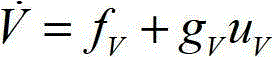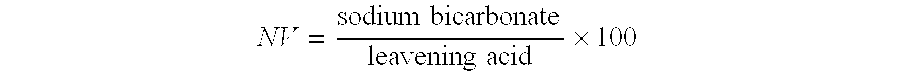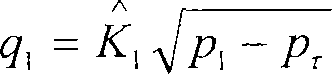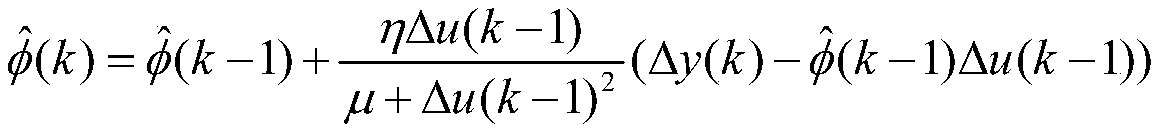Patents
Literature
83 results about "Discrete form" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
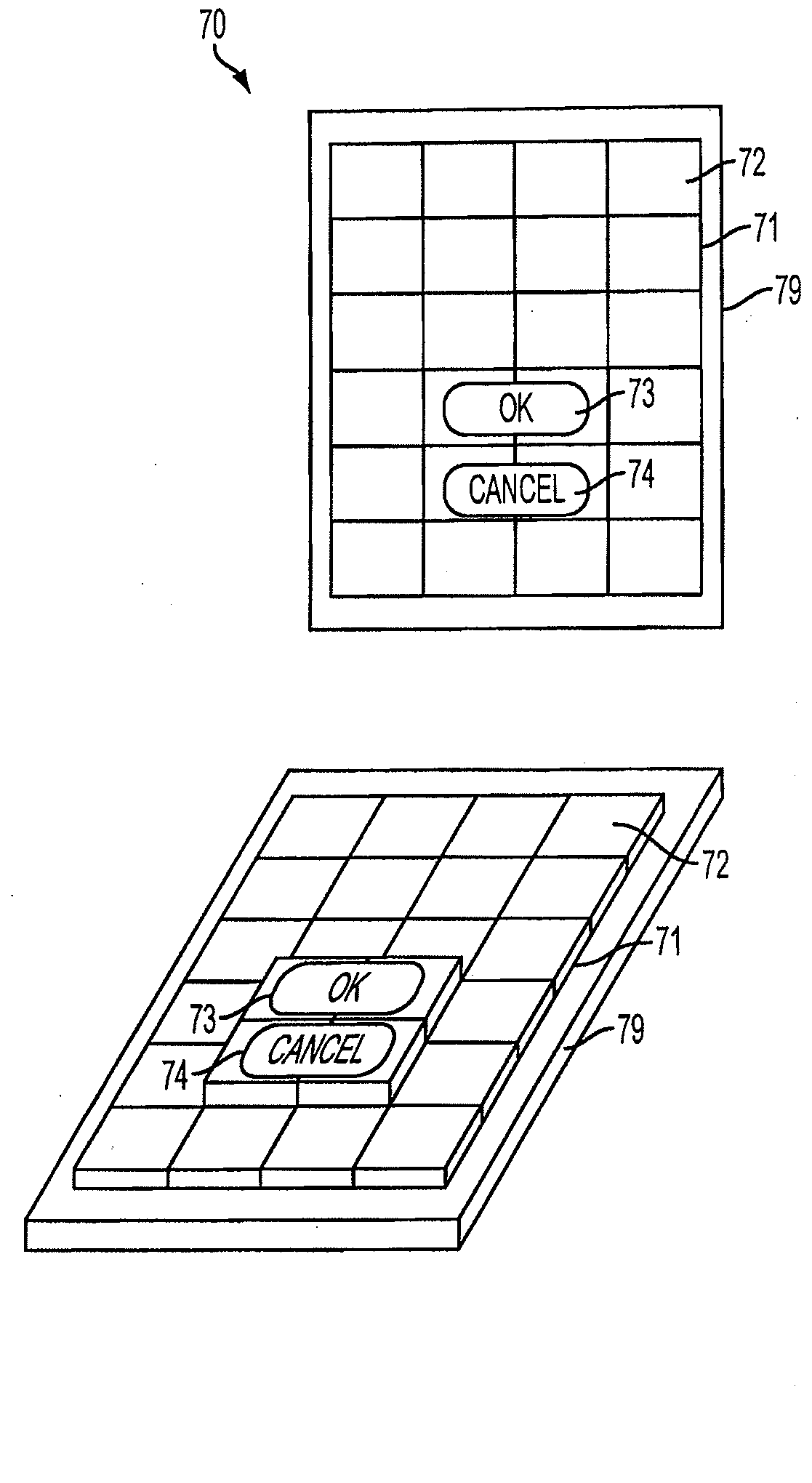
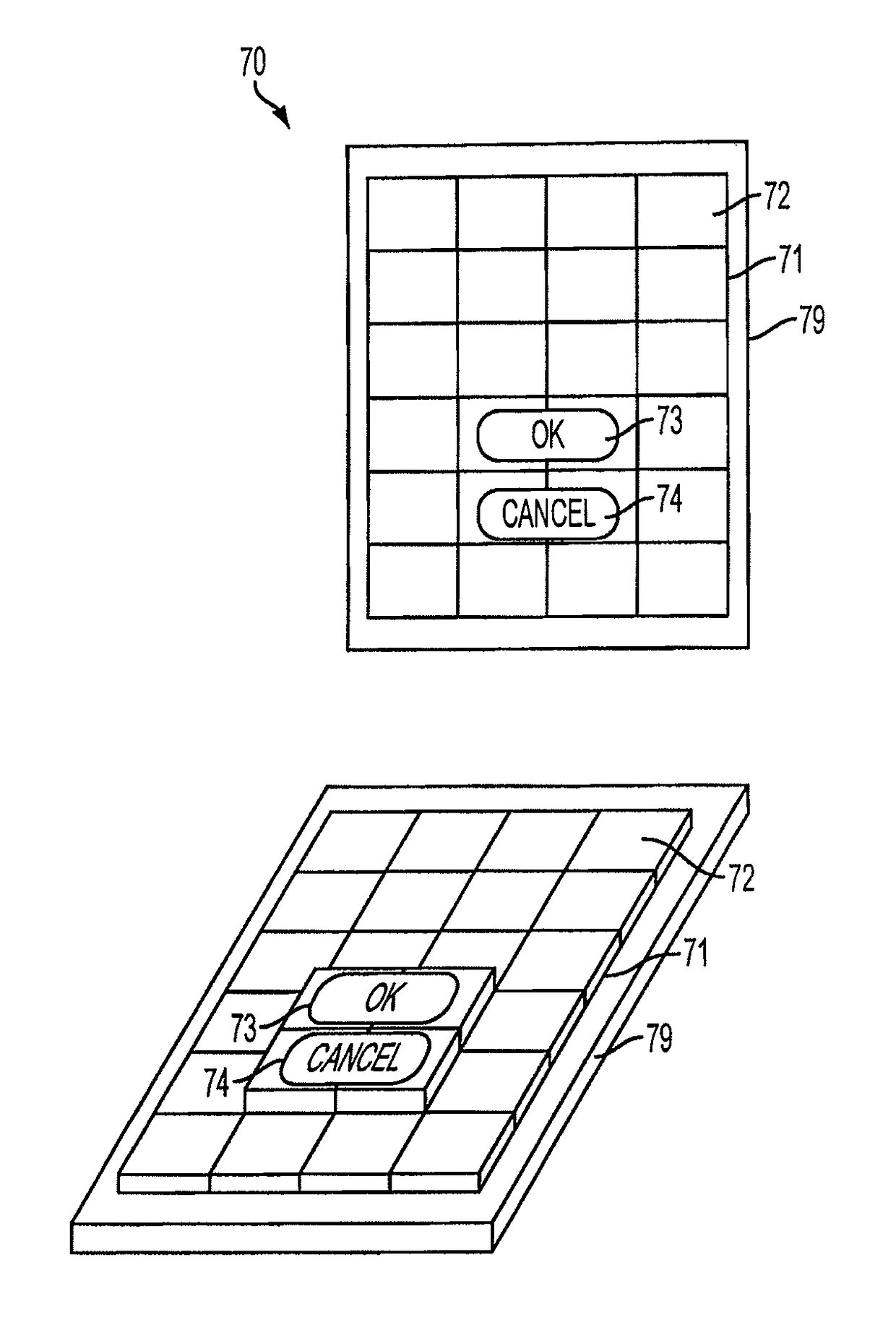
User interface having changeable topography
ActiveUS20100162109A1Input/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingInput selectionEngineering
Owner:APPLE INC
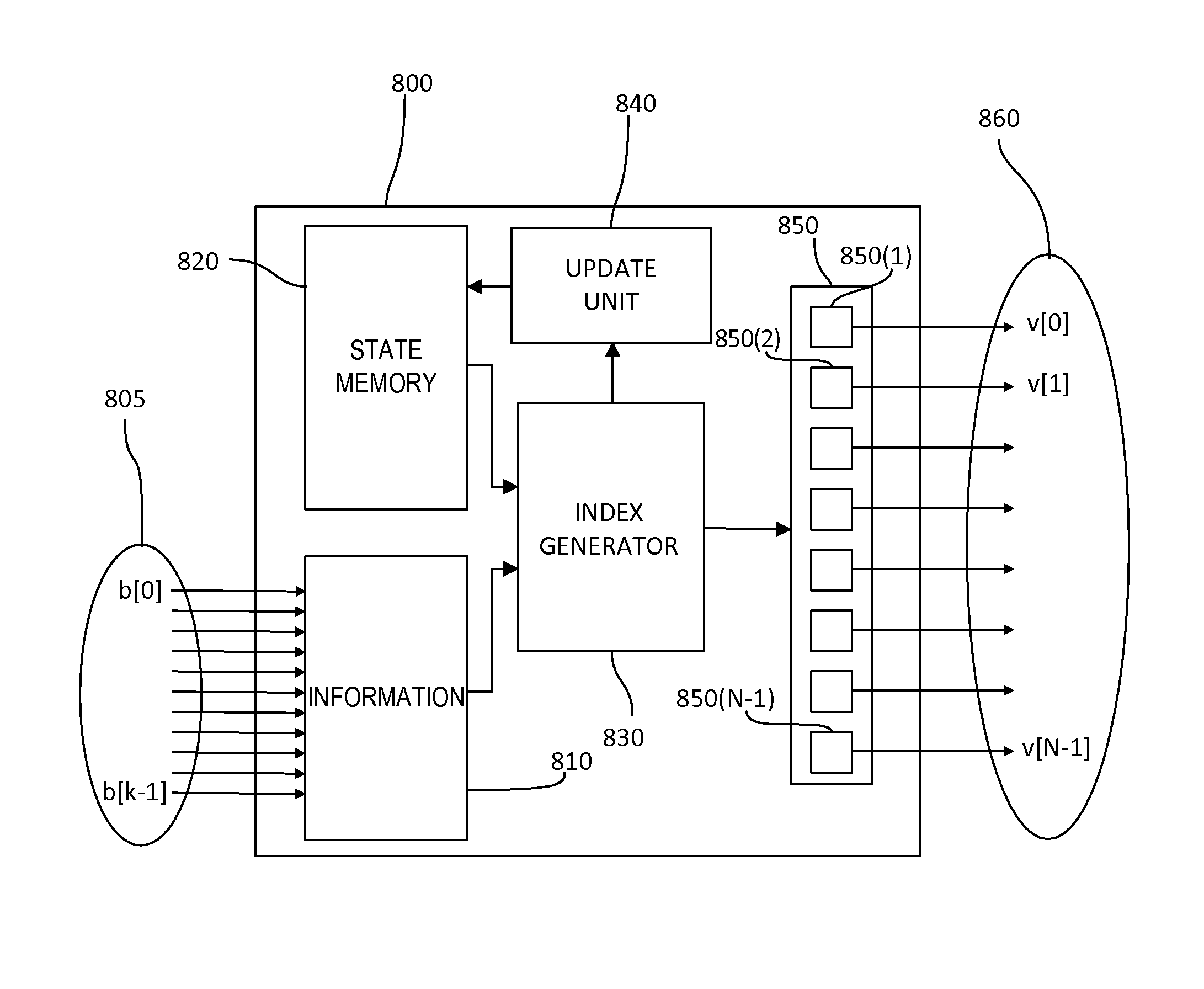
Finite state encoders and decoders for vector signaling codes
ActiveUS8718184B1Channel dividing arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemComputer science
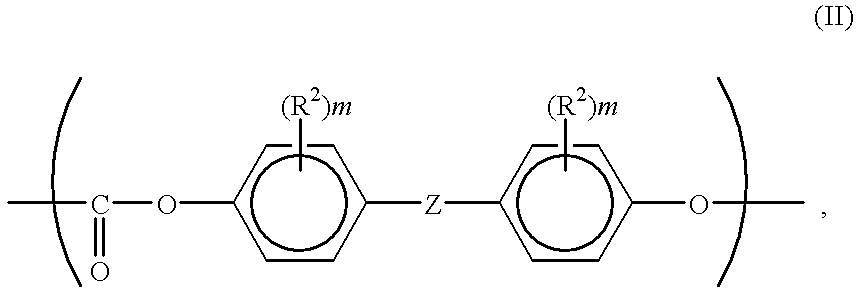
In a chip-to-chip communication system and apparatus, a set of physical signals to be conveyed over a communication bus is provided, and mapped to a codeword of a vector signaling code using the physical signals and a state information, wherein a codeword is representable as a vector of plurality of real-valued components, and wherein a vector signaling code is a set of codewords in which the components sum to zero and for which there is at least one component and at least three codewords having different values in that component; and wherein the state information is a plurality of information present in continuous or discrete form which may have been obtained from previous codewords transmitted over the communication bus.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
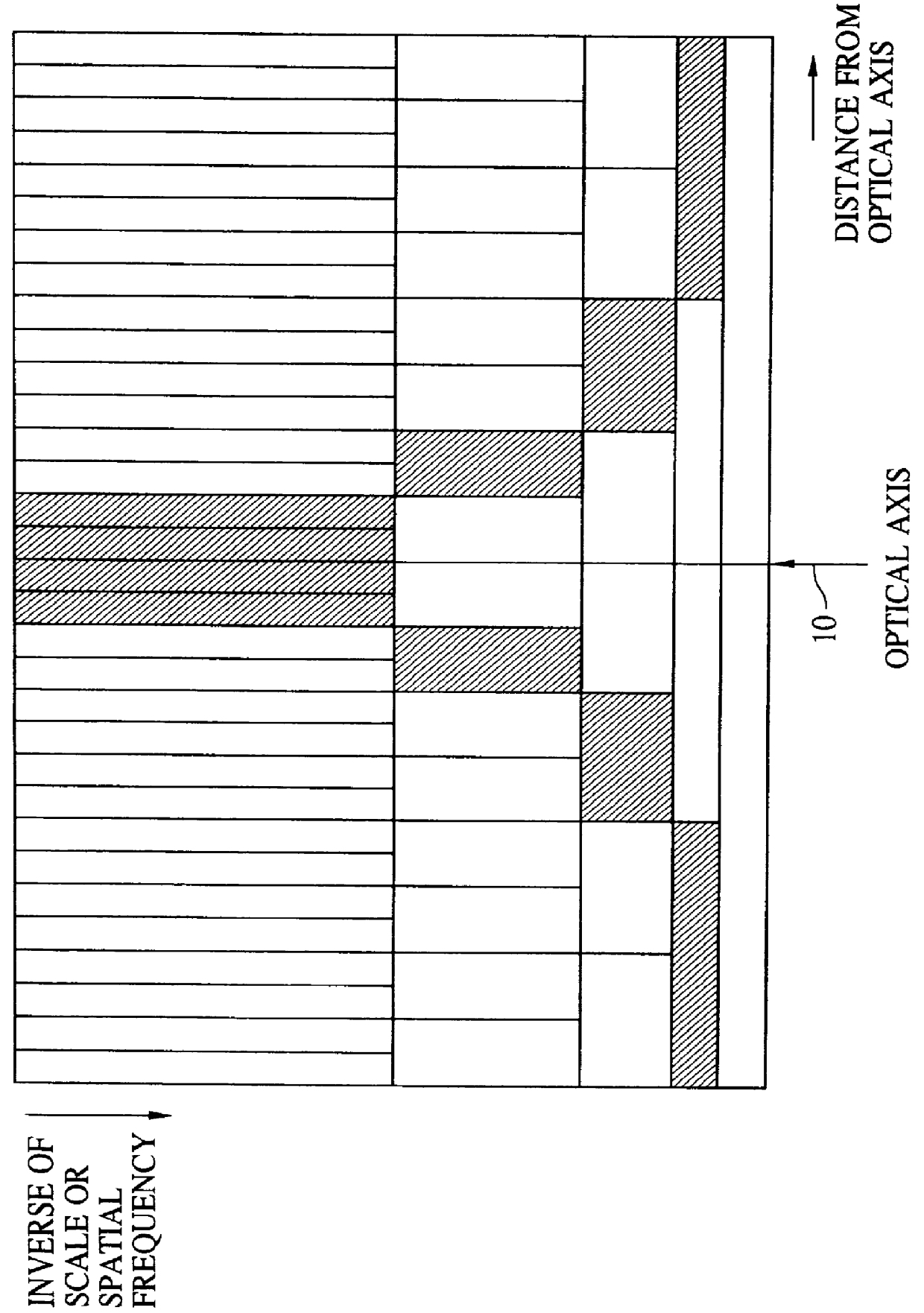
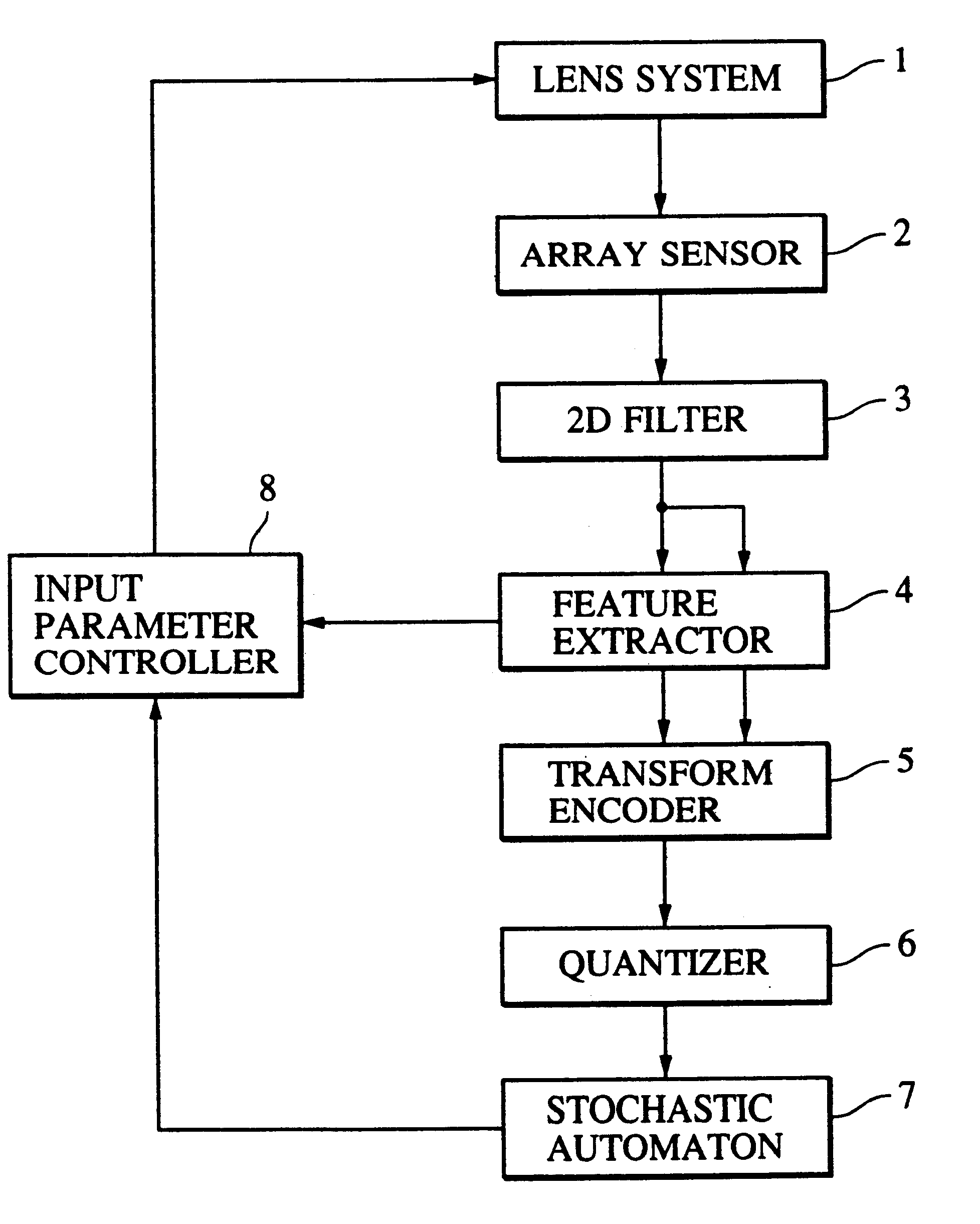
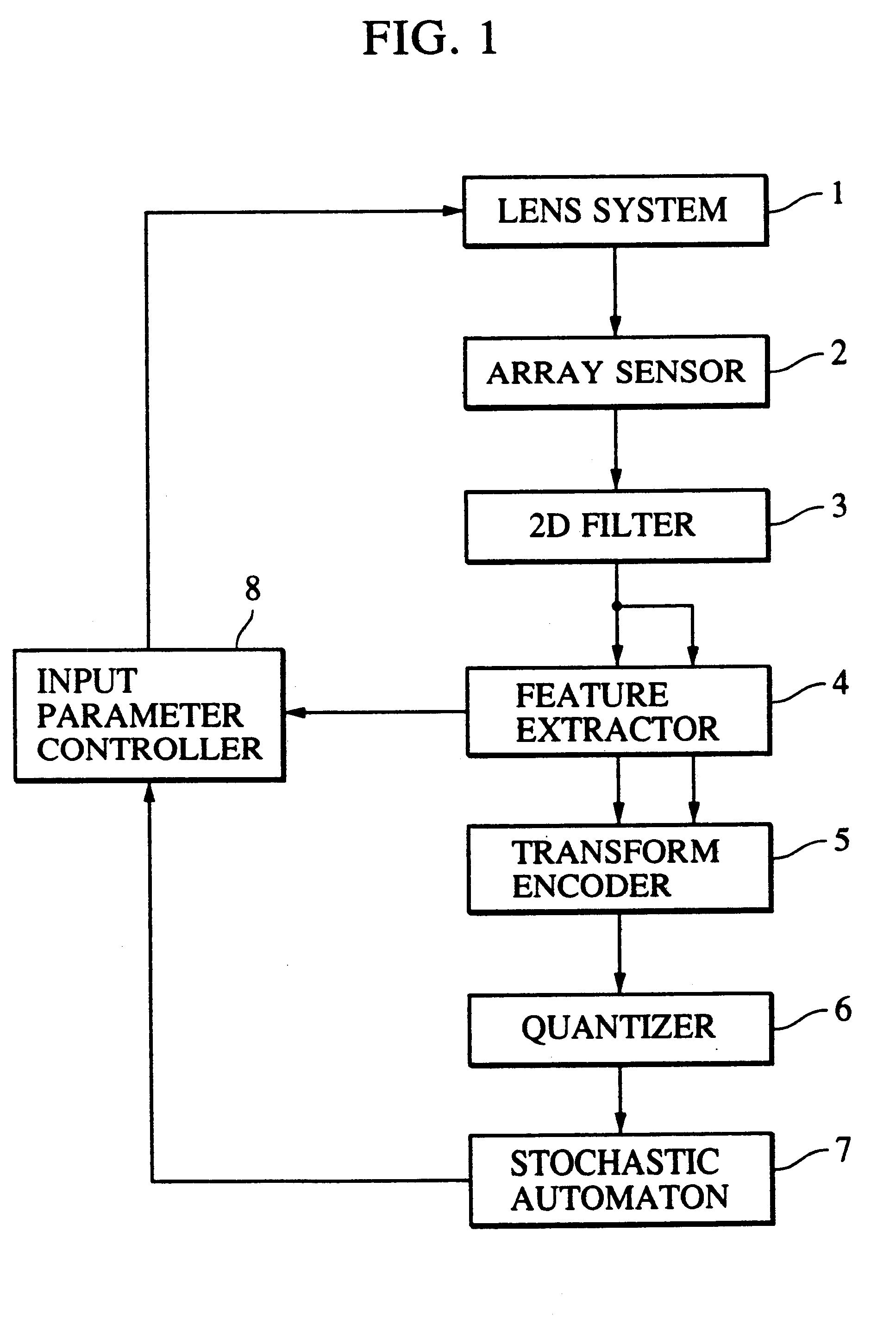
Method and apparatus for processing visual information
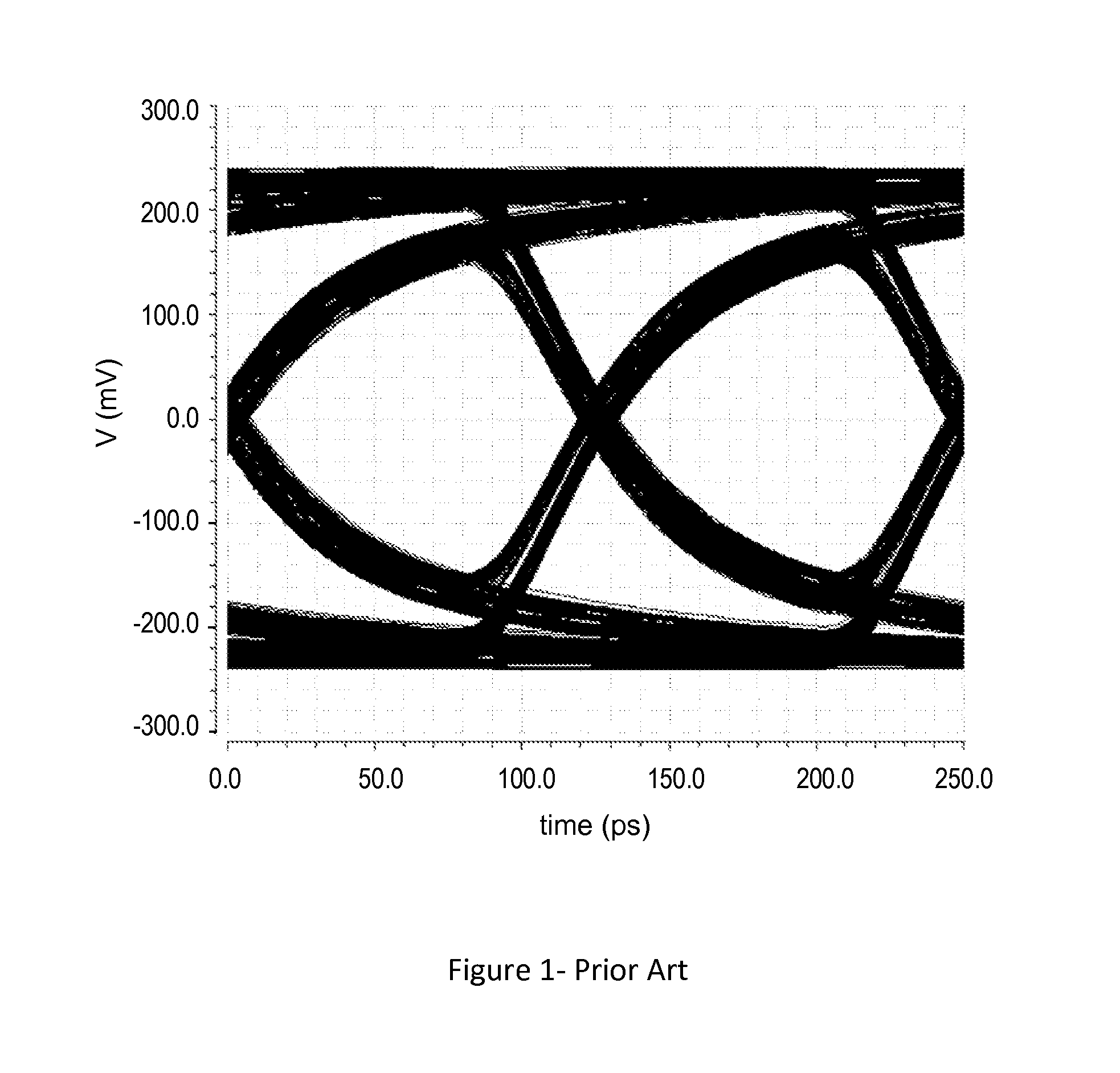
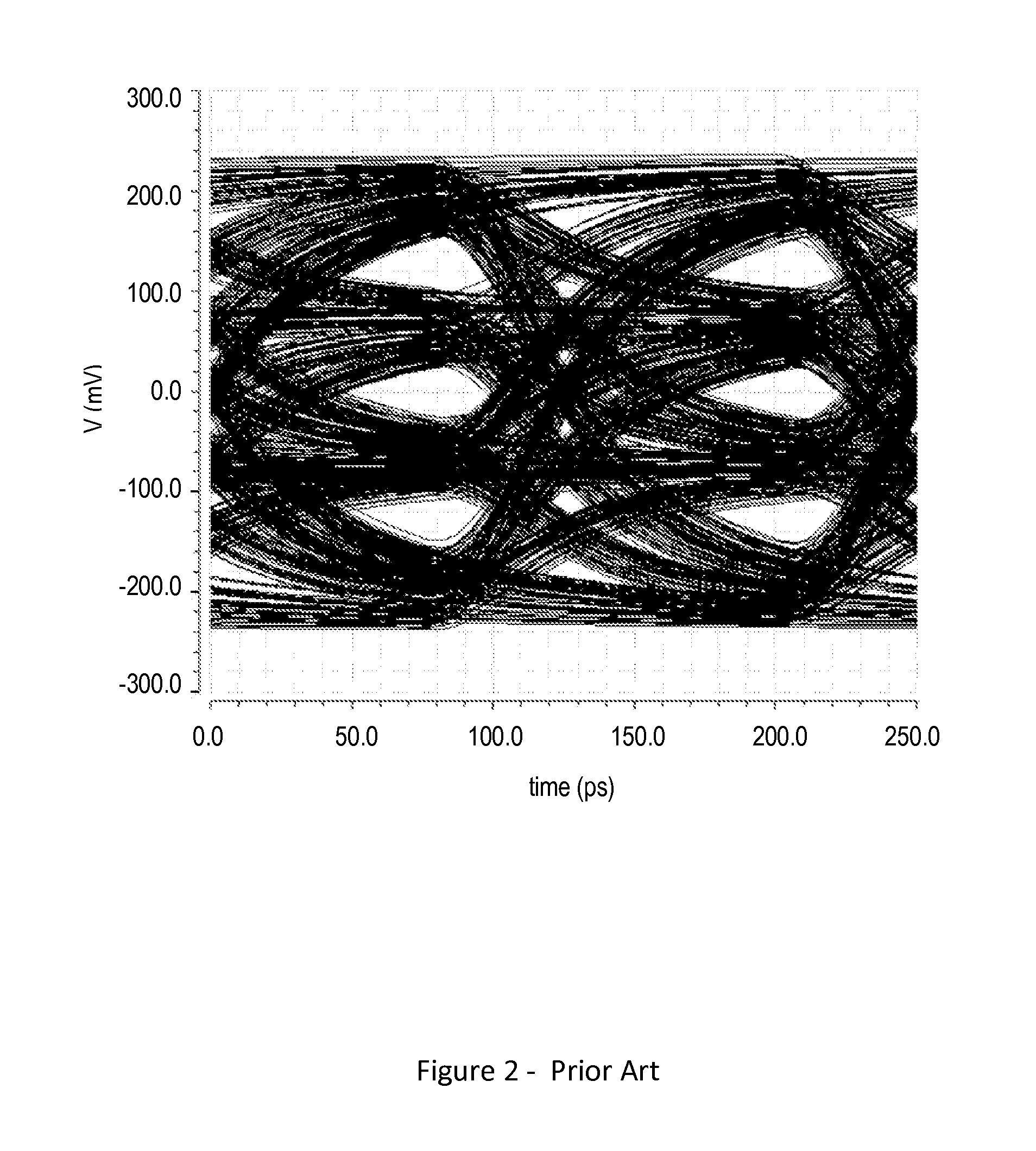
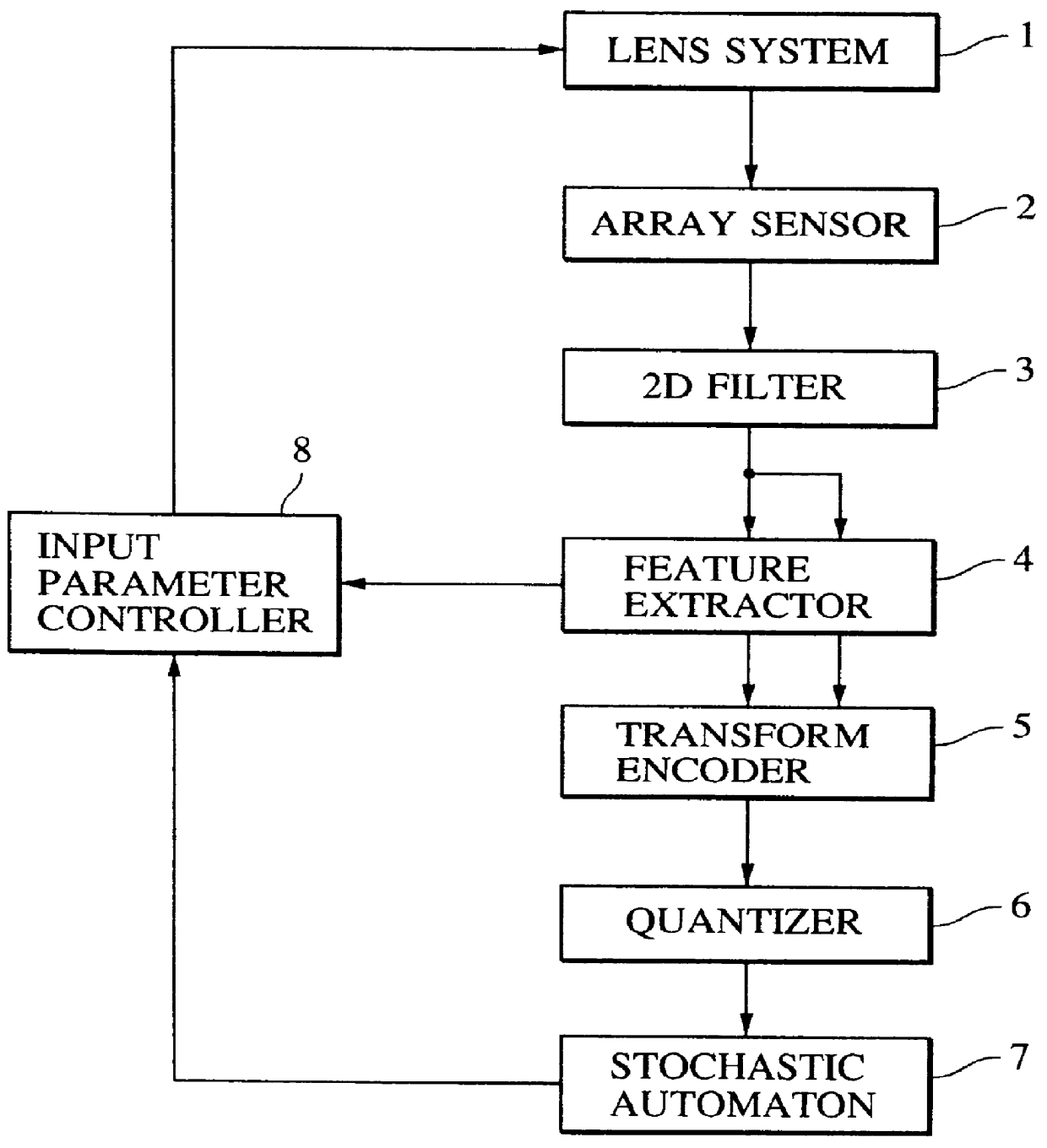
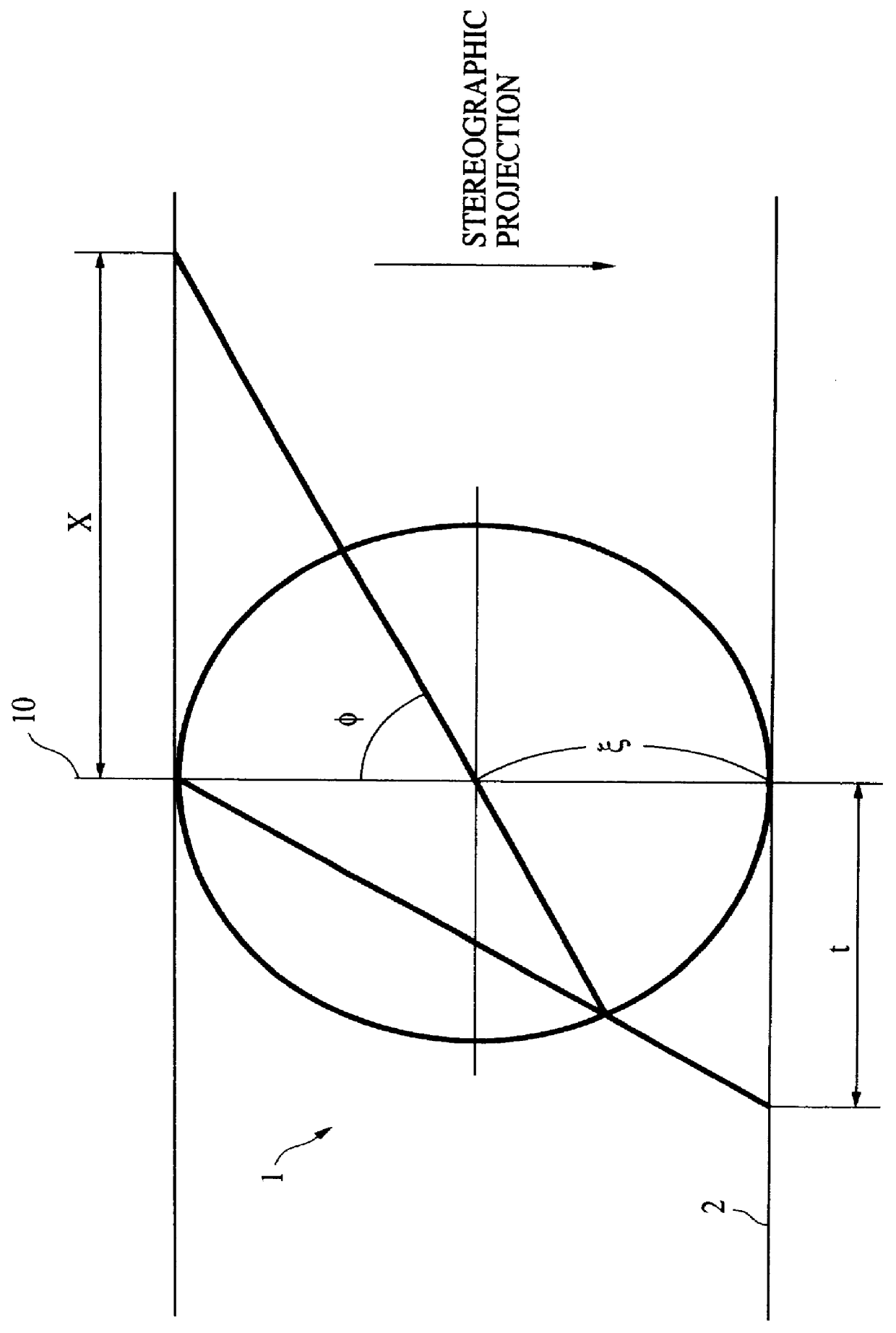
A 2D image supplied from an image input unit including a wide view lens is sampled into a discrete form by an array sensor, and then mapped to a multi-resolution space by a 2D filter. The feature of the supplied image is detected, and then the mapped image is transformed to a local pattern about the detected feature, and then the coordinates of the position of the feature and the code word of the local pattern are formed into a set which is then encoded. The code is supplied to each cell of a stochastic automaton. The quantity of visual information is calculated in accordance with the quantity of mutual information between different cells of the stochastic automaton consisting of cells in blocks, the coordinates of the position of the feature and the distance from the feature to the optical axis so as to control the optical axis of the image input unit in such a manner that the quantity of visual information is maximized.
Owner:CANON KK
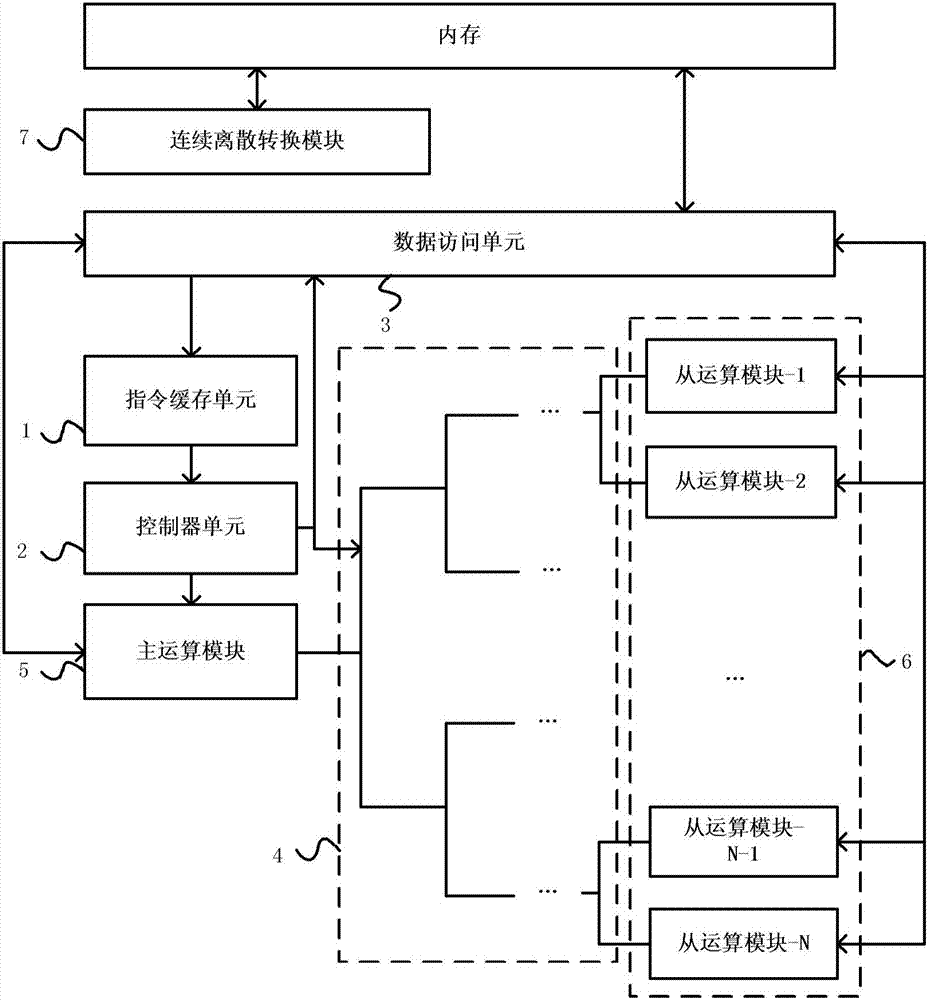
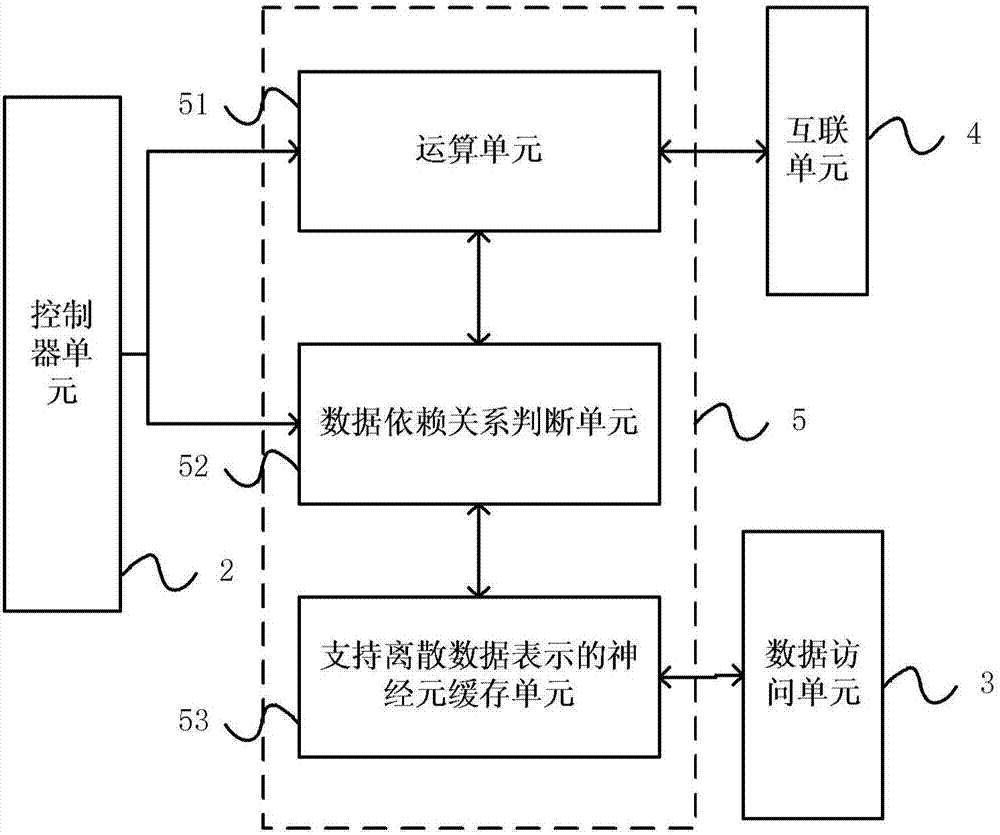
Artificial neural network forward calculation apparatus and method supporting discrete data representation
The invention provides an apparatus used for executing forward calculation of an artificial neural network and supporting discrete data representation. The apparatus comprises an instruction caching unit, a controller unit, a data access unit, an interconnection module, a master calculation module, a plurality of slave calculation modules, a discrete data calculation module and a continuous-discrete conversion module. By using the apparatus, the forward calculation of the multilayer artificial neural network supporting the discrete data representation can be realized; data such as weight values, neurons and the like in the forward calculation process can be represented in a discrete form; for example, -1, -1 / 2, 0, 1 / 2, 1 and the like are not continuous data; the module supporting discrete data calculation is provided; basic operations such as multiplication, addition and the like of the continuous data are replaced with different bit operations such as XOR operation, NOT operation and the like of the data according to discrete data values; the module for converting the continuous data into discrete data is provided; and batch normalization calculation is supported by utilizing the apparatus.
Owner:CAMBRICON TECH CO LTD
Porous nonwoven scrims in acoustical panels
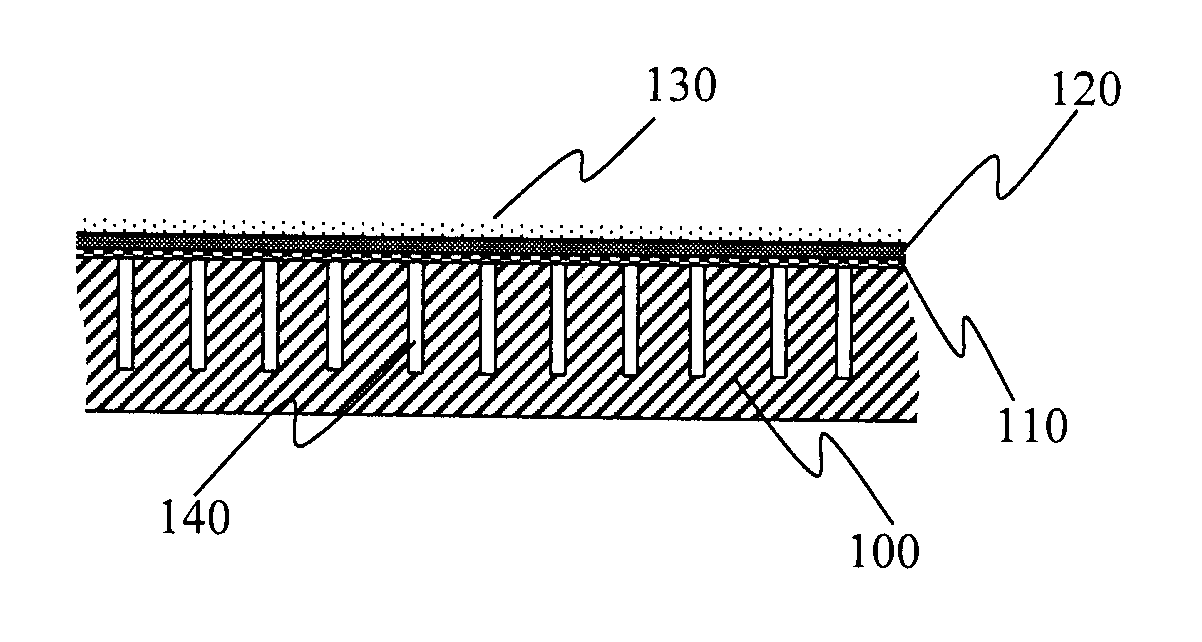
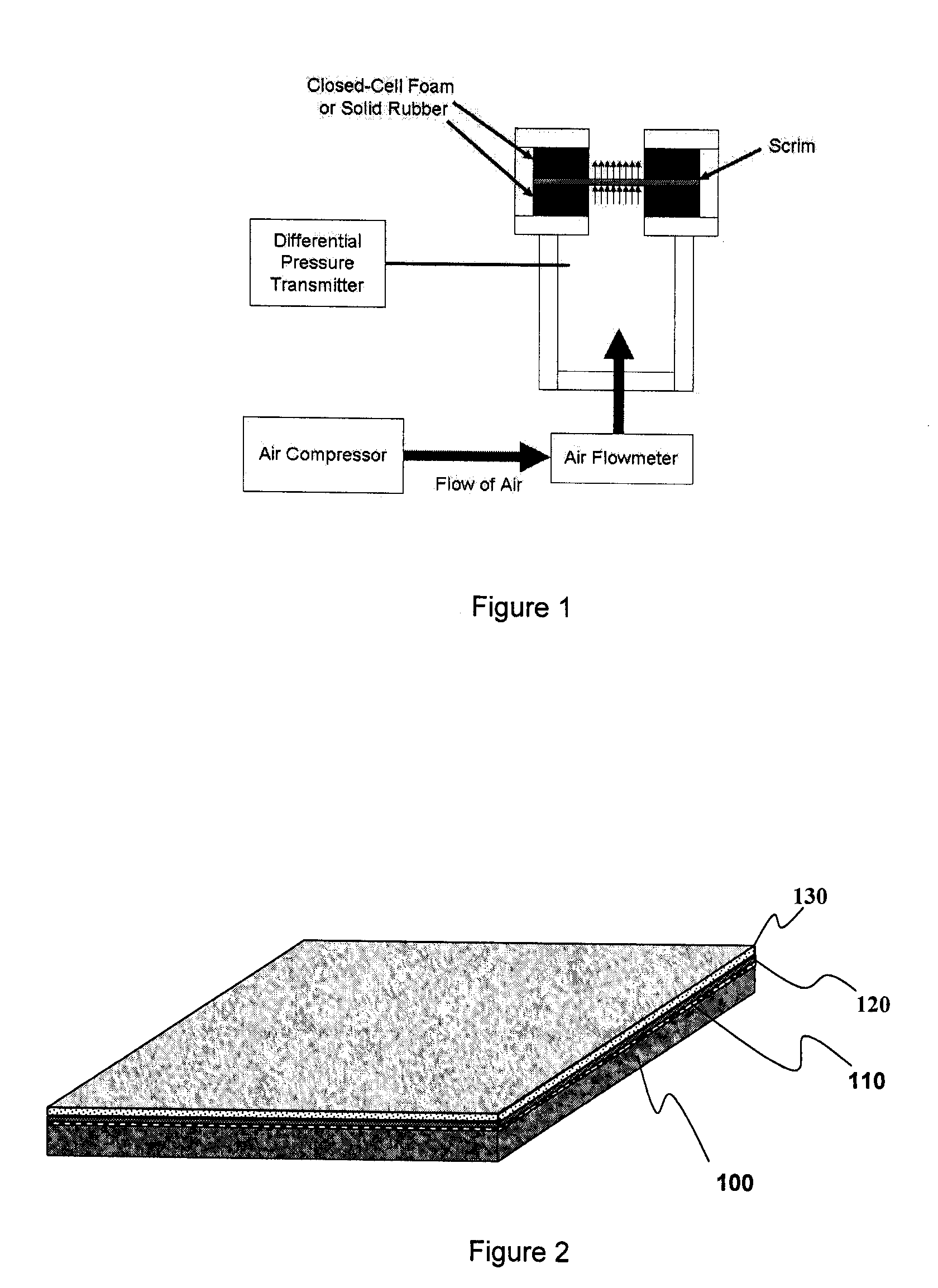
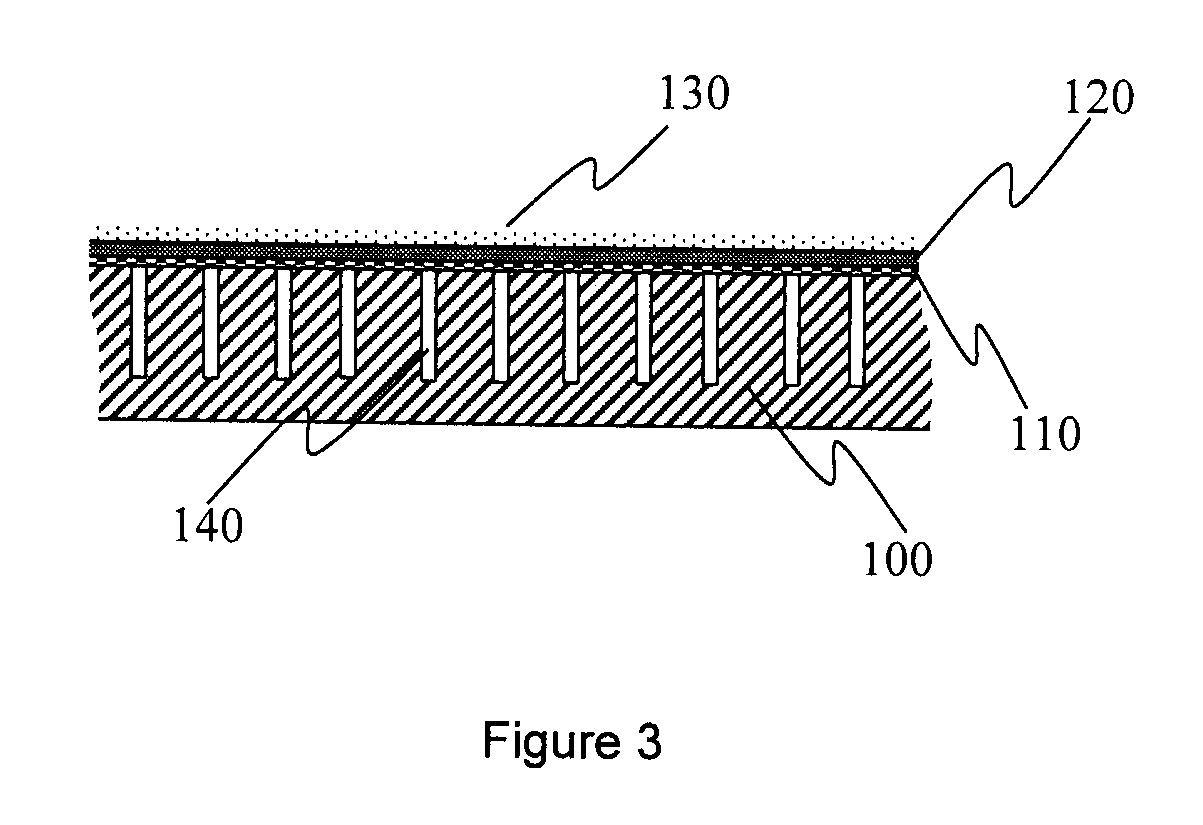
ActiveUS20110147119A1Reduce lossesReduce airflow resistanceCeilingsLamination ancillary operationsAdhesiveEngineering
An acoustical building panel and method of manufacturing it are disclosed. Embodiments of the panel include a porous nonwoven scrim, a coating deposited on the scrim, a base mat, and an adhesive deposited on either the base mat or the scrim in a discrete form such as in droplets. Embodiments of the method of manufacture include steps of perforating the base mat, applying the adhesive to the base mat in the discrete form, laminating the scrim onto the base mat, and applying the coating to the scrim surface.
Owner:USG INTERIORS LLC
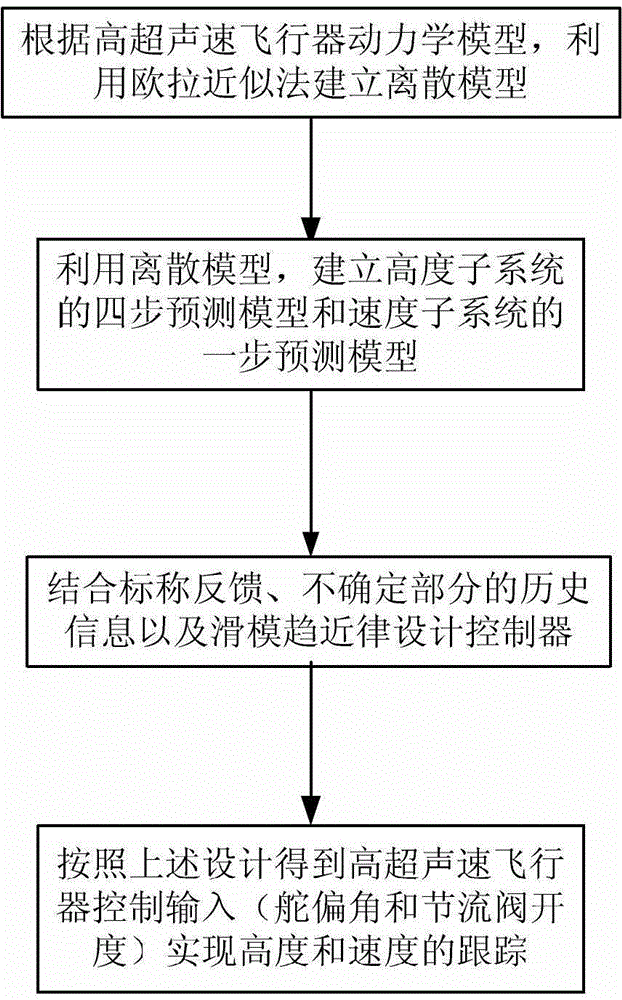
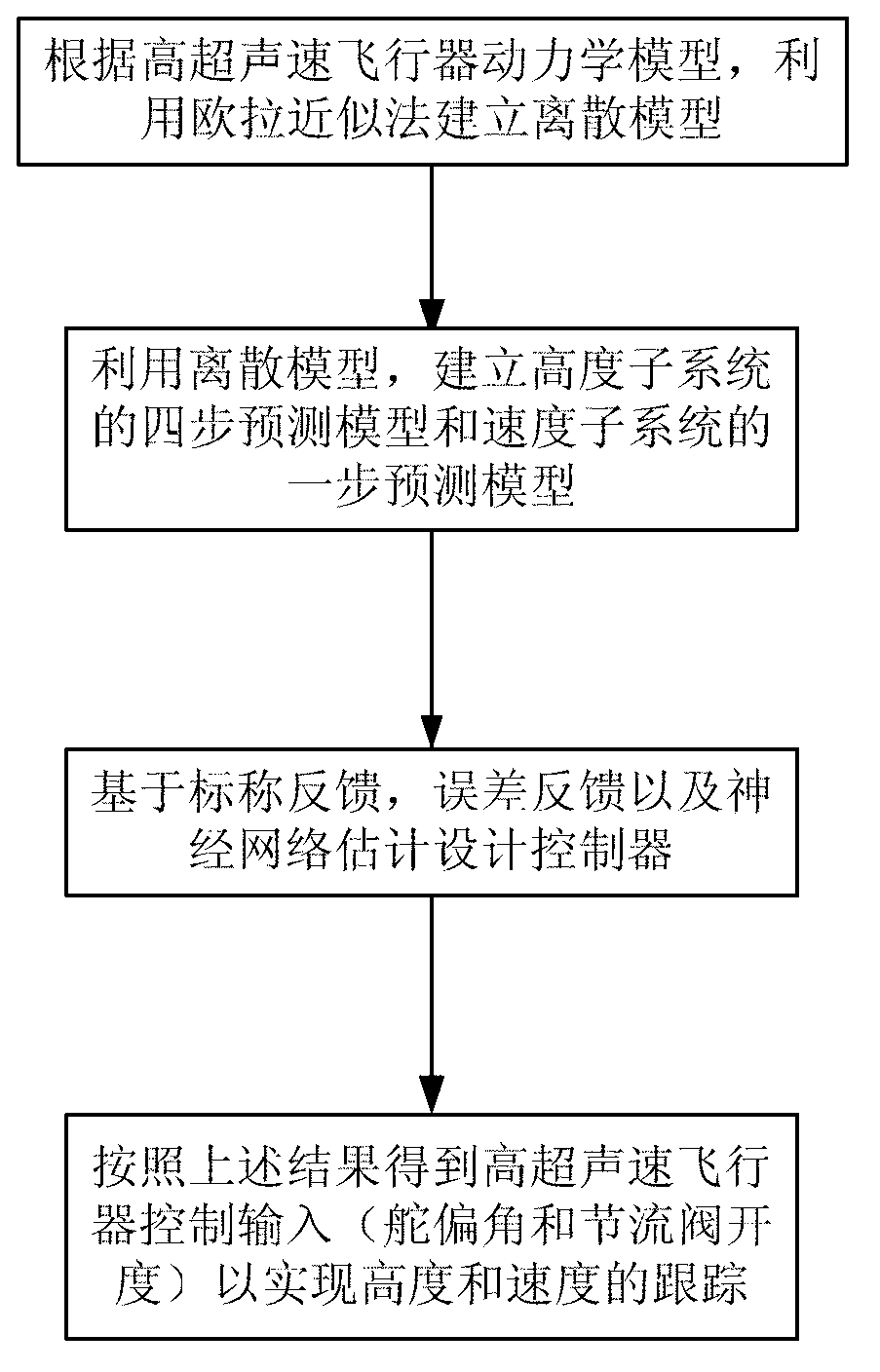
Prediction model based hypersonic aircraft sliding-mode control method
ActiveCN102880053AEasy to implementSolve non-causal problemsVehicle position/course/altitude controlAdaptive controlEulerian methodVirtual control
The invention discloses a prediction model based hypersonic aircraft sliding-mode control method. The method is used for solving the technical problem of difficulty in engineering realization by existing hypersonic aircraft adaptive discrete control. The method includes: obtaining a strict feedback form of a height subsystem by reasonable assumption, and building a discrete form of an original system through an Eulerian method; building a four-step prediction model of the original system by unceasing forward prediction, wherein the model only includes an equation; enabling the prediction model to provide the relation of height output at a future time and current system state and control input, wherein the relation can be used for computing numerical values of lumped uncertainties of the system at the historical moment, and the numerical values are used for feedback design of a controller; and combining lumped nominal information further, and using a discrete reaching law to design the sliding-mode controller so that robustness of the system is improved. The prediction model based hypersonic aircraft sliding-mode control method has the advantages that the discrete prediction model is built to acquire system nominal and uncertain information, design of virtual control variables is not needed, the controller is simple and practical in design, and the method is suitable for engineering application.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
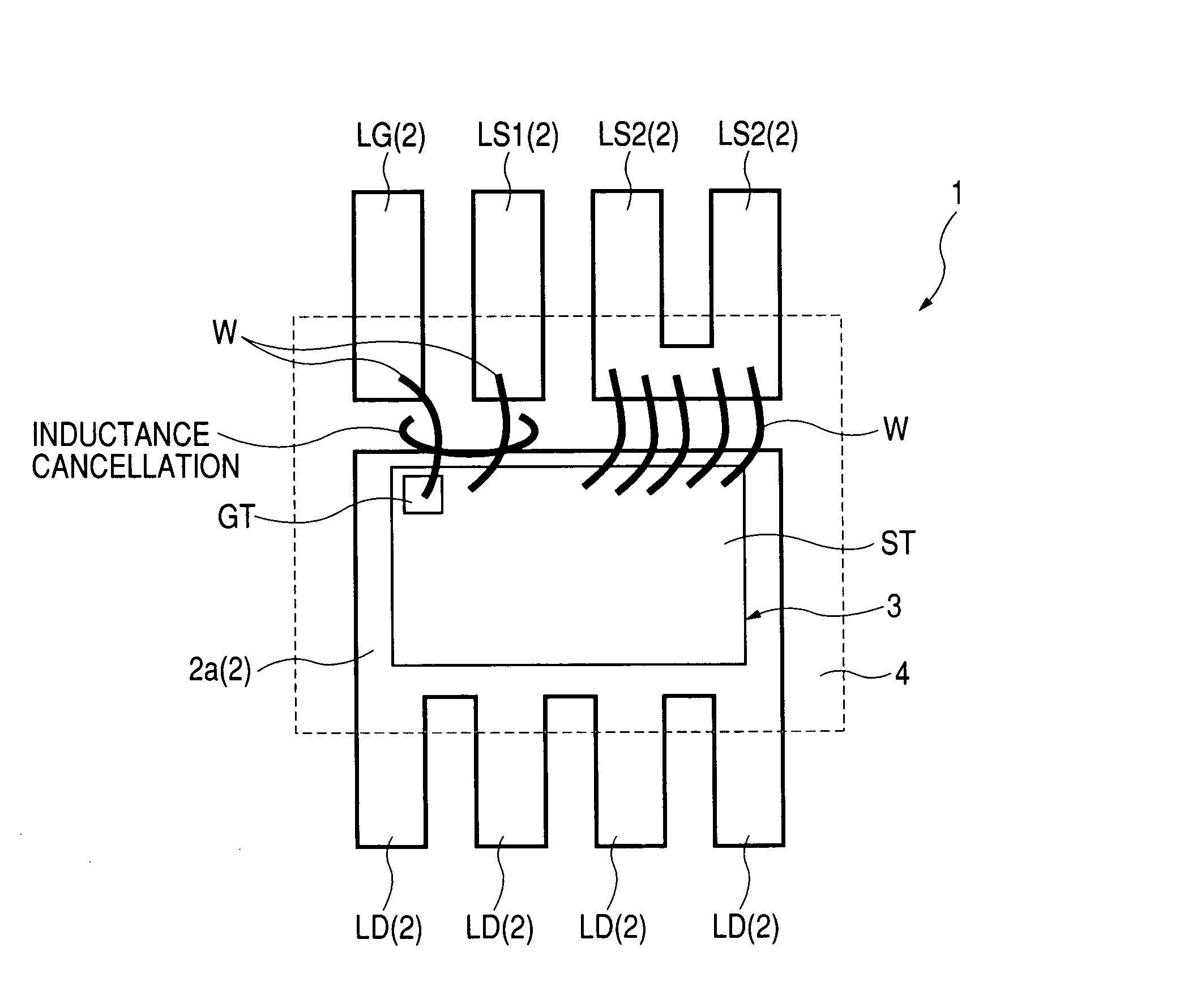
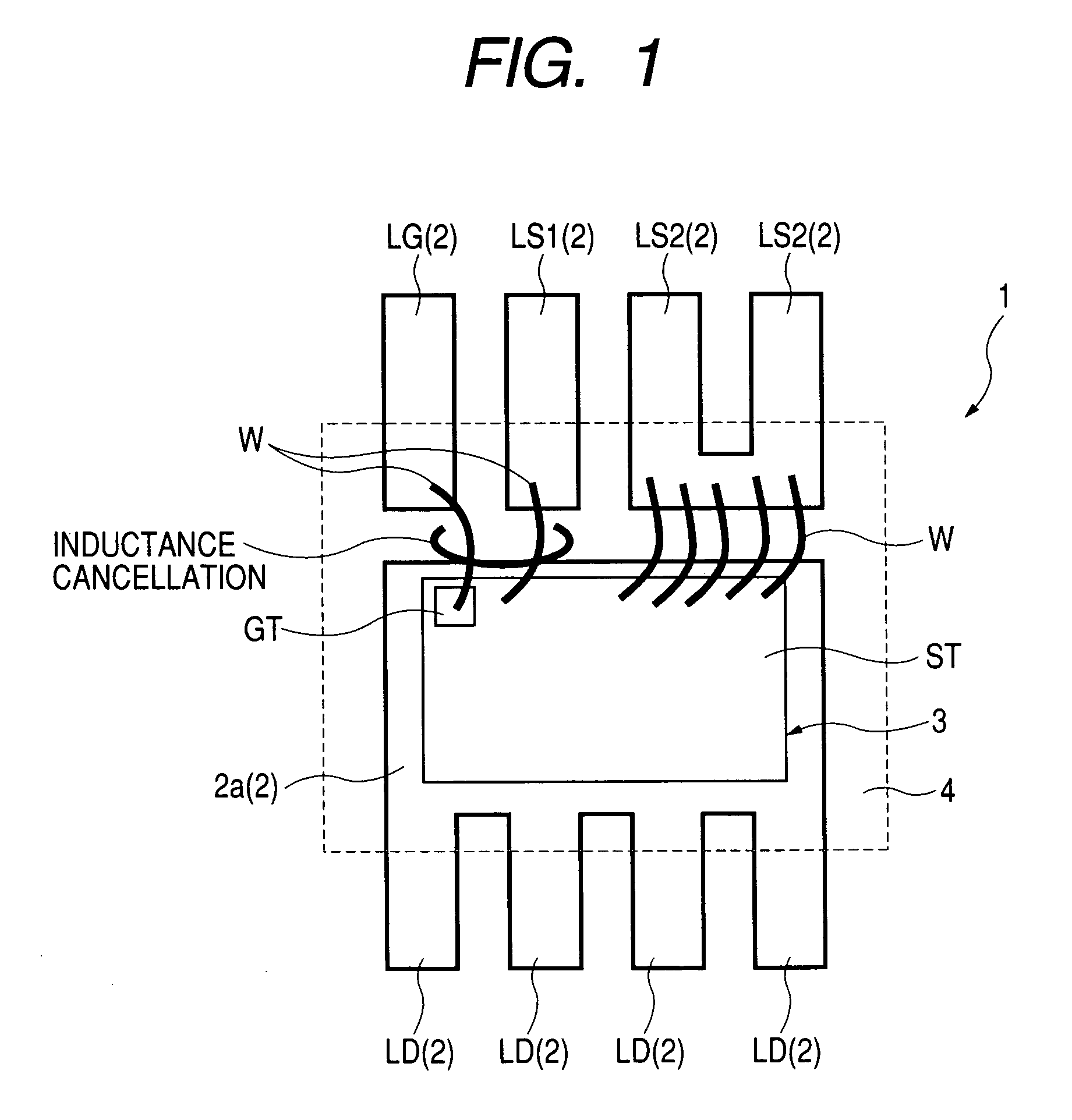
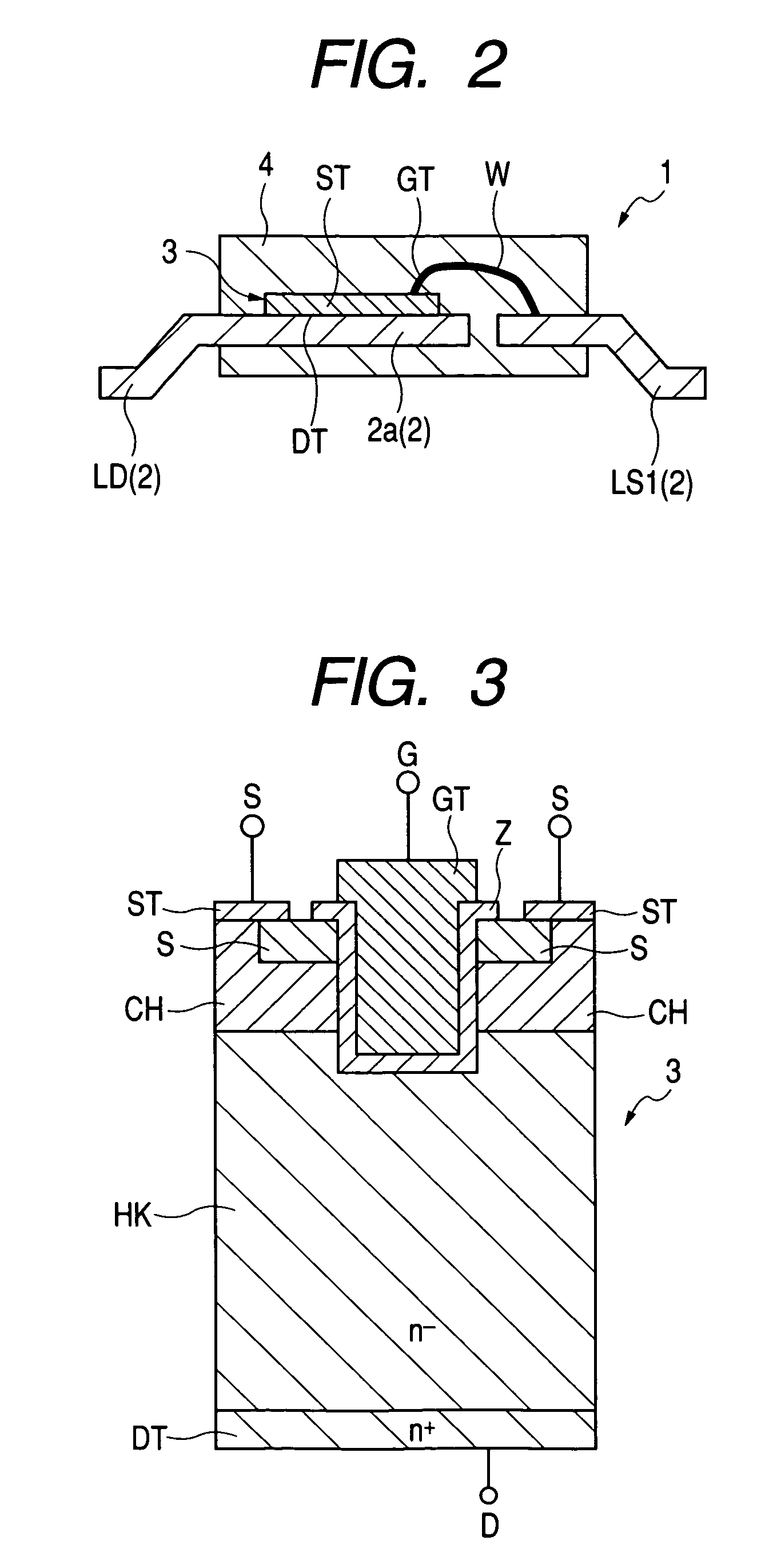
Semiconductor device and power supply system
ActiveUS7109577B2Reduce the impactImprove voltage conversion efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConversion constructional detailsPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A power MOS-FET is used as a high side switch transistor for a non-insulated DC / DC converter. An electrode section that serves as a source terminal of the power MOS-FET is connected to one outer lead and two outer leads via bonding wires respectively. The outer lead is an external terminal connected to a path for driving the gate. Each of the outer leads is an external terminal connected to a main current path. Owing to the connection of the main current path and the gate driving path in discrete form, the influence of parasitic inductance can be reduced and voltage conversion efficiency can be improved.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Time scale function decomposition based hypersonic aircraft actuator saturation control method
ActiveCN102880052ASimplify the number of variablesRealize the designVehicle position/course/altitude controlAdaptive controlDecompositionEulerian method
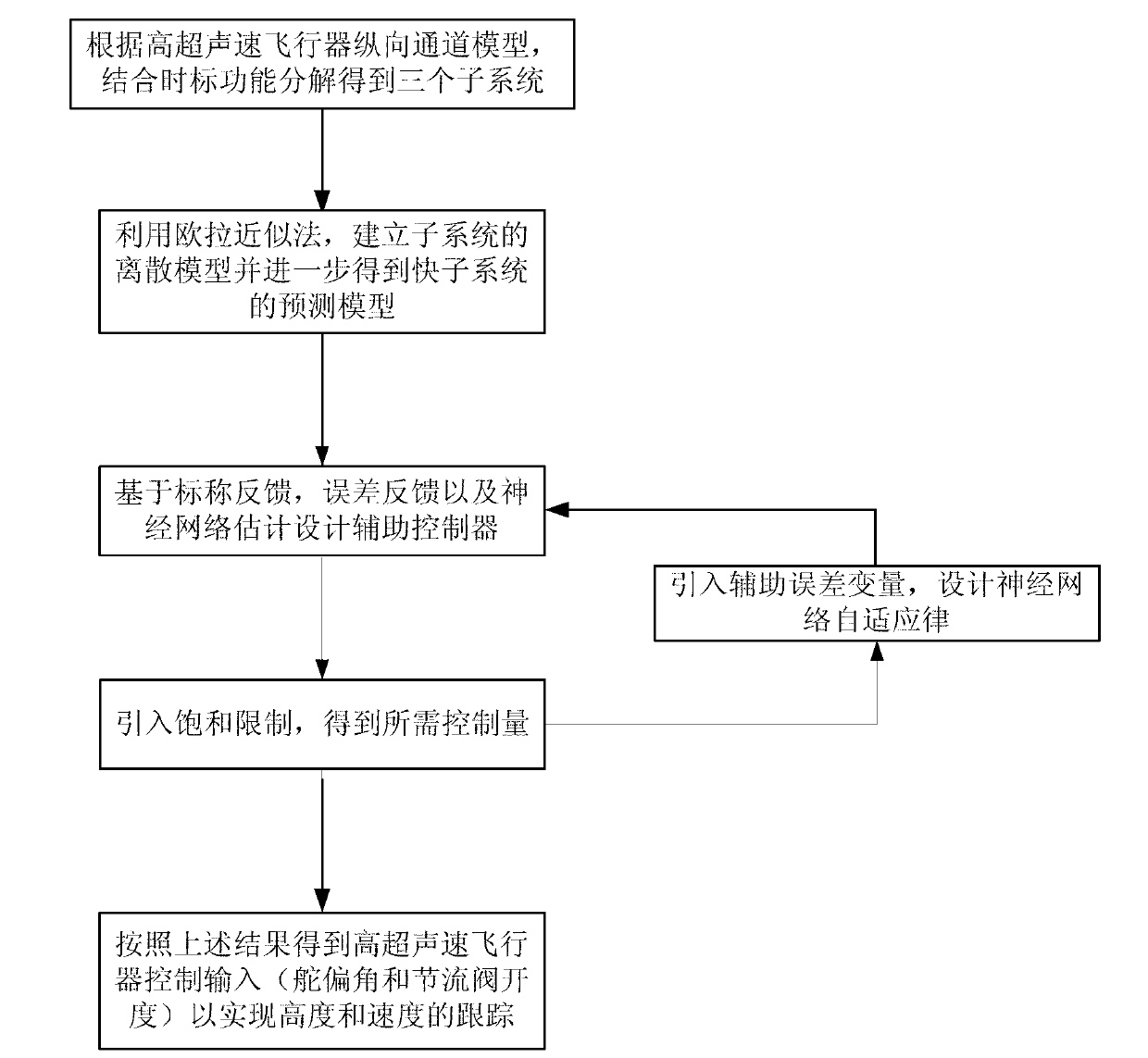
The invention discloses a time scale function decomposition based hypersonic aircraft actuator saturation control method. The method is used for solving the technical problem of difficulty in engineering realization under the existing hypersonic aircraft actuator saturation condition. The method includes: obtaining a high-speed slow variable subsystem, a speed slow variable subsystem and an attitude fast variable subsystem by time scale decomposition, and building a discrete form of an original system through an Eulerian method; regarding the height and the speed in a fast subsystem design process as constants so as to achieve model simplification; considering actuator saturation limitations, and importing auxiliary control variables to design throttling valve openness and the controlpiston deflexion angle; and designing an updating law of a neural network by importing an auxiliary error variable. The time scale function decomposition based hypersonic aircraft actuator saturation control method has the advantages that computer control characteristics are combined, a discrete model is built, the subsystems are designed according to time scale function decomposition, the actuator saturation condition is fully considered during controller design, and the method is suitable for engineering application.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Porous nonwoven scrims in acoustical panels
ActiveUS8100226B2Poor sag resistanceImprove humidity sag performanceCeilingsLayered product treatmentAdhesiveEngineering
An acoustical building panel and method of manufacturing it are disclosed. Embodiments of the panel include a porous nonwoven scrim, a coating deposited on the scrim, a base mat, and an adhesive deposited on either the base mat or the scrim in a discrete form such as in droplets. Embodiments of the method of manufacture include steps of perforating the base mat, applying the adhesive to the base mat in the discrete form, laminating the scrim onto the base mat, and applying the coating to the scrim surface.
Owner:USG INTERIORS INC
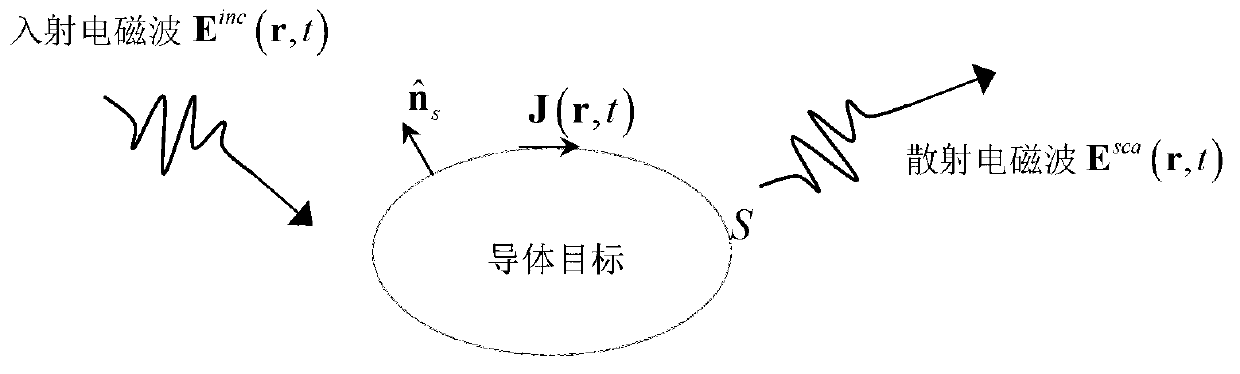
Method for simulating wide-band electromagnetic scattering property of conductor target
ActiveCN103279601AAccurate descriptionExact discrete fitSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorTime delays
The invention discloses a method for simulating the wide-band electromagnetic scattering property of a conductor target. The method comprises the following steps that the geometric model of the conductor target is built, and mesh generation is conducted on the surface of the conductor target by a curved surface triangle unit; a time domain electric field integral equation of the conductor target is determined; a surface induction current in the time domain electric field integral equation expands through a space CRWG primary function and a time delay primary function; an expanding surface induction current expression is substituted into the time domain electric field integral equation, and then the time domain electric field integral equation in a discrete form is tested in a time and space mode so as to obtain a system impedance matrix equation; singularity integrals are eliminated to obtain a sparse expression of a impedance matrix; the equation of the impedance matrix is solved to determine the distribution of the time domain current of the surface of the conductor target, and wide-band electromagnetic property parameters of the target are obtained according to the distribution of the time domain current so as to finish simulation. The method for simulating the wide-band electromagnetic scattering property of the conductor target has the advantages of being high in simulation precision, little in required time and low in memory consumption, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for controlling neural network of hypersonic aerocraft on basis of prediction model
ActiveCN102880055AAvoid approachingWell formedVehicle position/course/altitude controlAdaptive controlEulerian methodNetwork control
The invention discloses a method for controlling a neural network of a hypersonic aerocraft on the basis of a prediction model, and belongs to the field of control for aerocrafts. The method is used for solving the technical problem of difficulty in engineering implementation of discrete adaptive control for an existing hypersonic aerocraft. The method includes obtaining a strict feedback form of a height subsystem by means of reasonable assumption, and creating a discrete form of an original system by an Eulerian method; building the four-step prediction model of the original system by means of continuous forward prediction; and adopting a lumped nominal design and error feedback for a controller and estimating and compensating lumped uncertain portions by the neural network. The four-step prediction model contains only one equation and provides the relation among height output at future moments, a current system state and control input. The method has the advantages that features of computer control are combined with the method, the discrete prediction model is built, virtual control variables are not required to be designed, only the neural network is required, and the method is suitable for engineering application.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
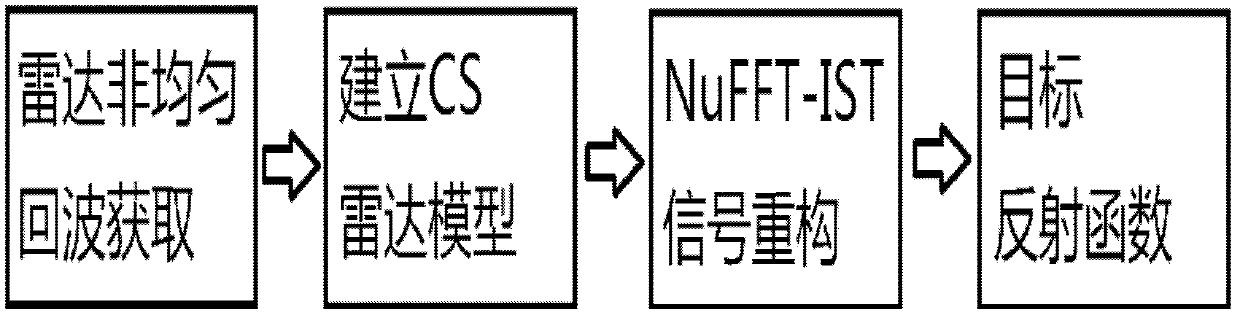
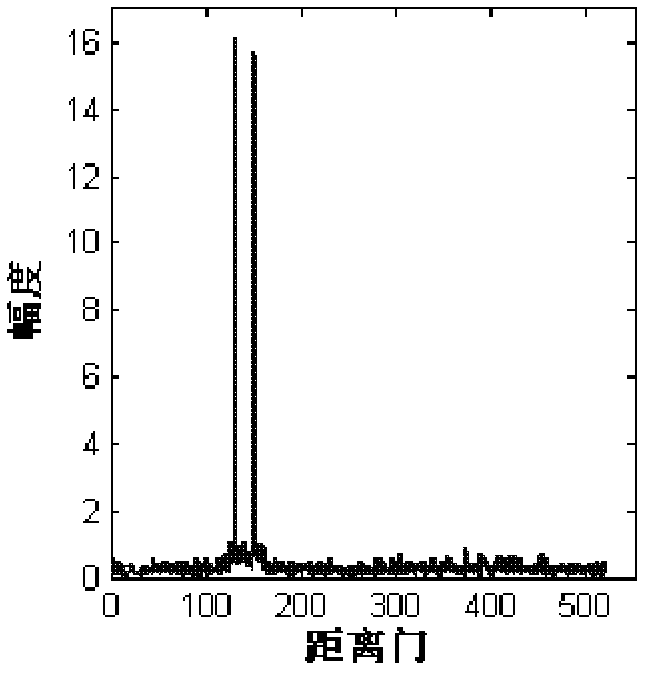
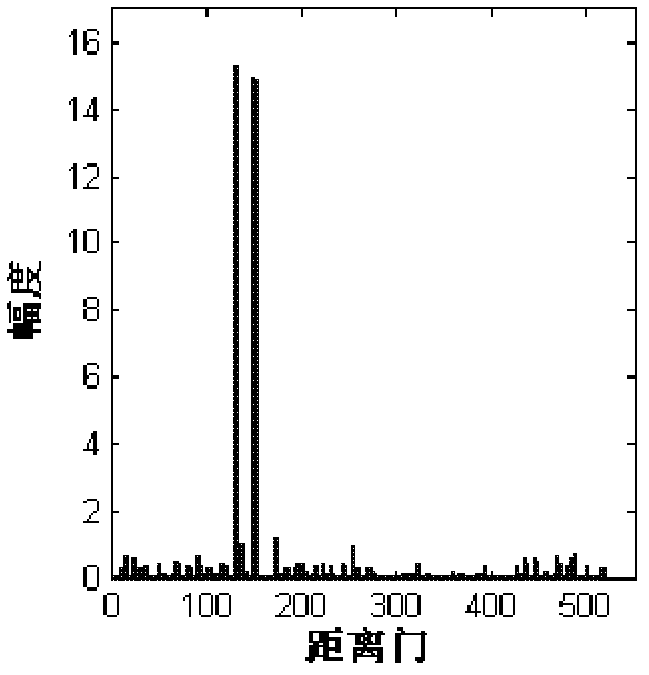
Compressive sensing radar reconstruction method
ActiveCN103364768AReduce complexityFast refactoringWave based measurement systemsRadarReconstruction method
The invention discloses a compressive sensing radar reconstruction method. The method comprises: receiving a target reflection echo in an imaging area and performing non-uniform sampling on echo signals so as to obtain a non-uniform sampling sequence in a discrete form; establishing a compressive sensing radar model through the non-uniform sampling echo sequence; and solving the compressive sensing radar model and reconstructing a target reflection function, wherein the matrix vector multiplication in the procedures of solving the compressive sensing radar model is calculated by means of the non-uniform Fourier transform. By adopting such a method, the complexity of algorithmic reconstruction is effectively reduced and the reconstruction speed of sparse signals is enhanced.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
User interface having changeable topography
ActiveUS9600070B2Input/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingInput selectionOutput device
Owner:APPLE INC
Adhesive articles having repositionability or slidability characteristics
An adhesive article exhibiting air release or egress, repositionability, and / or slidability characteristics. An adhesive article comprises an adhesive layer comprising an adhesive surface comprising discrete forms of non-adhesive material randomly distributed on the patterned surface and at least partially embedded in the adhesive layer. The discrete forms of non-adhesive material provide areas of no or minimal adhesion and provide the article with some level of repositionability or slidability. The adhesive surface comprising the non-adhesive forms may be patterned to provide an adhesive surface with a contact surface and recessed area or channels that provide the article with a route for air to flow out from under the construction. An article may be formed by providing a release liner, applying discrete forms of non-adhesive material to a surface of the release liner, at least partially embedding the non-adhesive forms, and embossing the release liner.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Batter-like compositions containing setting agent and methods of preparing and using same
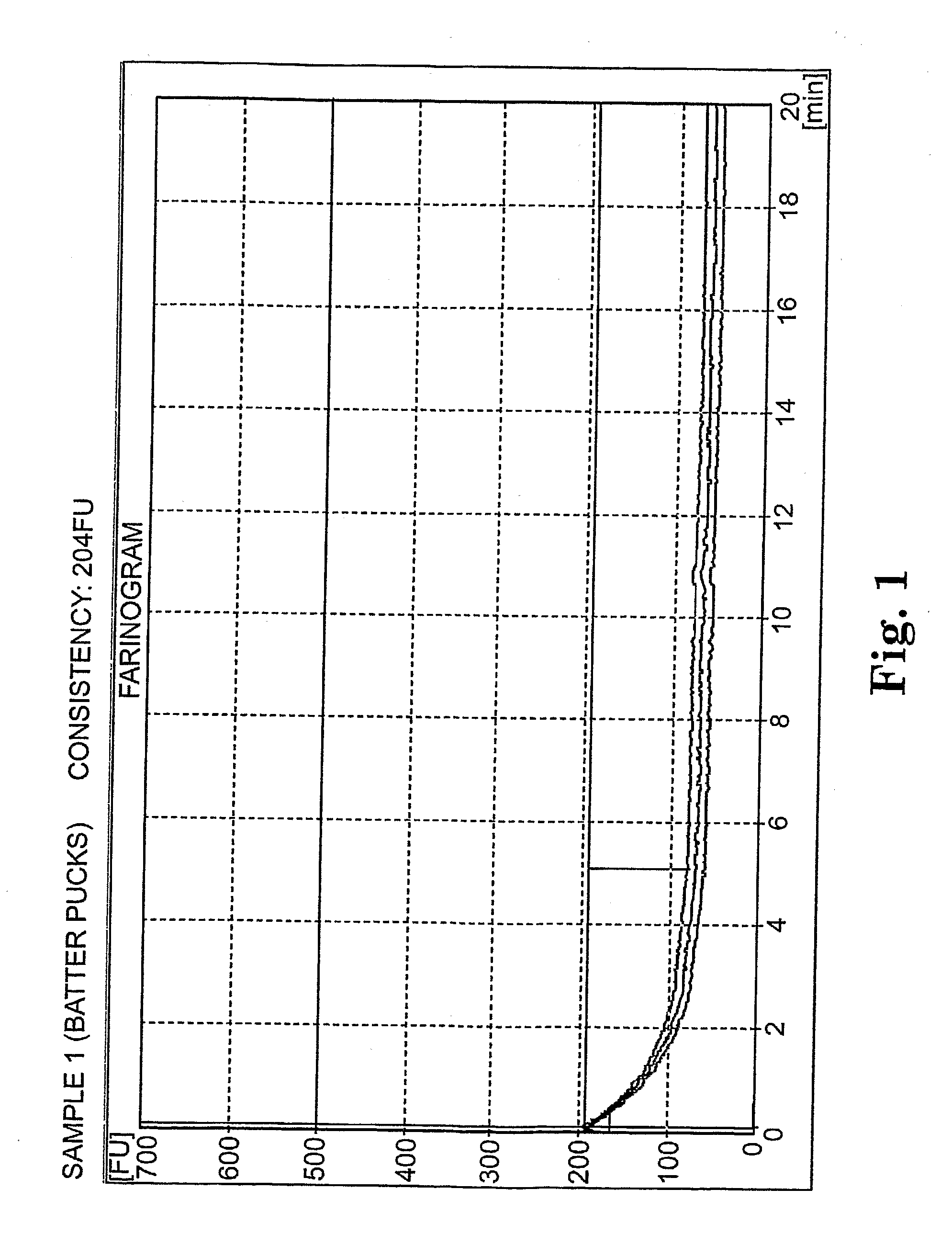
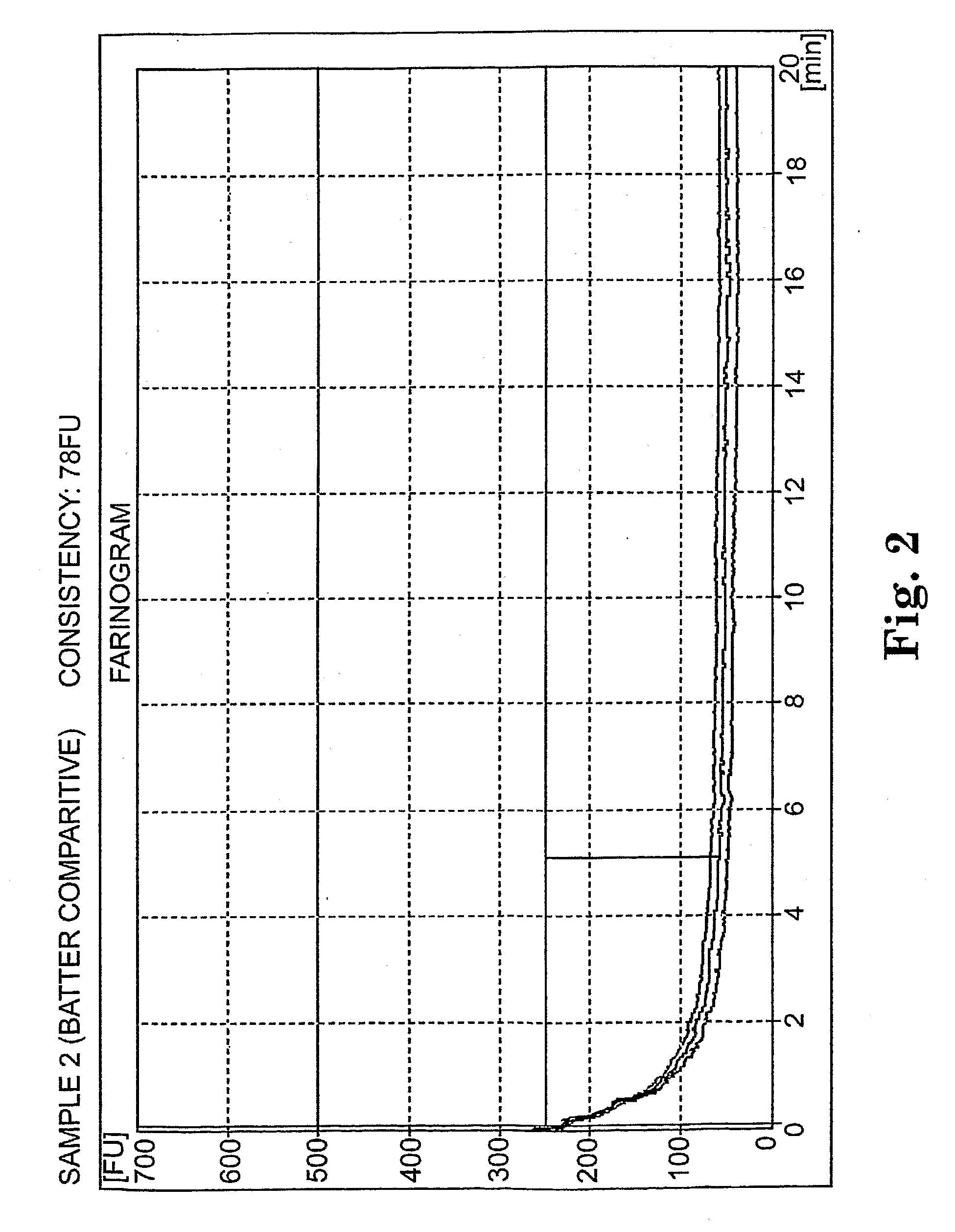
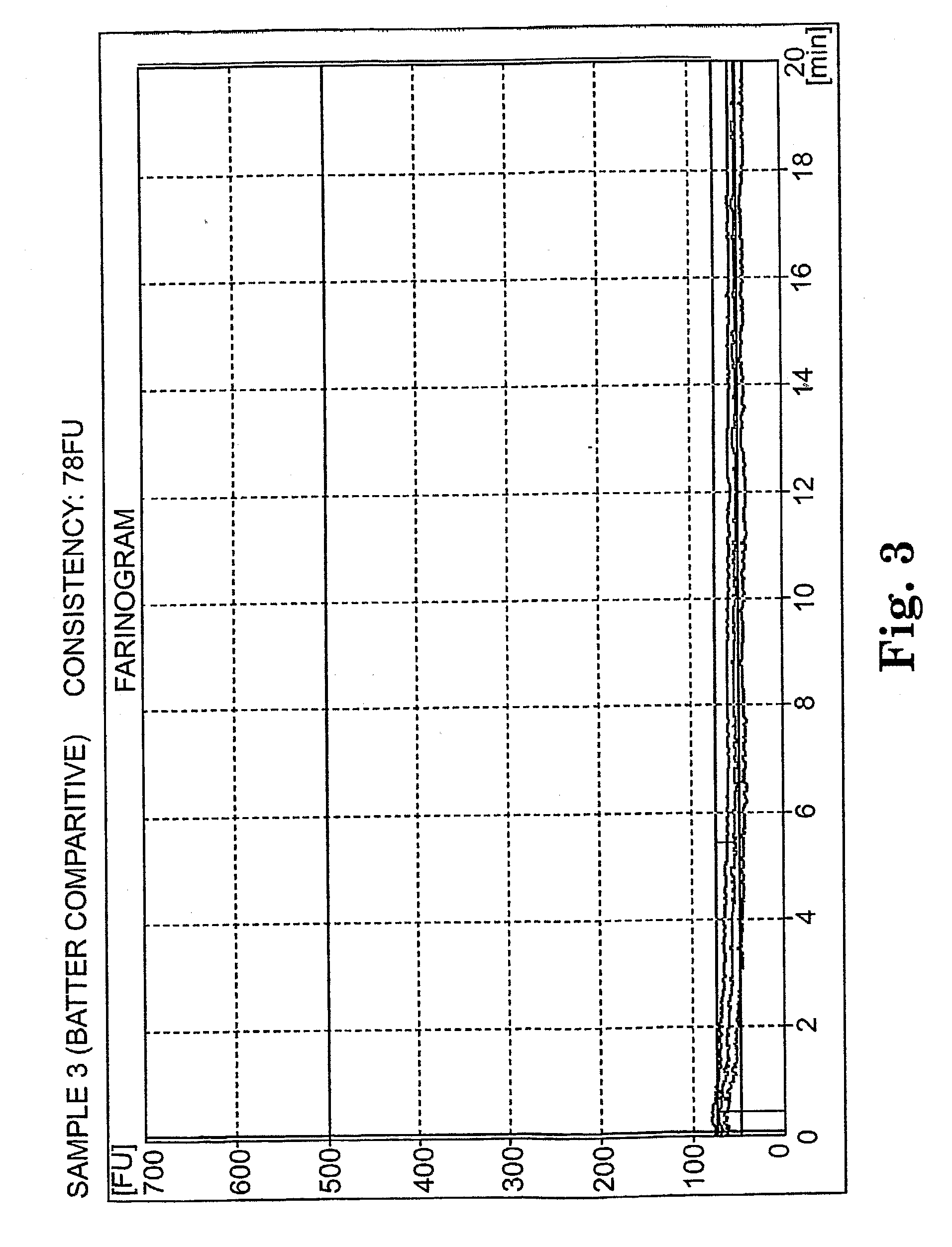
InactiveUS20070065554A1Easy to handleMaintain structural integrityDough treatmentDough/pre-mixesCooking & bakingAdditive ingredient
The invention provides batter-like compositions including flour or a flour replacement ingredient, sweetener, a fat source, a chemical leavening system, and a setting agent. The resulting batter-like compositions are capable of being formed into discrete product pieces (such as pucks), and maintaining the puck form throughout storage and handling of the batter-like composition prior to baking. The invention further provides methods of preparing batter-like compositions having a discrete form, and methods of using such batter-like compositions to provide baked goods.
Owner:GENERAL MILLS MARKETING INC
Toner for developing electrostatic images and image forming method
A toner suitable for use in electrophotography, etc., is composed of toner particles each containing a binder resin, a colorant and a wax component. The toner has a number-average particle size of 2-6 mum and a standard deviation in particle size of below 2.6 mum based on a number-basis distribution of circle-equivalent diameters, an average circularity of 0.970-0.995 and a standard deviation in circularity of below 0.030 based on a circularity frequency distribution, and a residual monomer content of at most 500 ppm. The toner particles have such a microtexture as to provide a particle cross section as observed through a transmission electron microscope (TEM) exhibiting a matrix of the binder resin and a particle of the wax dispersed in a discrete form in the matrix of the binder resin.
Owner:CANON KK
Microstructure array, mold for forming a microstructure array, and method of fabricating the same
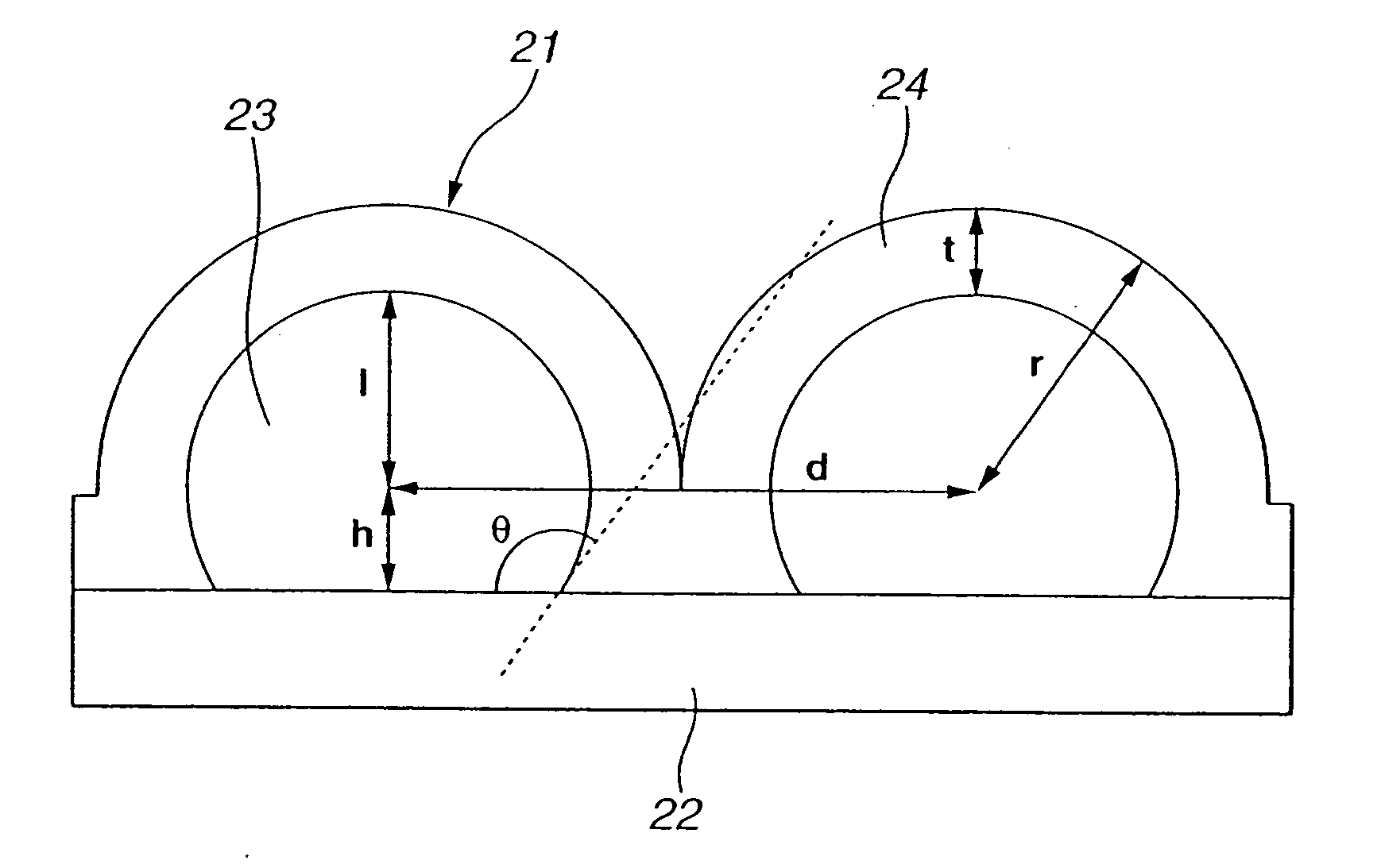
InactiveUS20050157396A1Reduced unusable regionEasy to makeLayered productsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingMicro lens arrayDiscrete form
A method for fabricating a microstructure array, such as a microlens array, and a mold for forming the microlens array, includes the steps of forming an array of microstructures with a curved profile in a discrete form on a substrate, and uniformly forming a continuous layer on the substrate and the discrete microstructures. Optically-unusable regions between the discrete microstructures, such as microlenses, can be readily reduced or eliminated by forming the continuous layer until flat portions between the microstructures disappear.
Owner:CANON KK
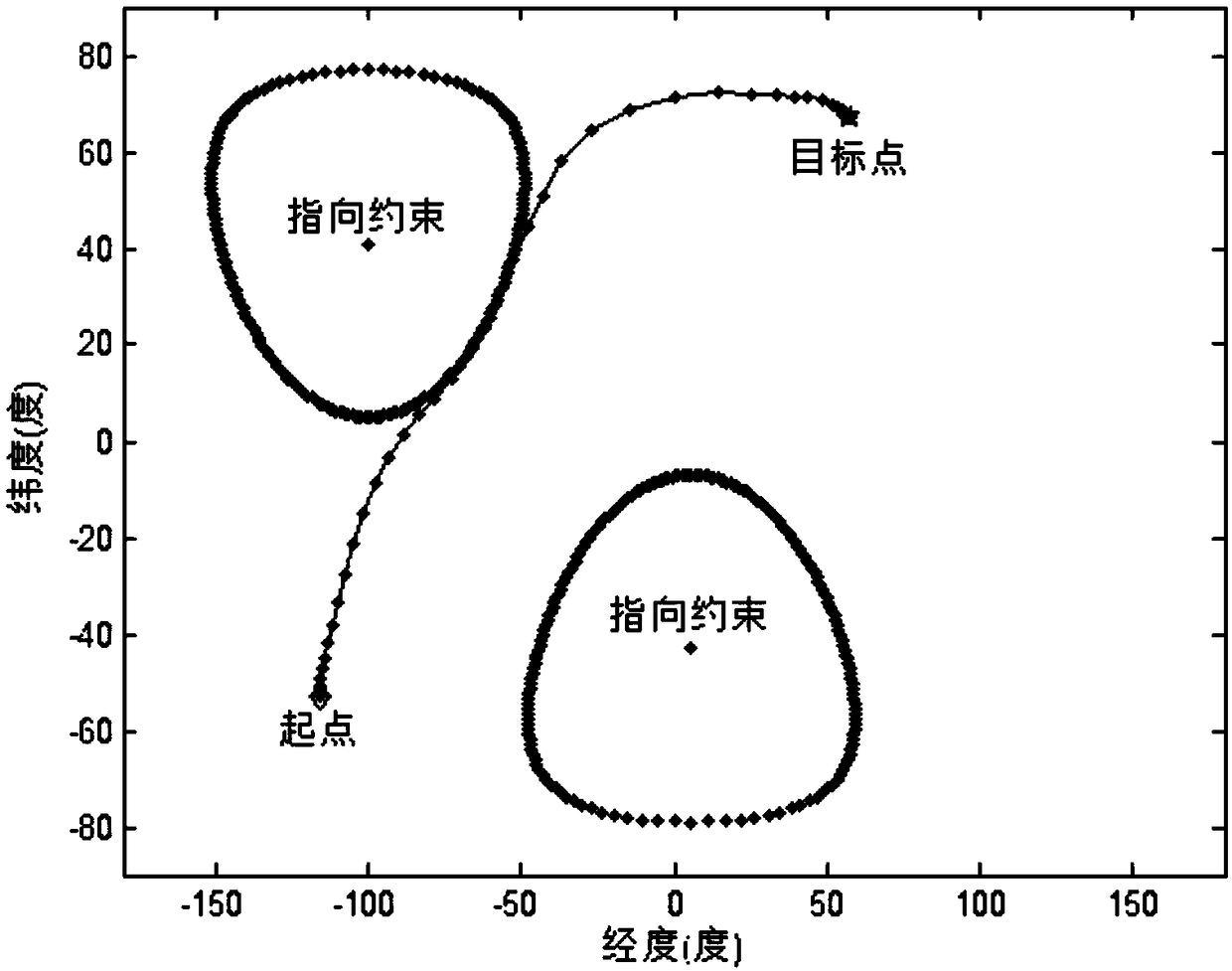
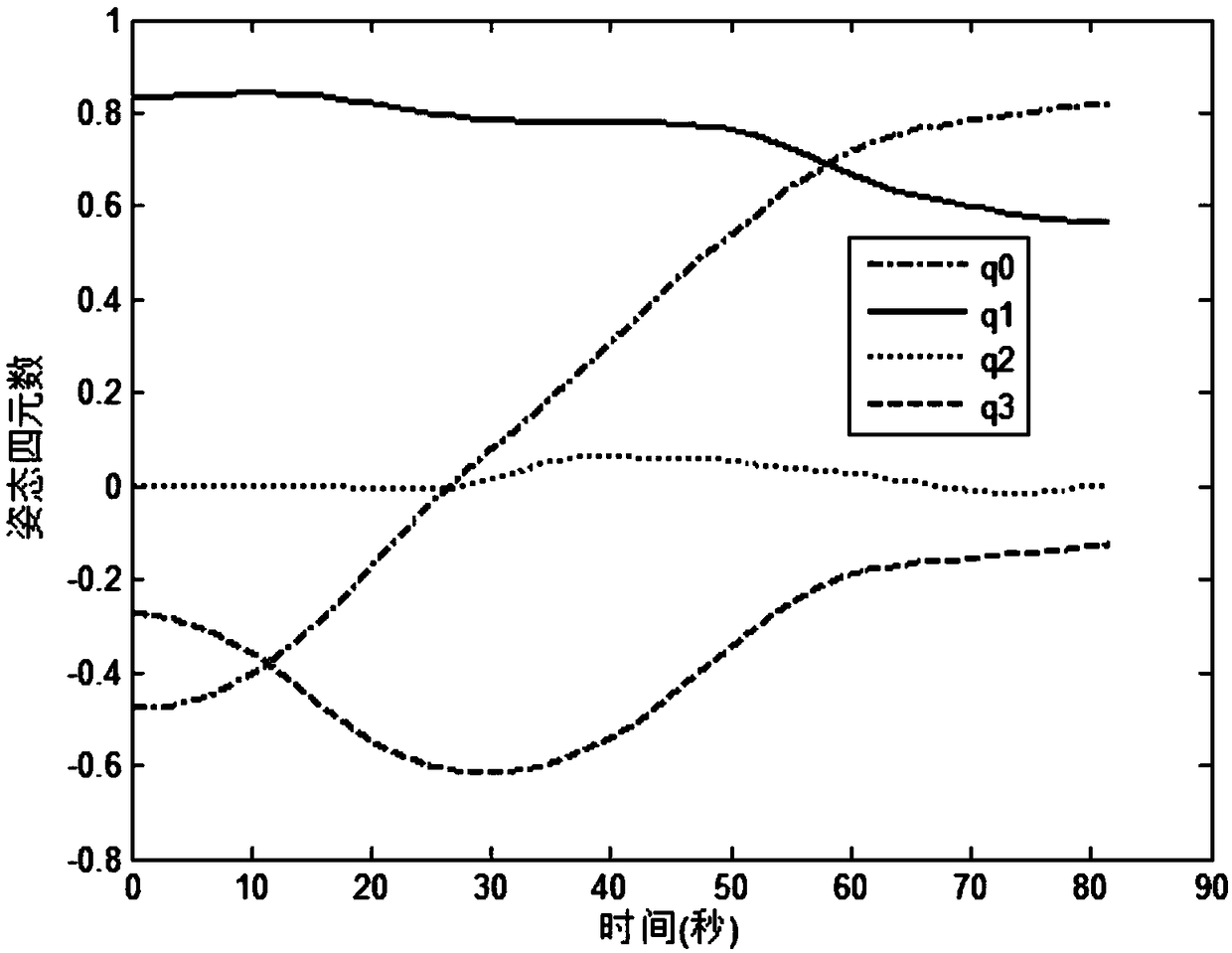
Spacecraft multi-constrained attitude maneuver optimization method based on rotating path quality
ActiveCN109283934AGood for attitude tracking controlUnwind lowerAttitude controlAdaptive controlPath lengthKinematics
The invention discloses a spacecraft multi-constrained attitude maneuver optimization method based on the rotating path quality, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft attitude planning andoptimization. The implementation method of the invention includes: establishing a rotating path quality evaluation model, and respectively giving a continuous form and a discrete form; evaluating therotation path quality by the reciprocal of the sum of the error distances of each path point and a target point; establishing a spacecraft attitude kinematics and dynamics model, and considering bounded constraints of the control torque and the angular velocity; determining a plurality of pointing constraints that the spacecraft needs to satisfy during the attitude maneuver; determining a startingattitude point and a target attitude point of the spacecraft attitude maneuvering process, and the starting angular velocity and the target angular velocity; solving the multi-constrained attitude maneuver based on the rotation path quality by using the optimization method, and obtaining the attitude path with high rotation path quality. The method can shorten the path length, reduce the path unwinding, obtain the attitude path with high rotation path quality, and is more beneficial to the actual attitude tracking control.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Toner for developing electrostatic images and image forming method
A toner suitable for use in electrophotography, etc., is composed of toner particles each containing a binder resin, a colorant and a wax component. The toner has a number-average particle size of 2-6 mum and a standard deviation in particle size of below 2.6 based on a number-basis distribution of circle-equivalent diameters, an average circularity of 0.970-0.995 and a standard deviation in circularity of below 0.030 based on a circularity frequency distribution, and a residual monomer content of at most 500 ppm. The toner particles have such a microtexture as to provide a particle cross section as observed through a transmission electron microscope (TEM) exhibiting a matrix of the binder resin and a particle of the wax dispersed in a discrete form in the matrix of the binder resin.
Owner:CANON KK
In-Line Continuous Flow Process for Making Cheese
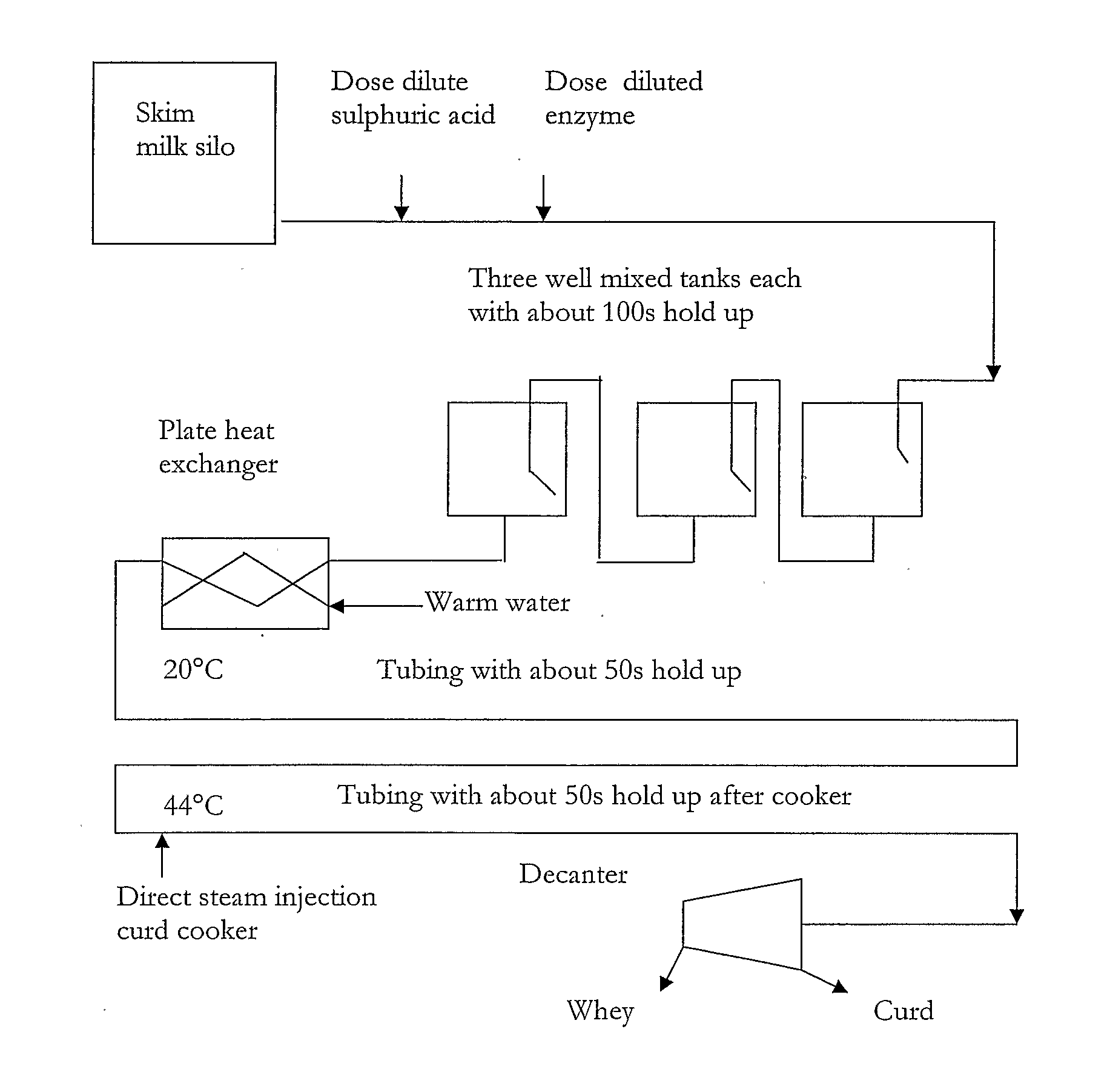
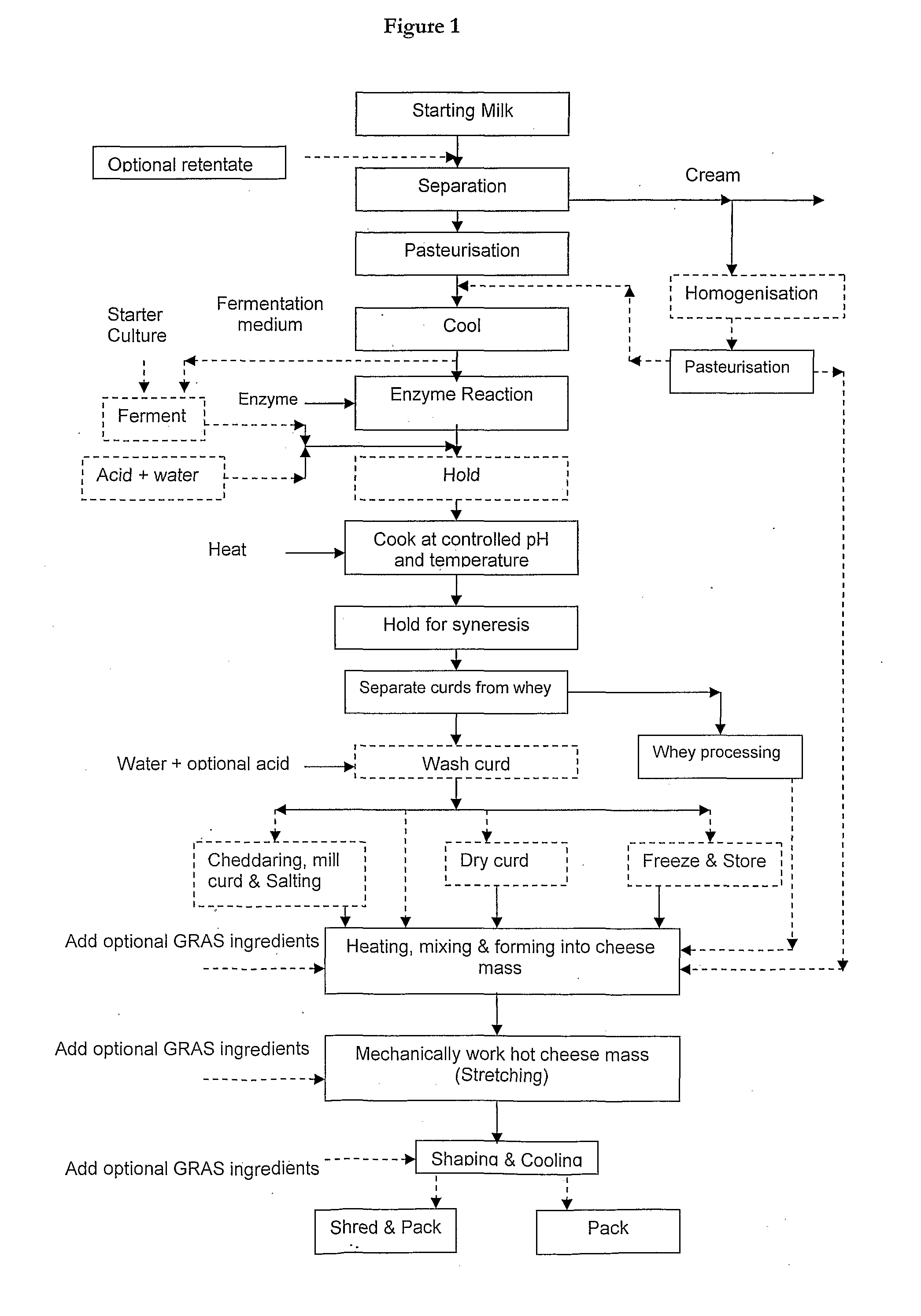
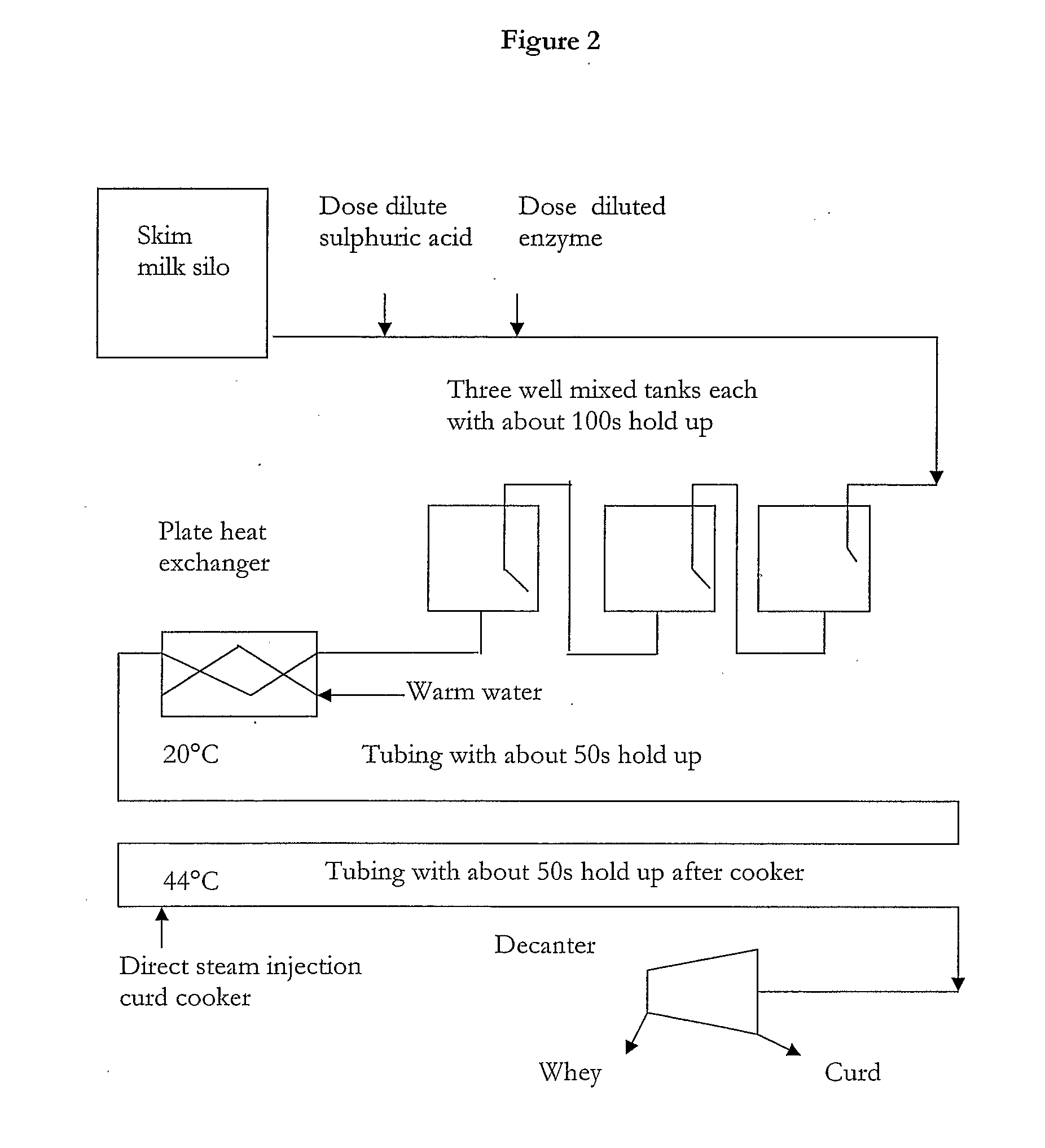
InactiveUS20100062110A1Enough timeEvenly dispersedMilk preparationCheese manufactureContinuous flowDiscrete form
The invention provides a novel process of making cheese including a quick and efficient coagulation step forming discrete form and uniform curd particles in an in-line continuous flow process, separation of the curd particles from the whey and subsequent processing to produce a desired soft, semi-soft, hard or extra hard cheese.
Owner:FONTERRA COOP GRP LTD
Batter-Like Compositions and Methods of Preparing and Using Same
InactiveUS20080280003A1Maintain structural integrityWithout risk of spoilageBakery battersEmulsionAdditive ingredient
The invention provides batter-like compositions including flour or flour replacement ingredient, sweetener, a fat source, and a chemical leavening system, wherein at least a portion of the fat source is provided as an emulsion to the batter-like composition. The resulting batter-like compositions are capable of being formed into discrete product pieces (such as pucks), and maintaining the puck form throughout storage and handling of the batter-like composition prior to baking. The invention further provides methods of preparing batter-like compositions having a discrete form, and methods of using such inventive batter-like compositions to provide baked goods.
Owner:GENERAL MILLS INC
Batter-like compositions containing setting agent and methods of preparing and using same
ActiveUS20070048426A1Easy to handleMaintain structural integrityDough treatmentDough/pre-mixesCooking & bakingAdditive ingredient
The invention provides batter-like compositions including flour or flour replacement ingredient, sweetener, a fat source, a chemical leavening system, and a setting agent. The resulting batter-like compositions are capable of being formed into discrete product pieces (such as pucks), and maintaining the discrete product form throughout storage and handling of the batter-like composition prior to baking. The invention further provides methods of preparing batter-like compositions having a discrete form, and methods of using such batter-like compositions to provide baked goods.
Owner:GENERAL MILLS INC
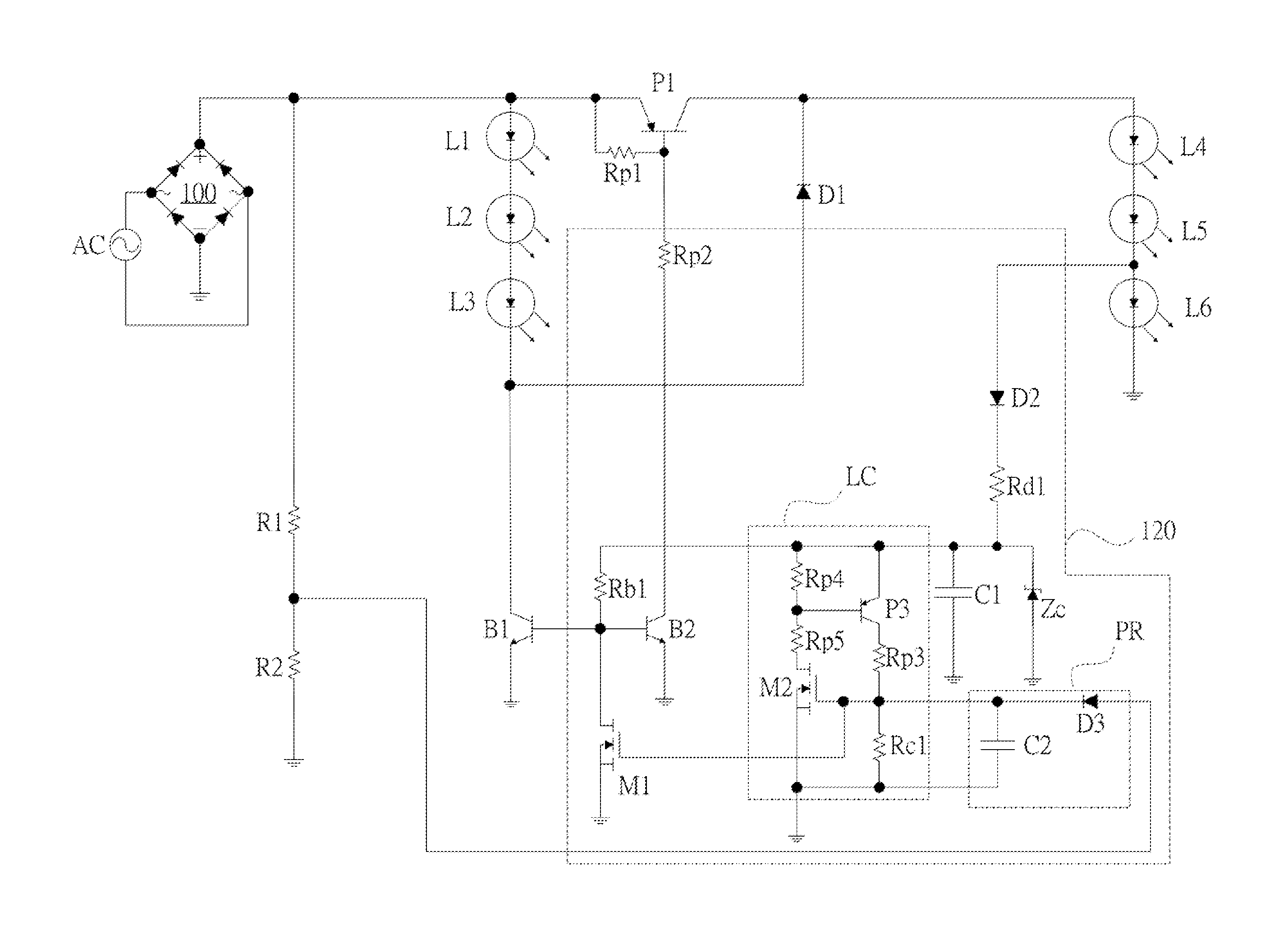
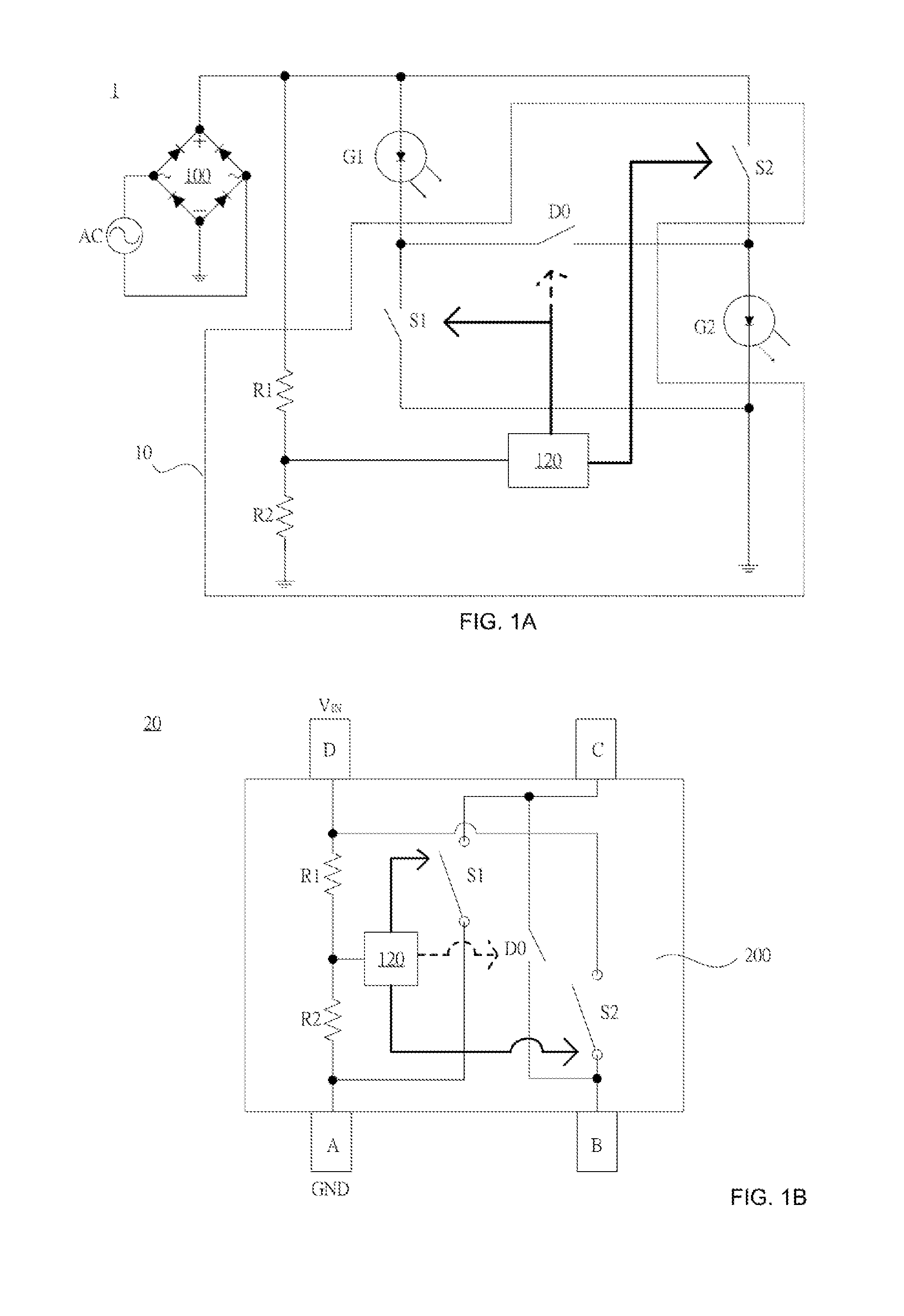
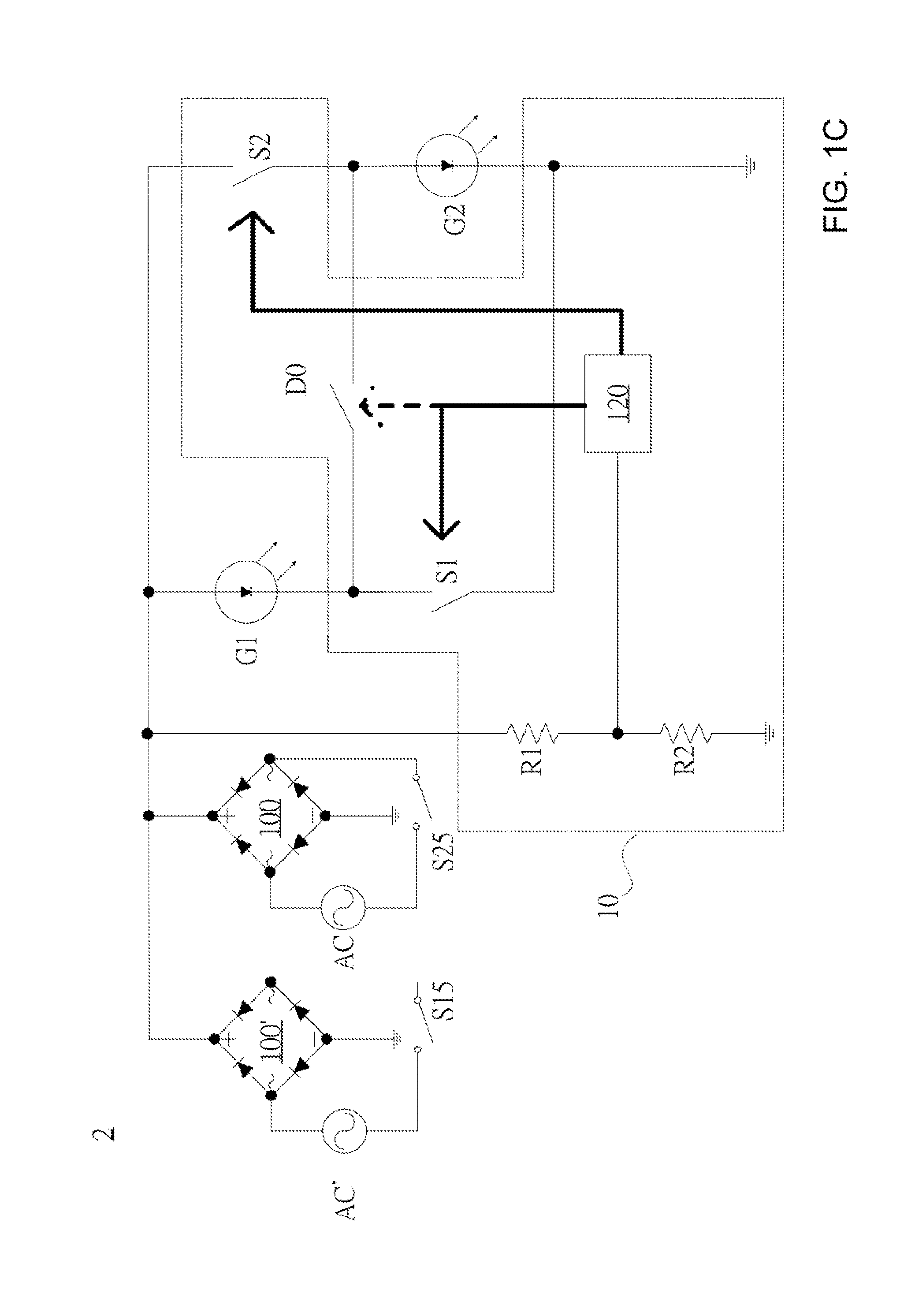
Control circuits, integrated circuits and illuminating apparatuses having the same
InactiveUS20150163869A1Wide range of adaptationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesVoltage amplitudeLed array
Disclosed are control circuits capable of auto-configuring two LED arrays either in parallel when the two LED arrays are operating off of 100±20% V AC voltage sources or in series when the two LED arrays are operating off of 200±20% V AC voltage sources according to the detection of the AC input voltage magnitude. The disclosed control circuits, ruling over the parallel or series configuration of the two LED arrays, could be implemented in discrete forms or as integrated circuits (IC).
Owner:GRP TECH
Production scheduling optimization method for beer saccharification process
The invention relates to a production scheduling optimization method for a beer saccharification process, wherein beer enterprises are not ideal in scheduling effect because of formulating production scheduling schemes by virtue of artificial experience presently. The production scheduling optimization method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: establishing a production scheduling mathematical model on the basis of a technological process mechanism and first, and then converting to a discrete form capable of solving by virtue of an ant colony optimization algorithm, and finally determining a production scheduling method for the beer saccharification process. The invention discloses a saccharification production scheduling method with a high global optimization capacity aiming at some problems in optimized scheduling for beer saccharification production, and the optimization method has the characteristics of openness, robustness, parallelism, global convergence, and no special requirements on problematic mathematical forms, and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
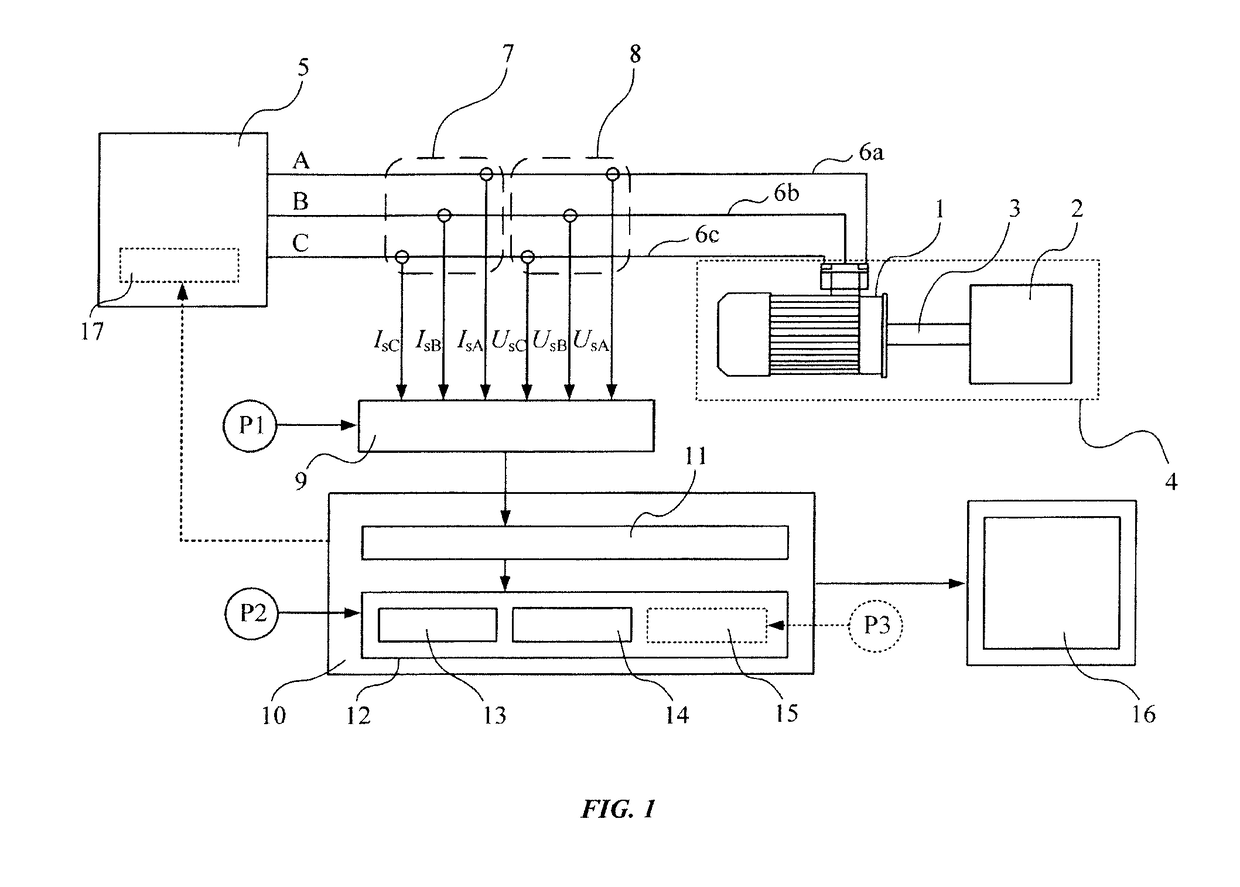
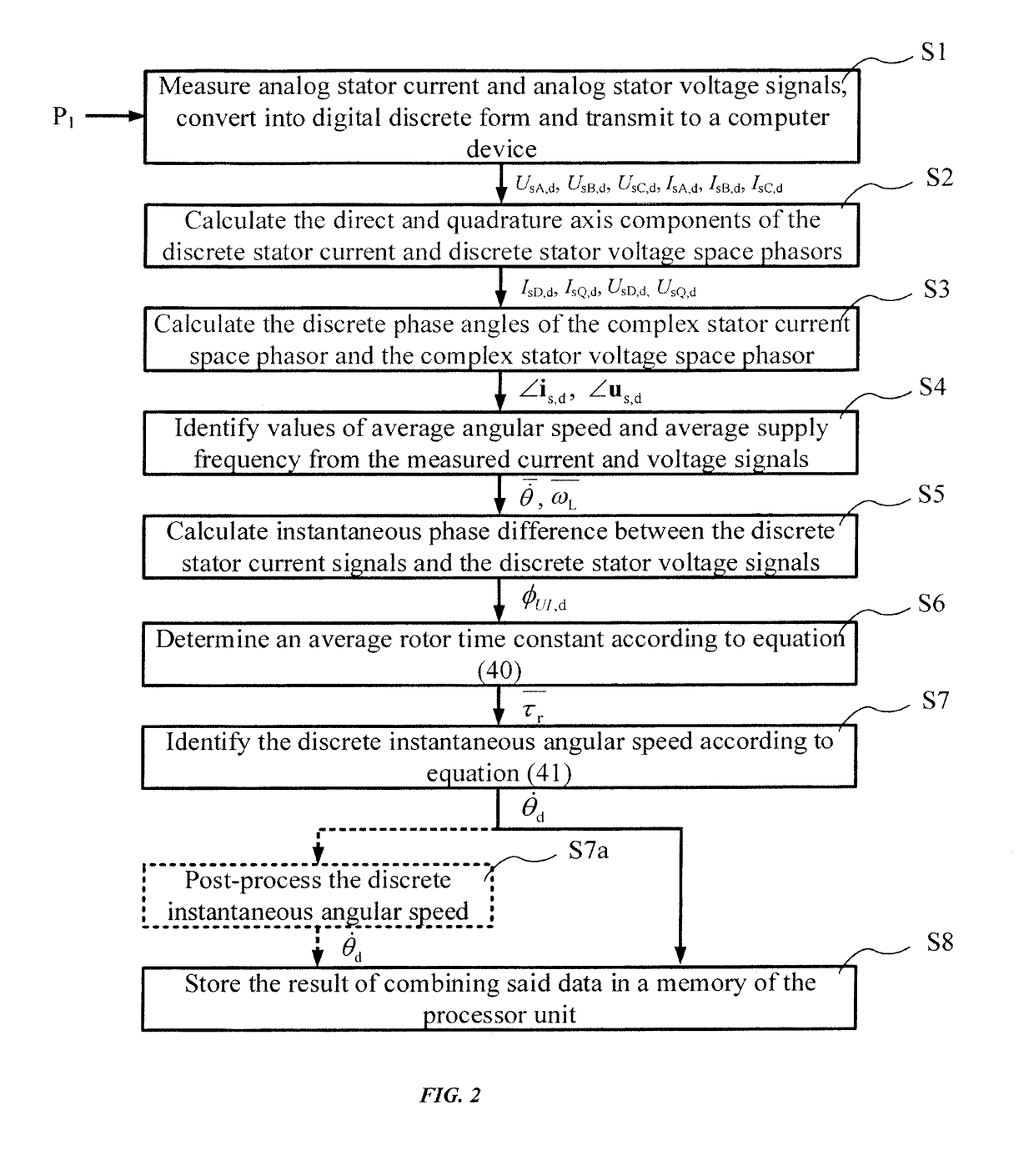
Method for identifying the discrete instantaneous angular speed of an electromechanical system
ActiveUS20180241332A1Minimize residual errorComputationally efficientElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlMathematical modelVIT signals
A method for identifying the discrete instantaneous angular speed of electromechanical systems in which electrical rotating machinery is used and in which at least one electrical signal is measured during an operation of the electromechanical system. The method includes measuring analog stator current signals and analog stator voltage signals for at least one phase A, B, C, converting the measurements into a digital discrete form, transmitting the digital discrete signals to a computer device wherein data analysis is performed in a processor unit on the basis of a simplified mathematical model of the dynamics of the motor or generator. During the data analysis an average rotor time constant is calculated, an average supply frequency value is identified, an average angular speed is obtained, and an instantaneous phase difference between the discrete stator current signals and the discrete stator voltage signals is determined. The discrete instantaneous angular speed is identified by combining the average supply frequency value, the instantaneous phase difference between the discrete stator current signals and the discrete stator voltage signals, the average rotor time constant, and a number of pole pairs of the electric motor, given by the user. The result of combining the data is stored in a memory of the processor unit.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
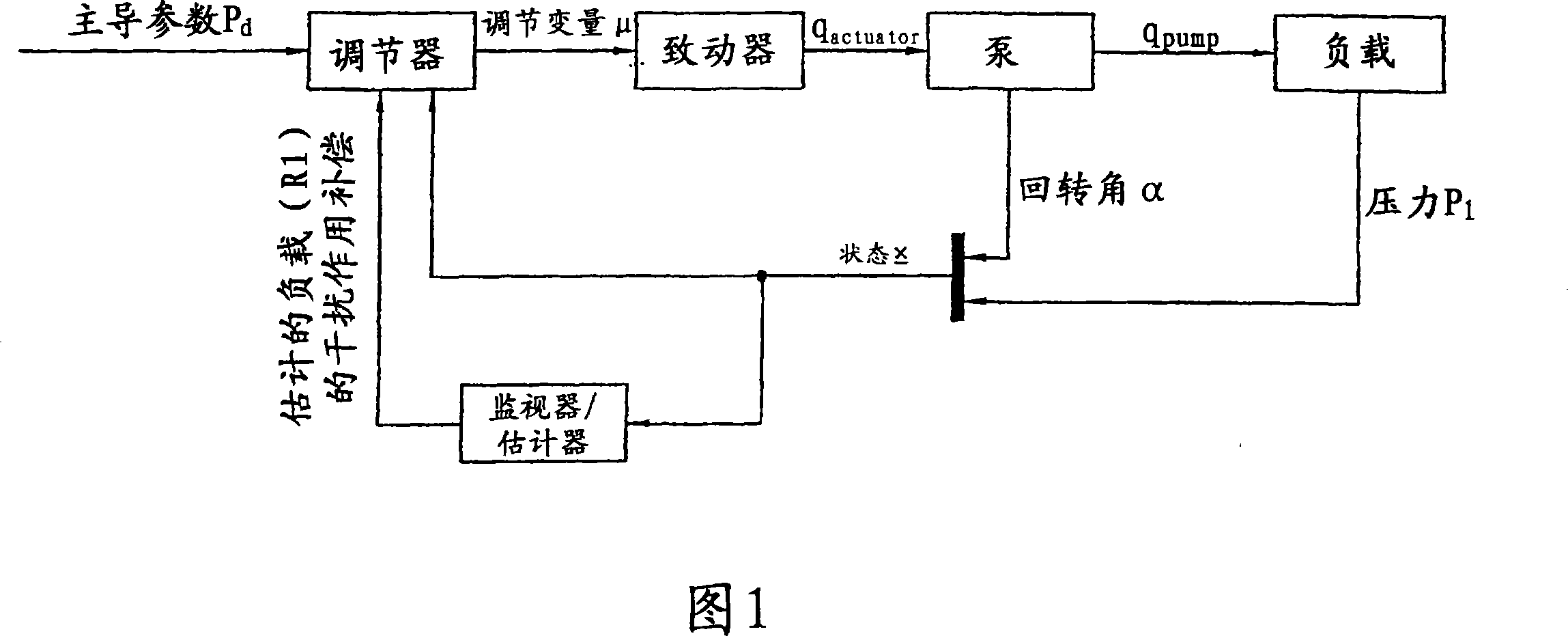
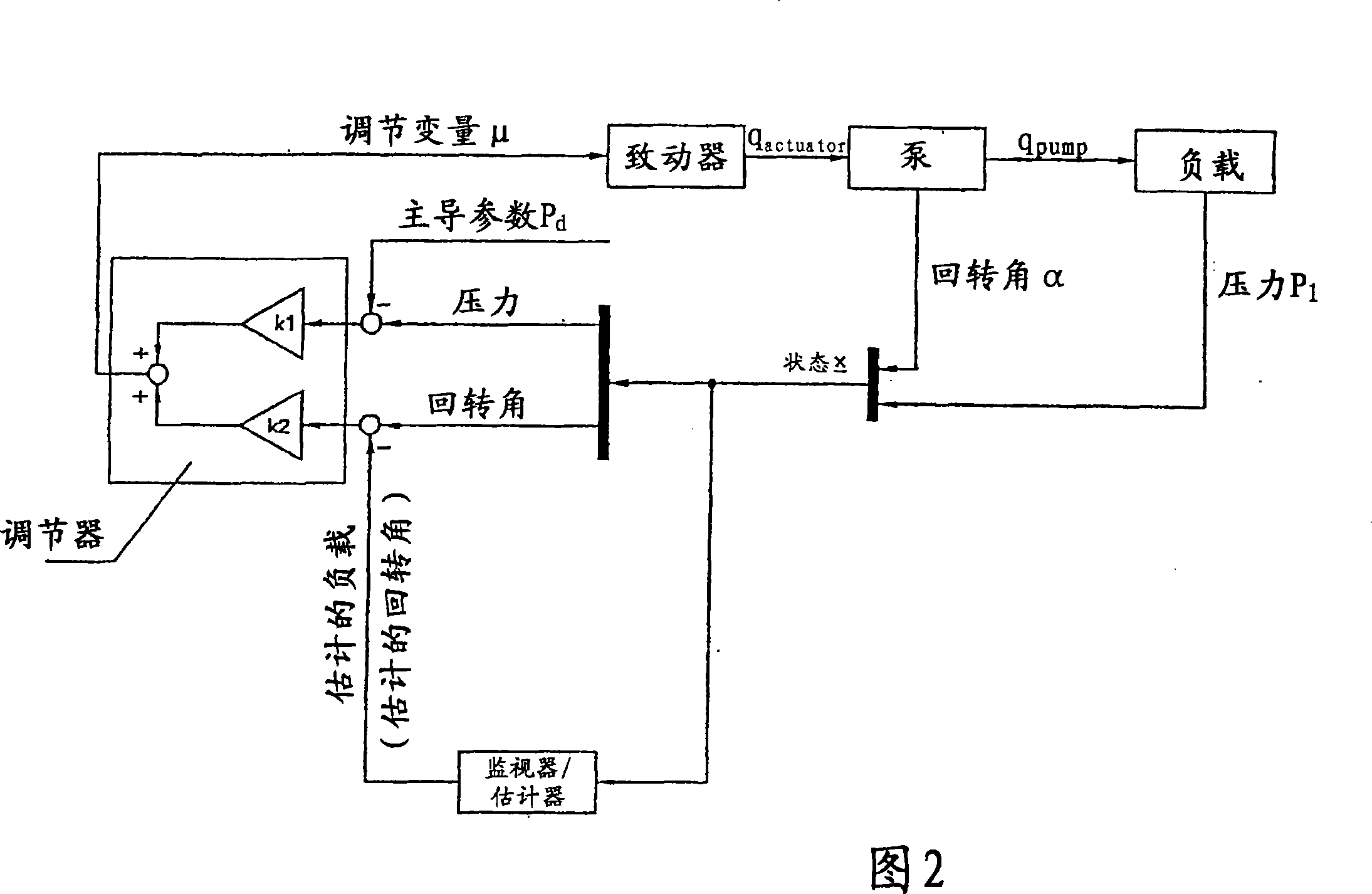
Regulator device and method for operating a regulator device
InactiveCN101189433AIncrease dynamicsHigh precisionFluid pressure control using electric meansPump controlDistribution controlHydraulic circuit
The invention relates to a regulator device, preferably as a component of a hydraulic circuit, in particular for regulating fluid-bearing units or units that are driven using a fluid, such as adjustable fluid pumps, which respectively co-operate with at least one actuator, which can be controlled by means of at least one governor in accordance with a predefinable guide variable (pd), said governor detecting output variables (alpha,pI) at least partially via a recirculation line. The fact that at least one recirculation line comprises at least one monitor (estimator), which estimates the output variables (condition x) that are at least in part unknown for the assignable governor, enables the provision of a regulator device, in which the governor comprises a linear or non-linear monitor for estimating the unknown load. Said regulator device continuously monitors the load, (load volumetric flow), independently of the regulation type, (volumetric and / or pressure regulation) and its implementation, (in analogous or discrete form), in order to regulate the operation in a dynamic, precise manner (devoid of spikes).
Owner:HYDAC ELECTRONICS GMBH
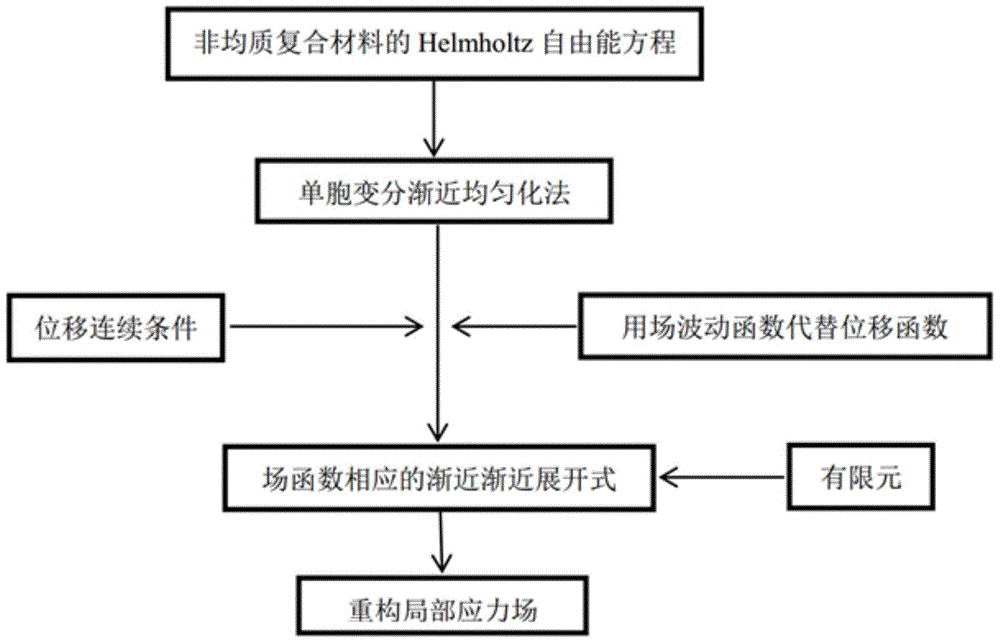
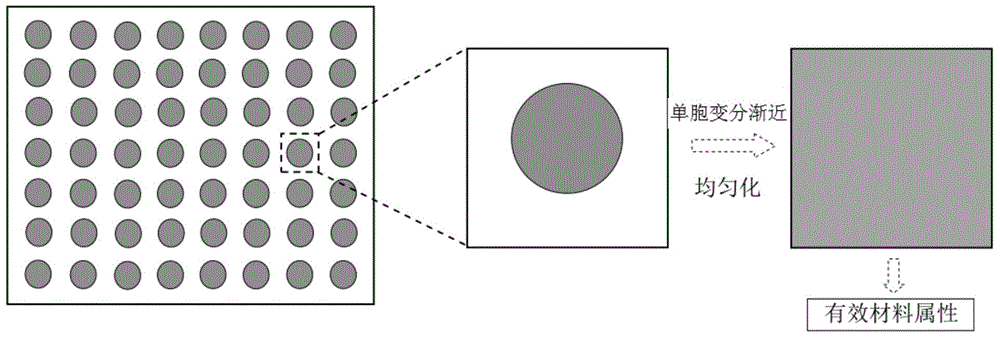
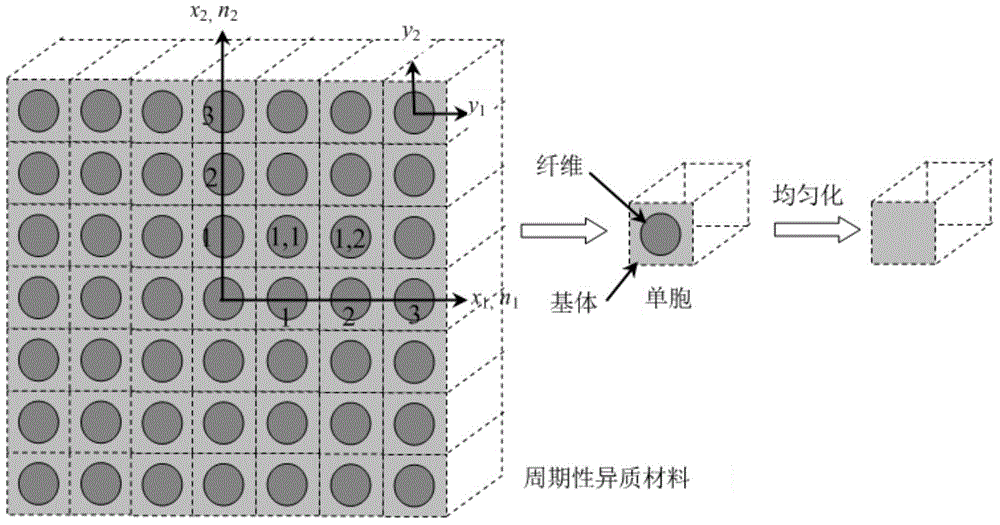
Method for forecasting thermoelasticity valid attribute and local field of composite material
InactiveCN103984869ATightnessEasy to repeat programsSpecial data processing applicationsResearch ObjectEuler–Lagrange equation
The invention provides a method for forecasting thermoelasticity valid attribute and local field of a composite material. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the sum of Helmholtz free energies stored in all unit cells by using heterogeneous and periodically-distributed microstructure of the composite material as a study object; converting thermoelasticity analysis and solution problem into the problem of minimizing-acquiring stationary value in an energy equation under a restricted condition; performing variational analysis for the energy equation to obtain an Euler-Lagrange equation set for solving a wave function and corresponding inhomogeneous boundary conditions; rewriting the energy equation into a discrete form by the numerical analysis technology-finite element method; solving to obtain the density of Helmholtz free energies of the unit cells; applying a constitutive model using the density as an effective medium to the composite material; then changing the load and temperature conditions of the composite material to analyze the local field of the composite material. The method is high in practicability, high in universality, and can obviously raise the calculating speed and efficiency for such problems.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Simulation method for rapidly extracting transient scattered signals of electric large-size metal cavity target
ActiveCN104731996AAccurate descriptionTrue discrete fitSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorDissection
The invention discloses a simulation method for rapidly extracting transient scattered signals of an electric large-size metal cavity target. The simulation method includes creating a geometric model of the metal cavity target, and performing mesh dissection on the surface of the metal cavity target by a curved-surface triangular unit; determining a time domain integral equation of the metal cavity target; unfolding a surface induced current in the time domain integral equation by a high-order lamination divergence conformal basis function in terms of space and a time and space-time hybrid basis function in terms of time; substituting a surface induced current expression into the time domain integral equation, and testing a time domain electric field integral equation in a discrete form in terms of time and space respectively to acquire a system impedance matrix equation; solving the impedance matrix equation by a time stepping method, determining time domain current distribution on the surface of the conductor target, and acquiring broadband electromagnetic characteristic parameters of the target according to time domain current distribution to complete simulation. The method has the advantages of high simulation accuracy, less time used and low memory consumption, thereby having a broad application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
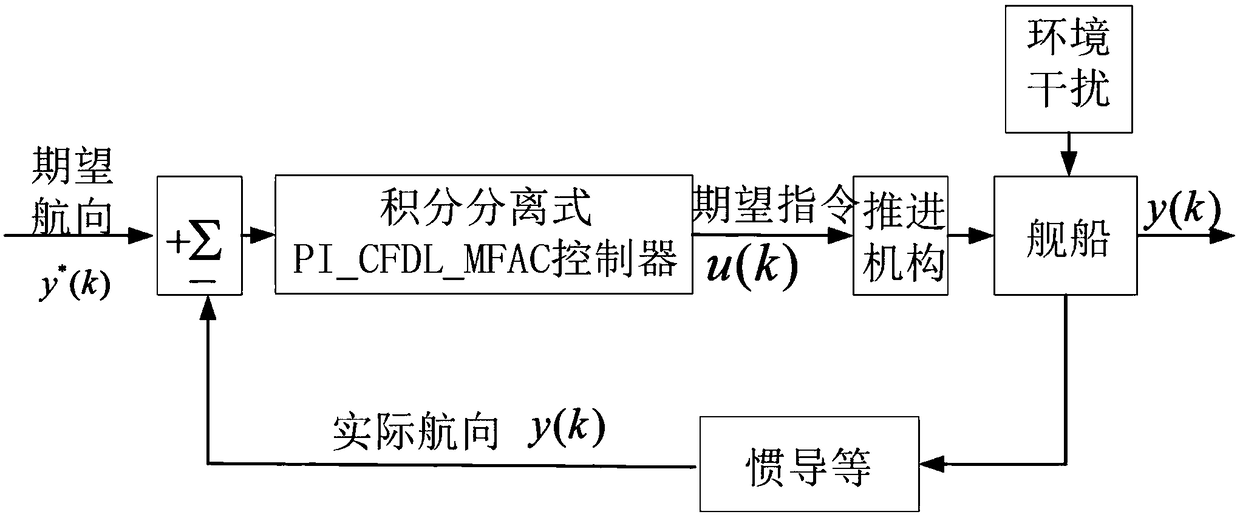
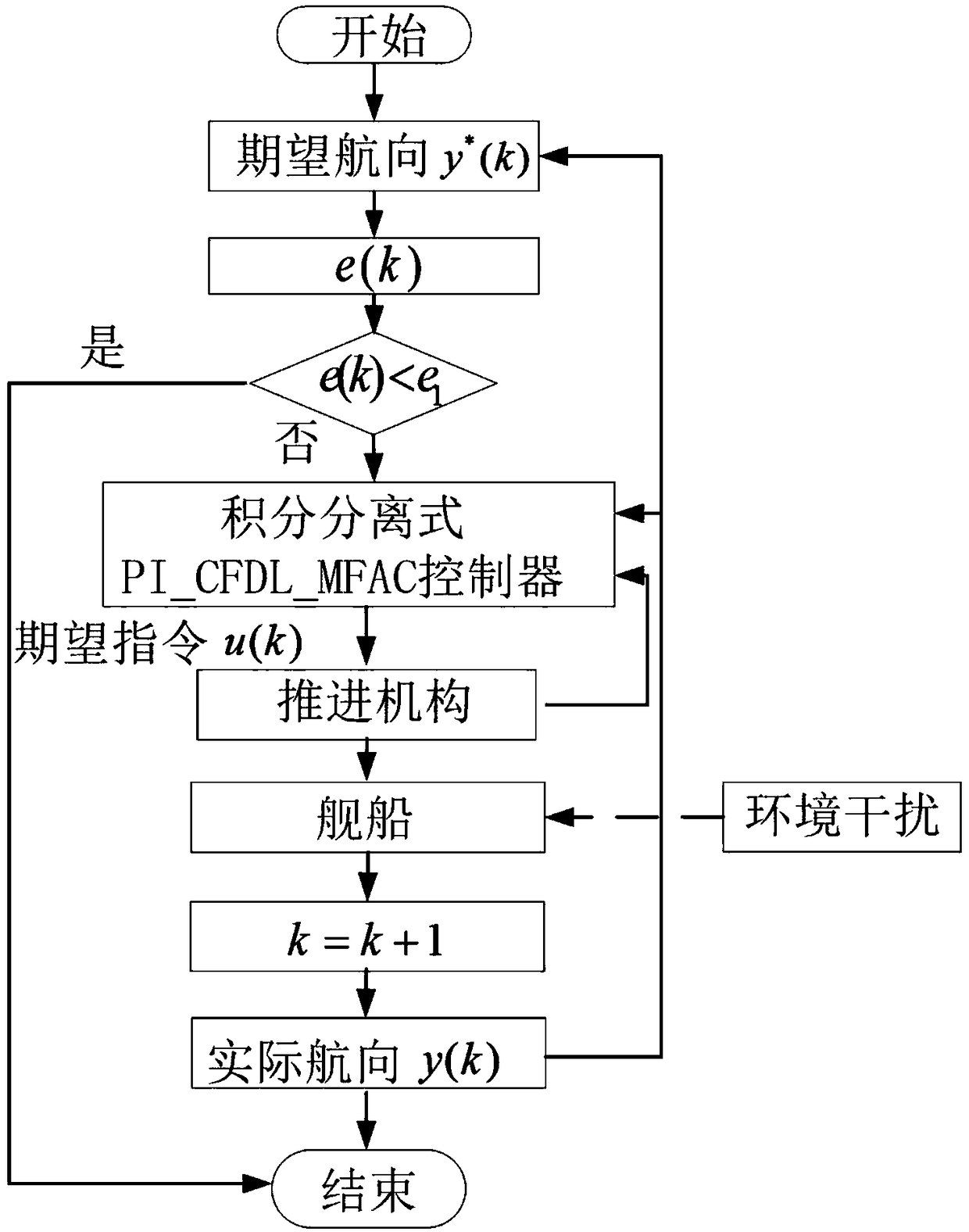
Integral separation type PI-Type tight format model free adaptive course control algorithm used for ships
ActiveCN109144066AConvergent stabilityQuick responseControllers with particular characteristicsPosition/course control in two dimensionsSelf adaptiveDiscrete form
The invention belongs to the field of ship motion control, and specifically relates to an integral separation type PI-Type tight format model free adaptive course control algorithm used for ships. Thealgorithm includes the following steps: a proportional item is introduced to form a PI-type CFDL_MFAC algorithm based on the tight format model free adaptive control algorithm, and a discrete form ofthe proportional item is k.[delta]e(k); a course deviation threshold e<0> is set; a course deviation e(k) is calculated, wherein e(k)=y<*>(k)-y(k); when an absolute value |e(k)| of the e(k) is greater than a threshold e<1> of a set course state deviation; according to the e(k), an integral separation type PI_CFDL_MFAC controller resolves expected input u(k) of a course system; and a formula ofk=k+1 is achieved, and a current course y(k) of a course ship is updated. By introduction of the proportional item in the control algorithm, the response speed of a system is improved; an idea of integral separation is introduced in the algorithm, thus avoiding the problem that an original control algorithm is directly applied to ship course control to cause system oscillation or even instabilitydue to integral saturation; and introduction of the proportional item and the integral separation idea makes an application range of a CFDL_MFAC theory extend, so that a ship course can quickly and stably converge to a desired course.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method and apparatus for processing visual information
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com