Patents
Literature
49 results about "Waveguide photodetector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
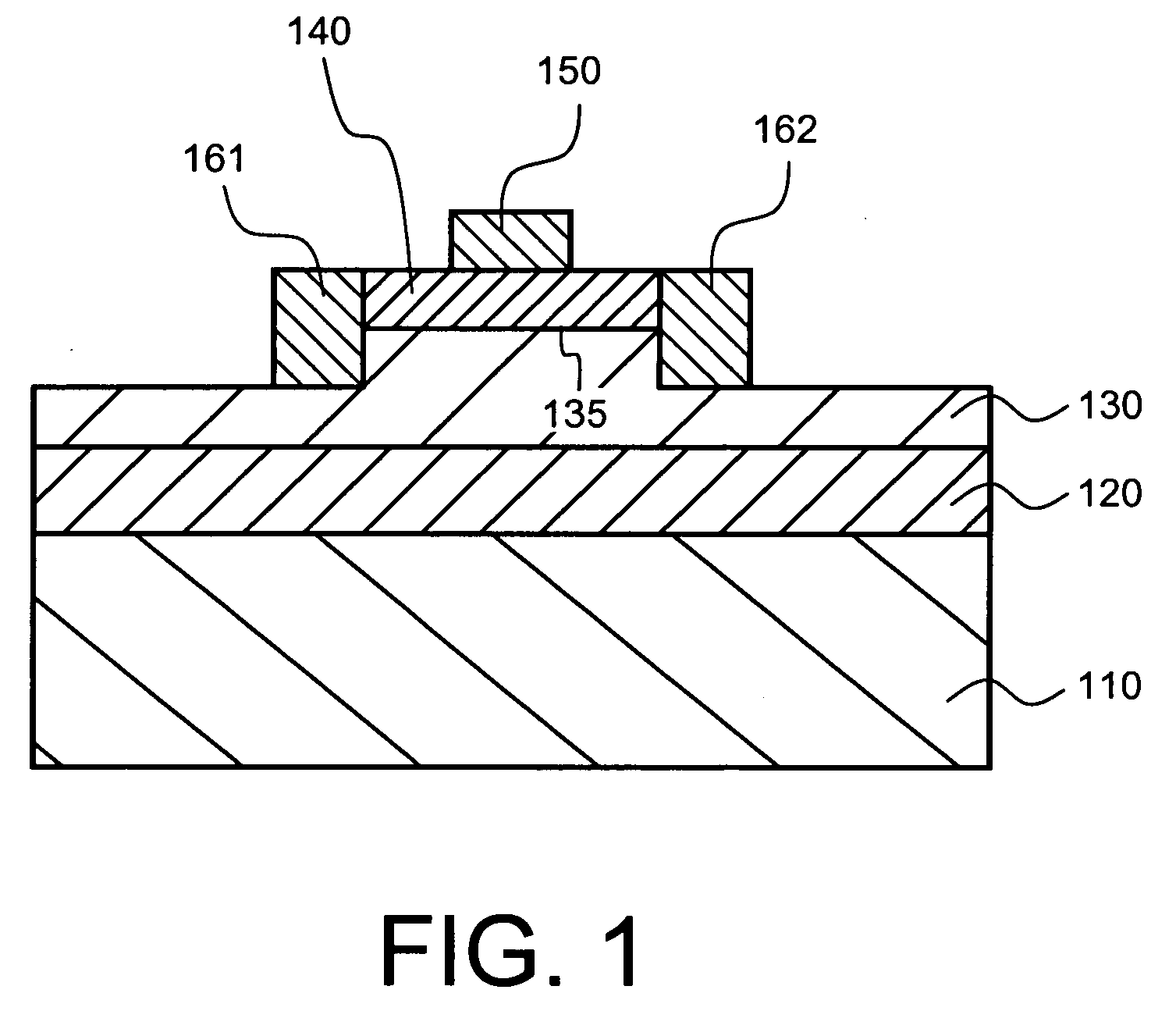
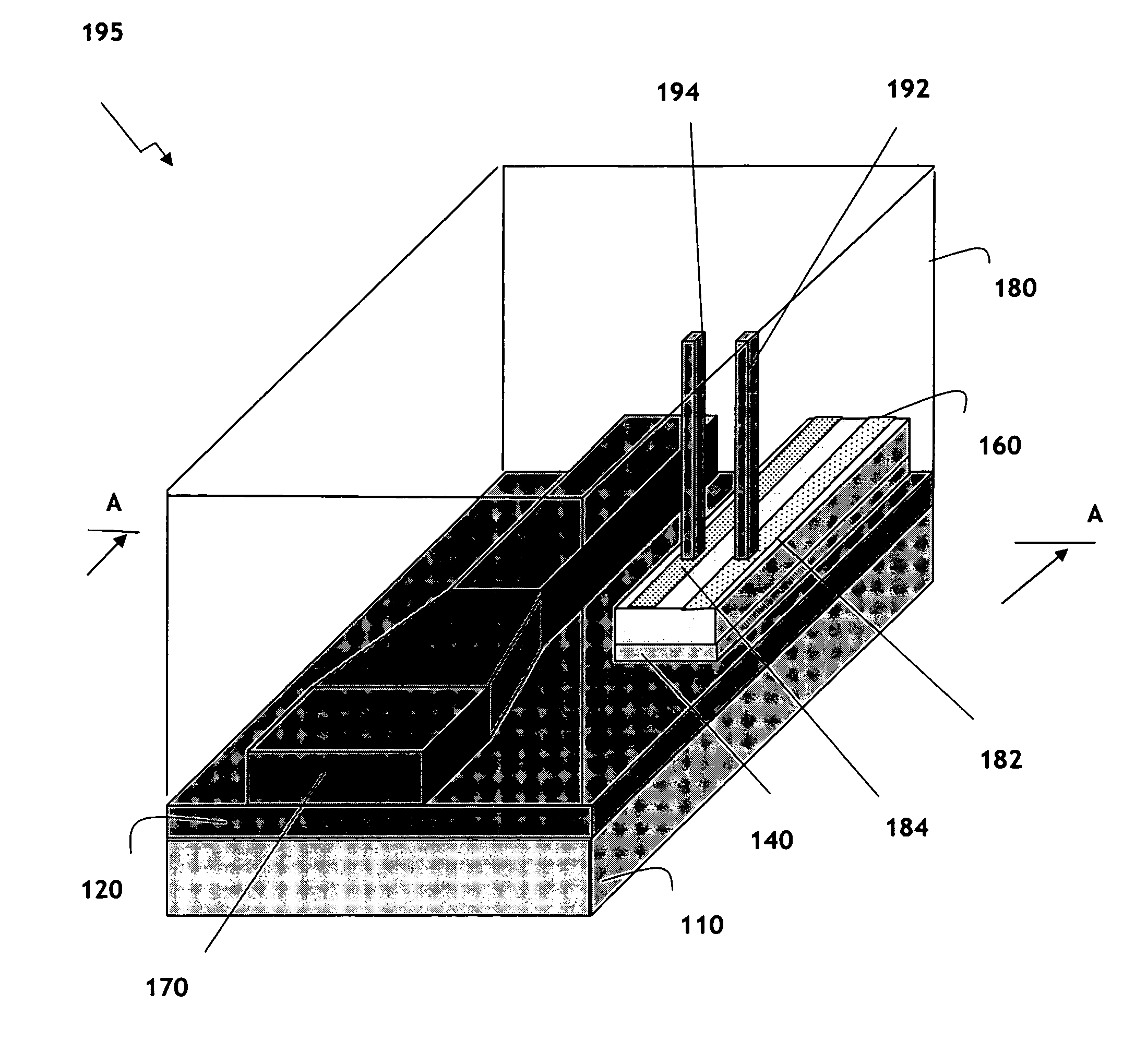
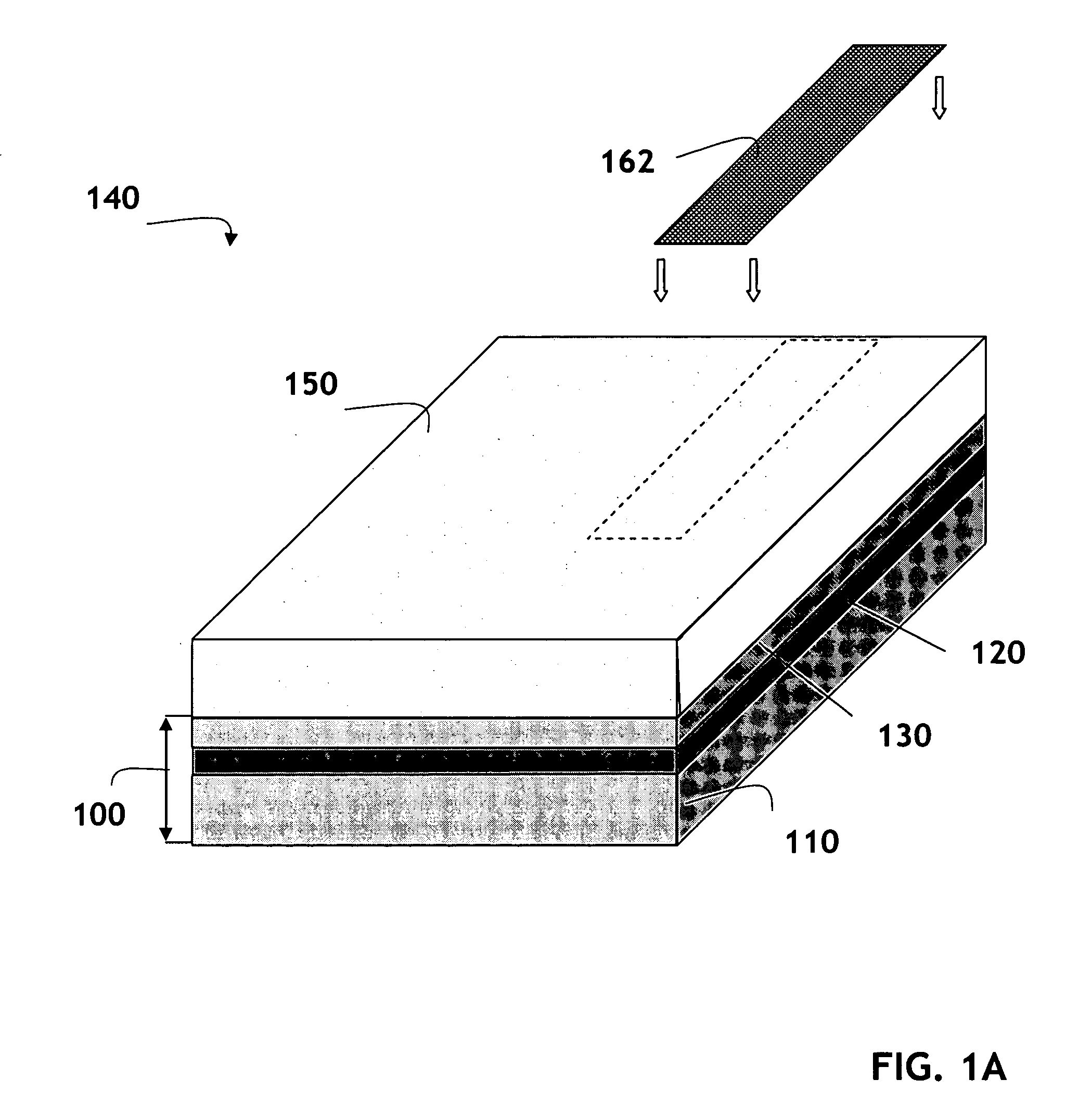
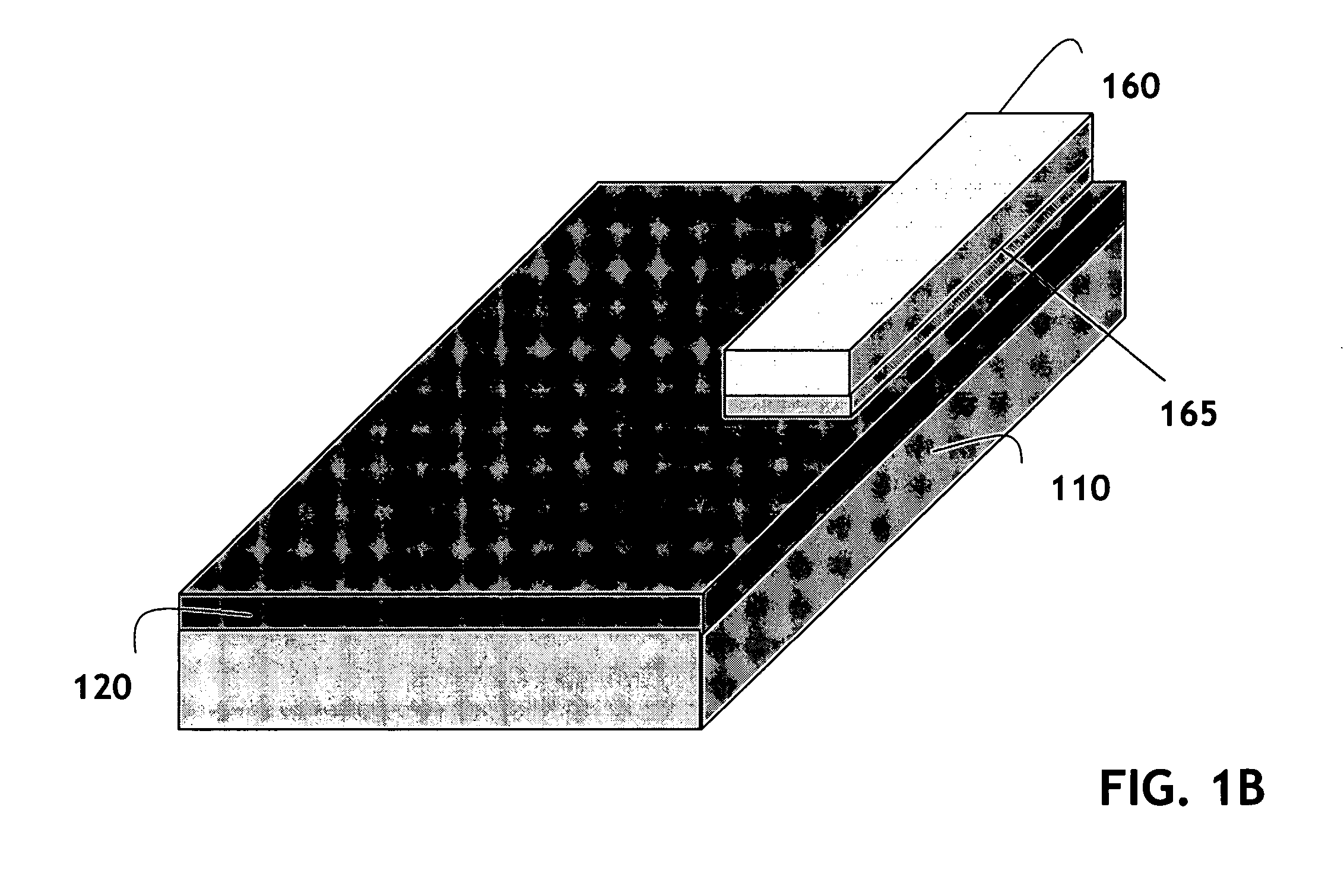
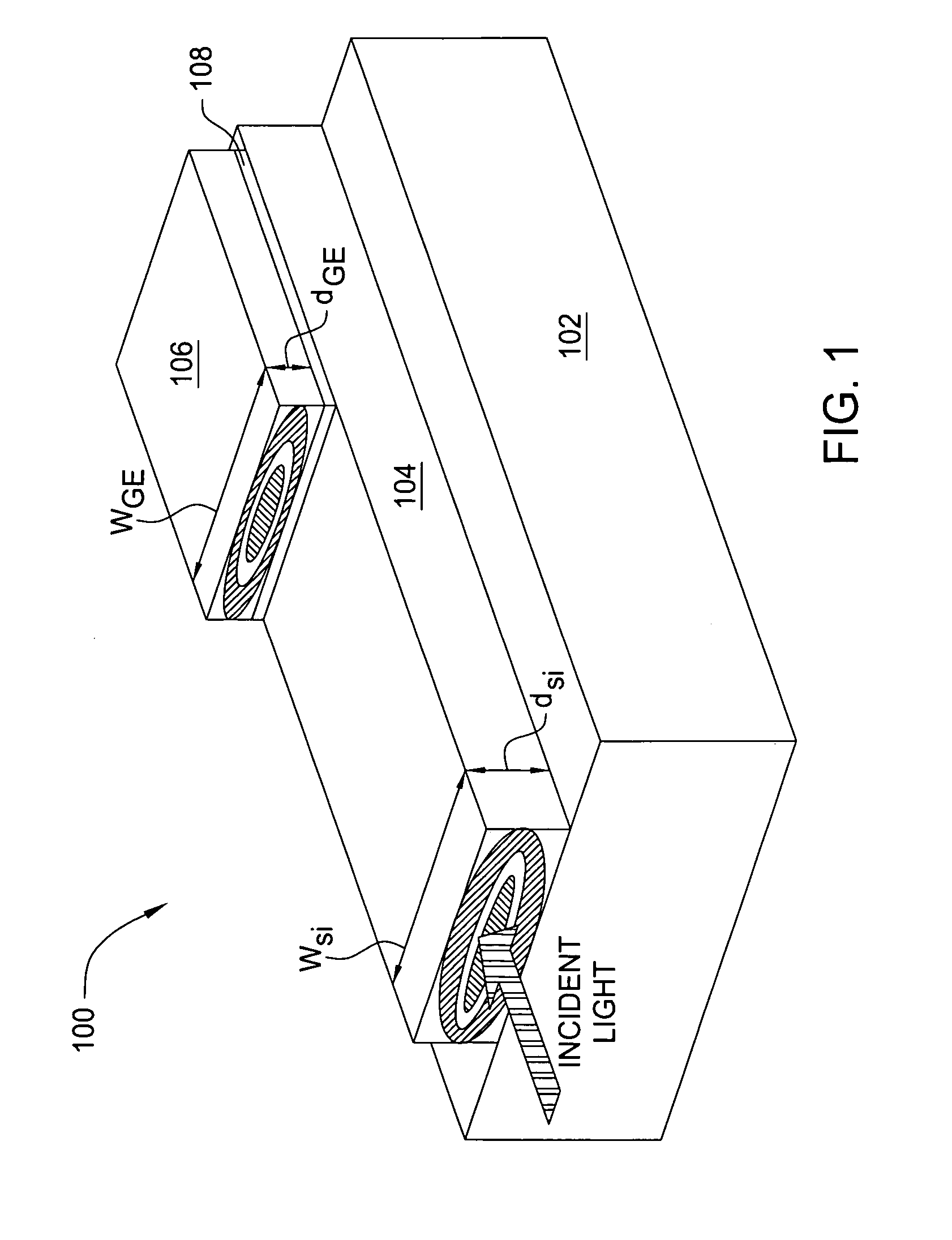
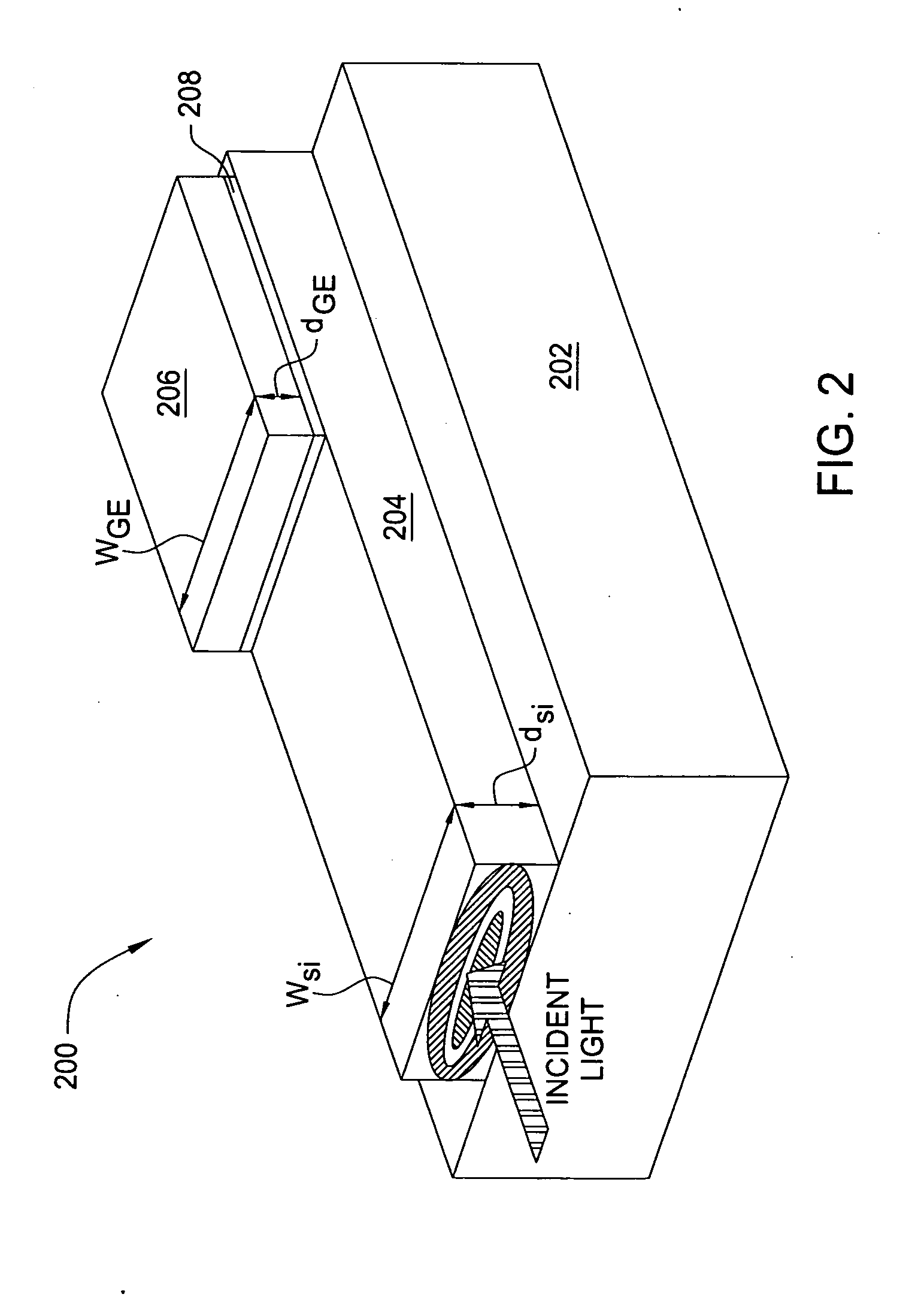
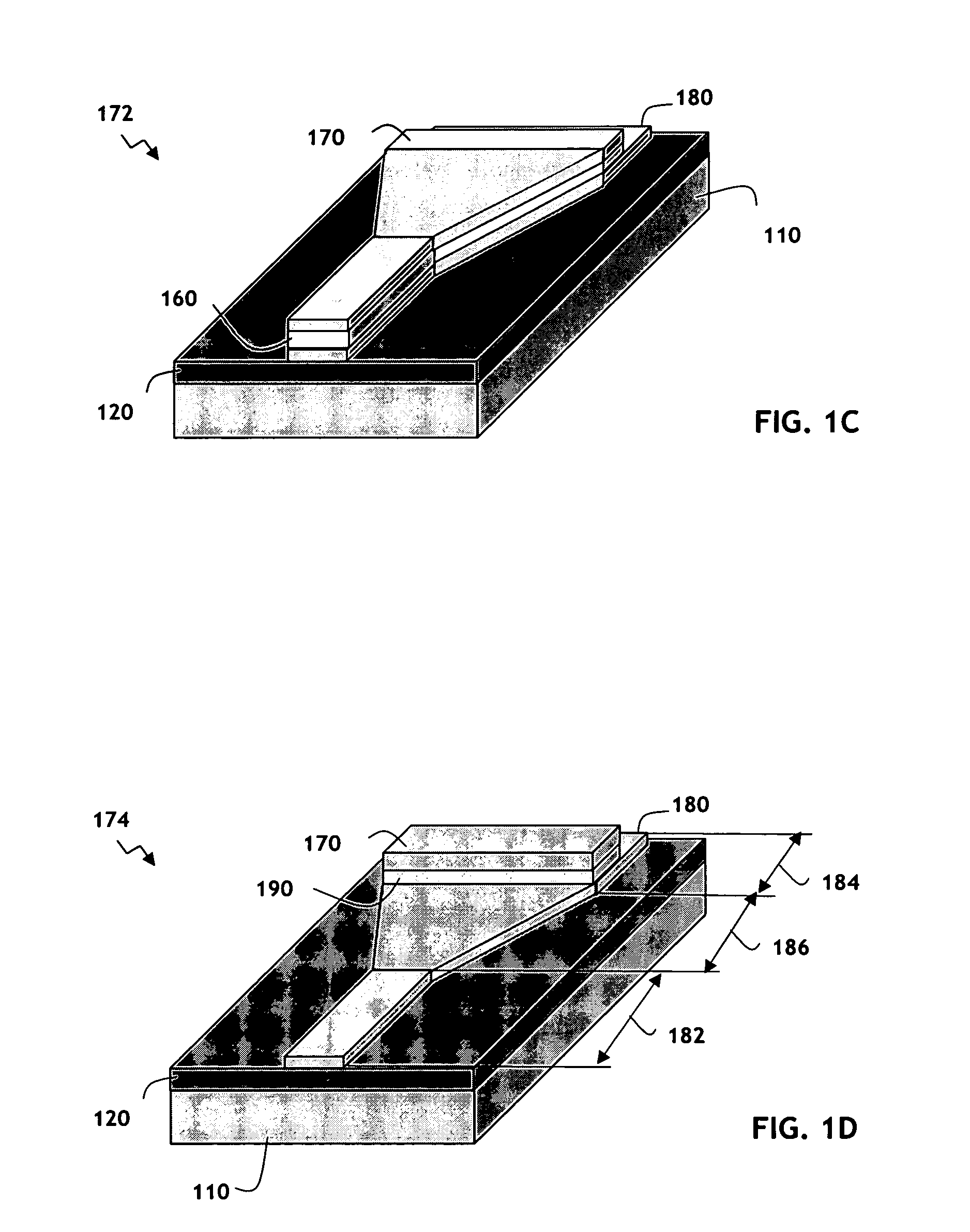
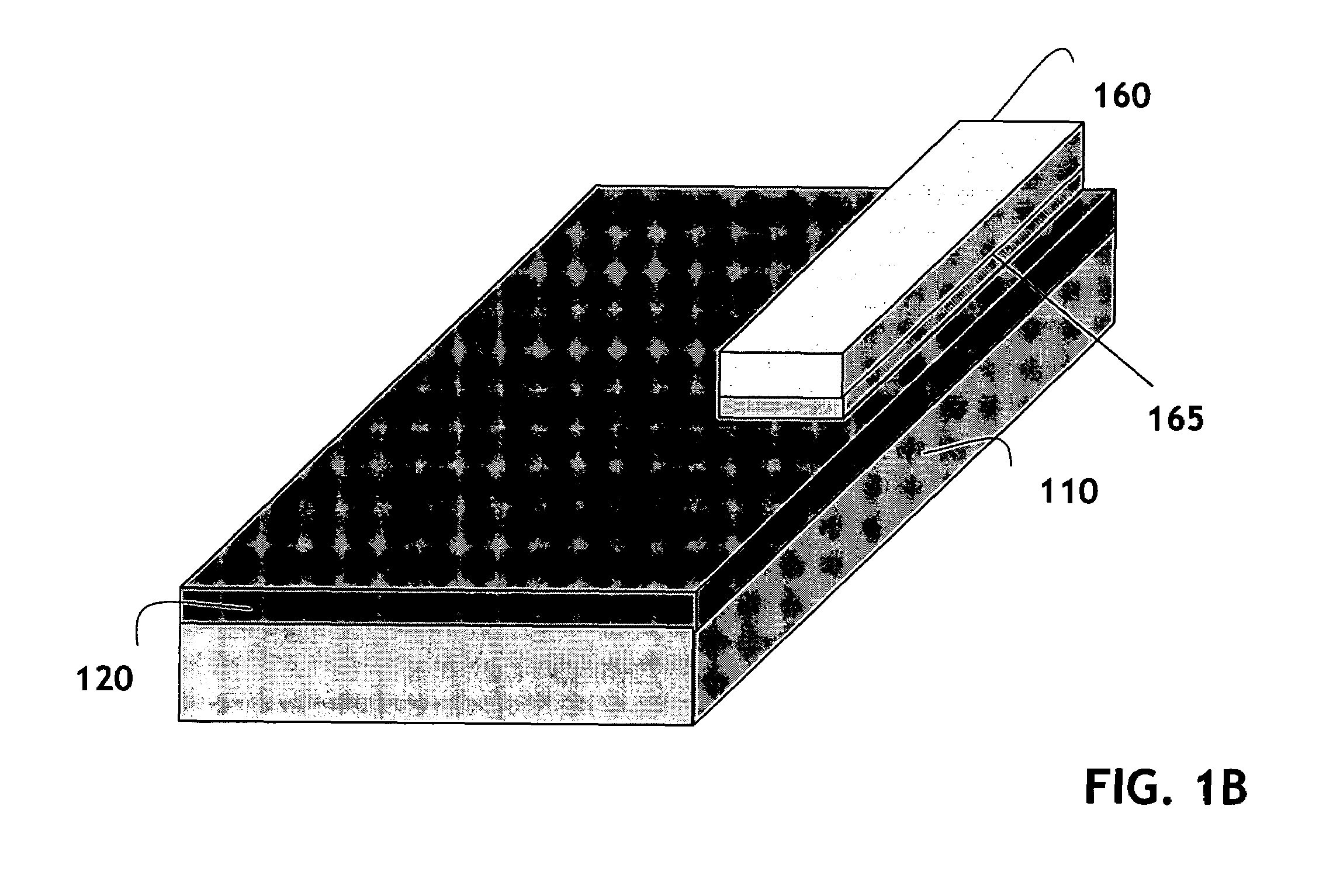
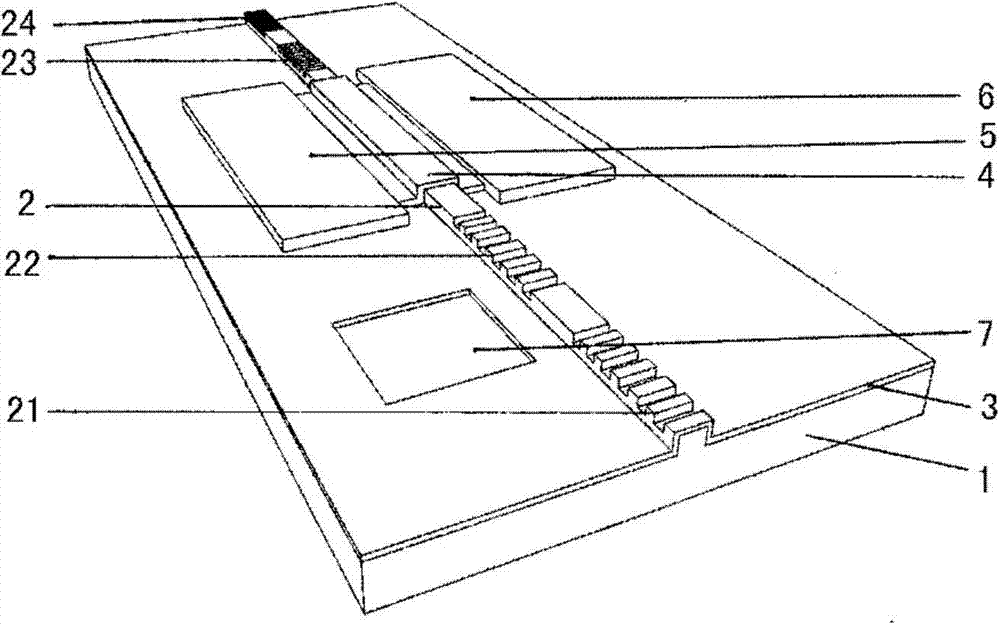
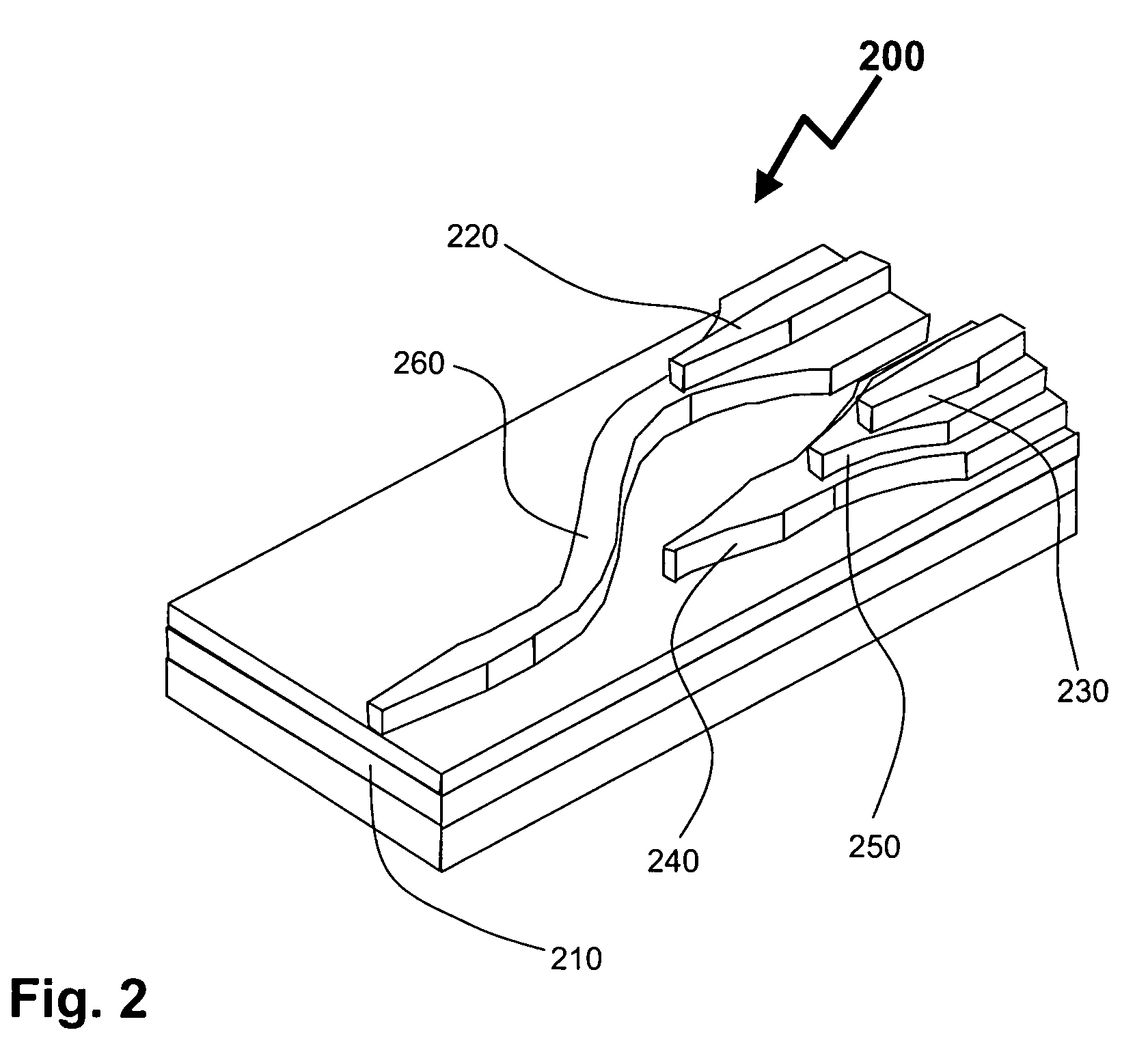
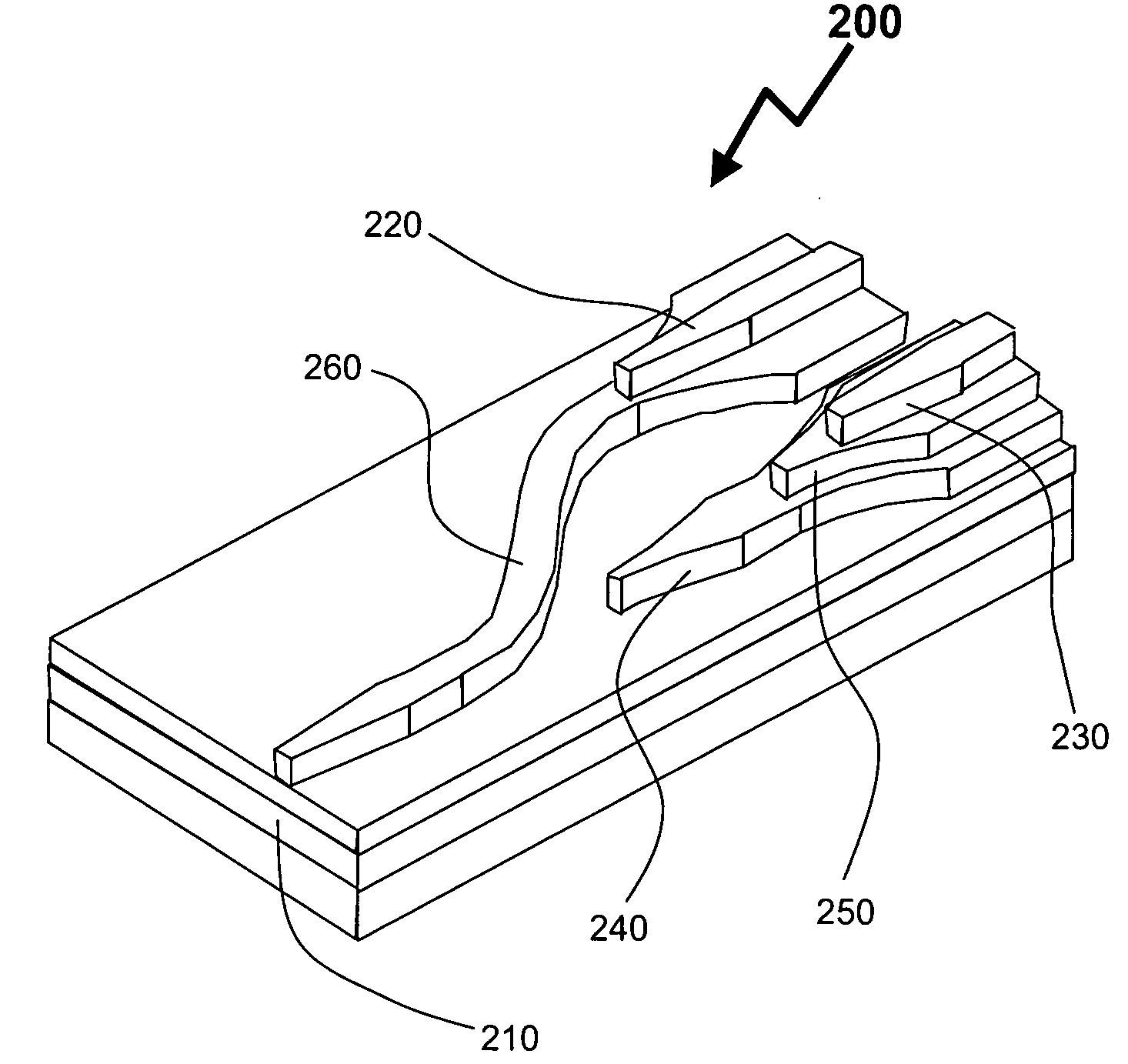
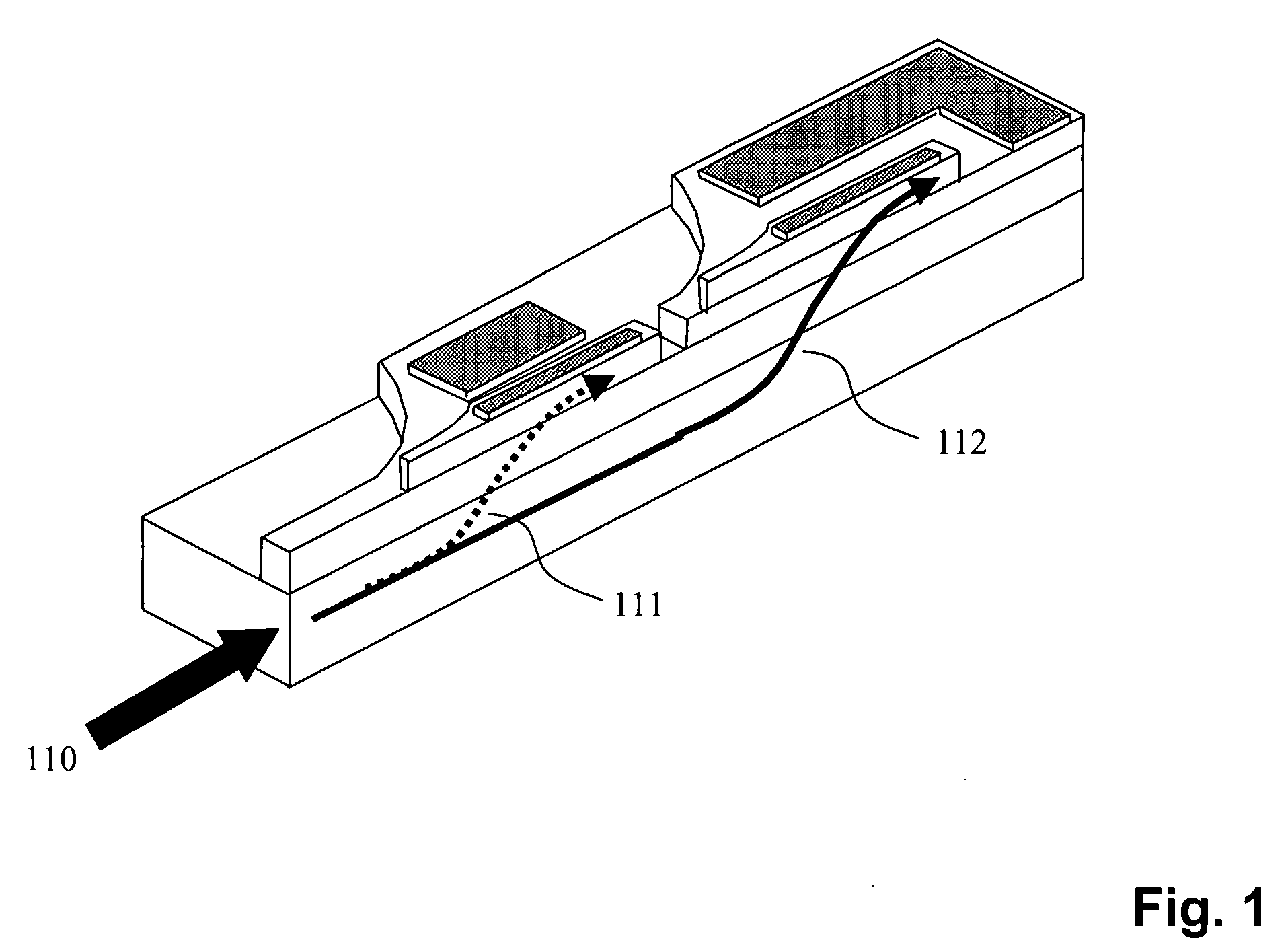
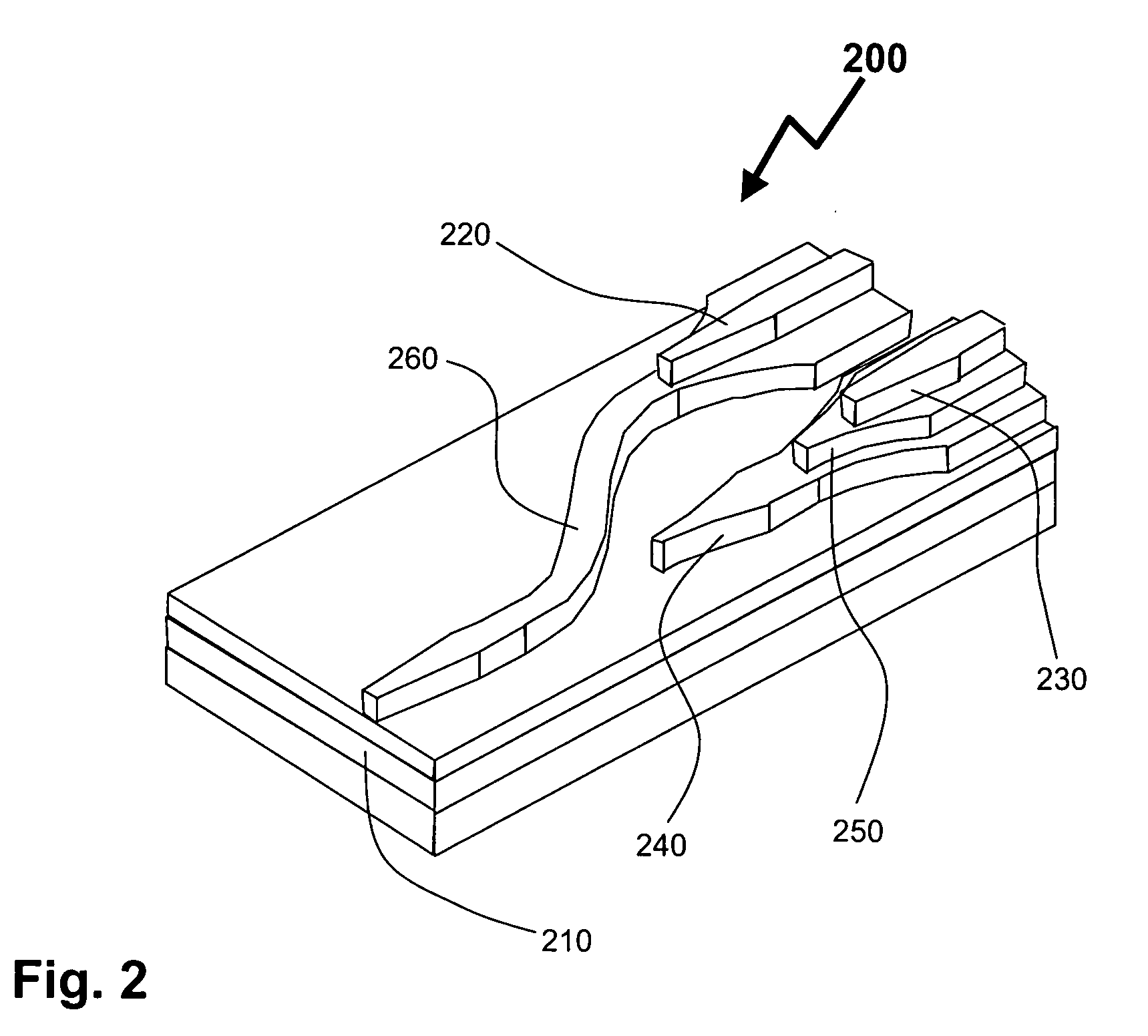
Laterally-integrated waveguide photodetector apparatus and related coupling methods
InactiveUS20070104441A1Increase data rateCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCMOSPhotovoltaic detectors
High-speed optoelectronic devices having a waveguide densely integrated with and efficiently coupled to a photodetector are fabricated utilizing methods generally compatible with CMOS processing techniques. In various implementations, the waveguide consists essentially of single-crystal silicon and the photodetector contains, or consists essentially of, epitaxially grown germanium or a silicon-germanium alloy having a germanium concentration exceeding about 90%.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Germanium integrated CMOS wafer and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7262117B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
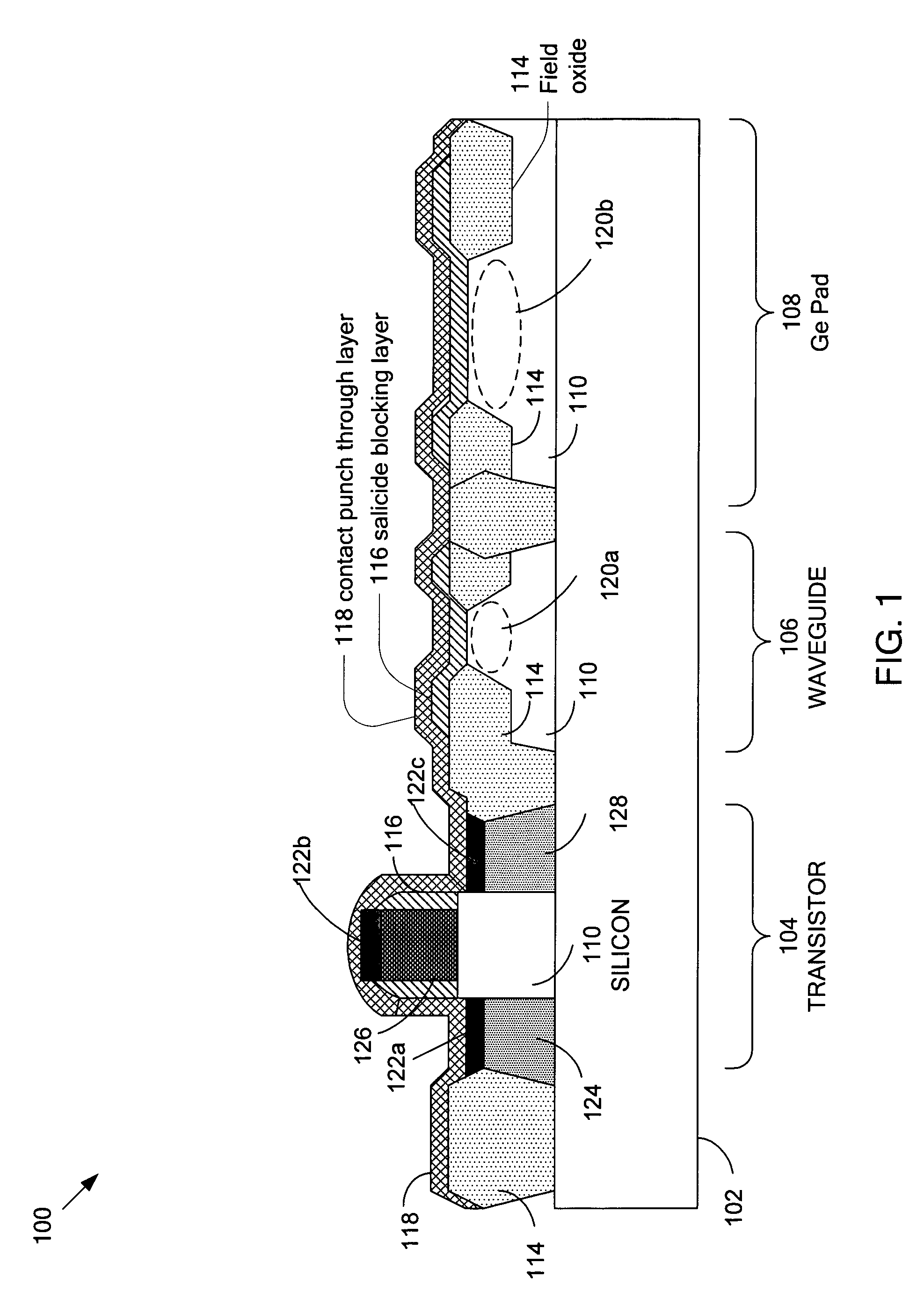
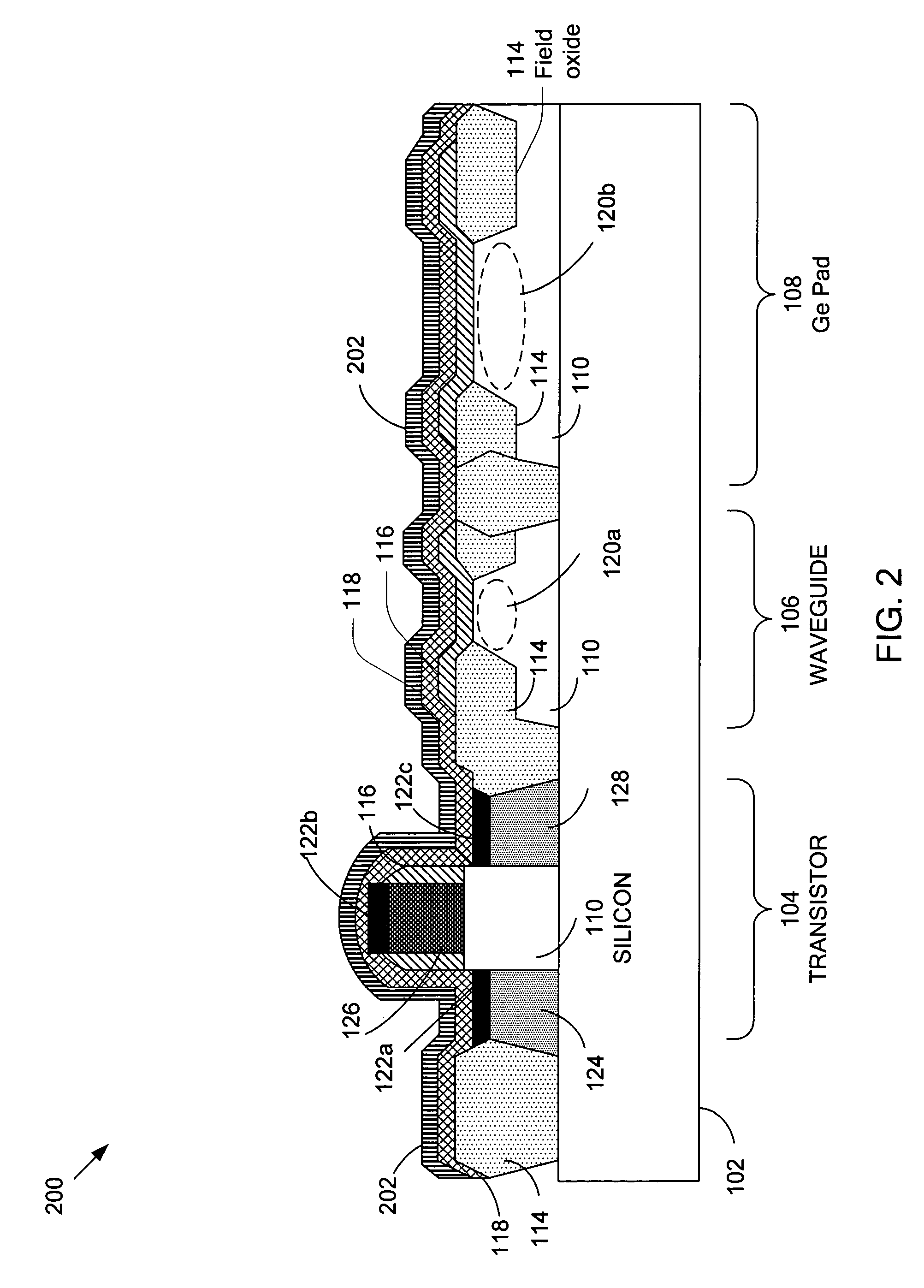
The present invention discloses an integration flow of germanium into a conventional CMOS process, with improvements in performing selective area growth, and implementing electrical contacts to the germanium, in a way that has minimal impact on the preexisting transistor devices. The present invention also provides methods to integrate the germanium without impacting the optical or electrical performance of these devices, except where intended, such as in a germanium photodetector, or germanium waveguide photodetector.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Silicon-graphene waveguide photodetectors, optically active elements and microelectromechanical devices
InactiveUS8554022B1Increase field strengthNanoinformaticsPhotovoltaic energy generationGratingRefractive index
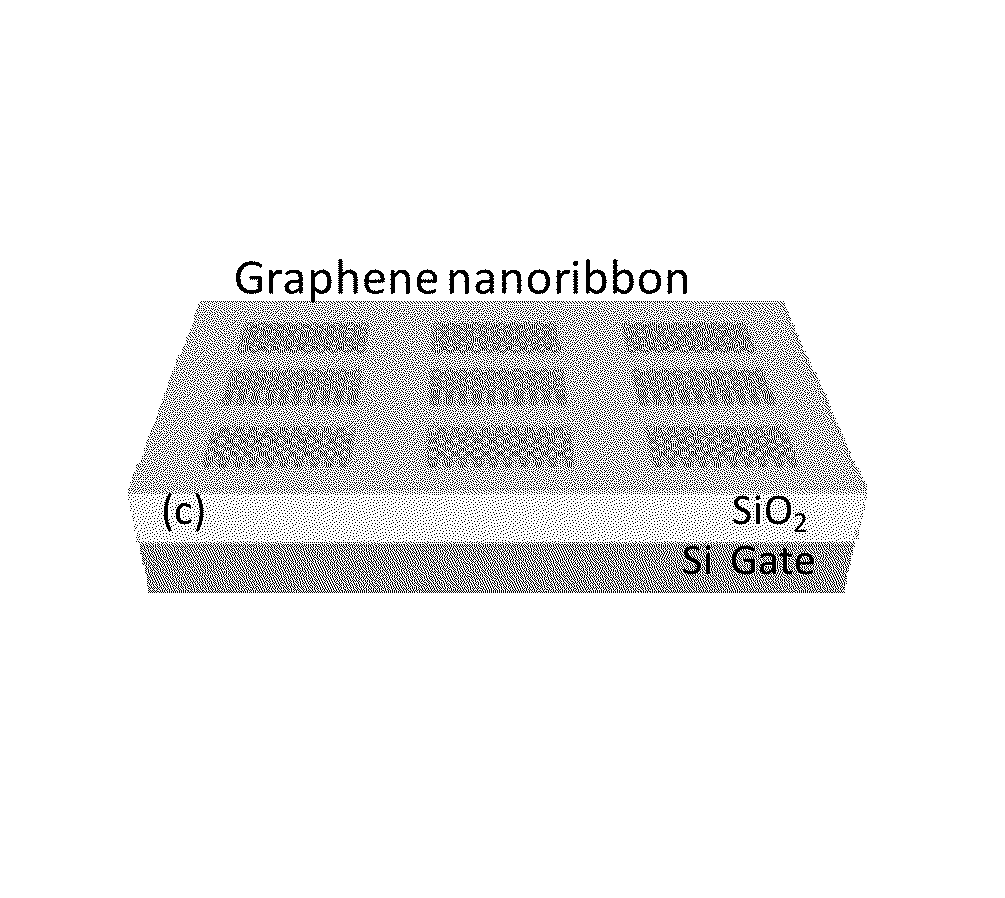
Systems and methods for modulating light with light in high index contrast waveguides clad with graphene. Graphene exhibits a large nonlinear electro-optic constant χ3. Waveguides fabricated on SOI wafers and clad with graphene are described. Systems and methods for modulating light with light are discussed. Optical logic gates are described. Waveguides having closed loop structures such as rings and ovals, Mach-Zehnder interferometer, grating, and Fabry-Perot configurations, are described. Optical signal processing methods, including optical modulation at Terahertz frequencies, are disclosed. Optical detectors are described. Microelectromechanical and nanoelectromechanical systems using graphene on silicon substrates are described.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
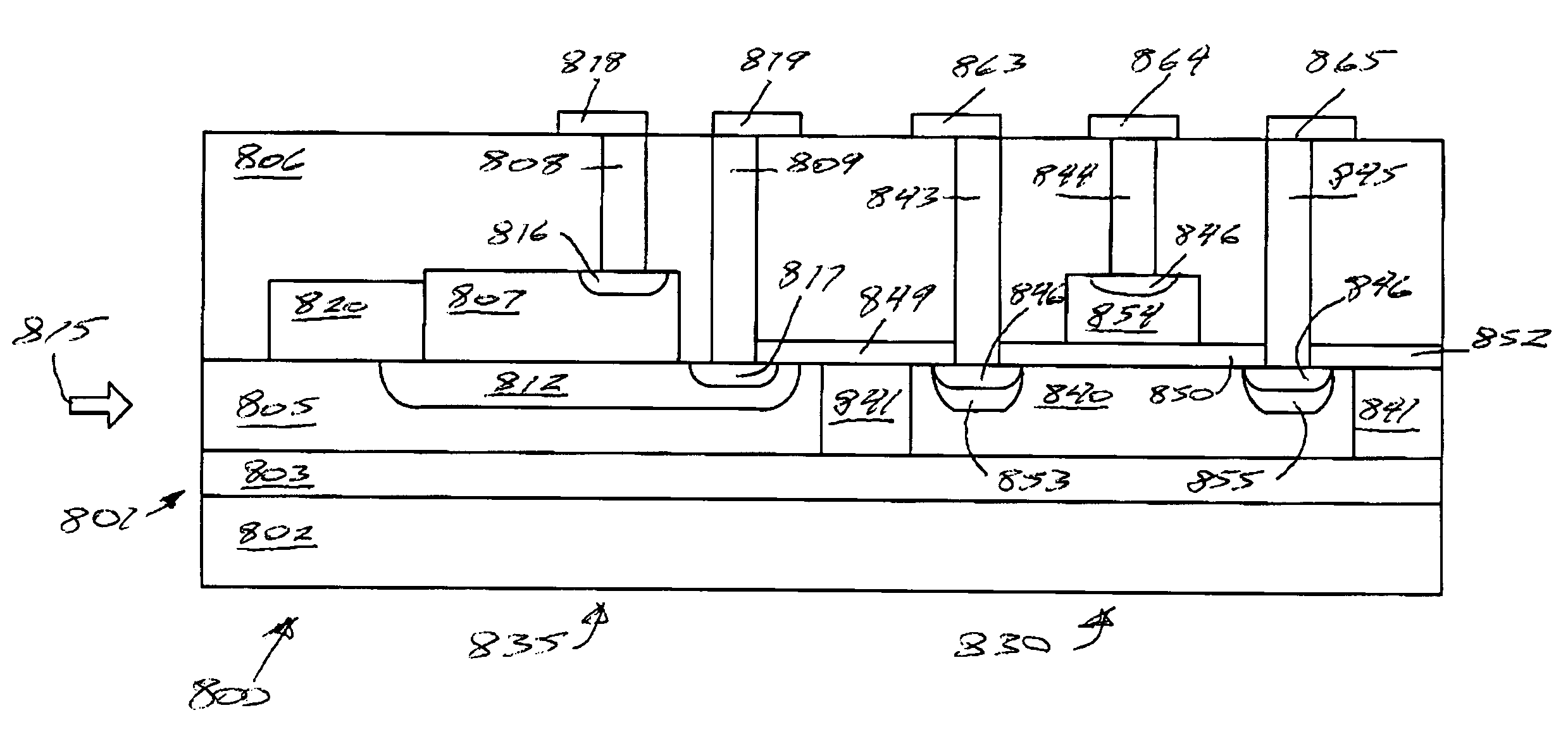
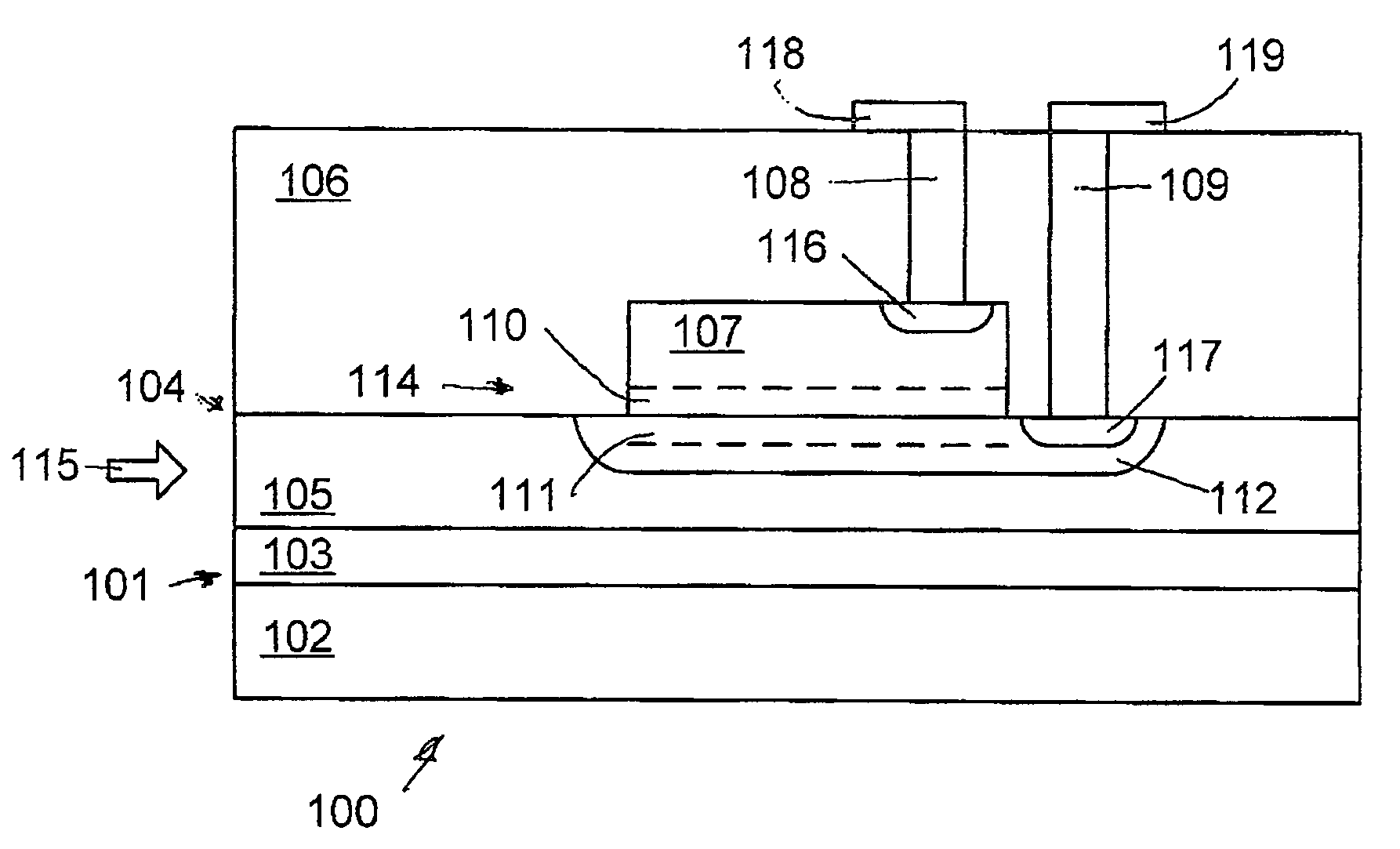
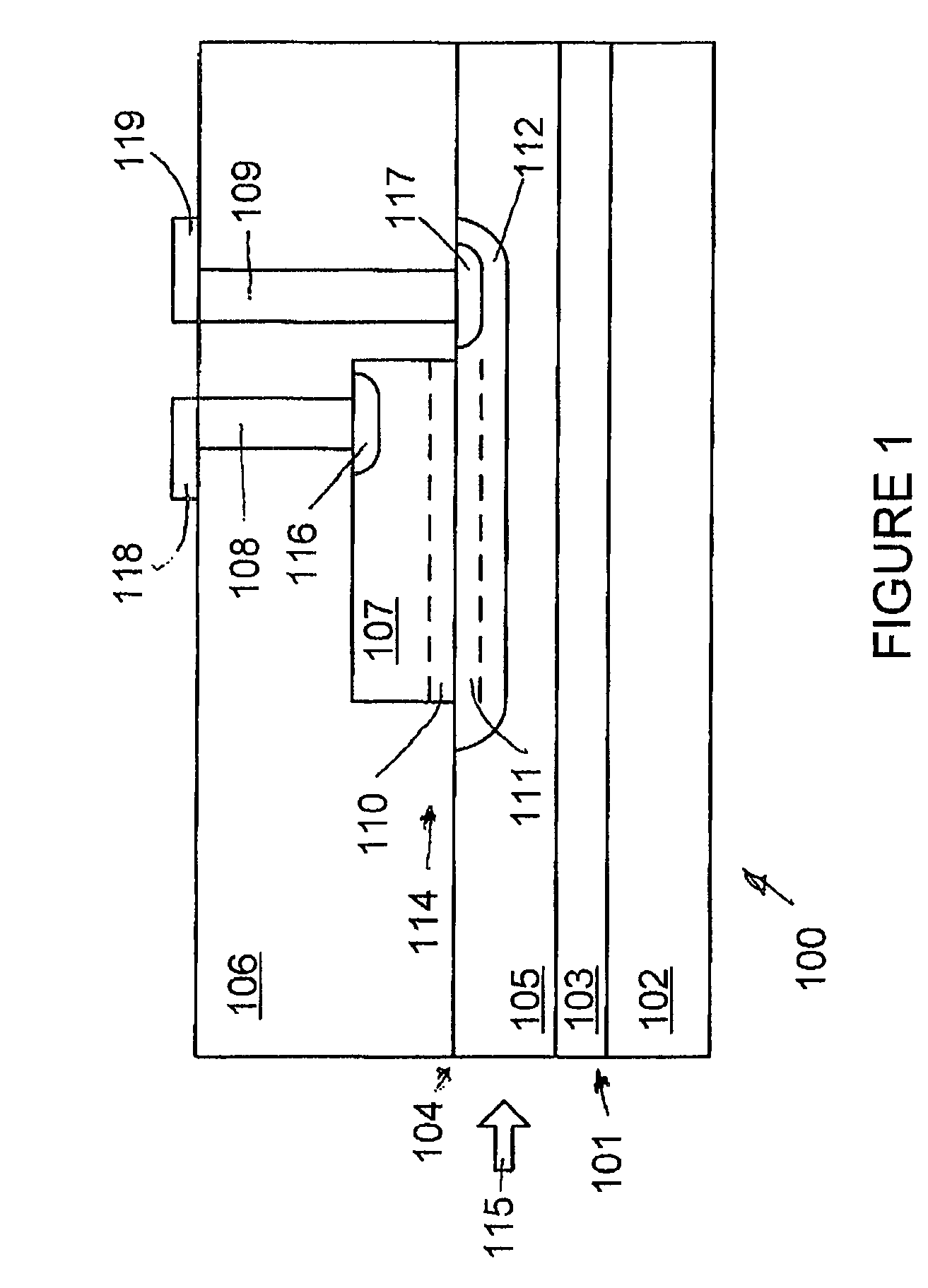
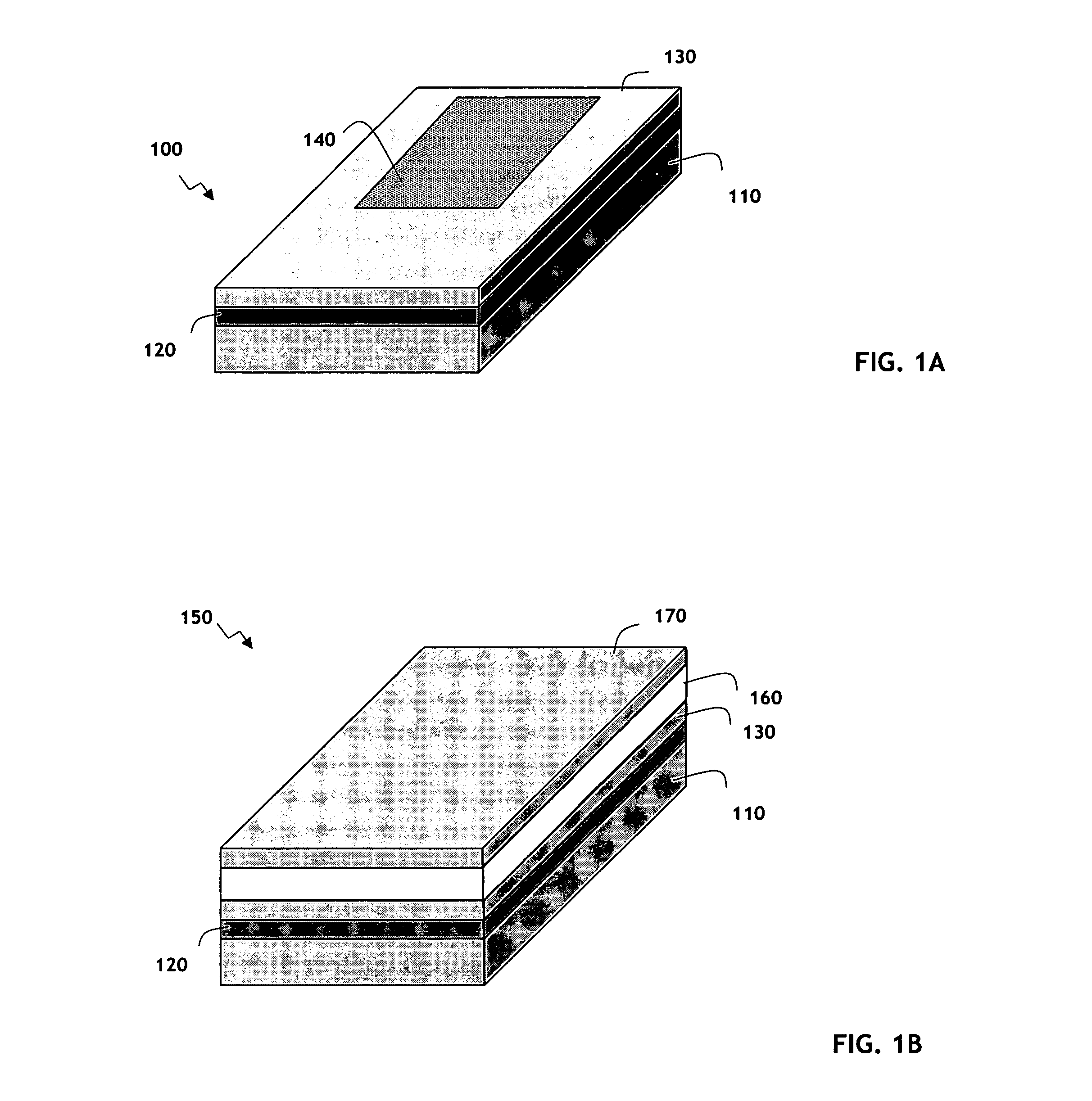
Waveguide photodetector with integrated electronics
A germanium on silicon waveguide photodetector disposed on a silicon on insulator (SOI) substrate. The photodetector is incorporated into a section of a planar silicon waveguide on the substrate. The photodetector generates an electric current as an infrared optical signal travels through the photodetector.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
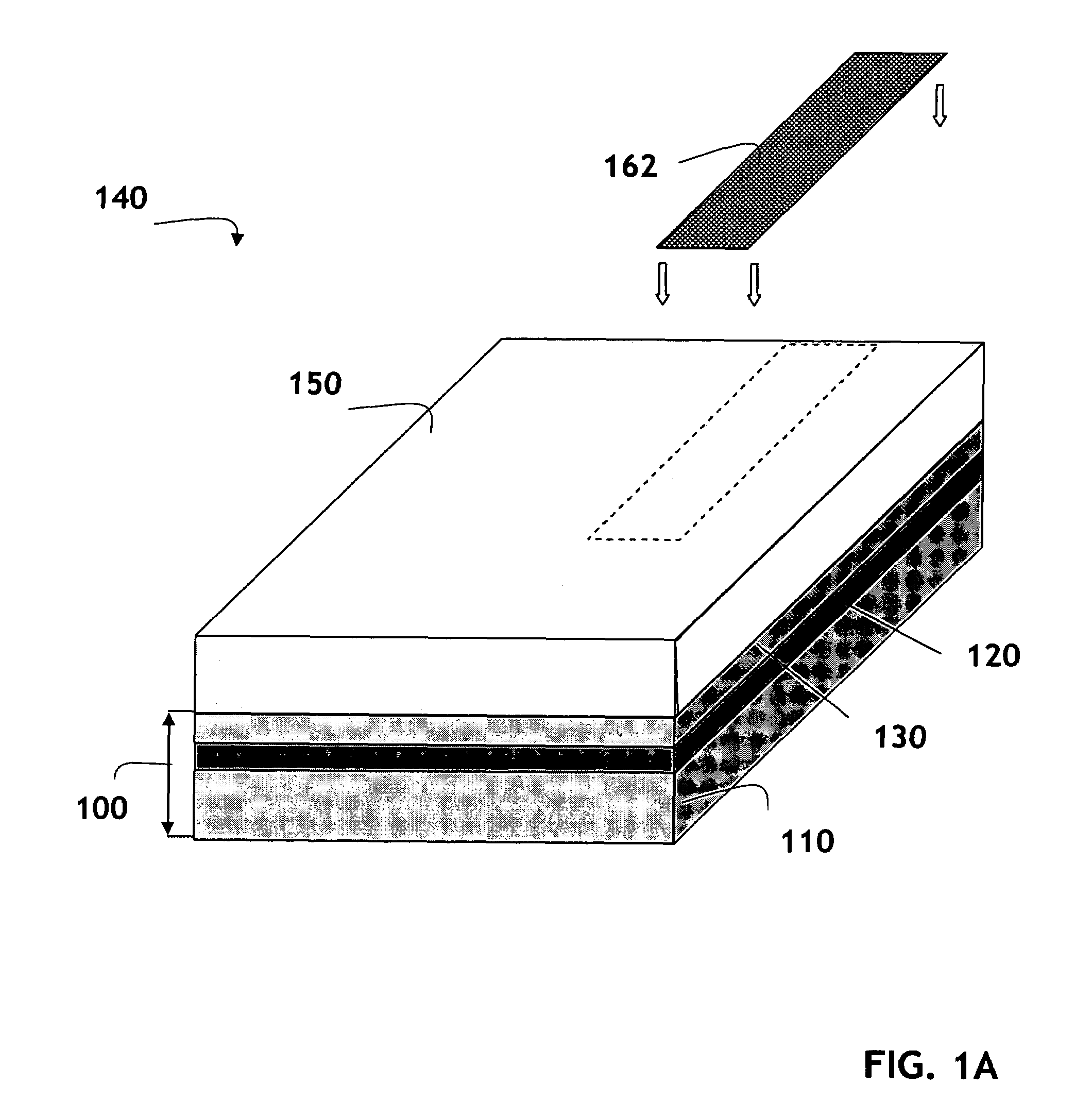
Waveguide photodetector device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20090324164A1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsOpto electronic
Embodiments of the present invention describe a waveguide-based photodetector device and its methods of fabrication. The waveguide photodetector device comprises a substrate having a cladding structure formed thereon. A waveguide element for receiving optical signals is disposed within the cladding structure. A portion of the waveguide element is encapsulated by a photodetector element that detects the optical signal received by the waveguide element and generates an electrical signal based on the optical signal. Encapsulating the waveguide element in the photodetector element improves coupling efficiency and enables a waveguide photodetector device with higher speeds and higher responsivity.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Waveguide photodetector with integrated electronics
A germanium on silicon waveguide photodetector disposed on a silicon on insulator (SOI) substrate. The photodetector is incorporated into a section of a planar silicon waveguide on the substrate. The photodetector generates an electric current as an infrared optical signal travels through the photodetector.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Vertically-integrated waveguide photodetector apparatus and related coupling methods
High-speed optoelectronic devices having a waveguide densely integrated with and efficiently coupled to a photodetector are fabricated utilizing methods generally compatible with CMOS processing techniques. In various implementations, the waveguide consists essentially of single-crystal silicon and the photodetector contains, or consists essentially of, epitaxially grown germanium or a silicon-germanium alloy having a germanium concentration exceeding about 90%.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
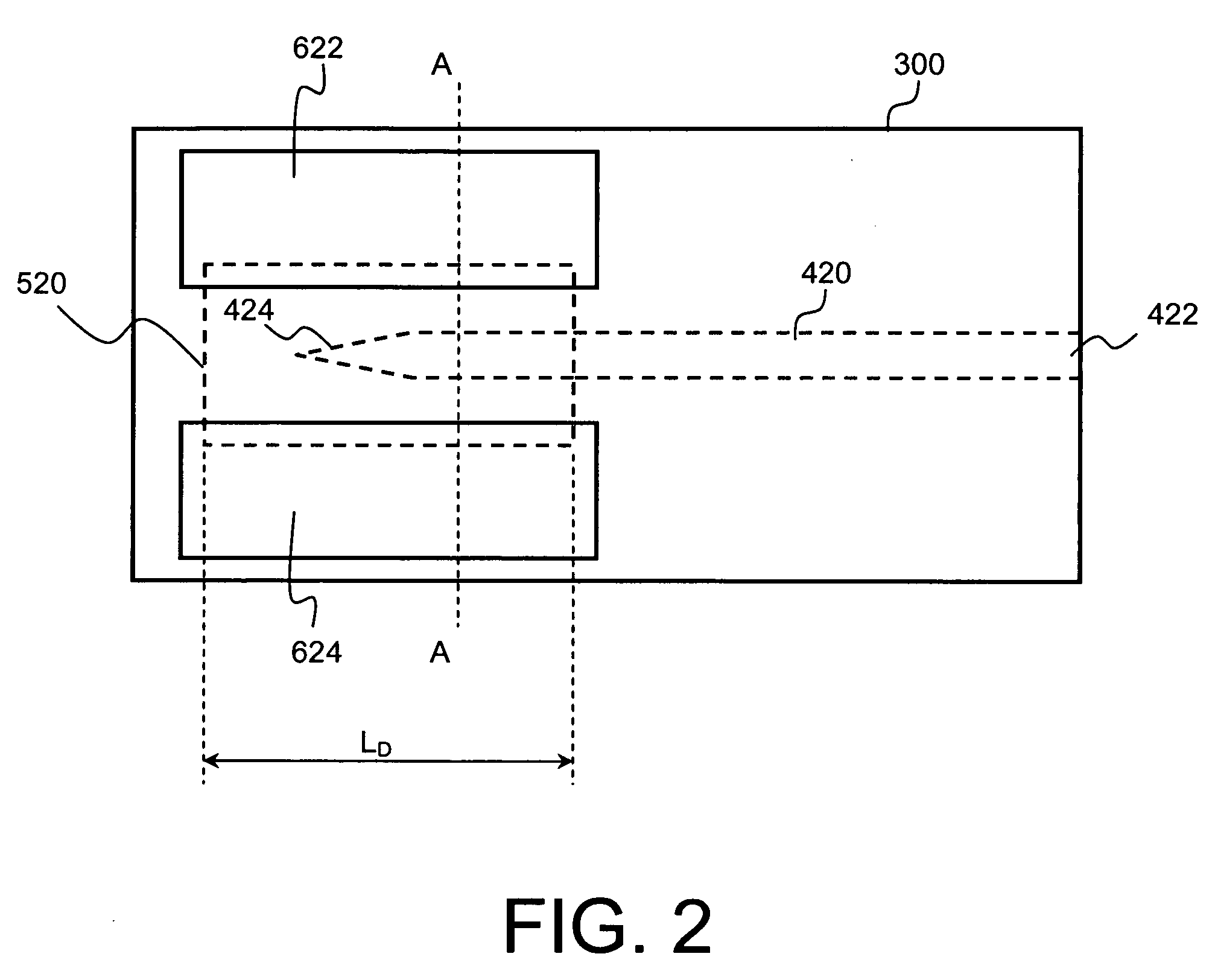
Integrated waveguide photodetector apparatus with matching propagation constants and related coupling methods
ActiveUS20070104410A1Increase data rateCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCMOSPhotovoltaic detectors
High-speed optoetectronic devices having a waveguide densely integrated with and efficiently coupled to a photodetector are fabricated utilizing methods generally compatible with CMOS processing techniques. In various implementations, the waveguide consists essentially of single-crystal silicon and the photodetector contains, or consists essentially of, epitaxially grown germanium or a silicon-germanium alloy having a germanium concentration exceeding about 90%.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
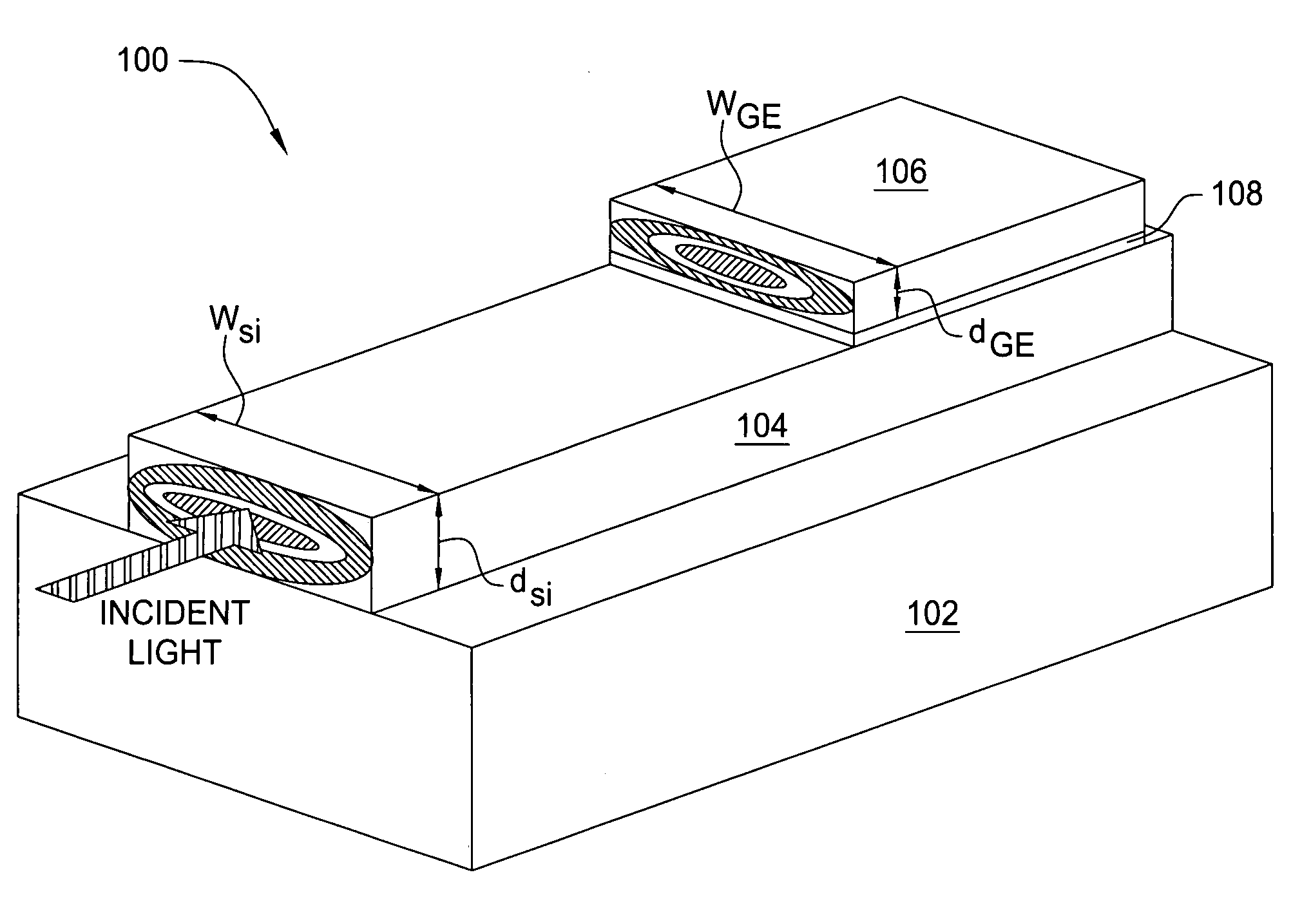
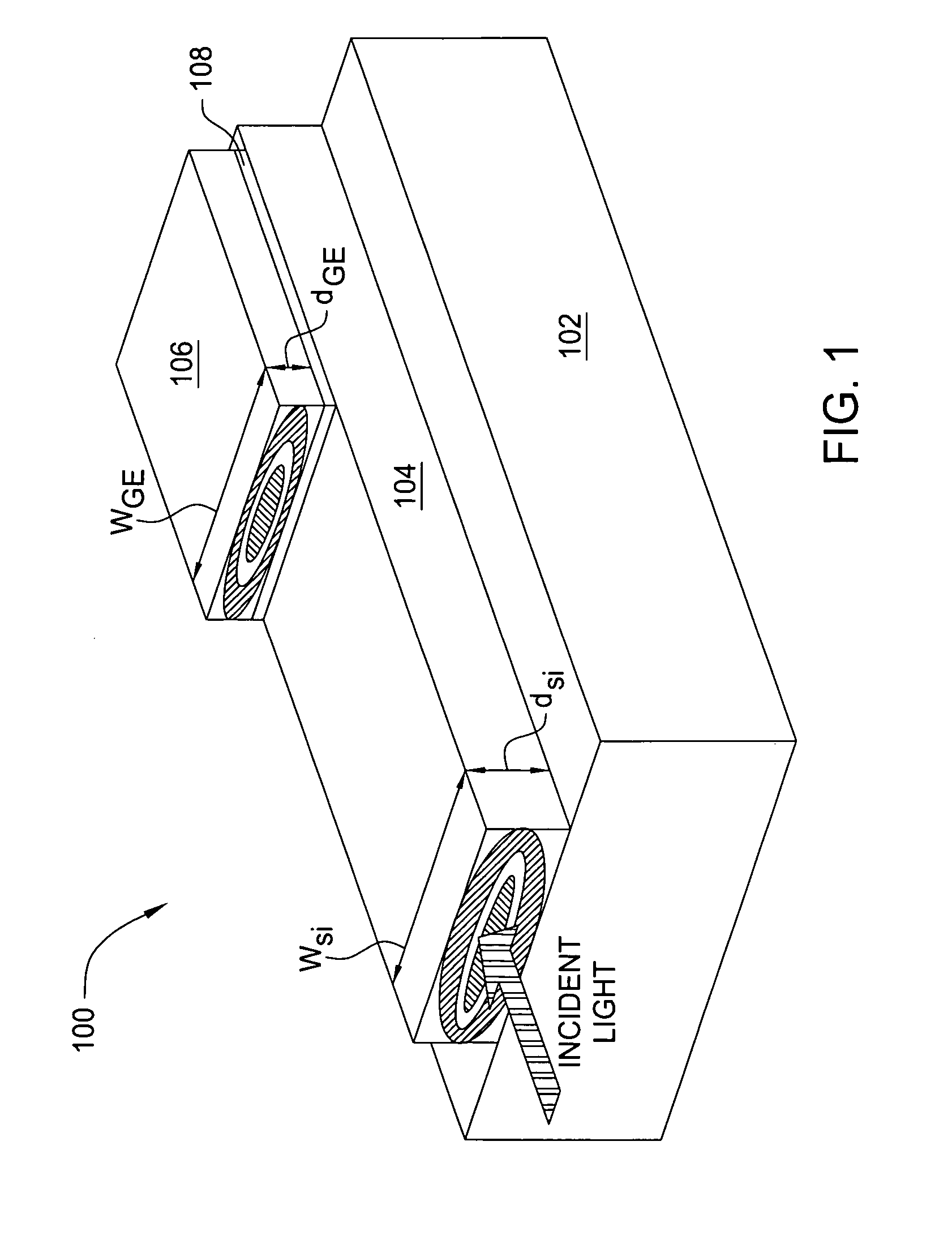
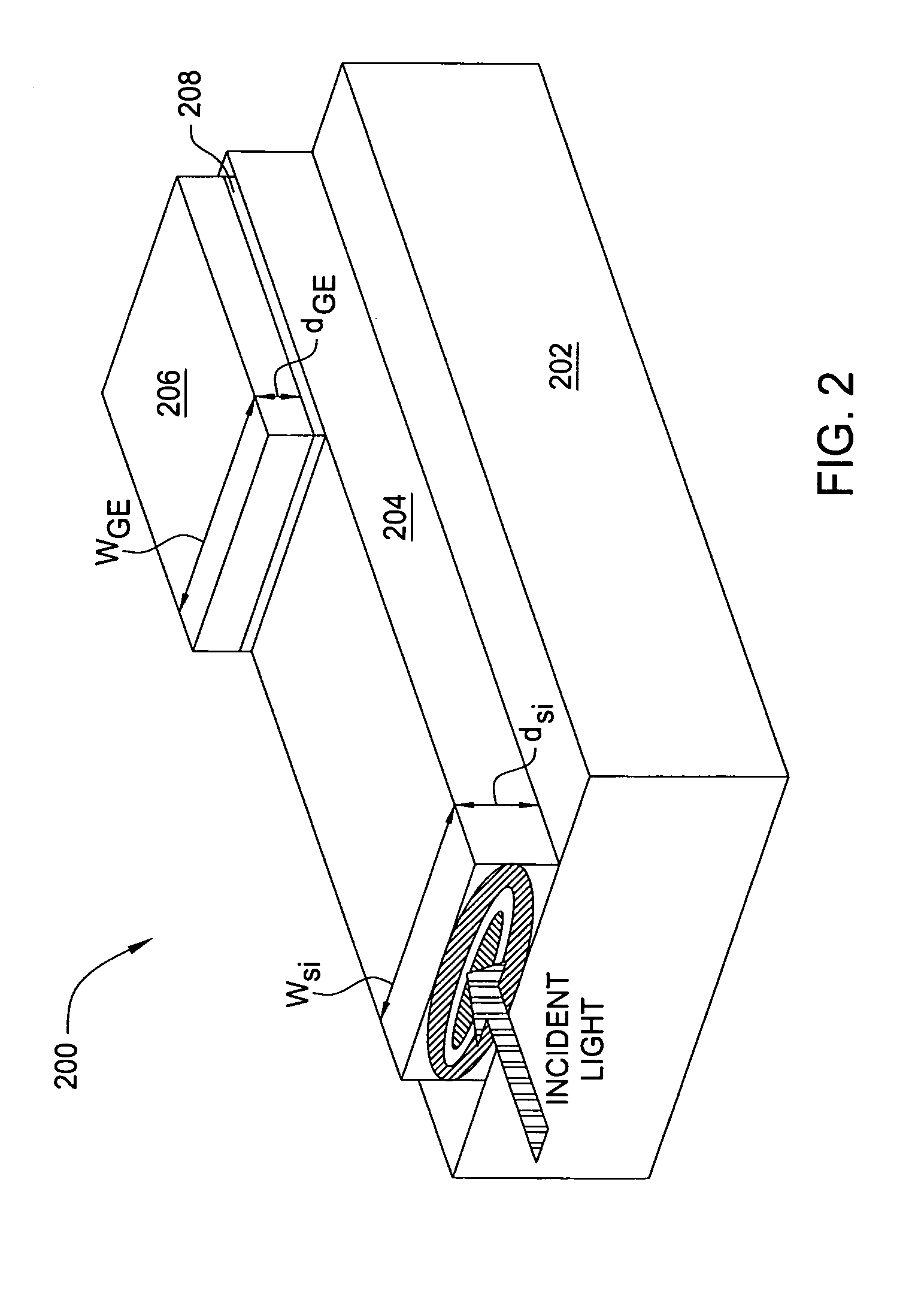
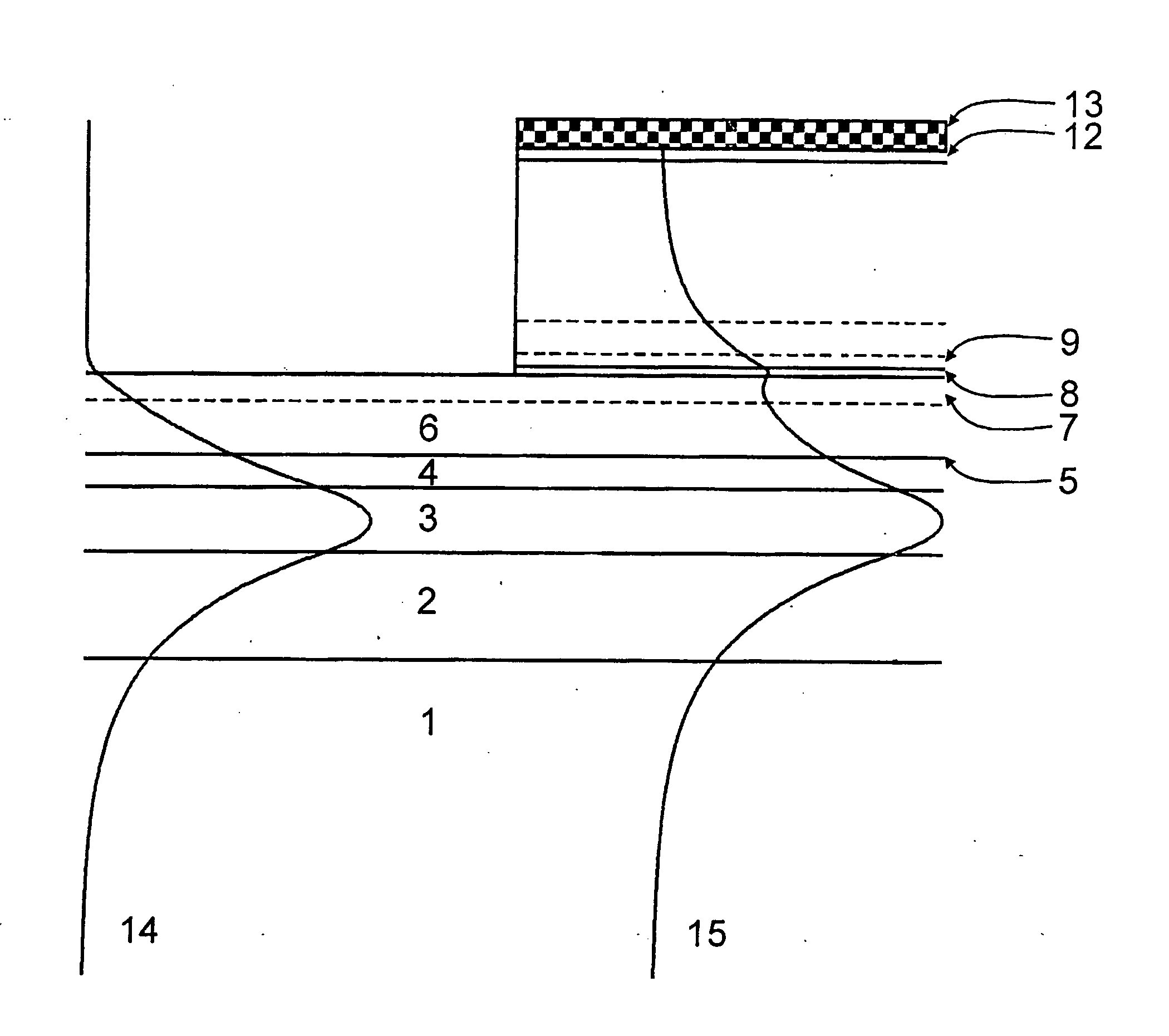
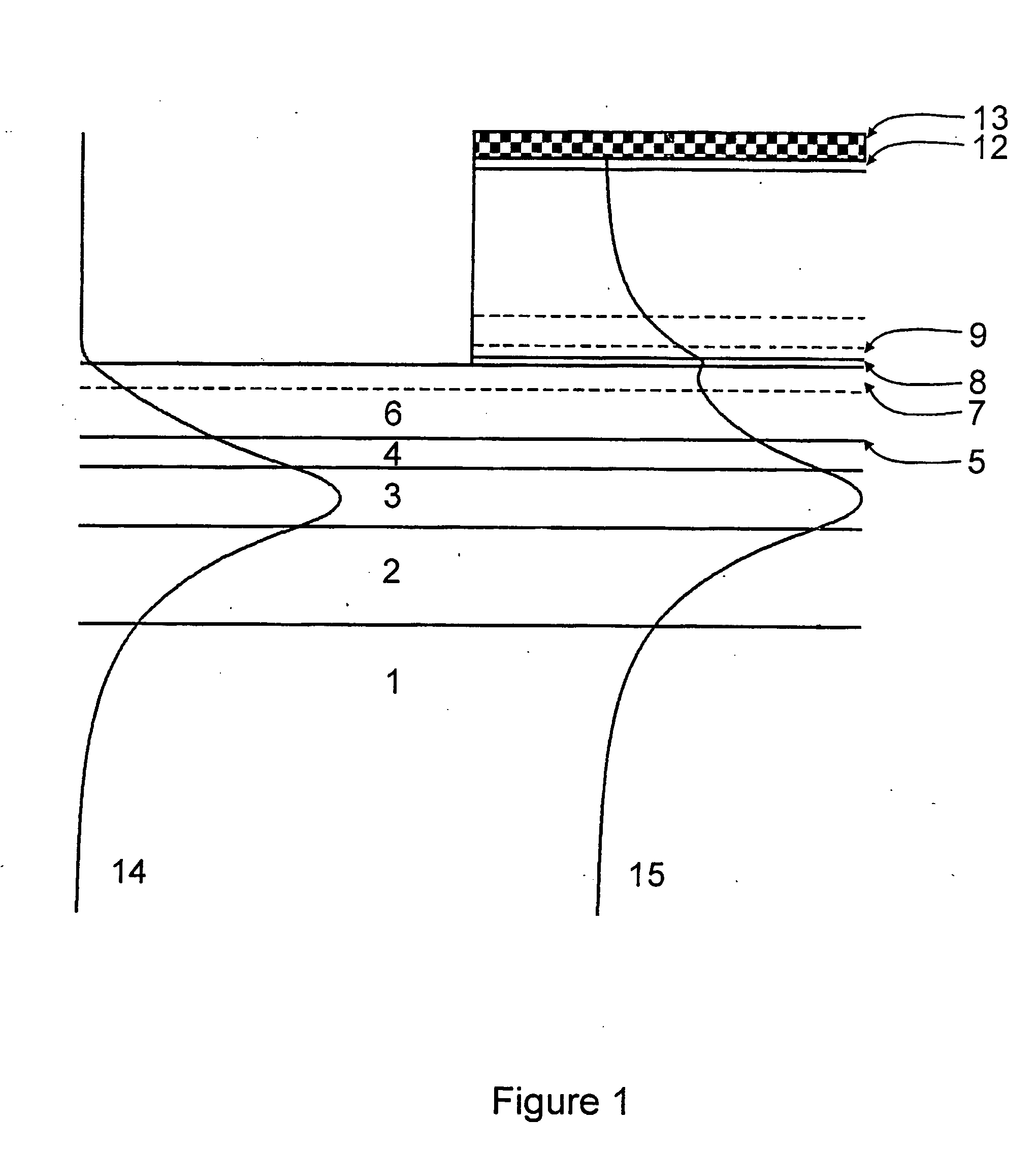
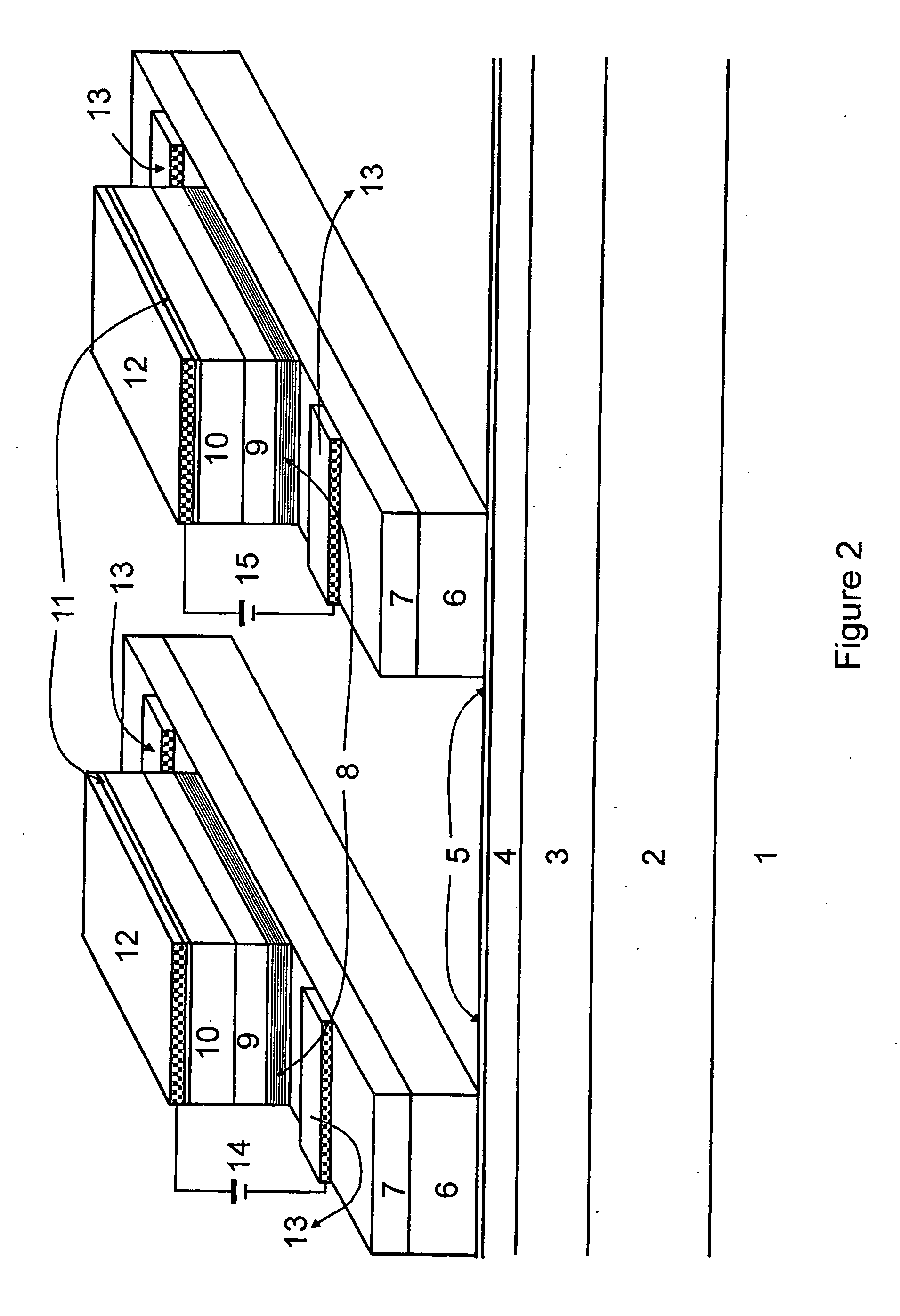
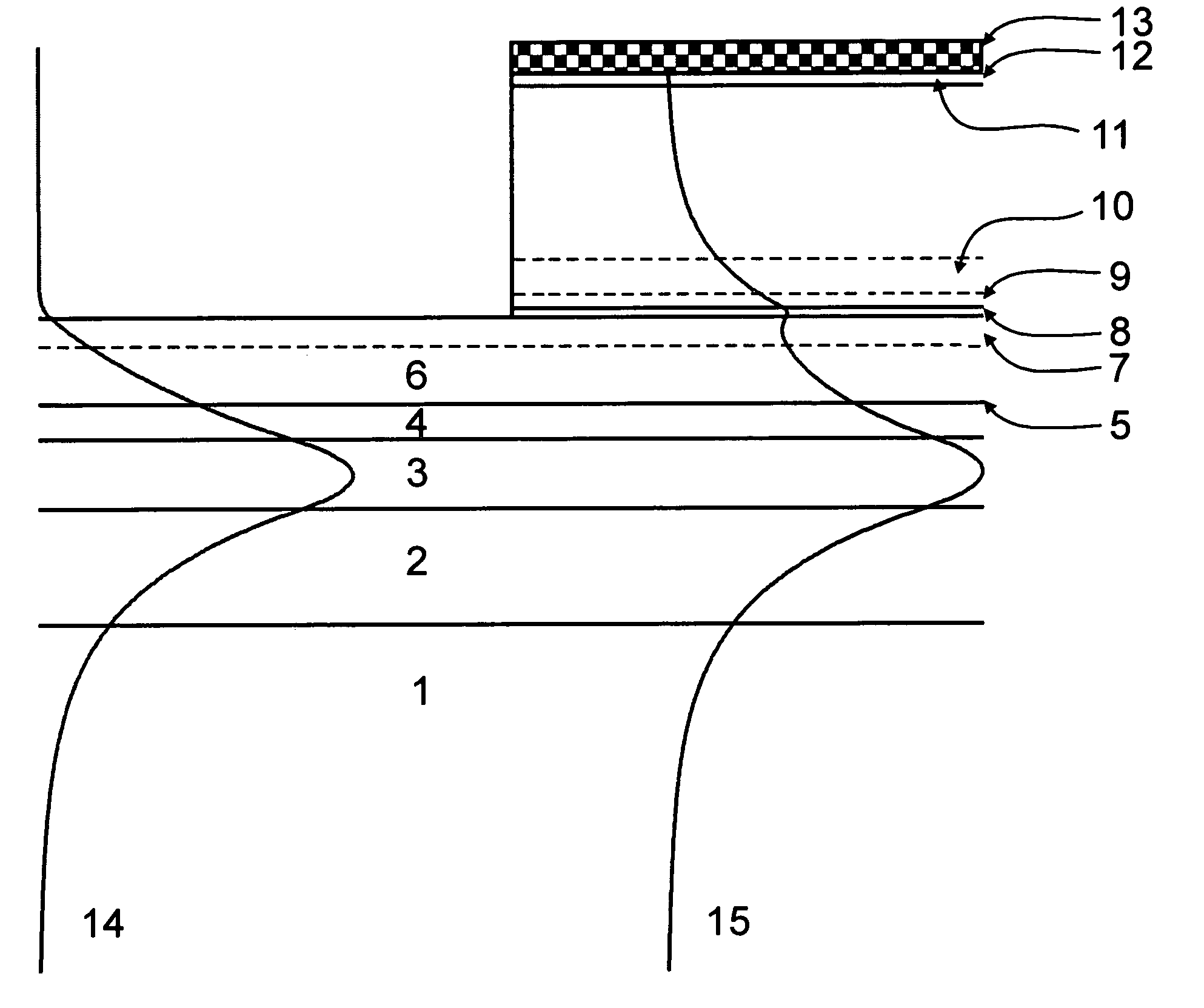
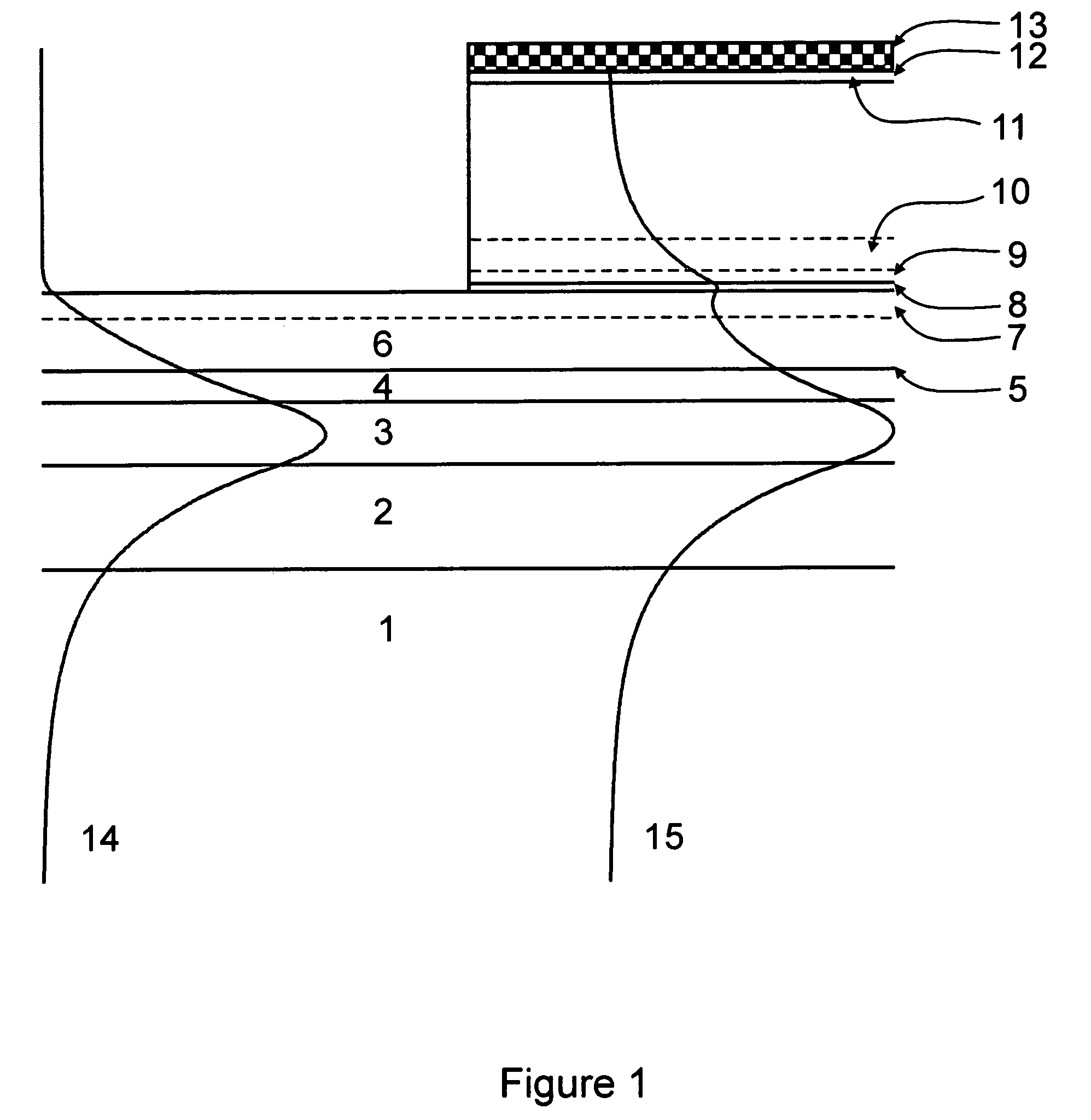
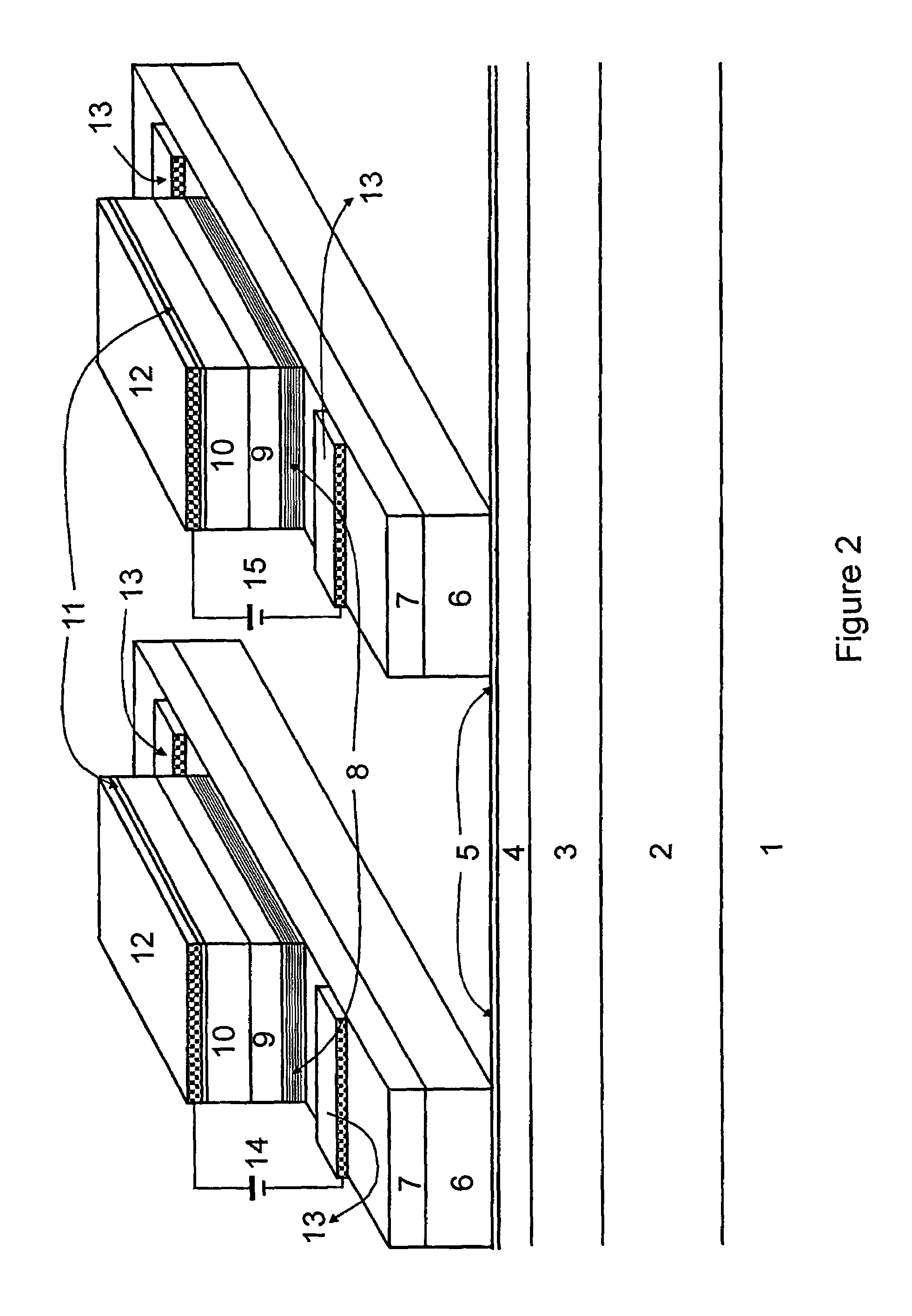
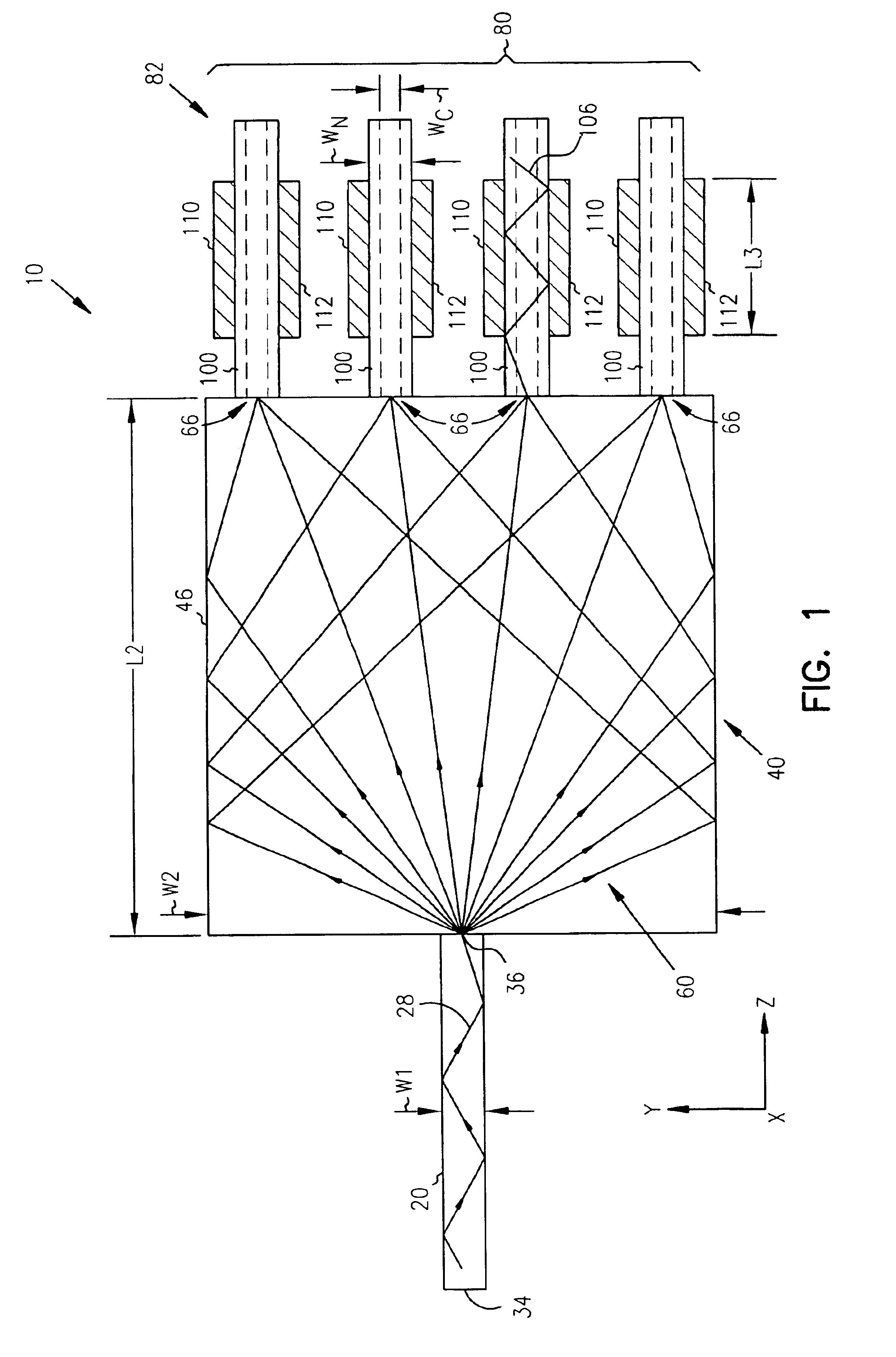
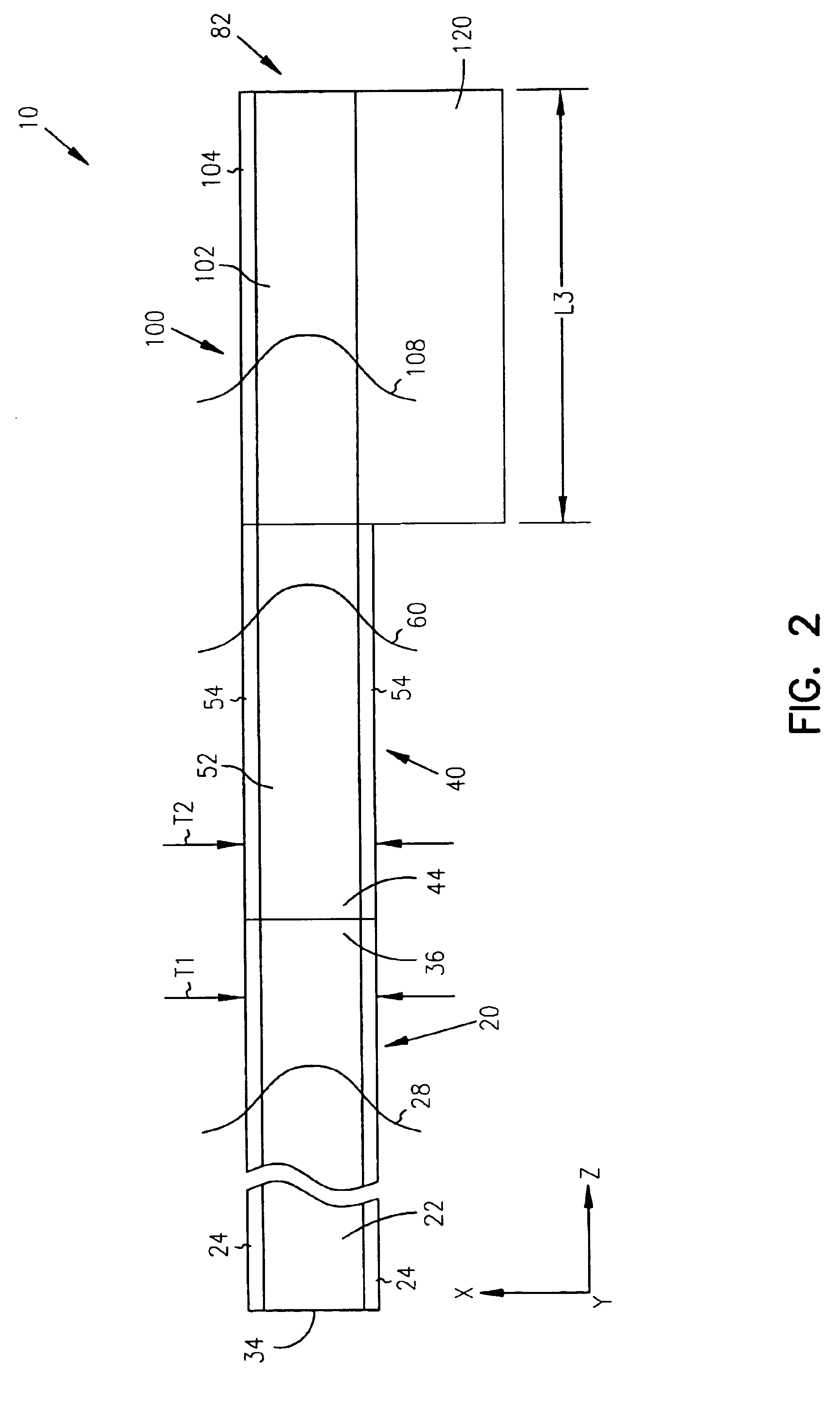
Waveguide photodetector
ActiveUS20070189688A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePhotovoltaic detectorsElectrical contacts
The present invention is a waveguide photodetector. In one embodiment, the waveguide photodetector includes a waveguide layer where light is guided or is confined and a detection layer formed on the waveguide layer where guided light is detected. Each of the waveguide layer and the detection layer allows for the guiding of no more than a single mode of light for a given polarization. In another embodiment, the waveguide photodetector includes a waveguide layer where light is guided or is confined, a detection layer formed on the waveguide layer where guided light is detected, a first electrical contact coupled to the detection layer, and a second electrical contact coupled to the detection layer. The first electrical contact and the second electrical contact are disposed in a spaced-apart, substantially parallel manner relative to each other.
Owner:IBM CORP
Vertically-integrated waveguide photodetector apparatus and related coupling methods
ActiveUS20070104411A1Increase data rateCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCMOSPhotovoltaic detectors
High-speed optoelectronic devices having a waveguide densely integrated with and efficiently coupled to a photodetector are fabricated utilizing methods generally compatible with CMOS processing techniques. In various implementations, the waveguide consists essentially of single-crystal silicon and the photodetector contains, or consists essentially of, epitaxially grown germanium or a silicon-germanium alloy having a germanium concentration exceeding about 90%.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Waveguide photodetector
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
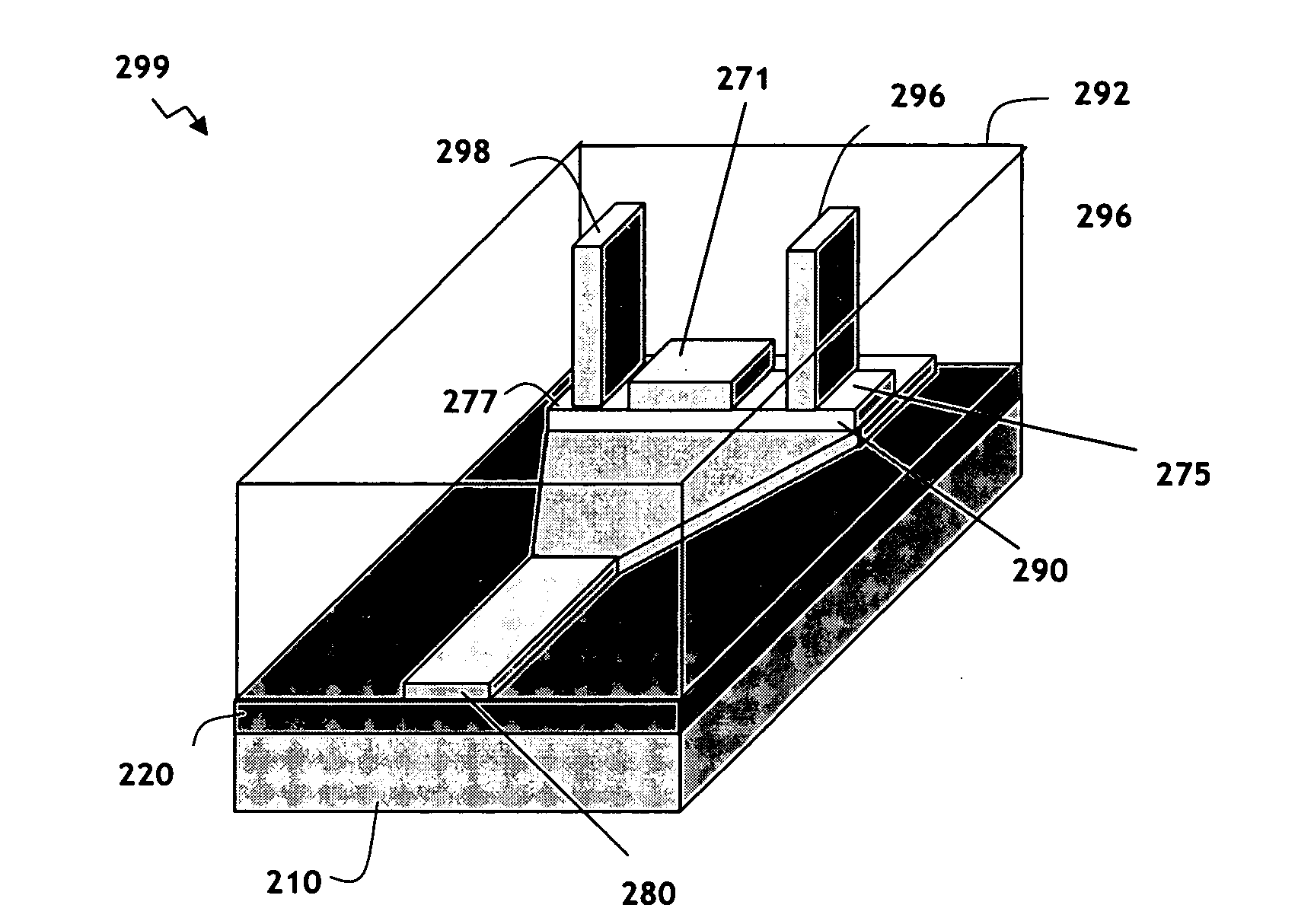
Single-mode vertical integration of active devices within passive semiconductor waveguides, a method and its applications for use in planar wdm components
InactiveUS20040096175A1Improve manufacturabilityOptical waveguide light guideSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsCommunications system
The invention discloses a method for monolithic integration of active devices within passive semiconductor waveguides and the application of this method for use in InP-based planar wavelength division multiplexing components of optical communication systems. The epitaxial device is grown in a single run and comprises a number of layers, such that the lower part of the structure acts as a single mode passive waveguide while the upper part of the structure contains a planar PIN diode. The PIN structure is present only in the active waveguide portion and absent in all the passive waveguide portions. The active and passive waveguide portions have substantially similar guiding properties with the exception of a mode tail above a top surface of the passive waveguide portion within the active waveguide portion. As a result, an optical signal portion penetrates the I-layer of the PIN structure and interacts with semiconductor material therein for actively affecting an intensity of the optical signal with no substantial changes in guiding properties of the semiconductor waveguide. Embodiments of invention in the form of monolithically integrated waveguide photodetector, electro-absorptive attenuator and semiconductor optical amplifier are disclosed in terms of detailed epitaxial structure, layout and performance characteristics of the device.
Owner:ENABLENCE
Vertical integration of active devices within passive semiconductor waveguides
InactiveUS7095938B2Optical waveguide light guideSemiconductor devicesElectricitySemiconductor materials
Owner:ENABLENCE
Integrated waveguide photodetector apparatus with matching propagation constants and related coupling methods
High-speed optoelectronic devices having a waveguide densely integrated with and efficiently coupled to a photodetector are fabricated utilizing methods generally compatible with CMOS processing techniques. In various implementations, the waveguide consists essentially of single-crystal silicon and the photodetector contains, or consists essentially of, epitaxially grown germanium or a silicon-germanium alloy having a germanium concentration exceeding about 90%.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
1 x N fanout waveguide photodetector
Owner:INTEL CORP
Enhanced graphene waveguide photodetector for integrally-distributed Bragg reflection grating
ActiveCN103943715ATo achieve the purpose of photoelectric detectionReduce volumeSemiconductor devicesResonant cavityGrating
The invention provides an enhanced graphene waveguide photodetector for an integrally-distributed Bragg reflection grating. The photodetector is manufactured on an SOI substrate and comprises an optical waveguide, an insulating transparent thin film, a graphene thin film, a first metal electrode, a second metal electrode and a gate electrode window. The optical waveguide is formed on the substrate in the longitudinal direction. The insulating transparent thin film is evenly manufactured on the substrate and covers the optical waveguide. The graphene thin film is manufactured on the insulating transparent thin film and covers the middle of the strip-shaped optical waveguide. The first metal electrode is provided with a contact end and a strip-shaped electrode end, the contact end of the first metal electrode is manufactured on one side of the insulating transparent thin film, and the electrode end of the first metal electrode is longitudinally manufactured on the graphene thin film. The second metal electrode is provided with a contact end and a strip-shaped electrode end, the contact end of the second metal electrode is manufactured on one side of the insulating transparent thin film, and the electrode end of the second metal electrode is longitudinally manufactured on the graphene thin film. The gate electrode window is formed on the insulating transparent thin film and located on any exposed surface of the insulating transparent thin film. The graphene photodetector is integrated with the waveguide, a resonant cavity and the like, and the defect of low optical responsivity is overcome.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coupled waveguide photo detector
An embodiment of the invention provides a coupled waveguide photo detector device. Optically, the device includes an input waveguide. An output waveguide is coupled to the input waveguide with a nonuniform coupling coefficient in a coupling section. An absorber is included in the coupling section to convert an absorbed portion of optical radiation into photo current. The location of absorber and the optical radiation intensity pattern in the coupling section are set to control the maximum intensity of output power absorbed by the output waveguide to be within a predetermined limit that avoids saturation. The absorber is also part of a transmission line collector which has a phase and group velocity to match those of the optical wave in the coupling section such that currents collected by the transmission line collector add in phase as the optical wave propagates in the output waveguide.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Waveguide photodetector device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS8290325B2Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsCoupling efficiency
Embodiments of the present invention describe a waveguide-based photodetector device and its methods of fabrication. The waveguide photodetector device comprises a substrate having a cladding structure formed thereon. A waveguide element for receiving optical signals is disposed within the cladding structure. A portion of the waveguide element is encapsulated by a photodetector element that detects the optical signal received by the waveguide element and generates an electrical signal based on the optical signal. Encapsulating the waveguide element in the photodetector element improves coupling efficiency and enables a waveguide photodetector device with higher speeds and higher responsivity.
Owner:INTEL CORP
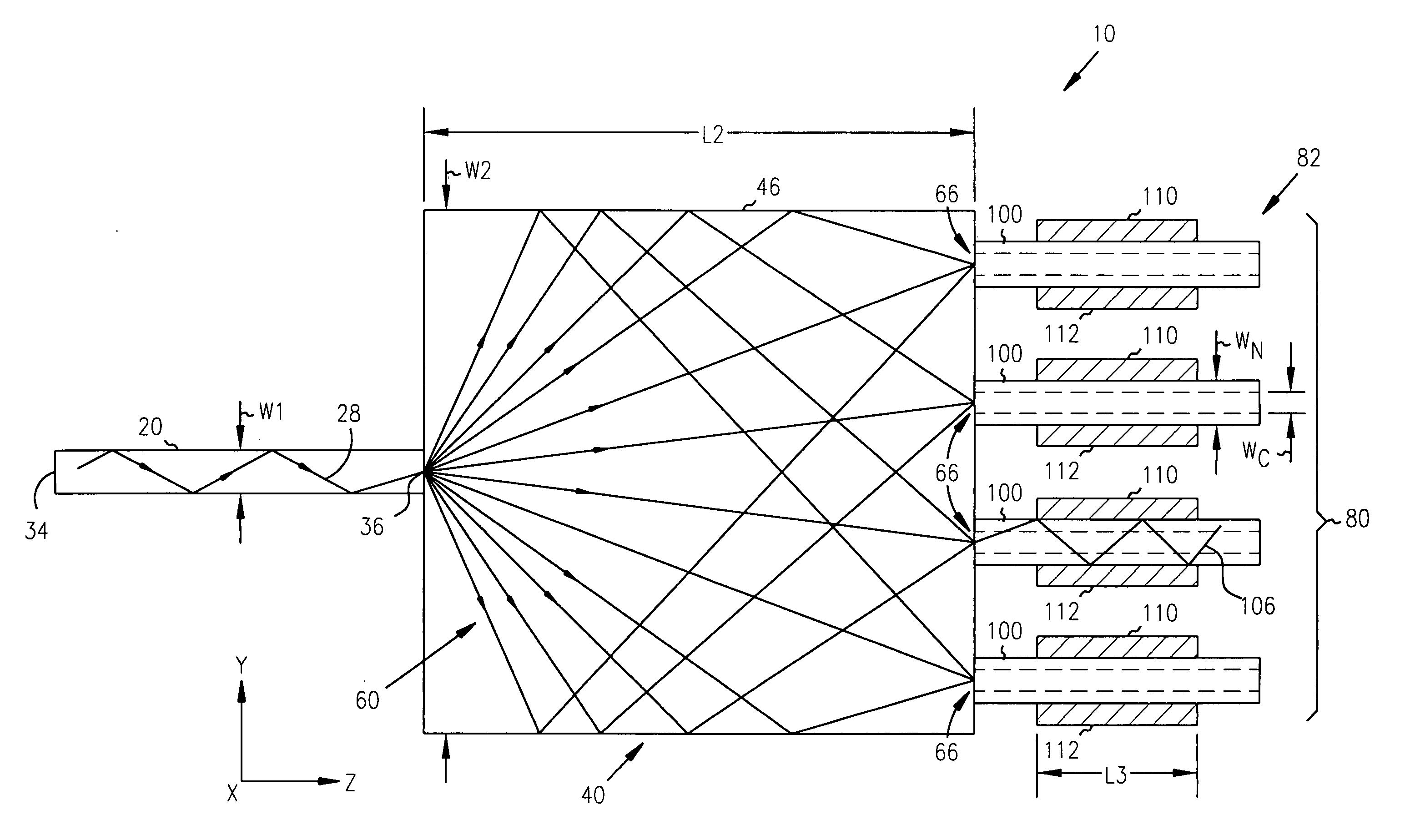
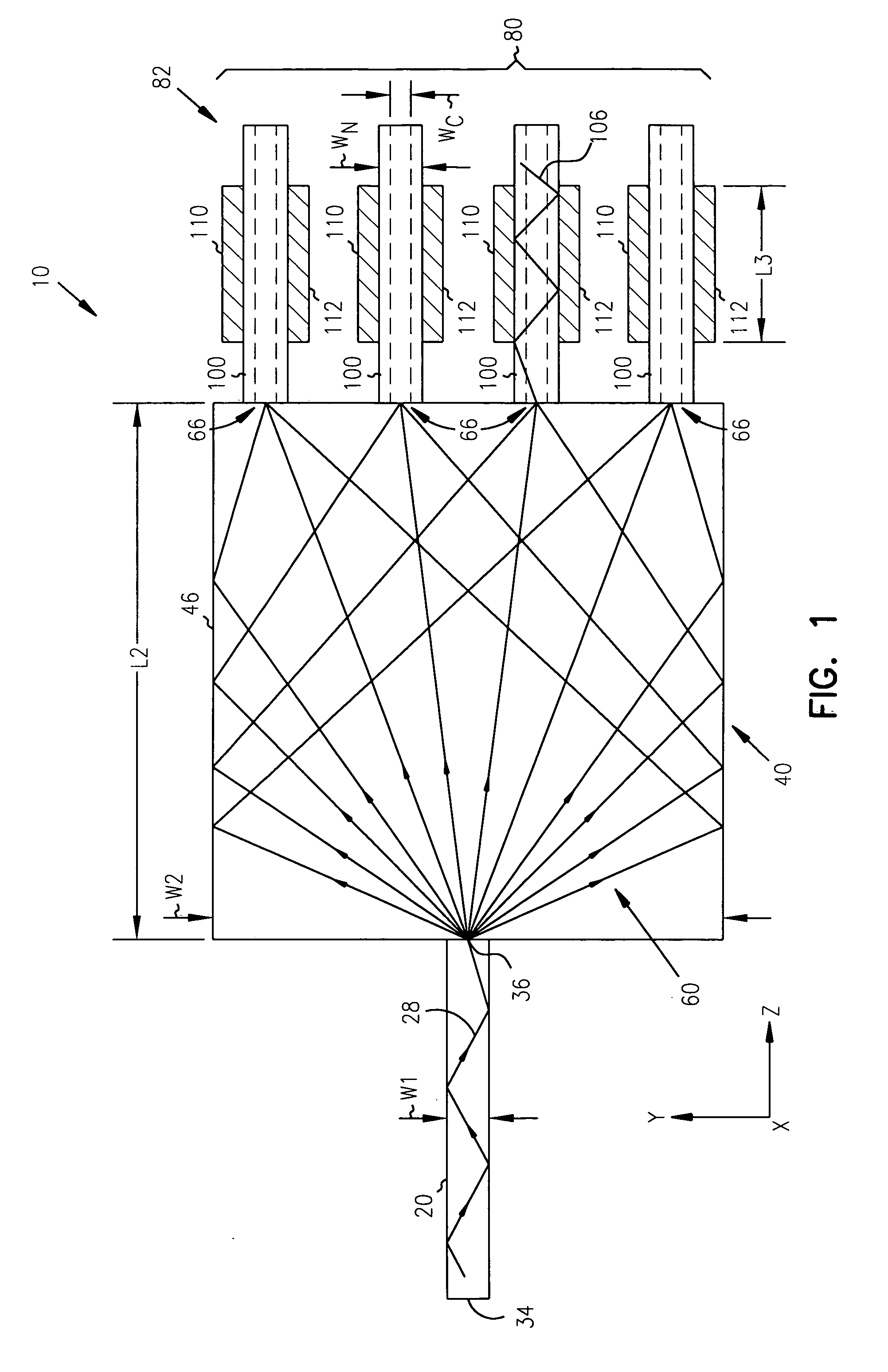
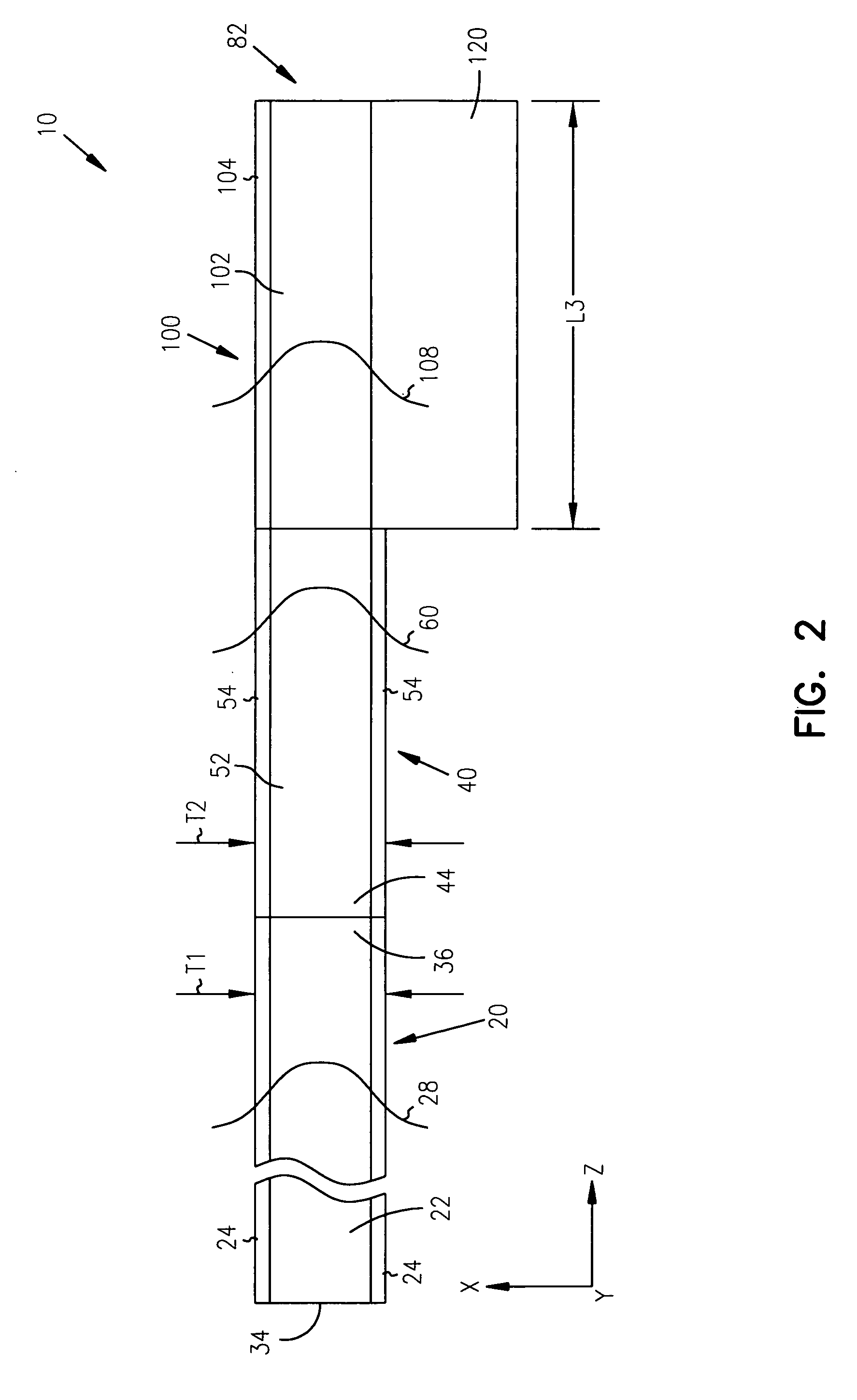
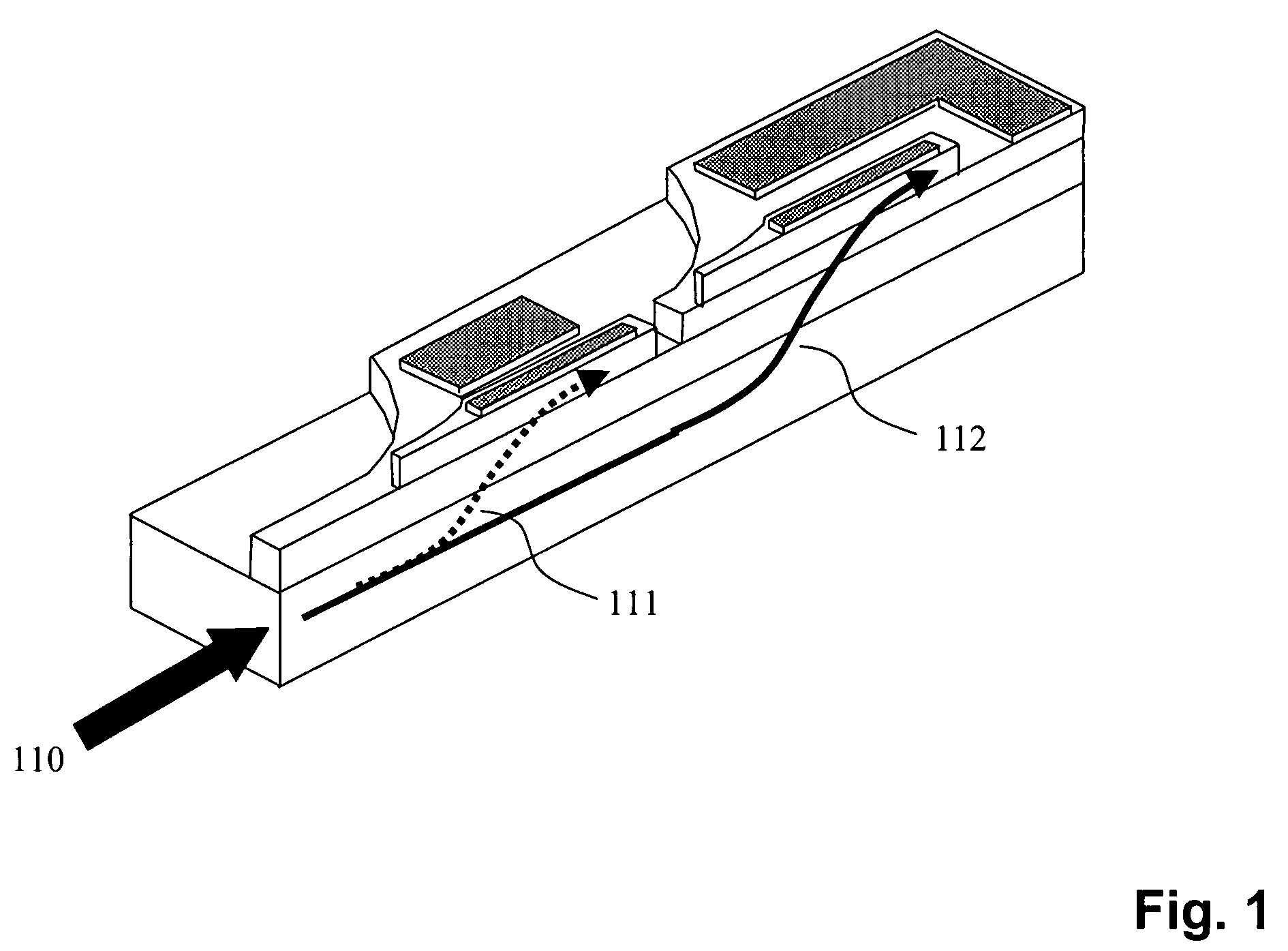
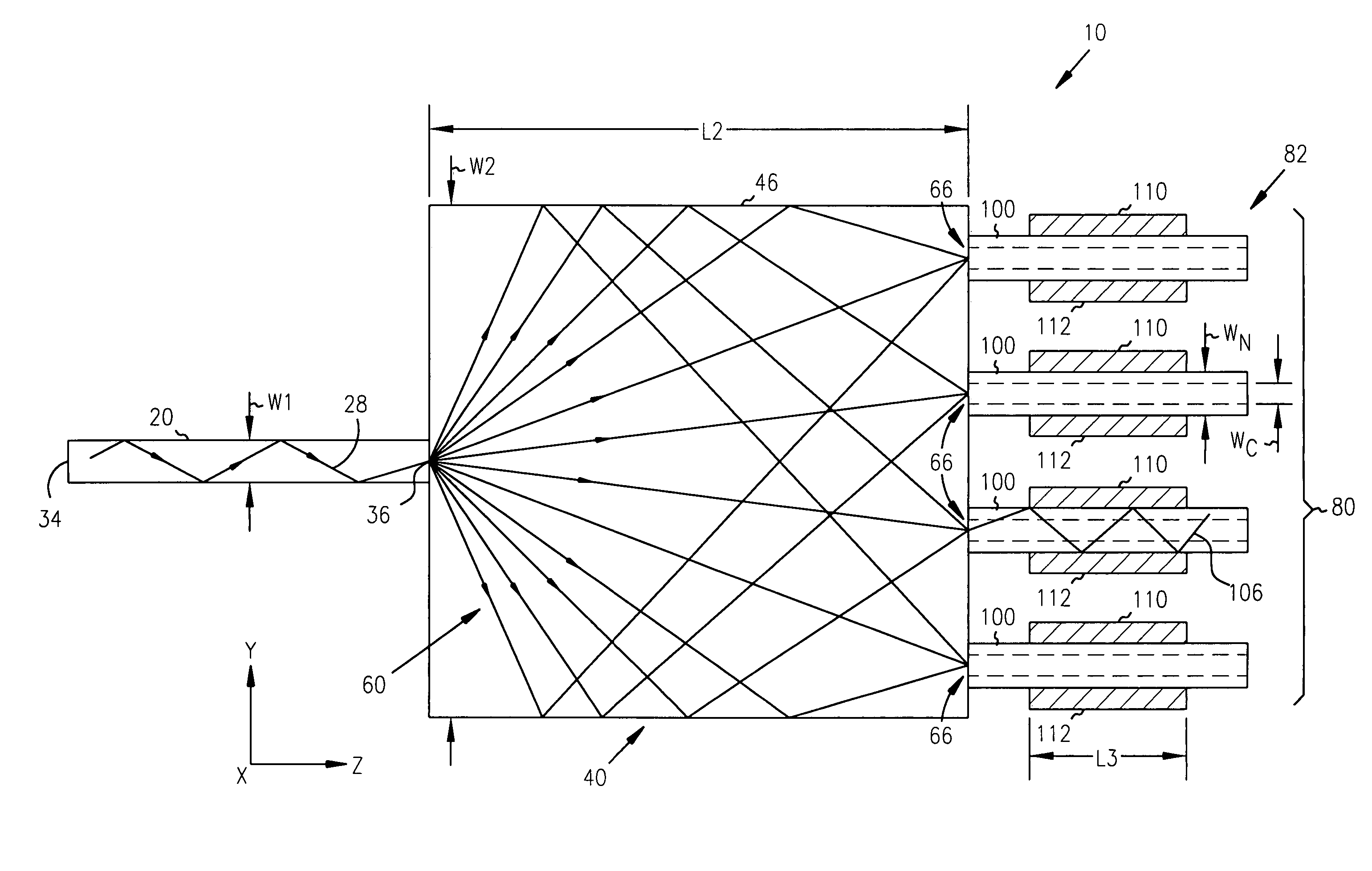
1xN fanout waveguide photodetector
InactiveUS6856733B2Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideQuantum efficiencyCharge carrier
A 1×N fanout waveguide detector is disclosed. The detector includes a multiple-mode interference (MMI) cavity with input and output ends. A single-mode waveguide is optically coupled to the input end of the MMI cavity so that the optical power in the guided mode is distributed over N modes. The MMI cavity forms N interference nodes at or near its output end. N waveguide detectors are optically coupled to the output end at or near the N interference nodes. The waveguide detectors each have a waveguide that is evanescently coupled to an intrinsic region of a PIN detector. The width of the detector waveguide core, which can be sub-micron, defines the carrier collection distance between the electrodes of the PIN detector. Further, the length of the detector waveguide can be selected to maximize optical absorption to provide optimum quantum efficiency. The waveguide detectors are connected in parallel to provide a high-output photocurrent.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
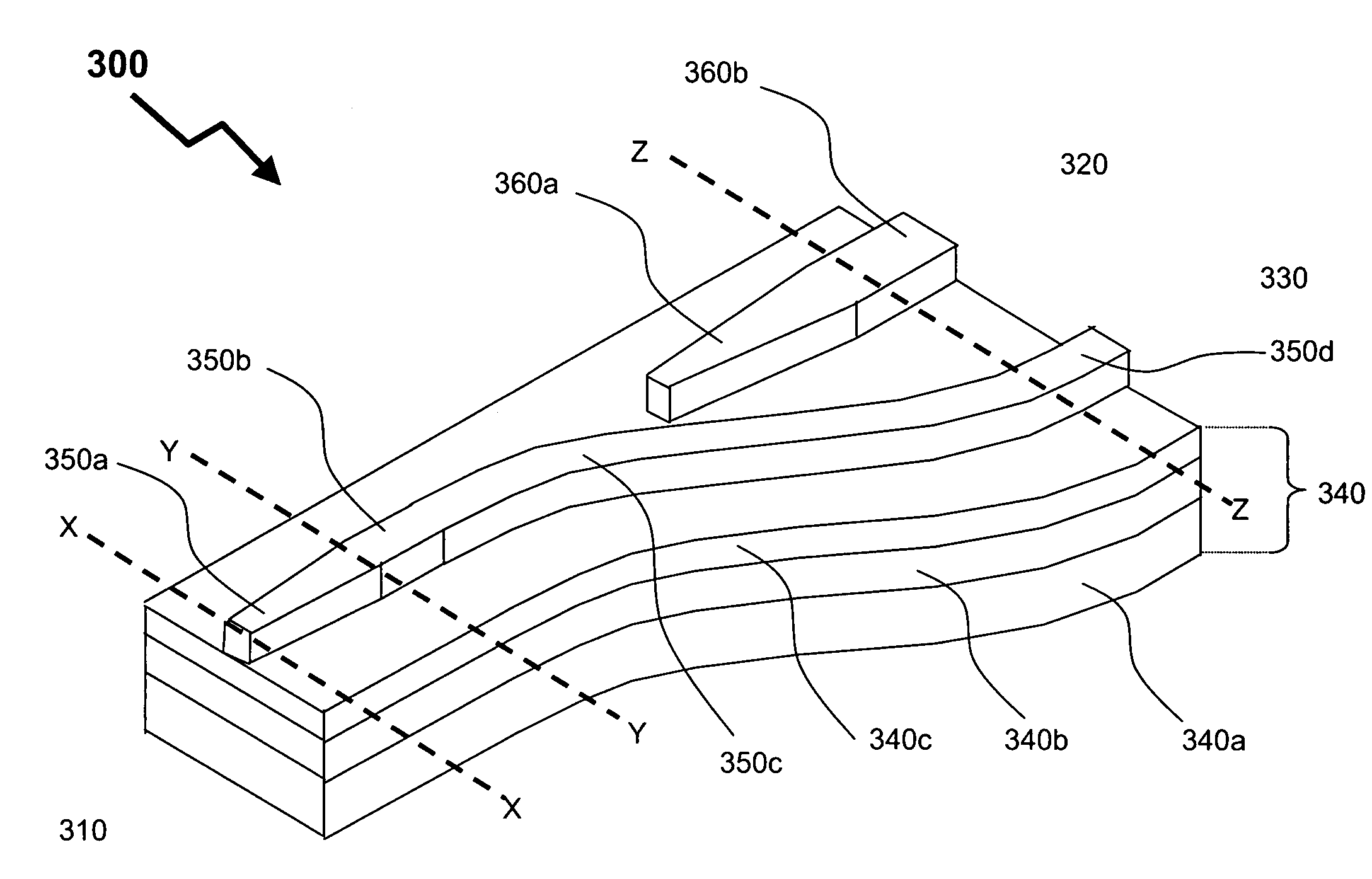
Integrated optics arrangement for wavelength (De)multiplexing in a multi-grade vertical stack
ActiveUS7444055B2Efficiently transitionImprove insertion lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMultiplexingTransceiver
The invention describes an integrated-photonics arrangement, implementable in a multi-guide vertical integration structure composed from III-V semiconductors and grown in one epitaxial growth run, that allows for vertical and lateral splitting of optical signals co- or bi-directionally propagating in the common passive waveguide into plurality of the vertically integrated passive or active wavelength-designated waveguides, therefore, enabling the wavelength-designated waveguides operating in different wavelengths to be monolithically integrated onto the same substrate and connected to the shared passive waveguide. In the exemplary embodiments of the invention, two active wavelength-designated waveguides, each of which either laser or photodetector, are vertically integrated with a common passive waveguide connected to the input / output optical port shared by both operating wavelengths, to form a single-fiber, two-wavelength receiver (both wavelength-designated waveguides are waveguide photodetectors) or transmitter (both wavelength-designated waveguides are edge-emitting semiconductor injection lasers) or transceiver (one wavelength-designated waveguide is waveguide photodetector and the other—edge-emitting semiconductor injection laser). Advantageously to the previous art, the proposed vertical splitting and lateral routing allows for a reduced footprint size while greatly improving design flexibility and / or device performance.
Owner:ONECHIP PHOTONICS
Integrated optics arrangement for wavelength (De)multiplexing in a multi-grade vertical stack
ActiveUS20080138008A1No longer transmittedEfficiently transitionWavelength-division multiplex systemsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransceiverWaveguide photodetector
The invention describes an integrated-photonics arrangement, implementable in a multi-guide vertical integration structure composed from III-V semiconductors and grown in one epitaxial growth run, that allows for vertical and lateral splitting of optical signals co- or bi-directionally propagating in the common passive waveguide into plurality of the vertically integrated passive or active wavelength-designated waveguides, therefore, enabling the wavelength-designated waveguides operating in different wavelengths to be monolithically integrated onto the same substrate and connected to the shared passive waveguide. In the exemplary embodiments of the invention, two active wavelength-designated waveguides, each of which either laser or photodetector, are vertically integrated with a common passive waveguide connected to the input / output optical port shared by both operating wavelengths, to form a single-fiber, two-wavelength receiver (both wavelength-designated waveguides are waveguide photodetectors) or transmitter (both wavelength-designated waveguides are edge-emitting semiconductor injection lasers) or transceiver (one wavelength-designated waveguide is waveguide photodetector and the other—edge-emitting semiconductor injection laser). Advantageously to the previous art, the proposed vertical splitting and lateral routing allows for a reduced footprint size while greatly improving design flexibility and / or device performance.
Owner:ONECHIP PHOTONICS
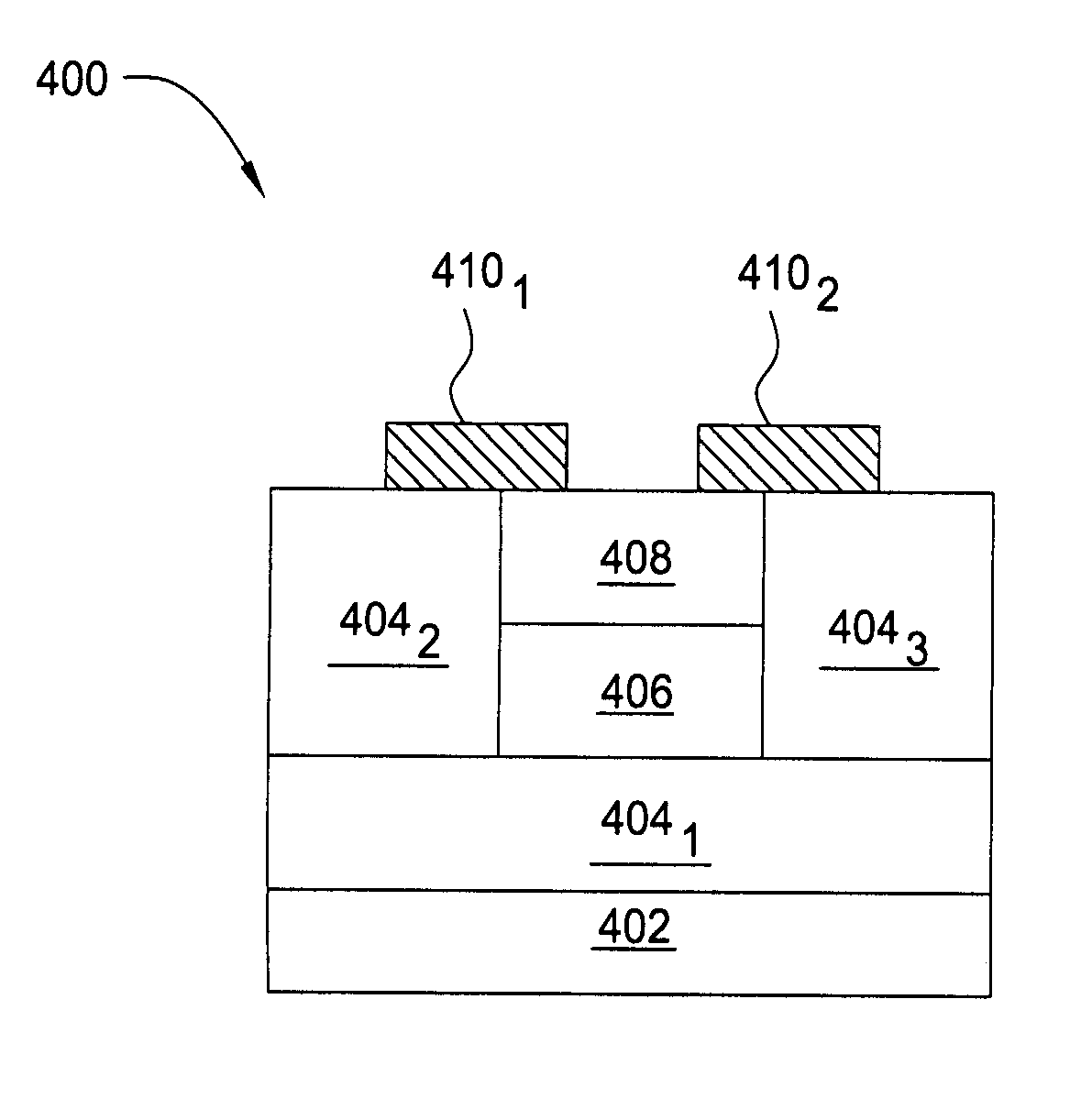
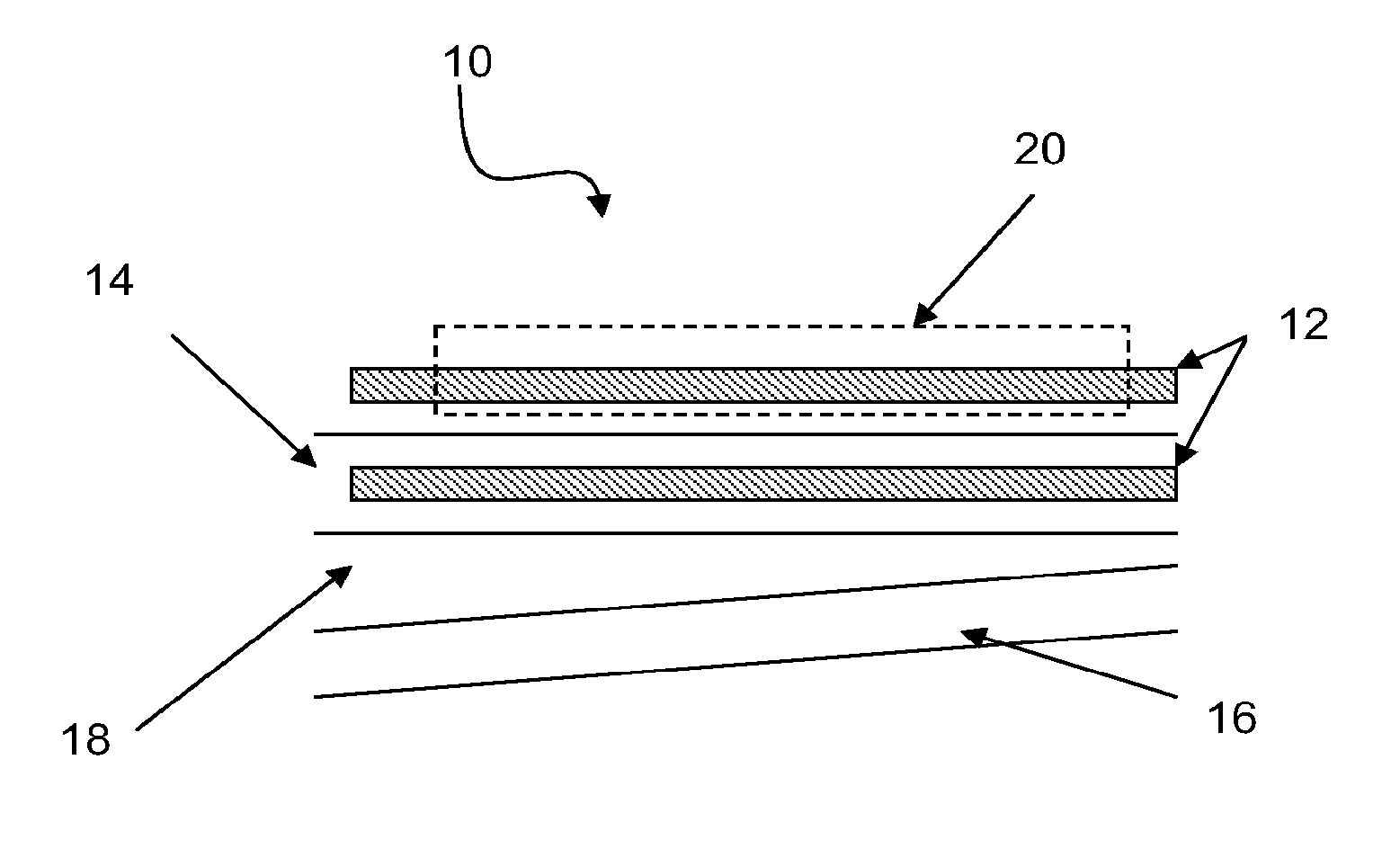
Photodetector employing slab waveguide modes
ActiveUS20060000976A1Low costThe preparation process is stableMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsGratingPhotovoltaic detectors
A photodetector for detecting infrared radiation (IR) using a slab waveguide is described. The slab waveguide photodetector operates by resonating transverse magnetic or electric modes within the slab from the incident IR. An IR absorbing layer is located within the slab waveguide photodetector where the magnitude of the electric field vector is greatest. This permits the use of a thinner IR absorbing layer without sacrificing photoresponse. Multi-color slab waveguide photodetectors are permitted because multiple transverse magnetic or electric modes resonate within the slab waveguide. A reflective or transmissive grating is used to launch the IR into the IR absorbing layer through a cladding or antireflection layer.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
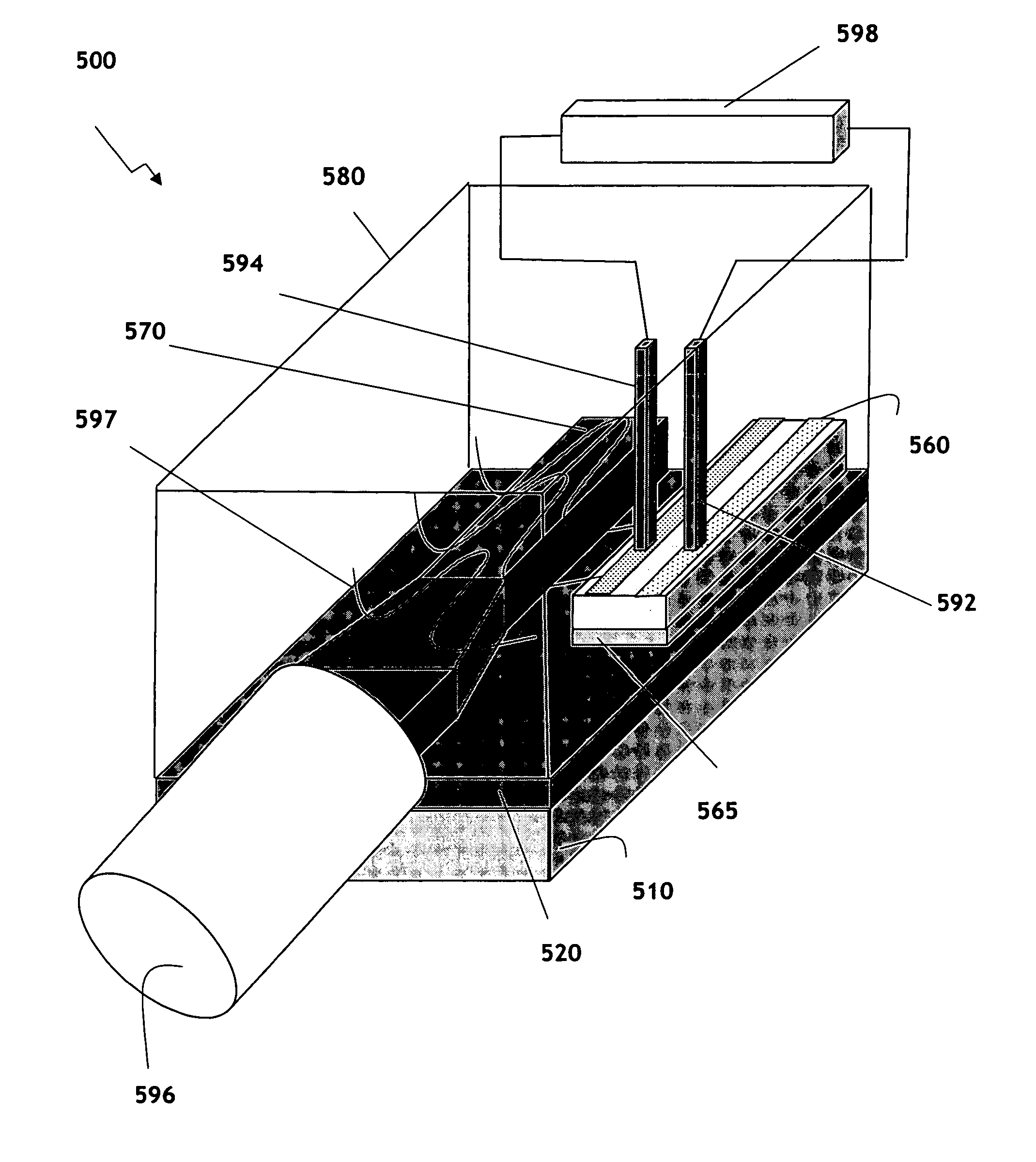
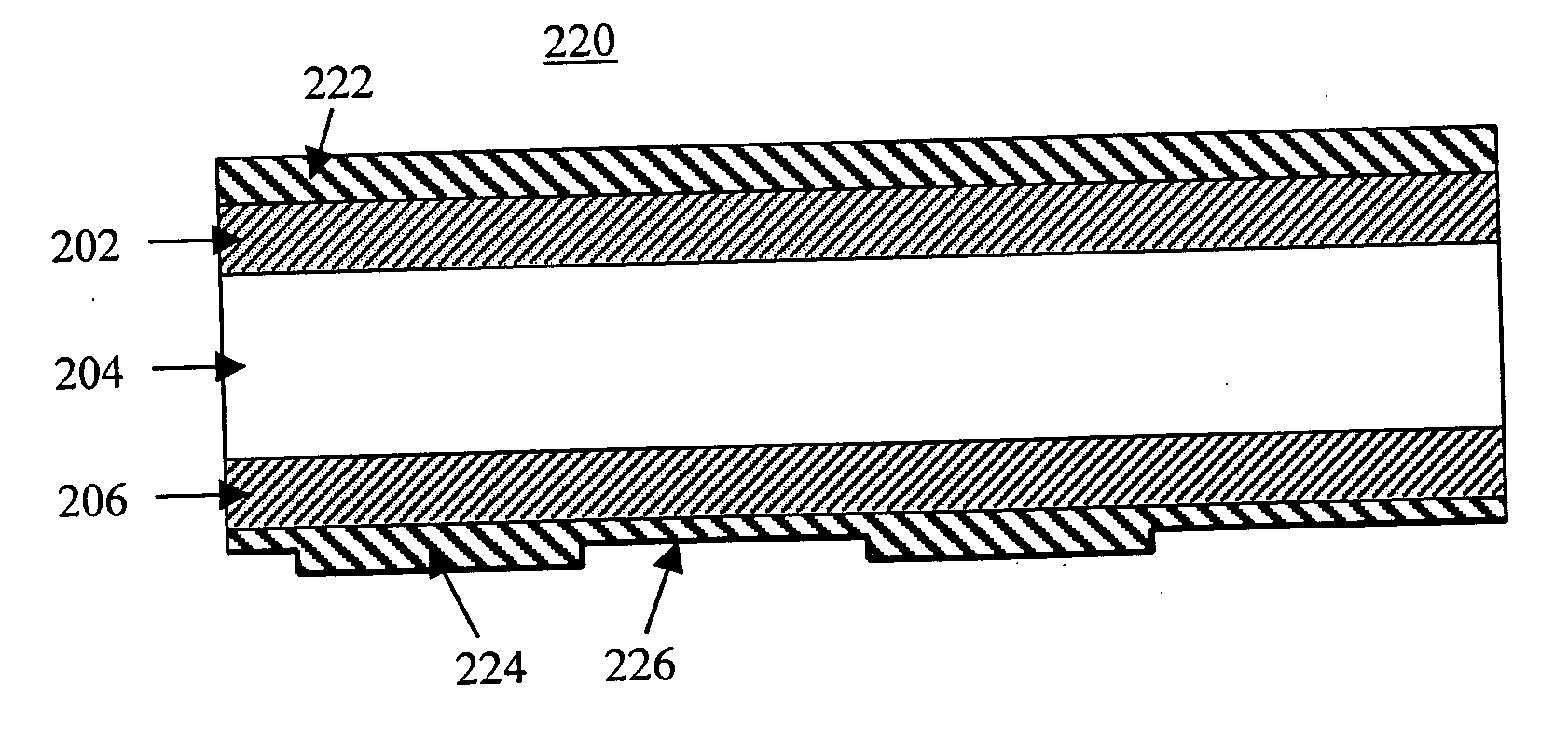
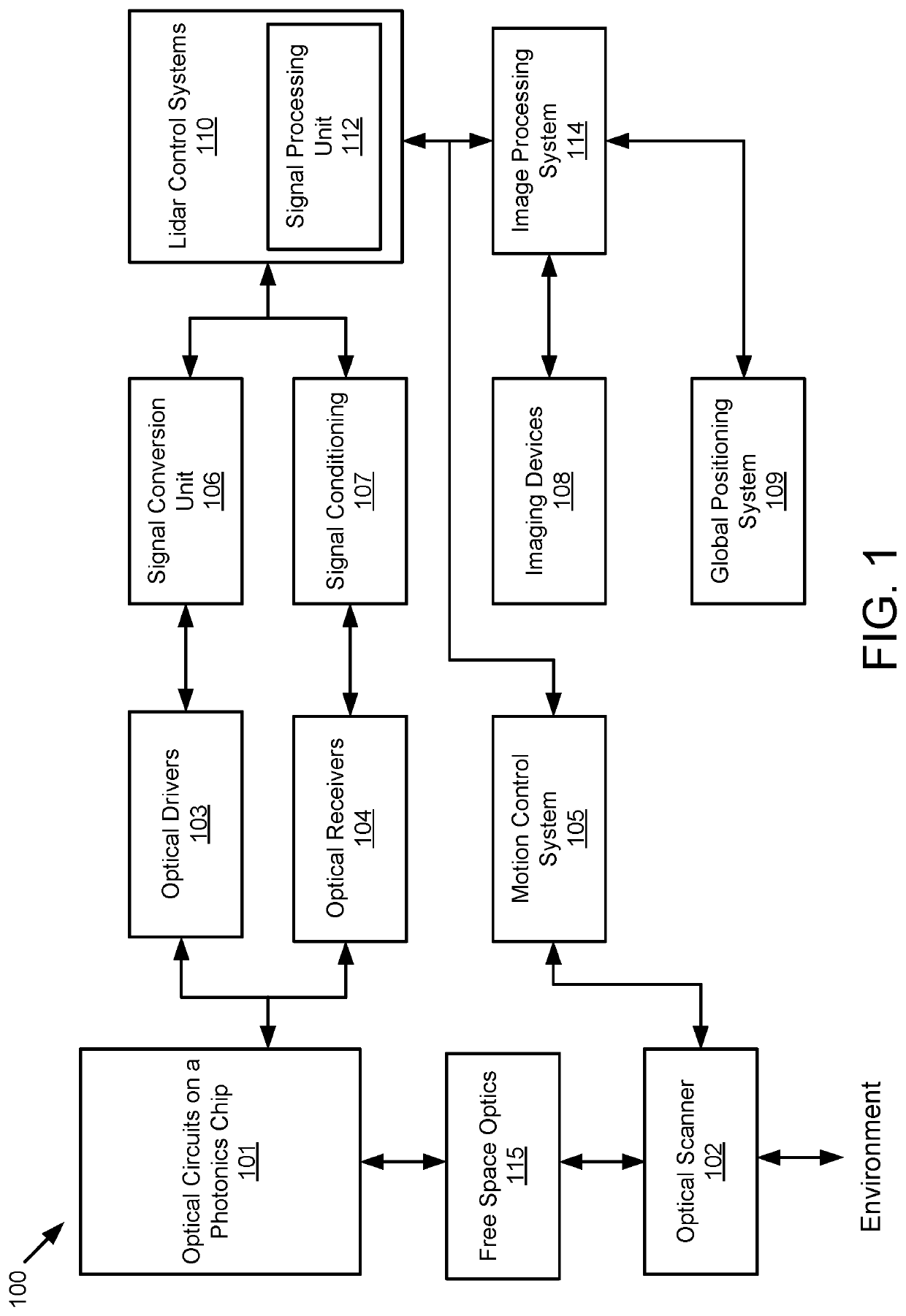
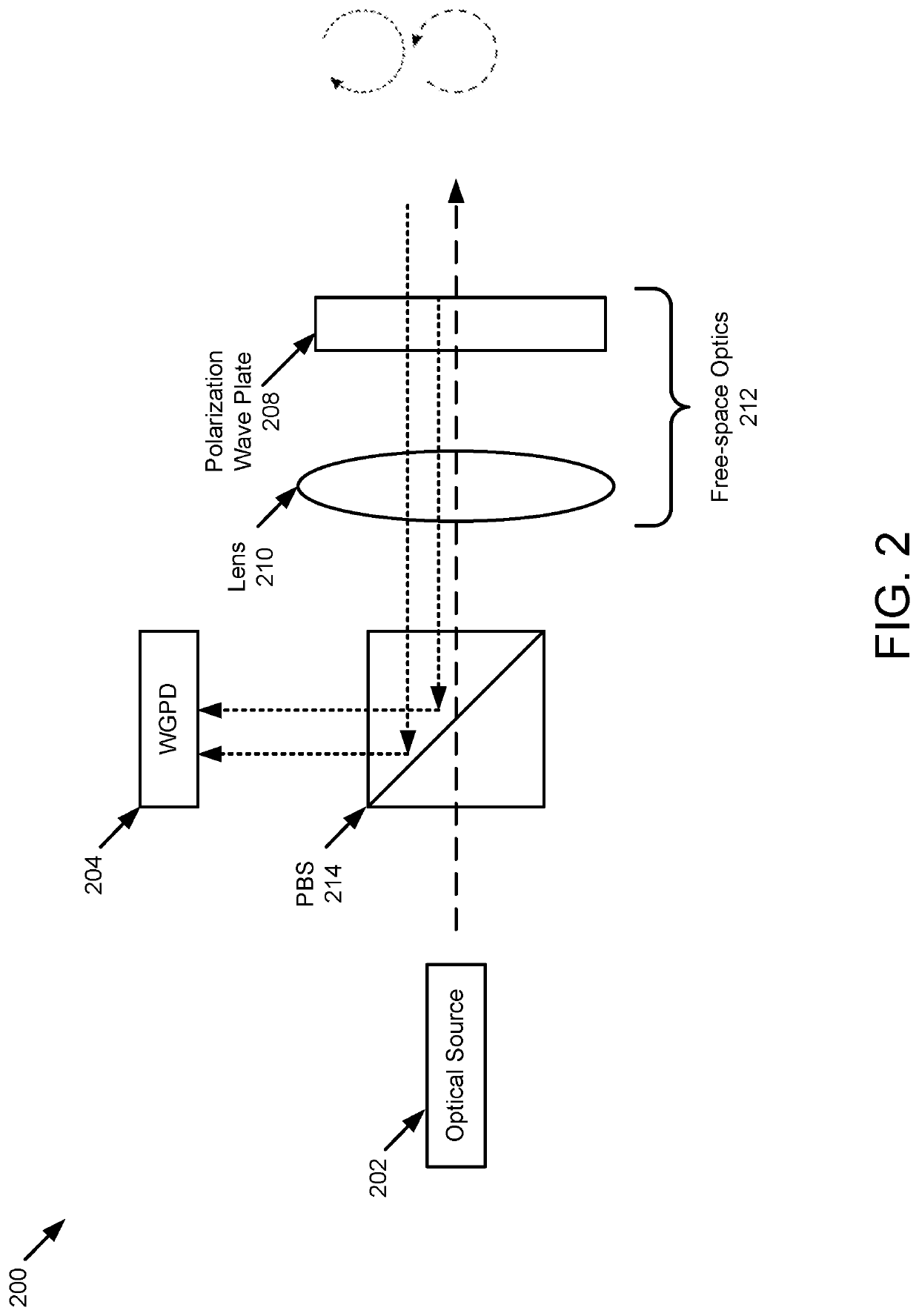
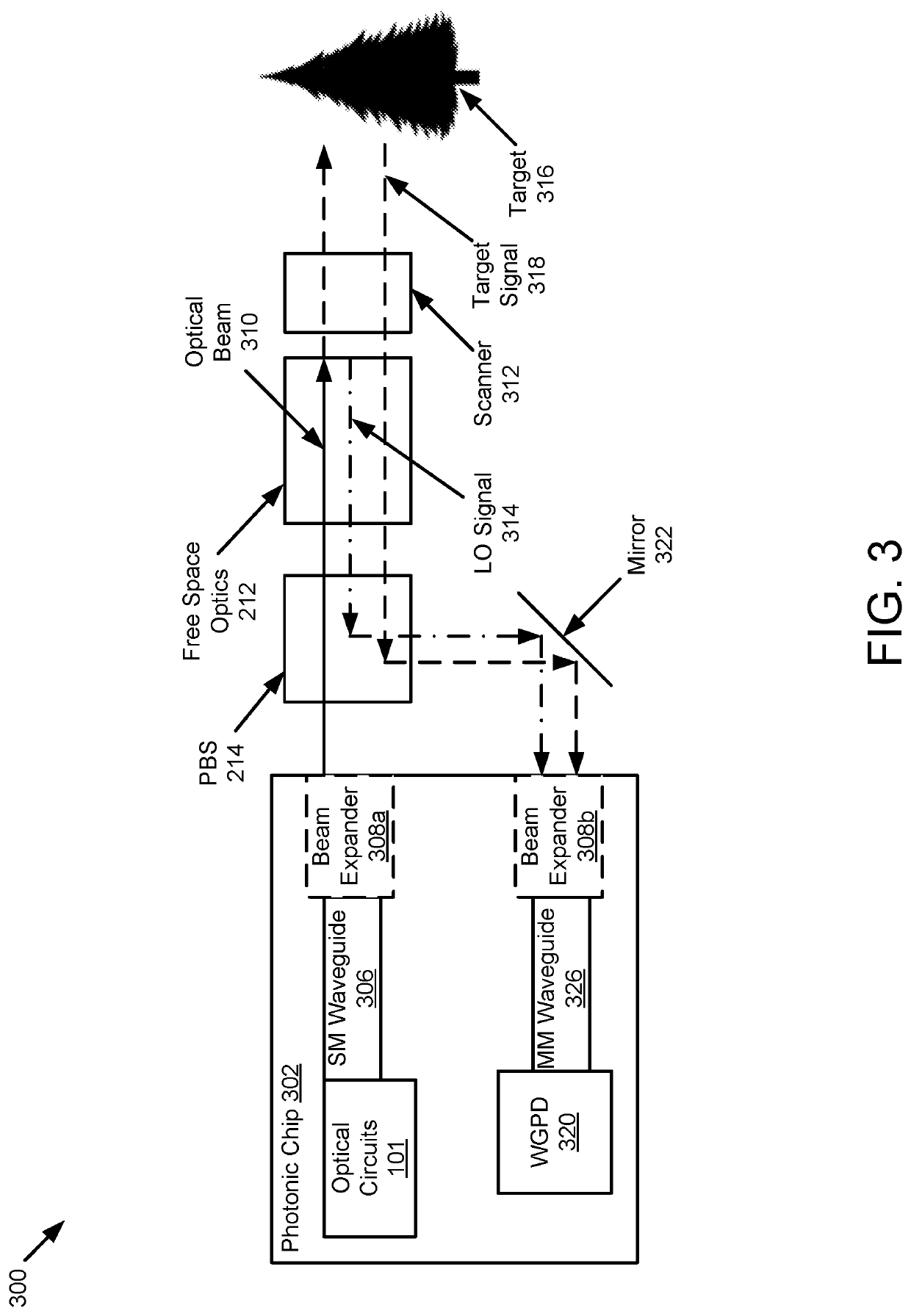
Lidar system with a multi-mode waveguide photodetector
ActiveUS20200319314A1Electromagnetic wave reradiationOptical elementsLocal oscillator signalTarget signal
A light detection and ranging (LIDAR) apparatus is provided that includes an optical source configured to emit an optical beam. The LIDAR apparatus further includes free space optics configured to receive a first portion of the optical beam as a target signal and a second portion of the optical beam as a local oscillator signal, and combine the target signal and the local oscillator signal. The LIDAR apparatus includes a multi-mode (MM) waveguide configured to receive the combined signal.
Owner:AEVA INC
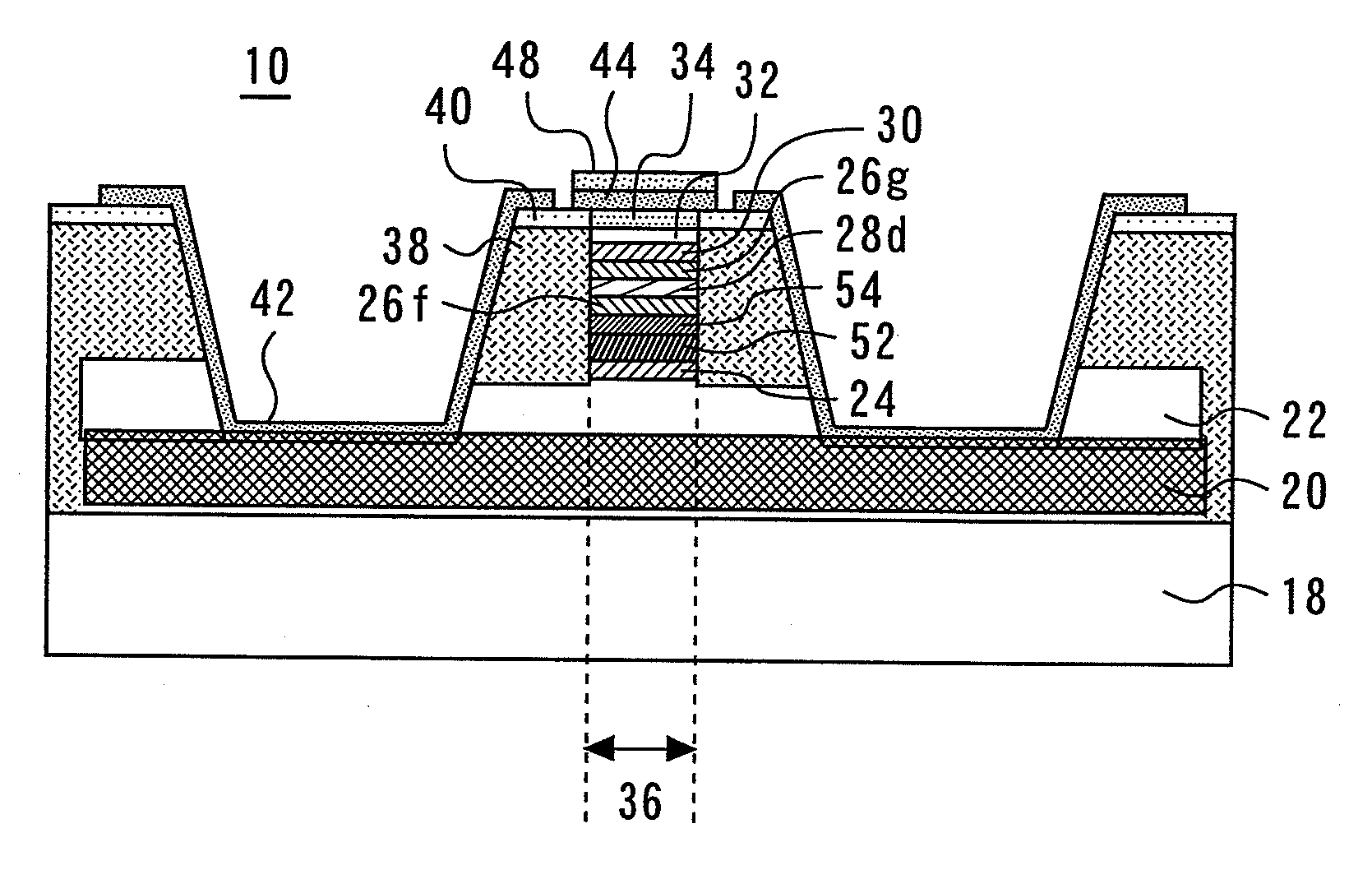
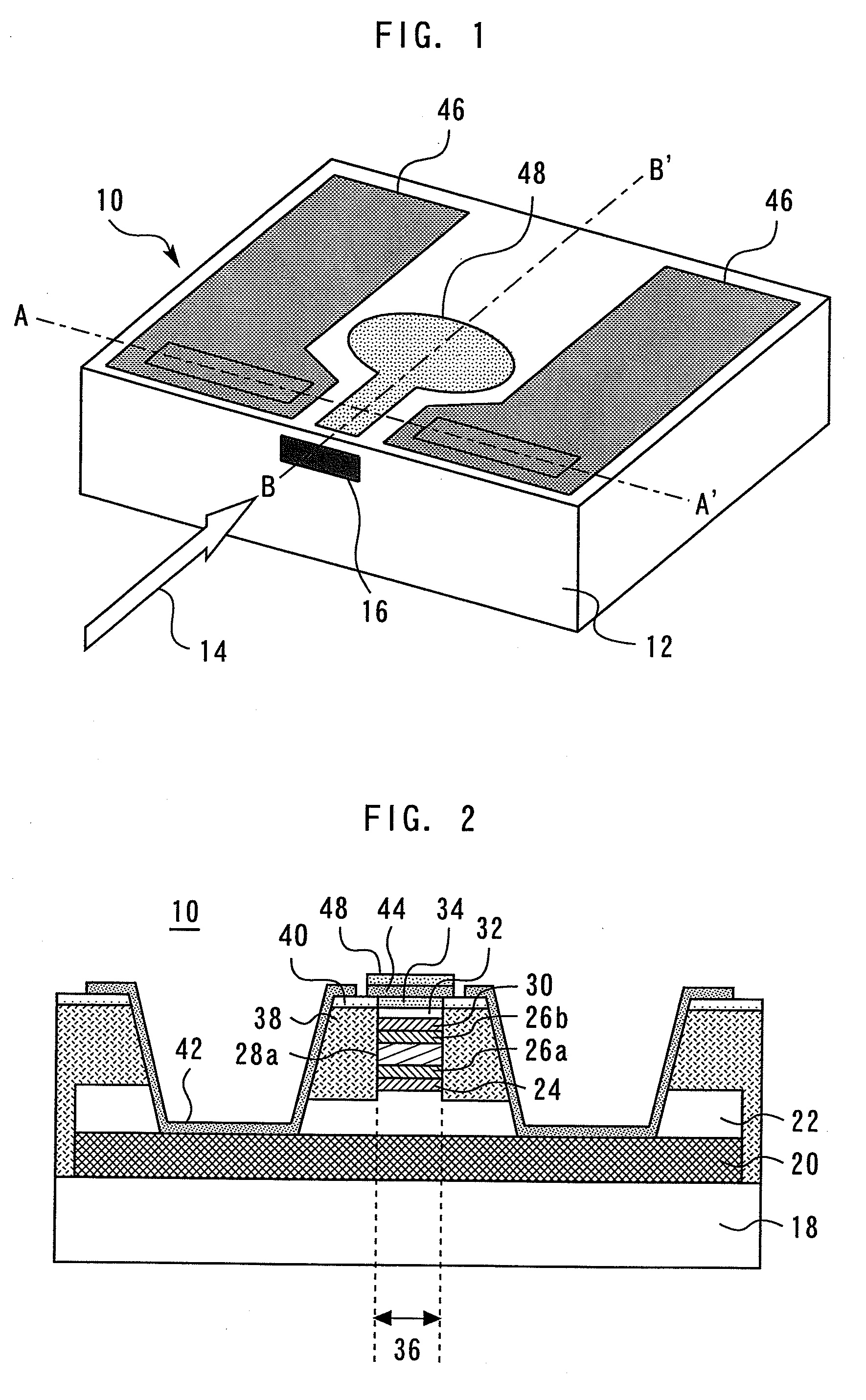
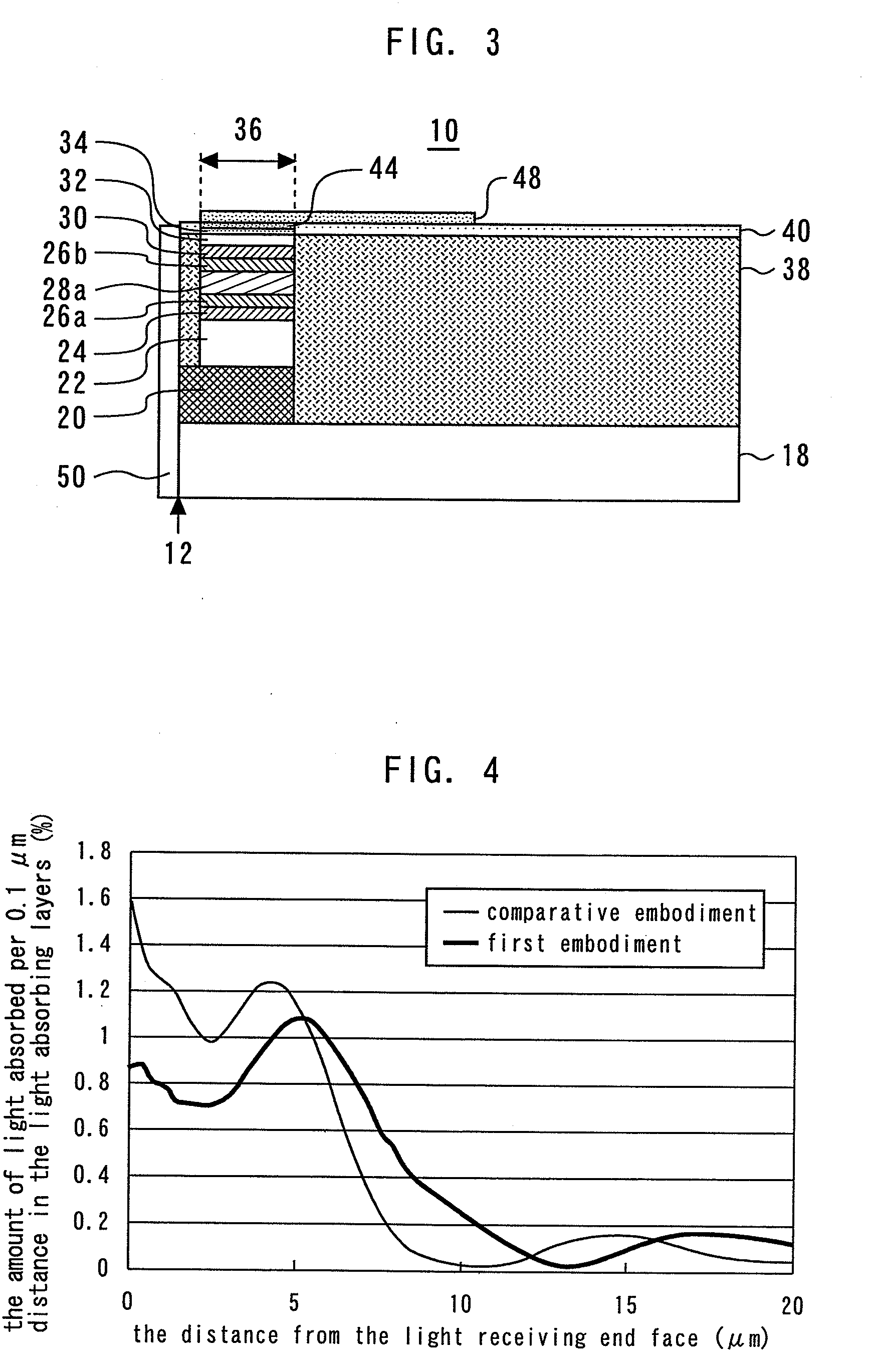
Waveguide photodetector
ActiveUS20090321868A1High speed responseImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLength waveSemiconductor
A waveguide photodetector detecting light incident on a light detecting end face includes: a substrate; and a layer stack structure on the substrate and including a semiconductor layer of a first conductivity type, an undoped semiconductor layer, and a semiconductor layer of a second conductivity type. The undoped semiconductor layer includes two or more undoped light absorbing layers and undoped non-light-absorbing layers. One non-light-absorbing layer is disposed between adjacent undoped light absorbing layers. The non-light-absorbing layers have a bandgap wavelength shorter than the wavelength of the incident light that is detected.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and System for Integrated Multi-Port Waveguide Photodetectors
ActiveUS20170329080A1Fibre transmissionCoupling light guidesLocal oscillator signalPhotovoltaic detectors
Methods and systems for integrated multi-port waveguide photodetectors are disclosed and may include an optical receiver on a chip, where the optical receiver comprises a multi-port waveguide photodetector having three or more input ports. The optical receiver may be operable to receive optical signals via one or more grating couplers, couple optical signals to the photodetector via optical waveguides in the chip, and generate an output electrical signal based on the coupled optical signals using the photodetector. The photodetector may include four ports coupled to two PSGCs. The optical signals may be coupled to the photodetector via S-bends and / or tapers at ends of the optical waveguides. A width of the photodetector on sides that are coupled to the optical waveguides may be wider than a width of the optical waveguides coupled to the sides. Optical signals may be mixed with local oscillator signals using the multi-port waveguide photodetector.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
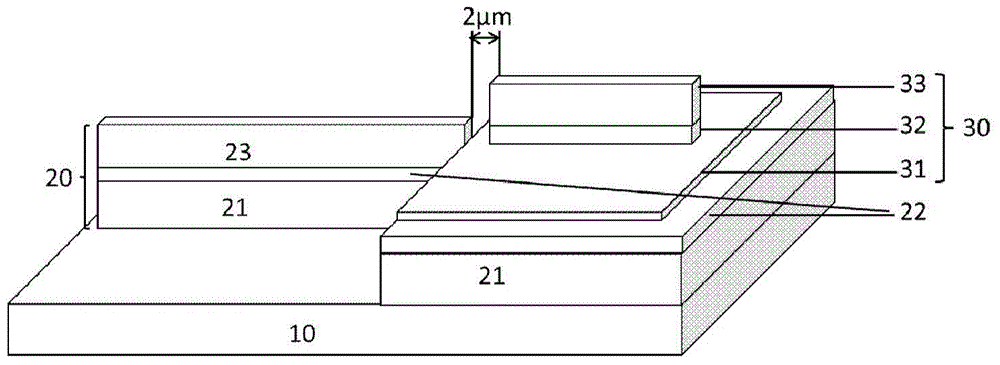
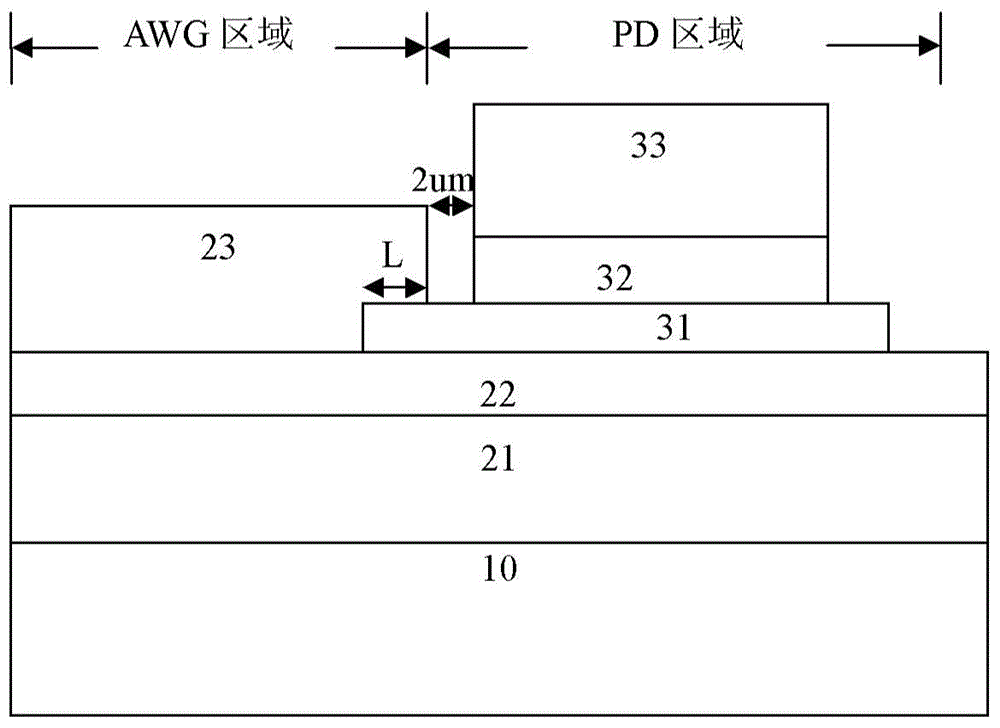
Integrated device for seamed butt joint of AWG (arrayed waveguide grating) output waveguide and detector and preparation method
ActiveCN104950382AAvoid coupling lossImprove coupling efficiencyOptical waveguide light guideCapacitanceCoupling loss
The invention provides an integrated device for seamed butt joint of an AWG (arrayed waveguide grating) output waveguide and a waveguide photodetector and a preparation method of the integrated device. The integrated device comprises a substrate, the AWG output waveguide and the waveguide photodetector, wherein the left area and the right area of the substrate are taken as an AWG area and a PD (photodetector) area respectively; the AWG output waveguide is located on the AWG area on the substrate, and an AWG lower coating layer and an AWG core layer extend to the PD area; the waveguide photodetector is formed above the AWG core layer in the PD area on the substrate, and a PD lower contact layer of the waveguide photodetector extends into an AWG upper coating layer of the AWG output waveguide and is located above the AWG core layer; a PD absorbing layer and a PD upper contact layer of the waveguide photodetector are spaced with the AWG upper coating layer of the AWG output waveguide by a narrow seam. According to the integrated device and the preparation method, excessive coupling loss generated during interconnection of discrete devices is avoided, and the energy efficiency of an optical link is improved through evanescent field coupling; meanwhile, by means of the seam between the AWG output waveguide and the waveguide photodetector, the capacitance of PD devices is reduced, and the device bandwidth is increased.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
1xN fanout waveguide photodetector
InactiveUS7233725B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansQuantum efficiencyCharge carrier
A 1×N fanout waveguide detector is disclosed. The detector includes a multiple-mode interference (MMI) cavity with input and output ends. A single-mode waveguide is optically coupled to the input end of the MMI cavity so that the optical power in the guided mode is distributed over N modes. The MMI cavity forms N interference nodes at or near its output end. N waveguide detectors are optically coupled to the output end at or near the N interference nodes. The waveguide detectors each have a waveguide that is evanescently coupled to an intrinsic region of a PIN detector. The width of the detector waveguide core, which can be sub-micron, defines the carrier collection distance between the electrodes of the PIN detector. Further, the length of the detector waveguide can be selected to maximize optical absorption to provide optimum quantum efficiency. The waveguide detectors are connected in parallel to provide a high-output photocurrent.
Owner:INTEL CORP
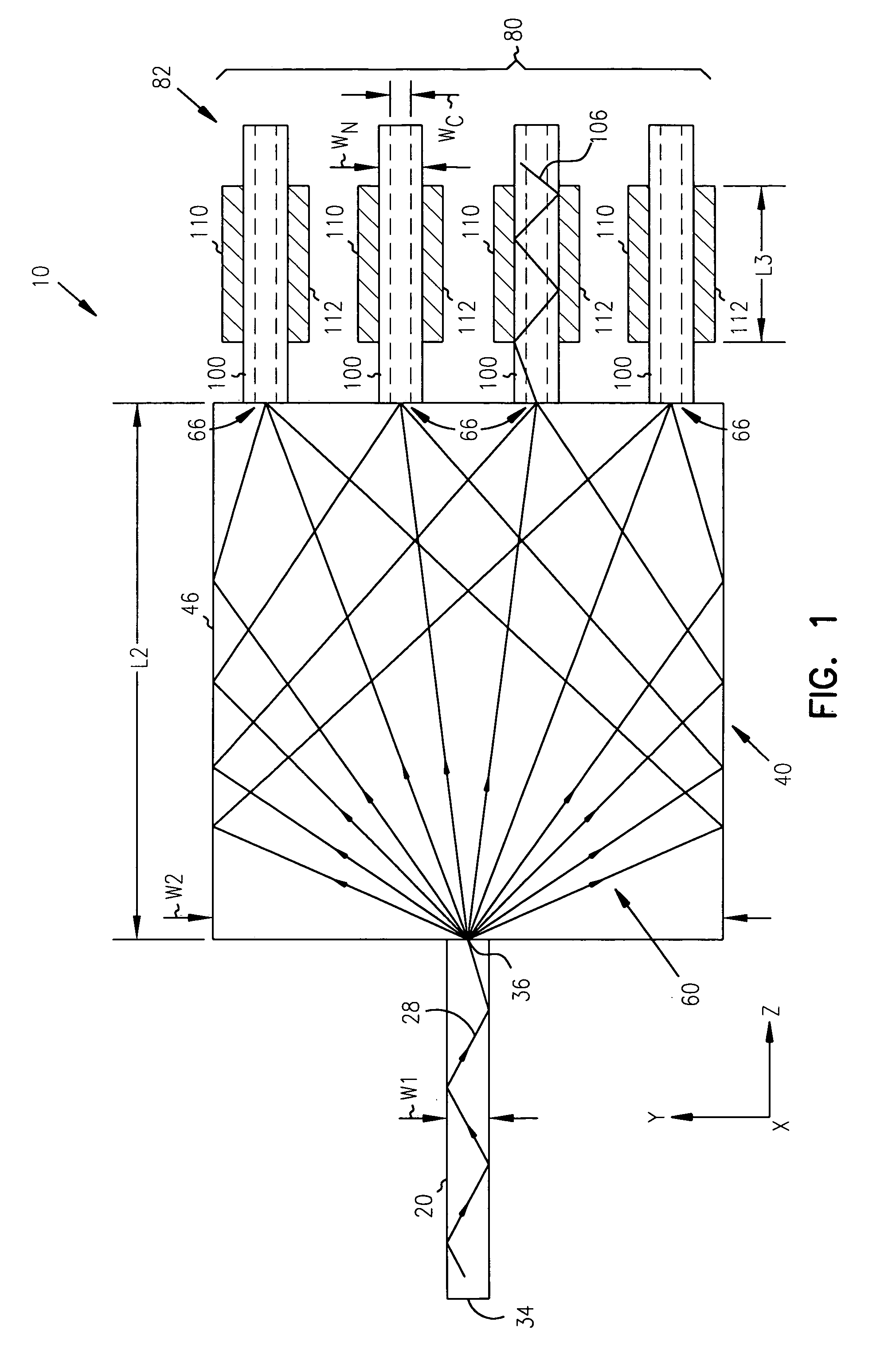
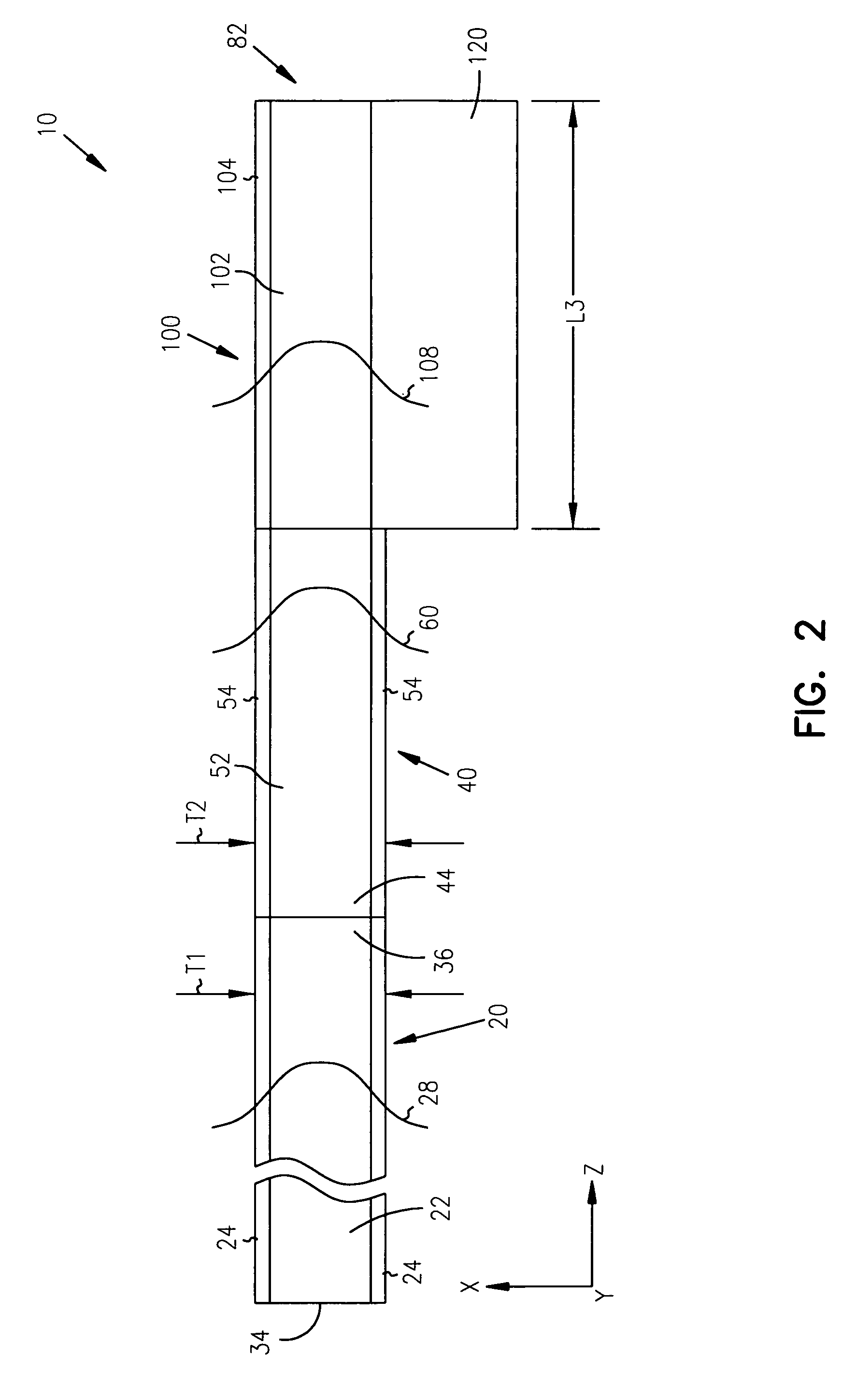
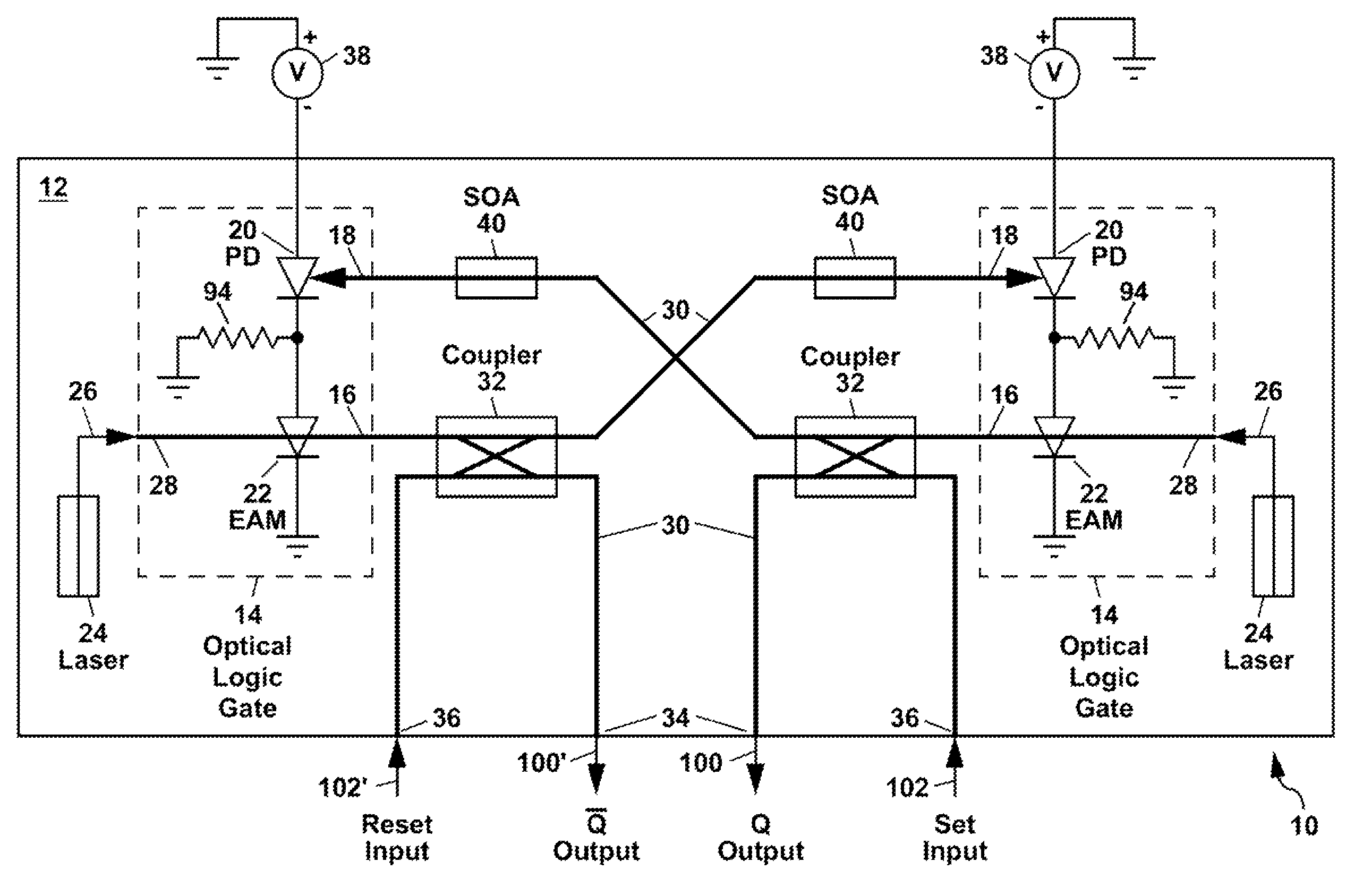
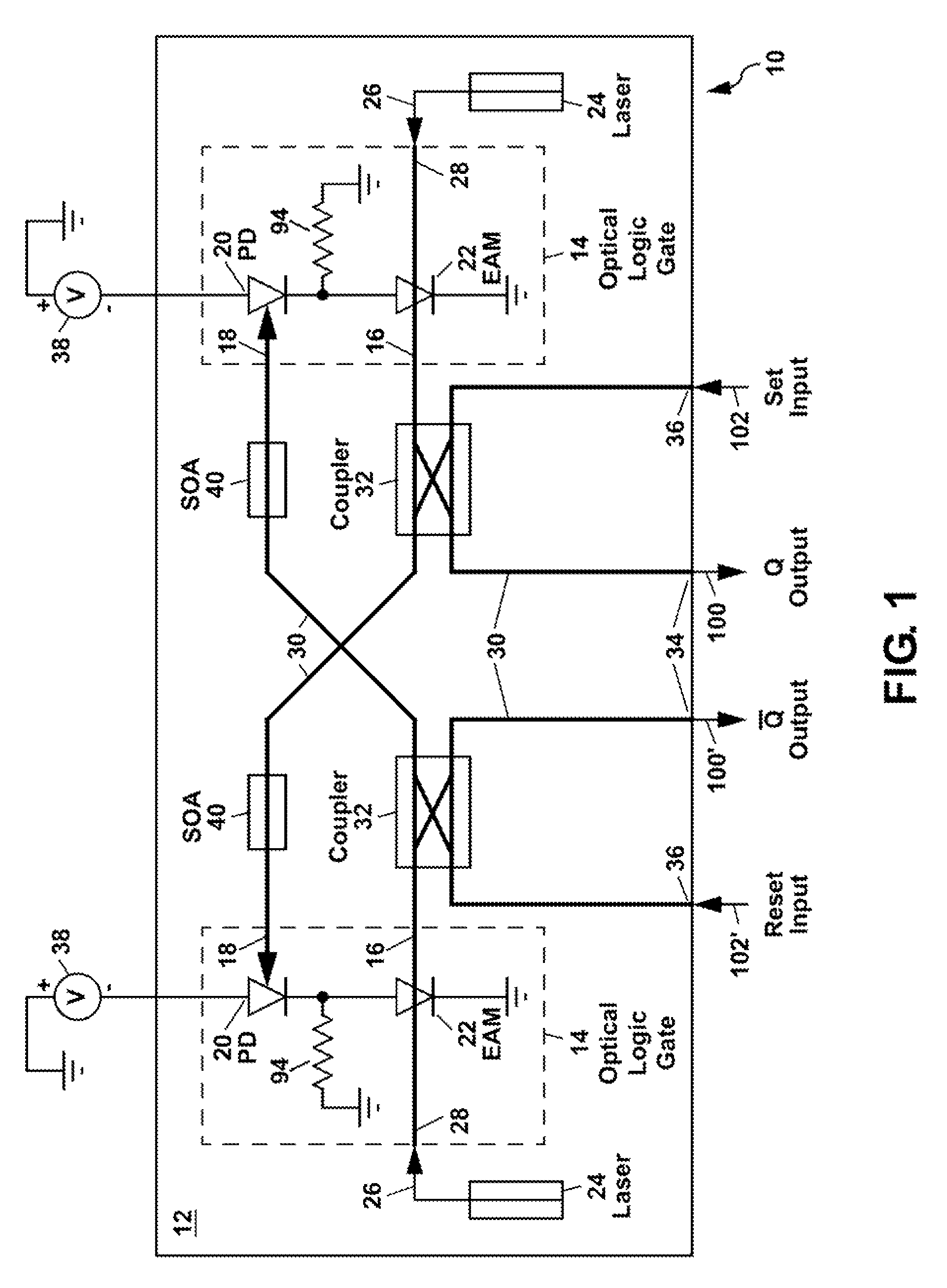
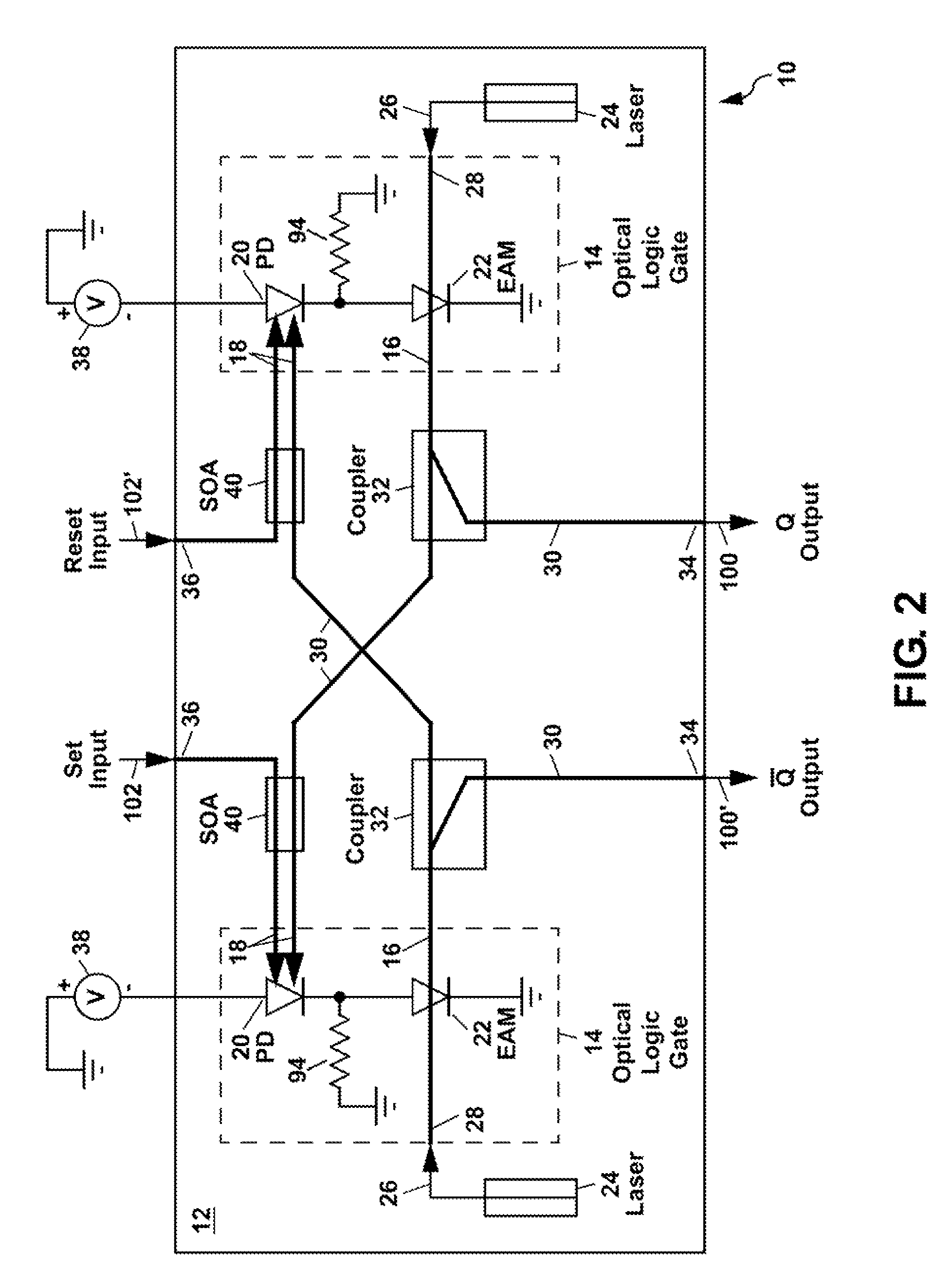
Optical data latch
ActiveUS7787719B1High speedGuaranteed high speed operationCladded optical fibreLogic circuits characterised by logic functionShift registerPhotodetector
An optical data latch is formed on a substrate from a pair of optical logic gates in a cross-coupled arrangement in which optical waveguides are used to couple an output of each gate to an photodetector input of the other gate. This provides an optical bi-stability which can be used to store a bit of optical information in the latch. Each optical logic gate, which can be an optical NOT gate (i.e. an optical inverter) or an optical NOR gate, includes a waveguide photodetector electrically connected in series with a waveguide electroabsorption modulator. The optical data latch can be formed on a III-V compound semiconductor substrate (e.g. an InP or GaAs substrate) from III-V compound semiconductor layers. A number of optical data latches can be cascaded to form a clocked optical data shift register.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
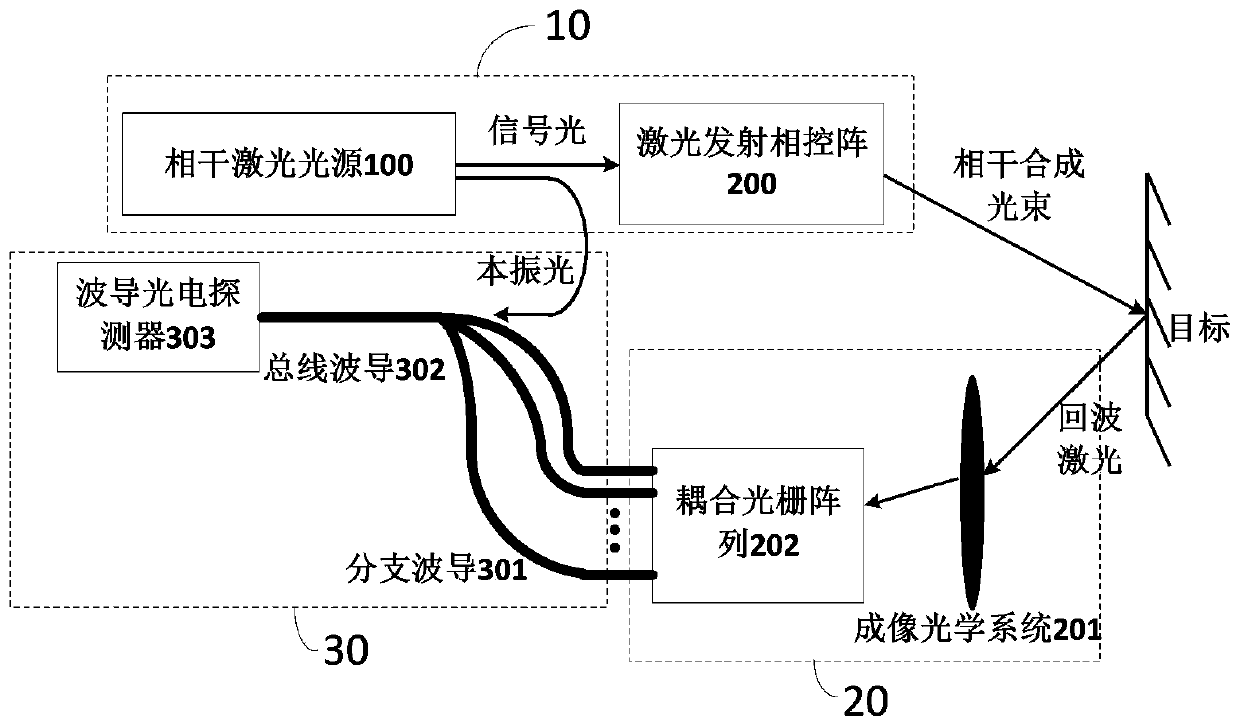
Integrated phased array laser radar system
ActiveCN110456324AModulation speedEnhance echo laser signalWave based measurement systemsSystem integrationRadar systems
The invention discloses an integrated phased array laser radar system comprising a laser phased array transmitting module, a coupled grating array receiving module, and a coherent detection module. The laser phased array transmitting module includes a coherent laser light source and a laser emission phased array. The coupled grating array receiving module includes an imaging optical system and a coupled grating array; the imaging optical system converges echo laser reflected from different object space target points to a corresponding position point on a focal plane in image space; and the incident surface of the coupled grating array is located on the focal plane in image space of the imaging optical system. The coherent detection module includes a branch waveguide, a bus waveguide, localoscillator light, and a waveguide photoelectric detector. According to the invention, the integrated phased array laser radar system has advantages of fast scanning speed, small size, high system integration, low cost, long detection distance, and strong noise suppression ability.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CENT CO LTD
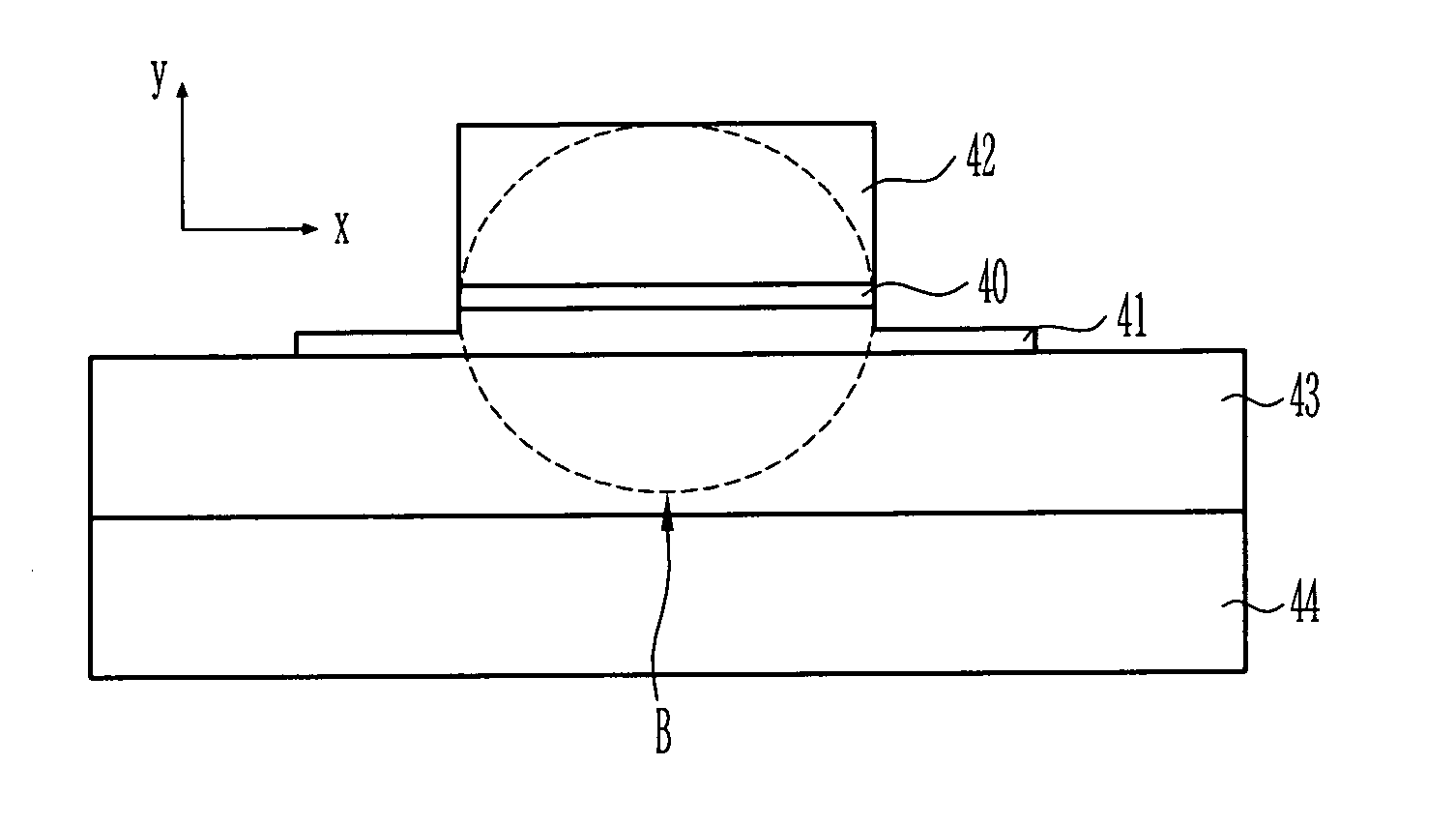
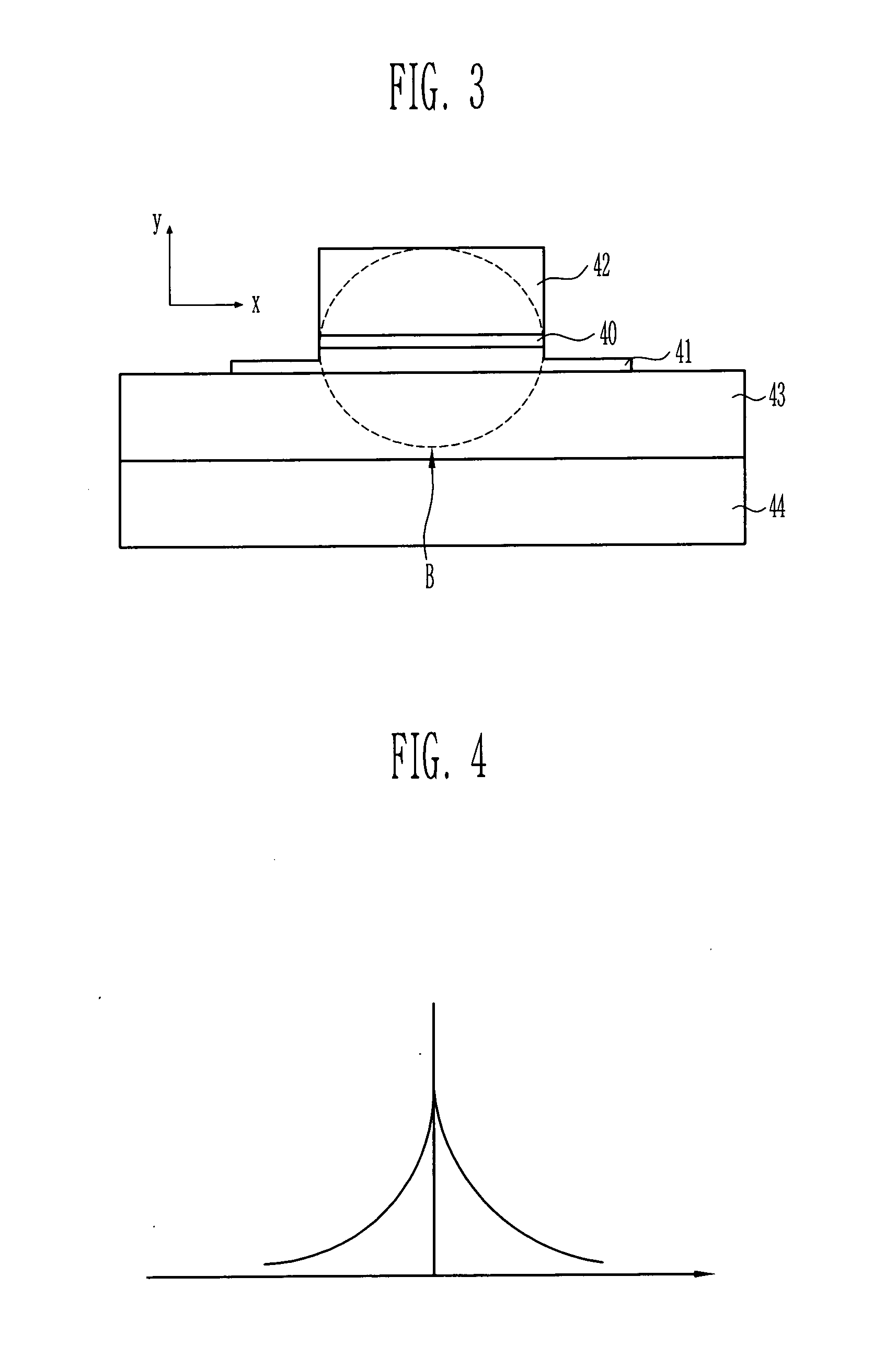
Waveguide photodetector
InactiveUS20050053349A1Reduce operating speedIncrease computing speedCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideTrappingRefractive index
The present invention relates to a waveguide photodetector having a good efficiency of coupling with an optical fiber or a PLC (Planar Light-wave Circuit). In order to increase size of mode beam and to effectively receive light from the optical fiber or the PLC, a thin absorbing layer is used as a core and a semiconductor having an index of refraction similar to that of the absorbing layer is used as a cladding layer. By doing so, it is possible to obtain a good efficiency of coupling with an optical fiber or a PLC. In addition, since a little amount of light proceeds along a waveguide, it is possible to obtain high operating speed even under a high power. Furthermore, by reducing difference between indexes of refraction of the absorbing layer and the cladding layer, it is possible to suppress the “carrier-trapping” generated from small difference between band gaps of the two materials.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com