Patents
Literature
696 results about "Ferroelectric thin films" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
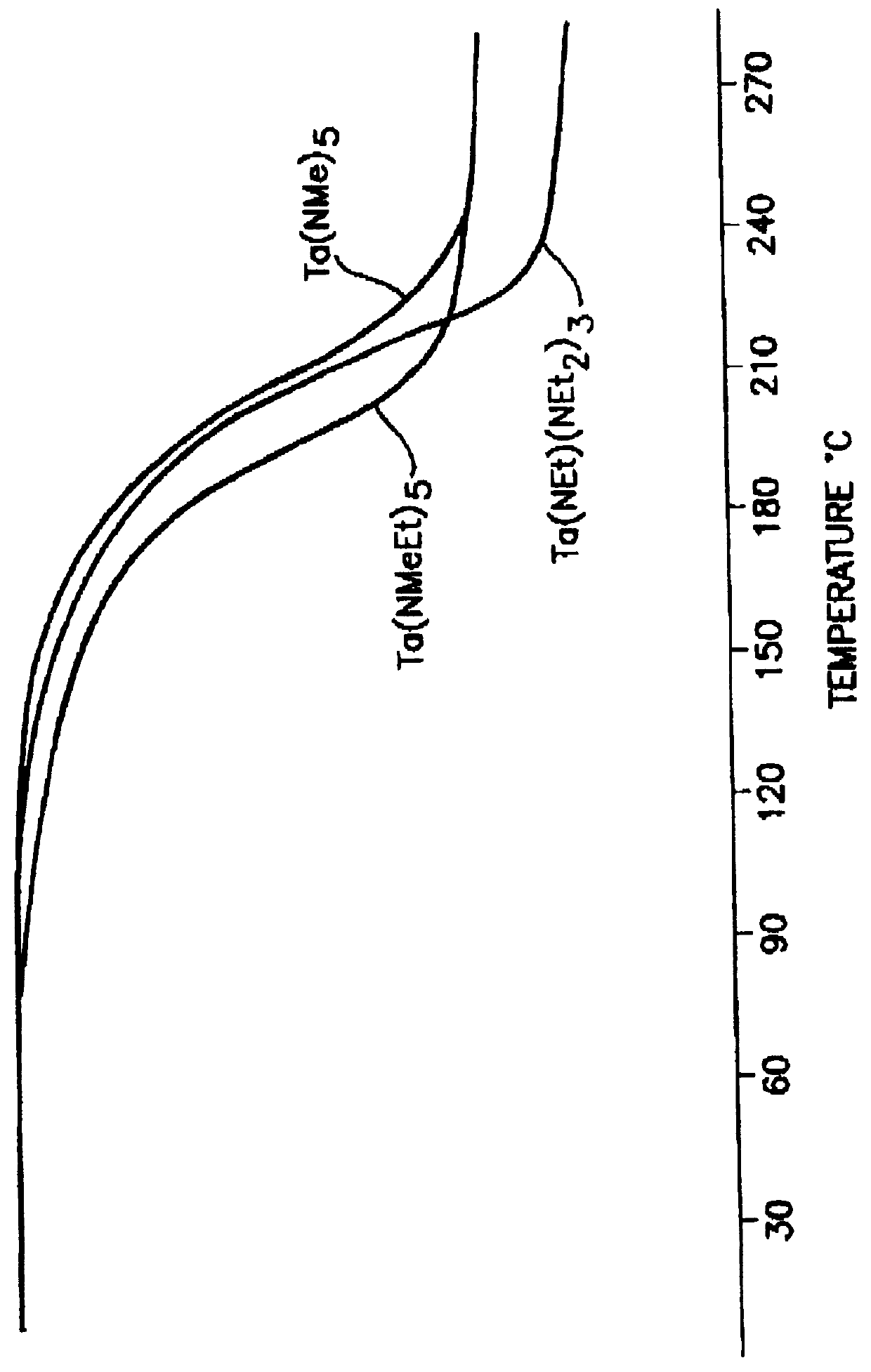
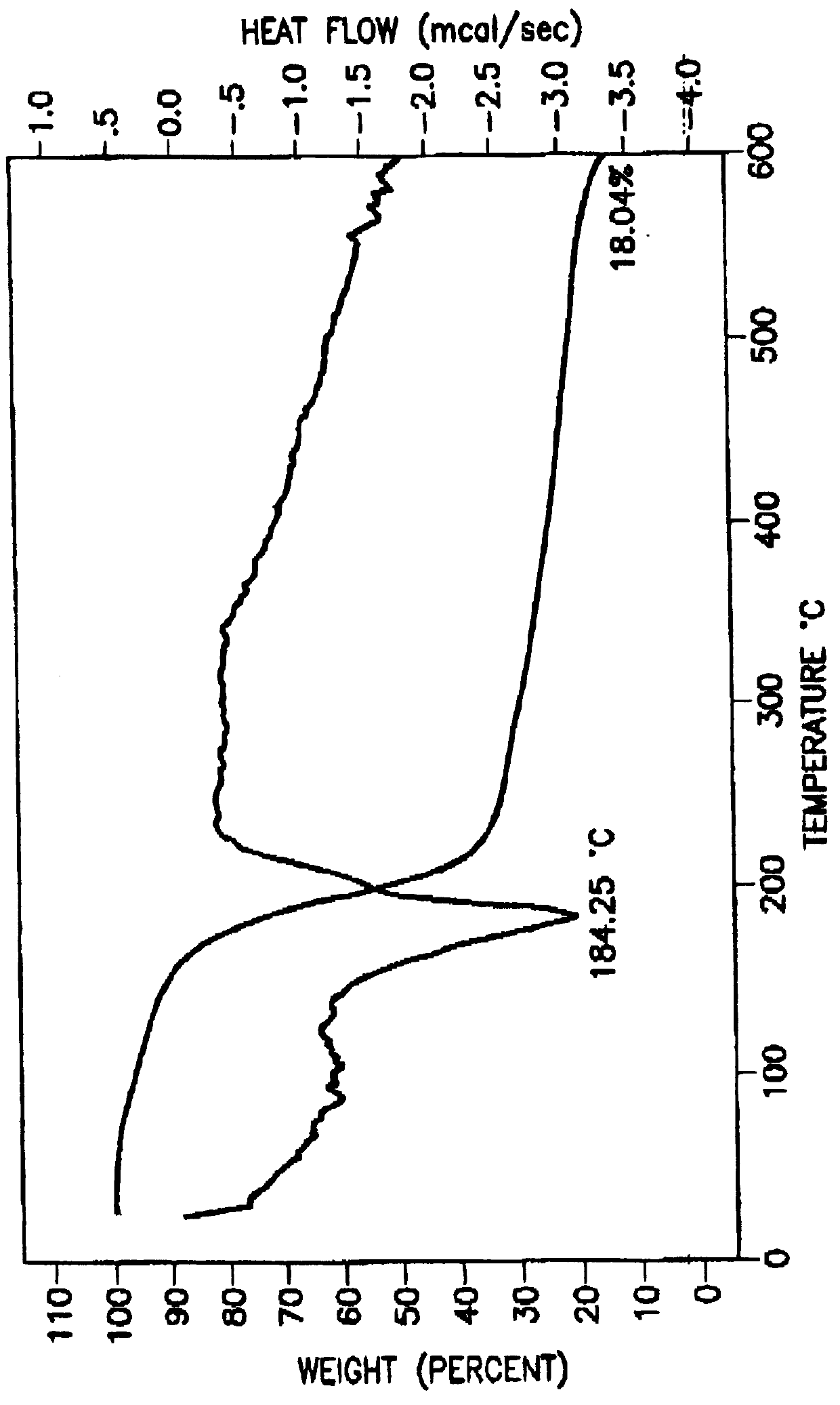
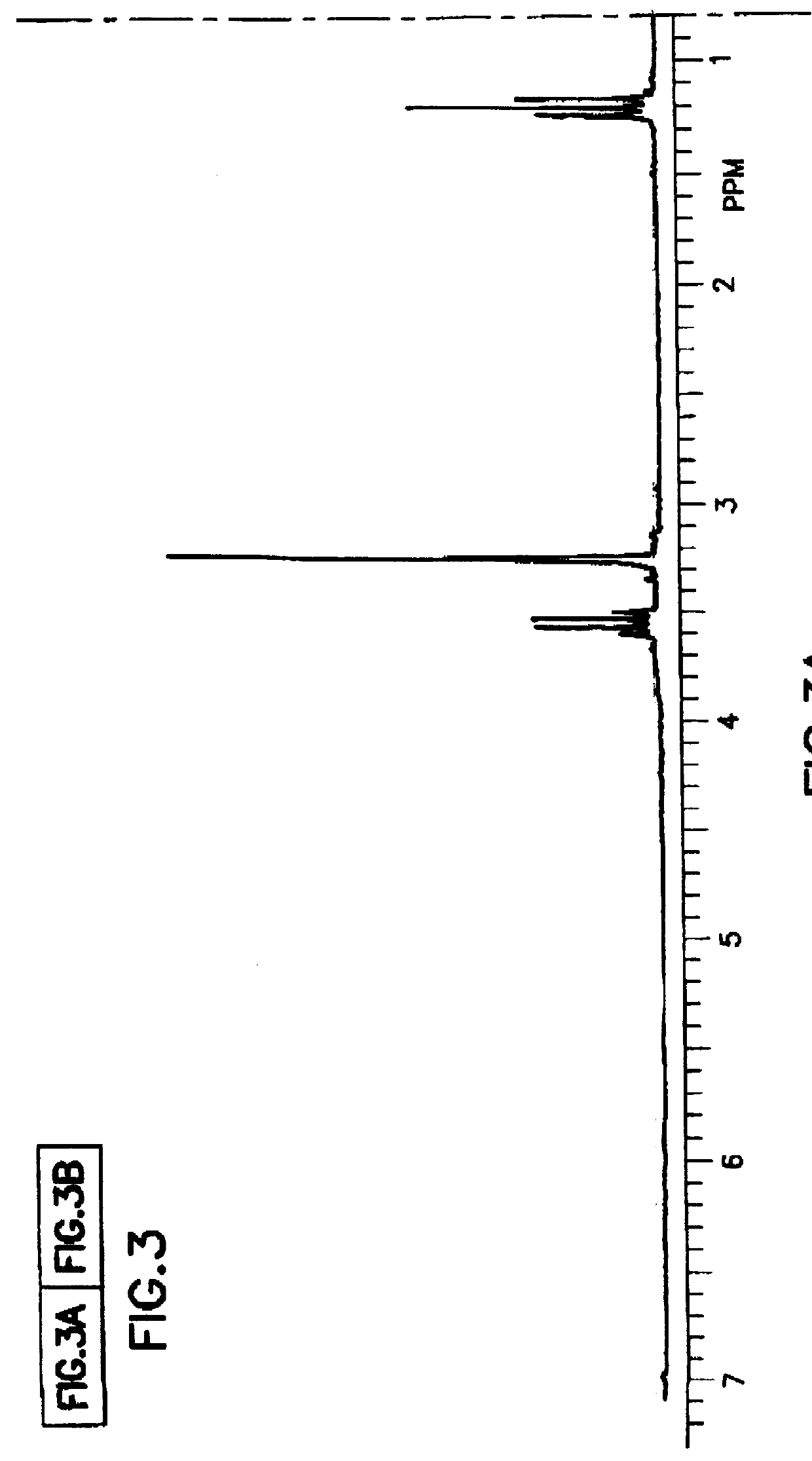
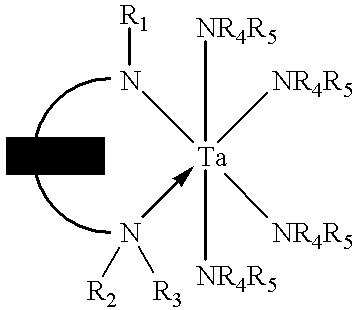
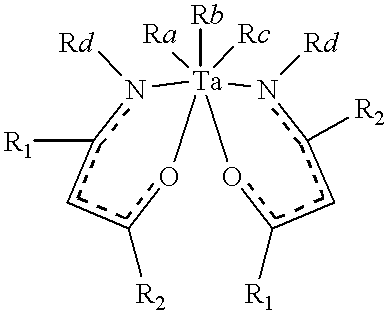
Tantalum amide precursors for deposition of tantalum nitride on a substrate
InactiveUS6015917ARapid heat treatmentSilicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthFerroelectric thin filmsChemical vapor deposition
Tantalum and titanium source reagents are described, including tantalum amide and tantalum silicon nitride precursors for the deposition of tantalum nitride material on a substrate by processes such as chemical vapor deposition, assisted chemical vapor deposition, ion implantation, molecular beam epitaxy and rapid thermal processing. The precursors may be employed to form diffusion barrier layers on microlectronic device structures enabling the use of copper metallization and ferroelectric thin films in device construction.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Tantalum amide precursors for deposition of tantalum nitride on a substrate
InactiveUS6379748B1Rapid heat treatmentSilicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthFerroelectric thin filmsChemical vapor deposition
Tantalum and titanium source reagents are described, including tantalum amide and tantalum silicon nitride precursors for the deposition of tantalum nitride material on a substrate by processes such as chemical vapor deposition, assisted chemical vapor deposition, ion implantation, molecular beam epitaxy and rapid thermal processing. The precursors may be employed to form diffusion barrier layers on microelectronic device structures enabling the use of copper metallization and ferroelectric thin films in device construction.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
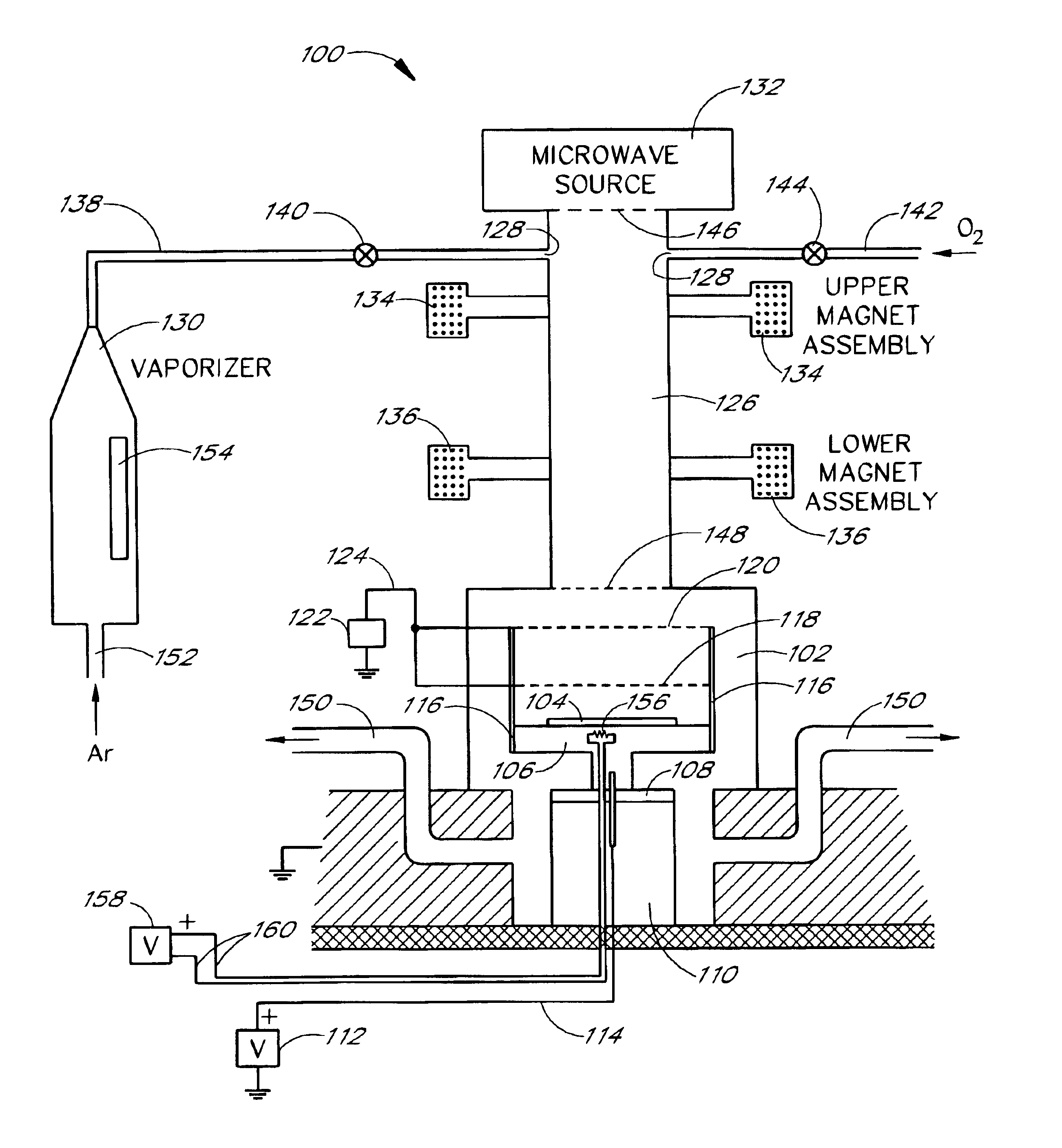
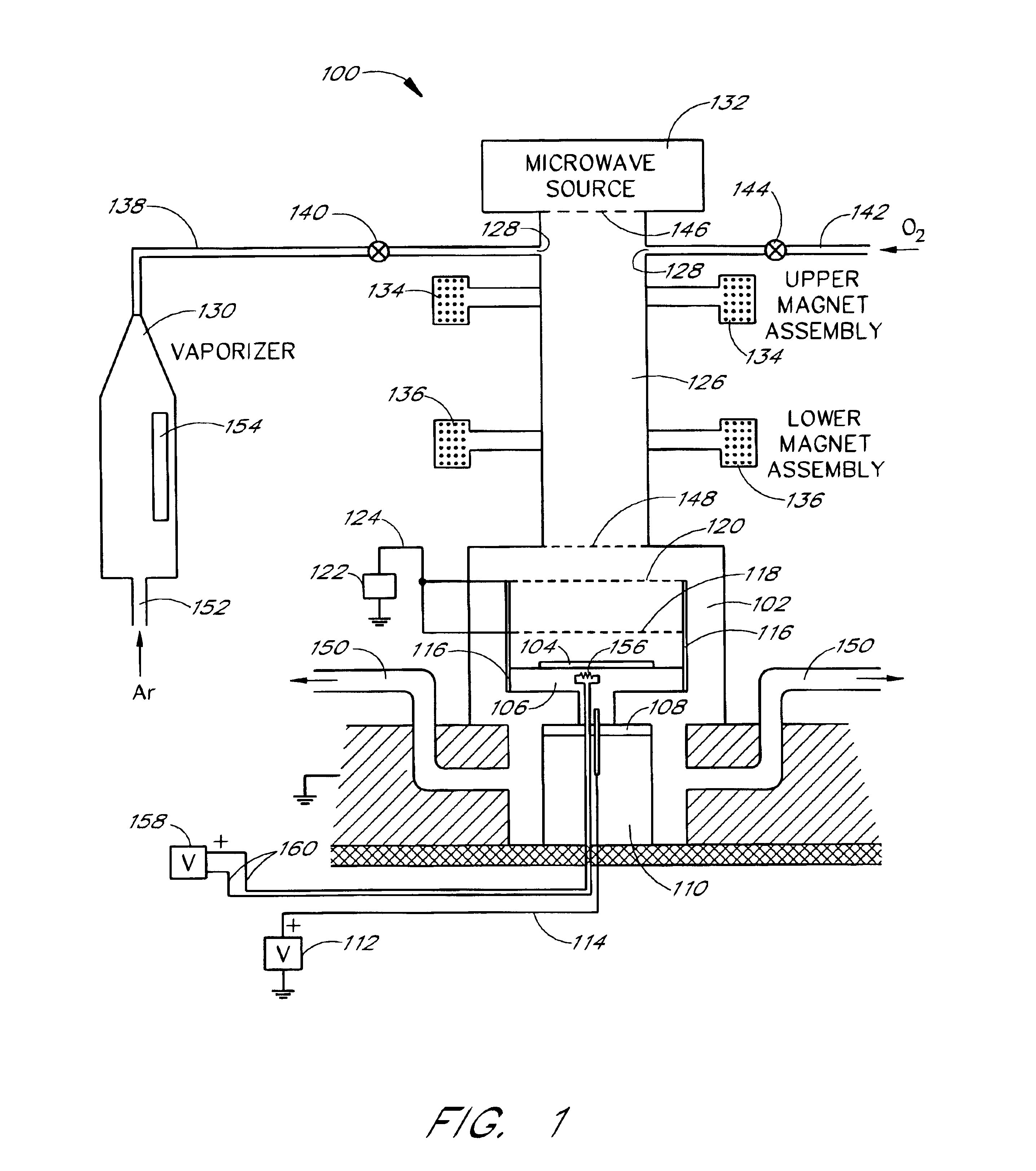
Method and apparatus for the fabrication of ferroelectric films
InactiveUS6858120B2Improve economyEasy to customizeCellsElectric discharge tubesFerroelectric thin filmsOxygen ions
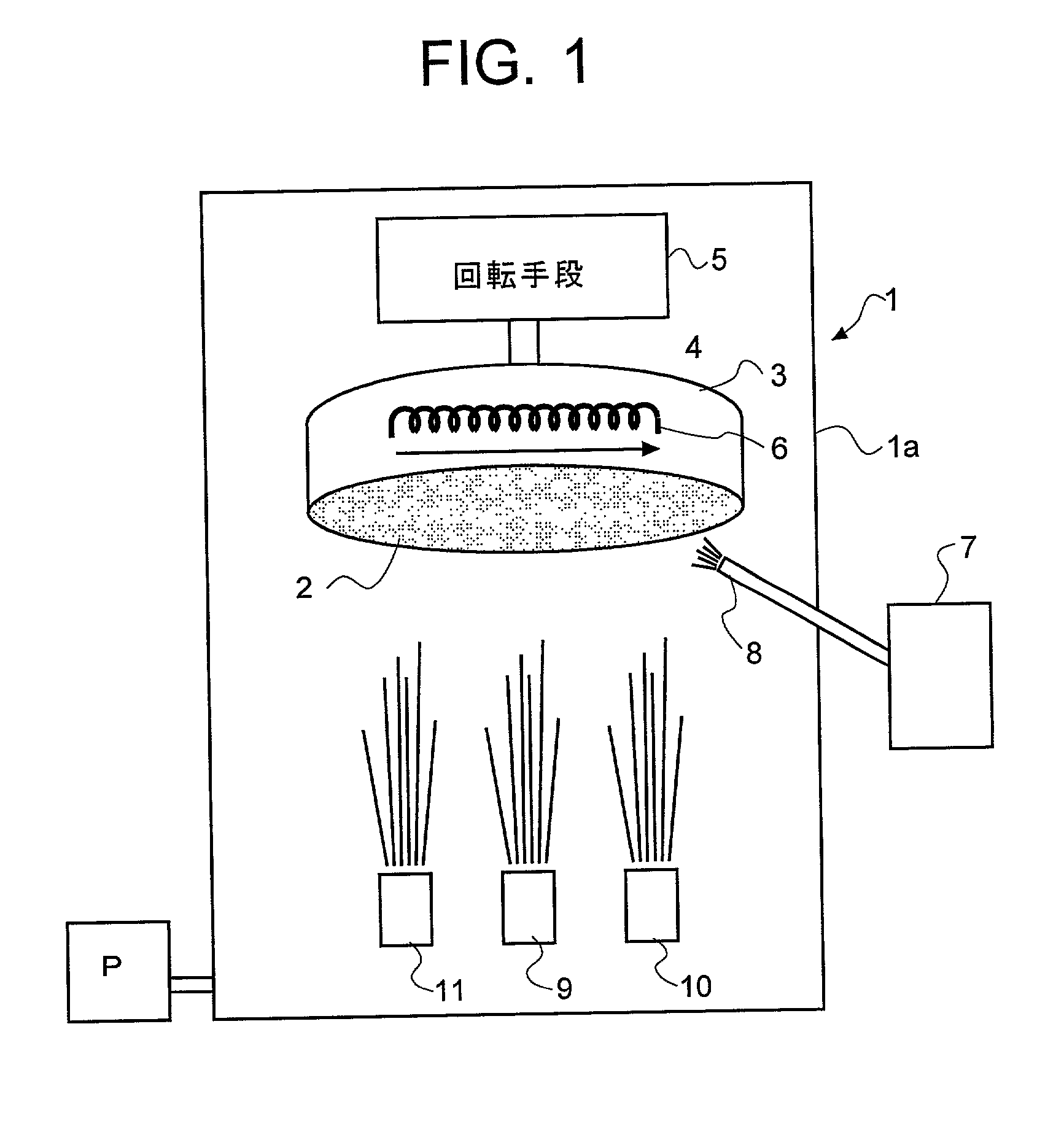
The present invention is related to methods and apparatus for processing weak ferroelectric films on semiconductor substrates, including relatively large substrates, e.g., with 300 millimeter diameter. A ferroelectric film of zinc oxide (ZnO) doped with lithium (Li) and / or magnesium (Mg) is deposited on a substrate in a plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition process such as an electron cyclotron resonance chemical vapor deposition (ECR CVD) process. Zinc is introduced to a chamber through a zinc precursor in a vaporizer. Microwave energy ionizes zinc and oxygen in the chamber to a plasma, which is directed to the substrate with a relatively strong field. Electrically biased control grids control a rate of deposition of the plasma. The control grids also provide Li and / or Mg dopants for the ZnO to create the ferroelectric film. A desired ferroelectric property of the ferroelectric film can be tailored by selecting an appropriate composition of the control grids.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
System and method for performing impact loading on micro test piece and measuring dynamic mechanical property
InactiveCN102135480ASolve the study of dynamic mechanical properties at high strain ratesLaunch fastStrength propertiesFerroelectric thin filmsStress–strain curve
The invention relates to a system and a method for performing impact loading on a micro test piece and measuring dynamic mechanical property. The method comprises the following steps of: instantly accelerating a bullet by using an electromagnetic pulse launch technology and launching the bullet at high speed; transmitting a stretching stress wave generated by collision of the bullet to the micro test piece by using a separated Hopkinson bar technology so as to generate the impact loading on the micro test piece; recording strain data of an input bar and an output bar, and acquiring an enlarged surface dynamic deformation image of the micro test piece; analyzing and obtaining a stress strain curve of the micro test piece subjected to the impact loading having different strain rates; and analyzing the surface dynamic deformation image of the micro test piece and obtaining a distribution of a bidimensional displacement field and a strain field during dynamic impact loading of the micro test piece. By the system and the method, the problem of research on the dynamic mechanical property of a micro electro mechanical system (MEMS), and membrane materials such as piezoelectric thin films, ferroelectric thin films and the like is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Stress control of thin films by mechanical deformation of wafer substrate
InactiveUS6156623AVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingFerroelectric thin filmsCurie temperature
A method of improving the physical and / or electrical and / or magnetic properties of a thin film material formed on a substrate, wherein the properties of the thin film material are stress-dependent, by selectively applying force to the substrate during the film formation and / or thereafter during the cooling of the film in the case of a film formed at elevated temperature, to impose through the substrate an applied force condition opposing or enhancing the retention of stress in the product film. The method of the invention has particular utility in the formation of ferroelectric thin films which are grown at temperature above the Curie temperature, and which may be placed in tension during the cooling of the film to provide ferroelectric domains with polarization in the plane of the film.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
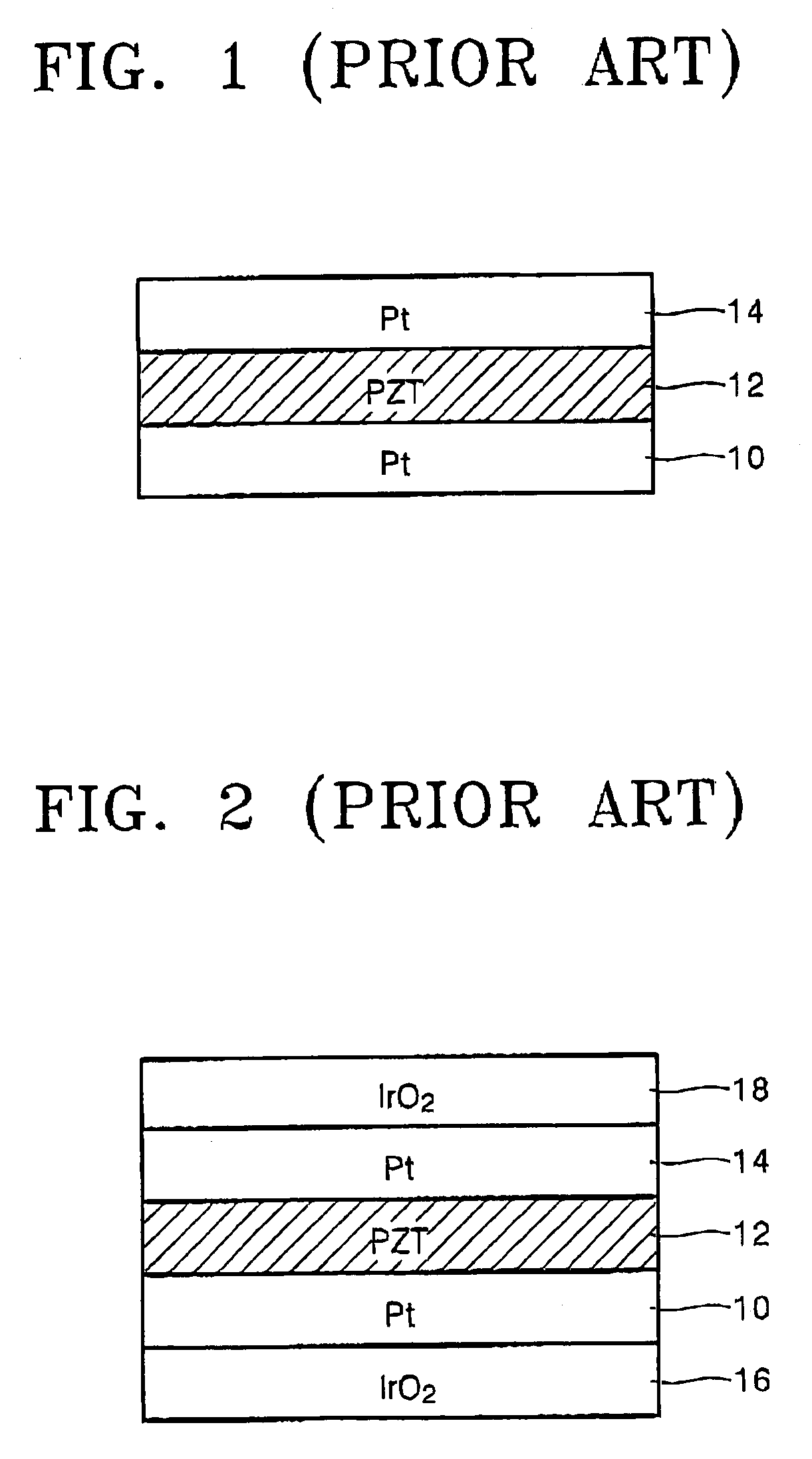
Ferroelectric capacitor
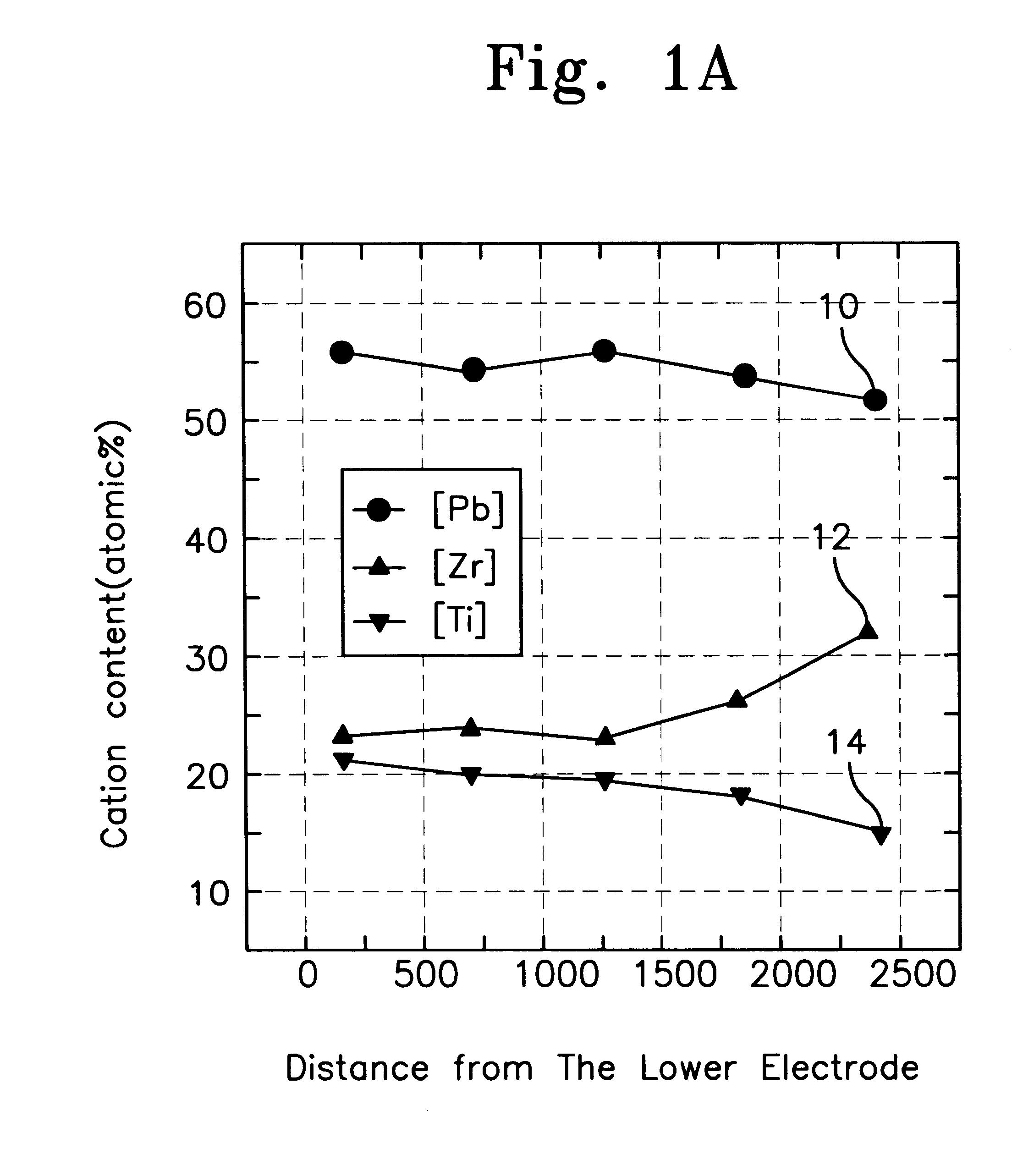
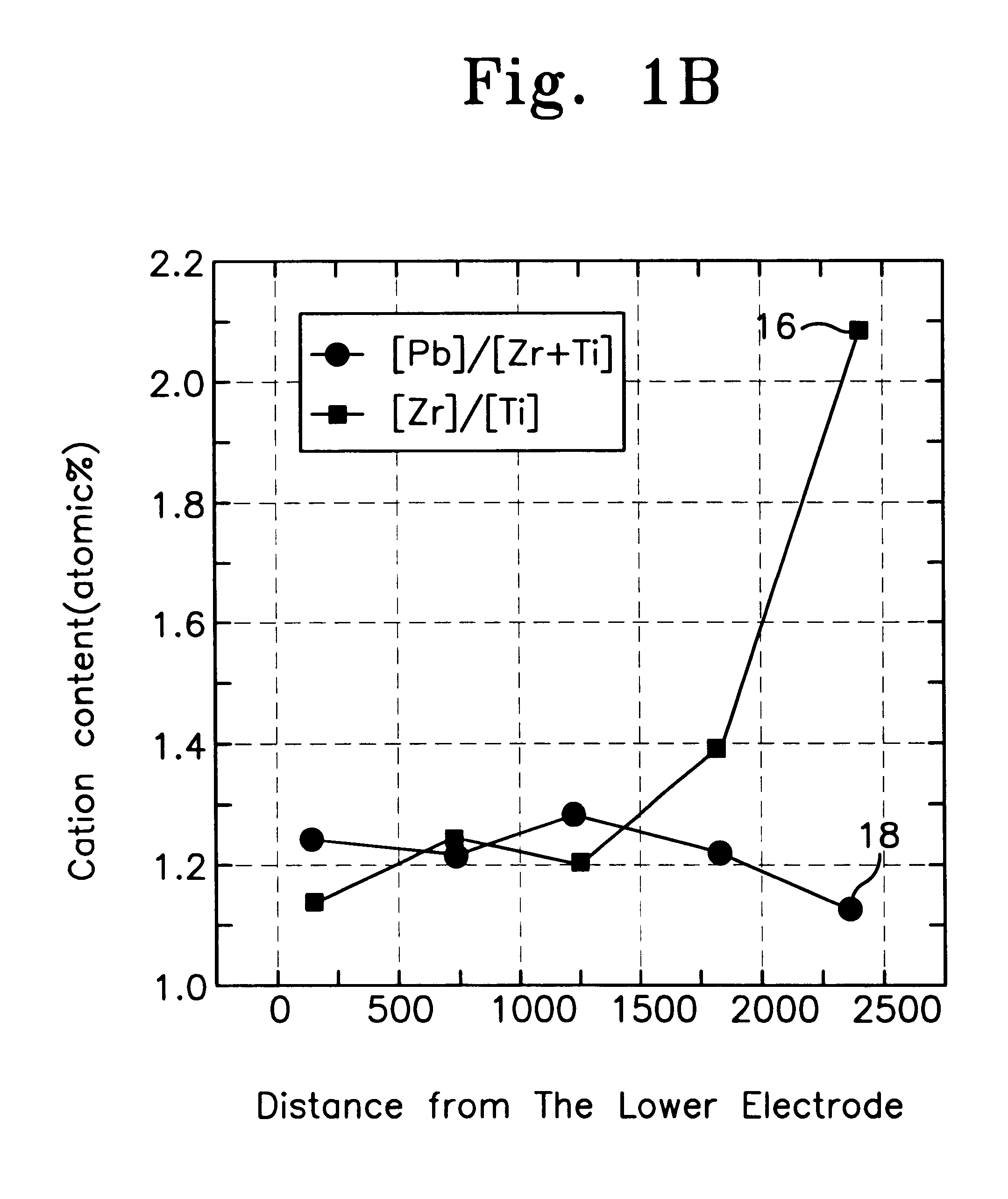
A ferroelectric capacitor with a multilayer ferroelectric film to prevent degradation of its ferromagnetic characteristics, wherein the ferroelectric film is made of a lower layer of PZT or PLZT formed on a lower electrode and an upper, titanium rich, layer of PZT, PLZT, or PbTiO3, an upper electrode formed on the upper layer of the ferroelectric film and a protective layer formed to cover the ferroelectric capacitor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Stress control of thin films by mechanical deformation of wafer substrate
InactiveUS6514835B1Vacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingFerroelectric thin filmsCurie temperature
A method of improving the physical and / or electrical and / or magnetic properties of a thin film material formed on a substrate, wherein the properties of the thin film material are stress-dependent, by selectively applying force to the substrate during the film formation and / or thereafter during the cooling of the film in the case of a film formed at elevated temperature, to impose through the substrate an applied force condition opposing or enhancing the retention of stress in the product film. The method of the invention has particular utility in the formation of ferroelectric thin films which are grown at temperature above the Curie temperature, and which may be placed in tension during the cooling of the film to provide ferroelectric domains with polarization in the plane of the film.
Owner:FELLOWS RES B V +1
Wake-up of ferroelectric thin films for probe storage
A method for improving the stability of ferroelectric storage devices comprises: providing a ferroelectric storage medium including a film of ferroelectric material; and repeatedly applying a voltage to the film of ferroelectric material to improve the stability of polarized bits in the film of ferroelectric material. An apparatus that is used to perform the method is also provided.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
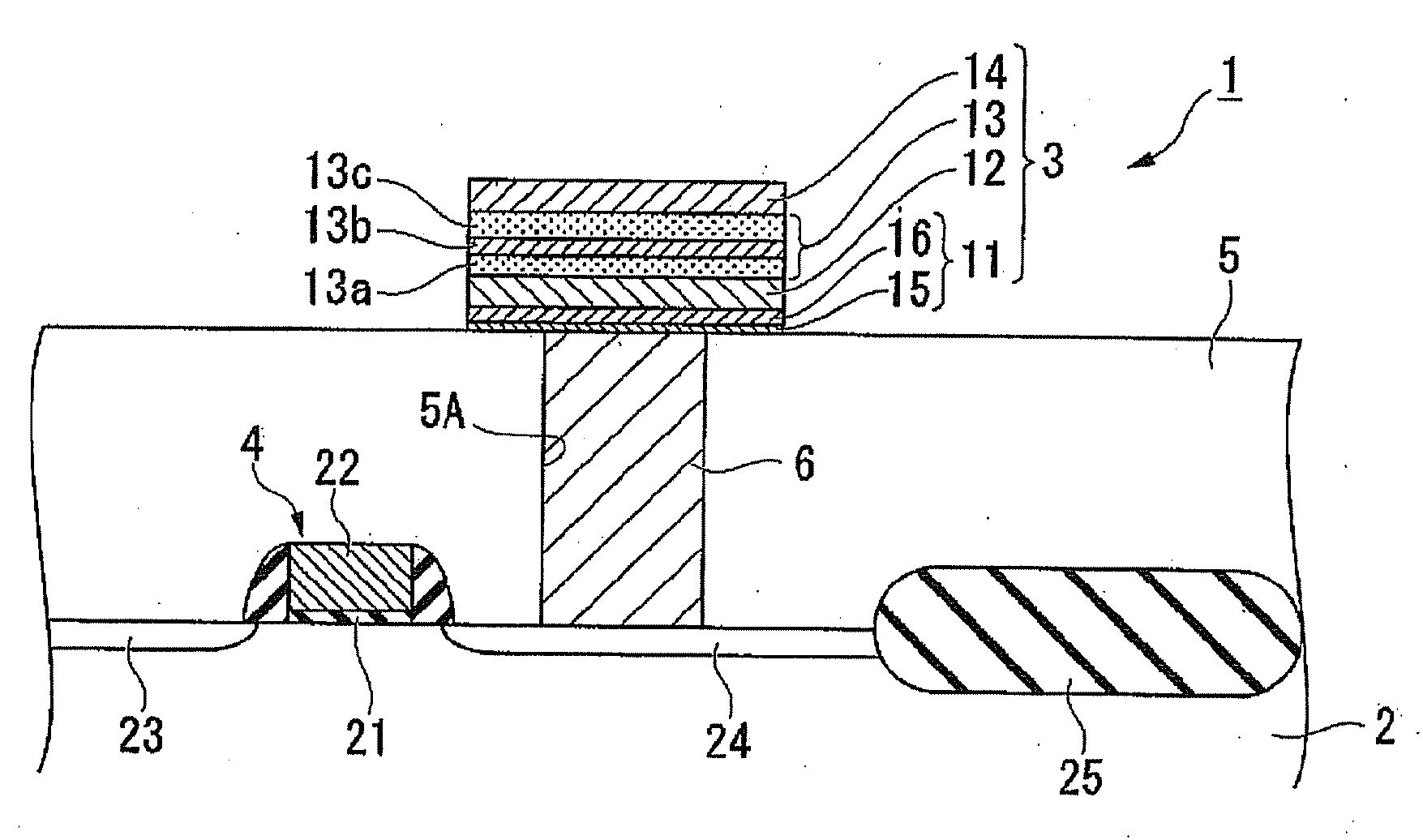
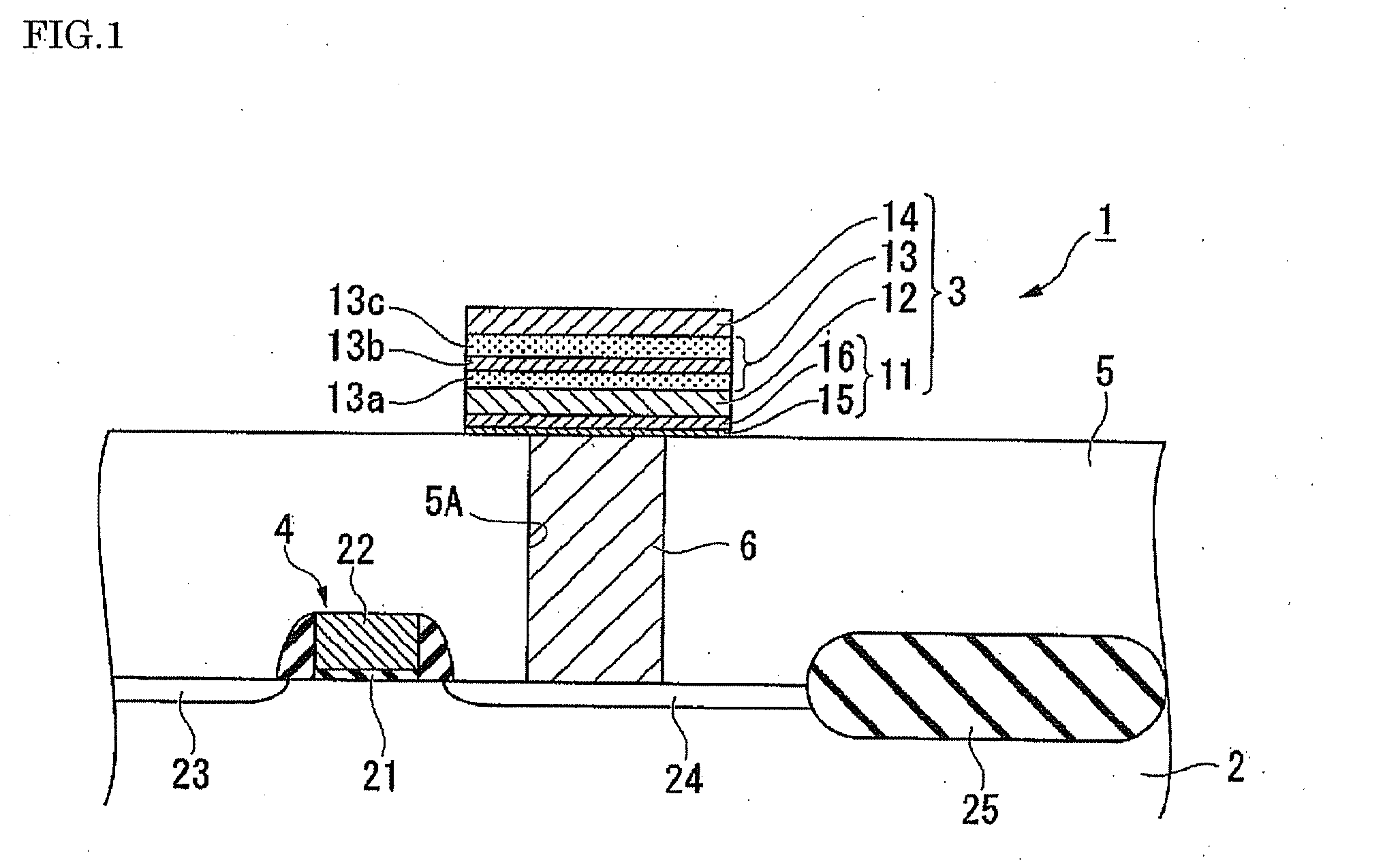
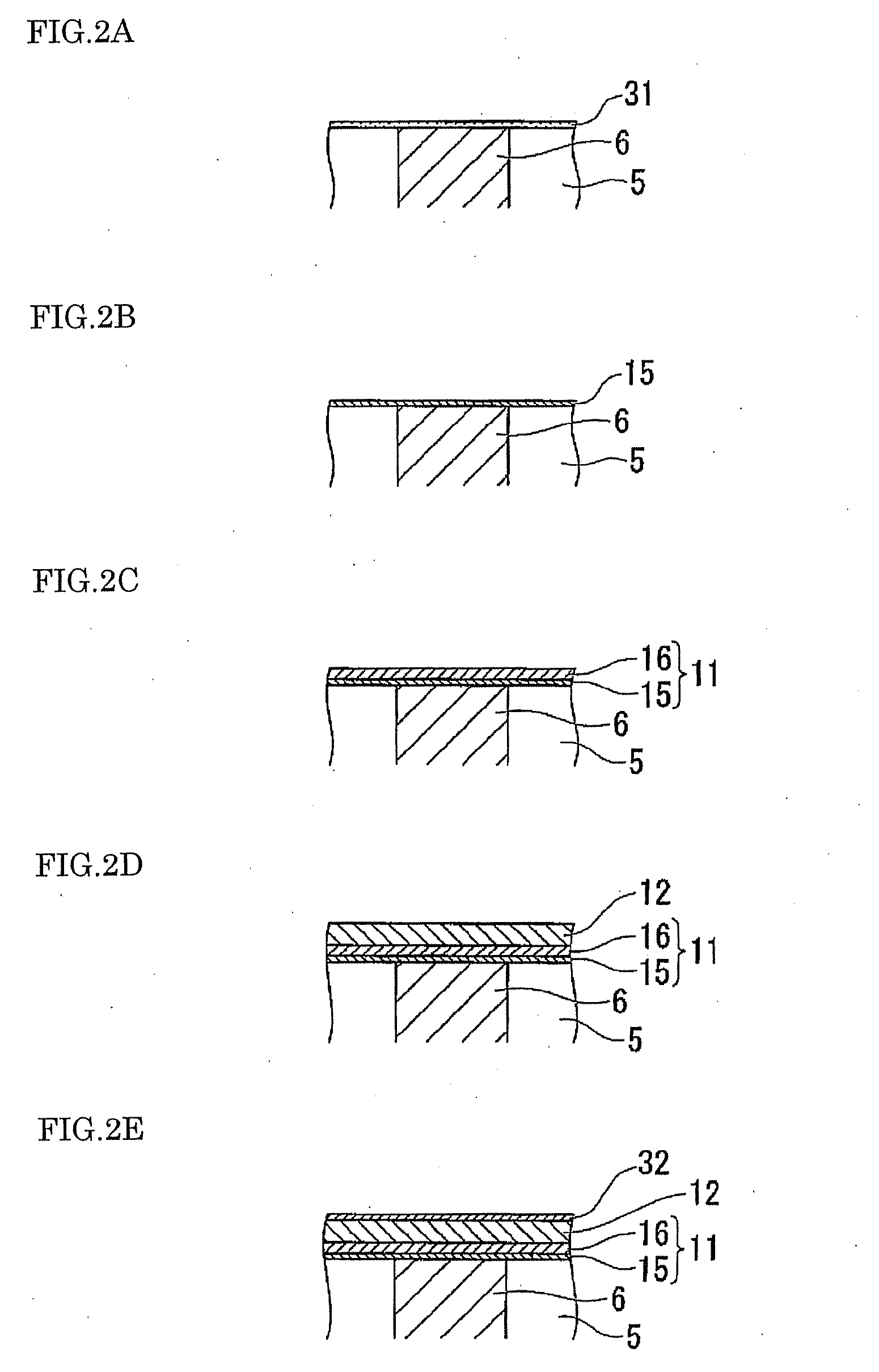
Piezoelectric device, liquid jetting head, ferroelectric device, electronic device and methods for manufacturing these devices
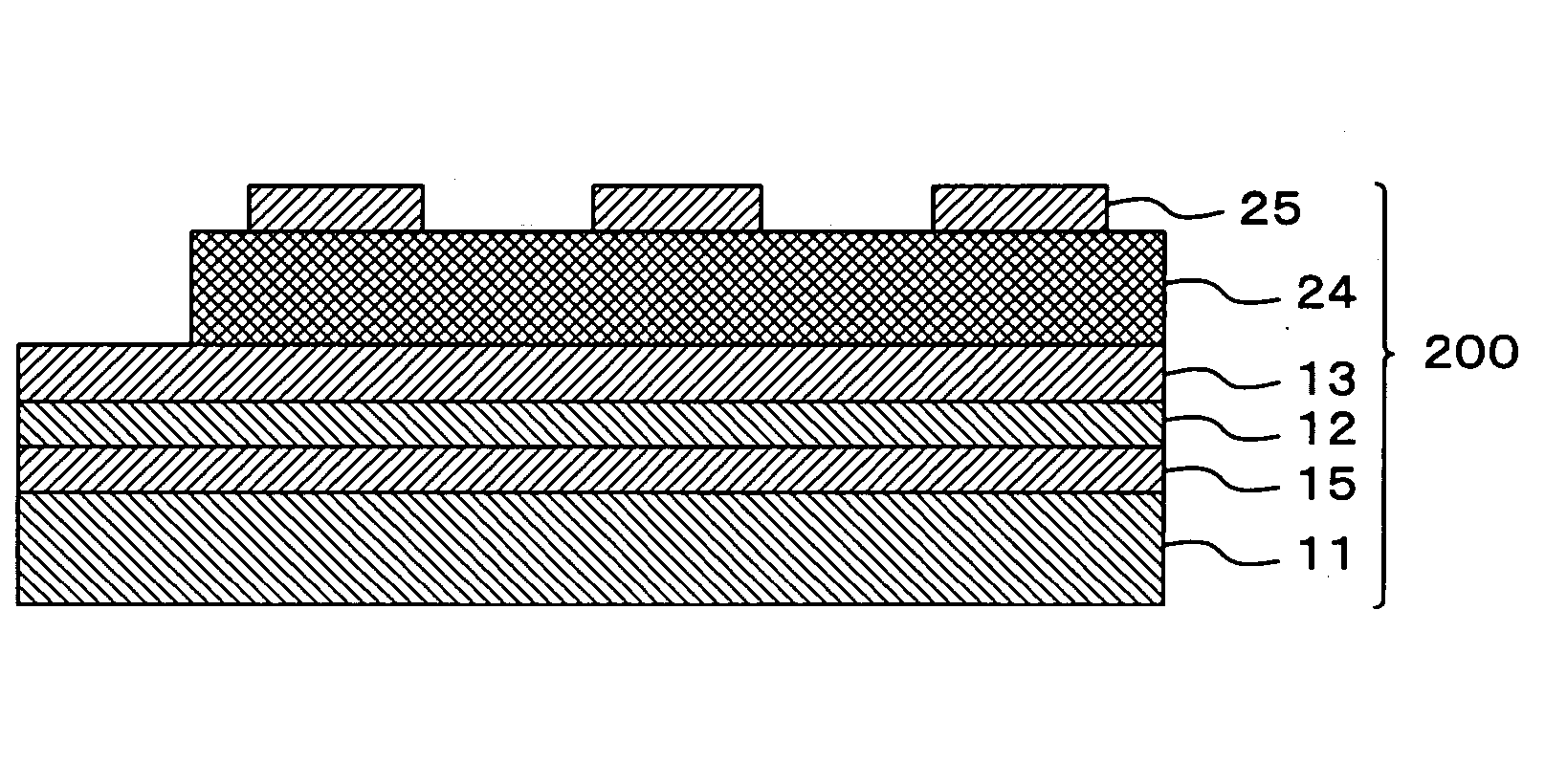
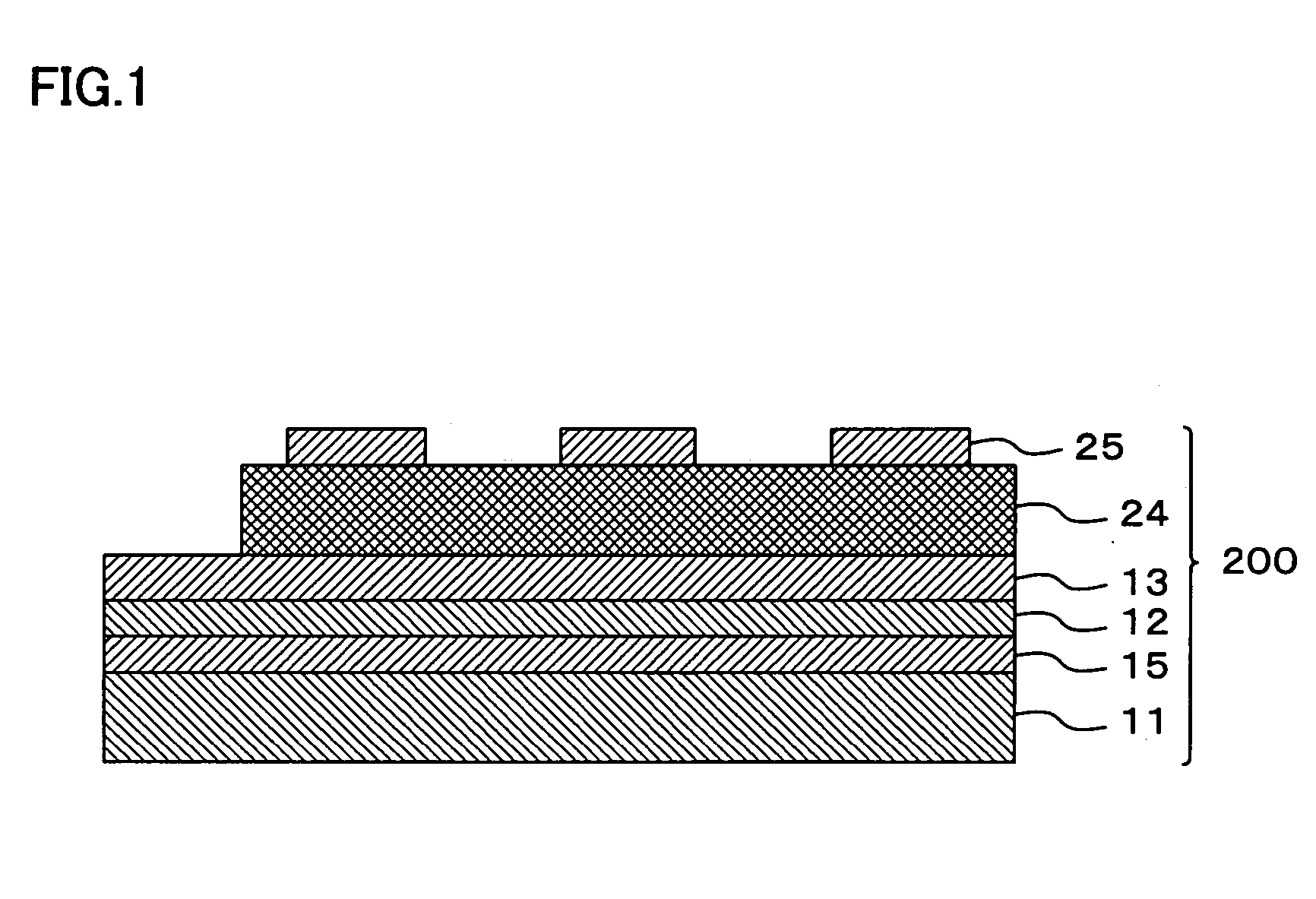
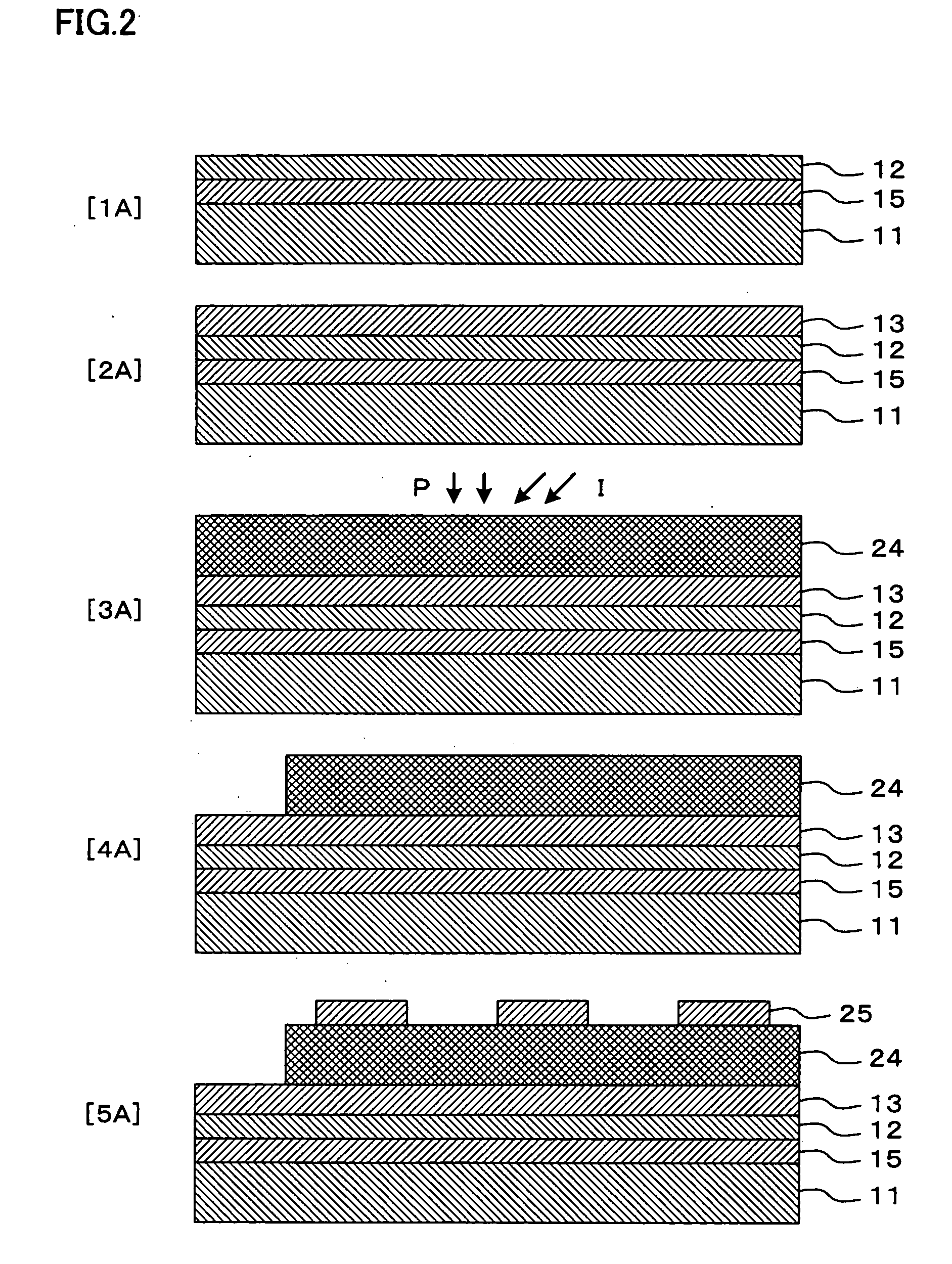
InactiveUS20050122005A1Efficient preparationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesIn planeFerroelectric thin films
An intermediate film (15, 12, 53) is formed on a substrate (11, 52), a bottom electrode (13, 542) is formed on top of this intermediate film, a ferroelectric film (24) or piezoelectric film (543) is formed on top of this bottom electrode by an ion beam assist method, and a top electrode (25, 541) is formed on top of this ferroelectric film or piezoelectric film. The ferroelectric film or piezoelectric film is formed by PZT, BST or a relaxer material. As a result of the use of an ion beam assist method in the formation of any one of the intermediate film, bottom electrode, ferroelectric film or piezoelectric film, a piezoelectric device or ferroelectric device which has a piezoelectric film or ferroelectric film with an in-plane orientation can be manufactured with good efficiency.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Tuneable electromagnetic bandgap structures based on high resistivity silicon substrates
ActiveUS7030463B1Small sizeSmall size and tunableCapacitor with electrode distance variationCapacitor with temperature varied dielectricFerroelectric thin filmsHigh resistivity silicon
Electrically tunable electromagnetic bandgap (“TEBG”) structures using a ferroelectric thin film on a semiconductor substrate, tunable devices that include such a TEBG structure, such as a monolithic microwave integrated circuit (“MMIC”), and a method producing such a TEBG structure are disclosed. The present invention provides a semiconductive substrate having an oxide layer, a first conductive layer positioned on the oxide layer, a ferroelectric layer covering the first conductive layer, and a second conductive layer positioned on a surface of the tunable ferroelectric layer. The use of the ferroelectric layer, which have a DC electric field dependent permittivity, enables a small size, tunable EBG structure.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON THE
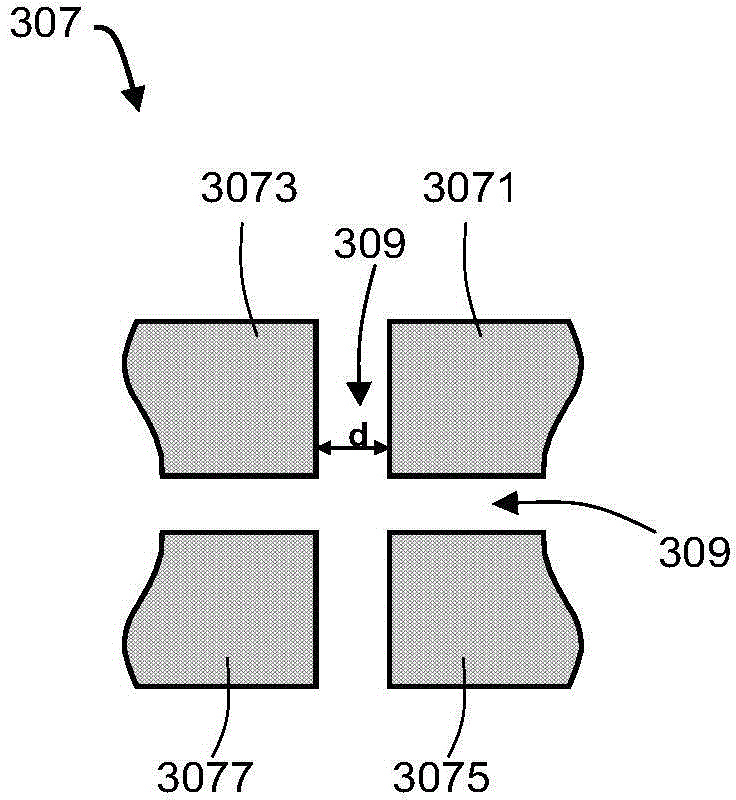
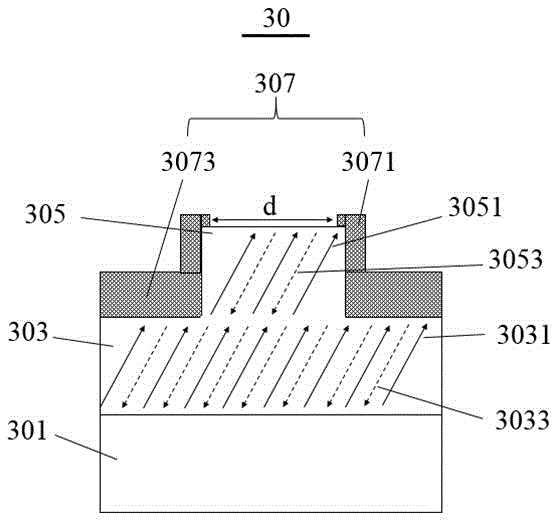
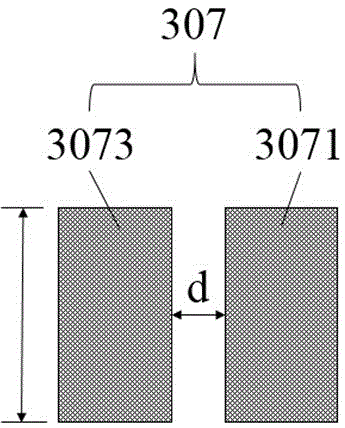
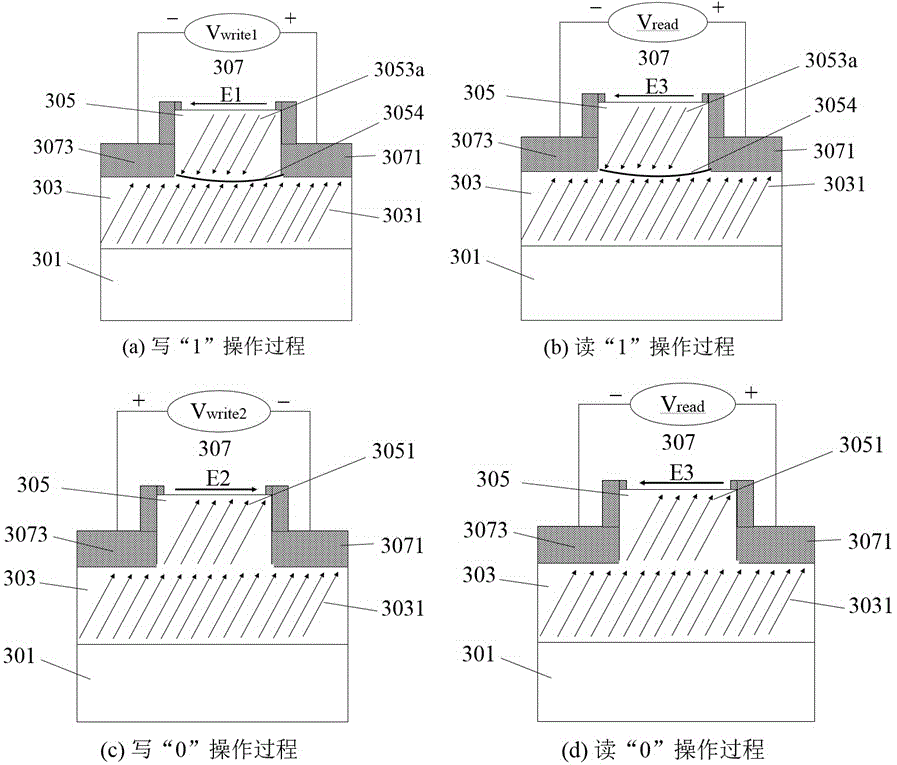
Non-destructive readout ferroelectric memory and manufacturing method and read/write operation method thereof
ActiveCN104637948ASimple structureEasy to makeSolid-state devicesDigital storageNon destructivePower flow
The invention belongs to the technical field of ferroelectric memory, in particular to a non-destructive readout ferroelectric memory and a manufacturing method and a read / write operation method thereof. The ferroelectric memory comprises a ferroelectric film layer and a read / write electrode layer which is arranged on the ferroelectric film layer, wherein a gap for partitioning the read / write electrode layer into at least two parts is formed in the read / write electrode layer; the polarization direction of the electric domain of the ferroelectric film layer is not basically parallel to the normal direction of the read / write electrode layer; read operation and write operation can be finished through the read / write electrode layer. The ferroelectric memory is simple in structure, is easiness to manufacture, is low in cost, and is suitable for high-density application; a non-destructive current readout way can be realized.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Ferroelectric nonvolatile memory and preparation method and read/write operation method thereof
ActiveCN105655342AGood retention propertiesFast read and writeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn planePower flow
The invention belongs to the technical field of ferroelectric storage, and particularly relates to a ferroelectric nonvolatile memory and a preparation method and a read / write operation method thereof. The ferroelectric memory comprises a ferroelectric thin film layer, a ferroelectric storage unit etched on the surface of the ferroelectric thin film layer, and in-plane read / write electrode layers prepared at the left and right of the ferroelectric storage unit; and a polarization direction of an electric domain is basically not parallel to a normal direction of the read / write electrode layer. When an in-plane structure of the storage unit is changed, the multi-bit information storage can be realized. A read operation and a write operation can be completed by virtue of a storage unit left / right deposited read / write electrode layer etched on the surface, and an additional read electrode and an additional read / write electrode can be additionally arranged on the top of the etched ferroelectric storage unit so as to realize the read operation. The ferroelectric memory is simple in structure, simple in preparation, low in cost and capable of nondestructively and rapidly reading the stored electric-domain logic information in a large-current way.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
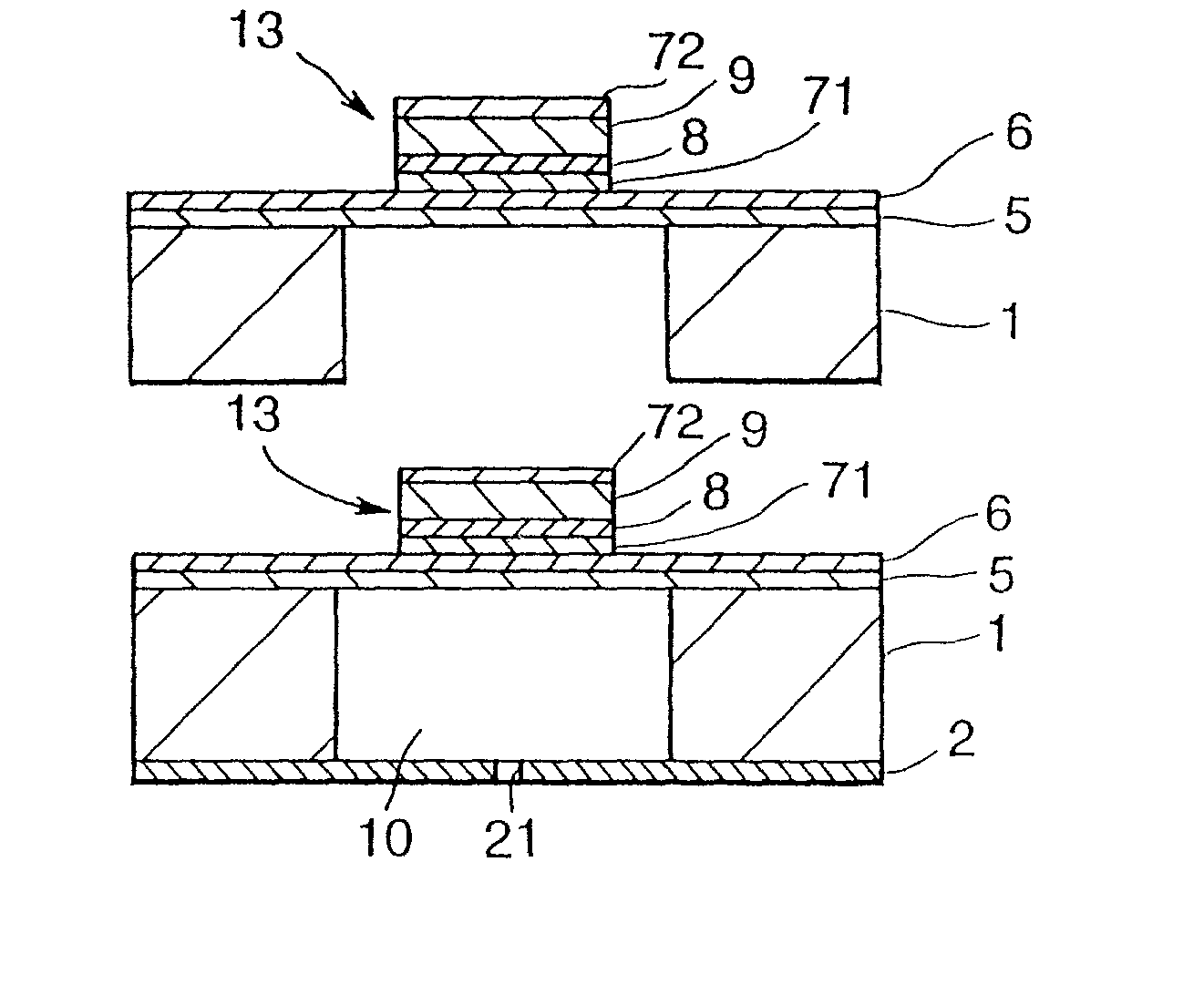
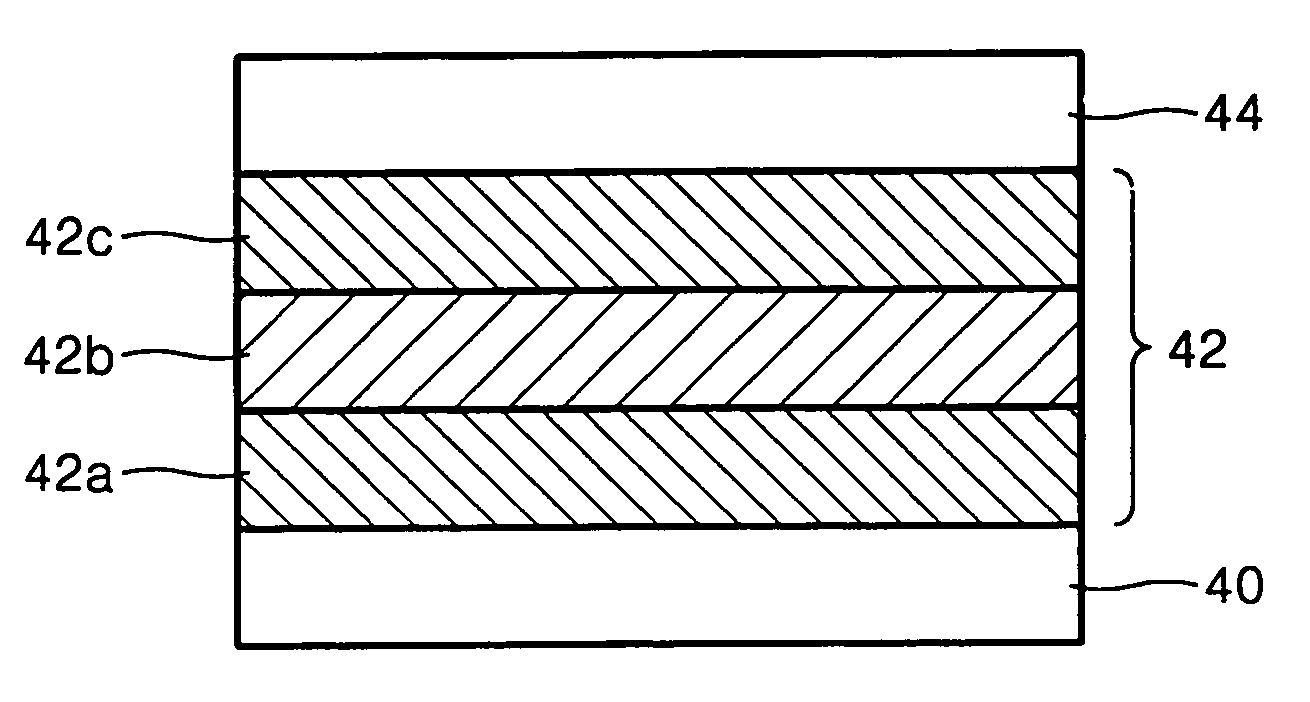
Ferroelectric capacitor and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20080225569A1Reduce roughnessReduce leakage currentThin/thick film capacitorSolid-state devicesFerroelectric thin filmsCrystal structure
A ferroelectric capacitor includes: a ferroelectric film, and a lower electrode and an upper electrode interposing the ferroelectric film, wherein the ferroelectric film includes a first ferroelectric layer of ferroelectric material having a perovskite type crystal structure expressed by a general formula ABO3 formed by a metal organic chemical vapor deposition method, a second ferroelectric layer of ferroelectric material in which a part of B site element in ferroelectric material having a perovskite type crystal structure expressed by a general formula ABO3 is replaced with Nb, and a third ferroelectric layer of ferroelectric material having a perovskite type crystal structure expressed by a general formula ABO3 formed by a sol-gel method, which are sequentially laminated from the side of the lower electrode.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Multilayer thin film and its fabrication process as well as electron device
InactiveUS20020015852A1Preferential (001) orientationRelaxation stressPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesFerroelectric thin filmsOptoelectronics
Owner:SNAPTRACK
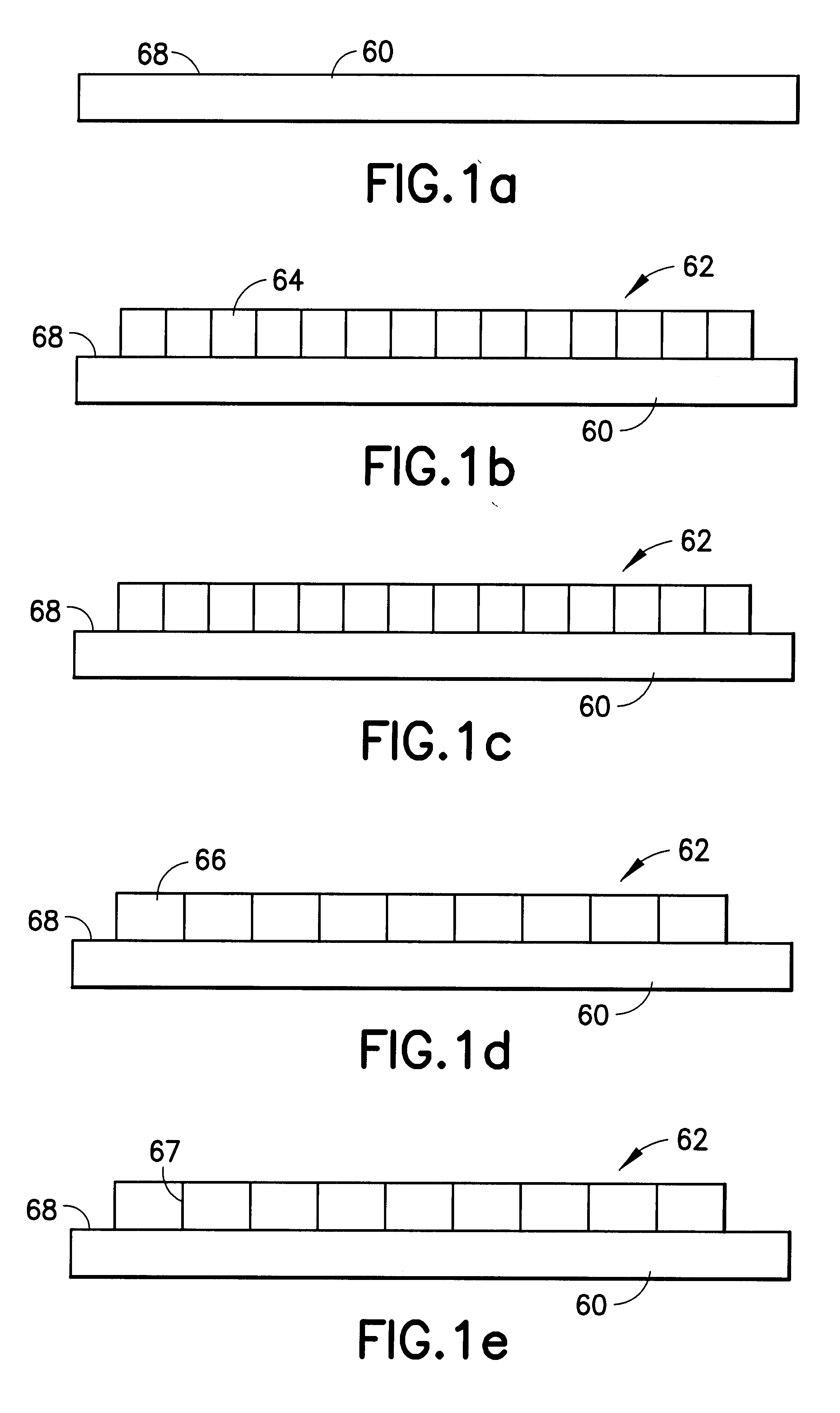
Ferroelectric stacked-layer structure, field effect transistor, and ferroelectric capacitor and fabrication methods thereof
InactiveUS20090152607A1Improve interface propertiesReduced carrier trap levelFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsFerroelectric thin filmsCrystal structure
A ferroelectric stacked-layer structure is fabricated by forming a first polycrystalline ferroelectric film on a polycrystalline or amorphous substrate, and after planarizing a surface of the first ferroelectric film, laminating on the first ferroelectric film a second thin ferroelectric film having the same crystalline structure as the first ferroelectric film. A field effect transistor or a ferroelectric capacitor includes the ferroelectric stacked-layer structure as a gate insulating film or a capacitor film.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Ferroelectric Thin Films and Devices Comprising Thin Ferroelectric Films
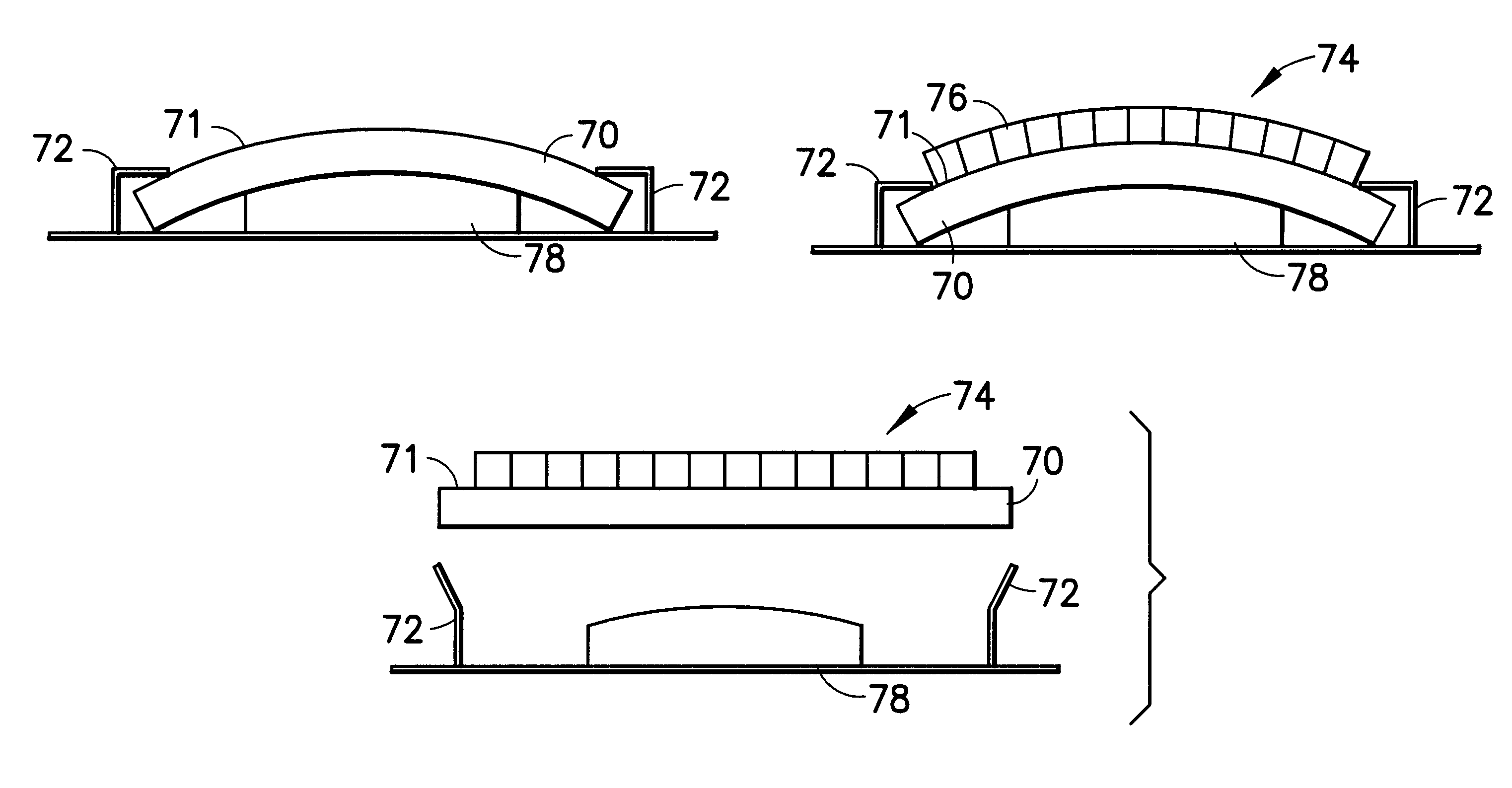
InactiveUS20080165565A1Small sizeAddress rising pricesThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyMicrometerFerroelectric thin films
A method of producing a device with a ferroelectric crystal thin film on a first substrate including the steps of providing a ferroelectric crystal, of irradiating a first surface of the ferroelectric crystal with ions so that a damaged layer is created underneath the first surface, of bonding a block of material including the first substrate to the ferroelectric crystal to create a bonded element, wherein an interface is formed between the first surface and a second surface of the block, and of heating the bonded element and separating it at the damaged layer, so that a ferroelectric crystal layer remains supported by the first substrate. By this method, very thin films—down to thicknesses of a fraction of a micrometer—of ferroelectric crystals may be fabricated without jeopardizing the monocrystalline structure.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
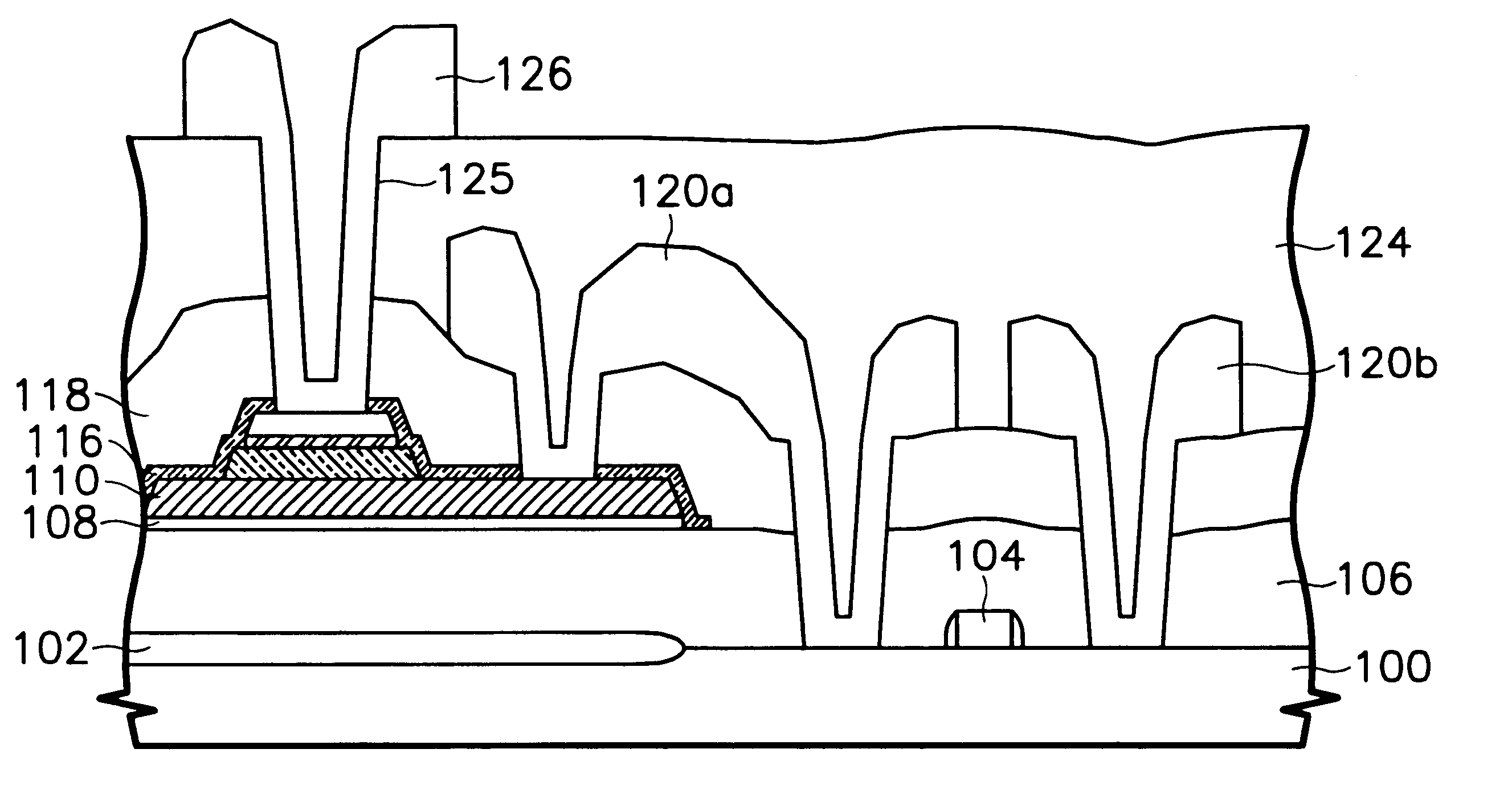
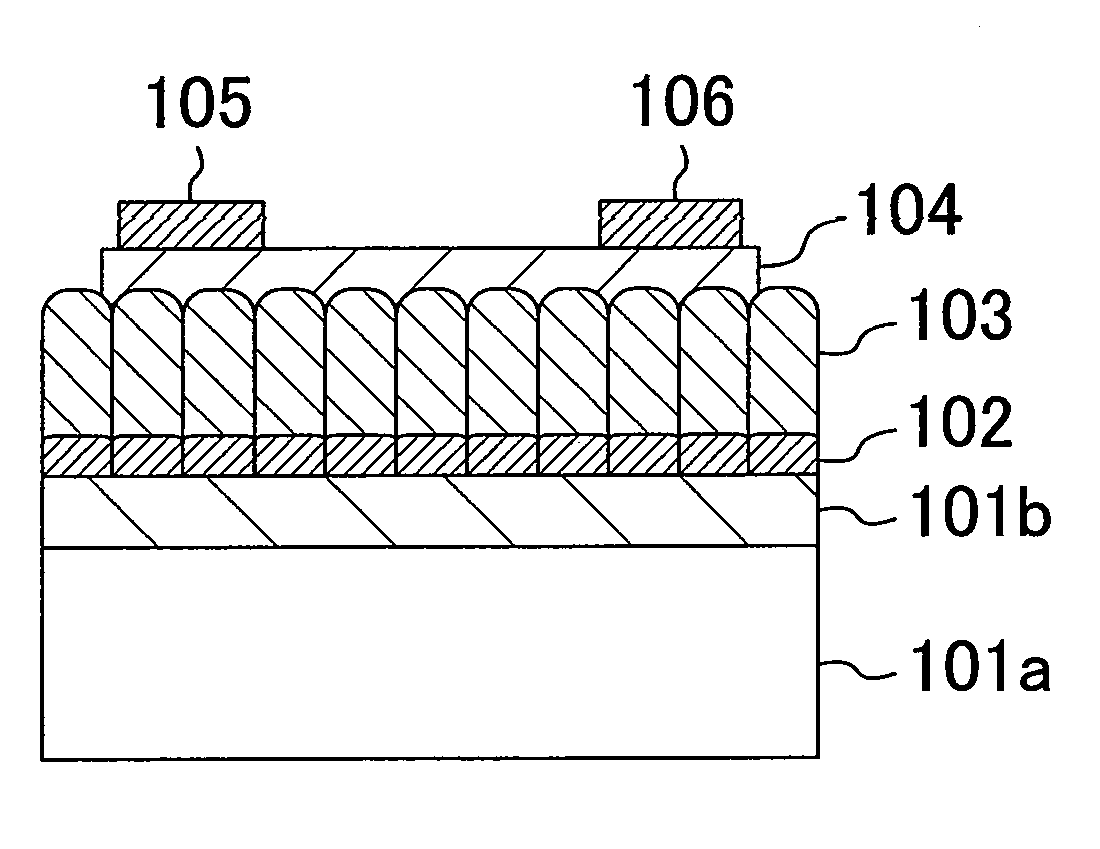
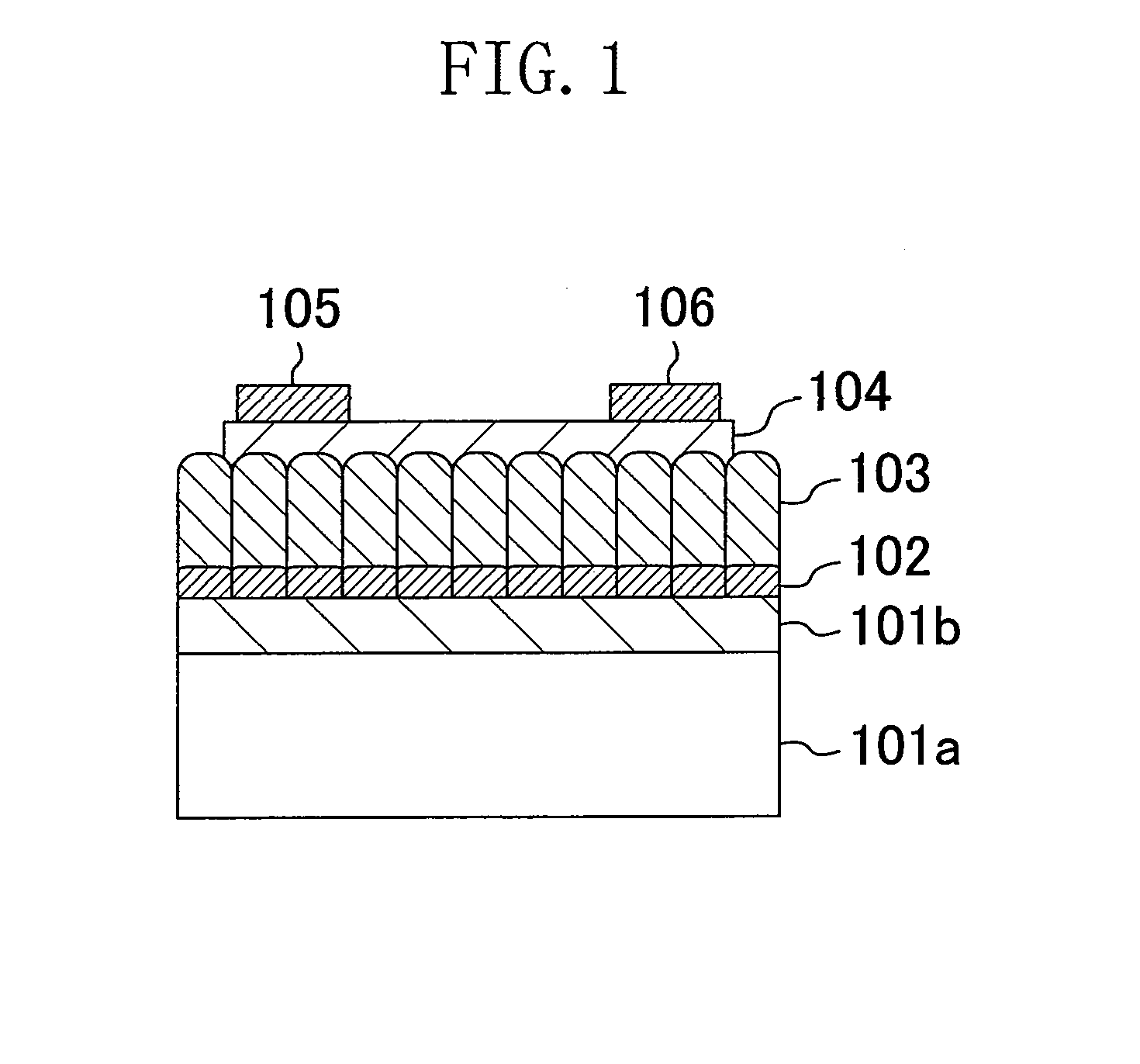
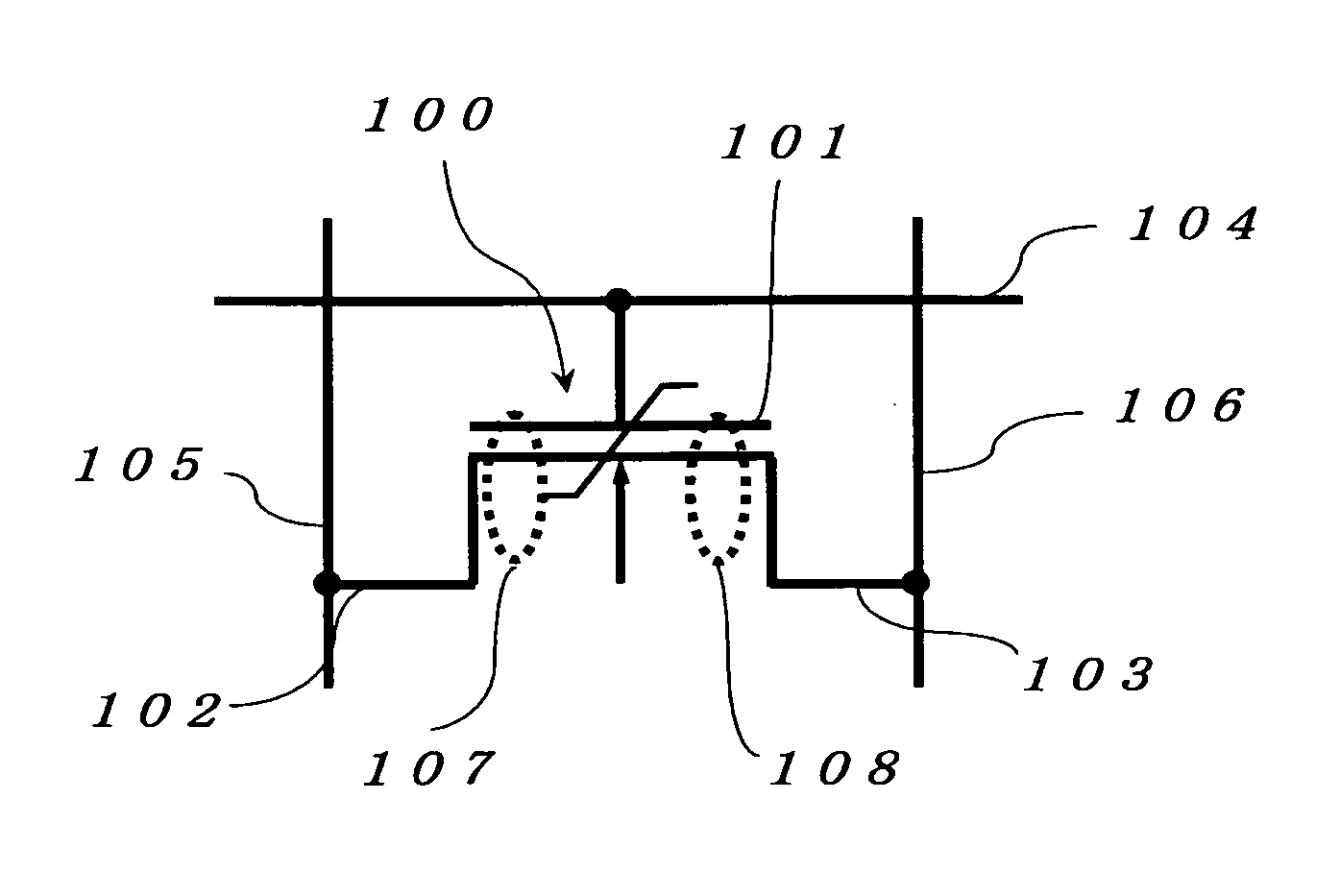
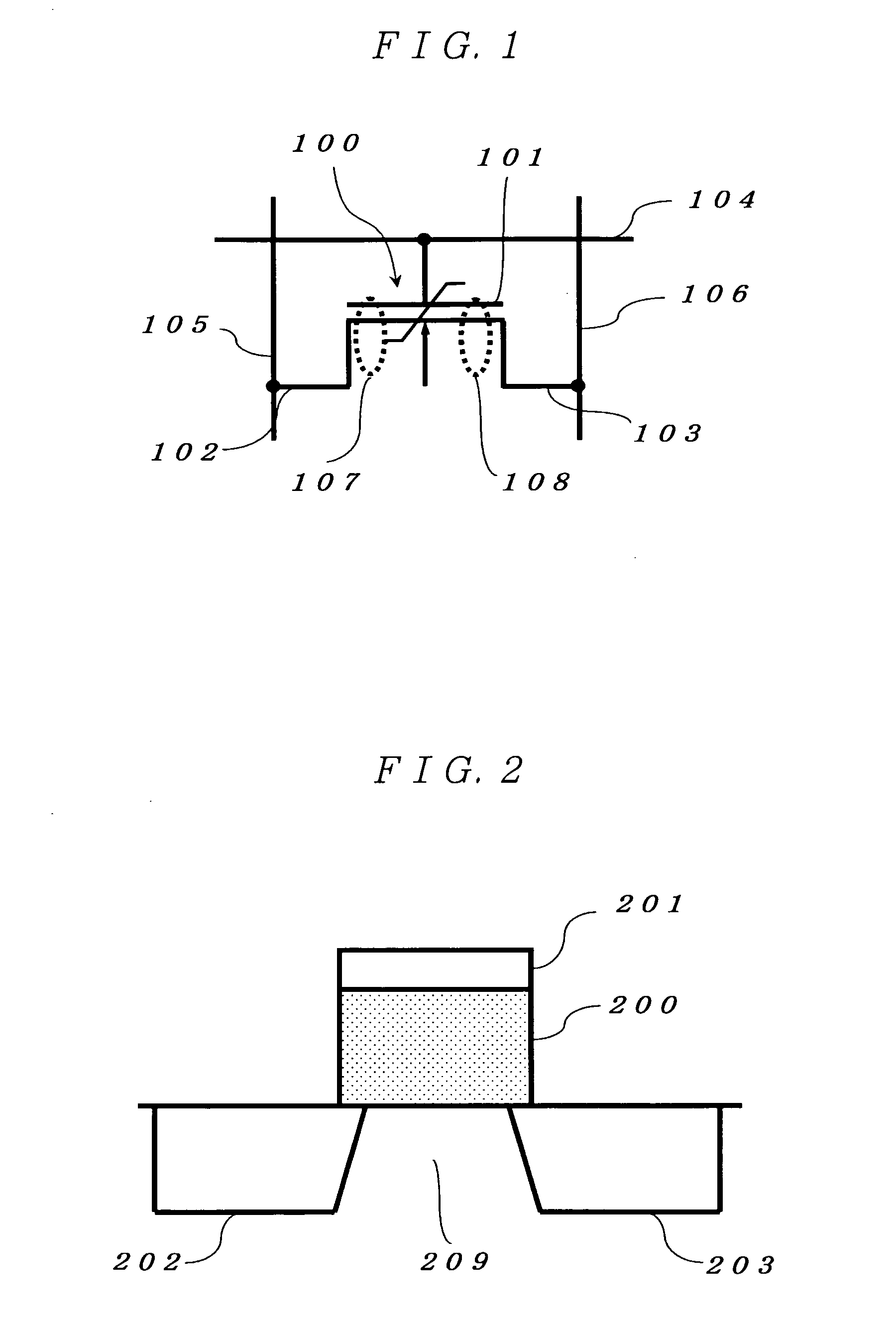
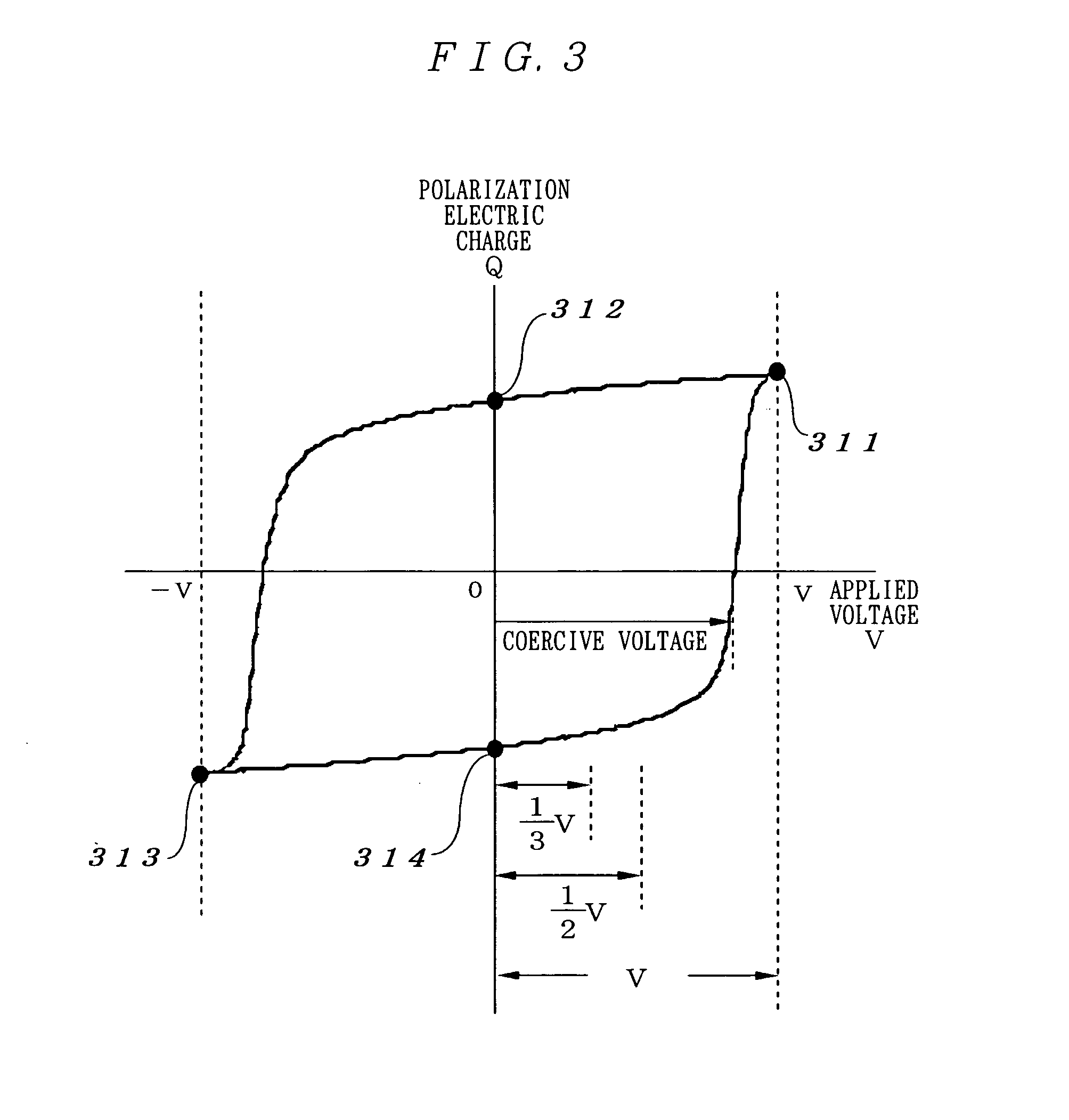
Ferroelectric memory device
To provide a nondestructive-read ferroelectric memory capable of realizing high speed, high integration, and long service life. The present invention is provided with an MFSFET 100 having a ferroelectric thin film at its gate portion, word line 104, bit line 105, and bit line 106 so as to apply voltage equal to or higher than the coercive electric field of the ferroelectric thin film between the bit line 105 and the word line 104 at first write timing and apply voltage equal to or higher than the coercive electric field between the bit line 106 and the word line 104 at second write timing, and applies voltage equal to or lower than the coercive electric field of the ferroelectric thin film between the bit line 105 and the word line 104 at first read timing to detect the current flowing between the both bit lines, and applies voltage equal to or lower than the coercive electric field between the bit line 106 and the word line 104 at second read timing to detect the current flowing between the both bit lines.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for manufactuing ferroelectric thin film device, ink jet recording head, and ink jet printer
InactiveUS20020123158A1Reliable drive characteristicReduce adhesionTransistorThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changeIridiumFerroelectric thin films
It is an object of the present invention to control the crystal orientation of a ferroelectric thin film as dictated by the application of a ferroelectric thin film device. To accomplished the stated object, a bottom electrode containing at least iridium is formed over a surface preparation layer whose main component is zirconium oxide, and an ultra-thin titanium layer is laminated over the bottom electrode. An amorphous layer containing the elemental metal and elemental oxygen that constitute the ferroelectric is formed over the titanium layer, and a crystallized ferroelectric thin film is formed by heat treating this amorphous layer. If the thickness of the titanium layer is kept between 2 nm and 10 nm in the lamination thereof, the ferroelectric thin film will have a priority orientation of (100), and if it is kept between 10 nm and 20 nm, the ferroelectric thin film will have a priority orientation of (111).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Ferroelectric memory device having a hydrogen barrier film
InactiveUS6982444B2Small degradation in characteristicGood ferroelectric propertiesTransistorSolid-state devicesHydrogenFerroelectric thin films
There is provided a semiconductor device having a ferroelectric capacitor formed on a semiconductor substrate covered with an insulator film, wherein the ferroelectric capacitor comprises: a bottom electrode formed on the insulator film; a ferroelectric film formed on the bottom electrode; and a top electrode formed on the ferroelectric film. The ferroelectric film has a stacked structure of either of two-layer-ferroelectric film or three-layer-ferroelectric film. The upper ferroelectric film is metallized and prevents hydrogen from diffusing in lower ferroelectric layer. Crystal grains of the stacked ferroelectric films are preferably different.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Tantalum amide complexes for depositing tantalum-containing films, and method of making same
InactiveUS6960675B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGroup 5/15 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGas phaseFerroelectric thin films
Tantalum precursors useful in depositing tantalum nitride or tantalum oxides materials on substrates, by processes such as chemical vapor deposition and atomic layer deposition. The precursors are useful in forming tantalum-based diffusion barrier layers on microelectronic device structures featuring copper metallization and / or ferroelectric thin films.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Method of fabricating semiconductor device
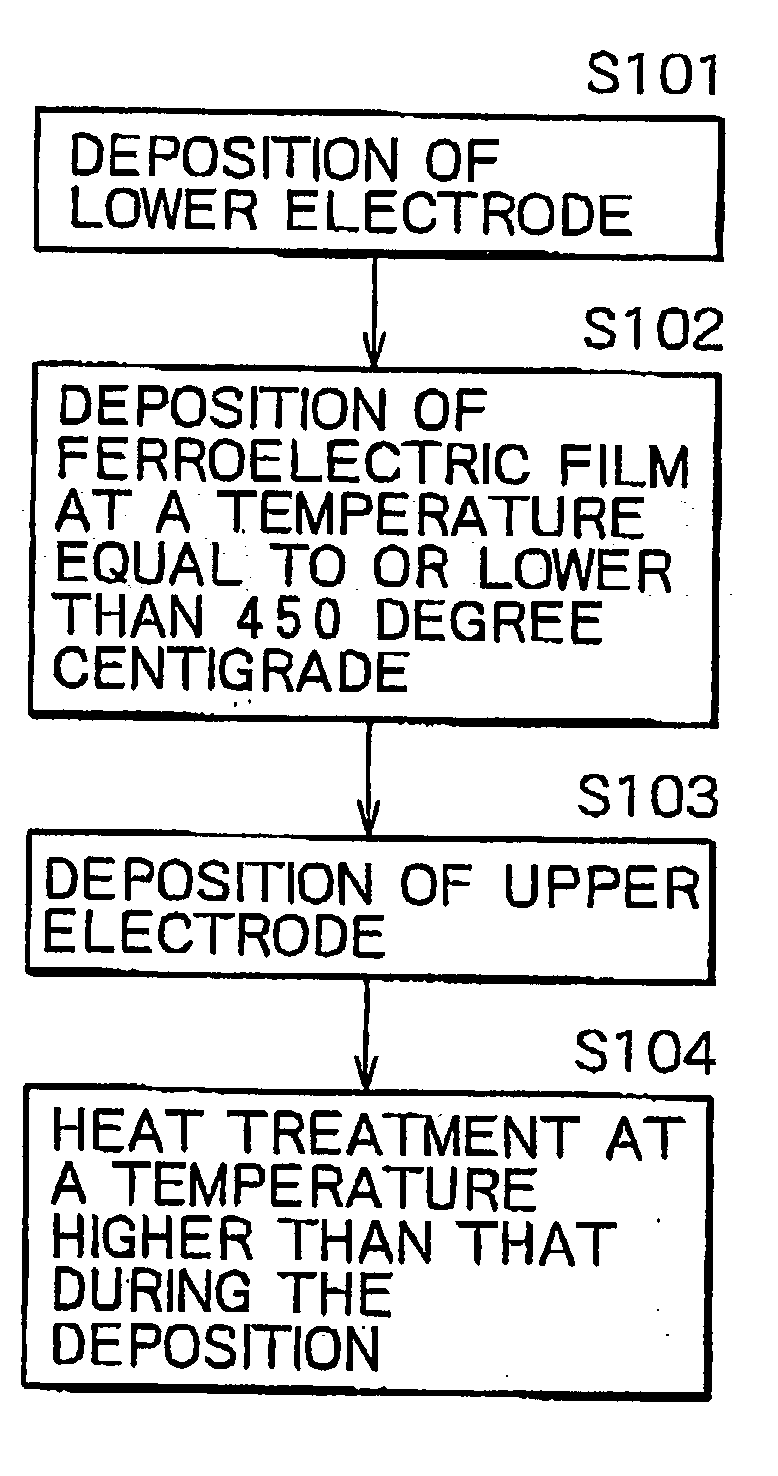
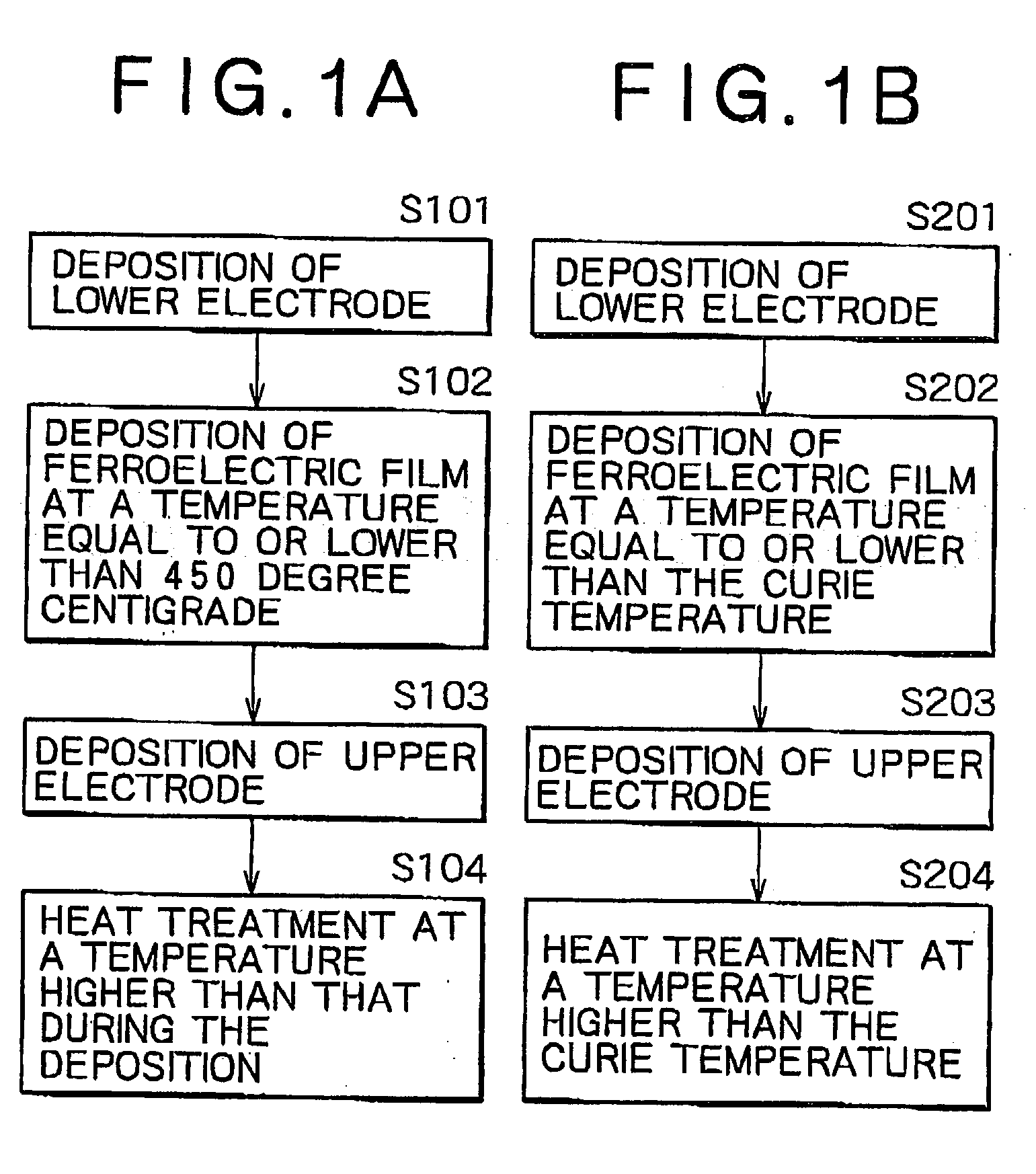
InactiveUS20030162394A1TransistorPolycrystalline material growthDeposition temperatureFerroelectric thin films
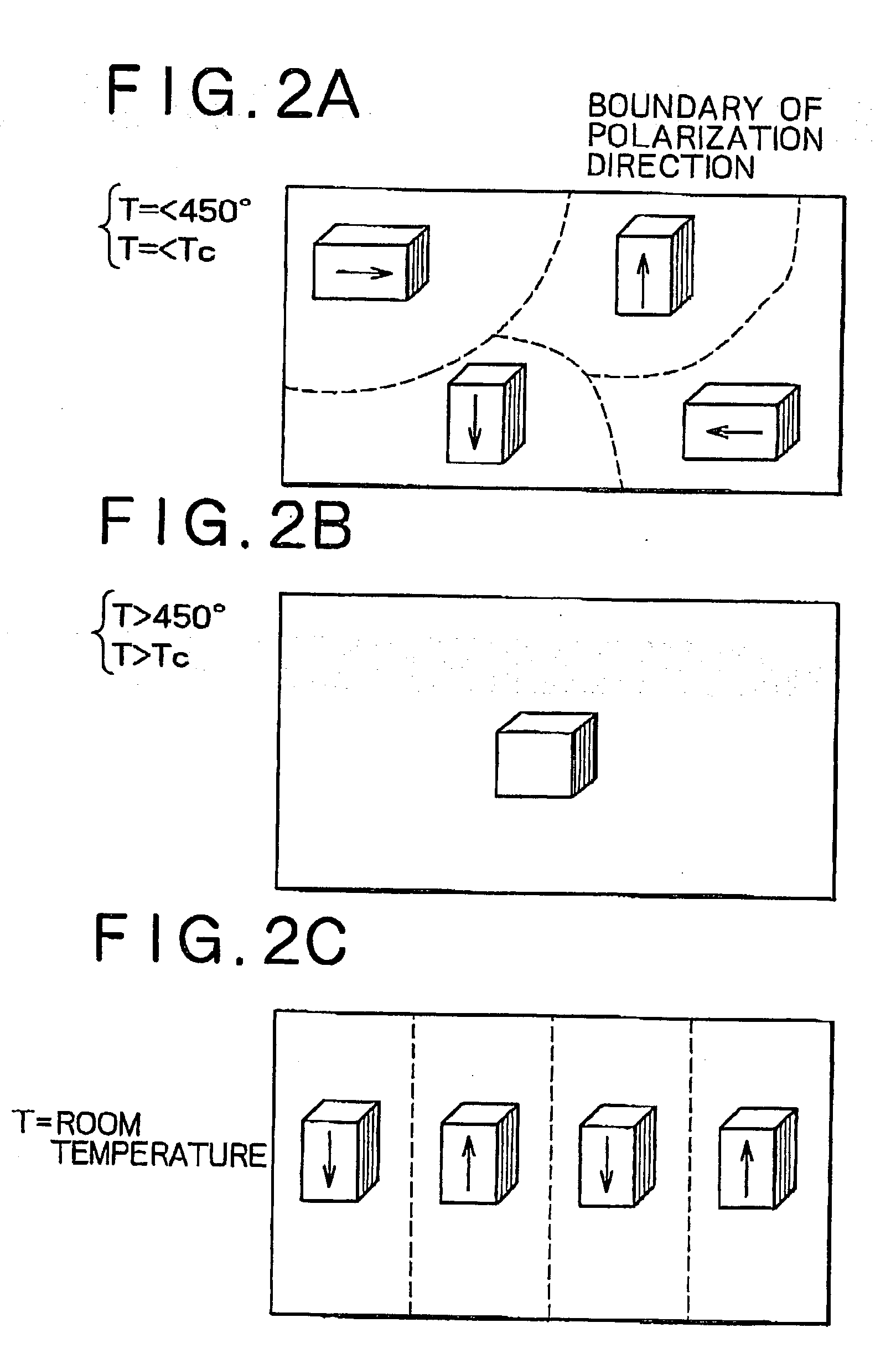
On an insulating film on a surface of a substrate a lower electrode is formed, and on the lower electrode a ferroelectric film is formed at a temperature equal to or less than 450 degree centigrade, or at a temperature equal to or less than the Curie temperature of the ferroelectric film. Thereafter, on the ferroelectric film an upper electrode is formed, and after the upper electrode is formed, heat treatment is applied at a temperature higher than the deposition temperature or the Curie temperature. Thereby, a ferroelectric film having a particular crystal orientation is formed, and when heat treatment at a temperature higher than the deposition temperature or the Curie temperature is applied to transform once to a paraelectric phase, without altering a crystal structure, a ferroelectric phase can be obtained, and thereby a ferroelectric film aligned in the spontaneous polarization orientations of the respective domains can be obtained.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Thermally oxidized seed layers for the production of textured electrodes and pzt devices and method of making
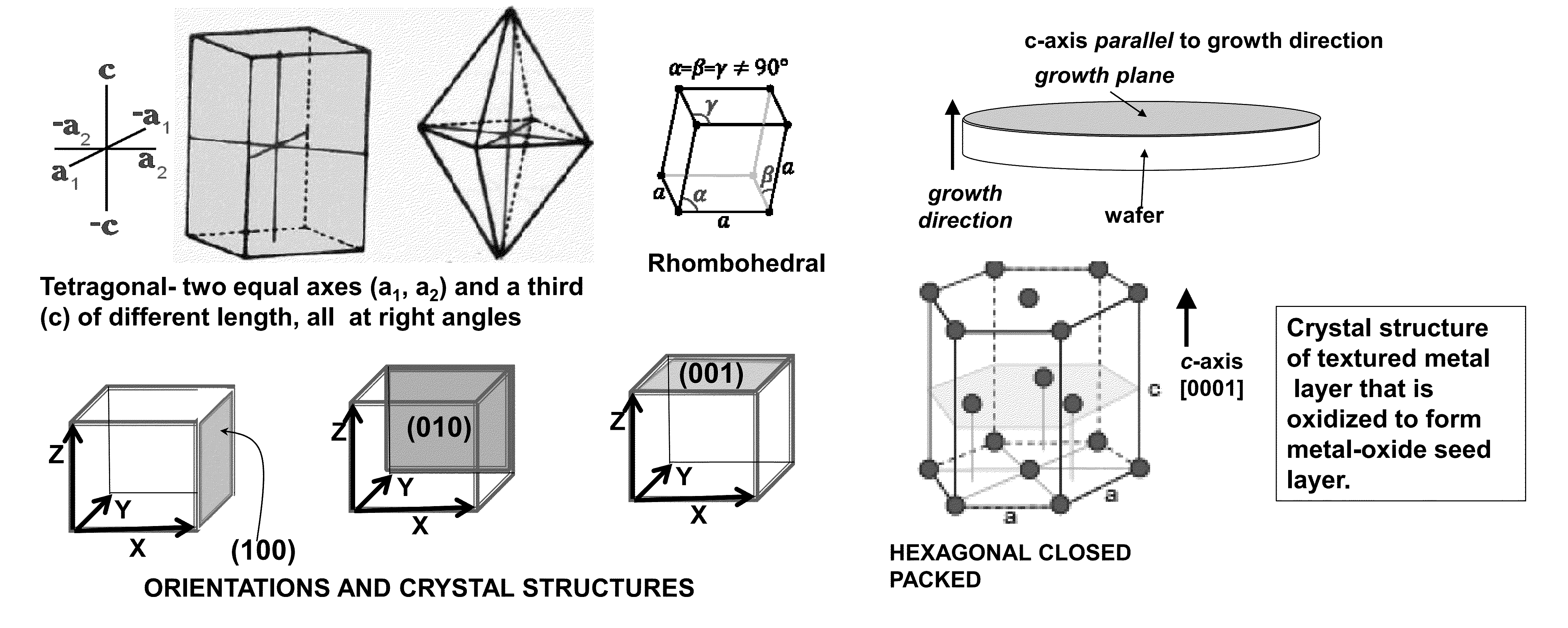
InactiveUS20130093288A1Improve texturePolycrystalline material growthPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCrystallographyFerroelectric thin films
A method for forming an electrical device having a {100}-textured platinum electrode comprising: depositing a textured metal thin film onto a substrate; thermally oxidizing the metal thin film by annealing to convert it to a rocksalt structure oxide with a {100}-texture; depositing a platinum film layer; depositing a ferroelectric film. An electrical device comprising a substrate; a textured layer formed on the substrate comprising metal oxide having a rocksalt structure; a first electrode film layer having a crystallographic texture acting as a template; and at least one ferroelectric material layer exhibiting spontaneous polarization epitaxially deposited on the first electrode film layer whereby the rocksalt structure of the textured layer facilitates the growth of the first electrode film layer with a {100} orientation which forms a template for the epitaxial deposition of the ferroelectric layer such that the ferroelectric layer is formed with an {001} orientation.
Owner:ARMY UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY THE
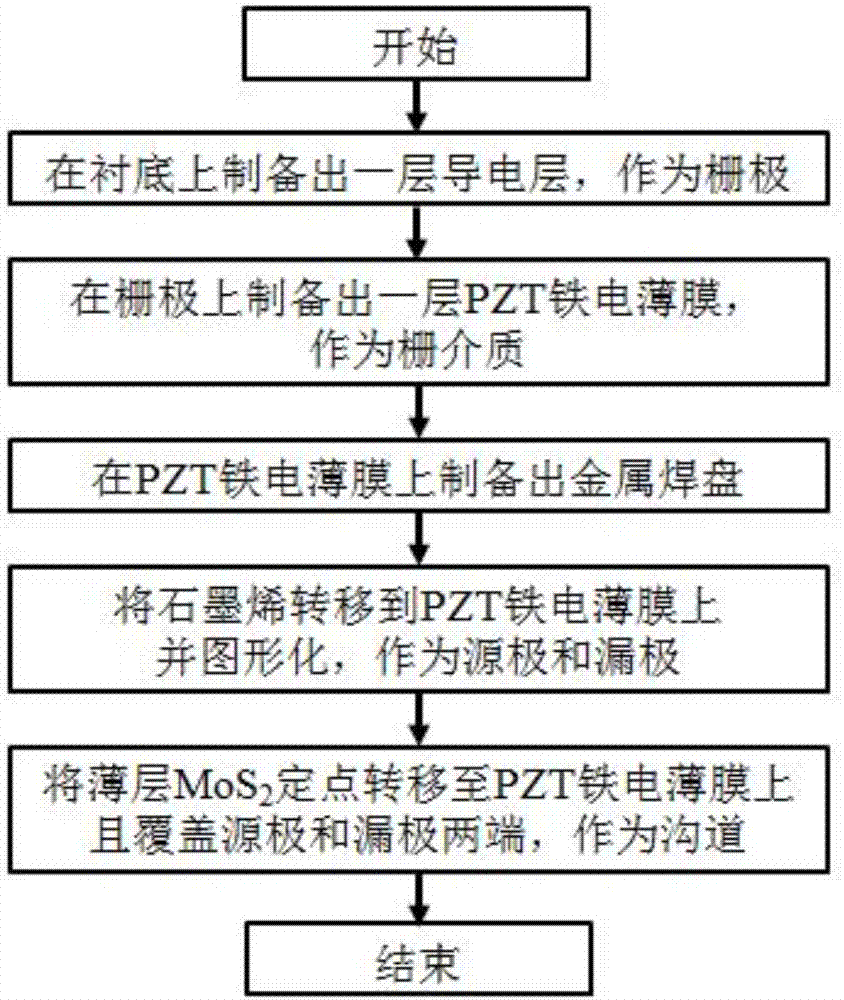
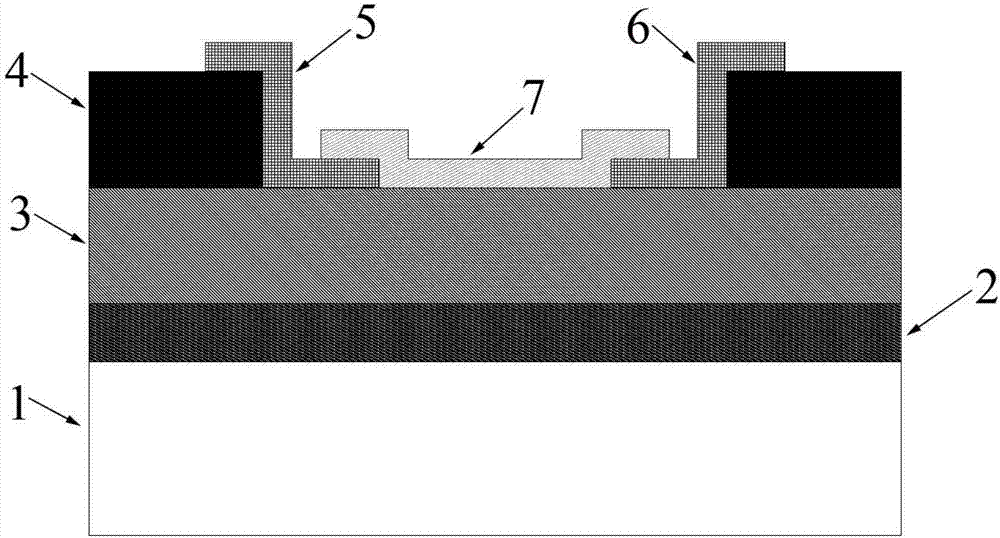
Phototransistor based on ferroelectric gate dielectric and thin layer MoS2 channel
The invention belongs to the field of micro-nano semiconductor optoelectronic devices, and particularly relates to a phototransistor based on a ferroelectric gate dielectric and a thin layer MoS2 channel and a preparation method thereof. The phototransistor comprises a source electrode, a leakage electrode, a channel, a gate electrode, a gate dielectric, a metal pad, and a substrate. The source electrode and the leakage electrode are graphene, the channel is thin layer MoS2, and the gate dielectric is a PZT ferroelectric membrane. Compared with existing similar phototransistor, the phototransistor has the following advantages that first, a high dielectric coefficienet of the PZT ferroelectric membrane helps improve the adjustment performance of the gate electrode for a channel carrier; second, the PZT ferroelectric membrane can adjust the channel carrier with surplus polarity field strength, so that the power consumption of the device is lowered; third, compared with organic ferroelectric material P (VDF-TrFE), the PZT ferroelectric membrane has the advantages of high surplus polarity, low coercive field strength, stable property and compatibility with microelectronic process; and fourth, as the source electrode and leakage electrode, the graphene can improve the signal light transmittance, and improve the light response degree and gain of the device.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
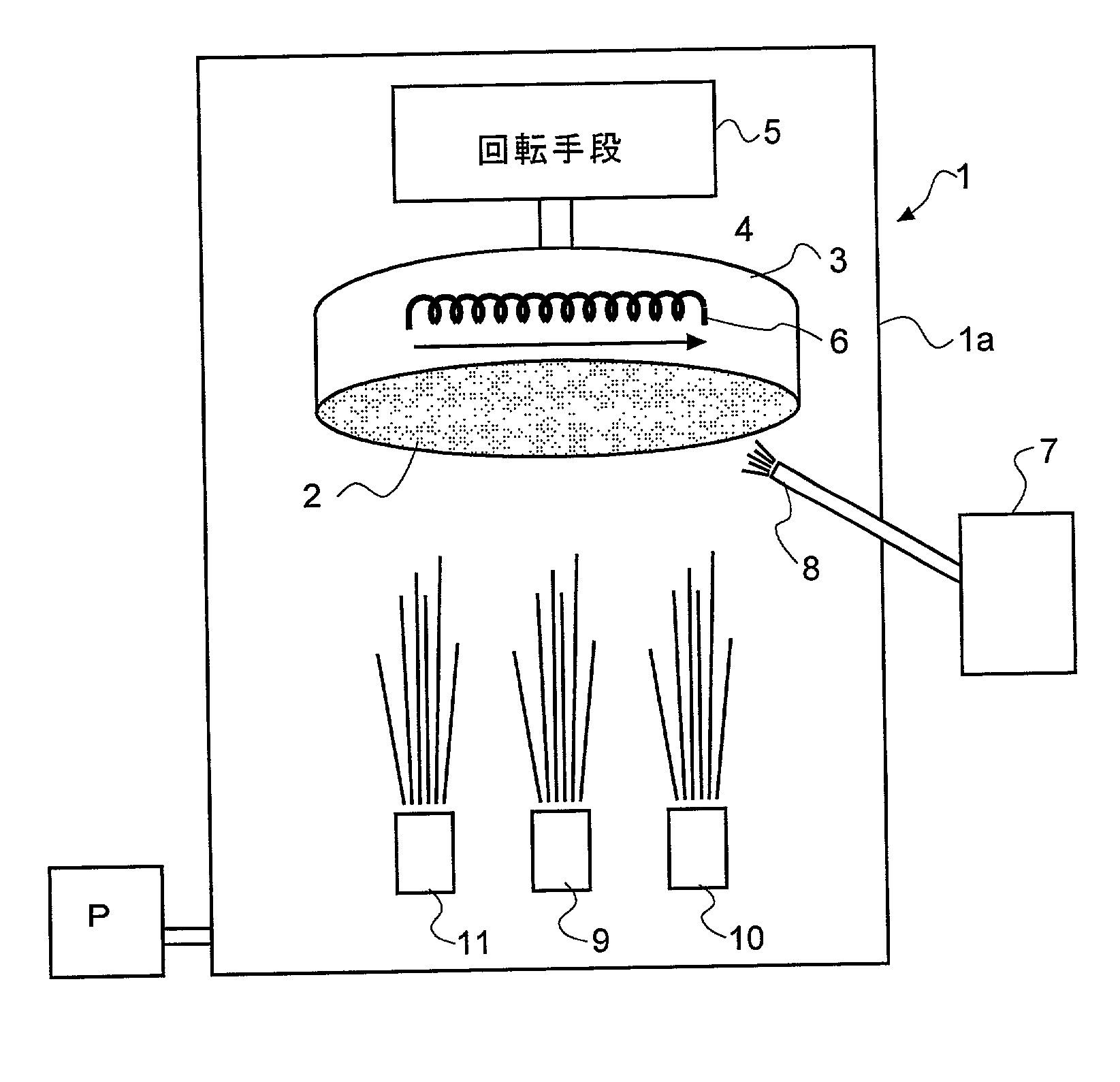
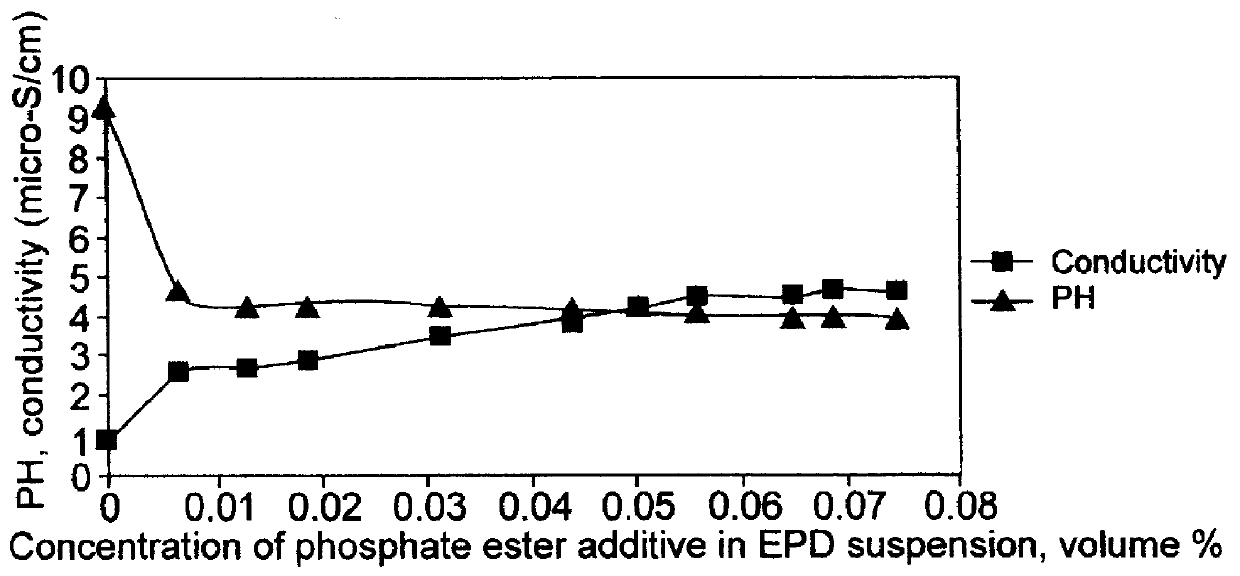
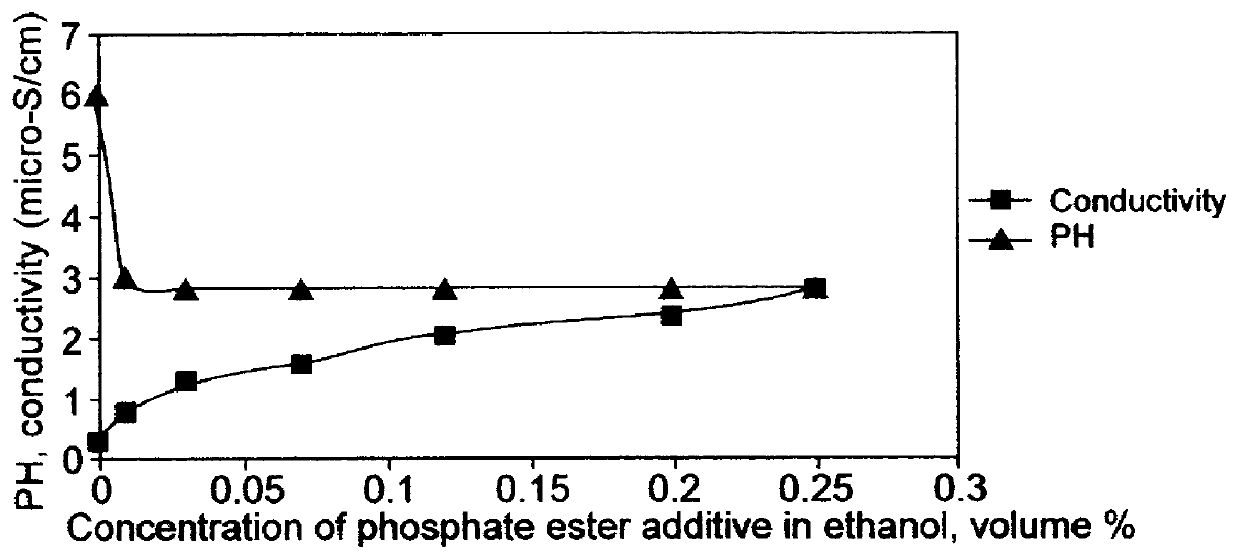
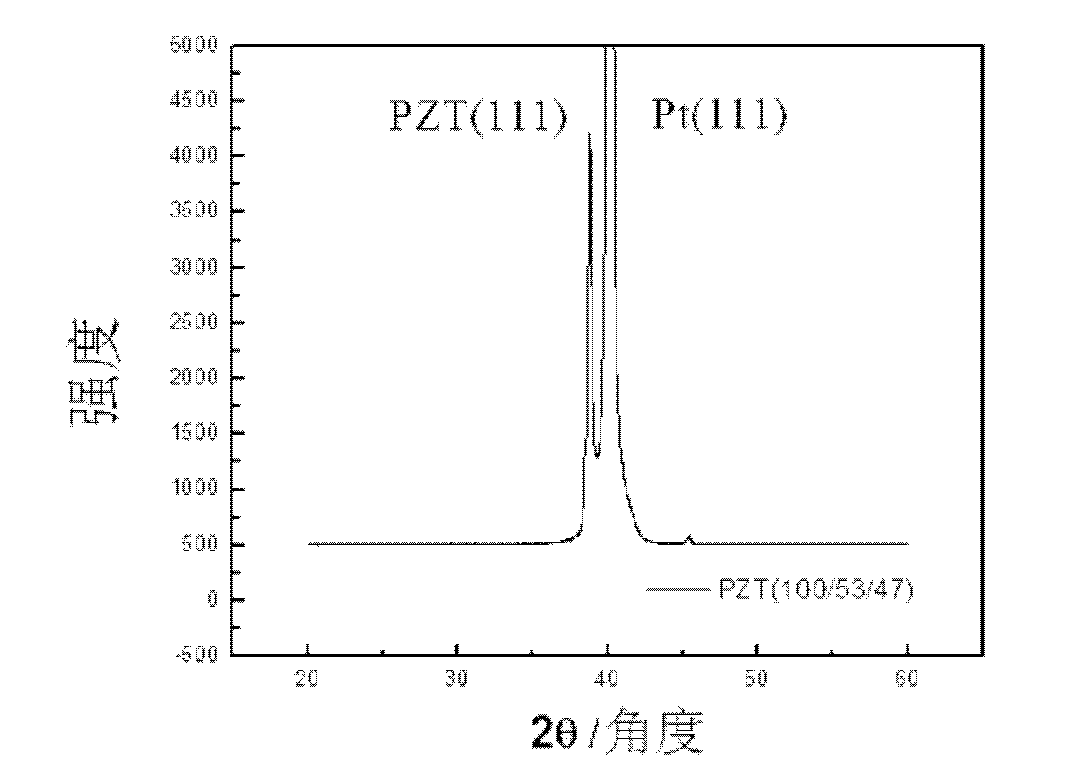
Method of electrophoretic deposition of ferroelectric films using a trifunctional additive and compositions for effecting same
InactiveUS6127283AEasy to manufactureSimple methodElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementParticulatesPhosphate
An improved method for depositing ferroelectric particles on a surface of a substrate to form films or stand-alone bodies. The improvement is based on electrophoretic deposition (EPD) of ferroelectric films by using a tri-functional phosphate ester additive having a concentration less than 10 volume percent in the EPD suspension, without the need for addition of a binder. The method includes preparation of the suspension by washing and dispersing ferroelectric particles, for example, commercially available PZT powder, in a polar solvent such as ethanol, followed by addition of the phosphate ester additive to the suspension, and an ultrasound treatment. The suspension is used in EPD of the ferroelectric particles on a prepared substrate. Following EPD, the green film is dried and sintered at high temperature. Visual and physical examination of stand alone and patterned PZT deposited films show excellent quality obtained in manufacturing a diversity of piezoelectric products, featuring exceptionally high green film uniformity, thickness distribution, and reproducibility to within + / -2 microns for 20 micrometer film thickness. The phosphate ester additive functions by improving stabilization and control of suspension characteristics and properties during the electrophoretic migration process, and by improving desired dimensions, characteristics, and electrical properties of the deposited green film. Thin or thick ferroelectric films, either as stand alone products, or formed on geometrically demanding patterned or non-patterned substrates are produced by using the method. The improved method is applicable to different ferroelectric particulate materials and to different substrates used for manufacturing piezoelectric elements and devices, in a cost effective manner.
Owner:CEREL CERAMIC TECH
Method for preparing piezoelectric-ferroelectric thin film
InactiveCN101885606AStructural solutionSolve Thickness ProblemsLead zirconate titanateFerroelectric thin films
The invention provides a method for preparing a piezoelectric-ferroelectric thin film, relating to the technical field of preparation of lead zirconate titanate ceramics and being realized by the steps of preparing a precursor solution, utilizing a PLD method to prepare a substrate and adopting a Sol-Gel method to prepare the piezoelectric-ferroelectric thin film on a PZT crystal seed layer. The invention utilizes a method combing PLD and Sol-Gel to prepare a PZT thick film, thus having strong applicability to different substrates; and the prepared PZT thick film has the obvious advantages of high preferred orientation, even crystal size and compact structure, and can be used for preparing a lead zirconate titanate thin film with the thickness of 3-6 microns, the residual polarization value Pr of 25-45 mu C / cm<2> and the coercive field Ec of 40-65 kV / cm. At the same time, the method in the invention has relative low cost, strong controllability of programs and high industrialized application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
In-plane reading/writing operation ferroelectric memristor and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN107123648AImprove storage densityEnables non-destructive readoutSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesNon destructiveIn plane
The invention belongs to the technical field of ferroelectric storage, and particularly relates to an in-plane reading / writing non-volatile ferroelectric memristor and a fabrication method and operation method thereof. The ferroelectric memristor comprises a ferroelectric thin film layer and reading / writing electrode pairs, wherein the reading / writing electrode pairs are arranged on a surface of the ferroelectric thin film layer, a gap between the reading / writing electrode pairs is an irregular pattern, the polarization direction of an electric domain of the ferroelectric thin film layer is not parallel to a normal direction of a reading / writing electrode plane, and different information can be stored with change of different writing voltages during writing voltage operation of a certain bias direction on the reading / writing electrode pairs. By the ferroelectric memristor, non-destructive reading in a current mode can be achieved with continuous change of the reading voltage, the ferroelectric memristor is suitable for high-density application, and moreover, the ferroelectric memristor is simple to fabricate and is low in cost.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Ferroelectric local field enhanced two-dimensional semiconductor photoelectric detector and preparation method
InactiveCN105762281AReduce dark currentReduce power consumptionFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesFerroelectric thin filmsElectron-beam lithography
The invention discloses a ferroelectric local field enhanced two-dimensional semiconductor photoelectric detector and a preparation method. The detector is characterized in that: the structure of the detector from top to bottom comprises a substrate, a two-dimensional semiconductor, a metal source and drain electrodes, a ferroelectric functional layer and a semi-transparent metal upper electrode in sequence. The preparation method of the detector comprises the steps: a transition-metal chalcogenide two-dimensional semiconductor is prepared on the substrate, an UV lithography or an electron-beam lithography is adopted and combines stripping technology to prepare a metal electrode serving as a source electrode and a drain electrode of a semiconductor channel, a ferroelectric thin film is prepared on the structure, a semi-transparent or transparent electrode is prepared on the ferroelectric thin film, so that a two-dimensional semiconductor detector structure is formed. The detector can make the two-dimensional semiconductor channel background carriers to be completely exhausted through using polarized ferroelectric materials, tiny voltage is applied between the source electrode and the drain electrode, and photoelectric detection is realized through detecting the current signal change under light. The detector has advantages of high sensitivity, fast response, good stability, low power consumption, wide spectrum detection and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for manufacturing ferroelectric thin film device, ink jet recording head, and ink jet printer
InactiveUS20030092203A1Reliable drive characteristicReduce adhesionTransistorThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changeIridiumFerroelectric thin films
It is an object of the present invention to control the crystal orientation of a ferroelectric thin film as dictated by the application of a ferroelectric thin film device. To accomplished the stated object, a bottom electrode containing at least iridium is formed over a surface preparation layer whose main component is zirconium oxide, and an ultra-thin titanium layer is laminated over the bottom electrode. An amorphous layer containing the elemental metal and elemental oxygen that constitute the ferroelectric is formed over the titanium layer, and a crystallized ferroelectric thin film is formed by heat treating this amorphous layer. If the thickness of the titanium layer is kept between 2 nm and 10 nm in the lamination thereof, the ferroelectric thin film will have a priority orientation of (100), and if it is kept between 10 nm and 20 nm, the ferroelectric thin film will have a priority orientation of (111).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Ferroelectric capacitor and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7148530B2Solve the lack of reliabilityLong processTransistorSolid-state devicesRetention timeRandom access memory
A ferroelectric capacitor and a method for manufacturing the same includes a lower electrode, a dielectric layer, and an upper electrode layer, which are sequentially stacked, wherein the dielectric layer has a multi-layer structure including a plurality of sequentially stacked ferroelectric films, and wherein two adjacent ferroelectric films have either different compositions or different composition ratios. Use of a ferroelectric capacitor according to an embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to hold stable polarization states of ferroelectric domains for a long retention time, and thus data written in the ferroelectric capacitor a long time ago can be accurately written, thereby improving the reliability of a ferroelectric random access memory (FRAM).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
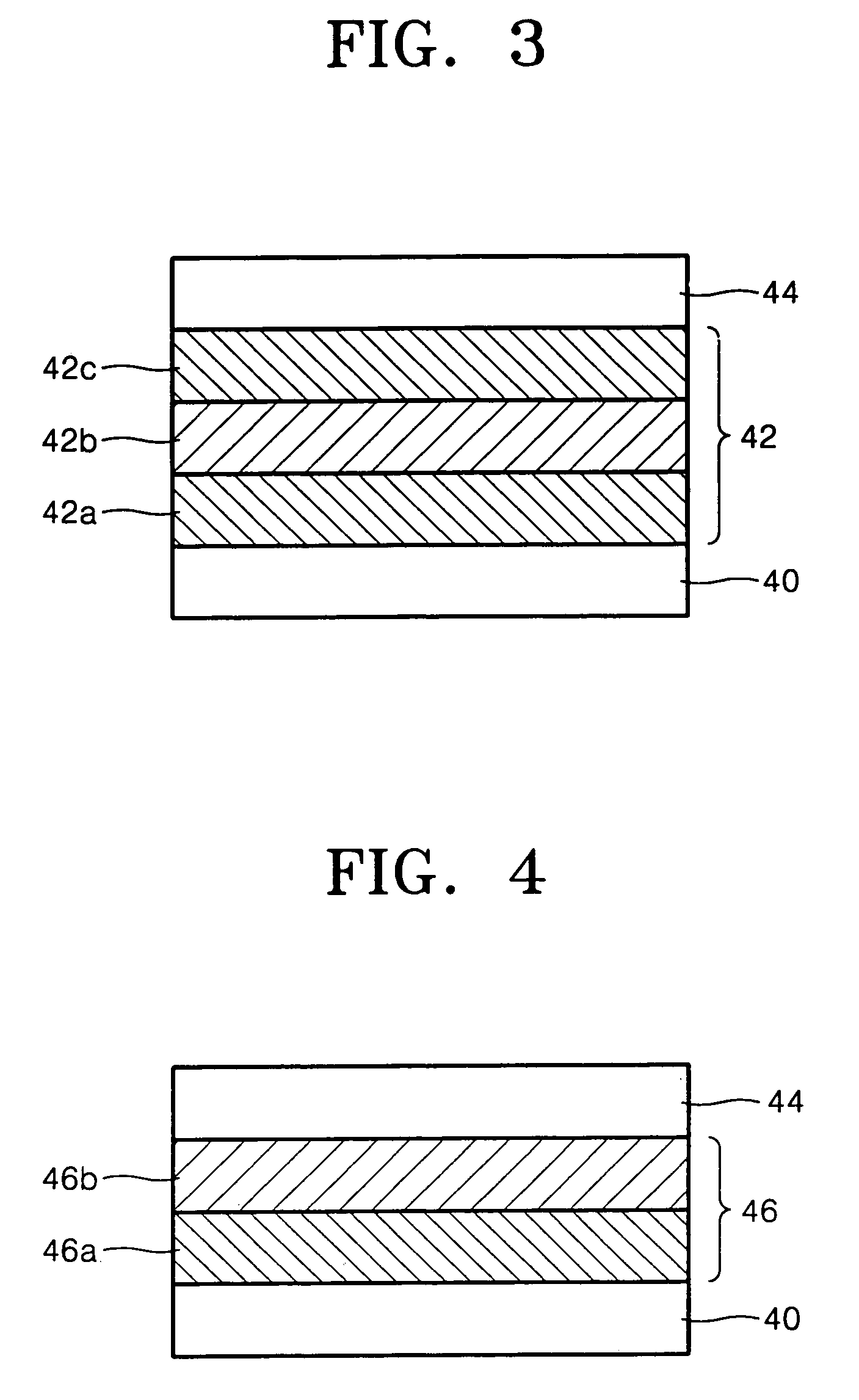
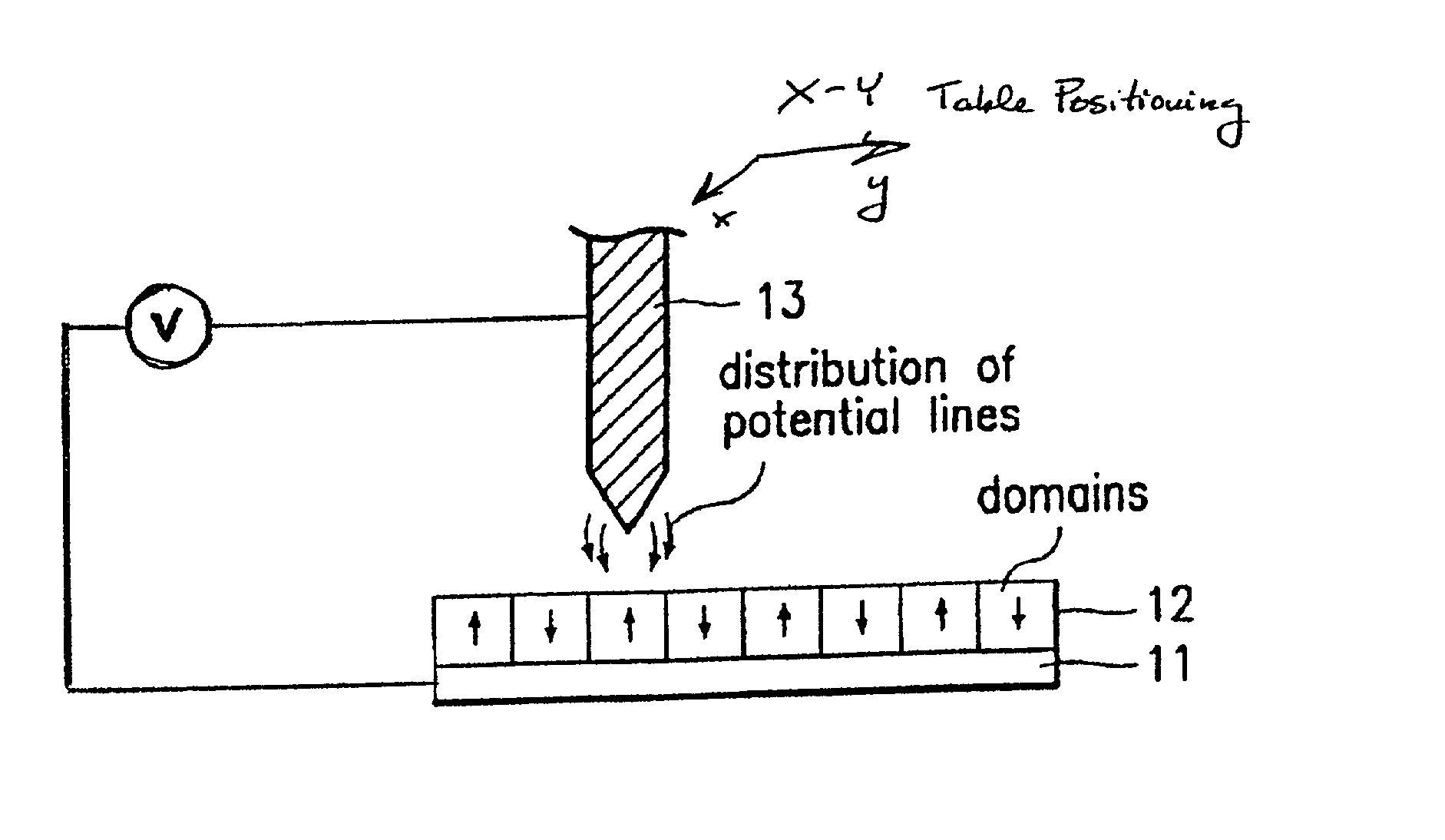
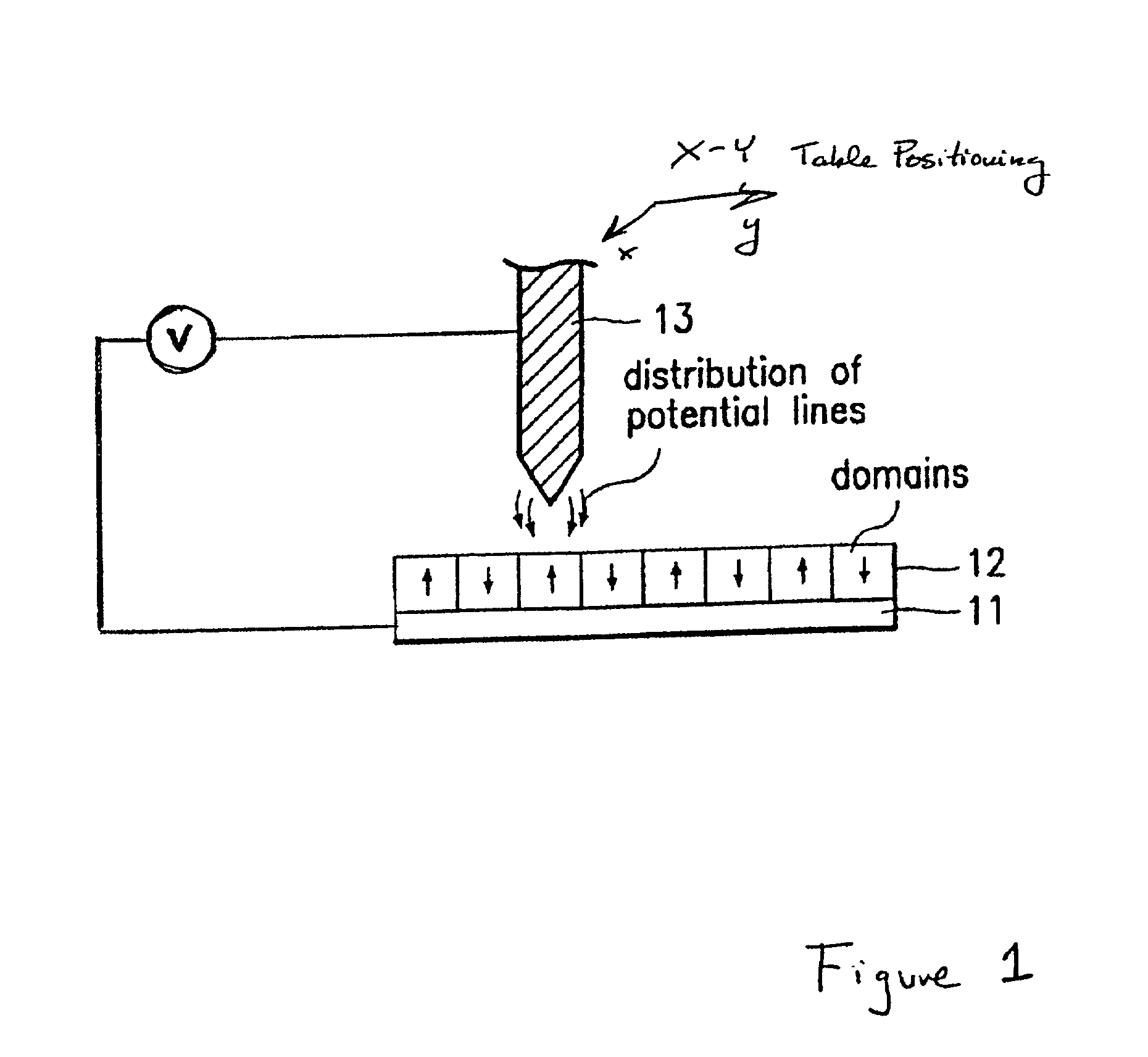
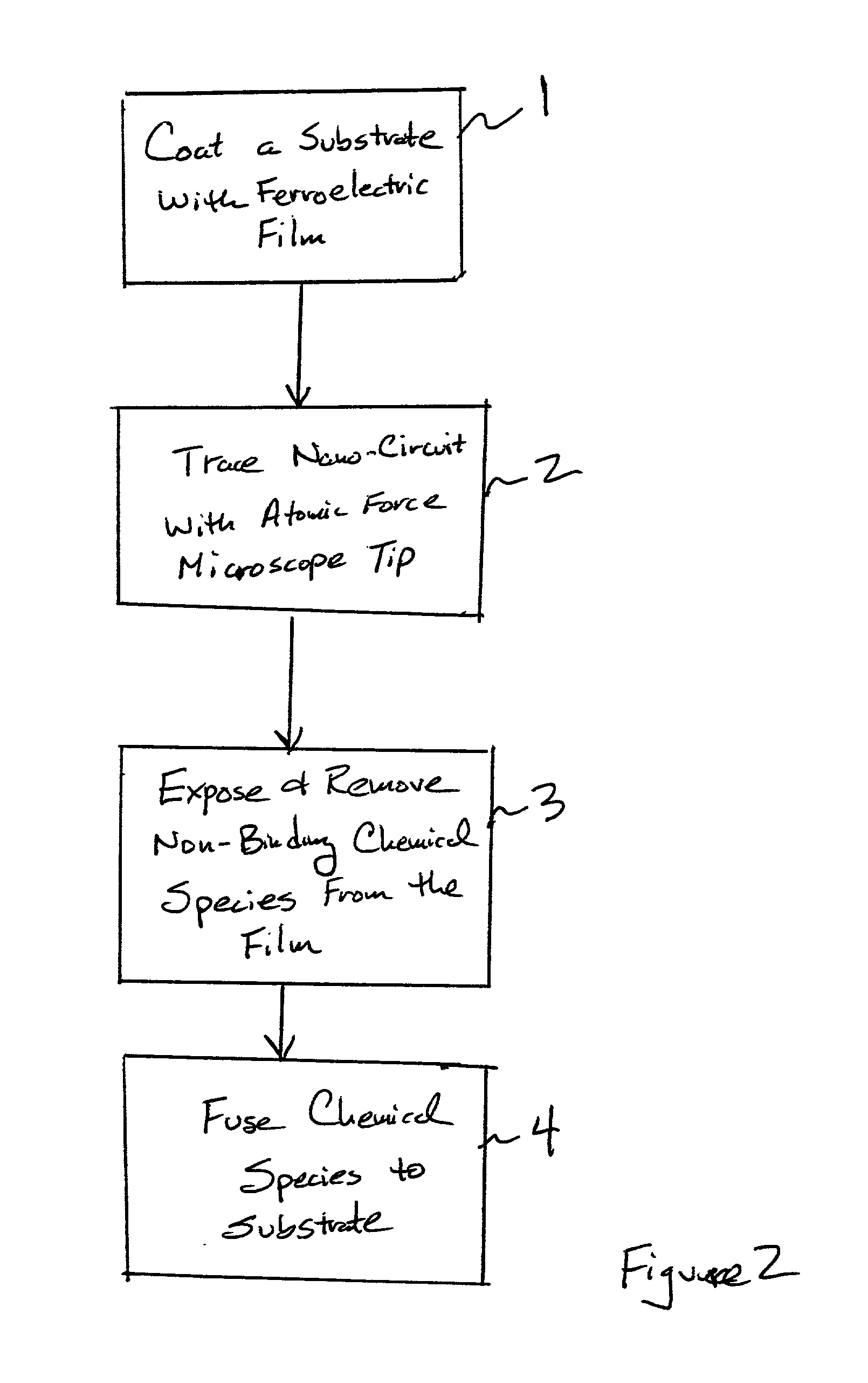
Assembling arrays of small particles using an atomic force microscope to define ferroelectric domains
InactiveUS20020118369A1Nanostructure manufactureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic force microscopeChemical species
A method of assembling arrays of small particles or molecules using an atomic force microscope to define ferroelectric domains includes depositing a ferroelectric thin film upon a substrate forming workpiece, then using an atomic force microscope having a conductive, tip for generating a pattern on this thin film to define desired nano-circuit patterns. Next, exposure of this thin film to a solution containing chemical species which selectively adsorb or accumulate under the influence of electrophoretic forces in selected regions of this thin film.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com