Method for forecasting thermoelasticity valid attribute and local field of composite material
A composite material and thermoelasticity technology, applied in the fields of instrumentation, calculation, electrical and digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of low analysis efficiency, inability to accurately predict the distribution of local field variables, and poor accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] 1. Theoretical formula.
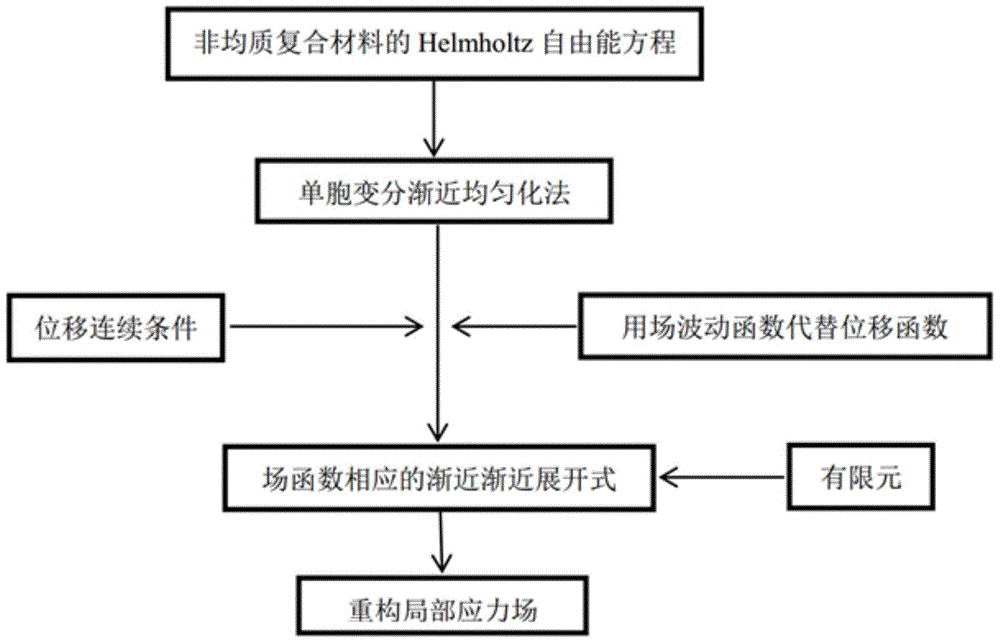
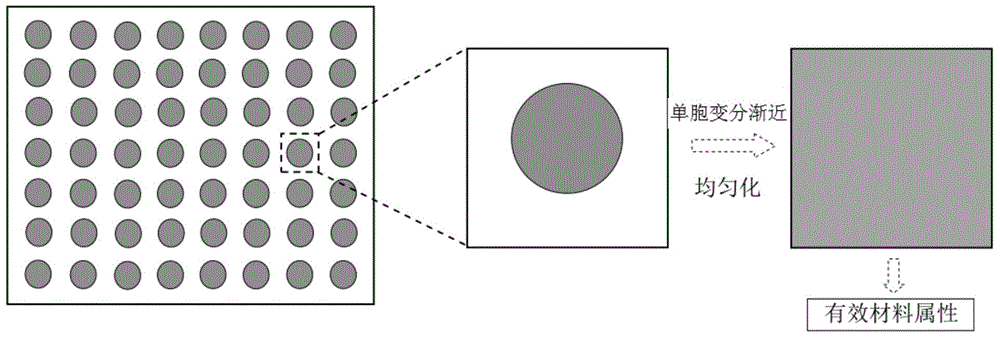
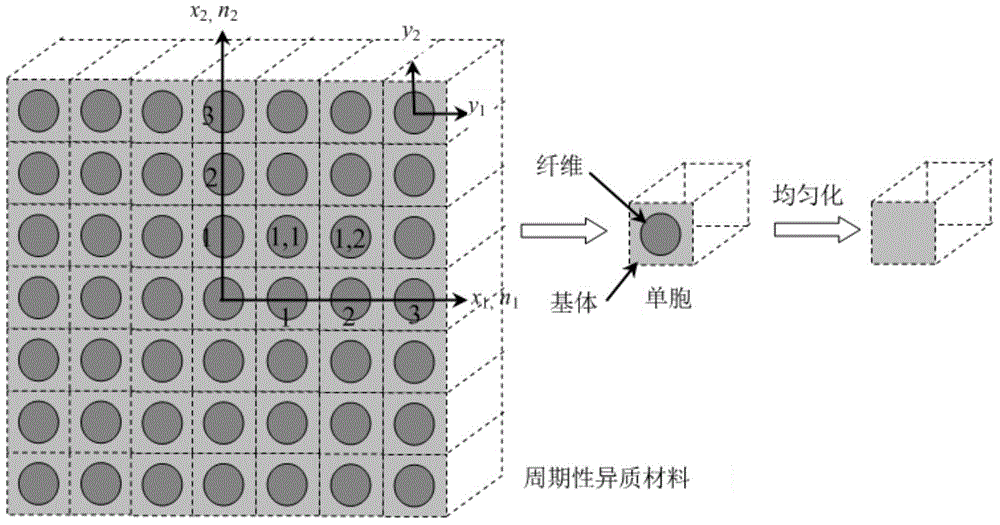
[0054] The flow chart of the effective attribute analysis method of the unit cell structure of the heterogeneous composite material of the present invention is as follows figure 1 Shown, the present invention is based on following two basic assumptions:
[0055] Assumption 1: According to the general discussion of the oscillation function, the macroscopic quantity must be the volume average of the corresponding quantity in the mesoscopic, such as the displacement u i volume average v i defined as:
[0056] v i = 1 Ω ∫ Ω u i dΩ = u j > - - - ( 1 )
[0057] In the formula: Ω represents the volume domain of the unit cell, and the angle bracket...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com