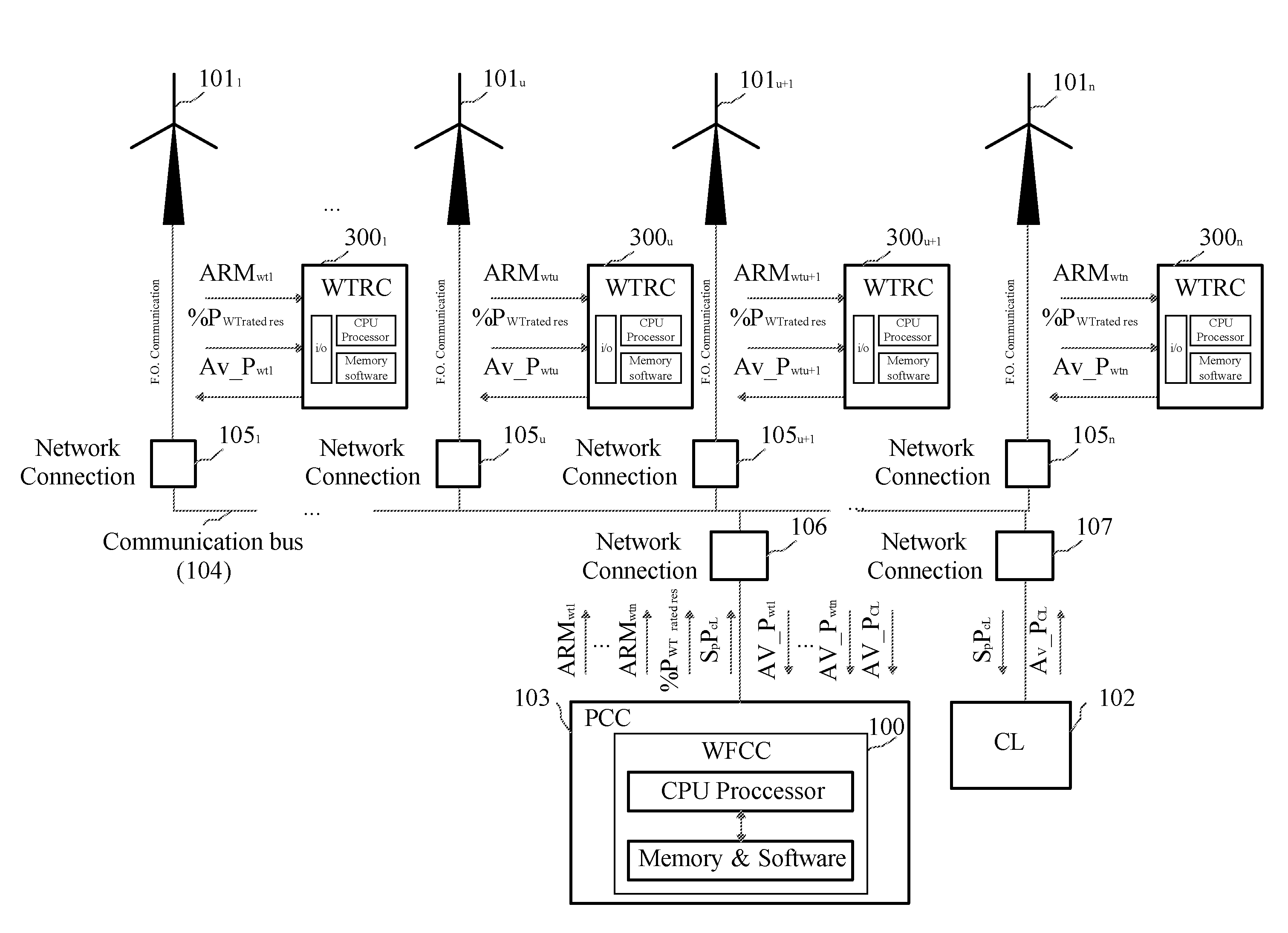
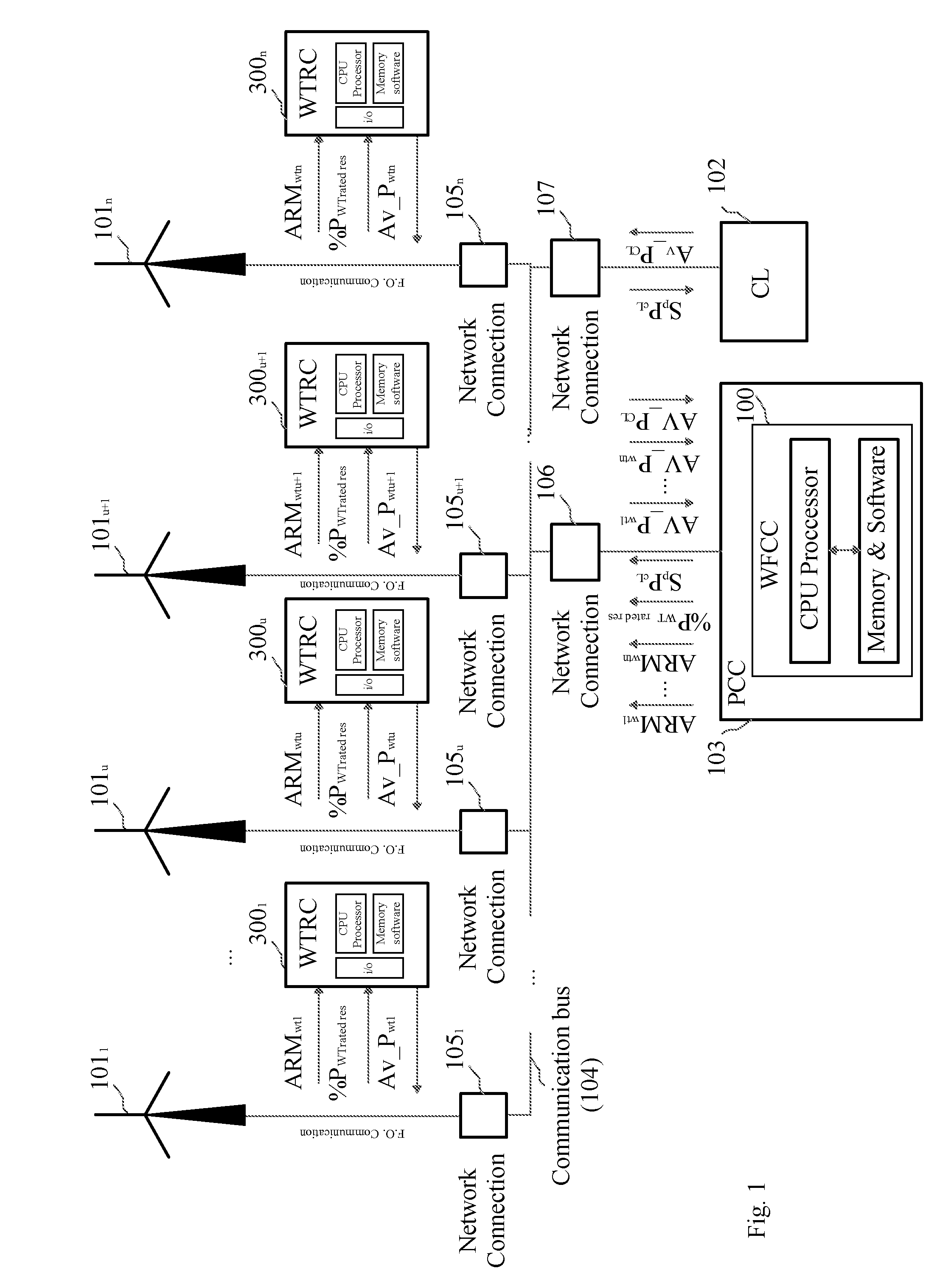
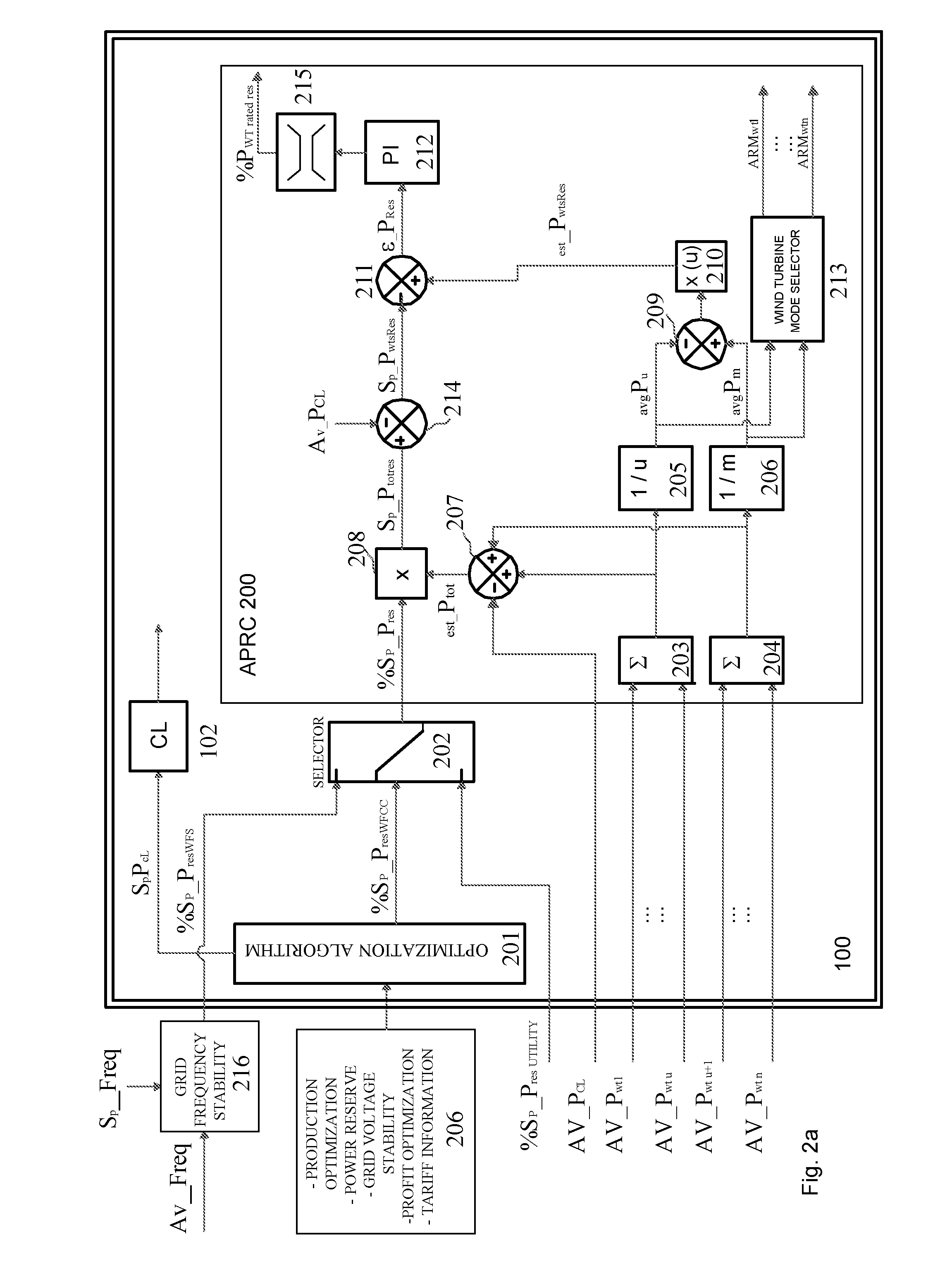
Control of active power reserve in a wind-farm
InactiveUS20090055030A1Easy to adjustMaintain frequency stabilityLevel controlWind motor controlPower gridEngineering
A method and system of active power reserve regulation in a wind farm with a communication network having a plurality of wind turbines that provide an active power reserve in order to support eventual power grid contingencies and to deliver an increase of power in case it is needed.
Owner:INGETEAM ENERGY
Method of controlling a wind turbine connected to an electric utility grid
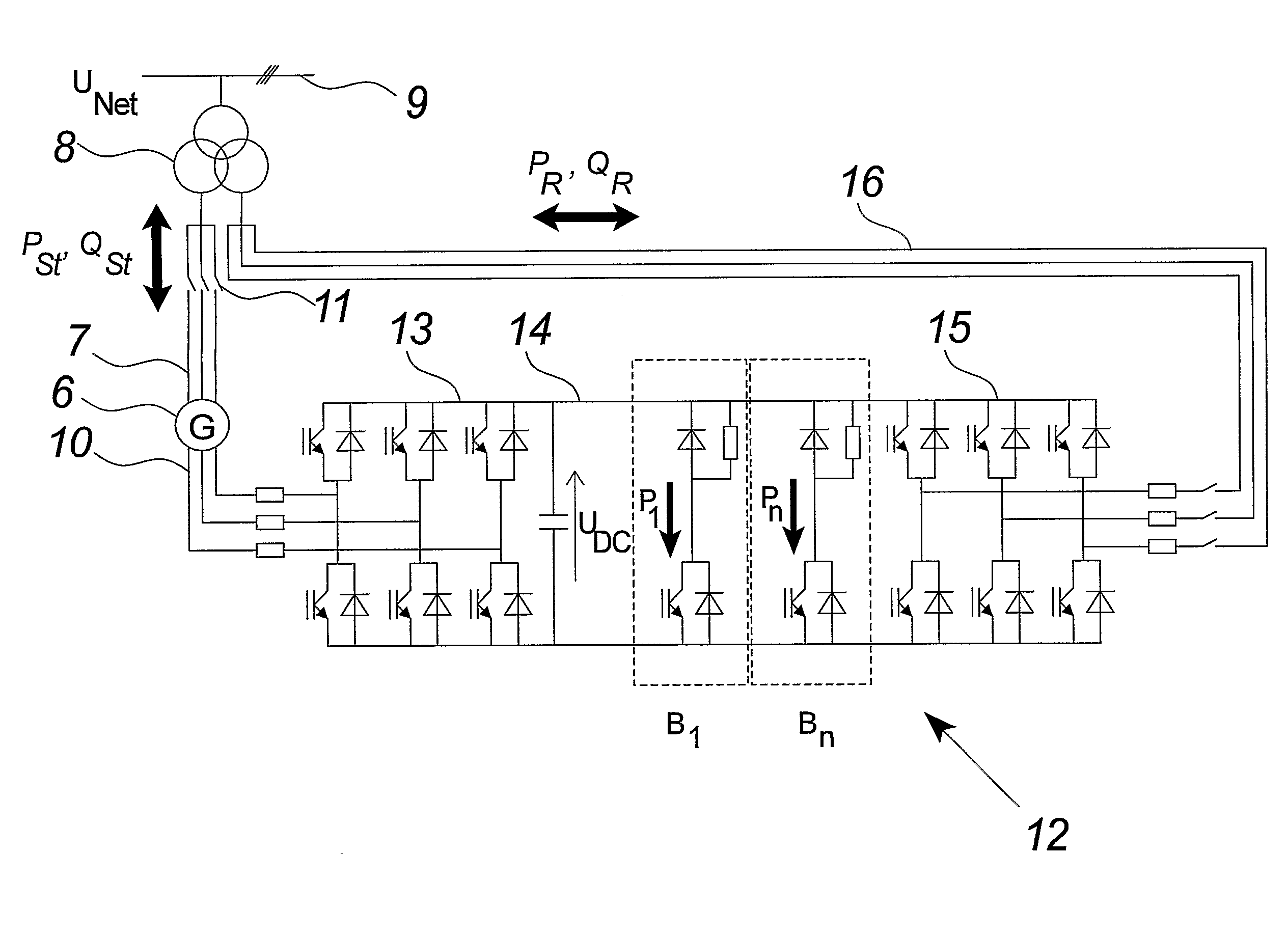
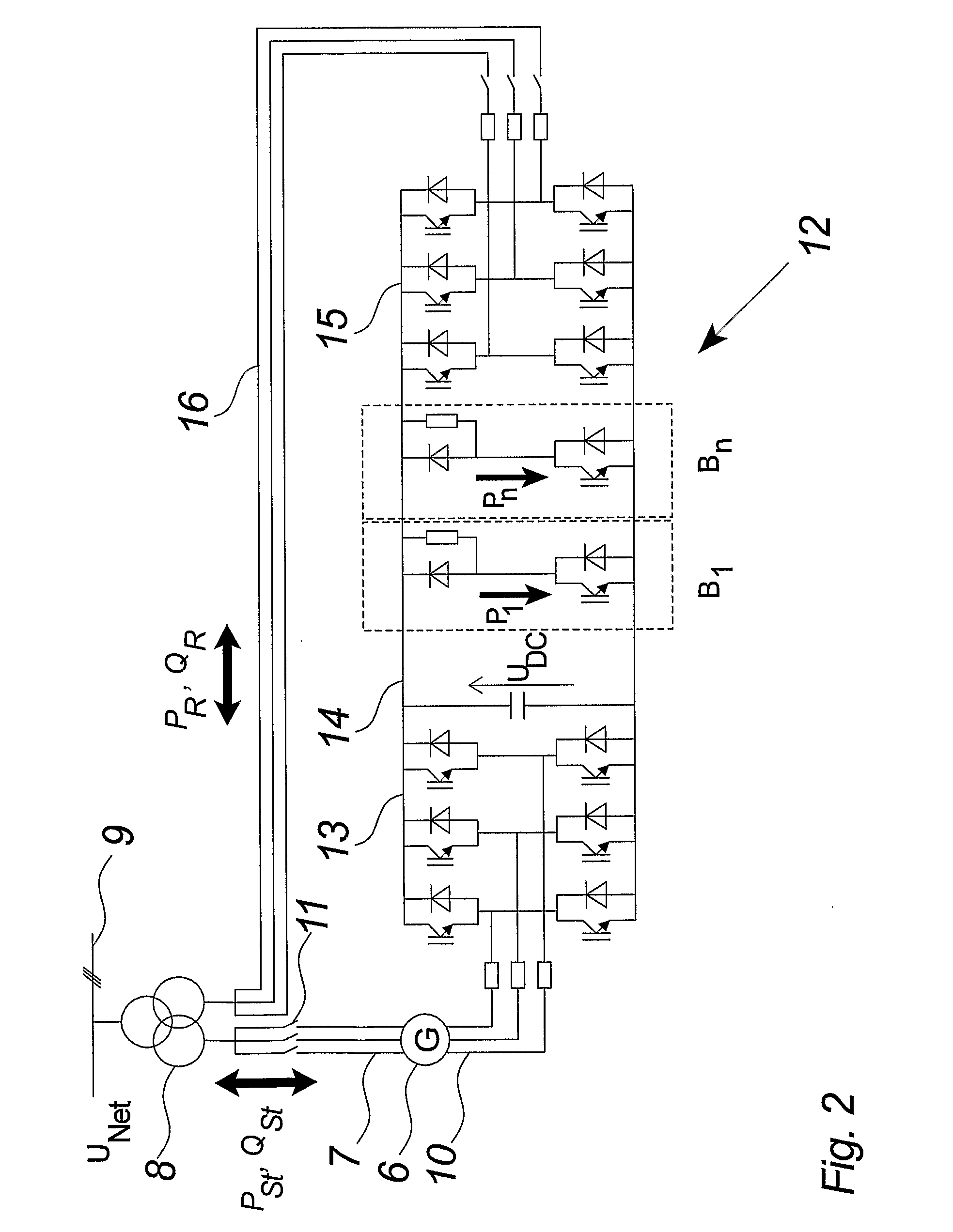
ActiveUS20090079193A1Reduce DC link voltageRelieve pressureWind motor controlWind motor combinationsControl systemEngineering
The invention relates to a method of controlling a wind turbine connected to an electric utility grid during malfunction in said electric utility grid (9). The method comprises the steps of detecting a malfunction in said electric utility grid and operating at least two control units of said power converter (12) in relation to at least one power converter limit value. The invention also relates to a control system for a wind turbine connected to a utility grid and a wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Methods and apparatus for reducing peak wind turbine loads
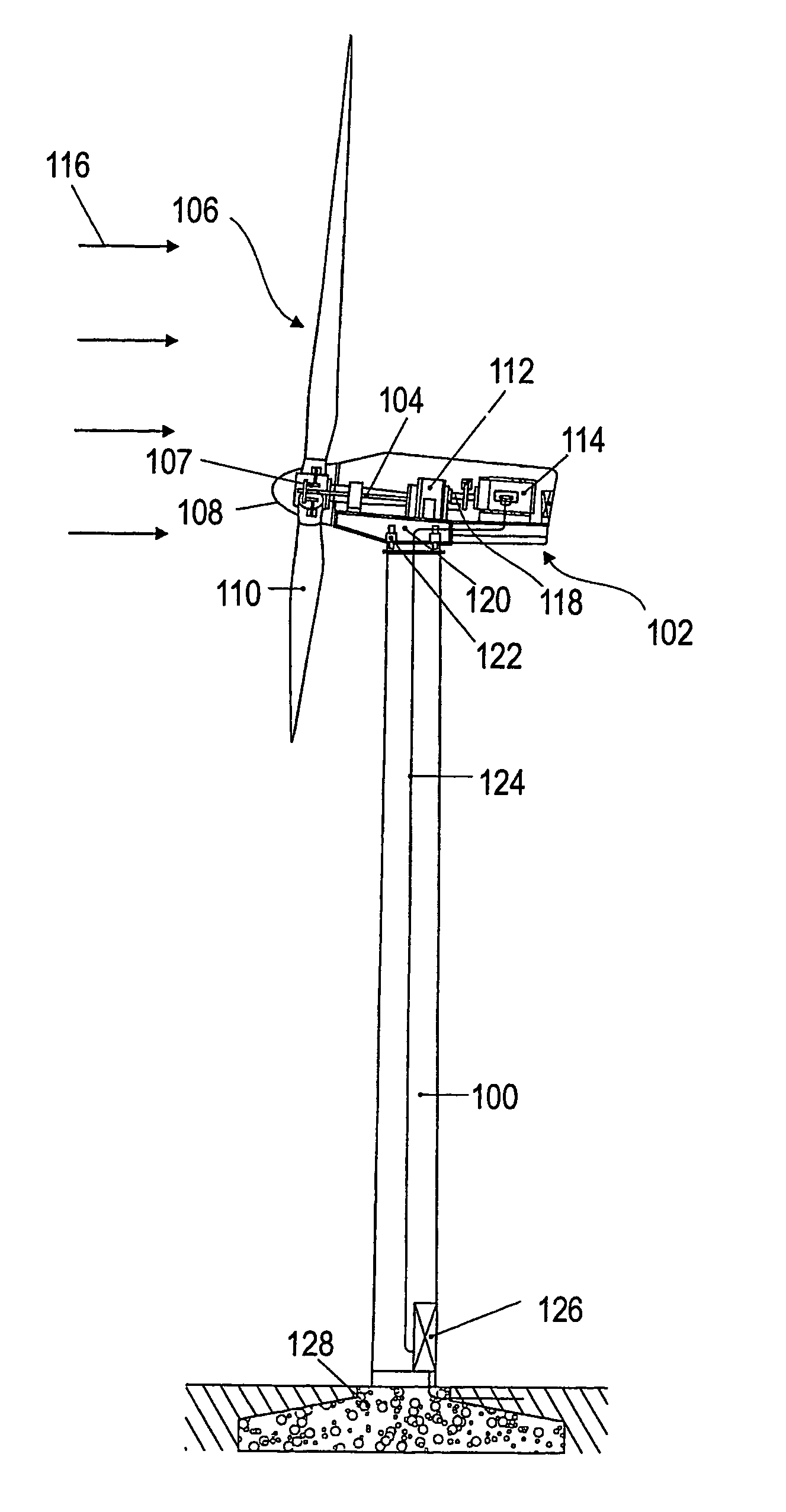
ActiveUS20060002791A1Reduce peak loadReduce the possibilityPropellersWind motor controlTurbinePeak load
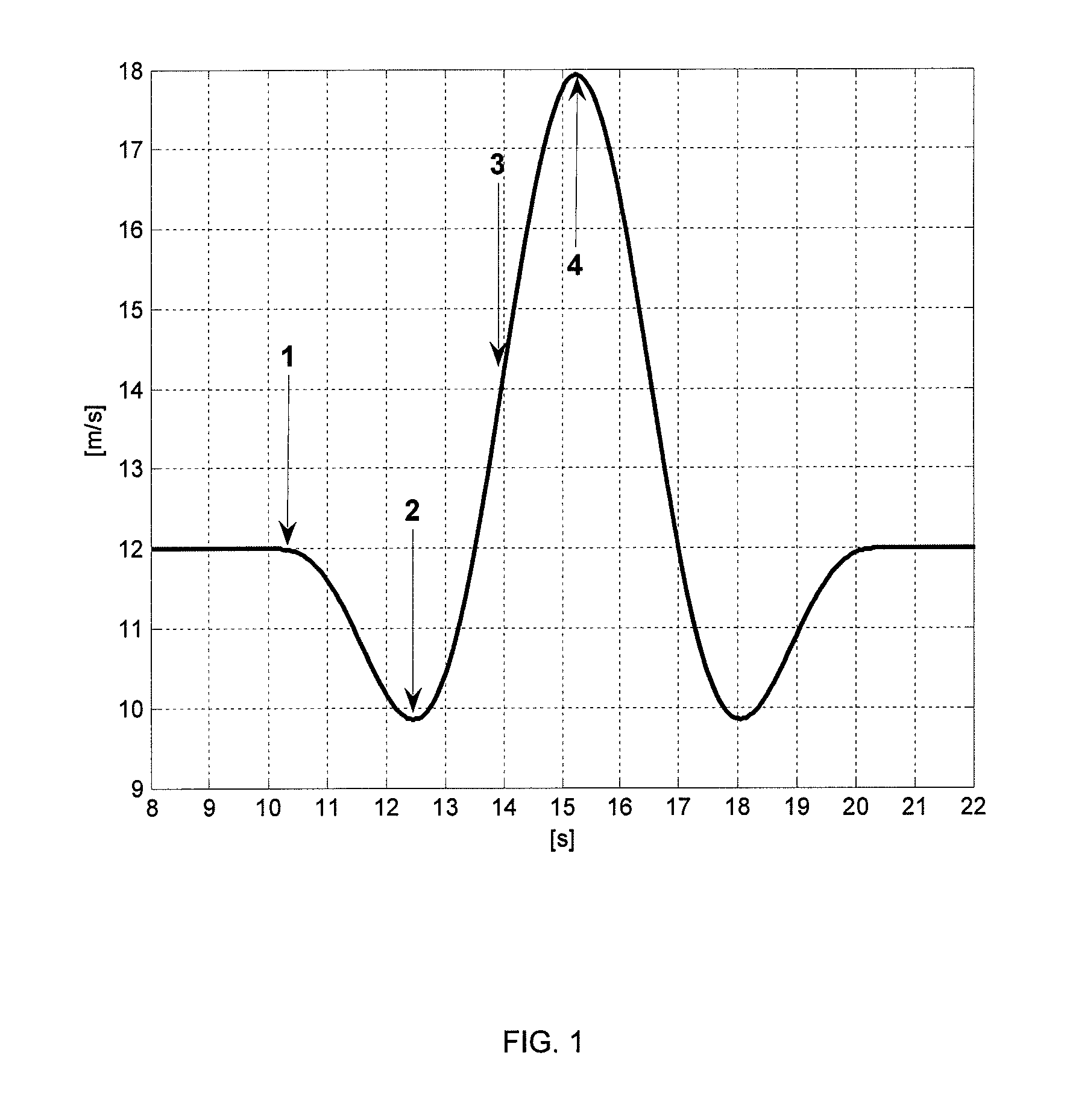
A method for reducing peak loads of wind turbines in a changing wind environment includes measuring or estimating an instantaneous wind speed and direction at the wind turbine and determining a yaw error of the wind turbine relative to the measured instantaneous wind direction. The method further includes comparing the yaw error to a yaw error trigger that has different values at different wind speeds and shutting down the wind turbine when the yaw error exceeds the yaw error trigger corresponding to the measured or estimated instantaneous wind speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind turbine system for satisfying low-voltage ride through requirement
A wind turbine system is provided with a wind turbine rotor, a pitch control mechanism, and an emergency power supply mechanism. The wind turbine rotor includes a blade having a variable pitch angle. The pitch control mechanism drives the blade to control the pitch angle. The emergency power supply mechanism generates electric power from rotation of the wind turbine rotor and feeds the electric power to the pitch control mechanism, in response to occurrence of an accidental drop of a system voltage of a power grid.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
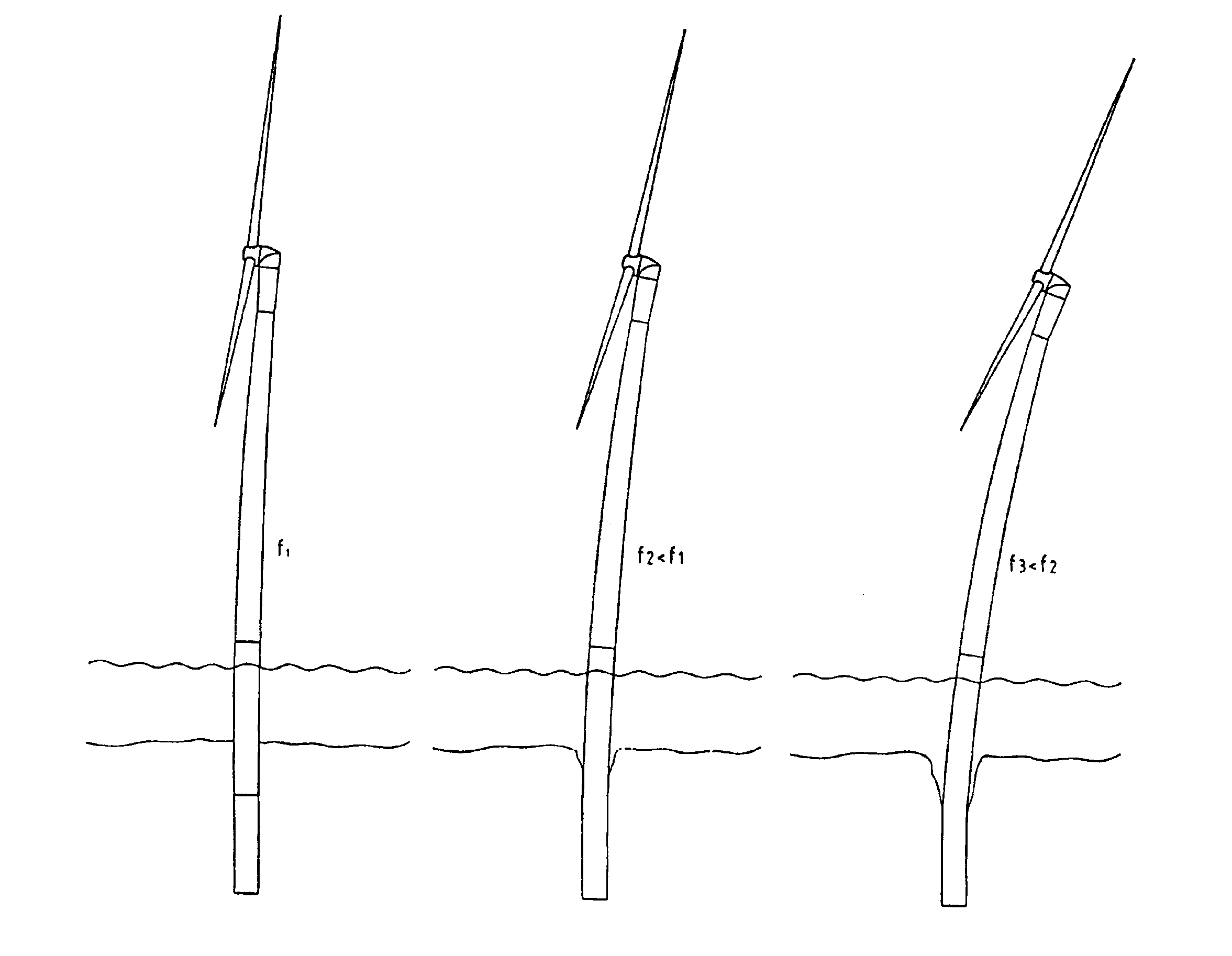
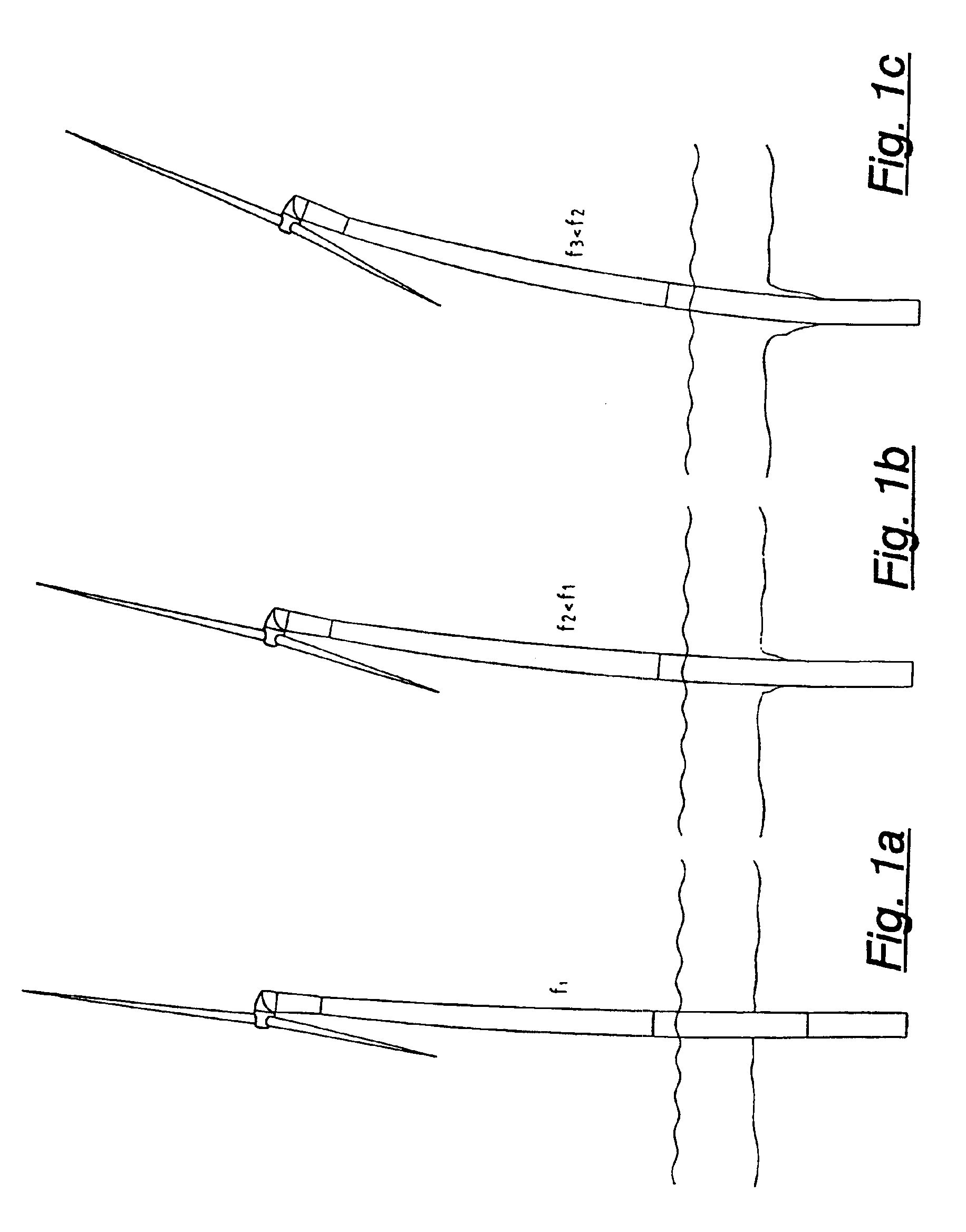
Method for operating offshore wind turbine plants based on the frequency of their towers
A method for operating a wind power plant which is provided with a device for regulating the speed of a rotor of the wind power plant. The method includes the steps of: determining the critical frequency of the respective turbine and / or turbine components, determining the speed range of the rotor in which the entire turbine and / or individual turbine components are excited in the vicinity of their critical frequencies and operation of the wind turbine plant only below and above the critical range; the latter being traversed rapidly.
Owner:MULTIBRID
Methods and apparatus for reducing peak wind turbine loads
A method for reducing peak loads of wind turbines in a changing wind environment includes measuring or estimating an instantaneous wind speed and direction at the wind turbine and determining a yaw error of the wind turbine relative to the measured instantaneous wind direction. The method further includes comparing the yaw error to a yaw error trigger that has different values at different wind speeds and shutting down the wind turbine when the yaw error exceeds the yaw error trigger corresponding to the measured or estimated instantaneous wind speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
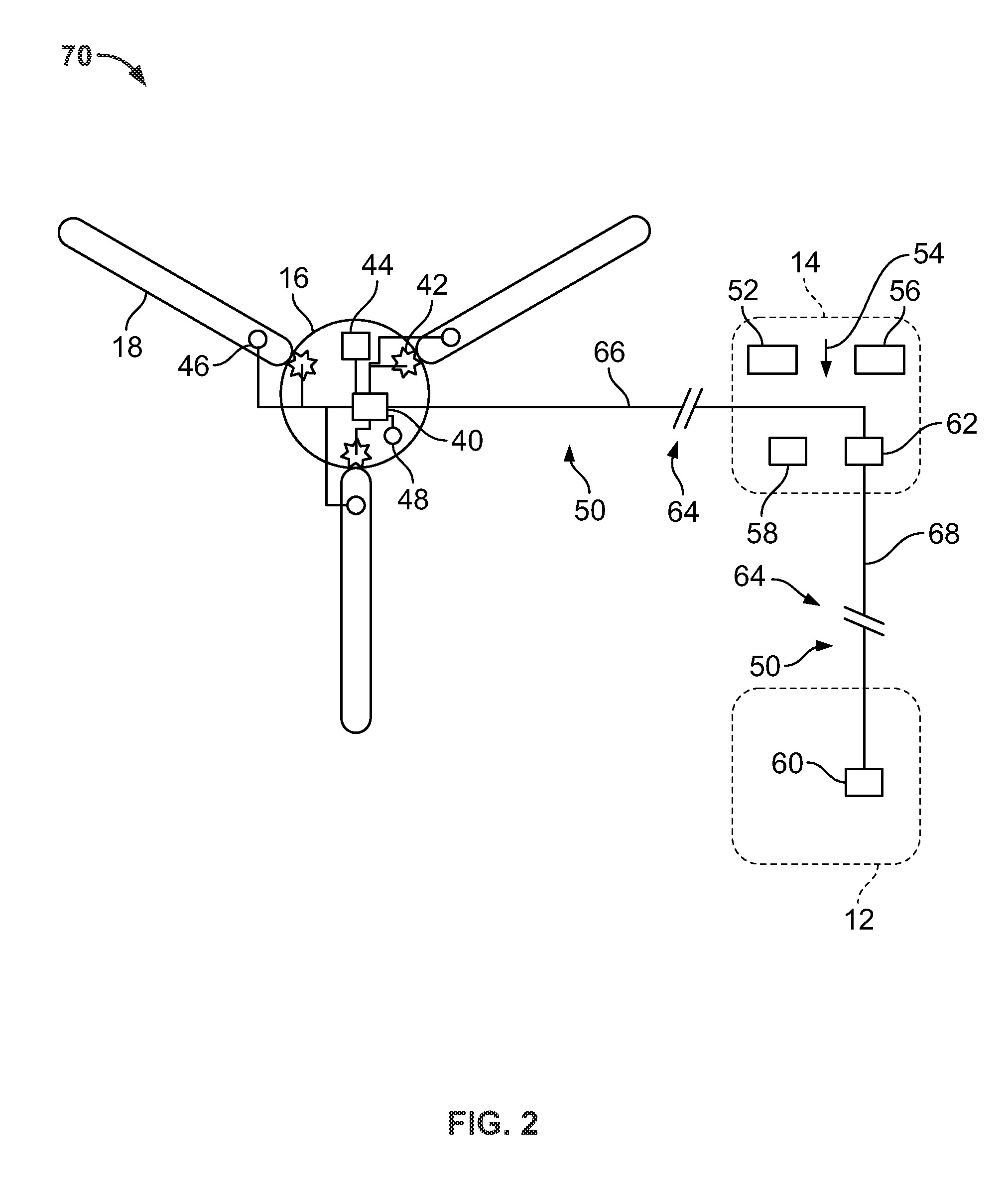
Wind turbine and operating method thereof
InactiveUS20080069692A1Prevent speedingControl moreRotational speed controlLevel controlClassical mechanicsControl theory
A pitch controller, uninterruptible power supply, and rotational speed detector are disposed in the rotor in a wind turbine. When a slip ring failure or wire breakage occurs, the pitch controller internally creates a pitch angle command so as to control the pitch angle.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and systems for operating a wind turbine using dynamic braking in response to a grid event
A method and system for dissipating energy in a direct current (dc) bus of a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) converter during a grid event is described. In one aspect, the method comprises monitoring operating conditions of an electrical system, the electrical system comprising at least a DFIG generator and a line side converter and a rotor side converter connected by a dc bus having a dynamic brake connected thereto; detecting an overvoltage on the dc bus or a condition indicative of an overvoltage on the dc link is detected, the overvoltage on the dc bus or condition indicative of the overvoltage caused by a grid event; and causing energy in the dc link to be dissipated using the dynamic brake.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
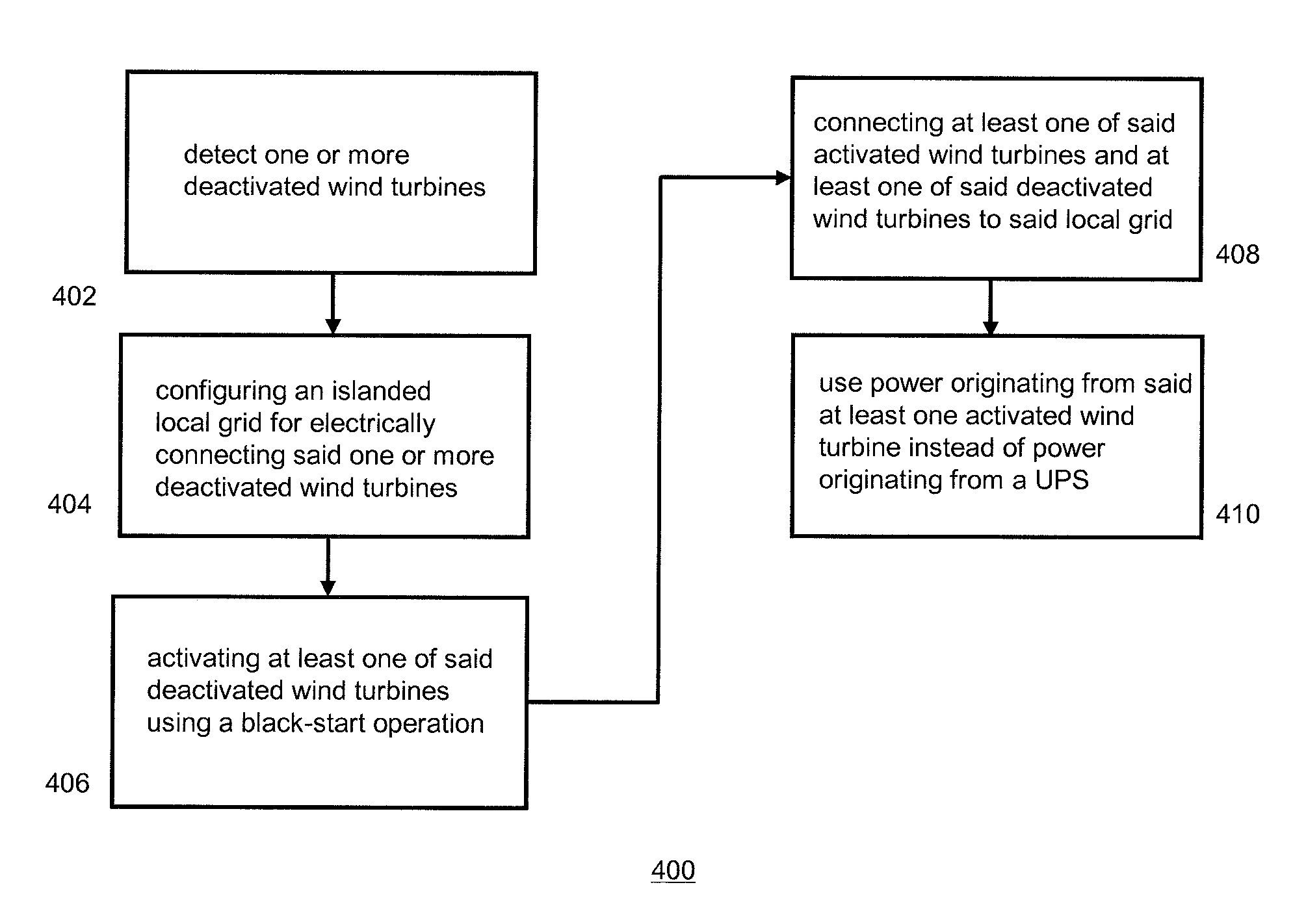
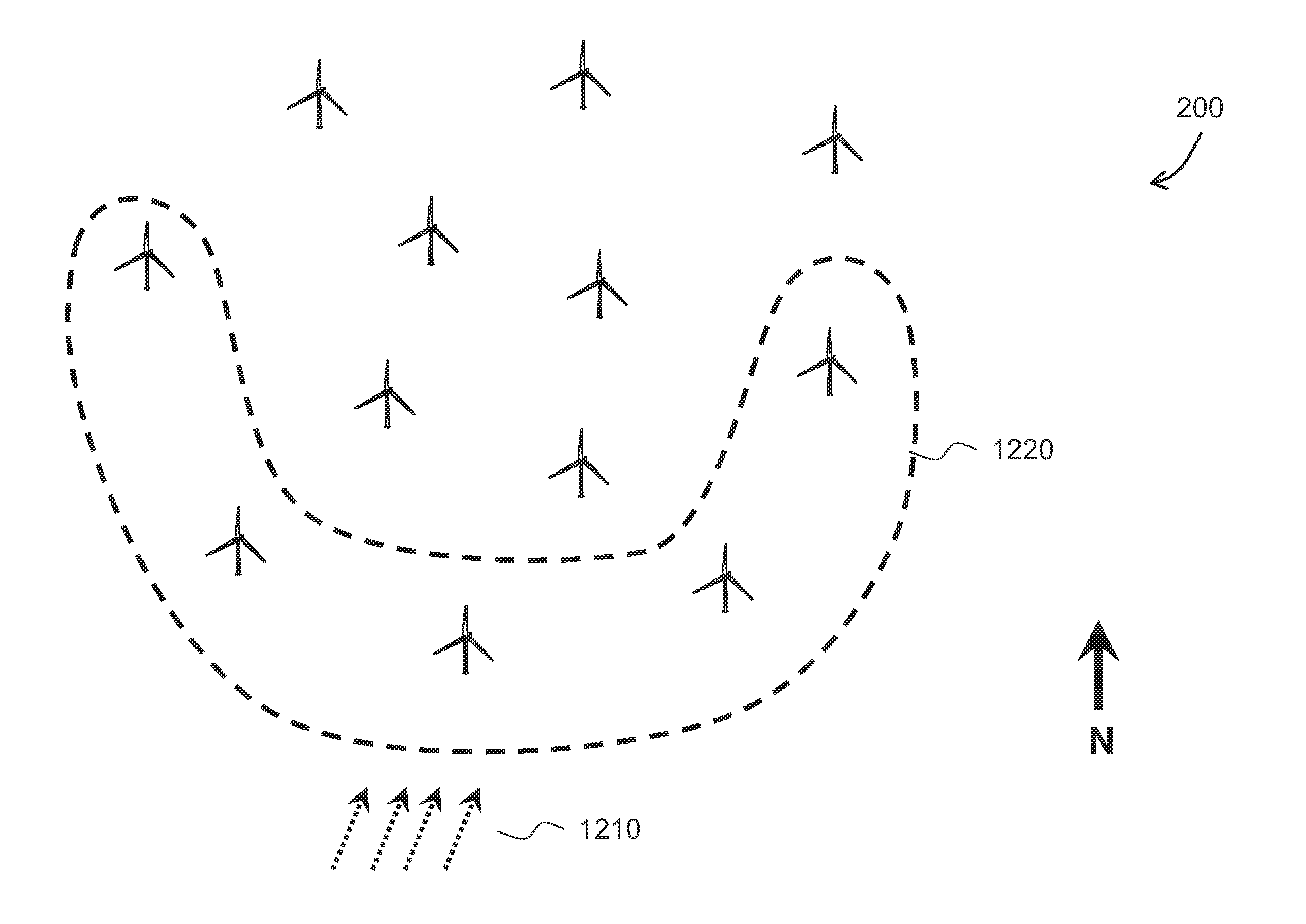
Wind farm island operation
ActiveUS20120146423A1Efficient and cheapReduce necessityDc network circuit arrangementsWind motor controlEngineeringTurbine
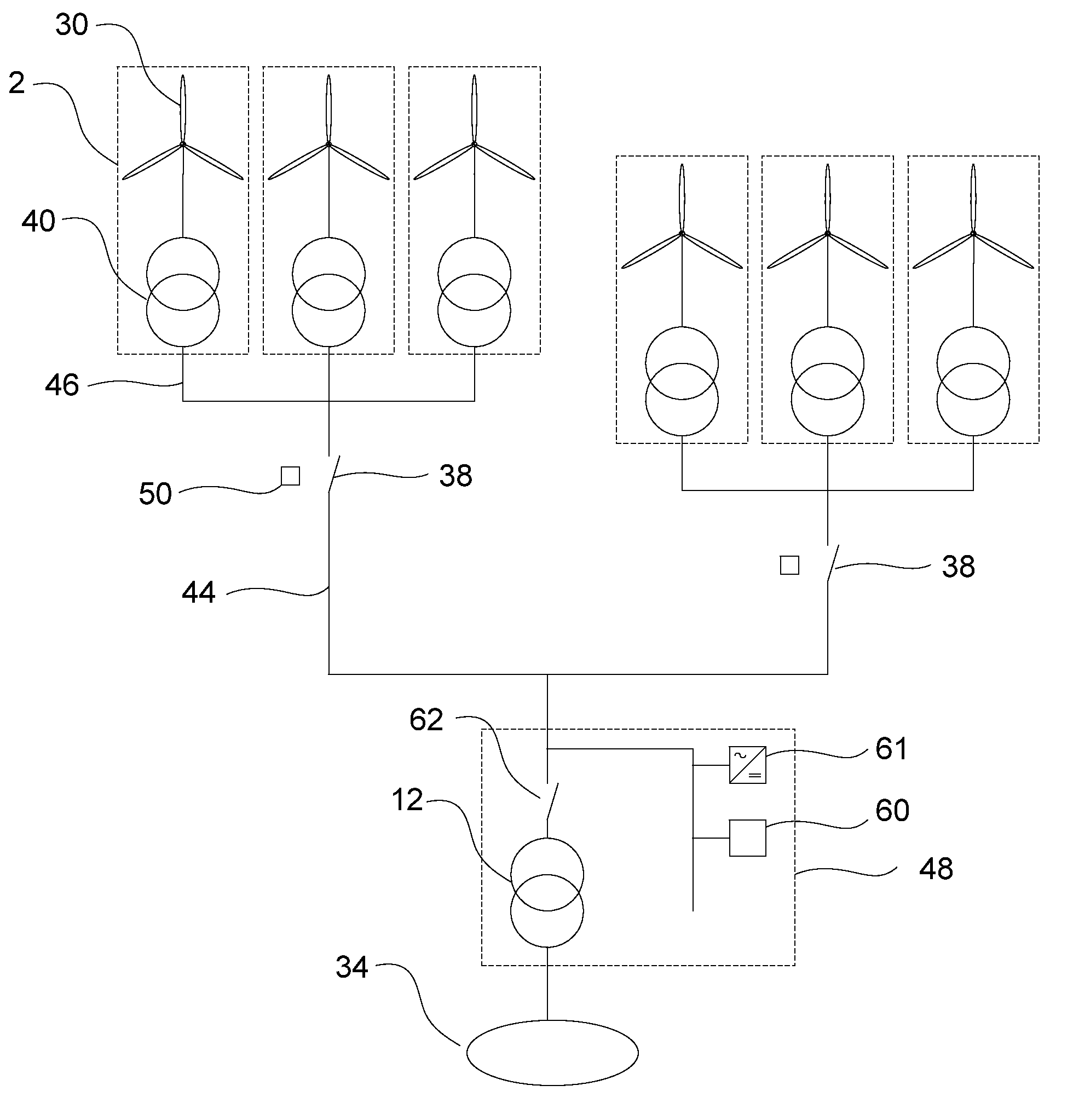
A method and a system are described for island operation of at least two wind turbines associated with a wind farm, wherein said wind farm is configured for providing power generated by wind turbines in said wind farm to a main grid and wherein the method comprises: detecting at least two or more deactivated wind turbines in said wind farm, said deactivated wind turbines being disconnected from said main grid; configuring at least one islanded local grid for electrically connecting said two or more deactivated wind turbines; activating at least one of said deactivated wind turbine using a black start operation; and, connecting said at least one activated wind turbine and at least one of said deactivated wind turbines to said local grid, said activated wind turbine acting as a power supply for said at least one deactivated wind turbine connected to said local grid.
Owner:XEMC DARWIND
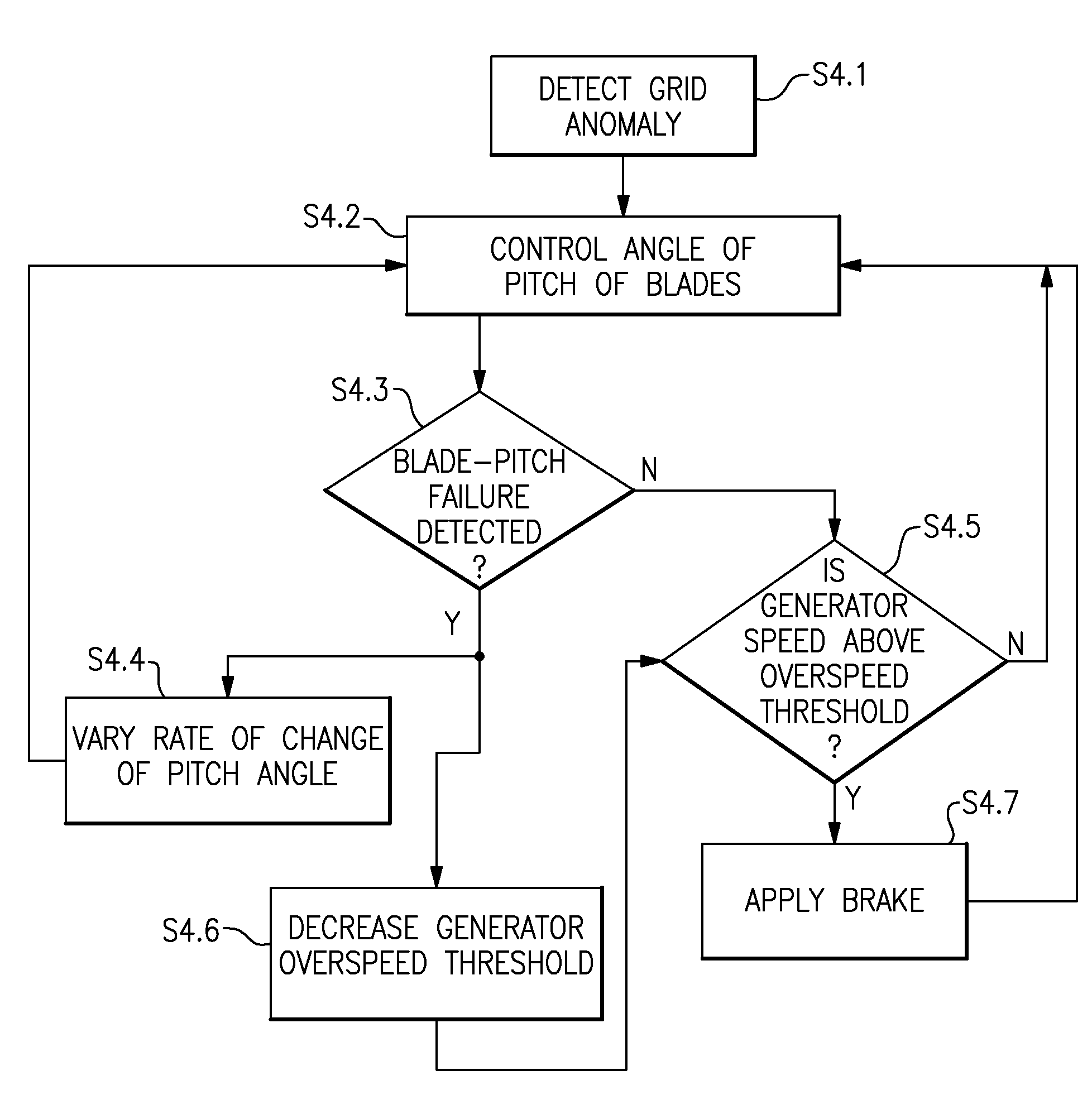
System and method for reducing rotor loads in a wind turbine upon detection of blade-pitch failure and loss of counter-torque
A system and method for reducing rotor loads in a wind turbine that includes a brake and one or more rotor blades coupled to a rotor. Upon detection of a loss of counter torque and a blade-pitch failure in at least one rotor blade, a processor reduces a generator overspeed threshold value by a predetermined amount and determines a brake-release threshold value. The brake is applied to slow the rotor if the generator / rotor speed exceeds the reduced generator / rotor overspeed threshold value. In addition, the brake is applied to slow the rotor until the generator / rotor speed is below the brake-release threshold value. The rate of change of the pitch angle of the rotor blade may be varied as the blade moves toward feather in response to the detected blade-pitch failure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
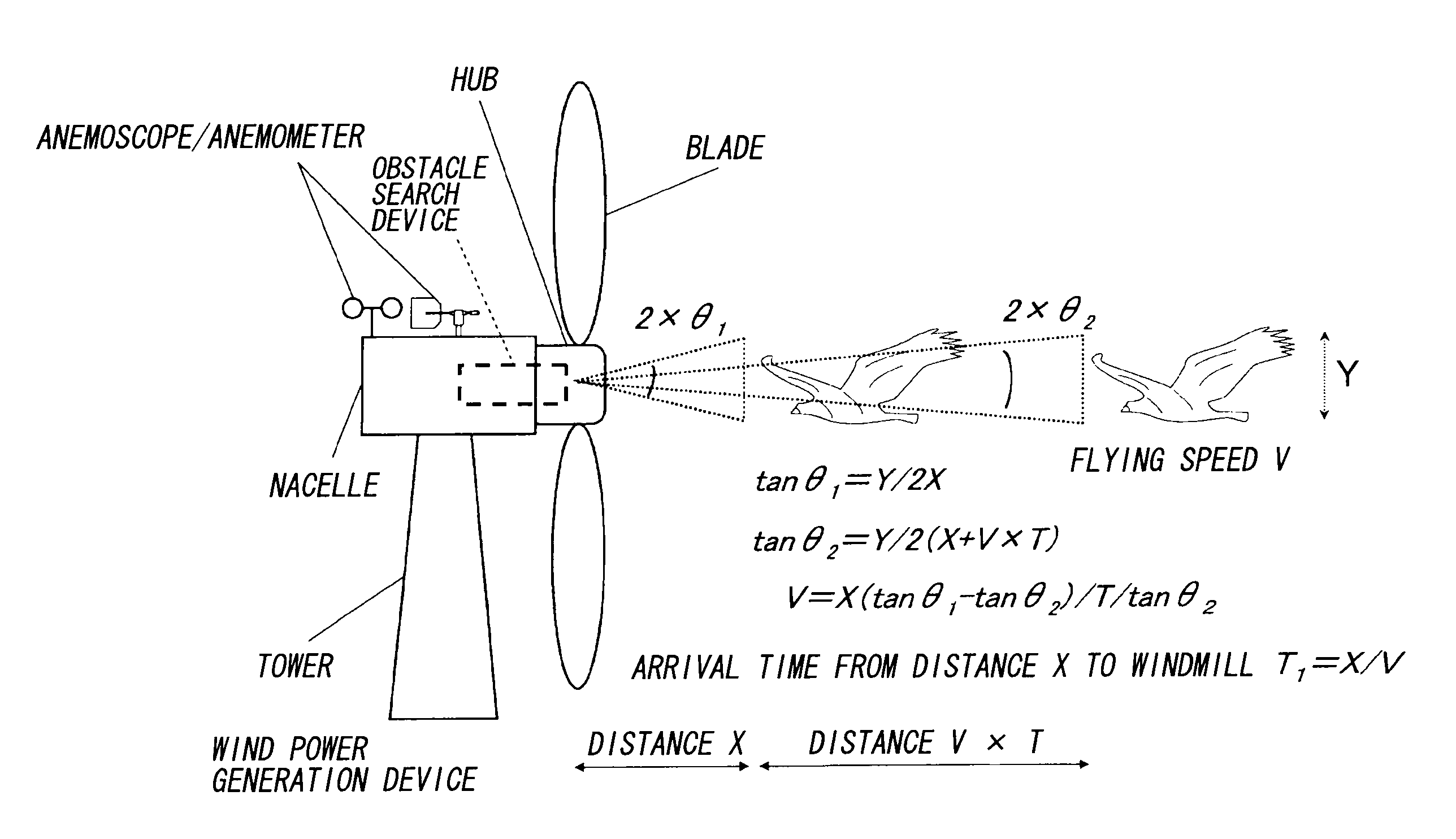
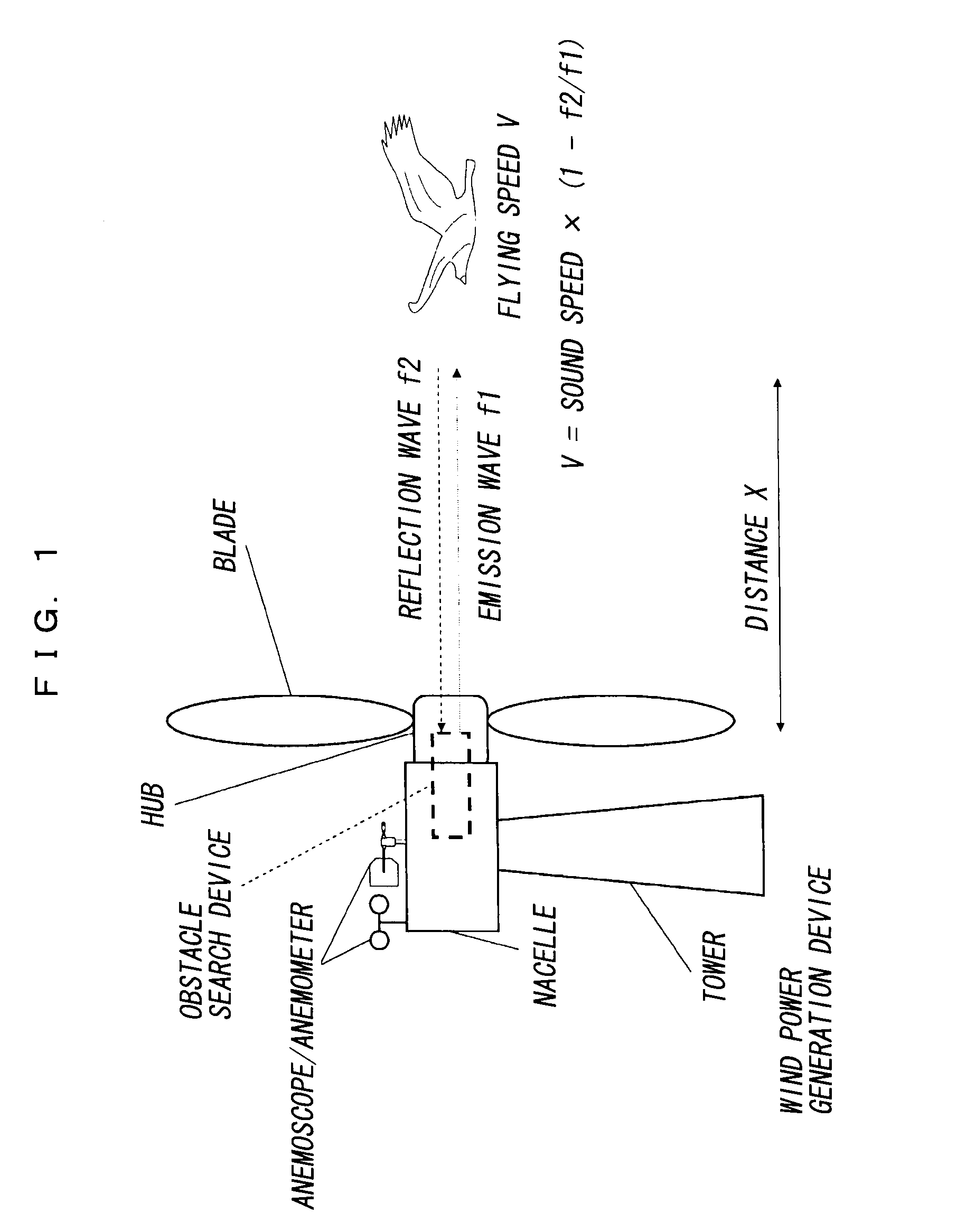
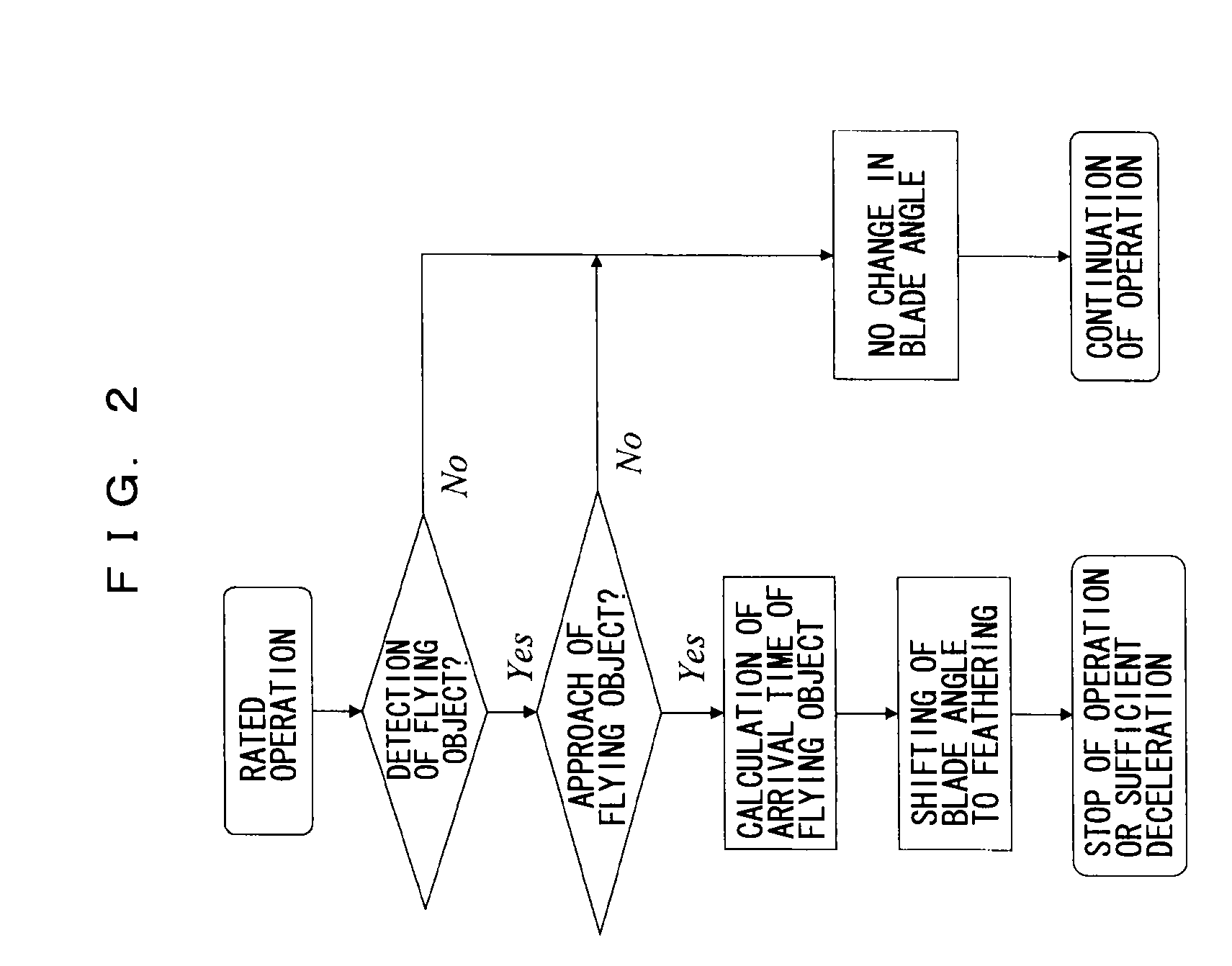
Wind-driven electricity generation device, method of controlling wind-driven electricity generation device, and computer program
InactiveUS20090185900A1Reduce breakageReduce breakage accidentsPropellersPump componentsWind drivenNacelle
The present invention provides a wind power generation device capable of reducing collision of a flying object against a blade or bird strike. The wind power generation device includes a tower set up on the ground, a nacelle fixed to the tower, a plurality of blades rotatably fixed to the nacelle via a hub, an obstacle search device capable of detecting a flying object existing in front, on the windward side, and a blade angle controller to control the change in angle of the blade including a rotation stop position. The obstacle search device searches for the flying object continuously, and when the flying object is determined to be approaching based on the continuous searching, the blade angle controller controls to change the blades to the rotation stop position.
Owner:THE TOKYO ELECTRIC POWER CO INC
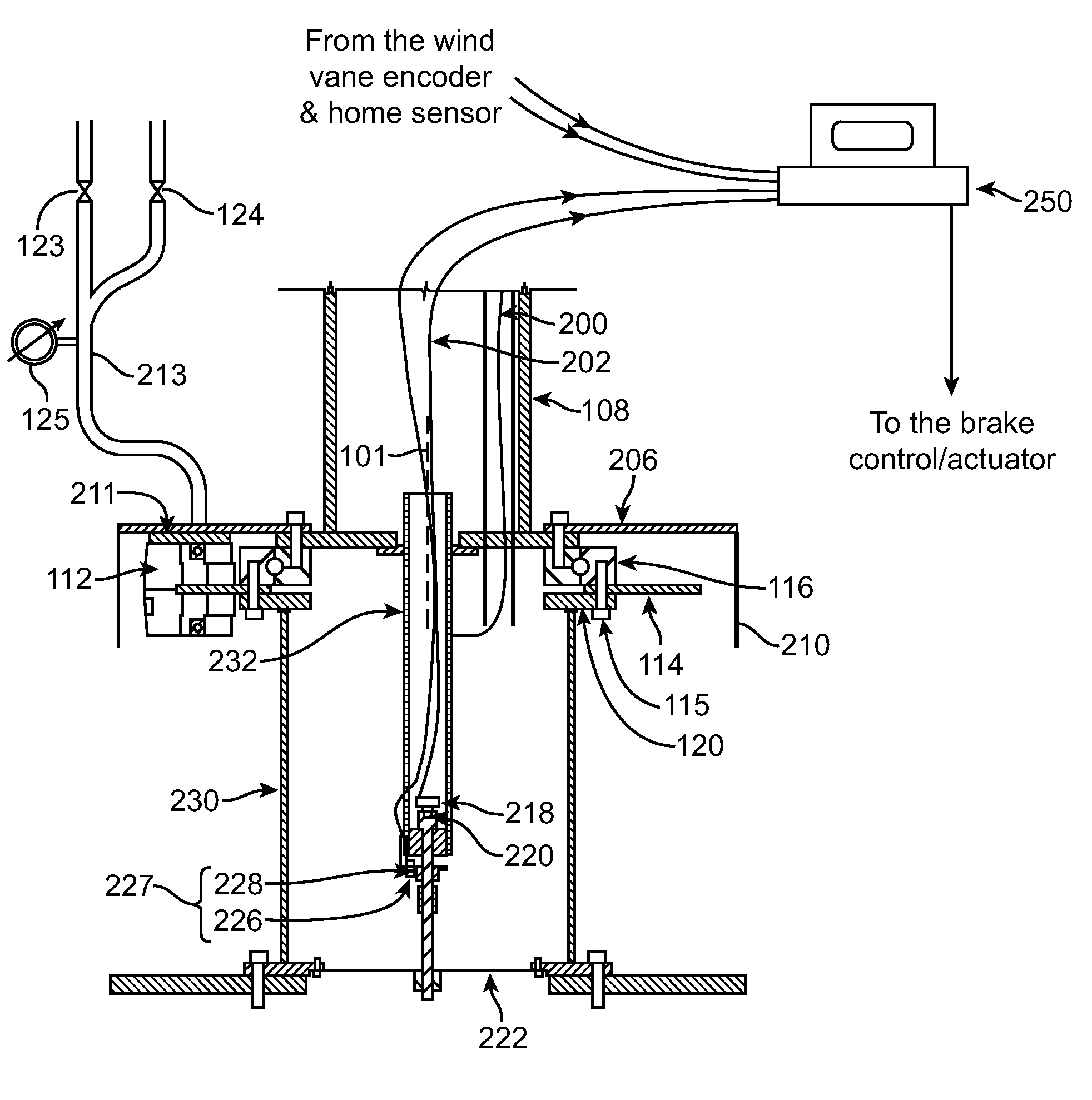
Yaw controller for downwind wind turbines
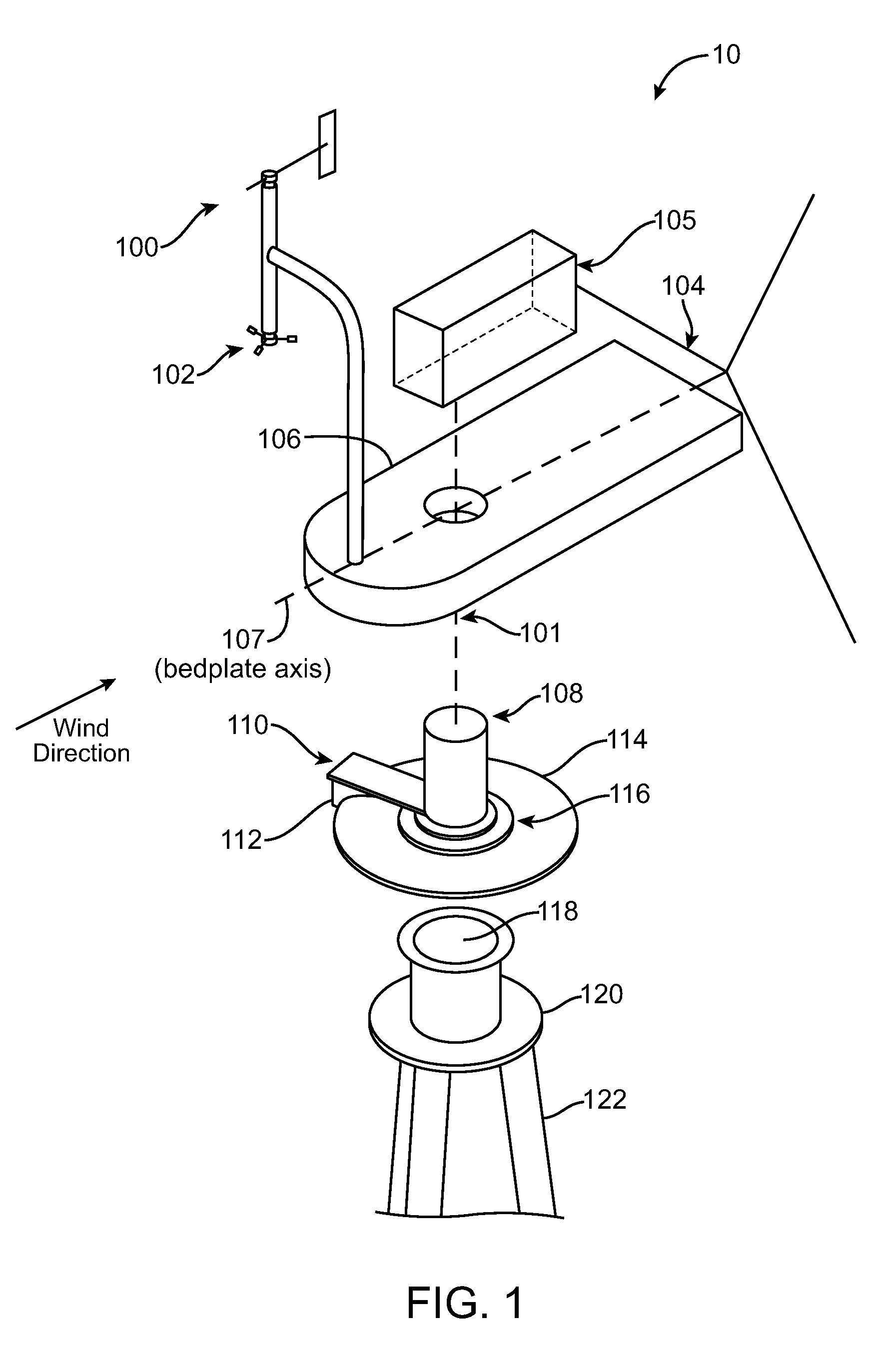
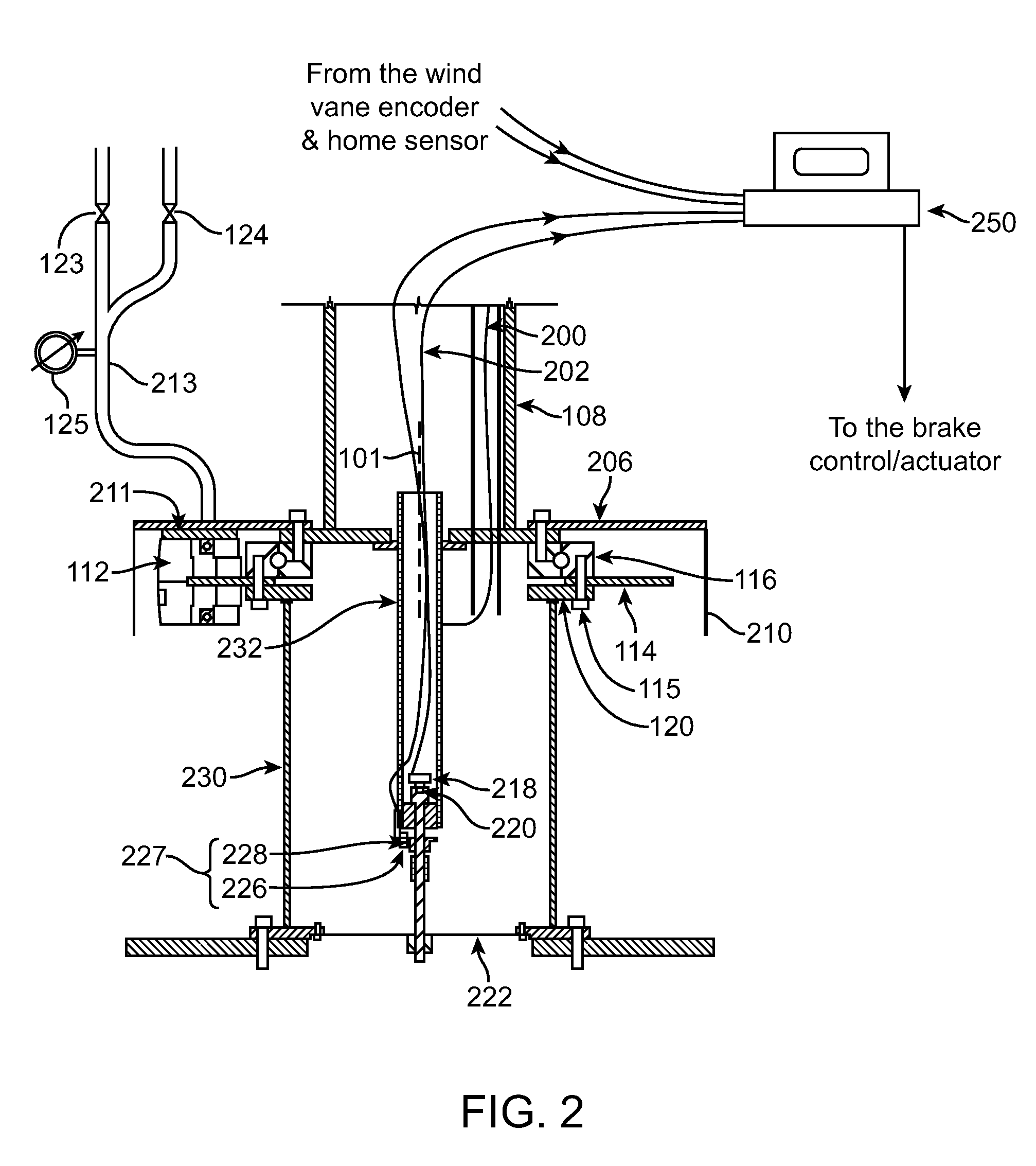
InactiveUS20100209246A1Preventing unsafe yaw brake releaseReduce rotationPropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeTower
Apparatuses and methods are disclosed for the wind turbine yaw control. A wind turbine bedplate is rotateably mounted on a stationary tower. The bedplate is connected to a yaw encoder, which provides angular position of the bedplate with respect to the stationary tower. A wind vane, which can be attached to the bedplate, is connected to a wind vane encoder. The yaw encoder and wind vane encoder send data to a turbine controller. When the bedplate orientation differs from the average wind direction by a predetermined amount, a yaw brake that keeps the bedplate in place is released in a controllable fashion, such that some amount of friction between the brake pads and the stationary disk remains. Consequently, the bedplate will controllably rotate to align itself with the newly established average wind vector, thus aligning the turbine blade rotation plane substantially perpendicularly against the average wind vector. When the bedplate arrives to its new position, as determined by the yaw encoder reading, the yaw brake can be fully applied again to fix the bedplate at its new position.
Owner:MIGLIORI ROBERT
Method for reducing loads in a wind turbine
InactiveUS20120139240A1Protect the loadMore speedWind motor controlWind motor combinationsControl systemTurbine blade
Loads reduction method in a wind turbine for power-grid disconnection during a wind gust, which uses a control system made up of three loops used to correct the speed at which the wind turbine blades are moved to the feathered position throughout a controlled emergency stop, with a non-linear law that takes into account blade position, tower vibrations and generator rotation speed limits.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Method for controlling a wind energy plant
ActiveUS20090081041A1The method is simple and reliableReduce loadRotational speed controlPropellersNacelleRest position
The present invention is related to a method for controlling a wind energy plant, with a nacelle disposed on a tower and with a rotor with at least one rotor blade, the blade adjustment angle of which can be adjusted by means of a blade adjustment equipment. The objective to provide a reduction of the loads acting on the plant when there is a malfunction of the blade adjustment equipment is resolved according to the present invention in that the function of the blade adjustment equipment is monitored, and when an error of the blade adjustment equipment occurs, the nacelle is rotated from an operating position into a rest position, in which there is a flow of the wind against the surface extended by the at least one rotor blade (4) in a rotation of the rotor which is reduced with respect to the operating position.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY SE & CO KG
Method for operating a wind energy installation and a wind energy installation
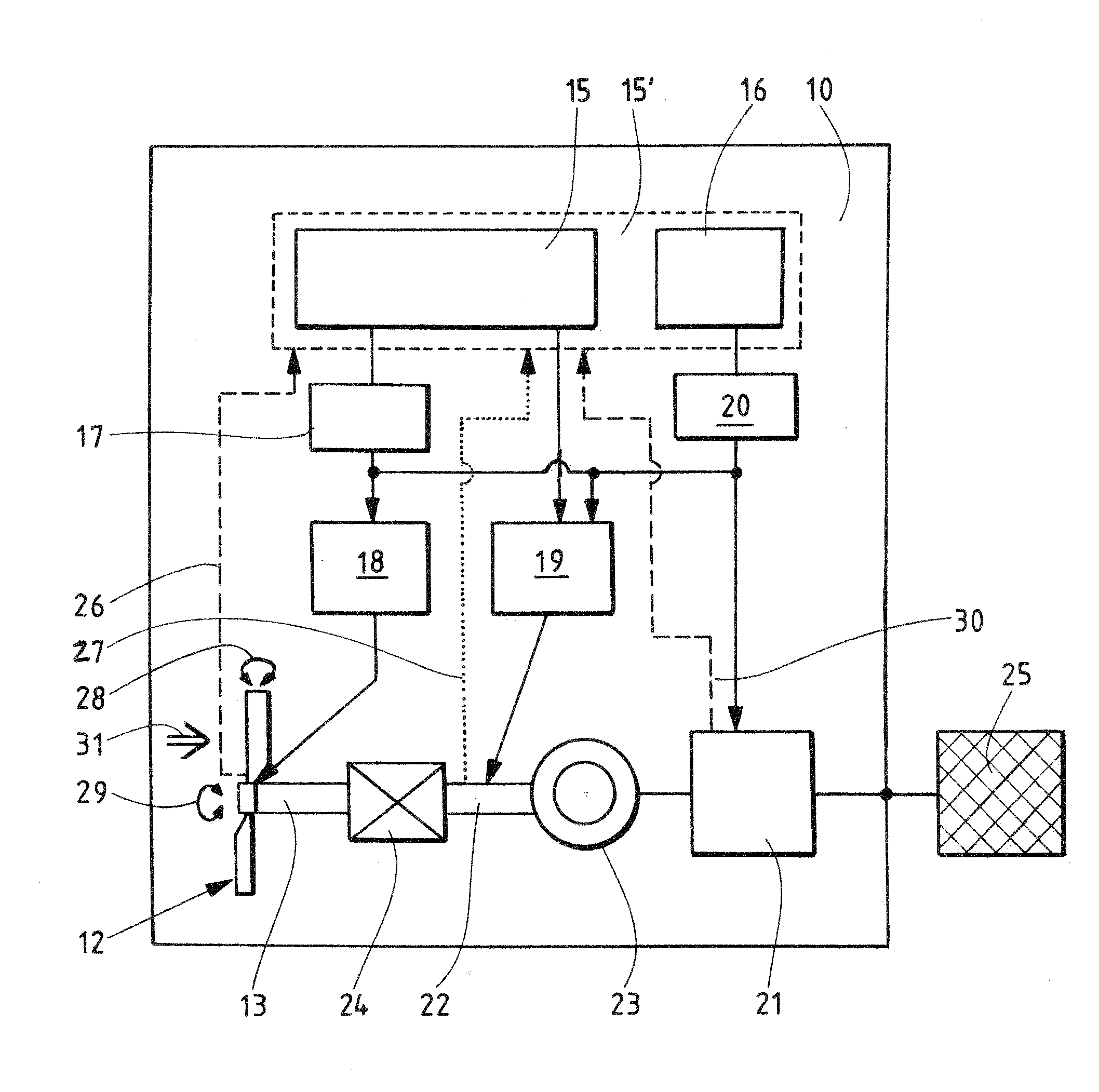
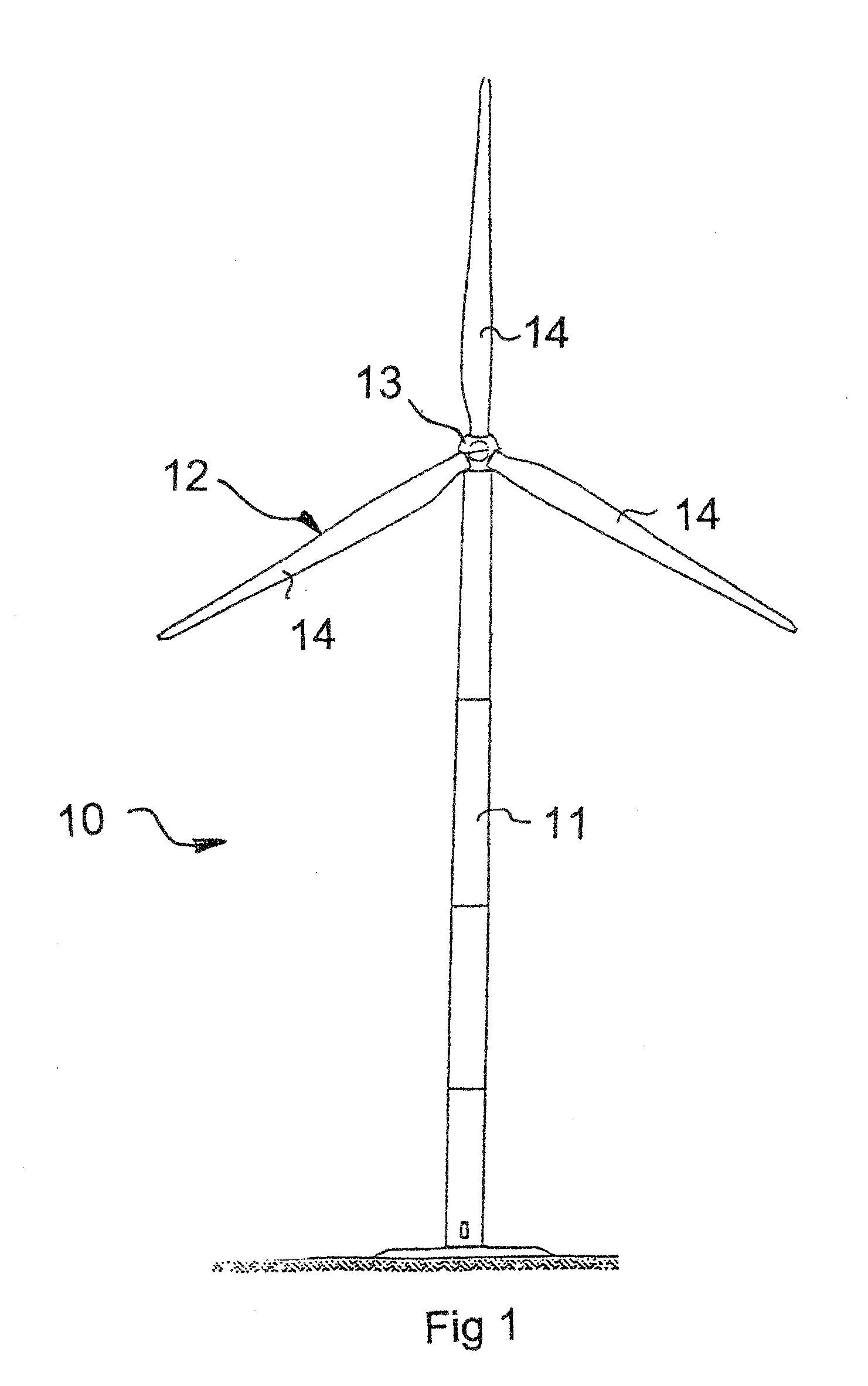
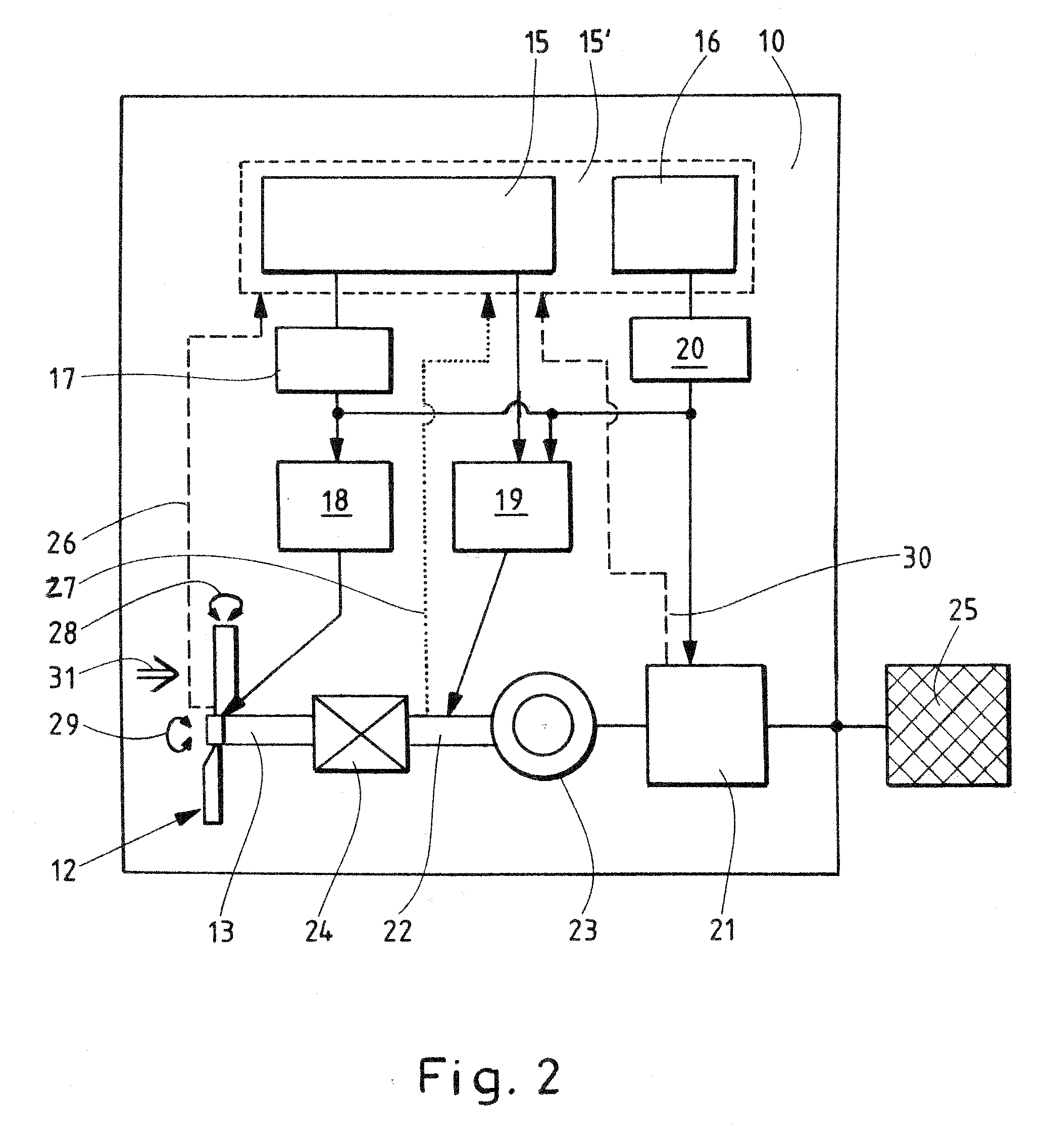
InactiveUS20090295161A1Reduce speedExtreme loadRotational speed controlWind motor controlEngineeringWind power
The invention relates to a method for operating a wind energy installation (10), in which the wind energy installation (10) has a rotor (12, 13, 22), at least one rotor blade (14) with an adjustable angle, a mechanical brake device (19) for braking the rotor (14), an operational control device (15, 15′) and a safety system (16, 20). The invention also relates to a corresponding wind energy installation (10). The method according to the invention is defined by the following method steps: braking of the rotor (12, 13, 22) by means of an angular adjustment (28) with an average angular adjustment rate of less than 8.5° / s of the at least one rotor blade (14) after a fault signal (30) occurs, braking of the rotor (12, 13, 22) by means of the mechanical brake device (19) as soon as the rotational speed of the rotor (12, 13, 22) exceeds a predefinable first rotational speed limit, and triggering of the safety system (16, 20) as soon as the rotational speed of the rotor (12, 13, 22) exceeds a predefinable second rotational speed limit.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
Method and Apparatus for Operating a Wind Turbine During a Loss of Communication
A method for operating a wind turbine during a loss of communication is described that includes coupling a pitch controller to at least one wind turbine blade and to a wind turbine controller, establishing communication between the pitch controller and the wind turbine controller, and detecting a loss of communication between the pitch controller and the wind turbine controller. After a loss of communication is detected, the method further includes waiting for a first predetermined amount of time to elapse, independently pitching the at least one wind turbine blade to a predetermined position, waiting for a second predetermined amount of time to elapse, and maintaining the at least one wind turbine blade in the predetermined position until a rotation of the at least one wind turbine blade stops.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Redundant blade pitch control system for a wind turbine and method for controlling a wind turbine
InactiveUS7717673B2Increase the angleDecreases the aerodynamic lift on the rotor bladesPropellersWind motor controlControl systemEngineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of operating a wind turbine
InactiveCN1900513AReduce power outputShorten speedOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlTurbineElectric generator
In a wind turbine and in a method of operating a wind turbine, the rotor speed and / or the power of the generator is reduced in response to a variable exceeding a predetermined value. Said variables belong to the group of variables consisting of wind direction and wind turbulence sensed by external sensors relative to the horizontal direction of the turbine main shaft and by one or Any other variable sensed by multiple sensors.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Warning a wind turbine generator in a wind park of an extreme wind event
ActiveUS20130144449A1Effective resourcesIncrease power generationMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlEngineeringDynamo
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
System and method for controlling a wind turbine during loss of grid power and changing wind conditions
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for controlling a wind turbine
A wind turbine includes a rotor, a plurality of rotor blades coupled to the rotor, and a blade pitch control system coupled to each rotor blade. A computer-implemented method for controlling the wind turbine includes determining at least one pitch position for a first blade. The method also includes determining whether there is a malfunction of the blade pitch control system associated with the first blade. The method further includes predicting a rotor imbalance using a model of at least a portion of the wind turbine. The method also includes comparing the predicted rotor imbalance with a predetermined threshold value. The method further includes one of regulating the pitch position for the second blade such that the predicted rotor imbalance is restored to a value below the predetermined threshold and regulating a pitch position for a second blade such that the predicted rotor imbalance does not exceed the predetermined threshold.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for controlling a wind turbine
InactiveUS20100314875A1Shorten speedMore speedRotational speed controlWind motor controlNacelleTurbine blade
A system for controlling the RPM of a wind turbine comprising using inverters to draw current from the wind turbine, thereby slowing the rotational speed of the wind turbine blades. In another aspect, a resistor and a switching mechanism attached between the resistor and a phase line is provided to increase the load on the phase line. A yaw motor is also used to yaw the facing direction of the wind turbine out of the wind. Moreover, a normally closed switching mechanism can redirect current from a phase line through a resistor. A normally closed brake is also used to mechanically engage the turbine when the control system fails. A normally open yawing clutch when disengaged allows the nacelle of the wind turbine to rotate freely into the down wind direction. The system also comprises a switch that can create an electrical short between the phase lines of the turbine.
Owner:REDRIVEN POWER
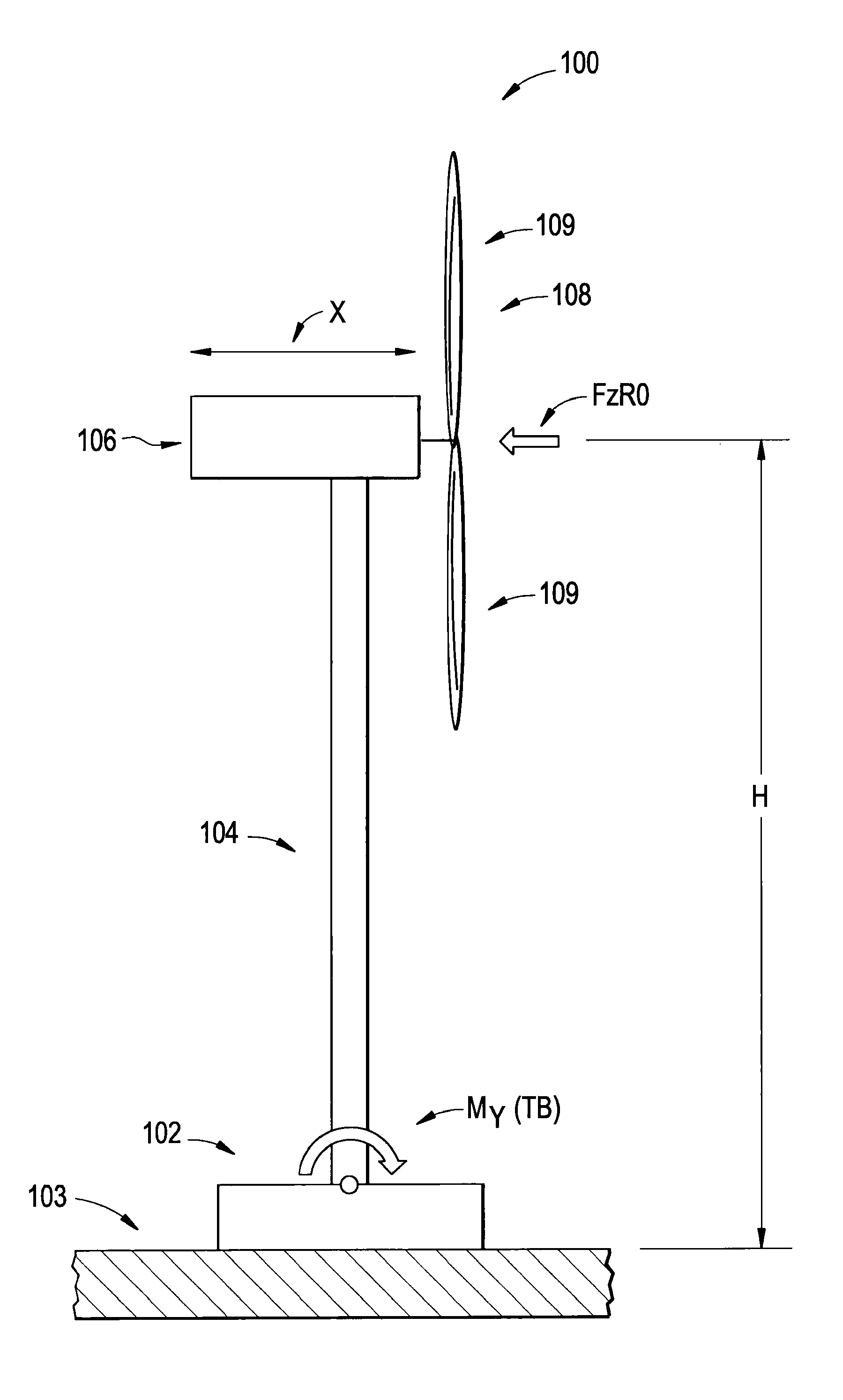
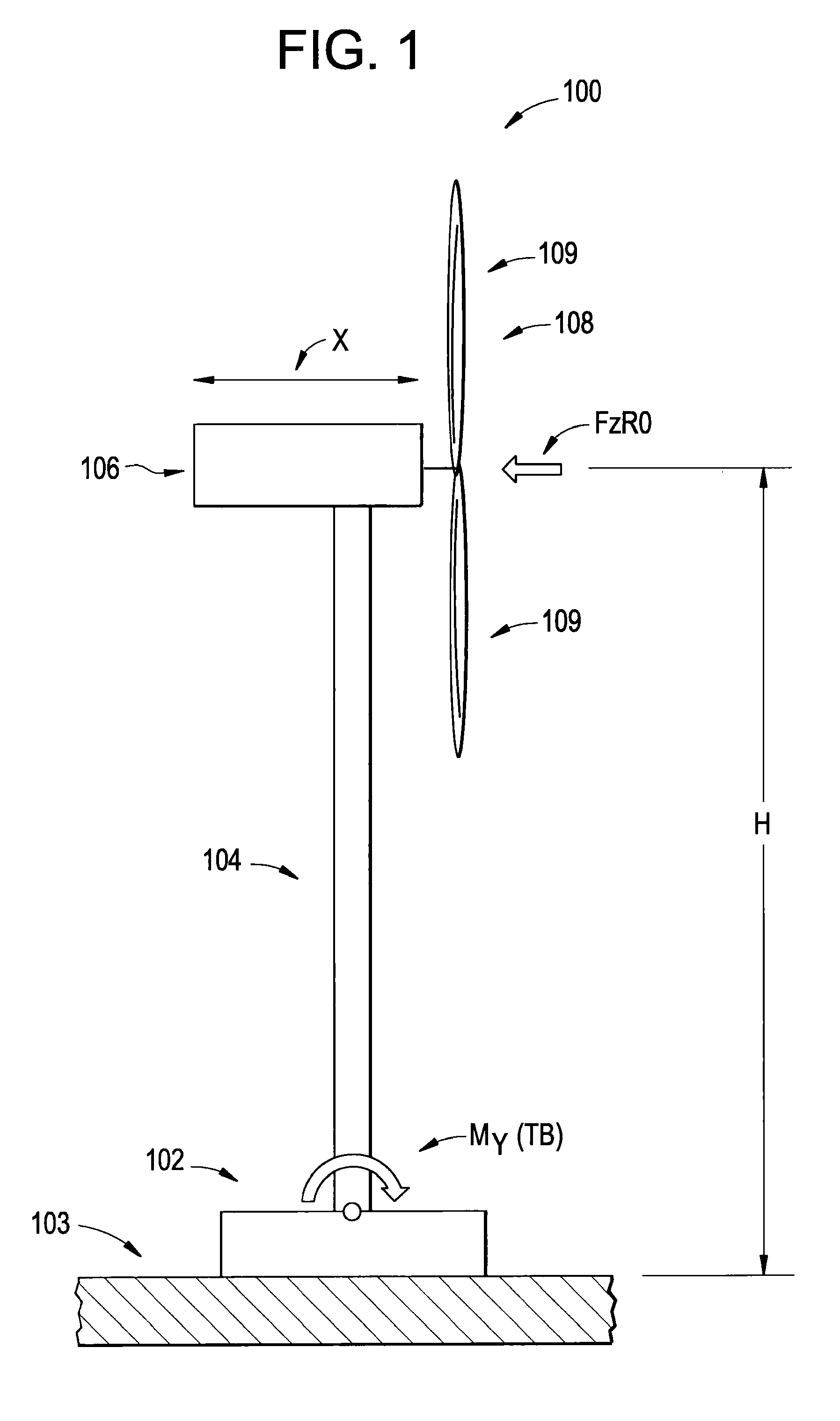
Systems and methods involving wind turbine towers for power applications
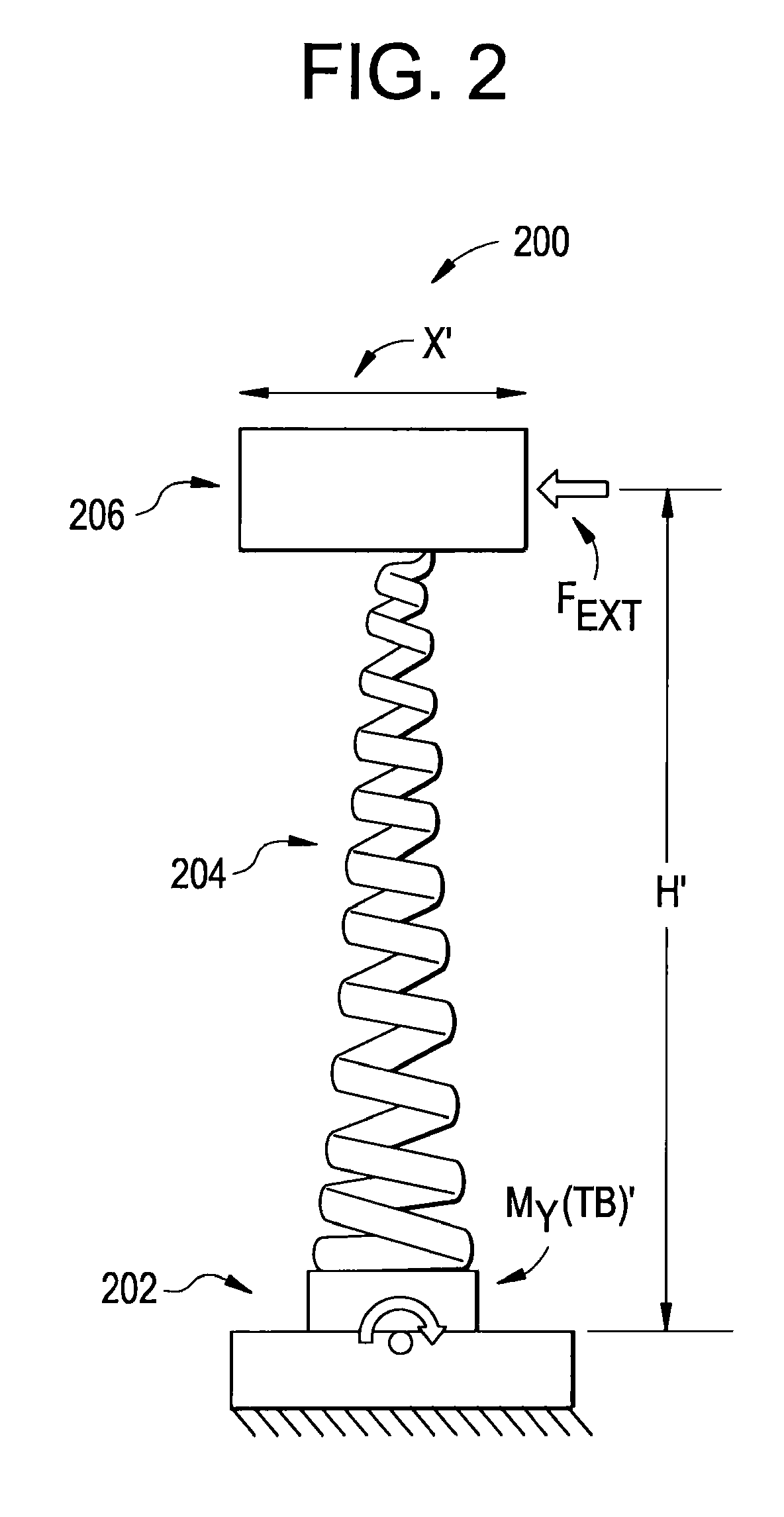
A system for determining wind turbine tower base torque loads including a controller configured to determine a torque load of a base of a tower of a wind turbine according to a computation of an effective height of the wind turbine multiplied by a wind force upon a rotor of the wind turbine, and generate a control signal representing the torque load. A method for determining wind turbine tower base torque loads including determining a torque load of a base of a tower of a wind turbine according to the foregoing computation, and generating a control signal representing the torque load.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind power plant predictive protection circuit
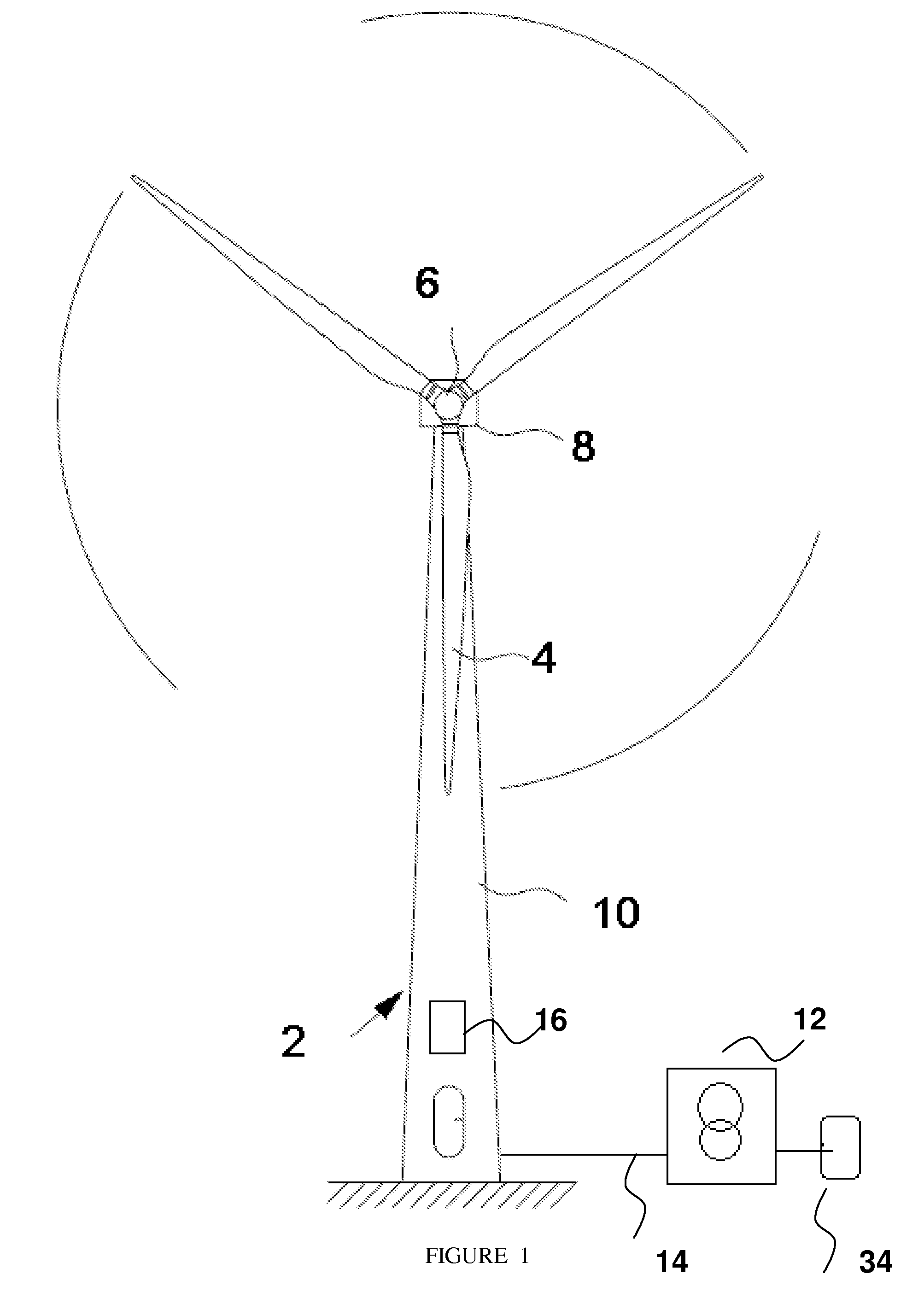
The present invention relates to a method of operating of a wind power plant comprising a circuit breaker and at least one wind turbine generator electrically connectable to an electrical grid through said circuit breaker, the method comprising the steps of detecting at least one condition for the circuit breaker to trip by means of a sensor; informing a control means of this detection prior to the circuit breaker disconnecting; and preparing the at least one wind turbine generator before said circuit breaker disconnects said at least one wind turbine generator from said electrical grid.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com