Patents
Literature
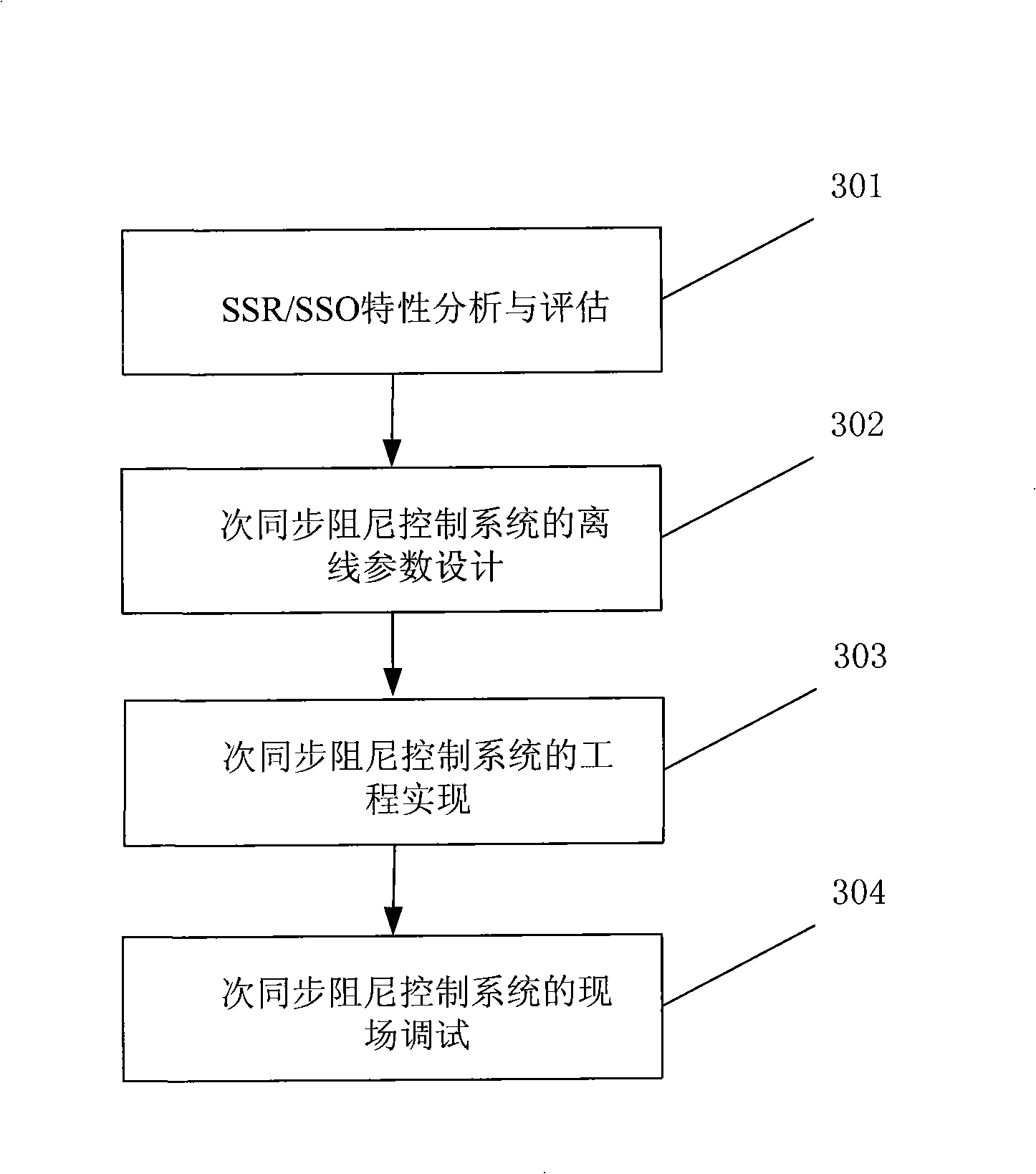
174 results about "Torsional oscillations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
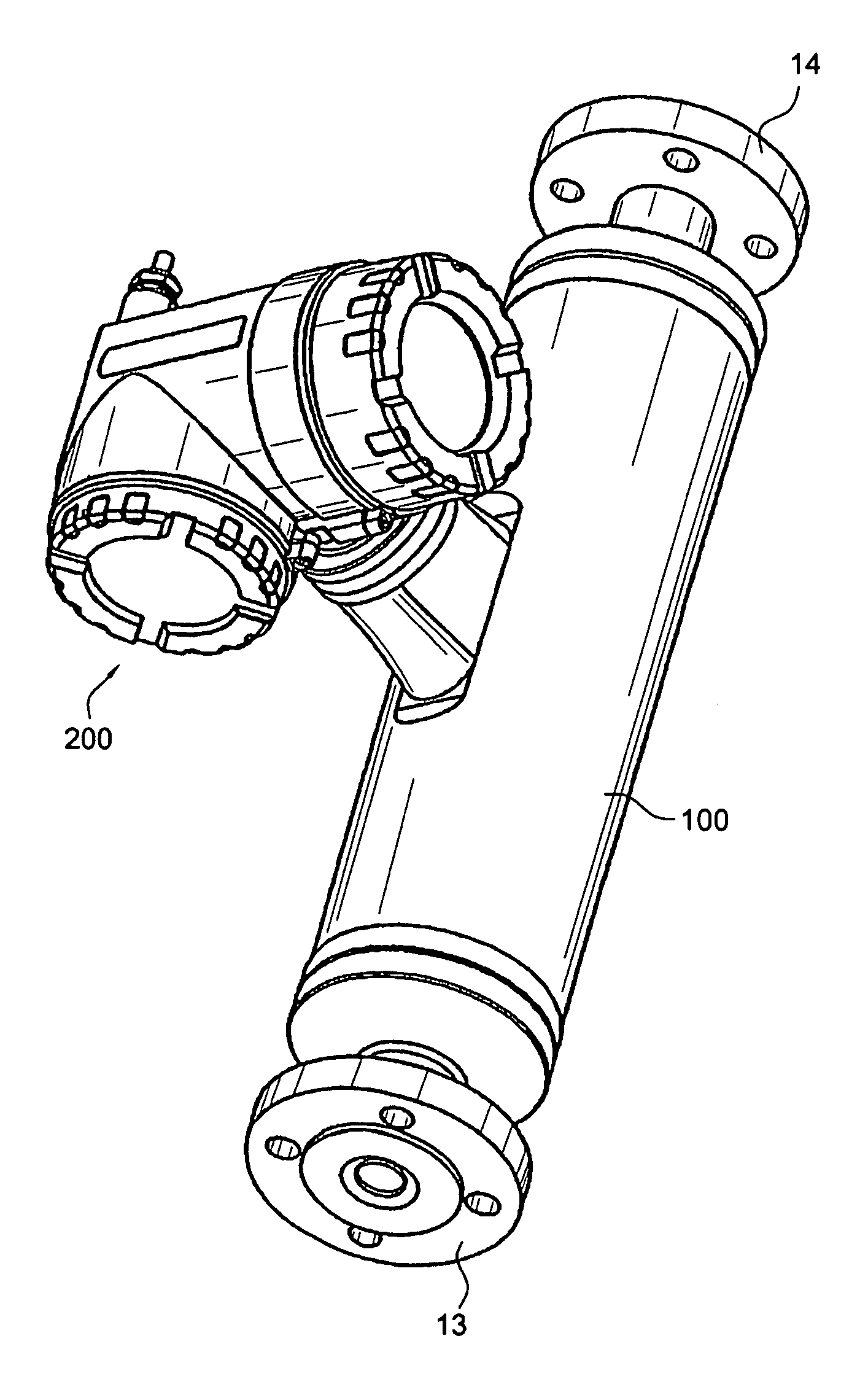
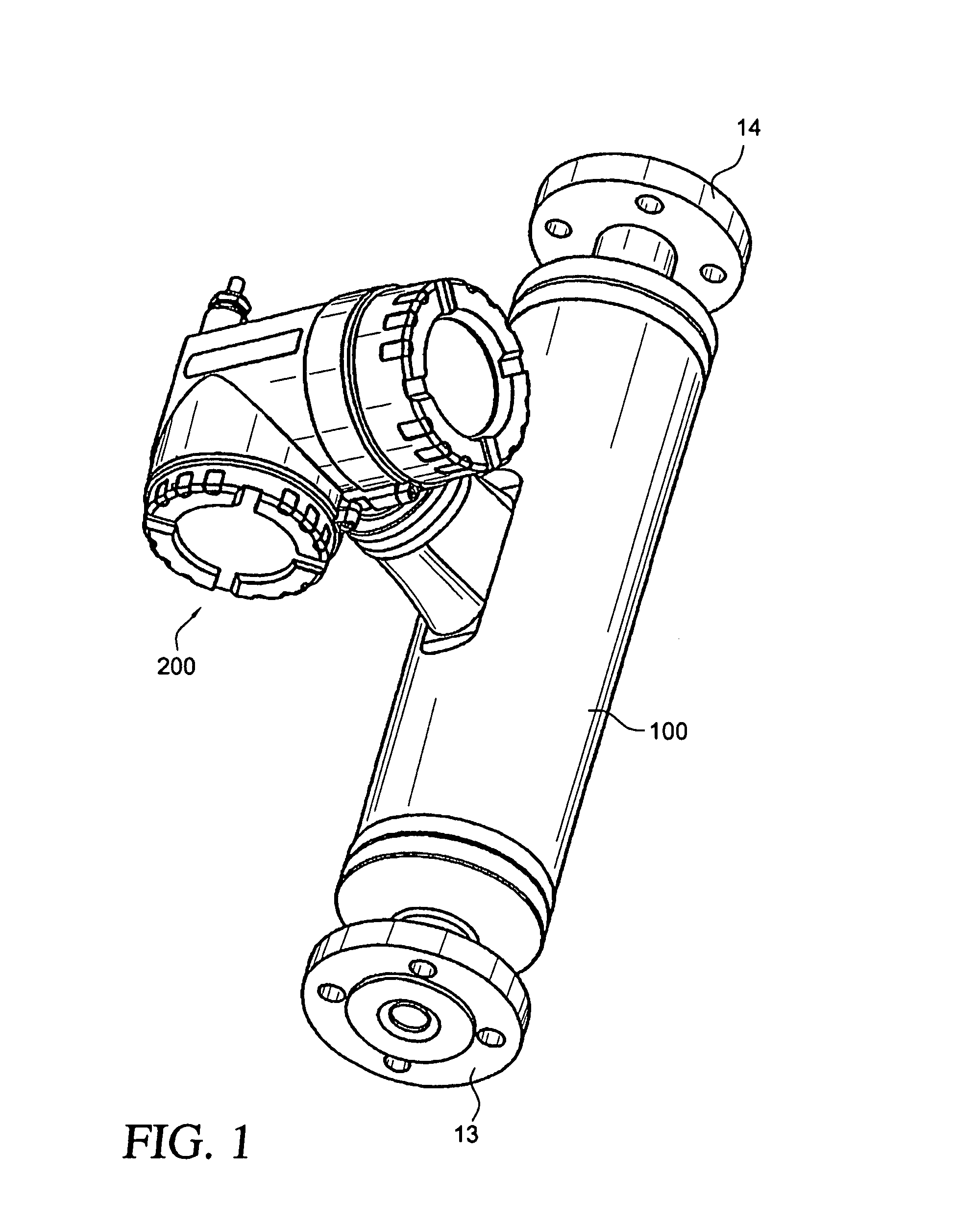
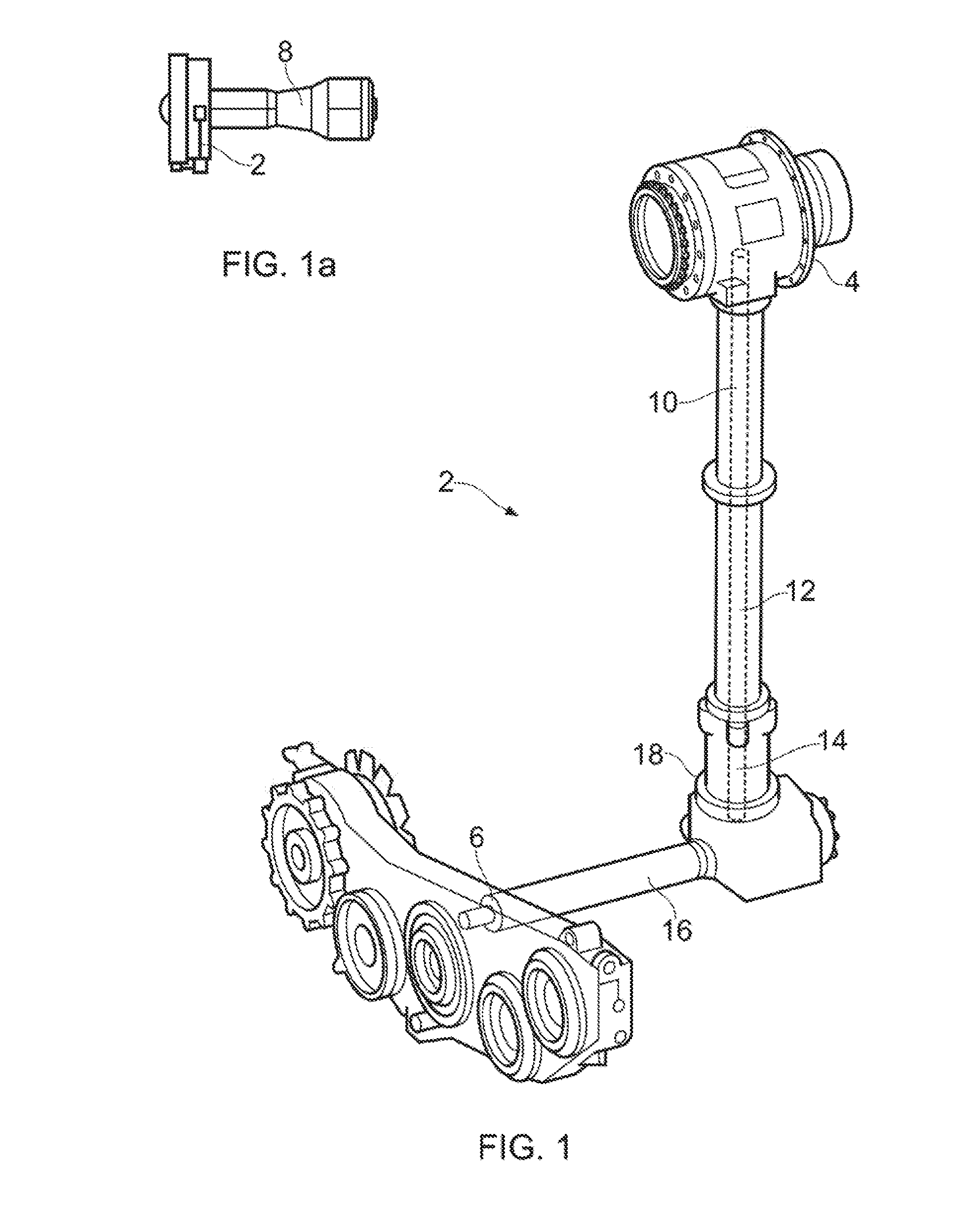
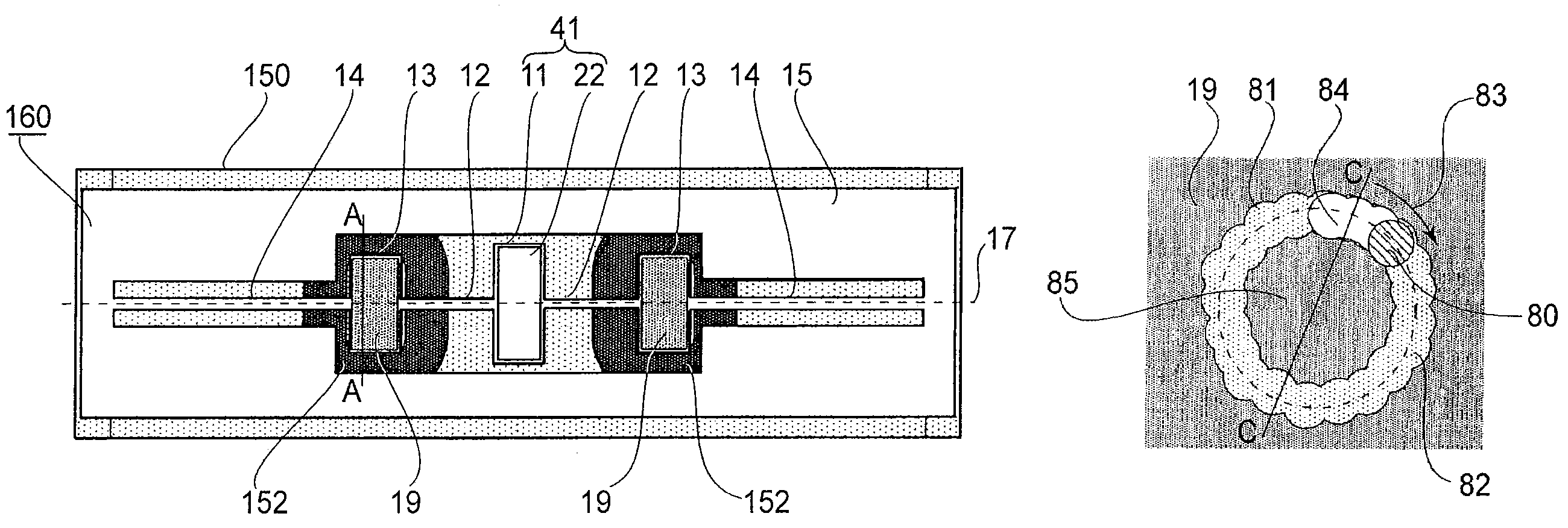
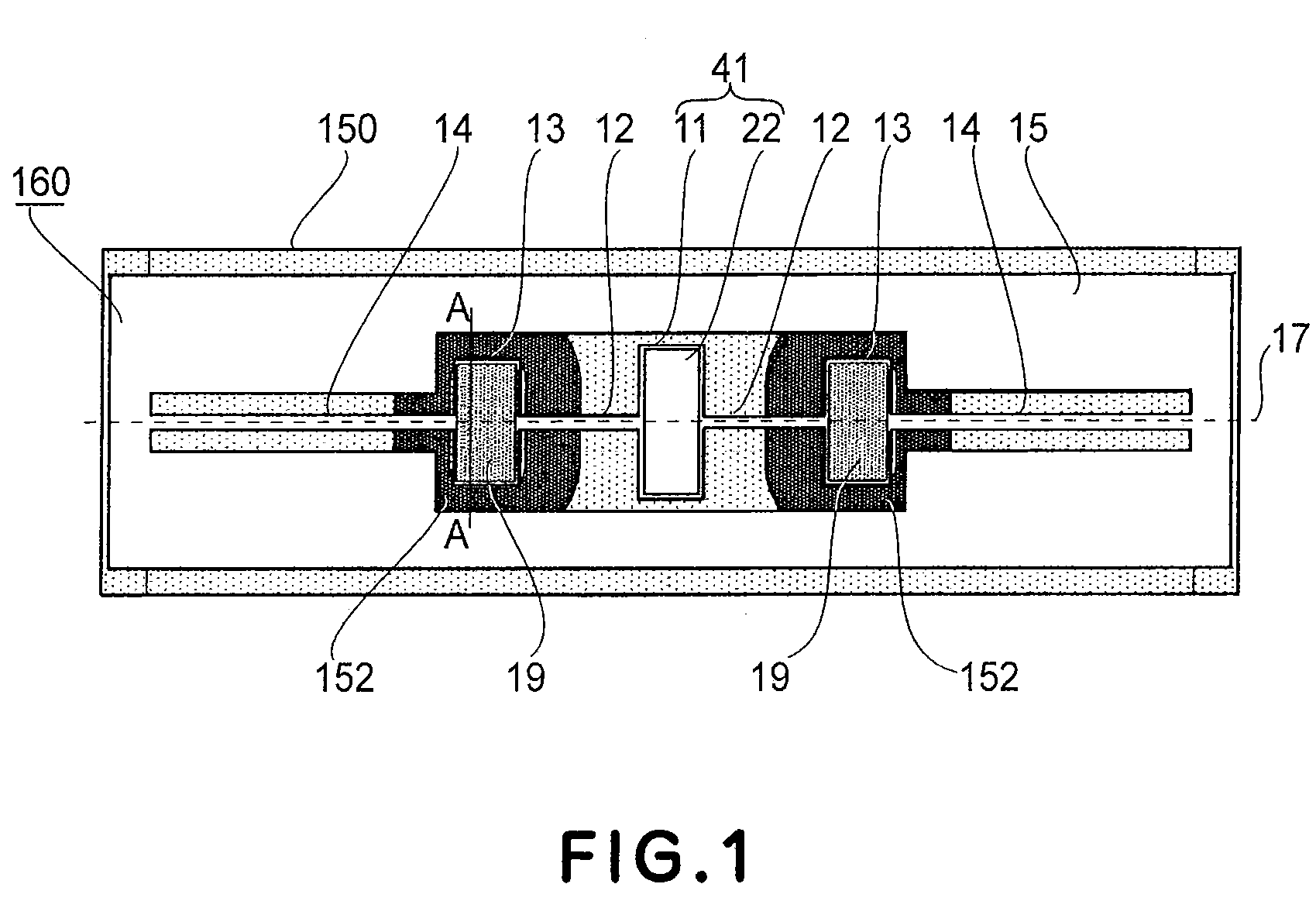
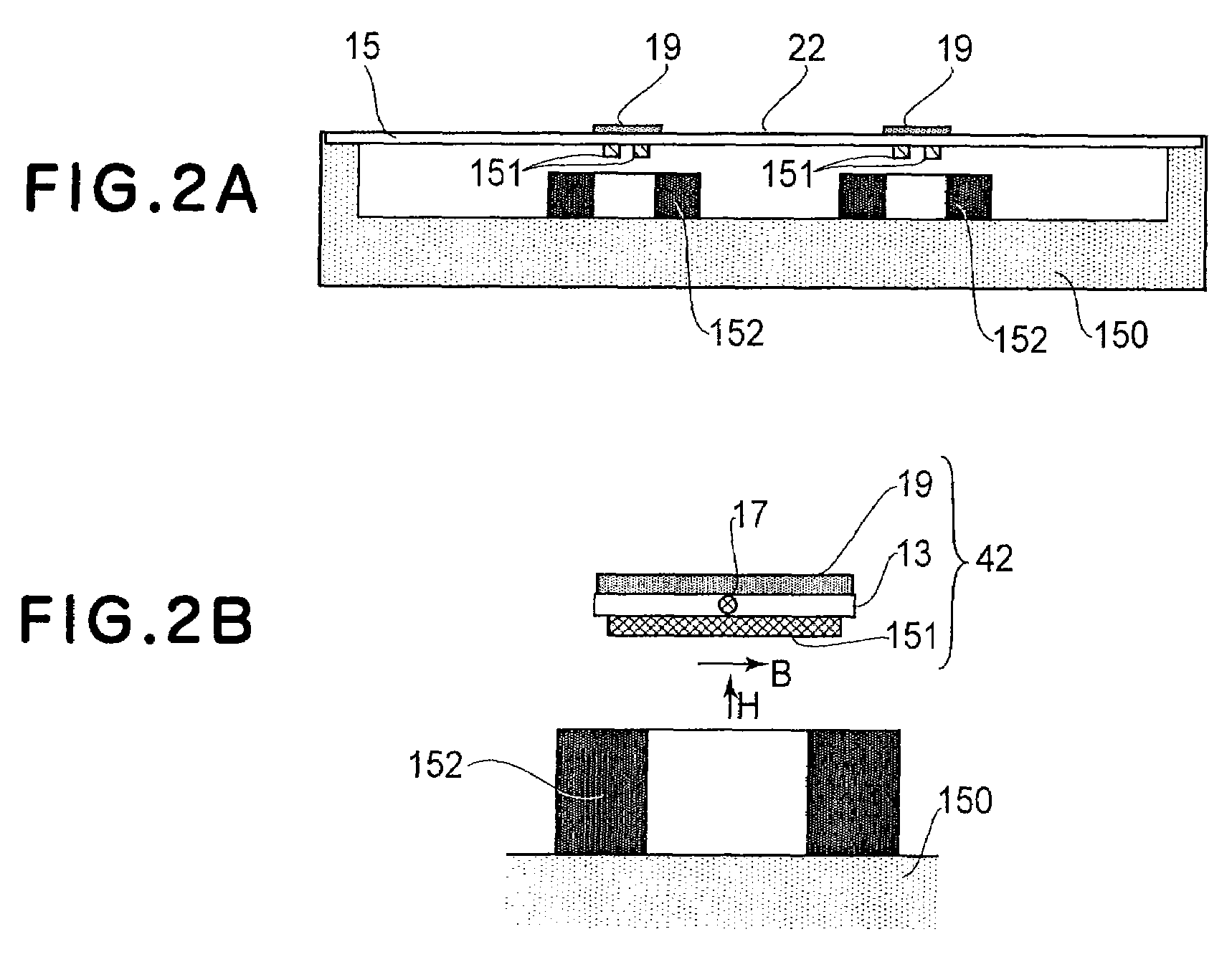
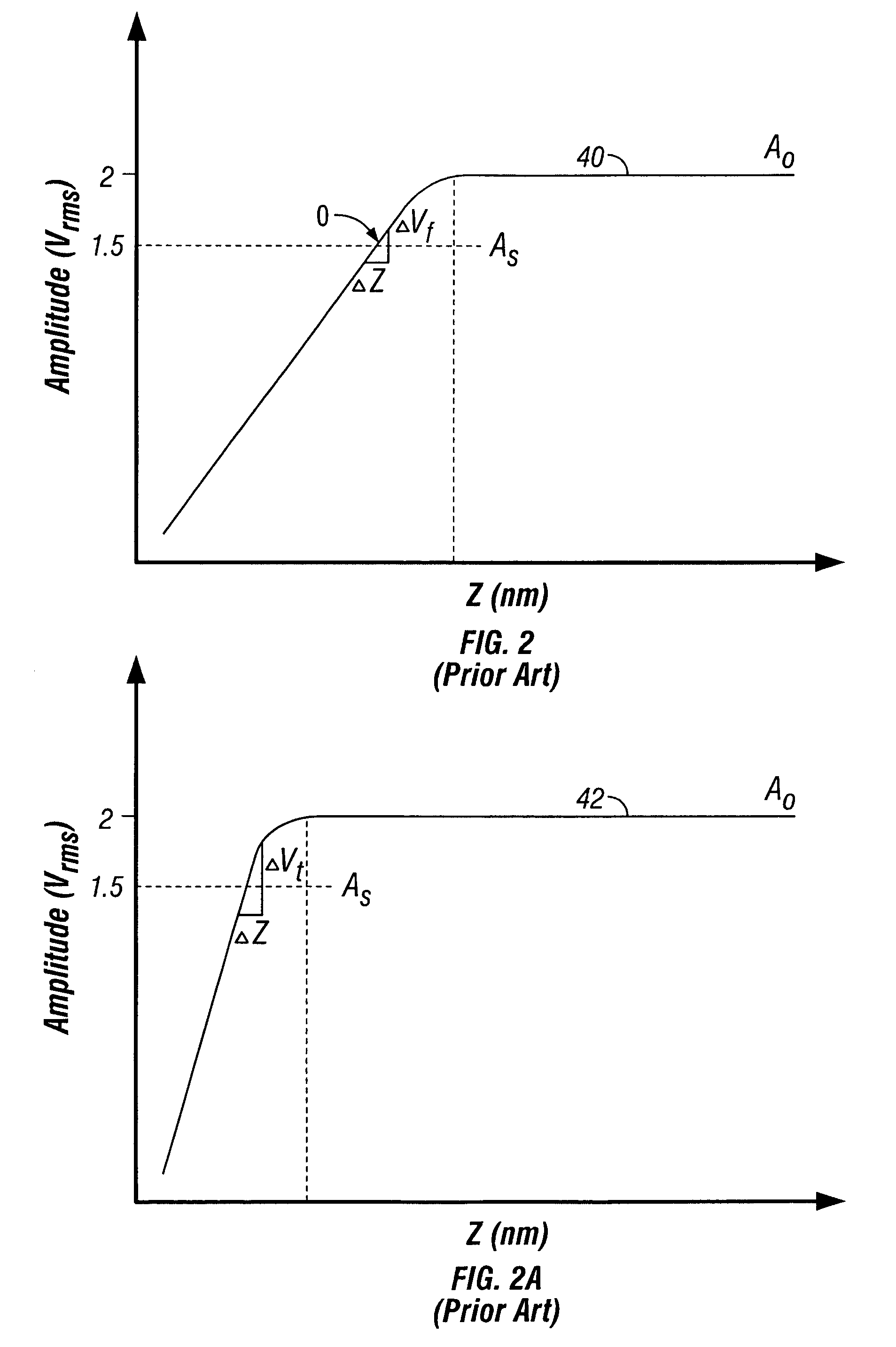
In-line measuring device
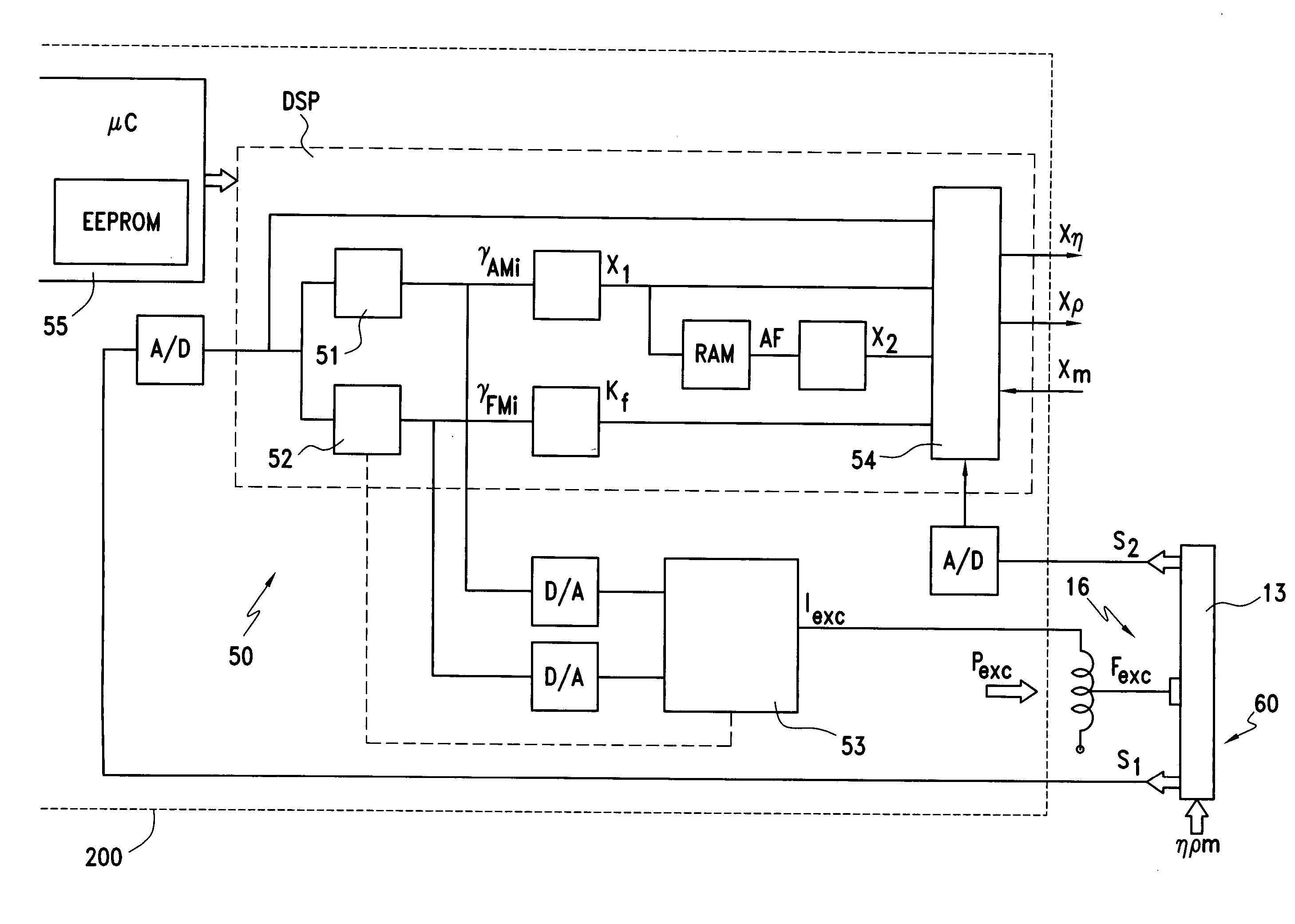
ActiveUS7284449B2Little effortFlow propertiesVolume meteringTorsional oscillationsElectrical current
An inline measuring device includes a vibration-type measurement pickup having at least one measuring tube, which has a medium to be measured flowing through it during operation. The measuring tube is made by means of an exciter arrangement to execute, at least at times and / or at least in part, lateral oscillations and, at least at times and / or at least in part, torsional oscillations about an imaginary measuring tube longitudinal axis. The torsional oscillations alternate with the lateral oscillations or are, at times, superimposed thereon. Also included is a sensor arrangement for producing oscillation measurement signals correspondingly representing oscillations of the measuring tube. Measuring device electronics controlling the exciter arrangement generates, by means of at least one of the oscillation measurement signals and / or by means of the exciter current, at least at times, at least one measured value, which represents the at least one physical quantity to be measured. Additionally, the measuring device electronics also determines a first intermediate value, which corresponds to the lateral current component of the exciter current serving to maintain the lateral oscillations of the measuring tube and / or to a damping of the lateral oscillations of the measuring tube, as well as a second intermediate value, which corresponds to a torsional current component of the exciter current serving to maintain the torsional oscillations of the measuring tube and / or to a damping of the torsional oscillations of the measuring tube. With the goal of producing the measured value at high accuracy, such value is determined also taking into consideration these two intermediate values. The measured value obtained in this way is distinguished especially by high accuracy also in the case of media of two, or more, phases.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
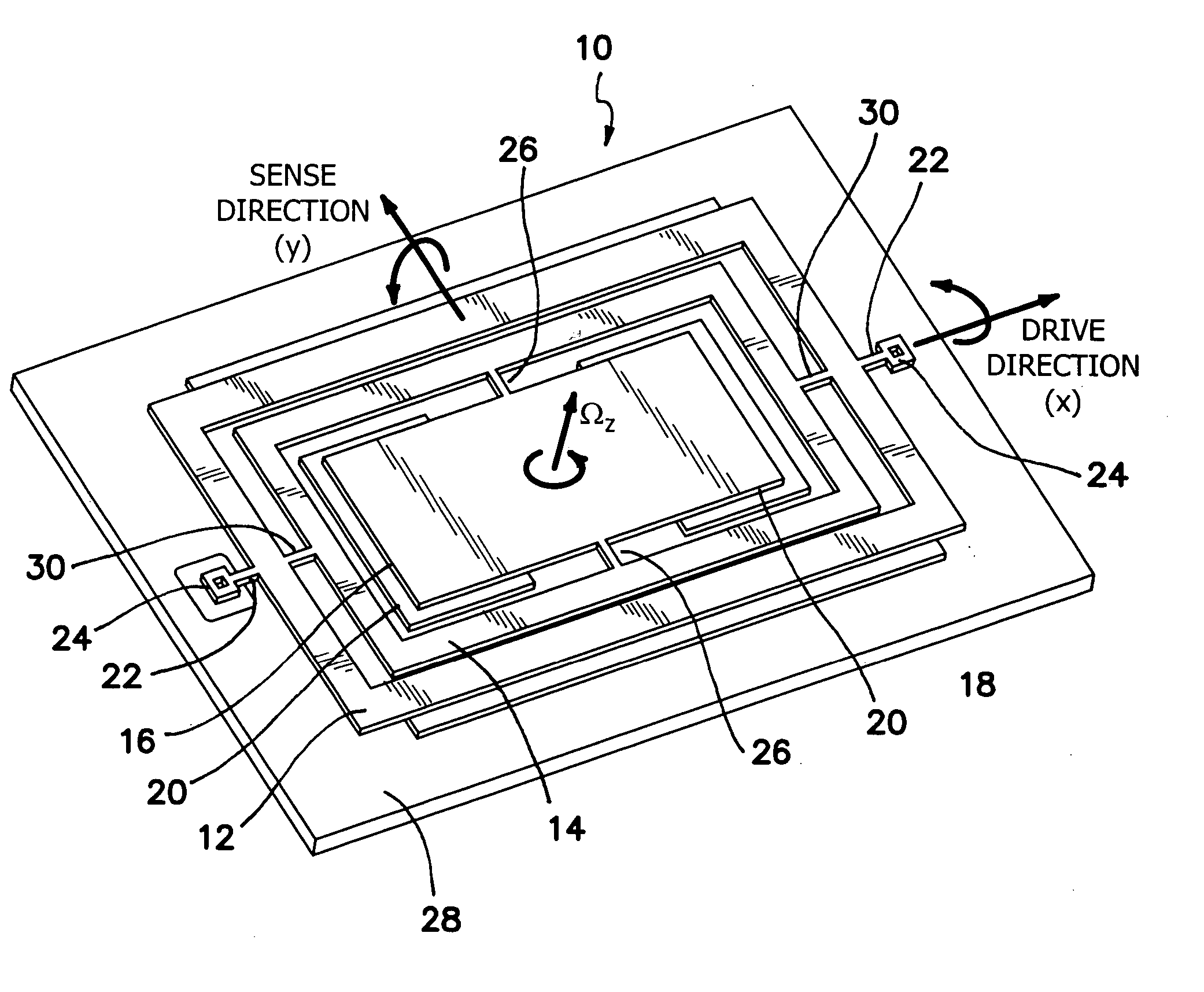
Torsional nonresonant z-axis micromachined gyroscope with non-resonant actuation to measure the angular rotation of an object
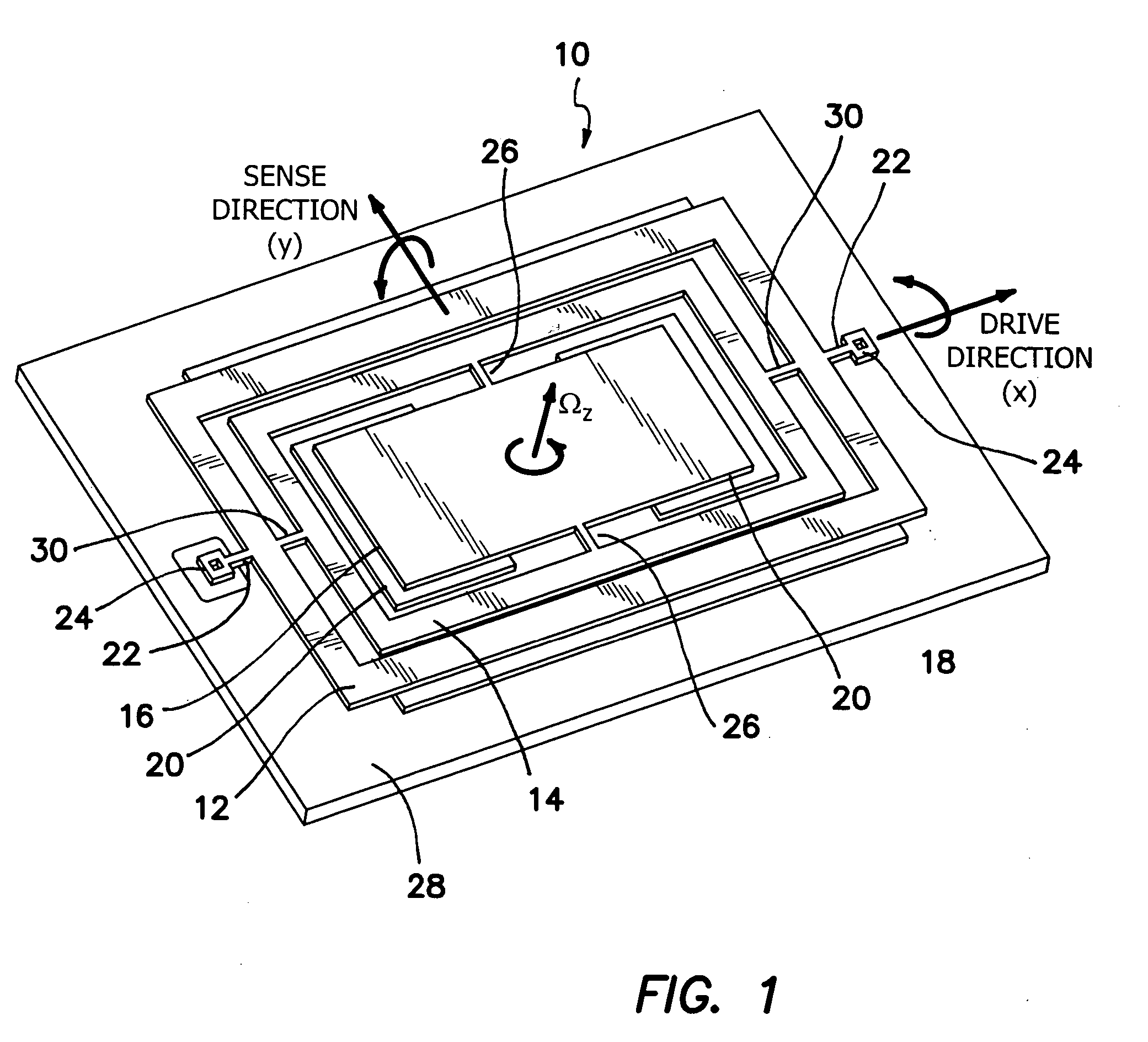
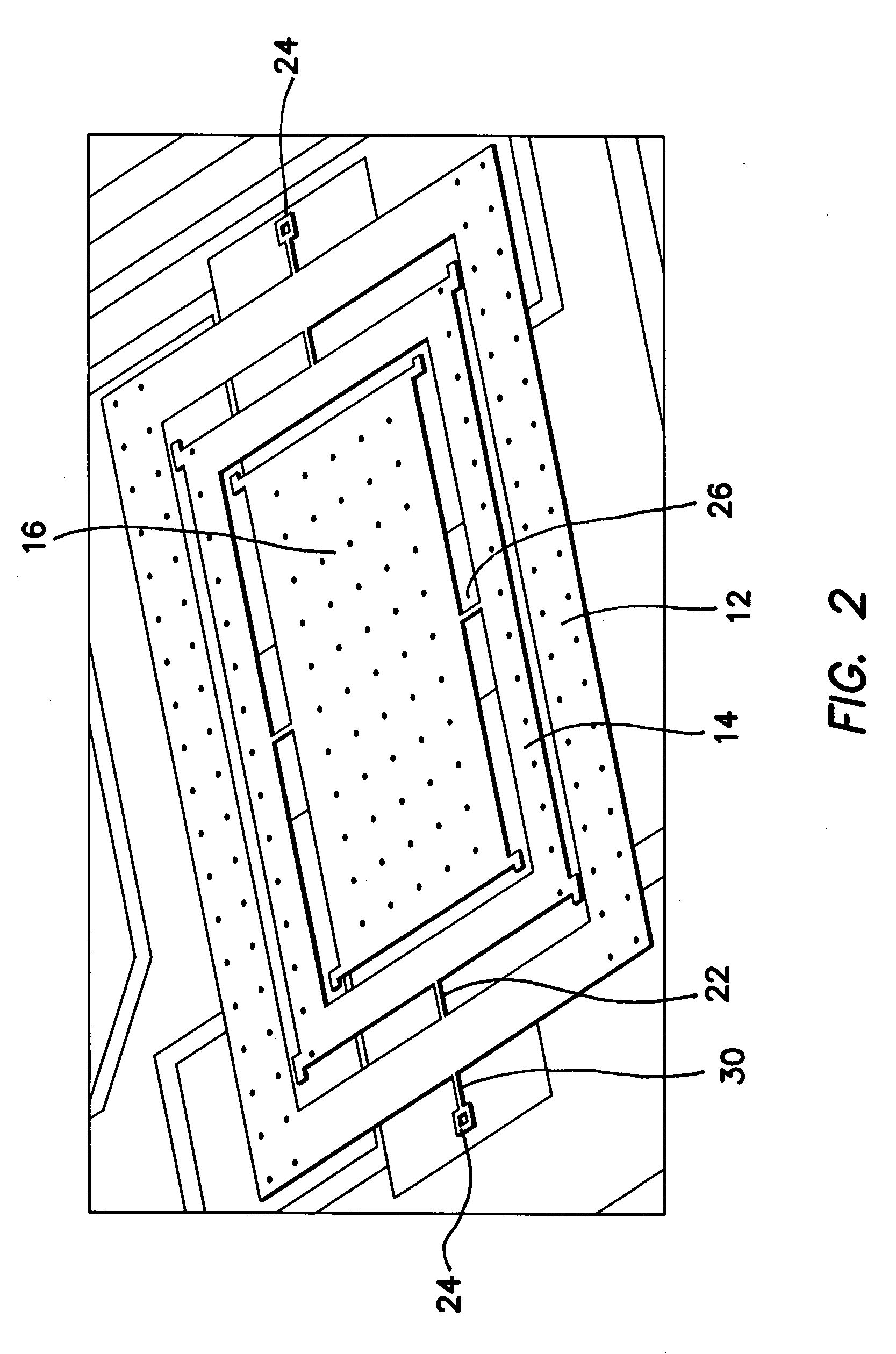
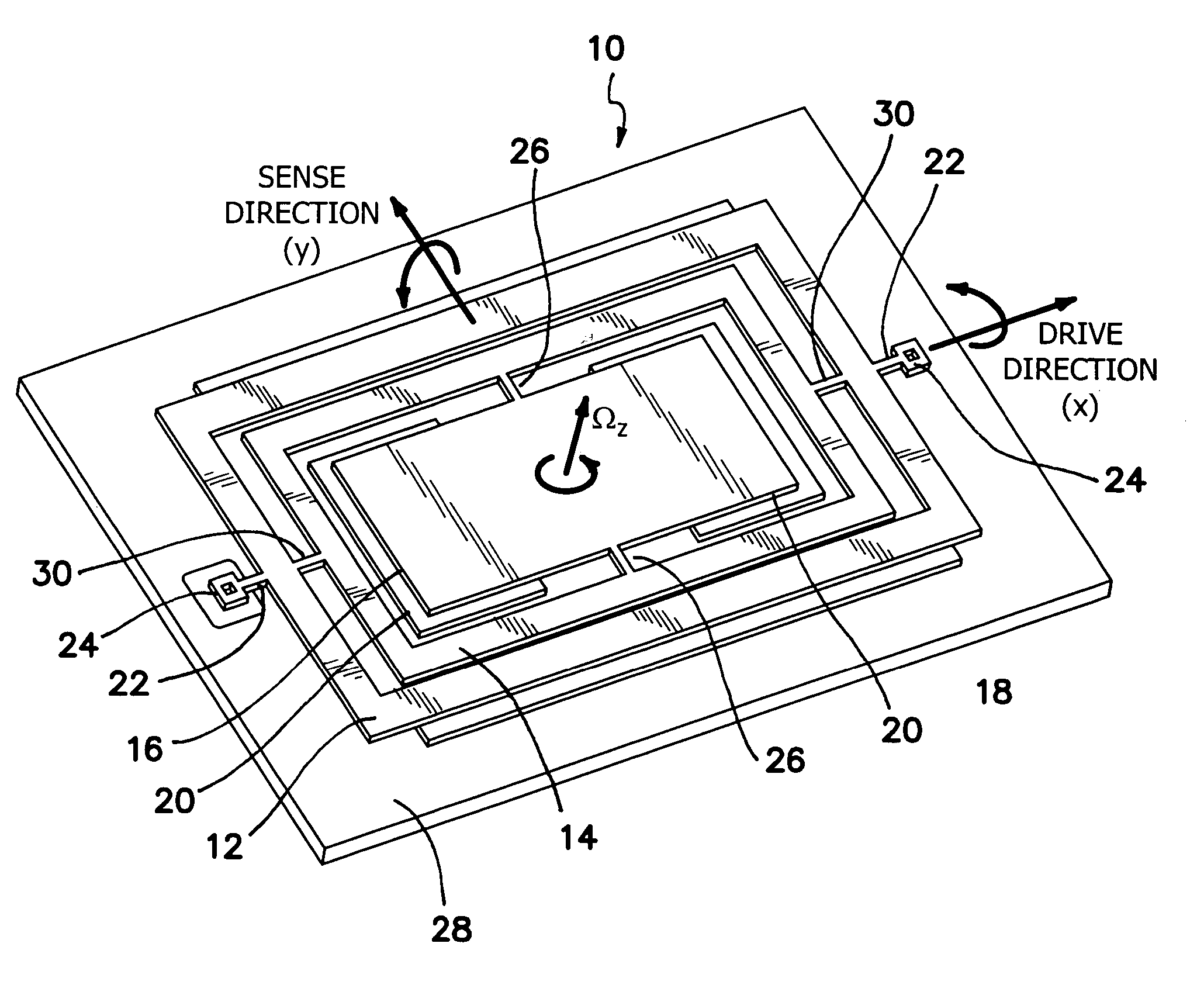
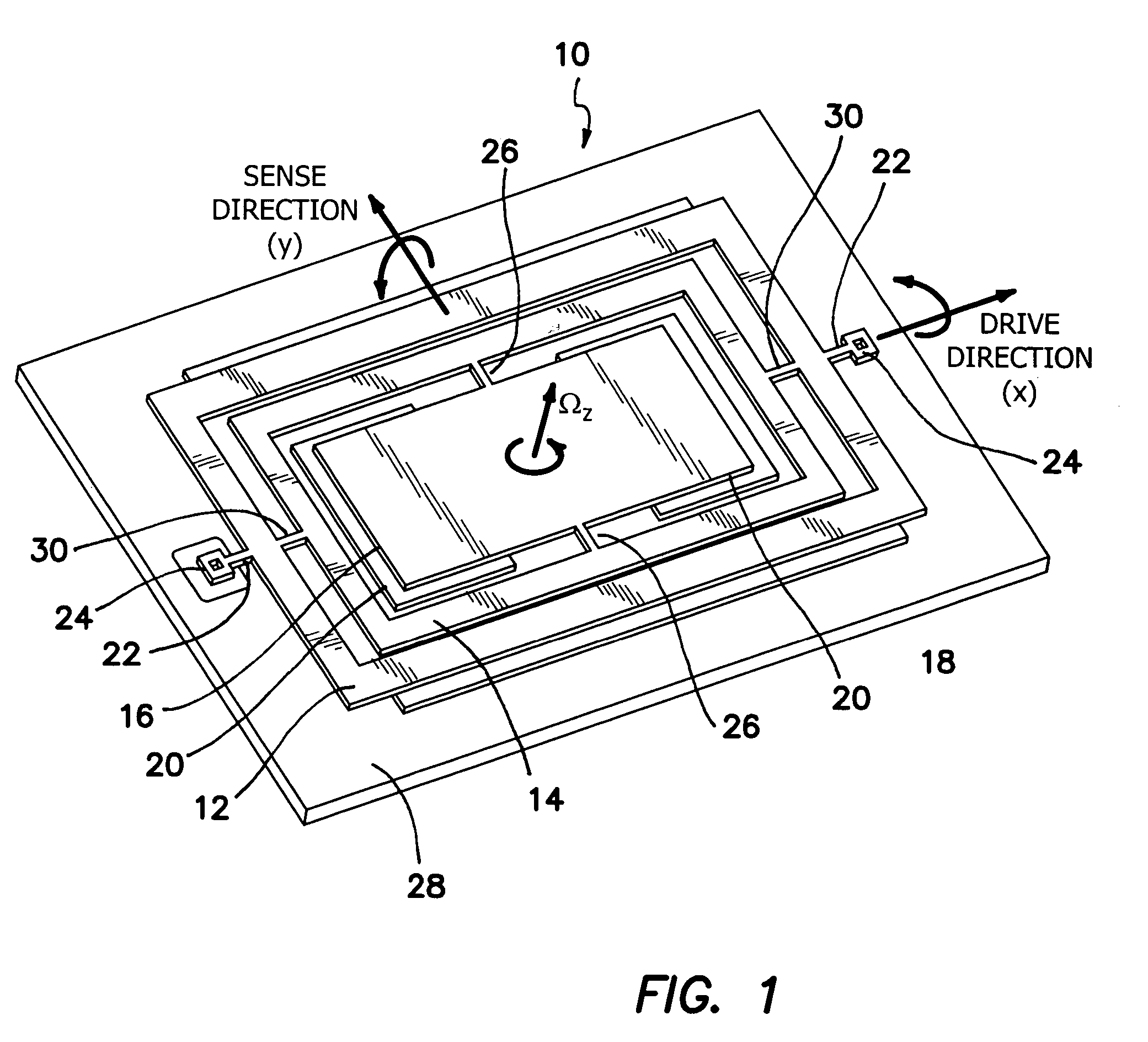
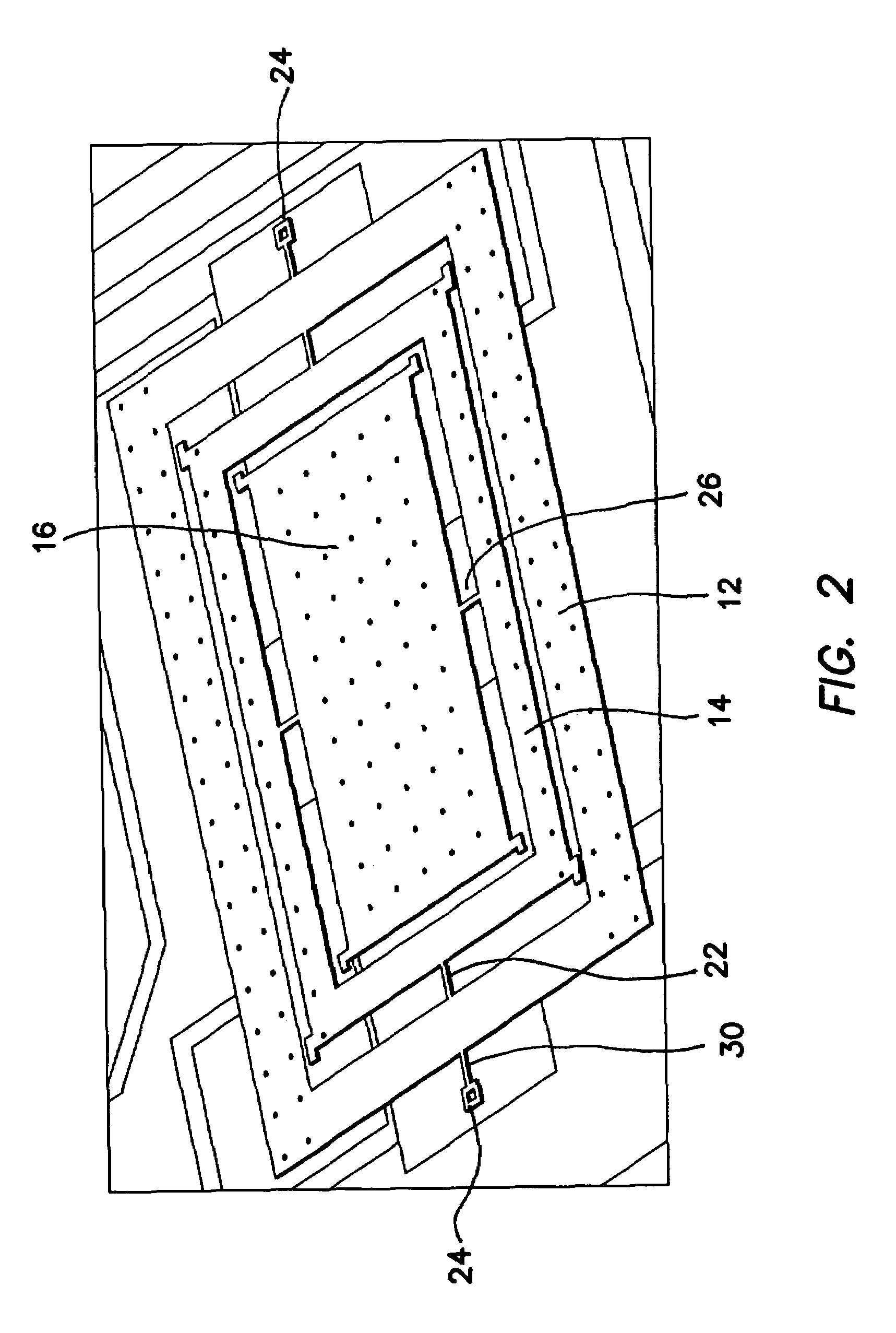
InactiveUS20060032308A1Minimizing nonlinear force profileMinimizing instabilityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeParallel plate
A gimbal-type torsional z-axis micromachined gyroscope with a non-resonant actuation scheme measures angular rate of an object with respect to the axis normal to the substrate plane (the z-axis). A 2 degrees-of-freedom (2-DOF) drive-mode oscillator is comprised of a sensing plate suspended inside two gimbals. By utilizing dynamic amplification of torsional oscillations in the drive-mode instead of resonance, large oscillation amplitudes of the sensing element is achieved with small actuation amplitudes, providing improved linearity and stability despite parallel-plate actuation. The device operates at resonance in the sense direction for improved sensitivity, while the drive direction amplitude is inherently constant within the same frequency band.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Micromachined piezoelectric x-axis gyroscope
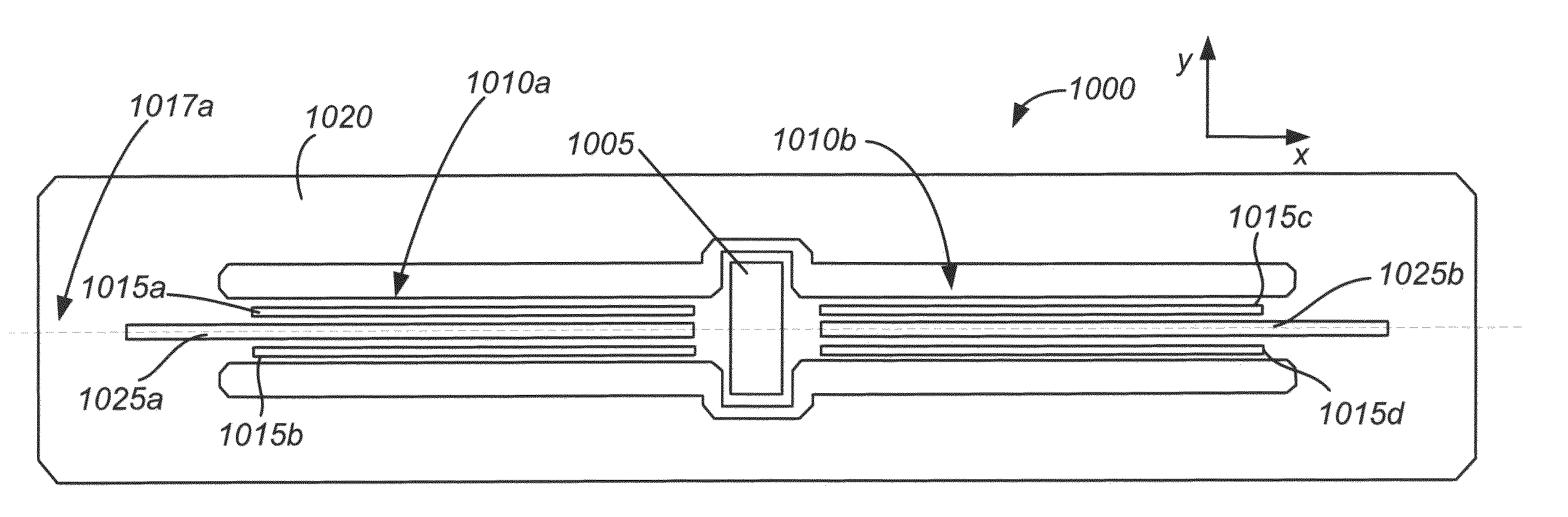
InactiveUS20110265564A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSolid-state devicesElectricityGyroscope
This disclosure provides systems, methods and apparatus, including computer programs encoded on computer storage media, for making and using gyroscopes. Such gyroscopes may include a sense frame, a proof mass disposed outside the sense frame, a pair of anchors and a plurality of drive beams. The plurality of drive beams may be disposed on opposing sides of the sense frame and between the pair of anchors. The drive beams may connect the sense frame to the proof mass. The drive beams may be configured to cause torsional oscillations of the proof mass substantially in a first plane of the drive beams. The sense frame may be substantially decoupled from the drive motions of the proof mass. Such devices may be included in a mobile device, such as a mobile display device.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Ultrasonic torsional mode and longitudinal-torsional mode transducer system
ActiveUS20090236938A1Improve performanceEasy to operatePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurgeryTorsional oscillationsEngineering
The present invention relates to the design of piezoelectric transducer subassemblies and systems primarily intended for medical and dental applications. The invention also provides transducer subassemblies and systems with improved performance and a capability to operate more efficiently in torsional or a combined longitudinal-torsional mode of vibration. The invention enables the size and weight of torsional mode transducers to be reduced. Additionally, the electrical characteristics of these transducer systems are improved, thus enabling the transducer end effector to deliver more power to the operative site.
Owner:PIEZOINNOVATIONS
Control system for suppressing impact speed drop and torsional oscillation of rolling mill transmission system
InactiveCN1803326AEasy to implementSimple structureMetal rolling arrangementsRoll speed control deviceMotor speedTorsional oscillations
The invention discloses a control system of dynamic deceleration and torsional to inhibit the driving system of rolling mill in the rolling mill driving control domain, which comprises the following parts: two-quality elastic driving system of rolling mill, control system and power variable-flow system, wherein two-quality elastic driving system of rolling mill contains rolling mill and roller to connect by connection axle; the control system contains load observer, state feedback gain amplifier and motor speed-adjusting system; the power variable-flow system is electric power electronic transformer, which transforms the electrical network voltage and current into fitful motor voltage and current to drive the motor speed-adjusting operation according to the control pressure.
Owner:AUTOMATION RES & DESIGN INST OF METALLURGICAL IND +1
Light-beam scanning device
ActiveUS20060245023A1Large torsional amplitudeEffective oscillationCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationElectricityTorsional oscillations
A light-beam scanning device includes a base plate having a torsion beam portion formed therein, and a mirror portion supported by the torsion beam portion and adapted to be oscillated. The light-beam scanning device includes one of a piezoelectric member, a magnetostrictive member and a permanent magnet member, which is fixed to or formed as a portion of the base plate. The mirror portion supported by the torsion beam portion is oscillated by a plate wave that is induced in the base plate by applying a voltage or electric field to the piezoelectric, magnetostrictive or permanent magnet member. The light-beam scanning device can efficiently generate a torsional oscillation in the mirror portion in a simplified structure.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Hyposynchronous damped control system
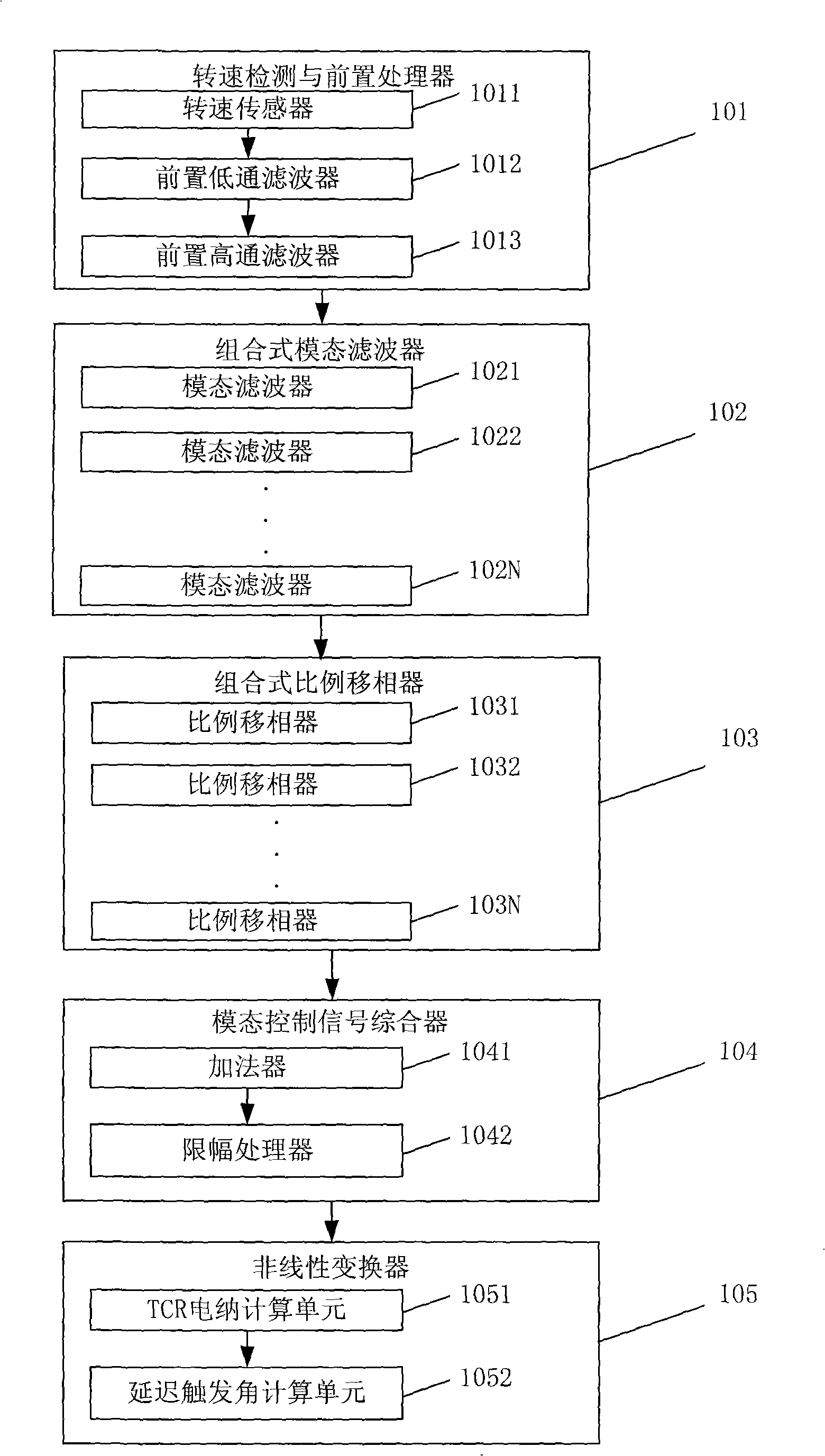
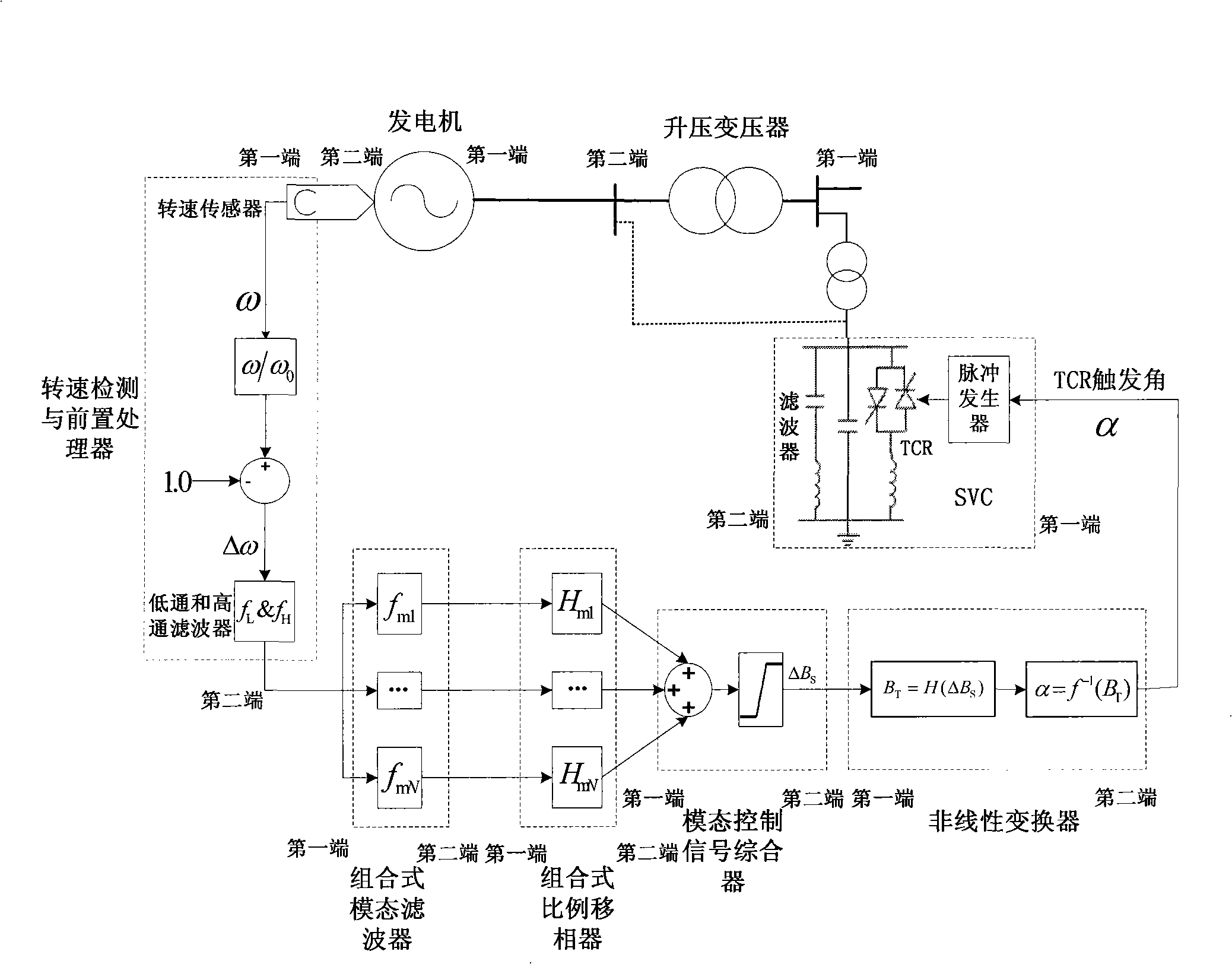
InactiveCN101325335AResolving Multimodal Subsynchronous ResonanceSolve Oscillation ProblemsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationElectric generator controlModal filterControl system
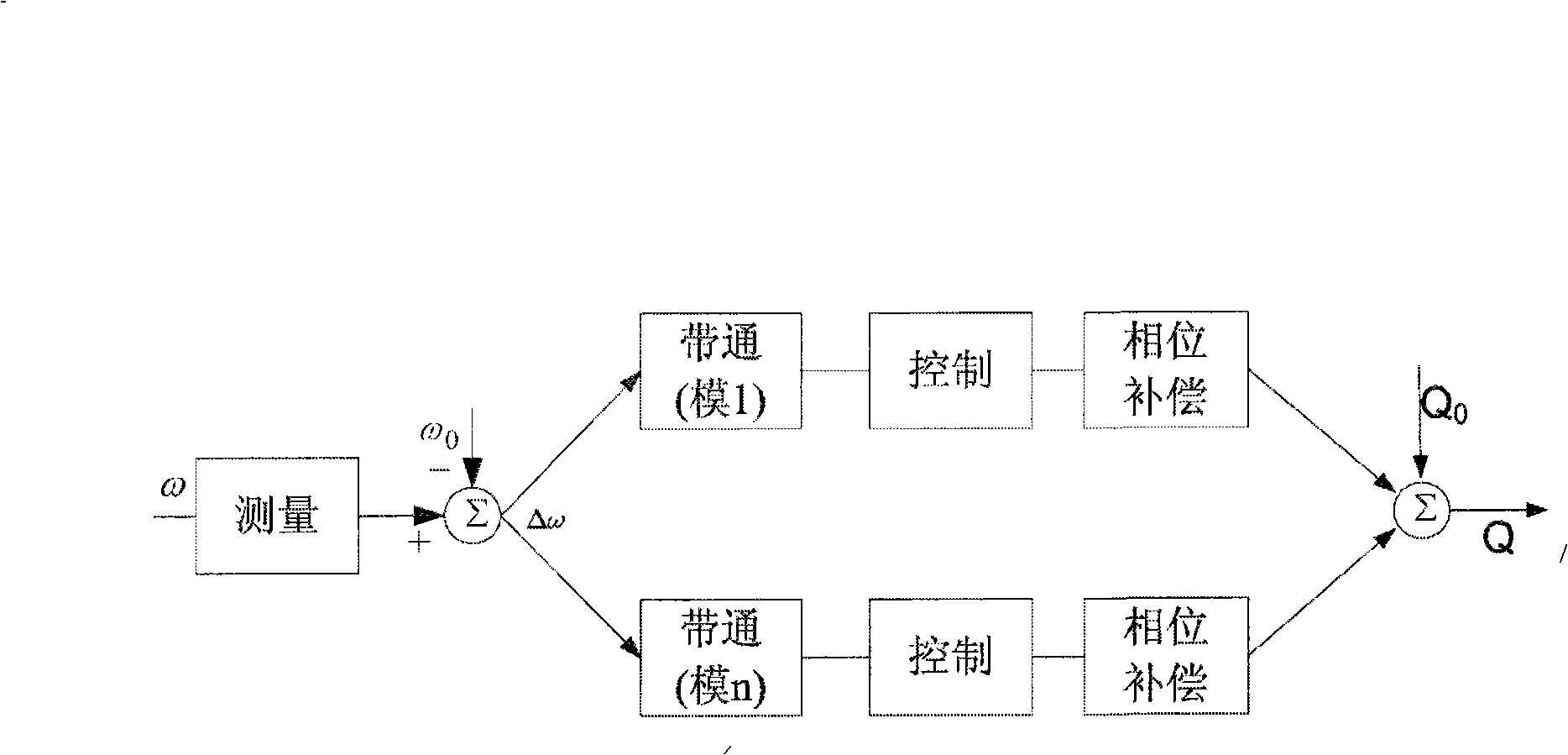
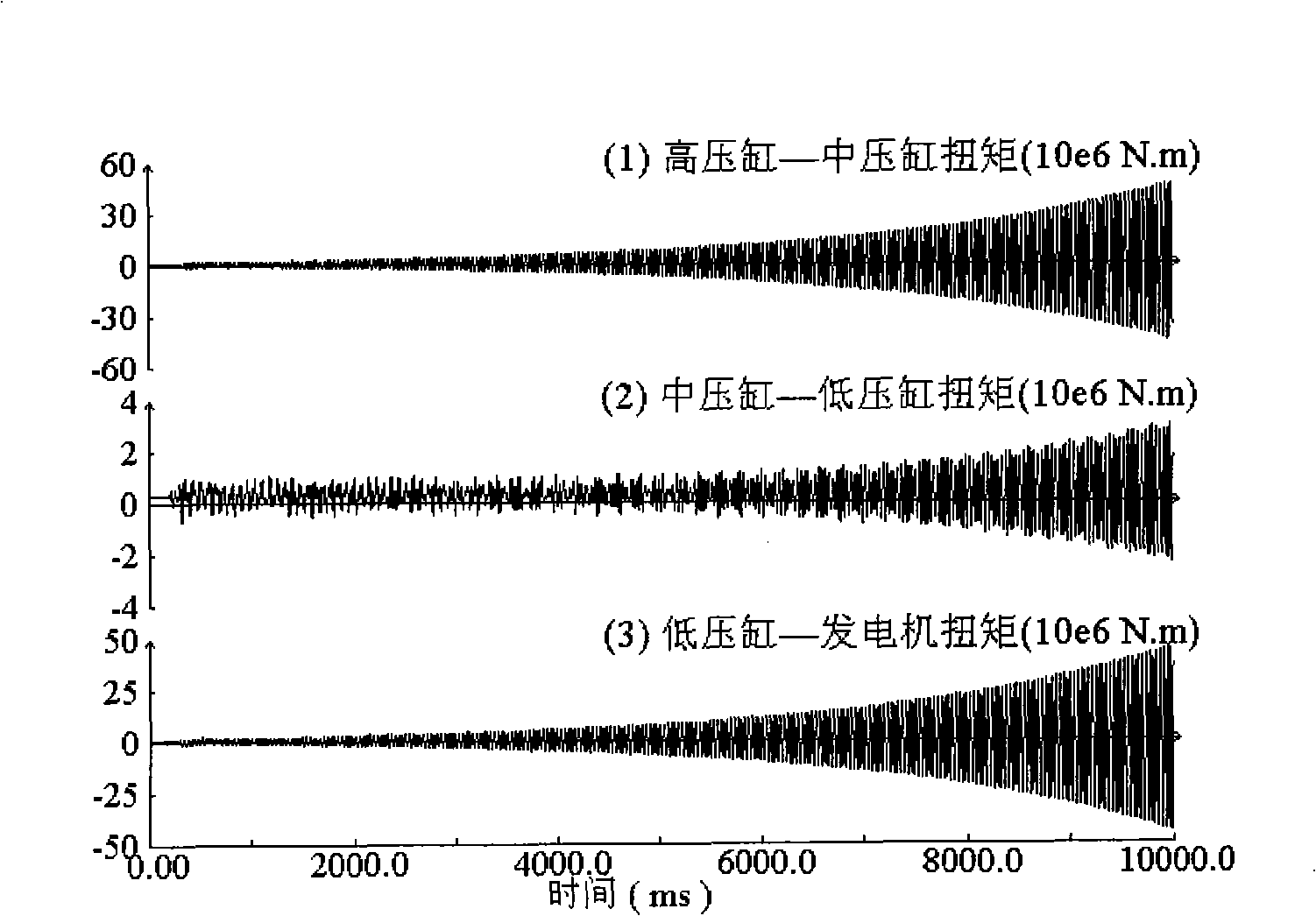
The invention discloses a subsynchronous damping control system, and belongs to the power system stabilization and control technology field. The system includes a rotate speed testing and preposing processor, a combined mode filter, a combined proportion phase shifter, a mode control signal synthesizer and a nonlinear transformer. The system solves the problem of multimode subsynchronous resonance and oscillation of a power system, improves the subsynchronous stability of the power system, and reduces the shafting torsional oscillation fatigue loss of a large-size steam turbo generator.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
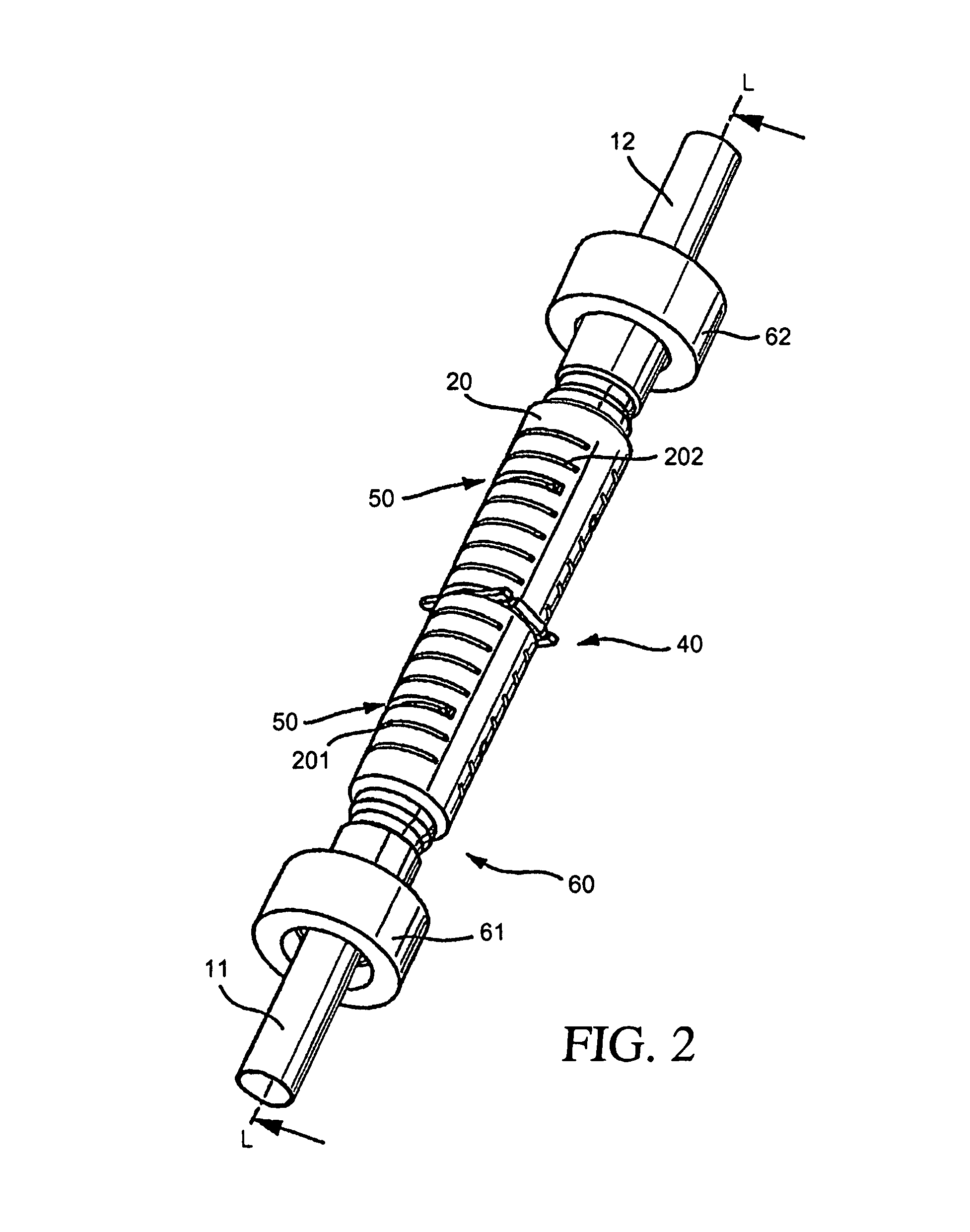
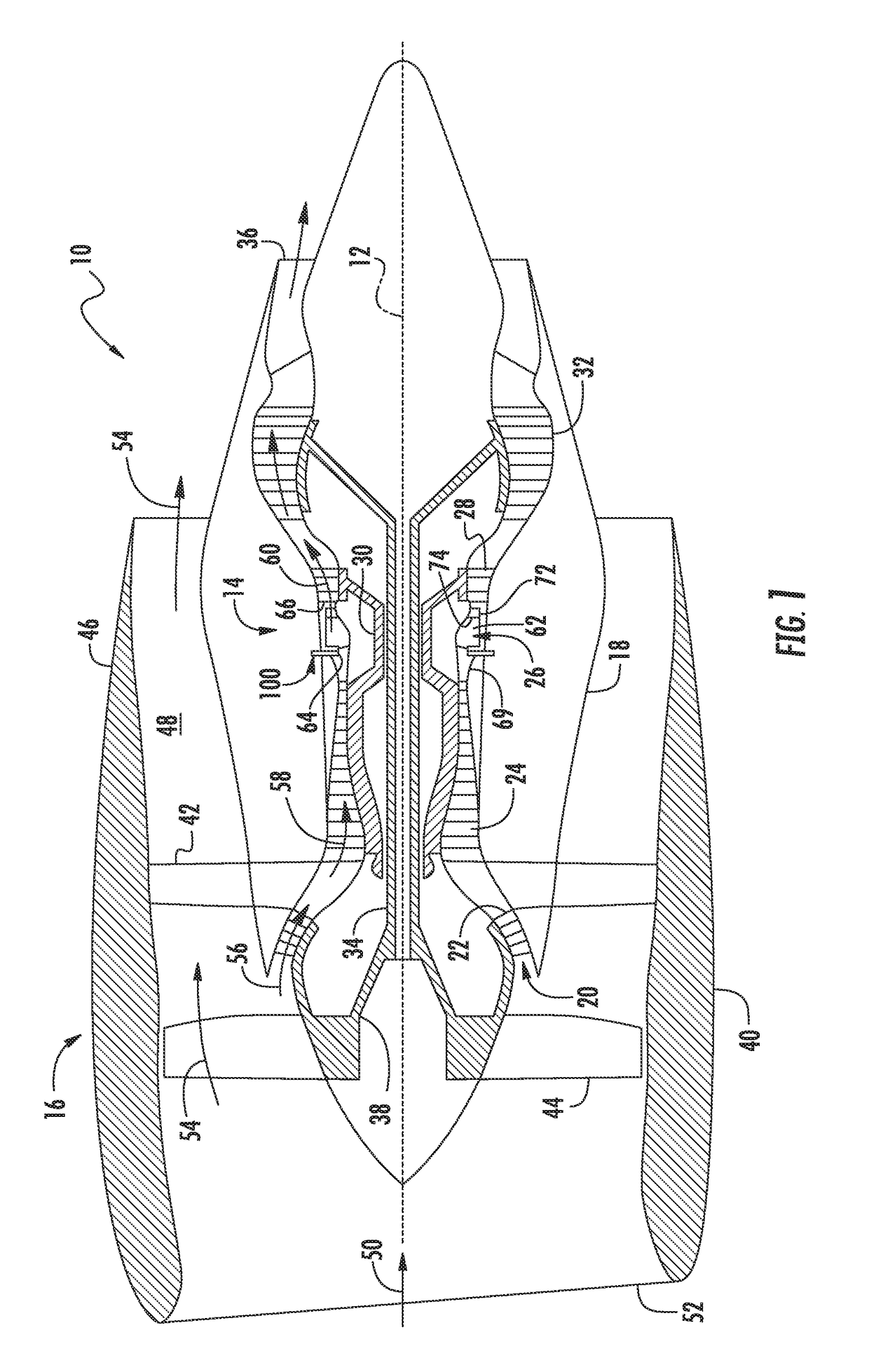
Inline measuring device
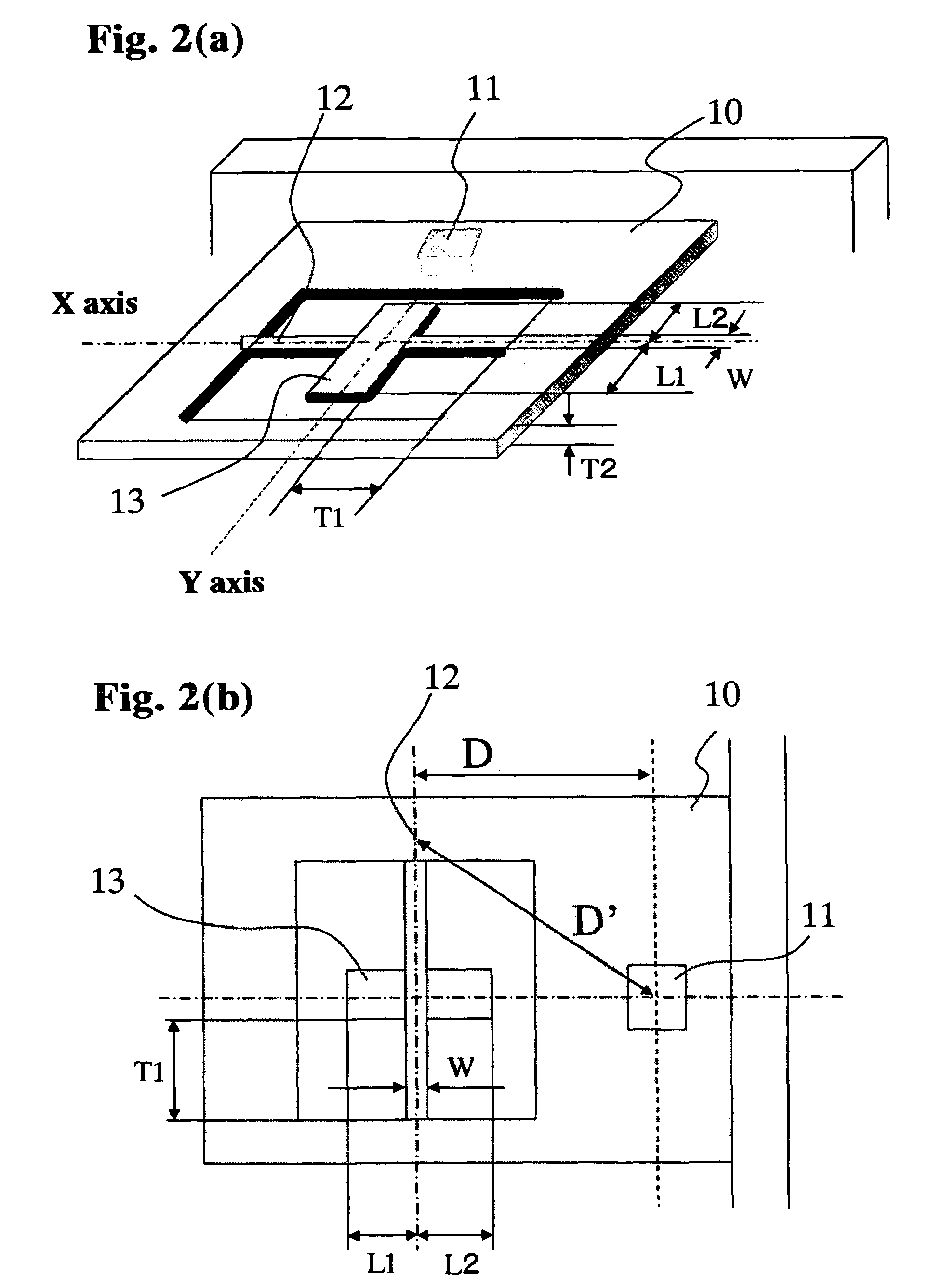
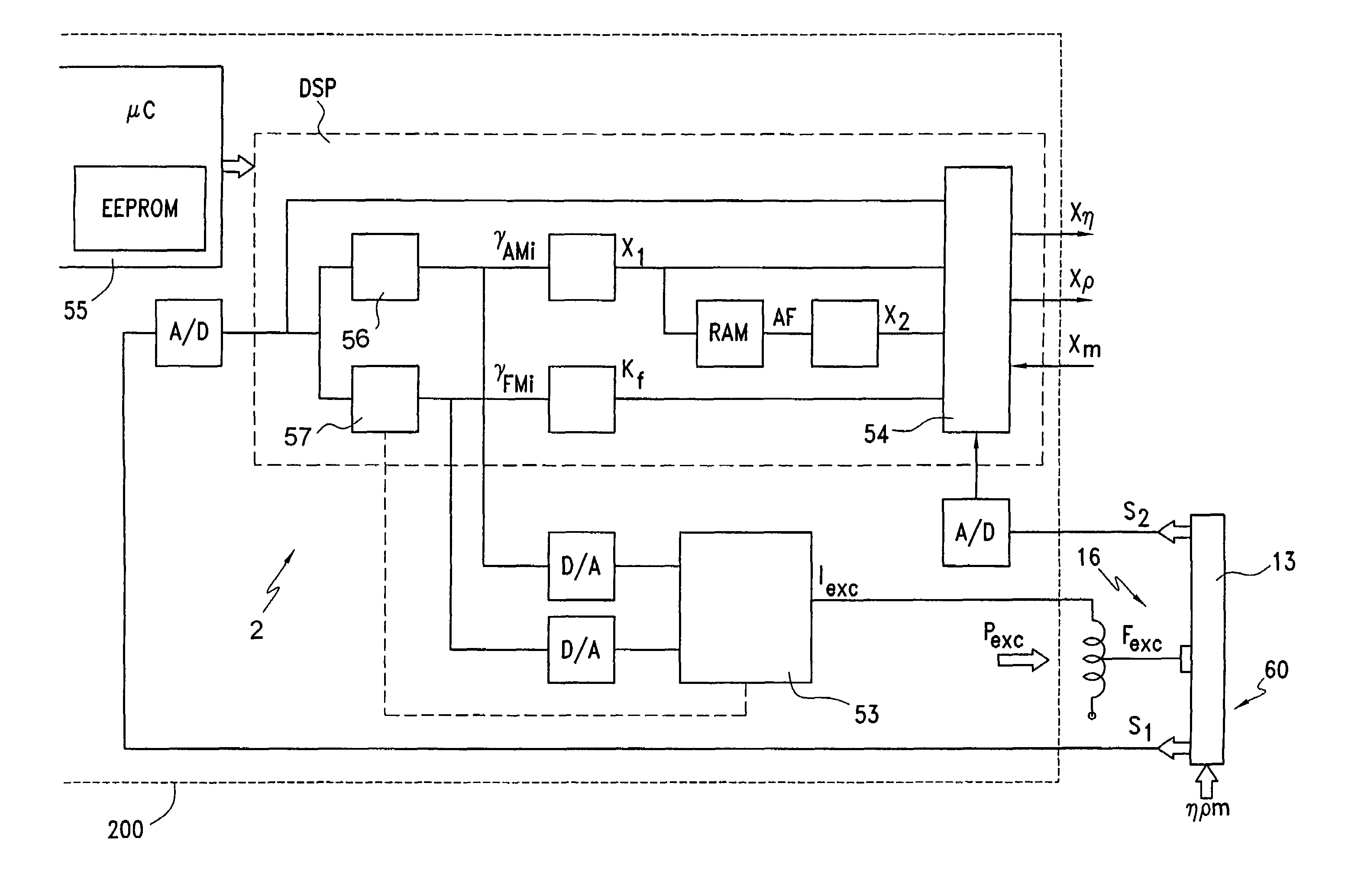
ActiveUS20070095153A1Accurate measurementVolume meteringDirect mass flowmetersElectricityMeasurement device
An inline measuring device which serves for measuring at least one physical, measured variable of a medium conveyed in a pipeline, includes a measurement pickup of vibration-type, as well as a measuring device electronics electrically coupled with the measurement pickup. The measurement pickup includes at least one, essentially straight measuring tube serving to convey the medium to be measured and communicating with the connected pipeline, an exciter mechanism acting on the measuring tube for causing the at least one measuring tube to vibrate, during operation, at least at times and / or at least in part, with torsional oscillations about a torsional oscillation axis imaginarily connecting an inlet end of the measuring tube and an outlet end of the measuring tube, as well as a sensor arrangement for registering vibrations of the at least one measuring tube and delivering at least one oscillation measurement signal representing oscillations of the measuring tube. The measuring device electronics delivers, at least at times, an exciter signal driving the exciter mechanism and generates, by means of the at least one oscillation measurement signal and / or by means of the exciter signal, at least at times, at least one measured value, which represents at least one physical, measured variable of the medium to be measured. Moreover, the measuring device electronics determines, on the basis of the at least one oscillation measurement signal and / or on the basis of the exciter signal, repetitively, an oscillation frequency of the torsional oscillations of the measuring tube and the measuring device electronics monitors, based on the oscillation frequency of the torsional oscillations, at least one operating condition of the at least one measuring tube. Additionally provided is an inline measuring device of the described kind used for monitoring an operating condition of a tube wall, especially also a section of the attached pipeline.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Torsional nonresonant z-axis micromachined gyroscope with non-resonant actuation to measure the angular rotation of an object
InactiveUS7421898B2Oscillation amplitude is largeLarge capacitanceAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeParallel plate
A gimbal-type torsional z-axis micromachined gyroscope with a non-resonant actuation scheme measures angular rate of an object with respect to the axis normal to the substrate plane (the z-axis). A 2 degrees-of-freedom (2-DOF) drive-mode oscillator is comprised of a sensing plate suspended inside two gimbals. By utilizing dynamic amplification of torsional oscillations in the drive-mode instead of resonance, large oscillation amplitudes of the sensing element is achieved with small actuation amplitudes, providing improved linearity and stability despite parallel-plate actuation. The device operates at resonance in the sense direction for improved sensitivity, while the drive direction amplitude is inherently constant within the same frequency band.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
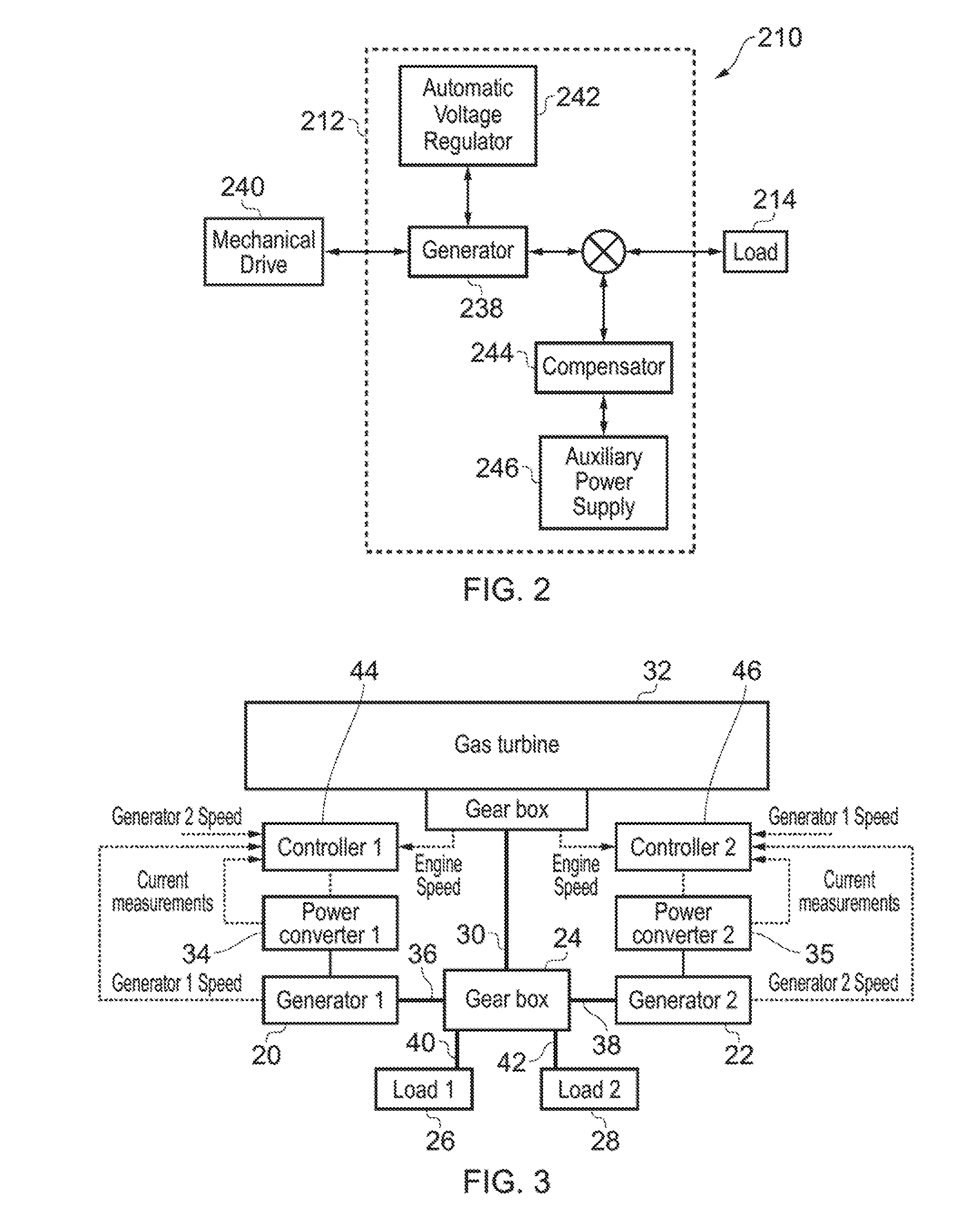
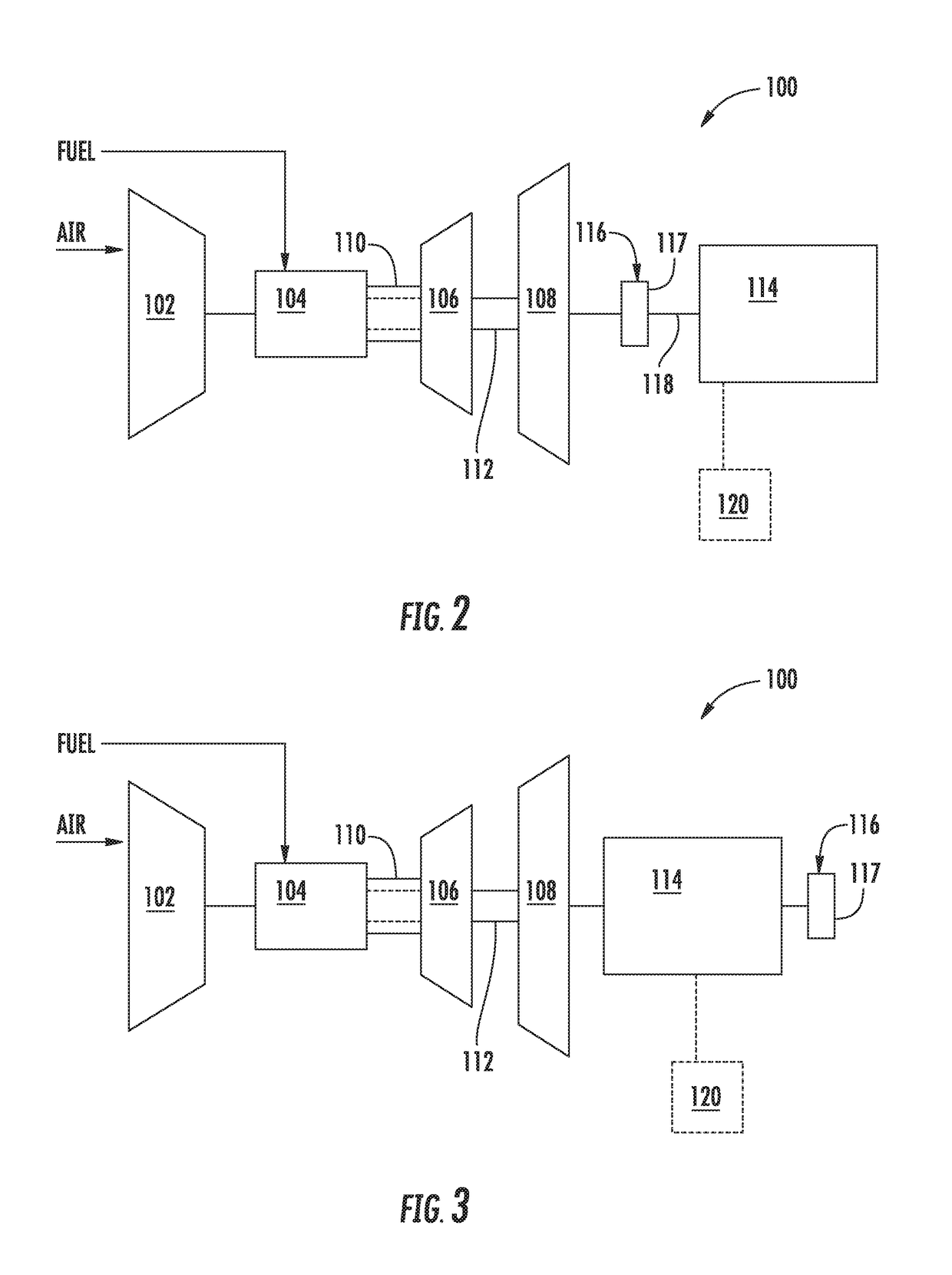
Method and system for damping torsional oscillations
InactiveUS20160218650A1Easy to controlAvoid complicationsRotating vibration suppressionEngine fuctionsAviationTorsional oscillations
The invention concerns the damping of torsional oscillations / vibrations, particularly during electrical power generation within a gas turbine such as a civil aviation engine. The method of the invention relies on actively generating compensating oscillations in a driveline of a system to actively damp undesirable oscillations existing in the system.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Light-beam scanning device
ActiveUS7394583B2Large torsional amplitudeEffective oscillationCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationTorsional oscillationsLight beam
A light-beam scanning device includes a base plate having a torsion beam portion formed therein, and a mirror portion supported by the torsion beam portion and adapted to be oscillated. The light-beam scanning device includes one of a piezoelectric member, a magnetostrictive member and a permanent magnet member, which is fixed to or formed as a portion of the base plate. The mirror portion supported by the torsion beam portion is oscillated by a plate wave that is induced in the base plate by applying a voltage or electric field to the piezoelectric, magnetostrictive or permanent magnet member. The light-beam scanning device can efficiently generate a torsional oscillation in the mirror portion in a simplified structure.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Method for monitoring an operating condition of a tube wall contacted by a flowing medium and inline measuring device therefore
ActiveUS7562586B2Accurate measurementVolume meteringDirect mass flowmetersElectricityTorsional oscillations
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Method for restraining hyposynchronous resonance of power system
ActiveCN101404475ASolve balance problemsSolve Overvoltage ProblemsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationPower oscillations reduction/preventionSub synchronous resonanceShunt reactor
The invention provides a method for using a controllable high-voltage shunt reactor to inhibit the sub-synchronous resonance of an electric power system. The shafting tachometry signal of the steam turbine generator unit in the electric power system is used as an input signal, and the shafting torsional oscillation property of the steam turbine generator unit can be discriminated from the input signal after being processed by digital signal algorithm. The method is characterized in that the shafting torsional oscillation property signal is calculated on line with a sub-synchronous resonance control strategy to gain the volume control command of the controllable high-voltage shunt reactor, so as to dynamically adjust the volume of the shunt reactor, thus correspondingly dynamically adjusting the reactive power, voltage, active power and rotating speed of the steam turbine generator unit, realizing the effect of inhibiting the sub-synchronous resonance of the steam turbine generator unit, and the effectiveness of the invention is validated by a numerical simulation aiming at certain planning system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Optical deflector and optical instrument using the same
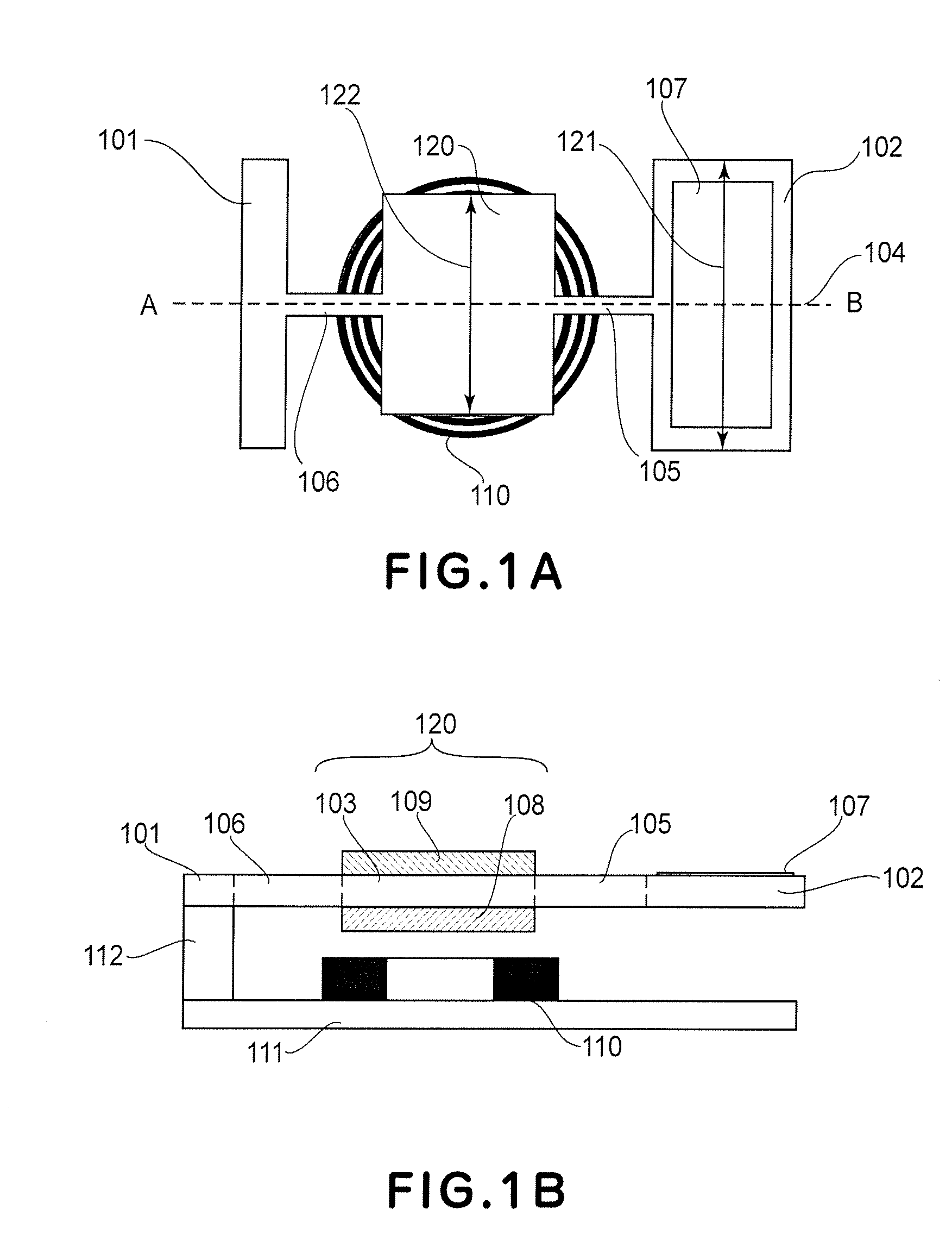
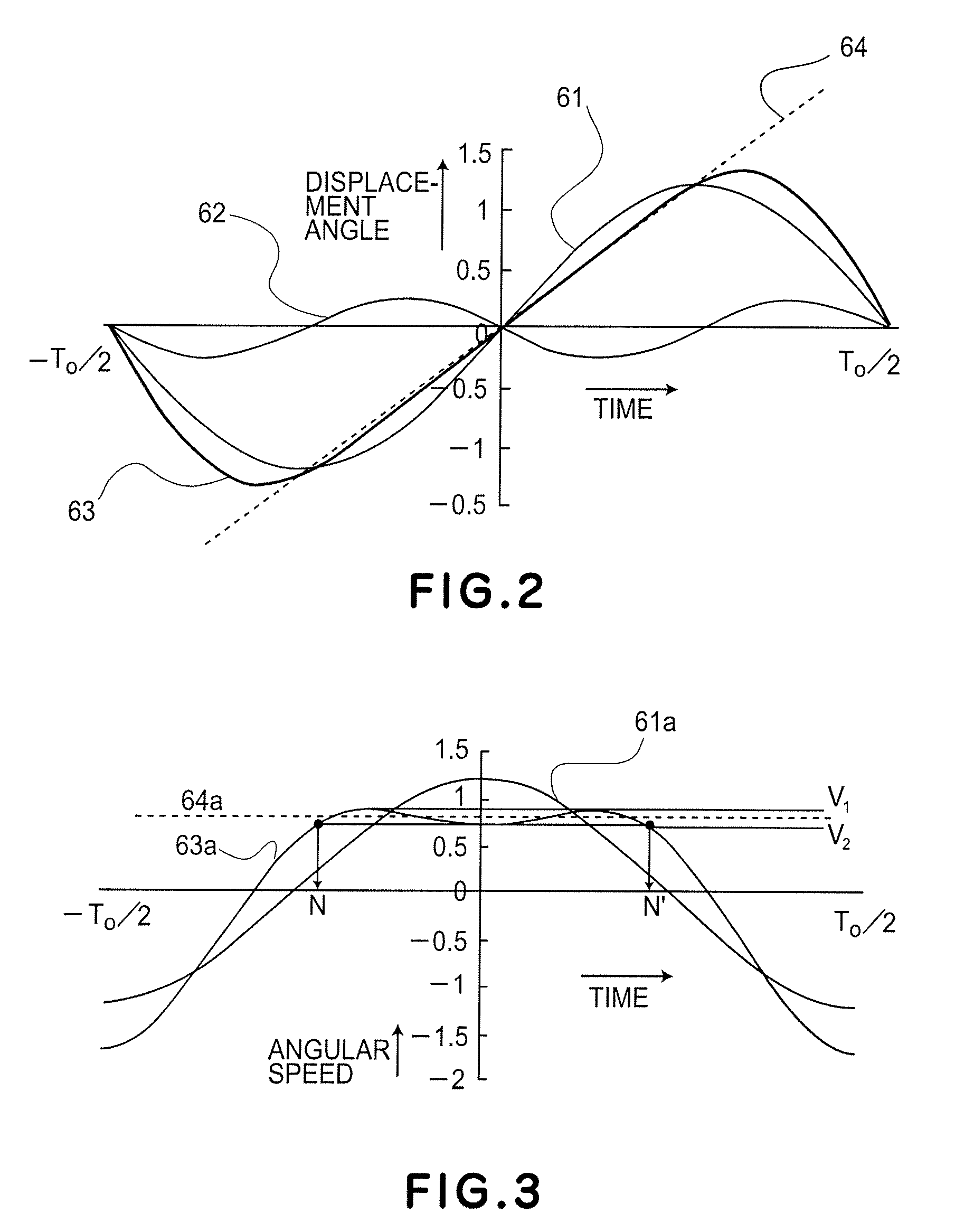
InactiveUS20070279720A1Easy to adjustLarge but stable displacement angleOptical elementsTorsional oscillationsMoment of inertia
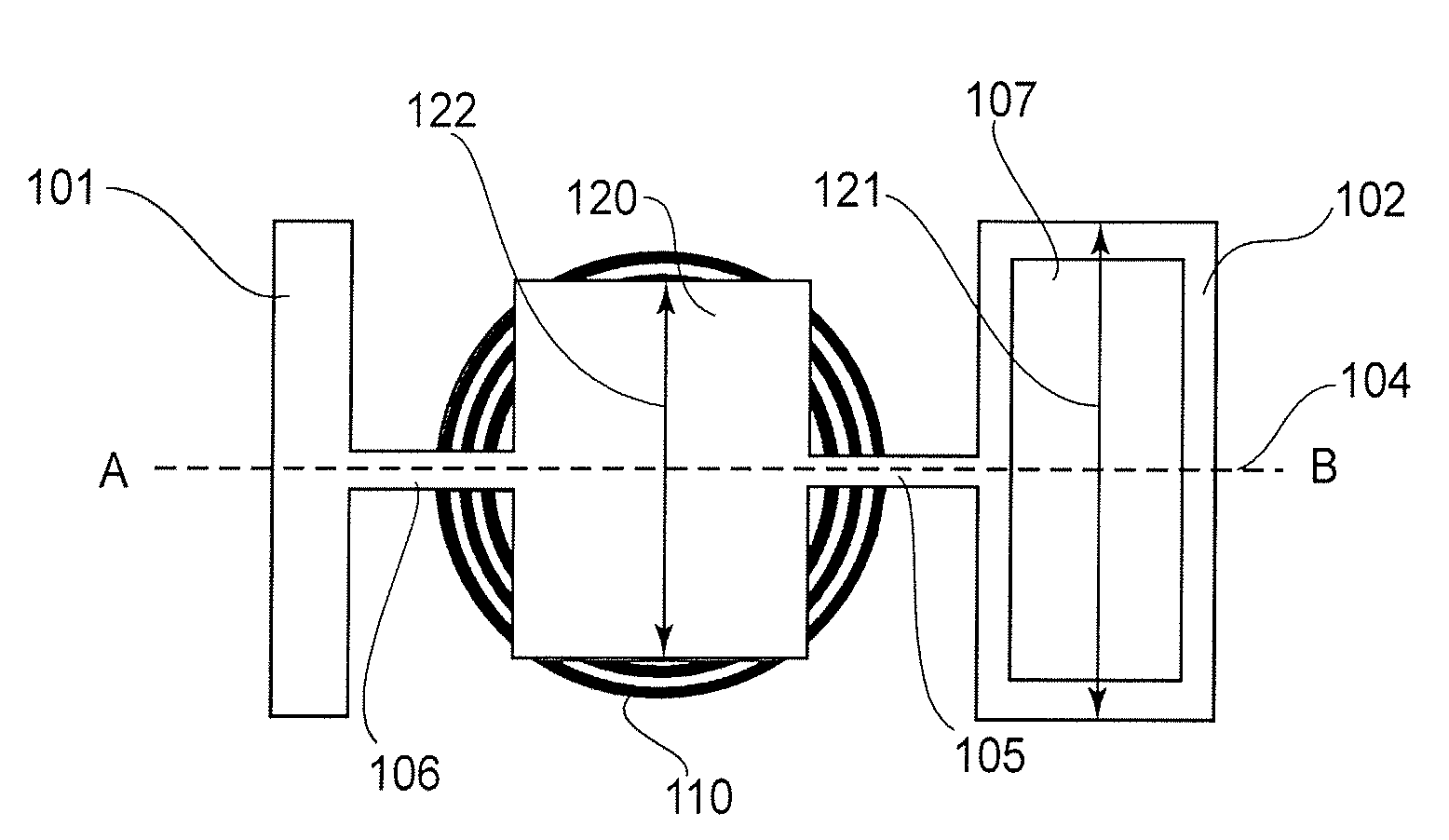
An optical deflector includes a supporting member, a first movable element having a light deflecting element, at least one second movable element, at least one first torsion spring configured to support the first and second movable elements, for torsional oscillation about an oscillation axis, at least one second torsion spring configured to support the second movable element and the supporting member, for torsional oscillation about the oscillation axis, and a driving system configured to apply a driving force to at least one of the first and second movable elements, wherein a moment of inertia of the second movable element with respect to the oscillation axis is larger than a moment of inertia of the first movable element with respect to the oscillation axis, and wherein a length of the second movable element in a direction perpendicular to the oscillation axis is equal to or less than a length of the first movable element in a direction perpendicular to the oscillation axis.
Owner:CANON KK
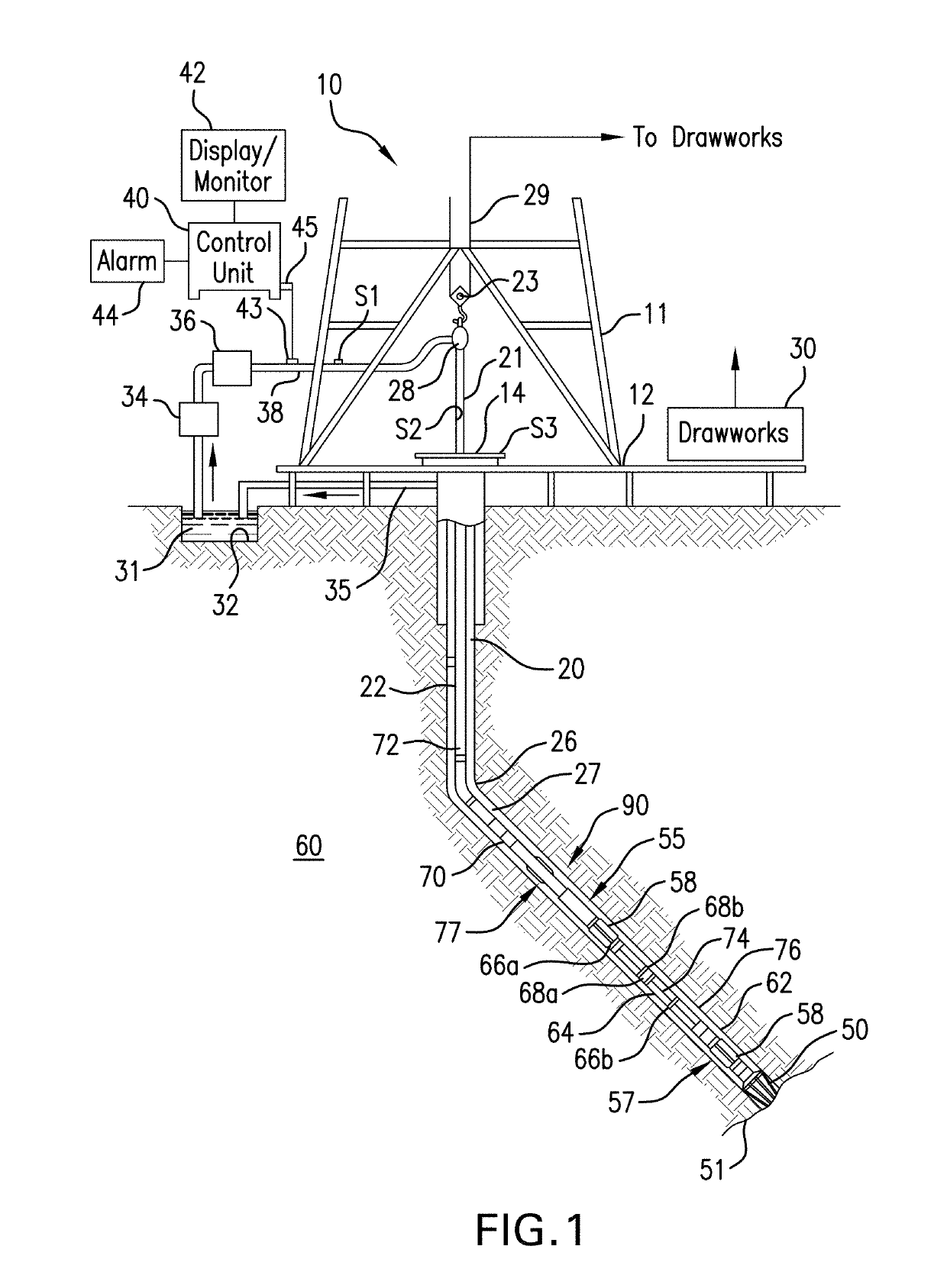
Drilling string torsional energy control assembly and method
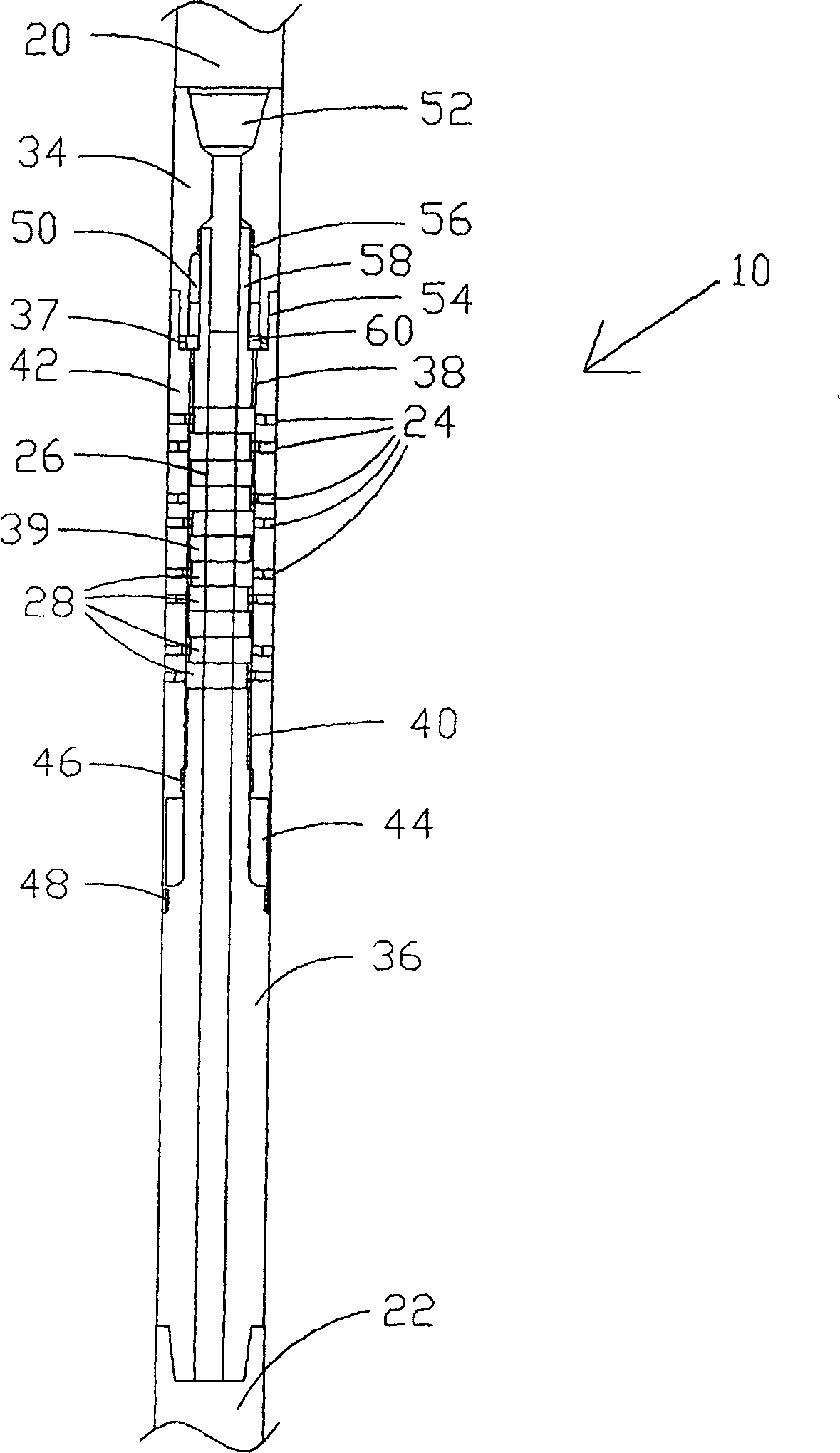
The present invention provides a torsional energy control assembly and method for eliminating slip-stick and / or drill bit oscillations comprising axial and / or rotational oscillations. In one preferred embodiment, the assembly permits slippage between an upper portion of the drilling string and a lower portion of a drill string. The rotational control assembly may be installed at any desired position in the drill string. The rotational control assembly could also be utilized as a component of other drilling mechanisms such as a downhole drilling motor. The rotational control permits slippage while drilling for a selected time or selected rotational distance or other criteria to thereby release torsional energy in the drilling string which otherwise may produce damaging slip-stick torsional oscillations such as slip-stick. The rotational control assembly may, in one embodiment, comprise an on-off clutch whereby torque is either substantially completely transmitted or substantially not transmitted through the assembly for brief periods.
Owner:STRATALOC TECH PROD
Optical deflector and optical instrument using the same
InactiveUS7423795B2Large scan angleGood reproducibilityOptical elementsTorsional oscillationsEngineering
An optical deflector includes an oscillating system and a driving system for driving the oscillating system, the oscillating system including a first oscillator, a first torsion spring, a second oscillator, a second torsion spring and a supporting member, the first oscillator including a first movable element having a light deflecting element configured to deflect light, the second oscillator including a second movable element having a mass adjusting member configured to adjust a mass, wherein the first movable element is resiliently supported by the second movable element through the first torsion spring, for torsional oscillation about an oscillation axis, wherein the second movable element is resiliently supported by the supporting member through the second torsional spring, for torsional oscillation about the oscillation axis, and wherein the oscillating system has at least two natural oscillation modes having different frequencies, about the oscillation axis.
Owner:CANON KK
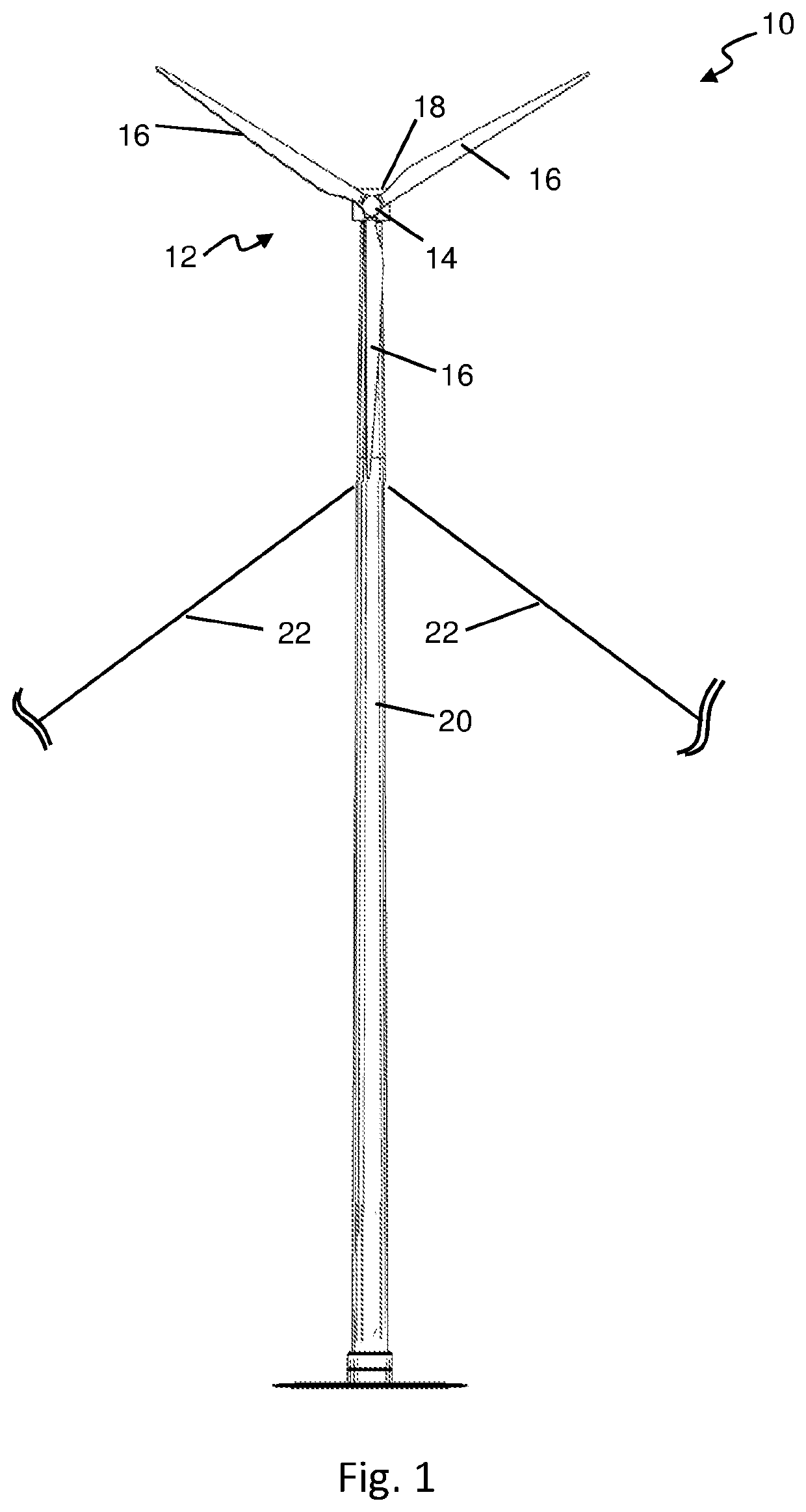
Torsional protection system and method for wind turbine
A torsional protection system and method is provided for protecting a wind turbine from undesired torsional oscillations. The torsional protection system includes a detection processing stage that isolates energy contained within a measured signal to a frequency band of interest. An input to the detection processing stage is obtained from at least one component in the wind turbine. A protection logic stage compares the energy to a threshold level to get an indication of an amount of the energy that is above a predetermined threshold. The torsional content of the signal can be measured and monitored so that if the torsional content exceeds the predetermined threshold for a predetermined time an alarm or trip signal can be generated.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
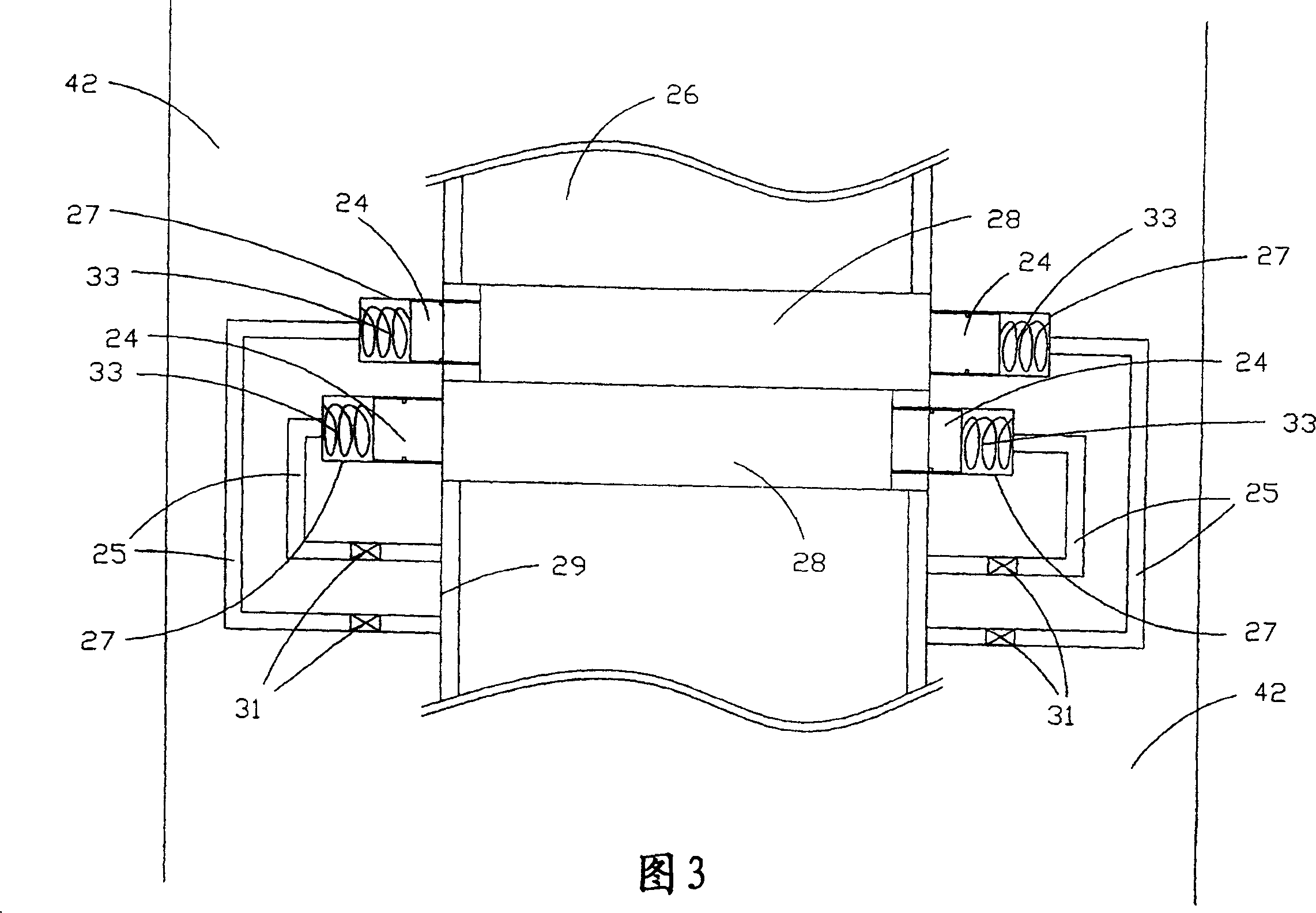
Device for damping torsional oscillations
InactiveUS20160153521A1Reducing and even avoiding axial impactAvoid it happening againRotating vibration suppressionTorsional oscillationsEngineering
A device for damping torsional oscillations comprises a support rotationally displaceable around an axis. A pendulum body comprises first and second axially spaced movable masses. Each mass arranged on a side of the support. A member connects the first and second masses. A bearing interacts with a raceway defined by the support and at least one raceway defined by the pendulum body. An interposition part arranged to prevent contact in the axial direction between one of the masses and at least one of the rolling member and the support. The interposition part comprises an interposition region preventing occurrence of contact in the axial direction, and a region for fastening onto one of the masses or onto one of the rolling member and the support. The fastening region comprises at least two fastening tabs and a reinforcement connecting the tabs.
Owner:VALEO EMRAYA
Method and apparatus of driving torsional resonance mode of a probe-based instrument
InactiveUS7168301B2Improve abilitiesMaximising amplitudeNanotechnologyScanning probe microscopyTorsional oscillationsEngineering
A method of operating a scanning probe microscope includes using a probe having a cantilever, and oscillating the probe at a torsional resonance frequency thereof. In addition, the method includes substantially increasing torsional drive efficiency with dual actuators disposed on the probe or the probe base. First and second actuators may be driven by corresponding first and second drive signals, the first and second drive signals being about 180° out of phase. The maximizing step includes altering at least one of the amplitudes of the first and second drive signals to maximize torsional oscillation. Torsional and flexural oscillation of the cantilever probe can be excited concurrently, sequentially or independently by adjusting the phase of the corresponding drive signals. A pair of cantilever components can be used to form a nanotweezer by rotating the respective arms having corresponding tip portions at the distal ends.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
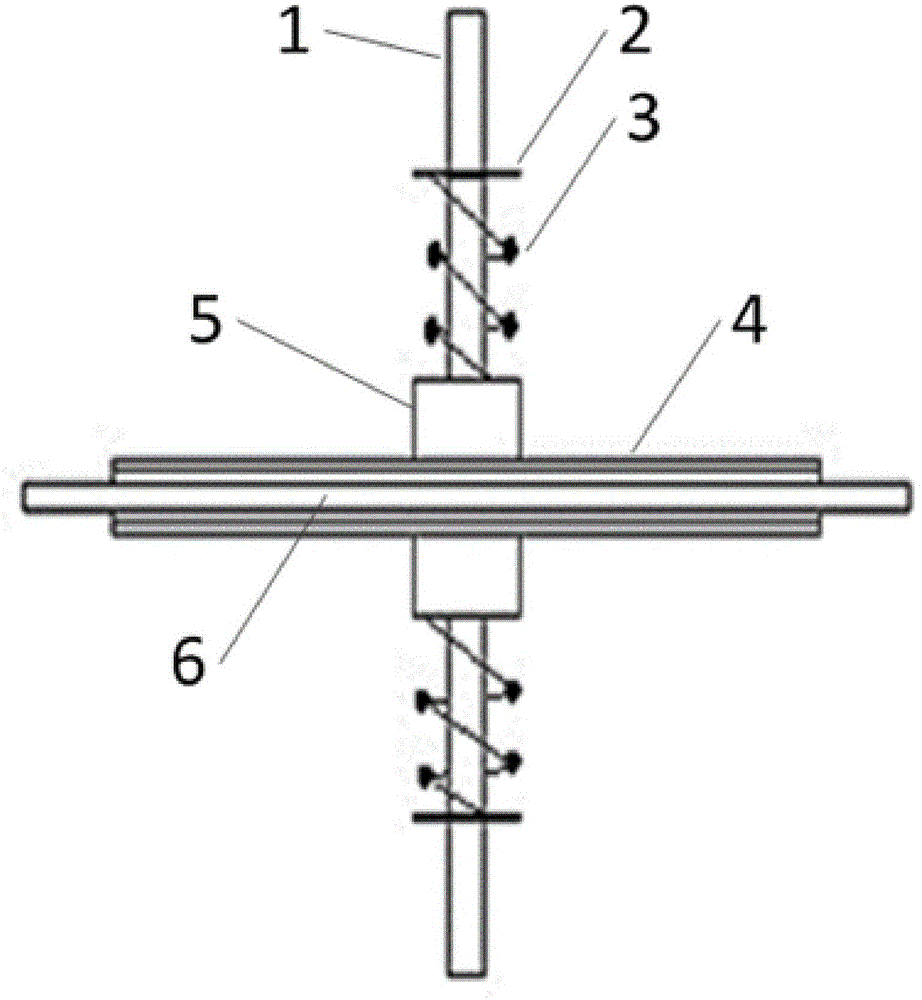
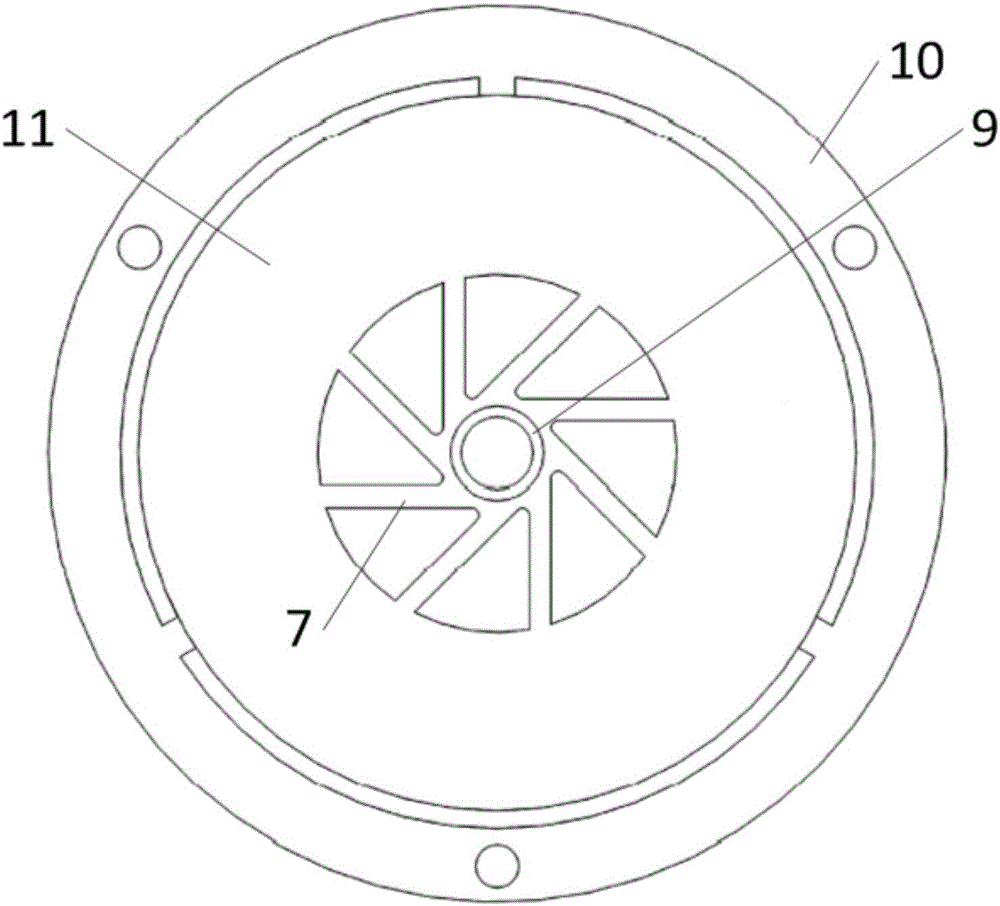
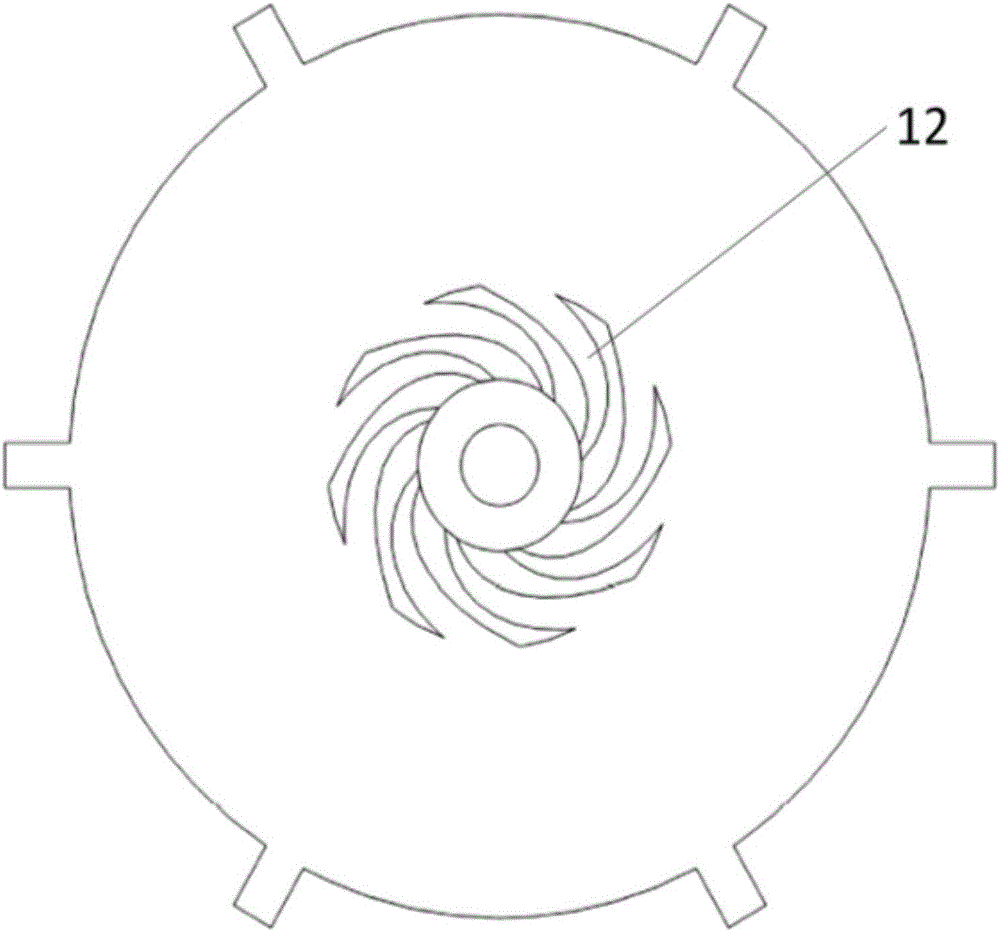
Thin reverse type ultrasonic motor
ActiveCN106059378ACompact structureSmall sizePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityTorsional oscillations
The invention discloses a thin reverse type ultrasonic motor. Vertical and radial vibration generated by piezoelectric ceramic sheets can be converted into torsional oscillation modal of a waveguide structure in a stator, and a rotor can be made to realize a high rotation speed through the torsional oscillation modal. The thin reverse type ultrasonic motor comprises a rotation shaft (1), wherein the rotation shaft (1) penetrates through a slot pad (2), a spring (3), the rotor (5) and the stator (6), the slot pad (2) is fastened on the rotation shaft (1) through a key slot on the rotation shaft (1), the piezoelectric ceramic sheets are attached to upper and lower surfaces of the stator (6), the rotor (5) is driven to rotate by the stator (6) through friction, the stator (6) is internally connected with the waveguide structure, and the waveguide structure comprises uniformly-distributed spoked beams in a tangent relationship with a center cylinder. The thin reverse type ultrasonic motor is suitable for the precise driving and transmission technology field.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for detecting shafting torsional oscillation mode of generator set appended with field excitation damp controller
ActiveCN101221085AEnsure safetyIncreased power delivery capabilityEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionInstrumentsPower stationTorsional oscillations
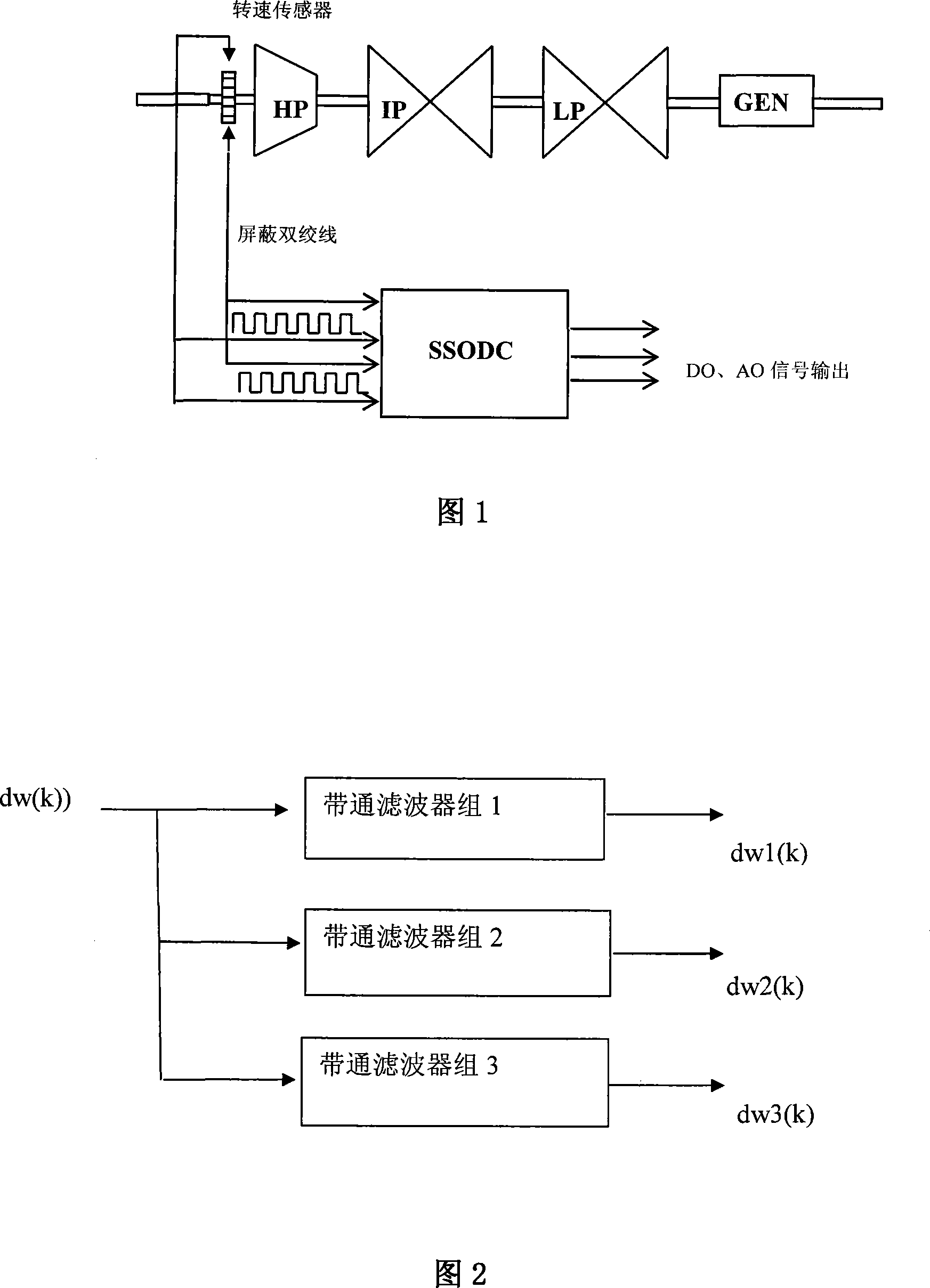
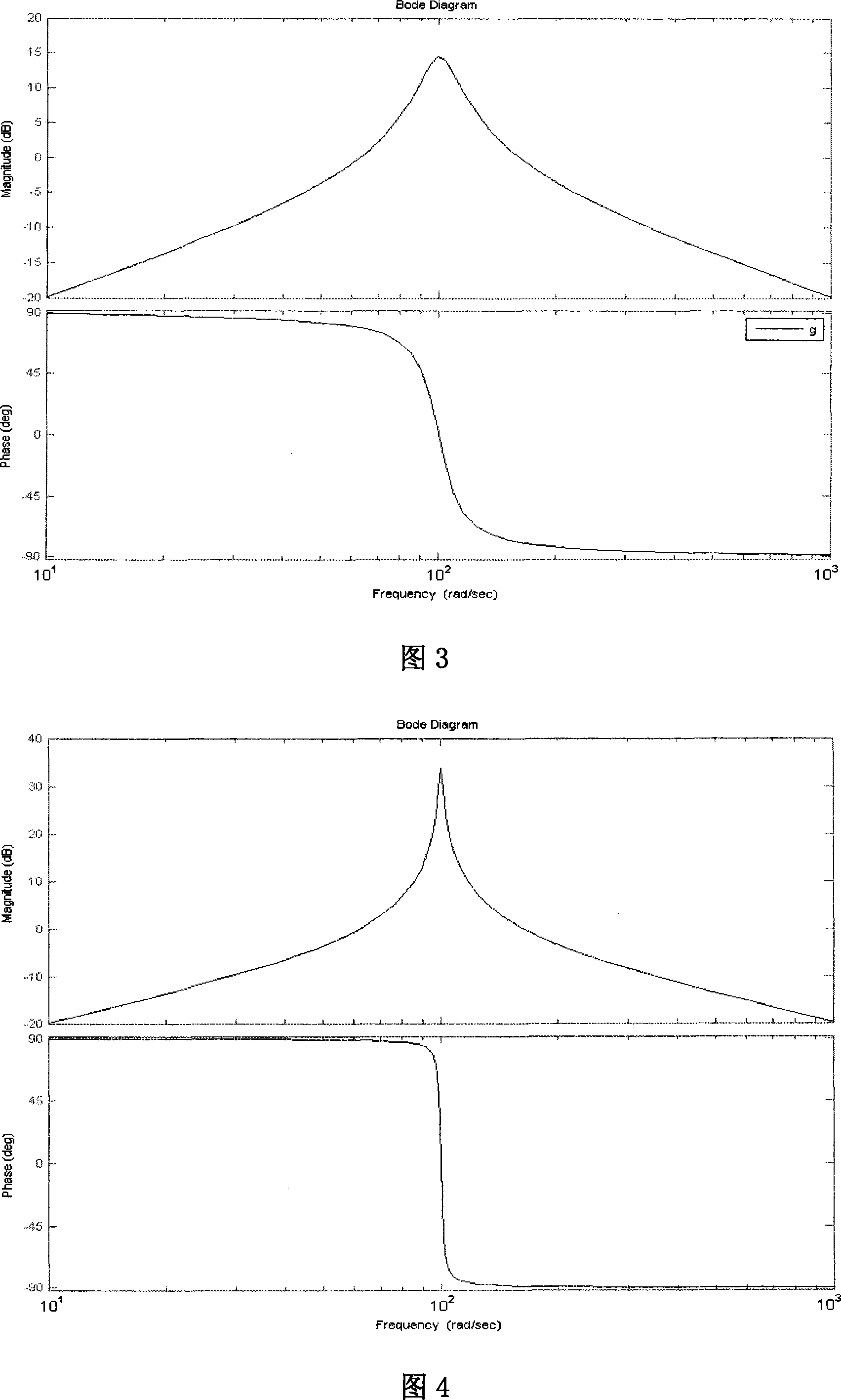
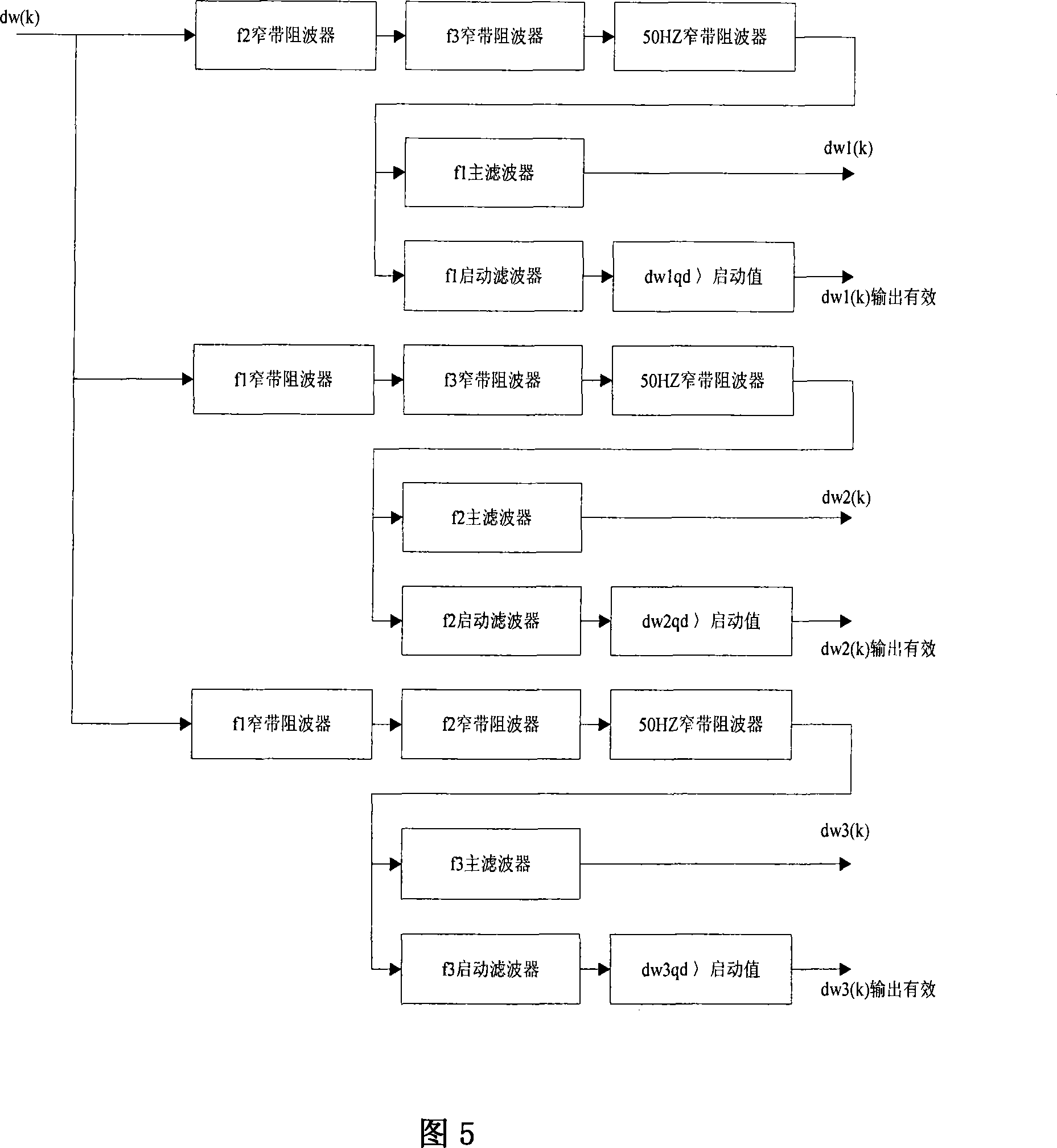
The invention relates to a method for monitoring and calculating a subsynchronous oscillation mode from an electric generating set in real-time when a power house and an electric power system generate subsynchronous oscillation (SSO) and discloses a method for obtaining a shafting torsional oscillation mode of a steamer electric generating set through combining a main filter, a starting filter and a narrow band wave-resistance filter. The method works out the change of a rotary palstance (dw) of an electric generating shafting through a rotary speed pulse of a rotary speed sensor arranged on the electric generating set shafting and works out an instant value of each mode of the electric generating set shafting torsional oscillation with linear phaseshift through the combination algorithm of a broad band filter combined by the main filter and the narrow band wave-resistance filter; a dw signal is combined with the narrow band wave-resistance filter by passing through the starting filter to be a mode starting condition. The method can be used for restraining the subsynchronous oscillation (SSO) steamer electric generating set into a subsynchronous oscillation damp controller (SSODC).
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION
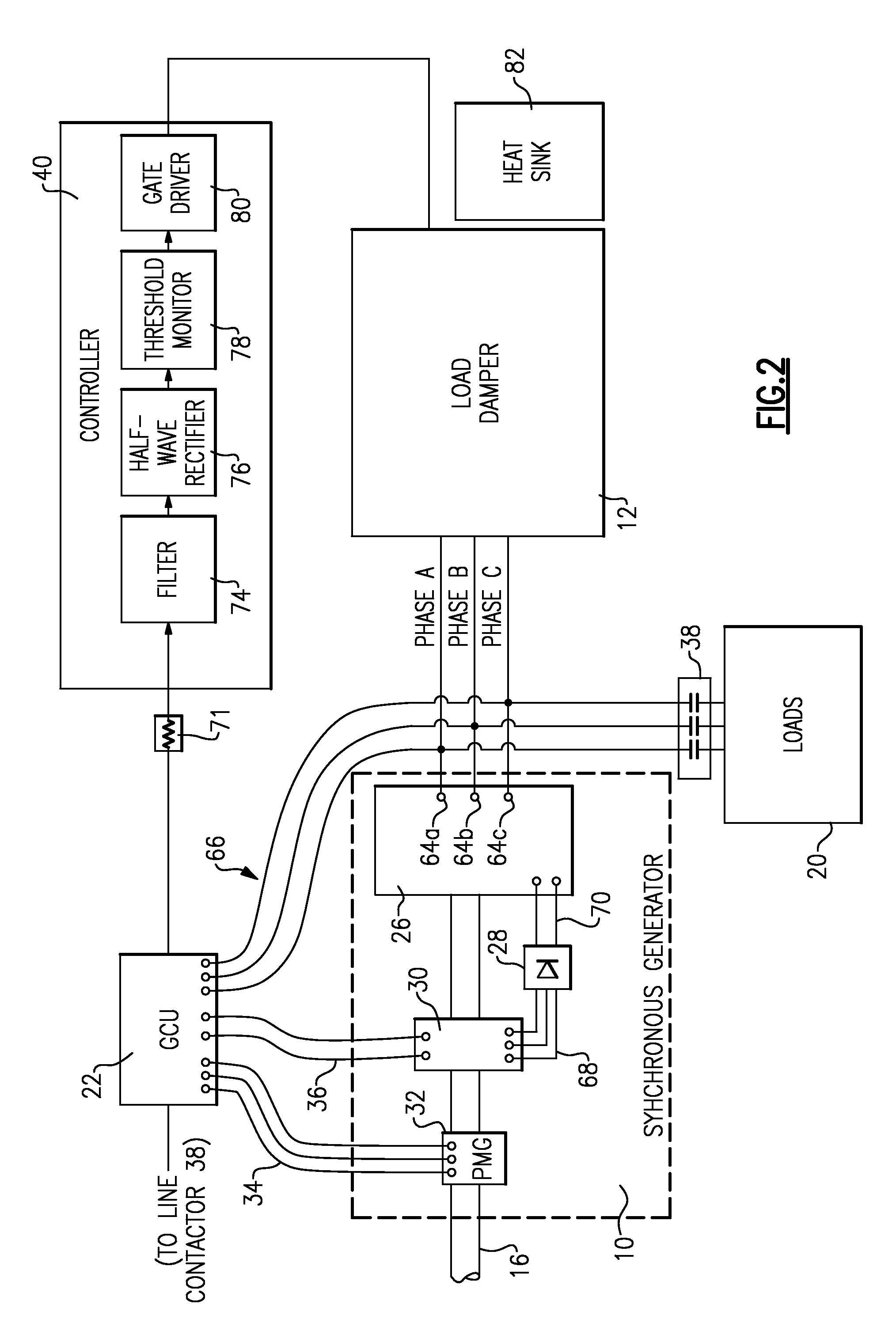
Electric load damper for damping torsional oscillation
ActiveUS8217630B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
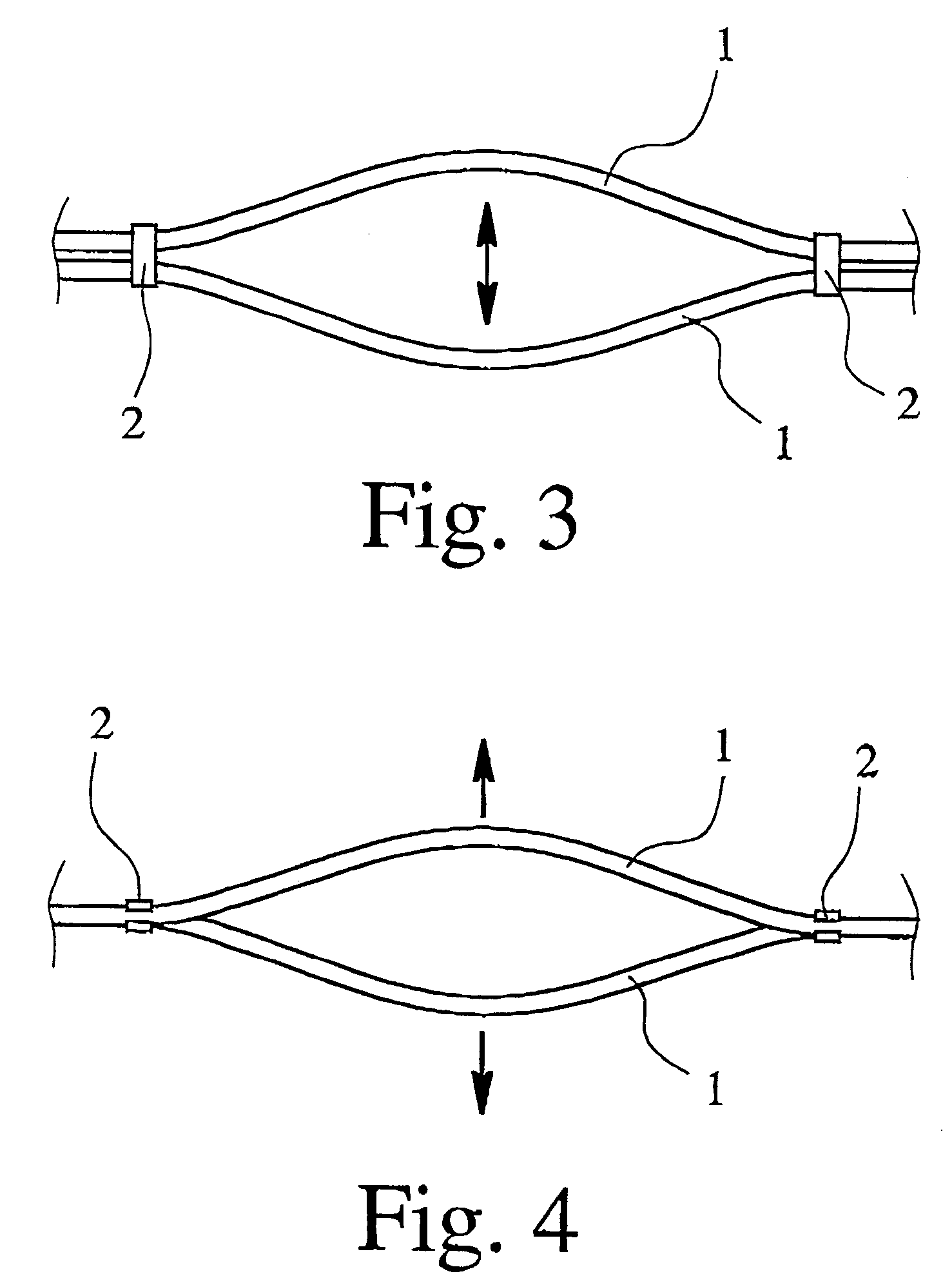
Mass flow meter composed of two measuring tubes with a connecting device between them
ActiveUS7275449B2Minimize impactReduce resistanceDirect mass flowmetersTorsional oscillationsFlexural strength
A mass flowmeter employing the Coriolis principle incorporates in at least one section two measuring tubes that extend along a common plane, as well as a connecting device that connects the two measuring tubes in the section in which they extend along the common plane. The connecting device is designed and positioned in a manner whereby its flexural strength for flections in the common plane of the measuring tubes is greater than its torsional rigidity for torsional oscillations around the connecting line between the two measuring tubes. This achieves good frequency separation between the excitation oscillations generated in the common plane of the measuring tubes and the oscillations of the measuring tubes perpendicular to the former.
Owner:KRONE GMBH
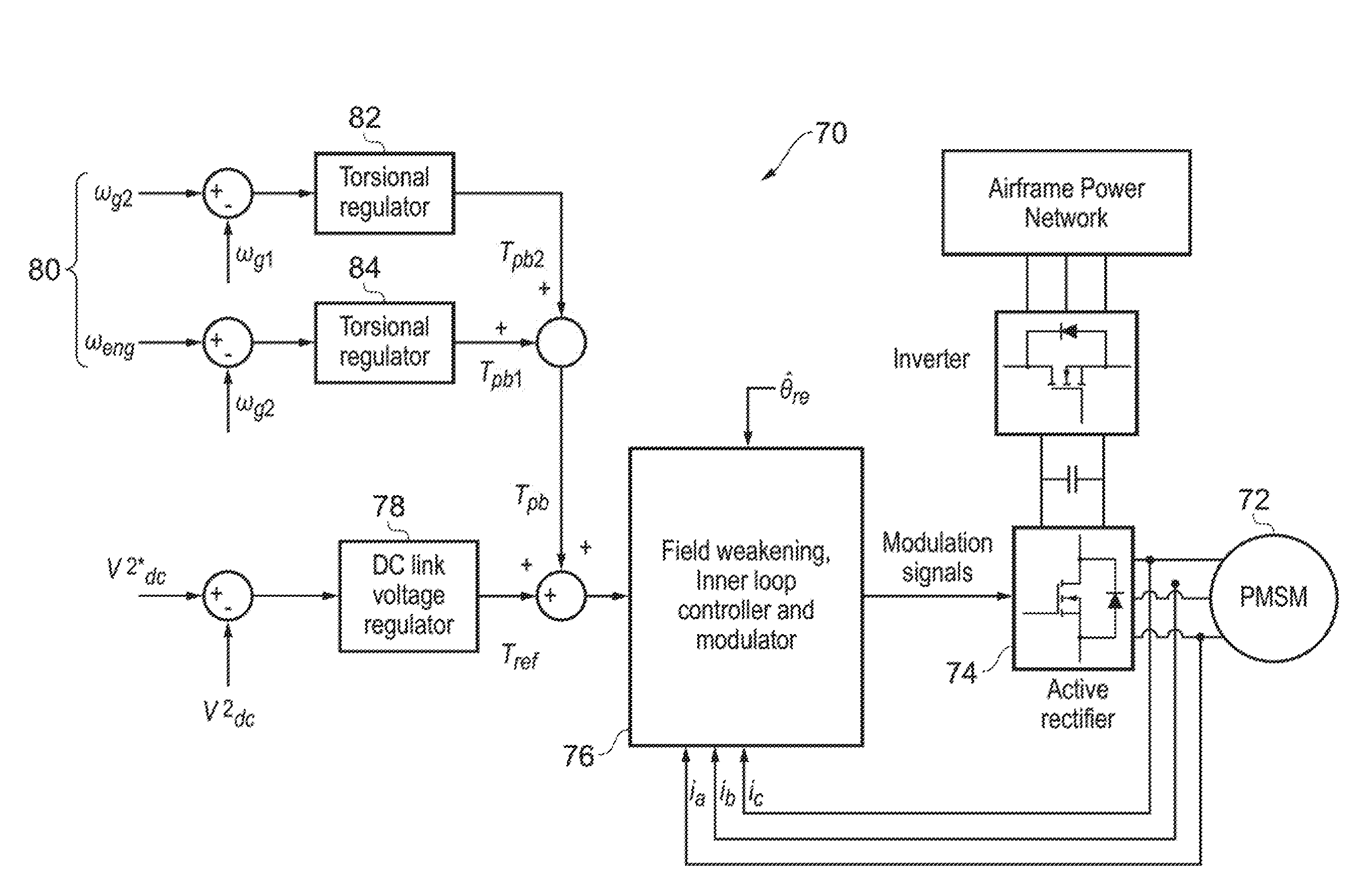
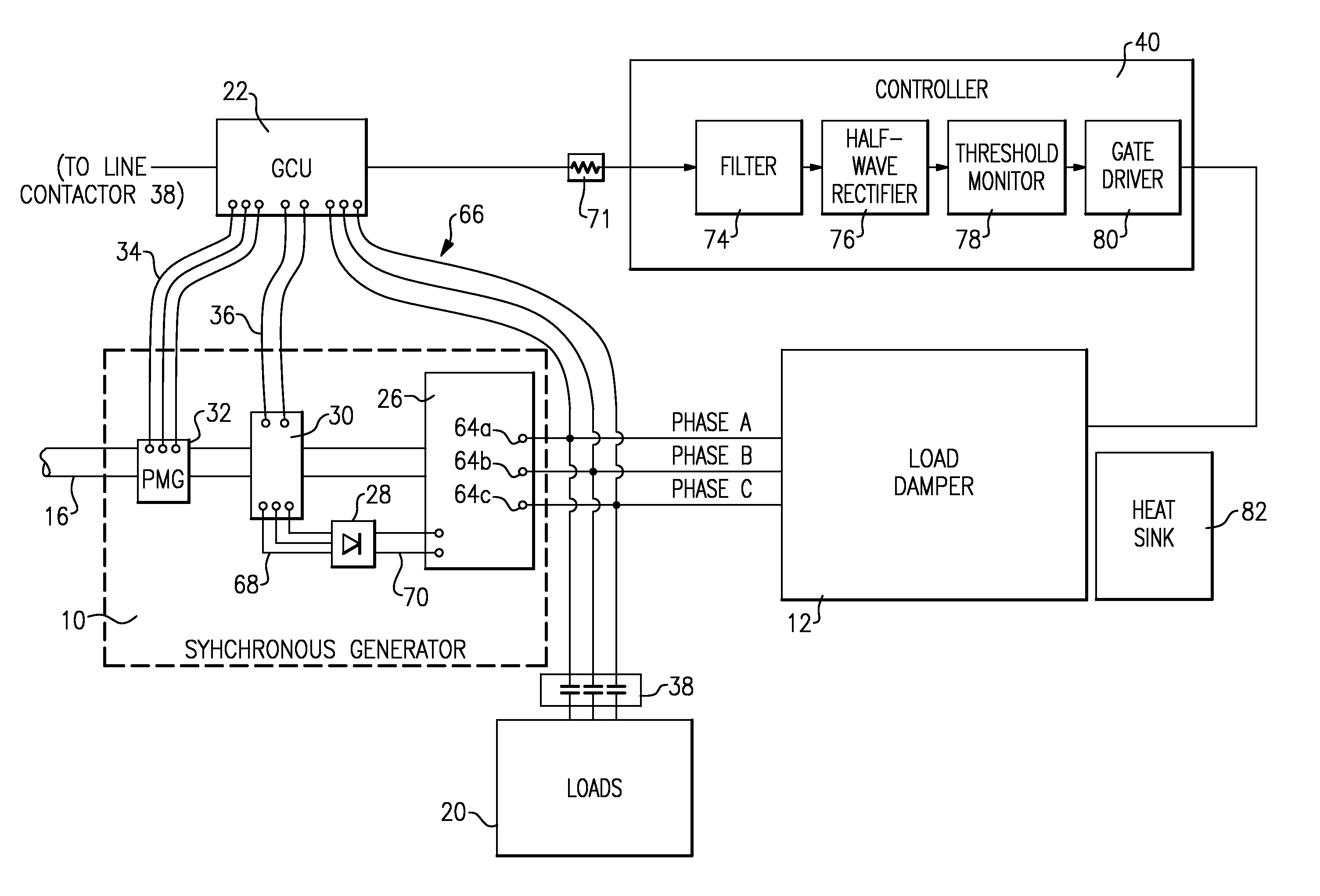
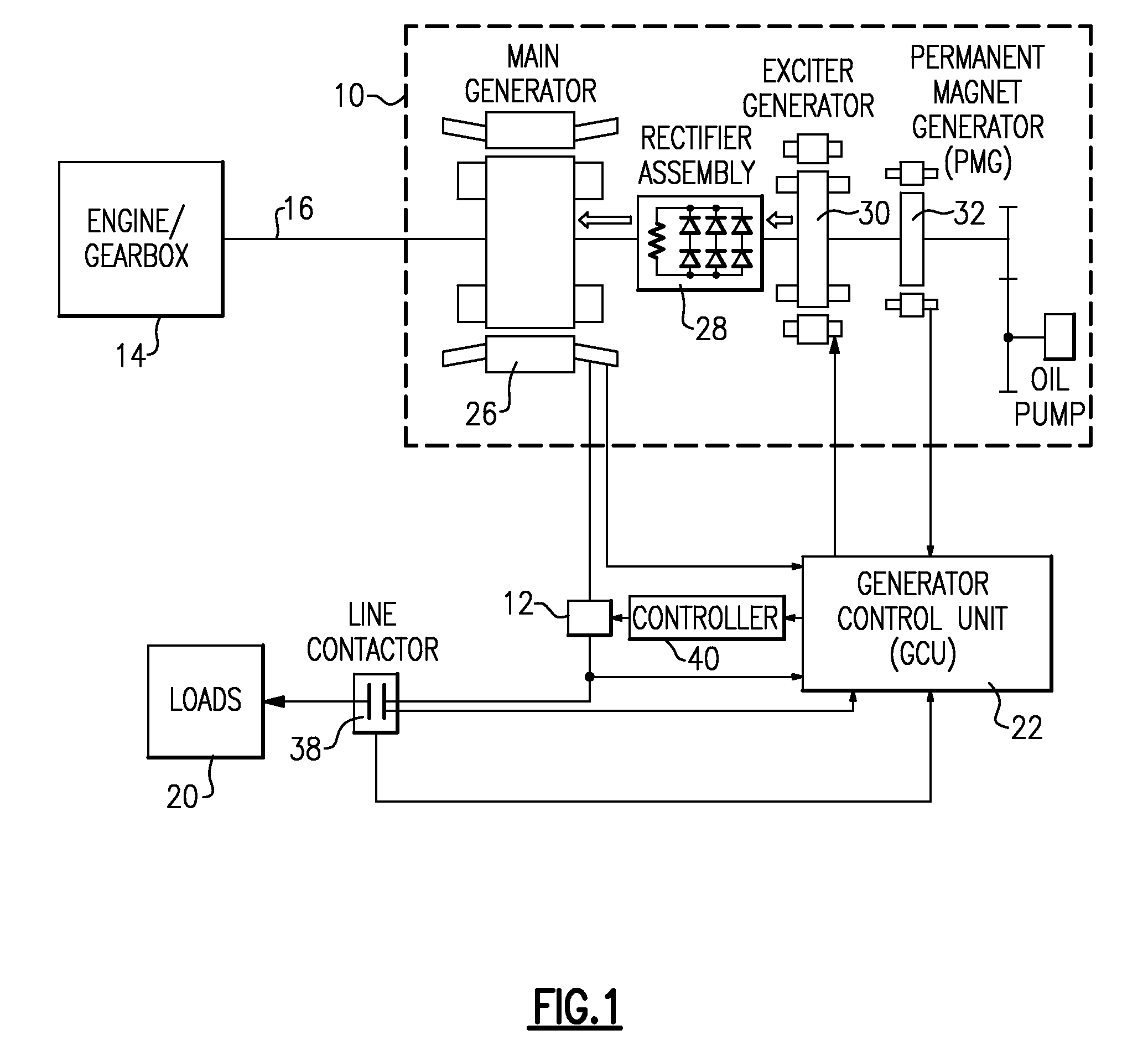
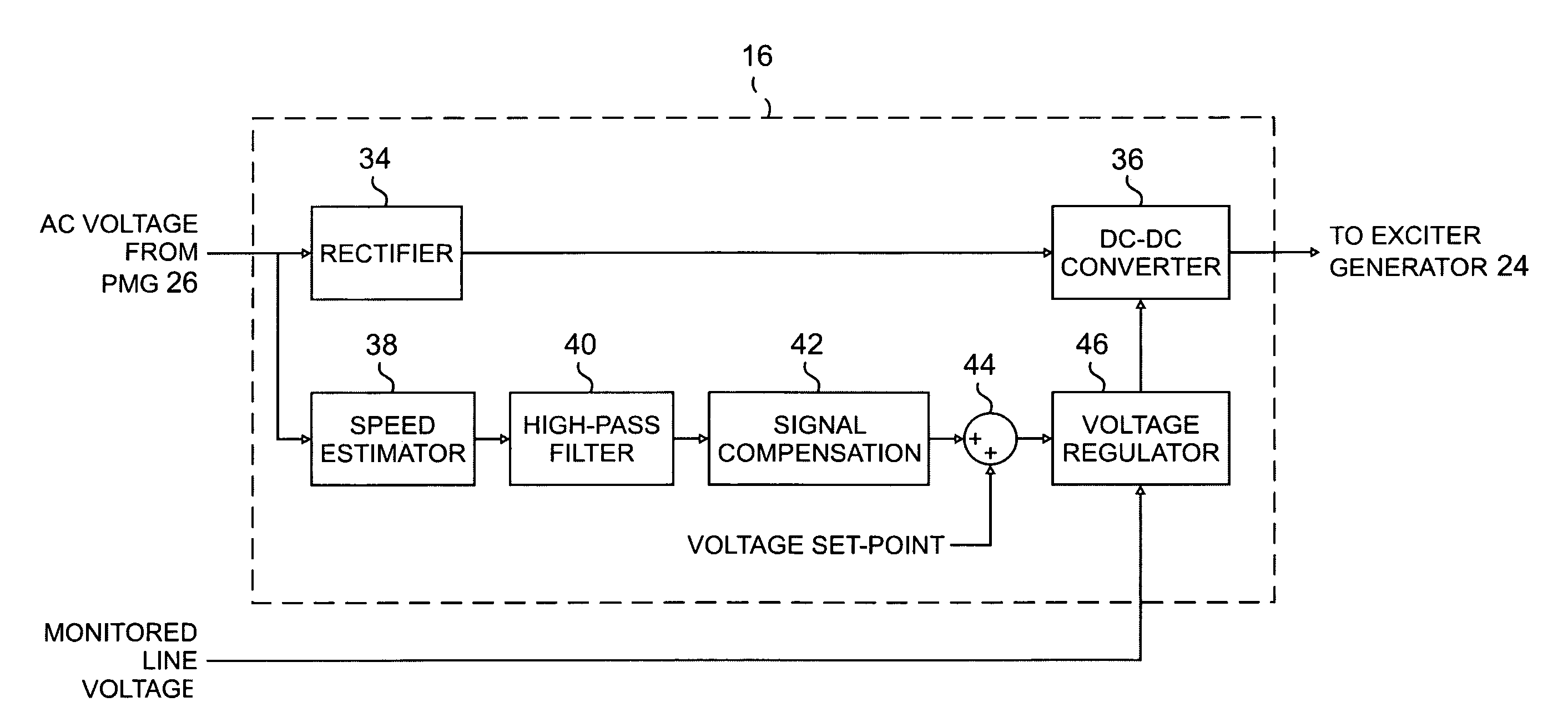
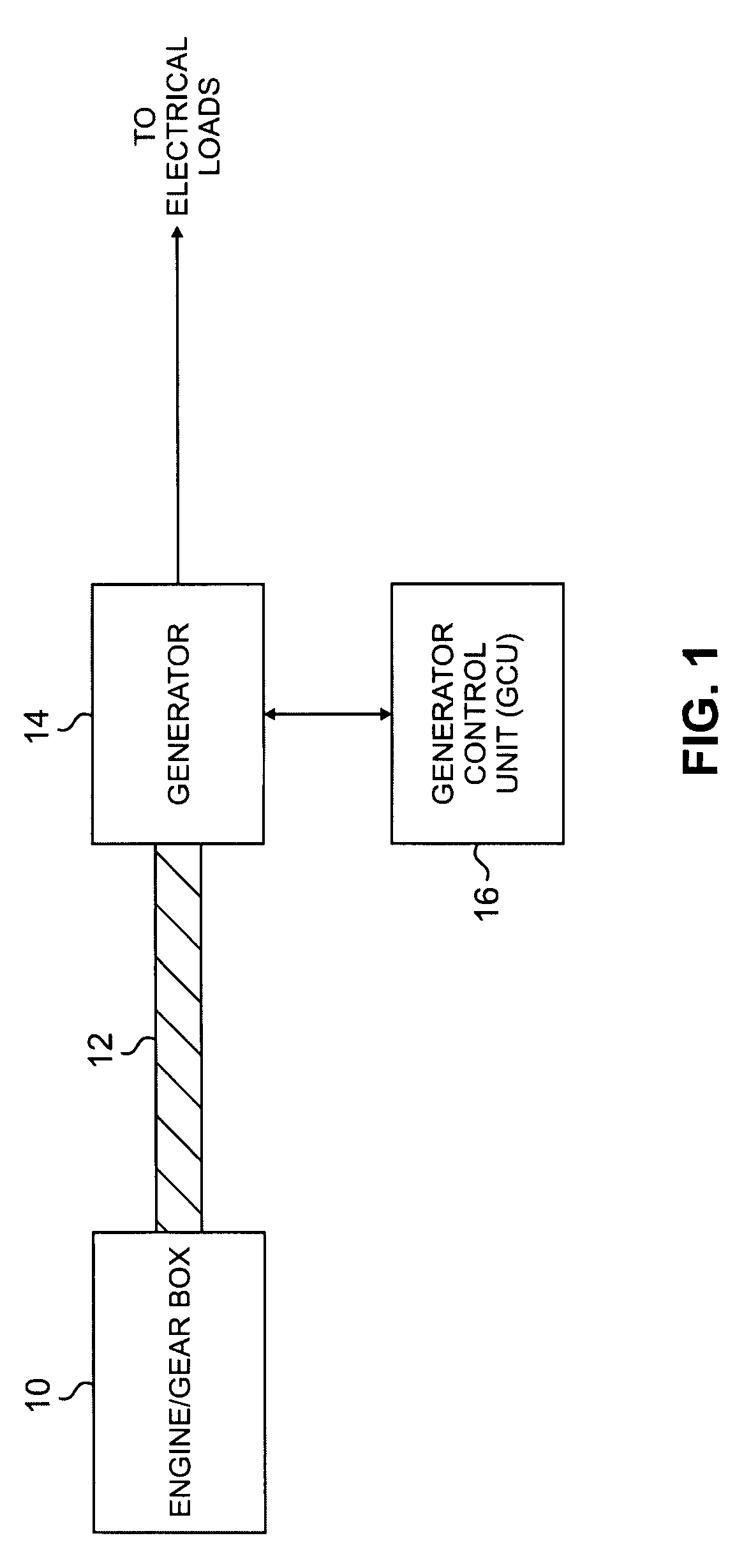
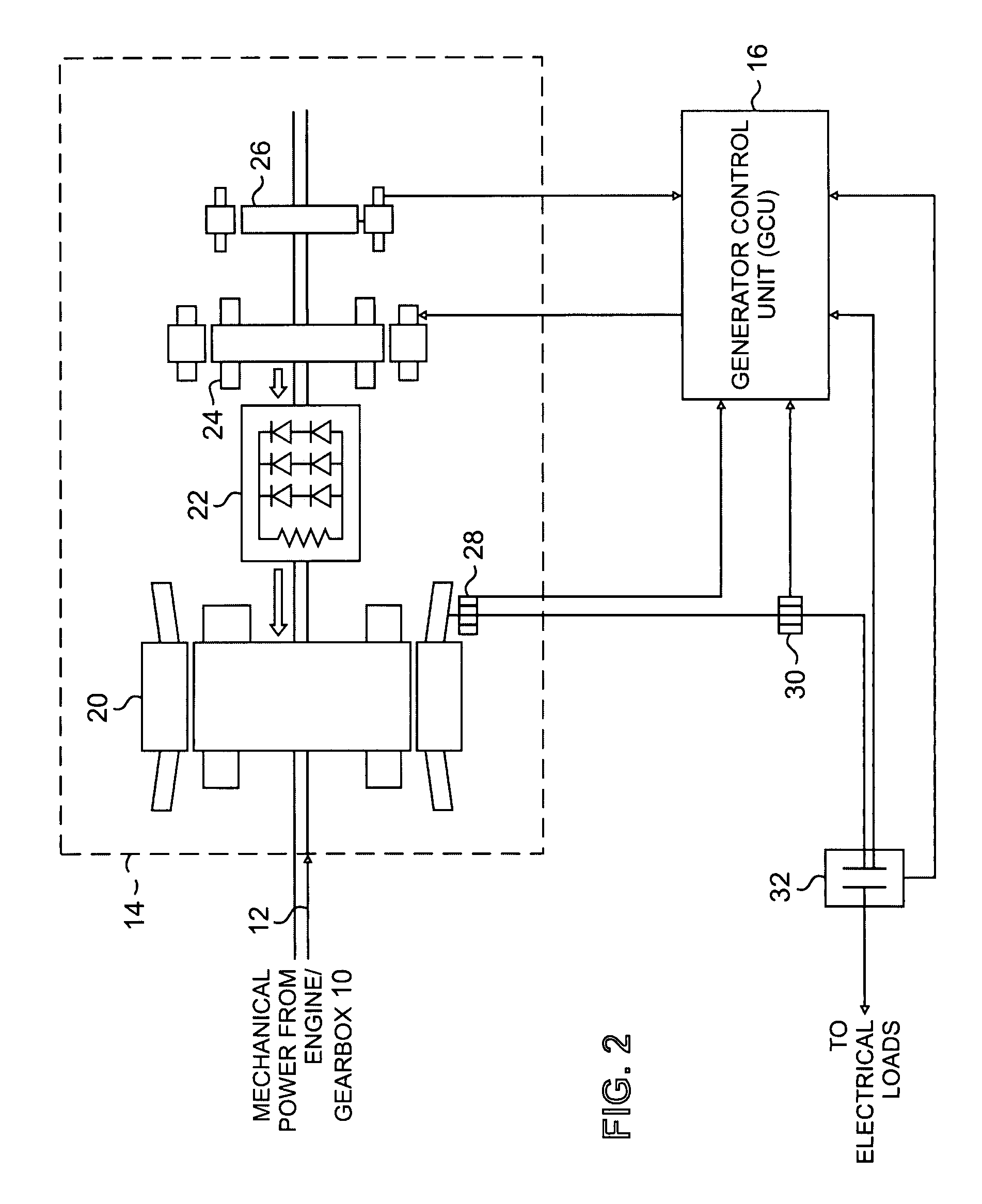
Active damping for synchronous generator torsional oscillations
ActiveUS7808215B2Reduce torsional oscillationsElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersTorsional oscillationsDrivetrain
A generator control unit (GCU) provides active damping of a synchronous generator by monitoring the speed of the synchronous generator and detecting oscillations in the monitored speed. The oscillations are indicative of torsional oscillations within the mechanical drivetrain including the synchronous generator or generators. In response to detected oscillations in the monitored speed, the GCU generates a varying set-point value that is used to control the excitation voltage provided to the synchronous generator. Varying the excitation voltage provided to the synchronous generator causes a variation in synchronous generator torque. By selectively varying the torque in the synchronous generator, the GCU provides active damping in the synchronous generator that decreases or dampens the torsional oscillations.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
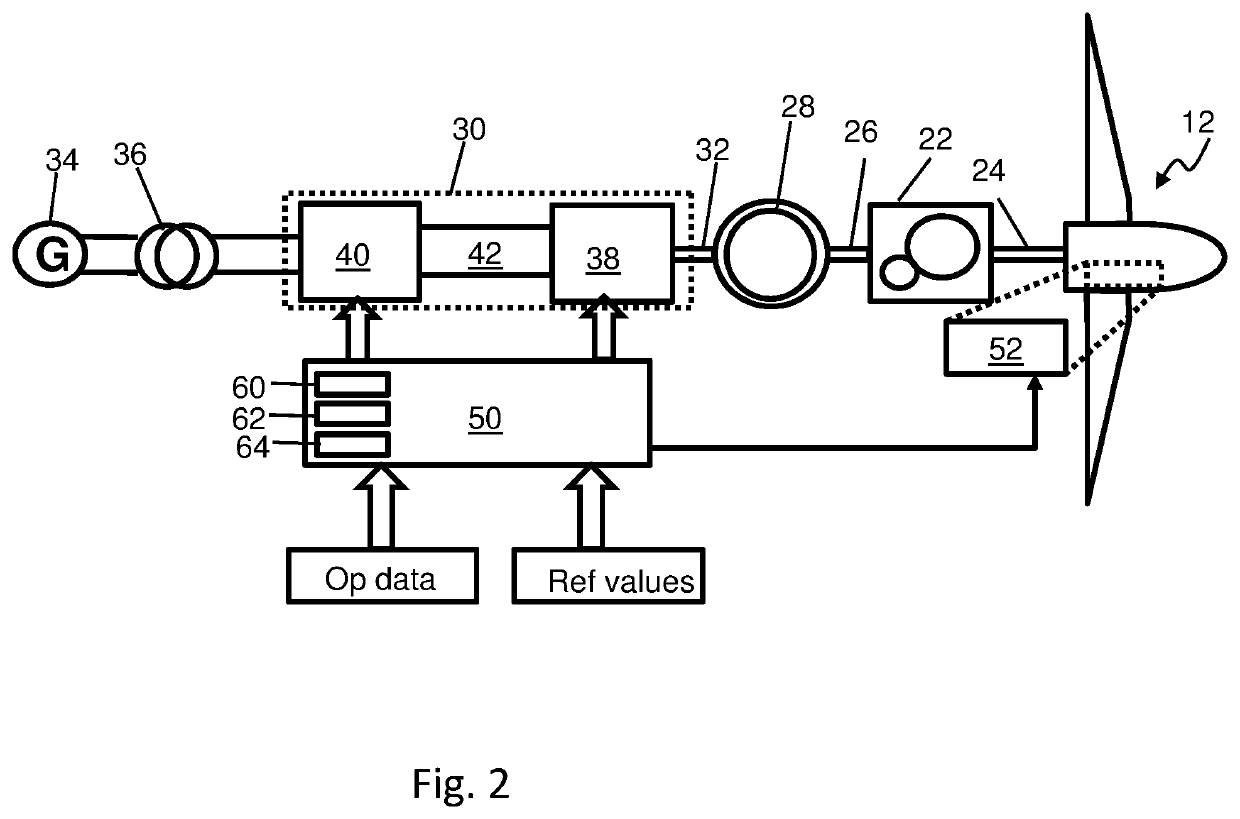
System and method to manage torsional oscillation of a wind turbine tower
ActiveUS20200088165A1Damp torsional oscillationReduce pitch activityWind motor controlEngine fuctionsNacelleTorsional oscillations
A wind turbine comprising a tower, a nacelle, a rotor including a plurality of blades, an electrical generator operatively coupled to the rotor, and a control system. The control system comprises: a sensing system operable to output a signal indicative of the torsional oscillation frequency of the nacelle; a torsional damping module configured to monitor the torsional oscillation signal and to determine one or more blade pitch command signals for damping the torsional oscillation of the tower, and a filter module configured to receive the one or more blade pitch command signals as inputs and to output a respective one or more modified blade pitch command signals, wherein the filter module is configured to filter the one or more blade pitch command input signals to exclude frequency components greater than the torsional oscillation frequency. Aspects of the invention also relate to a method, a computer program software product and a controller for implementing the method.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Dampers for mitigation of downhole tool vibrations
Systems and methods for damping torsional oscillations of downhole systems are described. The systems include a damping system configured on the downhole system. The damping system includes a first element and a second element in frictional contact with the first element. The second element moves relative to the first element with a velocity that is a sum of a periodic velocity fluctuation having an amplitude and a mean velocity, wherein the mean velocity is lower than the amplitude of the periodic velocity fluctuation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
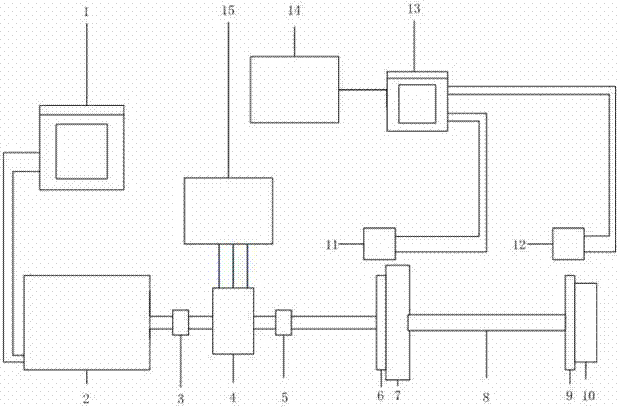
Device and method for testing torsional rigidity and mode of shafting
PendingCN108072488AEasy to implementEasy to operateMachine part testingStatic/dynamic balance measurementModal testingAccelerometer
The invention relates to a device and method for testing the torsional rigidity and mode of shafting, and belongs to the field of rigidity and mode test. In the device, a mass disc is bonded to the free end of a shaft to be tested, additional square blocks are bonded to the two sides, opposite to each other, in the side arm of the shaft to be tested respectively, and accelerometers are mounted onthe additional square blocks respectively. The device is easy to realize, convenient to operate and high in test precision, and fills the blanks in the field of torsional rigidity and mode test of theshafting. According to the method, the characteristic that the additional square blocks can act torsional moment excitation and test response of the tested shaft in the torsional direction is used, the mass disc is used to change the mass characteristic of the shaft, the torsional rigidity and moment of inertia of the tested shaft are calculated, the torsional rigidity and mode measured by the method can reflect the torsional oscillation characteristic of the shafting visually, and the method further has the advantage of high precision.
Owner:BRILLIANCE AUTO
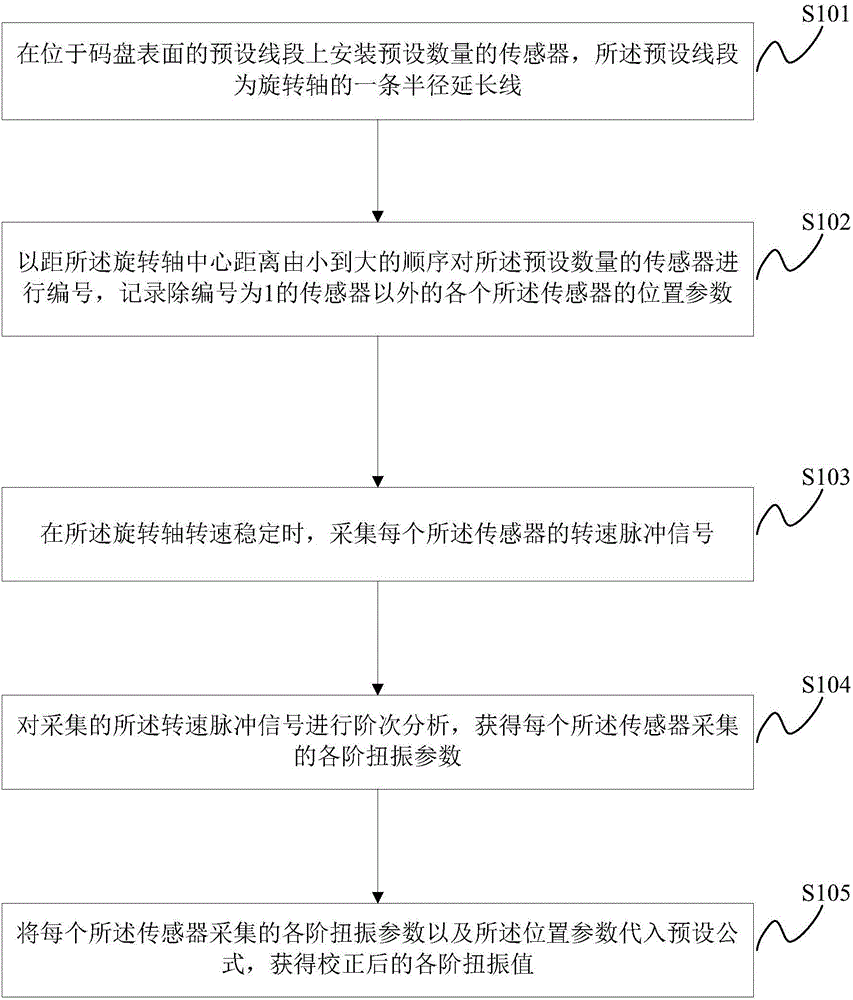
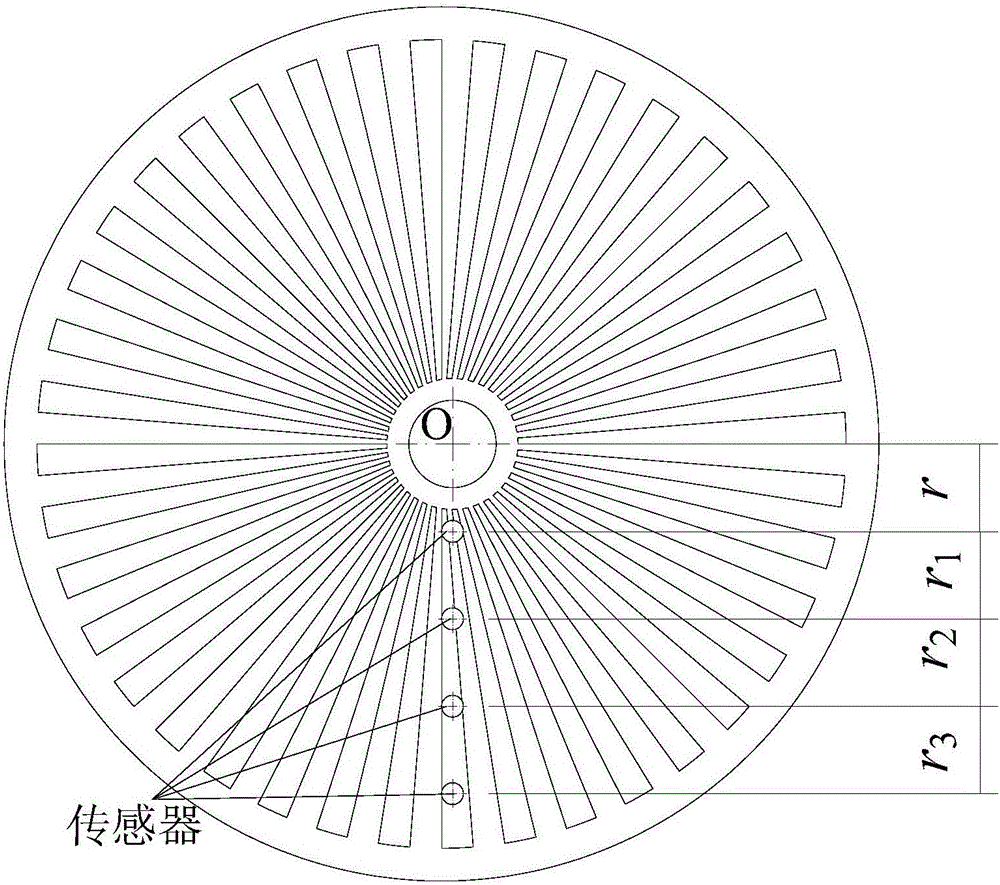
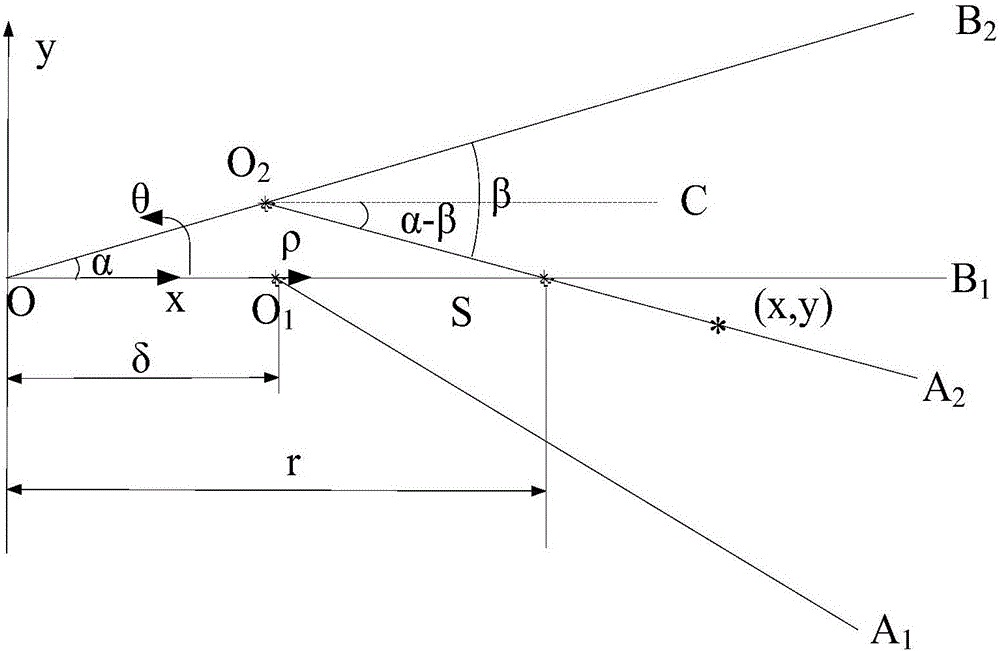
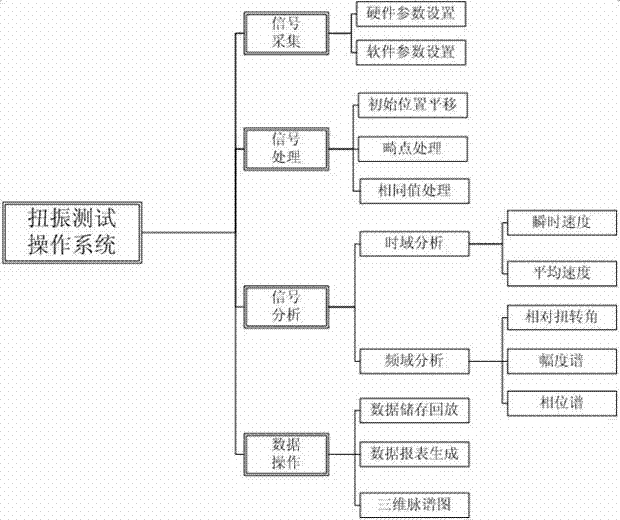
Torsional oscillation test error correction method
The application discloses a torsional oscillation test error correction method which is suitable for correcting torsional oscillation test errors generated by code disc eccentricity. The torsional oscillation test error correction method comprises steps of installing a preset number of sensors on a preset line segment on the surface of a code disc, wherein the preset line segment is a radius extending line of a rotary shaft; numbering the preset number of sensors according to distances to the center of the rotary shaft from small to large, and recording positional parameters of the sensors except a No.1 sensor; collecting a rotating speed pulse signal of each sensor when the rotary shaft has a stable rotating speed; carrying out order analysis of the collected rotating speed pulse signals to obtain a torsional parameter of each order of each sensor; and placing the torsional parameter of each order of each sensor and the positional parameter of each sensor in a preset formula to obtain a torsional value of each order after correction. As a result, the object of correcting the torsional oscillation test errors generated by code disc eccentricity is achieved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
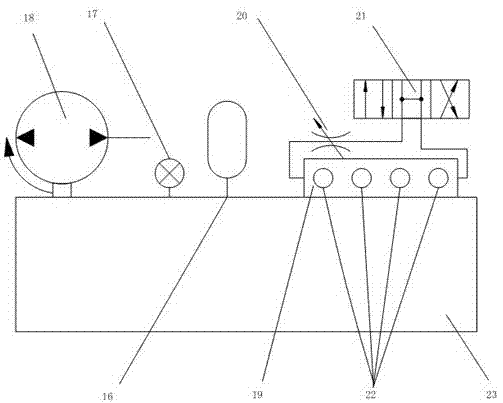
Performance parameter test system of silicon oil damper for vehicle
InactiveCN102221470AImprove securityAdjust the size of inertiaVehicle suspension/damping testingVibration testingContinuous measurementTorsional oscillations
The invention discloses a performance parameter test system of a silicon oil damper for a vehicle. The performance parameter test system comprises a frequency converter, a variable-frequency motor, an elastic coupling, a torsional oscillation exciting device, a coupling, a first measuring fluted disc, an adjustable inertia flywheel, a main shaft, a second measuring fluted disc and a damper, wherein the torsional oscillation exciting device is connected with a hydraulic pump station; a first magnetoelectric sensor is arranged above the first measuring fluted disc; a second magnetoelectric sensor is arranged above the second measuring fluted disc; the first and the second magnetoelectric sensors are connected with an NI-PXI6250 acquisition card respectively; and the NI-PXI6250 acquisition cards are connected with a computer. Due to the adoption of the performance parameter test system, engines of different cylinder numbers can be simulated, the inertia magnitude of an inertia disk can be adjusted, and the rotating speed can be adjusted in a large range; the test system can be used for continually measuring the instantaneous speed varying quickly and has high distinguishing capability on micro variation of the instantaneous speed and high responding speed; and due to the adoption of the test system, the cost of real vehicle test is saved, the risks of the real vehicle test are reduced, the function of efficiently measuring the internal performance of the damper at low cost is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
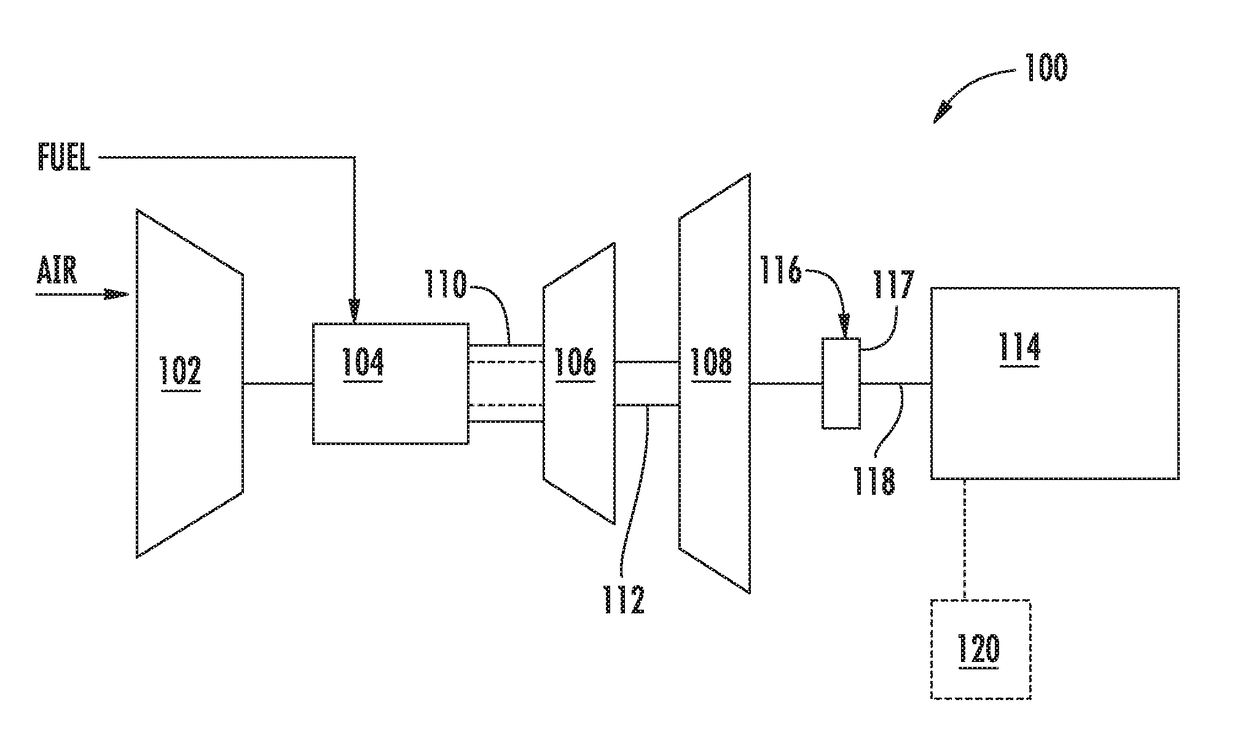
Torsional Damping for Gas Turbine Engines
ActiveUS20170114665A1Reduce power factorCreating lossRotating vibration suppressionGenerator control circuitsCombustion chamberTorsional oscillations
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com