Patents
Literature
474 results about "Impact loading" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
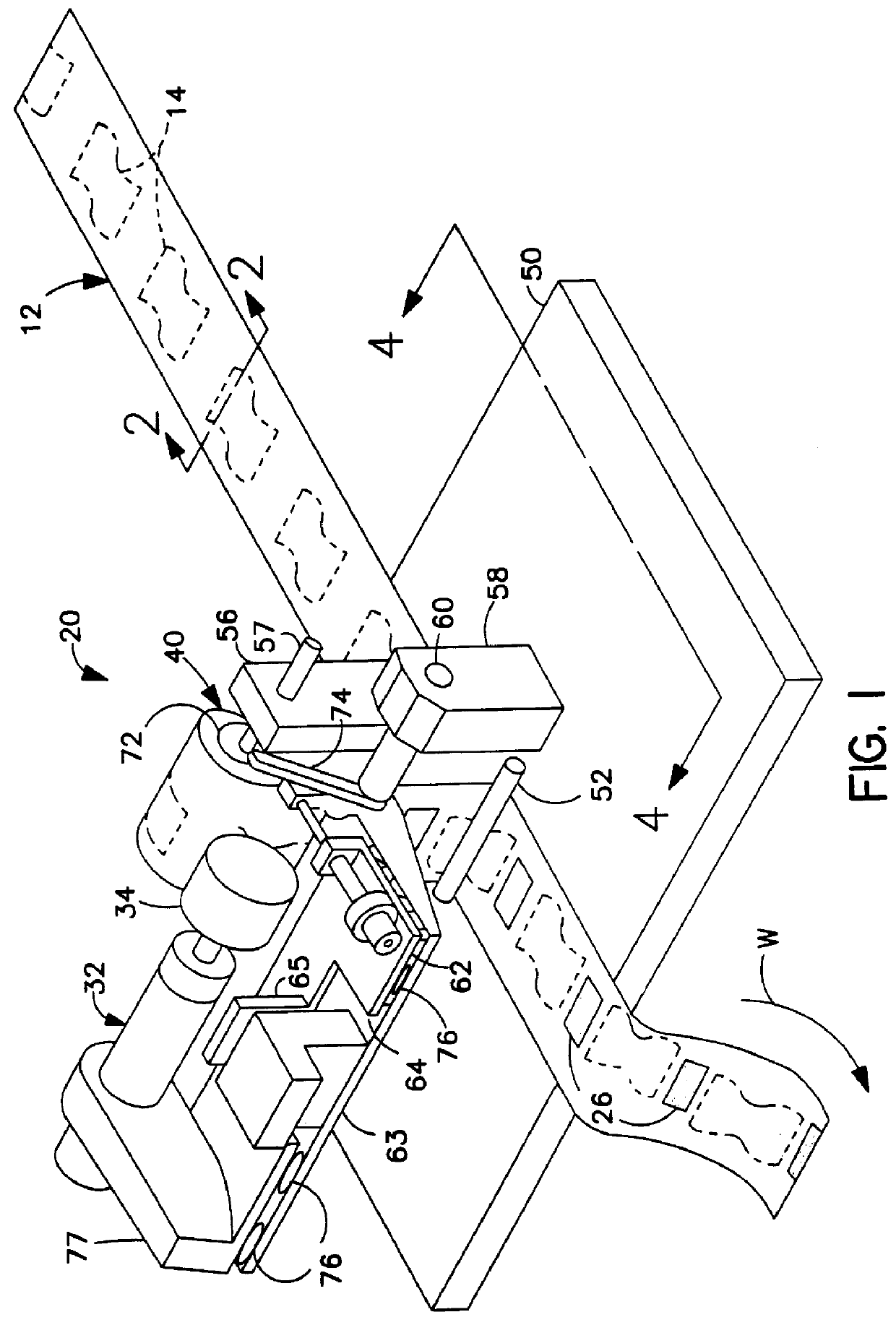
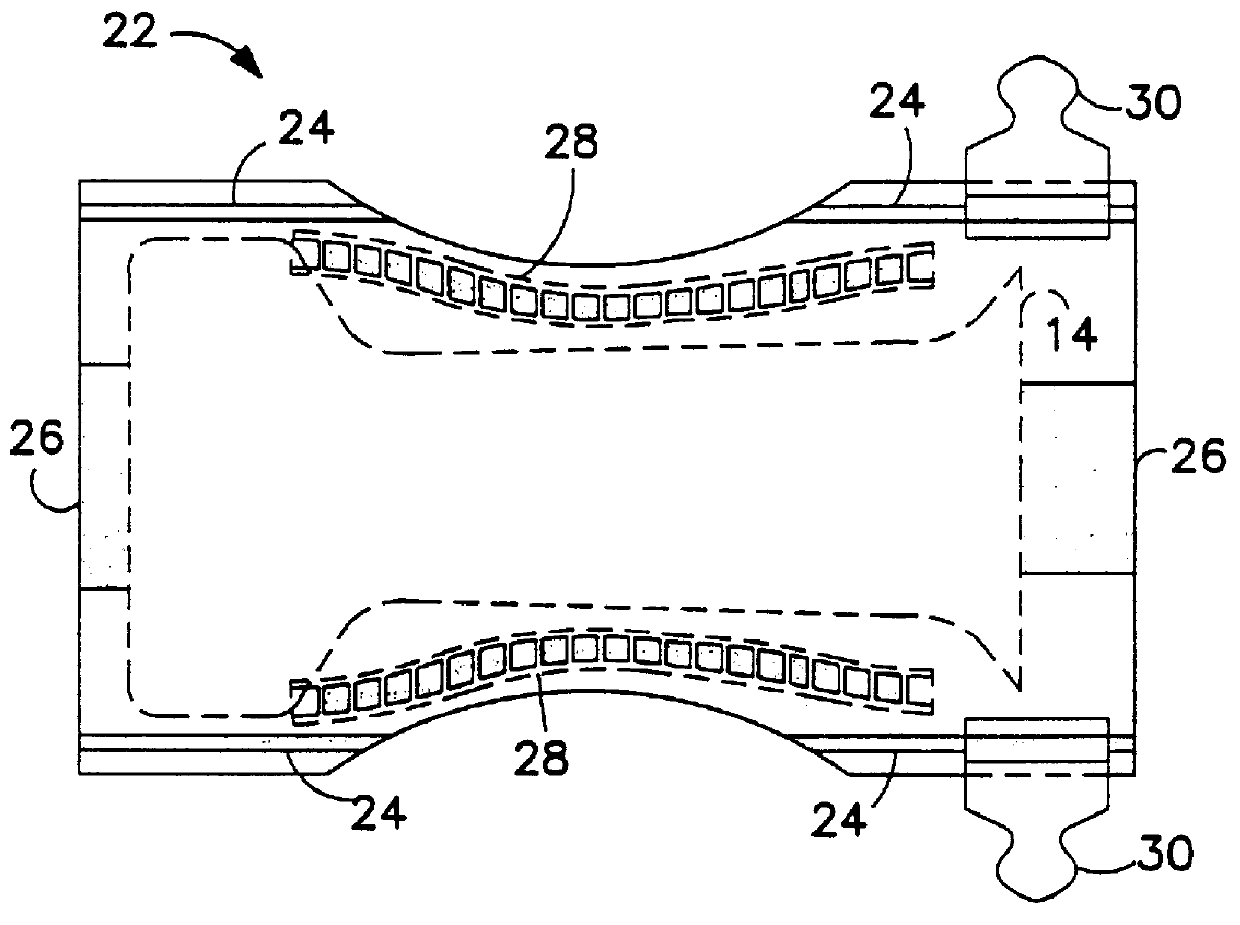
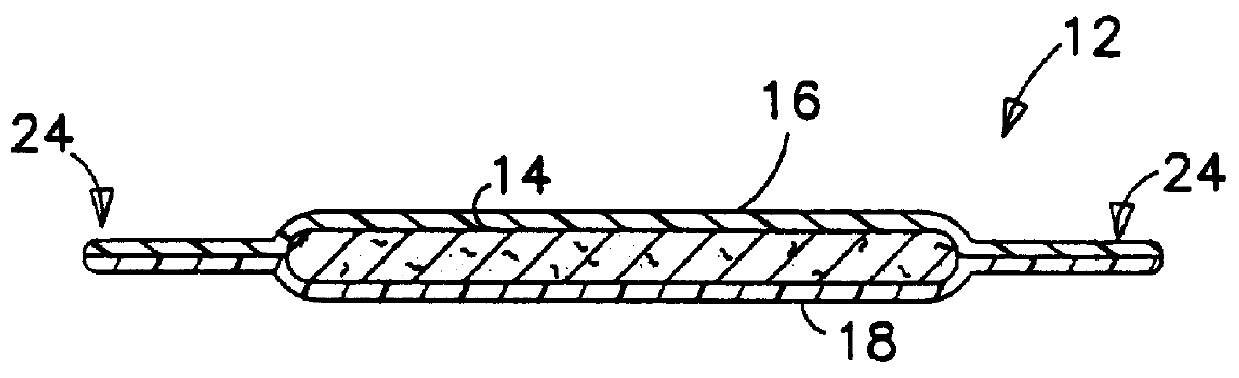
Methods and apparatus for intermittent rotary ultrasonic bonding system
InactiveUS6123792AAvoids deleterious bounceExtended service lifeLaminationLamination apparatusFiberSurface velocity
This invention relates to apparatus and methods for intermittently bonding a substrate web in fabricating a blank subassembly for an absorbent article. The invention comprises ultrasonic bonding apparatus including an anvil roll, a substrate web thereon, and at least one rotary ultrasonic horn. The substrate web can comprise at least first and second layers of material. The rotary ultrasonic horn, in combination with the anvil roll, ultrasonically bonds intermittent segments of the first and second layers of the substrate web to each other. Such intermittent bonds can comprise end seals for the absorbent articles. The ultrasonic horn and anvil roll are periodically separated from each other to provide the intermittent bonding of the substrate web. An actuator apparatus periodically moves the anvil roll and ultrasonic horn from engaging contact with each other preventing bond formation. The actuator apparatus can include a cam mechanism moving one of the anvil roll and ultrasonic horn from engaging contact with the other during rotation of the rotary ultrasonic horn. The cam mechanism can create a physical gap between the ultrasonic horn and the anvil roll. The cam mechanism moves either the ultrasonic horn and the anvil roll toward the other of the ultrasonic horn and anvil roll at a velocity of no more than about 80 millimeters / second to prevent bounce or impact loading when the horn and anvil roll are in engaging contact. The anvil roll comprises a substrate-receiving surface generally moving the substrate web through the nip at a surface speed of at least 300 meters per minute. The ultrasonic system generally creates bonds between the first and second layers of the substrate web at least about 600 times per minute.
Owner:DUKANE IAS LLC
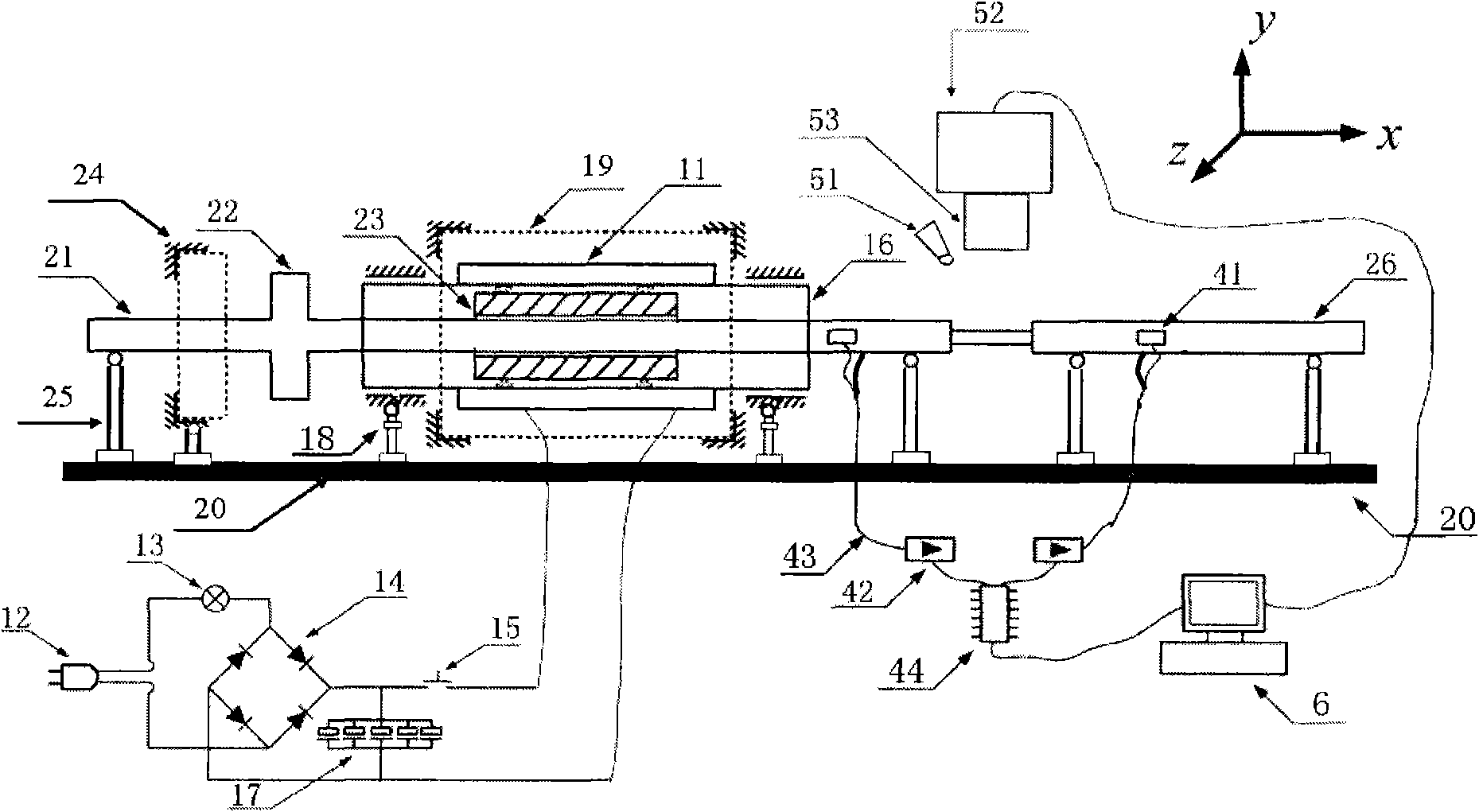
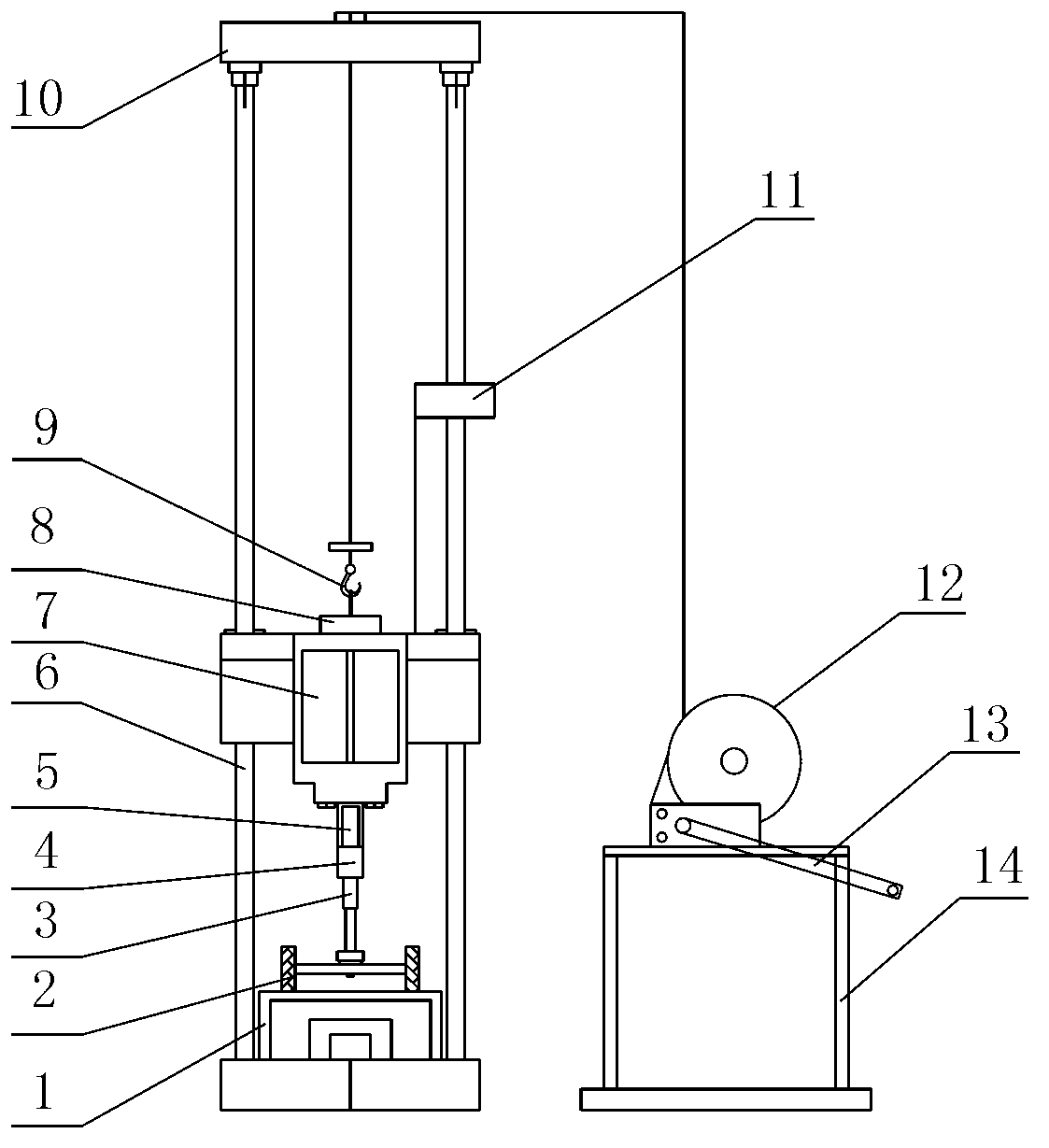
System and method for performing impact loading on micro test piece and measuring dynamic mechanical property
InactiveCN102135480ASolve the study of dynamic mechanical properties at high strain ratesLaunch fastStrength propertiesFerroelectric thin filmsStress–strain curve
The invention relates to a system and a method for performing impact loading on a micro test piece and measuring dynamic mechanical property. The method comprises the following steps of: instantly accelerating a bullet by using an electromagnetic pulse launch technology and launching the bullet at high speed; transmitting a stretching stress wave generated by collision of the bullet to the micro test piece by using a separated Hopkinson bar technology so as to generate the impact loading on the micro test piece; recording strain data of an input bar and an output bar, and acquiring an enlarged surface dynamic deformation image of the micro test piece; analyzing and obtaining a stress strain curve of the micro test piece subjected to the impact loading having different strain rates; and analyzing the surface dynamic deformation image of the micro test piece and obtaining a distribution of a bidimensional displacement field and a strain field during dynamic impact loading of the micro test piece. By the system and the method, the problem of research on the dynamic mechanical property of a micro electro mechanical system (MEMS), and membrane materials such as piezoelectric thin films, ferroelectric thin films and the like is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
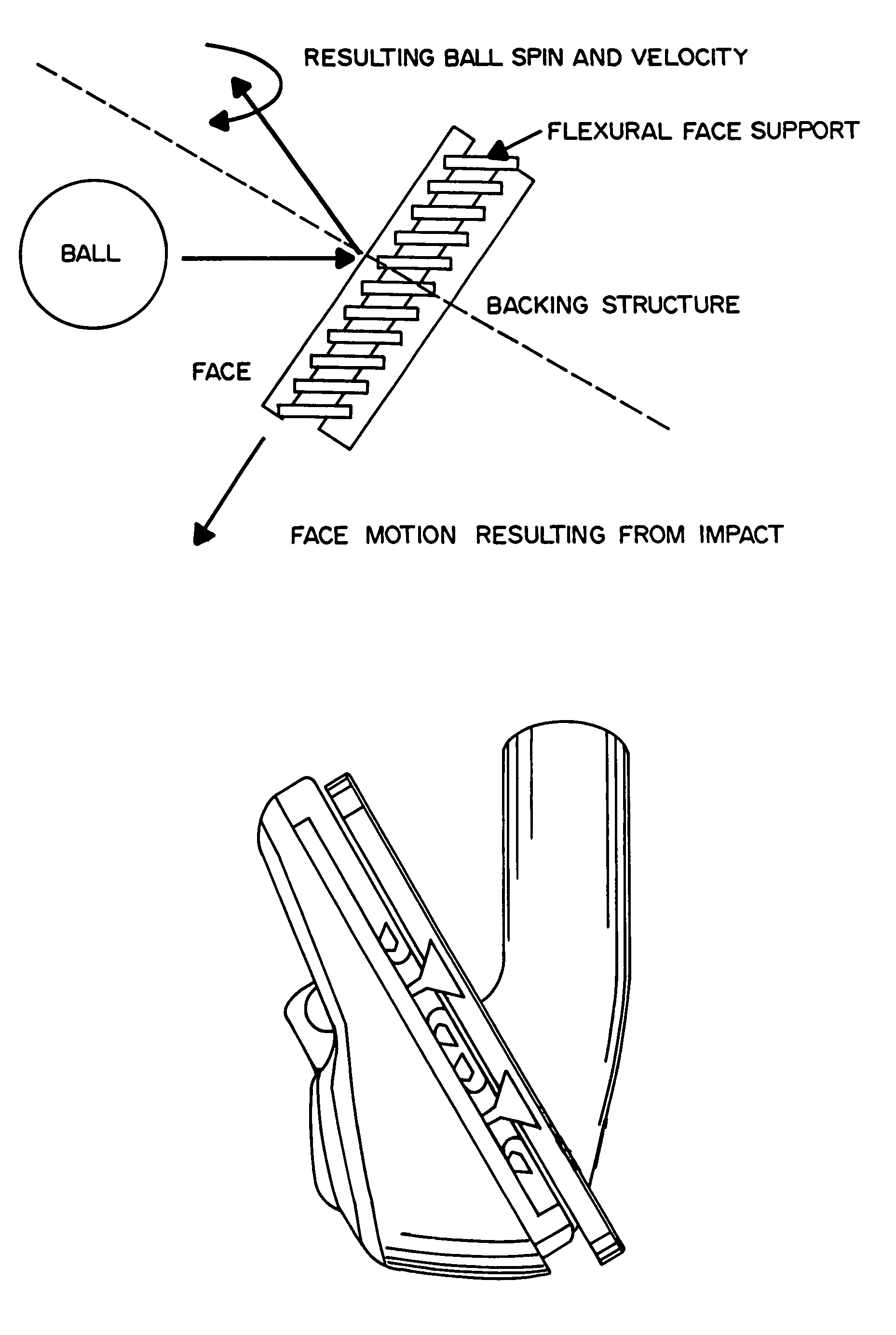
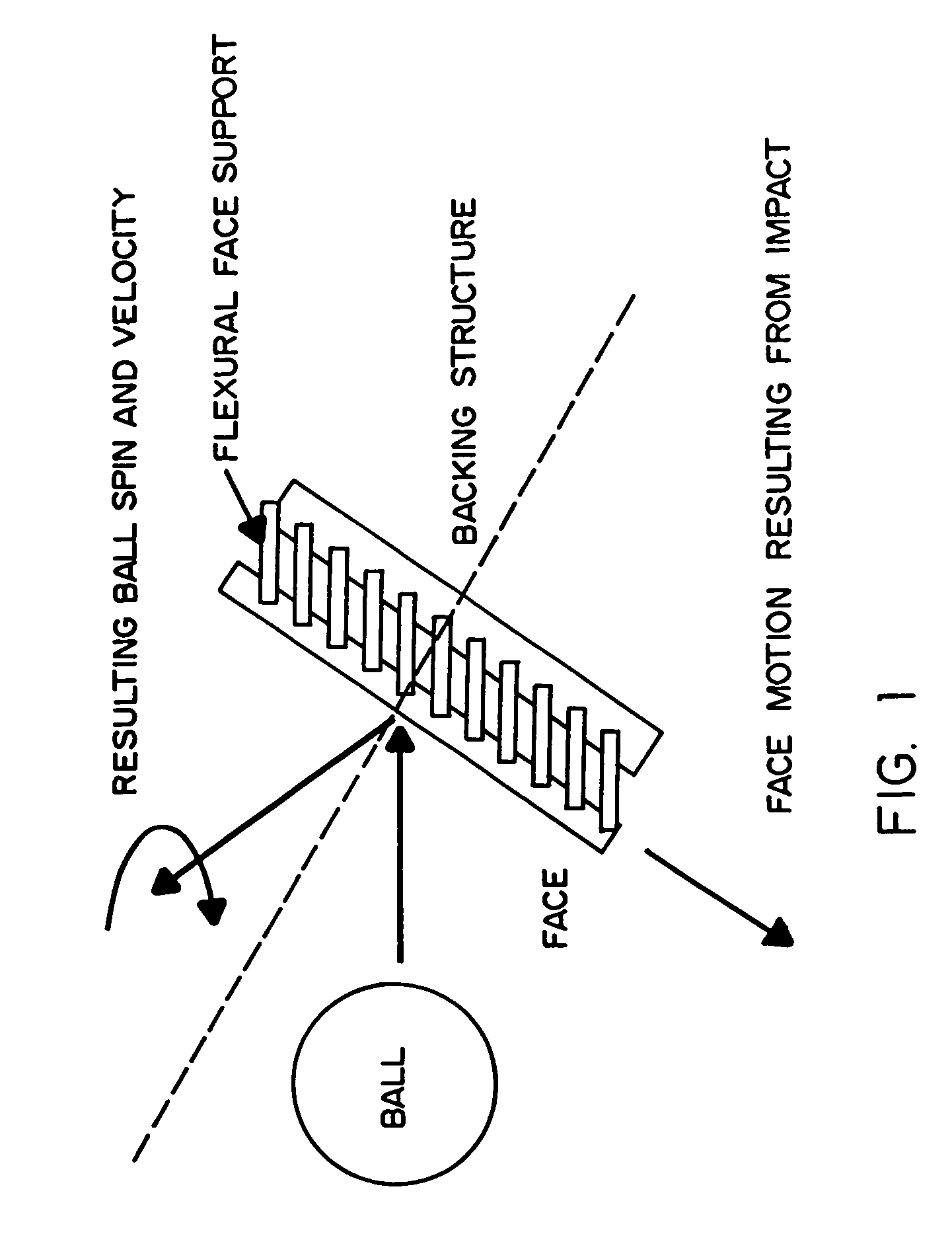
Method and apparatus for elastic tailoring of golf club impact
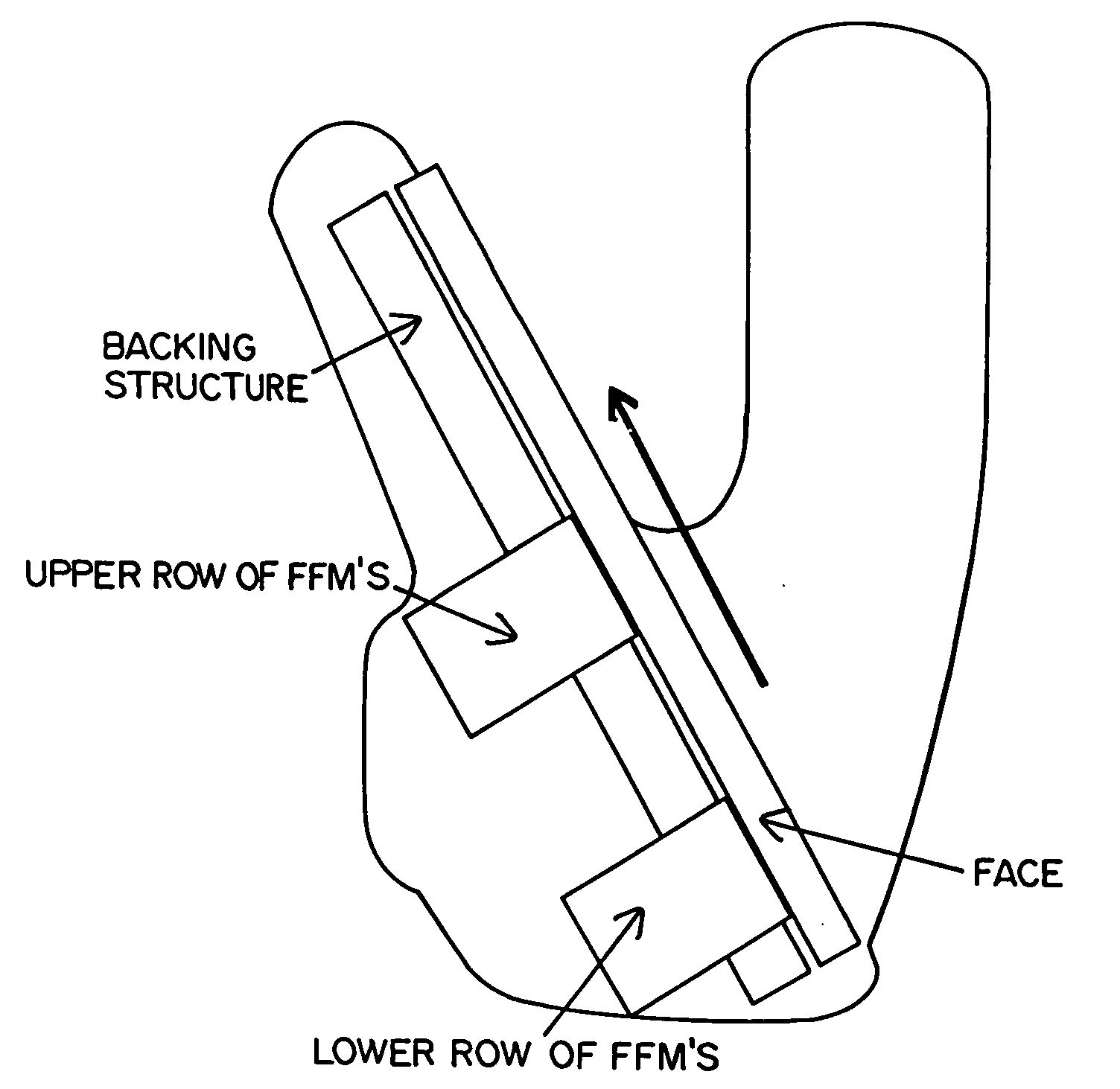
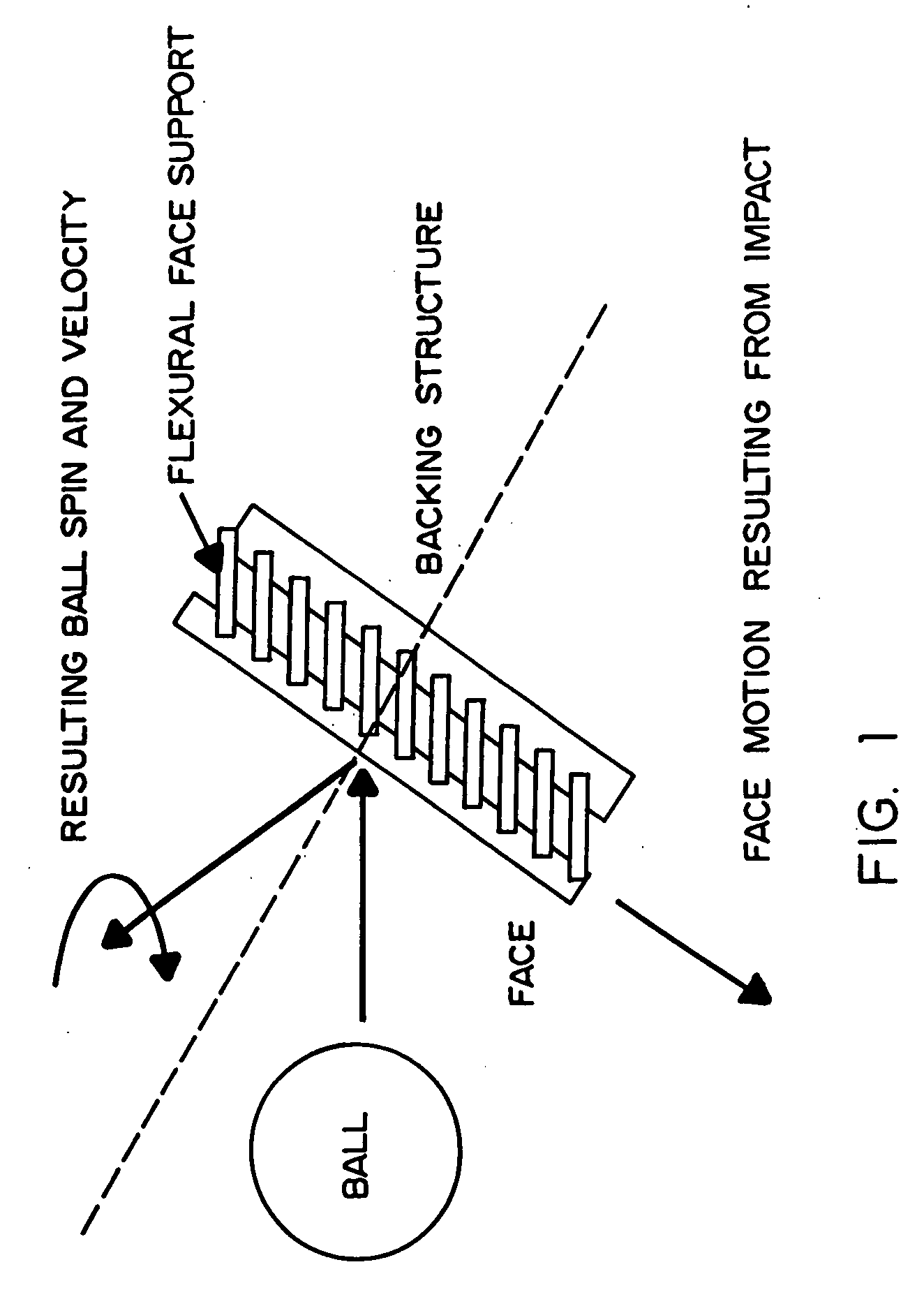
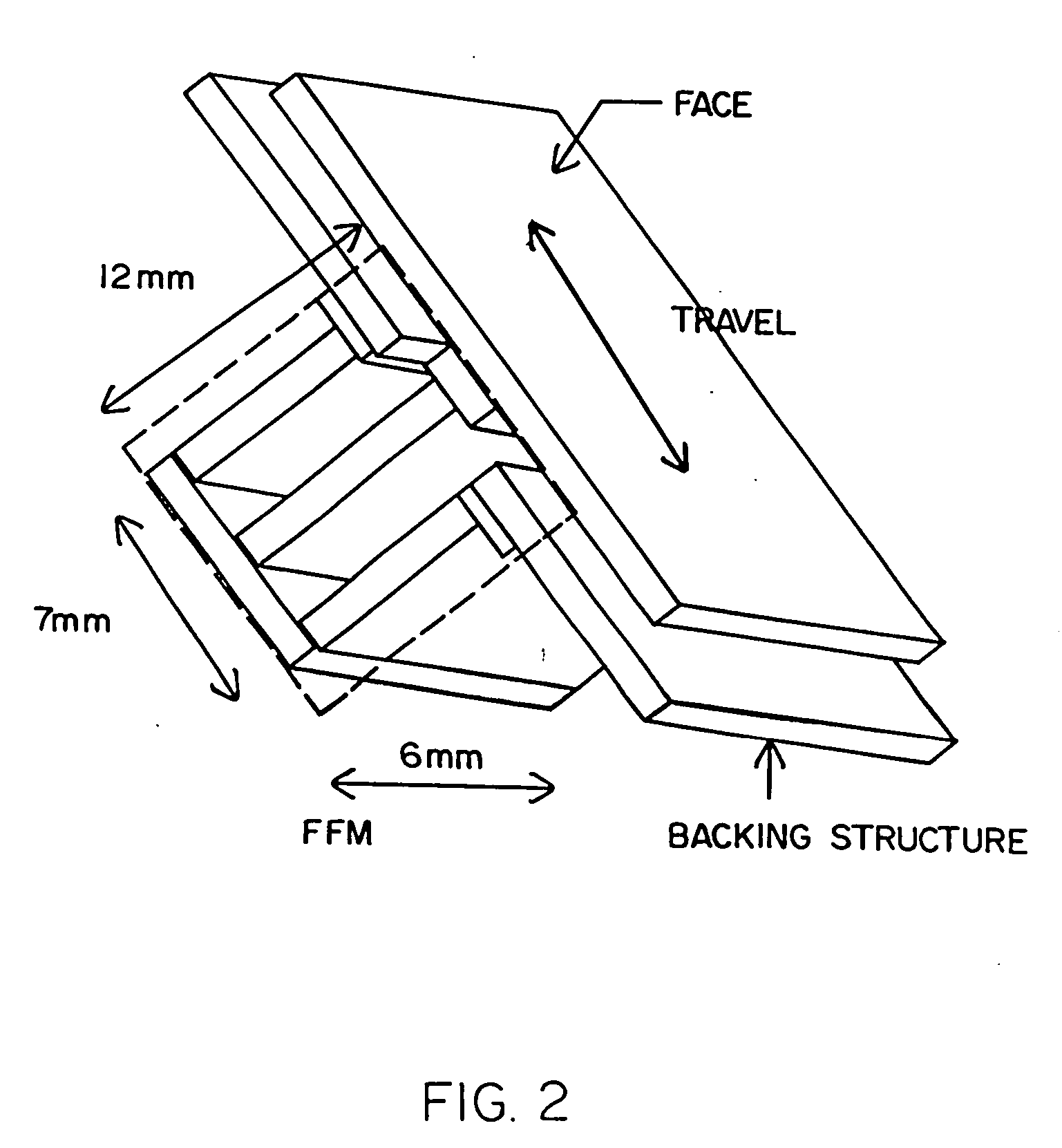
A method and apparatus for beneficially controlling the impact between a club head and a golf ball are described. A golf club head (such as on a driver, iron, or putter) has a body and a face mechanically supported thereon, wherein the face and body are elastically tailored to create beneficial face motion and deformation at impact. The tailored clubhead compliance is shown to influence impact properties and resulting ball parameters such as speed, direction and spin rates resulting from the impact event between the face of the club and the golf ball. Several embodiments are presented for controlling ball spin through design of the elastic and dynamic response of the face and body under impact loading.
Owner:HEAD TECHNOLOGY GMBH LTD
Corrugated steel deck system including acoustic features
ActiveUS20070000198A1Solve the slow construction speedReduce laborCeilingsCovering/liningsCarrying capacityEngineering
The present invention relates to a sound rated floor system for inhibiting sound transmission between floors. The system includes a corrugated steel deck; a first layer of cementitious material or board or sheet applied over the corrugated steel deck; a sound insulation mat or board applied over the first layer; a second layer of cementitious material applied over the sound insulation mat or board. The floor system has an IIC rating of at least 25 and the corrugated steel deck provides at least 50 percent of the ultimate load carrying capacity under static and impact loading of the floor system with a floor deflection of at most 1 / 360 of the floor span.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Multi-field coupled coal rock impact loading experimental device and method
ActiveCN103454164AResource securityEffective recoveryMaterial strength using single impulsive forceMulti fieldAmbient pressure
The invention relates to a multi-field coupled coal rock impact loading experimental device and method. The experimental device comprises an axial static pressure loading device, an axial static pressure loading hydraulic oil pump, an axial static pressure oil delivery pipe, an ambient pressure loading hydraulic oil pump, an ambient pressure loading oil delivery pipe, a radial ambient pressure loading device, a gas tank, a gas inlet pipe, a gas pressure regulating valve, an air extracting pump, a gas sensor, a gas outlet pipe, a cold and hot dual-purpose compressor, a servo oil pump and a cold and hot dual-purpose oil delivery pipe. By using the experimental device and method, a coal rock sample can be in a multi-field coupling state and the condition that the coal rock sample is in axial static loading, radial ambient pressure static loading, gas pressure and temperature coupling states, so that an experiment can be carried out aiming to the dynamic loading conditions.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Seat swivel with brake for infinite rotational position adjustment
A seat swivel for providing angular adjustment of a seat to an infinite number of rotational positions with respect to a seat base. The seat swivel includes a swivel assembly having a swivel plate rotatably supported between a pair of fixed plates, the swivel plate being adapted to be affixed to the seat and the fixed plates being adapted to be affixed to a seat base. The seat swivel further includes a brake assembly having a mechanism for releasably retaining the seat in any one of the infinite number of positions when the seat is subjected to a first dynamic impact loading, the mechanism being either mechanically or electrically actuated, the mechanism being adapted to withstand a dynamic impact loading of up to about 16 g in at least one rotational position of the seat.
Owner:BE AEROSPACE INCORPORATED
Laser direct-compounding micro-plastic forming device and method
InactiveCN102029317APrecise and controllable parametersGood repeatabilityLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingPunching
The invention discloses a laser direct-compounding micro-plastic forming device and method, belonging to the technical field of parts of a laser processing micro-electromechanical system (MEMS). The device comprises a laser loading system, a forming system and a control system. The method comprises the following steps: laser penetrates through a restraint layer after being focused by lens and acts on an energy-absorbing layer; the energy-absorbing layer absorbs the laser energy; a high pressure and high temperature plasmasphere is formed in a very short period of time and sprayed outward quickly; the expanded plasmas are limited by the restraint layer, so that the plasma pressure increases quickly and causes impact loading on a workpiece; the workpiece is extruded between the restraint layer and a compound micro-mould, so that the workpiece generates plastic deformation and copies the appearance of the compound micro-mould; and a compound process of stretching, punching and trimming a target workpiece is realized in one impact forming process by a stretching female mould, a trimming female mould and a punching male mould which are arrayed on the compound micro-mould, and simultaneously workpieces can be formed in batch.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Triaxial impact ground pressure true simulation test system
InactiveCN103471914AReduce intensityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using single impulsive forceEngineeringHigh stress
The invention discloses a triaxial impact ground pressure true simulation test system. The triaxial impact ground pressure true simulation test system is characterized by comprising a flexible loading unit, a confining pressure loading unit and an impact loading unit, wherein the flexible loading unit is used for applying vertical pressure on a test piece through a loading oil cylinder and a counterforce steel strand, the confining pressure loading unit is used for enabling the test piece to be under the condition of triaxial stress, the impact loading system is used for applying impact load on the test piece, the test piece is destroyed under the conditions of high stress and impact disturbance, the strength of the test piece is reduced, the test piece generates a certain displacement, in the process, the counterforce steel strand in the flexible loading unit is used for quickly supplementing load to the test piece, and further the extrusion and the action of external surrounding rocks to coal and rock masses are simulated. The triaxial impact ground pressure true simulation test system can be used for well simulating the occurring conditions of impact ground pressure, and the triaxial loading conditions are especially applicable to the simulation of gravity type impact ground pressure in a mining roadway.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Valve body with integral seal retention groove
InactiveUS7222837B1Easy to makeLittle finish machiningCheck valvesEqualizing valvesInterior spaceEngineering
A valve body having at least one internal hollow or space comprises two separately formed portions joined by at least one cylindrical web. Internal space may communicate with space outside the valve body via a fluid passage, and internal space may be filled with a substantially incompressible flowable substance to facilitate pressure equalization across the valve body. Forging or casting valve body portions to near-net-shape prior to joining minimizes machining necessary to achieve a final desired shape. Increased valve durability and reduced metal wear arise from the reduced valve body weight and correspondingly reduced impact loading as the valve body moves to seal against a valve seat. A single-durometer or dual-durometer elastomeric seal may be cast and cured in place in a peripheral integral seal retention groove, coupled thereto in part through welding flash protruding into the groove and / or through at least one serration in the groove.
Owner:NOVATECH HLDG CORP
Corrugated steel deck system including acoustic features
ActiveUS7908810B2Solve the slow construction speedReduce laborCeilingsCovering/liningsCarrying capacityEngineering
The present invention relates to a sound rated floor system for inhibiting sound transmission between floors. The system includes a corrugated steel deck; a first layer of cementitious material or board or sheet applied over the corrugated steel deck; a sound insulation mat or board applied over the first layer; a second layer of cementitious material applied over the sound insulation mat or board. The floor system has an IIC rating of at least 25 and the corrugated steel deck provides at least 50 percent of the ultimate load carrying capacity under static and impact loading of the floor system with a floor deflection of at most 1 / 360 of the floor span.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Pressure relieved thread connection
Lubricant escape passages are formed in the threads used to connect one tubular body to another. The passages conduct trapped thread lubricant out of the threaded area to prevent the creation of high lubricant pressure that may damage or cause improper make up of the threaded connection. The passages may be grooves in the crests of the thread teeth and / or may be corner bevels on the thread teeth. In a conductor pipe or other pipe assembly using axially spaced internal and external seals at each axial end of the threaded area, the escape passages form a helical flow path through the engaged thread area. The external seal prevents the entry of corrosive fluids into the threaded area and the internal seal prevents leakage through the threaded area from within the conductor pipe. When the lubricant pressure increases excessively during assembly or impact loading of the connection, the lubricant escapes past the seals to prevent connection damage. When used with a wedge or other metal-to-metal thread engaging designs, the escape passages may be interrupted at some point intermediate their helical path to provide a pressure seal at the point of interruption. Relieving trapped lubricant from a wedge thread connection permits consistent final makeup positions that ensure optimal pressure sealing.
Owner:GRANT PRIDECO LP
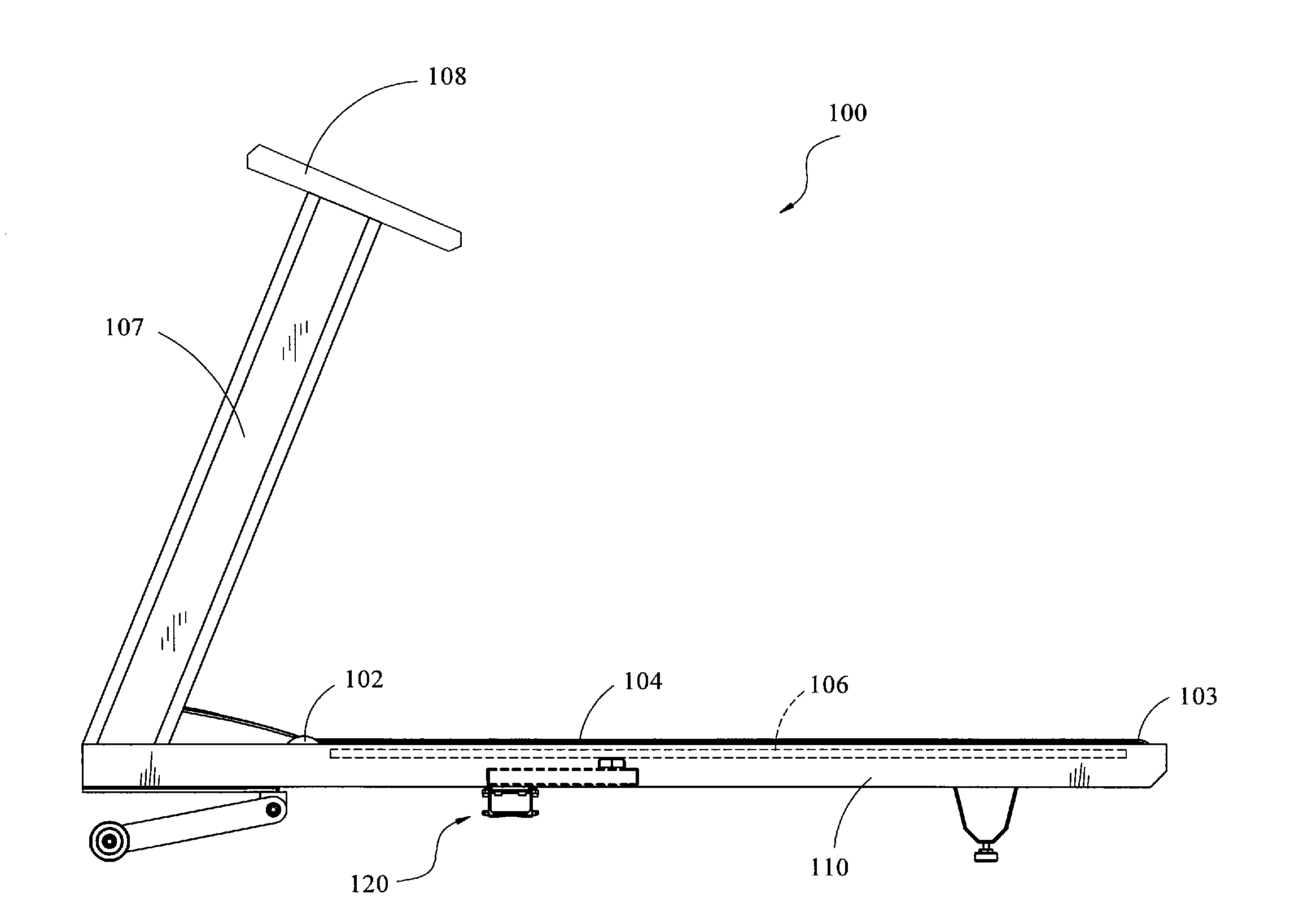
Treadmill with cushion assembly
InactiveUS7563205B2Increase shock loadTherapy exerciseMovement coordination devicesEngineeringImpact loading
A treadmill including a frame, an endless belt having an upwardly-exposed exercise section, a deck disposed underneath the exercise section of the belt, and a cushion assembly positioned between the deck and the frame for providing cushion in order to reduce high impact loads on the user's body. The cushion assembly comprises a lever having a first portion that is operably coupled to the deck and a second portion that is rotatably coupled to the frame. The cushion assembly also comprises a resilient member coupled to both the lever and the frame so that the resilient member resists rotation of the lever as the lever is rotated. The elastic deformation of the resilient member provides resistance to displacement of the deck and therefore creates a cushion effect on the user's feet, ankles and knees as the user's feet contact the belt.
Owner:JOHNSON HEALTH TECH
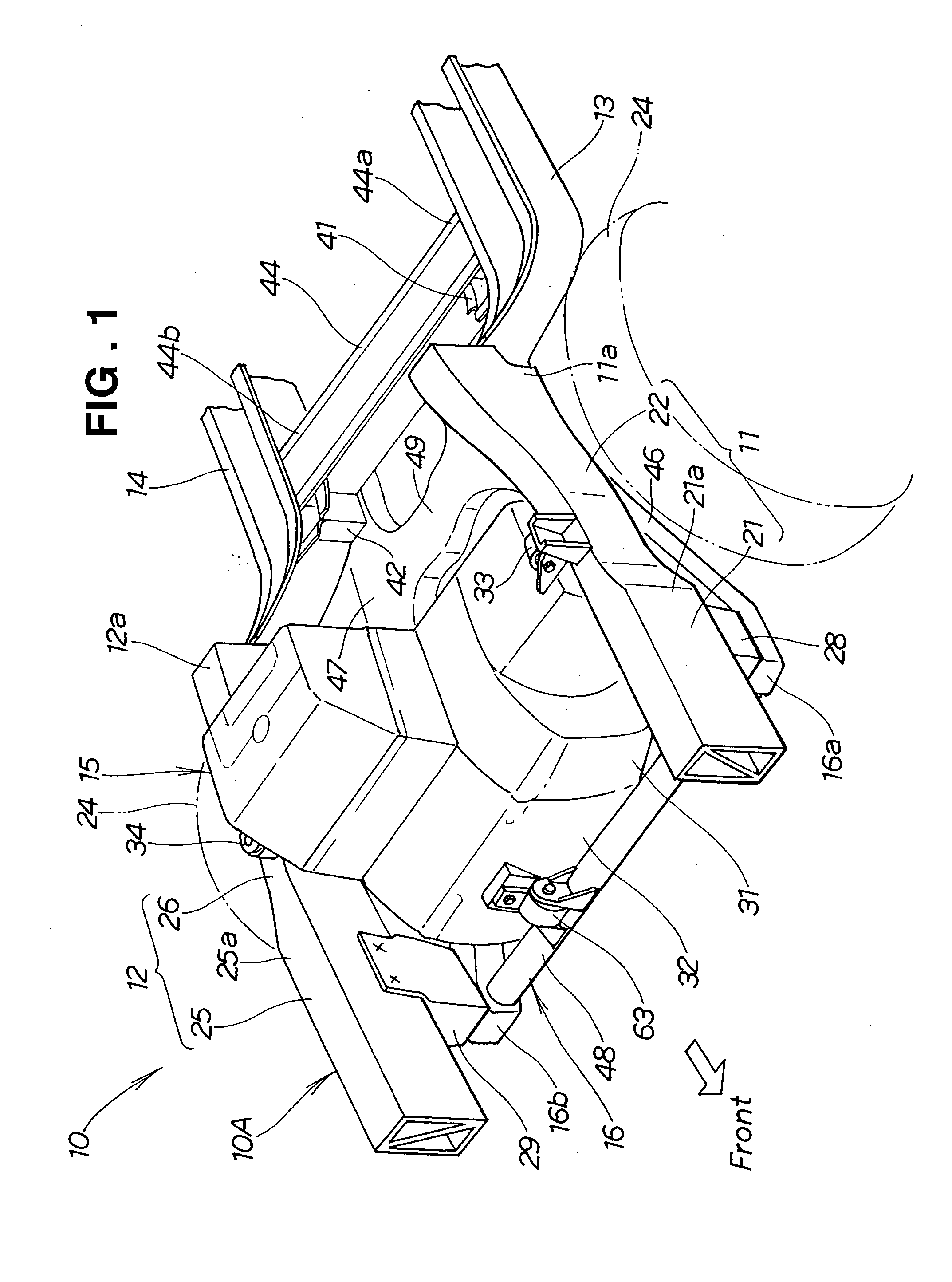
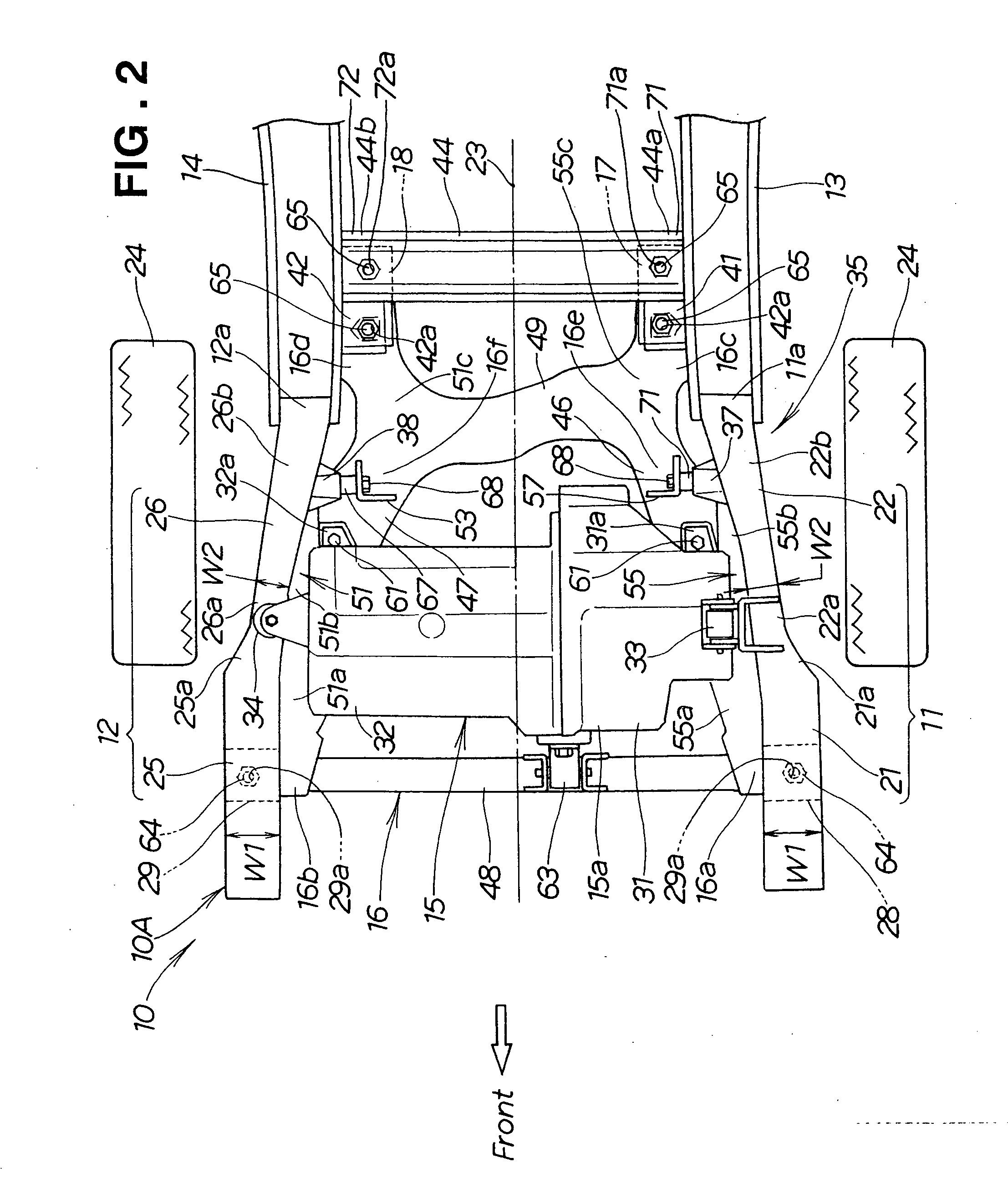
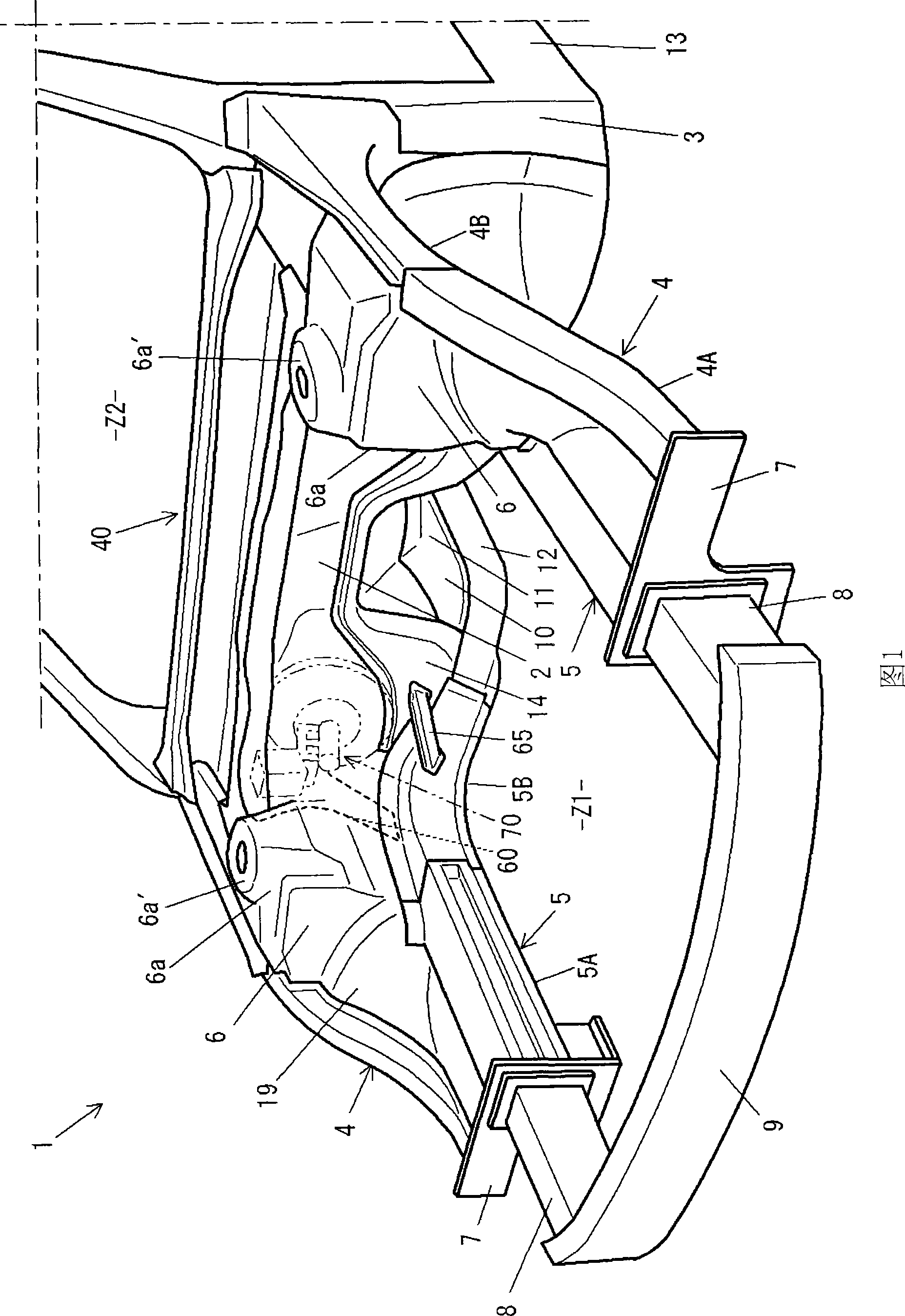
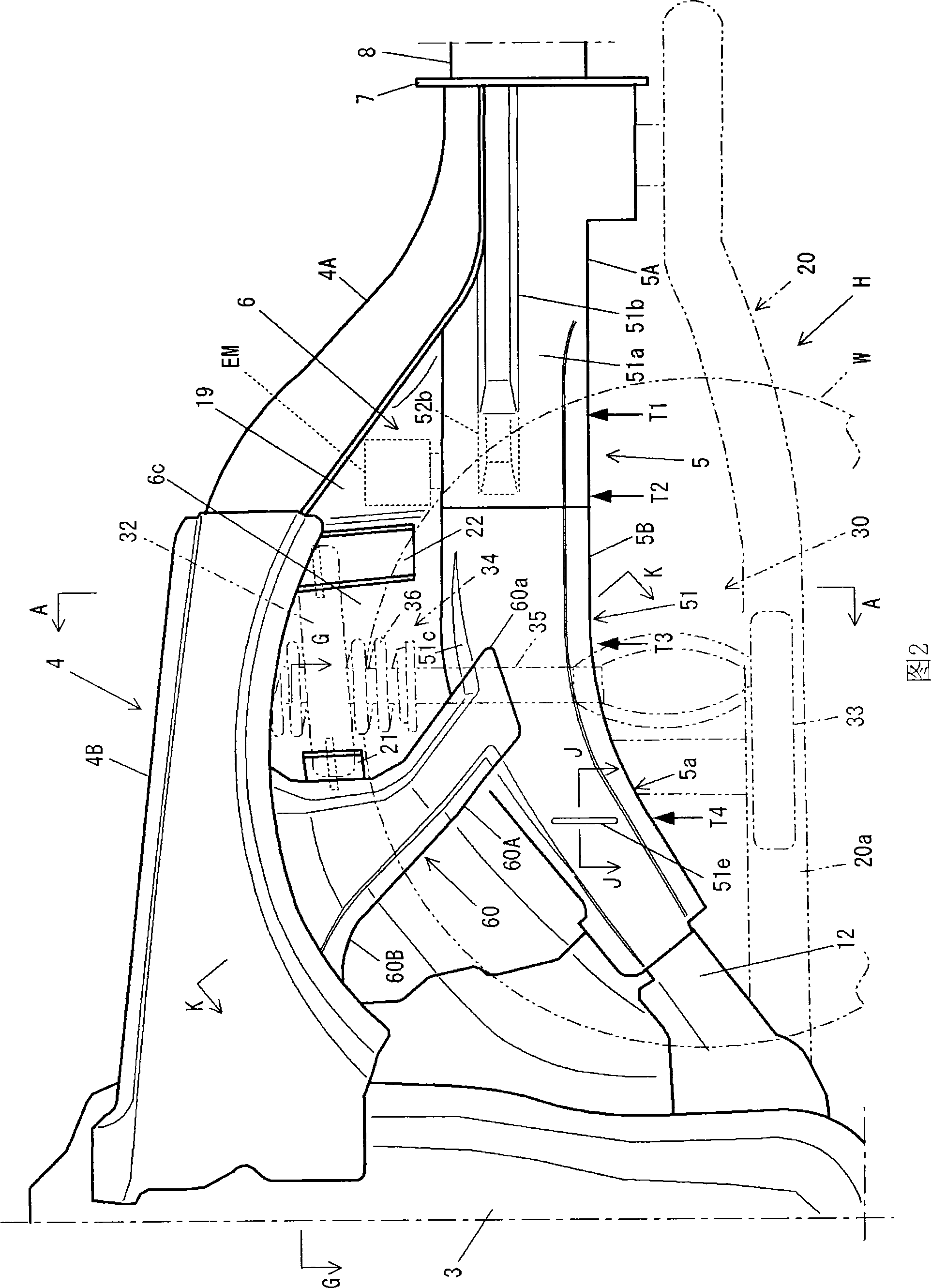
Front vehicle body structure
InactiveUS20060181071A1Reliable absorptionAvoid displacementSteering linkagesUnderstructuresEngineeringImpact loading
Front vehicle body structure includes left and right front side frames, a subframe provided on the undersides of the side frames, and left and right mounting brackets for connecting the side frames and subframe. Engine-transmission unit is mounted on the subframe. Respective rear half portions of the side frames extend toward the rear of the vehicle body while gradually approaching the centerline of the vehicle body. Left and right mounting brackets are provided, on the respective rear half portions, to project toward the centerline. The left and right mounting brackets are detachably connected to the subframe. When an impact load greater than a predetermined intensity has been applied, the left and right mounting brackets are detached from the subframe and then squashed by the engine-transmission unit while effectively absorbing the impact.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
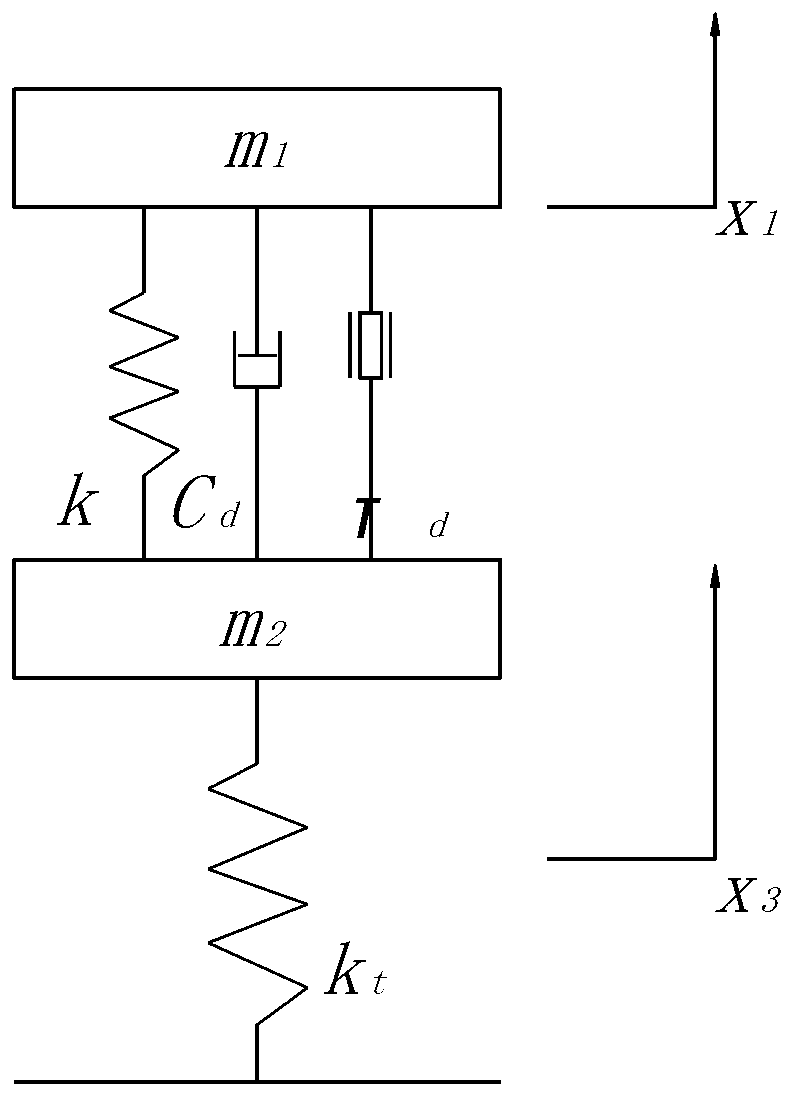
Three-dimensional impact loading experiment device
InactiveCN102169069AImprove accuracyAccuracy does not affectMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesData acquisitionImpact loading
The invention discloses a three-dimensional impact loading experiment device, which belongs to the technical field of impact dynamics experiment devices. The three-dimensional impact loading experiment device is characterized by comprising a loading device, an incidence rod, a test piece and a transmission rod which are arranged sequentially; foil gauges are arranged on the incidence rod and the transmission rod respectively; the foil gauges are connected with a data acquisition and processing unit; the test piece is a cube; three incidence rods and three transmission rods are provided; one end of each of the incidence rods corresponds to a loading device, and the other end of the incidence rod is vertical to three vertical side faces of the test piece; the transmission rods are vertically arranged on the other three side faces of the test piece; and the incidence rods and the transmission rods correspond to each other one to one. The invention aims at providing the three-dimensional impact loading experiment device which is capable of really realizing three-dimensional dynamic loading and used for researching the dynamics performance of engineering materials under the three-dimensional dynamic loading.
Owner:浣石
Dynamic impact loading test bed and test system thereof
InactiveCN101769838ASmall energy conversion rateReduce noise pollutionForce measurementStrength propertiesHigh energyMiniaturization
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
True triaxial simulation test device for three-directional rigid loading impact ground pressure
ActiveCN104390859AAvoid mutual influenceAvoid the impact of support effectMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringImpact loading
The invention provides a true triaxial simulation test device for three-directional rigid loading impact ground pressure. The problem that the simulation is not vivid in an existing impact ground pressure test device is solved. The true triaxial simulation test device comprises a pressure box, wherein the pressure box is internally provided with a pressure cavity, and further comprises a rigid loading unit and an impact loading unit; the inner periphery of the pressure cavity is provided with a flexible confining pressure loading jacket; the flexible confining pressure loading jacket has elastic deformation amounts in X, Y and Z directions; the rigid loading unit comprises loading oil cylinders of the pressure box in the X, Y and Z directions; telescopic shafts of the loading oil cylinders penetrate through the outer wall of the pressure box and the inner ends of the telescopic shafts are fixedly connected with loading base plates; the inner surfaces of the loading base plates abut against the outer surface of the flexible confining pressure loading jacket; and the impact loading unit comprises a lifting device in the Z direction and an impact weight is hung under the lifting device. According to the true triaxial simulation test device, the influences of deformation with one another in the three directions are solved, and the influences of a supporting effect are also avoided, so that the impact ground pressure is simulated relatively vividly.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Piping with integral force absorbing restraining system
InactiveUS6837523B2Reduce reaction forceReduce the impactPipe elementsCouplingsSuction stressEngineering
A force absorbing restraining system for a number of pipe sections, each having an integral restraining system which is subsequently connected and works in conjunction with the integral restraining system of adjacent pipe sections. It is known that during an explosive failure either of a pipe section or a joint between pipe sections, a tremendous amount of reaction force is generated by escaping effluent flow. This force, in turn, may energize equipment such as pipes, pumps, and the like to exhibit uncontrolled motion often at a rate of several hundred feet per second. The restraining system of the present invention is designed to absorb a sudden burst of explosive energy and to lessen the reaction forces generated by the explosion so as to ensure that equipment does not move about a service site in an uncontrolled manner which could injure people and damage buildings or other equipment. In short, the force absorbing restraining system in accordance with the present invention reduces the effects of impact loading during explosive failure by dissipating energy in the permanent mechanical deformation of an integral restraining tube assembly attached to each pipe section.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Pressure relieved thread connection
InactiveUS6905149B2Convenient and Accurate MonitoringDrilling rodsPipe elementsEngineeringImpact loading
Lubricant escape passages are formed in the threads used to connect one tubular body to another. The passages conduct trapped thread lubricant out of the threaded area to prevent the creation of high lubricant pressure that may damage or cause improper make up of the threaded connection. The passages may be grooves in the crests of the thread teeth and / or may be corner bevels on the thread teeth. In a conductor pipe or other pipe assembly using axially spaced internal and external seals at each axial end of the threaded area, the escape passages form a helical flow path through the engaged thread area. The external seal prevents the entry of corrosive fluids into the threaded area and the internal seal prevents leakage through the threaded area from within the conductor pipe. When the lubricant pressure increases excessively during assembly or impact loading of the connection, the lubricant escapes past the seals to prevent connection damage. When used with a wedge or other metal-to-metal thread engaging designs, the escape passages may be interrupted at some point intermediate their helical path to provide a pressure seal at the point of interruption. Relieving trapped lubricant from a wedge thread connection permits consistent final makeup positions that ensure optimal pressure sealing.
Owner:GRANT PRIDECO LP
Front body structure of automotive vehicle
A front side frame includes a bend portion which is operative to bend outward when an impact load acts on the front side frame from ahead. The bend portion is provided in a specified location such that the bend portion in a bending state substantially contacts a damper of the suspension from a vehicle front side. Accordingly, a rear end of the front side frame can be prevented properly from moving back when the impact load acts on the front side frame from ahead.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
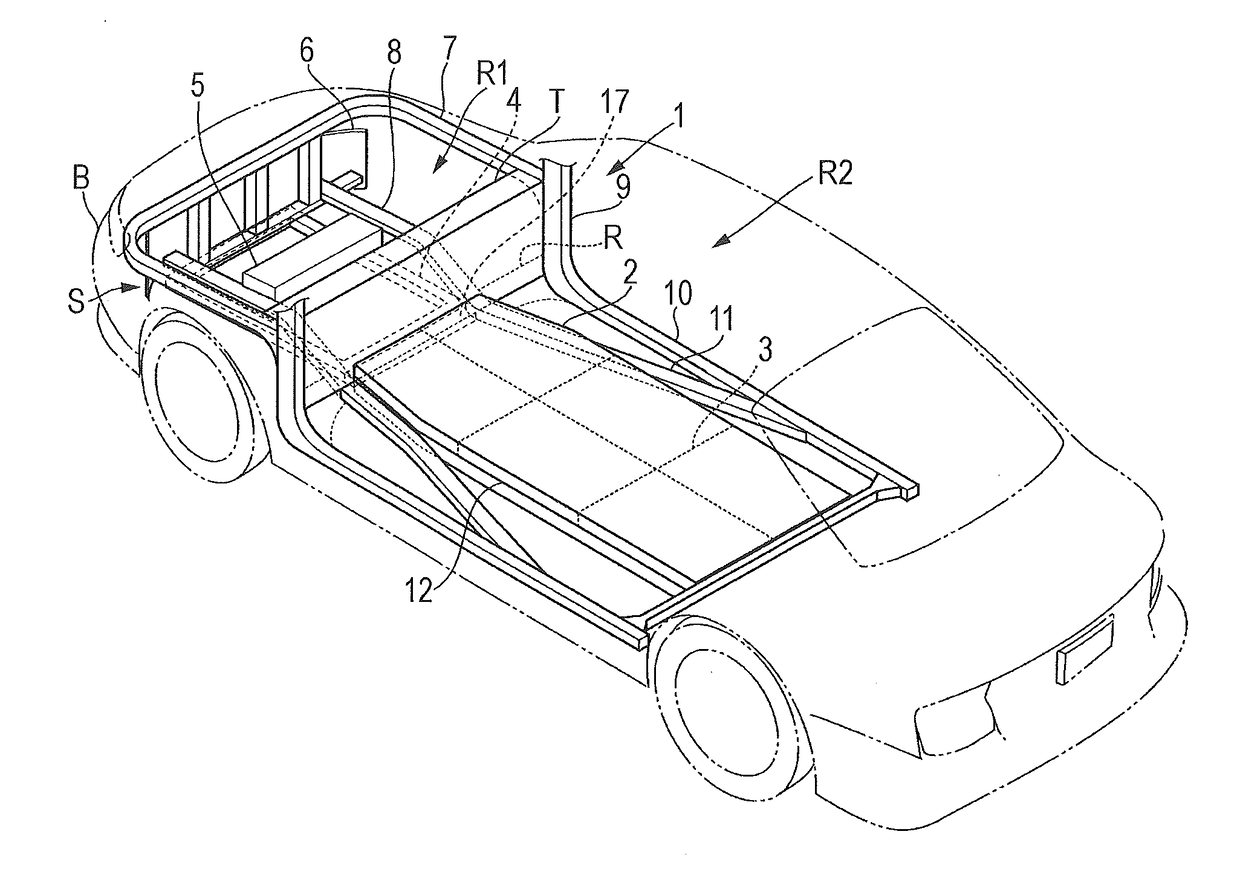
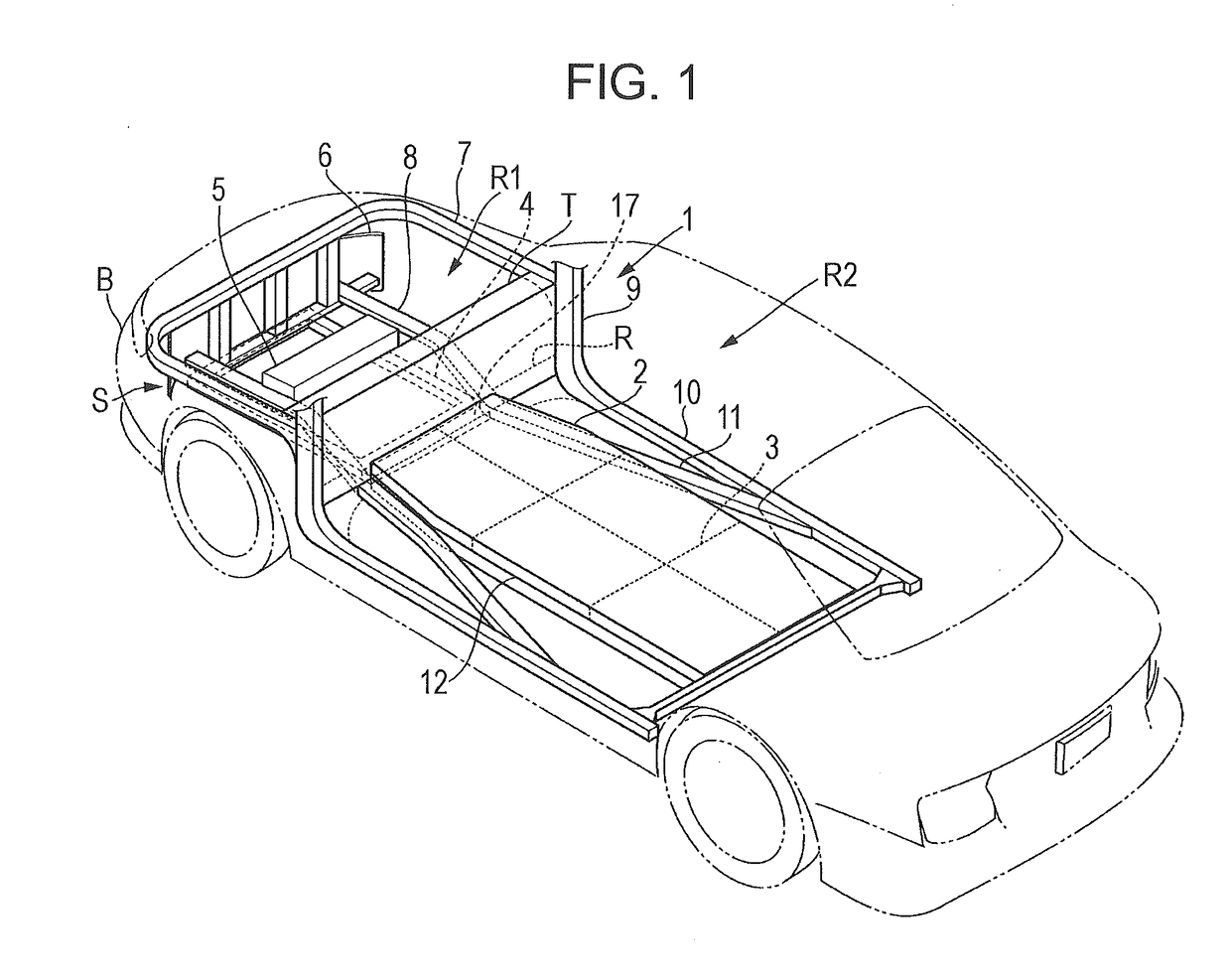
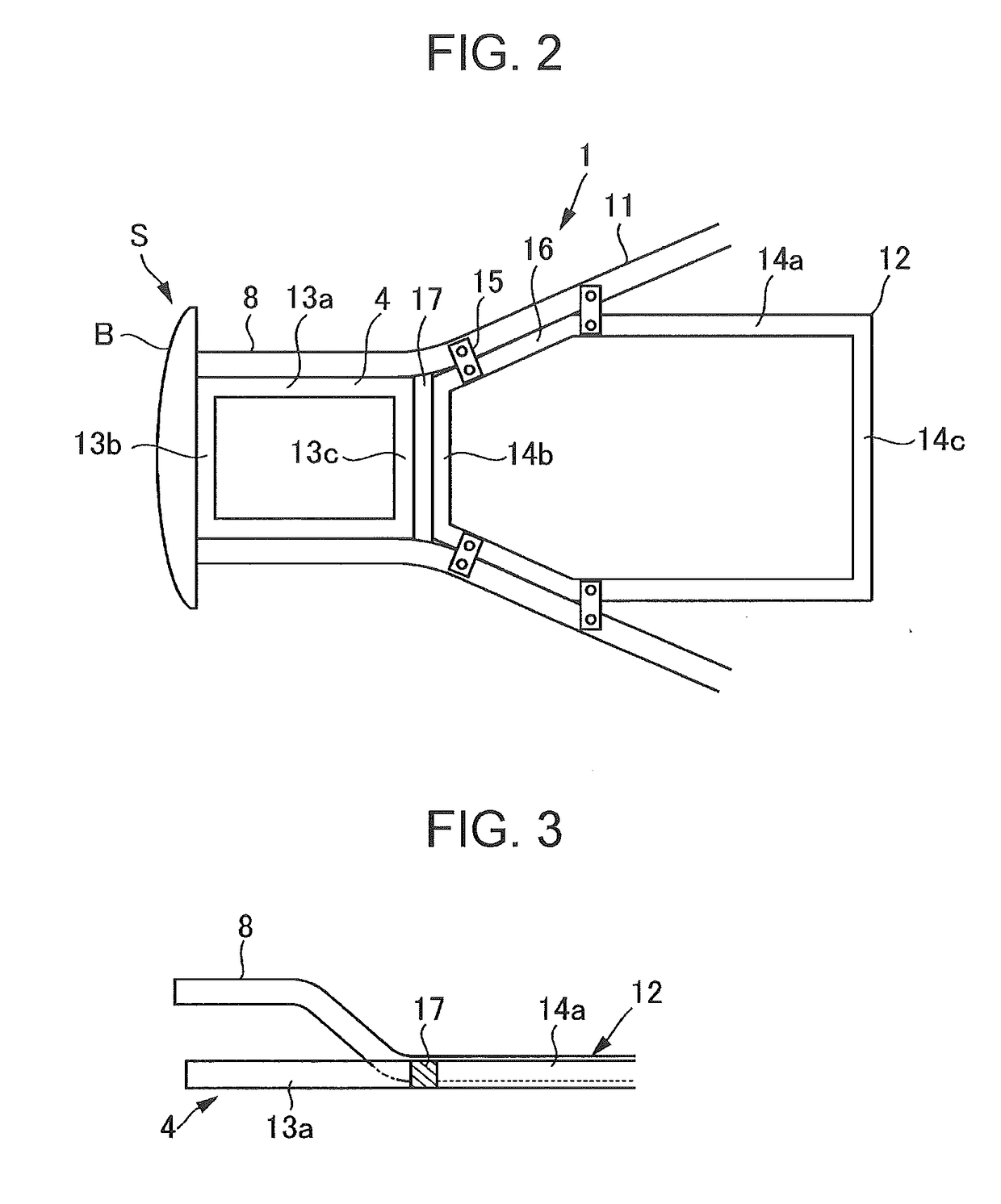
Impact load reduction structure
ActiveUS20170088178A1Reliably reducedReduce shock loadElectric devicesElectric propulsion mountingImpact loadingAutomotive engineering
An impact load reduction structure includes a battery frame, a load reduction frame, and a load absorber. The battery frame is fixed to a vehicle body frame of an electrically-powered vehicle and supports a battery. The load reduction frame extends in a front-rear direction on a front side of the battery frame and is disposed in a substantially same plane as the battery frame. The load absorber is disposed between the load reduction frame and the battery frame and absorbs an impact load to be transmitted from the load reduction frame to the battery frame.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
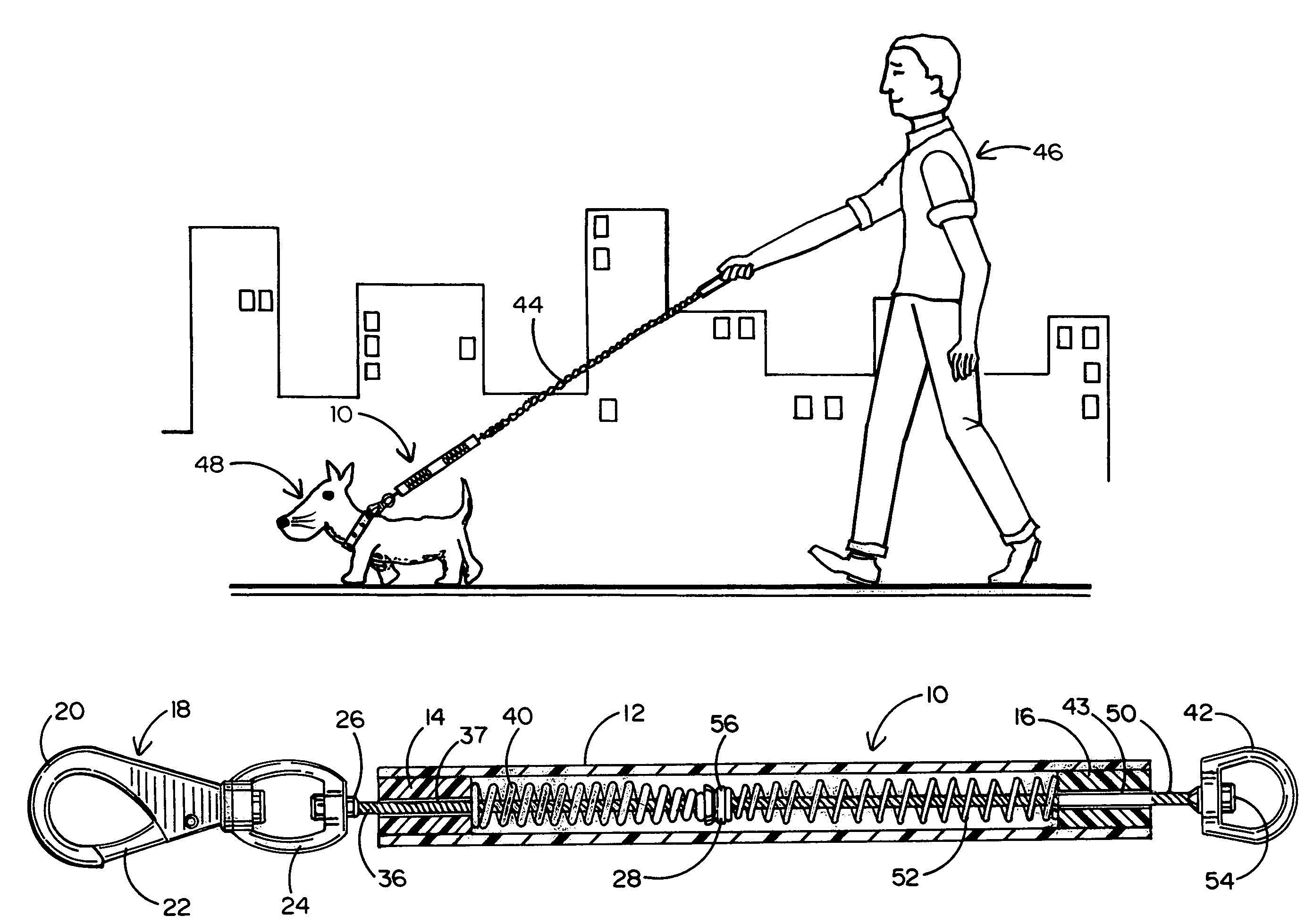
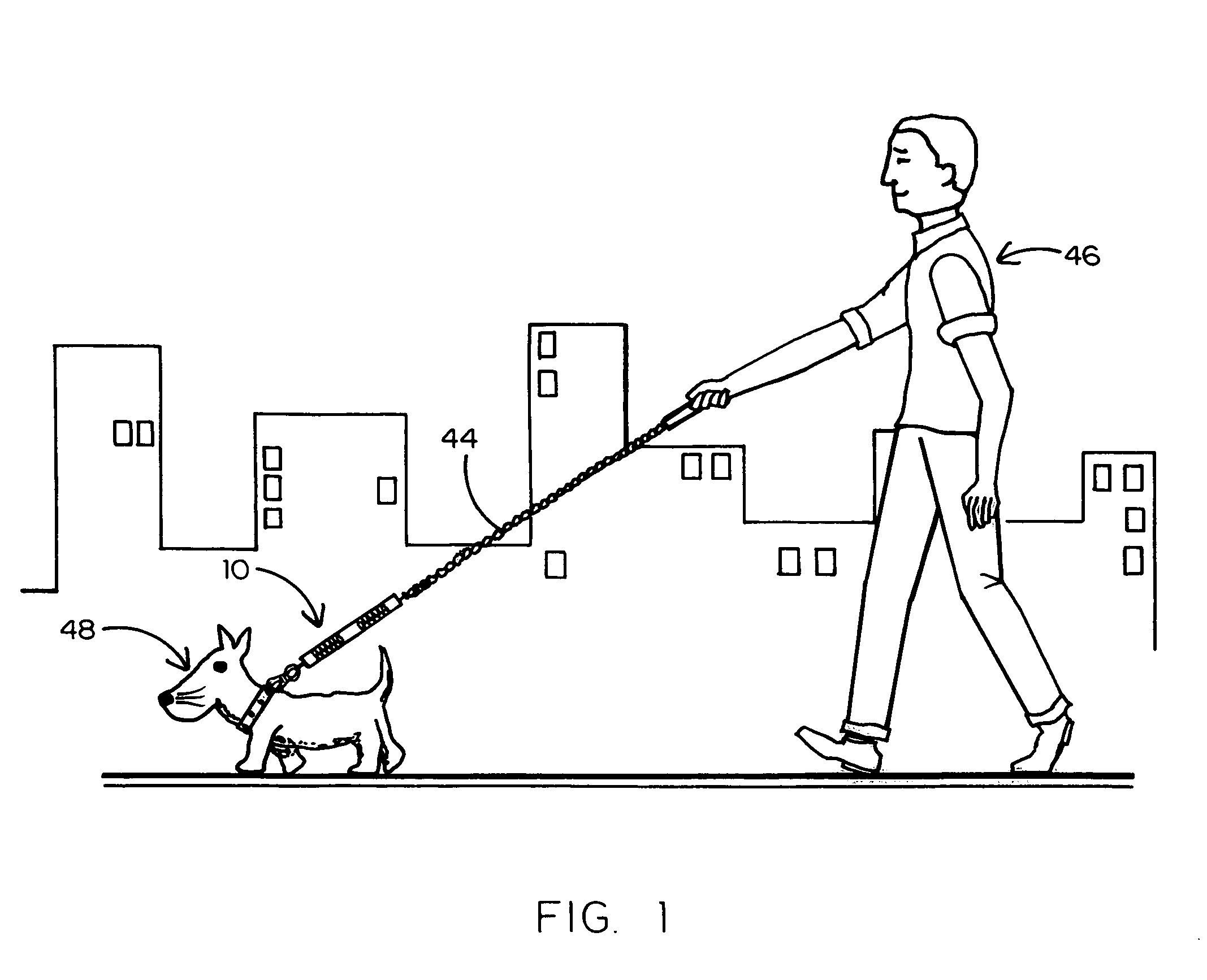
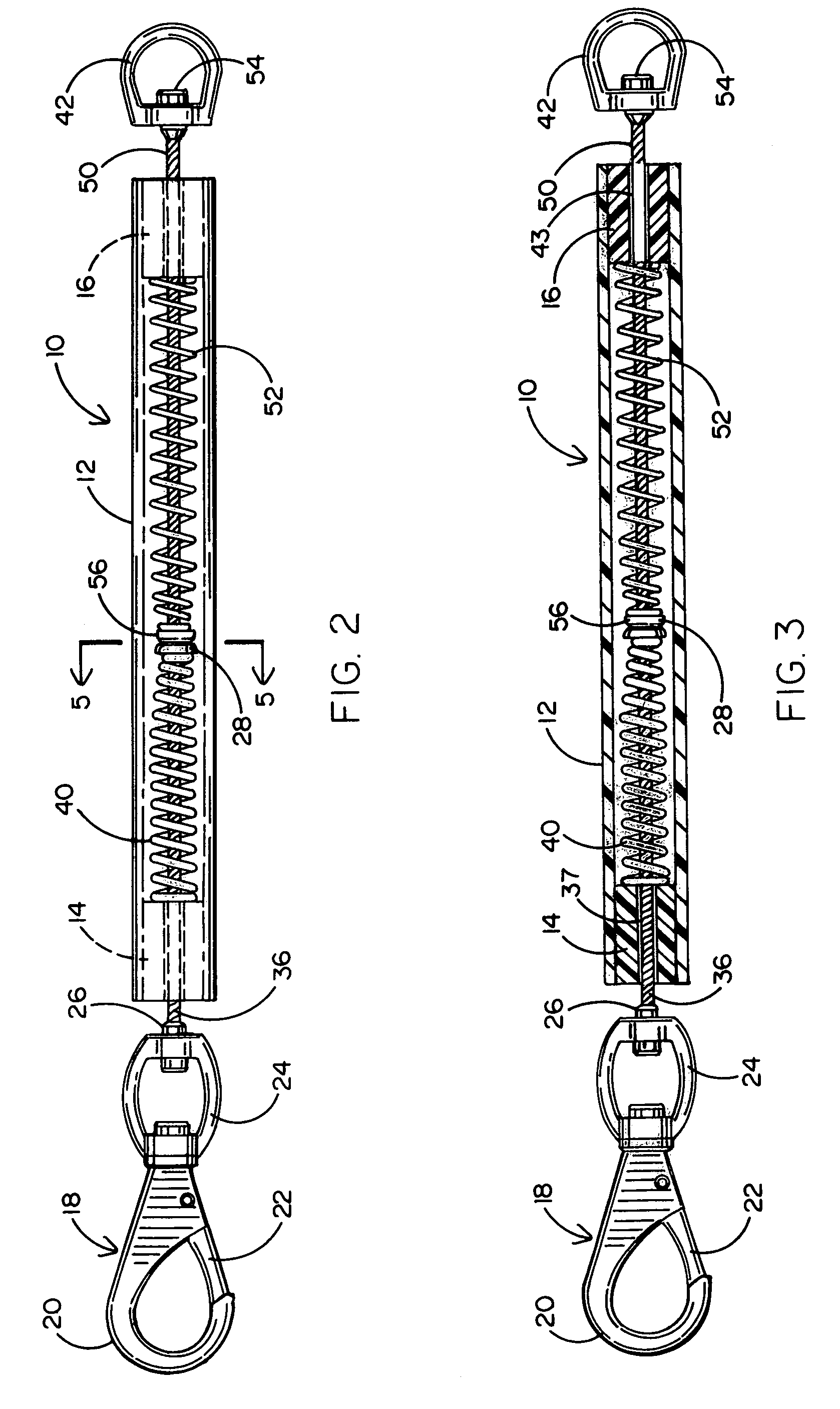
Shock absorber for attachment to a dog leash
The body of the shock absorber is made of lightweight flexible resilient tubular polymer material which will not cause injury when struck by it. The body has a stop in each end and two compression springs within the tubular body between the stops. Tension cables are attached to the compression springs and do not pneumatically engage within the tubular polymer body and extend out of the body and respectively carry a snap hook for attachment to a dog collar and a ring for attachment to a dog leash. Pull on the tension members causes compression of the springs to reduce shock-loading on the dog walker. After the springs are pulled solid, the resiliency of the body continues to absorb shock.
Owner:NAPOLITANO DENNIS
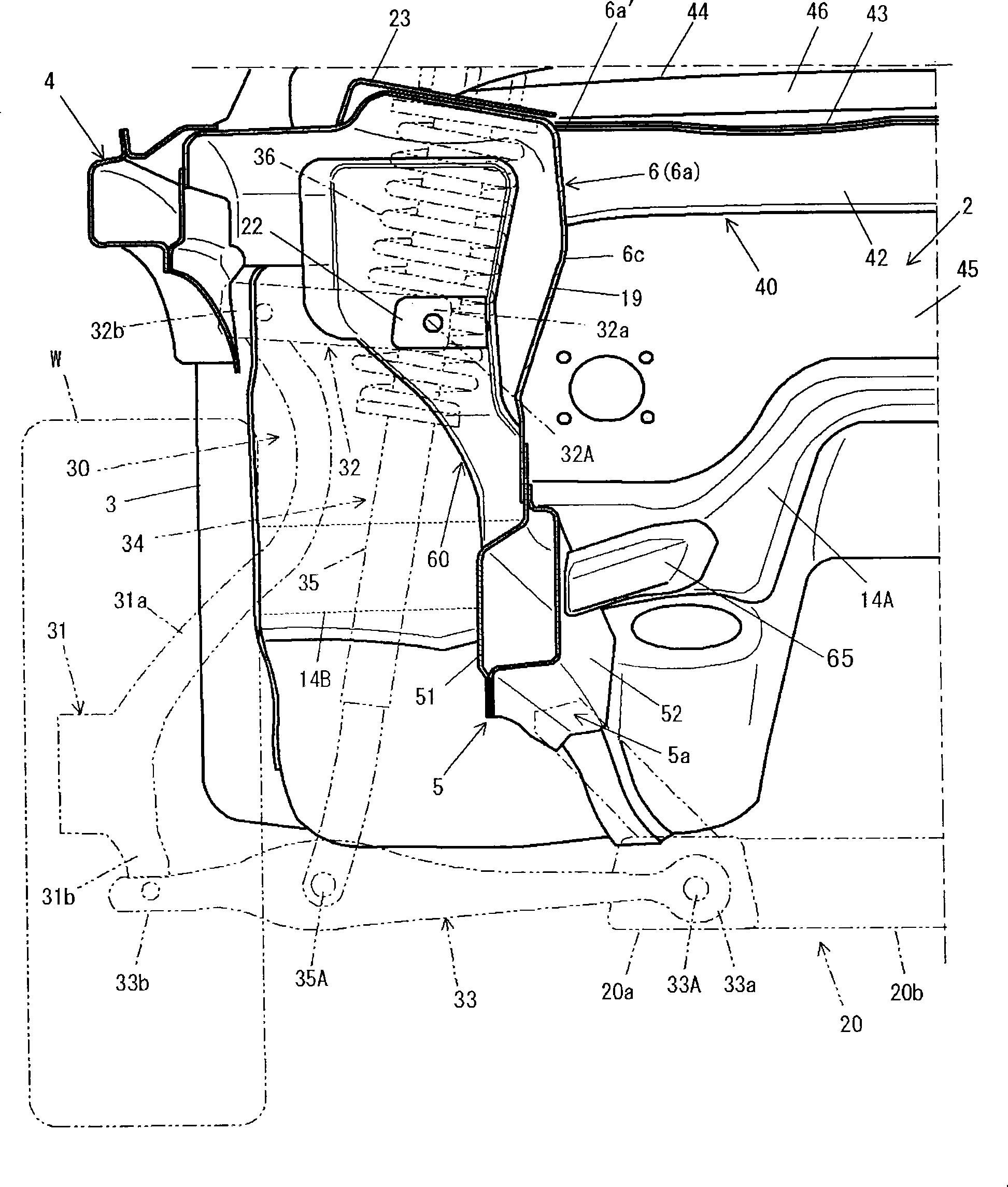
Vehicle front body structure
The vehicle front body structure of the present invention has a gusset (50), and the gusset (50) is connected to the front side member ( 30) The connecting part and the above-mentioned hinge pillar (20), the gusset (50) and the face of the engine room (2) side of the dash panel (11), along the vehicle compartment of the dash panel (11) ( 3) The closed cross-sectional structure on the side of the vehicle compartment formed by the side surface and the reinforcing member (40), forming a closed cross-sectional structure on the side of the engine compartment. According to the present invention, even when an impact load acts on the front side member (30) from the side, the front side member (30) can be prevented from collapsing inwardly.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Method and apparatus for elastic tailoring of golf club impact
A method and apparatus for beneficially controlling the impact between a club head and a golf ball are described. A golf club head (such as on a driver, iron, or putter) has a body and a face mechanically supported thereon, wherein the face and body are elastically tailored to create beneficial face motion and deformation at impact. The tailored clubhead compliance is shown to influence impact properties and resulting ball parameters such as speed, direction and spin rates resulting from the impact event between the face of the club and the golf ball. Several embodiments are presented for controlling ball spin through design of the elastic and dynamic response of the face and body under impact loading.
Owner:HEAD TECHNOLOGY GMBH LTD
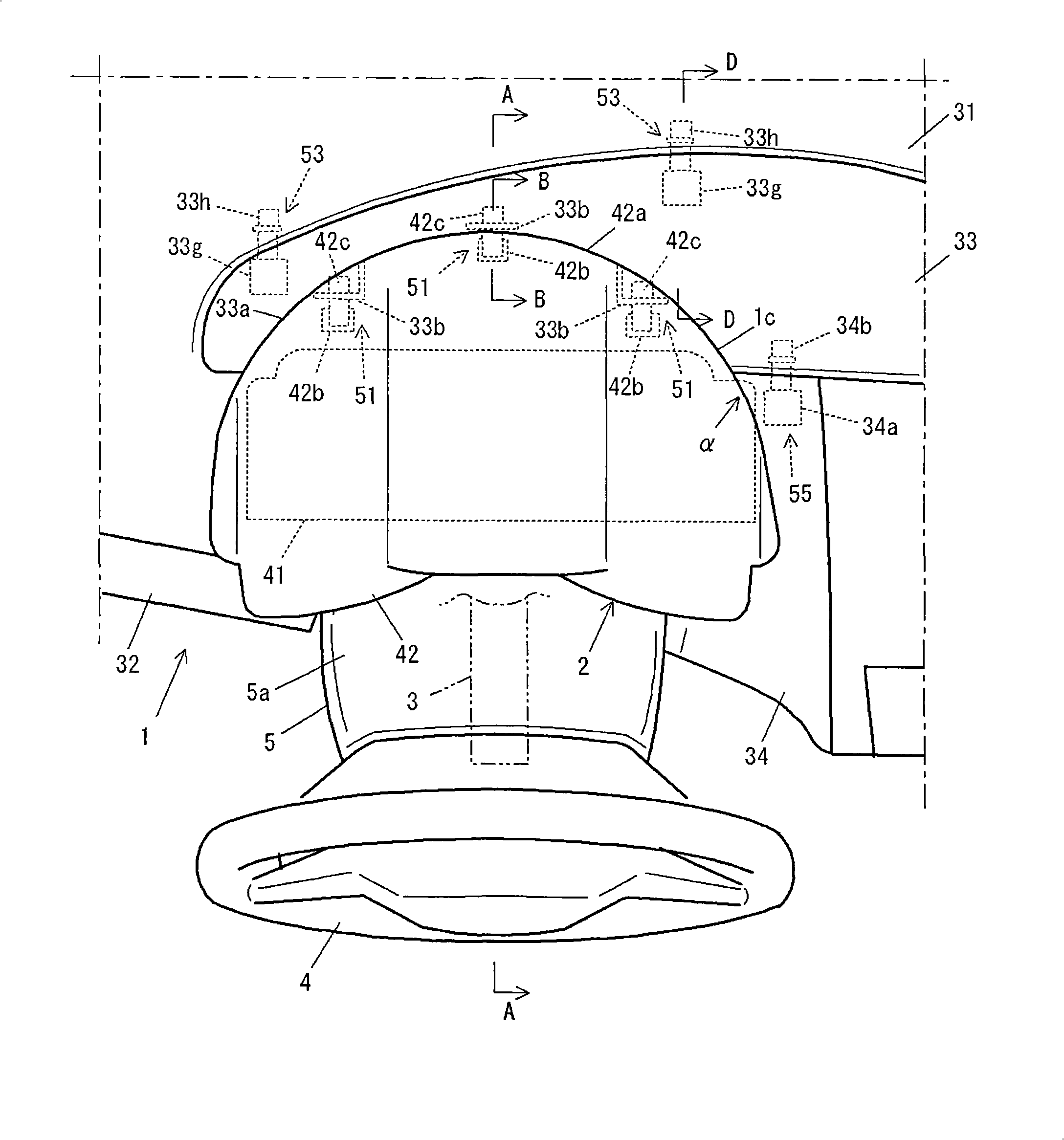
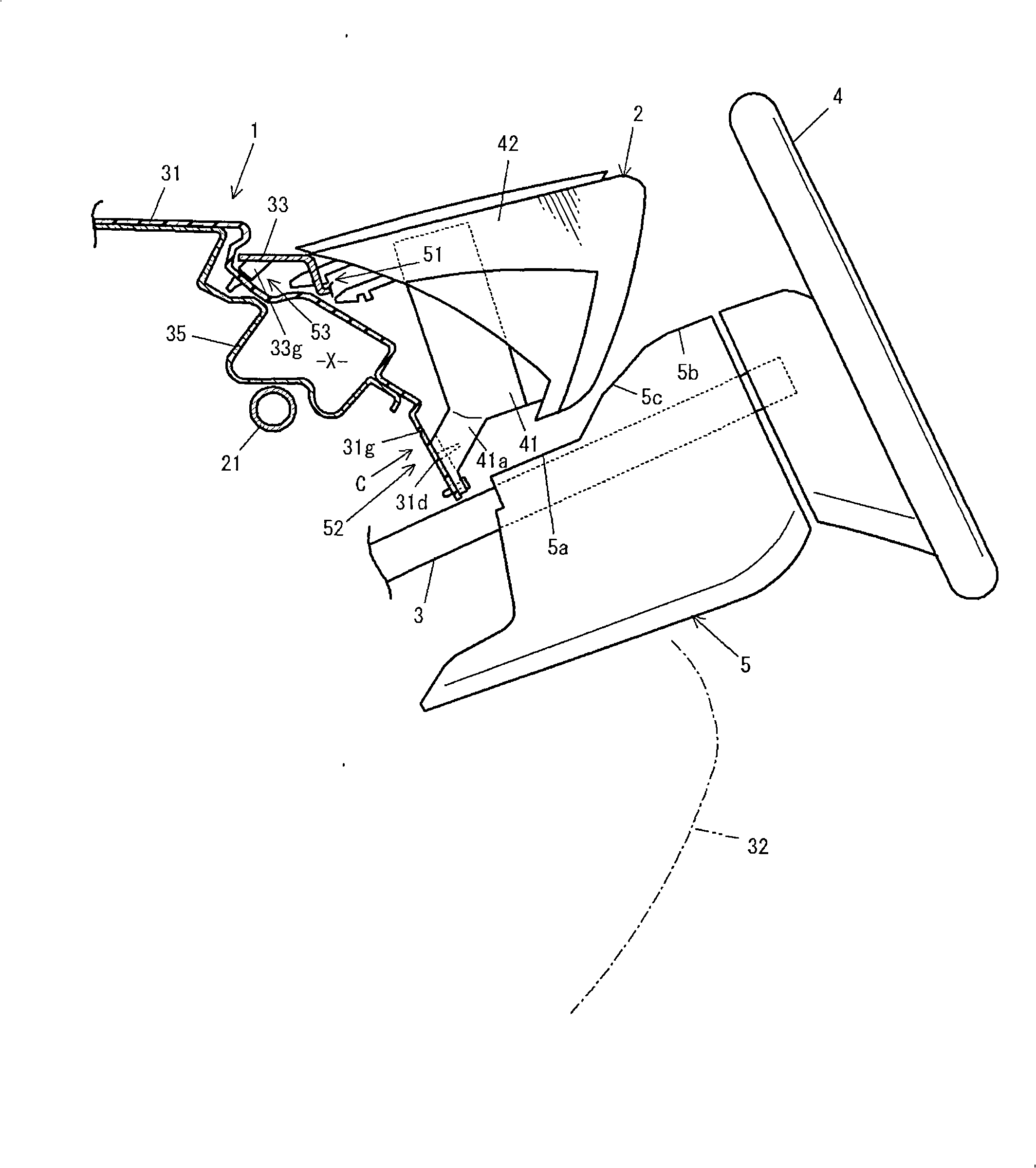
Structure of instrument panel area of vehicle
InactiveCN101402320AMake sure to move forwardEasy to movePedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSteering columnsDashboardSteering column
A structure of a vehicle instrument panel area, which is capable of sufficiently ensuring a frontward displacement of a steering column adapted to be displaced frontwardly in response to an impact load applied thereto frontwardly, even under a condition that a column cover is disposed to overlap with a meter unit when viewed in an axial direction of the steering column. A meter unit is attached to an instrument panel through brittles portions in such a manner as to allow the attachment therebetween to be released when a column cover is brought into contact with the meter unit.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP +1
Method and device for measuring dynamic contact heat exchange coefficient of high-temperature solid interface
InactiveCN101661009ARealize measurementEfficient heatingMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentContact pressureMeasurement device
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Differential pitch hammerless connection with hydraulic driving mechanism
A threaded connection assembly comprises a nut, a multiplier connected to the nut via a first threaded interface having a first number of threads per inch and a well servicing pipe coupling connected to the multiplier via a second threaded interface having a second number of threads per inch. A method of forming a threaded connection for a well servicing application comprises forming a pipe coupling between two well servicing pipe sections and threading a connector to the pipe coupling to form a threaded connection without impact loading the connector. Another method for forming a threaded connection comprises disposing a first pipe section partially within a nut, threading a multiplier into the nut, threading the multiplier onto a second pipe section, and leveraging the multiplier against the nut, or vice versa.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Drop hammer impact test device used for simulating vehicle collision
InactiveCN104913893ARealize limitRealize the collapse functionShock testingFree fallingImpact loading
The invention discloses a drop hammer impact test device used for simulating vehicle collision. The device comprises a drop hammer which can simulate vehicle crush. The drop hammer comprises a crushable hammerhead and a counterweight cap. The crushable hammer is used for impacting a test piece and transferring the impact force. A clump weight is arranged on the counterweight cap. The crushable hammerhead and the counterweight cap are coaxially assembled through a sliding structure. A crushable spring is arranged between the crushable hammerhead and the counterweight cap. The end part of the crushable spring is connected with the crushable hammerhead or the counterweight cap through a force sensor. Both ends of an impact simulation test column are respectively constrained and fixed on a test cap according a boundary condition. The whole drop hammer is lifted by a lifting mechanism, and free-fall impact loading is carried out on a part to be impacted on the test column. According to the invention, drop hammer test loading is used for simulating vehicle collision; the drop hammer impact test device has the advantages of real stress simulation, high test precision and being safe and reliable; the cost is far less than the cost of a conventional real vehicle collision test; and the drop hammer impact test device can be promoted in the fields of structure test and vehicle production and development.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Magnetorheological buffering unit structure based on impact load and control method thereof
InactiveCN103195858APrevent jumpingReasonable structureNon-rotating vibration suppressionAdaptive controlAviationMagnetic current
The invention discloses a magnetorheological buffering unit structure based on impact load and a control method thereof, aiming to mainly solve the technical problems that parameters of an oil-gas type buffer cannot be adjusted in working process, and accordingly a landing gear buffer cannot be balanced with a large power energy source required from outside for realizing ground sliding, landing off and actively controlling the landing gear. The magnetorheological buffering unit structure comprises a magnetorheological damper and a magnetorheological liquid chamber, and the magnetorheological liquid chamber can move in the magnetorheological damper through a sealing device. During testing, the unit structure main body is mounted on an impact test platform. Variable-structure oil holes of a conventional oil-gas type buffer are replaced by oil-needle-free constant-interface oil holes, passed oil damping force is controlled by applied magnetic field, and magnetic field is supplied by applied current. The magnetorheological buffering unit structure is reasonable in structure and capable of buffering impact energy produced by impact force effectively, and meanwhile, oil return holes can prevent wheels from jumping off the ground while landing. The magnetorheological buffering unit structure has functions of an oil-gas type passive-control buffer, realizes half-active buffer control effect, and is mainly applied to the technical field of aviation.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
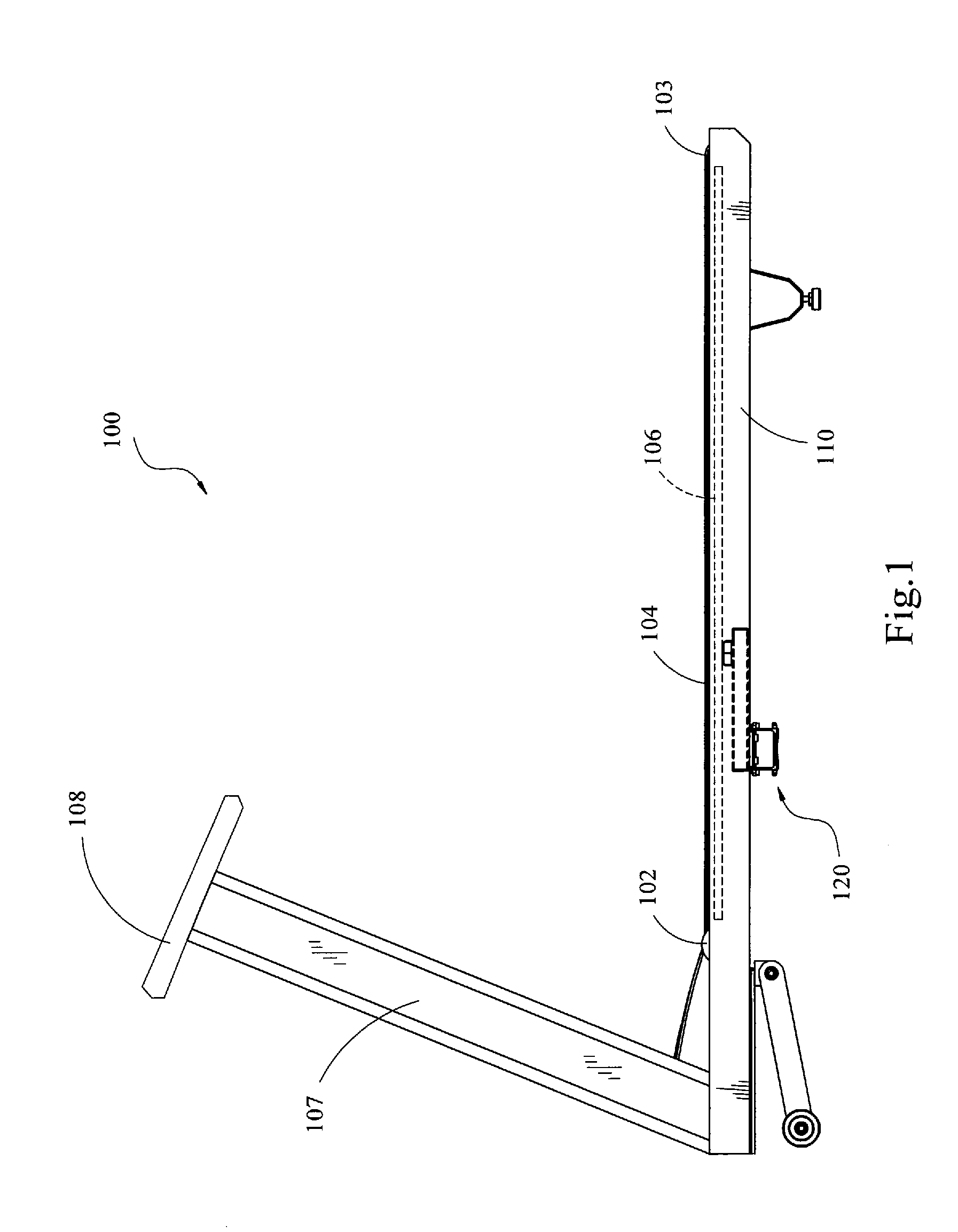
Treadmill with cushion assembly
InactiveUS20090088301A1Reduce high impact loadCushioning effectTherapy exerciseMovement coordination devicesEngineeringImpact loading
A treadmill including a frame, an endless belt having an upwardly-exposed exercise section, a deck disposed underneath the exercise section of the belt, and a cushion assembly positioned between the deck and the frame for providing cushion in order to reduce high impact loads on the user's body. The cushion assembly comprises a lever having a first portion that is operably coupled to the deck and a second portion that is rotatably coupled to the frame. The cushion assembly also comprises a resilient member coupled to both the lever and the frame so that the resilient member resists rotation of the lever as the lever is rotated. The elastic deformation of the resilient member provides resistance to displacement of the deck and therefore creates a cushion effect on the user's feet, ankles and knees as the user's feet contact the belt.
Owner:JOHNSON HEALTH TECH
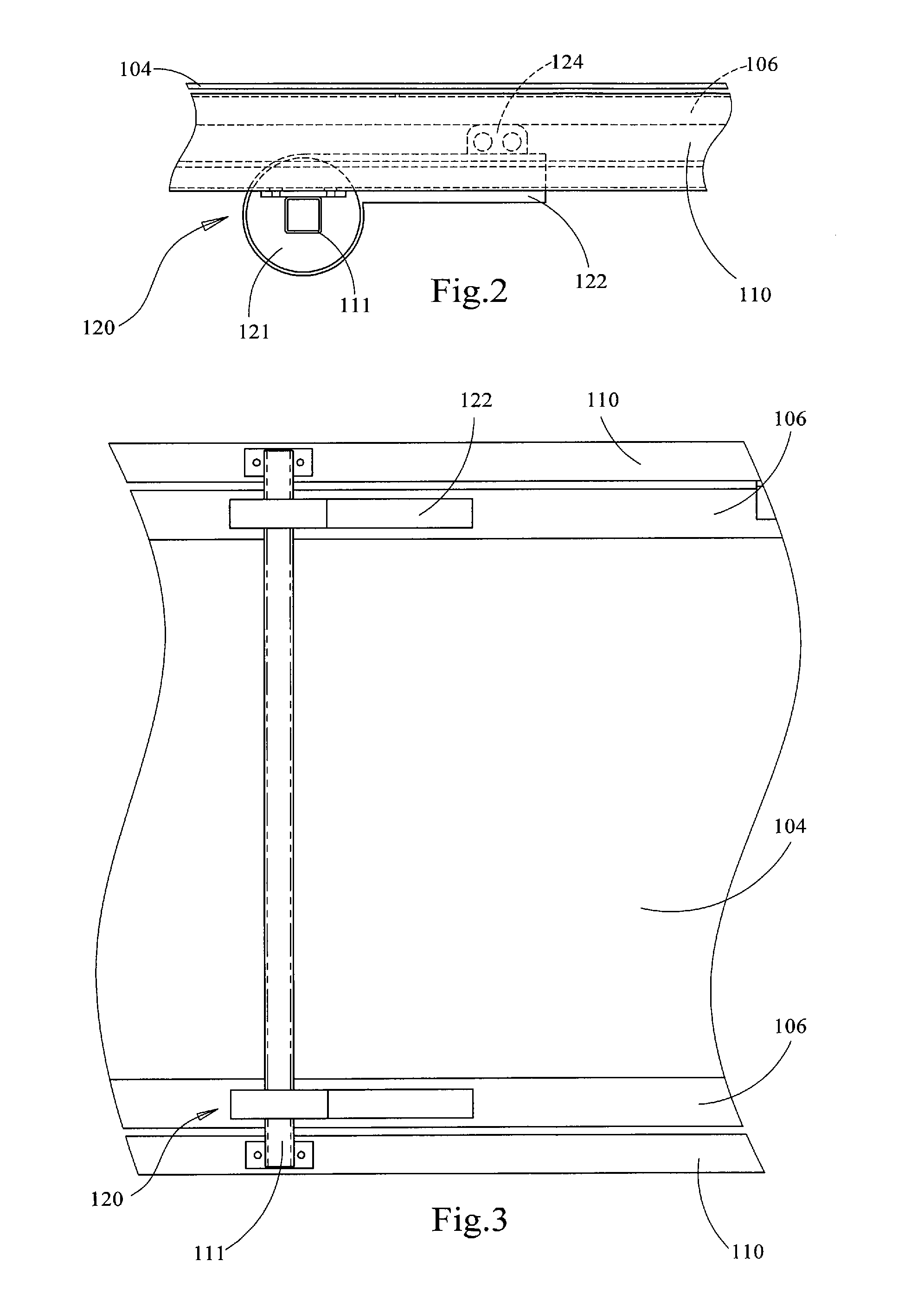
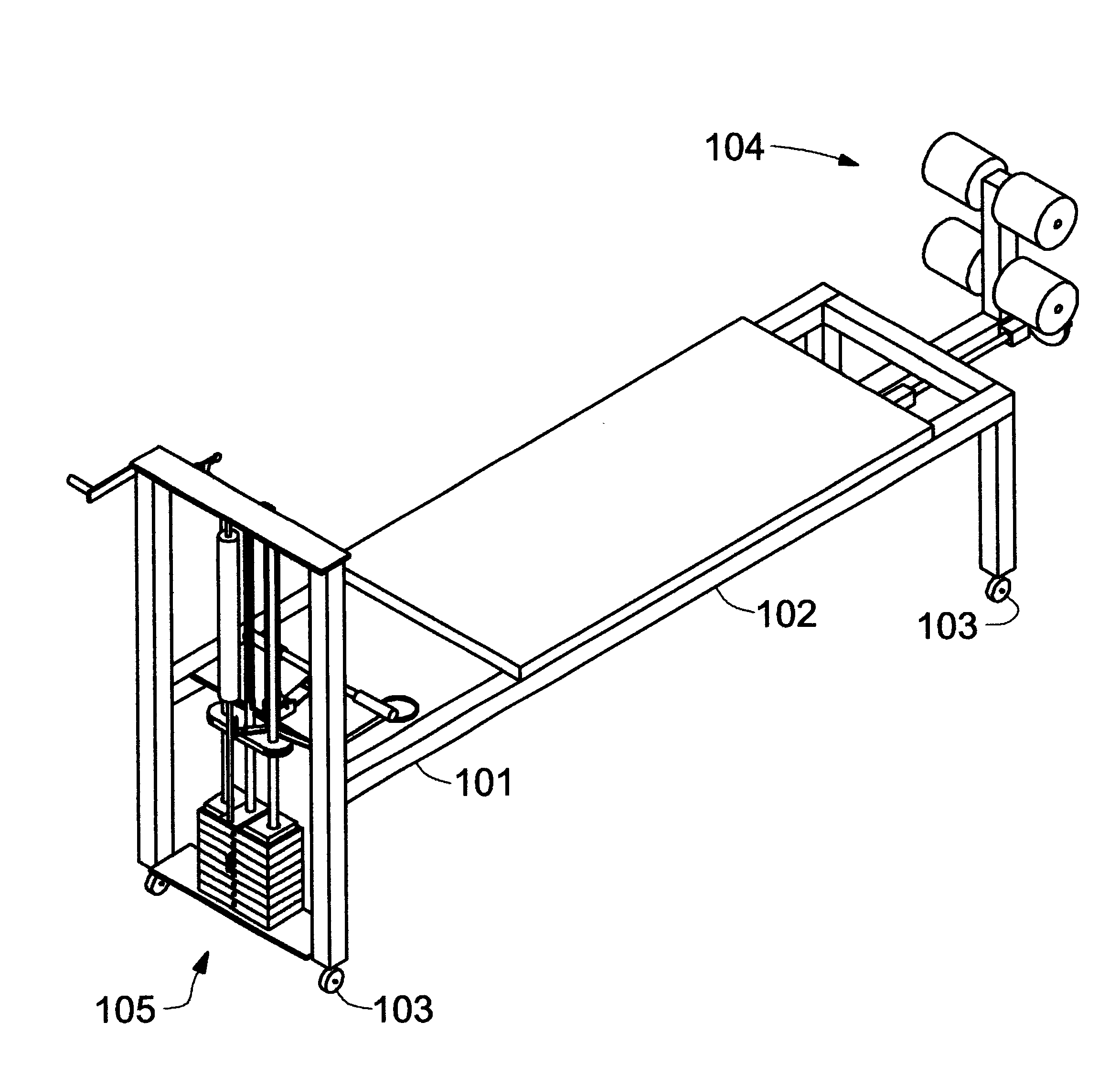
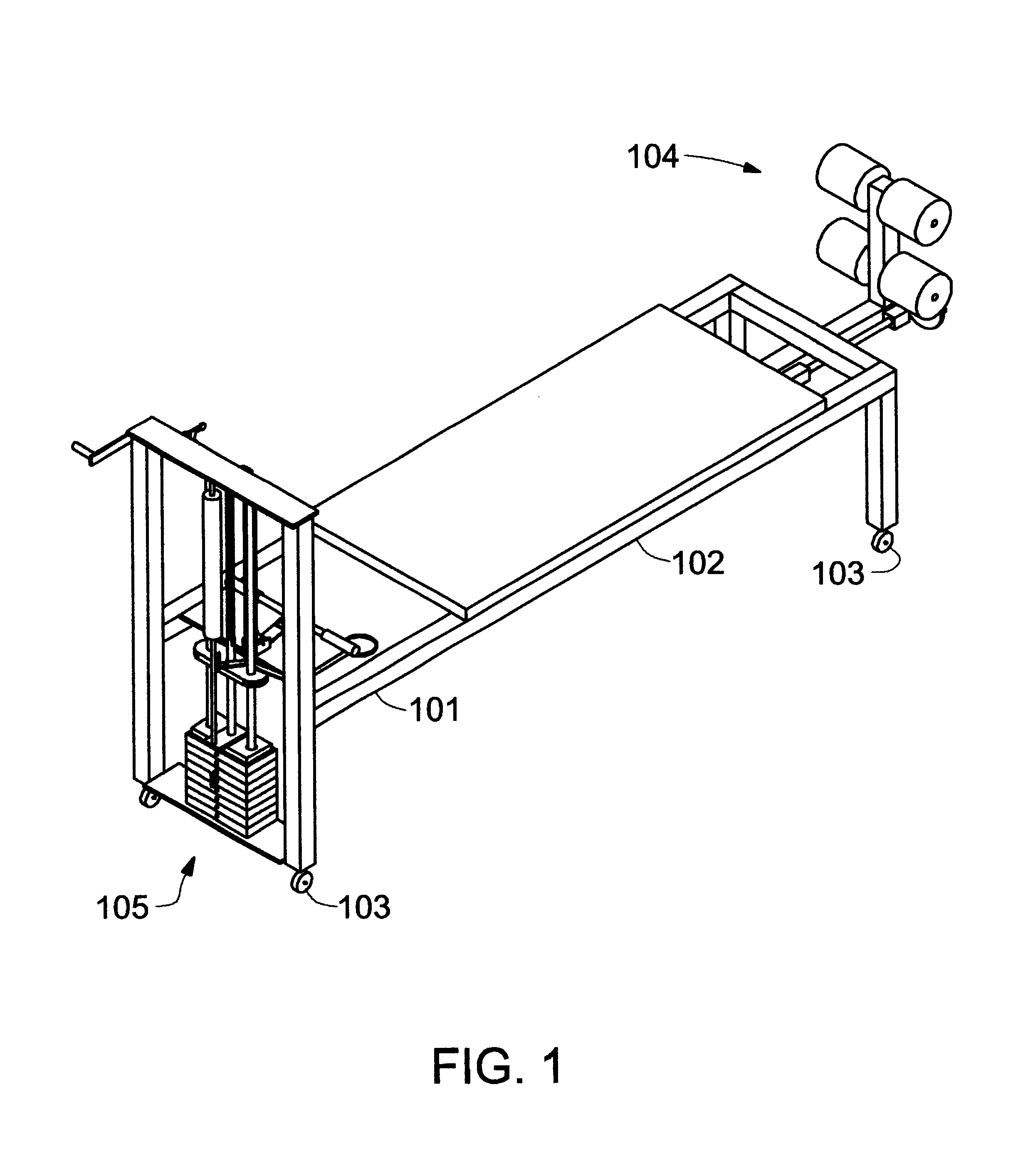
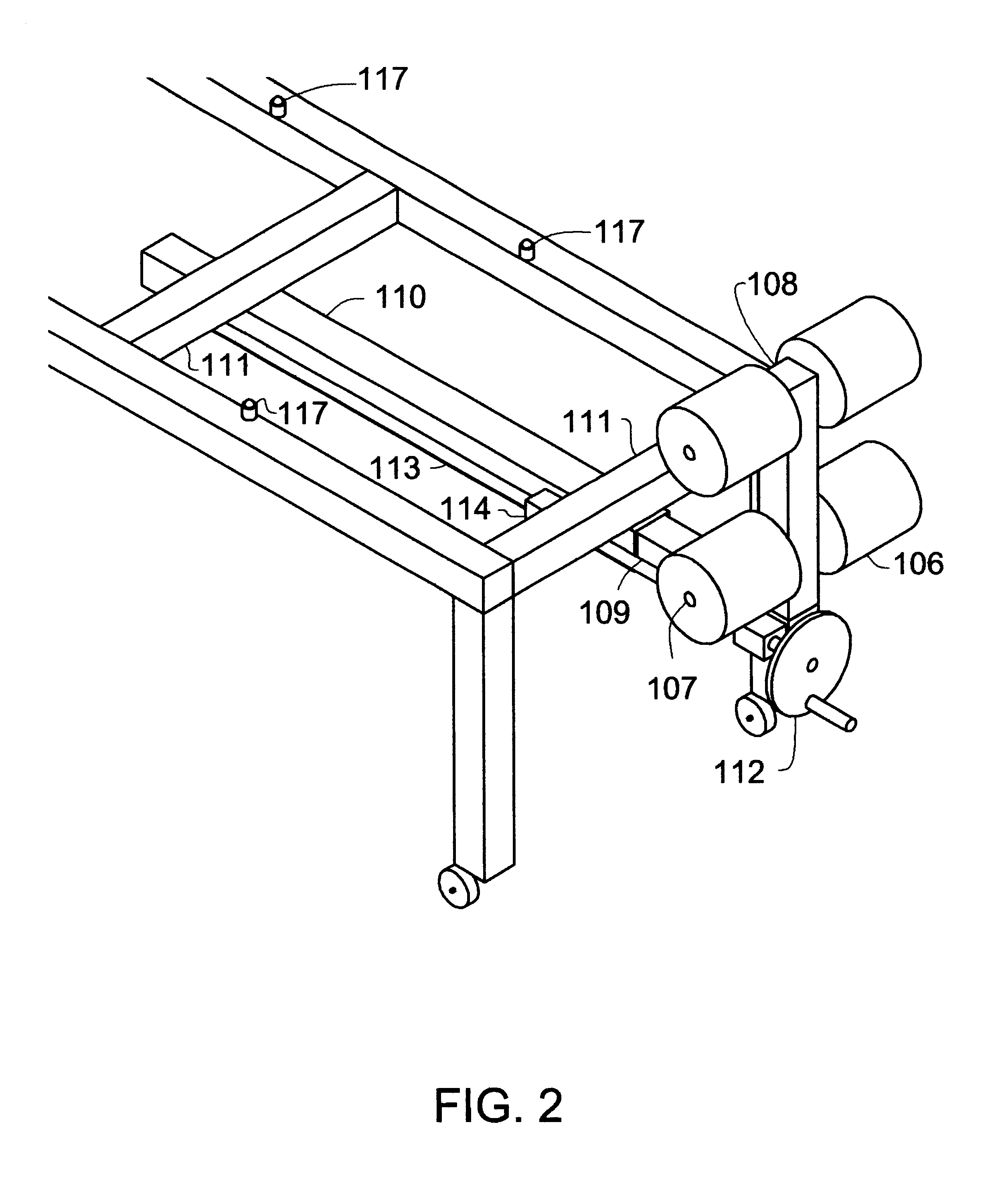
Body stretching apparatus and method
InactiveUS6814708B1Avoid risk of injuryMagnitude is and stableChiropractic devicesEye exercisersEngineeringImpact loading
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for stretching a human body in a substantially horizontal attitude. The apparatus places the body under a predetermined tensile load, uniformly distributed over the length of the body. The apparatus applies the loading force gradually in order avoid shock loads on the body. The apparatus may be operated easily and safely by the user, without assistance from another person.
Owner:JENNINGS RALPH ERNEST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com