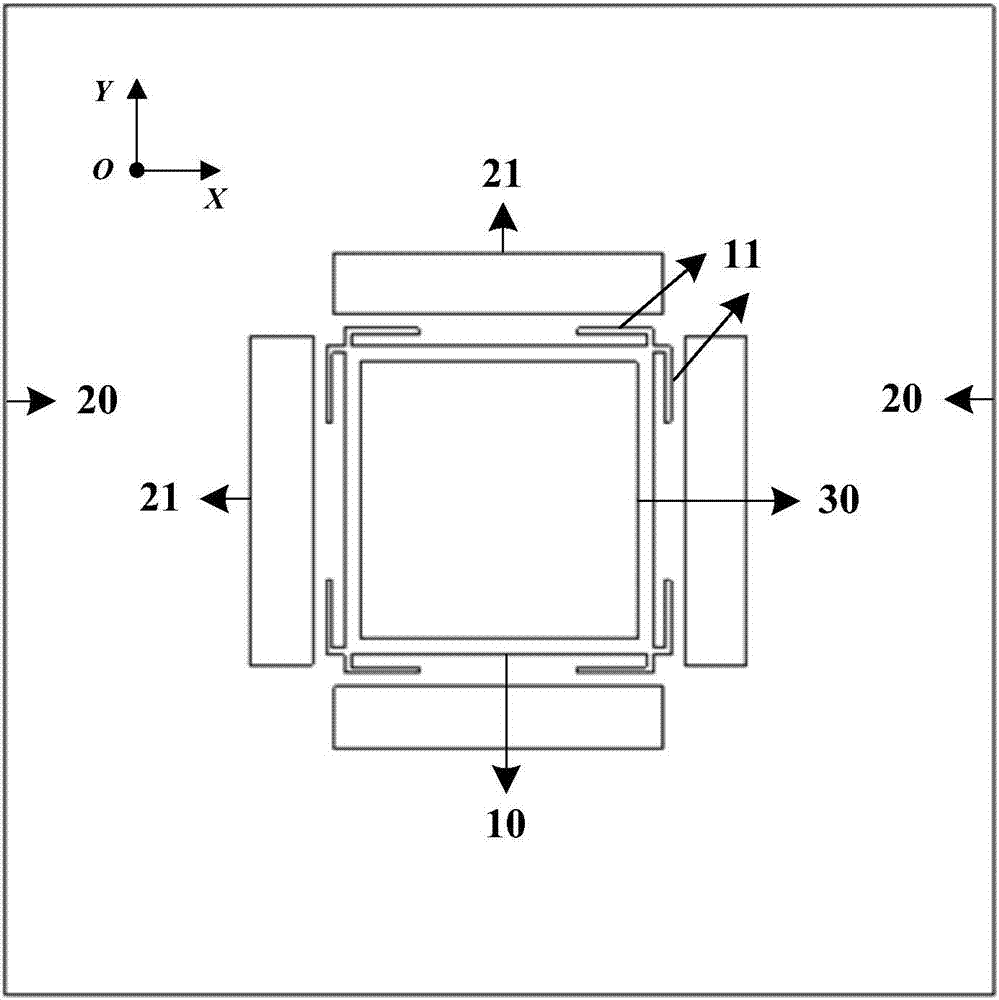
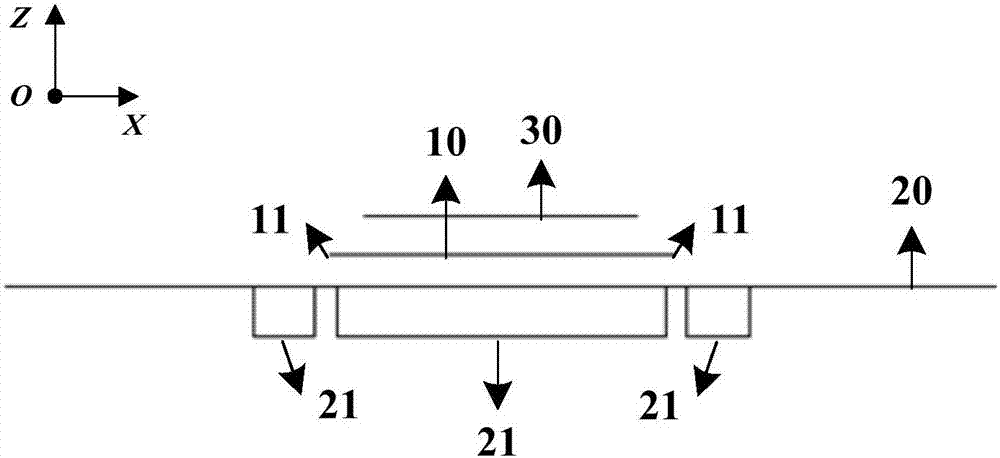
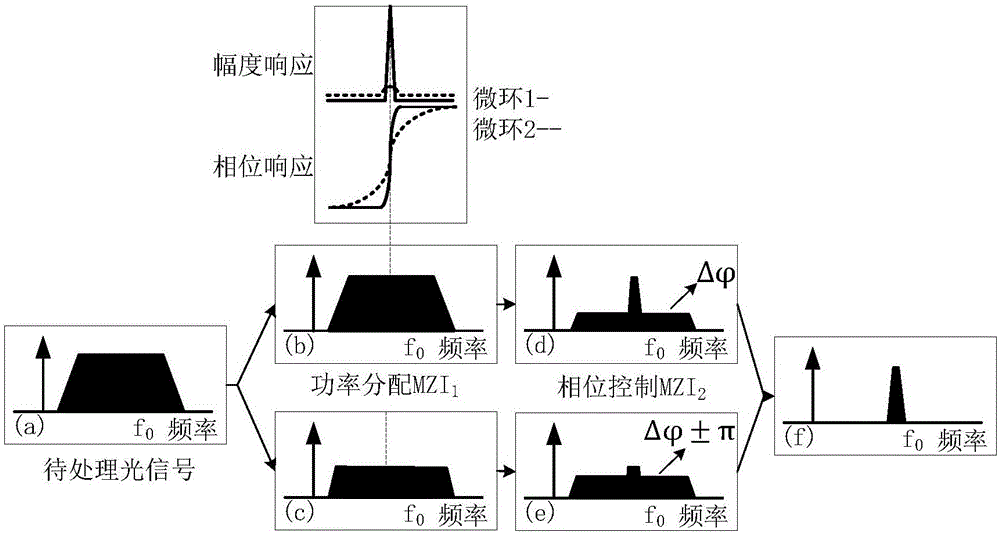
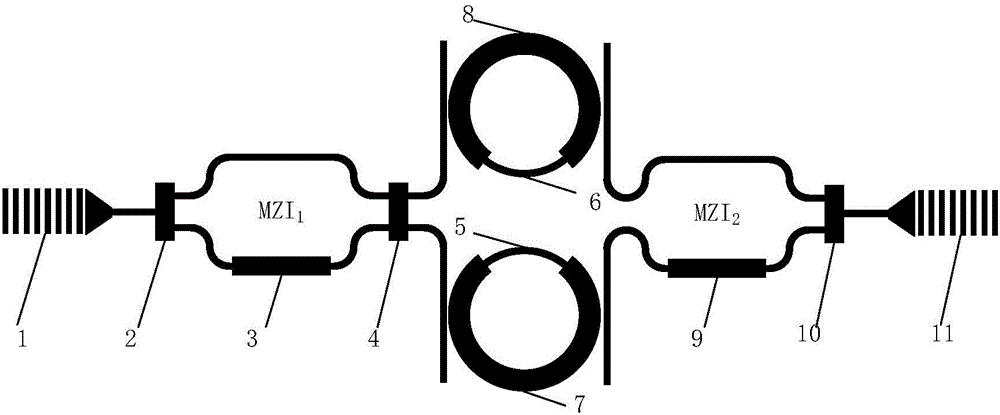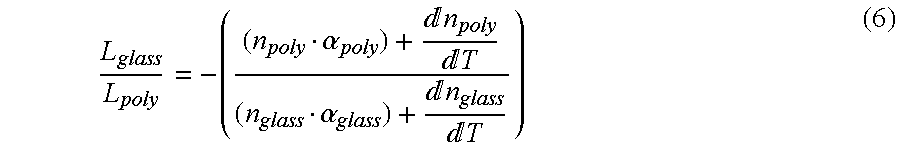Patents
Literature
257results about How to "Improve insertion loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
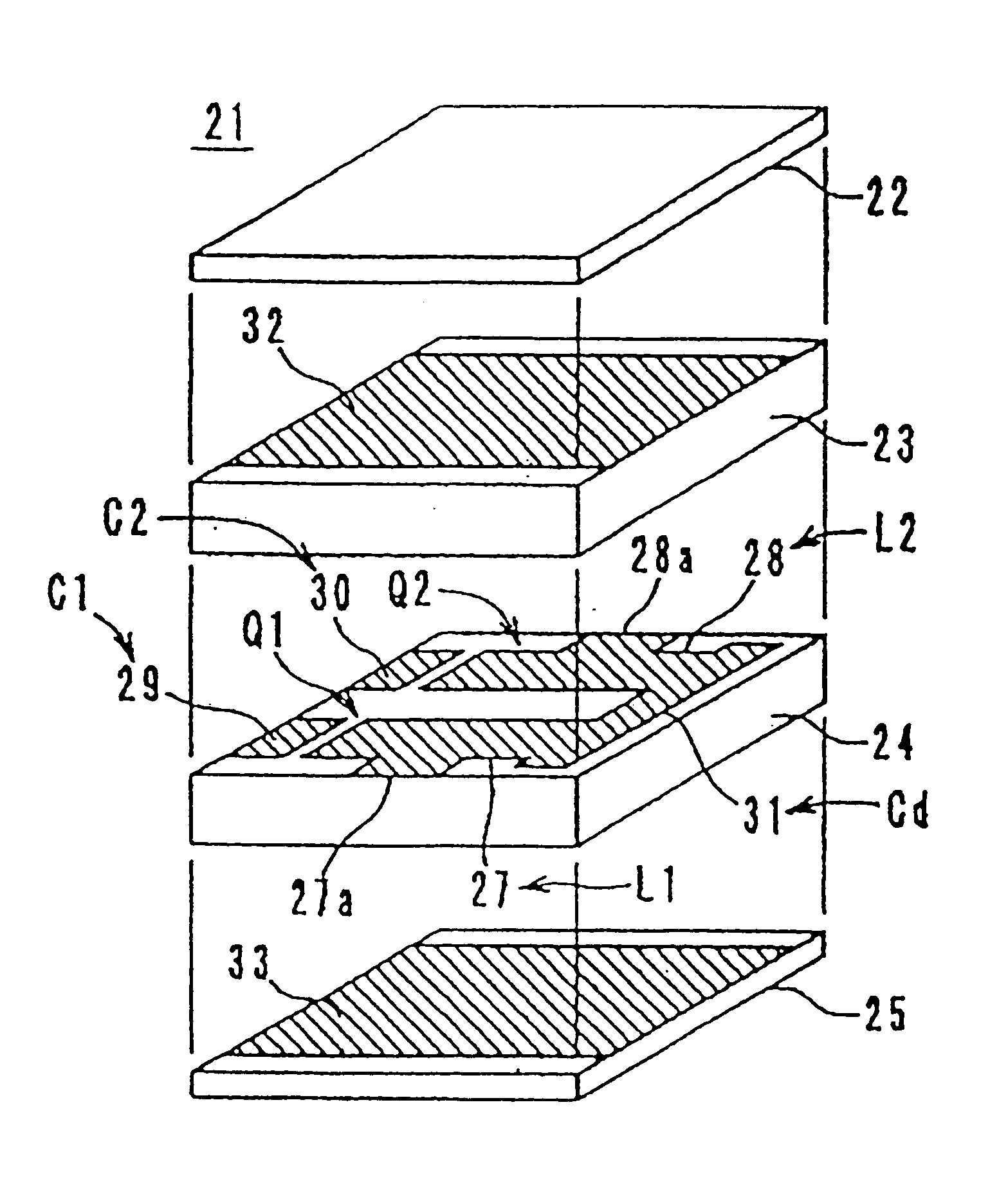
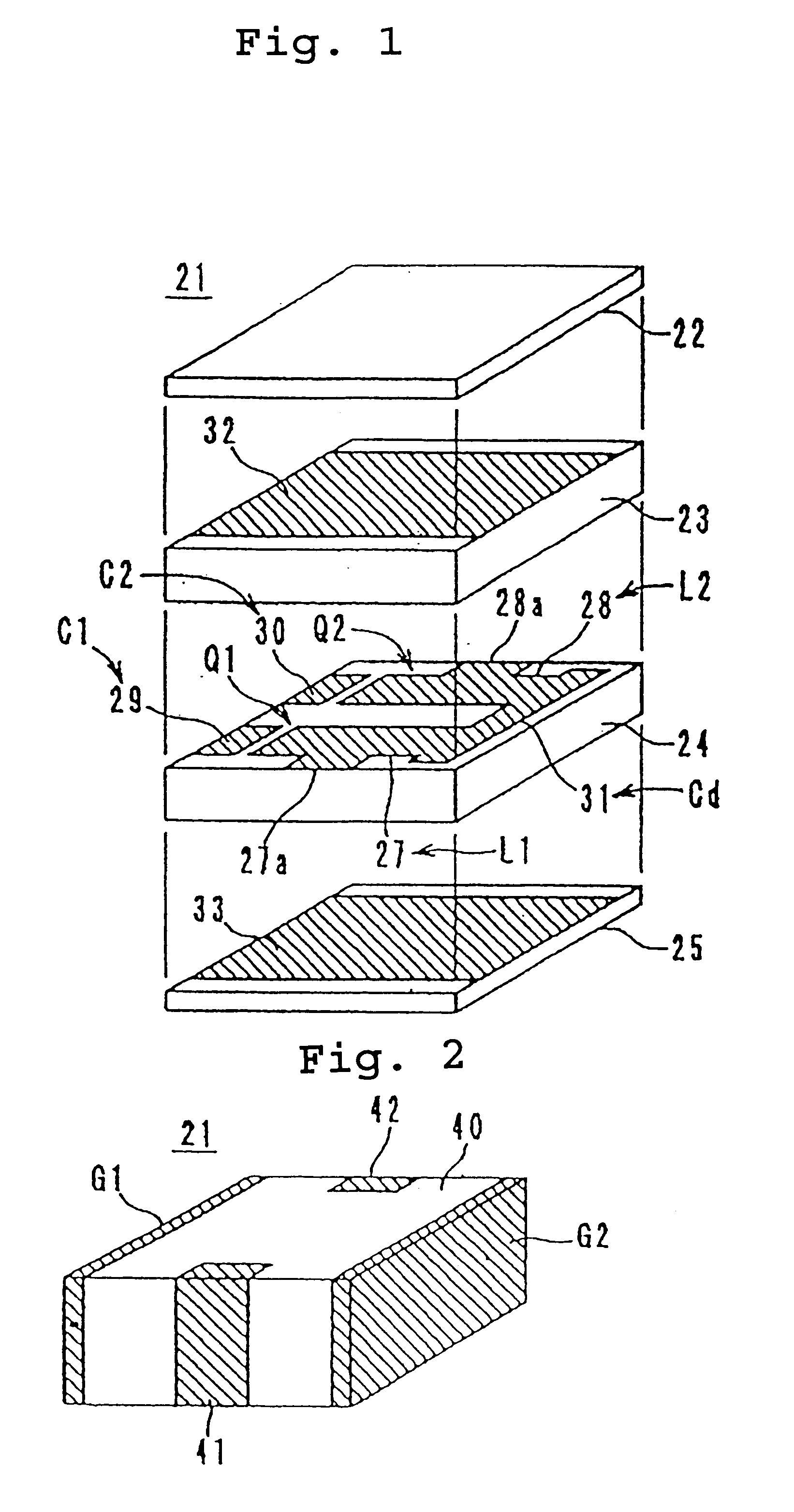
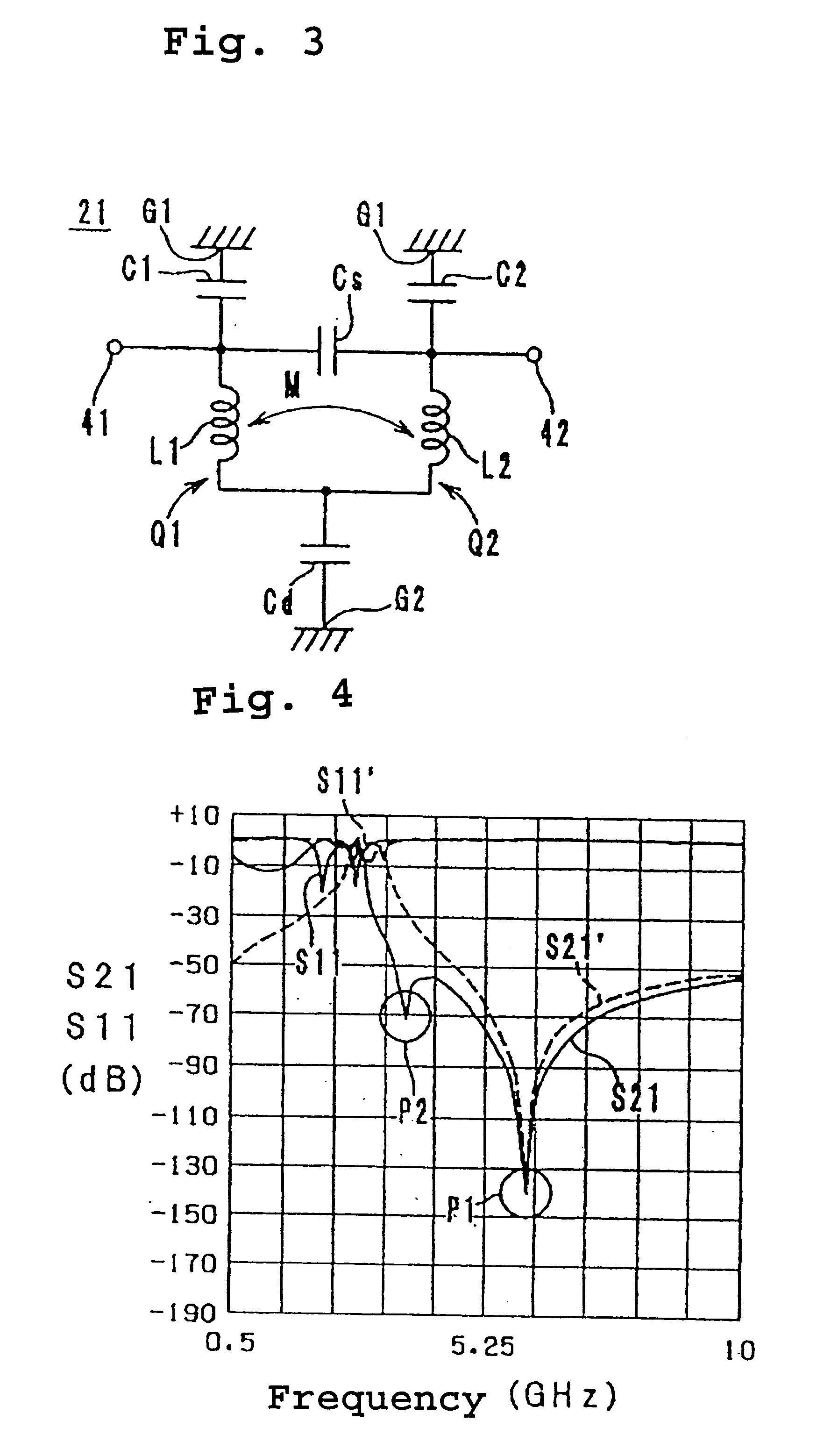
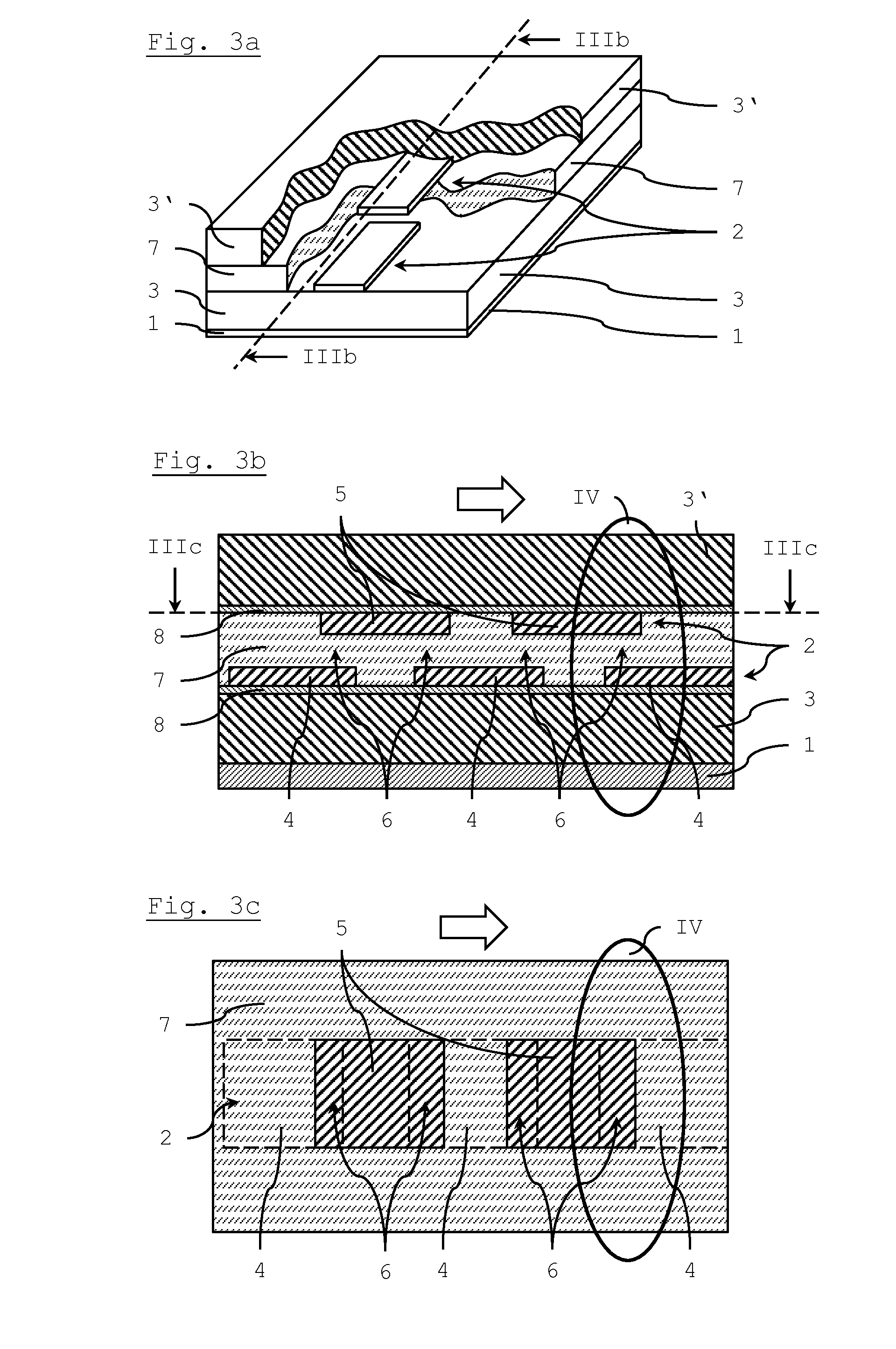
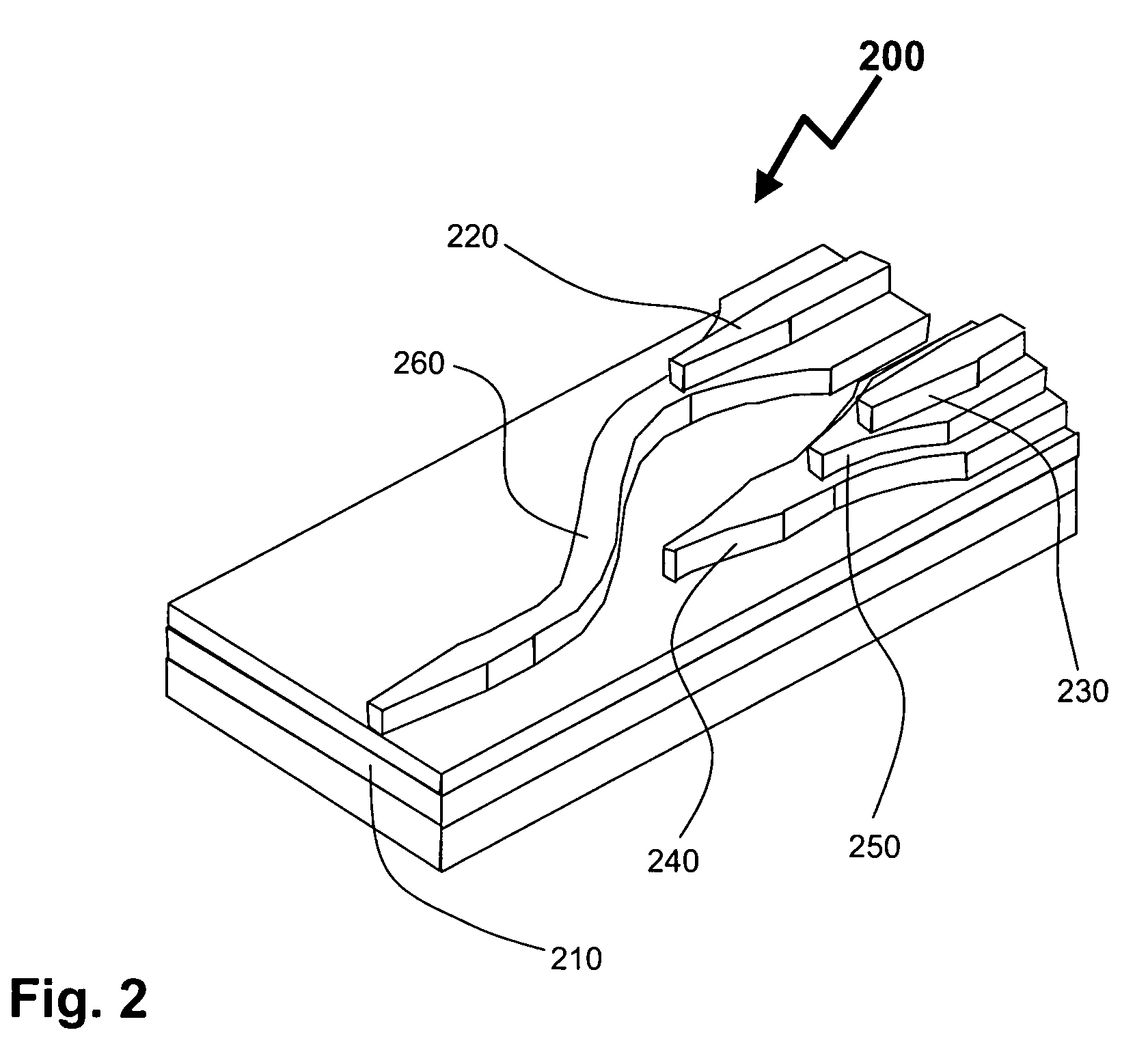
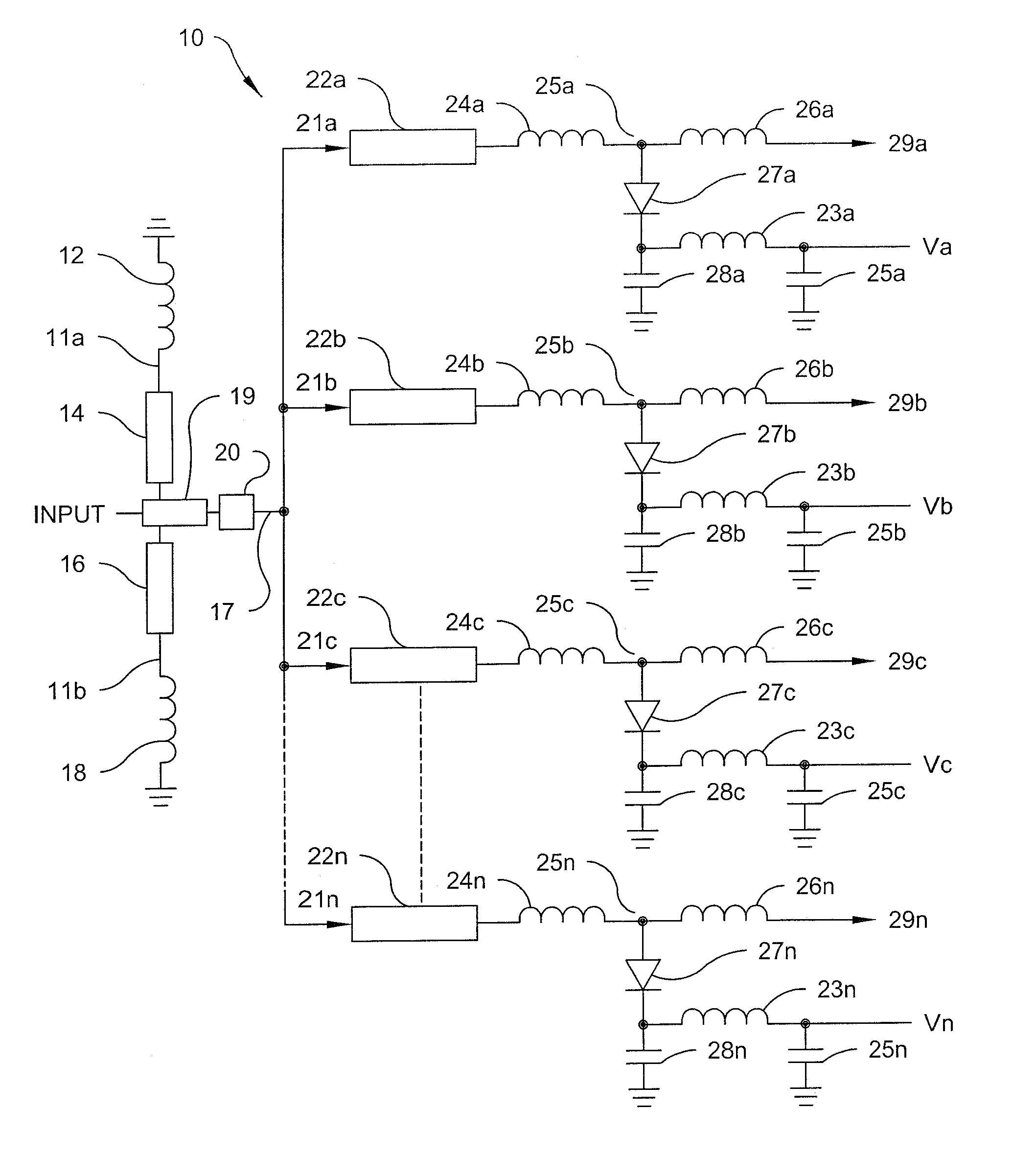
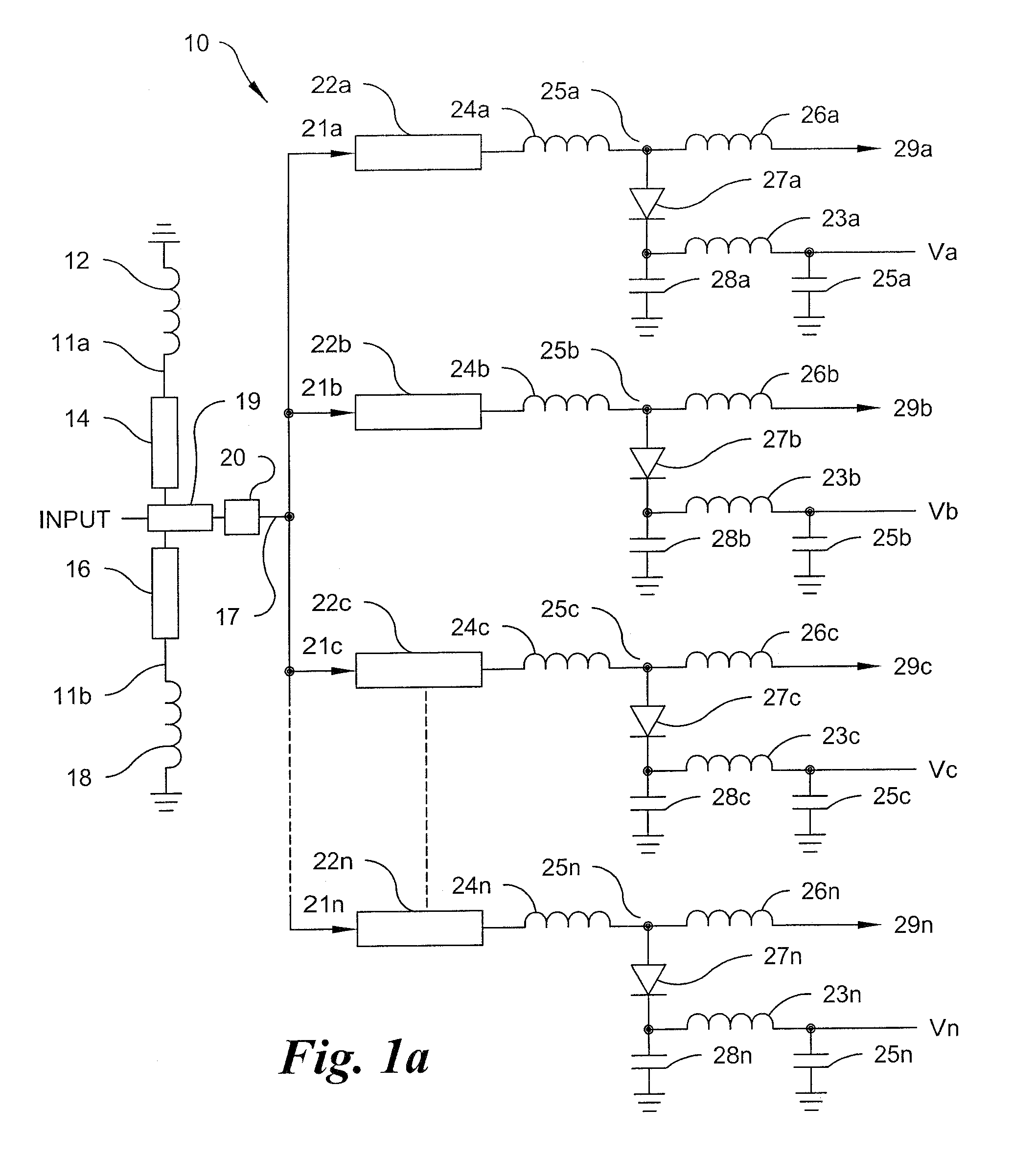
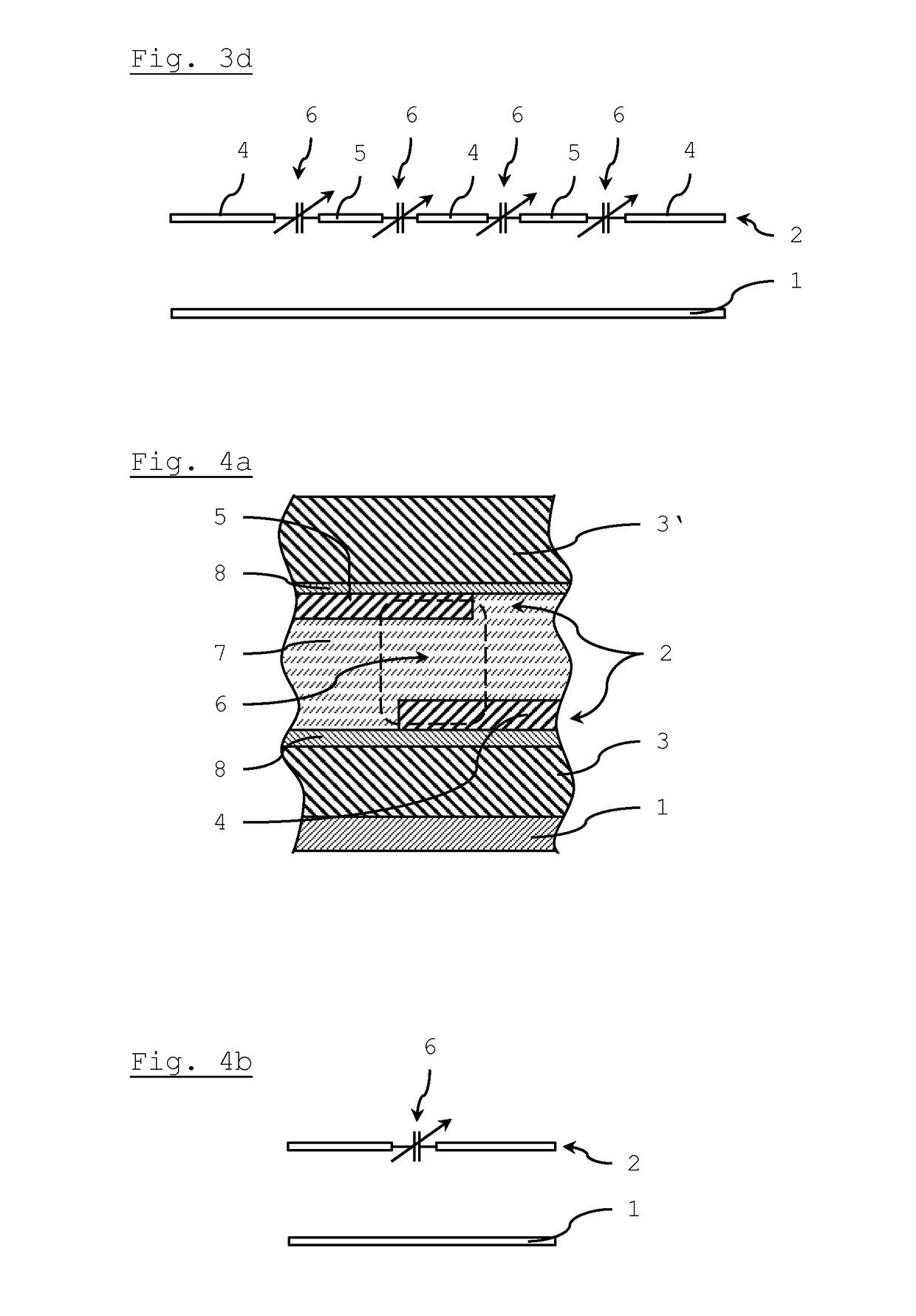
Multi-layered LC composite with a connecting pattern capacitively coupling inductors to ground
InactiveUS6504451B1Reduce the amount of solutionImprove insertion lossMultiple-port networksWaveguidesUltrasound attenuationCapacitance
A multi-layered LC composite component achieves greatly increased attenuation in the proximity of a central frequency without increasing insertion loss. In the arrangement of the multi-layered LC composite component, an end of each of inductor patterns is connected to a connecting pattern to be short-circuited. These inductor patterns define inductors. Frequency-adjusting capacitor patterns are opposed to open-circuited ends of the inductor patterns to define capacitors. As a result, the capacitors and the inductors define LC resonators. The connecting pattern is opposed to shield patterns via insulating sheets to define a common capacitor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Floating plate capacitor with extremely wide band low impedance
InactiveUS6272003B1Low inductanceImprove insertion lossAnti-noise capacitorsMultiple fixed capacitorsInsertion lossWide band
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Phase shift device
ActiveUS20150380789A1Easy and cost-saving fabricationFast and cheap fabricationCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricDelay linesMetal-insulator-metalElectricity
A phase shift device includes a planar transmission line that is formed by a signal electrode and a ground electrode which are separated by a dielectric substance, whereby the signal electrode of the planar transmission line is divided into several pieces and includes overlapping areas of adjacent pieces that are filled with a tunable liquid crystal material, thereby forming a dielectric tunable component (varactor) with a metal-insulator-metal type capacitor. The several pieces of the signal electrode are arranged at two or more different distance levels with respect to the ground electrode. The tunable liquid crystal material is arranged as a continuous layer between several pieces of the signal electrode that are arranged at two different distance levels.
Owner:ALCAN SYST GMBH
Common mode filtering method and device
ActiveUS20100052820A1Improve insertion lossReduce etch areaMultiple-port networksWaveguidesDual modeEngineering
Provided are common mode filtering method and device for use with a defected ground structure, the device including a substrate, coupled microstrip lines formed on the substrate and a ground plane formed underneath the substrate, the common mode filtering method being characterized by forming at least a defected ground structure on the ground plane and making dual mode signals pass through the coupled microstrip lines, thereby using the defected ground structure to suppress dual model noises within a specific frequency band and prevent signal distortion.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Optical element, optical drop module, optical add-drop module, and tunable light source
InactiveUS20050013000A1High speed responsePromote growthNon-linear opticsOptical elementsRefractive indexTransparent conducting film
An optical element has a structure in that a first mirror stack layer is formed on a substrate. A first transparent conductive film, a conductive buffer layer, a spacer layer having a primary or secondary electrooptic effect, a conductive buffer layer and a second transparent conductive film are stacked thereon in succession; and a second mirror stack layer is further formed thereon. A voltage is applied between the first and second transparent conductive films. The applied voltage change the refractive index of the spacer, changes a wavelength to be transmitted through or reflected from the layer.
Owner:SANTEC
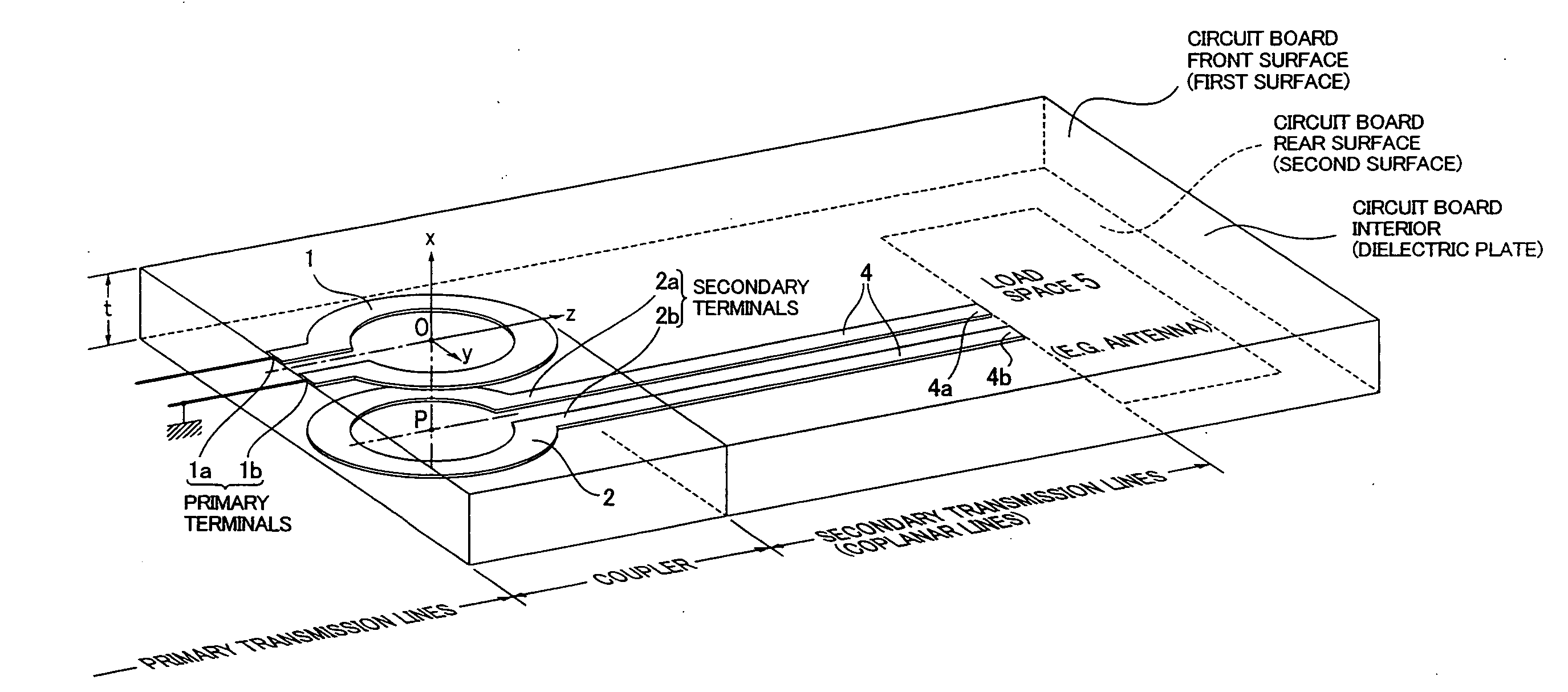
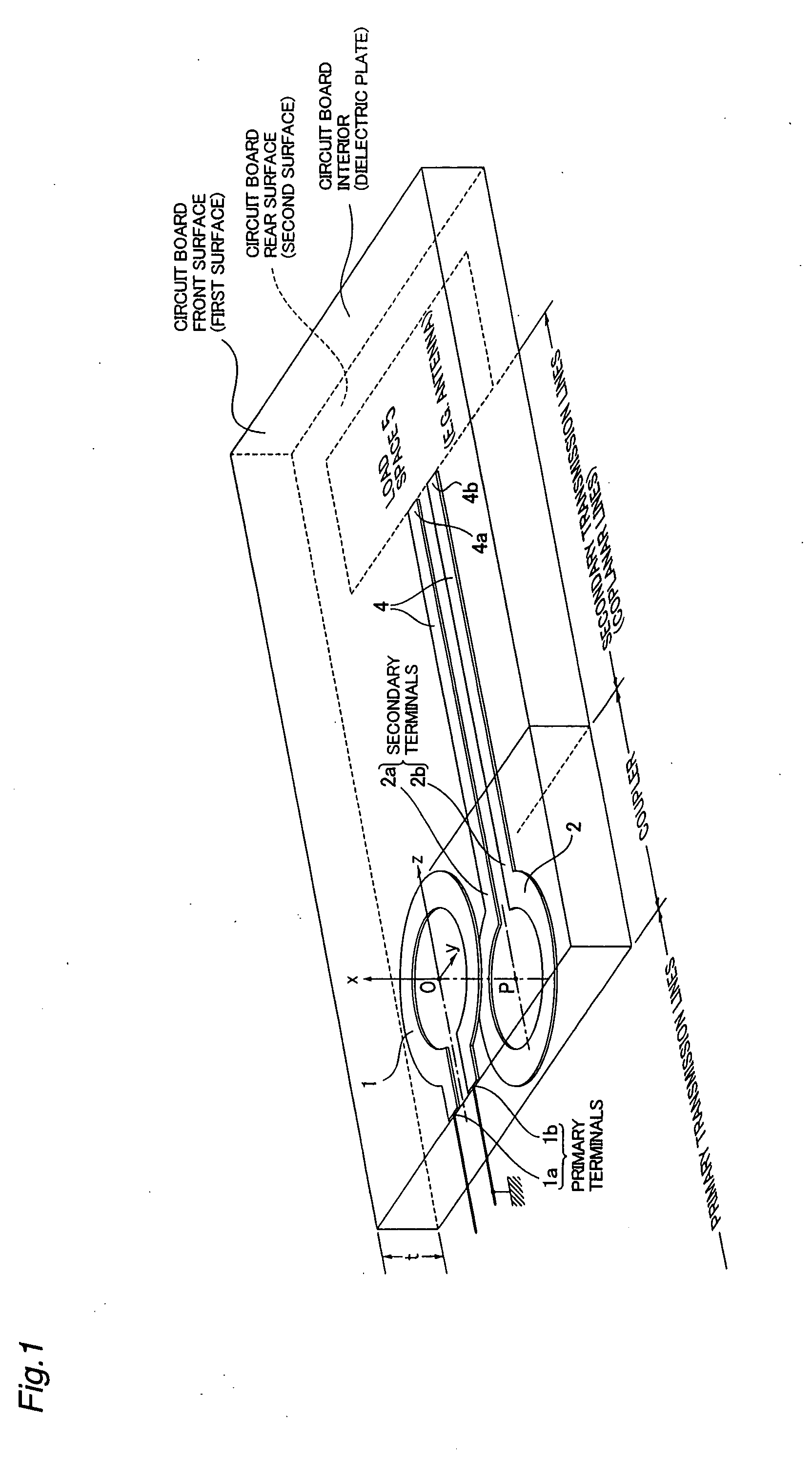
Planar coupler and integrated antenna system
InactiveUS20070229368A1Reduce manufacturing costSmall sizeSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectromagnetic couplingDielectric plate
Owner:HATA HIROSHI +2
Phase Shifter with Photonic Band Gap Structure Using Ferroelectric Thin Film
InactiveUS20080116995A1Improve insertion lossImproved loss return loss characteristicMultiple-port networksDelay linesPhotonic bandgapFerroelectric thin films
Provided are a phase shifter with a photonic band gap (PBG) structure using a ferroelectric thin film. The phase shifter includes a microstrip transmission line acting as a microwave input / output line and a plurality of tunable capacitors arranged in the microstrip transmission line at regular intervals. Electrodes disposed on a substrate apply DC voltages to the plurality of tunable capacitors. Radio frequency (RF) chokes and quarter wavelength radial-stubs are connected between the electrodes and the microstrip transmission line in order to prevent high frequency signals from flowing into a DC bias terminal. A plurality of PBGS are periodically arrayed on a ground plane of the substrate.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Combined waveguide
ActiveCN104241794AResolve connection matchReduce processing difficultyCoupling devicesWaveguideProcessing cost
The invention discloses a combined waveguide. The combined waveguide is formed by a gap waveguide and a rectangular waveguide in a horizontal or vertical transferring mode, or the combined waveguide is formed by a gap waveguide and a micro-strip line in a horizontal transferring mode. According to the combined waveguide, the effect of connecting and matching of the gap waveguide and the rectangular waveguide or the micro-strip line in the transferring process is achieved, and the gap waveguide can be applied to an existing high-frequency circuit structure; in comparison with the mode of adopting a traditional transmitting line, the loss of a system can be reduced, the transmitting efficiency is improved, the processing difficulty of a circuit is lowered, the processing cost is reduced, and the insertion loss of the system is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Surface Acoustic Wave Device and Communication Device
ActiveUS20100259341A1Improve clarityStrong vibrationImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringSurface acoustic wave
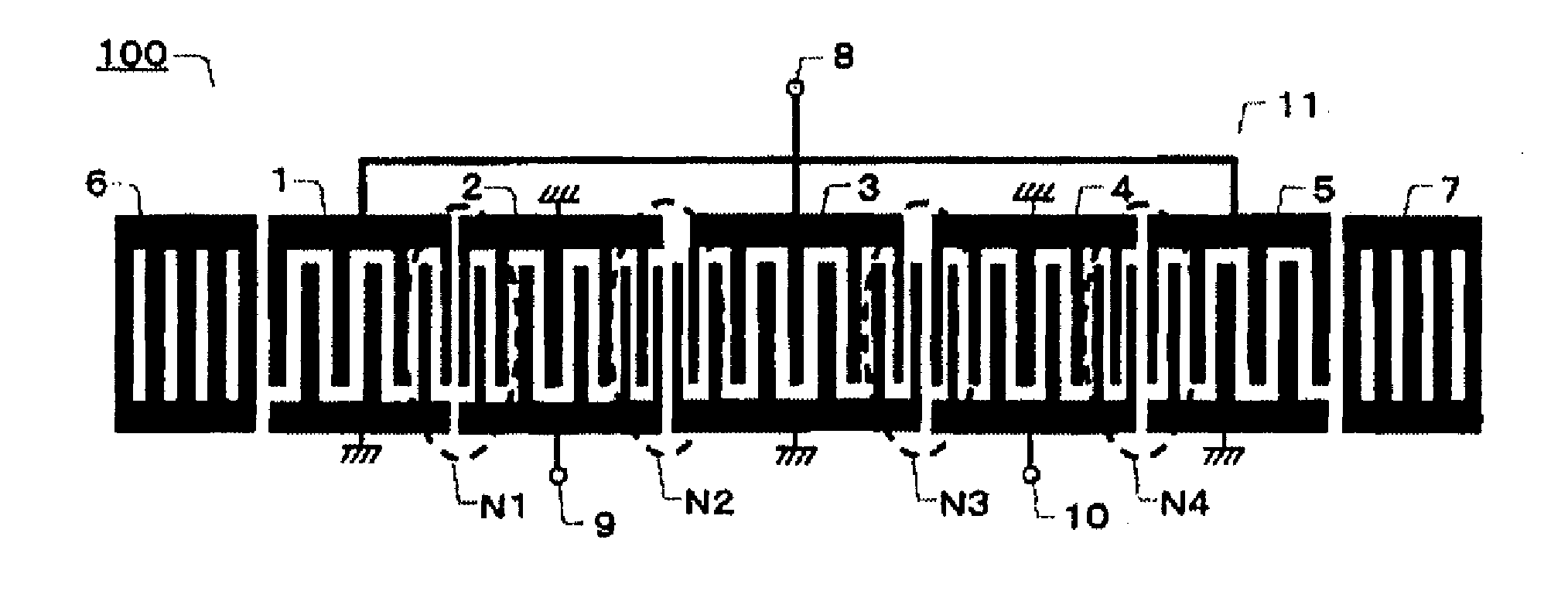
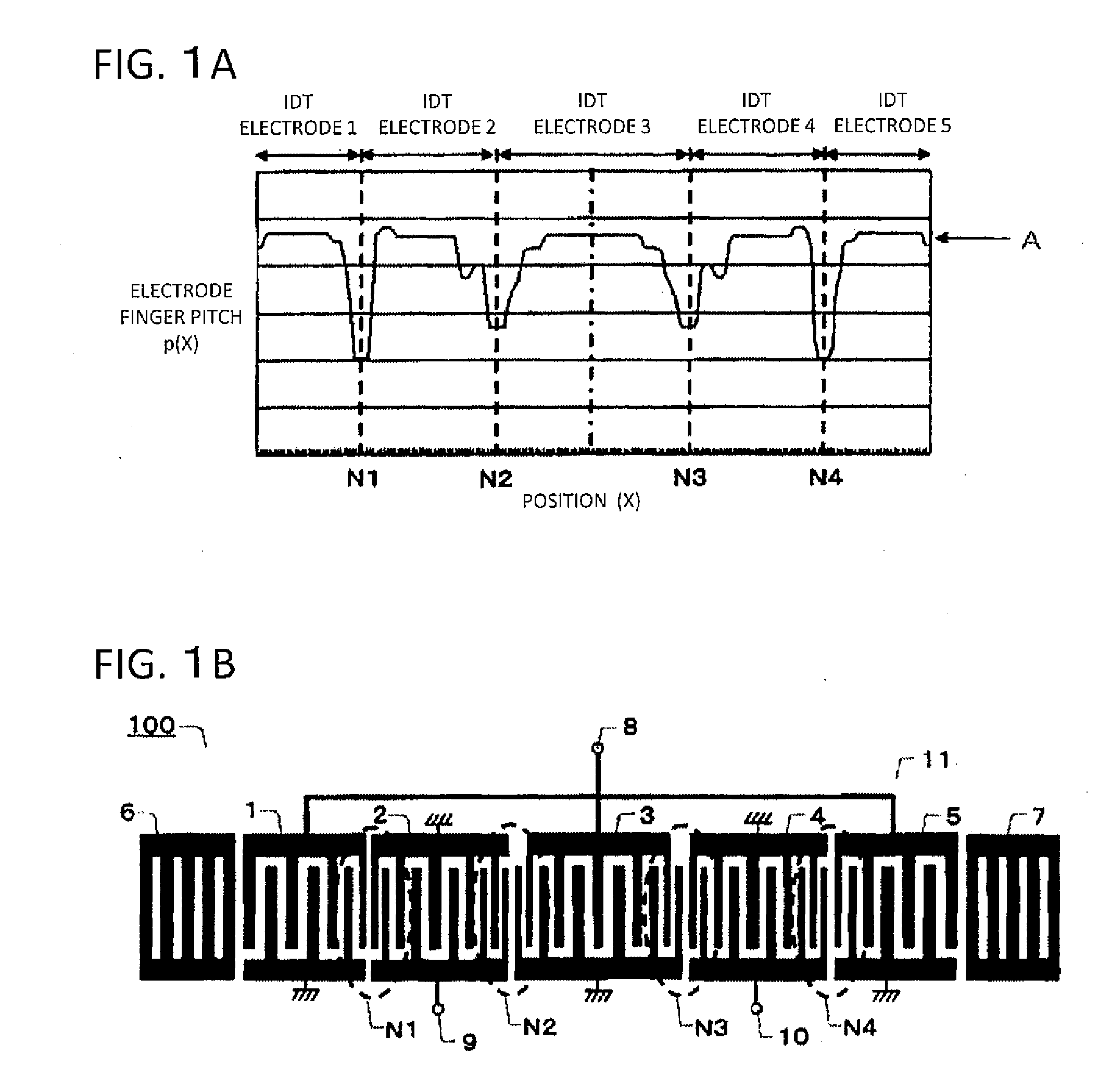
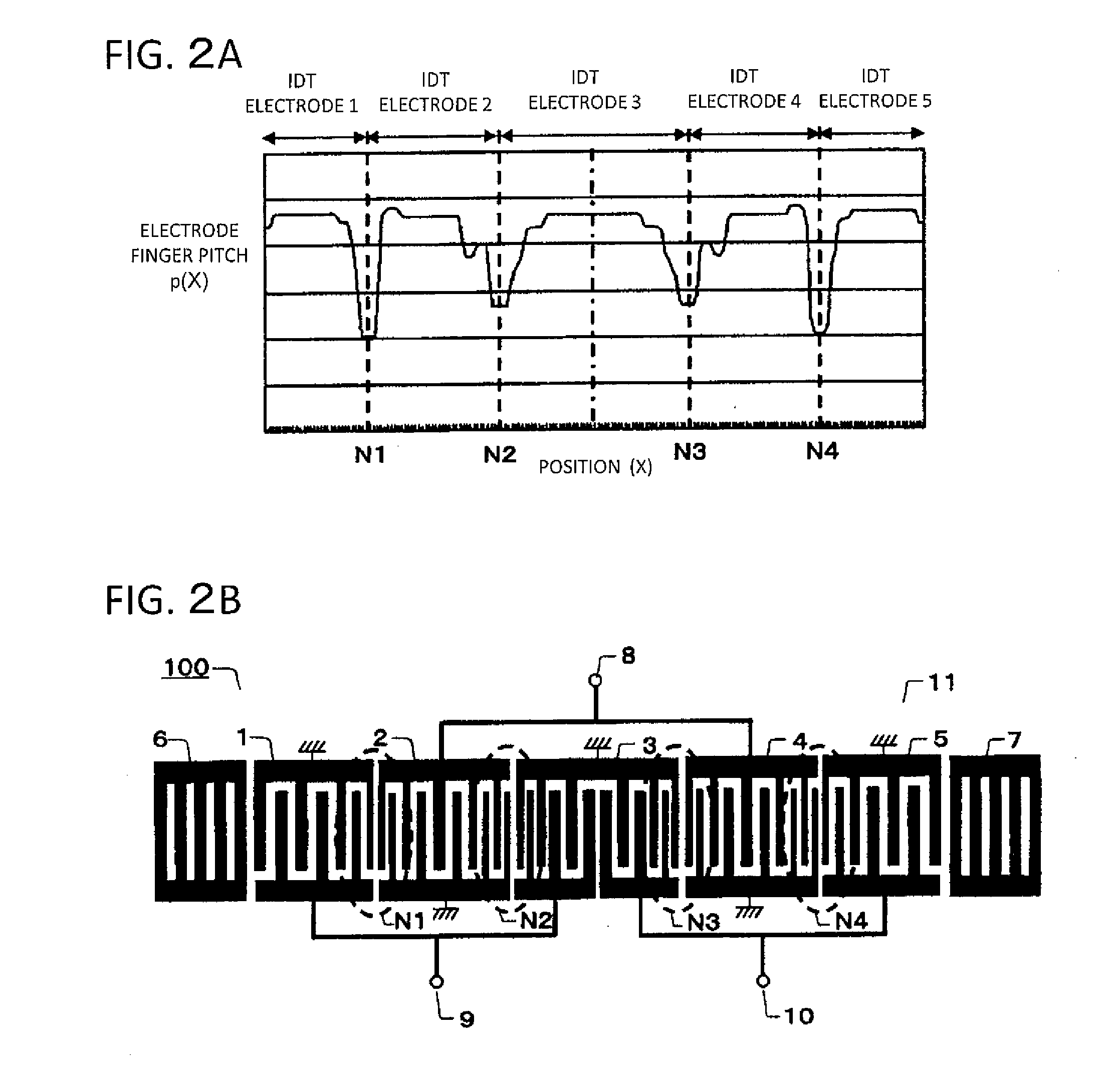
To provide a communication apparatus and a SAW device wherein the steepness in the vicinity of the outside of the lower frequencies of a passband can be improved. On a piezoelectric board 100, a SAW element 11 is formed which has first to fifth IDT electrodes 1-5 and reflector electrodes 6,7 with first to fourth electrode-finger narrow-pitch portions N1-N4 being formed in the respective ones of adjoining portions of the respective first to fifth IDT electrodes 1-5. An unbalanced signal terminal 8 and balanced signal terminals 9,10 are connected to the SAW element 11. The electrode finger pitches of the first to fourth electrode-finger narrow-pitch portions N1-N4 are formed symmetrically with respect to the third central IDT electrode 3 in such a manner that the electrode finger pitch of the first electrode-finger narrow-pitch portion N1 is narrower than that of the second electrode-finger narrow-pitch portion N2, while the electrode finger pitch of the fourth electrode-finger narrow-pitch portion N4 is narrower than that of the third electrode-finger narrow-pitch portion N3.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Integrated optics arrangement for wavelength (De)multiplexing in a multi-grade vertical stack
ActiveUS20080138008A1No longer transmittedEfficiently transitionWavelength-division multiplex systemsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransceiverWaveguide photodetector
The invention describes an integrated-photonics arrangement, implementable in a multi-guide vertical integration structure composed from III-V semiconductors and grown in one epitaxial growth run, that allows for vertical and lateral splitting of optical signals co- or bi-directionally propagating in the common passive waveguide into plurality of the vertically integrated passive or active wavelength-designated waveguides, therefore, enabling the wavelength-designated waveguides operating in different wavelengths to be monolithically integrated onto the same substrate and connected to the shared passive waveguide. In the exemplary embodiments of the invention, two active wavelength-designated waveguides, each of which either laser or photodetector, are vertically integrated with a common passive waveguide connected to the input / output optical port shared by both operating wavelengths, to form a single-fiber, two-wavelength receiver (both wavelength-designated waveguides are waveguide photodetectors) or transmitter (both wavelength-designated waveguides are edge-emitting semiconductor injection lasers) or transceiver (one wavelength-designated waveguide is waveguide photodetector and the other—edge-emitting semiconductor injection laser). Advantageously to the previous art, the proposed vertical splitting and lateral routing allows for a reduced footprint size while greatly improving design flexibility and / or device performance.
Owner:ONECHIP PHOTONICS
Integrated optics arrangement for wavelength (De)multiplexing in a multi-grade vertical stack
ActiveUS7444055B2Efficiently transitionImprove insertion lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMultiplexingTransceiver
The invention describes an integrated-photonics arrangement, implementable in a multi-guide vertical integration structure composed from III-V semiconductors and grown in one epitaxial growth run, that allows for vertical and lateral splitting of optical signals co- or bi-directionally propagating in the common passive waveguide into plurality of the vertically integrated passive or active wavelength-designated waveguides, therefore, enabling the wavelength-designated waveguides operating in different wavelengths to be monolithically integrated onto the same substrate and connected to the shared passive waveguide. In the exemplary embodiments of the invention, two active wavelength-designated waveguides, each of which either laser or photodetector, are vertically integrated with a common passive waveguide connected to the input / output optical port shared by both operating wavelengths, to form a single-fiber, two-wavelength receiver (both wavelength-designated waveguides are waveguide photodetectors) or transmitter (both wavelength-designated waveguides are edge-emitting semiconductor injection lasers) or transceiver (one wavelength-designated waveguide is waveguide photodetector and the other—edge-emitting semiconductor injection laser). Advantageously to the previous art, the proposed vertical splitting and lateral routing allows for a reduced footprint size while greatly improving design flexibility and / or device performance.
Owner:ONECHIP PHOTONICS
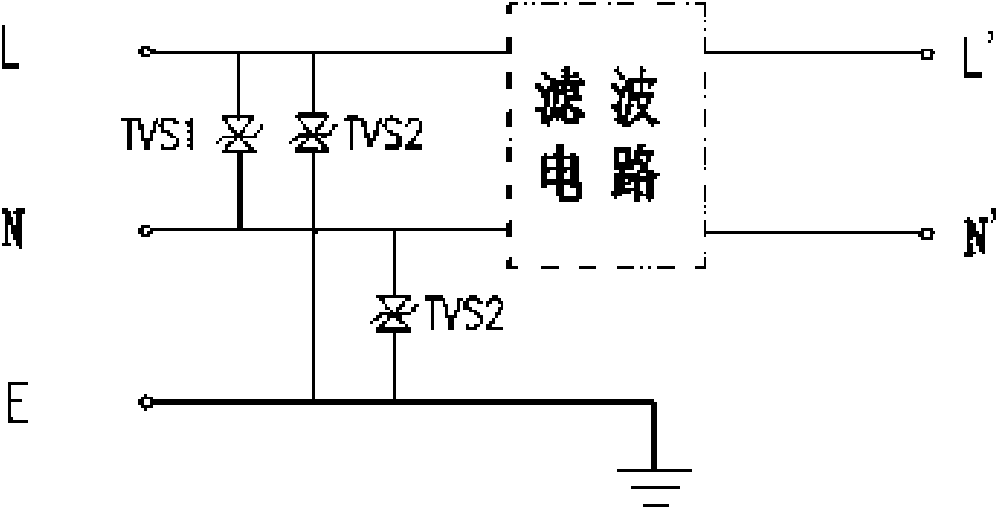
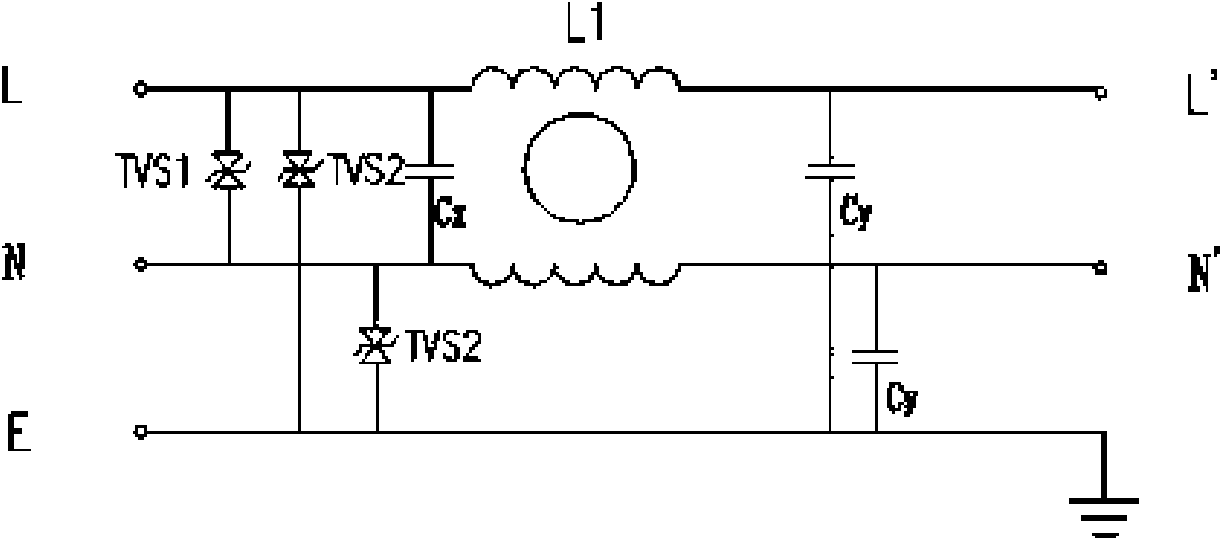
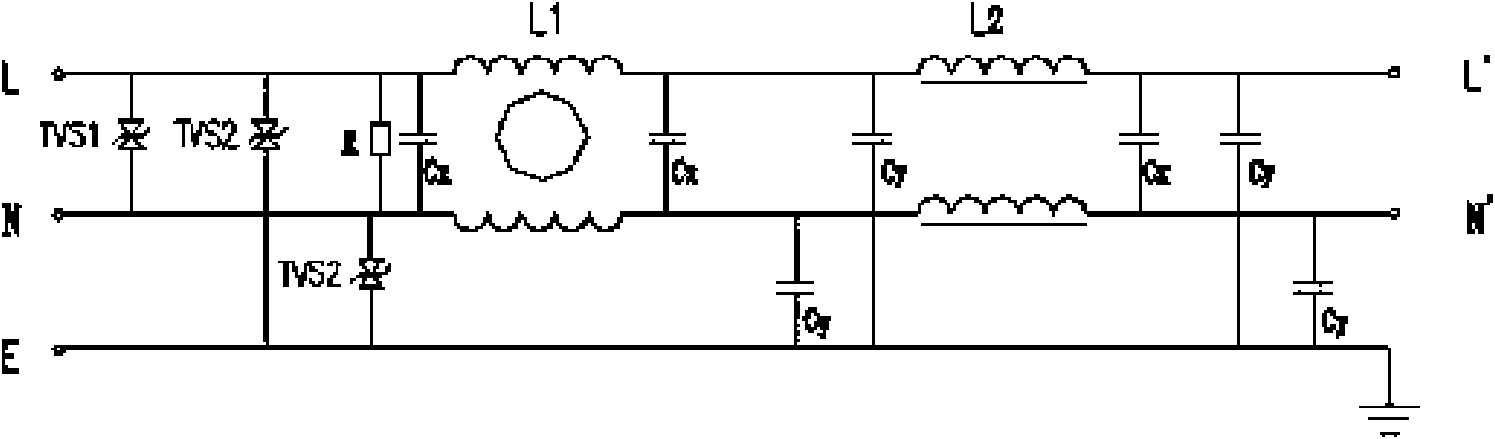
Transient state and stable state resisting combination interference power filter and design method thereof
InactiveCN101794999AReduce volumeQuick responseEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentHarmonic reduction arrangementStable stateTransient state
The invention relates to a power filter in a power filtering and protection technique, in particular to a transient state and stable state resisting combination interference power filter and a design method thereof. The power filter is characterized by at least comprising protection circuits and filter circuits, wherein the protection circuits are connected with the filter circuits in series; the filter circuits are packaged in a filter shell, which has a nickel-plated surface and is made of cold-rolled steel plates, at a constant temperature through epoxy resin; the filter circuits are type A, type U, type D and type F filter circuits; and the protection circuits are provided with TVS tubes on line-line and line-ground of input ends of the filter circuits respectively to form a line-line and line-ground transient protection module. The transient state and stable state resisting combination interference power filter not only has good common mode and difference mode filtering performance, but also can effectively inhibit surge interferences on a power line, and is particularly suitable for various types of direct current electronic devices having high requirements on CS116.
Owner:XIAN KAIRONG ELECTRONICS TECH
Aim satellite and data receiving circuit for satellite communication receiver
InactiveCN102013897AEasy to work with starsHigh sensitivityTransmissionLow-pass filterIntermediate frequency
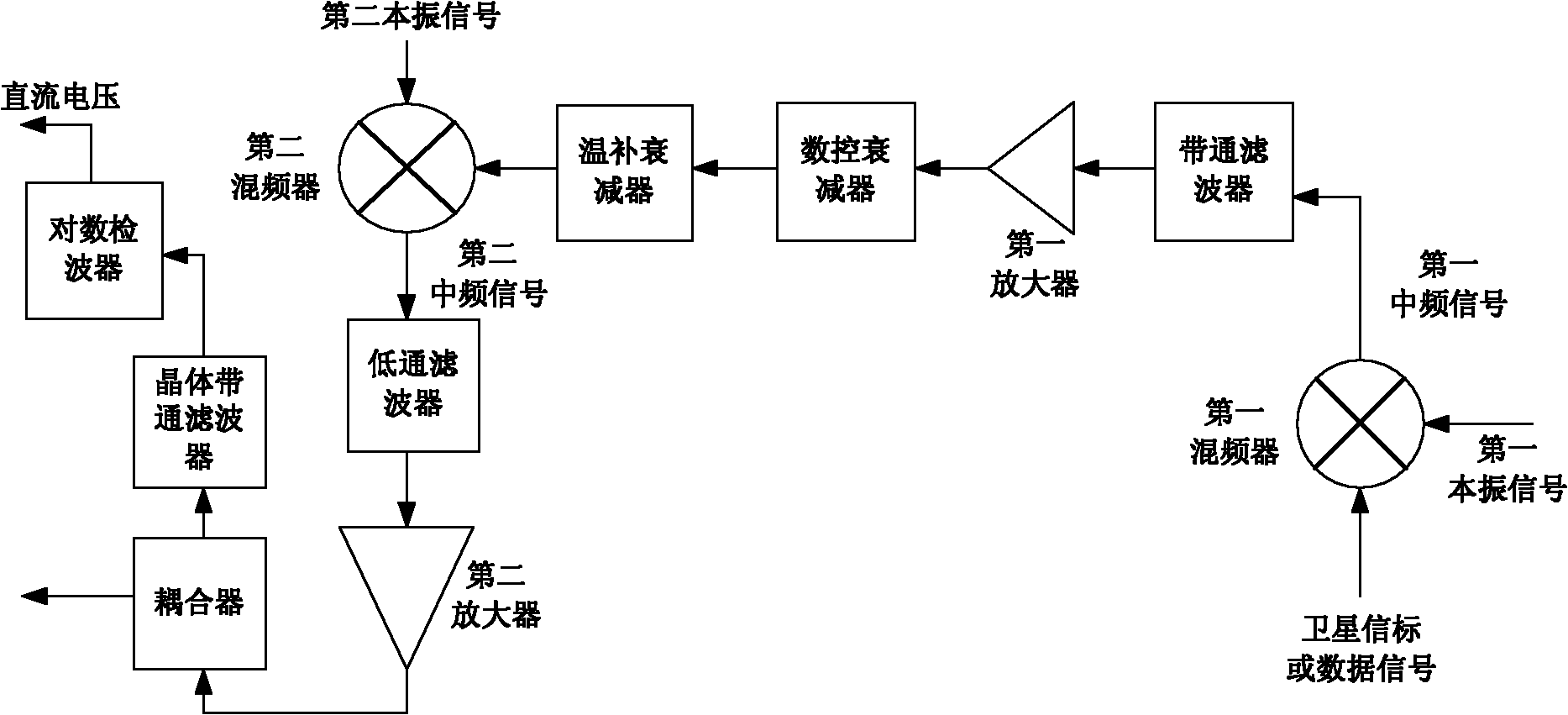
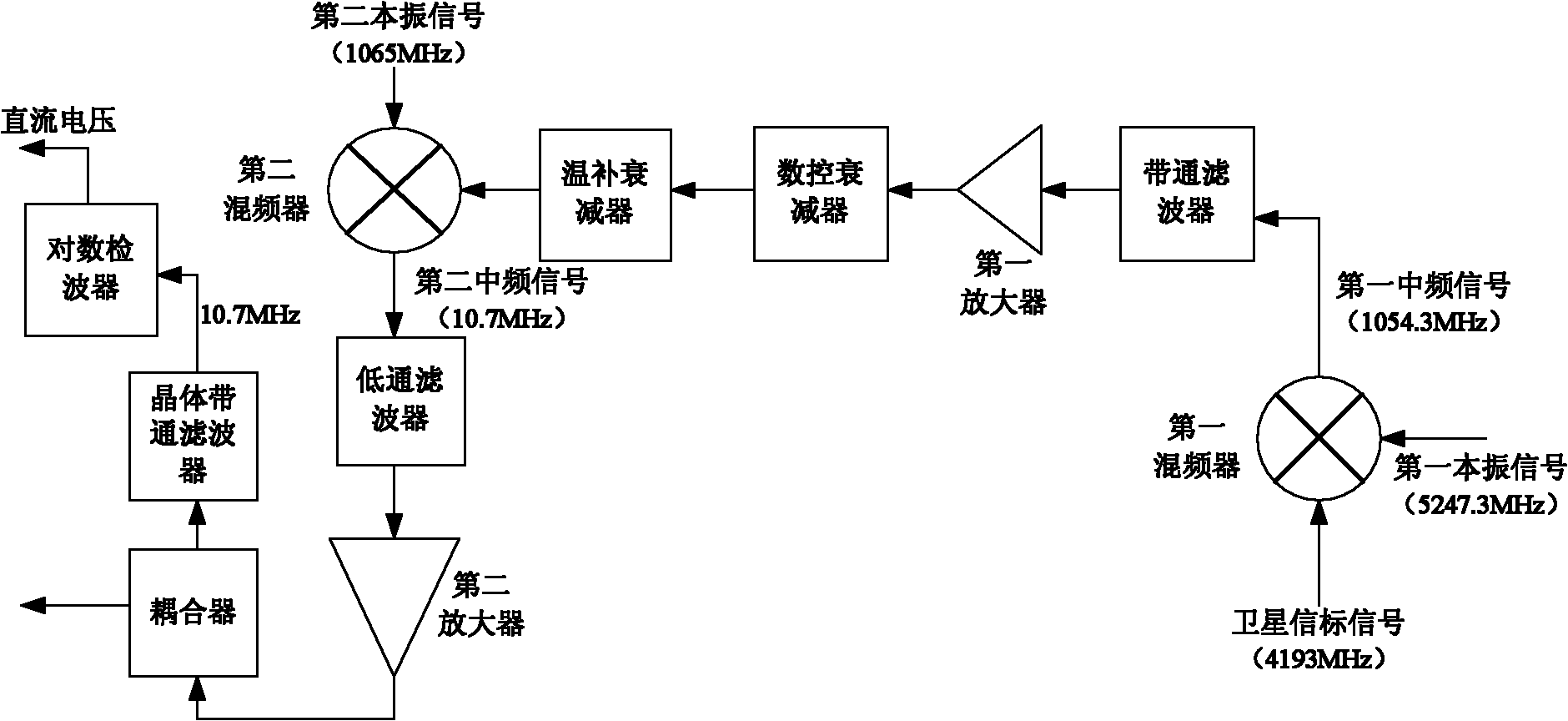
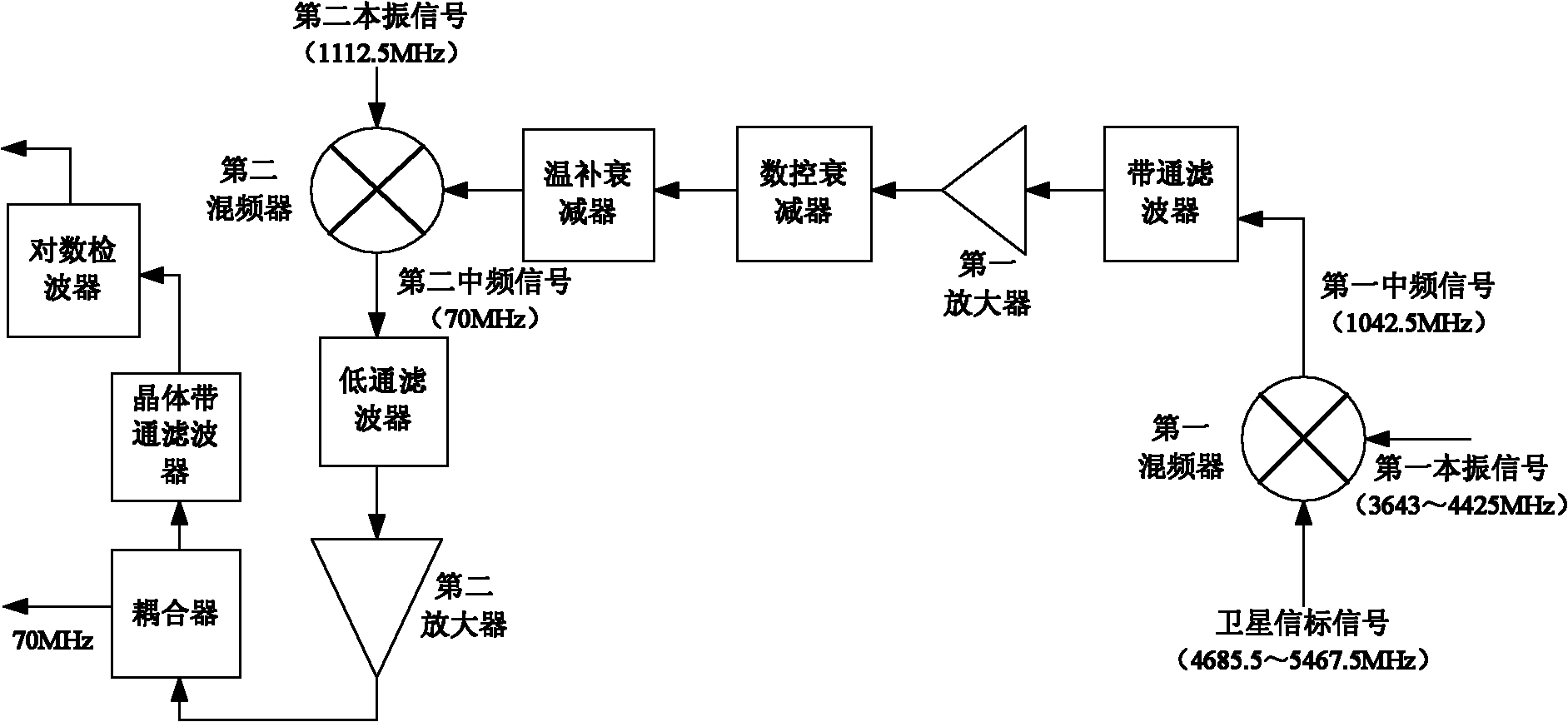
The invention discloses an aim satellite and data receiving circuit for a satellite communication receiver, belonging to the technical field of electronic communication. A satellite beacon signal or data signal is subject to down-conversion by a first mixer so that a first intermediate-frequency signal is obtained; the first intermediate-frequency signal successively passes through a band-pass filter, a first amplifier, a numeral control attenuator and a temperature-compensating attenuator, and then is subject to the down-conversion by a second mixer so that a second intermediate-frequency signal is obtained; and after the second intermediate-frequency signal successively passes through a low pass filter and a second amplifier, a one-way signal is output by the through output end of a coupler to be used for subsequent processing, and the other one-way signal is output by the coupling end of the coupler is filtered by a crystal band-pass filter and then is converted into a direct current voltage signal by a logarithmic detector. In the invention, the detector is arranged in the receiver so that the beacon signal is converted into a direct current voltage convenient for measurement, thereby being convenient for finishing aim satellite in the wild; and when the aim satellite work is completed, the circuit can also be utilized to receive the data signal. The circuit disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of good sensitivity, dynamic range, small noise jamming and the like, and is convenient for carrying.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Waveguide interface
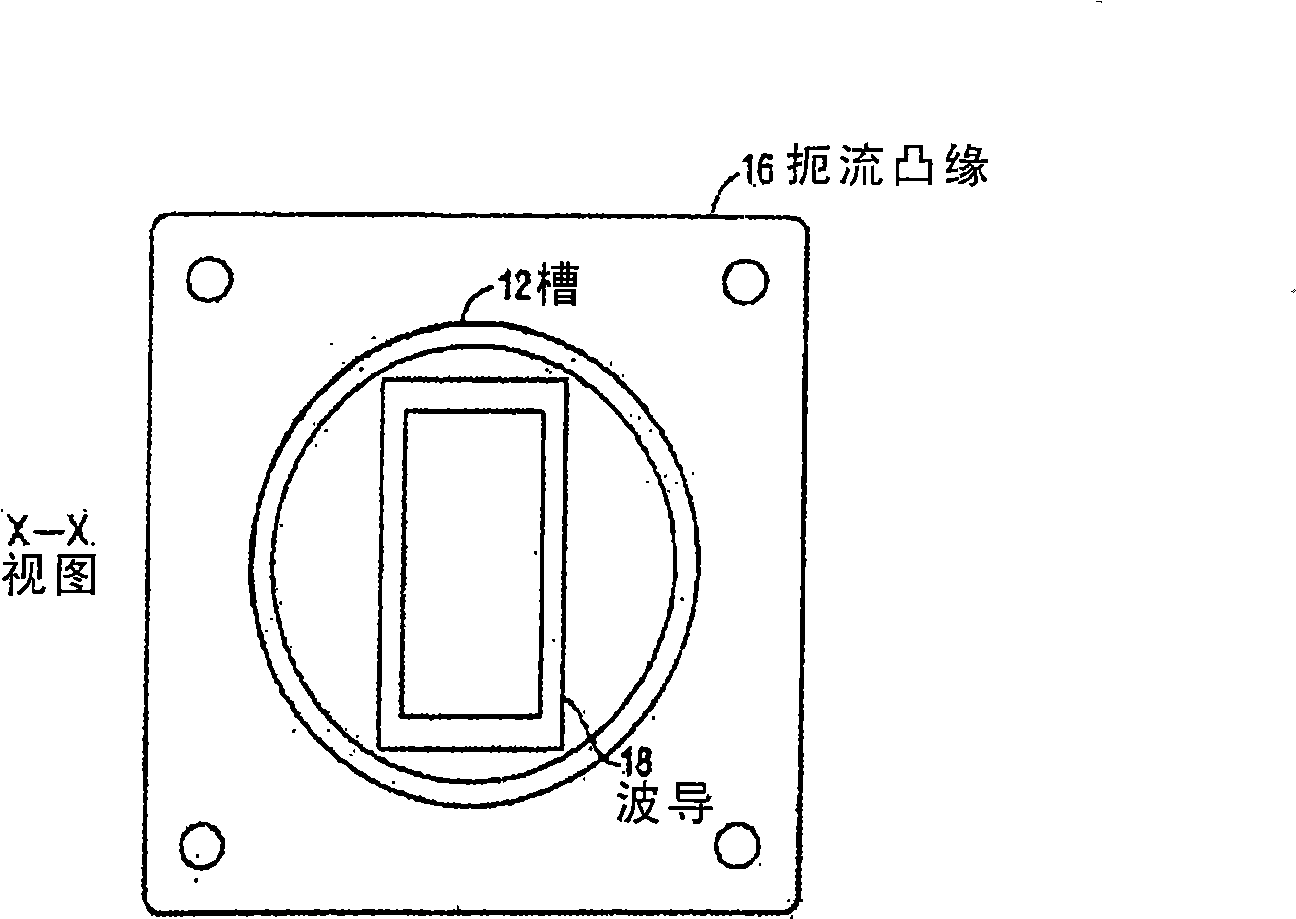
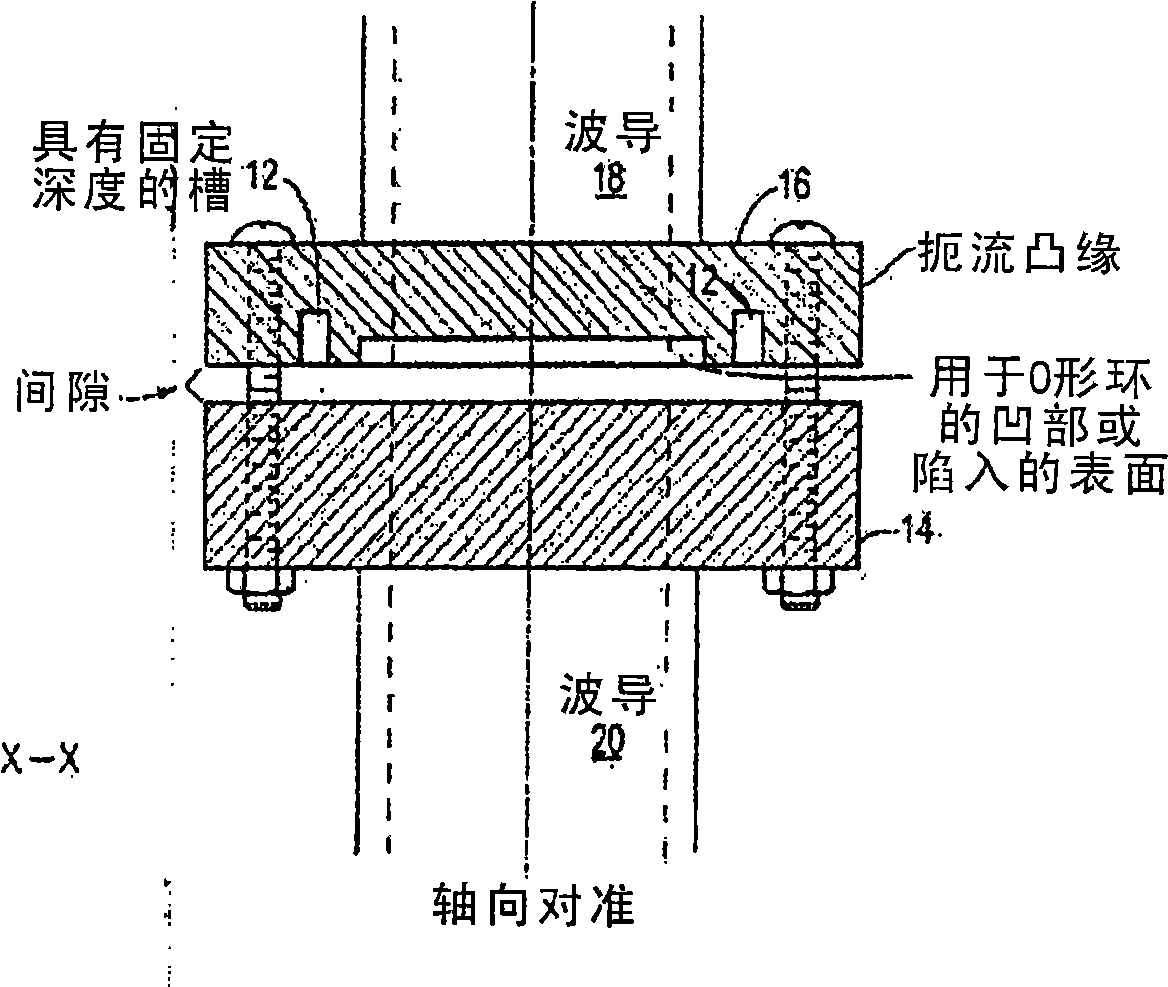
InactiveCN101485038ALow precision levelImprove insertion lossWaveguide type devicesElectricityEngineering
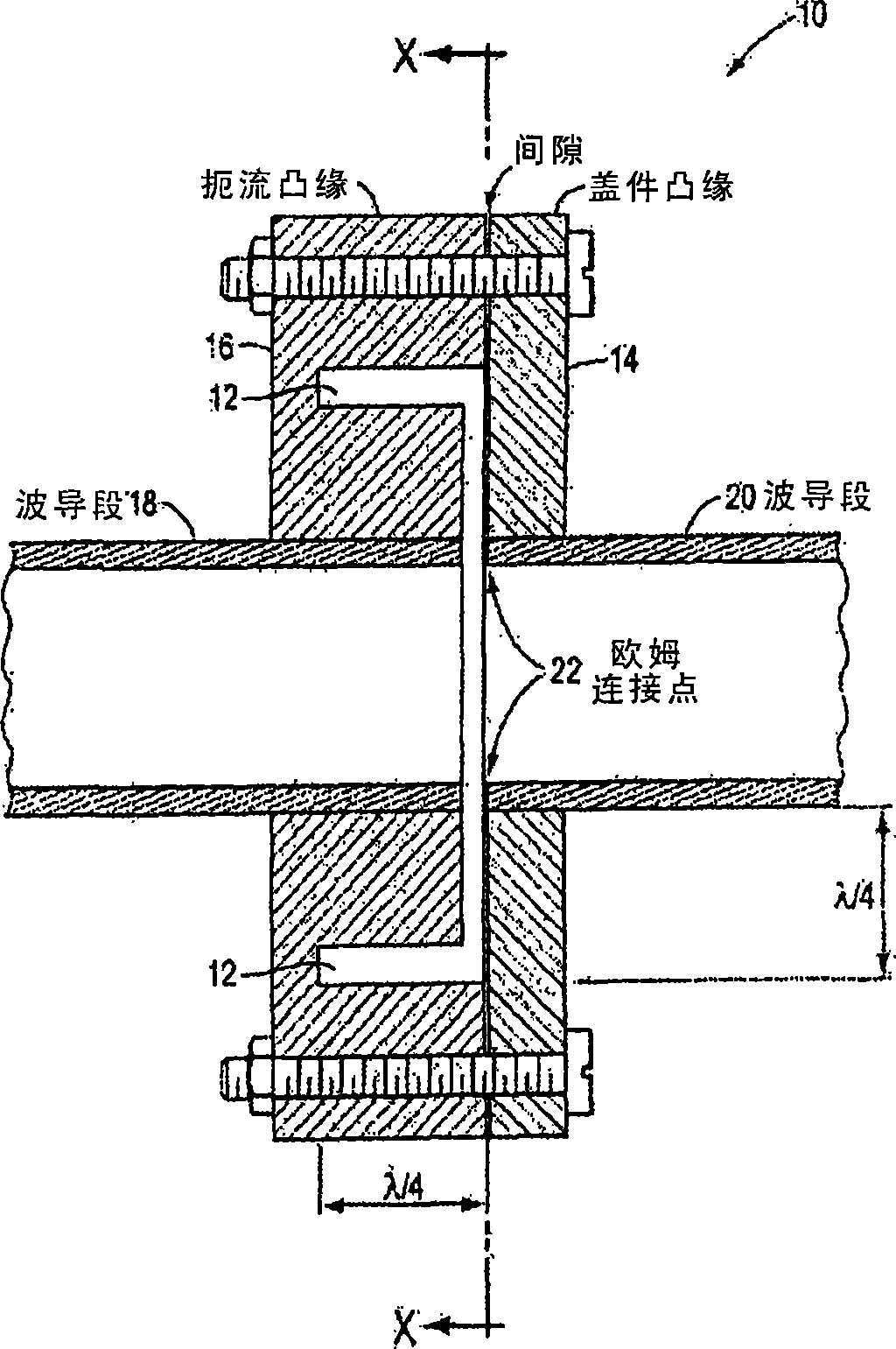
The present invention relates to a waveguide interface. Waveguide flanges for joining waveguide sections or components are designed to achieve mechanical strength and exhibit desired electrical properties such as low insertion loss and high return loss. The present invention contemplates waveguide interfaces with a choke flange designed to engage with a shield flange and provide a joint with improved electrical properties. The new choke designs produce a virtual continuity through the waveguide joints and minimize electrical energy leakage. The electrical and mechanical properties of the joint in the waveguide interfaces are robust and able to tolerate lower levels of parts precision, imperfect mating of the flanges without metal-to-metal contact and gaps up to 0.06'' or more between the mating flange surfaces.
Owner:HARRIS STRATEX NETWORKS OPERATING
Elastic wave filter, multiplexer, duplexer, high-frequency front end circuit, and communication device
A transmission filter includes five series resonators that include functional electrodes provided on a piezoelectric substrate, and connected in series with each other between a transmission input terminal and an antenna terminal, and parallel resonators. Frequency differences between the anti-resonant frequencies and the resonant frequencies of the series resonators other than the series resonator connected so as to be closest to the transmission input terminal and the series resonator connected so as to be closest to the antenna terminal are smaller than frequency differences of the series resonators, and anti-resonant frequencies of the series resonators are lower than the anti-resonant frequencies of the series resonators.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Ultra wide band rejection filter based on loading of multiple step impedance resonators
ActiveCN104091982AExpand stopband bandwidthReliable designWaveguide type devicesResonatorHigh impedance
The invention discloses an ultra wide band rejection filter based on loading of multiple step impedance resonators. The ultra wide band rejection filter comprises a double-faced copper-clad microstrip board. One end of a uniformity impedance resonator is connected with one end of an input end feeder line and one end of a first high impedance connecting line respectively, and the other end of the uniformity impedance resonator is open. The thin end of a microstrip line of the first step impedance resonator is connected with the other end of the first high impedance connecting line and one end of a second high impedance connecting line respectively, and the wide end of the microstrip line is open. The thin end of a microstrip line of the second step impedance resonator is connected with the other end of the second high impedance connecting line and an output end feeder line, and the wide end of the microstrip line is open. According to the ultra wide band rejection filter based on loading of the multiple step impedance resonators, the characteristic impedance of the uniformity impedance resonator and the two step impedance resonators is adjusted, so that the stop band range of the band rejection filter is greatly expanded.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
High-gain wideband microstrip patch antenna
ActiveCN107230840ALow costEasy to produceSubstantially flat resonant elementsMicrostrip patch antennaDielectric plate
The invention provides a high-gain wideband microstrip patch antenna. The high-gain wideband microstrip patch antenna comprises a floor, a dielectric plate arranged on the floor and a main radiation patch, wherein the main radiation patch is positioned at the position with the distance of Hp above the ground, and is in a rectangular shape; a top parasitism patch is arranged at the position with the distance of Hs above the main radiation patch, and is in the rectangular shape as well; four rectangular horizontal parasitism patches are arranged at the positions with the distances of Dp on the outer side of the peripheral edge of the main radiation patch, the heights of the four rectangular horizontal parasitism patches from the floor are Hc, and the lengths and widths of the four rectangular horizontal parasitism patches are Ls and Ws; and a feeding point is arranged on the main radiation patch, and is connected to a feeding network of the dielectric plate. Namely, a distance is reserved between the main radiation patch and the floor, and a distance is reserved between the top parasitism patch and the main radiation patch. A base station antenna which is high in gain, wide in band, dual in polarization, low in sidelobe or free of sidelobe, high in cross polarization, high in isolation, wide in wave beam, miniaturized, low in profile, low in cost and easy to produce is provided for micro cellular mobile communication.
Owner:TONGYU COMM INC
Optical bandpass filter based on double microring-Mach Zehnder interference structure
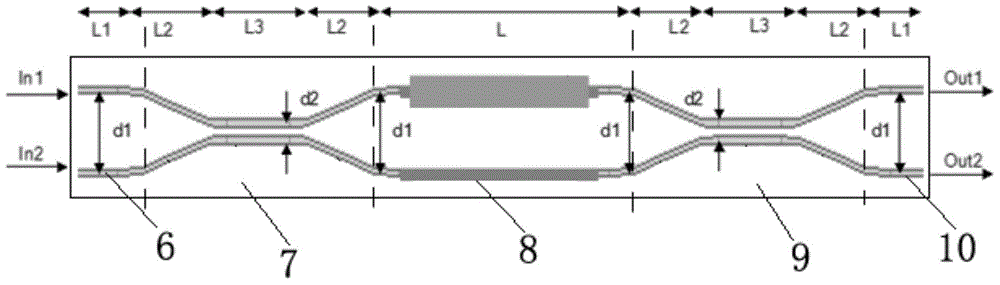
ActiveCN106371174AChanging the resonance wavelengthAchieving tunabilityOptical light guidesBandpass filteringGrating
The invention discloses an optical bandpass filter based on a double microring-Mach Zehnder interference structure. The optical bandpass filter is composed of a first multi-mode interference coupler, a second multi-mode interference coupler, a third multi-mode interference coupler, a first coupling grating, a second coupling grating, a first heating electrode, a second heating electrode, a third heating electrode, a fourth heating electrode, a first upload-download type micro ring, and a second upload-download type micro ring. According to the invention, on the basis of the design of the coupling states of two upload-download type micro rings, fully destructive interference is introduced based on a cascaded adjustable Mach Zehnder interference (MZI) structure; amplitude regulation is realized by adjusting the bias voltage on the heating electrode of the MZI1, so that amplitudes of passband external light signals of an upper arm and a lower arm becomes identical; and phase regulation is realized by adjusting the bias voltage on the heating electrode of the MZI2, so that phases of passband external light signals of the upper arm and the lower arm are opposite. Therefore, the extinction ratio of the filter increases under the circumstance that the passband insertion loss is not increased. The provided optical bandpass filter has advantages of narrow bandwidth, high extinction ratio, and low insertion loss.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Piezoelectric acoustic wave resonator, piezoelectric acoustic wave filter, duplexer and radio frequency communication module
ActiveCN108649920AImprove performanceImproved Lateral Path ImpedanceImpedence networksResonatorInsertion loss
The invention provides a piezoelectric acoustic wave resonator. The shape of an effective working area of the piezoelectric acoustic wave resonator is a polygon, a first side and a second side in theeffective working area correspond to an input side and an output side of the piezoelectric acoustic wave resonator respectively, and an outer frame of the effective working area is defined as a rectangle which can surround the effective working area and has the smallest area where one side coincides with the first side or the second side; one side of the outer frame that coincides with the first side or the second side has a first length, one side of the outer frame that is perpendicular to the side has a second length, and the ratio range of the first length to the second length is 1-4; and the ratio range of the sum of the lengths of the first side and the second side to the circumference of the effective working area is 0.4-0.7, wherein the ratio ranges of the lengths of the first sideand the second side to the circumference of the effective working area are both 0.2-0.35. The invention also provides a piezoelectric acoustic wave filter, a duplexer and a radio frequency communication module. Through the implementation of the invention, the electrical transmission loss of the piezoelectric acoustic wave resonator can be improved, and the insertion loss of the piezoelectric acoustic wave filter can be further improved.
Owner:SUZHOU HUNTERSUN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
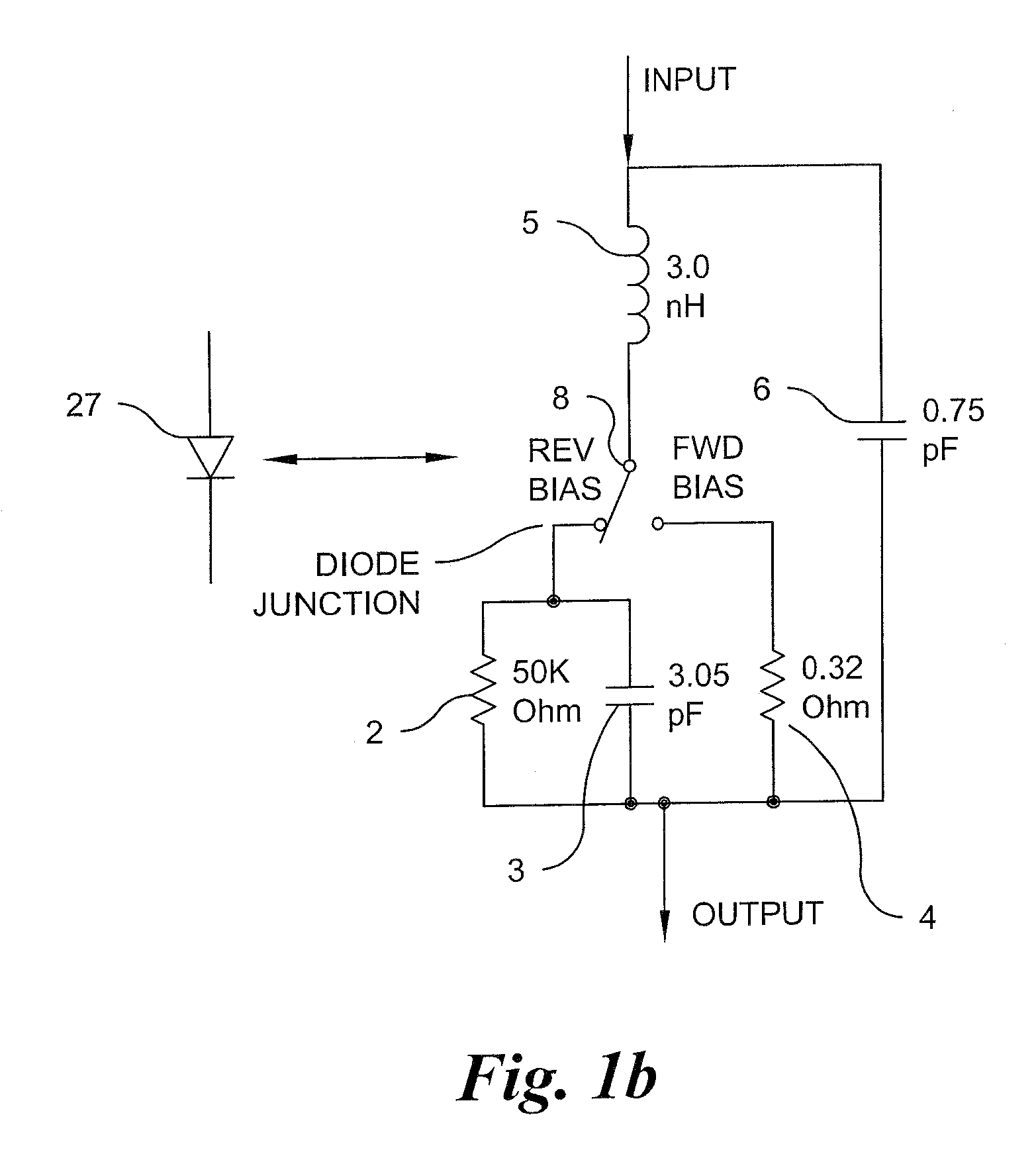
High power uhf single-pole multi-throw switch
ActiveUS20100289597A1Low insertion lossImprove insertion lossCoupling devicesEngineeringHigh pressure
A single pole multiple-throw switch for switching an RF signal to one of a plurality of outputs includes coupling the signal to a throw junction, said junction having connected thereto a plurality of switch legs, each leg includes a high voltage shunt diode spaced one quarter-wavelength from the throw junction; each diode mounted at its cathode end to a capacitor and adapted to receive a bias; wherein a controller applies a first DC bias to a selected one of the diodes to cause the selected diode to operate in reverse bias mode, such that the selected diode mounted on the corresponding capacitor provides a low insertion loss to pass the RF signal from the transmission line through the selected leg and to one of the outputs; and applies a second DC bias to the other diodes to cause the other diodes to operate in forward bias mode such that the other diodes mounted onto the corresponding capacitor provides a high insertion loss for blocking the RF signal to the remaining outputs.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
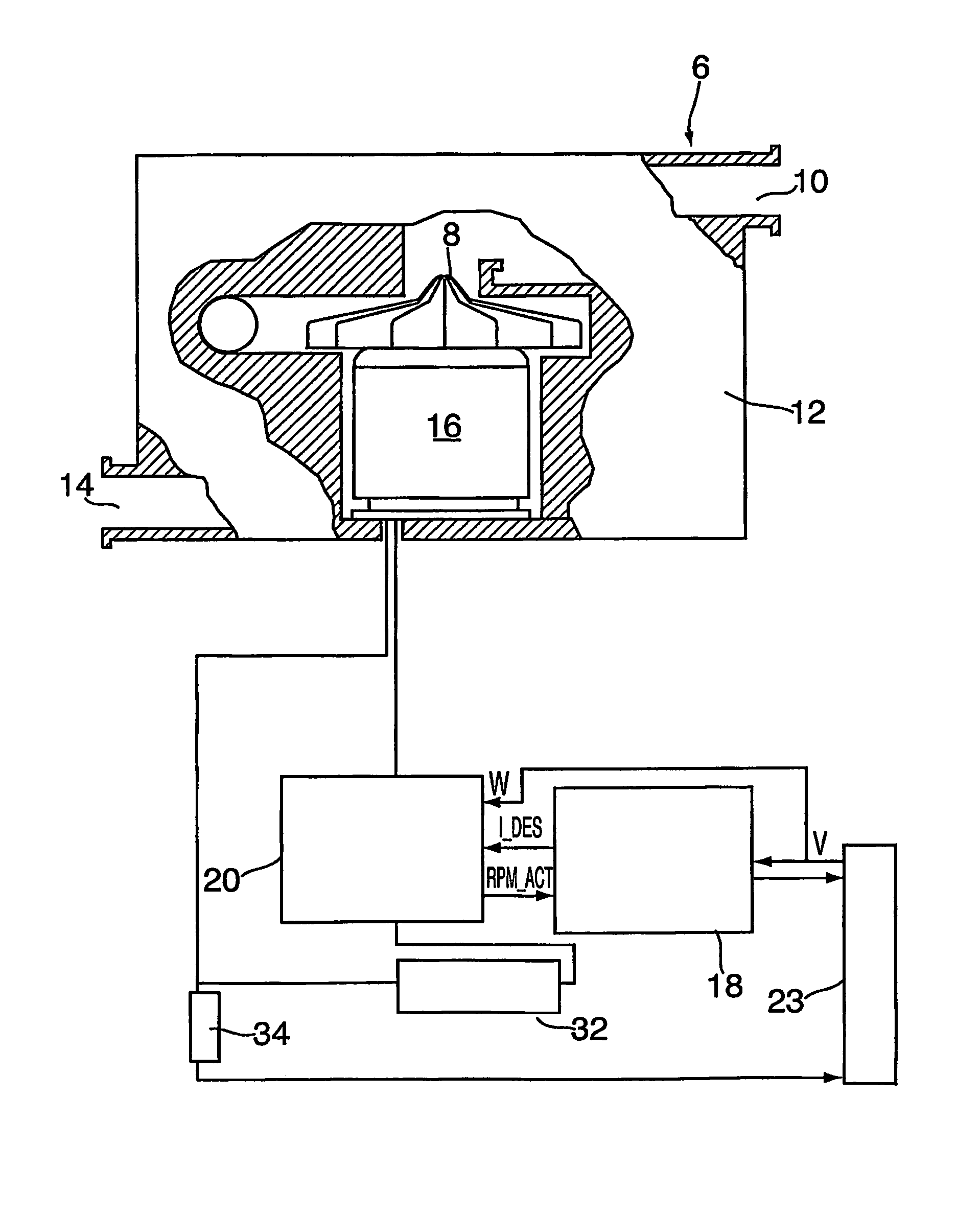
Using motor speed in a PAP device to estimate flow
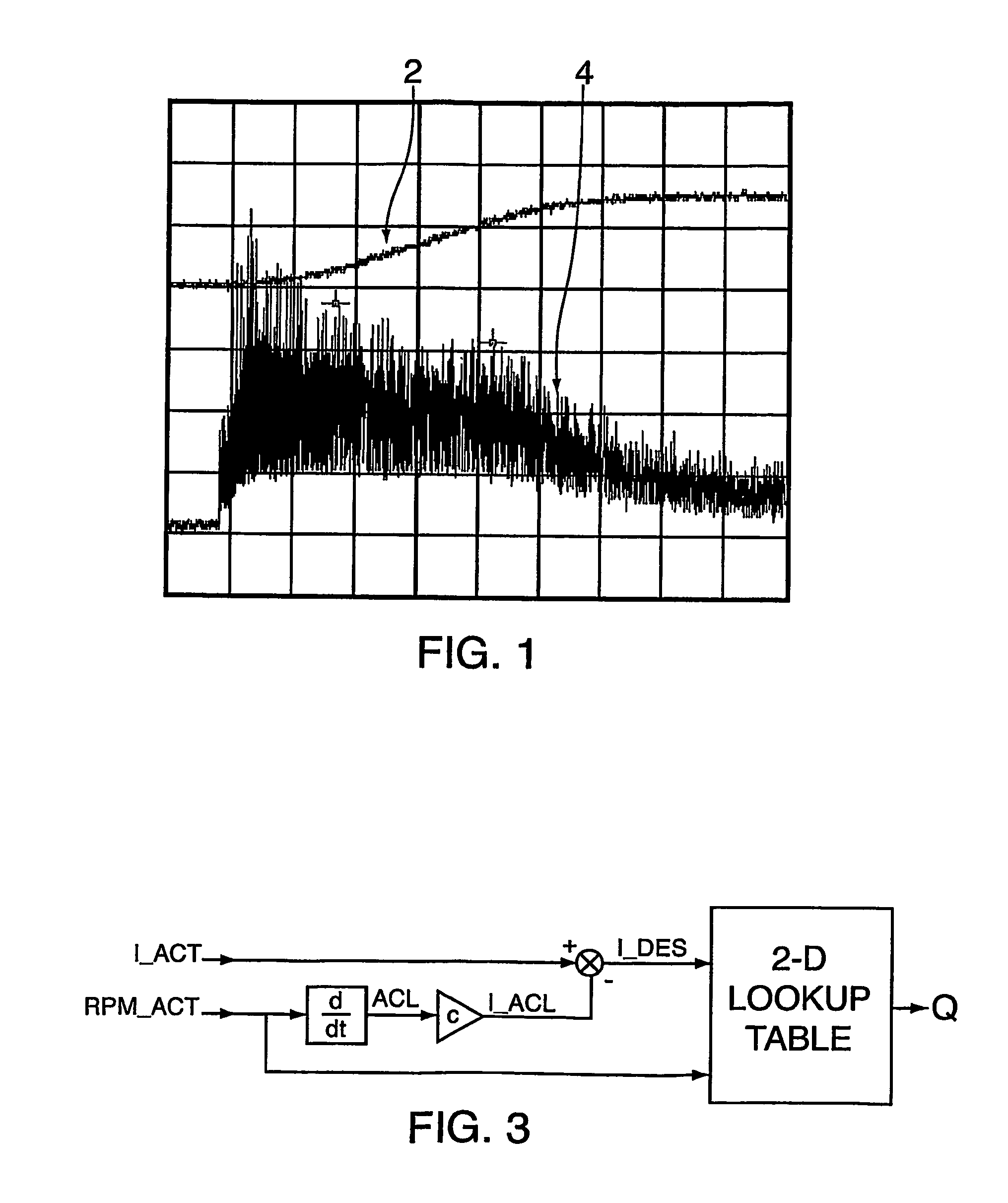
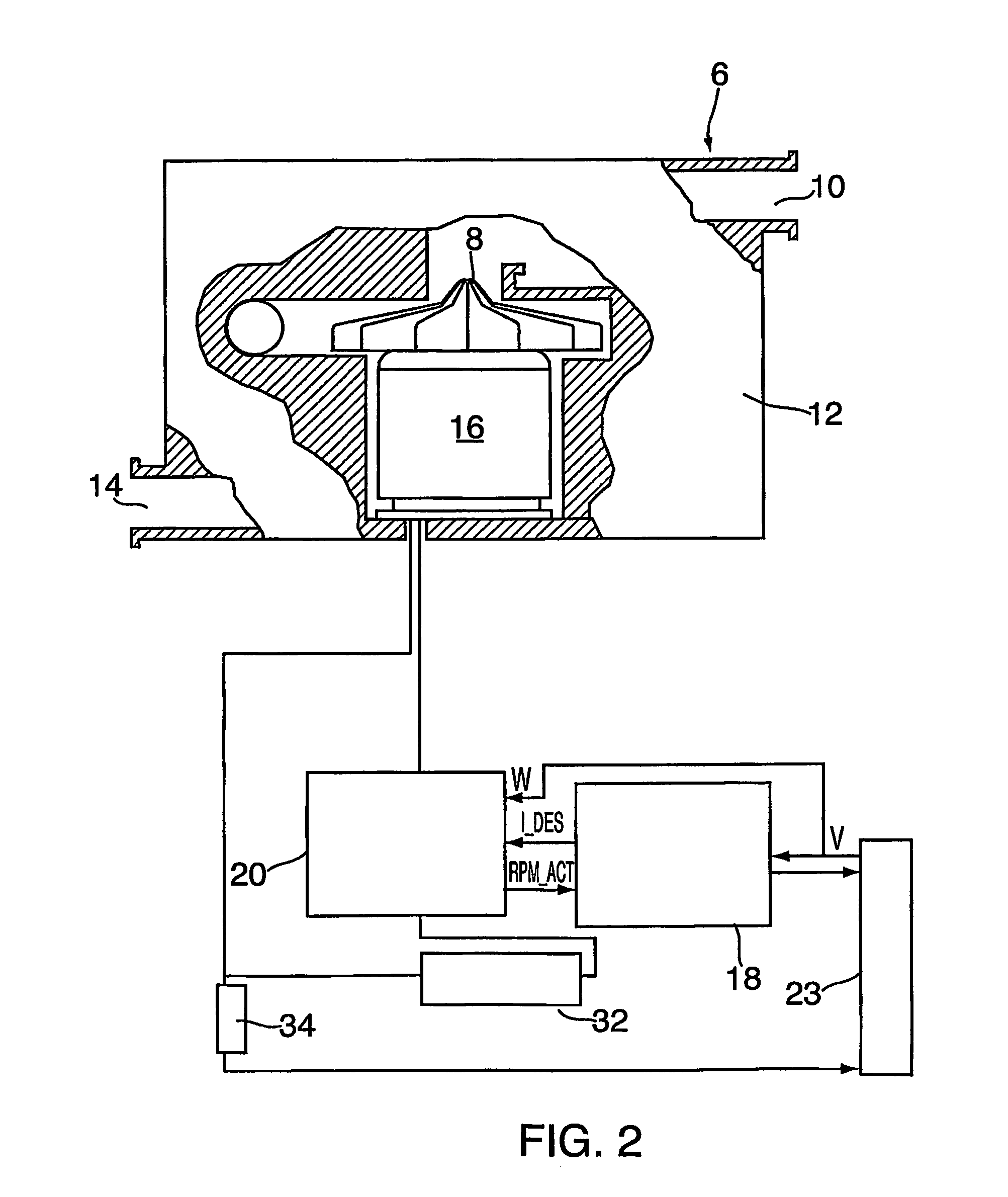
ActiveUS8353289B2Low costImprove insertion lossOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBreathing masksMotor speedElectrical current
A method and apparatus are disclosed for determining airflow through a PAP device while applying PAP therapy. The actual speed of a blower 6 is measured. The desired motor current IDES required for the actual speed to approach or maintain a desired speed is used, together with the actual speed RPM ACT, in a flow estimation algorithm to determine flow through the PAP device. The estimation algorithm consists of a two-dimensional look-up table, where the inputs are the desired motor current and actual motor speed, and the output is the flow through the PAP device.
Owner:RESMED LTD
EMI filter and power supply EMI filter access circuit
InactiveCN107482896AImprove insertion lossImprove filtering effectPower conversion systemsCapacitanceEngineering
The invention provides an EMI filter and a power supply EMI filter access circuit. The EMI filter comprises an adjustable common-mode inductor, a first differential-mode operating capacitor, a second differential-mode operating capacitor, an adjustable differential-mode inductor, a first common-mode operating capacitor and a second common-mode operating capacitor, wherein the first differential-mode operating capacitor is connected with an input end of the adjustable common-mode inductor in parallel; the second differential-mode operating capacitor is connected with an output end of the adjustable common-mode inductor in parallel; an input end of the adjustable differential-mode inductor is connected with the output end of the adjustable common-mode inductor in parallel; and the first common-mode operating capacitor and the second common-mode operating capacitor are connected in parallel with the input end of the adjustable differential-mode inductor, and a parallel structure is formed between the first common-mode operating capacitor and the second common-mode operating capacitor. According to the embodiment of the invention, the EMI filter can provide high insertion loss in a conducted interference frequency range, so as to attenuate EMI signals to the maximum, thus the electromagnetic property of equipment can meet the standard, and the filtering effect is effectively improved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Optical communication module having at least one monolithic semiconductor photonic integrated circuit chip
InactiveUS20050169640A1Few contactsHeat generationLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsIntegrated circuitOptical amplifier
An optical communication module comprises at least one monolithic semiconductor transmitter photonic integrated circuit chip having a plurality of optical signal channels approximating wavelengths on a standardized grid. Each of said channels comprises a laser source optically coupled to an electro-optic modulator. The outputs of the electro-optic modulators are coupled to inputs of an integrated optical combiner for combining the inputs to form a combined signal output from the chip. A booster optical amplifier is optically coupled to receive and amplify the combined signal output from the chip.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Antenna apparatus and electronic device comprising same
ActiveUS20190252757A1Low heat generationImprove antenna radiation efficiencyIndividually energised antenna arraysModular arraysAntenna elementHeat generation
The present invention relates to an antenna apparatus and an electronic device comprising the same. The antenna apparatus according to one embodiment of the present invention comprises an array antenna formed on a metal case of an electronic device, wherein the array antenna comprises at least two antenna elements, the at least two antenna elements may operate in the same frequency band. According to one embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to provide an antenna apparatus capable of reducing heat generation and increasing the radiation efficiency of an antenna.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
TSV structure applicable to adapter board and preparation method of TSV structure
ActiveCN103426864AImprove uniformityImprove insulation performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringDiffusion barrier
The invention relates to a TSV structure applicable to an adapter board and a preparation method of the TSV structure. The TSV structure comprises a substrate and is characterized in that TSV deep holes are formed in the substrate, the side wall and the bottom wall of each TSV deep hole are provided with first insulating layers, second insulating layers are arranged on the surfaces of the first insulating layers, diffusion blocking layers are arranged on the surfaces of the second insulating layers, seed layers are arranged on the surfaces of the diffusion blocking layers, and the TSV deep holes are filled with conductive metal. The preparation method of the TSV structure applicable to the adapter board comprises the following steps that (1) the substrate is etched to form the TSV deep holes; (2) silicon dioxide is grown on the front surface of the substrate in a thermal oxidation mode so that the first insulating layers can be obtained, TEOS is deposited on the surfaces of the first insulating layers by adopting PECVD or SACVD or APCVD so that the second insulating layers can be obtained, then, the diffusion blocking layers are deposited on the surfaces of the second insulating layers, the seed layers are deposited on the surfaces of the diffusion blocking layers, and finally, the TSV deep holes are filled with the conductive metal. The TSV structure applicable to the adapter board is simple in process, low in cost and good in quality, and improves uniformity and insulativity of the insulating layers of silicon via holes.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR ADVANCED PACKAGING
Phase shift device
ActiveUS10141620B2Improve insertion lossHigh metallic loss of the CPWCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricWaveguide type devicesMetal-insulator-metalPhase shifted
A phase shift device includes a planar transmission line that is formed by a signal electrode and a ground electrode which are separated by a dielectric substance, whereby the signal electrode of the planar transmission line is divided into several pieces and includes overlapping areas of adjacent pieces that are filled with a tunable liquid crystal material, thereby forming a dielectric tunable component (varactor) with a metal-insulator-metal type capacitor. The several pieces of the signal electrode are arranged at two or more different distance levels with respect to the ground electrode. The tunable liquid crystal material is arranged as a continuous layer between several pieces of the signal electrode that are arranged at two different distance levels.
Owner:ALCAN SYST GMBH
Microwave filter distributed on circuit board of wireless communication product
InactiveUS20050118978A1Improve insertion lossOvercomes drawbackCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted circuit aspectsNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
The present invention is to provide a microwave filter distributed on a circuit board of a wireless communication product, which comprises an input terminal, a resonant chamber of double frequencies, and an output terminal of the microwave filter directly distributed on the circuit board of the wireless communication product as a plurality of microstrips by utilizing a manufacturing technique of printed circuit board for eliminating the harmonic spurious of double frequencies and higher frequency caused by nonlinear distortion of a power amplifier of the wireless communication product.
Owner:ALPHA NETWORKS INC
Waveguide thermo-optic switch and manufacturing method thereof
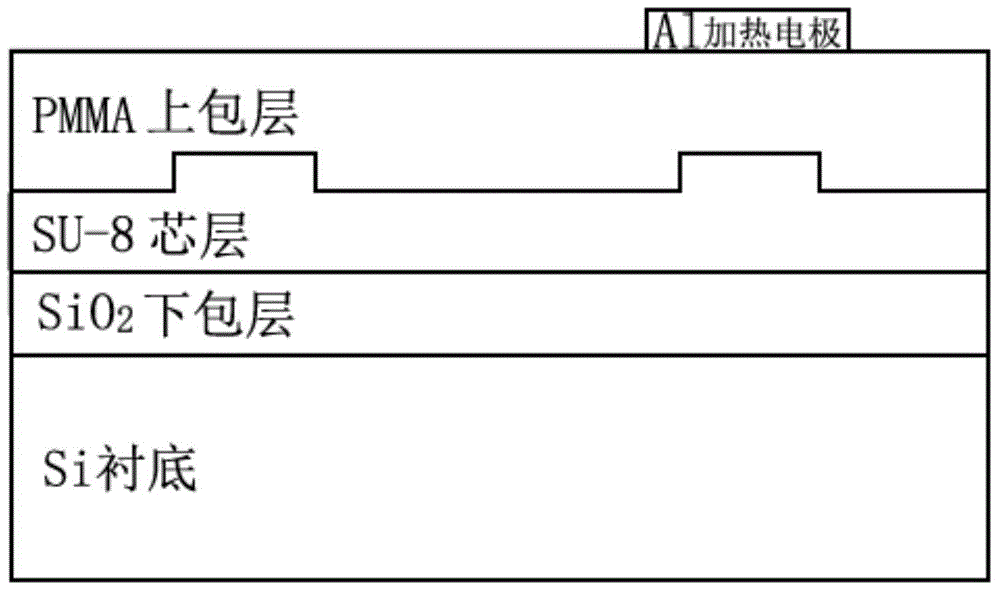
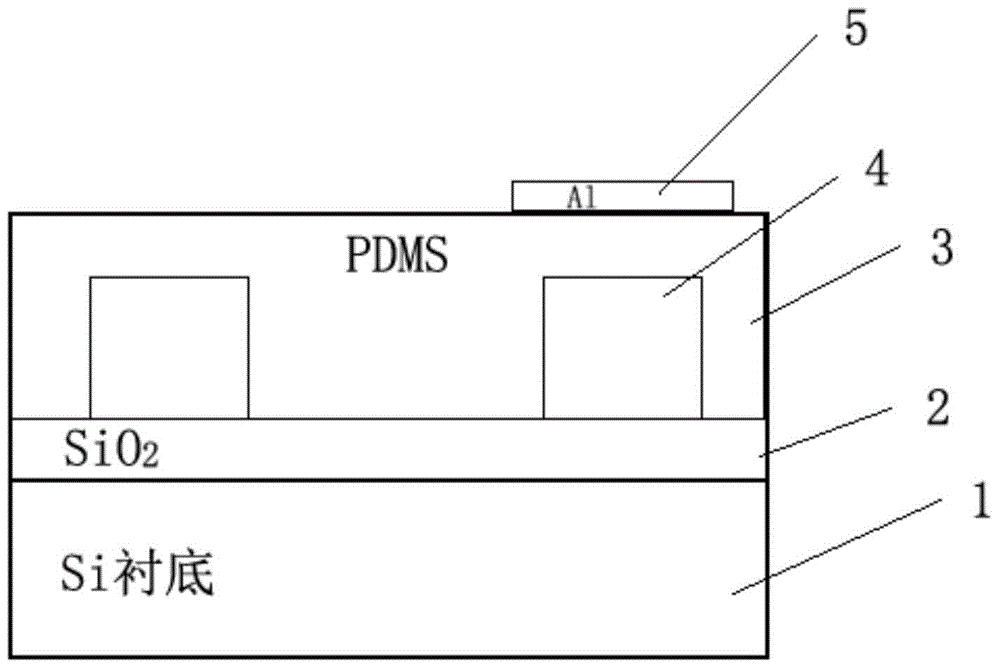
InactiveCN105759463ALow driving powerImprove performance indicatorsNon-linear opticsInsertion lossPolymer
The invention relates to a waveguide thermo-optic switch and a manufacturing method thereof. The waveguide thermo-optic switch sequentially comprises a substrate, a lower cladding, an upper cladding and a heating electrode, wherein the lower cladding is made from an SiO2 material, and the upper cladding is made from a polymer material; the waveguide thermo-optic switch is sequentially divided into an input waveguide area, a first beam splitting and combining area, a thermo-optic modulation area, a second beam splitting and combining area and an output waveguide area along the length direction; two waveguide cores arranged in the upper cladding in a penetrating way along the length direction of the waveguide thermo-optic switch are positioned between the lower cladding and the upper cladding; the waveguide cores in the thermo-optic modulation area are made from the polymer material, and the waveguide cores in the other areas are made from a doped SiO2 material. The technical problems that the existing thermo-optic switch having an organic / inorganic hybrid structure is high in insertion loss, low in reliability and poor in stability can be solved. Furthermore, a subsequent encapsulation process of the waveguide thermo-optic switch is also compatible with the existing mainstream encapsulation process, so that additional input is not increased.
Owner:苏州峰通光电有限公司
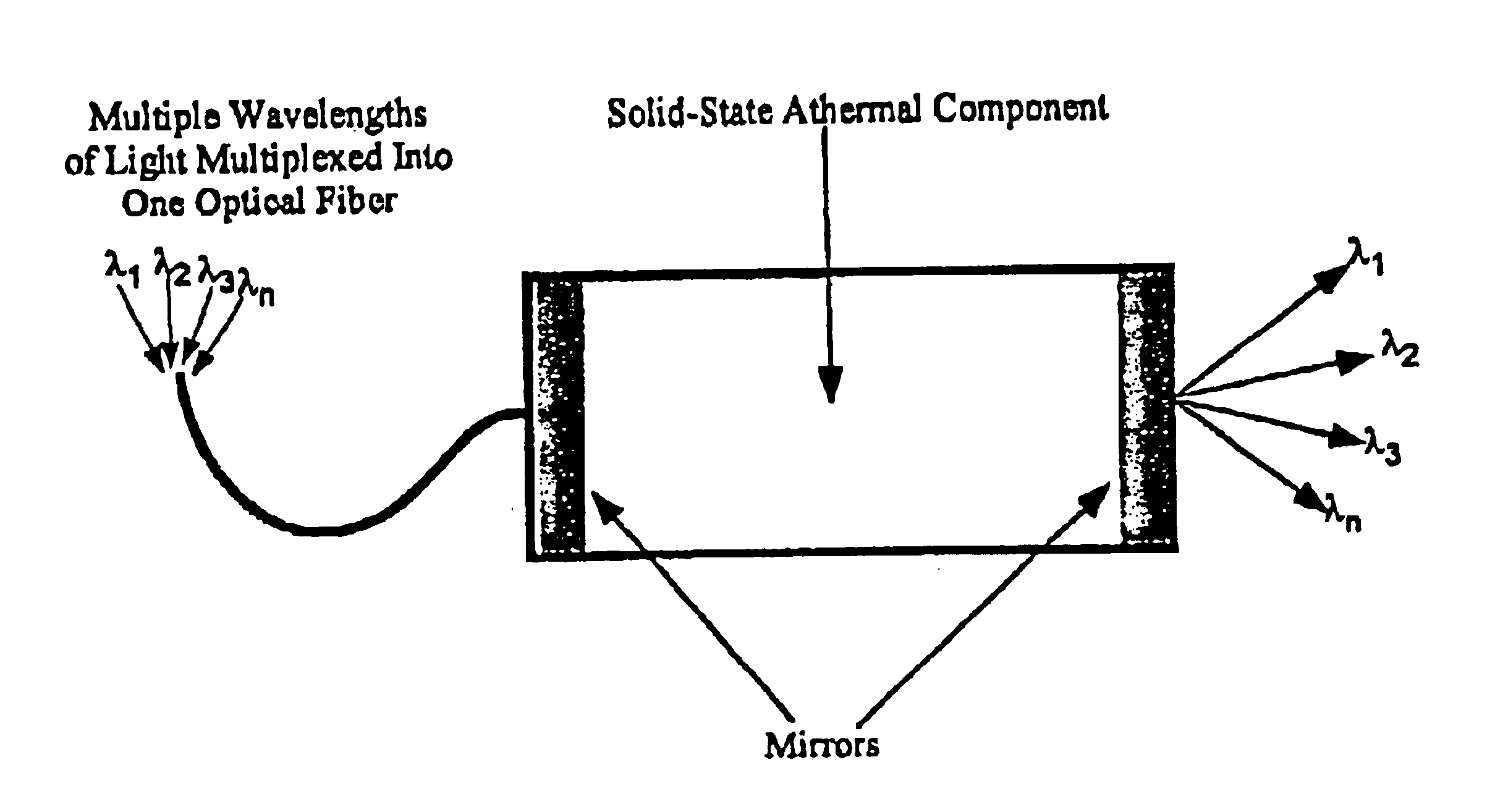
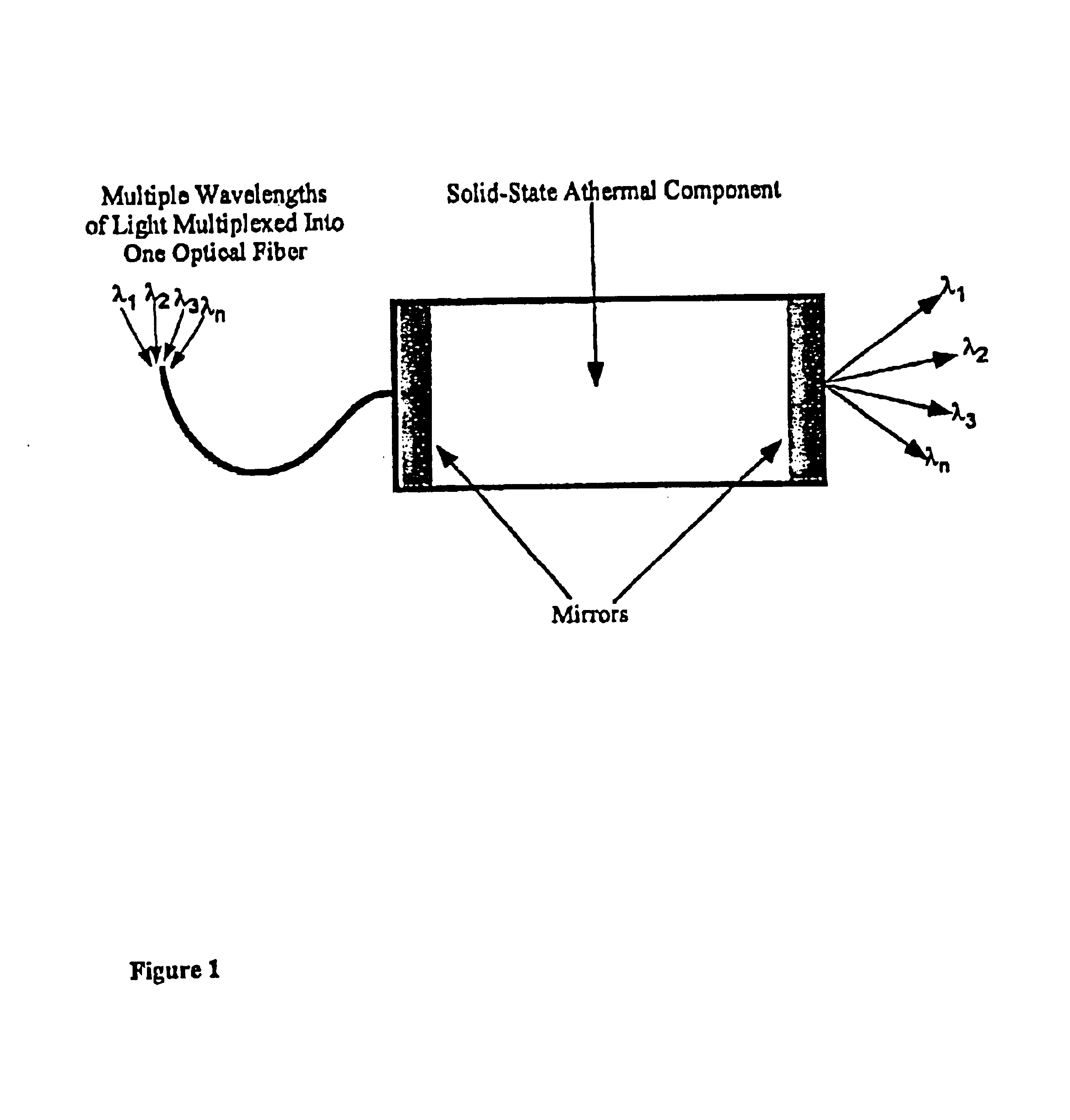
Athermal optical components
InactiveUS6865318B1High refractive indexImprove insertion lossCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesCrystalline materialsSilver chloride
Athermal optical components comprise cubic crystalline materials including silver chloride and cesium bromide, or comprise composites of at least two layers of different compositions wherein the total optical pathlength, nL, across said layers is essentially independent of temperature.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Calibrating tool, calibrating method, fiber inserting assembly and fiber connector
InactiveCN104181645ALow costImprove performanceCoupling light guidesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a calibrating tool used for calibrating the position of a fiber in the inner hole of a fiber inserting core. The calibrating tool comprises a high-precision external diameter aligning element and a fiber position high-precision calibrating element. The high-precision external diameter aligning element is used for aligning the outer cylinder of the fiber inserting core to the outer cylinder of the fiber position high-precision calibrating element. One end of the fiber passes through the inner hole of the fiber inserting core and is inserted into the calibrating hole of the fiber position high-precision calibrating element in order that the axis of the fiber inserted into the inner hole of the fiber inserting core us is aligned to a central axis determined by the outer cylinder of the fiber inserting core. Therefore, a high-precision fiber connector is produced by the low-precision fiber inserting core and production cost is reduced. The invention also discloses a calibrating method and a high-precision fiber connector produced by using the calibrating tool and the calibrating method and provided with precision equal to or more than that of a single-mode fiber connector.
Owner:ADC TELECOMM (SHANGHAI) DISTRIBUTION CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com