Patents
Literature
4646 results about "Insertion loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunications, insertion loss is the loss of signal power resulting from the insertion of a device in a transmission line or optical fiber and is usually expressed in decibels (dB). If the power transmitted to the load before insertion is PT and the power received by the load after insertion is PR, then the insertion loss in dB is given by, IL(dB)=10log₁₀PT/PR
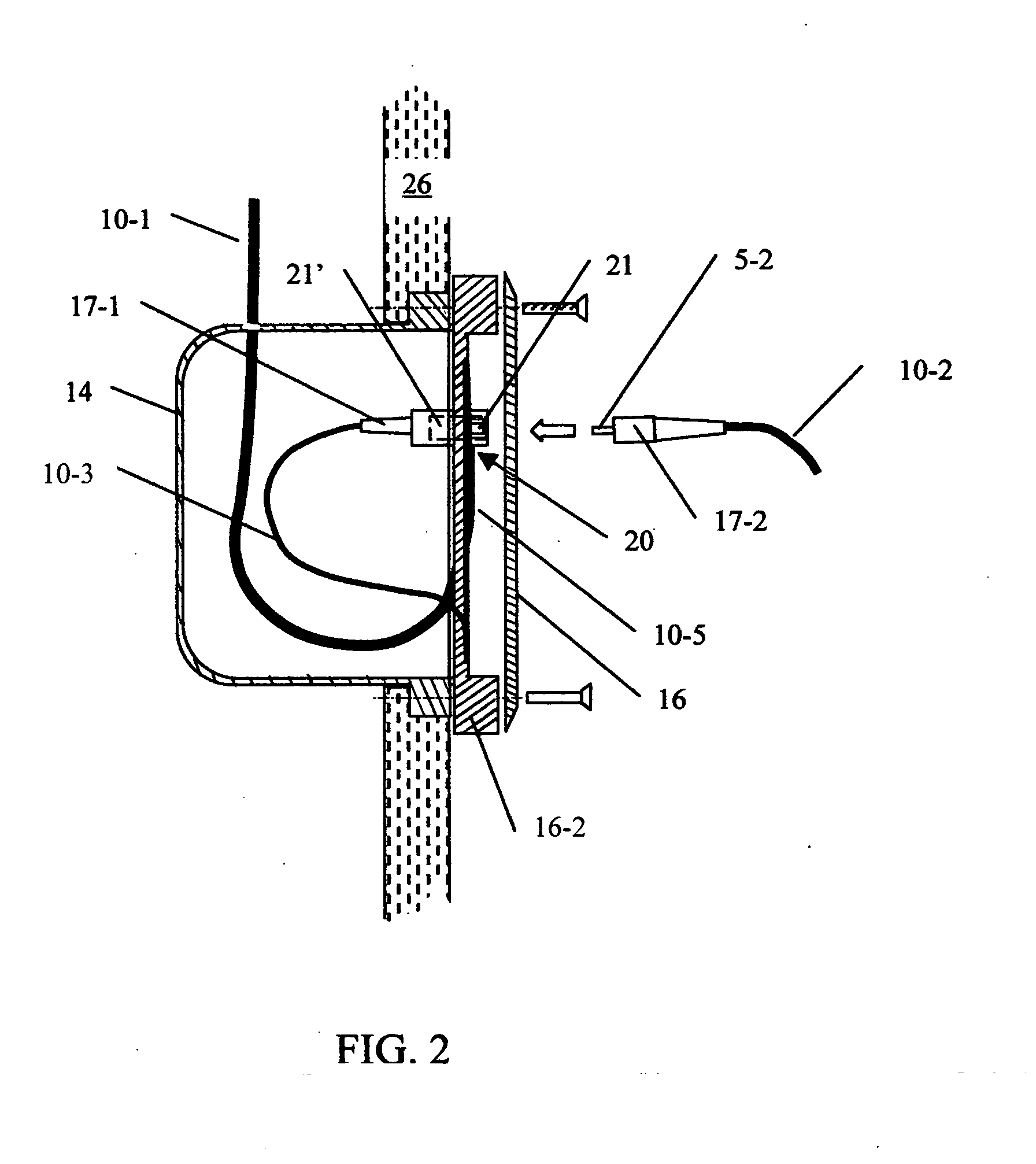
Coaxial cable-connector termination
InactiveUS7381089B2Eliminate spaceEliminates a longitudinal electric fieldElectrically conductive connectionsCoupling device detailsInterference fitElectrical conductor
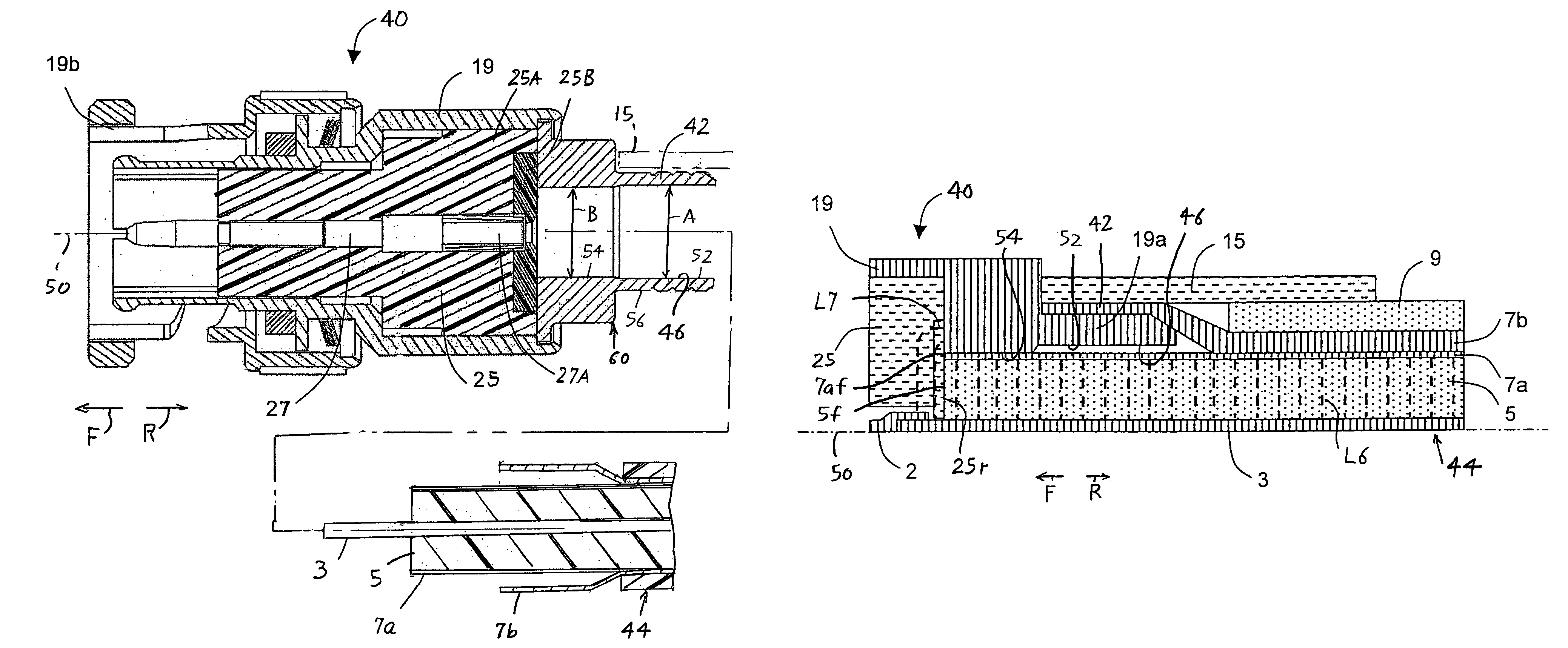
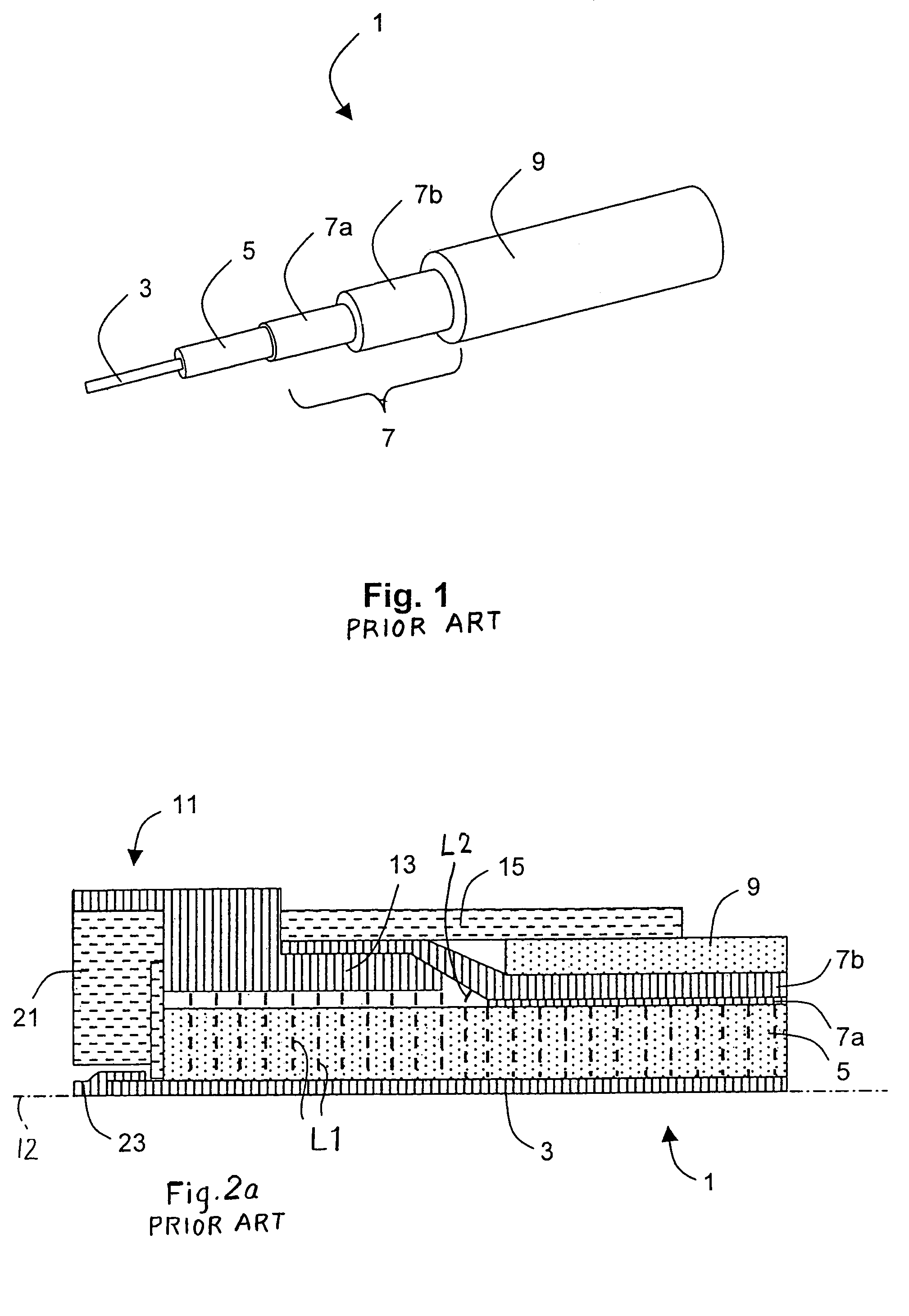
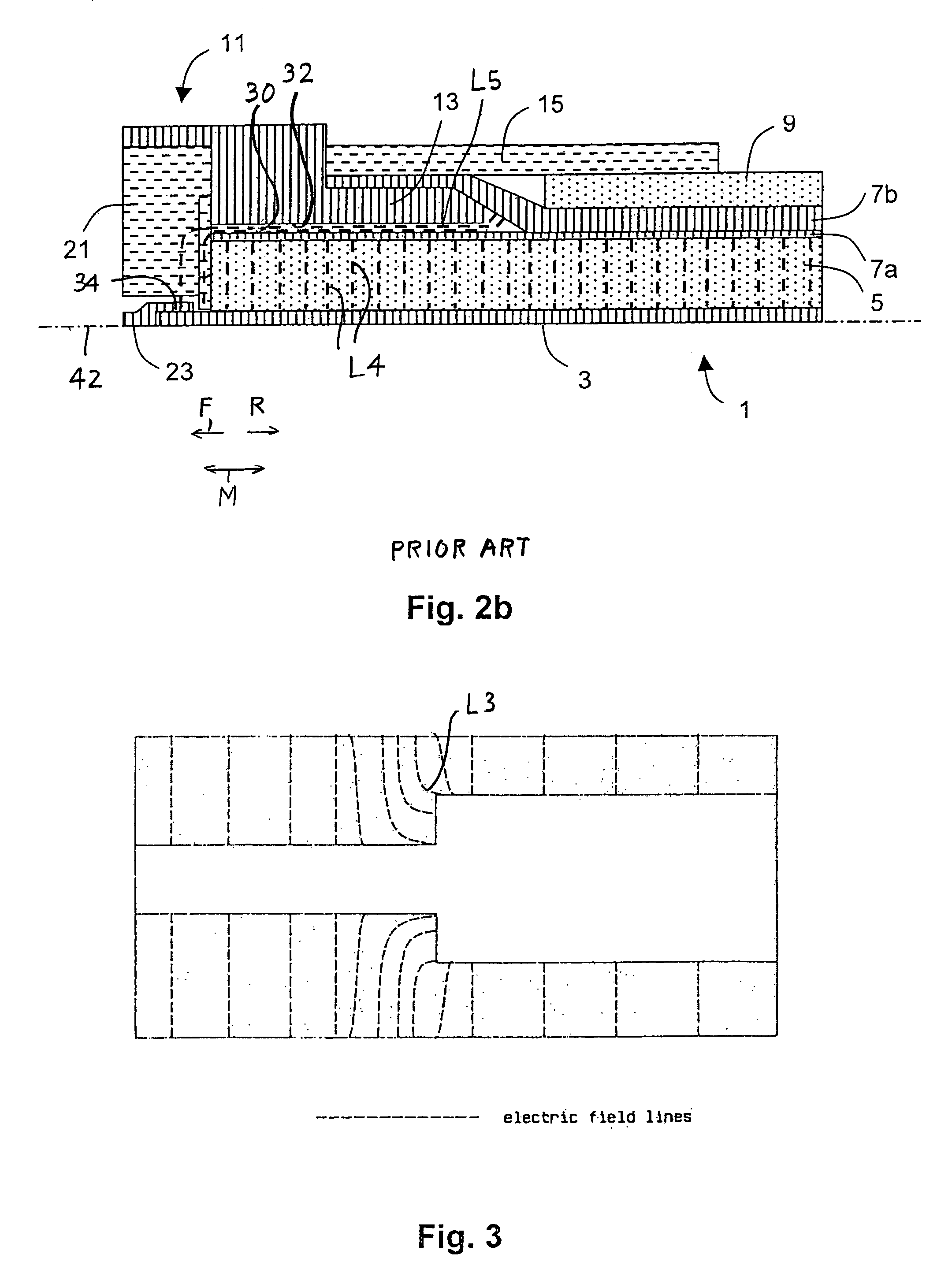
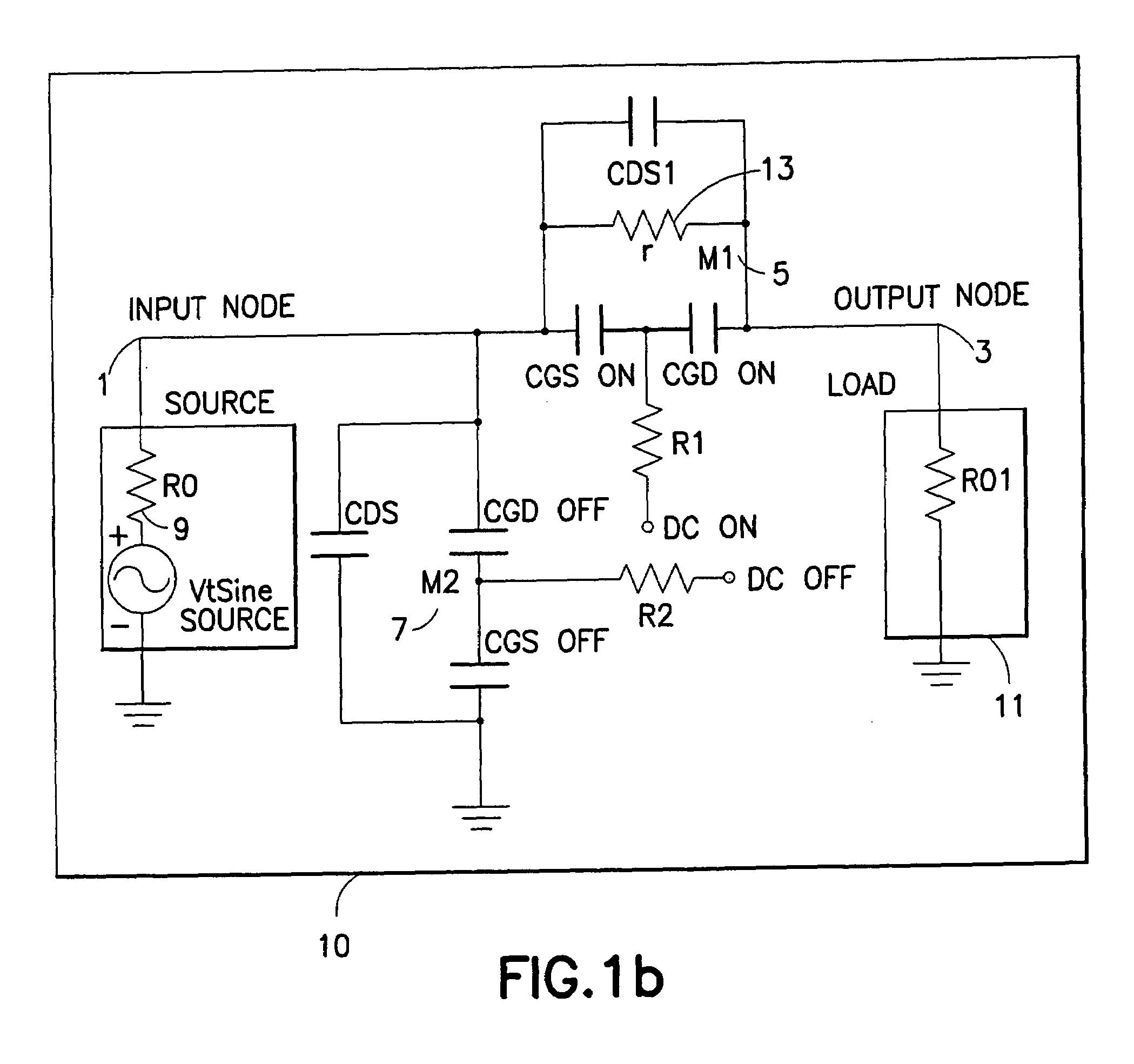
A high frequency coaxial cable having a foil (7a) between the cable insulator (5) and cable braid (7b), is terminated to a coaxial connector (40) in a manner that allows fast and easy cable preparation and results in a termination with minimal axial electric field lines that cause a high insertion loss and a high VSWR (voltage standing wave ratio). A bore (46) at the rear portion of the connector outer conductor, receives the cable insulator with foil around the cable insulator. The bore has a front part (54) that forms an interference fit around the foil, to avoid an axially-extending gap which might contain axially-extending field lines. The front of cable insulator and foil are flush and both abut the insulation (25) of the connector.
Owner:ITT MFG ENTERPRISES LLC
Chromatic dispersion compensating fiber
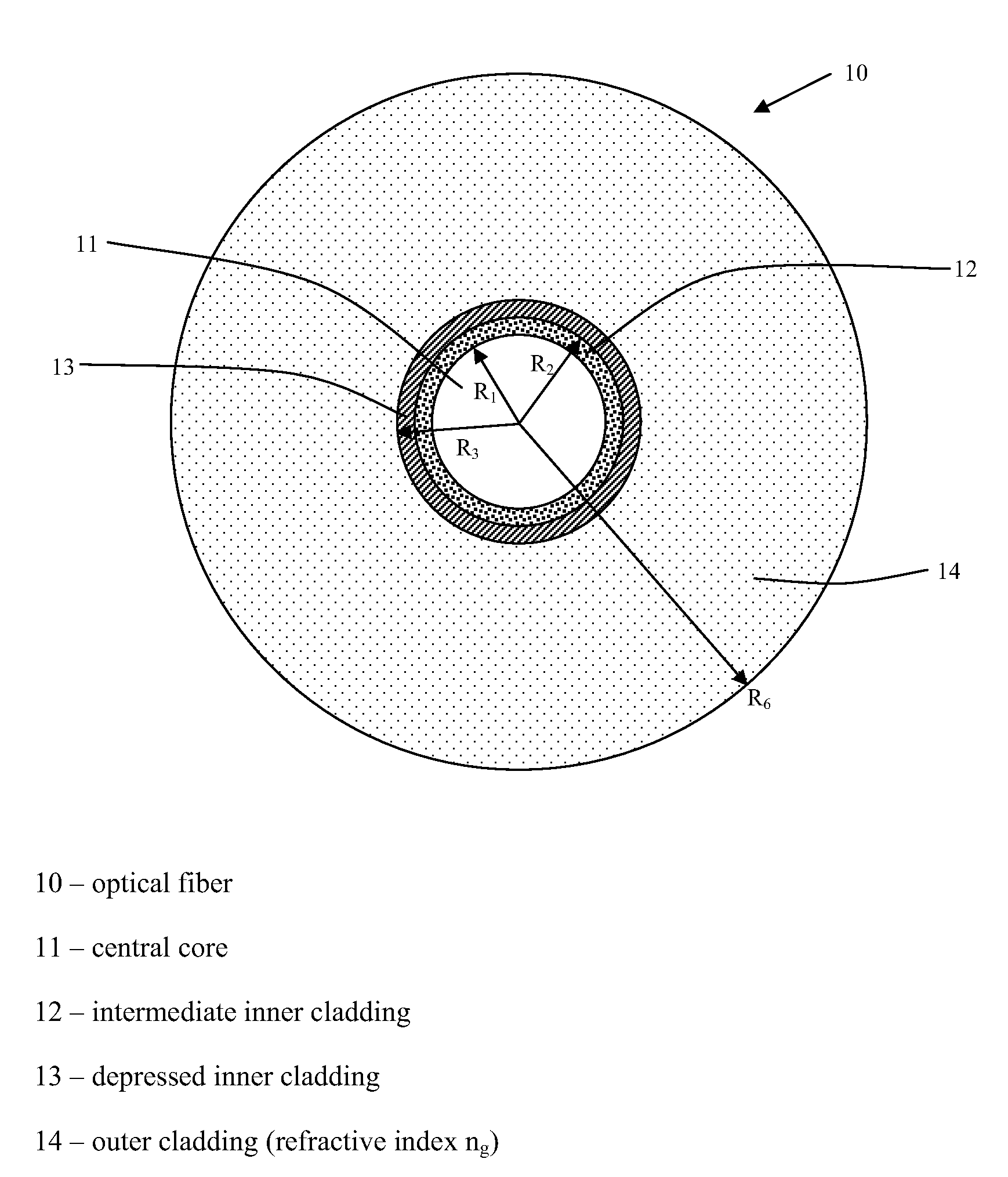
ActiveUS7356234B2Improved FOM valueLimited bending and micro-bending lossesOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideOptical ModuleRefractive index
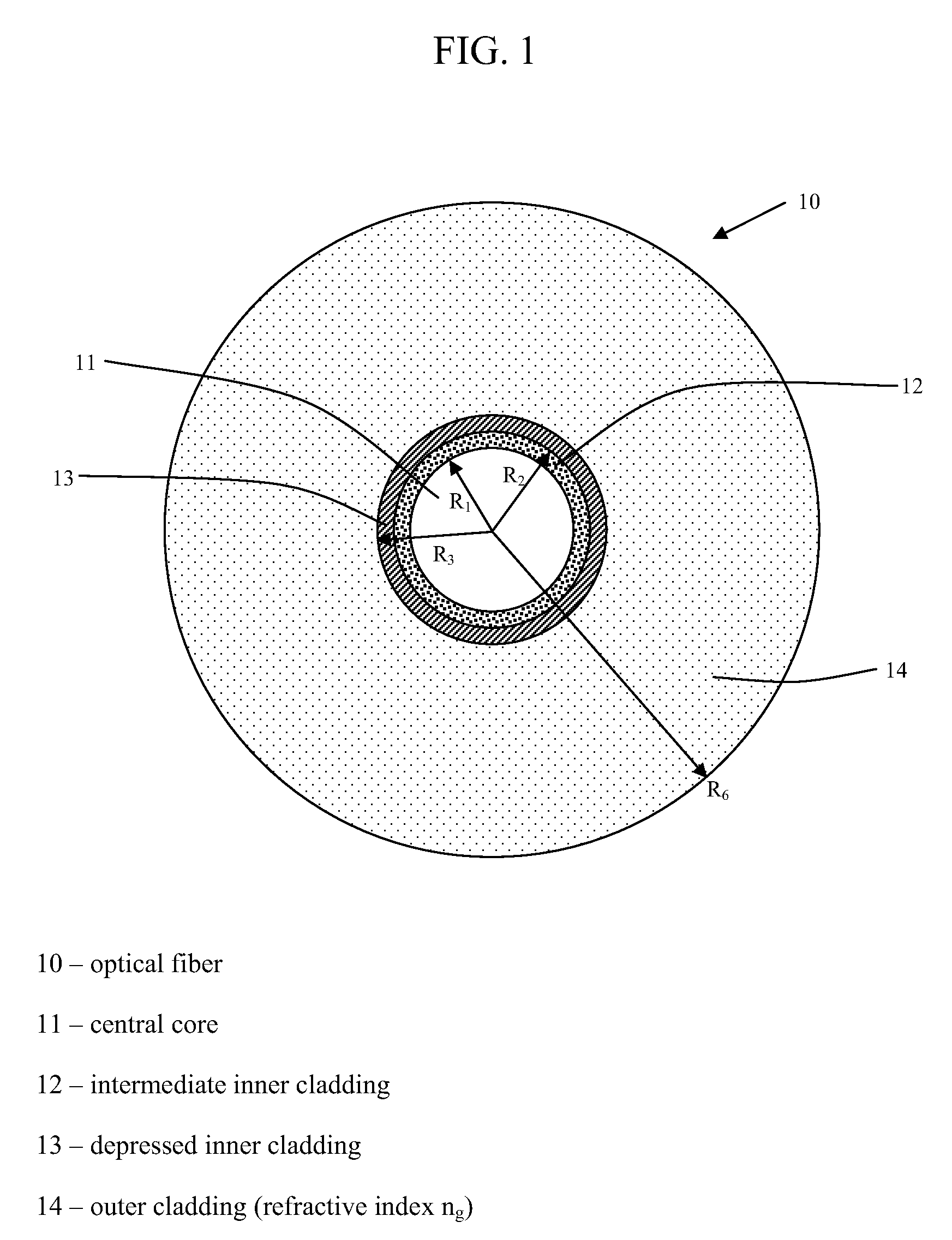
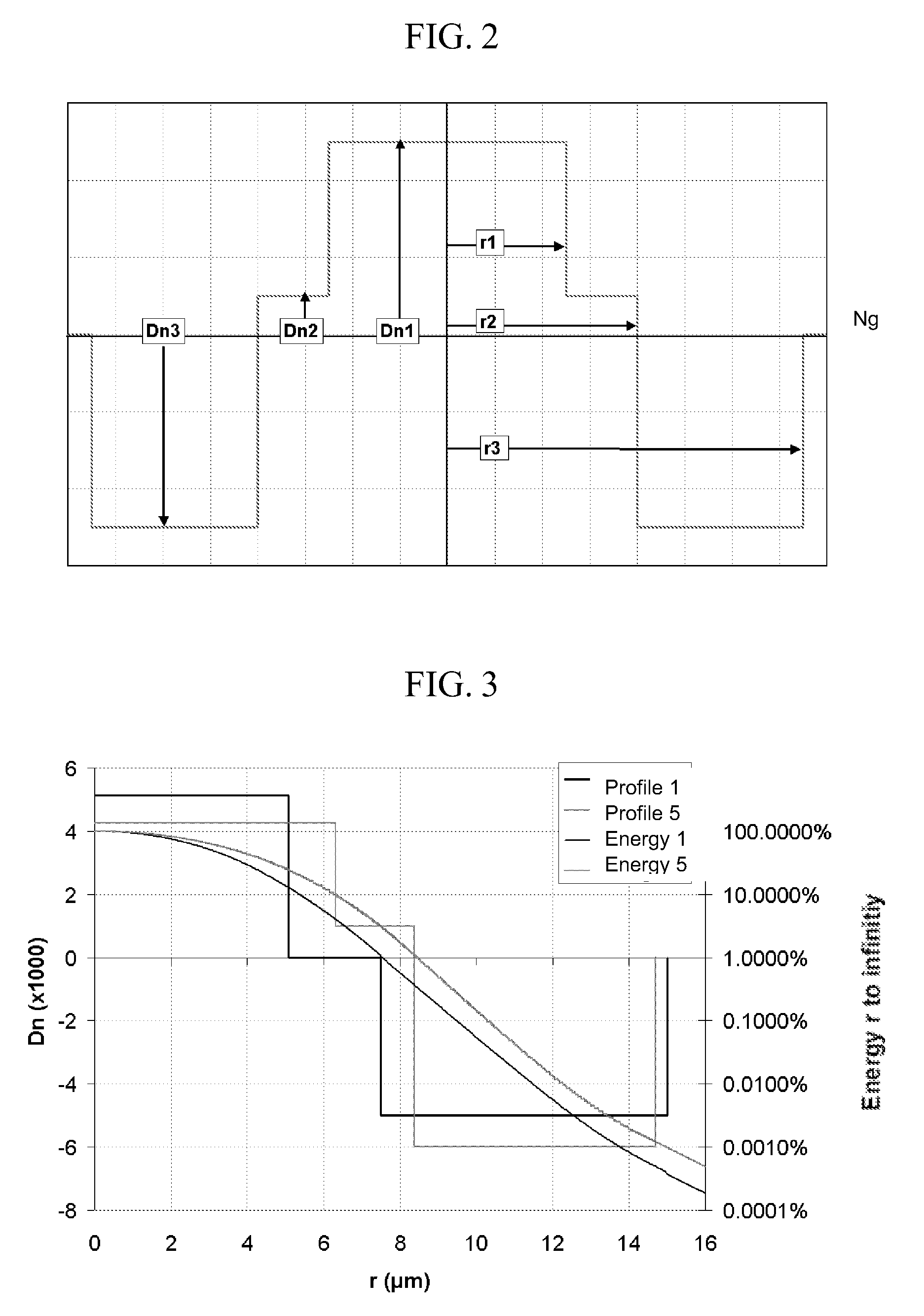
Disclosed is a chromatic dispersion compensating optical fiber comprising a central core, an intermediate cladding having a width (r2−r1) of 2.0 microns or greater, and a depressed inner cladding having a refractive index difference Dn3 with the external optical cladding of −3.0×10−3 or lower. At a wavelength of 1550 nm, the optical fiber exhibits a positive chromatic dispersion of 21 ps / (nm·km) or higher and a ratio of mode radius to intermediate cladding radius of (W02 / r2) of 0.7 or less. The present optical fiber has a good figure of merit value and limited bending and microbending losses. The optical fiber can be rolled up in a housing of reduced size in a chromatic dispersion compensating optical module having limited insertion losses and reduced polarization mode dispersion.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Radio frequency identification for transfer of component information in fiber optic testing
InactiveUS7165728B2Easy data transferMaterial analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesFiberOptical test
The device includes a connector, a transponder, an optical test unit, an antenna, and a transceiver. The transponder is attached to the connector. The antenna is attached to the optical test unit. The transceiver is electrically connected to the antenna. When the connector is attached to the optical test unit and the optical test unit performs diagnostic testing on the connector and its associated optical fiber, the results or data of the diagnostic testing are stored in the optical test unit for later downloading from the optical test unit to the transponder. The test data can include attenuation loss, insertion loss, and back reflection test data. Once the connector is connected to a host device, the data associated with the specific connector can uploaded from the transponder to the host device.
Owner:STRATOS INT
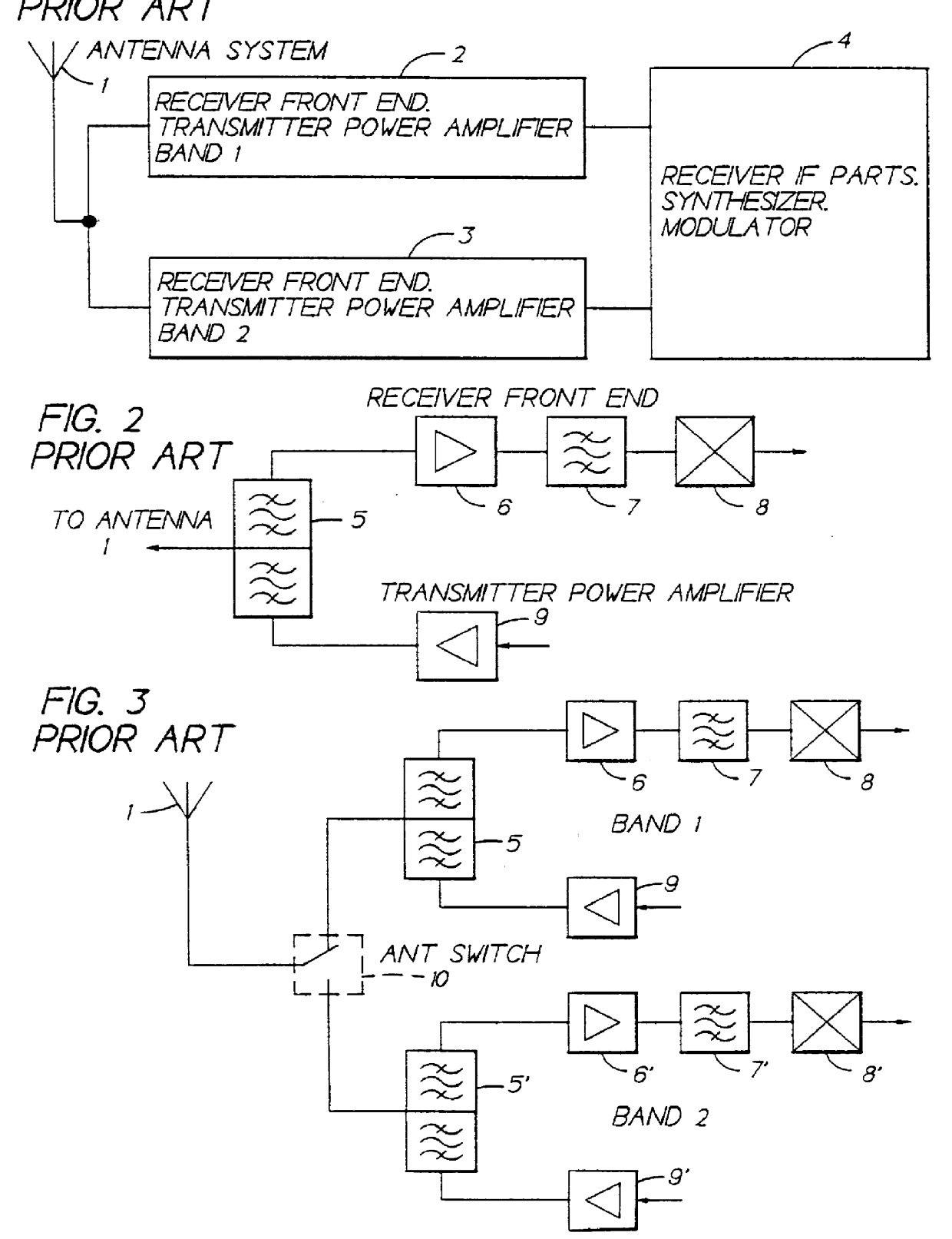
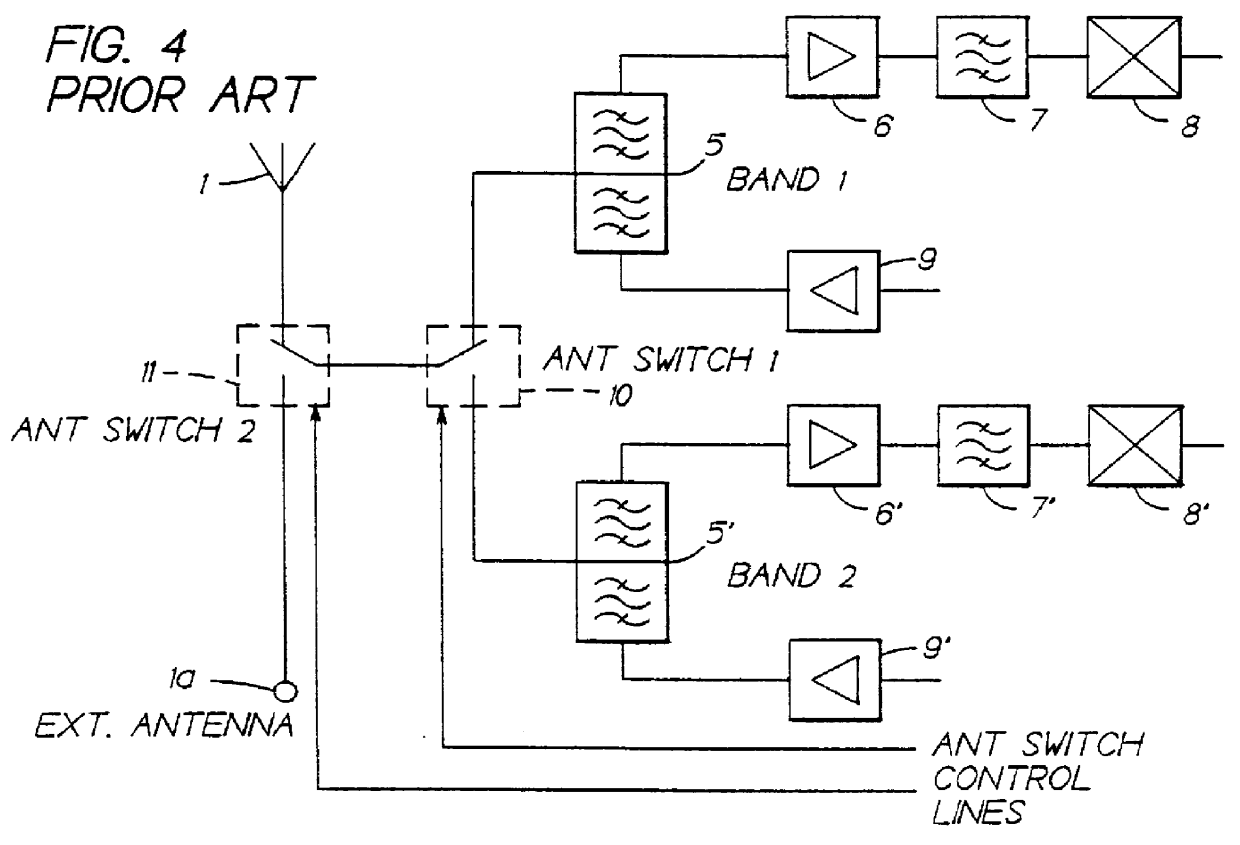
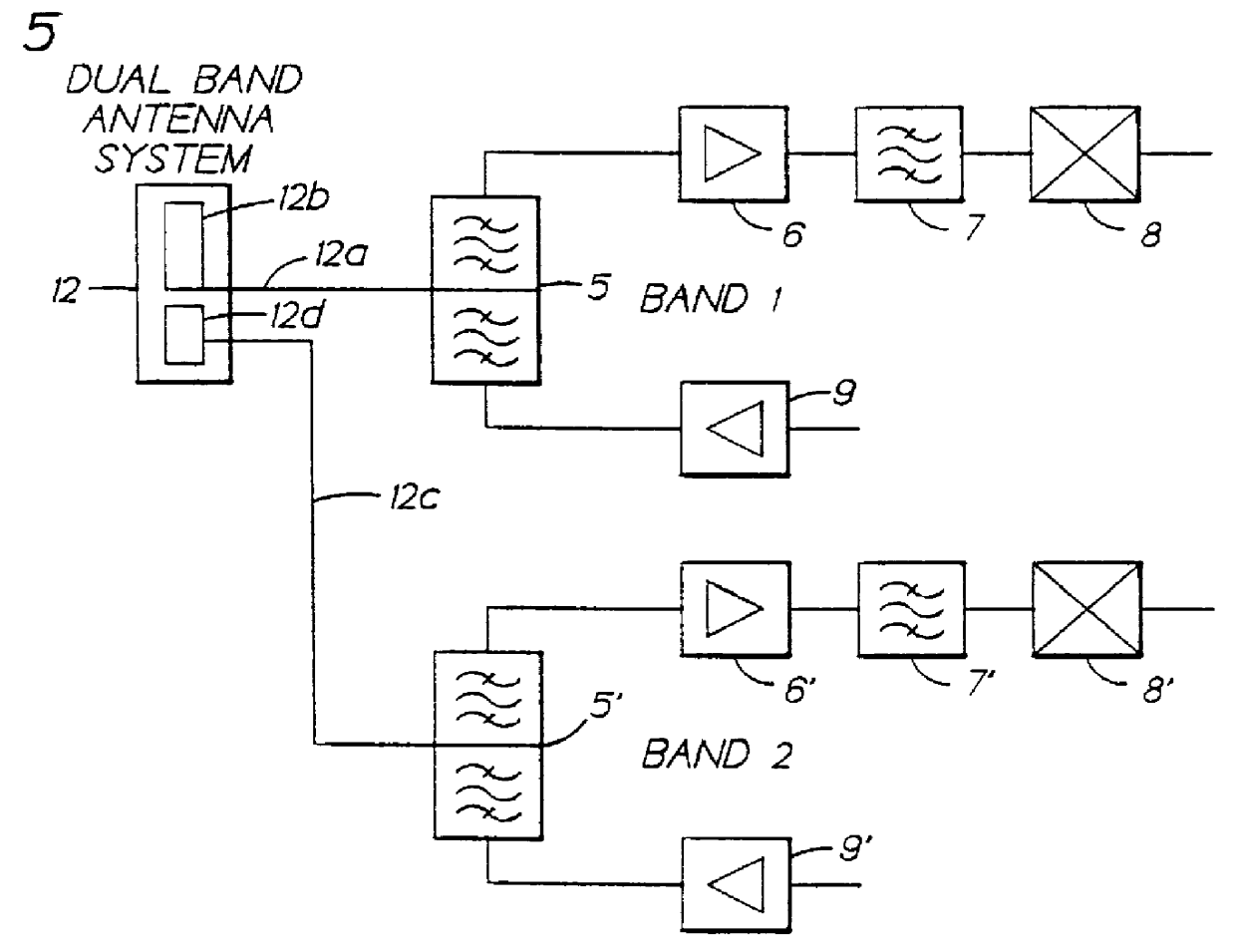
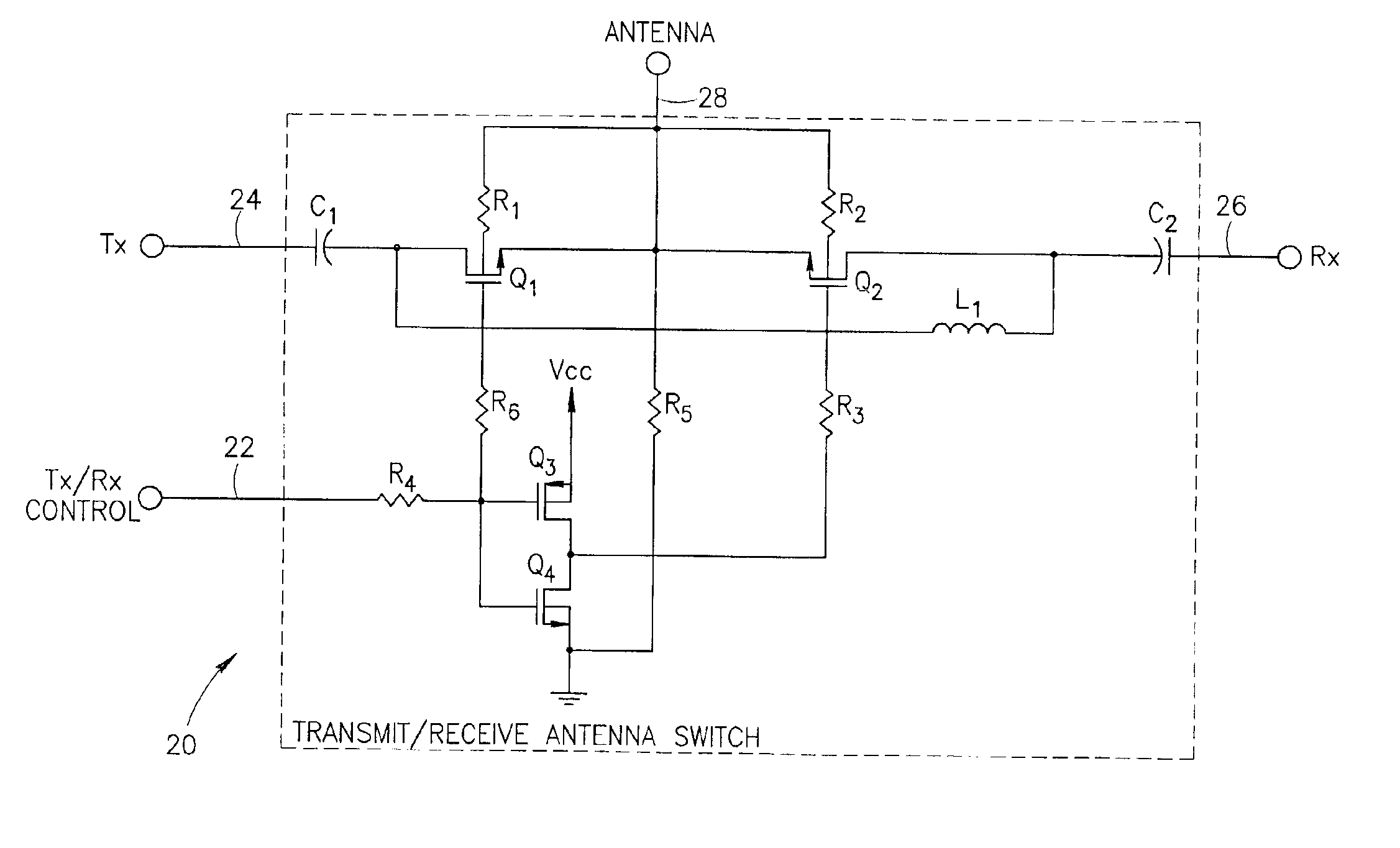
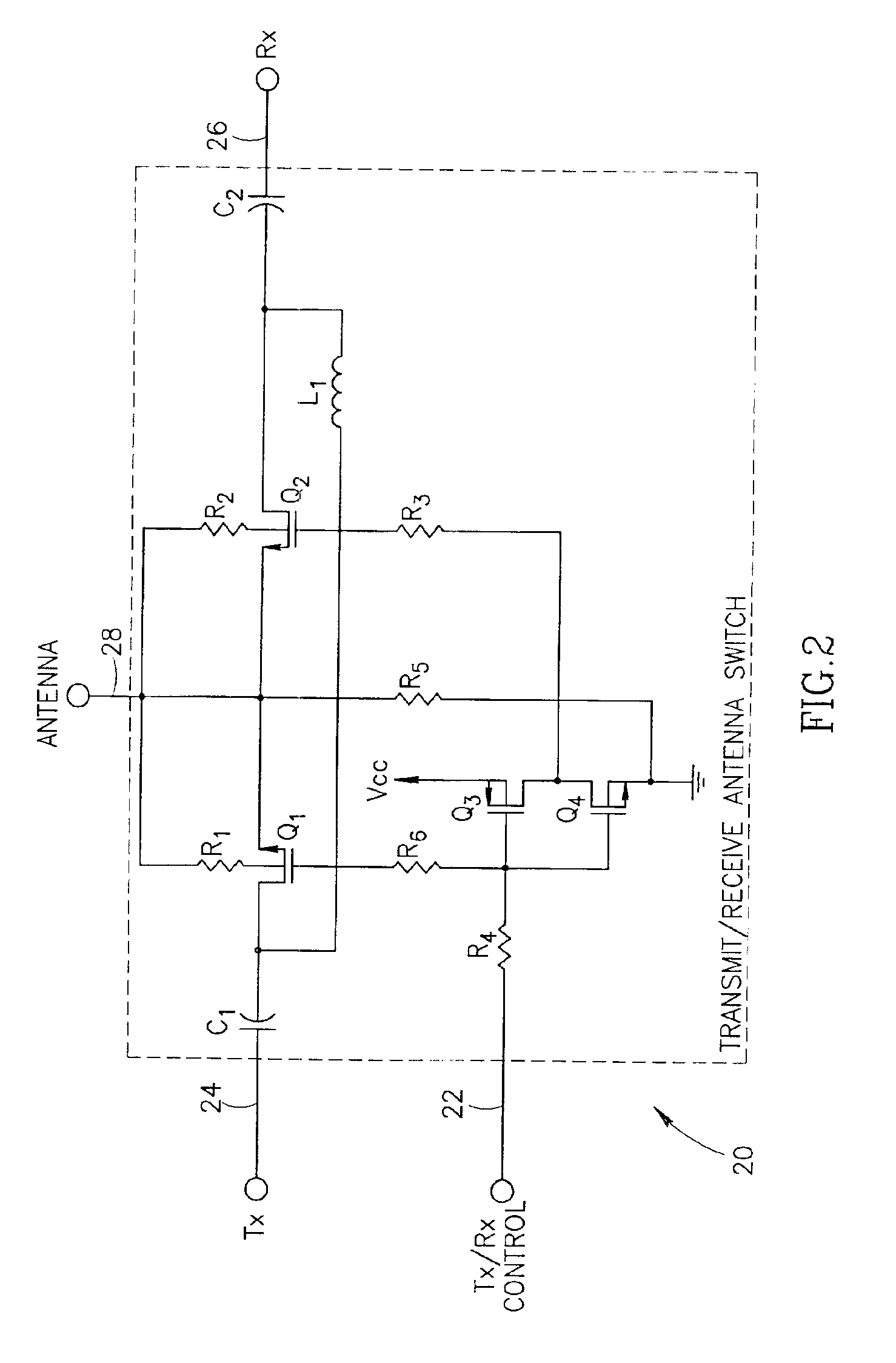
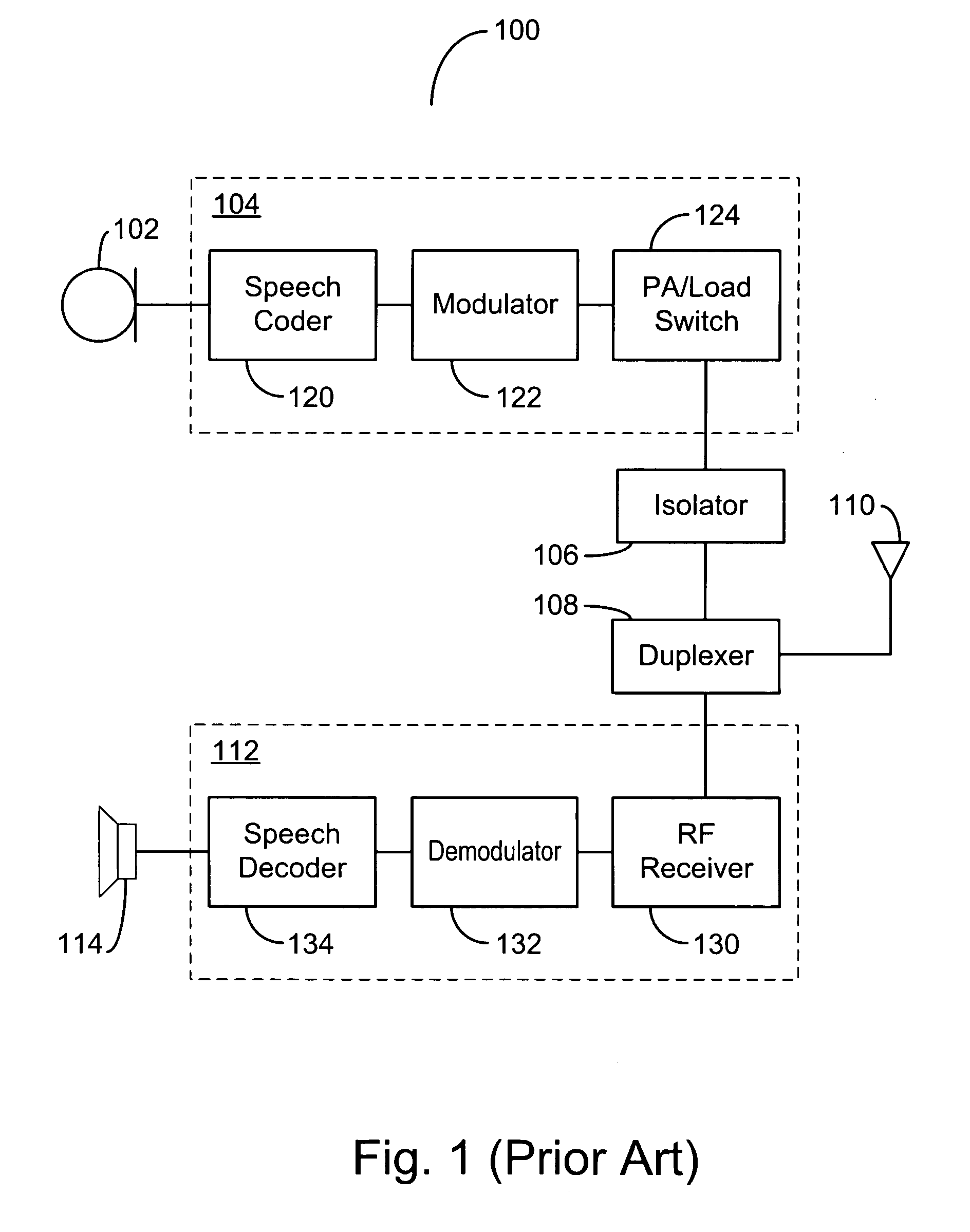
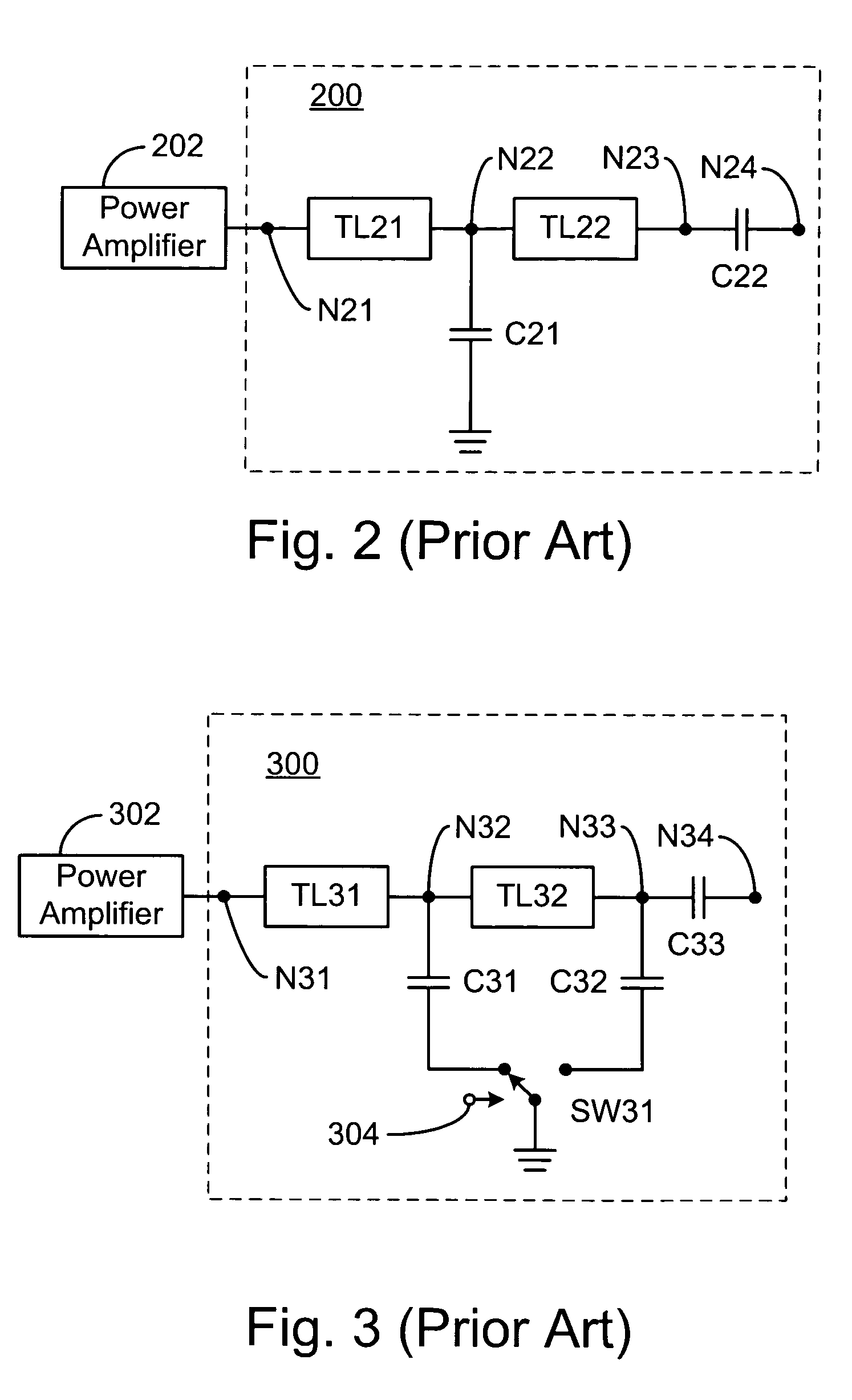
Antenna switching circuits for radio telephones
InactiveUS6115585AEliminate requirementsFunction increaseSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsTransceiverEngineering
Disclosed are various embodiments of circuitry for coupling first and second transceivers of a dual band radio telephone to integral and external antennas. The circuitry uses impedance matching lengths of transmission lines and switches arranged to provide a minimum insertion loss. Also disclosed is an embodiment for use with a single band radio telephone, such as a digital TDMA radio telephone that either transmits or receives at any given time. Also disclosed is an antenna switching arrangement for a dual band phone that eliminates a requirement for duplexers.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
Component functioning with bulk acoustic waves having coupled resonators
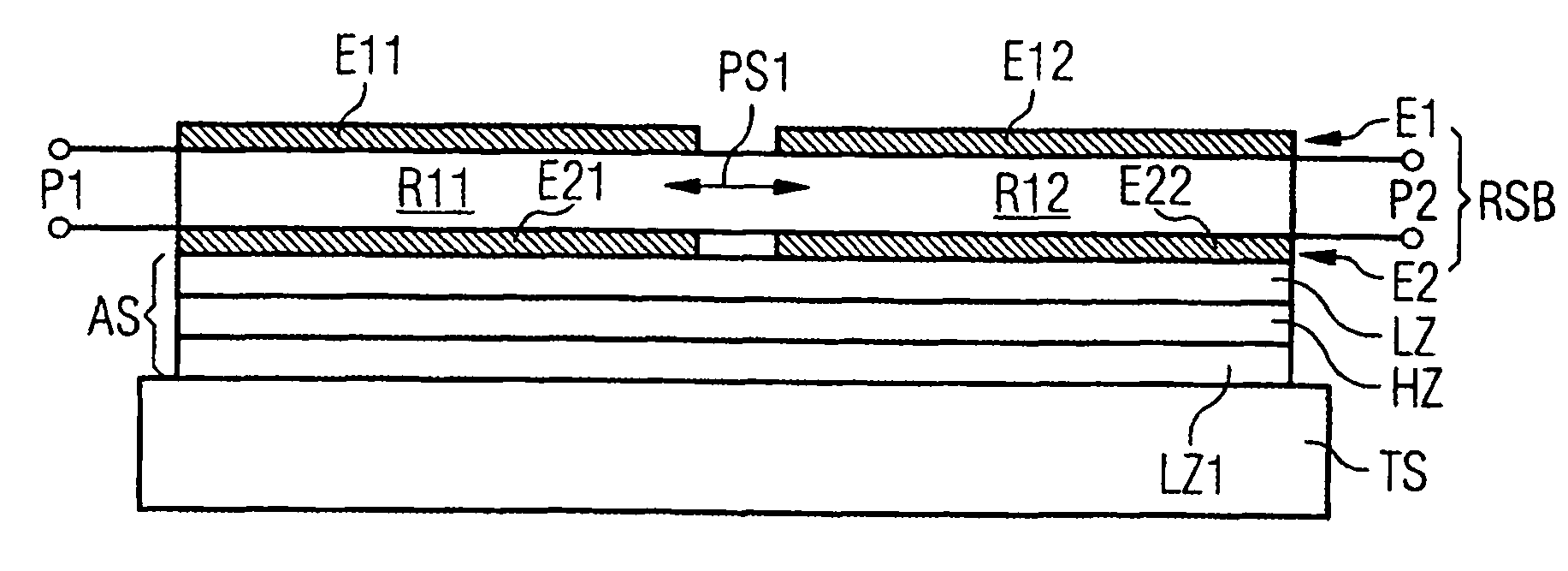
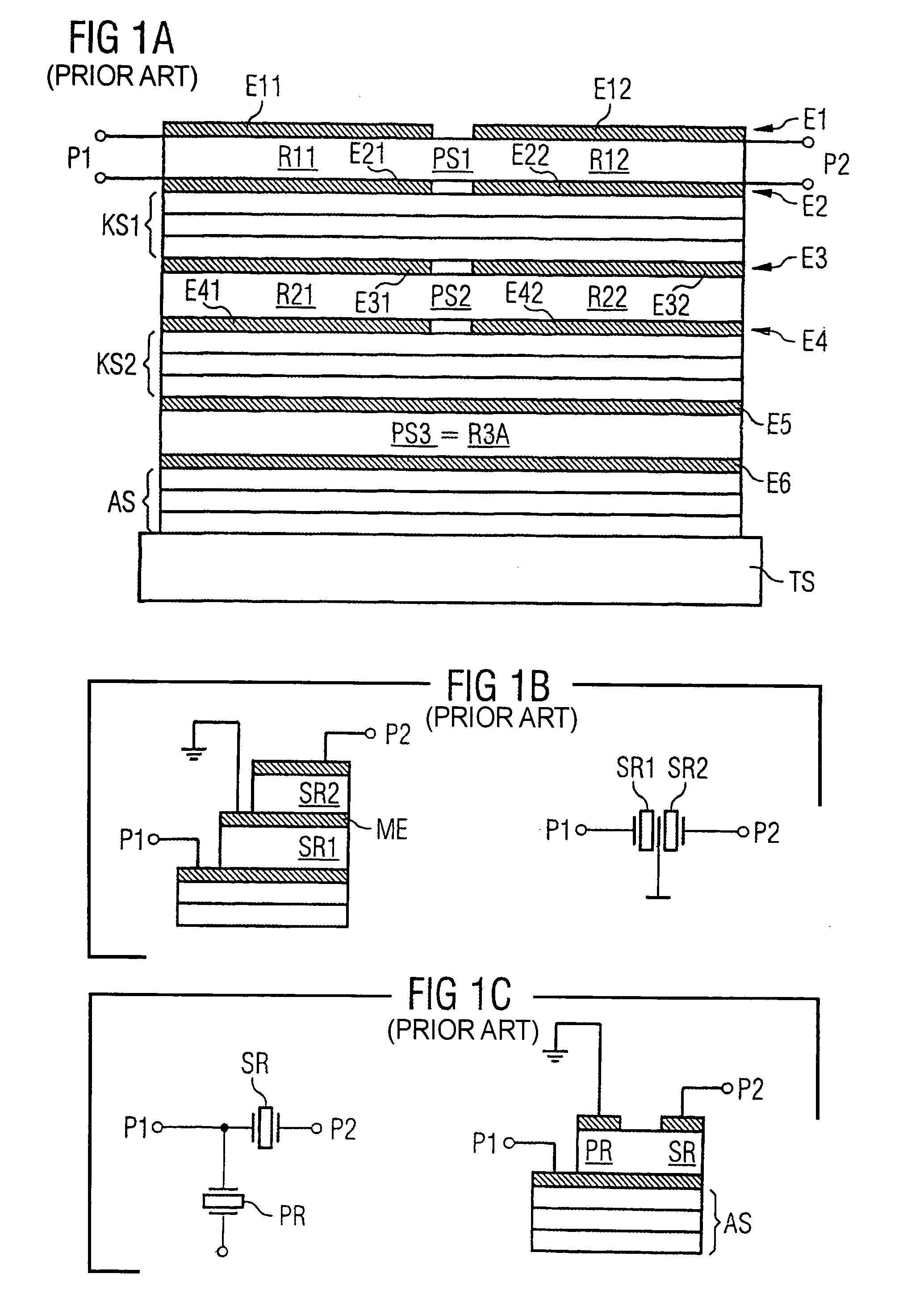
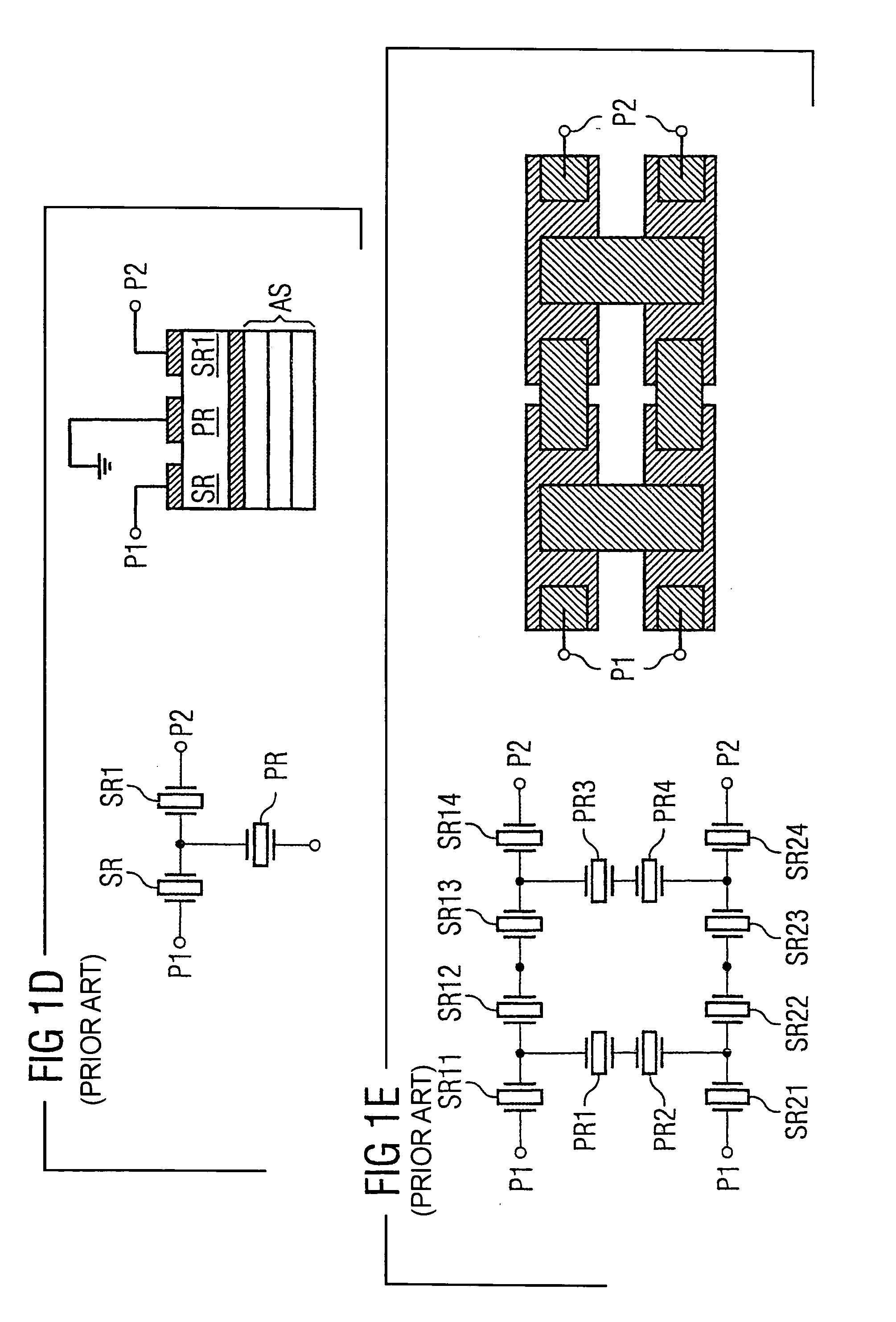
ActiveUS20050012570A1Improve transmission characteristicsImprove featuresImpedence networksBandpass filteringCoupling
A component that functions with bulk acoustic waves, particularly a bandpass filter, has an increased number of degrees of design freedom in order to improve the transmission characteristics of the component. The component has BAW resonators coupled acoustically in the vertical and / or lateral direction through common electrodes, coupling layer systems and through the excitation of lateral acoustic modes. Through the acoustic coupling of the resonators, it is possible to create additional pole points in the transfer function so that in this manner, the rejection band characteristics of a bandpass filter can be improved. Through acoustic paths which are added in addition to the electrical connection, the insertion loss can be reduced. Through an acoustic coupling instead of an electrical connection, decoupling between input and output loops of a circuit can be achieved.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Oct optical probe and optical tomography imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20090198125A1Inexpensive and safeImprove accuracySurgeryEndoscopesOptical reflectionInterior space
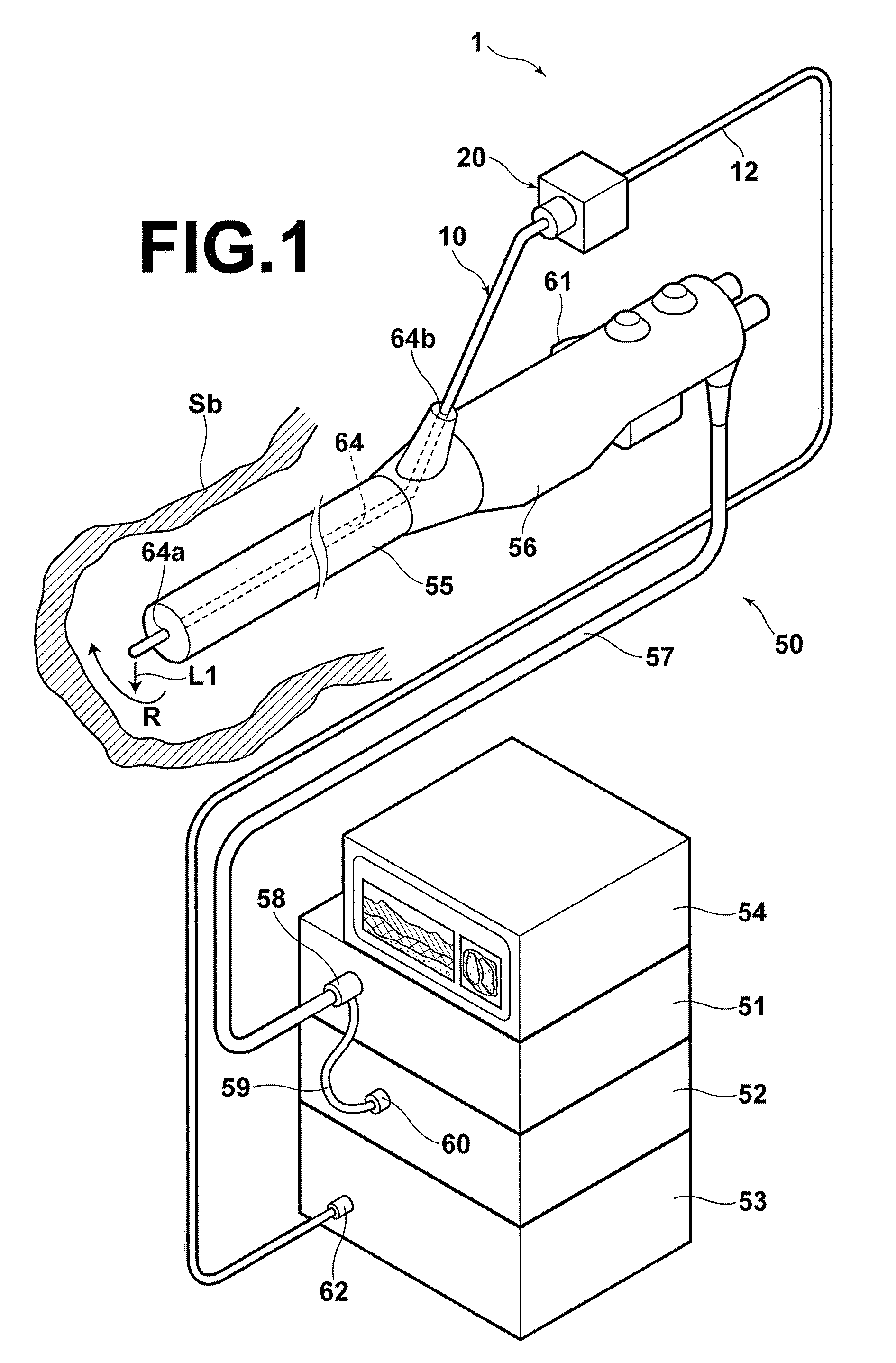
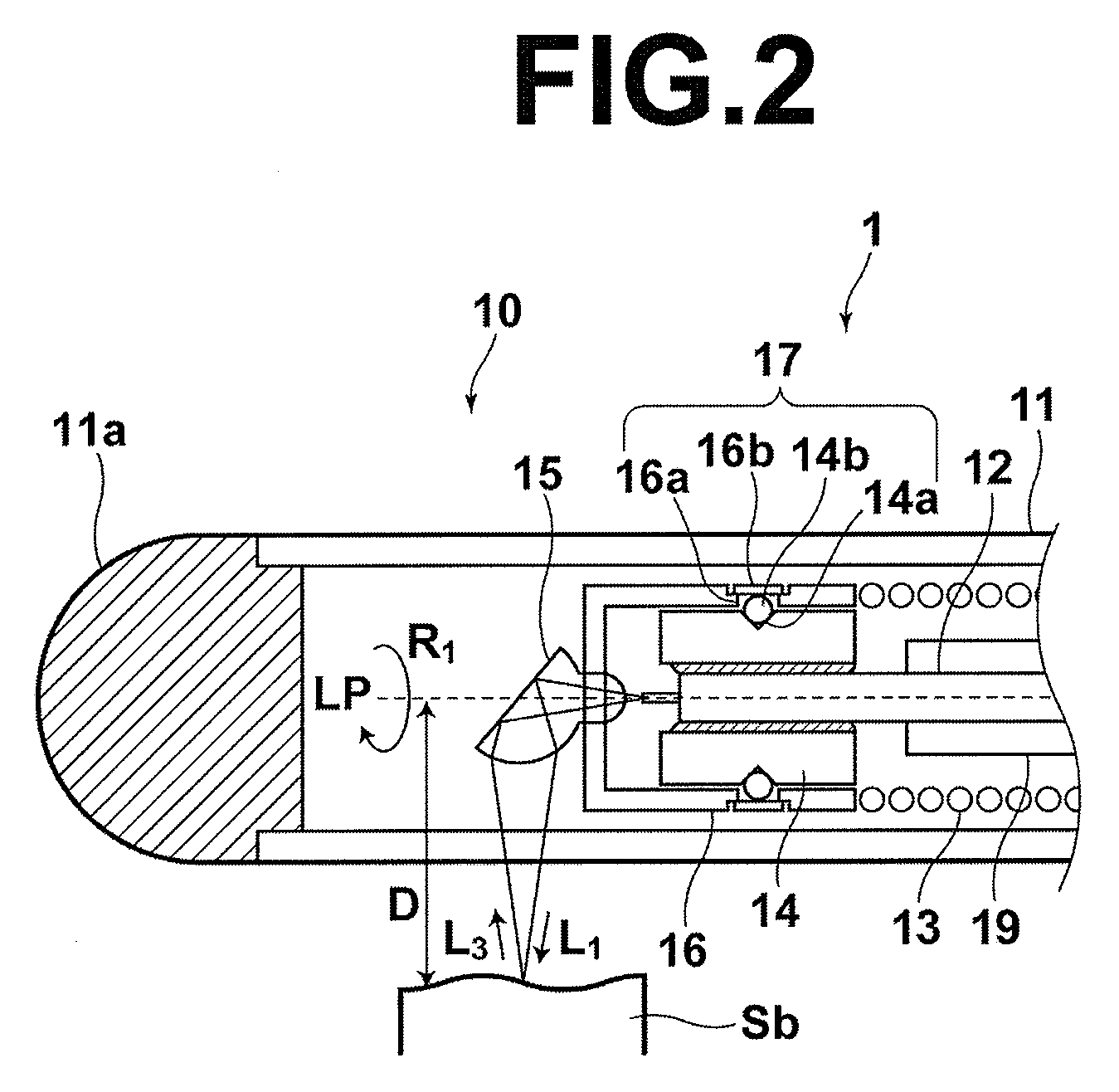
An OCT optical probe to be inserted into a subject includes: a cylindrical sheath to be inserted into a subject; an optical fiber disposed in the internal space of the sheath; a rotatably-supporting portion fixed to the optical fiber in the vicinity of a distal end of the optical fiber; a distal optical system to deflect light emitted from the distal end of the optical fiber toward the subject; a holding portion to hold the distal optical system such that the optical system is rotatably supported by the rotatably-supporting portion; and a flexible shaft covering the optical fiber in the internal space, wherein the holding portion is fixed to a distal end of the flexible shaft. Using the OCT optical probe of the invention, the problem of degradation of measurement accuracy due to optical insertion loss and optical reflection loss at a rotary joint can be eliminated inexpensively and safely.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Switch circuit and method of switching radio frequency signals
InactiveUS7123898B2Easy to switchImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETDigital control
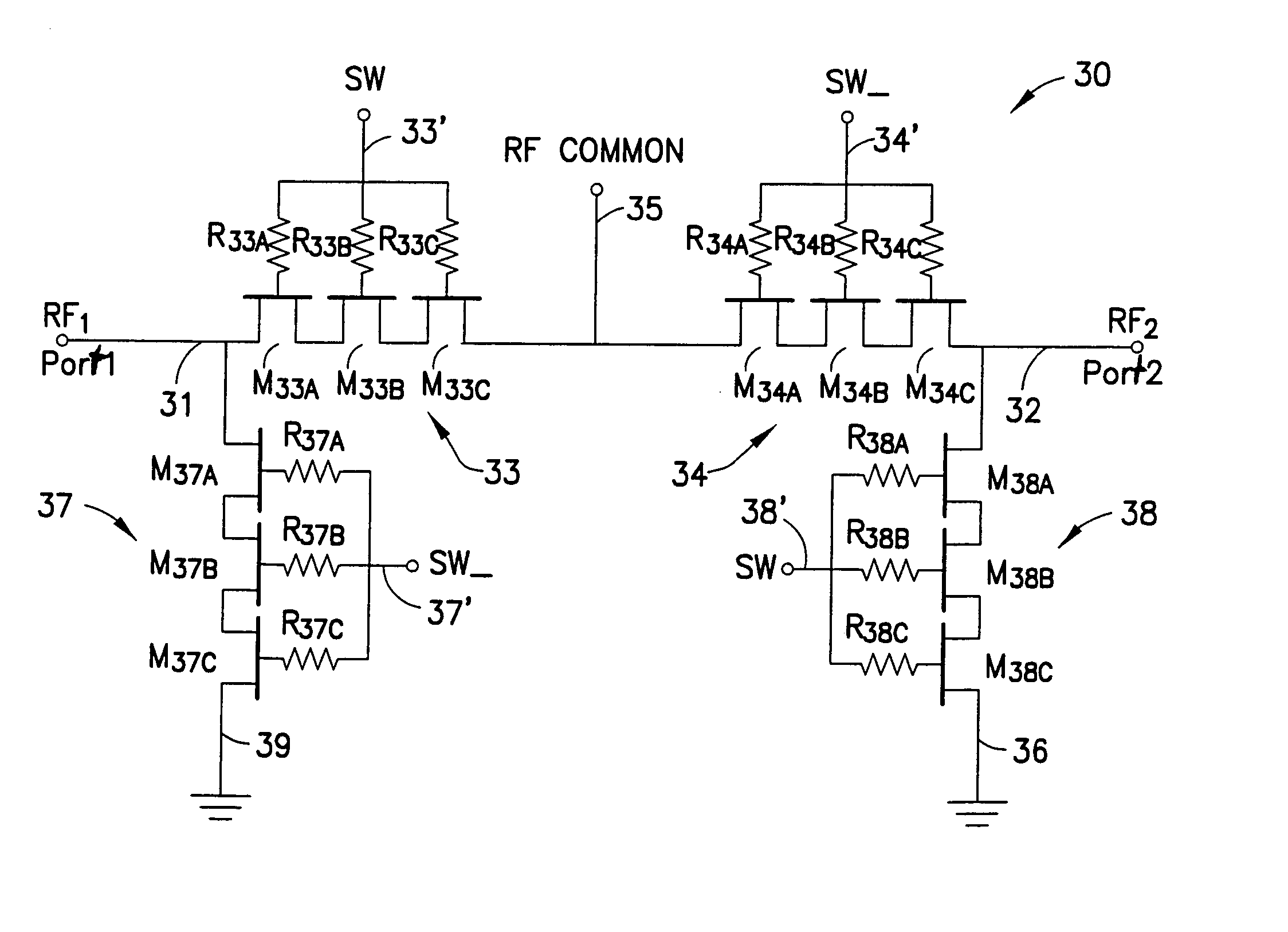
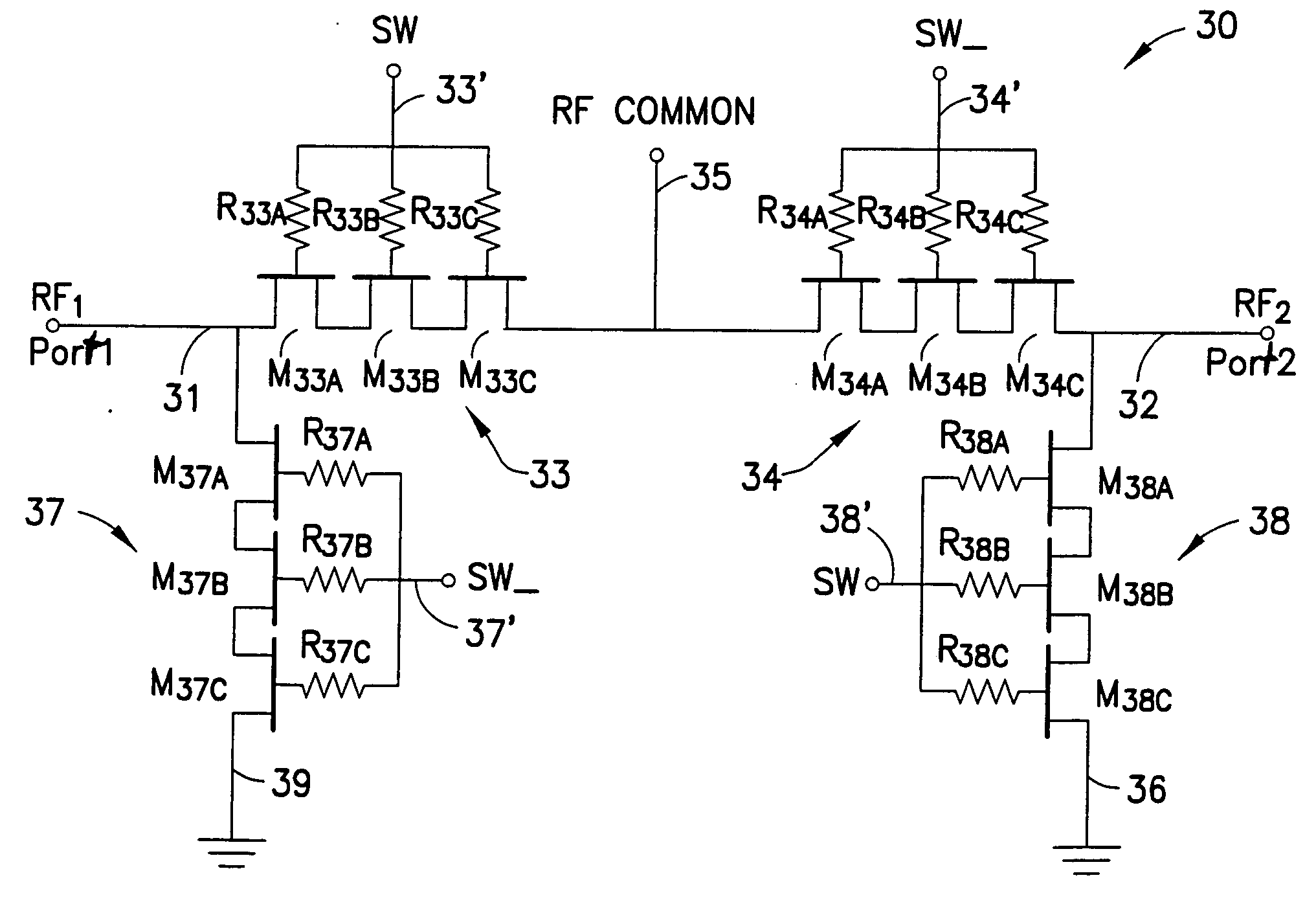
A novel RF buffer circuit adapted for use with an RF switch circuit and method for switching RF signals is described. The RF switch circuit is fabricated in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology. The RF switch includes pairs of switching and shunting transistor groupings used to alternatively couple RF input signals to a common RF node. The switching and shunting transistor grouping pairs are controlled by a switching control voltage (SW) and its inverse (SW_). The switching and shunting transistor groupings comprise one or more MOSFET transistors connected together in a “stacked” or serial configuration. The stacking of transistor grouping devices, and associated gate resistors, increase the breakdown voltage across the series connected switch transistors and operate to improve RF switch compression. A fully integrated RF switch is described including digital control logic and a negative voltage generator integrated together with the RF switch elements. In one embodiment, the fully integrated RF switch includes a built-in oscillator, a charge pump circuit, CMOS logic circuitry, level-shifting and voltage divider circuits, and an RF buffer circuit. Several embodiments of the charge pump, level shifting, voltage divider, and RF buffer circuits are described. The inventive RF switch provides improvements in insertion loss, switch isolation, and switch compression.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Impedance control in electrical connectors
InactiveUS6981883B2Coupling contact membersTwo-part coupling devicesDifferential signalingElectrical connector
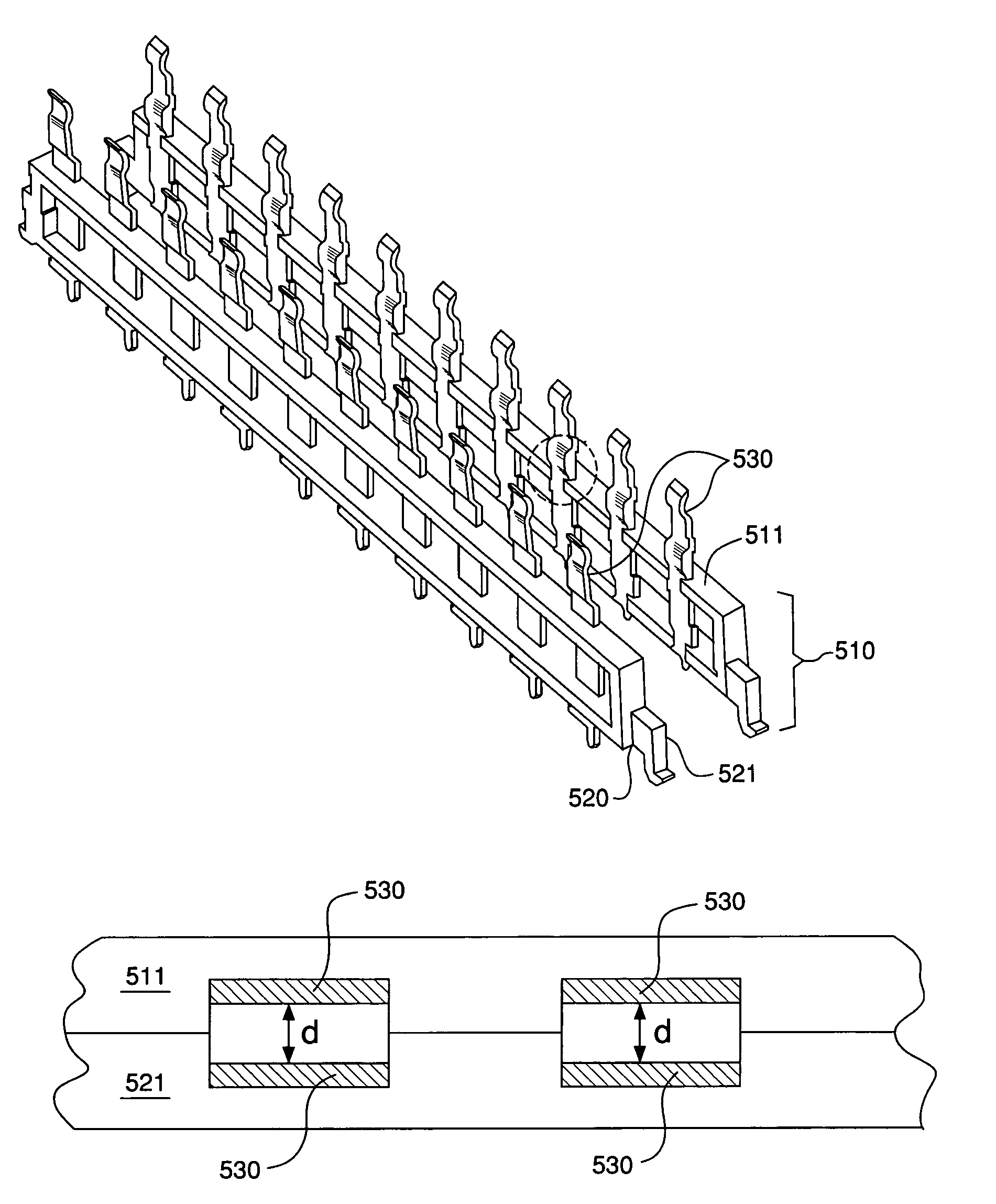
The invention provides a high speed connector wherein differential signal pairs are arranged so as to limit the level of cross talk between adjacent differential signal pairs. The connector comprises lead frame assembly having a pair of overmolded lead frame housings. Each lead frame housing has a respective signal contact extending therethrough. The lead frame housings may be operatively coupled such that the signal contacts form a broadside-coupled differential signal pair. The contacts may be separated by a gap having a gap width that enables insertion loss and cross talk between signal pairs to be limited.
Owner:FCI AMERICAS TECH LLC
Cross talk reduction and impedance-matching for high speed electrical connectors
InactiveUS6976886B2Reduce weightReduced insertion lossTwo-part coupling devicesPrinted circuitsGround contactInterference (communication)
Lightweight, low cost, high density electrical connectors are disclosed that provide impedance controlled, high-speed, low interference communications, even in the absence of shields between the contacts, and that provide for a variety of other benefits not found in prior art connectors, such as low insertion loss. Signal contacts and ground contacts within the connectors can be scaled and positioned relative to one another such that a differential signal in a first differential signal pair produces a high field in the gap between the contacts that form the signal pair and a low field near an adjacent signal pair. Consequently, cross talk between adjacent signal contacts can be limited to acceptable levels for the particular application. In such connectors, the level of cross talk between adjacent signal contacts can be limited to the point that the need for (and cost of) shields between adjacent contacts is unnecessary, even in high speed, high signal integrity applications.
Owner:FCI USA LLC
High-frequency switch, and electronic device using the same
A high-frequency switch comprises: a substrate; a main line electrode provided between two terminals; a stub line electrode with one end thereof connected to the side edge of the main line electrode and the other end thereof grounded; and a ground electrode provided adjacent to the stub line electrode in the width direction thereof; wherein the substrate has a semiconductor activation layer which extends to below the stub line electrode and the ground electrode between at least one side edge of the stub line electrode and the ground electrode; and wherein a gate electrode which extends in the longitudinal direction of the stub line electrode is provided on the semiconductor activation layer between the stub line electrode and the ground electrode, thereby forming an FET structure, thus providing a high-frequency switch and electronic device therewith, capable of using high frequencies, having reduced insertion loss, and high signal cut-off capabilities.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
High performance, small form factor connector with common mode impedance control
Techniques for improving electrical performance of a connector. The techniques are compatible with the form factor of a standardized connector, such as an SFP connector or stacked SFP. The resulting connector has reduced insertion loss for high speed signals. Such techniques, which can be used separately or together, include shaping of conductive elements within the connector while still retaining the same mating contact arrangement. Changes may be made at the contact tail portions or in the intermediate portions where engagement to a connector housing occurs. The techniques also include the incorporation of lossy bridging members between conductive elements designated to be ground conductors. For connectors according to the stacked SFP configuration, multiple bridging members may be incorporated at multiple locations within the connector.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
High performance, small form factor connector
ActiveUS20130012038A1Improve electrical performanceImprove performanceElectric discharge tubesCoupling contact membersElectricitySmall form factor
Techniques for improving electrical performance of a connector. The techniques are compatible with the form factor of a standardized connector, such as an SFP connector or stacked SFP. The resulting connector has reduced insertion loss for high speed signals. Such techniques, which can be used separately or together, include shaping of conductive elements within the connector while still retaining the same mating contact arrangement. Changes may be made at the contact tail portions or in the intermediate portions where engagement to a connector housing occurs. The techniques also include the incorporation of lossy bridging members between conductive elements designated to be ground conductors. For connectors according to the stacked SFP configuration, multiple bridging members may be incorporated at multiple locations within the connector.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
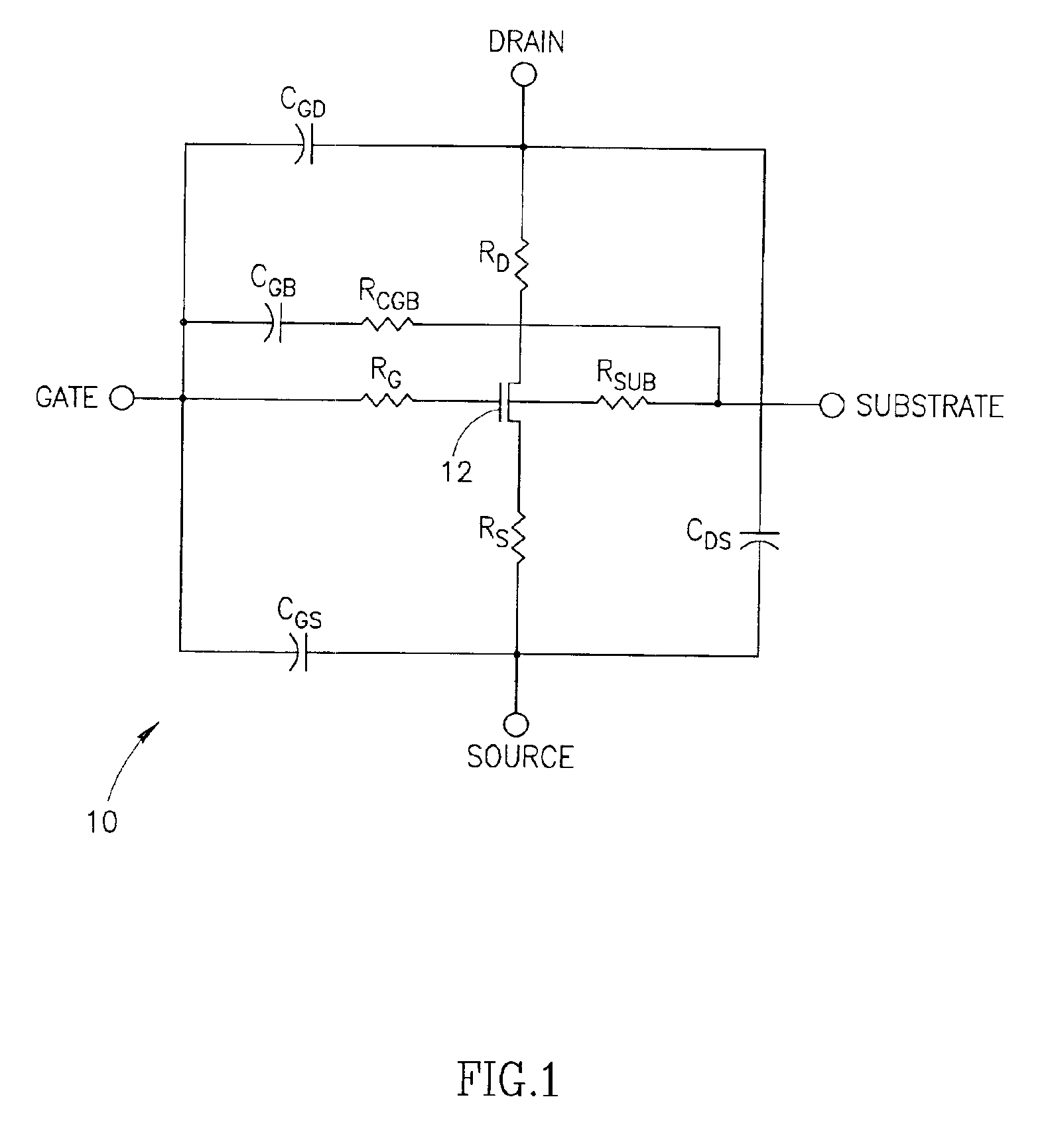
Integrated circuit incorporating RF antenna switch and power amplifier
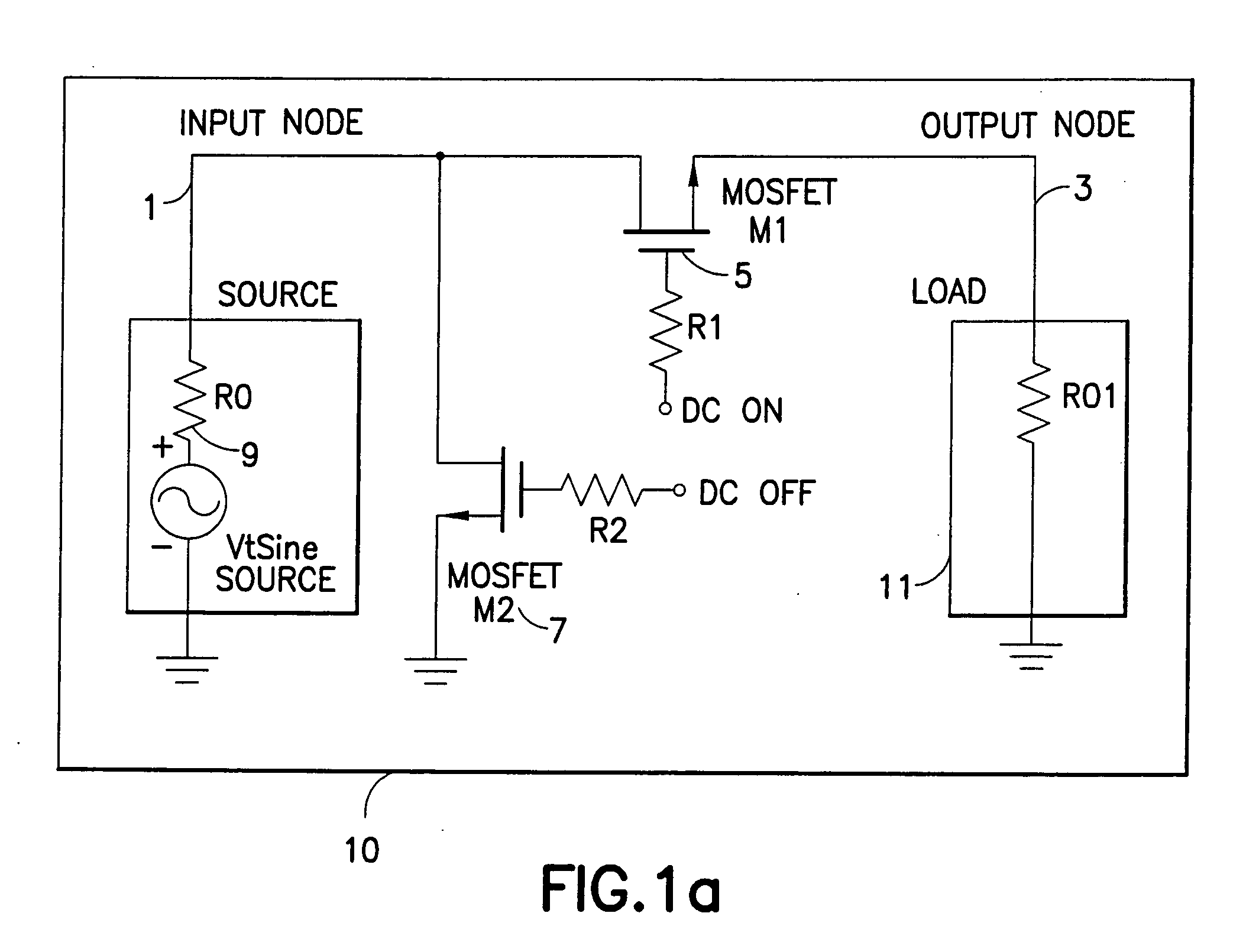
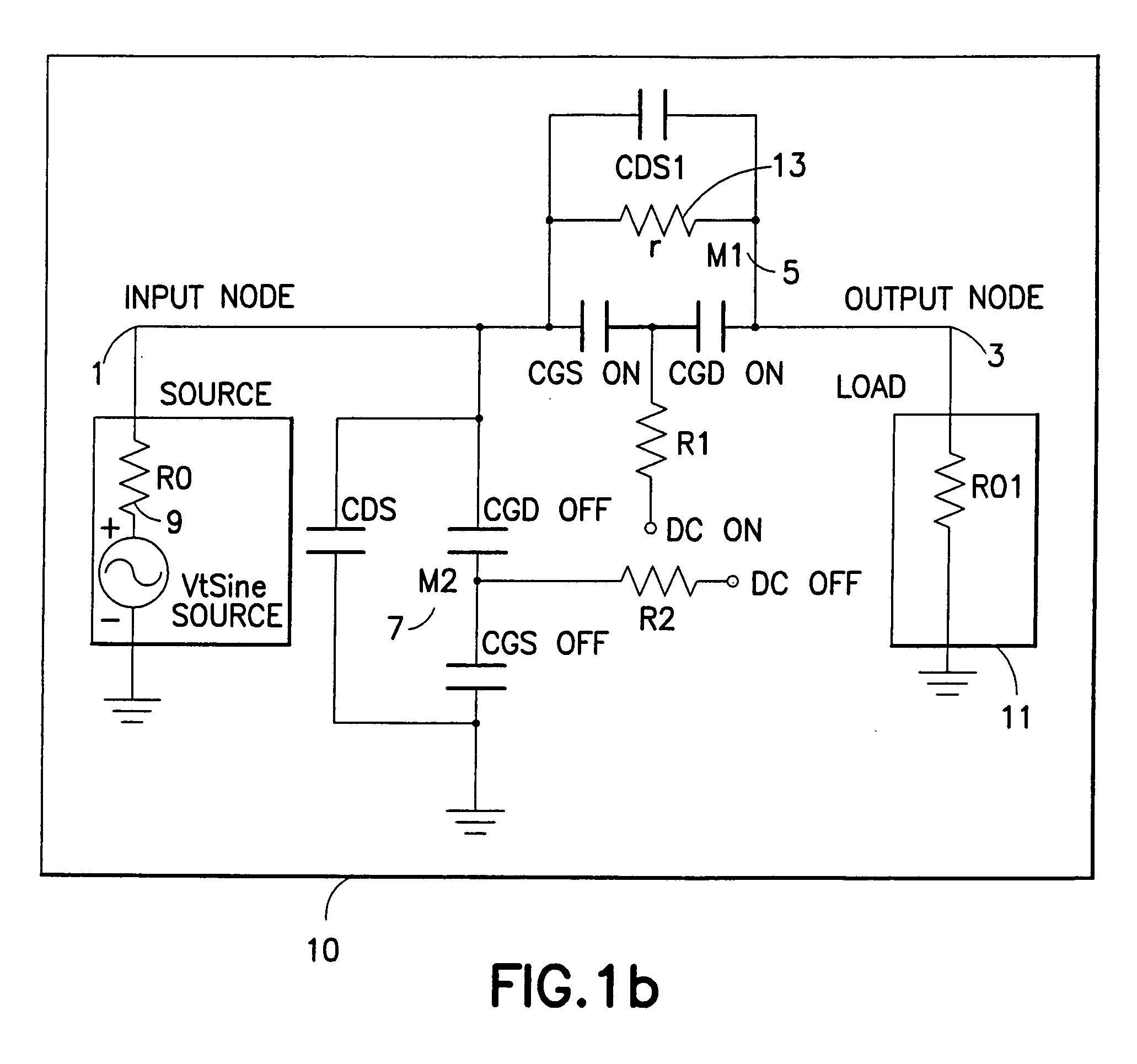
A novel integrated circuit incorporating a transmit / receive antenna switch capable of being integrated using silicon based RF CMOS semiconductor processes and a power amplifier on the same substrate. The switch circuit is constructed whereby the substrate (i.e. bulk) terminals of the FETs are left floating thus improving the isolation and reducing the insertion loss of the switch. Floating the substrate of the transistors eliminates most of the losses caused by leakage paths through parasitic capacitances internal to the transistor thus improving the isolation and reducing the insertion loss of the switch. Alternatively, the substrate can be connected to the source or to ground via a resistor of sufficiently high value to effectively float the substrate.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
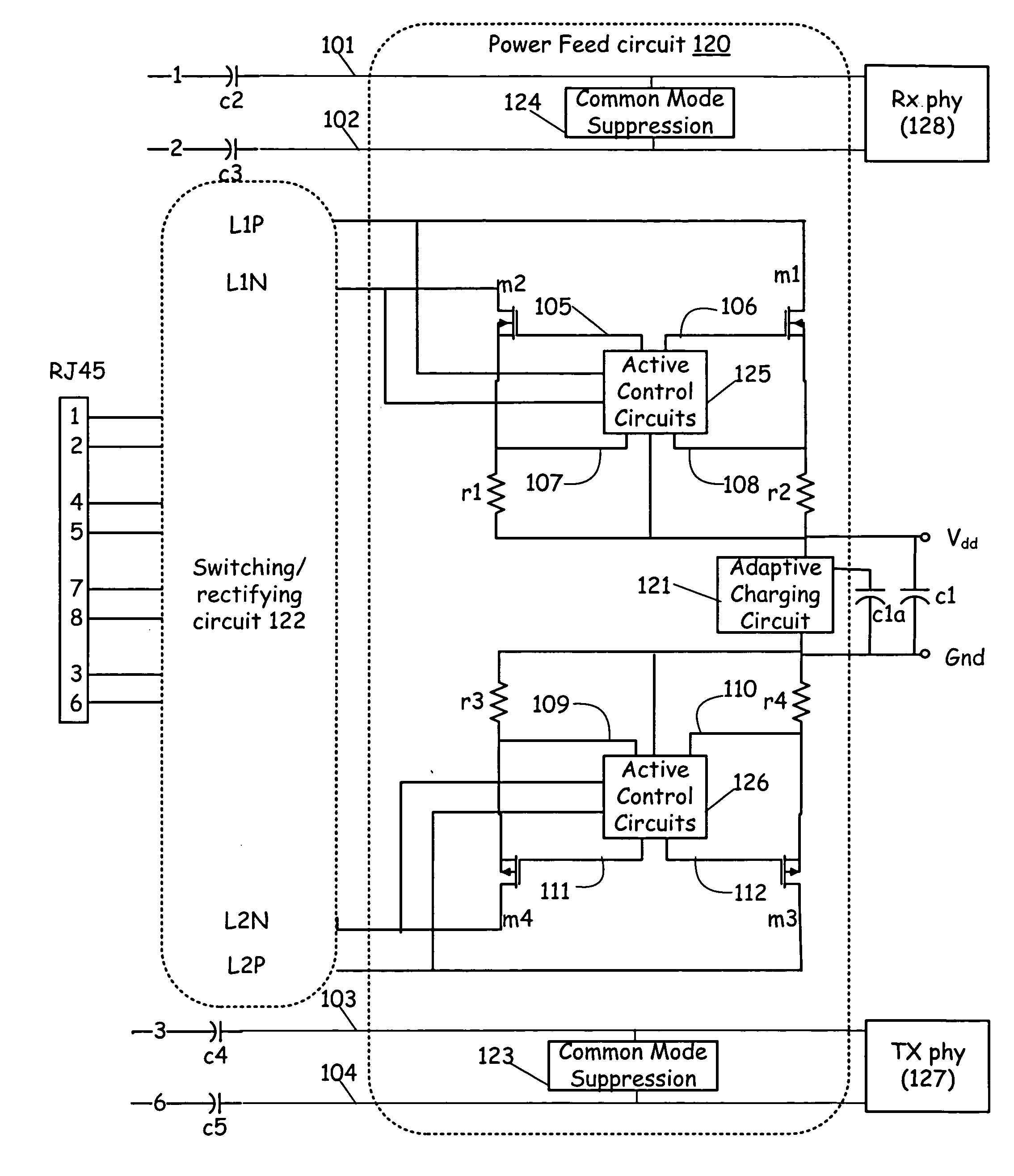
Method for dynamic insertion loss control for 10/100/1000 mhz ethernet signaling
ActiveUS20060238250A1Suppression of insertion lossReduced insertion lossResistance/reactance/impedenceDigital data processing detailsNetworking protocolNetwork connection
The present invention provides for dynamic insertion loss control for a 10 / 100 / 1000 megahertz Ethernet power on differential cable pairs. A power feed circuit supplies power to a network attached device (PD). An insertion loss control circuit limits power loss in a coupled power feed circuit. The insertion loss control circuit determines an insertion loss limit and senses an average power of the power signals to produce a common mode feedback signal to the power feed circuit. The insertion loss limit is determined for the received signals based on a differential RMS of the received Ethernet power signals as seen by a differential transistor pair. Alternatively, the insertion loss limit may be determined logically by the higher layers of the network protocol based on the AC differential portion of the network power signal. When the insertion loss limit is determined based on the differential RMS, the insertion loss control circuit is operable to automatically reduce the insertion loss based upon transmission losses experienced over the network connection between the power sending equipment and network-attached device.
Owner:KINETIC TECH INT HLDG LP
Component functioning with bulk acoustic waves having coupled resonators
A component that functions with bulk acoustic waves, particularly a bandpass filter, has an increased number of degrees of design freedom in order to improve the transmission characteristics of the component. The component has BAW resonators coupled acoustically in the vertical and / or lateral direction through common electrodes, coupling layer systems and through the excitation of lateral acoustic modes. Through the acoustic coupling of the resonators, it is possible to create additional pole points in the transfer function so that in this manner, the rejection band characteristics of a bandpass filter can be improved. Through acoustic paths which are added in addition to the electrical connection, the insertion loss can be reduced. Through an acoustic coupling instead of an electrical connection, decoupling between input and output loops of a circuit can be achieved.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
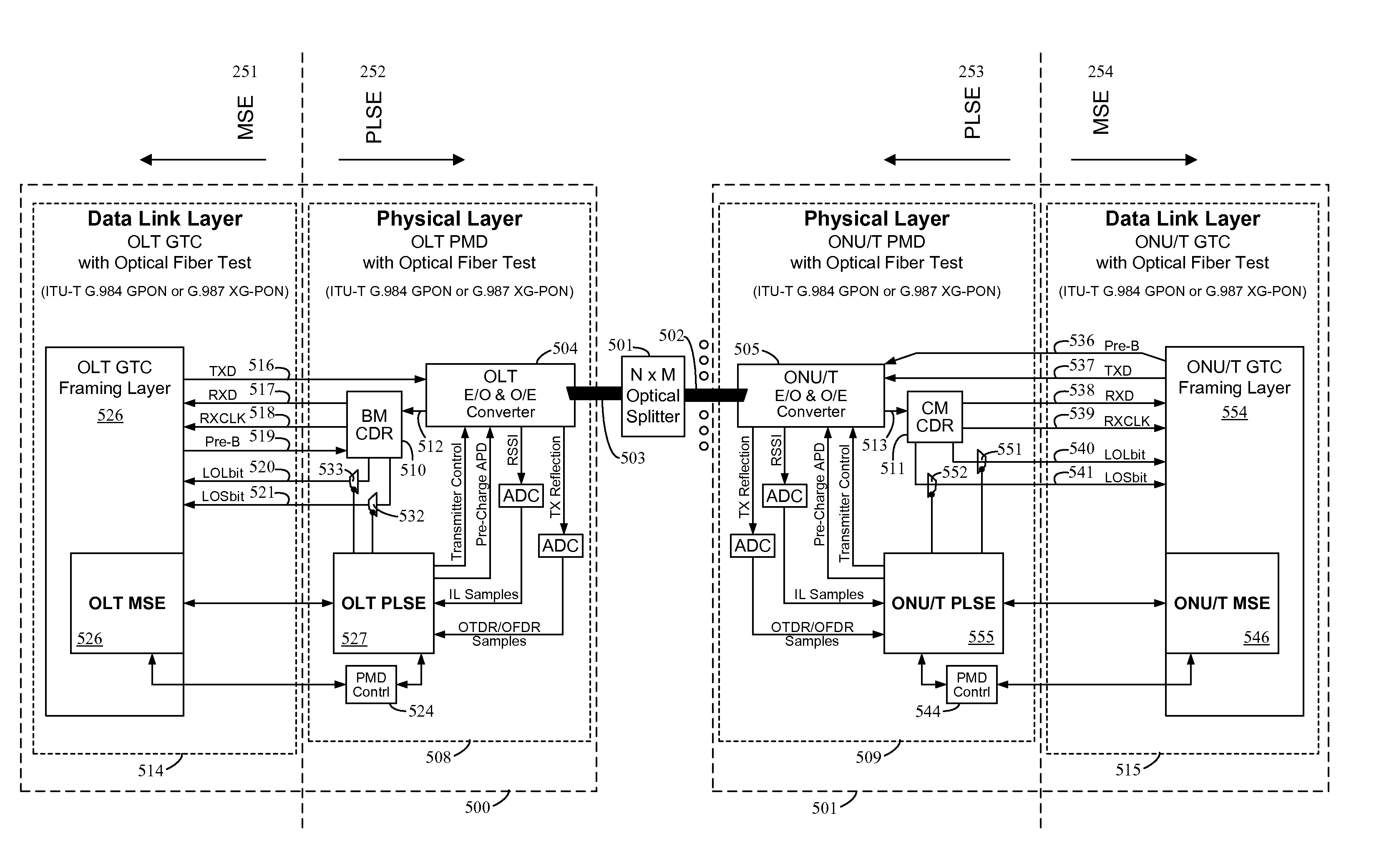
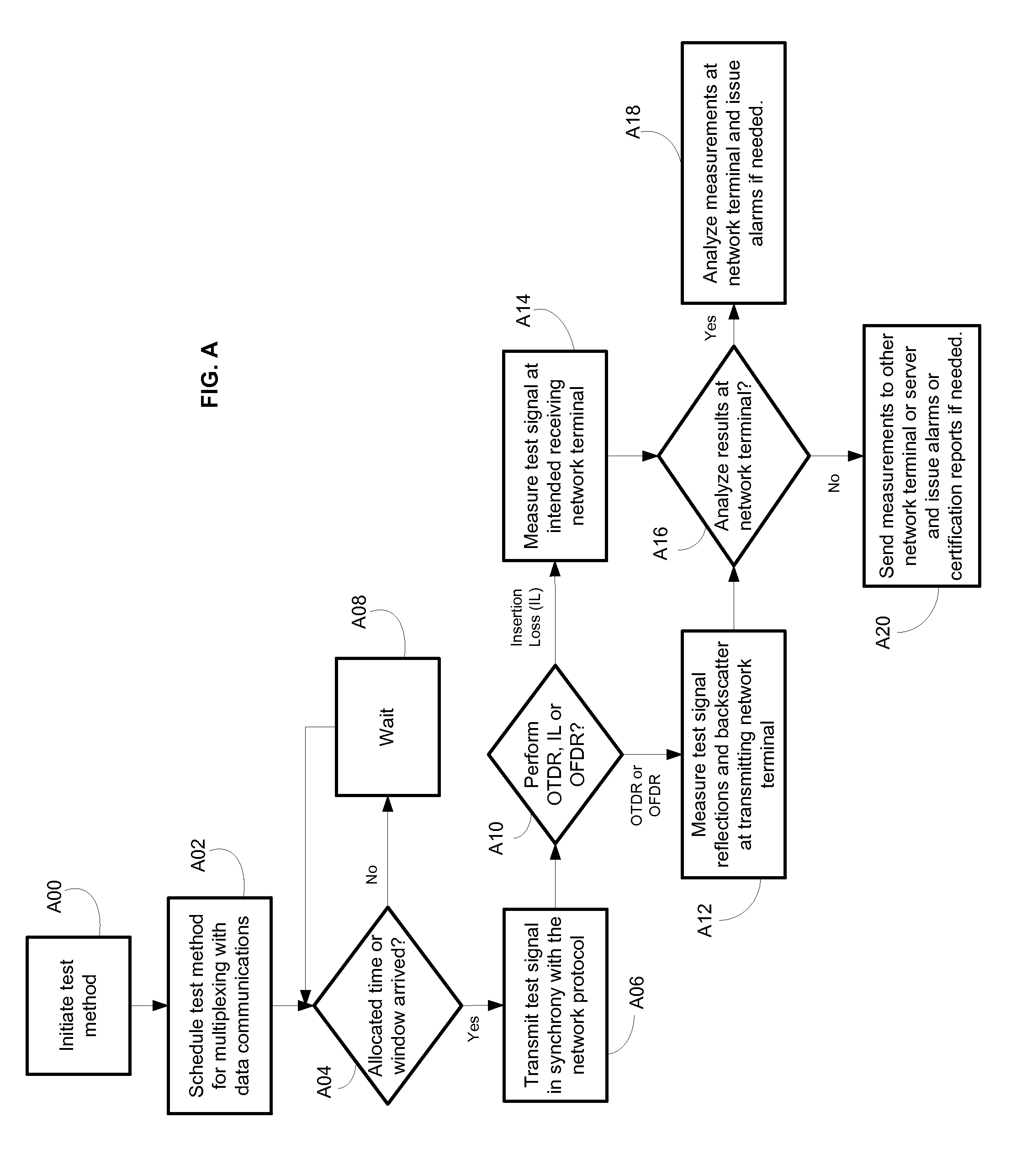
System and method for performing in-service optical network certification
ActiveUS20140016926A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsNetwork communicationLength wave
A system and method for performing an in-service optical time domain reflectometry test, an in-service insertion loss test, and an in-service optical frequency domain reflectometry test using a same wavelength as the network communications for point-to-point or point-to-multipoint optical fiber networks while maintaining continuity of network communications are disclosed.
Owner:SOTO ALEXANDER IVAN +1
Rectangular waveguide directional coupler
The invention discloses a rectangular waveguide directional coupler. The rectangular waveguide directional coupler comprises a main rectangular waveguide serving as a main microwave channel, a sub-rectangular waveguide serving as a sampling signal channel, and coupling holes serving as coupling channels, wherein the main mode H-surface of the main rectangular waveguide is parallel to that of the sub-rectangular waveguide; the main rectangular waveguide is isolated from the sub-rectangular waveguide; the main rectangular waveguide is communicated with the sub-rectangular waveguide through one or two coupling holes; at least one coupling hole includes a hollow coupling pipe attached with the sidewall of the main rectangular waveguide or / and the sidewall of the sub-rectangular waveguide; the sidewall of the hollow coupling pipe close to the rectangular waveguide is connected with a coupling cavity with three opening ends; and the coupling cavity is communicated with the hollow coupling pipe, and is located between and communicated with the main rectangular waveguide and the sub-rectangular waveguide. The rectangular waveguide directional coupler provided by the invention is compact in structure and easy in processing, and has the outstanding advantage of low insertion loss in comparison with the common single-hole directional coupler, particularly in the millimeter wave band and the Terahertz wave band.
Owner:成都赛纳赛德科技有限公司
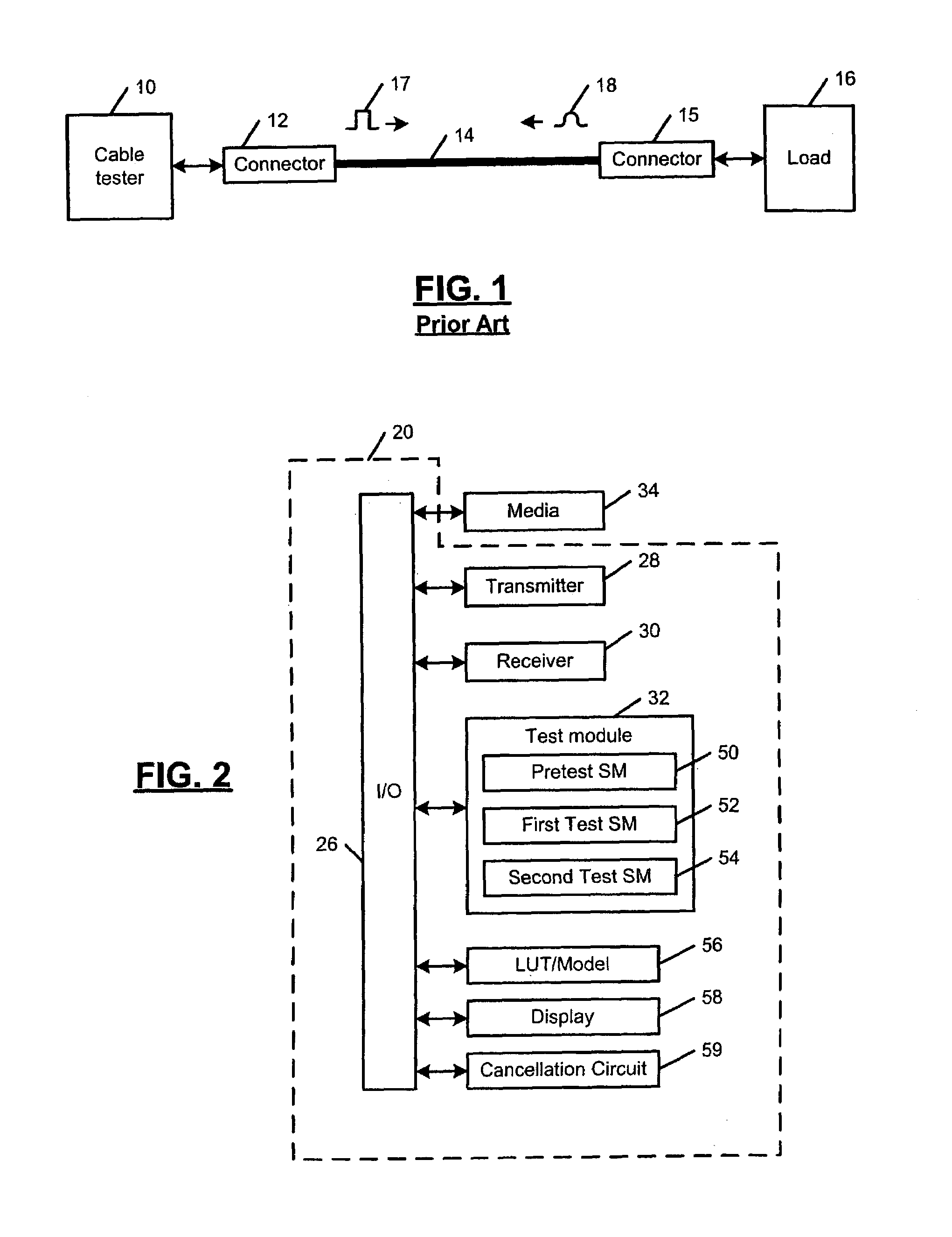
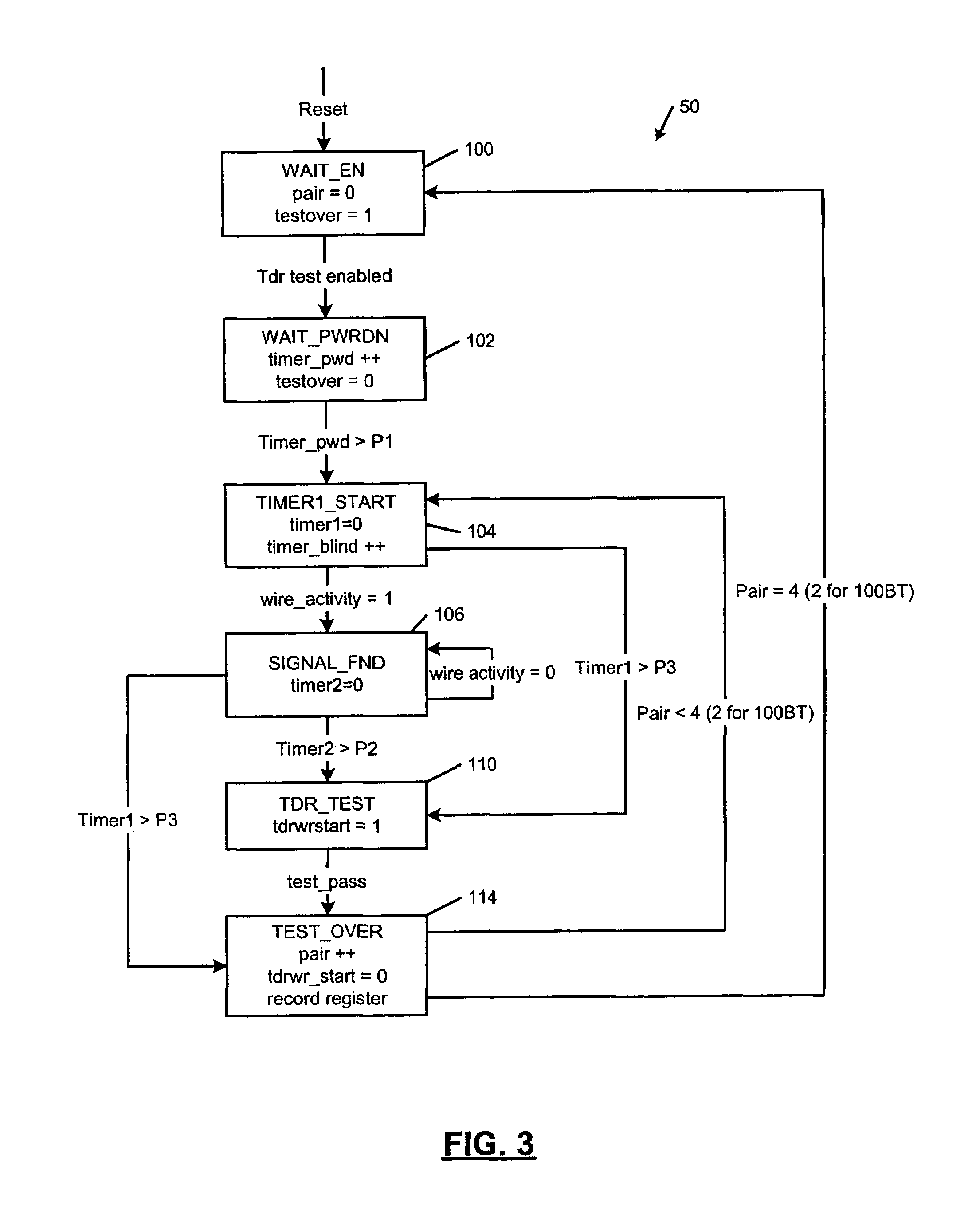
Cable tester with insertion loss and return loss estimators
InactiveUS6980007B1Fault location by conductor typesFault location by pulse reflection methodsInsertion lossEngineering
A physical layer device that communicates over a cable comprises a cable tester that determines a cable status, which includes an open status, a short status, and a normal status. The cable tester includes a pretest module that senses activity on the cable and selectively enables testing based on the sensed activity. A test module is enabled by the pretest module, transmits a test pulse on the cable, measures a reflection amplitude, calculates a cable length, and determines the cable status based on the measured amplitude and the calculated cable length. An insertion loss estimator communicates with the cable tester and estimates insertion loss of the cable. A return loss estimator communicates with the cable tester and estimates return loss of the cable based on gain parameters of the physical layer device.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Isolated Fiber Optic Union Adapters
InactiveUS20070196053A1Reduce the possibility of damageLow costCoupling light guidesEngineeringInterconnection
Devices to enhance the reliability of optical networks and to reduce the cost of repair are disclosed in this invention. In particular, fiber optic union adapters with built-in protective isolation prevent a damaged, connectorized fiber optic cable from degrading other fiber optic terminations within the network should they be physically connected. The fiber optic union comprises a split sleeve with an interior channel and a fiber stub centrally located within the interior channel. The fiber stub prevents the ferrules of two different cables from making direct physical exchange but allows them to make efficient optical exchange. Opposite ends of the fiber stub are optically polished to enable physical contact to the ferrules of fiber optic cables with low insertion loss and low backreflection. Devices to achieve low loss isolated interconnection between cables containing dissimilar fiber types by use of a fiber taper are further disclosed.
Owner:KEWITSCH ANTHONYS
High performance, small form factor connector with common mode impedance control
Techniques for improving electrical performance of a connector. The techniques are compatible with the form factor of a standardized connector, such as an SFP connector or stacked SFP. The resulting connector has reduced insertion loss for high speed signals. Such techniques, which can be used separately or together, include shaping of conductive elements within the connector while still retaining the same mating contact arrangement. Changes may be made at the contact tail portions or in the intermediate portions where engagement to a connector housing occurs. The techniques also include the incorporation of lossy bridging members between conductive elements designated to be ground conductors. For connectors according to the stacked SFP configuration, multiple bridging members may be incorporated at multiple locations within the connector.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
Method and device for generating optical signals
ActiveUS8831440B2Simple structureLow costElectromagnetic transmittersOptical NRZ to RZ conversionReturn-to-zeroSoftware engineering
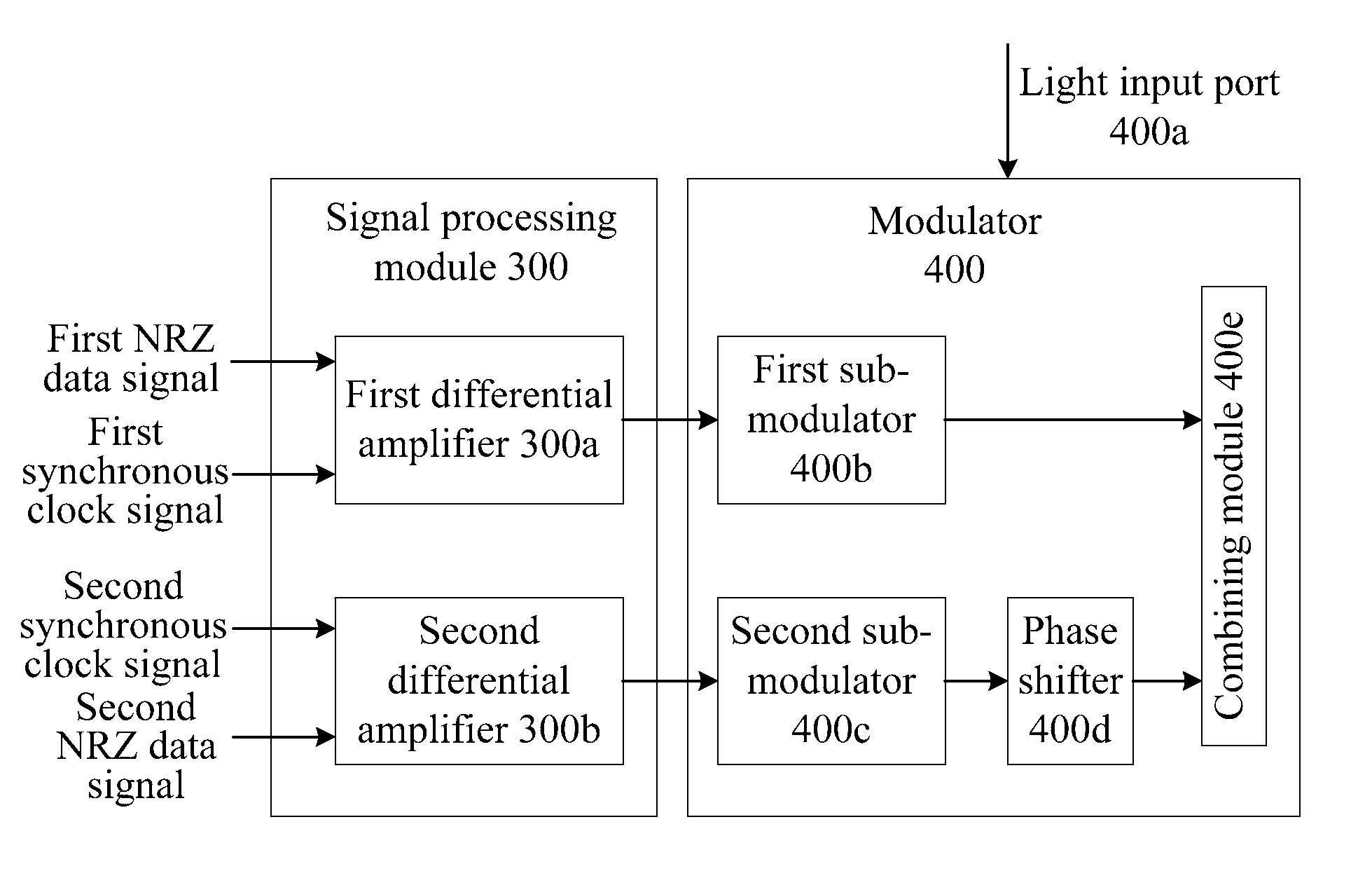
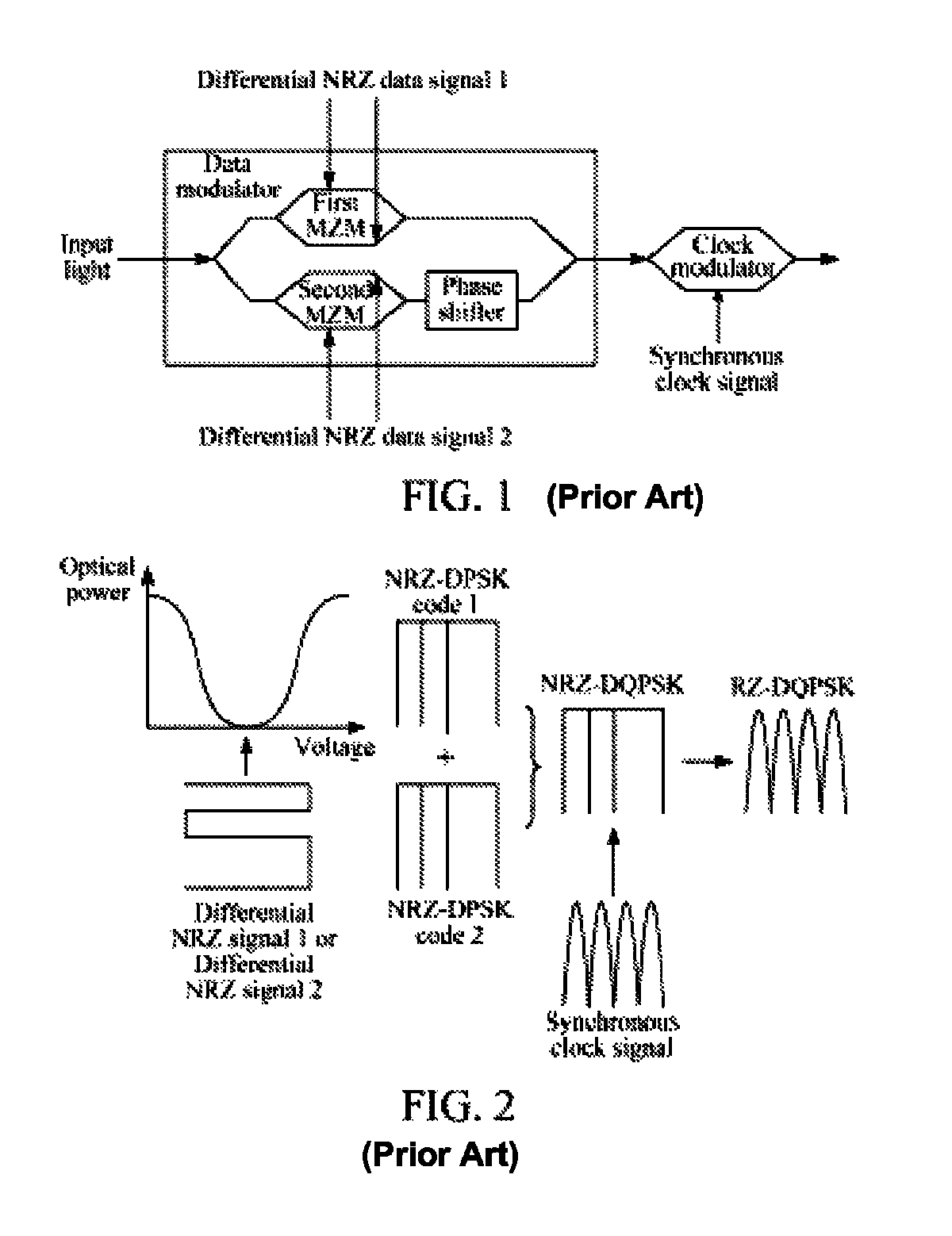
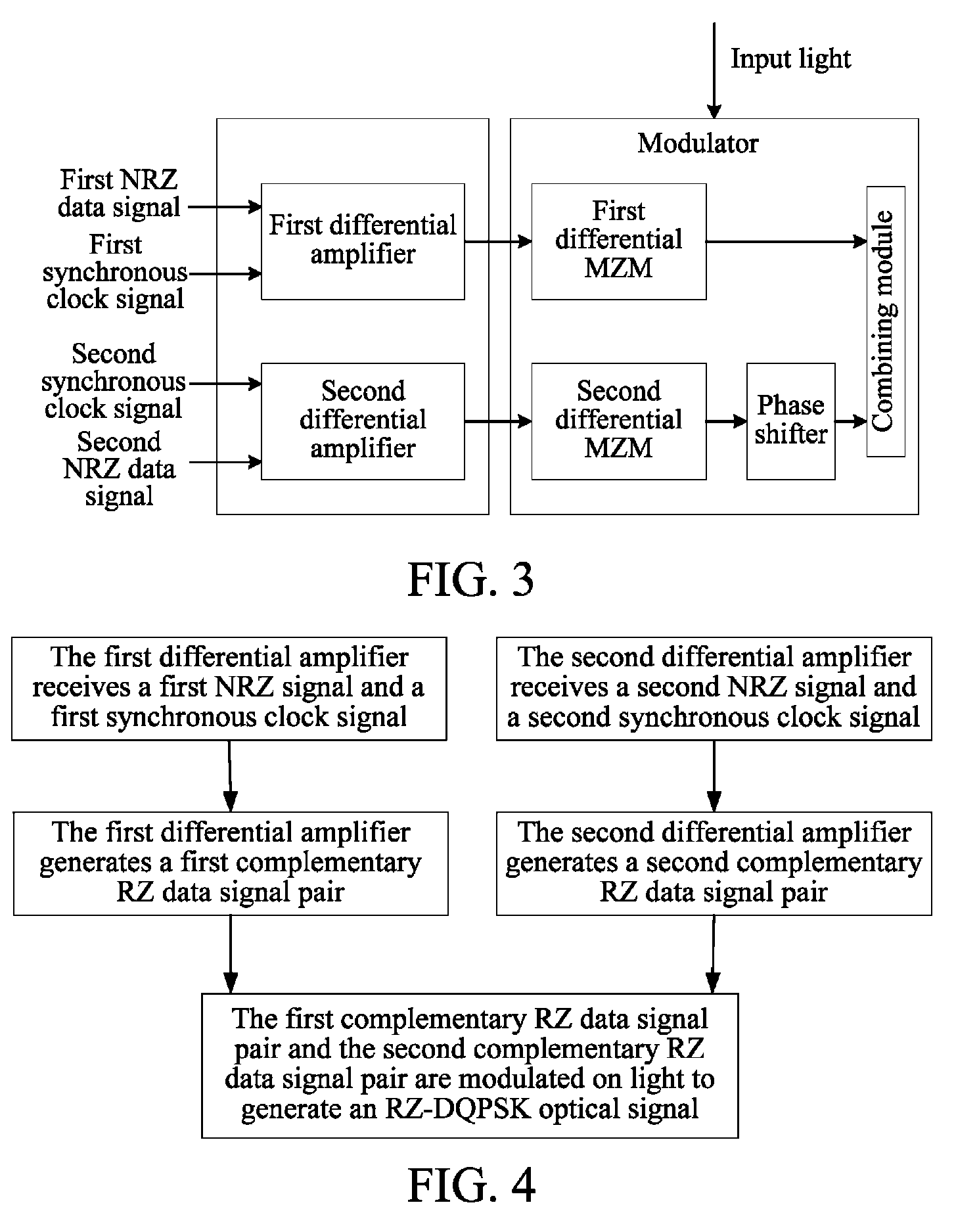
The method includes: receiving a first Non Return to Zero (NRZ) data signal and a synchronous clock signal, and performing Return to Zero (RZ) processing to generate a first complementary RZ data signal pair; receiving a second NRZ data signal and a synchronous clock signal, and performing RZ processing to generate a second complementary RZ data signal pair; and modulating the first complementary RZ data signal pair and the second complementary RZ data signal pair on light to generate an RZ-Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (RZ-DQPSK) optical signal. Through the method and device, RZ processing are performed on the NRZ data signals to generate the complementary RZ data signal pairs, and the complementary RZ data signal pairs are modulated on the light, thereby reducing the cost and the insertion loss of the entire device, lowering the requirements for input optical power and reducing the complexity of loop circuit control.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Multi-layered LC composite with a connecting pattern capacitively coupling inductors to ground
InactiveUS6504451B1Reduce the amount of solutionImprove insertion lossMultiple-port networksWaveguidesUltrasound attenuationCapacitance
A multi-layered LC composite component achieves greatly increased attenuation in the proximity of a central frequency without increasing insertion loss. In the arrangement of the multi-layered LC composite component, an end of each of inductor patterns is connected to a connecting pattern to be short-circuited. These inductor patterns define inductors. Frequency-adjusting capacitor patterns are opposed to open-circuited ends of the inductor patterns to define capacitors. As a result, the capacitors and the inductors define LC resonators. The connecting pattern is opposed to shield patterns via insulating sheets to define a common capacitor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Electric component for communication device and semiconductor device for switching transmission and reception
ActiveUS20050047038A1Reduce component countImprove installation densityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGated amplifiersAudio power amplifierCommunications system
There are provided a transmission / reception switching circuit which is small in insertion loss and harmonic distortion and allows an increase in the output power of a power amplifier and an electronic component for communication on which the transmission / reception switching circuit is mounted. As an element composing a transmission / reception switching circuit in a wireless communication system, series-connected FETs or a multi-gate FET are used in place of a diode. Gate resistors connected between the individual gate terminals and a control terminal are designed to have resistance values which become progressively smaller from the gate to which a highest voltage is applied toward the gate to which a lowest voltage is applied.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
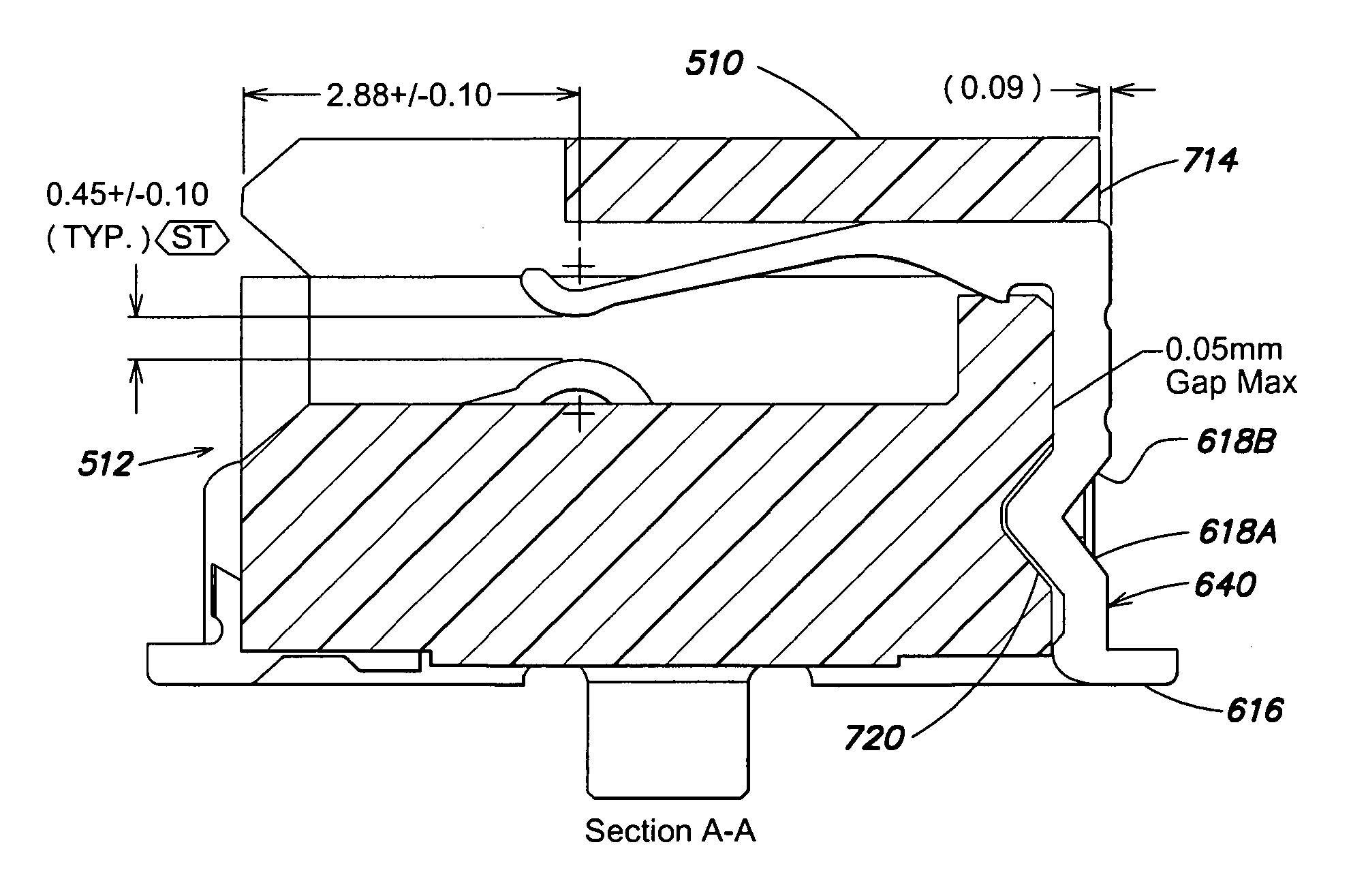
Optical connector plug, optical connector adapter and optical connector
To provide an optical connector promoting reliability by reducing insertion loss of an optical fiber and downsized, there is provided an optical connector plug having a ferrule including a cylindrical member for the ferrule for holding an optical fiber and a flange member provided at a rear end portion of the cylindrical member for the ferrule, an urge spring provided on a side of a rear end portion of the flange member of the ferrule, and a plug housing for holding the ferrule and the urge spring directly at inside thereof and directly engaged with an optical connector adapter inserted with a front end portion of the ferrule to carry out optical connection, in which the plug housing is formed with a slit capable of inserting the optical fiber in a radius direction thereof at a portion of an outer periphery thereof over an axial direction.
Owner:SEIKOH GIKEN
Switch circuit and method of switching radio frequency signals
InactiveUS20050017789A1Improving RF switch isolationRaise the compression pointTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETEngineering
A novel RF buffer circuit adapted for use with an RF switch circuit and method for switching RF signals is described. The RF switch circuit is fabricated in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology. The RF switch includes pairs of switching and shunting transistor groupings used to alternatively couple RF input signals to a common RF node. The switching and shunting transistor grouping pairs are controlled by a switching control voltage (SW) and its inverse (SW_). The switching and shunting transistor groupings comprise one or more MOSFET transistors connected together in a “stacked” or serial configuration. The stacking of transistor grouping devices, and associated gate resistors, increase the breakdown voltage across the series connected switch transistors and operate to improve RF switch compression. A fully integrated RF switch is described including digital control logic and a negative voltage generator integrated together with the RF switch elements. In one embodiment, the fully integrated RF switch includes a built-in oscillator, a charge pump circuit, CMOS logic circuitry, level-shifting and voltage divider circuits, and an RF buffer circuit. Several embodiments of the charge pump, level shifting, voltage divider, and RF buffer circuits are described. The inventive RF switch provides improvements in insertion loss, switch isolation, and switch compression.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
CDMA power amplifier design for low and high power modes
InactiveUS7202736B1Improve responseLow insertion lossHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlPower modeAudio power amplifier
An amplifier circuit responsive to a power mode signal improves efficiency at low power levels without compromising efficiency at high power levels. At low power levels, high impedance is presented with suitable adjustment in the phase of the signal. Also, providing for predistortion linearization improves high power efficiency and switching the predistortion linearizer OFF at low power levels contributes little more than a small insertion loss. The power amplifier also uses a bias circuit incorporating a dual harmonic resonance filter to provide high impedance at a fundamental frequency and low impedance at a second harmonic. These properties are of particularly advantageous since amplifiers in cell-phones are used in low power modes most of the time although they are designed to be most efficient at primarily the highest power levels.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
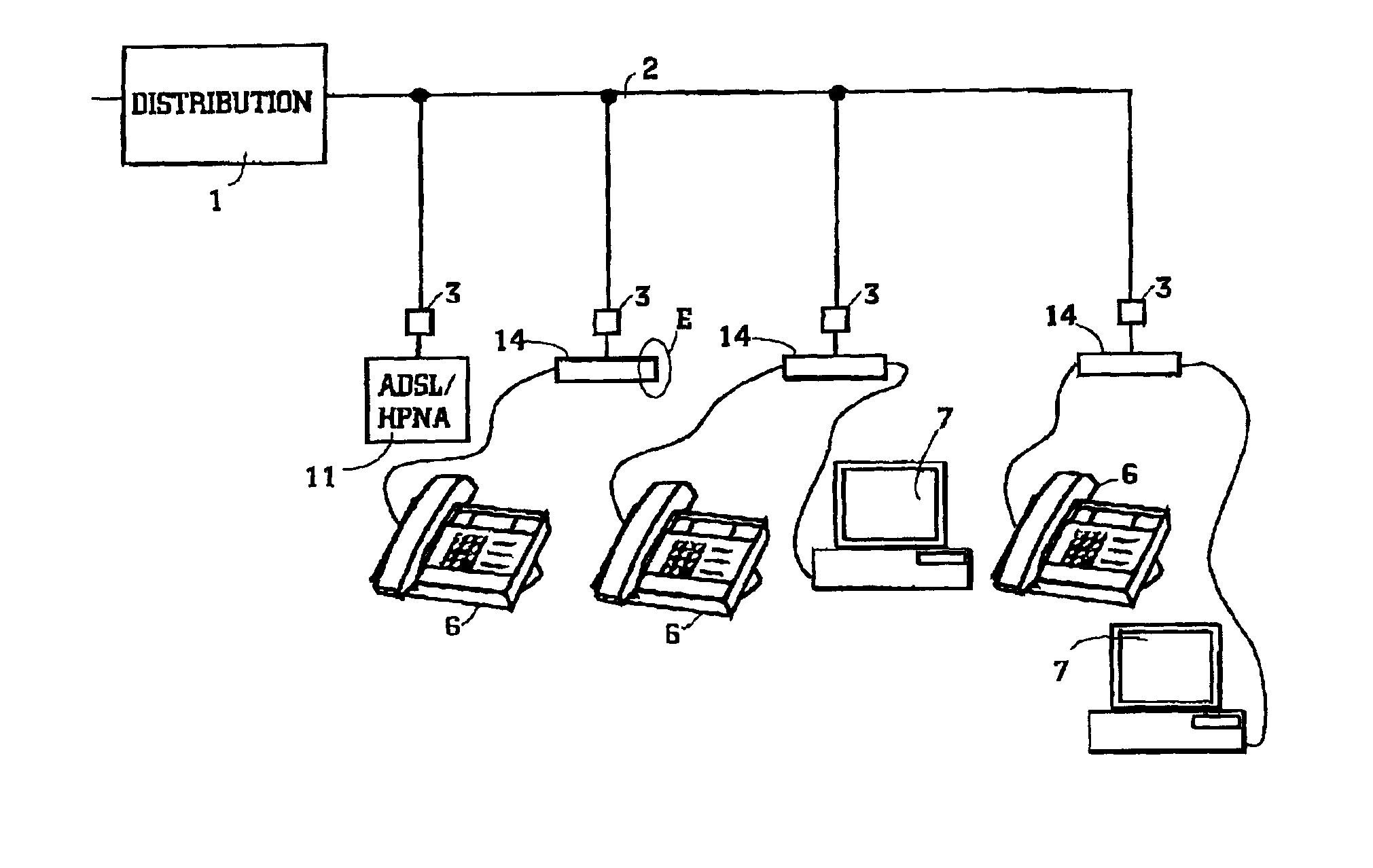
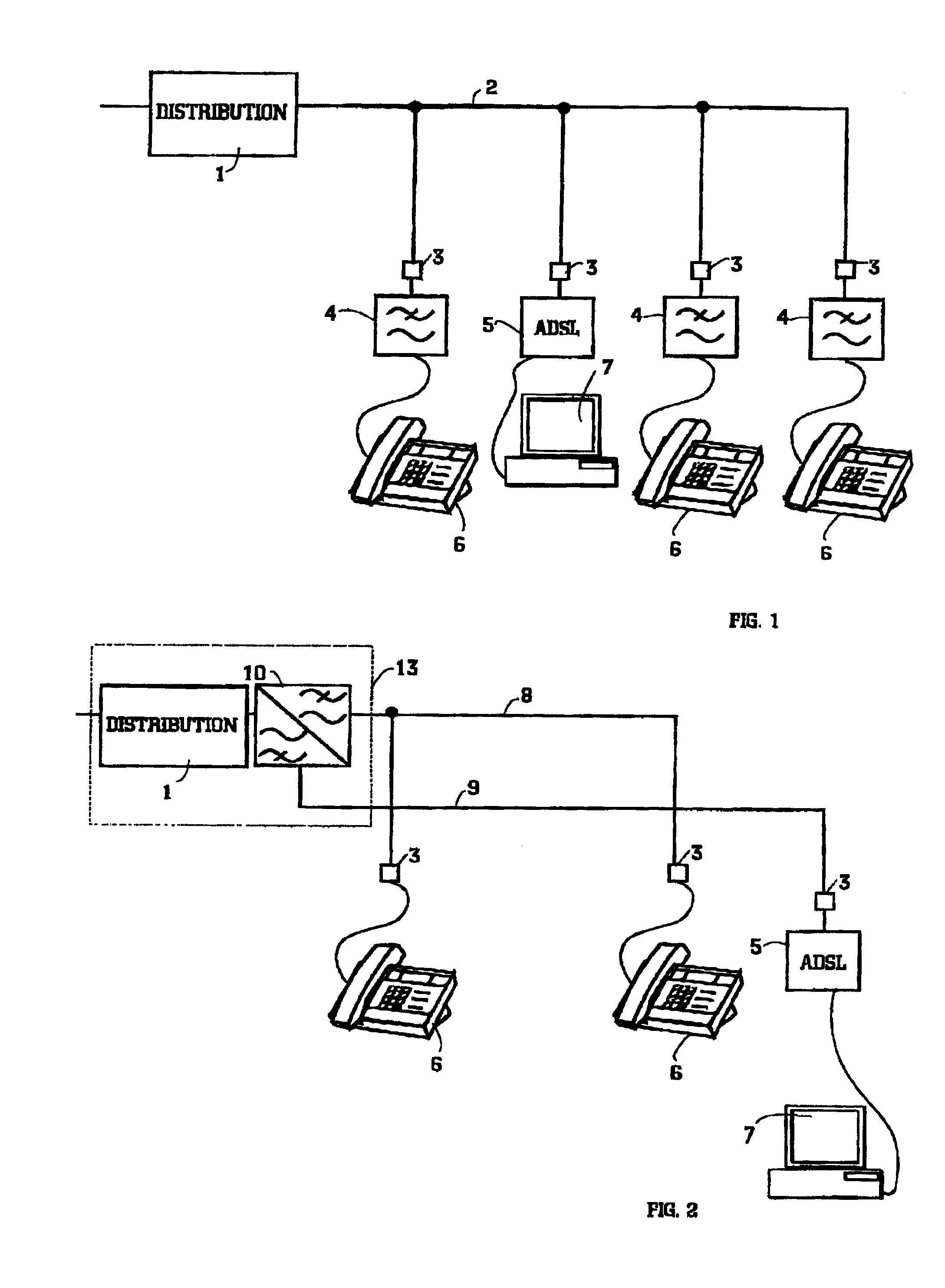
Arrangement of local area network
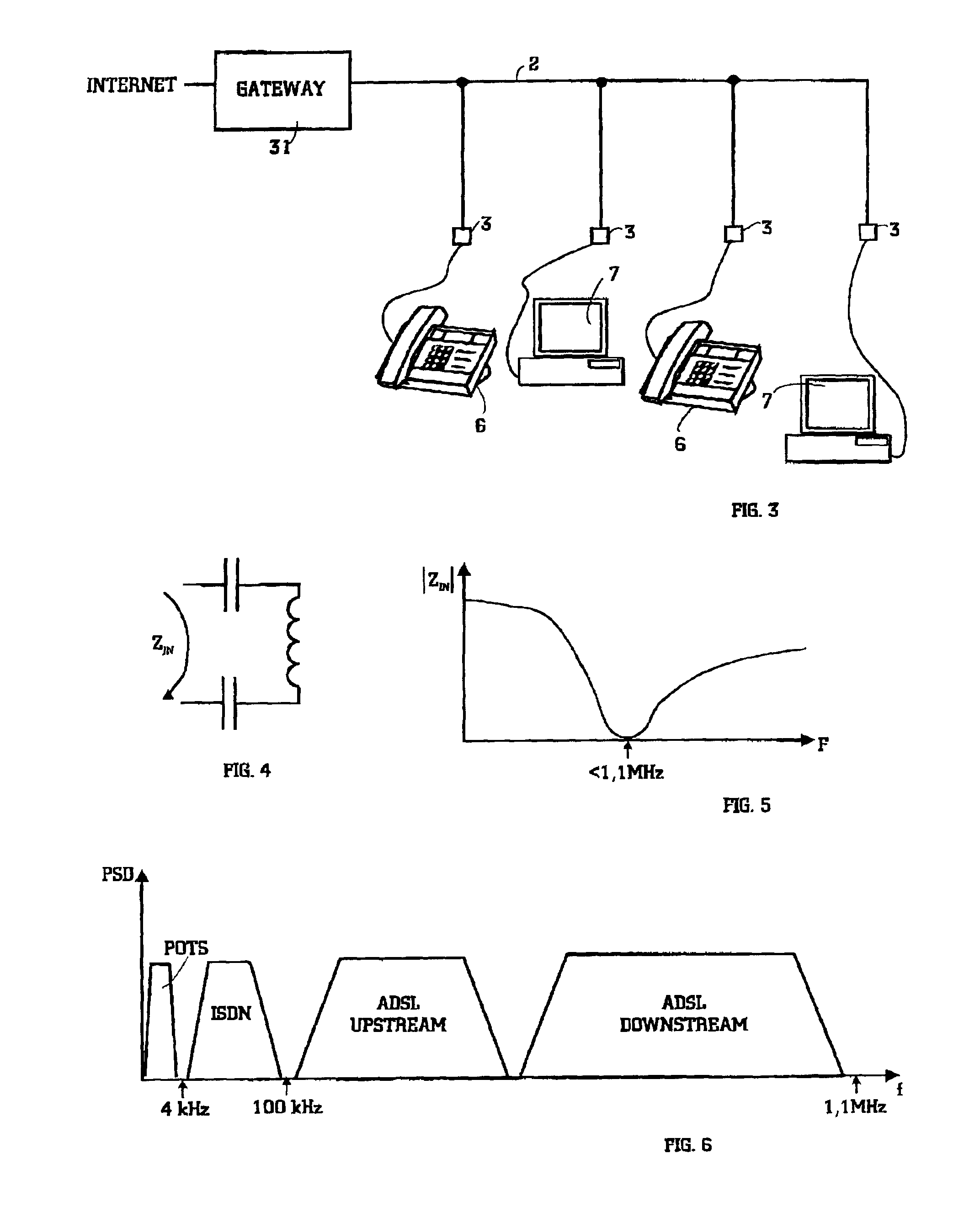
InactiveUS6963559B2Maximizing insertion lossMaximizing impedanceTelephonic communicationCircuit switching systemsEngineeringDistribution networks
This invention relates to LANs at a customers' premise, especially to the HomePNA technique. The idea of the invention is that voice band terminals and HomePNA (HPNA) stations are hidden from a distribution network by a band division filter in a way that performance of ADSL is not degraded by presence of an HPNA LAN. The band division filter incorporates two subfilters: a POTS filter and an HPNA filter. The latter implements a band stop function maximizing insertion loss at the ADSL band The band division filter can be installed to needed telephone sockets.
Owner:WI LAN INC
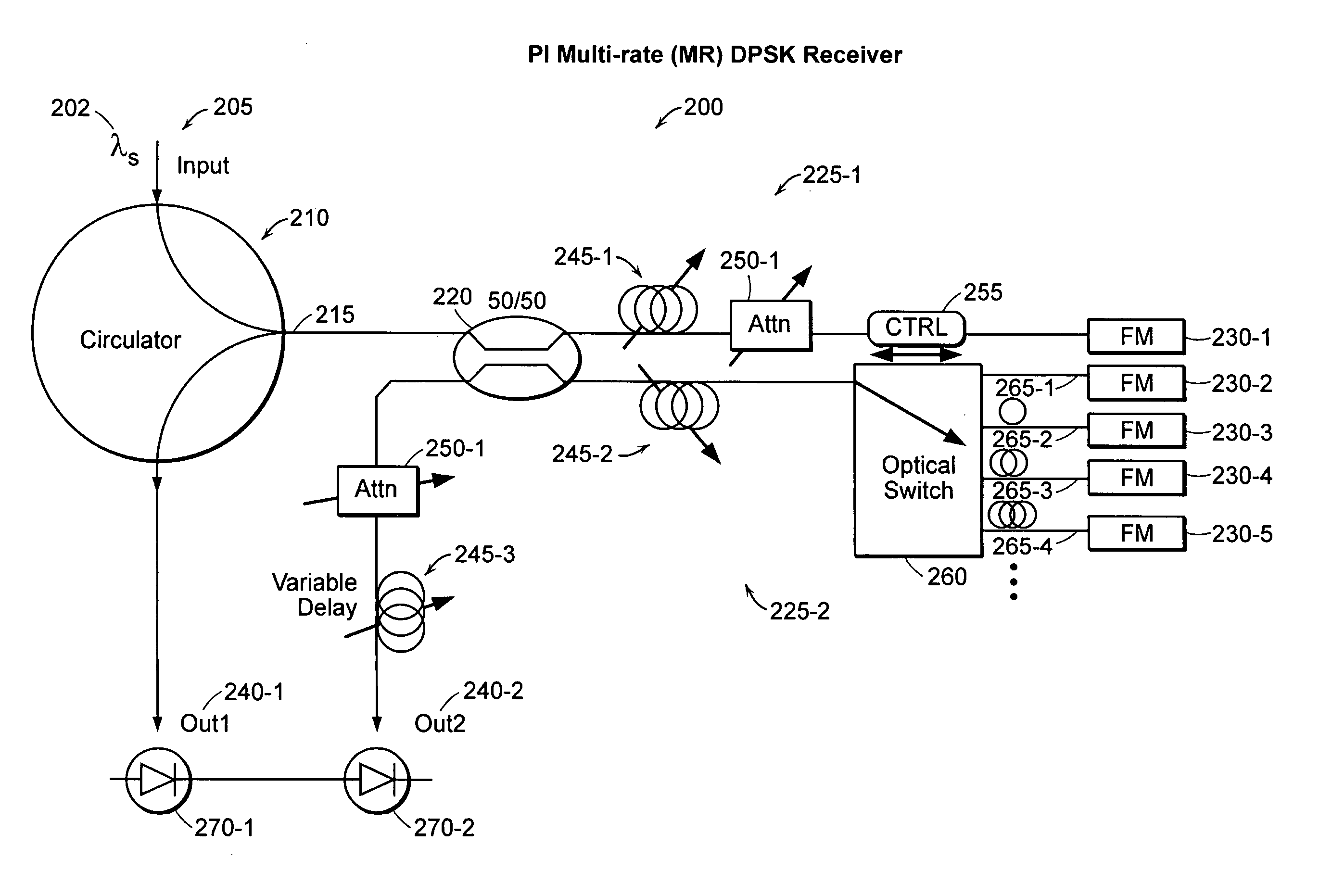
Reconfigurable polarization independent interferometers and methods of stabilization
A polarization independent (PI) interferometer design that can be built from standard optical components is described. Based upon a Michelson interferometer, the PI interferometer uses a 50 / 50 splitter and Faraday Rotator Mirrors (FM's). The interferometer achieves good optical characteristics, such as high extinction ratio (ER) and low insertion loss (IL). Lack of polarization sensitivity reduces interferometer construction tolerances and cost, enhances performance and utility, and expands the scope of interferometric based devices. Such characteristics can be used to construct flexible, high performance, polarization insensitive, multi-rate, self-calibrating, optical DPSK receivers, power combiners, optical filters and interleavers, all-optical switches, and cascaded interferometers. Since polarization is not maintained in standard fiber optic networks, a PI-DPSK receiver allows for use of more sensitive DPSK communications over fiber, without need for costly polarization control hardware. Other applications of PI interferometers include optical CDMA, secure communications, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and temporal gratings with ultra-precise timing.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Optical add/drop multiplexing systems
ActiveUS20050105909A1Improve efficiencyOvercome problemsMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingGrating
The present invention overcomes problems associated with switch isolation, noise and crosstalk suppression, insertion loss, spurious reflections, wavelength tolerance, and compactness that are present in varying degrees in other add / drop systems. The present invention includes devices or components that include, but are not limited to high efficiency switchable gratings. In one embodiment of the invention, each of the “base” gratings have substantially identical spatial frequencies and each of the “vertex” gratings have substantially identical spacial frequencies. However, the “vertex” gratings have higher grating frequencies than the “base” gratings. In another embodiment of the invention, the “base” and “vertex” gratings have substantially the same grating frequencies. Further embodiments of the invention, for example, deal with multiple add / drop grating pairs, variations of fixed and switchable gratings, the use of grating pairs to spatially separate the wavelength division multiplexed components of input beams into individual beams, and the replacement of lenses and waveguides with detectors or emitters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Aligned duplex antennae with high isolation
InactiveUS20070057860A1Improve isolationReduce signal lossRadiating element housingsIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsEngineeringHigh isolation
Integrating dual antennae into a single rigid assembly guarantees parallel alignment between the antennae and provides higher isolation with lower insertion loss than duplexing methods can achieve through a single antenna. The resulting higher performance at lower cost can benefit two-way communication systems using time division duplexing, frequency division duplexing, or polarization division duplexing; or combinations of these methods.
Owner:RADIOLINK NETWORKS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com