Groundwater flow calculation method
A calculation method and groundwater technology, applied in calculation, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems that are not suitable for engineering projects, strict assumptions, and non-unique unit boundary flow values
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
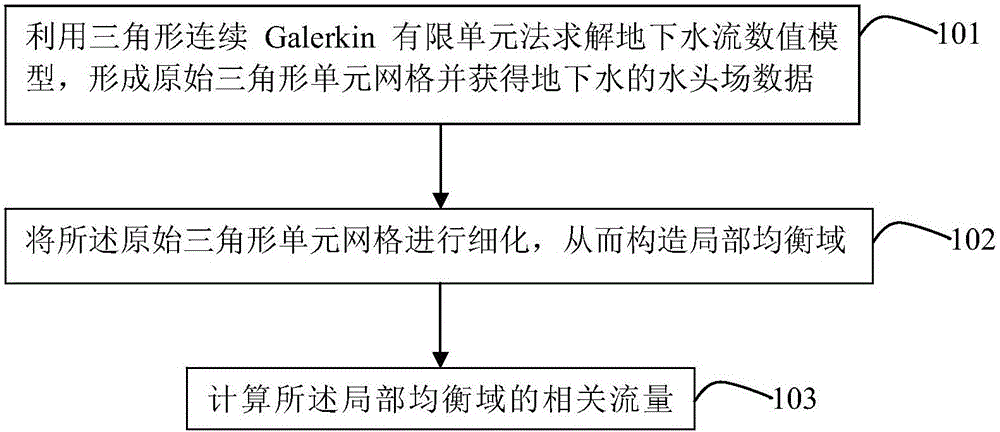
[0058] Refer to attached figure 1 , is a schematic flow chart of the calculation method for groundwater flow provided by the present invention. As an embodiment of the present invention, the calculation method of the groundwater flow includes:
[0059] Step 101: using the triangular continuous Galerkin finite element method to solve the groundwater flow numerical model, forming an original triangular element grid and obtaining groundwater head field data.
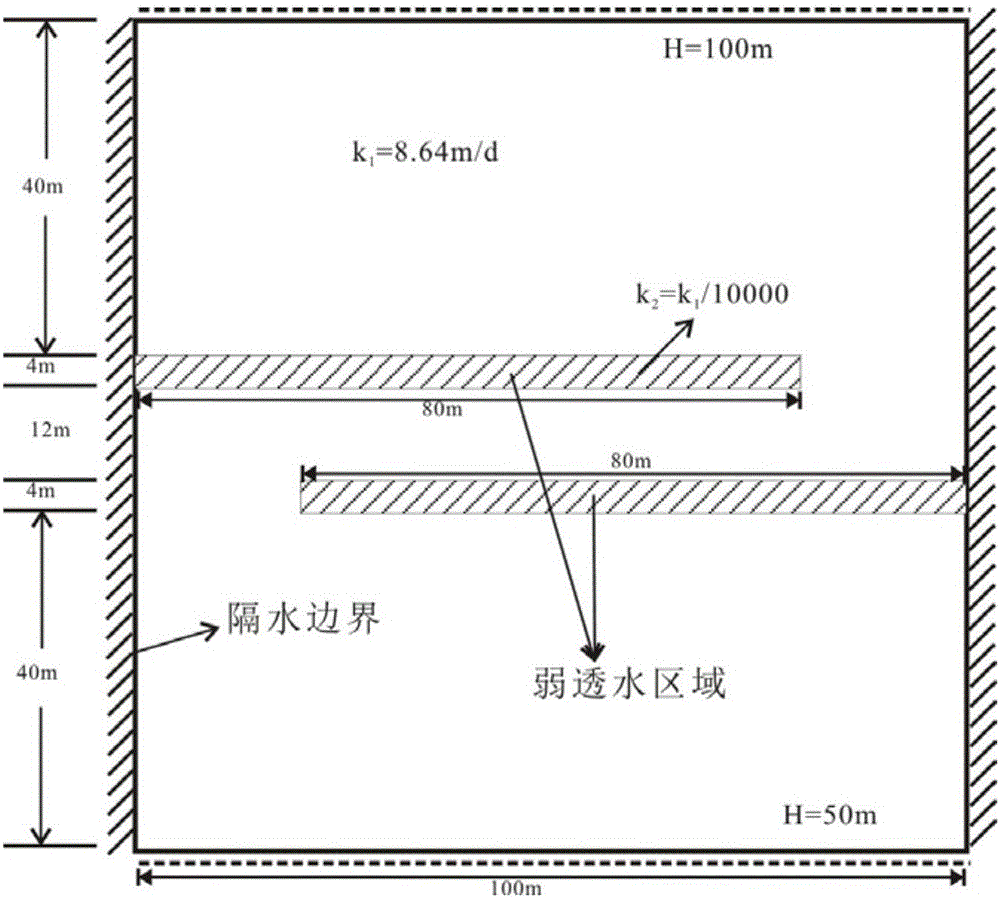
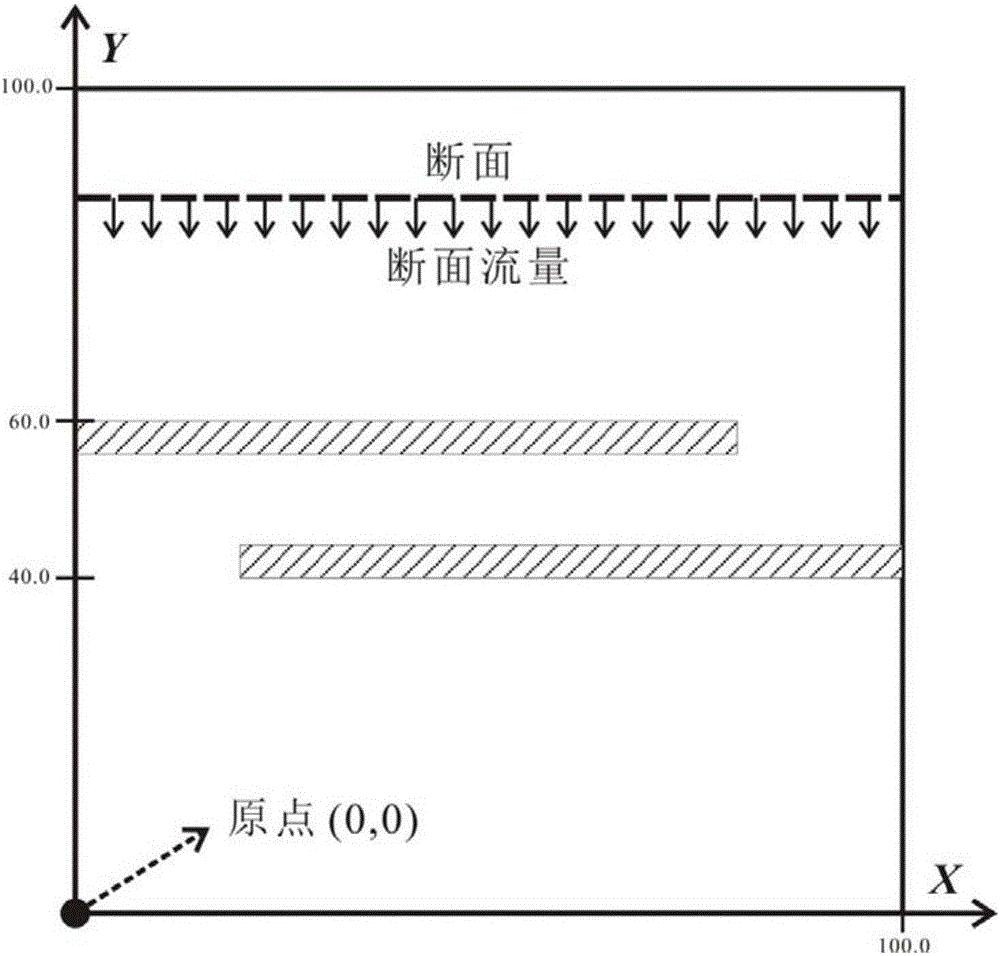
[0060] The hydraulic head field refers to any point in the study area corresponding to a hydraulic head value. In the present invention, it means that any triangle mesh vertex corresponds to a water head value. Other points in the study area can be obtained by inter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com