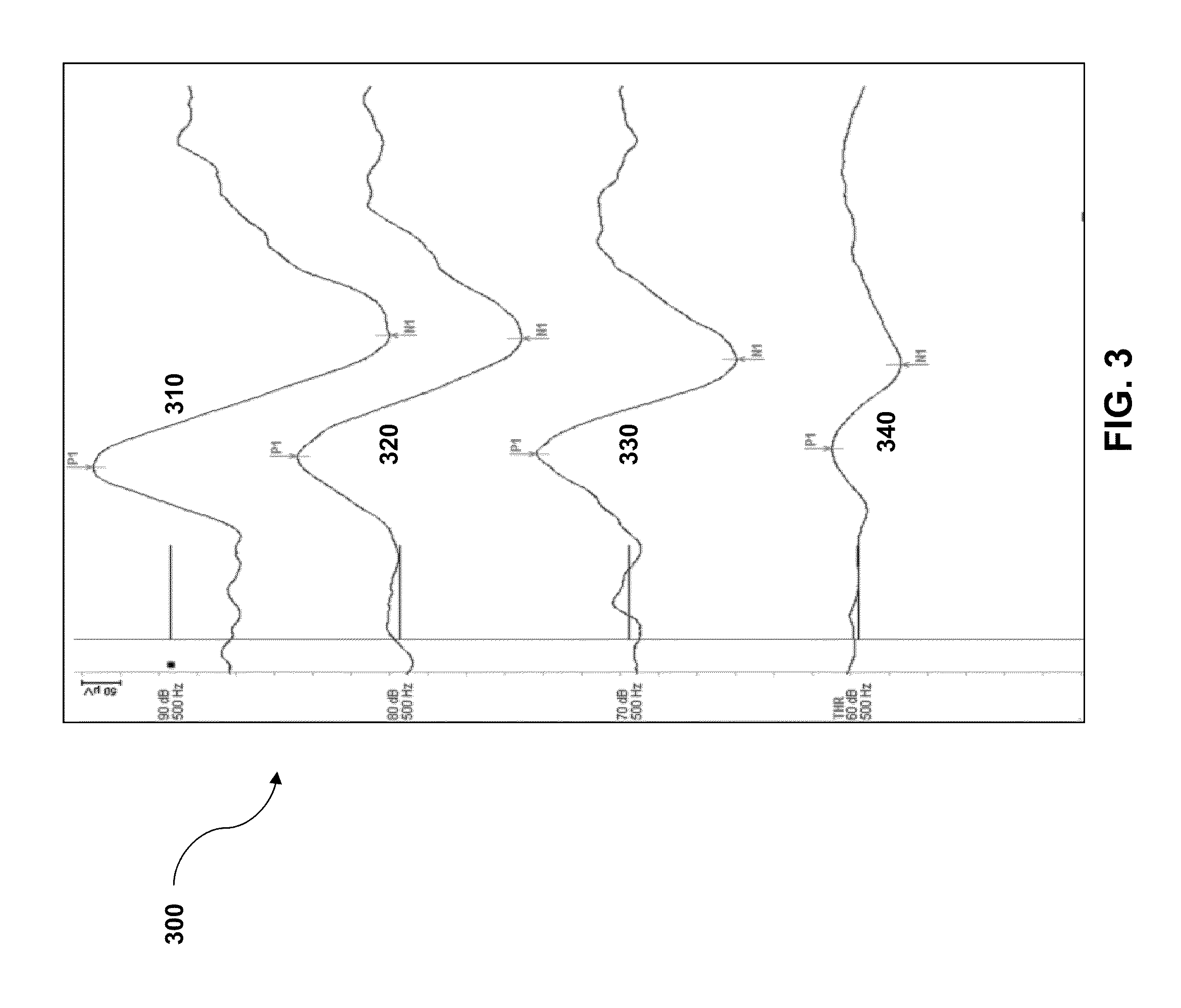
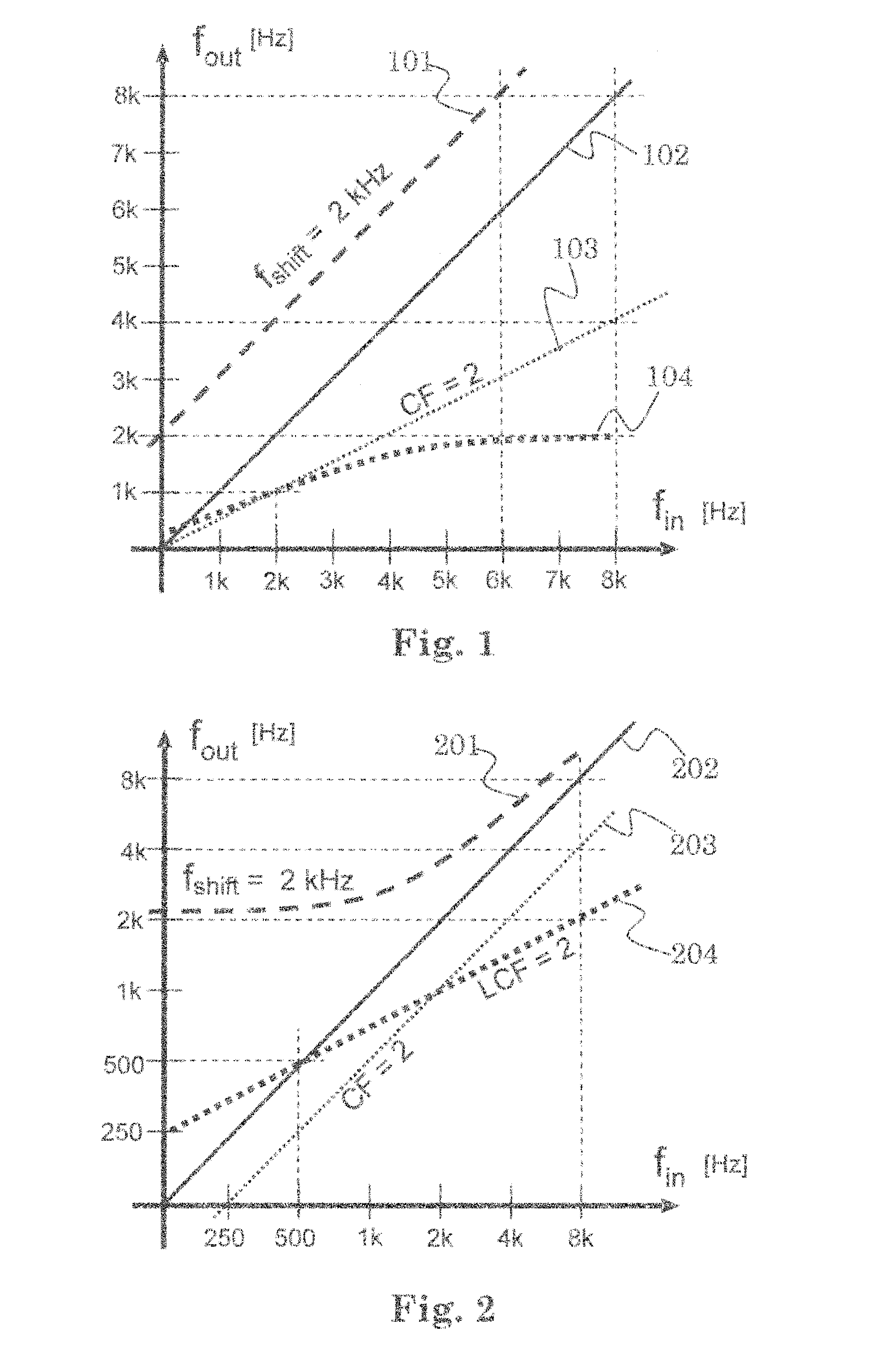
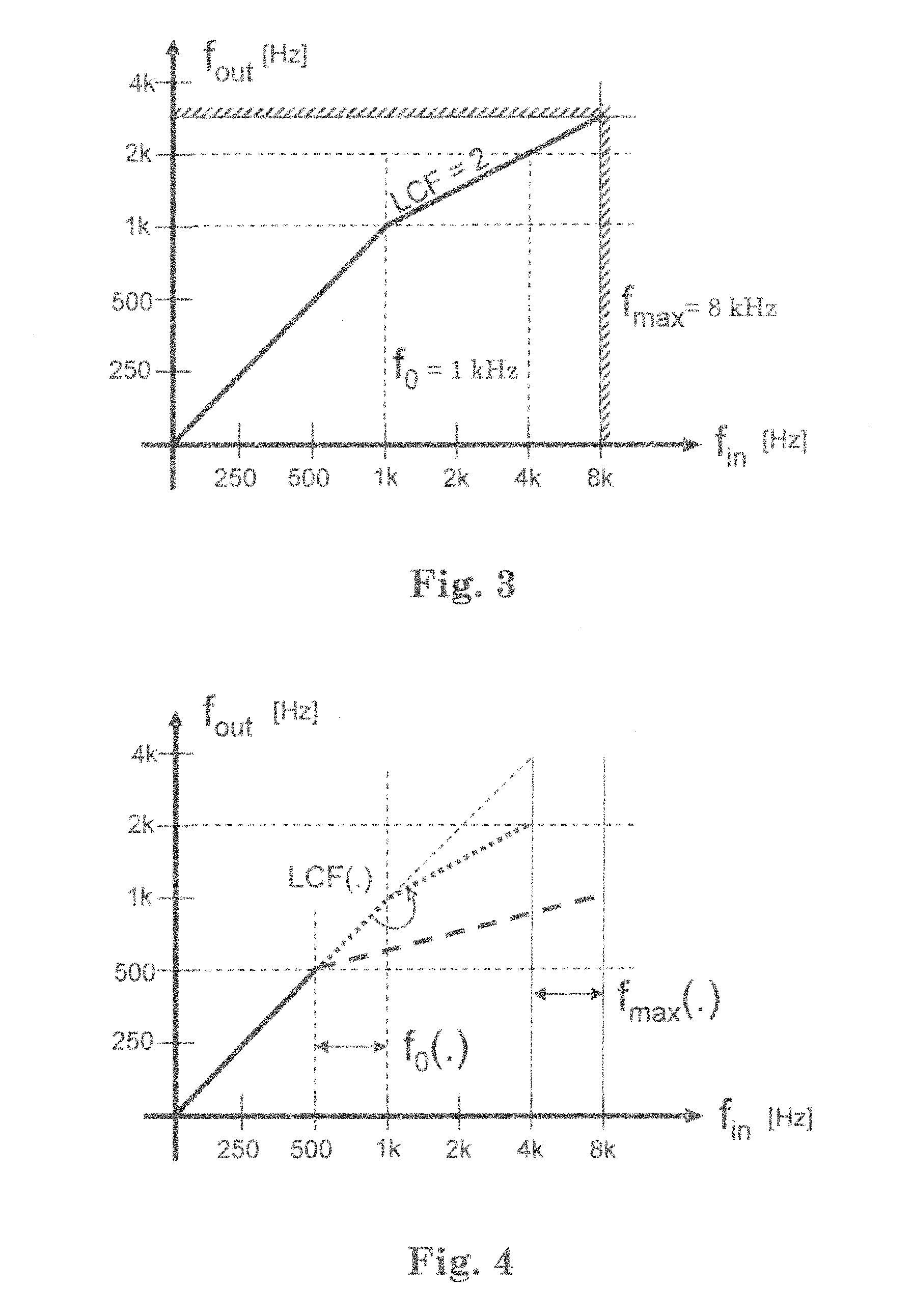
Patents
Literature
1457 results about "Noise (signal processing)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In signal processing, noise is a general term for unwanted (and, in general, unknown) modifications that a signal may suffer during capture, storage, transmission, processing, or conversion. Sometimes the word is also used to mean signals that are random (unpredictable) and carry no useful information; even if they are not interfering with other signals or may have been introduced intentionally, as in comfort noise.
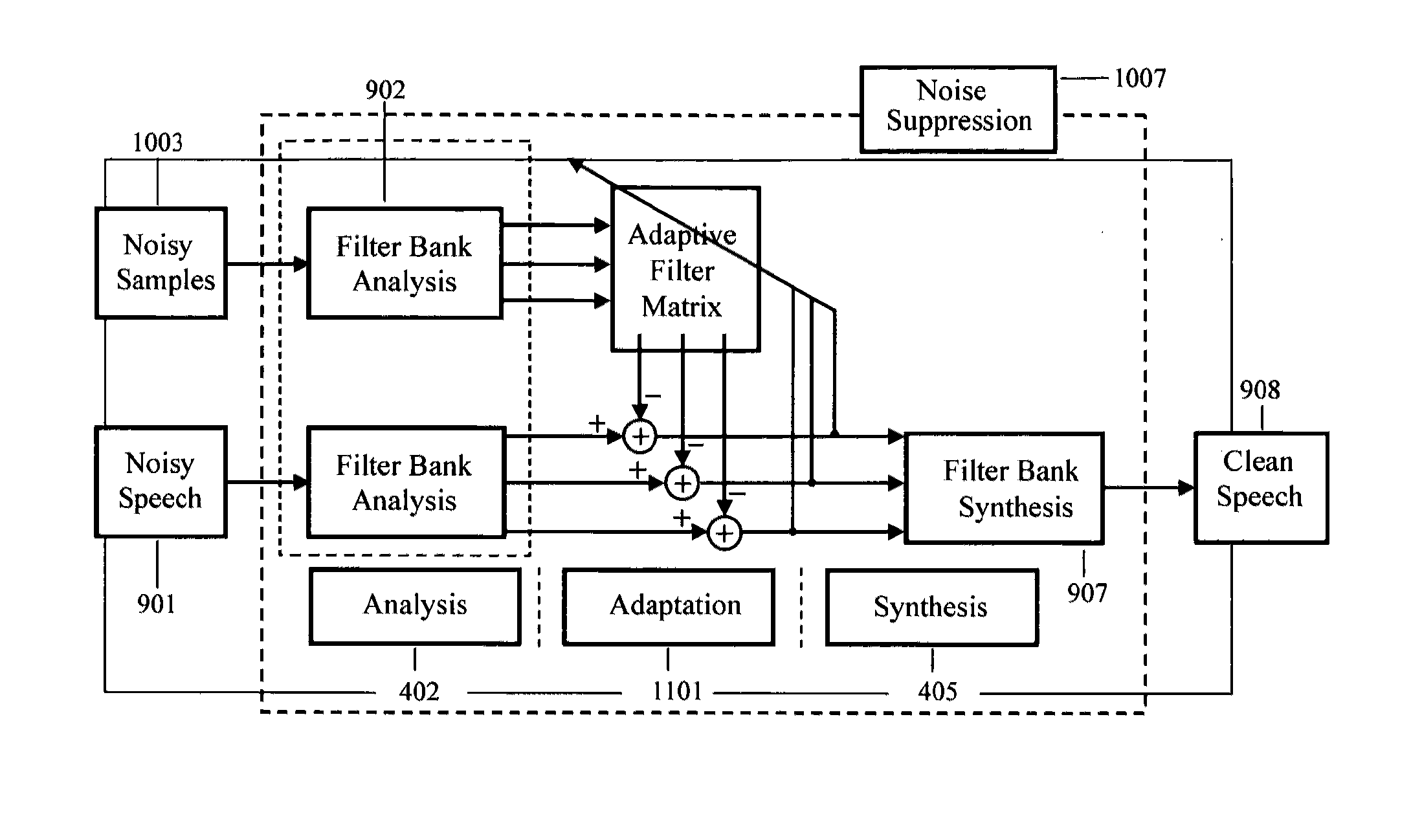
Noise-reducing arrangement and method for signal processing
InactiveUS6963626B1Effective noise reductionImprove noiseError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemDatapath
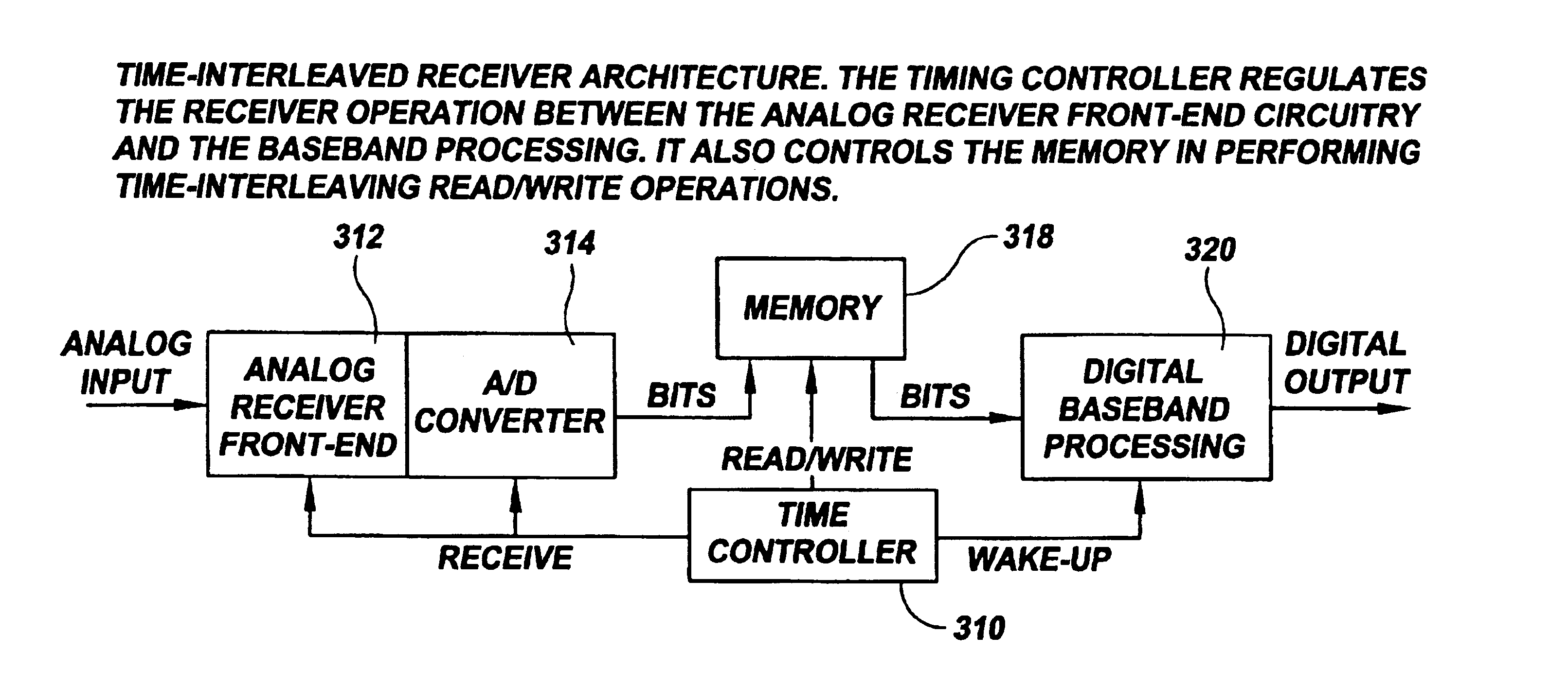
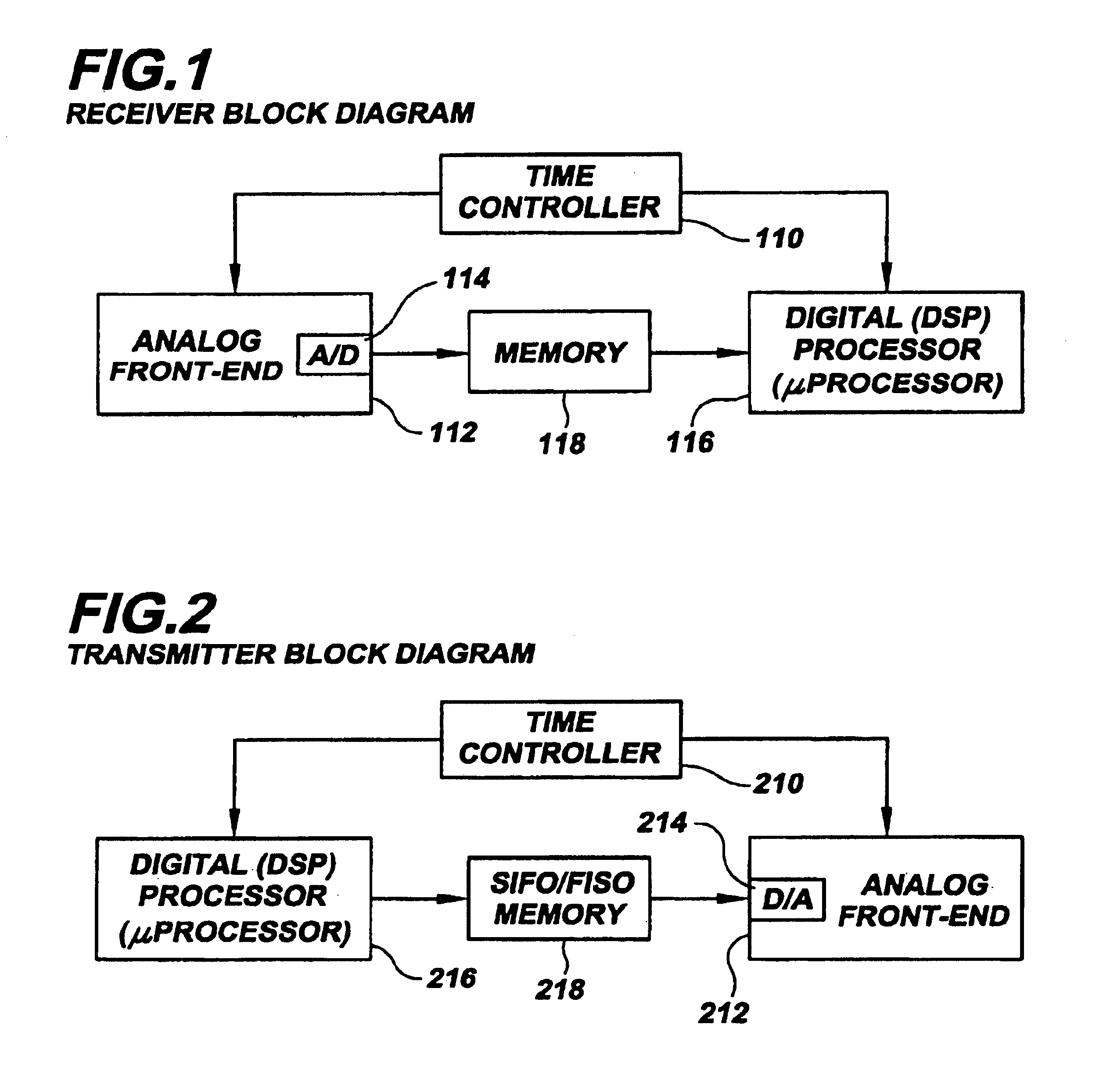
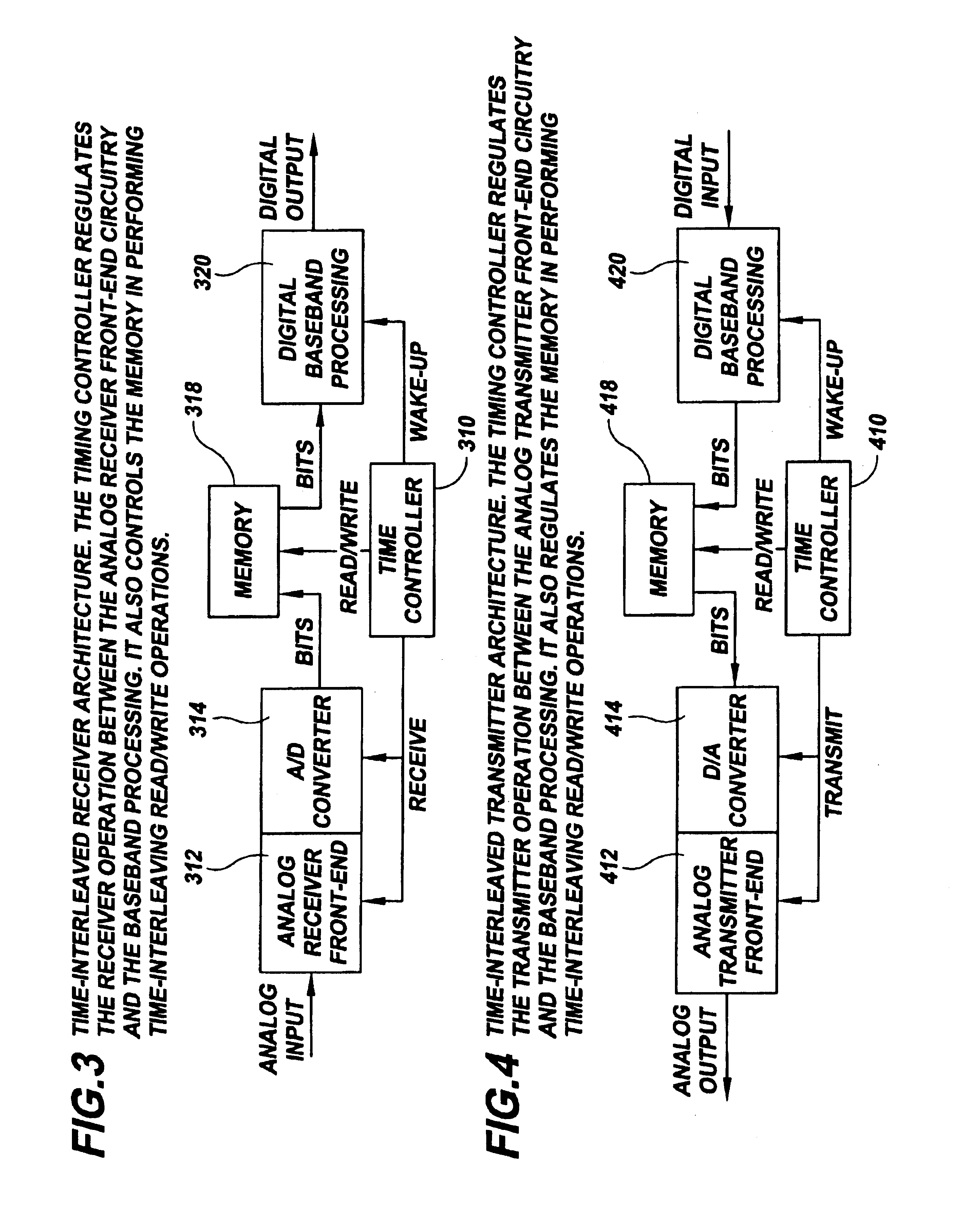
A communication system uses analog and digital circuits along the same data path in a manner that permits the analog circuitry to avoid adverse affects caused by the digital circuitry. Consistent with one embodiment directed to a signal processing system that detects faint incoming signals, the analog and digital circuits are implemented on a single piece of silicon. In such signal processing systems, noise generated by digital processing blocks can degrade the performance of sensitive analog portions. The effective noise is reduced by causing the analog and digital portions of the system to function during separate time intervals. The noise-generating portions of the system may then be turned off during a first data-communication interval while the analog block operates. The data acquired during this period is stored for subsequent processing by the digital portion during a second shorter data-communication interval. Other aspects are applicable to reception arrangements in which part of the incoming signal may be disregarded without significant degradation in performance of the rest of the system, and other aspects are directed to transmission arrangements in which the inverse of the above reception arrangement is used.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Signal processing method and device for signal-to-noise improvement
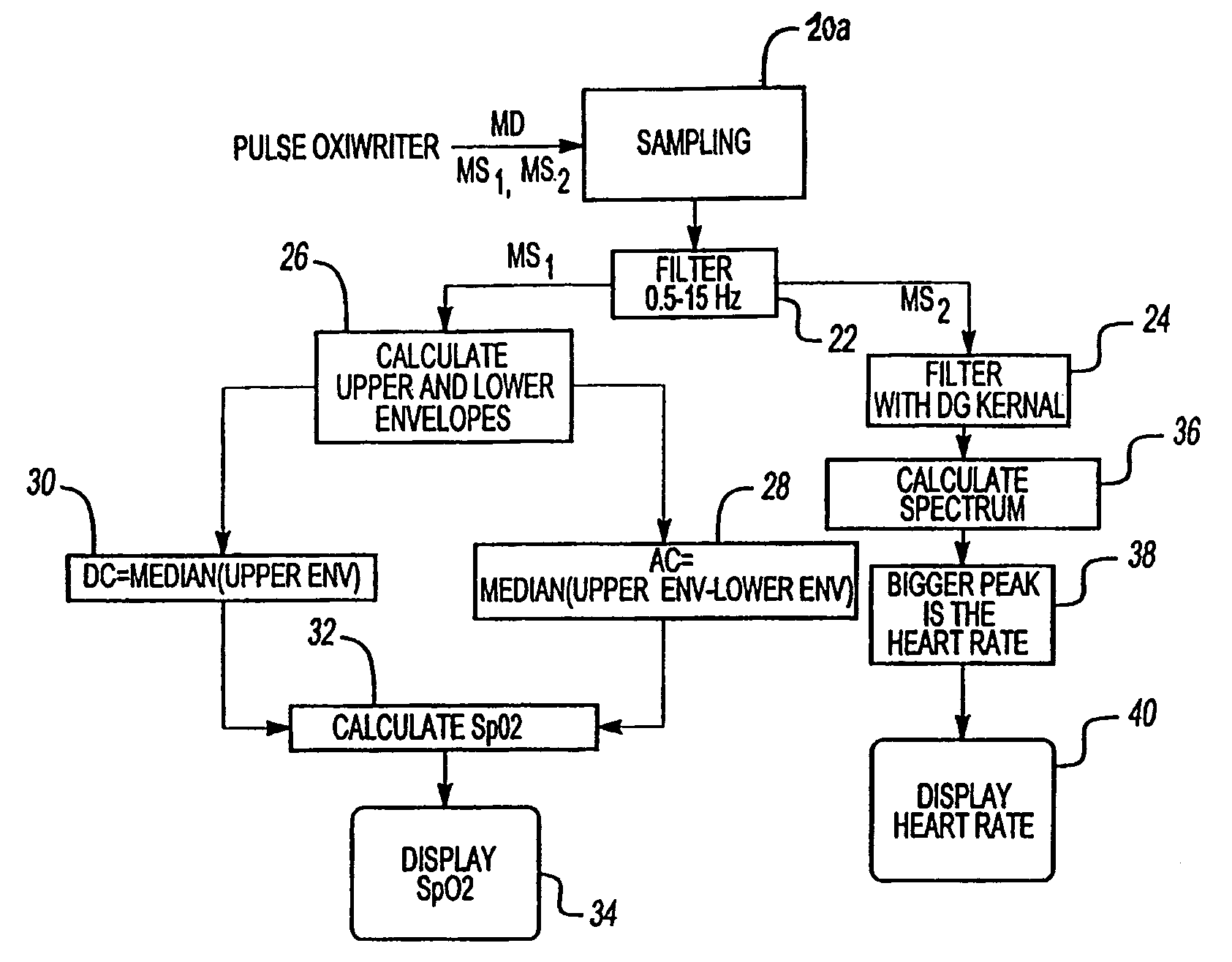
InactiveUS7027850B2Increase heightAdditional componentCatheterSensorsEngineeringSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
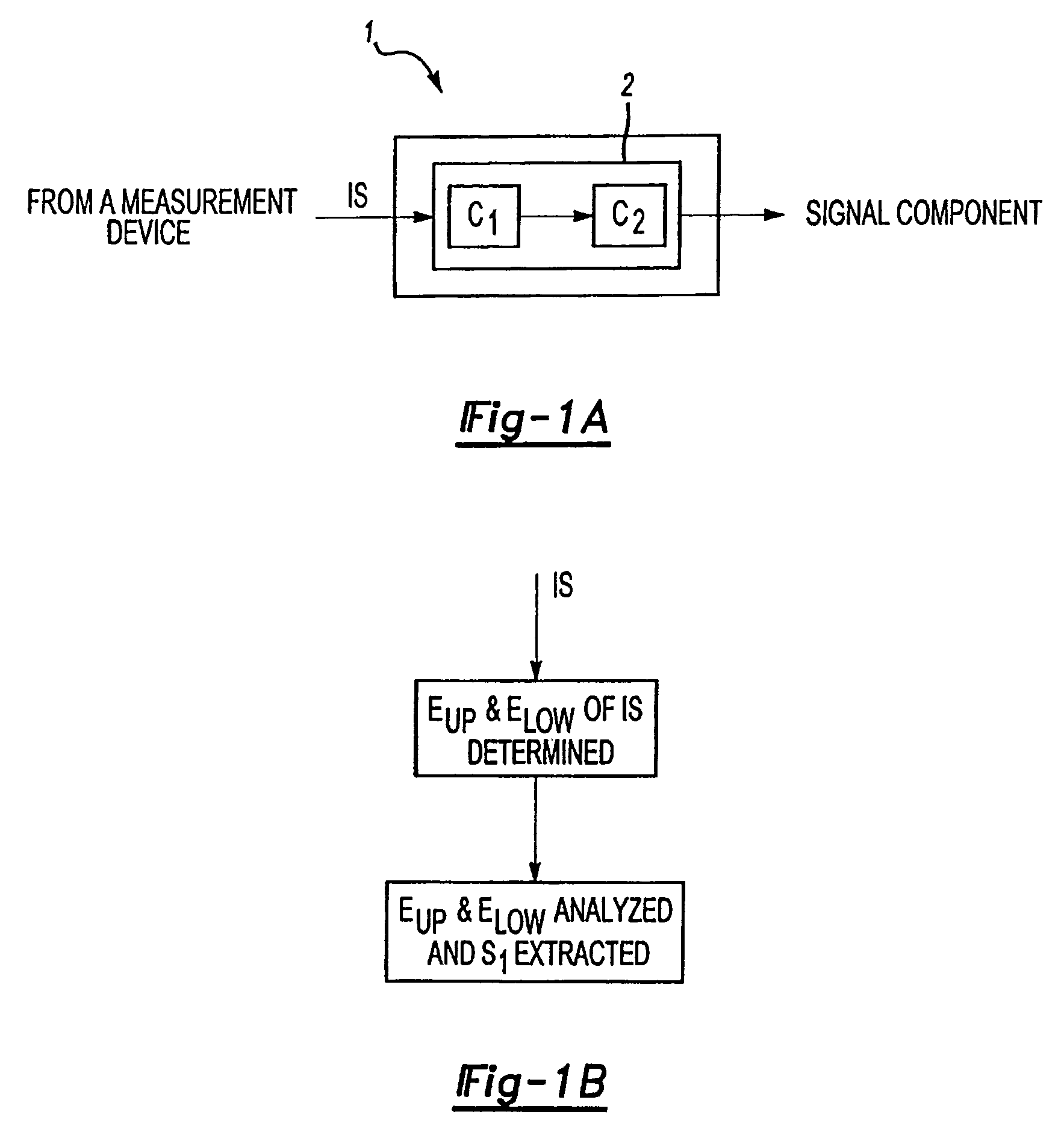
A method and apparatus extract a signal component of a measured signal using one of two methods. If the signal component in the measured signal is a periodic signal with a certain well-defined peak-to-peak intensity value, upper and lower envelopes of the measured signal are determined and analyzed to extract said signal component of the measured signal. This signal component can further be used to calculate a desired parameter of the sample. The DC component of the signal is determined as the median value of the upper envelope, and the AC component is determined as the median value of the difference between the upper and lower envelopes. If the signal component of the measured signal is a periodic signal characterized by a specific asymmetric shape, a specific adaptive filtering is applied to the measured signal, resulting in the enhancement of the signal component relative to a noise component. This adaptive filtering is based on a derivative of the Gaussian Kernel having specific parameters matching the characteristics of the signal component.
Owner:CONMED CORP
Method and system for detecting and classifying the modulation of unknown analog and digital telecommunications signals
InactiveUS7428270B1Accurate classificationHigh precisionModulation type identificationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSignal classificationCarrier signal
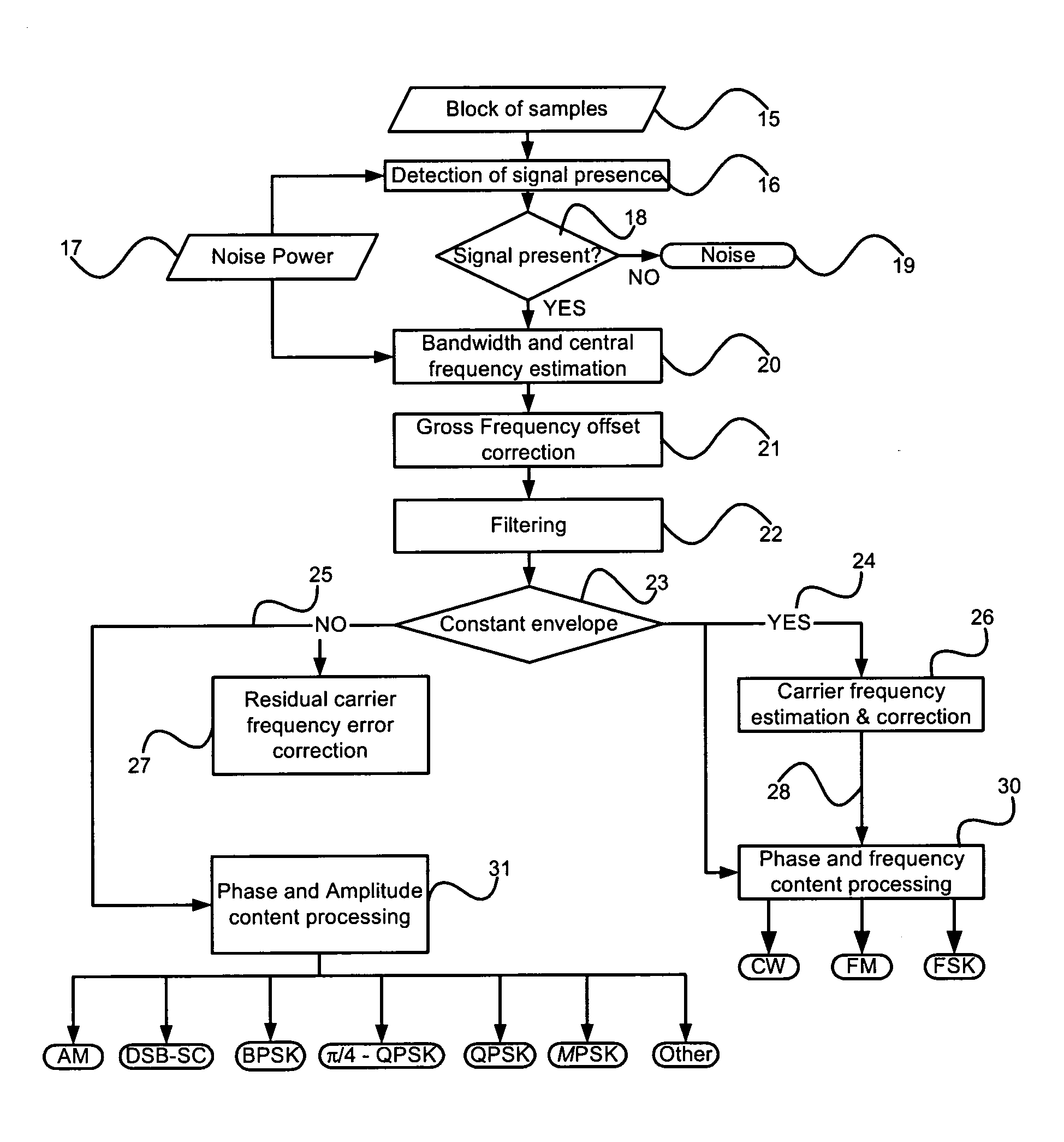
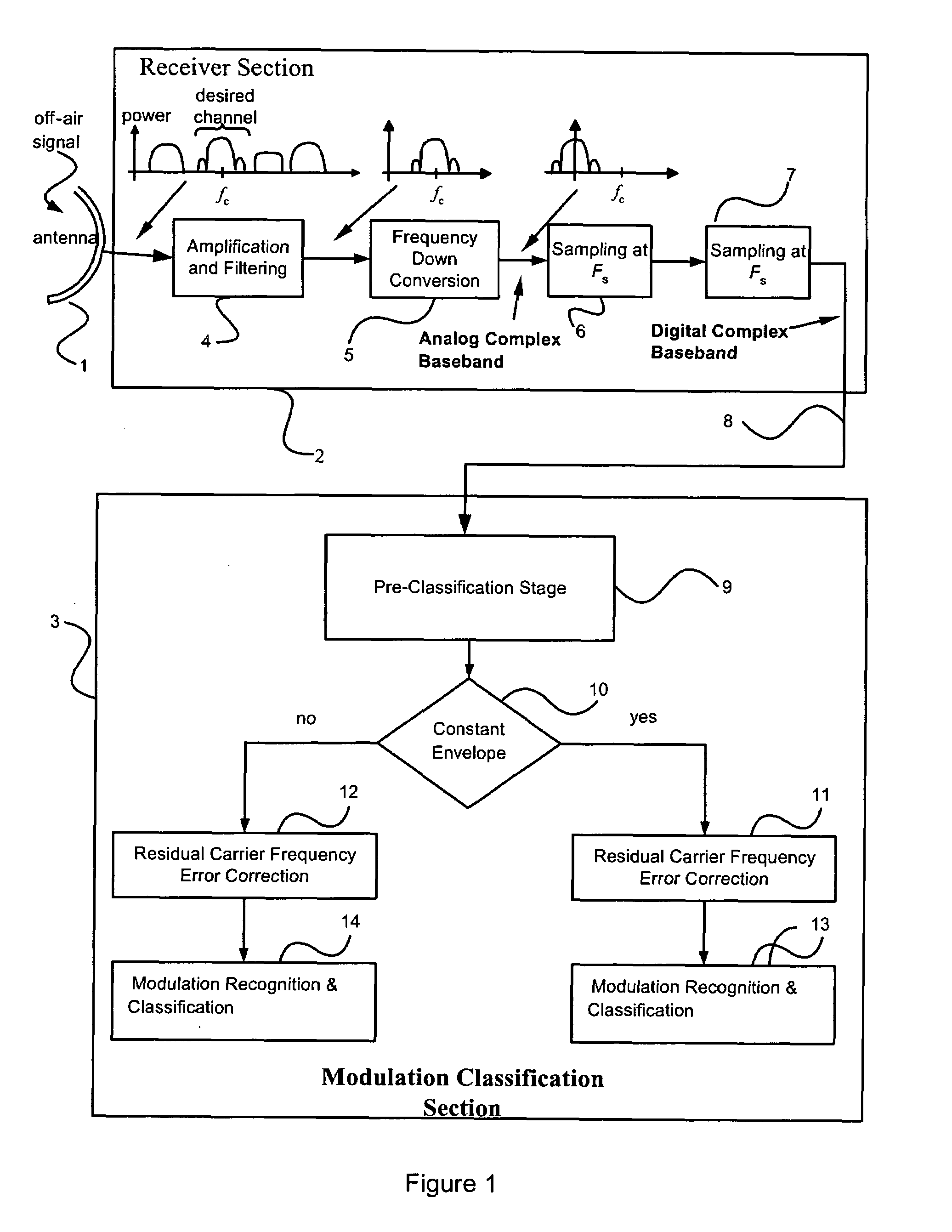
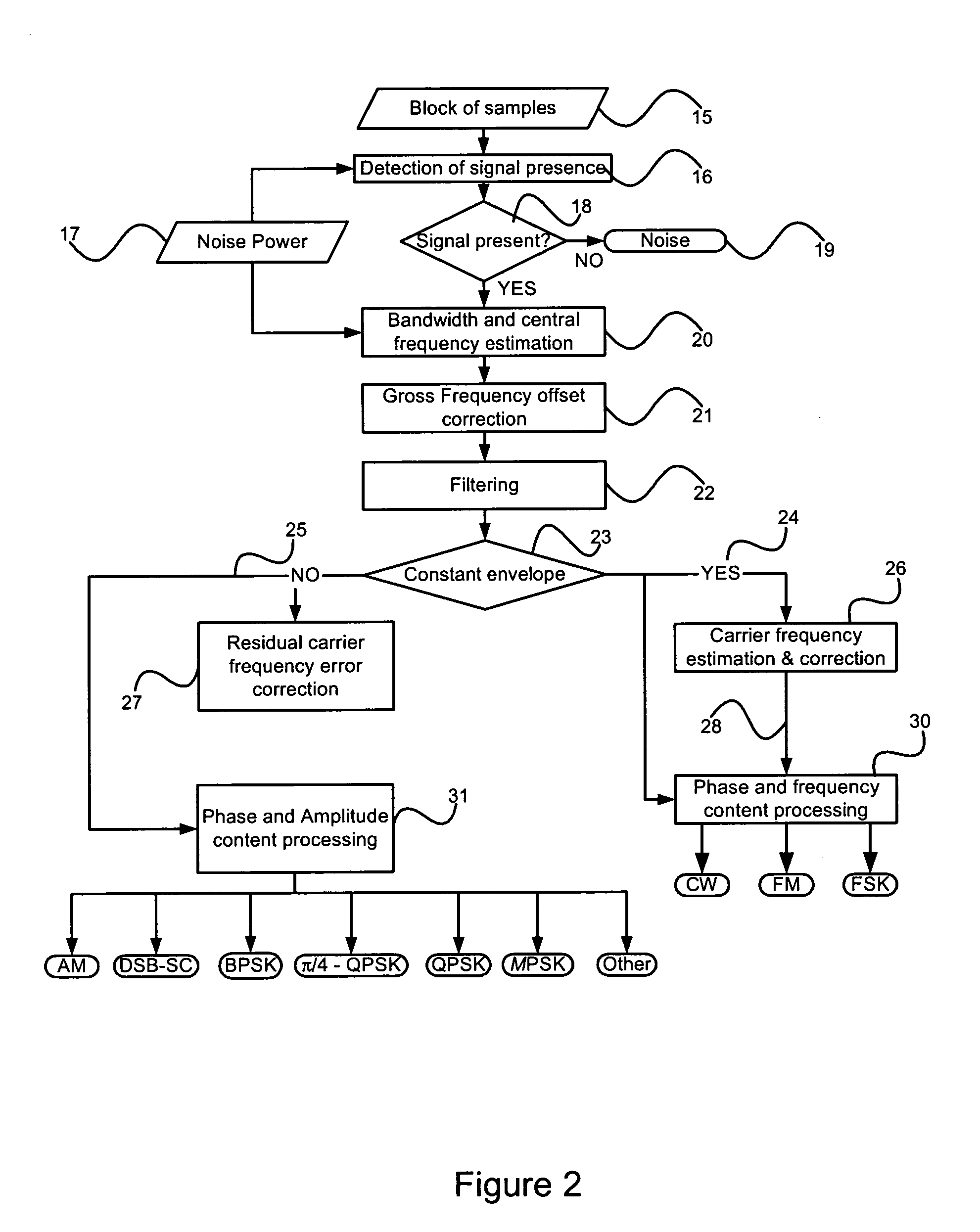
Disclosed is a unique system and method for recognizing the type of modulation embedded in an unknown complex baseband signal, comprising a receiver section for extracting the complex baseband signal from a modulated signal having a carrier frequency, and comprising an orderly series of signal processing functions for (a) estimating the bandwidth of the unknown signal, (b) removing the out-of-band noise and correcting gross carrier frequency errors, (c) discriminating between constant envelope and irregular envelope signals, (d) estimating and correcting residual carrier frequency errors, (e) classifying a constant envelope signal into one of the following modulation formats: {Continuous Wave (CW), Frequency Modulation (FM), Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)}, and (f) classifying an irregular envelope signal into one of the following modulation formats: {Amplitude Modulation (AM), Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC), Binary Shift Keying (BPSK), Quaternary Phase Shift Keying (QPSK), π / 4-shifted QPSK, M-ary PSK (MPSK), and OTHER classes}.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Binaural signal processing techniques
InactiveUS6987856B1Easy to zeroImprove localizationDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesTransmission noise suppressionFrequency spectrumSound sources
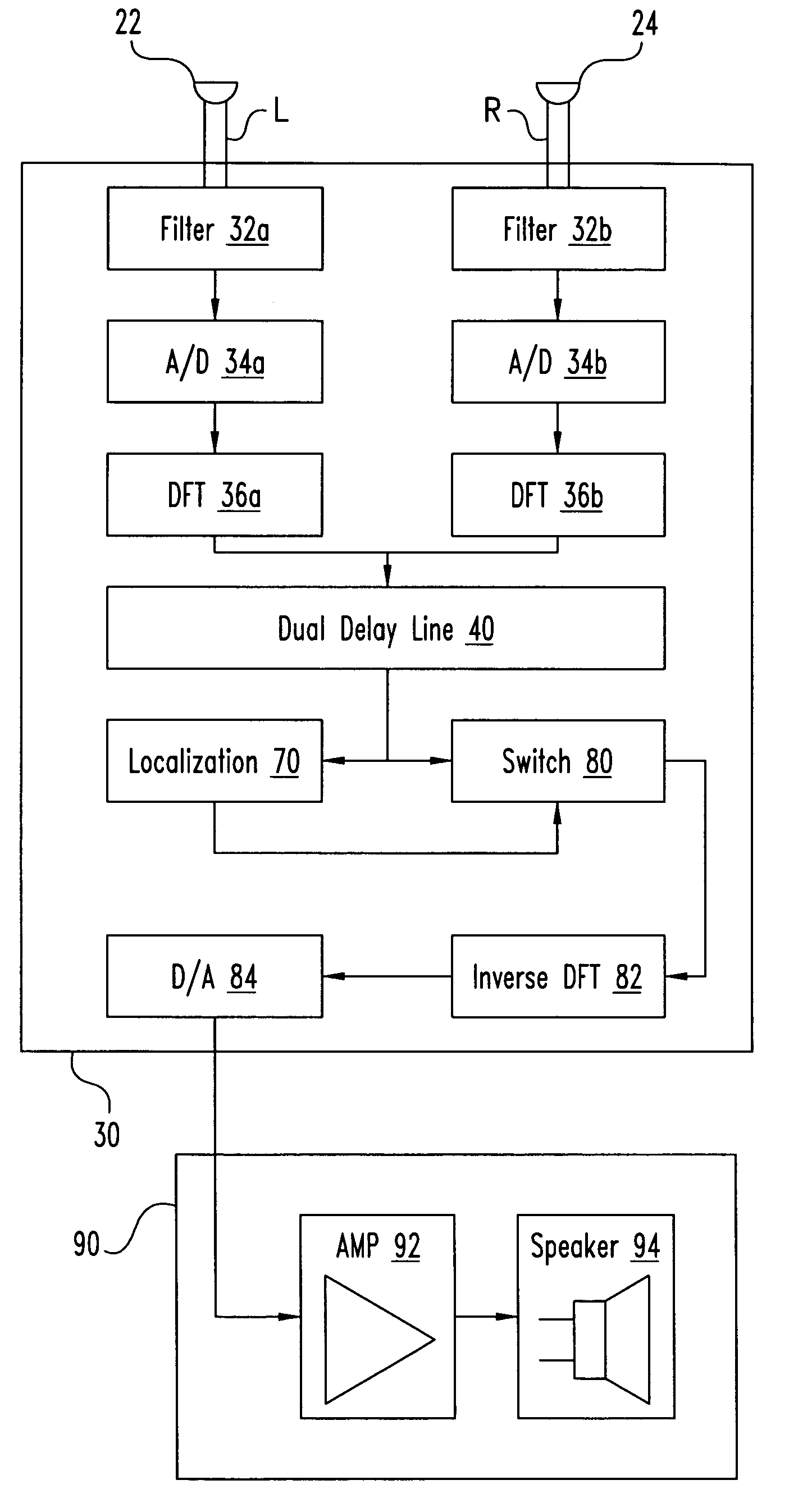
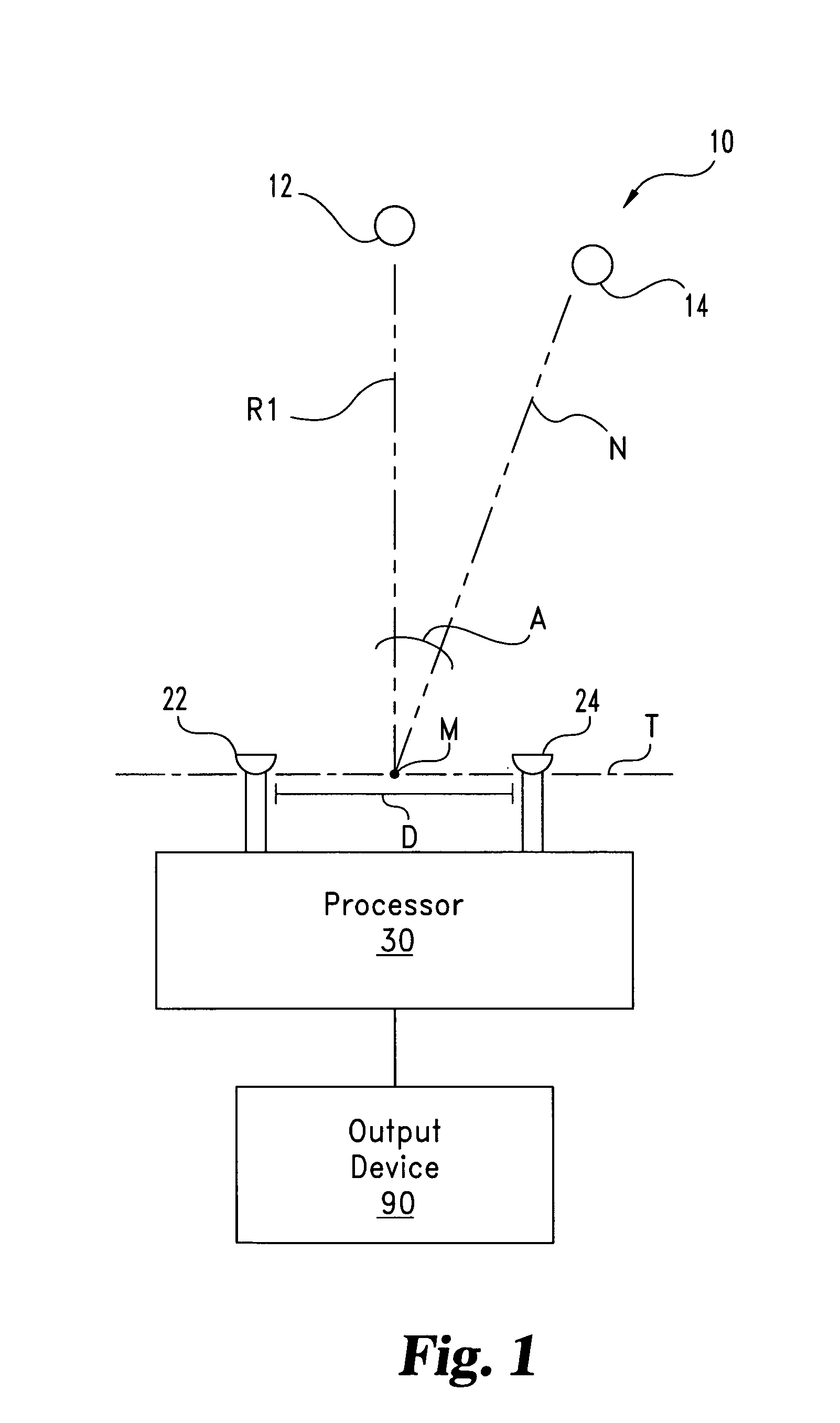
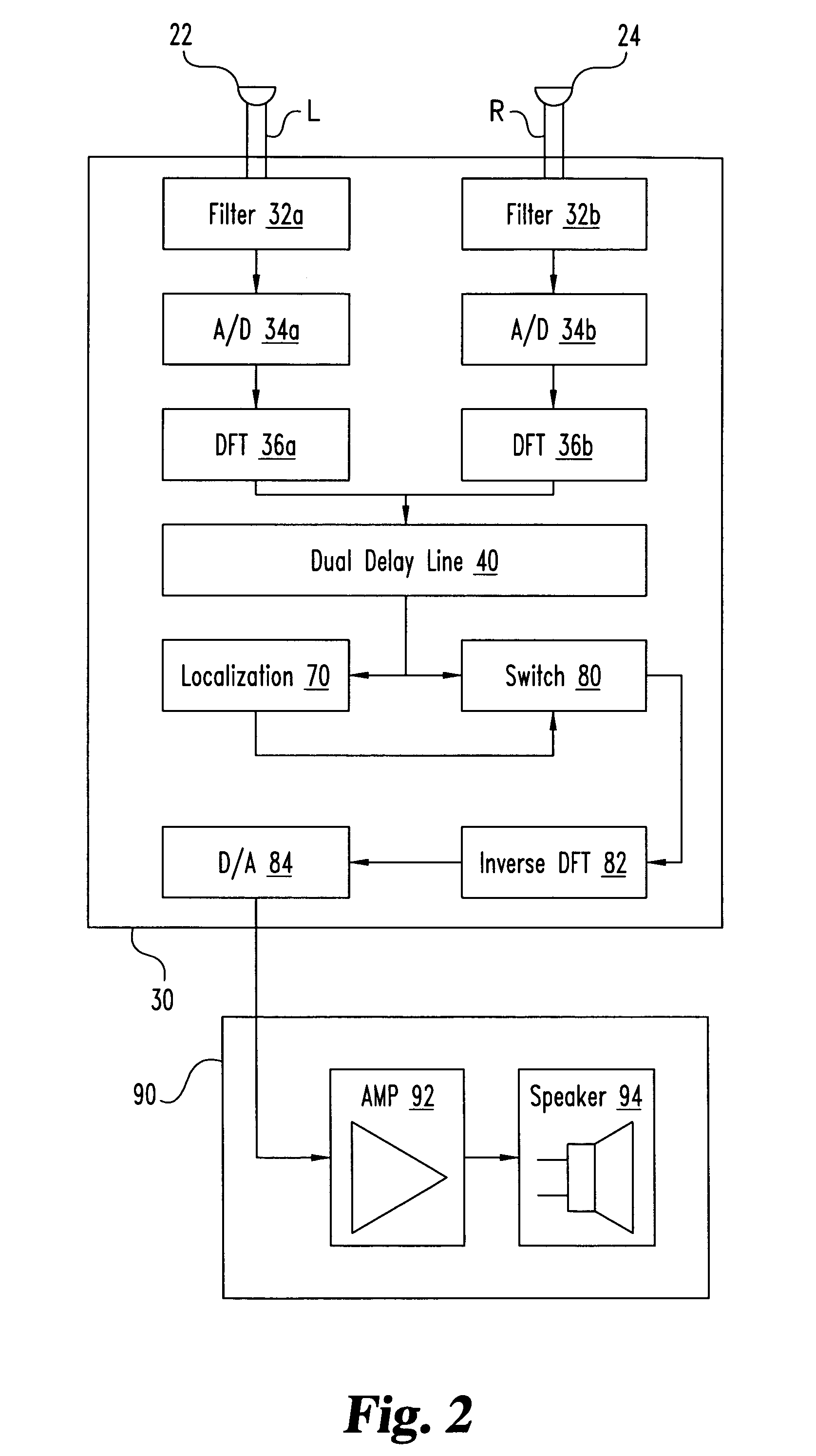
A desired acoustic signal is extracted from a noisy environment by generating a signal representative of the desired signal with a processor. The processor receives aural signals from two sensors each at a different location. The two inputs to the processor are converted from analog to digital format and then submitted to a discrete Fourier transform process to generate discrete spectral signal representations. The spectral signals are delayed by a number of time intervals in a dual delay line to provide a number of intermediate signals, each corresponding to a different spatial location relative to the two sensors. Locations of the noise source and the desired source are determined and the spectral content of the desired signal is determined from the intermediate signal corresponding to the noise source locations. Inverse transformation of the selected intermediate signal followed by digital to analog conversion provides an output signal representative of the desired signal. Techniques to localize multiple acoustic sources are also disclosed. Further, a technique to enhance noise reduction from multiple sources based on two-sensor reception is described.
Owner:ILLINOIS UNIV OF BOARD OF TRUSTEES THE
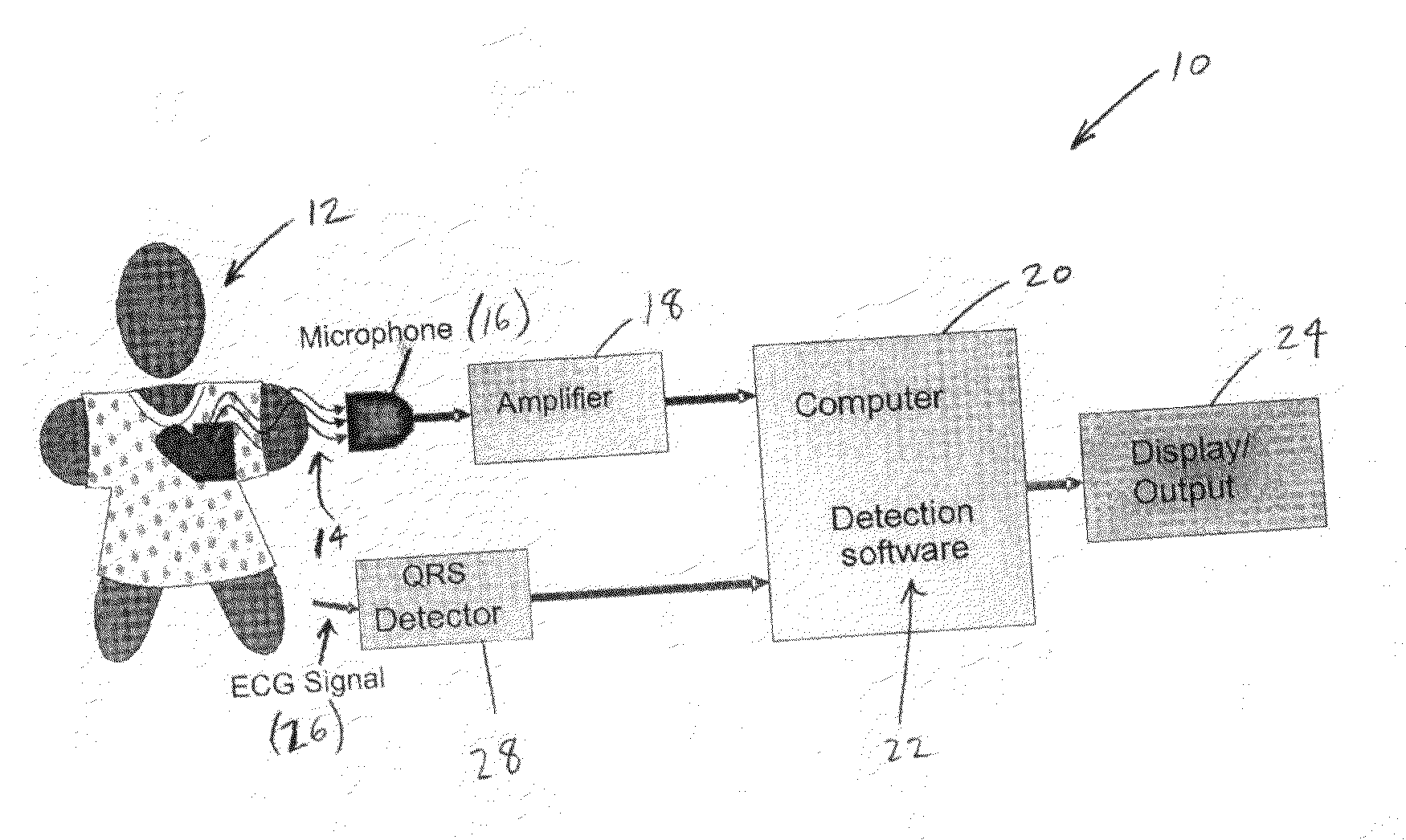
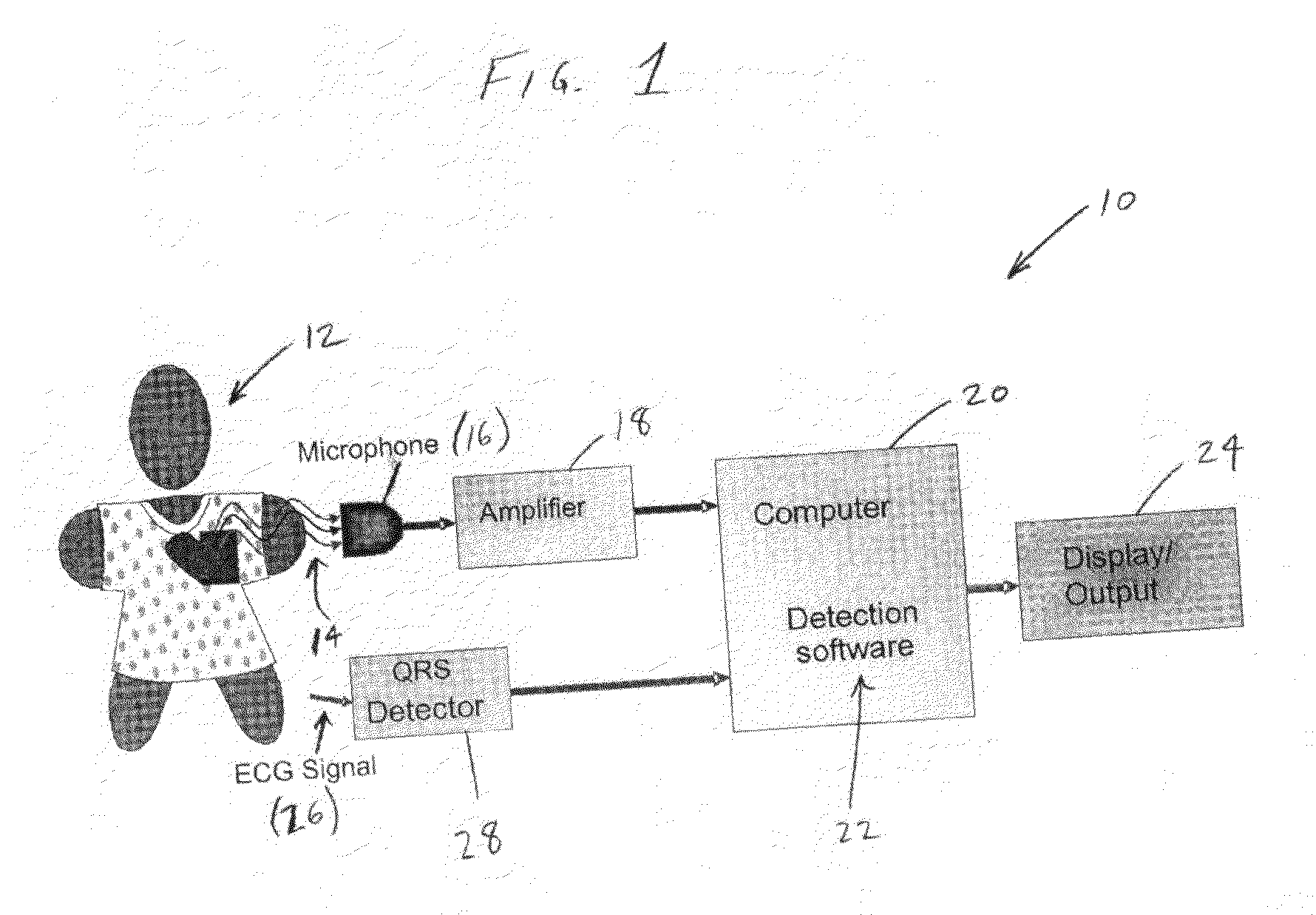
System and method for acoustic detection of coronary artery disease
InactiveUS20100094152A1Eliminate artifactsEliminate in signalStethoscopeCatheterDiseaseCoronary heart disease
A system and method for acoustic detection of coronary artery disease (CAD) are provided. The system includes a transducer for acoustically detecting heart signals of a patient and a computer system which executes detection software for processing the detected heart signals to identify the presence of CAD from the heart signals. The software allows for the automatic definition of a diastolic “window” of the acoustic signal for analysis, and automatically edits the sampled acoustic signal to eliminate unwanted artifacts and / or noise in the acoustic signal. The edited signal is then processed by a plurality of signal processing algorithms, including spectral analysis algorithms, time-frequency algorithms, global feature algorithms, kurtosis algorithms, mutual information algorithms, negenthropy algorithms, and principal component analysis algorithms, to generate a disease vector. The disease vector is then classified to determine whether CAD is present in the patient. Classification can be accomplished using linear discriminant analysis or a support vector machine.
Owner:NEW JERSEY UNIVESITY OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF
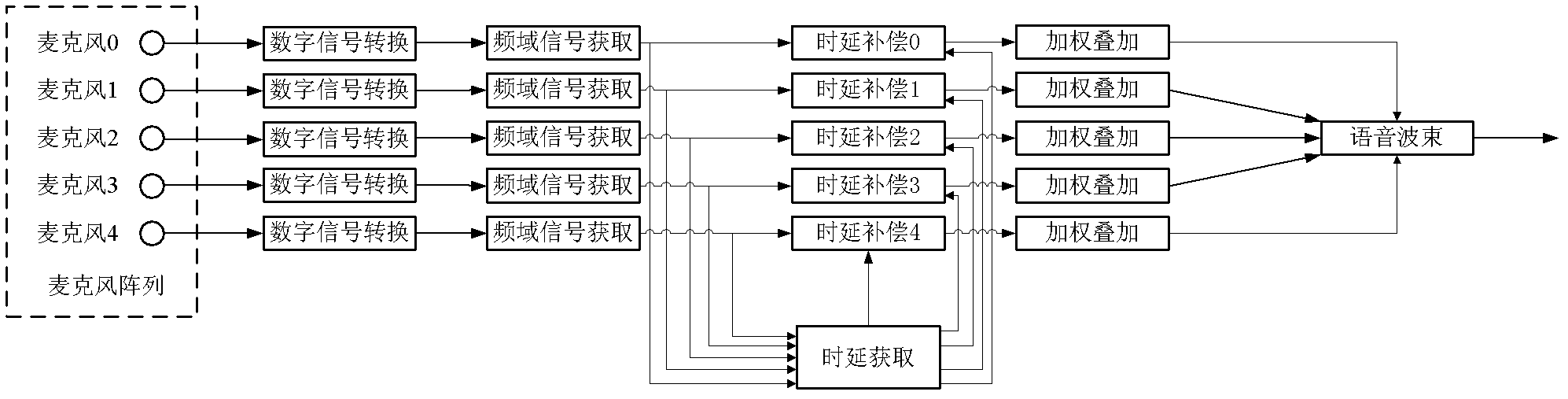
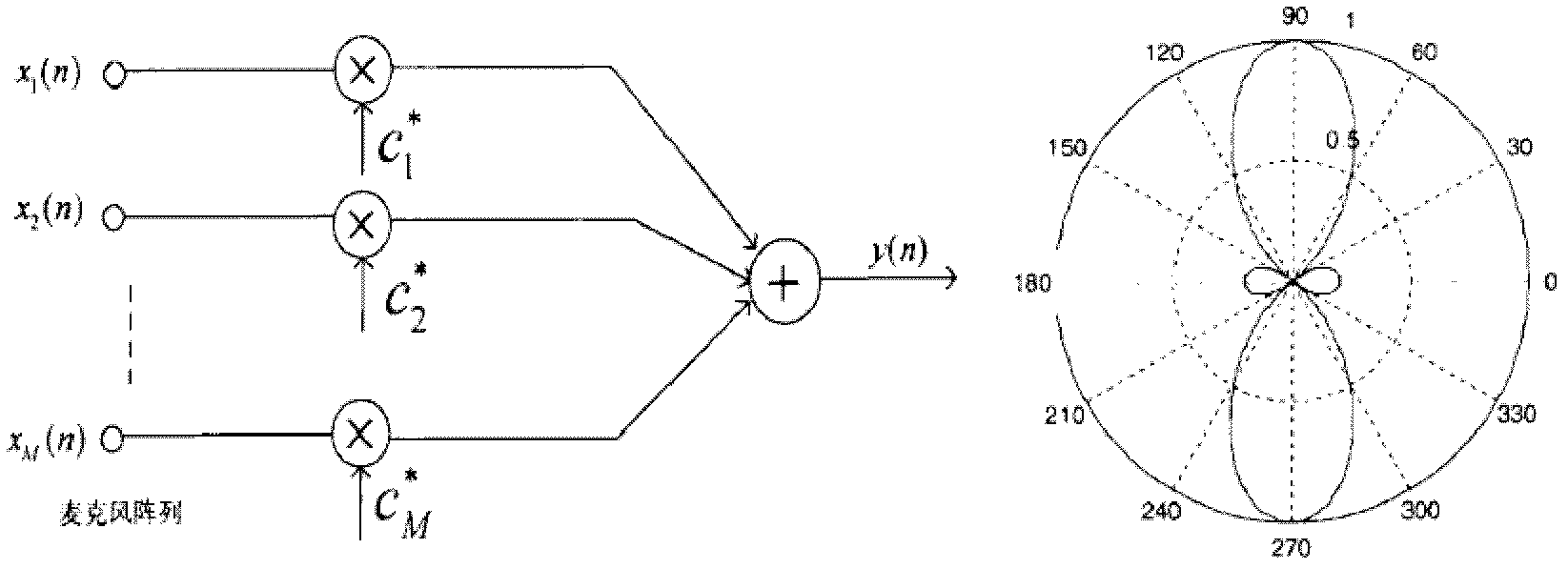
Microphone-array speech-beam forming method as well as speech-signal processing device and system
InactiveCN102324237AHigh positioning accuracyImprove directivitySpeech analysisSound producing devicesPhase conversionSound sources
The embodiment of the invention discloses a microphone-array speech-beam forming method, which comprises a digital-signal converting step, a frequency-region signal-obtaining step, a time-delay obtaining step, a time-delay compensating step and a weighted stacking step, wherein time-delay estimation based on phase conversion is adopted particularly in the time-delay obtaining step, thereby a beam-forming signal pointed to a target sound-source spatial position after enhancement processing is obtained. Compared with the prior art, the positioning precision and the directivity of a three-dimensional space are enhanced, the long-distance sound-picking capability in a complicated acoustics environment is greatly enhanced, high-quality voice signals are obtained, and noise and other interferences are reduced. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a speech-signal processing device and a system.
Owner:深圳市顺畅声学科技有限公司
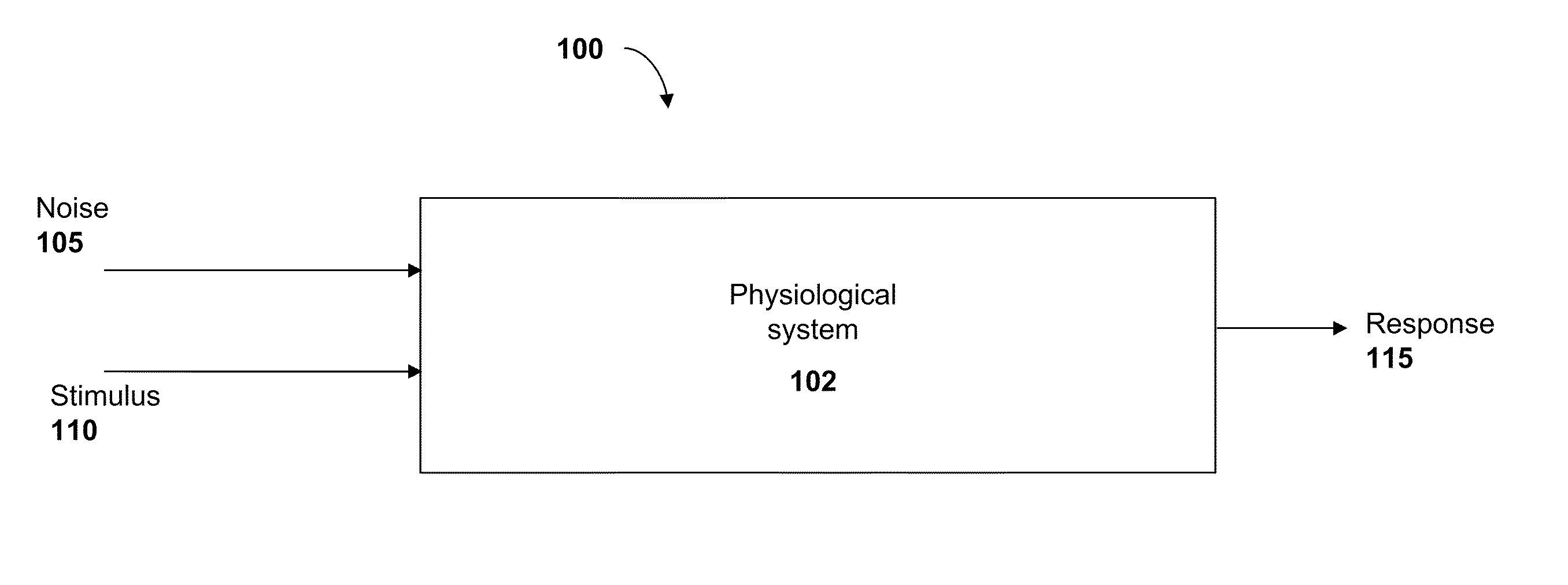
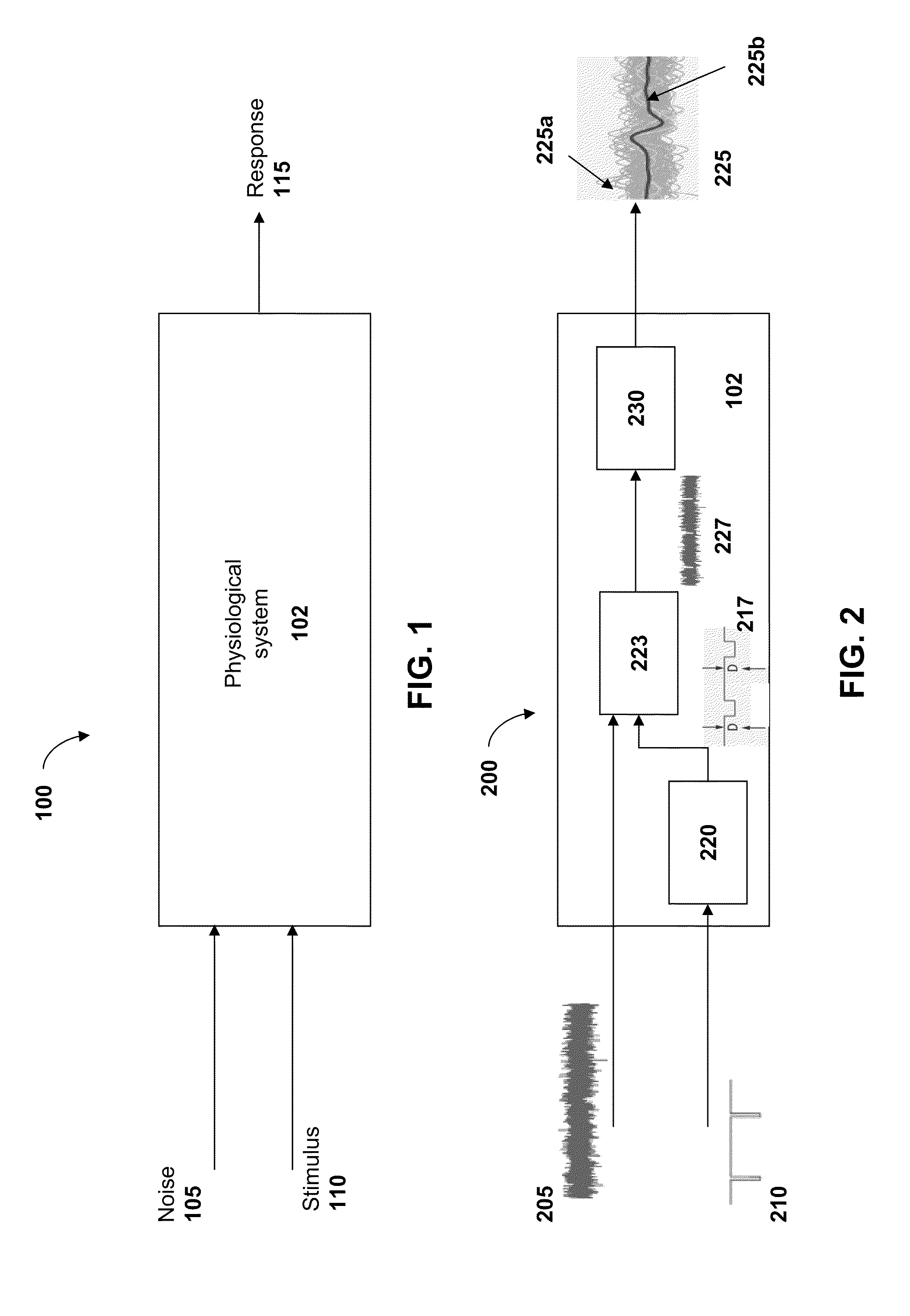
Signal Processing in Physiological Noise
InactiveUS20100292606A1Ease of evaluationReduce inter-subjectElectromyographyMedical automated diagnosisEngineeringSignal processing
The invention relates to systems and methods for estimating a response of at least a part of a physiological system to a first deterministic stimulus signal. The methods include separating a measured first signal into a plurality of segments, each segment representing a response of the physiological system to a corresponding portion of the first stimulus signal and generating a template signal representing the plurality of segments. The methods further include calculating a measure of similarity of each segment in the plurality of segments to the template signal to provide a set of scalar quantities, and determining a metric representing a characteristic of the response of at least a part of the physiological system to the first stimulus signal.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS EYE & EAR INFARY
Virtual speaker demonstration system and virtual noise simulation
ActiveUS7899656B2Eliminate the effects ofNear-field transmissionEar treatmentEngineeringHuman–computer interaction
A virtual speaker demonstration system is disclosed that permits a retail outlet to use a reference speaker to demonstrate the performance of multiple different demonstration speakers. A user interface permits a user to select a demonstration speaker and signal processing is performed so that the output from the reference speaker simulates the output of the selected demonstration speaker. The invention provides benefits to all three of the consumer, the retailer, and the manufacturer. The consumer can listen to and compare multiple demonstration speakers easily and conveniently from the same reference speaker. The retailer to use a single (or few) reference speaker to demonstrate the performance of multiple demonstration speakers, saving costs and space. The manufacturer to be able to display and demonstrate to consumers a broader range of the manufacturer's product line.
Owner:CRUTCHFIELD
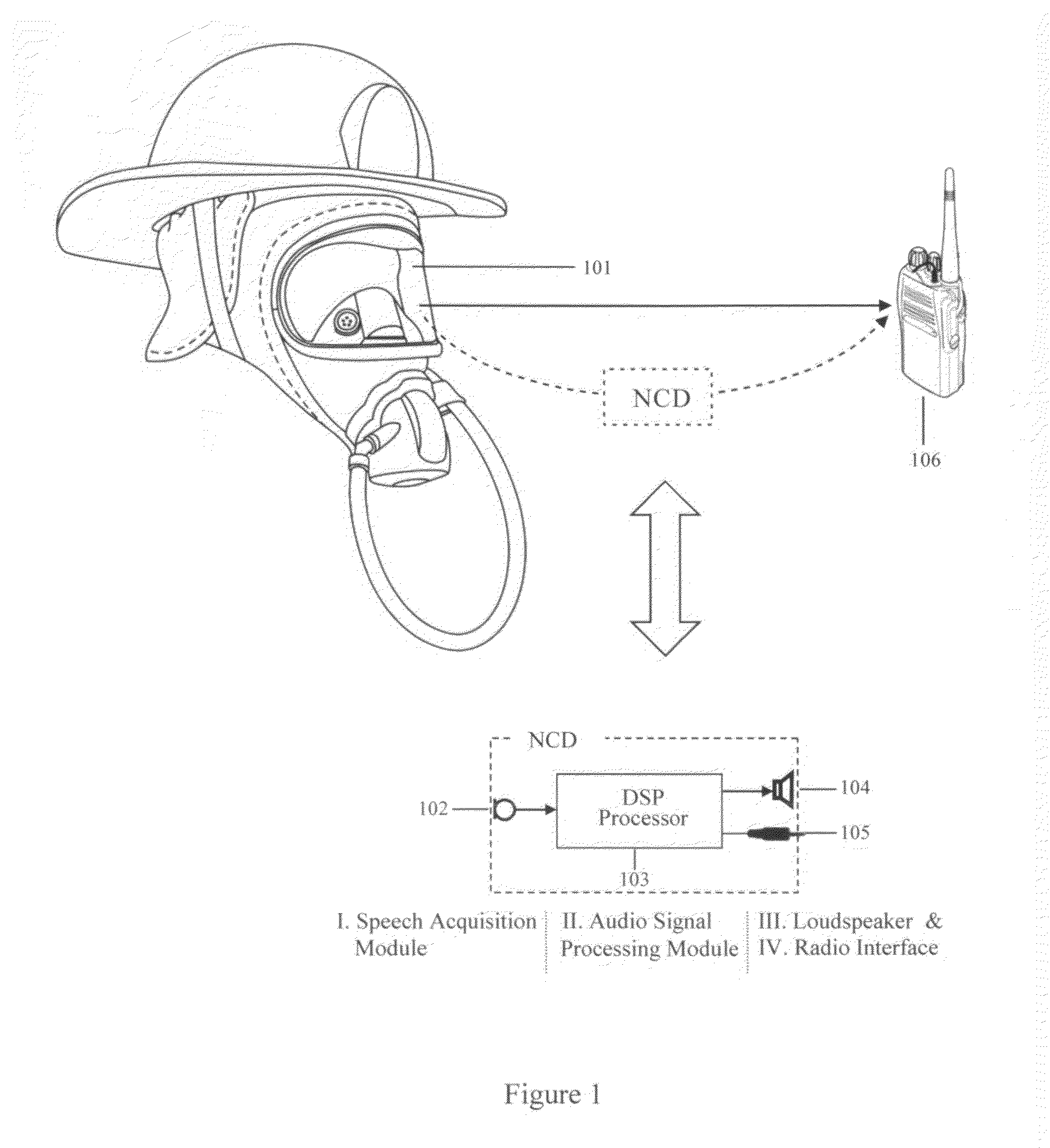
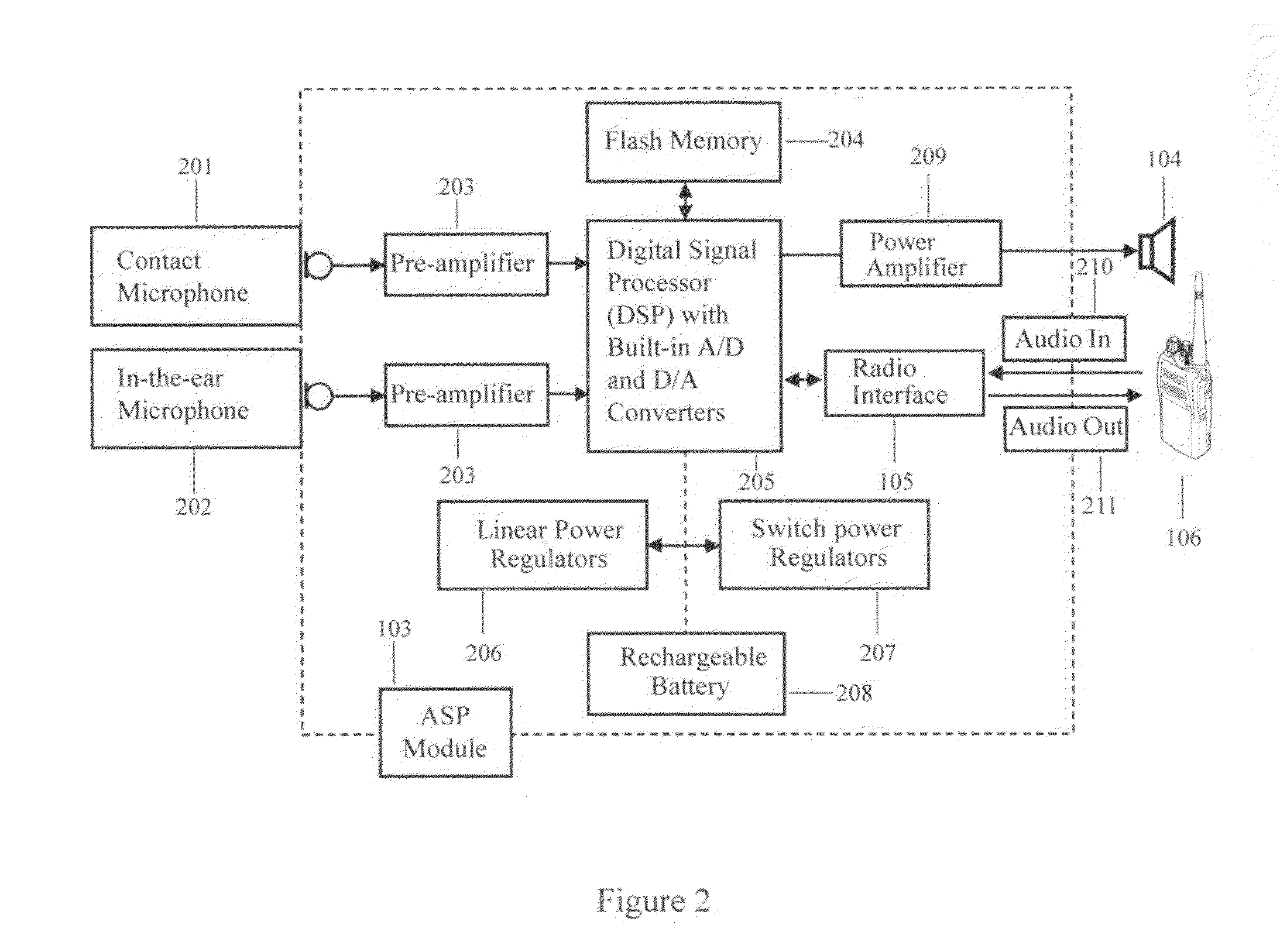
Noise cancellation device for communications in high noise environments
ActiveUS20120084084A1Novel noise cancellationEasy to useSpeech recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
This invention presents a noise cancellation device for improved personal face-to-face and radio communications in high noise environments. The device comprises speech acquisition components, an audio signal processing module, a loudspeaker, and a radio interface. With the noise cancellation device, the signal-to-noise ratio can be improved by as much as 30 dB.
Owner:LI CREATIVE TECH
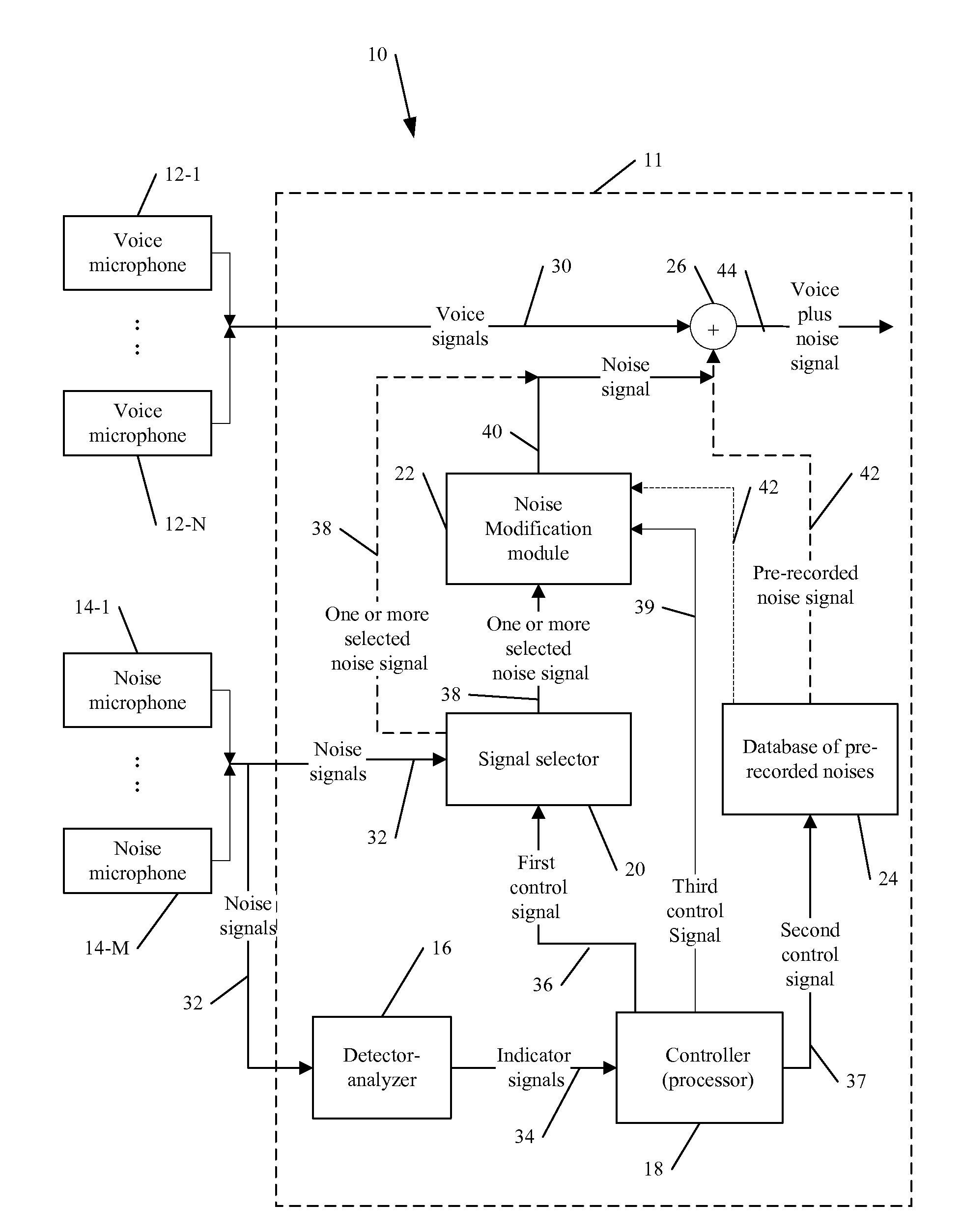
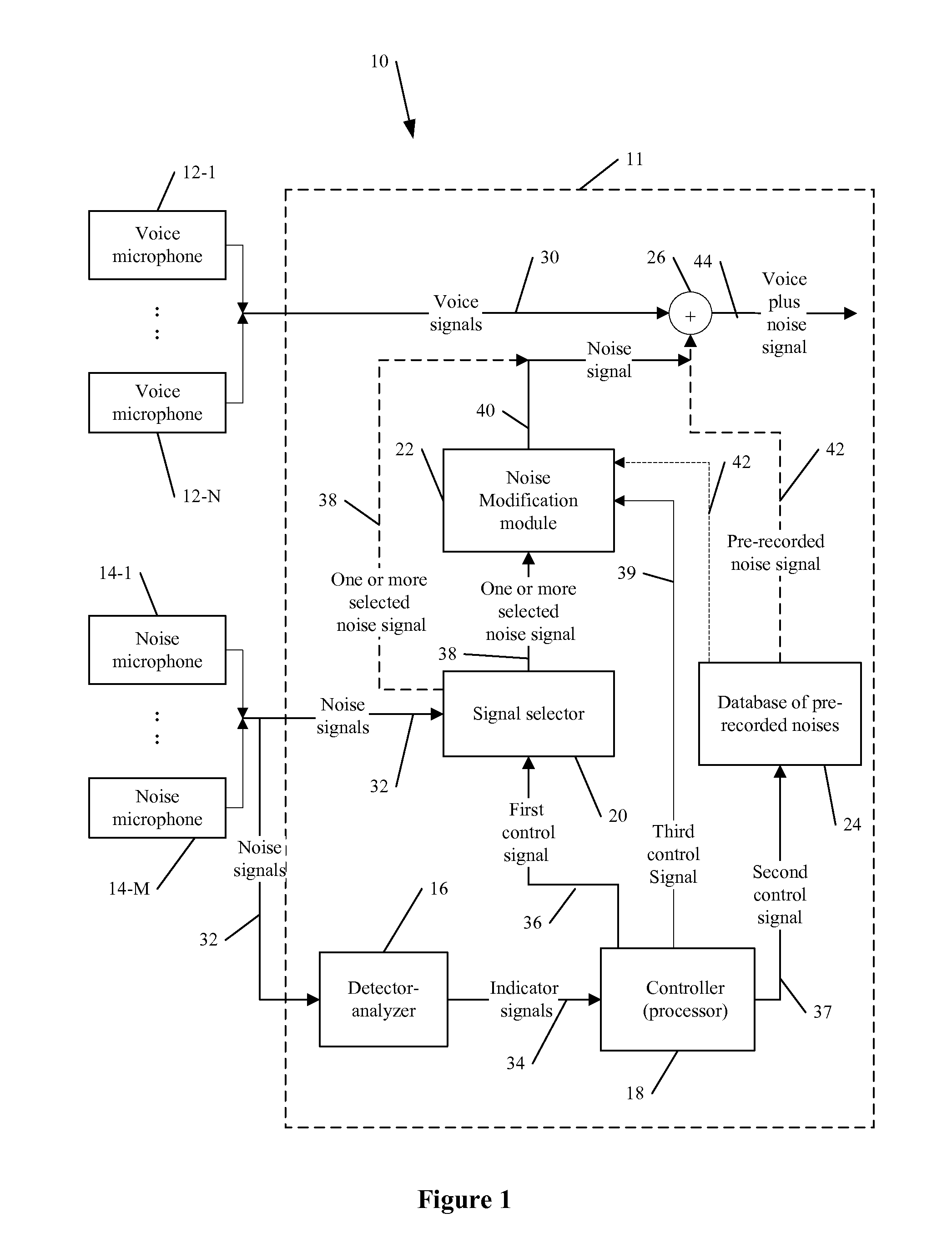
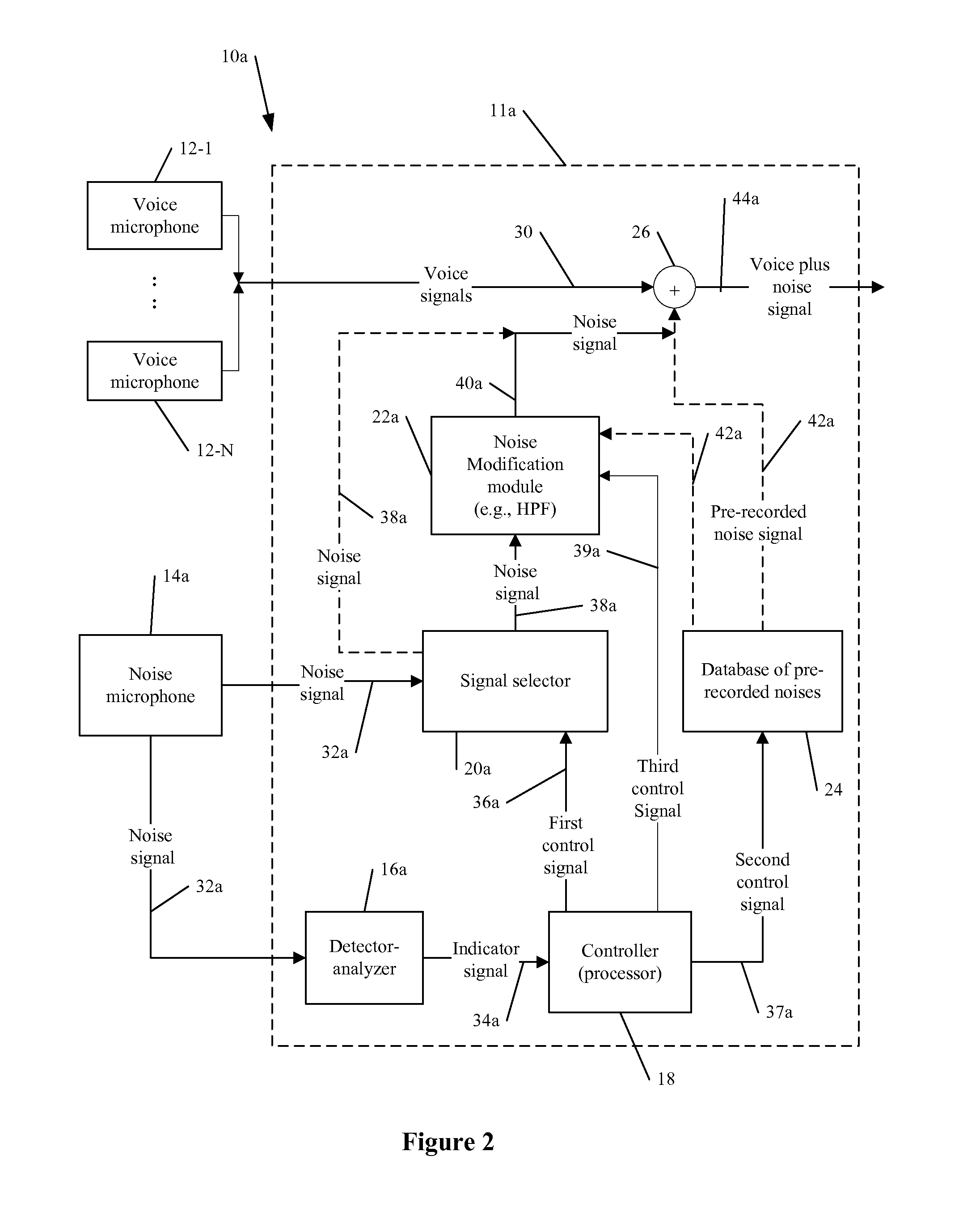
Audio noise modification for event broadcasting
An signal processing apparatus, system and software product for audio modification / substitution of a background noise generated during an event including, but not be limited to, substituting or partially substituting a noise signal from one or more microphones by a pre-recorded noise, and / or selecting one or more noise signals from a plurality of microphones for further processing in real-time or near real-time broadcasting.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
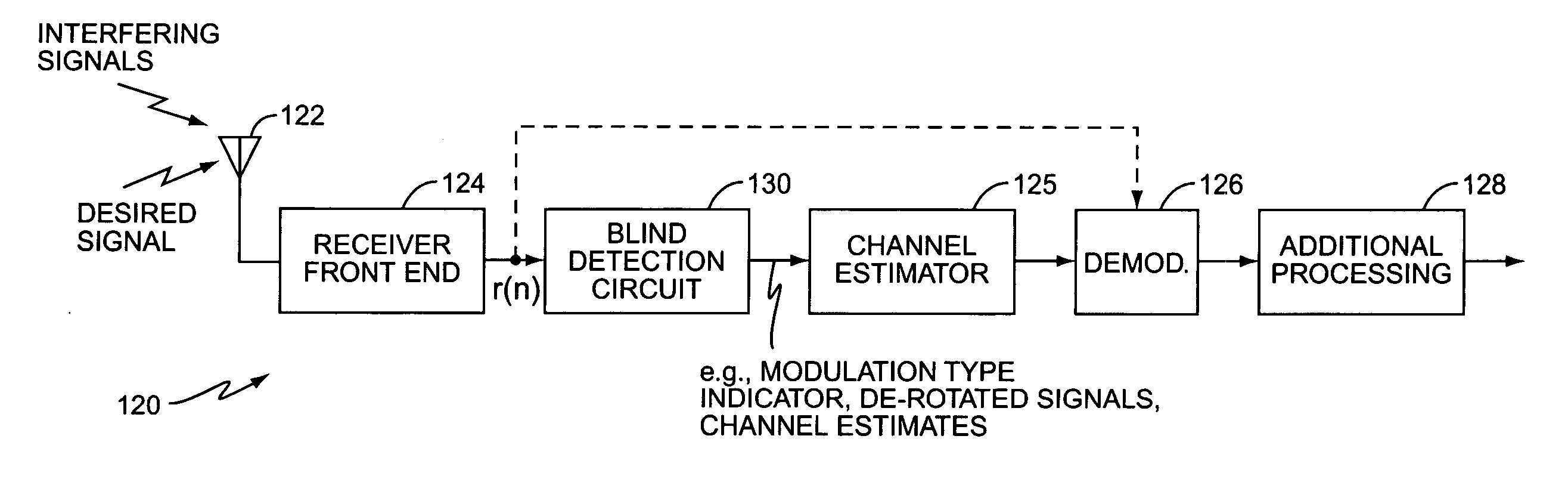
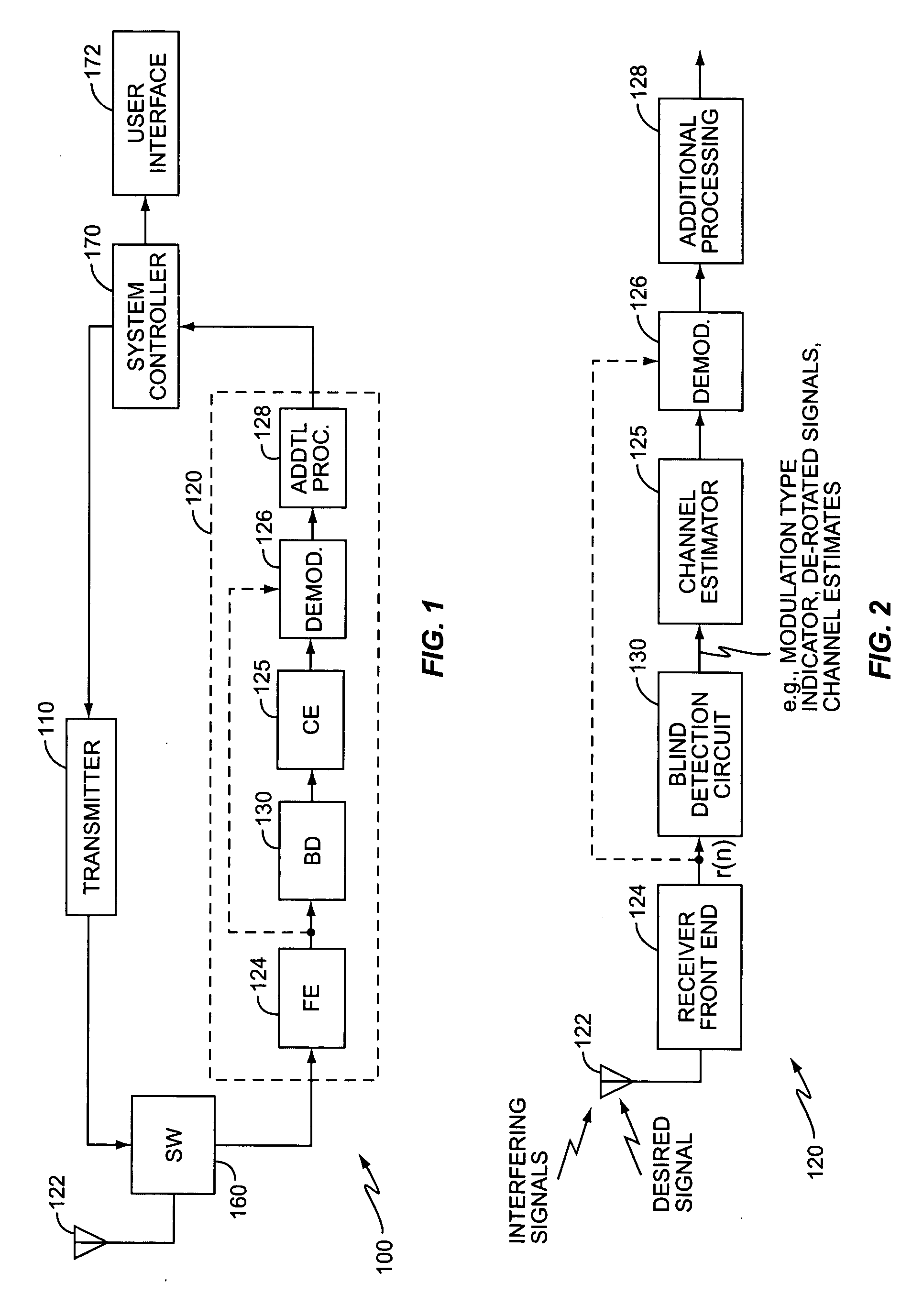
Method and apparatus for interference cancellation in communication signal processing
ActiveUS20050254600A1Reduce distractionsPolarisation/directional diversityModulation type identificationSpatial correlationIn-phase and quadrature components
A method and apparatus blindly detects a received signal's modulation type characterizing an impairment component of the received signal for each postulated modulation type by determining spatial correlations between In-phase and Quadrature components of the received signal. The blind detection circuit then detects the modulation type based on the characterized impairment component. A metric generator generates a postulation metric for each postulated modulation type based on the characterized impairment component. After evaluating the postulation metrics, an evaluation circuit identifies the postulated modulation type having the best postulation metric as the modulation type of the received signal. According to an exemplary embodiment, the blind detection circuit determines a whitened noise estimate for each postulated modulation type and generates the postulation metrics based on the whitened noise estimate to reduce interference effects in the postulation metrics.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for numeral sound signal processing and digital type sound frequency directional loudspeaker
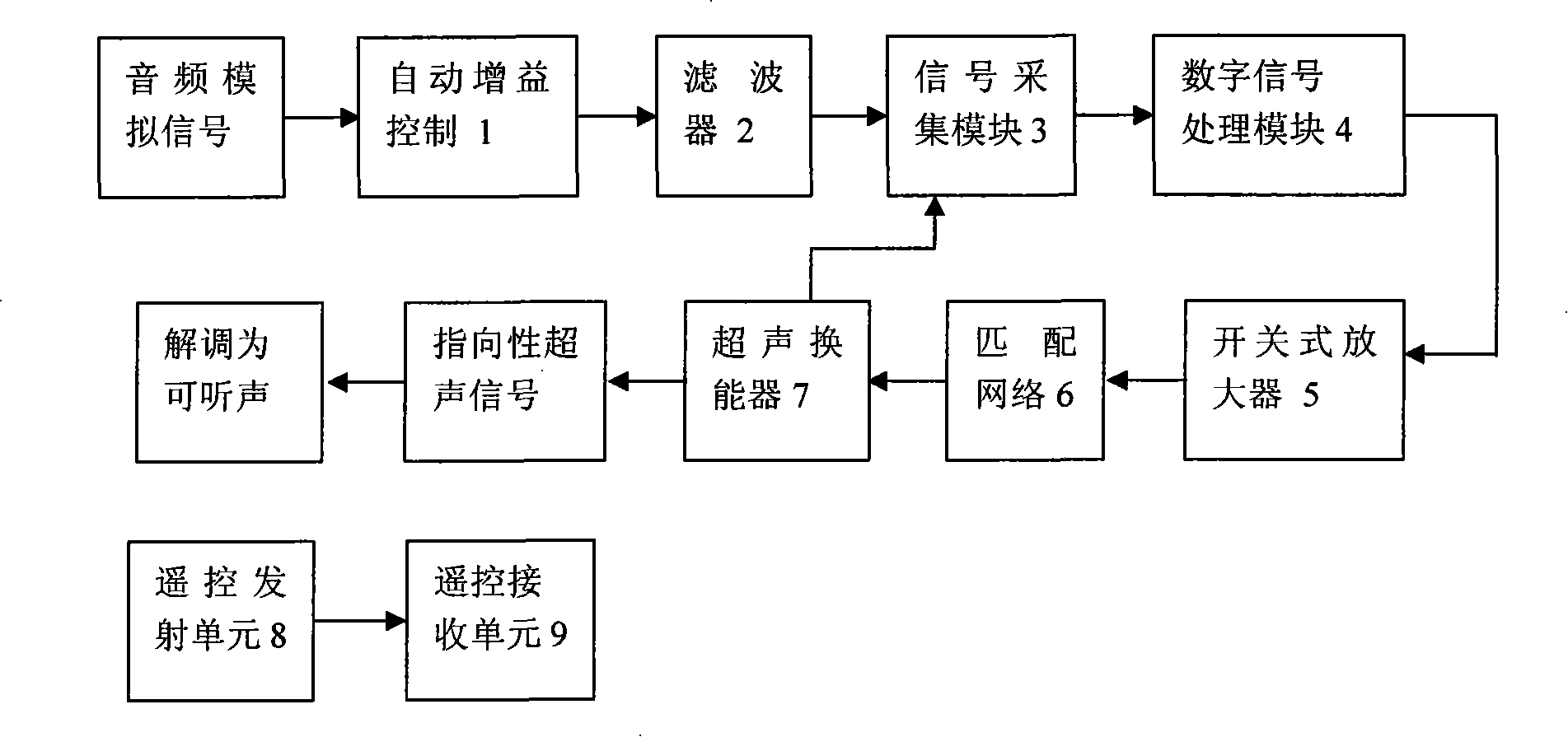
InactiveCN101203062AImplement video extensionRealize remote controlSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionTransducer circuitsDigital signal processingSound sources
The invention discloses a digital audio directional loudspeaker and a digital audio signal processing method. An automatic gain control module adjusts the amplitude of a sound source signal; then, a filter filters out elements beyond a audio signal belt so as to reduce noises; a signal input module changes an audio analog signal into a digital signal; the processing of approximate square root algorithm or other algorithms to the audio digital signal is finished in the digital signal processing module; two state levels are output into a switch type power amplifier to match with the network to assure impedance matching; an ultrasonic transducer is used for changing an electric signal into a sound pressure signal. The ultrasonic signal which is emitted from the transducer carries the input audio signal information, does the nonlinear interaction in the air and is demodulated into audible sound. A remote control receiving unit receives orders sent by a remote control transmission unit to control parameters such as point angle, volume, transmission distance, sound effect and point sound, etc.
Owner:徐利梅
Method for adapting sound in a hearing aid device by frequency modification and such a device
InactiveUS20110150256A1Reduce presenceLess distortionOcclusion effect electronic compensationHearing device energy consumption reductionDistortionDigital hearing aid
In a digital hearing aid device (1) frequency modification is employed above a lower spectral bound and in accordance with a compression factor. The frequency modification is dynamically adjusted in dependence on a sound environment analysis (10) or an end-user input (30), by modifying the frequency modification parameters such as a lower spectral bound and a compression factor. The adjustment can be based on an interpolation between predefined parameters. In certain sound environments, such as loud noise, own-voice and telephone conversations, frequency modification is reduced or switched off. The proposed solutions have the advantage that the occurrence of disturbing noise and of distortions of harmonic relationships at the end-user's ear is reduced and signal processing resources as well as battery resources are saved.
Owner:SONOVA AG
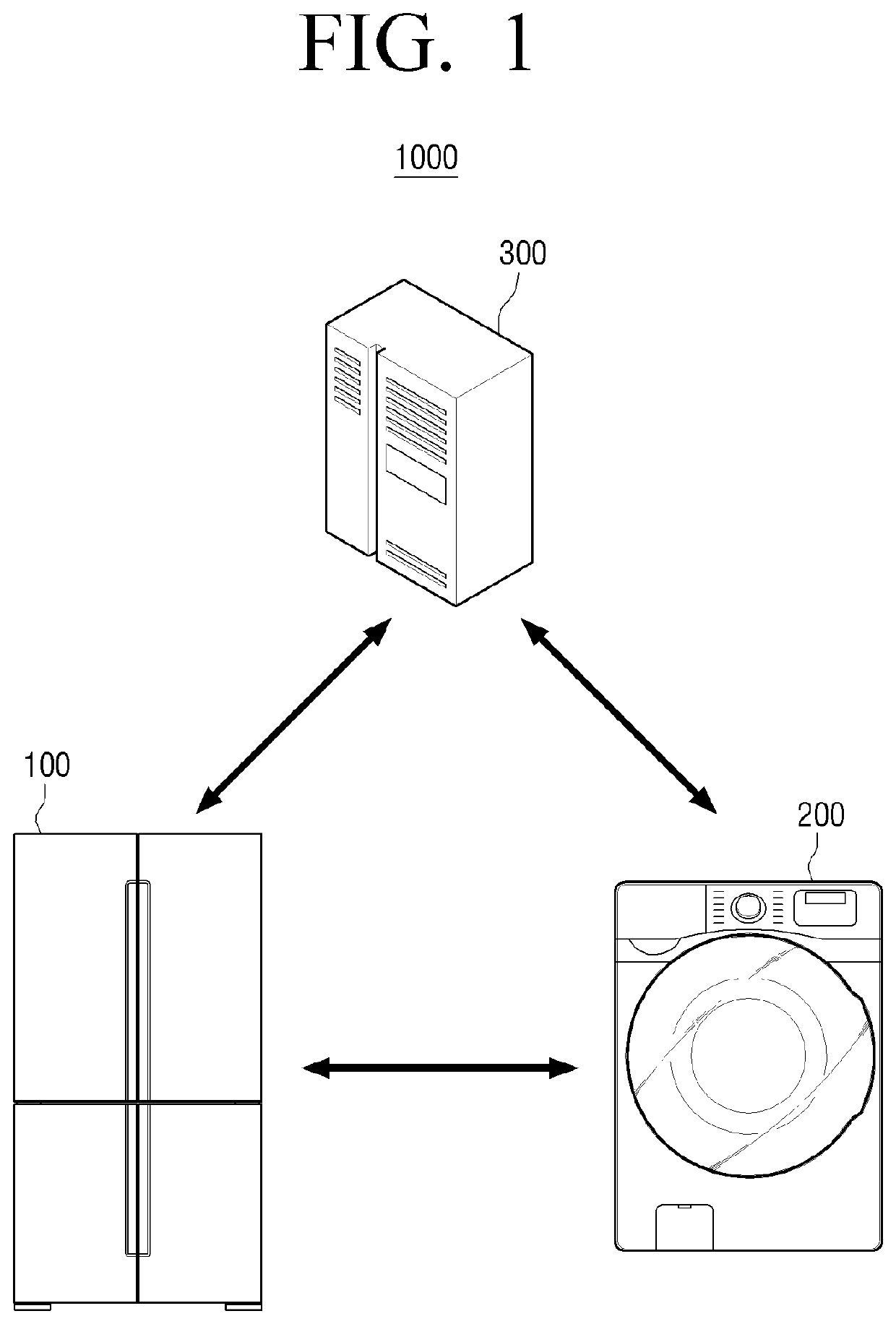
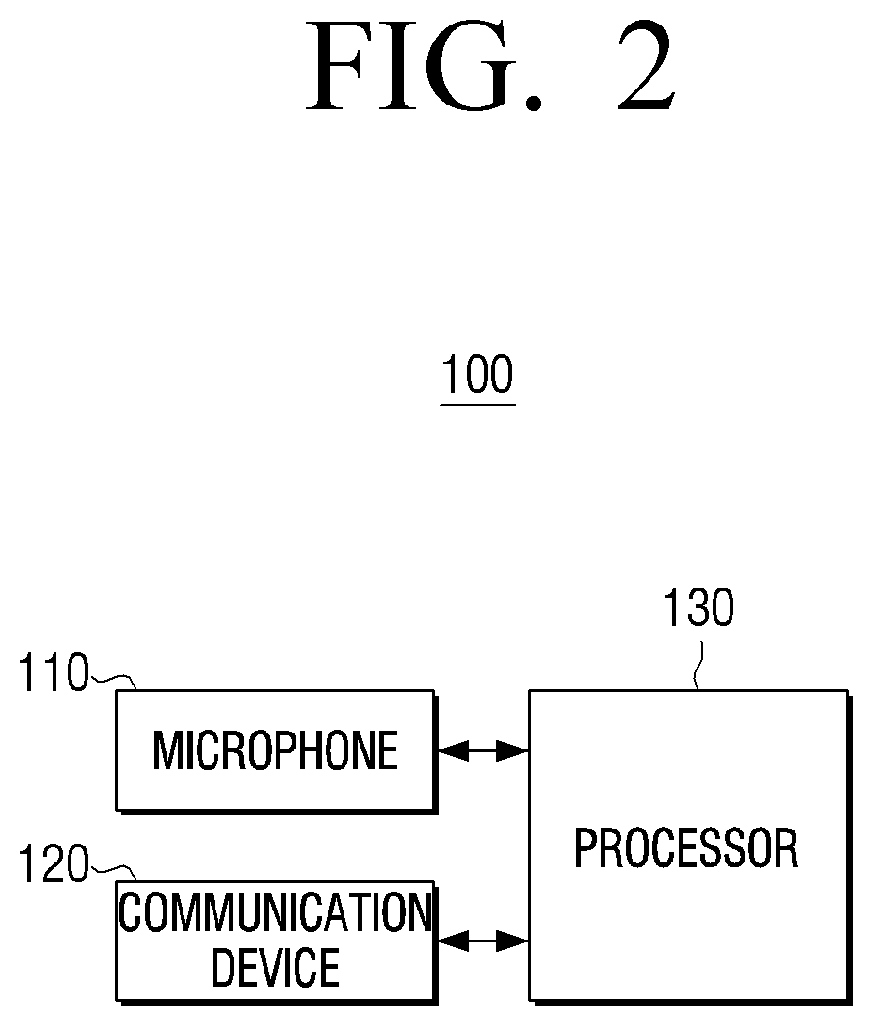
Home appliance and method for voice recognition thereof
ActiveUS20200211539A1Lower estimation noiseImprove speech recognition rateSpeech recognitionEngineeringHome appliance
A home appliance including a communication device configured to communicate with another home appliance, a microphone configured to receive a voice from a user, and a processor configured to perform signal processing on first voice data obtained from the microphone and perform voice recognition using the signal-processed first voice data. Wherein the processor generates noise data using second voice data received from the other home appliance and performs the signal processing on the first voice data using the generated noise data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
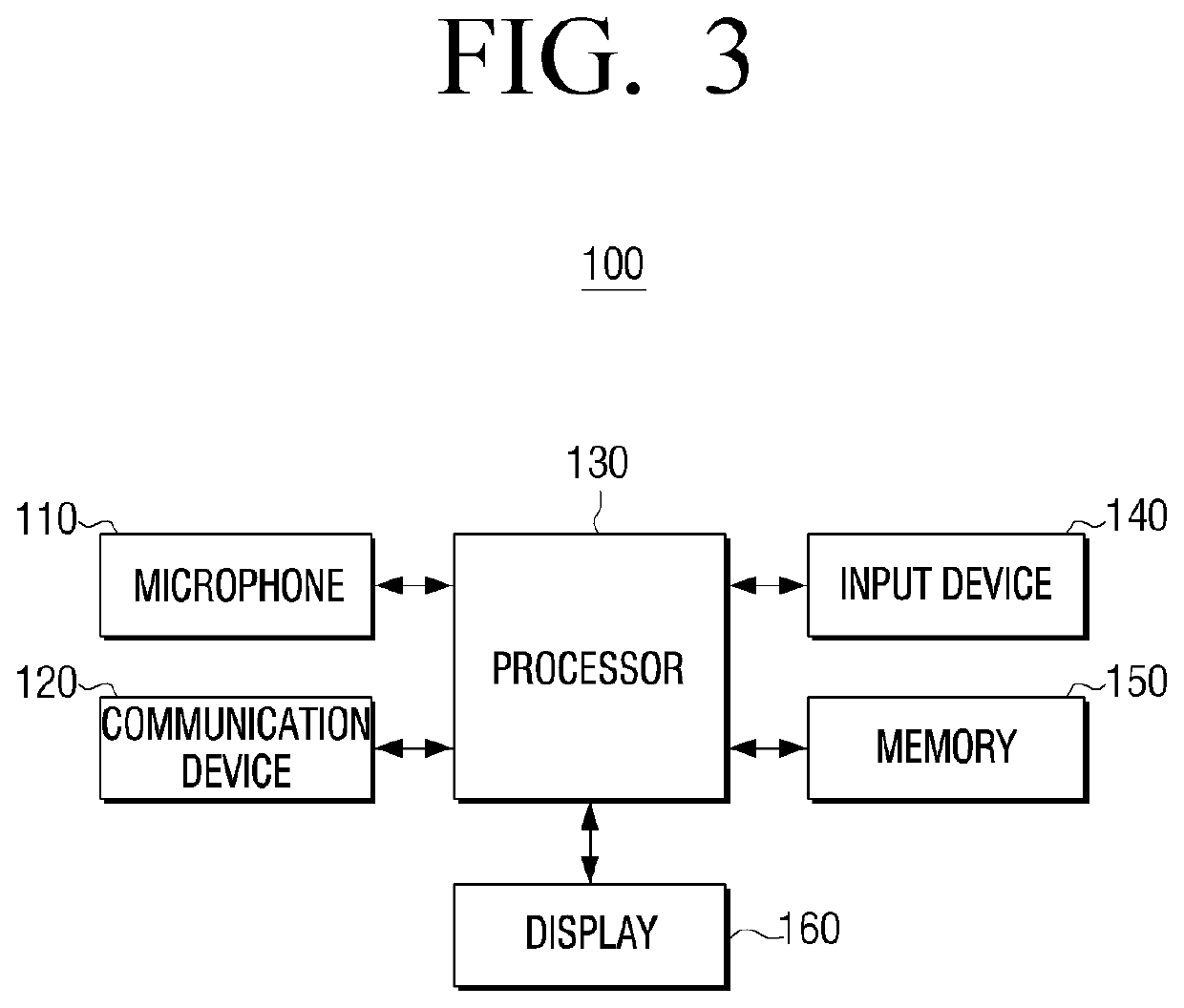
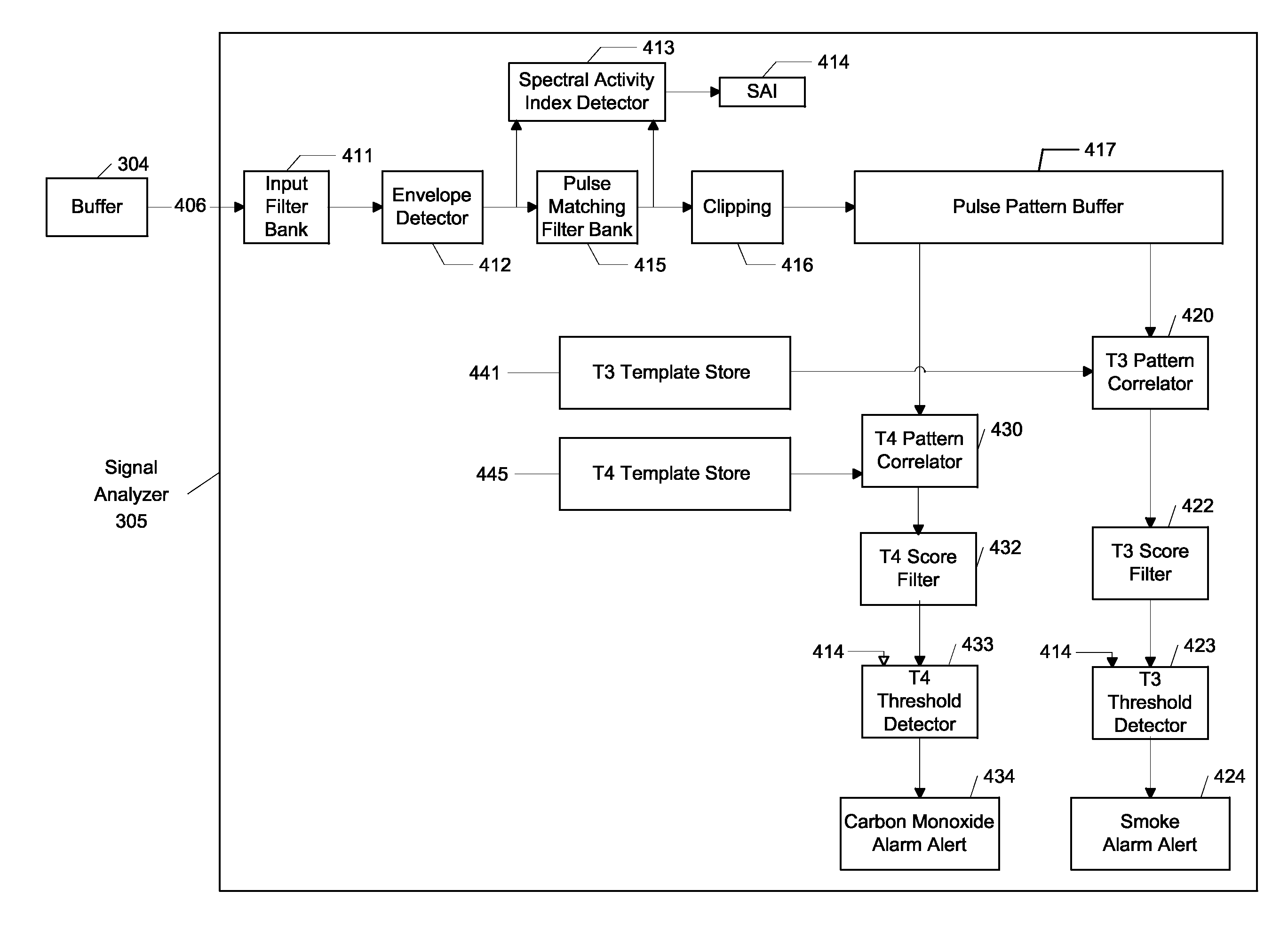
Signal processing system and methods for reliably detecting audible alarms
ActiveUS8269625B2Electrical apparatusElectric transmission signalling systemsCarbon monoxide detectorUltimate tensile strength
A signal processing system and associated methods are disclosed for reliably detecting audible alert signals, such as Temporal-3 (or Code-3) and Temporal-4 (or Code-4) alert signals generated by commercially available smoke, fire, and carbon monoxide detectors. The system and methods are capable of detecting audible alert signals of different intensities in the presence of dynamic background environment (e.g., television programming, music, noise, and the like). The system and methods are capable of detecting audible alert signals generated by far away smoke, fire, and carbon monoxide detectors. The signal processing system and methods may, in some embodiments, be incorporated into a bedside or other unit that generates a supplemental alert signal capable of alerting individuals who might not otherwise respond to the alarm condition, such as individuals who are asleep, children, hearing impaired, or intoxicated.
Owner:INNOVALARM
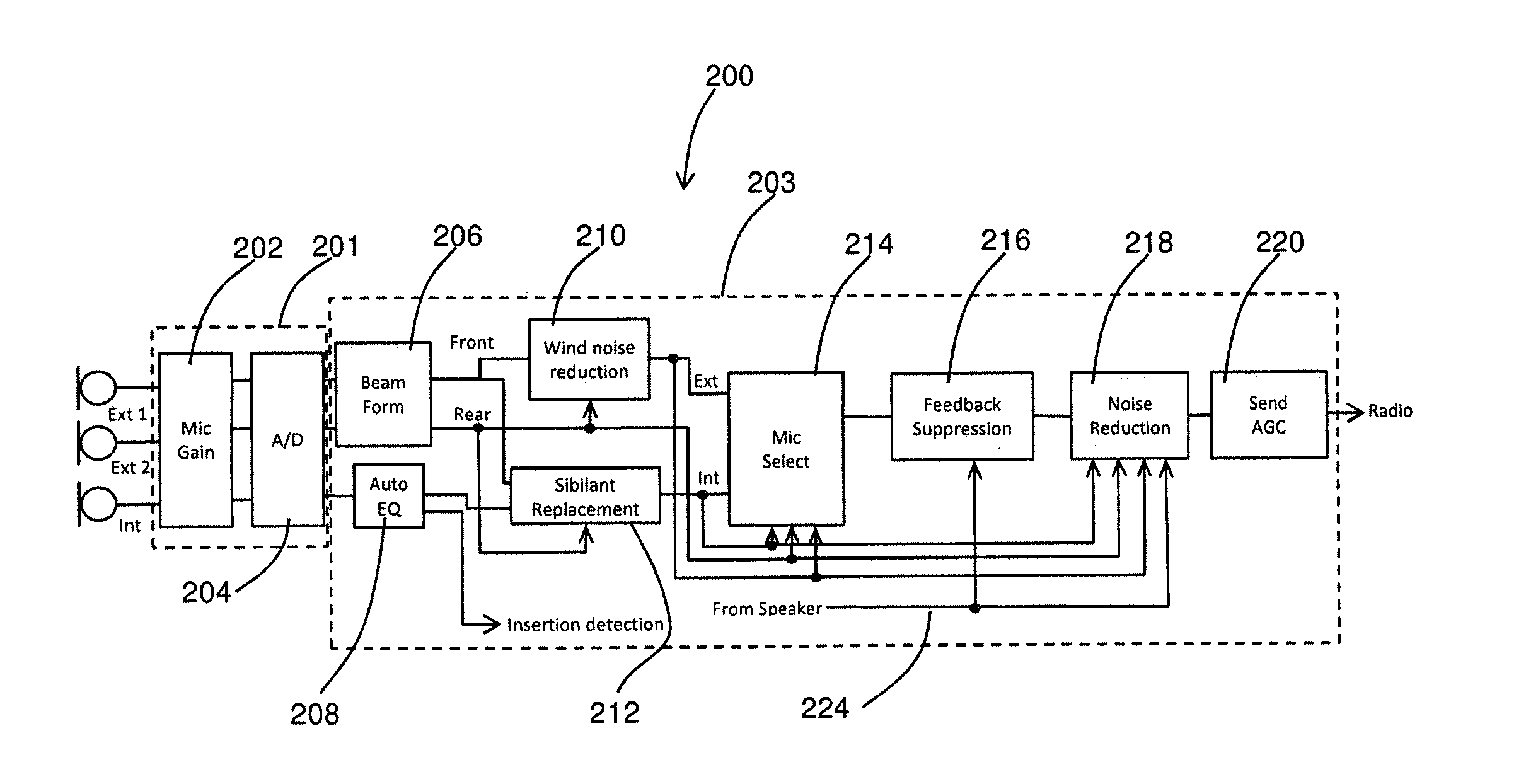
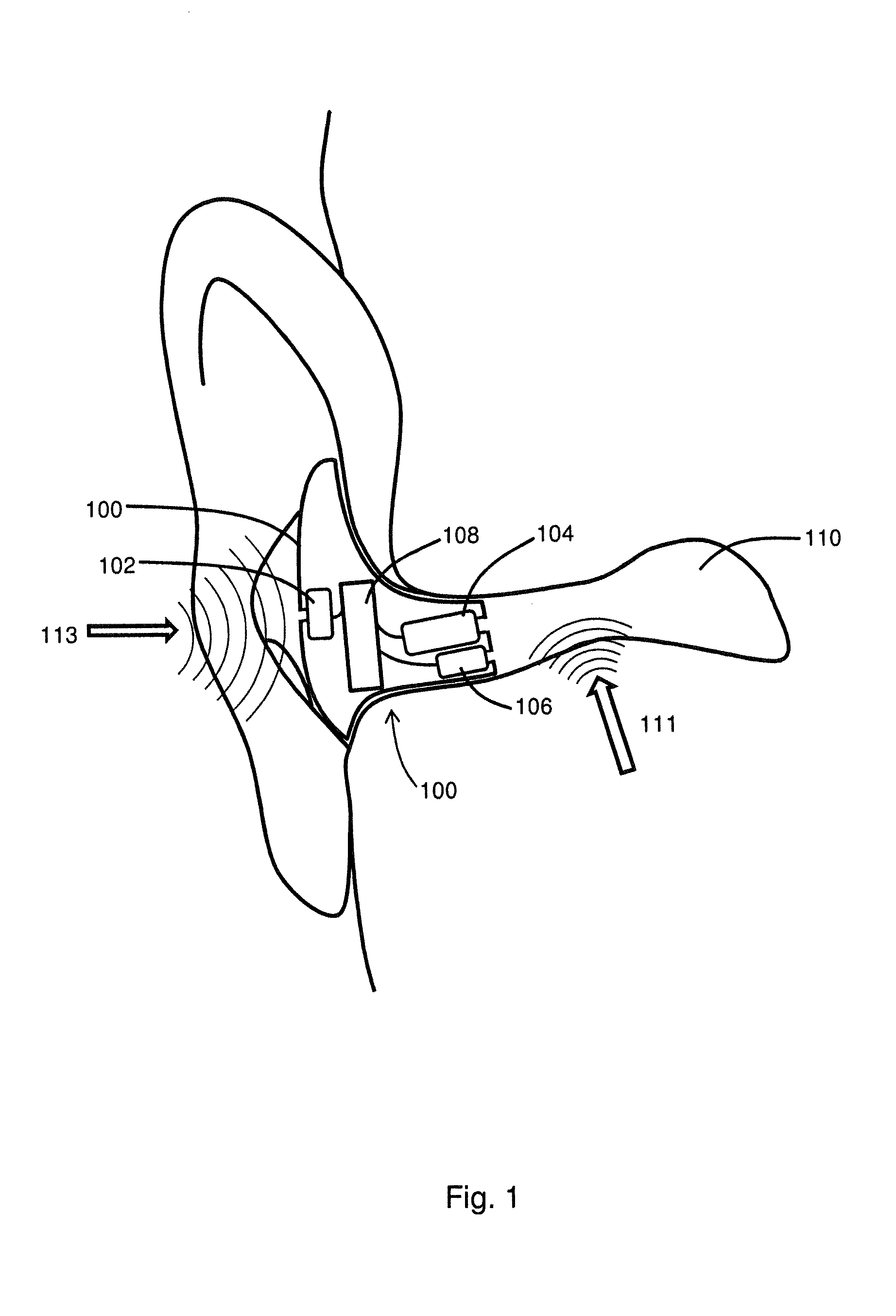
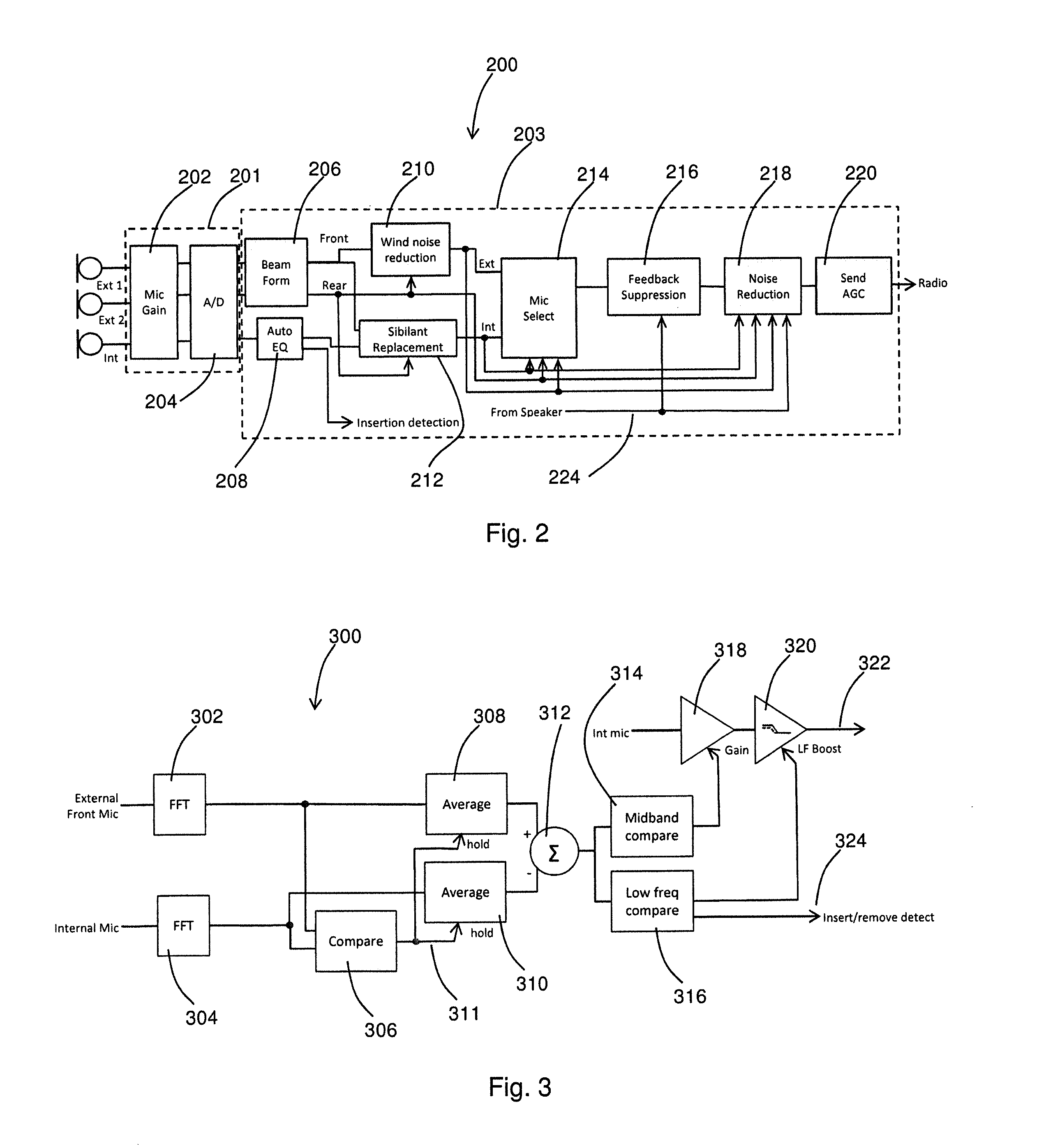
Apparatus and method for digital signal processing with microphones
At least a partial seal between a housing of a hearing instrument and an ear canal is provided. First signals are received from an internal microphone disposed in the ear canal. Second signals are received from an external microphone disposed outside of the ear canal. A condition of the at least a partial seal is determined, and when the condition of the at least a partial seal indicates a leak, one or more of the level and the spectrum of the first signals is adjusted to compensate for the leak and producing first adjusted signal. A first amount of the first adjusted signals is blended with a second amount of the second signals to produce a blended signal, the first amount and the second amount selected based upon a level of noise.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
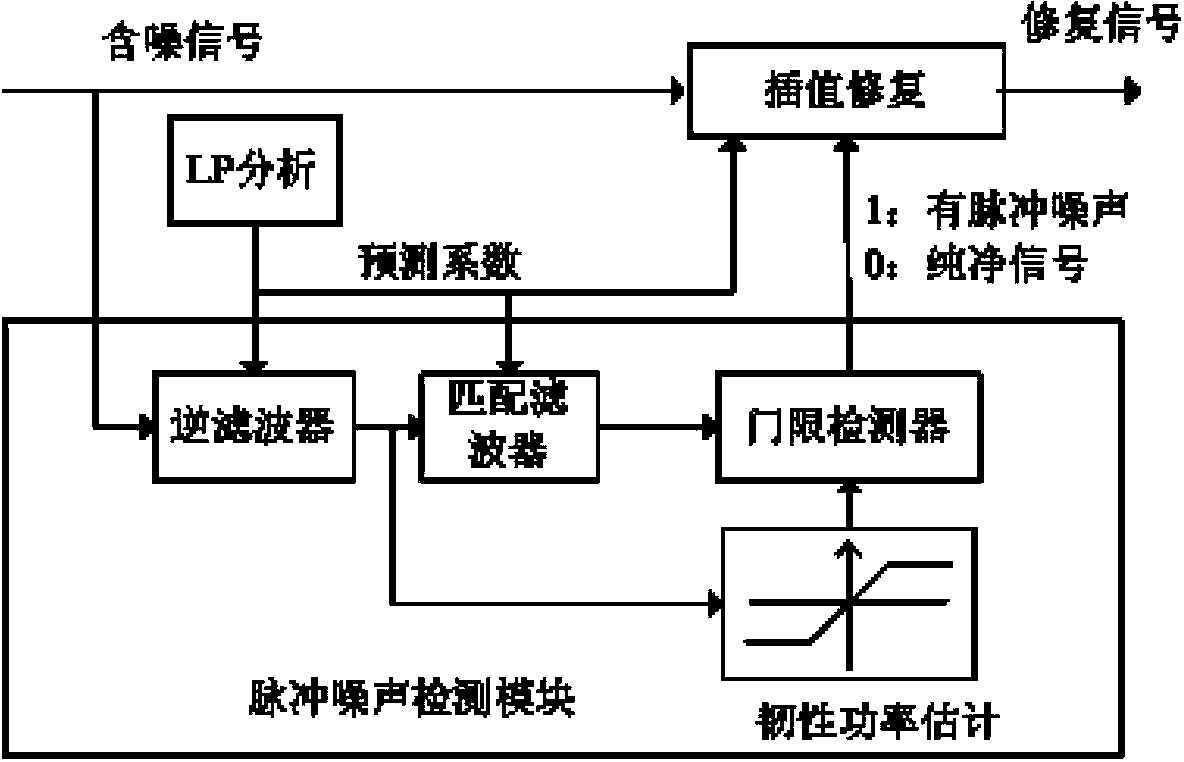
Method for suppressing transient noise in voice
The invention discloses a method for suppressing transient noise in voice, and belongs to the technical field of signal processing. The method for suppressing transient noise in voice is characterized by comprising a gamma through frequency cepstrum coefficient extraction module, a transient noise detection module and a voice signal reconstruction module, wherein the input end of the gamma through frequency cepstrum coefficient extraction module receives a voice signal containing noise, the output end of the gamma through frequency cepstrum coefficient extraction module is connected with the input end of the transient noise detection module, the output end of the transient noise detection module is connected with the input end of the voice signal reconstruction module, the input end of the voice signal reconstruction module receives the voice signal containing noise and is also connected with the output end of the transient noise detection module, and the voice signal reconstruction module outputs the voice with noise removed.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Signal processing apparatus and method
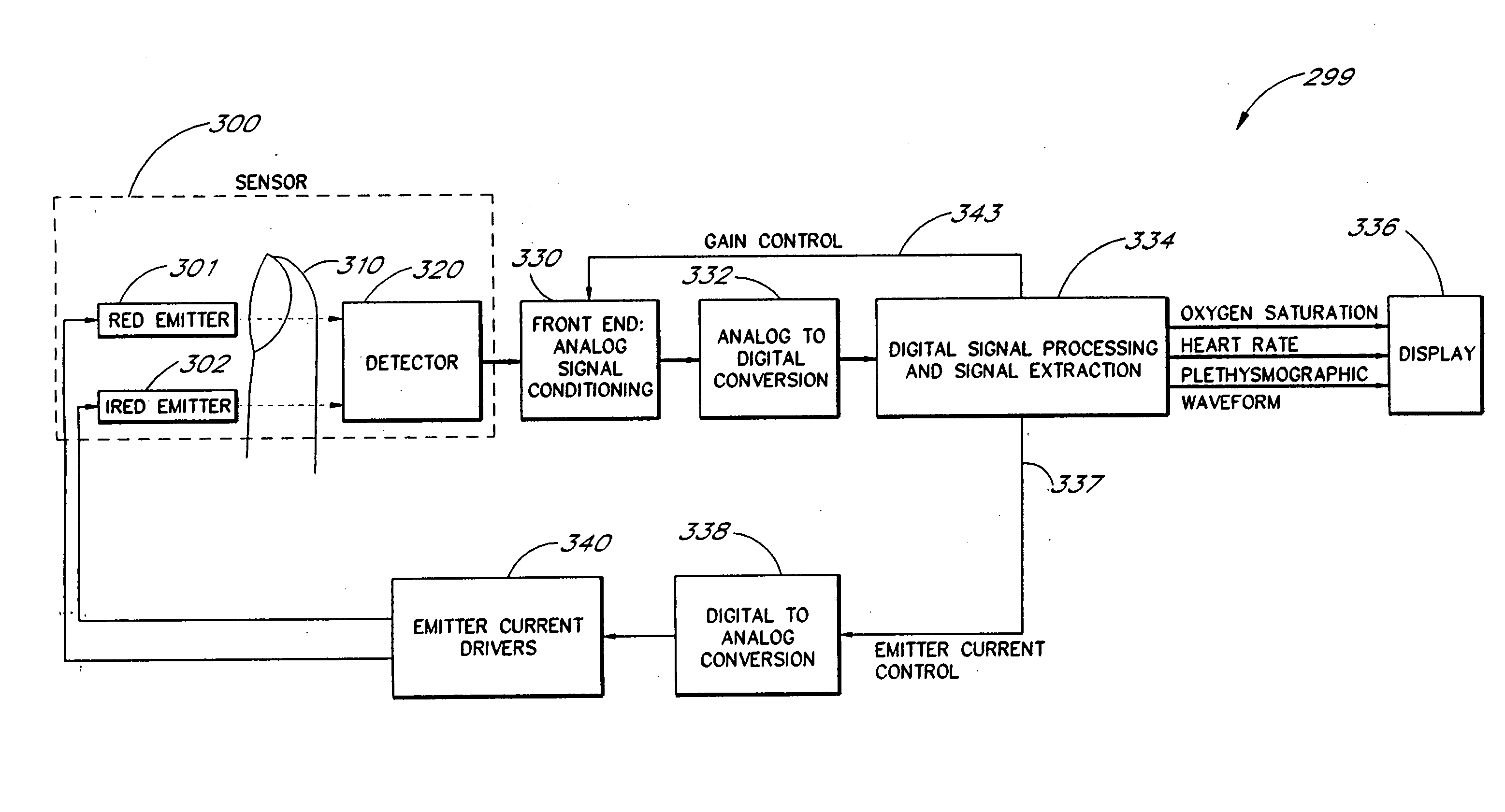
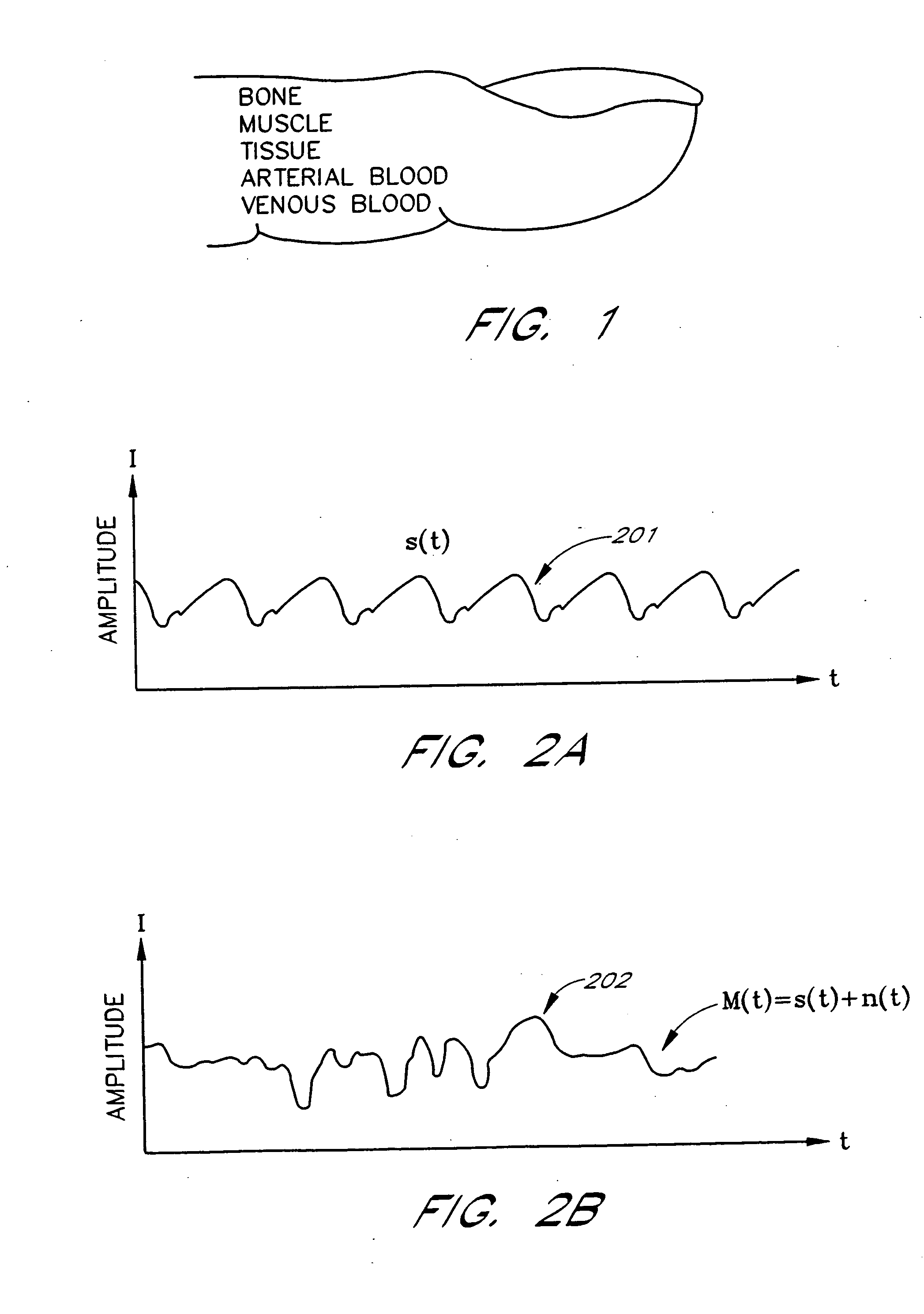
A method and an apparatus to analyze two measured signals that are modeled as containing desired and undesired portions such as noise, FM and AM modulation. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, a transformation is used to evaluate a ratio of the two measured signals in order to find appropriate coefficients. The measured signals are then fed into a signal scrubber which uses the coefficients to remove the unwanted portions. The signal scrubbing is performed in either the time domain or in the frequency domain. The method and apparatus are particularly advantageous to blood oximetry and pulserate measurements. In another embodiment, an estimate of the pulserate is obtained by applying a set of rules to a spectral transform of the scrubbed signal. In another embodiment, an estimate of the pulserate is obtained by transforming the scrubbed signal from a first spectral domain into a second spectral domain. The pulserate is found by identifying the largest spectral peak in the second spectral domain.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Apparatus And A Method For Audio Signal Processing
InactiveUS20150172807A1Suppress noiseExcessive noiseMicrophonesLoudspeakersEngineeringMicrophone signal
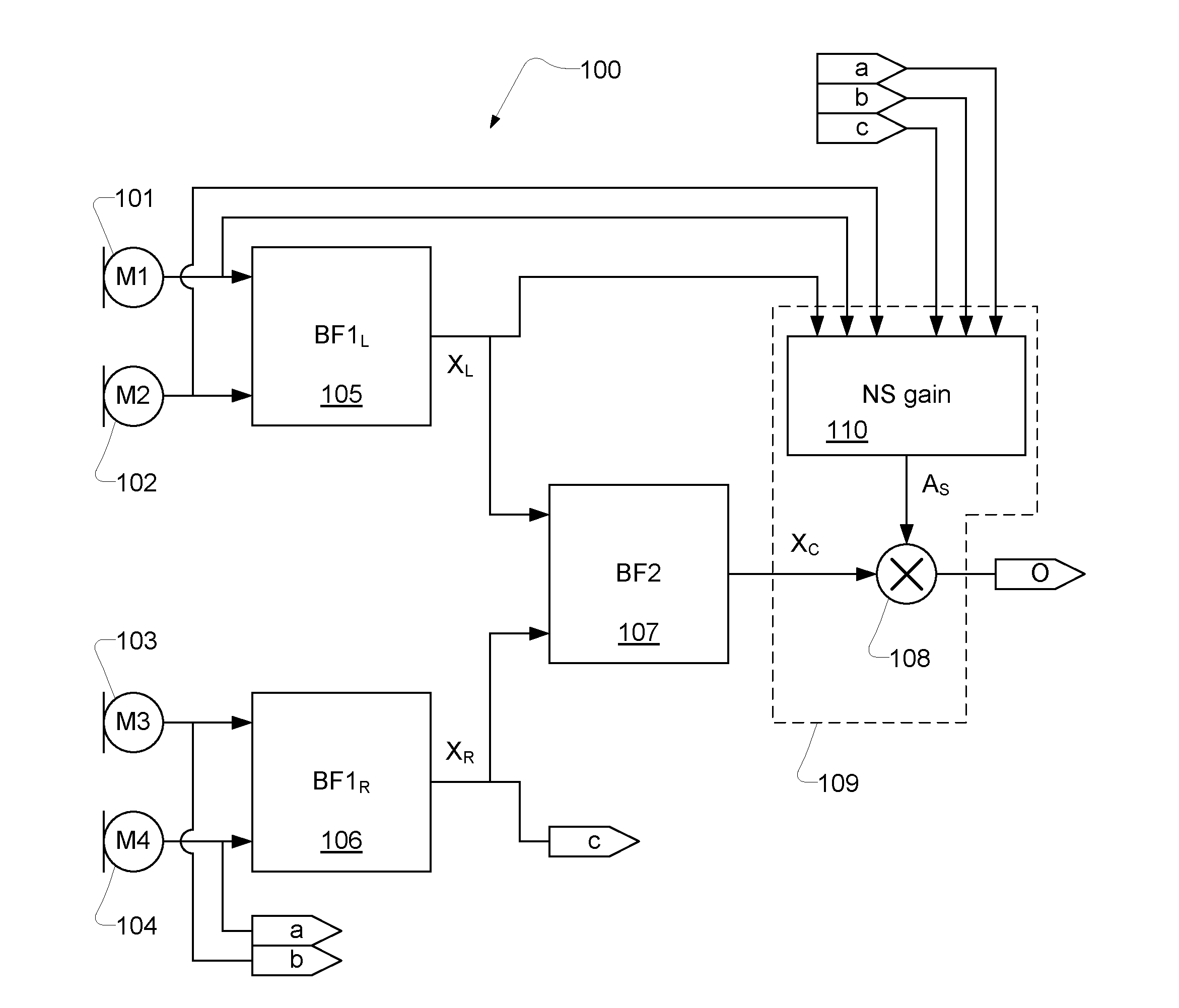
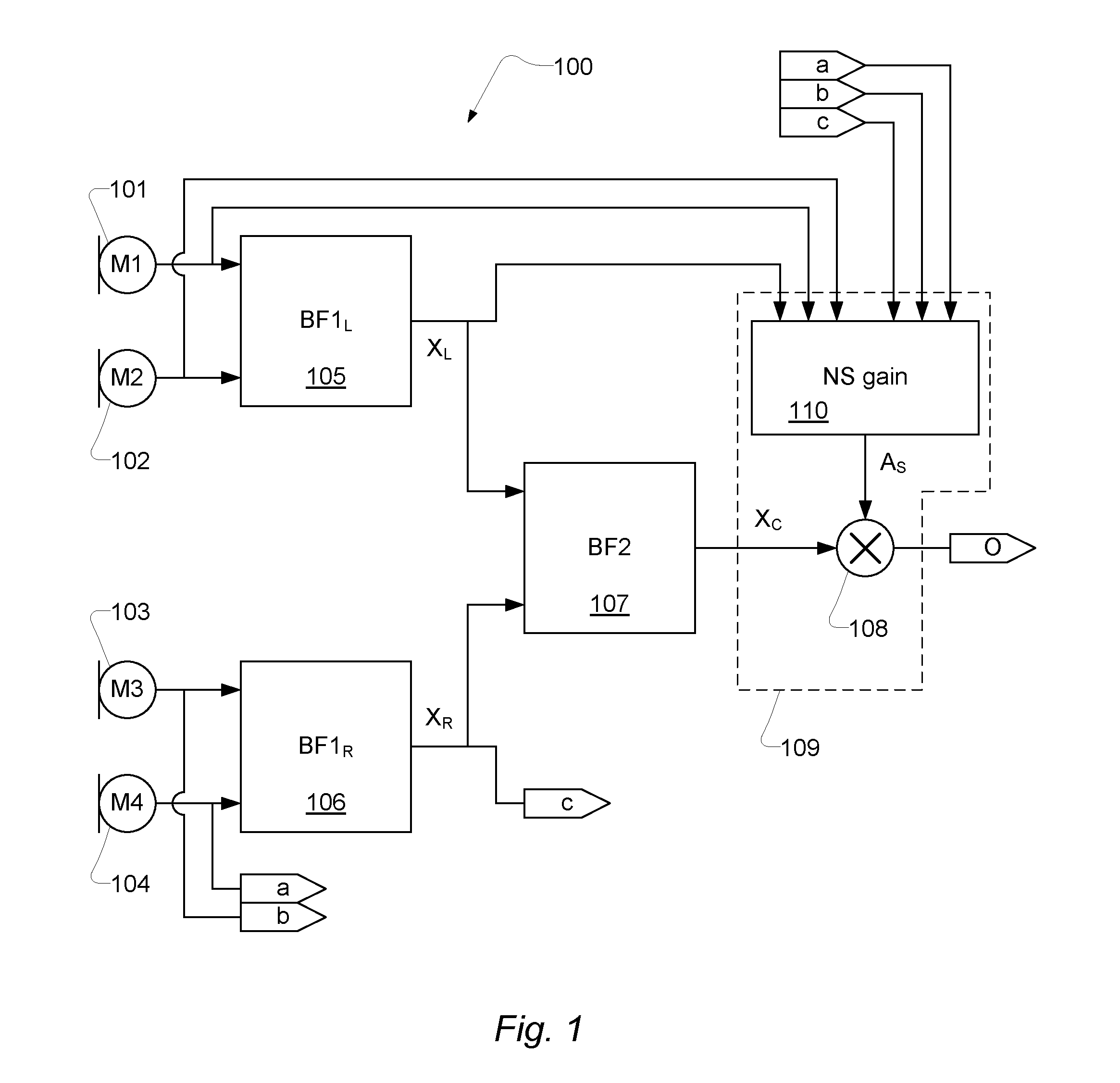
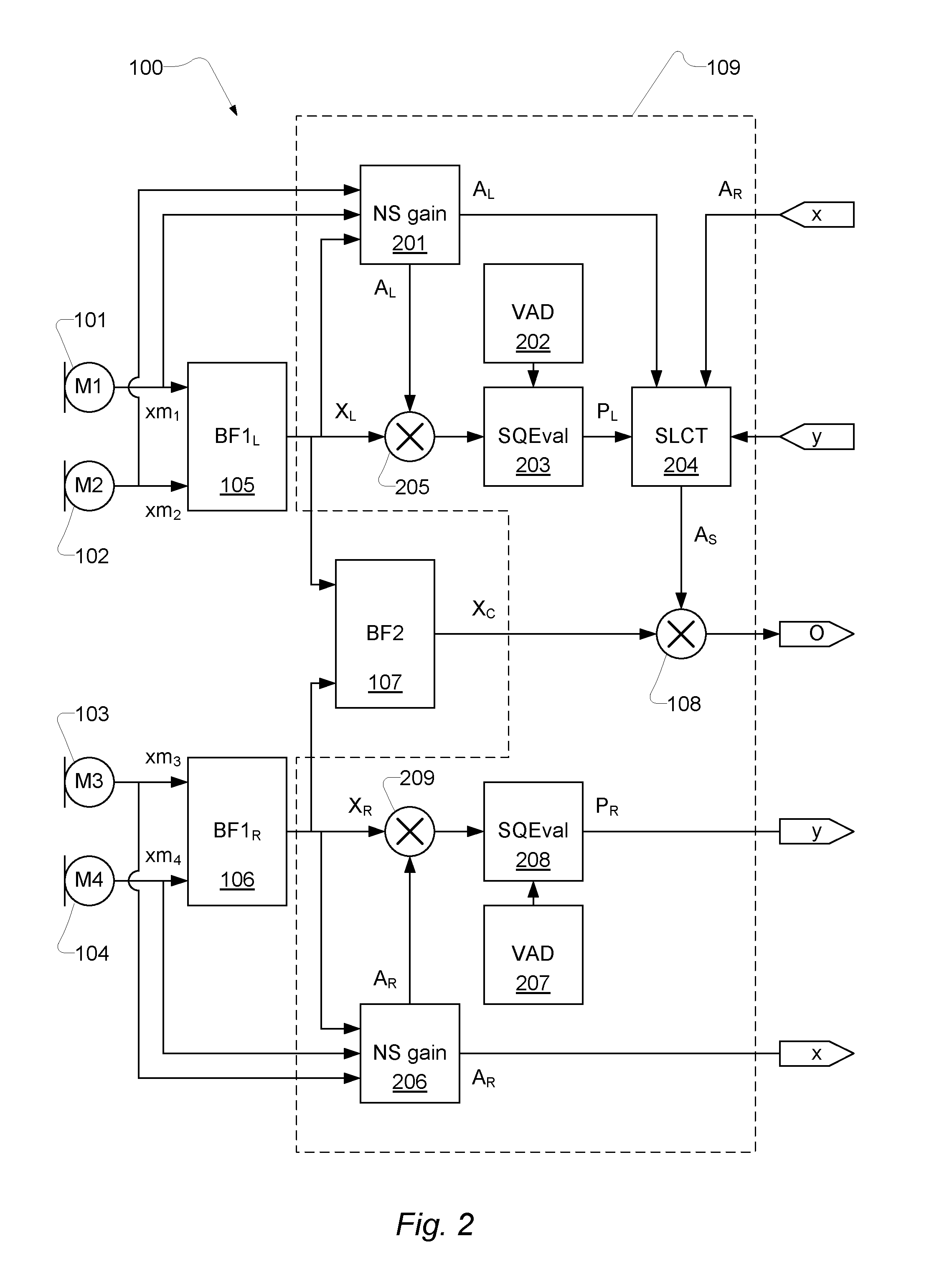
An apparatus, such as a headset, configured to process audio signals from multiple microphones, comprising: a first pair of microphones (101, 102) outputting a first pair of microphone signals and a second pair of microphones (103, 104) outputting a second pair of microphone signals; a first beamformer (105) and a second beamformer (106) each configured to receive a pair of microphone signals and adapt the spatial sensitivity of a respective pair of microphones as measured in a respective beamformed signal (XL; XR) output from a respective beamformer (105; 106); wherein the spatial sensitivity is adapted to suppress noise relative to a desired signal; a third beamformer (107) configured to dynamically combine the signals (XL; XR) output from the first beamformer (105) and the second beamformer (106) into a combined signal (XC); wherein the signals are combined such that signal energy in the combined signal is minimized while a desired signal is preserved; and a noise reduction unit (109) configured to process the combined signal (XC) from the third beamformer (107) and output the combined signal such that noise is reduced.
Owner:GN NETCOM
Method and apparatus for instantaneouslly inspecting motor vehicle fault
InactiveCN101029855AIncrease productivityImprove accuracyVibration measurement in solidsVehicle suspension/damping testingDriver/operatorTransducer
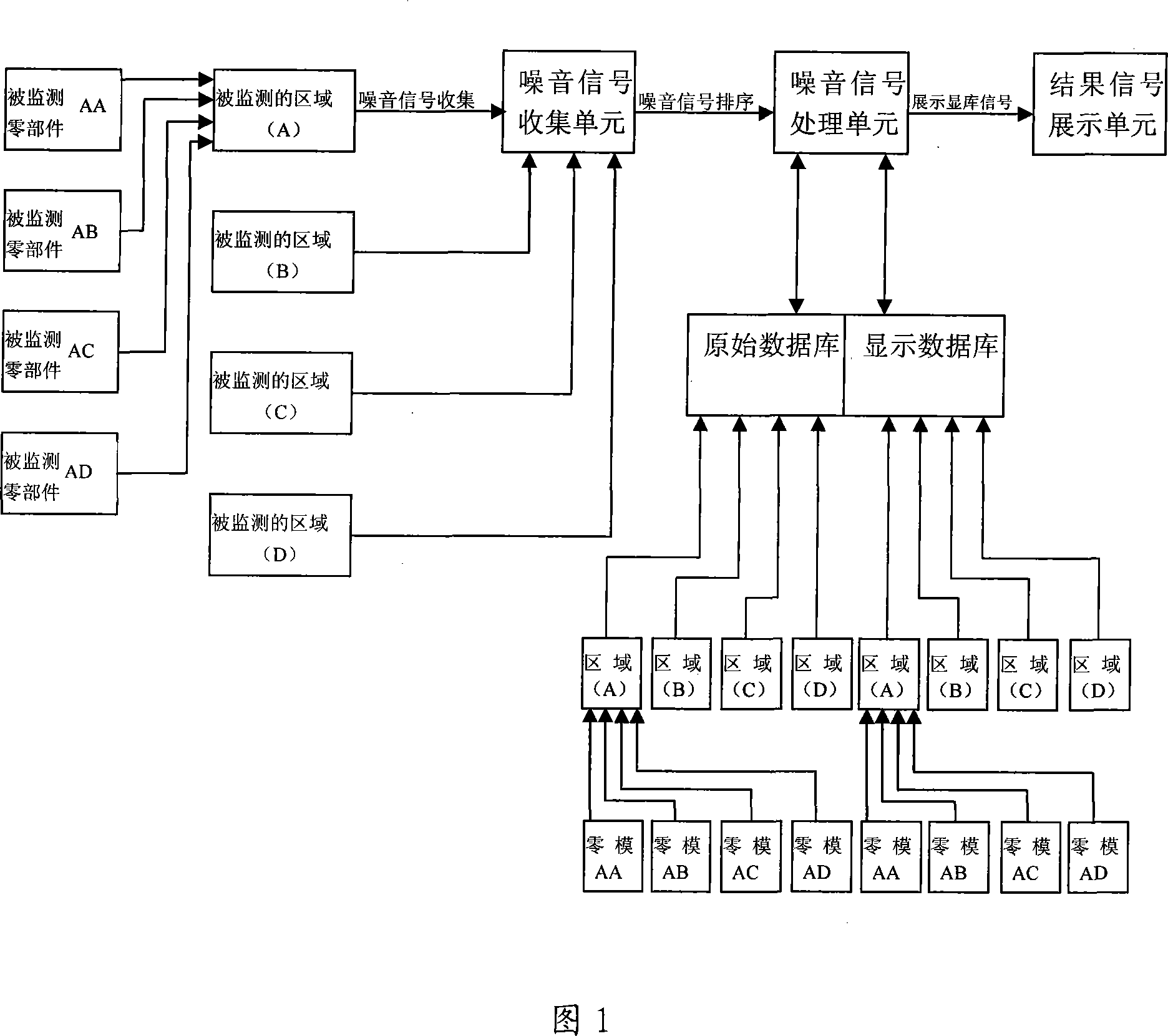
A method for detecting demand fault of motor vehicle includes setting sound transducer near to key parts of motor vehicle operation, comparing sound detected by said transducer with original sound information stored in noise signal databank by noise signal processing unit for knowing information that detected parts is damaged or not then informing said information to motor vehicle driver through information display unit.
Owner:童军
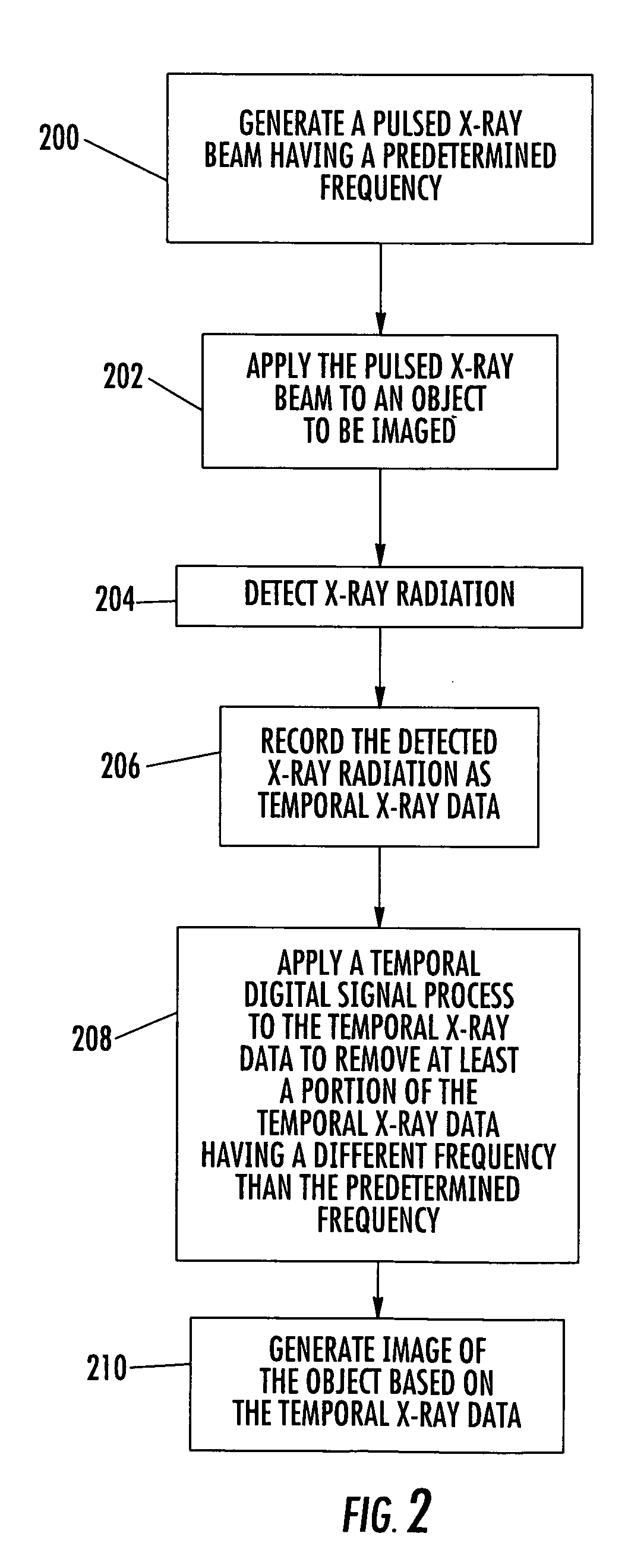
X-ray imaging systems and methods using temporal digital signal processing for reducing noise and for obtaining multiple images simultaneously
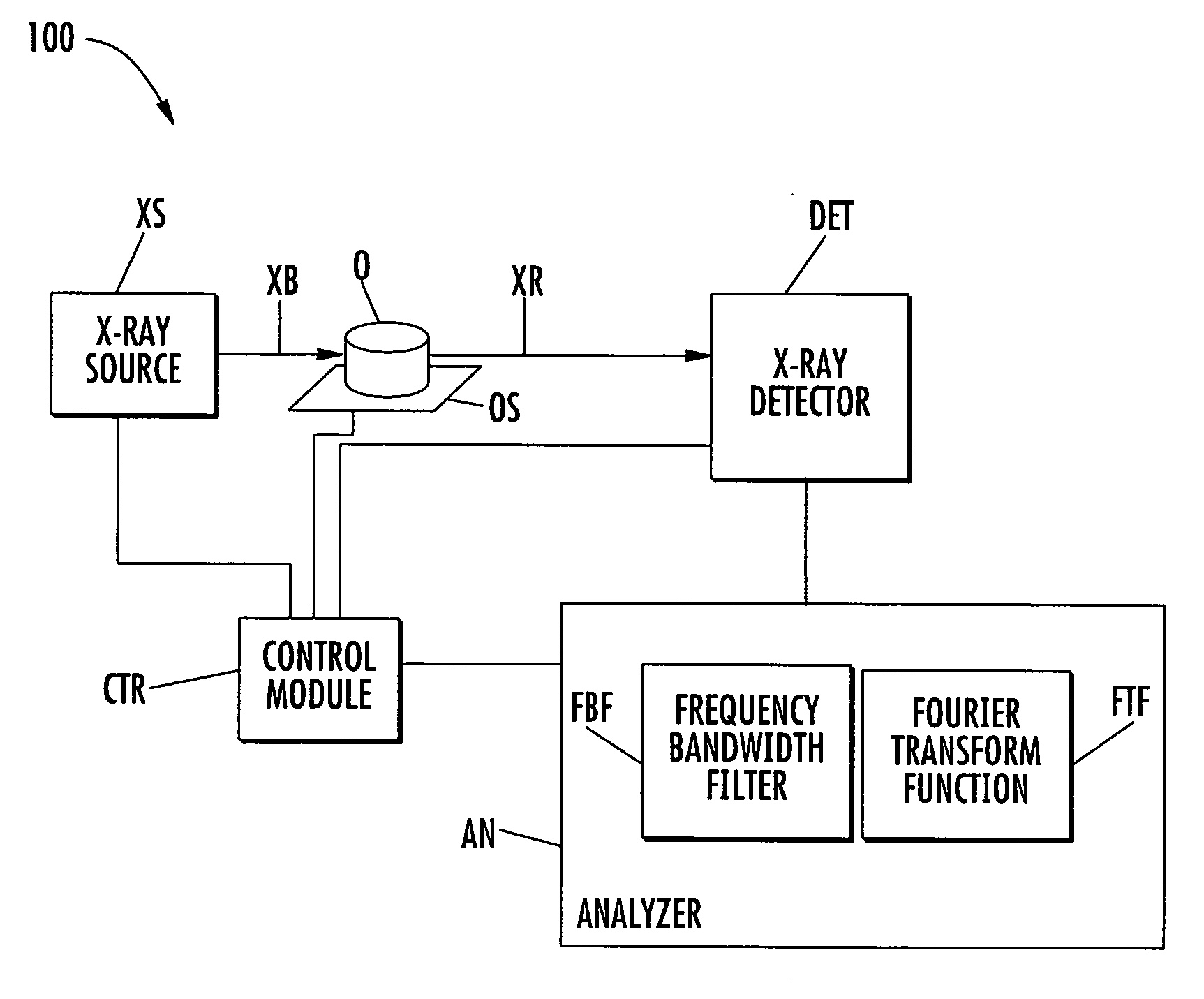
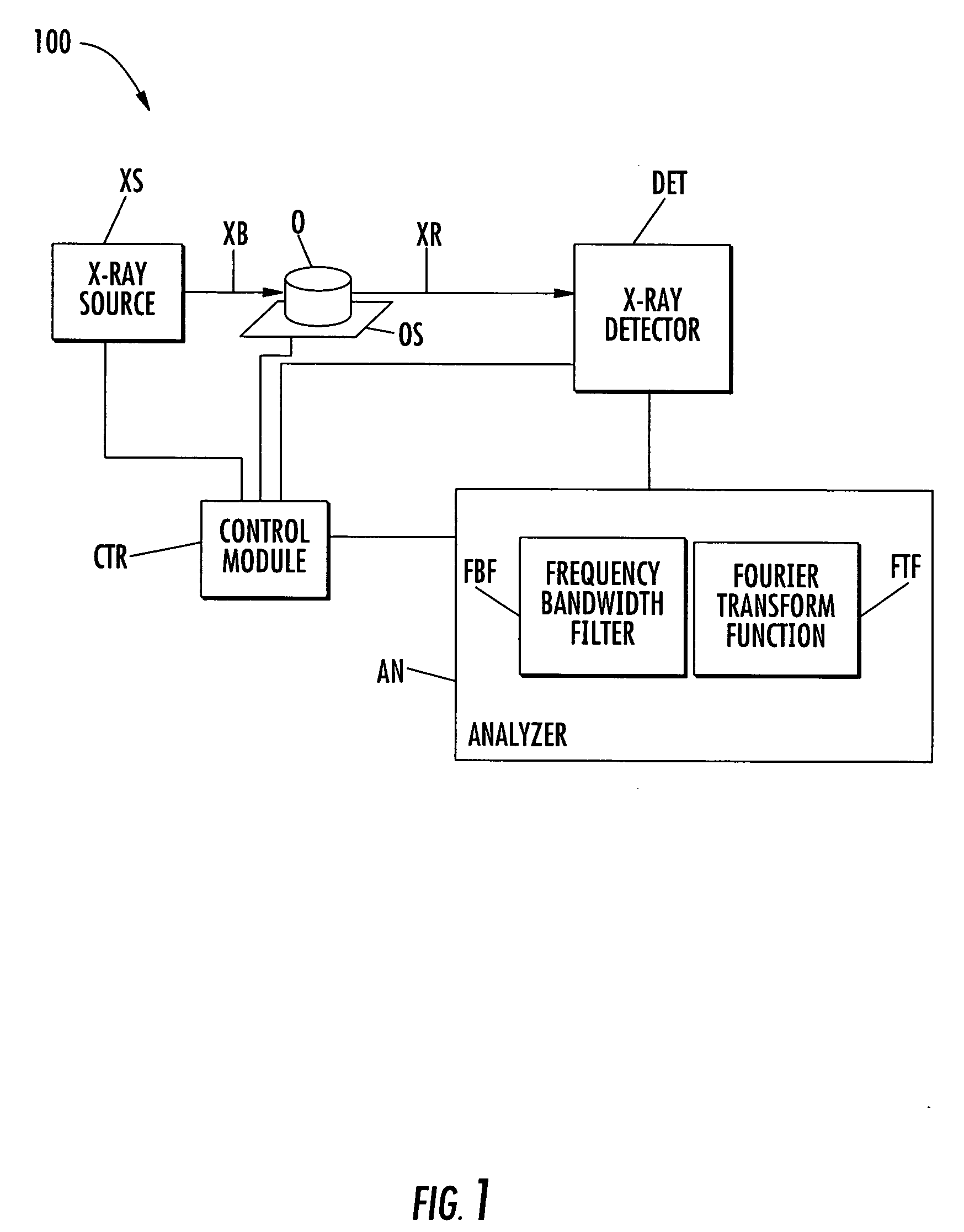
ActiveUS7245692B2Reduce noiseRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsDigital signal processingRadiology
X-ray imaging systems and methods are provided that use temporal digital signal processing for reducing noise and for obtaining multiple images simultaneously. An x-ray imaging system can include an x-ray source adapted to generate a pulsed x-ray beam having a predetermined frequency and apply the pulsed x-ray beam to an object to be imaged. An x-ray detector can be adapted to detect x-ray radiation from the object and generate temporal data based on the x-ray radiation. A temporal data analyzer can be adapted to apply a temporal signal process to the temporal data to remove at least a portion of the temporal data having a different frequency than the predetermined frequency.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
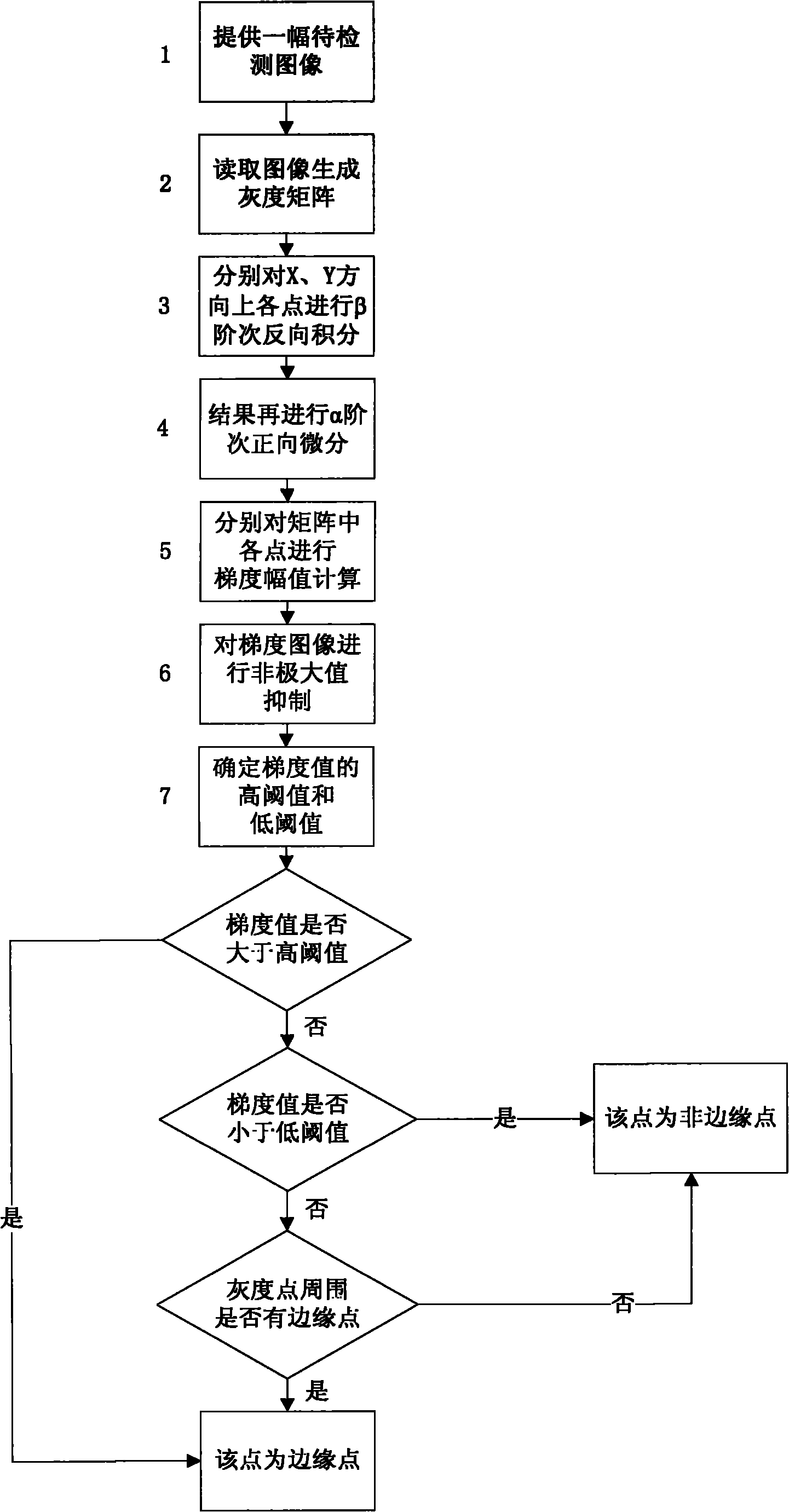
Edge detection method based on fractional-order signal processing
InactiveCN101841642AAdjustment sensitivityEffective filteringTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAlgorithmThresholding
The invention discloses an edge detection method based on fractional-order signal processing, aiming at solving edge detection which is a traditional trouble in the pattern recognition field. The method is a novel algorithm which can conduct gradient operation to all target pixel points in an image by using the fractional-order signal processing to obtain an edge, and comprises that a gray-level matrix is generated from any image, the gradient operation is conducted respectively to each pixel point in the matrix by adopting detection operators to obtain the gradient amplitude of each pixel point, then non-maximum value suppression is conducted to the gradient image and finally a double-threshold method is adopted for judging whether the target pixel points are edge points and are connected with the edge or not. The invention omits the process of smooth filtering preprocessing conducted to the image and utilizes a novel derivative algorithm based on the fractional-order signal processing to conduct the gradient operation. Fractional integrals in the algorithm can suppress the interference introduced during derivation. The entire method has the advantages that the signal-to-noise ratio is good, the edge positioning is accurate and the false edge can be effectively suppressed. The algorithm can be used in the fields such as the automatic target recognition and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU HENGSHENG ELECTRONICS TECH +4
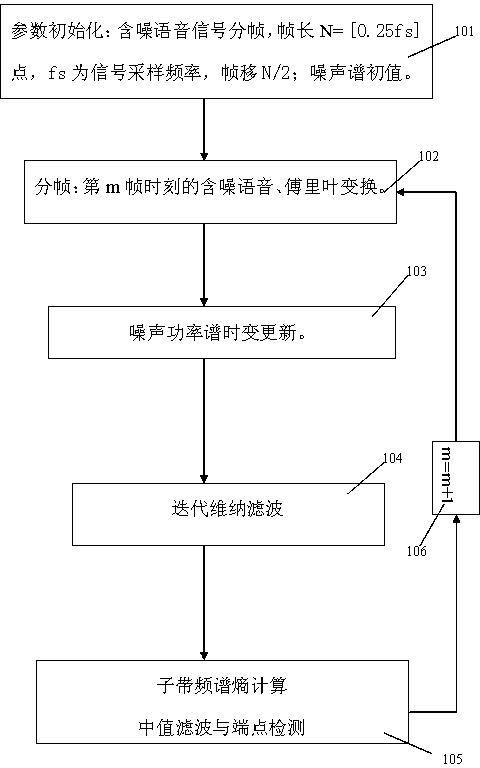
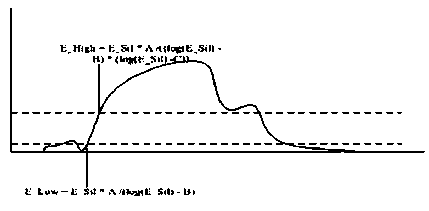
Noised voice end point robustness detection method
InactiveCN105023572AImprove signal-to-noise ratioSimple calculationSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumNoise power spectrum
The invention discloses a noised voice end point robustness detection method. The method comprises the following steps of constructing an estimation method of a noise power spectrum of each frame of acoustical signals in filtering and providing a time-varying updating mechanism of a noise spectrum; firstly, carrying out iterative wiener filtering on a frequency spectrum of each frame of voices; then, dividing into several sub-band and calculating a frequency spectrum entropy of each sub-band; and then making successive several frames of sub-band frequency spectrum entropies pass through one group of median filters so as to acquire each frame of the frequency spectrum entropies; according to values of the frequency spectrum entropies, classifying input voices. By using the algorithm, the voices and noises, and a voice state and a voiceless state can be effectively distinguished. Under different noise environment conditions, robustness is possessed. The algorithm has low calculating cost, is simple, is easy to realize and is suitable for application of real-time voice signal processing system of various kinds of systems needing voice end point detection. The method is a real-time voice end points detection algorithm which adapts to a complex environment, and voice end point detection and voice filtering enhancement are completed together in a one-time state.
Owner:王景芳
Interference noise matrix reconstitution-based self-adaptive wave beam forming method
InactiveCN103778102AImprove robustnessComplex mathematical operationsSignal classificationEngineering
The invention relates to an interference noise matrix reconstitution-based self-adaptive wave beam forming method and belongs to the field of array signal processing. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing the signal model of a minimum variance distortionless response wave beam forming problem, then under the condition that the angle range of an expected signal wave arrival direction is known, utilizing a multiple signal sorting spatial spectrum to reconstitute an interference noise covariance matrix in a region without containing expected signals, based on the matrix, solving the estimation value of a guide vector of the real expected signal by using the maximizing of an array output power and the constrain condition that the estimation value of the guide vector of the expected signal is prevented from being converged to the guide vector of any interference or the linear combination of the interference. According to the method, a simulation result shows that when random pointing errors and local scattering of the expected signal and a interference source exist, the output signal to interference plus noise power ratio in a very large input signal-to-noise ratio range is still close to a theoretical value and is superior to that of other self-adaptive wave bean forming methods.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
MR spectroscopy system and method for diagnosing painful and non-painful intervertebral discs
ActiveUS8825131B2Eliminate the effects ofMedical imagingMagnetic measurementsFrequency spectrumSpectroscopy
An MR Spectroscopy (MRS) system and approach is provided for diagnosing painful and non-painful discs in chronic, severe low back pain patients (DDD-MRS). A DDD-MRS pulse sequence generates and acquires DDD-MRS spectra within intervertebral disc nuclei for later signal processing and diagnostic analysis. An interfacing DDD-MRS signal processor receives output signals of the DDD-MRS spectra acquired and is configured to optimize signal-to-noise ratio by an automated system that selectively conducts optimal channel selection, phase and frequency correction, and frame editing as appropriate for a given acquisition series. A diagnostic processor calculates a diagnostic value for the disc based upon a weighted factor set of criteria that uses MRS data extracted from the acquired and processed MRS spectra for multiple chemicals that have been correlated to painful vs. non-painful discs. A display provides an indication of results for analyzed discs as an overlay onto a MRI image of the lumbar spine.
Owner:ACLARION INC
Image processing apparatus and image display apparatus using same
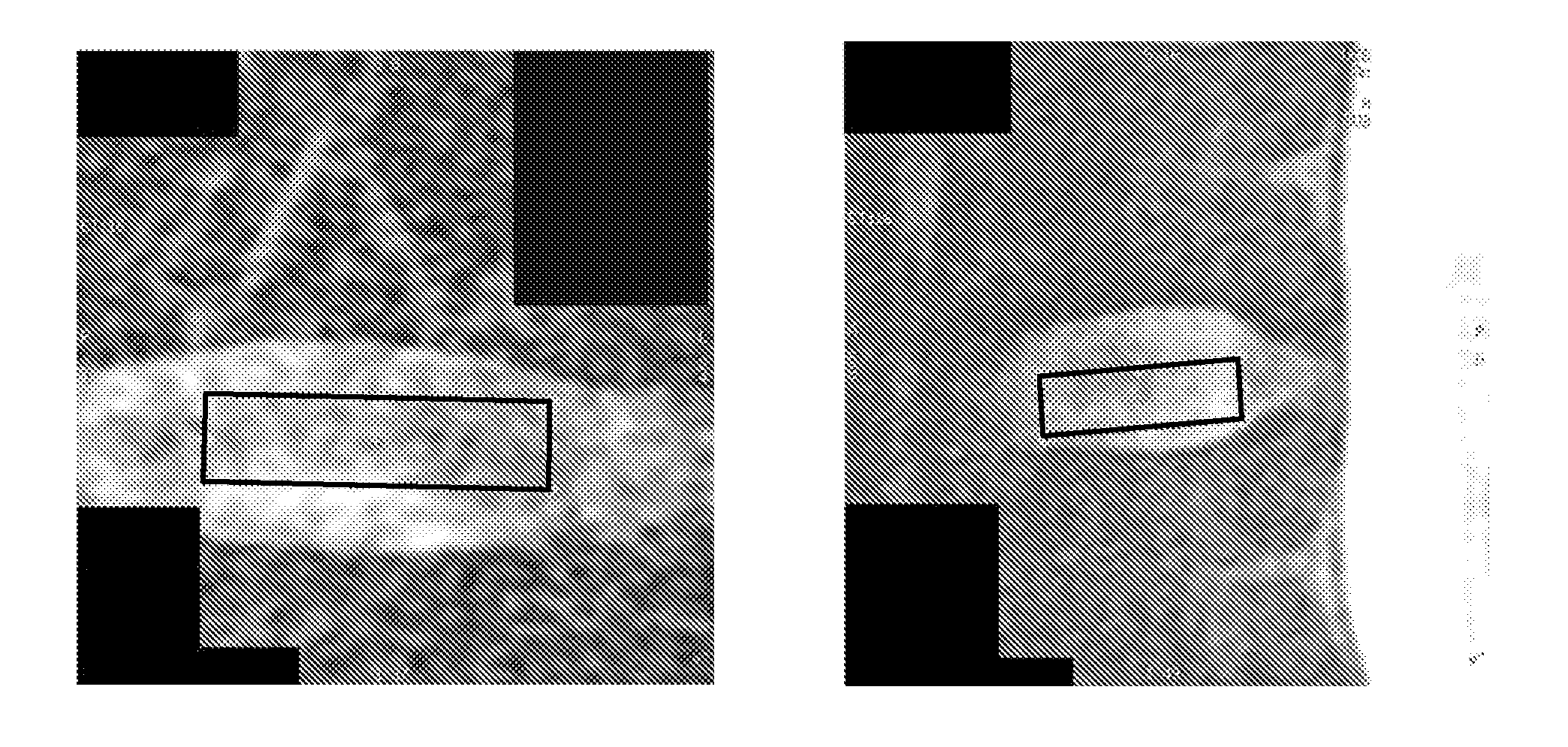
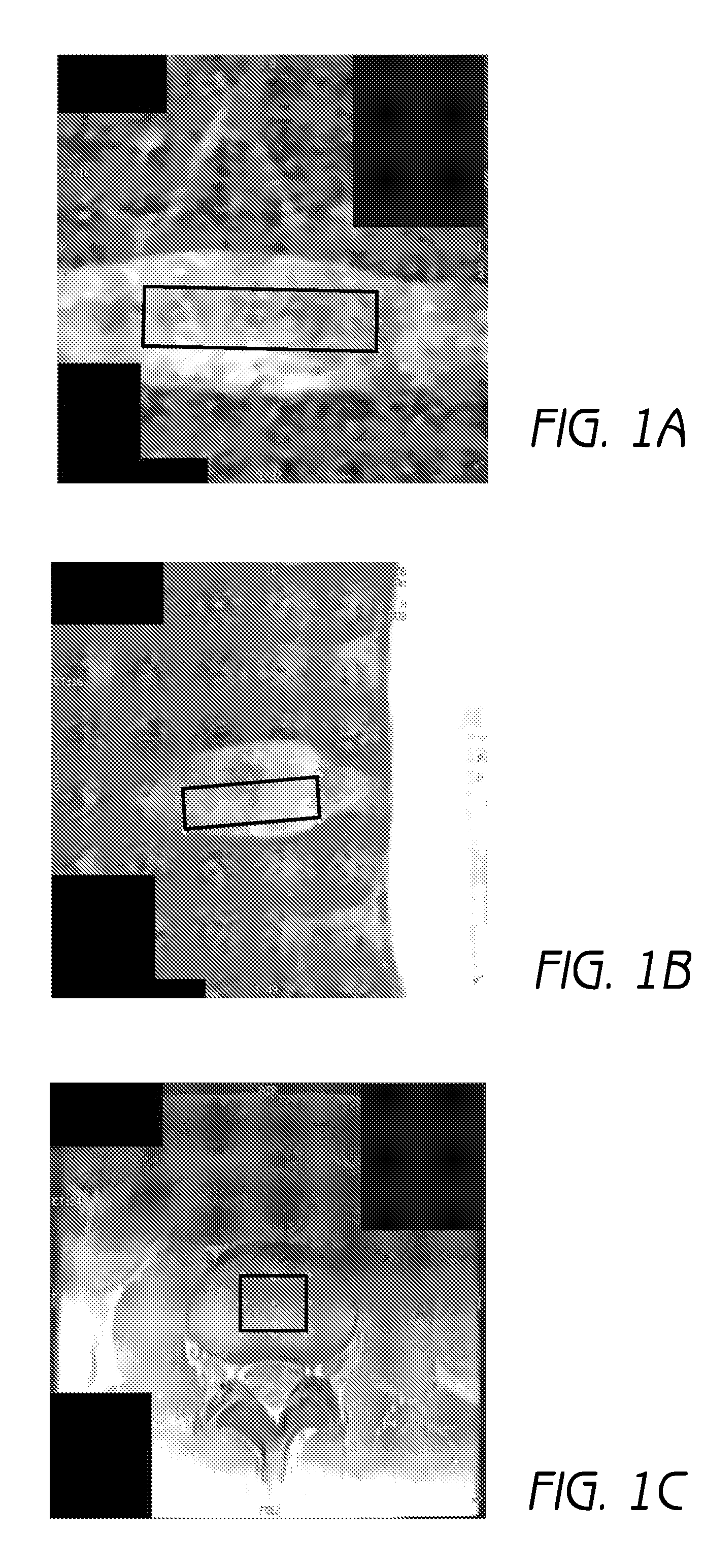
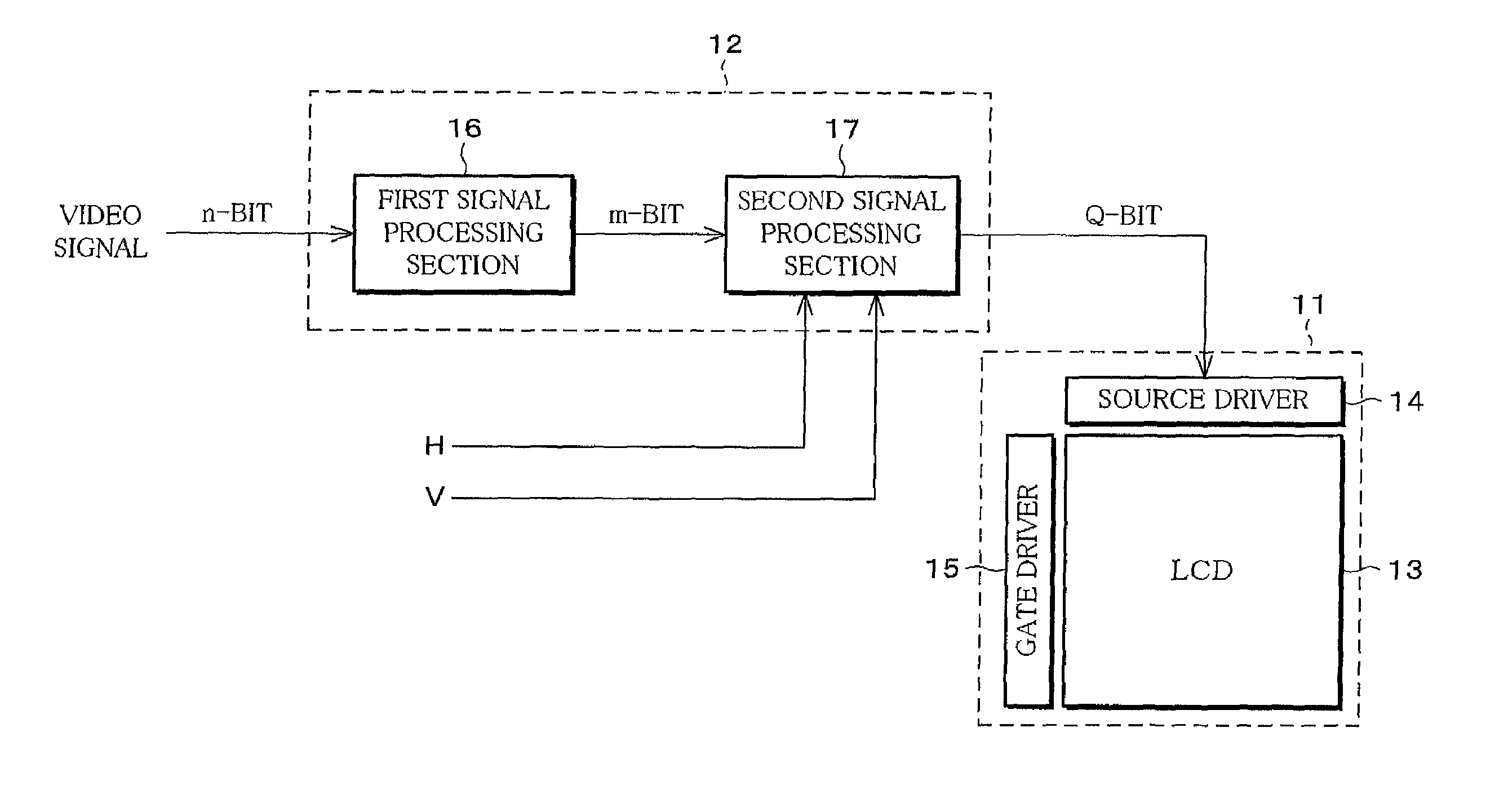
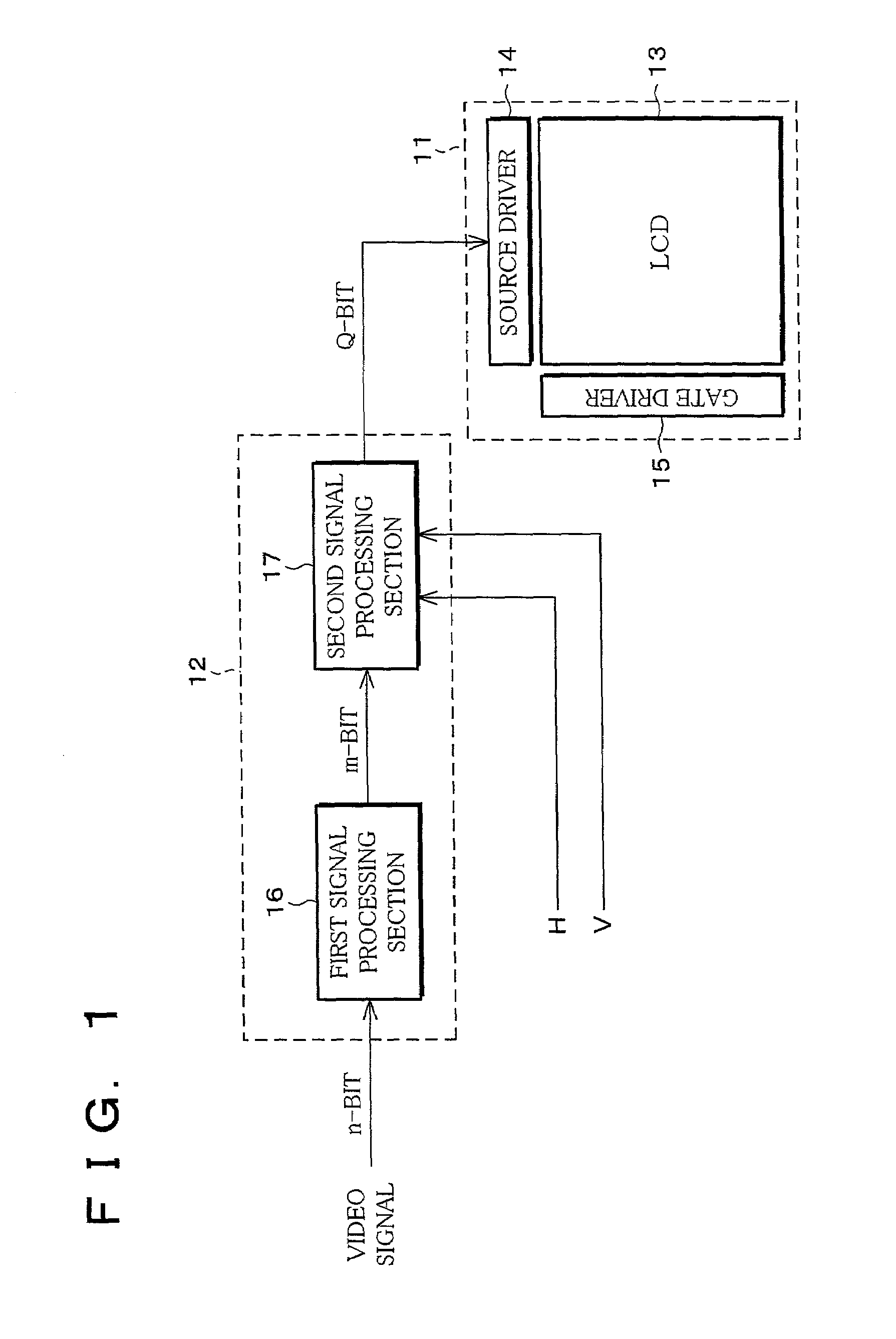
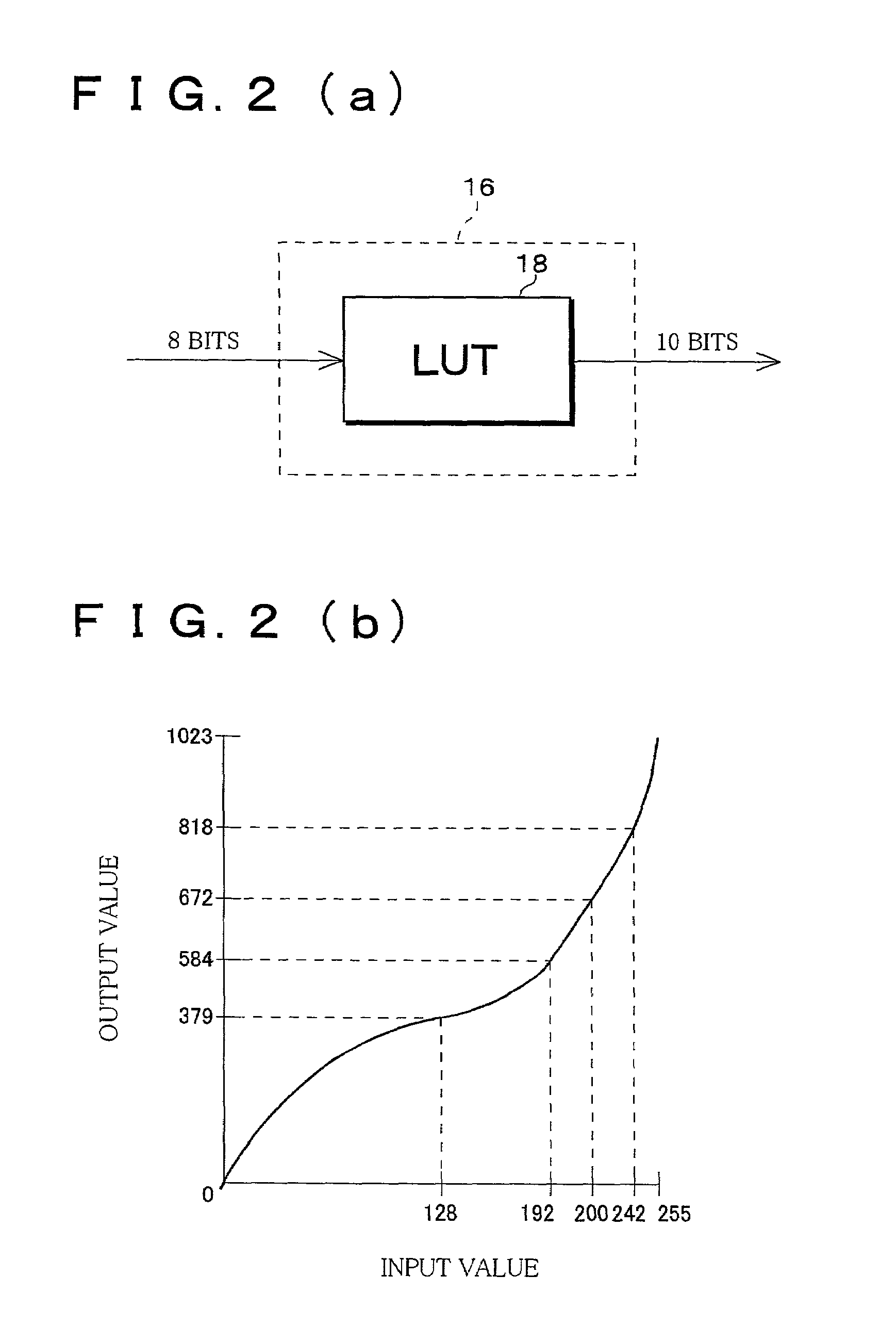
InactiveUS7002594B2Low costReduction of pseudo contourTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging processingSignal processing circuits
An image processing apparatus of the present invention comprising (a) a first signal processing circuit for applying gamma correction to an n-bit (n: a natural number) digital signal inputted as a video signal and for converting the n-bit digital signal into an m-bit (m>n, m: a natural number) digital signal, and (b) a second signal processing circuit for adding a noise signal, which is used for pseudo contour reduction, into the m-bit digital signal from the first signal processing circuit and for outputting a Q-bit (Q: a natural number) digital signal, which is obtained from rounding off a less significant (m−Q) bit (Q≦n) from the m-bit digital signal, to a display section.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
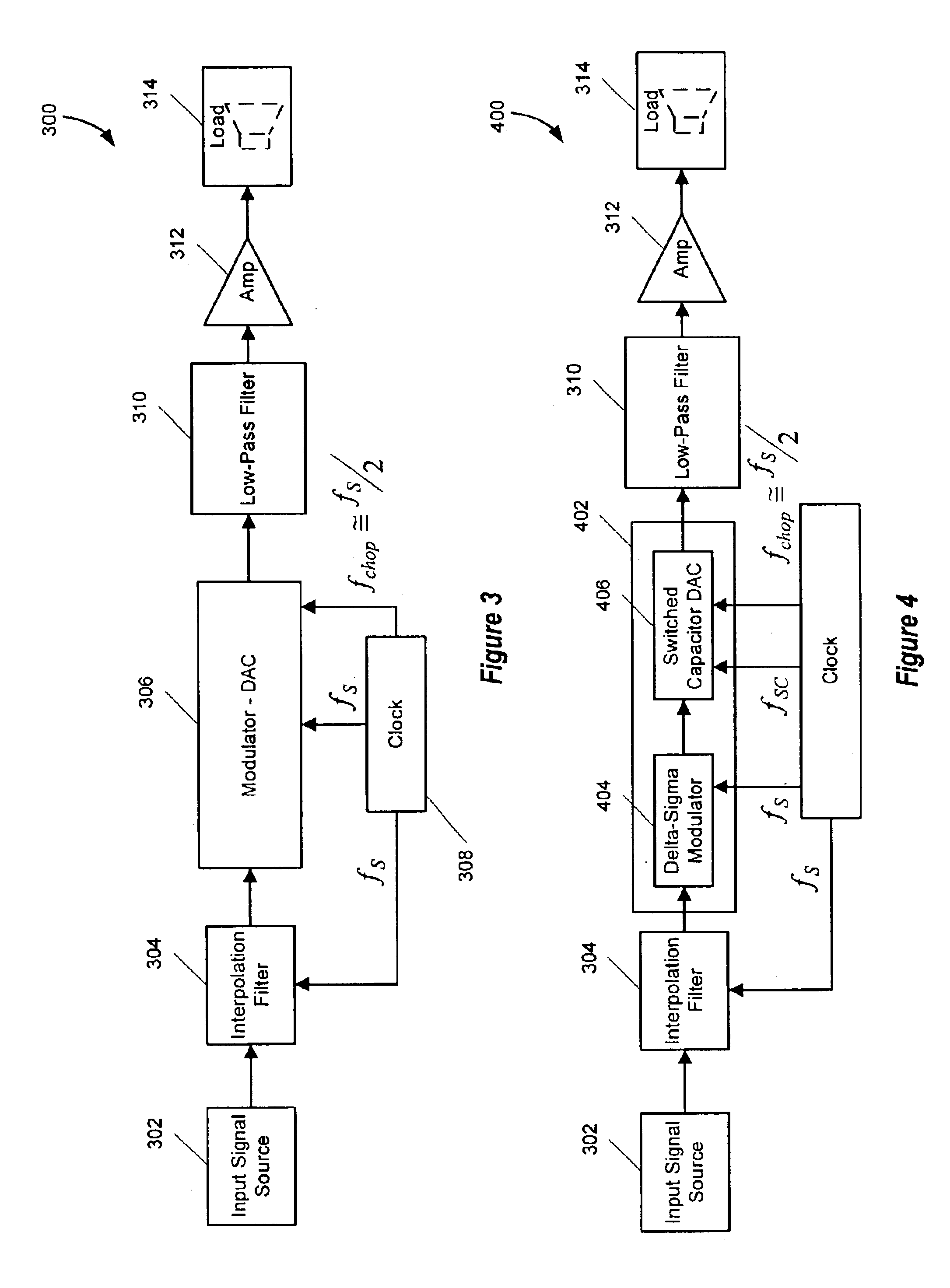
Signal processing system with baseband noise modulation and noise fold back reduction
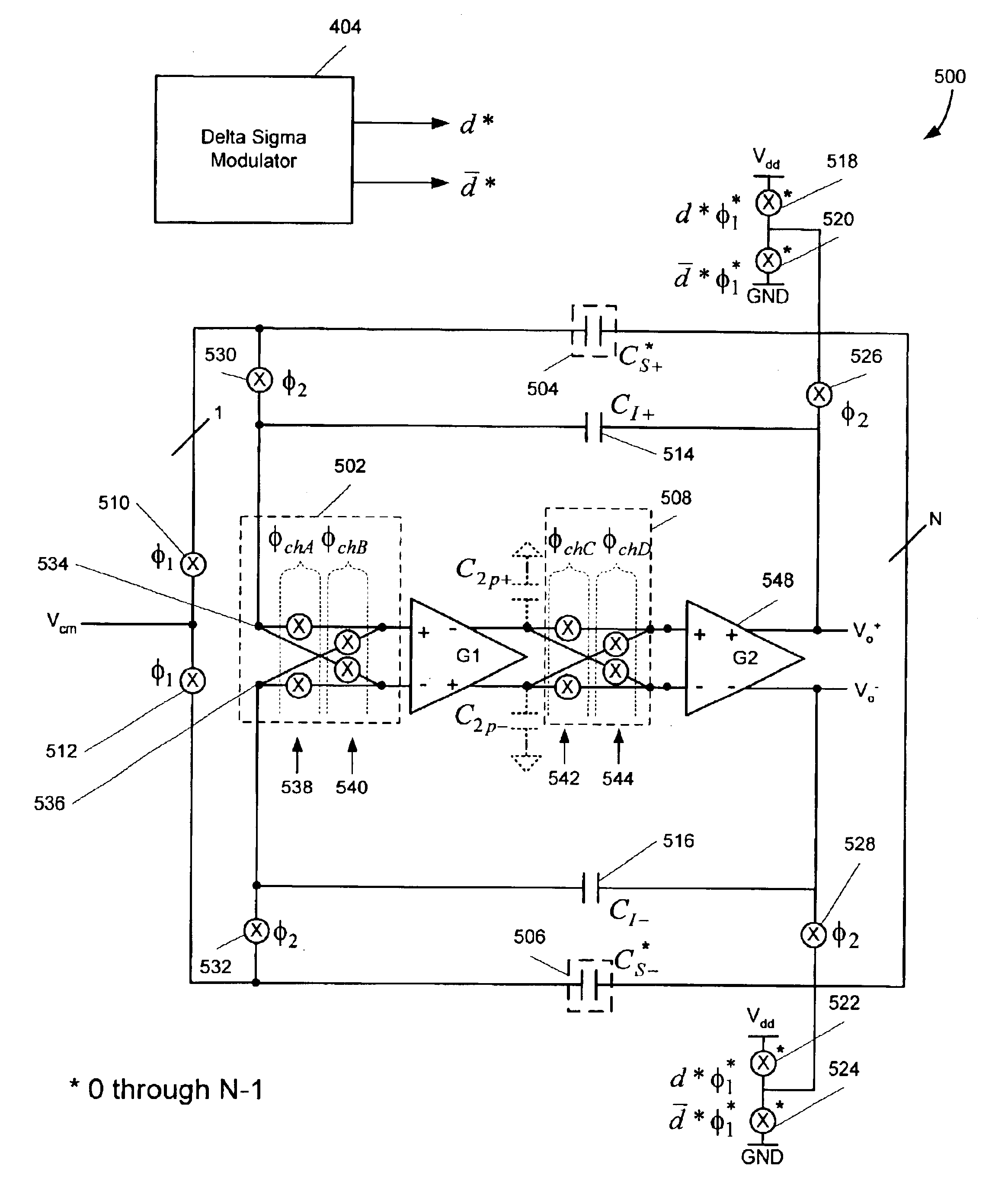
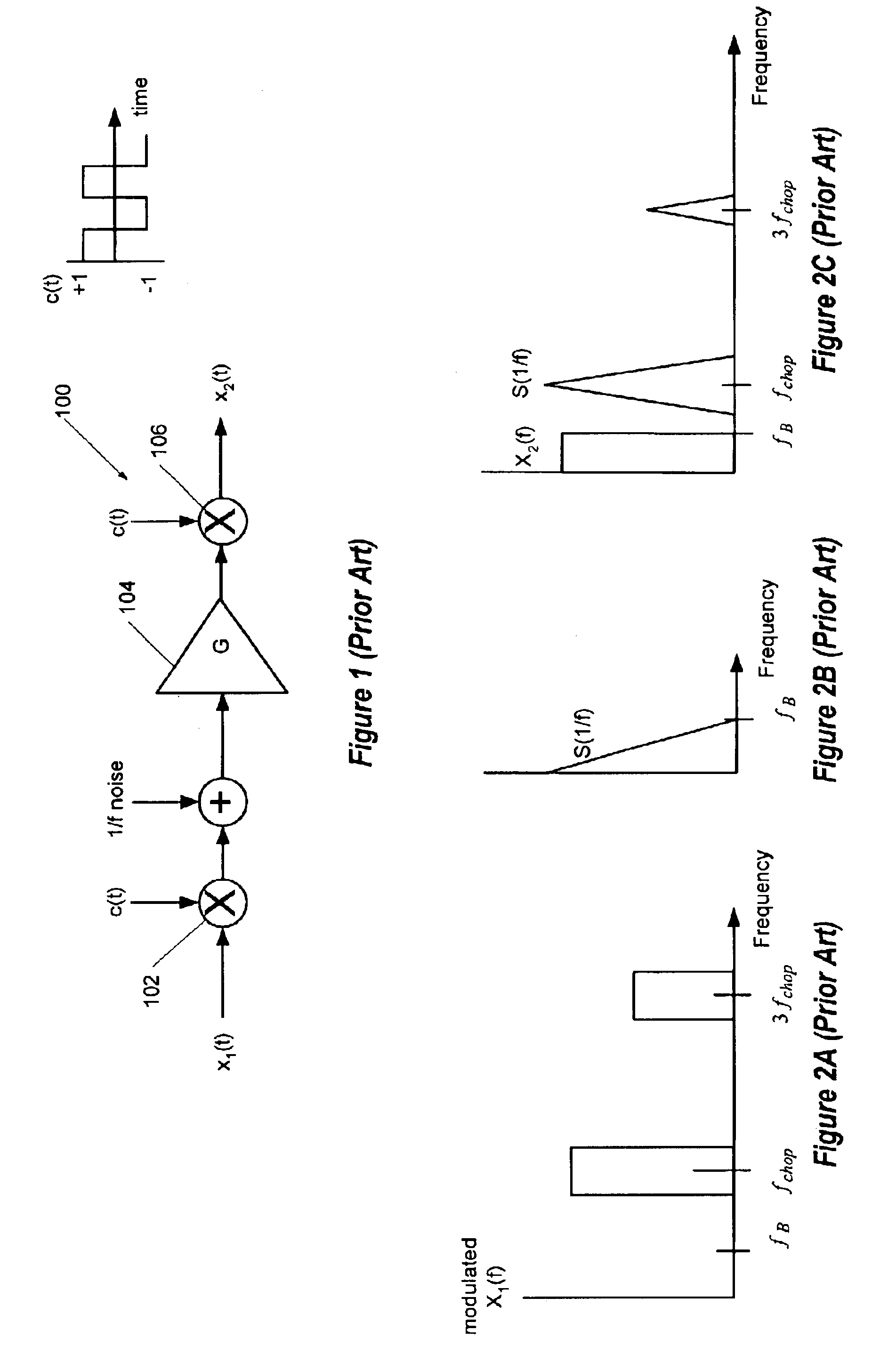
ActiveUS6842486B2Reduce fold backReducing fold back of quantization noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower amplifiersSignal of interestSignal frequency
A digital-to-analog converter (“DAC”) system utilizes chopping modulation technology to remove 1 / f and other baseband noise from a baseband of a signal of interest. Chopping modulation and demodulation circuitry of the DAC operate at a chopping frequency equal to approximately one-half of a digital input signal sampling frequency. Chopping at one-half the sampling frequency allows fold back into the baseband of the input signal's frequency components and reduces fold back of noise, such as quantization noise, residing outside the baseband. In a further embodiment, a notch filter attenuates signals having frequencies around the chopping frequency prior to chopping to reduce fold back of noise into the baseband due to parasitic modulation. Coordination of chopping timing also reduces noises in the output of the DAC system.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
MR spectroscopy system and method for diagnosing painful and non-painful intervertebral discs
An MR Spectroscopy (MRS) system and approach is provided for diagnosing painful and non-painful discs in chronic, severe low back pain patients (DDD-MRS). A DDD-MRS pulse sequence generates and acquires DDD-MRS spectra within intervertebral disc nuclei for later signal processing & diagnostic analysis. An interfacing DDD-MRS signal processor receives output signals of the DDD-MRS spectra acquired and is configured to optimize signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) by an automated system that selectively conducts optimal channel selection, phase and frequency correction, and frame editing as appropriate for a given acquisition series. A diagnostic processor calculates a diagnostic value for the disc based upon a weighted factor set of criteria that uses MRS data extracted from the acquired and processed MRS spectra along regions associated with multiple chemicals that have been correlated to painful vs. non-painful discs. A diagnostic display provides a scaled, color coded legend and indication of results for each disc analyzed as an overlay onto a mid-sagittal T2-weighted MRI image of the lumbar spine for the patient being diagnosed. Clinical application of the embodiments provides a non-invasive, objective, pain-free, reliable approach for diagnosing painful vs. non-painful discs by simply extending and enhancing the utility of otherwise standard MRI exams of the lumbar spine.
Owner:ACLARION INC +1
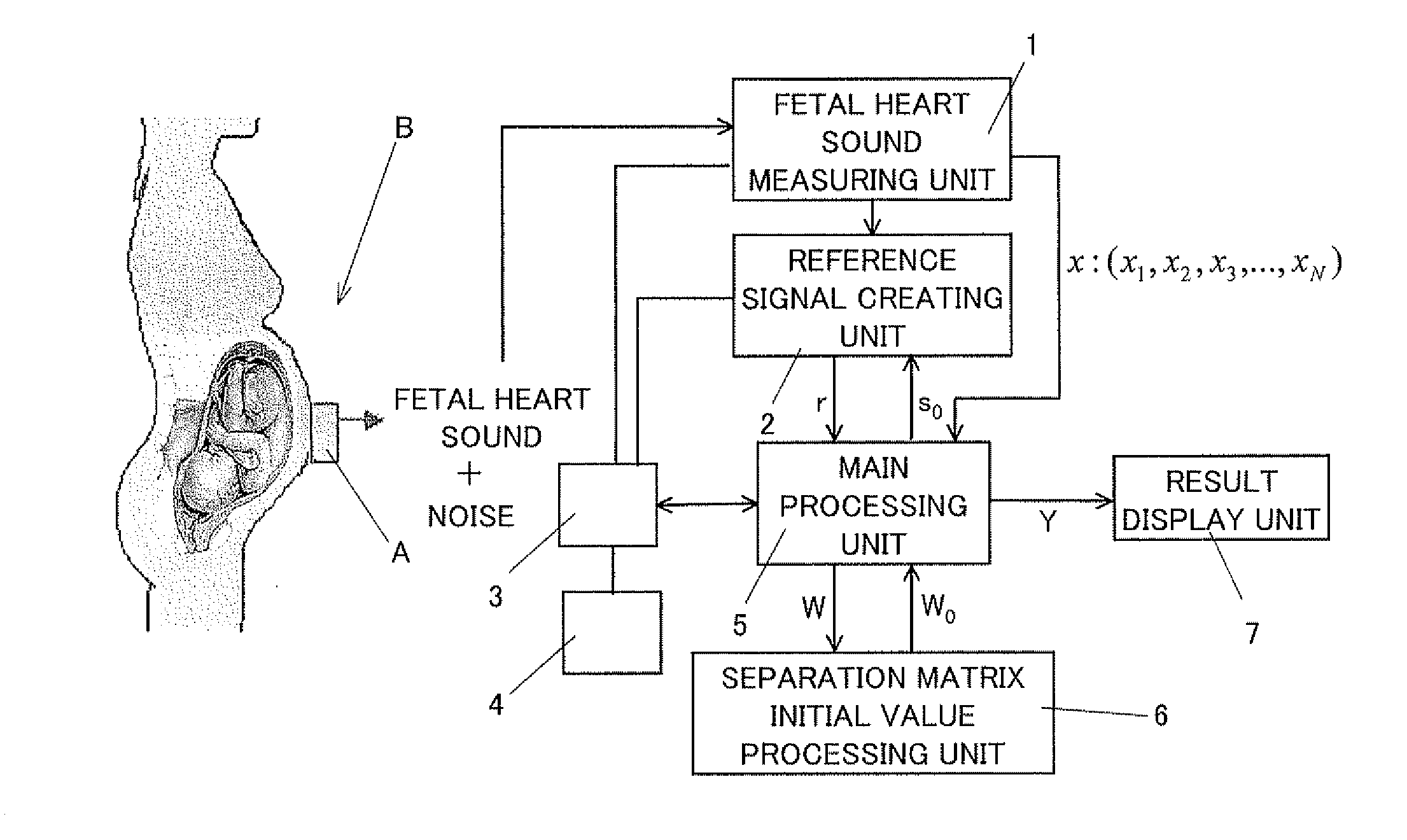
Signal extracting apparatus
ActiveUS20120232418A1Accurate extractionStable separationElectrocardiographyElectromyographyMain processing unitTarget signal
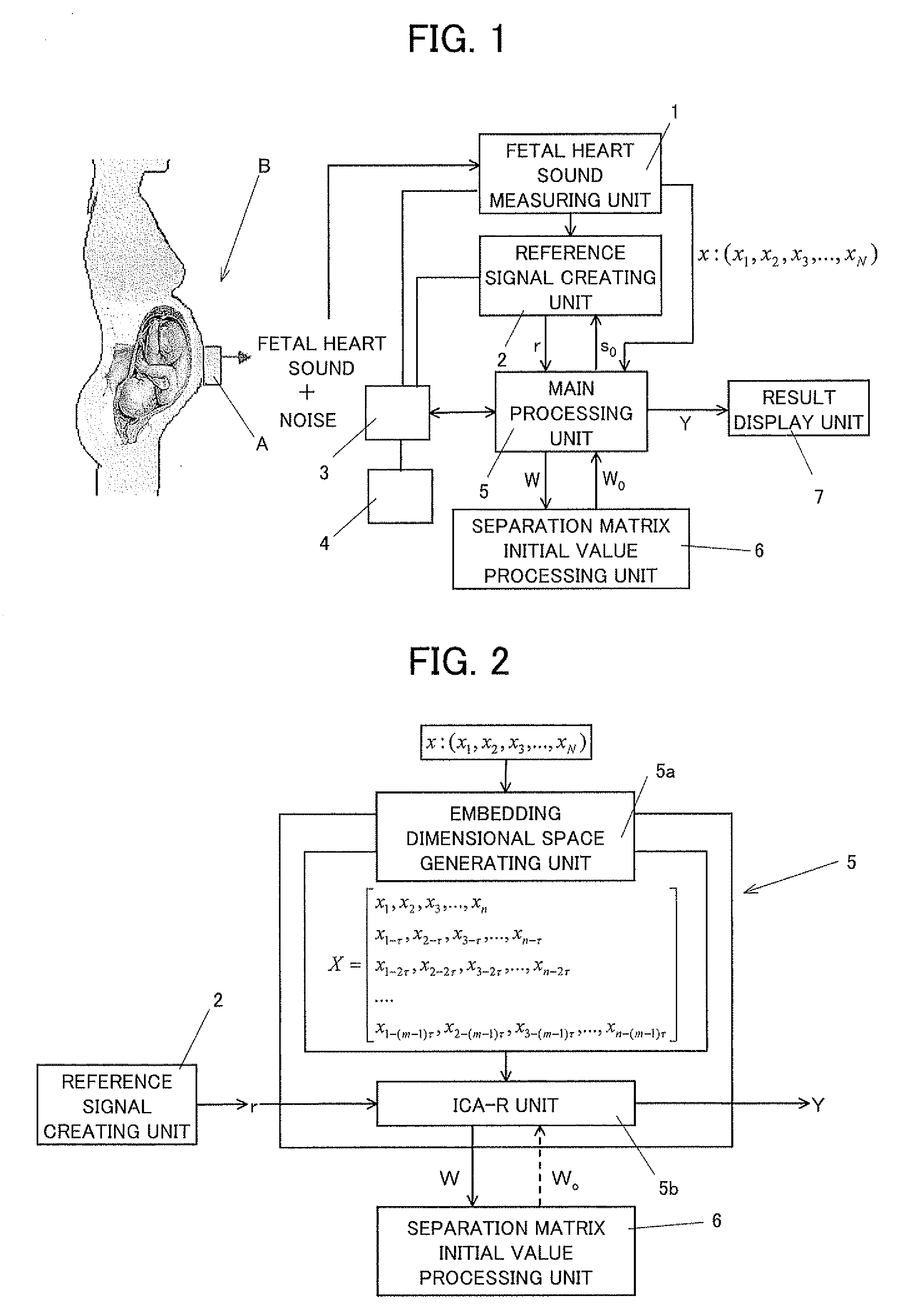
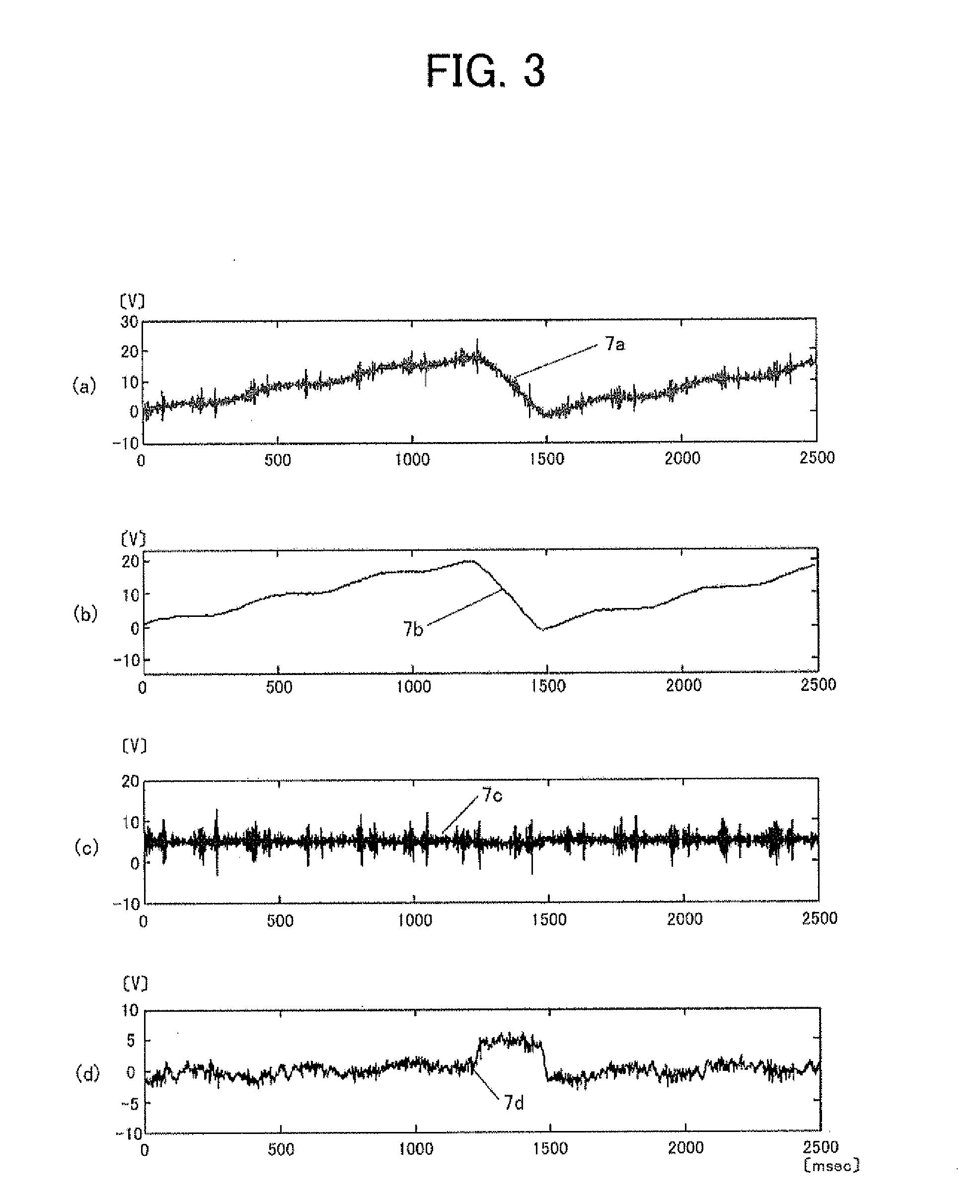
A signal extracting apparatus is provided based on independent component analysis with reference for a single measured signal as a signal processing technique that allows stable and quick extraction of a target signal from single measured signal even in a high-noise environment with a high noise ratio against a target signal to be extracted. The signal extracting apparatus includes: a single-signal measuring unit to measure a measured signal as a single time-series signal containing a target signal obtained by measurement by a single channel; a reference signal creating unit (2) to create a reference signal provided with timing-axis information based on the time-series signal obtained by the single-signal measuring unit; and a main processing unit (5) to perform independent component analysis with reference for a single measured signal by capturing the reference signal obtained by the reference signal creating unit (2) and providing the timing-axis information for an algorithm in a reference system to extract an independent component.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
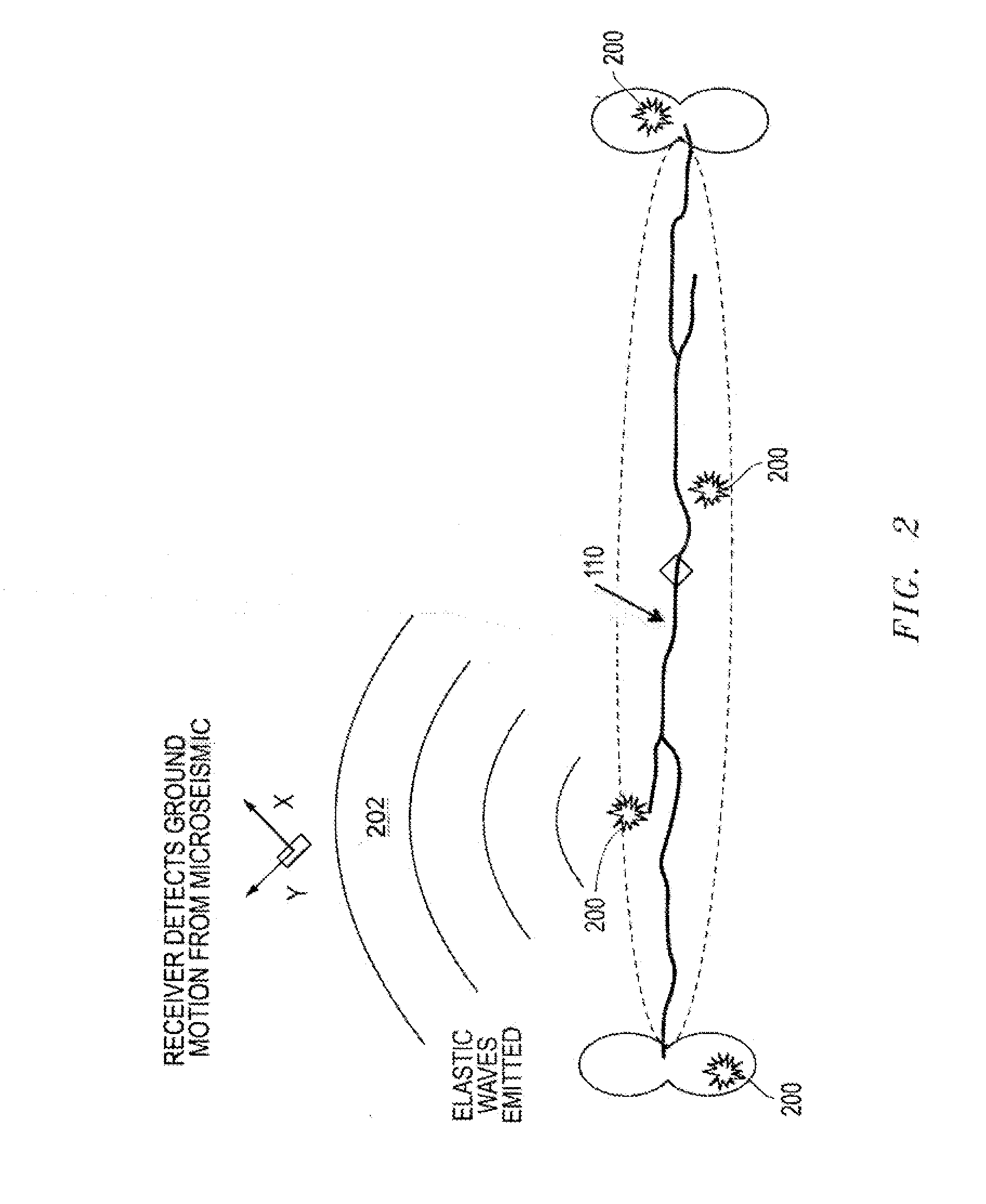
Neural Network Signal Processing of Microseismic Events
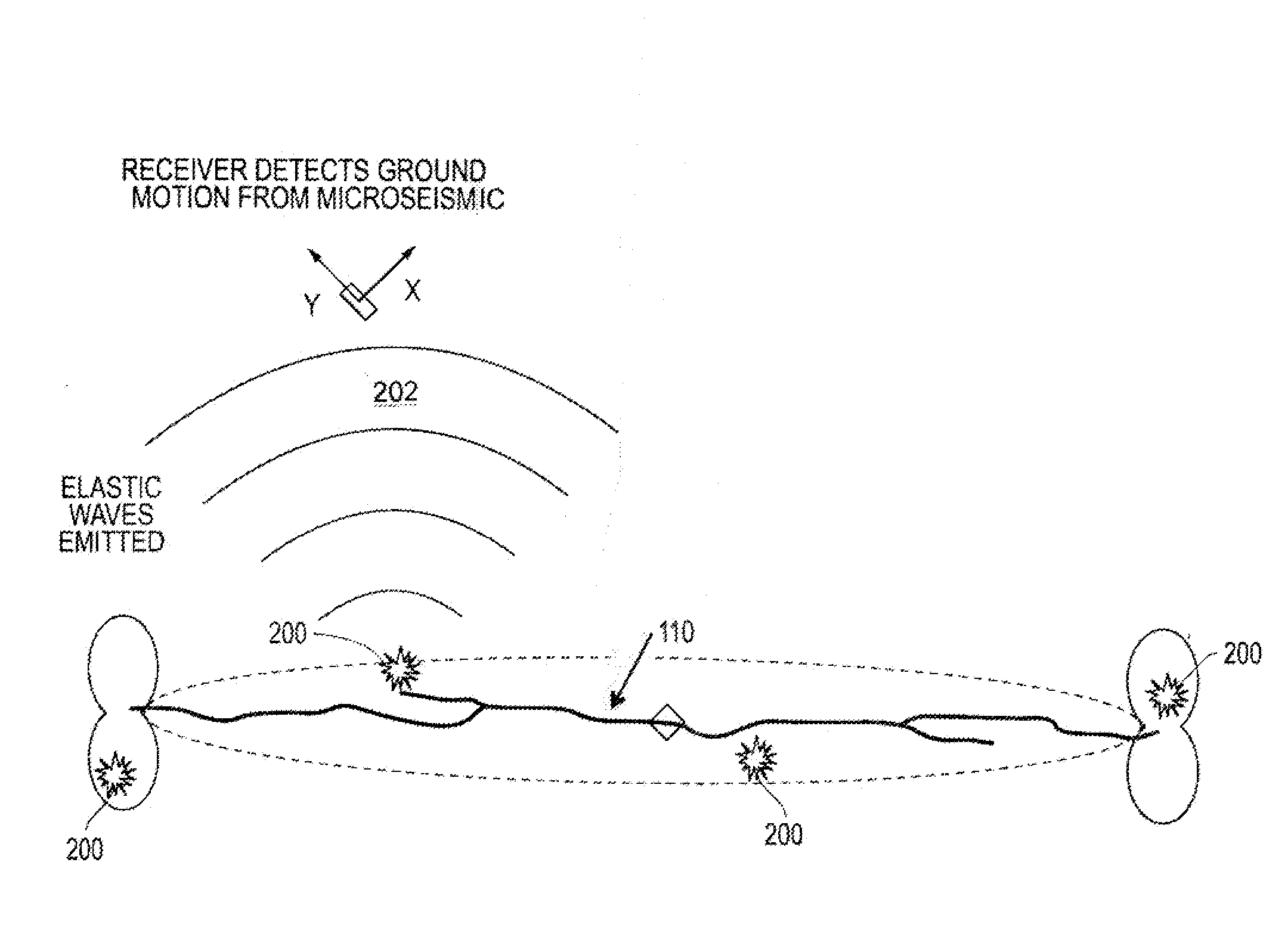
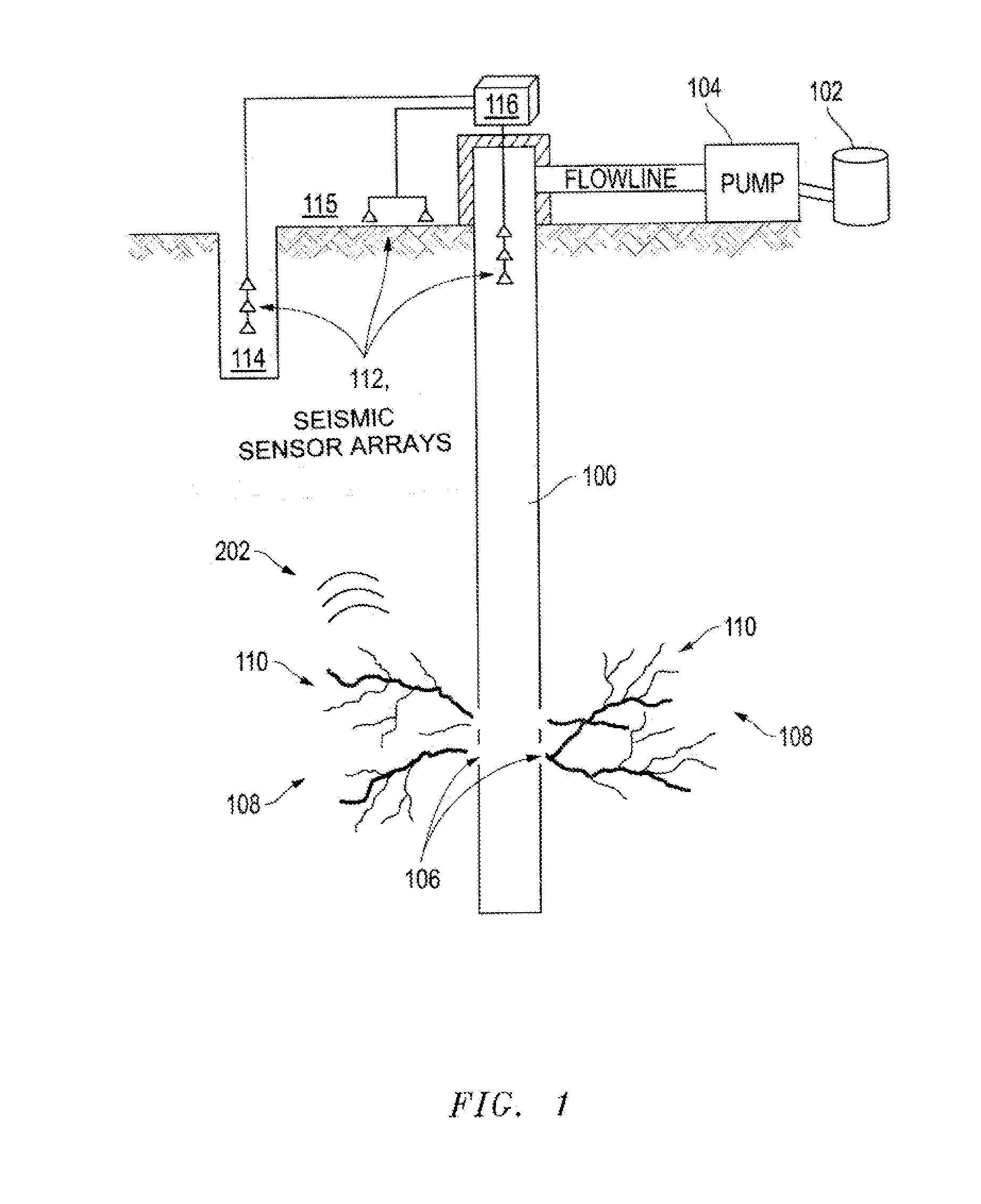
InactiveUS20140334260A1Cancel noiseSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingAcoustic emissionData signal
Systems, apparatuses and methods for neural network signal processing of microseismic events. A series of sensors are disposable in at least one first well positioned about a second well disposed in a subterranean formation. The series of sensors obtain a data signal measurement including noise events and microseismic acoustic emission events. A processor includes a first neural network. The processor may remove the noise events from the data signal measurement and determine with the first neural network an arrival time for each microseismic acoustic emission event. An interface can output the arrival time for each microseismic acoustic emission event.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com