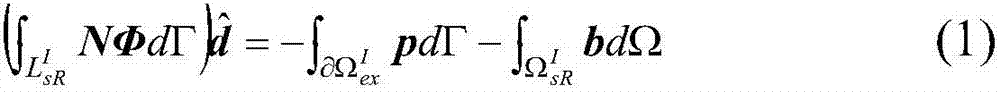Patents
Literature
140 results about "Triangular cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
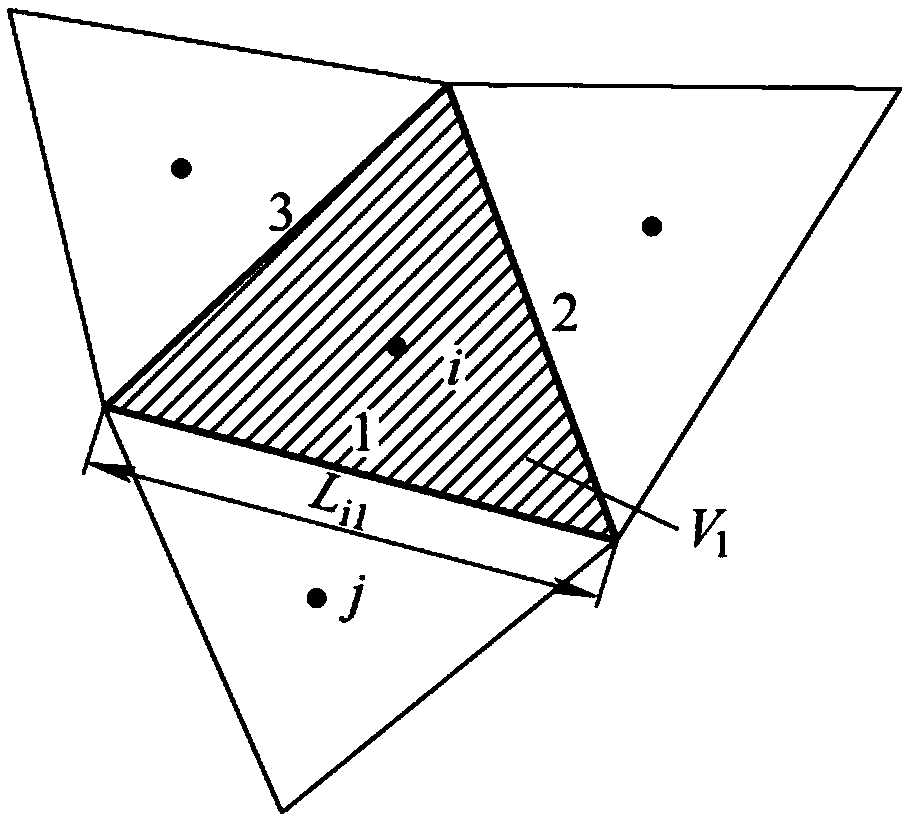
A triangular board has been cut into 100 small triangular cells by the lines parallel to its sides. Two cells that share a side are said to be neighbors. In each cell there is a grasshoper.
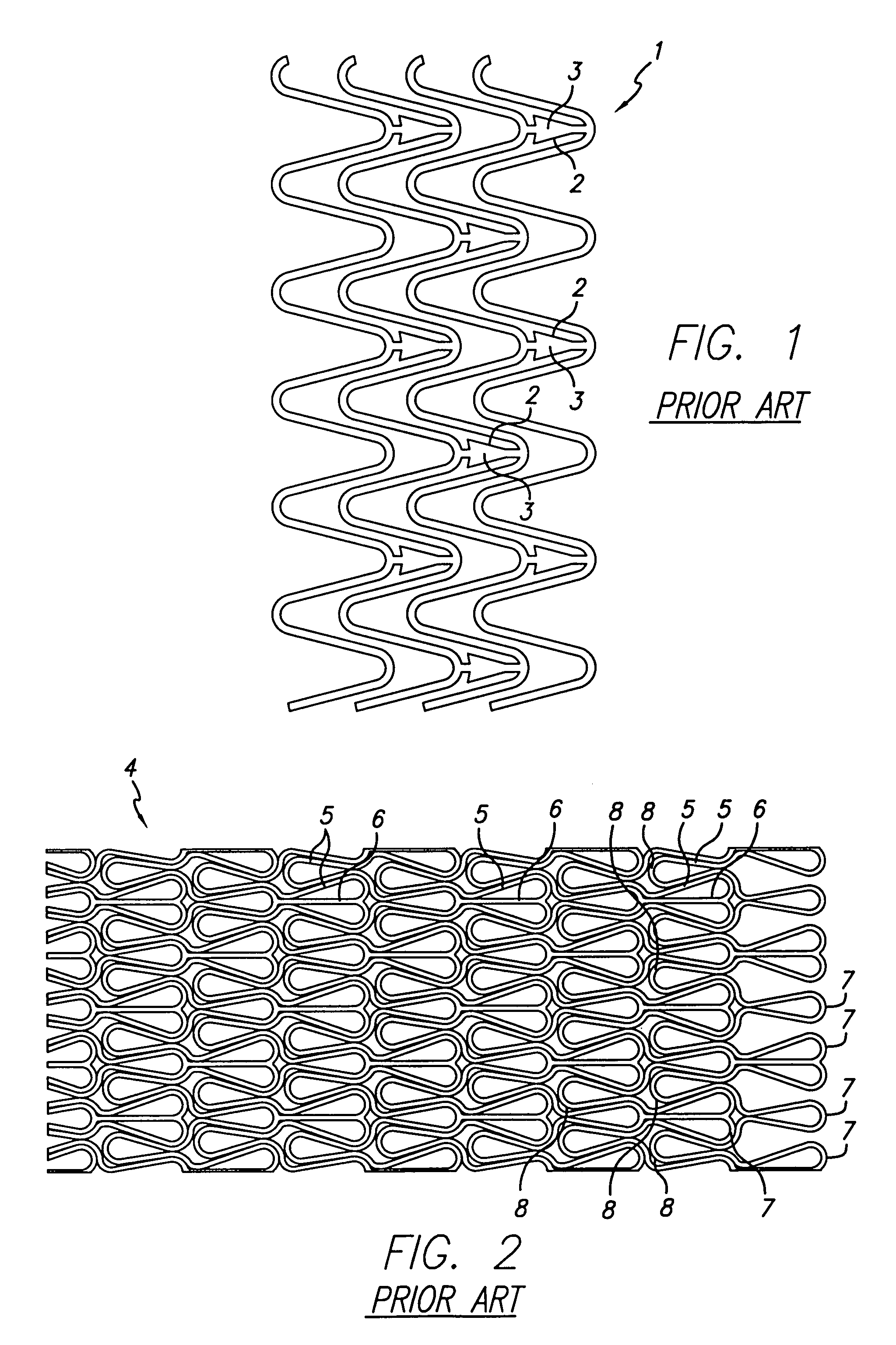
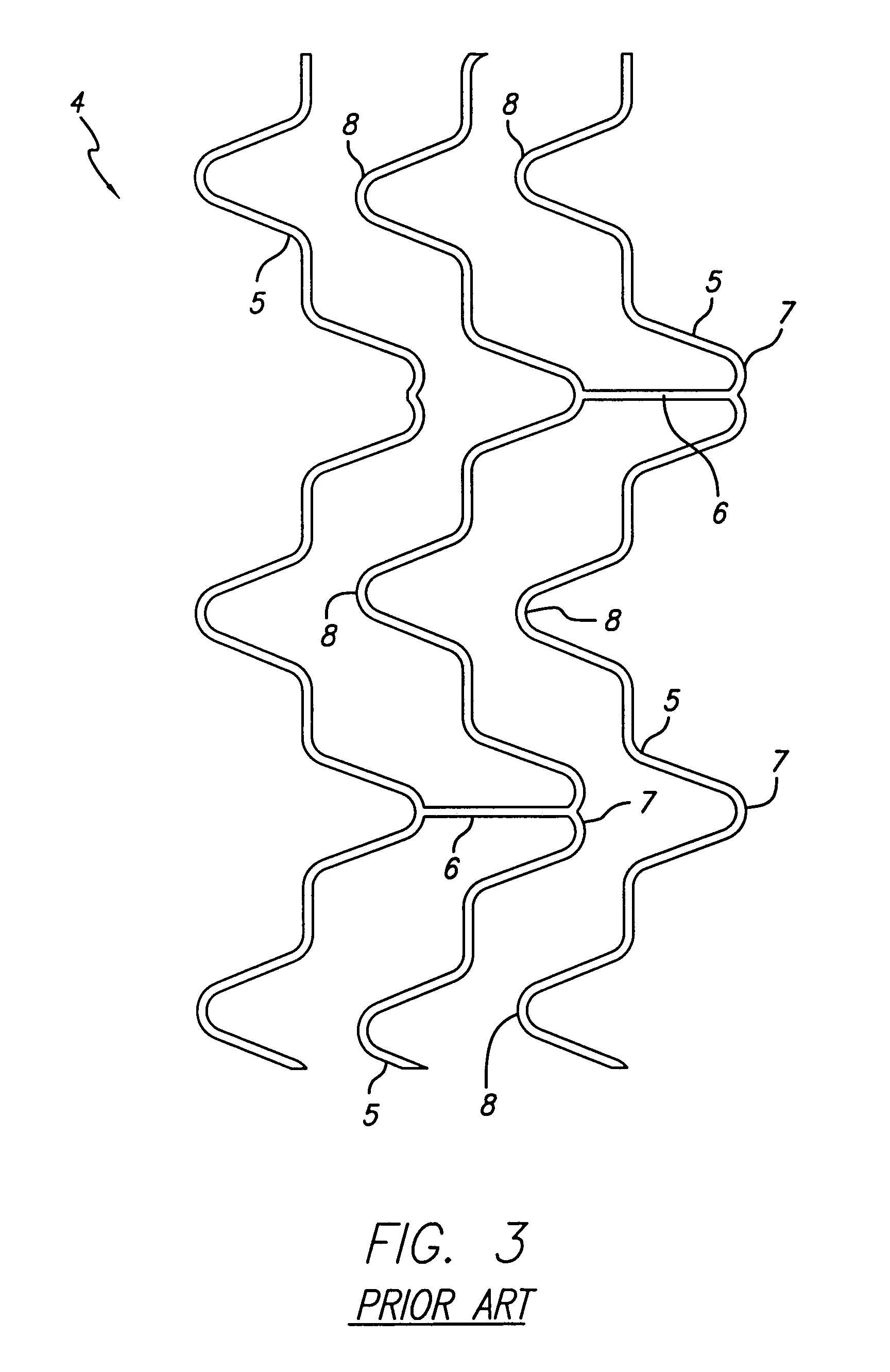
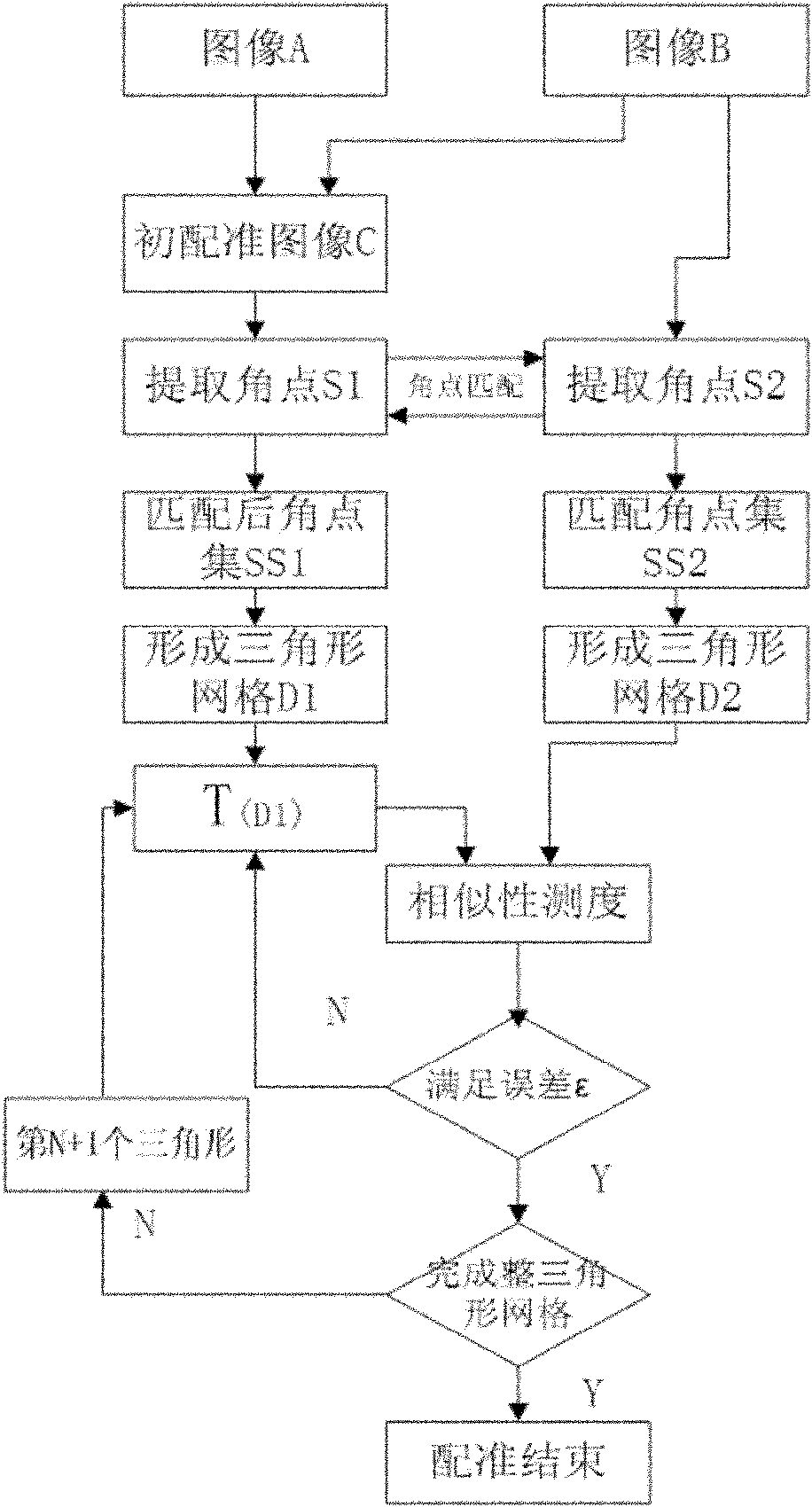
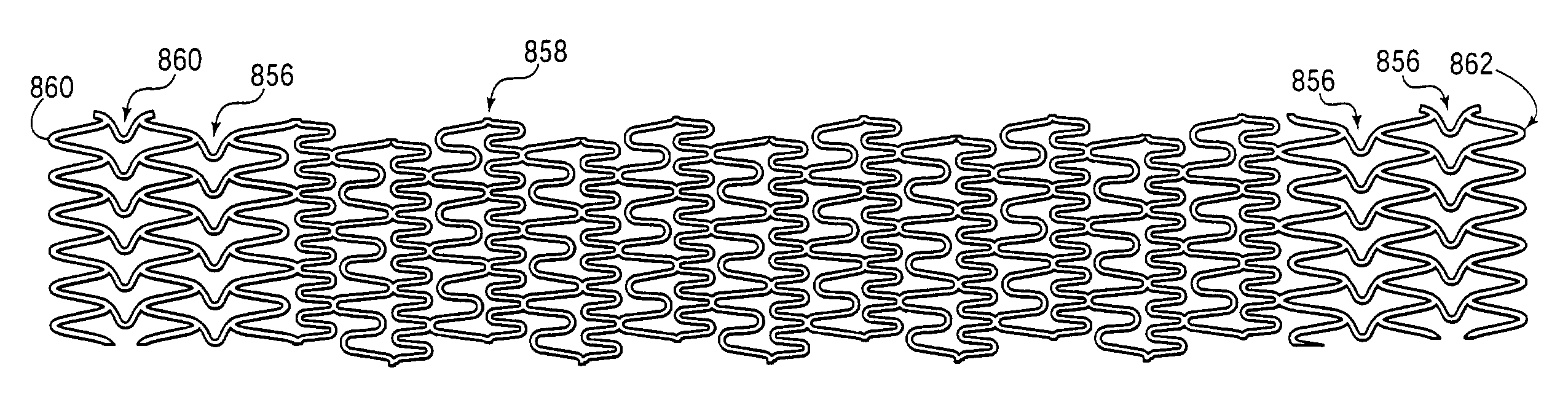
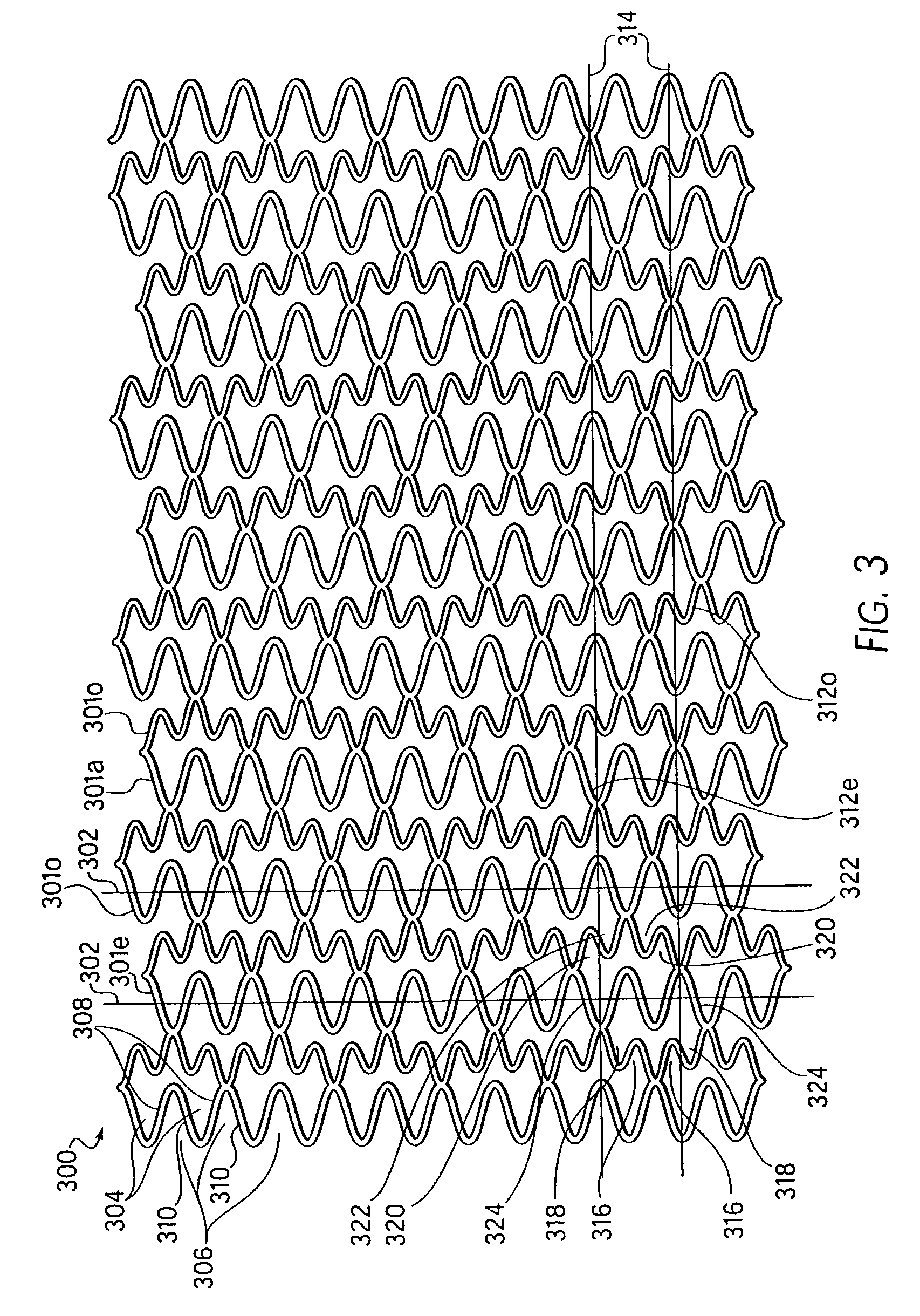
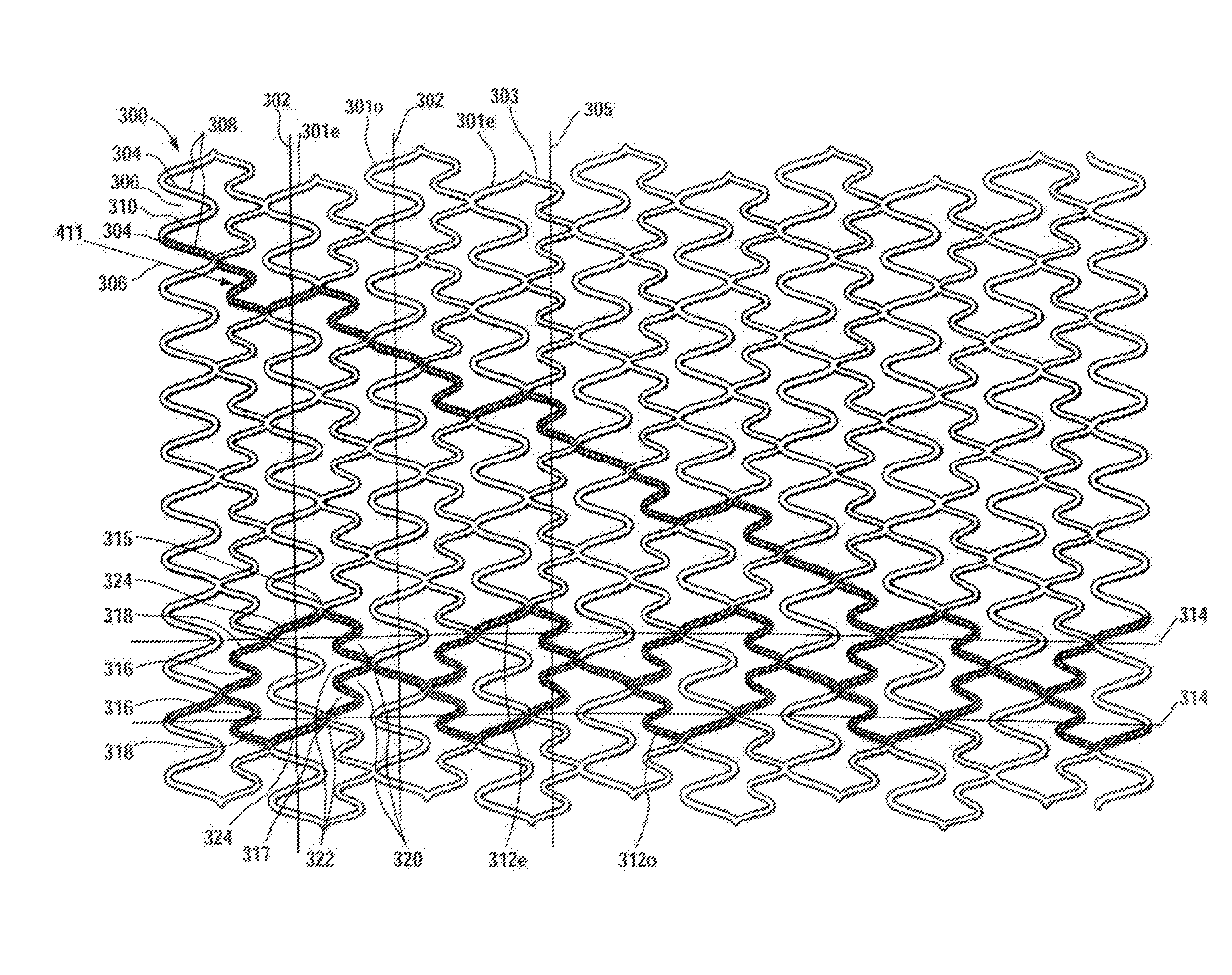
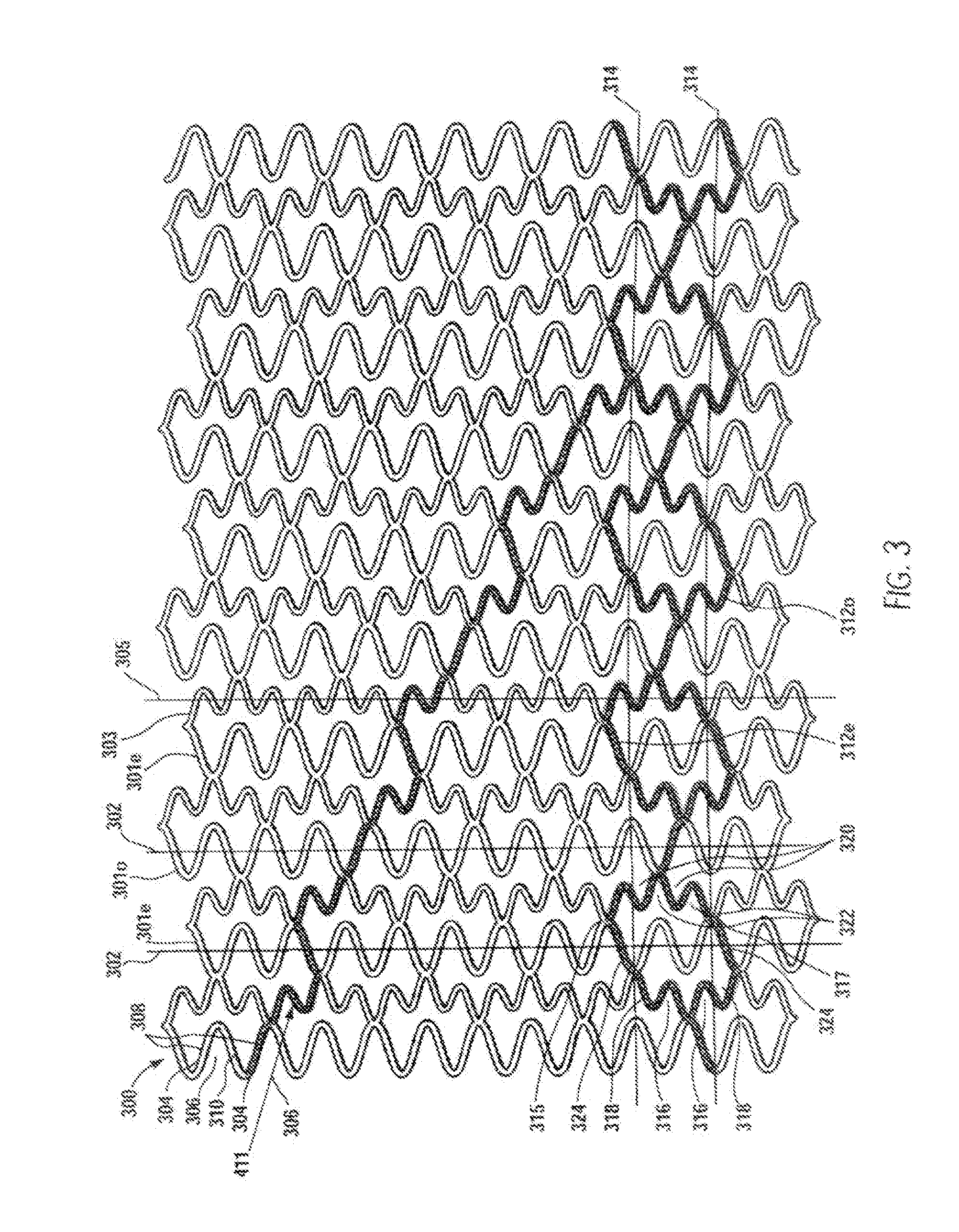
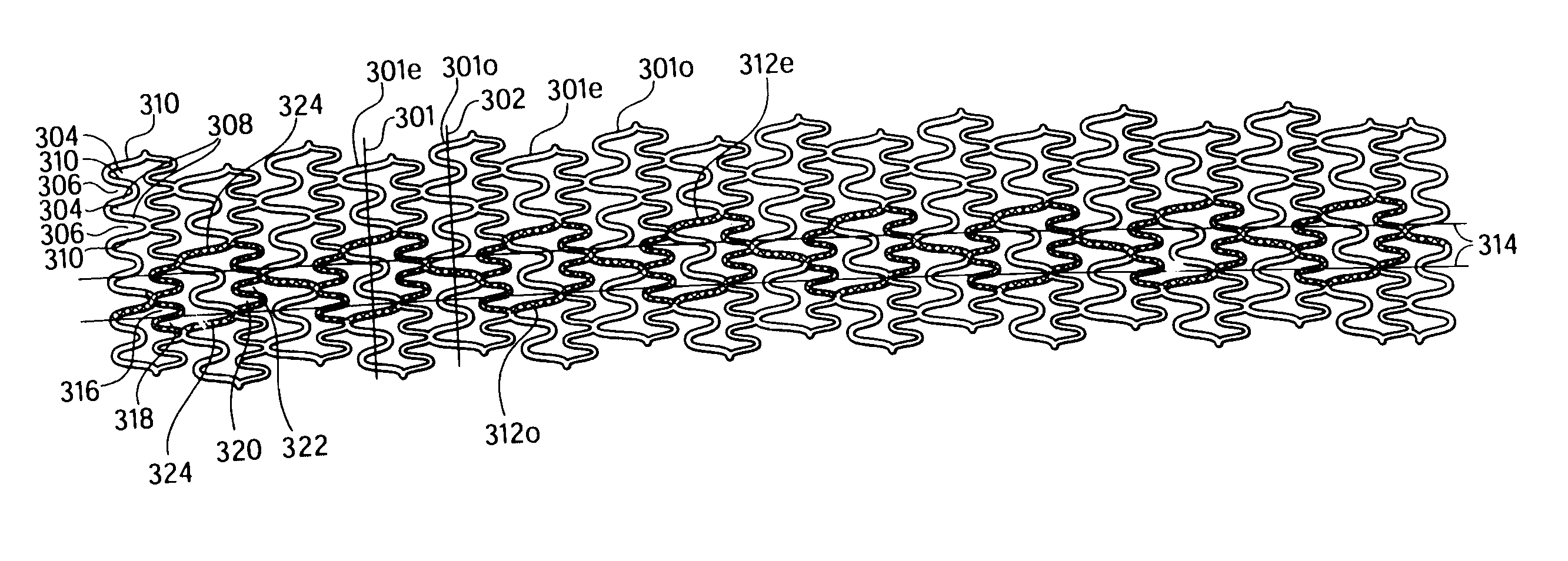
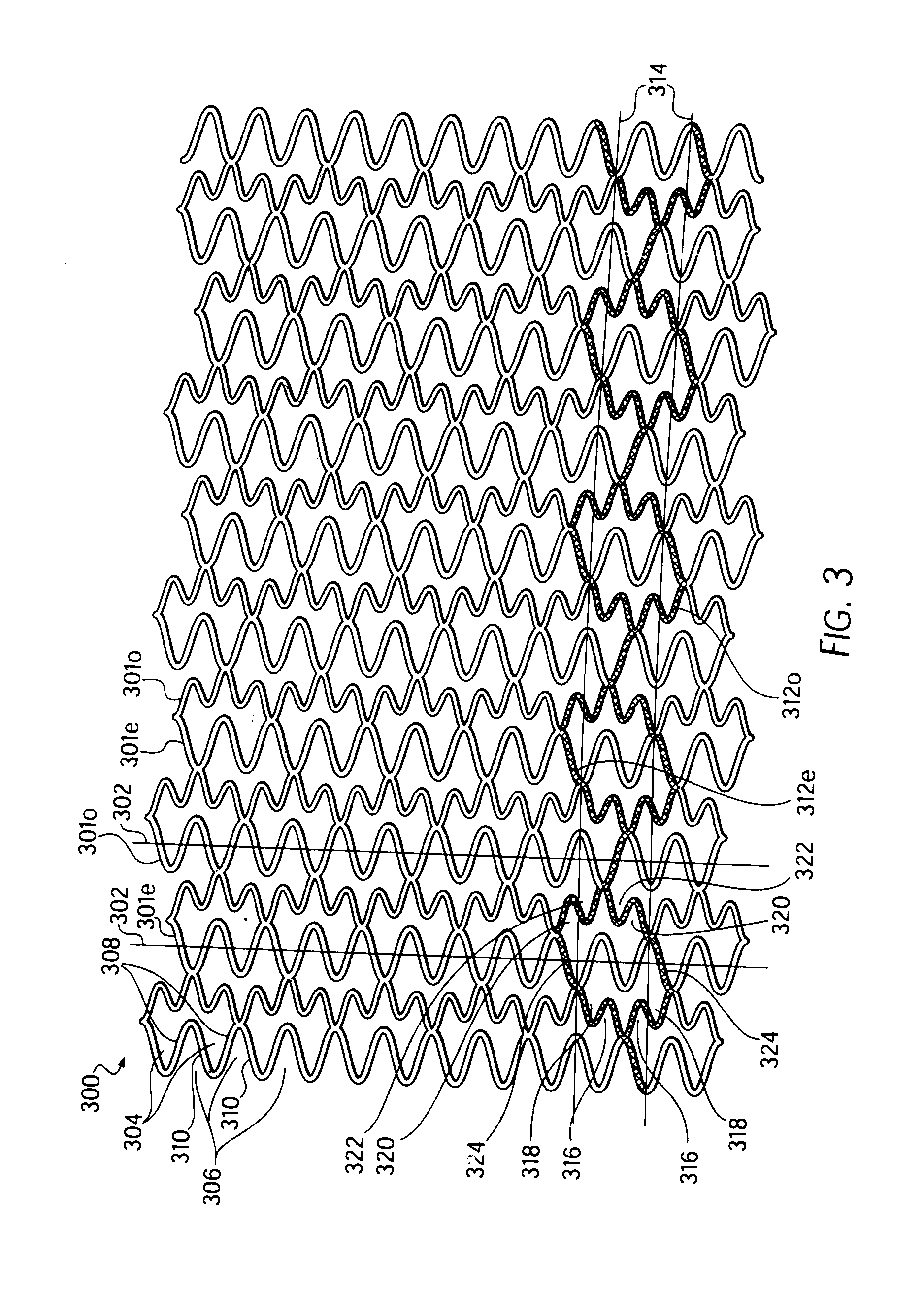
Longitudinally flexible stent
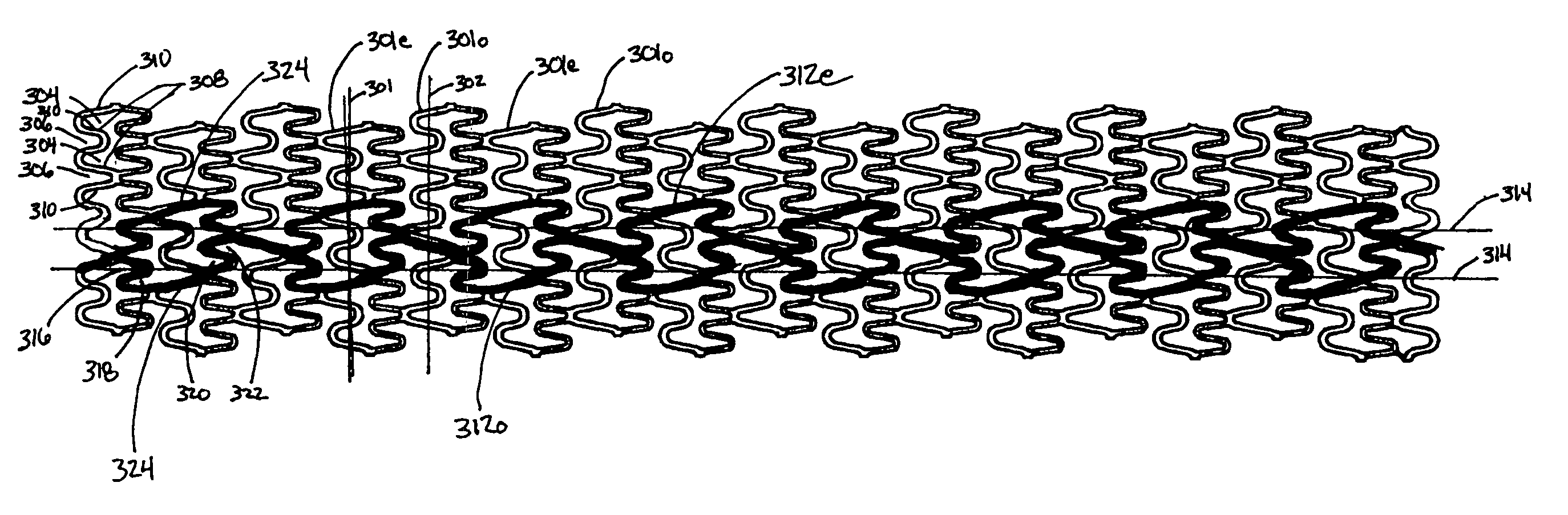
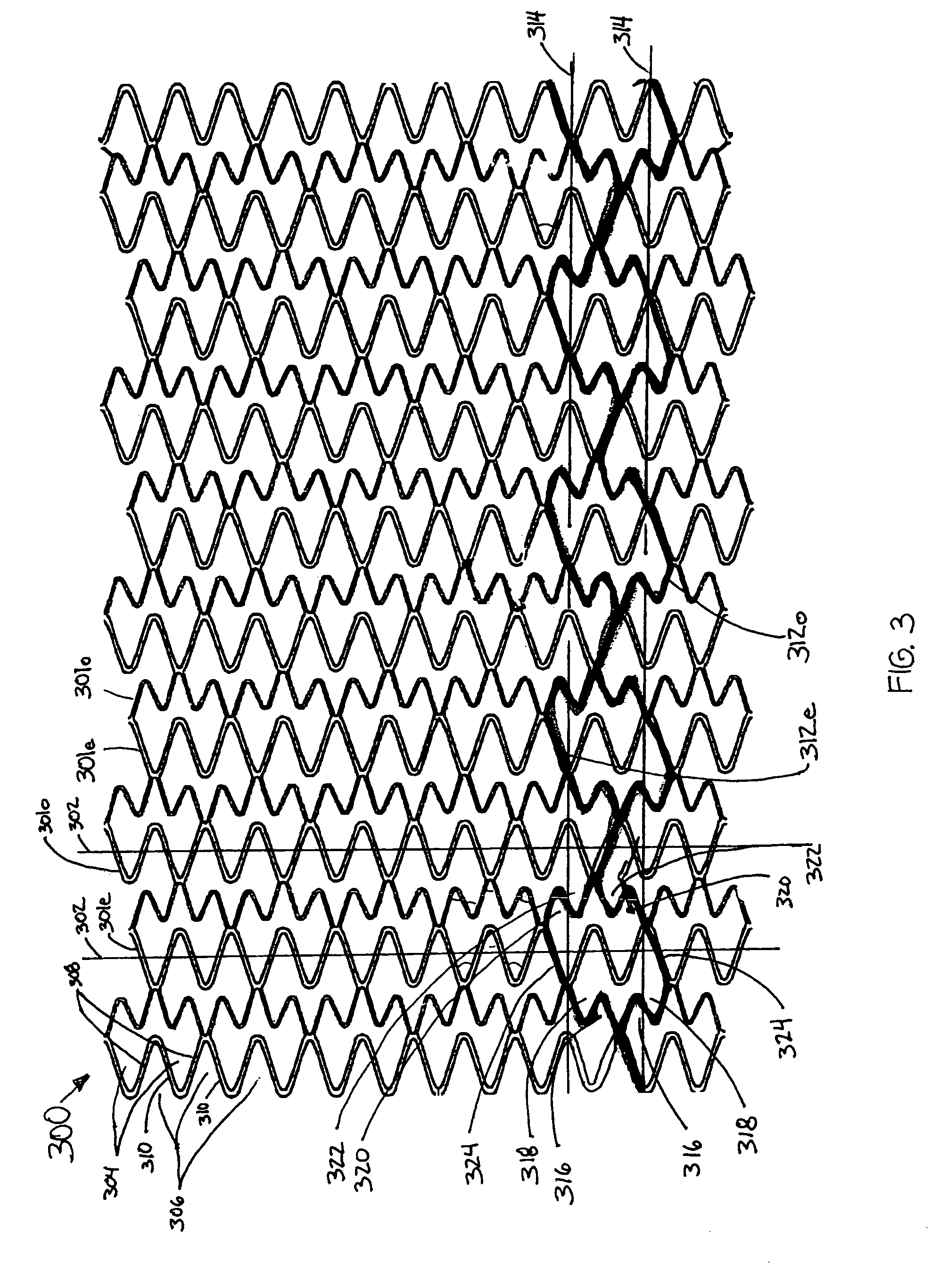
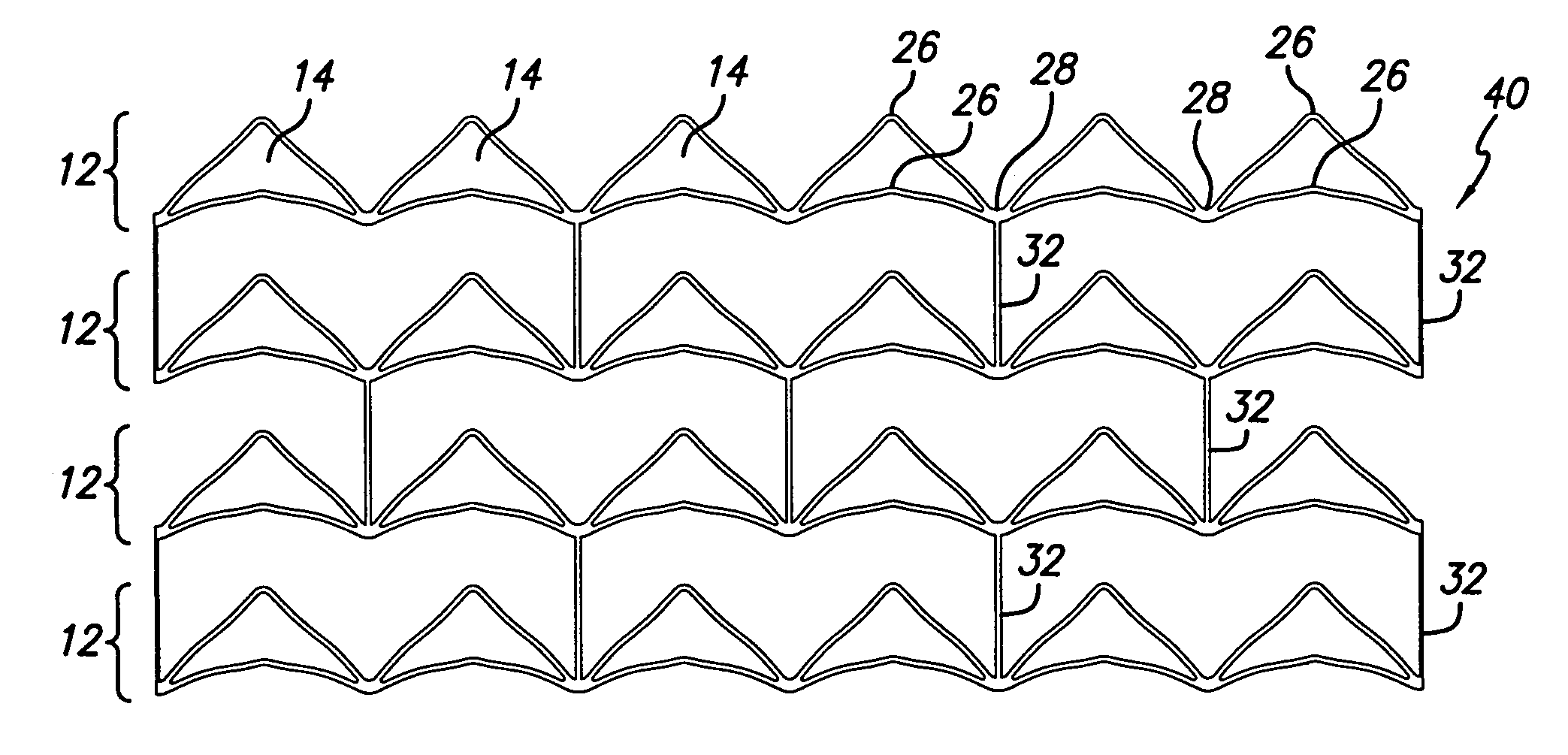
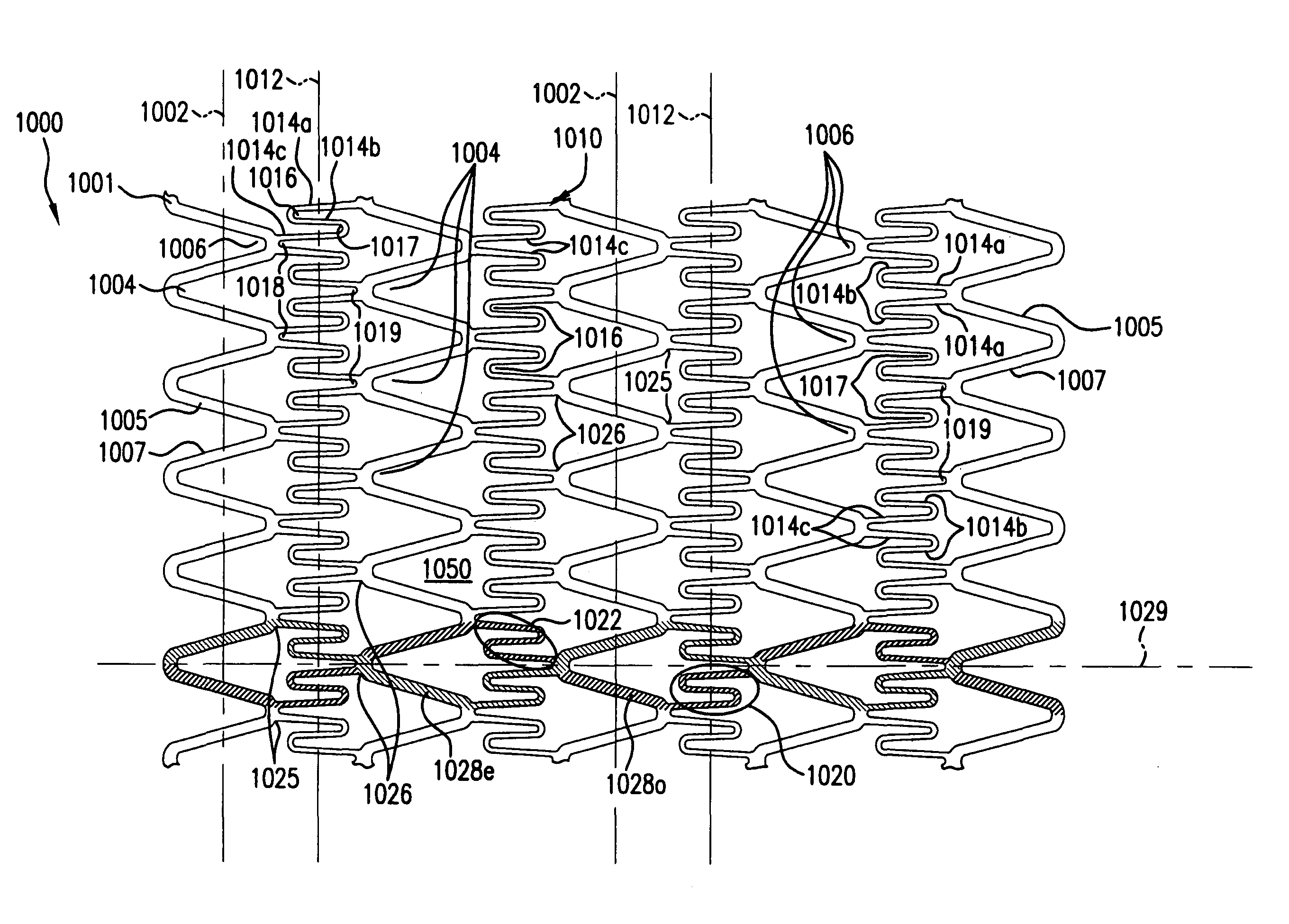
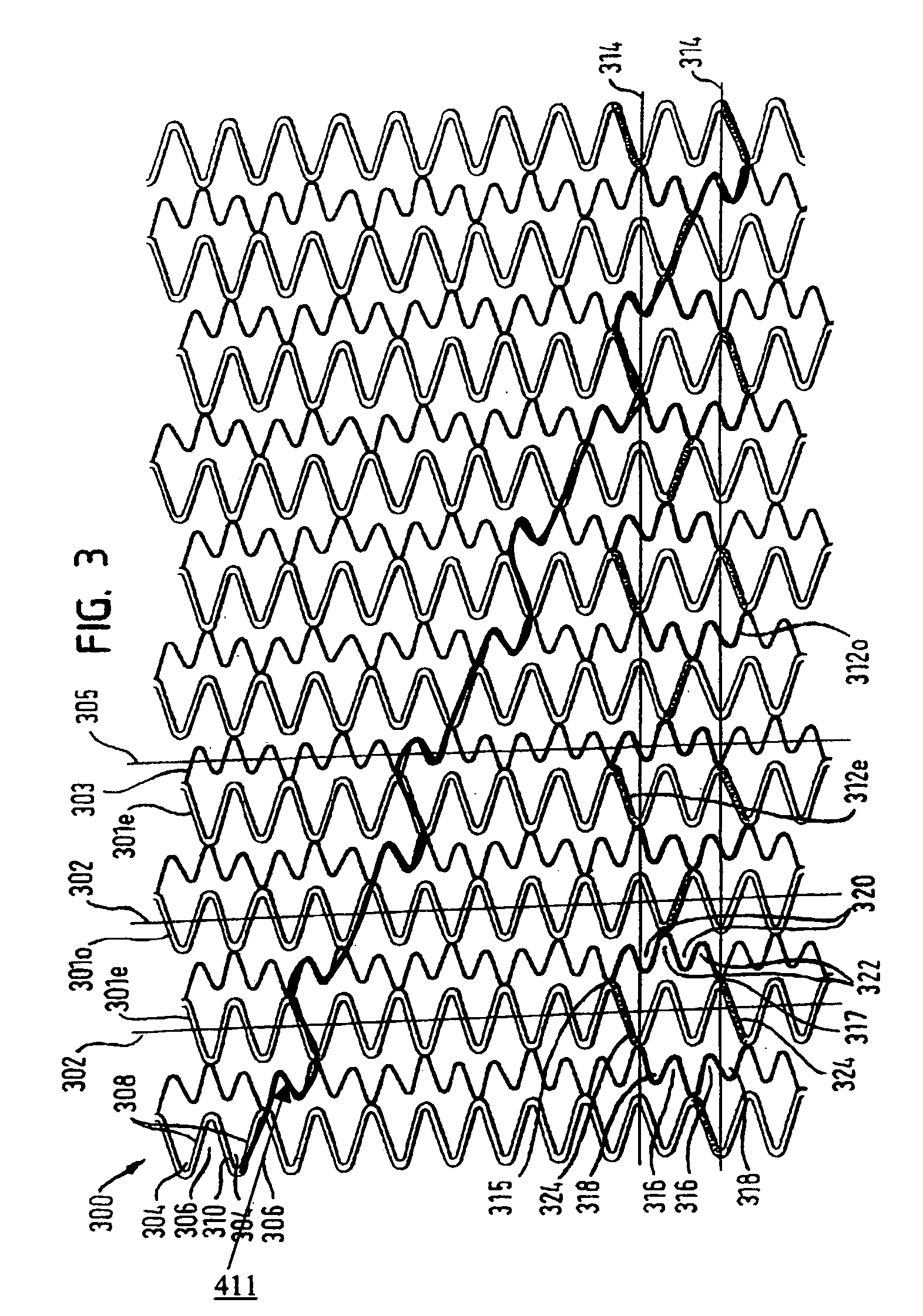
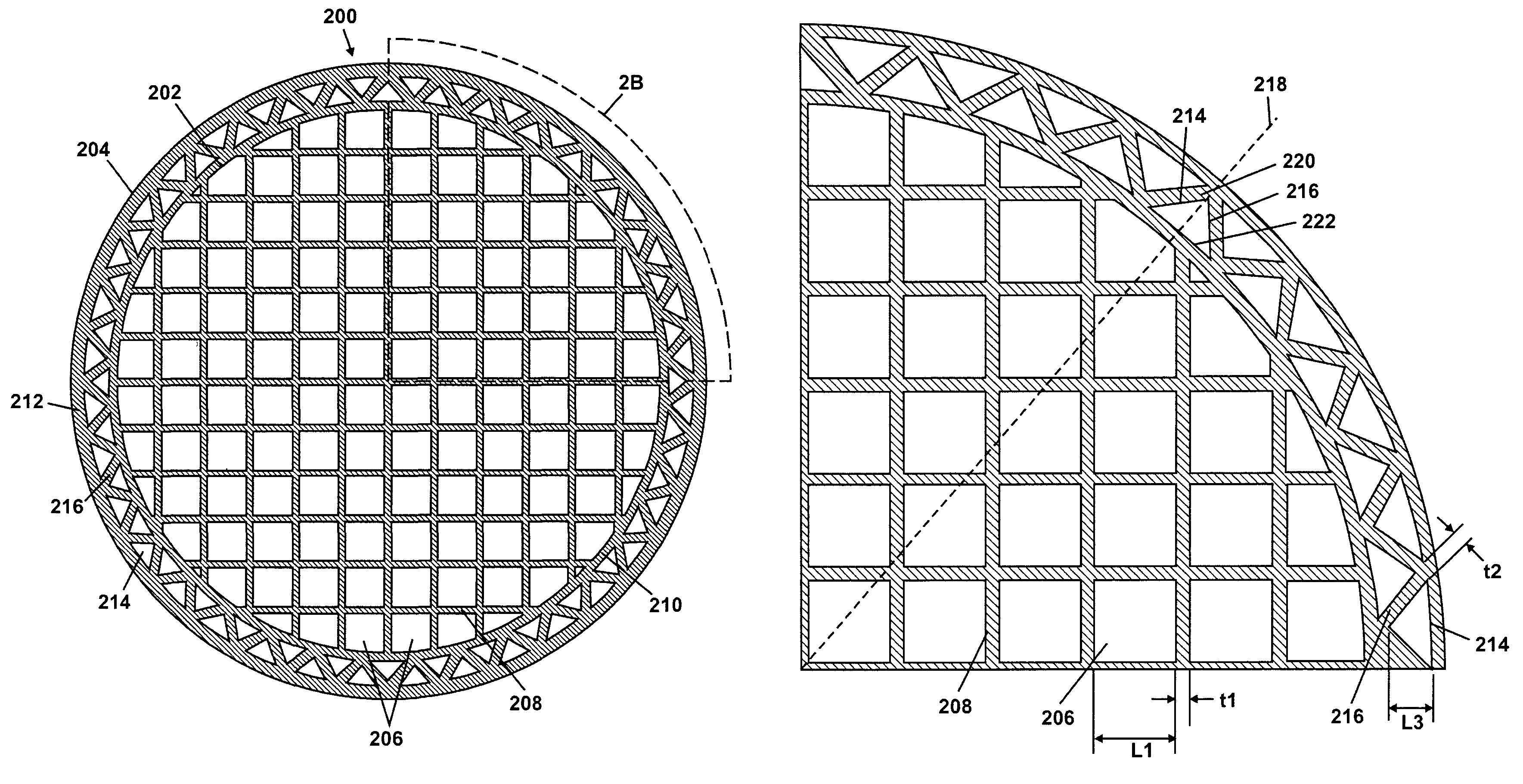
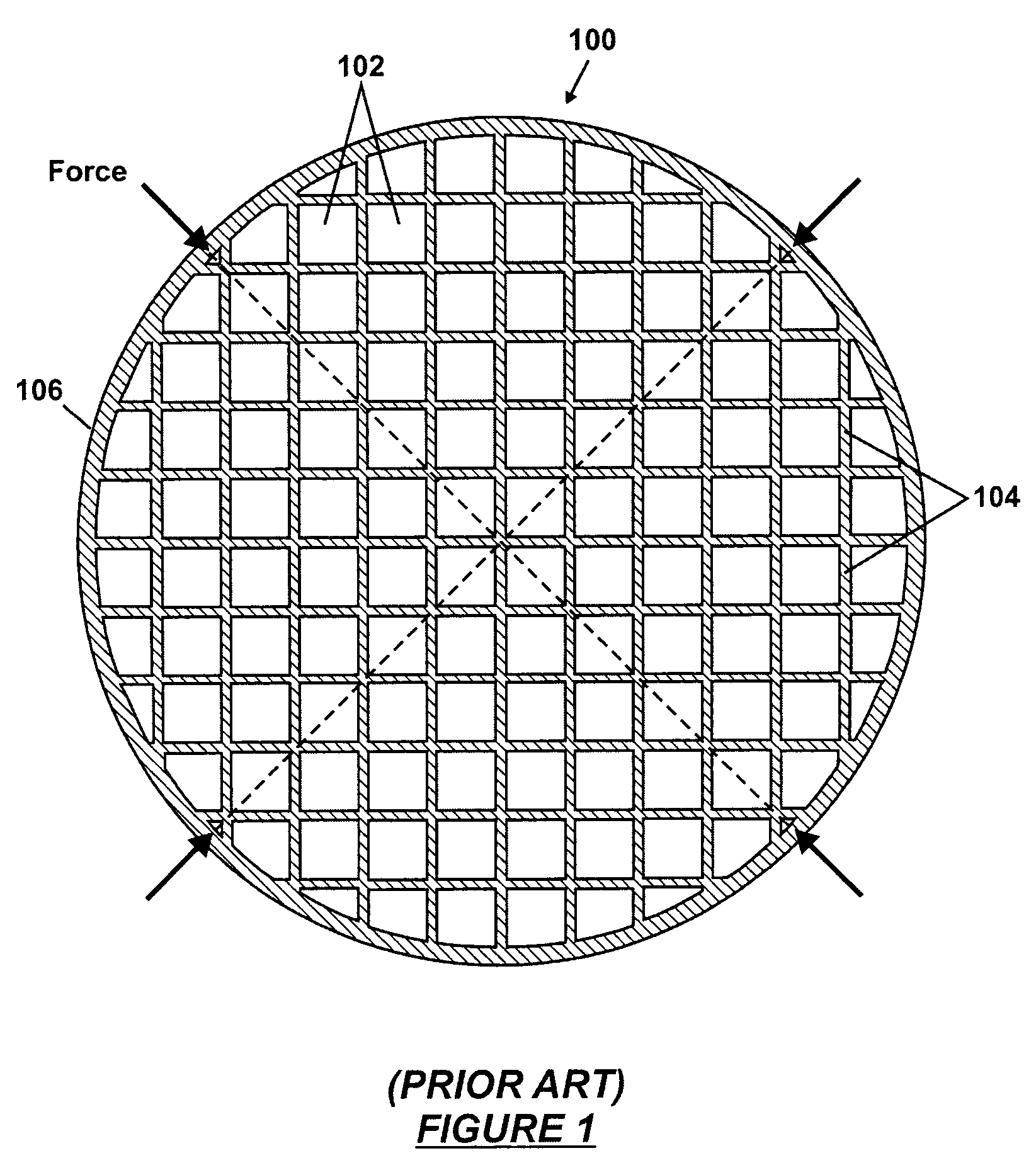
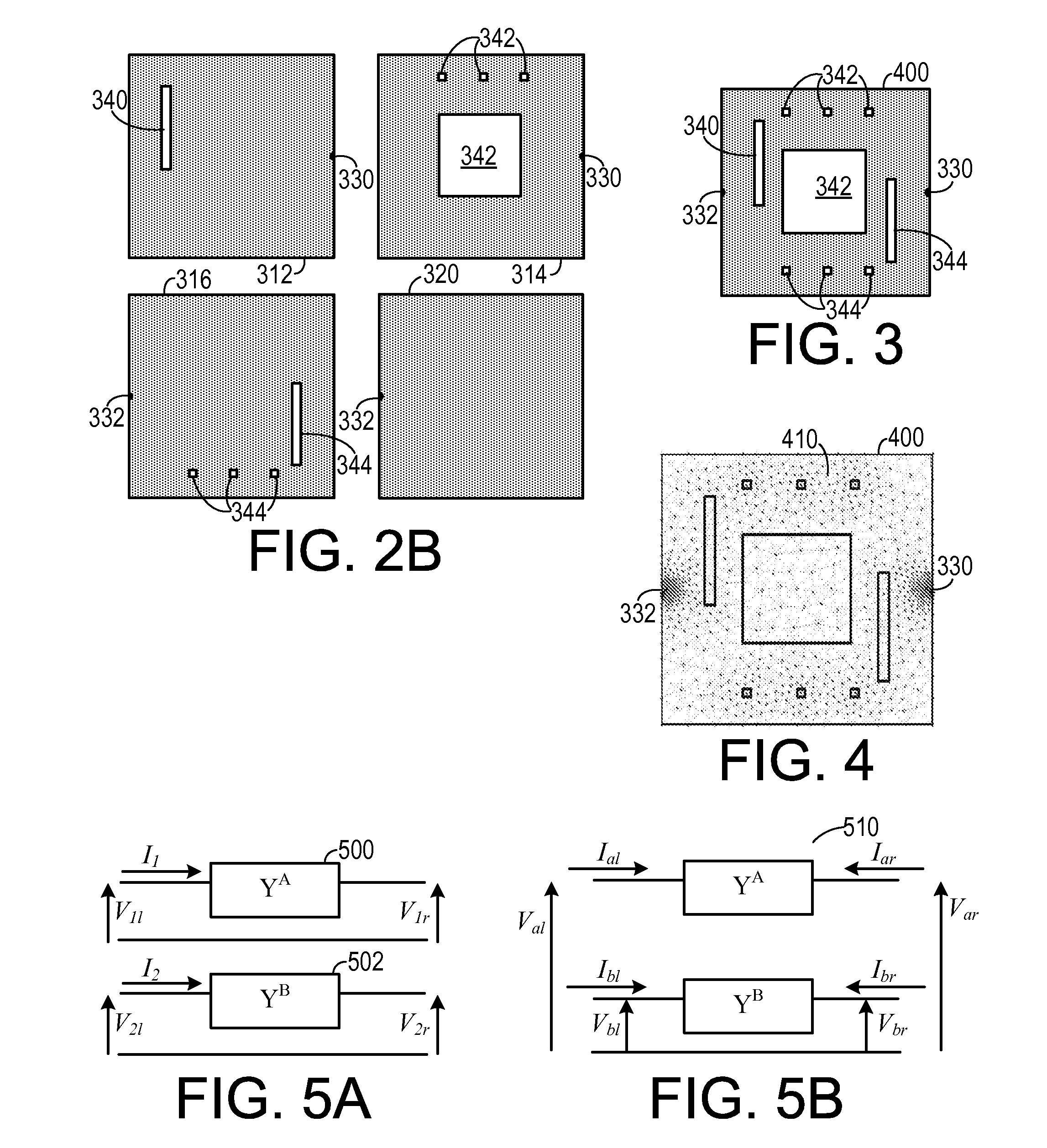
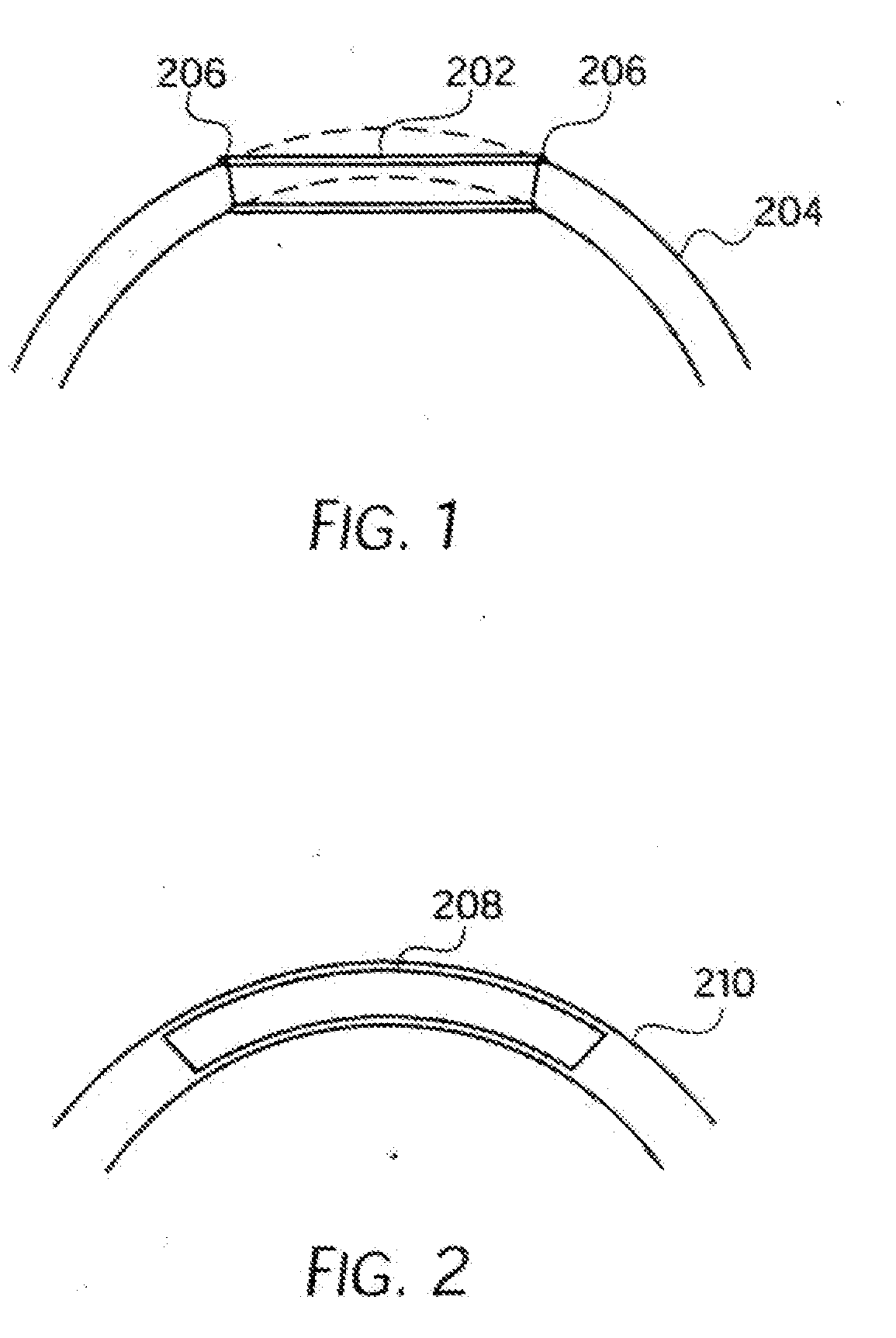
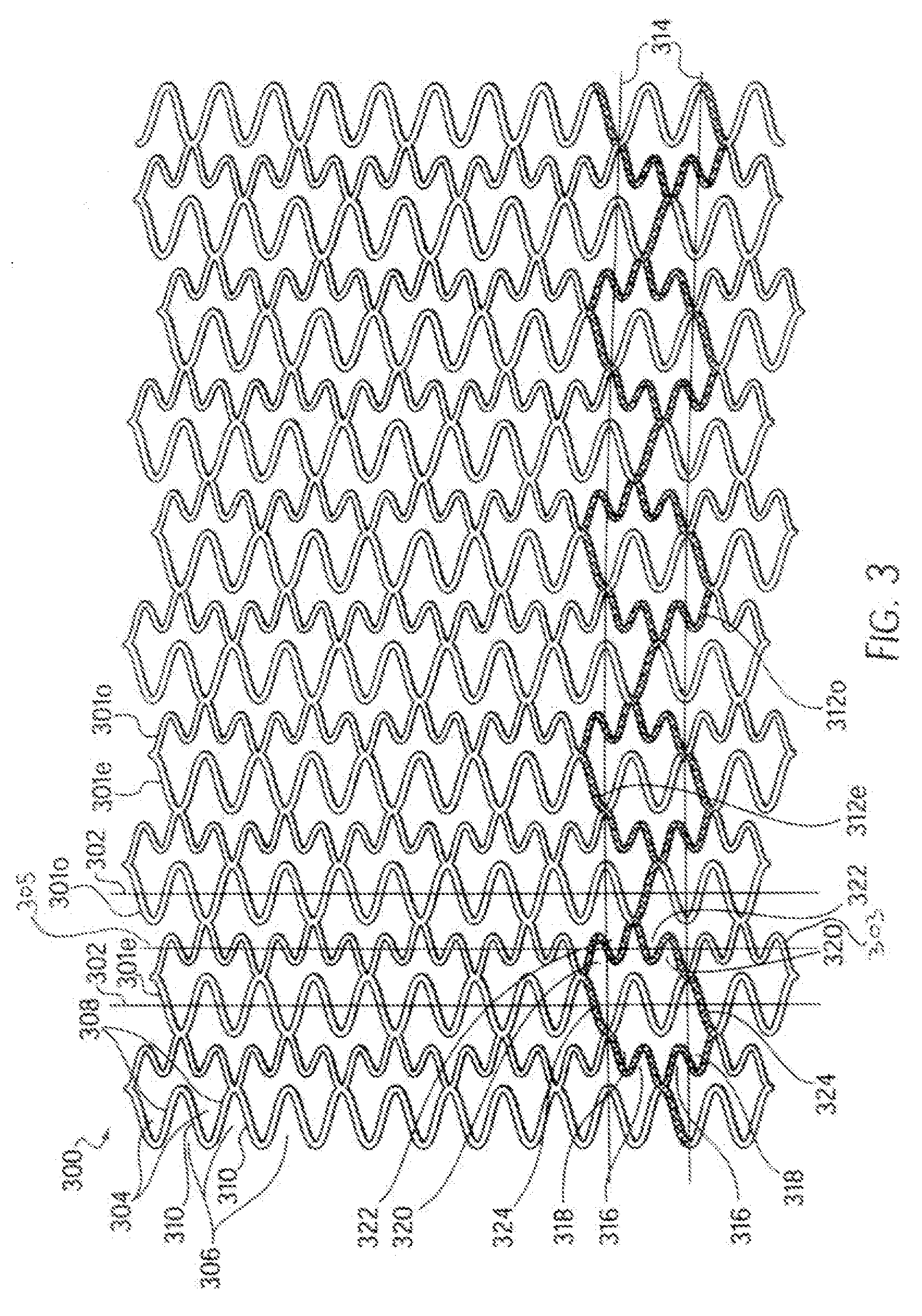
An intravascular stent especially suited for implanting in curved arterial portions. The stent retains longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The stent is formed of intertwined meander patterns forming triangular cells. The triangular cells are adapted to provide radial support, and also to provide longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The triangular cells provide increased coverage of a vessel wall. The stent can have different portions adapted to optimize radial support or to optimize longitudinal flexibility. The stent can be adapted to prevent flaring of portions of the stent during insertion.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Apparatus and method for decreasing stent gap size
InactiveUS6997944B2Reduce deliveryIncreased vessel coverageStentsBlood vesselsTriangular cellVascular wall
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
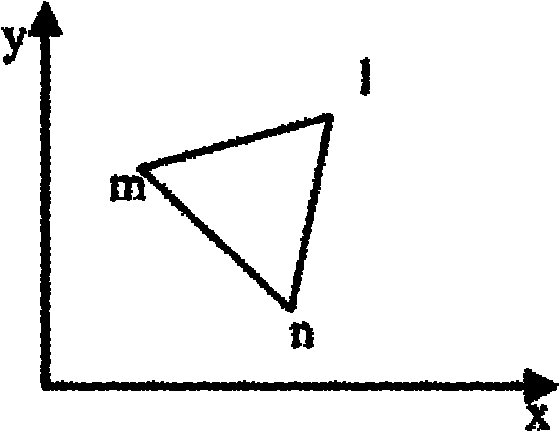
Nonrigid medical image registration method based on self-adapting triangular meshes
ActiveCN102136142ADeal with distractionsStrong anti-noise abilityImage analysisImaging processingAngular point
The invention discloses a nonrigid medical image registration method based on self-adapting triangular meshes in the field of image processing technology. In the method, the thought of graded registration is adopted to implement overall registration on a standard image to be registered and a reference image; then the angular points of the images are used to restrain the interested regions of the overall registration image and the reference image to generate irregular triangular meshes, and generate triangular units with smaller shapes and more quantity at places with larger deformation in theinterested region of the image; the triangular meshes generated by the triangular units with larger shapes and less quantity at places with smaller deformation in the interested region of the image are changed according to the changes of the image contents; and finally, the thought of near-rigid registration is used for realizing local accurate registration of the images. The nonrigid medical image registration method based on self-adapting triangular meshes can effectively improve the accuracy of nonrigid medical image registration and enhance the noise resisting capacity of registration.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
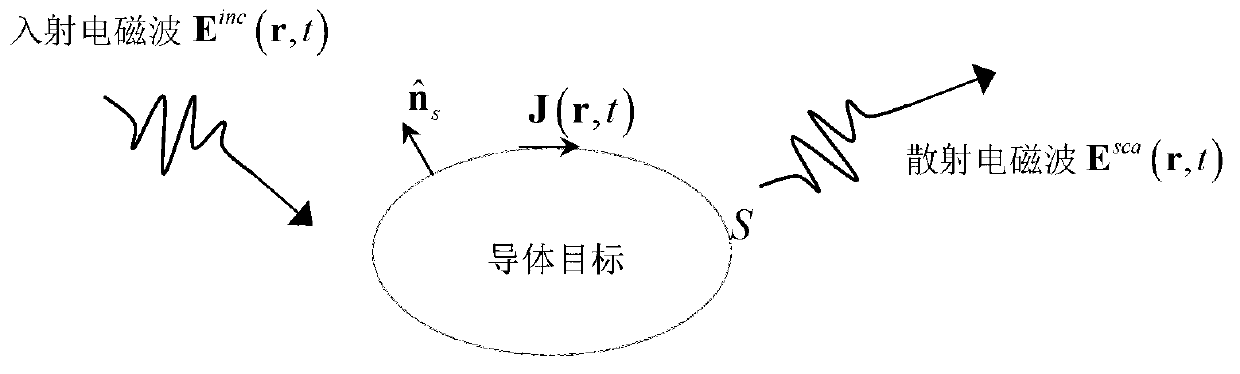
Method for simulating wide-band electromagnetic scattering property of conductor target
ActiveCN103279601AAccurate descriptionExact discrete fitSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorTime delays
The invention discloses a method for simulating the wide-band electromagnetic scattering property of a conductor target. The method comprises the following steps that the geometric model of the conductor target is built, and mesh generation is conducted on the surface of the conductor target by a curved surface triangle unit; a time domain electric field integral equation of the conductor target is determined; a surface induction current in the time domain electric field integral equation expands through a space CRWG primary function and a time delay primary function; an expanding surface induction current expression is substituted into the time domain electric field integral equation, and then the time domain electric field integral equation in a discrete form is tested in a time and space mode so as to obtain a system impedance matrix equation; singularity integrals are eliminated to obtain a sparse expression of a impedance matrix; the equation of the impedance matrix is solved to determine the distribution of the time domain current of the surface of the conductor target, and wide-band electromagnetic property parameters of the target are obtained according to the distribution of the time domain current so as to finish simulation. The method for simulating the wide-band electromagnetic scattering property of the conductor target has the advantages of being high in simulation precision, little in required time and low in memory consumption, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Longitudinally flexible stent
InactiveUS7758627B2Increased longitudinal flexibilityIncrease circumferential widthStentsSurgeryMeanderInsertion stent
An intravascular stent especially suited for implanting in curved arterial portion. The stent retains longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The stent is formed of intertwined meander patterns forming triangular cells. The cells are adapted to provide radial support, and also provide longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The cells also provide increase coverage of a vessel wall. Loops in the stent are disposed and adapted to cooperate, so that after expansion of said stent within a curved lumen, the stent is curved and cells on the outside of the curve open in length, but narrow in width, whereas cells on the inside of the curve shorten in length, but thicken in width to maintain a density of the stent element area which is much more constant than otherwise between the inside and outside of the curve. The stent also minimizes flaring out by eliminating free loops of the radially supporting circumferential bands of loops.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Contact judgment method of spherical particles and triangular meshes in discrete element simulation
InactiveCN103235854ASolve the problem of contact judgmentAvoid the problem of separately establishing the contact judgment algorithmSpecial data processing applicationsDiscrete element simulationGraphics
The invention relates to a contact judgment method of spherical particles and triangular meshes in discrete element simulation. The contact judgment method of the spherical particles and the triangular meshes in the discrete element simulation comprises steps of searching neighbor meshes of a target particle to confirm a boundary triangle unit which performs intersecting detection with the target particle; confirming primary contacting information between the target particle and the boundary triangle unit in combination with a symbolic assembly of triangular Voronoi space and center-of-mass coordinates; and judging effectiveness of the primary contacting information, eliminating invalid contacting information and adding the effective contacting information into a contacting linked list to calculate the contact force of particles through a discrete element simulation program. The contact judgment method of the spherical particles and the triangular meshes in the discrete element simulation has the advantages of avoiding respectively building contact judgment algorithms for every kind of basic graphic elements; providing a method for directly positioning an area generating contact to save execution steps of the contact judgment; building judging criteria for eliminating the invalid contact information among multiple contact information; and finally effectively solving the contact judgment problem of the spherical particles and complex geometry boundaries in the discrete element simulation.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Extrusion die for making a double-skin honeycomb substrate
A honeycomb substrate includes an inner body having an inner skin and an array of inner webs defining an array of inner cells within the inner skin. The honeycomb substrate further includes an outer body having an outer skin formed concentric with the inner skin and an array of outer webs defining an array of triangle cells between the inner skin and the outer skin. The triangle cells are oriented along a radial direction with respect to a center of the inner body. An extrusion assembly for forming the honeycomb substrate includes an inner cell forming die, an outer cell forming die, and a skin forming mask, all mounted coaxially. An outer skin slot formed between the outer cell forming die and the skin forming mask is in communication with feedholes in the inner cell forming die through an opening in the outer cell forming die.
Owner:CORNING INC
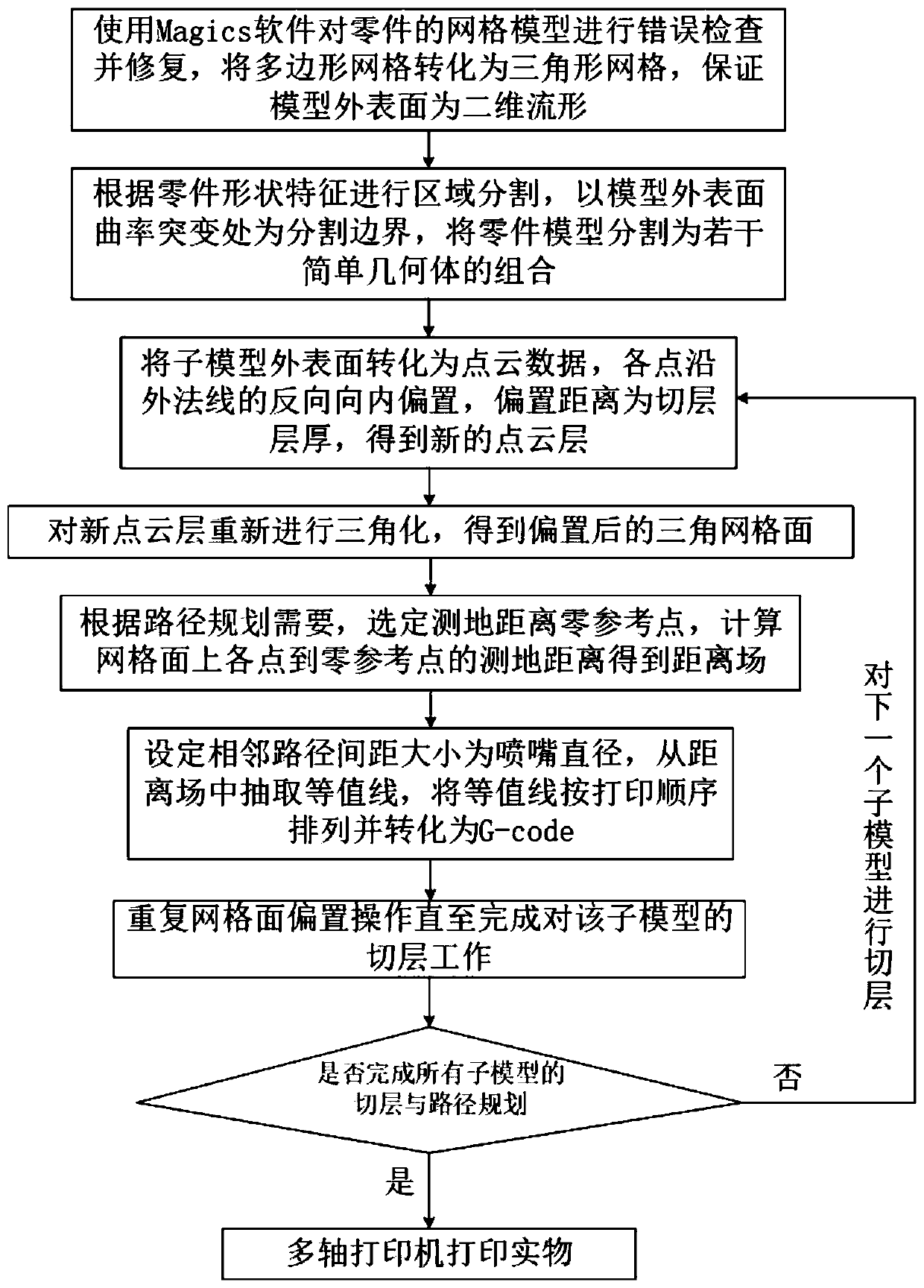
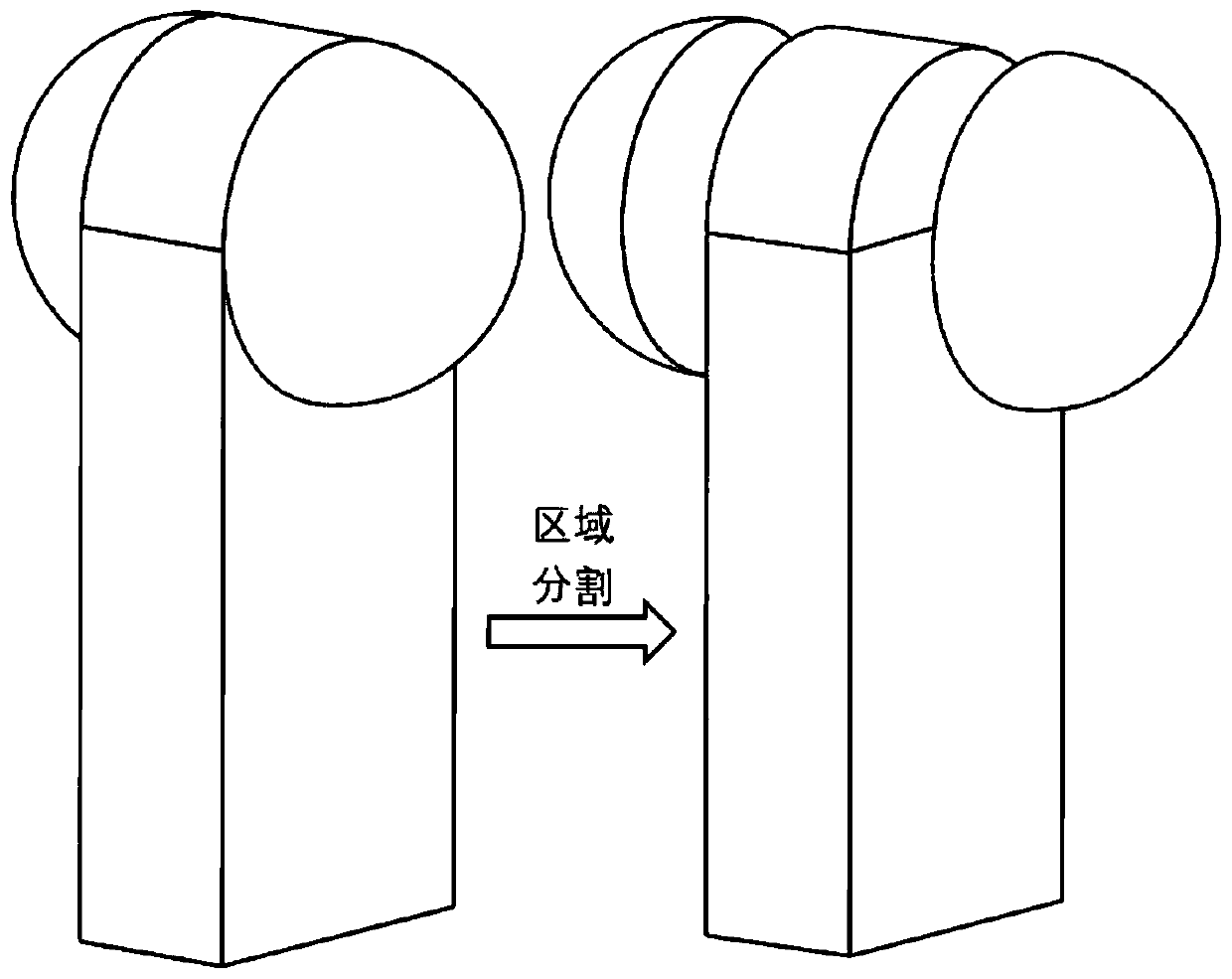
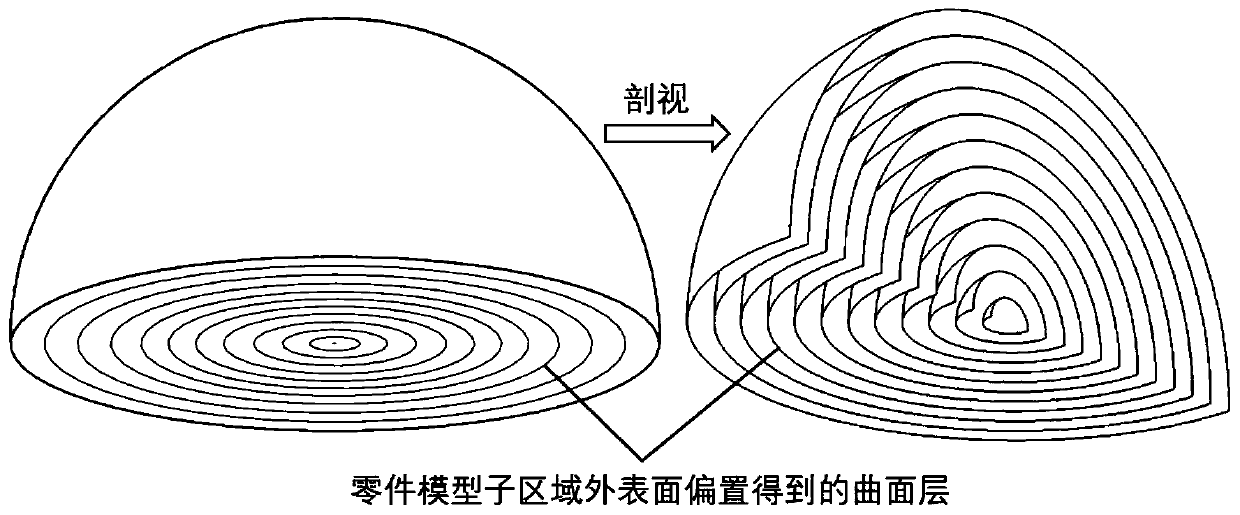
Conformal cutting layer and path planning method for curved surface 3D printing
ActiveCN110126279AUniform distanceImprove layering accuracyAdditive manufacturing apparatusManufacturing data aquisition/processingSurface layerPoint cloud
The invention discloses a conformal cutting layer and path planning method for curved surface 3D printing. The conformal cutting layer comprises a conformal curved surface cutting layer method and a three-dimensional space path planning method, the conformal curved surface cutting method comprises the following steps that defect inspection and repairing are carried out on a grid model, it is ensured that the outer surface of the model is a two-dimensional flow shape, if the grid surface is not an all-triangular unit, triangular formation is carried out on the grid surface; then regional segmentation is carried out, the printing sequence of each sub-portion and the approximate direction of the sub-layer are determined; the outer surface is converted into point cloud data, and the point cloud is biased inwards; the offset point cloud data is fit to form a triangular mesh surface; and the model is correspondingly divided into a plurality of curved surface layers to obtain a curved surfaceset; and the three-dimensional space path planning method comprises the following steps of checking whether the curved surface in the curved surface set is the two-dimensional flow shape or not, homogenizing the triangular unit, calculating the geodesic distance of each vertex of the grid relative to the designated reference point, extracting equivalent points, fitting to be a contour line, and converting into a G-code to obtain a printing path. According to the conformal cutting layer and path planning method, the special requirements of curved surface printing can be met.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
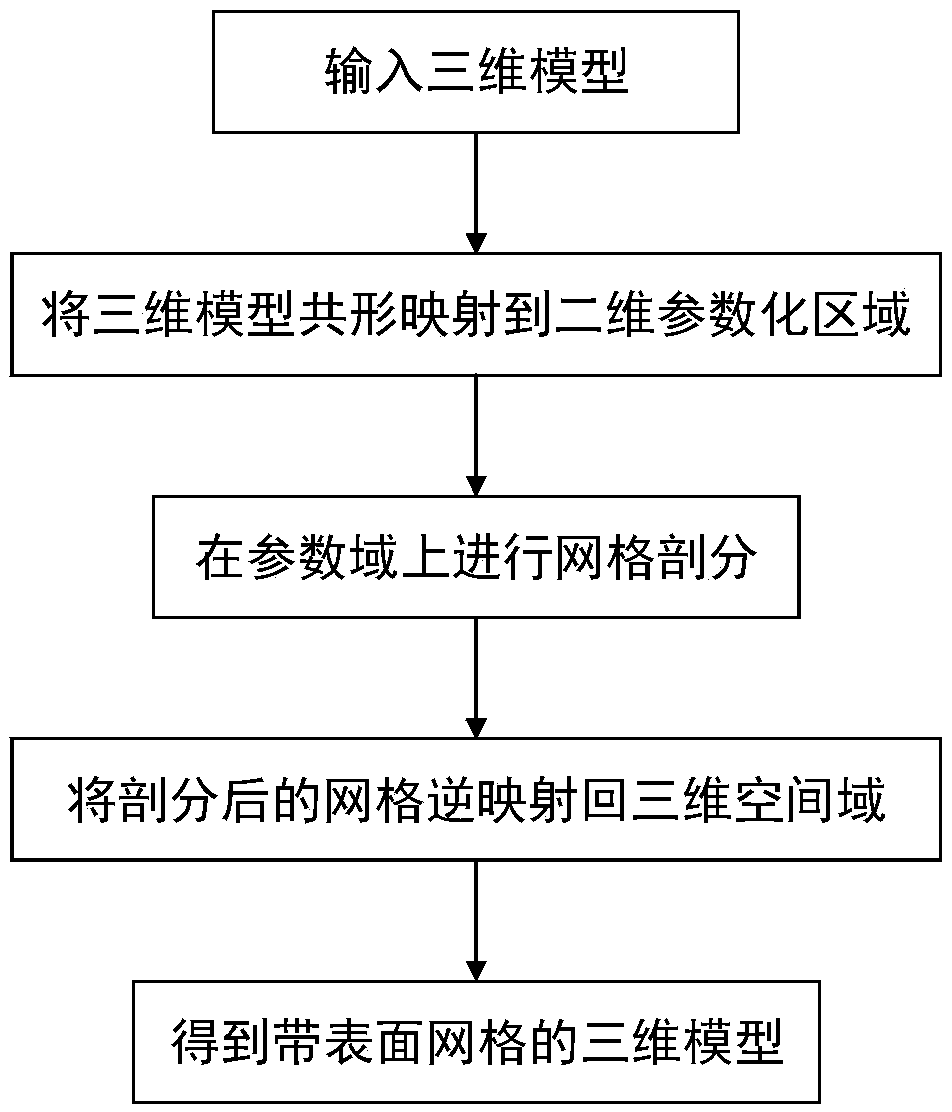
A surface mesh generation method of a digital model based on conformal geometry
PendingCN109377561AEasy split operationQuality improvement3D modellingNODALComputer graphics (images)
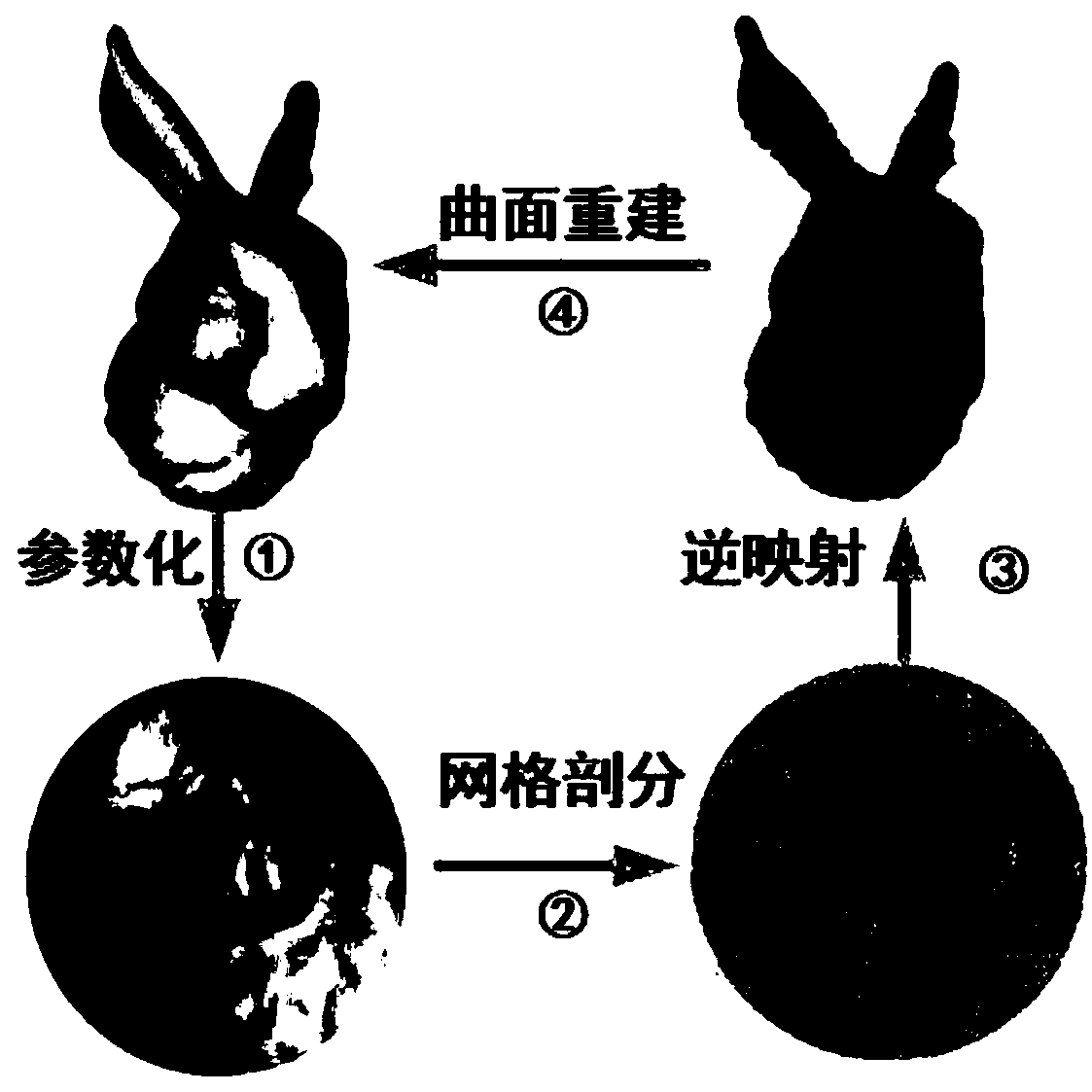
The invention provides a surface mesh generation method of a digital model based on conformal geometry, which aims at simplifying the surface mesh generation problem of a three-dimensional model to atwo-dimensional plane for processing, wherein the method comprises according to the topological information of the three-dimensional model, selecting the conformal mapping function from the three-dimensional model to the two-dimensional parameter region, and then generating the finite element mesh on the parameter region, in the mesh generation of parametric domain, generating the triangular element or quadrilateral element, and then mapping the mesh of parametric domain into the mesh of spatial domain by conformal inversion according to the mapping function from parametric domain to spatial domain, and keeping the topological relationship between nodes unchanged, so that the mesh of spatial domain is the surface mesh of the 3D model. Compared with the mesh generation on the surface of 3Dmathematical model directly, the mesh generation on parameterized area is simpler and has less computational complexity. The surface mesh generated by this method is of high quality and high precision.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
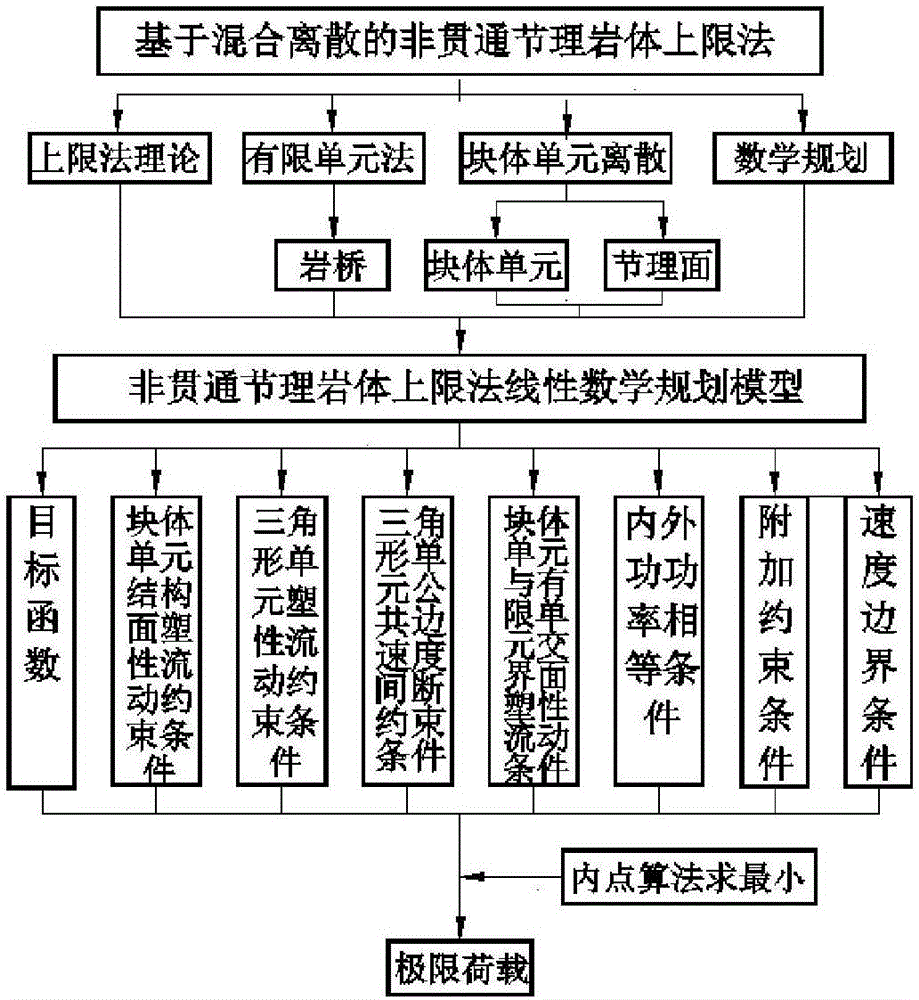
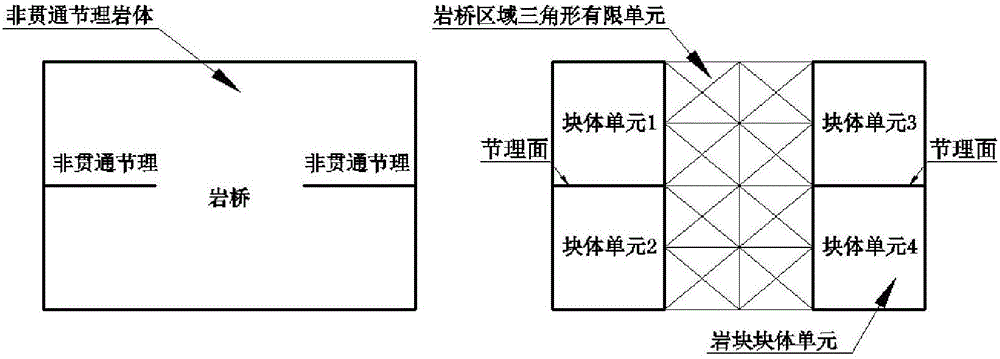
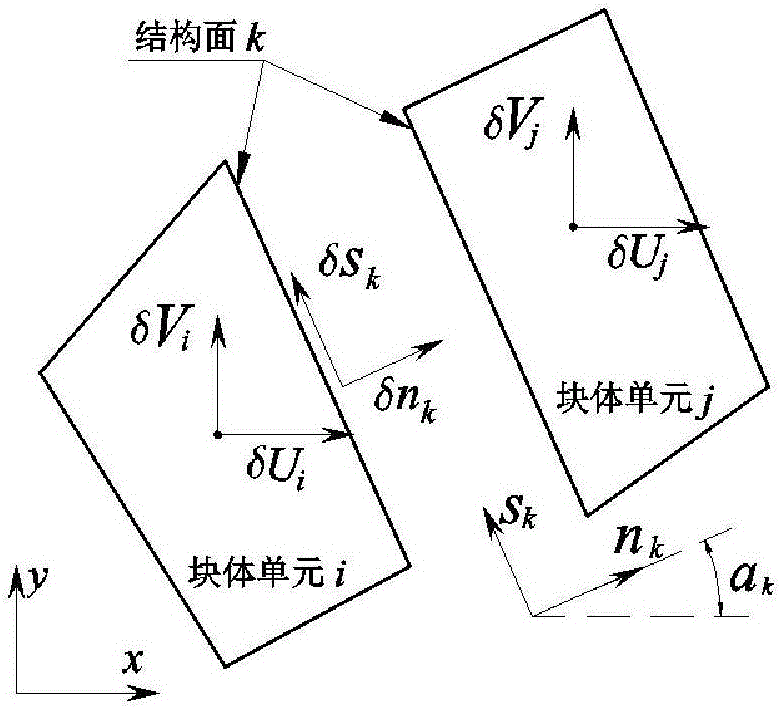
Hybrid numerical discretization-based plasticity limit analysis upper-bound method of non-across jointed rock mass
ActiveCN106557608ASimulate the mechanical properties of discontinuous mediaMethod concept is clearDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALDiscretization
The invention relates to a plasticity limit analysis upper-bound method of a non-across jointed rock mass, and belongs to the field of bearing capacity analysis of the rock mass in rock mechanics. The method comprises the steps of: on the basis of an upper-bound method theory in plasticity limit analysis, discretizing a non-across jointed rock slope by adopting a hybrid element method, namely constructing a kinematically admissible velocity field which simultaneously meets block and structural surface deformation compatibility conditions, plasticity flowing constraint conditions, internal and external power equivalence conditions, block element and triangular element interface plasticity flowing conditions and velocity boundary conditions by adopting a rigid block element discretization rock, a finite element discretization rock bridge, a block element centroid speed and a triangular element node velocity as unknown quantities; and building a linear mathematical programming model of solving an ultimate load of the non-across jointed rock mass, solving the linear mathematical programming model by adopting an interior point algorithm and obtaining an upper-bound solution of the ultimate load of the non-across jointed rock mass. The plasticity limit analysis upper-bound method has the characteristics of clear concepts, high calculation accuracy and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Longitudinally flexible stent
InactiveUS7621947B2Add supportIncreased longitudinal flexibilityStentsEar treatmentMeanderInsertion stent
An intravascular stent especially suited for implanting in curved arterial portions. The stent retains longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The stent is formed of intertwined meander patterns forming triangular cells. The triangular cells are adapted to provide radial support, and also to provide longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The triangular cells provide increased coverage of a vessel wall. The stent can have different portions adapted to optimize radial support or to optimize longitudinal flexibility. Loops in the stent are disposed and adapted to cooperate so that after expansion of said stent within a curved lumen, the stent is curved and cells on the outside of the curve open in length, but narrow in width whereas cells on the inside of the curve shorten in length but thicken in width to maintain a density of stent element area which much more constant than otherwise between the inside and the outside of the curve. As a result, when the stent is coated with a medicine the more constant density of stent elements results in an even dose being applied to the inside wall of the lumen, avoiding the possibility that a toxic dose be supplied at one area while a less than effective dose is applied to another area.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
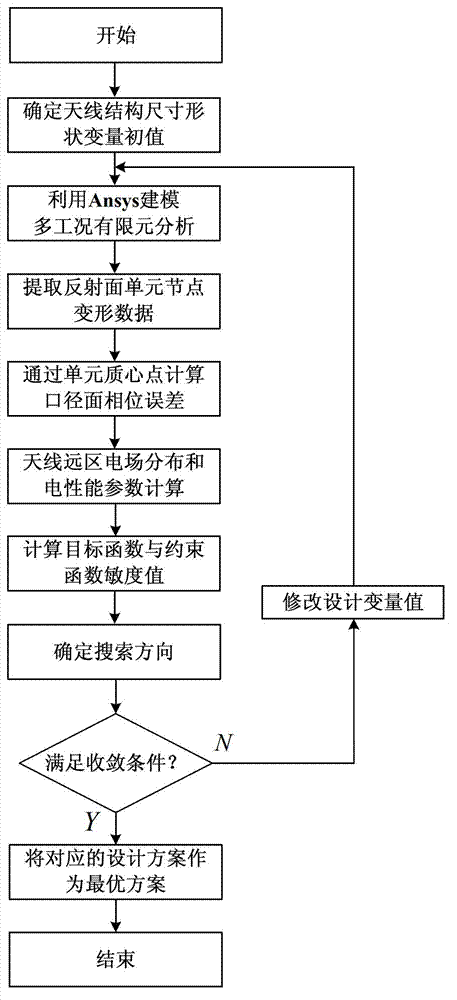
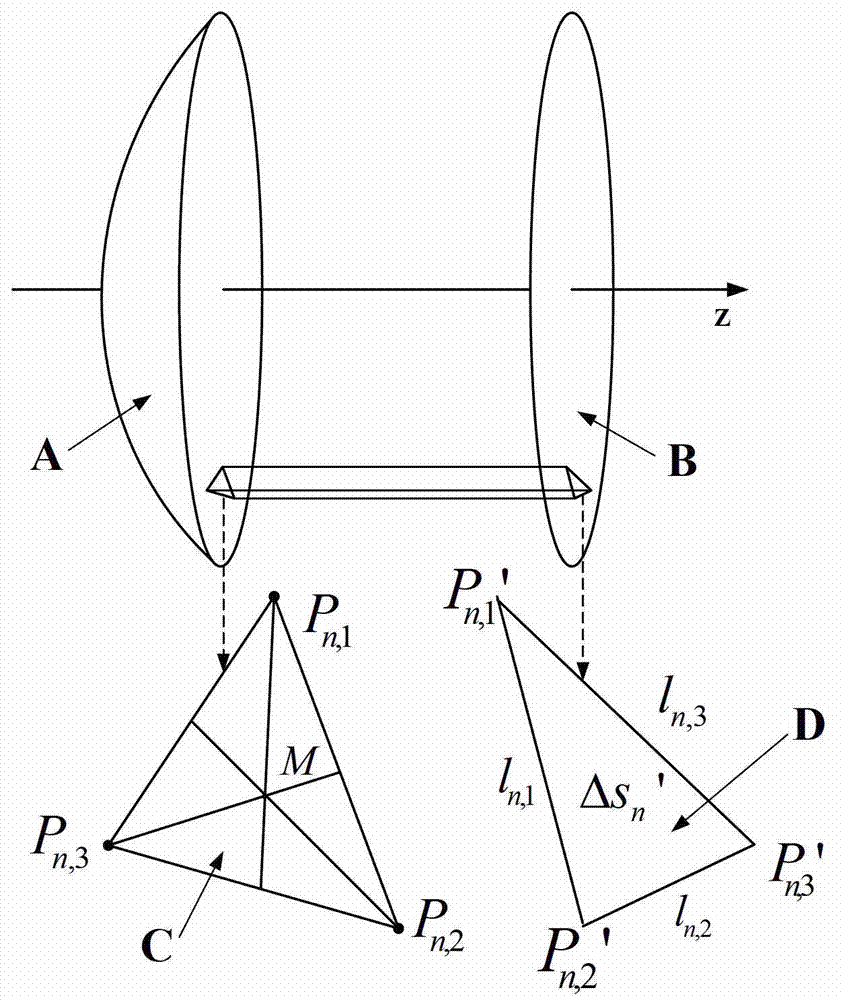
Electromechanical integration design method of 65m-aperture large-size reflector antenna structure
InactiveCN102968532AAccurately calculate the phase error of the aperture surfaceRealize comprehensive electromechanical analysisSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityAntenna design
The invention discloses an electromechanical integration design method of a 65m-aperture large-size reflector antenna, mainly aiming at solving the problem in electromechanical integration in large-size antenna design. The electromechanical integration design method comprises the following steps of: obtaining node displacement information after a reflector is distorted on the basis of finite element analysis of an antenna structure; designing a relation between coordinates and coordinate spatial positions after the reflector is distorted according to a node theory, and calculating theoretical coordinates and displacement of centroid points of triangular units; calculating optical path difference of the centroid points of the triangular units and phase errors on the corresponding aperture; projecting the units onto the aperture and calculating far-zone electric field distribution to obtain electrical performance parameters; building an optimization model by taking the structural parameters of the antenna as design variables and optimization of the electrical performance parameter of the antenna as a target; and solving the optimization model by adopting a sequential quadratic programming method to obtain an optimum mechanical electromagnetic comprehensive design scheme, so as to realize the electromechanical integration design of the reflector antenna. The electromechanical integration design method can be used for guiding the structural design of the large-size reflector antenna, and the analysis and the evaluation of the electromechanical comprehensive performance of the antenna under different working conditions.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
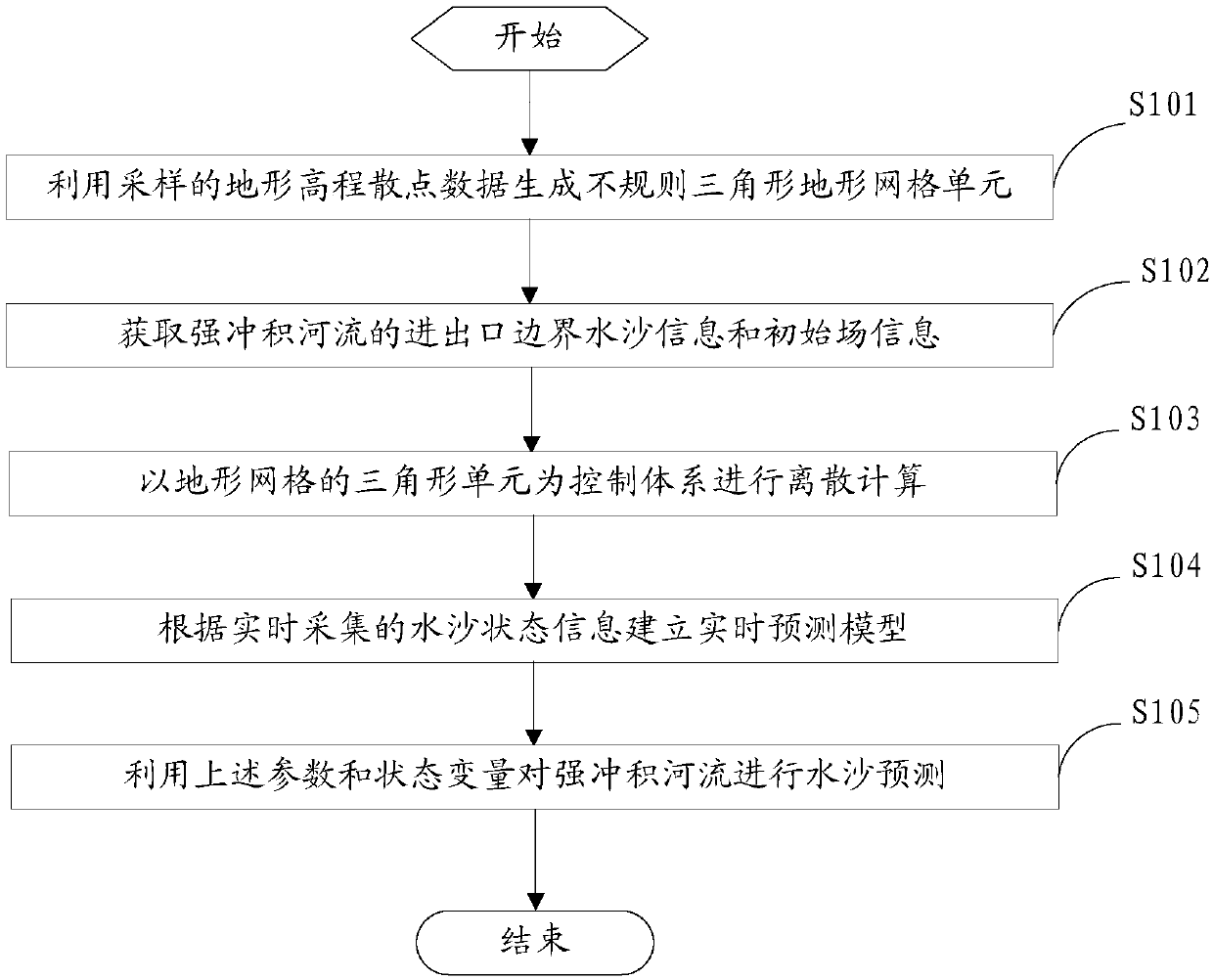
Water and sand prediction method and system for strong alluvial river based on data assimilation
ActiveCN108334660ASupport regulationGet water level in real timeClimate change adaptationForecastingFluvialLandform
The invention provide a water and sand prediction method and system for a strong alluvial river based on data assimilation. The method particularly comprises the steps of using terrain elevation scatter data obtained by sampling to generate an irregular triangular terrain grid unit; obtaining water-sand information and initial field information of strong alluvial river inlet and outlet boundaries;taking triangular elements of terrain grids as control bodies, discretizing a two-dimensional water-sand model of the strong alluvial river, selecting a solution method for calculation, and obtainingcalculated values of the control bodes; acquiring riverway water and sand state information of the strong alluvial river in real time, establishing a real-time prediction model based on the data assimilation according to the water and sand state information, and obtaining assimilation state variables and parameter variables; finally, using a two-dimensional water and sand data assimilation modelto conduct water and sand prediction on the strong alluvial river. Through the above treatment, the real-time status of water and sand of the strong alluvial river can be effectively predicted, so that water and sand regulation can be regulated, and a basis is provided for flood control and disaster alleviation, water environmental protection and water resource management.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Longitudinally flexible stent
InactiveUS20080215133A1Increased longitudinal flexibilityMinimize flareStentsEar treatmentMeanderIntravascular stent
An intravascular stent especially suited for implanting in curved arterial portion. The stent retains longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The stent is formed of intertwined meander patterns forming triangular cells. The cells are adapted to provide radial support, and also provide longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The cells also provide increase coverage of a vessel wall. The stent has a reduced crimped profile due to the differing lengths of adjacent structural members within the cells, resulting in loops which are not aligned around the circumference of the stent. Also, this stent may contain a second type of square cells, which are adapted predominately to minimize flaring of the stent ends and to provide additional stiffness.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Triangular mesh ray tracing global method of two-dimensional complex construction
ActiveCN101533102AHigh precisionImprove reliabilitySeismic signal processingWave fieldDirection information
The invention relates to a travel tomographic inversion of two-dimensional complex construction and a ray tracing method of wave field calculation based on Maslov ray theory. For two-dimensional complex external geometric boundary and complex space structure within domain, a medium is parameterized by using a triangle model with uniform slowness subblocks, and nodes are set on the boundary of a triangle unit. A traveling wave surface is used for replacing a wave front surface so that the expansion of the traveling wave surface and the transmission of the wave are transferred with the vibration of the triangle unit and the adjacent triangle unit, and can self-transfer backwards when encountering reverse branch without other shrinkage; the secondary source position of each node and the minimum travel time calculation are realized in the process of travel wave surface expansion; and the ray path from the receiving point to the source point is picked by using the travel time and direction information of each node secondary source and by means of the minimum travel time search. The calculation method is applied to any polygonal mesh.
Owner:CHANGJIANG GEOPHYSICAL EXPLORATION & TESTING WUHAN CO LTD
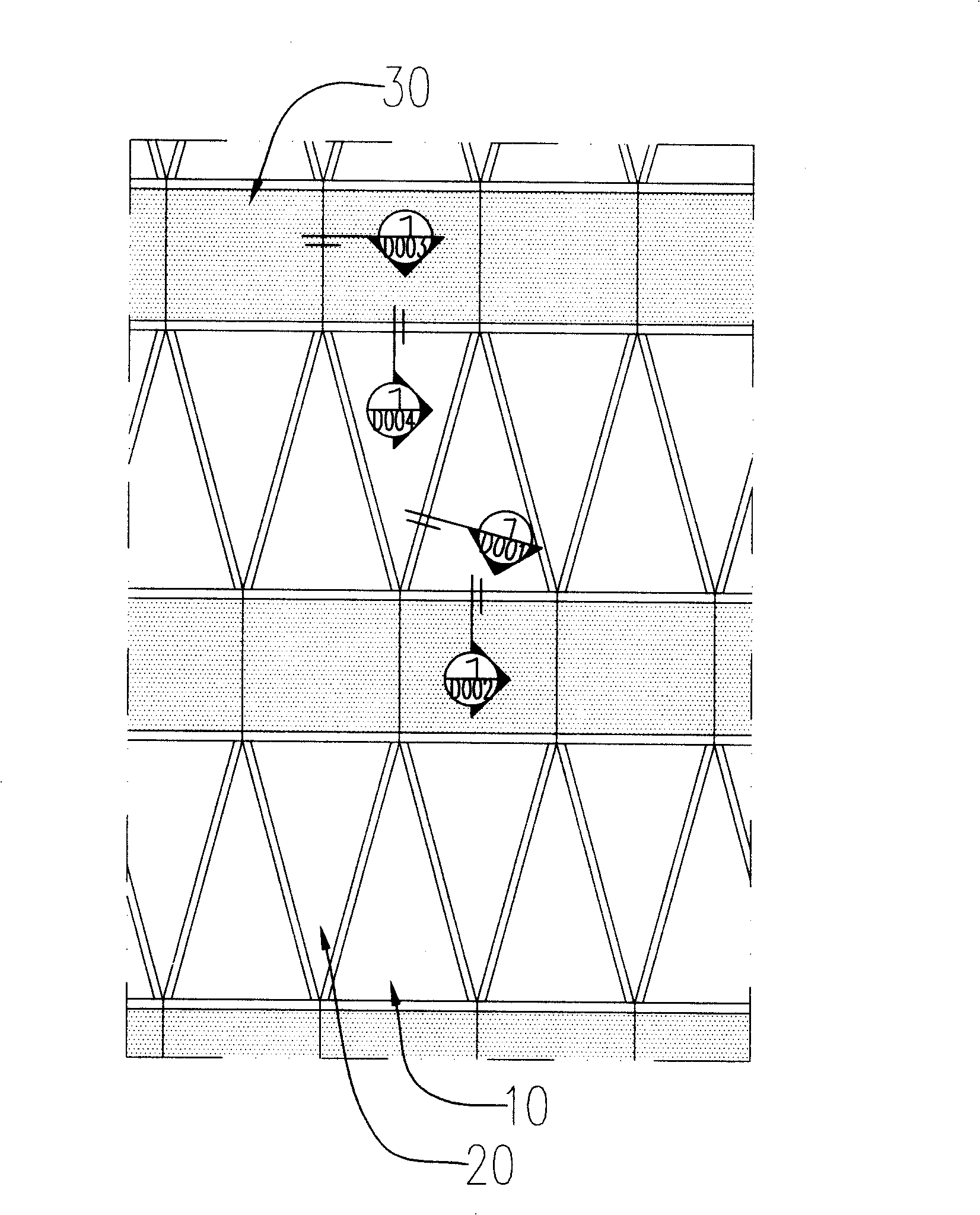
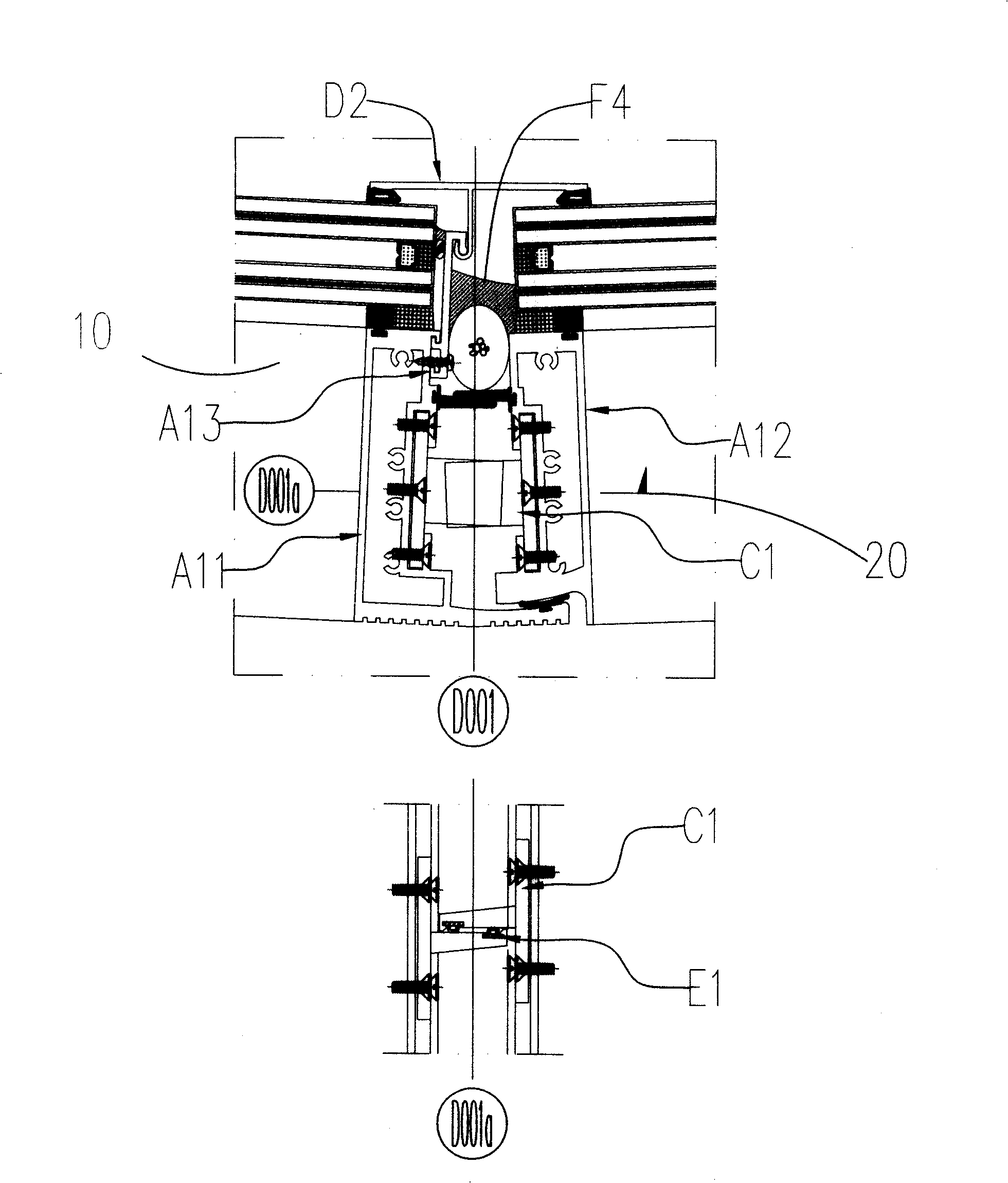
Double-trough curved surface unit type panel wall
A double trough curved surface unit type curtain wall comprises a tetragonal unit plate, a regular triangle unit plate and an inversed triangle unit plate, wherein, the adjacent tetragon unit plates are not coplanar. And with the structure, the regular triangle unit plate and the inversed triangle unit plate connect the interlaminar adjacent tetragonal unit plates to a whole curved surface. When the above structure is adopted, the curtain wall can get rid of the restraint of the coplanar board. A plurality of curtain wall units which are not coplanar can be connected together for forming the complicated anomalistic spacial curved surface curtain wall forms of spherical surface or other double curved surface and the like in order to realize the request of various forms of building.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINYUE CURTAIN WALL DECORATION ENG
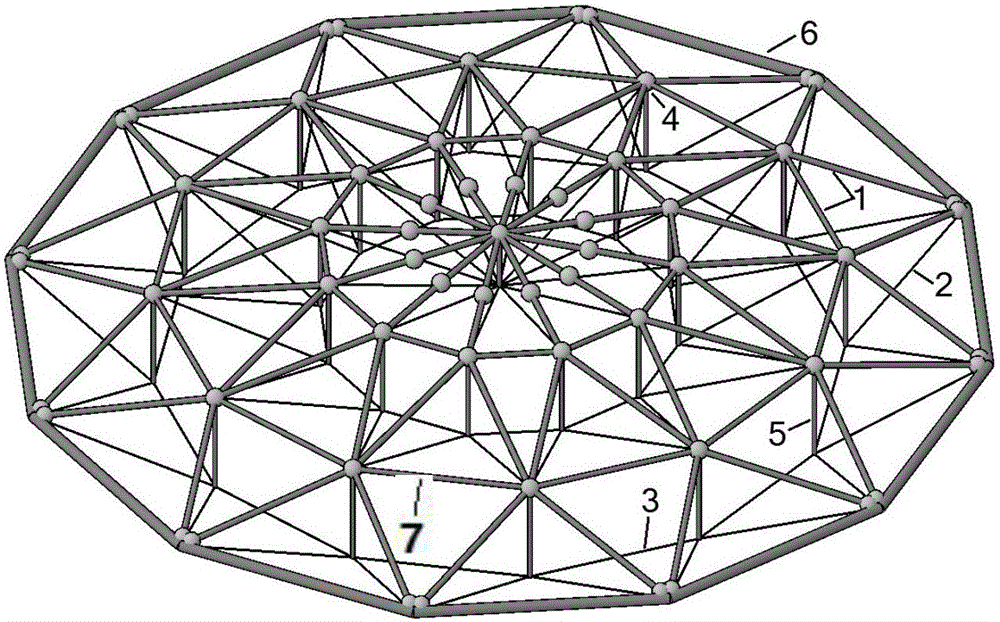
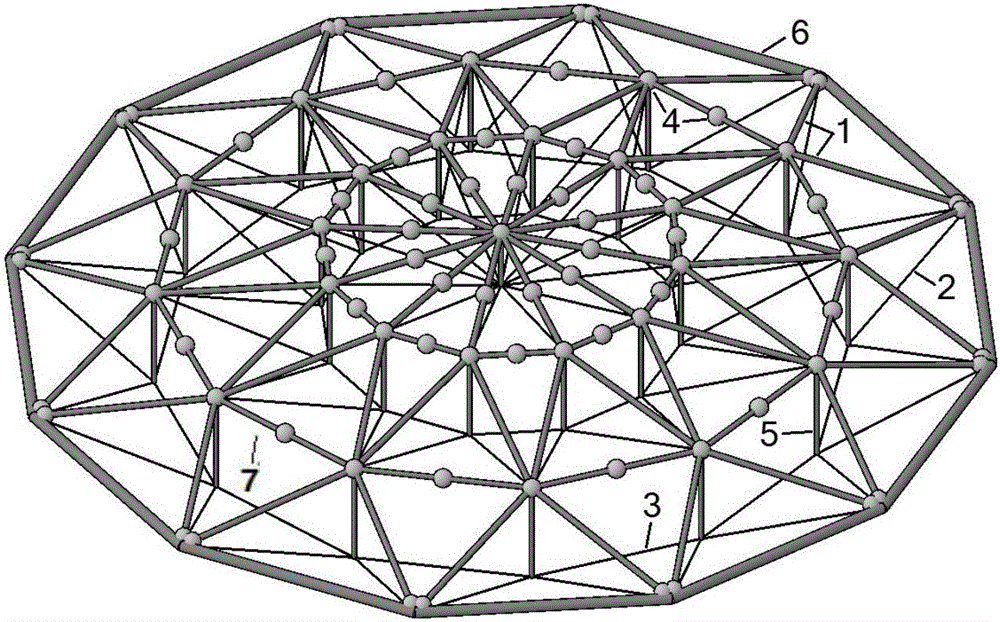
Straining beam cable rod dome structure and construction method thereof
InactiveCN105888065ASmall sizeReduce deflectionArched structuresVaulted structuresLow altitudeTriangular cell
The invention discloses a straining beam cable rod dome structure and a construction method of the straining beam cable rod dome structure. The straining beam cable rod dome structure comprises radial straining beams, circumferential straining beams, stay cables, pressing rods, annular cables, outer pressing rings and staining beam hinges, wherein different shapes and different sizes of triangular units are formed by the radial straining beams and the circumferential straining beams; the triangular units are connected to each other and share one edge to form a straining beam grid; connecting positions of the triangular units stretch downwards to form the pressing rods; each stay cable is connected with the lower ends of the pressing rods arranged at the inner sides of every two adjacent rings and the upper end of the pressing rod arranged at the outer side nearest to the stay cable, or is connected with the lower end of the pressing rod arranged at the outmost ring and the outer pressing rings; the annular cables are connected with the lower ends of the pressing rods in the same ring; the straining beam hinges are arranged at the end parts or the middle parts of the radial straining beams and the circumferential straining beams in the straining beam grid; the straining beam grid, the outer pressing rings, the pressing rods and the stay cables are mutually hinged. The invention also provides the construction method for low-altitude assembly and high-altitude tension forming. The invention provides a space tension structure for paving rigid roof materials, and construction is carried out by adopting an integrated pulling and lifting mechanism expansion method.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
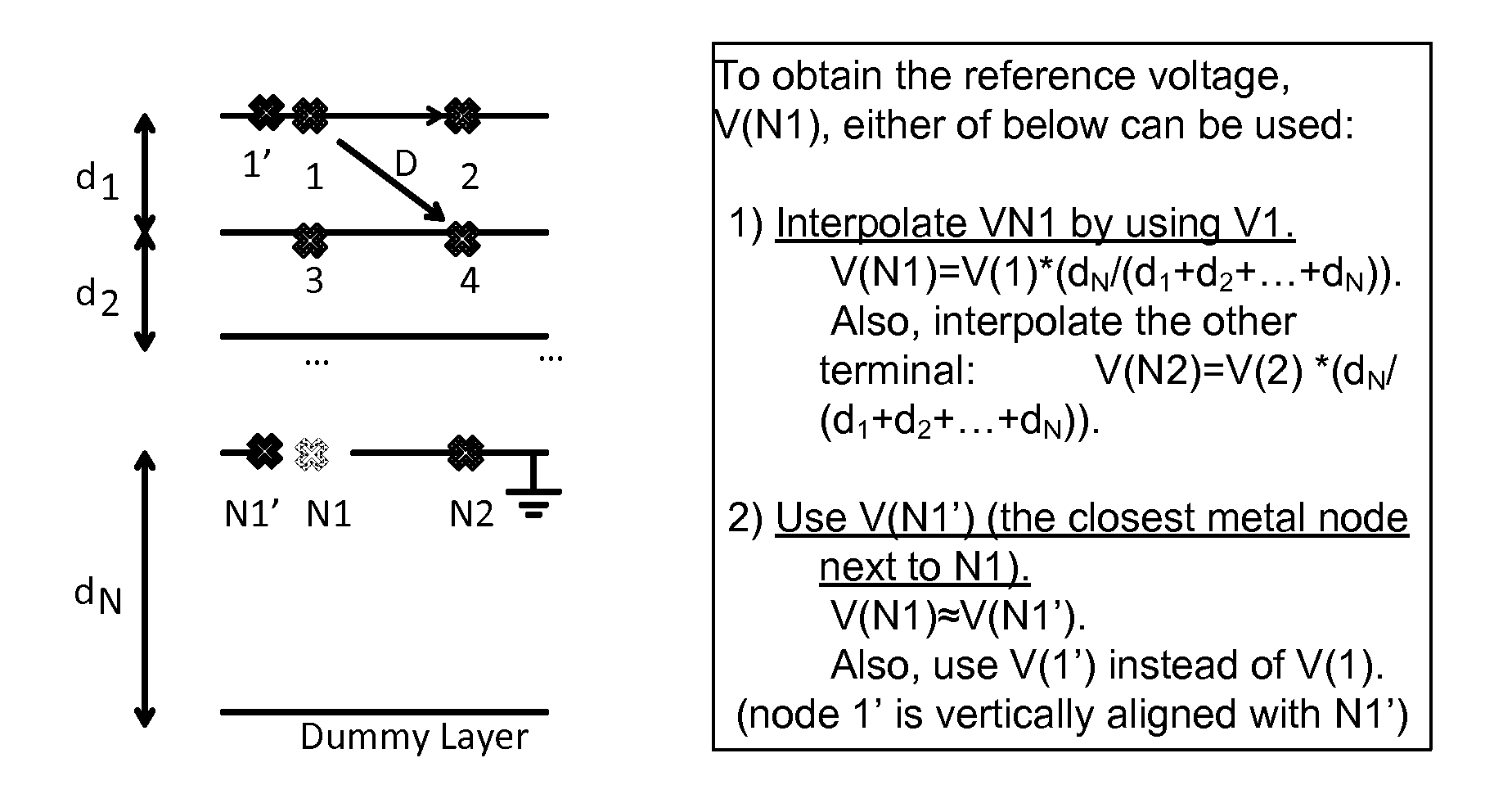
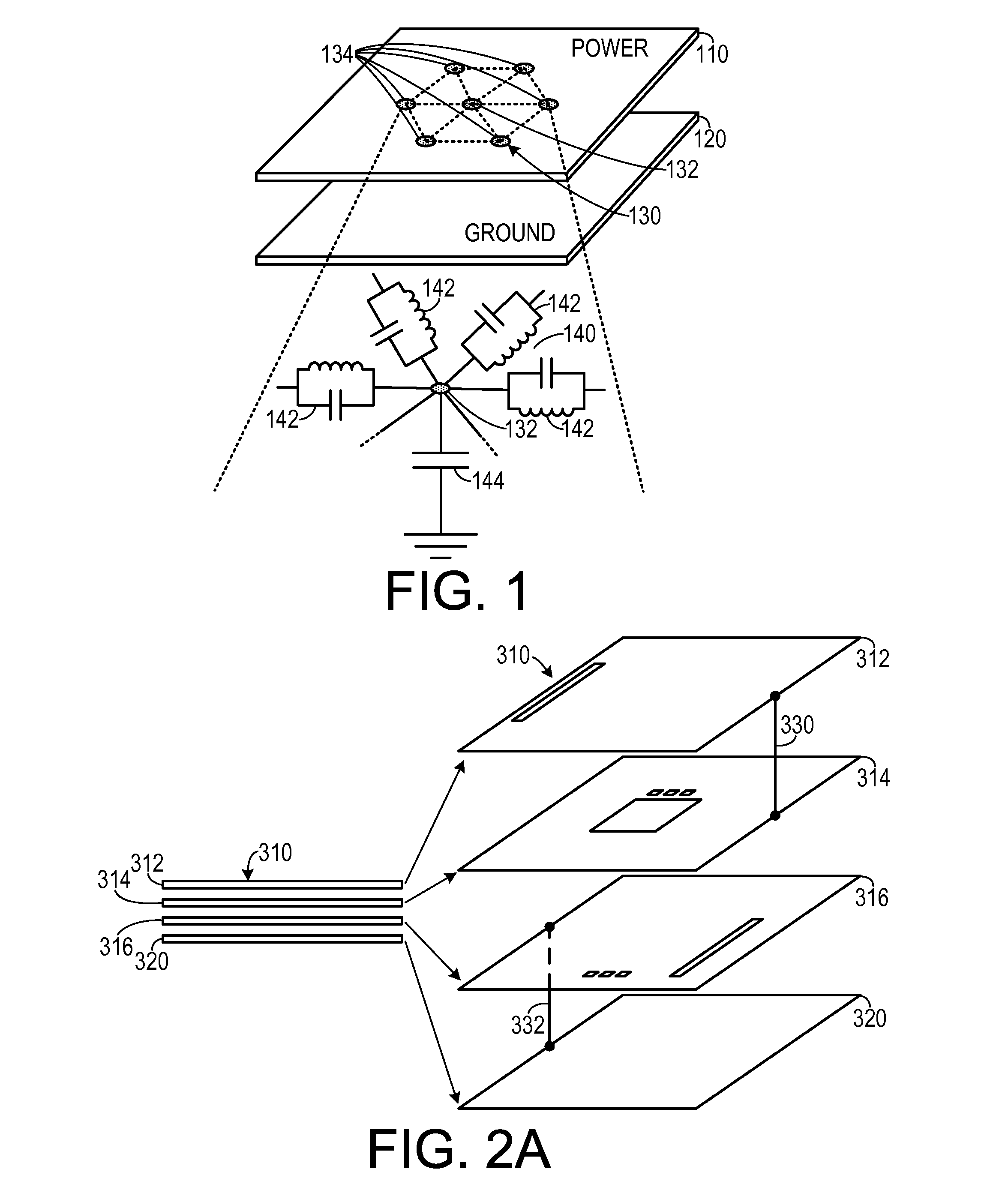
Modeling of Multi-Layered Power/Ground Planes using Triangle Elements
InactiveUS20120150523A1High densityLow densityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityGround plane
In a method of simulating electrical characteristics of a circuit board having a plurality of features, the plurality of features is projected onto a planar construct. A Delaunay triangulation routine for generating a triangular mesh that corresponds to the single planar construct is executed on the digital computer. A routine that generates a Voronoi diagram corresponding to the triangular mesh. An equivalent circuit for each triangle is determined. The equivalent circuit includes exactly three sub-circuits that couple a vertex within the triangle to a vertex within an adjacent triangle and exactly one sub-circuit that couples the vertex within the triangle to a reference plane. A routine solves, for each triangle, an equation describing an electrical characteristic value based on the equivalent circuit corresponding to the triangle. A routine for generating a human-perceptible indication of the electrical characteristic value for each triangle is executed on the digital computer.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Longitudinally flexible stent
InactiveUS20100100166A1Add supportIncreased longitudinal flexibilityStentsSurgeryMeanderInsertion stent
An intravascular stent especially suited for implanting in curved arterial portions. The stent retains longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The stent is formed of intertwined meander patterns forming triangular cells. The triangular cells are adapted to provide radial support, and also to provide longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The triangular cells provide increased coverage of a vessel wall. The stent can have different portions adapted to optimize radial support or to optimize longitudinal flexibility. Loops in the stent are disposed and adapted to cooperate so that after expansion of said stent within a curved lumen, the stent is curved and cells on the outside of the curve open in length, but narrow in width whereas cells on the inside of the curve shorten in length but thicken in width to maintain a density of stent element area which much more constant than otherwise between the inside and the outside of the curve. As a result, when the stent is coated with a medicine the more constant density of stent elements results in an even dose being applied to the inside wall of the lumen, avoiding the possibility that a toxic dose be supplied at one area while a less than effective dose is applied to another area.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Multi-claw space-extensible structure
InactiveCN104294914AEasy to transportEasy to rebuildBuilding constructionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a multi-claw space-extensible structure. The multi-claw space-extensible structure comprises a disc joint, six shear type assembly members, sliding groove guide rails, a rigid connection ring and enclosure rods. The disc joint is located in the center. The six shear type assembly members are symmetrically arranged around the disc joint. Each shear type assembly member is formed by hinging shear type units. Each shear type unit is composed of triangular units. Each triangular unit is formed by connecting three rods end to end. Every two triangular units are hinged mutually at the obtuse angle apex to form the corresponding shear type unit. Every three shear type units are connected vertically to form the corresponding shear type assembly member. A wheel is installed at one end of each shear type assembly member. A hexagon structure is formed by the enclosure rods in an enclosure mode. The rigid connection ring is arranged in the center of the hexagon structure composed of the enclosure rods. The sliding groove guide rails are arranged between the rigid connection ring and six corners of the enclosure rods. The wheels can move back and forth in the sliding groove guide rails. The multi-claw space-extensible structure can be quickly installed anywhere to build a large and stable usage space. The multi-claw space-extensible structure is folded into a small size after being used, and can be detached into rods to be transported and reused. The constituent basic rods are the same, so that mass production is convenient.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Simulation method for rapidly extracting transient scattered signals of electric large-size metal cavity target
ActiveCN104731996AAccurate descriptionTrue discrete fitSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorDissection
The invention discloses a simulation method for rapidly extracting transient scattered signals of an electric large-size metal cavity target. The simulation method includes creating a geometric model of the metal cavity target, and performing mesh dissection on the surface of the metal cavity target by a curved-surface triangular unit; determining a time domain integral equation of the metal cavity target; unfolding a surface induced current in the time domain integral equation by a high-order lamination divergence conformal basis function in terms of space and a time and space-time hybrid basis function in terms of time; substituting a surface induced current expression into the time domain integral equation, and testing a time domain electric field integral equation in a discrete form in terms of time and space respectively to acquire a system impedance matrix equation; solving the impedance matrix equation by a time stepping method, determining time domain current distribution on the surface of the conductor target, and acquiring broadband electromagnetic characteristic parameters of the target according to time domain current distribution to complete simulation. The method has the advantages of high simulation accuracy, less time used and low memory consumption, thereby having a broad application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Double platform filling structure with double protection
InactiveCN110645298AAchieve double protectionImprove energy absorptionSpringsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementMicrocellMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a double platform filling structure with double protection. The double platform filling structure with double protection comprises at least four microcells. Each microcell is formed by combining two symmetrical concave triangular cell bodies. Each concave triangular cell body comprises a first energy absorbing part and a second absorbing parts same in structure. The top ends of the first energy absorbing part and the second absorbing part are connected through a connecting block. The first energy absorbing part comprises an upper horizontal connecting part, a first energy absorbing portion, a second energy absorbing portion, a force transfer portion, a third energy absorbing portion and a lower horizontal connecting portion. The microcells are successively arrangedand combined in X direction and Y direction and an octagonal energy absorbing area is formed between adjacent two microcells. The filling structure can be used for achieving bidirectional protection functions of human and an automobile by means of the octagonal energy absorbing areas.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
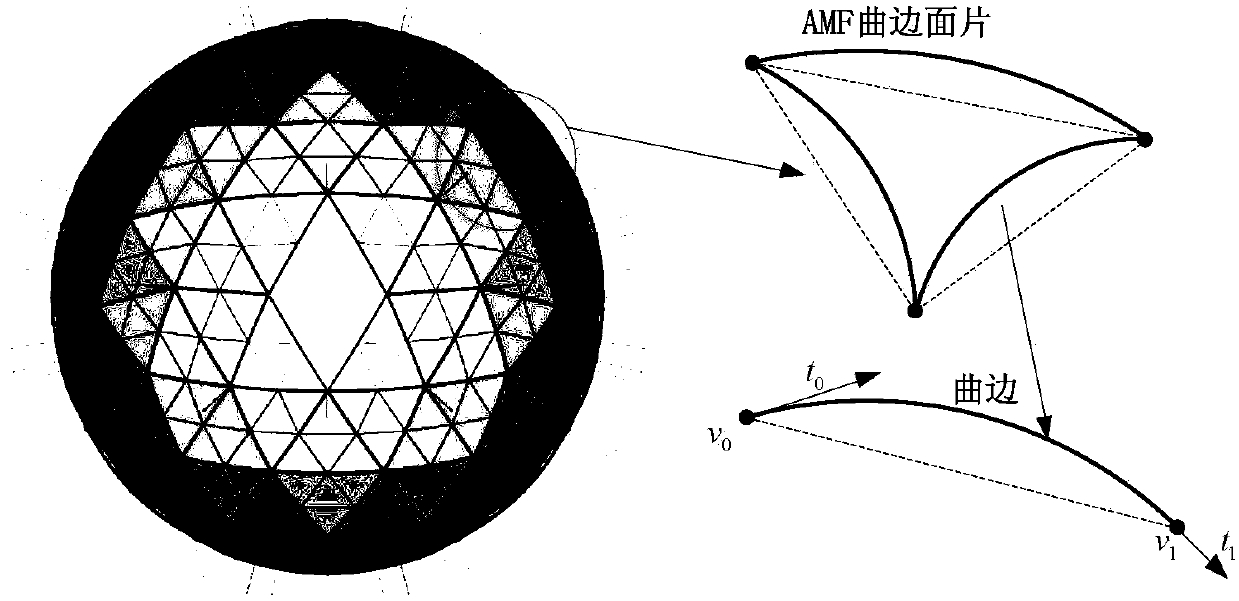
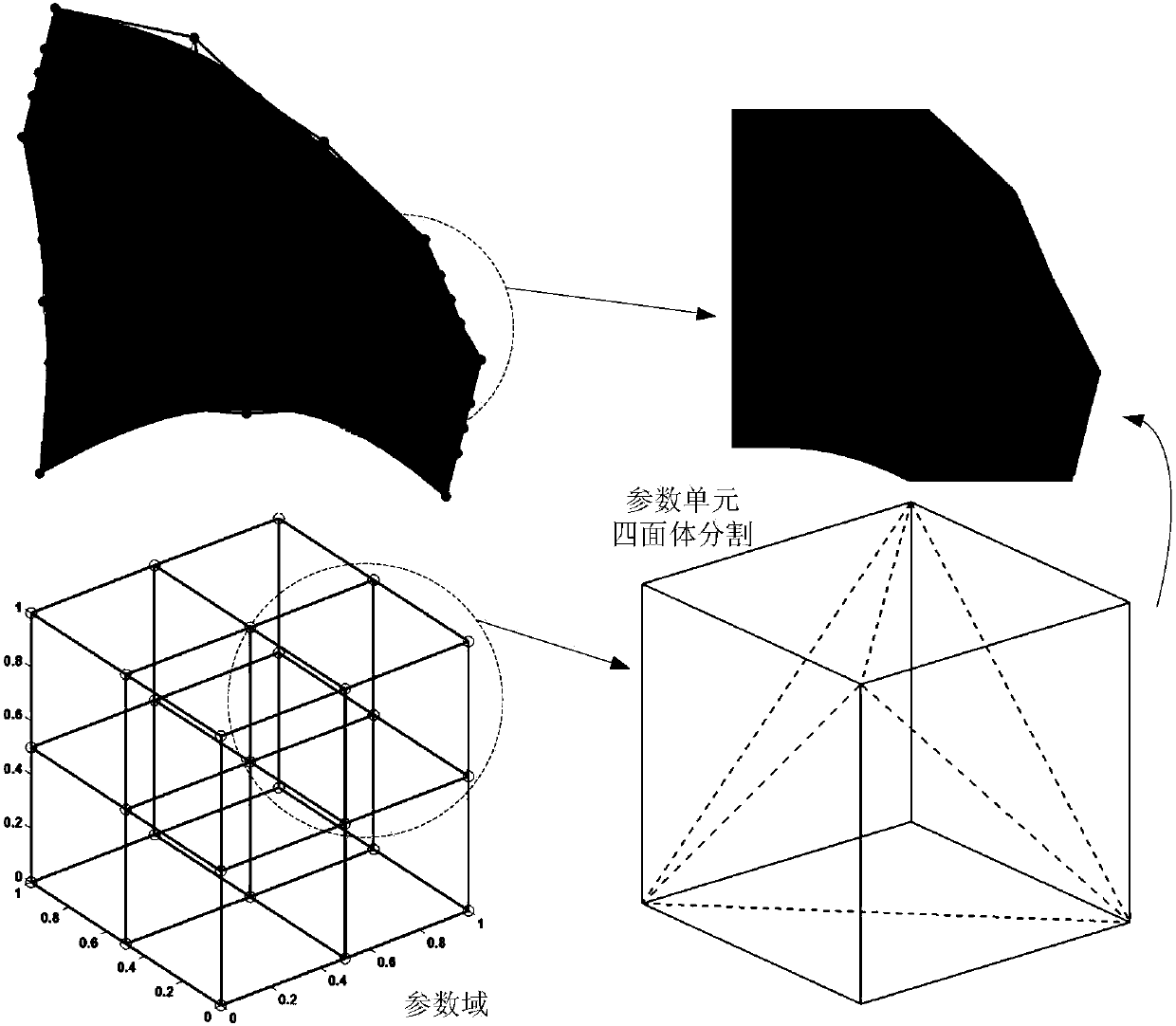
Method for converting gradient material models into additive manufacturing data formats
ActiveCN106777477AImprove efficiencyHigh precision transferGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusNODALGradient material
The invention relates to a method for converting gradient material models into additive manufacturing data formats. The method includes carrying out tetrahedron or triangle patch division on parameter domains; acquiring curve-edge tetrahedron and triangle units adaptable to AMF (additive manufacturing formats) by the aid of mapping relations; reading information of corresponding materials, colors and the like at grid nodes; writing the information into AMF files according to standard formats; organizing acquired curve-edge mesh units and other acquired information in the form of XML (extensive markup language) documents and completely carrying out transmission between the gradient material models and the additive manufacturing format files.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for connecting and installing unit curtain walls
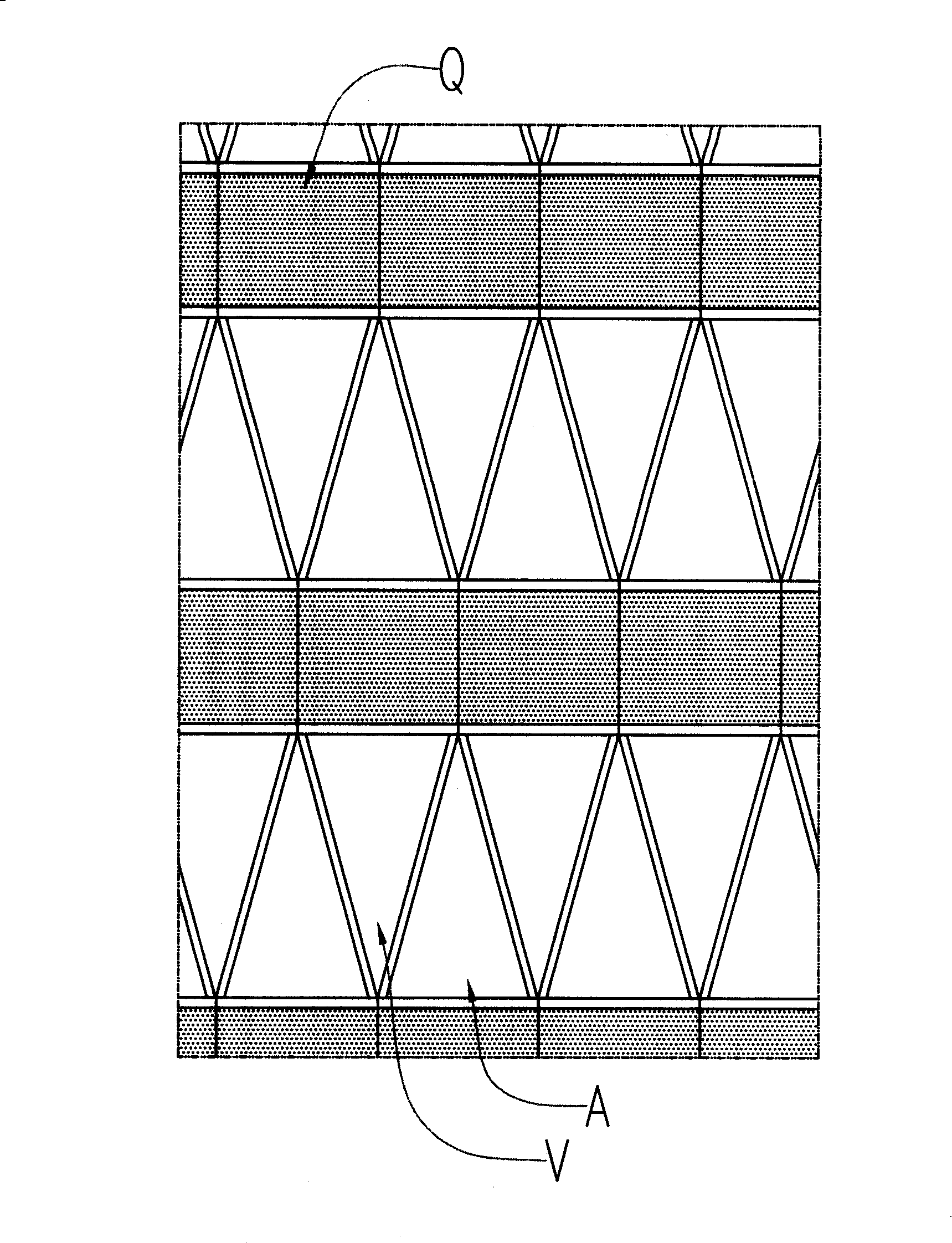
The invention relates to a connecting and installing method of a unit curtain wall, which comprises the procedures that: a floor unit Q is hinged with a body structure in four points, which forms a banding pattern curtain wall supporting system, as same as a secondary supporting system attached to the body structure; an interlayer regular triangle unit plate A is arranged temporarily between the floor units Q, and forms a third supporting system with the floor unit Q; an interlayer inverted triangle unit plate V is arranged in the triangle opening formed by the floor unit Q and the regular triangle unit plate A, which forms a whole curtain wall system. The connecting and installing method of a unit curtain wall has the advantages of taking every floor as an independent work section, finishing installing curtain wall via the space in room, improving control ability of the time limit for a project, and adapting to more complex space curved surface.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINYUE CURTAIN WALL DECORATION ENG
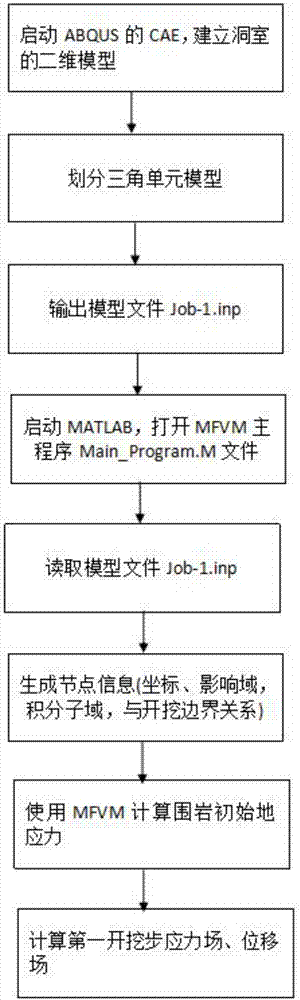
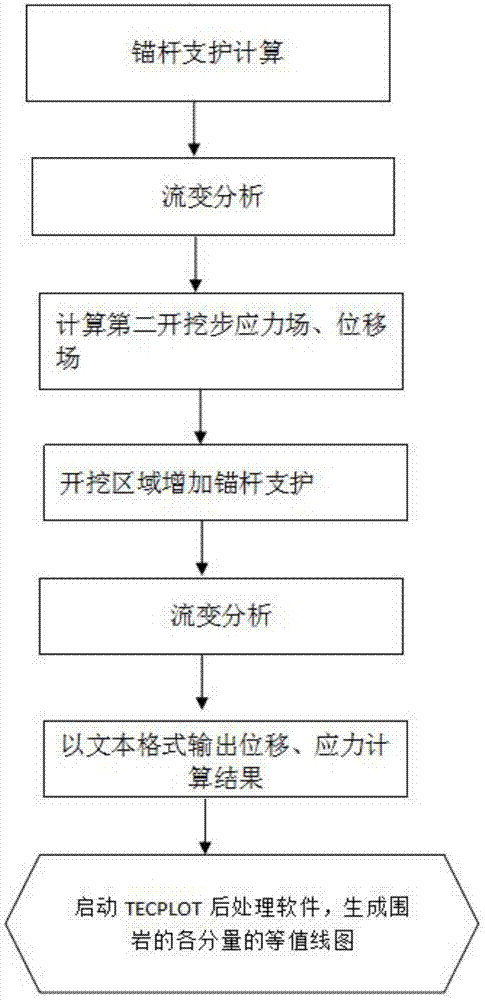
Meshless method for analyzing excavation and support of tunnel
InactiveCN107391820AAdaptableEasy to analyzeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALApproximation function
The invention relates to the technical field of tunnels, in particular to a meshless method for analyzing excavation and support of a tunnel. The method comprises the following steps of (1) starting CAE of ABQUS, and establishing a two-dimensional model of a chamber; (2) dividing a triangular cell model; (3) outputting a model file, Job-1. Inp; (4) starting MATLAB, opening a main program file, Main_Program. M, of MFVM; (5) reading the model file, Job-1. inp; (6) generating node information; (7) using the MFVM to calculate the initial ground stress of surrounding rocks; (8) calculating a stress field and a displacement field in the first step of the excavation. The method has the advantages that since an approximation function of the meshless method has no dependence on meshes, the difficulty caused by grid distortion is reduced, interface connection with CAD software can be achieved more easily, and the method is suitable for solving large-scale scientific and engineering problems; besides, since the adaptability of the meshless method is very strong, node position information rather than mesh information is needed in the pretreatment of the meshless method, and a complex three-dimensional structure can be analyzed easily; moreover, an obtained graph of meshless calculation is smooth and continuous, so no stress smoothing is needed.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
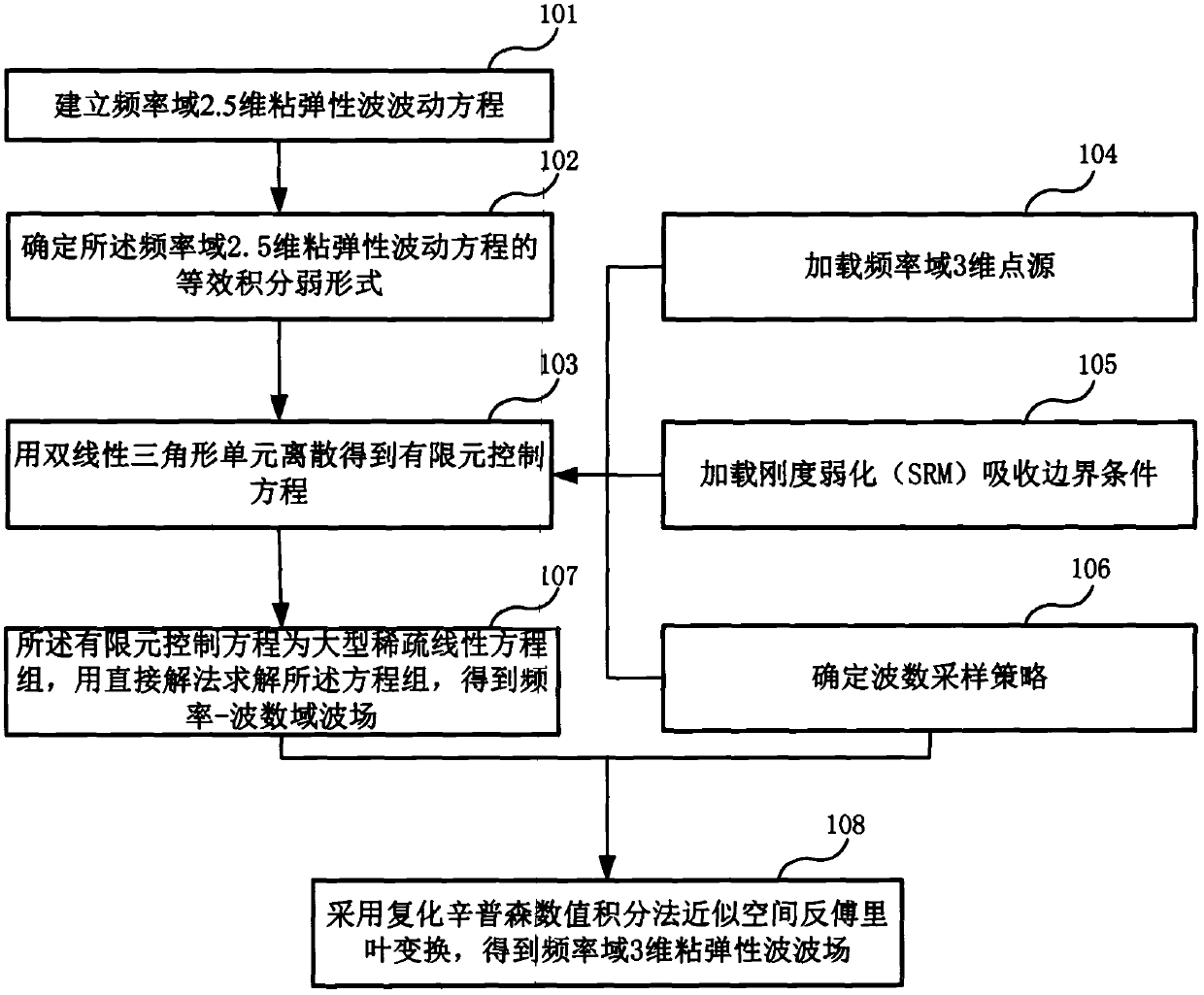
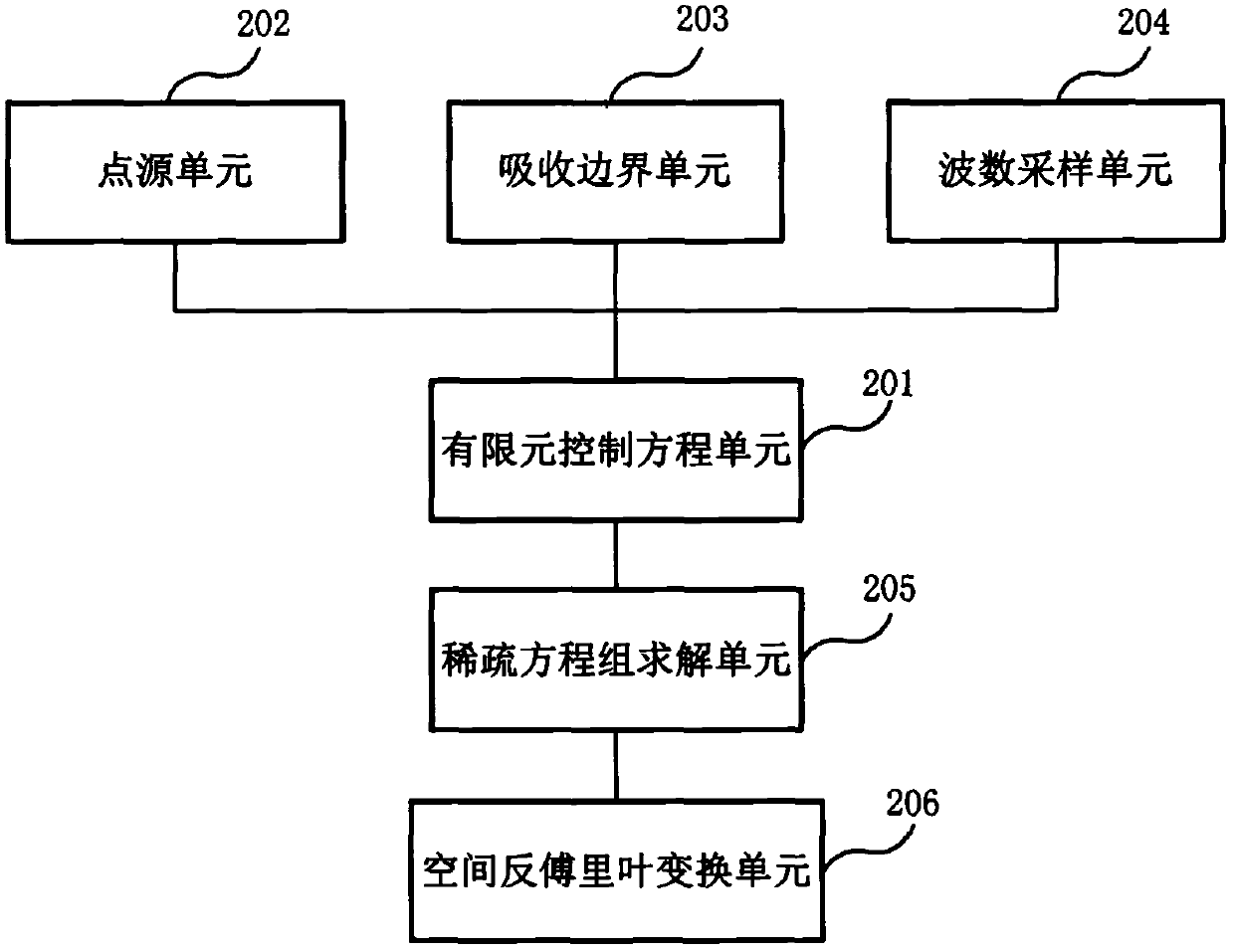
2.5-dimensional viscoelastic wave numerical simulation method and apparatus in frequency domain
InactiveCN107798156ANot affected by positive definitenessSimple loading processDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWave equationWave field
Embodiments of the present invention provide a 2.5-dimensional viscoelastic wave numerical simulation method and apparatus in the frequency domain. The method comprises: establishing a 2.5-dimensionalviscoelastic wave equation in the frequency domain; determining an equivalent integral weak form of the 2.5-dimensional viscoelastic wave equation in the frequency domain; obtaining a finite elementcontrol equation by using the discrete of bilinear triangular elements; loading 3D point sources in the frequency domain; loading the stiffness to weaken the absorption boundary condition; determininga wavenumber sampling strategy, wherein the finite element control equation is large sparse linear equations, and a direct solution method is used to solve the equations to obtain a frequency-wavenumber domain wave field; and using a complex Simpson numerical integration method to approximate the spatial inverse Fourier transform to obtain a three-dimensional viscoelastic wave field in the frequency domain. The present invention provides an accurate forward modeling method for 2.5-dimensional viscoelastic wave multi-scale full waveform inversion, and the method can adapt to any undulating surface complex medium, has a good absorption effect of the absorption boundary condition, and has high calculation efficiency.
Owner:赵建国 +2
Longitudinally flexible stent
InactiveUS20110022156A1Add supportIncreased longitudinal flexibilityStentsEar treatmentMeanderInsertion stent
An intravascular stent especially suited for implanting in curved arterial portions. The stent retains longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The stent is formed of intertwined meander patterns forming triangular cells. The triangular cells are adapted to provide radial support, and also to provide longitudinal flexibility after expansion. The triangular cells provide increased coverage of a vessel wall. The stent can have different portions adapted to optimize radial support or to optimize longitudinal flexibility. Loops in the stent are disposed and adapted to cooperate so that after expansion of said stent within a curved lumen, the stent is curved and cells on the outside of the curve open in length, but narrow in width whereas cells on the inside of the curve shorten in length but thicken in width to maintain a density of stent element area which much more constant than otherwise between the inside and the outside of the curve. As a result, when the stent is coated with a medicine the more constant density of stent elements results in an even dose being applied to the inside wall of the lumen, avoiding the possibility that a toxic dose be supplied at one area while a less than effective dose is applied to another area.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
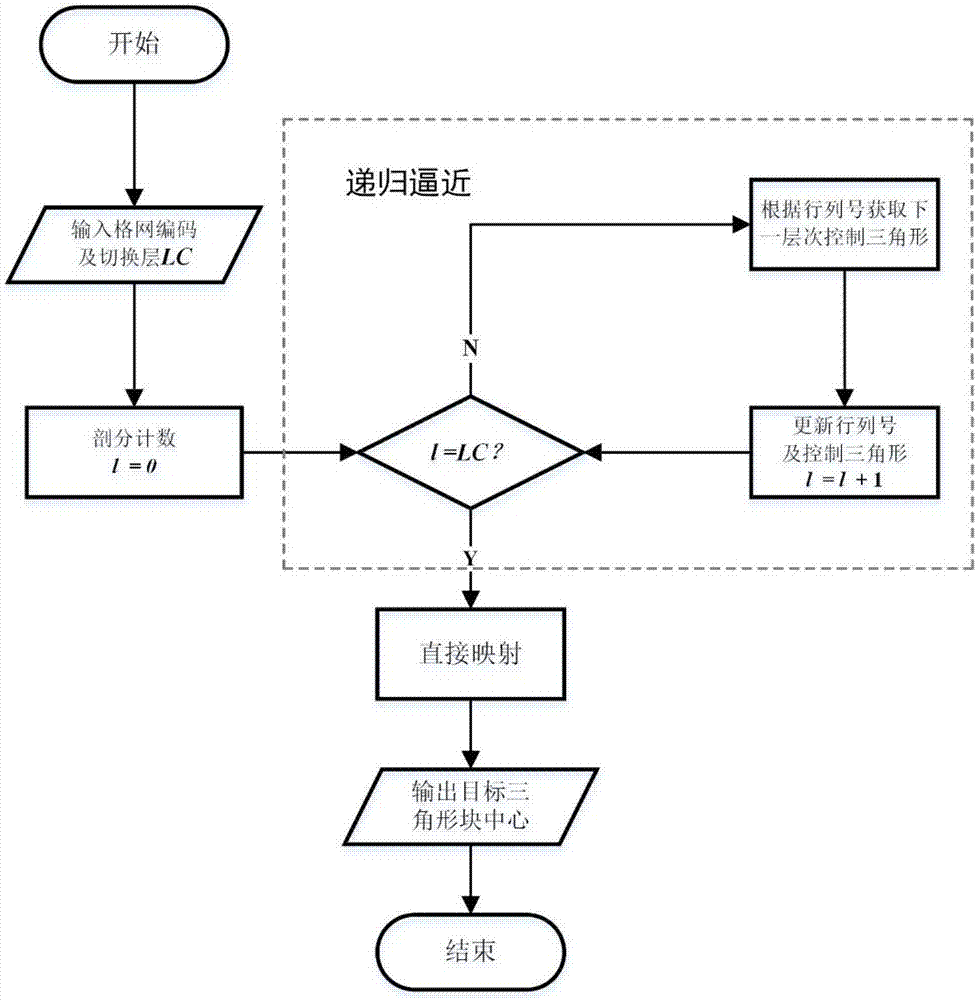
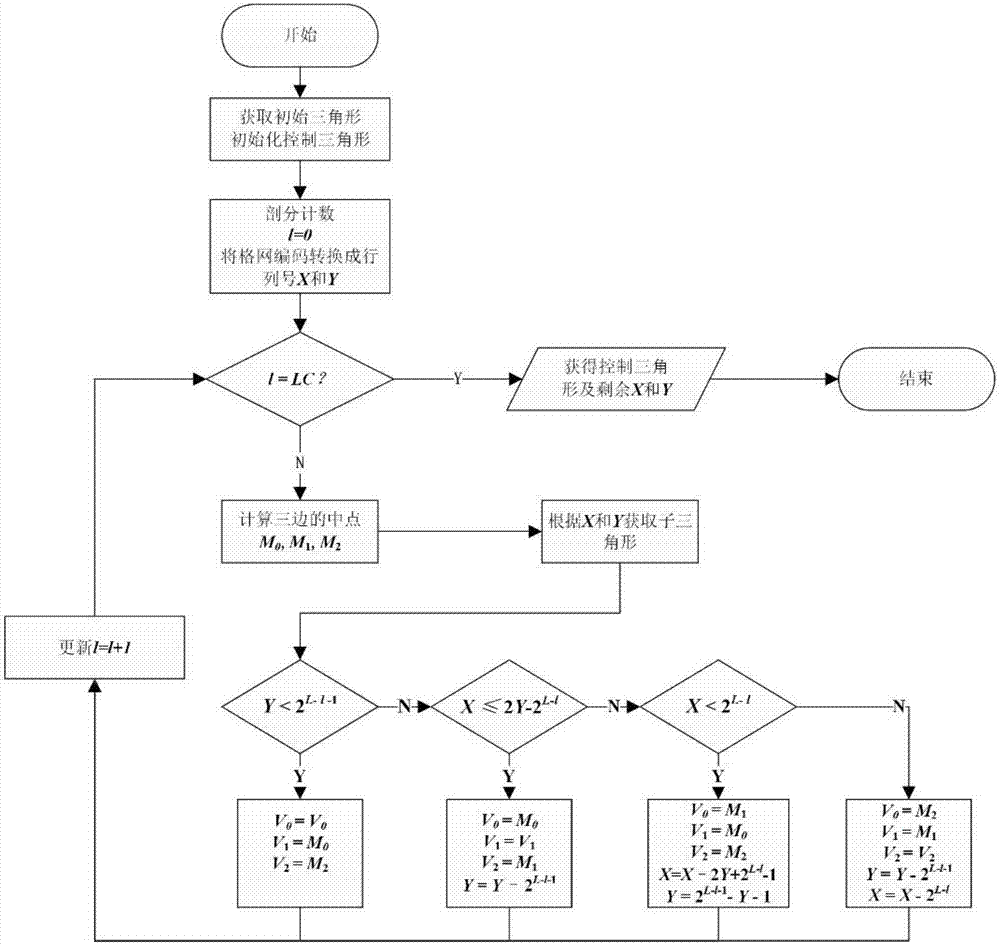
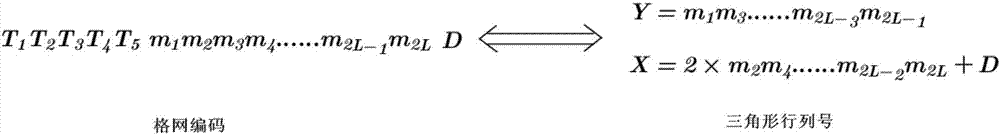
Method for rapidly converting spherical triangle discretization grid codes into geographic longitude and latitude coordinates
ActiveCN107273466AGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsLinear growthRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses a method for rapidly converting spherical triangle discretization grid codes into geographic longitude and latitude coordinates. The method comprises the following steps of inputting grid codes, and converting the grid codes into rank numbers; according to dissection layers of the codes, determining a control dissection layer; in a stage lower than the control dissection layer, adopting a recursive approaching method for determining a control triangular unit corresponding to the grid codes on the control dissection layer and the rank number of the target code cell inside the control triangle; when the control dissection layer is converted, adopting a direct mapping method for directly dividing the control triangle into grids in a halving mode, and then finding a target triangular cell according to the rank number inside the control triangle; calculating coordinates of the central point of the target triangular cell, converting the rectangular coordinates into longitude and latitude coordinates, and outputting the coordinates to complete conversion. The efficiency of converting spherical triangle discretization grid codes into geographic longitude and latitude coordinates can be obviously improved, and the algorithm time complexity is increased along with the dissection layers and increased linearly.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
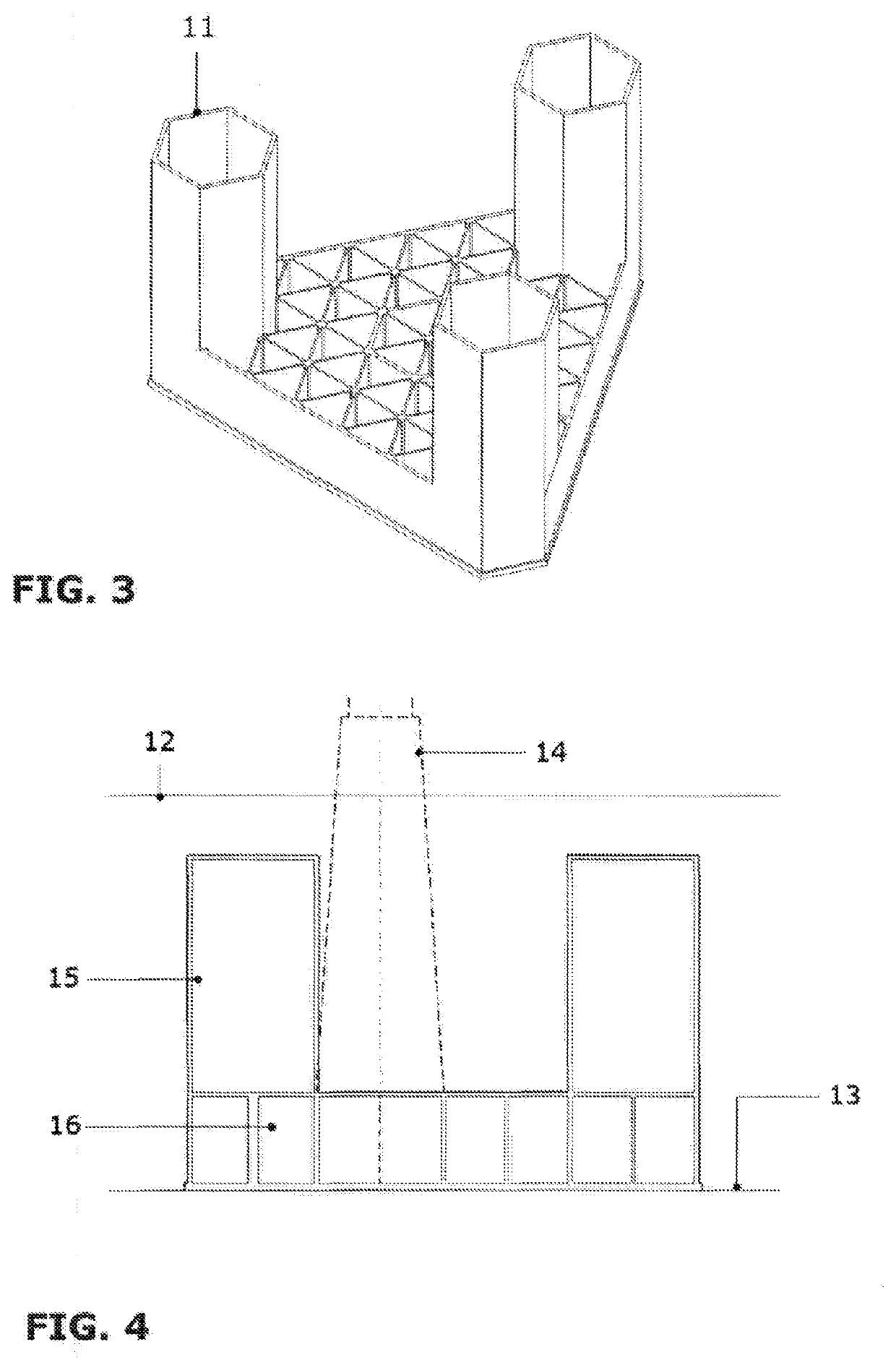
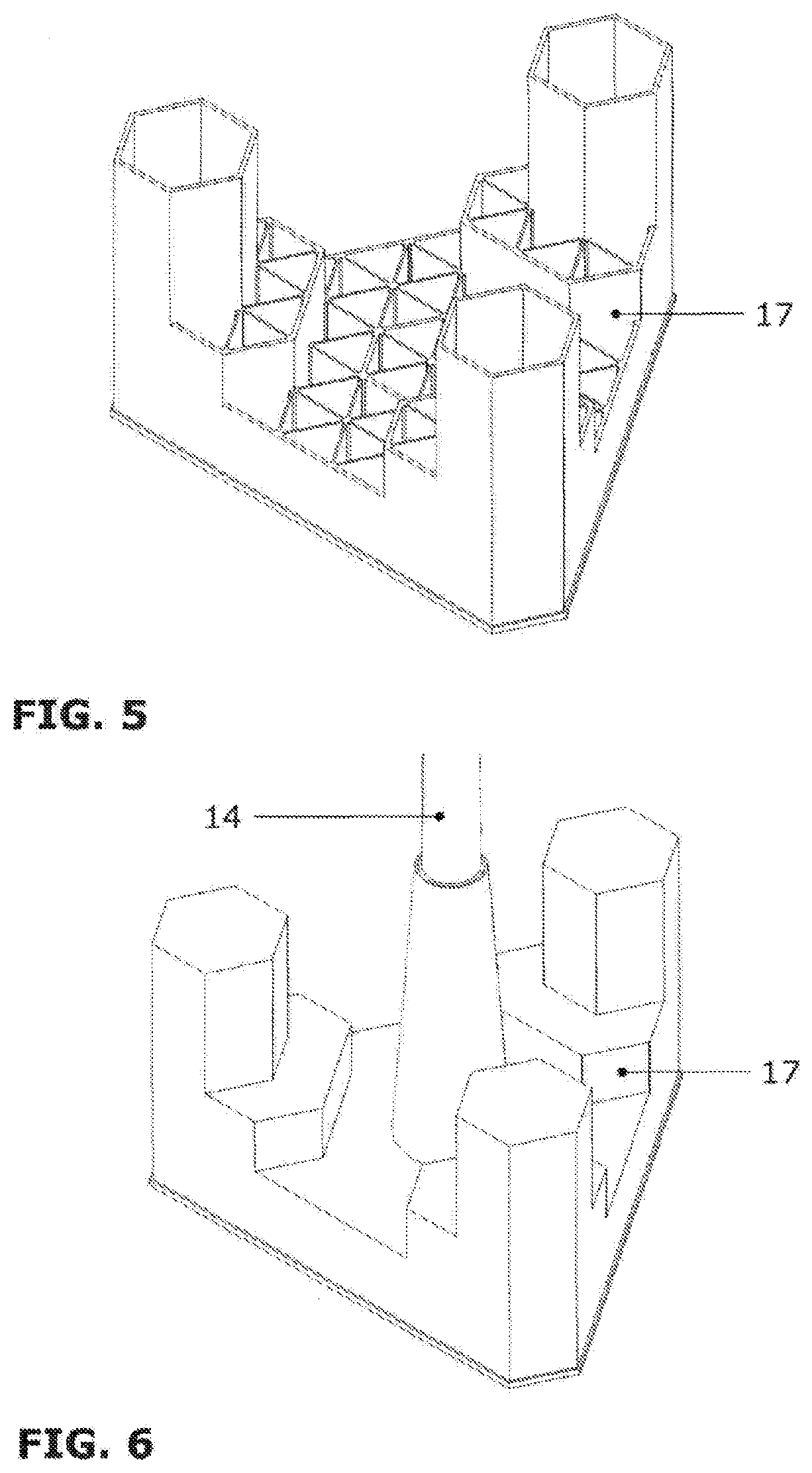
Maritime structure for laying the foundations of buildings, installations and wind turbines by means of gravity in a marine environment
ActiveUS20200032473A1Solve insufficient capacityAvoid the needArtificial islandsWind motor assemblyShip stabilityTower
The invention relates to a maritime structure for laying the foundations of buildings, installations or wind turbines by means of gravity in a marine environment, which has significant advantages for constructing, transporting, positioning and operating same, owing to the novel features introduced into the design thereof in comparison with existing types. The structure comprises a base in the shape of a chamfered equilateral triangle, having a sufficient height to optimise navigability, the base being formed by a frame of vertical walls that form hexagonal or triangular cells closed at the ends by a lower slab and an upper slab, and three closed towers having a regular hexagonal or circular cross section which are located in the corners of the base. The structure can be towed, completely installed, with a wind turbine or superstructure that same supports, and has low initial draft, high naval stability and low resistance to movement. The anchoring process is performed by using gravity to ballast the cells with seawater, without needing any additional means, auxiliary large-capacity vessels or floating elements external to the structure itself. The structure can be positioned as a gravity foundation at a depth of 20 to 50 meters and can be re-floated to be transferred whole again to a port for dismantling.
Owner:BERIDI MARITIME SL
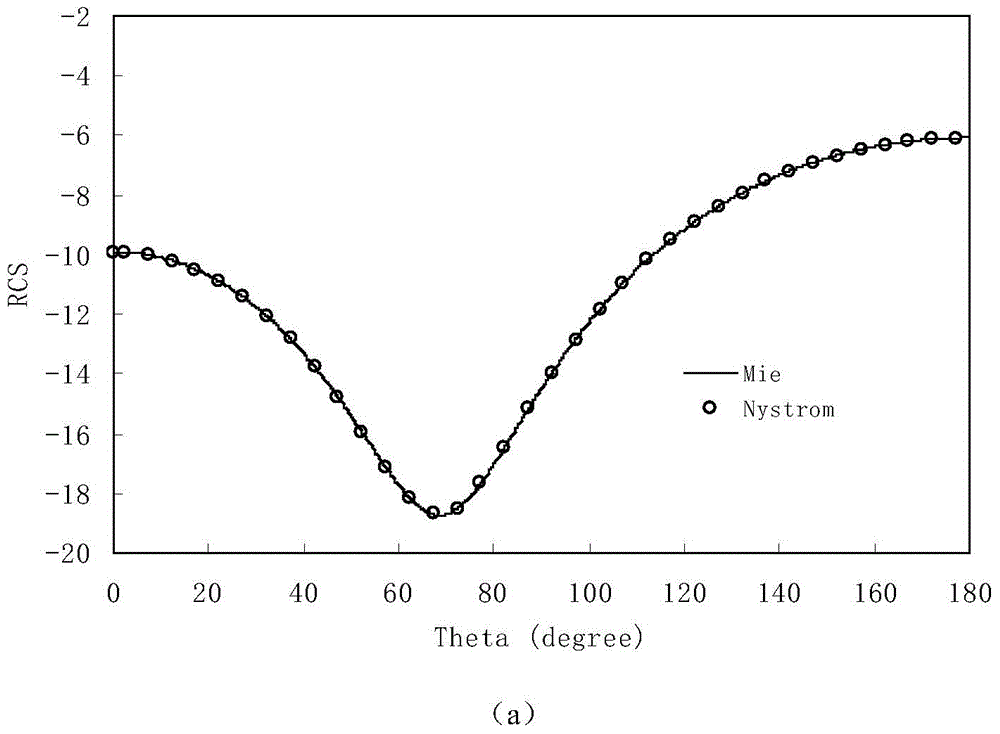
Time-domain high-order Nystrom method for analyzing transient electromagnetic scattering property of conductor
InactiveCN105224780ASpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorTime domain integral equation
The invention discloses a time-domain high-order Nystrom method for analyzing a transient electromagnetic scattering property of a conductor. The method comprises: establishing a conductor surface time-domain integral equation; performing time discretization on the conductor surface time-domain integral equation by adopting a triangular basis function, and performing spatial discretization by adopting a two-order curved surface triangular unit; forming a to-be-solved matrix equation by adopting a Galerkin test in time and point matching in space, wherein an unknown current is a transient surface current of the conductor; and solving the matrix equation to obtain a transient surface current coefficient of the conductor, and calculating a transient electromagnetic scattering parameter by the current coefficient according to a reciprocal theory. Compared to a conventional RWG basis function based time domain integral equation method, the time-domain high-order Nystrom method has the advantage of robustness of a discrete grid.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com