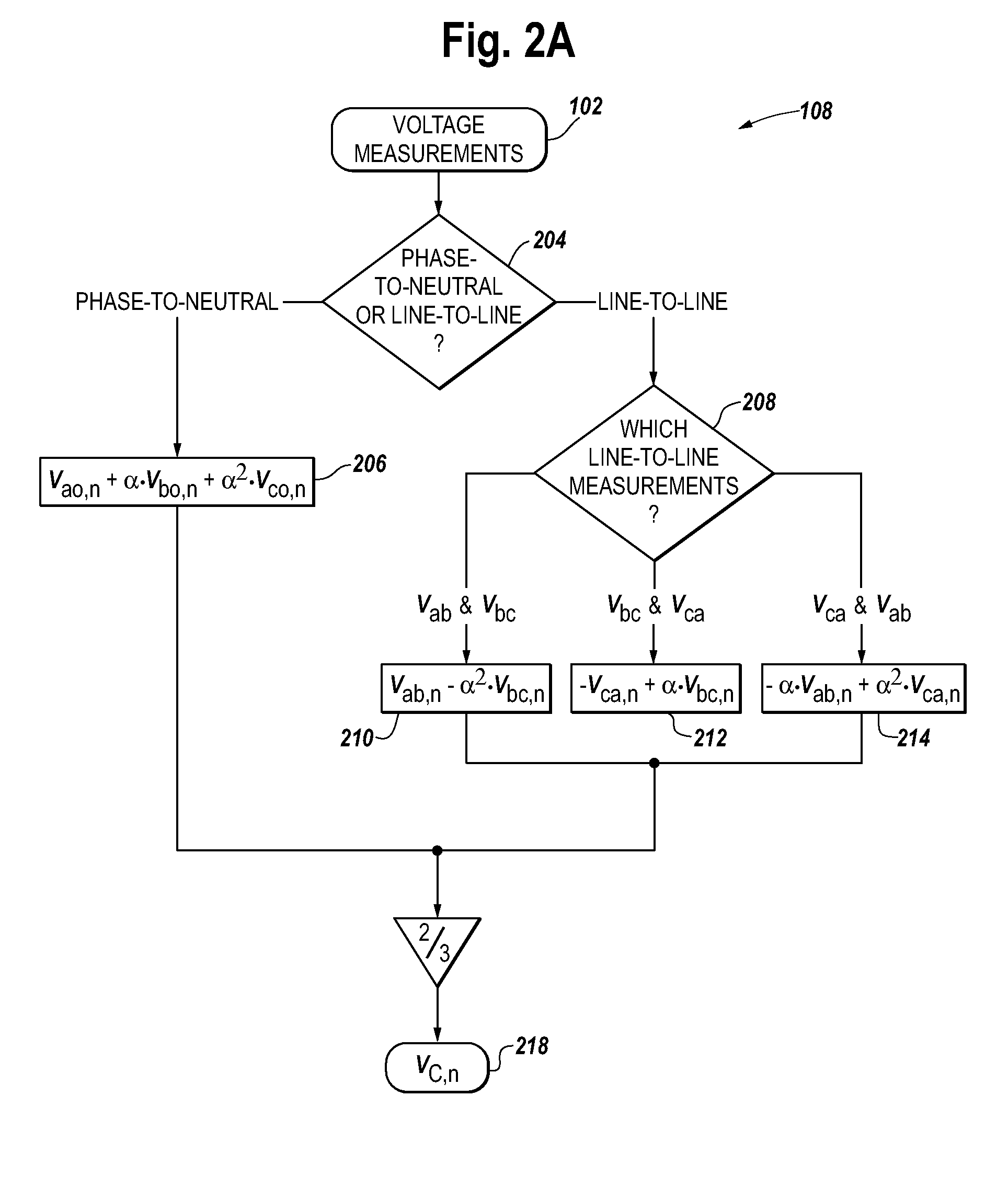
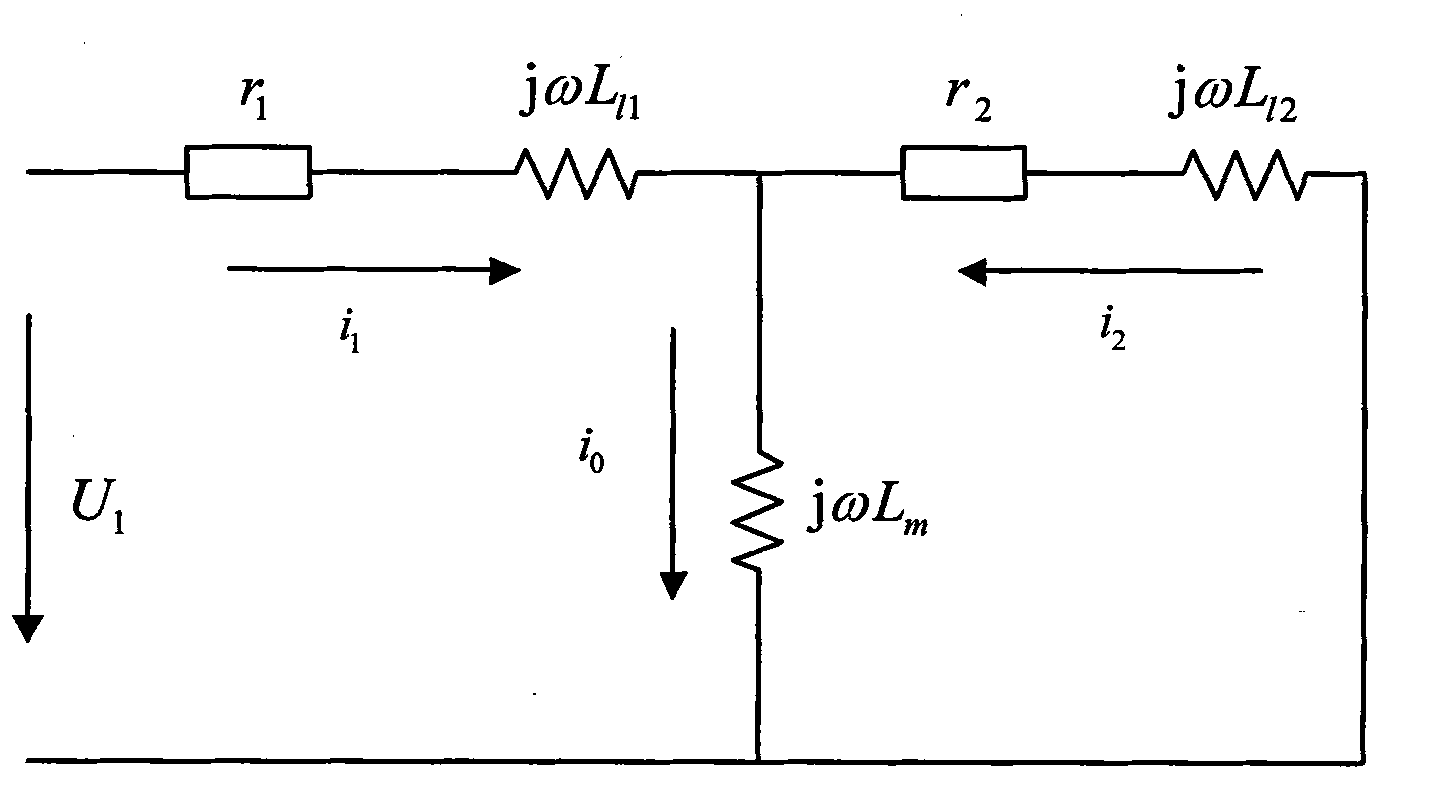
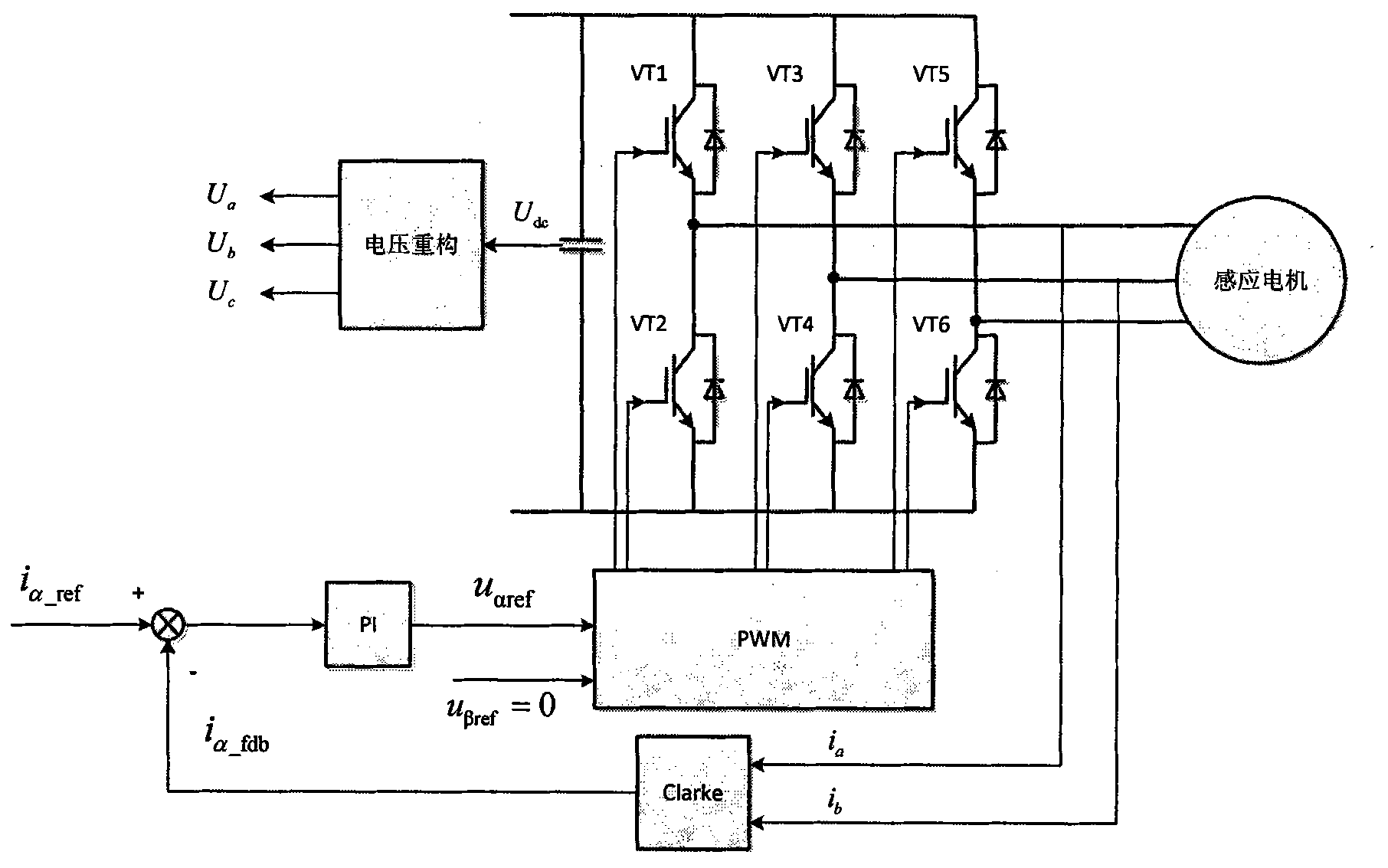
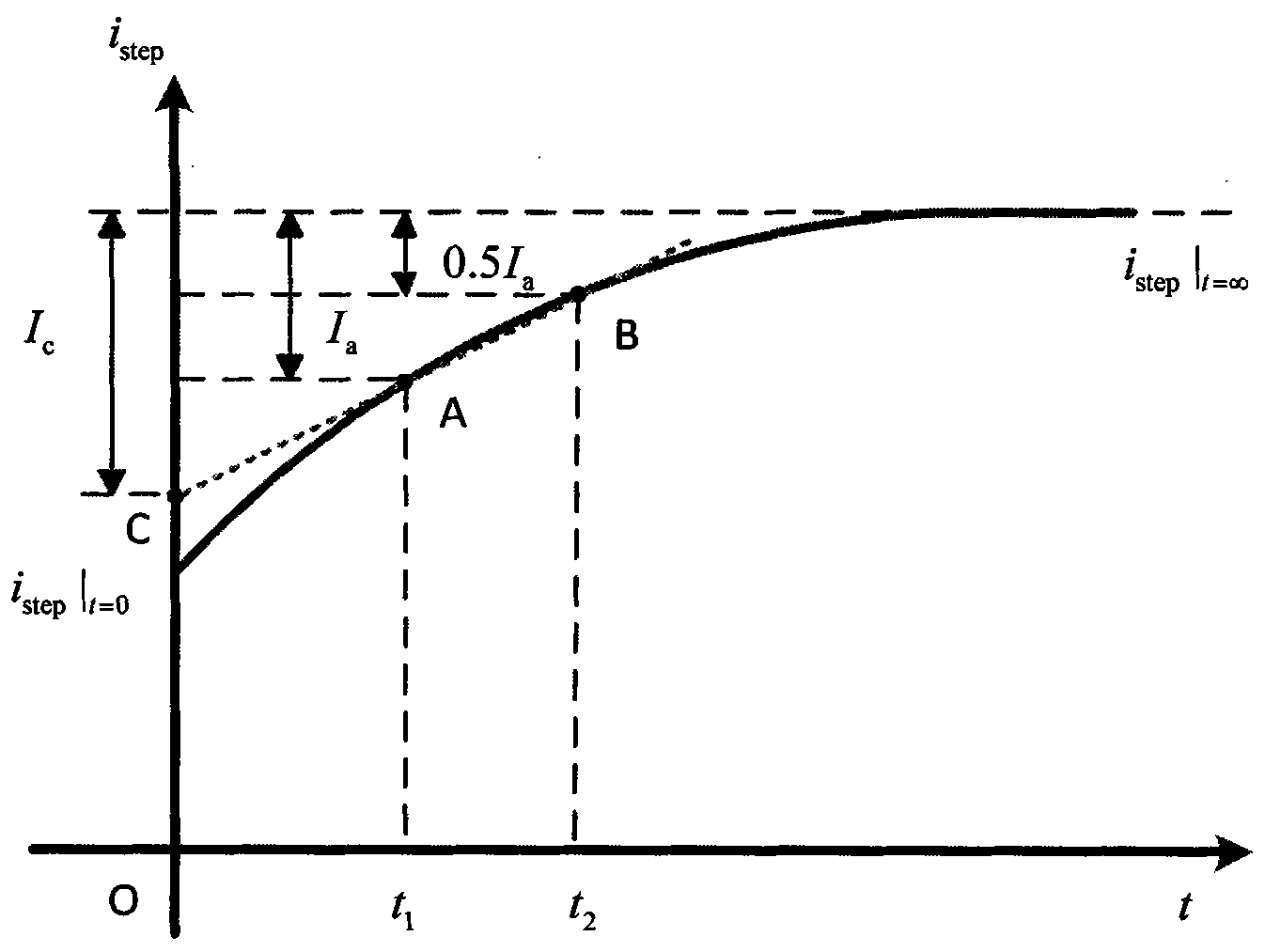
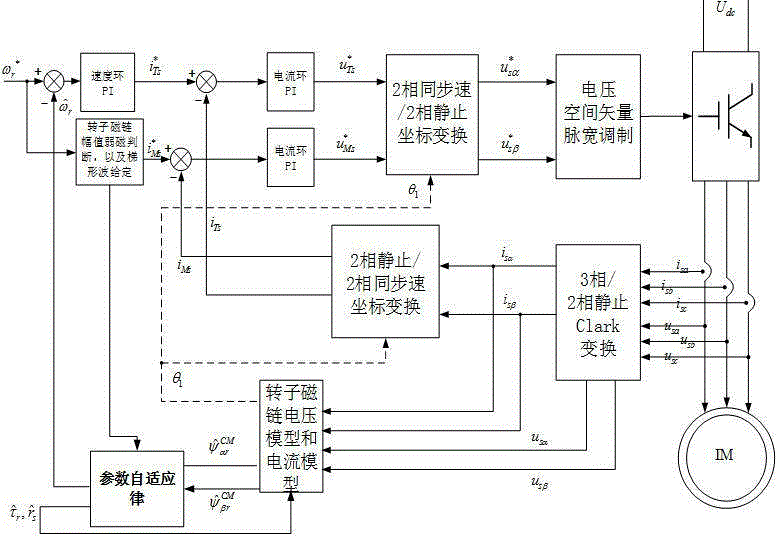
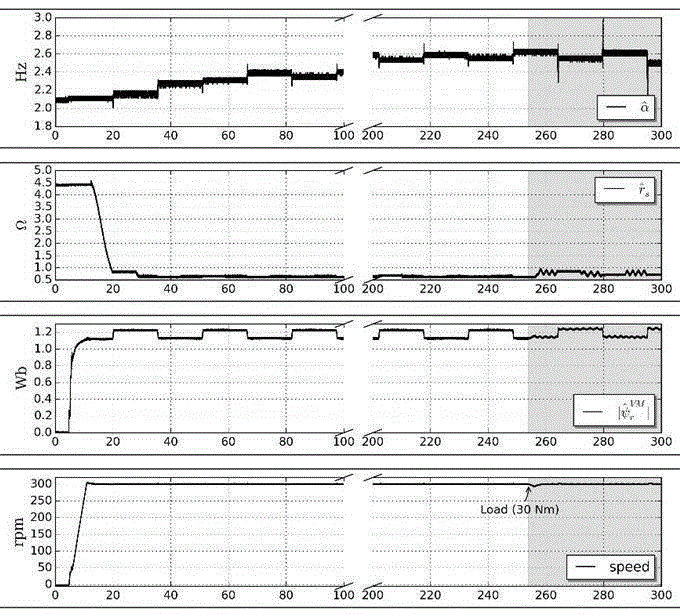
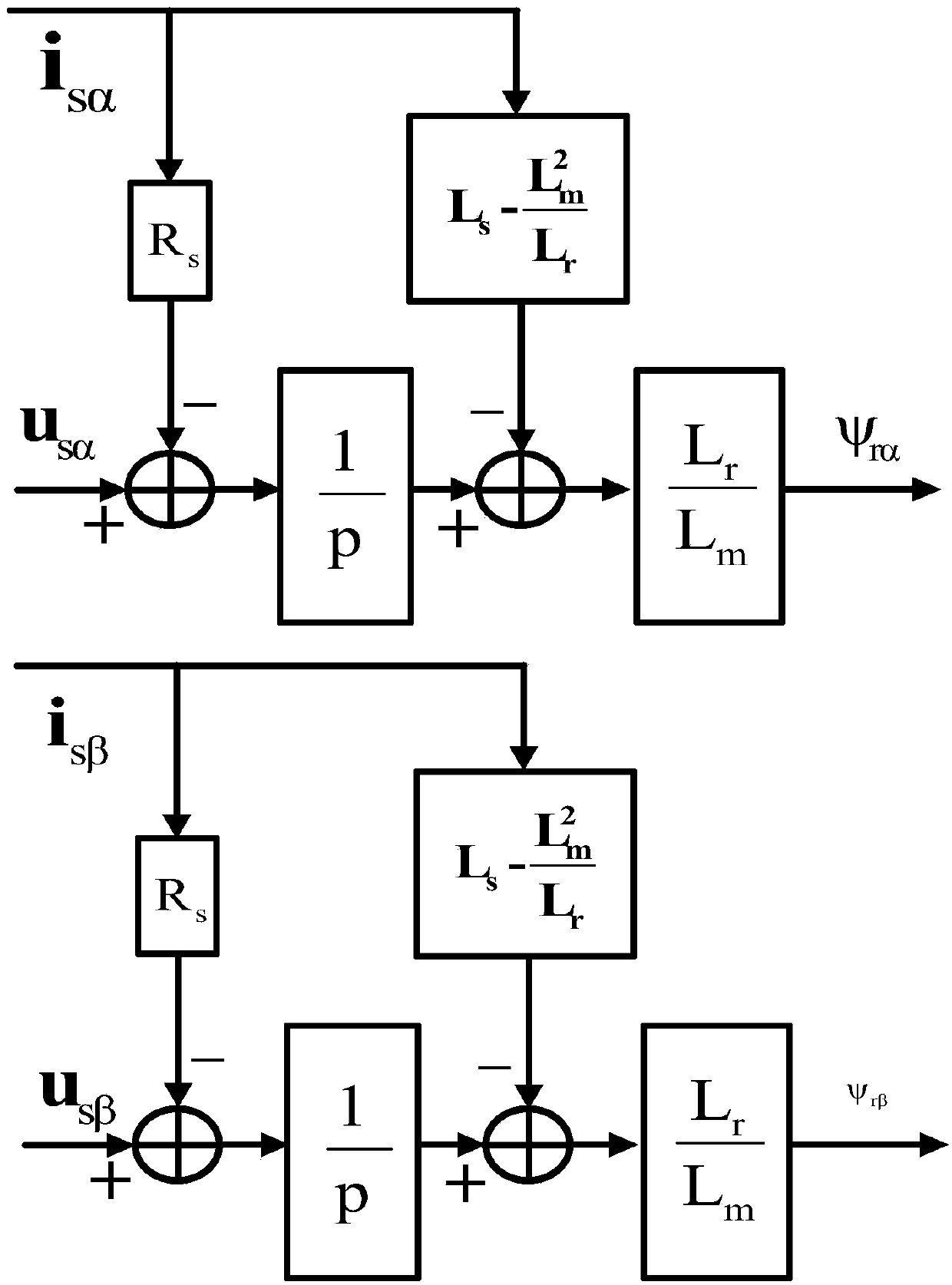
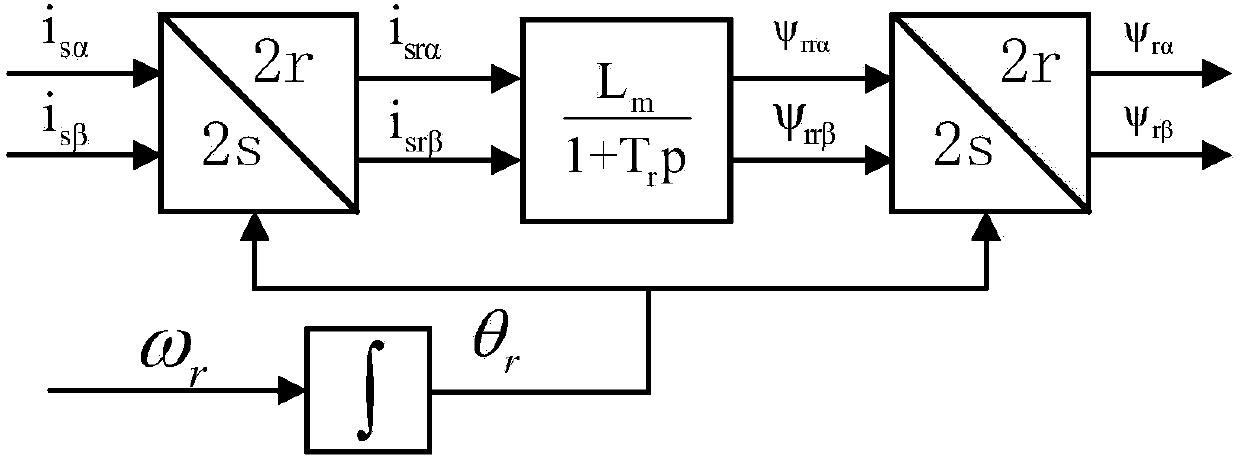
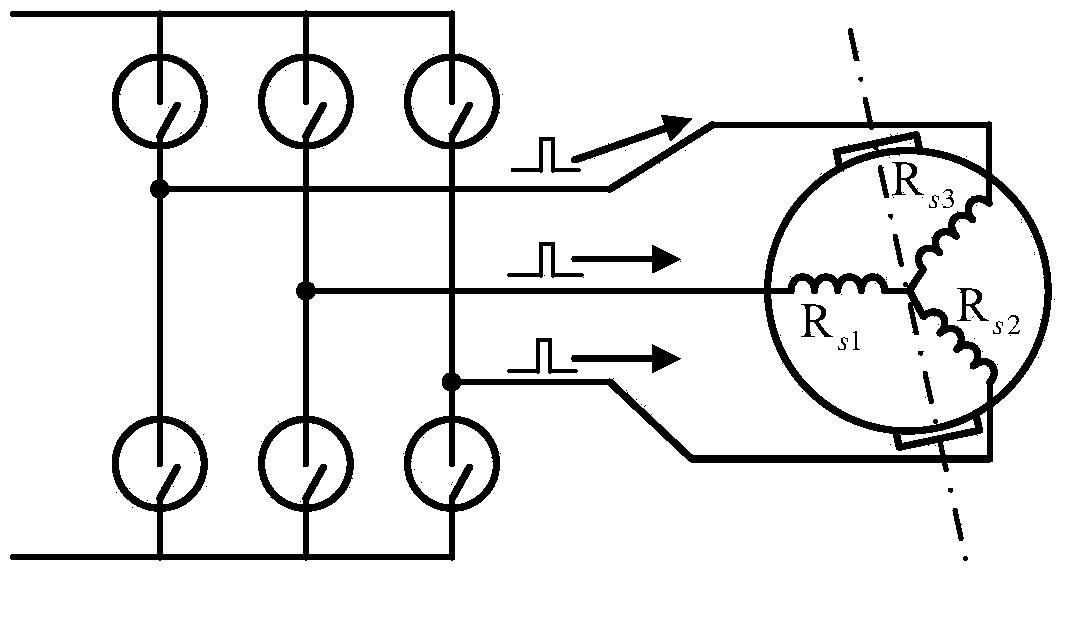
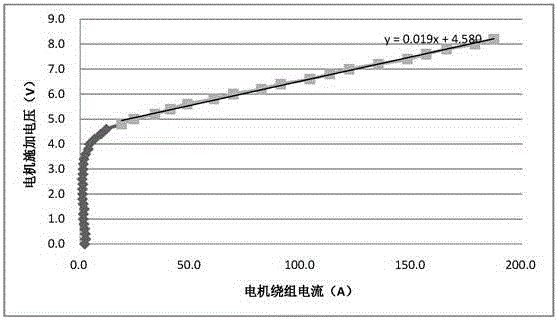
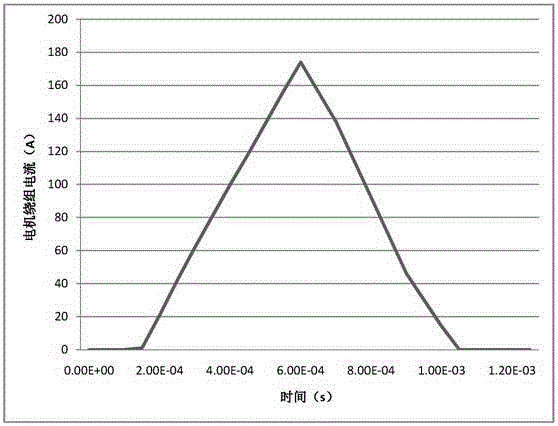
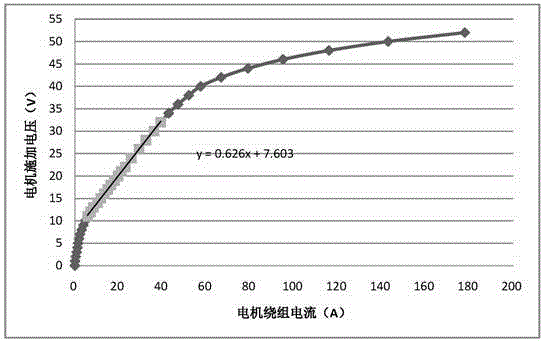
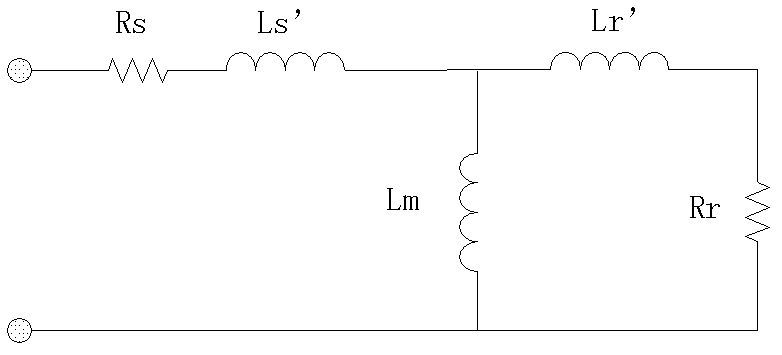
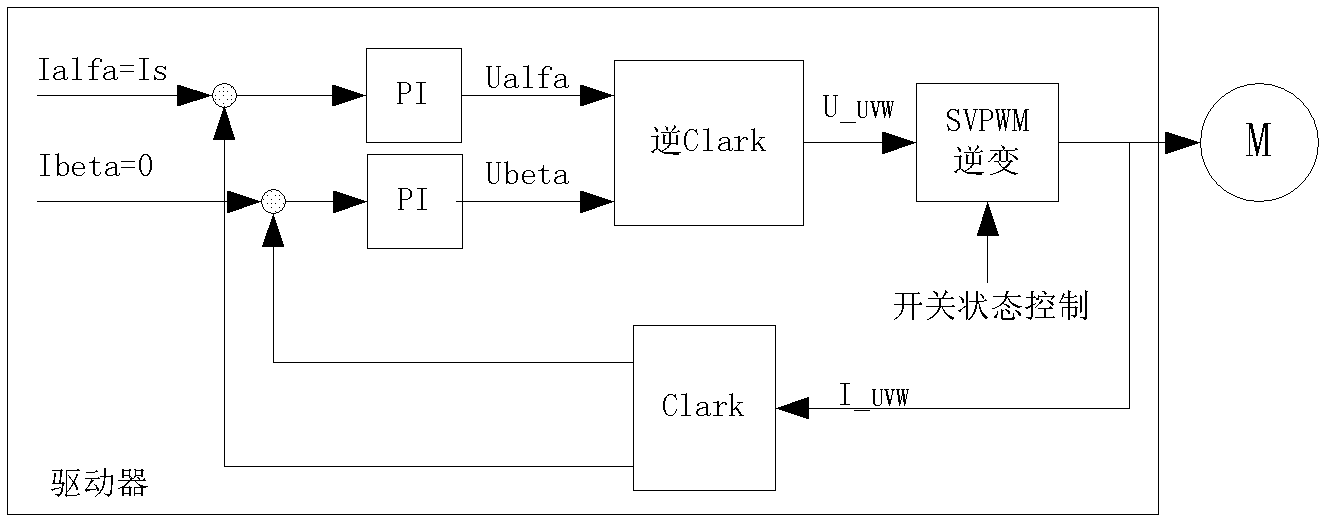
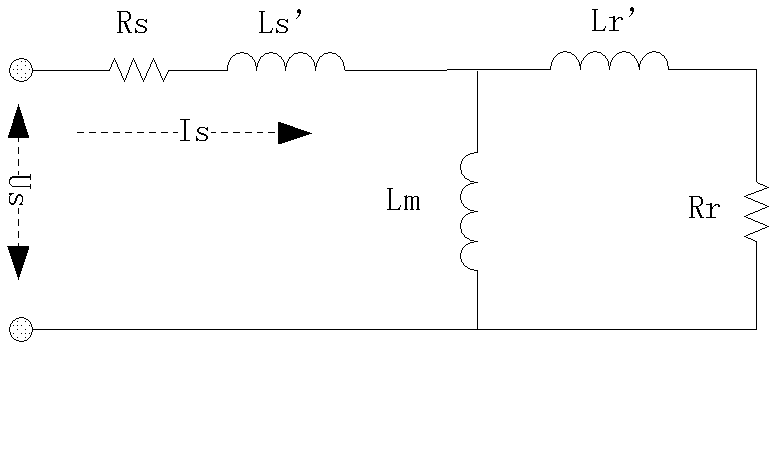
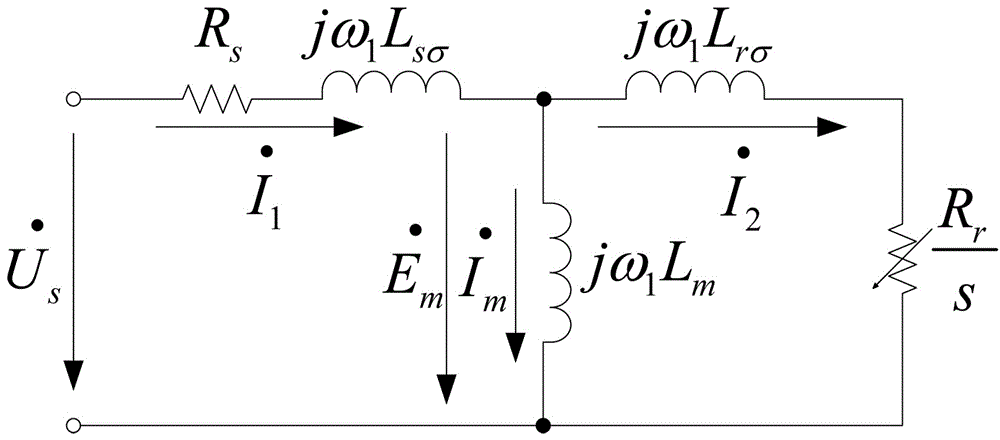
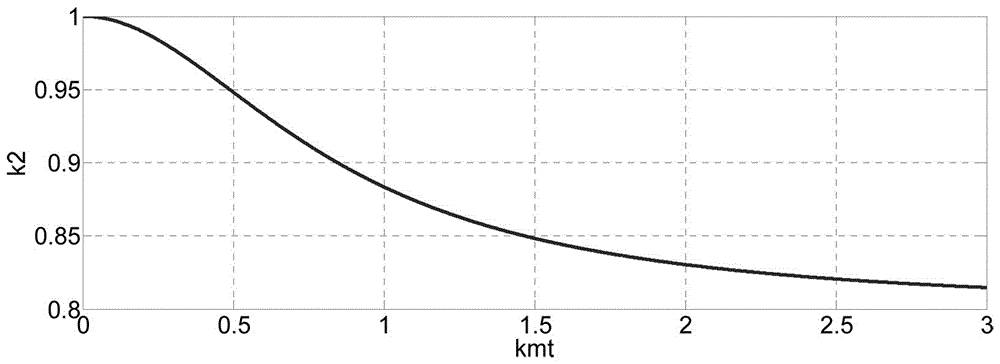
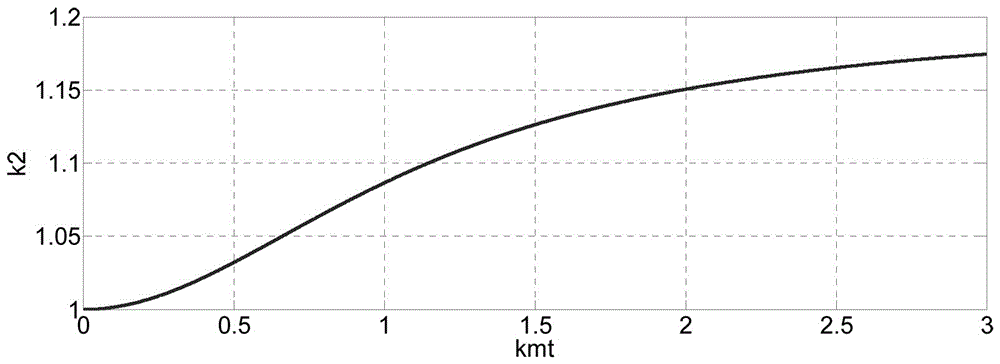
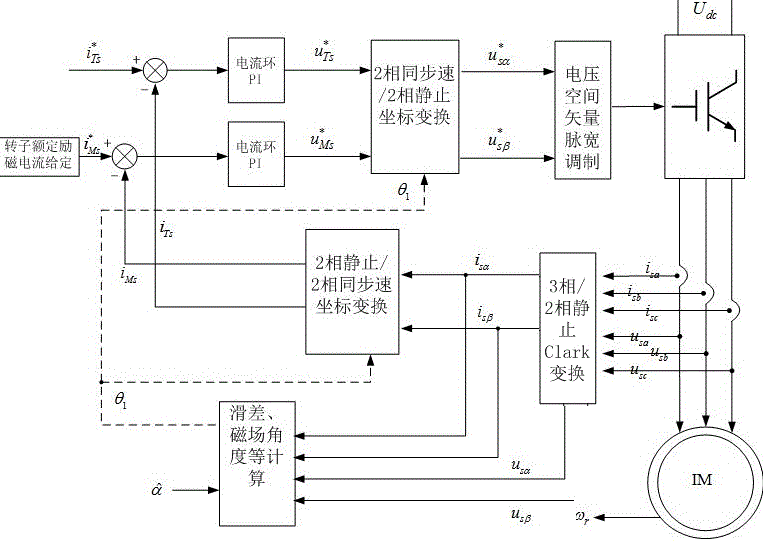
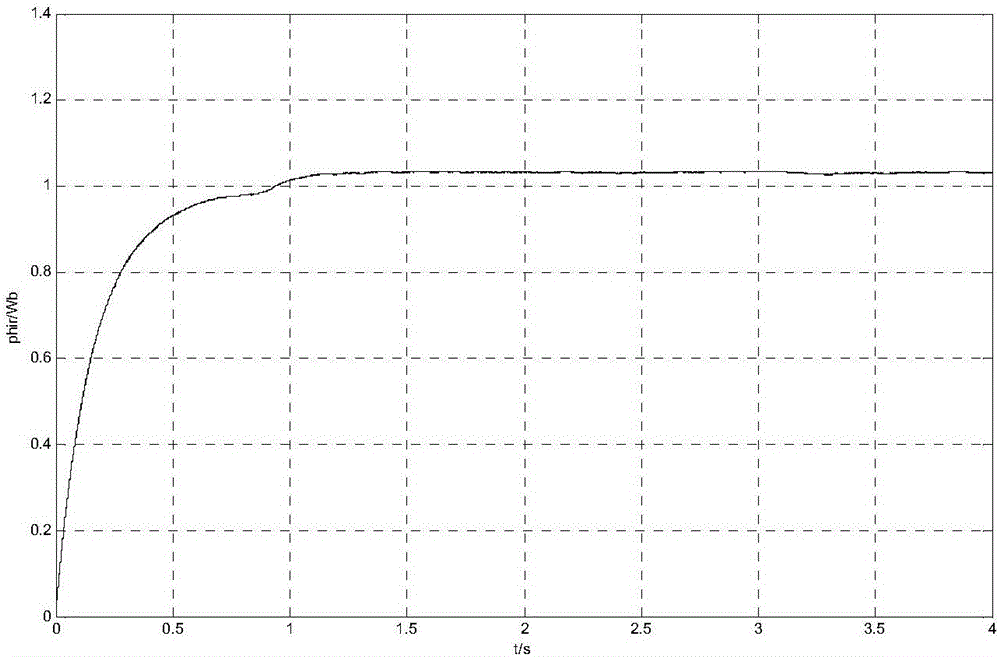
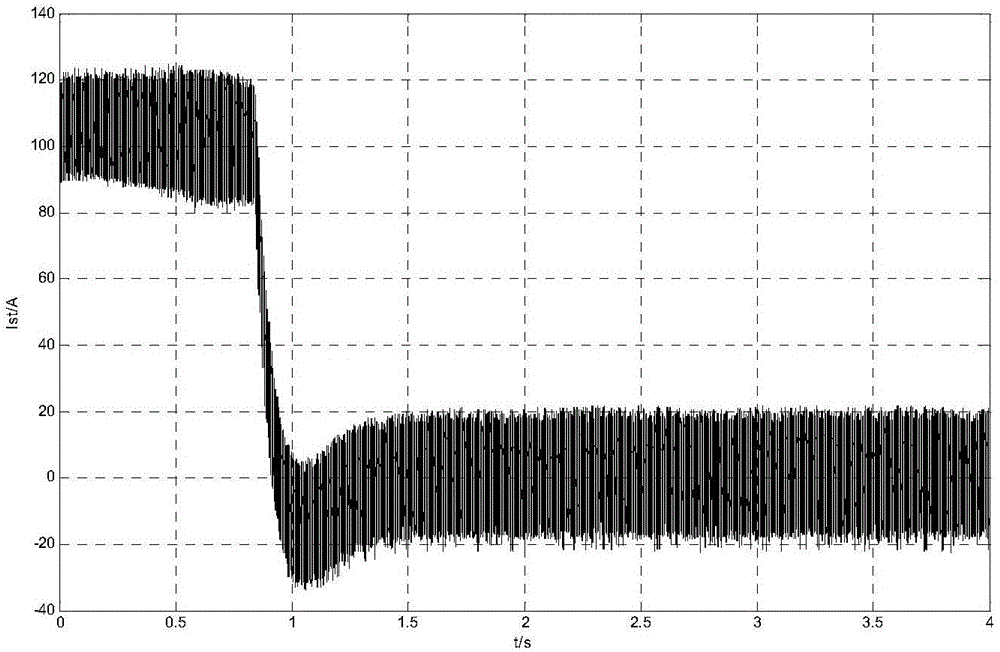
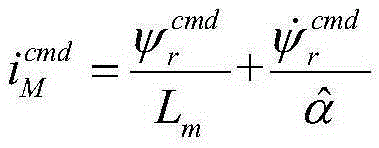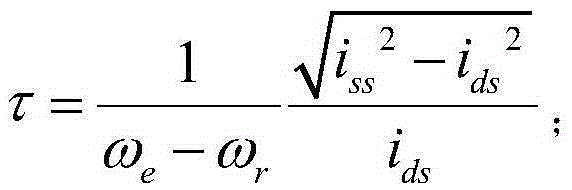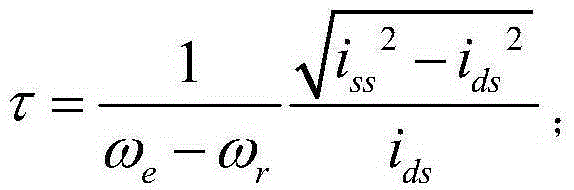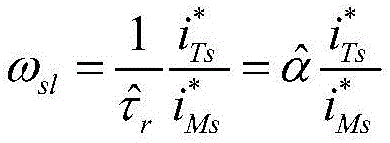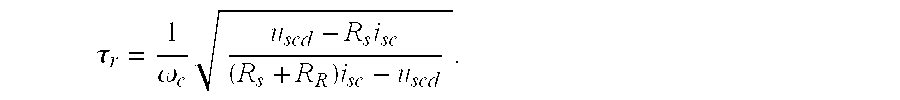Patents
Literature
79 results about "Rotor time constant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The rotor time constant is normally in the hundreds of milliseconds to seconds order of magnitude. I imagine that your filter has a cut off frequency well above 100 Hz, which corresponds to a 1.5 ms time constant.
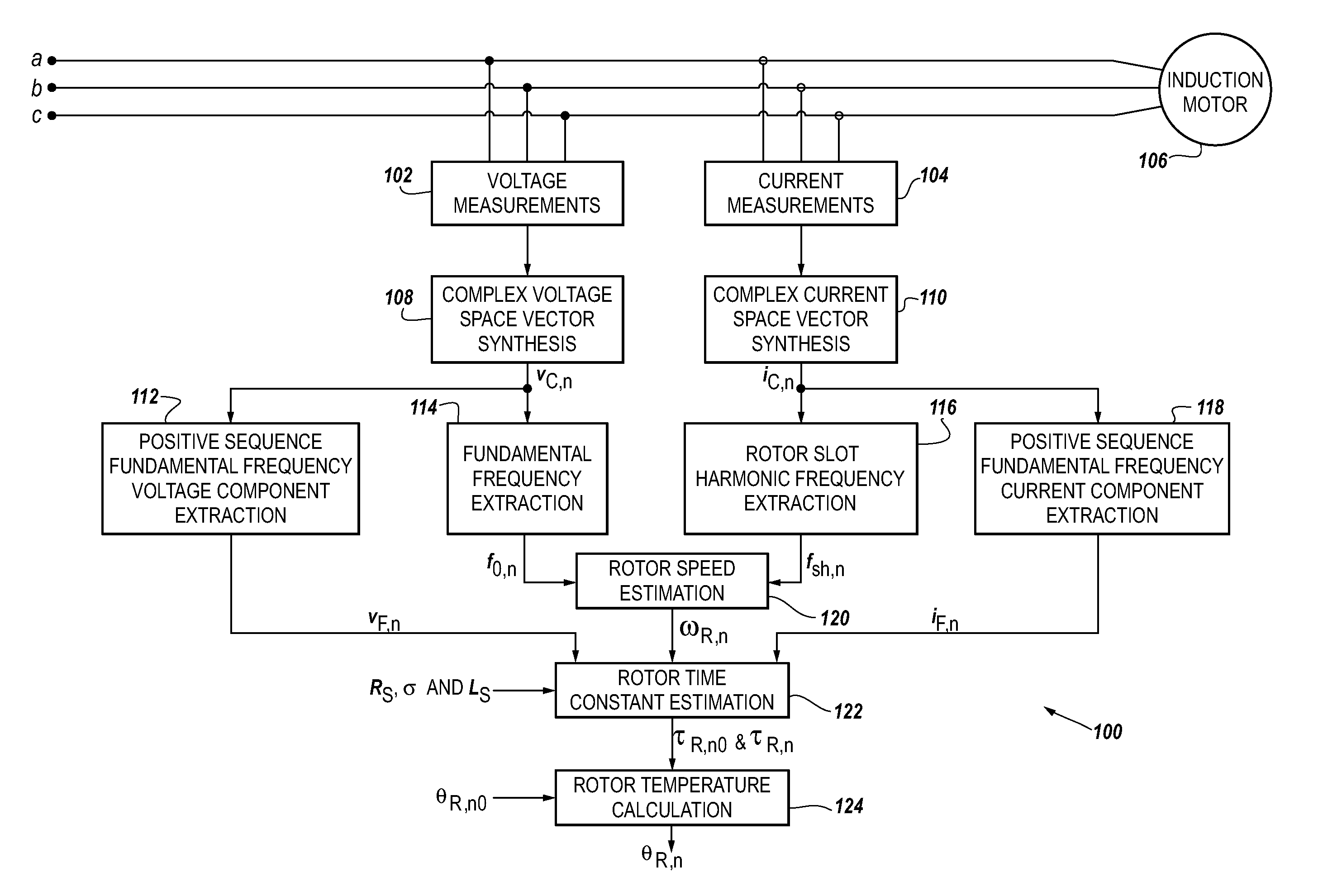
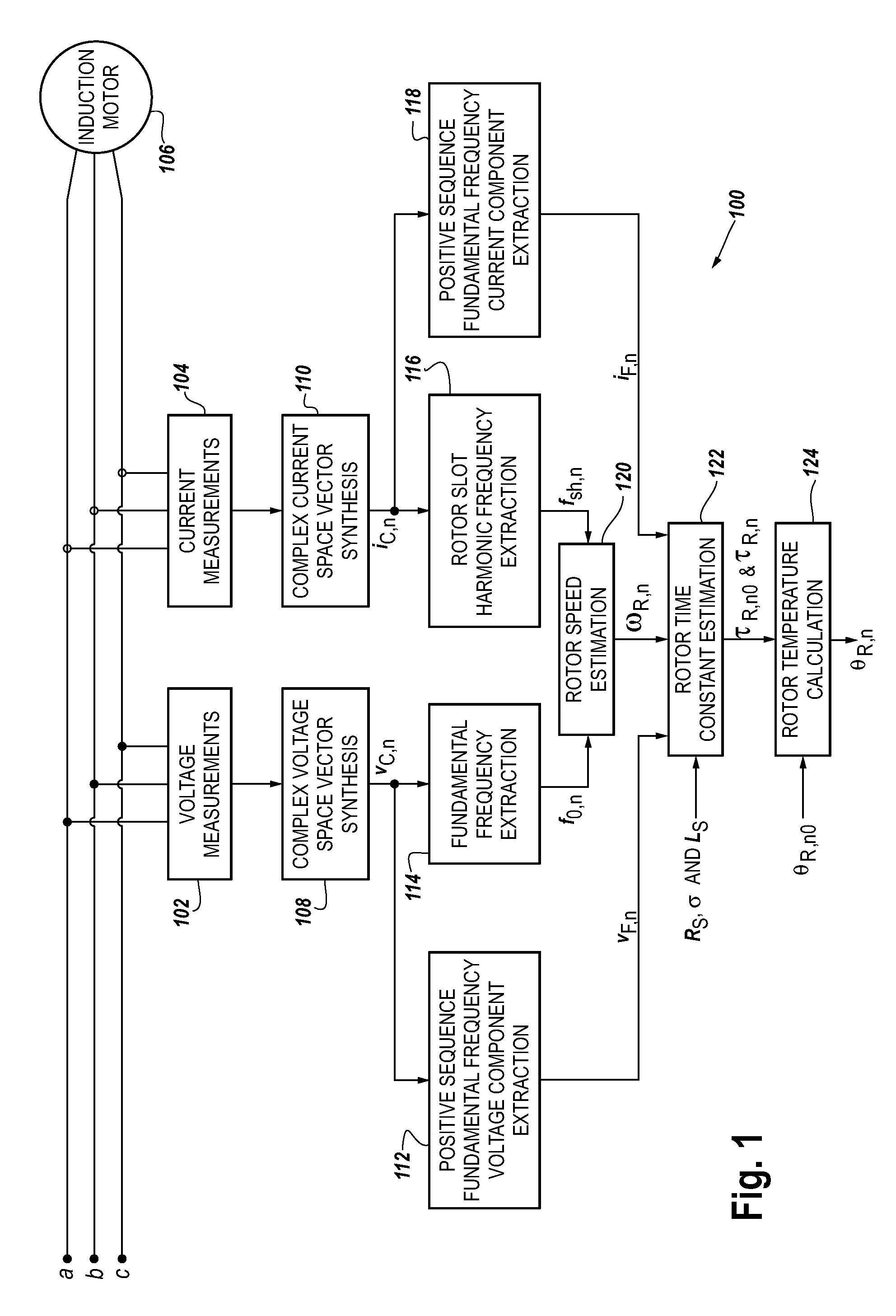
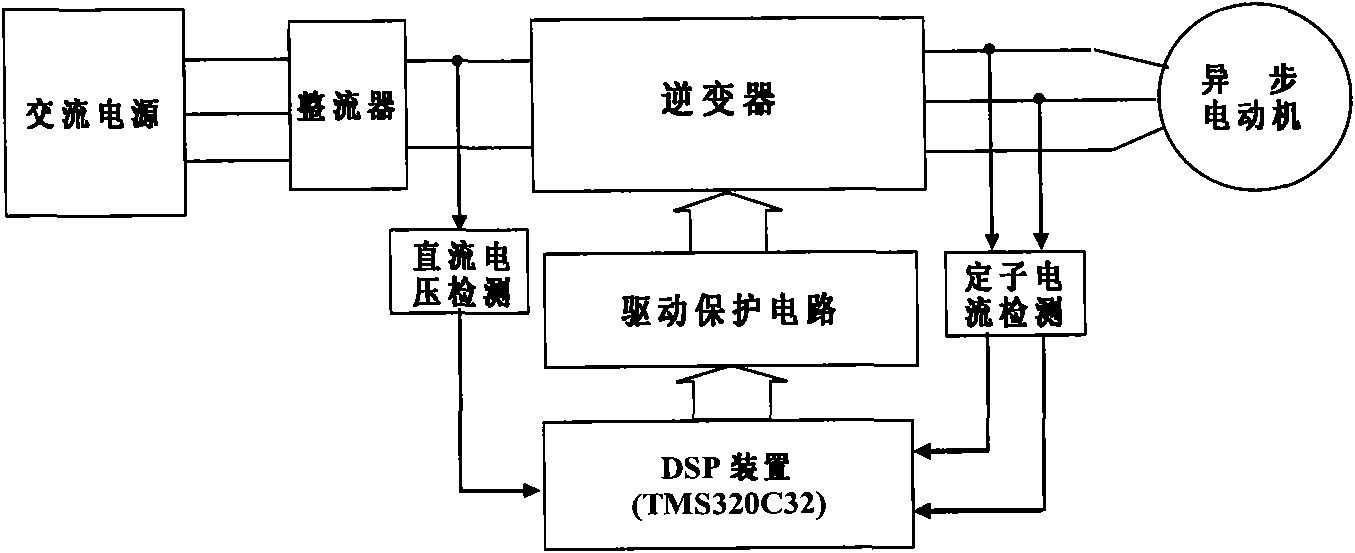
Method and apparatus for estimating induction motor rotor temperature
InactiveUS20090284204A1Low costSingle-phase induction motor startersDC motor speed/torque controlLinear relationshipEngineering
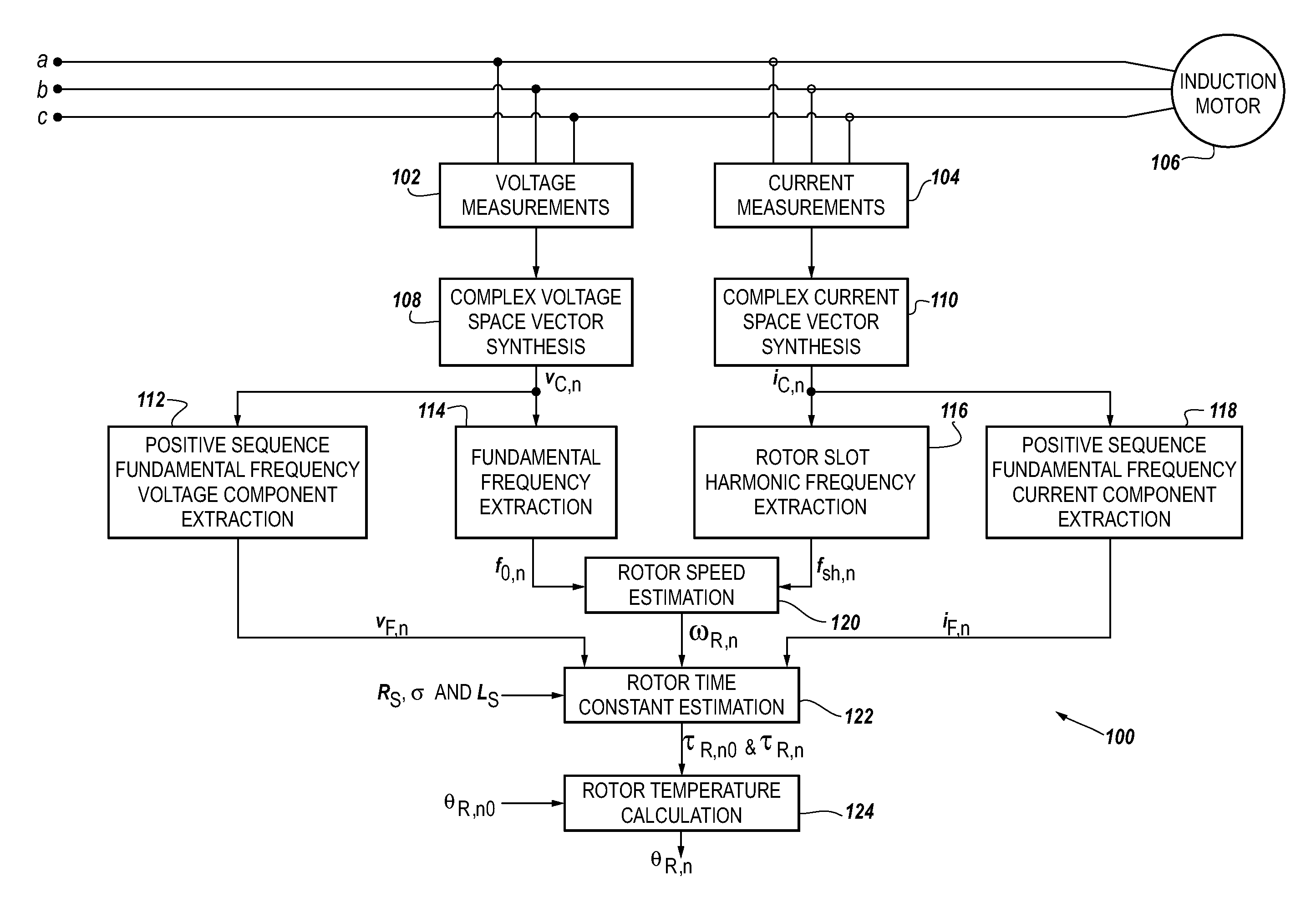
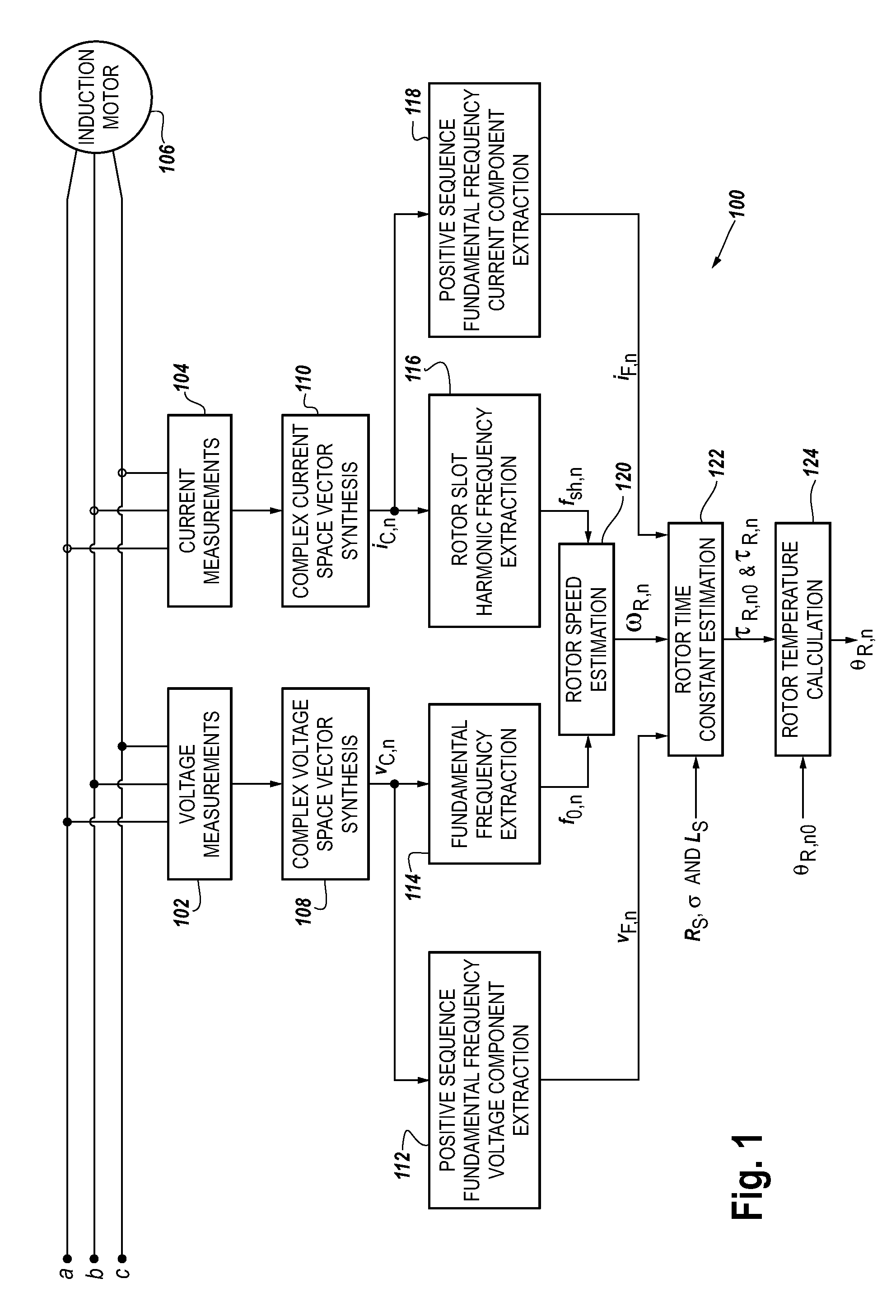
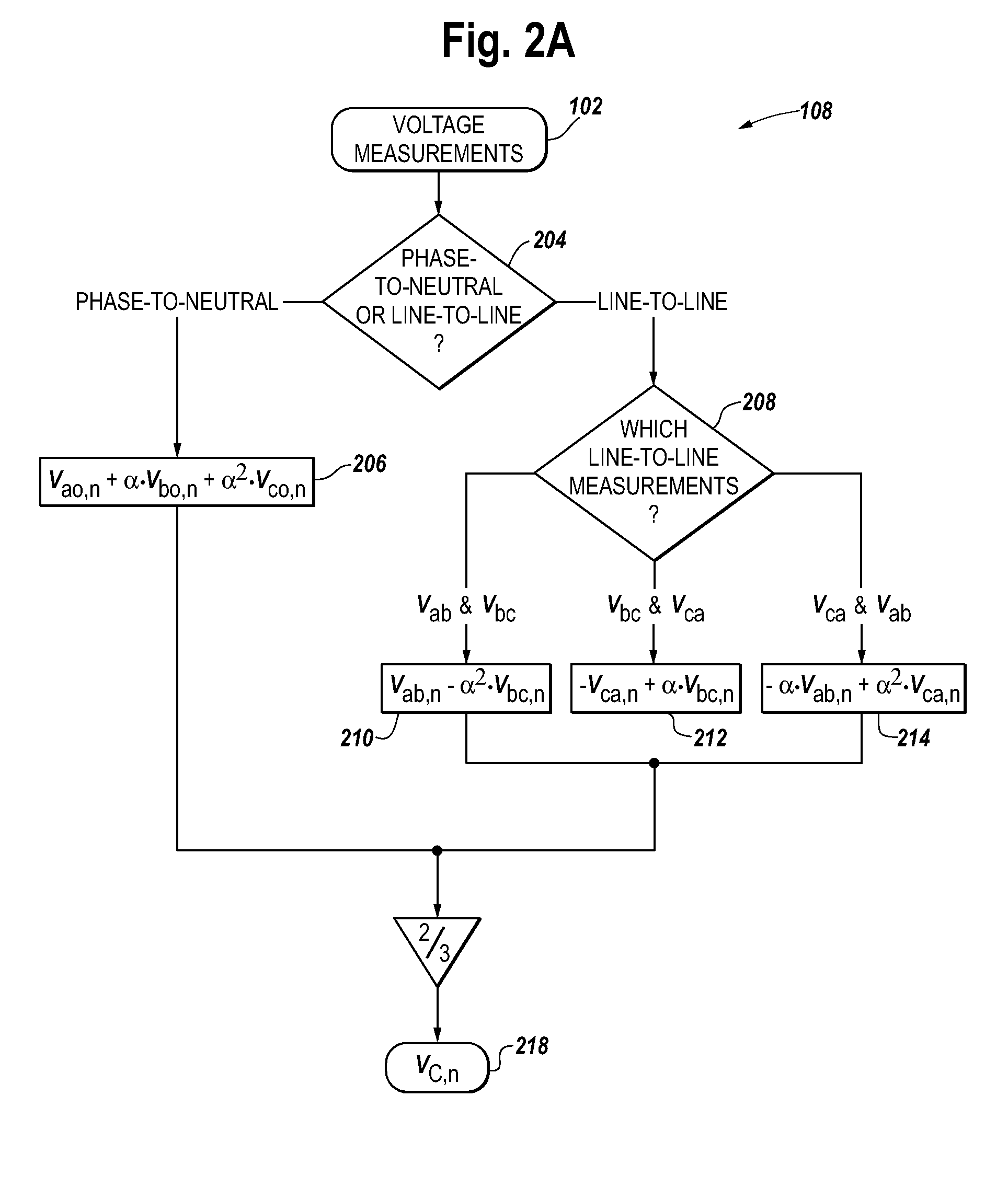
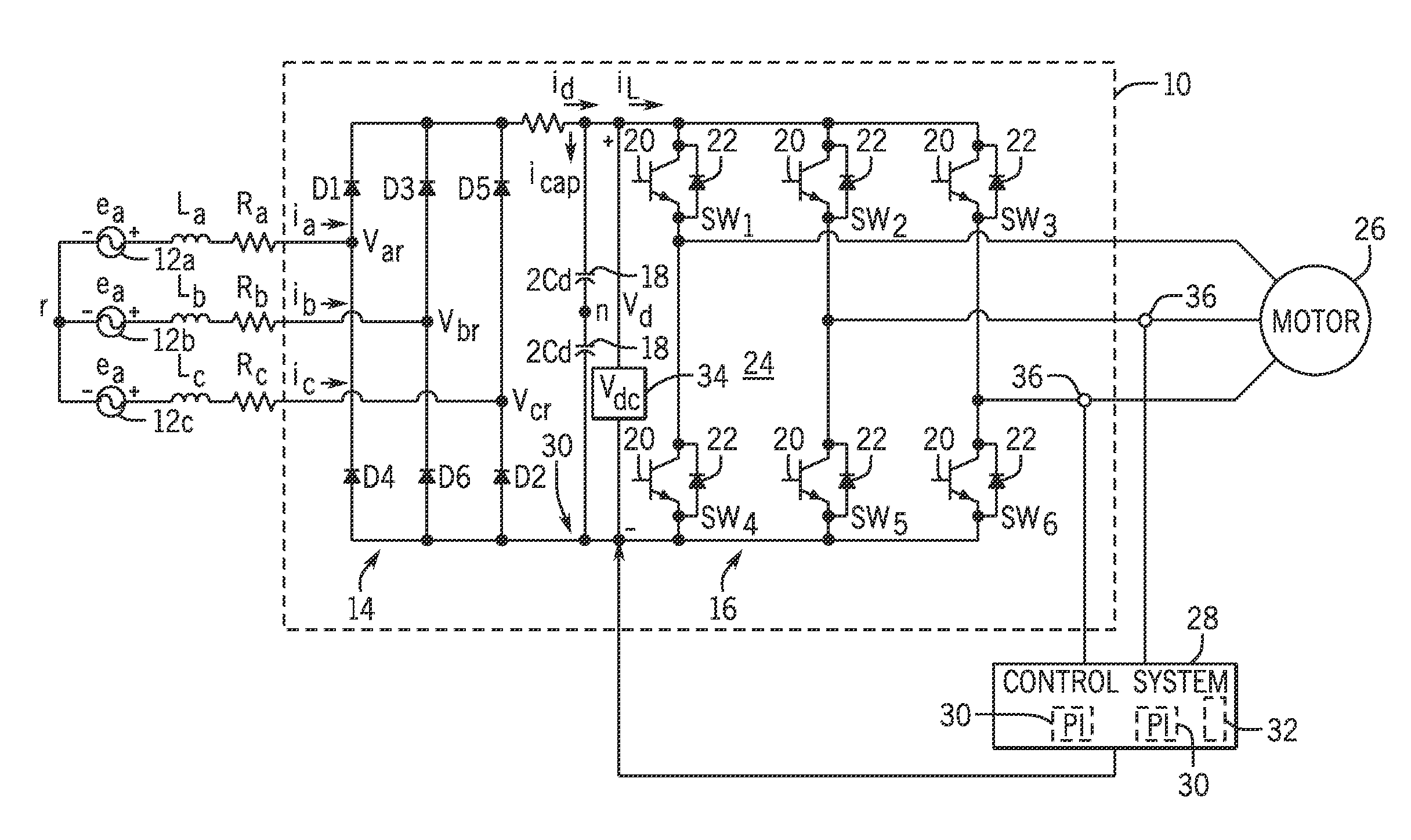
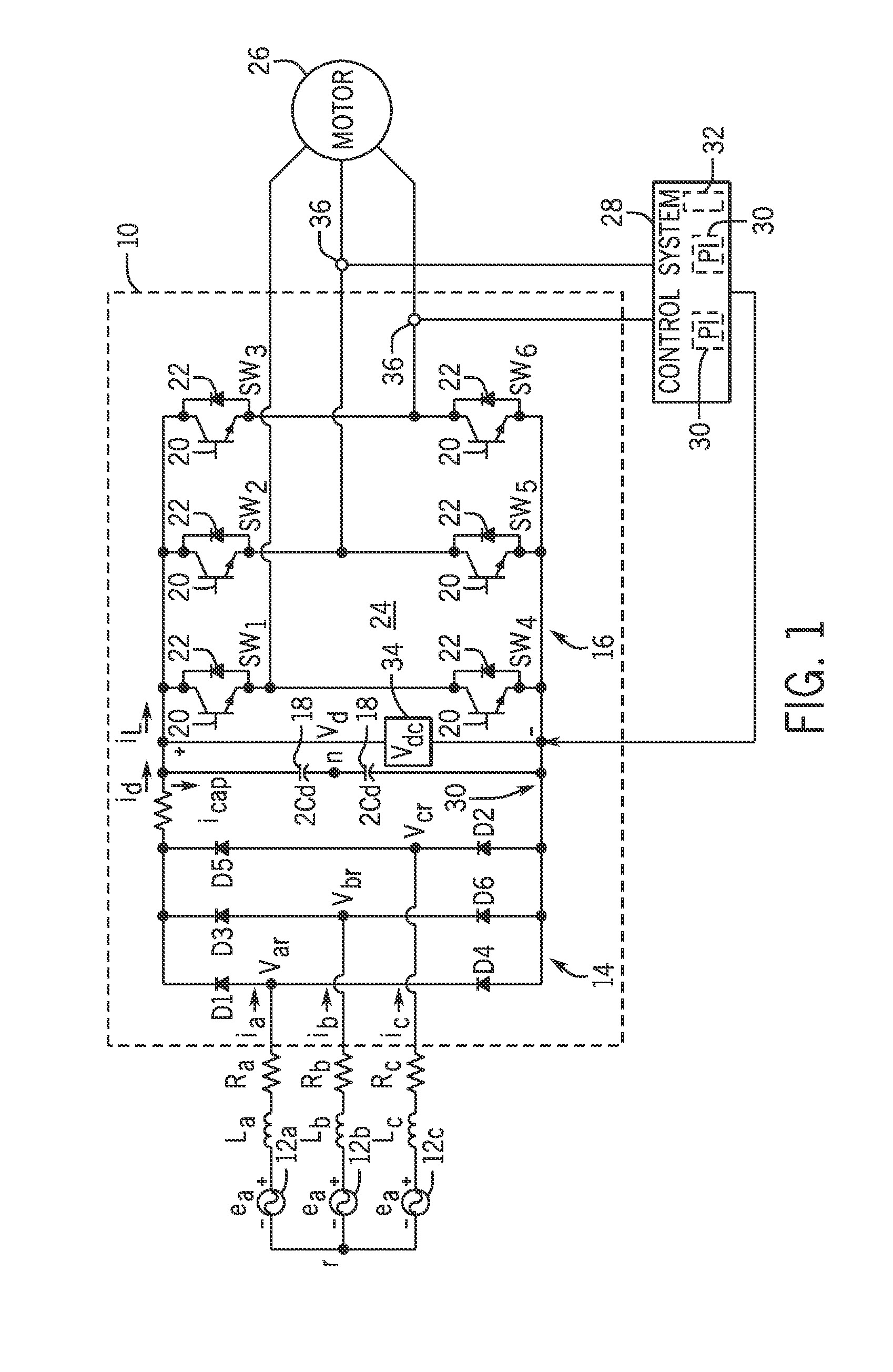
A method and apparatus to provide continuous and reliable rotor temperature estimates for line-connected induction motors during steady-state and / or dynamic motor operations. Rotor temperature is calculated from voltage and current measurements without any temperature or speed sensors. First, complex space vectors are synthesized from voltage and current measurements. Second, the instantaneous rotor speed is detected by calculating the rotational speed of a single rotor slot harmonic component with respect to the rotational speed of the fundamental frequency component. Third, the positive sequence fundamental frequency components are extracted from complex space vectors. Fourth, the rotor time constant is estimated in a model-reference adaptive system based on a dynamic induction motor equivalent circuit model. Finally, the rotor temperature is calculated according to the linear relationship between the rotor temperature and the estimated rotor time constant. Real-time induction motor thermal protection is achieved through this continuous tracking of the rotor temperature.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
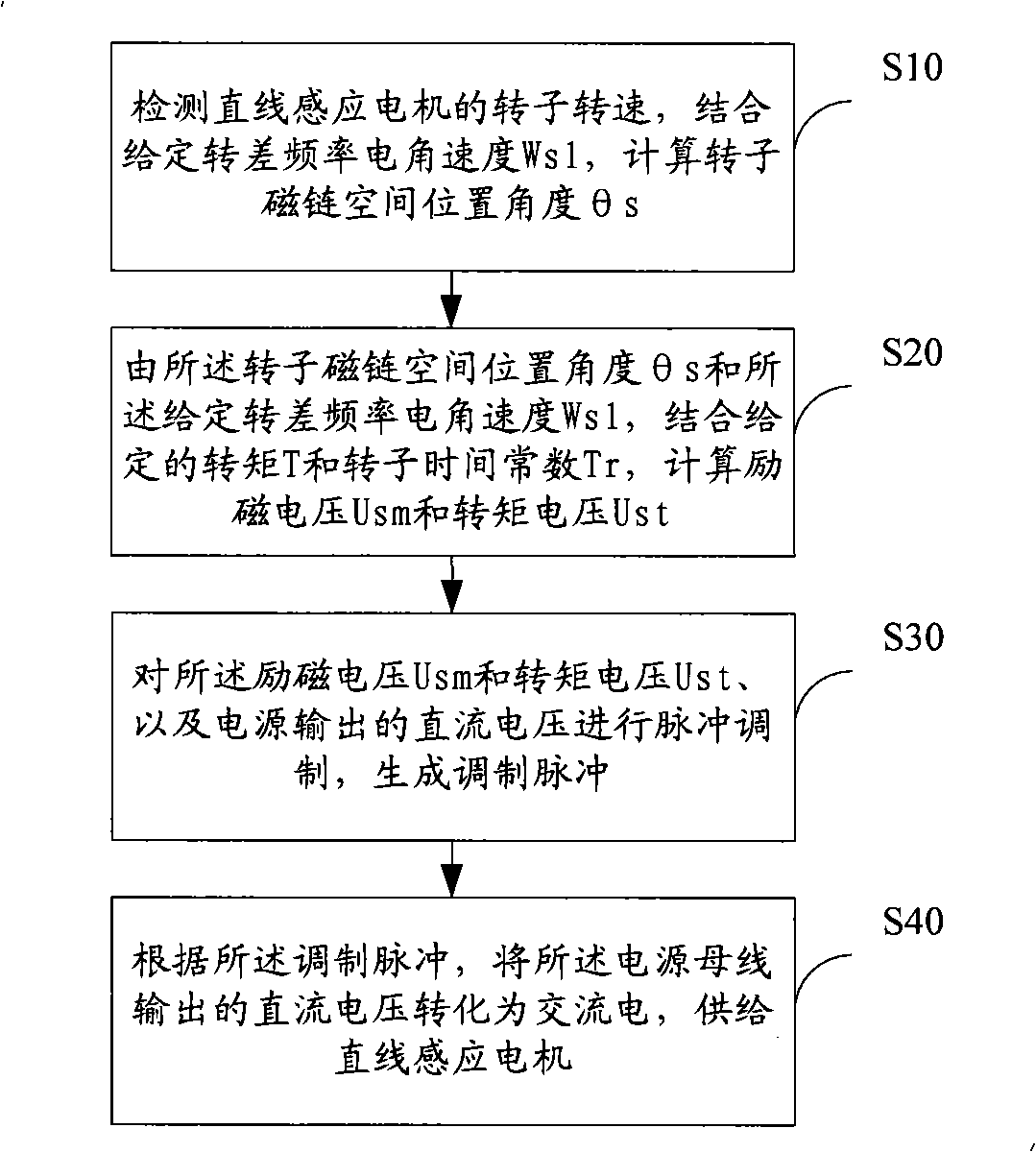
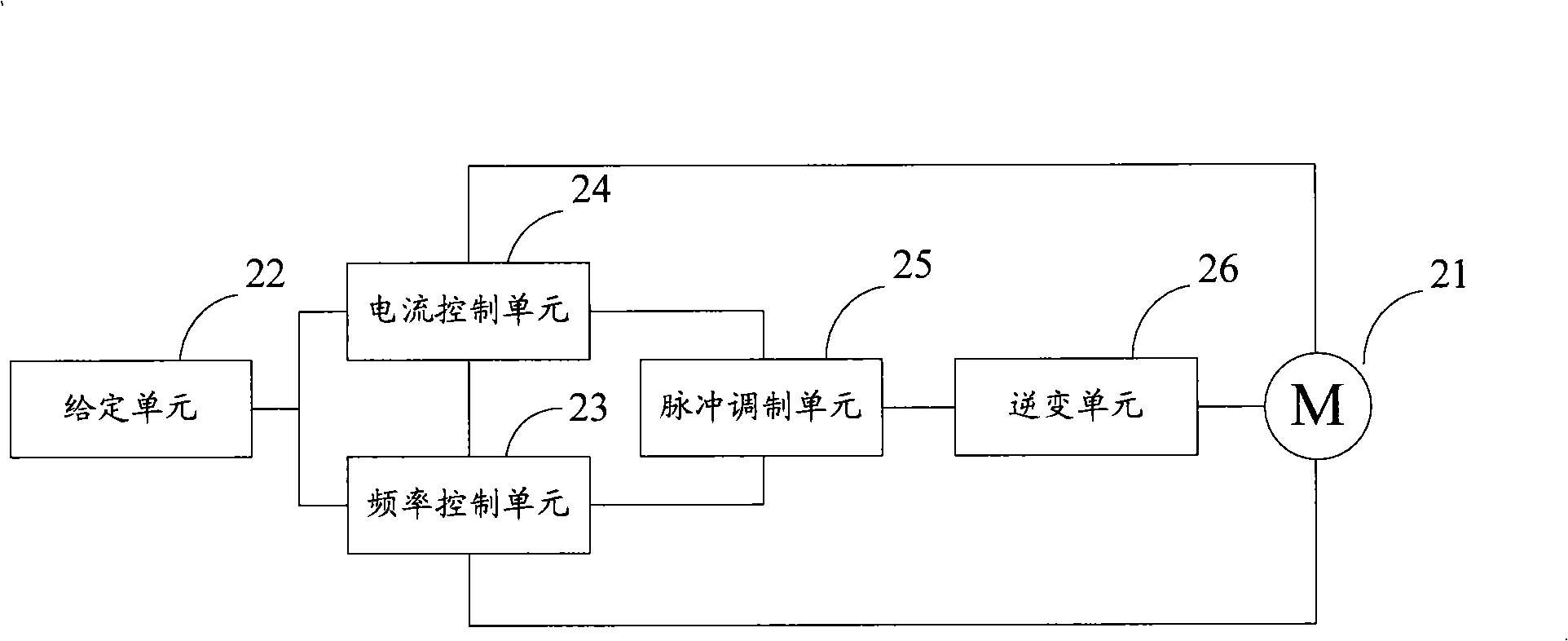
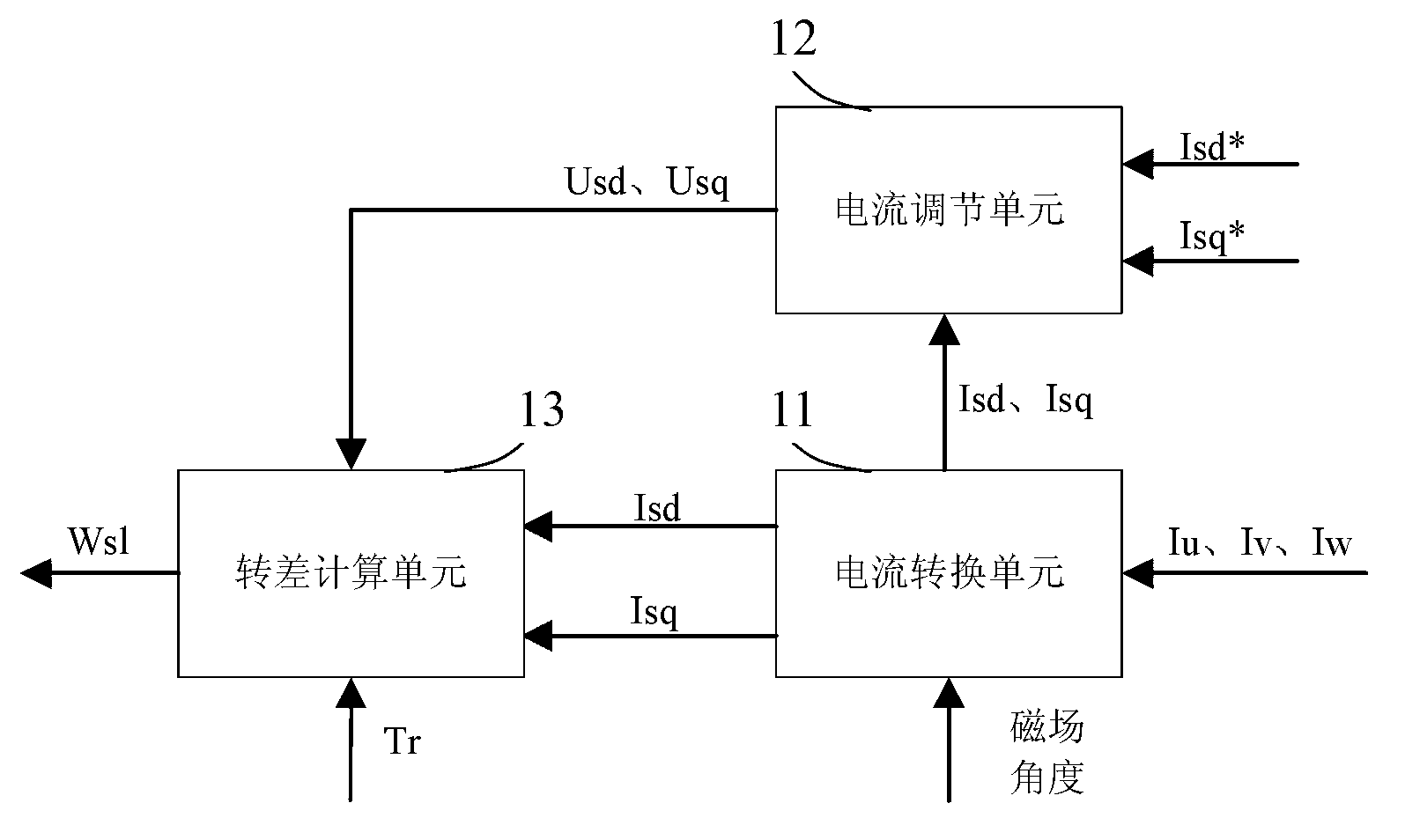
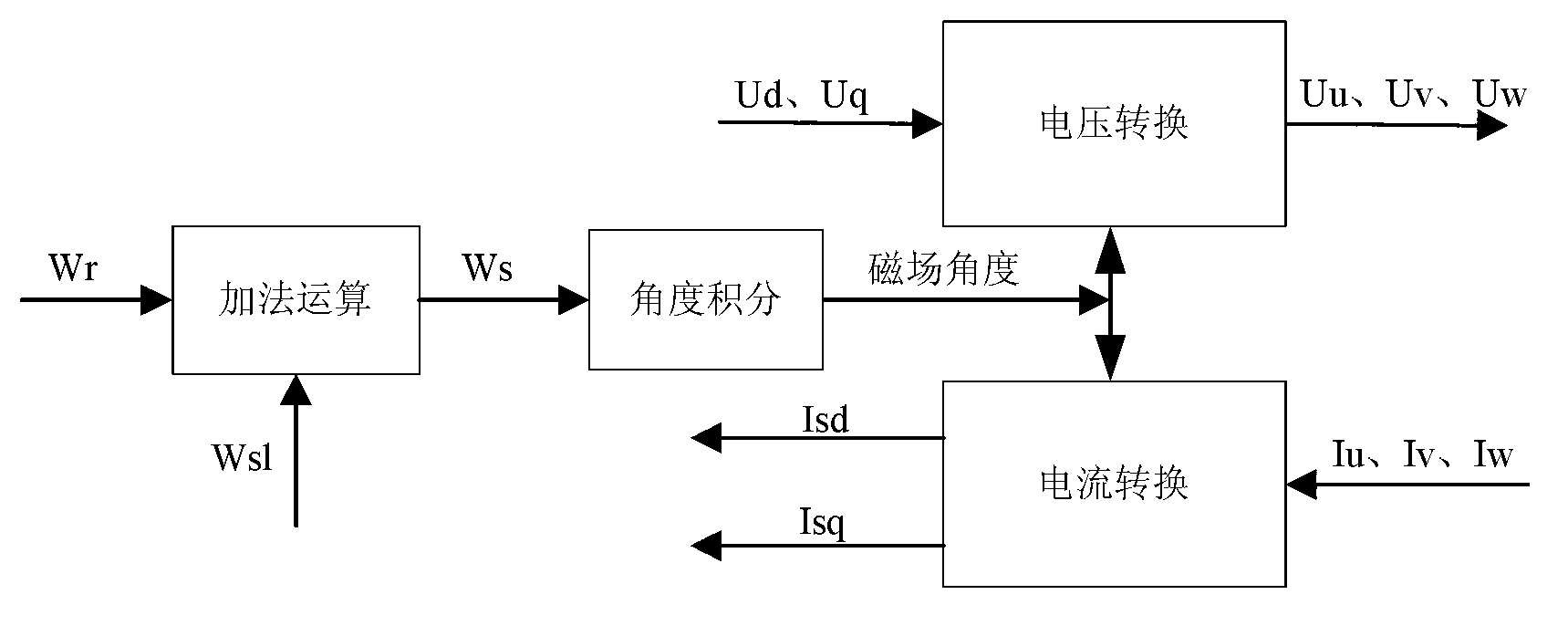
Constant slip frequency vector control method and system for linear induction motor
ActiveCN101316093AExcellent slip frequency electrical angular velocitySmooth orientation angleElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPosition angleAngular velocity
The invention discloses a linear induction motor constant slip frequency vector control method. The method comprises the steps as follows: detecting the rotation speed of a rotor of a linear induction motor, calculating the magnetic chain space position angle Theta<s> of the rotor according to the given slip frequency electric angular velocity Wsl; calculating the excitation voltage Usm and torque voltage Ust according to the magnetic chain space position angle Theta<s> and the given slip frequency electric angular velocity Wsl and combining a given torque T and a rotor time constant Tr; generating modulation pulses by pulse-modulating the excitation voltage Usm and the torque voltage Ust and the DC voltage output by the power supply; converting the DC voltage output by the power supply into the AC electricity so as to be supplied to the linear induction motor according to the modulation pulse. The invention also discloses a linear induction motor constant slip frequency vector control system. The linear induction motor constant slip frequency vector control method and system of the invention can realize the constant slip frequency vector control of the linear induction motor.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and apparatus for estimating induction motor rotor temperature
InactiveUS7769552B2Low costSingle-phase induction motor startersDC motor speed/torque controlLinear relationshipFundamental frequency
A method and apparatus to provide continuous and reliable rotor temperature estimates for line-connected induction motors during steady-state and / or dynamic motor operations. Rotor temperature is calculated from voltage and current measurements without any temperature or speed sensors. First, complex space vectors are synthesized from voltage and current measurements. Second, the instantaneous rotor speed is detected by calculating the rotational speed of a single rotor slot harmonic component with respect to the rotational speed of the fundamental frequency component. Third, the positive sequence fundamental frequency components are extracted from complex space vectors. Fourth, the rotor time constant is estimated in a model-reference adaptive system based on a dynamic induction motor equivalent circuit model. Finally, the rotor temperature is calculated according to the linear relationship between the rotor temperature and the estimated rotor time constant. Real-time induction motor thermal protection is achieved through this continuous tracking of the rotor temperature.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
Motor parameter detection method and motor parameter detection apparatus
ActiveCN102426337AReduce calculation stepsImprove work efficiencyDynamo-electric machine testingElectrical resistance and conductanceRC time constant
The invention discloses a motor parameter detection method and a motor parameter detection apparatus. The motor parameter detection method comprises the following steps that: open circuit is carried out on a phase winding of the motor; a motor stator resistance detection step is realized; that is, a pulse direct current voltage is applied between other two phases of the motor and the motor stator resistance is detected; and a motor rotor time constant detection step is realized; that is, a stepped direct current voltage is applied between the other two phases of the motor; different time and current values of the time are measured as well as a current-time linear equation is obtained; a current value at zero time and the motor stator resistance are introduced into the current-time linear equation to obtain an approximate value of the rotor time constant. According to the invention, a motor parameter detection method and a motor parameter detection apparatus are provided on the condition that an induction machine rotor is in a static state; and high accuracy of motor parameter detection can be realized only by successively applying currents or voltages at different frequencies between two phases of the motor as well as reducing voltage errors and an influence of a sink effect.
Owner:PEITIAN ROBOTICS CO LTD
Online calibrating method and device for rotor time constant of asynchronous motor and control system
ActiveCN102843093ARealization of online correctionLower requirementElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlStator voltageRC time constant
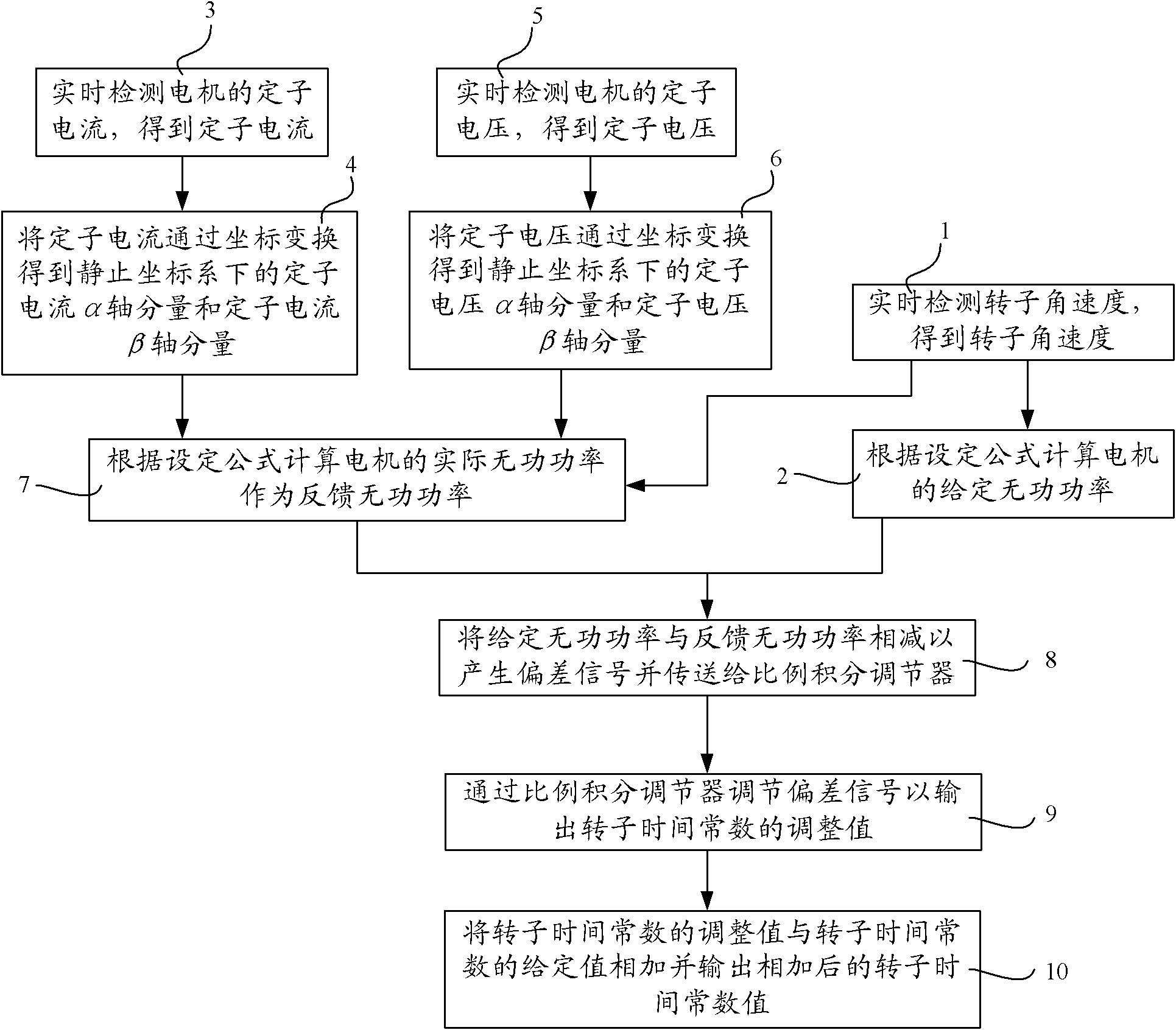
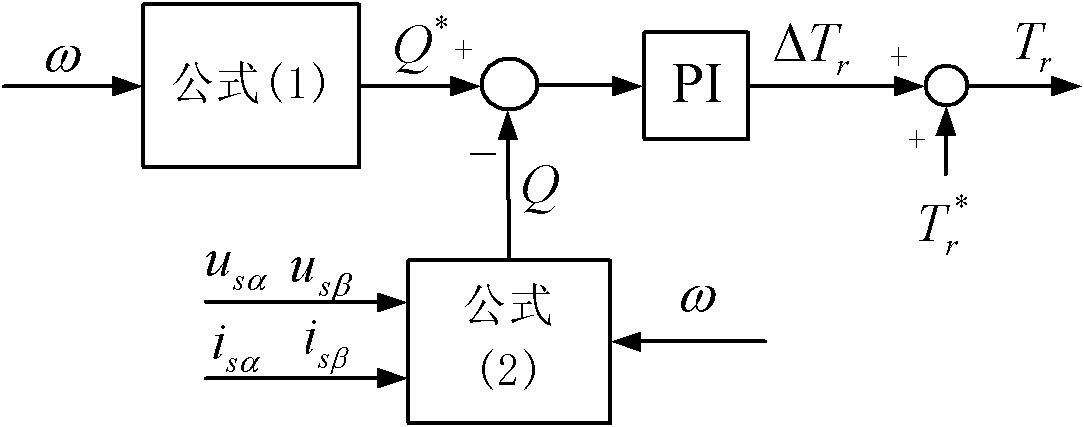
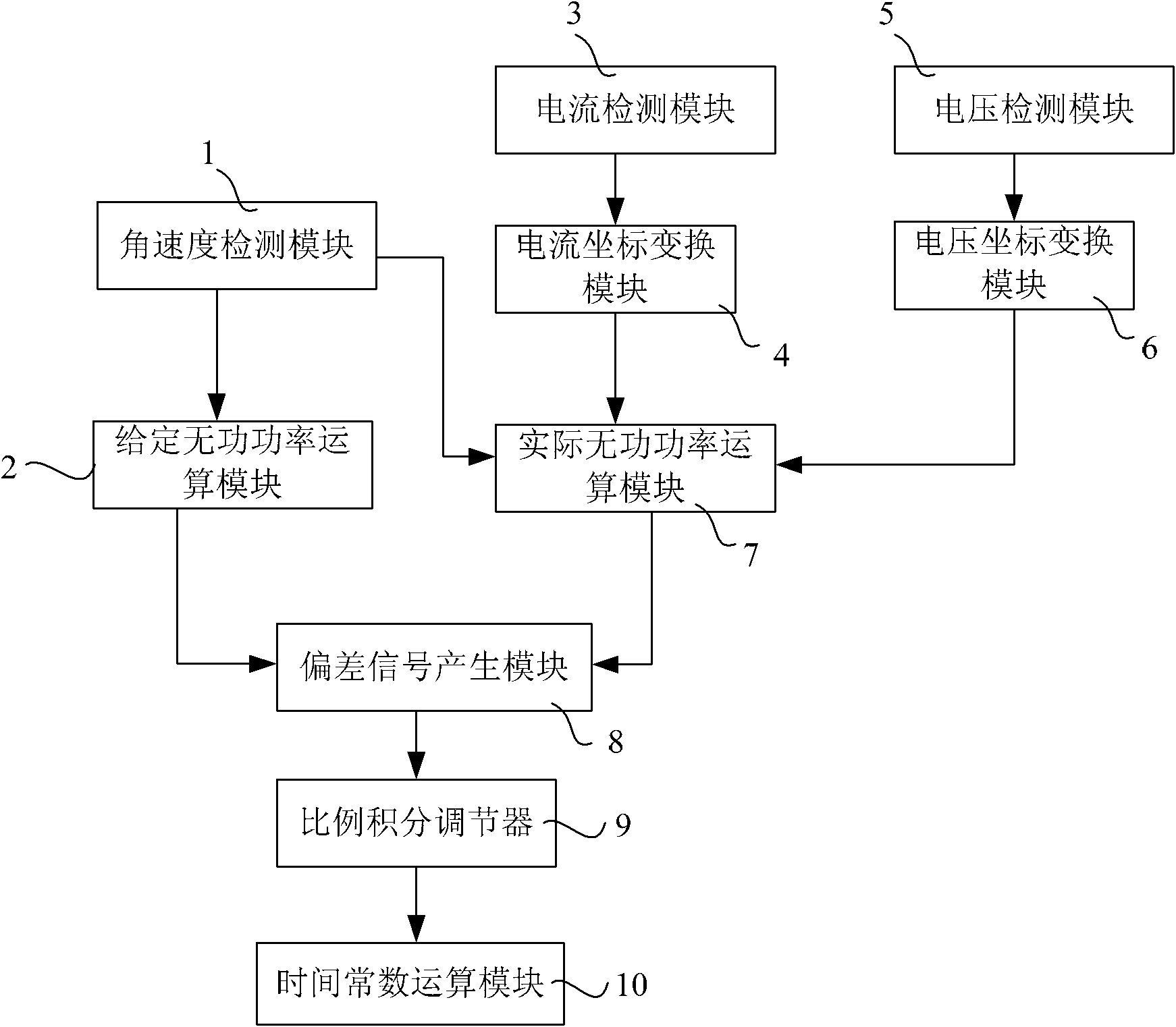
The invention discloses an online calibrating method and device for a rotor time constant of an asynchronous motor, and an asynchronous motor driving control system. The calibrating method comprises the following steps: measuring the angular velocity of a rotor, the current of a stator and the voltage of the stator; calculating a given reactive power and an actual reactive power of a motor based on a formula; making a comparison between the given reactive power and the calculated actual reactive power served as a feedback reactive power, so as to generate a deviation signal; adjusting the deviation signal through a proportional-integral controller in order to output an adjusting value of a rotor time constant; calibrating the setting value of the rotor time constant based on the adjusting value, thus meeting the setting value of the rotor time constant in line with the actual value. The calibrating method is simple, and is low in requirement on hardware.
Owner:CRRC YONGJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and device for measuring time constant of asynchronous motor rotor on line
InactiveCN102916647AHigh precisionReduce occupancyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsRC time constantElectromotive force
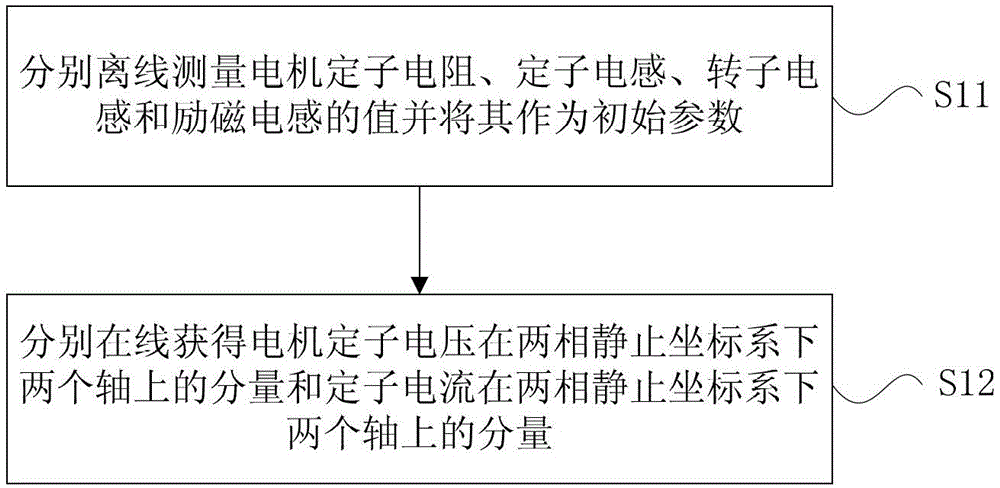
The invention relates to a method for measuring the time constant of an asynchronous motor rotor on line. The method comprises the following steps of: giving initial parameters in advance; obtaining induced electromotive force of a rotor flux linkage on a stator winding; processing the induced electromotive force of the rotor flux linkage on the stator winding to obtain a value of synchronous angular speed; obtaining a value of slip frequency from the synchronous angular speed; and obtaining a value of time constant of the rotor according to a slip frequency formula. The invention further relates to a device for implementing the method for measuring the time constant of the asynchronous motor rotor on line. The method and device for measuring the time constant of the asynchronous motor rotor on line, disclosed by the invention, have the beneficial effects of simple algorithm, small occupying area on CPU (Central Processing Unit) resources and higher precision of measured time constant of the rotor.
Owner:SHENZHEN HANGSHENG ELECTRONICS
Method for identifying stator resistance and rotor resistance online in asynchronous motor speed sensorless system
InactiveCN105281630ARealize identificationImprove control effectElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMotor speedRotor flux
The invention discloses a method for identifying the stator resistance and the rotor resistance online in an asynchronous motor speed sensorless system. According to the method, a controller constructs an adaptive observer using direct or indirect field-oriented control. First, the given signal of the motor rotor flux amplitude is a trapezoidal wave (including DC component), and the given signal can be composed of a flat given part and a slope given part; and then, the observer self-adapts to the stator resistance and speed when the actual rotor flux amplitude keeps up with the flat given part, and the observer self-adapts to the rotor time constant and speed when the actual rotor flux amplitude tracks the slope given part. The method is of high universality. The problem that simultaneous identification of the stator resistance and the rotor resistance in a speed sensorless system is difficult is overcome. The accuracy of speed identification is improved. The control performance of rotors in a full-speed range is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for identifying traction induction motor parameter of high-speed train
ActiveCN104201962AImprove observation accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsLow speedModel parameters
A method for identifying a traction induction motor parameter of a high-speed train is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: running two magnetic flux linkage observers synchronously and calibrating main model parameters such as a magnetic inductance and a rotor time constant set in a controller respectively in high-speed and low-speed running regions of the traction induction motor by utilizing respective advantages of a voltage type observer and a current type observer to enable the traction induction motor to be in a full-speed running range and enable the observation effects of the two magnetic flux linkage observers to be optimal. The method for identifying the traction induction motor parameter of the high-speed train can overcome the negative influence such as temperature rise of the motor and the excitation characteristic change, and realizes high-performance traction control.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Induction motor parameter identification method
ActiveCN106452241ASimple methodImprove accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectrical resistance and conductanceControl vector
The invention discloses an induction motor parameter identification method. The method comprises steps of S10, identifying motor stator phase resistance Rs; S2, identifying motor stator phase leakage inductance Lssigma; S30, identifying motor stator / rotor equivalent excitation inductance Lm, equivalent stator self-inductance Ls and equivalent rotor self-inductance Lr; S40, detecting a motor rotor time constant initial value Tr0; S50, calculating a rotor resistor initial value Rr0; S60, calculating a rotor resistor correction value Rr; and S70, calculating a motor rotor time constant correction value Tr. Through the method, not any equipment is required to add such as a three-phase voltage regulator and a three-phase power meter, and online induction motor parameter identification vector control is carried out. The method is advantaged in that the method is simple and easy for operation, and quite high accuracy is realized.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
Method for measuring time constant of rotor of asynchronous machine
ActiveCN102540076AEasy to measureOptimizationAC motor controlDynamo-electric machine testingObservational errorRC time constant
The invention discloses a method for measuring a time constant of a rotor of an asynchronous machine. An inverter or a servo driver connected with the asynchronous machine comprises an inverter bridge; when the inverter bridge is in an inversion state, stator current is given to be Is0 and the working time is given to be tm under the condition that the stator current and voltage are zero, and the magnetizing current reaches the maximum Im0 which is recorded; after excitation is carried out for tm, the inverter bridge is immediately in a closed state, and the stator current is zero after a period of time; after a stator is cut off, the inverter bridge is set to be in a three-phase short circuit state, the stator current Is is gradually raised from zero, when the Is reaches the maximum Isz, the Isz is recorded, and the current of the asynchronous machine is waited to be subjected to excitation attenuation to reach zero; and the Isz is compared with IszO, and when the compared difference is in a set error range, the time constant of the rotor of the asynchronous machine is working time tm1. By the method, calculation can be simplified and measurement errors can be effectively reduced.
Owner:杭州兆鼎科技实业有限公司
Asynchronous motor rotor time constant on-line identification system and method
ActiveCN102983807AImproving the effect of magnetic field orientationImprove torque control accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectric machine
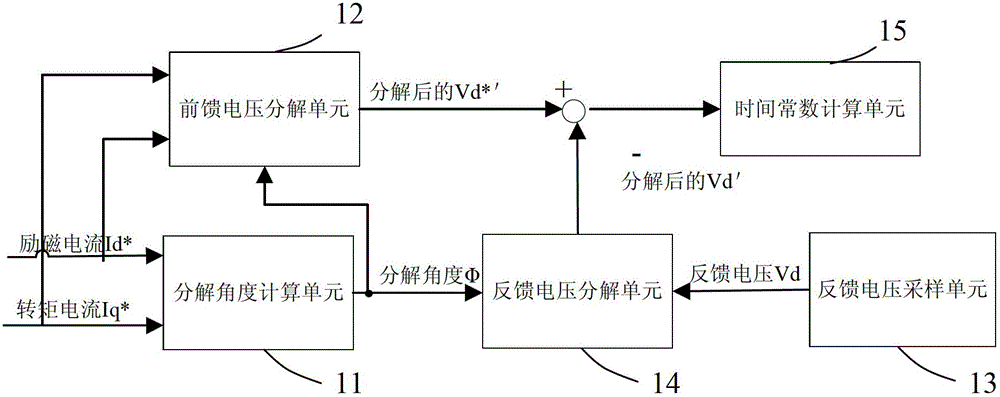
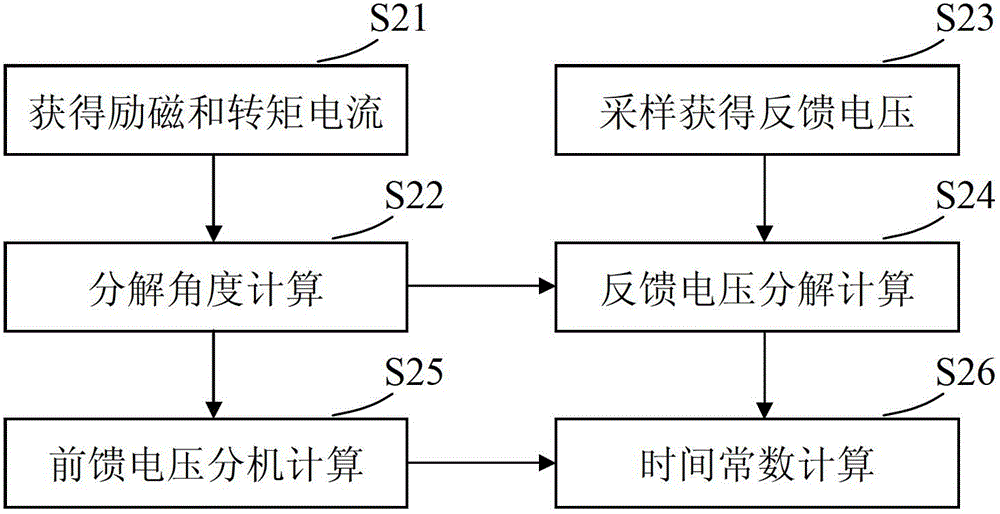
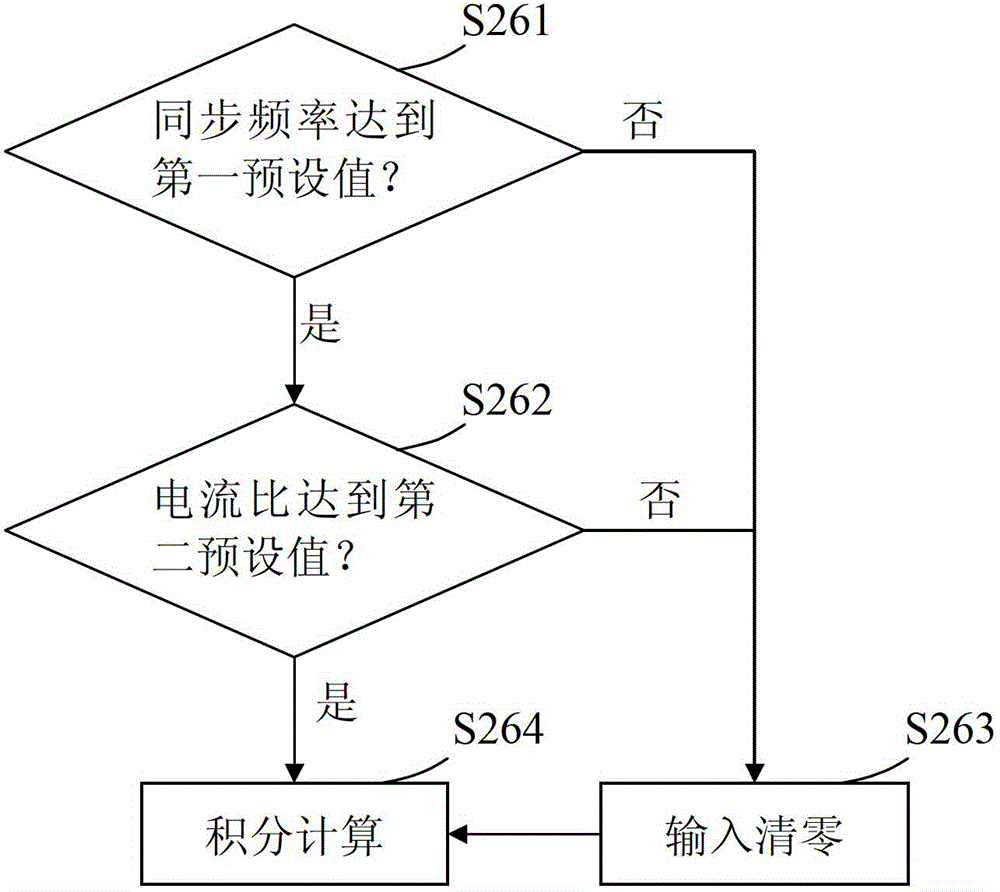
The invention provides an asynchronous motor rotor time constant on-line identification system. The system comprises a decomposition angle calculation unit, a feedforward voltage decomposition unit, a feedback voltage sampling unit, a feedback voltage decomposition unit and a time constant calculation unit, wherein the decomposition angle calculation unit is used for acquiring a decomposition angle according to exciting current and torque current; the feedforward voltage decomposition unit is used for performing decomposition calculation on the feedforward voltage by using the decomposition angle; the feedback voltage sampling unit is used for sampling the output end of a controlled motor to acquire the feedback voltage; the feedback voltage decomposition unit is used for performing decomposition calculation on the feedback voltage by using the decomposition angle; and the time constant calculation unit is used for calculating and updating the rotor time constant according to the decomposition results of the feedforward voltage and the feedback voltage. The system realizes on-line real-time identification of the rotor time constant through voltage decomposition, and the process is not influenced by the change of stator resistance.
Owner:SUZHOU INOVANCE TECH CO LTD
Method for determining optimal time constant of three-phase asynchronous motor rotor
ActiveCN103731081AImprove execution efficiencyBypass the identification processElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorExcitation current
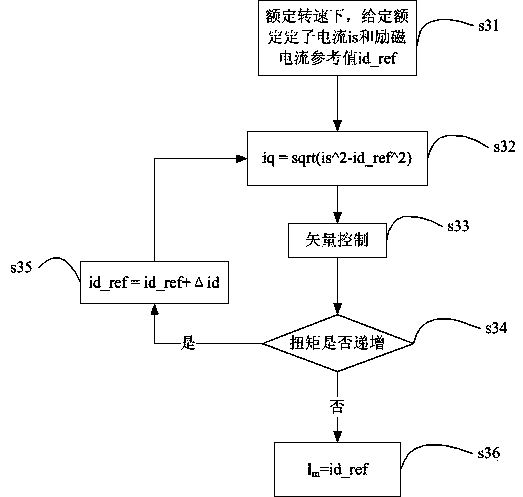
The invention provides a method for determining an optimal time constant of a three-phase asynchronous motor rotor. The method includes the step s11 of setting a rotor time constant reference value tau[r]_ref, the step s12 of selecting an excitation current value id and a corresponding torque current value iq, wherein at the moment, iq=id; the step s13 of calculating the slip ratio Ws=iq / (tau[r]_ref*id) at the moment, the step s14 of conducting vector control, the step s15 of judging whether the torque progressively increases or not, the step s16 of enabling tau[r]_ref to be equal to tau[r]_ref plus delta tau[r] if the torque progressively increases, and executing the step s13 again, wherein delta tau[r] is the increment; the step s17 of determining the optimal time constant tau[r] which is equal to tau[r]_ref if the torque does not progressively increase. According to the method, the defects in the prior art are overcome, the executing efficiency of software is improved, the characteristics of parameter dynamic changes is also taken into consideration, and the method can be easily achieved in terms of projects under the condition that efficient output of a system is ensured.
Owner:SHENZHEN HANGSHENG ELECTRONICS
System and method of rotor time constant online identification in an ac induction machine
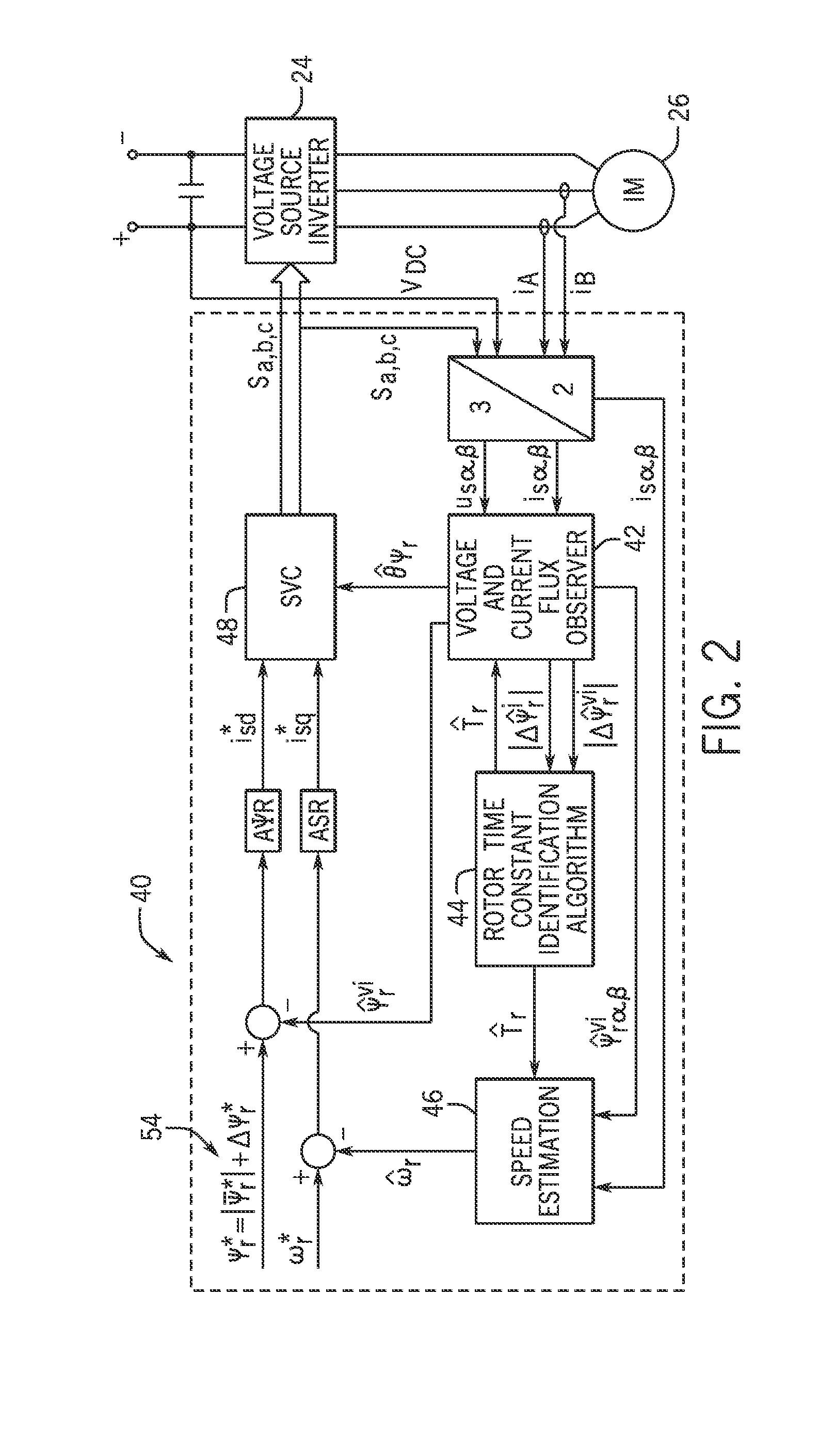
ActiveUS20150002071A1Electronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlRotor fluxRotor time constant
A system and method for determining a rotor time constant of an AC induction machine is disclosed. During operation of the induction motor, a flux signal is injected into a rotor flux command so as to generate a time-variant rotor flux. A voltage-current flux observer determines amplitudes of rotor flux variations resulting from the time-variant rotor flux, with the amplitudes of the rotor flux variations comprising an amplitude of a rotor flux variation based on a current model of the voltage-current flux observer and an amplitude of a rotor flux variation based on a combined voltage-current model of the voltage-current flux observer. A rotor time constant of the induction motor is then estimated based on the determined amplitudes of the rotor flux variations.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Torque calibration method for AC induction motor of electric vehicle
ActiveCN104158457AOutput is smooth and accurateMeet the requirements of torque control accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectric machineryElectric cars
The invention discloses a torque calibration method for an AC induction motor of an electric vehicle. The torque calibration method comprises the following steps: when the AC induction motor of the electric vehicle controls the electric vehicle, adopting the torque computational formula to convert an expected torque T<o>e into an expected torque current I<0>g, and realizing the torque control according to the directional vector control algorithm of the rotor field; before the torque calibration is carried out, adjusting the time constant parameter Tt and the mutual induction parameter Lm of the motor rotor by comparing the error tendency between an expected torque curve and an actual torque curve, so as to enable the actual torque to be close to the expected torque and to realize the actual torque calibration. According to the torque calibration method, on the basis of the conventional vector control algorithm, by the calibration of the time constant Tt and the mutual induction Lm of the motor rotor based on the conventional motor parameters in sequence, the actual torque calibration is completed; in the entire calibration process, a control motor is smooth and accurate in torque output, the requirement on torque control accuracy of a driving system of the electric vehicle can be met, and cumbersome torque calibration by adopting the table look-at method is further avoided.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRIC CORP LTD
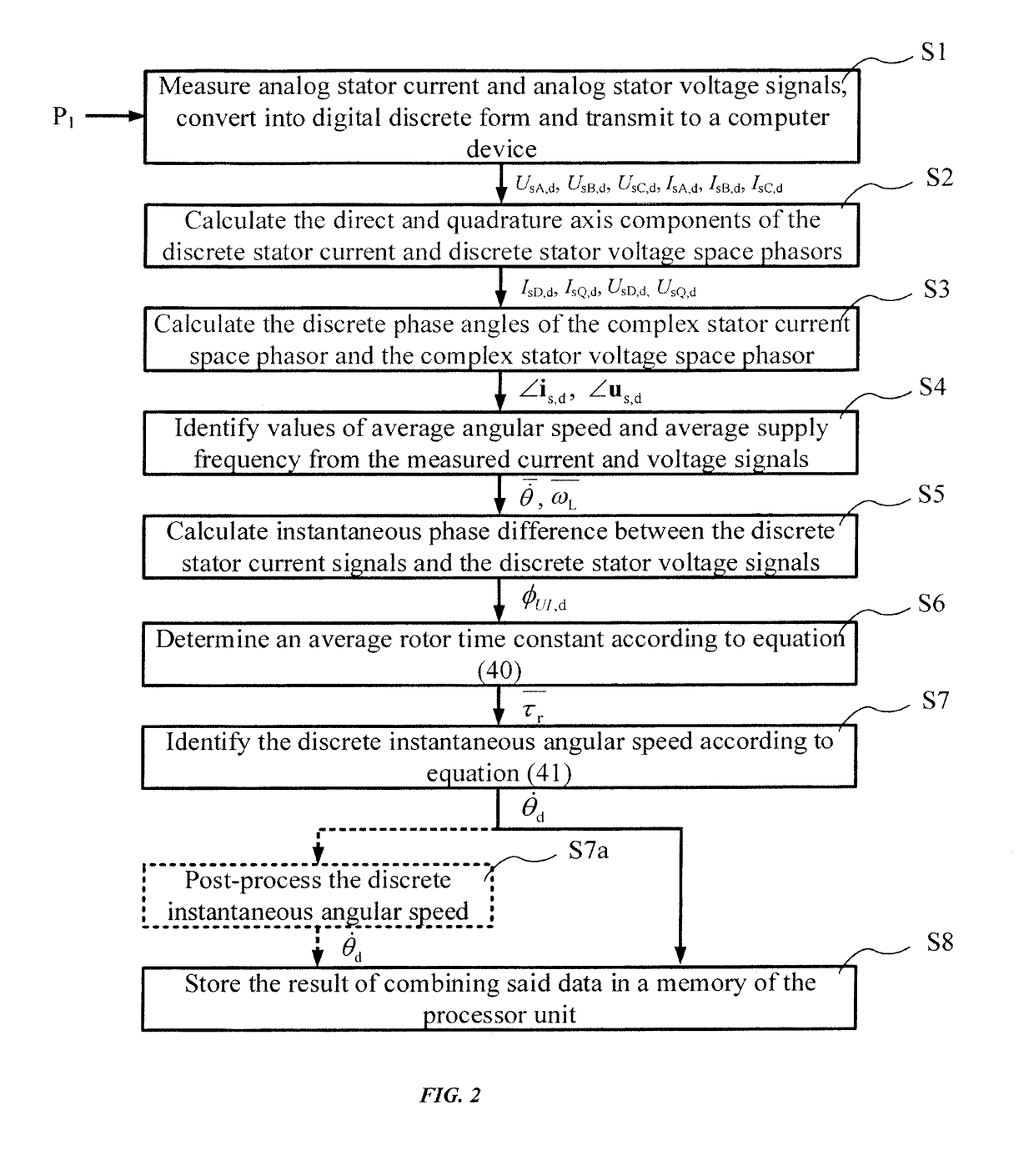
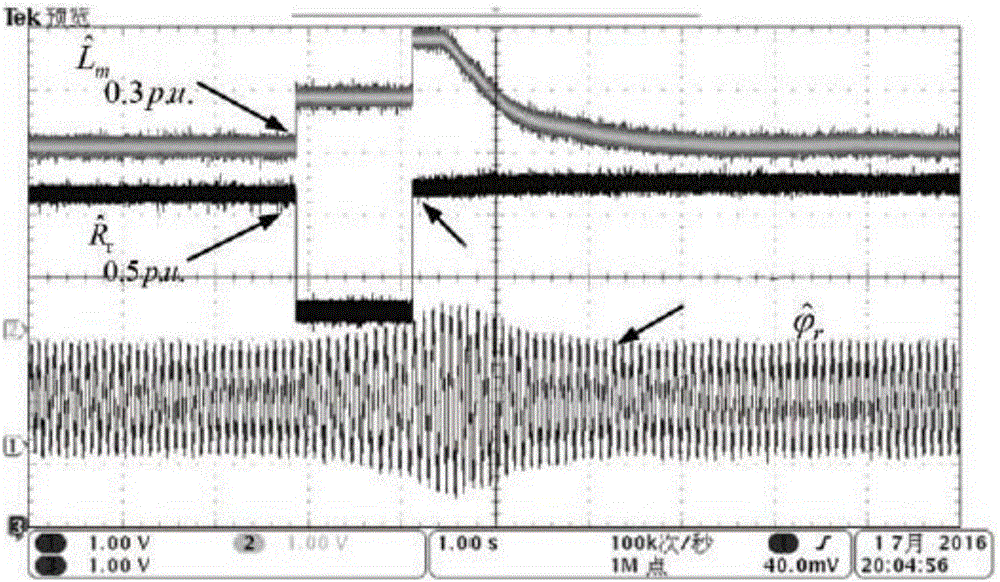
Method for identifying the discrete instantaneous angular speed of an electromechanical system
ActiveUS20180241332A1Minimize residual errorComputationally efficientElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlMathematical modelVIT signals
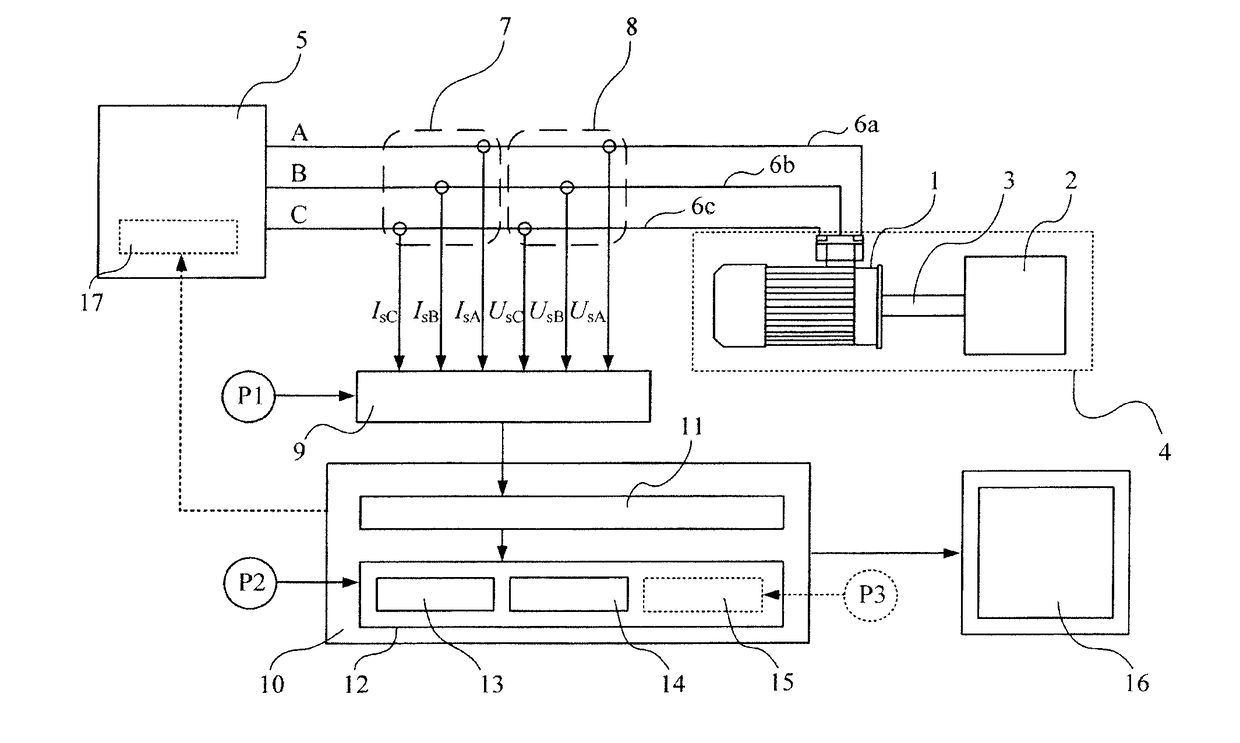
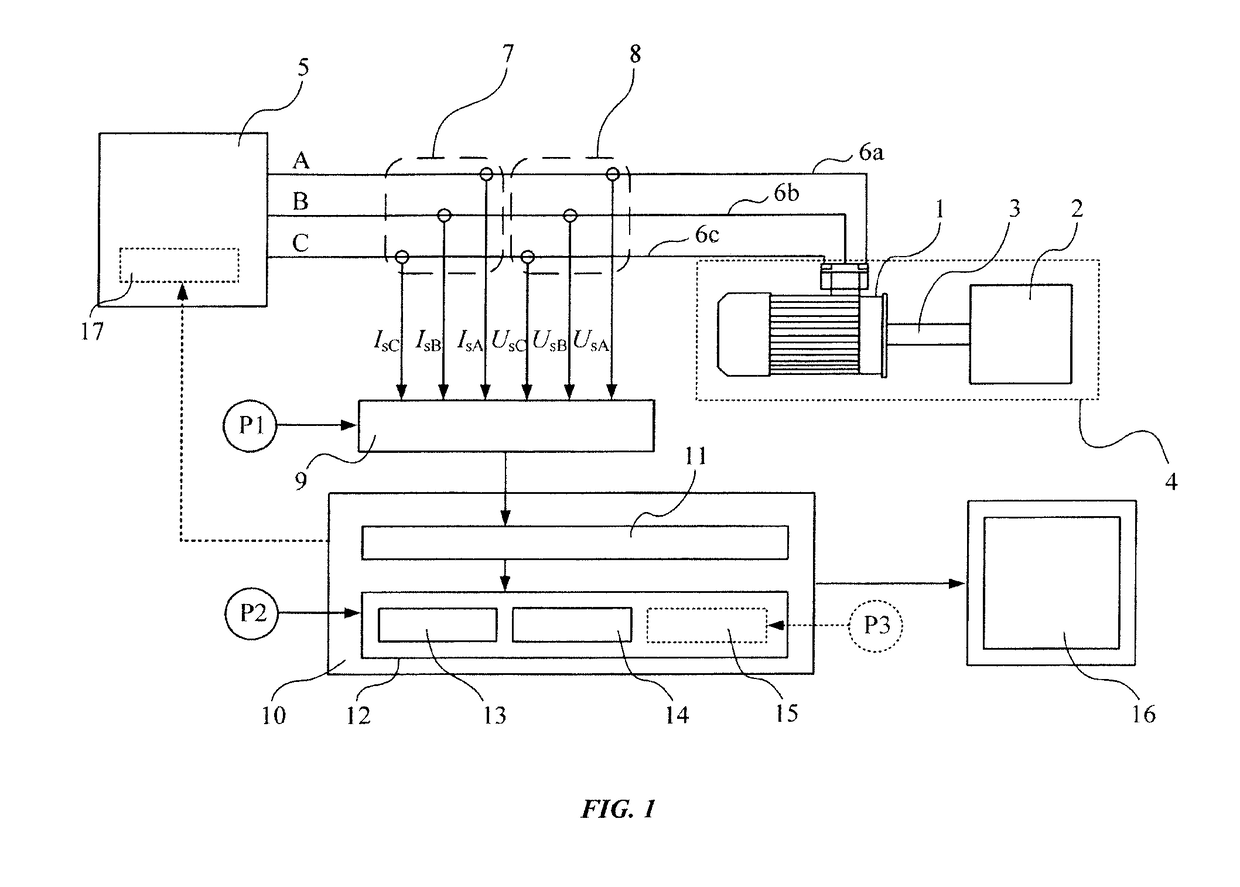
A method for identifying the discrete instantaneous angular speed of electromechanical systems in which electrical rotating machinery is used and in which at least one electrical signal is measured during an operation of the electromechanical system. The method includes measuring analog stator current signals and analog stator voltage signals for at least one phase A, B, C, converting the measurements into a digital discrete form, transmitting the digital discrete signals to a computer device wherein data analysis is performed in a processor unit on the basis of a simplified mathematical model of the dynamics of the motor or generator. During the data analysis an average rotor time constant is calculated, an average supply frequency value is identified, an average angular speed is obtained, and an instantaneous phase difference between the discrete stator current signals and the discrete stator voltage signals is determined. The discrete instantaneous angular speed is identified by combining the average supply frequency value, the instantaneous phase difference between the discrete stator current signals and the discrete stator voltage signals, the average rotor time constant, and a number of pole pairs of the electric motor, given by the user. The result of combining the data is stored in a memory of the processor unit.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Asynchronous motor parameter online correction method based on rotor flux observer
ActiveCN106452256ARealize online identificationAccurate rotor time constantElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase differenceAngular velocity
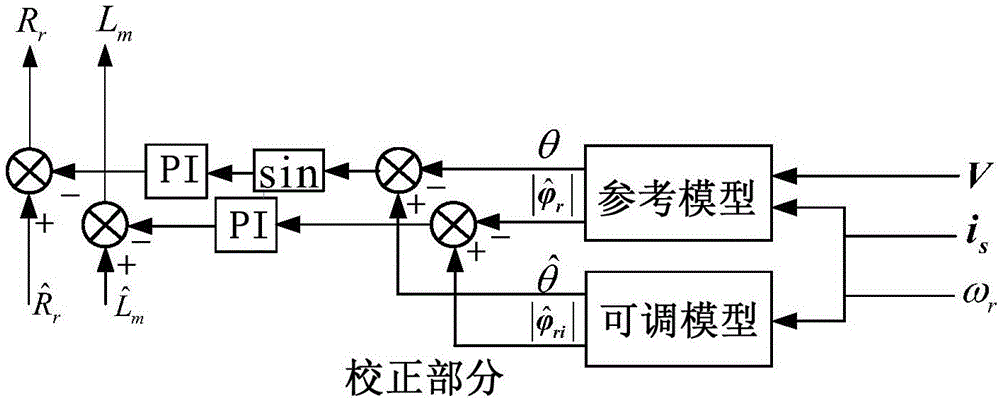
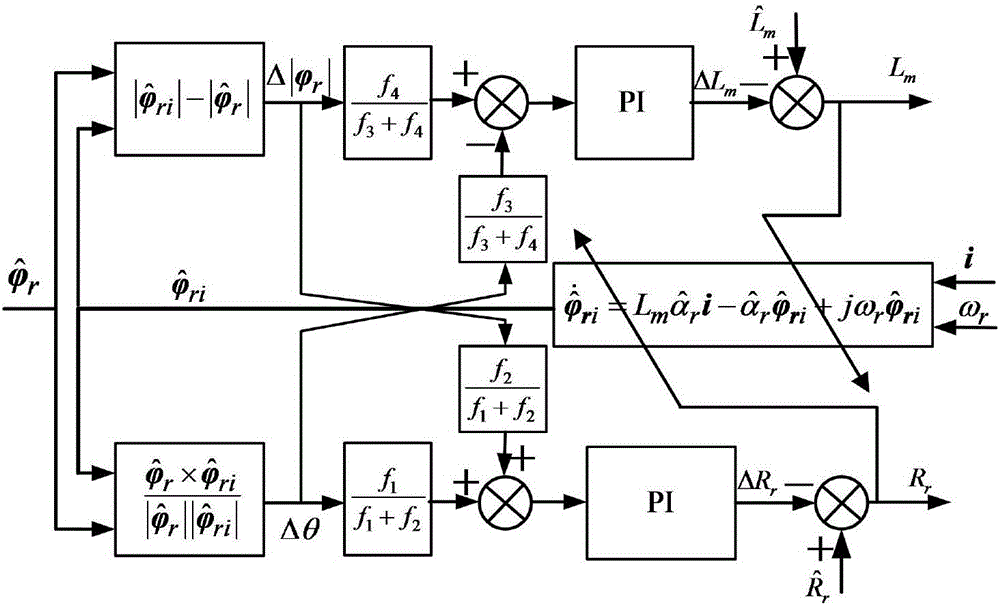
The invention discloses an asynchronous motor parameter online correction method based on a rotor flux observer. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: getting an accurate counter electromotive force e through a high-order current sliding-mode observer according to a motor stator voltage vector v, a stator current vector i and a rotor electrical angular velocity omega(r) under a two-phase static coordinate system (alpha-beta) obtained through acquisition and operation; setting up an asynchronous motor state space expression based on the relationship between the counter electromotive force and the rotor flux; constructing a rotor flux sliding-mode observer according to the space expression to observe a rotor flux vector phi(r); getting the calculated value phi<hat>(ri) of the rotor flux vector according to a current flux model; and further getting the phase difference sinusoidal quantity sin(delta theta) and the amplitude difference delta|phi(r)|; and using the phase difference sinusoidal quantity sin(delta theta) to correct a given rotor resistance R<hat>(r) in the system, and using the amplitude difference delta|phi(r)| to correct a given excitation inductance L<hat>(m) in the system. The integral problem caused by flux is overcome. Moreover, there is no transient flux problem, an accurate rotor time constant can be obtained, and online identification of excitation inductance is realized.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Power calculation based slip estimation system and power calculation based slip estimation method
ActiveCN103023421AHigh control precisionSmall magnetic field orientation errorElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageRC time constant
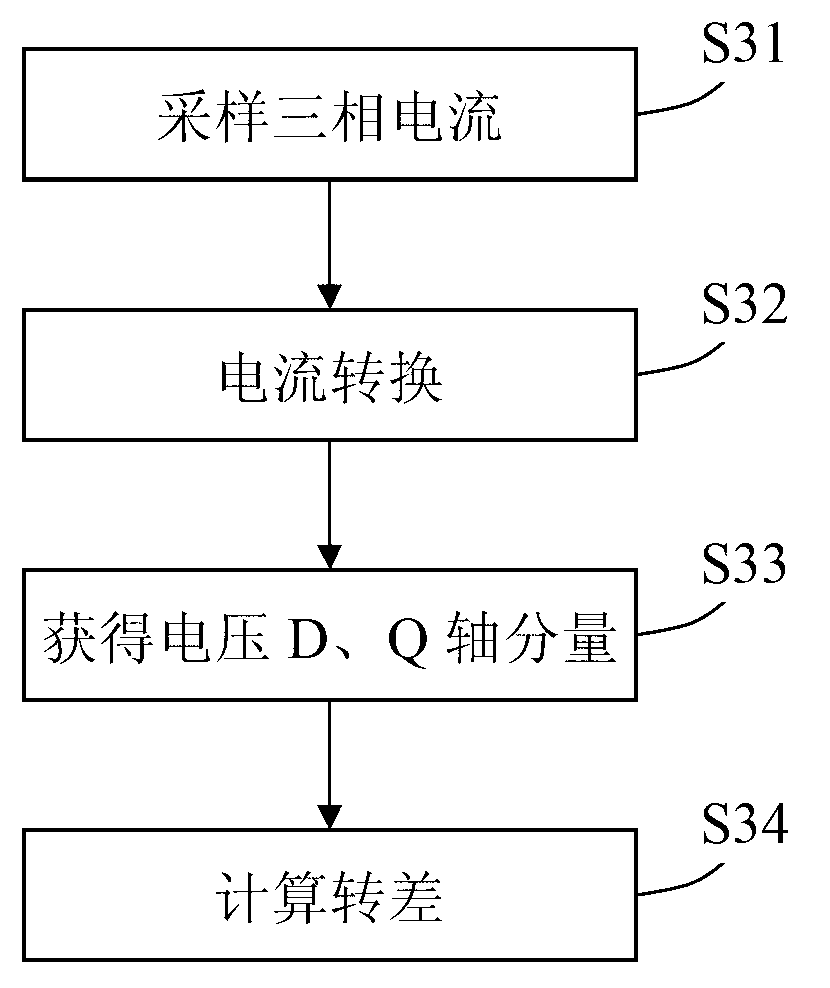
The invention provides a power calculation based slip estimation system. The power calculation based slip estimation system comprises a current sampling unit, a current conversion unit, a current regulation unit and a slip calculation unit, wherein the current sampling unit is used for sampling three-phase current of an asynchronous motor, the current conversion unit is used for obtaining feedback current D-axis component and Q-axis component, the current regulation unit is used for obtaining D-axis stator voltage and Q-axis stator voltage, and the slip calculation unit is used for obtaining slip according to the D-axis stator voltage, the Q-axis stator voltage, the feedback current D-axis component, the Q-axis component and a rotor time constant. The invention further provides a corresponding method. The system and the method have the advantages that the slip is estimated according to the ratio of active power to reactive power to enable rotor field orientation error caused by the rotor time constant Tr during speed regulation to become smaller, so that rotor field orientation effect of the asynchronous motor is improved effectively, and torque control precision is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU INOVANCE TECH CO LTD
Asynchronous motor rotor time constant online recognition method based on improved reactive power model
InactiveCN105227022AEasy to set upElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsFour quadrantsLow speed
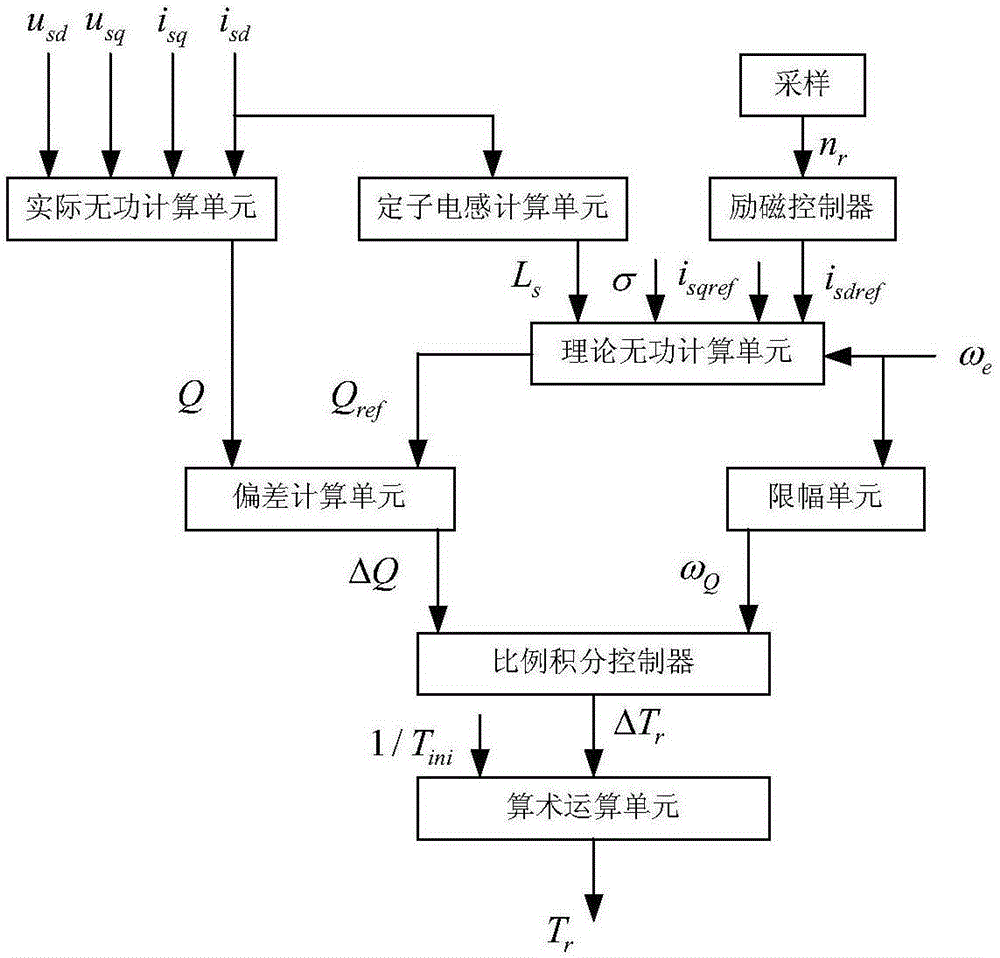
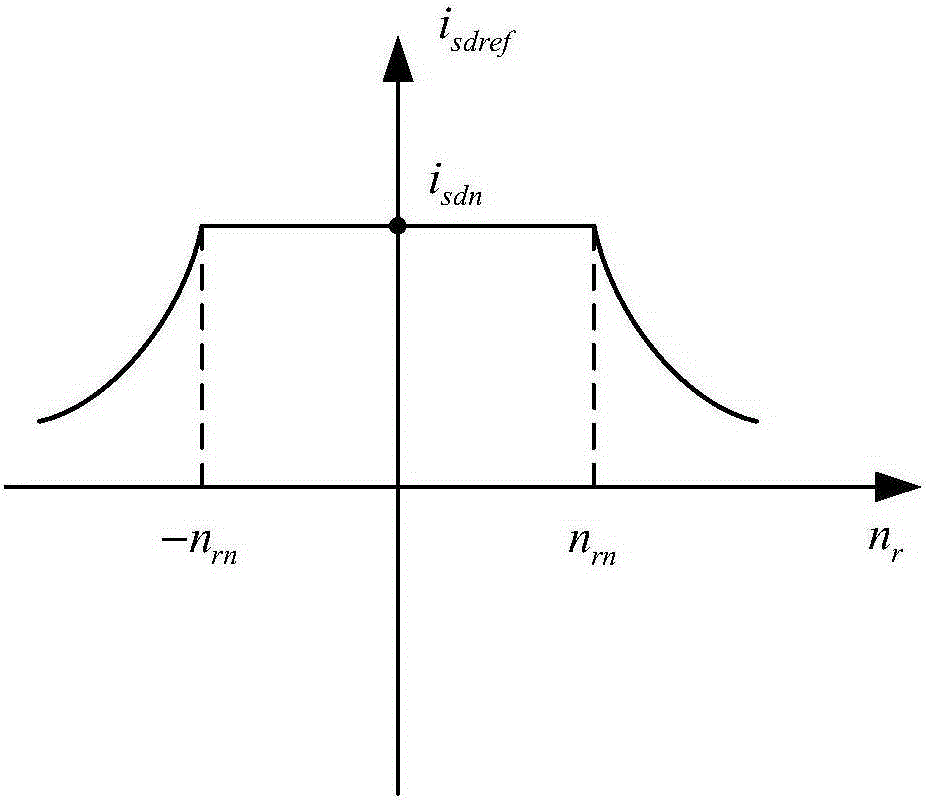
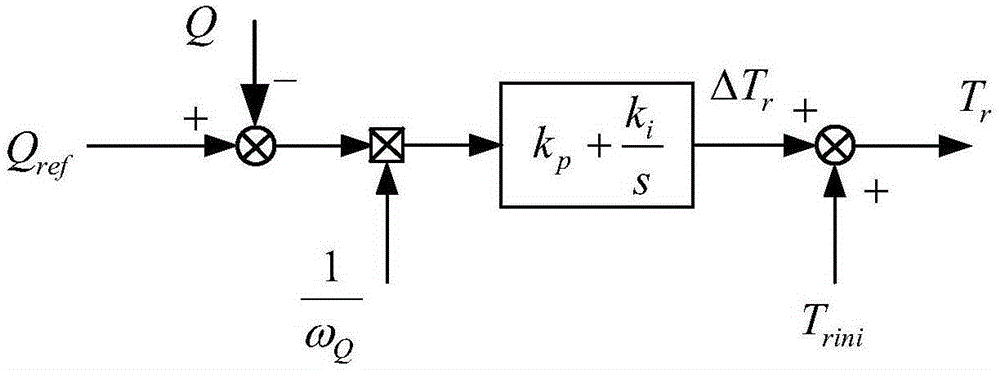
The invention discloses an asynchronous motor rotor time constant online recognition method based on an improved reactive power model. According to the invention, a feed-forward for a motor stator frequency, subjected to the amplitude limiting treatment, is introduced in a conventional reactive power model. The method comprises the steps of sampling and obtaining the actual reactive power Q of a motor by an actual reactive power calculation unit; obtaining the stator inductance Ls of the motor by a stator inductance calculation unit; obtaining the reference value Isdref of the d-axis component of the stator current of the motor by an excitation controller; obtaining the theoretical reactive power Qref of the motor by a theoretical reactive power calculation unit; obtaining the reactive power deviation delta Q by a deviation calculation unit; obtaining a feed-forward value omega Q by an amplitude limiting unit; obtaining a correction value delta Tr for the rotor time constant Tr of the motor by a proportional-integral controller; and calculating the rotor time constant Tr of the motor by an arithmetic operation unit. The above method can be applied in the four-quadrant operation scenarios for the motor. By means of the method, the proportional-integral controller of the reactive power model is easy to set. At the same time, the similar rotor time constant convergence dynamic process can be obtained during the high-speed and low-speed operation process of the motor.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for measuring parameter of asynchronous motor
InactiveCN102914741AHigh precisionReduce mistakesDynamo-electric machine testingRotor time constantControl theory
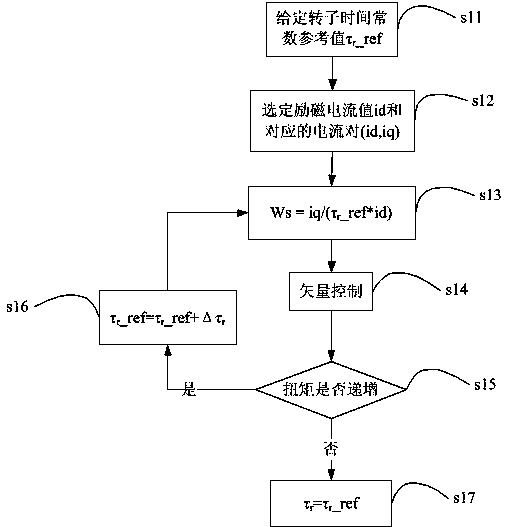
The invention relates to a method for measuring a parameter of an asynchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps of: presetting a reference exciting current and a reference torque current, setting a first rotor time constant and a second rotor time constant; obtaining a first slip frequency and a second slip frequency which respectively correspond to the first rotor time constant and the second rotor time constant by using a slip frequency formula; respectively obtaining a first output torque and a second output torque which correspond to the first rotor time constant and the second rotor time constant; and respectively substituting the first output torque, the second output torque, the first slip frequency and the second slip frequency into a torque formula to work out an actual rotor time constant, wherein an output torque in the torque formula is a product of a first coefficient and an expression including the rotor time constants and the slip frequency product. The invention also relates to a method for realizing the device. The method and device for measuring the parameter of the asynchronous motor have the beneficial effect that the measured rotor time constant is high in accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN HANGSHENG ELECTRONICS
Method for automatically identifying asynchronous motor rotor time constant by frequency converter
ActiveCN105281633AReduce workloadAchieve the intended effectElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPrimary screeningRotor time constant
The invention discloses a method for automatically identifying asynchronous motor rotor time constant by a frequency converter. The method comprises following steps: a, calculating the probable value tau of the rotor time constant; b, selecting at least five numbers including tau[1], tau[2] and the like...tau[n] between 0.1 tau to 3 tau as primary screening rotor time constants; c, driving the asynchronous motor to rotate by the frequency converter according to the selected first primary screening rotor time constant tau[1], and obtaining a first primary screening speed deviation accumulated value after the asynchronous motor finishing the operation process; d, obtaining a primary second screening speed deviation accumulated value based on a similar way of the step c; e, performing the same process until obtaining the n-th primary screening speed deviation accumulated value by the frequency converter; f, comparing the obtained n primary screening speed deviation accumulated values, and using the primary screening rotor time constant corresponding to the minimum primary screening speed deviation accumulated value as an identification result. Through adoption of the method, neither debugging performed by professional staff nor additional hardware equipment is needed, and the method has good identification effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI STEP ELECTRIC +1
Asynchronous motor rotor time constant adjusting method
ActiveCN105897104AAccurate Rotor Time ConstantImprove efficiencyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsFrequency changerPower flow
The invention discloses an asynchronous motor rotor time constant adjusting method. The asynchronous motor rotor time constant adjusting method comprises the steps: judging whether the rated field current is accurate; commanding the motor to operate with high speed under zero load, recording and extracting several practical modulation coefficients for a frequency converter in different rotating speed stages, obtaining the due theoretical modulation coefficient in the normal situation through calculation, comparing the values of the two modulation coefficients and adjusting the excitation current value set by the system until the two modulation coefficients for several different speed points become approximate; and on the basis of determining that the excitation current value set by the system is approximate to the rated excitation current value, commanding the motor to run with moderate load or heavy load in the high speed stage, recording and extracting several practical modulation coefficients for the frequency converter in different rotating speed stages, calculating the modulation coefficients under the corresponding rotating speed at the same time, and comparing the values of the two coefficients at several different speed points. The asynchronous motor rotor time constant adjusting method is high in efficiency and low in consumed time, and can be quickly mastered and applied to field debugging to enable the motor rotor time constant to be approximate to a true value so as to guarantee the motor to work in the optimal state.
Owner:中国船舶重工集团公司第七一二研究所
Method for verifying induction motor rotor time constant based on magnetic field orientation accuracy
InactiveCN106602953AEasy to implementElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsValidation methodsExcitation current
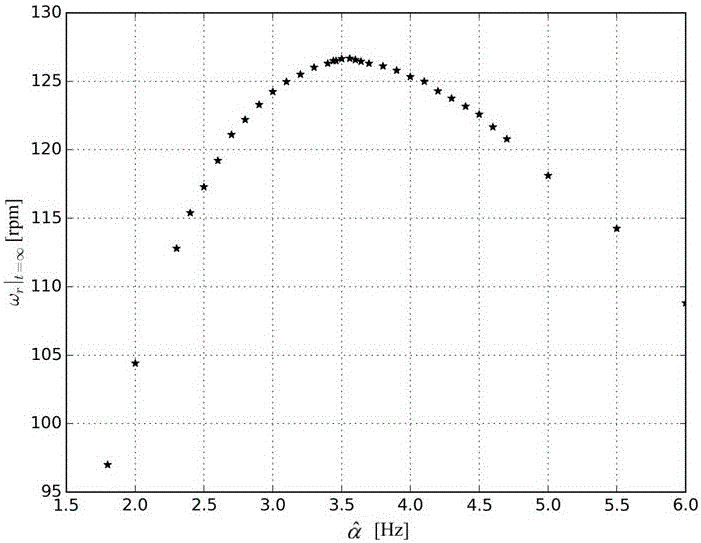
The invention discloses a method for verifying an induction motor rotor time constant based on magnetic field orientation accuracy. The implementation steps are as follows: firstly, in an indirect rotor magnetic field orientation controller a given torque current and exciting current are ensured to be equal; secondly, a motor drags a direct current generator load to rotate in an operation mode with given torque; then, a rotor time constant value in the controller is constantly changed, and corresponding motor steady state rotation speed values are recorded; and finally, when the steady state rotation speed of the motor corresponding to a certain rotor time constant value reaches the highest is observed, and the rotor time constant value is an accurate value. The method can automatically run and complete verification, and does not need people to judge an experiment phenomenon, and a result is fairly accurate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
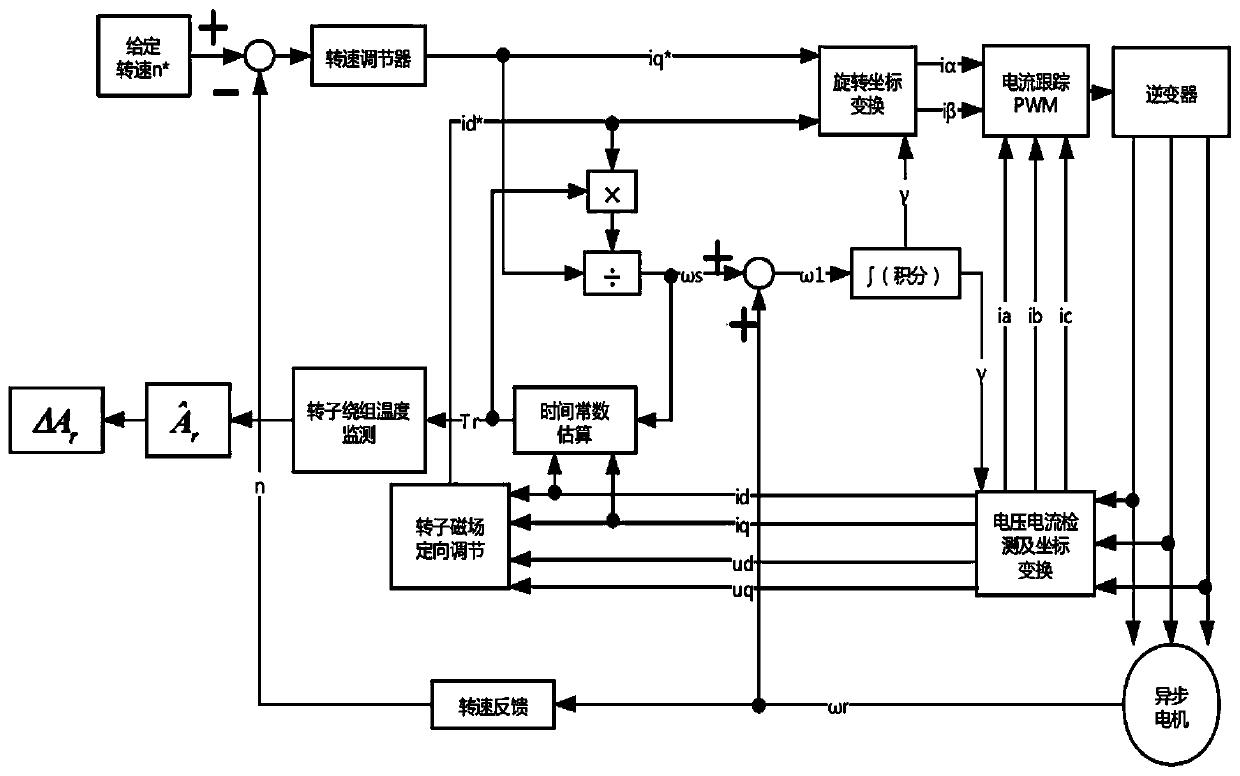
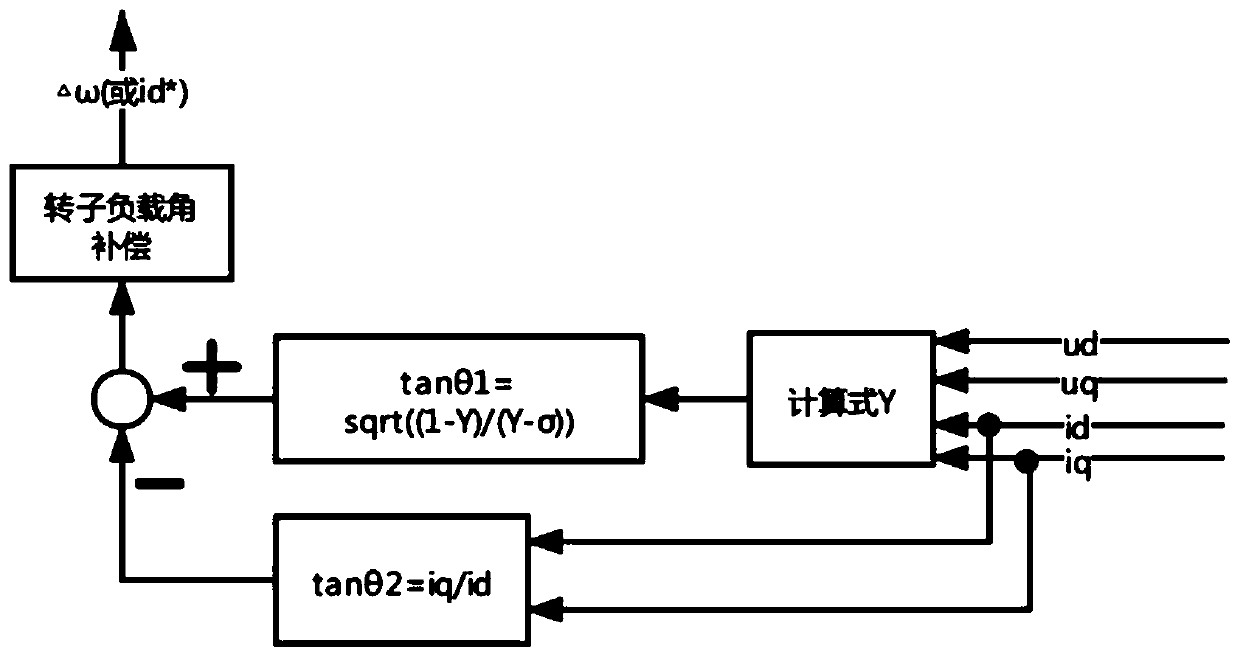
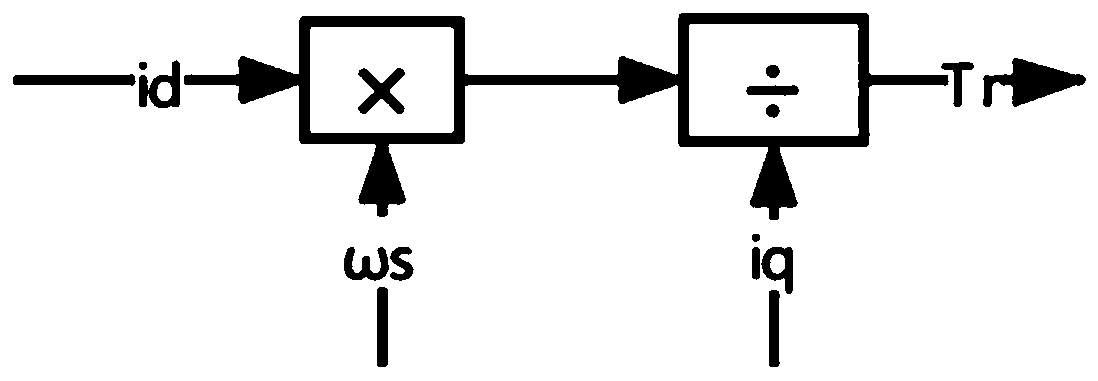
Asynchronous motor vector control rotor winding temperature on-line monitoring method
ActiveCN111049450AOrientation is accurateAchieve independent controlElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlElectric machineWorking environment
The invention relates to an asynchronous motor vector control rotor winding temperature on-line monitoring method comprising the following steps: 1) carrying out rotor magnetic field accurate orientation based on load angle compensation correction according to current and voltage signals under d-q synchronous rotation coordinates; 2) estimating a rotor time constant on the basis of accurate orientation of a rotor magnetic field and correction and compensation of slip frequency; 3) estimating the rotor time constant value in a short time when the motor is started for the first time to reach stable rotating speed, and obtaining a motor cooling medium detection temperature; 4) estimating the current rotor time constant value in the normal working process of the motor, obtaining the motor cooling medium detection temperature corresponding to the moment, and estimating the rotor winding temperature in real time; and 5) obtaining the temperature rise of the rotor winding. Compared with the methods in the prior art, the method has the advantages that the rotor magnetic field orientation is accurate, the robustness is good, the temperature monitoring of the rotor winding is conveniently realized, and the method is not influenced by the characteristics of hardware equipment, the electromagnetic interference of a working environment and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
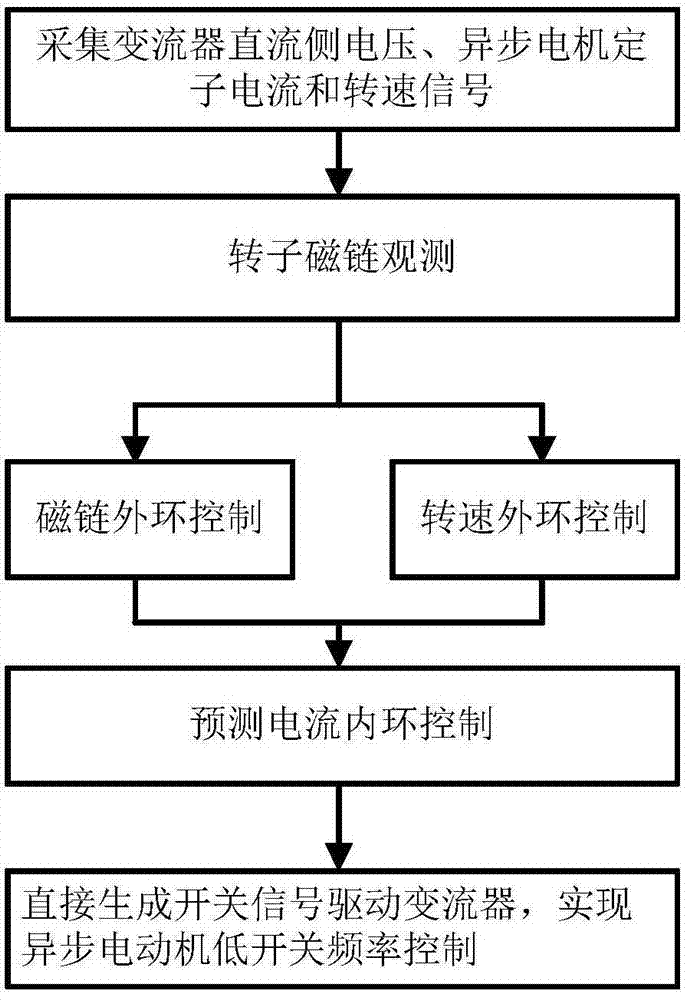
Low switching frequency operation control method for new-type high power asynchronous motor
ActiveCN107231109AImprove reliabilityEfficiencyElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlClosed loopLinear modulation
The invention discloses a low switching frequency operation control method for a new-type high power asynchronous motor. The method comprises the steps of signal collection, flux linkage observation, flux linkage outer ring control and rotation speed outer ring control, and prediction current inner ring control. An inverter direct current side voltage and a motor stator current are obtained through utilization of collection signals; rotor flux linkage is obtained through calculation; flux linkage closed loop is realized to obtain a d-axis current reference value; the rotation speed of an asynchronous motor is obtained through utilization of the collection signals; rotation speed closed loop is realized to obtain a q-axis current reference value; and a switching signal is directly generated through the prediction current inner ring control, thereby realizing the control of the inverter over the motor. According to the method, a boundary is appointed to be an oval with a long d-axis and a short q-axis in a dq synchronous coordinate system, so the switching frequency operation control with a relatively low linear modulation mode is realized; the switching frequency is reduced by releasing relatively high errors to a d-axis; moreover, the problem of increasing an additional harmonic current is avoided through utilization of the feature that a motor rotor time constant is relatively high; and the motor system operation reliability and high efficiency under the low switching frequency are improved.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Self-setting method in vector control system of asynchronous motor
InactiveCN102710207AReduce test errorReduce phase currentElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVector control systemSteady state
The invention relates to a self-setting method in a vector control system of an asynchronous motor, which mainly adopts rotor time constant self testing under the magnetic circuit saturation. The self-setting method aims to achieve the effect of controlling the performance in a speed control system of the vector control asynchronous motor through the rotor time constant self testing under the magnetic circuit saturation. The rotor time constant self testing is carried out through a voltage type inverter. When direct current voltage is excited and added, the current of a rotor circuit of the asynchronous motor is zero, and the current of a stator is a steady-state current value Id. If a transient process occurs in the current of the stator, the current initial value of the rotor circuit is not zero. Therefore, the zero current of a rotor can be determined through the characteristic, so that a rotor time constant is obtained by adopting a least square method. The self-tested rotor time constant particularly considers the measurement and the acquisition of the rotor time constant under the magnetic circuit saturation and the dead-time compensation, so that the performance of the vector control system of the asynchronous motor is improved.
Owner:北京建筑工程学院
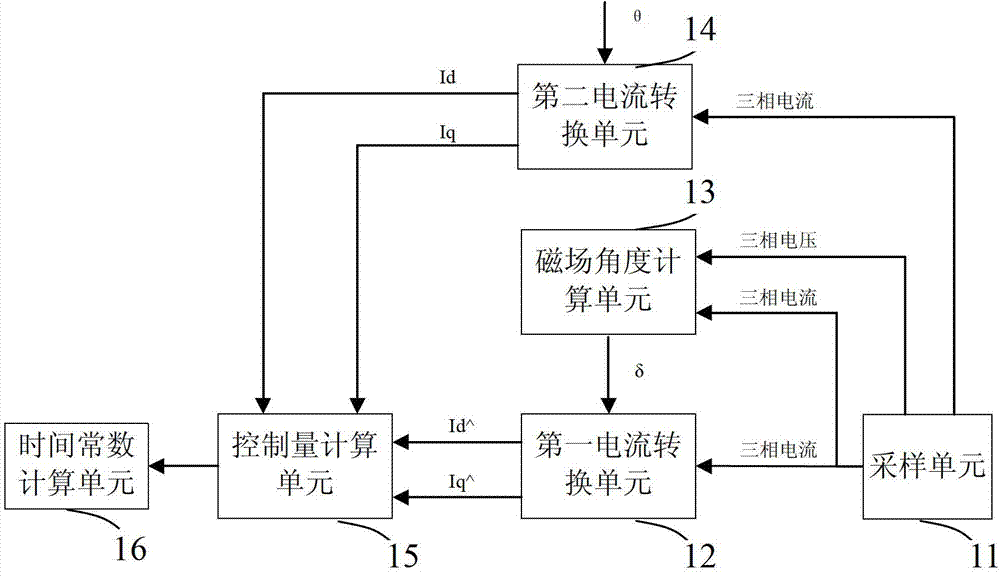
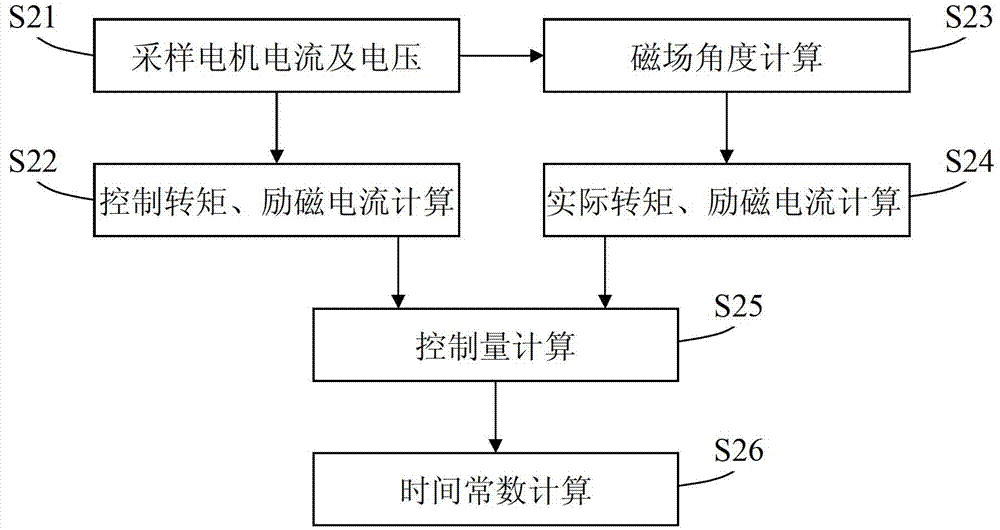
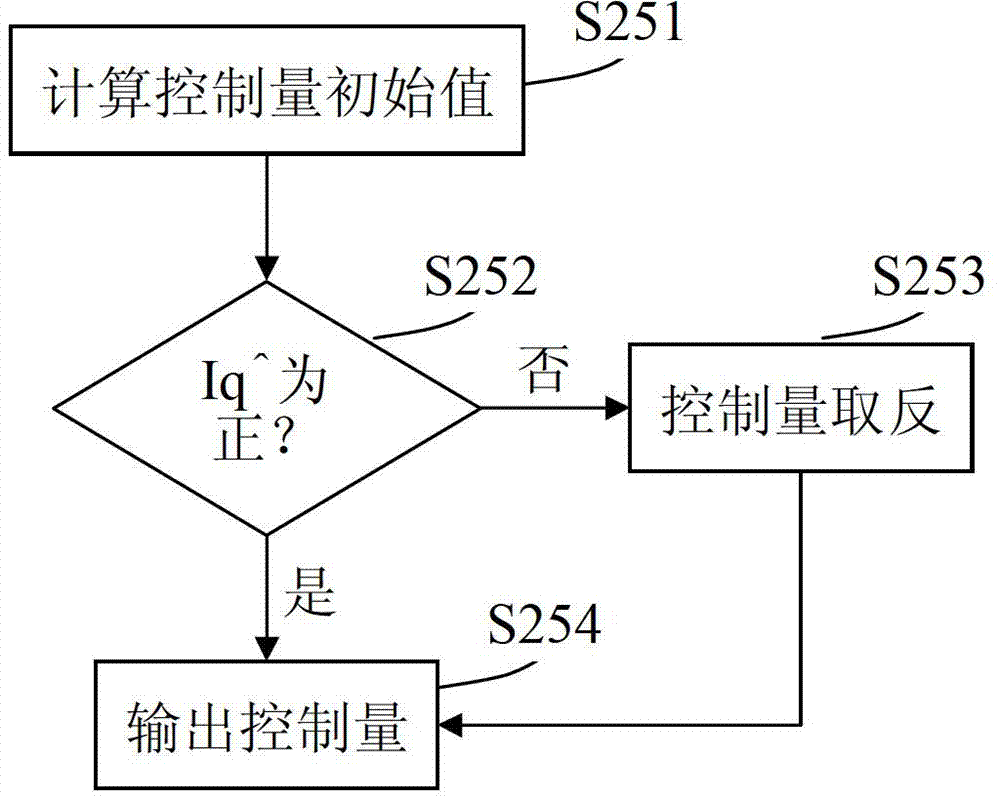
Rotor time constant online identifying system and method based on flux estimator
ActiveCN103051278ARealize online real-time identificationImproving the effect of magnetic field orientationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsExcitation currentThree-phase
The invention provides a rotor time constant online identifying system based on a flux estimator. The system comprises a sampling unit, a magnetic field angle calculating unit, a first current converting unit, a second current converting unit, a controlled quantity calculating unit and a time constant calculating unit, wherein the sampling unit is used for sampling the three-phase voltage and three-phase current of the output end of an asynchronous motor; the magnetic field angle calculating unit is used for calculating an estimated magnetic field angle; the first current converting unit is used for acquiring practical exciting current and practical torque current; the second current converting unit is used for acquiring control exciting current and control torque current; the controlled quantity calculating unit is used for calculating a controlled quantity; and the time constant calculating unit is used for calculating and updating a rotor time constant. The invention further discloses a corresponding method. According to the system and method, the rotor time constant is calculated by a relation between estimated magnetic field angle decomposing current and control angle decomposing current, so that the torque control accuracy is increased.
Owner:SUZHOU INOVANCE TECH CO LTD
Method for calibrating key parameters of asynchronous motor of electric vehicle
ActiveCN110620536AFine state adjustmentSpeed controllerElectronic commutation motor controlMaximum torqueMotor controller
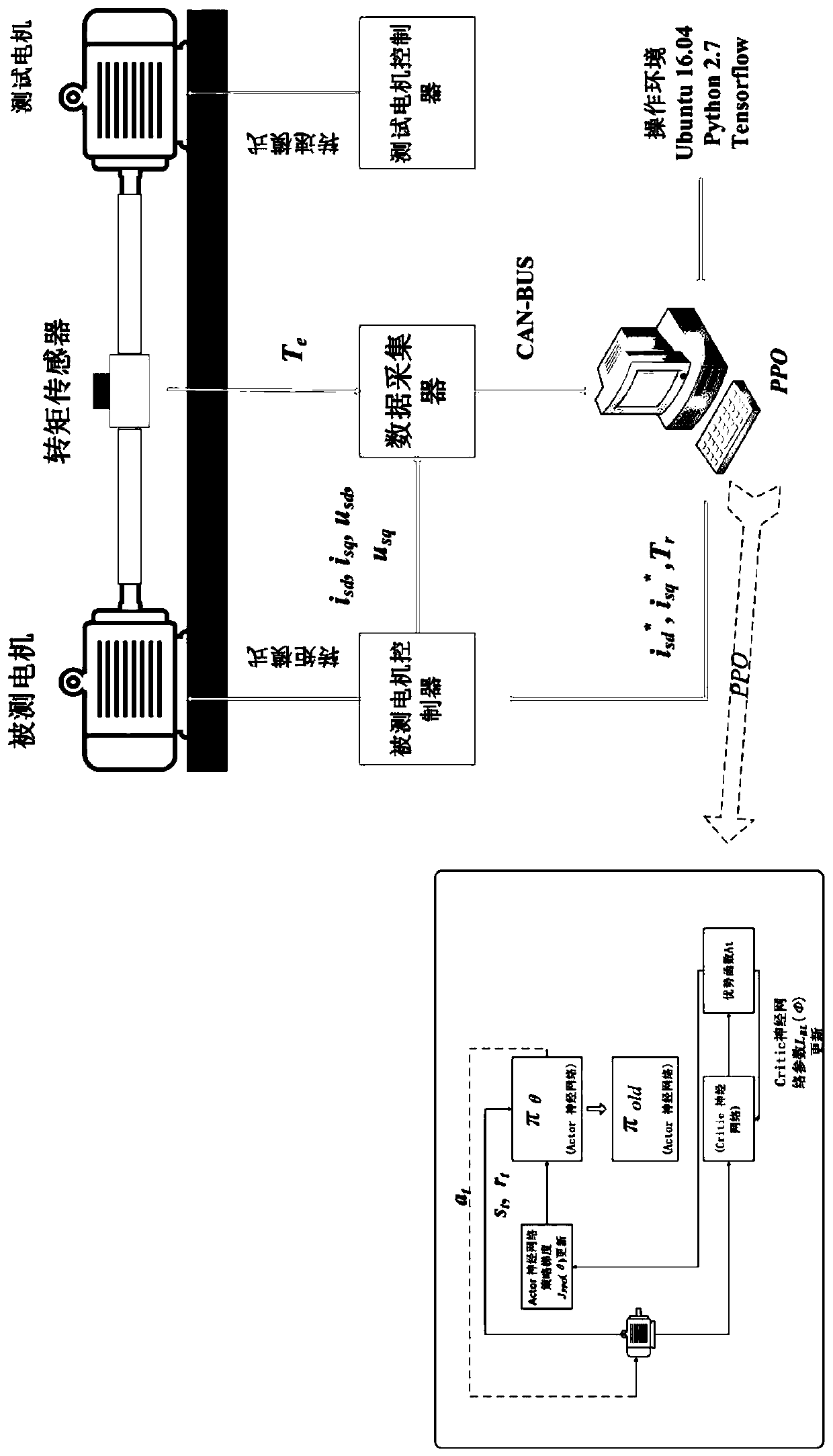
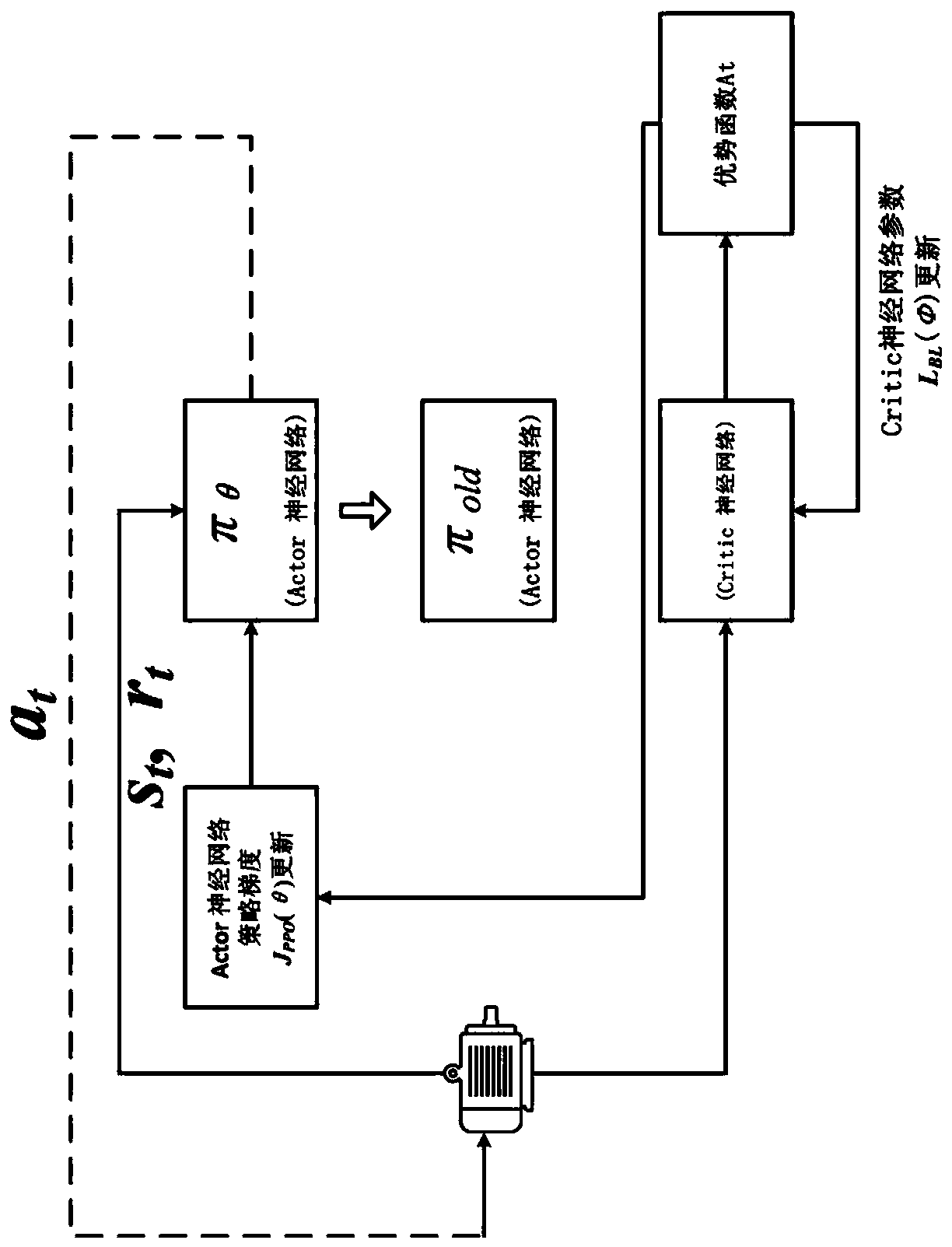
The invention discloses a method for calibrating key parameters of an asynchronous motor of an electric vehicle. The method comprises the steps: on a motor twin-trawling table, for different rotatingspeeds n and different torque instructions Te* under a current rotating speed, calibrating a d-axis given current value, a q-axis given current value and a rotor time constant value of the asynchronous motor of the electric vehicle by adopting a Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm; storing a calibrated result in a motor controller in a form of a table so that the asynchronous motor of theelectric vehicle queries and uses the parameter can be inquired during actual operation. According to the method, the rotor time constant of the asynchronous motor of the electric vehicle is calibrated, and the d-axis given current and the q-axis given current of the motor are also calibrated; meanwhile, the calibrated parameters can enable the motor to have the maximum torque-current ratio characteristic under any rotating speed n and torque instruction Te*.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Induction motor feedback type indirect vector control system and control method thereof
ActiveCN105763126AWidely used valueRealize decoupling controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsHysteresisIndirect vector control
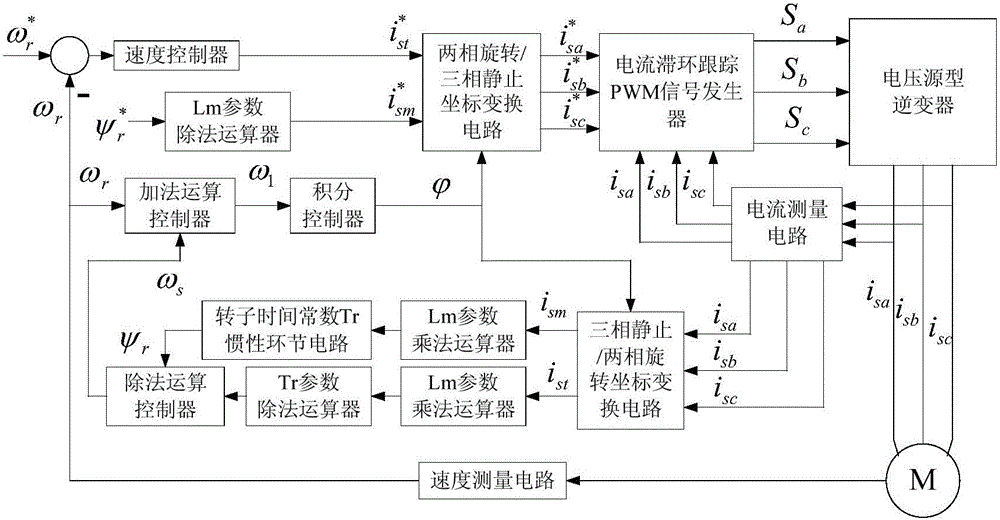
The invention relates to induction motor feedback type indirect vector control system and a control method thereof.The control system includes a speed controller, an Lm parameter division arithmetic unit, an addition operation controller, an integral controller, a division operation controller, a Tr parameter division arithmetic unit, a high cut-off frequency low-pass filter, a three-phase static / two-phase rotating coordinate transformation circuit, a two-phase rotating / three-phase static coordinate transformation circuit, a current hysteresis tracking PWM signal generator, a voltage source inverter and an induction motor.Compared with the prior art, the induction motor feedback type indirect vector control system needs an Lm parameter multiplication arithmetic unit and a rotor time constant Tr inertial link circuit no longer, and the high cut-off frequency low-pass filter is added, so that the problem that the rotor flux linkage vector amplitude of a traditional control system monotonically rises, dynamic response is slow and the induction motor cannot perform constant acceleration and quick starting at an accelerating-starting stage, and the dynamic response of the induction motor feedback type indirect vector control system is improved.
Owner:国家电投集团河南电力有限公司
Asynchronous motor rotor resistance and excitation inductance decoupling correction method
ActiveCN106685294ARealize online identificationAccurate rotor time constantElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase differenceAngular velocity
The invention discloses an asynchronous motor rotor resistance and excitation inductance decoupling correction method. The method comprises the steps of obtaining accurate counter electromotive force e via a high-order sliding-mode observer according to the acquired and calculated motor stator voltage vector V, stator current vector i and rotor electrical angular velocity omega r under a two-phase static coordinate system alpha beta, and establishing an asynchronous motor state space expression according to the relation between the counter electromotive force and the rotor flux, thus realizing accurate observation of a rotor flux vector phi r; obtaining a rotor flux vector calculation value which is defined in the specification according to a current flux model, then obtaining a phase difference delta theta and an amplitude difference which is defined in the specification, analyzing and deducing a correlation function of a parameter error and a flux error to obtain a weighting coefficient, correcting given rotor resistance which is defined in the specification in the system by using a decoupling correction function I which is defined in the specification, and correcting given excitation inductance in the system by using a decoupling correction function II which is defined in the specification. The method does not have the flux transient problem while solving the problem of integration of flux acquisition, and can obtain an accurate rotor time constant and realize on-line identification of the excitation inductance.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for estimating the rotor time constant of an induction machine
ActiveUS7250739B2Accurate estimateSimple and accurate estimationSingle-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersStator voltageDc current
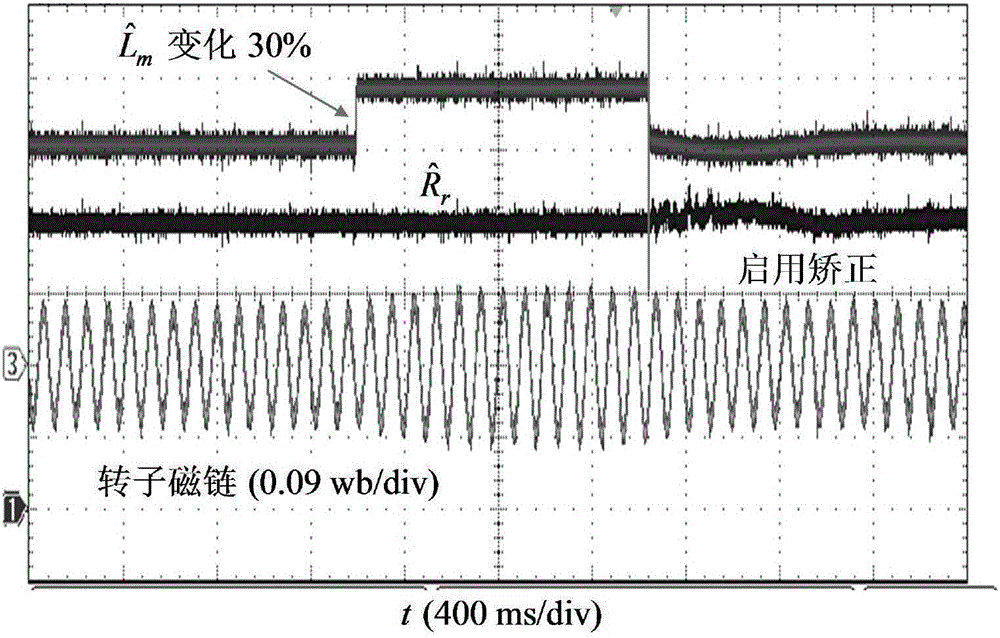
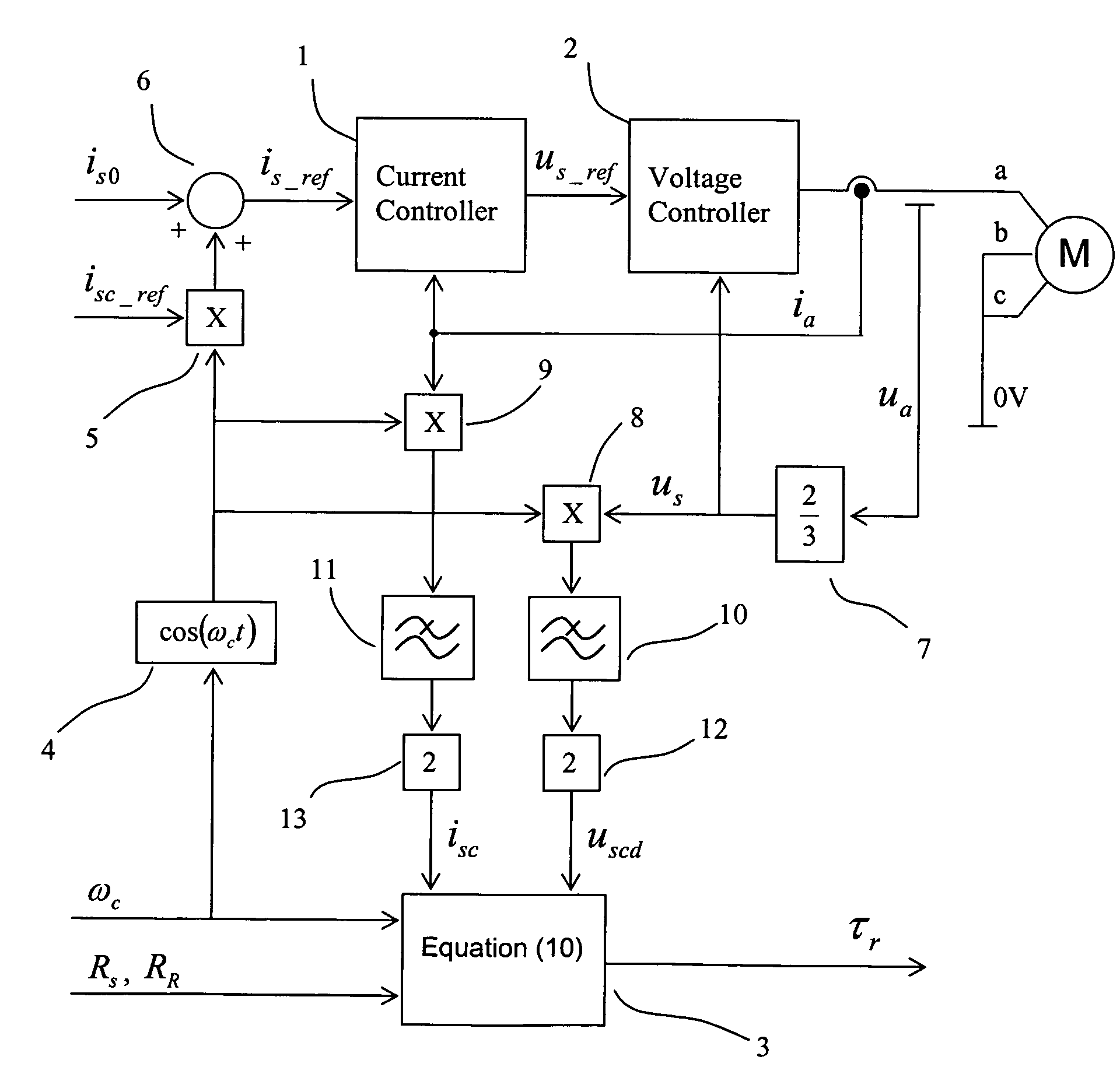
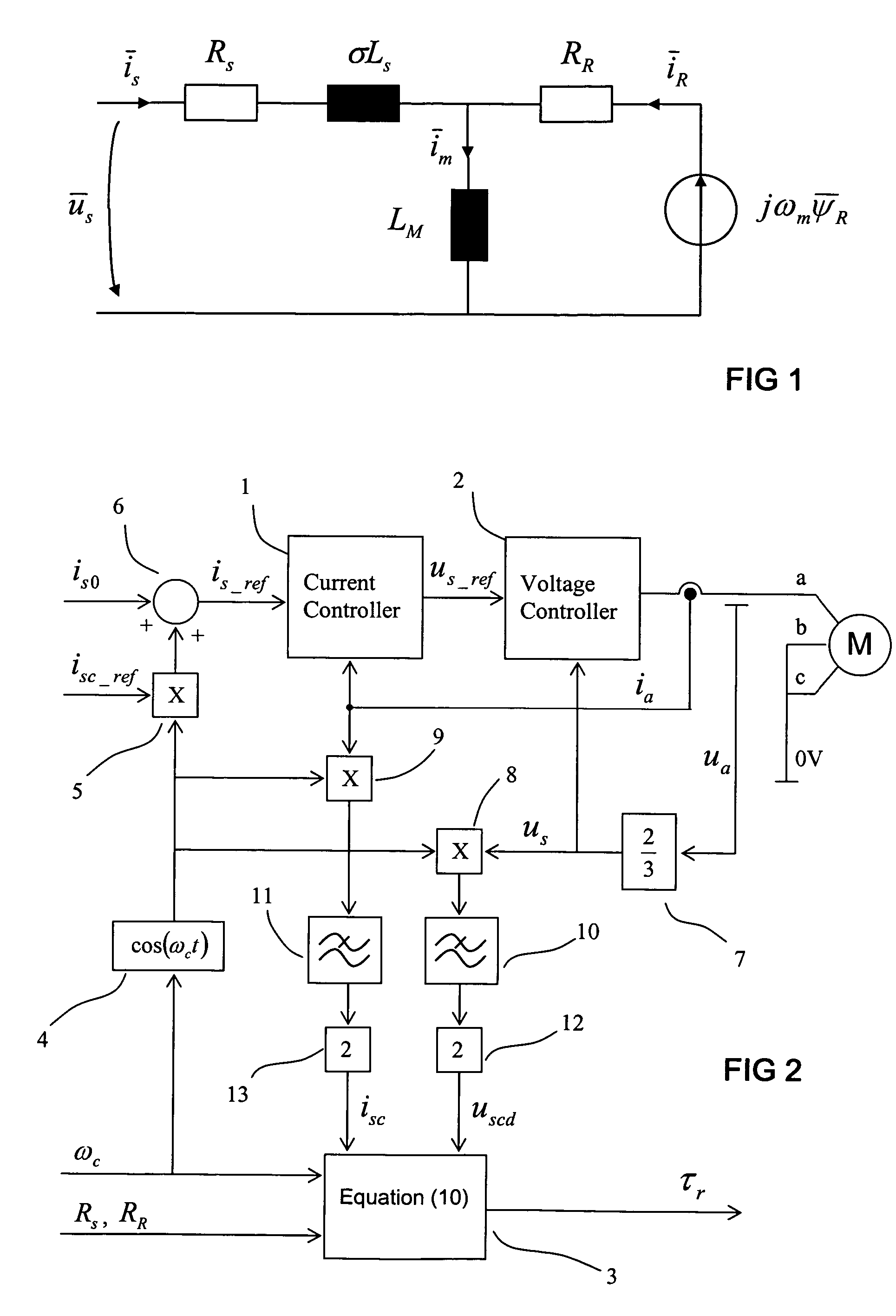
A method for estimating the rotor time constant (τr) of an induction machine when the stator resistance (Rs) and rotor resistance (Rr) of the induction machine are known. The method comprises the steps of feeding a DC current to the stator of the induction machine, injecting a sine-wave current component into the stator of the induction machine, the current having an amplitude (isc) and an angular frequency (ωc), measuring the voltage component (uscd) of the stator voltage of the induction machine in the same direction and with the same angular frequency as the injected current, and calculating the rotor time constant using equationτr=1ωcuscd-Rsisc(Rs+RR)isc-uscd.
Owner:OY ABB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com