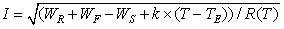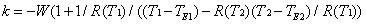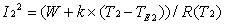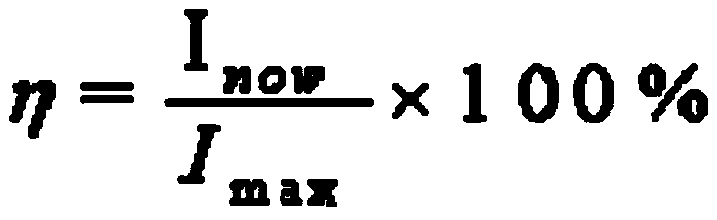Patents
Literature
206 results about "Ampacity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ampacity is a portmanteau for ampere capacity defined by National Electrical Codes, in some North American countries. Ampacity is defined as the maximum current, in amperes, that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating. Also described as current-carrying capacity.
Real-Time Power Line Rating
InactiveUS20100114392A1Well formedMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlTraffic capacityAmpacity
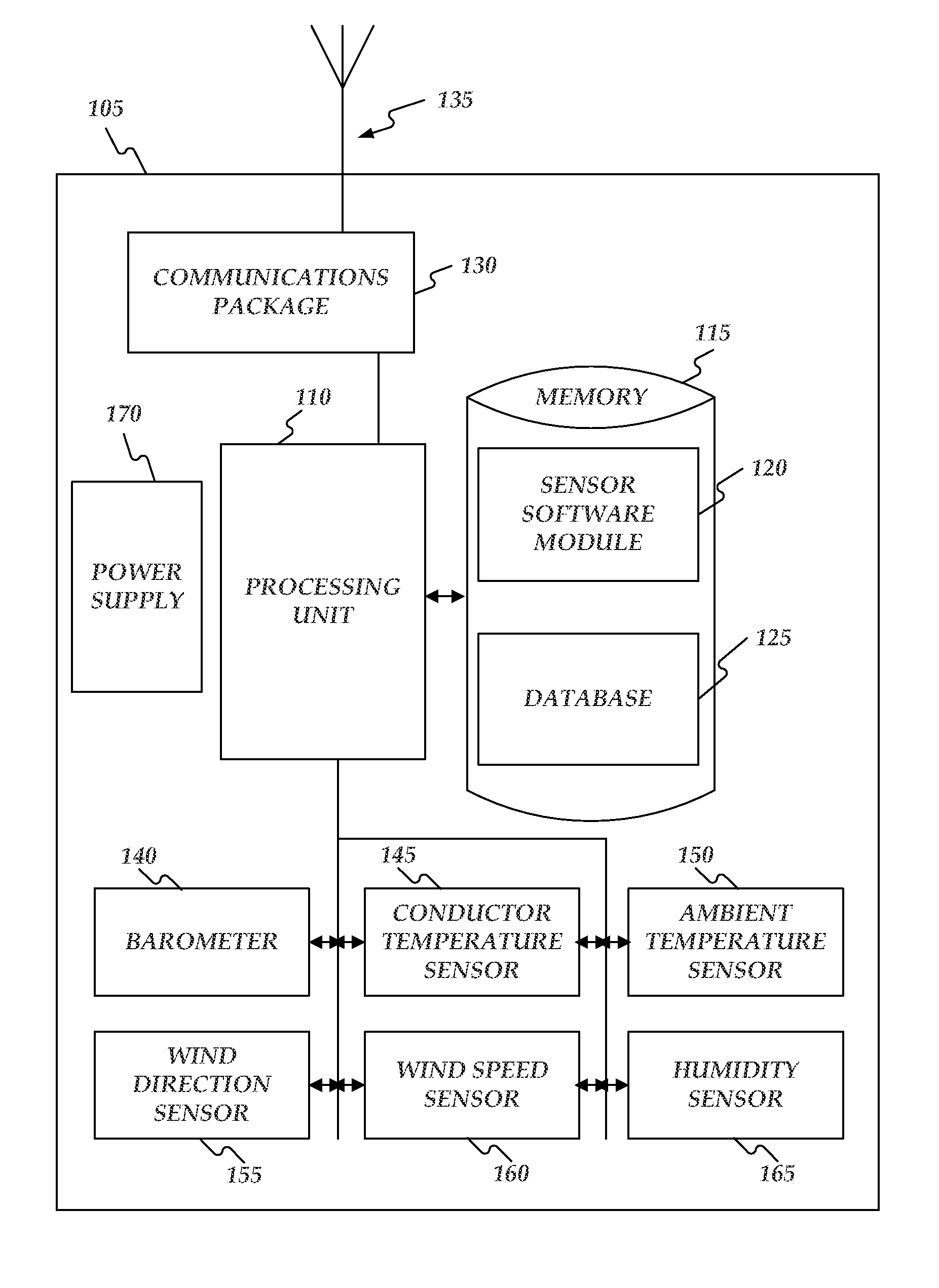
Real-time power line rating may be provided. First, sensor data may be received corresponding to a conductor of a power line. The sensor data may provide real-time weather conditions for the conductor's environment. The sensor data may be received from a sensor device configured to collect the sensor data. The sensor data may correspond to the weather conditions at a location of the sensor device on the power line. Next, design limitations for the power line having the conductor may be received. The conductor of the power line may have a design ampacity based upon the design limitations and assumed weather conditions for the conductor's environment. Then a dynamic ampacity may be calculated for the power line based upon the received sensor data and the received design limitations for the power line. The power line may then be operated according to the calculated dynamic ampacity instead of the design ampacity.
Owner:SOUTHWIRE CO LLC
Efficient high-ampacity bowl-shaped tubular conductors
ActiveUS20100051342A1Better currentAccelerated dissipationBus-bar/wiring layoutsMagnetic/electric field screeningIsosceles trapezoidBusbar
A high ampacity busbar includes a pair of oppositely facing bowl-shaped conductors, each of whose cross sections resembles half of a hexagon or an open isosceles trapezoid, separated by an air gap in both horizontal and vertical configurations. The air gap increases cooling efficiency by natural convection by exposing more surface area of the conductors directly to the air flow within the electrical distribution equipment cabinet. As a result, the overall temperature of the bus system is reduced. The shaped conductors have smoother transitions presented to the electrical current between the bends of the conductors. These smooth transitions improve current distribution throughout the conductor, reducing skin effects. As a result of improved thermal dissipation and reduced skin effects, the amount of copper needed to maintain the same ampacity is significantly reduced. Magnetic shields can be placed between adjacent busbars, reducing proximity effects.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
Calculation method of real-time current-carrying capacity of cable connector
InactiveCN106326572AThe calculation result is accurateAccurately calculate the structureDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCarrying capacityElectrical conductor
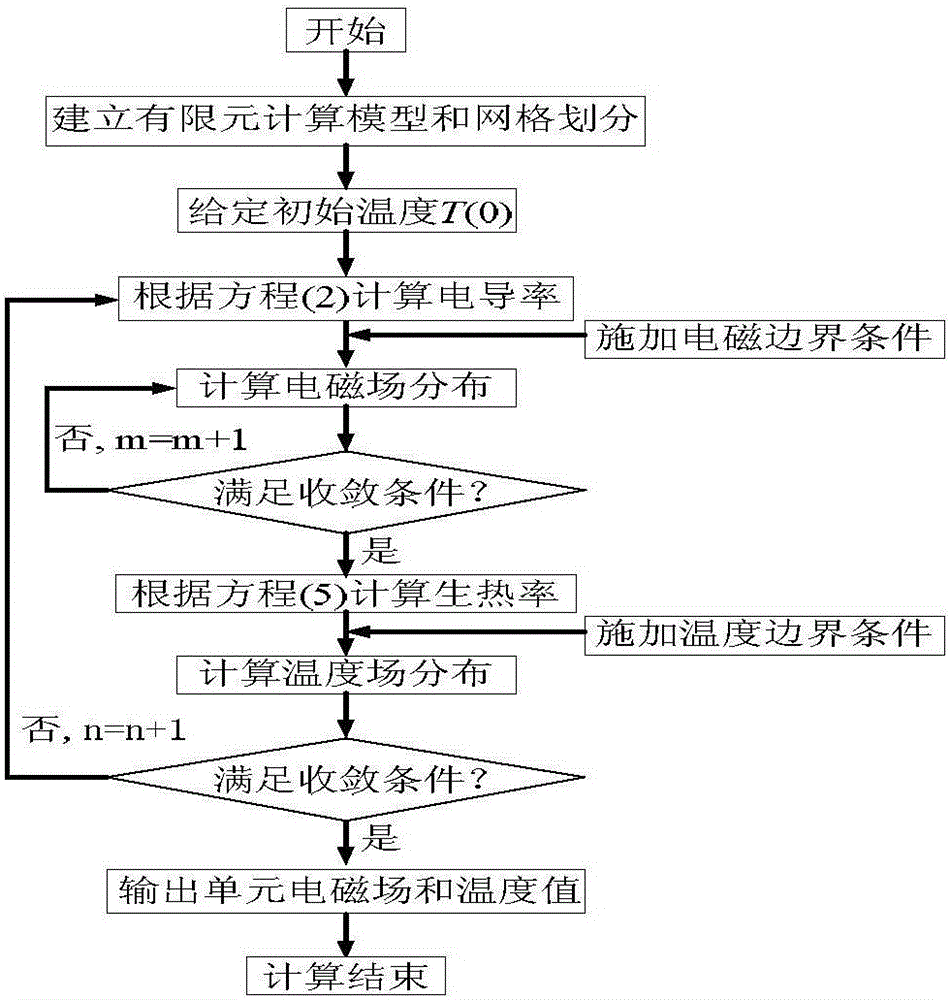
The invention discloses a calculation method of a real-time current-carrying capacity of a cable connector. The calculation method comprises: firstly, carrying out cable connector modeling in COMSOL; subdividing a model by utilizing tetrahedron non-uniform subdivision; furthermore, carrying out simulation calculation on the model by utilizing an electromagnetic-thermal coupling double-layer iterative algorithm; obtaining temperature distribution of a cable when considering influences, caused by temperature, on the electric conductivity of a cable conductor; simulating the temperature distribution of the cable under different current-carrying capacities; finally, backstepping the size of the current-carrying capacity of the cable at the moment by applying a current-carrying capacity calculation formula.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Efficient high-ampacity bowl-shaped tubular conductors
ActiveUS7786384B2Better currentAccelerated dissipationBus-bar/wiring layoutsElectrically conductive connectionsIsosceles trapezoidBusbar
A high ampacity busbar includes a pair of oppositely facing bowl-shaped conductors, each of whose cross sections resembles half of a hexagon or an open isosceles trapezoid, separated by an air gap in both horizontal and vertical configurations. The air gap increases cooling efficiency by natural convection by exposing more surface area of the conductors directly to the air flow within the electrical distribution equipment cabinet. As a result, the overall temperature of the bus system is reduced. The shaped conductors have smoother transitions presented to the electrical current between the bends of the conductors. These smooth transitions improve current distribution throughout the conductor, reducing skin effects. As a result of improved thermal dissipation and reduced skin effects, the amount of copper needed to maintain the same ampacity is significantly reduced. Magnetic shields can be placed between adjacent busbars, reducing proximity effects.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
High-strength heat-resistant aluminum alloy single line and wire for smart power grid and processing process of single line
ActiveCN105369073AHigh strengthImprove the safety of useConductive materialInsulated cablesSmart gridPower grid
The invention discloses a high-strength heat-resistant aluminum alloy single line and wire for a smart power grid and a processing process of the single line. The high-stretching-rate high-strength heat-resistant aluminum alloy single line is prepared from, by weight percent, 0.05%-0.15% of Zr, 0.01%-0.30% of Y or La, 0.15%-0.30% of Fe, 0.01%-0.40 of Si, 0.01%-0.50% of Mg, 0.10% or less of other impurity elements and the balance aluminum. The strength of the wire formed by stranding single lines can be greatly increased, the draw-weight ratio can be increased, and the use safety of the wire can be improved; meanwhile, the operating temperature of the wire is greatly increased, the operating temperature of the wire is increased to 150 DEG C from conventional 70 DEG C, and therefore the carrying capacity is greatly improved; and the use requirements of high-capacity and large-span extra-high-voltage lines can be met.
Owner:FAR EAST CABLE +2
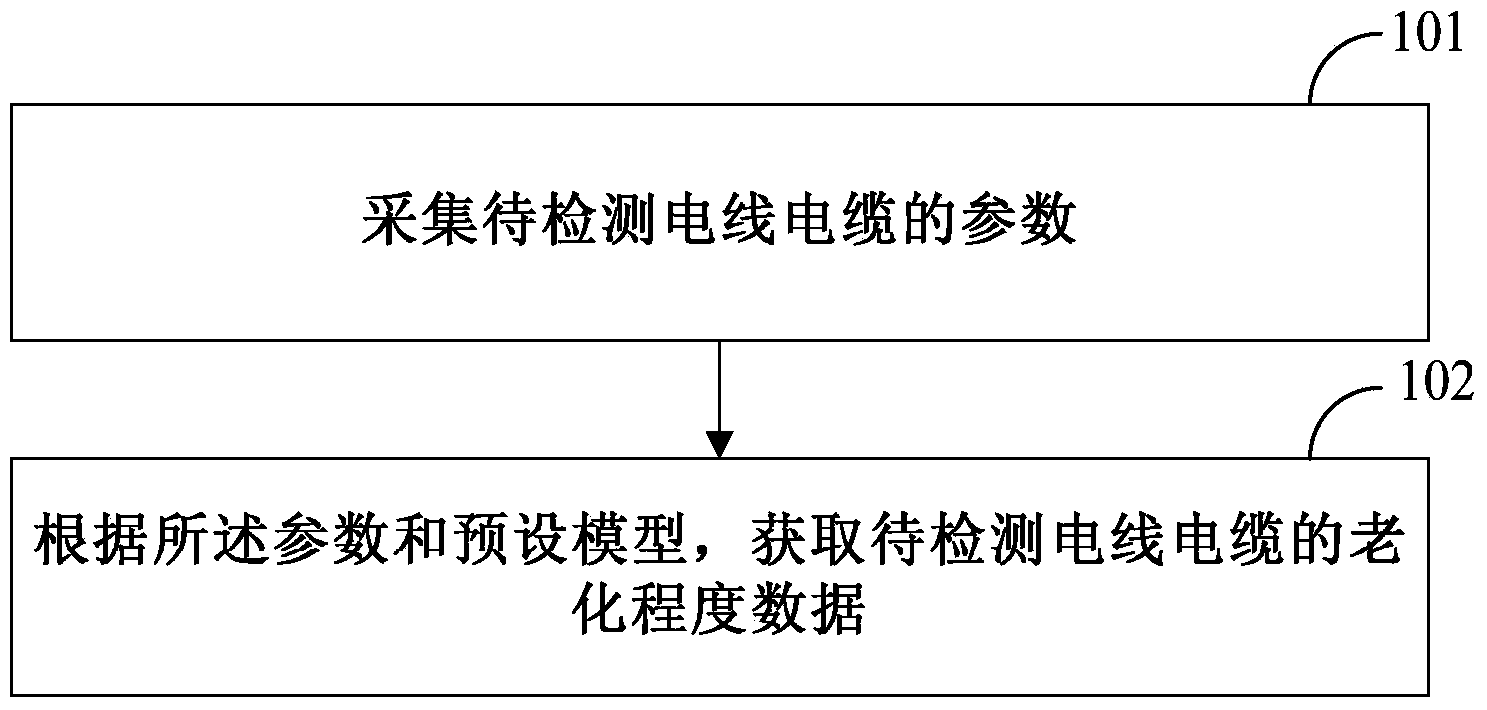
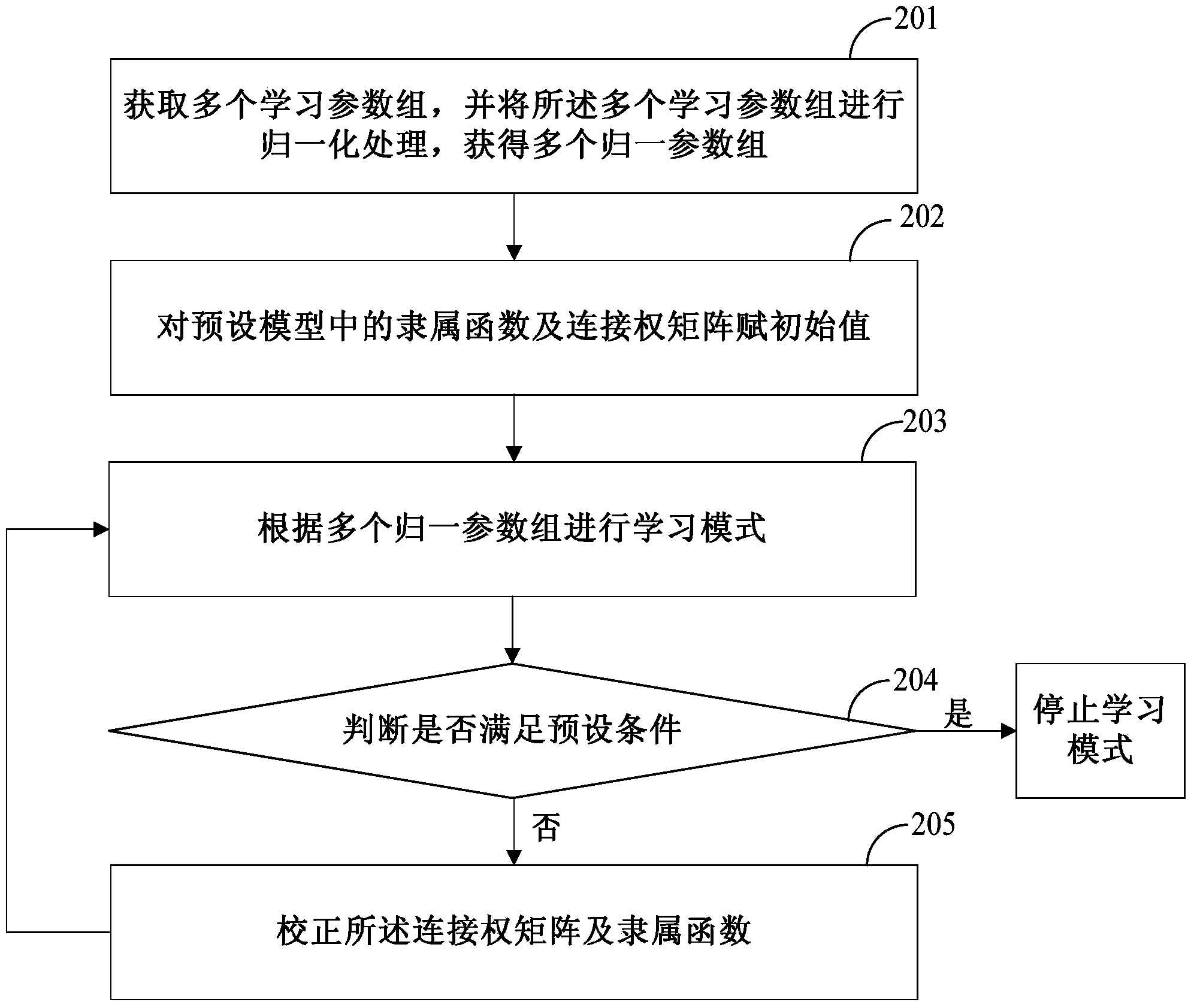
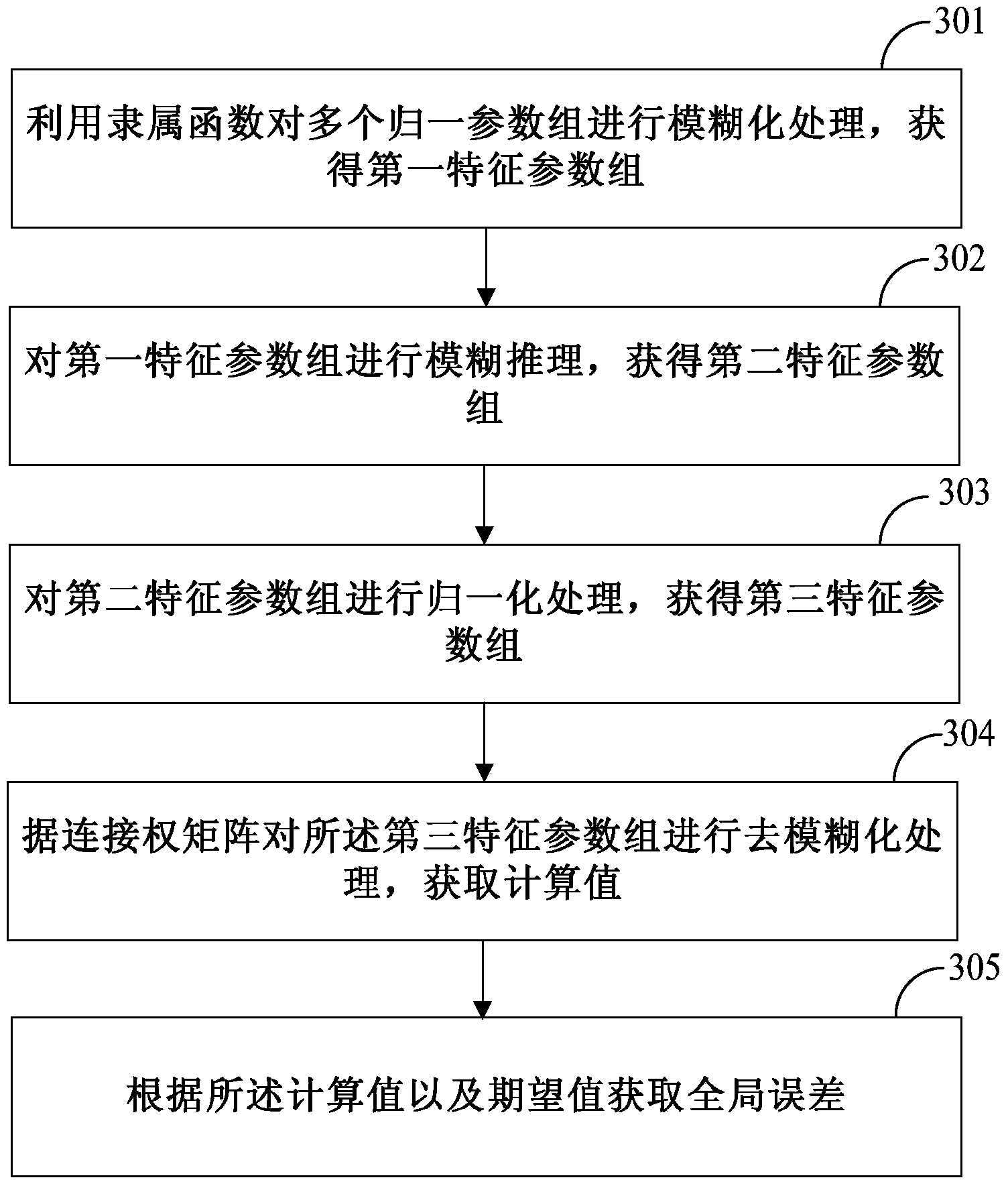
Ageing degree detecting method and device
The embodiment of the invention discloses an ageing degree detecting method. The method comprises the following steps: collecting parameters of to-be detected electric wires and cables, wherein the parameters comprise ampacity, leakage current, temperature, humidity, use time and historical load of the to-be detected electric wires and cables; acquiring ageing degree data of the to-be detected electric wires and cables according to the parameters and preset models. The ageing degree detecting method can detect ageing degrees of the electric wires and the cables.
Owner:彭浩明
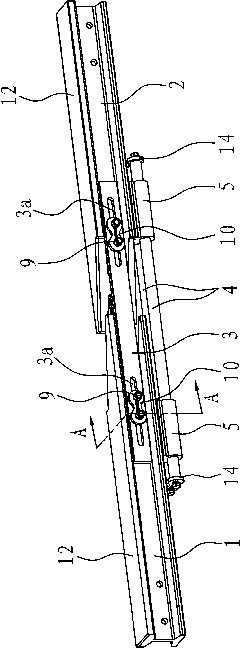
External sliding type expansion junction for contact rail
The invention discloses an external sliding type expansion junction for a contact rail, belonging to the field of traffic facilities. The invention solves the problems that the traditional expansion junctions are easy to wear and power-off, or installation and sliding are affected due to high strength, or ampacity is unstable and the like. The invention is characterized in that the external sliding type expansion junction for the contact rail is used to be connected with a contact rail I and a contact rail II which are in the same straight line and have 'I' shaped cross sections; the junction comprises a guide plate arranged between the two contact rails, the backs of the two contact rails are provided with at least one conductive rigid guide rail which is parallel to the guide plate; and electric connectors are respectively arranged between the rigid guide rail and the back of the contact rail I as well as the rigid guide rail and the the back of contact rail II, which can lead the rigid guide rail to be electrically conducted with the contact rail I and the contact rail II. The invention has the advantages of uneasy abrasion and crack and long service life. And whether the contact rail elongates or shortens, the contact areas between the contact rail and the electric connectors as well as the electric connectors and the rigid guide rail maintain unchanged from beginning to end, thereby ensuring constant and steady ampacity.
Owner:浙江旺隆轨道交通设备有限公司
7 split conductor with cable copper core section of 3500mm<2> and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102347104AReduce loss and heatLarge carrying capacityNon-insulated conductorsInsulated cablesSkin effectStructural engineering
The invention discloses a 7 split conductor with a cable copper core section of 3500mm<2> and a manufacturing method thereof, and the conductor provided by the invention is used for transmitting high-capacity high-pressure energy, overcoming the problem that the use effect is bad in an higher temperature environment, increasing the cable section, and causing the cable copper core section to be 3500mm<2>. In addition, a conductor-splitting mode is adopted, so that the structure of a conductor with a large copper core section is more disperse, thus the heat losses of the conductor are reduced effectively, the influence of the 'skin effect' on current transmission of a cable is reduced, and the current-carrying capacity of the conductor is increased, thereby improving the practicability of the cable.
Owner:SICHUAN MINGXING CABLE
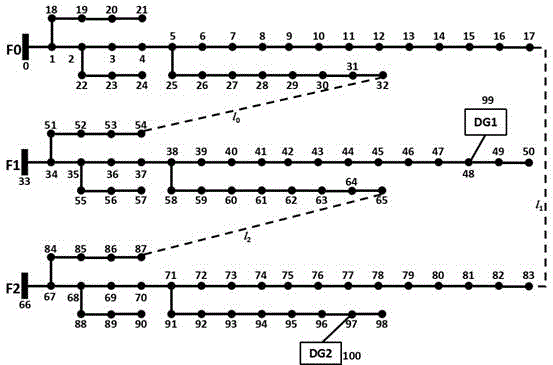
Nonlinear integer programming-based distribution network load transfer optimization model with distributed power supplies
InactiveCN105762795AData processing applicationsSystems intergating technologiesNonlinear integer programmingPower factor
The invention provides a nonlinear integer programming-based distribution network load transfer optimization model with distributed power supplies. In view of access of the distributed power supplies, ideas of a branch switch state matrix, a path, a reachability matrix and a loop is introduced, a path reachability and node branch number relationship is used for describing tree topology constraints and power flow constraints for the distribution network with the distributed power supplies, a load transfer optimization model when the distribution network with the distributed power supplies fails is obtained, an objective function is the sum of absolute values of differences between known load power of all nodes and node calculation injection power, constraint conditions comprise the tree topology constraints, the power flow constraints, ampacity constraints of a feeder line and node permissible voltage offset constraints, and a standard nonlinear integer programming analytic form is provided. The distributed power supply considered in the invention is an asynchronous generator-type distributed power supply with determined active power and stably-kept power factor, and a PQ node with negative load is processed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Method of calculating steady-state heat capacity of power circuit
InactiveCN102620846ASteady-state heat capacity deviation is smallReduce predicted temperature errorsThermometer detailsEngineeringAlternating current
A method of calculating steady-state heat capacity of a power circuit relates to the technical field of monitoring of the power circuit, solving the technical problem that the calculated result in the conventional method has a large deviation. The method comprises the following specific steps: 1), measuring a ambient temperature and a conductor temperature of a sample conductor in two measuring environments, and calculating an ambient temperature influencing coefficient of the sample conductor according to a measured value; 2) taking the ambient temperature influencing coefficient of the sample conductor as a circuit ambient temperature influencing coefficient of the power circuit, and establishing a steady-state heat capacity formula of the power circuit; and 3) when a current circuit ampacity of the power circuit is required to be calculated, firstly, measuring a current circuit temperature and a current ambient temperature of the power circuit, and obtaining a current alternating current resistance of the power circuit, and then, according to the current circuit temperature, the current ambient temperature, the current alternating current resistance and the steady-state heat capacity formula of the power circuit, calculating the current circuit ampacity of the power circuit. According to the method, the calculated result of the circuit ampacity has a relatively small deviation.
Owner:SHANGHAI SUNRISE POWER TECH
Method and System for Determining the Thermal Power Line Rating
ActiveUS20160178681A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionEngineeringAmpacity
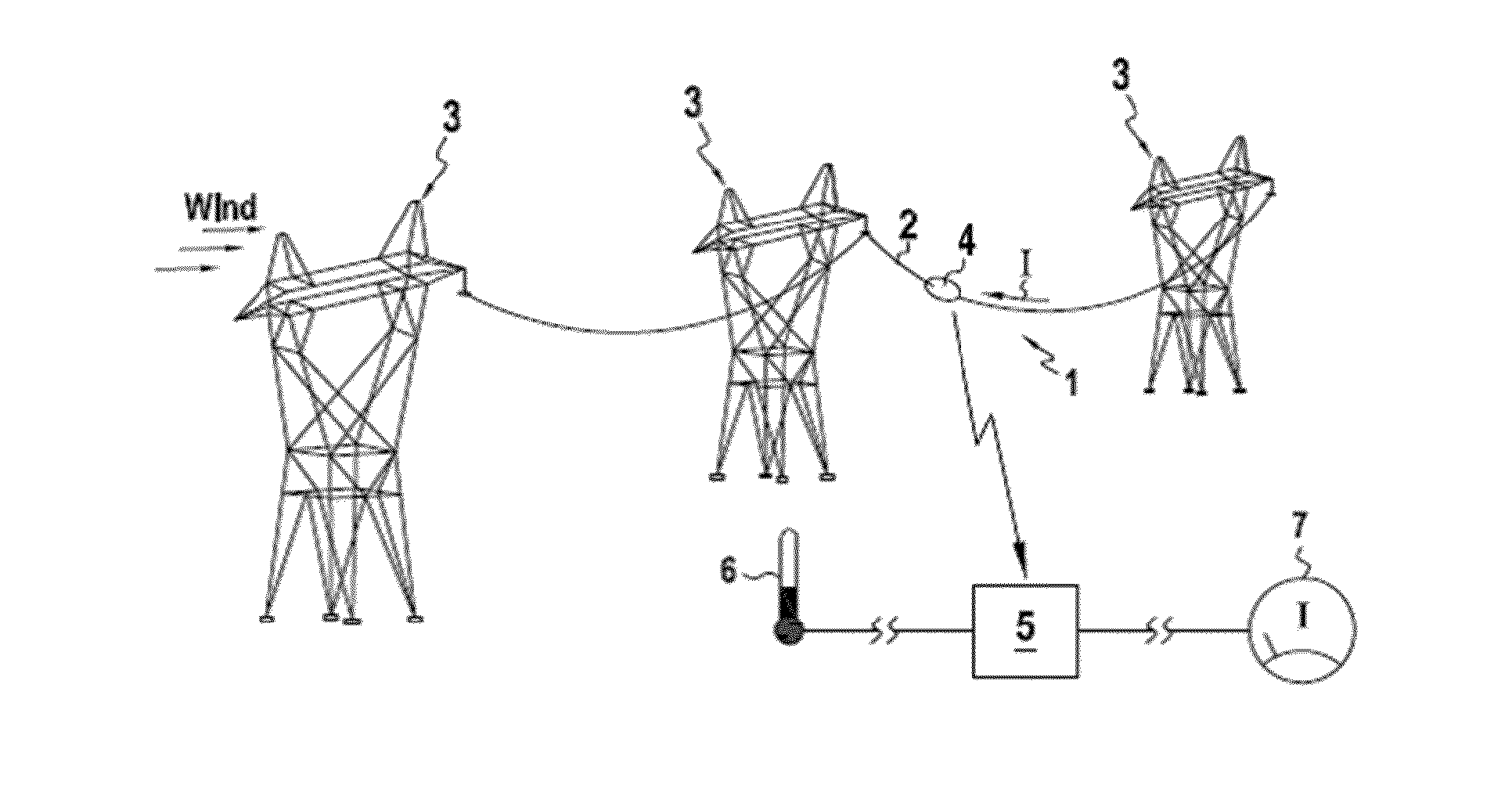
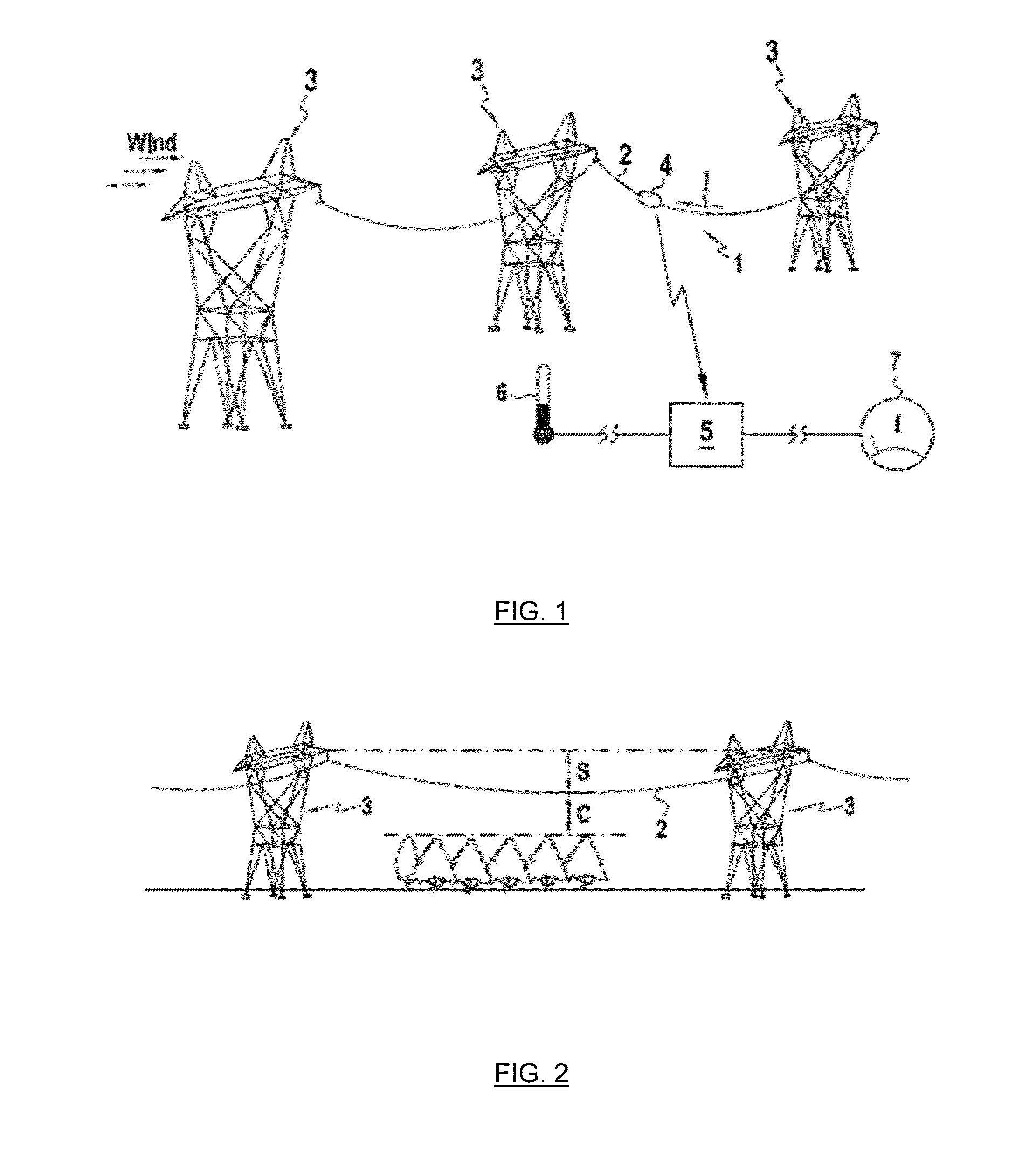
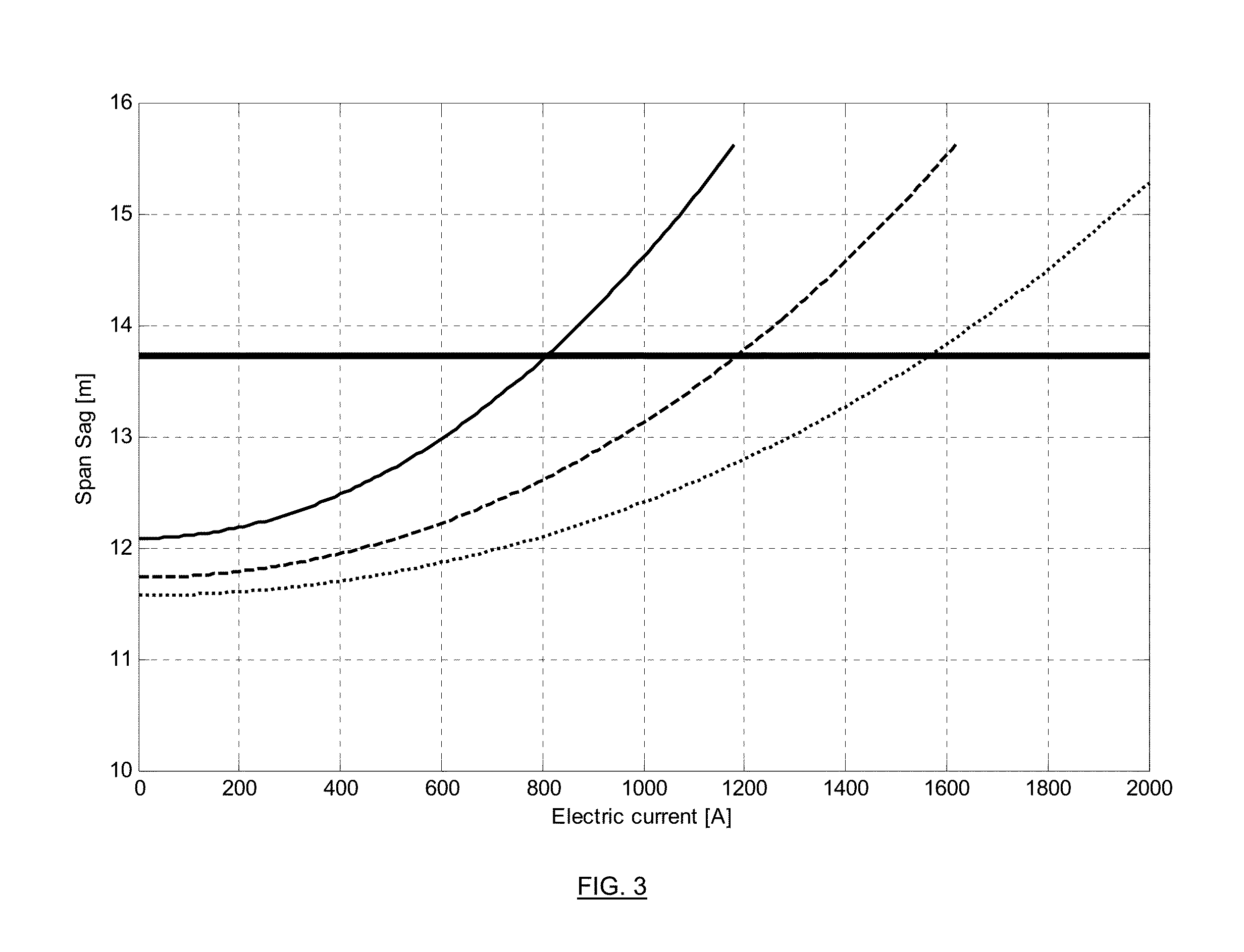
Method for measuring the power line thermal rating or maximum allowable current rating of an overhead power line with respect to a suspended / anchored cable span (2), comprising at least the following steps of:monitoring a motion of at least one point P of said suspended / anchored cable span (2) over a time interval;monitoring actual line current I, in A, over said time interval;determining an actual sag of said suspended / anchored cable, as a variable of actual line current;measuring or determining the effective wind speed of said suspended / anchored cable span (2) over said time interval;determining a sag reserve DF, in m, for thermal rating, which is the distance between the actual sag and a maximum allowable sag;determining the rate of change, tan(α), in m / A2, of the actual sag versus the square of the line current for the effective wind speed; anddetermining the power line thermal rating of the overhead power line, or ampacity, linked to a corresponding safety clearance, at measured or determined effective wind speed, by adding the square of actual current I to the ratio of the sag reserve DF by the sag rate of change, tan(α), at the effective wind speed, and taking the square root of that addition, i.e.Ampacity=I2+DFtan(α),wherein ampacity is in amperes.
Owner:AMPACIMON
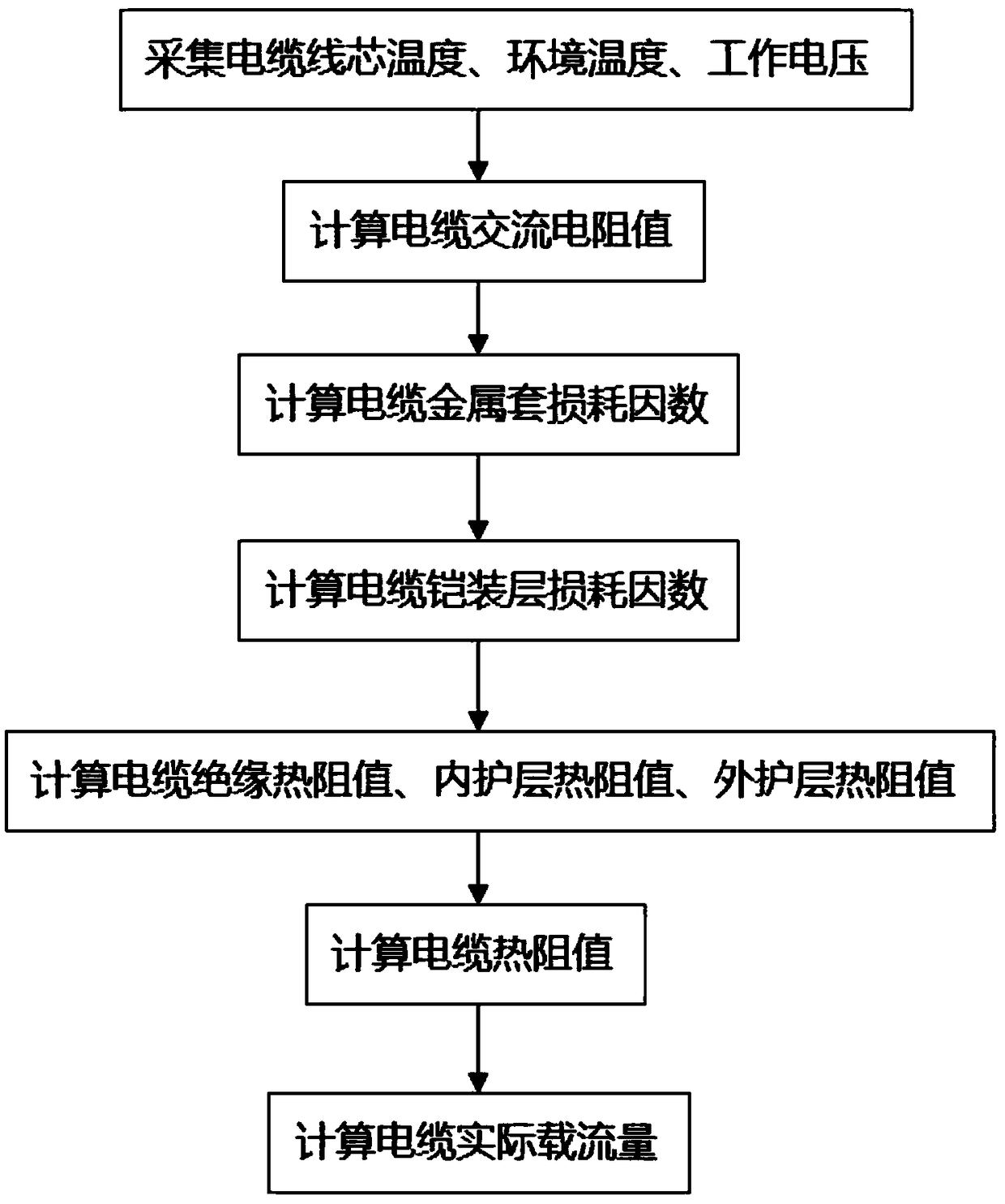
Actual current-carrying capacity calculating method of underground laid power distribution line cable
InactiveCN109490664AHigh working reliabilityIncrease job securityElectrical testingComplex mathematical operationsElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
The invention provides an actual current-carrying capacity calculating method of an underground laid power distribution line cable. The actual current-carrying capacity calculating method comprises the following steps that 1, cable core temperature, environment temperature and working voltage are acquired; 2, an alternating-current resistance value of the cable is calculated; 3, a metal sheath loss factor of the cable is calculated; 4, an armor layer loss factor of the cable is calculated; 5, an insulating thermal resistance value of the cable, an inner protective layer thermal resistance value and an outer protective layer thermal resistance value are calculated; 6, a thermal resistance value of the cable is calculated; 7, the actual current-carrying capacity of the cable is calculated. By adopting the actual current-carrying capacity calculating method of the underground laid power distribution line cable, the actual current-carrying capacity of the cable is calculated according to parameters of the cable and acquired temperature and voltage information, appropriate working current is selected, and accordingly the reliability and security of the cable in work are improved.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD NANTONG POWER SUPPLY BRANCH
Control cable for solar photovoltaic power stations and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a control cable for solar photovoltaic power stations and a manufacturing method thereof and relates to the technical field of cables. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: carrying out the wire drawing on metallic copper; annealing the metallic copper, and wiring into a conductor; sheathing insulating material on the outer surface of the conductor in an extruding mode to form an insulating wire core; winding the insulating wire core and filling material by a winding band; arranging a metal shield outside the winding band; and sheathing an internal protective sleeve outside the metal shield in an extruding mode. The control cable has the advantages of easy production, high heat, cold and weather resistance, ozone resistance, high hydrolysis property, ultraviolet resistance, microbe and chemical corrosion resistance, strong capability of short-time overload, high ampacity, wear resistance, oil resistance, corrosion resistance, termite resistance, favorable mechanical properties, favorable lightening-proof effect, flame retardance, low smoke density, recovering performance, environmental protection and the like, and can meet the requirementsfor solar power stations and photovoltaic power systems.
Owner:江苏晨曦光伏科技有限公司
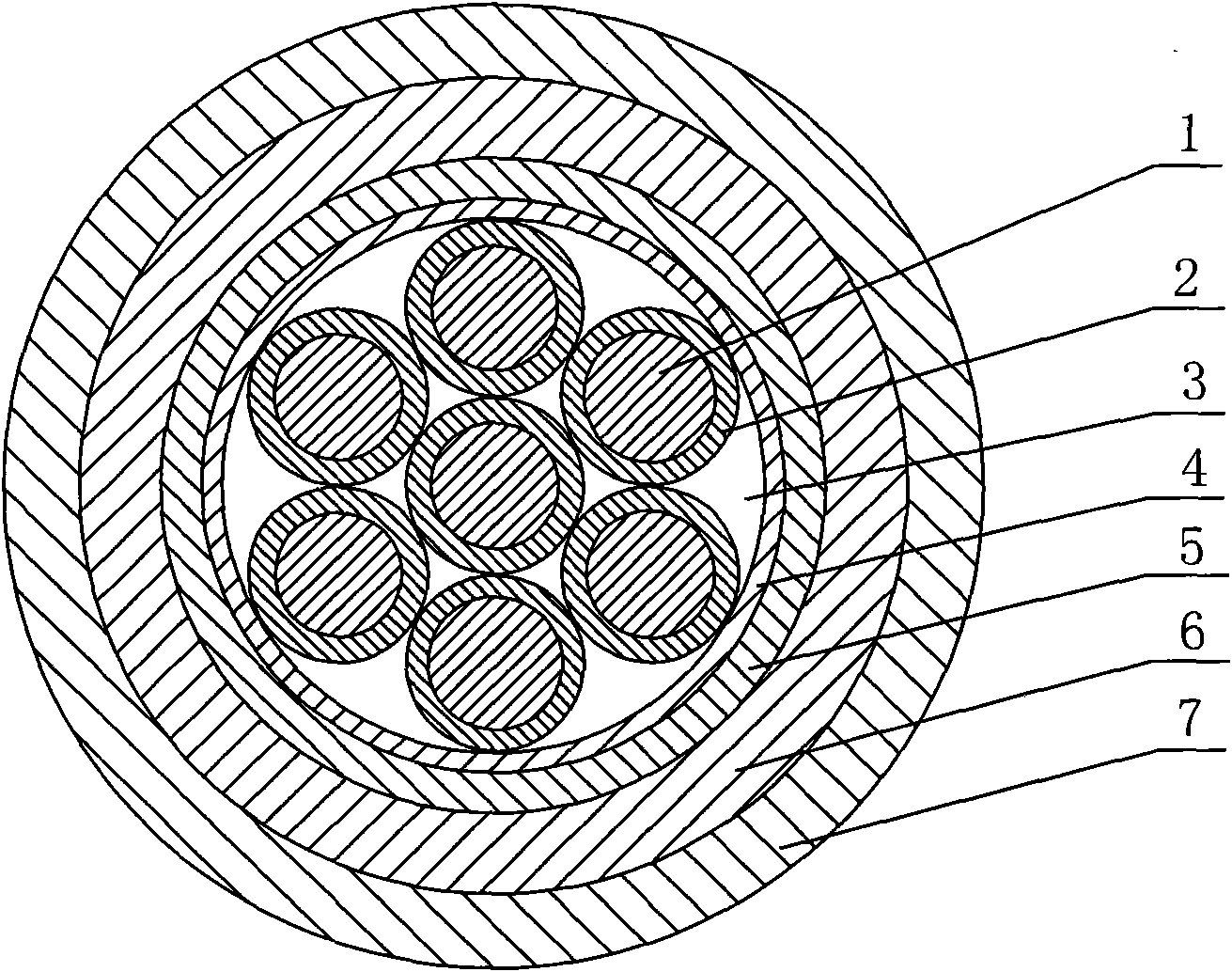
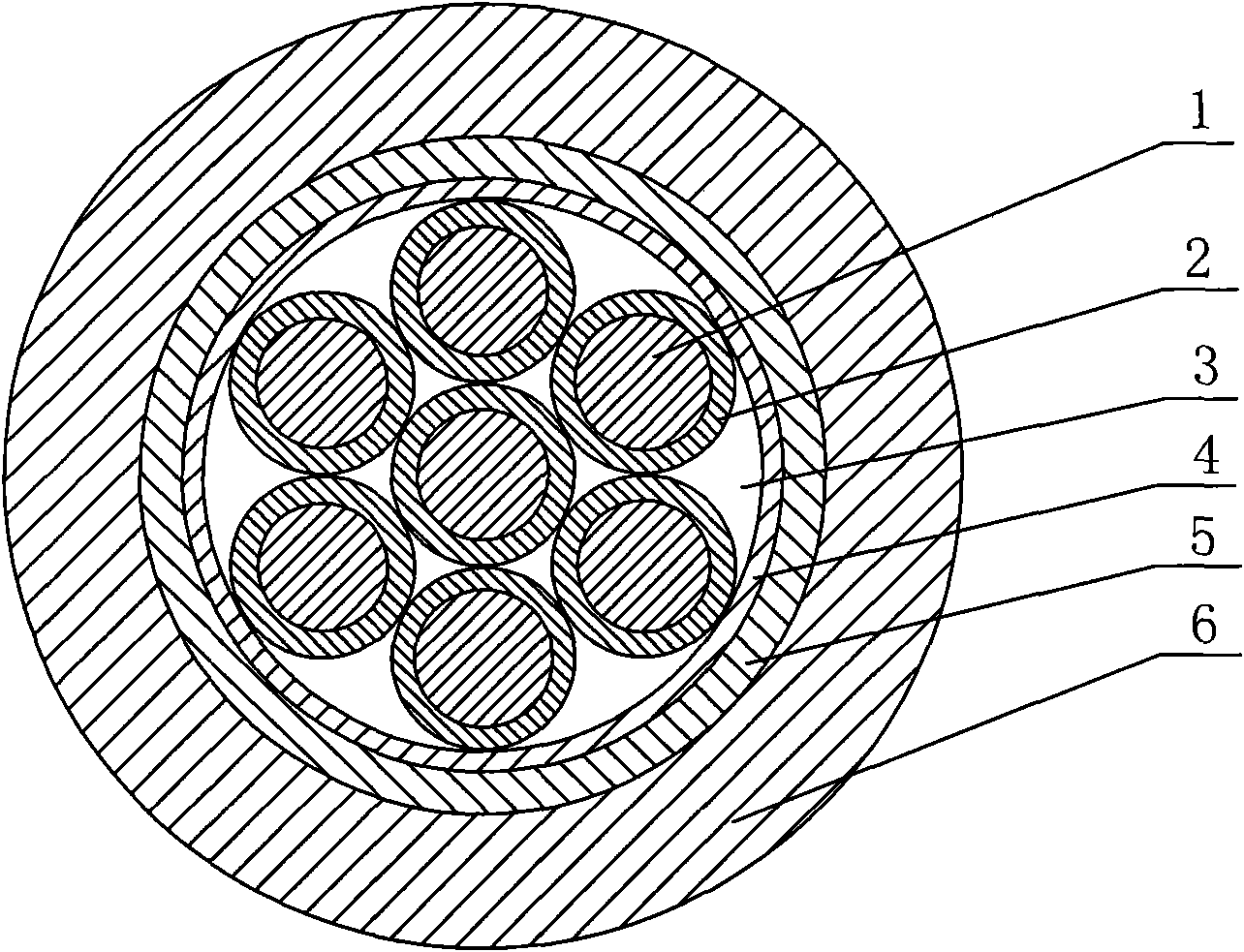
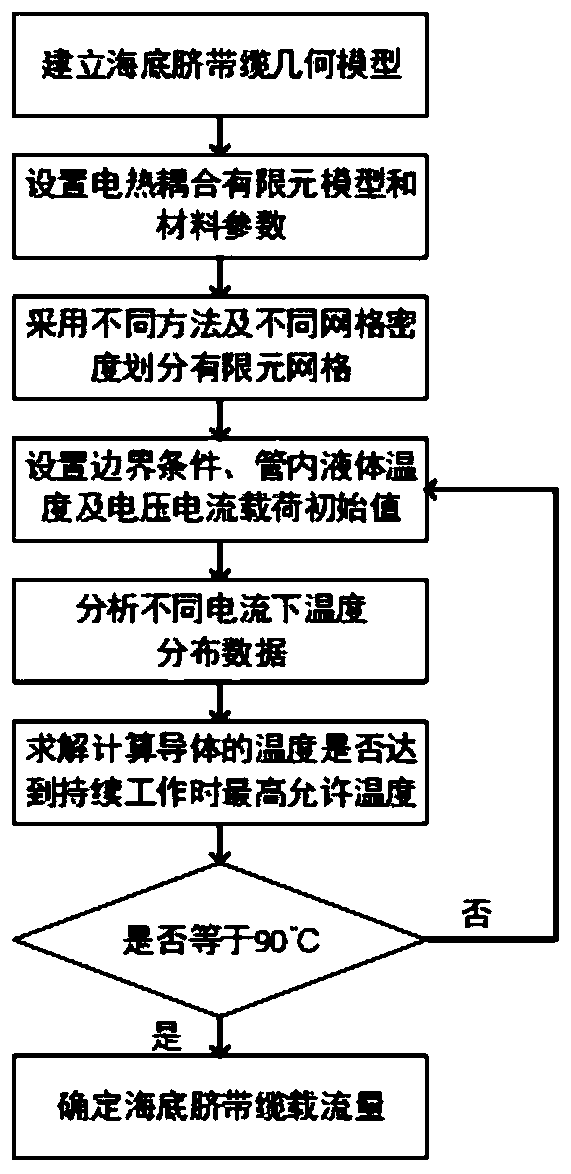
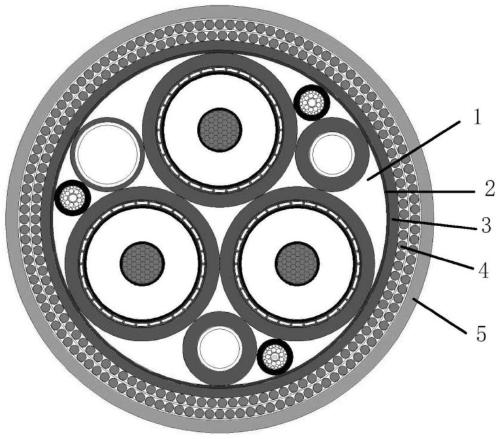
Submarine umbilical cable conductor current-carrying capacity evaluation method
PendingCN111539148AOvercoming implementation difficultiesOvercome costsDesign optimisation/simulationConstraint-based CADElement modelGrid density
The invention discloses a submarine umbilical cable conductor current-carrying capacity evaluation method, and relates to the field of transmission submarine cable simulation. At present, the internalstructure of the submarine umbilical cable is complex, materials of all layers are different, and the performance difference is too large. When the current-carrying capacity is analyzed through simulation, simulation data are large, calculation is complex, the current-carrying capacity is troublesome to determine, and the risk that an analysis result is uncertain exists. The method comprises thefollowing specific steps: establishing a submarine umbilical cable geometric model; setting an electro-thermal coupling finite element model and material parameters; dividing finite element grids by adopting different methods and grid densities; boundary conditions, the temperature of liquid in the pipe and initial values of voltage and current loads are set; and analyzing the temperature field distribution condition under different current magnitudes, and solving and calculating whether the conductor temperature reaches the maximum allowable temperature during continuous working or not. According to the technical scheme, the defects of difficult test, difficult data collection and the like are overcome, evaluation of the current-carrying capacity of the submarine umbilical cable conductorin a conventional environment is realized, and calculation and analysis are convenient and efficient.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Elastic jack contact
InactiveCN101635402AHighly reliable electrical connectionSimple structureSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersCoupling contact membersInterference fitLow insertion force
The invention relates to an elastic jack contact comprising a sleeve, elastic pieces and a jack. Each elastic piece is rolled stock or wire stock bent in a shape comprising an arc contact part and a hook-shaped fixed part; and the elastic pieces are uniformly arranged in the circumference of the jack; the fixed parts of the elastic pieces are fixed at the end part of the jack by the interference fit between the sleeve and the elastic pieces; the arc contact part is suspended towards the center of the jack to form a gliding fulcrum and form an inscribed round jack in the radial direction of the jack. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, low insertion force and great ampacity and is more suitable for high-density multicore electric connection occasions.
Owner:GUIZHOU SPACE APPLIANCE CO LTD
Overhead transmission line current-carrying capacity calculation method, system and device
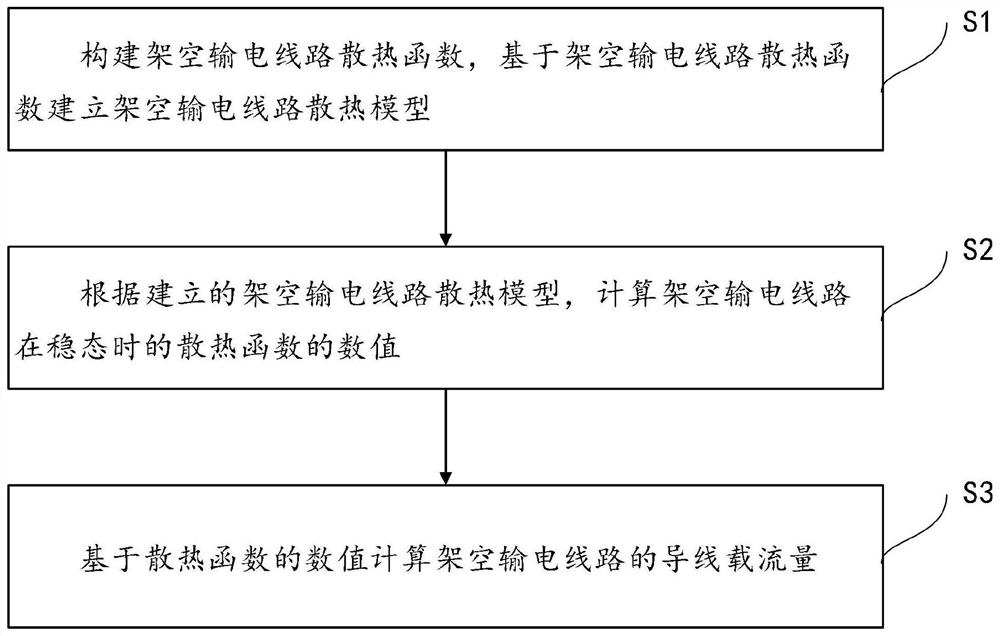
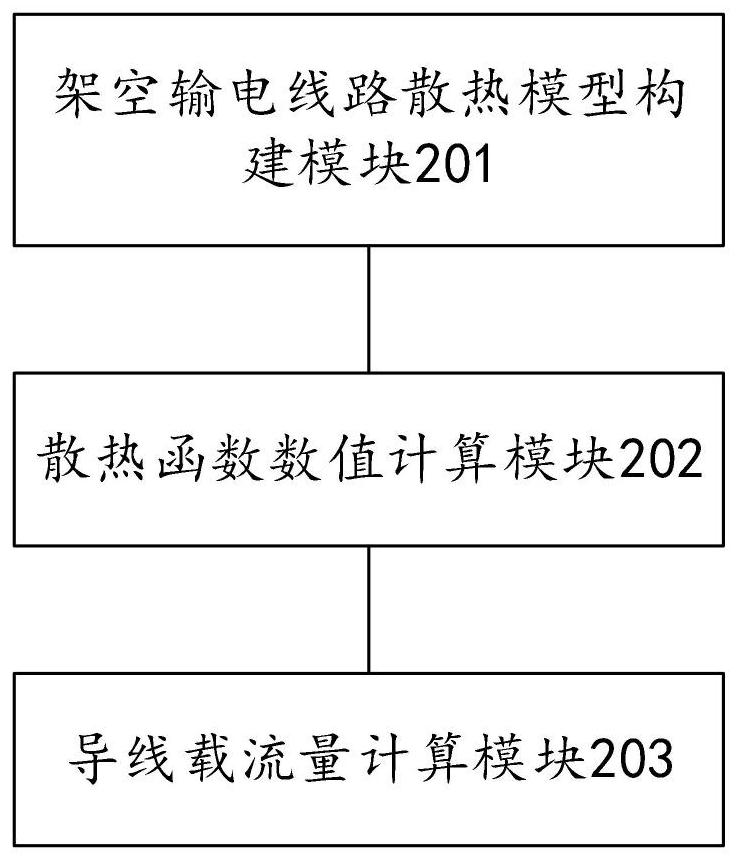
InactiveCN111814344ARealize computingFew parametersDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAmpacityComputer science
The invention discloses an overhead transmission line current-carrying capacity calculation method, system and device. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a heat dissipation function of the overhead transmission line, establishing a heat dissipation model of the overhead transmission line, solving a numerical value of the heat dissipation function of the overhead transmission line by utilizing the heat dissipation model of the overhead transmission line, and calculating a wire current-carrying capacity of the overhead transmission line according to the numerical value of theheat dissipation function. According to the invention, the calculation of the current-carrying capacity of the overhead transmission line is realized through the heat dissipation model of the overhead transmission line, the number of parameters required to be measured in the calculation process is small, excessive sensors are not required, and the accuracy of calculating the current-carrying capacity of the overhead transmission line can be effectively improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
High temperature superconducting tape conductor having high critical ampacity
ActiveUS20130210635A1High transfer currentIncrease layer thicknessSuperconductors/hyperconductorsRecord information storageHigh-temperature superconductivityInter layer
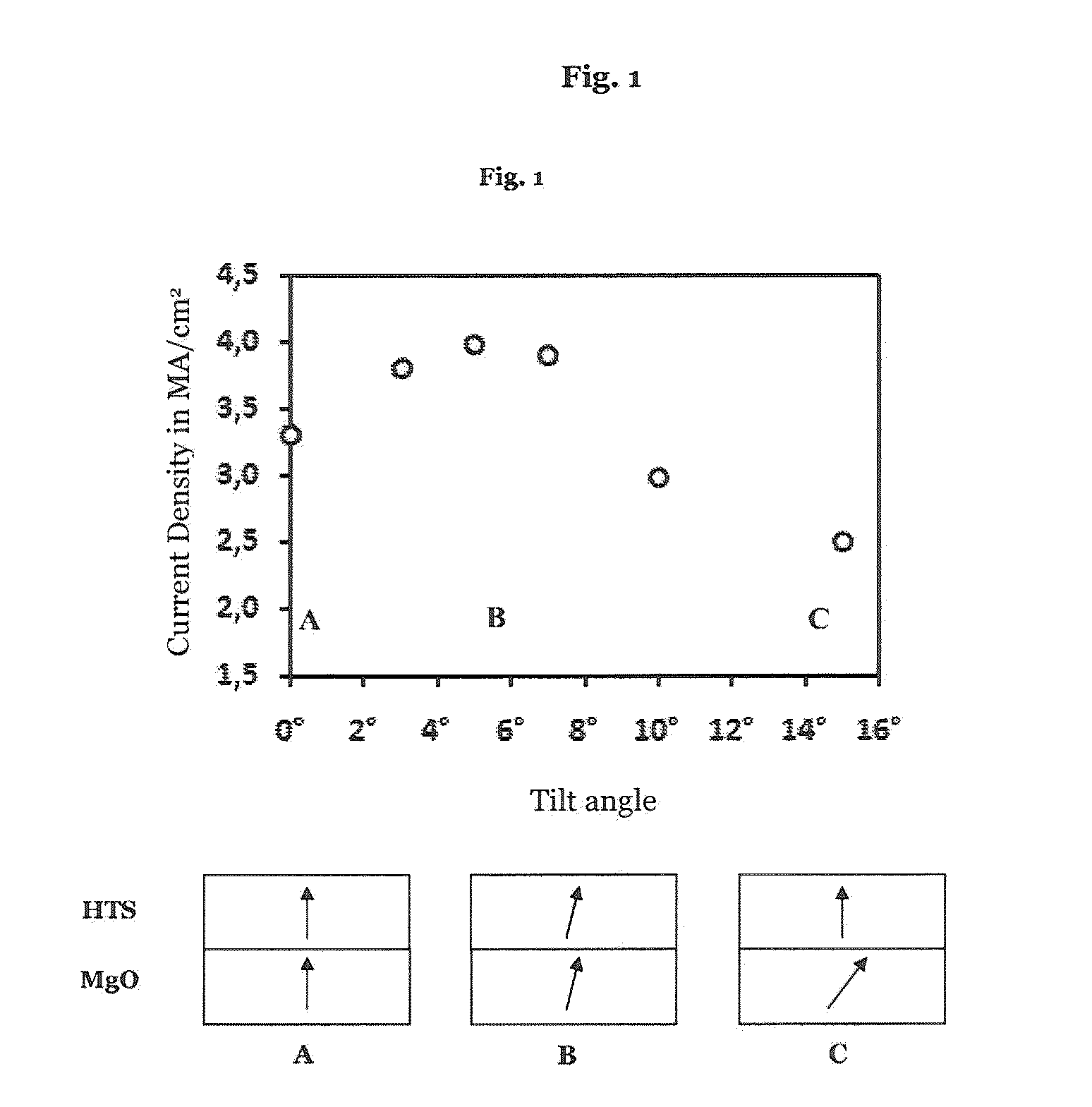
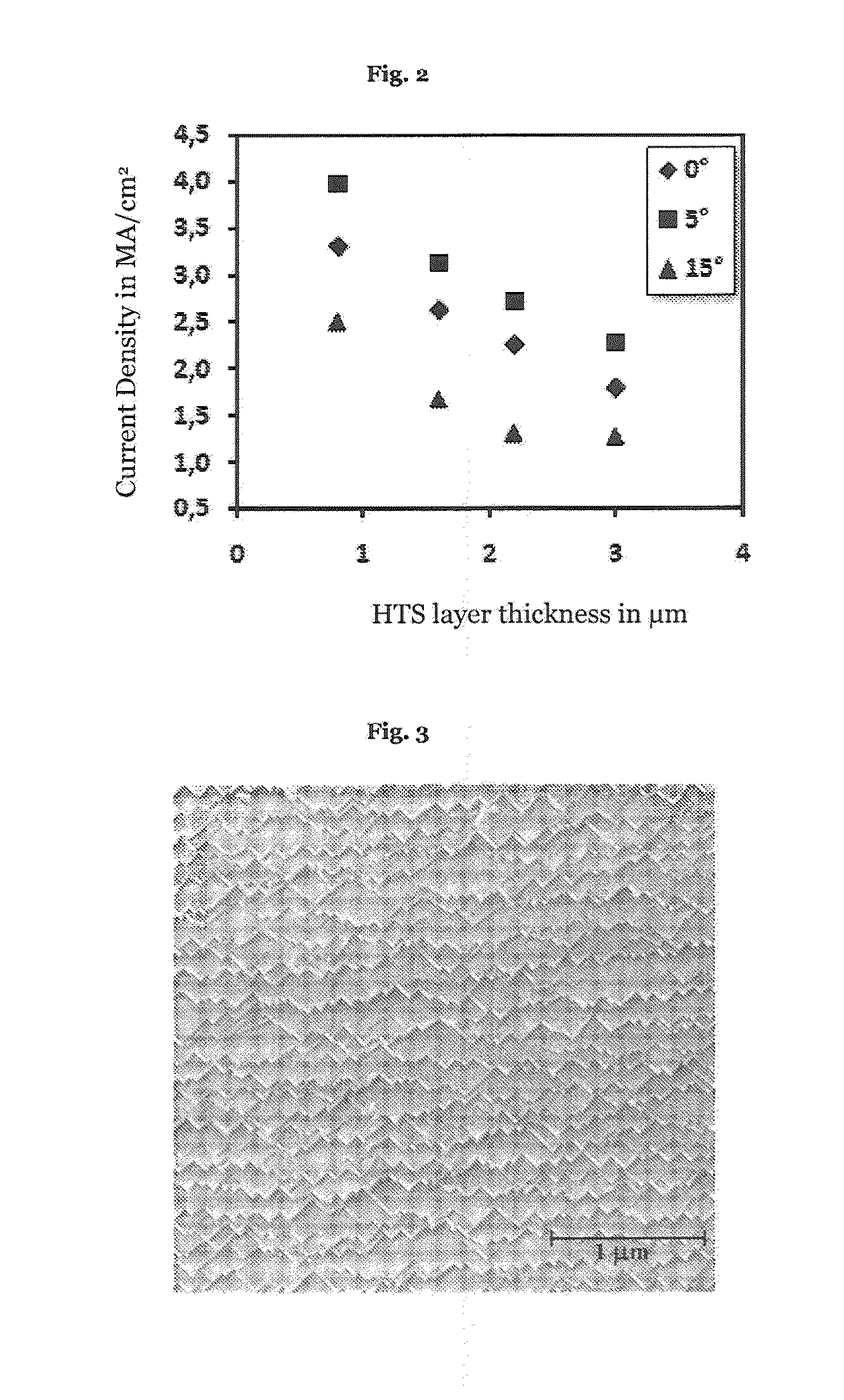
The invention relates to a high temperature superconducting tape conductor having a flexible metal substrate that comprises at least one intermediate layer disposed on the flexible metal substrate and comprising terraces on the side opposite the flexible metal substrate, wherein a mean width of the terraces is less than 1 μm and a mean height of the terraces is more than 20 nm, and that comprises at least one high temperature superconducting layer disposed on the intermediate layer, which is disposed on the at least one intermediate layer and comprises a layer thickness of more than 3 μm. The ampacity of the high temperature superconducting tape conductor relative to the conductor width is more than 600 A / cm at 77 K.
Owner:THEVA DUENNSCHICHTTECHN
Power transmission line current-carrying capacity boundary dynamic evaluation method
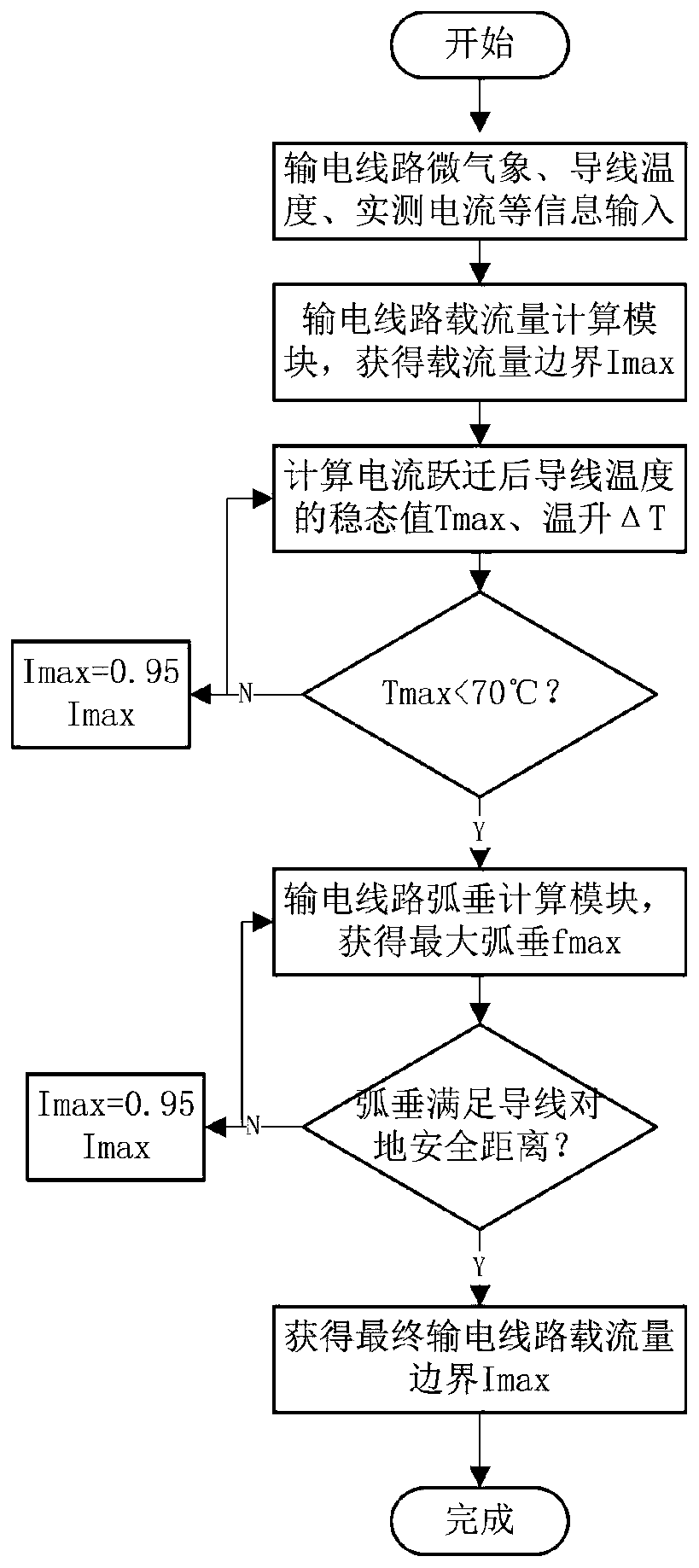
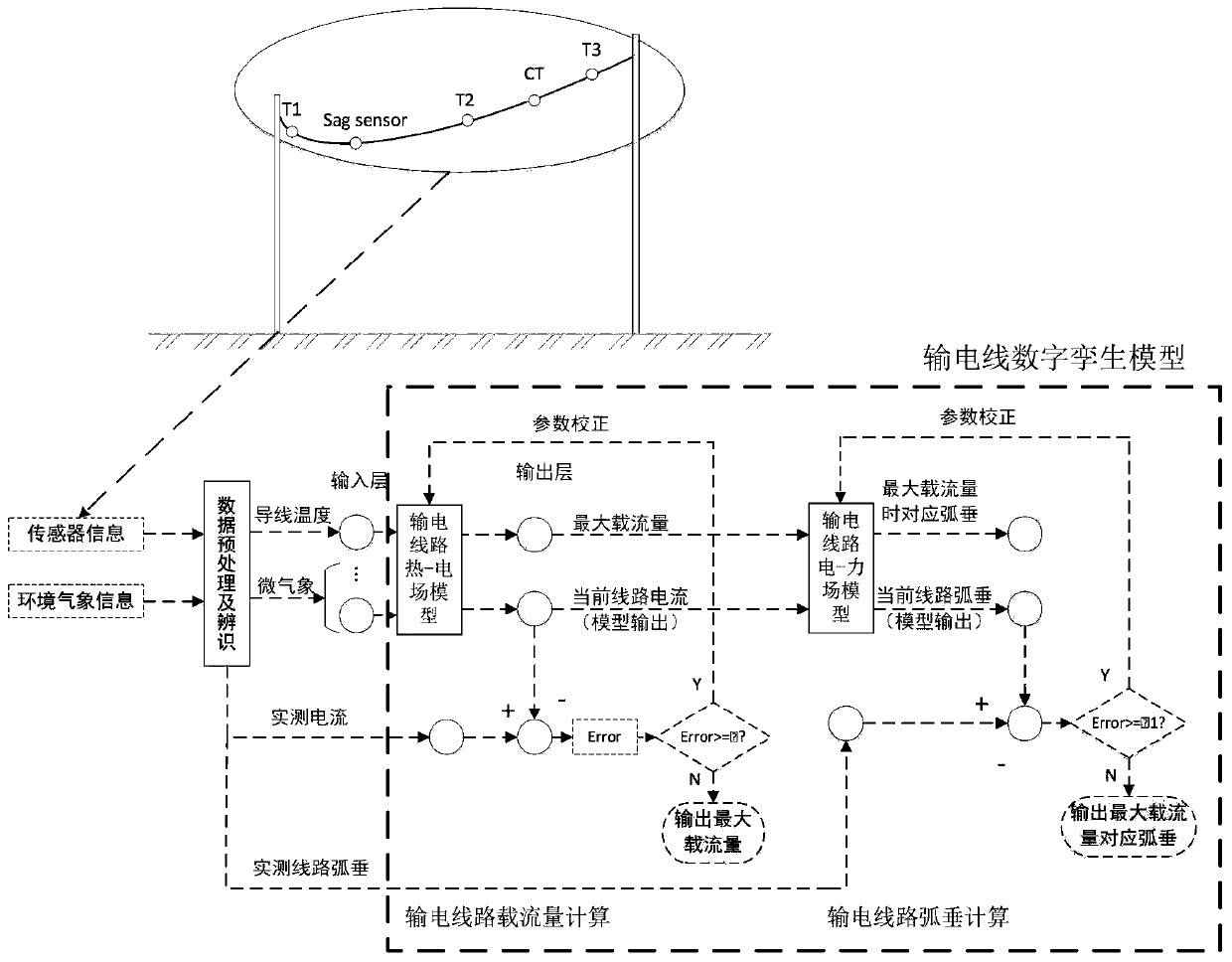
InactiveCN111398736AImprove forecast accuracyOvercoming the influence of output resultsFault location by conductor typesCurrent measurements onlyThermodynamicsAmpacity
The invention discloses a power transmission line current-carrying capacity boundary dynamic evaluation method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting sensor information and environmental meteorological information collected by a power transmission line into a power transmission line digital twinning model; (2) calculating a current-carrying capacity boundary; (3) calculating a steady-state value and a temperature rise value of the wire temperature after current transition; (4) judging whether the steady-state value of the conductor temperature exceeds a preset temperature value or not to determine whether the current-carrying capacity boundary needs to be reduced or not to recalculate the steady-state value of the conductor temperature, and outputting the reduced current-carrying capacity boundary as a reference; (5) calculating the maximum conductor sag corresponding to the maximum current-carrying capacity of the power transmission line; (6) judging whether the maximum conductor sag corresponding to the maximum current-carrying capacity of the power transmission line meets the requirement of the power transmission line for the safe distance to the ground; and (7) obtaining the final current-carrying capacity boundary of the power transmission line. On the premise of ensuring stable operation of the system and equipment safety, the credibility and accuracy oftransmission capacity evaluation of the power transmission line are improved.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD
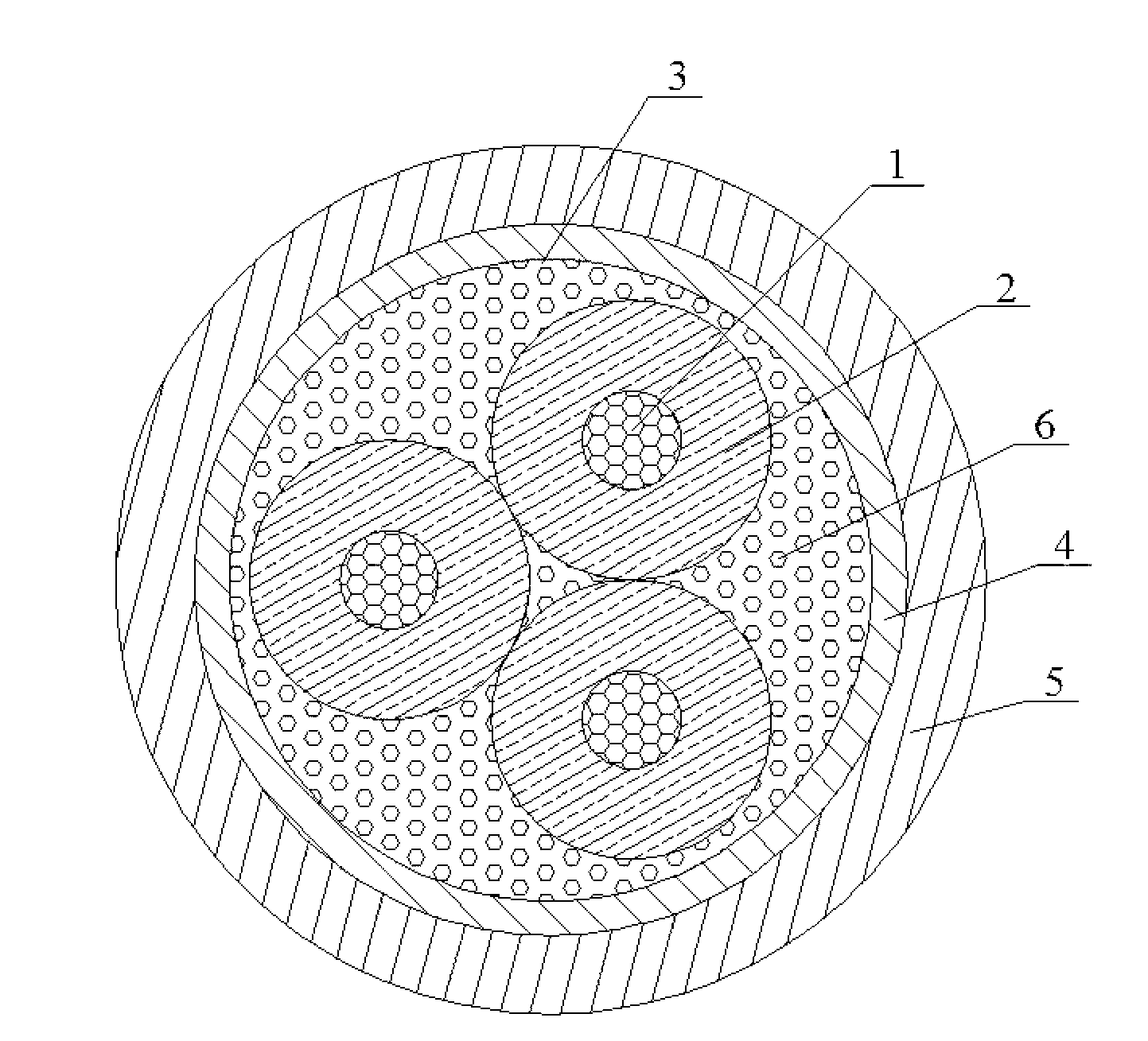
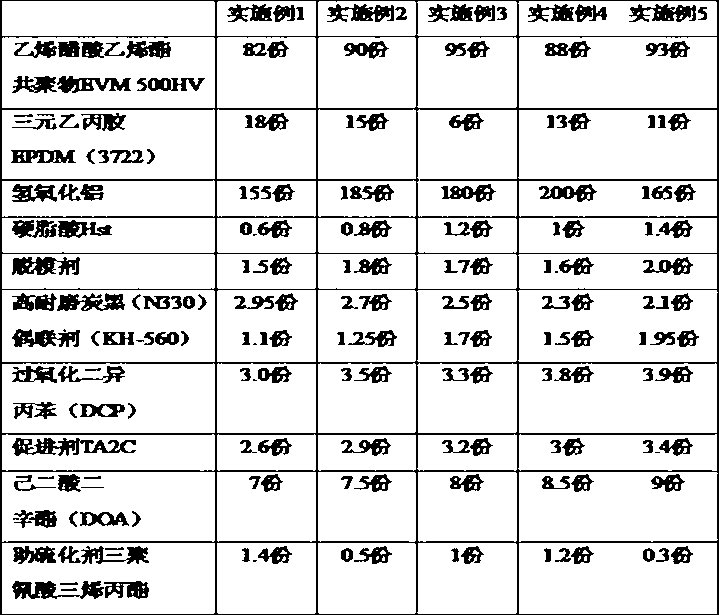
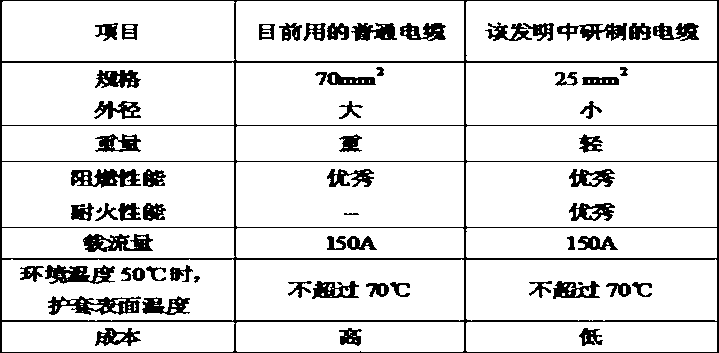
High current-carrying capacity low conduction temperature fire resistant cable for accident network analysis and preparation technology
ActiveCN103077775AReduce sizeFlame retardantPower cables including communication wiresInsulated cablesCopper conductorPolyolefin
The invention discloses a high current-carrying capacity low conduction temperature fire resistant cable for accident network analysis and a preparation technology. A ceramic composite belt is wrapped on the outer surface of a cable core; a high thermal resistance low smoke zero halogen polyolefin sheath layer is coated on the outer surface of the ceramic composite belt; and the high thermal resistance low smoke zero halogen polyolefin sheath layer comprises the following components in parts by weight: 80 to 100 parts of ethylvinylacetate, 5 to 20 parts of ethylene-propylene diene copolymer EPDM, 150 to 200 parts of aluminium hydroxide, 0.5 to 1.5 parts of stearic acid Hst, 1.5 to 2.0 parts of release agent, 2.0 to 3.0 parts of high abrasion carbon black, 1.0 to 2.0 parts of coupling agent, 3.0 to 4.0 parts of dicumyl peroxide, 2.5 to 3.5 parts of accelerating agent TA2C, 7 to 9 parts of dioctyl adipate, and 0.3 to 1.4 parts of auxiliary curing agent cyanuric acid triallyl ester. The cable can reduce the diameter of a copper conductor, and lock a great amount of heat produced by the copper conductor in the cable core, thereby ensuring that the surface temperature of the sheath layer is not over 70 DEG C.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGTONG POWER CABLE
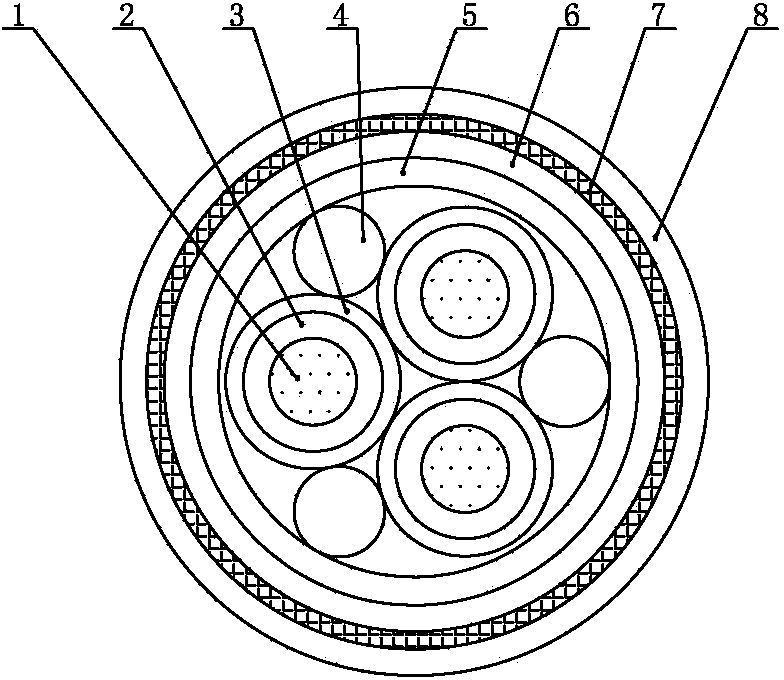
Ship and warship protection cable high in current carrying capacity and low in surface temperature rise and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN103489525AReduce the temperatureIncrease ampacityRubber insulatorsPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsCross-linkCopper conductor
The invention relates to a ship and warship protection cable high in current carrying capacity and low in surface temperature rise and a manufacture method thereof. A flame-retardant fire-resistant insulating layer high in thermal resistivity evenly wraps a stranded copper conductor in an extruding mode. A filament glass fiber woven reinforcing layer wraps the flame-retardant fire-resistant insulating layer high in thermal resistivity so as to form an electric cable insulating wire core. A plurality of electric cable insulating wire cores are mutually stranded to form an electric cable core. Flame-retardant fire-resistant padding high in thermal resistivity is filled into clearance between the electric cable insulating wire cores so as to enable the cable core to be round and neat. A flame-retardant fire-resistant longitudinal wrapping band high in thermal resistivity wraps the electric cable core. A chemical cross-linked polyolefin inner protection sleeve high in thermal resistivity wraps the flame-retardant fire-resistant longitudinal wrapping band high in thermal resistivity in an extruding mode. An armoured braid layer wraps the inner protection sleeve. A chemical cross-linked polyolefin outer protection sleeve high in thermal resistivity wraps the armoured braid layer. The high protection cable can reduce the temperature of the outer wall of cables, and can be improved in current-carrying capacity on the condition that section areas of conductors are the same.
Owner:江苏远桥电气科技有限公司
Method for reducing heating of electric joint and copper bars adopting method
ActiveCN105226478ACoupling device connectionsLine/current collector detailsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention relates to a method for reducing heating of an electric joint, and copper bars adopting the method for reducing the heating of the electric joint. Serial connection of contact resistors of conductors of the electric joint is changed into parallel connection, and a single-face feed connection mode is changed into a double-face or multi-face feed connection mode, so a current density of each contact face is reduced, and the object of heating reduction is achieved. On the basis that the current-carrying capacity of the cross section of each conductor is guaranteed, a busbar connection piece adopts a thin copper plate folded, bent and flattened structural piece, a change for adaption of the fact that an electric element is connected to a copper bars structural piece is comprised, transition plates and backing plates are increased, copper materials are saved, good heat radiation performance is also possessed, and certain practical value especially in frequency converter structure thermal design is possessed.
Owner:CHENGDU SHENLAN HIGH TECH DEV
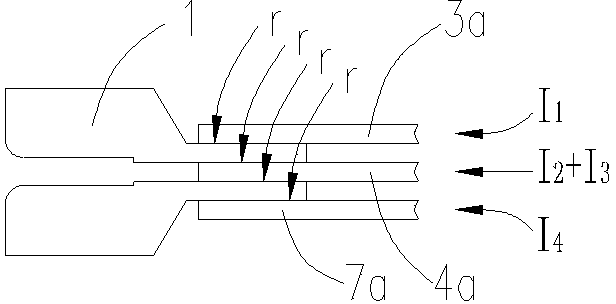
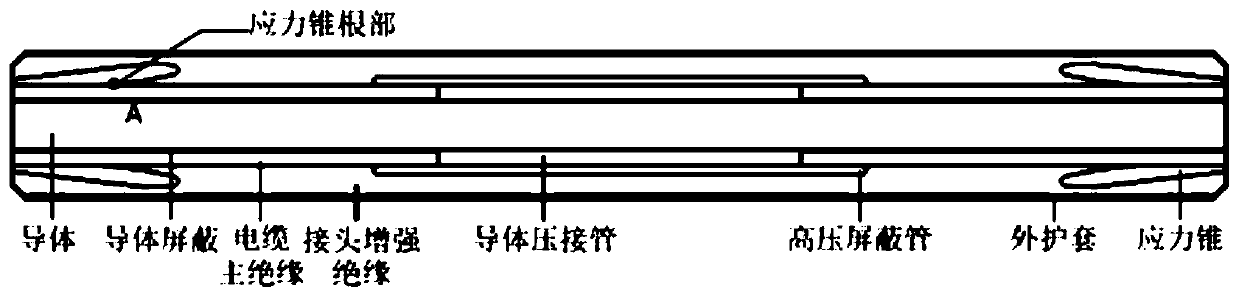
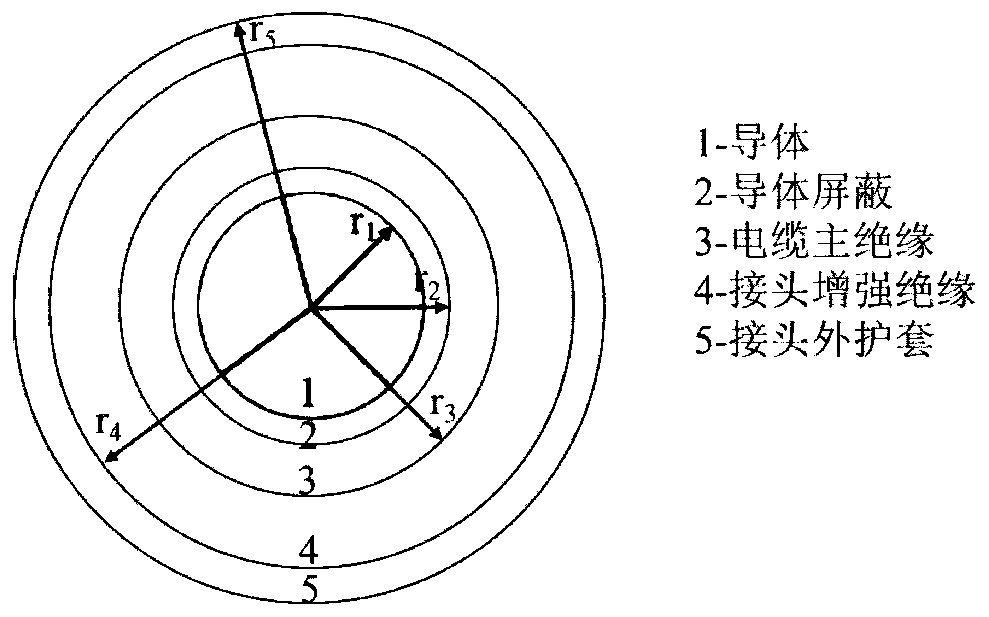
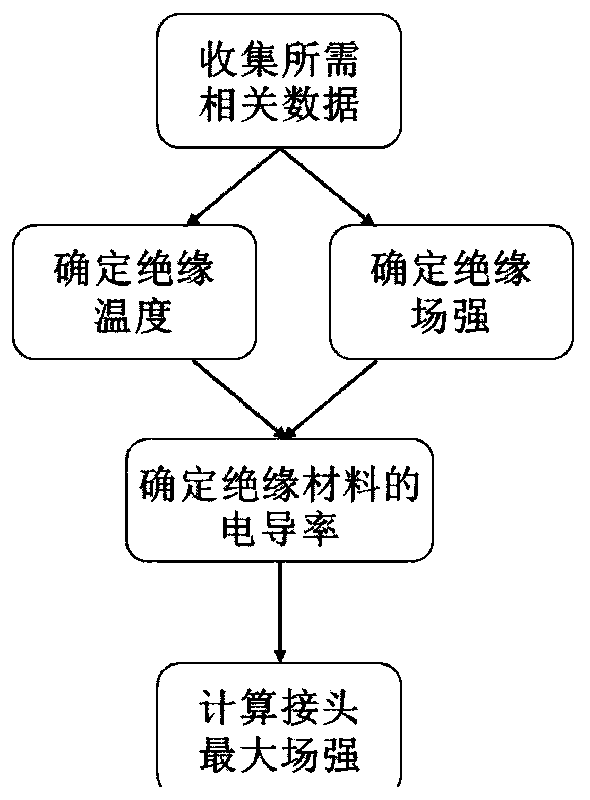
Method for determining maximum field intensity of intermediate joint for medium-low-voltage direct-current XLPE cable
ActiveCN111324975ACalculation method is simpleReduce data volumeDesign optimisation/simulationPower gridAmpacity
The invention discloses a method for determining the maximum field intensity of an intermediate joint for a medium-low-voltage direct-current XLPE cable. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting the structure and operating parameters of the joint; determining characteristic parameters in a relational expression that the conductivity of the main insulation material and the joint reinforced insulation material of the used cable changes along with the temperature and the field intensity through a direct current conductivity test; then calculating the temperature and the fieldintensity of the main insulation part of the cable and the enhanced insulation part of the joint so as to determine the conductivity of the two insulation materials, and finally solving the maximum field intensity value in the joint; according to the method, complex simulation modeling is avoided, and the calculation time is saved; conductivity characteristic parameters are easy to obtain; a powerful reference is provided for determination of current-carrying capacity and operation voltage in engineering of transforming an XLPE cable line from alternating current to direct current, and the method has important significance for enhancing safety and reliability of a power grid.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
High capacity rectangular flexible cable and preparation technology thereof
InactiveCN102063957AIncrease capacityHigh tensile strengthNon-insulated conductorsFlexible cablesCarrying capacityElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a high capacity rectangular flexible cable and a preparation technology thereof. The preparation technology of the high capacity rectangular flexible cable is characterized in that the lamination copper bar is superposed with 2 layers or more than 2 layers copper bar, and carrys out by adopting approximate common round cable pay-off equipment to pay-off, a conductor outer layer formed by the lamination copper bar is an insulating layer, the insulating layer is extruded by a cable extrusion machine with a rectangular extruding mold, and the cross section of the high capacity rectangular flexible cable is rectangular or approximately rectangular. The high capacity rectangular flexible cable has the advantages that the capacity is higher, and the current carrying capacity is larger: the cross section of the cable is rectangular, if the cross section is same, the rectangular cable has larger electric current than that of the round cable; the bending radius is smaller: the bending radius is smaller than that of the round cable with the same cross section; the high capacity rectangular flexible cable is convenient to install: manual installation requires smaller space, and special equipment is not required in installation; the high capacity rectangular flexible cable is more convenient to connect, a terminal is not required to install, and installation time is saved; and the tensile strength is extremely high: because the rectangular cable conductor uses the copper bar, and the strain distribution on the width of the cable is uniform.
Owner:NANJING QUANXIN CABLE TECH
Vessel high-carrying-capacity low-surface-temperature-rise power cable and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103474158AReduce the temperatureIncrease ampacityInsulated cablesPower cablesGlass fiberCopper conductor
The invention relates to a vessel high-carrying-capacity low-surface-temperature-rise power cable and a manufacturing method thereof. A high-thermal-resistance-coefficient inflaming retarding fire-resistant insulating layer evenly wraps the periphery of a twisted copper conductor in a squeezing mode, a filament glass fiber woven reinforcement layer wraps the periphery of the high-thermal-resistance-coefficient inflaming retarding fire-resistant insulating layer to form power cable insulating cable cores, the power cable insulating cable cores are mutually twisted to form a power cable core, and gaps among the power cable insulating cable cores are filled with high-thermal-resistance-coefficient inflaming retarding fire-resistant filling cores so that the cable core can be rounded off. A high-thermal-resistance-coefficient inflaming retarding fire-resistant longitudinal wrapping belt wraps the periphery of the power cable core, and at last, a high-thermal-resistance-coefficient chemical crosslinking polyolefin outer sheath wraps the periphery of the high-thermal-resistance-coefficient inflaming retarding fire-resistant longitudinal wrapping belt in a squeezing mode. According to the power cable, the temperature of the outer wall of the power cable can be reduced, and the carrying capacity can be improved under the condition that the cross sections of conductors are the same.
Owner:山东大河机械制造股份有限公司
Calculation method and system for obtaining current-carrying capacity critical environment temperature of direct-current cable
PendingCN109858100AImprove work efficiencyIncreased level of controlSpecial data processing applicationsInsulation layerElectric power system
The invention discloses a calculation method and system for obtaining the critical environment temperature of the current-carrying capacity of a direct-current cable, and belongs to the technical field of power systems. The method comprises: acquiring direct-current cable insulation material parameters, performing function fitting on the direct-current cable insulation material parameters, and generating a conductivity numerical model; obtaining the equivalent conductivity of the DC cable insulation material, the intermediate point electric field value and the temperature value of the DC cableinsulation material insulation layer and the leakage current of the DC cable insulation material insulation layer according to the conductivity numerical model, and determining the electric field distribution of the DC cable insulation material insulation layer; when it is determined that the electric field in the insulating layer of the insulating material is maximum, the outer-layer temperatureand the maximum temperature gradient of the insulating material of the direct-current cable are obtained; and obtaining an environment temperature relational expression according to the maximum temperature gradient, and calculating the critical environment temperature of the direct current cable by combining a thermal circuit model between the current-carrying capacity and the wire core temperature. Under different environment temperatures, the maximum temperature gradient and the environment temperature critical value of the current-carrying capacity of the cable are controlled through the wire core temperature.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Preparation method of energy-saving overhead wire
InactiveCN103788782AImprove delivery capacityIncrease ampacityCable/conductor manufactureReflecting/signal paintsEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention provides a preparation method of an energy-saving overhead wire. The preparation method provided by the invention enhances the surface heat scattering coefficient and reduces the heat absorption coefficient by coating a coating on the basis of a common steel-cored aluminum strand wire, thereby increasing the current capacity of the common steel-cored aluminum strand wire without increasing the temperature of the common steel-cored aluminum strand wire.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
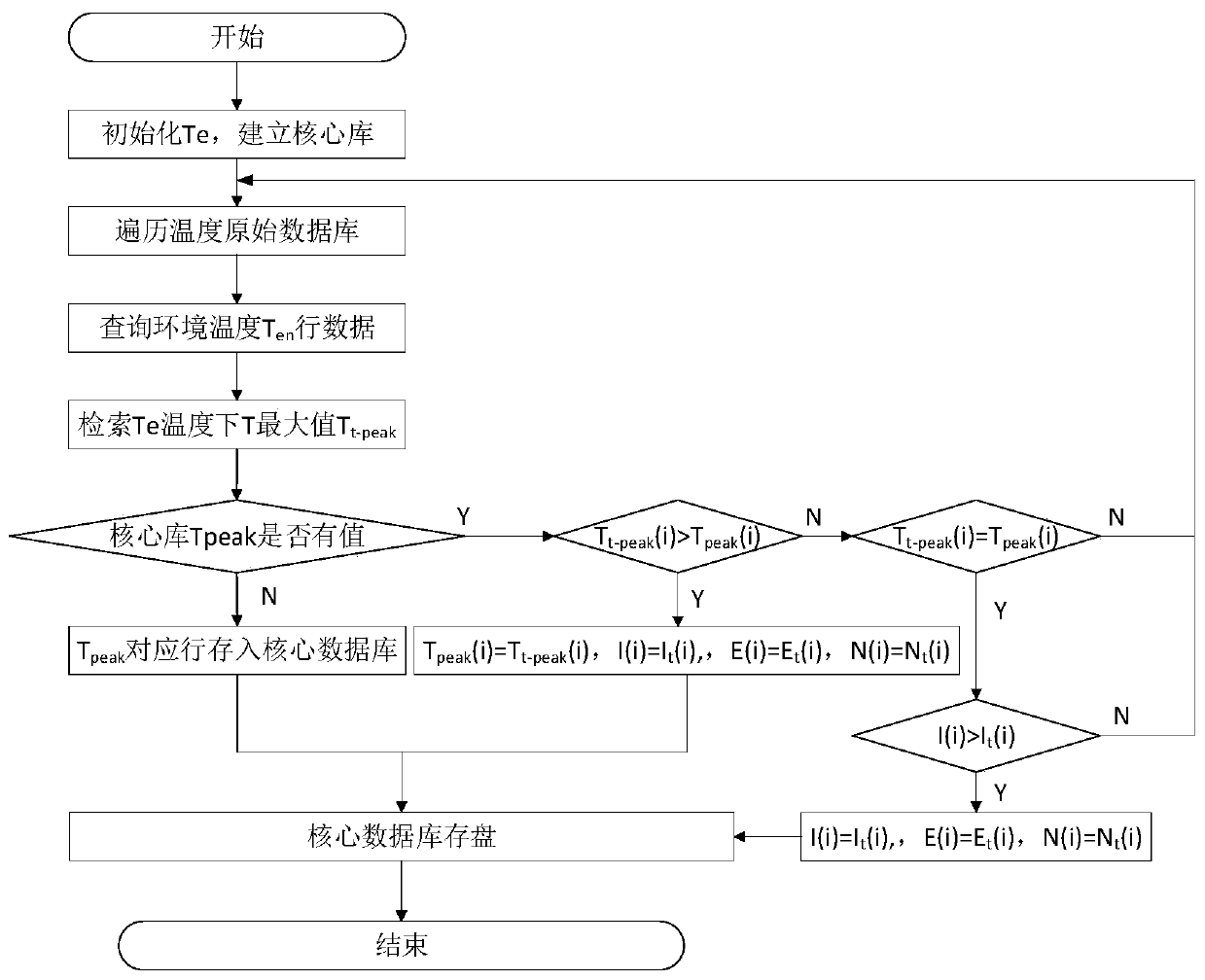
Management method for intelligent cable state online measurement and control
ActiveCN110108983ARealize dynamic capacity expansionGuaranteed uptimeFault location by conductor typesFull life cycleEngineering
The invention relates to a management method of intelligent cable state online measurement and control. The management method comprises the following steps that S1, cable temperature data are obtained, state monitoring and control in real time are conducted, and an original temperature database is established; S2, ampacity adjustable and controlling logic is started off, the utilization rate of ampacity is analyzed, and dynamic capacity increasing is obtained; S3, the cable fault location analysis is conducted and an early warning is carried out; and S4 a life cycle of a cable is analyzed anda conclusion is obtained. The invention has the advantages that cable fault early warning, testing, location and navigation are obtained, dynamic capacity control is operated, full life cycle aging states are evaluated, and management and maintenance guidance functions are operated by a cable system.
Owner:深圳市壹电电力技术有限公司
Novel structure cable and manufacturing method
InactiveCN104200910AEasy to prepareEasy to masterInsulated cablesPower cablesIsolation layerMaterial consumption
The invention belongs to the technical field of power and cables and particularly relates to a novel structure cable. The novel structure cable comprises a conductor, an isolation layer and a sheath layer and is characterized in that multiple filling strips are arranged on the outside of the conductor, gaps are reserved among adjacent filling strips, the filling strips are wrapped by the isolation layer, and the sheath layer is extruded and wrapped on the isolation layer. The filling strips adhere to the surface of the conductor. The invention further discloses a manufacturing method of the novel structure cable. The novel structure cable has the main following advantages that under the condition of the same current carrying capacity, the outer diameter is smaller, material consumption is lower, and the price is lower; the heat radiating performance of the cable is excellent; the manufacturing method is simple and easy to master.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
Copper bar current-carrying capacity testing device and testing method
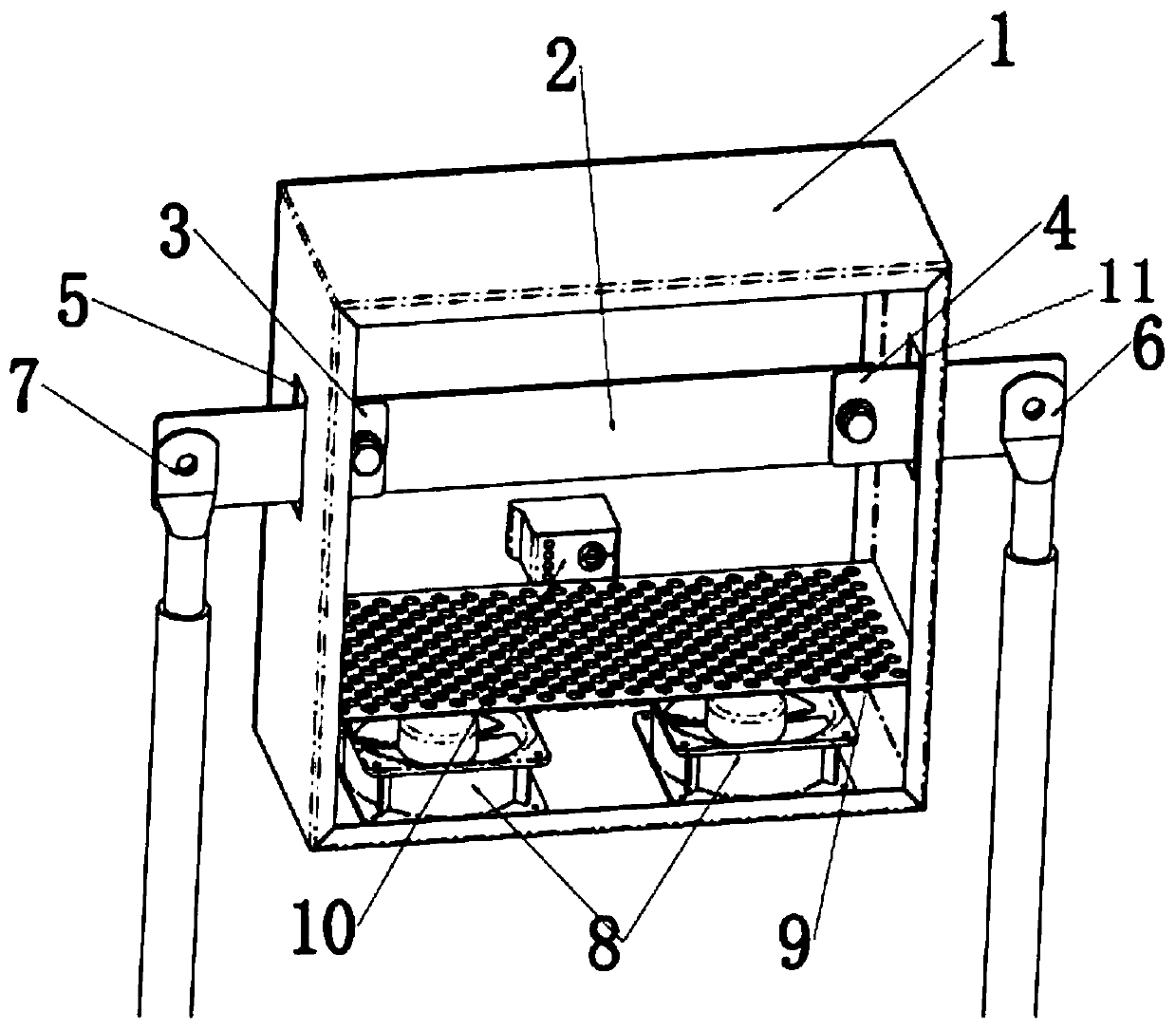
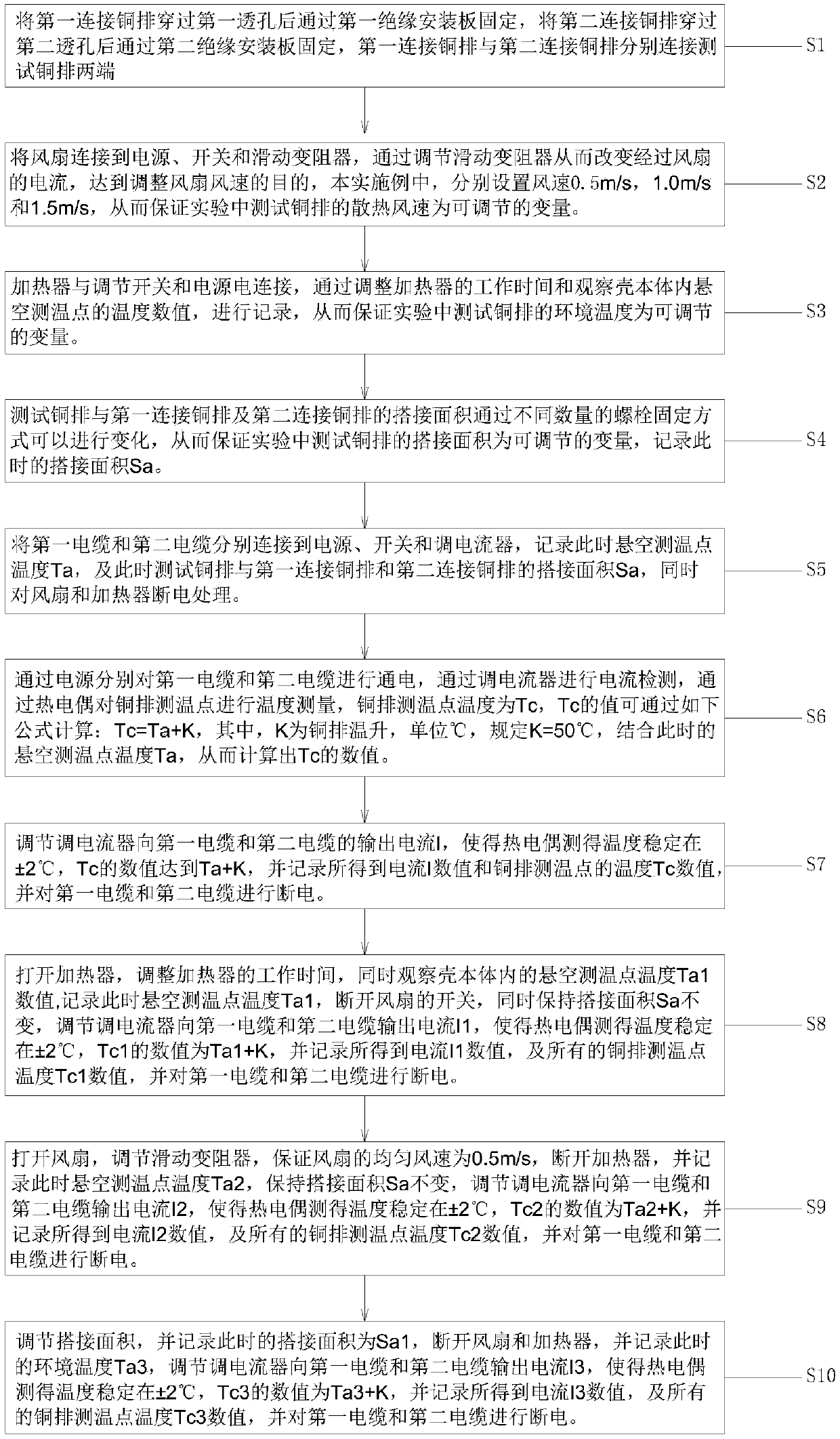
PendingCN110907737AAdjustable environmental factorsAccurate measurementEnvironmental/reliability testsStructural engineeringAmpacity
The invention provides a copper bar current-carrying capacity testing device including a shell body, a first through hole and a second through hole are respectively formed in opposite sides of the shell body; a first connecting copper bar is arranged in the first through hole; a second connecting copper bar is arranged in the second through hole; a test copper bar is arranged in the shell body, two ends of the test copper bar are respectively connected with one end of a first connecting copper bar and one end of a second connecting copper bar, the other end of the first connecting copper bar is connected with a first cable, the other end of the second connecting copper bar is connected with a second cable, and a plurality of temperature measuring points, a heater and a fan are arranged atthe bottom of the test copper bar. The device is simple in structure, convenient to operate and low in production cost, the test cost can be effectively reduced, the environmental factors of the copper bar can be adjusted, multiple groups of numerical values can be measured, and the copper bar current-carrying capacity measurement result is accurate. In actual use, waste caused by too large copperbar specification selection or risks caused by too small copper bar specification selection are reduced, and the product quality is improved.
Owner:RENERGY ELECTRIC TIANJIN
High-flame-retardant, long-service-life and high-load low-smoke halogen-free building cloth wire and preparing technology
ActiveCN106024169AImprove overall lifespanLow Smoke GuaranteeClimate change adaptationInsulated cablesCopper conductorCross-link
The invention discloses a high-flame-retardant, long-service-life and high-load low-smoke halogen-free building cloth wire and a preparing technology. The high-flame-retardant, long-service-life and high-load low-smoke halogen-free building cloth wire comprises a copper conductor layer, conductor winding layers, a semiconducting medium coating, an inner insulating layer and an outer insulating layer. The outer side of the single copper conductor is coated with the multiple conductor winding layers formed by winding thin copper wires, the inner insulating layer is arranged on the outer sides of the conductor winding layers, gaps between the conductor winding layers and the inner insulating layer are filled with the semiconducting medium coating, and the outer insulating layer is fixedly arranged on the outer surface of the inner insulating layer. The current-carrying capacity of a cable conductor is increased through the composite conductor formed by the single core, the winding structure and the semiconducting medium coating. EVA and PE serve as base materials, corresponding-component assistants are added, an irradiation-cross-linking polyolefin material is modified, extrusion processing and irradiation are carried out, and the cloth wire cable has the long service life, the high flame resistance and the high cold resistance accordingly. The whole cable is completely designed through the low-smoke halogen-free system, the good fire-resistant effect and the good flame-retardant effect are achieved accordingly, toxic gas can not be generated, and harm to the human body is avoided under the fire condition.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN TECH IND WIRE&CABLE SYST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com