Patents
Literature
2625 results about "Television programming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
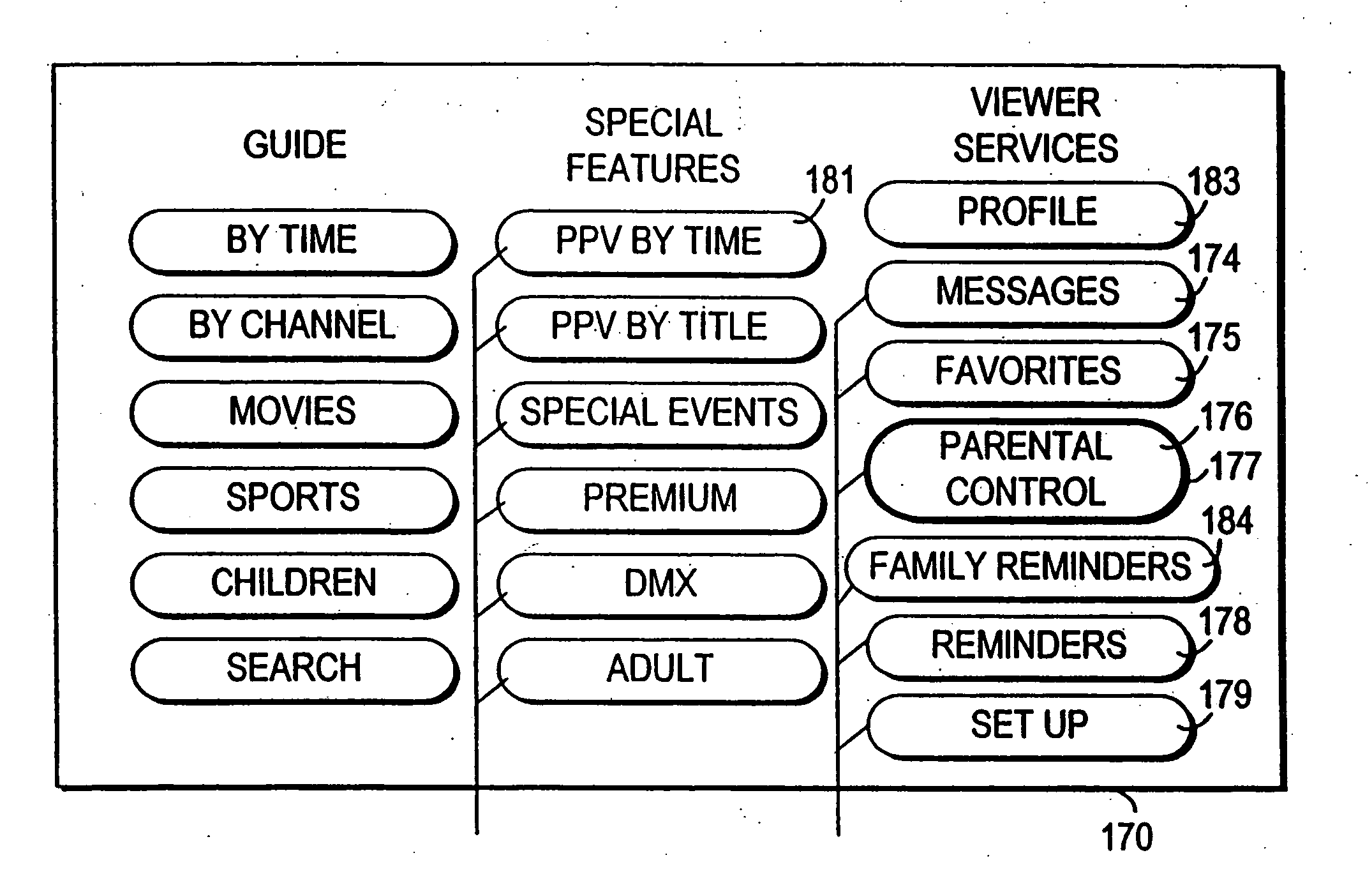
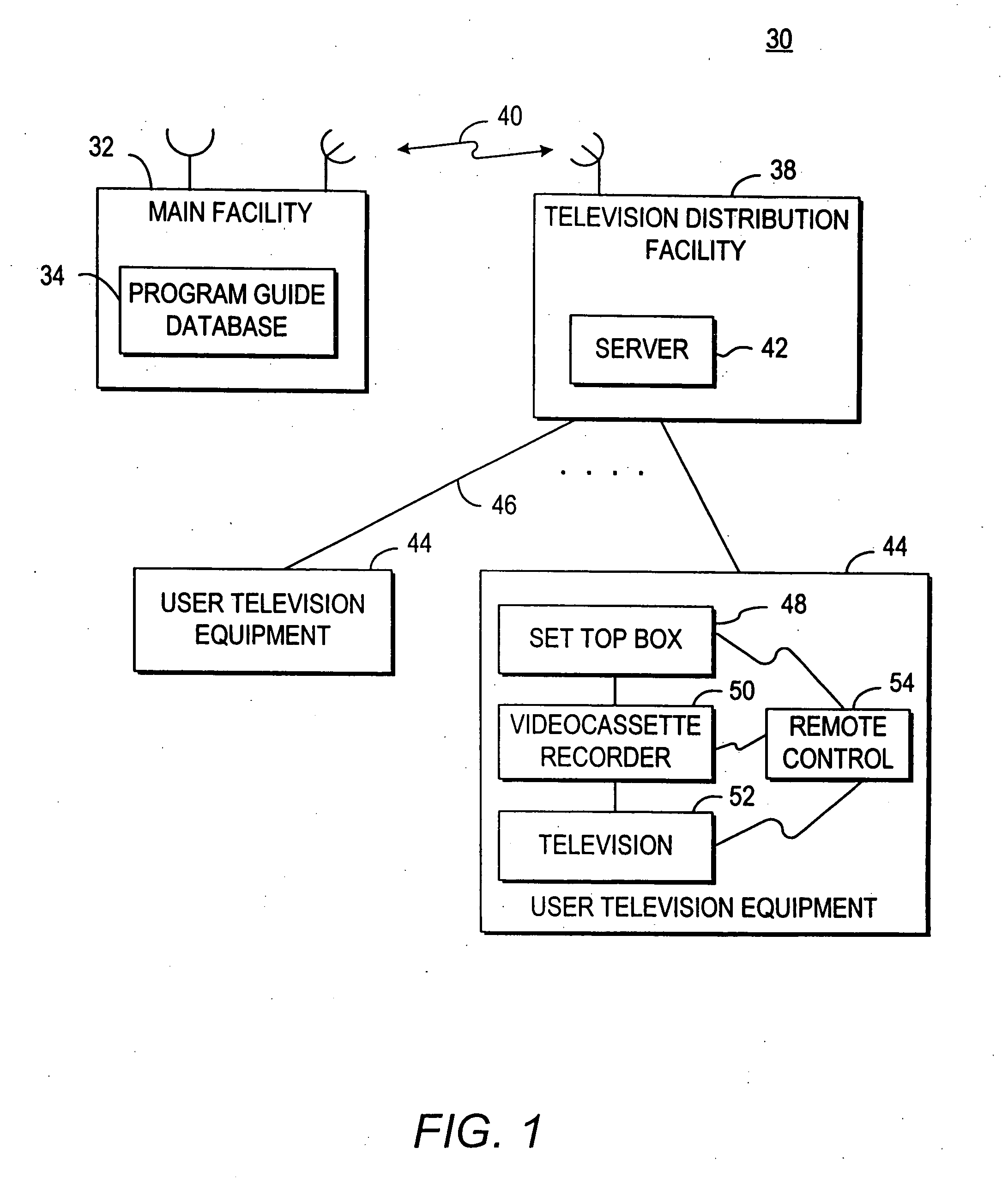
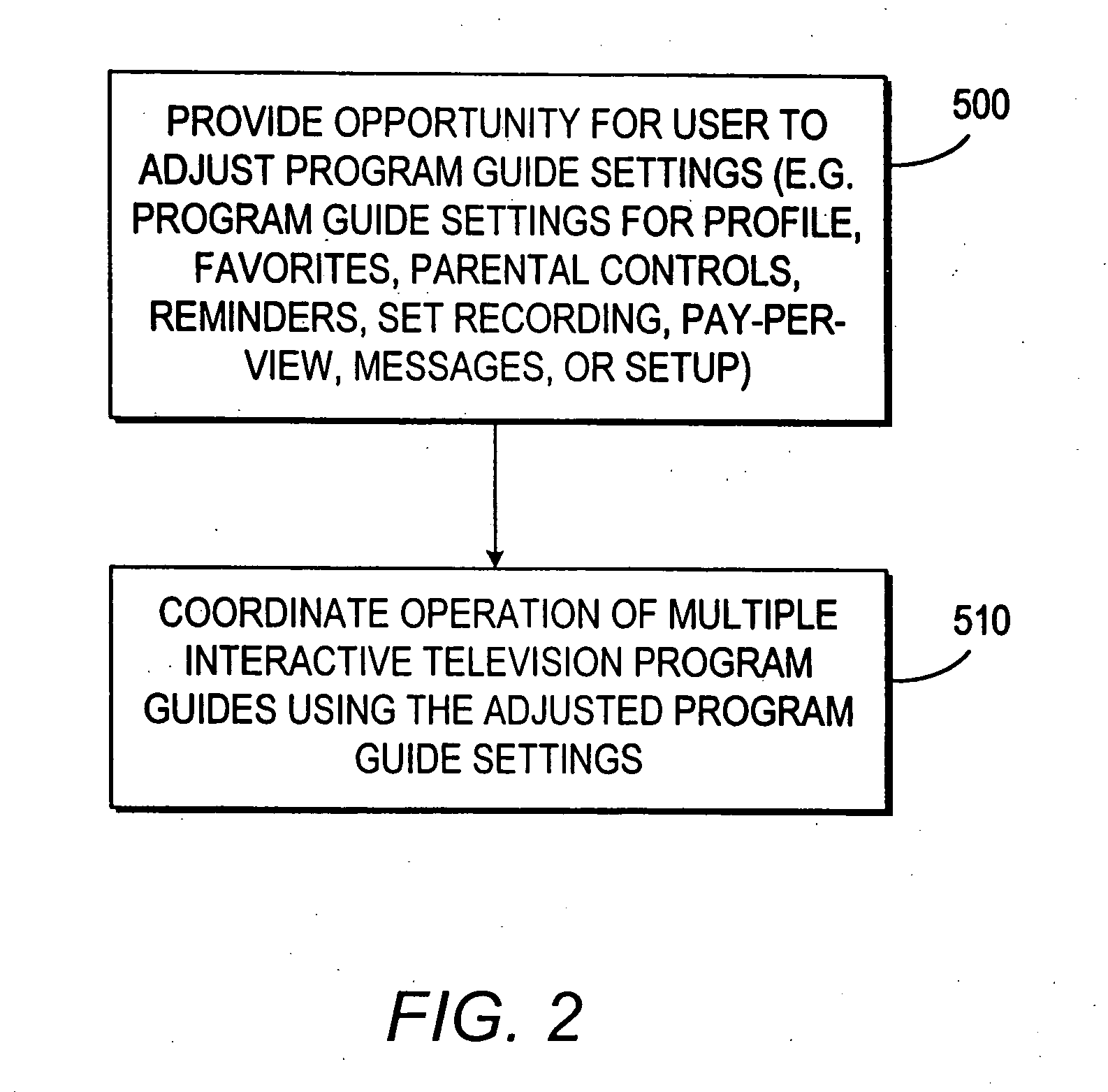
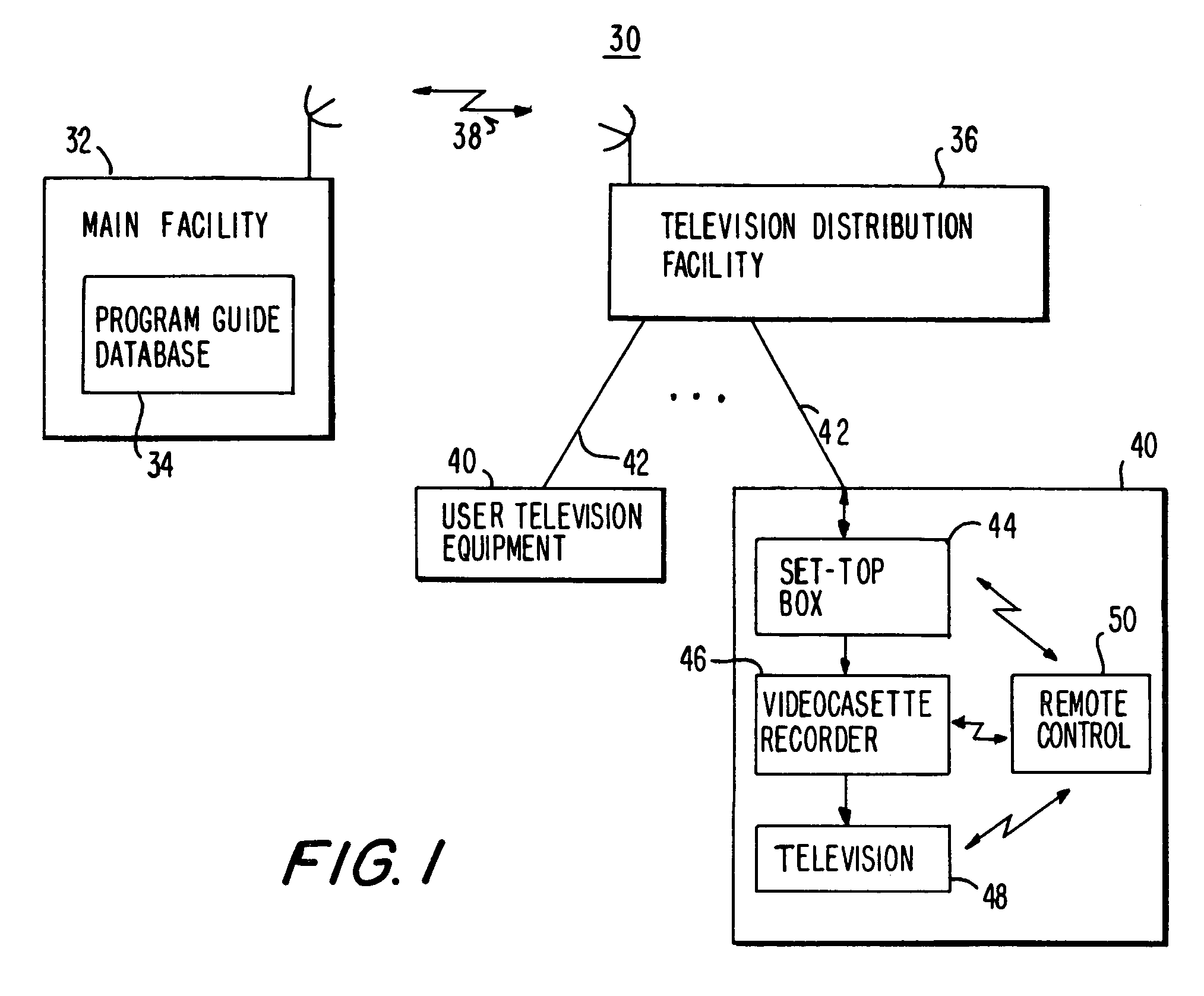
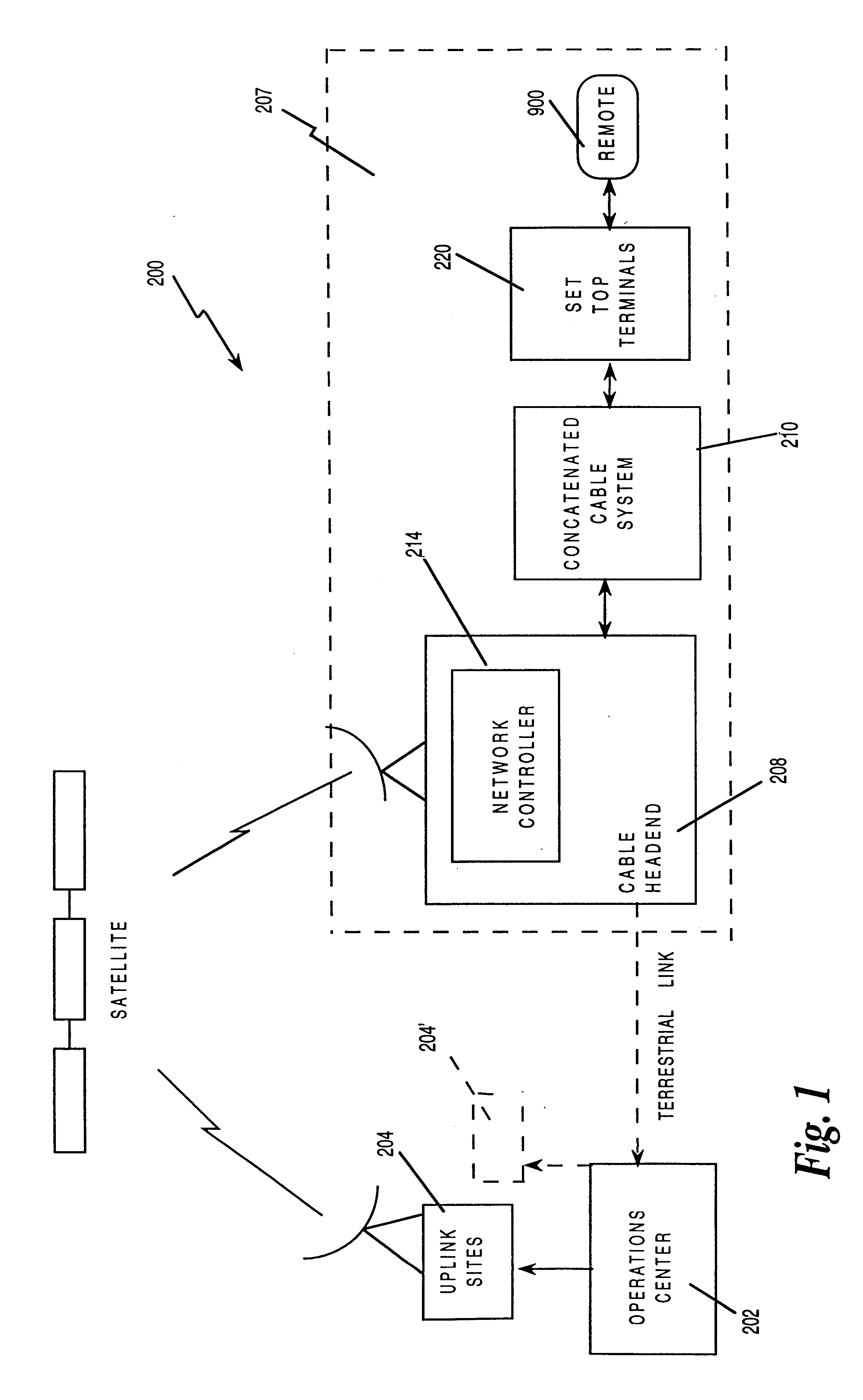
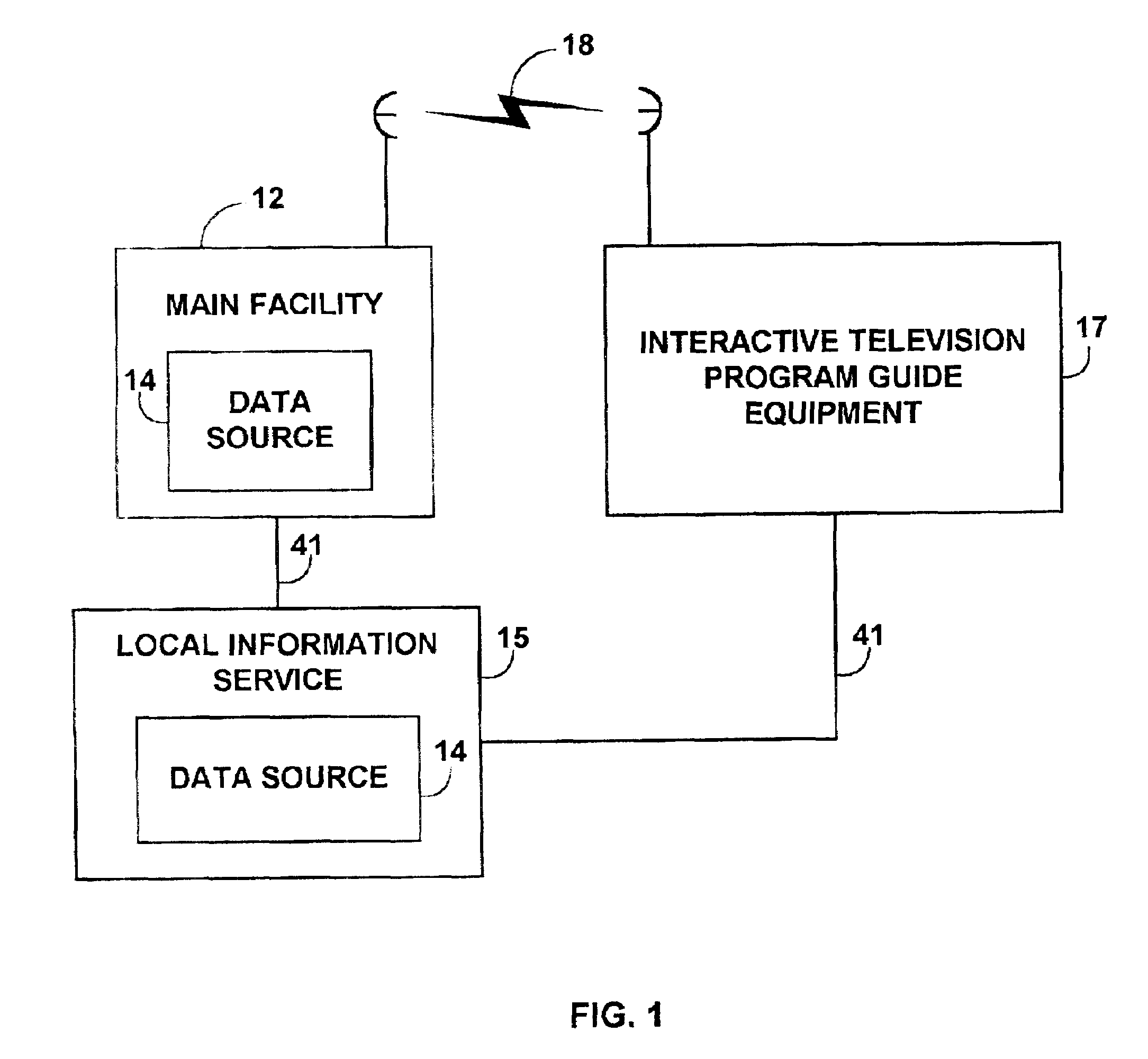
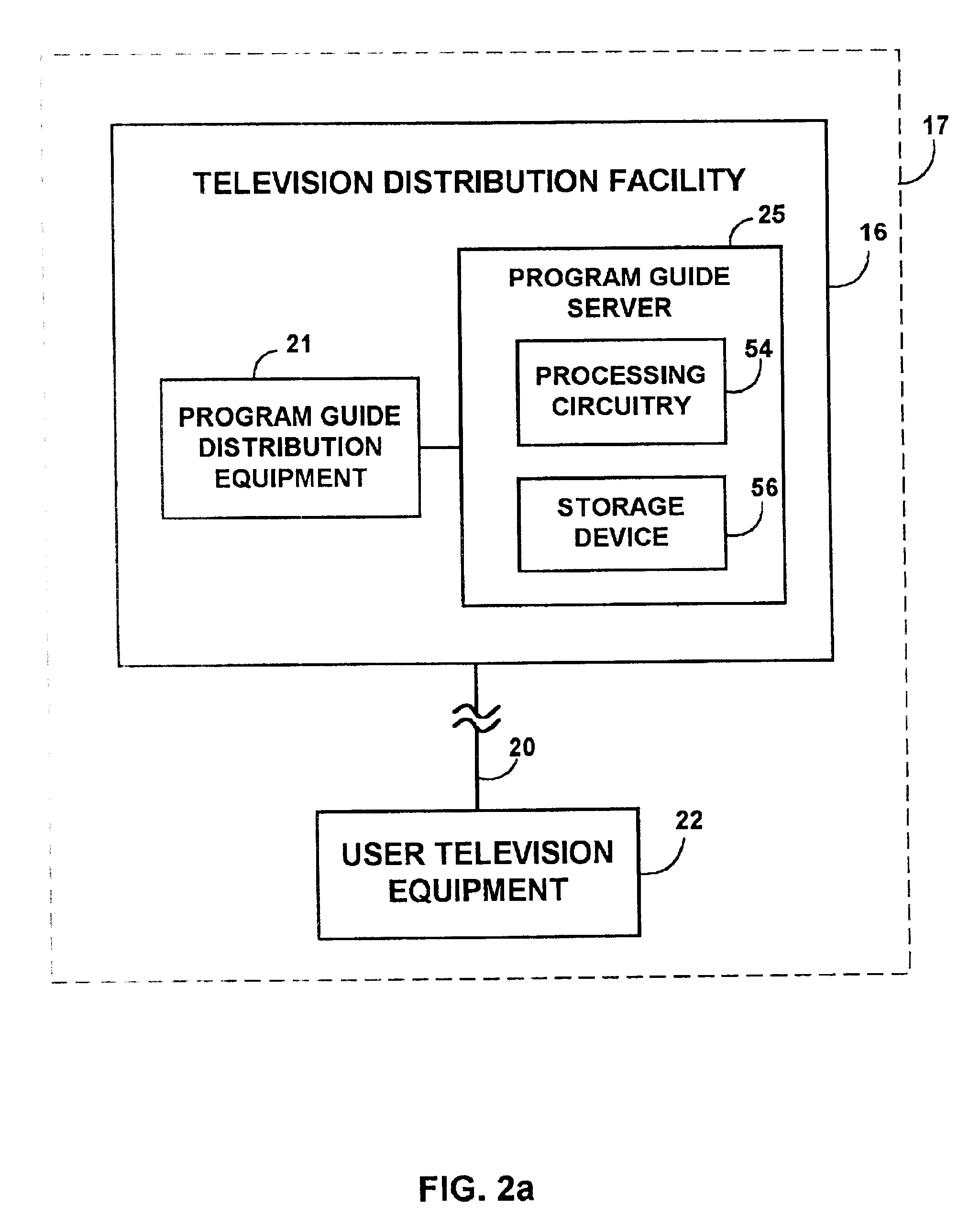
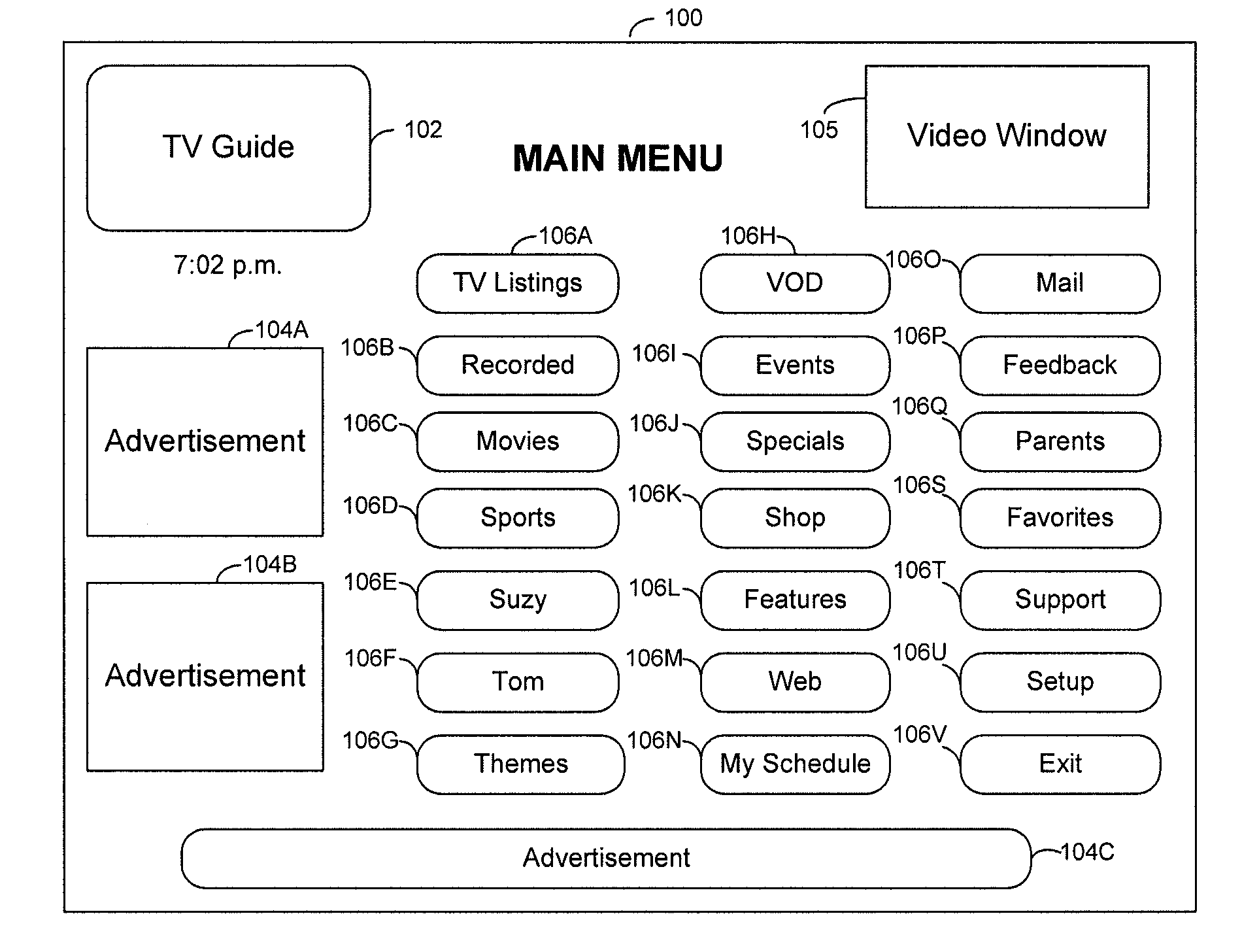
Interactive television program guide system having multiple devices within a household
InactiveUS20050251827A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsWeb browserInteractive television
An interactive television program guide system based on multiple user television equipment devices in a single household is provided. The system provides a user with an opportunity to adjust program guide settings with a given one of the interactive television program guides. The system coordinates the operation of the interactive television program guides so that the program guide settings that were adjusted with the given interactive television program guide are used by the other interactive television program guides. Program guide setting include features related to setting program reminders, profiles, program recording features, messaging features, favorites features, parental control features, program guide set up features (e.g., audio and video and language settings), etc. The operation of applications such as web browser applications, home shopping applications, home banking applications, game applications, etc. may also be coordinated.
Owner:UNITED VIDEO PROPERTIES
On-line schedule system with personalization features
InactiveUS7165098B1Increase flexibilityEasy accessMultiple digital computer combinationsSelective content distributionPersonalizationApplication software
An on-line scheduling application allows users to personalize how television-related, entertainment-related, and social event related information is provided. Users may select one or more sources from which the information is obtained. Users may set up a date book that is also used as a source. Users may select one or more delivery schemes that the application uses to provide the information. One or more of the personalization features of the scheduling application may be incorporated into an on-line television programming guide.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
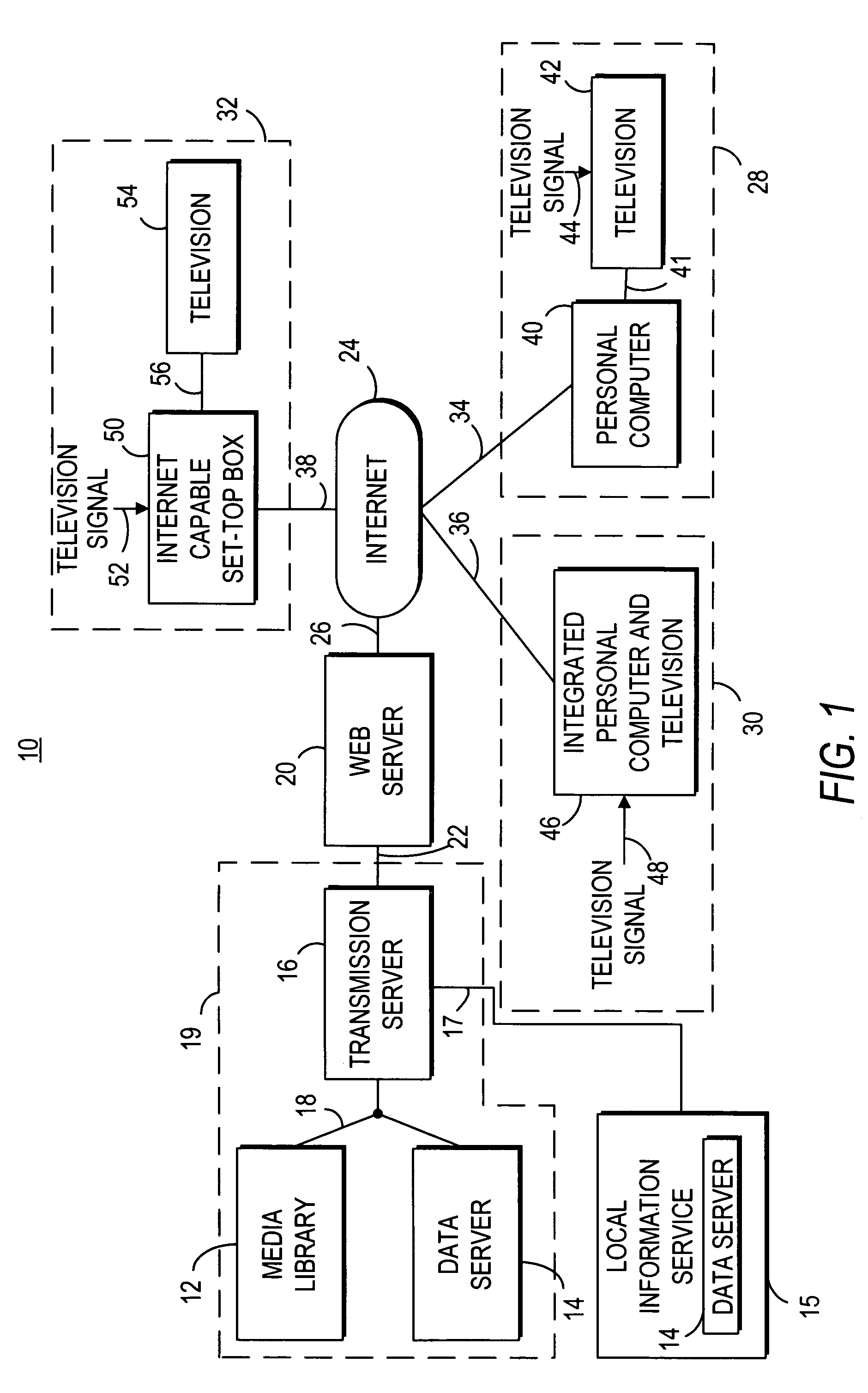
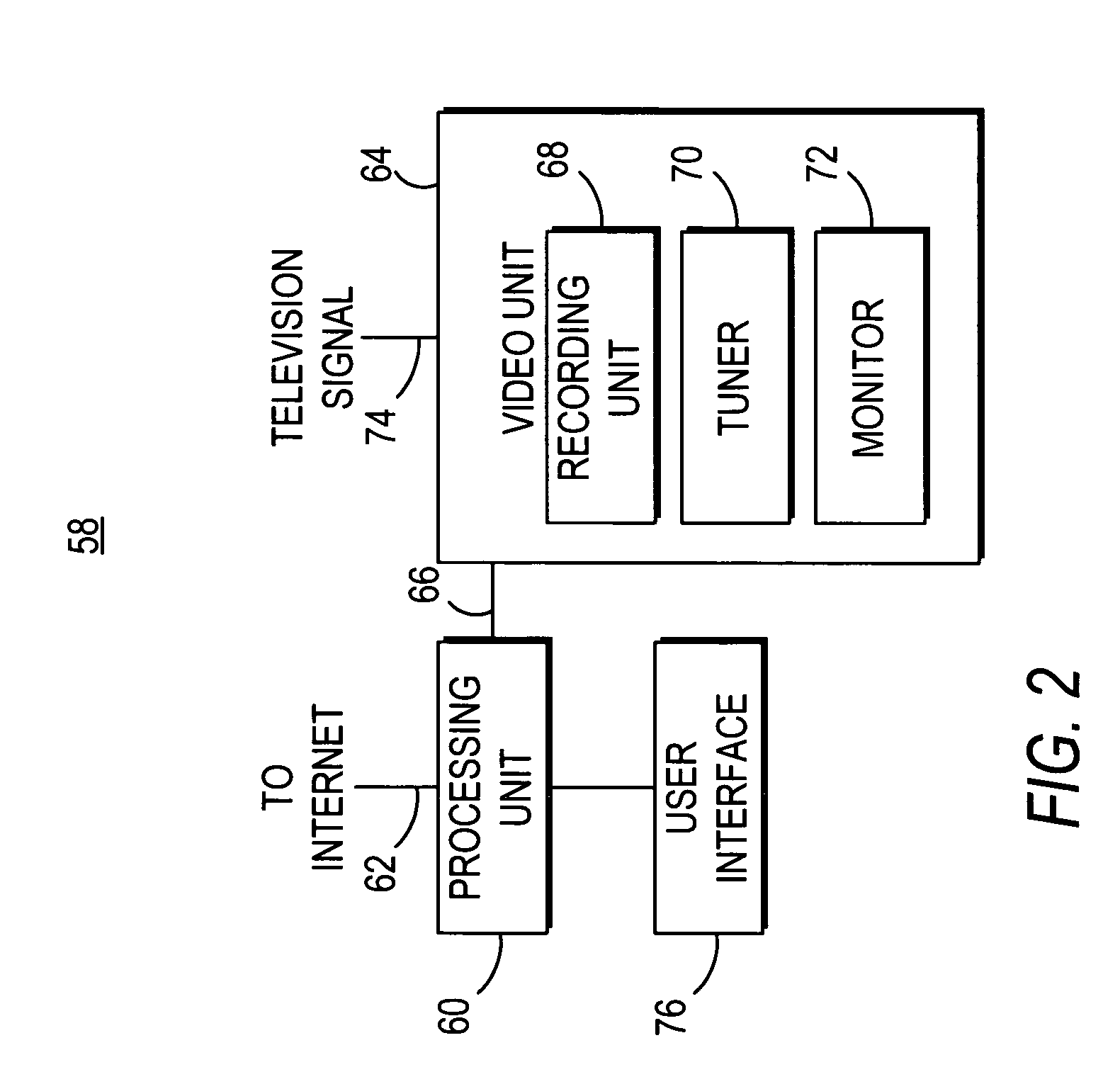
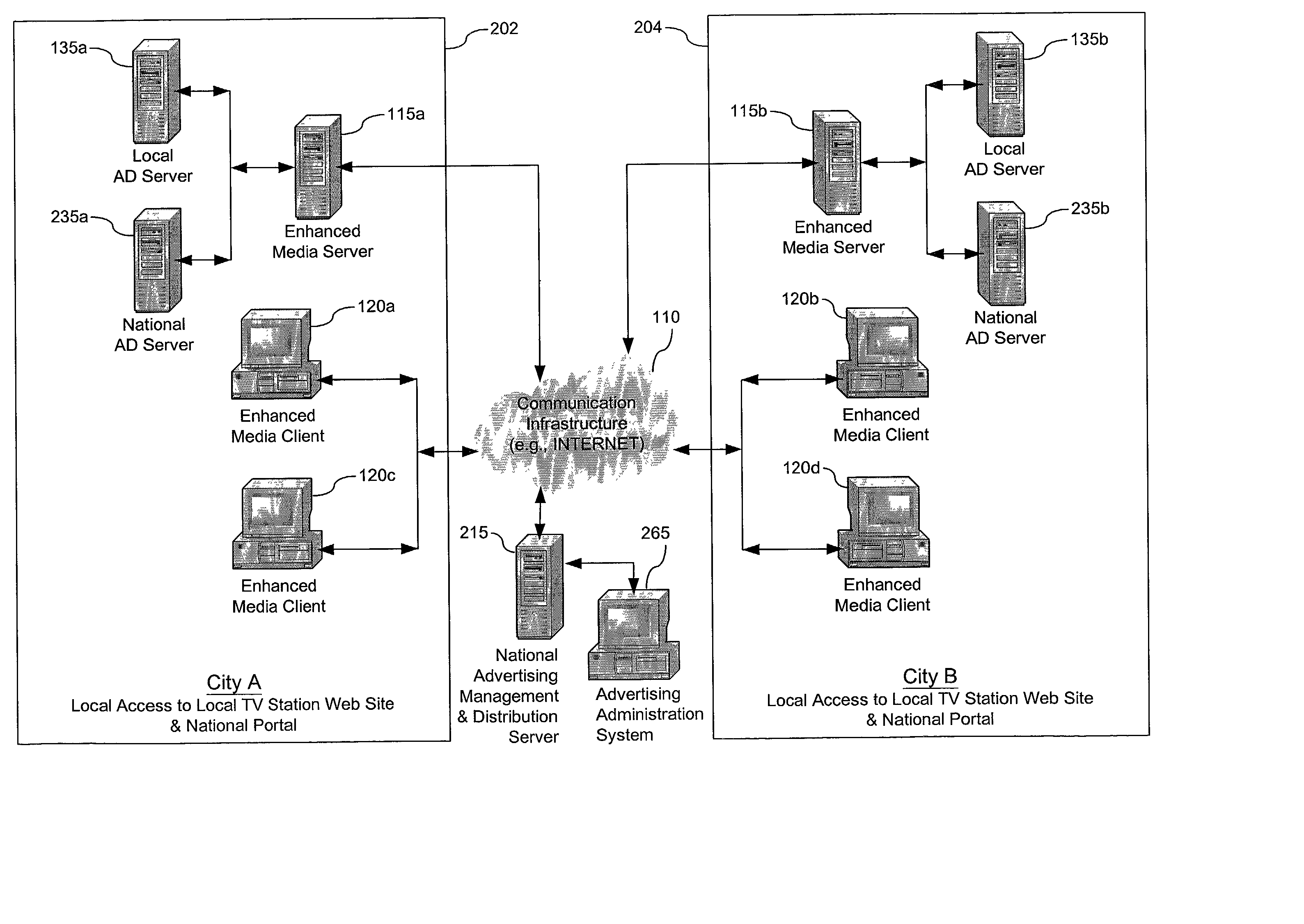
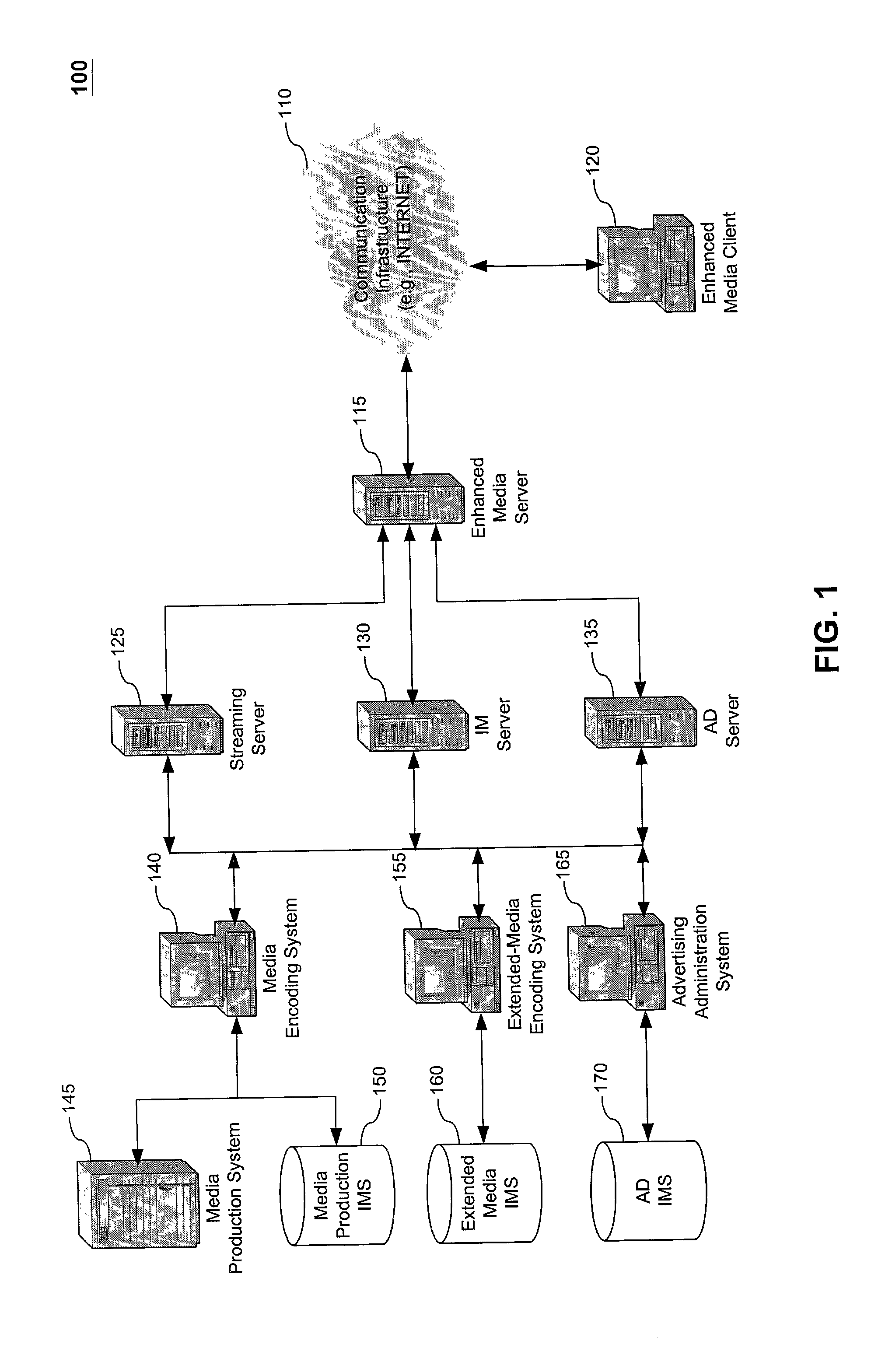
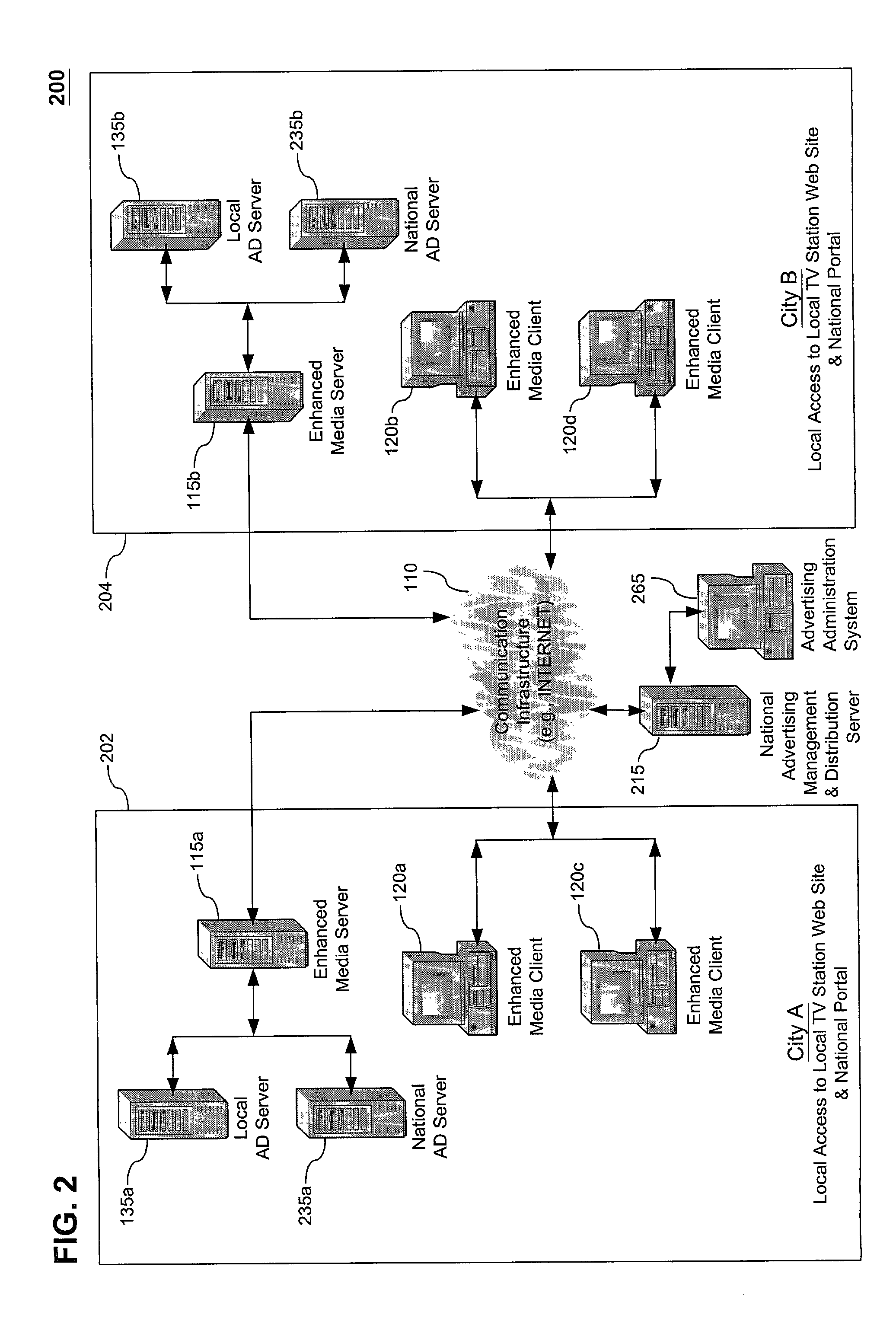
Method, system and computer program product for producing and distributing enhanced media downstreams
InactiveUS20020053078A1Fair and equitableEasy retrievalTelevision system detailsRecord information storageThe InternetTelevision station
A multimedia production and distribution system collects or assembles a media production (such as, a news program, television programming, or radio broadcast) from a variety of sources, including television stations and other media hosting facilities. The media production is categorized and indexed for retrieval and distribution across a wired or wireless network, such as the Internet, to any client, such as a personal computer, television, or personal digital assistant. A user can operate the client to display and interact with the media production, or select various options to customize the transmission or request a standard program. Alternatively, the user can establish a template to generate the media production automatically based on personal preferences. The media production is displayed on the client with various media enhancements to add value to the media production. Such enhancements include graphics, extended play segments, opinion research, and URLs. The enhancements also include advertisements, such as commercials, active banners, and sponsorship buttons. An advertisement reporting system monitors the sale and distribution of advertisements within the network. The advertisements are priced according to factors that measure the likelihood of an advertisement actually being presented or viewed by users most likely to purchase the advertised item or service. The advertisement reporting system also collects metrics to invoice and apportion income derived from the advertisements among the network participants, including a portal host and / or producer of the content.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
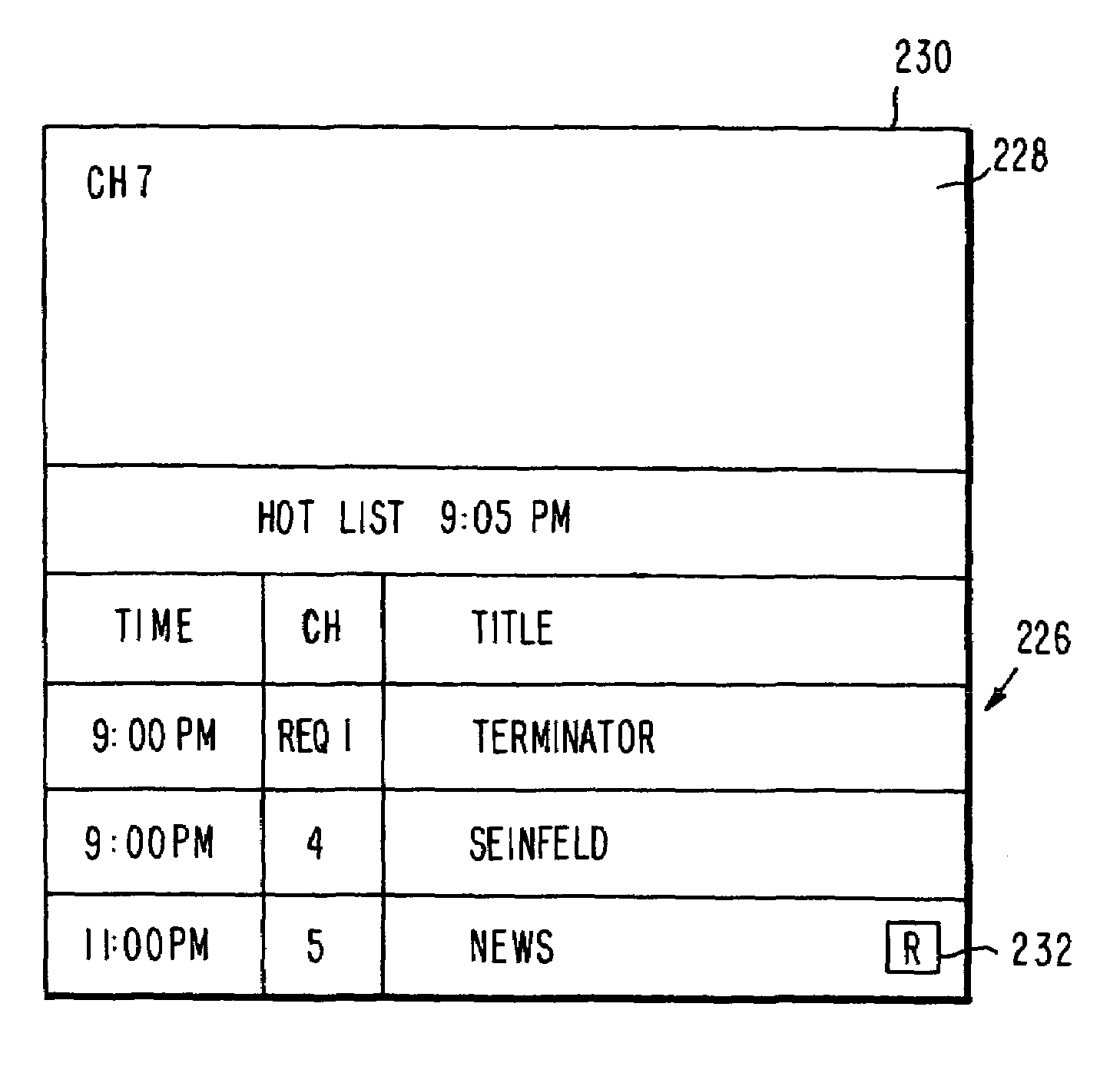
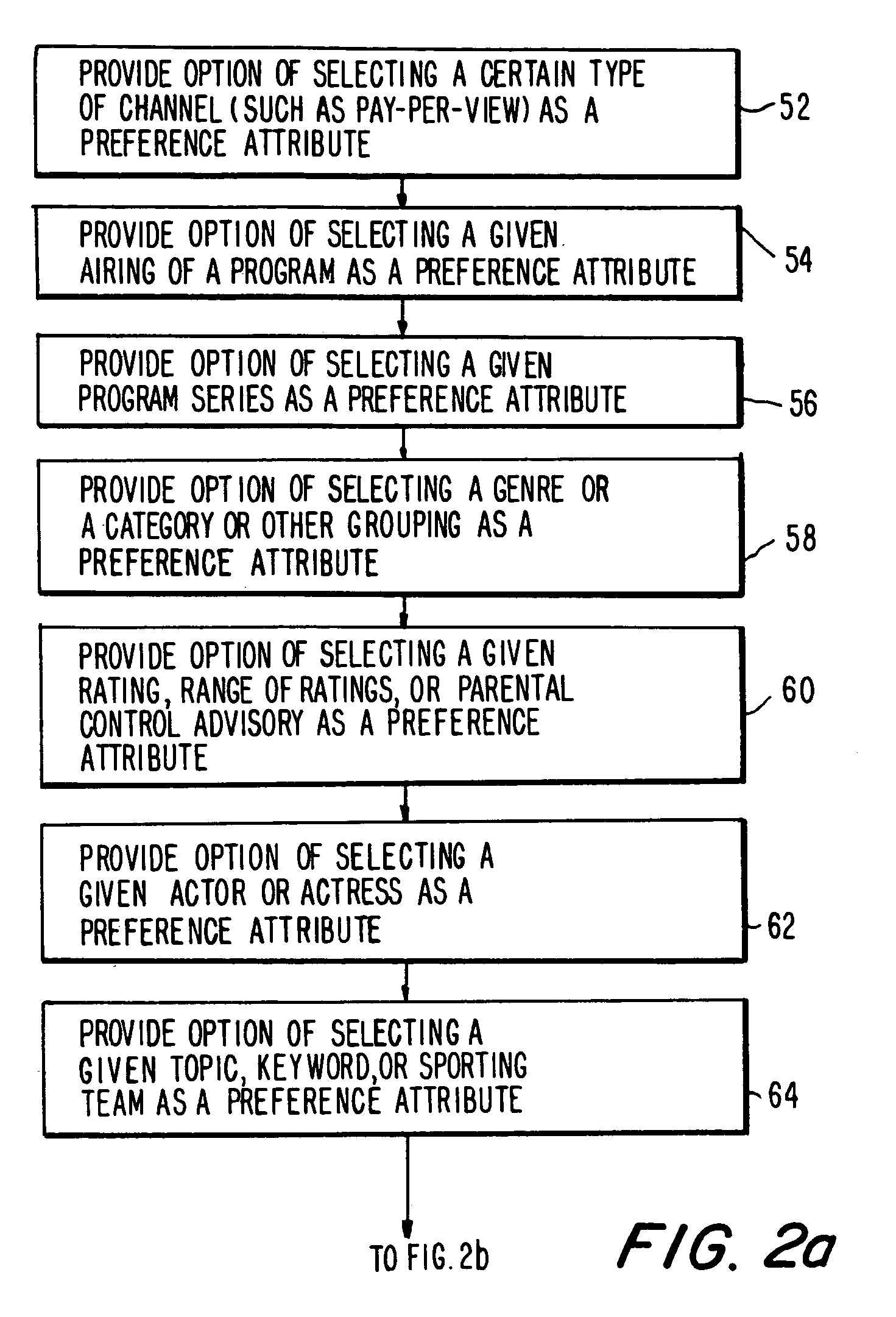
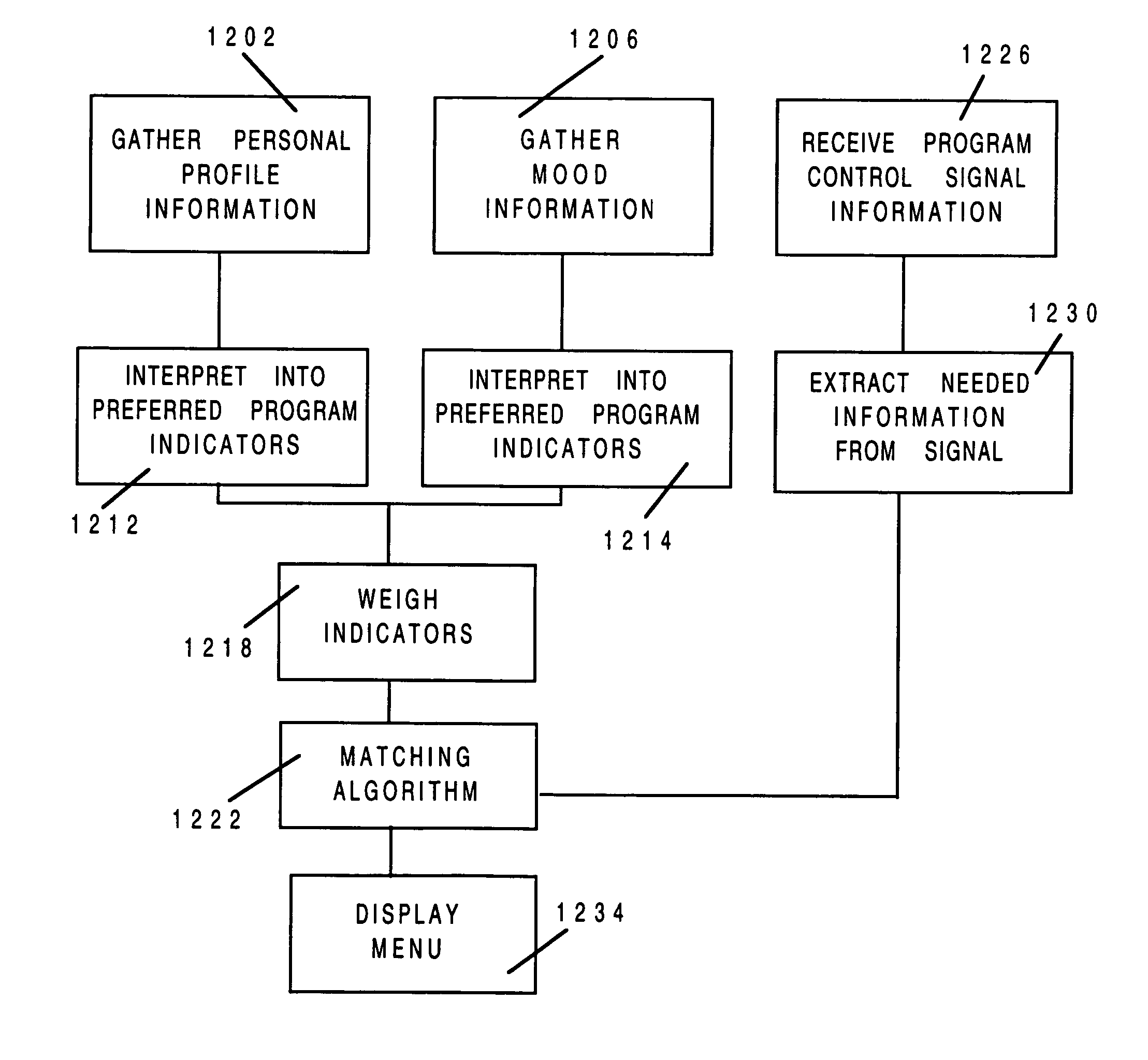
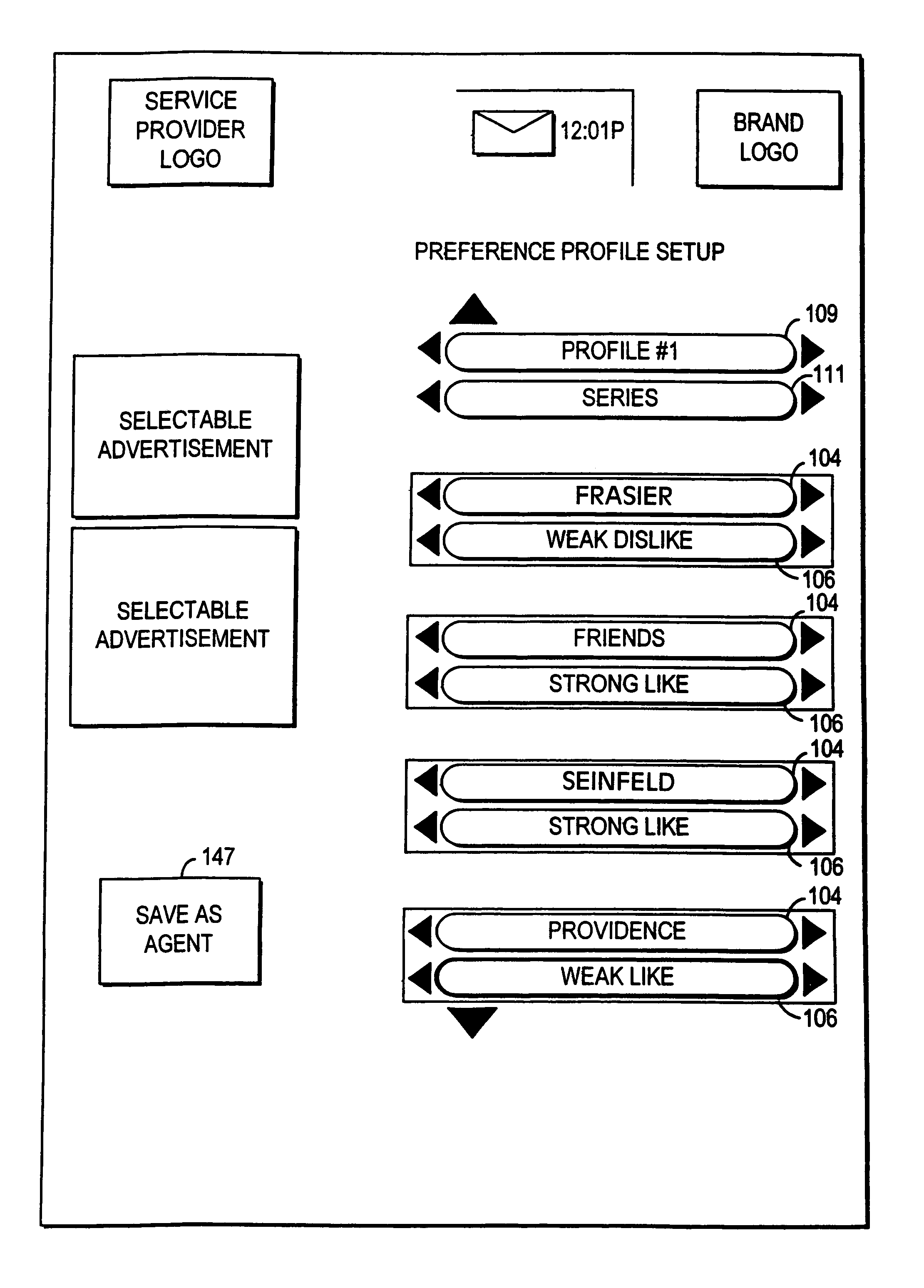
Program guide system with preference profiles
InactiveUS7185355B1Television system detailsColor television detailsInteractive televisionBroadcasting
An interactive television program guide system is provided in which a user may inform a program guide of the user's interests. Information on the user's interests may be stored in a preference profile. There may be more than one preference profile, each for a different user. Each preference profile contains a number of preference attributes (program titles, genres, viewing times, channels, broadcast characteristics, etc.). A preference level (e.g., strong or weak like, strong or weak dislike, illegal, mandatory, don't care, etc.) that is indicative of the user's level of interest is associated with each preference attribute. Preference profiles may be used to restrict the programs that are listed in various program listings display screens and may be used to limit the channels to which the program guide allows the user to tune.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
Method and apparatus for providing entertainment content on a gaming machine
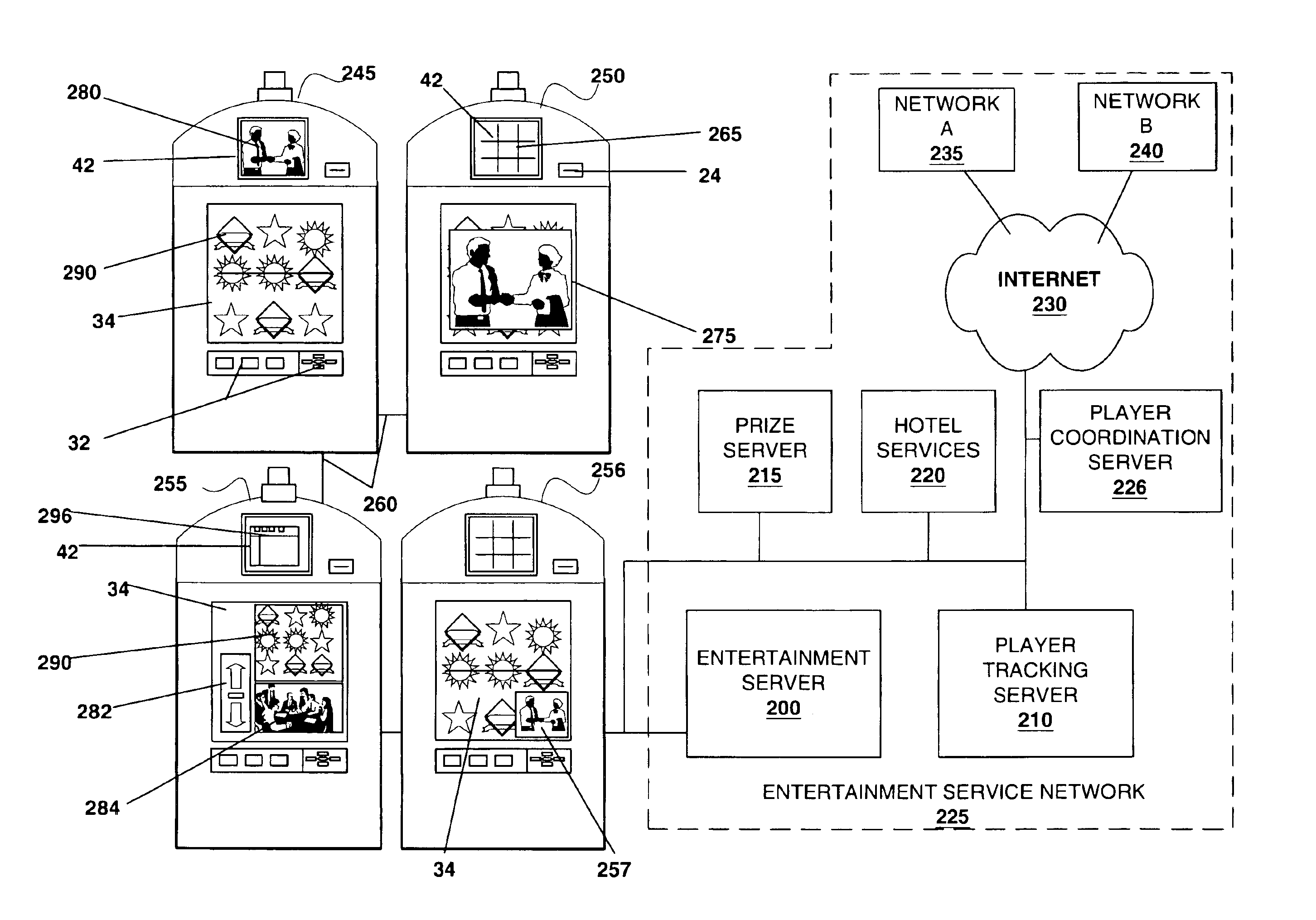
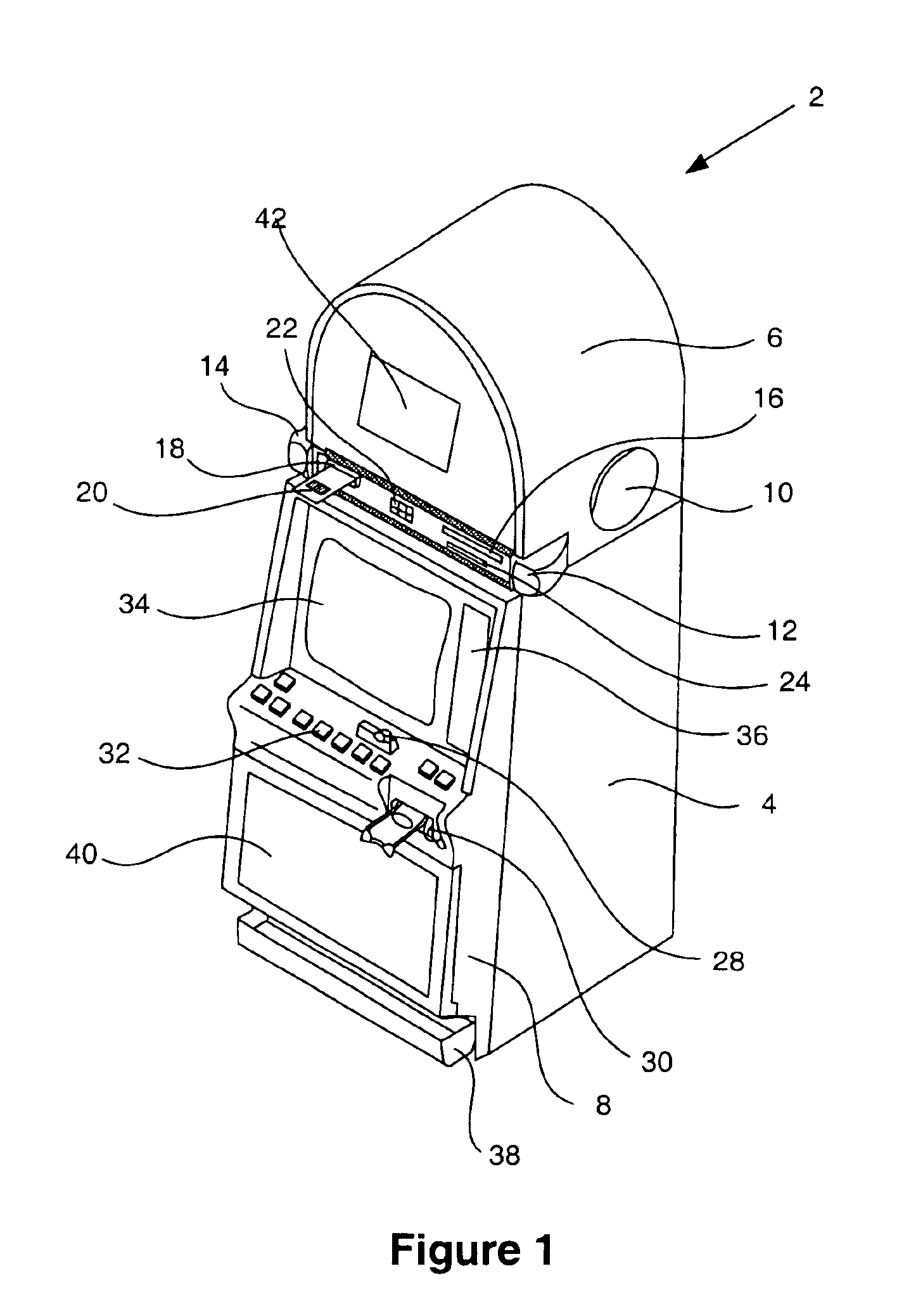
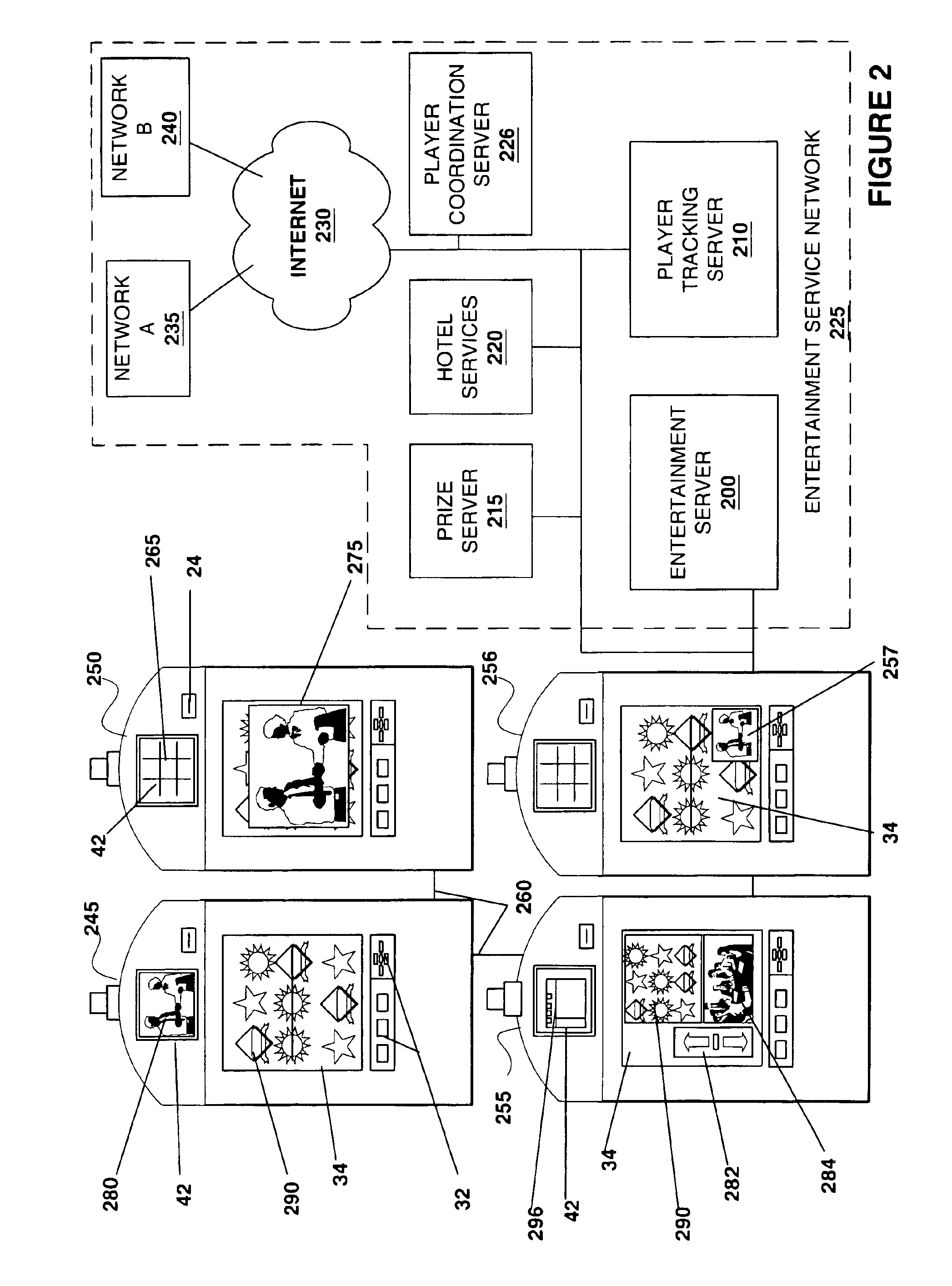
A gaming machine with devices able to output entertainment content (e.g. movies, TV programming, audio programs and advertising) from entertainment content sources located within the gaming machine or outside of the gaming machine is described. A player utilizing the gaming machine may access, independently of game play, entertainment content on the gaming machine where access to the entertainment content is granted according to a predetermined fee. In addition, the player utilizing the gaming machine may receive personal messages on the gaming machine. For example, while utilizing the gaming machine, a player may receive, e-mail, stock quotes, news and advertising that is of particular interest to the player utilizing the gaming machine.
Owner:IGT
Advertising methods for advertising time slots and embedded objects
ActiveUS20050137958A1Increase flexibilityShort timeFinanceAdvertisementsCombined techniqueWorld Wide Web
Disclosed is a process for an advertising bidding system in which advertisers can bid on advertising time slots or enhanced ads that can be inserted in either prerecorded or live television programming. A high degree of flexibility is provided by allowing embedded ads to be purchased and displayed in a very short time period. This allows TV broadcasters to increase revenues and allows advertisers to have more flexibility in advertising. Objects can be inserted in the display video broadcast using enhancements such as by using mark-up language overlay pages or by video combination techniques. The effect of these ads can be evaluated for advertising campaigns.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
Smart filtering
InactiveUS6172674B1Reduce settingsFind quicklyTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsComputer scienceElectronic program guide
A system and method for implementing an electronic programming guide that allows a television viewer to access and interact with television scheduling information. The electronic programming guide provides the viewer with a grid which lists channels, titles and show times. To help the viewer locate information about shows the viewer is interested in, the guide can filter the data prior to display. Only the data that meets certain filter criteria will be displayed. The filter criteria are set by the viewer. The filter criteria can be changed by manipulating a variable selection element such as a slider.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM MANAGEMENT LLC
Advertising with video ad creatives
InactiveUS20070157228A1Good serviceAdvertisementsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsRelevant informationThe Internet
The serving of advertisements with (e.g., on) video documents may be improved in a number of ways. For example, a system may (a) accept information defining at least one ad spot associated with at least one instance of an video document, (b) accept offers to have advertisements served in the ad spot(s), and (c) arbitrate among competing advertisements, using at least the offers, to determine at least one advertisement to be served in that ad spot(s). As another example, a system may (a) accept relevance information for an advertisement, (b) determine at least one video document using the accepted relevance information, (c) present information about the video document(s) to an advertiser associated with the advertisement, and (d) accept, from the advertiser, an offer to have its advertisement served with at least one of the video document(s) accepted. As yet another example, a system may (a) accept relevance information for an video document, (b) determine a plurality of advertisements relevant to the video document using the relevance information and serving constraints of the advertisements, and (c) select at least one of the determined relevant advertisements to be served with the video document. Examples of video documents include video files published on the Internet, television programs, live or recorded talk shows, video-voice mail, segments of an video conversation, etc.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
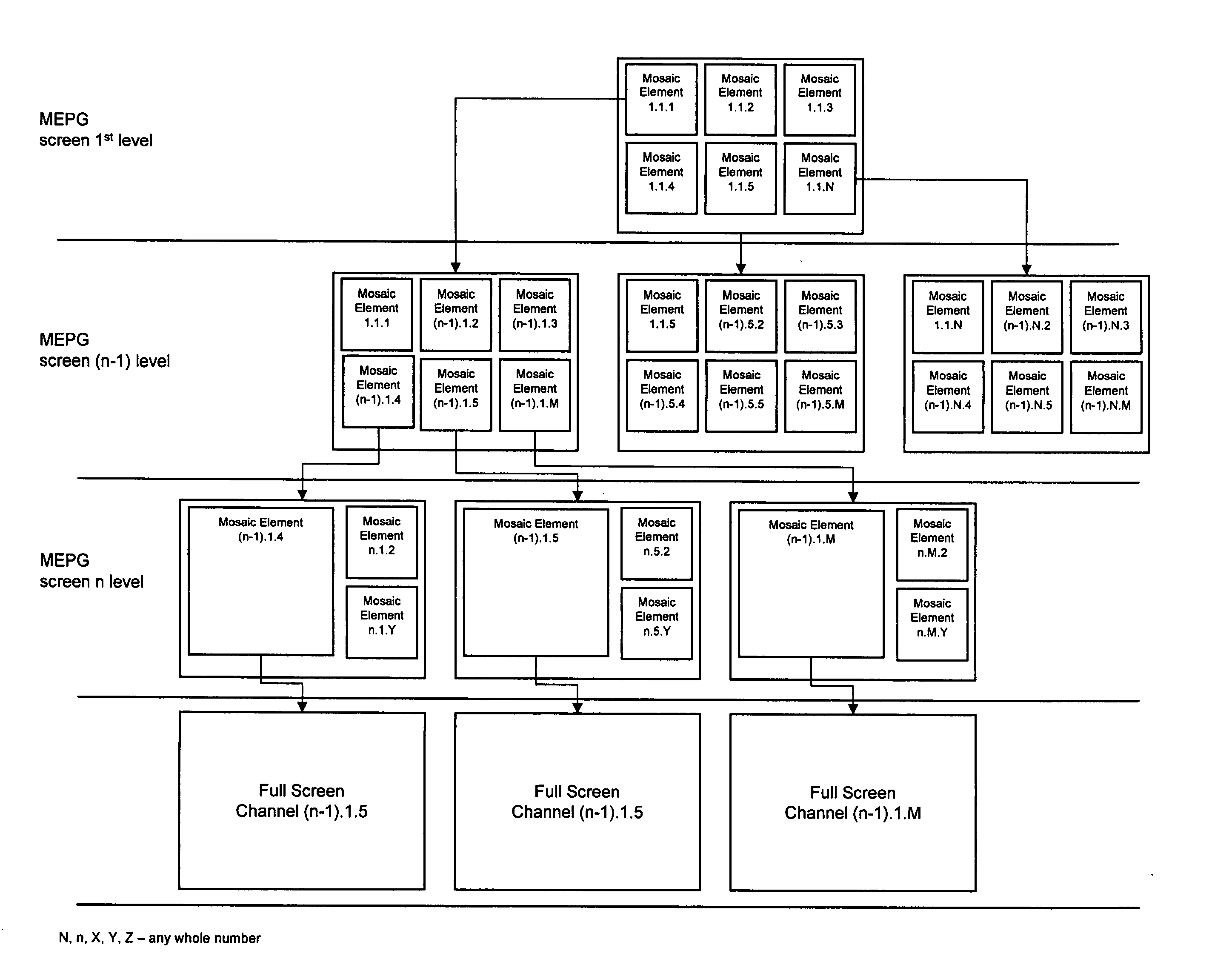
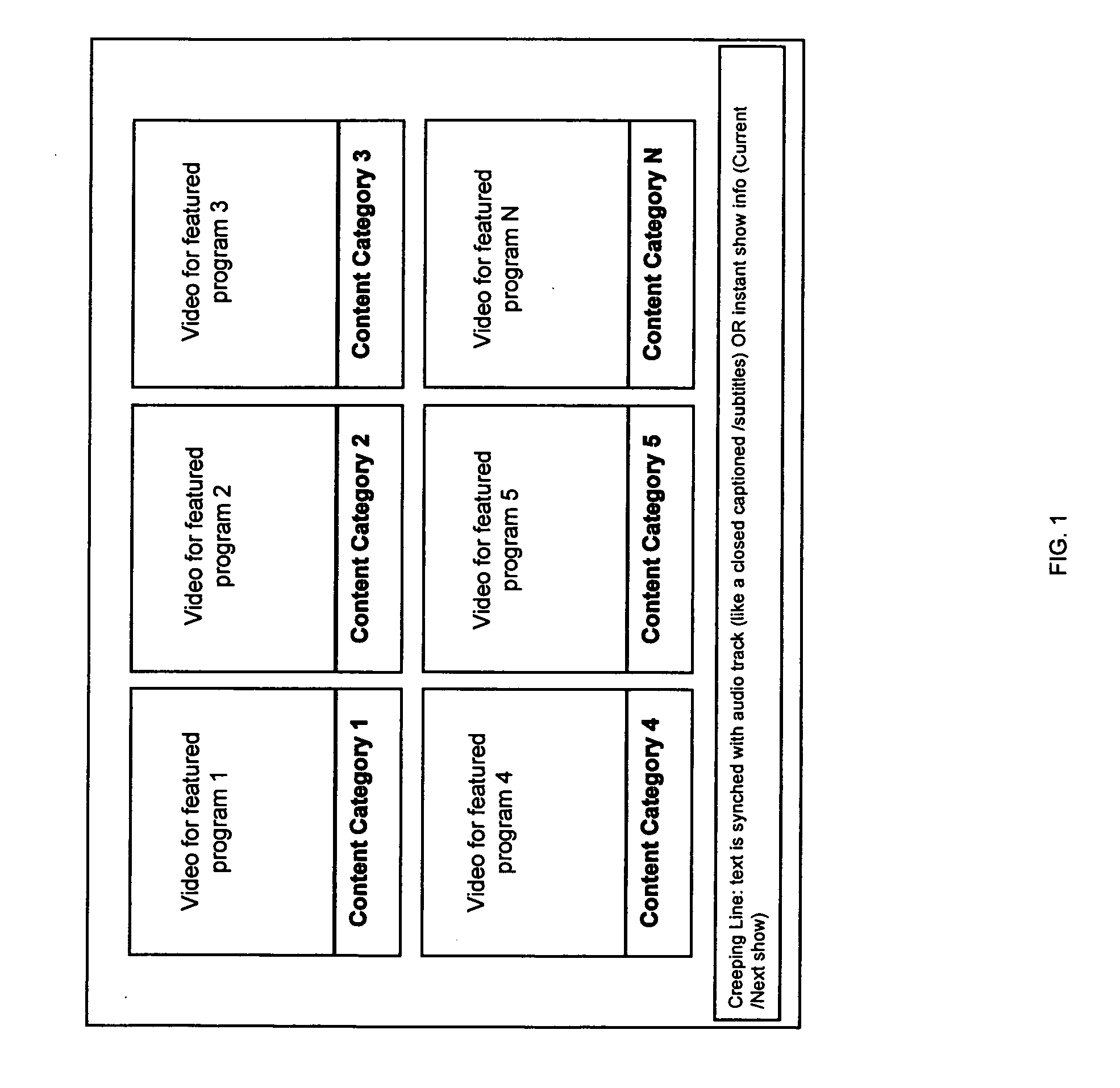
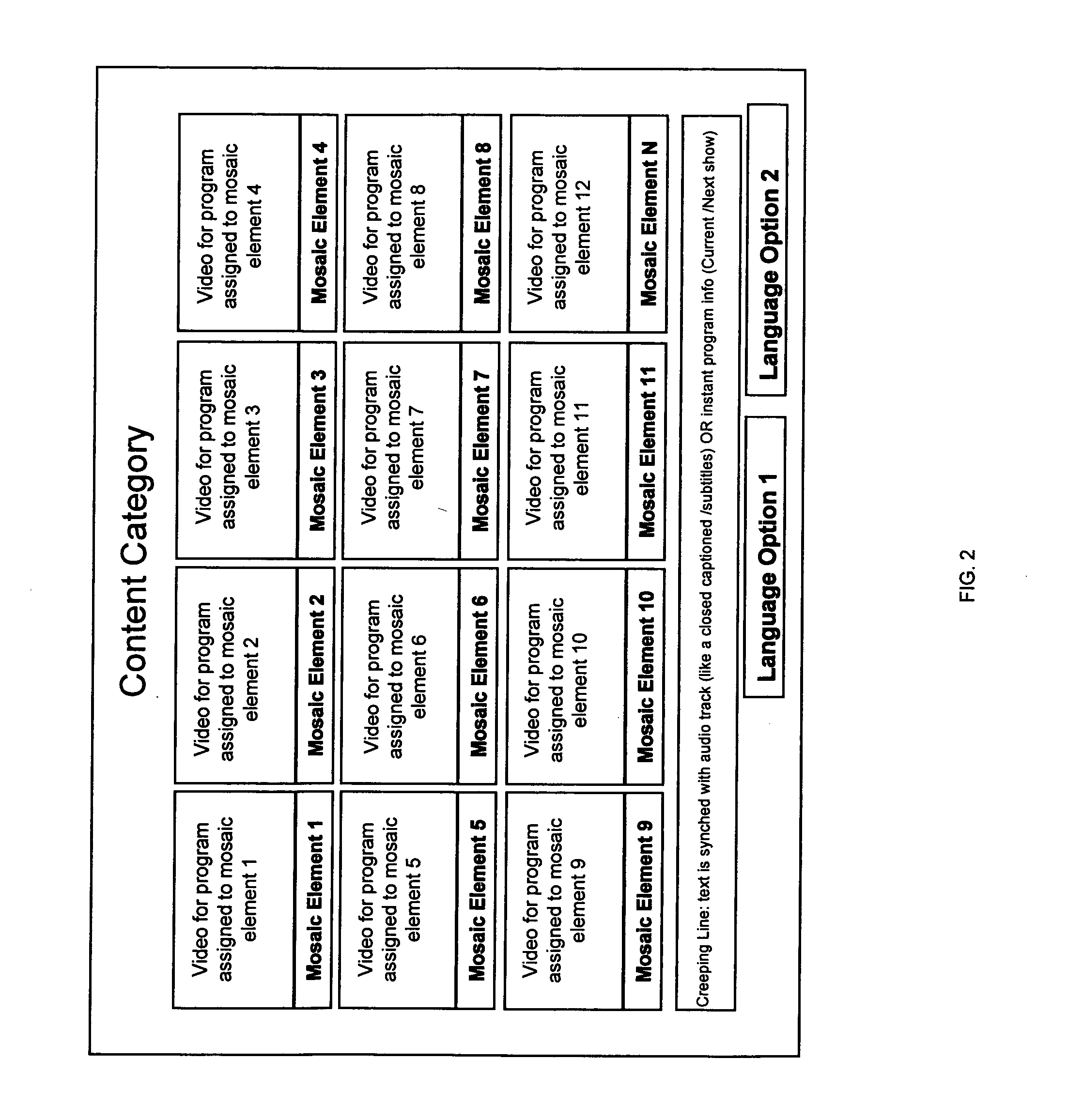
Dynamic mosaic extended electronic programming guide for television program selection and display
Owner:WEBTUNER CORP
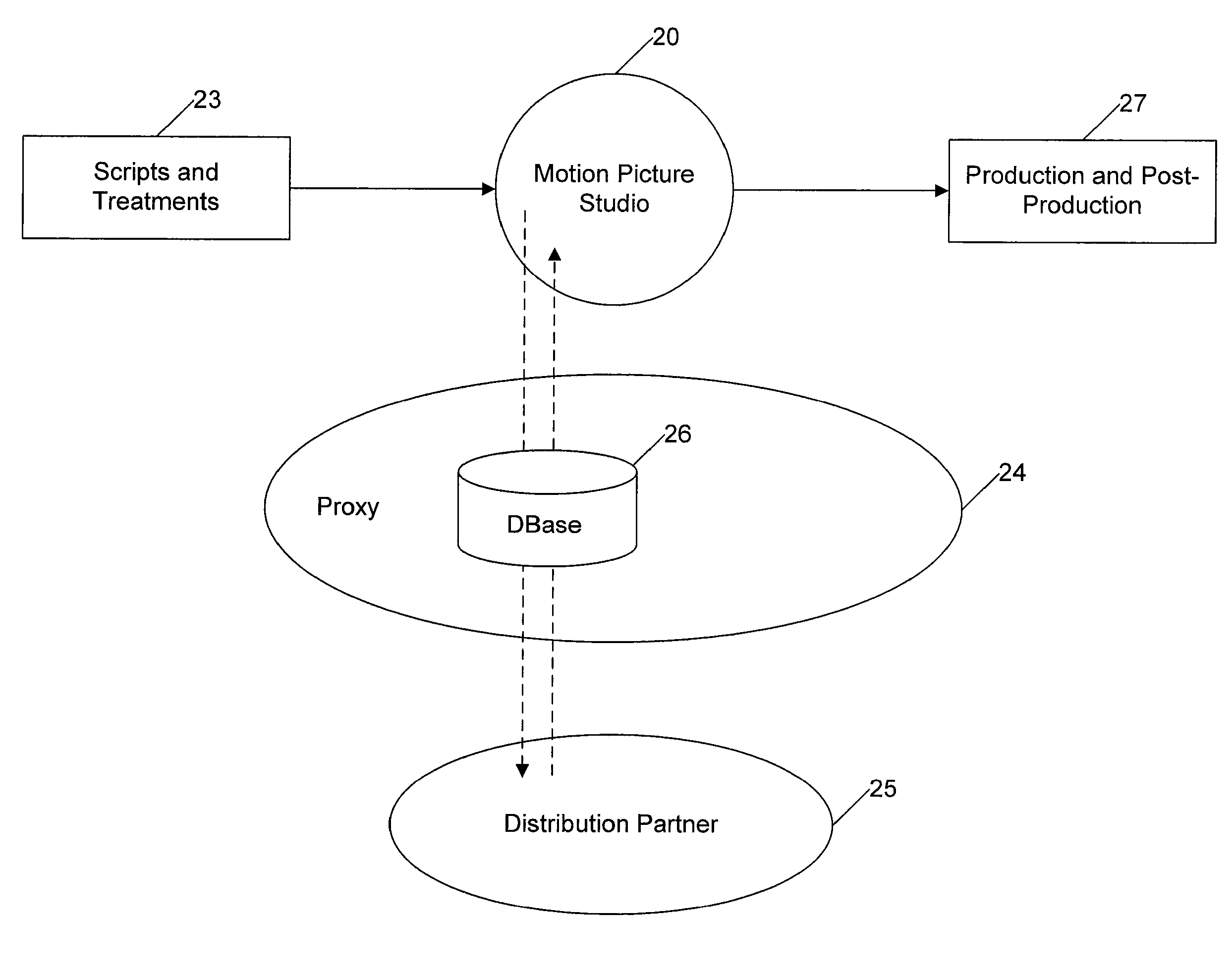
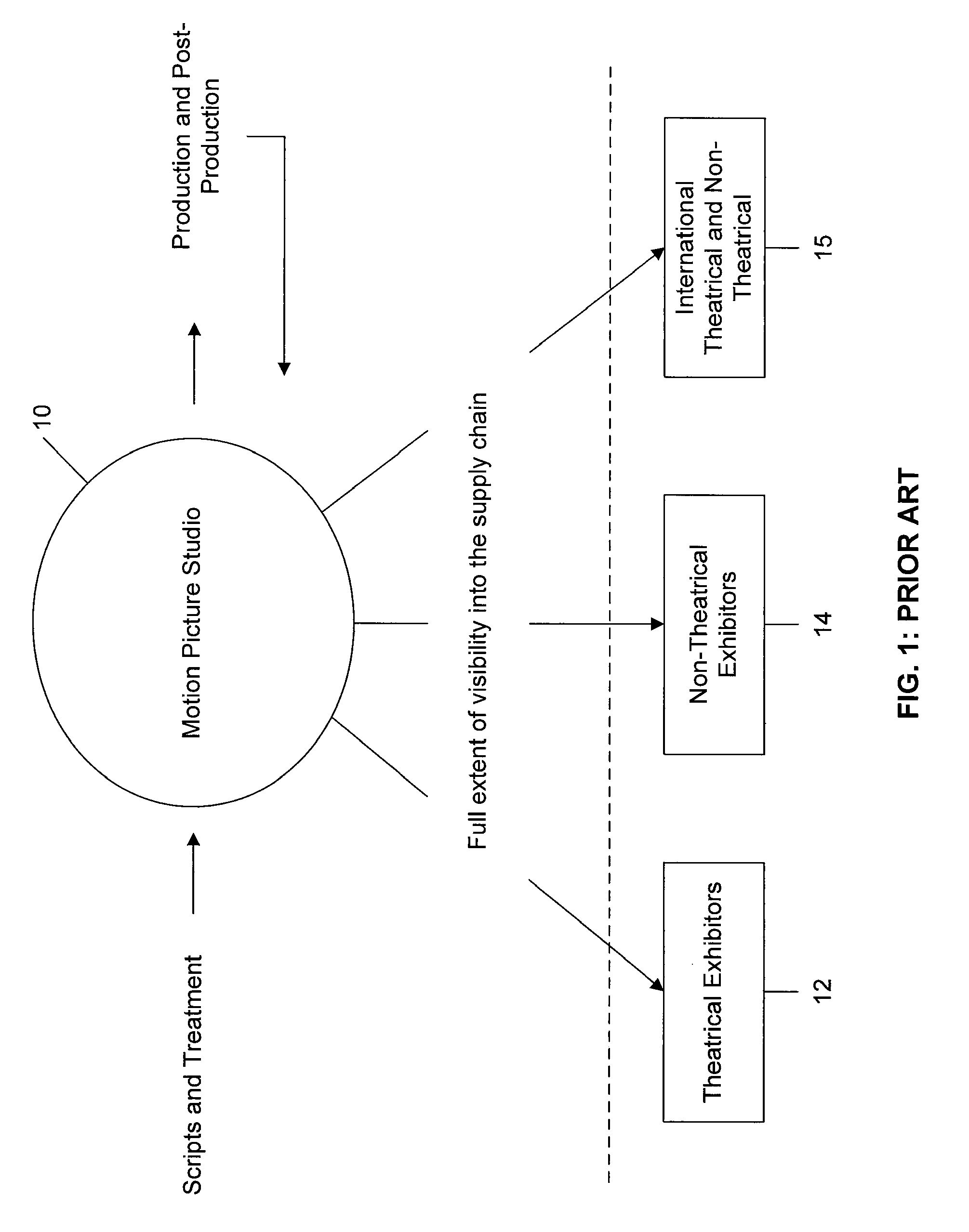
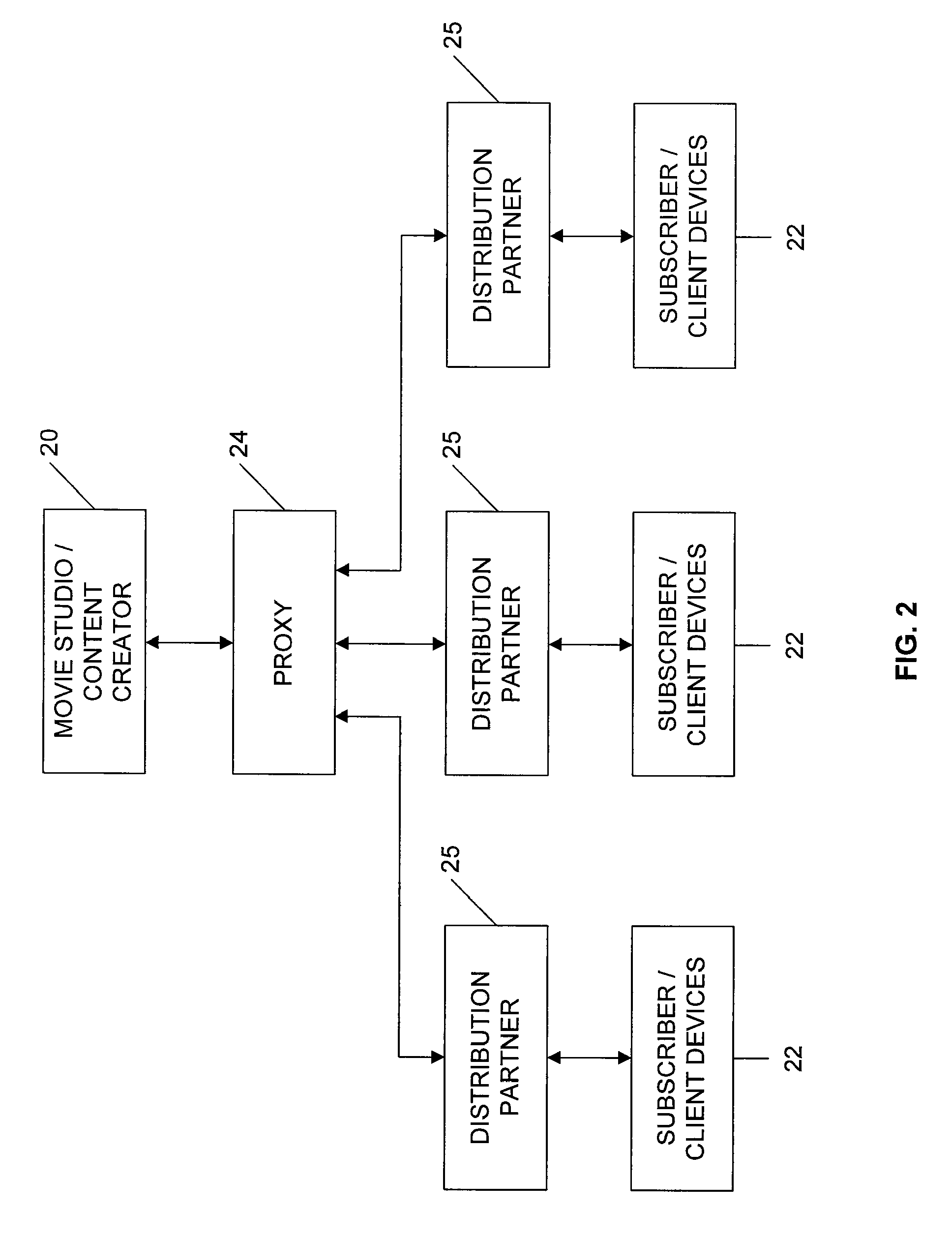
Movie studio-based network distribution system and method
ActiveUS20070220575A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsAccess networkDigital content
Digital content files containing entertainment media such as movies, TV shows, and the like are distributed from at least one content source primarily responsible for the original creation of the media to subscribers over a network system. The content source is connected over at least one content source network to a plurality of distribution partners, and each distribution partner is connected with a selected group of subscribers over an access network. A requested digital content file is distributed from the content source to a subscriber in a network distribution path comprising at least the content source network, the distribution partner associated with the subscriber, and the second network. A profile information package containing subscriber preferences is transmitted from the subscriber to the content source by way of a proxy over the network distribution path, and the profile information package is stored at the content source.
Owner:VERIMATRIX INC
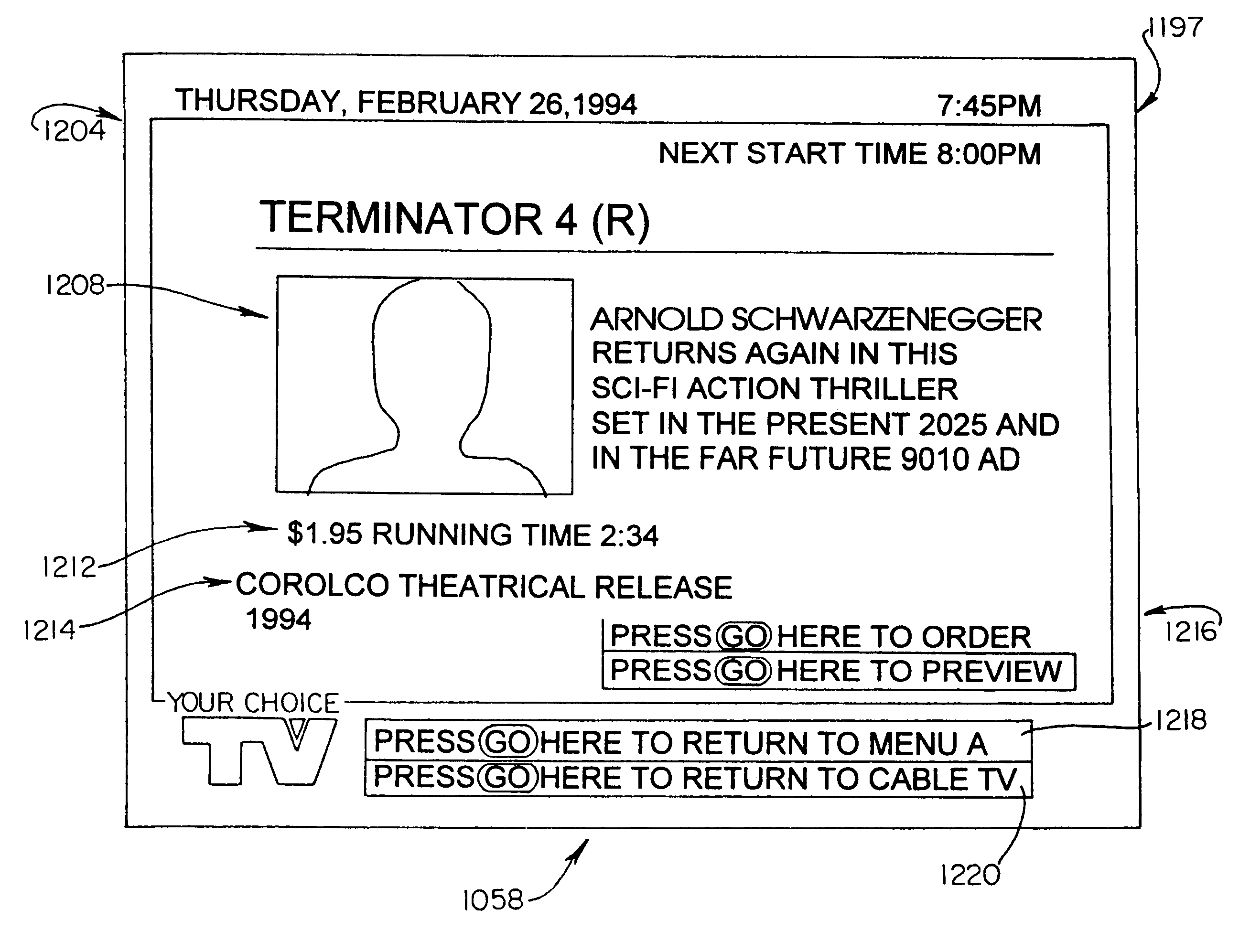
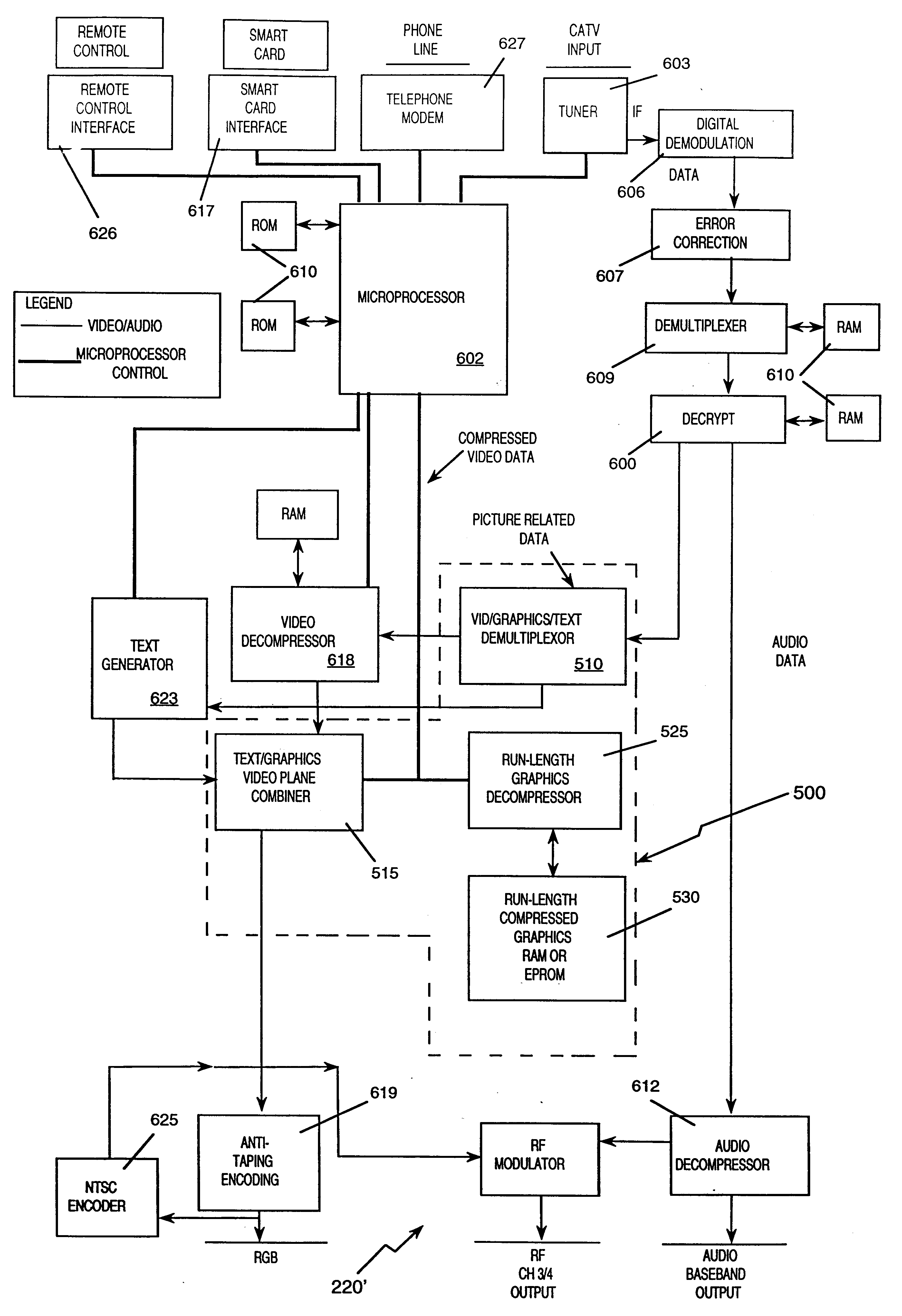
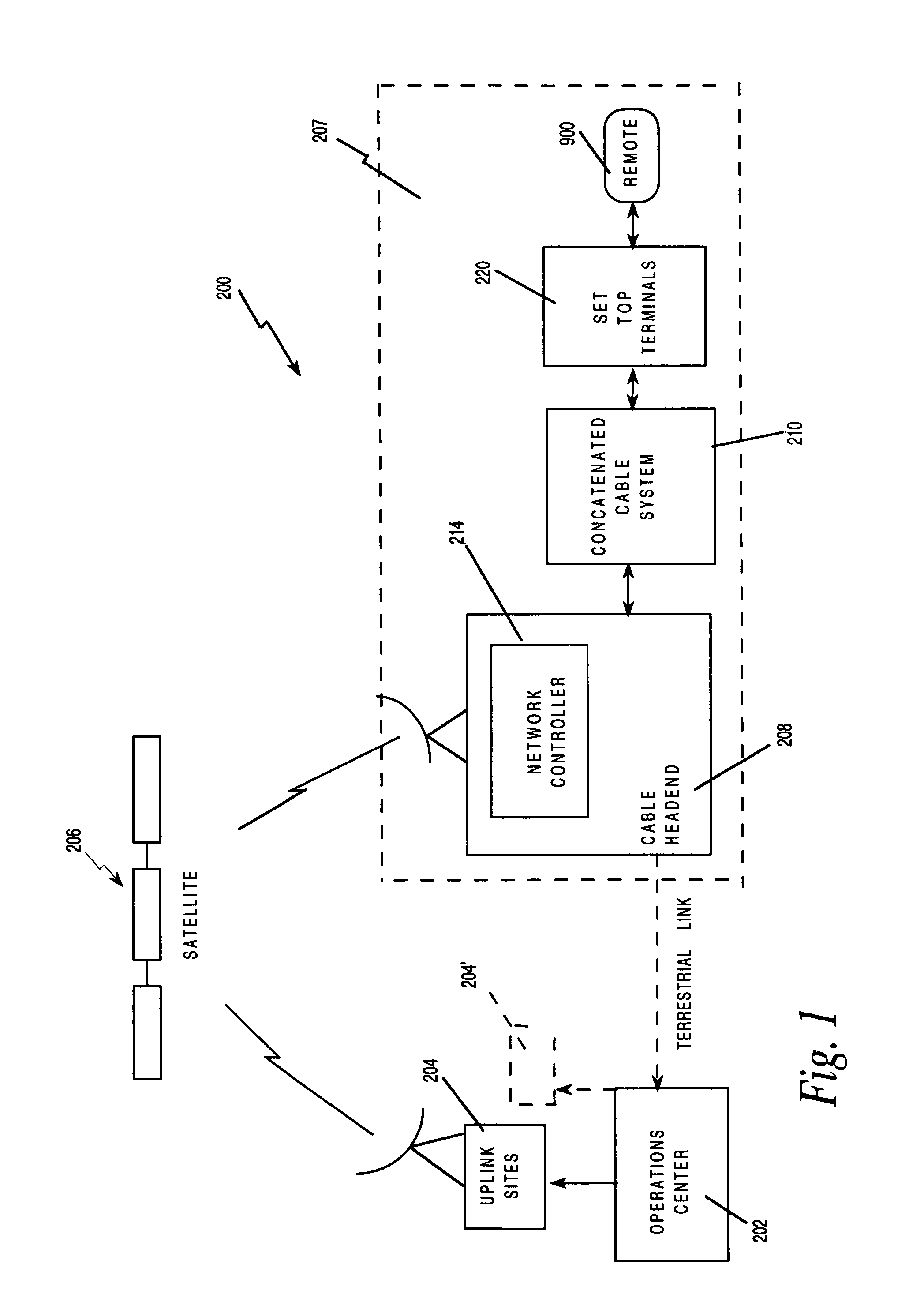
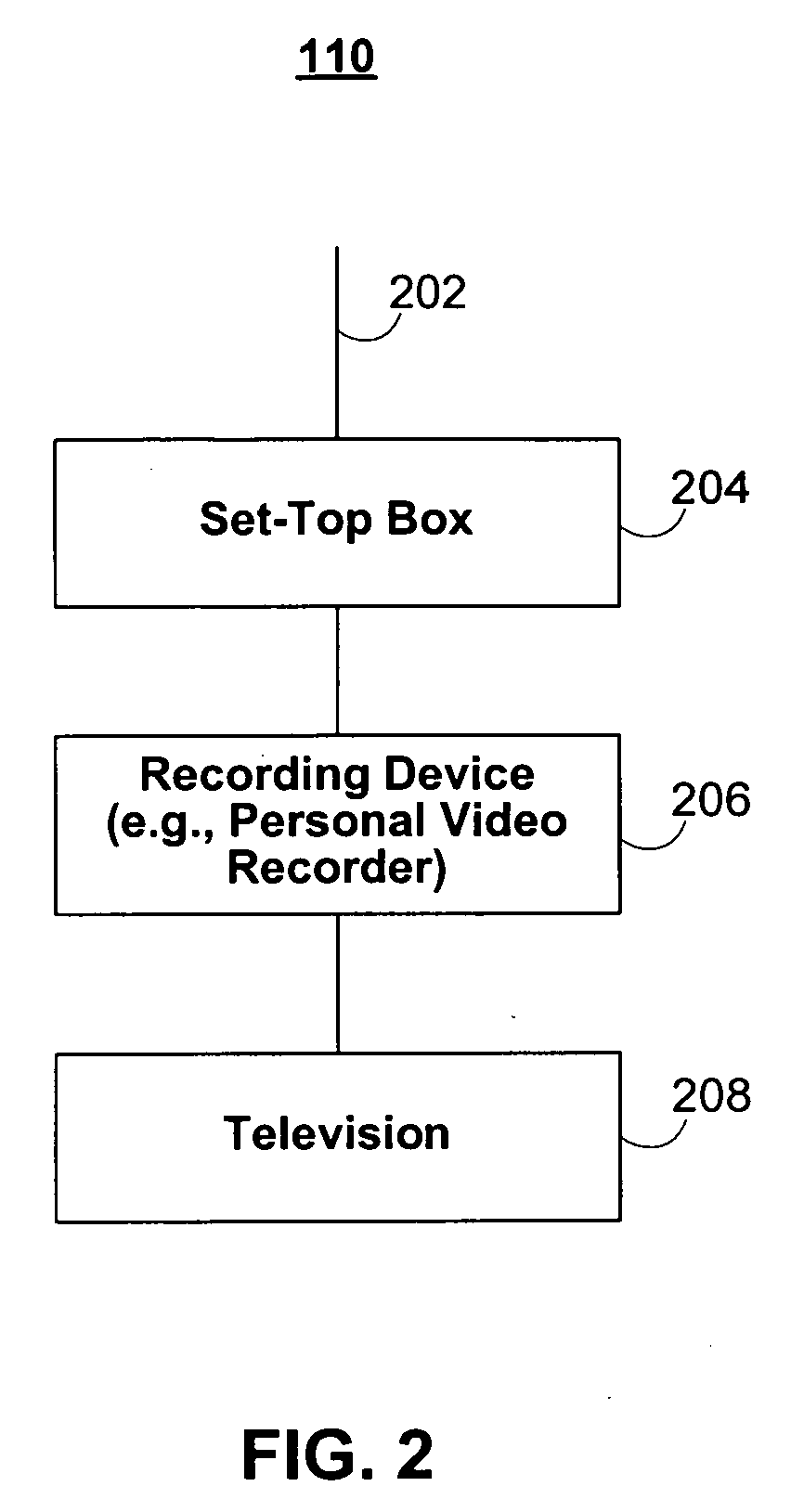
Set top terminal for television delivery system
InactiveUS6515680B1Easy to browseImprove user friendlinessPulse modulation television signal transmissionBroadcast information characterisationData signalComputer terminal
A viewer interface for a television program delivery system is described. The innovation relates to methods and devices for viewer pathways to television programs. Specifically, the interface involves hardware and software used in conjunction with a television at the viewer home to create a user friendly menu based approach to television program access. The device is particularly useful in a program delivery system with hundreds of programs and a data signal carrying program information. The disclosure describes menu generation and menu selection of television programs.
Owner:COMCAST IP HLDG I
Second screen interactive platform
InactiveUS20130111514A1Broadcast systems characterised by additional dataAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsData storeSocial web
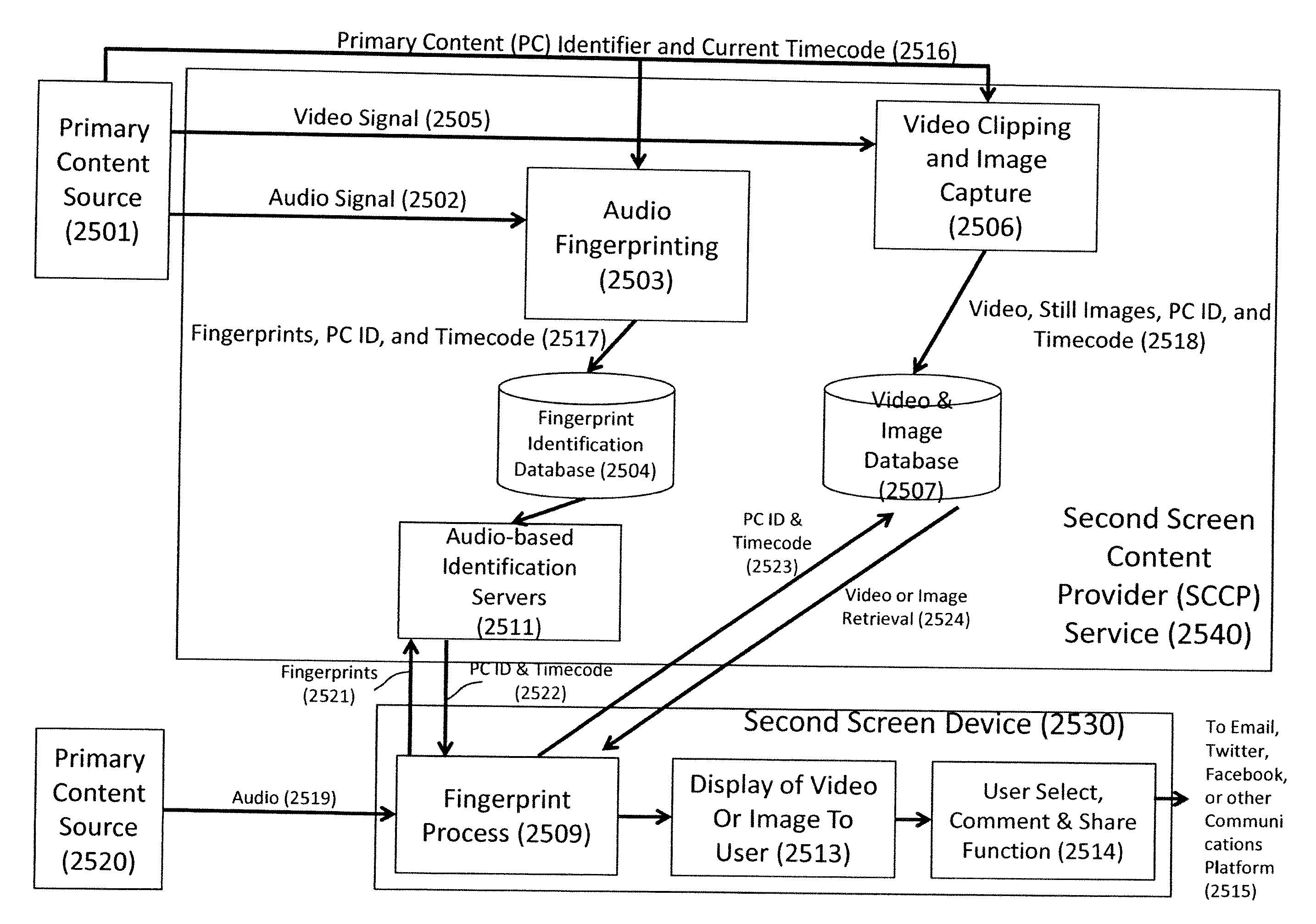
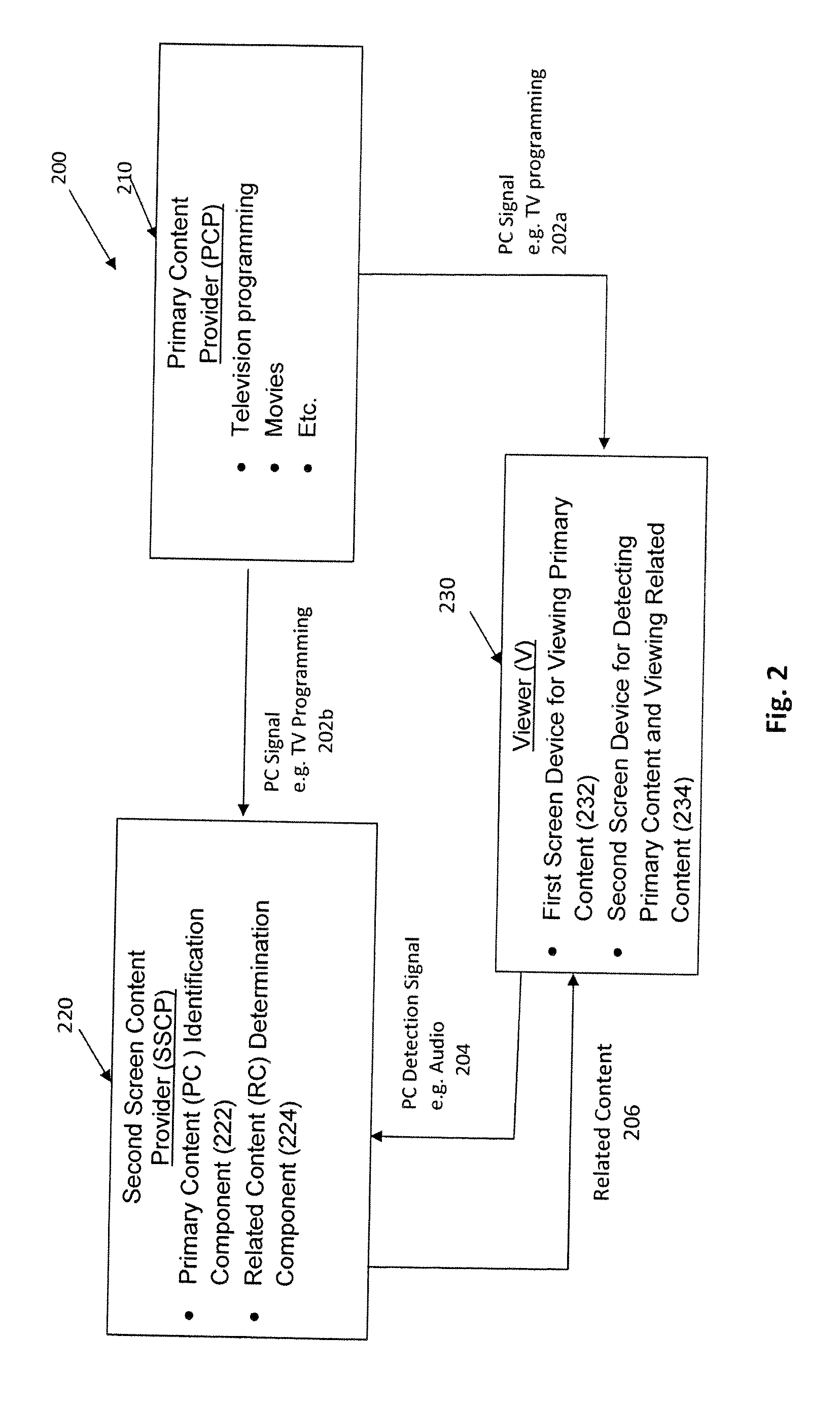
Interactive digital media platform, methods and apparatus for detecting and dynamically synchronizing to media content (e.g., television (TV) programs or movies) that a viewer is watching while providing related content on a second screen for enhancing the viewer experience. In one embodiment, the primary content is determined by detecting an audio signal of the primary content via the second screen device; the audio signal may then be processed to generate a fingerprint for comparison with a data store of primary content. The primary content can be classified by various categories (e.g., unique program, advertising, repeat airing, theme song . . . ) and the classification used to aid in the identification and / or in selection of the content to be presented on the interactive second screen device. The system allows a substantially real time comparison and recognition of what primary content a viewer is watching on a first screen device and presentation to the user of content that is substantially synchronous to the viewer's location in the primary content. The viewer can actively engaged with the content presented and can share the content with others via social networking and the like.
Owner:UMAMI
Card for a set top terminal
InactiveUS6181335B1Speed up searchImprove throughputTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionData signalUser Friendly
An apparatus for upgrading a viewer interface for a television program delivery system (200) is described. The invention relates to methods and devices for viewer pathways to television programs and services. Specifically, the apparatus involves hardware and software used in conjunction with the interface and a television at the viewer home to create a user friendly menu based approach to accessing programs and services. The apparatus is particularly useful in a program delivery system (200) with hundreds of programs and a data signal carrying program information. The disclosure describes menu generation and menu selection of television programs.
Owner:COMCAST IP HLDG I
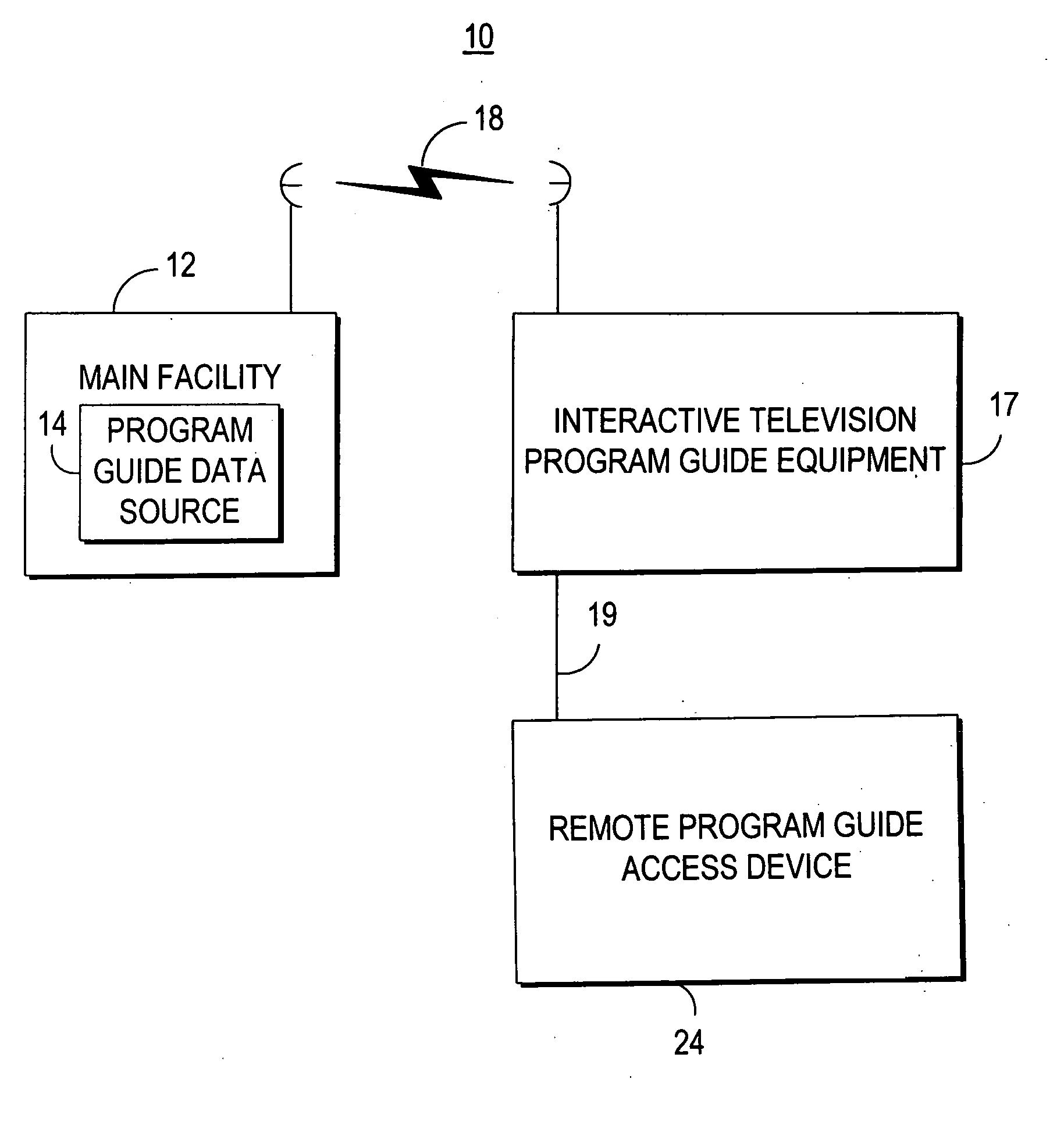
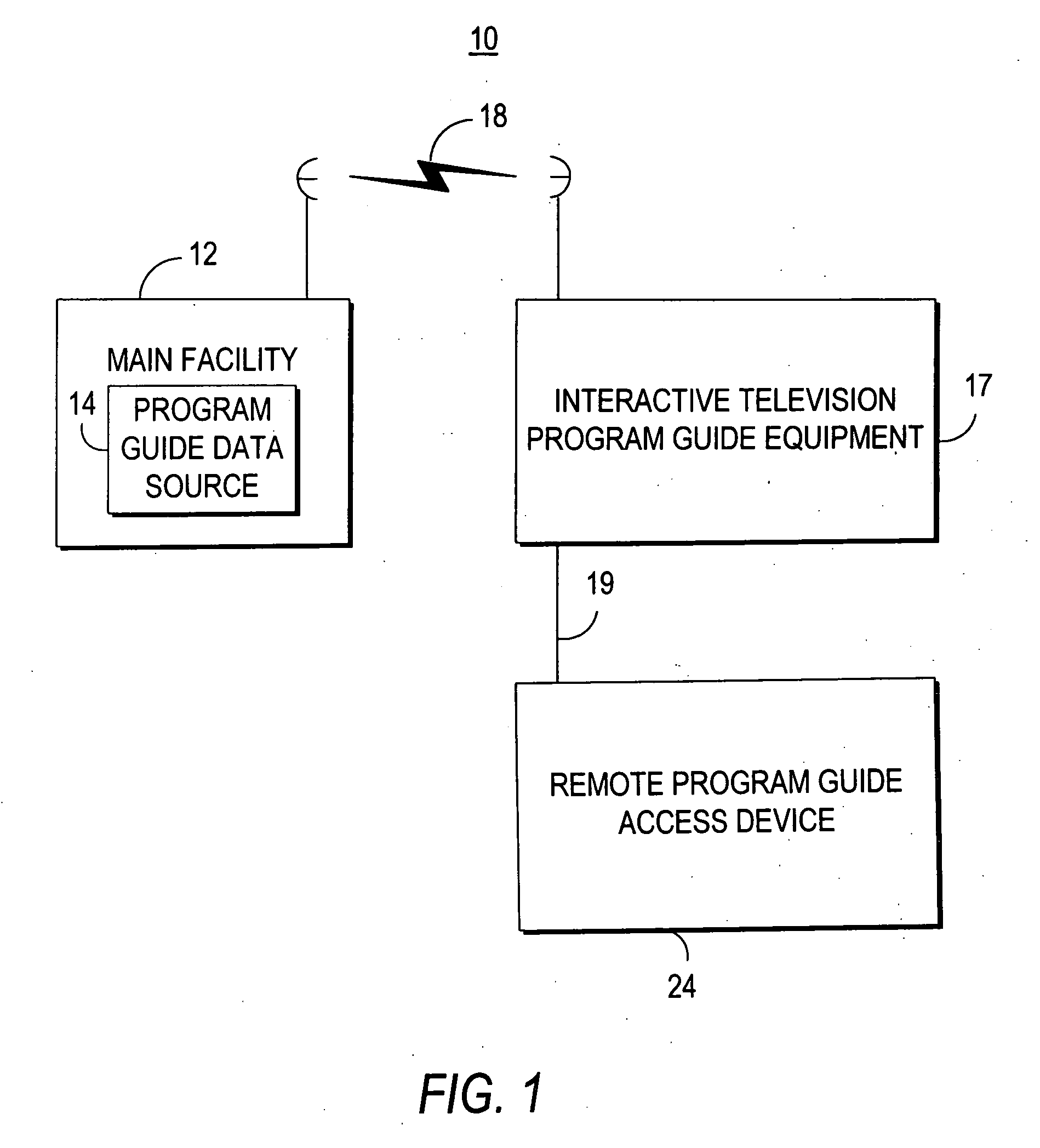
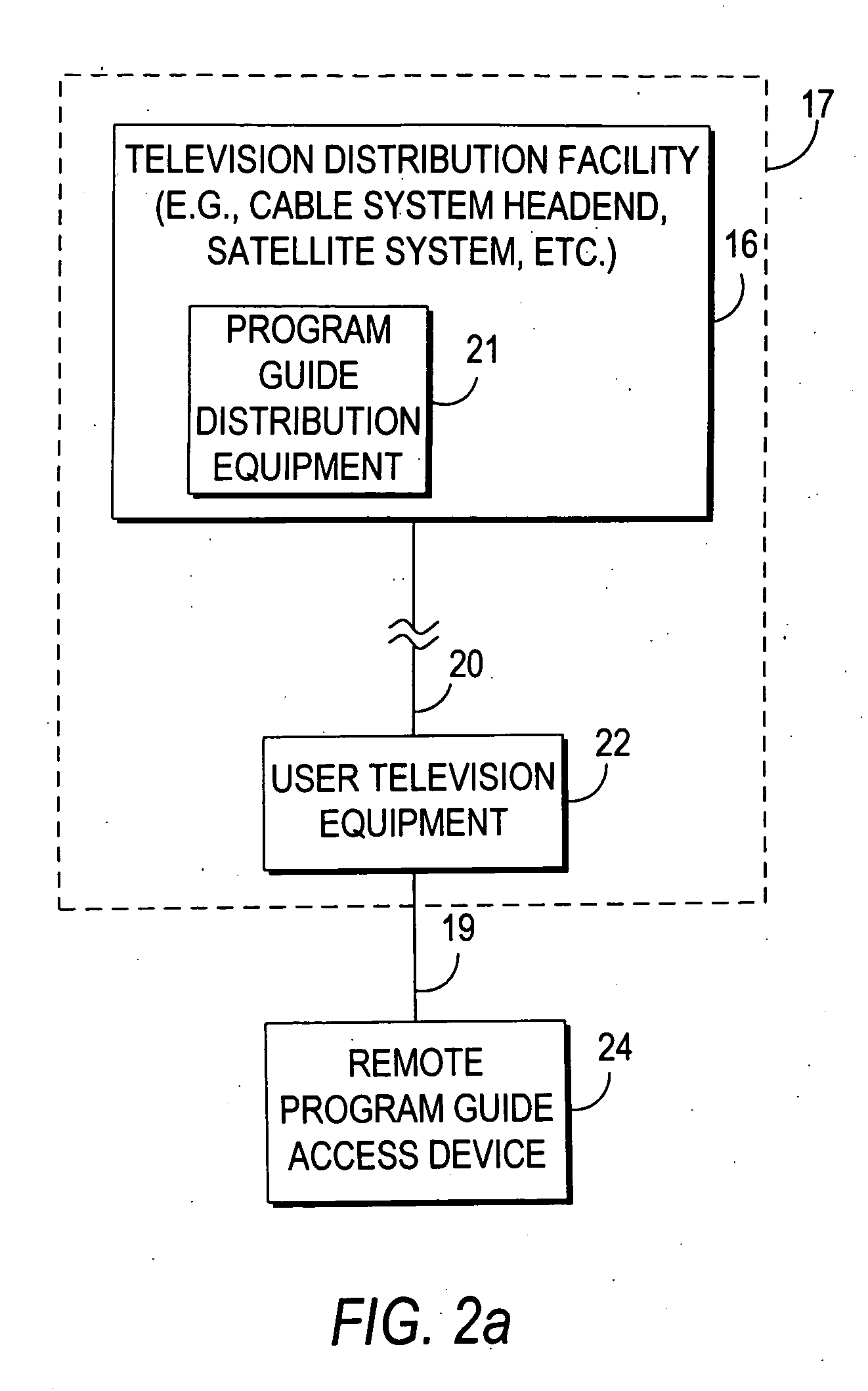
Interactive television program guide with remote access
InactiveUS20060031883A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInteractive televisionCable television
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
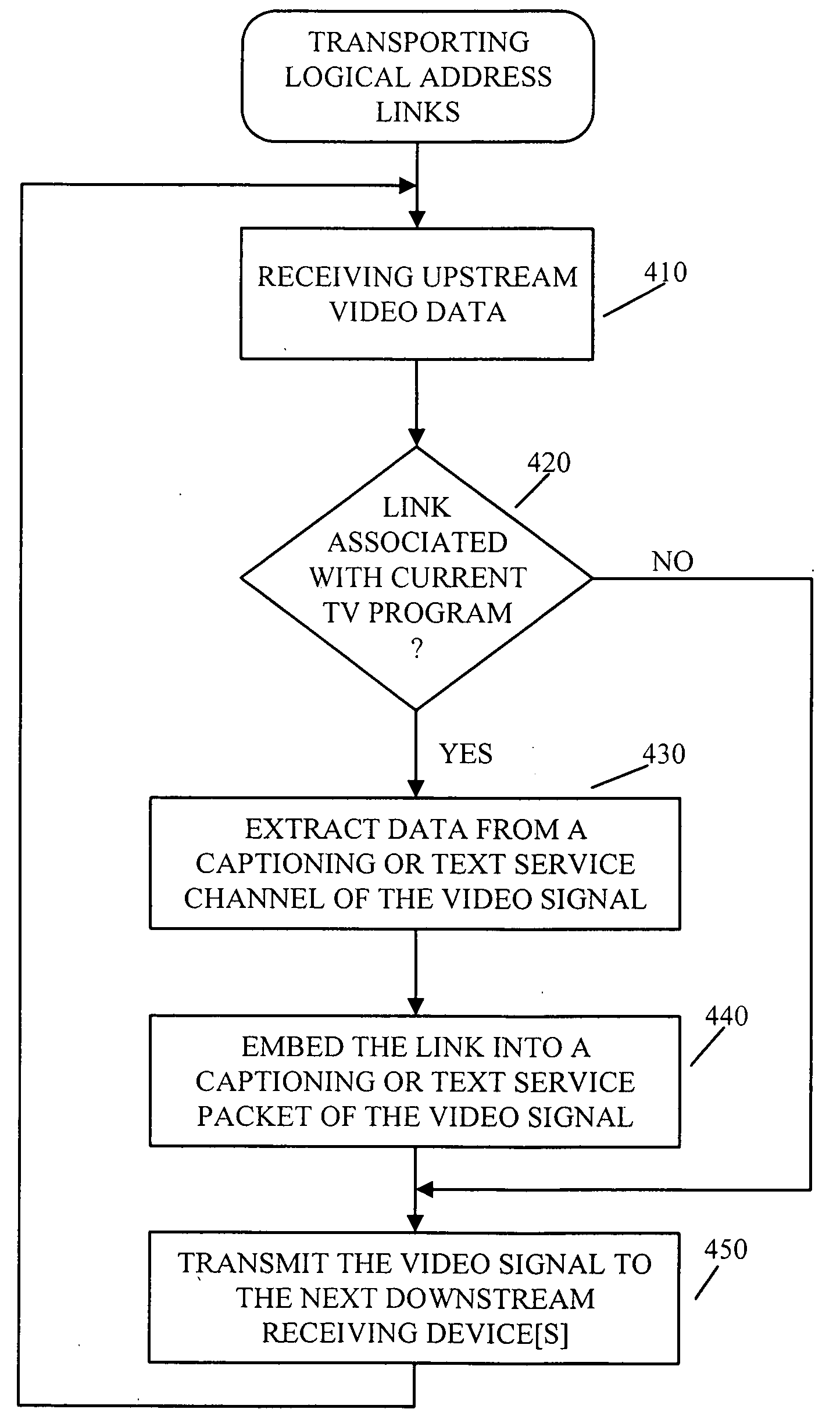
Pausing television programming in response to selection of hypertext link
InactiveUS6973669B2Television system detailsColor television signals processingHyperlinkRecording duration
A time sequential signal comprising audiovisual content and hyperlinks is received and displayed on a display device by the systems of the invention in a time sequential manner. The display of the time sequential signal is paused whenever a displayed hyperlink is selected. While pausing the display, data corresponding to any selected hyperlink is accessed and displayed on the display device. The corresponding data may comprise a web page accessed through the Internet or an interval page that is transmitted within the vertical blanking intervals of the time sequential signal. While pausing the display of the time sequential signal, the time sequential signal is recorded so that it can be viewed in the order it was recorded as soon as a resume display command is received by the system.
Owner:ROVI TECH CORP
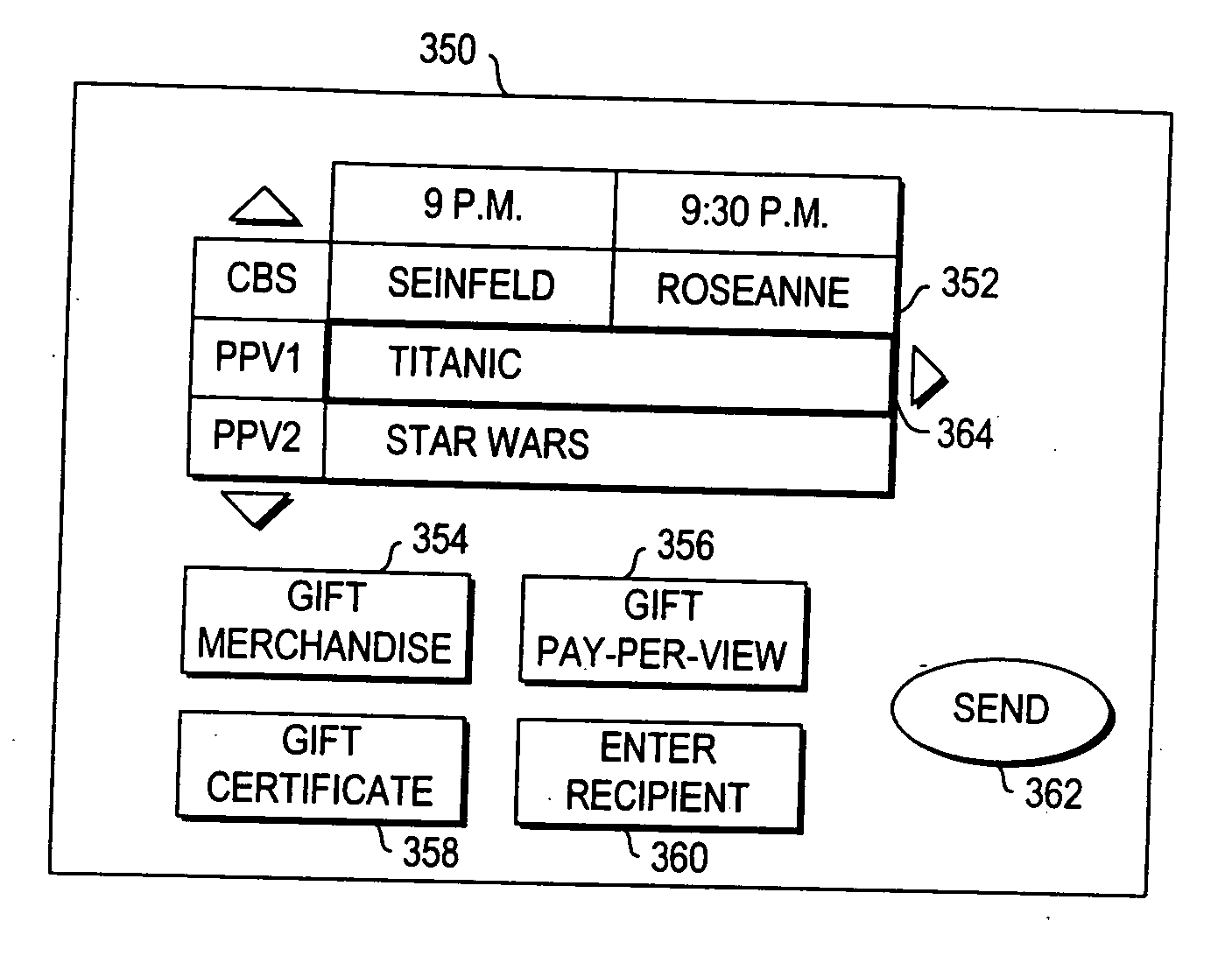
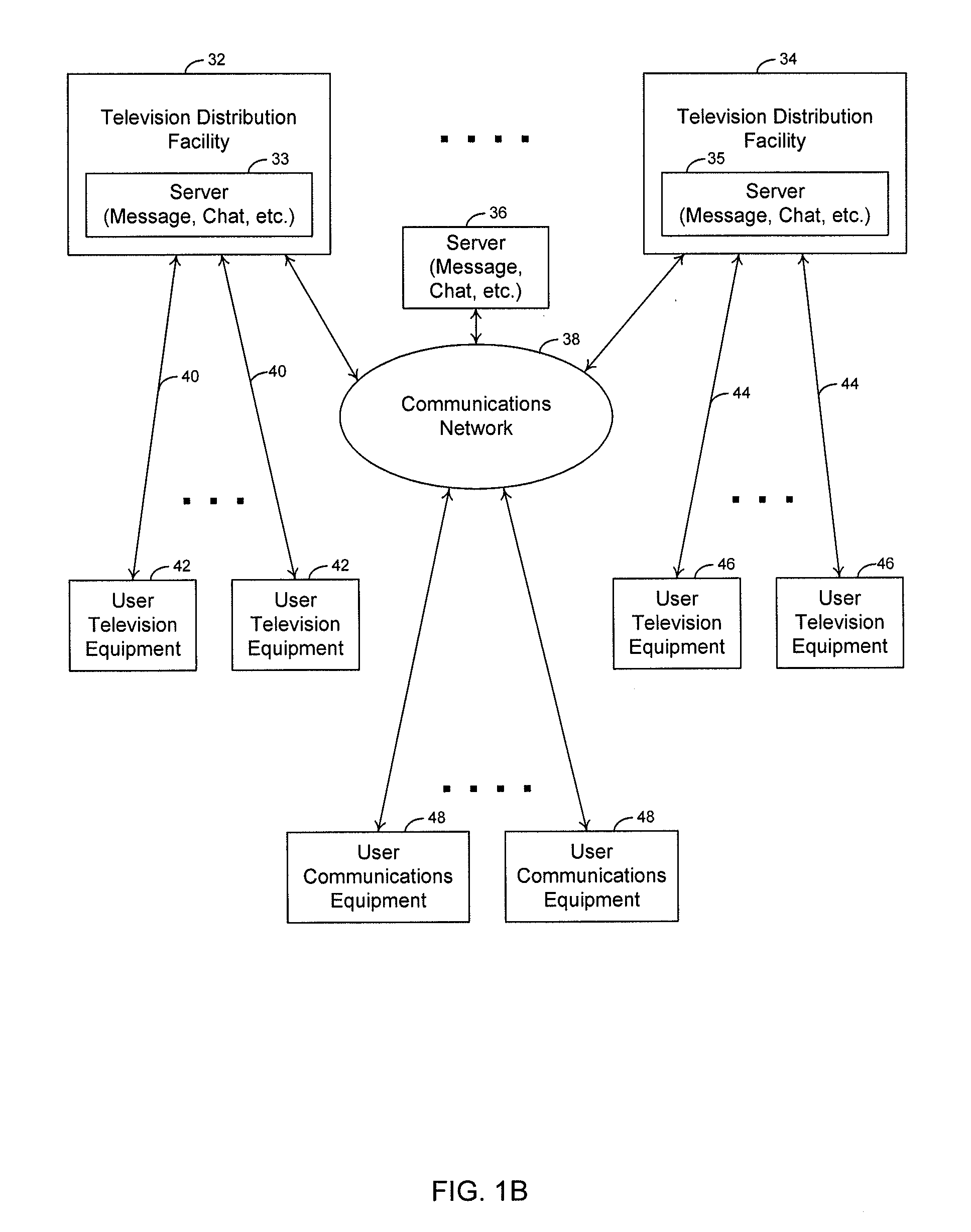
Systems and methods for providing a program as a gift using an interactive application
InactiveUS20060190966A1Eliminate needTelevision system detailsAcutation objectsNetwork connectionInteractive television
A television message system is provided that allows users at user television equipment devices that are connected to a television distribution facility to transmit messages to each other relating to a television program or other suitable subject. The television message system permits users to participate in evaluations, contests, promotions, and surveys related to a television program while watching that television program. The television message system also permits users to compose and send a message to a television program entity. Users can send messages through the television message system to users at personal computers who are connected to the user's television distribution facility through a communications network. The television message system also allows a user to purchase a gift related to television programming for a recipient. The gift may be an electronic gift certificate for pay-per-view programming. The television message system may be based on an interactive television program guide or a set-top box application implemented on a set-top box.
Owner:UNITED VIDEO PROPERTIES
Navigating through television programs
InactiveUS6405371B1Improve convenienceReduce brightnessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTelevision receiversComputer science
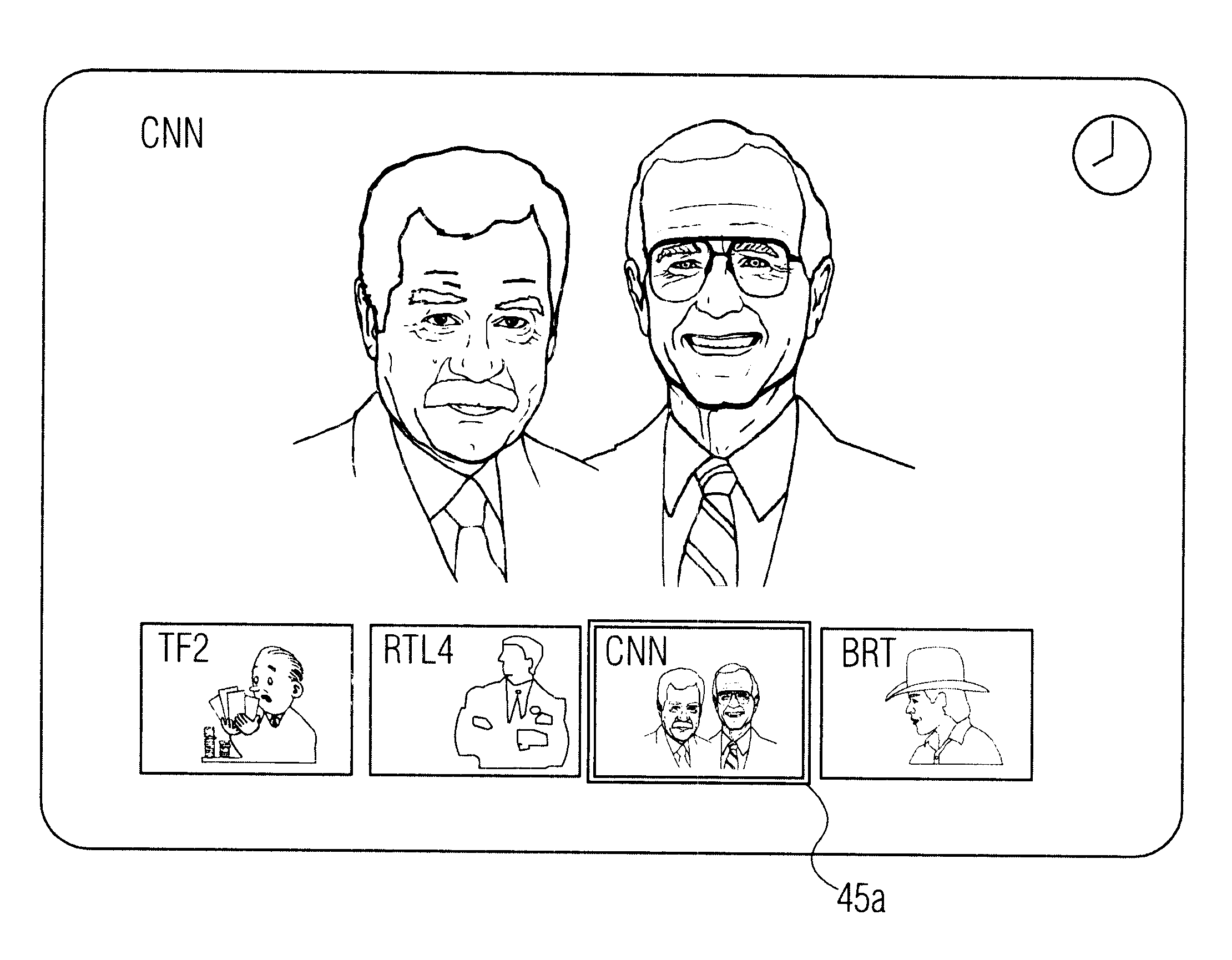
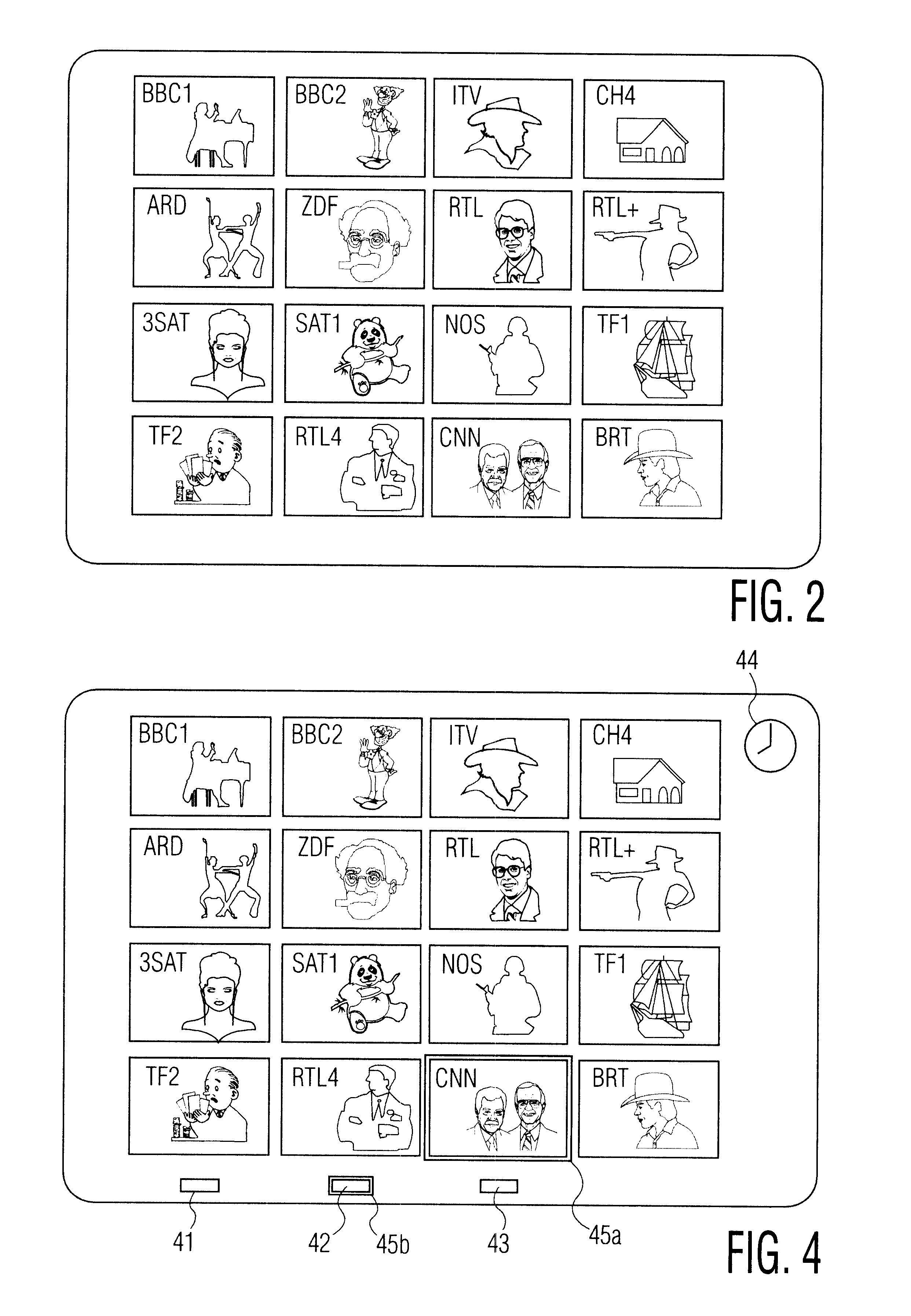
A method of navigating through television programs is disclosed. A television receiver displays a mosaic image with sub-images representing the available programs. The receiver further receives an electronic program guide with program descriptions. Upon activating a "theme" button (42), the viewer can enter a desired program type, e.g. "movie". In response thereto, the brightness of the sub-images representing programs that are not desired is reduced. The user is thus assisted in navigating through programs he is interested in, while maintaining the mosaic structure he is familiar with, and without losing the association between channels and their positions on the mosaic screen.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
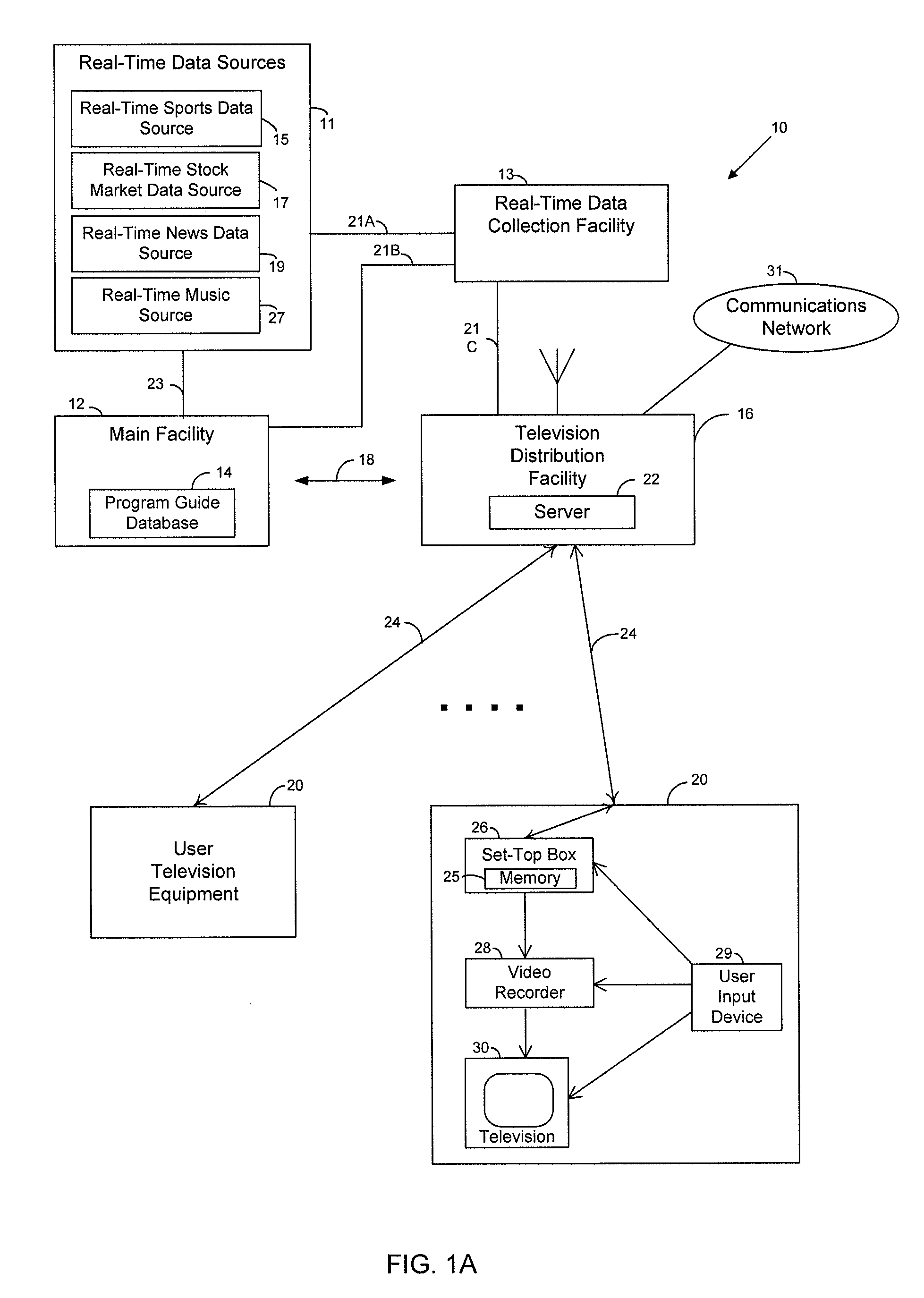
System and method for personalized TV
InactiveUS20060206912A1Television system detailsRecording carrier detailsPersonalizationCable television
A Personal TV System receives a plurality of video segments constituting a TV program and information describing each segment, and controls the display of the segments to a viewer in accordance with preferences of the viewer and with the description of each segment. Segments may be omitted or replaced with substitute segments. The viewer may review his preferences and edit or replace them. In a multi-viewer household, the system may prompt a viewer to confirm her preferences. A TV program may contain interactive segments, and when the viewer chooses to interact with a particular segment, the system automatically stores all subsequently received segments for later viewing while the viewer interacts with the selected segment. The system may present TV program choices to the viewer selected and arranged in accordance with her preferences.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
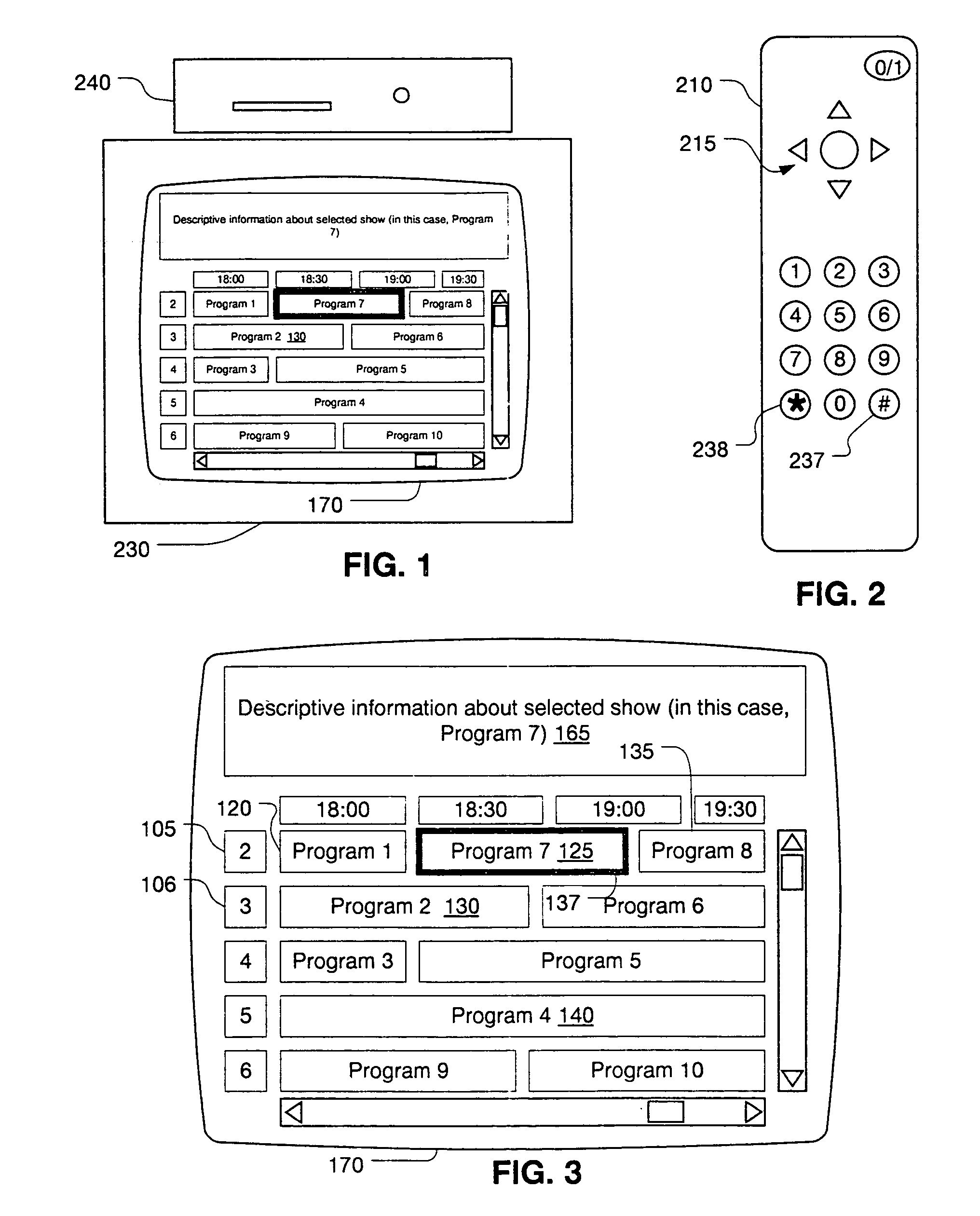
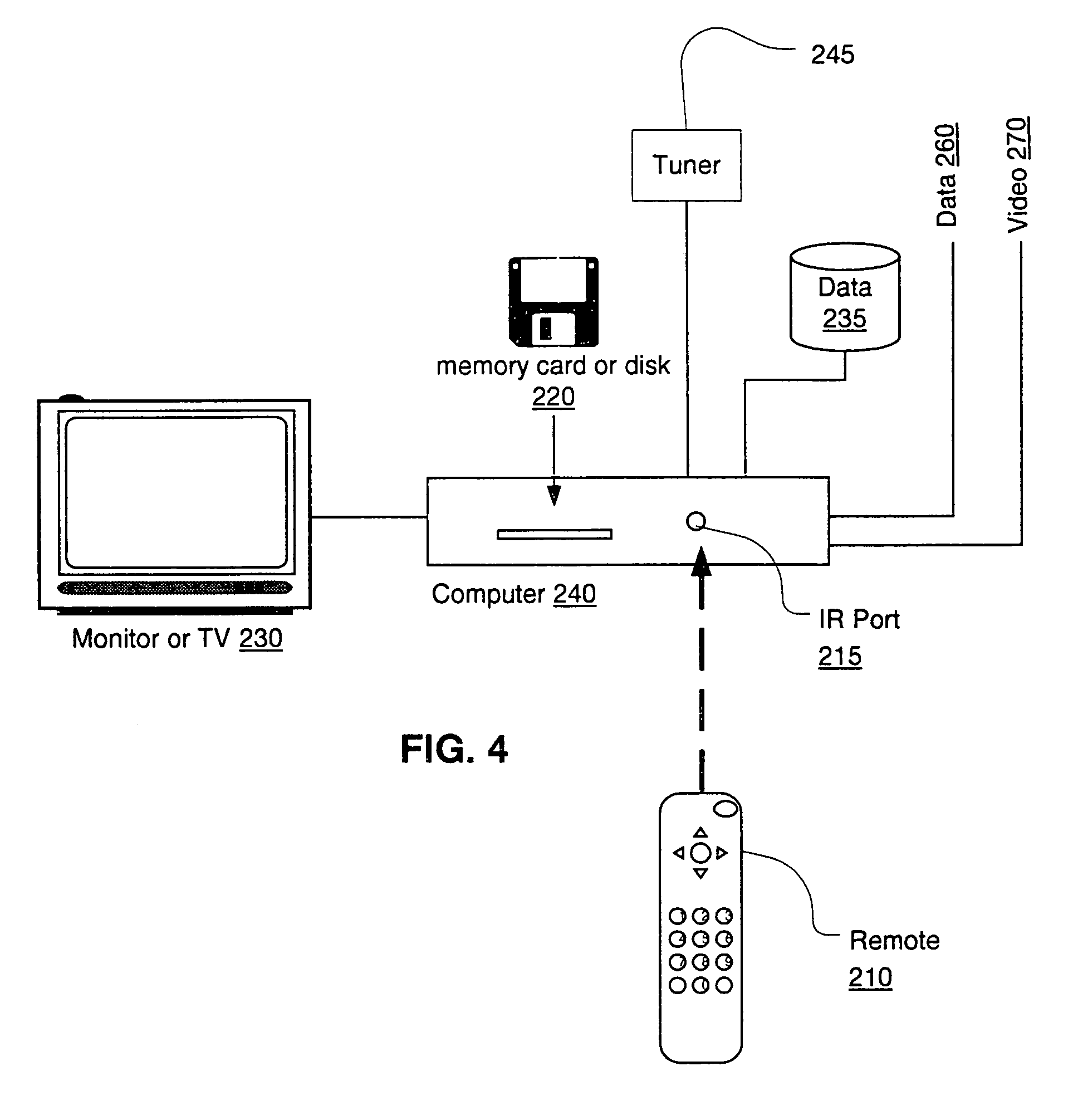
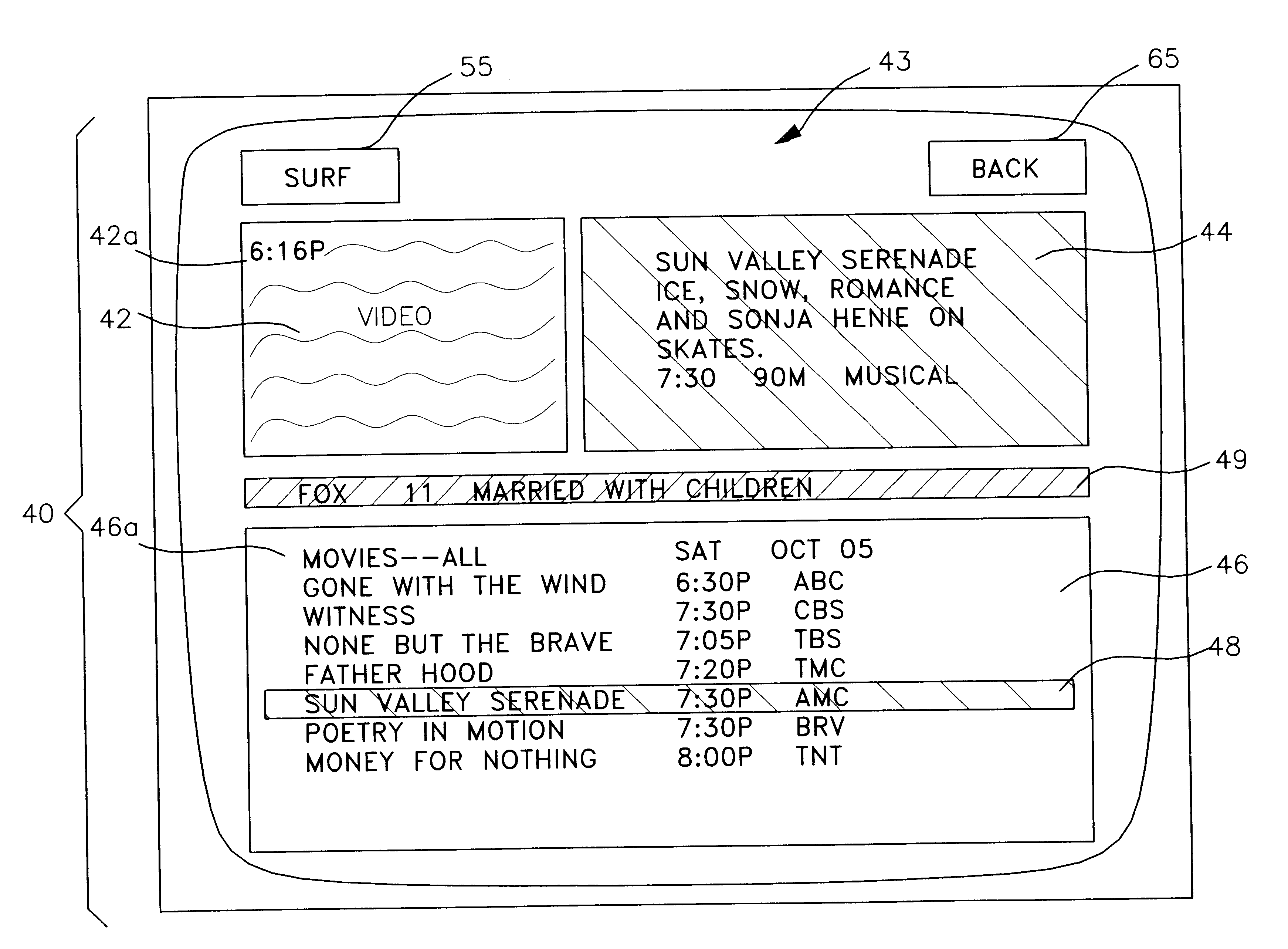
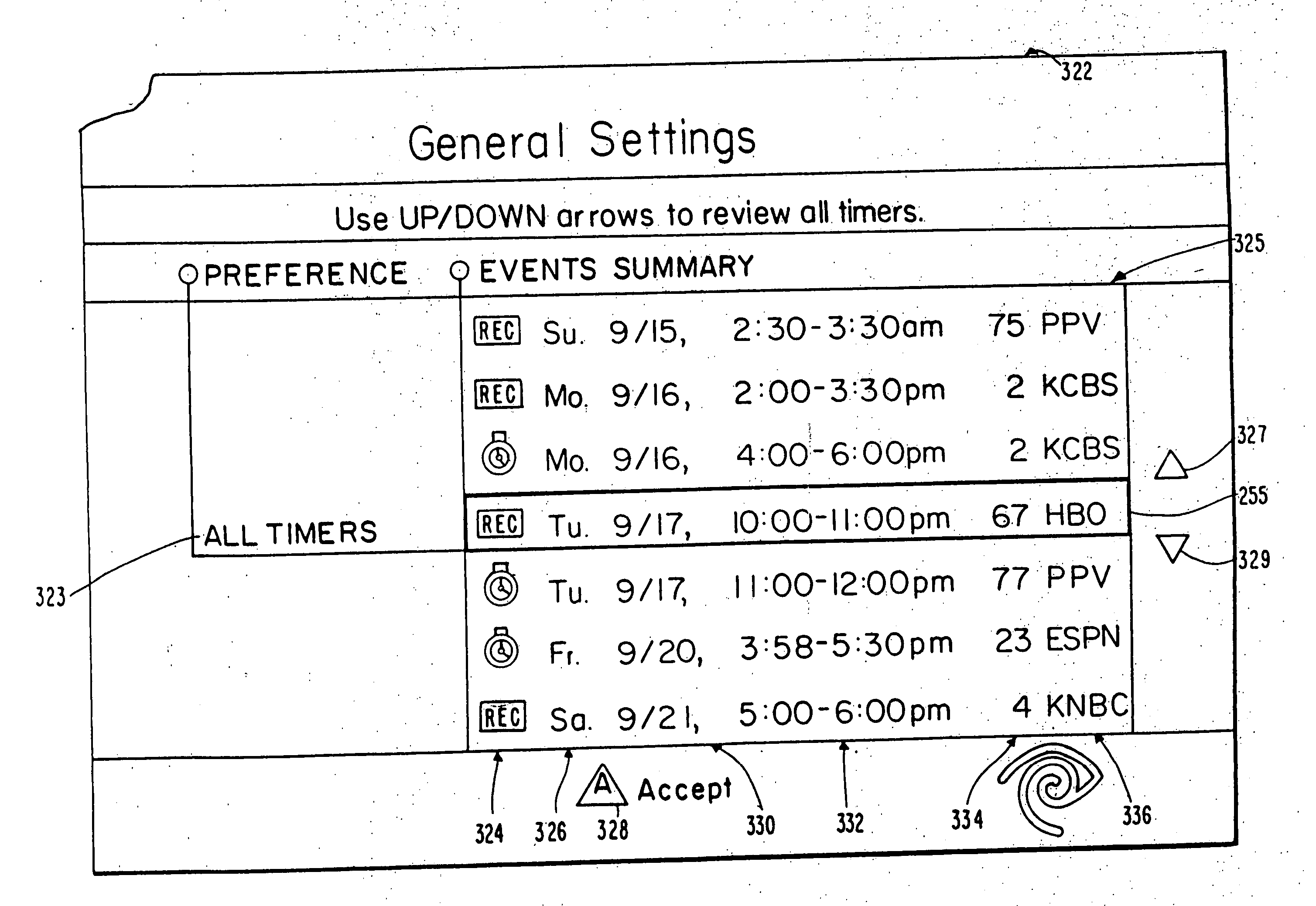
User interface for television schedule system
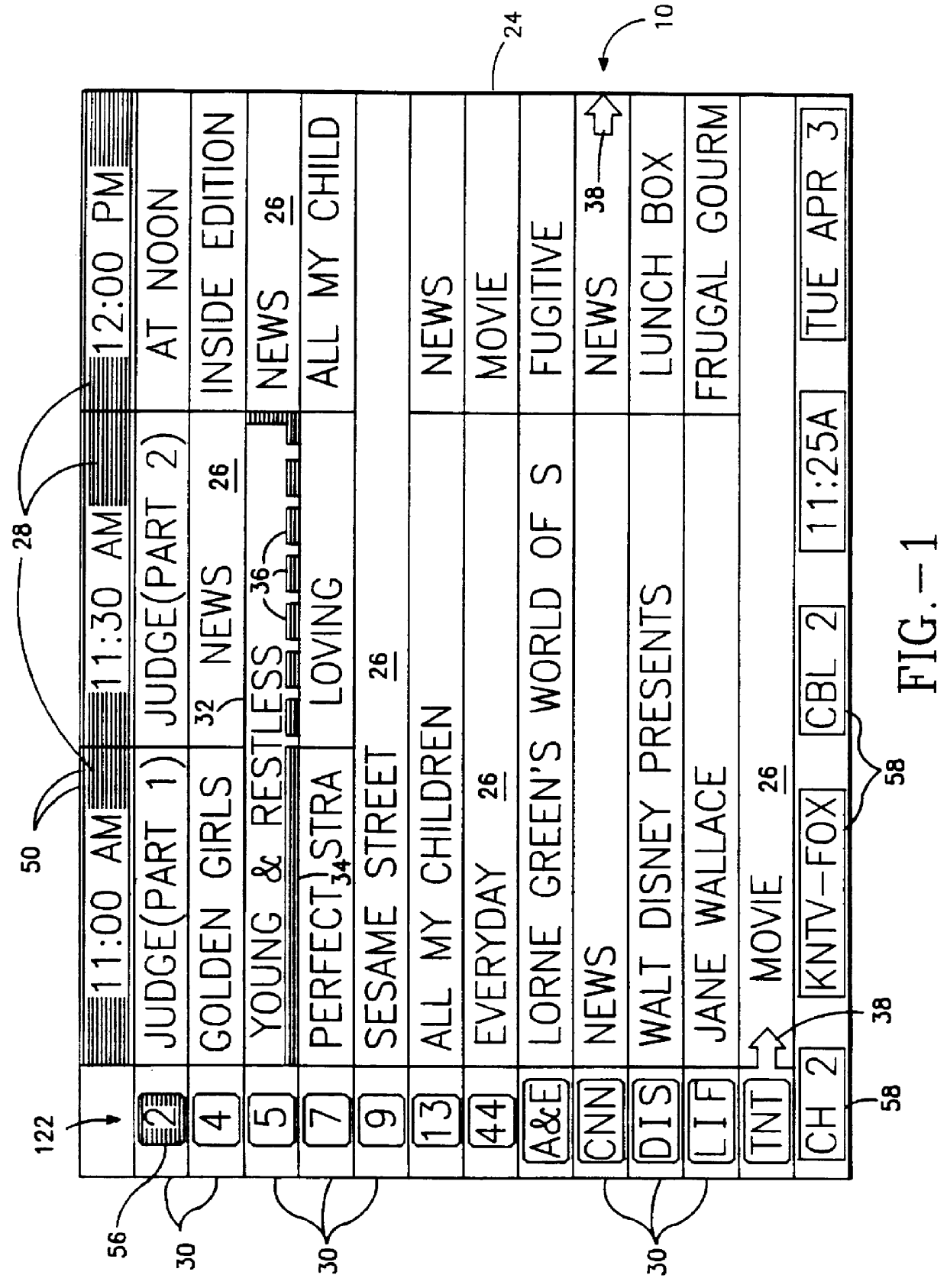
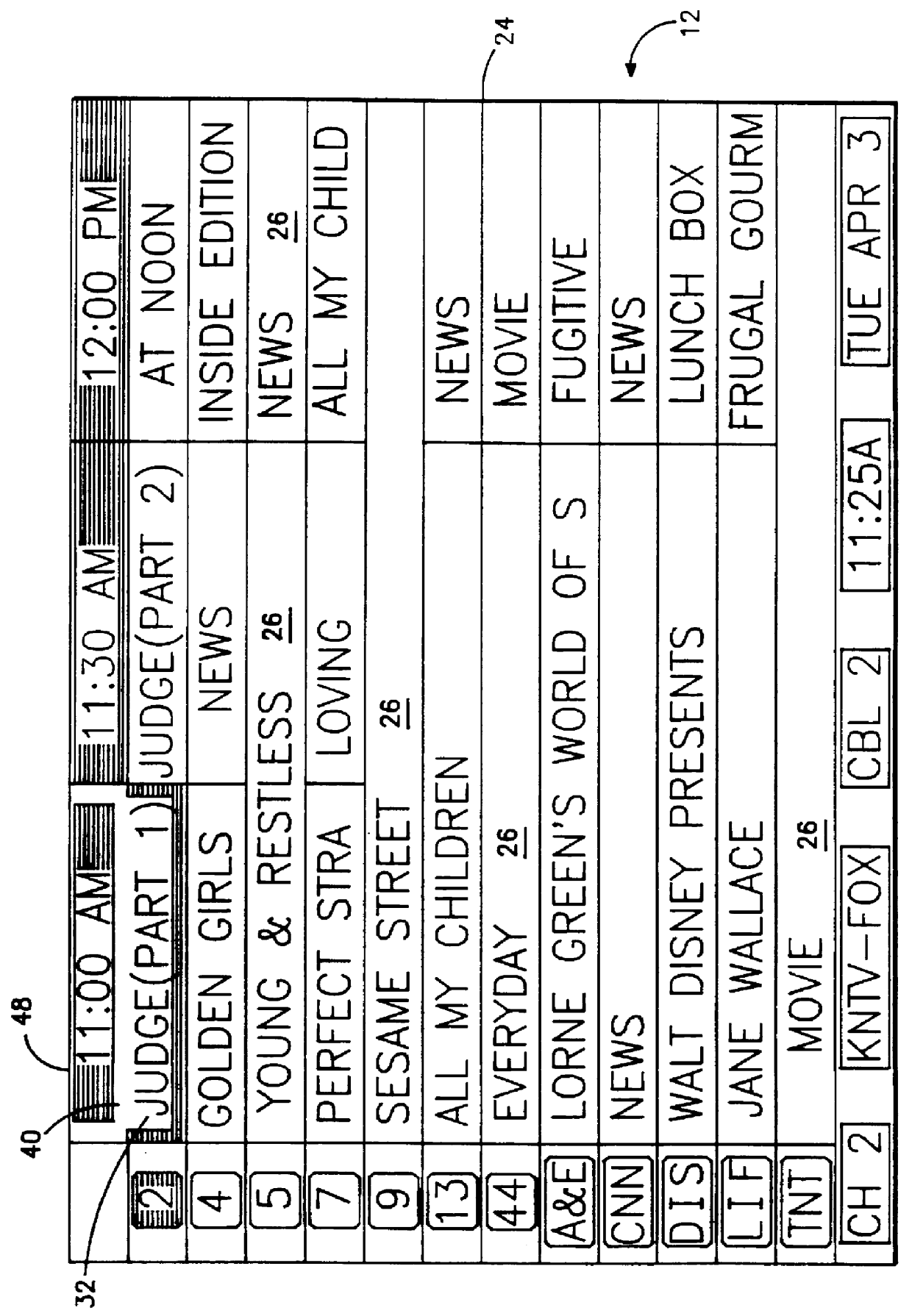
Screen (10) for a user interface of a television schedule system and process consists of an array (24) of irregular cells (26), which vary in length, corresponding to different television program lengths of one half hour to one-and-one half hours or more. The array is arranged as three columns (28) of one-half hour in duration, and twelve rows (30) of program listings. Some of the program listings overlap two or more of the columns (28) because of their length. Because of the widely varying length of the cells (26), if a conventional cursor used to select a cell location were to simply step from one cell to another, the result would be abrupt changes in the screen (10) as the cursor moved from a cell (26) of several hours length to an adjacent cell in the same row. An effective way of taming the motion is to assume that behind every array (24) is an underlying array of regular cells. By restricting cursor movements to the regular cells, abrupt screen changes will be avoided. With the cursor (32), the entire cell (26) is 3-D highlighted, using a conventional offset shadow (34). The offset shadow (34) is a black bar that underlines the entire cell and wraps around the right edge of the cell. To tag the underlying position-which defines where the cursor (32) is and thus, where it will move next-portions (36) of the black bar outside the current underlying position are segmented, while the current position is painted solid.
Owner:STARSIGHT TELECAST
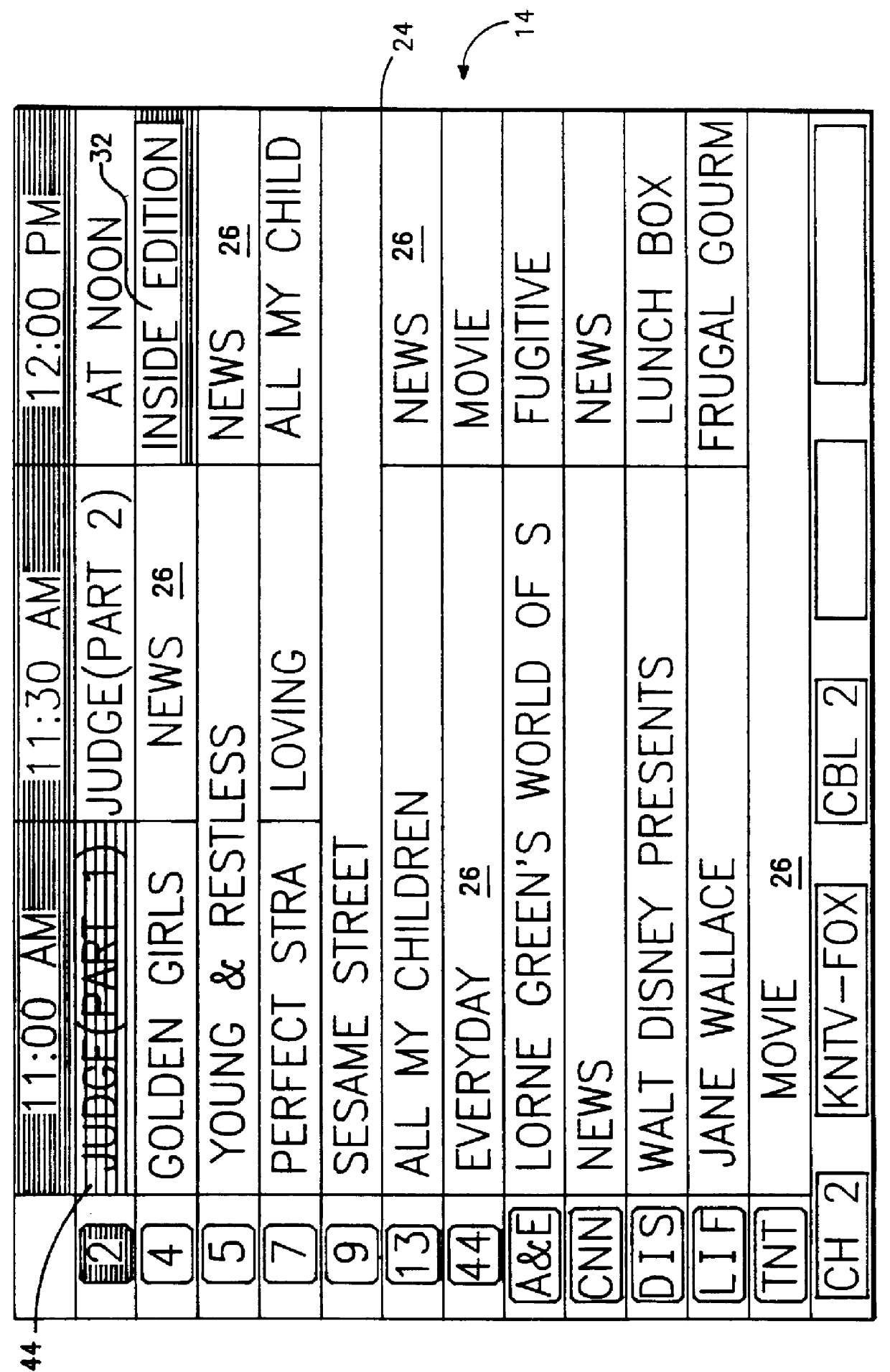
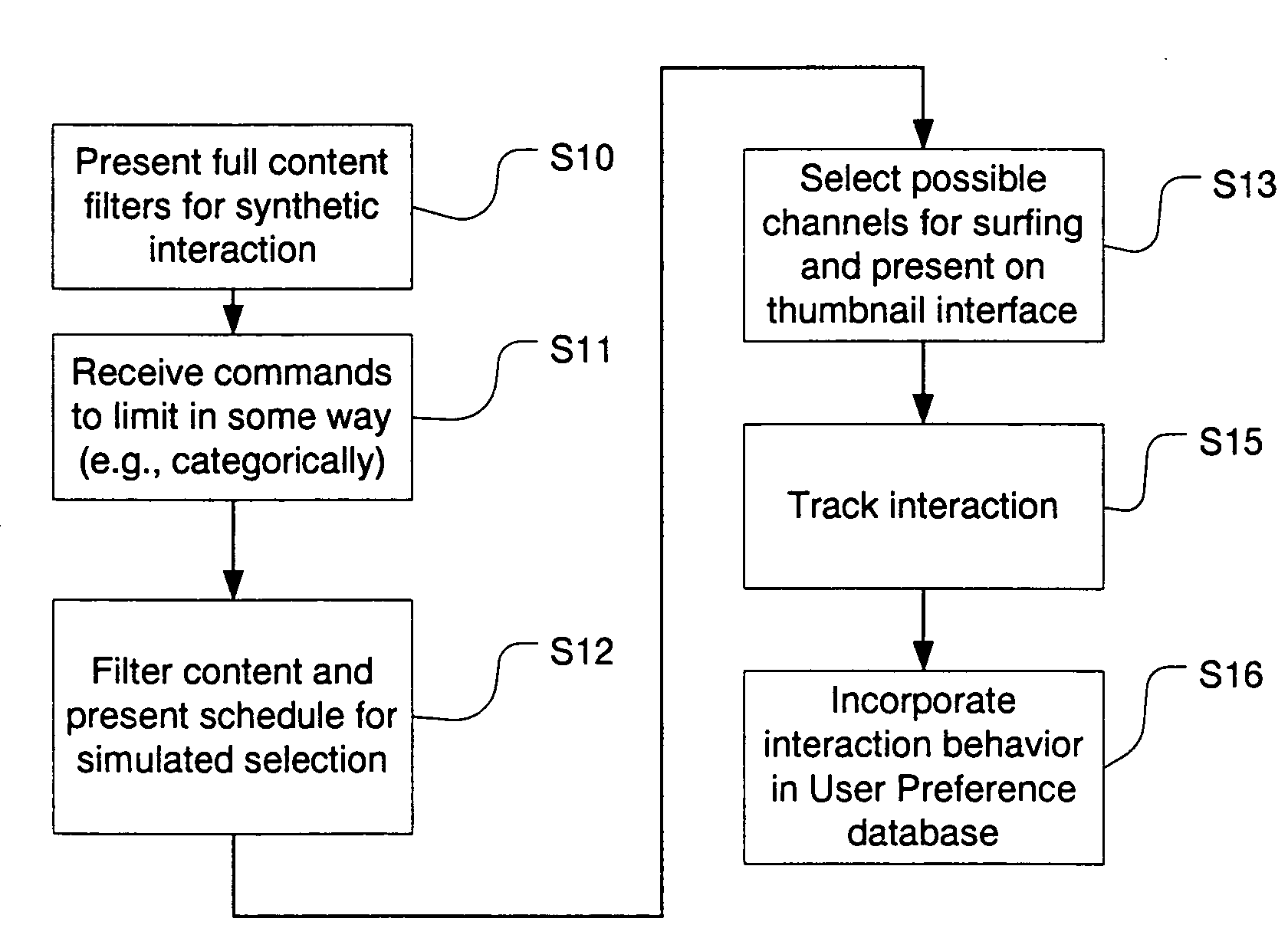
Electronic program guide viewing history generator method and system
InactiveUS6934964B1Quick buildClear resolutionTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsPersonalizationTelevision watching
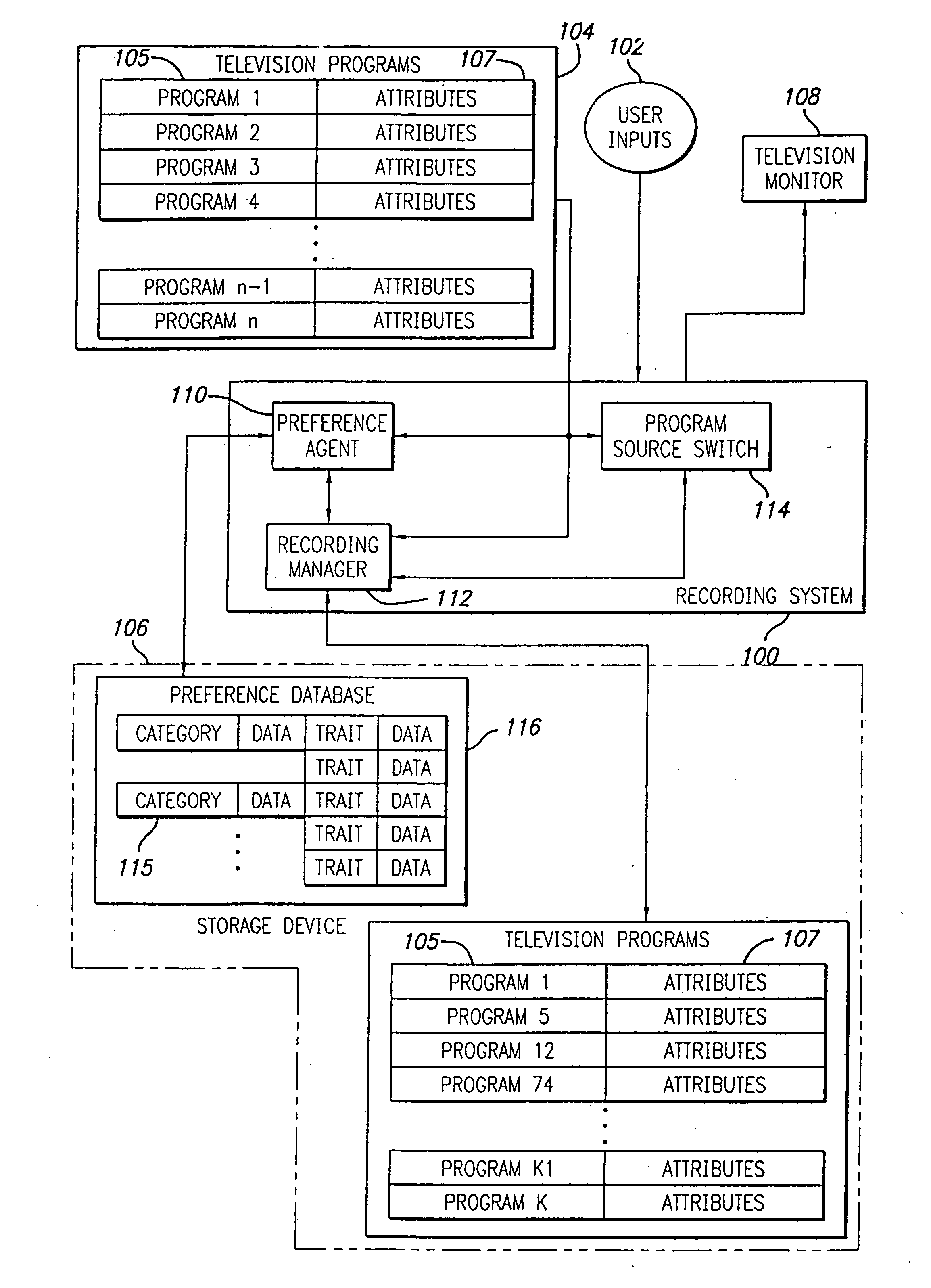
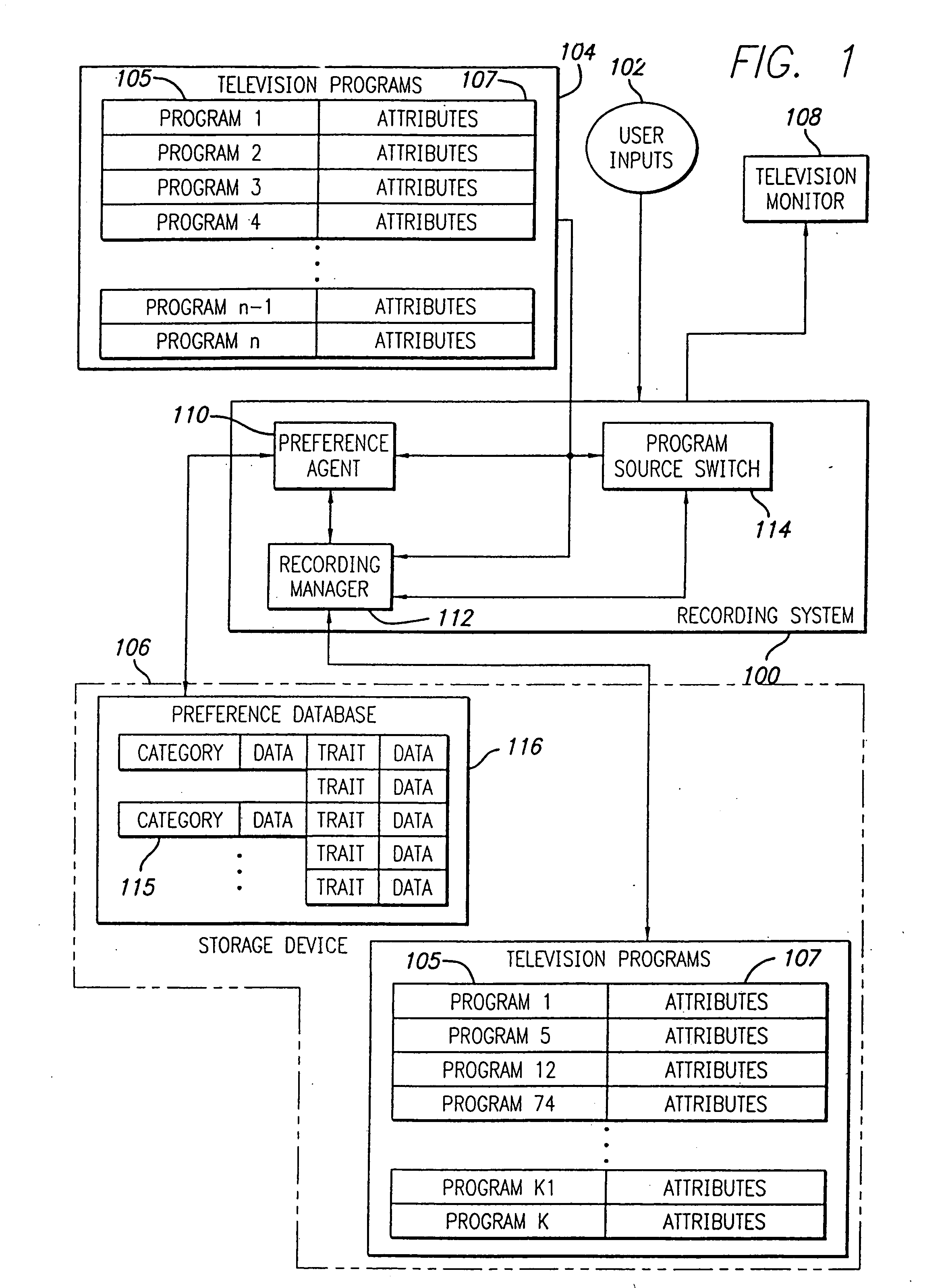
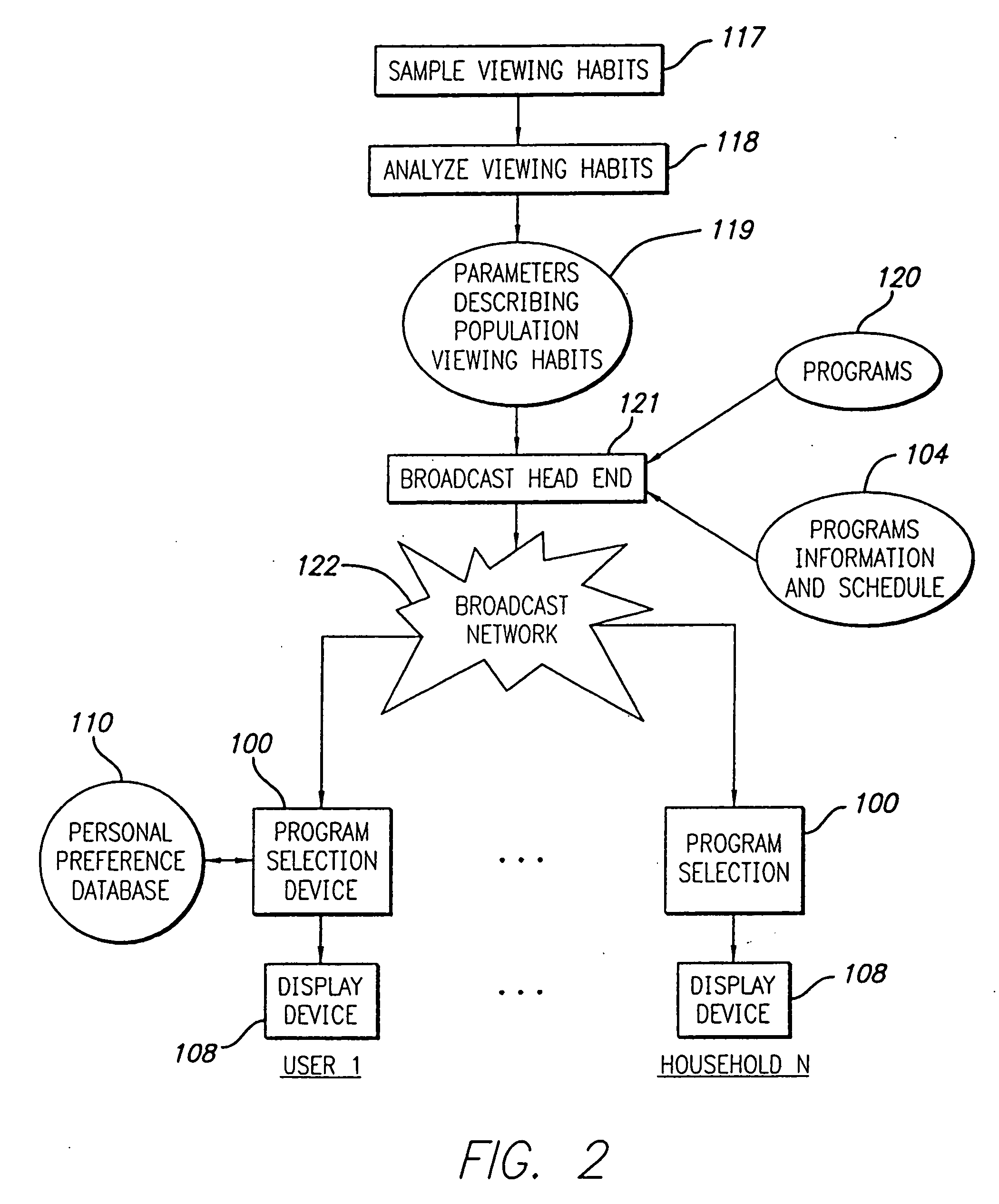
An electronic programming guide (EPG) system employs a preference engine and processing system that learns viewers' television watching preferences by monitoring their viewing patterns. The system operates transparently to build a profile of a viewer's tastes. The profile is used to provide services, for example, recommending or automatically recording television programs the viewer might be interested in watching. To permit the personalization of the preferences database, a user interface is provided to allow the user to simulate various kinds of interaction with the system. This allows the system to build a profile rapidly without requiring a long interaction history to personalize the system.
Owner:S I SV EL SOC ITAL PER LO SVILUPPO DELLELETTRONICA SPA
Television/Internet terminal user interface
InactiveUS20050097622A1Easy to switchTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsRemote controlThe Internet
A viewer of television programming is alerted to the availability of content related to the programming (e.g. an associated Internet web page) by an icon momentarily displayed on the screen. Using a remote control, the viewer can select the icon. A control panel then appears, superimposed over the television image, and provides additional detail about the related content. By further operating the remote control, the viewer can select the associated content for viewing, or return to watching the television. Various other features and variations are disclosed.
Owner:ROVI TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for transmitting, storing, and processing electronic program guide data for on-screen display
InactiveUS6477705B1Facilitate grazingTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTime scheduleBackground information
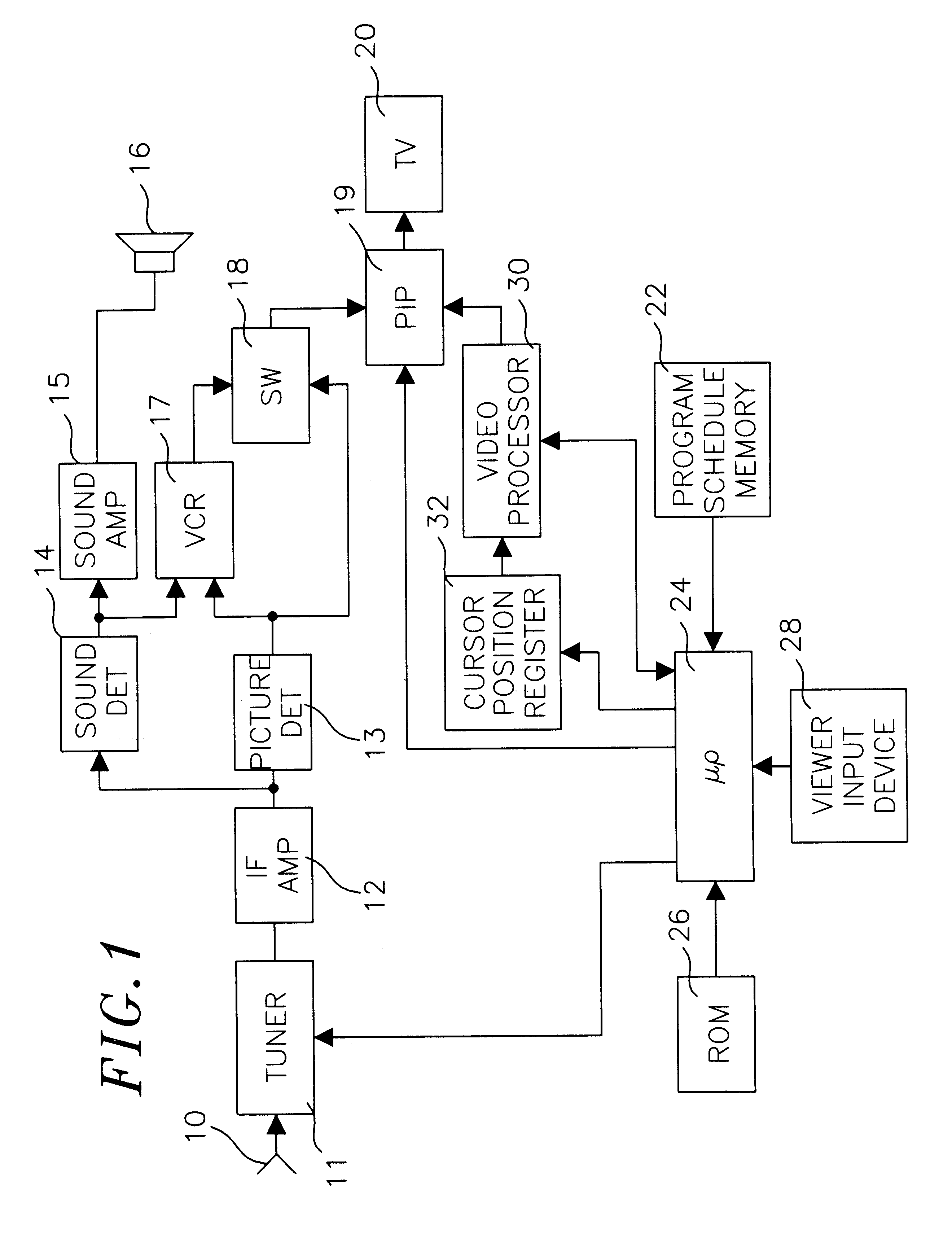
A television viewer uses a PIP format for display of program related information such as television program listings from a program schedule data base in the background and moving, real time images of a program selected from the displayed listings in the PIP window. All the text of the background information lies outside the PIP window. In one embodiment, as the viewer selects a particular program from the display of current television program listings by means of a cursor or a code number, the corresponding program automatically appears in the PIP window.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
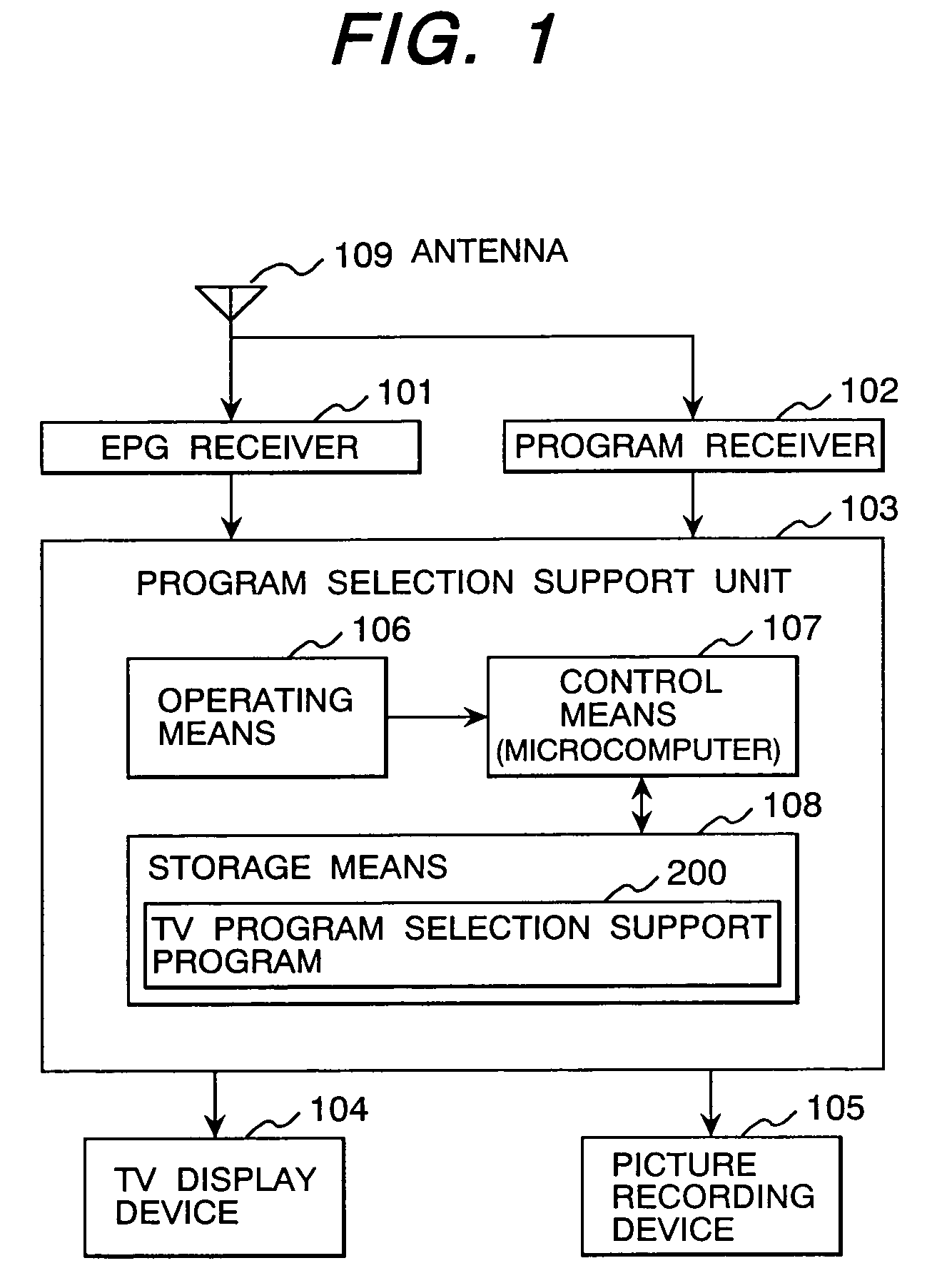
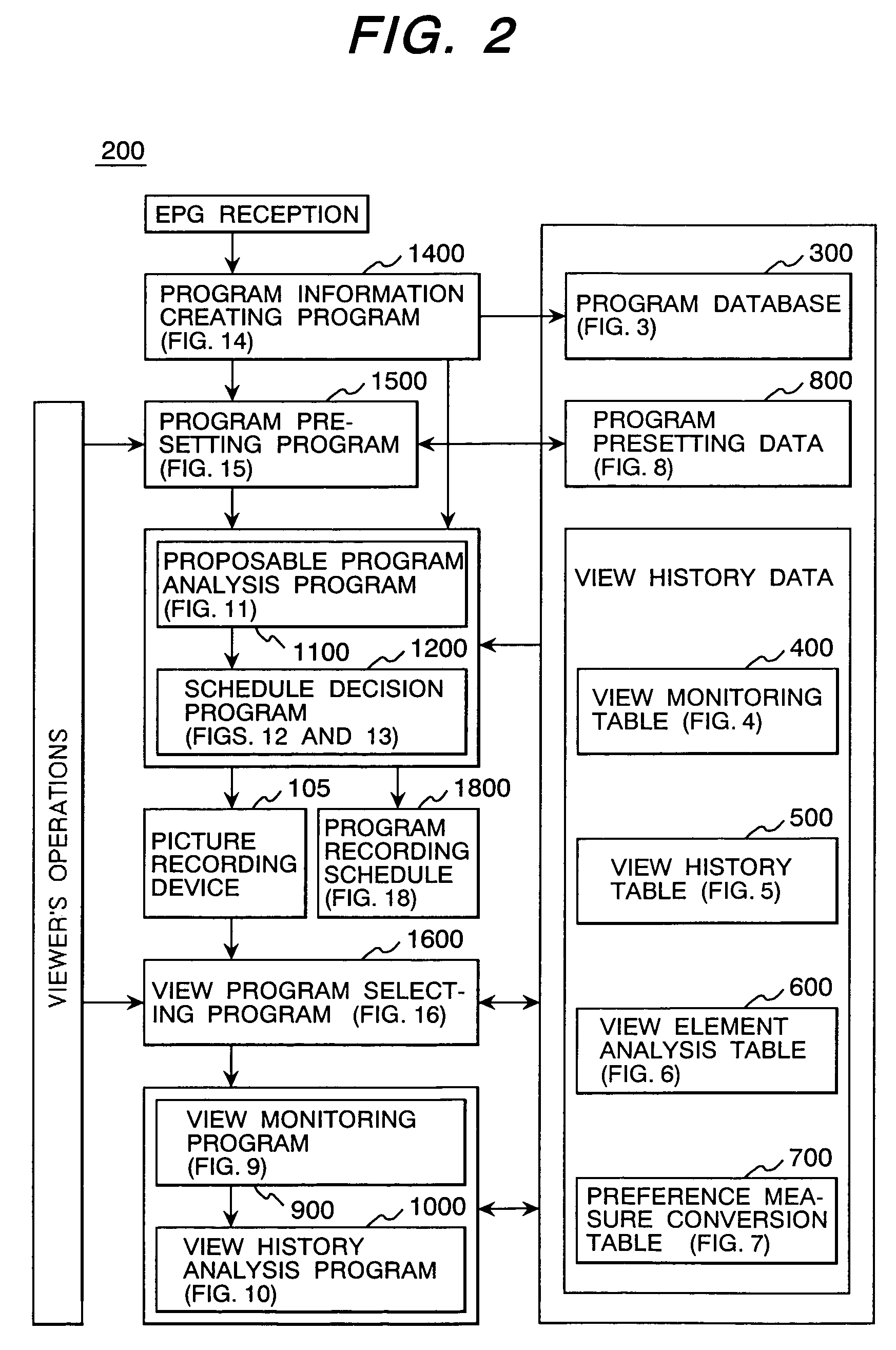
TV program selection support system
InactiveUS7096486B1Television system detailsColor television detailsSupporting systemElectronic program guide
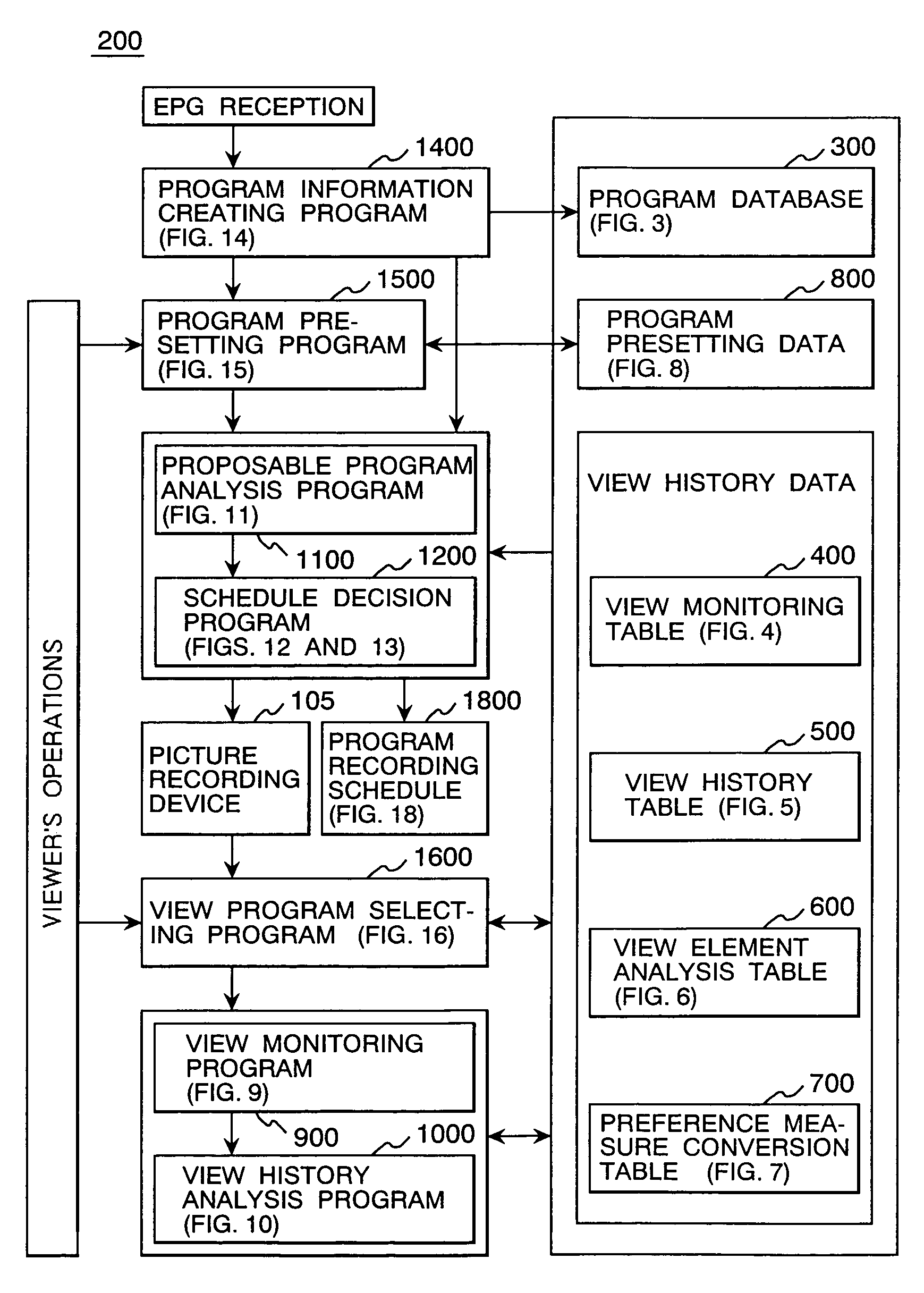
A TV program selection support system selects only programs suiting viewer's preference or necessary for a viewer from a large number of programs to be broadcast and proposes the selected programs to the viewer. The TV program selection support system comprises a program receiver for receiving broadcast TV programs, an EPG receiver for receiving an electronic program table listing TV programs, an EPG storage device for storing an EPG received by the EPG receiver, an operating means to be operated by the viewer to select a program from the stored electronic program table, a program selection support program for determining viewer's view tendency by analyzing the operation made by the viewer, creating an electronic program table on the basis of the view tendency and displaying the created electronic program table.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Method and apparatus for interactive program suggestion
InactiveUS7013478B1Television system detailsBroadcast information characterisationComputer terminalElectronic book
A method and an apparatus suggests programs for viewing by a subscriber. Terminals installed at a subscriber's home and at central locations, such as bookstores, video rental stores and libraries, provide responsive or intelligent search functions to suggest programs for viewing according to a subscriber's viewing preferences. Responsive searching includes posing questions to and receiving answers from the subscribers. Intelligent searching includes gathering historical data, such as the subscriber's history of programs watched. The programs include videotapes, videodiscs, television programs and electronic books. Subscribers indicate their selection and order the programs using a menu system. An automated billing system tracks the programs ordered.
Owner:COX COMMUNICATIONS
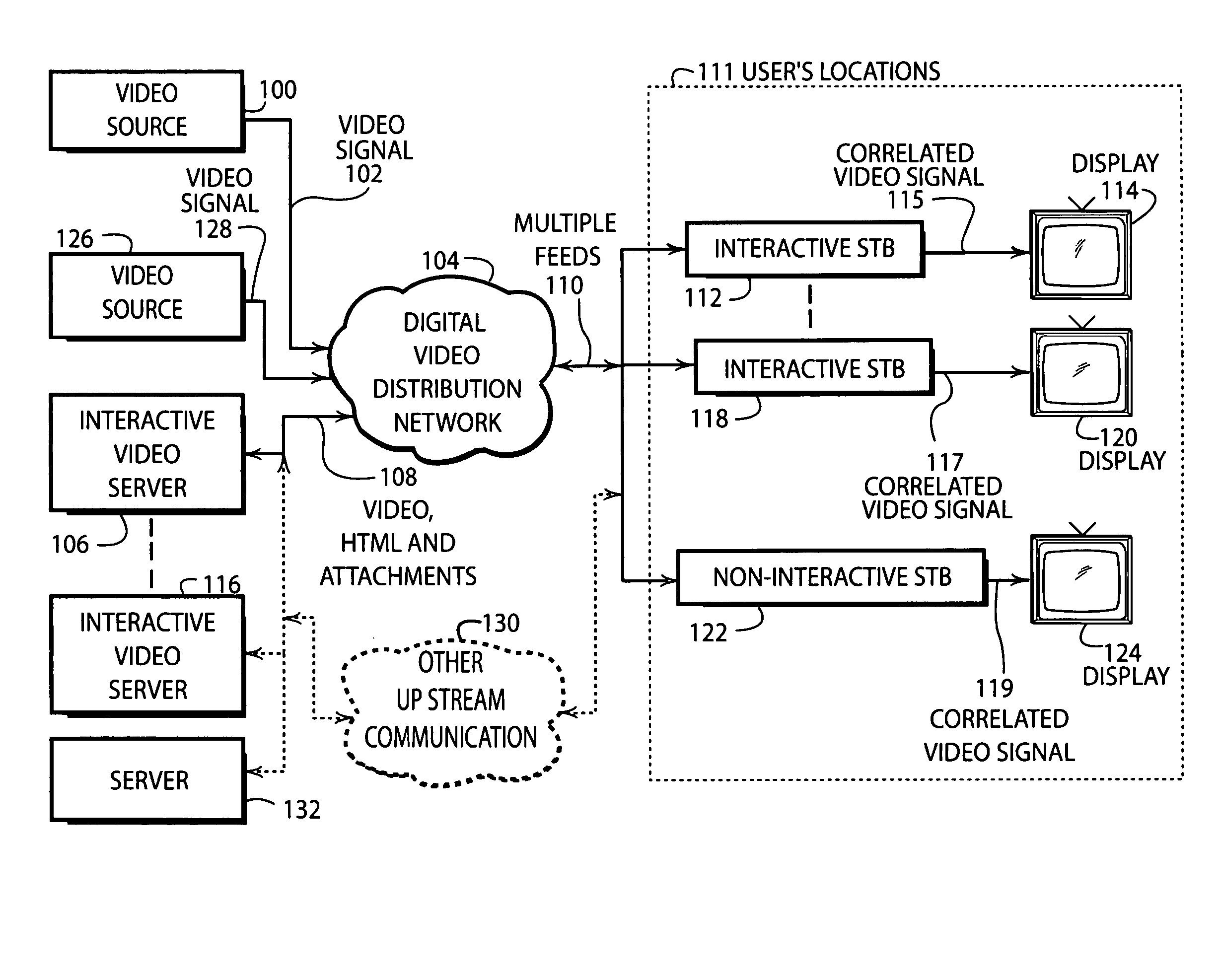
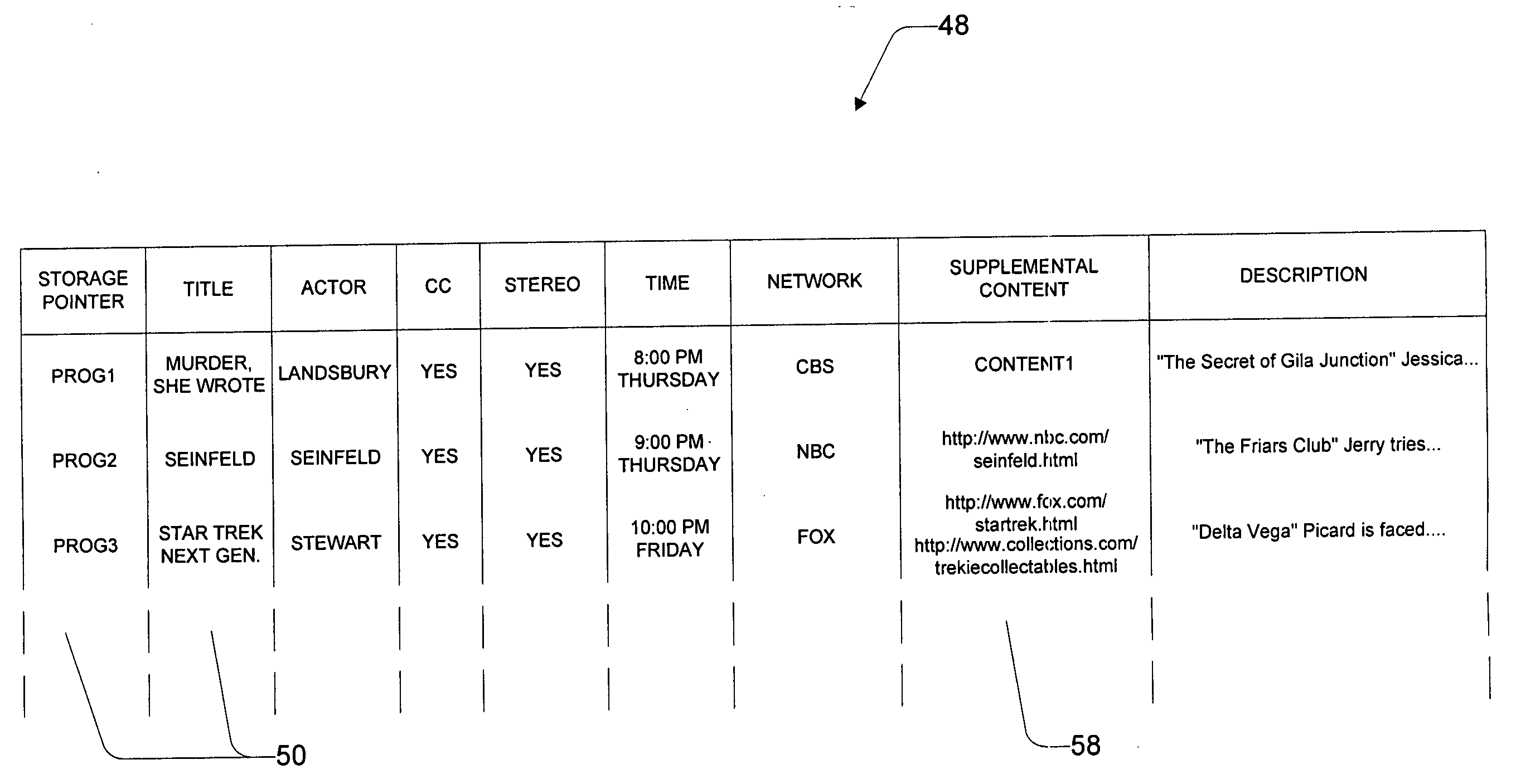
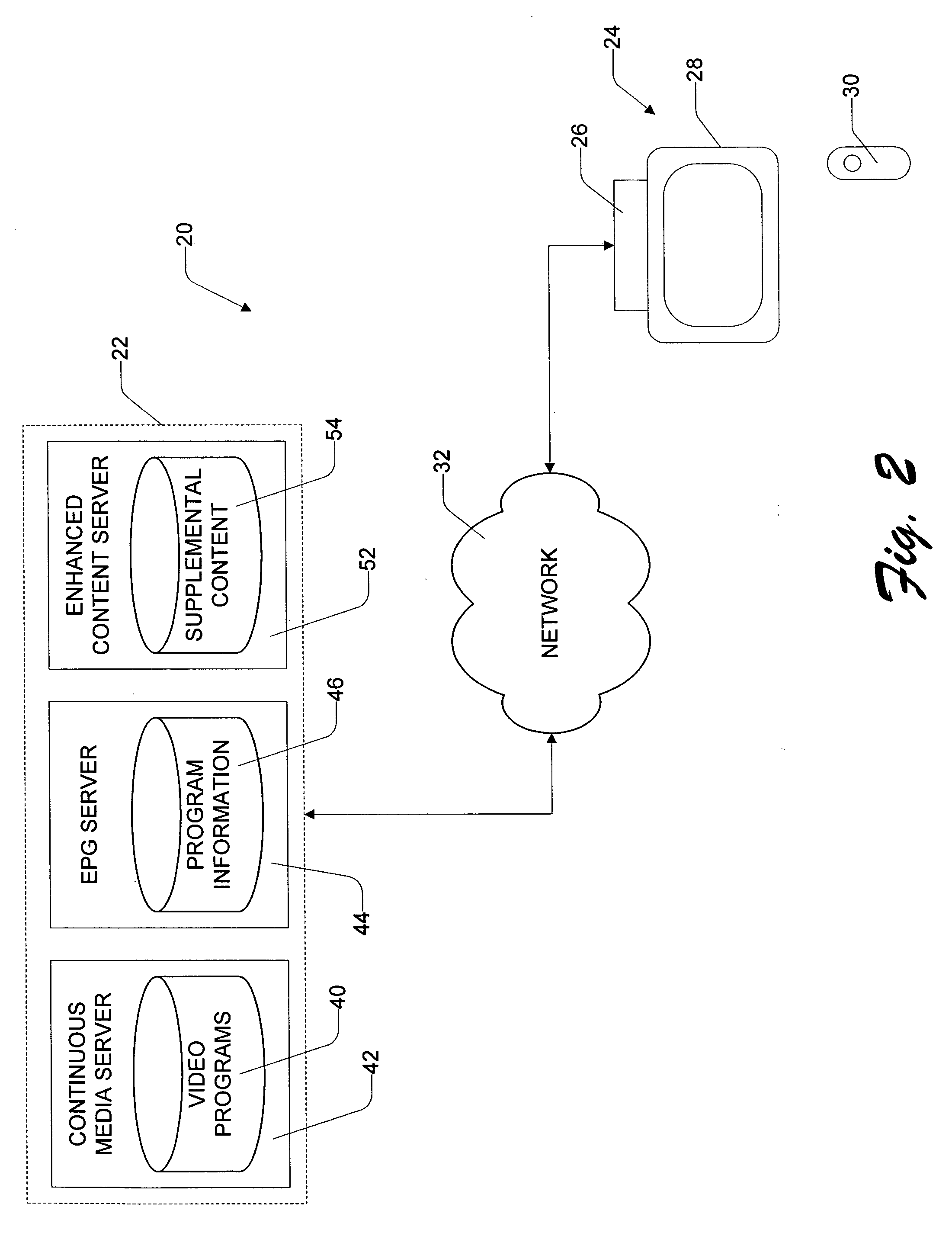
Interactive entertainment system for presenting supplemental interactive content together with continuous video programs
InactiveUS20050015815A1Not be restrictTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInteractive contentDistribution networks
An interactive entertainment system enables presentation of supplemental interactive content along side traditional broadcast video programs, such as television shows and movies. The programs are broadcast in a conventional manner. The supplemental content is supplied as part of the same program signal over the broadcast network, or separately over another distribution network. A viewer computing unit is located at the viewer's home to present the program and supplemental content to a viewer. When the viewer tunes to a particular channel, the viewer computing unit consults an electronic programming guide (EPG) to determine if the present program carried on the channel is interactive. If it is, the viewer computing unit launches a browser. The browser uses a target specification stored in the EPG to activate a target resource containing the supplemental content for enhancing the broadcast program. The target resource contains display layout instructions prescribing how the supplemental content and the video content program are to appear in relation to one another when displayed. When the data from the target resource is downloaded, the viewer computing unit is responsive to the layout instructions obtained from the target resource to display the supplemental content concurrently with the video content program. Embedding the layout instructions in the supplemental content advantageously places control of the presentation to the content developers. The developers are free to arrange the data and video in any manner they choose.
Owner:ROVI TECH CORP
Client-server electronic program guide
InactiveUS7065709B2Improve experienceMinimize memory requirementTelevision system detailsVideo data queryingInteractive televisionTelevision equipment
A client-server interactive television program guide system is provided. An interactive television program guide client is implemented on user television equipment. The interactive television program guide provides users with an opportunity to define expressions that are processed by the program guide server. The program guide server may provide program guide data, schedules reminders, schedules program recordings, and parentally locks programs based on the expressions. Users' viewing histories may be tracked. The program guide server may analyze the viewing histories and generates viewing recommendations, targets advertising, and collects program ratings information based on the viewing histories.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
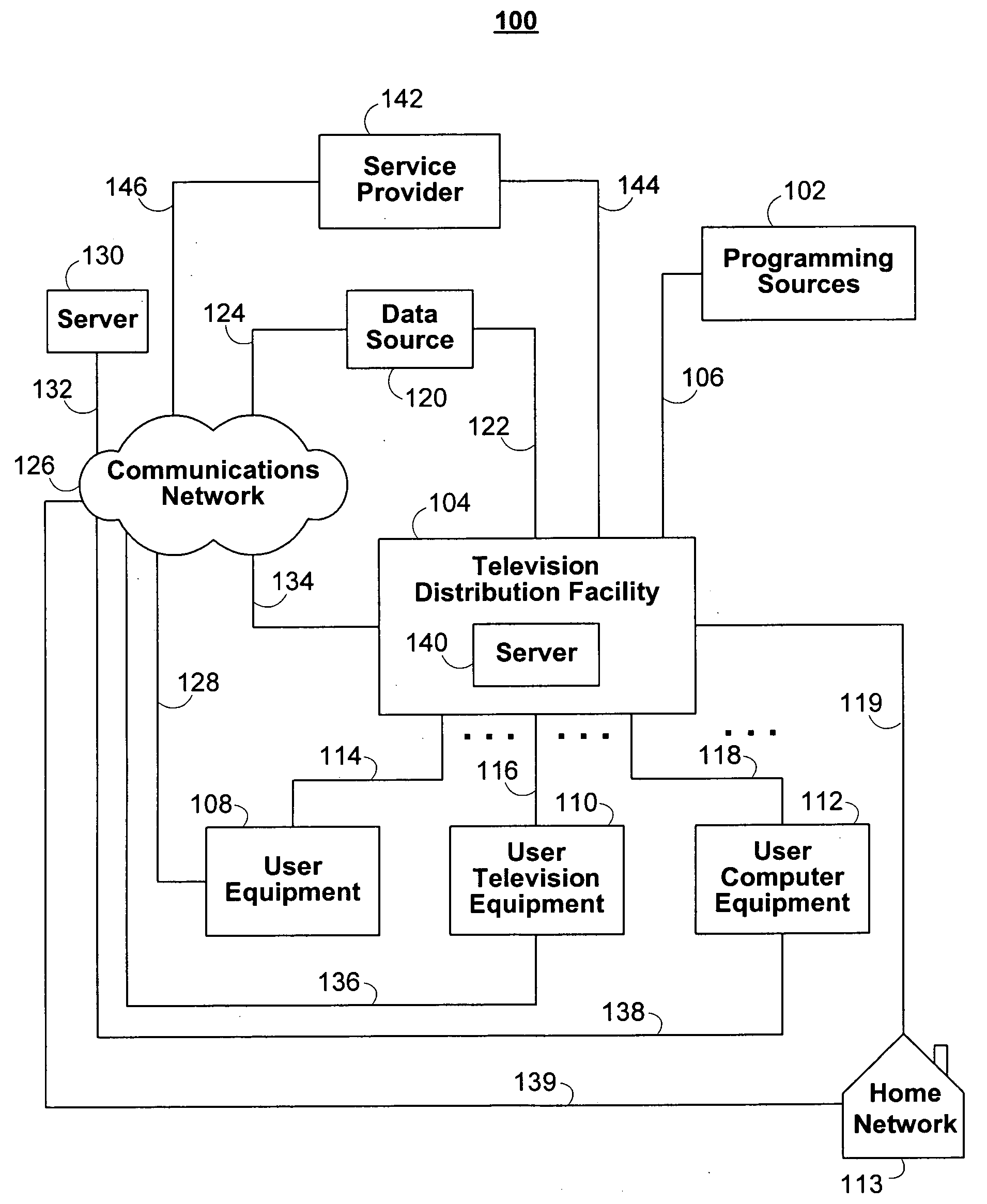
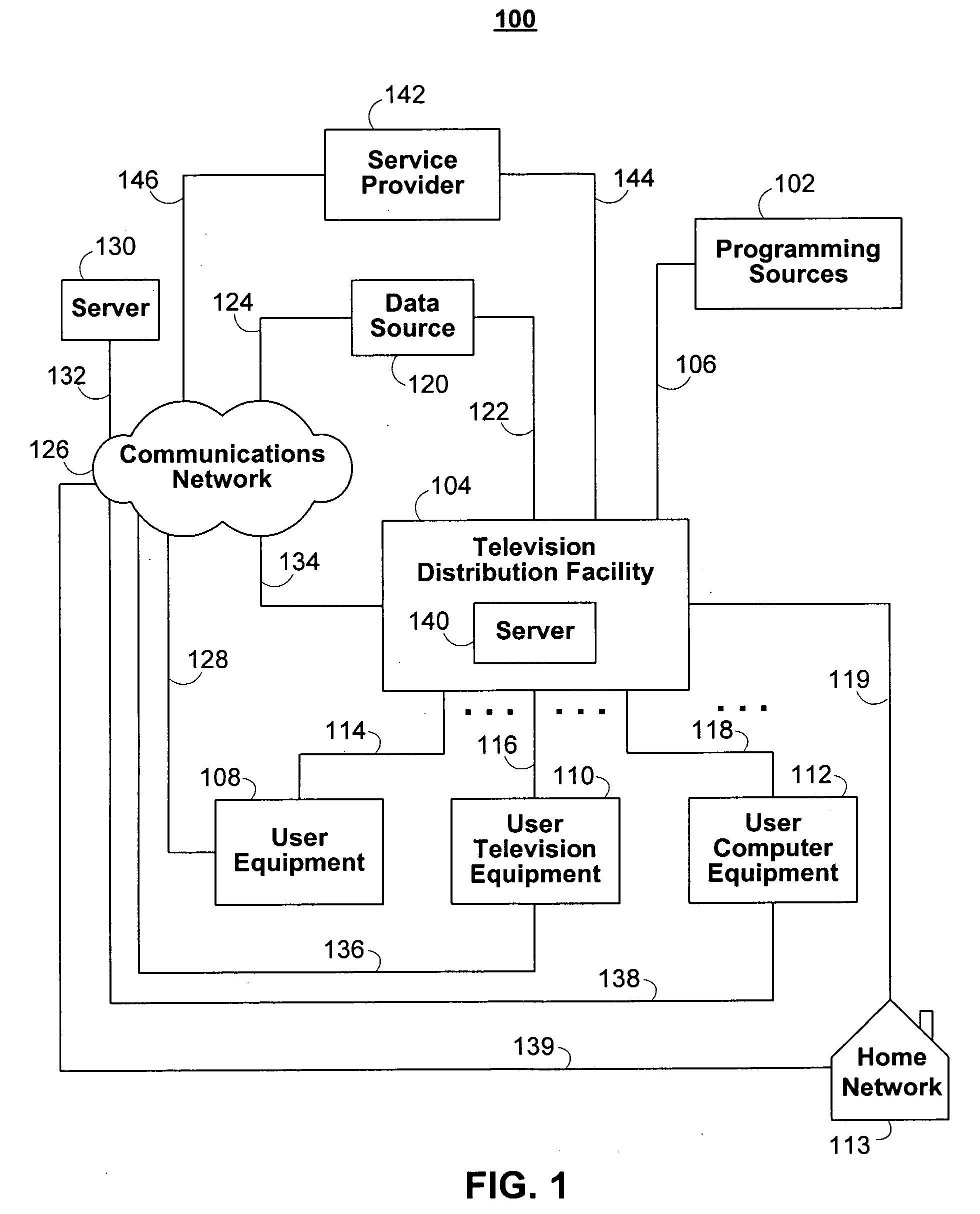
Interactive media guidance system having multiple devices
ActiveUS20080141303A1Limitation of display capacityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesGuidance systemComputer network
When selecting a television program for recording, a user may configure the delivery of the selected television program and associated data and interactive applications to different user equipment devices in a home network, which may have different capabilities. Because the user equipment devices in the home network may have different capabilities, the user may wish to deliver different types and amount of content, different amounts of data, and different versions of interactive applications to the user equipment devices in the home network.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
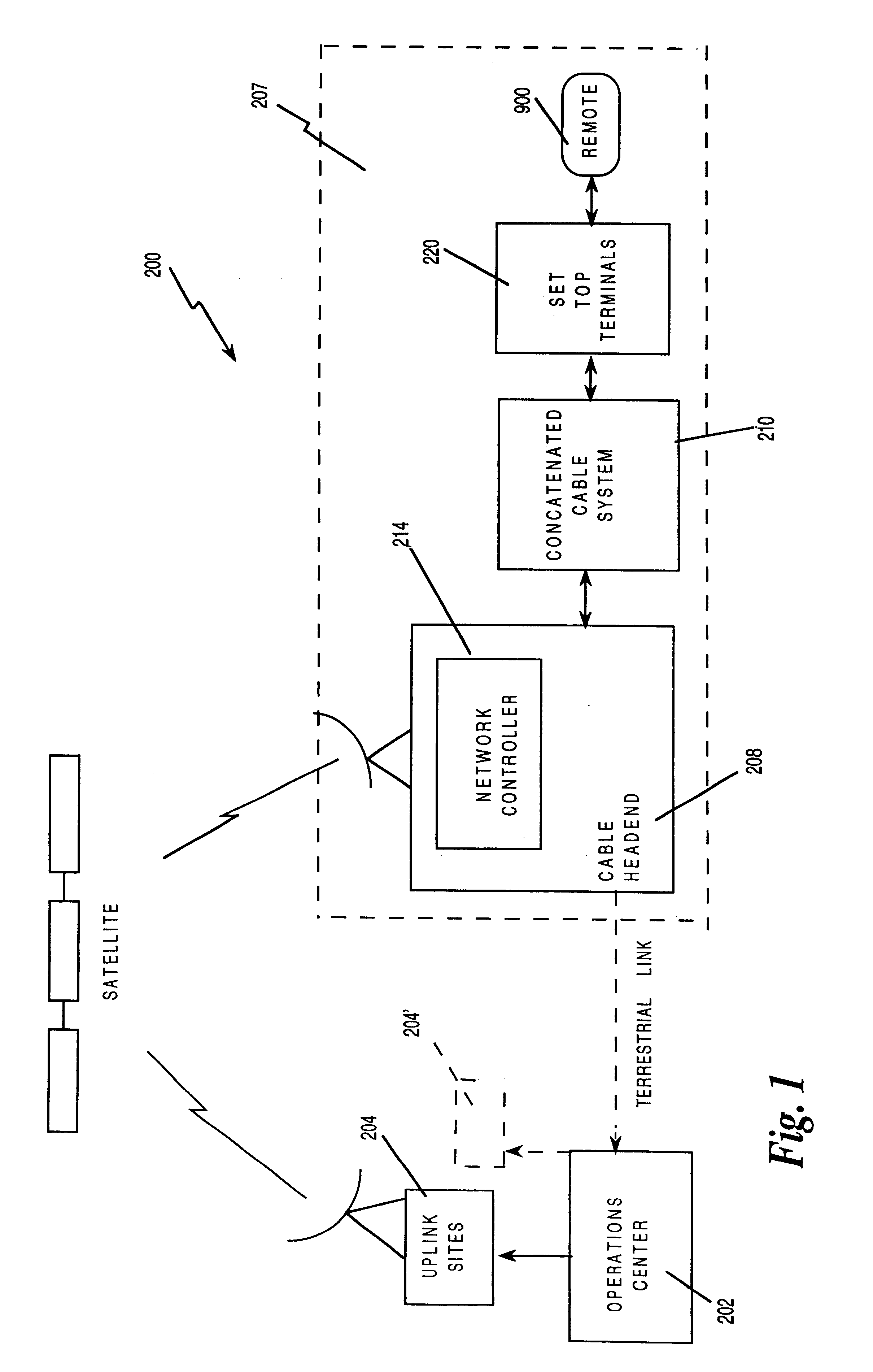
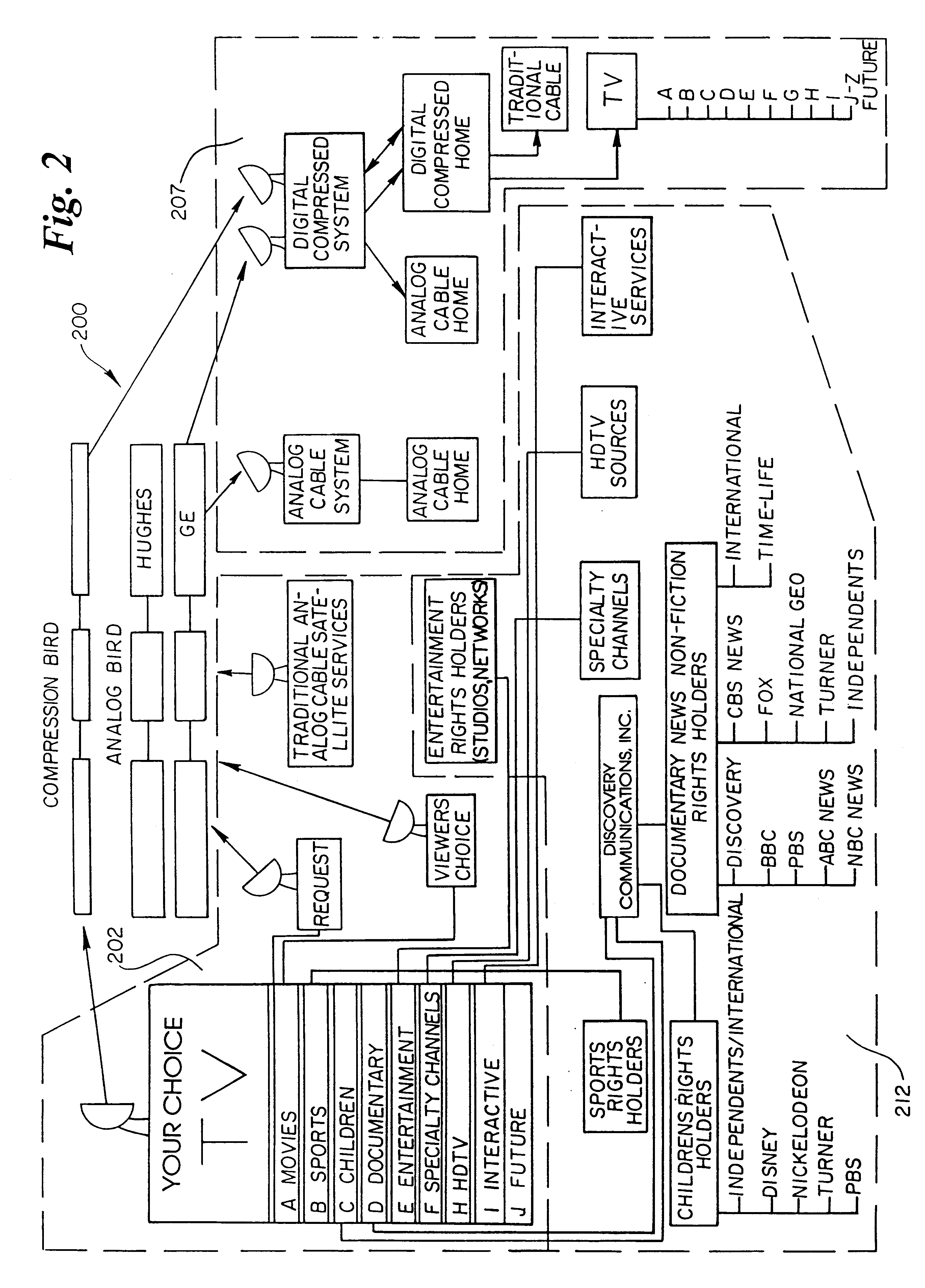
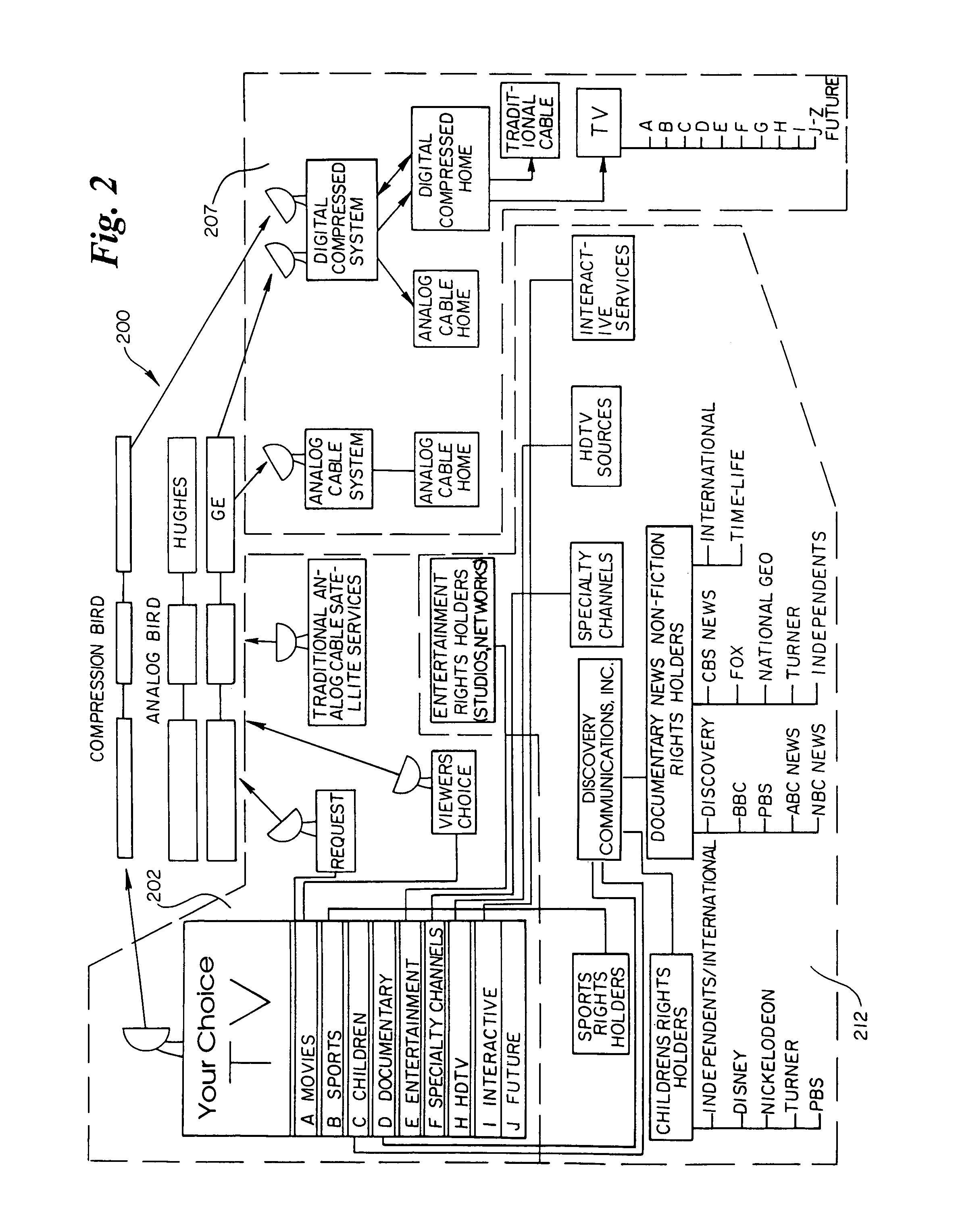
Interactive television program guide display
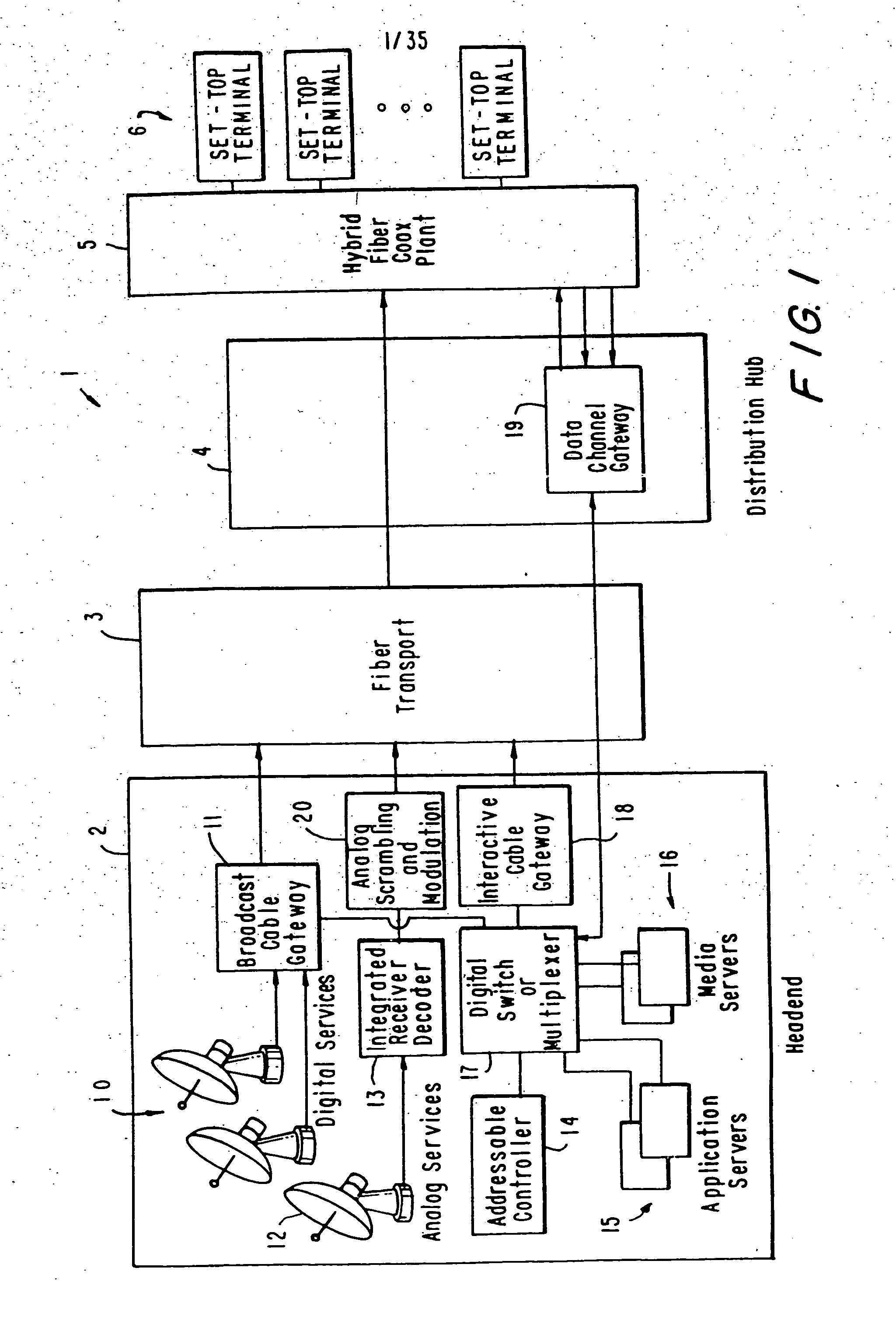
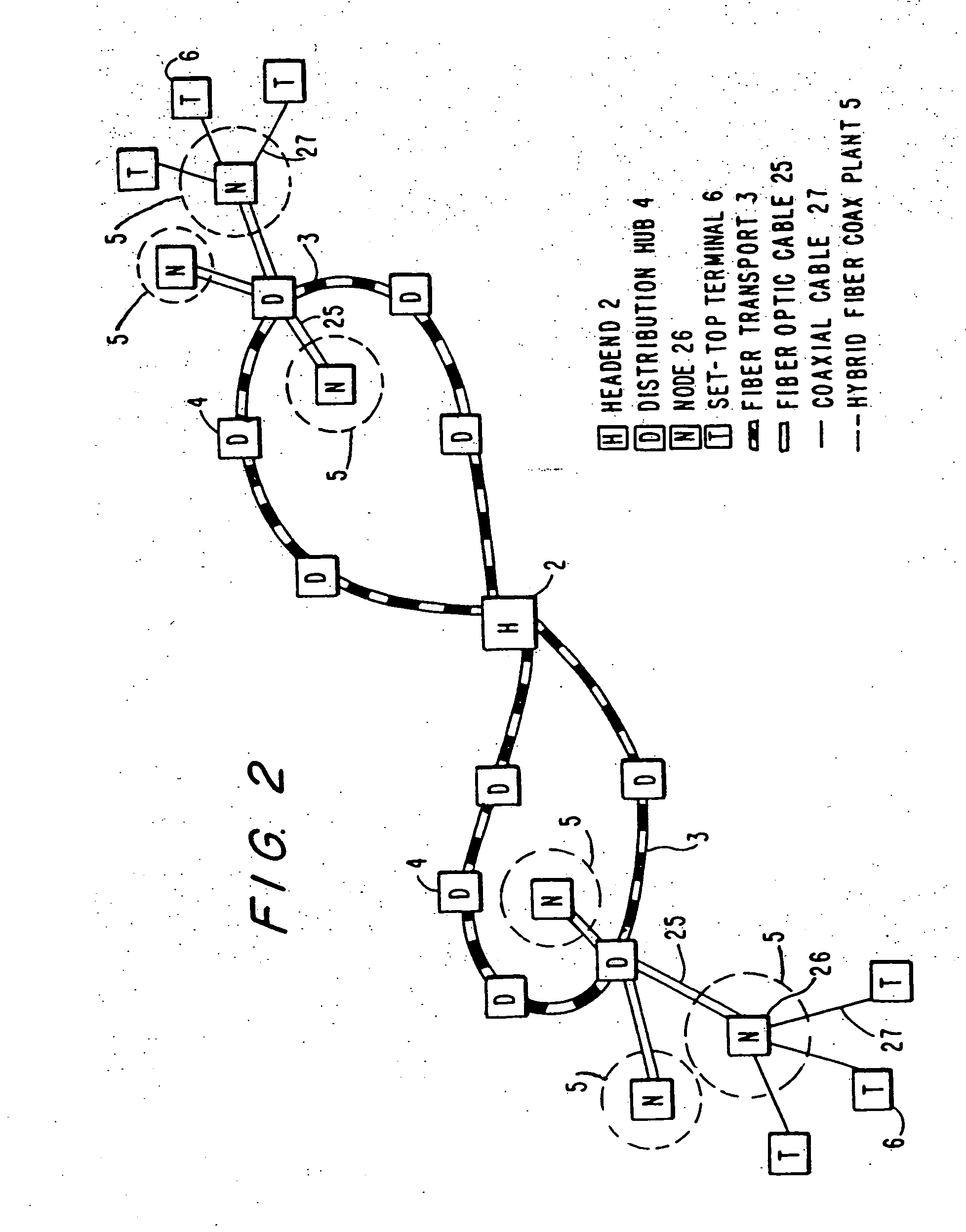
InactiveUS20050015804A1Increase the number ofEnhanced signalTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsThe InternetHybrid fibre-coaxial
A full service cable television system and method are provided. The system comprises a cable headend, at least one fiber transport, at least one distribution hub, at least one hybrid fiber coax plant, and a plurality of set-top terminals. The system delivers television programs, advanced cable services, and online services. Programs and services are transmitted to the set-top terminals in both digital and analog formats to maintain downward compatibility with existing systems. The set-top terminal includes a central processing unit, a unified memory architecture, a memory management unit, communications circuitry, I / O control circuitry, and audio and video output circuitry. Through these components, the set-top terminal provides advanced cable services such as a comprehensive channel navigator, an interactive program guide, impulse Pay-Per-View, Near-Video-On-Demand and Video-On-Demand programming, and advanced configuration controls. The set-top terminal also provides online services such as World Wide Web browsing, Internet e-mail, and home shopping.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
Interactive television program guide system and method with niche hubs
InactiveUS20090019485A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsWeb siteInteractive television
A system for providing interactive television program guide features and other features and information related to a specific user interest or programming category in niche hubs is provided. All of the television programming features provided by user television equipment that relate to a specific user interest or programming category may be accessed from the niche hub. For example, a movie lovers niche hub may provide programming features such as television program listings for movies, video-on-demand listings for movies, pay-per-view listings for movies, web site links related to movies, movie-related merchandise, movie news groups, movie chat groups, movie e-mail clubs, movie contests, movie trivia questions, movie actor interviews, movie reviews, movie channel package ordering, etc. The programming features of the niche hubs may be transmitted from a server, database, or other storage facility via a television distribution facility. User television equipment may be connected via two-way communications paths to transmit messages to each other.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
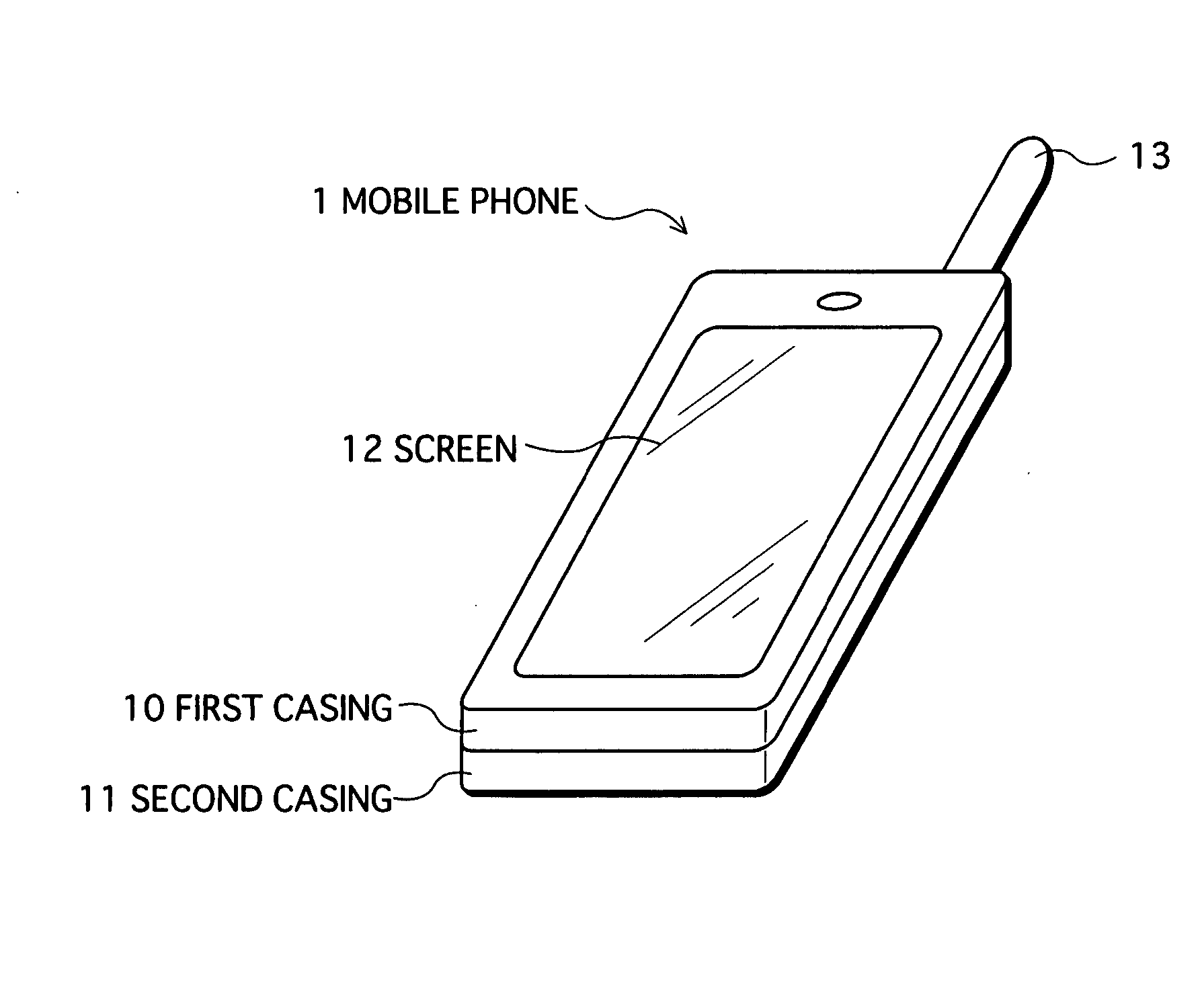
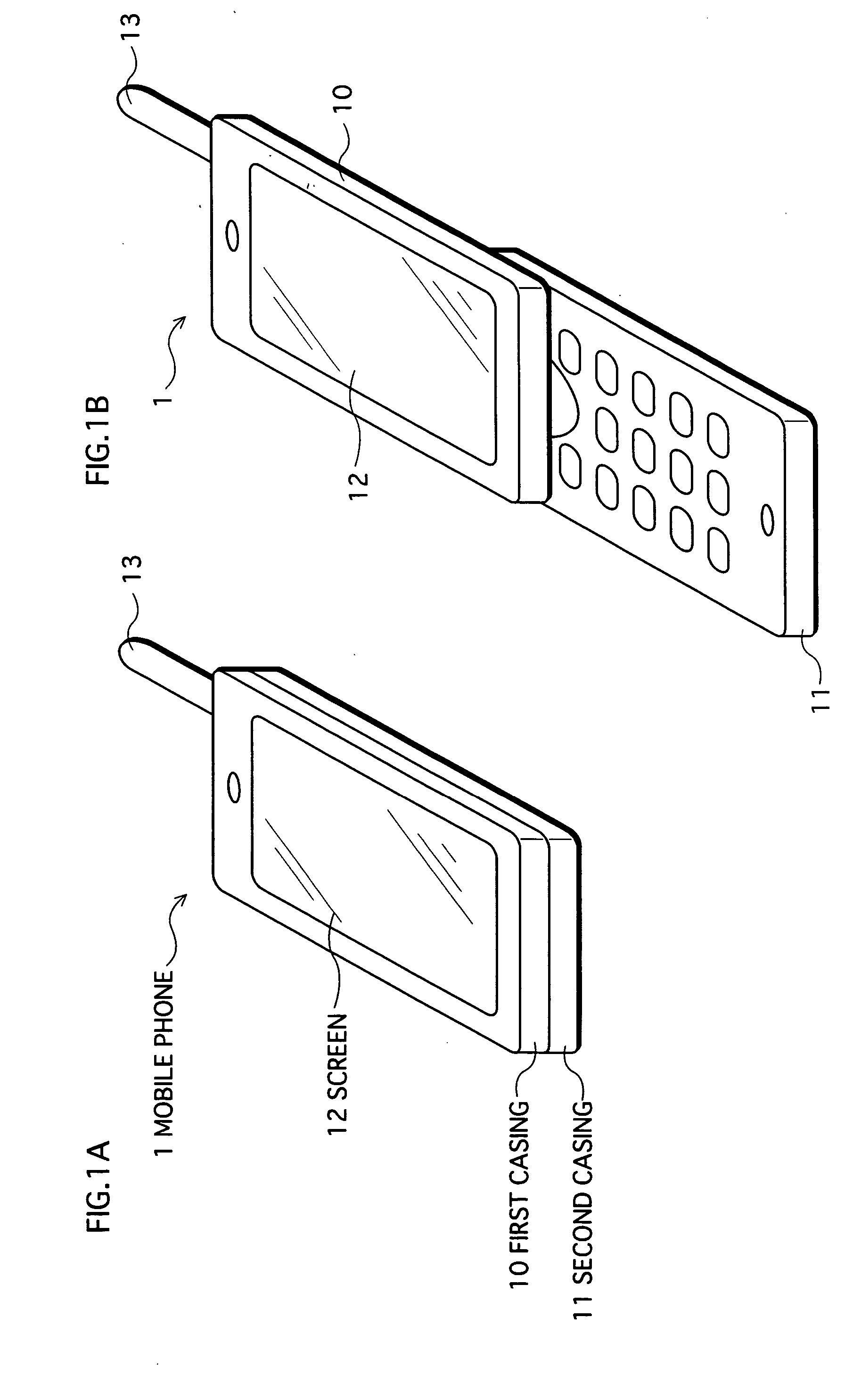
Mobile Phone, Display Method, and Computer Program
InactiveUS20070265031A1Television system detailsColor television detailsUser FriendlyMobile telephony
A mobile phone capable of displaying video and other information in a user-friendly manner without interrupting video display in the case where other information is displayed during the display of received video. The mobile phone, on receipt of an external event via a wireless unit during display by a display unit of video constituting a TV program received by a tuner, partitions a screen based on a partition ratio stored in a partition information storage unit, and displays both video constituting the TV program and information composed of information showing the occurrence of an external event, information related to an originator, and the like.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com