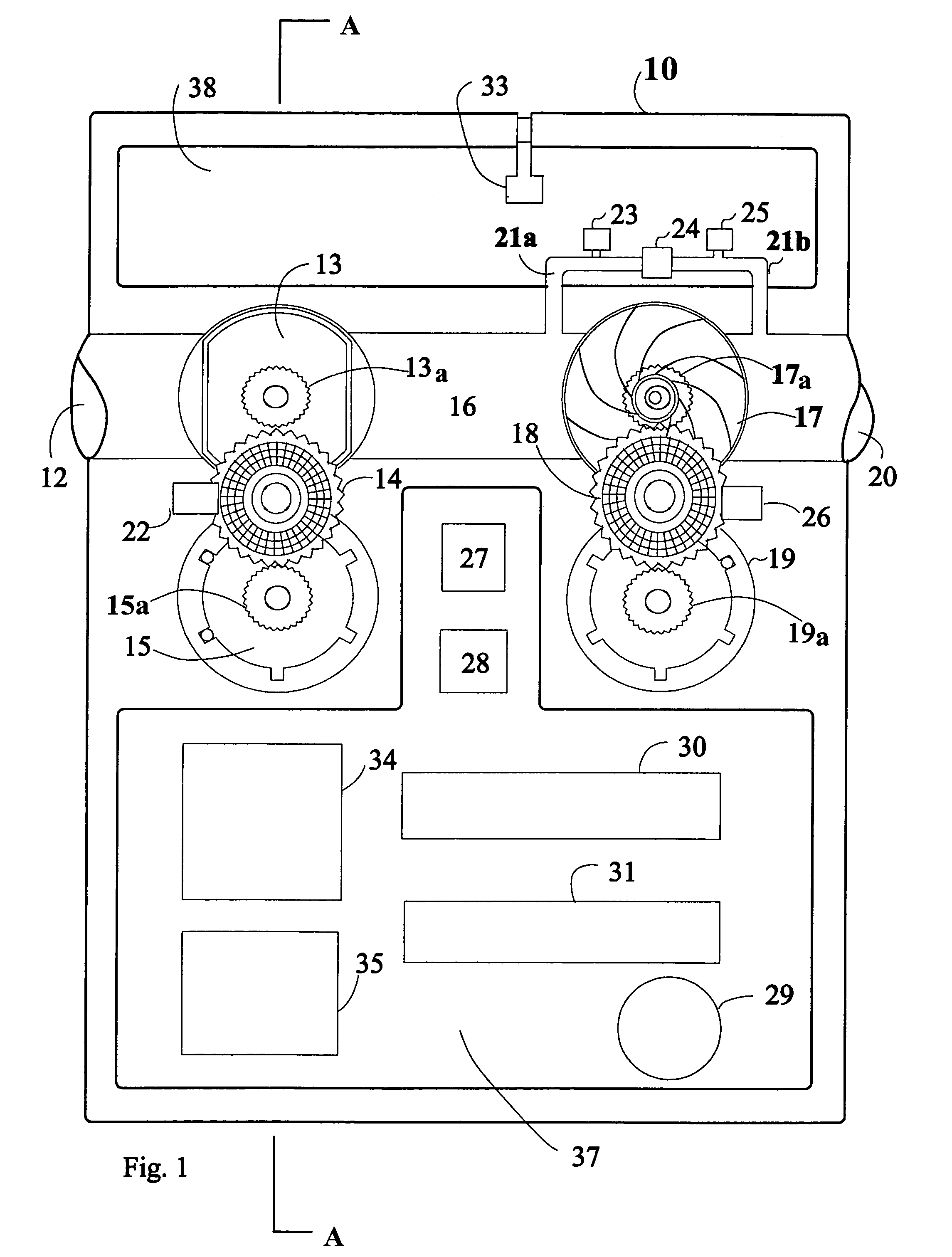
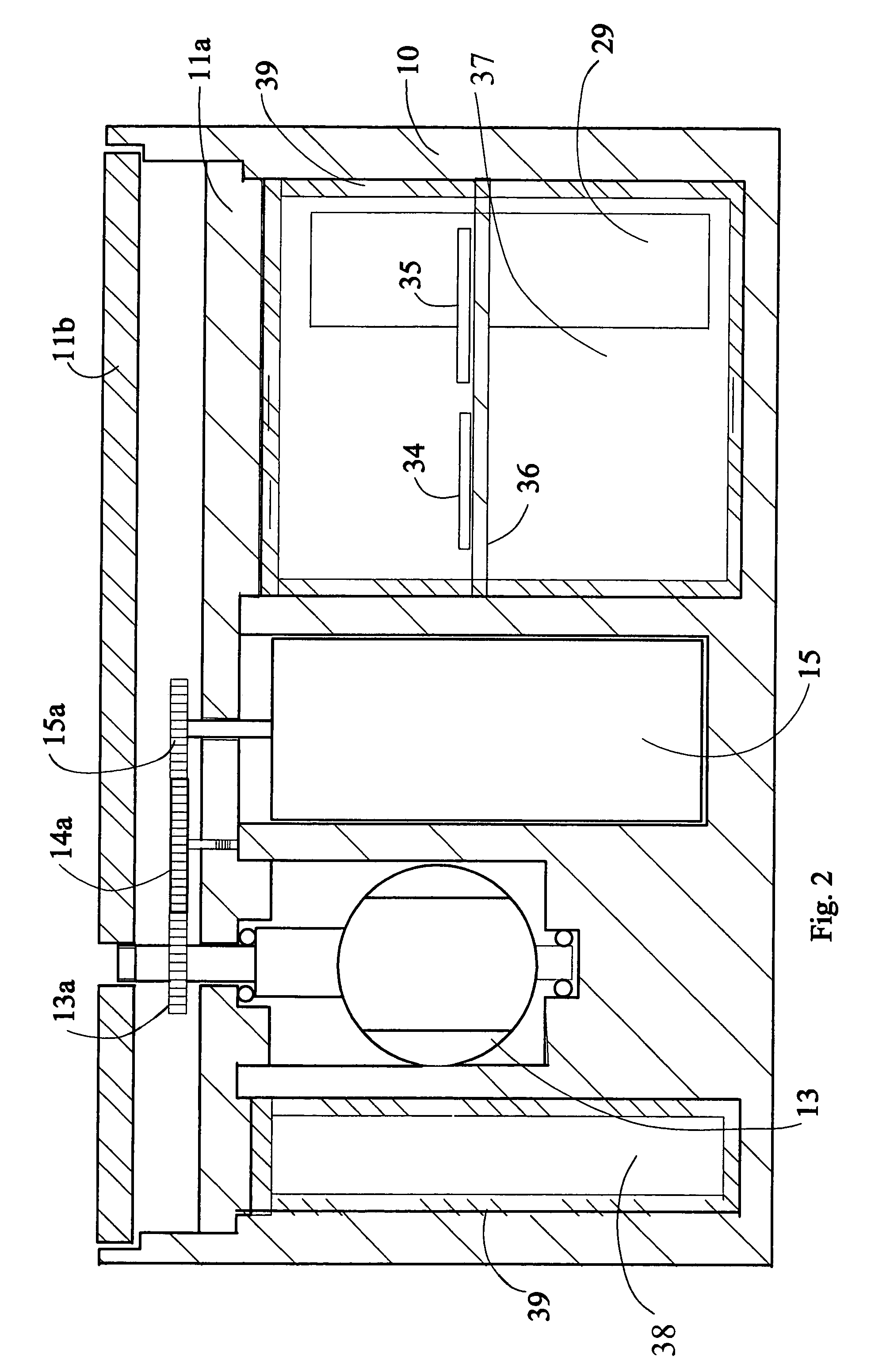
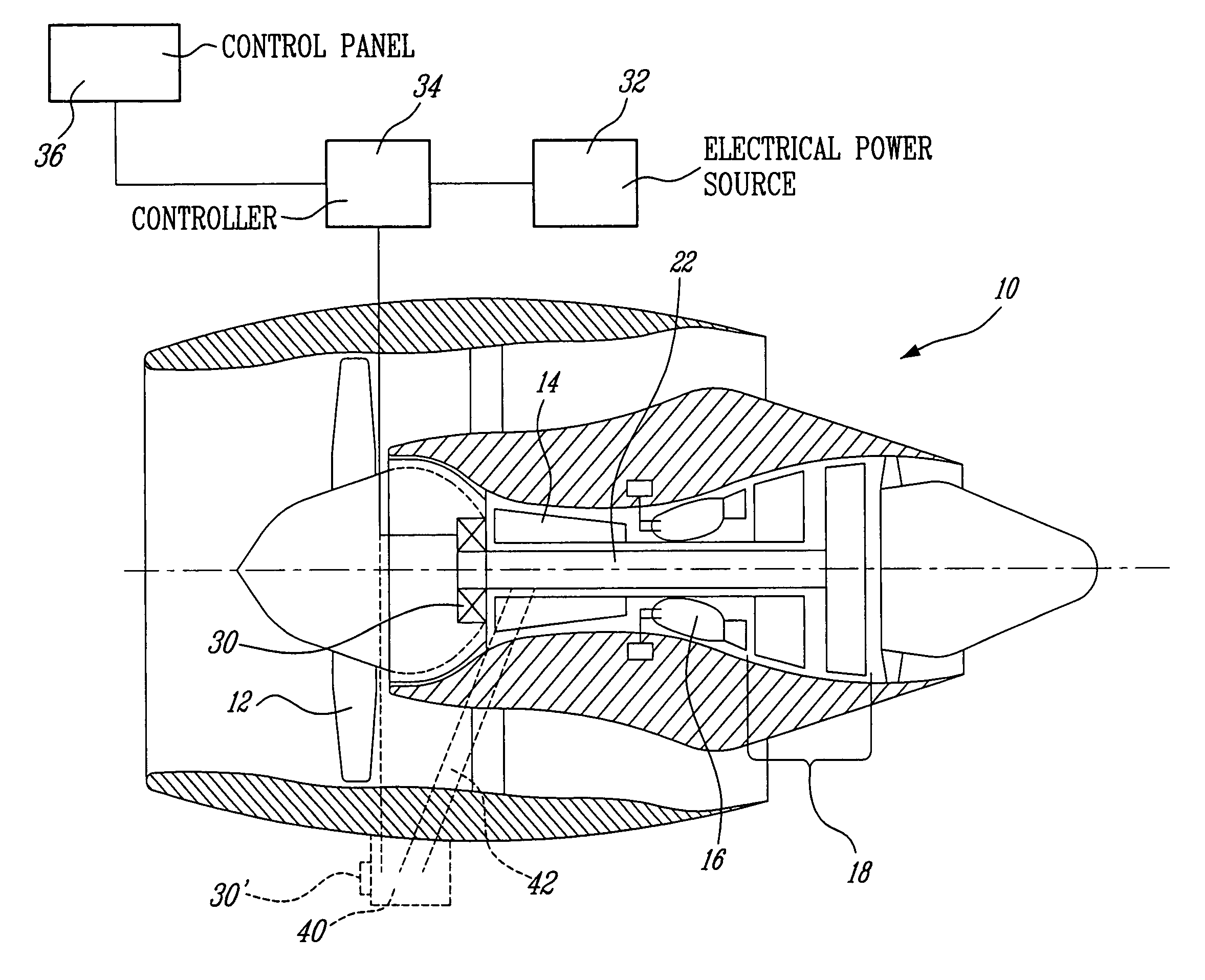
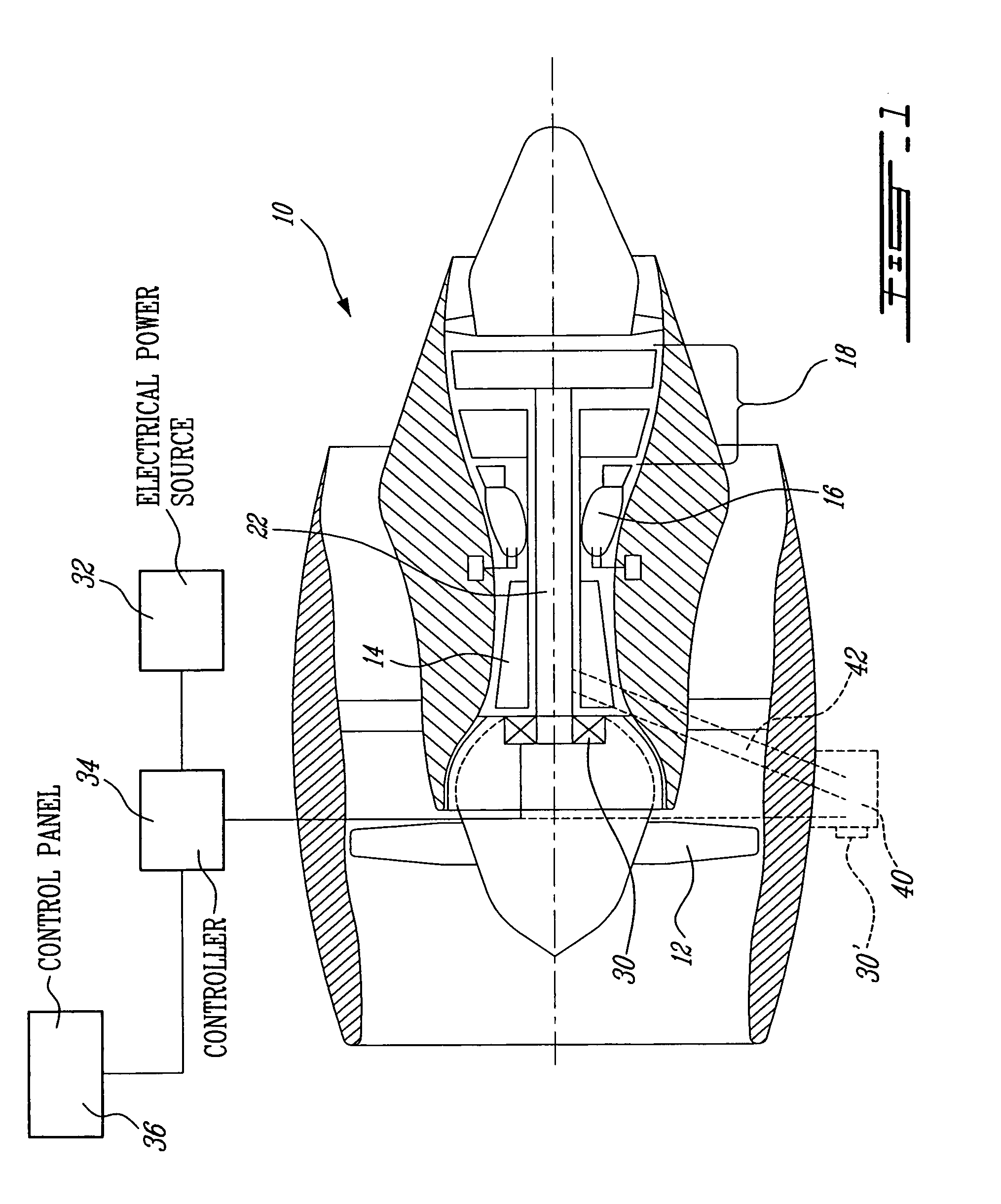
Patents
Literature
4091 results about "Rotor (electric)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The rotor is a moving component of an electromagnetic system in the electric motor, electric generator, or alternator. Its rotation is due to the interaction between the windings and magnetic fields which produces a torque around the rotor's axis.
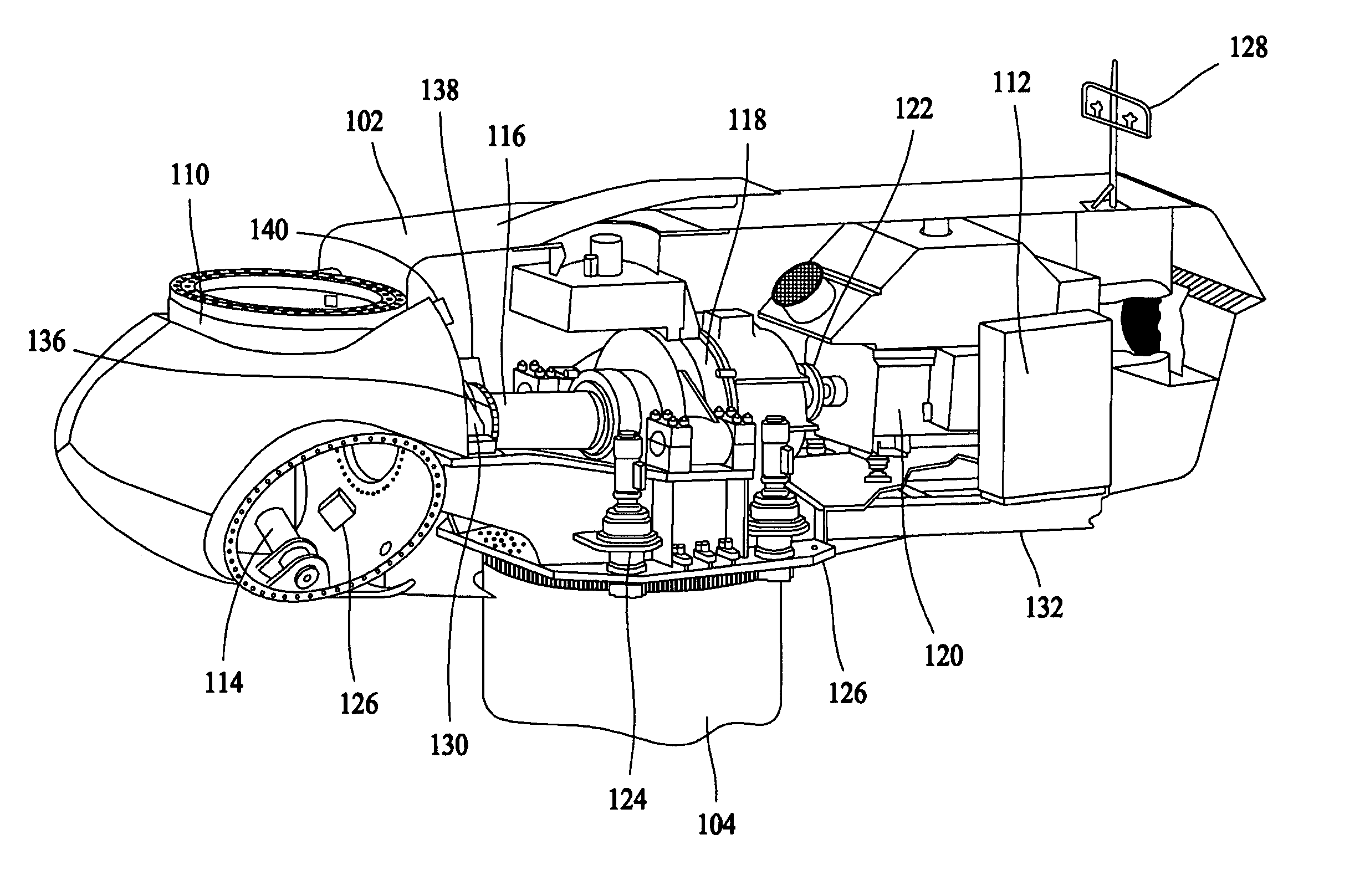
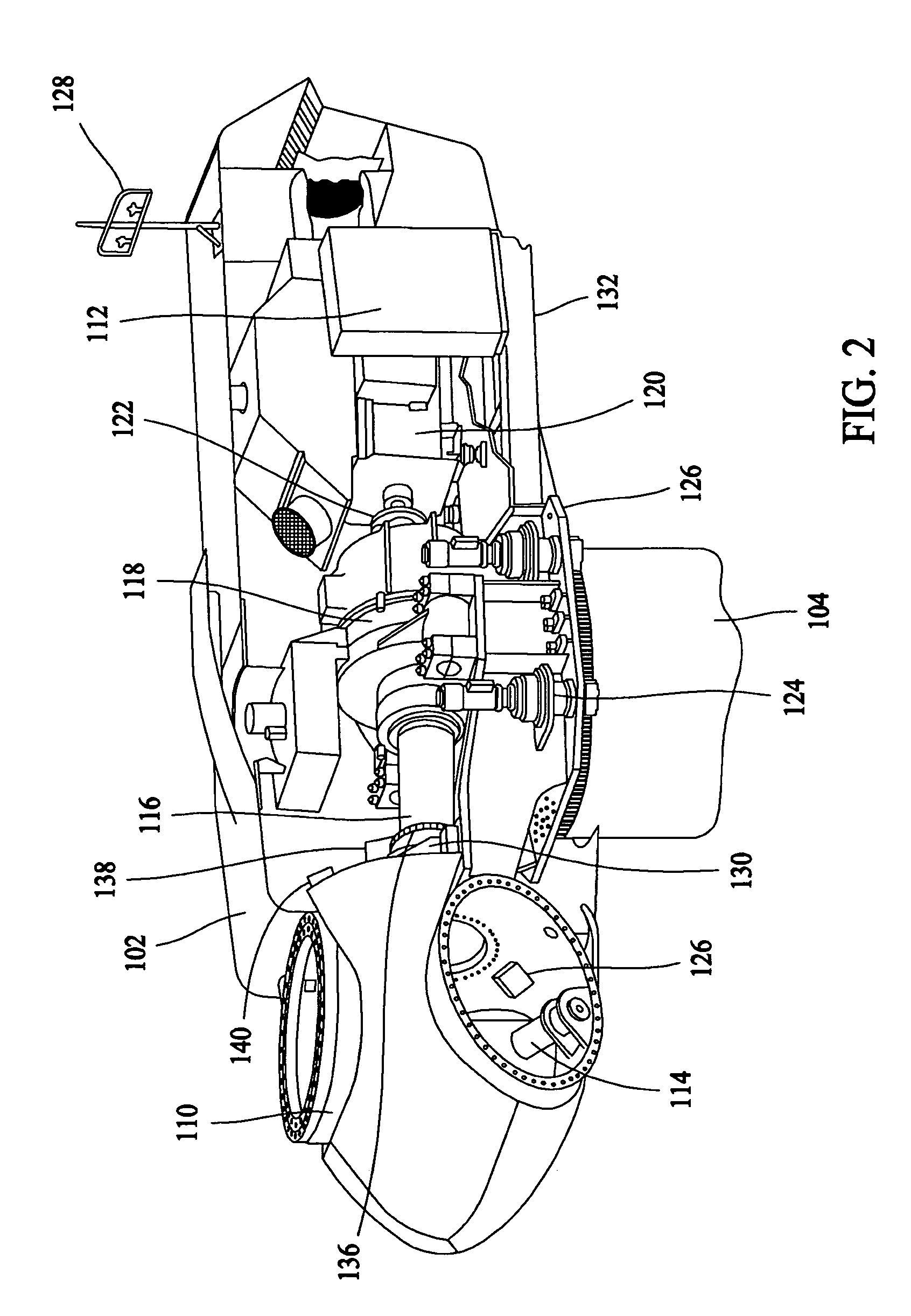
Method for operating a wind turbine
InactiveUS6965174B2Voltage fluctuationUnwanted fluctuationWind motor controlMachines/enginesPower gridWind force
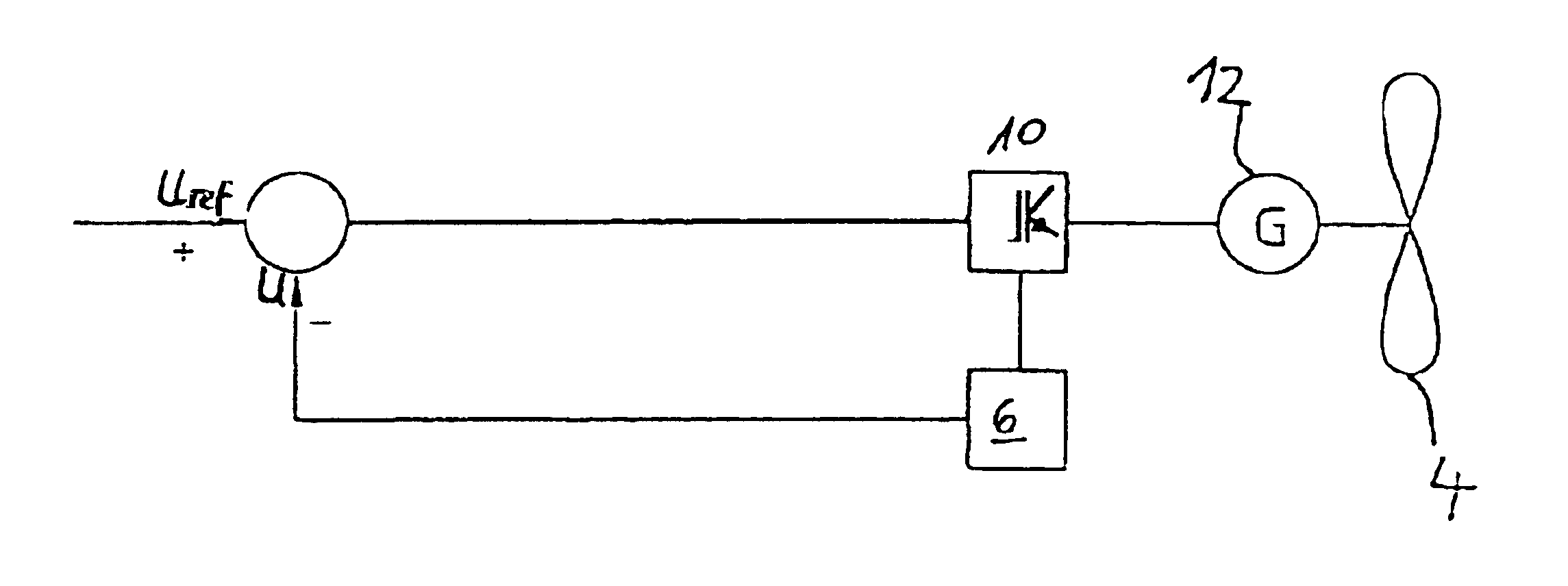
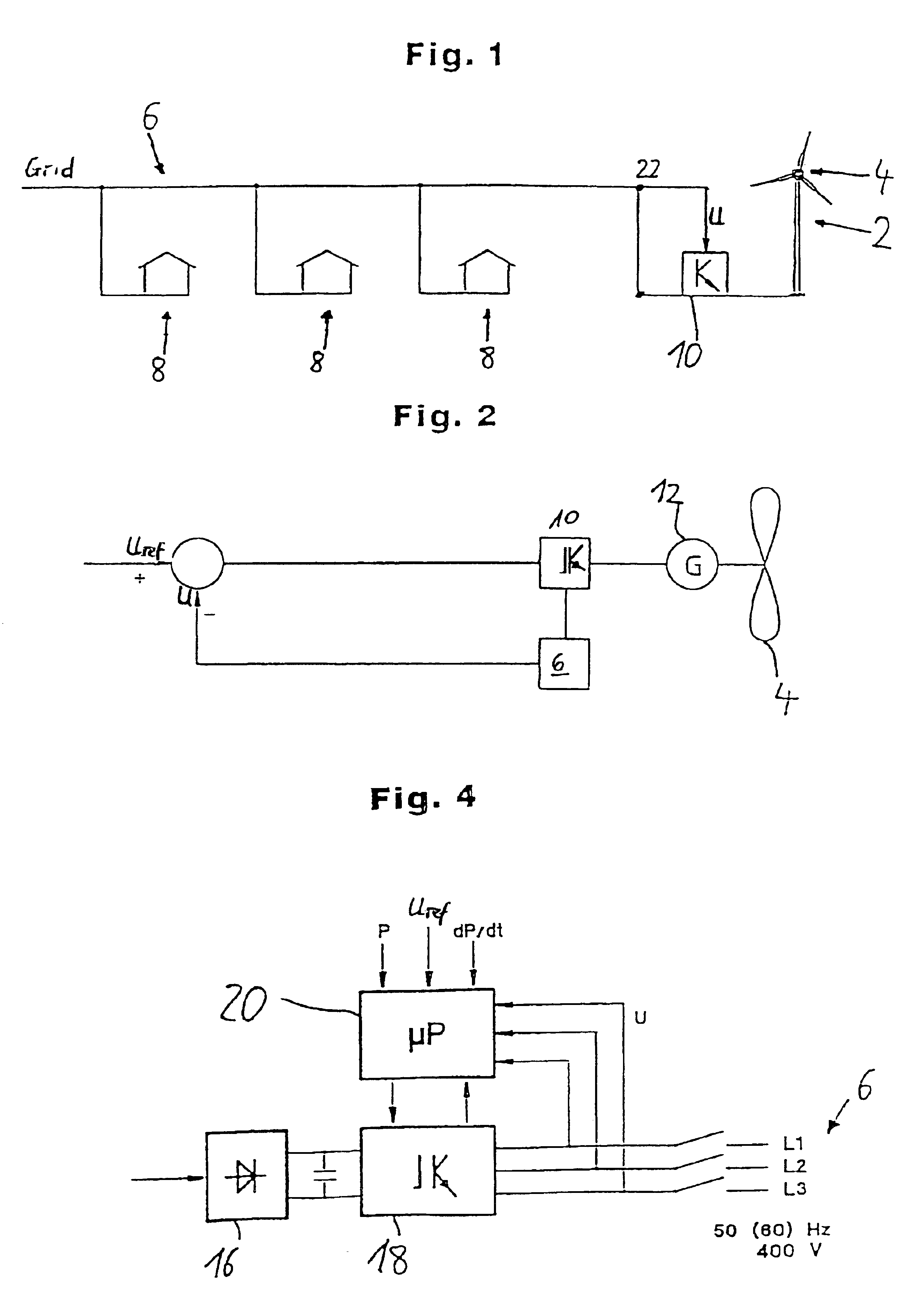
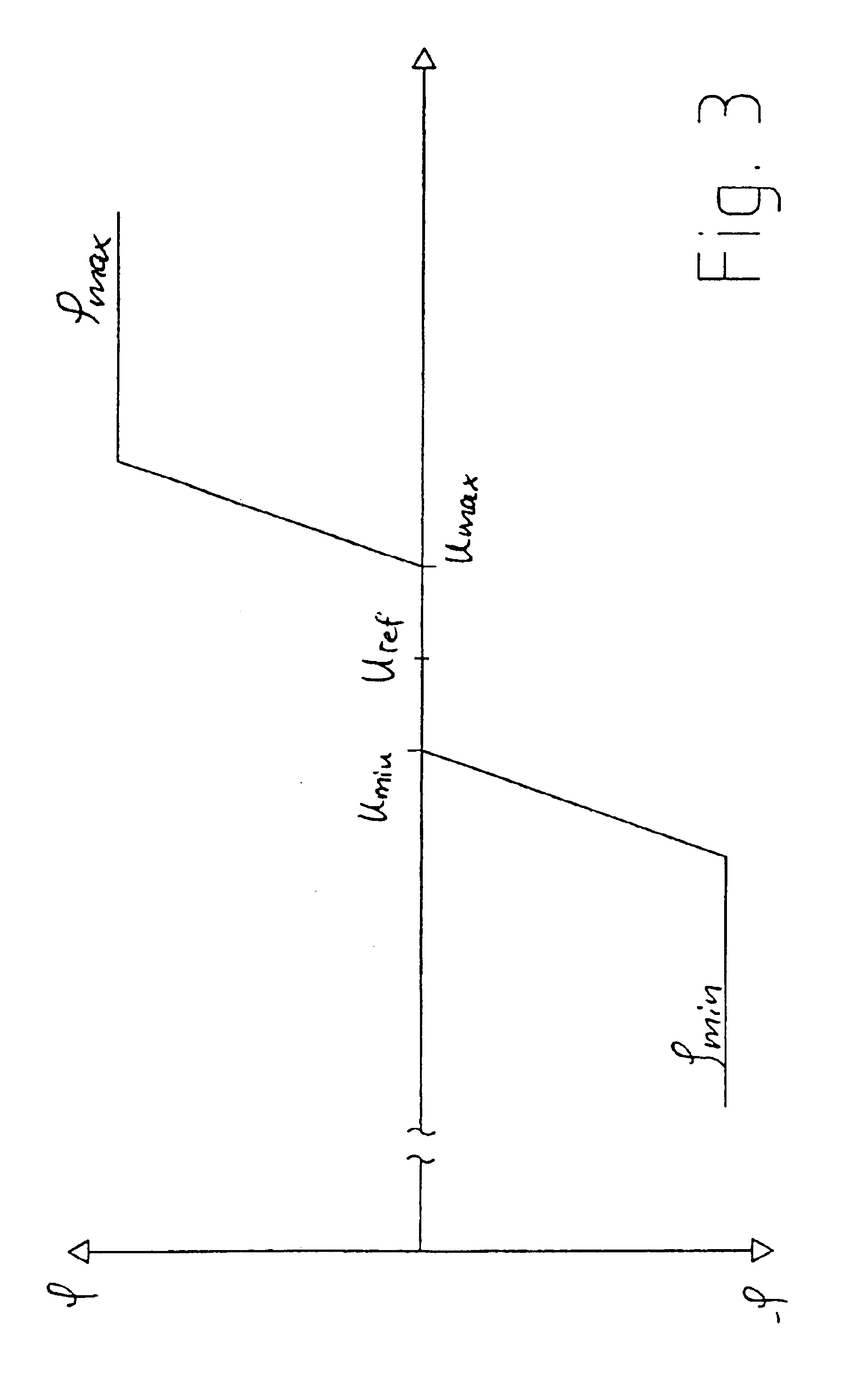
The present invention relates to a method for operating a wind turbine with an electrical generator, drivable by a rotor, for supplying electrical power to an electric grid, in particular to the loads connected thereto. The object of the present invention is to define a method for operating a wind turbine and to provide a wind turbine and / or a wind farm that is capable, even when the output of non-reactive power fluctuates, of reducing or at least of insignificantly increasing the unwanted fluctuation in voltage at a predefined point in the grid compared to the situation with no wind turbine(s). Method for operating a wind turbine with an electrical generator, drivable by a rotor, for supplying electrical power to an electric grid, in particular to the loads connected thereto, characterized in that the phase angle φ is changed in response to at least one voltage measured in the grid.A method for operating a wind turbine and to provide a wind turbine and / or a wind farm that is capable, even when the output of non-reactive power fluctuates, of reducing or at least of insignificantly increasing the unwanted fluctuation in voltage at a predefined point in the grid compared to the situation with no wind turbines. Method for operating a wind turbine with an electrical generator, drivable by a rotor, for supplying electrical power to an electric grid, in particular to the loads connected thereto, characterized in that the phase angle φ is changed in response to at least one voltage measured in the grid.
Owner:WOBBEN ALOYS
System and method for controlling a tethered flying craft using tether attachment point manipulation
InactiveUS20110121570A1Increase speedIncrease loadWind motor controlWind motor combinationsPrevailing windsTurbine
A tethered airborne electrical power generation system which may utilize a strutted frame structure with airfoils built into the frame to keep wind turbine driven generators which are within the structure airborne. The primary rotors utilize the prevailing wind to generate rotational velocity. Electrical power generated is returned to ground using a tether that is also adapted to fasten the flying system to the ground. The flying system is adapted to be able to use electrical energy to provide power to the primary turbines which are used as motors to raise the system from the ground, or mounting support, into the air. The system may use an attachment mechanism for the tether adapted to move the tether attachment point relative to the flying craft.
Owner:BEVIRT JOEBEN +1
Electrodynamic field generator
This device is a brushless high-voltage electrical generator, requiring suitable means of input rotary torque, for purposes of producing a very-high-energy external electrodynamic field or continuous quasi-coherent DC corona or arc discharge of uniform current density which completely encloses the machine's conductive housing. This housing is divided into distinct electrical sections and contains a flat conductive rotor which electrically links separate negative and positive housing sections and upon which a plurality of toroidal generating coils are rotatably mounted. Circular arrays of stationary permanent magnets are affixed within the housing which induce a constant DC voltage within said coils upon their rotation. The primary voltage so-generated is electrostatically impressed across the rotor such that great quantities of electronic charge may be transported between the opposite polarity sections of the housing, in such a manner that a much higher secondary voltage is caused to appear across interposed neutral sections thereof, and the resulting external breakdown current once initiated is independent of the generating coils' ampacity. Ancillary mechanical, electrical, an / or electronic features may be attached upon or within the housing to aid in harnessing and controlling the useful effects associated with the external dynamic electric field produced by the device.
Owner:LV DYNAMICS
Braking mechanisms
ActiveUS20120055740A1Improve braking effectEffective meanSafety beltsSelf acting brakesEngineeringEddy current
An eddy-current braking mechanism including a rotor, rotatable about a rotor axis; at least one electrically conductive member coupled to the rotor for rotation therewith; at least one magnet configured to apply a magnetic field extending at least partially orthogonal to the plane of rotation of the conductive member, and characterised in that upon rotation of the rotor, the conductive member is configured to move at least partially radially from the rotor axis into the applied magnetic field.
Owner:EDDY CURRENT PARTNERSHIP
Anti-icing system for wind turbines
InactiveUS20050242233A1Lower Level RequirementsAvoid and reduce accretionPump componentsEngine fuctionsNacelleEngineering
A de-icing and anti-icing arrangement for a Wind Energy Converting System (WECS), a WECS comprising a de-icing and anti-icing arrangement and a method for preventing and eliminating ice accretion on the rotor blades of a WECS are provided. The WECS comprises a tower, a rotor having a plurality of blades that rotate due to wind force, a nacelle including a first means for transforming the rotor's rotational movement to electric power, and a second means for permitting the flow of fluid from volumes defined by the rotor blades, the rotor blades comprising an external surface having openings in fluid connection with the volumes inside the blades for permitting the flow of fluid to the outside of the blades to fluid-thermodynamically interact with the wind hitting the part of the blade surface, and thereby prevent or eliminate the accretion of ice on the external surface of the blade.
Owner:BATTISTI LORENZO
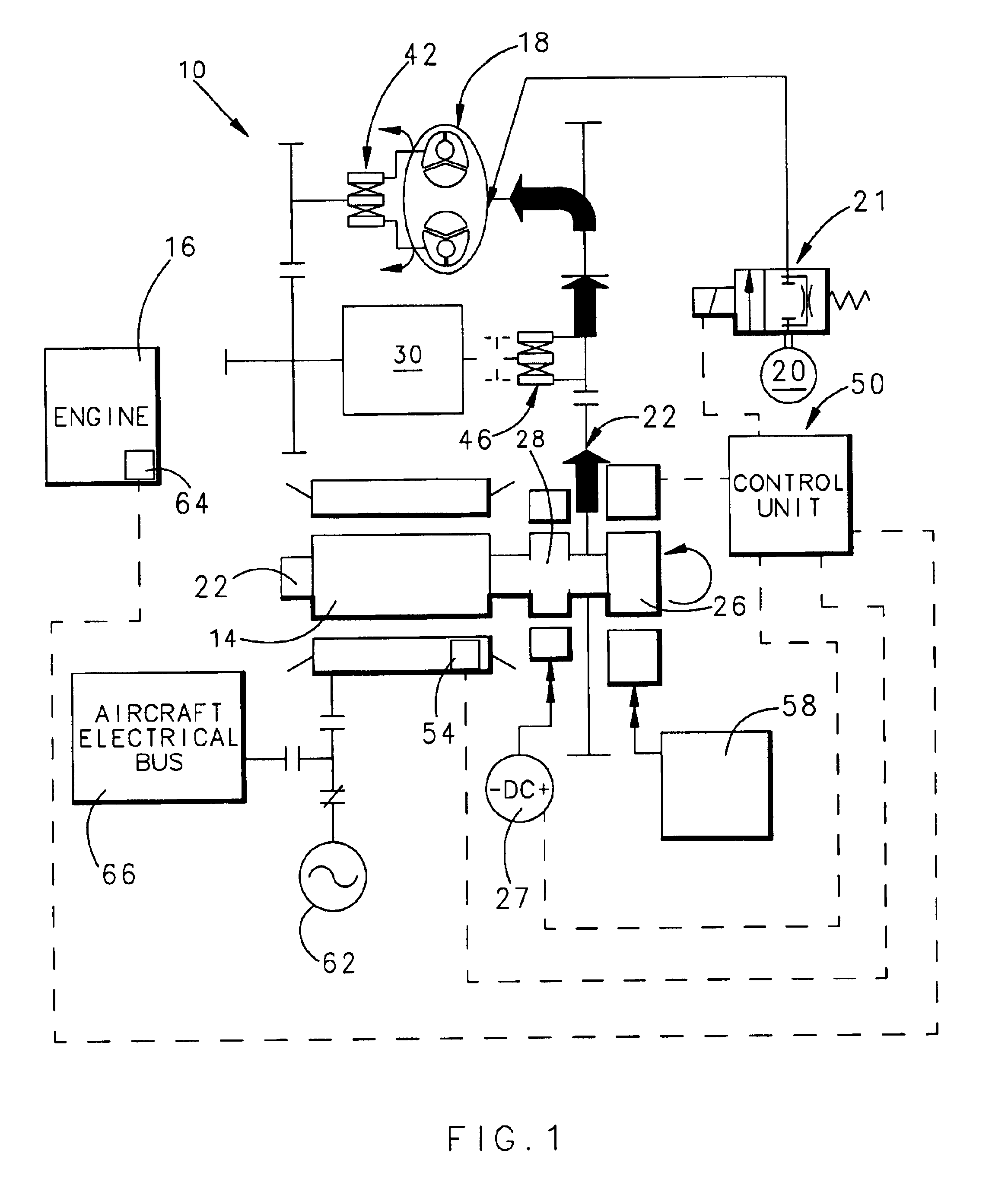
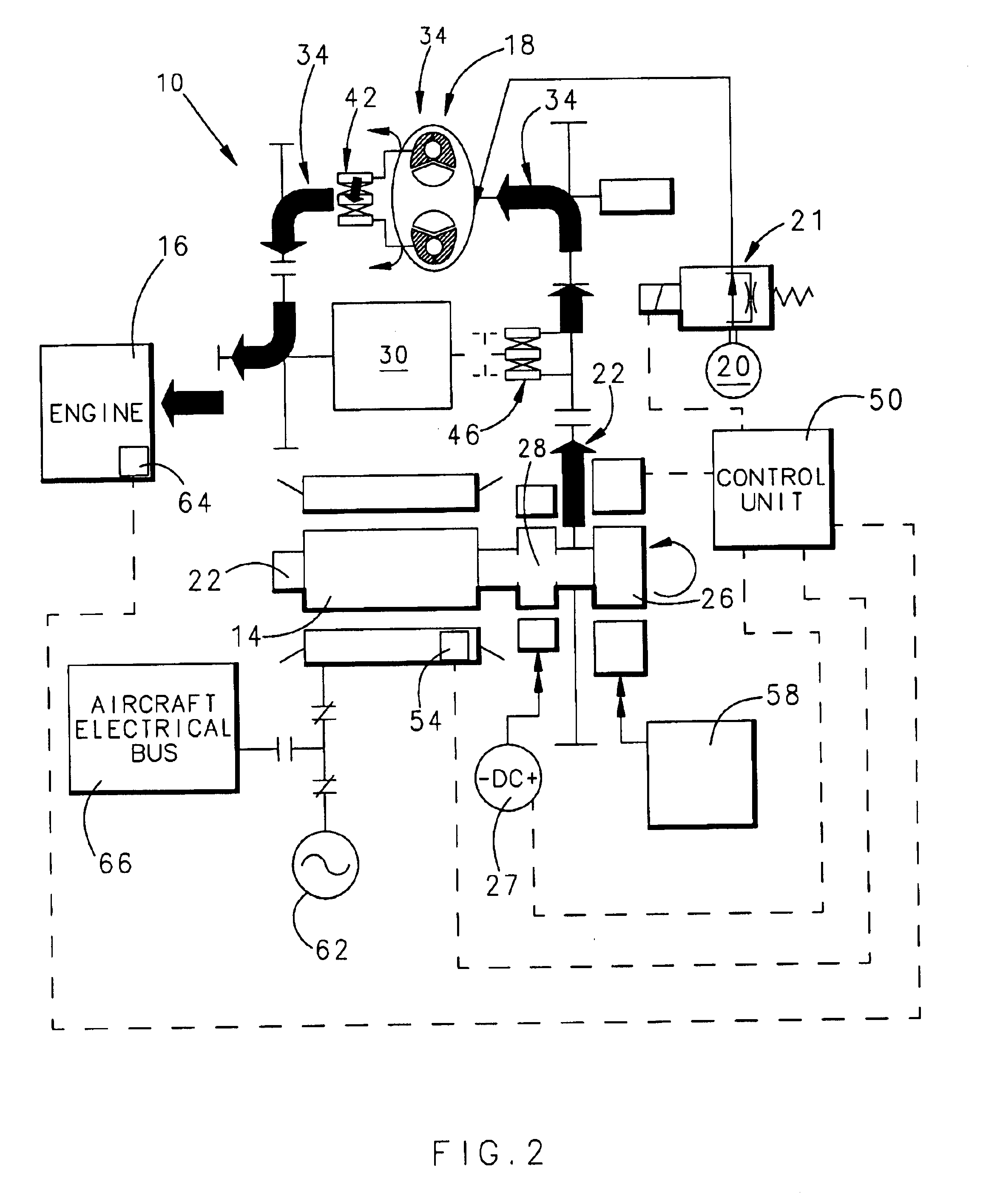
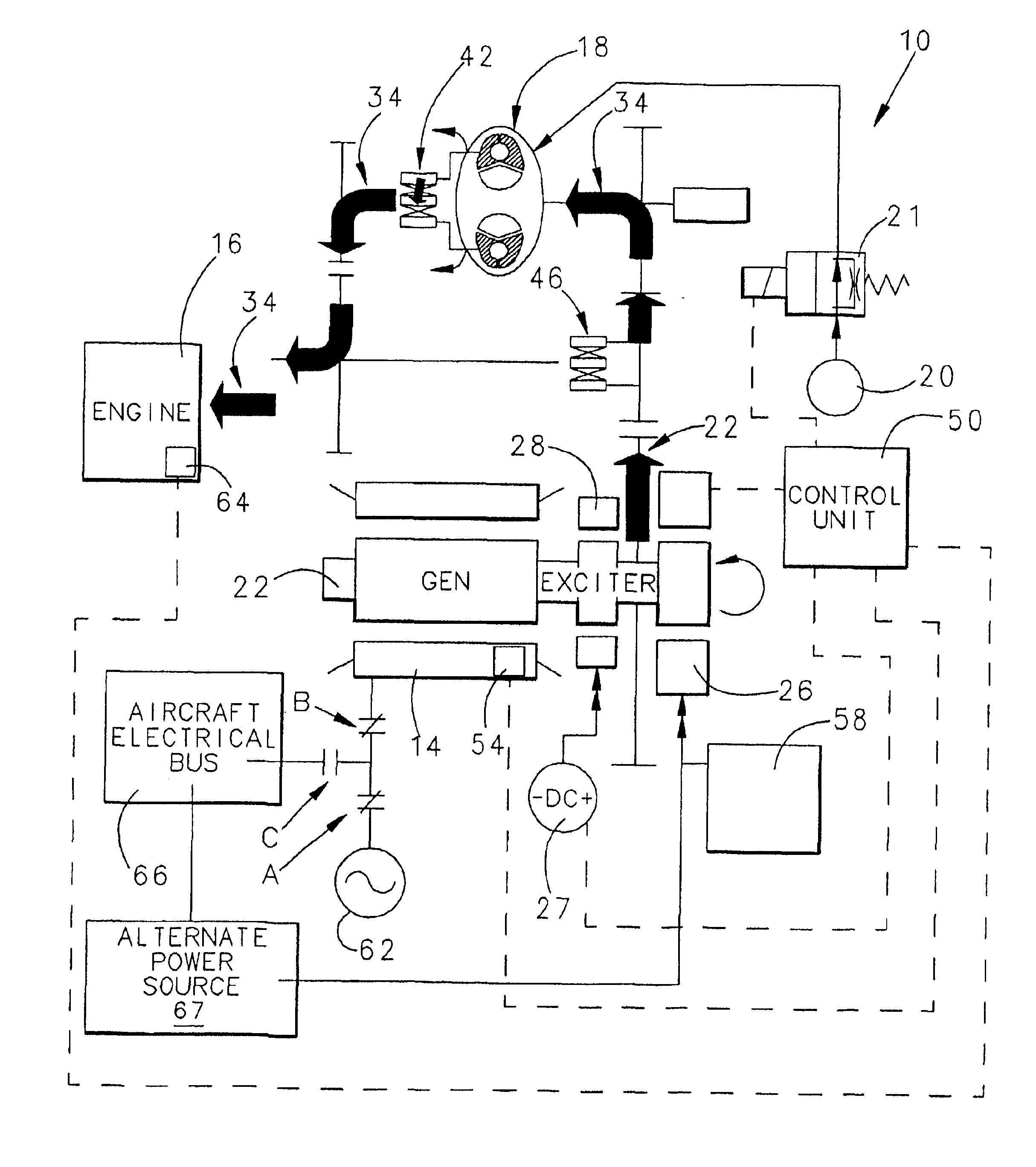
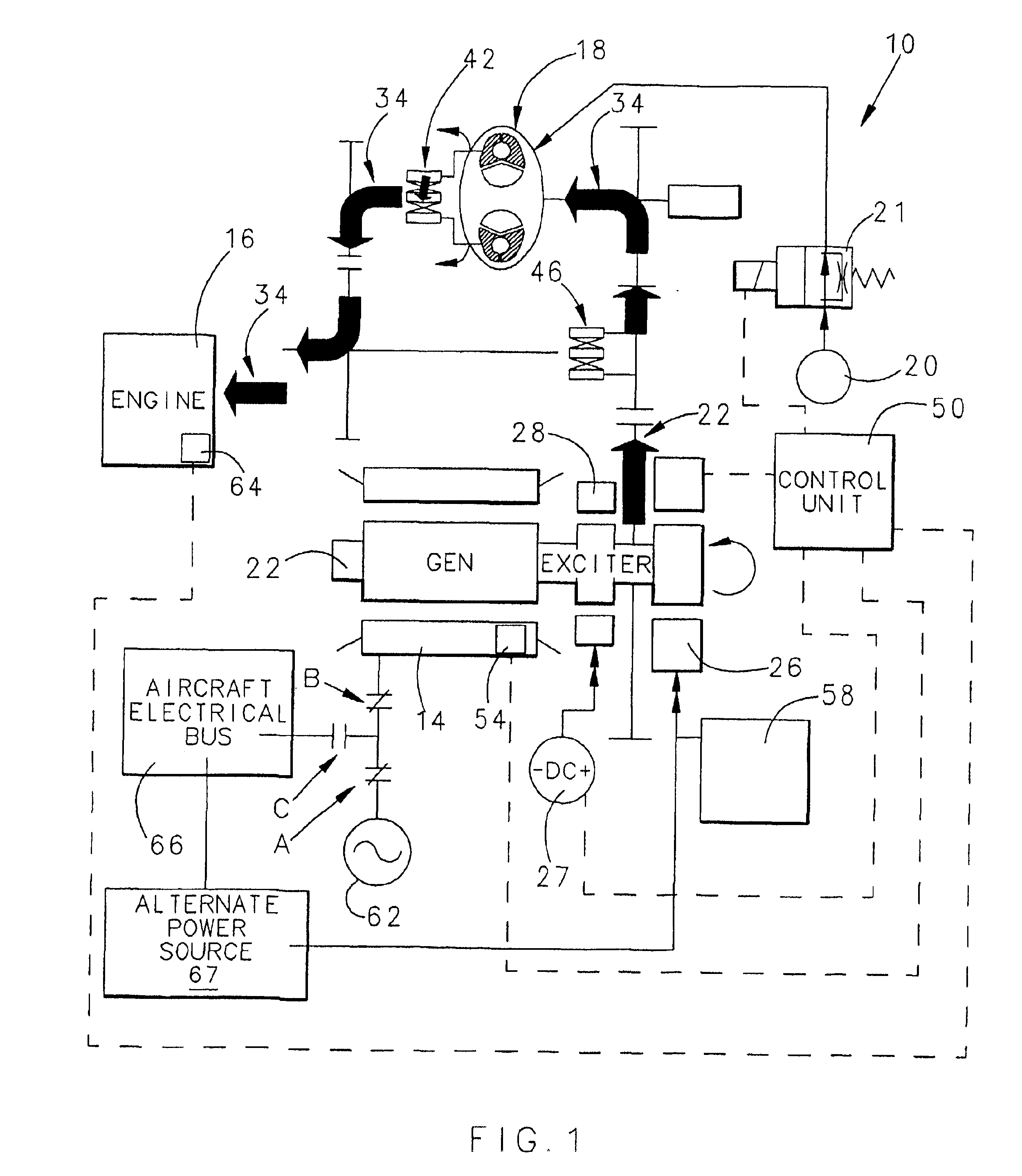
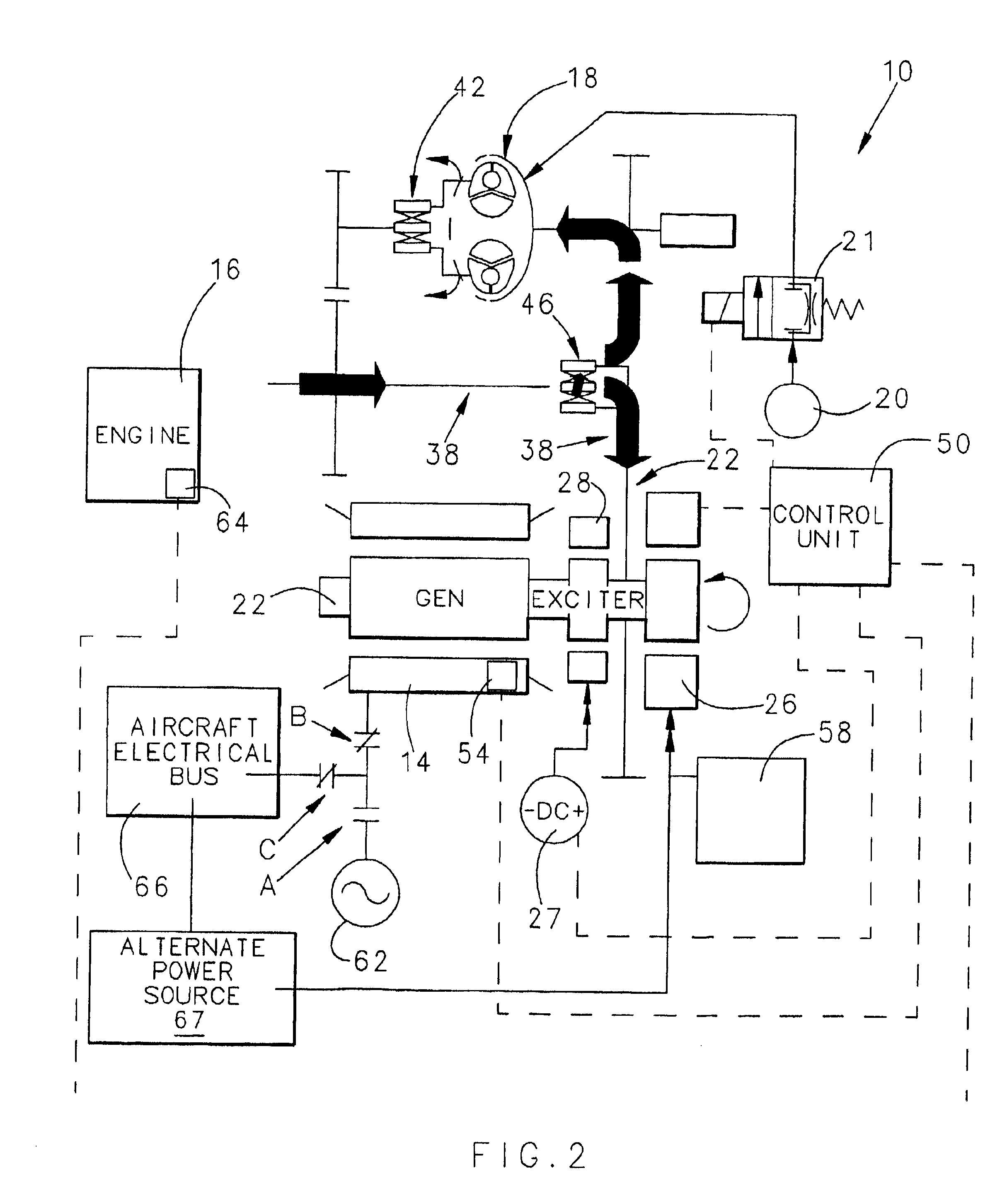
Integrated starter generator drive having selective torque converter and constant speed transmission for aircraft having a constant frequency electrical system
InactiveUS6838778B1Reduce loadStarters with fluid-driven auxillary enginesTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionStarter generatorConstant frequency
A starter-generator for an aircraft engine comprises a dynamoelectric machine alternatively operable as a motor or as a generator, having a rotor. A support motor is coupled to the dynamoelectric machine to assist the machine. A torque converter selectively couples and decouples the rotor to the engine, coupling the rotor to the engine at some point when dynamoelectric machine is operated as a motor. A constant speed transmission has an input adapted to be connected to the engine and an output to be connected to the rotor. The unit provides a desired speed relation between input and output. The engine may be started by the dynamoelectric machine when operated as a motor through a first power train including the torque converter and may drive the dynamoelectric machine as a generator through a second power train including the constant speed transmission.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Aircraft starter generator for variable frequency (vf) electrical system
InactiveUS6838779B1Reduce loadPower operated startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersStarter generatorElectric machine
A starter-generator for an aircraft engine comprises a variable dynamoelectric machine alternatively operable as a motor or as a generator, having a rotor. A support motor is coupled to the variable dynamoelectric machine to assist the machine. A torque converter selectively couples and decouples the rotor to the engine, coupling the rotor to the engine at some point when the dynamoelectric machine is operated as a motor. The engine may be started by the dynamoelectric machine when operated as a motor through a first power train including the torque converter and may drive the dynamoelectric machine as a generator through a second power train.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
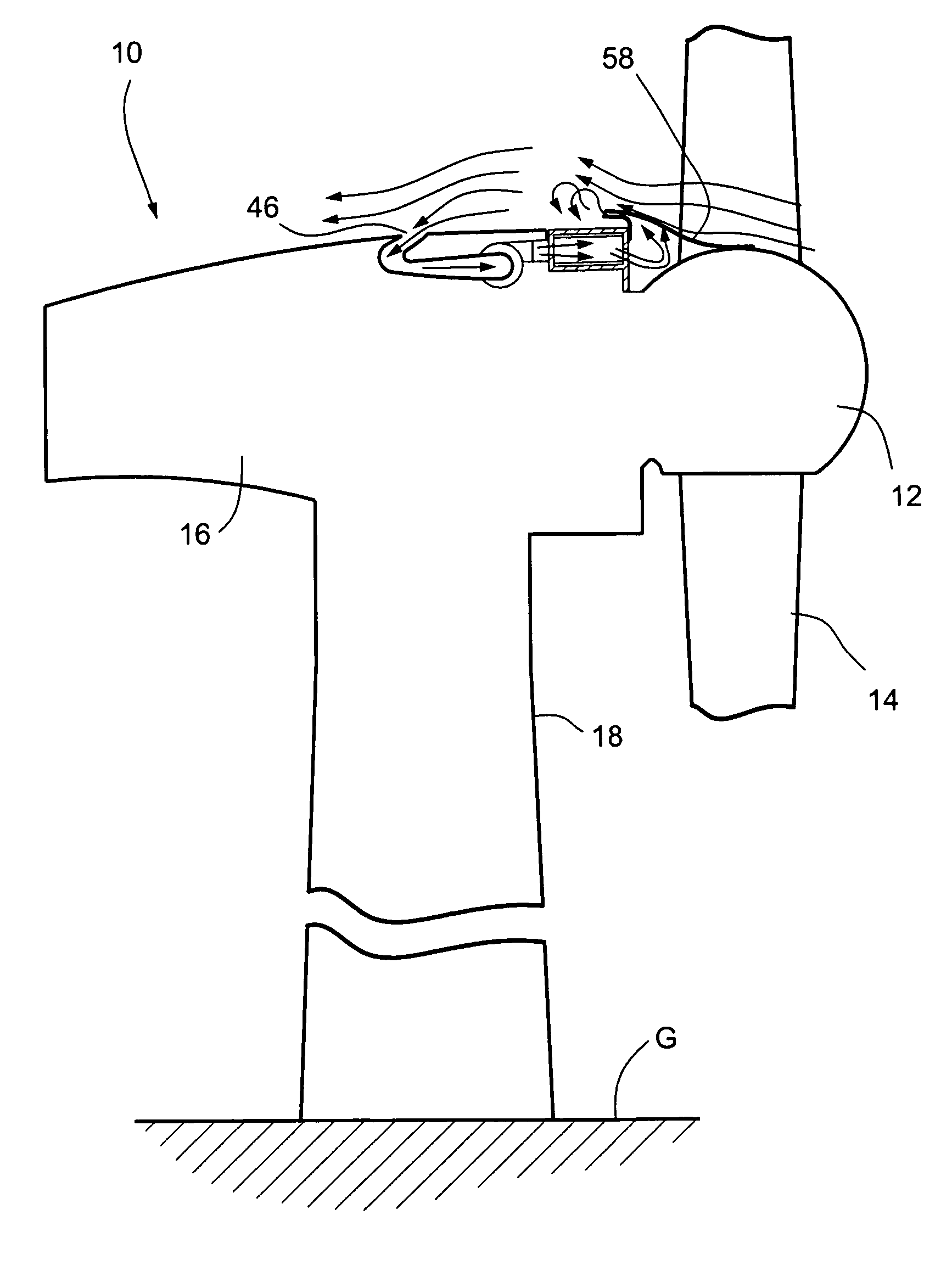
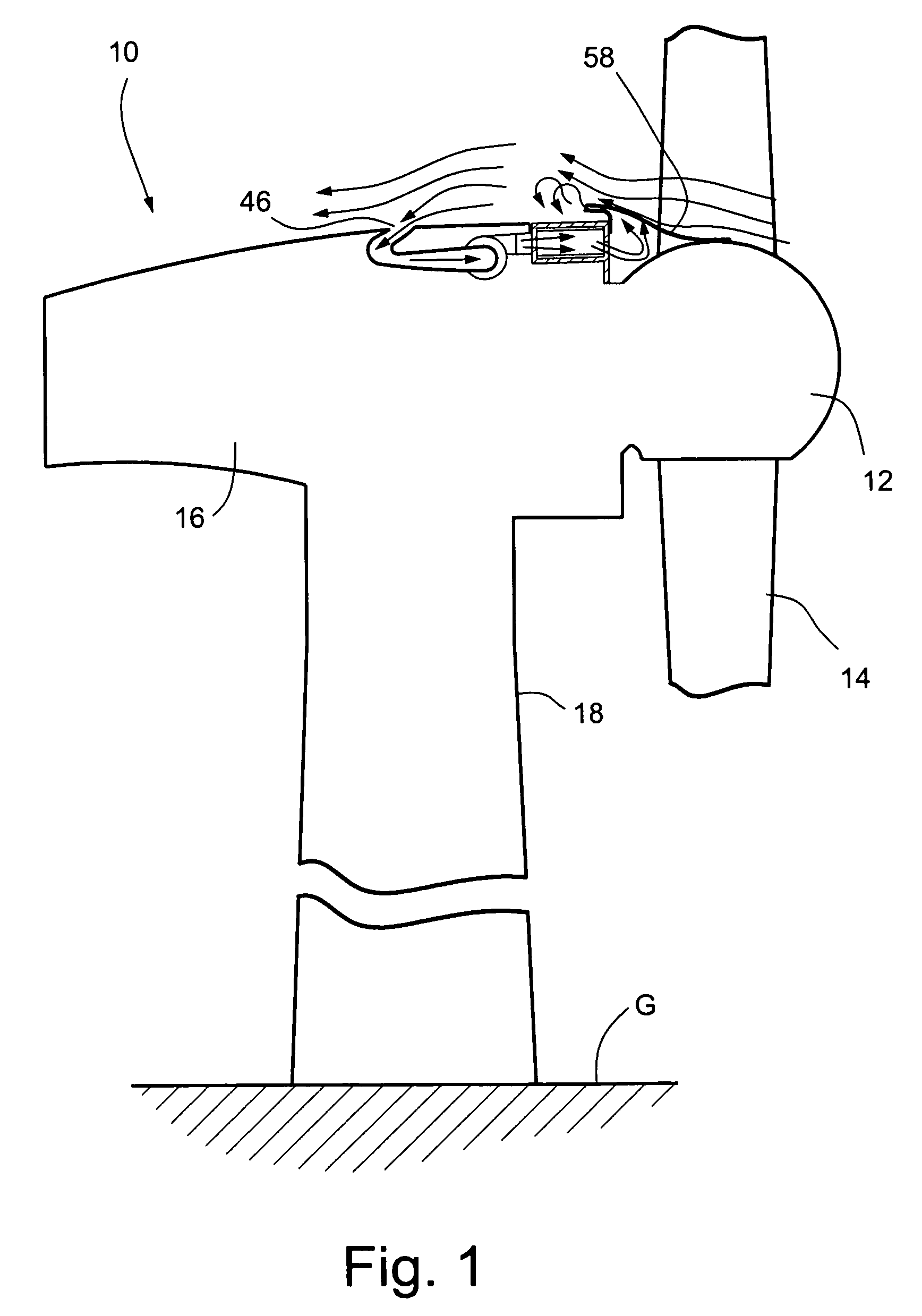
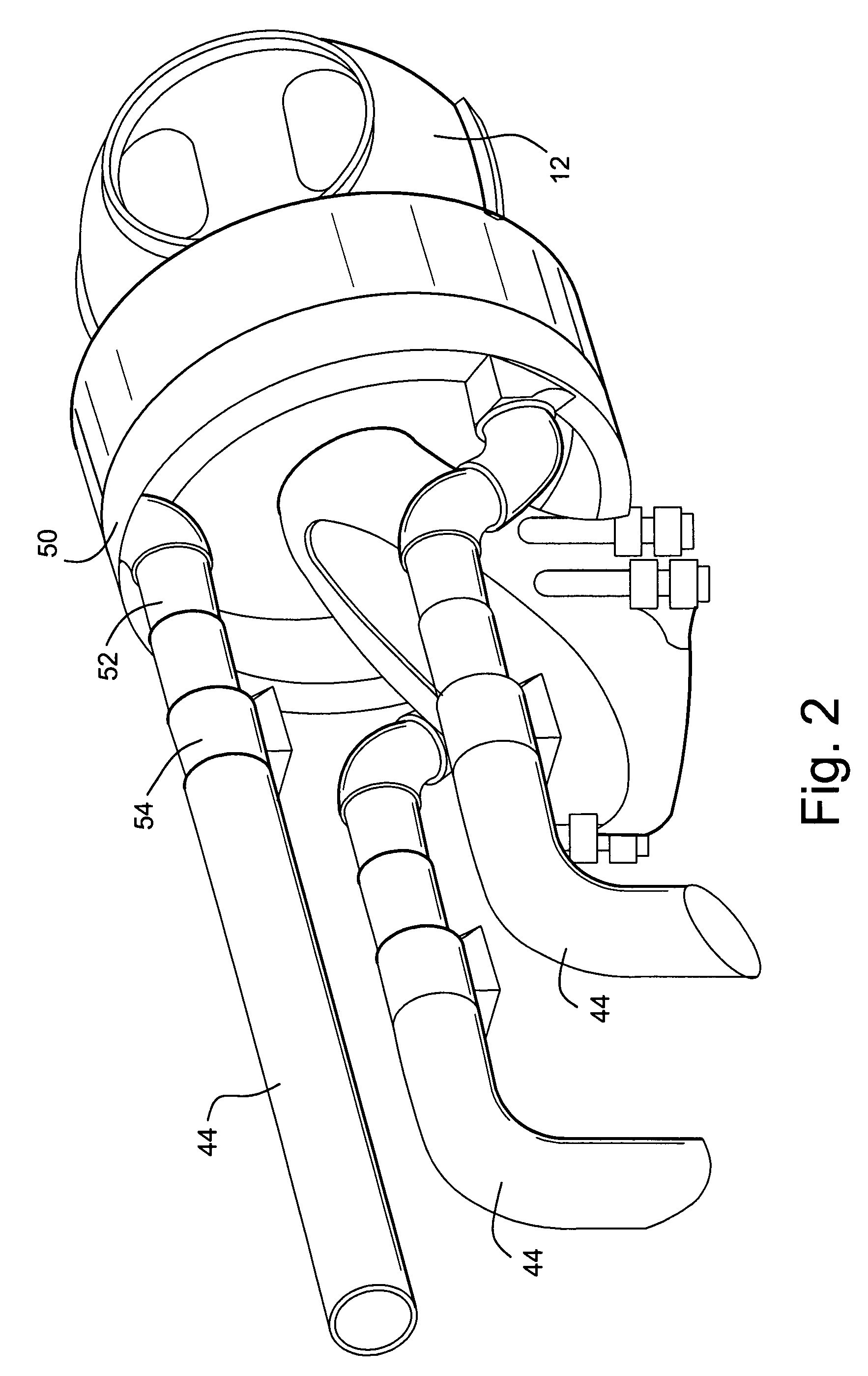
Wind turbine generators having wind assisted cooling systems and cooling methods
A wind generator includes: a nacelle; a hub carried by the nacelle and including at least a pair of wind turbine blades; and an electricity producing generator including a stator and a rotor carried by the nacelle. The rotor is connected to the hub and rotatable in response to wind acting on the blades to rotate the rotor relative to the stator to generate electricity. A cooling system is carried by the nacelle and includes at least one ambient air inlet port opening through a surface of the nacelle downstream of the hub and blades, and a duct for flowing air from the inlet port in a generally upstream direction toward the hub and in cooling relation to the stator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for rotor load control in wind turbines
ActiveUS7095129B2Reduce loadReduce wind loadsWind motor controlGeneration protection through controlClassical mechanicsPower grid
A wind turbine having a rotor, at least one rotor blade, and a plurality of generators, of which a first generator is configured to provide power to an electric grid and a second generator is configured to provide power to the wind turbine during times of grid loss. The wind turbine is configured to utilize power provided by the second generator to reduce loads on the wind turbine during times of grid loss.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
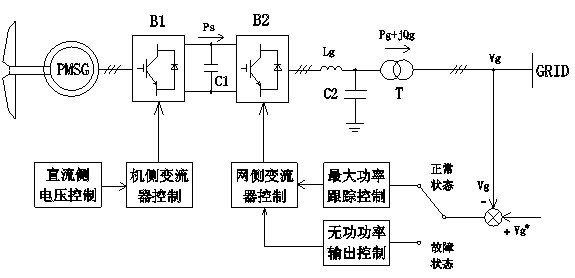
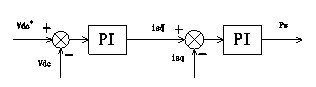
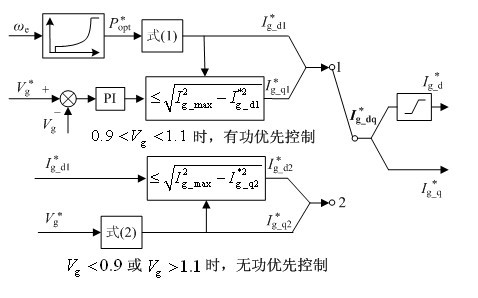
Active and reactive coordination control method for permanent-magnet direct-driven wind turbines in low-voltage ride-through process
InactiveCN102664427AReduce active power lossDC voltage fluctuation is smallSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationDC - Direct currentRotor (electric)
Enclosed is an active and reactive coordination control method for permanent-magnet direct-driven wind turbines in the low-voltage ride-through process. Two different control strategies are employed for a grid side converter according to amplitude change of power grid voltage: when the power grid voltage is in a normal state, the grid side converter is in an active-priority maximum power tracing control mode so that the wind turbines capture wind energy to the maximum extent; when the power grid voltage is beyond the normal range, the grid side converter is in an active priority control mode so that the dynamic reactive current which is injected into an electricity system meets the requirements of grid combining. An engine side converter is in a direct-current voltage control mode based on rotor energy storage, power unbalance of the direct-current side of the engine side converter is relieved and the direct-current voltage is stabilized by utilizing the self rotating speed of the permanent-magnet direct-driven wind turbines and the change of the kinetic energy. The active and reactive coordination control for the wind turbines before or after the sudden change of the power grid voltage is realized according to the amplitude change of the power grid voltage, the fluctuation of the direct-current bus voltage is restrained by releasing or storing the rotor kinetic energy, so that the low-voltage ride-through capability of the permanent-magnet direct-driven wind turbines is improved, reactive power support is rapidly and accurately provided for the power grid, and certain support is given to restoration of the power grid voltage.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
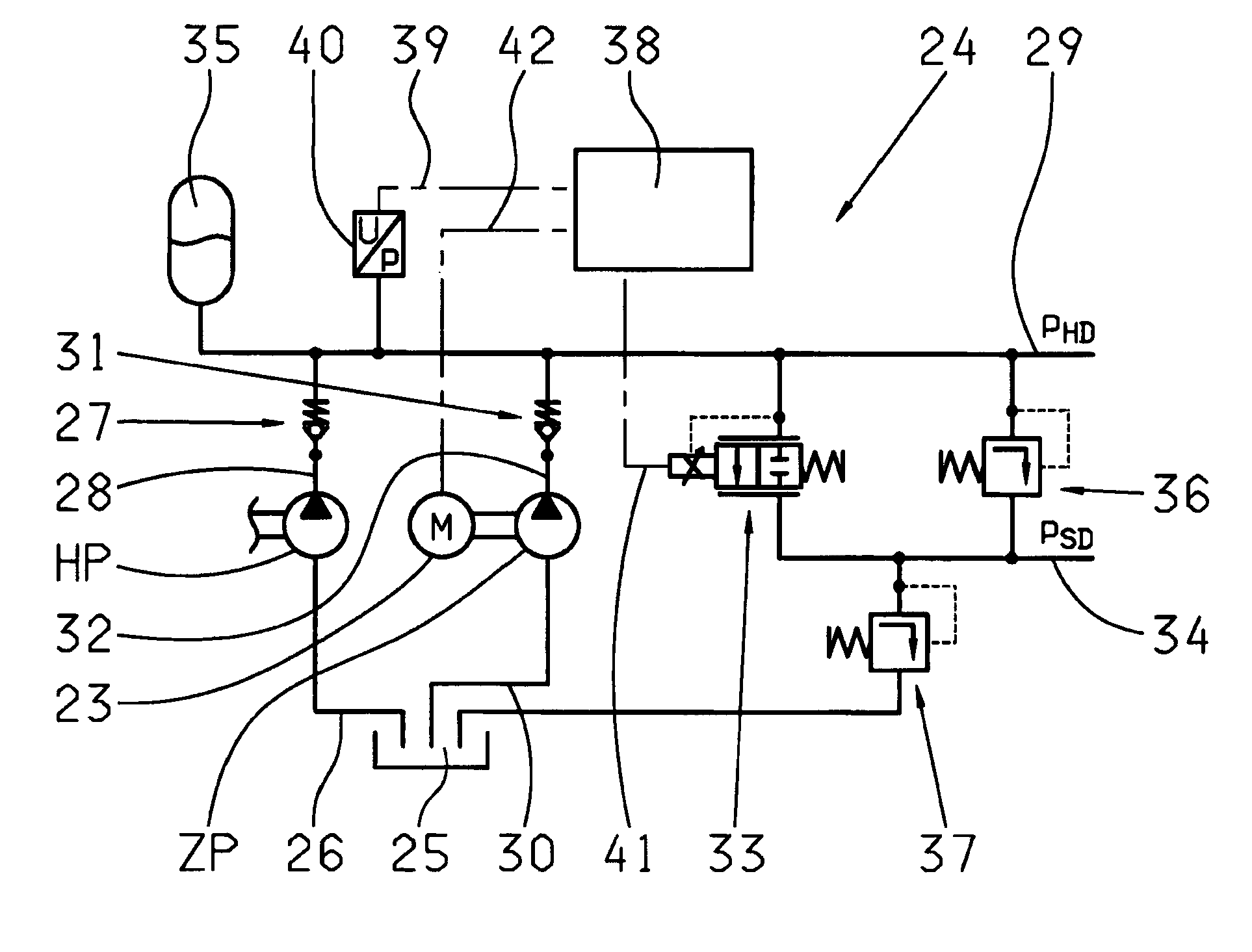
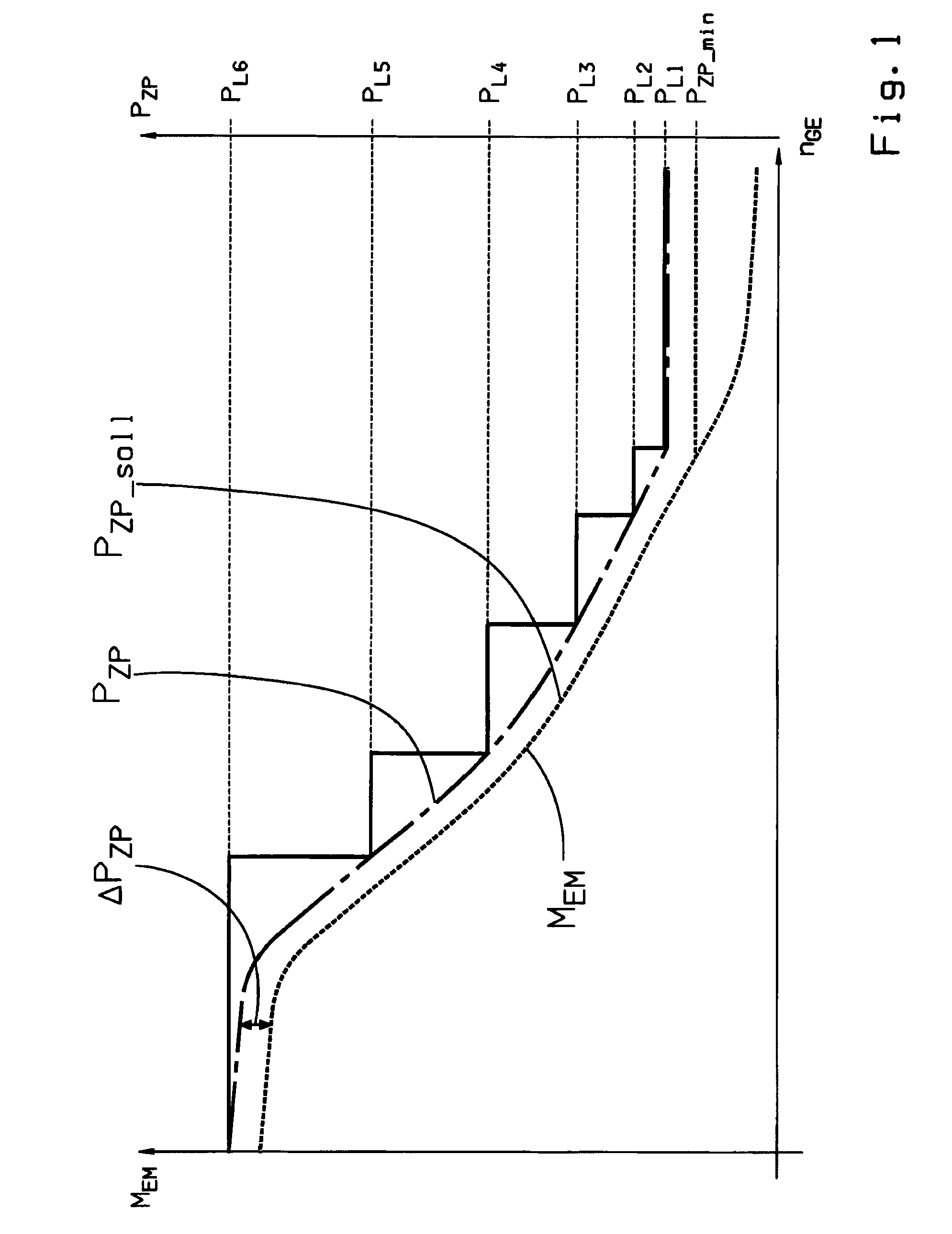
Method for controlling the oil supply of an automatic planetary transmission
InactiveUS20100018808A1Improve accessibilityIncrease installation spaceElectric propulsion mountingGear lubrication/coolingEngineeringInternal combustion engine
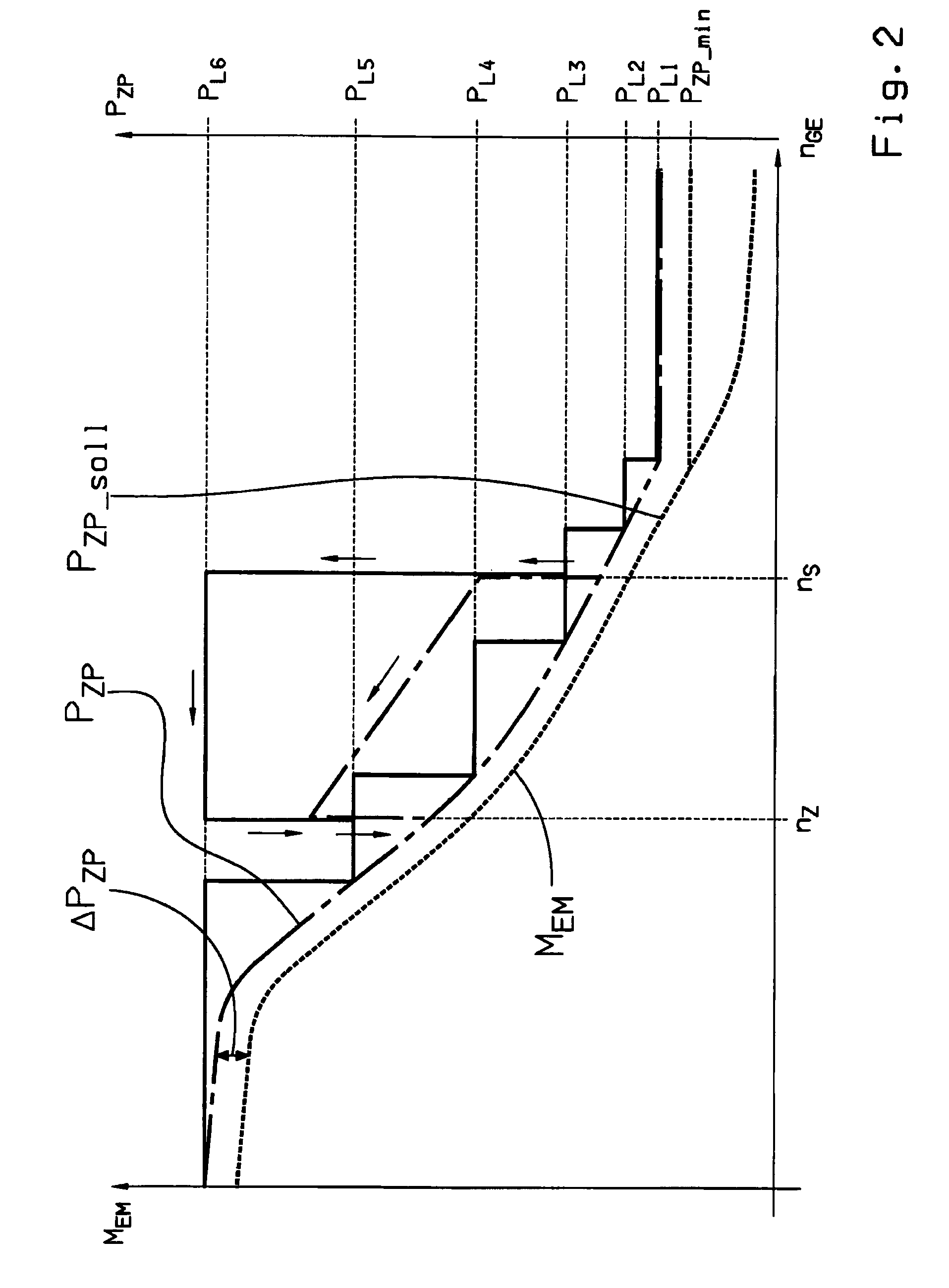
The invention relates to a method for controlling the oil supply device of an automatic planetary transmission, comprising a main oil pump (HP), which is mechanically drivably connected to the drive shaft of an internal combustion engine (VM), and an auxiliary oil pump (ZP) that may be driven via a controllable electric motor, the automatic transmission (ATG) being part of a parallel hybrid powertrain of a motor vehicle having an input shaft (5), which may be connected via a separating clutch (K) to the drive shaft (2) of the internal combustion engine (VM) and is permanently drivably connected to the rotor (4) of an electric machine (EM).In order to achieve an oil supply to the automatic transmission (ATG) as and when needed, it is provided that the current oil requirement (PHD<sub2>—< / sub2>soll) of the automatic transmission is determined as a function of at least one currently captured operating parameter, and that the delivery rate (PZP) of the auxiliary oil pump (ZP) is set, by a correspondingly actuation of the associated electric motor, in the combustion and combined driving mode below a minimum input speed of the main oil pump (HP) and in the electric driving mode to at least the total oil requirement, and at least in the combined driving mode above the minimum input speed of the main oil pump (HP) is set to at least the residual oil requirement exceeding the delivery rate (PHP) of the main oil pump.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Novel electric driving control system and method for vehicle air conditioner compressor
InactiveCN101051806AImprove operational efficiencySmooth startSingle motor speed/torque controlElectric machinesElectricityControl system
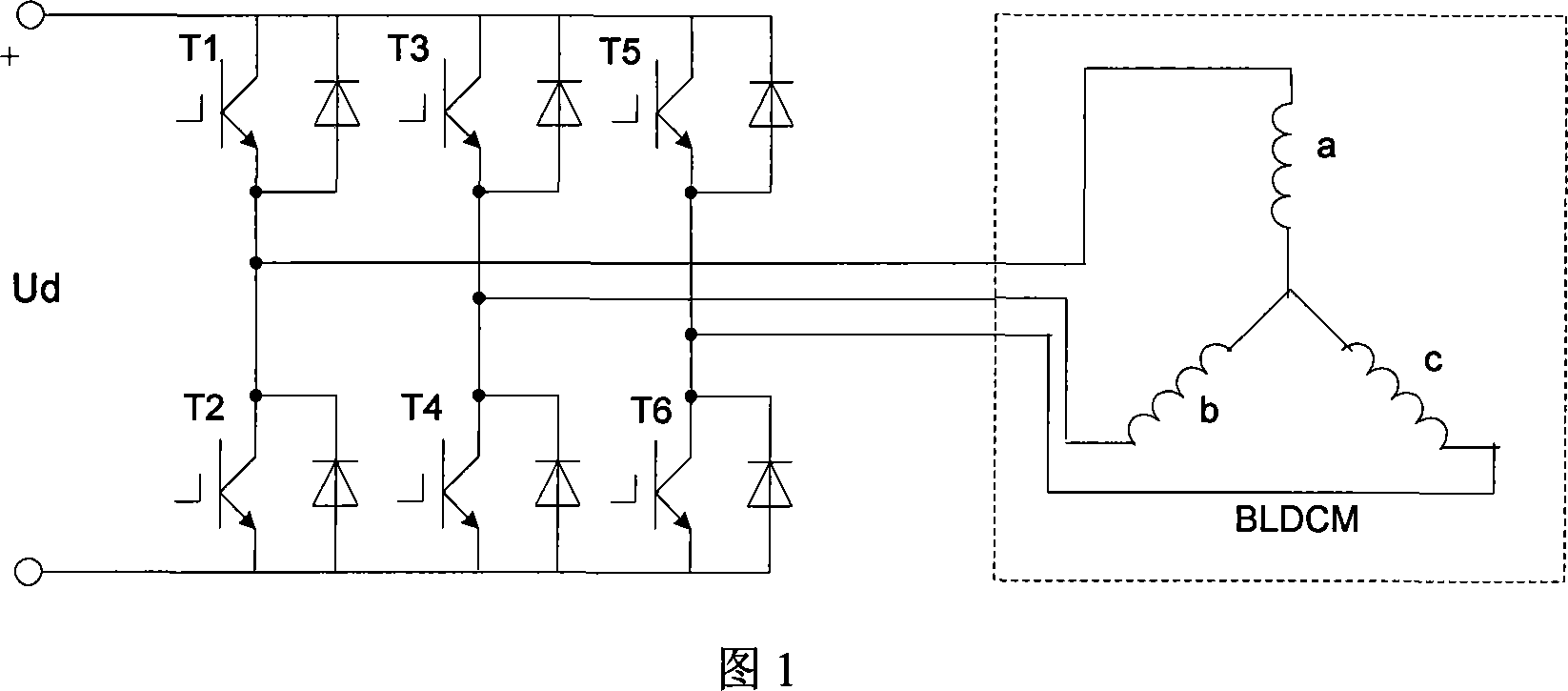
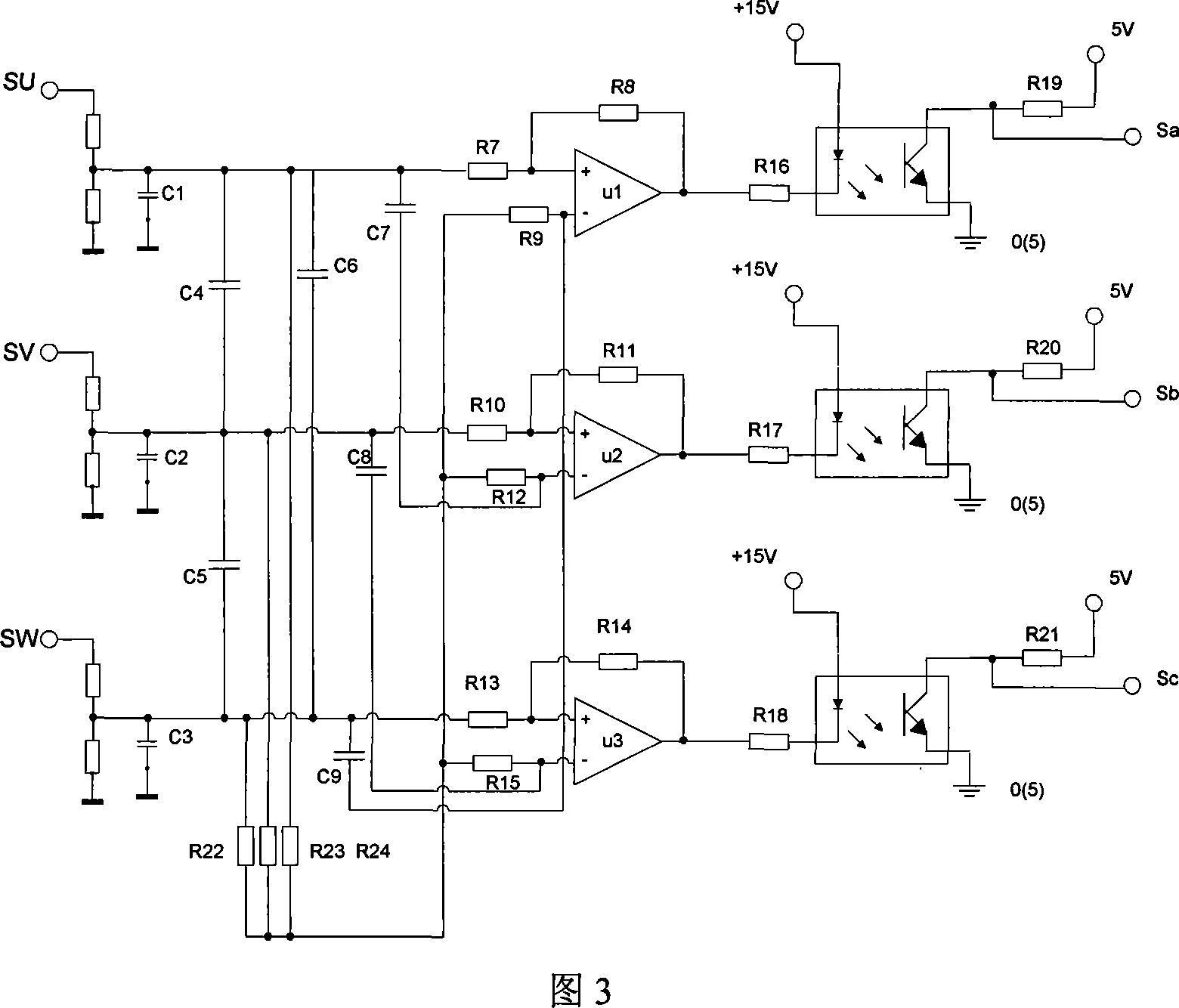
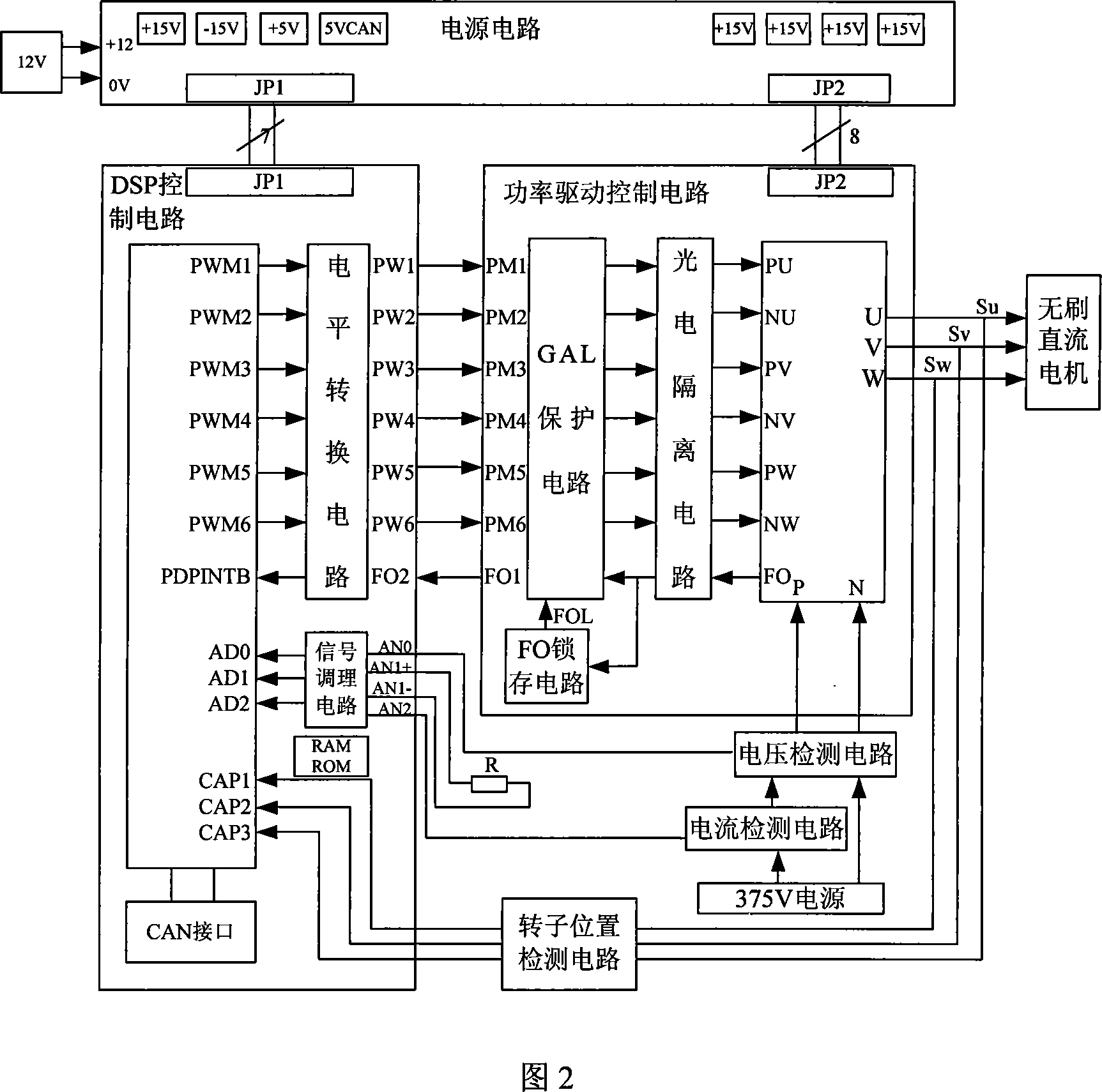
The system and method for controlling electrical motor with no position sensor and brushless are based on angle self-learned, and switching self-optimized optimized efficiency. The system is composed of power supply circuit, power drive circuit unit, DSP control circuit, detection circuit unit for rotor position, voltage detection unit, current detection unit, and temperature detection unit etc. The software part includes following modules: initialization module, external synchronization starting up module, module for switching external synchronization to self - synchronization, self adaptive raising speed module for self - synchronization, hardware module for computing signal of position, and module for optimizing operating efficiency. The disclosed driving controller makes motor with no position sensor and brushless start up smoothly and operate in high efficiency under large dynamic load range. Including CAN comm interface, the system guarantees reliable comm to bus of vehicle.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Liquid ring pumps with hermetically sealed motor rotors
ActiveUS7465375B2Easy maintenanceMaximize energy efficiencyGeneral water supply conservationDistillation regulation/controlDrive shaftDistillation
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Remotely operated self-powered gas safety valve
InactiveUS6994309B2Plug valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringRotation control
An apparatus for the remote measurement, control, and supervision, via a wired or wireless network connection, of the flow of gas, allowing fully opening or closing a valve in case of an emergency or for administrative purposes. The apparatus also provides for flow pressure, barometric pressure, and a temperature compensated gas flow meter. The apparatus obtains the number of revolutions of a rotor which delivers a fixed amount of gas per revolution and compensates for gas bypassing the rotor. The apparatus is self-powered by the energy produced by an electric generator coupled to the flow measurement rotor. The surplus energy not used by the electronic components in measuring and reporting is stored for the operation of the rotary control valve. The apparatus is housed in a planar base plate that allows servicing from one side of the system. The apparatus uses an energy storage management system for the controlled charging and use of the apparatus in an intrinsically safe manner.
Owner:FERNANDEZ SEIN RAFAEL
Method and system for taxiing an aircraft
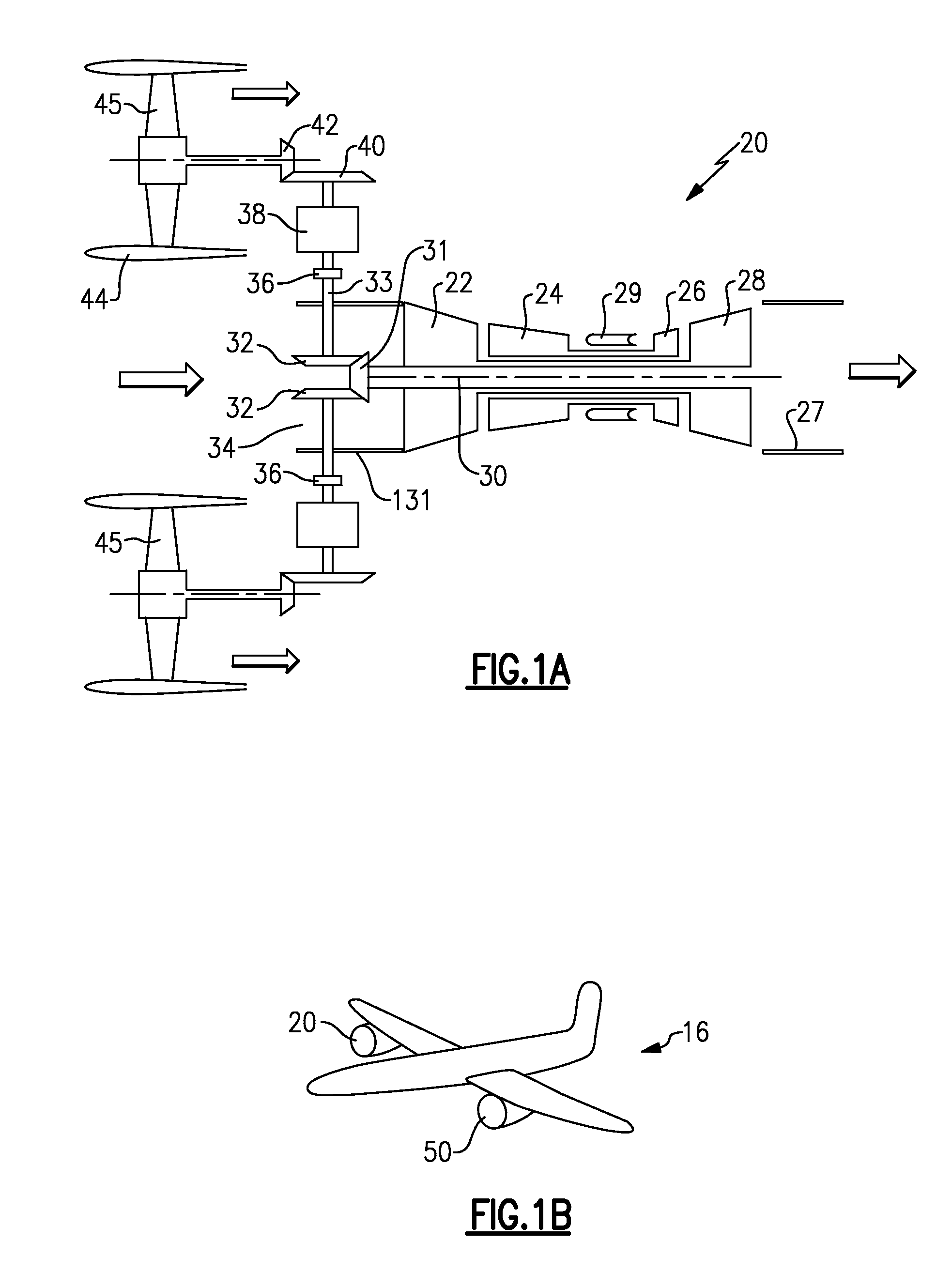
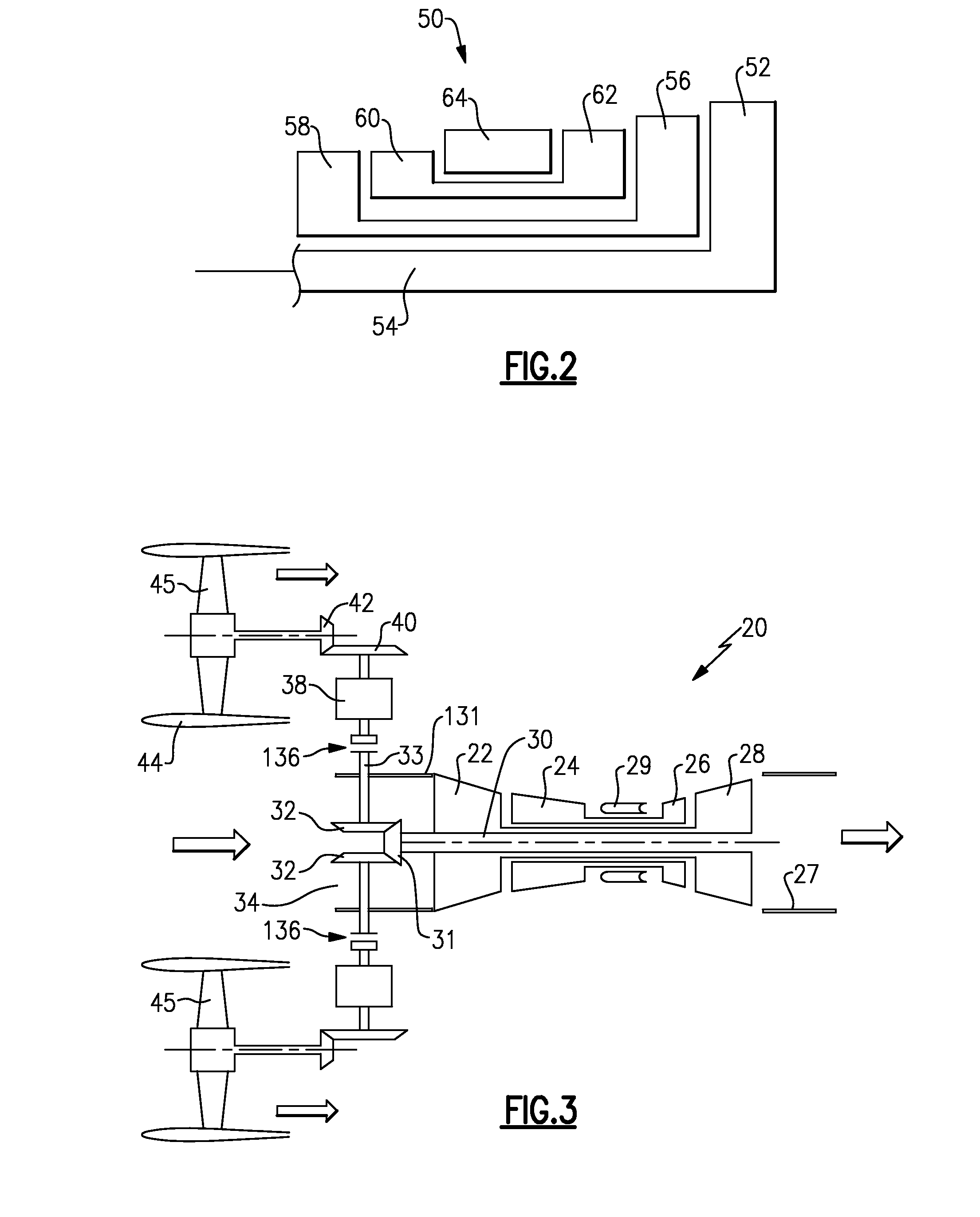
The system is used for taxiing an aircraft and comprises at least one multi-spool gas turbine engine, the engine having an electrical motor in a torque-driving engagement with a low pressure spool of the engine. The low pressure spool has a propulsor connected thereon to generate thrust when rotated. A controller is connected to the electrical motor and an electrical power source to control an amount of electrical power provided from the power source to the electrical motor so as to drive the propulsor and cause at least a major portion of the thrust to be generated by the propulsor for moving the aircraft during taxiing.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Motor with RPM pickup via a hall sensor
PCT No. PCT / DE98 / 00393 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 7, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 7, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 12, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 40751 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 17, 1998The invention is based on an electrically operated motor, having a shaft with a magnet rotor body, the RPM of the shaft can be picked up by a Hall sensor disposed on a circuit board. The circuit board is embodied with soldered pins or contact shoes and is integrated into a component of the motor, and that contacts, supply and signal lines for the circuit board are injected and / or plugged into the component of the motor.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
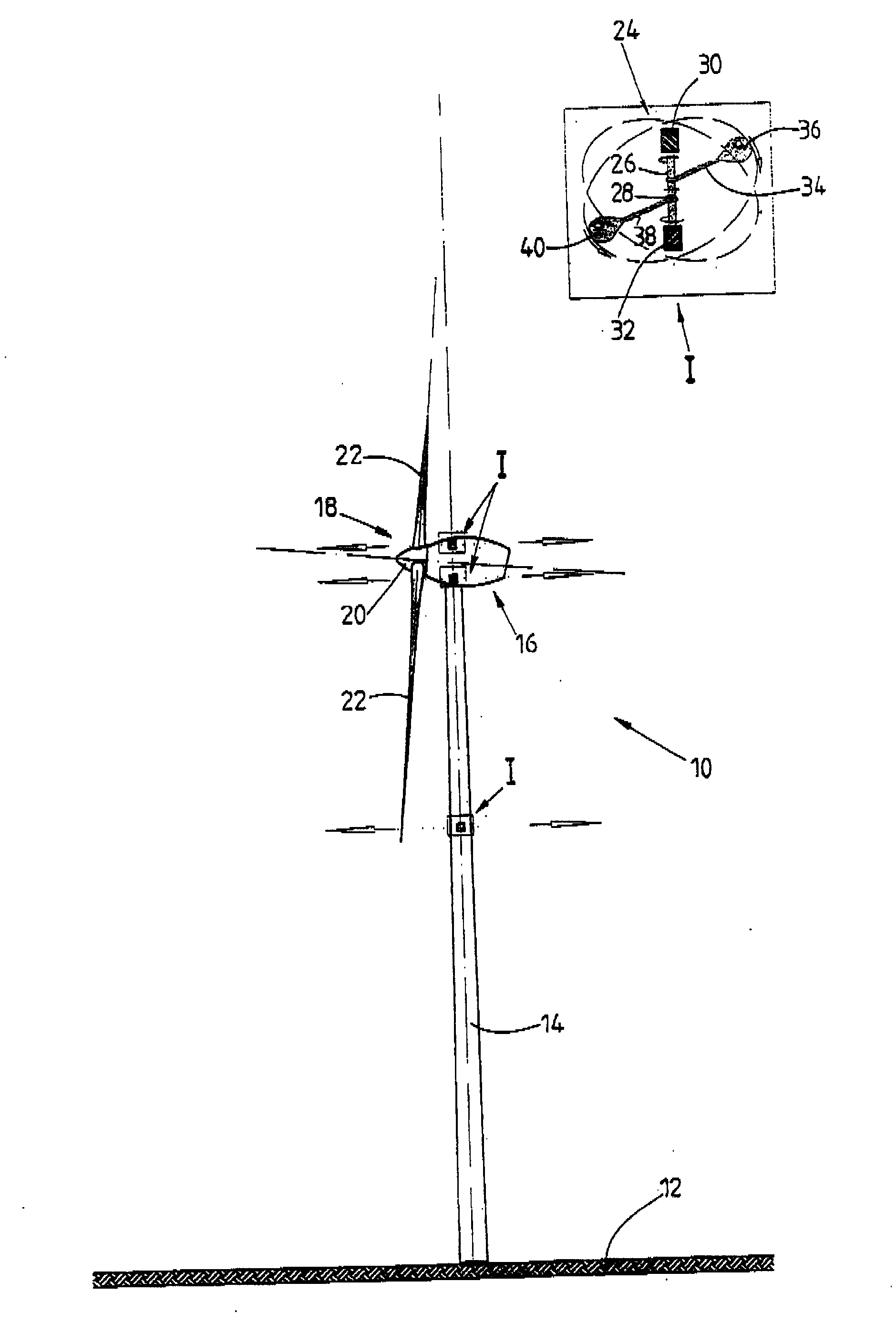
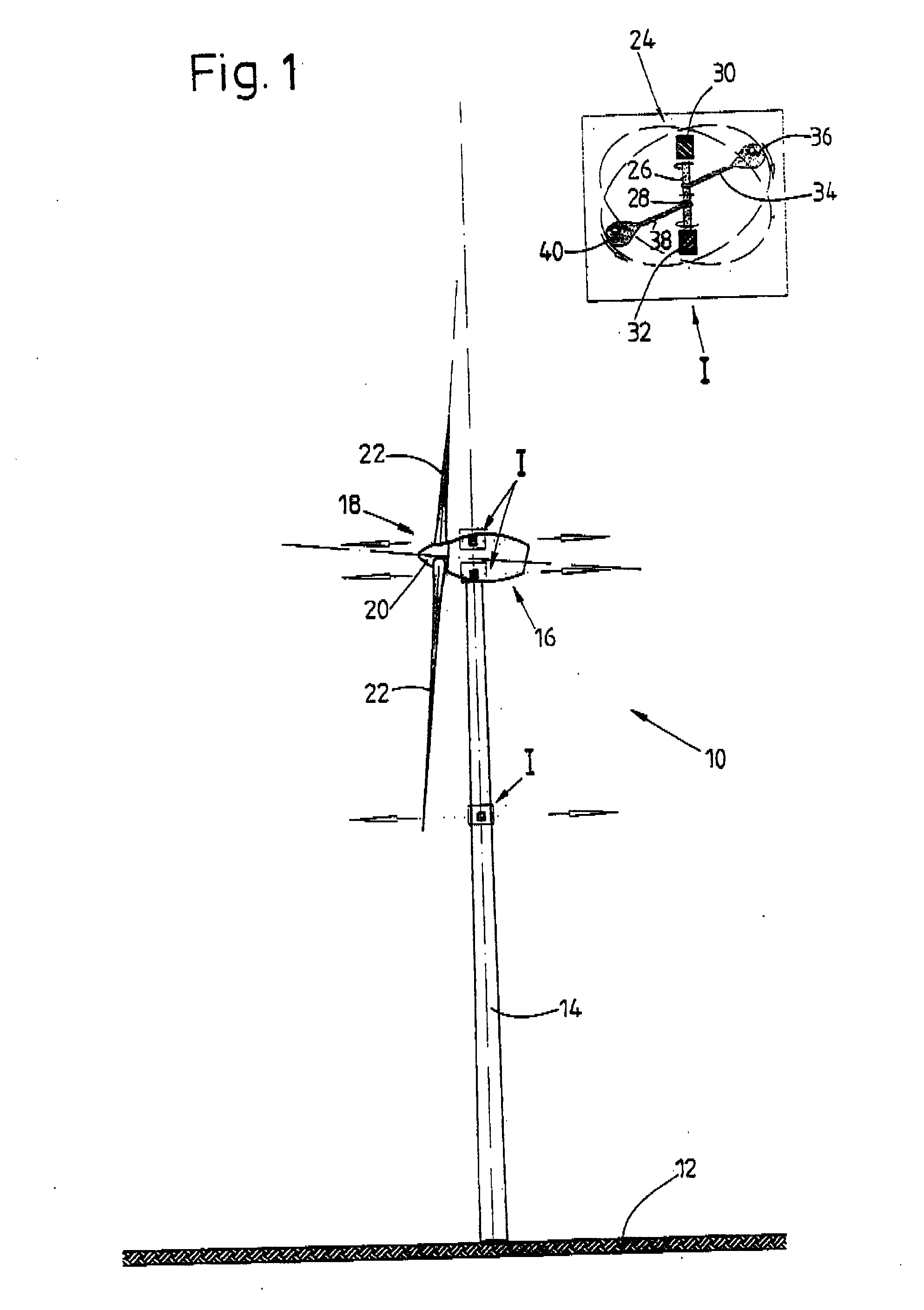
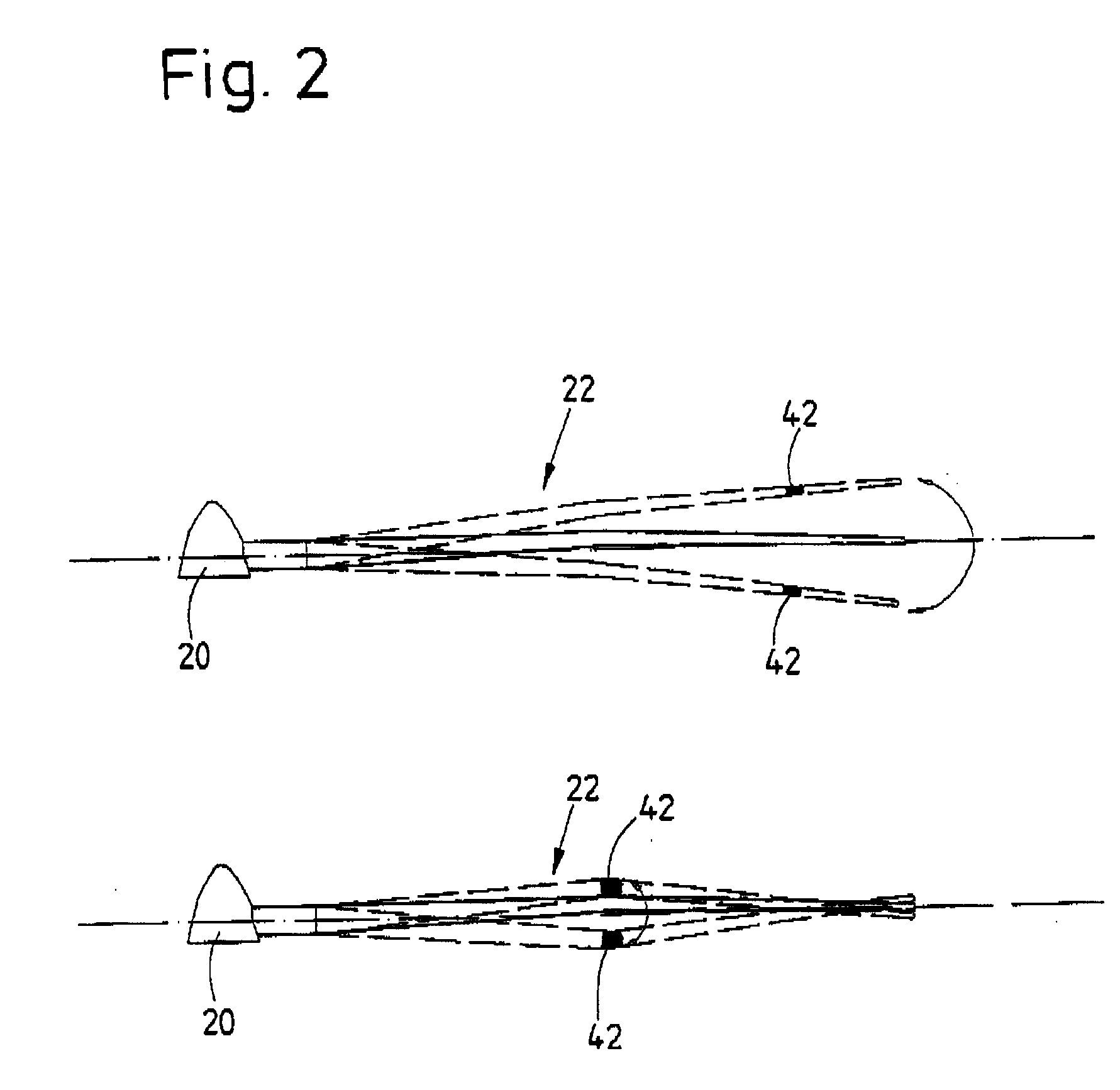
Method for adapting a wind energy installation to given wind conditions
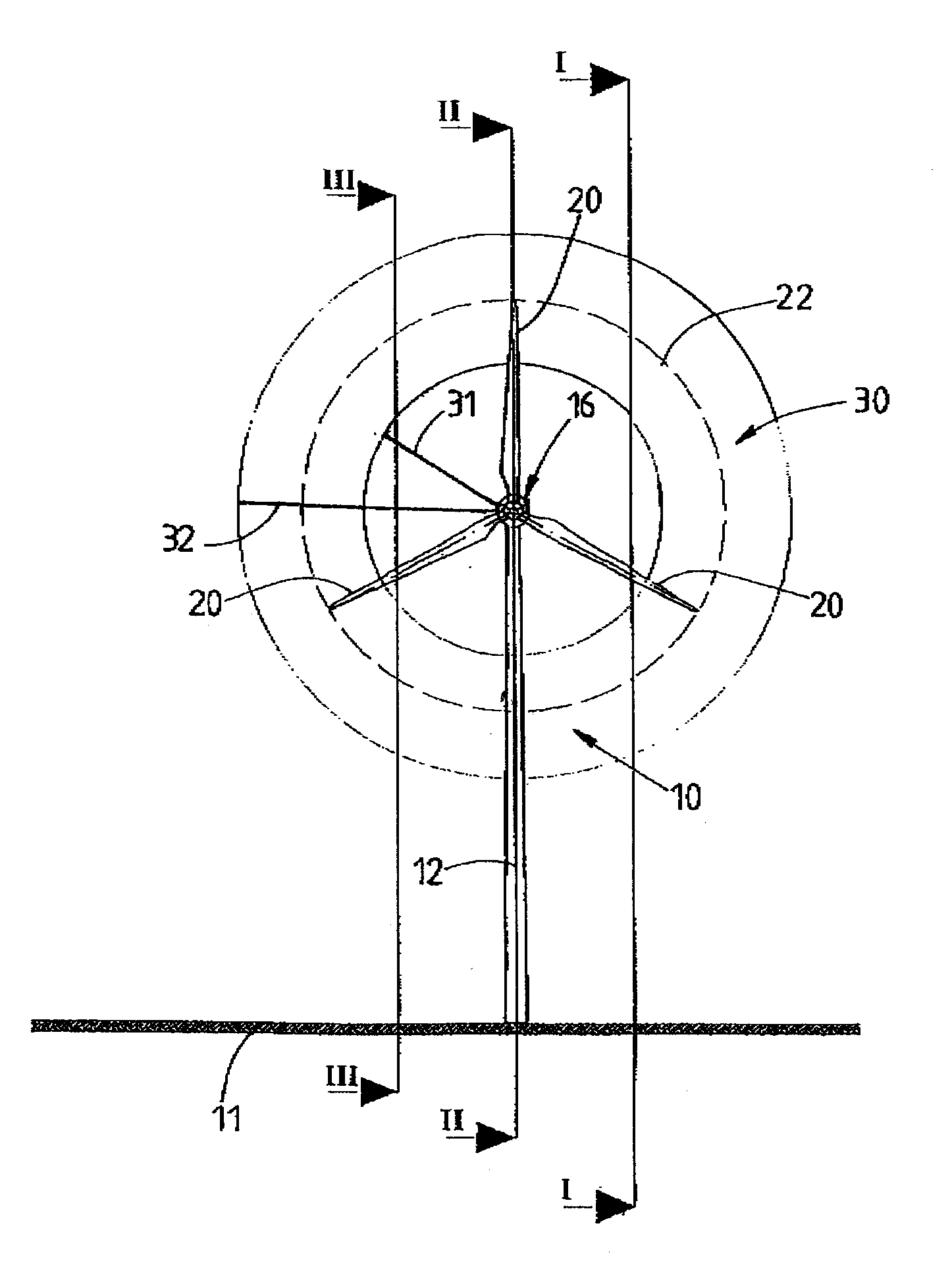
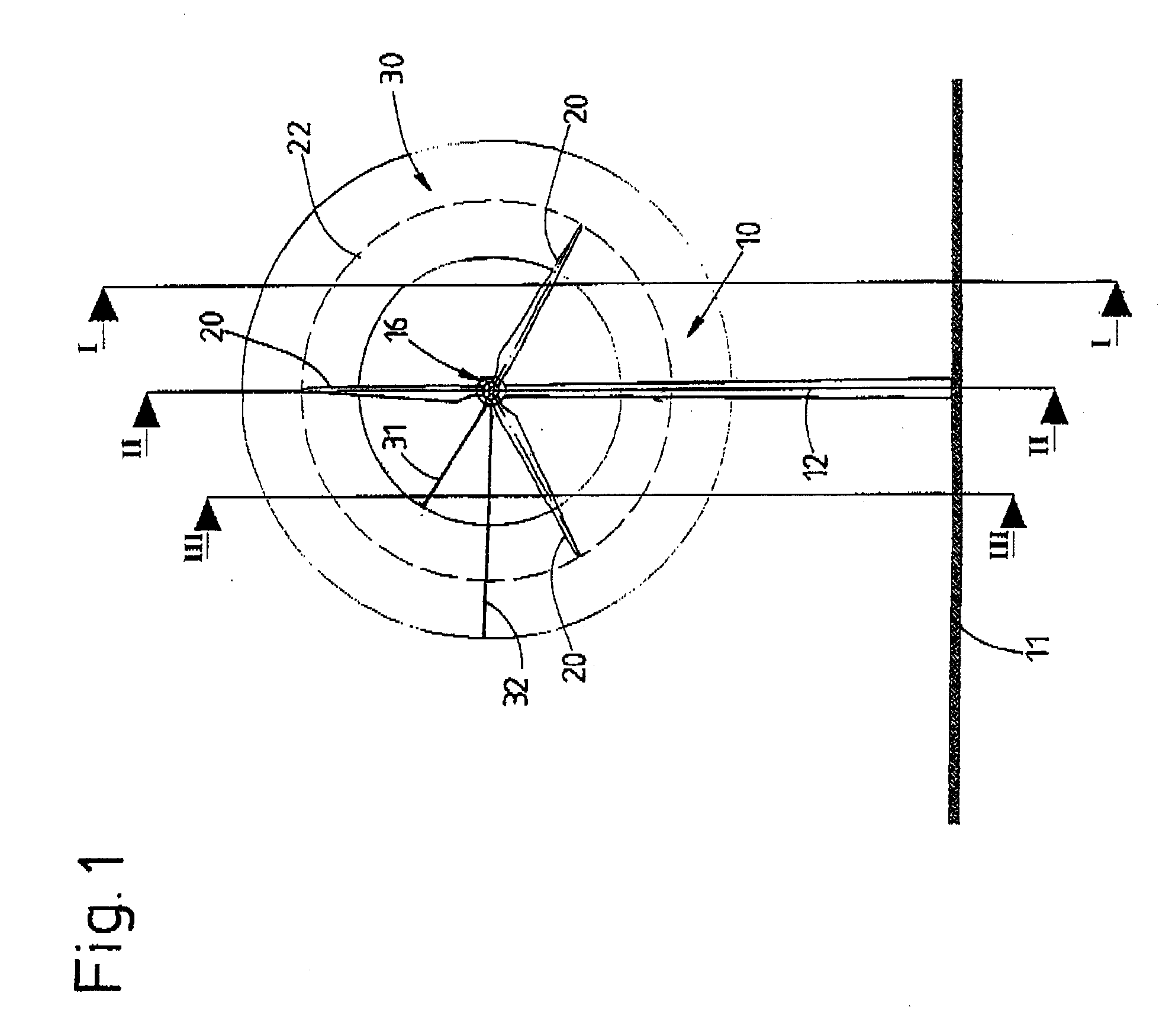
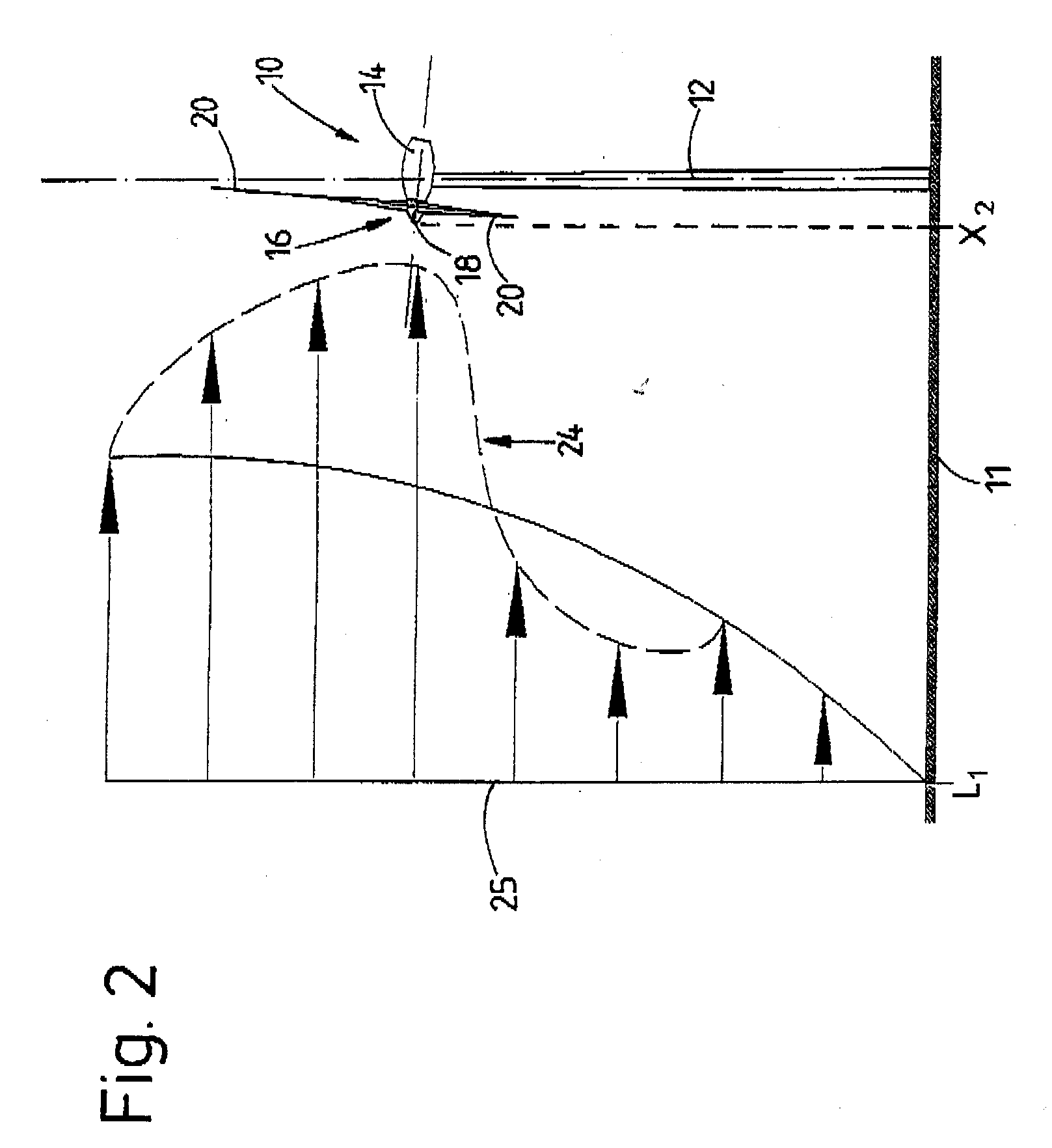
InactiveUS20070067067A1Short response timeFull adjustmentPropellersLevel controlAngle of incidenceTemporal resolution
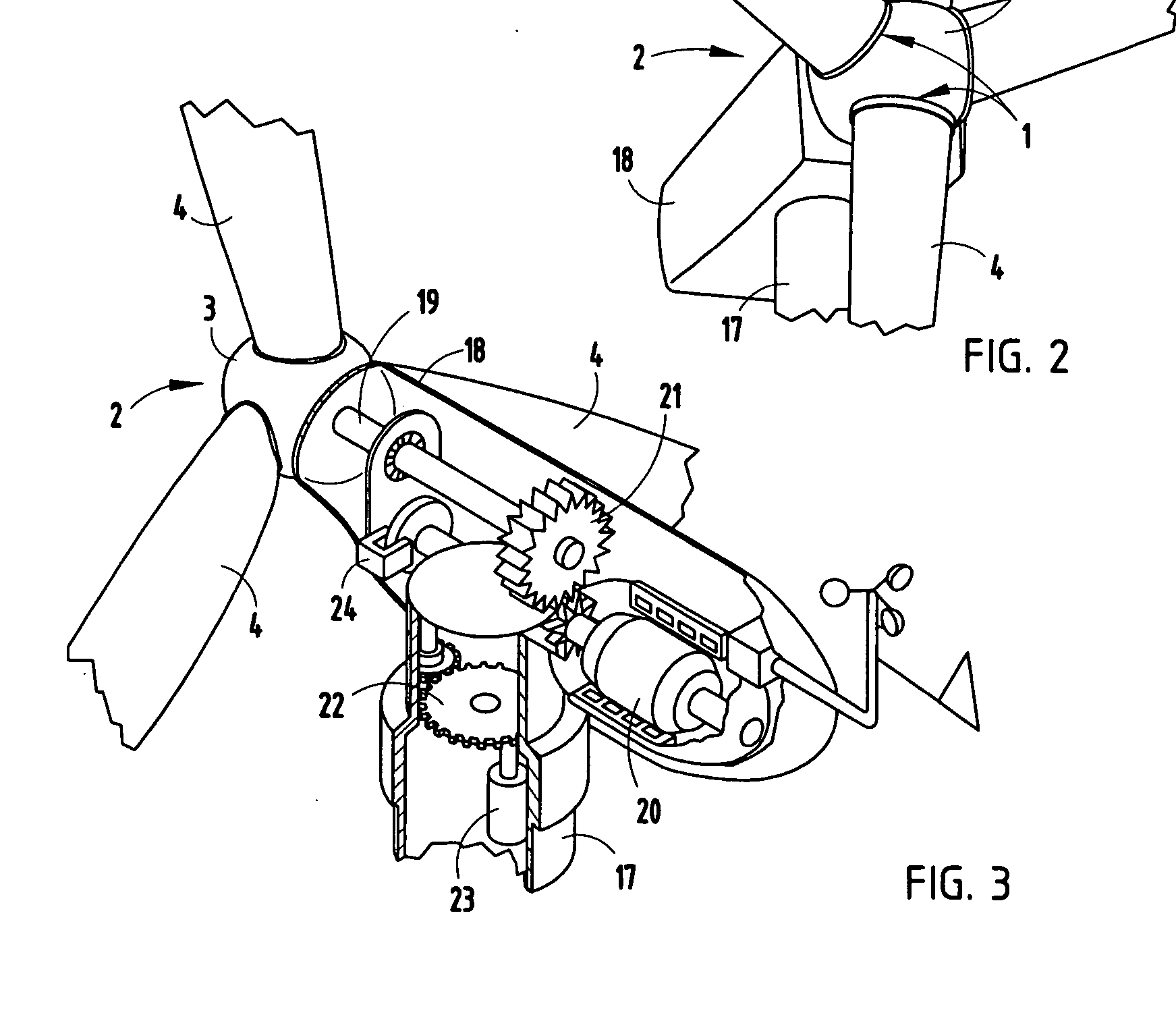
A method for operating a wind energy installation, in particular for adapting a wind energy installation (10) to given wind conditions, the wind energy installation (10) having a rotor (16), which can be driven by wind, with at least two rotor blades (20), whose respective angles of incidence of the wind can be adjusted by means of at least one adjustment device, and having a generator for converting the mechanical energy of the rotor (16) to electrical energy. During operation of the wind energy installation, parameters are measured with spatial and / or temporal resolution on the side of the wind energy installation (10) facing the wind, said parameters describing the wind conditions in the measurement region, preferably the wind speed and / or the wind direction. The wind parameters are measured at various vertical distances from the ground, namely various heights, and at horizontal distances from the rotor (16), which are selected such that the angles of incidence of the wind on the individual rotor blades (20) can be adapted in response to the measured wind parameters before the wind on which the wind parameters are based, in particular a wind front or a gust of wind, reaches the rotor (16). Values are predicted or calculated, in particular continuously or periodically, from the measured wind parameters—prognosis values—which describe wind conditions occurring in the future at the rotor blades for various heights. The angles of incidence of the wind on the individual rotor blades (20) are adjusted individually and independently of one another, preferably a plurality of times during a complete revolution of a rotor blade, depending on these predicted or calculated prognosis values at the various heights.
Owner:VOLKSWIND
Method of controlling a group of engines, and an aircraft
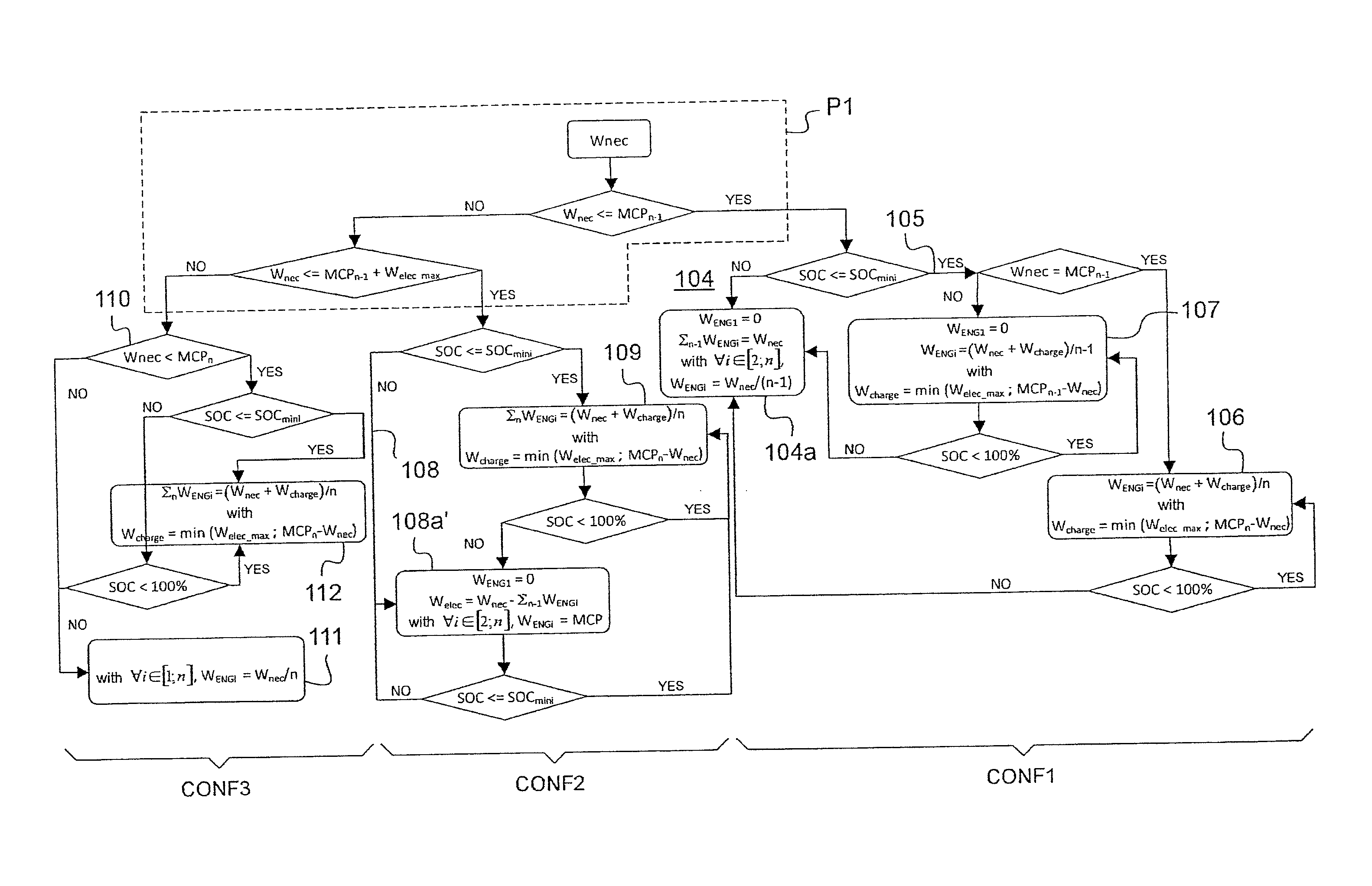
ActiveUS20130184958A1Improve energy efficiencyAnalogue computers for vehiclesEnergy saving arrangementsElectricityAirplane
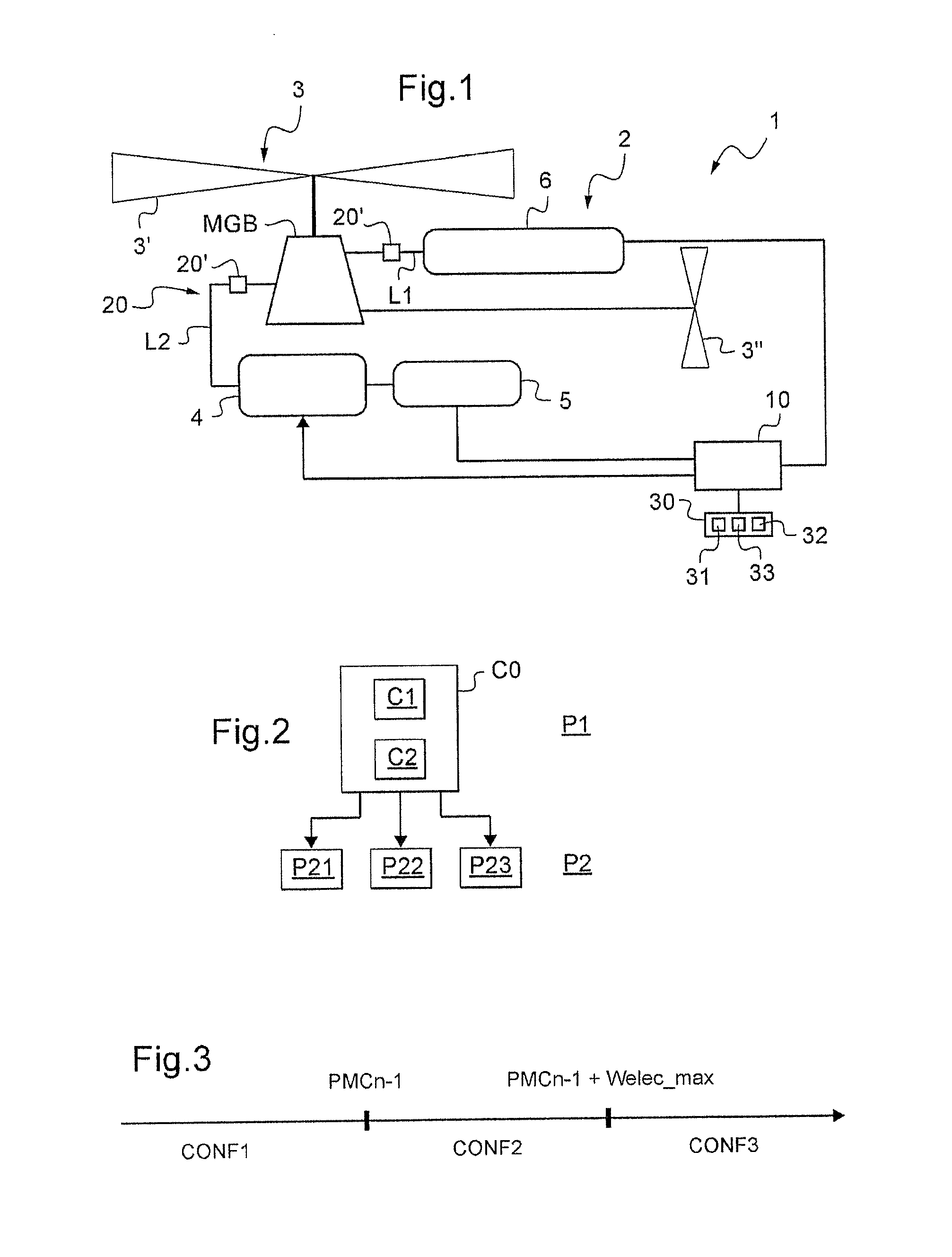
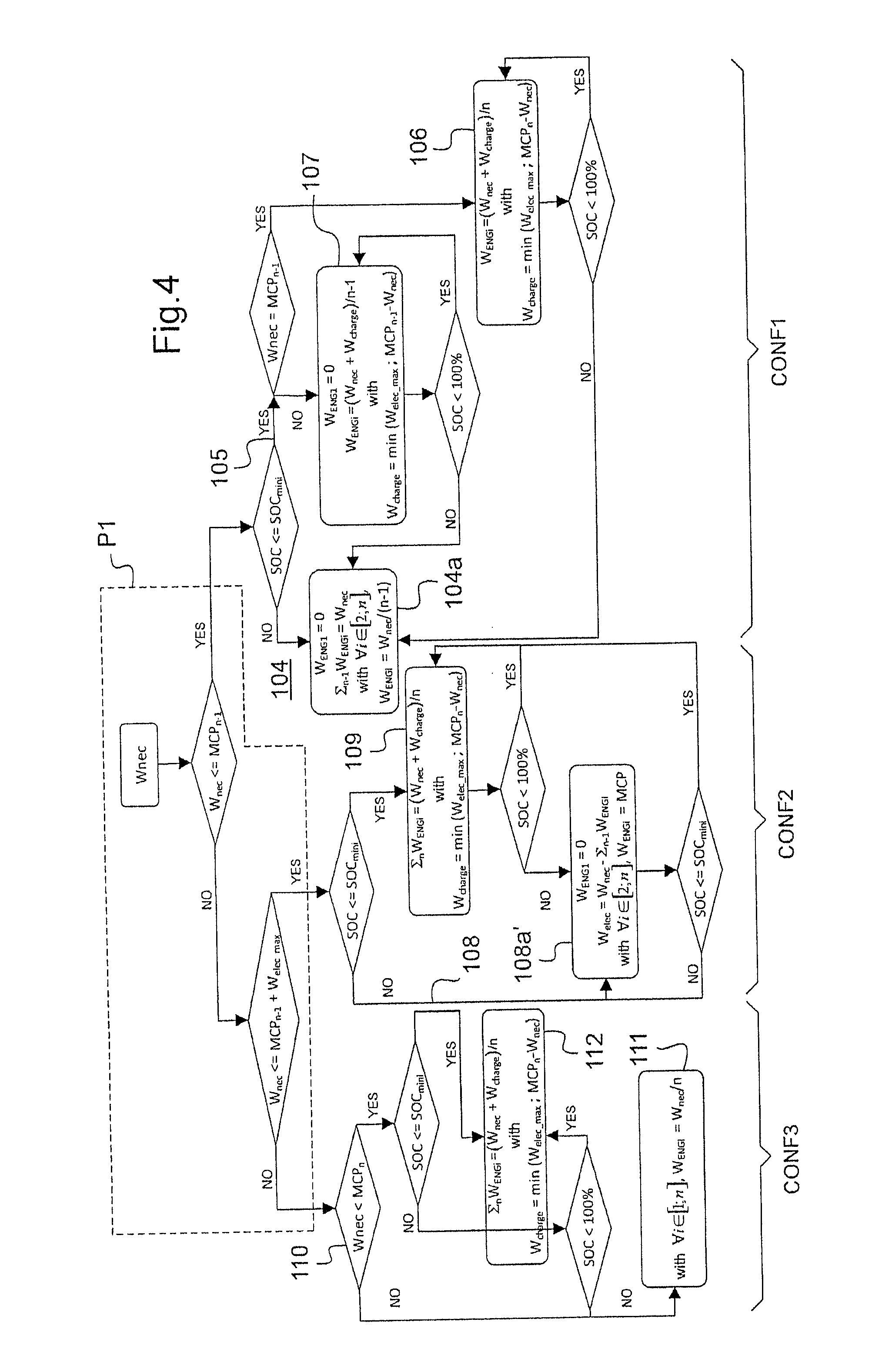
A method of controlling a group (2) of engines developing a necessary power (Wnec) for driving a rotor (3), said group (2) of engines having at least one electrical member (4), electrical energy storage means (5), and a first number n of engines (6) that is greater than or equal to two. A processor unit (10) executes instructions for evaluating a main condition as to whether the group of engines can develop the necessary power while resting one engine, and if so for resting one engine and accelerating a second number engines not at rest, and for causing the electrical member to operate in motor mode, if necessary, the electrical member operating temporarily in electricity generator mode when the storage means are discharged.
Owner:EUROCOPTER +1
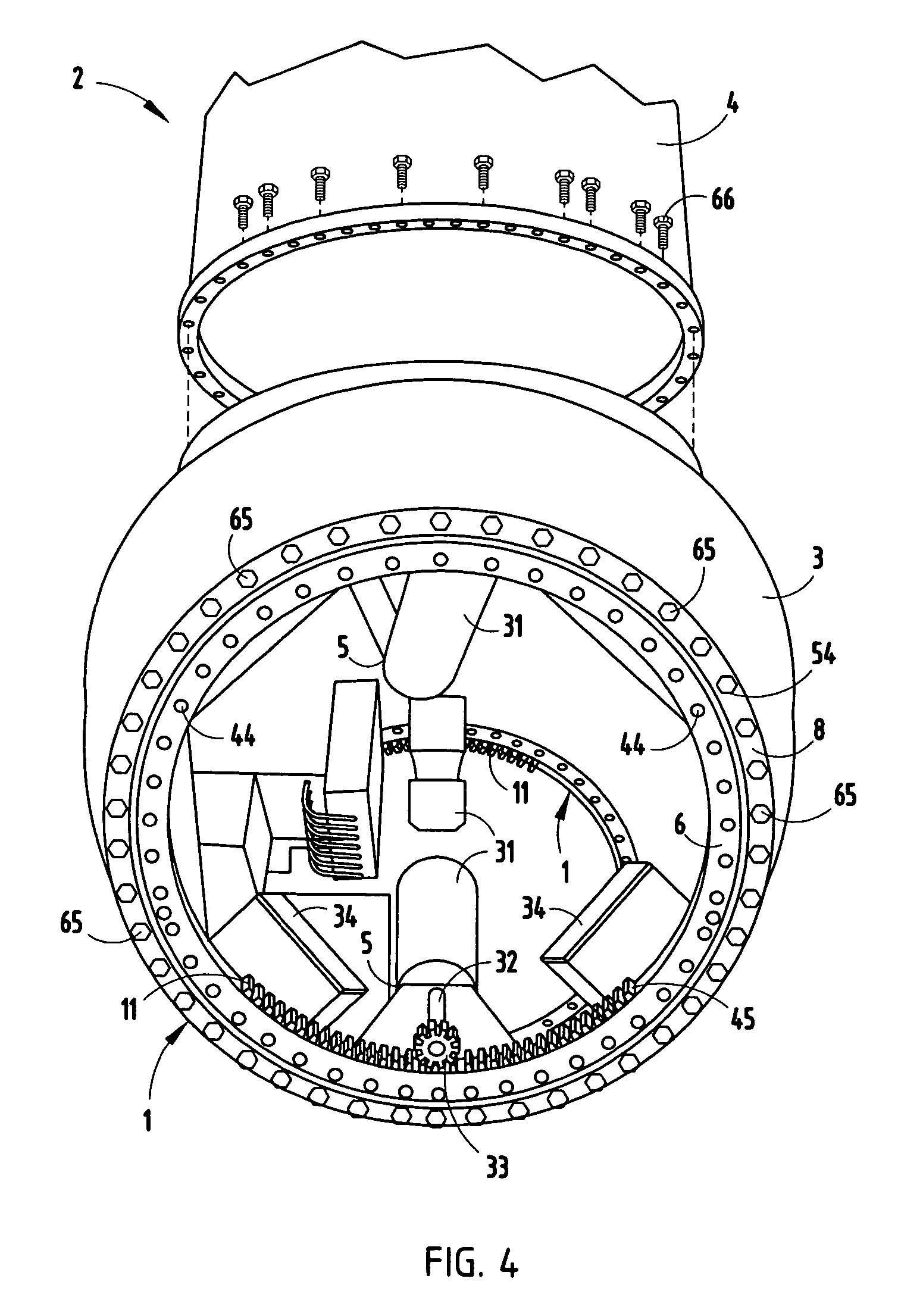
Wind turbine pitch bearing and method
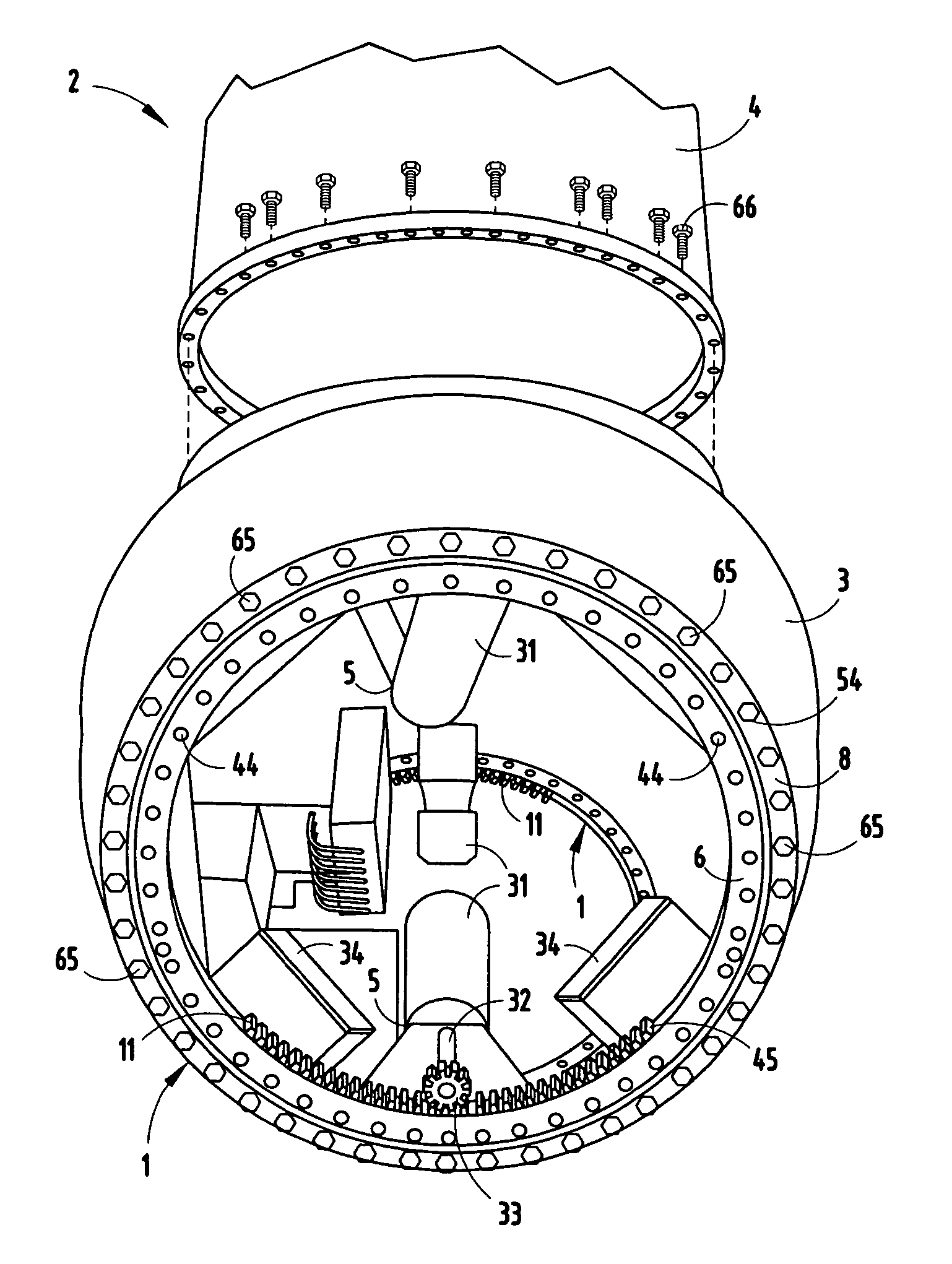
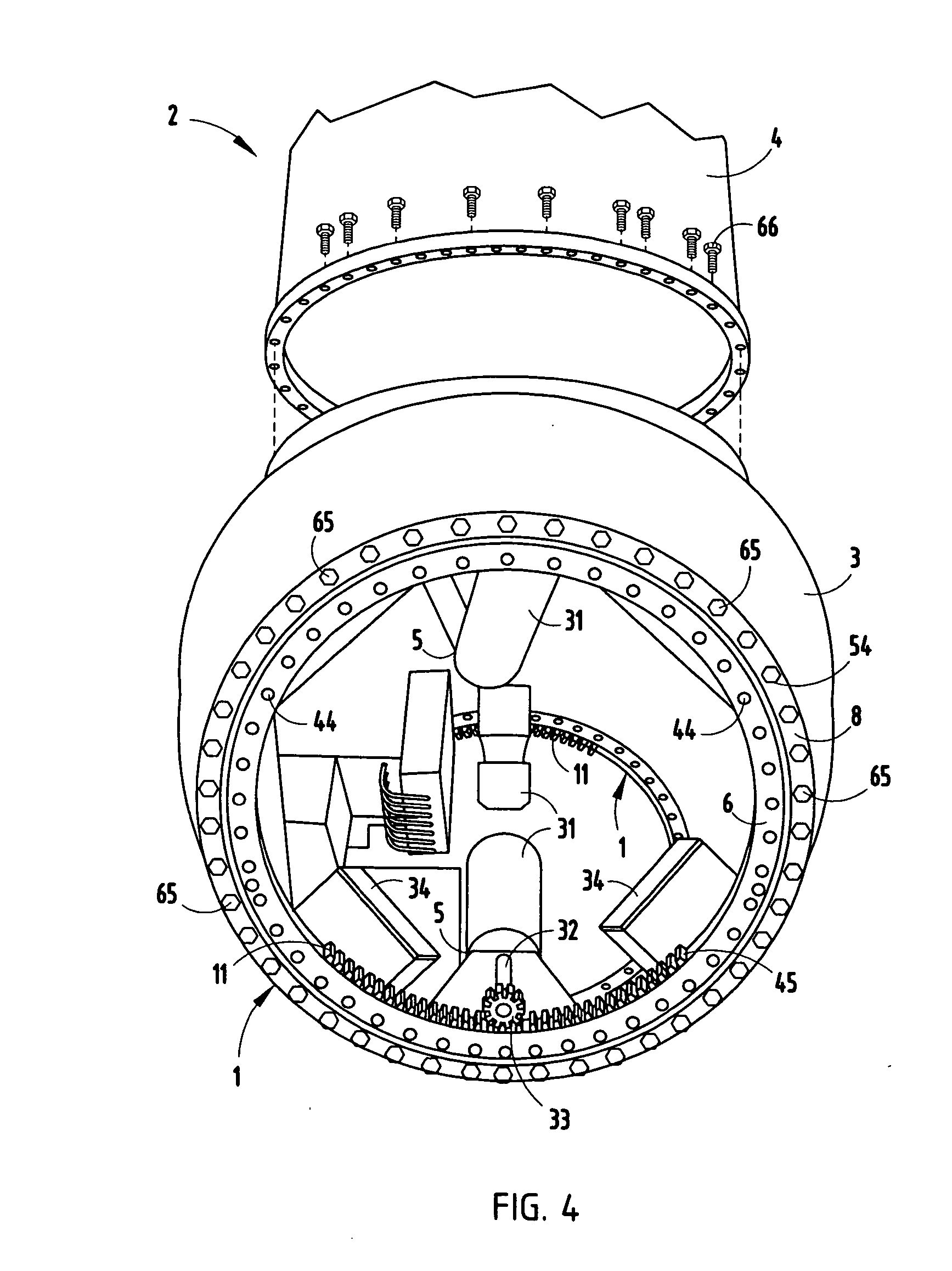
InactiveUS7331761B2Reduce manufacturing costEasy to useRotary bearingsPropellersTurbine bladeWind force
A pitch bearing and related method for wind electric turbines has an annularly-shaped first bearing ring connected with an associated wind turbine blade, and includes a first raceway groove. An annularly-shaped second bearing ring is connected with the rotor portion of the wind turbine, and includes a second raceway groove aligned with the first raceway groove. Rolling elements are positioned in the first and second raceway grooves to rotatably interconnect the two bearing rings. A gear segment is formed on one of the bearing rings, and is configured to engage a pitch drive portion of the wind turbine to pivot the blade axially between different pitch angles. The gear segment has an arcuate measure of less than 200 degrees to facilitate economical manufacture.
Owner:KAYDON CORP
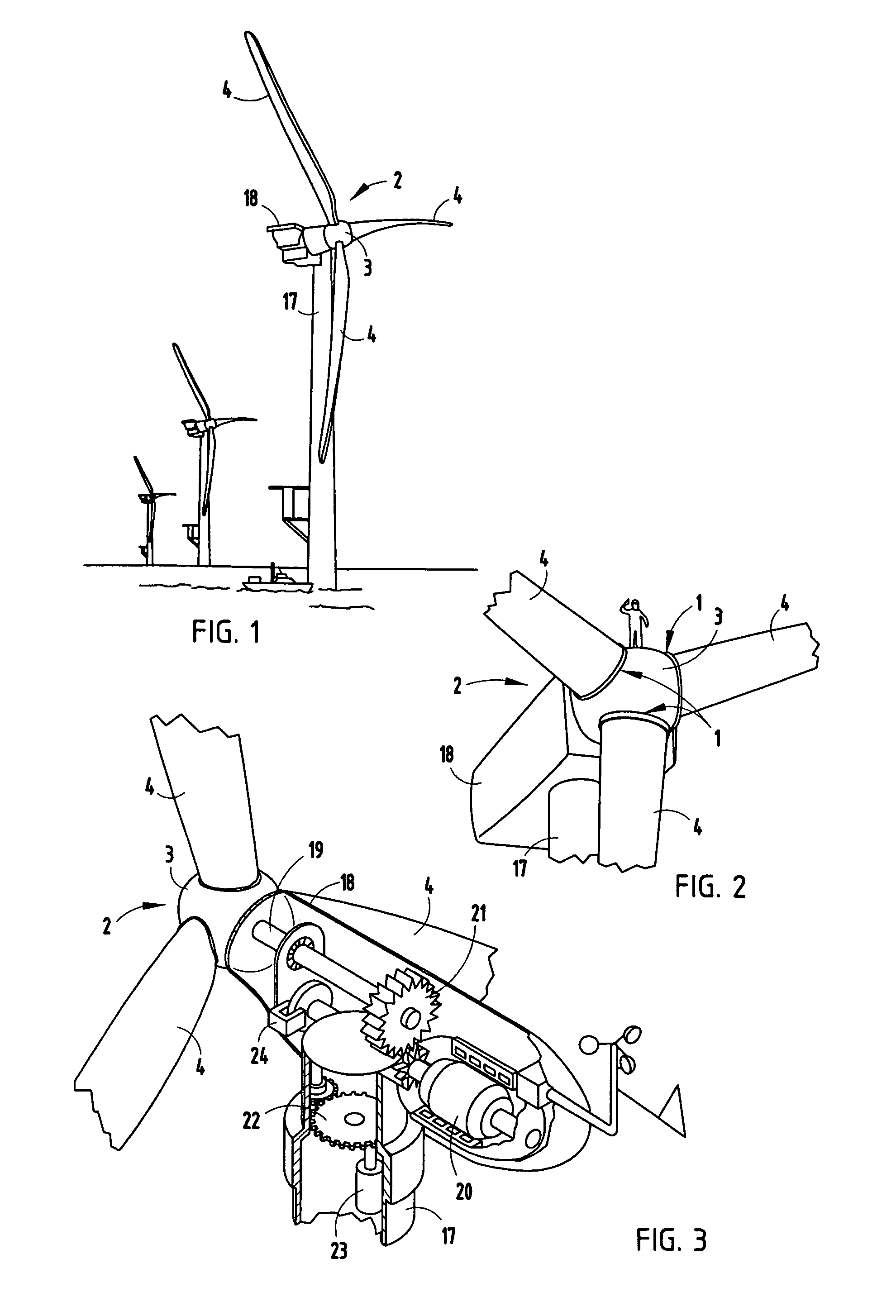
Wind energy installation
The invention relates to a wind energy installation (10) having a rotor (18) which can be driven by wind and has at least one rotor blade (22), having a generator for conversion of the mechanical energy of the rotor (18) to electrical energy, and having a tower (14) on which the rotor (18) is arranged, in which the rotor blade (22) has one or more additional masses (36, 40) and / or active and / or passive oscillation dampers (24), which are designed in such a manner that movements of the rotor blade (22), in particular oscillations, which are initiated by external influences and are directed towards the tower or away from it are prevented and / or damped. The invention also relates to a method for operation of a wind energy installation, preferably of an off-shore wind energy installation, in which one or more components of the wind energy installation, preferably the tower (14), have opposing vibration applied to them in order to reduce / prevent sound waves which result from component vibration and disturb animals and / or people, which opposing vibration counteracts vibration (which produces sound) of the component (14), and reduces or prevents this component vibration.
Owner:DAUBNER & STOMMEL BAU WERK PLANUNG
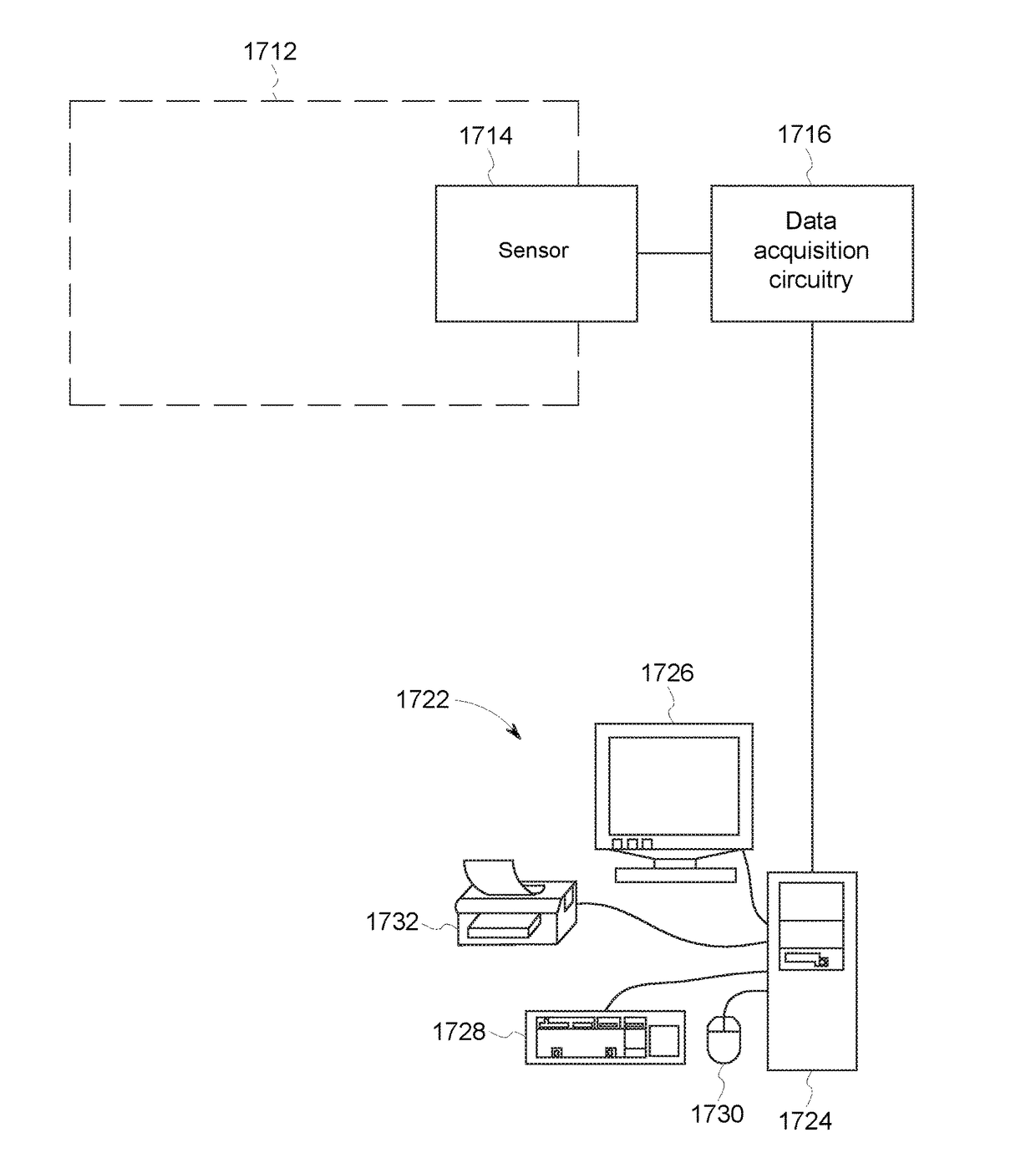
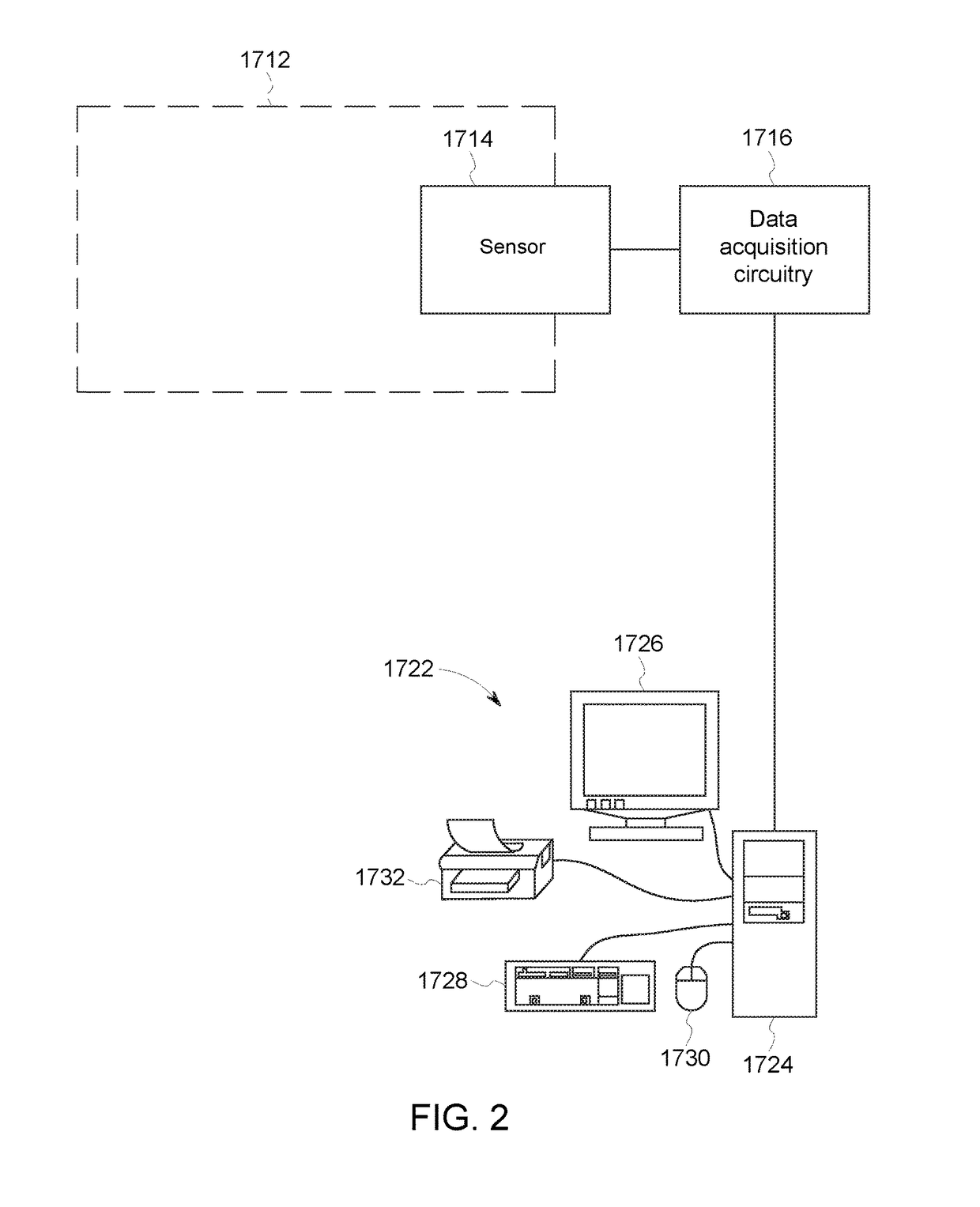
Sensing system and method
ActiveUS20170138922A1Quality improvementDecreased performance of machineMachine gearing/transmission testingMachines/enginesElectricityAnalyte
A system includes a resonant sensor in contact with oil within a gearbox of a rotor system, such as a wind turbine, and one or more processors. The sensor includes electrodes and a sensing circuit that generates electrical stimuli having frequencies applied to the oil at different times during a life of the gearbox. The processors receive electrical signals from the resonant sensor representative of impedance responses of the oil to the electrical stimuli. The processors analyze the impedance responses and determine a concentration of a polar analyte in the oil at different times. The processors calculate a degradation value for the gearbox based on the concentration of the polar analyte. Responsive to the degradation value exceeding a designated threshold, the processors at least one of schedule maintenance for the rotor system, provide an alert to schedule maintenance, or prohibit operation of the rotor system until maintenance is performed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multiple axle driving system for oil-electricity mixed power automobile
ActiveCN1810557AImprove fuel economyImprove efficiencyHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerElectricityElectric machine
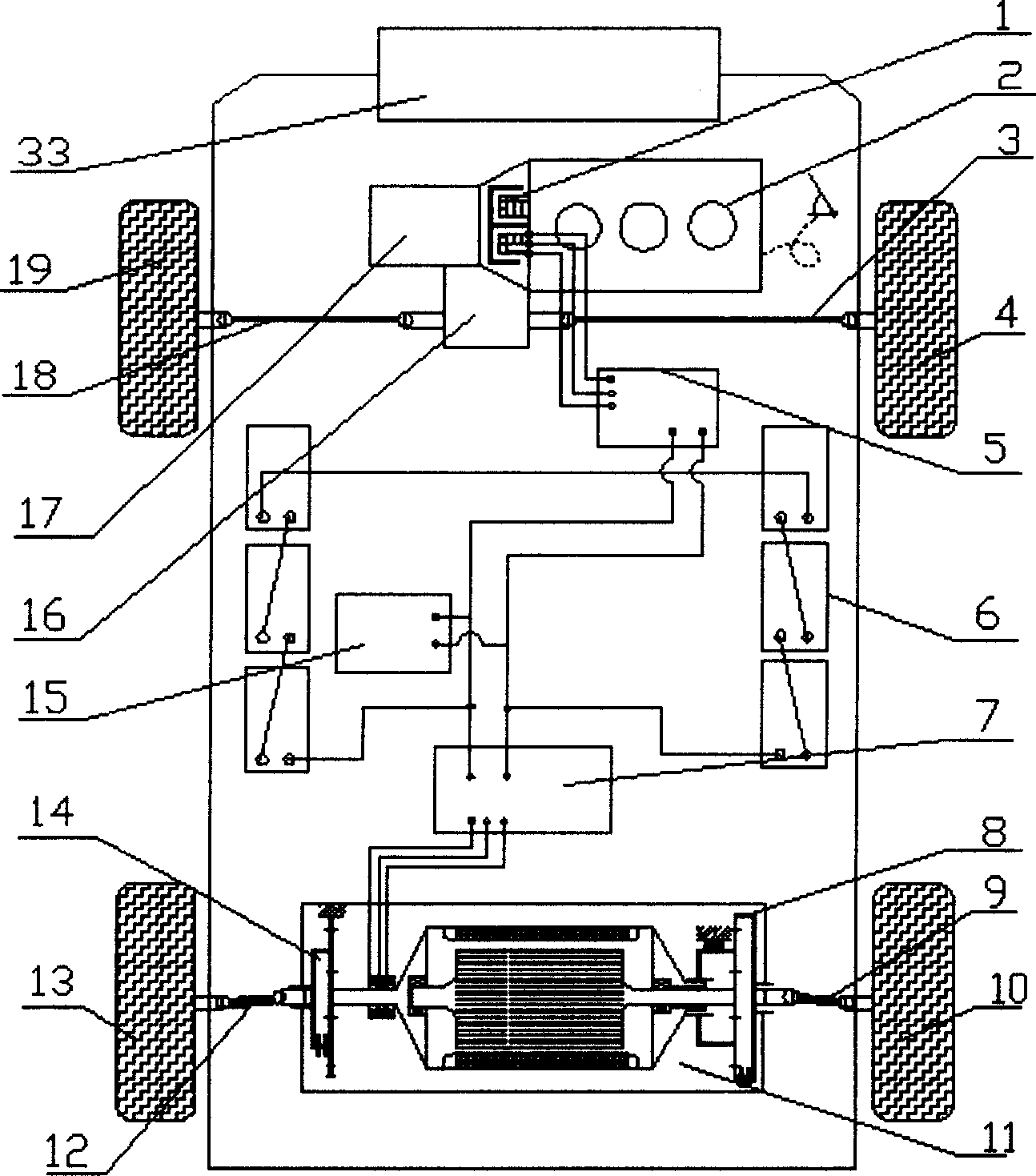
The multiple axle driving system for mixed power automobile with fuel oil and electric energy as power source includes at least one mechanical driving axle assembly, at least one electric driving axle assembly, one power source assembly, one general controller, one monitoring and communication network system, and one engine and one multifunctional double-rotor motor to drive different axles separately. The double-rotor motor consists of one outer rotor and one inner rotor, the outer rotor is connected to the hub in one side through the reducing mechanism and the versatile transmission mechanism, and the inner rotor is connected to the hub in the other side through the reducing mechanism and the versatile transmission mechanism. The multiple axle driving system integrates the technology and functions of complete mixed power, multiple axle driving, etc. and makes the automobile possess the advantages of easy realization, low cost, raised running smoothness and stability, etc.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Control method of IPM electromotor for driving electric motor car
InactiveCN101567655AReduce dependenceCutting costsSingle motor speed/torque controlElectronic commutatorsTrailing edgeControl theory
The invention discloses a control method of an IPM electromotor for driving an electric motor car. According to the working characteristics of the IPM electromotor used on the electric motor car and the characteristics and advantages of various control methods, a segmental control strategy and a method for accurately detecting the start of the electromotor as well as the position and the rotational speed of a rotator during the operation provided are provided. A hall sensor is used for carrying out the method of rough positioning first and scanning next, so that the relatively accurately positioning of the initial position of the rotation in a static state can be realized, the electromotor can be successfully and easily started no matter in the case of idle load, light load or heavy load,and the reliability of the start and operation of the electromotor can be greatly improved. After the IPM electromotor is successfully started, output signals of the hall position sensor undergo rising edge capturing and trailing edge capturing by using software. According to a signal jumping edge, the position of the rotator is corrected in the cases of a low rotational speed and a high rotational speed. When the electromotor operates, a T method is adopted for speed measurement, and an algorithm undergoes certain adjustment in the cases of the low rotational speed and the high rotational speed. When the position and the rotational speed of the rotator during the operation are correctly detected, the segmental control strategy such as peak torque current control and field-weakening control can be adopted so as to ensure that a peak torque is output during the operation of the electromotor.
Owner:マイウェイ技研
Method and apparatus for automatically identifying electrical parameters in a sensor-less pmsm
ActiveUS20100060210A1Effective parameter estimationAccurately model saturation effectElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectricityPermanent magnet synchronous machine
A method and apparatus for determining electrical parameters for commissioning a sensor-less permanent magnet synchronous machine uses knowledge of the rotor position to apply balanced pulses along the rotor magnet axis and perpendicular to the rotor magnet axis allowing measurement of q- and d-inductance at multiple current levels without substantial rotor movement.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Fixed frequency high-pressure high reliability pump drive
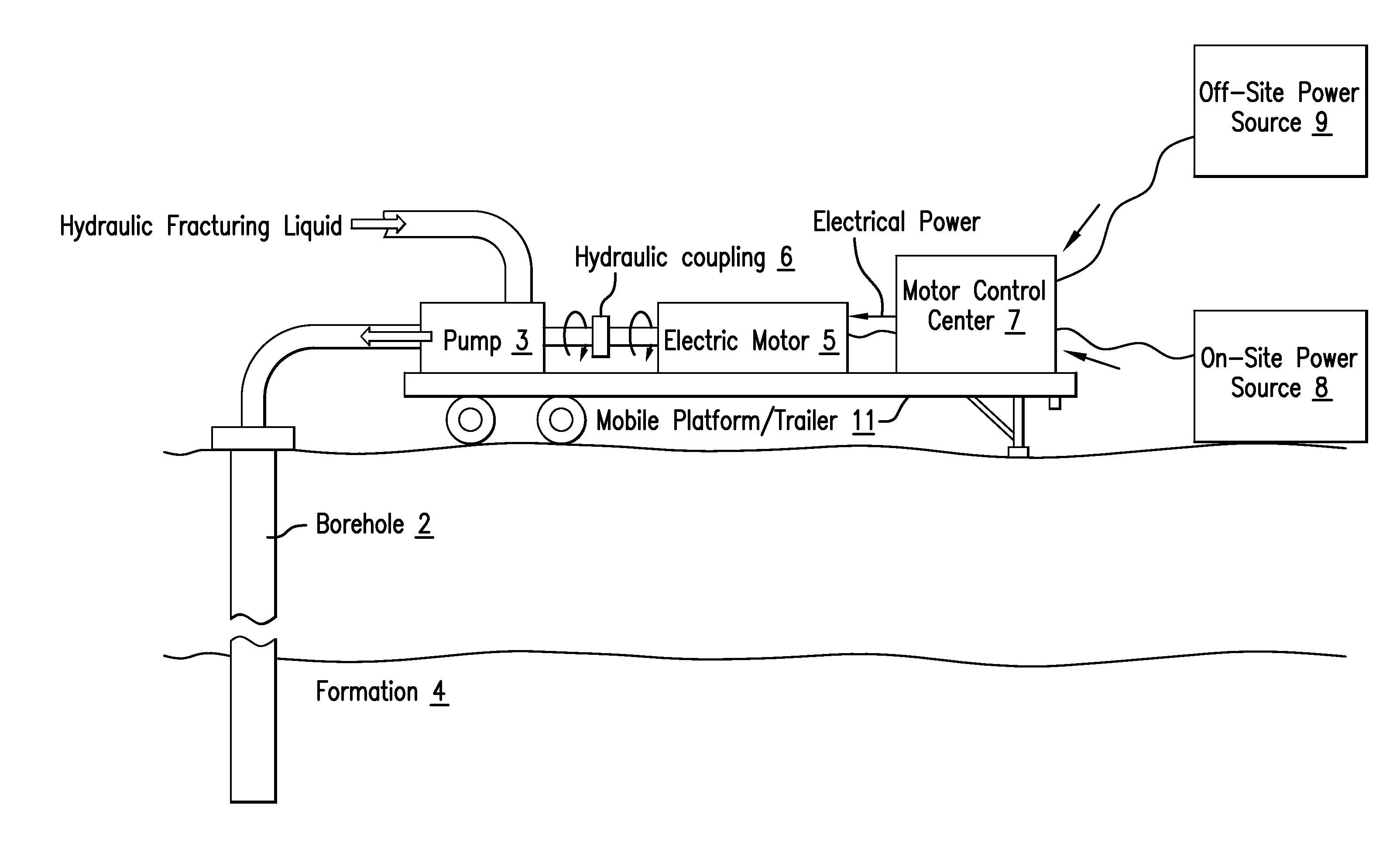
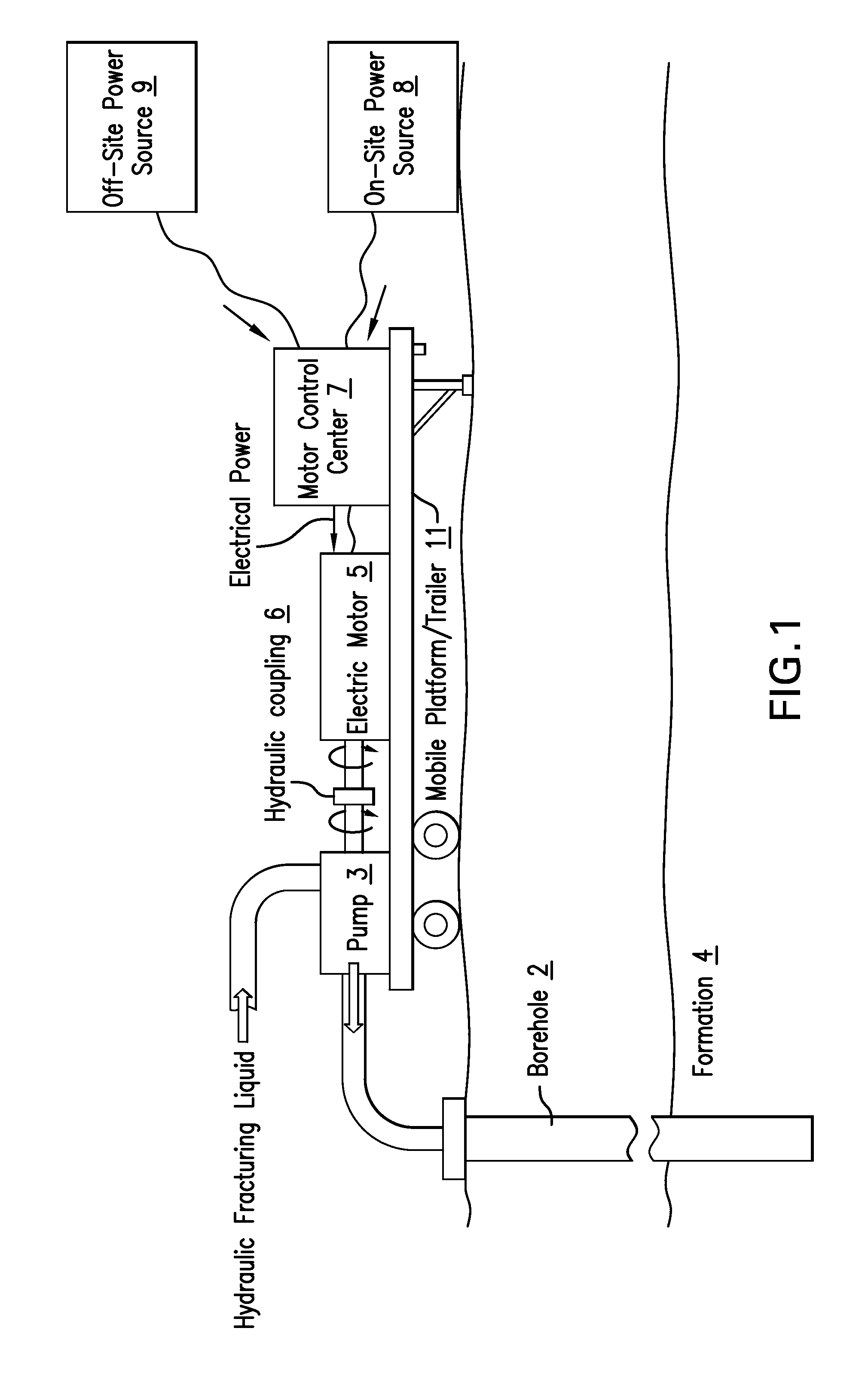
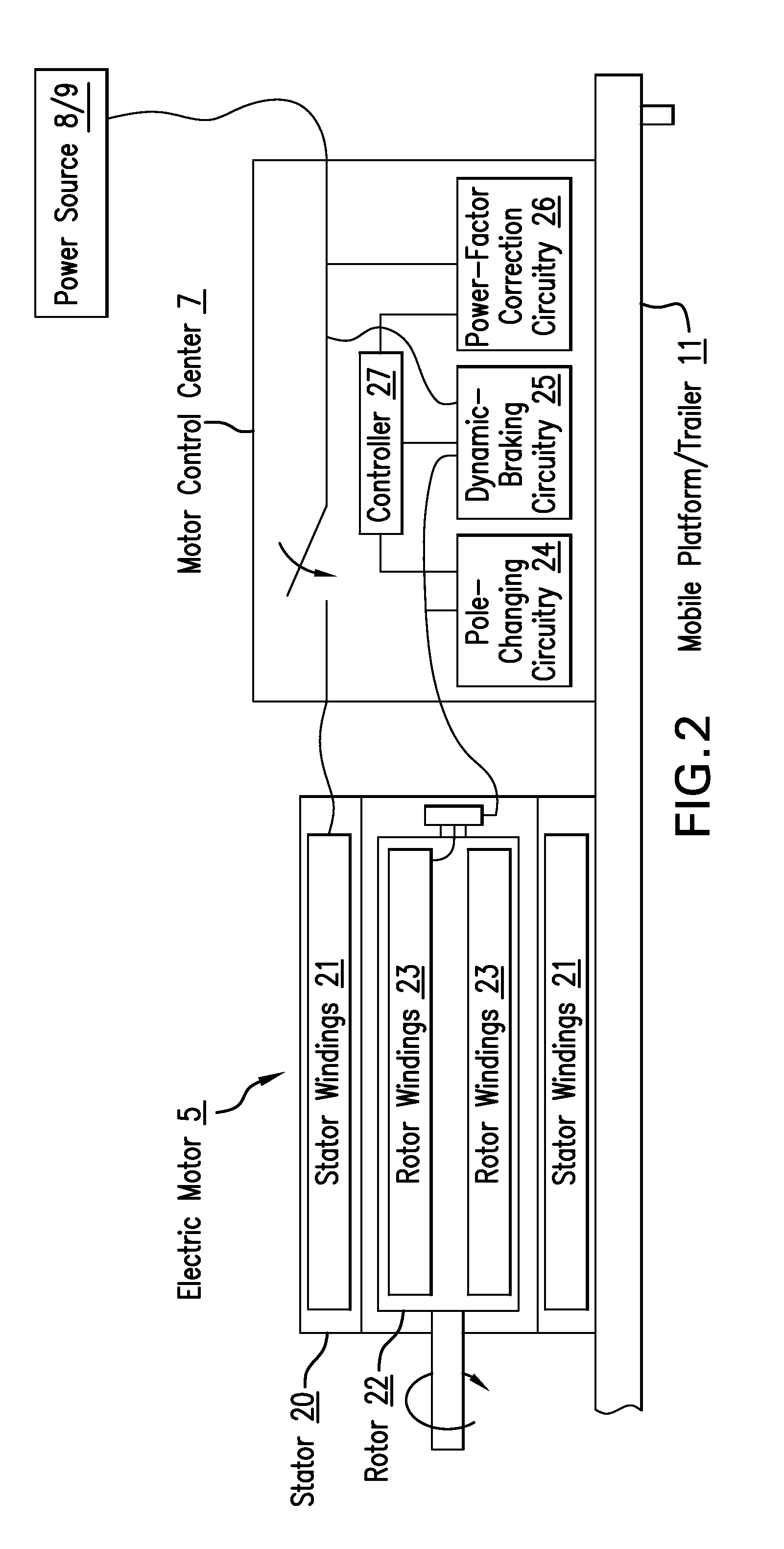
An apparatus configured to hydraulically fracture an earth formation, includes a pump configured to hydraulically fracture the earth formation by pumping a fracturing liquid into a borehole penetrating the earth formation and an electric motor having a rotor coupled to the pump and a stator. A motor control center is configured to apply an alternating electrical voltage having a fixed-frequency to the stator in order to power the electric motor, wherein the apparatus and motor control center do not have a variable frequency drive.
Owner:BJ ENERGY SOLUTIONS LLC FORMERLY TES ASSET ACQUISITION LLC
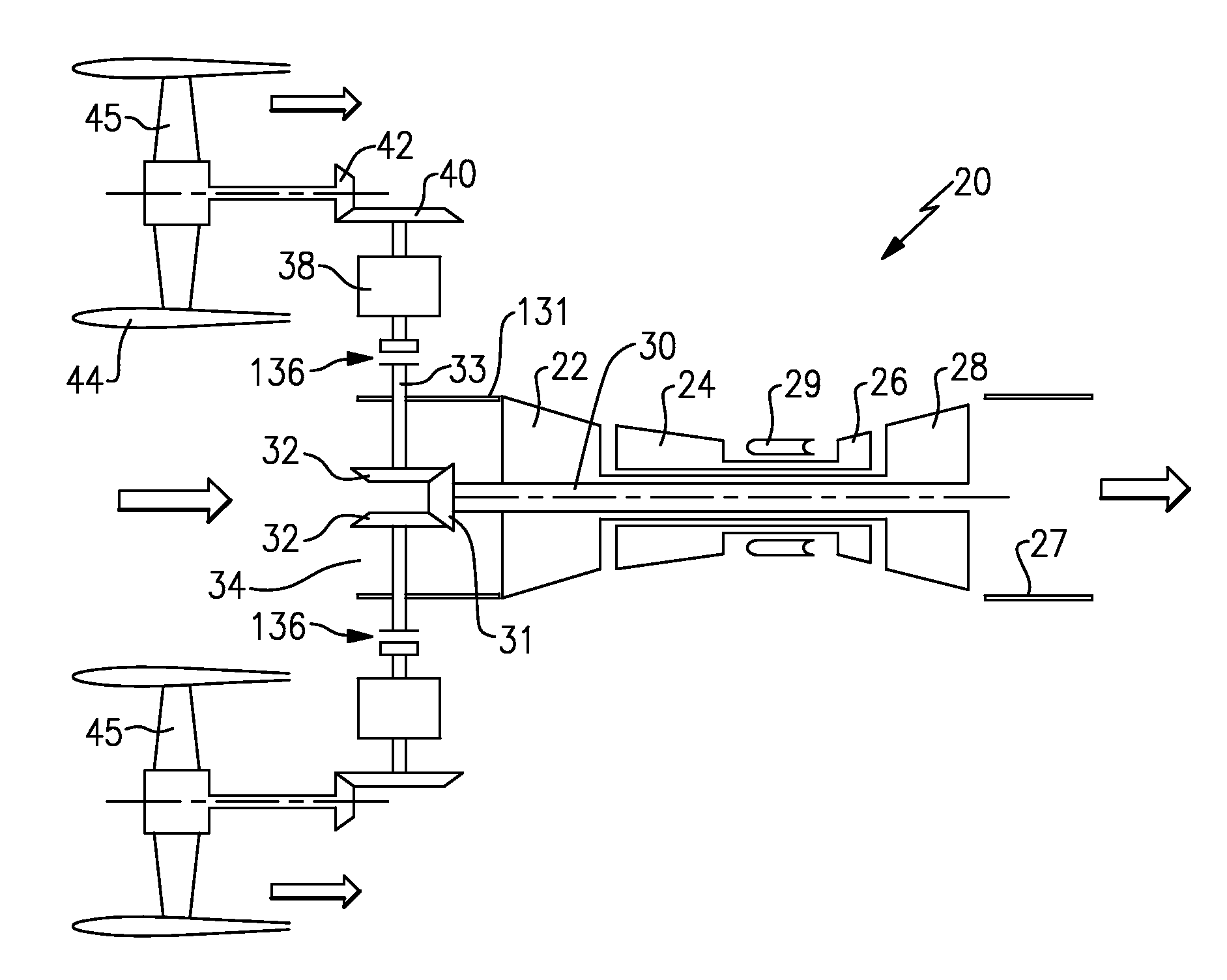
Hybrid drive for gas turbine engine
A gas turbine engine has a fan drive turbine for selectively driving a fan rotor. A drive shaft between the fan drive turbine and the fan rotor includes a clutch, and an electric motor. The electric motor is positioned such that it is not downstream of a flow path relative to the fan drive turbine. A method of operating a gas turbine engine is also disclosed.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Method of operating a supercharger
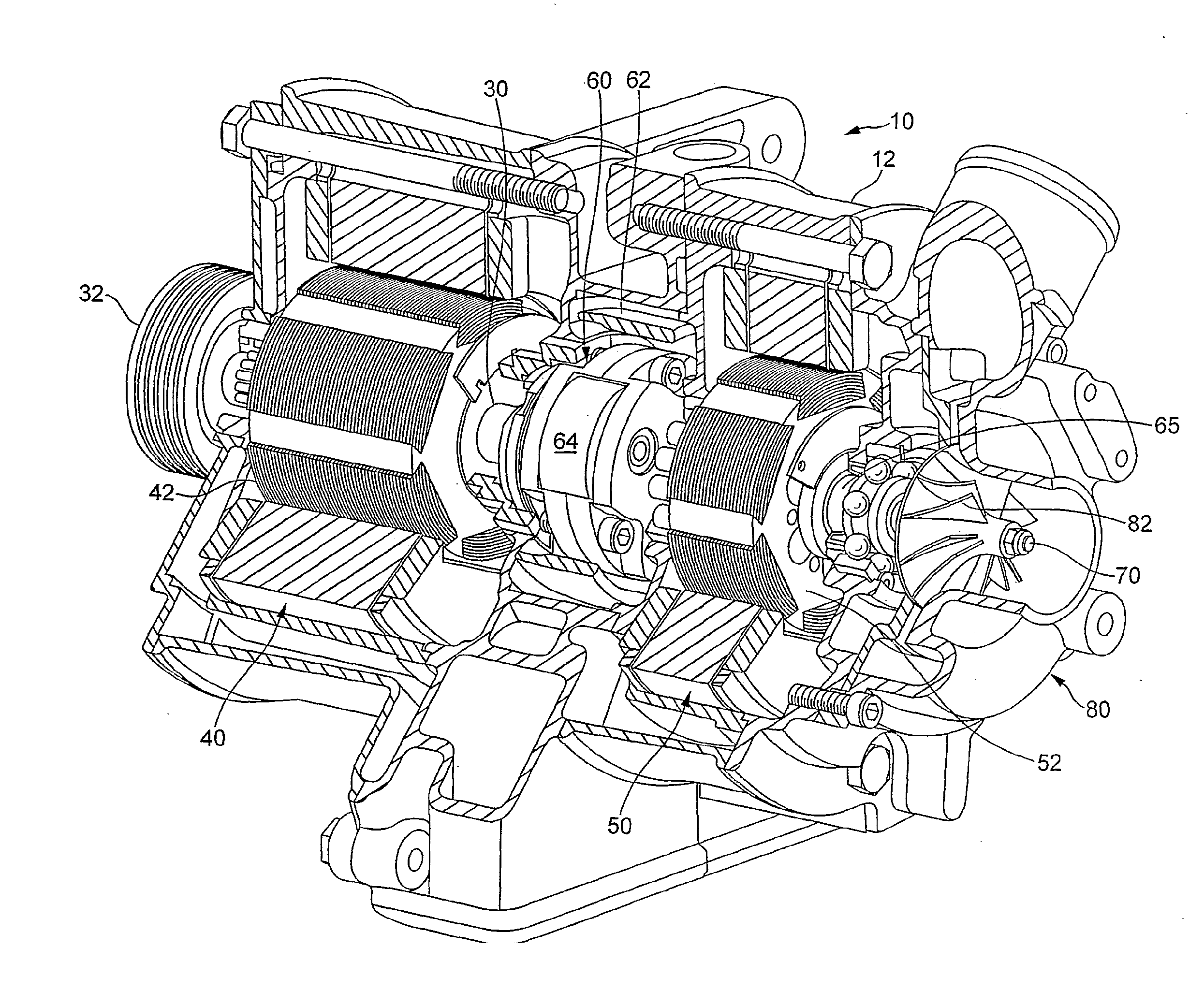
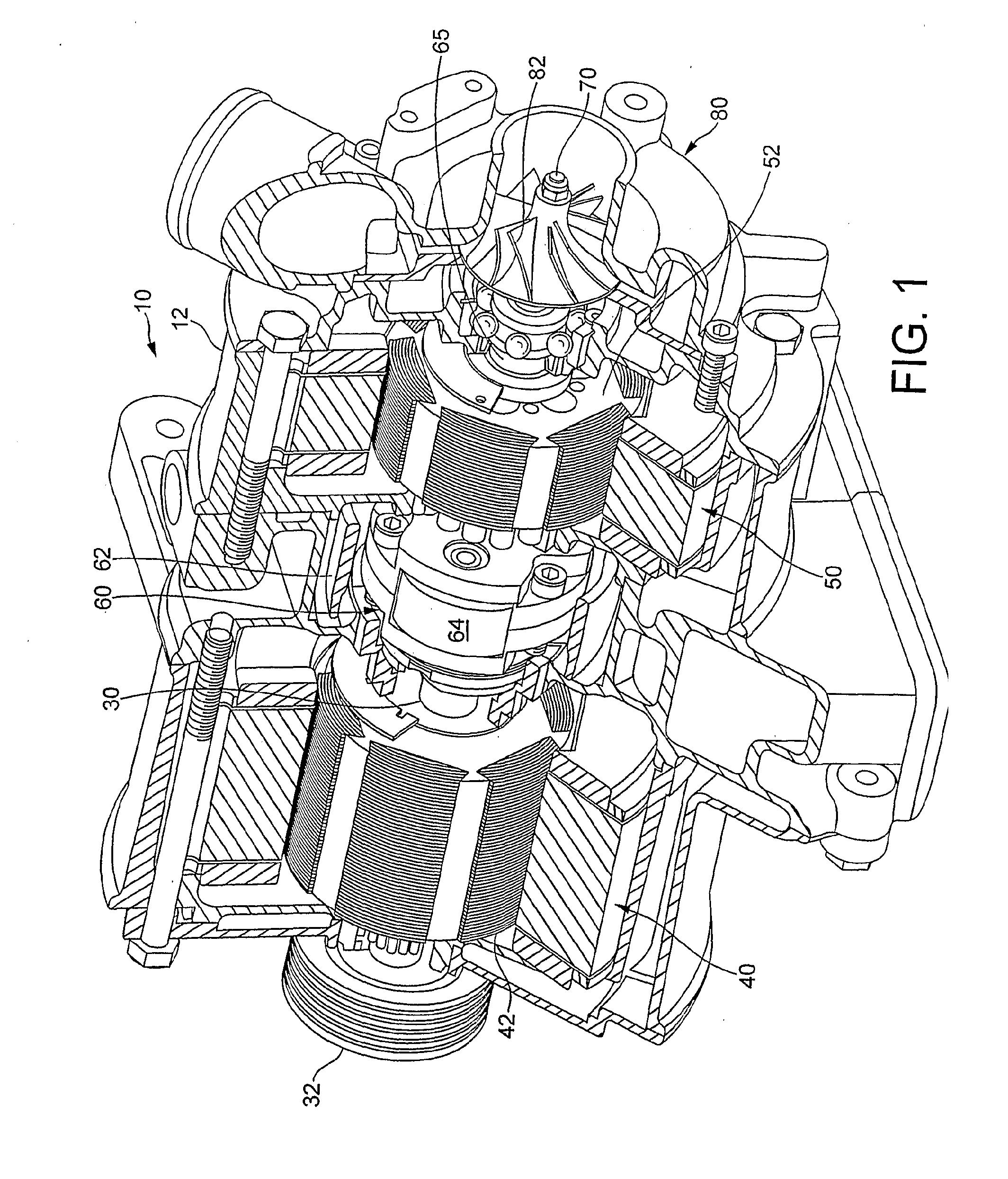
ActiveUS20100275890A1Constant speedReduce cycle variationCombustion enginesPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingCrankshaftElectric generator
A method of operating a supercharger (10) for an automotive engine (20) is disclosed. A supercharger (10) has an input shaft (30) for coupling to a crank shaft (22) of the engine and also for coupling to the rotor of a first electrical machine (40) and the annulus of an epicyclic gear train (60). An output shaft (70) is connected to a compressor (80) and a sun gear of the epicyclic gear train (60). A carrier carrying planet gears of the epicyclic gear train (60) is connected to the rotor of a second electrical machine (50). The first electrical machine (40) is selectively operable to supply electrical energy to the second electrical machine (50). The second electrical machine (50) is selectively operable as a motor or a generator to accelerate or decelerate the compressor (80), thereby tending to increase or decrease the power output of the engine. The first electrical machine (40) is selectively operable as a motor or a generator to control the torque transmitted from the input shaft (30) back to the crank shaft (22) caused by operation of the second electrical machine (50).
Owner:NEXXTDRIVE LTD +1
Motor in which an electric leakage to a shaft is prevented
InactiveUS20070138902A1Avoid accidentsHigh strengthMagnetic circuit rotating partsOther washing machinesRotational axisElectric machine
The present invention relates to motors each having a rotor with a metal rotor frame, a metal rotation shaft, and a rotation shaft supporting member connected between the rotor frame and the rotation shaft for transmission of a rotating power from the rotor to the rotation shaft, and, more particularly, to a motor in which the rotation shaft supporting member is constructed of a metal and an insulating material, for insulating the rotation shaft from the rotor frame while enhancing a structural strength of the rotation shaft supporting member. The motor for preventing current leakage to a rotation shaft, having a rotor with a rotor frame of metal, a rotation shaft of metal, and a rotation shaft supporting member connected between the rotor frame and the rotation shaft to transmit a rotation power from the rotor to the rotation shaft, the rotation shaft supporting member includes a supporting portion of metal for receiving and supporting the rotation shaft, and an insulating portion for electric insulation between the rotor frame and the rotation shaft.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
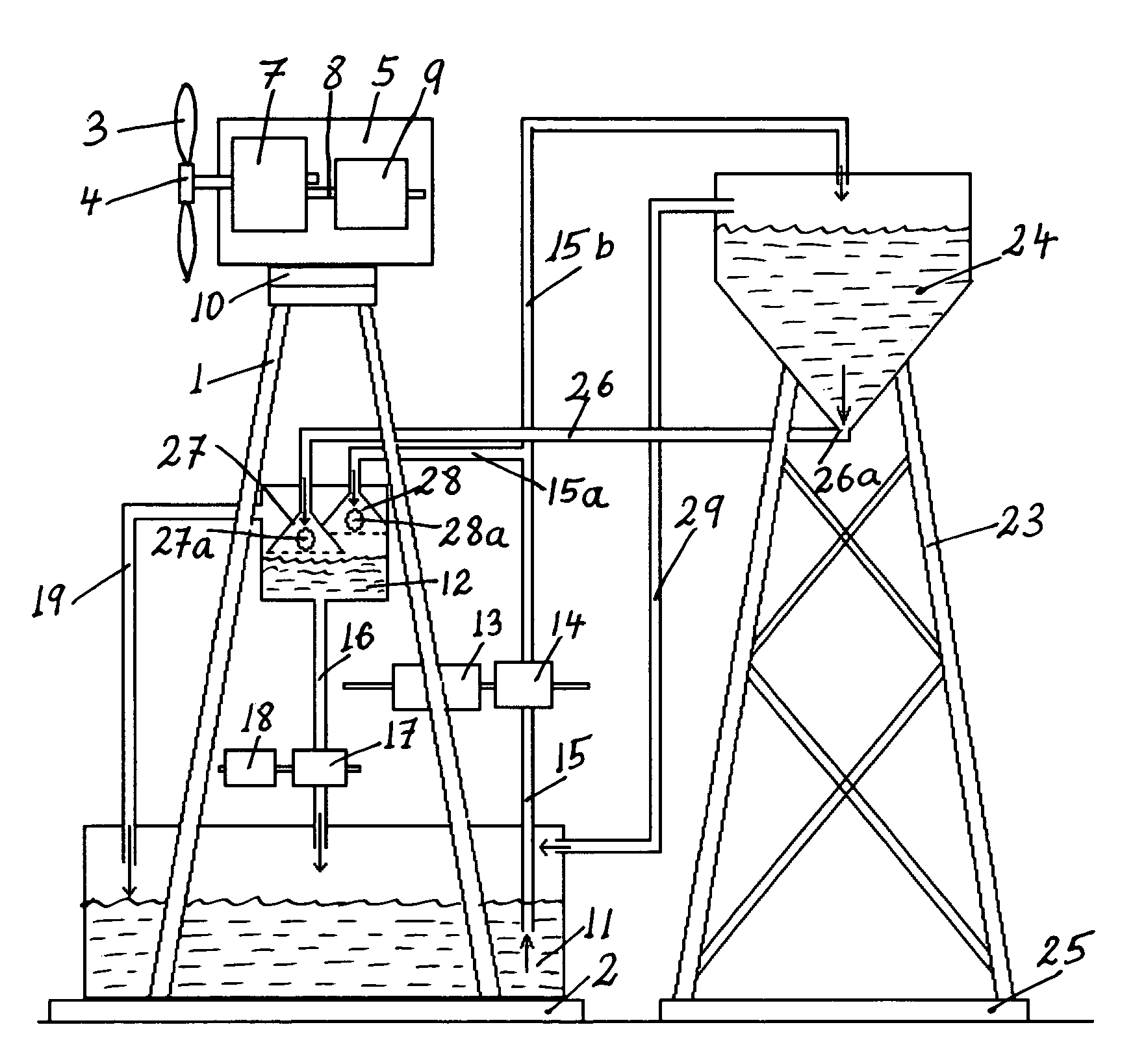
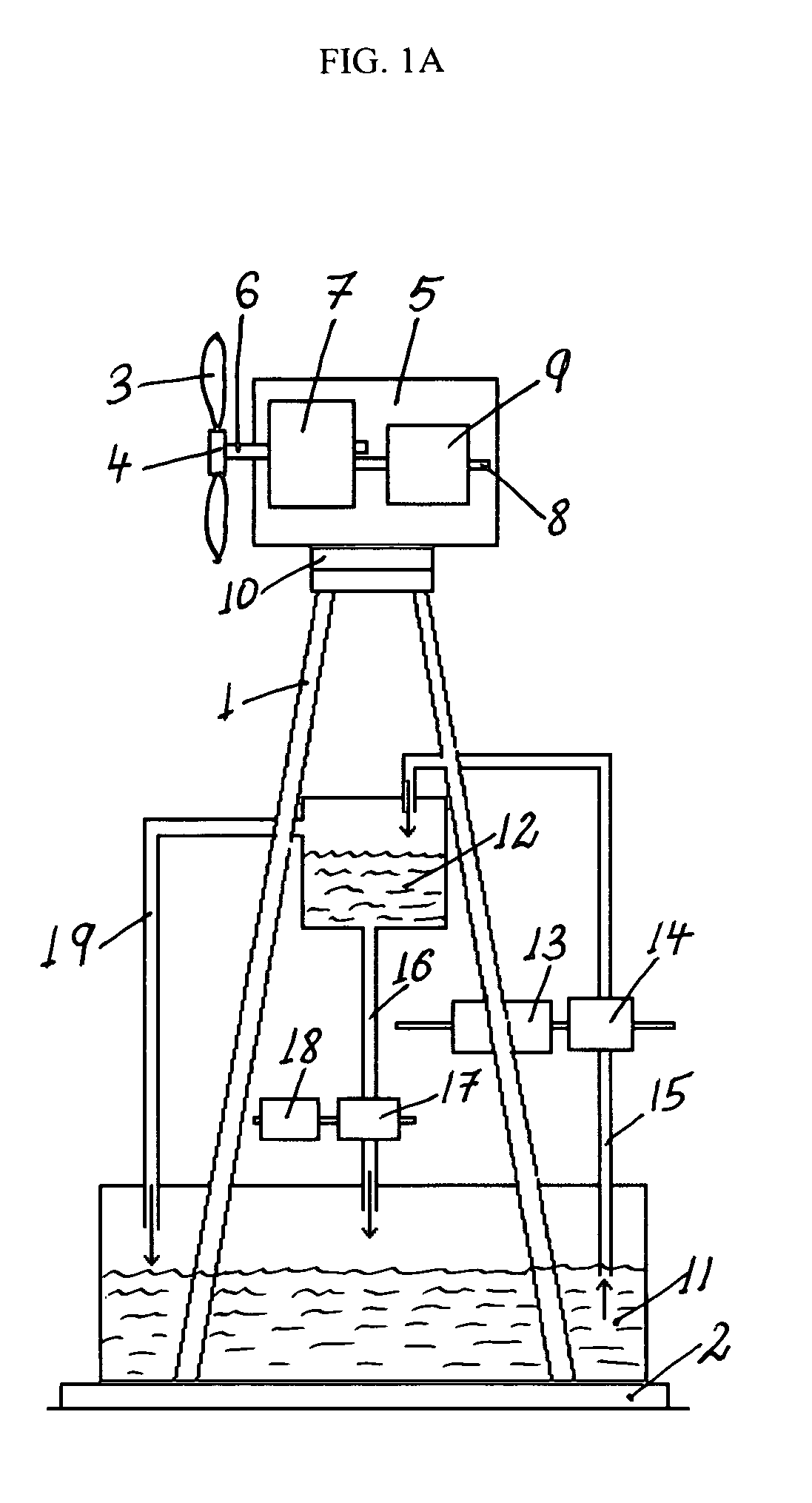
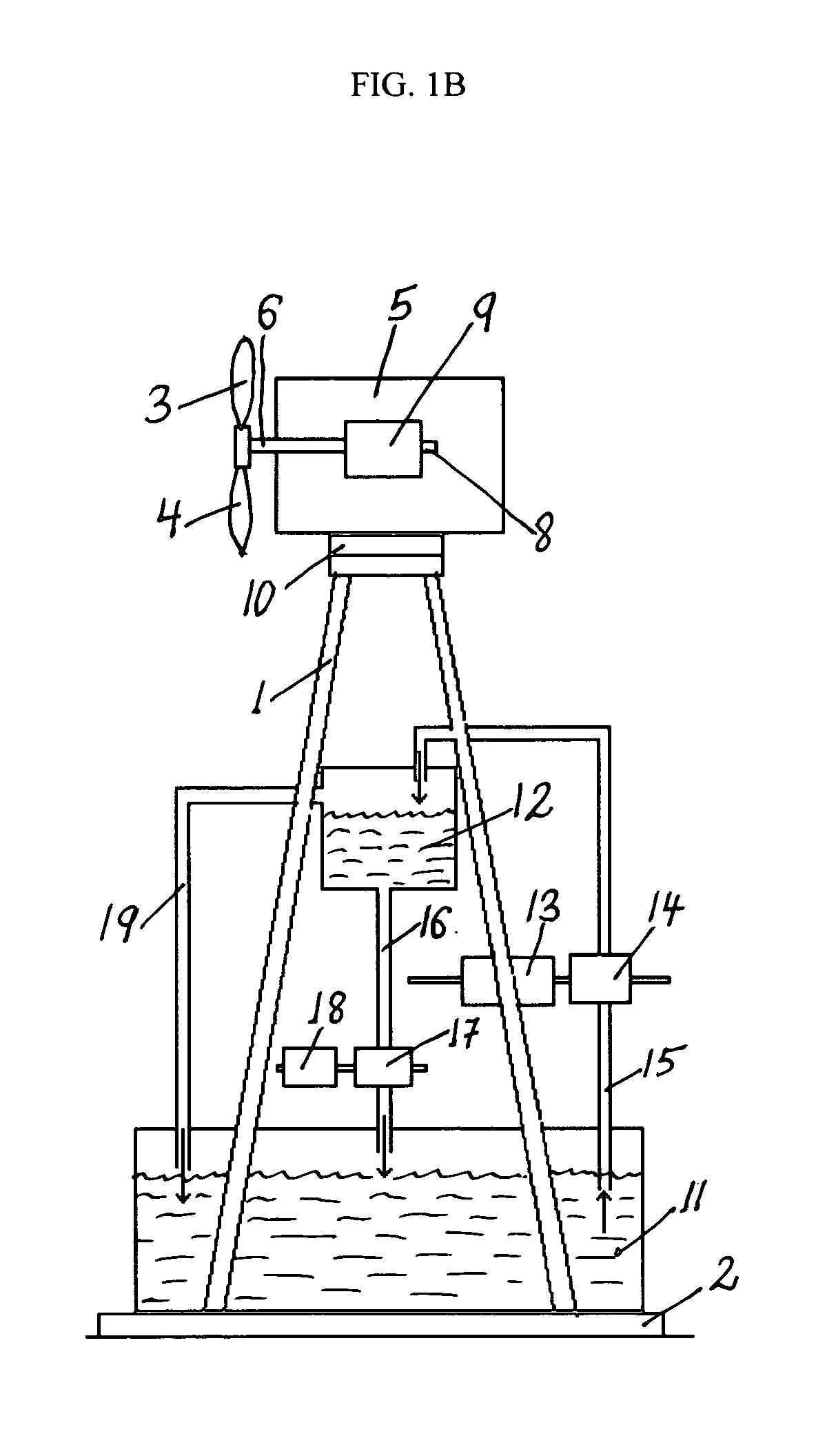
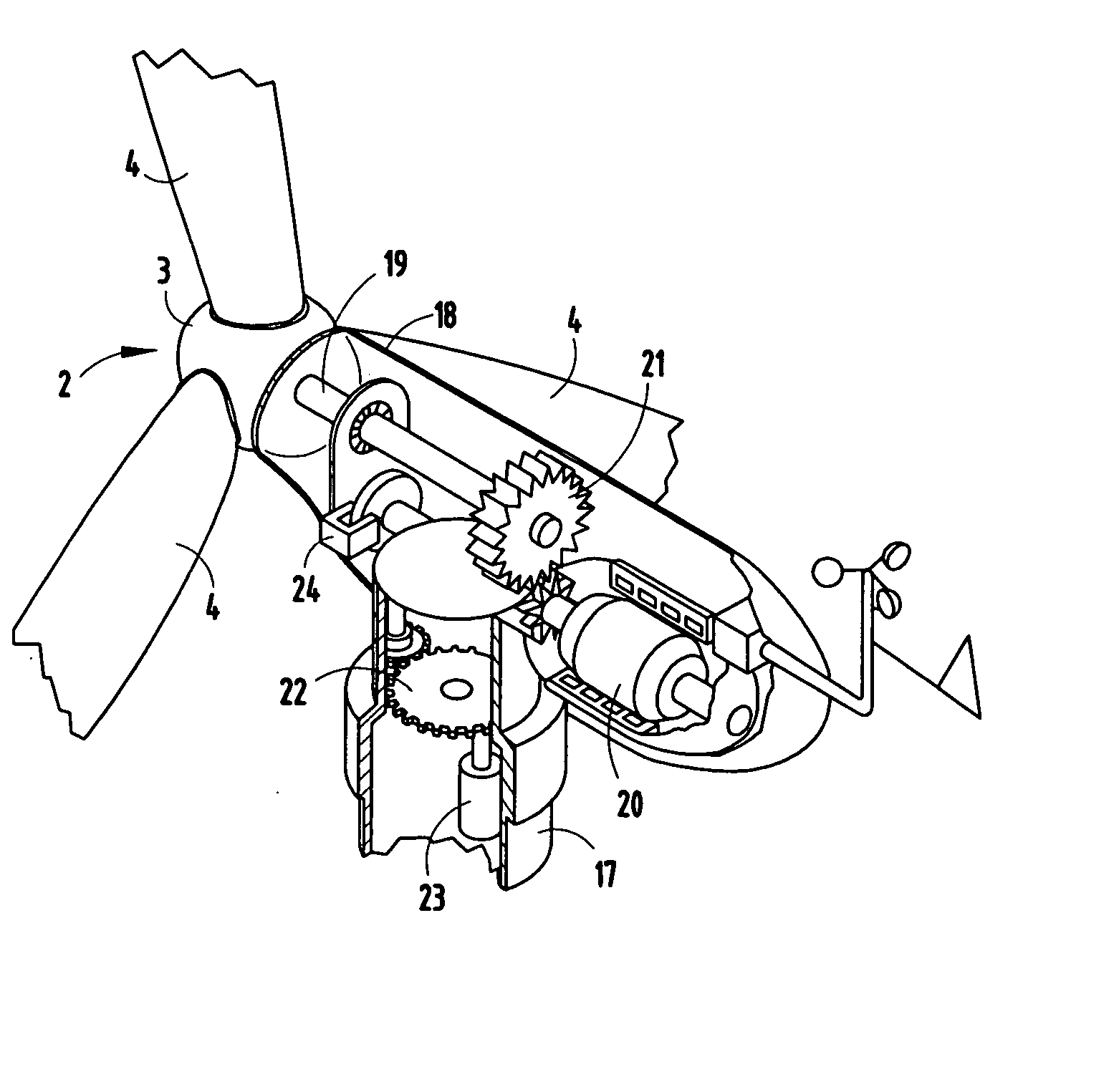
Hybrid water pressure energy accumulating wind turbine and method
A hybrid water pressure energy accumulating, wind turbine tower assembly used to directly propel water pumps to raise water from low elevation reservoir(s) to high elevation reservoir(s) where it is used as a potential energy. The wind tower assembly includes a wind turbine having propeller with a rotor, a generator driven by the rotor and a yaw assembly attached to a tower with a foundation. The tower includes in-tower storage reservoirs configured for storing water. The in-tower storage reservoirs could be defined by lower and upper water storage containers attached to the inner or outer surface of the tower that might be connected to other neighboring reservoir(s). The wind turbine may be of the vertical or horizontal-axis type and may be installed inside a residential or commercial building. The lifted water is used to generate electricity utilizing a hydropower generator.
Owner:KAMENOV KAMEN GEORGE
Wind turbine pitch bearing and method
InactiveUS20070104577A1Easy and economical to makeReduce manufacturing costRotary bearingsPropellersTurbine bladeWind force
A pitch bearing and related method for wind electric turbines has an annularly-shaped first bearing ring connected with an associated wind turbine blade, and includes a first raceway groove. An annularly-shaped second bearing ring is connected with the rotor portion of the wind turbine, and includes a second raceway groove aligned with the first raceway groove. Rolling elements are positioned in the first and second raceway grooves to rotatably interconnect the two bearing rings. A gear segment is formed on one of the bearing rings, and is configured to engage a pitch drive portion of the wind turbine to pivot the blade axially between different pitch angles. The gear segment has an arcuate measure of less than 200 degrees to facilitate economical manufacture.
Owner:KAYDON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com