Patents
Literature
124 results about "High resistivity silicon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
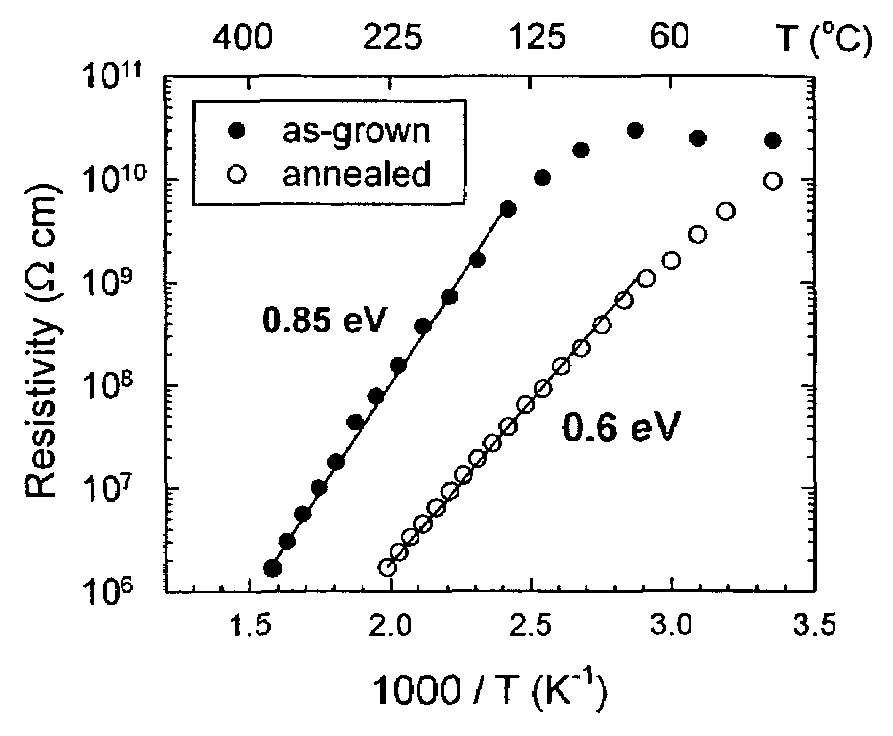
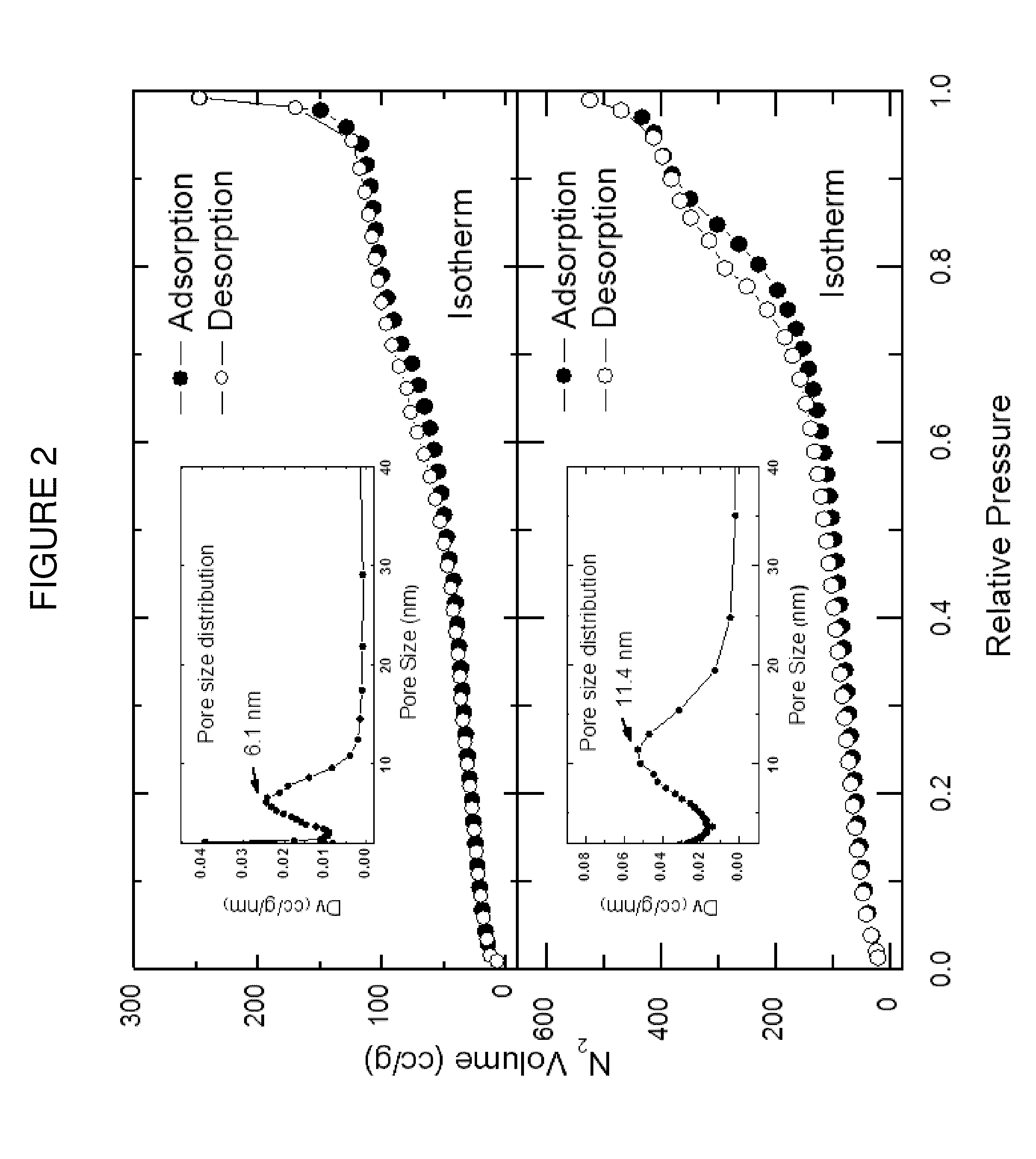
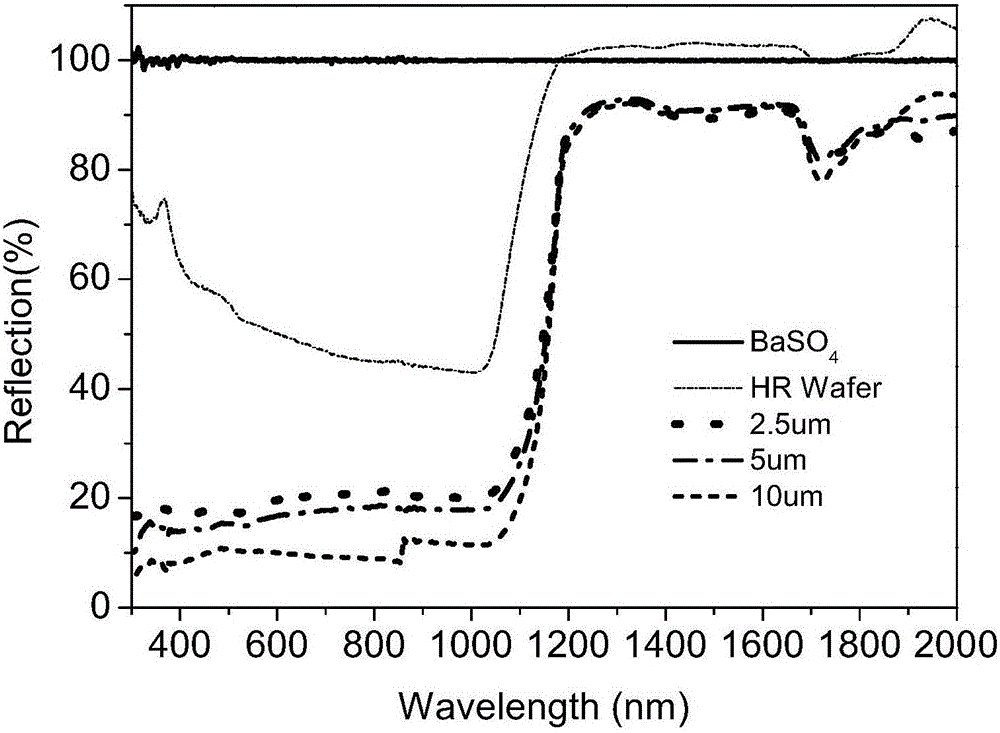
High resistivity silicon is an ideal candidate for a substrate for a GHz &THz transmission line because of the low loss tangent and, thus, the high effective dielectric constant. Several papers have demonstrated the usefulness of high resistivity silicon as a substrate for low loss waveguide transmission line devices.
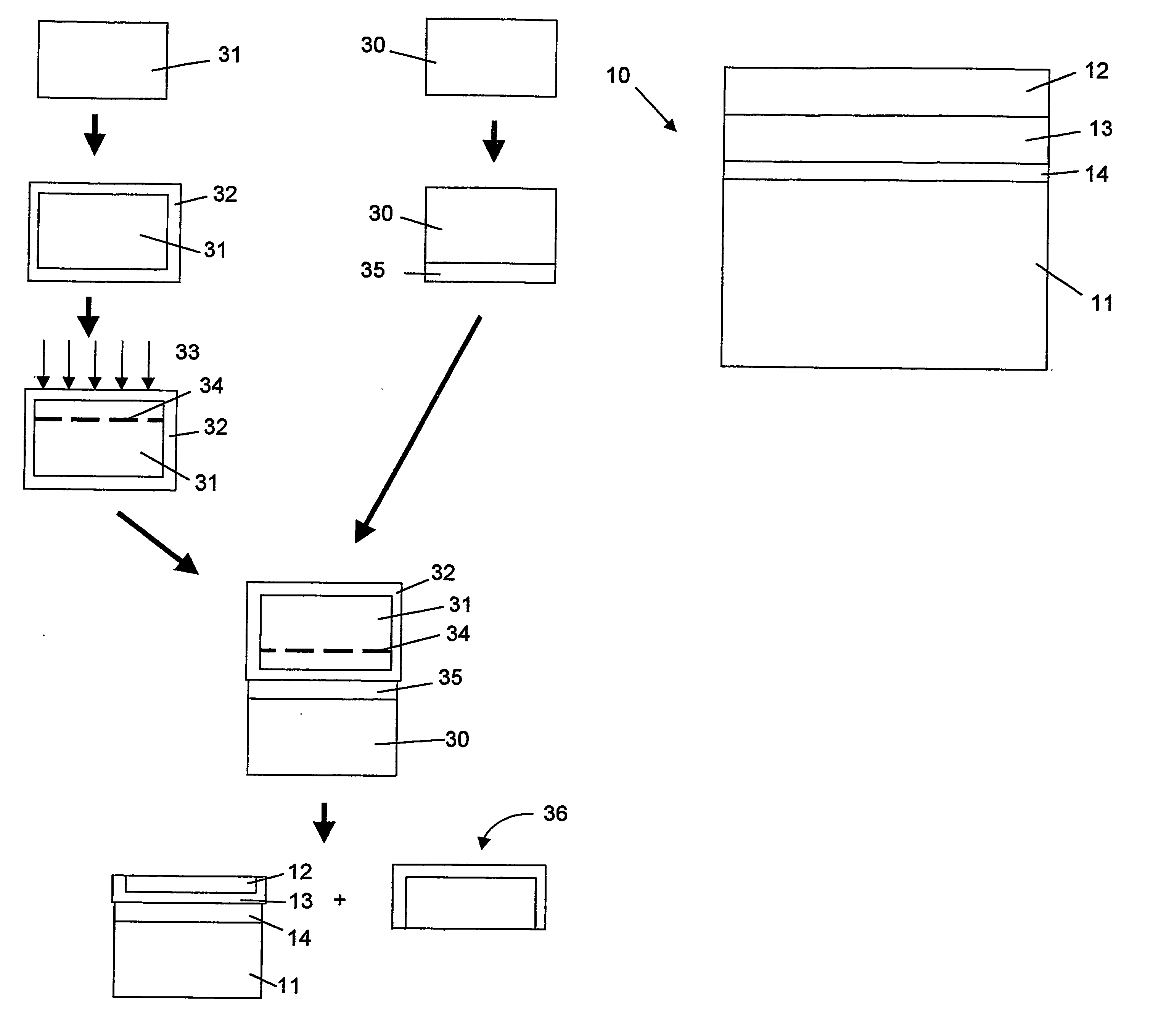
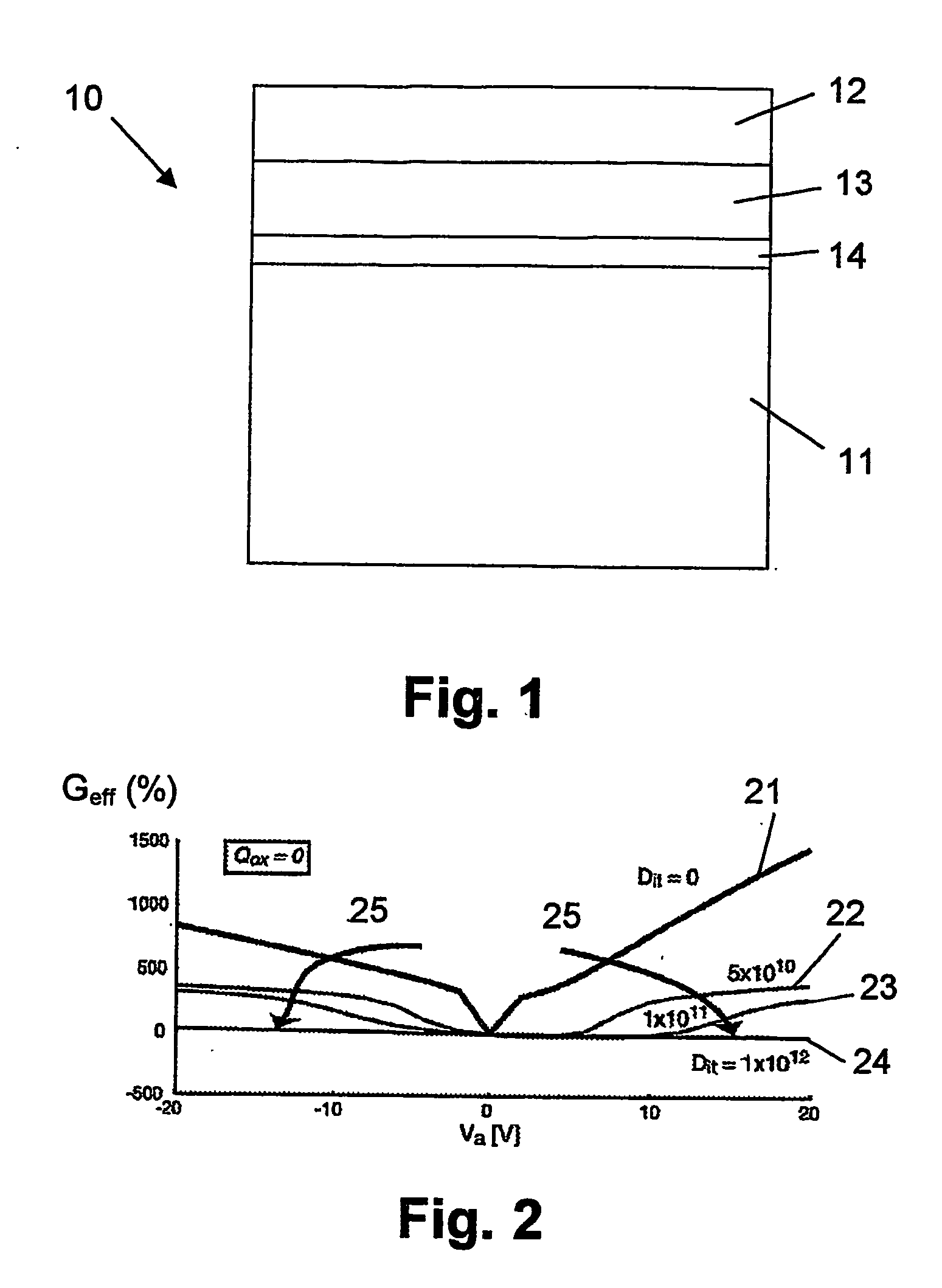
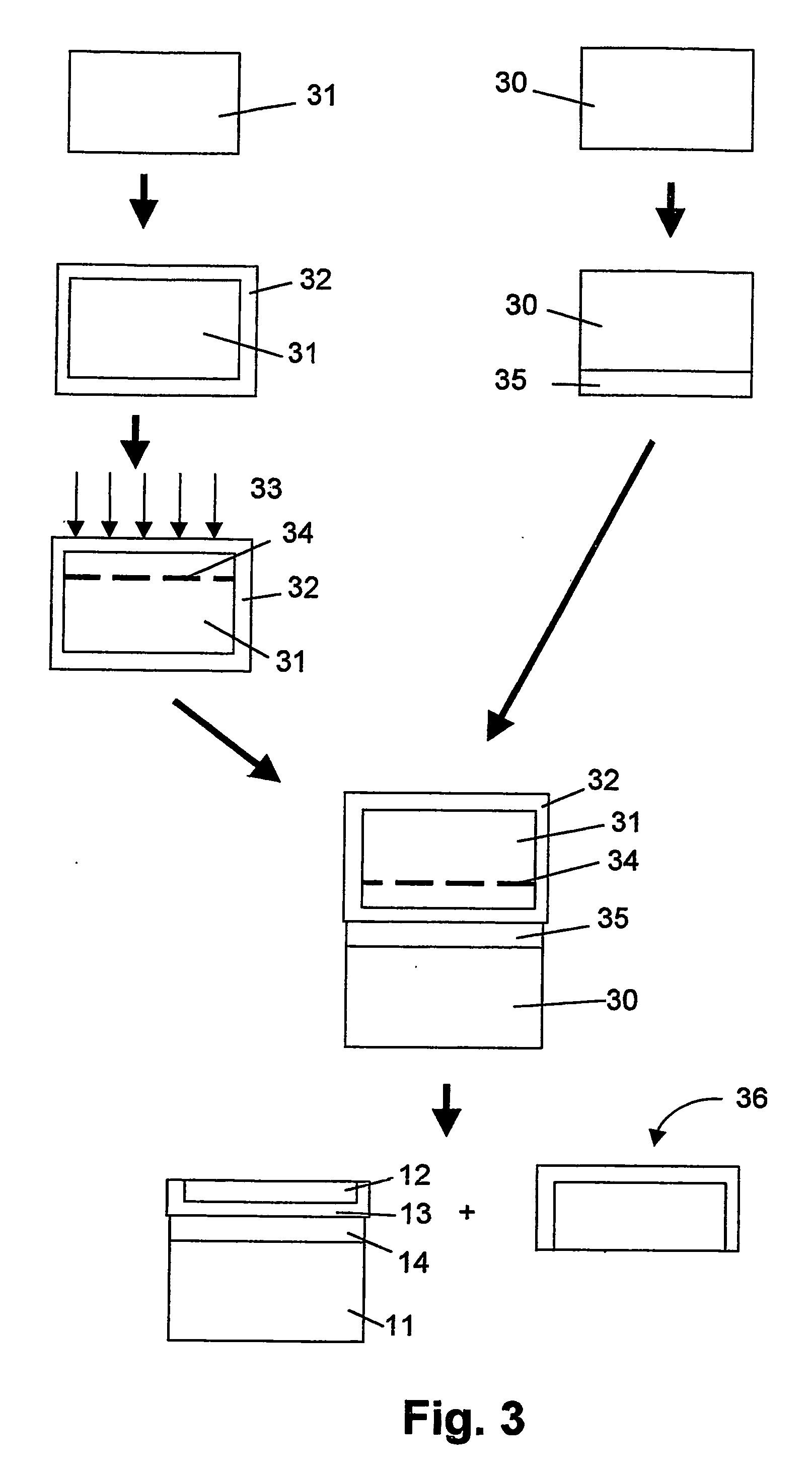
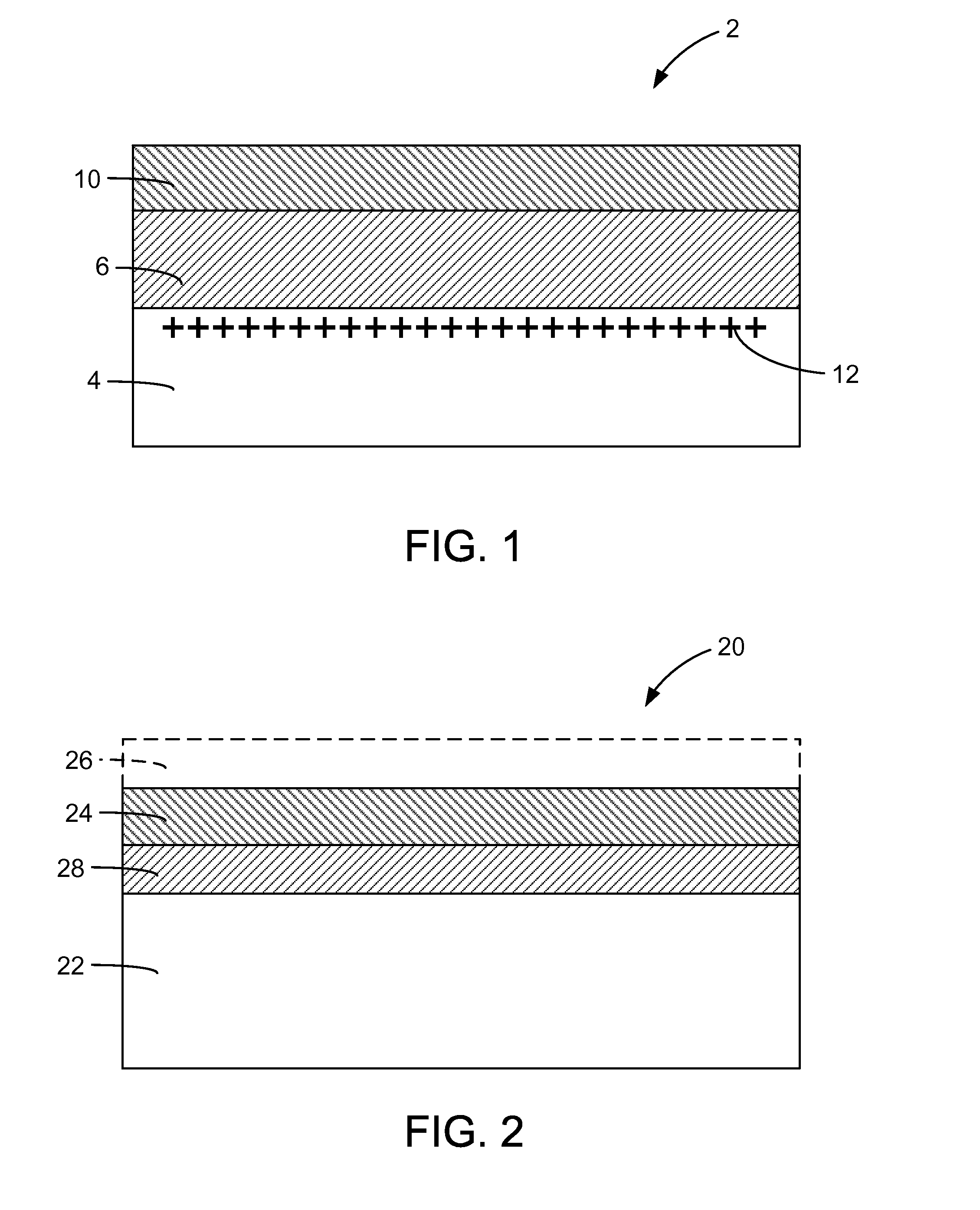
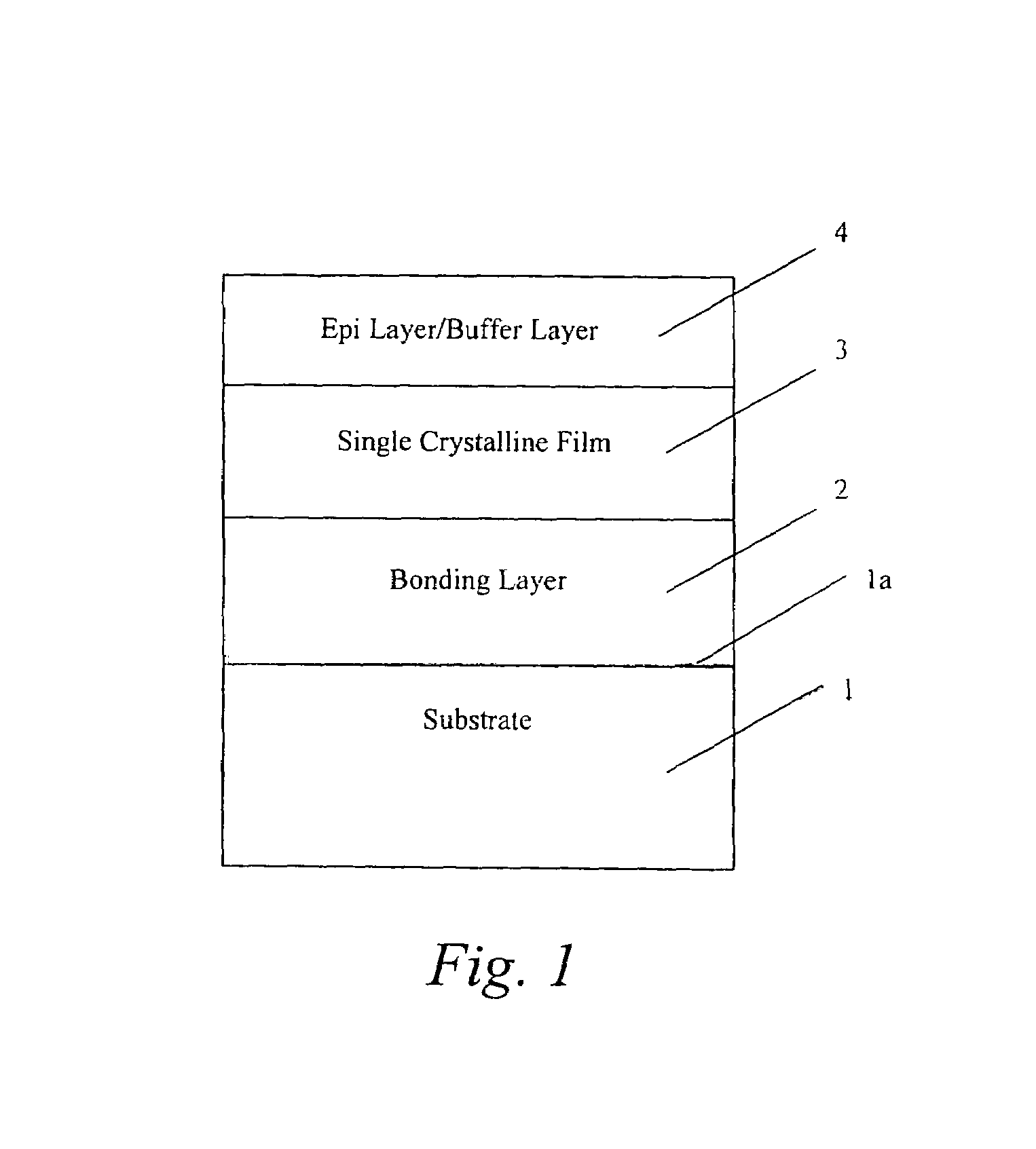
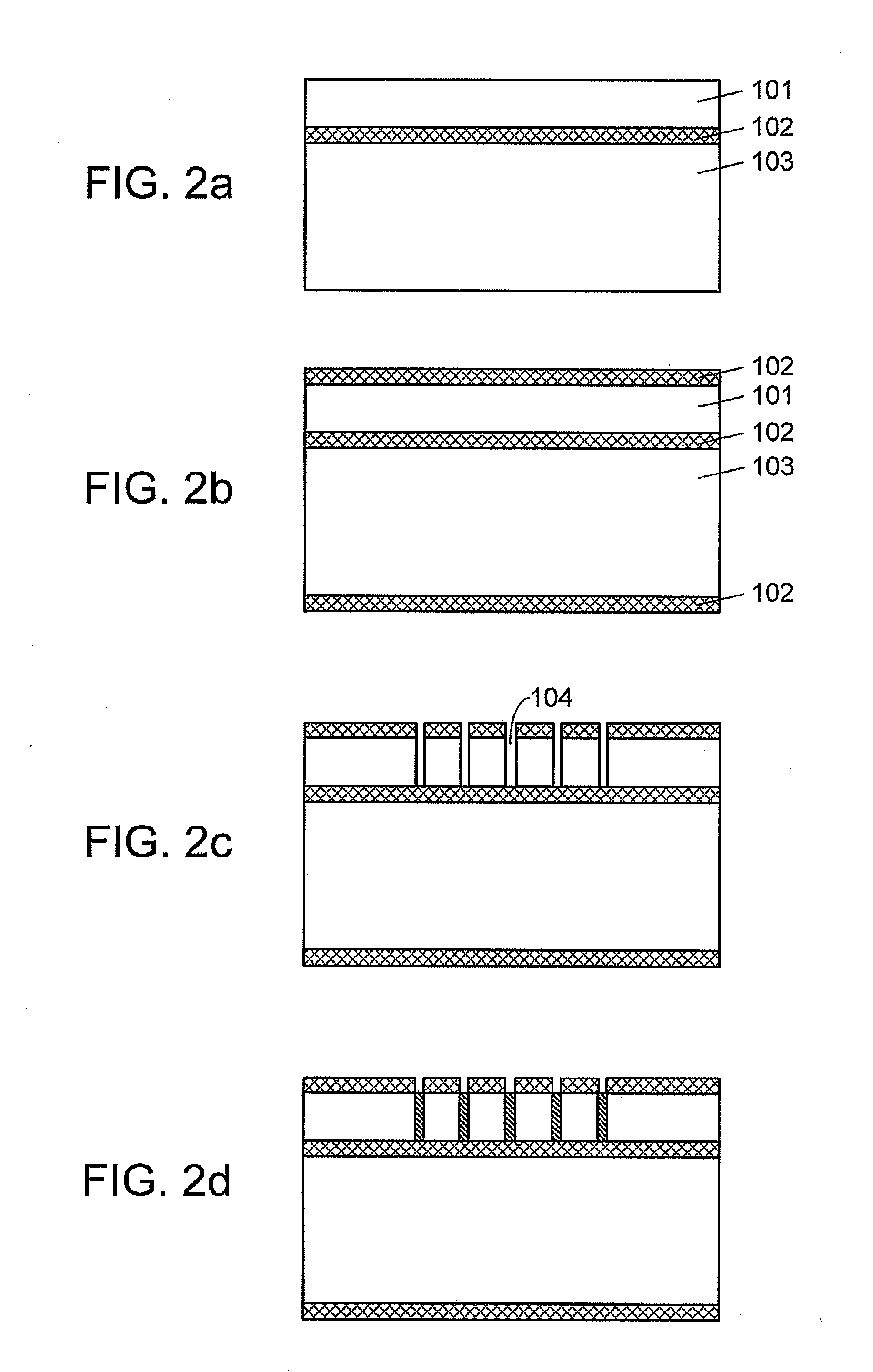
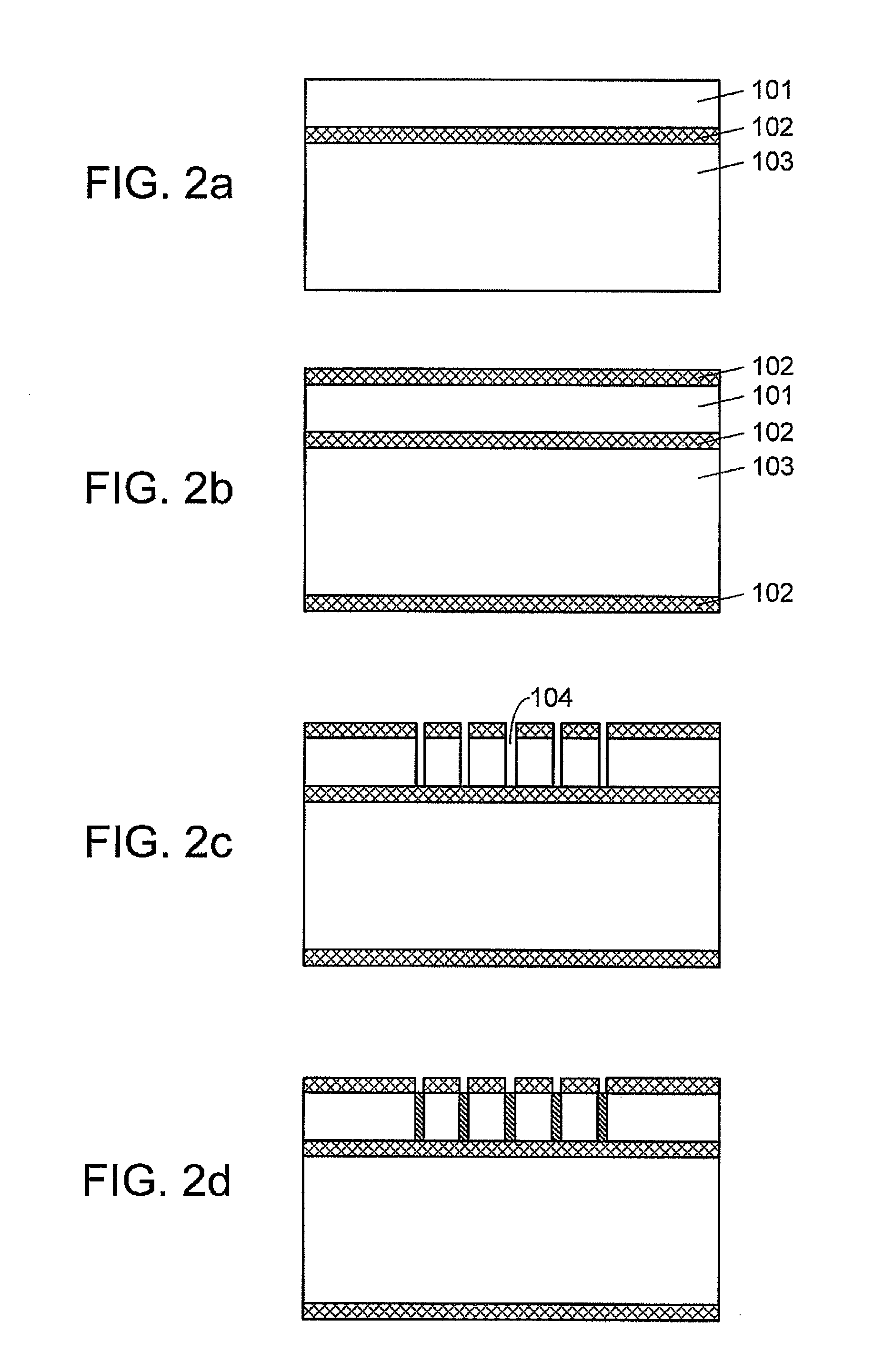
Method of manufacturing a multilayer semiconductor structure with reduced ohmic losses
InactiveUS20070032040A1Reduce and minimiseElectrical losses are reducedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInter layerSemiconductor structure
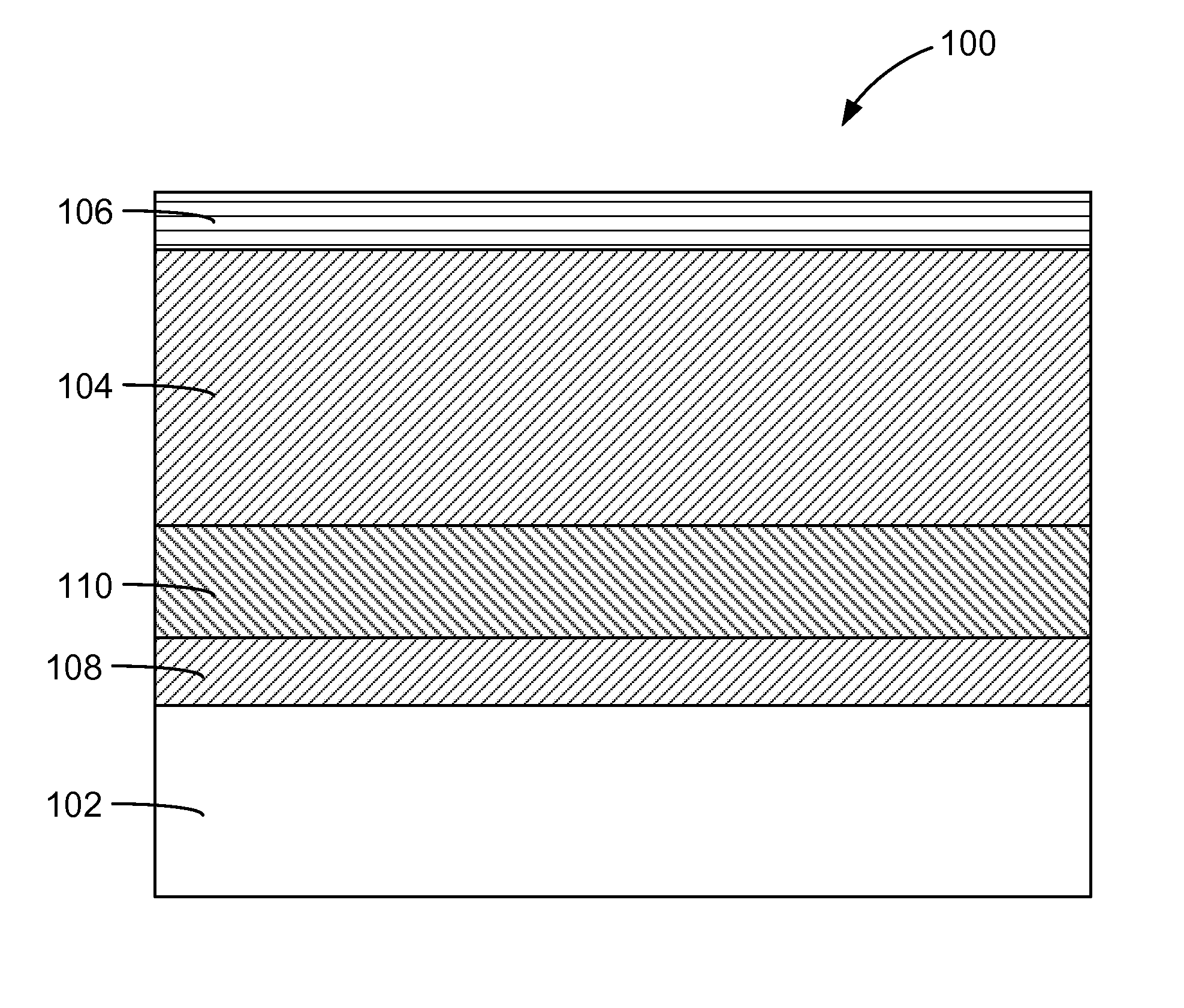
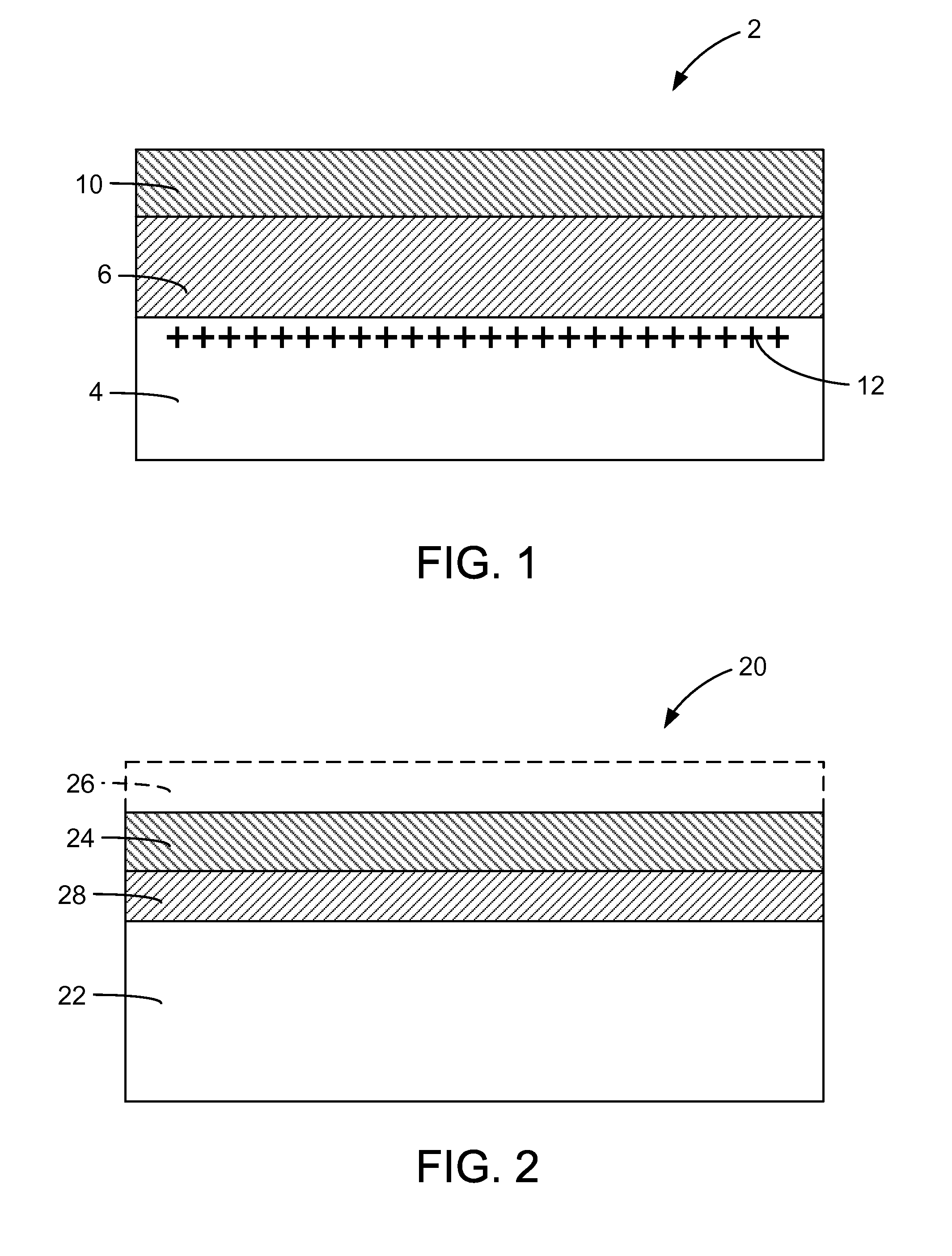
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a multilayer semiconductor structure featuring reduced ohmic losses with respect to standard multilayer semiconductor structures. The semiconductor structure comprises a high resistivity silicon substrate with resistivity higher than 3 KΩ.cm, an active semiconductor layer and an insulating layer in between the silicon substrate and the active semiconductor layer. The method comprises suppressing ohmic losses inside the high resistivity silicon substrate by increasing, with regard to prior art devices, charge trap density between the insulating layer and the silicon substrate. In particular this may be obtained by applying an intermediate layer in between the silicon substrate and the insulating layer, the intermediate layer comprising grains having a size, wherein the mean size of the grains of the intermediate layer is smaller than 150 nm, preferably smaller than 50 nm.
Owner:UNIV CATHOLIQUE DE LOVAIN
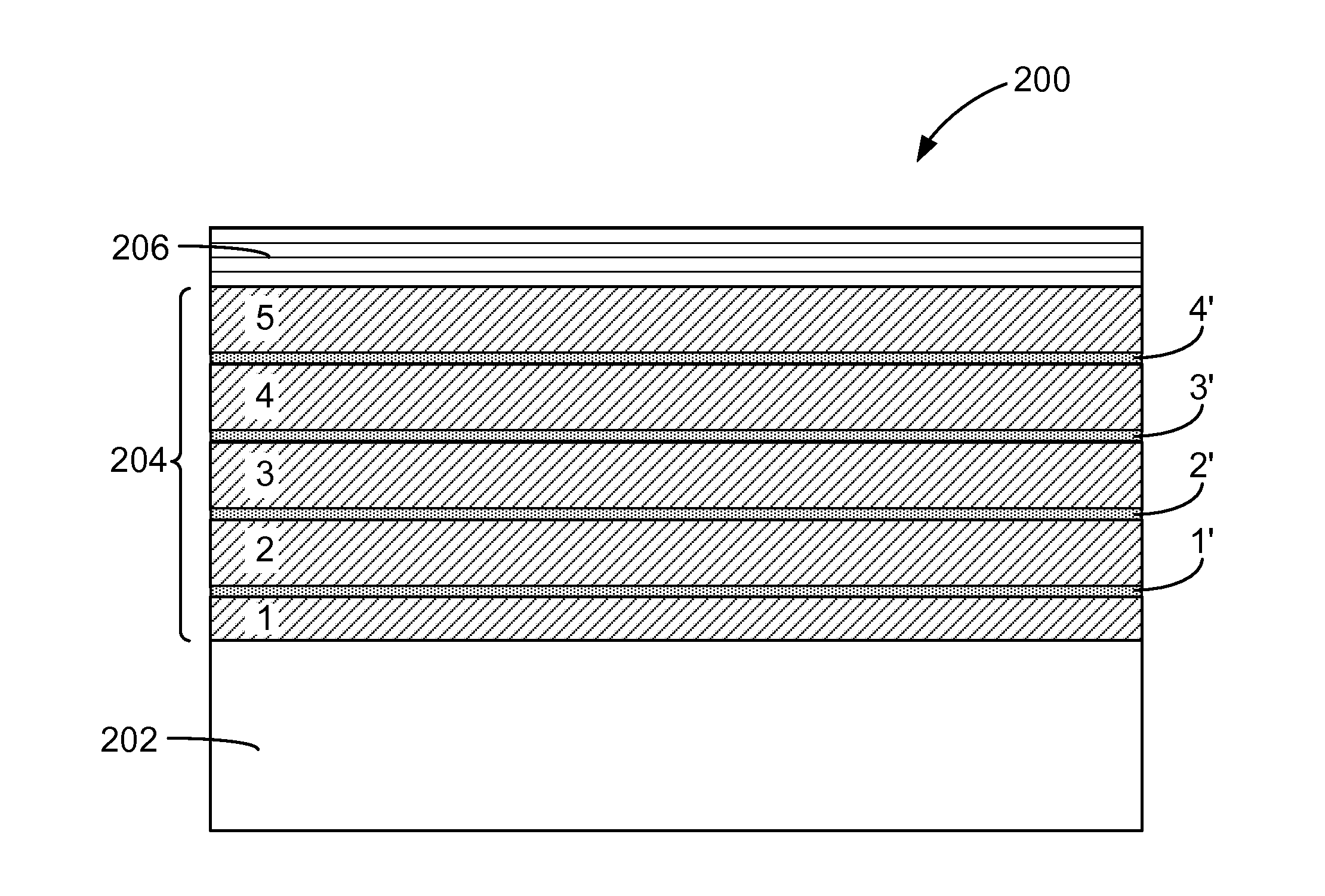
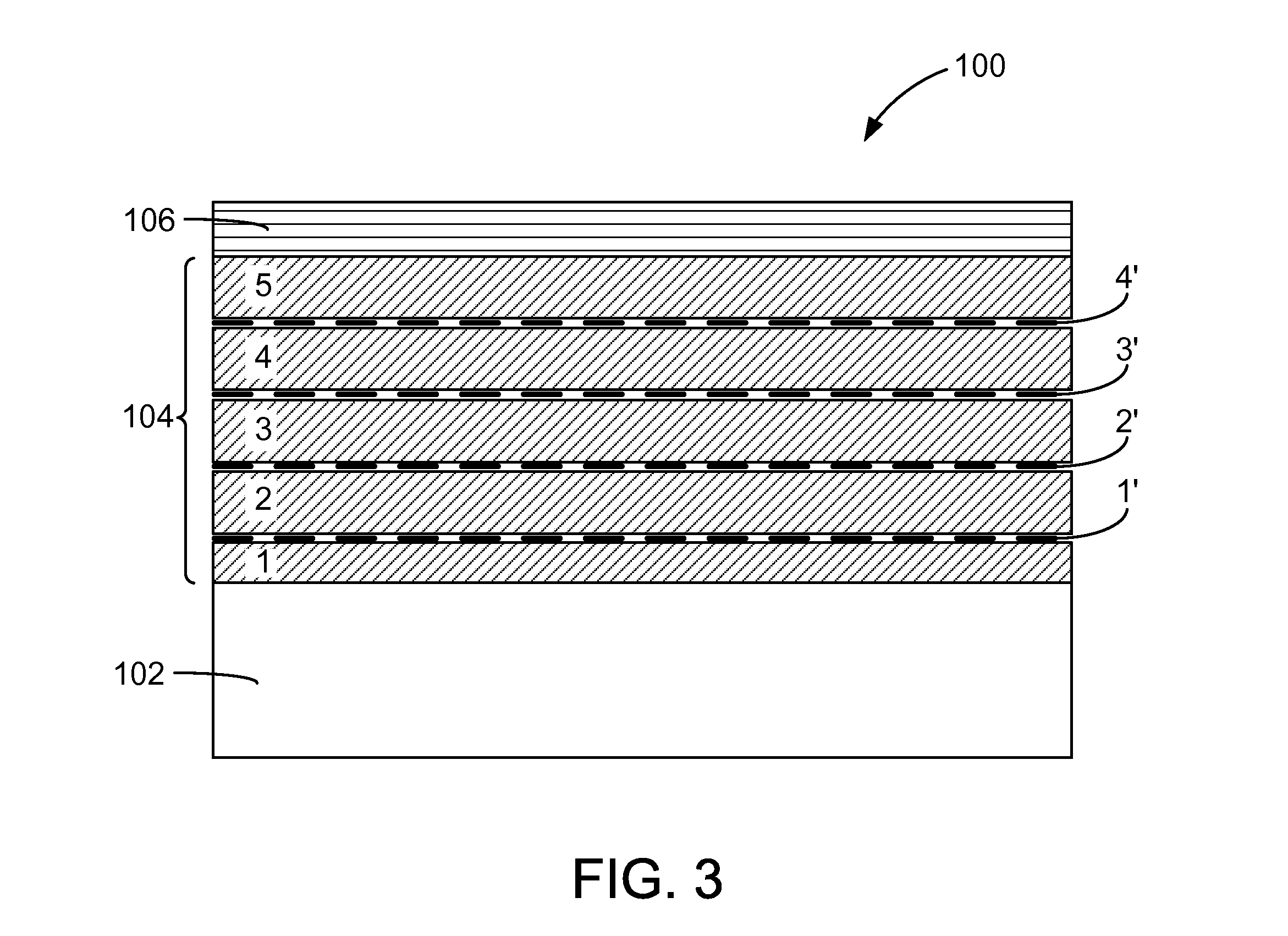
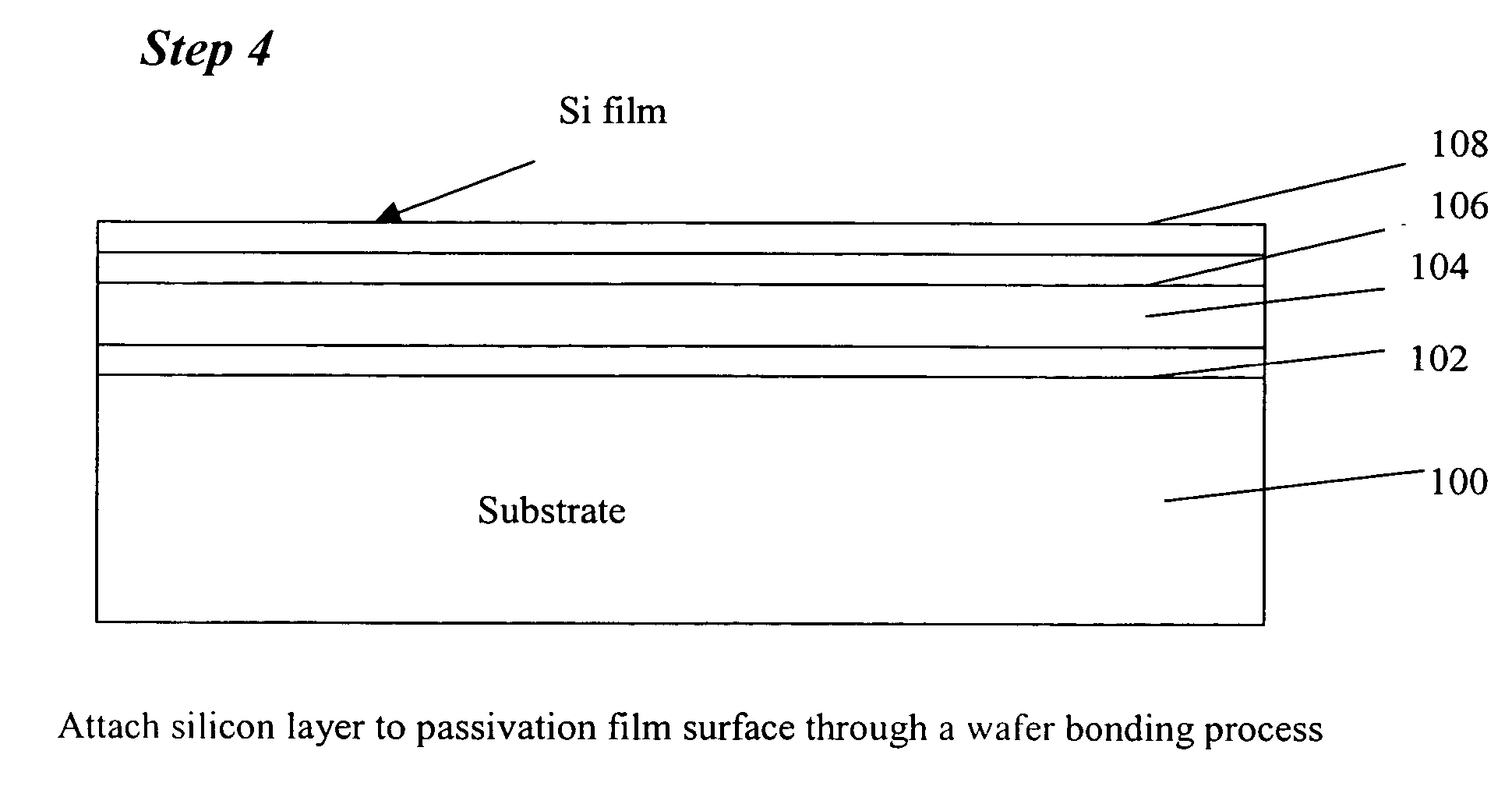
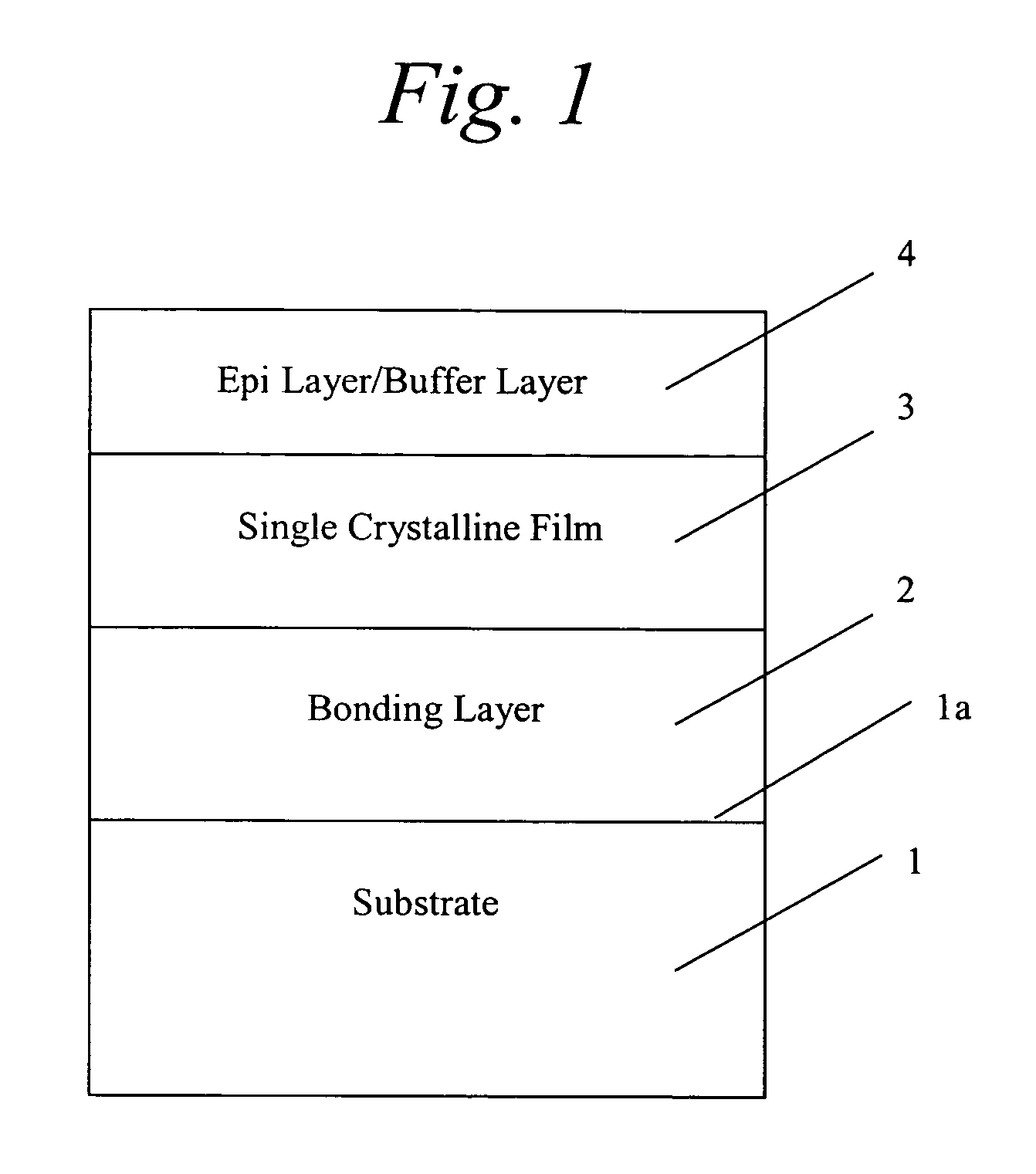
Method of manufacturing high resistivity soi wafers with charge trapping layers based on terminated si deposition
ActiveUS20150115480A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingSemiconductor structure
A method of preparing a single crystal semiconductor handle wafer in the manufacture of a silicon-on-insulator device is provided. The method comprises forming a multilayer of passivated semiconductors layers on a dielectric layer of a high resistivity single crystal semiconductor handle wafer. The method additionally comprises forming a semiconductor oxide layer on the multilayer of passivated semiconductor layers. The multilayer of passivated semiconductor layers comprise materials suitable for use as charge trapping layers between a high resistivity substrate and a buried oxide layer in a semiconductor on insulator structure.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
Novel method for integrating silicon CMOS and AlGaN/GaN wideband amplifiers on engineered substrates
ActiveUS20060284247A1Eliminate the problemSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSThin layer
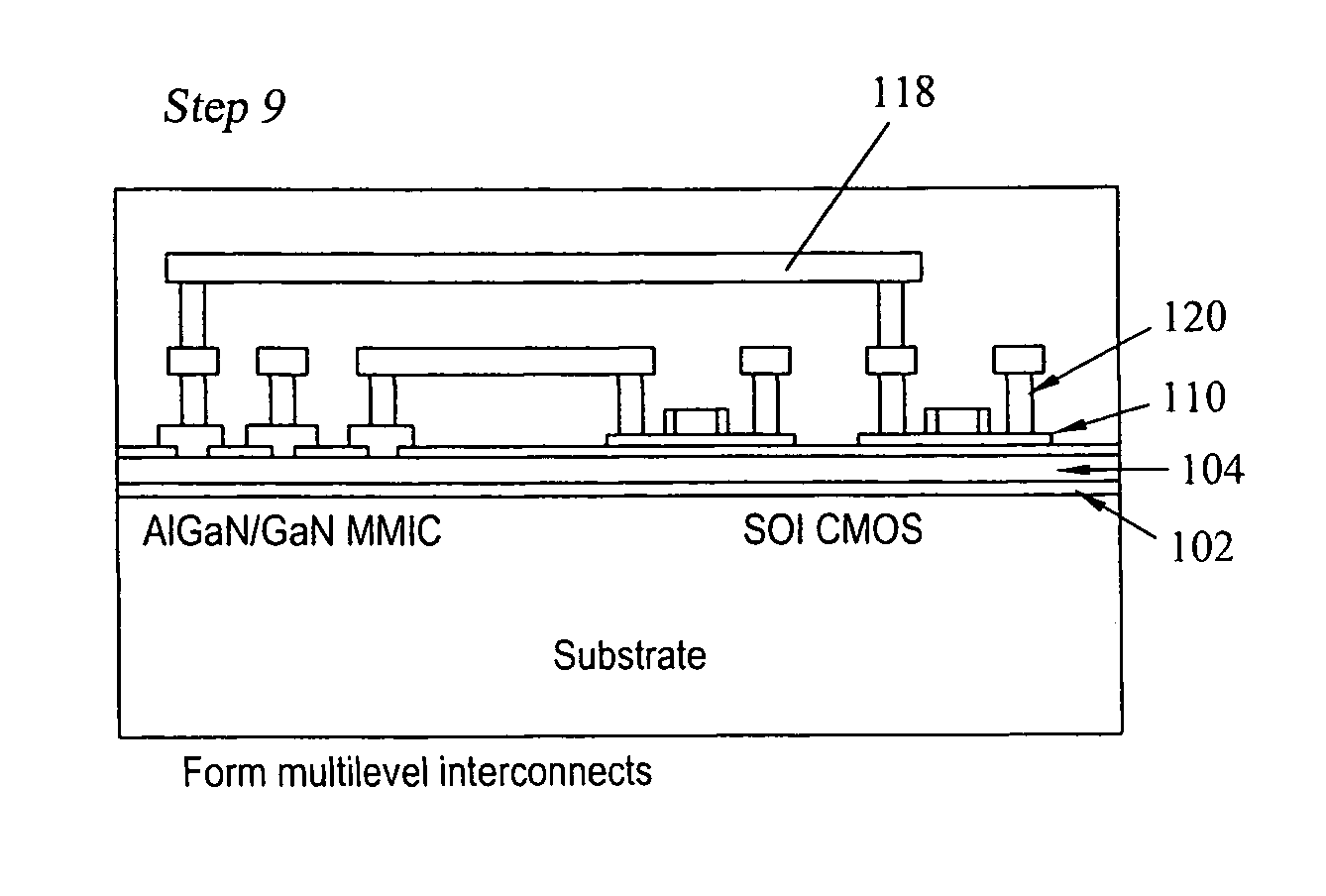
High-speed silicon CMOS circuits and high-power AlGaN / GaN amplifiers are integrated on the same wafer. A thin layer of high resistivity silicon is bonded on a substrate. Following the bonding, an AlGaN / GaN structure is grown over the bonded silicon layer. A silicon nitride or a silicon oxide layer is then deposited over the AlGaN / GaN structure. Following this, a thin layer of silicon is bonded to the silicon nitride / silicon oxide layer. An area for the fabrication of AlGaN / GaN devices is defined, and the silicon is etched away from those areas. Following this, CMOS devices are fabricated on the silicon layer and AlGaN / GaN devices fabricated on the AlGaN / GaN surface.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Low-resistivity photon-transparent window attached to photo-sensitive silicon detector
InactiveUS6025585ALow resistivityHigh resistivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOS sensorX-ray
The invention comprises a combination of a low resistivity, or electrically conducting, silicon layer that is transparent to long or short wavelength photons and is attached to the backside of a photon-sensitive layer of silicon, such as a silicon wafer or chip. The window is applied to photon sensitive silicon devices such as photodiodes, charge-coupled devices, active pixel sensors, low-energy x-ray sensors and other radiation detectors. The silicon window is applied to the back side of a photosensitive silicon wafer or chip so that photons can illuminate the device from the backside without interference from the circuit printed on the frontside. A voltage sufficient to fully deplete the high-resistivity photosensitive silicon volume of charge carriers is applied between the low-resistivity back window and the front, patterned, side of the device. This allows photon-induced charge created at the backside to reach the front side of the device and to be processed by any circuitry attached to the front side. Using the inventive combination, the photon sensitive silicon layer does not need to be thinned beyond standard fabrication methods in order to achieve full charge-depletion in the silicon volume. In one embodiment, the inventive backside window is applied to high resistivity silicon to allow backside illumination while maintaining charge isolation in CCD pixels.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Porous and non-porous nanostructures
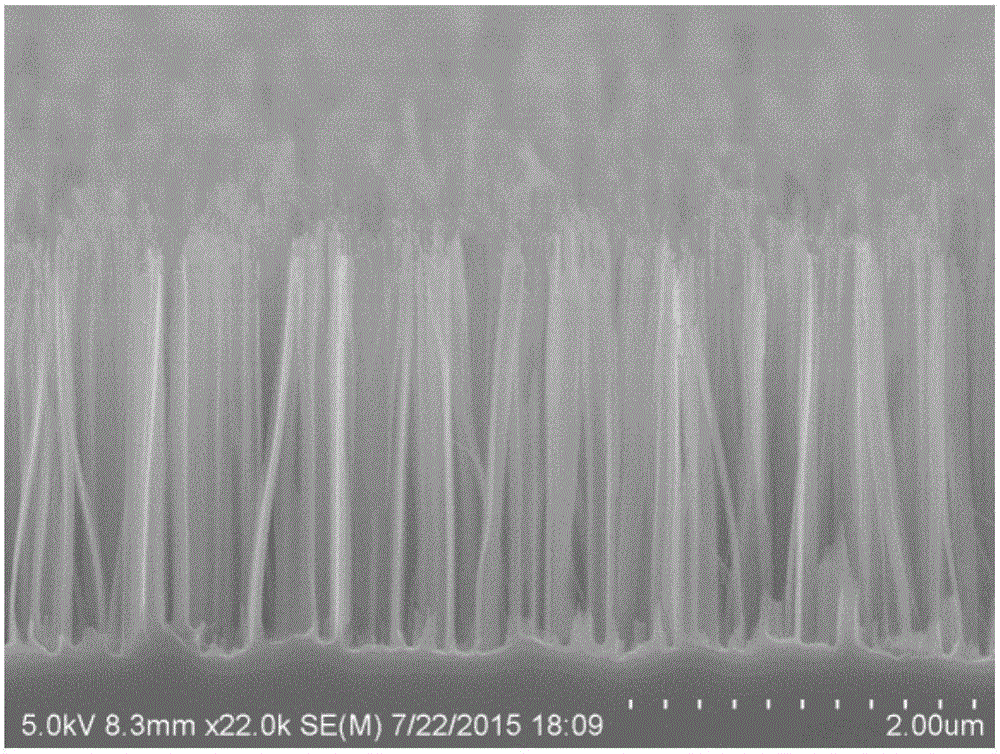
ActiveUS20110266521A1Material nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsHigh resistivity siliconMicroscopic scale
Disclosed are a variety of porous and non-porous wire-like structures of microscopic and nanoscopic scale. For instance, disclosed are structures that comprise a porous object that comprises: (i) a first region; and (ii) a second region adjacent to the first region along an axis of the object, where the first region has at least one porous property different from that of the second region. Also disclosed are structures that include: (i) a high resistivity silicon; and (ii) a cross-section that is substantially perpendicular to an axis of the object. Also disclosed are methods of making and using such structures. For instance, the present invention provides methods of making a porous object by: (i) obtaining an etchable substrate; (ii) forming on a surface of the substrate a patterned porosification assisting metal layer that has at least one opening; and (iii) subsequently exposing the substrate to a first etching solution and a second etching solution to form respectively a first region and a second region of a porous object.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
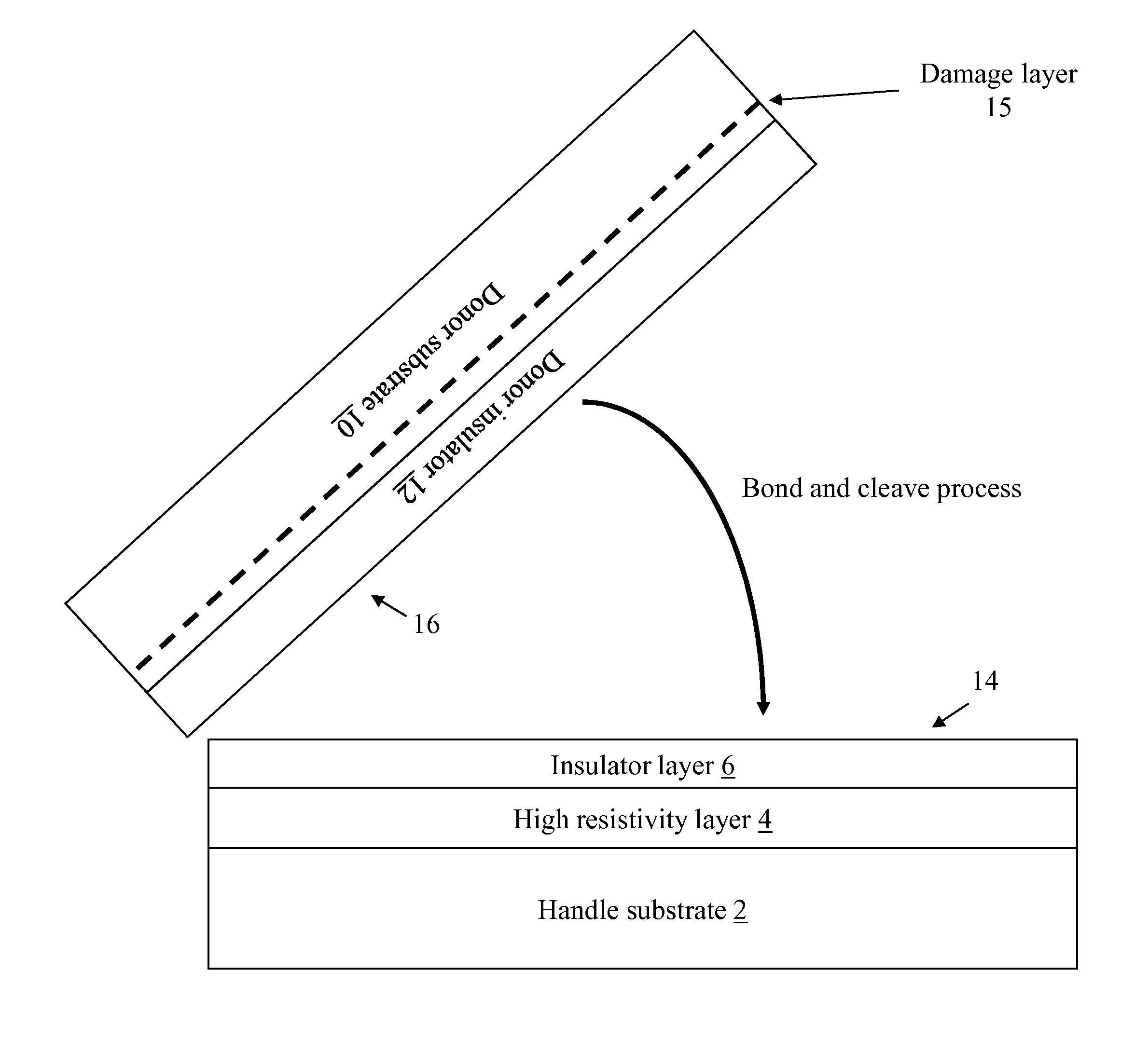
High resistivity silicon-on-insulator substrate and method of forming
InactiveUS20140124902A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingSemiconductor structure
A semiconductor structure and a method of forming the same. In one embodiment, a method of forming a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafer substrate includes: providing a handle substrate; forming a high resistivity material layer over the handle substrate, the high resistivity material layer including one of an amorphous silicon carbide (SiC), a polycrystalline SiC, an amorphous diamond, or a polycrystalline diamond; forming an insulator layer over the high resistivity material layer; and bonding a donor wafer to a top surface of the insulator layer to form the SOI wafer substrate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
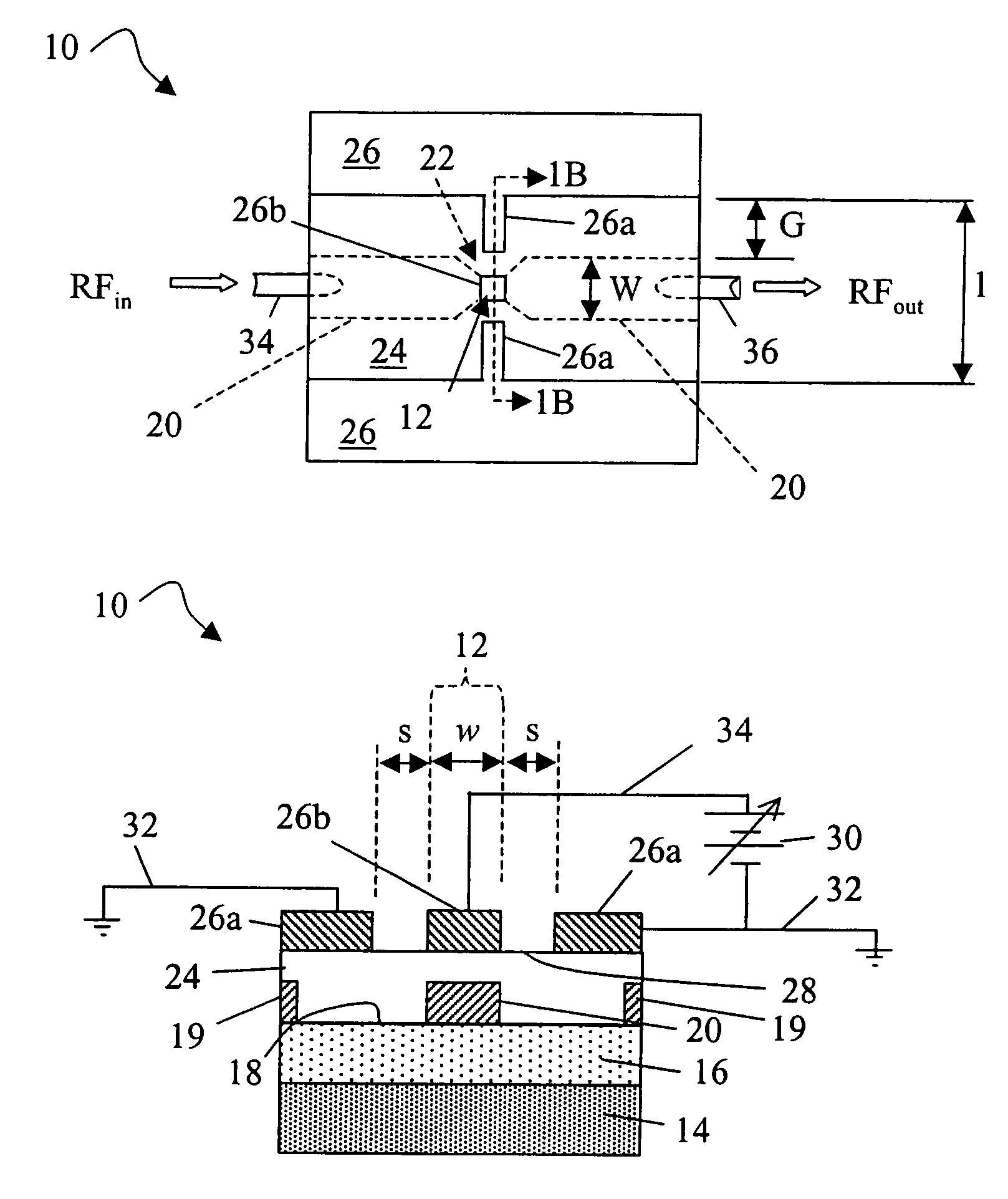
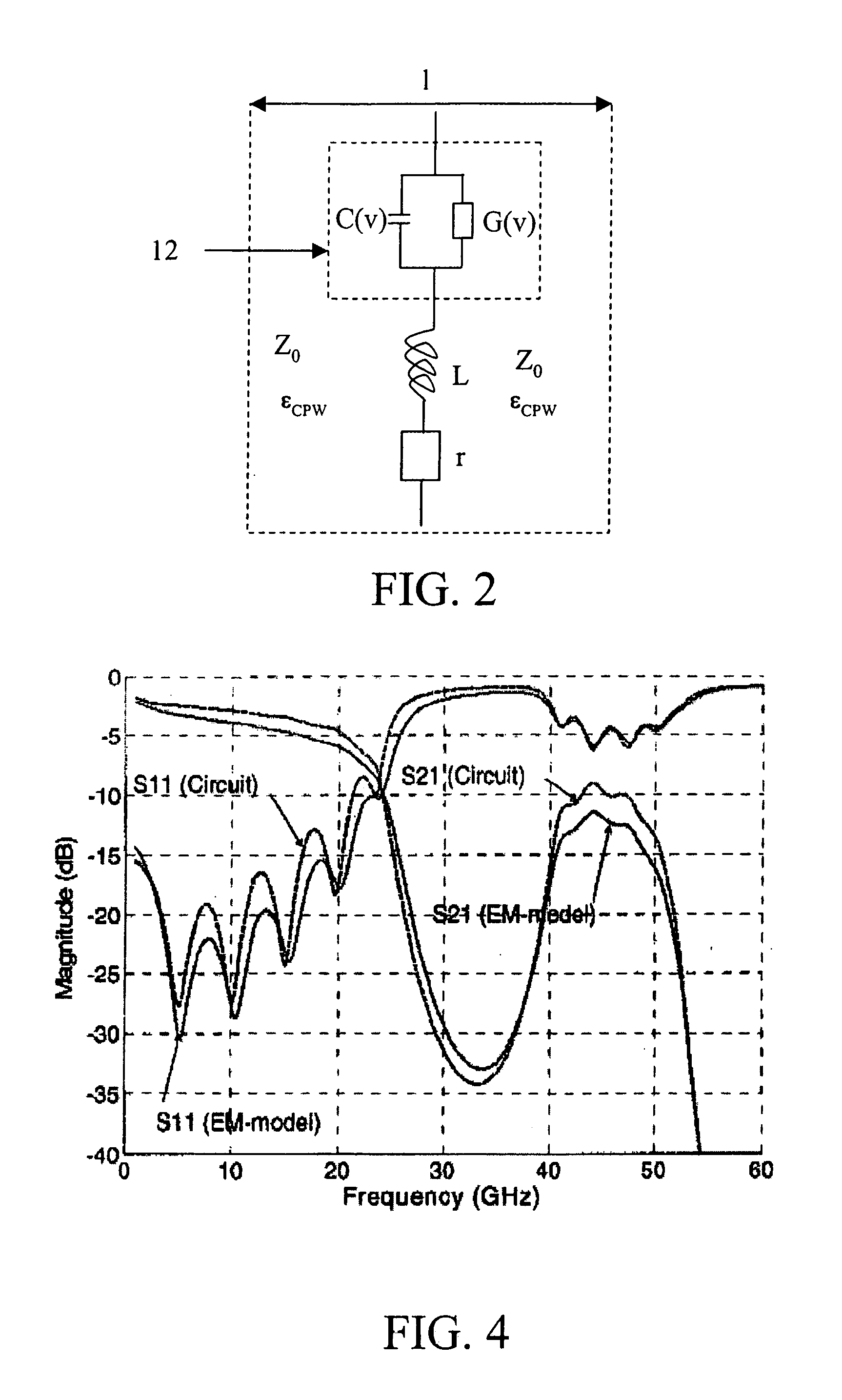
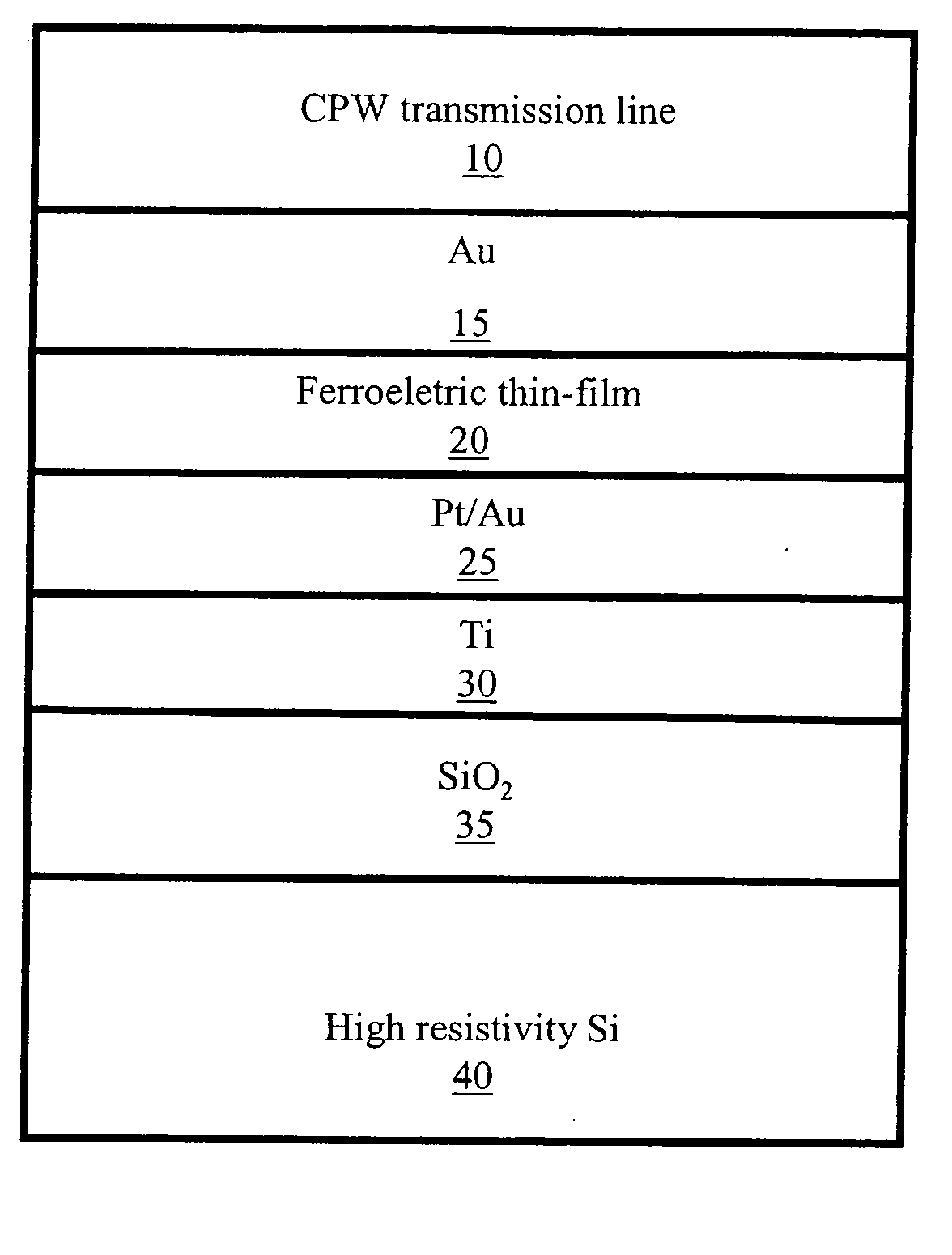
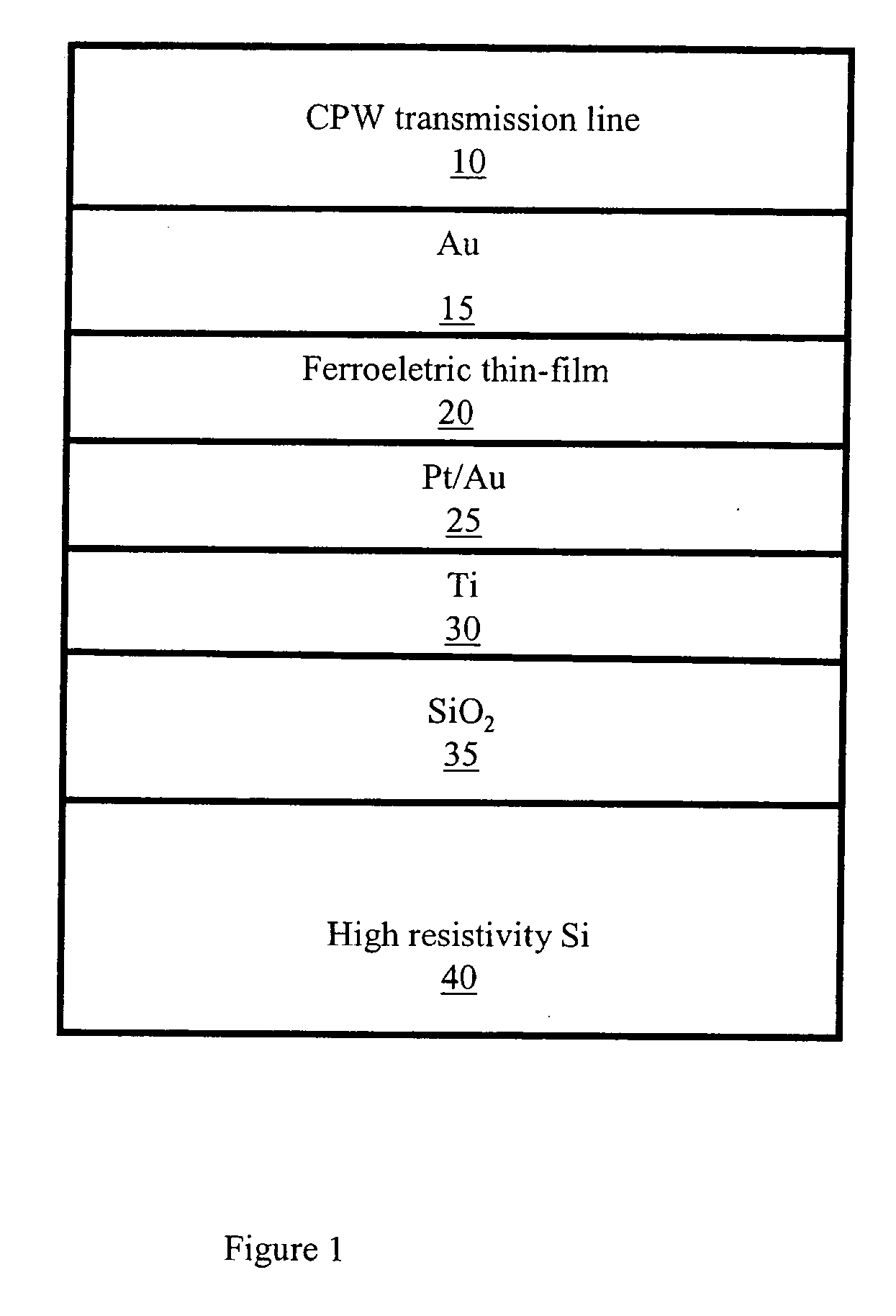
Tuneable electromagnetic bandgap structures based on high resistivity silicon substrates
ActiveUS7030463B1Small sizeSmall size and tunableCapacitor with electrode distance variationCapacitor with temperature varied dielectricFerroelectric thin filmsHigh resistivity silicon
Electrically tunable electromagnetic bandgap (“TEBG”) structures using a ferroelectric thin film on a semiconductor substrate, tunable devices that include such a TEBG structure, such as a monolithic microwave integrated circuit (“MMIC”), and a method producing such a TEBG structure are disclosed. The present invention provides a semiconductive substrate having an oxide layer, a first conductive layer positioned on the oxide layer, a ferroelectric layer covering the first conductive layer, and a second conductive layer positioned on a surface of the tunable ferroelectric layer. The use of the ferroelectric layer, which have a DC electric field dependent permittivity, enables a small size, tunable EBG structure.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON THE
High resistivity silicon-on-insulator structure and method of manufacture thereof
ActiveUS20180158721A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureTrapping
A multilayer structure is provided, the multilayer structure comprising a semiconductor on insulator structure comprises an insulating layer that enhances the stability of the underlying charge trapping layer.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
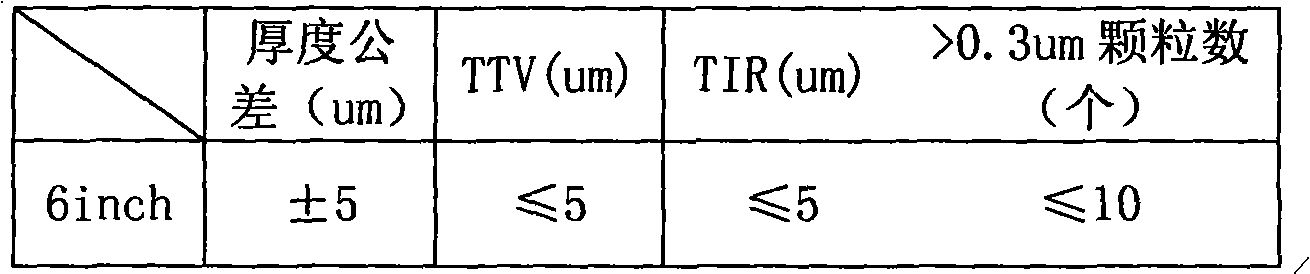
High resistivity silicon wafer and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100224968A1Avoid it happening againHigh mechanical strengthPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantCzochralski method
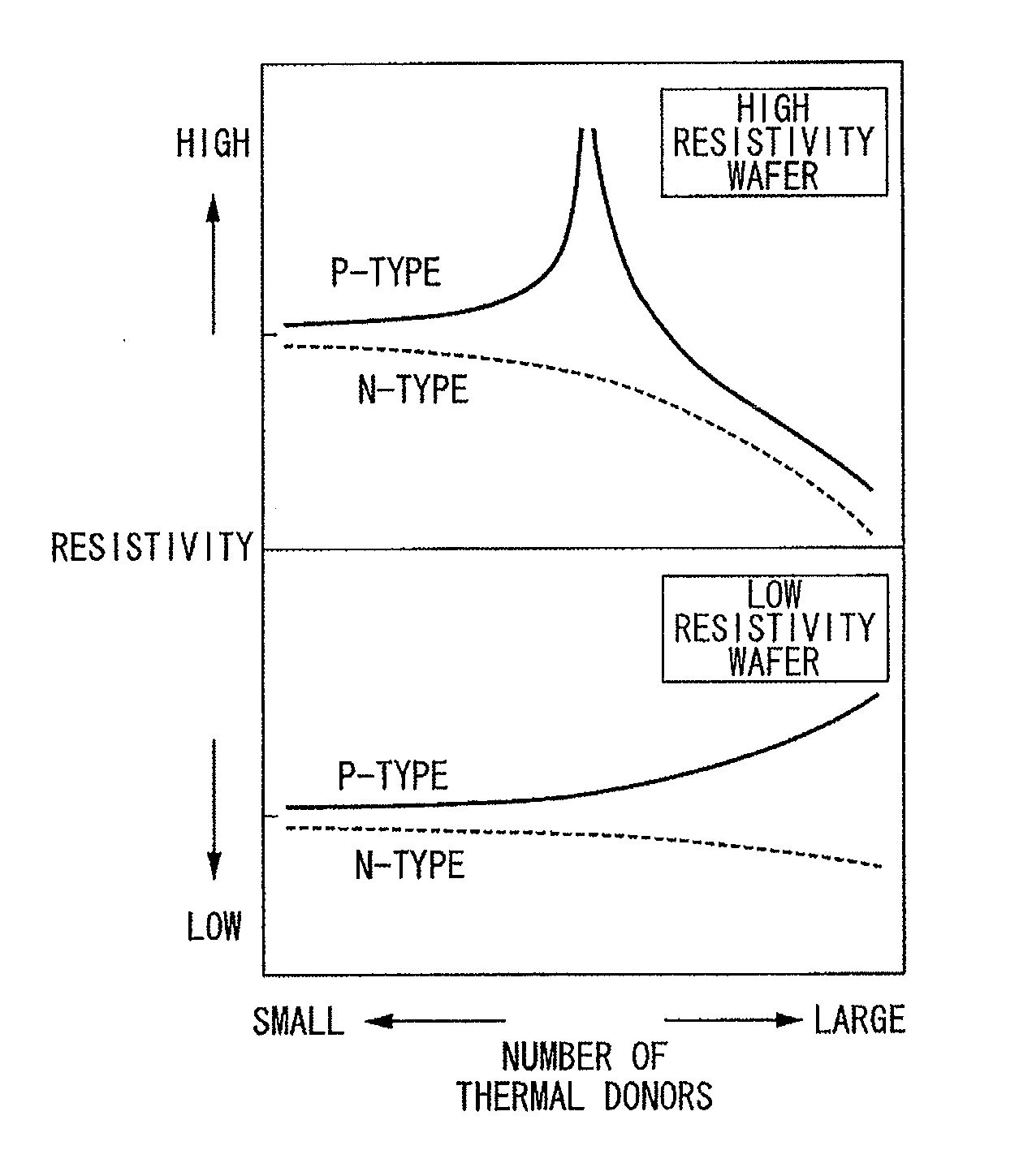
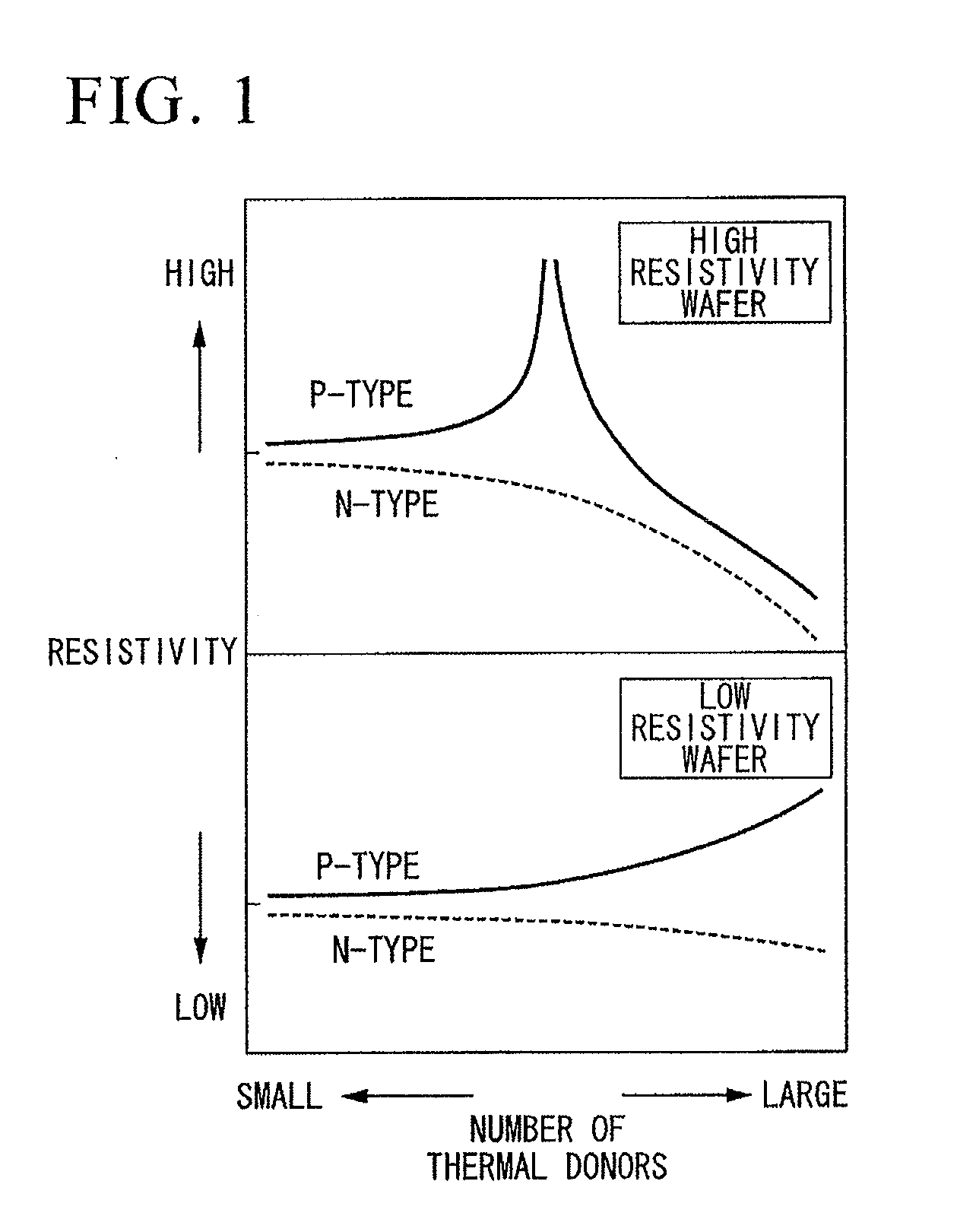
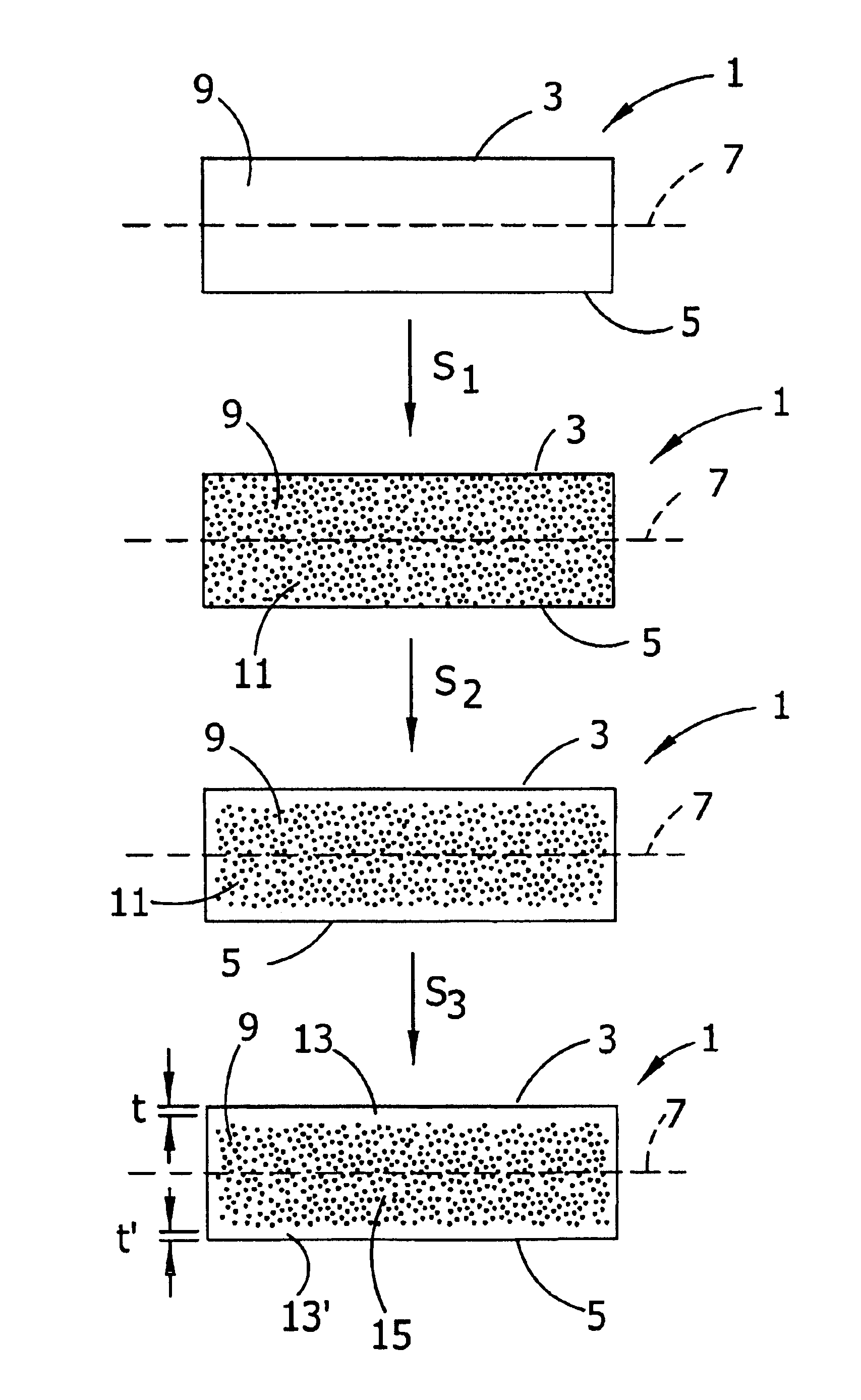
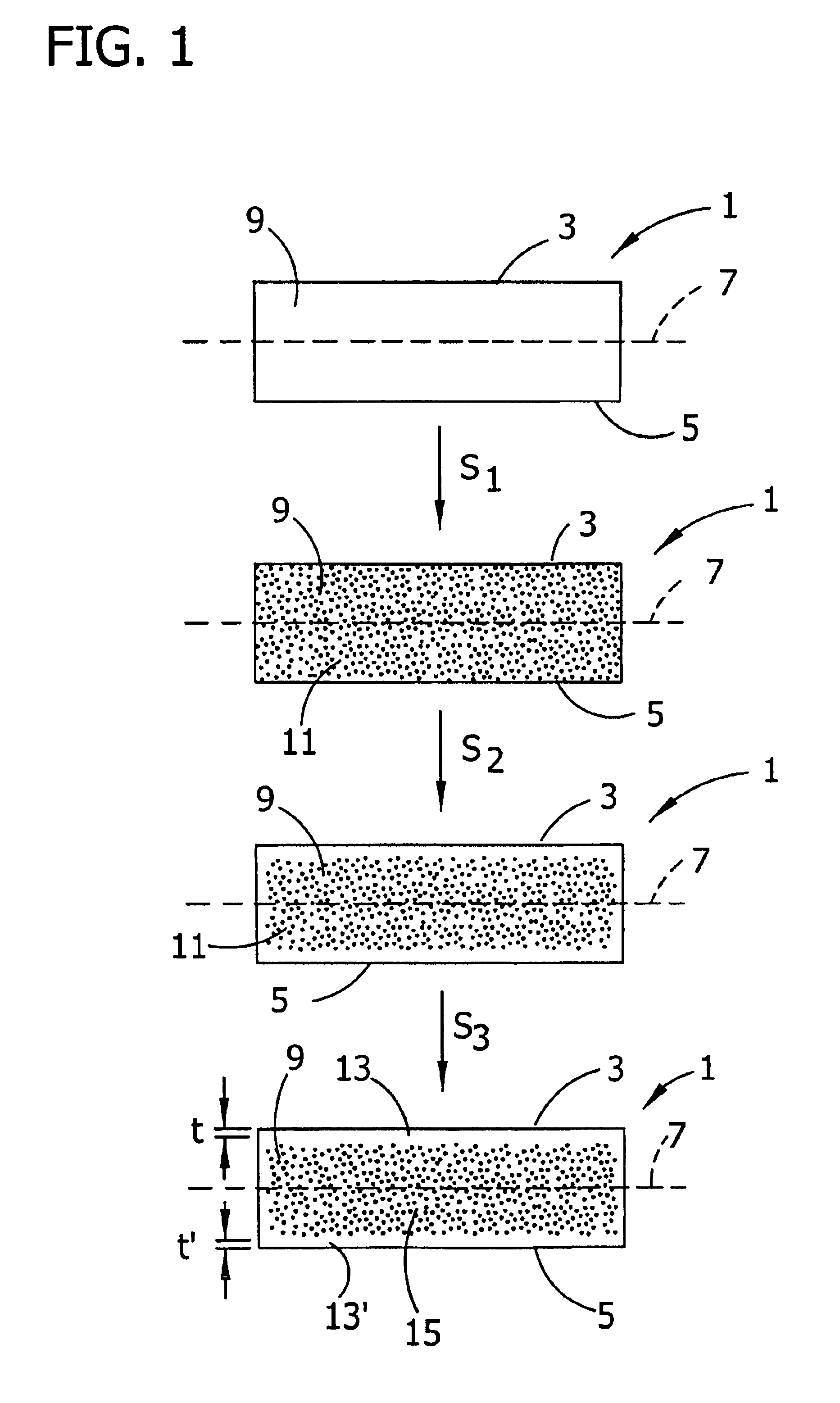
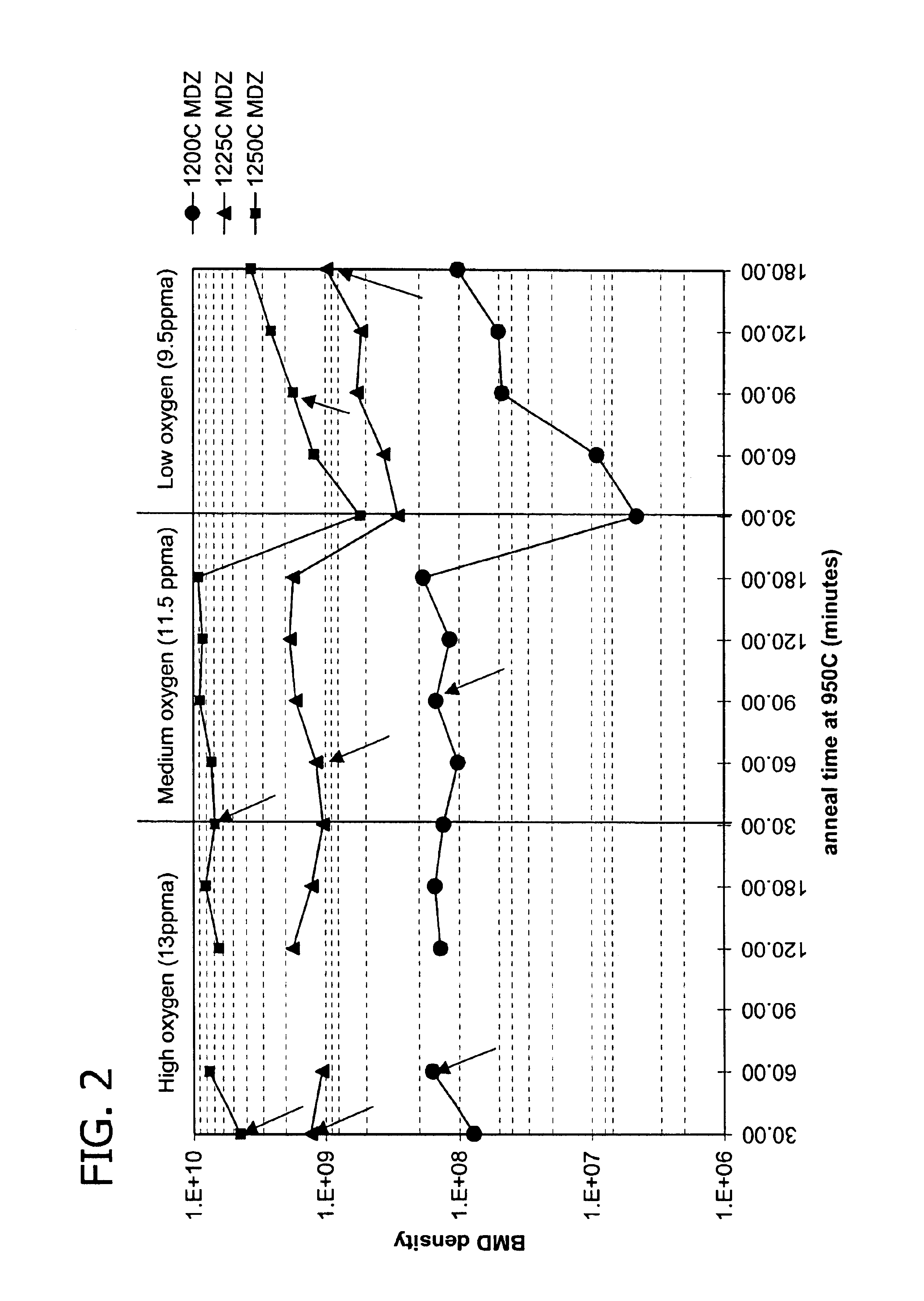
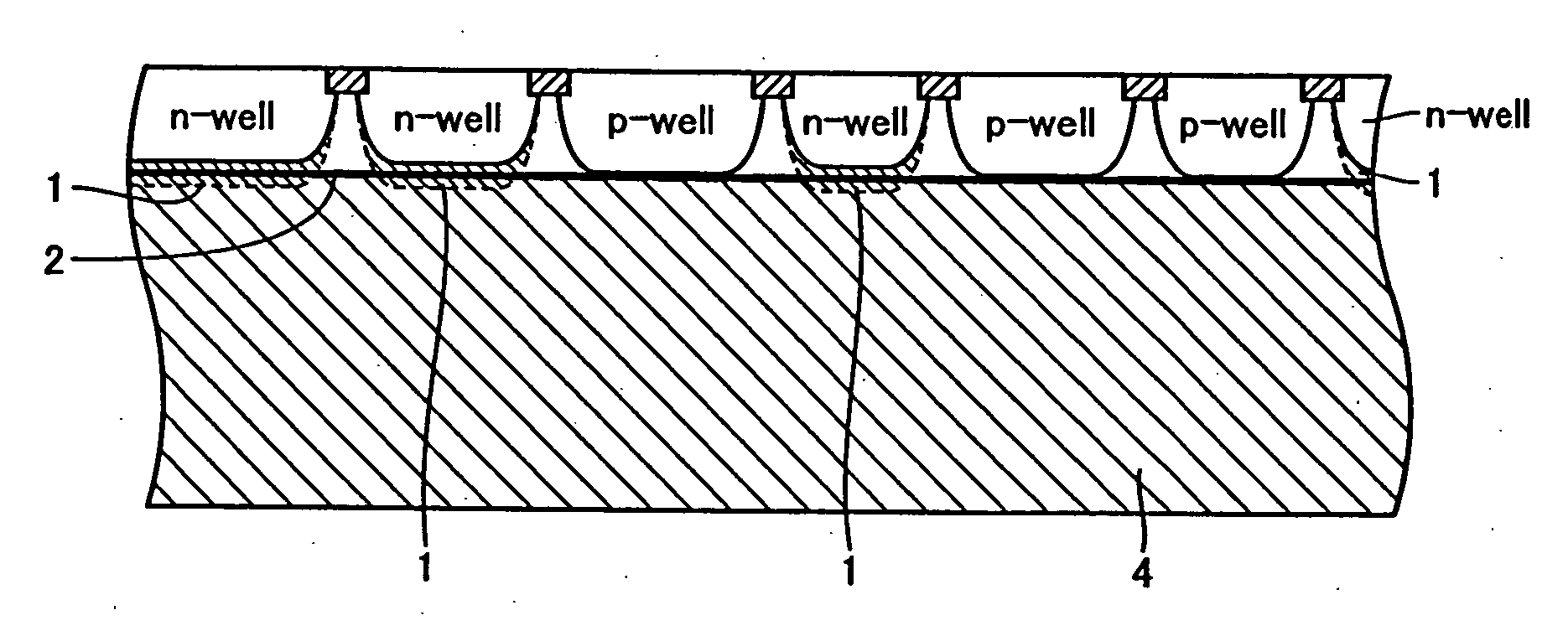
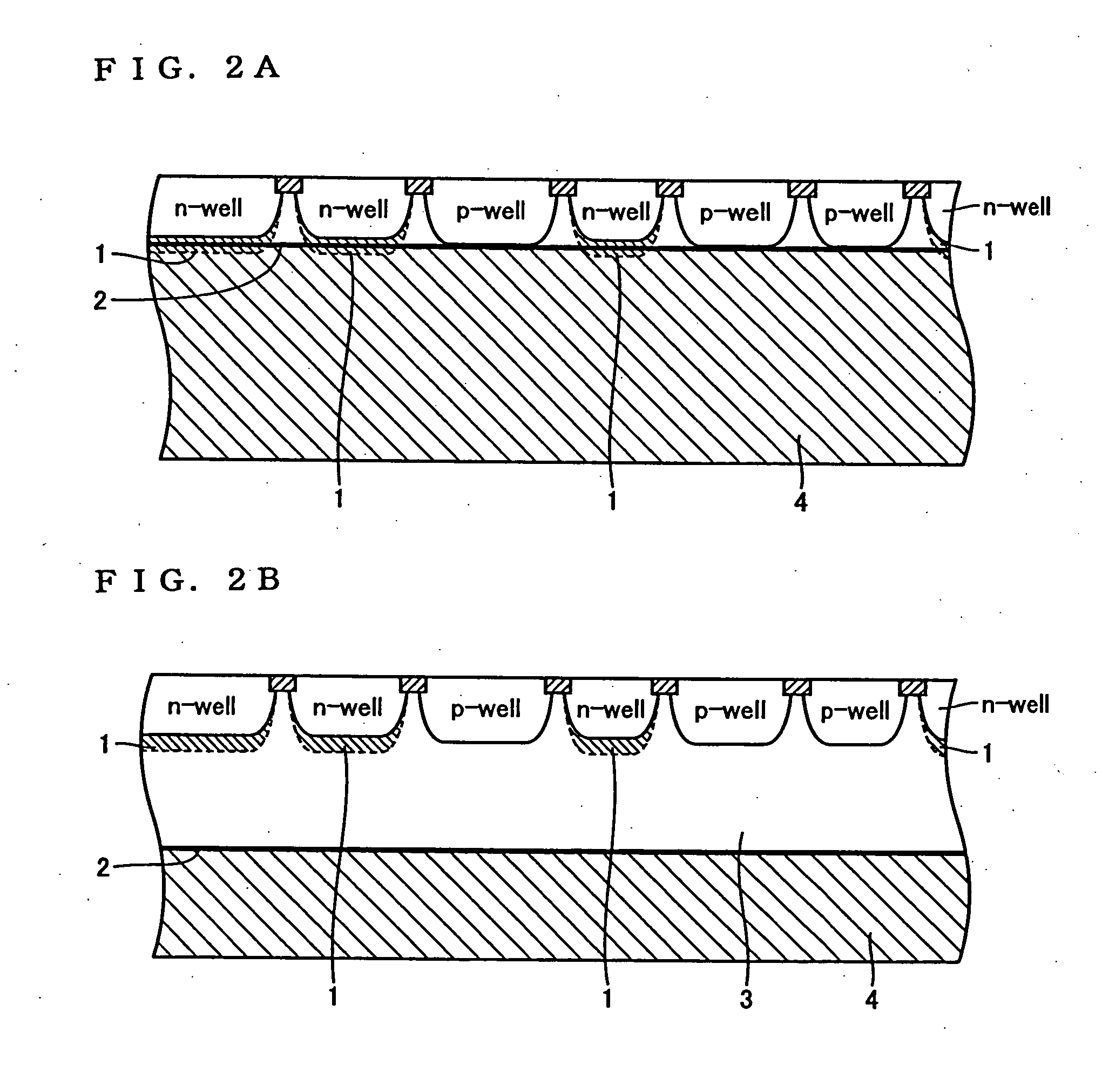
This method for manufacturing a high resistivity silicon wafer includes pulling a single crystal such that the single crystal has a p-type dopant concentration at which a wafer surface resistivity becomes in a range of 0.1 to 10 kΩcm, an oxygen concentration Oi of 5.0×1017 to 20×1017 atoms / cm3 (ASTM F-121, 1979), and either one of a nitrogen concentration of 1.0×1013 to 10×1013 atoms / cm3 (ASTM F-121, 1979) and a carbon concentration of 0.5×1016 to 10×1016 atoms / cm3 or 0.5×1016 to 50×1016 atoms / cm3 (ASTM F-123, 1981) by using a Czochralski method, processing the single crystal into wafers by slicing the single crystal, and subjecting the wafer to an oxygen out-diffusion heat treatment process in a non-oxidizing atmosphere. A peak position of a resistivity serving as a boundary between a p-type region of a wafer surface side and a p / n conversion region of an inner side of a thickness direction is adjusted by the nitrogen concentration or the carbon concentration such that the peak position is set to a boundary depth in a range of 10 to 70 μm from the wafer surface.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
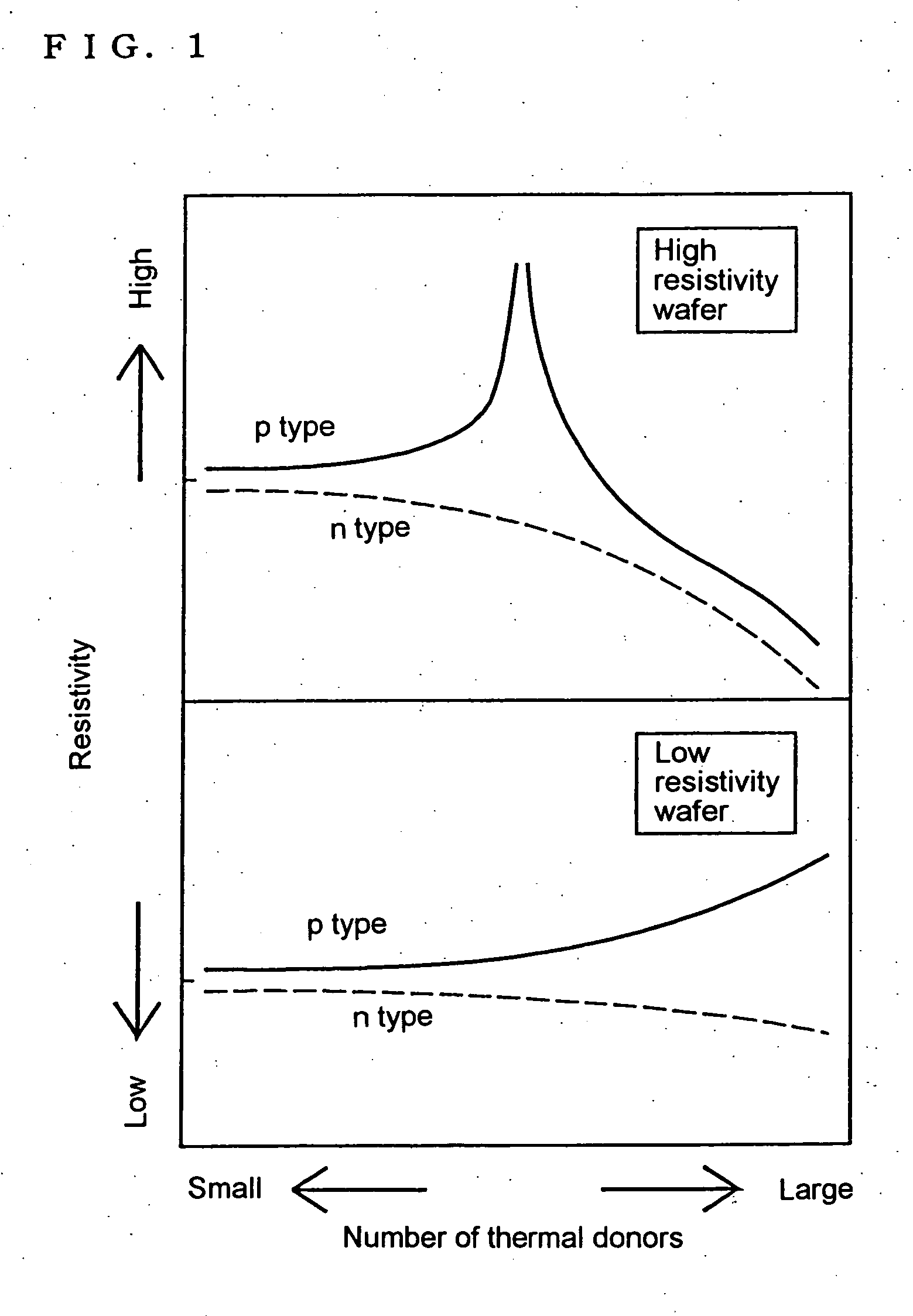
Control of oxygen precipitate formation in high resistivity CZ silicon
InactiveUS6897084B2Layer is highHigh resistivityAfter-treatment detailsSolid-state devicesSurface layerHigh resistivity
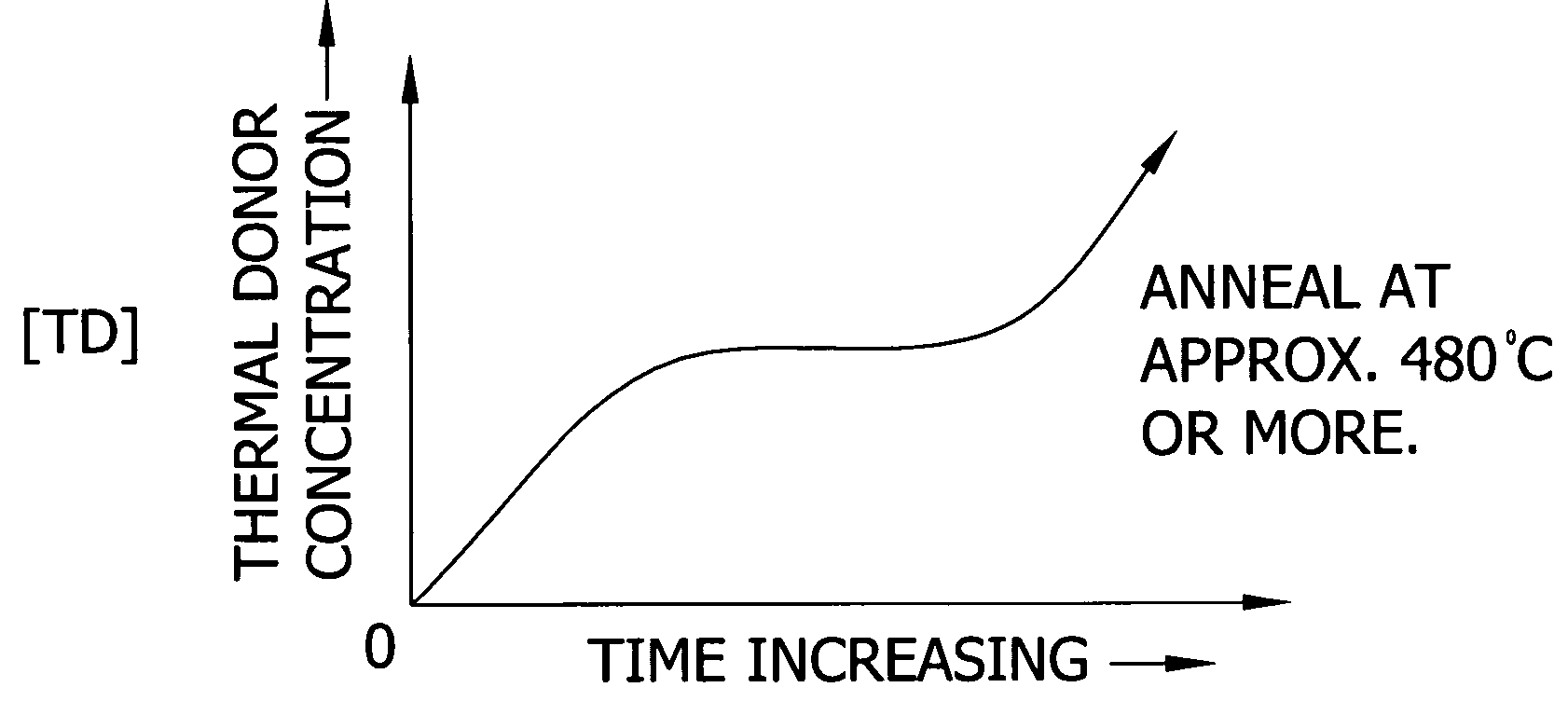
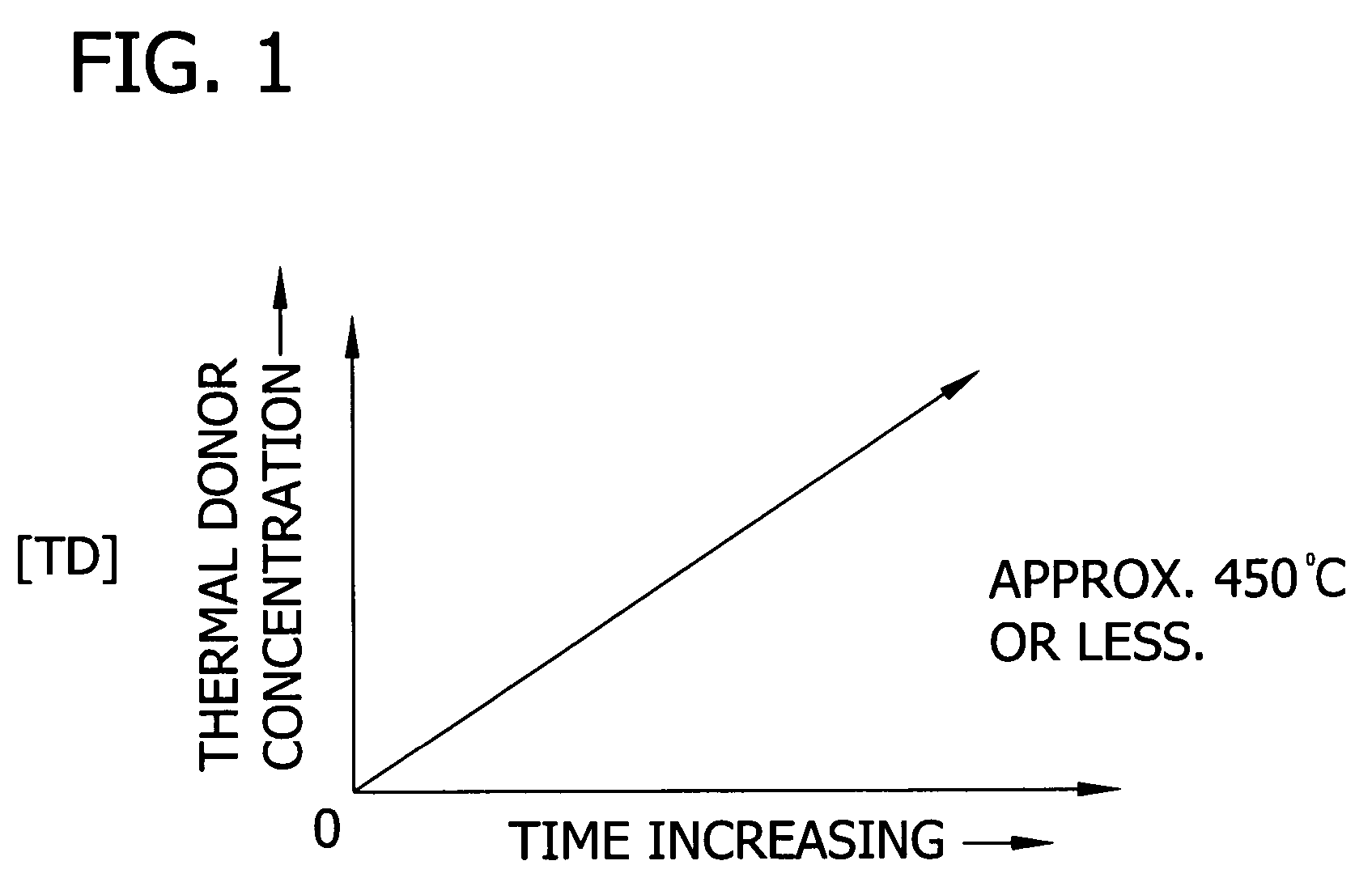
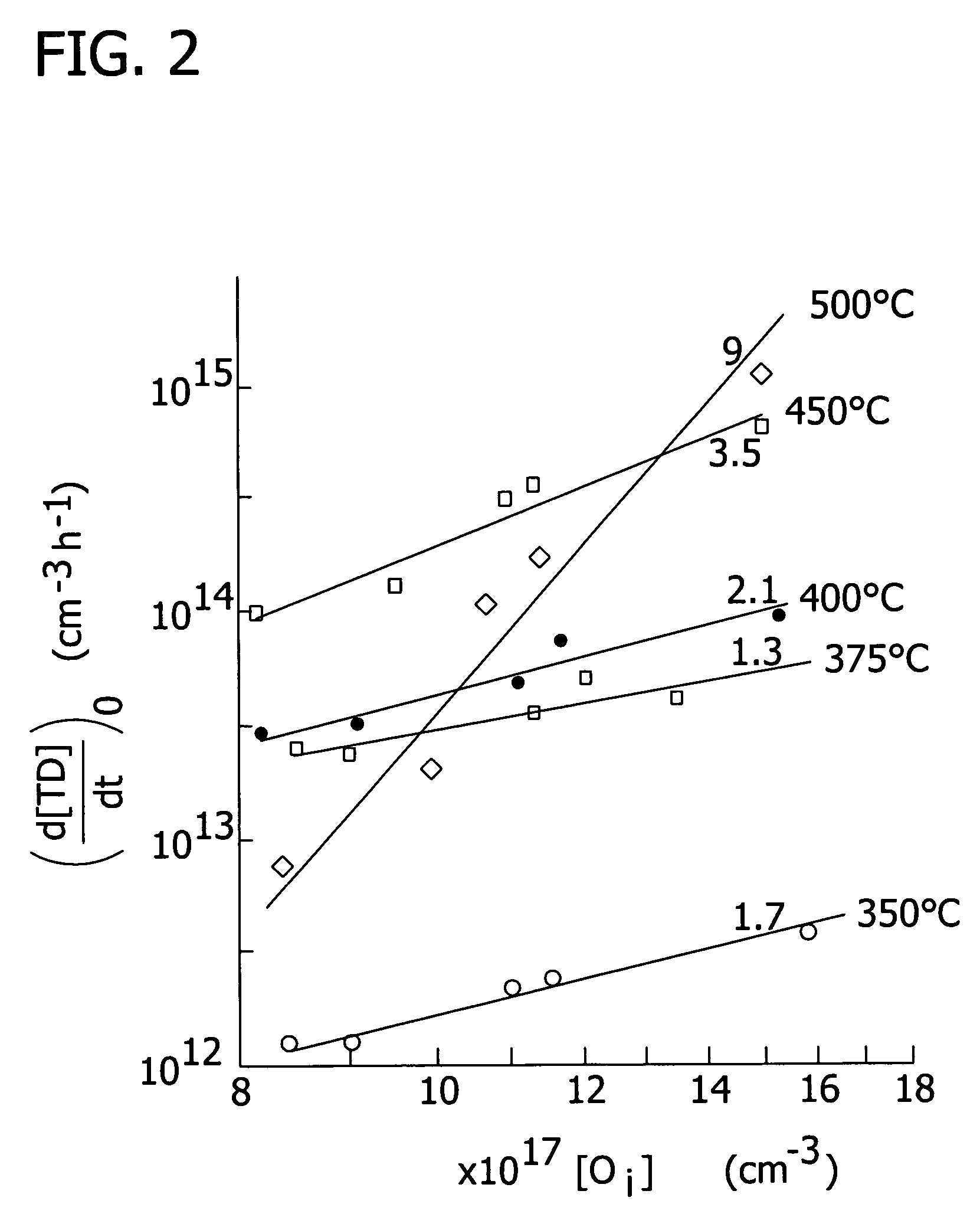
The present invention is directed to a single crystal Czochralski-type silicon wafer, and a process for the preparation thereof, which has at least a surface layer of high resistivity, the layer having an interstitial oxygen content which renders it incapable of forming thermal donors in an amount sufficient to affect resistivity upon being subjected to a conventional semiconductor device manufacturing process. The present invention further directed to a silicon on insulator structure derived from such a wafer.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
Method for integrating silicon CMOS and AlGaN/GaN wideband amplifiers on engineered substrates
ActiveUS7420226B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSHigh resistivity silicon
High-speed silicon CMOS circuits and high-power AlGaN / GaN amplifiers are integrated on the same wafer. A thin layer of high resistivity silicon is bonded on a substrate. Following the bonding, an AlGaN / GaN structure is grown over the bonded silicon layer. A silicon nitride or a silicon oxide layer is then deposited over the AlGaN / GaN structure. Following this, a thin layer of silicon is bonded to the silicon nitride / silicon oxide layer. An area for the fabrication of AlGaN / GaN devices is defined, and the silicon is etched away from those areas. Following this, CMOS devices are fabricated on the silicon layer and AlGaN / GaN devices fabricated on the AlGaN / GaN surface.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
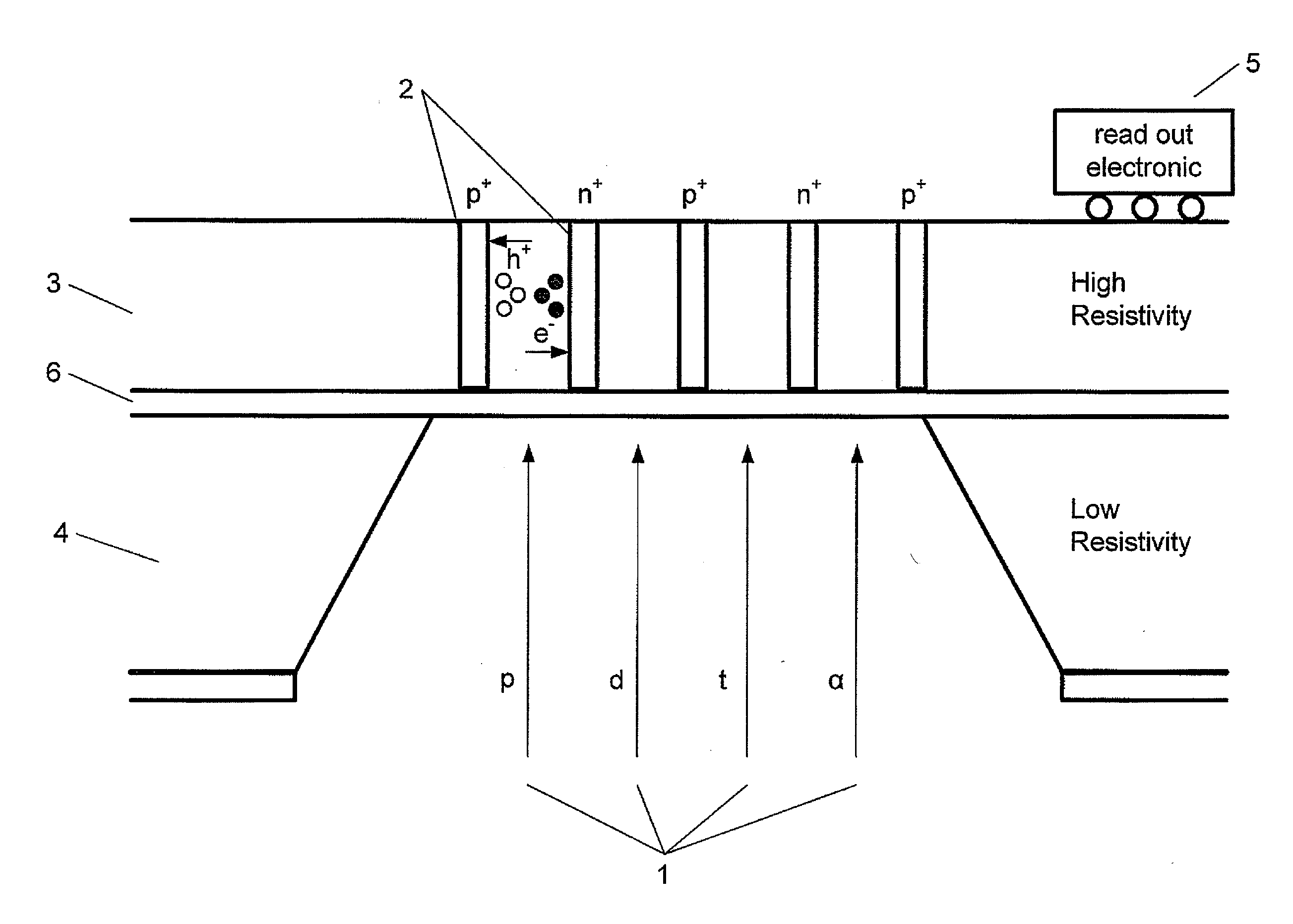
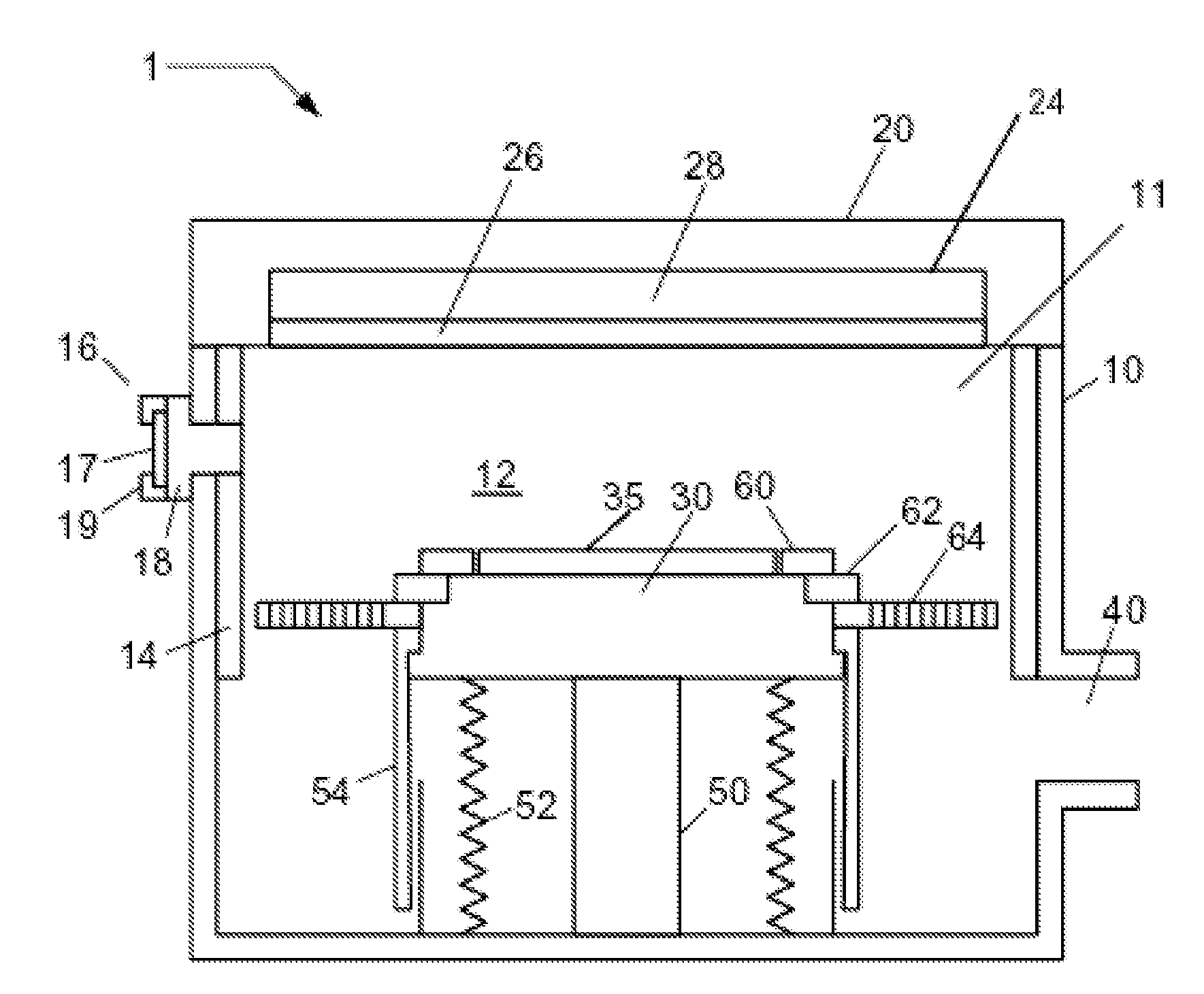
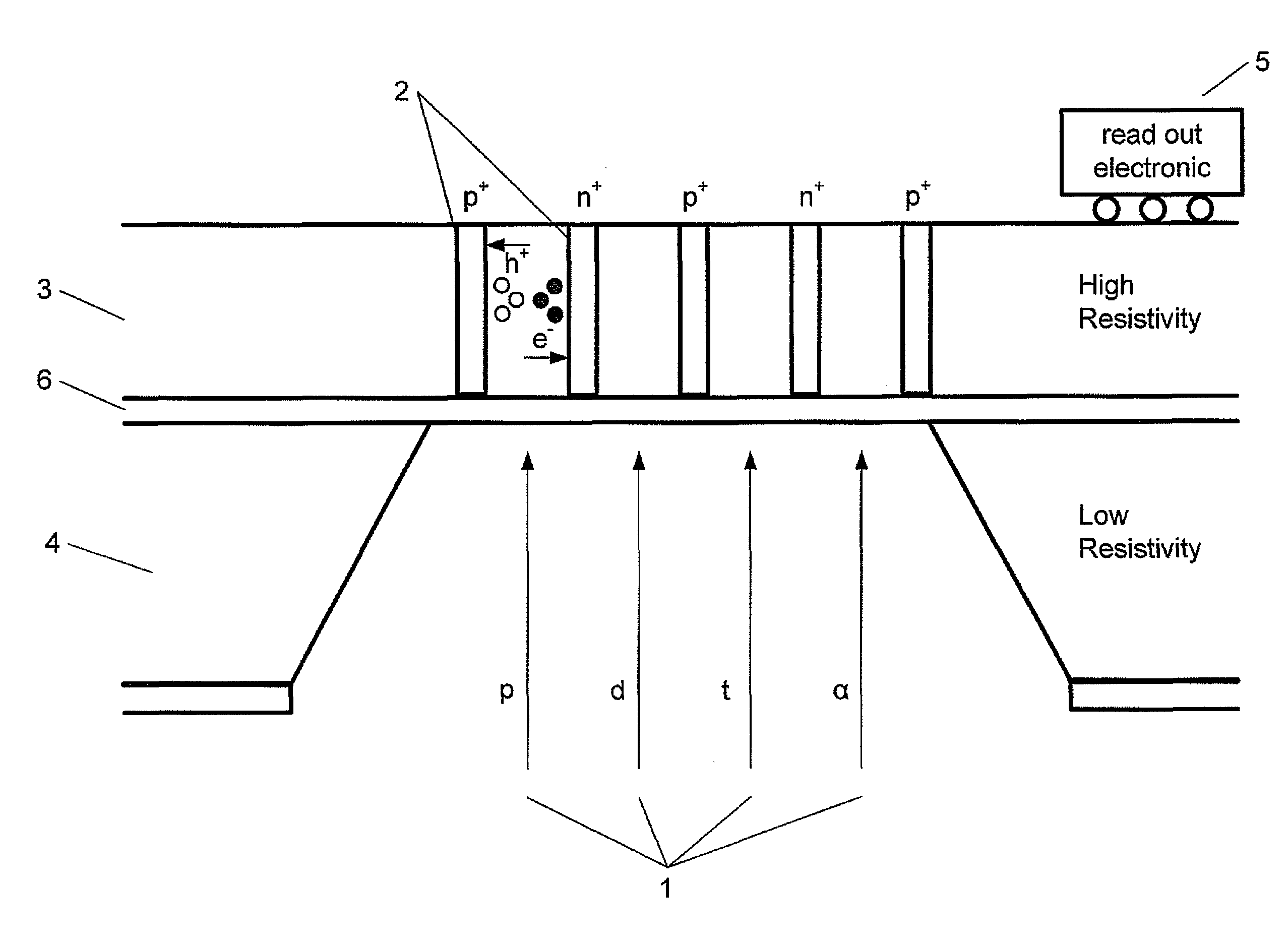
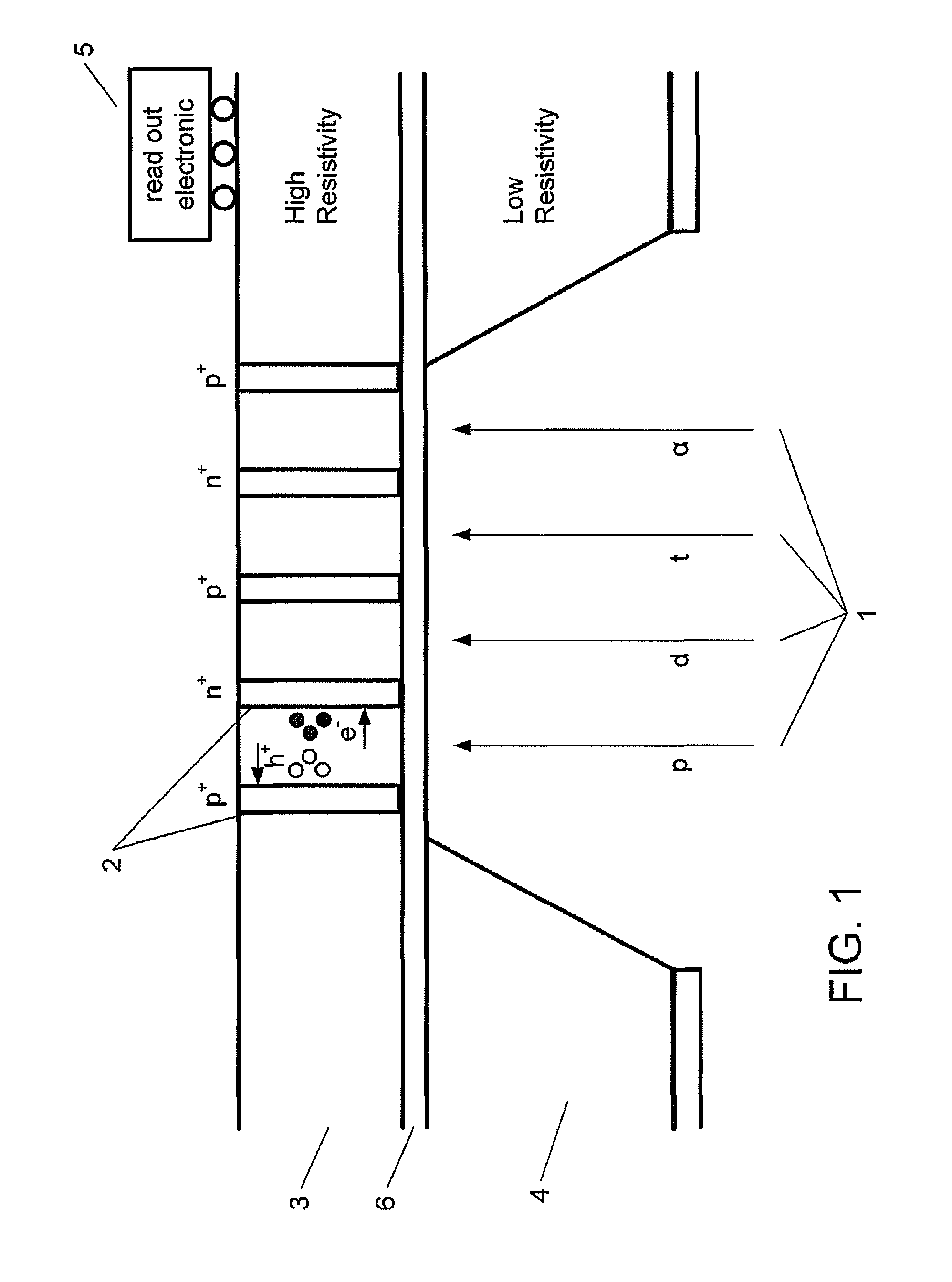
Radiation detector, method of manufacturing a radiation detector and use of the detector for measuring radiation
ActiveUS20110079728A1Slow energyWeaken energyMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesHigh resistivity siliconVertical channel
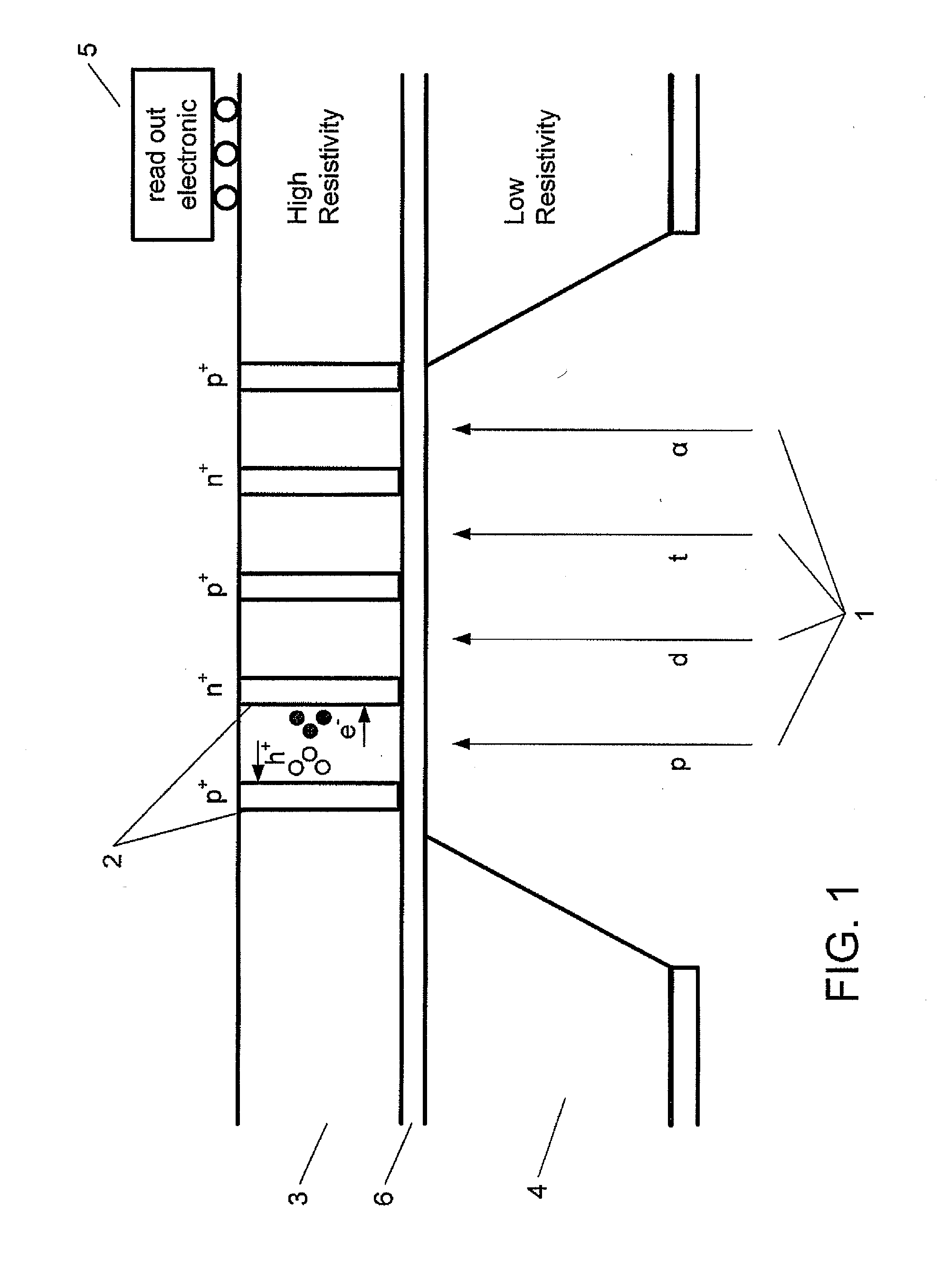
A radiation detector is disclosed. The detector has an entrance opening etched through a low-resistivity volume of silicon, a sensitive volume of high-resistivity silicon for converting the radiation particles into detectable charges, and a passivation layer between the low and high-resistivity silicon layers. The detector also has electrodes built in the form of vertical channels for collecting the charges generated in the sensitive volume, and read-out electronics for generating signals based on the collected charges.
Owner:FINPHYS OY SENCE CENT
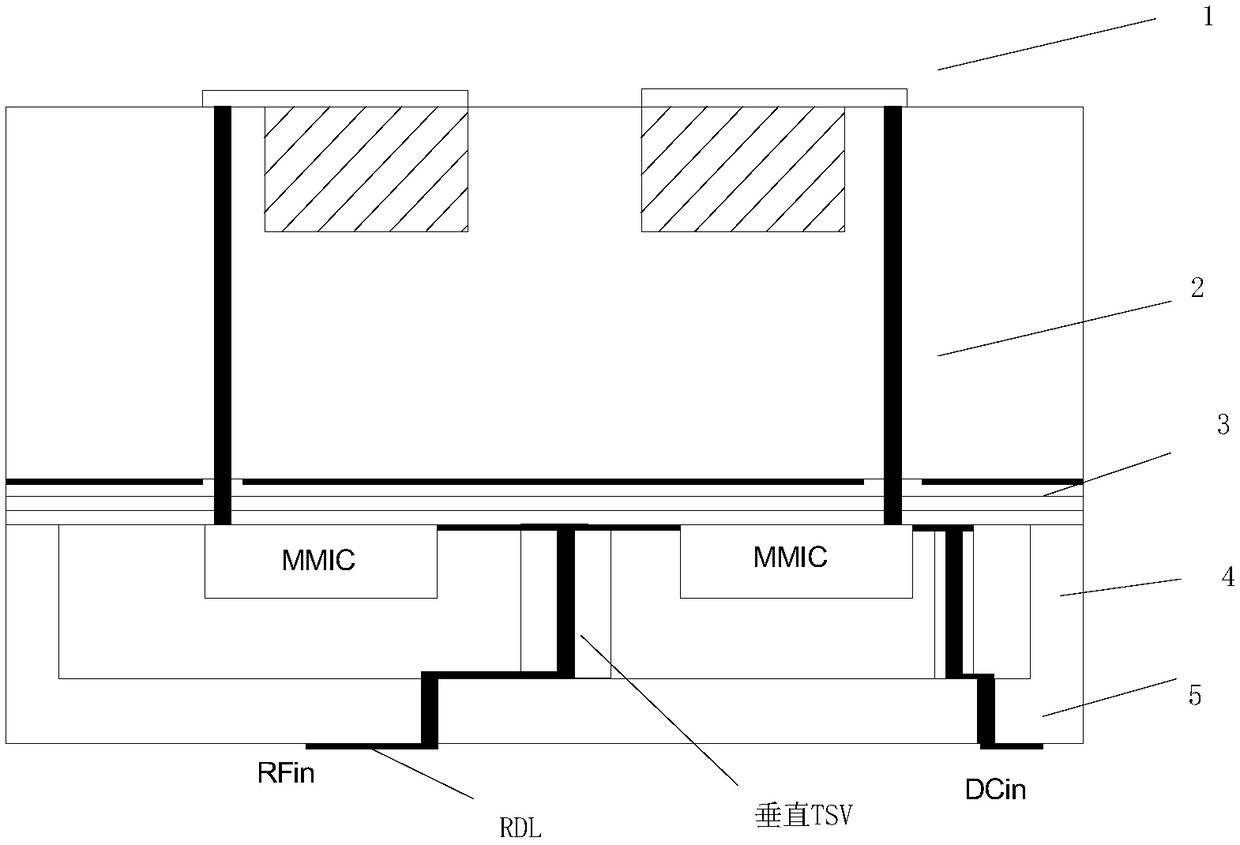
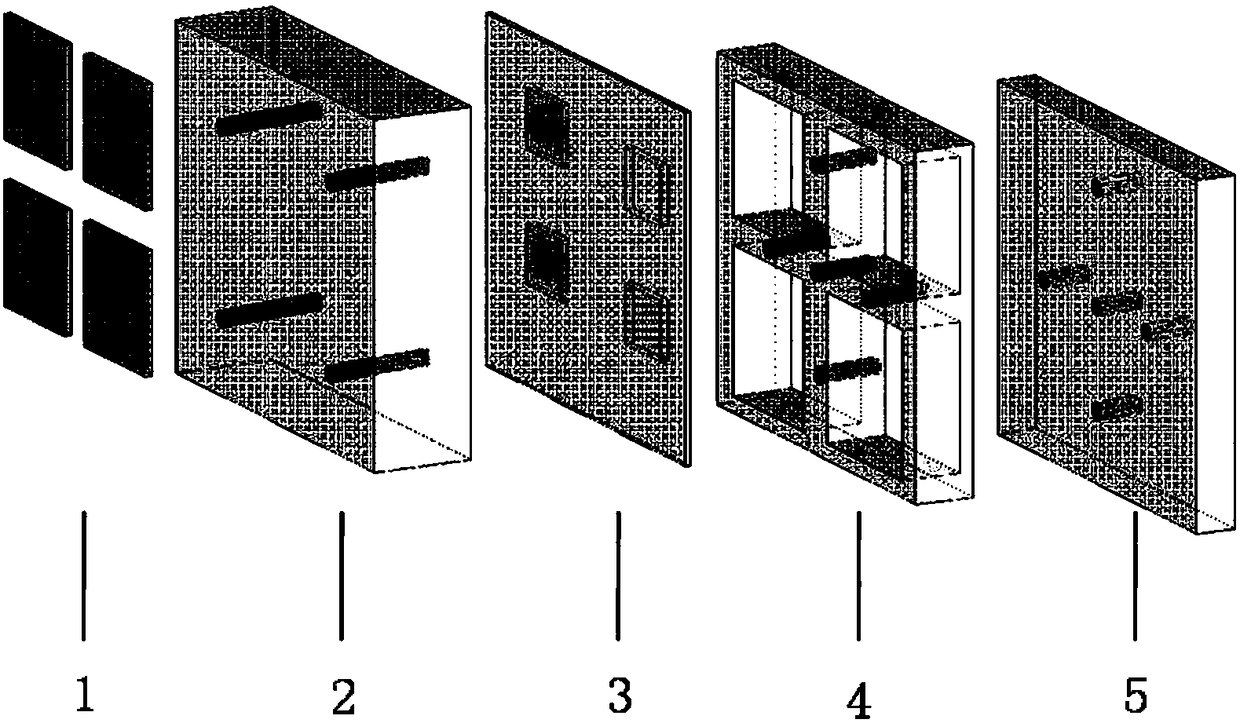
Three-dimensional integrated packaging based on millimeter wave antenna and silicon-based component
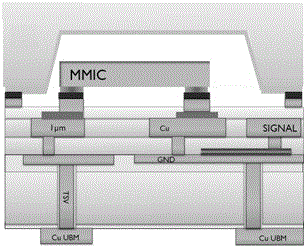
ActiveCN108172564AHighly integratedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAntenna supports/mountingsHigh resistivity siliconMiniaturization
The present invention discloses a three-dimensional integrated packaging based on a millimeter wave antenna and a silicon-based multi-channel component. The packaging comprises a radiation layer, wherein the radiation layer is a micro-strip patch antenna array; a high resistivity silicon substrate with a TSV feeding structure; a dielectric wiring layer with microwave wirings and digital wirings; asurrounding frame with a TSV three-dimensional vertical transmission structure and an air-tightness packaging cover plate with a TSV transmission structure. According to the packaging, by integratingthe micro-strip patch antenna array, microwave chip(s), digital chip(s) and passive device(s) in a same module via a MEMS process at the same time, the middle part of the surrounding frame has the TSV structure capable of realizing vertical transmission of microwave signal(s), so that integration degree is relative high, the microwave properties are good, the multi-functionalization and the miniaturization of the components can be realized.
Owner:南京国微电子有限公司
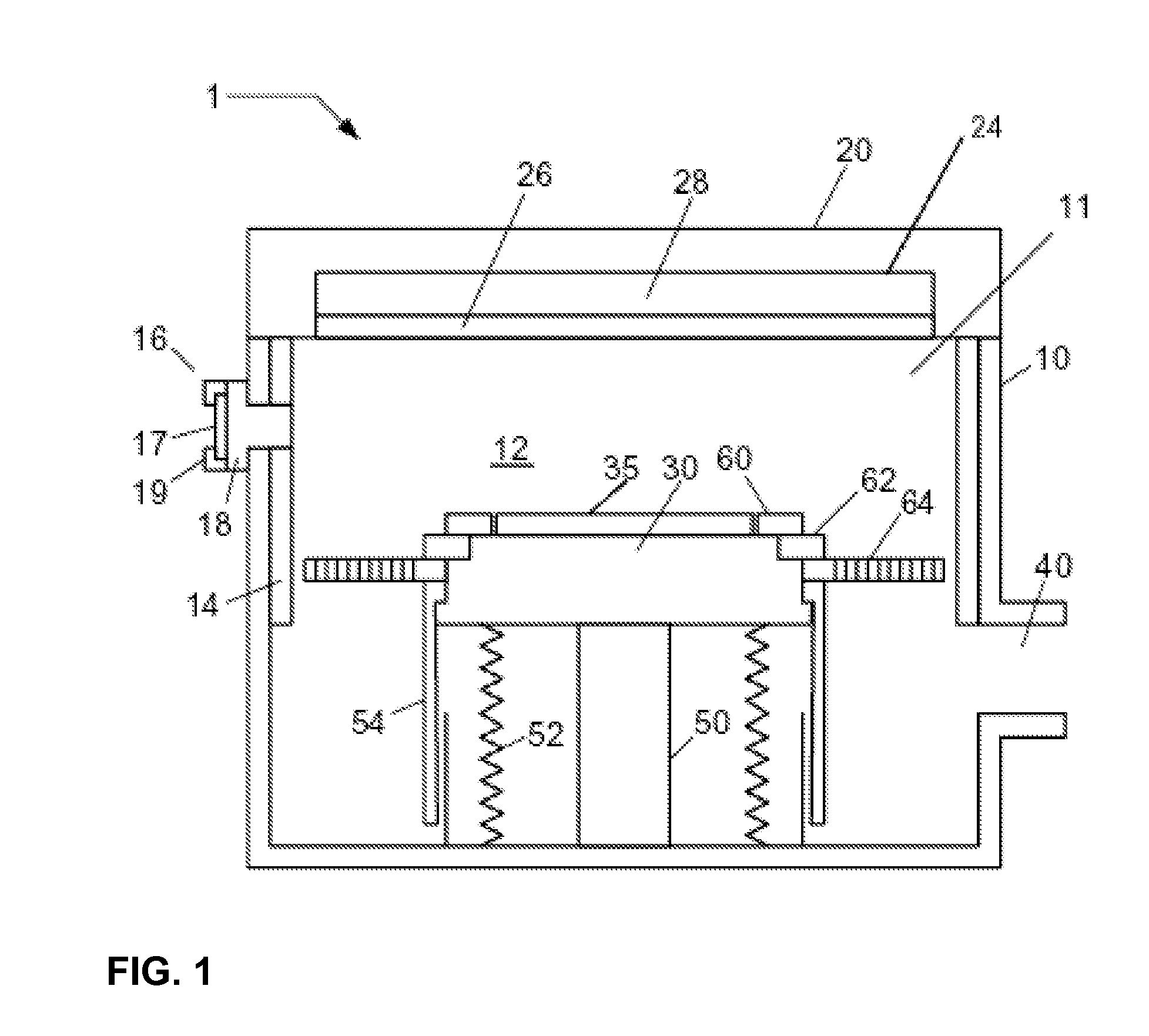
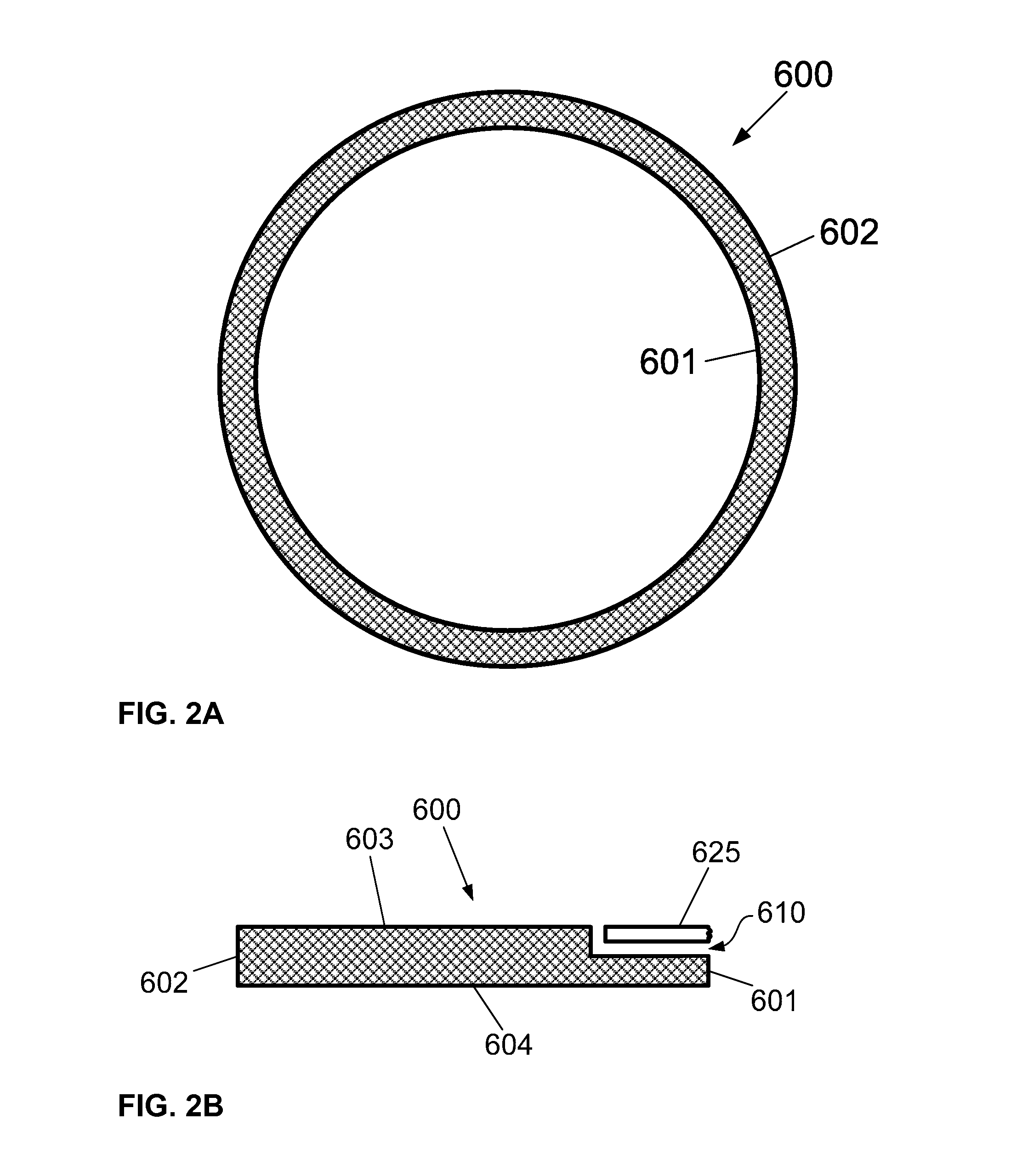
Silicon carbide focus ring for plasma etching system
InactiveUS20090151870A1High resistivityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistivity siliconCarbide
A high resistivity silicon carbide focus ring for use in a plasma etching system is described. The focus ring comprises an upper surface, a lower surface, an inner radial edge, and an outer radial edge, and is configured to surround a substrate on a substrate holder in a plasma processing system. The focus ring comprises high resistivity silicon carbide having a resistivity greater than or equal to about 100 ohm-cm.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Monolithic x-ray image detector and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS6072224AHigh resolutionEnhance the imageSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansIntegratorX-ray
An x-ray imaging detector comprised of read-out electronics and PIN diodes formed on a high resistivity silicon-on-insulator substrate that permits cell pitches as small as 20 microns. The read-out electronics are fabricated in the thin, top silicon layer of the SOI substrate. The read-out electronics produced provide circuits such as integrators and transimpedance amplifiers which are required to transform the electrical current from PIN diode detectors into an analog voltage. The anodes of the PIN sensor diodes are formed by etching through an oxide barrier layer in the substrate and implanting a heavily doped p+ region into a high resistivity intrinsic silicon layer. X-ray imaging detectors produced by the methods disclosed herein can be assembled into multi-chip modules that can be used in a large panel x-ray imaging apparatus. With a suitable printed circuit board and an edge connector, these panels, using the x-ray image detectors of the present invention, can provide a form, fit and function replacement of film cassettes in existing x-ray equipment.
Owner:ALLIANT TECHSYST INC
Swill-cooked dirty oil detecting system and detecting method
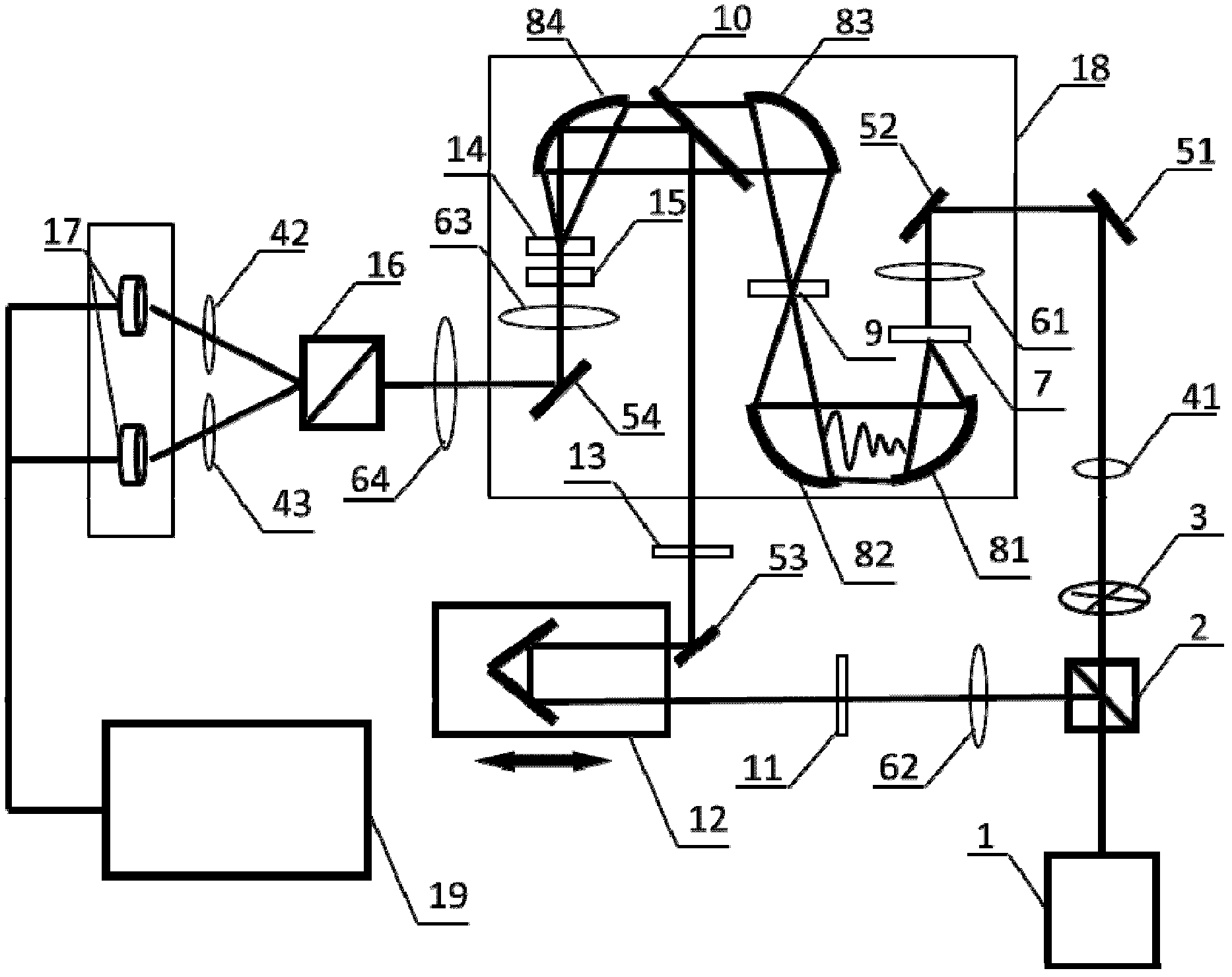
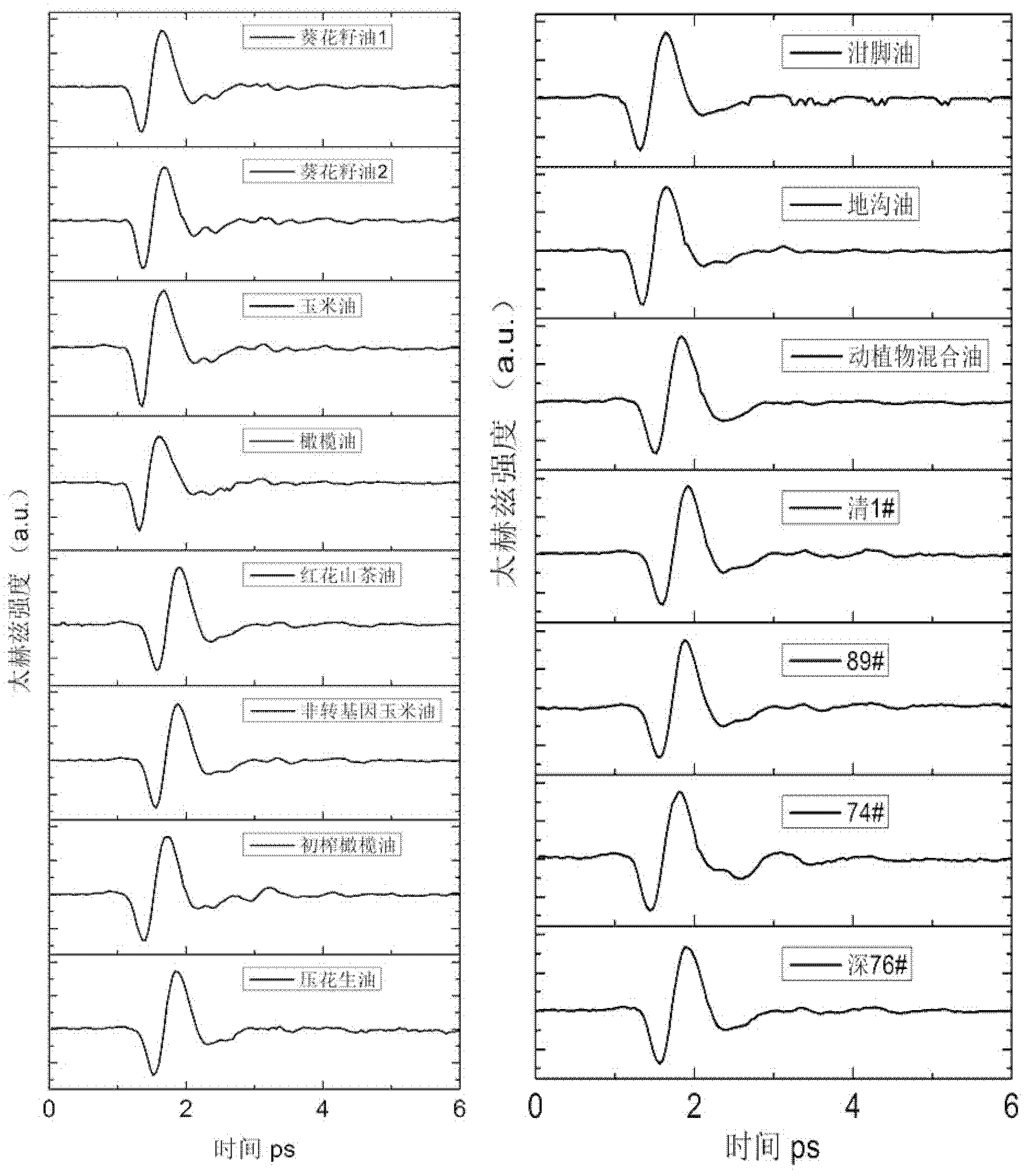
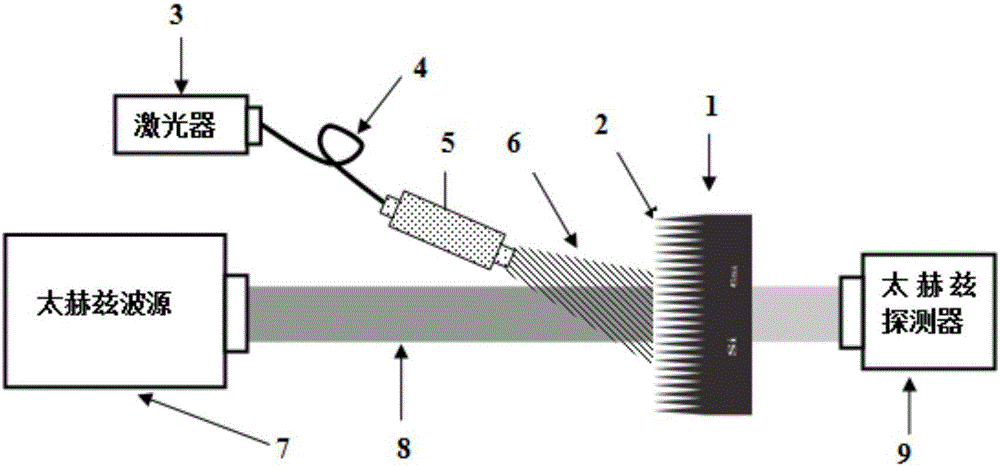
InactiveCN102564996ASimple processGood for healthColor/spectral properties measurementsBeam splitterHigh resistivity silicon
The invention provides a swill-cooked dirty oil detecting system. A semi-reflection and semi-transmission beam splitter is arranged at an emission port of a femtosecond laser; a pulse laser light is split into a pump light path and a detecting light path; the pump light path is connected with a photochopper, a first attenuation sheet, a first reflecting mirror, a second reflecting mirror, a first focusing lens and a gallium arsenide photoconductive antenna in sequence; a sample box is arranged on a confocal point of second and third paraboloidal mirrors; a second collimating lens, a half wave plate, a light path delay device, a third reflecting mirror, a polarizer and a high resistivity silicon reflecting mirror are arranged on the detecting light path in sequence; the femtosecond laser after being sampled by an electrooptic crystal is detected by being directed with a photoelectric detector via a quarter wave plate, a third focusing lens, a fourth reflecting mirror, a fourth focusing lens, a Wollstone prism as well as second and third attenuation sheets; and the variation of voltage magnitude caused by terahertz waves is recorded, so that a time domain terahertz signal including swill-cooked dirty oil information is obtained. The swill-cooked dirty oil detecting system provided by the invention has the advantages of simple detecting process, high efficiency, rapidness and accurate detecting result.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH +2
Manufacturing method of three-dimensional bonding stack interconnect integration for radio-frequency microsystem device
InactiveCN106783847AImprove efficiencyImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBond interfaceHigh resistivity silicon
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a three-dimensional bonding stack interconnect integration for a radio-frequency microsystem device. The method comprises the steps as follows: high-resistivity silicon is taken as a substrate or an adapter plate; multi-layer dielectric-metal alternate wiring is completed for radio-frequency signal transmission and control on the substrate or the adapter plate; heterogeneous compound chips achieve heterogeneous integration through chip to wafer bonding, all chips are connected with metal bumps on the silicon substrate or the adapter plate through a bottom bonding pad to achieve signal transmission among different layers, and three-layer structure stacking and chip protection are achieved through bonding of wafers with silicon cavities and the wafer of the silicon substrate or the adapter plate; and leading-out of signals of a whole device is achieved by adopting a through-silicon via technology. The method has the advantages that the heterogeneous chips are integrated together through three-layer stacking, so that the original function of the device is greatly improved, leading-out of the signals from bonding interfaces is achieved by adopting the through-silicon via technology, a closed and compact chip structure is formed, three-dimensional heterogeneous integration of a radio-frequency device is really achieved, the technology is simplified, packaging is low in cost and the yield is high.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
High resistivity silicon carbide single crystal
InactiveUS7018597B2Stable and linear characteristicHigh resistivityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistivity siliconCarbide
The purpose of the invention is to provide a high resistivity silicon carbide substrate with electrical properties and structural quality suitable for subsequent device manufacturing, such as for example high frequency devices, so that the devices can exhibit stable and linear characteristics and to provide a high resistivity silicon carbide substrate having a low density of structural defects and a substantially controlled uniform radial distribution of its resistivity.
Owner:OKMETIC OY
High resistivity silicon-on-insulator substrate having enhanced charge trapping efficiency
ActiveUS20180114720A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantTrapping
A multilayer semiconductor on insulator structure is provided in which the handle substrate and an epitaxial layer in interfacial contact with the handle substrate comprise electrically active dopants of opposite type. The epitaxial layer is depleted by the handle substrate free carriers, thereby resulting in a high apparent resistivity, which improves the function of the structure in RF devices.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
Method of manufacturing a multilayer semiconductor structure with reduced ohmic losses
InactiveCN1856873ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInter layerSemiconductor structure
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a multilayer semiconductor structure featuring reduced ohmic losses with respect to standard multilayer semiconductor structures. The semiconductor structure comprises a high resistivity silicon substrate with resistivity higher than 3 Kohm.cm, an active semiconductor layer and an insulating layer in between the silicon substrate and the active semiconductor layer. The method comprises suppressing ohmic losses inside the high resistivity silicon substrate by increasing, with regard to prior art devices, charge trap density between the insulating layer and the silicon substrate. In particular this may be obtained by applying an intermediate layer in between the silicon substrate and the insulating layer, the intermediate layer comprising grains having a size, wherein the mean size of the grains of the intermediate layer is smaller than 150 nm, preferably smaller than 50 nm.
Owner:ЮНІВЕРСИТЕ КАТОЛІК ДЕ ЛУВЕН
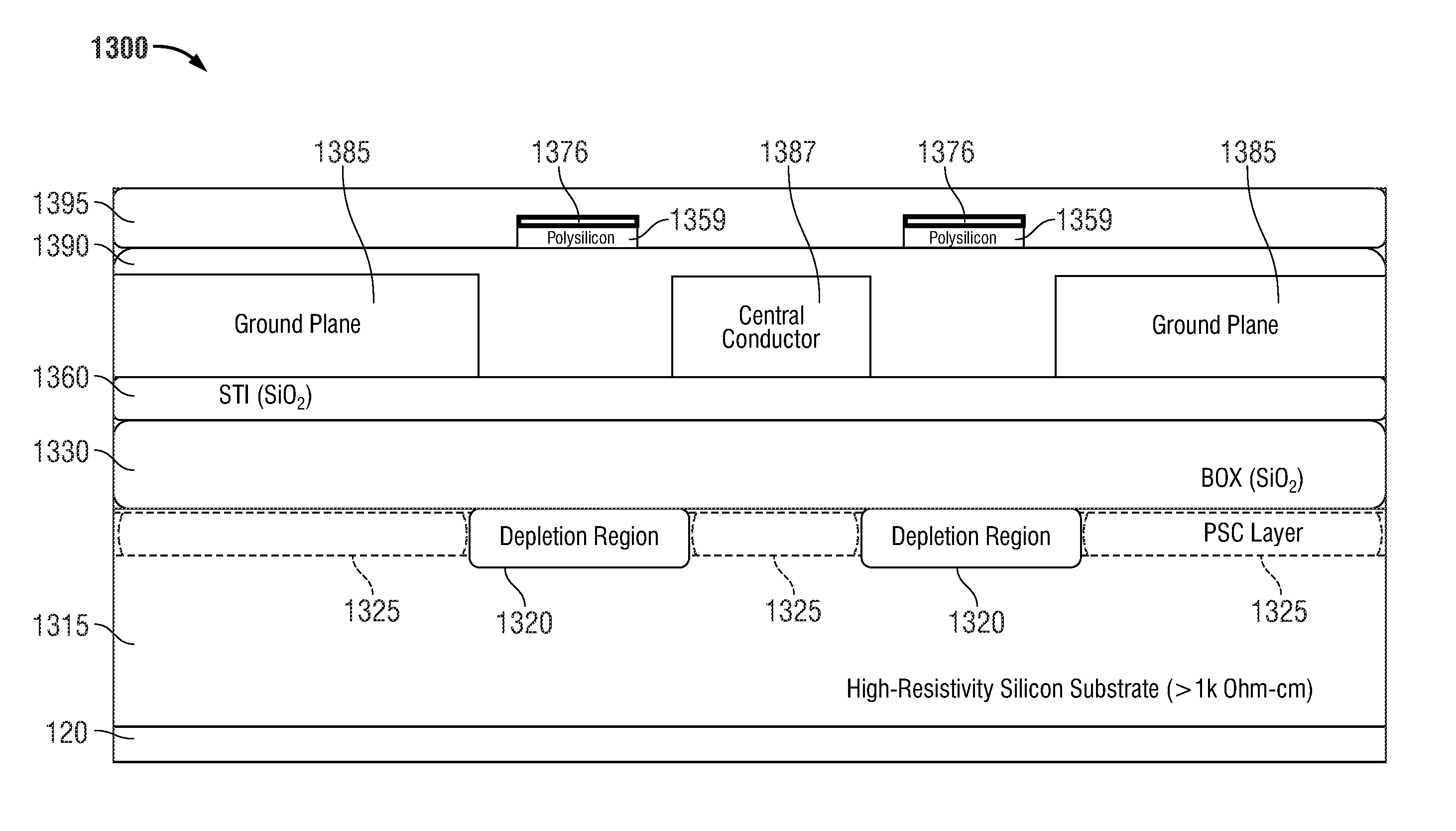
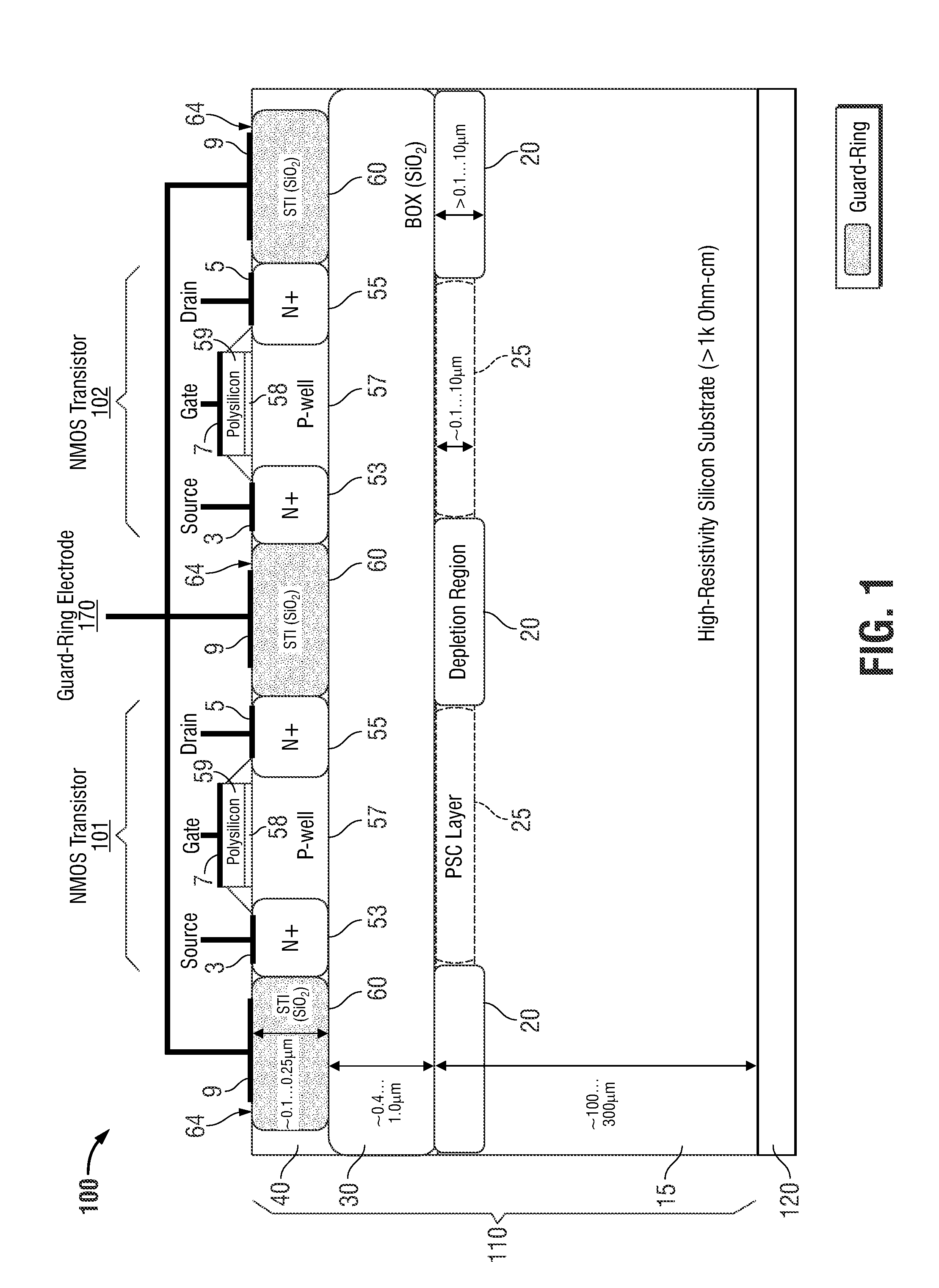
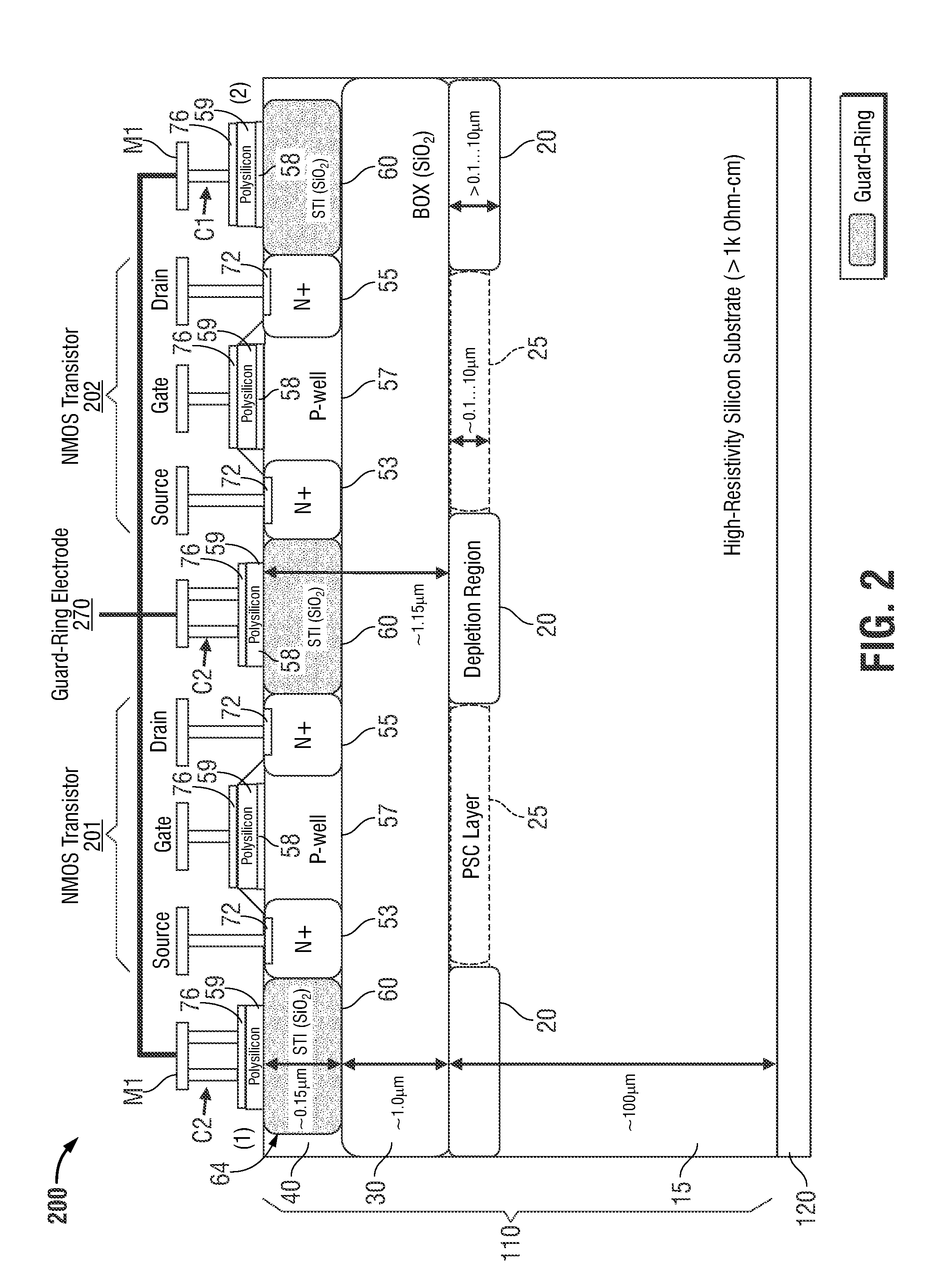
Isolation methods for leakage, loss and non-linearity mitigation in radio-frequency integrated circuits on high-resistivity silicon-on-insulator substrates
InactiveUS20150228714A1Minimize couplingReduce the impactSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh resistivity siliconHigh resistivity
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Method of manufacturing high resistivity silicon-on-insulator substrate
ActiveUS20160071959A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh resistivity siliconAmorphous silicon
A multilayer composite structure and a method of preparing a multilayer composite structure are provided. The multilayer composite structure comprises a semiconductor handle substrate having a minimum bulk region resistivity of at least about 500 ohm-cm; a silicon dioxide layer on the surface of the semiconductor handle substrate; a carbon-doped amorphous silicon layer in contact with the silicon dioxide layer; a dielectric layer in contact with the carbon-doped amorphous silicon layer; and a semiconductor device layer in contact with the dielectric layer.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
Porous and non-porous nanostructures
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Silicon-on-insulator radio frequency device and silicon-on-insulator substrate
ActiveUS20140175598A1High surface resistanceHigh resistivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceRadio frequency signal
A silicon-on-insulator radio frequency device and a silicon-on-insulator substrate are provided. In the silicon-on-insulator radio frequency device, a pit is formed on a surface of a high resistivity silicon plate which is close to a buried oxide layer. The pit may be filled with an insulating material, thereby increasing an equivalent surface resistance of the high resistivity silicon plate; or no insulating material is filled into the pit, that is, the pit remains a vacuum state or is only filled with air, which can increase the equivalent surface resistance of the high resistivity silicon plate as well. In such, an eddy current generated on a surface of the high resistivity silicon plate under the action of a radio frequency signal may be reduced. As a result, loss of the radio frequency signal is reduced and the linearity of the radio frequency signal is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
High resistivity silicon wafer and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050127477A1Avoid conversionIncrease release ratePolycrystalline material growthAluminium silicatesCMOSElectrical resistance and conductance
A high resistivity p type silicon wafer with a resistivity of 100 Ωcm or more, in the vicinity of the surface being formed denuded zone, wherein when a heat treatment in the device fabrication process is performed, a p / n type conversion layer due to thermal donor generation is located at a depth to be brought into contact with neither any device active region nor depletion layer region formed in contact therewith or at a depth more than 8 μm from the surface, and a method for fabricating the same. The high resistivity silicon wafer can cause the influence of thermal donors to disappear without reducing the soluble oxygen concentration in the wafer, whereby even if various heat treatments are performed in the device fabrication process, devices such as CMOS that offer superior characteristics can be fabricated. The wafer has wide application as a substrate for a high-frequency integrated circuit device.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
Optical control terahertz wave amplitude modulator based on silicon nanoneedle
InactiveCN105914565AIncrease modulation depthGreat modulation depthSolid masersRefractive indexHigh resistivity silicon
The invention belongs to the field of terahertz imaging technologies, relates to a modulation device in the related field of terahertz imaging, and in particular provides an optical control terahertz wave amplitude modulator based on a silicon nanoneedle. The optical control terahertz wave amplitude modulator comprises a semiconductor laser, an optical fibre, an optical fibre modulator and a terahertz amplitude modulation structure; laser generated by the semiconductor laser enters the optical fibre modulator through optical fibre coupling; the optical control terahertz wave amplitude modulator is characterized in that the terahertz amplitude modulation structure is composed of a silicon-based bottom layer and a silicon nanoneedle tip array on the surface; and the optical fibre modulator outputs modulated laser incident to the surface of the silicon nanoneedle tip array. According to the optical control terahertz wave amplitude modulator disclosed by the invention, a dual-layer structure including the silicon nanoneedle tip array and a high-resistivity silicon / intrinsic silicon layer is adopted; the silicon nanoneedle tip array has the gradient change of a refractive index on the surface of high-resistivity silicon / intrinsic silicon; reflection of terahertz wave and pumping laser can be reduced simultaneously; the insertion loss of the device is obviously reduced; the pumping laser utilization rate is increased; and the device has relatively high modulation depth under relatively low pumping laser power.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
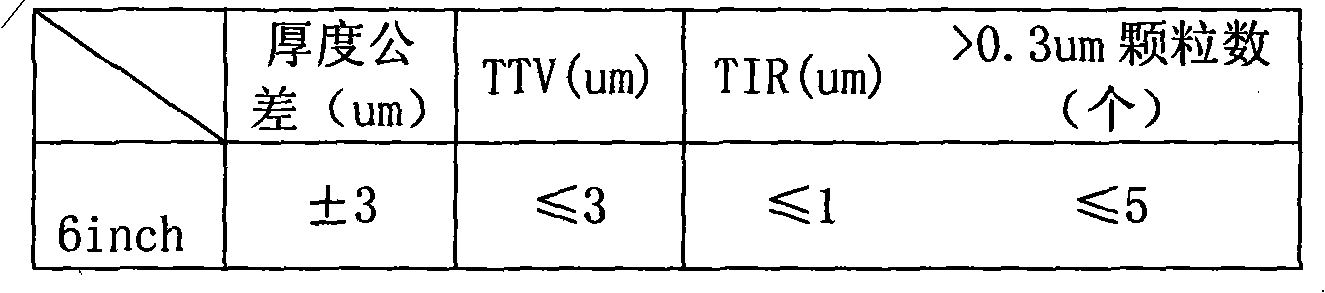
Polishing process for ultrahigh-resistivity silicon polished wafer
The invention relates to a polishing process for an ultrahigh-resistivity zone-melting silicon polished wafer. Wax-free single-surface polishing is adopted in the process and comprises rough polishing and fine polishing; the rough polishing and the fine polishing are respectively carried out according to pressure and time parameters set in four steps; the polishing solution temperature of the rough polishing and the fine polishing is controlled in a range of 30-40 DEG C; and the large disk temperature of a polishing machine is controlled in a range of 40-60 DEG C. In the process, polishing pressure and time suitable for producing an ultrahigh-resistivity silicon wafer are worked out, quality indexes of flatness, and the like of the polished surface of the silicon wafer are improved by adopting wax-free polishing, especially, an wafer adhering agent is discarded, the contamination of organic matter, and the like is reduced to the greatest extent and the polishing wafer is easy to clean, thereby simplifying wax removal cleaning program and equipment, reducing the cost of the polishing silicon wafer and improving the labor productivity.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Radiation detector, method of manufacturing a radiation detector and use of the detector for measuring radiation
ActiveUS8461541B2Slow energyWeaken energyMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesHigh resistivity siliconVertical channel
Owner:FINPHYS OY SENCE CENT
Ferroelectric varactors suitable for capacitive shunt switching and wireless sensing
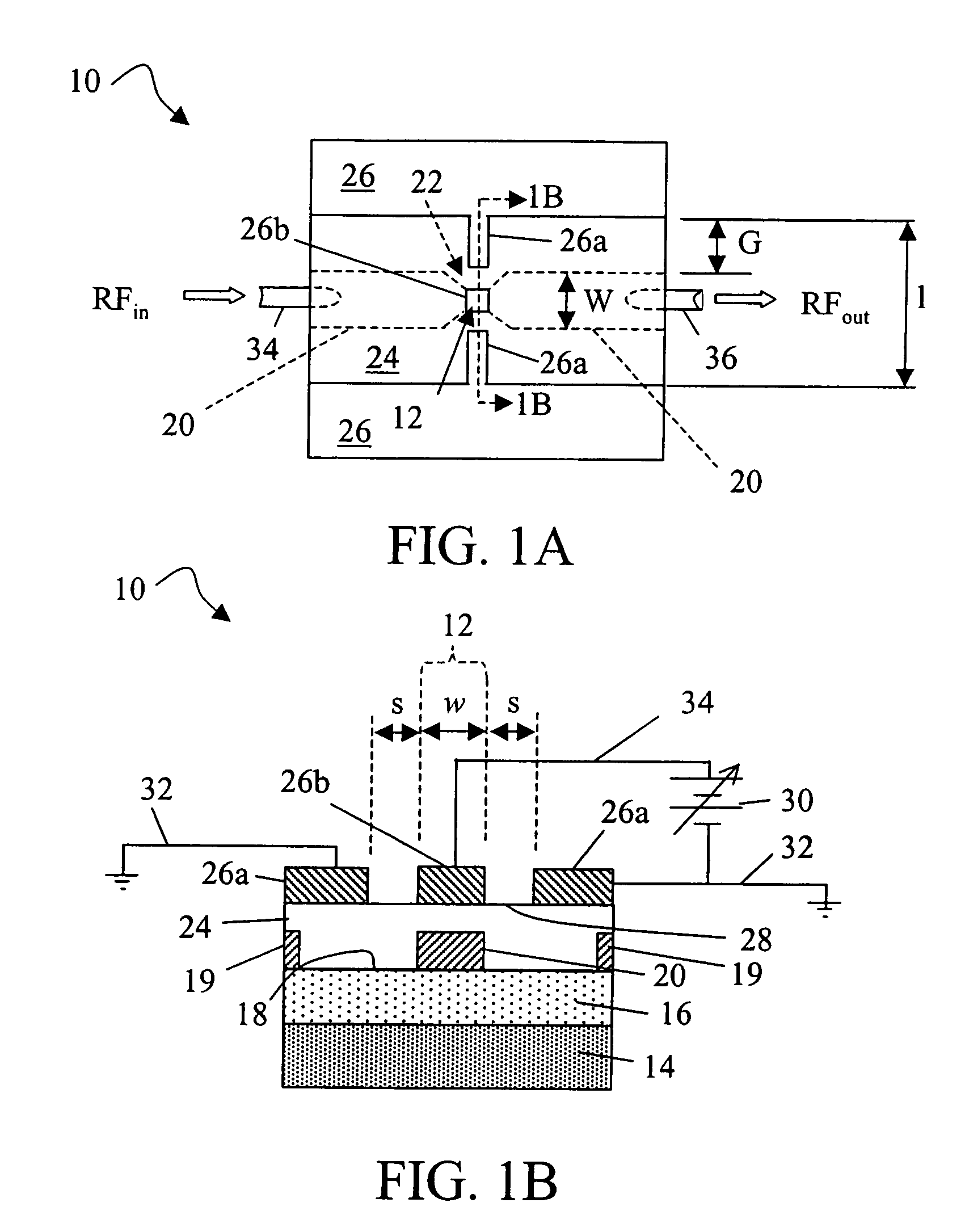
InactiveUS20070069264A1High resistivityEliminate needTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A ferroelectric varactor suitable for capacitive shunt switching is disclosed. High resistivity silicon with a SiO2 layer and a patterned metallic layer deposited on top is used as the substrate. A ferroelectric thin-film layer deposited on the substrate is used for the implementation of the varactor. A top metal electrode is deposited on the ferroelectric thin-film layer forming a CPW transmission line. By using the capacitance formed by the large area ground conductors in the top metal electrode and bottom metallic layer, a series connection of the ferroelectric varactor with the large capacitor defined by the ground conductors is created. The large capacitor acts as a short to ground, eliminating the need for vias. In one embodiment, the varactor shunt switch can be used as passive sensor with the capability of being wireless.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com