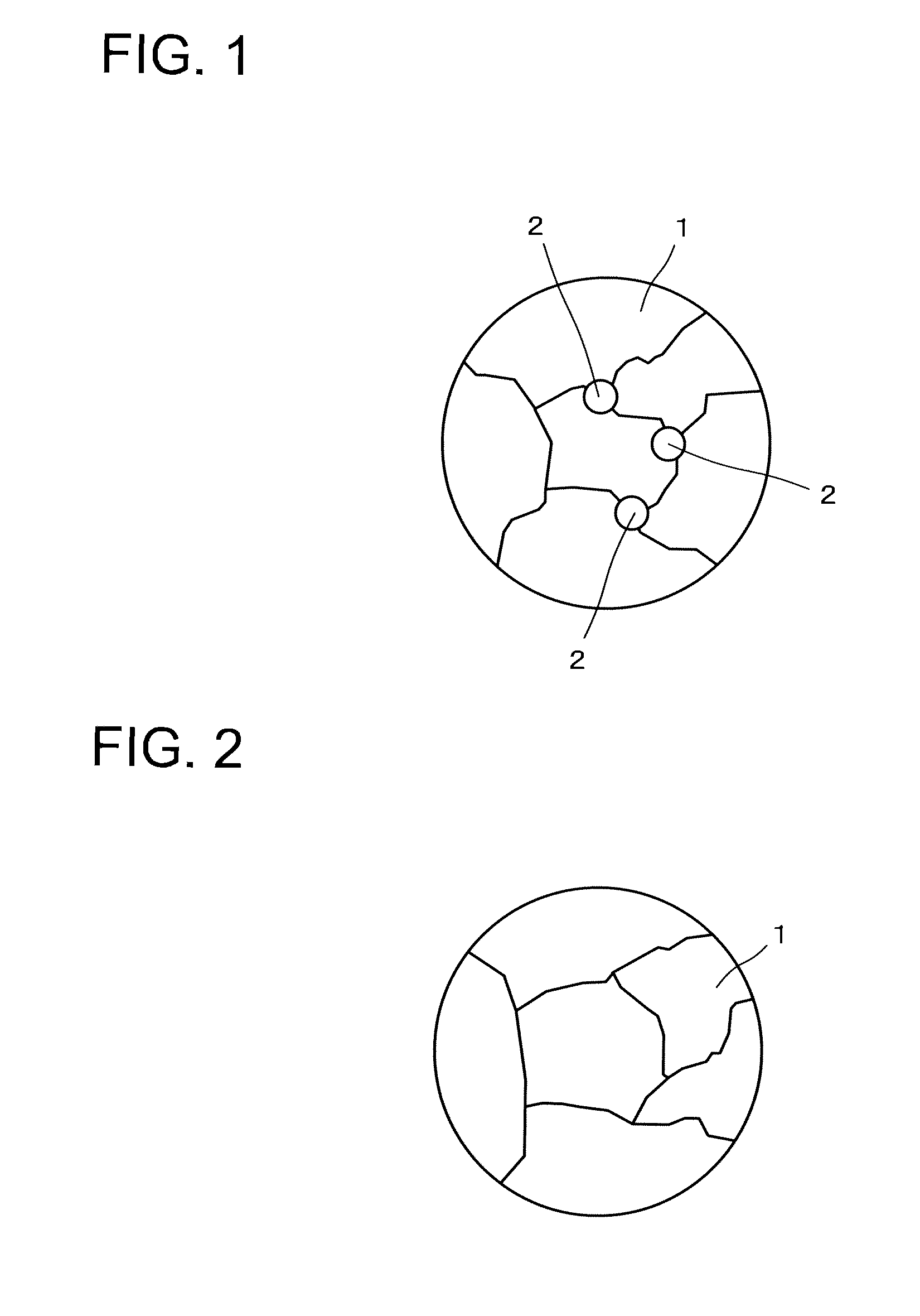
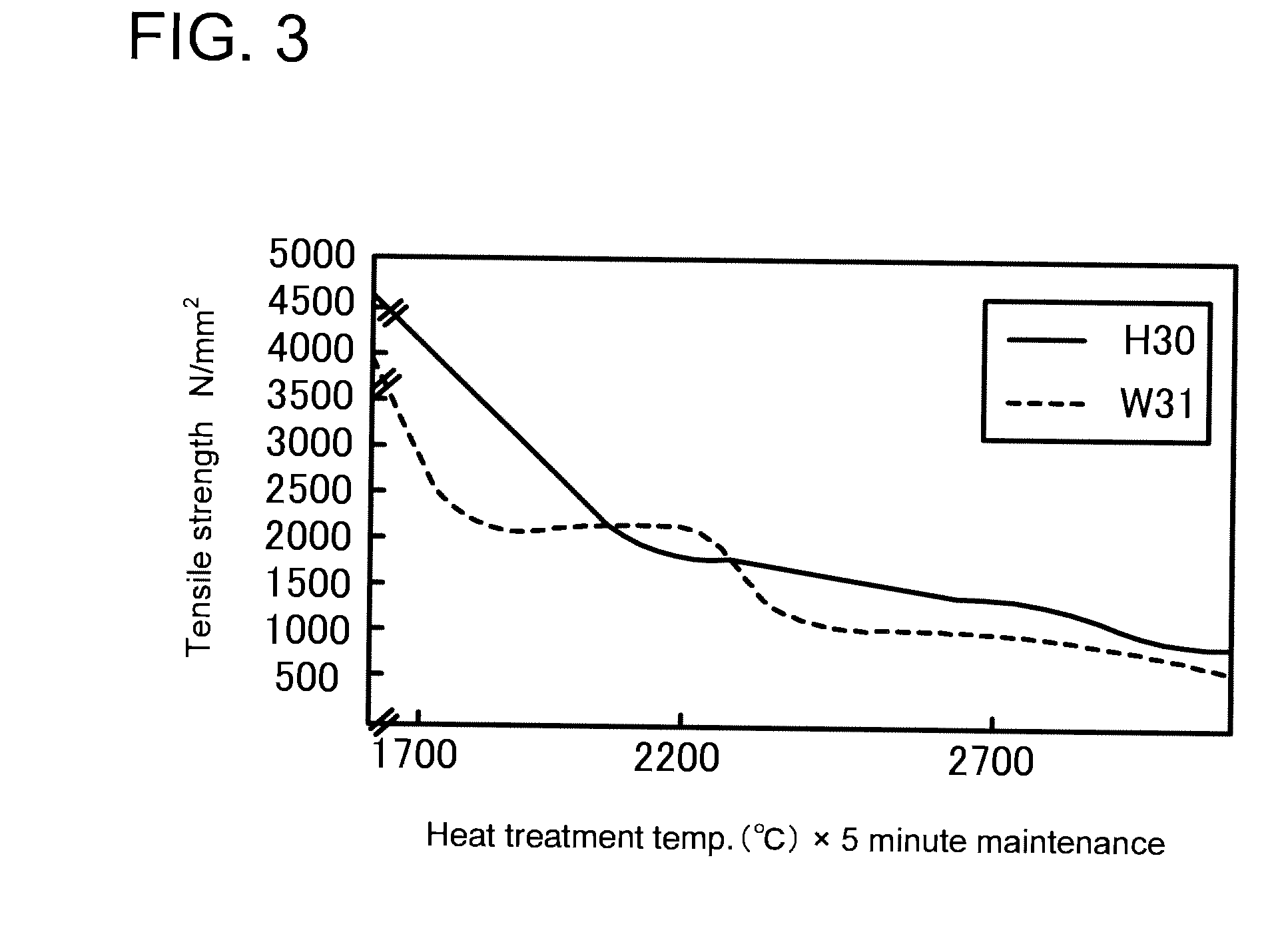
Patents
Literature
771 results about "Tantalum carbide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tantalum carbides form a family of binary chemical compounds of tantalum and carbon with the empirical formula TaCₓ, where x usually varies between 0.4 and 1. They are extremely hard, brittle, refractory ceramic materials with metallic electrical conductivity. They appear as brown-gray powders, which are usually processed by sintering. Being important cermet materials, tantalum carbides are commercially used in tool bits for cutting applications and are sometimes added to tungsten carbide alloys. The melting points of tantalum carbides peak at about 3880 °C depending on the purity and measurement conditions; this value is among the highest for binary compounds. Only tantalum hafnium carbide may have a slightly higher melting point of about 3942 °C, whereas the melting point of hafnium carbide is comparable to that of TaC.
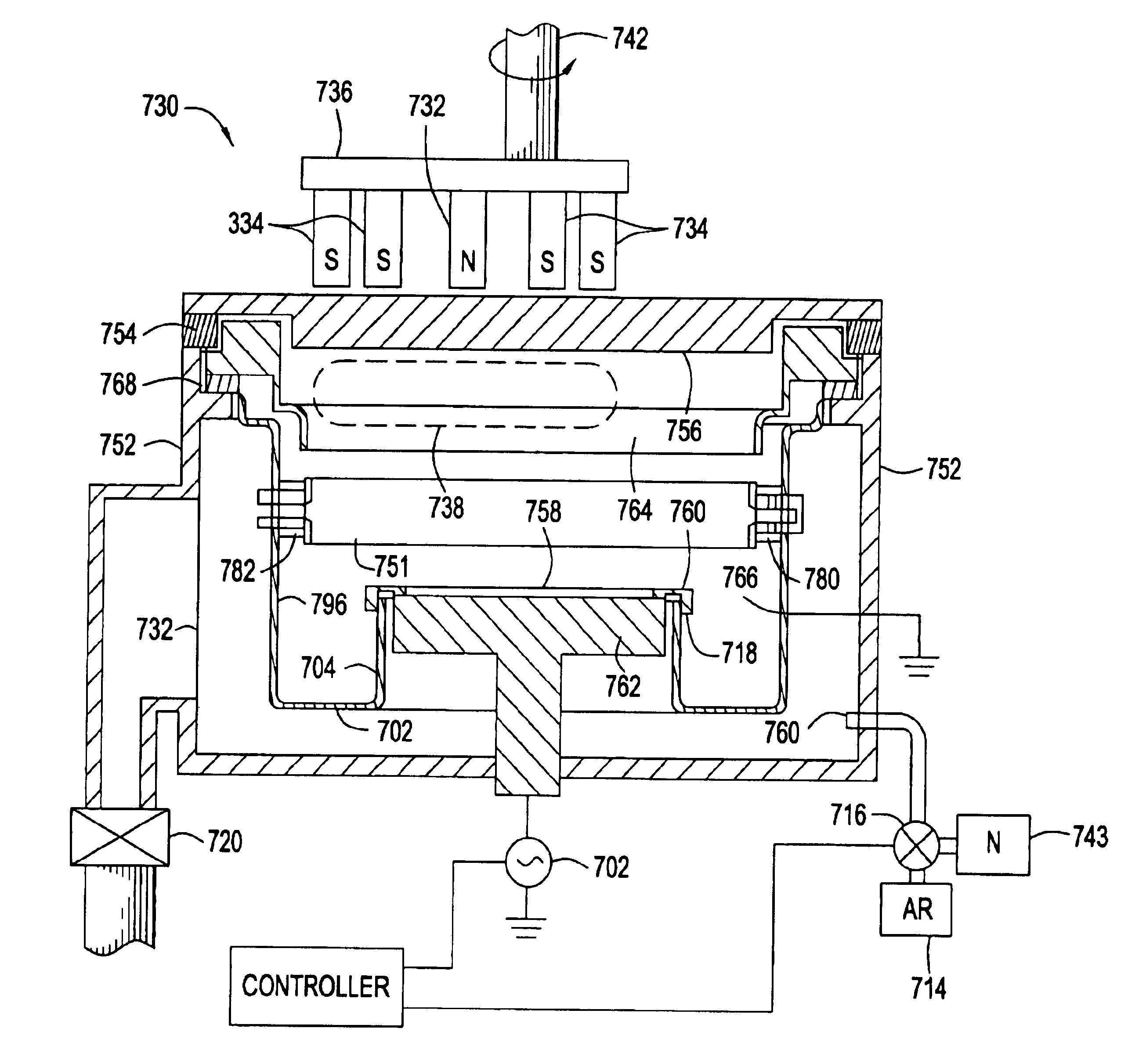
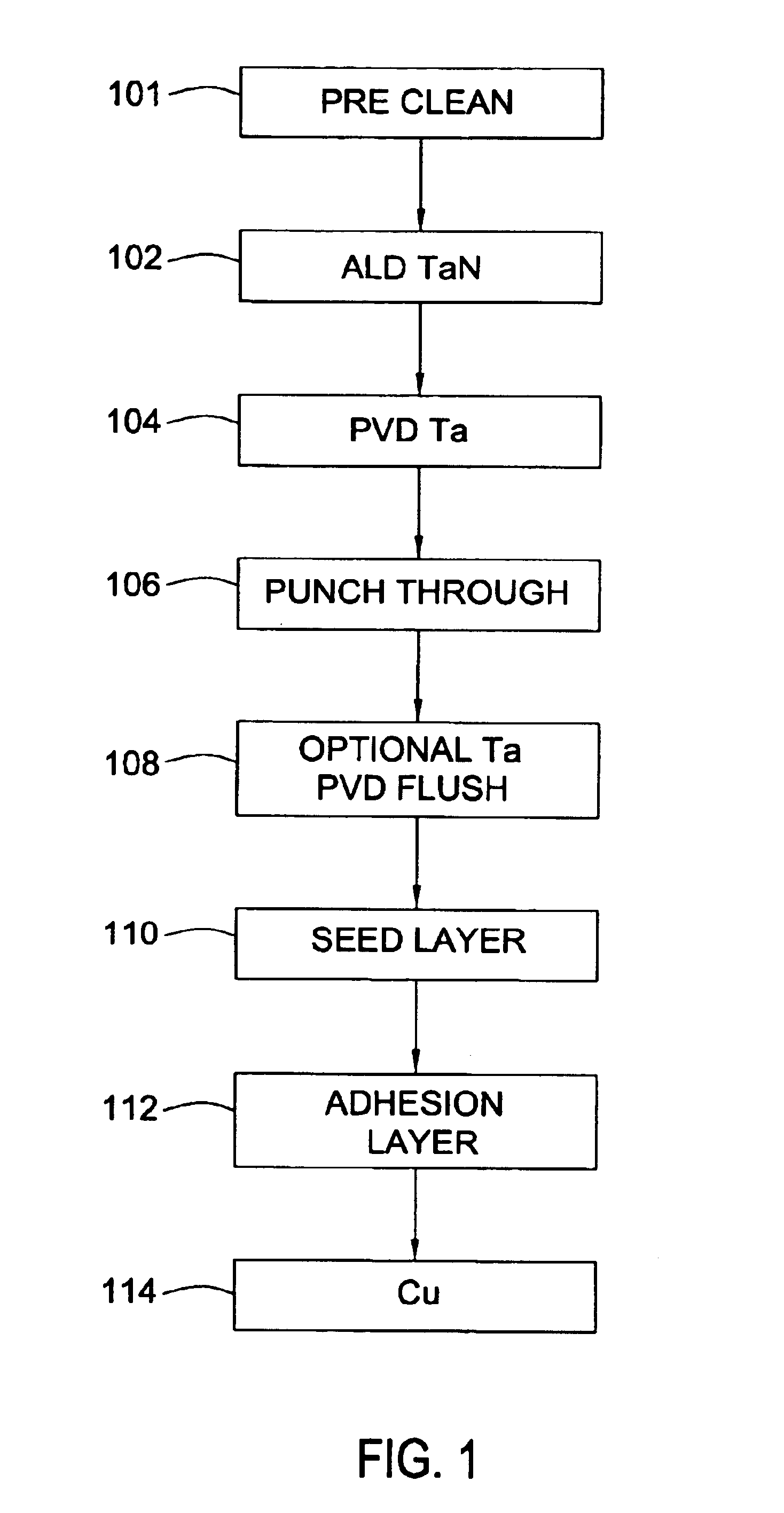
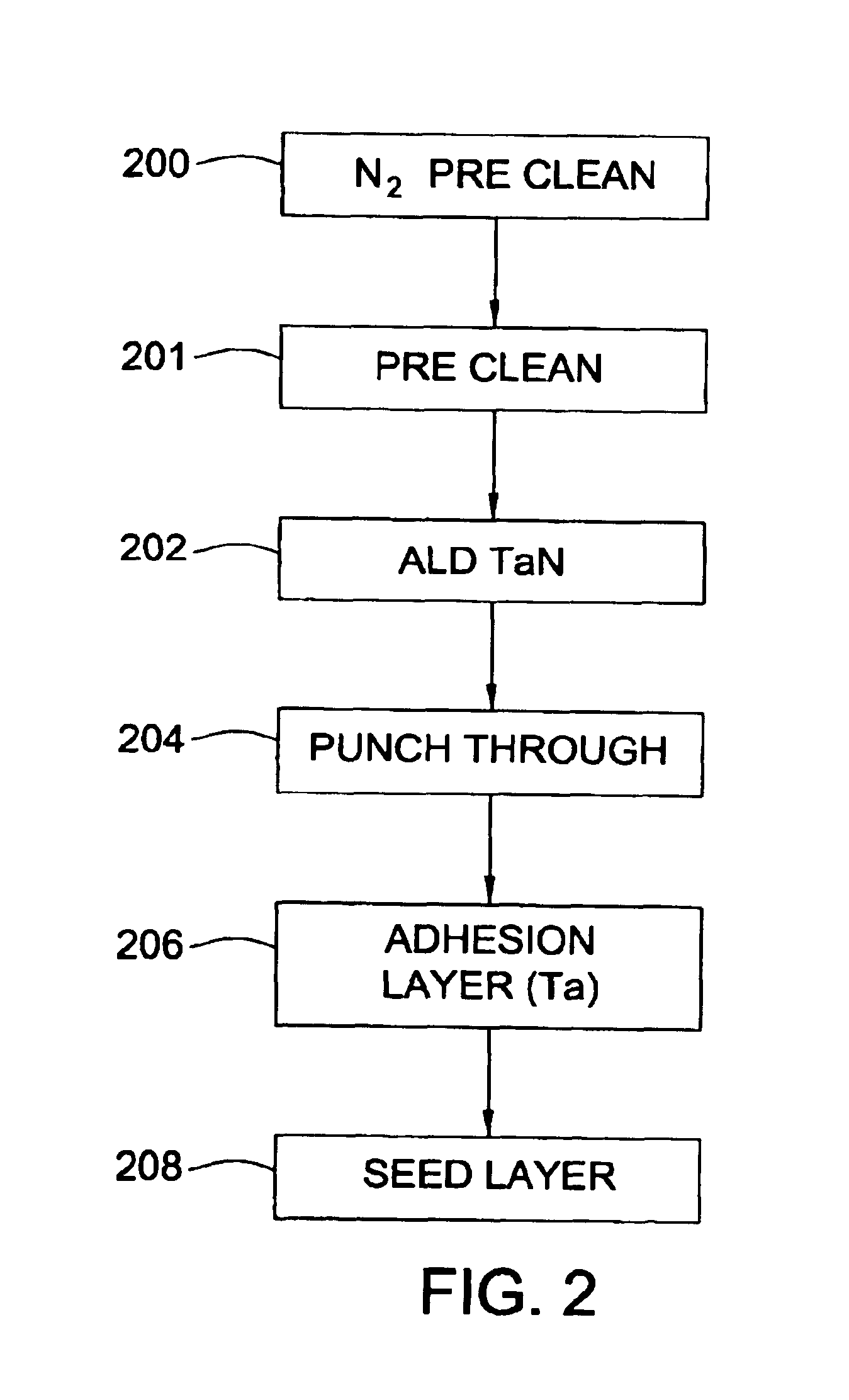
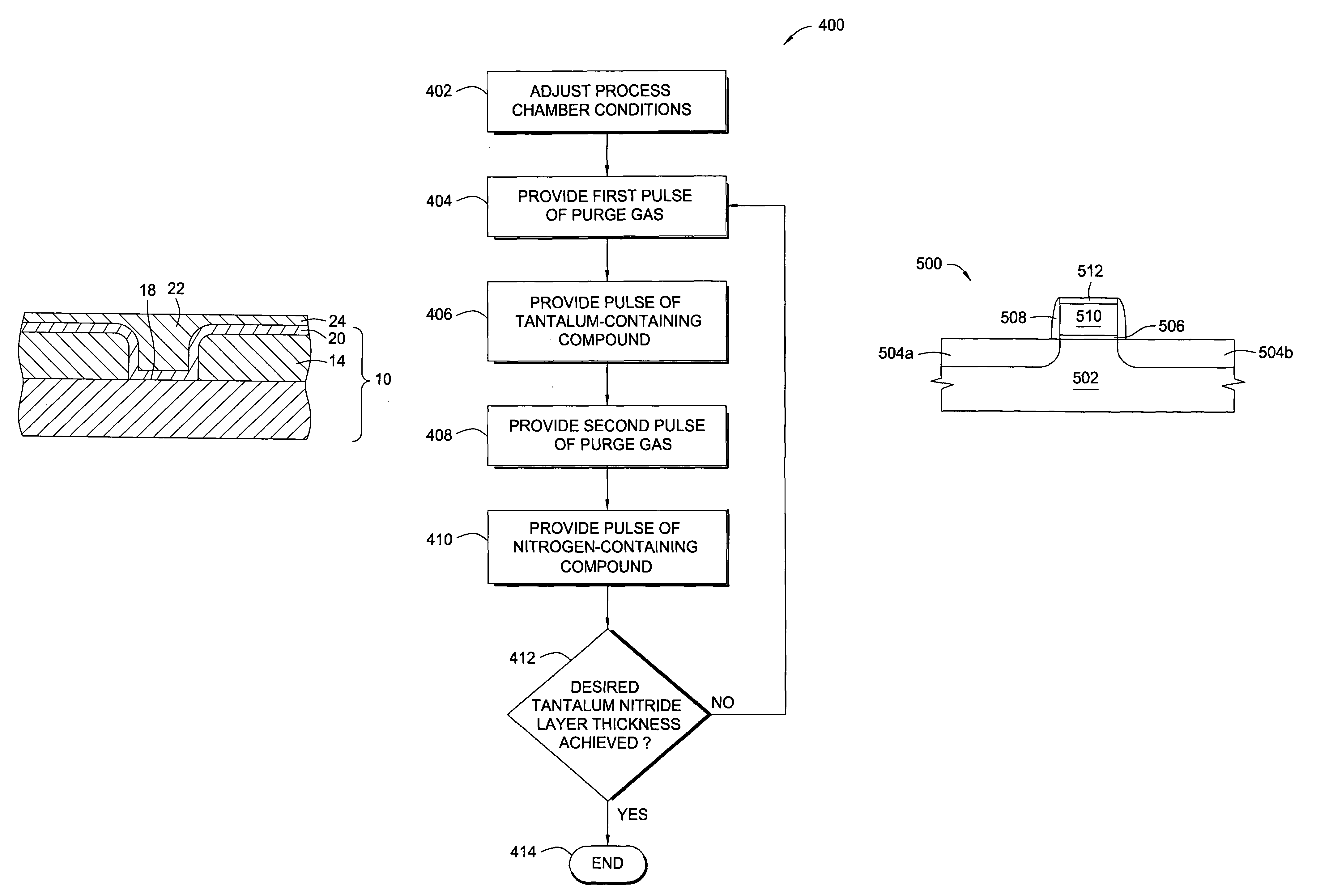
Integration of ALD tantalum nitride for copper metallization
InactiveUS7049226B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTantalum nitrideConductive materials
A method and apparatus for depositing a tantalum nitride barrier layer is provided for use in an integrated processing tool. The tantalum nitride is deposited by atomic layer deposition. The tantalum nitride is removed from the bottom of features in dielectric layers to reveal the conductive material under the deposited tantalum nitride. Optionally, a tantalum layer may be deposited by physical vapor deposition after the tantalum nitride deposition. Optionally, the tantalum nitride deposition and the tantalum deposition may occur in the same processing chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
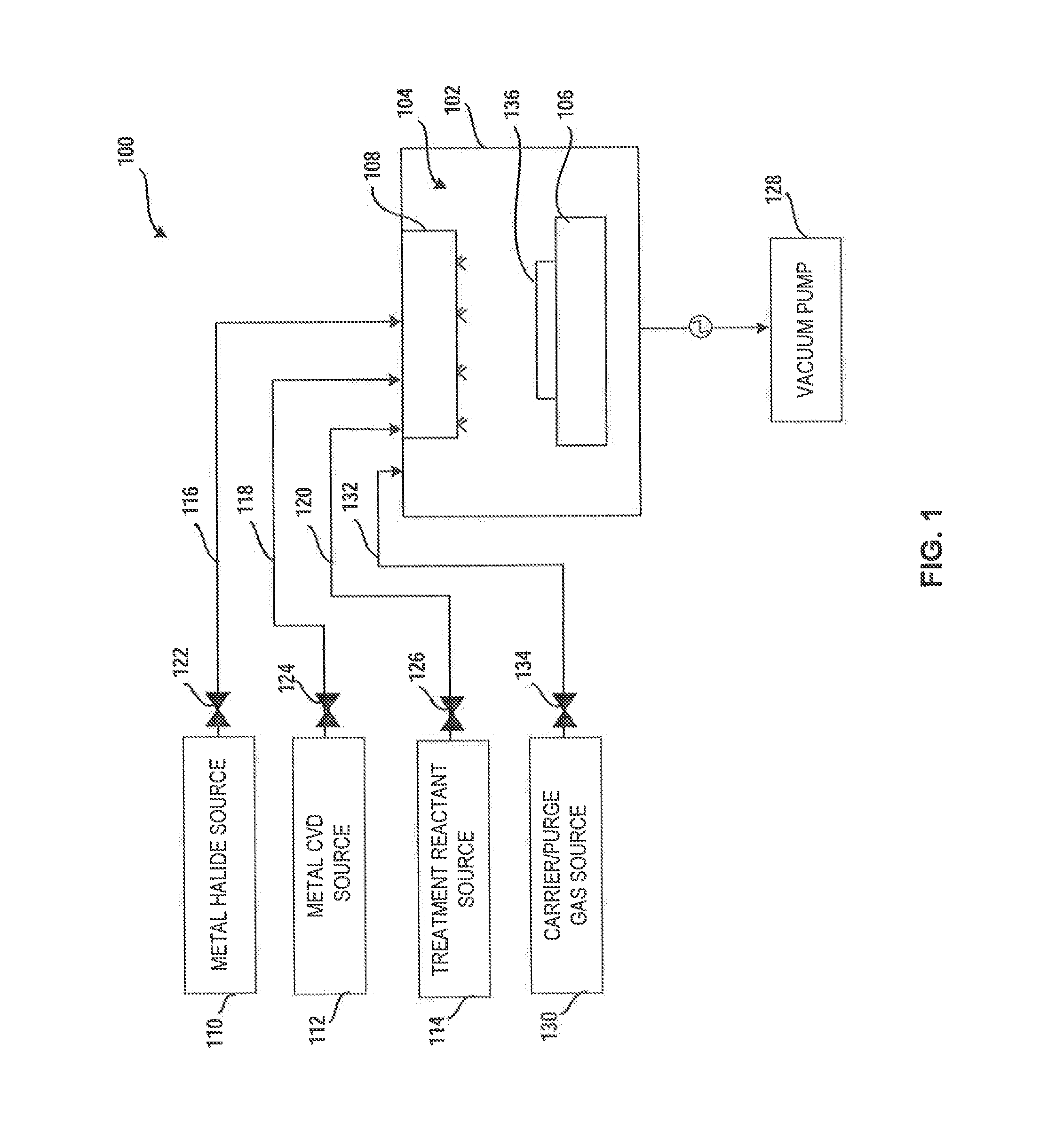
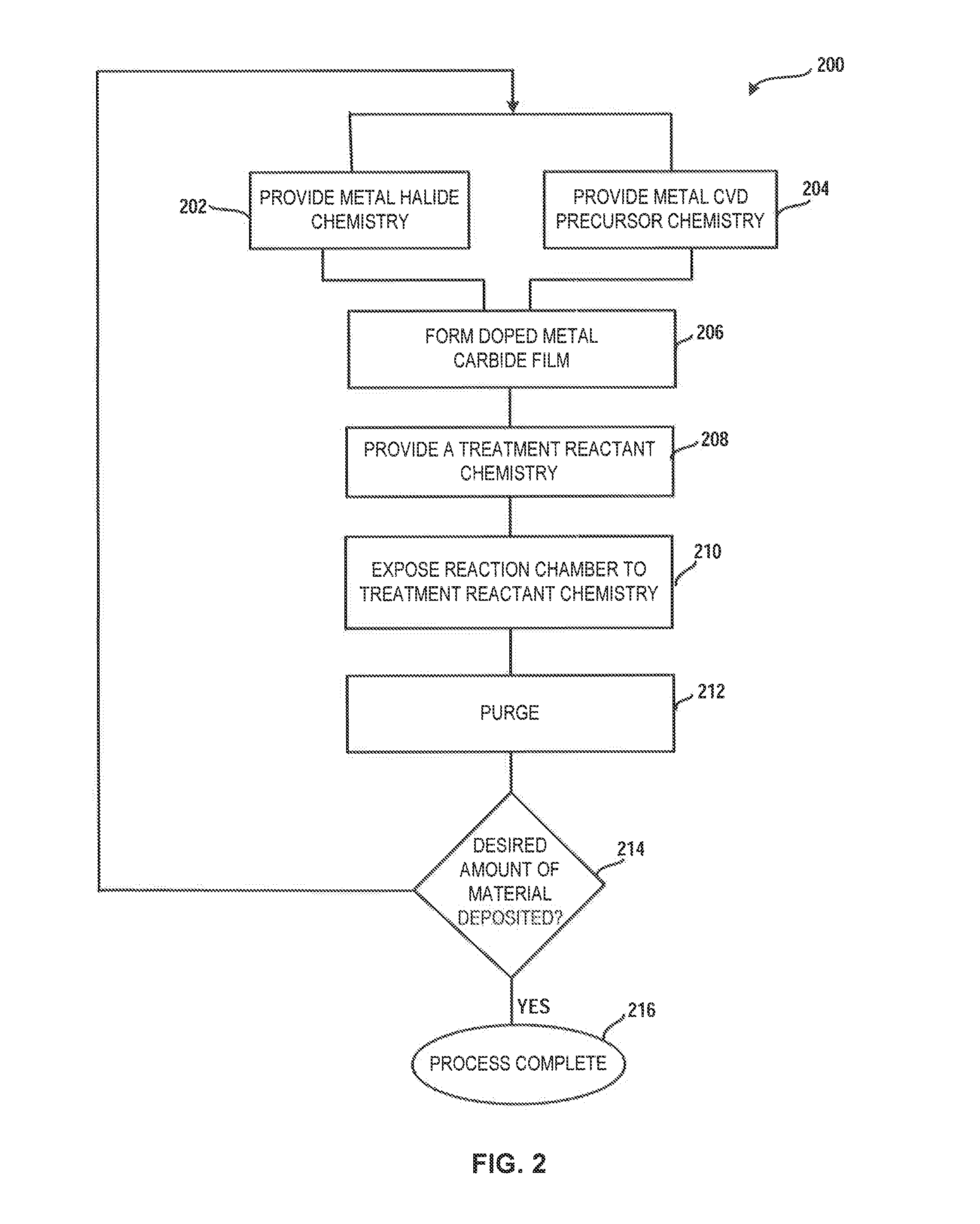
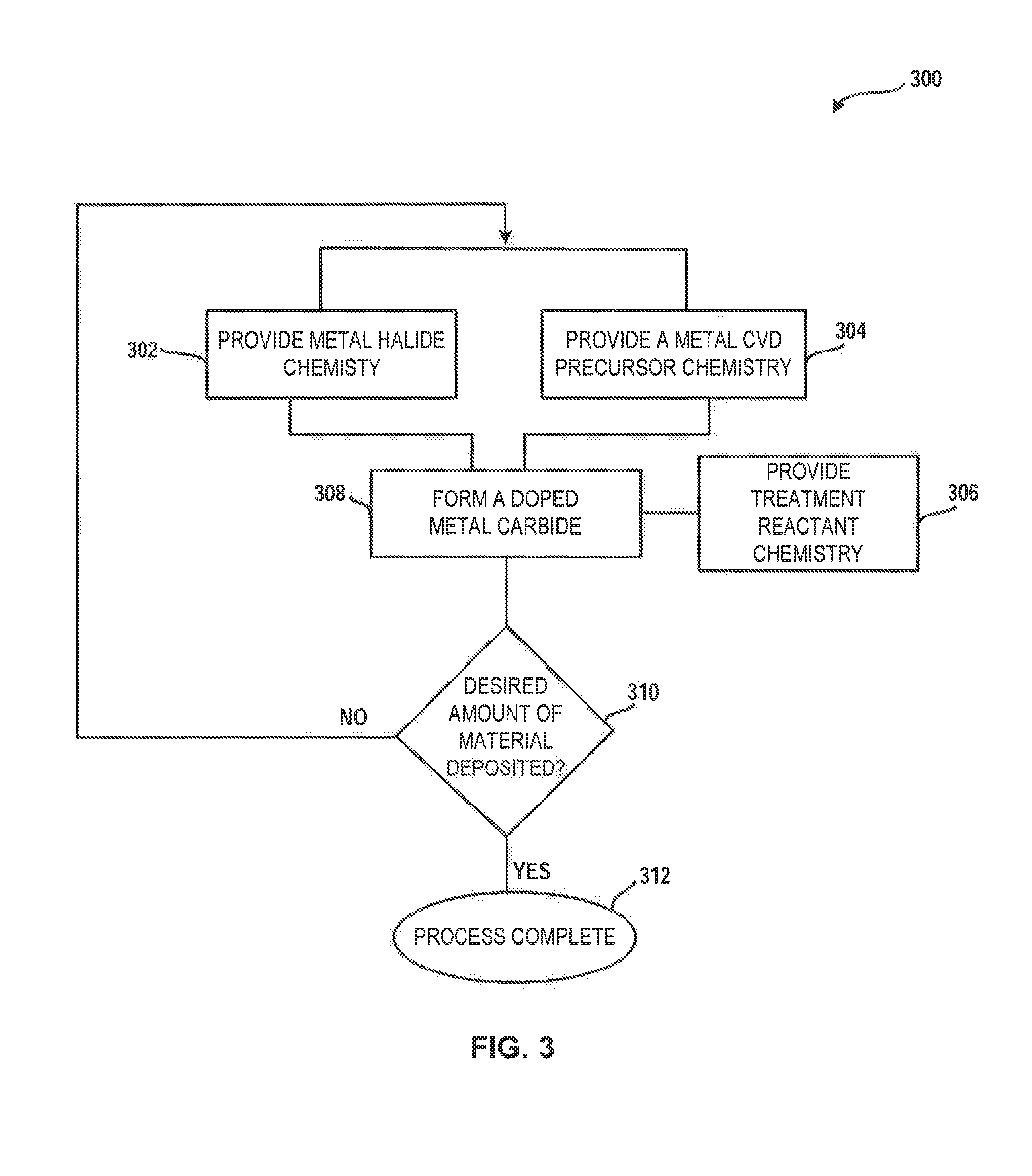
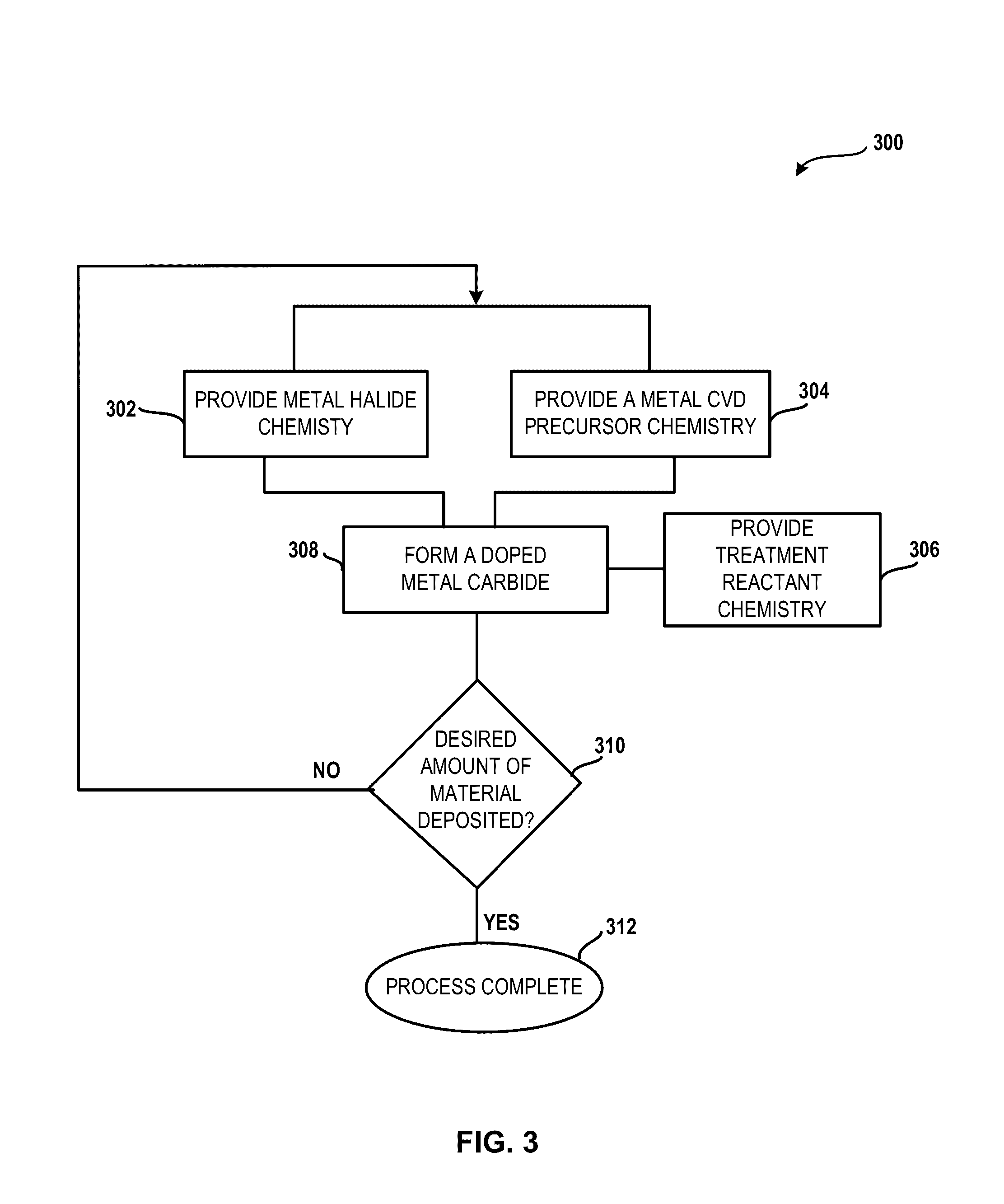
Method and system for treatment of deposition reactor
ActiveUS20140220247A1Substrate throughput can be increasedReduce operating costsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTitanium carbideMetal membrane
A system and method for treating a deposition reactor are disclosed. The system and method remove or mitigate formation of residue in a gas-phase reactor used to deposit doped metal films, such as aluminum-doped titanium carbide films or aluminum-doped tantalum carbide films. The method includes a step of exposing a reaction chamber to a treatment reactant that mitigates formation of species that lead to residue formation.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
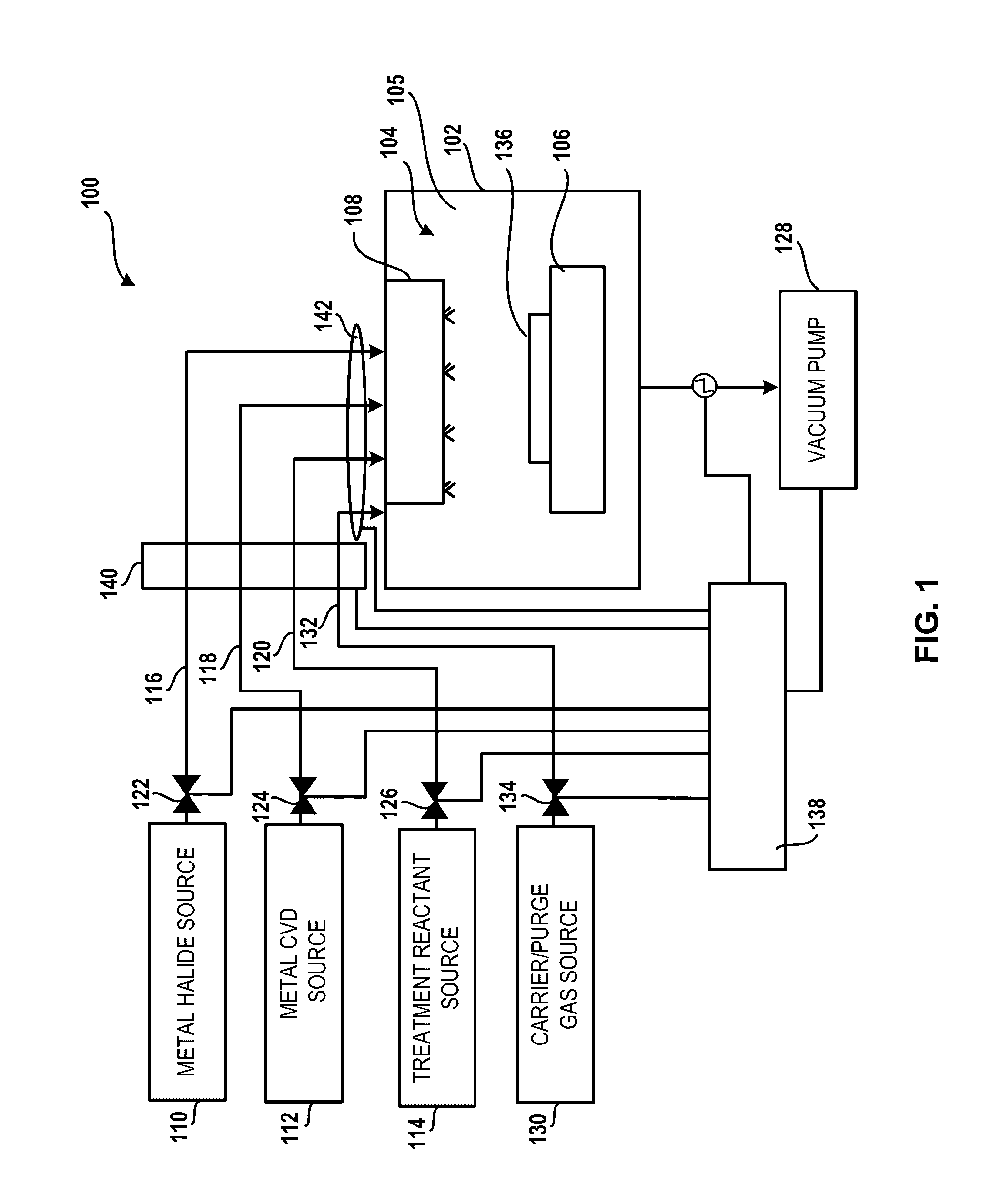
System for treatment of deposition reactor
InactiveUS20160376700A1Improve throughputReduce operating costsElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseTitanium carbide
A system and method for treating a deposition reactor are disclosed. The system and method remove or mitigate formation of residue in a gas-phase reactor used to deposit doped metal films, such as aluminum-doped titanium carbide films or aluminum-doped tantalum carbide films. The method includes a step of exposing a reaction chamber to a treatment reactant that mitigates formation of species that lead to residue formation.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Tantalum amide precursors for deposition of tantalum nitride on a substrate
InactiveUS6015917ARapid heat treatmentSilicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthFerroelectric thin filmsChemical vapor deposition
Tantalum and titanium source reagents are described, including tantalum amide and tantalum silicon nitride precursors for the deposition of tantalum nitride material on a substrate by processes such as chemical vapor deposition, assisted chemical vapor deposition, ion implantation, molecular beam epitaxy and rapid thermal processing. The precursors may be employed to form diffusion barrier layers on microlectronic device structures enabling the use of copper metallization and ferroelectric thin films in device construction.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
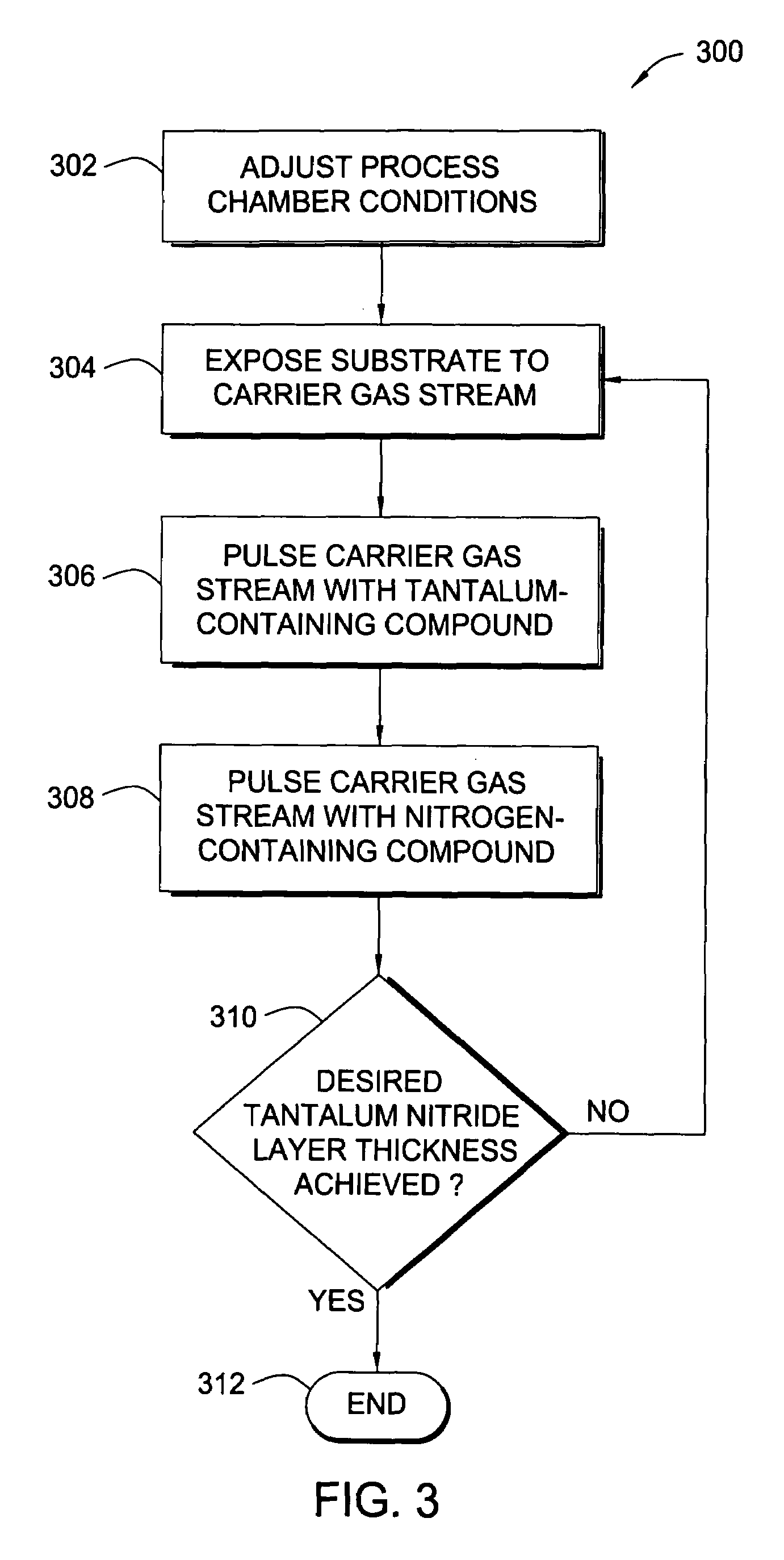
Atomic layer deposition of tantalum-containing materials using the tantalum precursor TAIMATA
InactiveUS7241686B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBoron nitrideAtomic layer deposition
In one example of the invention, a method for depositing a tantalum-containing material on a substrate in a process chamber is provided which includes exposing the substrate to a tantalum precursor that contains TAIMATA and to at least one secondary precursor to deposit a tantalum-containing material during an atomic layer deposition (ALD) process. The ALD process is repeated until the tantalum-containing material is deposited having a predetermined thickness. Usually, the TAIMATA is preheated prior to pulsing the tantalum precursor into the process chamber. Subsequently, a metal layer, such as tungsten or copper, may be deposited on the tantalum-containing material. The tantalum-containing material may contain tantalum, tantalum nitride, tantalum silicon nitride, tantalum boron nitride, tantalum phosphorous nitride, or tantalum oxynitride. The tantalum-containing material may be deposited as a barrier or adhesion layer within a via or as a gate electrode material within a source / drain device.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
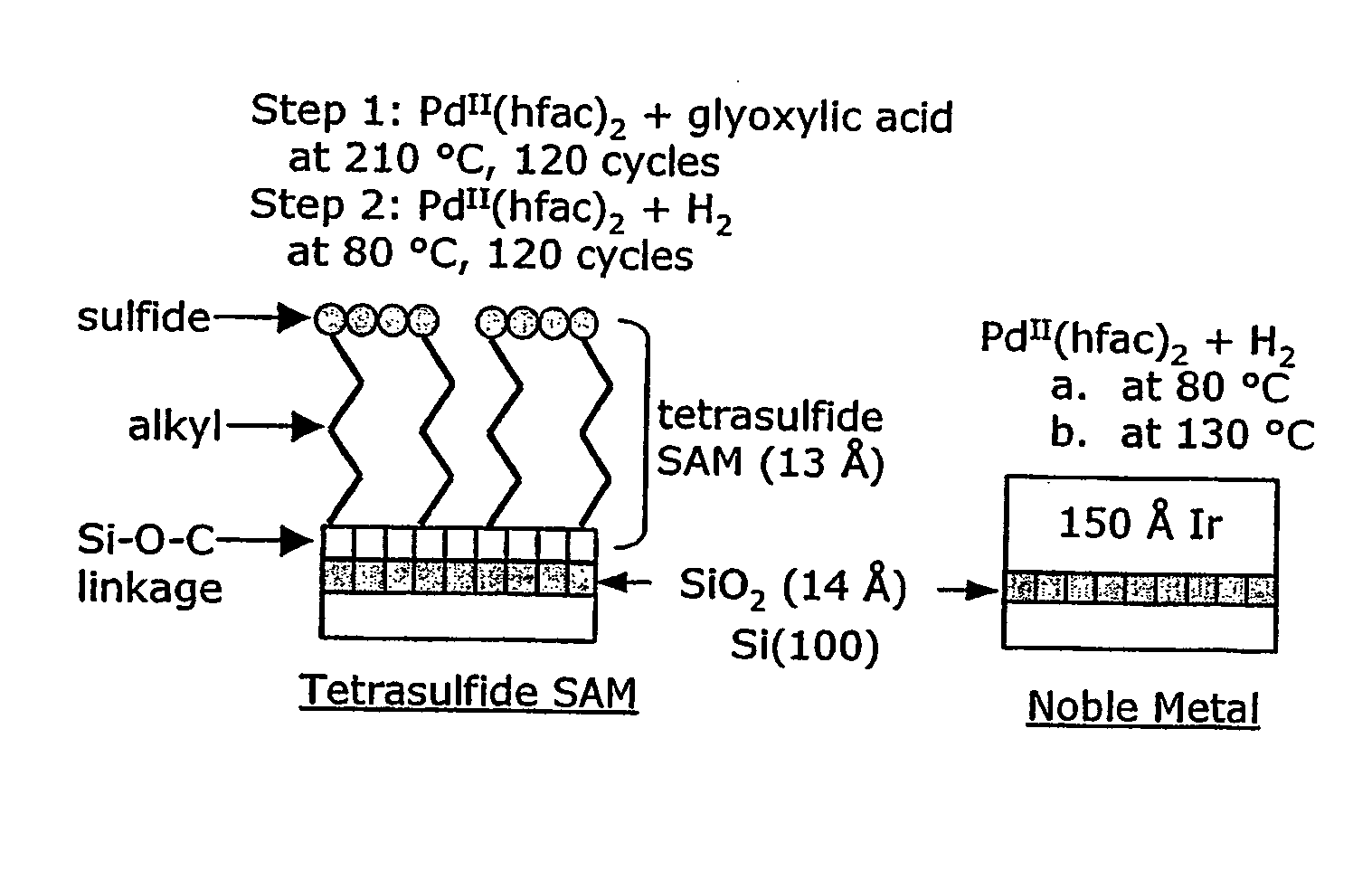
Atomic layer deposition of noble metals
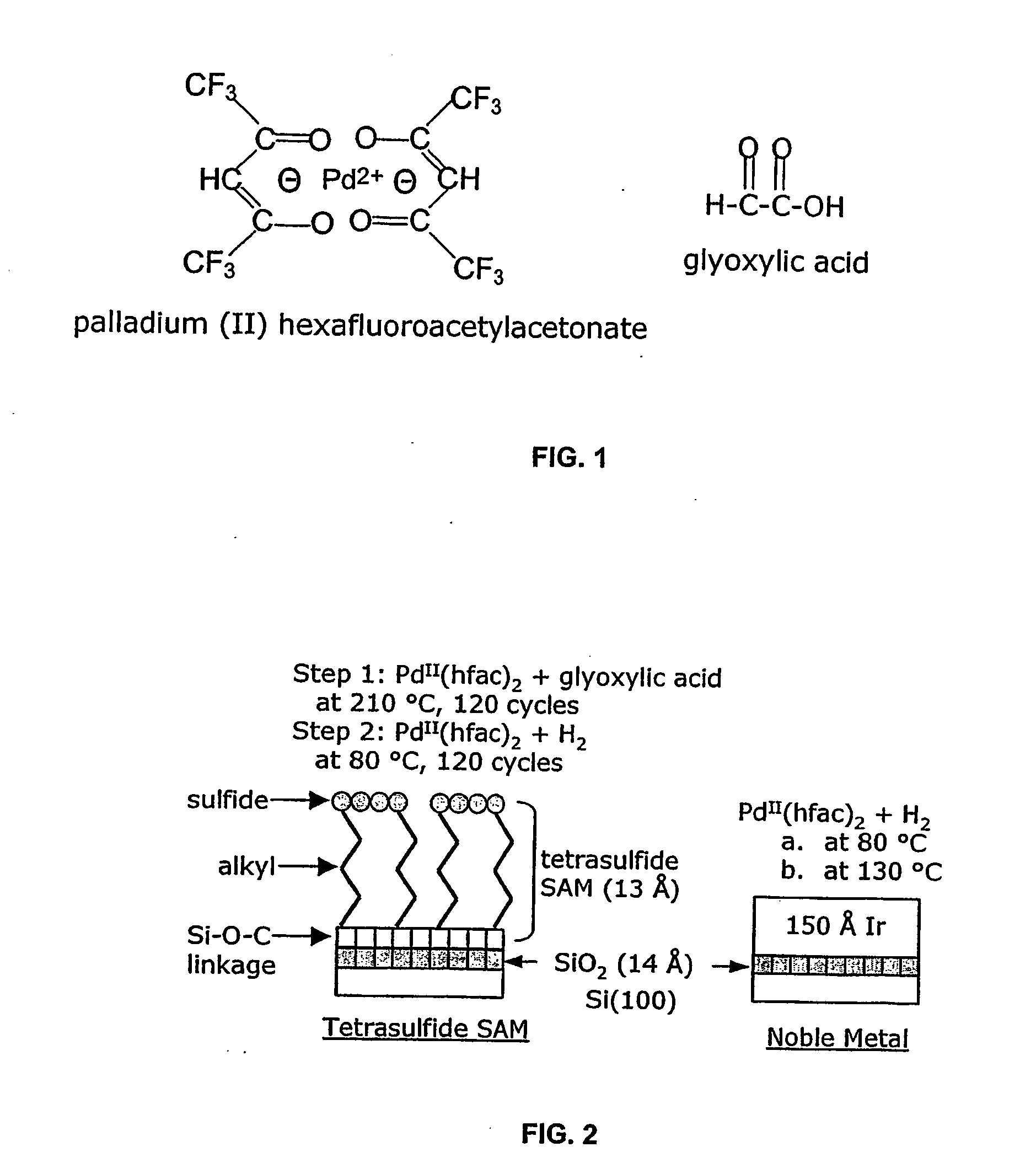
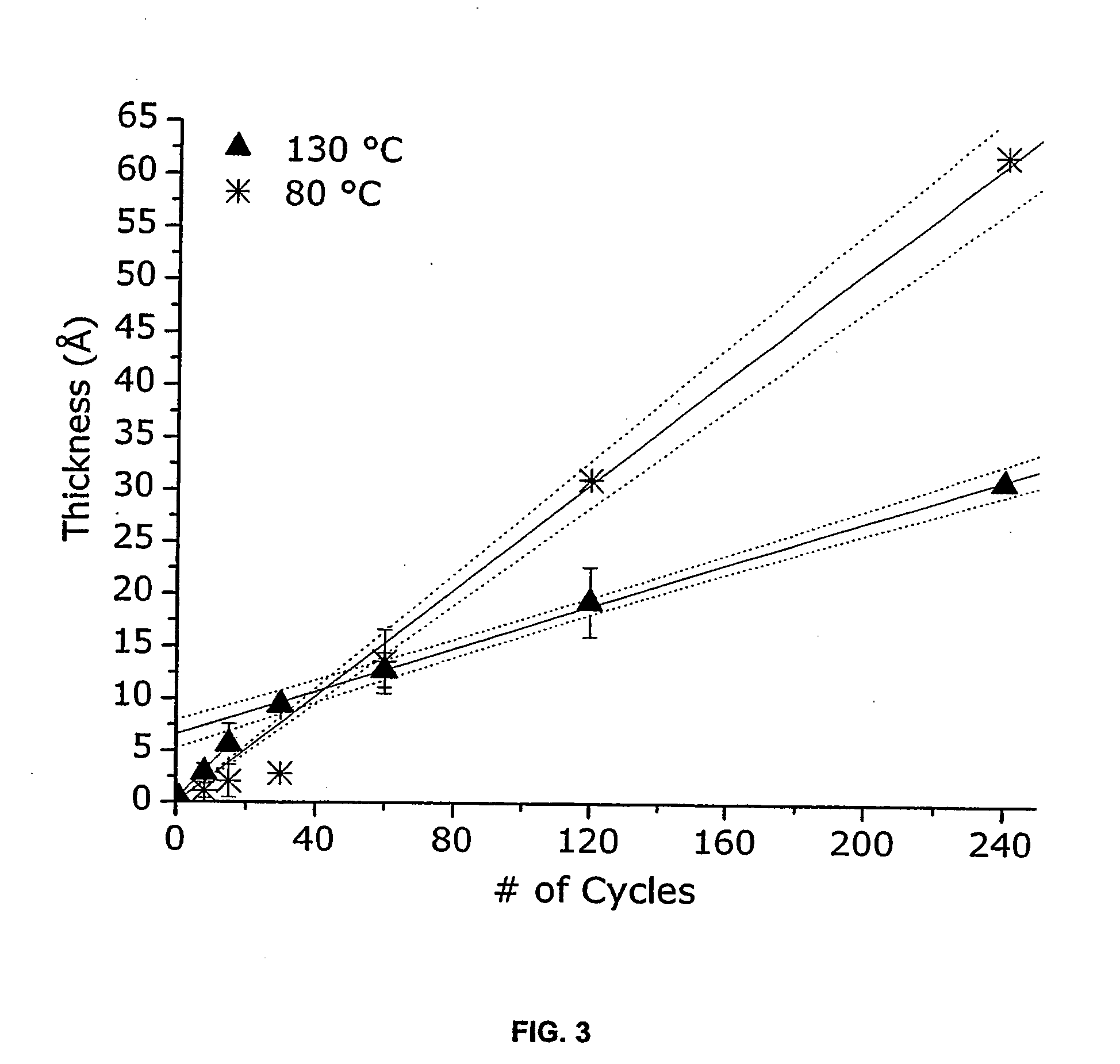
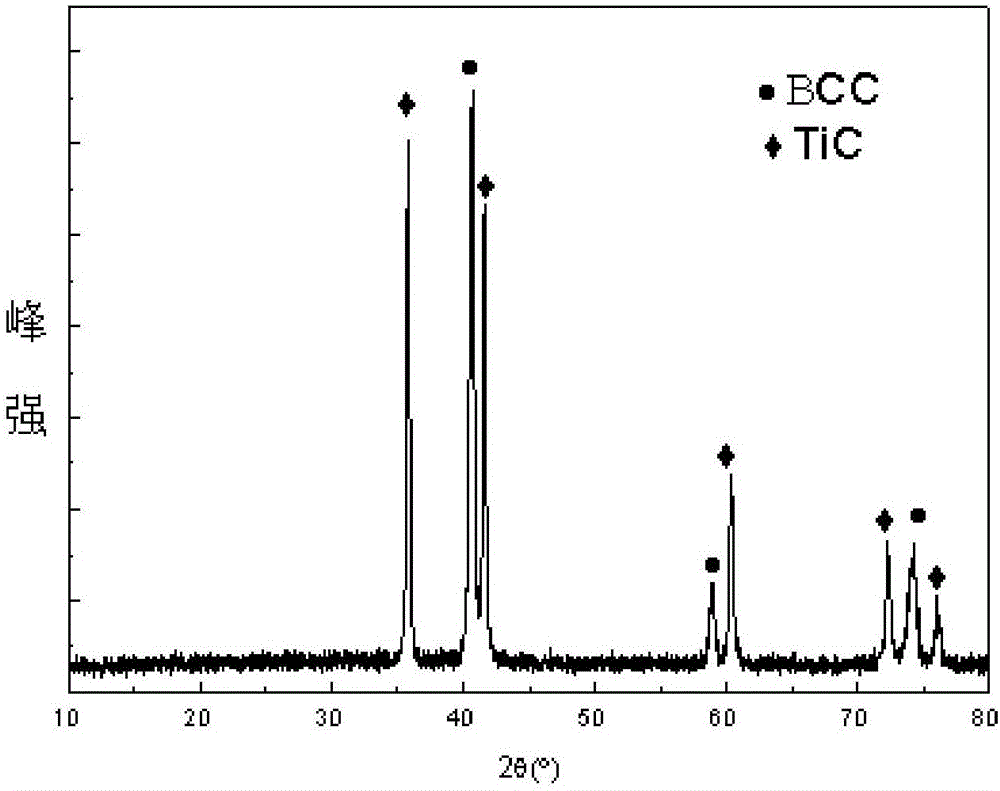
The present invention relates to ALD processes for deposition of a metal selected from Pd, Rh, Ru, Pt and Ir wherein a layer including the metal is formed on a surface composed of a material selected from W, Ta, Cu, Ni, Co, Fe, Mn, Cr, V Nb, tungsten nitride, tantalum nitride, titanium nitride, dielectrics and activated dielectrics at a temperature ranging from >60° C. to <260° C. The layer is formed by sequentially pulsing into a chamber containing the surface a precursor for the metal and a reducing gas selected from hydrogen, glyoxylic acid, oxalic acid, formaldehyde, 2-propanol, imidazole and plasma-activated hydrogen.
Owner:SENKEVICH JOHN JOSEPH +1
Refractory high-entropy alloy/titanium carbide composite and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a refractory high-entropy alloy / titanium carbide composite. A refractory high-entropy alloy serves as a matrix phase, and titanium carbide serves as a wild phase; and elements in the refractory high-entropy alloy are selected from at least four kinds of elements of W, Mo, Ta, Nb, V, Ti, Zr, Hf and Cr. A preparation method of the refractory high-entropy alloy / titanium carbide composite comprises the steps that at least four kinds of carbonization metal powder in tungsten carbide, molybdenum carbide, tantalum carbide, niobium carbide, vanadium carbide, the titanium carbide, hafnium carbide, zirconium carbide and chromium carbide are selected and mixed according to the equal molar ratio or the ratio close to the equal molar ratio to form high-entropy matrix powder; and after the high-entropy matrix powder and titanium powder are mixed, alloy mechanization is carried out, then spark plasma sintering or hot-press sintering is carried out, and the refractory high-entropy alloy / titanium carbide composite is obtained. The density and cost of the composite are reduced while the hardness of the composite is improved, excellent high-temperature performance is achieved, and the requirement for manufacturing a high-temperature structural component is met.
Owner:江西咏泰粉末冶金有限公司
Friction stir welding tool
InactiveUS20100258612A1Easy to useReduce sensitivityWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesHard metalTitanium carbide
The invention relates to a friction stir welding tool (1) with an essentially cylindrical shank (2), which has a peg (3) with a smaller diameter projecting on one end (5) starting from a shoulder region (4) of the shank (2). According to the invention it is provided in order to create a friction stir welding tool (1) for welding steel, that the friction stir welding tool (1), at least in the region of the peg (3) and in the shoulder region (4), is made of a hard metal containing 80% by weight to 98% by weight tungsten carbide with an average grain size of more than 1 μm and up to 20% by weight cobalt as well as optionally a total of up to 18% by weight titanium carbide, tantalum carbide, niobium carbide and / or mixed carbides thereof and at least in one of the referenced regions has a coating of one or more layers.
Owner:BOEHLERIT GMBH & CO KG
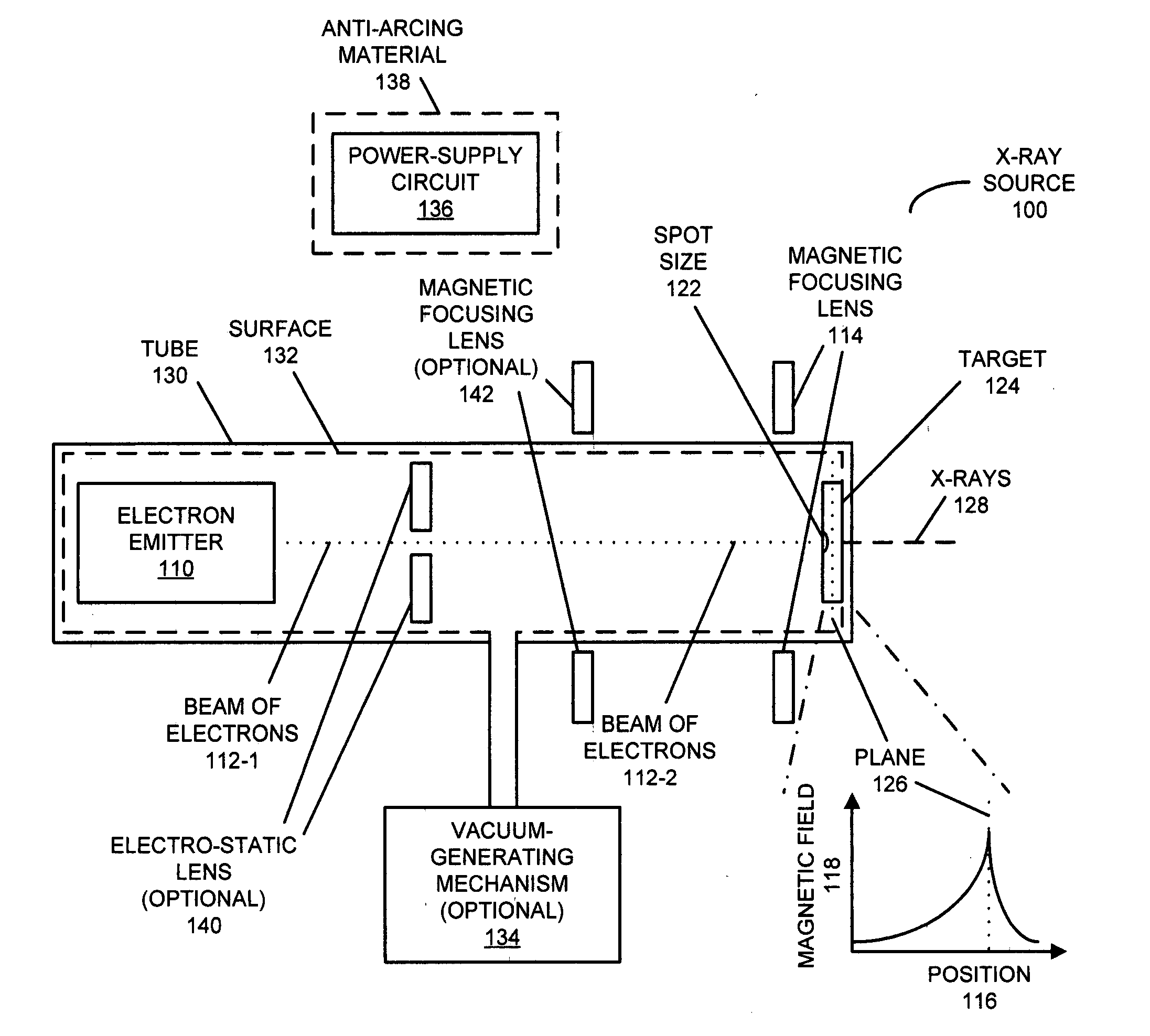
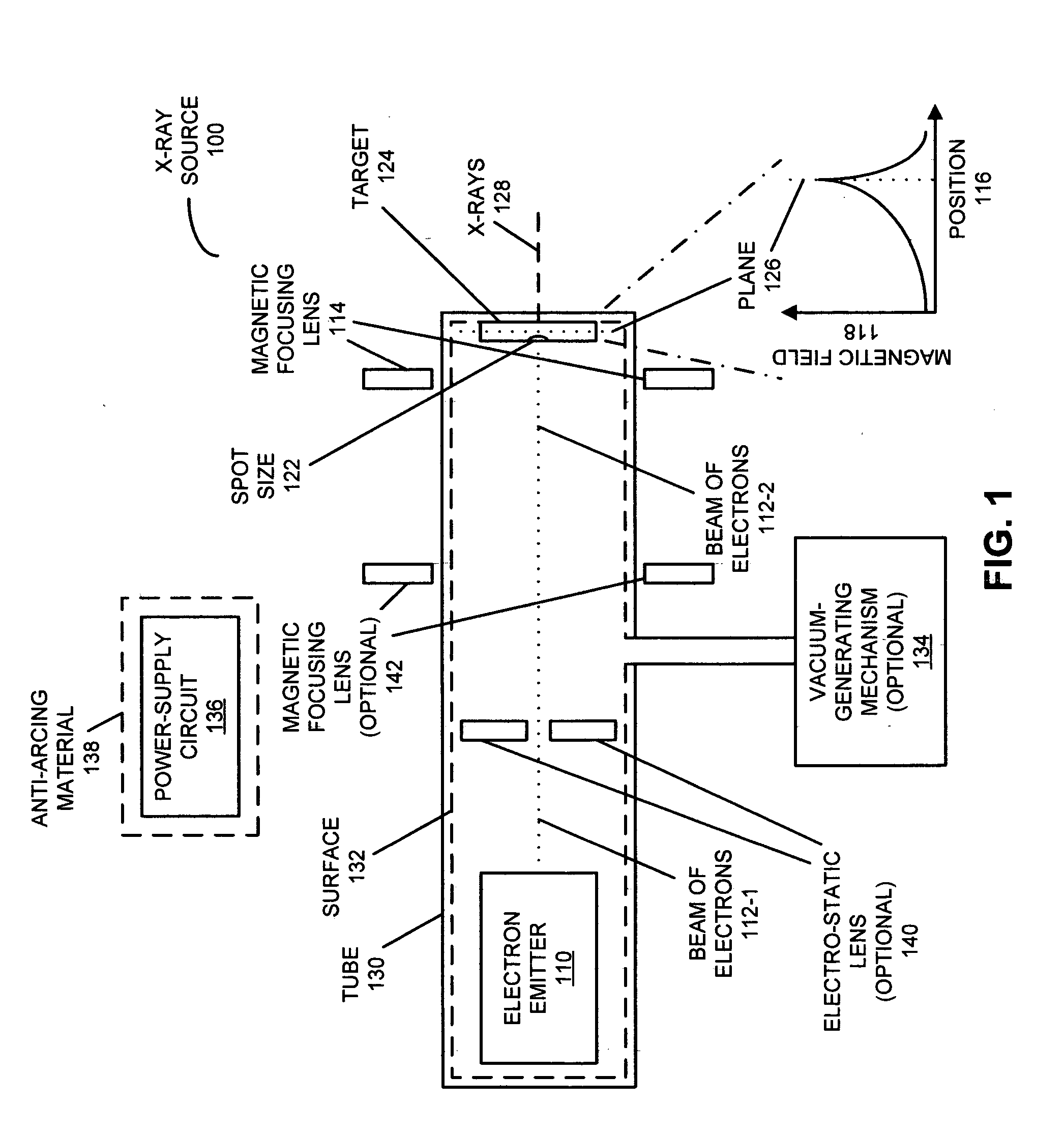
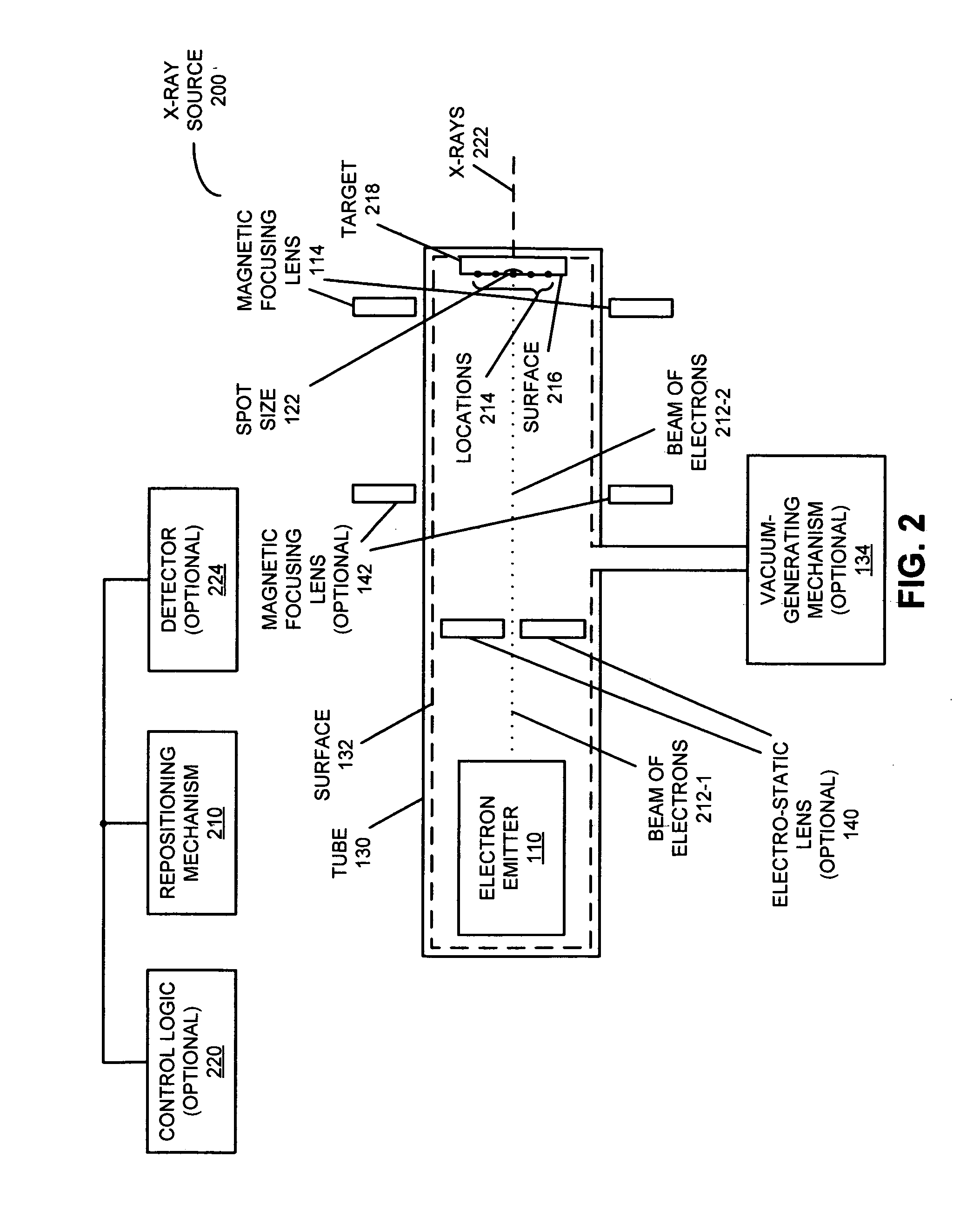
X-ray source with high-temperature electron emitter
InactiveUS20120269326A1X-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingElectron sourceX-ray
An x-ray source is described. This x-ray source includes an electron source with a refractory binary compound having a melting temperature greater than that of tungsten. For example, the refractory binary compound may include: hafnium carbide, zirconium carbide, tantalum carbide, lanthanum hexaboride and / or compounds that include two or more of these elements.
Owner:ADLER DAVID L +1
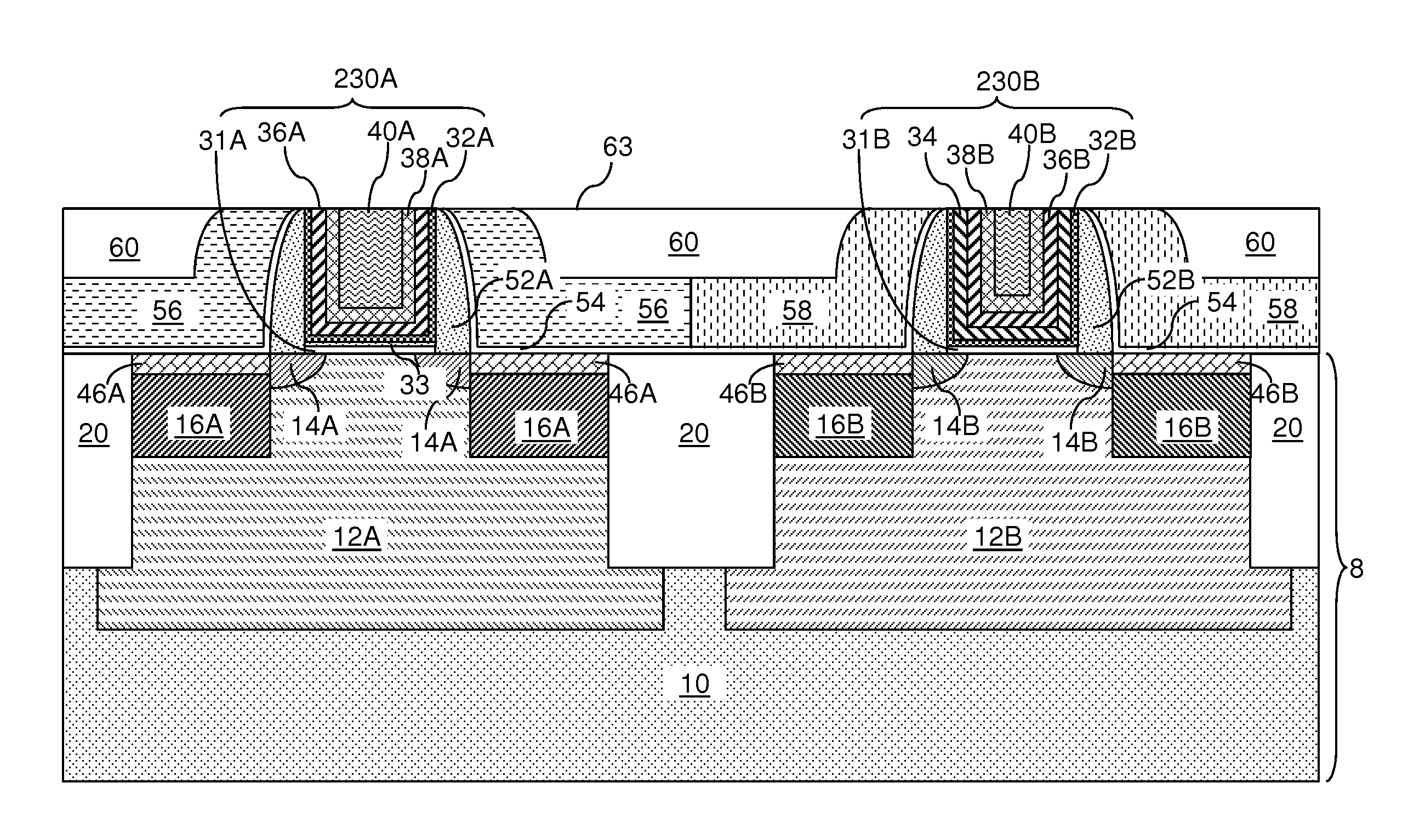
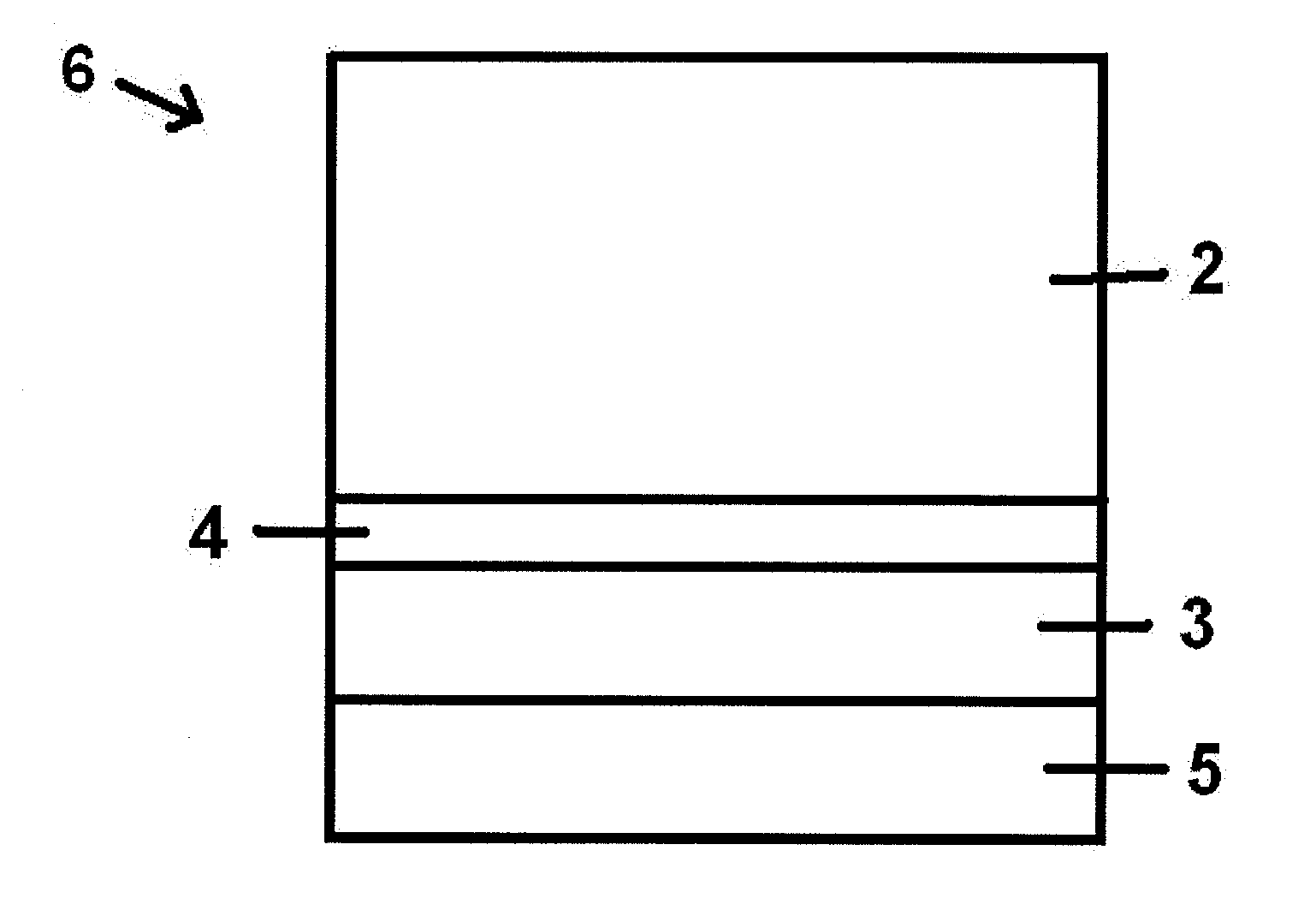
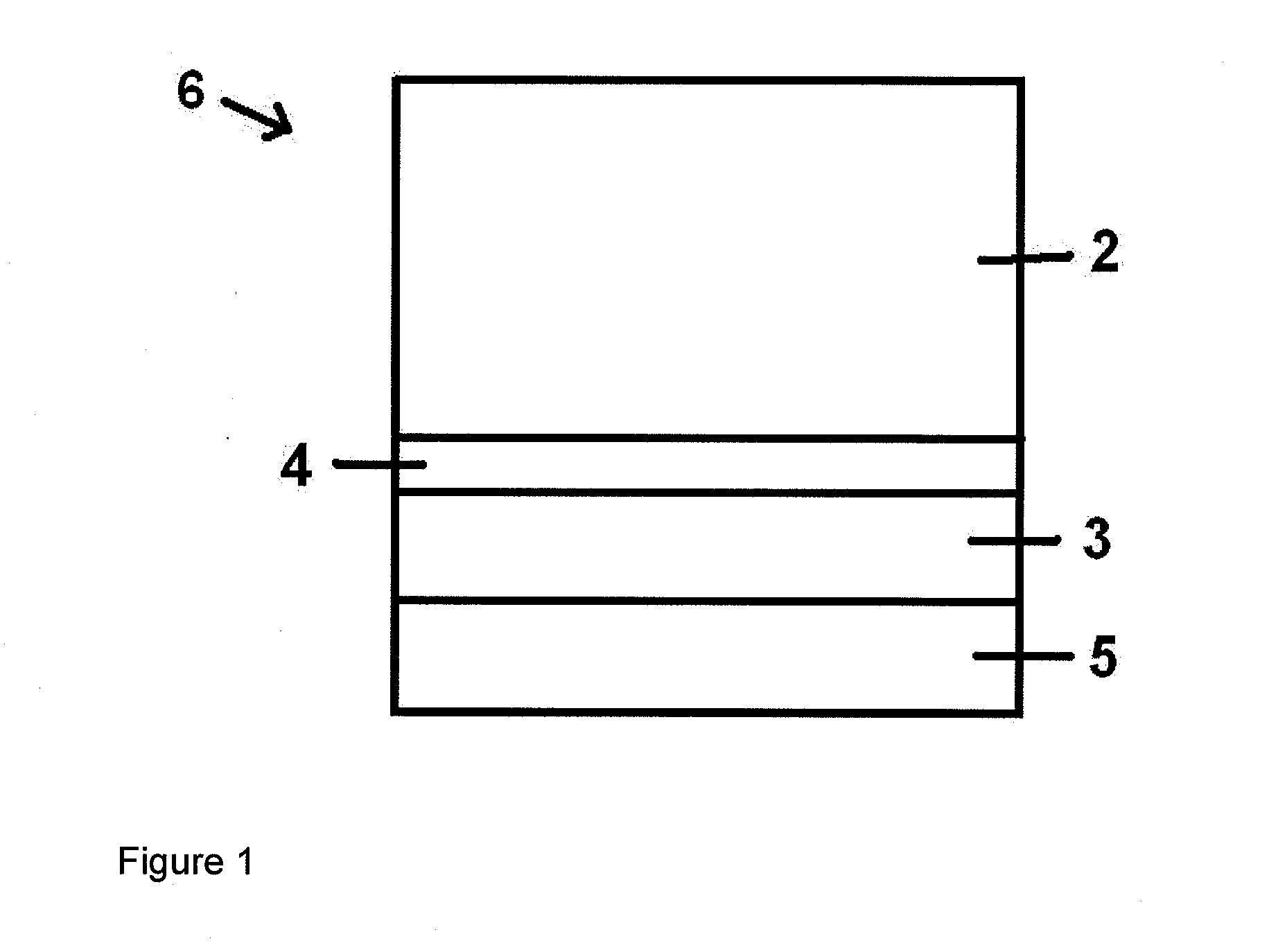
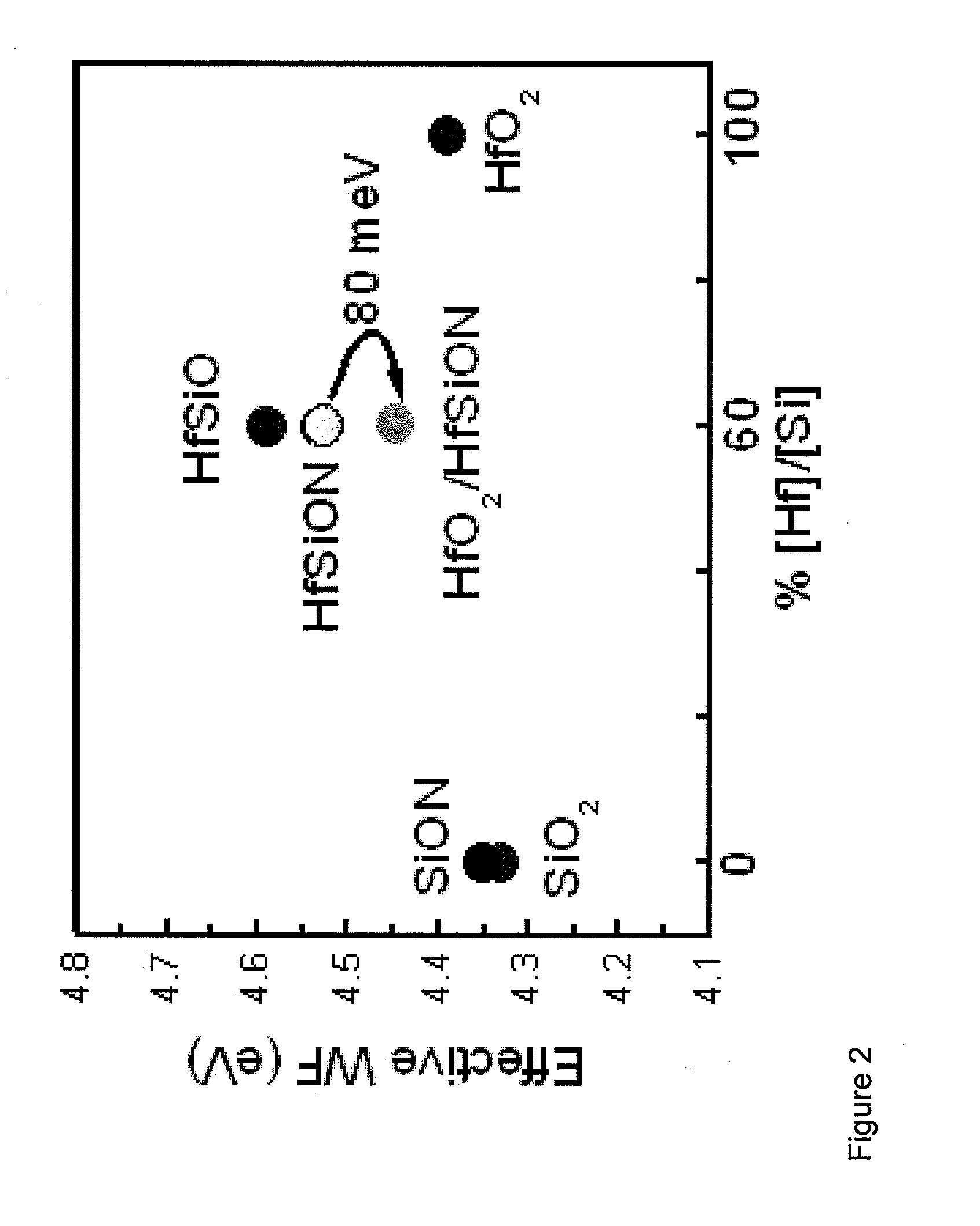
Replacement gate with reduced gate leakage current
InactiveUS20130260549A1Improve performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSilicon alloy
Replacement gate work function material stacks are provided, which provides a work function about the energy level of the conduction band of silicon. After removal of a disposable gate stack, a gate dielectric layer is formed in a gate cavity. A metallic compound layer including a metal and a non-metal element is deposited directly on the gate dielectric layer. At least one barrier layer and a conductive material layer is deposited and planarized to fill the gate cavity. The metallic compound layer includes a material, which provides, in combination with other layer, a work function about 4.4 eV or less, and can include a material selected from tantalum carbide, metallic nitrides, and a hafnium-silicon alloy. Thus, the metallic compound layer can provide a work function that enhances the performance of an n-type field effect transistor employing a silicon channel. Optionally, carbon doping can be introduced in the channel.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
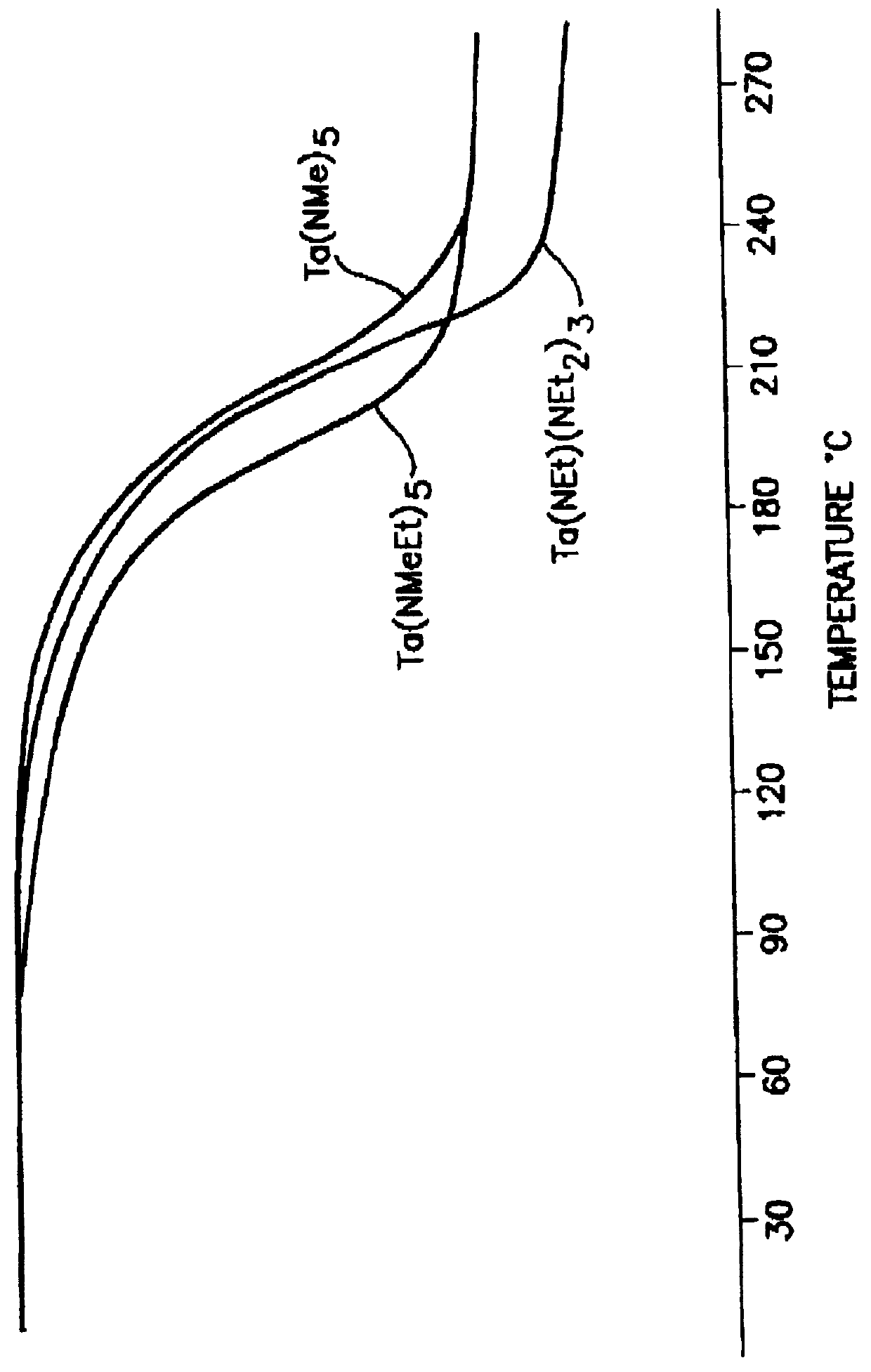
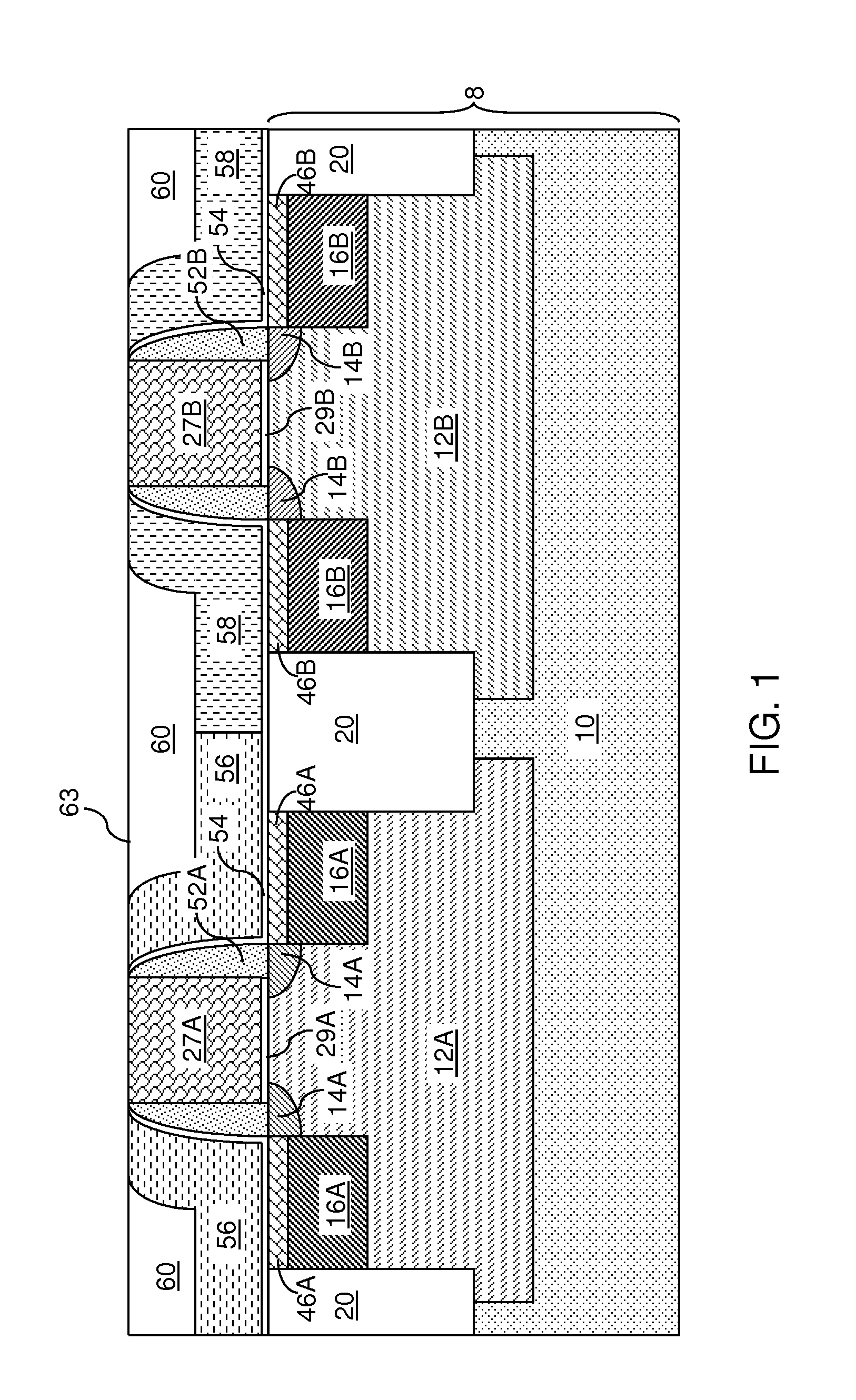
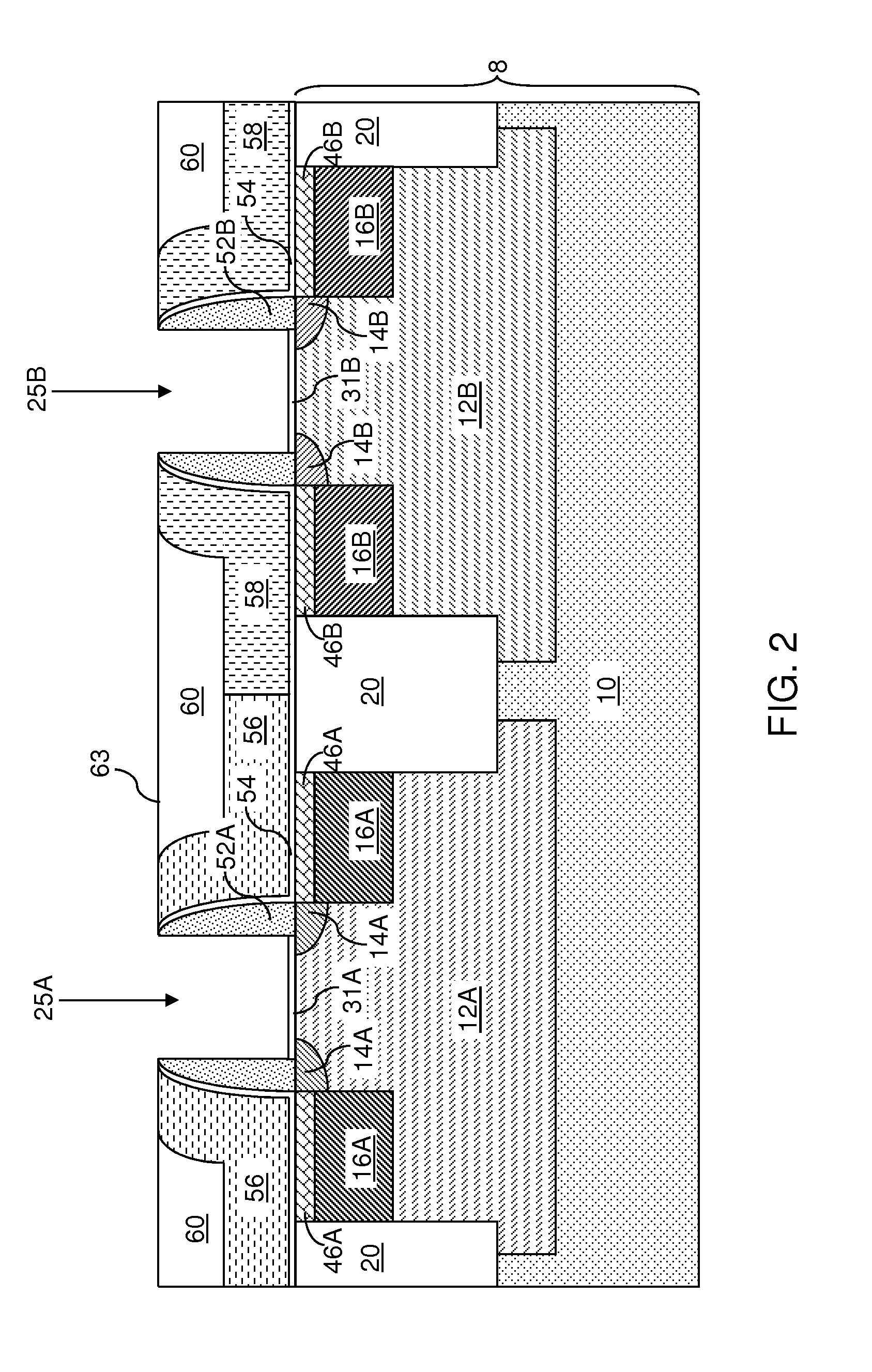
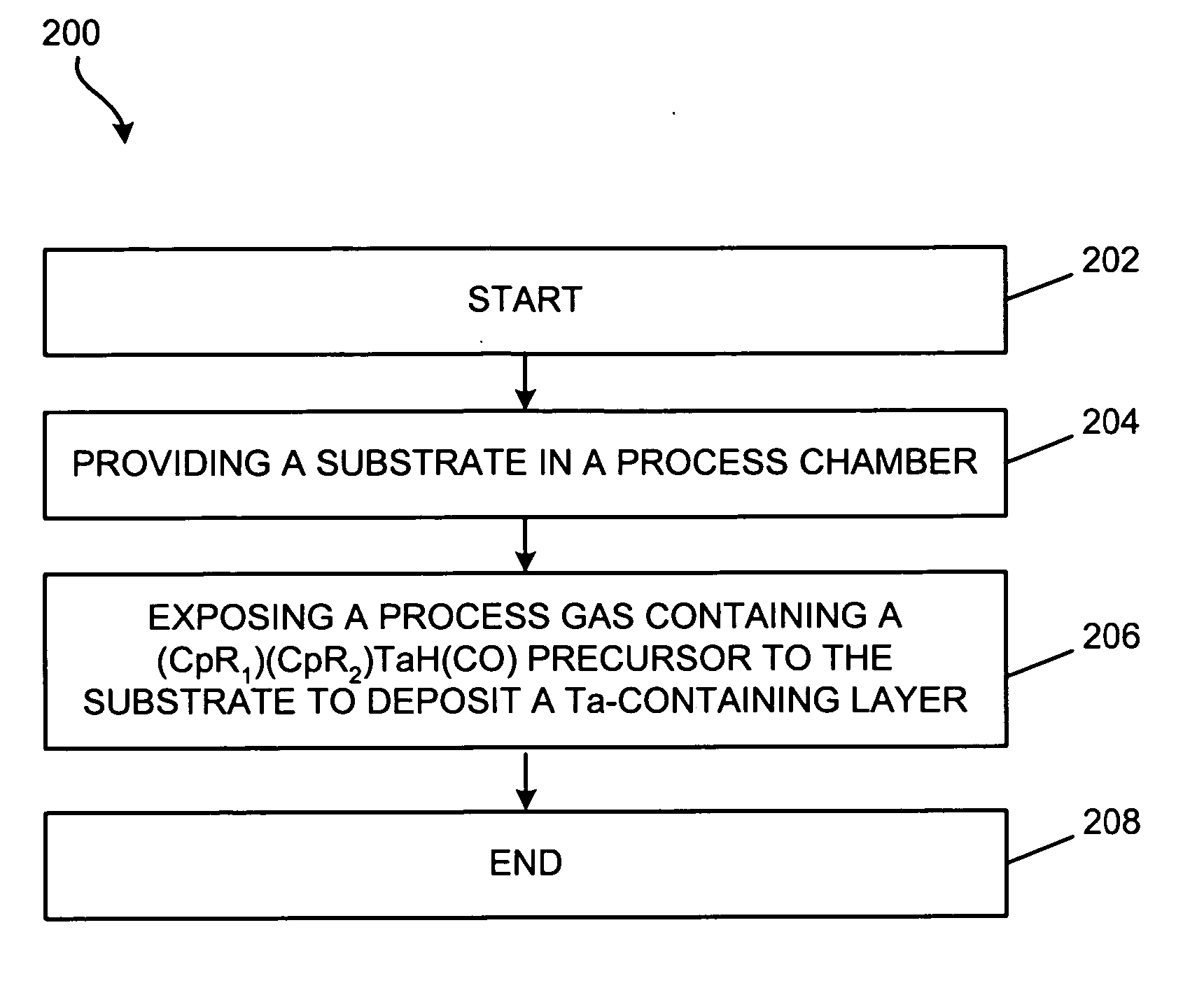
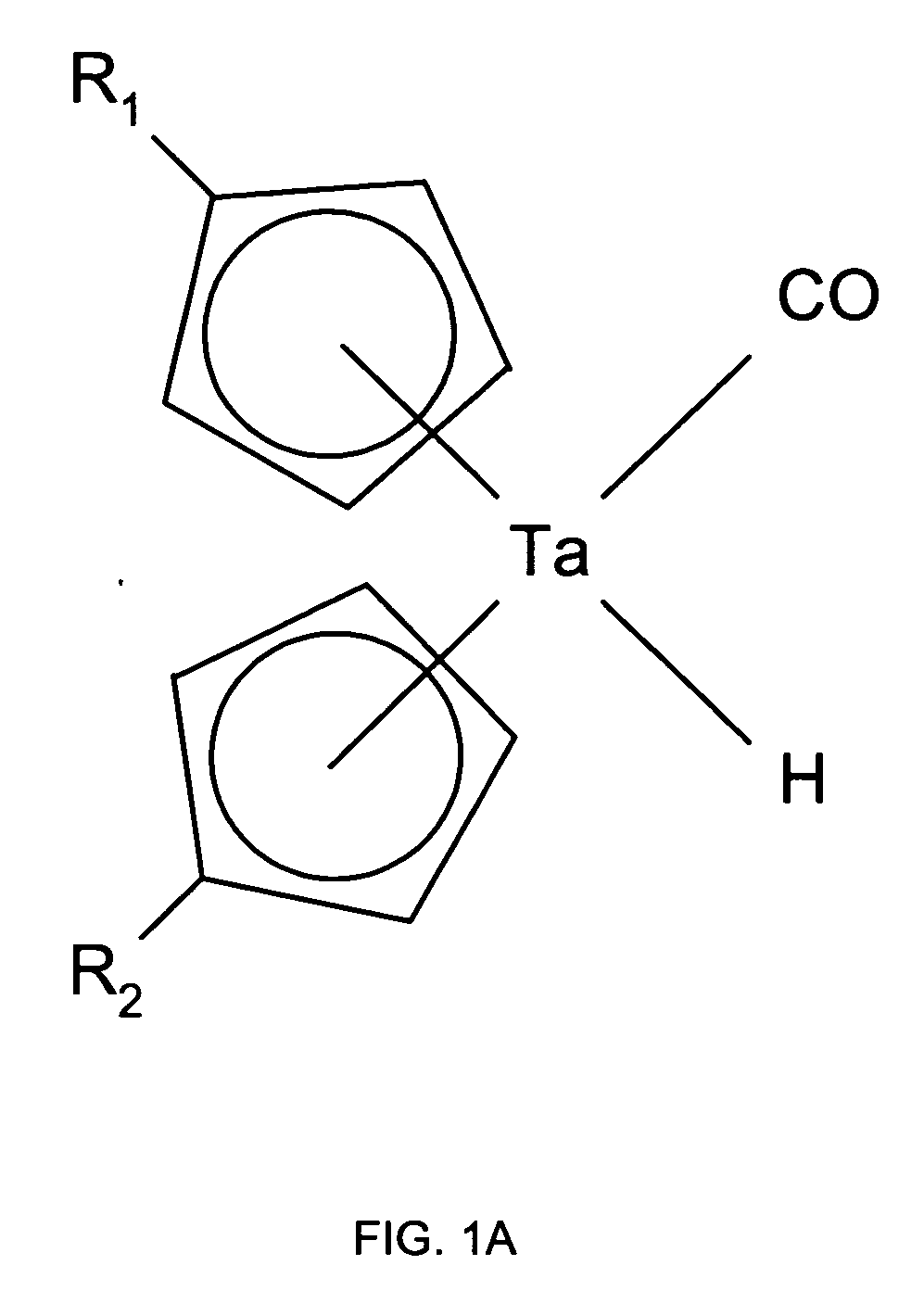
Method of forming a tantalum-containing layer from a metalorganic precursor
InactiveUS20070054046A1Improve thermal stabilityChemical vapor deposition coatingTantalum nitrideDevice material
A method and precursor for forming and integrating a Ta-containing layer in semiconductor processing. The tantalum precursor has the formula (CpR1)(CpR2)TaH(CO), where Cp is a cyclopentadienyl functional group and R1 and R2 are H or alkyl groups. The method includes providing a substrate in a process chamber of a deposition system, and exposing a process gas comprising the tantalum precursor to the substrate to form the Ta-containing layer. The Ta-containing layer may be treated to remove contaminants and modify the layer. The Ta-containing layer may contain tantalum metal, tantalum carbide, tantalum nitride, or tantalum carbonitride, or a combination thereof, and may be deposited in a TCVD, ALD, or PEALD process. A semiconductor device containing a Ta-containing layer formed on a patterned substrate containing one or more vias or trenches is provided.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Ceramic cladding powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101423398AThere will be no phenomenon of grain aggregation and growthEvenly distributedCeramic coatingTitanium nitride
The invention relates to ceramic coating powder the ceramic phase of which is coated by a metallic phase cobalt or / and a metallic phase nickel. The metallic phase cobalt and the metallic phase nickel are obtained by means of a liquid phase reduction method; and the ceramic phase is at least one of titanium carbonitride, titanium carbide, titanium nitride, tungsten carbide, silicon carbide, niobium carbide, tantalum carbide, aluminum oxide, zirconium oxide, magnesium oxide, boron nitride and silicon nitride. A method for preparing the ceramic coating powder is the liquid phase reduction method to carry out a reduction reaction between cobalt or / and nickel ions in a plating solution to generate the metallic phase cobalt or / and nickel which is deposited on the surface of a ceramic core to form the ceramic coating powder; and the process steps are as follows: (1) pre-treatment of the ceramic powder; (2) preparation of the plating solution; (3) liquid-phase reduction reaction; and (4) plating post treatment.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Powder metallurgy crucible for aluminum nitride crystal growth
A crucible for growing III-nitride (e.g., aluminum nitride) single crystals is provided. The crucible includes an elongated wall structure defining an interior crystal growth cavity. Embodiments include a plurality of grains and a wall thickness of at least about 1.5 times the average grain size. In particular embodiments, the crucible includes first and second layers of grains the first layer including grains forming an inside surface thereof and the second layer being superposed with the first layer. The crucible may be fabricated from tungsten-rhenium (W—Re) alloys; rhenium (Re); tantalum monocarbide (TaC); tantalum nitride (Ta2N); hafnium nitride (HfN); a mixture of tungsten and tantalum (W—Ta); tungsten (W); and combinations thereof.
Owner:CRYSTAL
Replacement Gate With Reduced Gate Leakage Current
InactiveUS20130256802A1Improve performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSilicon alloy
Replacement gate work function material stacks are provided, which provides a work function about the energy level of the conduction band of silicon. After removal of a disposable gate stack, a gate dielectric layer is formed in a gate cavity. A metallic compound layer including a metal and a non-metal element is deposited directly on the gate dielectric layer. At least one barrier layer and a conductive material layer is deposited and planarized to fill the gate cavity. The metallic compound layer includes a material, which provides, in combination with other layer, a work function about 4.4 eV or less, and can include a material selected from tantalum carbide, metallic nitrides, and a hafnium-silicon alloy. Thus, the metallic compound layer can provide a work function that enhances the performance of an n-type field effect transistor employing a silicon channel. Optionally, carbon doping can be introduced in the channel.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Tantalum barrier removal solution
InactiveUS20030181345A1Reduce erosionMaterial removalPigmenting treatmentSoap detergents with inorganic compounding agentsGuanidine derivativesTantalum nitride
A chemical mechanical planarization solution is useful for removing tantalum barrier materials. The solution includes by weight percent 0 to 25 oxidizer, 0 to 15 inhibitor for a nonferrous metal and 0 to 20 complexing agent for the nonferrous metal, 0.01 to 12 tantalum removal agent selected from the group consisting of formamidine, formamidine salts, formamidine derivatives, guanidine derivatives, guanidine salts and mixtures thereof, 0 to 5 abrasive, 0 to 15 total particles selected from the group consisting of polymeric particles and polymer-coated coated particles and balance water. The solution has a tantalum nitride to TEOS selectivity of at least 3 to 1 as measured with a microporous polyurethane polishing pad pressure measure normal to a wafer less than 20.7 kPa.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Tantalum barrier removal solution
InactiveUS7491252B2Pigmenting treatmentSoap detergents with inorganic compounding agentsGuanidine derivativesNonferrous metal
A chemical mechanical planarization solution is useful for removing tantalum barrier materials. The solution includes by weight percent 0 to 25 oxidizer, 0 to 15 inhibitor for a nonferrous metal and 0 to 20 complexing agent for the nonferrous metal, 0.01 to 12 tantalum removal agent selected from the group consisting of formamidine, formamidine salts, formamidine derivatives, guanidine derivatives, guanidine salts and mixtures thereof, 0 to 5 abrasive, 0 to 15 total particles selected from the group consisting of polymeric particles and polymer-coated coated particles and balance water. The solution has a tantalum nitride to TEOS selectivity of at least 3 to 1 as measured with a microporous polyurethane polishing pad pressure measure normal to a wafer less than 20.7 kPa.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
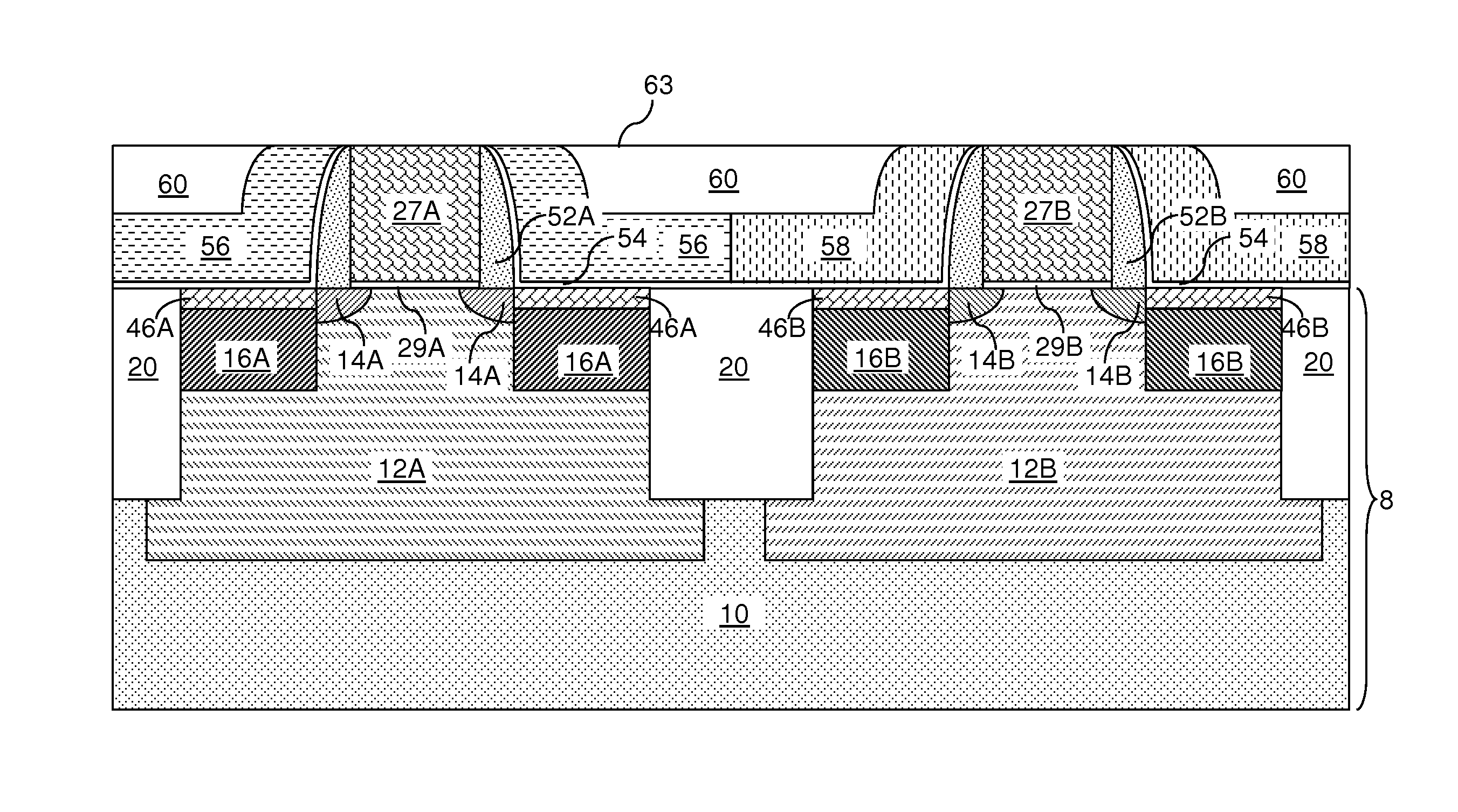
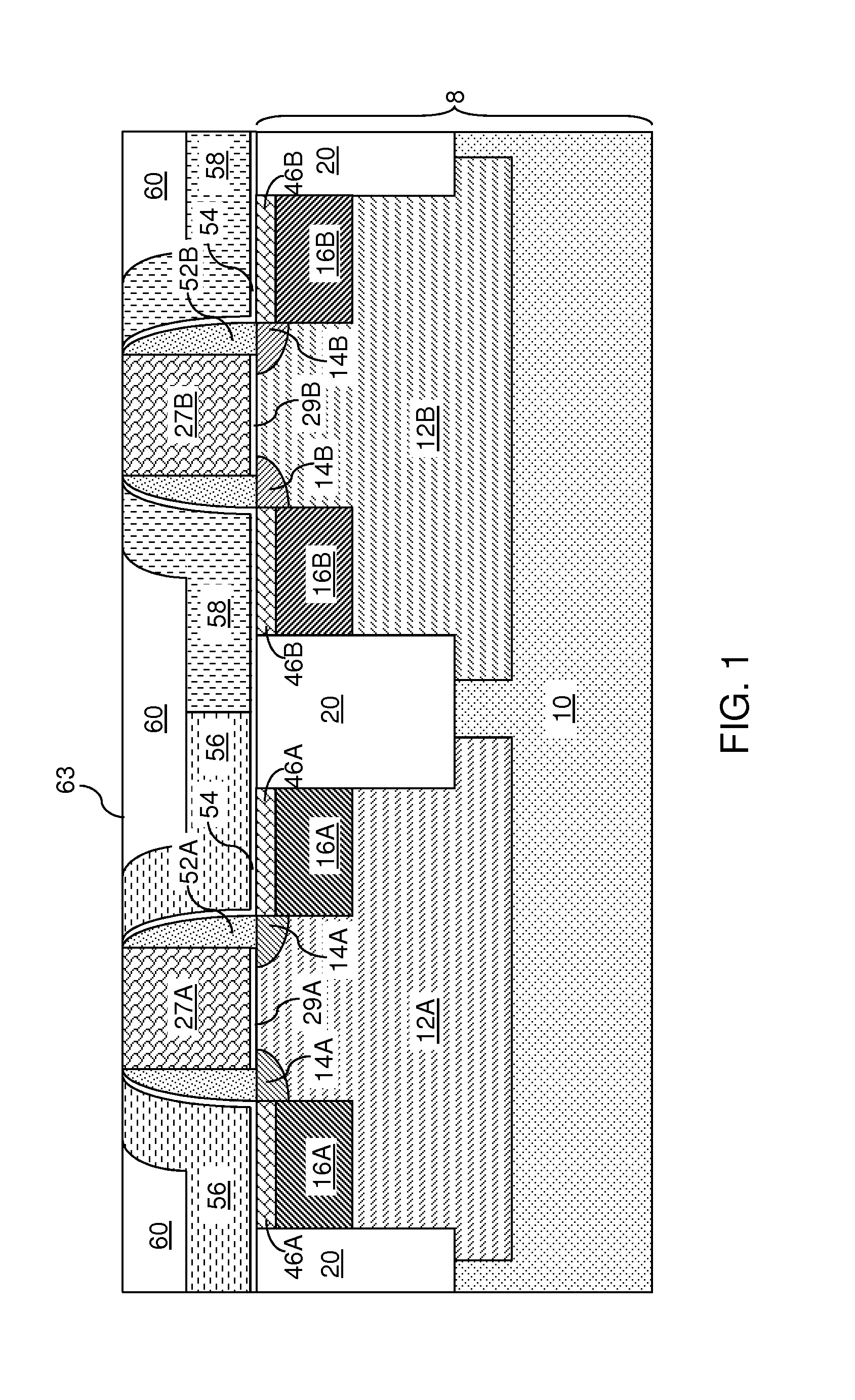
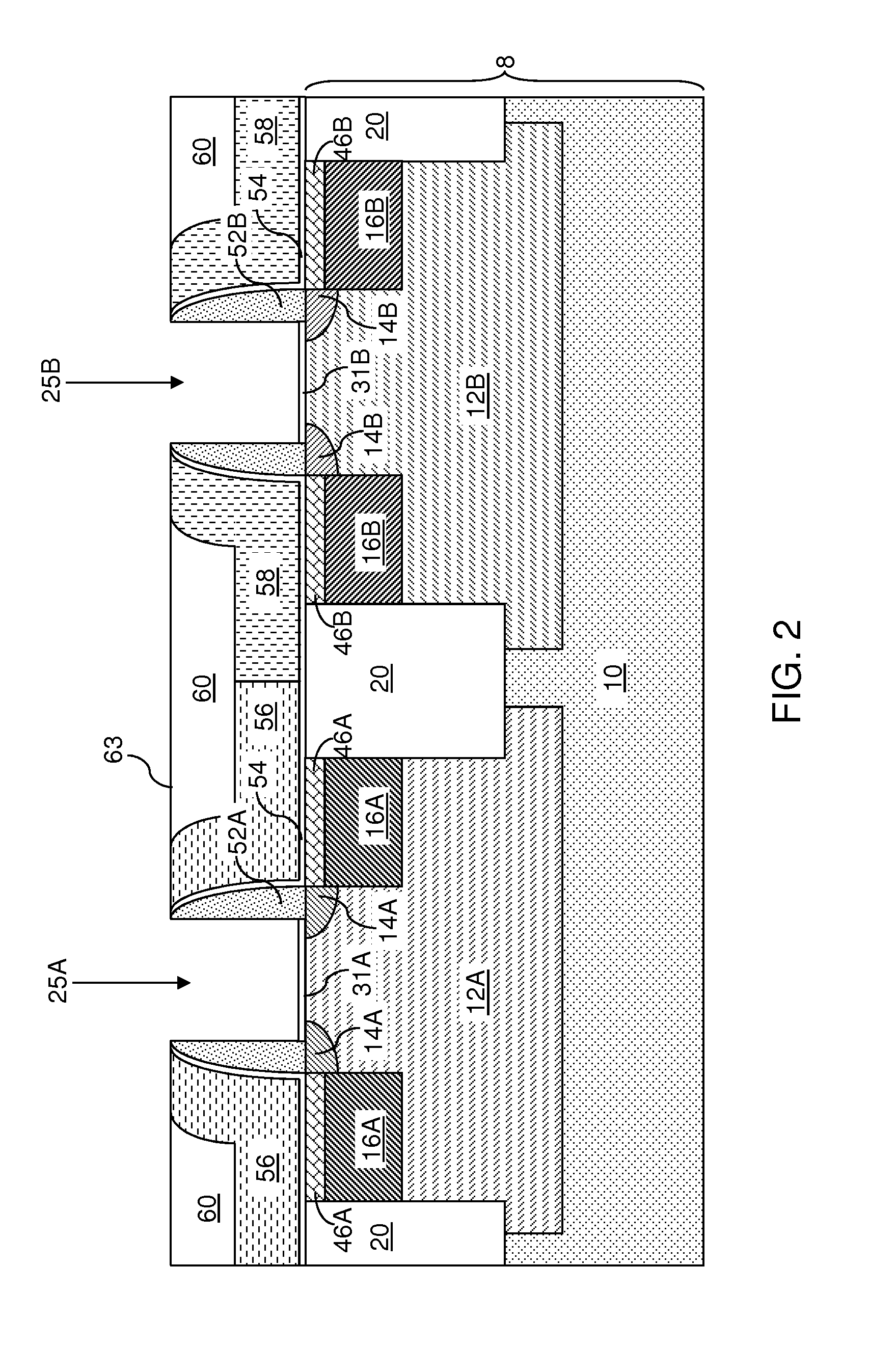
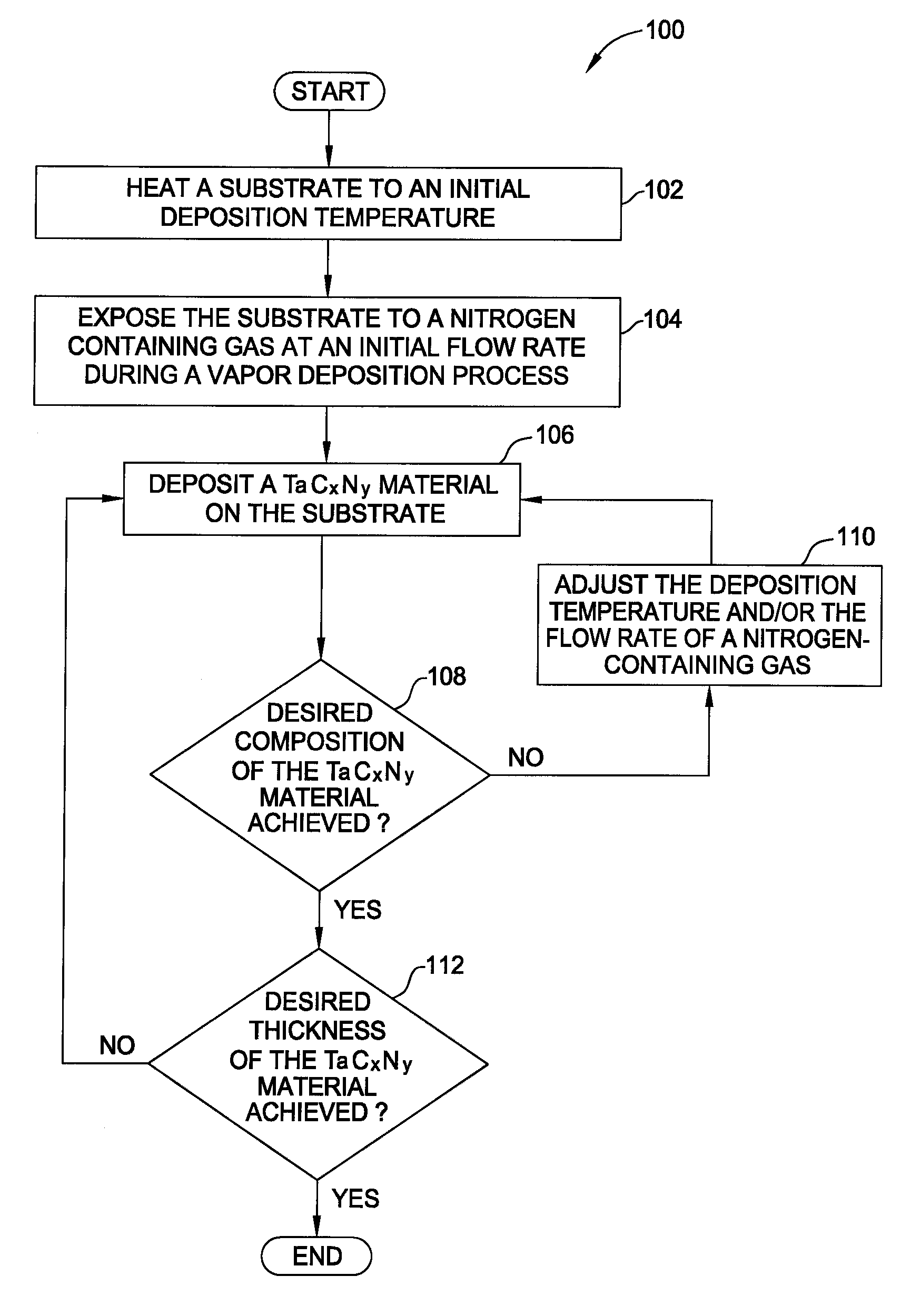
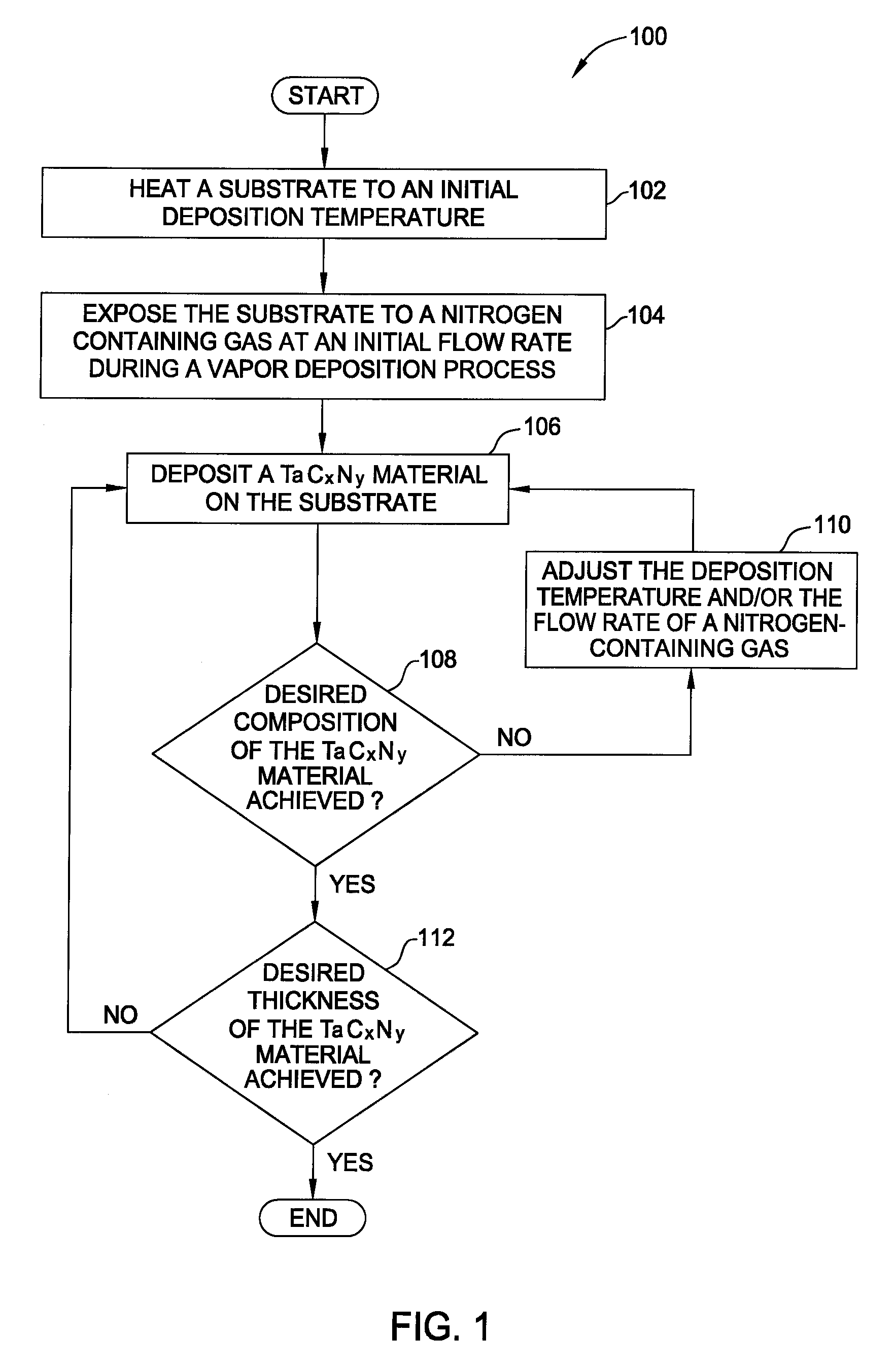
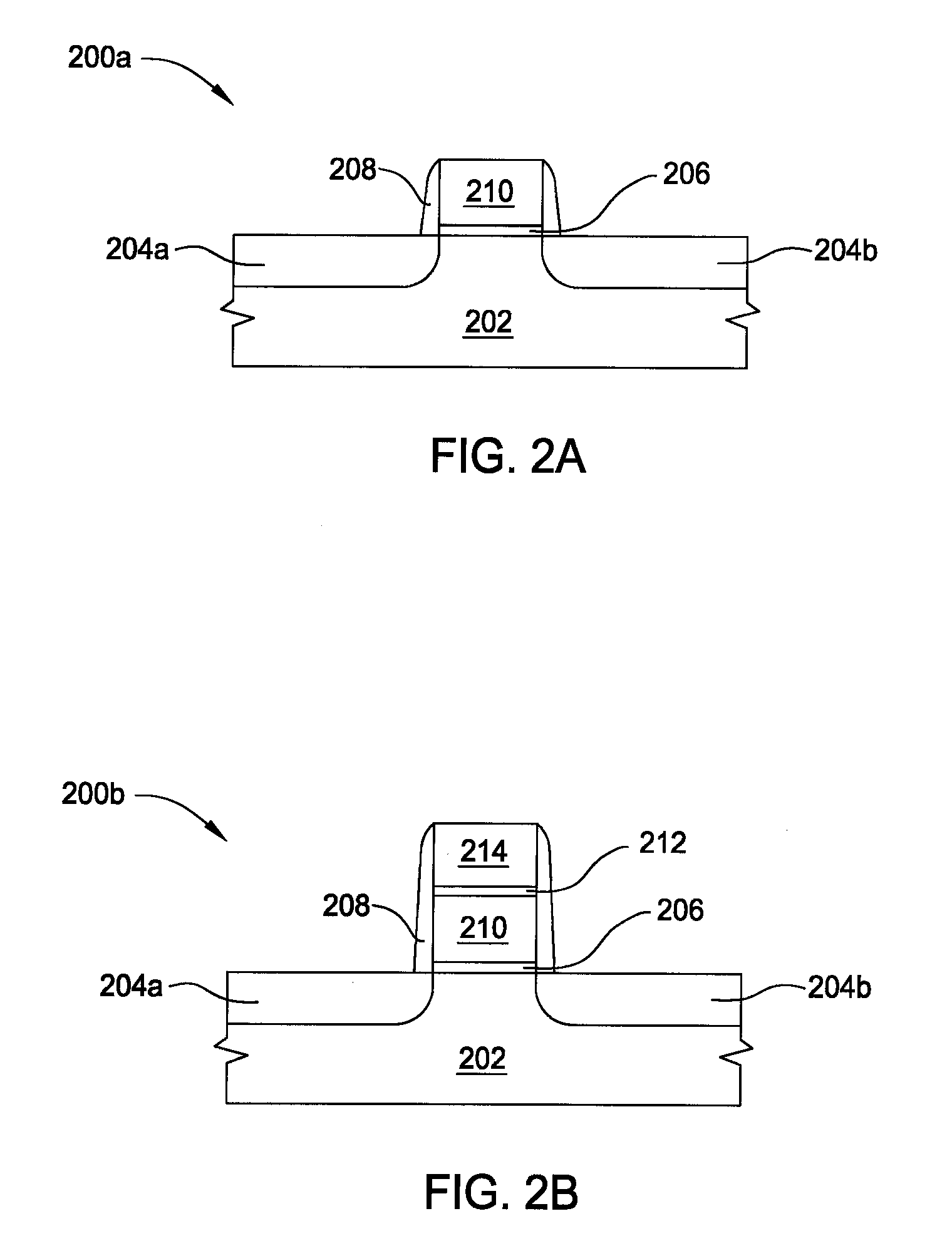
Vapor deposition processes for tantalum carbide nitride materials
ActiveUS20090081868A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseElemental carbon
Embodiments of the invention generally provide methods for depositing and compositions of tantalum carbide nitride materials. The methods include deposition processes that form predetermined compositions of the tantalum carbide nitride material by controlling the deposition temperature and the flow rate of a nitrogen-containing gas during a vapor deposition process, including thermal decomposition, CVD, pulsed-CVD, or ALD. In one embodiment, a method for forming a tantalum-containing material on a substrate is provided which includes heating the substrate to a temperature within a process chamber, and exposing the substrate to a nitrogen-containing gas and a process gas containing a tantalum precursor gas while depositing a tantalum carbide nitride material on the substrate. The method further provides that the tantalum carbide nitride material is crystalline and contains interstitial carbon and elemental carbon having an interstitial / elemental carbon atomic ratio of greater than 1, such as about 2, 3, 4, or greater.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
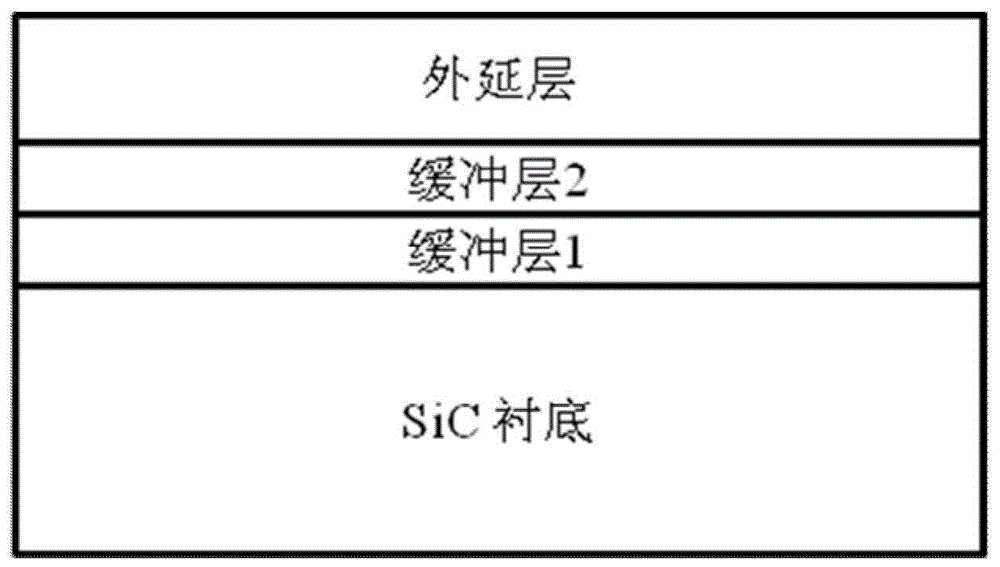
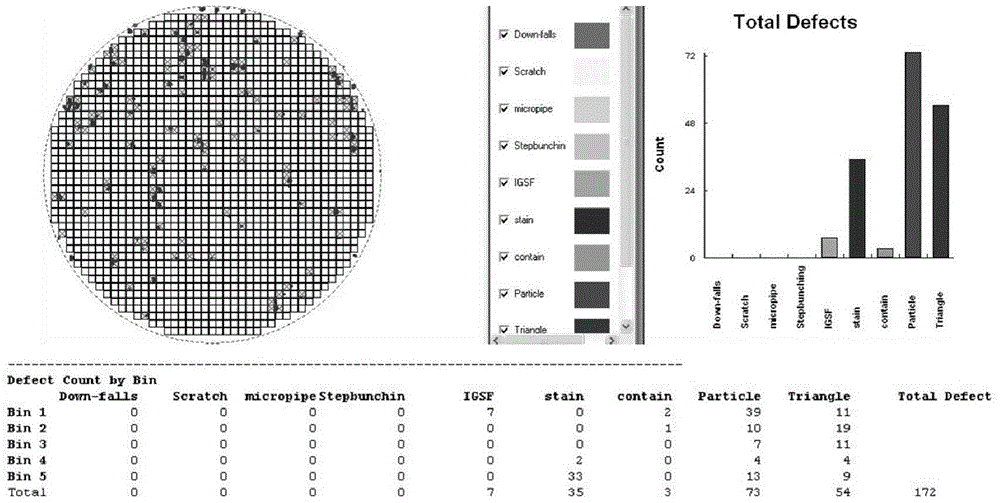
Growing method for high-surface-quality silicon carbide epitaxial layer
ActiveCN105826186AReduce triangle defectsGrowth inhibitionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenHigh surface
The invention discloses a growing method for a high-surface-quality silicon carbide epitaxial layer. The method comprises the steps of 1) selecting a silicon-surface silicon carbide substrate at a deflecting <11-20> direction of 4 degrees, placing the substrate on a graphite base with a tantalum carbide coating inside a reaction chamber of a SiC epitaxial system; 2) heating the reaction chamber of the SiC epitaxial system to increase the temperature in the reaction chamber to be 1450 DEG C, setting the pressure in the reaction chamber to be 90-200 mbar, maintaining the temperature in the reaction chamber for 5-10 minutes with the flow rate of H2 to be 68-80 L / min, and etching the substrate by utilizing the pure hydrogen H2; 3) after the step 2), pumping a small amount of hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas into the reaction chamber to etch the substrate for facilitating the H2 at the flow ratio selection range of HCl / H2 is 0.01%-0.15%, continuously increasing the temperature till the growth temperature of a buffer layer reaches 1650 DEG C-1670 DEG C, wherein the heating process lasts for 10-30 minutes. Based on the above method, triangle defects occurred in epitaxial wafers are effectively reduced. Meanwhile, the formation of the stepped bunching morphology in the epitaxial layer is avoided by utilizing the low-temperature and low-carbon-silicon-ratio buffer layer.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
Electronic device and process for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080164581A1Lighting and heating apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLanthanideHafnium
An electronic device and a process for manufacturing the same are disclosed. In one aspect, the device comprises an electrode comprising a metal compound selected from the group of tantalum carbide, tantalum carbonitride, hafnium carbide and hafnium carbonitride. The device further comprises a high-k dielectric layer of a hafnium oxide comprising nitrogen and silicon, the high-k dielectric layer having a k value of at least 4.0. The device further comprises a nitrogen and / or silicon and / or carbon barrier layer placed between the electrode and the high-k dielectric layer. The nitrogen and / or silicon and / or carbon barrier layer comprises one or more metal oxides, the metal of the metal oxides being selected from the group of lanthanides, aluminium or hafnium.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Probe needle material, probe needle and probe card each using the same, and inspection process
ActiveUS20100194415A1Maintain contact stabilityNot abraded heavilyElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingProbe cardHafnium
Disclosed is a probe needle material used for producing a probe needle which is used in contact with an inspection object to inspect electrical characteristics of the inspection object, comprising not less than 0.1% by volume but not more than 3.5% by volume of at least one compound selected from the group consisting of titanium boride, zirconium boride, hafnium boride, niobium boride, tantalum boride, chromium boride, titanium carbide, zirconium carbide, hafnium carbide, vanadium carbide, niobium carbide, tantalum carbide, zirconium oxide, hafnium oxide and chromium oxide and the balance of a tungsten alloy mainly consisting of tungsten.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
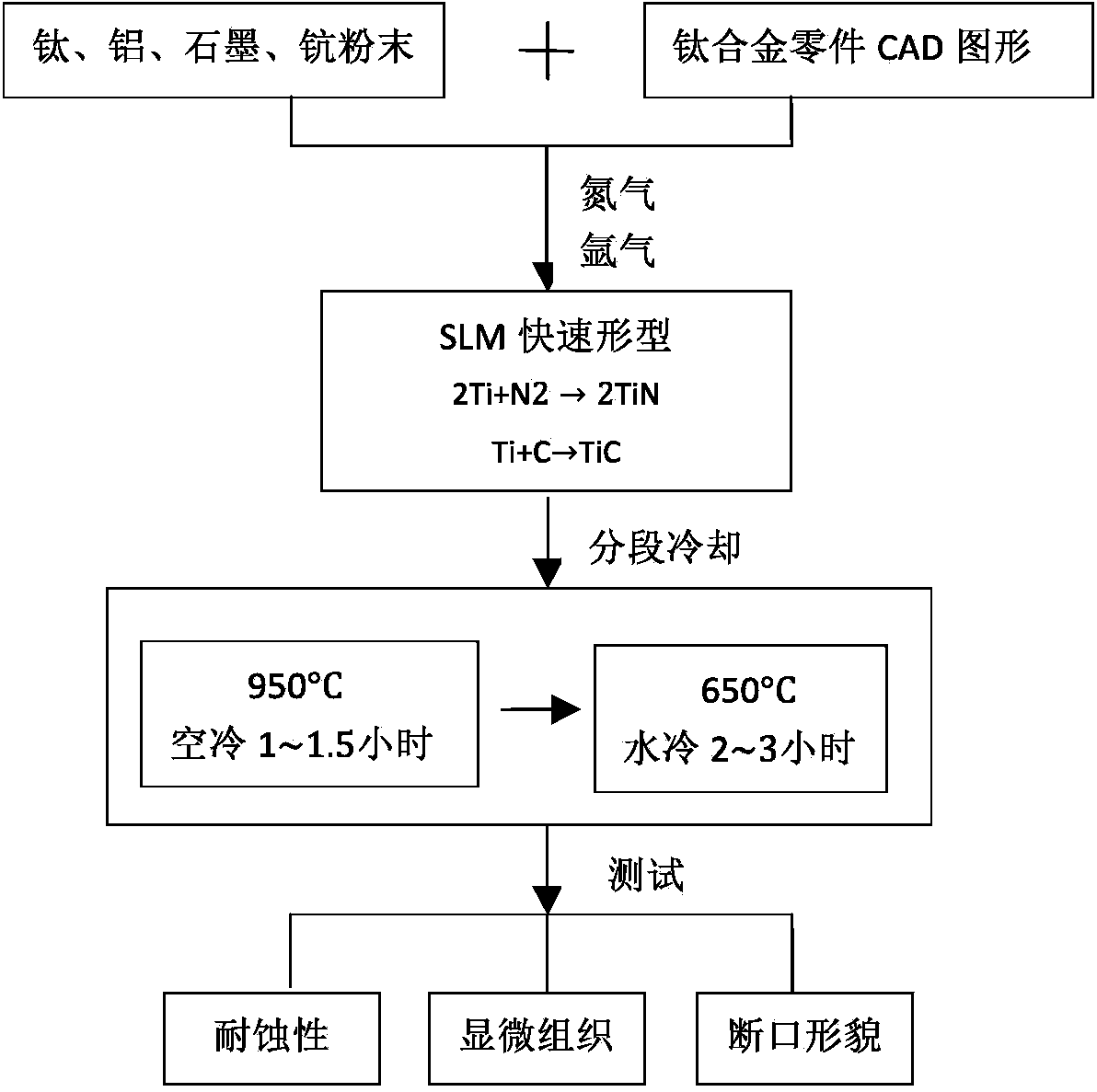
Selective laser melting forming method for preparing titanium alloy component
ActiveCN104174845AEasy to peel offLow costMetallic material coating processesSelf-propagating high-temperature synthesisSelective laser melting
The invention provides a selective laser melting forming method for preparing a titanium alloy component. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, after being subjected to ball-milling and mixing, titanium alloy powder is delivered to a selective laser melting quick forming device, and the titanium alloy component is formed according to a component CAD image imported into the selective laser melting quick forming device; secondly, during a forming process, a mixture of 35-45% of nitrogen and 55-65% of argon is input by the flow rate of 3-5 liter per minute at the same time, a self-propagating high-temperature synthetic reaction is performed on the titanium and the nitrogen under the temperature ranging from 1220 DEG C to 1480 DEG C so as to generate titanium nitride, and titanium carbide is generated through the reaction of the titanium and the carbon in graphite under the temperature ranging from 1260 DEG C to 1523 DEG C under the argon condition; thirdly, the titanium nitride and the titanium carbide generated from the reactions are melted with the titanium alloy component as an organic whole; fourthly, the formed titanium alloy component is subjected to segmental cooling. Through adopting the technical scheme of the method, the generated titanium alloy component has better abrasive resistance and corrosion resistance, and besides, the fact that the film layers of the traditional titanium nitride and titanium carbide composite coatings are easy to peel off from the titanium alloy is avoided, and the surface of the titanium alloy is not needed to be subjected to coating and anticorrosive treatment additionally, so that the cost is saved, and no other additional processing procedures are required.
Owner:南京博乔机械有限公司
Semiconductor device with metal gate and high-k tantalum oxide or tantalum oxynitride gate dielectric
ActiveUS7060571B1Reduce leakage currentReduce thermal instabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricOxygen
Microminiaturized semiconductor devices are fabricated with a replacement metal gate and a high-k tantalum oxide or tantalum oxynitride gate dielectric with significantly reduced carbon. Embodiments include forming an opening in a dielectric layer by removing a removable gate, depositing a thin tantalum film, as by PVD at a thickness of 25 Å to 60 Å lining the opening, and then conducting thermal oxidation, as at a temperature of 100° C. to 500° C., in flowing oxygen or ozone to form a high-k tantalum oxide gate dielectric layer, or in oxygen and N2O or ozone and N2O ammonia to form a high-k tantalum oxynitride gate dielectric. Alternatively, oxidation can be conducted in an oxygen or ozone plasma to form the high-k tantalum oxide layer, or in a plasma containing N2O and oxygen or ozone to form the high-k tantalum oxynitride gate dielectric layer.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
High wear resistance, high toughness titanium carbide base hard alloy capable of welding
A carbonized hard Ti-base alloy with high weldability, anti-wear nature and toughness is prepared proportionally from the hard phase (TiC or the mixture of TiC and WC), adhesive phase chosen from Ni, Co and Fe, Cu and Mn or Mn compound, C, tantalum carbonate and / or niobium carbonate, V or V compound, Cr or Cr compound, and Mo or Mo compound.
Owner:帅进 +1
Ultra-fine hard alloy coated powder and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101186990AReduced tendency to aggregate and growWell mixedLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingCarbonizationTitanium carbide
The invention discloses a super-fine cemented carbide coating powder and process of preparation thereof. Super-fine hard-phase carbonization tungsten in the cemented carbide coating powder and other carbides such as titanium carbide, tantalum carbide, niobium carbide, vanadium carbide and / or chromium carbide are composed around by cobalt-phase ultra-fine powder particles. Karl Fischer's mean particle size of the super-fine cemented carbide coating powder is <=1 mu m. The super-fine tungsten carbide of the invention is put into the liquor of water-soluble metal cobalt-salt after being activated and dispersed with other hard-phase of carbide powder, the super-fine carbide powder and other hard-phase of carbide powder are taken as the core, chemical coprecipitation coating is employed in the reaction, and a uniform cobalt carbonate or cobalt hydroxide inhibitory coating is formed on the surface of the tungsten carbide powder and other hard-phase of carbide powder. The coprecipitation coating powder can be made into the super-fine cemented carbide coating powder by filtering, washing, and drying and low temperature reduction. The invention has the advantages of simple technique and low cost, which can take place the existing cemented carbide wet grinding mixture and the preparation method. High quality super-fine cemented carbide can be prepared by utilizing the powder of the invention.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Erosion and corrosion resistant coating system for compressor
InactiveUS20110165433A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove erosion resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsBlade accessoriesCoating systemVanadium nitride
Process for providing a protective coating to a metal surface by applying a nickel or tantalum plate layer to the surface and dispersing particles of a hard material such as diamond, alumina, vanadium nitride, tantalum carbide and / or tungsten carbide within the nickel or tantalum plate layer as the plating is occurring.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
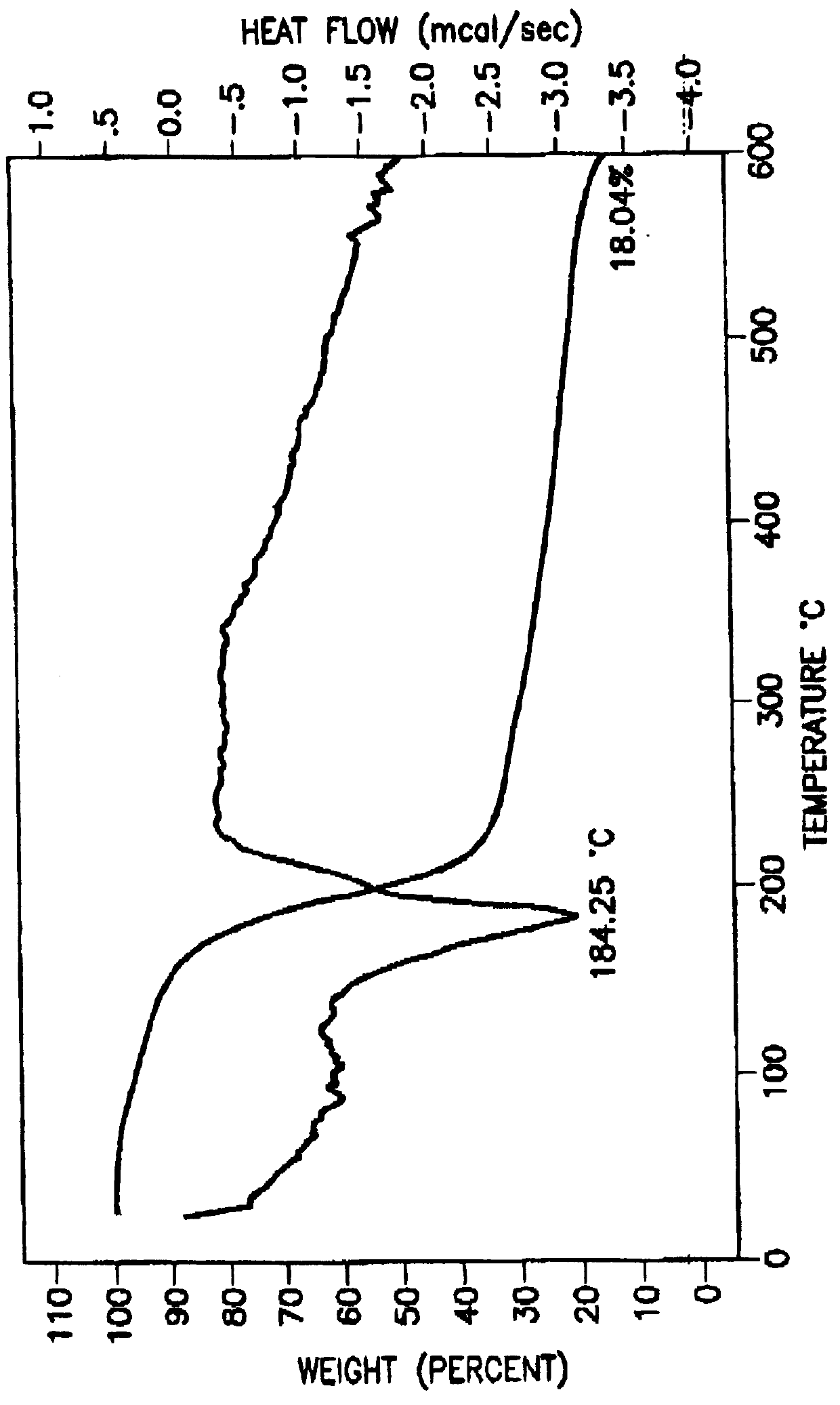
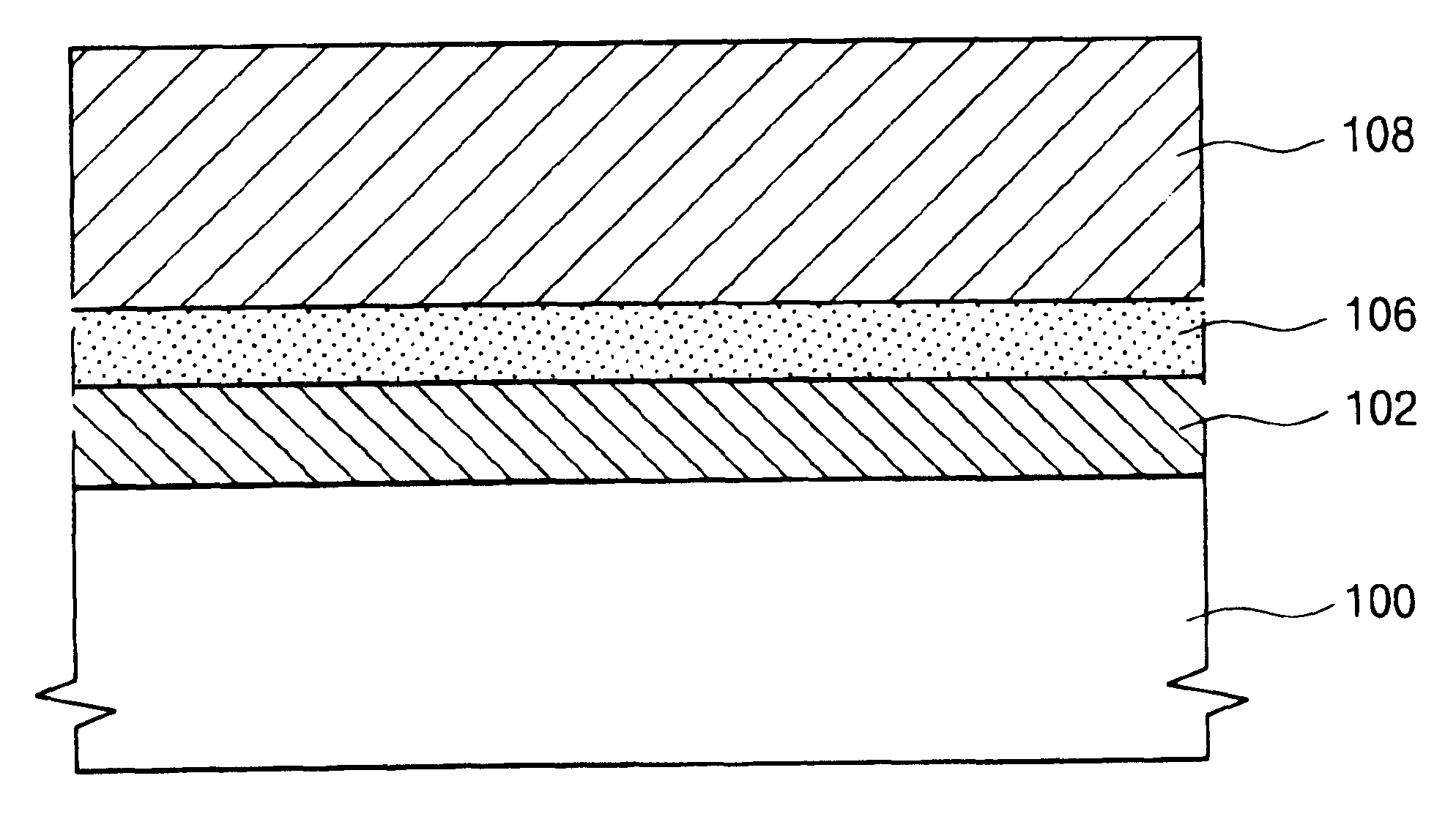
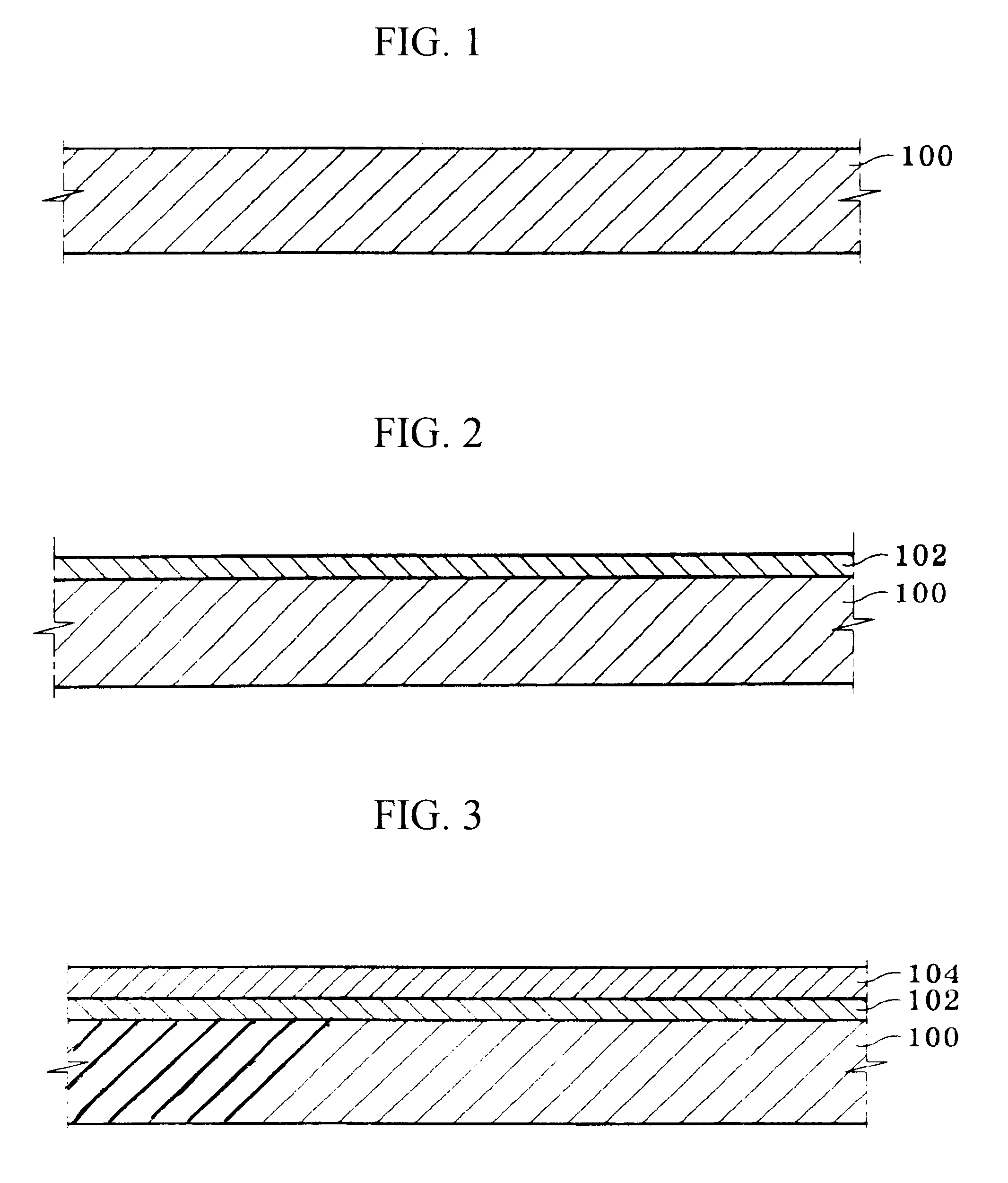
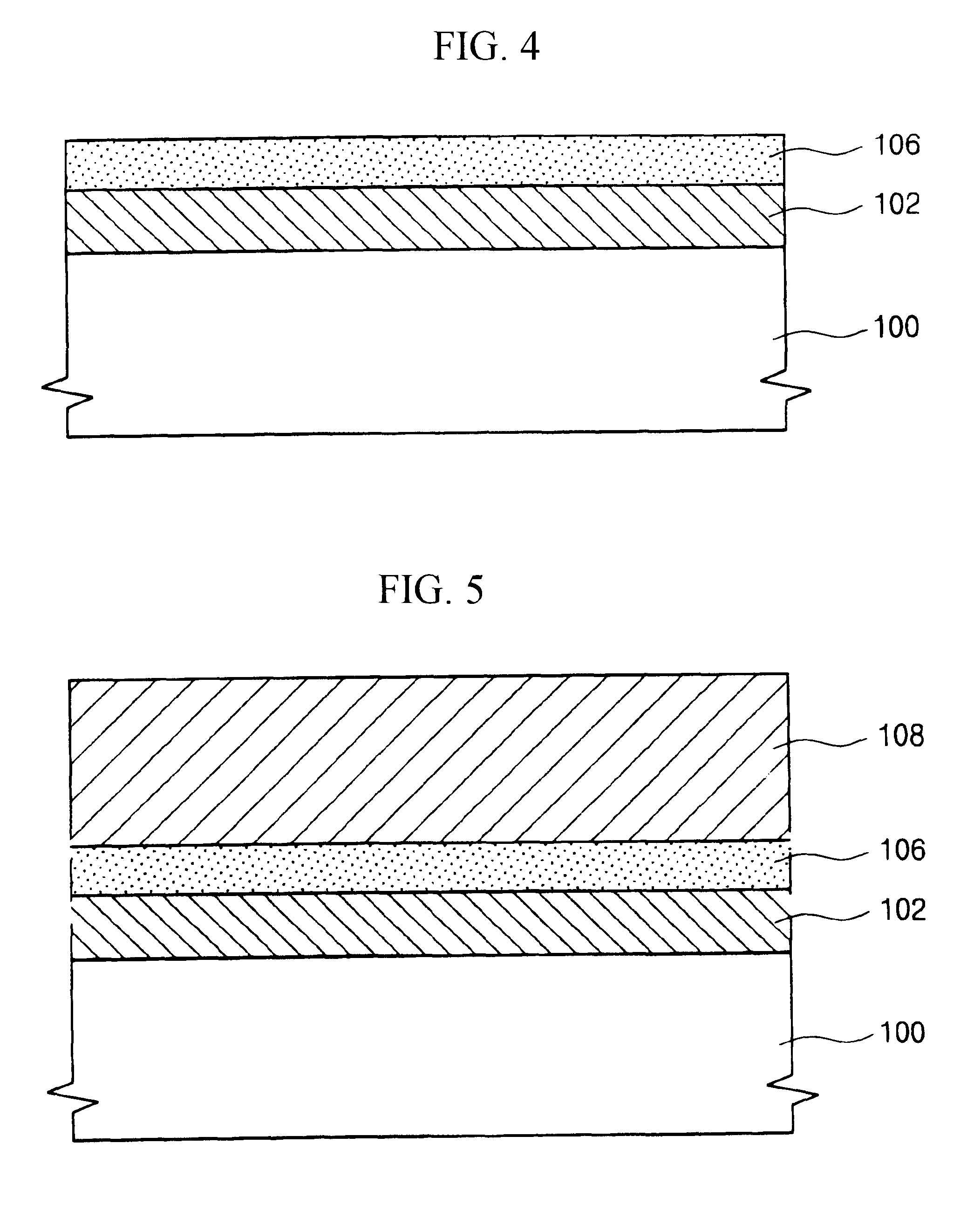
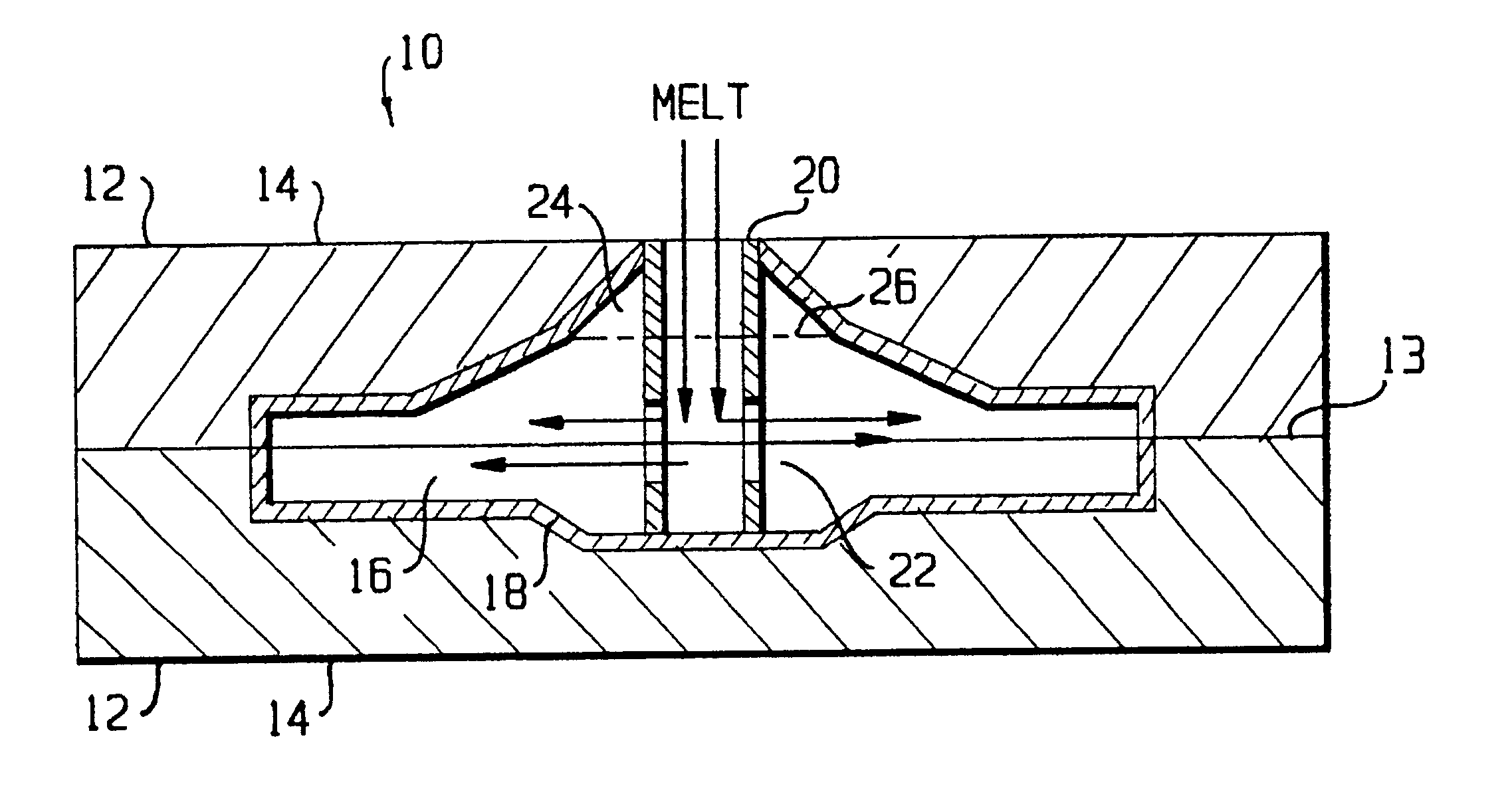
Tantalum carbide-covered carbon material and process for producing the same
This invention provides a tantalum carbide-covered carbon material, which has excellent corrosion resistance to reducing gases and thermal shock resistance at high temperatures, and a process for producing the same. The tantalum carbide-covered carbon material comprises a carbon base material and a covering film provided on the carbon base material directly or through an intermediate layer. The covering film is formed of a large number of densely aggregated fine crystals of tantalum carbide. Preferably, the covering film exhibits such an X-ray diffraction pattern that the diffraction intensity based on (220) face of tantalum carbide is the highest intensity. More preferably, this diffraction intensity is not less than four times higher than the second highest diffraction intensity.
Owner:TOYO TANSO KK
Method for forming a tantalum oxide capacitor
InactiveUS6551873B2Improve featuresEnhance layeringTransistorSolid-state devicesMetallurgyAtomic layer deposition
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Castings of metallic alloys with improved surface quality, structural integrity and mechanical properties fabricated in titanium carbide coated graphite molds under vacuum
Molds are fabricated having a substrate of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, and having a mold cavity coated with titanium carbide. The molds may be made by making the substrate (main body) of high density, high strength ultrafine grained isotropic graphite, by, for example, isostatic or vibrational molding, machining the substrate to form the mold cavity, and coating the mold cavity with titanium carbide via either chemical deposition or plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition, magnetron sputtering or sputtering. The molds may be used to make various metallic alloys such as nickel, cobalt and iron based superalloys, stainless steel alloys, titanium alloys and titanium aluminide alloys into engineering components by melting the alloys in a vacuum or under a low partial pressure of inert gas and subsequently casting the melt in the graphite molds under vacuum or low partial pressure of inert gas.
Owner:SANTOKU CORP
Ceramic material suitable for repair of a space vehicle component in a microgravity and vacuum environment, method of making same, and method of repairing a space vehicle component
A precursor of a ceramic adhesive suitable for use in a vacuum, thermal, and microgravity environment. The precursor of the ceramic adhesive includes a silicon-based, preceramic polymer and at least one ceramic powder selected from the group consisting of aluminum oxide, aluminum nitride, boron carbide, boron oxide, boron nitride, hafnium boride, hafnium carbide, hafnium oxide, lithium aluminate, molybdenum silicide, niobium carbide, niobium nitride, silicon boride, silicon carbide, silicon oxide, silicon nitride, tin oxide, tantalum boride, tantalum carbide, tantalum oxide, tantalum nitride, titanium boride, titanium carbide, titanium oxide, titanium nitride, yttrium oxide, zirconium, diboride, zirconium carbide, zirconium oxide, and zirconium silicate. Methods of forming the ceramic adhesive and of repairing a substrate in a vacuum and microgravity environment are also disclosed, as is a substrate repaired with the ceramic adhesive.
Owner:COI CERAMICS
Ultrafine cemented carbide coating blade suitable for numerical control machining center and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103801746AHigh hardnessImprove flexural strengthMilling cuttersTurning toolsChromium carbideNumerical control
The invention provides an ultrafine cemented carbide coating blade suitable for a numerical control machining center, the ultrafine cemented carbide coating blade is prepared from the following components by weight: 0.5-2% of tantalum carbide, 0.5-2% of chromium carbide, 0-0.5% of niobium carbide, 6-10% of cobalt and the balance of ultrafine tungsten carbide, and the invention also provides a manufacturing method of the ultrafine cemented carbide coating blade. The manufacturing method of the ultrafine cemented carbide coating blade is low in cost, and the manufactured ultrafine cemented carbide coating blade is excellent in performance, stable in quality, and suitable for the numerical control machining center, satisfies ever-growing market demands of mechanical processing industry of the numerical control machining center, and gradually replaces expensive imported products.
Owner:HUNAN RUIFENG CEMENTED CARBIDE PROD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com