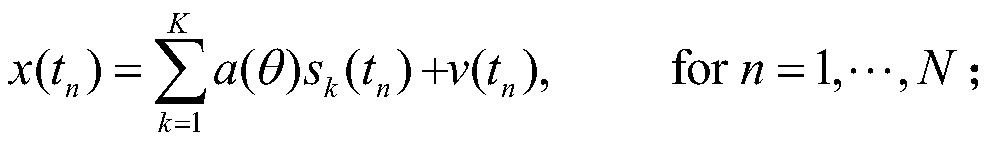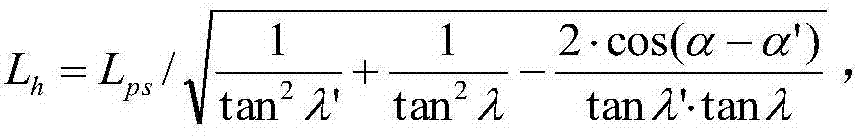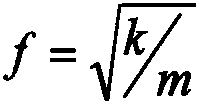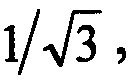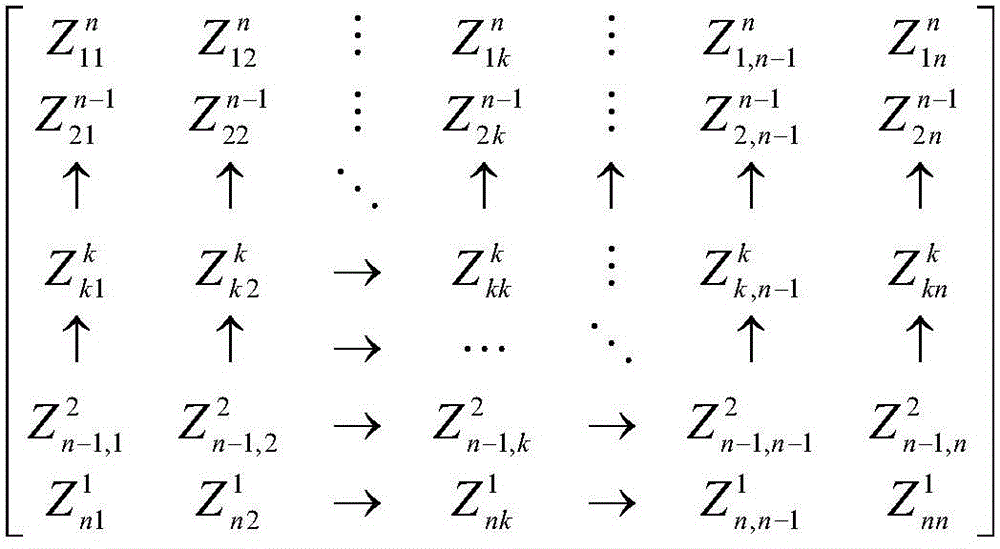Patents
Literature
72 results about "Triangular element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
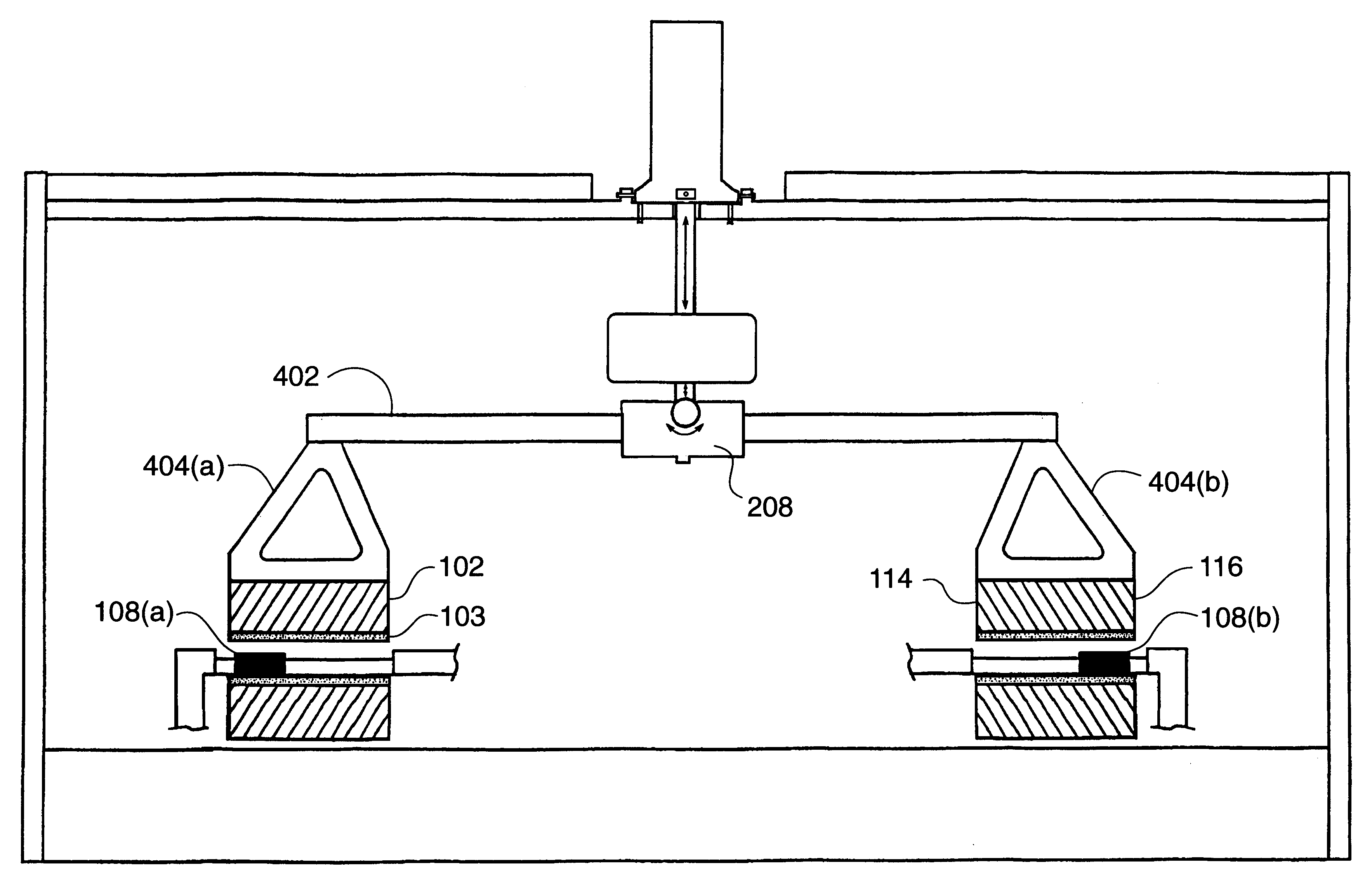
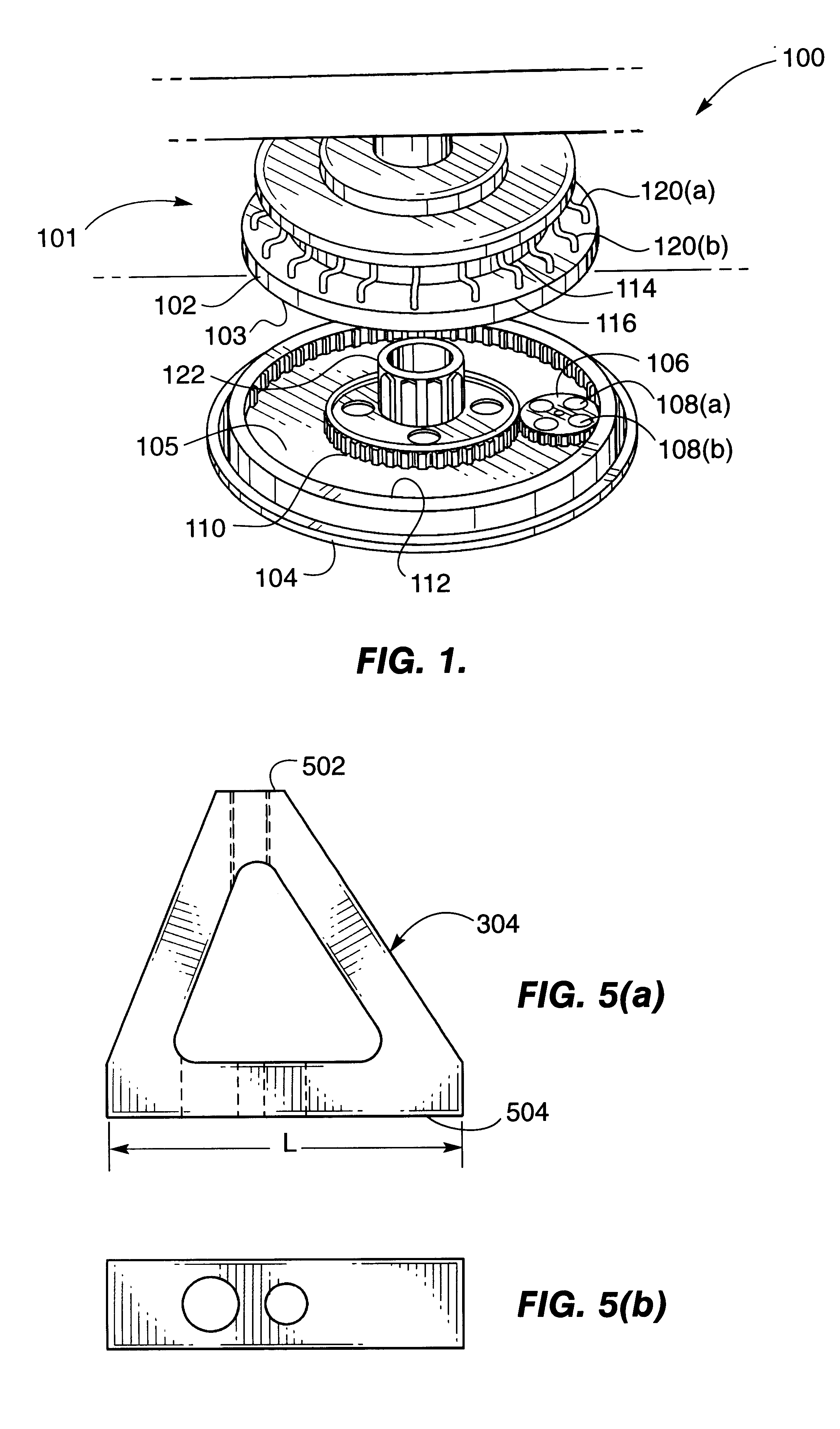
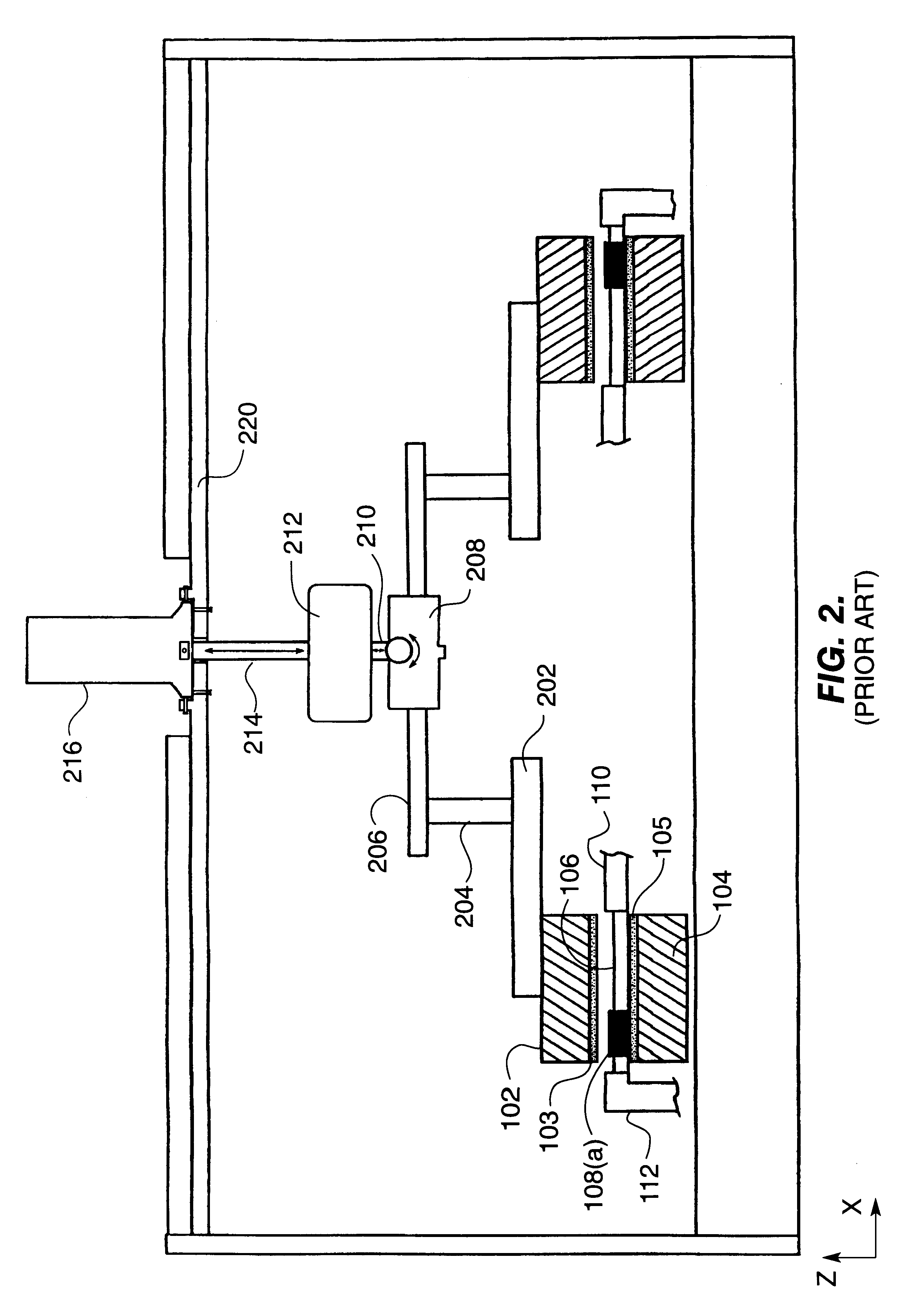
Apparatus for polishing using improved plate supports
InactiveUS6168506B1Reduce stress changesConstantEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesRadial stressEngineering
A set of supports are advantageously disposed on a top plate having a polishing surface useful for polishing workpieces, thereby applying substantially uniform pressure to the top plate. In a preferred embodiment, the supports are non-isosceles triangular elements distributed evenly at 45 degree increments around a ring-shaped top plate. This structure effectively compensates for radial stress variations arising from non-optimum positioning of support points with respect to the inner and outer diameters of the polishing surface.
Owner:SPEEDFAM IPEC
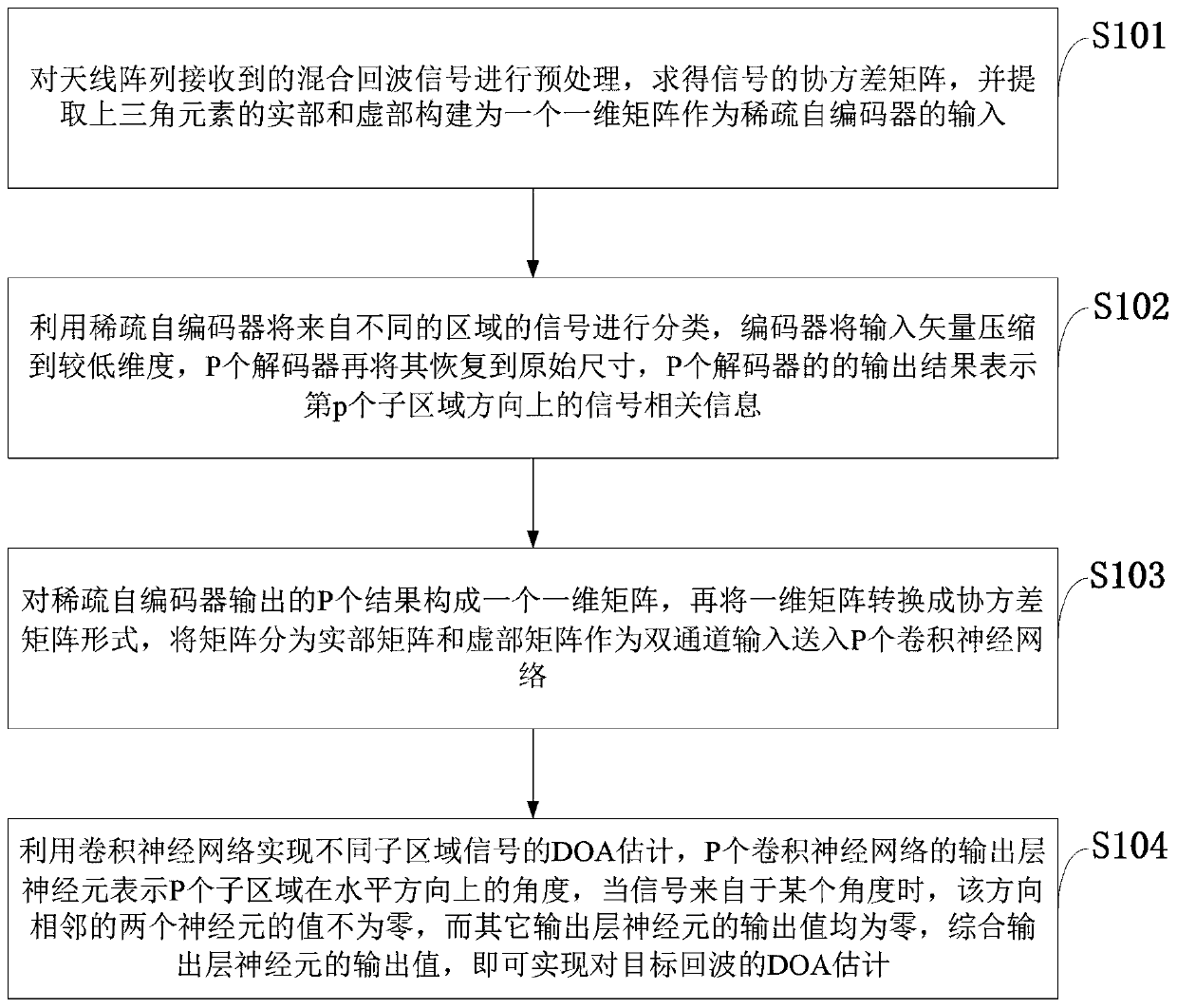
DOA estimation method for moving target echoes under multiple external radiation sources
InactiveCN110967665ARadio wave finder detailsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAlgorithmAutoencoder
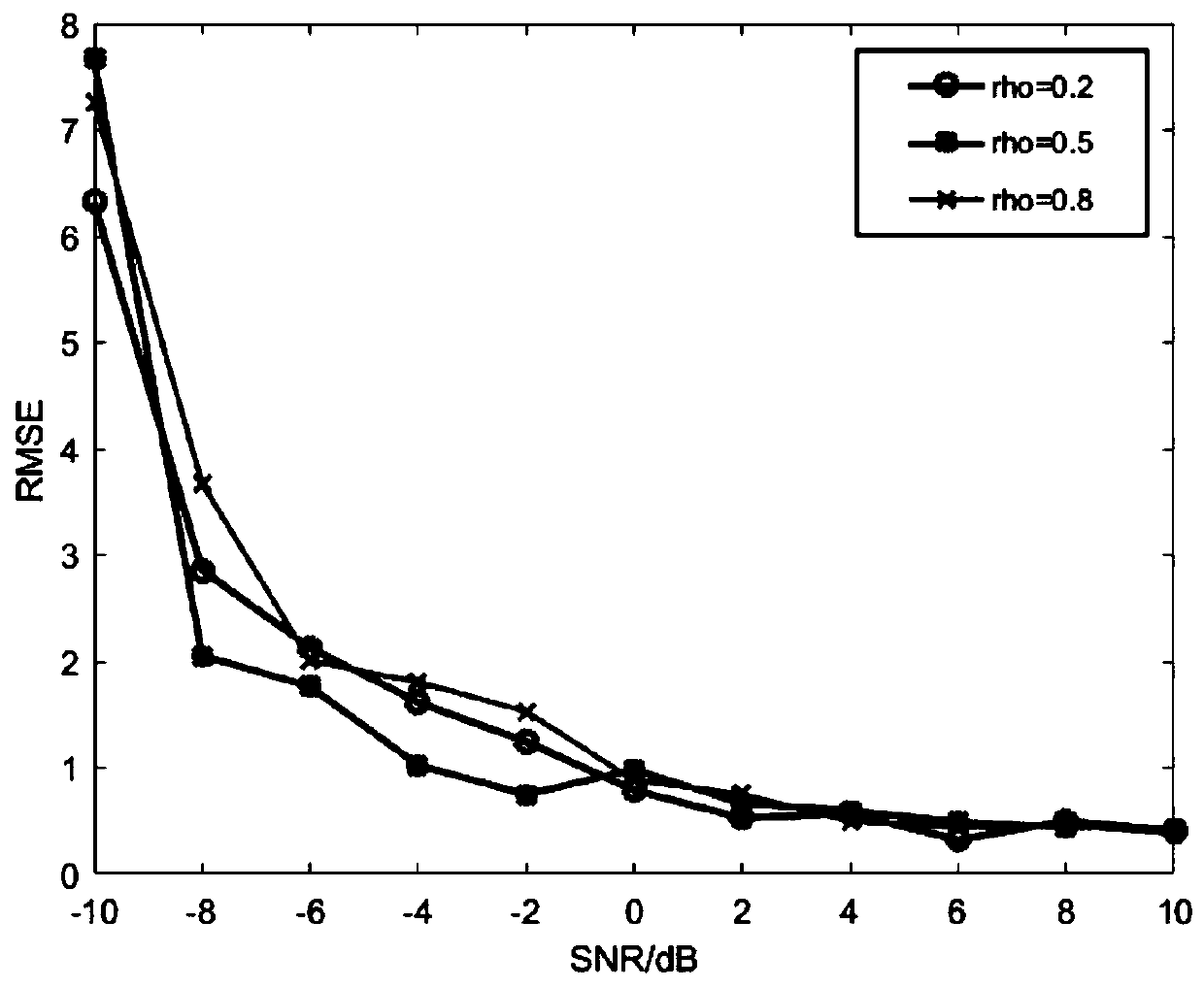
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication technology and signal processing, and discloses a DOA estimation method for moving target echoes under multiple external radiation sources, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of a mixed echo signal received by an antenna array, solving a covariance matrix of the signal, extracting a real part and an imaginary part of an upper triangular element, and constructing a one-dimensional matrix as the input of a sparse auto-encoder; classifying the signals from different regions by using a sparse auto-encoder; p results output by the sparse auto-encoder forming a one-dimensional matrix, then converting the one-dimensional matrix into a covariance matrix form, and dividing the matrix into a real part matrix and an imaginary part matrix to serve as dual-channel input to be sent to P convolutional neural networks; realizing DOA estimation of different subarea signals by using the convolutional neural network, and output layer neurons of the P convolutional neural networks representing the angles of the P sub-regions in the horizontal direction; and when the signal-to-noise ratio is greater than 0dB,the normalized mean square error of signal-to-noise ratio estimation being less than 1.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Delaunay triangular net-based road center line extraction method
ActiveCN106528740AKeep topologyAvoid reacquisitionGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsRoad networksApplication areas
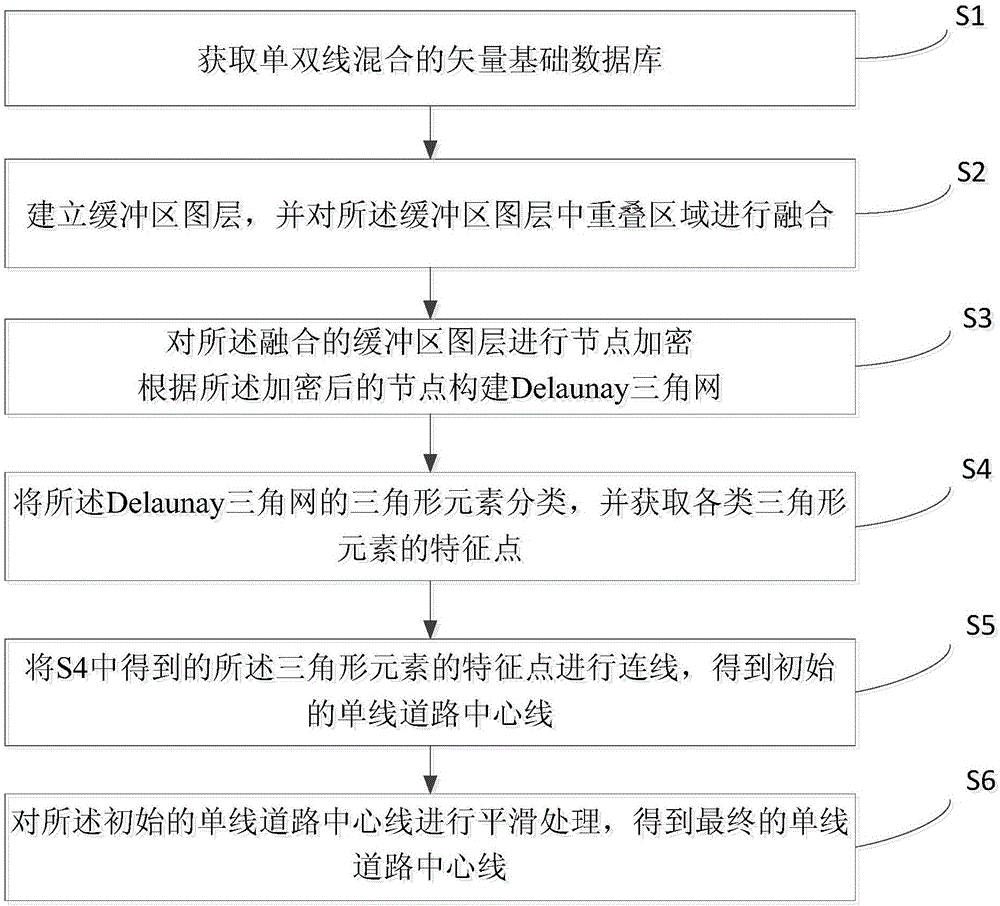
The invention discloses a Delaunay triangular net-based road center line extraction method, and belongs to the technical field of geographic information data processing. The method comprises the steps of establishing buffer regions of road line data, and performing buffer region fusion; performing node encryption based on a graphic layer of the established buffer regions, and establishing a Delaunay triangular net by utilizing encrypted nodes; classifying triangular elements forming the triangular net according to geometric features, thereby obtaining feature points of all the triangular elements; connecting the feature points in sequence to obtain single-line data, and obtaining a final result through curve smoothing. Single-line road network data is obtained by single and double-line mixed road data, so that complex manual processing or a data re-collection process is avoided when data is obtained in the field of scientific research such as road network analysis and the like or application, a topological relation of the road data can be well kept, and result data meeting the requirements is obtained.
Owner:MAPUNI TECH CO LTD
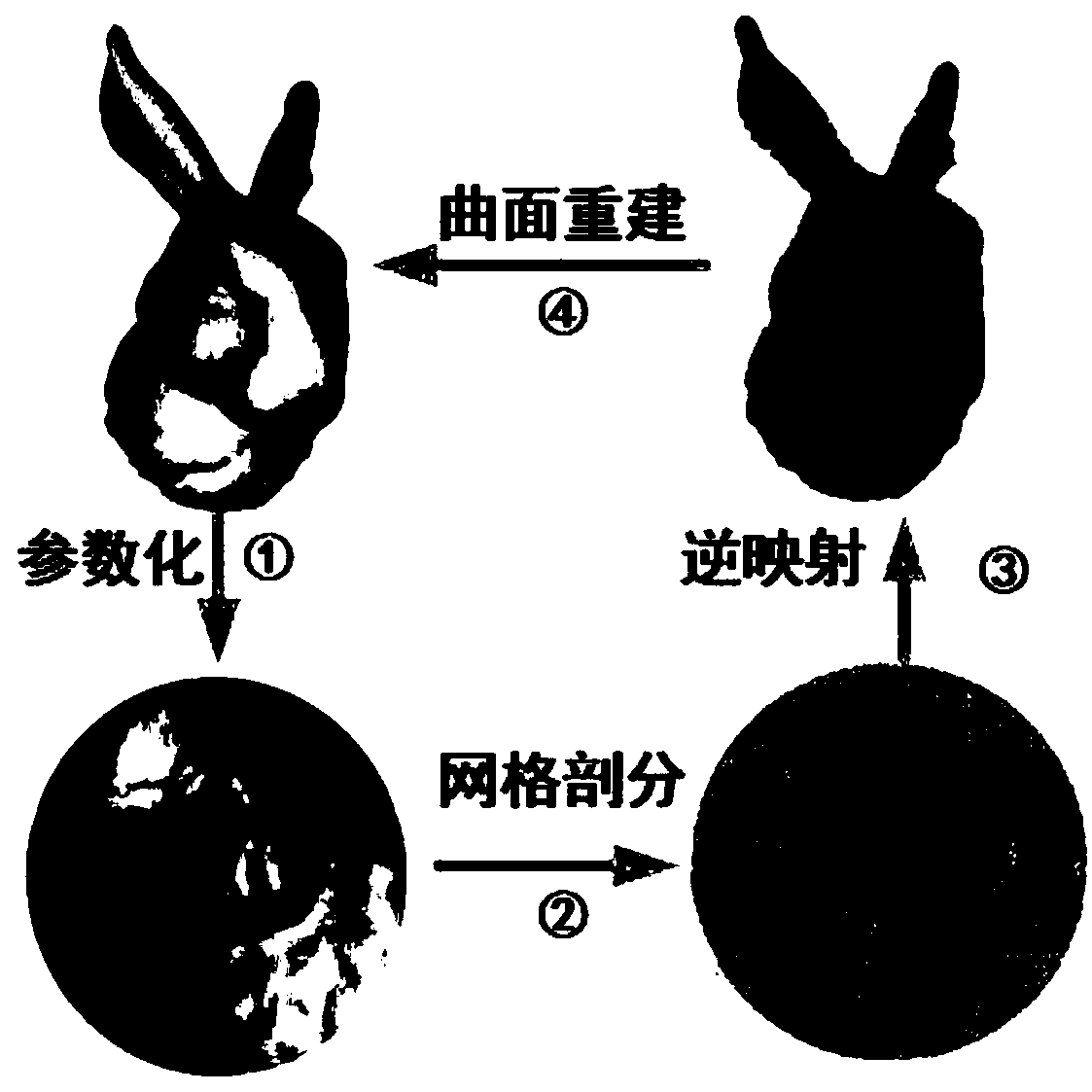
A surface mesh generation method of a digital model based on conformal geometry
PendingCN109377561AEasy split operationQuality improvement3D modellingNODALComputer graphics (images)
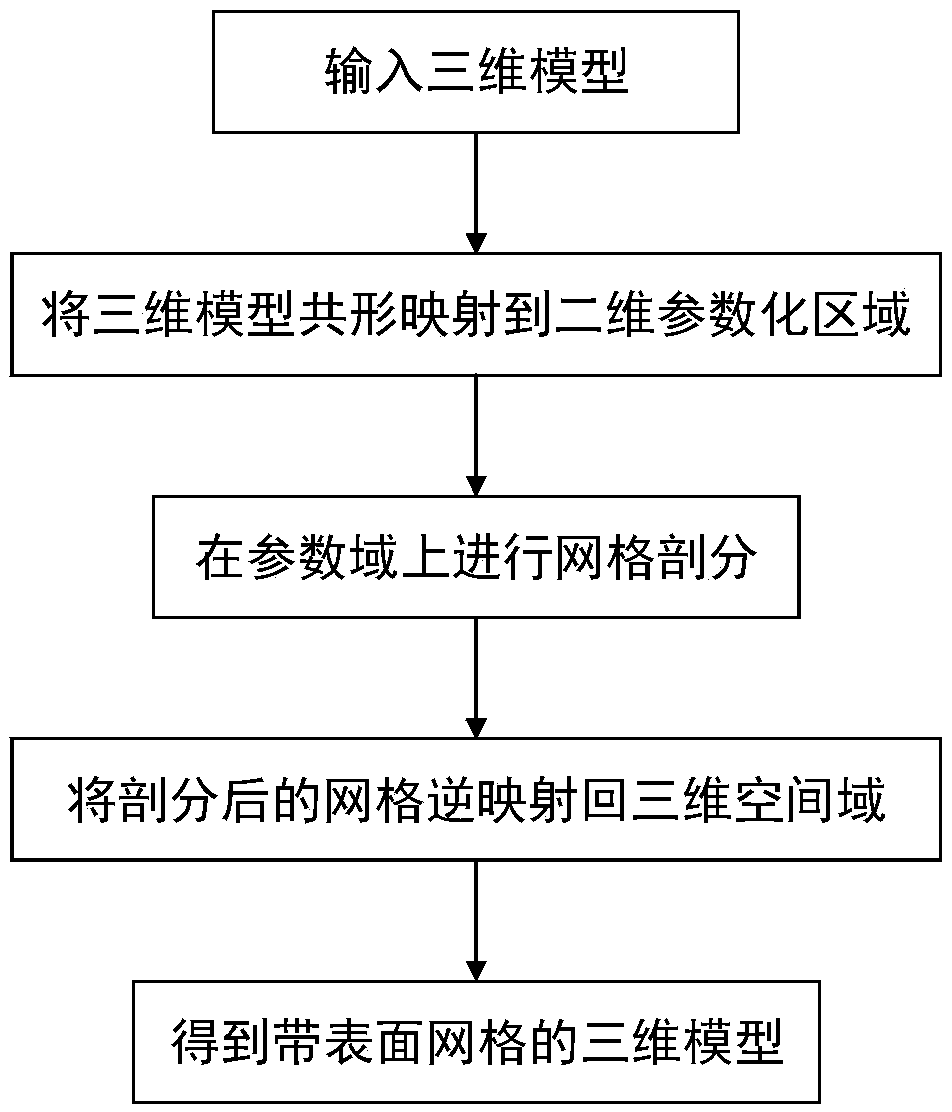
The invention provides a surface mesh generation method of a digital model based on conformal geometry, which aims at simplifying the surface mesh generation problem of a three-dimensional model to atwo-dimensional plane for processing, wherein the method comprises according to the topological information of the three-dimensional model, selecting the conformal mapping function from the three-dimensional model to the two-dimensional parameter region, and then generating the finite element mesh on the parameter region, in the mesh generation of parametric domain, generating the triangular element or quadrilateral element, and then mapping the mesh of parametric domain into the mesh of spatial domain by conformal inversion according to the mapping function from parametric domain to spatial domain, and keeping the topological relationship between nodes unchanged, so that the mesh of spatial domain is the surface mesh of the 3D model. Compared with the mesh generation on the surface of 3Dmathematical model directly, the mesh generation on parameterized area is simpler and has less computational complexity. The surface mesh generated by this method is of high quality and high precision.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
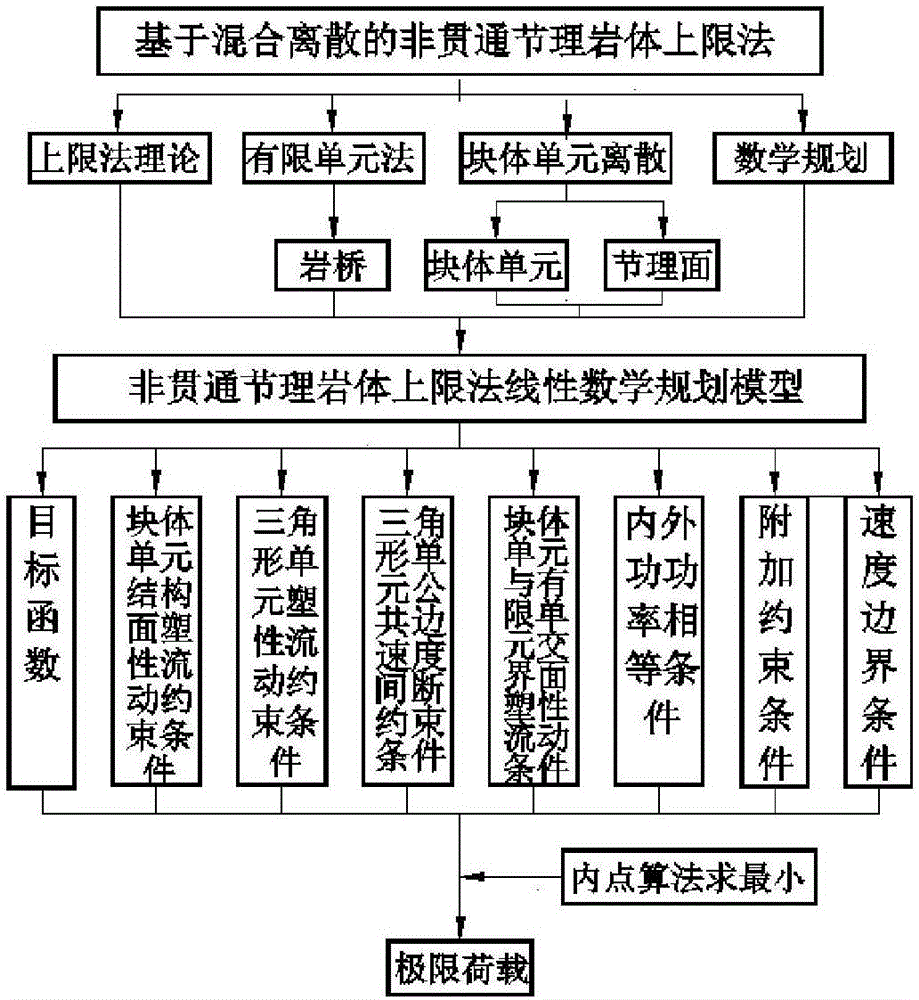
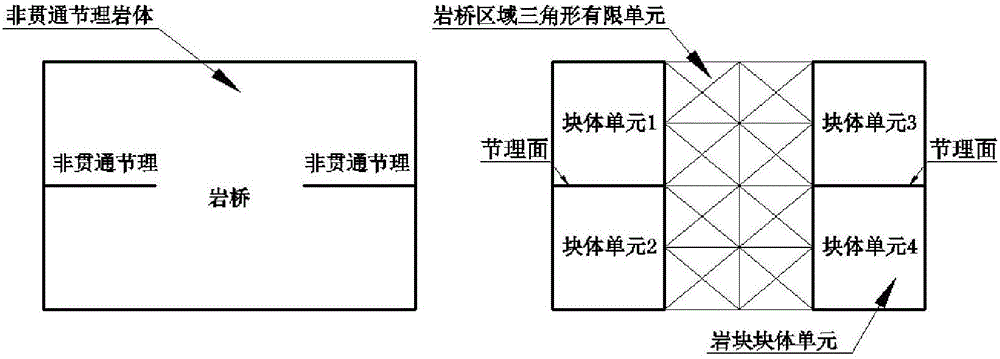
Hybrid numerical discretization-based plasticity limit analysis upper-bound method of non-across jointed rock mass
ActiveCN106557608ASimulate the mechanical properties of discontinuous mediaMethod concept is clearDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALDiscretization
The invention relates to a plasticity limit analysis upper-bound method of a non-across jointed rock mass, and belongs to the field of bearing capacity analysis of the rock mass in rock mechanics. The method comprises the steps of: on the basis of an upper-bound method theory in plasticity limit analysis, discretizing a non-across jointed rock slope by adopting a hybrid element method, namely constructing a kinematically admissible velocity field which simultaneously meets block and structural surface deformation compatibility conditions, plasticity flowing constraint conditions, internal and external power equivalence conditions, block element and triangular element interface plasticity flowing conditions and velocity boundary conditions by adopting a rigid block element discretization rock, a finite element discretization rock bridge, a block element centroid speed and a triangular element node velocity as unknown quantities; and building a linear mathematical programming model of solving an ultimate load of the non-across jointed rock mass, solving the linear mathematical programming model by adopting an interior point algorithm and obtaining an upper-bound solution of the ultimate load of the non-across jointed rock mass. The plasticity limit analysis upper-bound method has the characteristics of clear concepts, high calculation accuracy and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Direction-of-arrival estimation method based on sparse representation
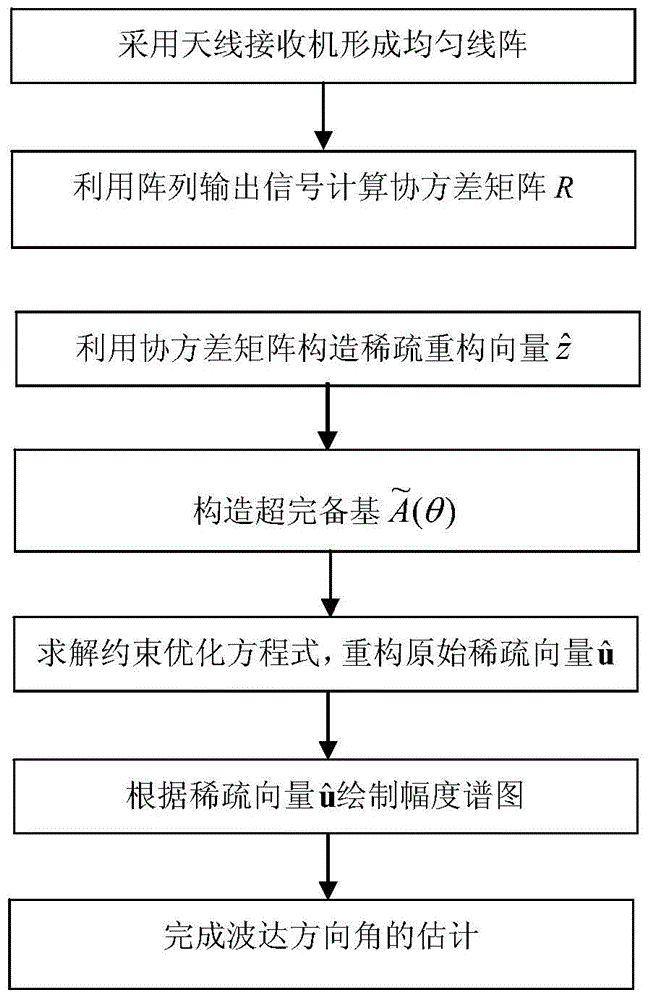
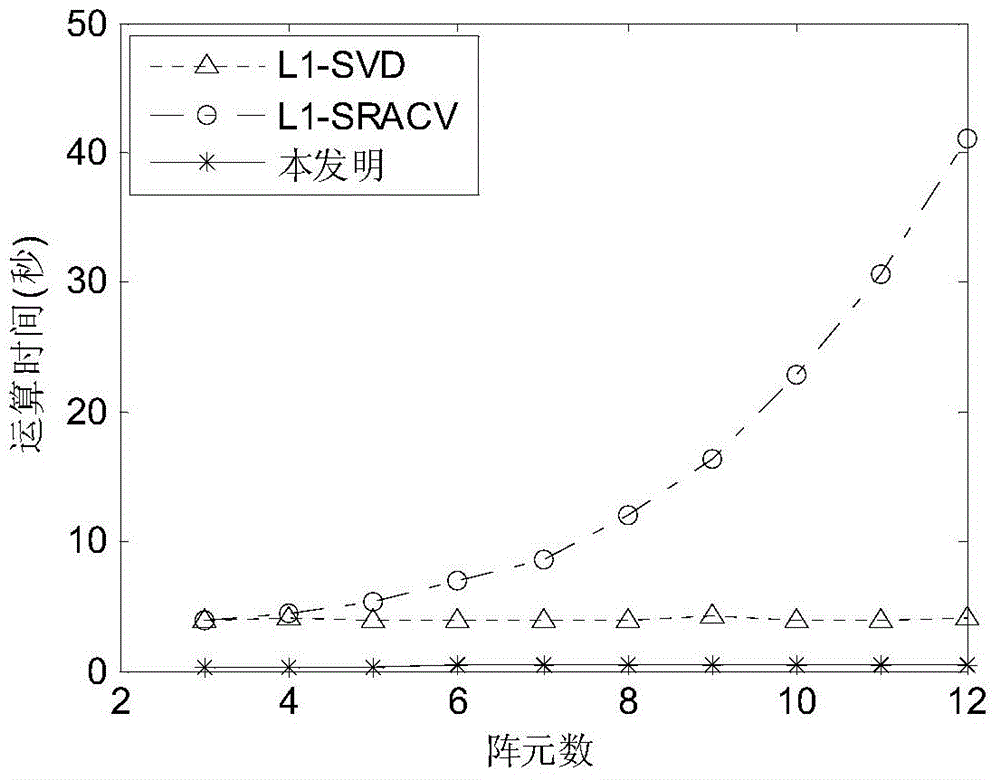
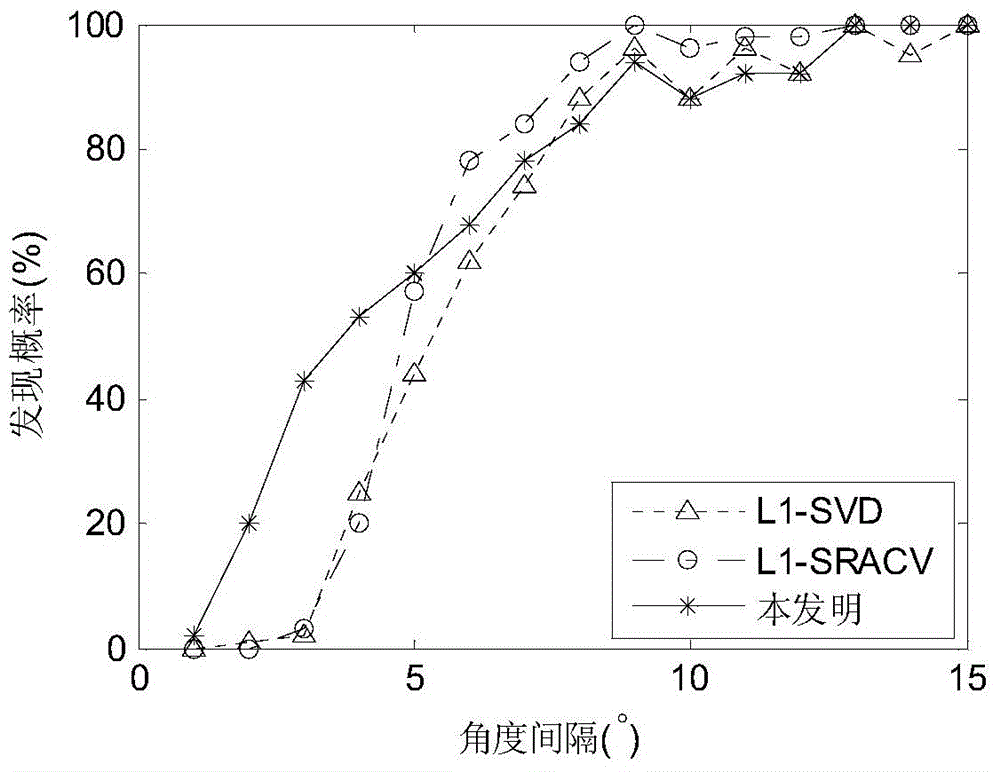
InactiveCN104020438AAvoid anglesBreaking through the Rayleigh limit of resolutionRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsEstimation methodsImage resolution
The invention discloses a direction-of-arrival estimation method based on sparse representation. The method mainly solves the problems that because a similar technology is large in calculation amount and low in angular resolution, the estimation speed of target reconnaissance and passive location is low and estimation errors in target reconnaissance and passive location are large. The method comprises the implementation steps: (1) acquiring output signals of an array and calculating a covariance matrix R of the signals, (2) constructing reconstructed sparse vectors through lower triangular elements of the covariance matrix R, (3) carrying out mesh generation on a spatial domain to construct a perfect base, (4) converting the direction-of-arrival estimation issue into the issue of solving a constrained optimization equation according to the sparse representation relation between the reconstructed sparse vectors and the perfect base, (5) solving the constrained optimization equation according to the convex optimization method to obtain the optimal estimation vectors, (6) drawing a magnitude spectrum according to the one-to-one correspondence of the optimal estimation vectors and spatial domain angles to obtain the direction-of-arrival value. By means of the method, the calculation speed of target reconnaissance and passive location is decreased, and the estimation errors in target reconnaissance and passive location are reduced. The method can be applied to target reconnaissance and passive location.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
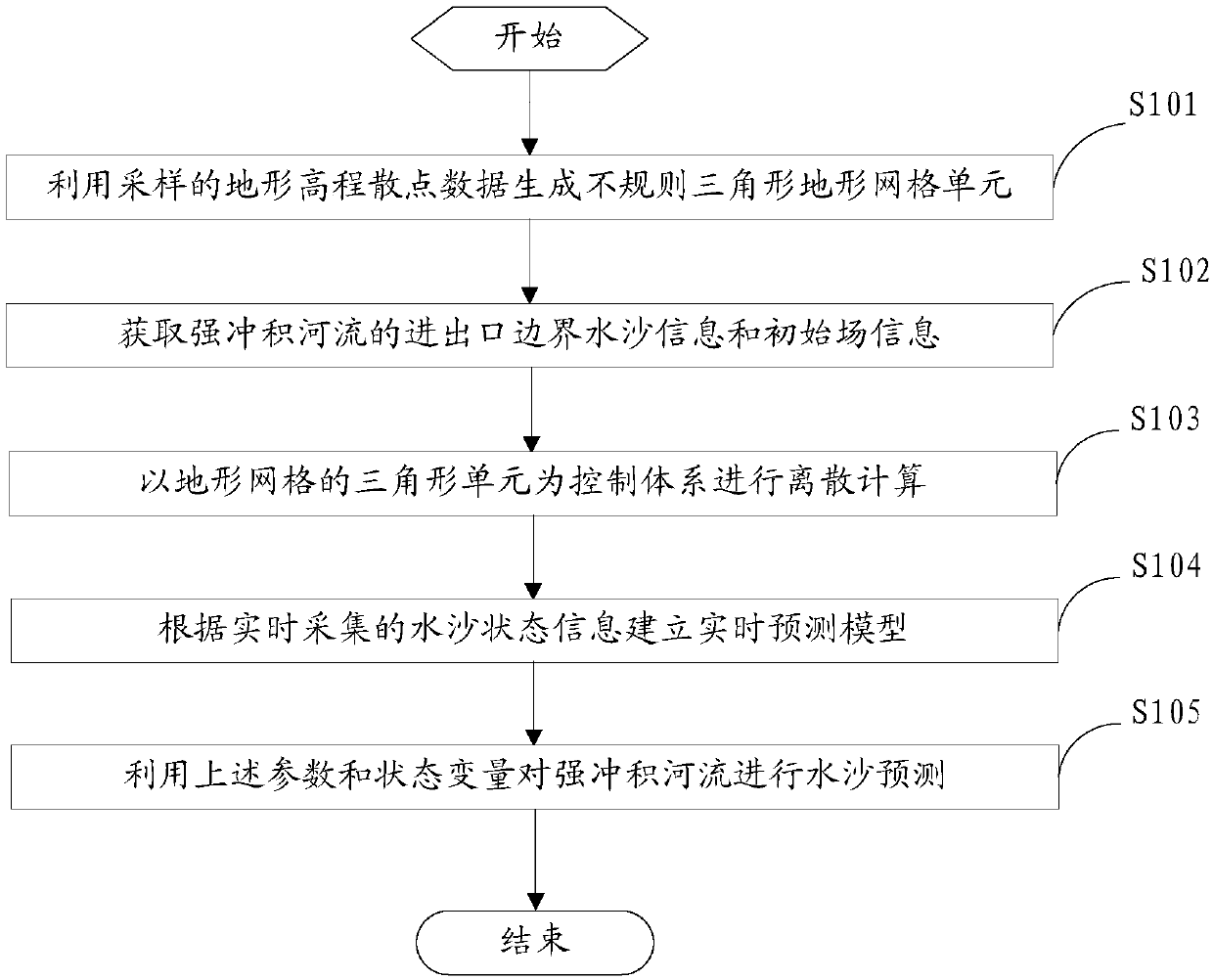
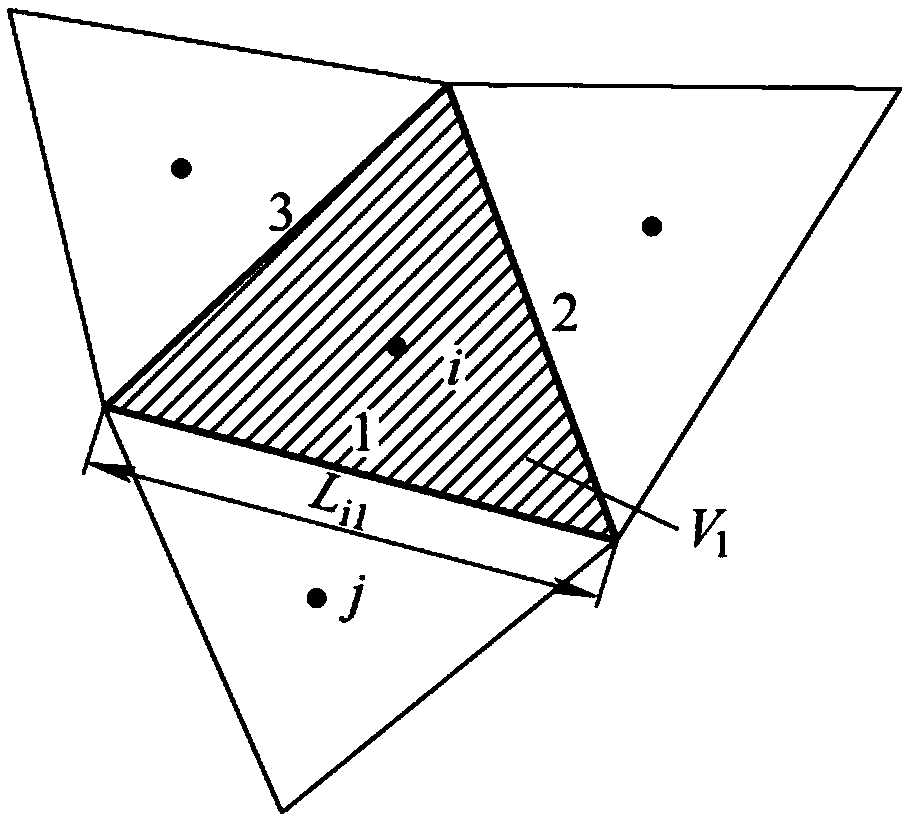
Water and sand prediction method and system for strong alluvial river based on data assimilation
ActiveCN108334660ASupport regulationGet water level in real timeClimate change adaptationForecastingFluvialLandform
The invention provide a water and sand prediction method and system for a strong alluvial river based on data assimilation. The method particularly comprises the steps of using terrain elevation scatter data obtained by sampling to generate an irregular triangular terrain grid unit; obtaining water-sand information and initial field information of strong alluvial river inlet and outlet boundaries;taking triangular elements of terrain grids as control bodies, discretizing a two-dimensional water-sand model of the strong alluvial river, selecting a solution method for calculation, and obtainingcalculated values of the control bodes; acquiring riverway water and sand state information of the strong alluvial river in real time, establishing a real-time prediction model based on the data assimilation according to the water and sand state information, and obtaining assimilation state variables and parameter variables; finally, using a two-dimensional water and sand data assimilation modelto conduct water and sand prediction on the strong alluvial river. Through the above treatment, the real-time status of water and sand of the strong alluvial river can be effectively predicted, so that water and sand regulation can be regulated, and a basis is provided for flood control and disaster alleviation, water environmental protection and water resource management.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
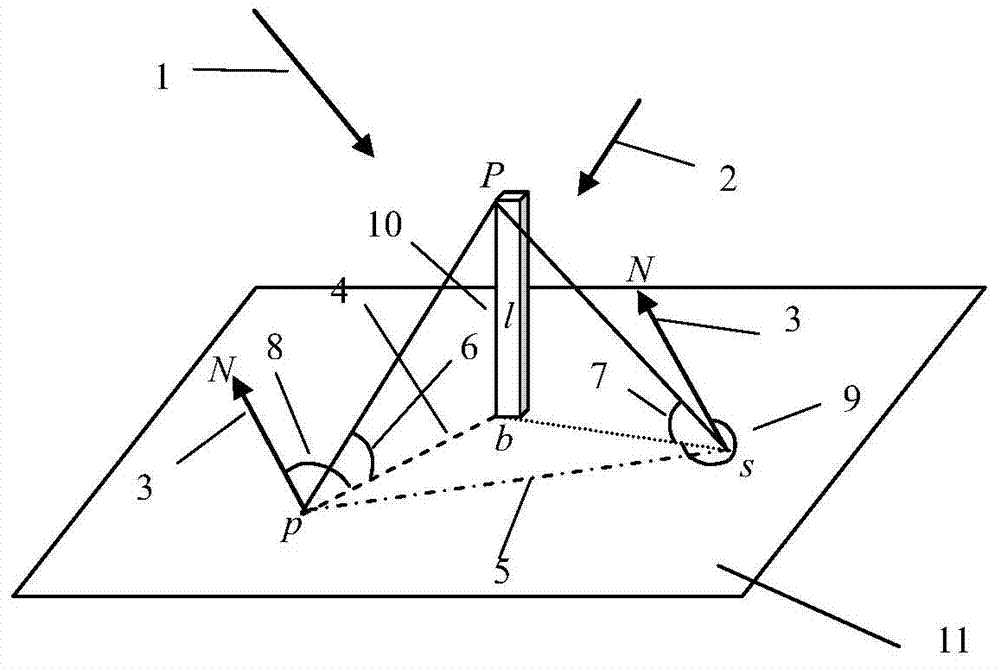
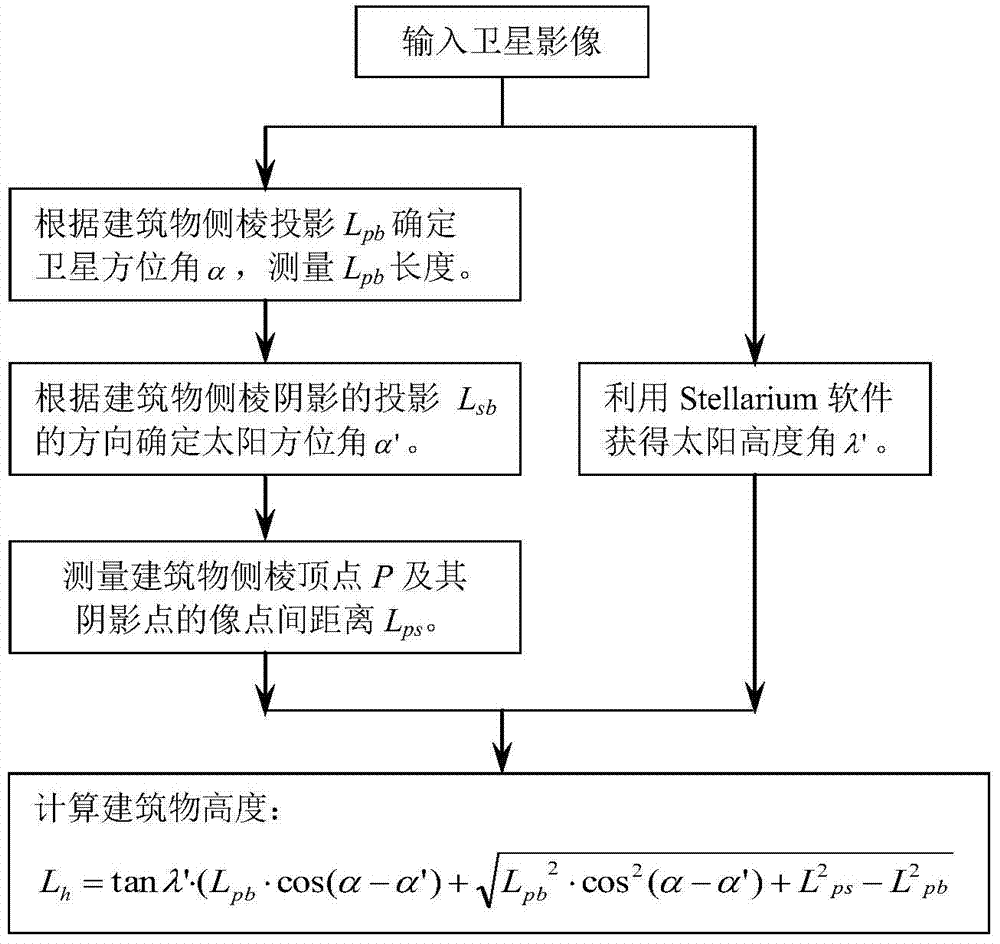
Single satellite image-oriented self-acquired triangular element height calculation method
ActiveCN103791885AThe solution is not easy to obtainAltitude calculation works wellAngle measurementHeight/levelling measurementElevation angleNatural satellite
The invention provides a single satellite image-oriented self-acquired triangular element height calculation method. The method comprises the steps of calculating three angle parameters, namely a sun elevation angle, a sun azimuth angle and a satellite azimuth angle, according to direction information in a single satellite image and a relation between the sun azimuth angle and the sun elevation angle, performing equivalent expression on a satellite elevation angle through a building height and a building projection length, and finally calculating a triangular element height which does not contain the satellite elevation angle. The effect of realizing calculation on the height of a building in the single satellite image is good.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
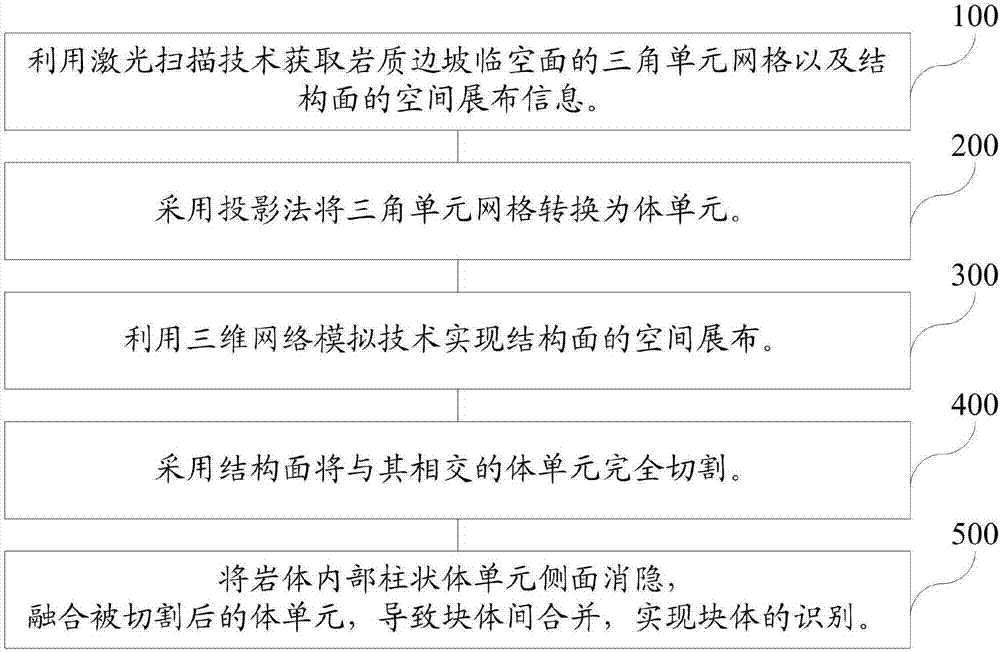
Method for refined modeling and block recognition of rock slope structure
ActiveCN106934826ARealize identificationUnrestricted formImage enhancementImage analysisBody identificationLaser scanning
The invention which relates to the field of the geological modeling technology, provides a method for refined modeling and block recognition of a rock slope structure. The method comprises: (1), obtaining a triangular element grid and a structural plane geometric parameter of a slope free face by using a laser scanning technique; (2) transforming a triangular face unit into a body unit by a projection method; (3) realizing spatial distribution of a structural surface by using a three-dimensional network simulation technology; (4) with a plane where the structural plane is located, cutting an intersected body unit completely; and (5) carrying out blanking on a side surface of a cylindrical unit inside a rock mass, carrying out fusion with the cut body unit, and thus forming block body merging between structural surfaces, thereby realizing block body identification. Therefore, the field measurement data and the block identification are combined; the precision is high and the speed is fast; and the identified block form and number are not limited.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Lionsphere, a three-dimenstional puzzle
A puzzle formed by splitting of a 3-D body by three pairs of symmetrical conical surfaces. The body has a hollow sphere inside with three main axes coincided with the axes of each pair. The elements are a result of splitting by the conical surfaces and comprise outer and inner junction means providing two adjacent elements sliding with respect to each other. There are three types of elements with orientation means: six polar, twelve median and eight triangular elements. The elements adjacent to one conical surface comprise key open means providing elements move apart. The goal of the three-dimensional puzzle is to put the body in right order by 90 degrees rotations of elements spaced from one side of conical surfaces, to the initial ordered orientation, where the body can be separated for two parts providing access to the space located inside the hollow sphere.
Owner:LIONSHPERE PUZZLES PARTNERSHIP
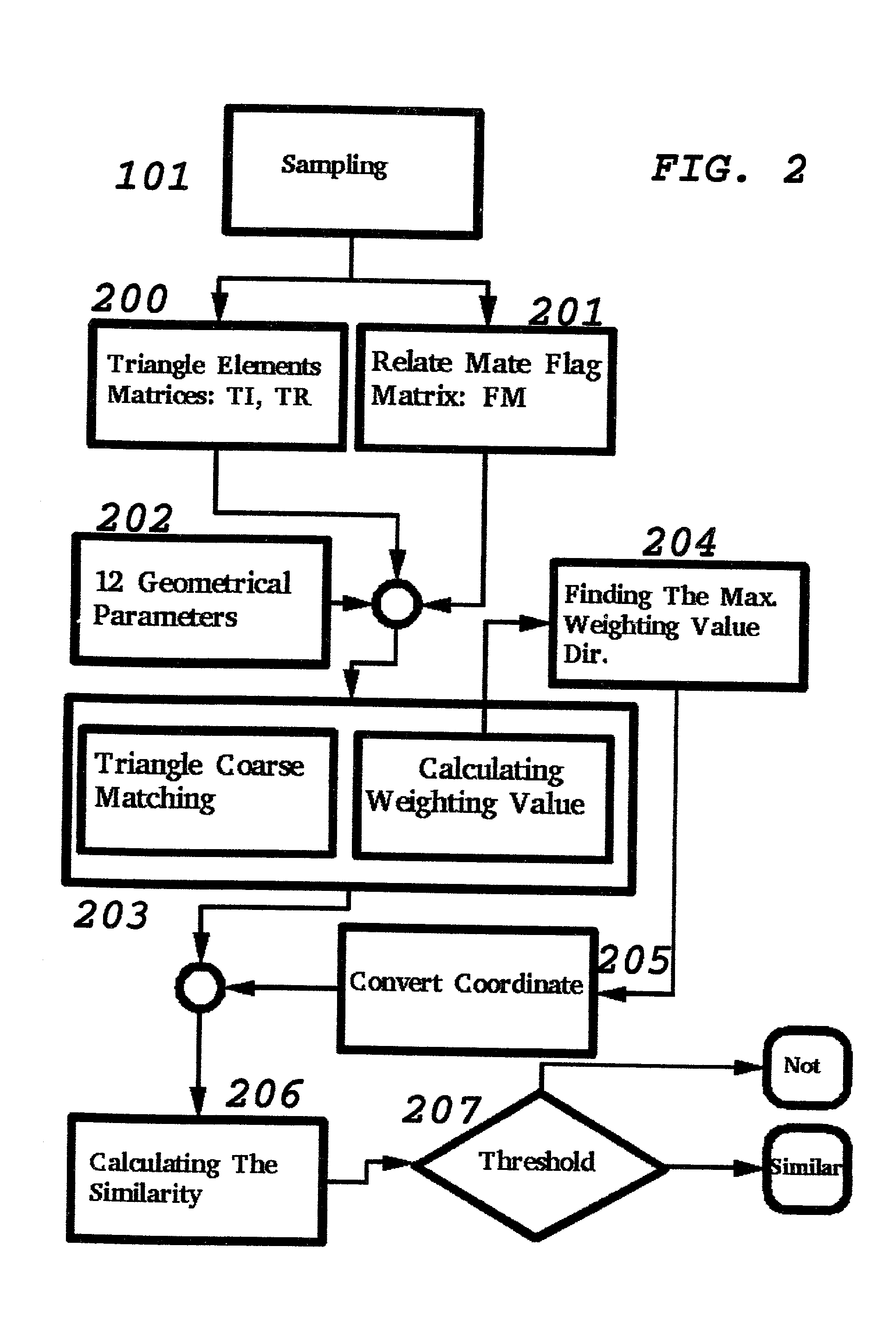
Triangle automatic matching method
Owner:COMETRUE CONSULTING
Three-dimensional puzzle
A puzzle formed by splitting of a 3-D body by three pairs of symmetrical conical surfaces. The body has a hollow sphere inside with three main axes coincided with the axes of each pair. The elements are a result of splitting by the conical surfaces and comprise outer and inner junction means providing two adjacent elements sliding with respect to each other. There are three types of elements with orientation means: six polar, twelve median and eight triangular elements. The elements adjacent to one conical surface comprise key open means providing elements move apart. The goal of the three-dimensional puzzle is to put the body in right order by 90 degrees rotations of elements spaced from one side of conical surfaces, to the initial ordered orientation, where the body can be separated for two parts providing access to the space located inside the hollow sphere.
Owner:LIONSHPERE PUZZLES PARTNERSHIP
Three-dimensional visualization architecture
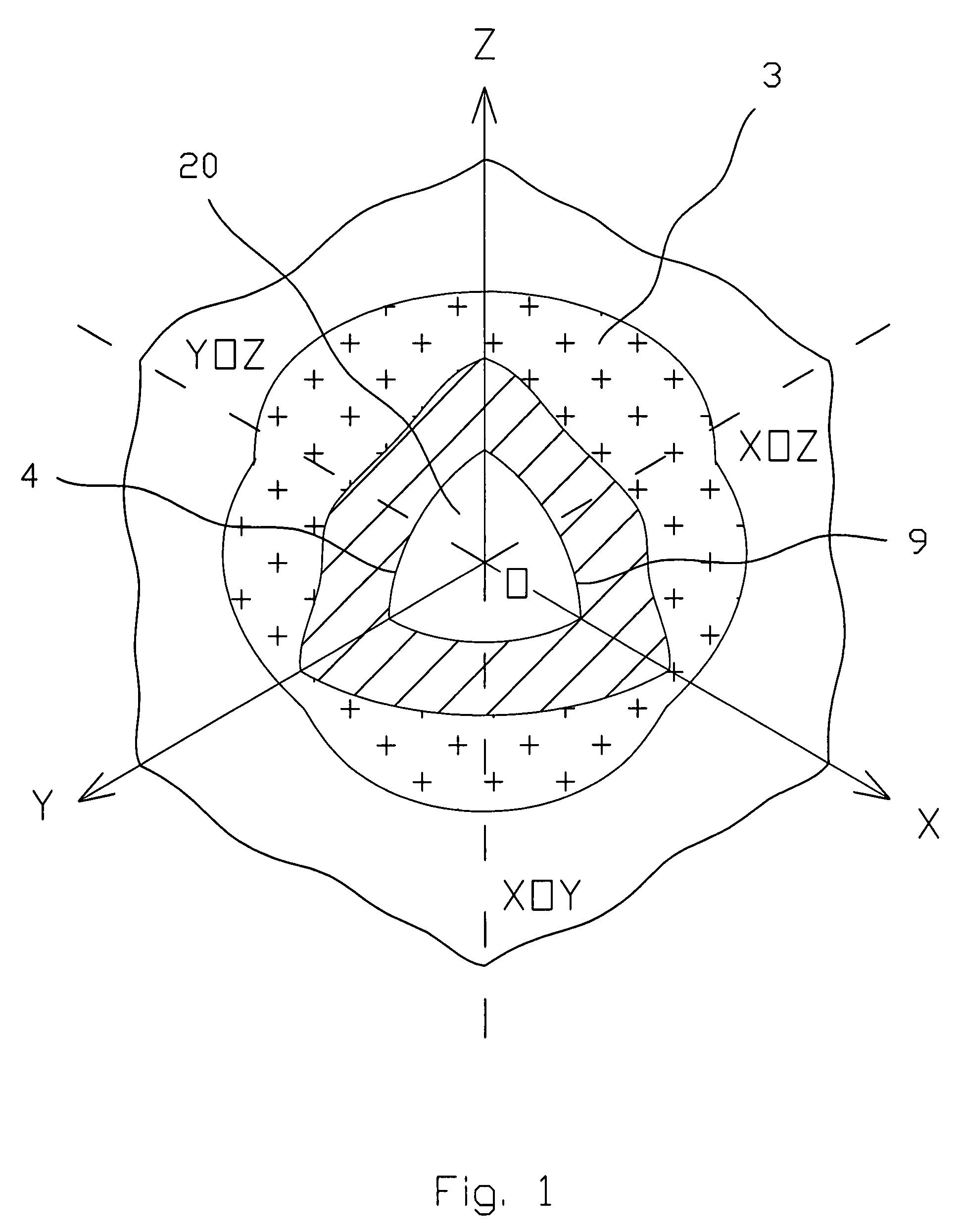
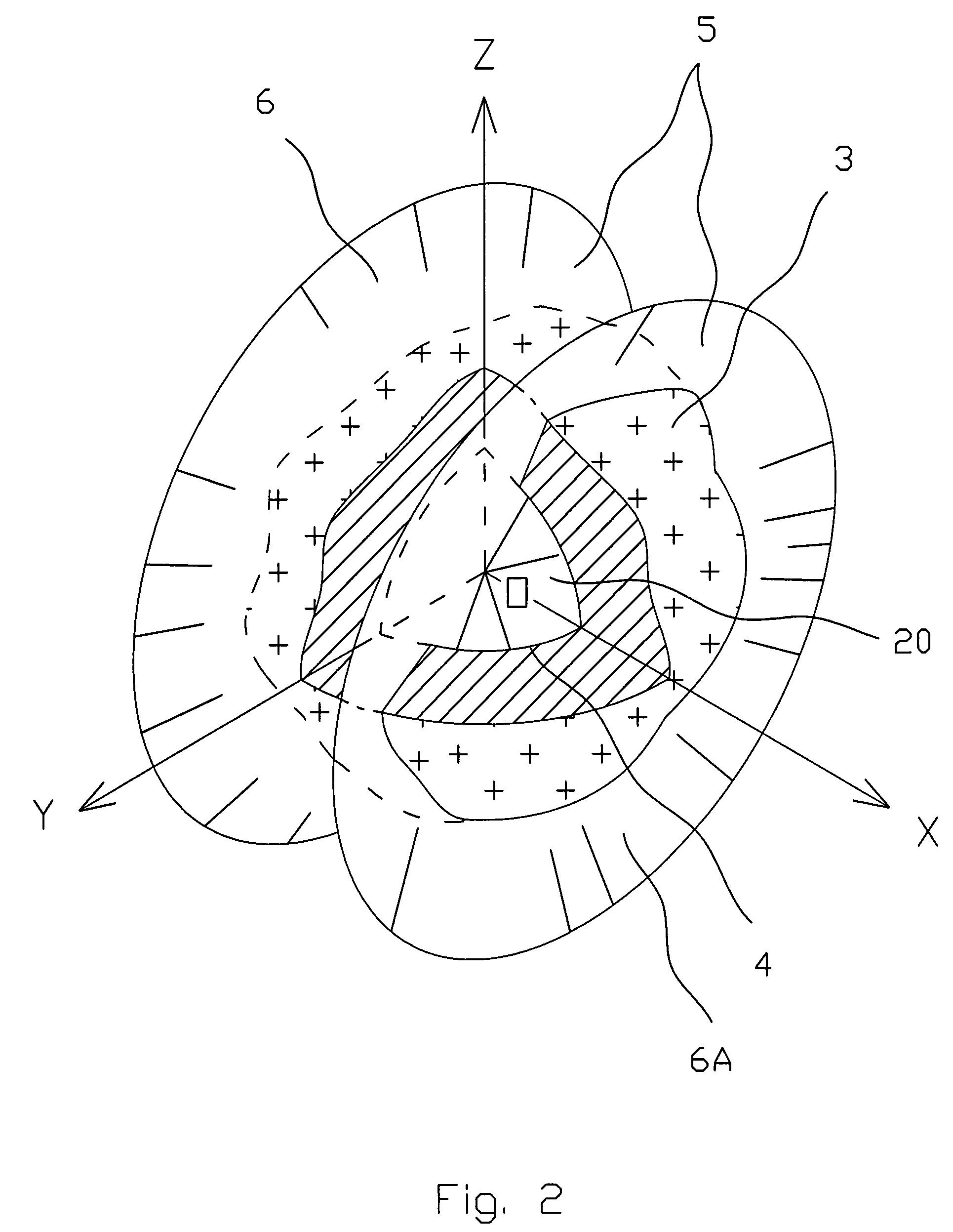
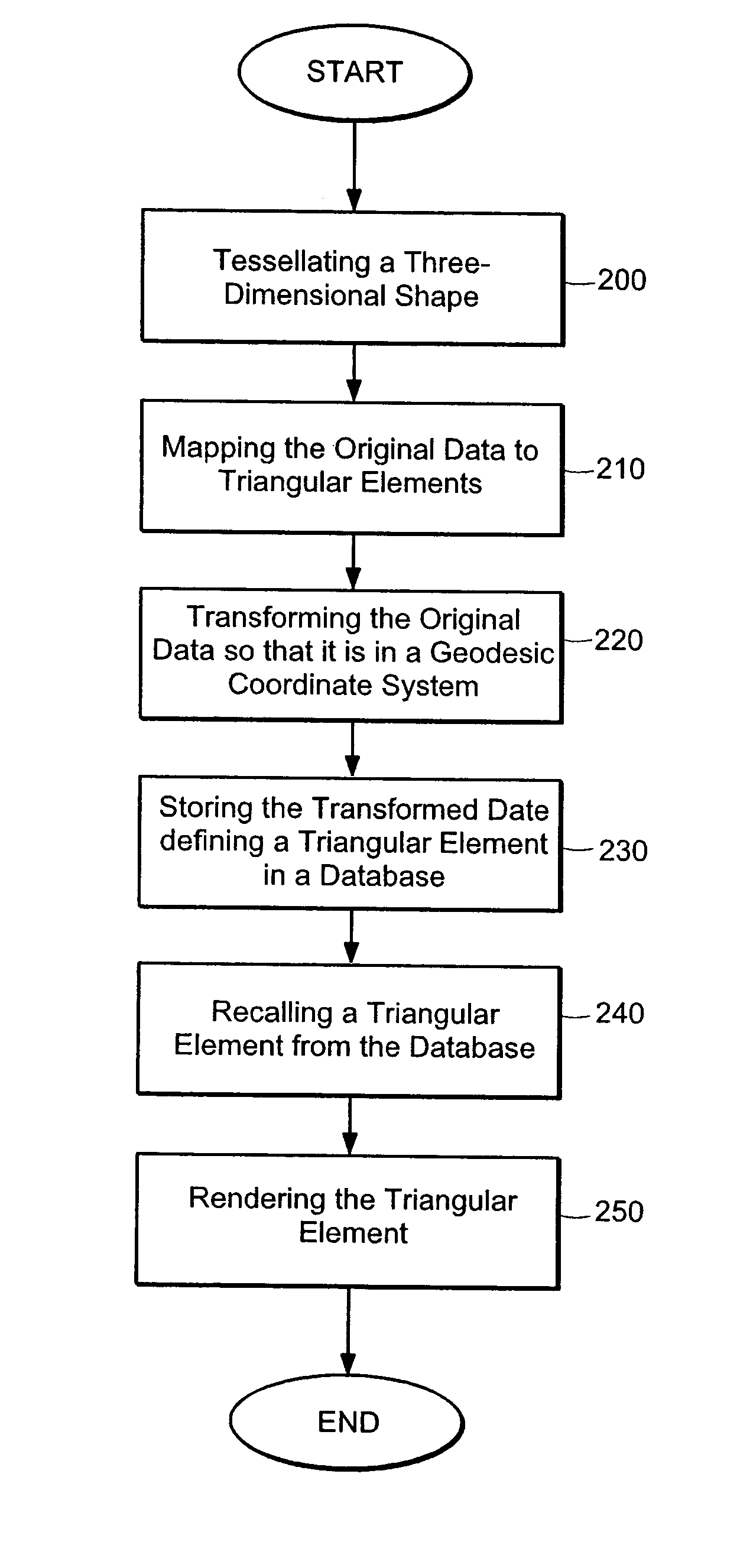
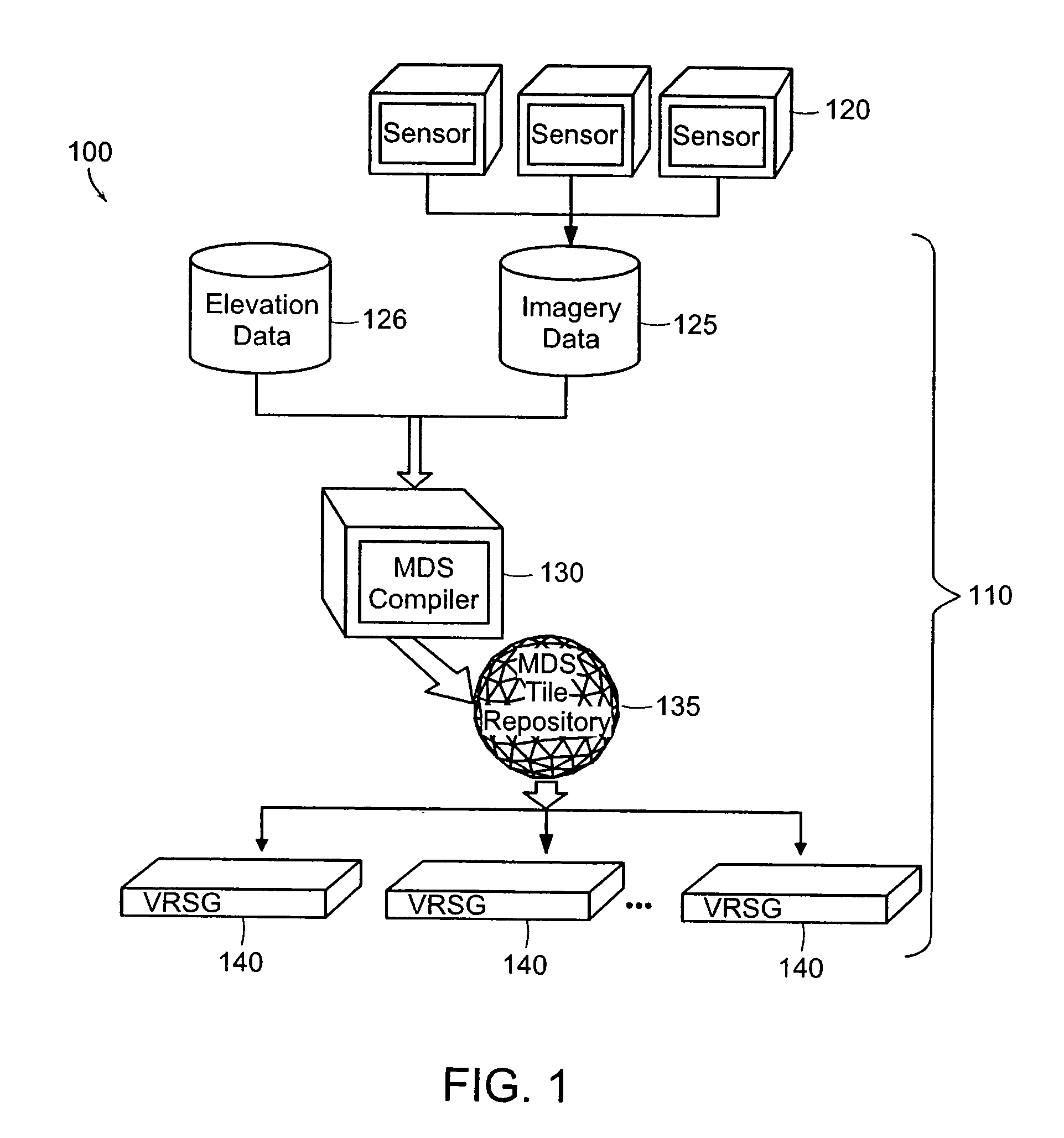
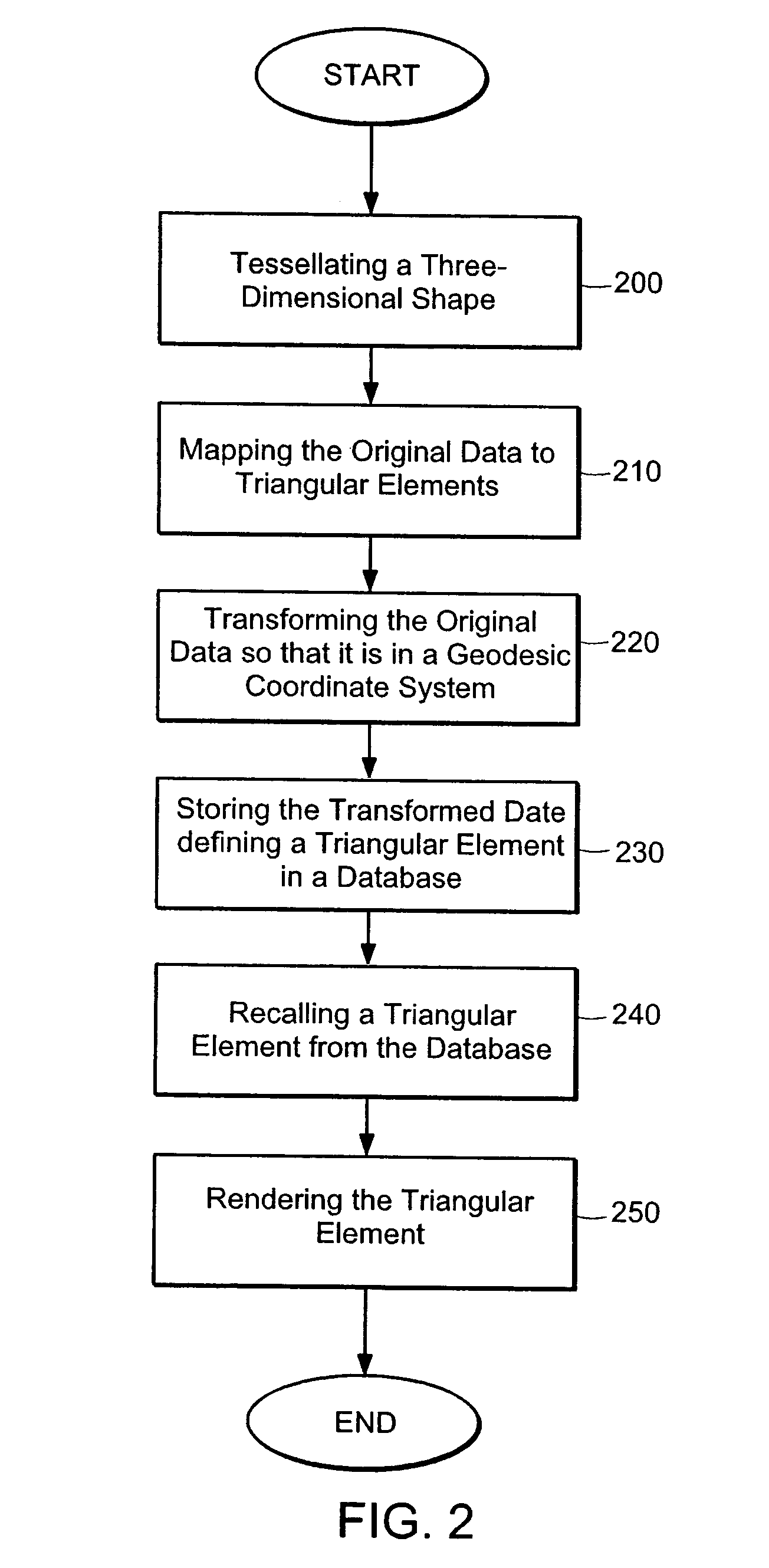
ActiveUS7425952B2Accurate representationCharacter and pattern recognition3D-image renderingTerrainImage resolution
A virtual terrain architecture and computer program product for employing a geocentric coordinate system, using a tessellated three-dimensional shape for representing a celestial body, and mapping terrain data to the tessellated three-dimensional shape is disclosed. In one embodiment, the methodology begins with a seed polyhedron such as an ellipsoid model. The seed ellipsoid is preferably composed of a plurality of triangle primitives. After selection of the seed ellipsoid, the ellipsoid is subdivided using tessellation. Each triangular element is subdivided into four sub-elements which are also triangular in shape. As the elements are further subdivided, the triangles of the ellipsoid model create a sphere that is representative of the earth or other celestial body. Tessellation continues until a desired resolution is reached for each triangular element. Once a sphere has been substantially formed, terrain data is mapped to the triangular elements and the data is converted to geocentric coordinates and stored in a database. Each triangular element is separately indexed according to the triangular elements name. By creating a geocentric representation, the earth's curvature and polar regions can be accurately represented. By using a tessellation process, tiling for the geocentric coordinate system is achieved. Thus, the tiles can be paged as discrete elements.
Owner:MVRSIMULATION INC
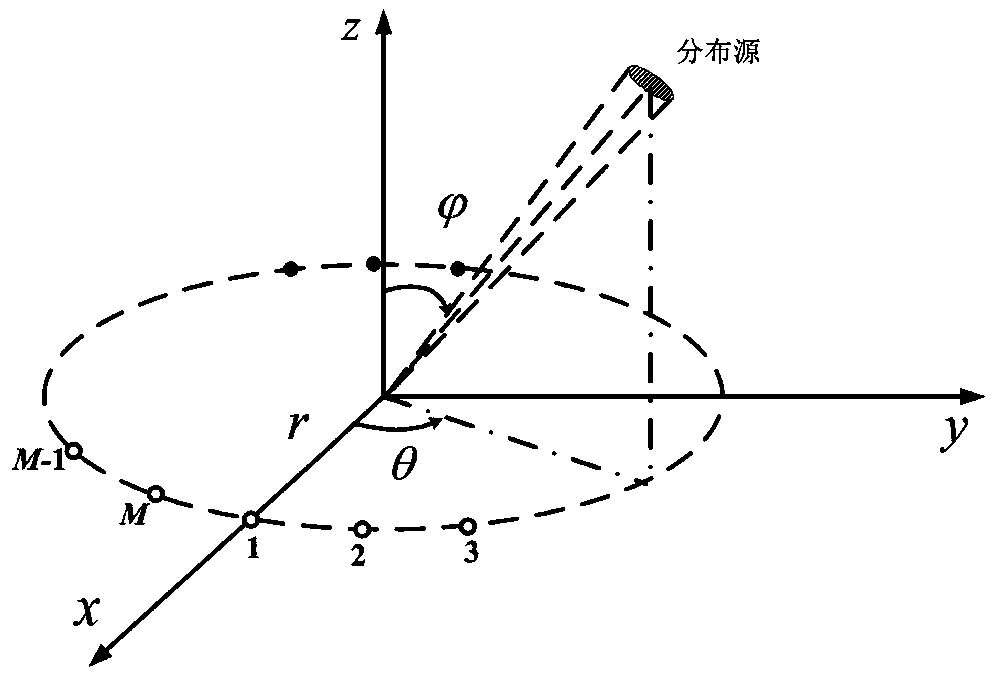
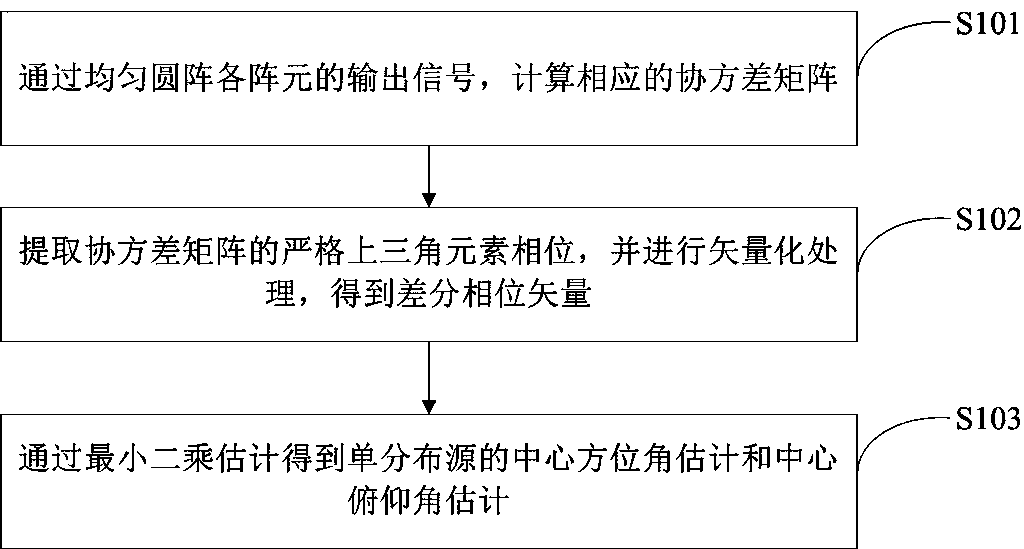
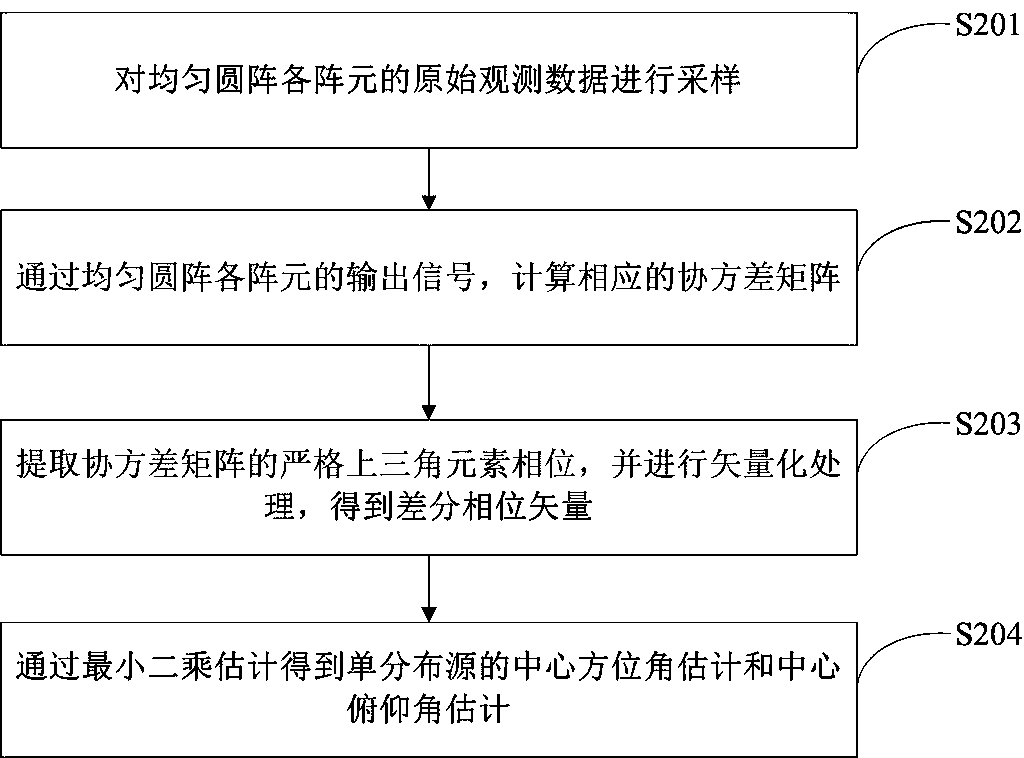
Uniform circular array differential phase based single distributed source DOA estimation method
InactiveCN107907853AQuick estimateEffective estimateRadio wave finder detailsDistributed sourceDecomposition
The invention relates to the technical field of array signal processing technology, especially relates to DOA (Direction Of Arrival) estimation of a wireless signal source, and particularly relates toa uniform circular array differential phase based single distributed source DOA estimation method. The method includes calculating a corresponding covariance matrix through output signals of different array elements of the uniform circular array; extracting exact upper triangular element phases of the covariance matrix and performing vectorization treatment, and obtaining a differential phase vector; obtaining single distributed source central azimuth angle estimation and central pitch angle estimation through least squares estimation. According to the invention, a two-dimensional DOA closed-form solution is obtained directly through the least squares method, spectrum peak search and eigenvalue decomposition calculation are avoided and complexity is reduced substantially.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
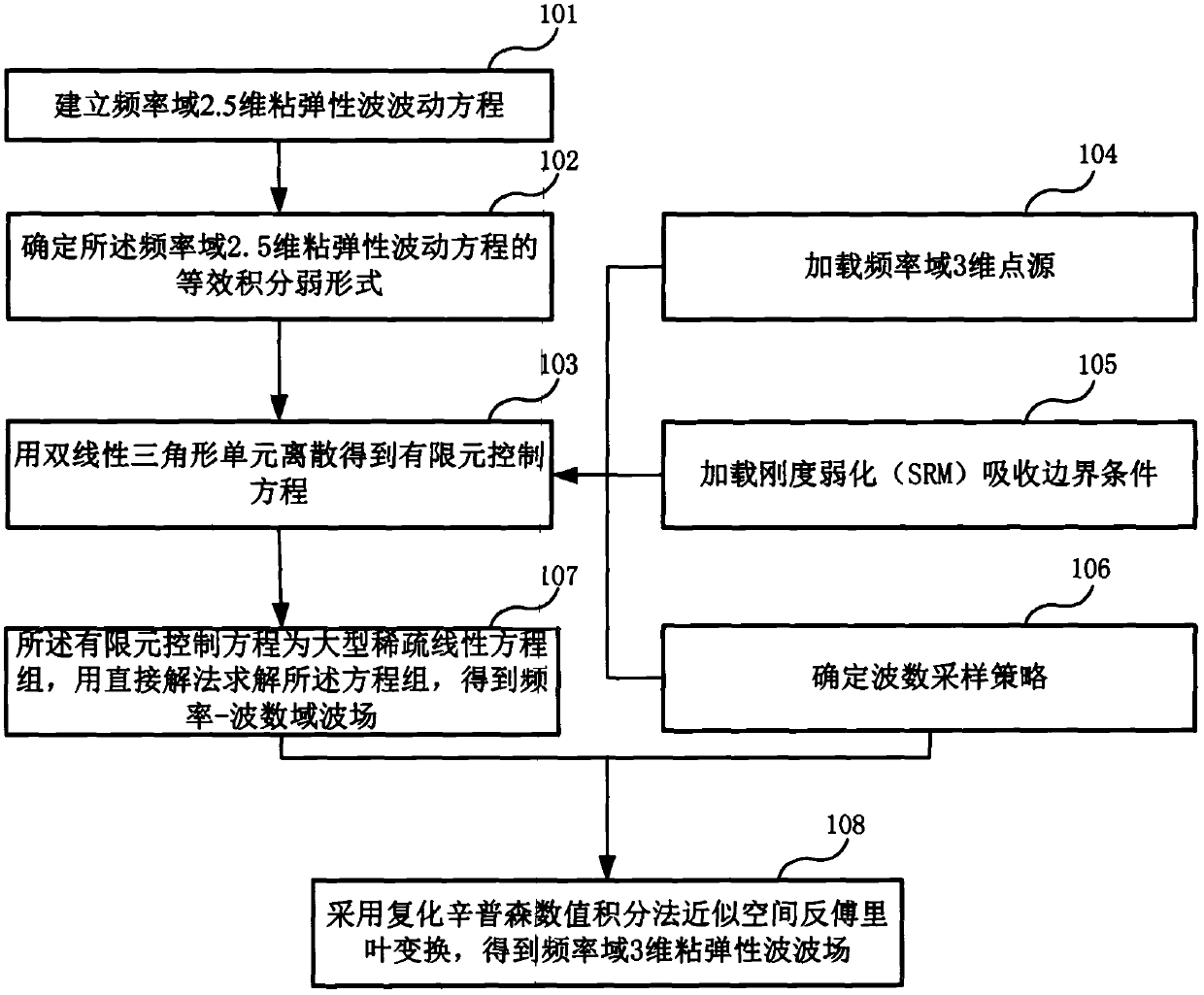
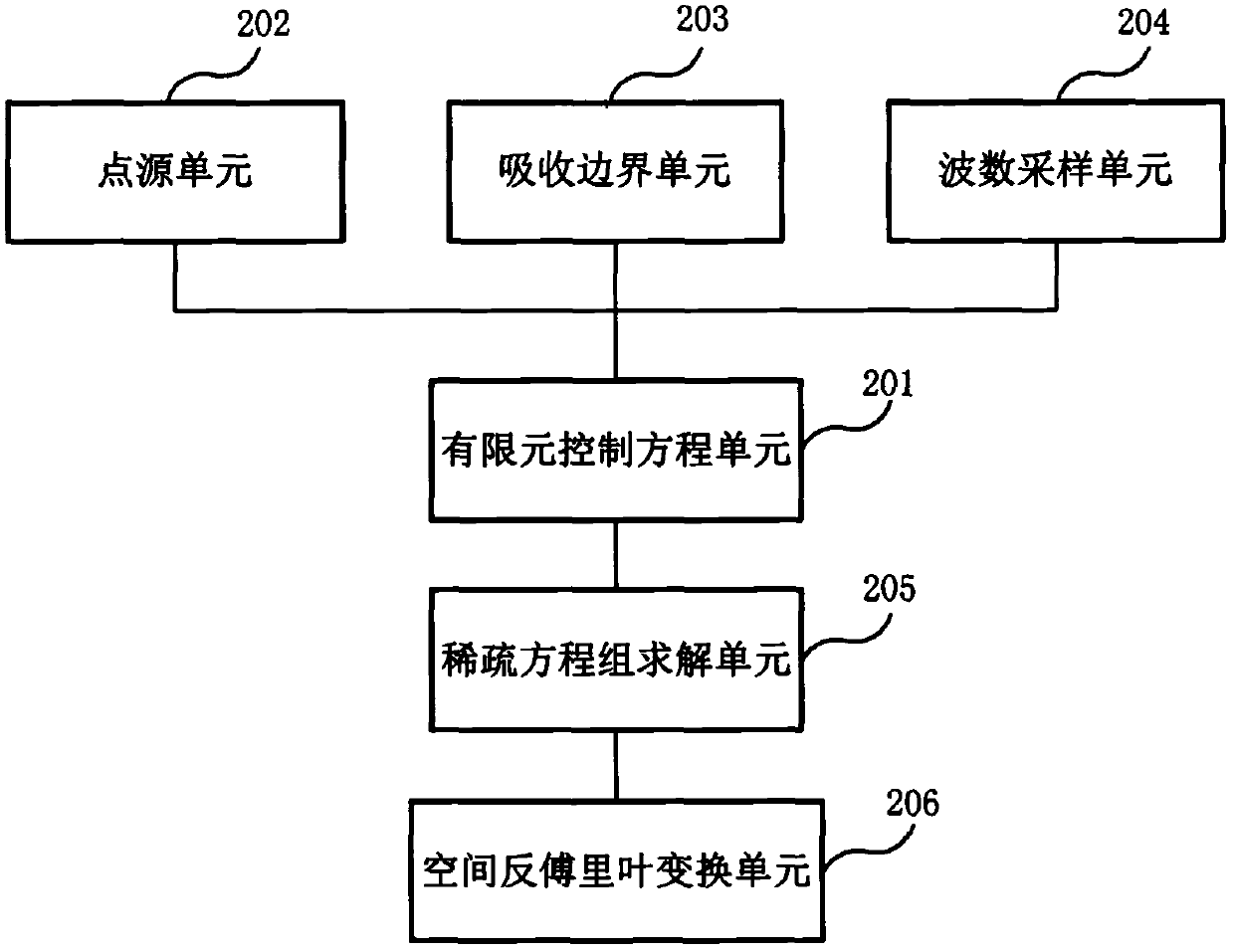
2.5-dimensional viscoelastic wave numerical simulation method and apparatus in frequency domain
InactiveCN107798156ANot affected by positive definitenessSimple loading processDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWave equationWave field
Embodiments of the present invention provide a 2.5-dimensional viscoelastic wave numerical simulation method and apparatus in the frequency domain. The method comprises: establishing a 2.5-dimensionalviscoelastic wave equation in the frequency domain; determining an equivalent integral weak form of the 2.5-dimensional viscoelastic wave equation in the frequency domain; obtaining a finite elementcontrol equation by using the discrete of bilinear triangular elements; loading 3D point sources in the frequency domain; loading the stiffness to weaken the absorption boundary condition; determininga wavenumber sampling strategy, wherein the finite element control equation is large sparse linear equations, and a direct solution method is used to solve the equations to obtain a frequency-wavenumber domain wave field; and using a complex Simpson numerical integration method to approximate the spatial inverse Fourier transform to obtain a three-dimensional viscoelastic wave field in the frequency domain. The present invention provides an accurate forward modeling method for 2.5-dimensional viscoelastic wave multi-scale full waveform inversion, and the method can adapt to any undulating surface complex medium, has a good absorption effect of the absorption boundary condition, and has high calculation efficiency.
Owner:赵建国 +2
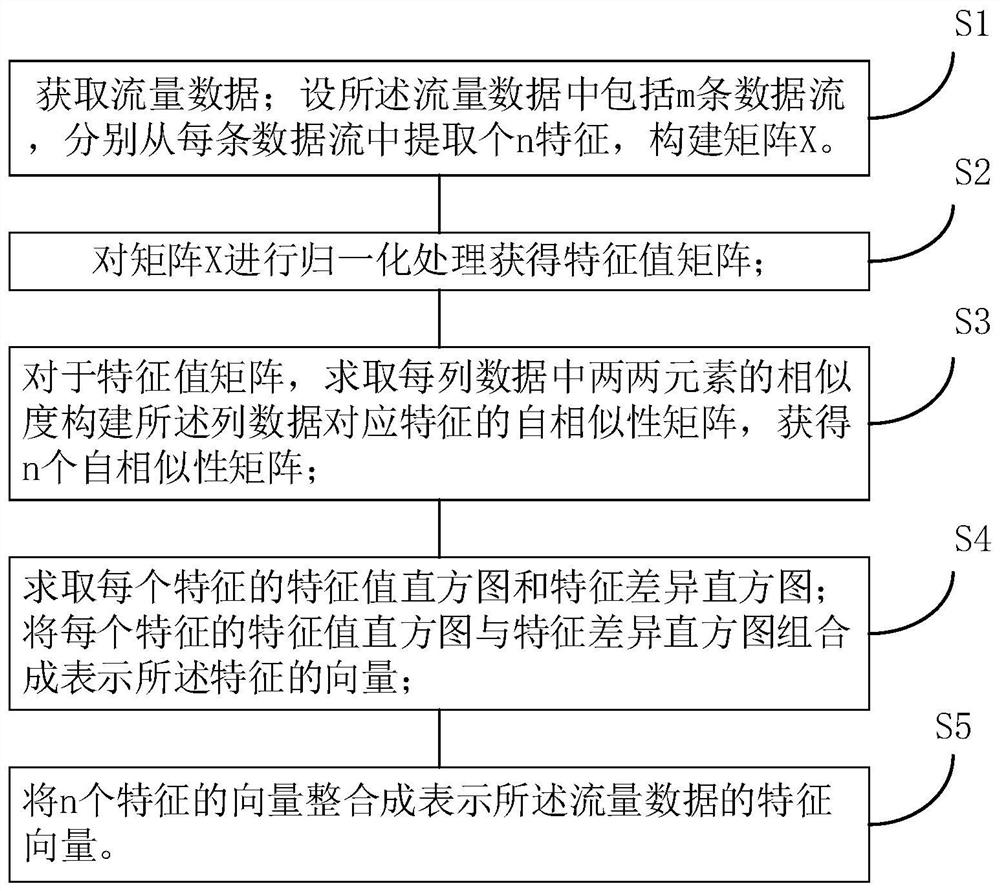
Traffic data feature extraction method, malicious traffic identification method and network system
ActiveCN111786951AAccurate distinctionImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionData switching networksFeature vectorData stream
The invention discloses a traffic data feature extraction method, a malicious traffic identification method and a network system. The feature extraction method comprises the steps of S1, obtaining traffic data including m data streams, extracting n features from each data stream, and constructing a matrix X; S2, performing normalization processing on the matrix X to obtain a feature value matrix;S3, solving the similarity of every two elements in each column of data for the feature value matrix to construct a self-similarity matrix of corresponding features of the column of data; S4, solvinga feature value histogram of features corresponding to each column of data of the feature value matrix; taking an upper triangular element of the self-similarity matrix of each feature to obtain a feature difference histogram; combining the feature value histogram and the feature difference histogram of each feature into a feature vector; and S5, integrating the vectors of the n features into a feature vector of the traffic data. The feature vectors have variation tolerance capability for the traffic features and are used as input of the classification model, so that the classifier can accurately identify malicious traffic and variants thereof.
Owner:中国星网网络应用有限公司
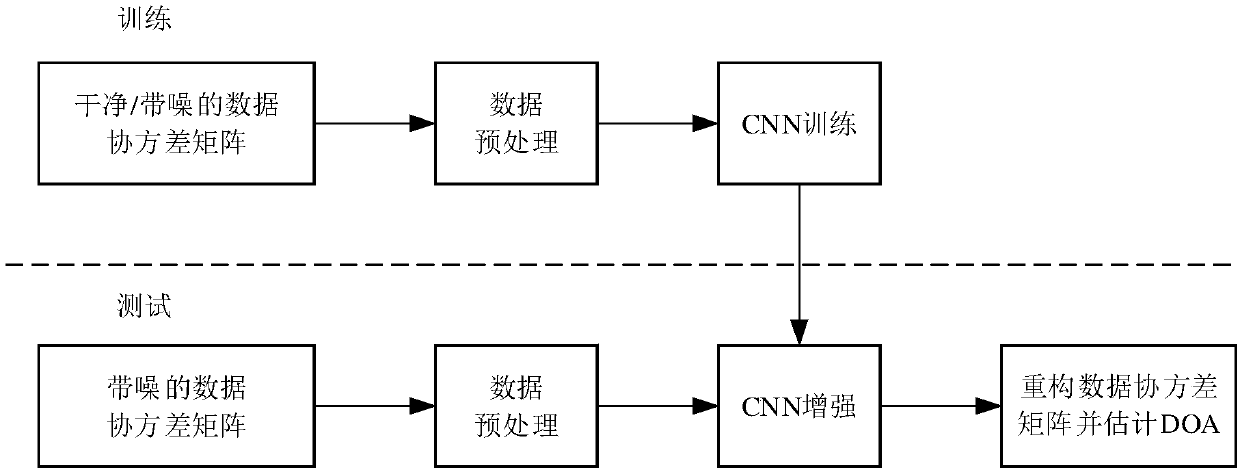
Method for estimating DOA (direction of arrival) of meter wave radar based on two-dimensional convolution neural network
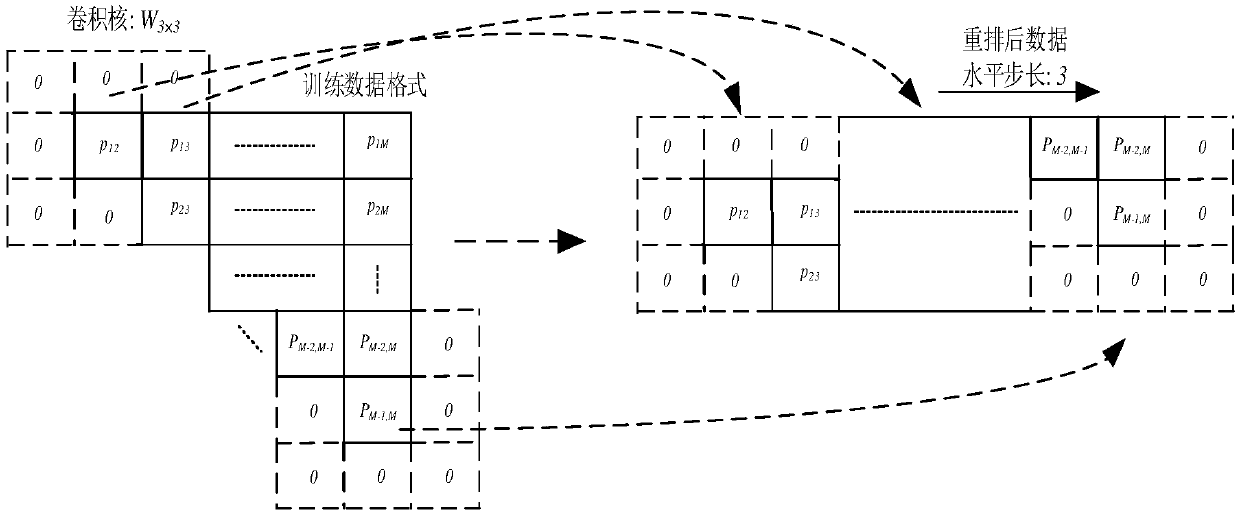
PendingCN109597048AWave based measurement systemsICT adaptationPhase.standard deviationCovariance matrix
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar, and discloses a method for estimating the DOA (direction of arrival) of a meter wave radar based on a two-dimensional convolution neural network.The method comprises the steps of obtaining P plots as a training set; calculating the covariance matrix of each plot in the training set and obtaining the corresponding phase average matrix and phase standard deviation matrix, wherein phases corresponding to upper triangular elements form an upper triangular element phase matrix; using the phase matrix corresponding to the i plot and subjected to zero filling and rearrangement as the input of the convolution neural network, and the output matrix of the convolution neural network corresponding to the i plot is obtained; modifying thenetwork parameters of the convolution neural network according to an objective function; and obtaining an actually measured target plot, and inputting the phase matrix of the actually measured targetplot into the convolution neural network to reconstruct the covariance matrix of the actually measured target plot to estimate the DOA of the target plot. Thus the DOA estimation problem is transformed into a pure regression problem.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Near-field source positioning method based on factor analysis
PendingCN112014790AReduce the numberImprove generalization abilityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsPosition fixationFeature DimensionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a near-field source positioning method based on factor analysis, and aims to solve the problems that a traditional subspace method is complex in calculation, cannot perform real-time processing and is poor in parameter estimation performance under a low signal-to-noise ratio. According to a neural network method, upper triangular elements of a covariance matrix of trainingsample signals are generally used as features of the signals to perform network training, and in a large array with a large number of array elements, the upper triangular elements of the covariance matrix of the signals are used as input signal features, so that the complexity of a neural network is improved, and the network training time is prolonged. Therefore, the invention provides the near-field source signal positioning method for dimension reduction by using the factor analysis method. According to the method, a few reconstructed feature variables are used for replacing original featurevariables to research and analyze things, so that the feature dimension of the network input signals is reduced, the input signal features after dimension reduction are used for training of the neural network, the training speed is increased, the real-time performance of the algorithm is high, and the engineering application value of the method is enhanced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Foldable mandrel for production of a single curvature folded core for a sandwich panel
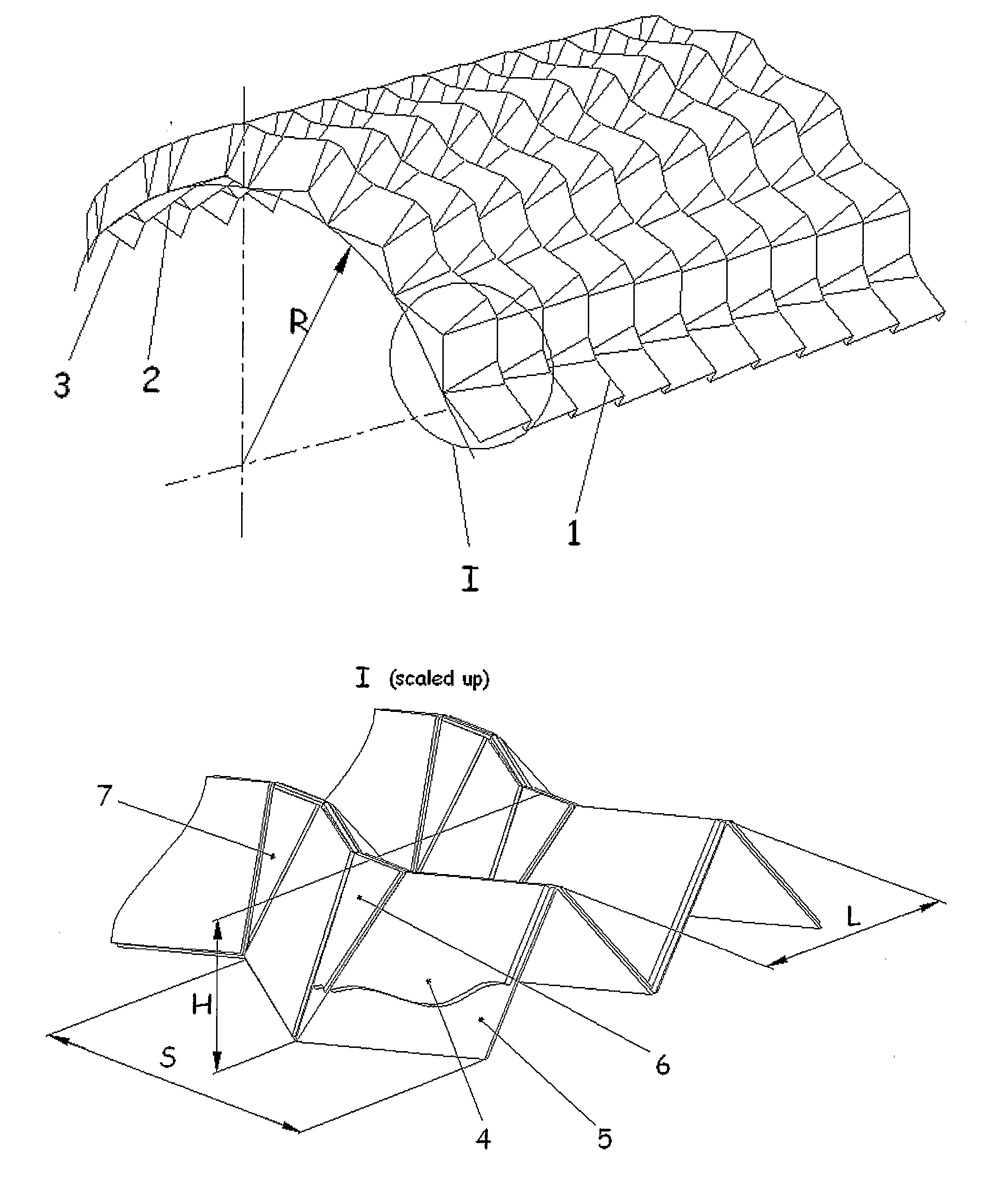
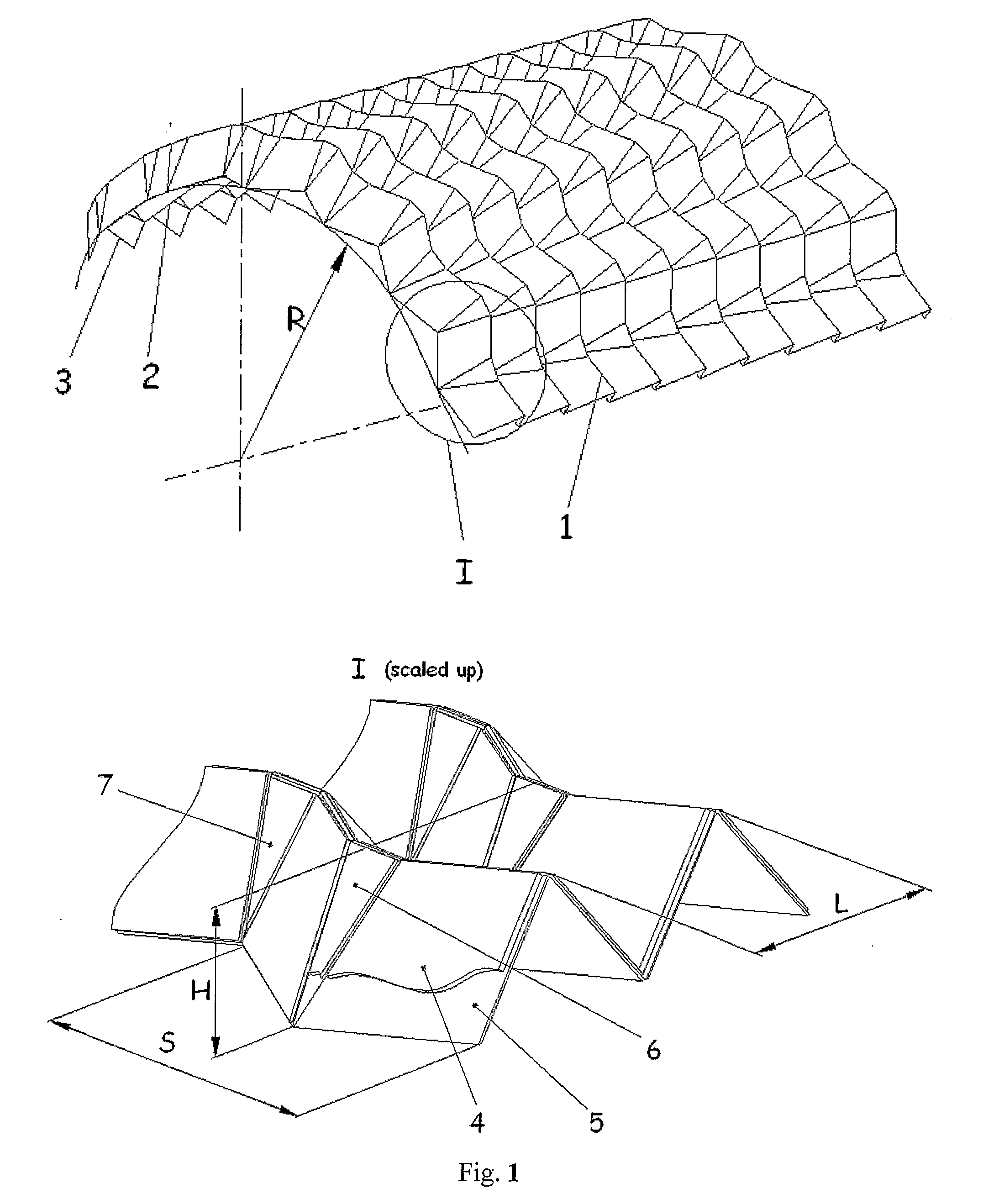
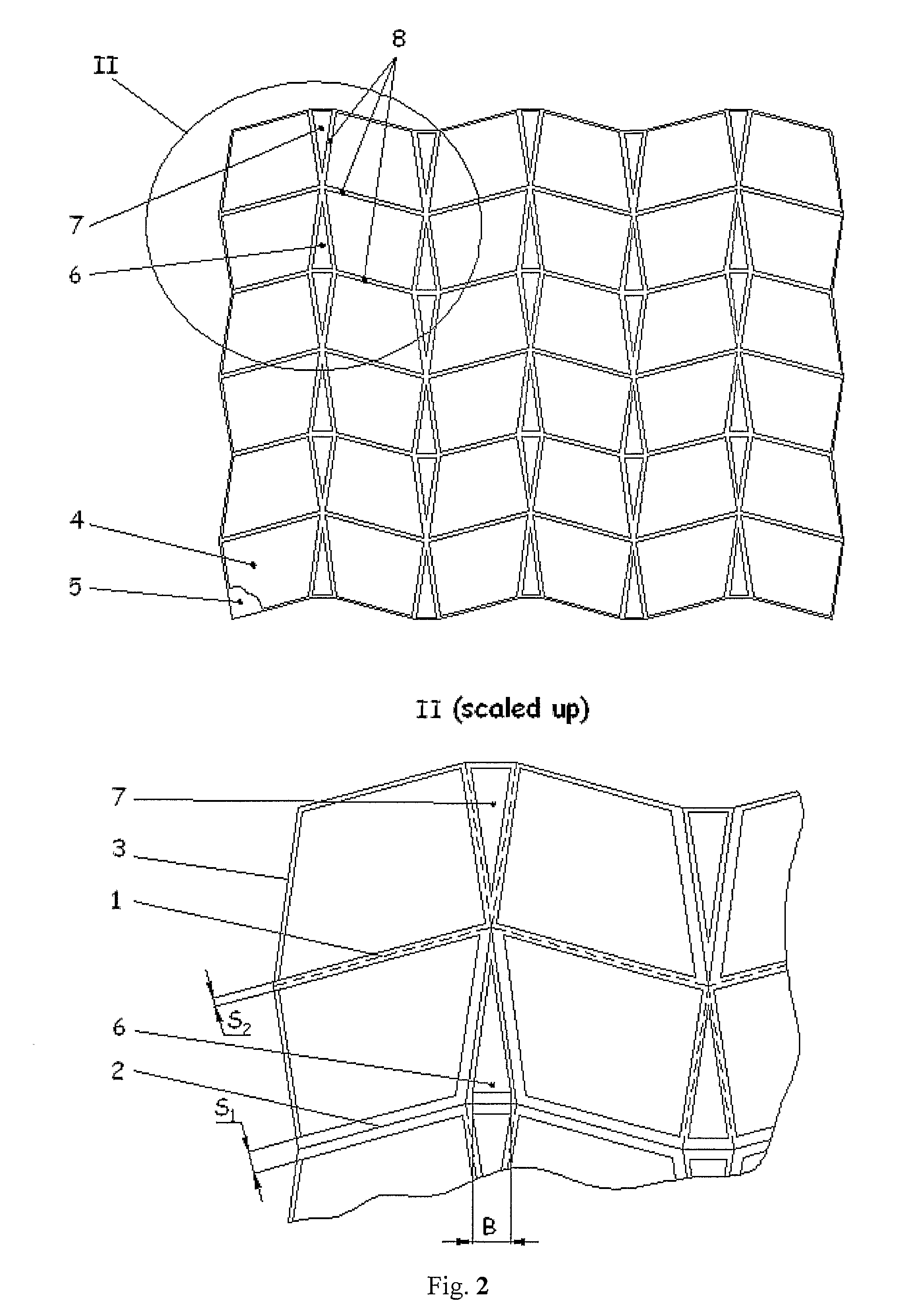
The invention can be defined in its most general form as a device for sheet material corrugation by means of bending and can be applied in the devices for production of single curvature folded core used in production of aircraft and craft curvilinear panels. The invention has for its object to broaden the technological capabilities. For that the mandrel is made in the form of a set of alternating rows of plane elements (4, 6, 7) made in the form of trapeziums (4) and isosceles triangles (6, 7) fixed on the flexible material of the base (5) forming thus the gap-pivots between the elements. At the same time the bases of the triangular elements (6, 7) face each other in pairs along the bending lines while said bending lines correspond to the protrusions lines of the core folded structure. The base of the triangular elements (6, 7) is the function of the folded core block curvature radius and the geometrical parameters of the zigzag crimp structure. The width of the gap-pivots is taken so that to provide the folding of the mandrel together with the blank forming thus the single curvature zigzag corrugated structure with the lateral direction of crimps.
Owner:AIRBUS +1
Brain function network feature classification method
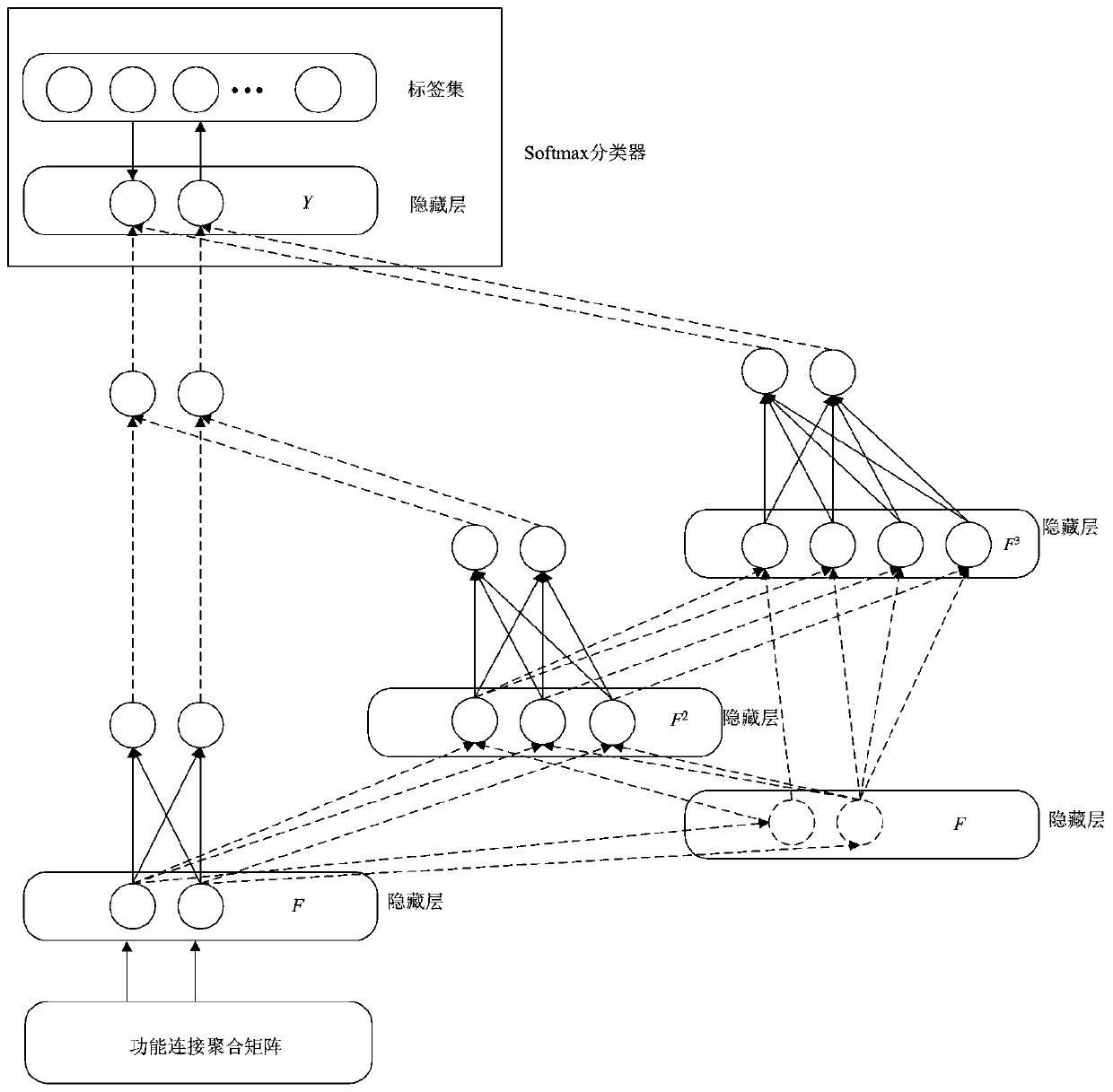
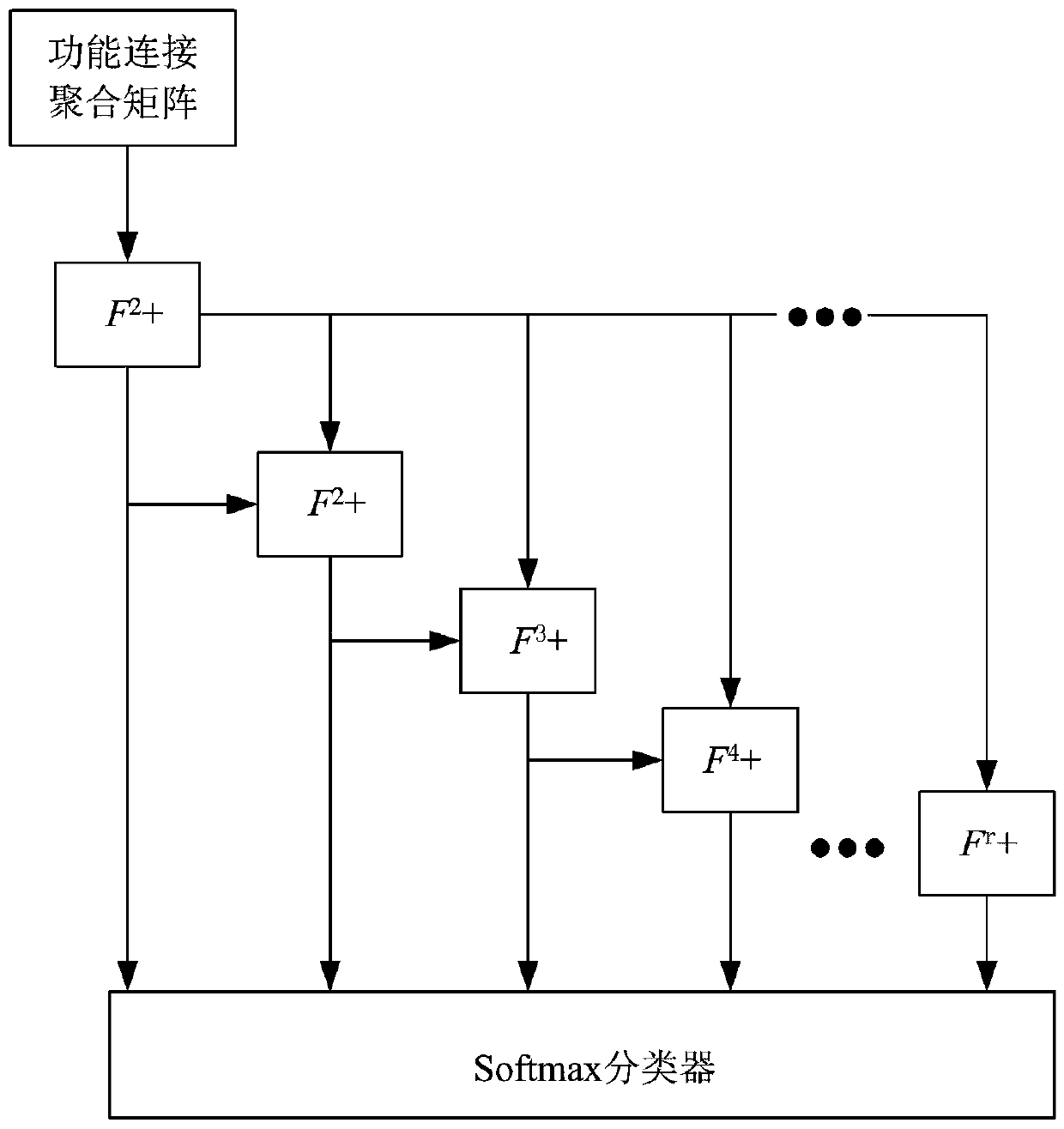
ActiveCN110598793ACharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringFunctional connectivityClassification methods
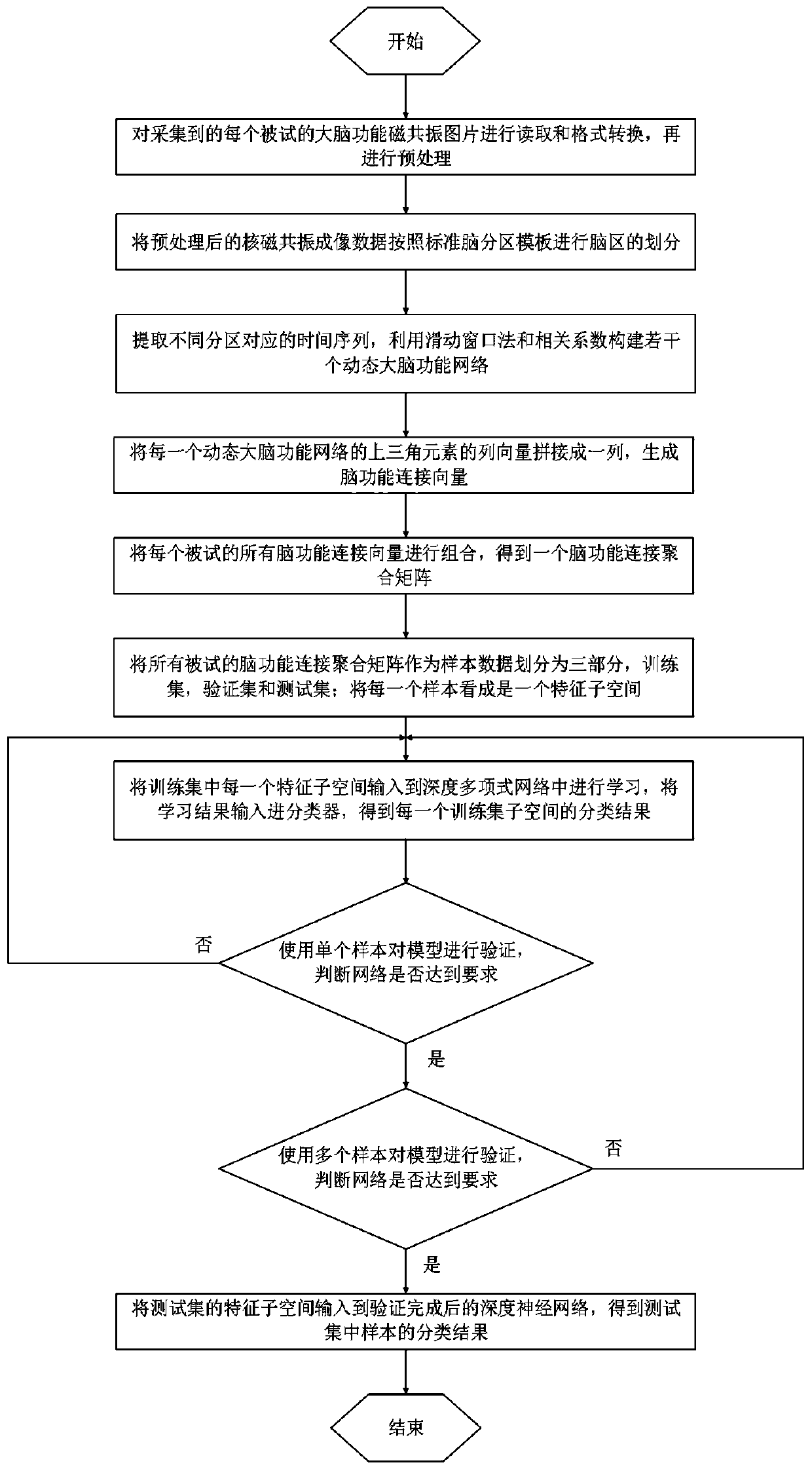
The invention relates to a brain function network feature classification method, which comprises the following steps of: performing format conversion and preprocessing on functional magnetic resonanceimaging, and extracting a time sequence of each brain region; dividing the time sequence into overlapping sub-segments with fixed lengths, and calculating correlation coefficients among the sub-segments to construct a plurality of dynamic function networks; splicing the column vectors of the upper triangular elements of each dynamic brain function network into a function connection vector, and combining all the tested function connection vectors into a successful aggregation matrix; dividing all the tested aggregation matrixes into three parts as samples, wherein each sample is used as a feature subspace; learning and classifying each feature subspace by the training set to obtain a training result; evaluating the network model by the verification set, and adjusting network parameter by the verification set; and classifyings each feature subspace by the test set to obtain a final classification result. The method has a certain reference value for researching cognitive impairment of the brain.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
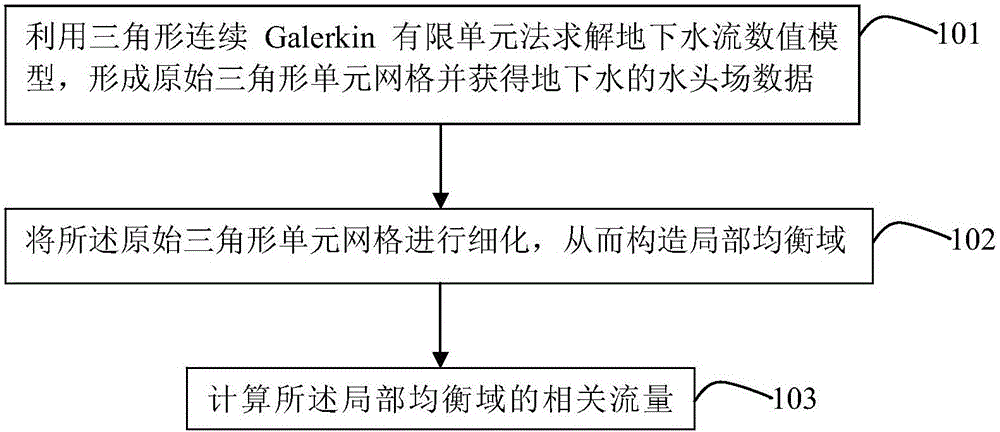
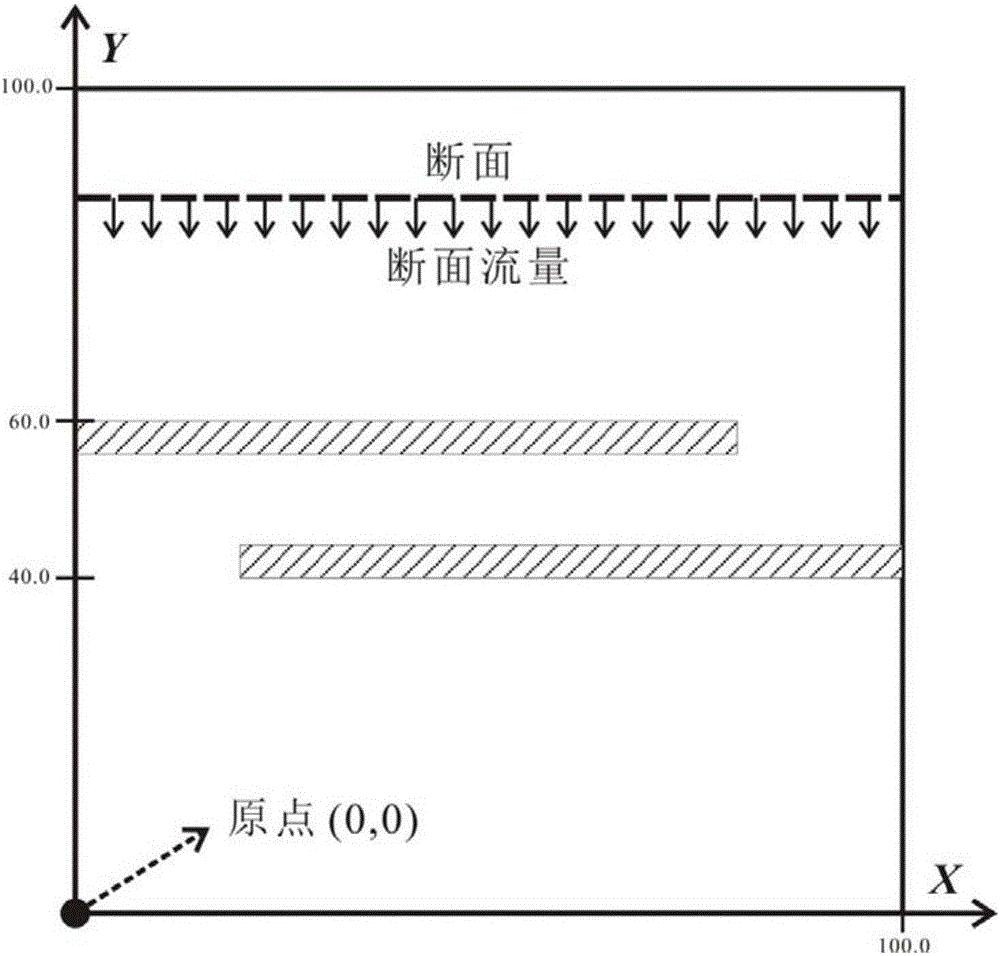
Groundwater flow calculation method
The present invention discloses a groundwater flow calculation method. The method comprises steps: S1. solving a numerical model of a groundwater flow by using a triangular continuous Galerkin finite element method, and forming an original triangular element mesh and obtaining water head field data of the groundwater; S2. carrying out refinement of the original triangular element mesh to construct a partial equilibrium domain; and and S3. calculating a relevant flow value of the partial equilibrium domain. The method disclosed by the invention proposes two flow calculation methods that can ensure conservation of mass in an equilibrium domain by using the continuous Galerkin finite element method to calculate a water head field of the groundwater, so as to improve the accuracy of a flow field of the groundwater based on the triangular continuous Galerkin finite element method and the relevant calculations thereof.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
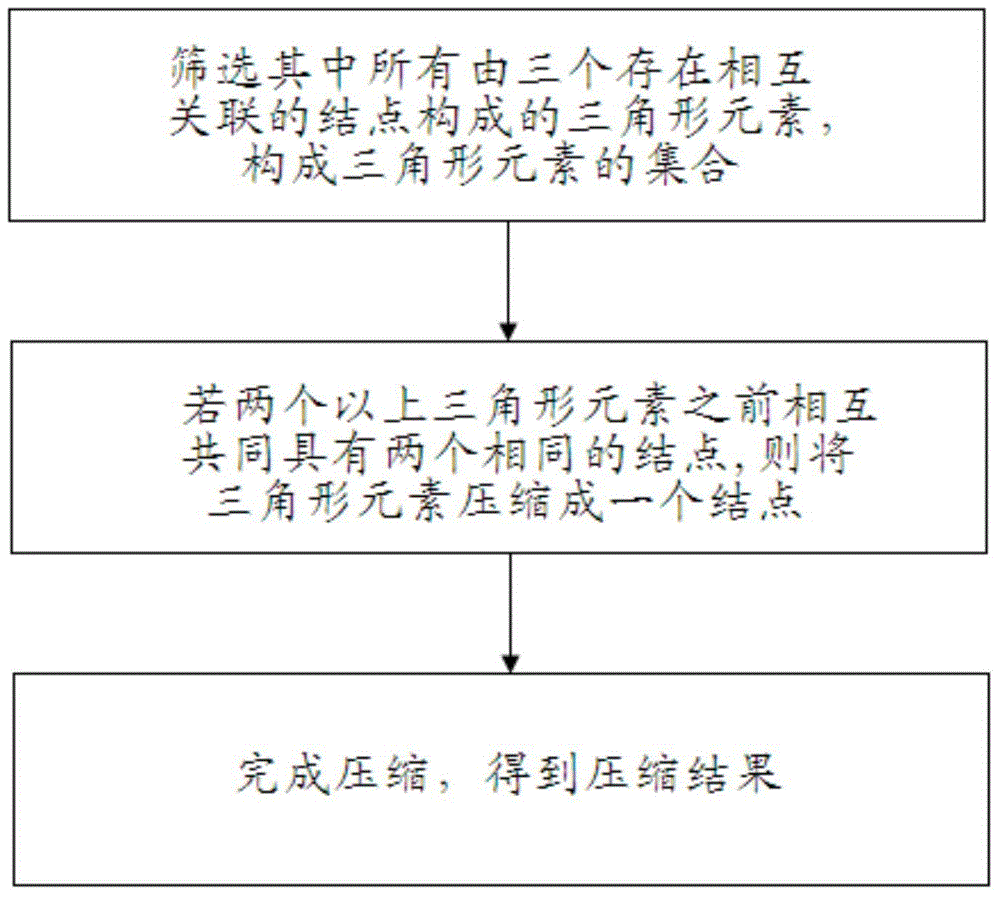
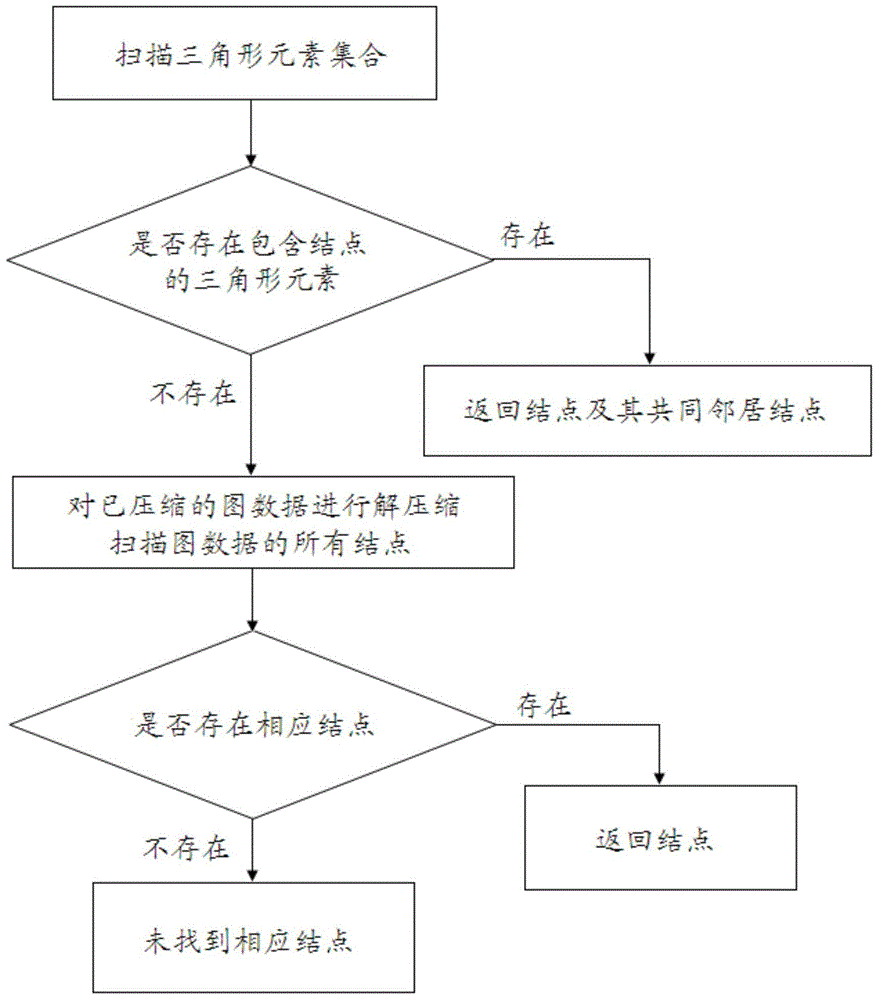
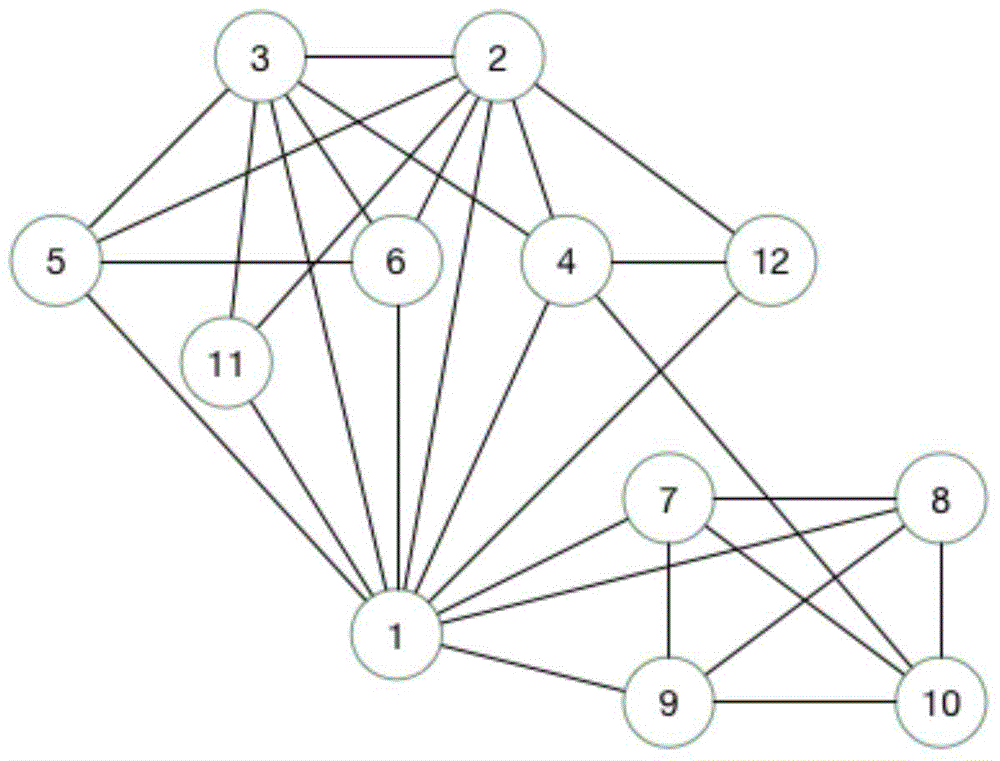
Graph data compression method and query method based on triangular statistics
InactiveCN105530011AImprove query efficiencyImprove compression efficiencyCode conversionData compressionMutual correlation
The invention discloses a graph data compression method based on triangular statistics, which comprises the steps of: acquiring a group of graph data, screening all triangular elements composed of three nodes having a correlation in the group of graph data, and forming a set of the triangular elements; and compressing the triangular elements into one node to obtain a compression result if more than two triangular elements comprise two identical nodes in the set. The graph data compression method increases a compression ratio by transforming an original storage form utilizing a node pair to represent a correlation between two nodes into a feature of utilizing a common node of the triangular elements. The invention further discloses an optimized query method for the graph data obtained by adopting the graph data compression method based on triangular statistics.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Modeling of multi-layered power/ground planes using triangle elements
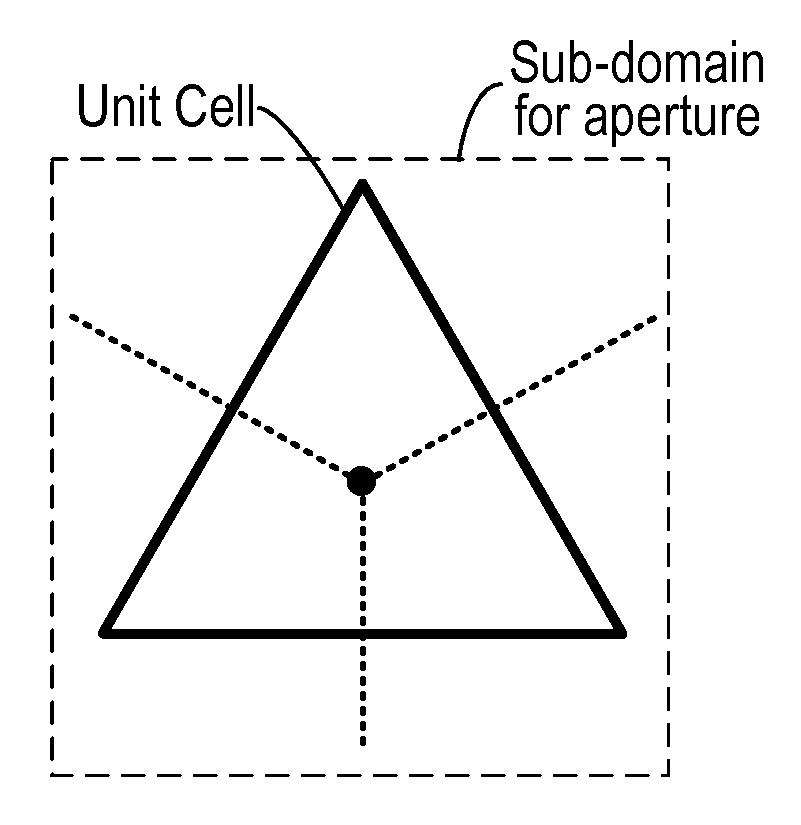
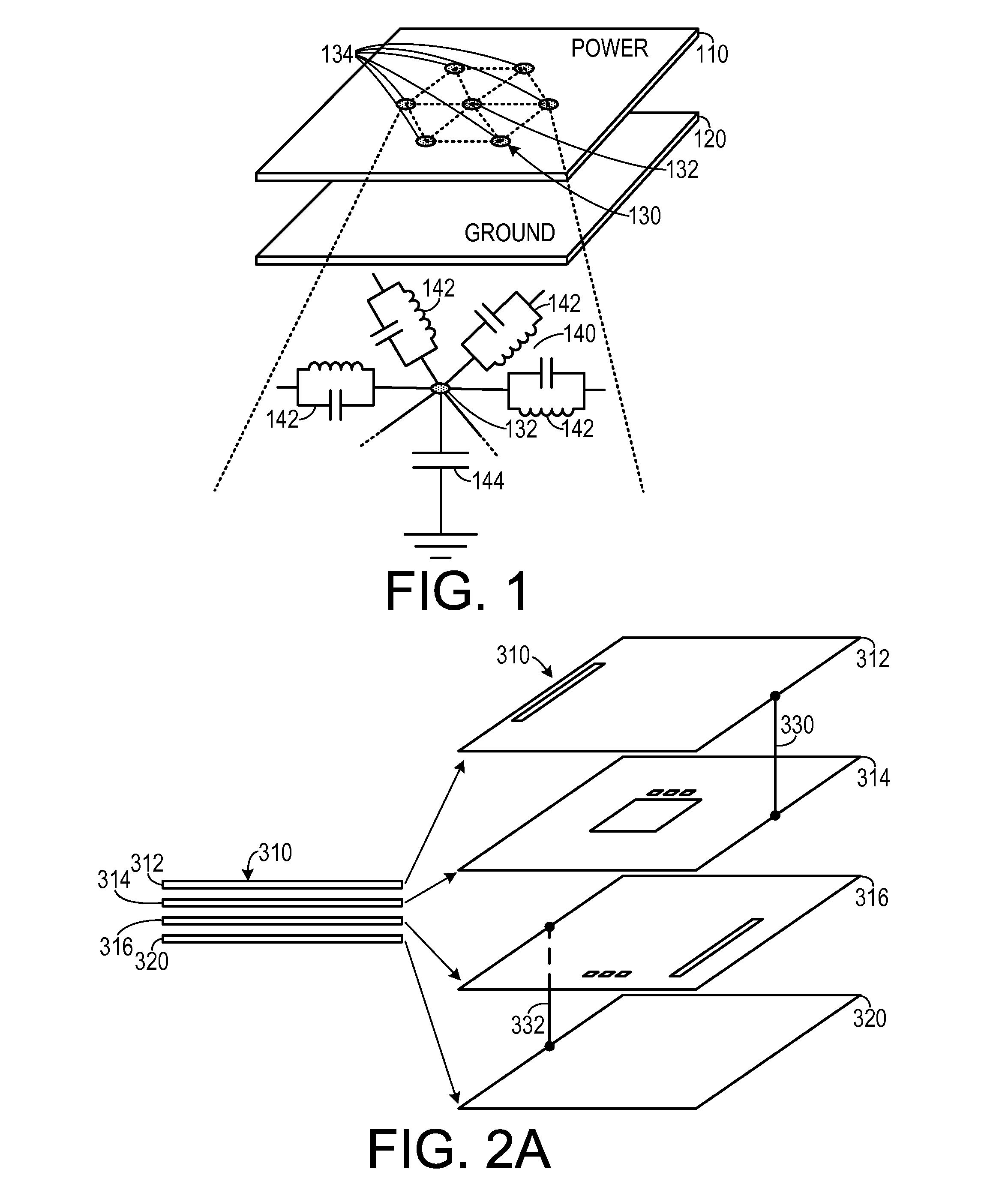
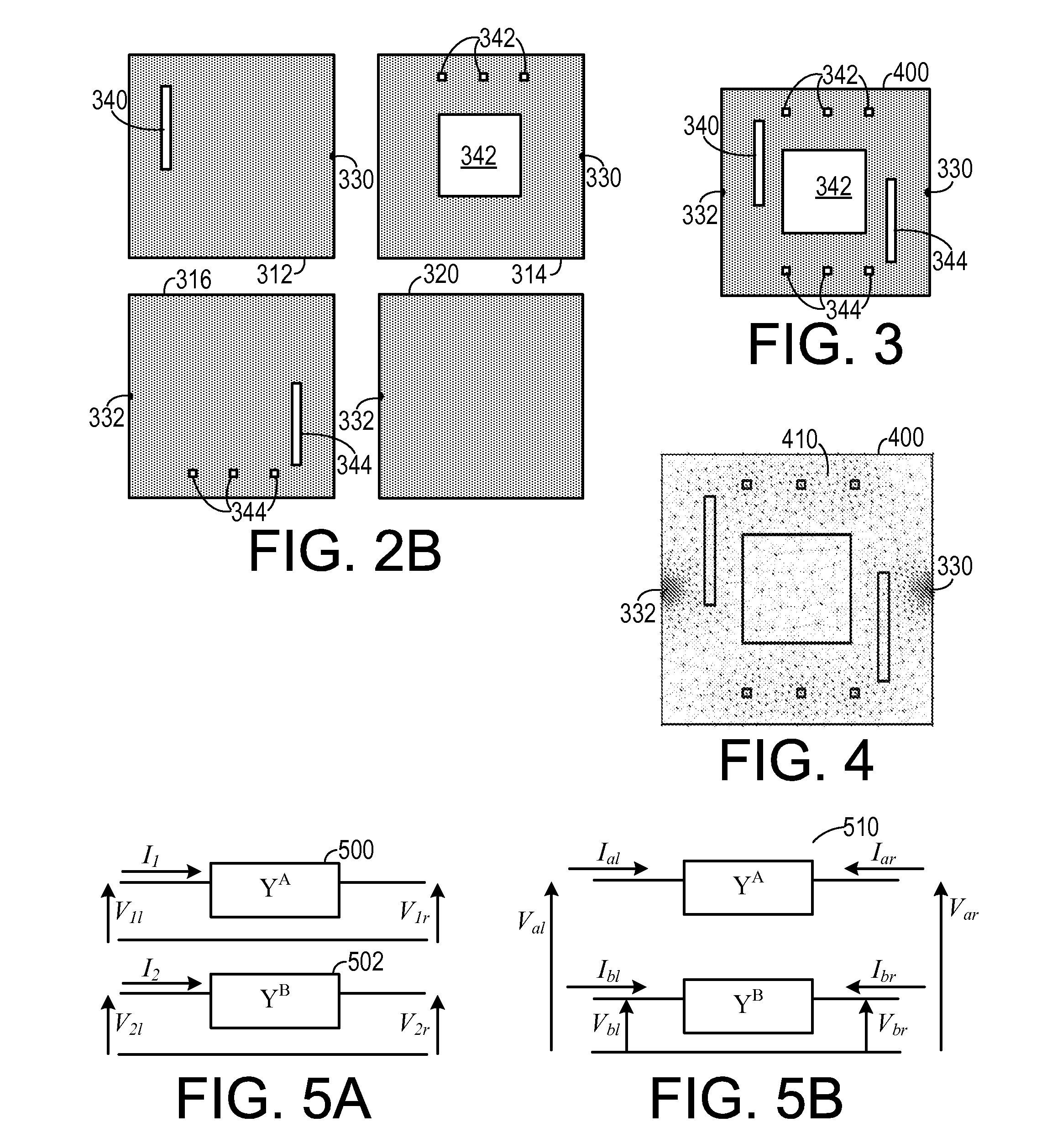
InactiveUS8954308B2Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityGround plane
In a method of simulating electrical characteristics of a circuit board having a plurality of features, the plurality of features is projected onto a planar construct. A Delaunay triangulation routine for generating a triangular mesh that corresponds to the single planar construct is executed on the digital computer. A routine that generates a Voronoi diagram corresponding to the triangular mesh. An equivalent circuit for each triangle is determined. The equivalent circuit includes exactly three sub-circuits that couple a vertex within the triangle to a vertex within an adjacent triangle and exactly one sub-circuit that couples the vertex within the triangle to a reference plane. A routine solves, for each triangle, an equation describing an electrical characteristic value based on the equivalent circuit corresponding to the triangle. A routine for generating a human-perceptible indication of the electrical characteristic value for each triangle is executed on the digital computer.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
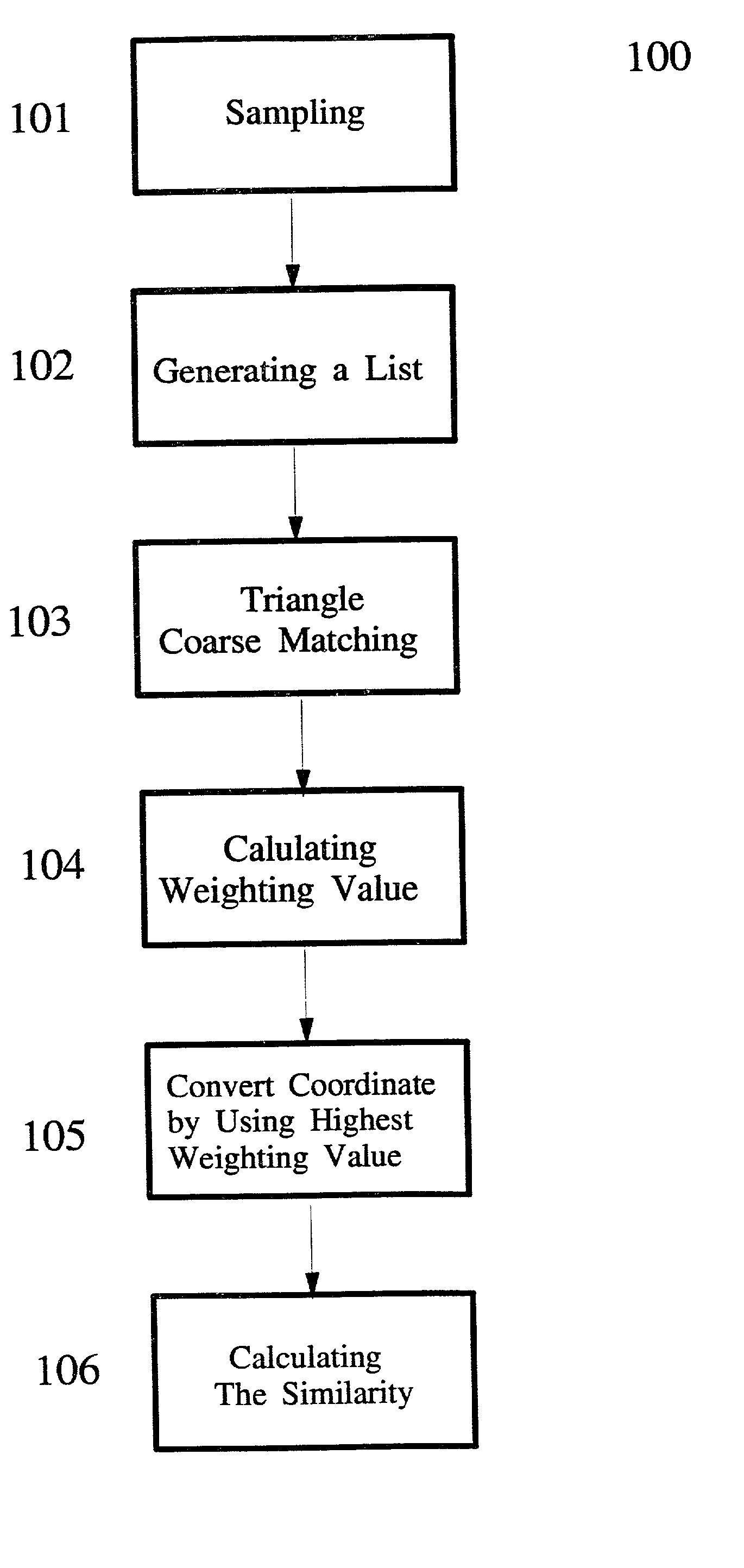
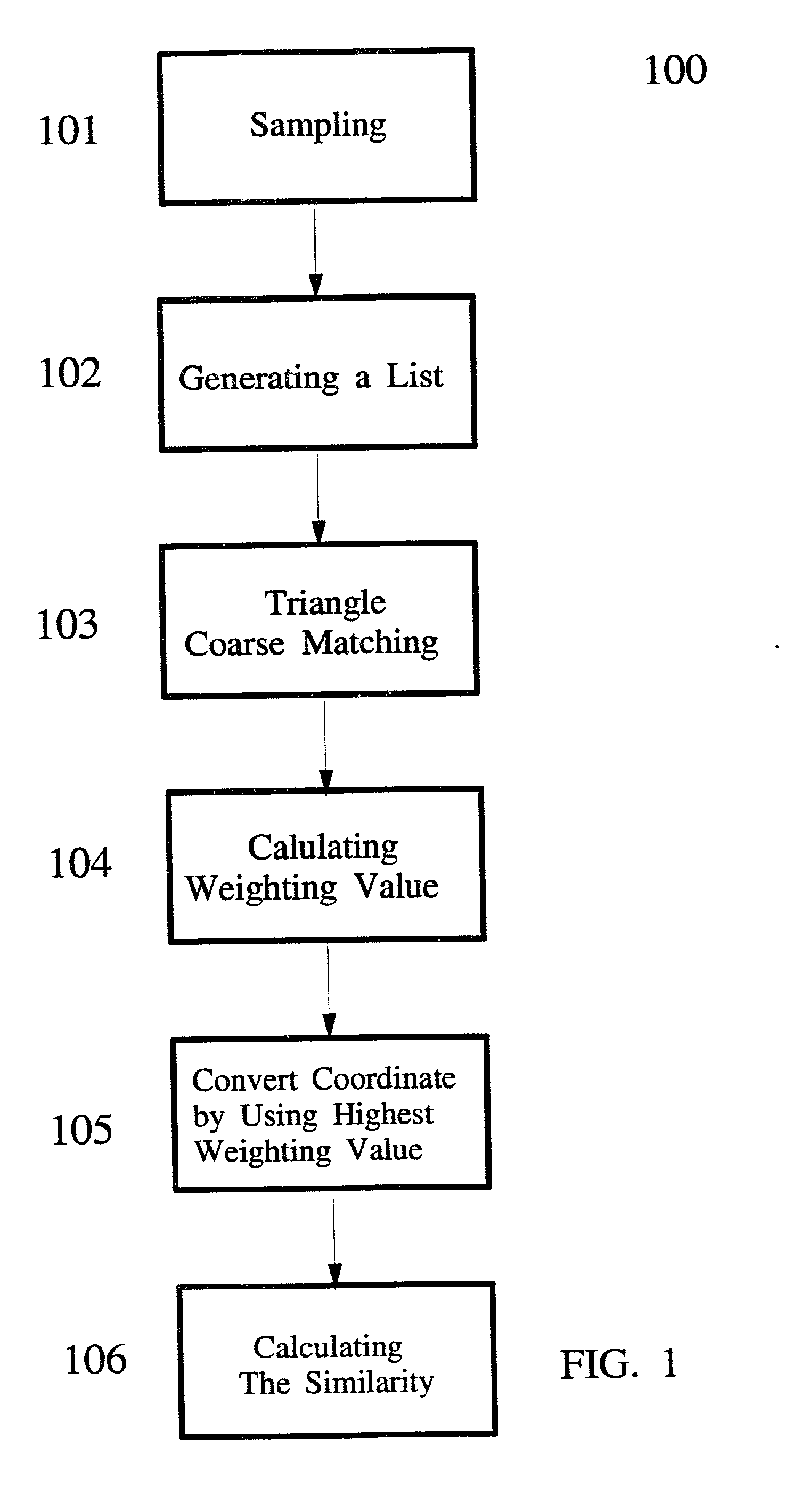
A method for improving the accuracy of the frame antenna profile
ActiveCN108401577BImprove theoretical surface accuracyShorten side lengthCollapsable antennas meansEngineeringMechanical property
A method to improve the accuracy of the frame antenna profile. Firstly, the reflective mesh surface is separated from the folded rods and the faceplate nodes, and an adjustable support column of a certain height is added to the faceplate nodes, and then the reflective mesh surface is decomposed. Add adjustable cables on top, add straps between the adjustable support columns and adjustable cables, divide the triangular units on the upper surface of each frame into several small triangular units, and finally sew the reflective mesh on the straps . This method adopts the design idea of separating the frame structure from the reflective mesh surface, re-decomposes the reflective mesh surface, and increases the number of basic triangular units while keeping the quality characteristics, mechanical properties, and expansion methods of the main structure of the frame unchanged. The side length of the triangle unit is shortened, thereby improving the theoretical surface accuracy of the reflective mesh surface.
Owner:中国航天科技集团公司第五研究院第五0四研究所
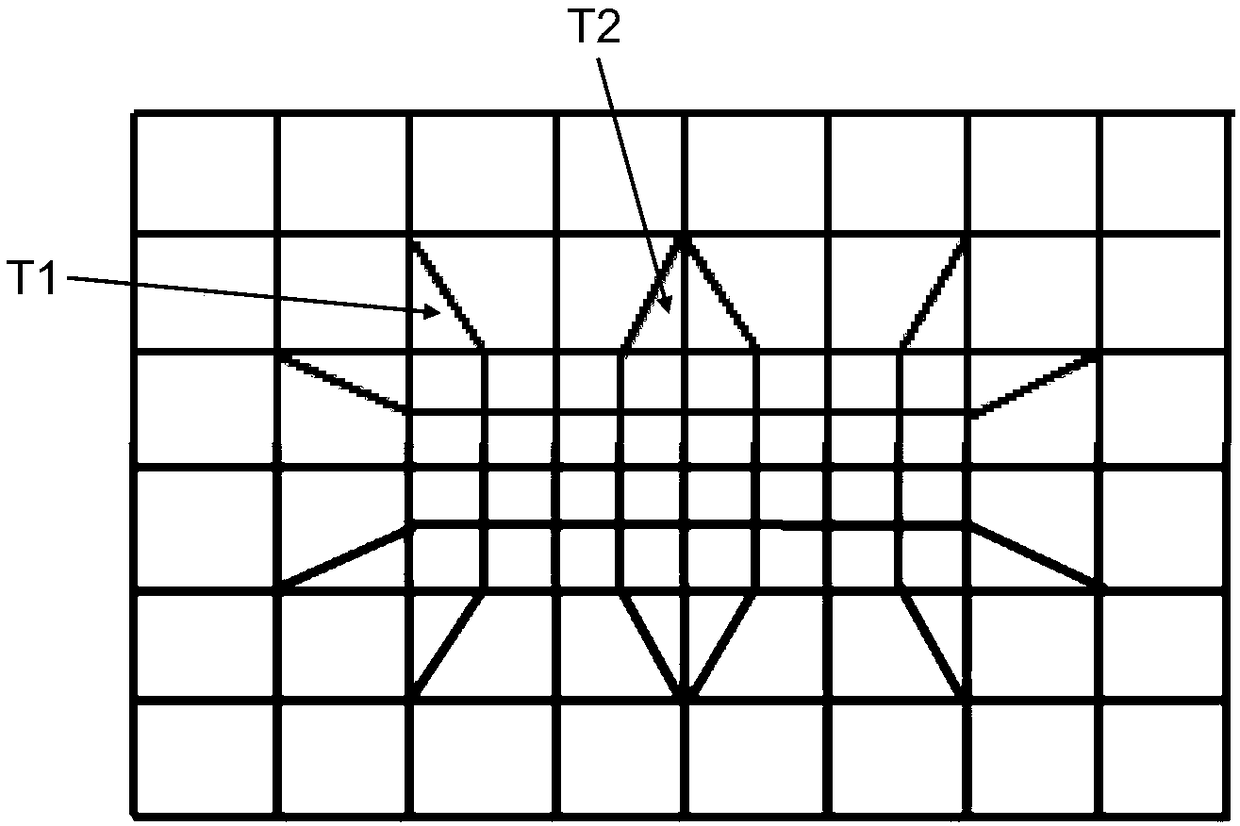
A method for improving the local refinement quality of a finite element mesh
InactiveCN109165475AImprove local encryption qualityEasy to divideGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationHigh densityComputer science
The invention discloses a method for improving the local refinement quality of a finite element mesh. The method includes: an encryption partition step: a region to be refined is determined on an initial region which has been refined by a finite element two-dimensional element mesh, in the region to be refined, the region to be refined is refined by a finite element two-dimensional element mesh with a smaller mesh cell size and a higher density, and after refinement, a triangular element exists in the peripheral region of the region to be refined; a triangular element removal step: a triangular element is selected, one or more mesh elements adjacent to the triangular element are selected, the triangular element and the mesh element form a transition region together, and the transition region has a quadrilateral contour, in the transition region, the original triangular element and the mesh element are eliminated, and the transition region is refilled with a plurality of quadrilateral elements. For each triangle element in the peripheral region of the area to be encrypted, a triangle removal step is sequentially performed until all the triangle elements are removed.
Owner:SAIC VOLKSWAGEN AUTOMOTIVE CO LTD
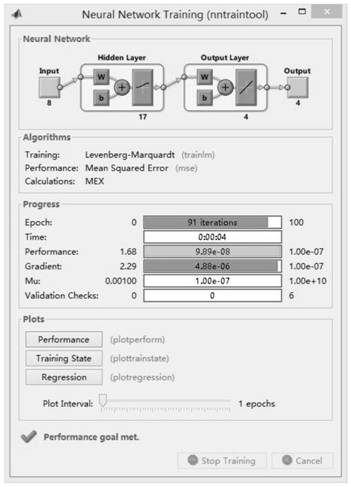
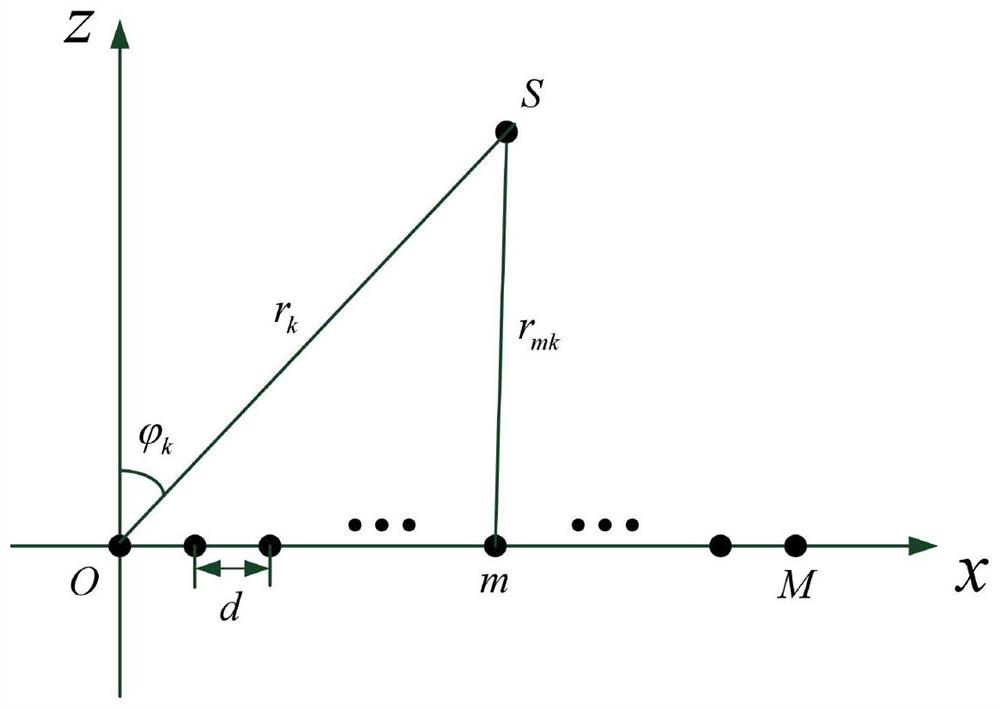
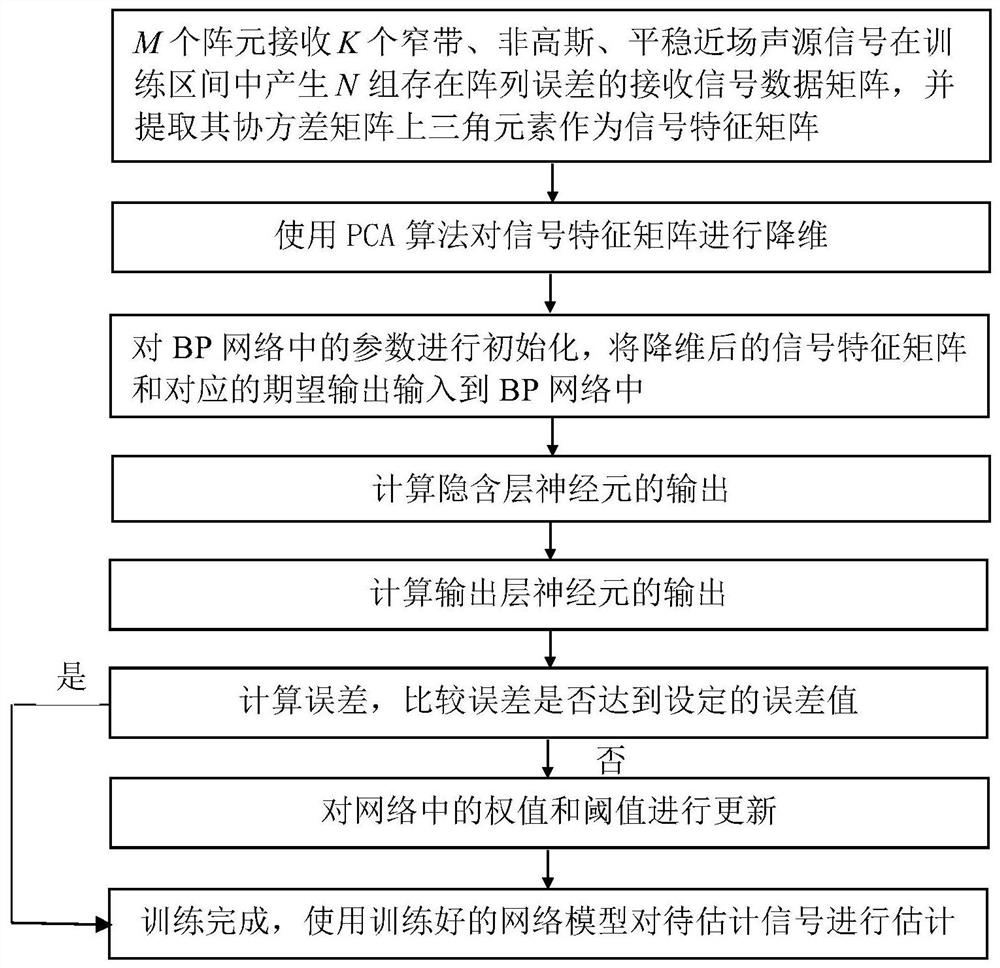
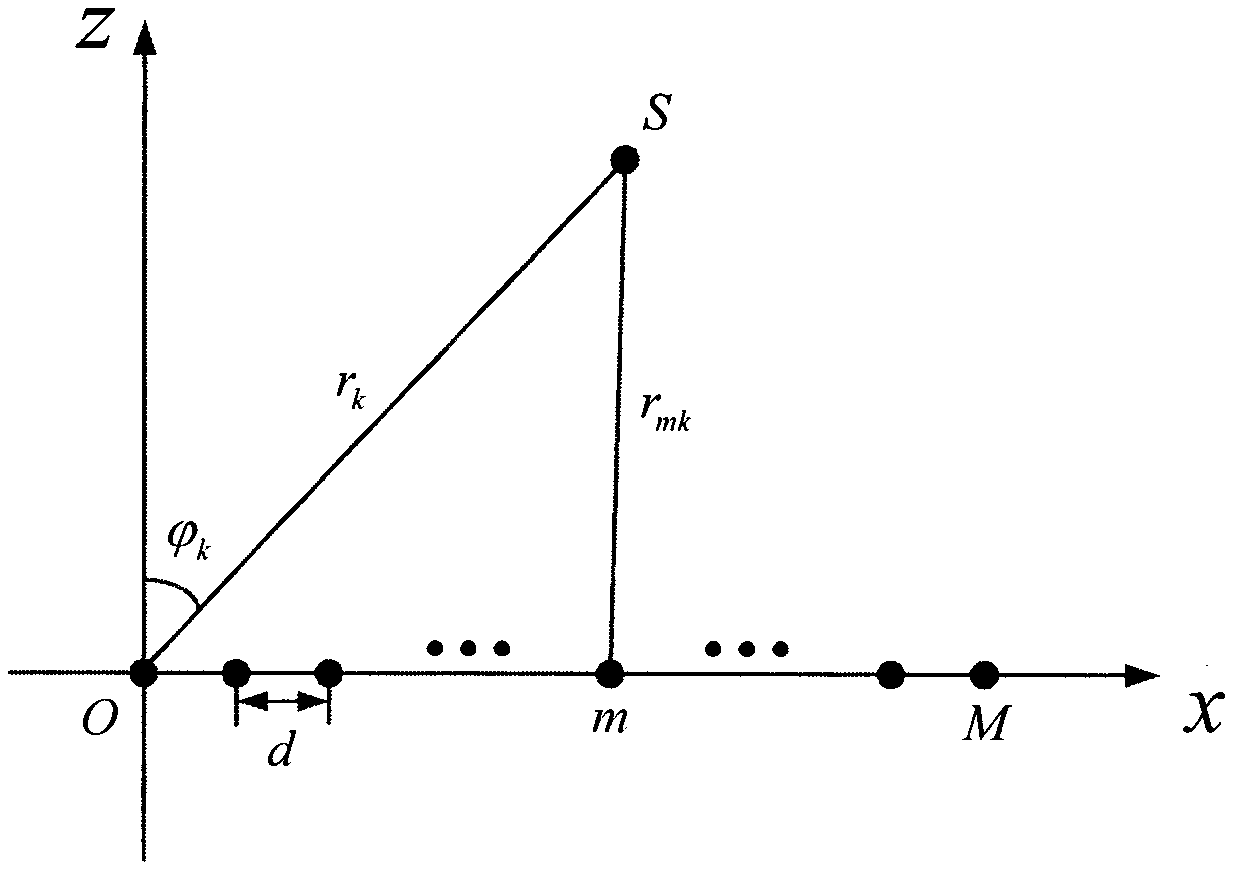
Near-field source positioning method of array PCA-BP algorithm with array errors
PendingCN112014791ASmall amount of calculationImprove noise immunityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionSound sourcesAlgorithm
The invention discloses a near-field source positioning method of an array PCA-BP algorithm with array errors. The method comprises the steps of Receiving K narrow-band, non-Gaussian and stable near-field sound source signals by using a uniform linear array, generating N groups of array receiving signal data in a training interval, extracting an upper triangular element of a covariance matrix of the array receiving signal data as a signal feature matrix, and performing PCA dimension reduction to obtain a dimension-reduced signal feature matrix; inputting the dimension-reduced signal feature matrix and the corresponding expected output into a BP neural network for training, and including the array error in the BP network through training, thereby obtaining a trained network estimation modelin the presence of the array error; and estimating near-field source parameters by using the trained network model. By using the array PCA-BP algorithm, errors are prevented from being corrected, thecalculation amount of the algorithm is reduced, the estimation performance of the algorithm under the low signal-to-noise ratio is improved, and good noise immunity is achieved.
Owner:SHAANXI SCI TECH UNIV
Near-field sound source positioning method based on partial least squares regression
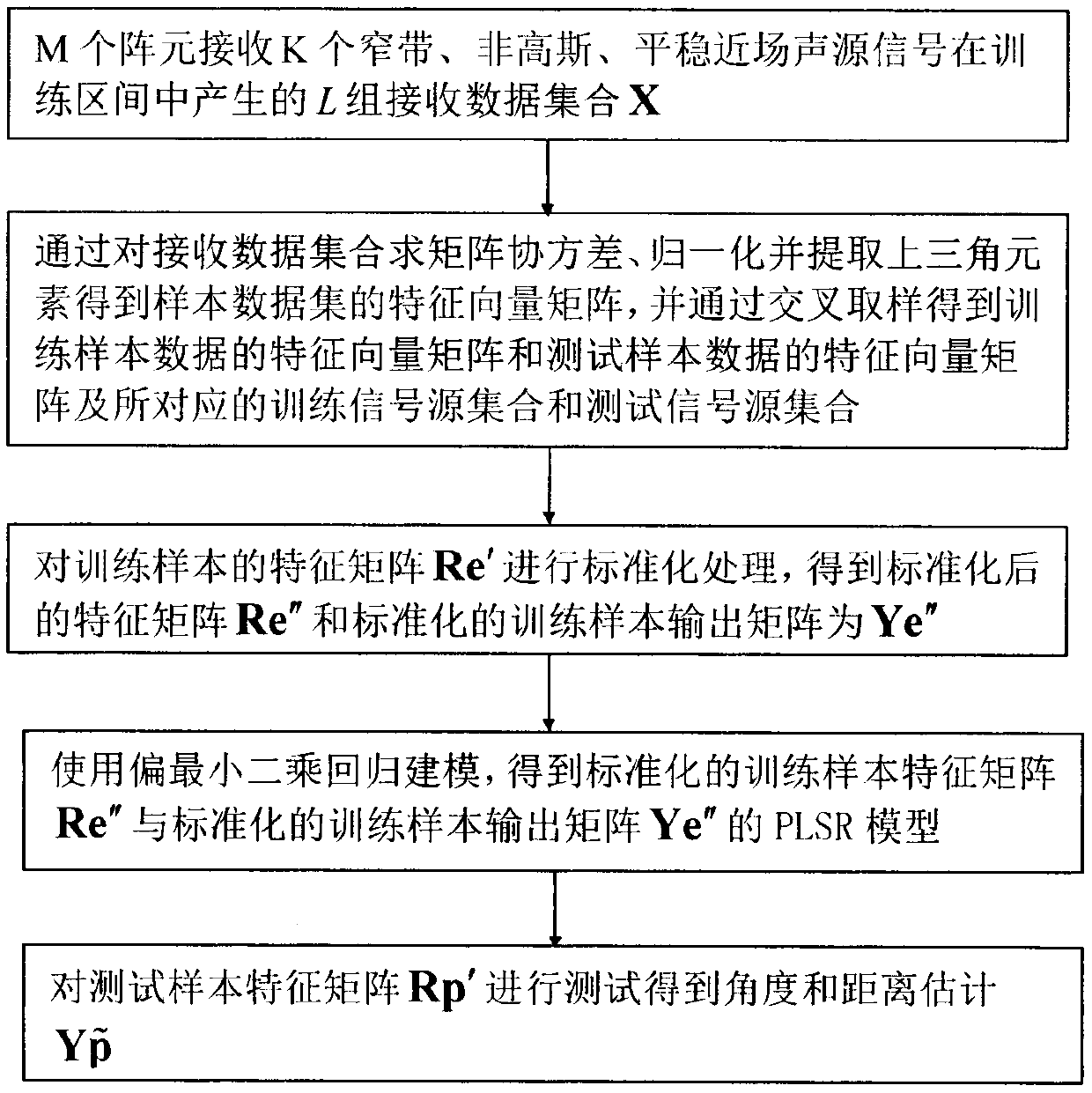
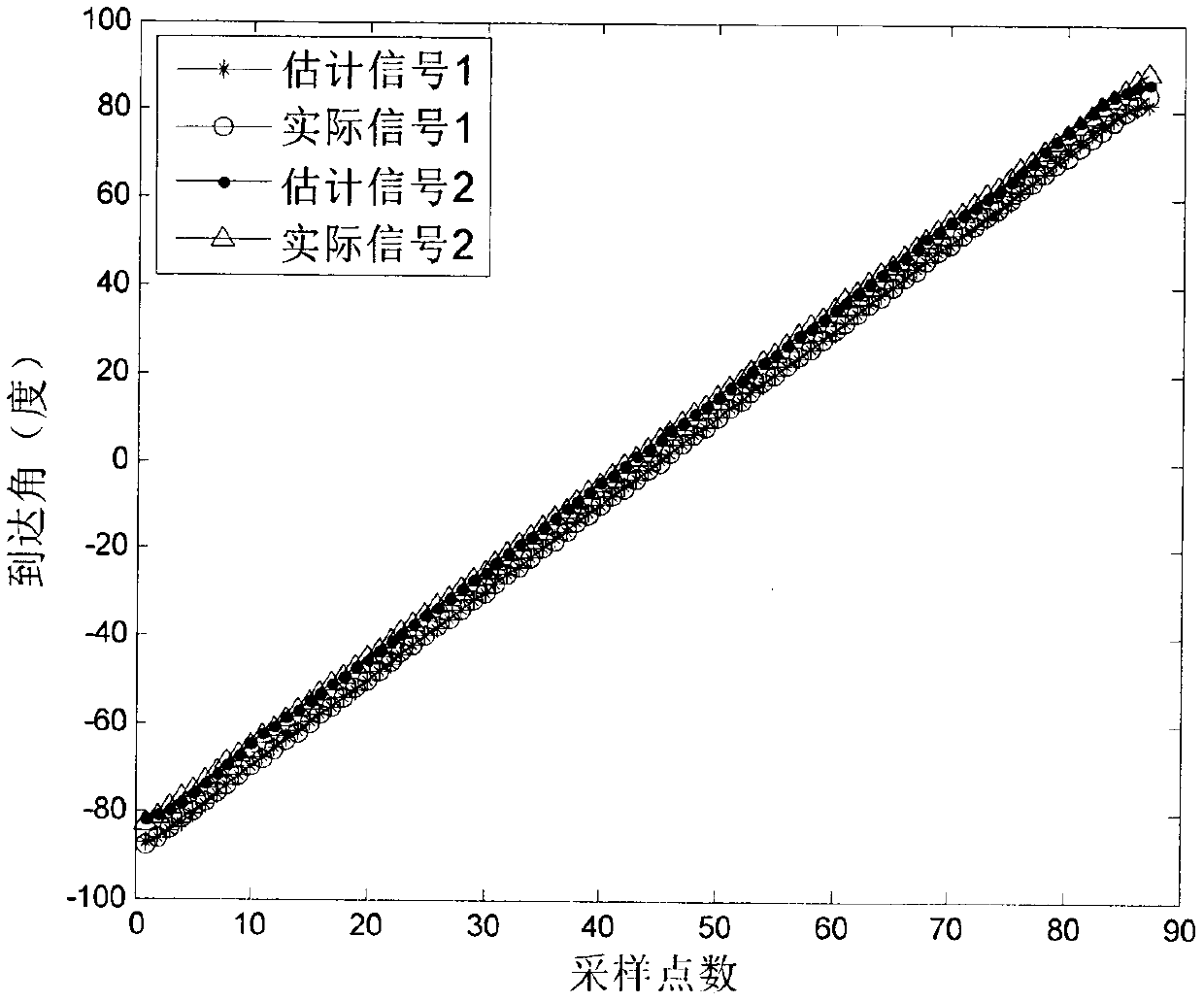
InactiveCN109901111ASimple calculationEstimated time is shortPosition fixationSound sourcesAlgorithm
The invention relates to a near-field sound source positioning method based on partial least squares regression and can effectively solve multiple correlation problems between variables. The method ischaracterized in that L sets of receiving data generated by K narrowband, non-Gaussian and stationary near-field sound source signals in a training interval are received by a uniform linear array, after each set of receiving data is subjected to covariance to obtain a corresponding covariance matrix, upper triangular elements of the data covariance matrix are extracted, standardization processingis performed, a training sample source set is subjected to standardization processing, the number of extracted components is determined based on the cross validity, and thereby a satisfactory estimation model is obtained; test data is estimated through utilizing the trained near-field source partial least squares regression model, the angle and the distance of a test source are estimated; the components extracted by partial least squares regression are not only a good summary of the information in an independent variable system, but also explains dependent variables well, and eliminates noiseinterference in the system, and the predicted angle and the distance are highly accurate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
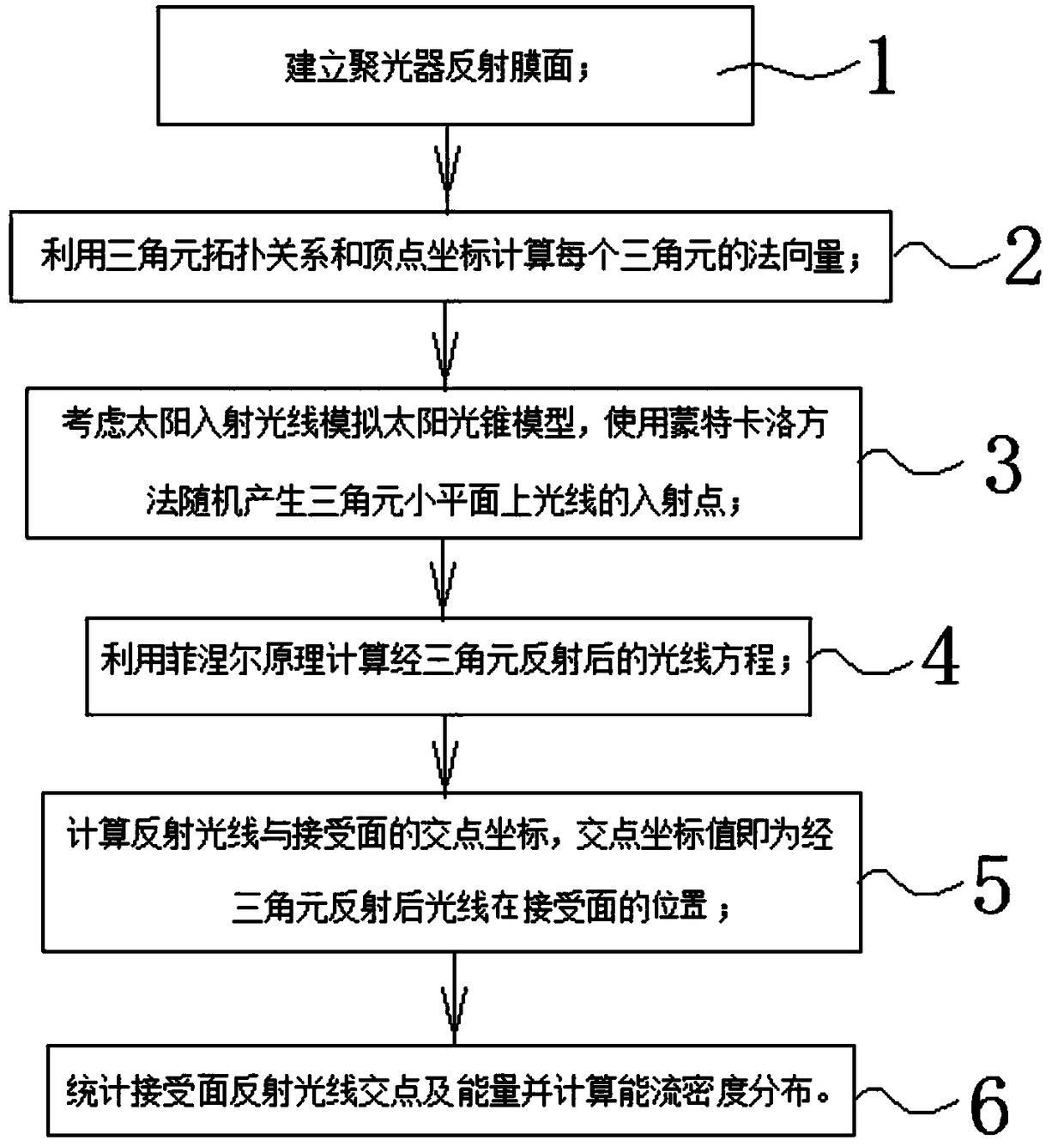
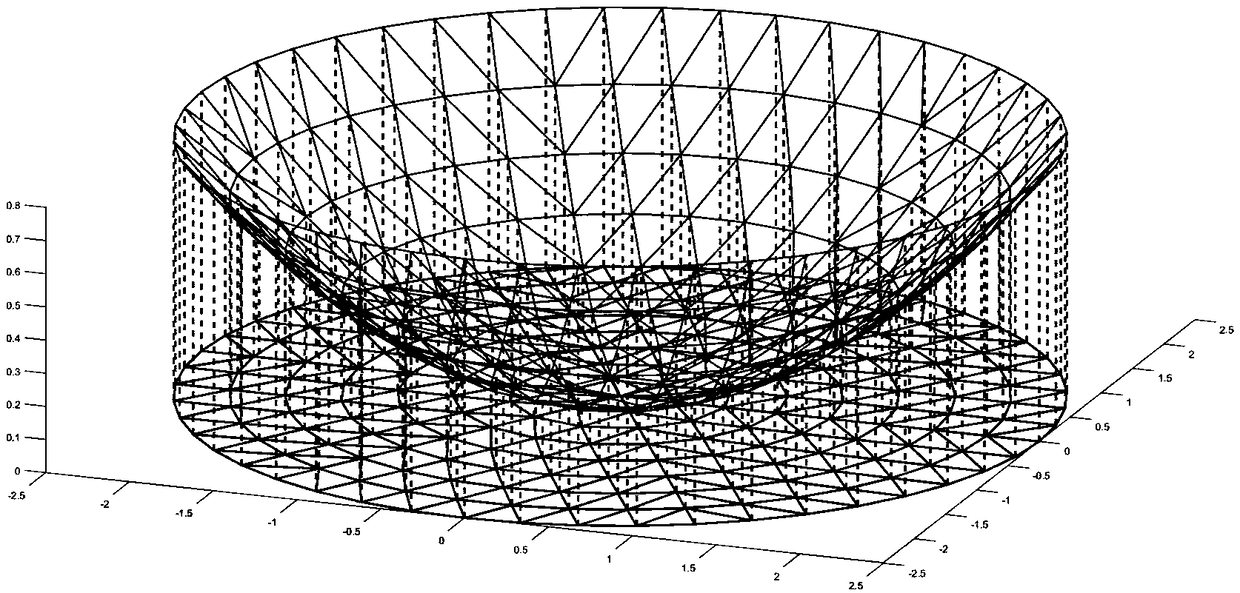
A method for predict that condensing performance of a dish-type triangular element splice parabolic film condenser
A method for predict that condensing performance of a triangular element splice parabolic film condenser is characterized in that the method at least comprises the follow steps: step 1, establishing areflective film surface of the condenser; 2, calculate that normal vector of each triangular element by using the topological relation of the triangular element and the vertex coordinates; 3, simulate a solar cone model by considering incident solar ray, and generating incident points of rays on a small flat surface of a triangular element at random by use a Monte Carlo method; 4, calculate thatray equation reflected by the triangular element by use the Fresnel principle; 5, calculate that coordinate of the intersection point of the reflected light ray and the receive surface, wherein the coordinate value of the intersection point is the coordinate of the light ray reflected by the triangular element and the receiving surface; 6, collect that intersection point and the energy of the light reflected by the receive surface and calculating the distribution of the energy flow density. The invention can simulate the distribution of the received surface energy flow density under the conditions of different incident angles of the light rays.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
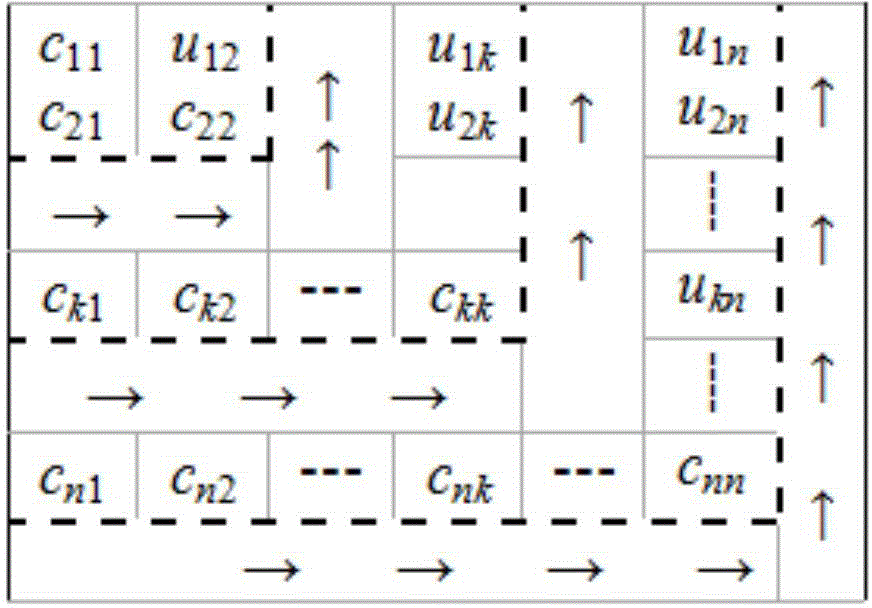
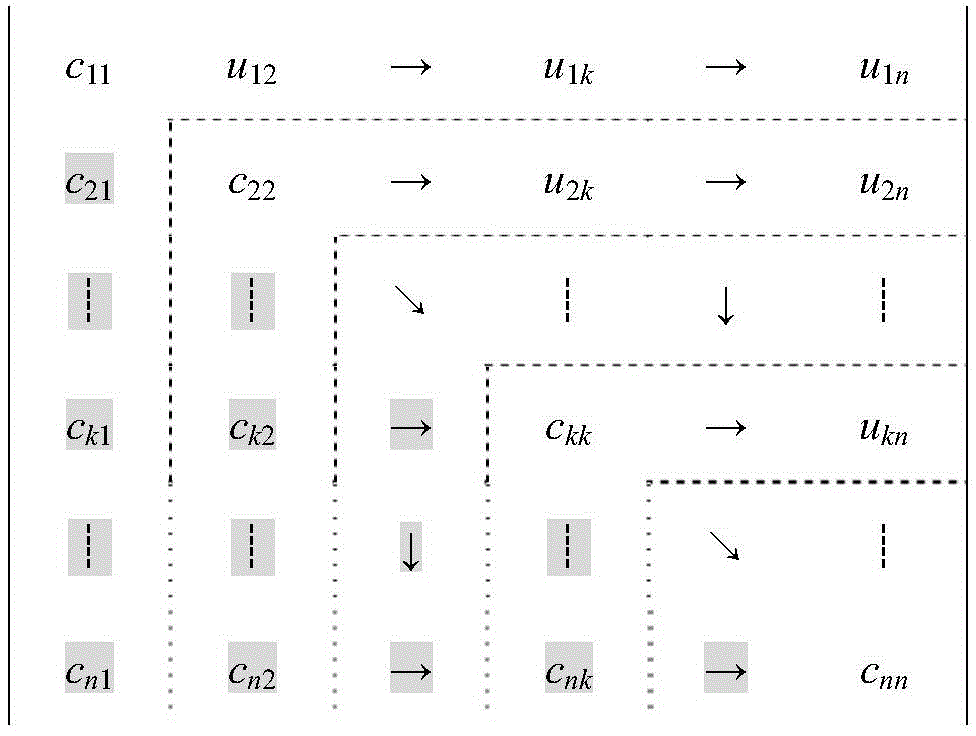
Electric power system node impedance matrix Z solving method based on CU triangular decomposition
ActiveCN104657337AImprove computing efficiencySave storage unitComplex mathematical operationsNODALElectric power system
The invention relates to an electric power system node impedance matrix Z solving method based on CU triangular decomposition and belongs to the field of electric power system analysis and computing. The method mainly includes the steps of forming a node admittance matrix Y; performing quick CU triangular decomposition on the matrix Y; solving a matrix Wk through CWk=Ek; solving non-diagonal elements of a diagonal element Zkk and the diagonal element above the diagonal element Zkk of a matrix Zk through UZk=Wk; solving non-diagonal elements on the left of the diagonal element Zkk in accordance with the symmetry; writing data of a matrix Z to a data file. According to the electric power system node impedance matrix Z solving method based on CU triangular decomposition, a CU triangular decomposition method higher in calculation efficiency than a LDU triangular decomposition method is used for solving elements of the matrix Z, the symmetrical relationship between elements of a matrix Y and elements of a matrix C and a matrix U is used for quickly forming a composite matrix of a factor matrix C and a factor matrix U, and the symmetry of the matrix Z and the calculation order of elements of the matrix Zk is used for omitting back substitution solving of lower triangular elements of the matrix Z for achieving direct solving, so that the speed of formation of the matrix Z is greatly improved. Compared with the traditional LDU triangular decomposition method, the electric power system node impedance matrix Z solving method based on CU triangular decomposition has the calculation speed increased by about 33% when the method is used for IEEE-30, IEEE-57 and IEEE-118 node system checking calculation.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
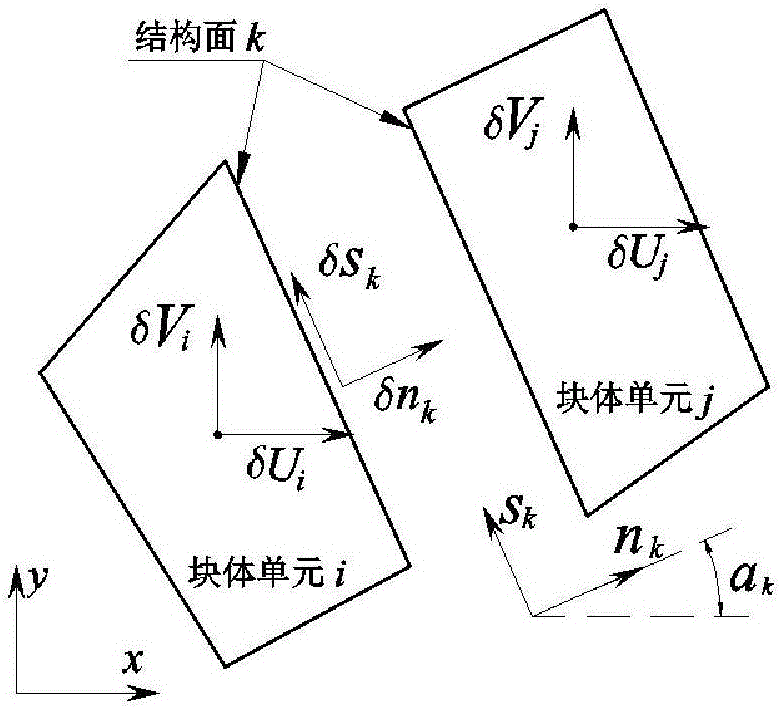
Method for measuring deformation of discontinuous body containing structural plane and application
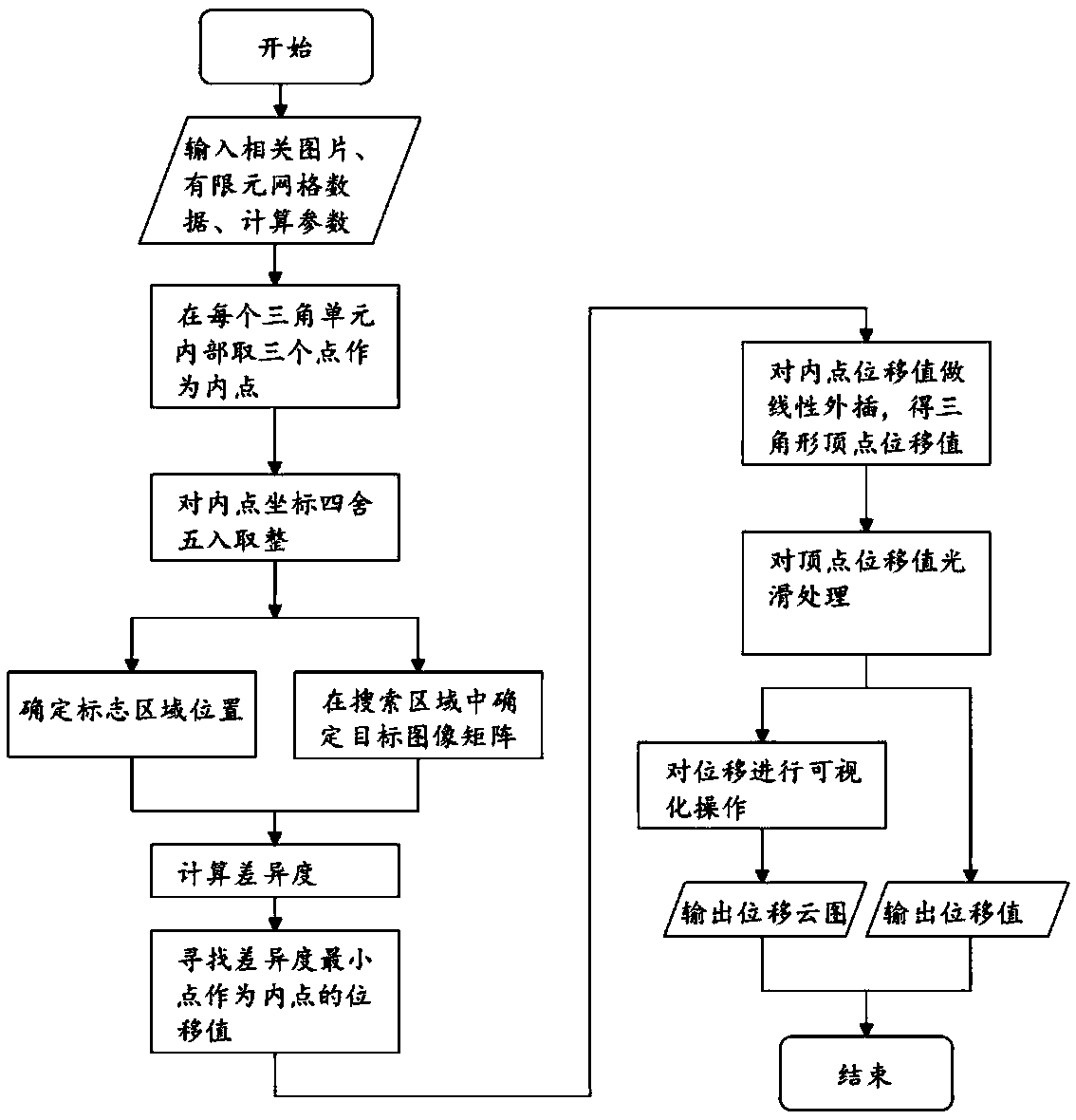
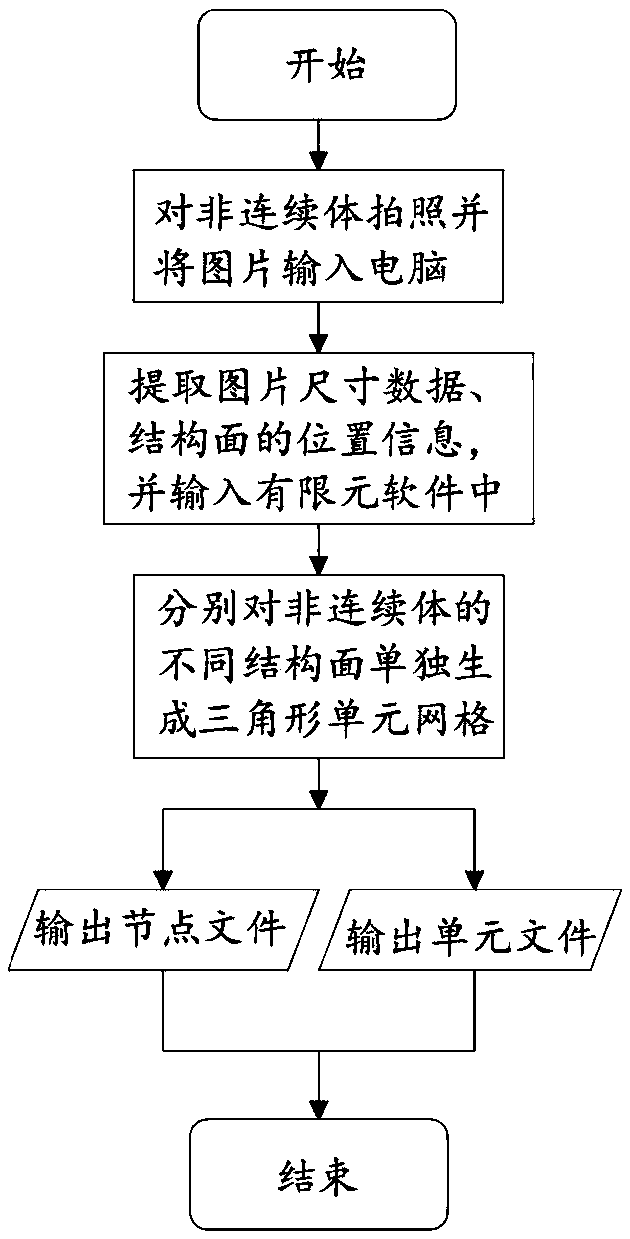
ActiveCN109448122ADiscontinuous deformation field accurateImprove deformationUsing optical means3D modellingRock sampleFinite element software
The invention relates to a method for measuring deformation of a discontinuous body containing a structural plane. The method comprises the following steps of (1) taking photos of a given discontinuous body containing a structural plane and inputting the photographs into finite element software; separately generating triangular elements for different structural planes of the discontinuous body andoutputting corresponding node files and element files; (2) generating interior points; (3) solving the displacement of the interior point; (4) solving the vertex deformation function of triangular block; 5) converting that vertex displacement to physical displacement; (6) visualizing the displacement. The method of the invention can be specially used for the deformation measurement of the discontinuous body, and can better reflect the displacement situation of the discontinuous body, so that the method can be better applied to the deformation measurement of a rock sample containing a joint ora crack surface.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com