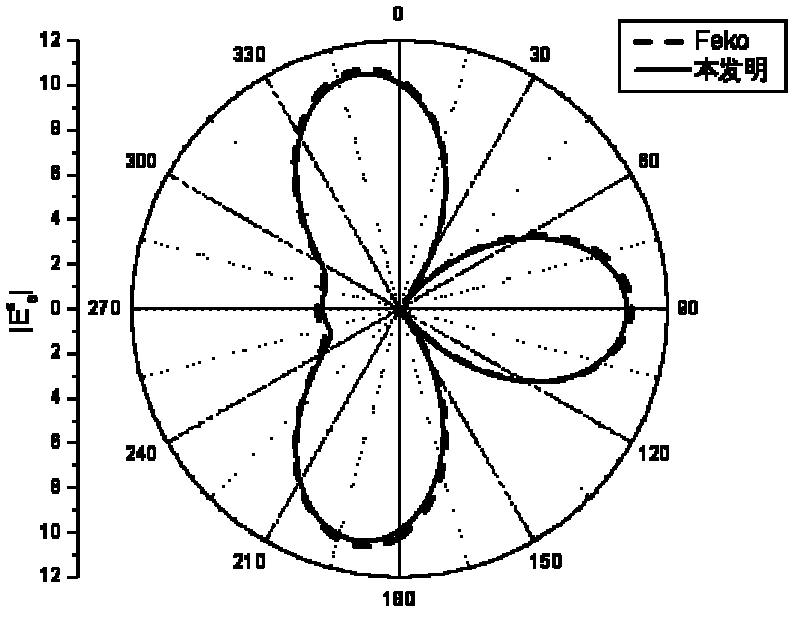
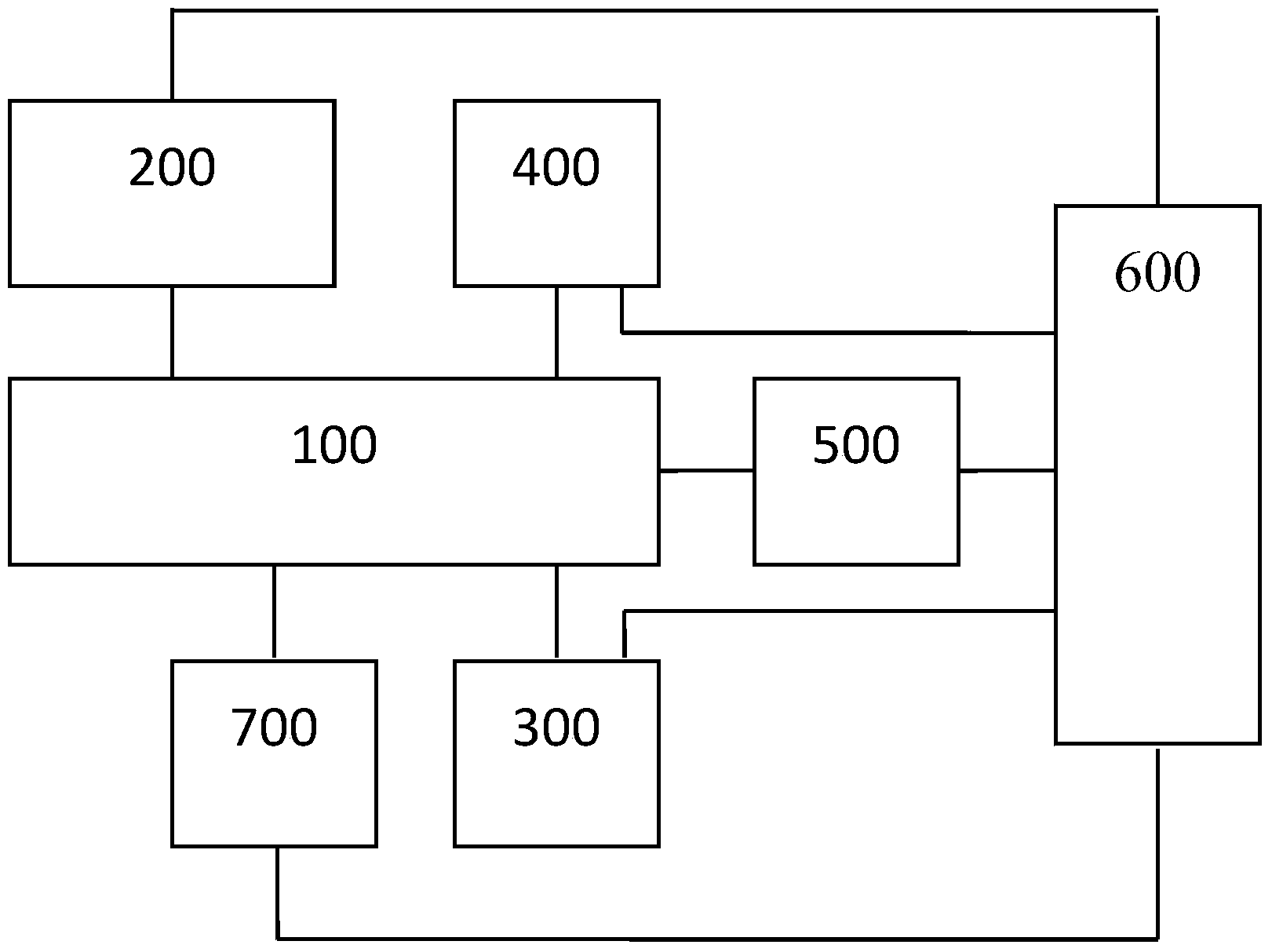
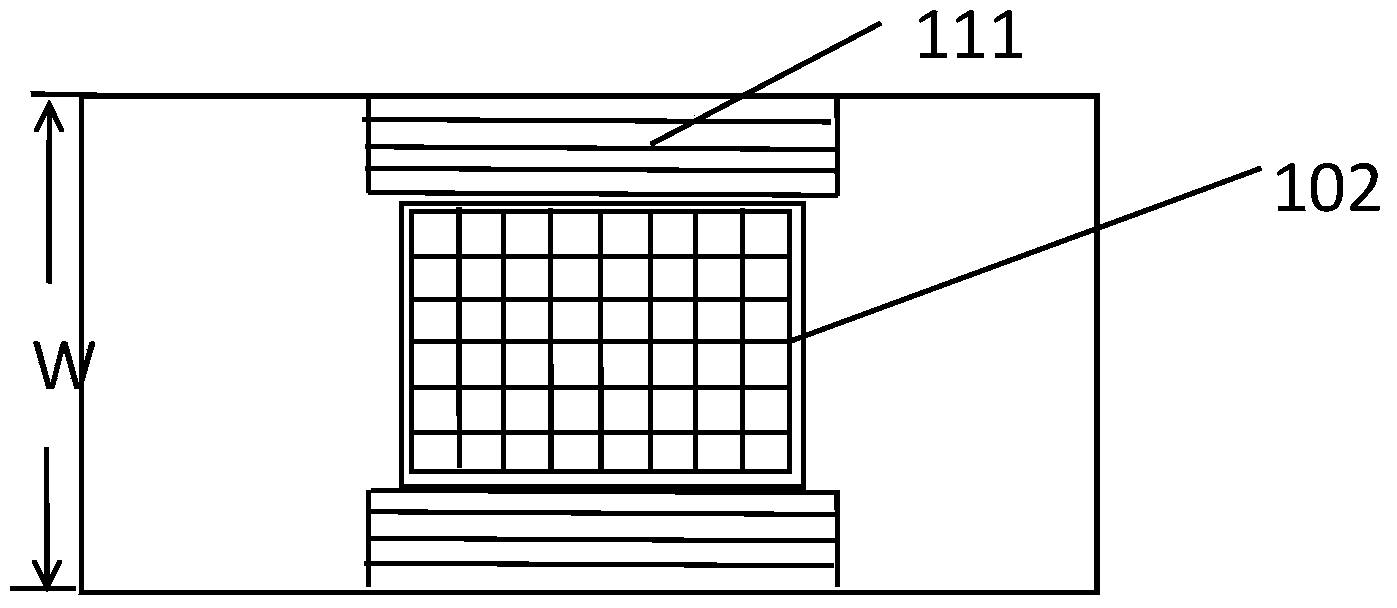
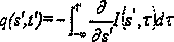Patents
Literature
34 results about "Electric-field integral equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
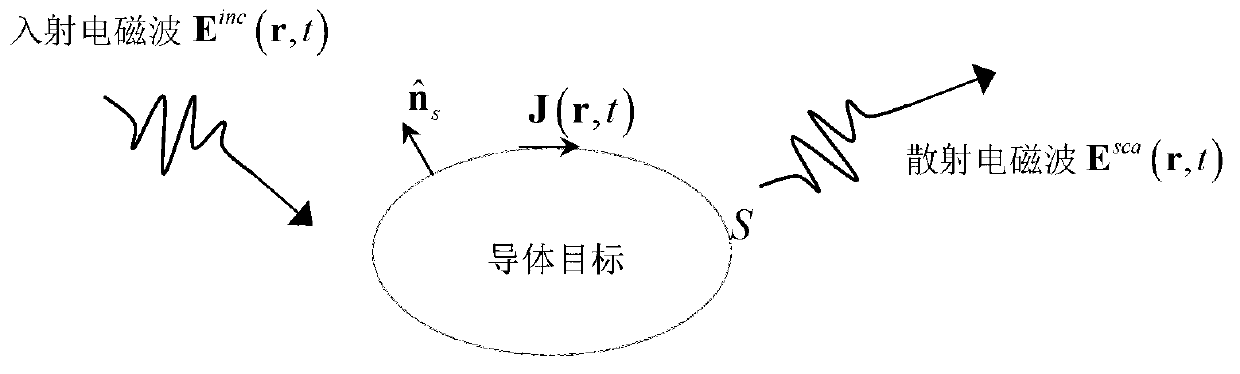
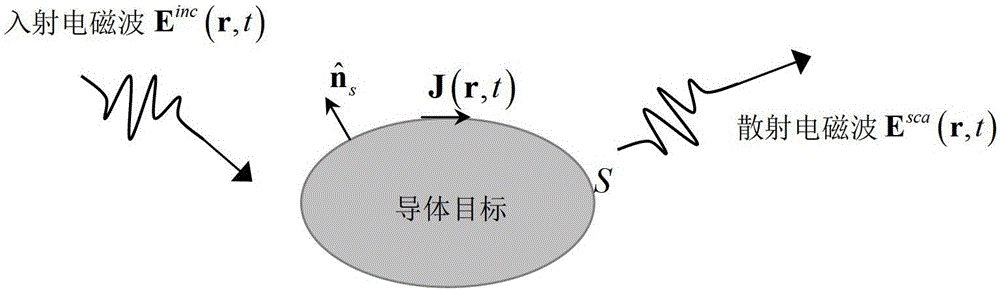
The electric-field integral equation is a relationship that allows the calculation of an electric field (E) generated by an electric current distribution (J).
Method for simulating wide-band electromagnetic scattering property of conductor target
ActiveCN103279601AAccurate descriptionExact discrete fitSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorTime delays
The invention discloses a method for simulating the wide-band electromagnetic scattering property of a conductor target. The method comprises the following steps that the geometric model of the conductor target is built, and mesh generation is conducted on the surface of the conductor target by a curved surface triangle unit; a time domain electric field integral equation of the conductor target is determined; a surface induction current in the time domain electric field integral equation expands through a space CRWG primary function and a time delay primary function; an expanding surface induction current expression is substituted into the time domain electric field integral equation, and then the time domain electric field integral equation in a discrete form is tested in a time and space mode so as to obtain a system impedance matrix equation; singularity integrals are eliminated to obtain a sparse expression of a impedance matrix; the equation of the impedance matrix is solved to determine the distribution of the time domain current of the surface of the conductor target, and wide-band electromagnetic property parameters of the target are obtained according to the distribution of the time domain current so as to finish simulation. The method for simulating the wide-band electromagnetic scattering property of the conductor target has the advantages of being high in simulation precision, little in required time and low in memory consumption, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rotationally symmetric target electromagnetic scattering rapid calculation method of thin-medium-coated metal
InactiveCN103177193AGood iterative solution behaviorSimplify the build processSpecial data processing applicationsInternal memorySurface charges
The invention discloses a rotationally symmetric target electromagnetic scattering rapid calculation method of thin-medium-coated metal. For a metal-medium mixing structure, an electric field integral equation only needs to be built for a metal part rather than a medium part, so that an equation building process is simple, and the equation belongs to second integral equations; and therefore, the method is good in iterative solution behavior. When the iterative solution is adopted, the required calculation accuracy can be quickly converged. According to the rotationally symmetric characteristic of the target, a three-dimensional problem is reduced into a two-dimensional problem to be analyzed, so that the solution speed can be increased, and the solution internal memory can be reduced. The metal surface charge density, the medium body polarization current density and the polarization current density on and under the surface of a medium layer are expressed by the metal surface current density, so that the mesh generation is only carried out on the metal part rather than the medium part; and therefore, the generation regions can be reduced, and the method is convenient to operate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for determining protection space between ultra-high-voltage DC (direct current) transmission line and wireless station
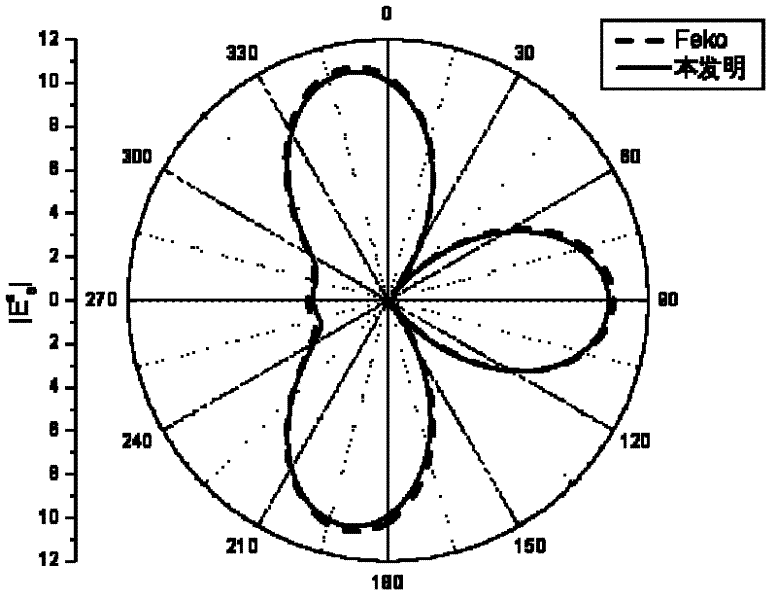
The invention relates to a method for determining the protection space between an ultra-high-voltage DC (direct current) transmission line and a wireless station. The method comprises the methods of constructing a passive jamming line-surface model of an ultra-high-voltage DC transmission line and solving an electric field integral equation corresponding to the model. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a passive jamming simulation surface model of the line according to the real space truss structure of transmission towers of the line, and constructing the passive jamming line-surface model of the transmission line in combination with the line model of an overhead wire and ground wire; solving induced current of each part of the ultra-high-voltage DC transmission line by using a moment method checked by RWG (Rao-Wilton- Glisson) basis function and Galerkin method, and calculating secondary radiation intensity vector generated by the induced current; and superposing the vector with a source electromagnetic filed to obtain the jamming level of the ultra-high-voltage DC transmission line to the wireless station. Comparison of test data obtained through the test proves that the method provided by the invention has higher accuracy, and can be used for accurately determining the passive jamming protection space between high-voltage transmission line and adjacent wireless stations in the future.
Owner:STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Surface exciting method applicable to calculation of direction diagrams of waveguides in different shapes
ActiveCN102411676AAchieve motivationSave resourcesSpecial data processing applicationsMagnetic currentRadiation field
The invention provides a surface exciting method applicable to calculation of direction diagrams of waveguides in different shapes. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, setting an exciting surface of a shape corresponding to the shape of the cross section of a waveguide according to the the shape of the cross section of a waveguide; 2, dividing the exciting surface into even two-dimensional meshes, wherein an equivalent electric dipole source and a magnetic dipole source are arranged in the center of each mesh; 3, obtaining electric current of all the equivalent electric dipole sources and magnetic current of all the magnetic dipole sources on the exciting surface according to an equivalence principle, wherein an electromagnetic filed on the exciting surface is a main mode in which electromagnetic wave spreads in the waveguide; 4, carrying out mesh generation on the surface of the waveguide by virtue of triangular binning so as to obtain radiation fields generated by all the equivalent electric dipole sources, wherein the radiation fields serve as exciting fields of the surface of the waveguide; establishing an electric filed integral equation according to boundary conditions of the surface of the waveguide and obtaining the induction current of the surface of the waveguide by solving the equation according to a moment method; and 5, calculating the scattering direction diagram of the waveguide according to the induction current. Waveguides in different structures and shapes can be excited by the method provided by the invention instead of different methods separately.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
Electromagnetic scattering analysis method of target with cavity on the basis of moment method and parabolic equation
ActiveCN104778151AWell formedQuick and easy to formComplex mathematical operationsAnalysis methodRadar cross-section
The invention discloses an electromagnetic scattering analysis method of a target with a cavity on the basis of a moment method and a parabolic equation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, filling the cavity body of the target with the cavity with solid metal, establishing a discrete model, determining the axial direction of a parabola as an x axis, and dispersing a target along the axial direction of the parabola by a mesh; in an x-axis direction, utilizing a CN (Crank-Nicolson) difference scheme to obtain a relationship between two adjacent tangent planes; in y-axis and z-axis directions, independently adopting an RPIM (Radial Point Interpolation Method) constructing fractal function and a spatial derivative to construct a matrix equation; successively carrying out recursive solving on a node electric field value on each tangent plane; carrying out solving on a cavity body part in the target separately by a fast multipole algorithm, applying an electric field integral equation to obtain current on the surface of the cavity body, and obtaining the electric field value of each discrete point required by the parabolic equation on an opening surface of the cavity body; and finally, carrying out postprocessing on the electric field on a last tangent plane to obtain a radar scattering sectional area. A meshless parabola and a fast multipole acceleration moment method are combined, and the electromagnetic scattering analysis method has the advantages of being efficient and reliable.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aviation transient electromagnetic conductivity three-dimensional inversion method based on bonn iterative method
InactiveCN107121706ACalculation speedEliminate the effects ofElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationAviationTime domain response
A three-dimensional inversion method for airborne transient electromagnetic conductivity based on the Bornn iterative method, involving electromagnetic exploration. Provide a set of three-dimensional conductivity inversion algorithm based on the frequency domain to improve the calculation speed of the inversion; the algorithm uses the fitting of the secondary field value to perform the inversion calculation, thereby removing the influence of the ground response of the direct wave on the signal and improving the inversion calculation speed. Acting precision. Firstly, the time-domain signal of the total field is obtained from the transient electromagnetic system, and then the time-domain response of the corresponding theoretical uniform half-space is calculated to extract the secondary field signal required for the inversion. First use the electric field integral equation to solve the electric field distribution in the calculation area, and calculate the secondary field value through the definition of the contrast function. Then use the Born iterative method to establish the inversion process, fit the secondary field values in the frequency domain, and iteratively solve the contrast function, so as to obtain the distribution of the medium in the underground calculation area, and realize the three-dimensional inversion of the conductivity of the transient electromagnetic system. play.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
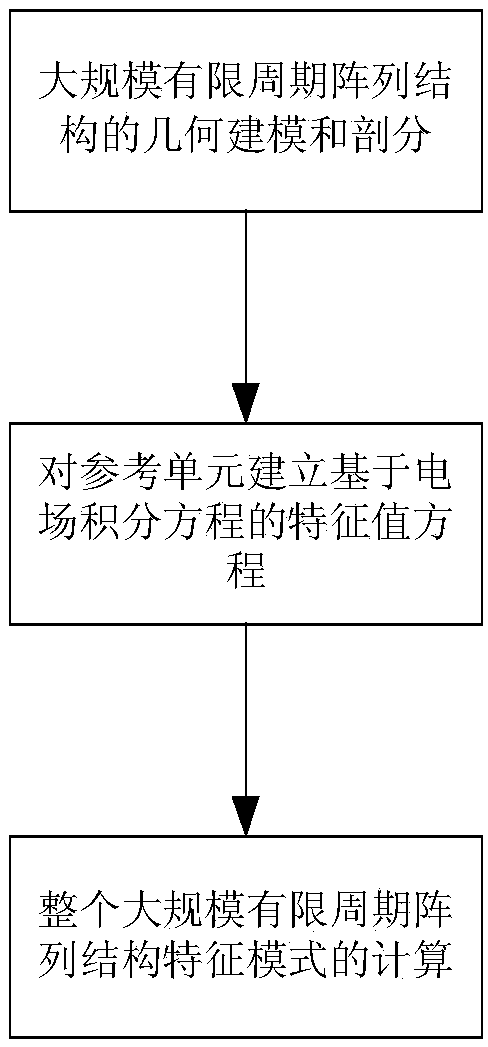
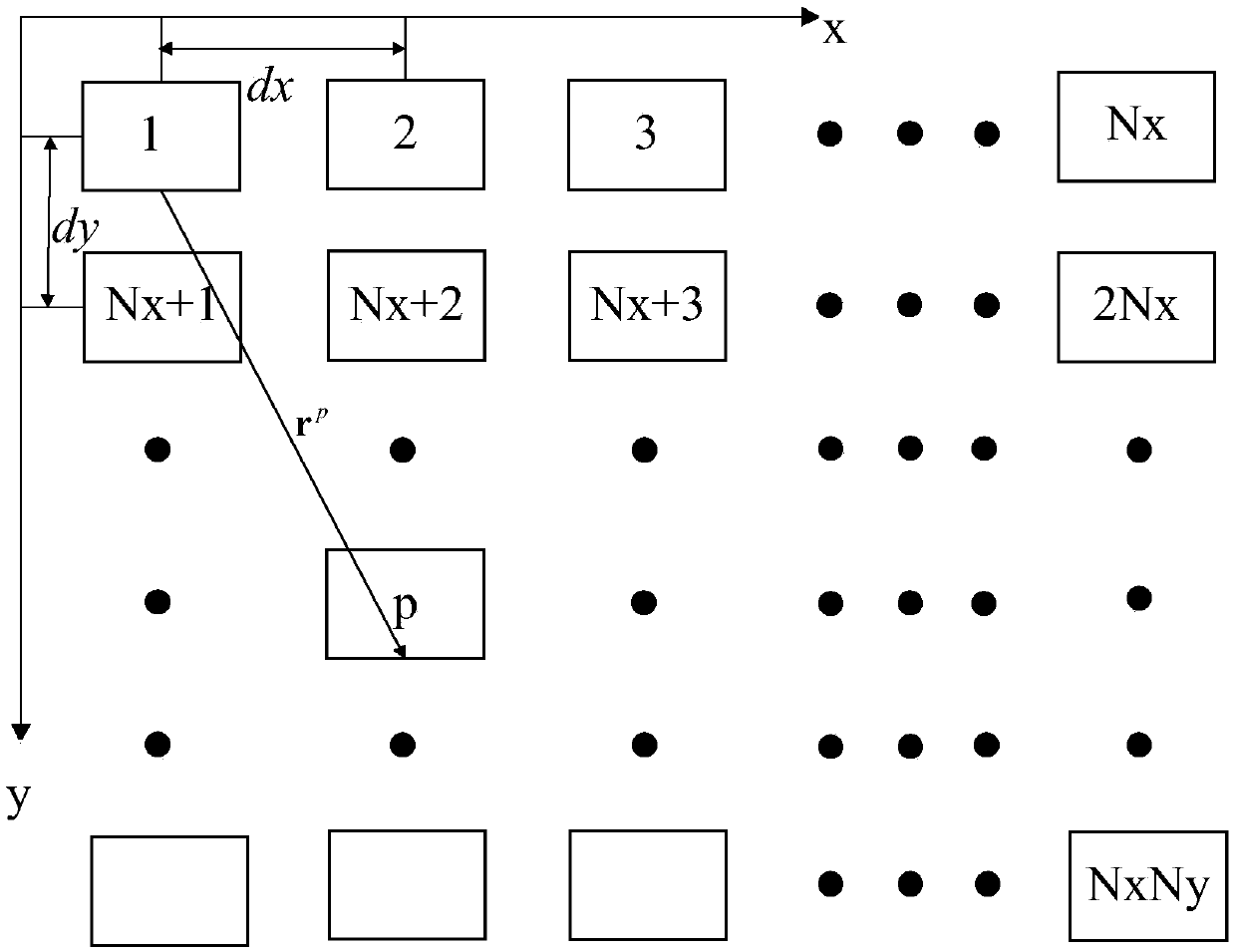
A large-scale finite period array structure characteristic mode analysis method
ActiveCN108959772AReduce the number of unknownsReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsGeometric modelingComputer science
The invention relates to a large-scale finite period array structure characteristic mode analysis method, which solves the defect that the characteristic mode analysis method cannot be applied to thelarge-scale finite period array structure compared with the prior art. The invention comprises the following steps: carrying out geometric modeling and division of a large-scale finite period array structure; establishing an eigenvalue equation based on the electric field integral equation for the reference cell; performing computation of the eigenmodes of a large-scale finite-period array structure. The invention can remarkably reduce the number of unknown quantities of the matrix characteristic equation of the periodic array, and greatly reduce the calculation memory and the calculation timerequired.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Efficient analyzing method for superfine line structure object electromagnetic property
InactiveCN104112044AFind out quicklySpecial data processing applicationsCurrent distributionAnalysis method
The invention provides an efficient analyzing method for a superfine line structure object electromagnetic property, and belongs to the field of analyzing of a computational electromagnetic moment method. A section wavelet serves as a primary function in the moment method, fast wavelet transform is used, a sparse matrix can be obtained through calculation, and therefore the defects caused by a dense matrix are overcome, and a effect more accurate and efficient than that of traditional analyzing can be obtained. The method comprises the steps that firstly, an object is placed in an appropriate geometry coordinate system, and an electric field integral equation to which the surface current conforms is listed; secondly, the section wavelet serves as the primary function to carry out expansion on an unknown current; thirdly, geometry mapping is established and is substituted into an original matrix equation; fourthly, the matrix equation is solved; fifthly, the current distribution is obtained through solving, and the scattering problem is dealt with to obtain far field distribution. The method can serve as an efficient and accurate means for studying a wire antenna, and plays a significant role.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Simulation method for rapidly extracting transient scattered signals of electric large-size metal cavity target
ActiveCN104731996AAccurate descriptionTrue discrete fitSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorDissection
The invention discloses a simulation method for rapidly extracting transient scattered signals of an electric large-size metal cavity target. The simulation method includes creating a geometric model of the metal cavity target, and performing mesh dissection on the surface of the metal cavity target by a curved-surface triangular unit; determining a time domain integral equation of the metal cavity target; unfolding a surface induced current in the time domain integral equation by a high-order lamination divergence conformal basis function in terms of space and a time and space-time hybrid basis function in terms of time; substituting a surface induced current expression into the time domain integral equation, and testing a time domain electric field integral equation in a discrete form in terms of time and space respectively to acquire a system impedance matrix equation; solving the impedance matrix equation by a time stepping method, determining time domain current distribution on the surface of the conductor target, and acquiring broadband electromagnetic characteristic parameters of the target according to time domain current distribution to complete simulation. The method has the advantages of high simulation accuracy, less time used and low memory consumption, thereby having a broad application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
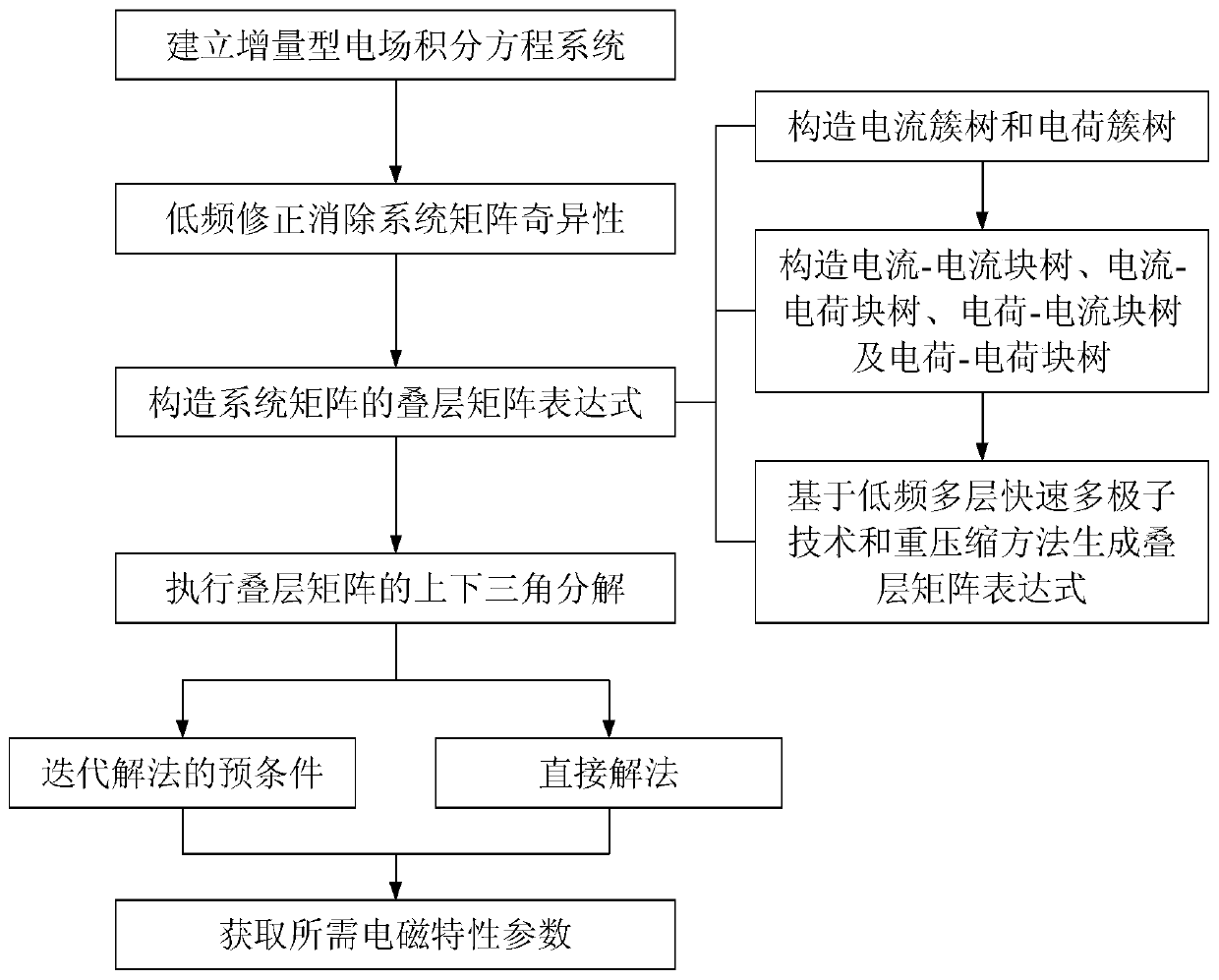
A laminated matrix decomposition-based low frequency electromagnetic property simulation method
ActiveCN106991222AImprove performanceIterative convergence is fastDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsMatrix decompositionComputation complexity
The invention provides a laminated matrix decomposition-based low frequency electromagnetic property simulation method. Firstly, the problem of low frequency collapse of the conventional electric field integral equation method is eliminated by employing an augmented electric field integral equation method; a low frequency multi-level fast multi-pole method is adopted to establish a laminated matrix expression for the coefficient matrix of the augmented electric field integral equation; the laminated matrix is further compressed by using a double compression method to remove redundant information; finally, a laminated matrix format algorithm is adopted to perform upper-lower triangular decomposition on the compressed laminated matrix. The laminated matrix decomposition can reduce calculating complexity and memory consumption to be almost linear; a precondition technology is constructed for an iteration solution and a direct solution is constructed. The method has the advantages of high solving speed, low memory consumption and precision controllability and can be applied to various kinds of low frequency electromagnetic property analysis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Numerical method of satellite electromagnetic scattering characteristics within millimeter wave band
ActiveCN103235193AReduce computing timeSave storage memoryElectromagentic field characteristicsClassical mechanicsMillimeter
The invention discloses a numerical method of satellite electromagnetic scattering characteristics within a millimeter wave band. Aiming at such a metal and medium mixed structure of a satellite, an electric field integral equation is established only for the metal part of the satellite, an equation does not need to be established for the medium part, and finally, an equation with good conditions is formed, so as to be convenient for iterative solution. Mesh generation is performed only on the metal surface of the satellite, the mesh generation does not need to be performed on the medium coated part, and the strangeness is easily processed. Because of a structural feature of the inclined long satellite, the directionality of a transfer factor component is strong, an acceleration method is adopted for a far field effect on the basis of a multi-level fast multipole algorithm, computational memory requirements are effectively reduced, and the computing time is saved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
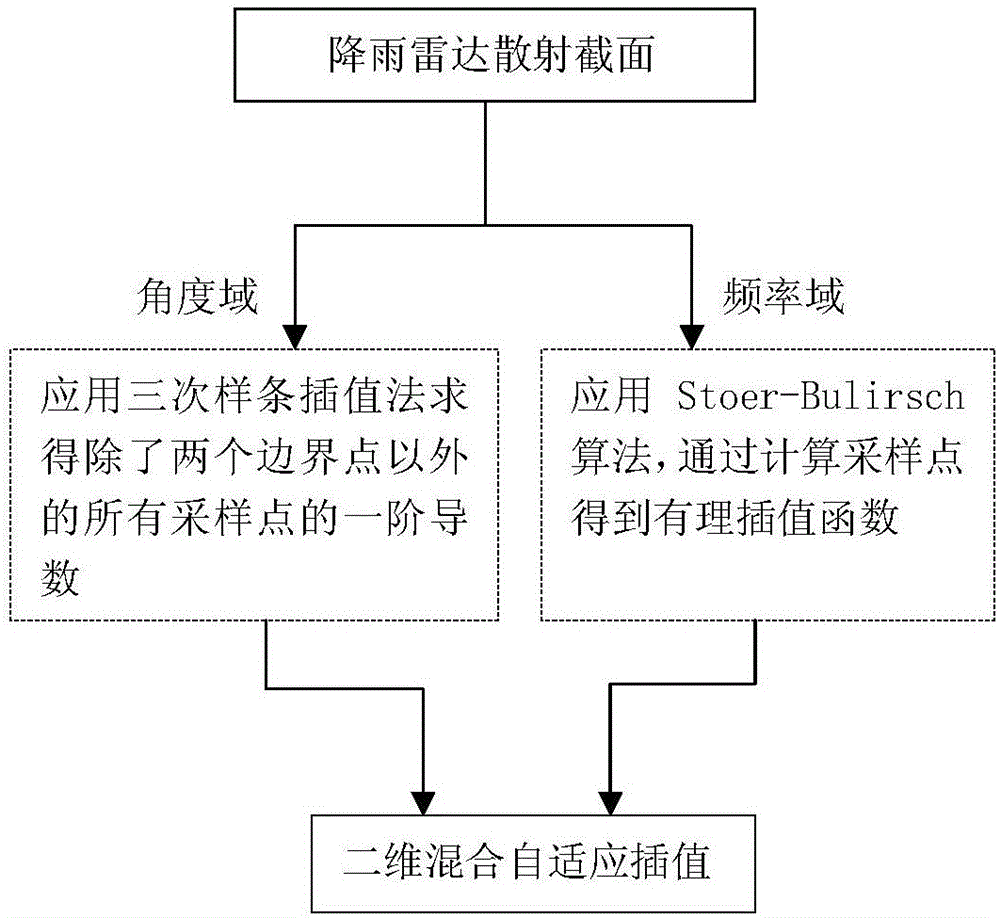
Frequency angle two-dimensional mixed interpolation based rainfall particle scattering operation accelerating method
InactiveCN106294284AShorten operation timeAvoid singularity problemsComplex mathematical operationsRegular gridAngular scan
The invention discloses a frequency angle two-dimensional mixed interpolation based rainfall particle scattering operation accelerating method. A cubic spline interpolation method and Stoer-Bulirsch are combined as a model, a RCS (radar cross section) contains frequency and angle information, and RCS acquisition at frequency and angle zones of interested wave bands is repeated. The method is characterized in that cubic spline interpolation is applied to wide-induced-current angle zones, and Stoer-Bulirsch is applied to wide frequency zones. In order to effectively calculate electromagnetic scattering characteristics and improve operation efficiency of matrix-vector multiplication in an electric field integral equation, SM / CG (sparse matrix / canonical grid) is applied. By adoption of the method, operation time is greatly saved in frequency and angle scanning, and rainfall particle swarm bandwidth scattering operation speed is increased effectively.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
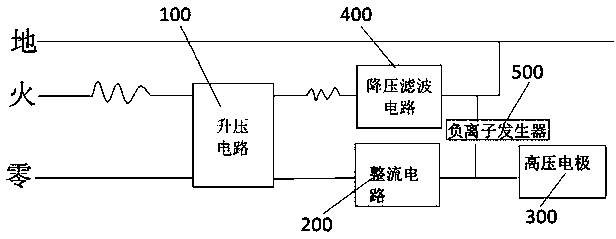
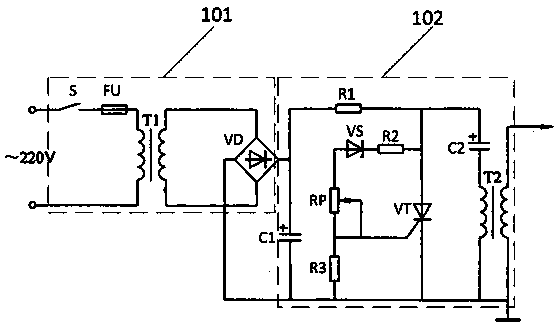
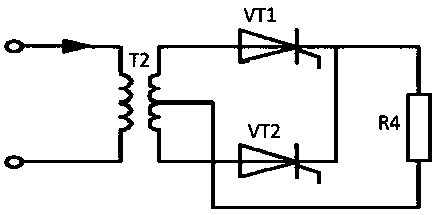
Electric field generating device and electric field fresh-keeping refrigerator
InactiveCN110200188AExtended shelf lifeHigh activityDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusHigh pressureAlternating current
The invention discloses an electric field generating device and an electric field fresh-keeping refrigerator. A boost circuit is utilized to output an alternating current voltage, for example, 220 V can be boosted into alternating current voltage of 1,000-8,000 V through a rectifier circuit; an energy field can be generated through vibration due to electric field interaction between high voltage electrodes in the device, the proper energy field can be combined with the refrigerator, so that the activity of the free radical scavenging systems (including SOD, POD, CAT and other various antioxidant enzymes) in fruits and vegetables at the proper energy field environments can be strengthened, the generation and removing of free radicals are returned to balance again, and therefore, the shelf life of the fruits and vegetables can be prolonged; and a negative ion generator is connected, and plasma active substances can be generated through the discharging of the negative ion generator, so that skin bacterial viruses can be further killed on the basis of the fresh-keeping of food.
Owner:ANHUI KONKA TONGCHUANG HOUSEHOLD APPLIANCES
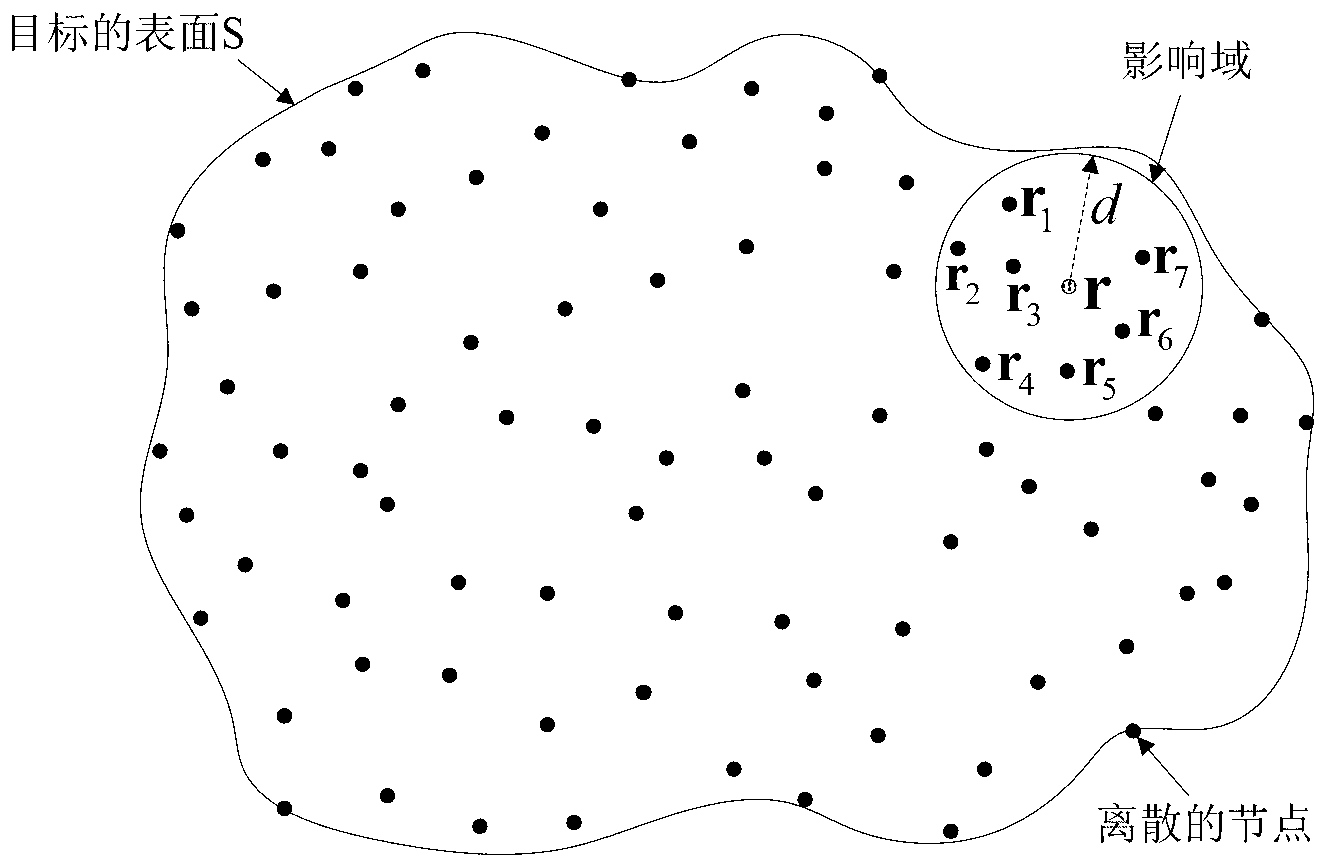
Electromagnetic scattering no-grid simulation method for appearance-complicated metal target
ActiveCN103246827AGood iterative solution behaviorThe implementation process is flexible and simpleSpecial data processing applicationsNODALPower flow
The invention discloses an electromagnetic scattering no-grid simulation method for an appearance-complicated metal target, which comprises the following steps that local integral domains of nodes are established: the local integral domain at the periphery of each node is constructed by a region growing algorithm according to distribution information of the discrete nodes on the surface of the appearance-complicated metal target; an electric field integral equation of the metal target is established; surface current at the discrete nodes is decomposed; surface current in the center of each integral domain is constructed; the electric field integral equation is tested by point matching; an impedance matrix equation is obtained and solved; a current coefficient is obtained; and a radar cross section is determined according to the current coefficient. The method is independent of modeling grid subdivision on the surface of the target; quick electromagnetic scattering simulation can be conducted on the target only after the distribution information of the discrete nodes on the surface of the target is known in advance; an implementation process of the method is flexible and free; and the method has a very high practical engineering application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for analyzing a non-uniformly divided target electromagnetic scattering characteristic
InactiveCN108038313AShorten the timeSave memoryDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorPower flow
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a non-uniformly divided target electromagnetic scattering characteristic. The method includes the following steps of establishing an electromagnetic scattering integral equation based on an electric field boundary condition of an ideal conductor; establishing adaptive octree grouping to index a near field and a far field of each group; placing an equivalent source on each group, and converting action matrixes of two far field groups into equivalent source action of the two far field groups; filling the electric field integral equation with near field matrixes, generating a compression matrix corresponding to the far field groups of each group and storing; solving for a matrix equation to obtain a current coefficient, and calculating electromagnetic scattering parameters based on the current coefficient. The method saves computing time and memory, and has higher flexibility and effectiveness.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
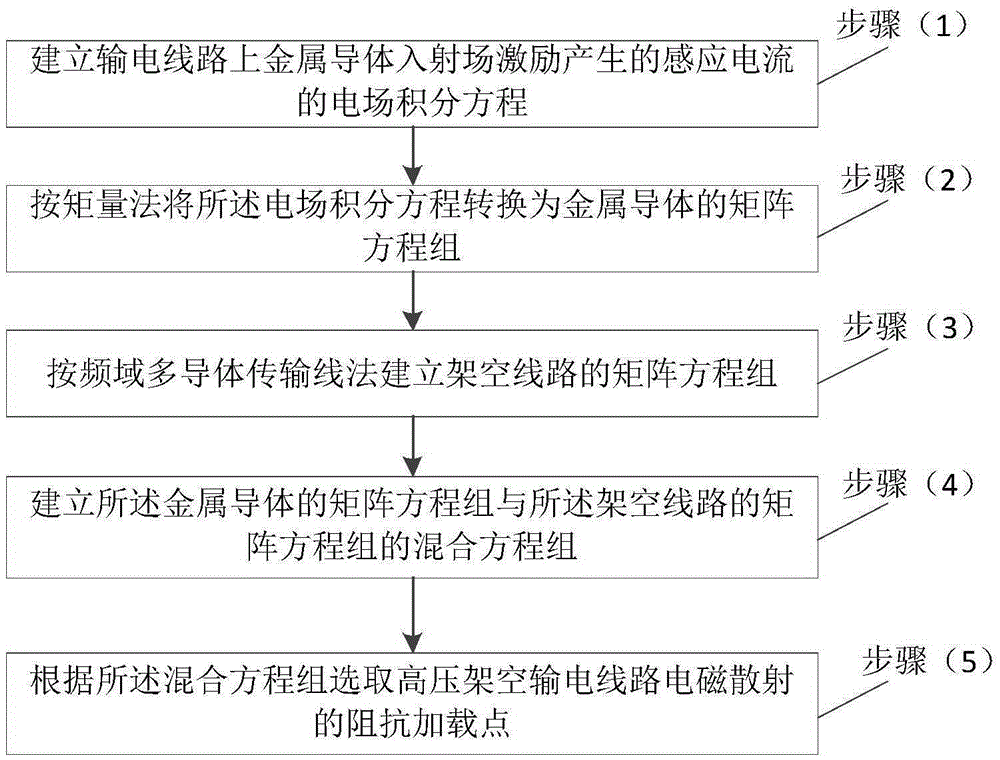
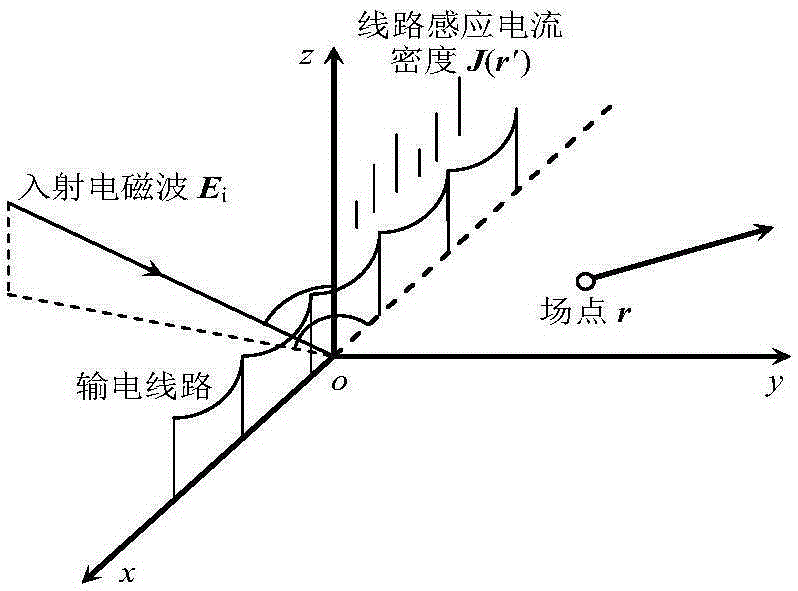
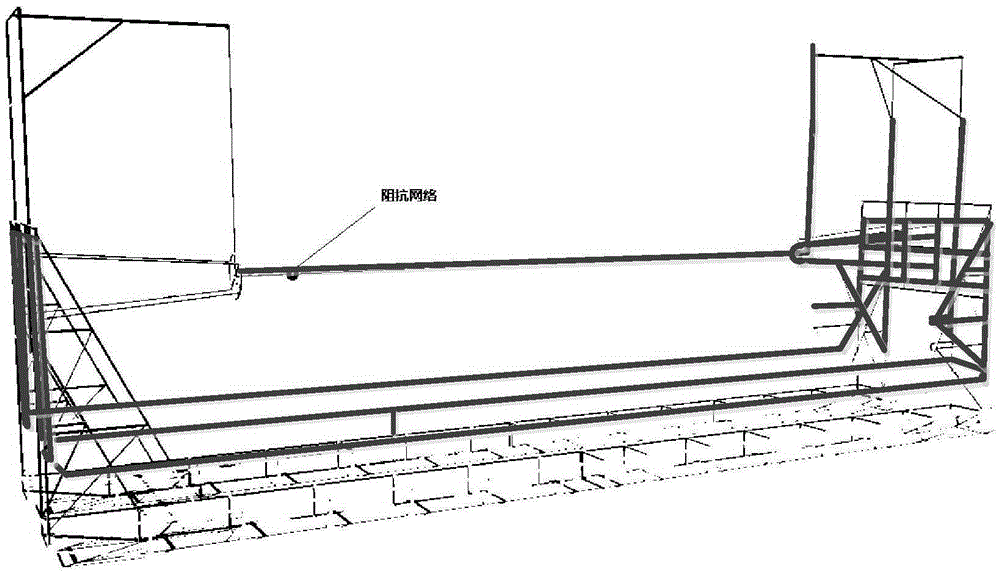
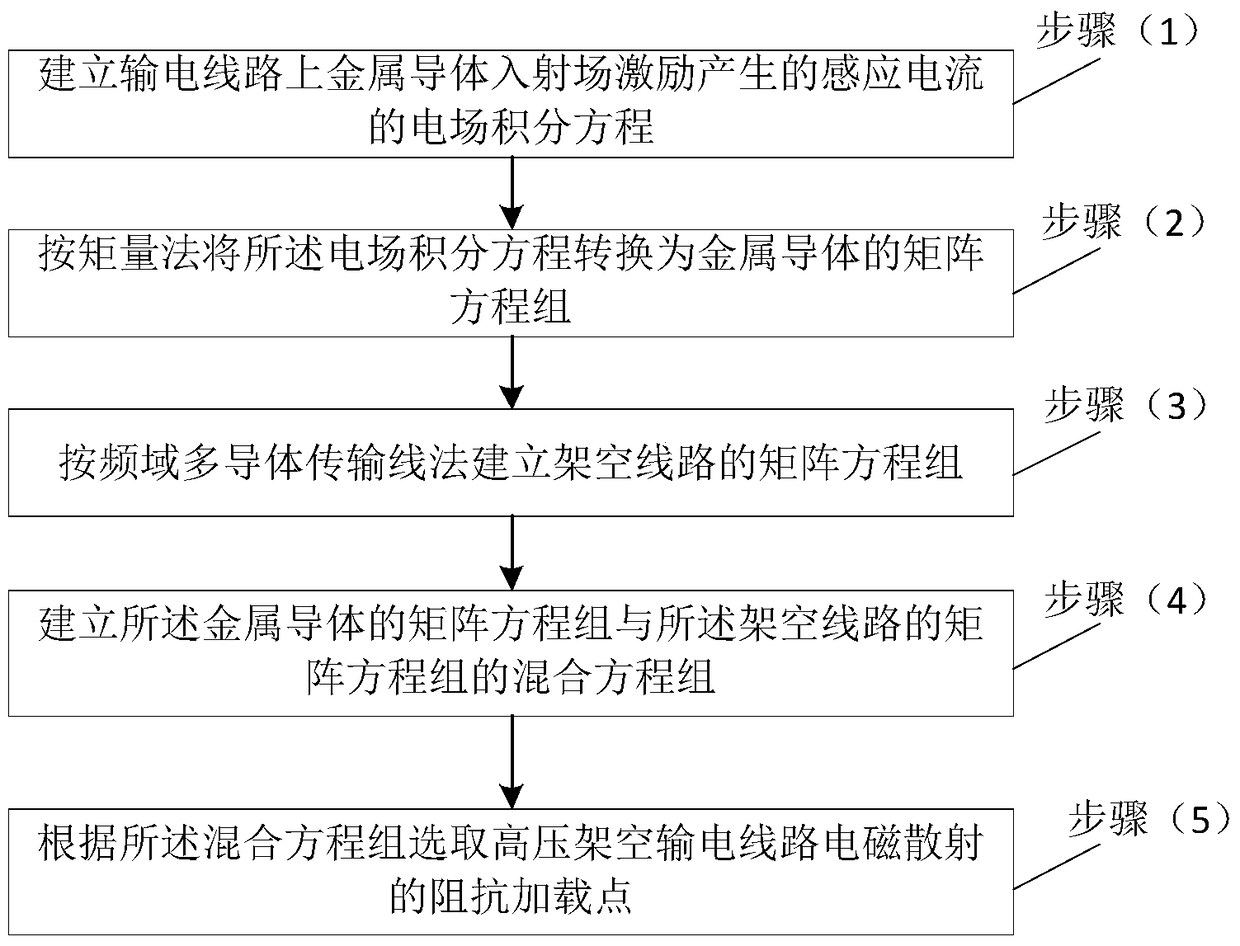
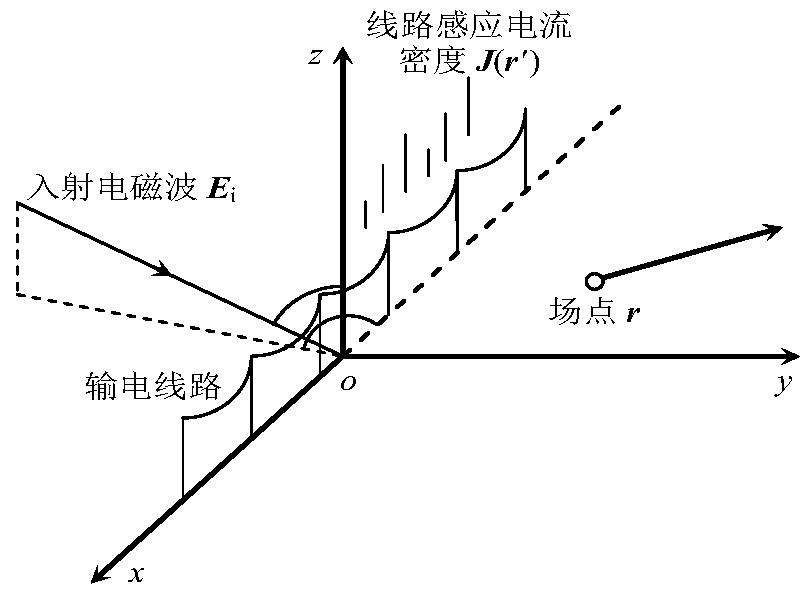
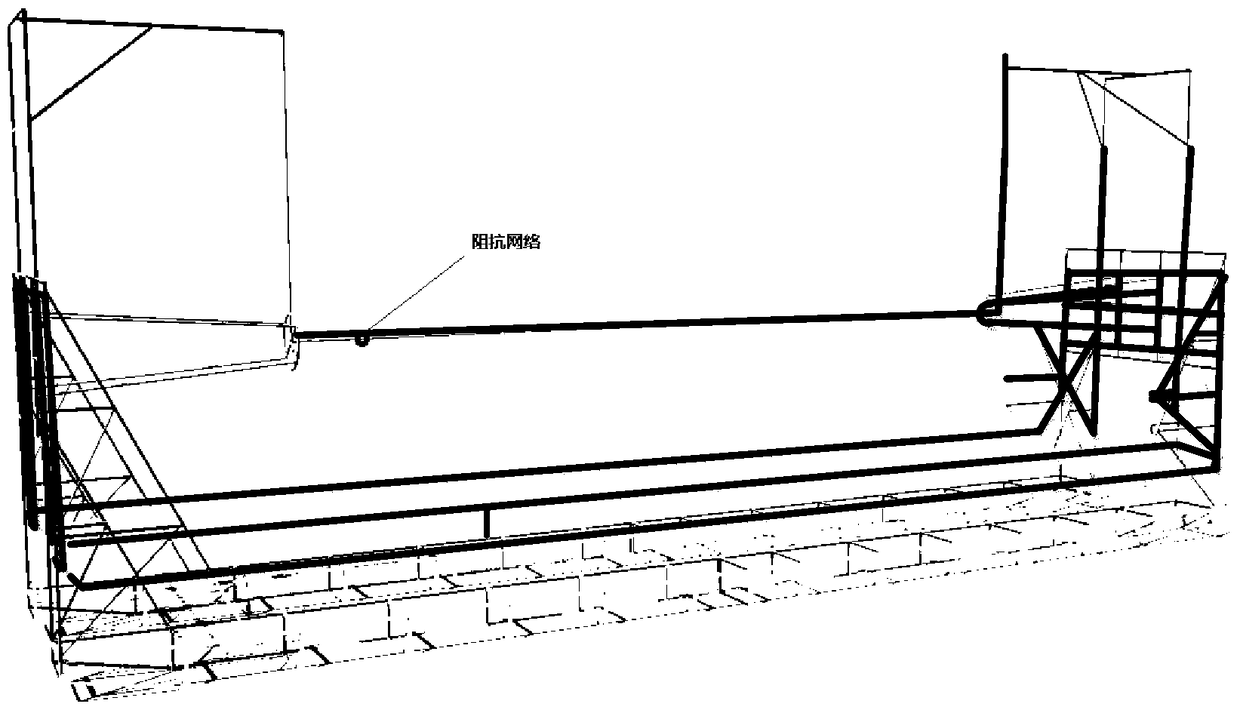
Impedance load point selection method for electromagnetic scattering of high tension overhead transmission lines
ActiveCN105388368AThe effect of suppressing electromagnetic scatteringImprove accuracyElectromagentic field characteristicsElectrical conductorMatrix method
The invention relates to an impedance load point selection method for electromagnetic scattering of high tension overhead transmission lines. The method comprises that (1) an electric field integration equation of induction current generated by excitation of a metal conductor incident field of the transmission lines is established; (2) the electric field integration equation is converted into a metal-conductor matrix equation set based on a matrix method; (3) an overhead-line matrix equation set is established based on frequency-domain multi-conductor transmission line method; (4) a mixed equation set of the metal-conductor matrix equation set and the overhead-line matrix equation set is established; and (5) the impedance load point of electromagnetic scattering of the high tension overhead transmission lines is selected according to the mixed equation set. The provided method is highly accurate, and can be used to select the optimal load point when the electromagnetic scattering for electromagnetic waves of specific frequency of the high tension transmission lines is inhibited, and thus, electromagnetic scattering for different types of radio stations of the high tension transmission lines can be inhibited in an economical and efficient way.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
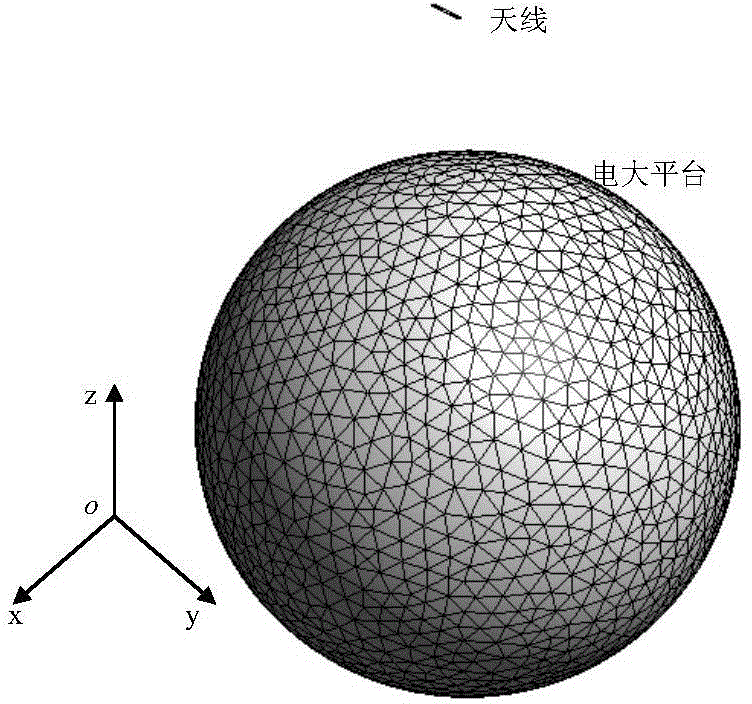
Prediction method of antenna pattern disturbance on electrically large platform
InactiveCN104933212ASmall sizeSplit bigSpecial data processing applicationsPower flowGeometric modeling
The present invention discloses a prediction method of antenna pattern disturbances on an electrically large platform. Firstly, a geometrical model of an antenna and an electrically large platform is established and grid division is performed on the model; secondly, an electric field integral equation is established according to boundary conditions, antenna and electrically large platform surface sensing current is represent by a spherical wave phase primary function, the electric field integral equation is tested through a galerkin approach to obtain a matrix equation system, solving the matrix equation system to obtain a current expansion coefficient; and ultimately, calculating a disturbance pattern of the antenna. With adoption of the prediction method, division grids of the electrically large platform and the antenna structure can be greatly reduced, thereby saving computing resources.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method for stably solving an electric field integral equation in a time domain
InactiveCN108984472AEfficient solutionAvoid cumbersomeComplex mathematical operationsTime domainEngineering
A method for stably solving an electric field integral equation in a time domain is disclosed. Another form of a thin-line time-domain electric field integral equation suitable for a finite differencesolution is deduced, and in the fine wire structure, symbols shown in the description are considered to be the line current and charge density respectively. The invention does not need to introduce an expansion function, directly discretizes the temporal and spatial differentials of the unknown current, and further advances the solution in time.
Owner:苏州峰极电磁科技有限公司
Ionized layer irregular shape body diffraction imaging method based on p band satellite borne synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
InactiveCN103033810ASolve the problem of large storage capacitySimple methodRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarPerformed Imaging
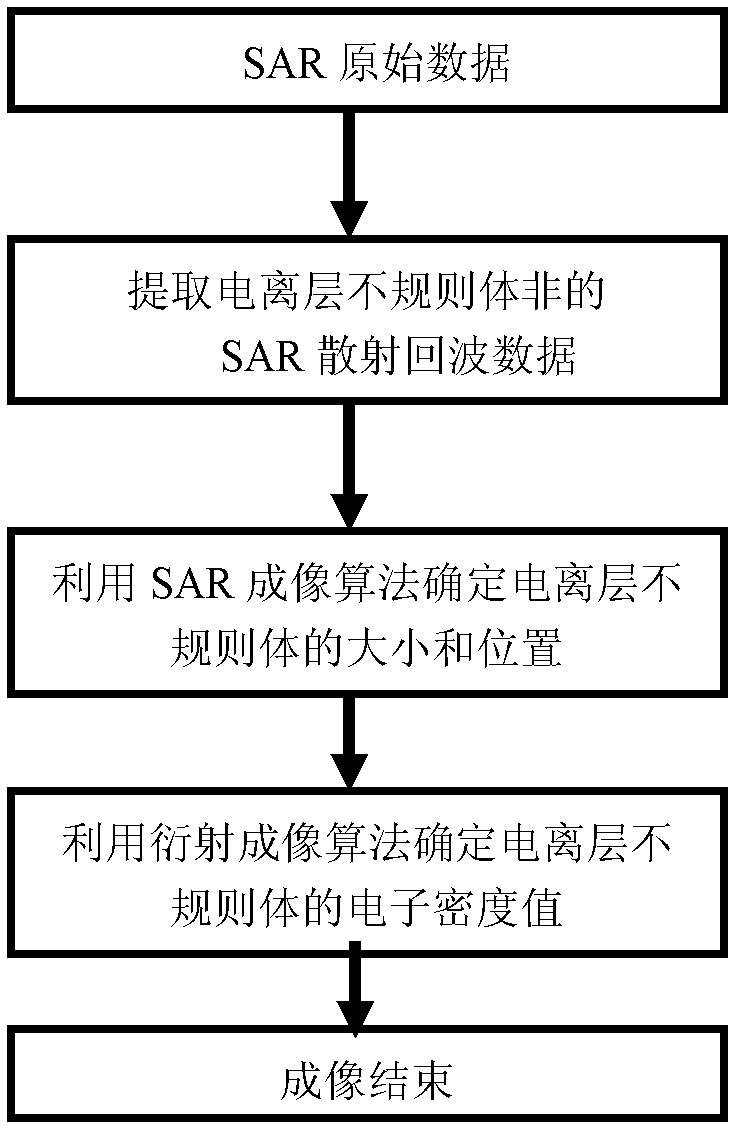
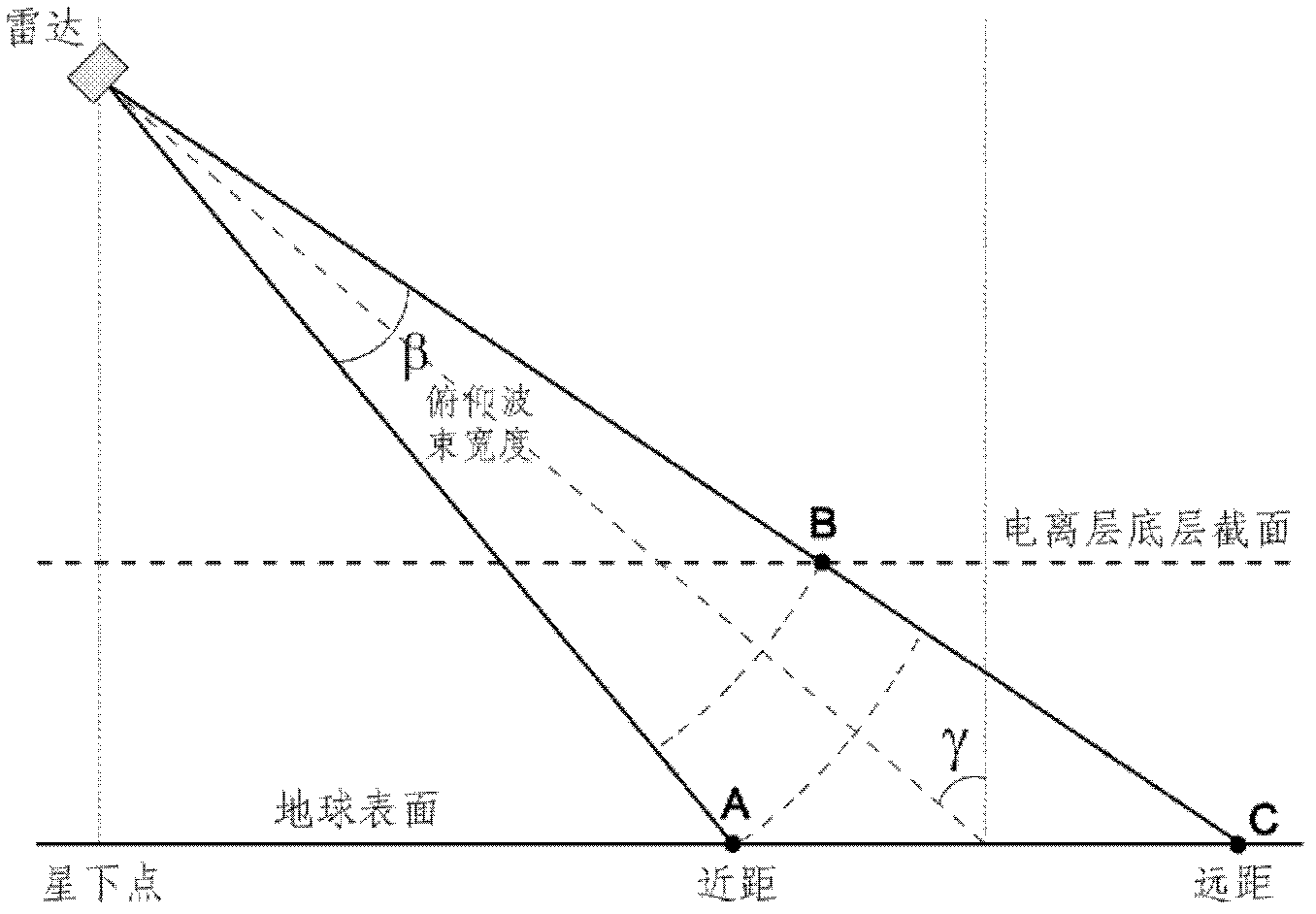
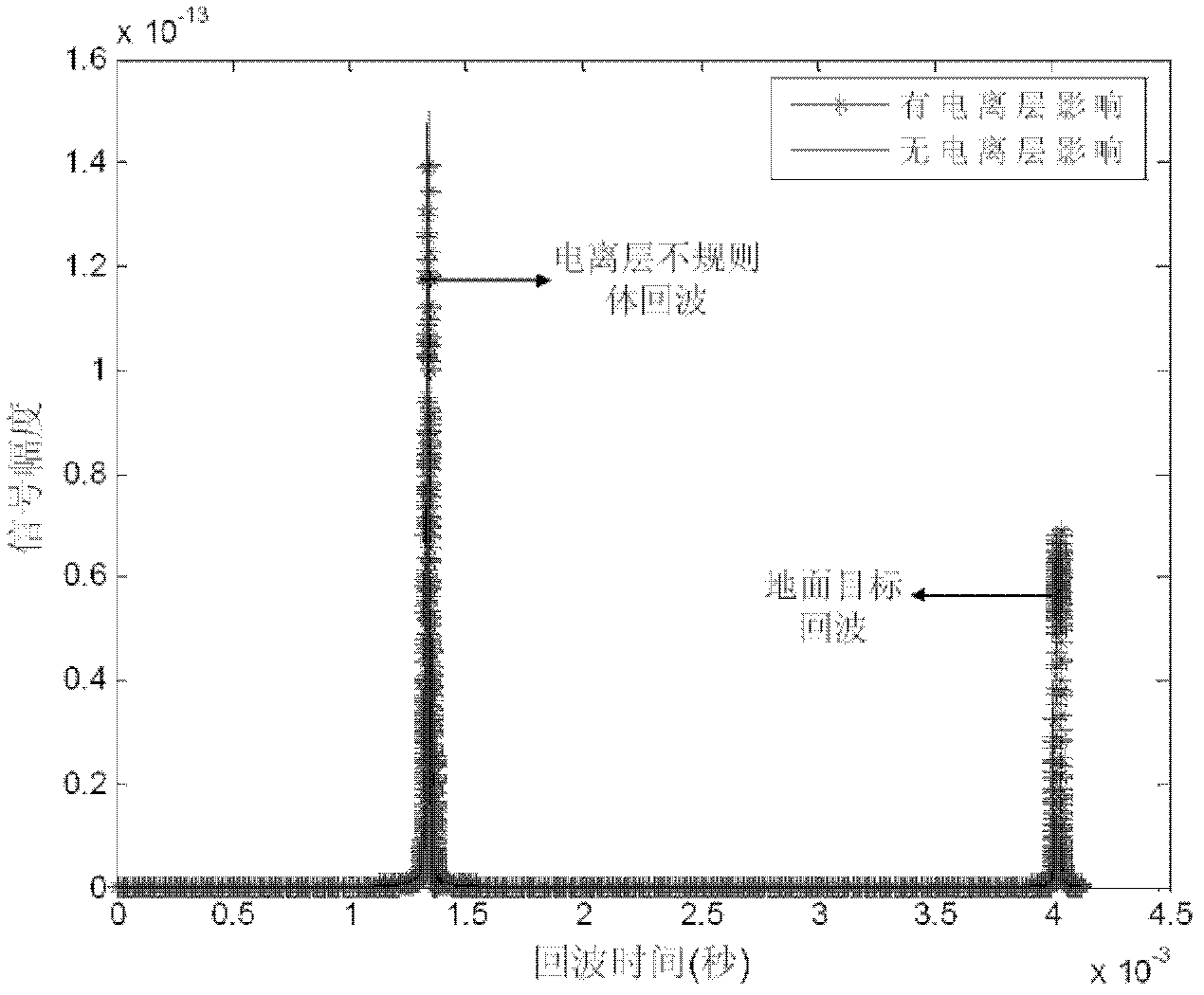
The invention discloses an ionized layer irregular shape body diffraction imaging method based on p band satellite borne synthetic aperture radar (SAR), and relates to a radar imaging technique. The steps are as follows. (1). An ionized layer signal is separated from a time domain echo signal of satellite borne p band SAR. (2). SAR diffraction imaging is used to confirm a rough range and a location of a target. (3). The relationship between radar echo and ionized layer electron density is built according to an electric-field integral equation. (4). Diffraction imaging method is used to image an irregular shape body. The ionized layer irregular shape body diffraction imaging method based on p band satellite borne SAR is simple and easy, and solves a problem of a big calculated amount and a big storage volume in an ionized layer irregular shape body diffraction imaging method.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
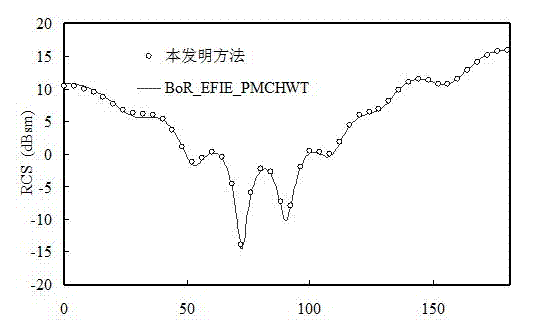
Simulation Method of Broadband Electromagnetic Scattering Characteristics of Conductive Targets
ActiveCN103279601BAccurate descriptionExact discrete fitSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorTime delays
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Adaptive nested crossover approximation method for analyzing low-frequency electromagnetic characteristics
ActiveCN108170647AEasy programmingLow frequency numerical stabilityWave based measurement systemsComplex mathematical operationsWave parameterComputer science
The invention discloses an adaptive nested crossover approximation method for analyzing low-frequency electromagnetic characteristics. The method comprises the steps of firstly extracting a grid fileof an electromagnetic analysis target, and setting an incident electromagnetic wave parameter; secondly grouping to-be-analyzed target grids by adopting an octree according to an average grid number in each group, defining discrete grids and groups where the discrete grids are located, and performing statistics on a basis function number in each non empty group; thirdly establishing a subordination relationship between the groups of adjacent layers, establishing an electrical field integral equation in a discrete grid region, and dividing the region into a near-field region and a far-field region according to the distances between the groups; fourthly calculating an impedance matrix formed between the non-adjacent groups by adopting the adaptive nested crossover approximation method; and finally obtaining a solution of the electrical field integral equation through iterative solving, thereby obtaining the low-frequency electromagnetic characteristics. The method has the advantages of stable low-frequency value, simple programming realization and high calculation efficiency, and realizes efficient analysis on the low-frequency electromagnetic characteristics.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
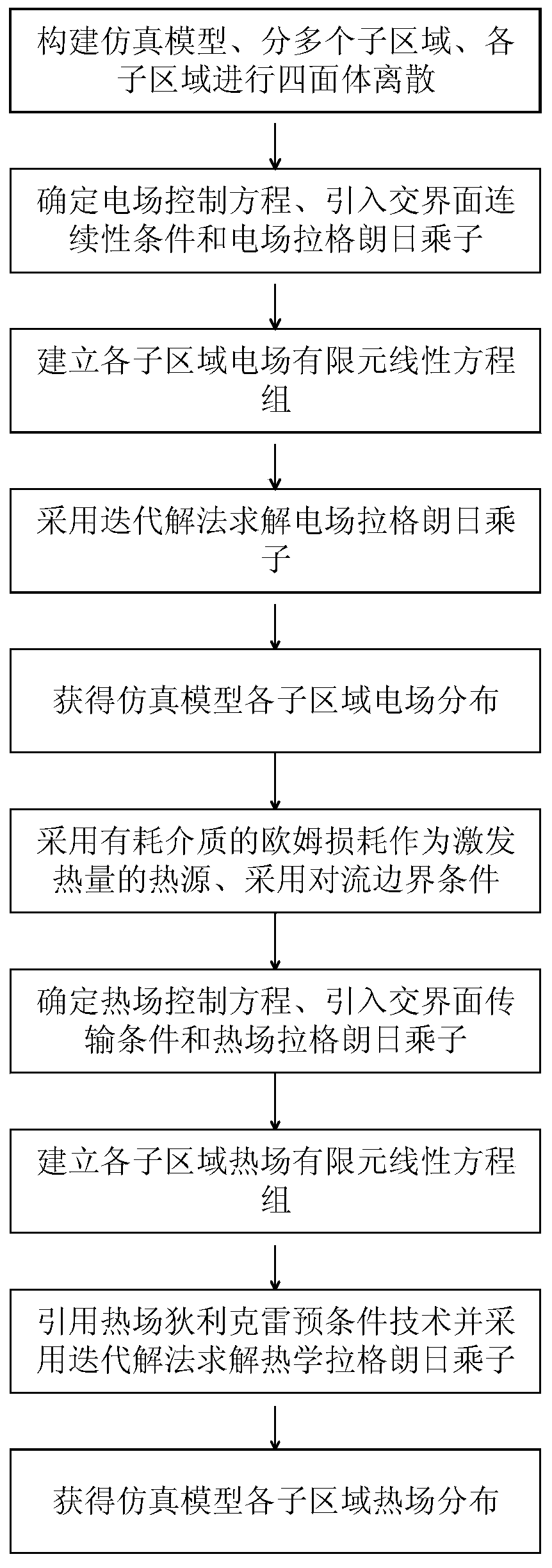
Simulation method of three-dimensional electromagnetic heat effect based on regional decomposition method
InactiveCN110096799AWide iterationsReduce the number of iterationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectromagnetic fieldElectric field computation
The invention discloses a simulation method of a three-dimensional electromagnetic heat effect based on a regional decomposition method, which comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a simulation model for a target structure, dividing the simulation model into a plurality of complementary overlapped sub-regions, and then performing grid dispersion; secondly, establishing an electric field control equation set of the sub-regions based on the time-coordinated electromagnetic field characteristics, introducing continuity conditions and electric field Lagrangian multipliers on interfaces of the sub-regions, and obtaining electric field distribution conditions of the sub-regions by solving the electric field Lagrangian multipliers; wherein ohmic loss of a consumed medium in each sub-region is taken as a heat source of excitation heat, a convection boundary condition is adopted in each sub-region for truncation; determining a thermal control equation based on a heat conduction characteristic, and meanwhile, introducing a thermal field transmission condition and a thermal field Lagrangian multiplier into an interface of each sub-region; and finally, introducing a thermal field Dirichlet pre-condition technology, accelerating the iterative solution of the thermal field Lagrangian multiplier, and obtaining the thermal field distribution condition in each sub-region. The method is wide in application range, high in convergence speed and high in solving precision.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multi-point thin coating aircraft RCS prediction method with uncertain source
ActiveCN110287549AImprove computing efficiencyHigh simulationSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationGeometric modelingMetallic Object
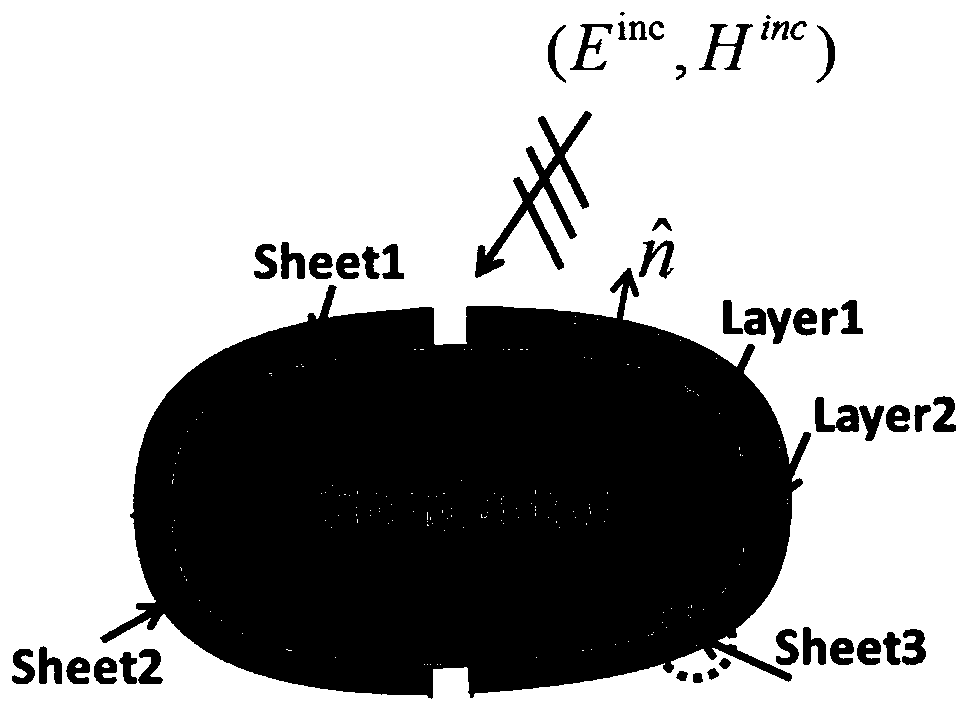
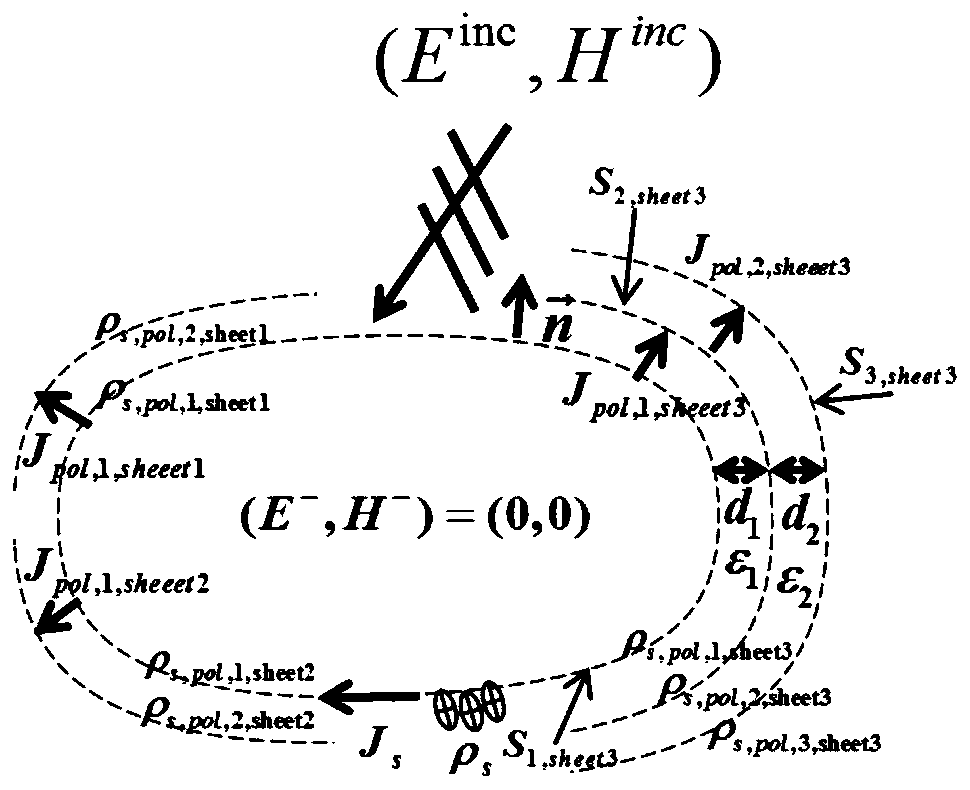
The invention discloses a multi-point thin coating aircraft RCS prediction method with uncertain source. The method comprises the following steps of establishing an MTDS electric field integral equation; establishing a geometric model of a multi-point thin coating aircraft with shape uncertainty; extracting the shape uncertain parameters of the multi-point thin coating aircraft; analyzing the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of the multi-point thin coating aircraft with the shape uncertainty. According to the method, the uncertainty of the geometric shape of the shape uncertainty is introduced into a matrix equation of an MTDS integral equation method through a primary function with random variables; furthermore, the RCS of the multi-position thin coating aircraft with the uncertain appearance can be effectively and quantitatively predicted through a disturbance method, and the method can better simulate a metal object with multi-position multi-medium sheet thin coating.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method for selecting impedance loading points for electromagnetic scattering of high-voltage overhead transmission lines
ActiveCN105388368BThe effect of suppressing electromagnetic scatteringImprove accuracyElectromagentic field characteristicsElectrical conductorMatrix method
The invention relates to an impedance load point selection method for electromagnetic scattering of high tension overhead transmission lines. The method comprises that (1) an electric field integration equation of induction current generated by excitation of a metal conductor incident field of the transmission lines is established; (2) the electric field integration equation is converted into a metal-conductor matrix equation set based on a matrix method; (3) an overhead-line matrix equation set is established based on frequency-domain multi-conductor transmission line method; (4) a mixed equation set of the metal-conductor matrix equation set and the overhead-line matrix equation set is established; and (5) the impedance load point of electromagnetic scattering of the high tension overhead transmission lines is selected according to the mixed equation set. The provided method is highly accurate, and can be used to select the optimal load point when the electromagnetic scattering for electromagnetic waves of specific frequency of the high tension transmission lines is inhibited, and thus, electromagnetic scattering for different types of radio stations of the high tension transmission lines can be inhibited in an economical and efficient way.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
A Simulation Method of Low Frequency Electromagnetic Characteristics Based on Laminated Matrix Decomposition
ActiveCN106991222BImprove performanceIterative convergence is fastDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsMatrix decompositionComputation complexity
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Surface exciting method applicable to calculation of direction diagrams of waveguides in different shapes
ActiveCN102411676BAchieve motivationSave resourcesSpecial data processing applicationsMagnetic currentRadiation field
The invention provides a surface exciting method applicable to calculation of direction diagrams of waveguides in different shapes. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, setting an exciting surface of a shape corresponding to the shape of the cross section of a waveguide according to the the shape of the cross section of a waveguide; 2, dividing the exciting surface into even two-dimensional meshes, wherein an equivalent electric dipole source and a magnetic dipole source are arranged in the center of each mesh; 3, obtaining electric current of all the equivalent electric dipole sources and magnetic current of all the magnetic dipole sources on the exciting surface according to an equivalence principle, wherein an electromagnetic filed on the exciting surface is a main mode in which electromagnetic wave spreads in the waveguide; 4, carrying out mesh generation on the surface of the waveguide by virtue of triangular binning so as to obtain radiation fields generated by all the equivalent electric dipole sources, wherein the radiation fields serve as exciting fields of the surface of the waveguide; establishing an electric filed integral equation according to boundary conditions of the surface of the waveguide and obtaining the induction current of the surface of the waveguide by solving the equation according to a moment method; and 5, calculating the scattering direction diagram of the waveguide according to the induction current. Waveguides in different structures and shapes can be excited by the method provided by the invention instead of different methods separately.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
Observation device for cell biological behaviors in direct current electric field
InactiveCN103525702BImprove stabilityHeight adjustableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImage recordingEngineering
The invention provides an observation device for cell biological behaviors in a direct current electric field. The observation device is used for observing the biological behaviors of cells in the direct current electric field and comprises an electric field generation part, a cell bearing part, a current monitoring part, a fluid exchange part, an image recording part, a control part and a plurality of cover plates used for adjusting the height of a culture medium on the cells. An observation area and two corresponding step structures are arranged in the cell bearing part. An observation area and two identical step structures are arranged in a middle area of a base tank, wherein the two corresponding step structures are arranged on the two sides of the observation area, the number of steps is m, and distances between the steps at the same level of the two step structures are respectively l1, l2... and lm. The number of the cover plates is n, and the widths of the cover plates are respectively w1, w2... and wn, wherein the width wi of the cover plate i (1<=i<=n) is greater than or equal to li and less than or equal to li+1. By means of the observation device, the height of the culture medium on the cells can be changed more quickly and can be adjusted conveniently at the time of an experiment.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
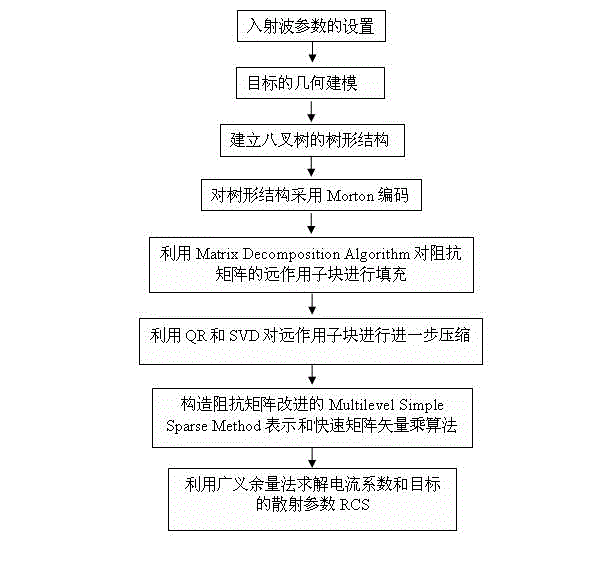
Full-wave Analysis Method for Microstrip Circuit
ActiveCN103150415BReduce memory requirementsReduce computational complexitySpecial data processing applicationsSingular value decompositionComputation complexity
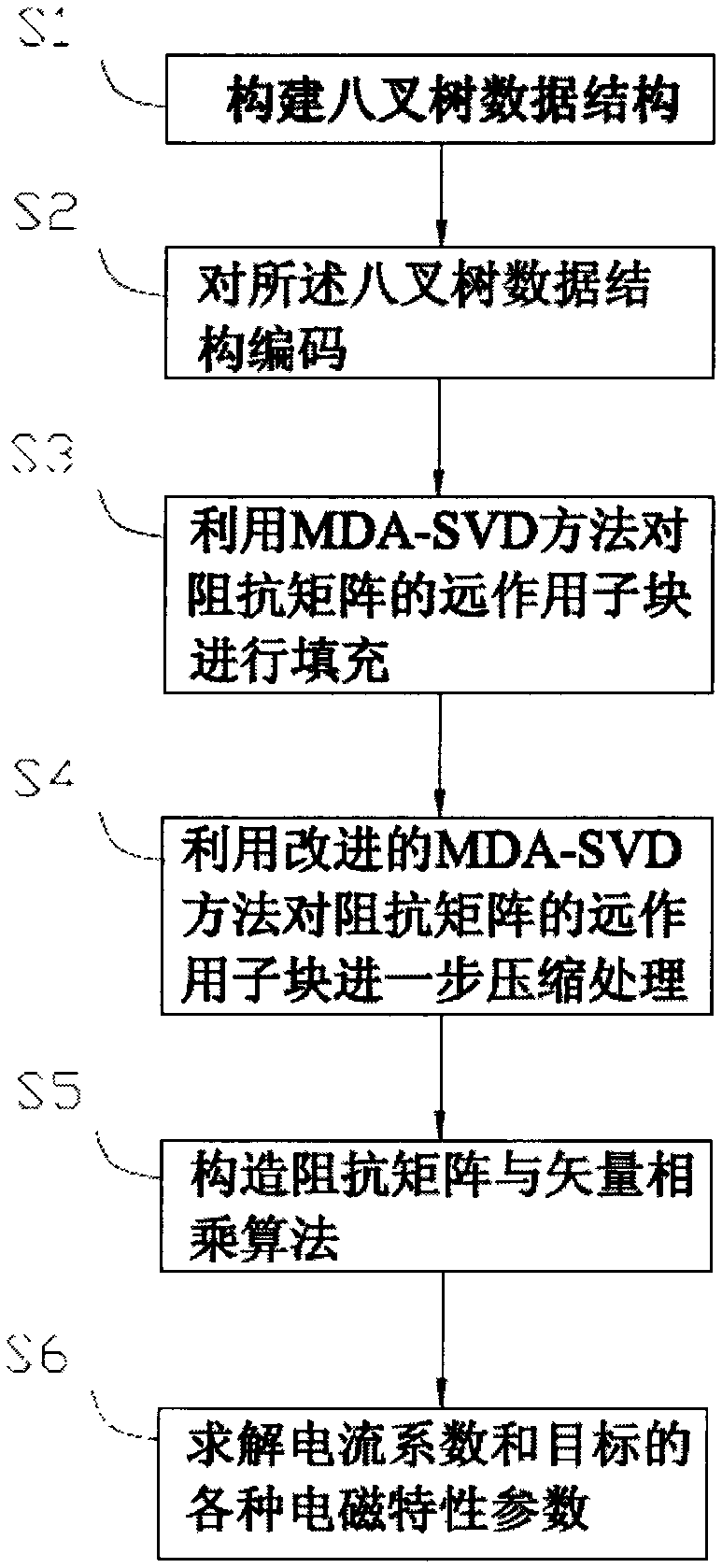
The invention provides a full wave analysis method for a microstrip circuit based on improved MDA (model driven arthitecture) -SVD (singular value decomposition) compression representation. The method comprises the following steps of establishing an octree structure for a target to be analyzed; acquiring sparse low rank representation which is formed by a discrete electric field integral equation and corresponds to a far field action part in a dense impedance matrix by the MDA-SVD method; then representing the part which is represented by the low rank in the impedance matrix by the improved MDA-SVD method; and finally, constructing an algorithm which quickly calculates matrix vectors and is suitable for iteration computation on the basis of the MDA-SVD method representation. According to the full wave analysis method for the microstrip circuit, on the basis of the traditional MDA-SVD method, a new compressed format is constructed to represent the impedance matrix, so that memory requirements and computation complexity can be effectively reduced, and computation time is shortened.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Simulation Method of Electromagnetic Scattering Characteristics of Rotationally Symmetric Body Based on Matrix Nested Compression
ActiveCN103279589BIncrease computing speedReduce memory consumptionSpecial data processing applicationsMatrix decompositionDiscretization
The invention discloses a rotational symmetric body electromagnetic scattering property simulation method based on matrix nest compression. The method includes the following steps: building a generatrix of a rotational symmetric body, performing subdividing and discretization to obtain subdivided line segments, establishing a binary tree grouping relation among the subdivided line segments, establishing an index relation between a near-field group and a far-field group, establishing an electric field integral equation of the rotational symmetric body, determining a simulating vector and the total number of modes, breaking every thinnest-layer far-field group mode impedance matrix into two strip-shaped matrixes to be stored respectively with a matrix extraction method, dividing the far-field group impedance matrixes into parent layer near fields and parent layer far fields through the index of layers, performing nest processing layer by layer, breaking each far-field impedance matrix into small matrixes, sequentially determining mode impedance matrixes of all the modes, solving the equations of the mode impedance matrixes one by one, calculating and obtaining far-field information according to the reciprocal theorem to complete the simulation. The method is low in memory consumption, high in equation iteration speed, and capable of efficiently simulating electromagnetic scattering properties of the rotational symmetric body in a large size.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
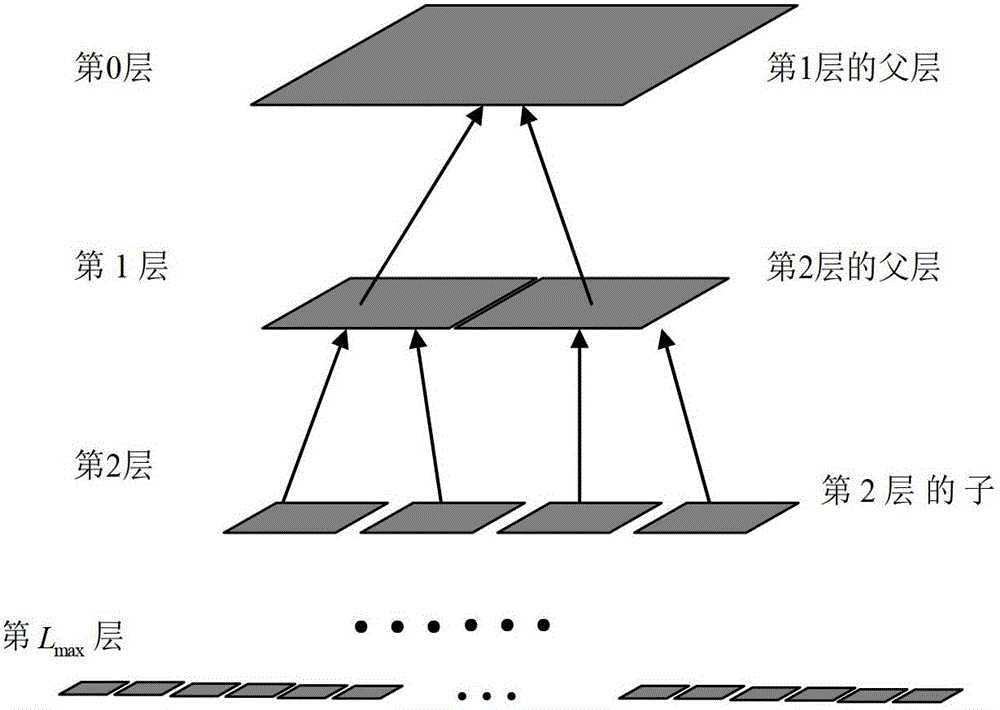
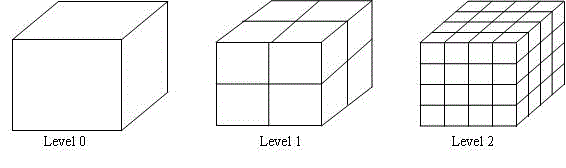
Method for analyzing electromagnetic scattering of complex target through MDA and MLSSM
ActiveCN102129523BReduce memory requirementsEasy to handleSpecial data processing applicationsSparse methodsElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a method for analyzing the electromagnetic scattering of a complex target through an MDA (Model-Driven Architecture) and an MLSSM (Multilevel Simply Sparse Method). The method comprises the steps of: at first, establishing an octree structure of a target object, obtaining, through the MDA method, a far-field action portion corresponding sparse low-rank representation in a dense impedance matrix formed by a discrete electric field integral equation, then by using the improved MLSSM, representing the low-rank-represented portion in the impedance matrix, and in the end, on the basis of the improved MLSSM representation, constructing an algorithm for rapidly calculating matrix-vector product, which is suitable for iterative solution. The method can greatly reduce the calculation time and the memory requirement which are required by using an electric field integral equation method for analyzing the electromagnetic scattering of the complex target.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com