Patents
Literature
317 results about "Functional connectivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Functional Connectivity. Functional connectivity is defined as the temporal correlation (measured as a Pearson’s r) in the high amplitude, low-frequency spontaneously generated BOLD signal between voxels (cubic “pixel” in a three-dimensional brain image) or brain regions (Fox & Raichle, 2007). From: Neurobiology of Language, 2016.
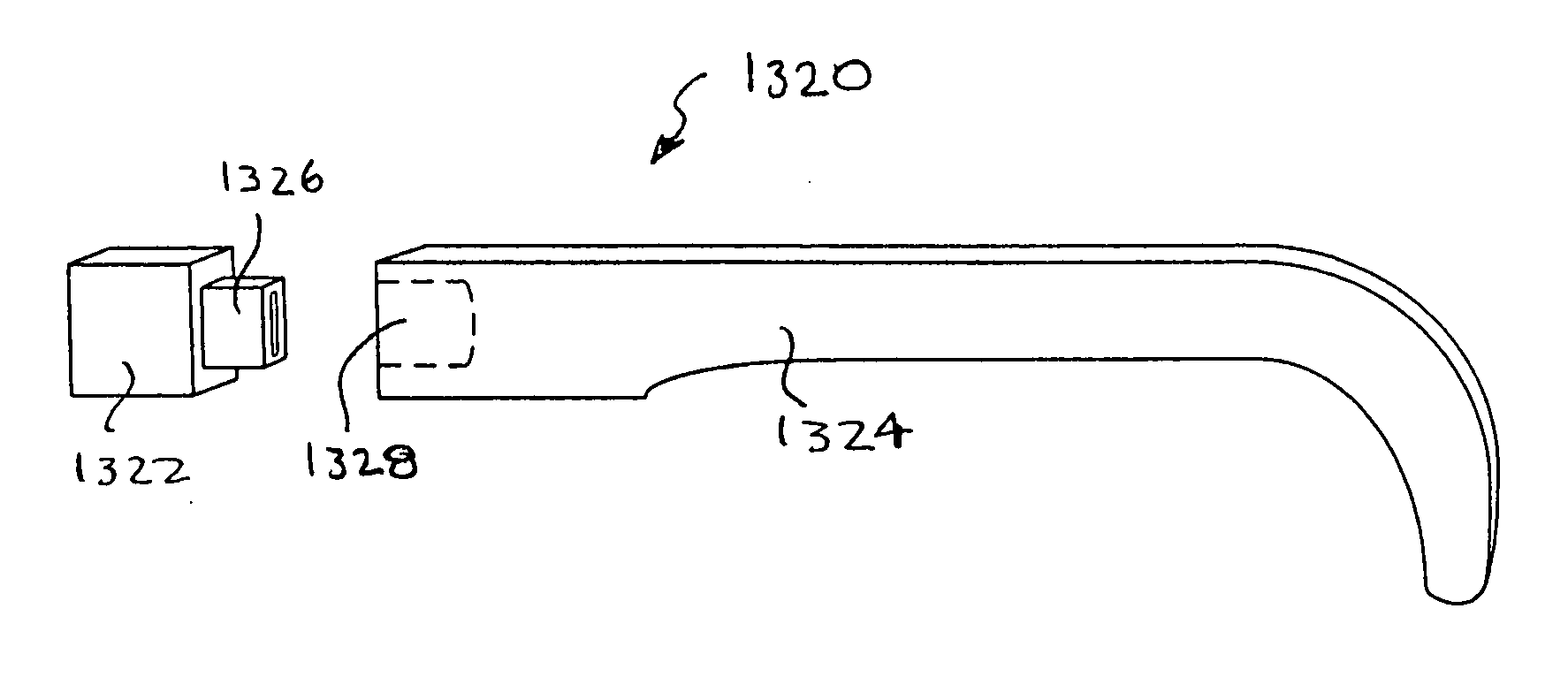
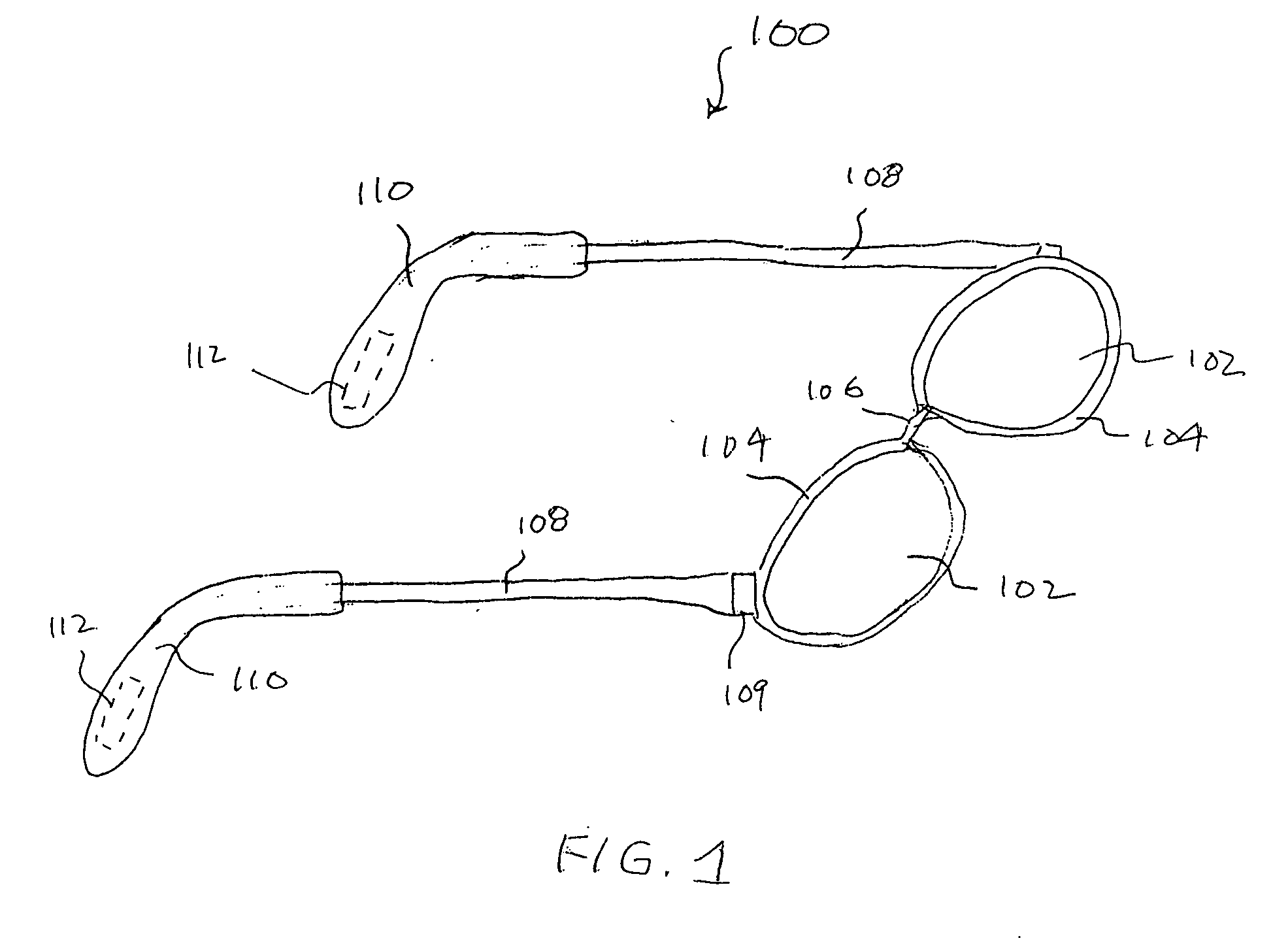
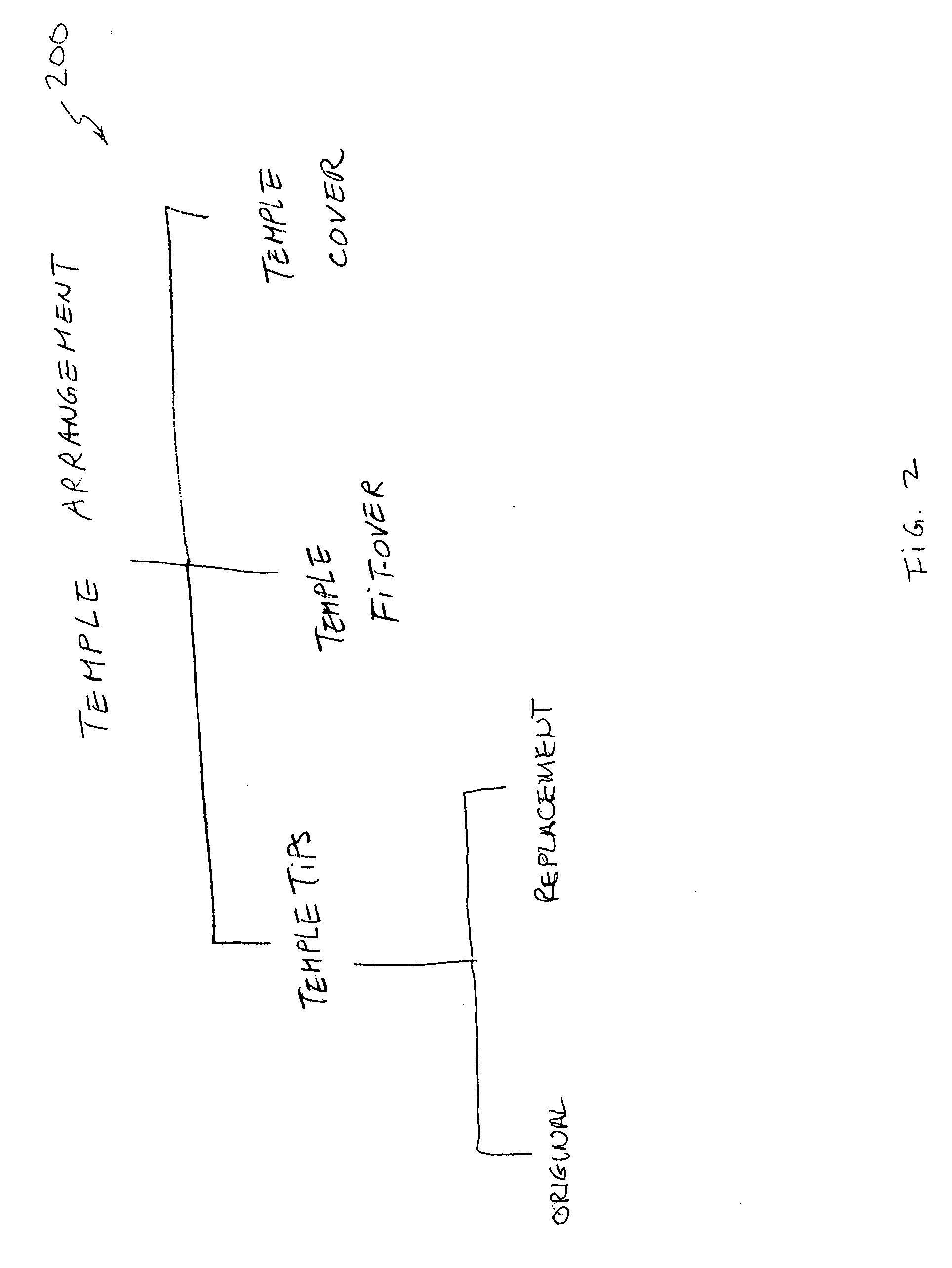
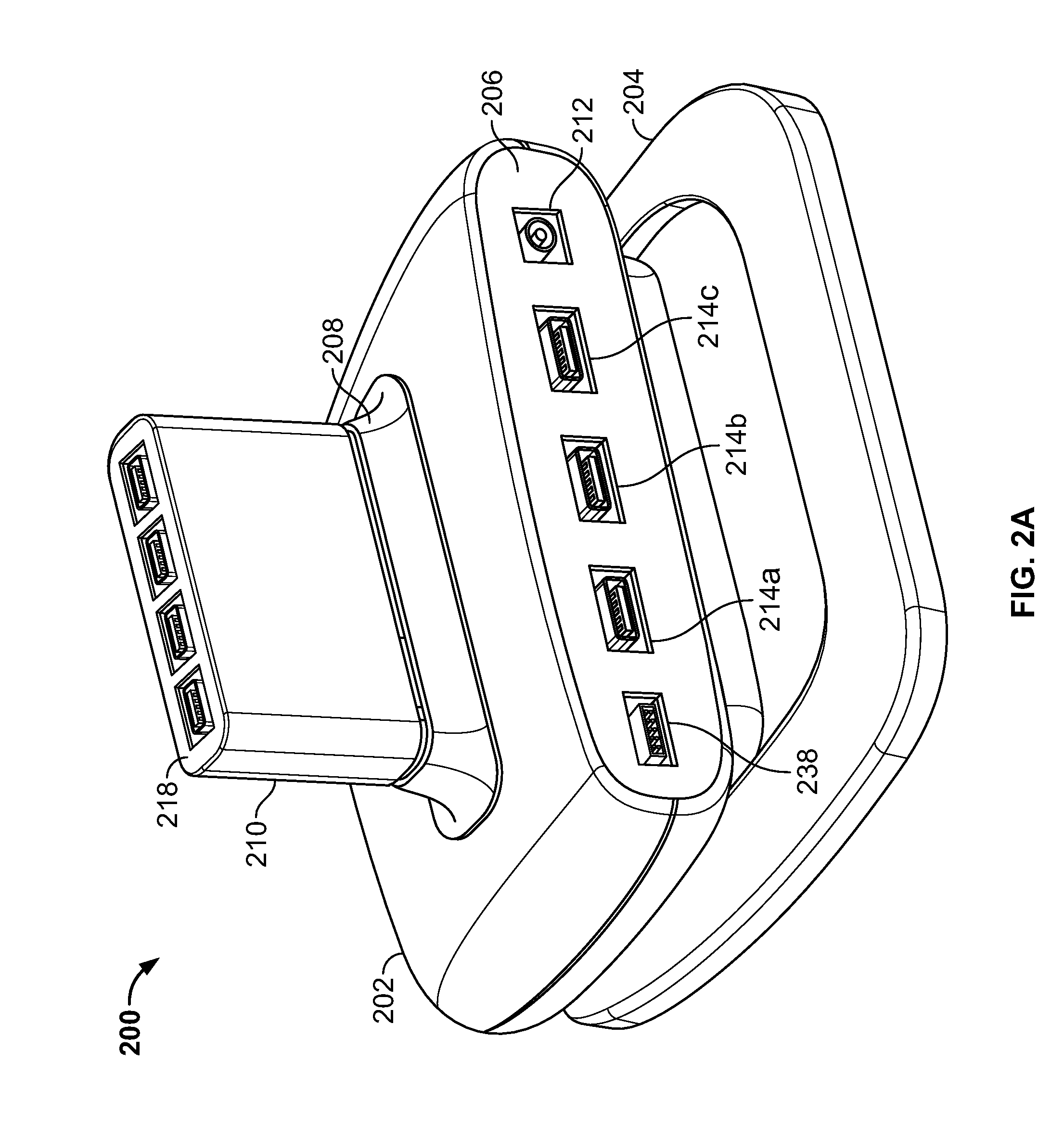
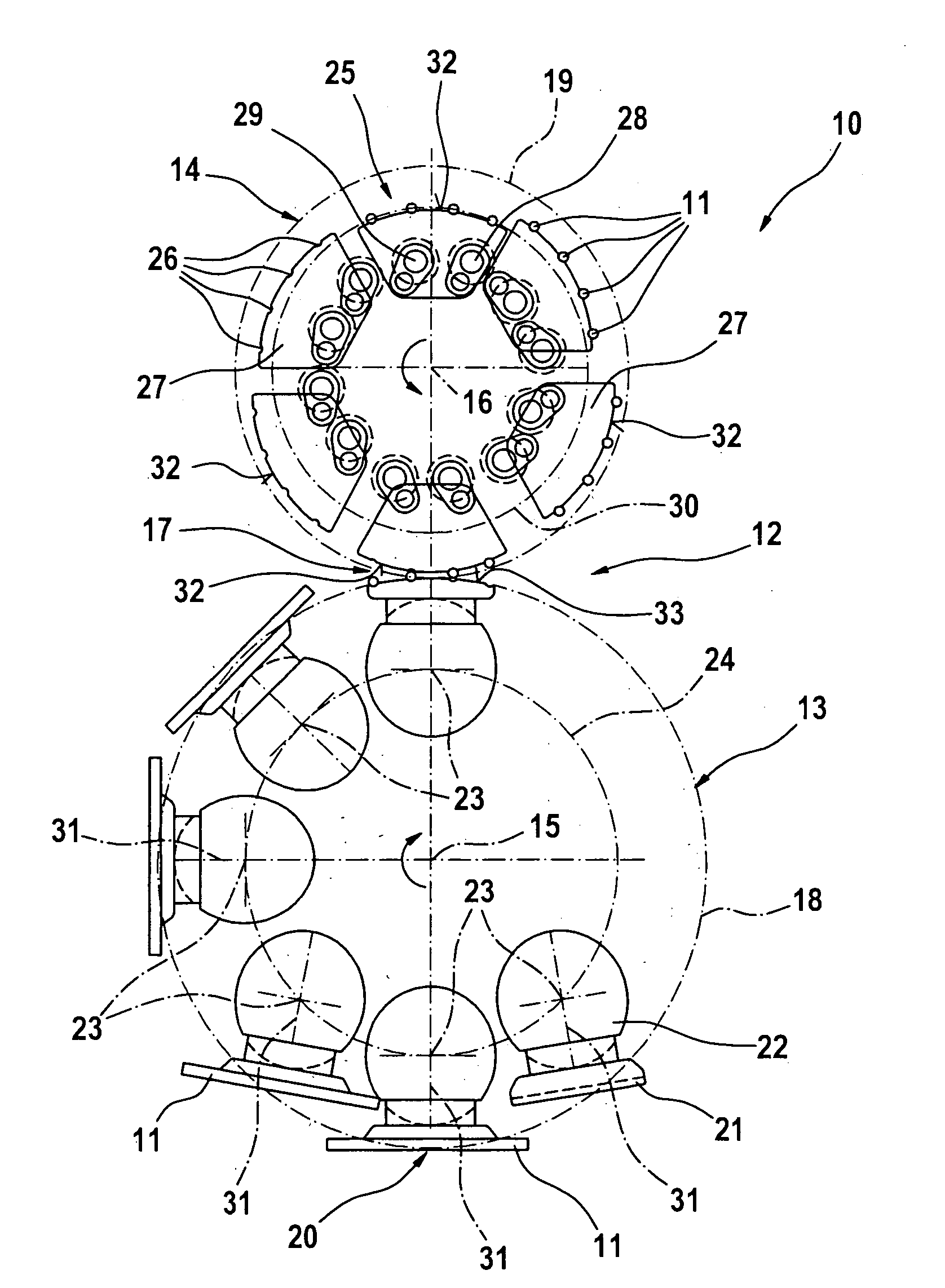
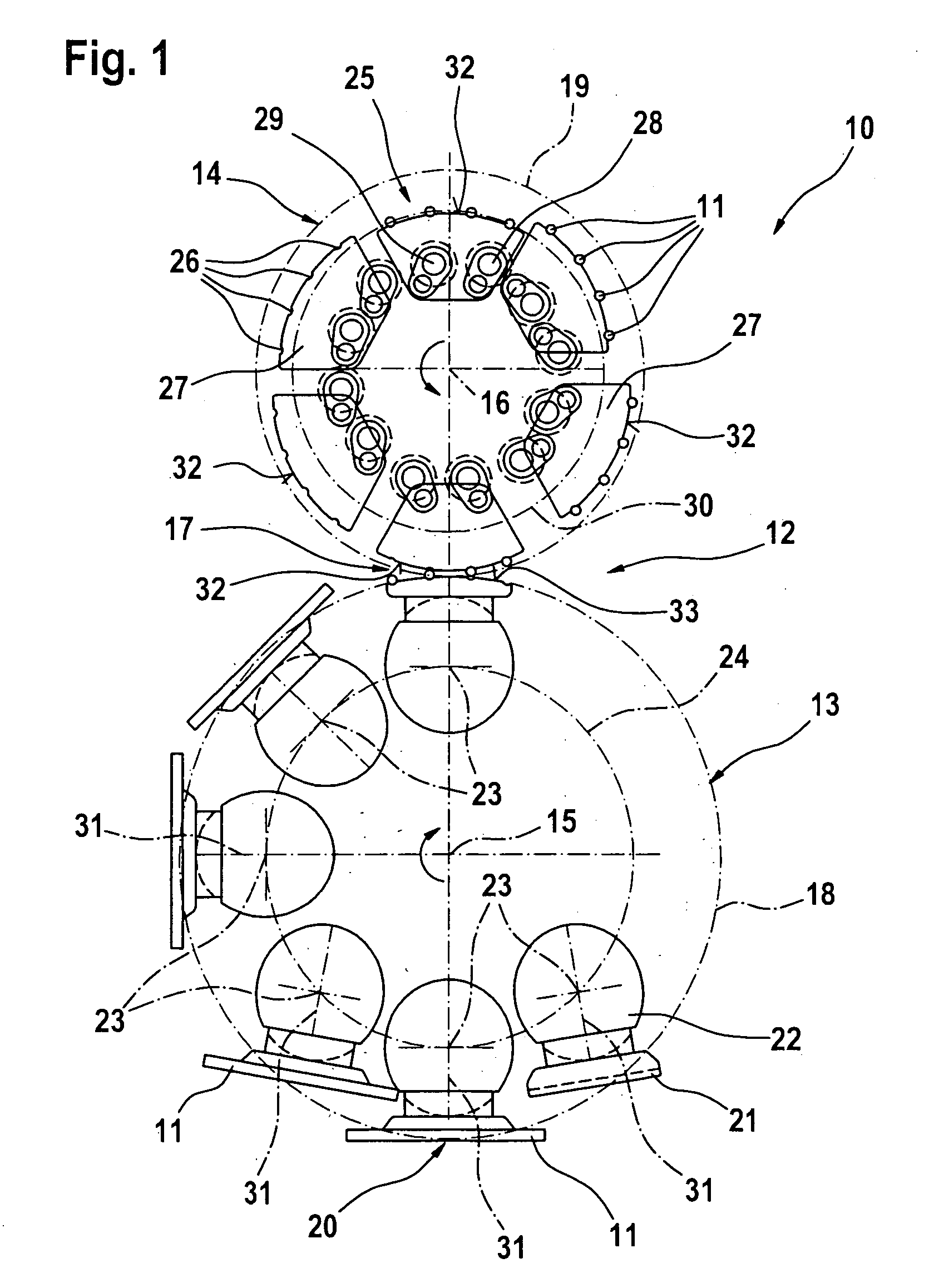
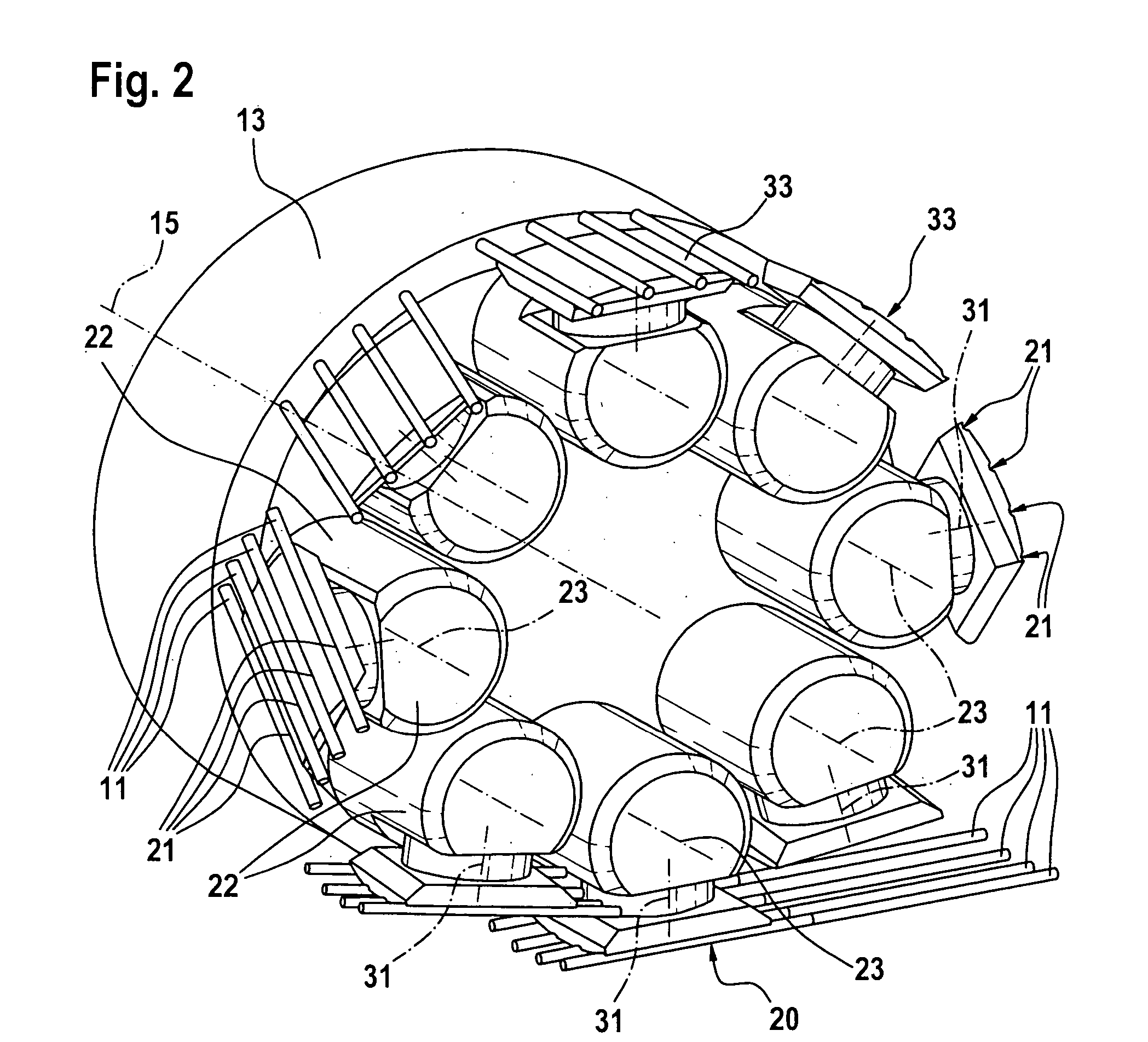
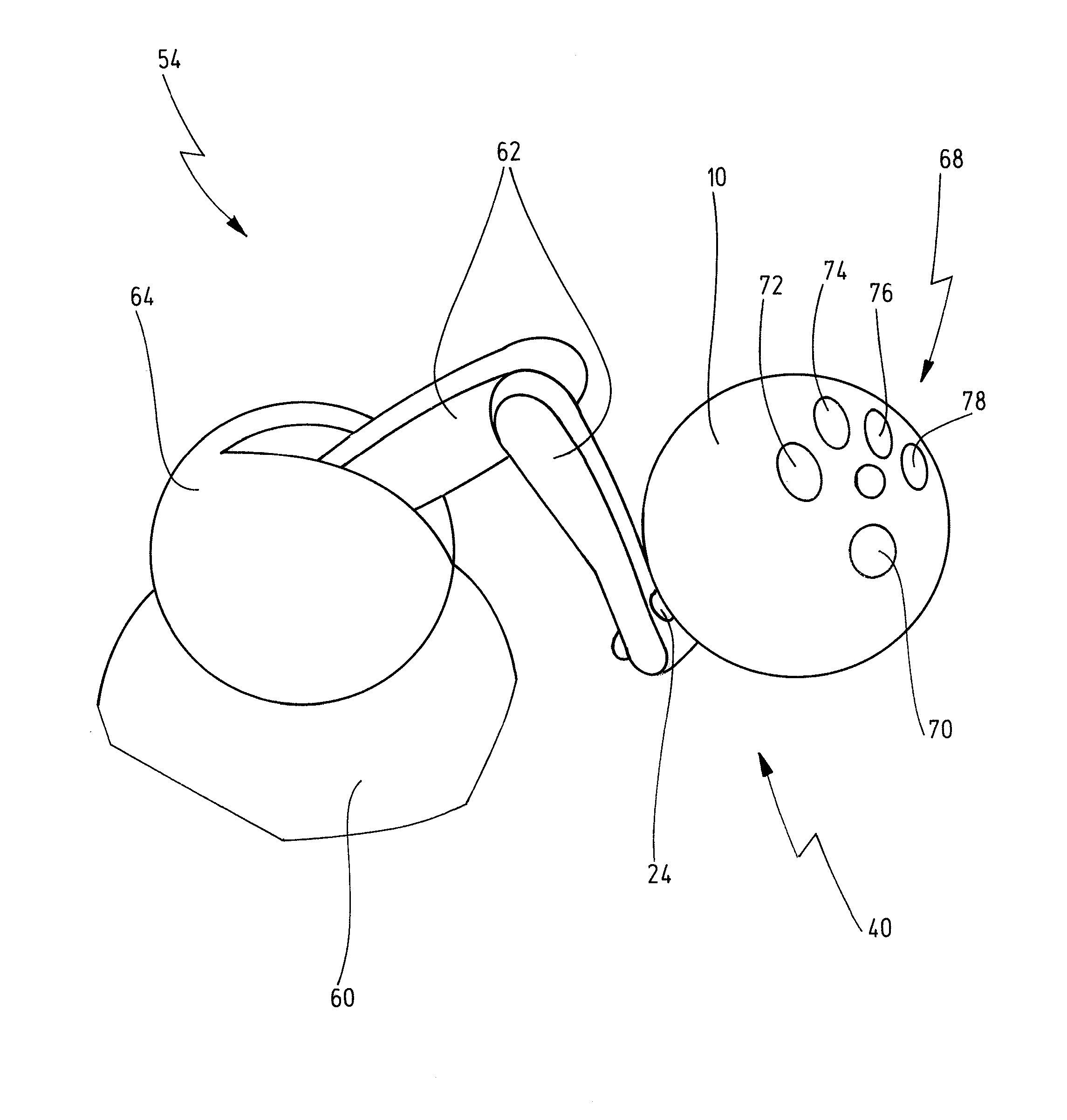
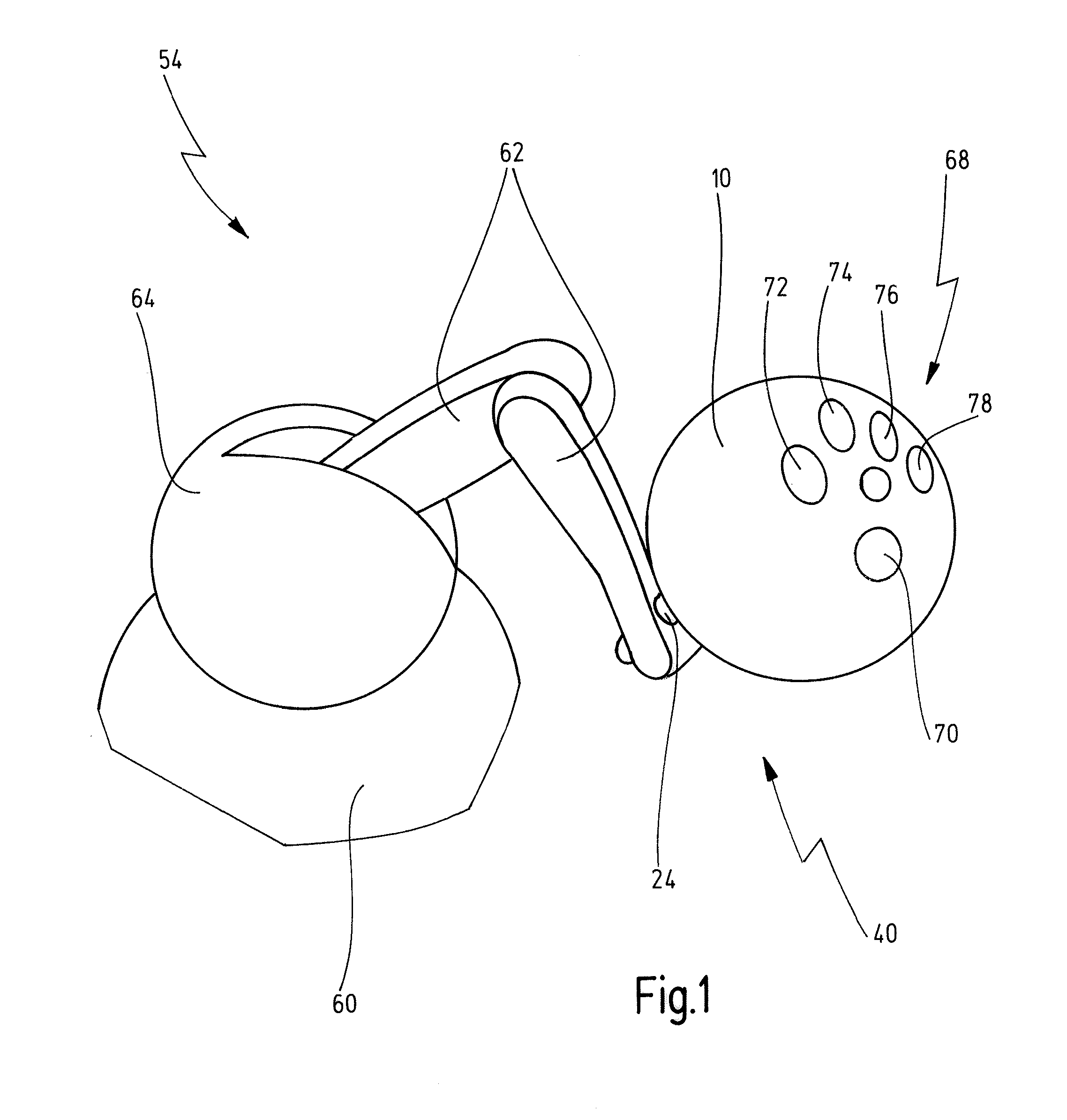
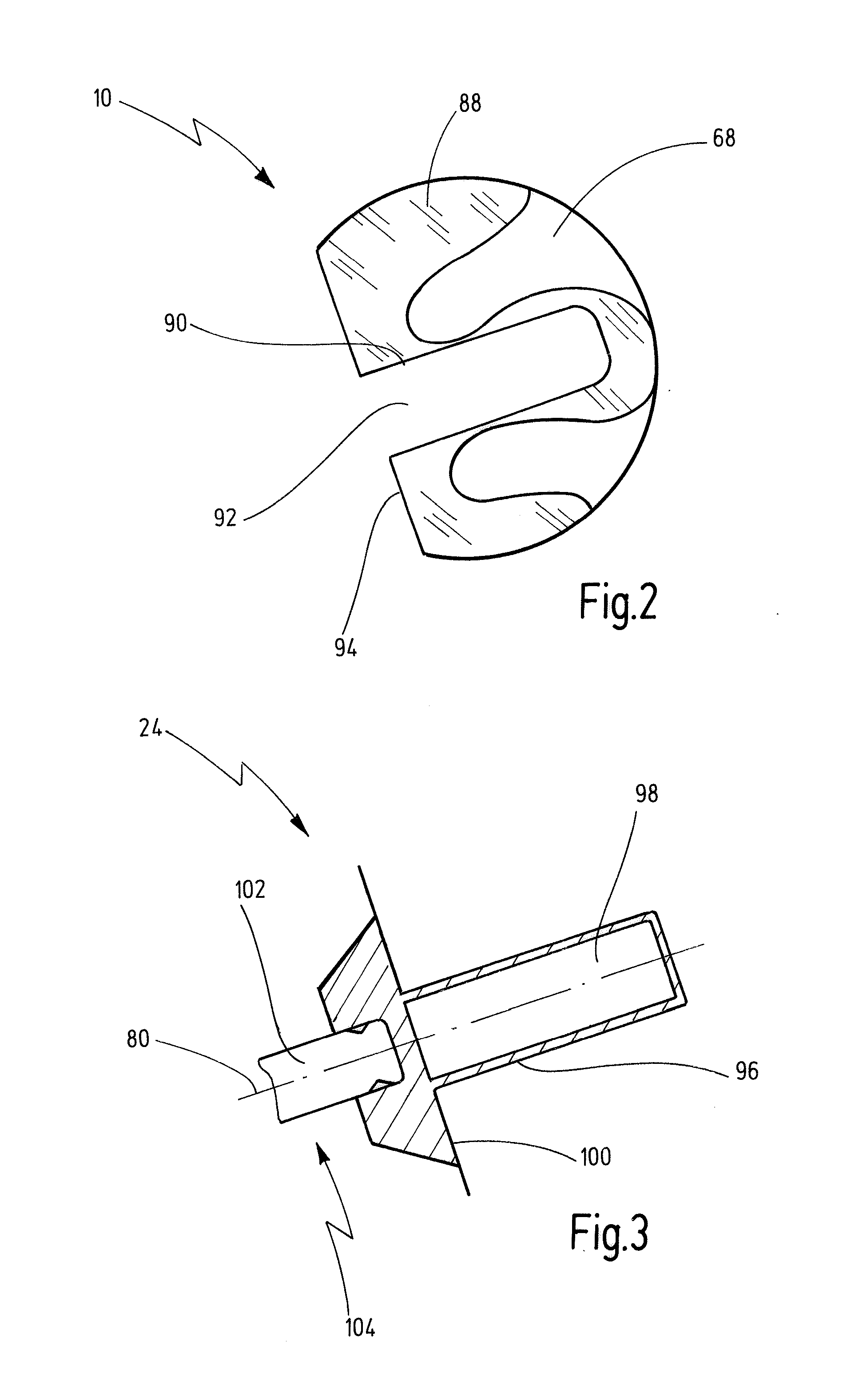
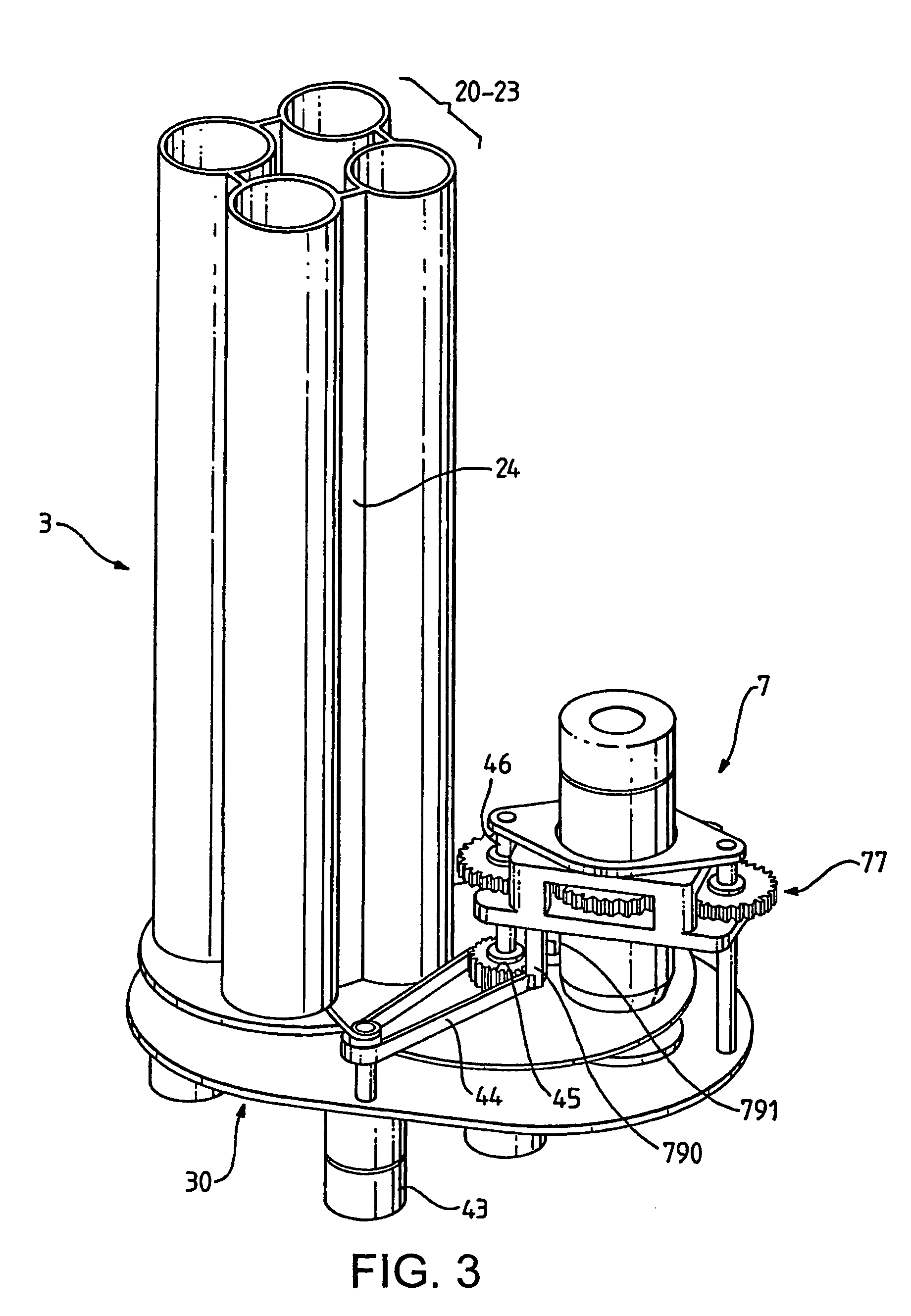
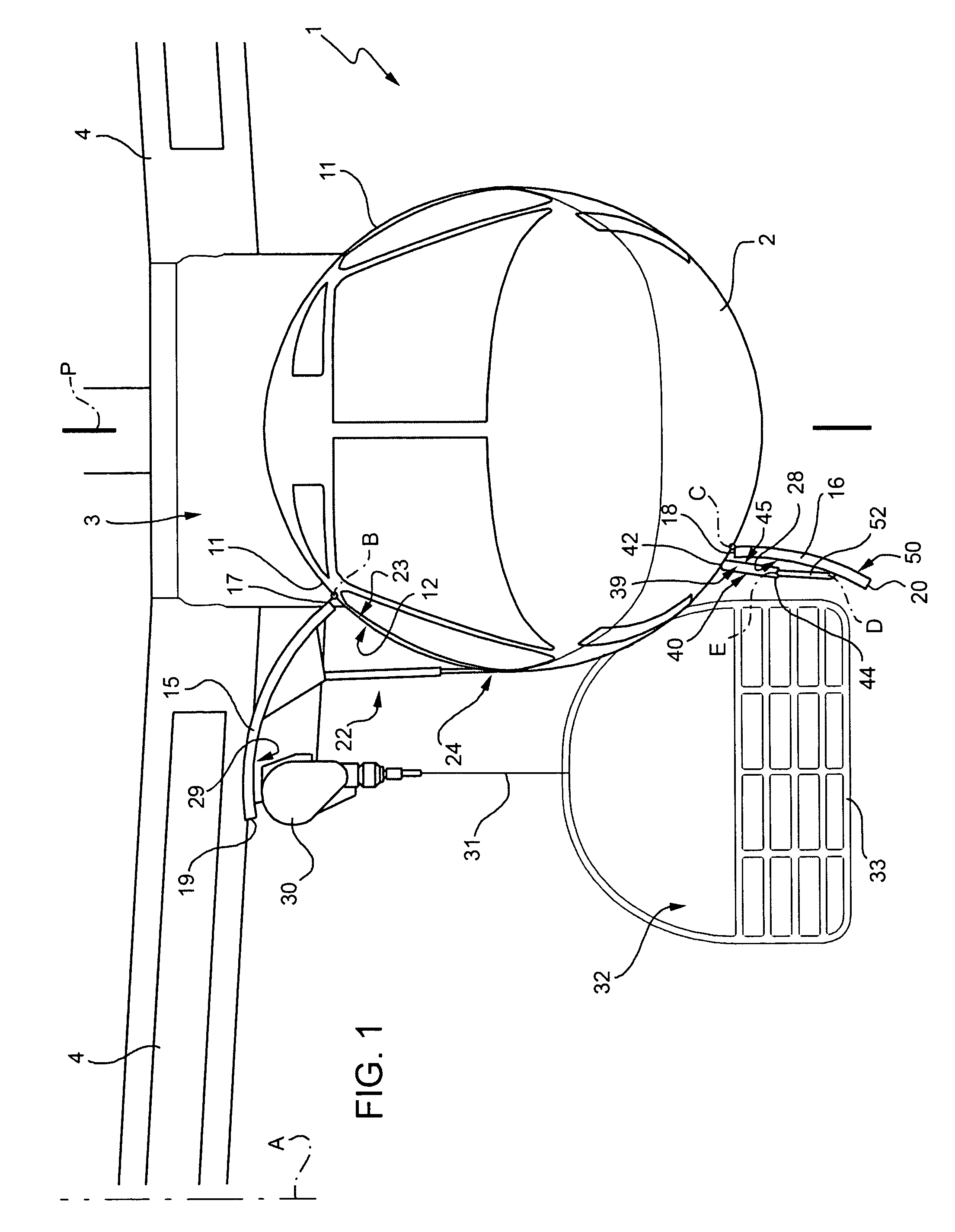
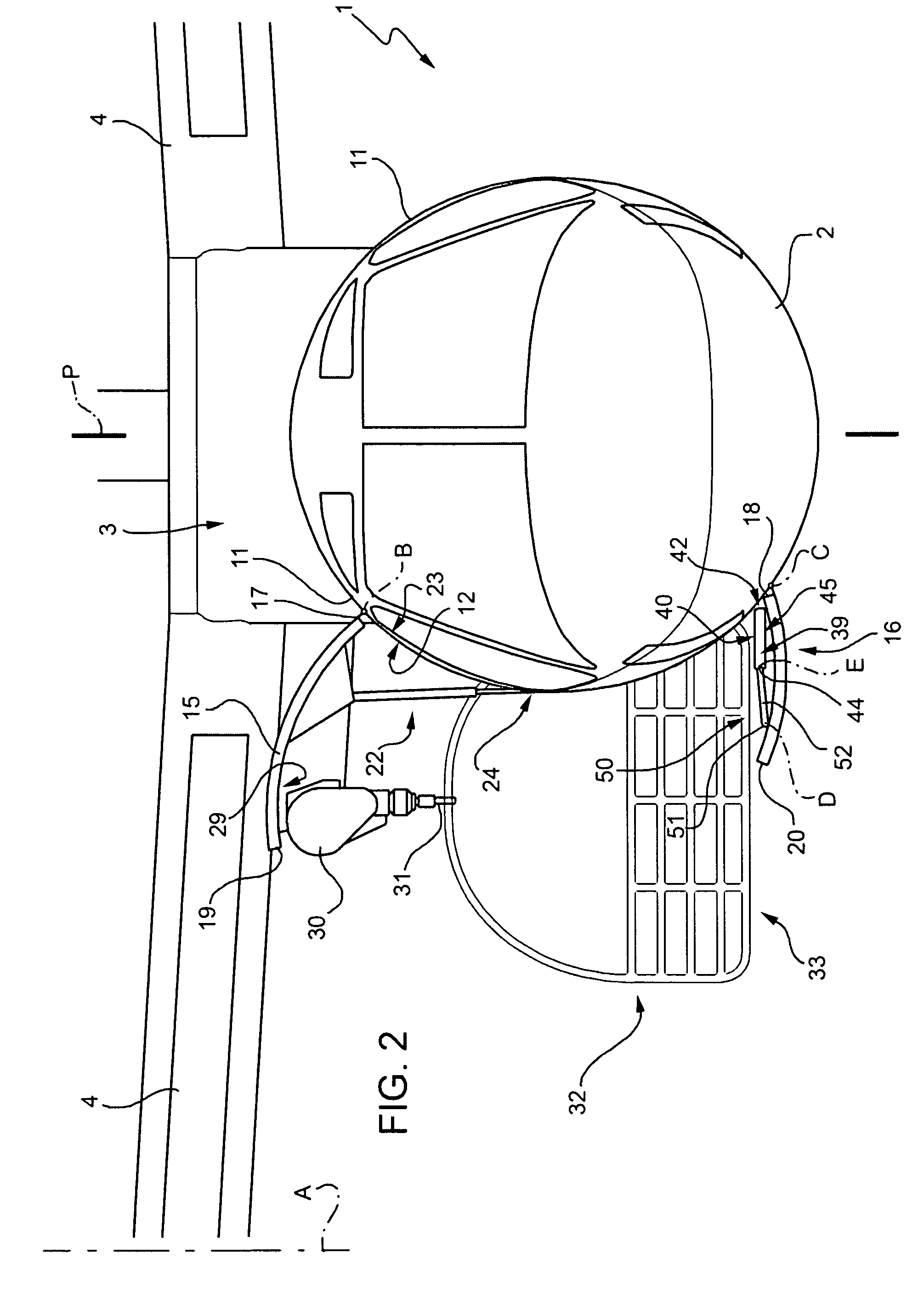
Eyewear supporting after-market electrical components
Techniques for providing eyewear with electrical components are disclosed. The electrical components can provide electrical technology to eyewear without having to substantially compromise aesthetic design principles of the eyewear. The electrical components can be partially or completely internal to eyewear. The electrical components can also be attached to the eyewear as an after-market enhancement. The electrical components can operate independently or together with other electrical components provided elsewhere.
Owner:INGENIOSPEC
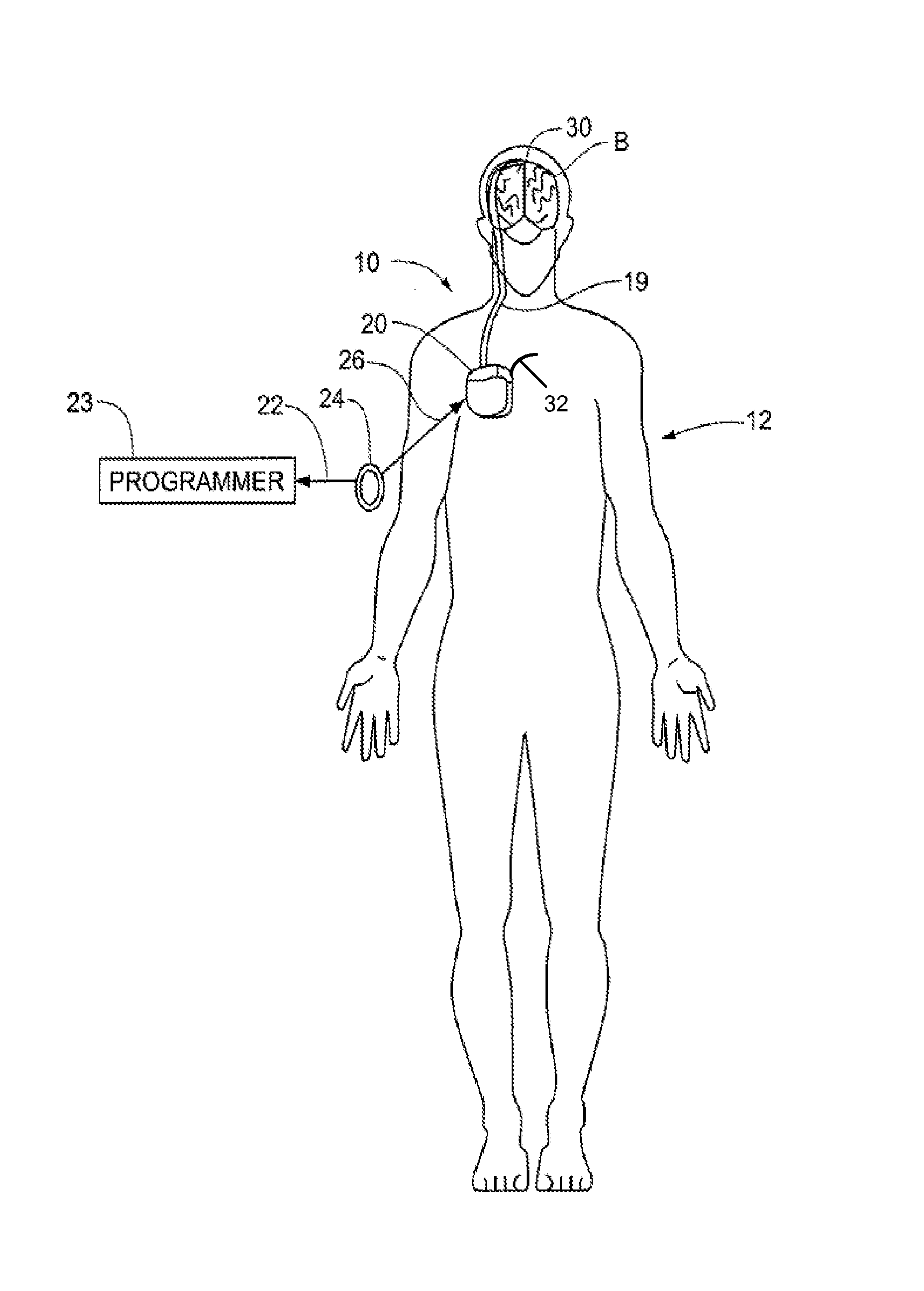
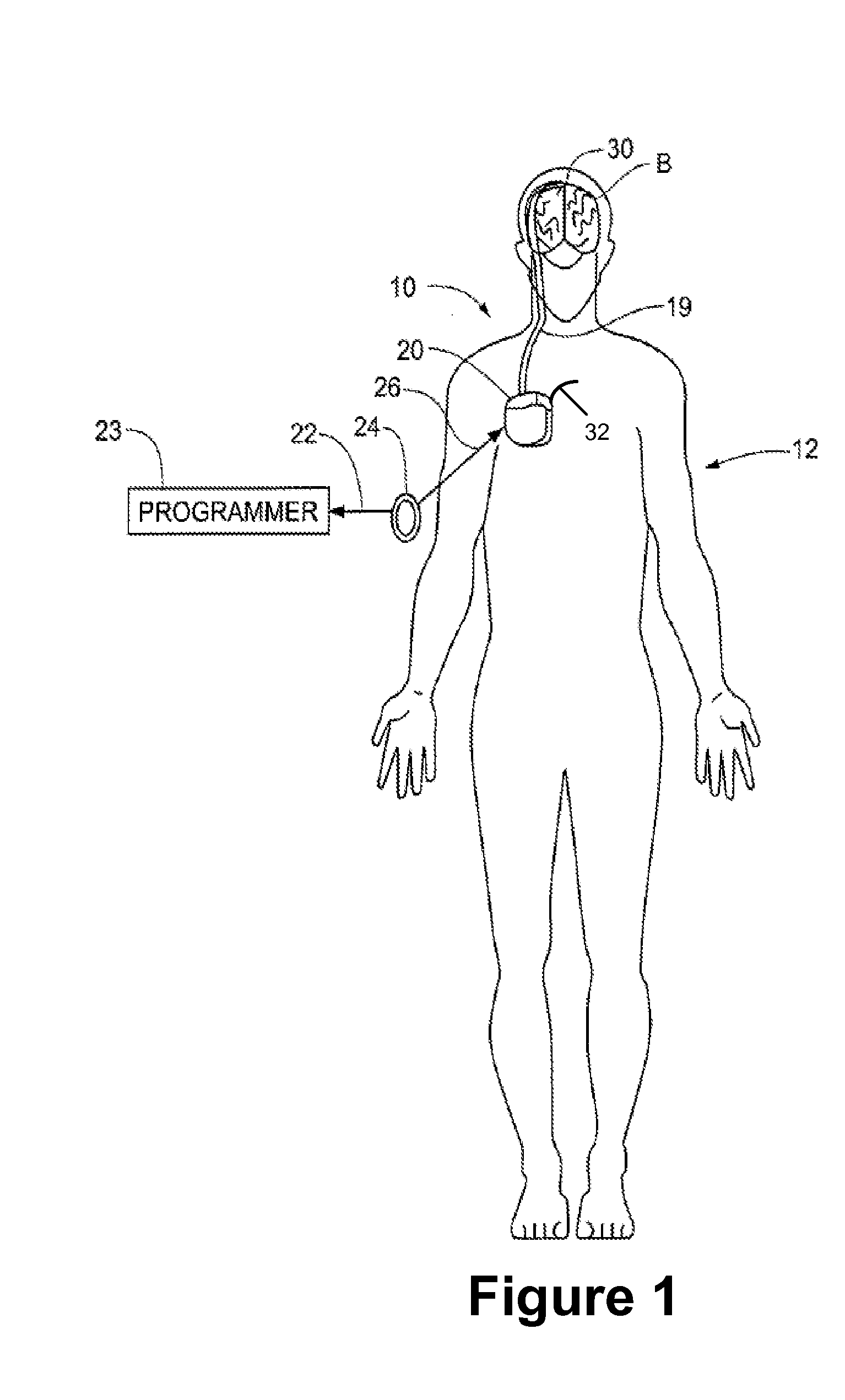
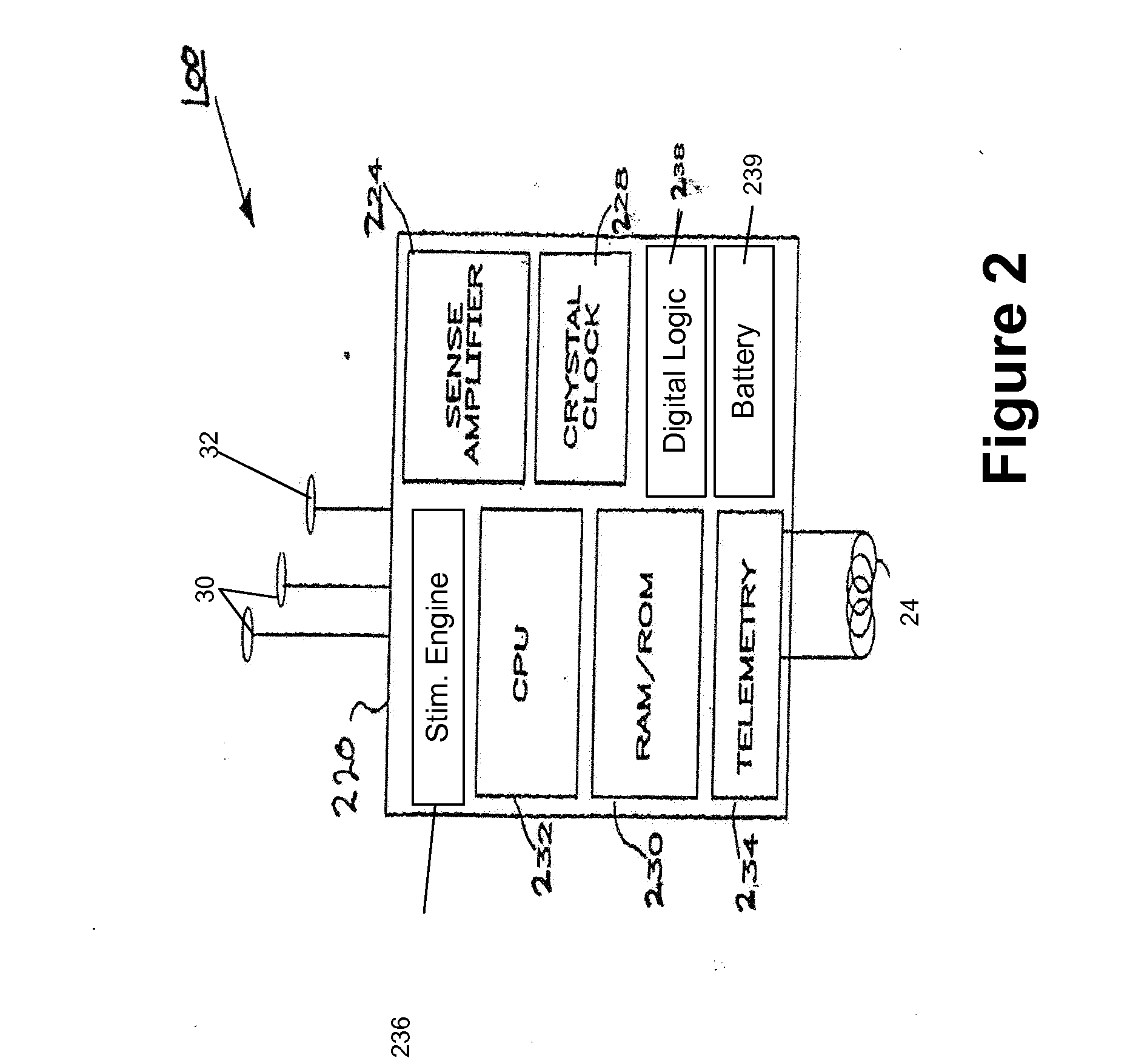
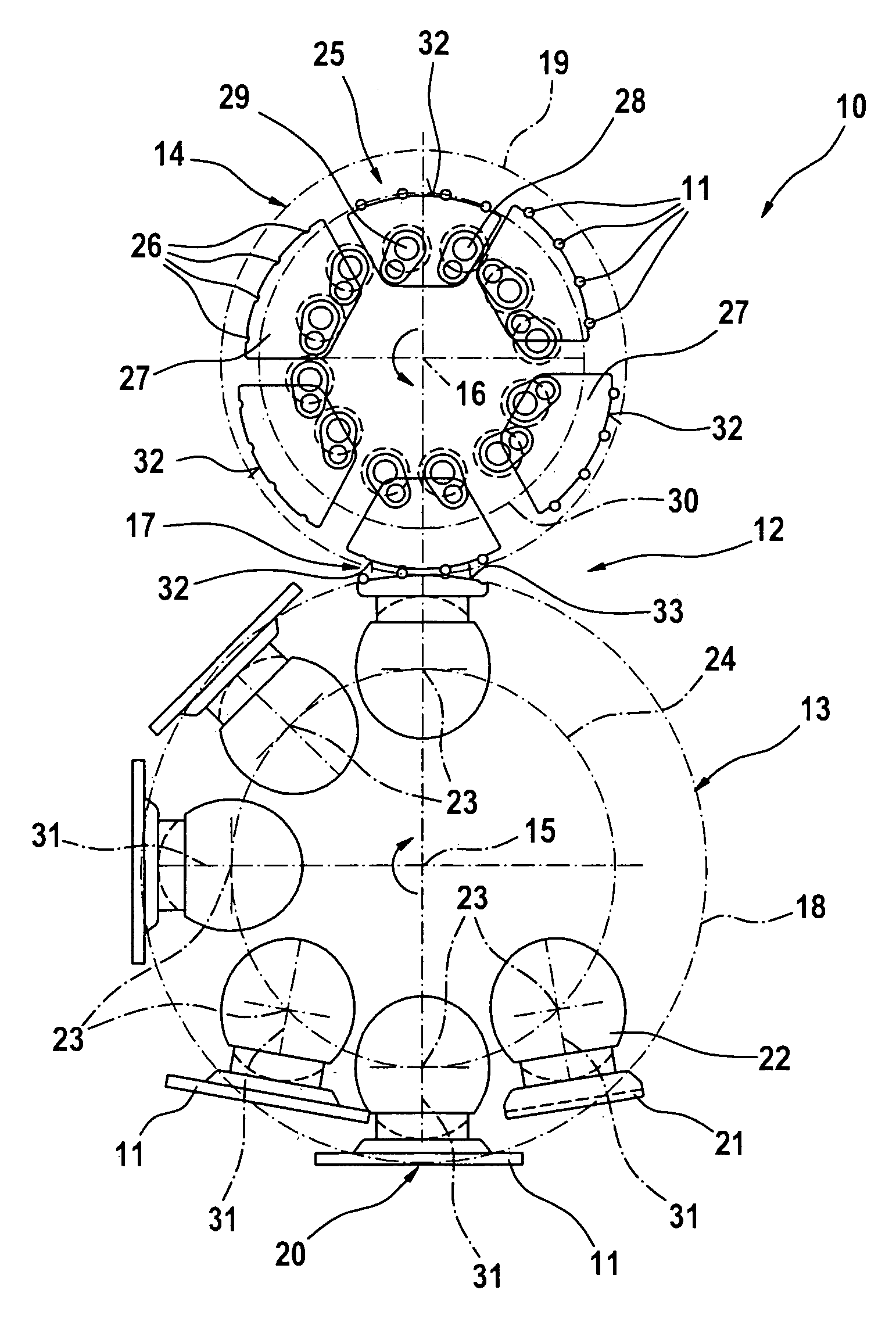
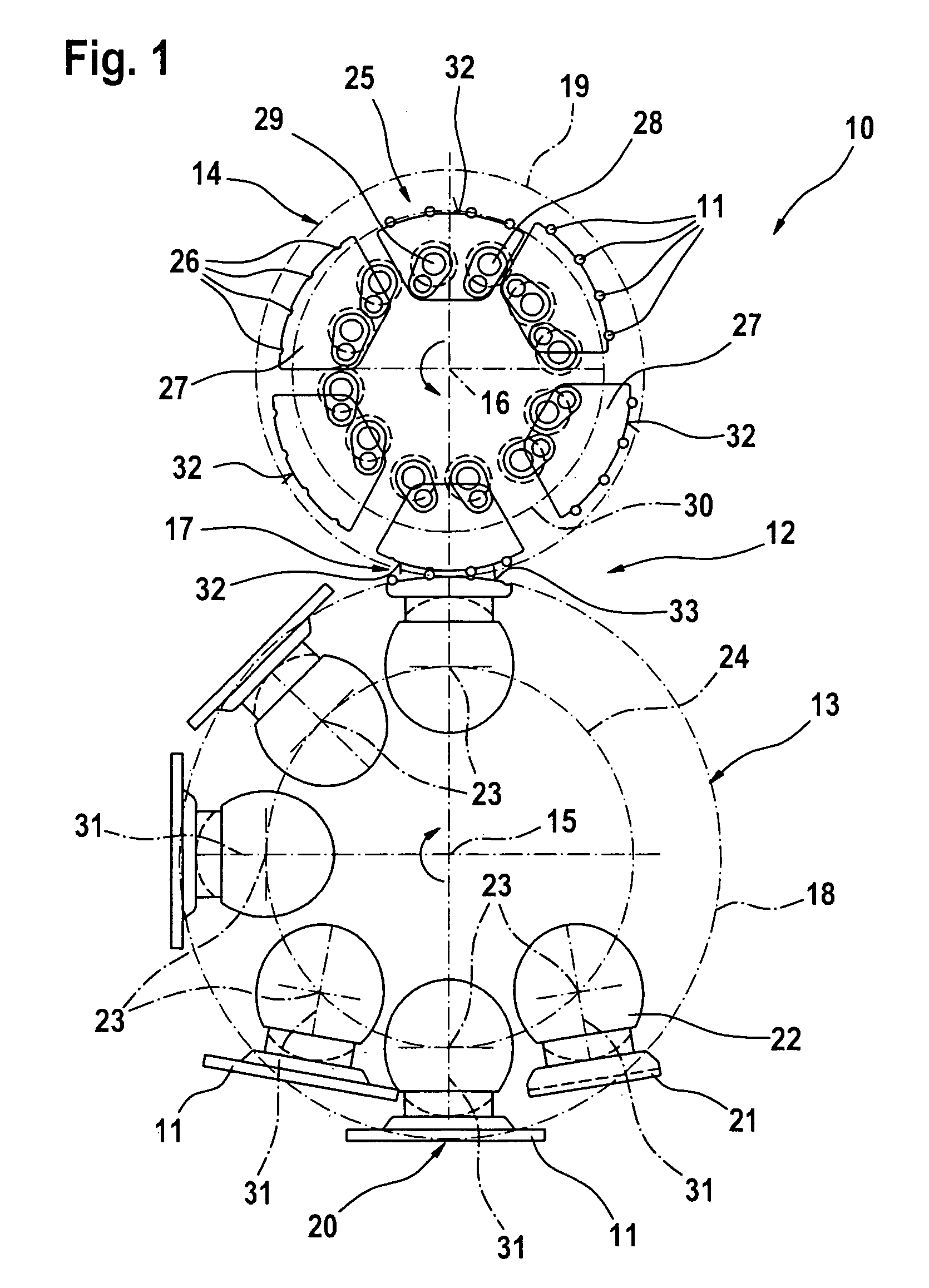
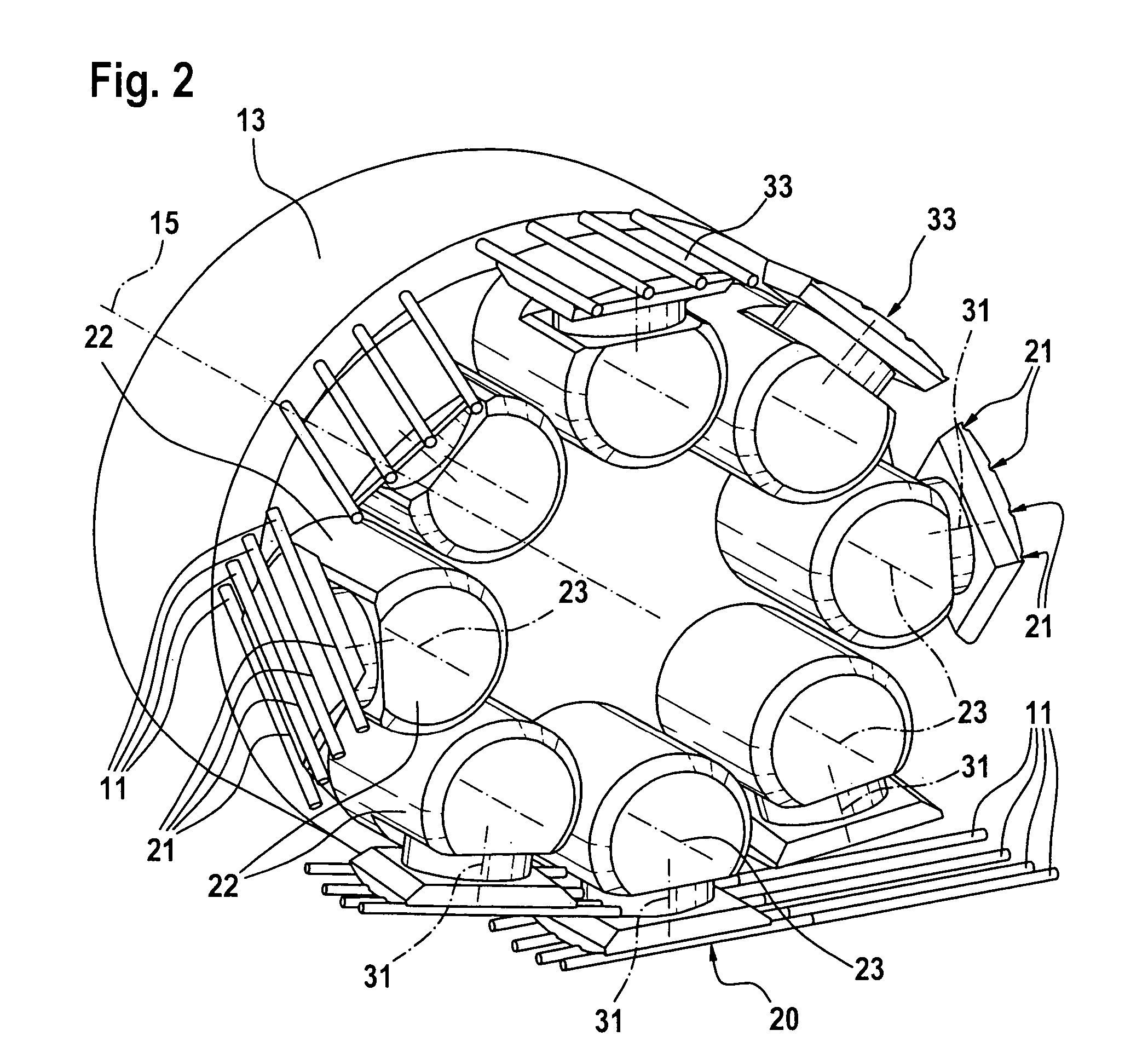
Evoked Response to Stimulation
InactiveUS20070244407A1ElectroencephalographyImplantable neurostimulatorsFunctional connectivityConfiguration design
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Multipart medical engineering system
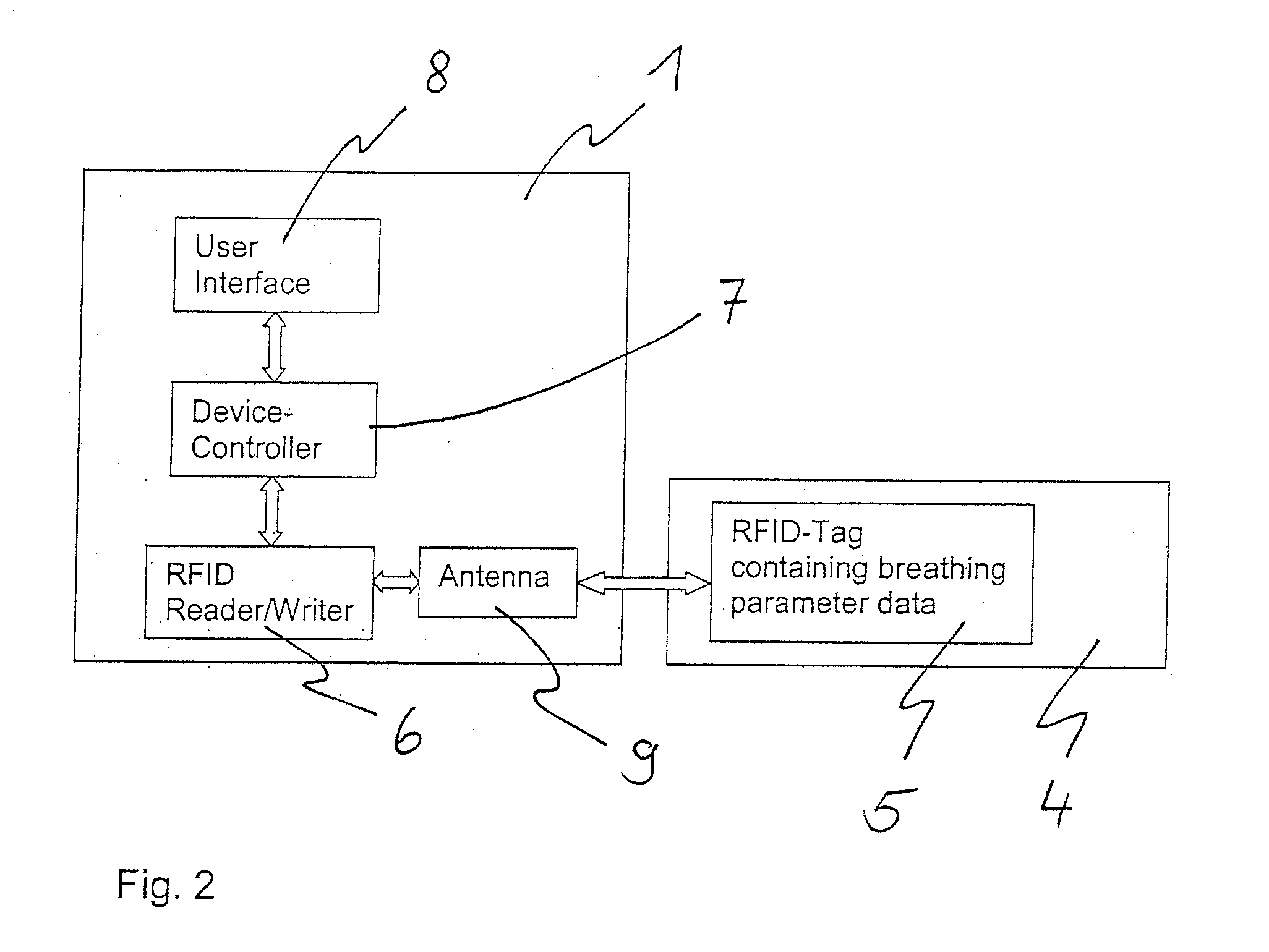
InactiveUS20060278222A1Reduce riskImprovement effortsRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFunctional connectivityBiomedical engineering
A multipart medical engineering system, which comprises at least two components that can be connected via positioning-determining connection feature (410, 411). At least one component (44) is intended to remain in the vicinity of the patient in the connected and unconnected states of the system and at least one component (41) can be removed or replaced with other components in the unconnected state. The component (44) intended to remain in the vicinity of the patient contains a data storage element (45) that can be written to and read via an interface (46) that is mechanically integrated in the position-determining connection means (410, 411).
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
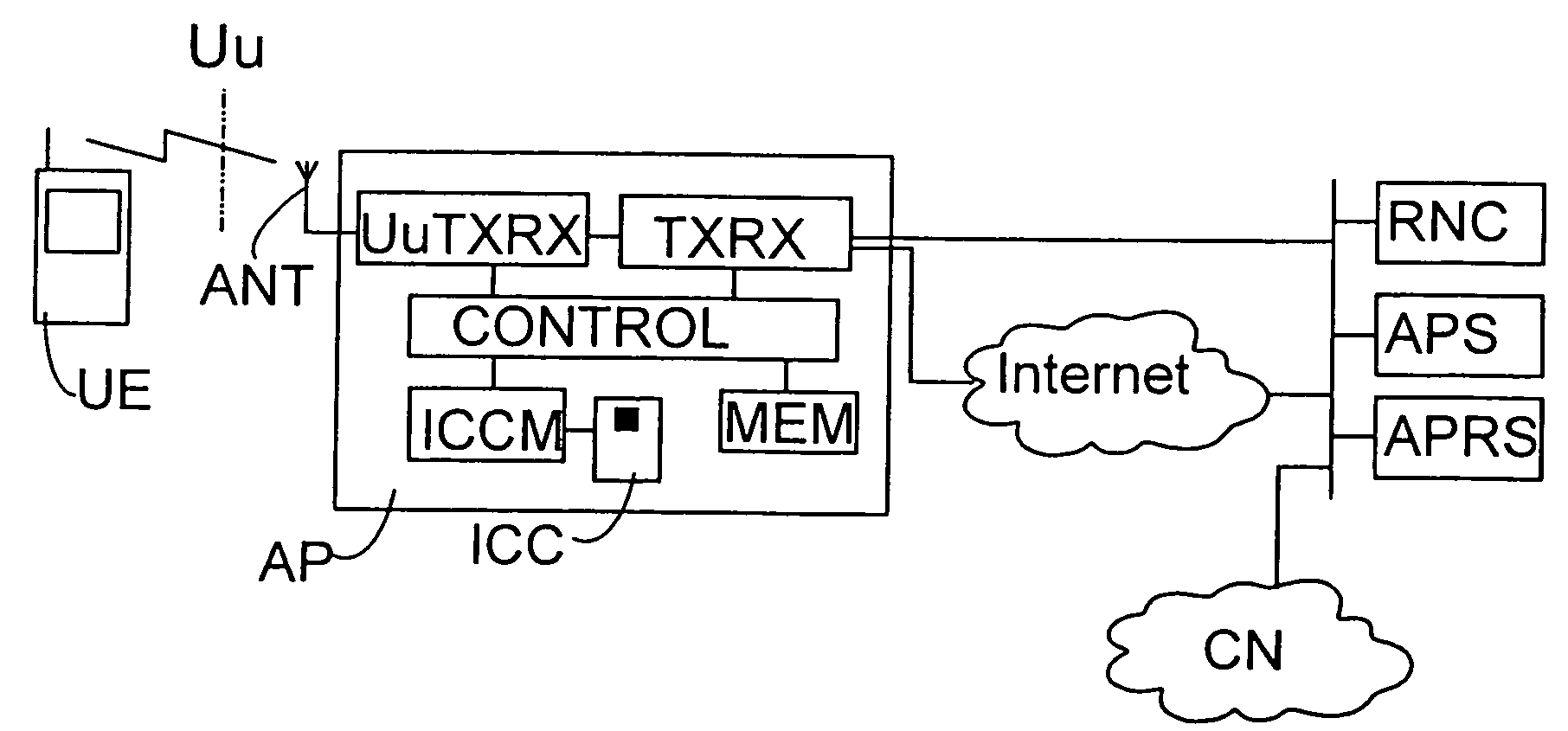
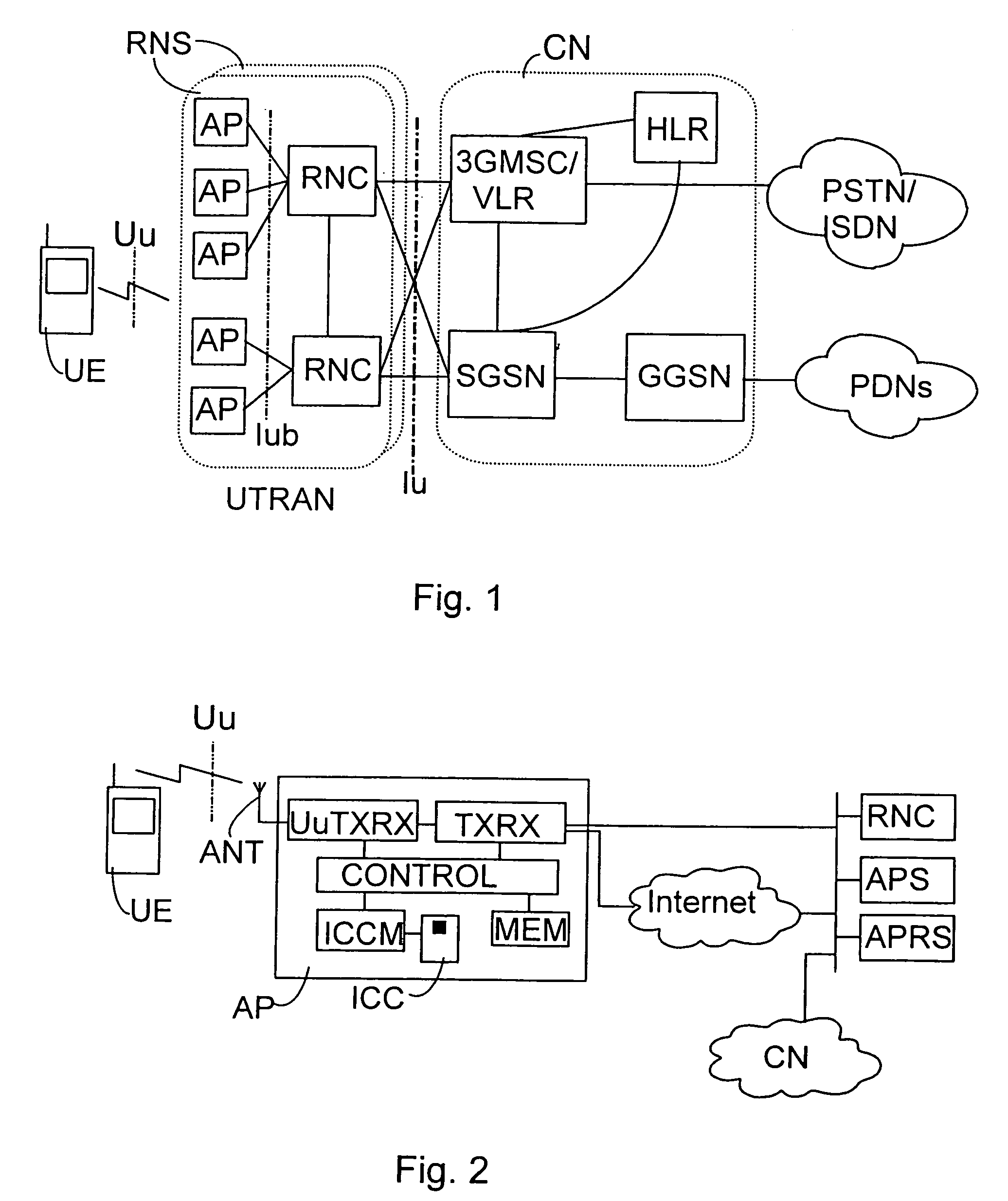
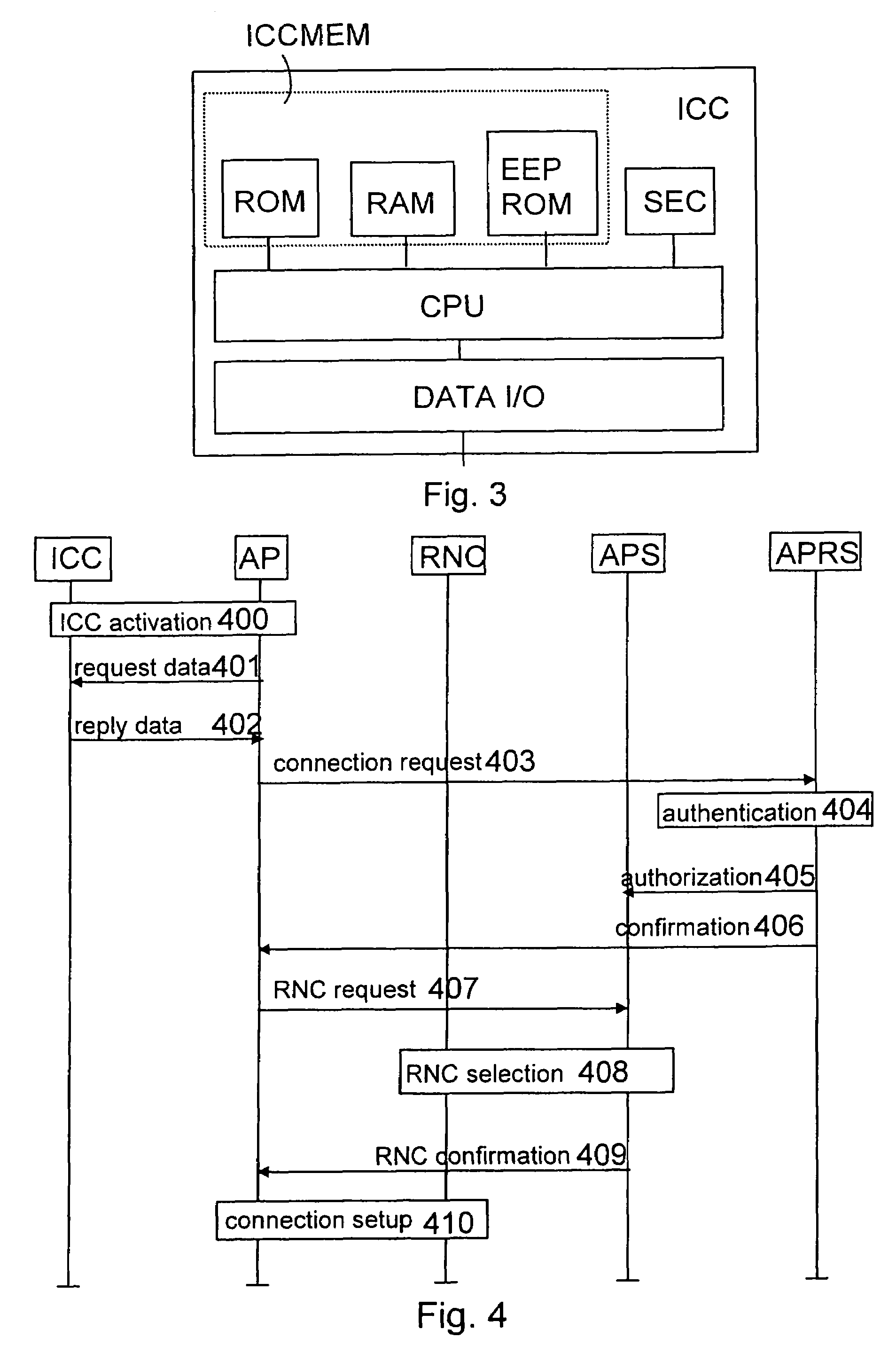
Connecting access points in wireless telecommunications systems
InactiveUS7266393B2Easily and reliably controlFirmly connectedUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsFunctional connectivityData connection
A method of connecting an access point to other network elements in a wireless telecommunication system having at least one access point offering wireless connections, and at least one fixed network part, includes storing data on an IC card for connecting at least one access point to a functional connection with the fixed network part. The IC card is connected to a functional connection with the access point when the access point is to be connected to the fixed network part. Necessary resources of the fixed network part are connected to a functional connection with the access point on the basis of said stored data. As a precondition for the connection, the IC card's rights to use the resources of the fixed network part can be checked in the fixed network part.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD +1
System, method and apparatus for performing facial recognition
InactiveUS20150317511A1Efficiently and accurately understandingCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsFunctional connectivityFacial recognition system
A method for recognizing a face in an image is performed by a facial recognition system. The system retrieves an image and detects a face within the image. The system then determines a set of facial feature positions for a set of facial features. The set of facial feature positions are used to separate the face into a set of facial feature parts. For each part, the system extracts a set of image features. The extracted features are concatenated into a full feature. The system performs dimension reduction on the full feature to derive a final feature.
Owner:ORBEUS LLC
Connectivity hub with a stationary base station and a removable second hub
InactiveUS7899970B2Easy to transportElectric digital data processingFunctional connectivityTelecommunications
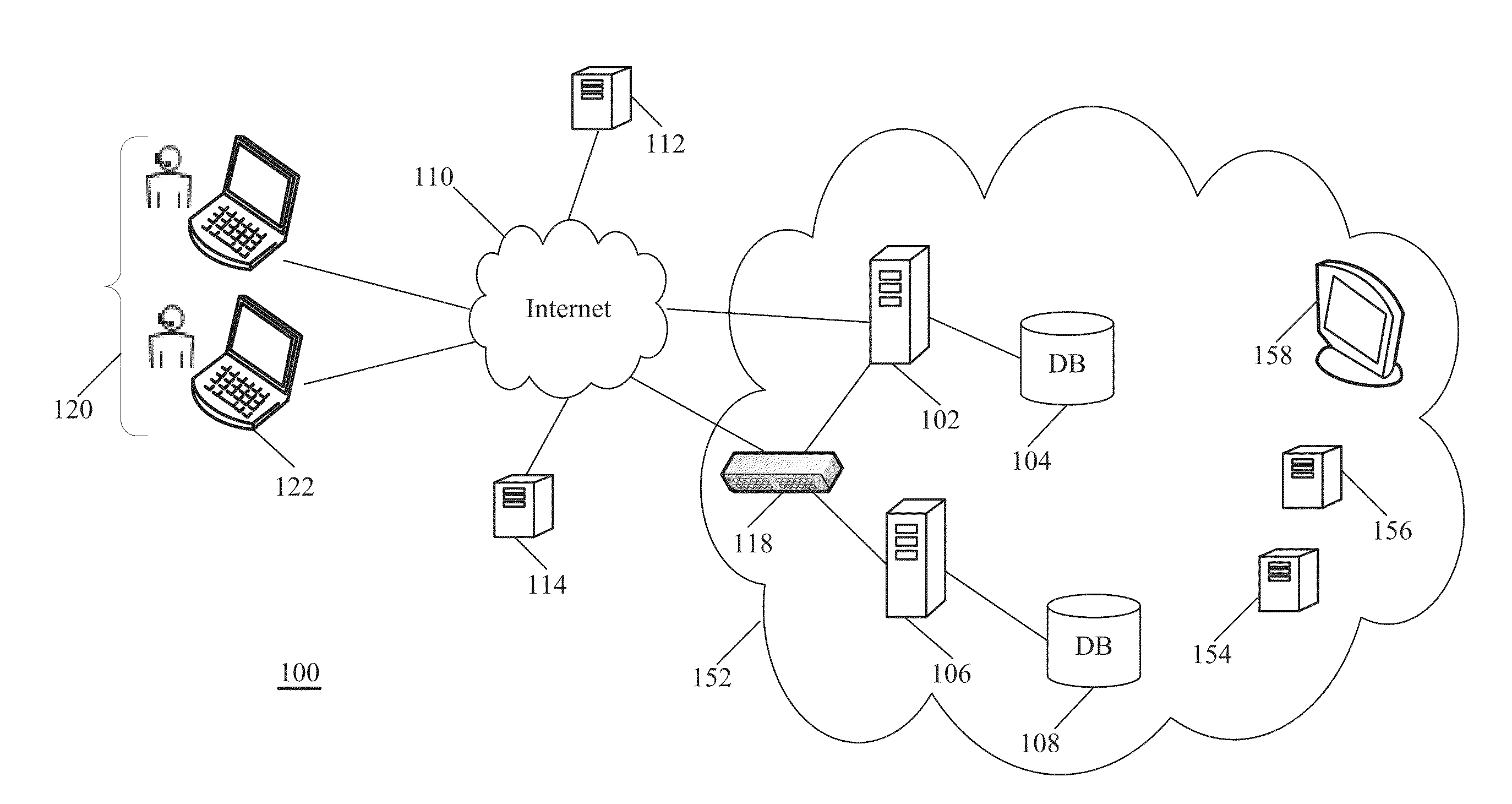
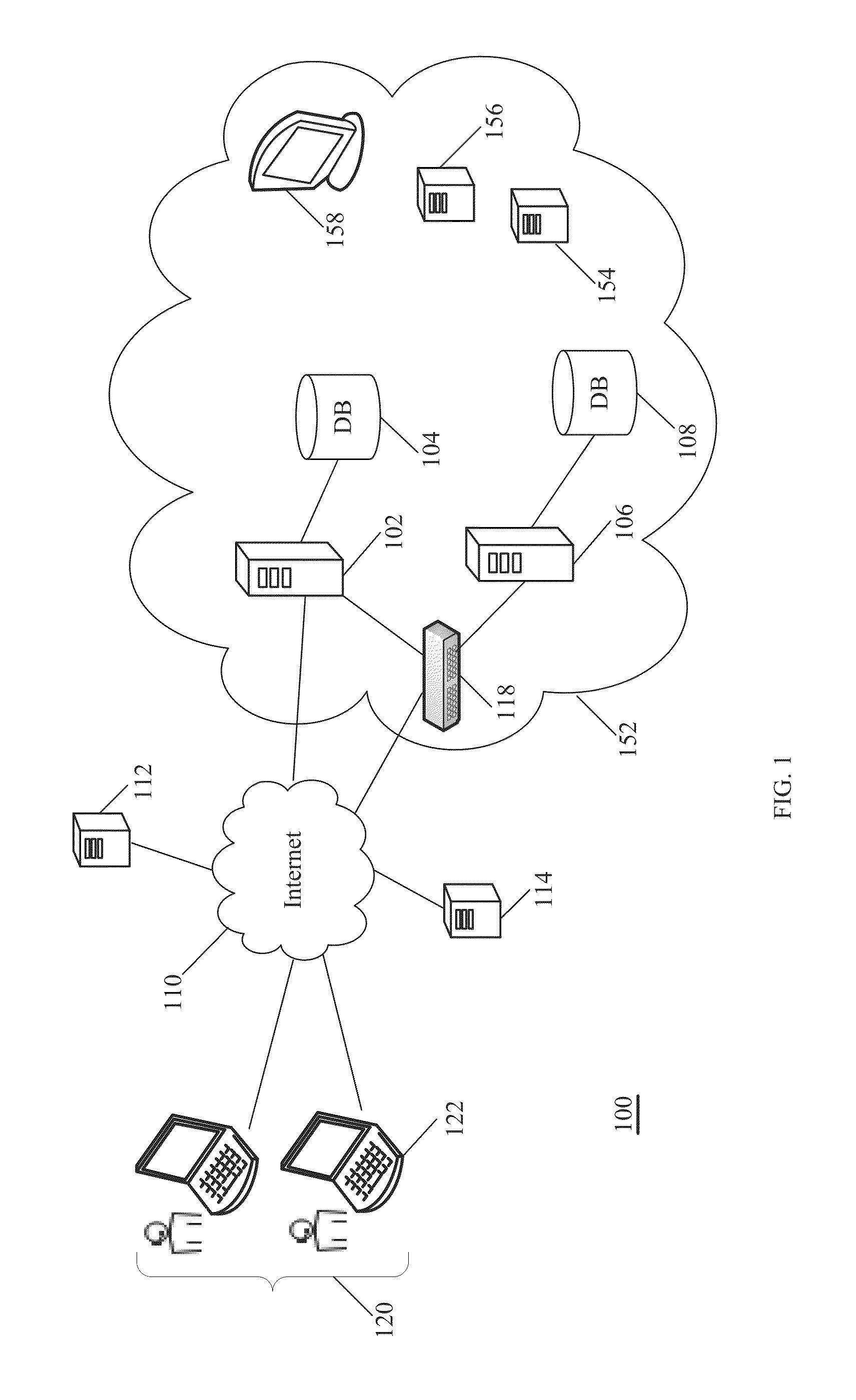
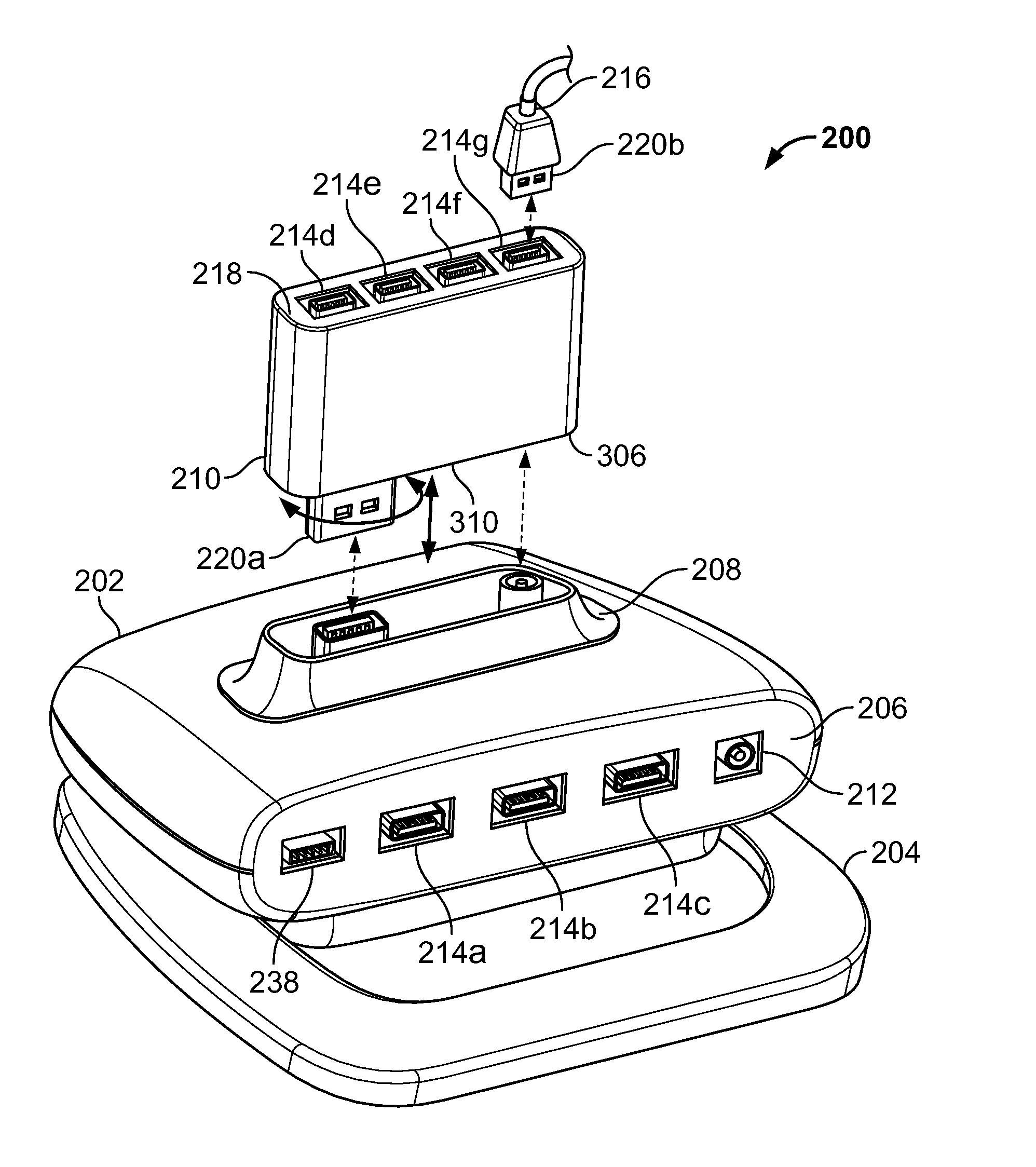
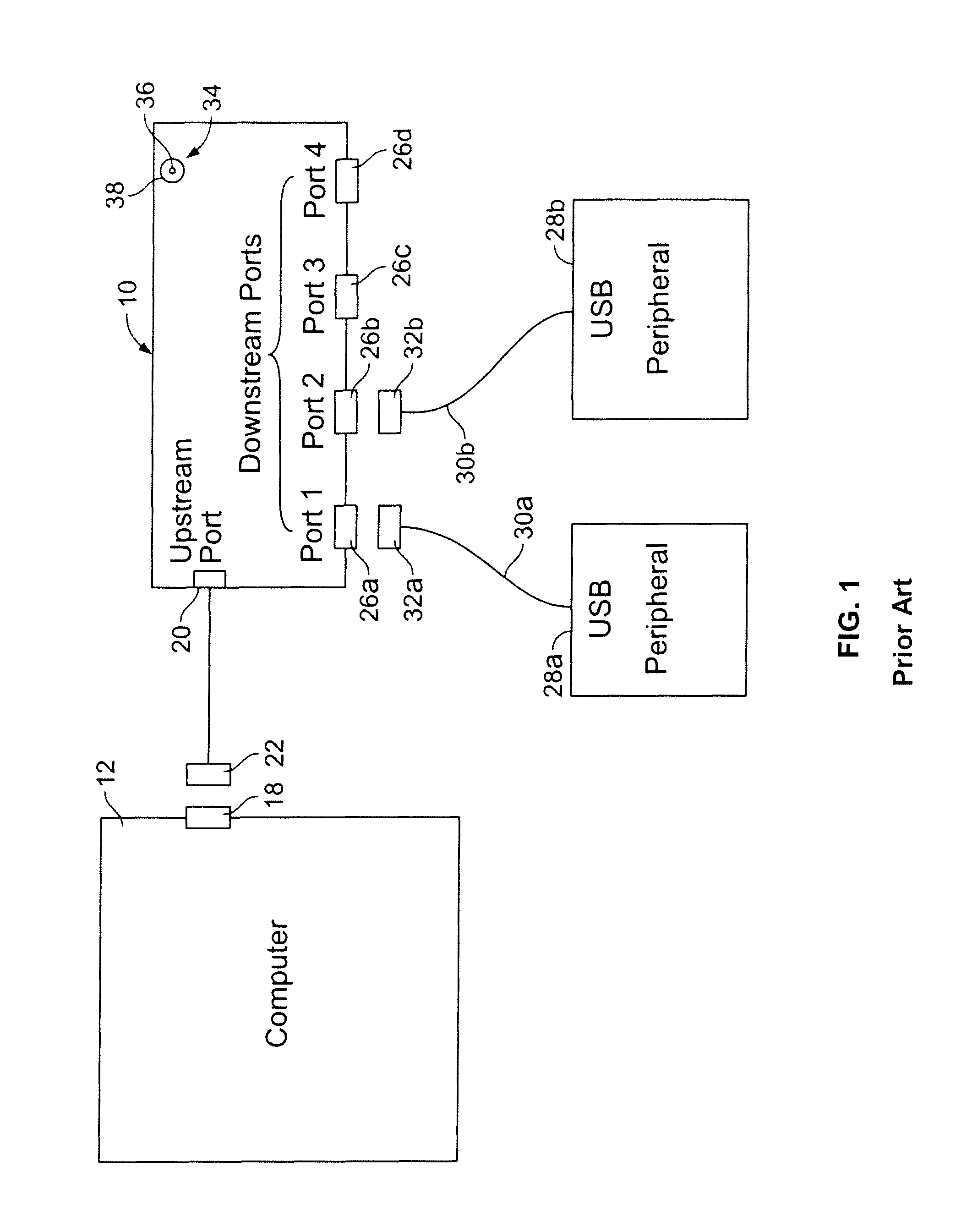
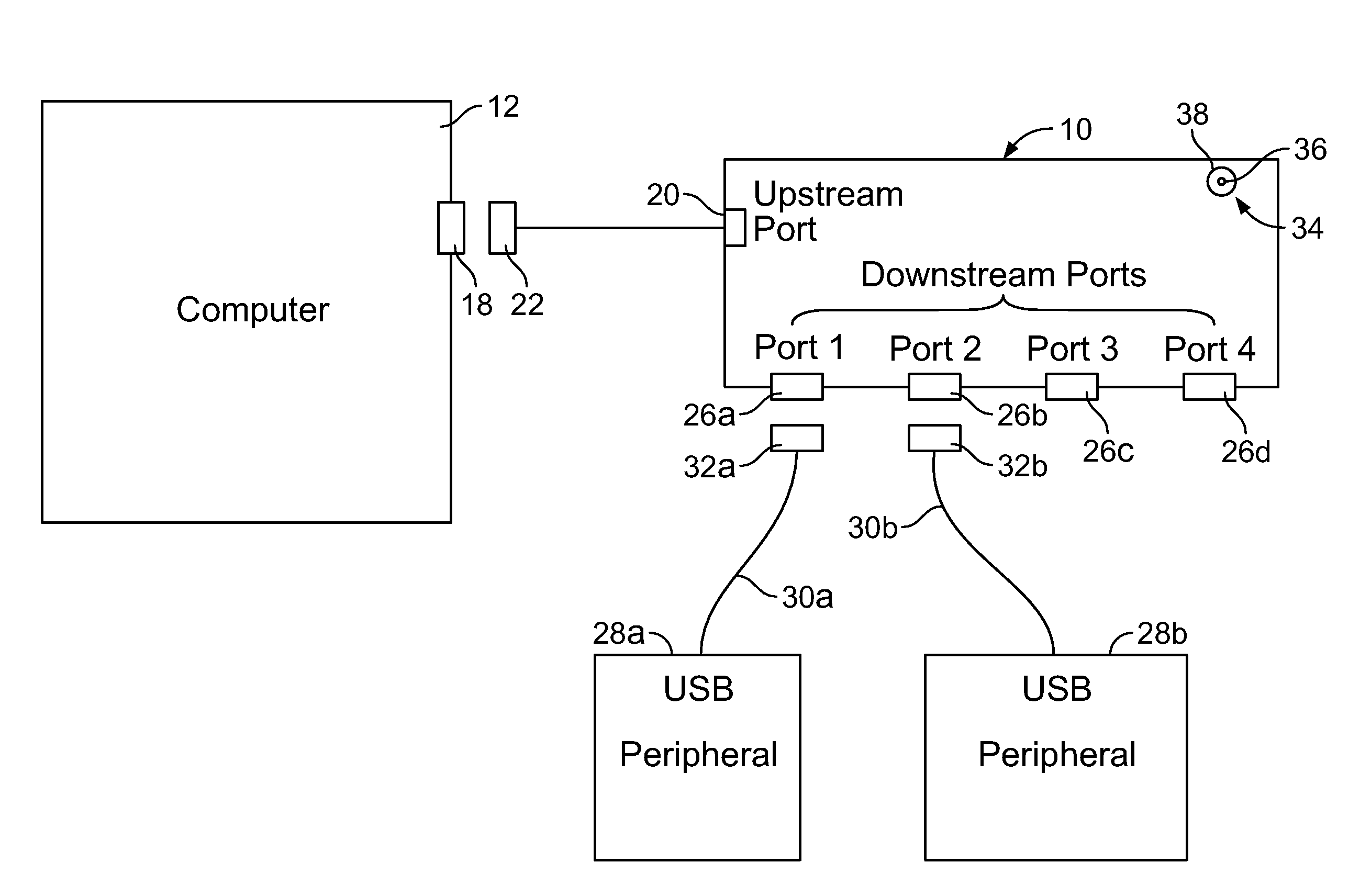
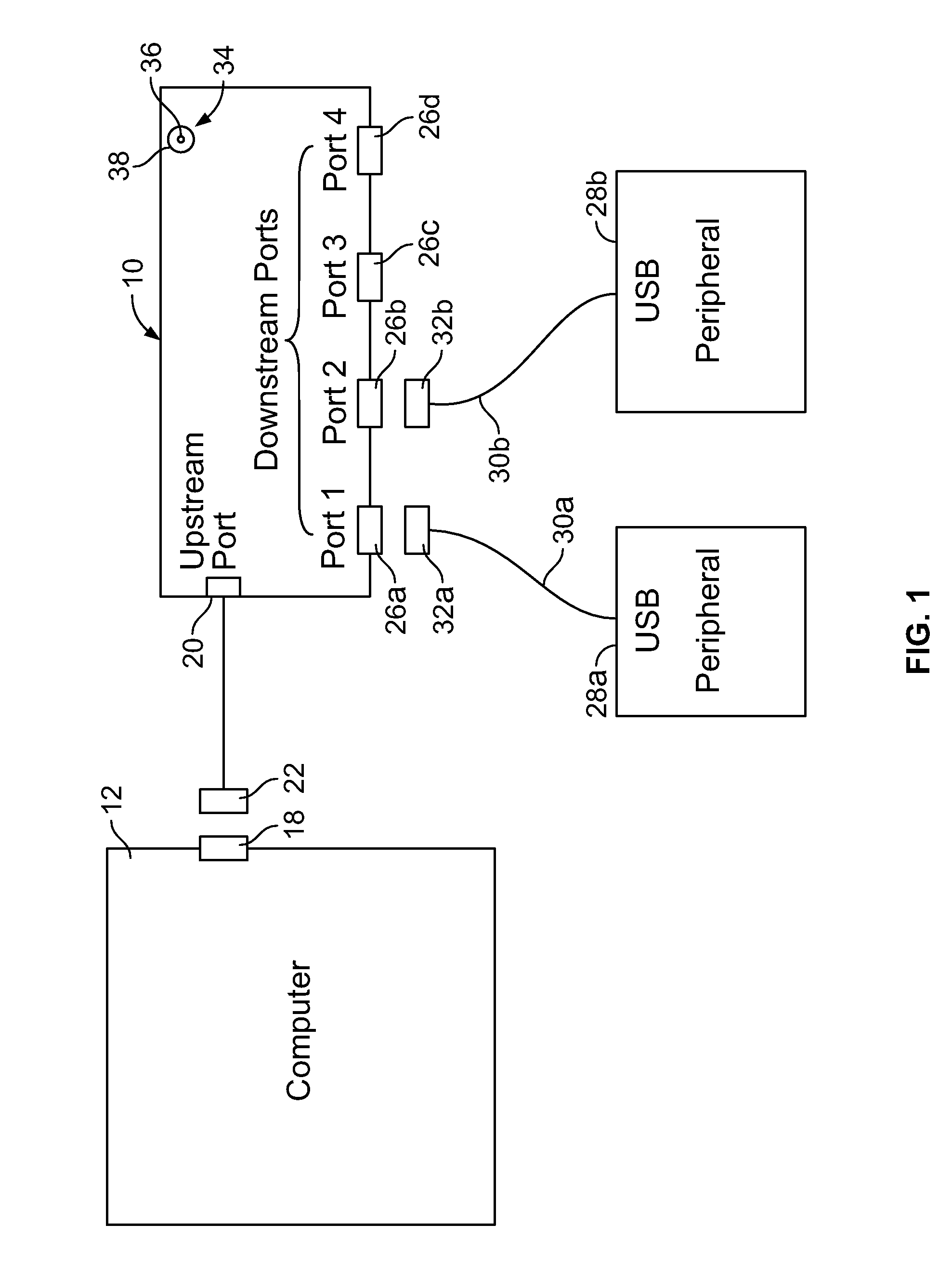
A connectivity hub enabling multiple peripheral devices to be connected with a computer includes a stationary base station functioning as a connectivity hub and a removable connectivity hub functioning by itself as a travel connectivity hub. The removable travel hub can be plugged into the stationary base station by connecting an upstream port of the removable hub to a downstream port of the base station. Thus, a user of the connectivity hub achieves the functionality of a full-featured connectivity base station as well as that of a small, easily transportable travel hub without having to purchase multiple units.
Owner:BELKIN INT
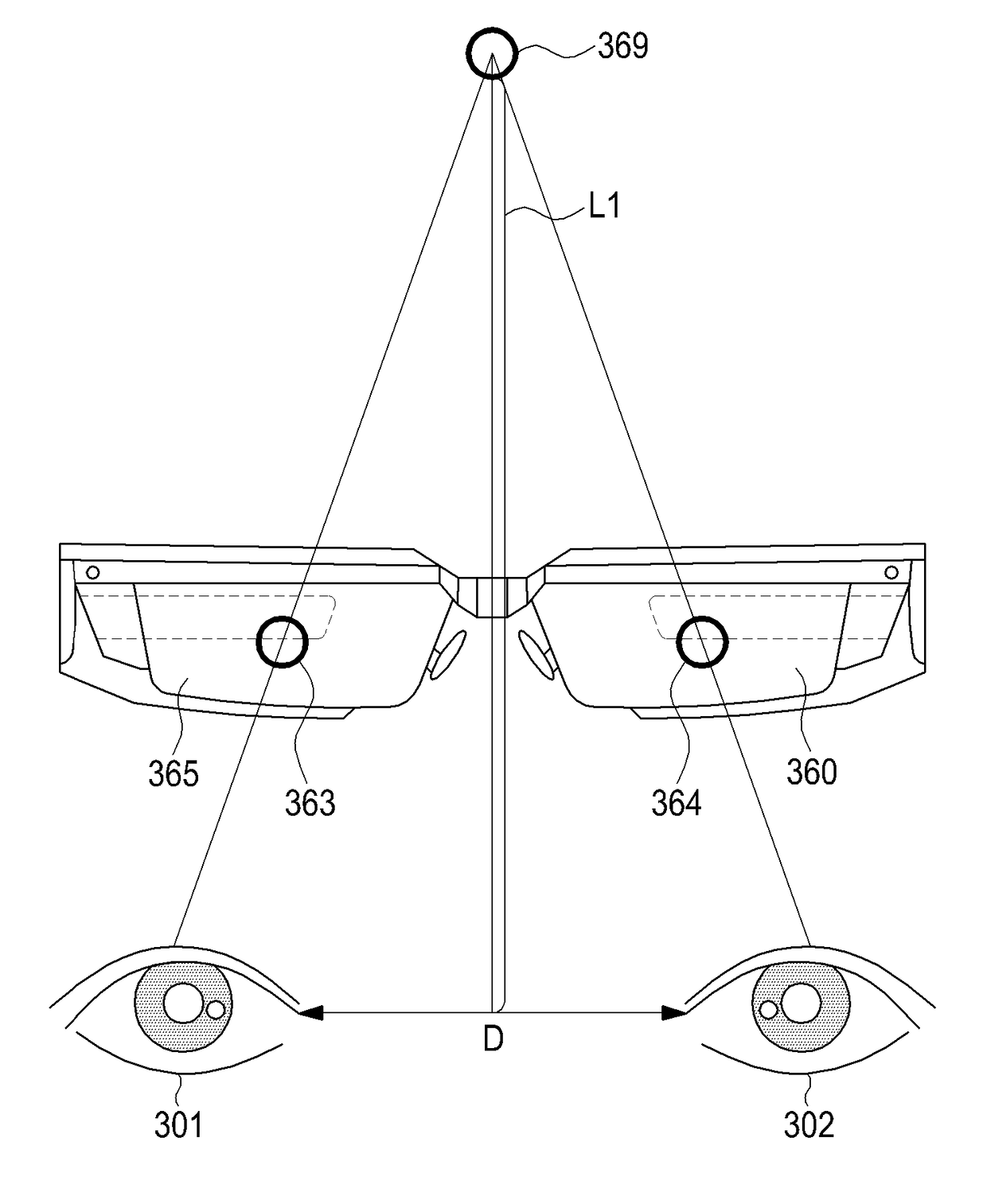
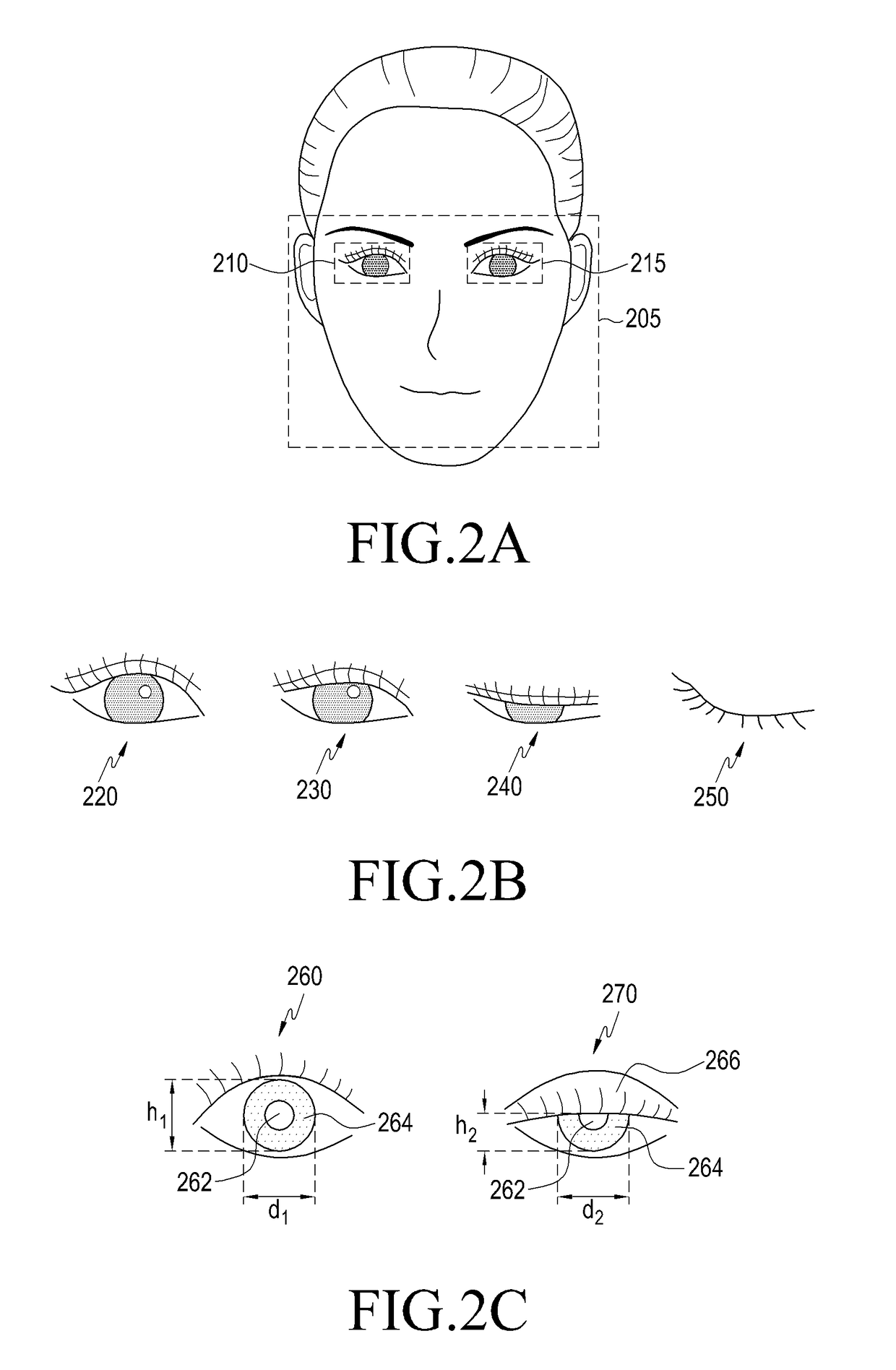
Method for displaying virtual image, storage medium and electronic device therefor
ActiveUS20180239425A1Easy to identifyInput/output for user-computer interactionImage analysisFunctional connectivityDisplay device
An electronic device comprises a first camera module, a display device, and a processor functionally connected with the first camera module and the display device. The processor may be configured to determine a size of at least one eye area included in an image obtained by the first camera module while displaying a virtual image using the display device and to control a degree of display of the virtual image corresponding to the size of the at least one eye area. Other various embodiments are also available.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Onboard apparatus, navigation system, and method for setting display screen
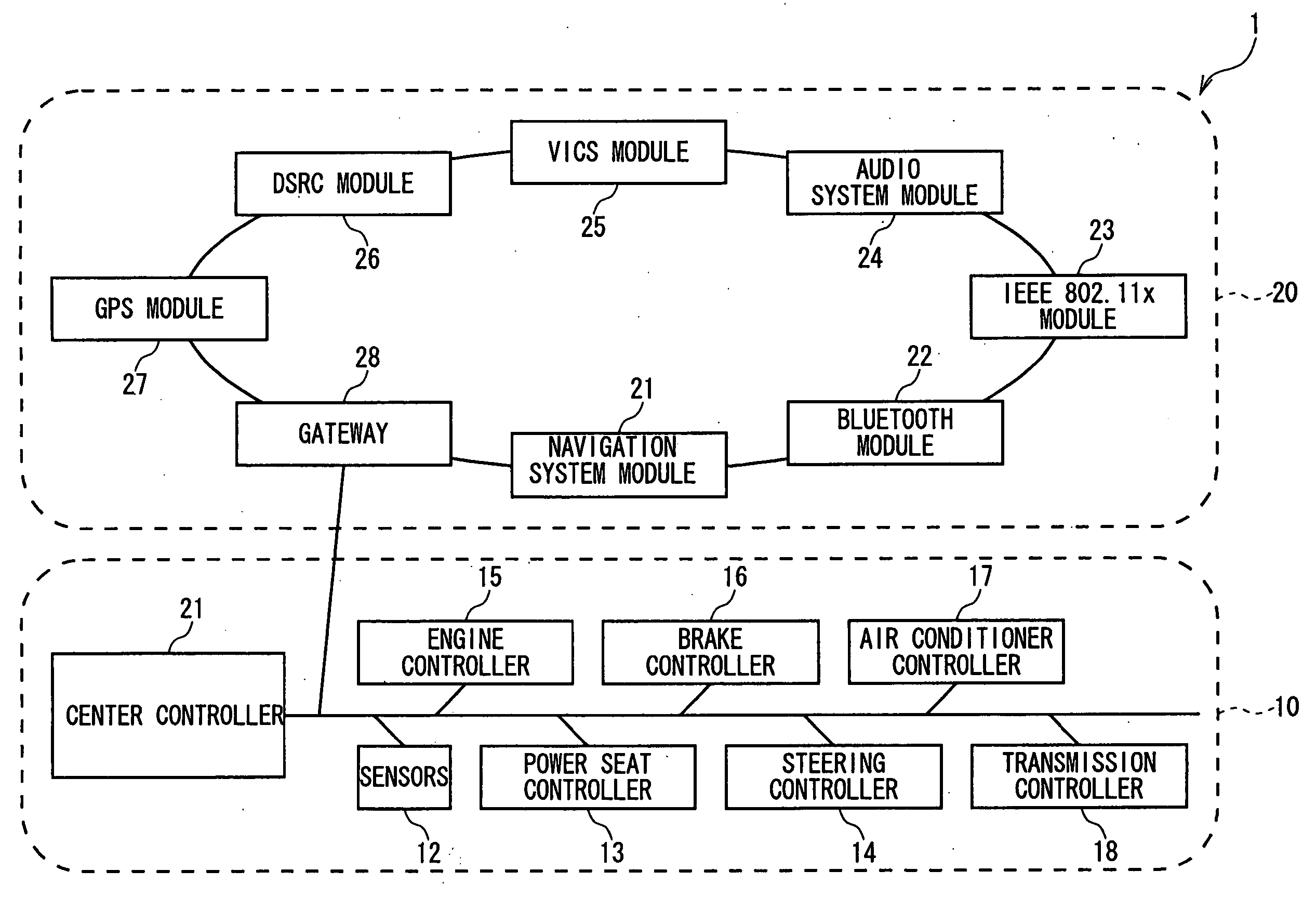
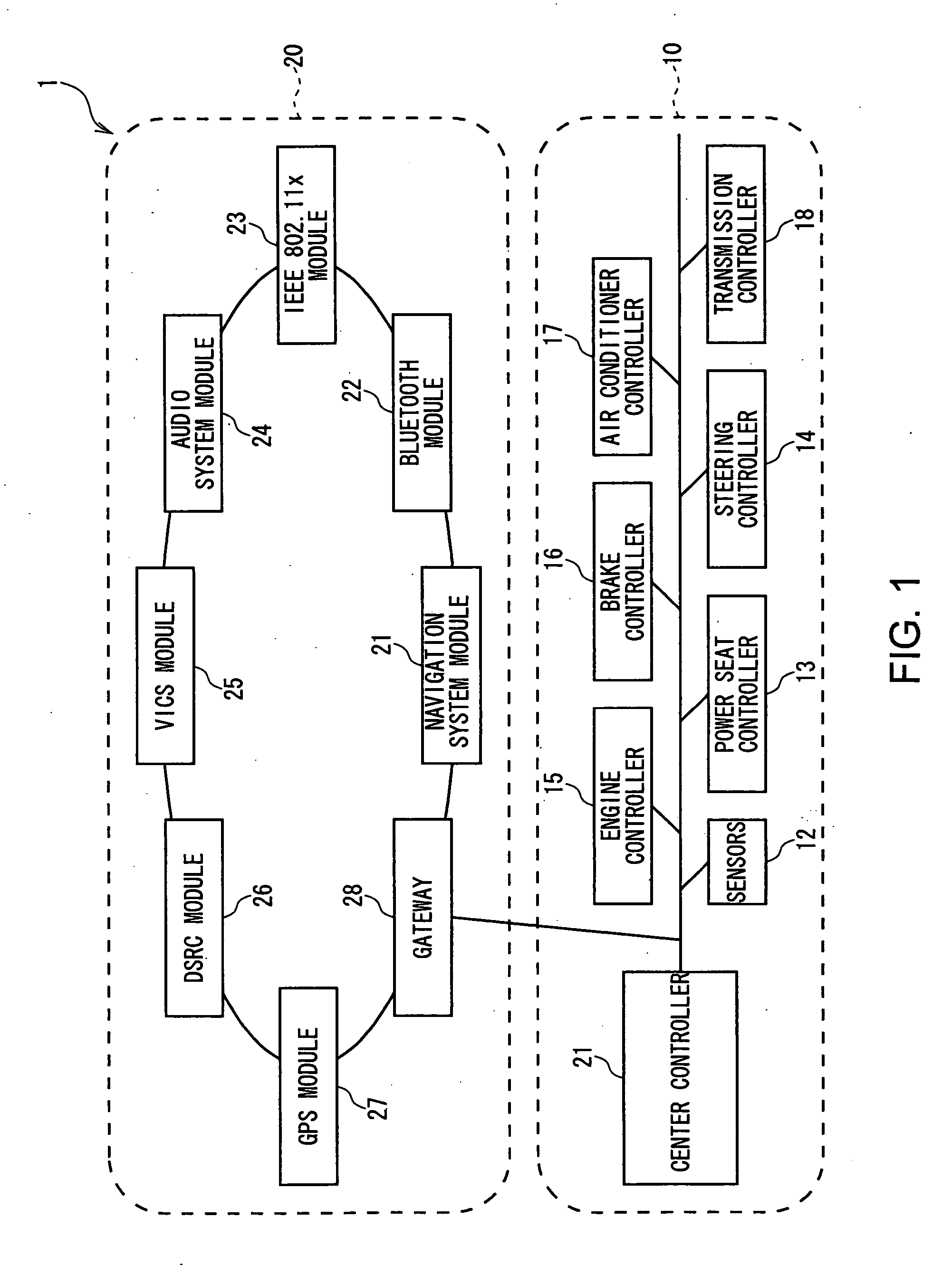
ActiveUS20040254690A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlFunctional connectivityScreen design
To use the same onboard apparatus and navigation system in many kinds of vehicles. A table in which manufacturers and vehicle types are connected with designs and functions has been previously stored in a navigation system module 21. The navigation system module 21 itself sends the center controller 11 a query about vehicle information (the country that manufactured, manufacturer, vehicle type, using country, manufacturing number), recognizes the vehicle information supplied from the center controller 11, and automatically sets the screen design, function, etc., suitable to the vehicle on which the onboard apparatus is mounted.
Owner:SONY CORP
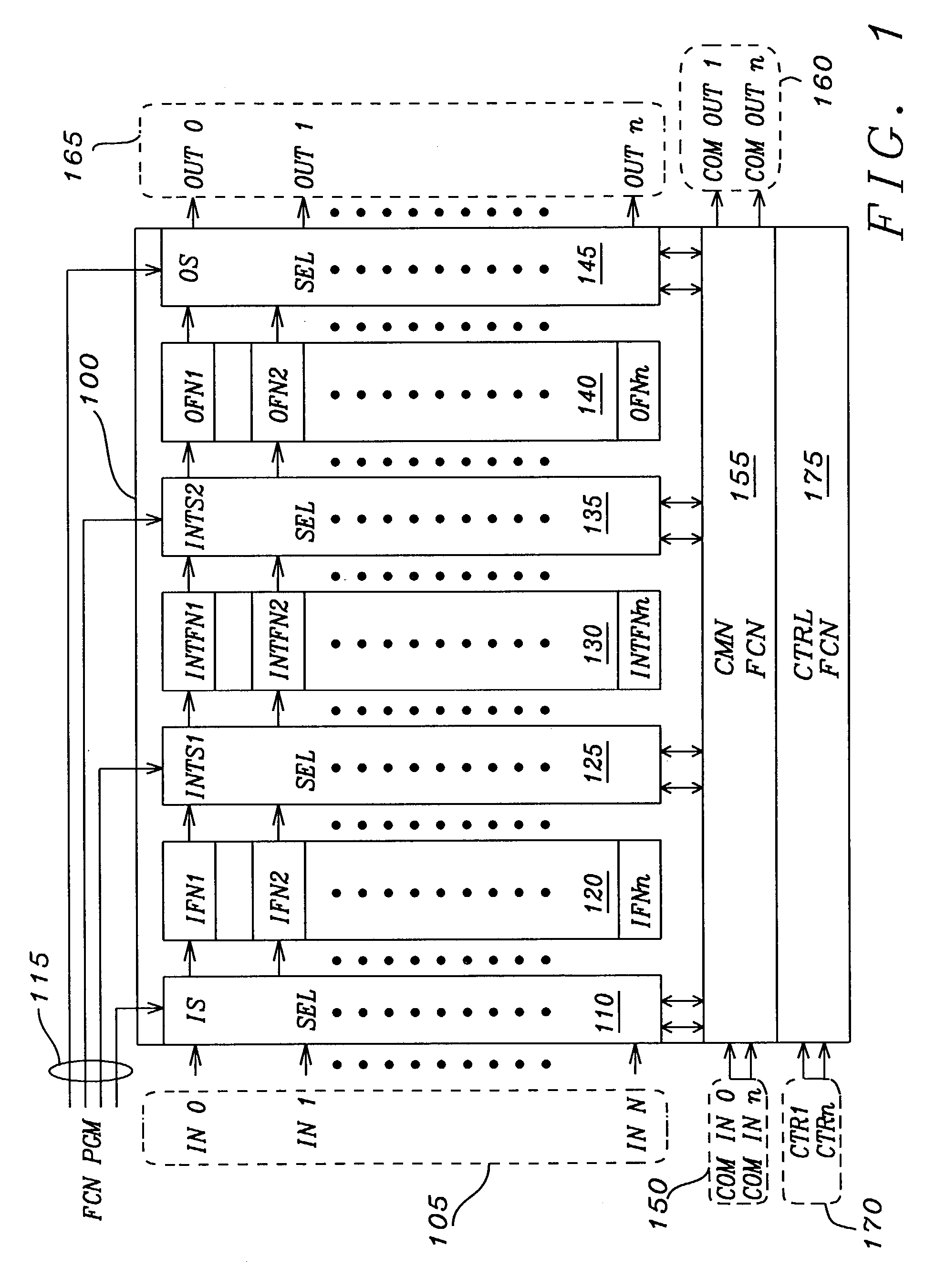
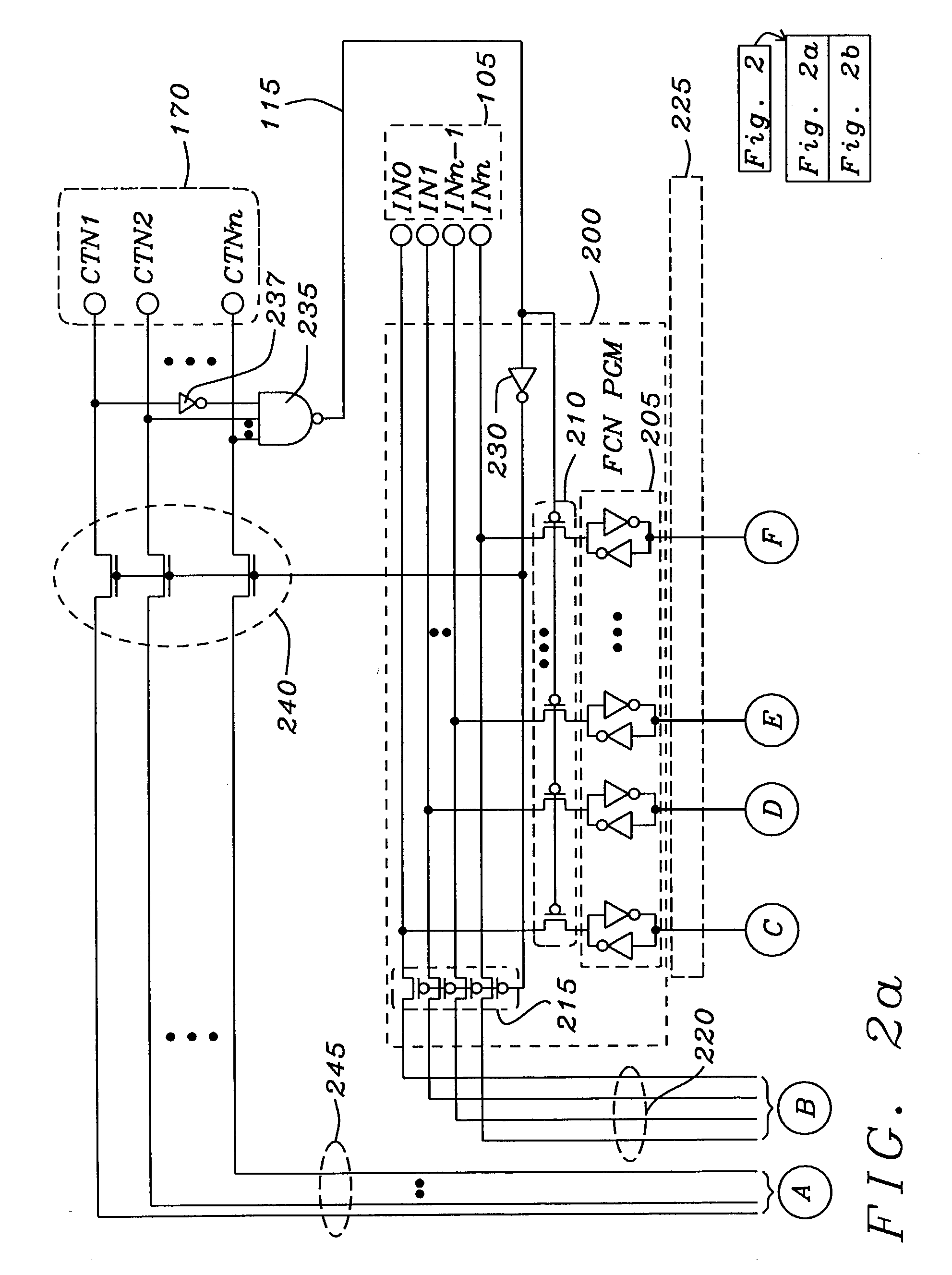
Software programmable multiple function integrated circuit module
InactiveUS7360005B2Slow to programSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementCurrent/voltage measurementFunctional connectivityElectricity
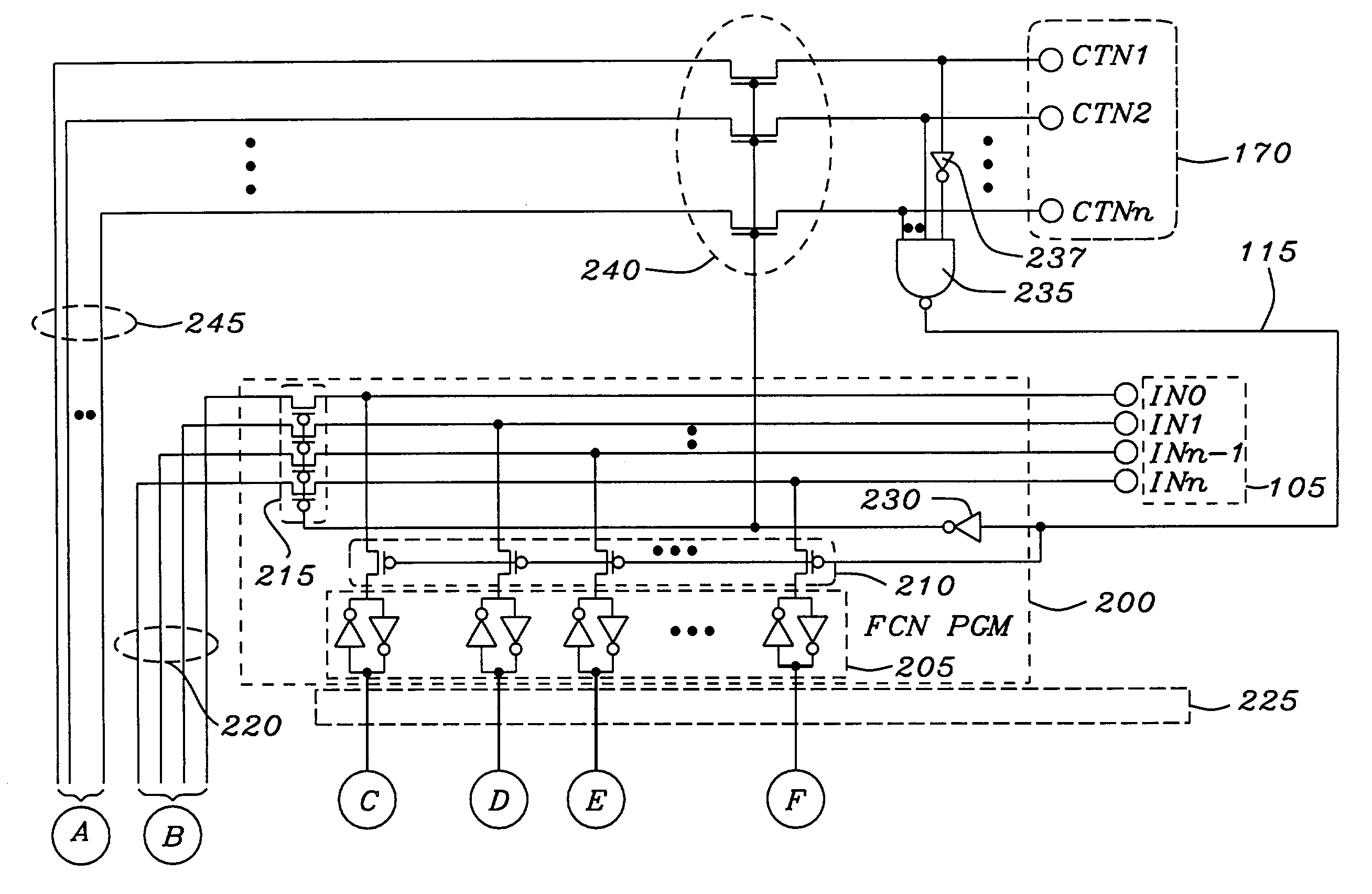
An electrically programmable multiple selectable function integrated circuit module has a plurality of optionally selectable function circuits, which receive and manipulate a plurality of input data signals. The outputs of the plurality of optionally selectable function circuits are either interconnected to each other or connected to a plurality of output connectors to transmit manipulated output data signals to external circuitry. The electrically programmable multiple selectable function integrated circuit module has at least one configuration connector, which may be multiplexed with input control and timing signals, connected to a function configuration circuit to receive electrical configuration signals indicating the activation of a program mode and which of the optionally selectable function circuits are to be elected to manipulate the input data signals. The function configuration circuit is connected to the optionally selectable function circuits to selectively elect, which of the optionally selectable function circuits are to is manipulate the input data signals. The electrically programmable multiple selectable function integrated circuit module optionally has common function circuit connected to common function connectors and the plurality of optionally selectable function circuits to manipulate common data signals, and transmit common output data signals to the selectable function circuits.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
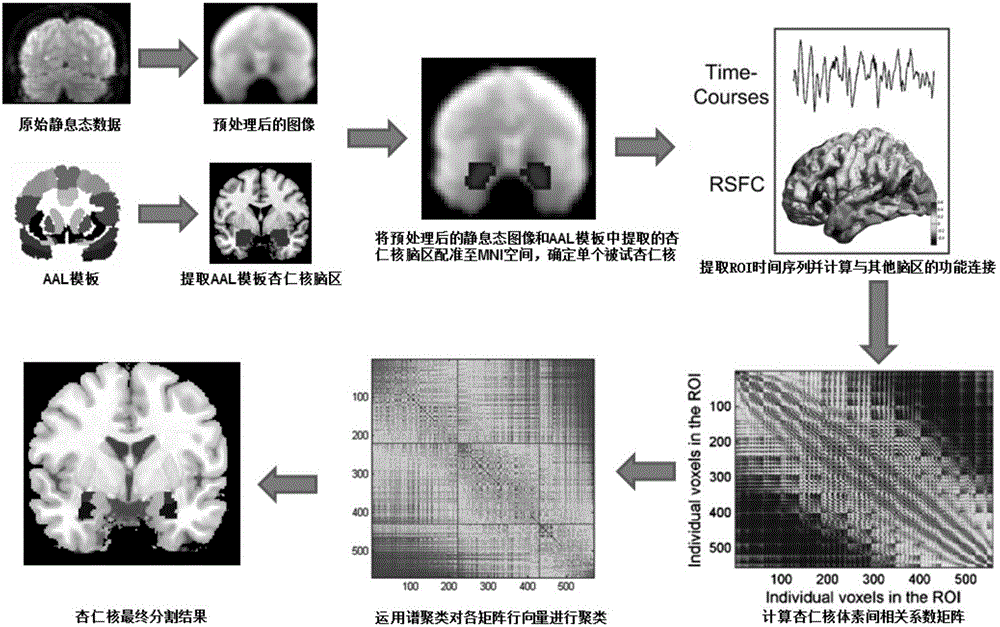
Amygdaloid nucleus spectral clustering segmentation method based on resting state function connection
ActiveCN106023194AGood repeatabilityImage enhancementImage analysisFunctional connectivityPattern recognition
The invention discloses an amygdaloid nucleus spectral clustering segmentation method based on resting state function connection, and the method is used for carrying out the automatic high-efficiency segmentation of an encephalic region based on a spectral clustering algorithm according to the similarity of internal voxel functions of an amygdaloid nucleus. The method comprises the steps: firstly carrying out the preprocessing of resting state magnetic resonance data; secondly carrying out the extraction of the encephalic region of the amygdaloid nucleus; thirdly carrying out the connection calculation of internal voxel whole-brain functions of the amygdaloid nucleus; and finally carrying out the spectral clustering segmentation of a function connection matrix. The automatic segmentation algorithm proposed by the invention and an amygdaloid nucleus clinic dissection result are enabled to be greatly consistent with each other, and the stability and noise interference resistance are enabled to be more satisfying. Compared with a conventional manual segmentation method, the method is simpler and more convenient and efficient, and is high in repeatability.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for detecting brain network function connectivity lateralization based on modality fusion
ActiveCN103345749ALaterality detectionImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityFunctional connectivity
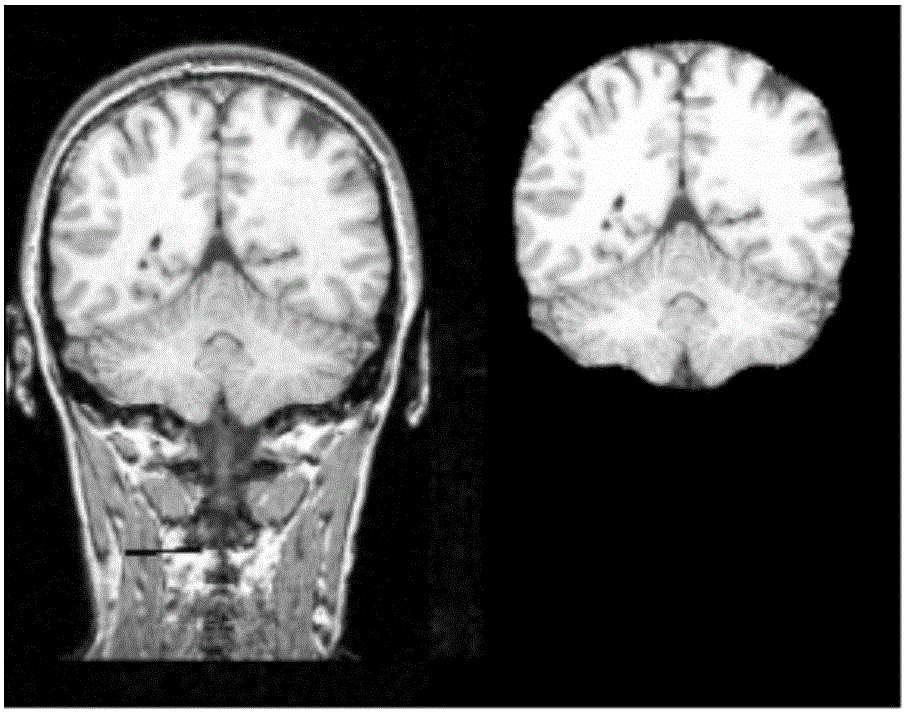
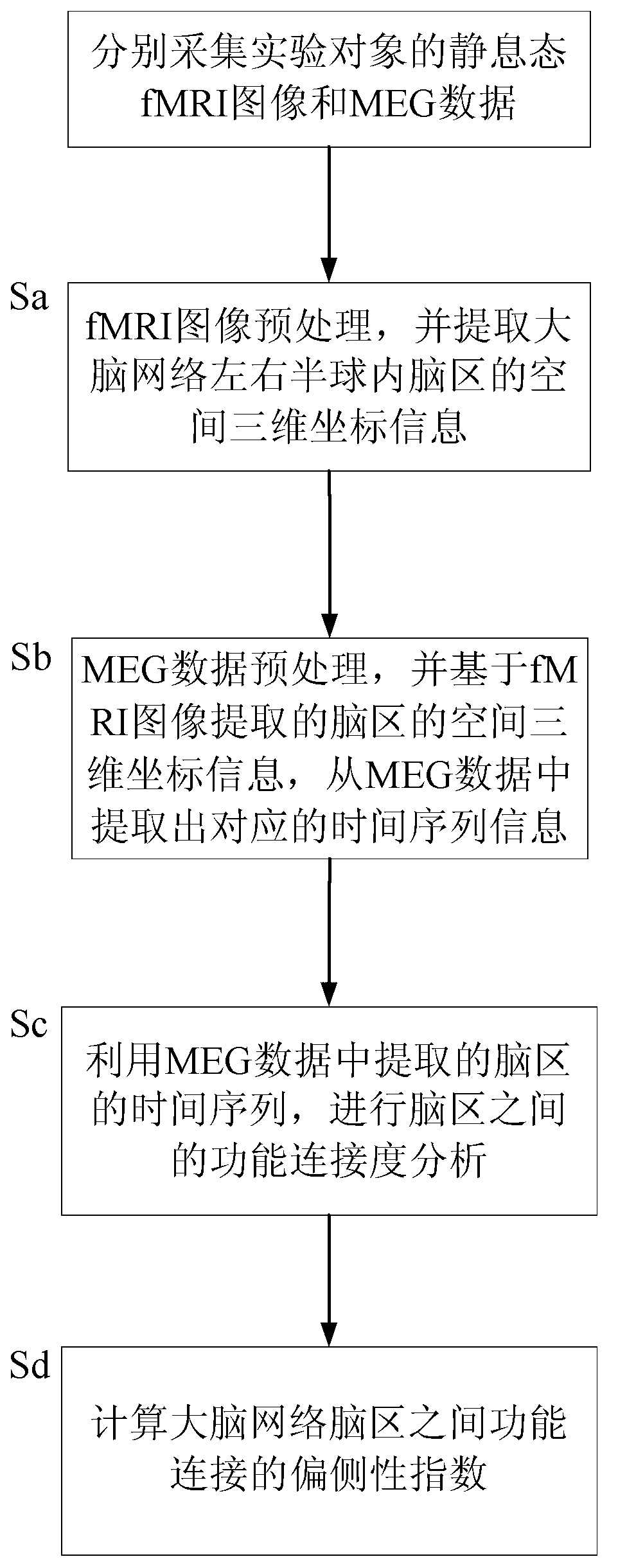
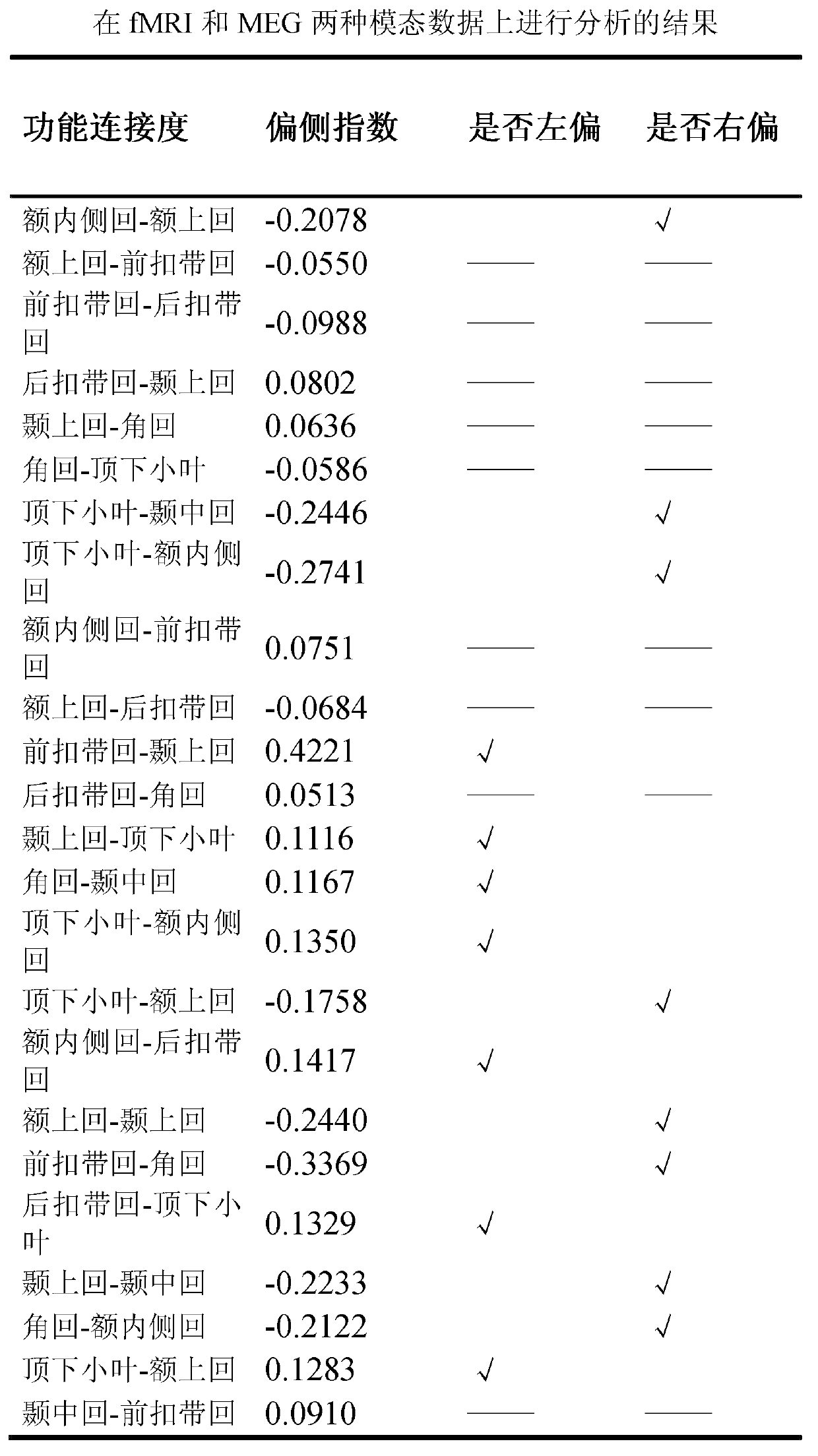
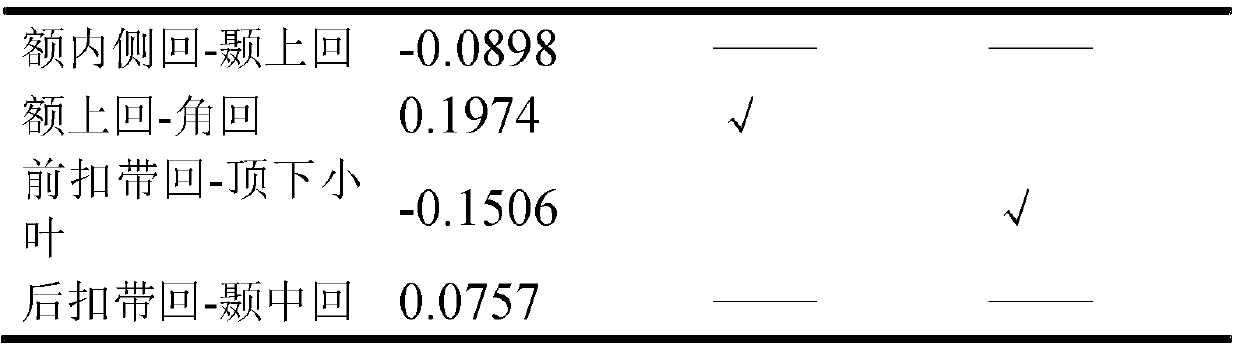
The invention relates to a method for detecting brain network function connectivity lateralization based on modality fusion. The method includes the steps that first, pretreatment is conducted on an fMRI image, and three-dimensional space coordinate information of brain areas inside a left hemisphere and a right hemisphere of a brain network is extracted; then, corresponding time series information is extracted from pretreated MEG data based on the three-dimensional space coordinate information of the brain areas extracted through the fMRI image; afterwards, the time series of the brain areas extracted from the MEG data can be used for analyzing the function connectivity between the brain areas; ultimately, the lateralization index of the function connectivity between the brain areas of the brain network is calculated. The method is an effective method for detecting the brain network function connectivity lateralization based on magnetic resonance and magnetoencephalogram modality fusion, and the method can detect the brain network function connectivity lateralization more completely and comprehensively compared with a traditional detection method which only uses the fMRI image.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and method for the delivery of rod-shaped articles
InactiveUS20050082141A1Shorten speedWithout reducing “ output ” and capacityCigarette manufactureConveyor partsFunctional connectivityMechanical engineering
Owner:HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG
Gripping Element And Gripper Input Module For A Haptic Input System
ActiveUS20140165770A1Easy to cleanImprove the bactericidal effectMechanical apparatusJointsFunctional connectivityEngineering
A gripping element for arrangement on an adapter element in order to form a gripper input module for a haptic input system for controlling an object, including a receptacle for holding at least two fingers of a user therein, wherein, at least in one portion, the receptacle has a functional connection to at least one sensor means, and at least one connection element for arranging the gripping element on the adapter element, wherein the receptacle is configured such that movement information of a movement of at least one finger of the user in the receptacle can be detected by the sensor means and hence the movement information can be transmitted for controlling the at least one object. There is also disclosed a corresponding adapter element, a gripper input module consisting of a gripping element and adapter element, and also to a haptic input system and medical instrument system.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
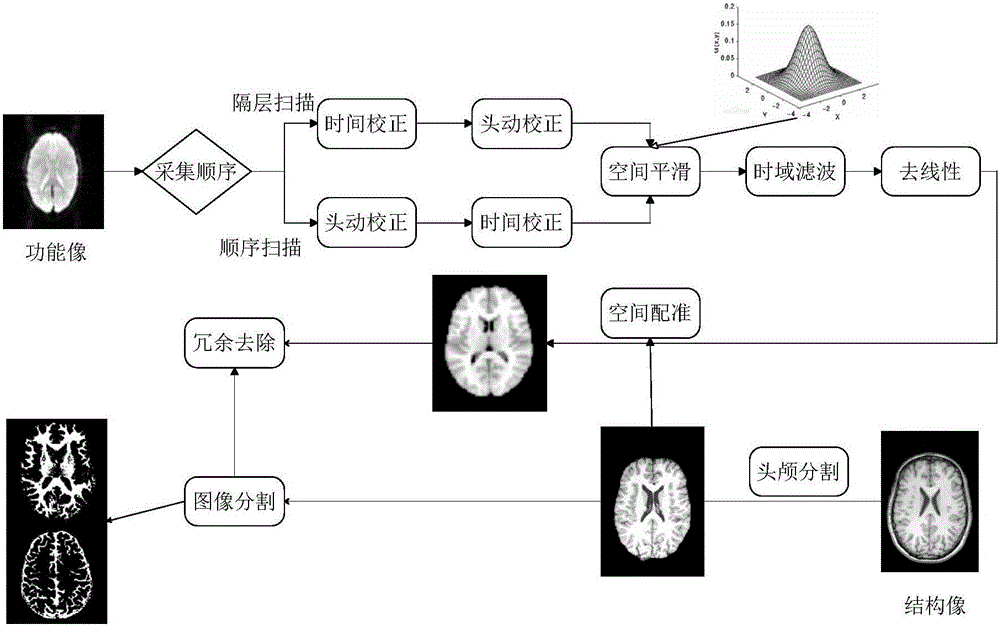
Method and system for extracting abnormal parameters of brain
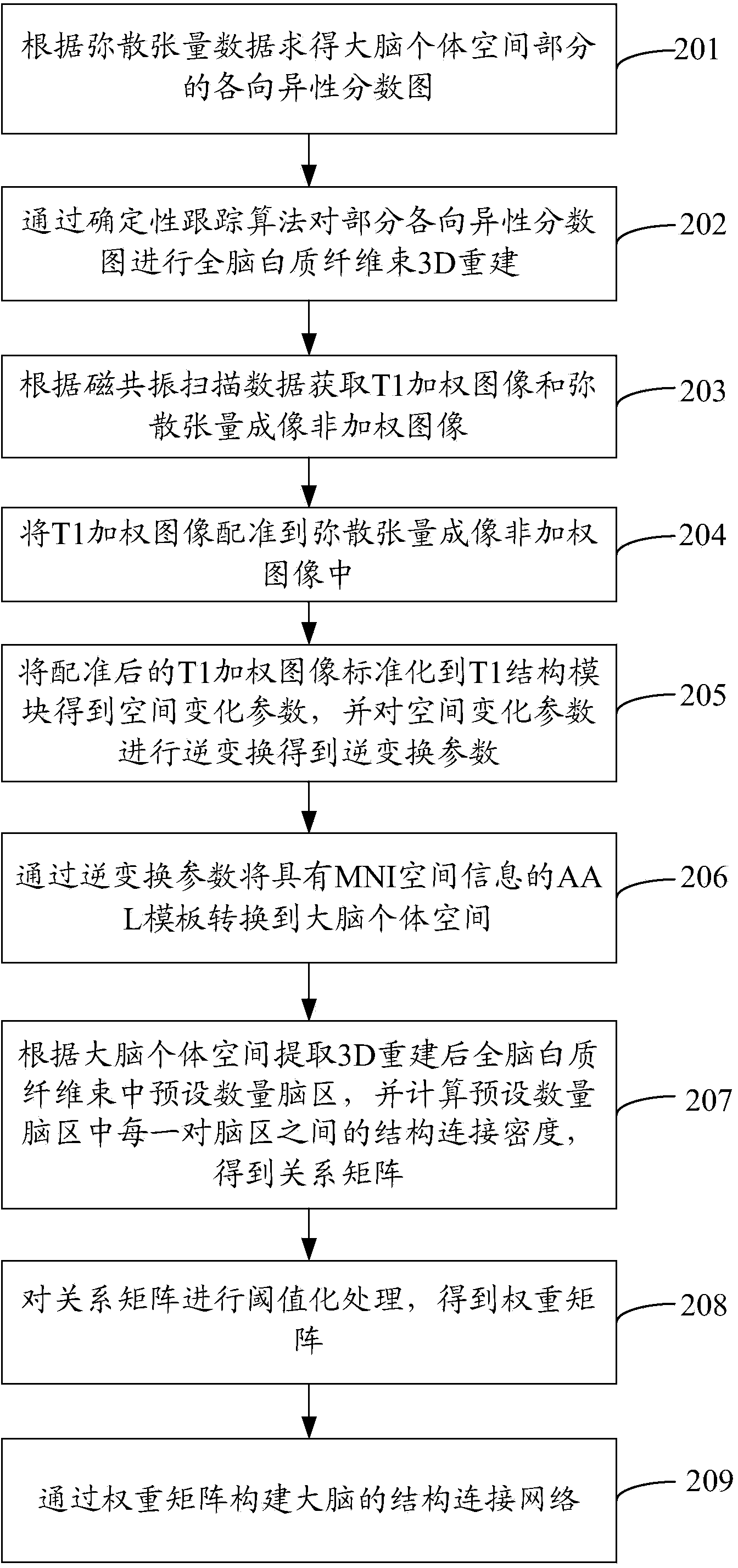
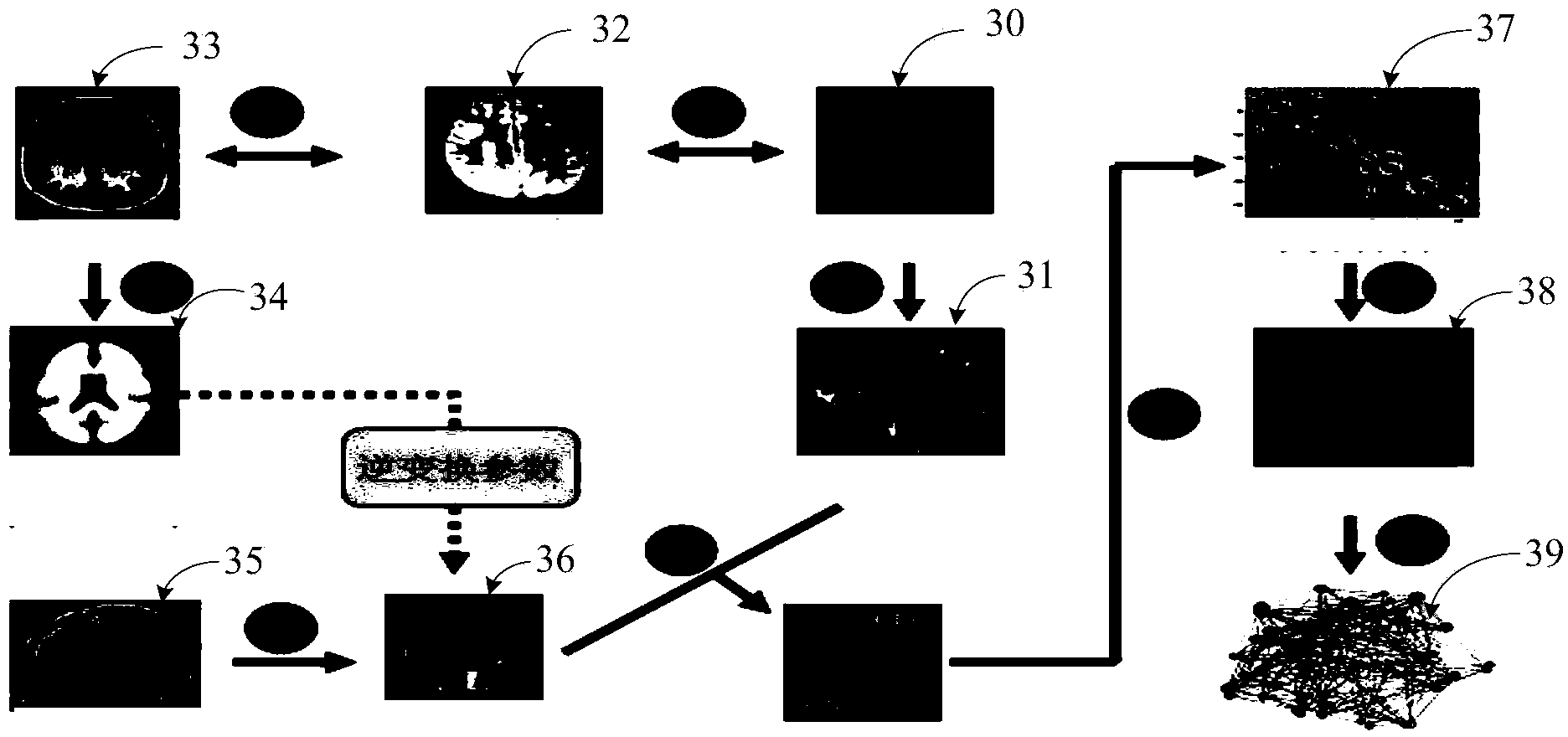
InactiveCN104346530AEasy extractionSpecial data processing applicationsDiffusionFunctional connectivity
The invention provides a method and system for extracting abnormal parameters of the brain. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging and resting-state functional imaging scanning for the brain, and obtaining diffusion tensor data and resting-state functional data of the brain; building the structural connection network of the brain according to the diffusion tensor data; building the functional connection network of the brain according to the resting-state functional data; coupling the structural connection network with the functional connection network to obtain network coupling indexes; arraying and verifying the network coupling indexes and normal network coupling indexes, and extracting the parameters which are different from the normal network coupling indexes in the network coupling indexes. The method and the system are used for conveniently extracting the parameters sensitively reflecting the abnormity of the structure and the function of the brain.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-group transmission of a motor vehicle
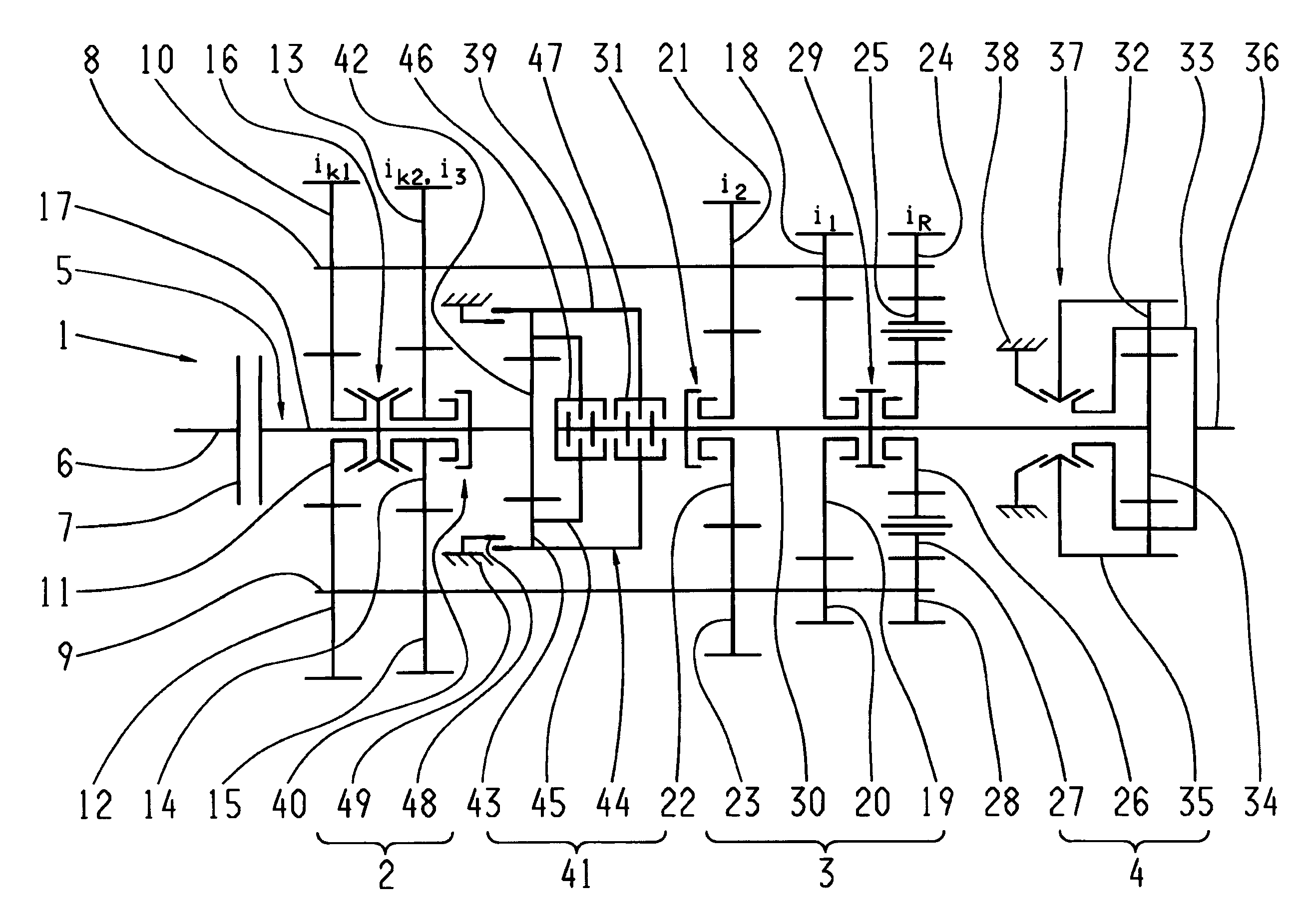
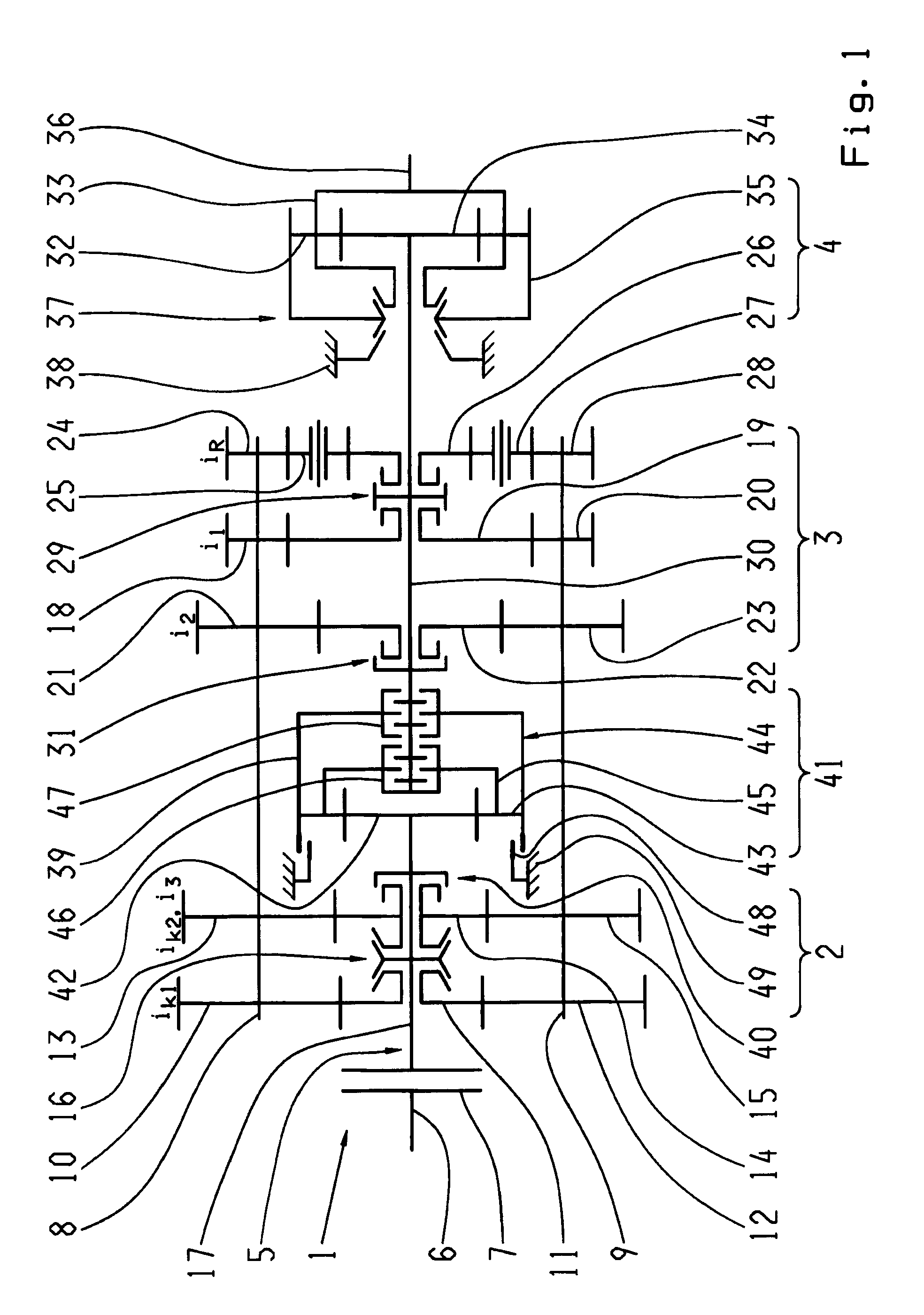
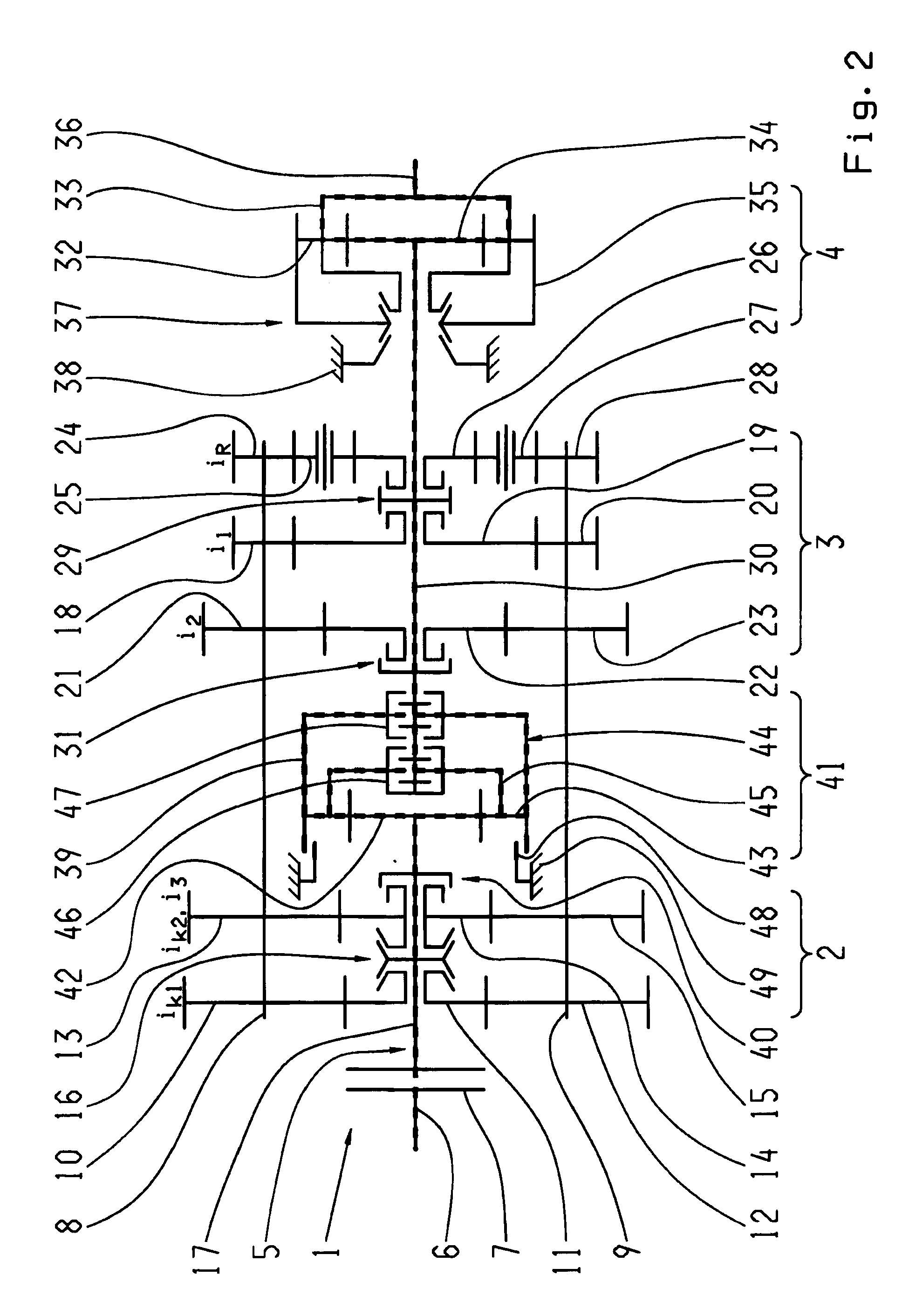
InactiveUS20090264241A1Efficient and low-wear operationEasy to operateToothed gearingsGearing controlFunctional connectivityGear wheel
The invention relates to a multi-group transmission of a motor vehicle with at least two transmission groups (2, 3) arranged in a drive train, in which the means for switching an intermediate gear are provided, in order to diminish or avoid interruptions in tractive force during gear changes. A planetary transmission (41) is arranged between a first transmission group (2) and a second transmission group (3), in order to enable gear changes without interruptions in tractive force with a variably selectable intermediate gear, as well as efficient operation that involves as little wear as possible, whereby a transmission input shaft (17) can be brought into a functional connection with a transmission main shaft (30) via the planetary transmission (41). According to a method of operating the multi-group transmission, a functional connection is established between a transmission input shaft (17) and a transmission main shaft (30), in order to switch an intermediate gear with the help of a planetary transmission (41) which can be engaged by means of the associated clutches (46, 47), so that at least one main group (3) is load-free, when a starting element (7) arranged between a drive motor and the transmission main shaft (17) is at least partially closed, an engaged initial gear is disengaged, the rotational speed of the drive motor in a slippage mode of at least one of the clutches (46, 47) of the planetary transmission (41) is synchronized with a connecting rotational speed of a target gear, and, when the connecting rotational speed is reached, a target gear is engaged, and the planetary transmission (41) is one again deactivated.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
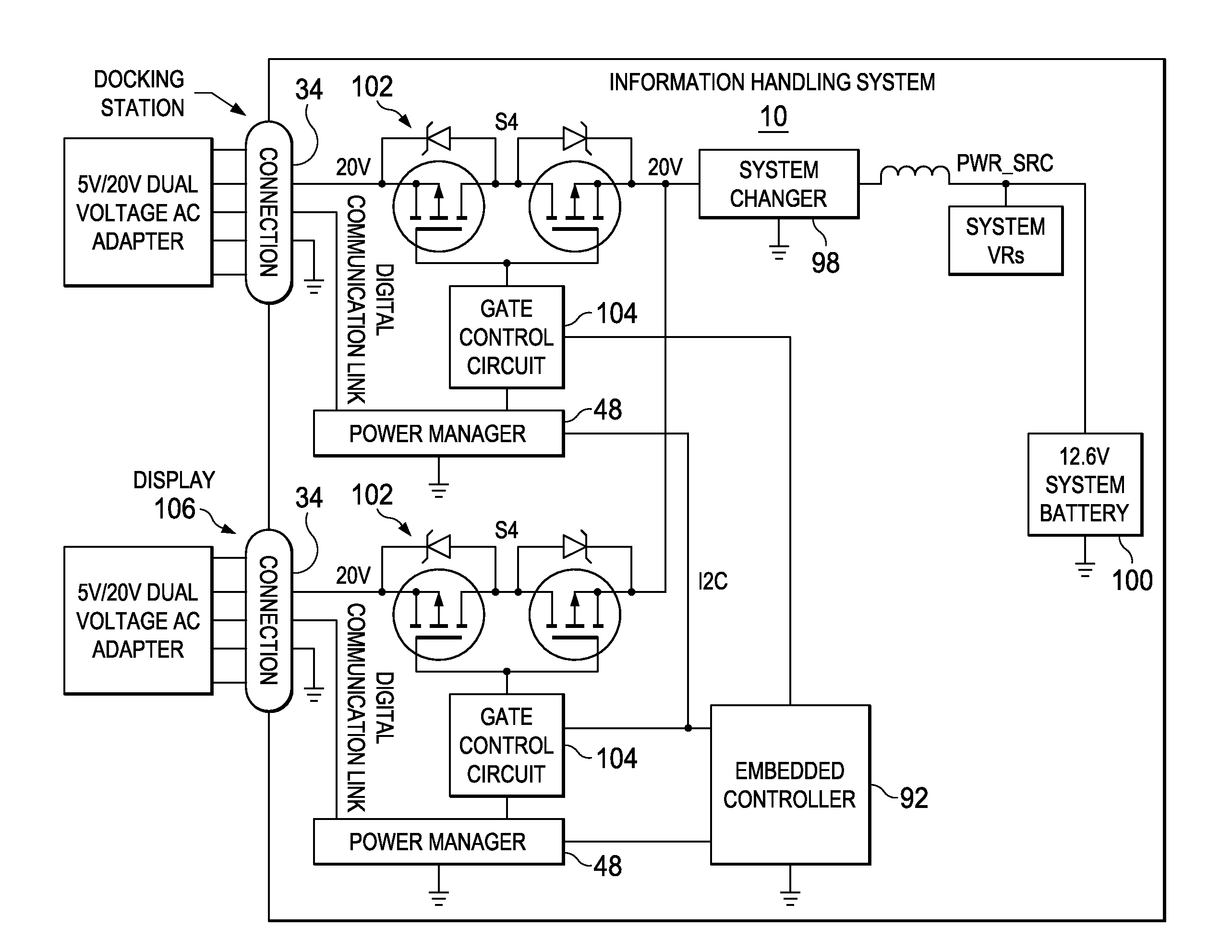
Information Handling System Multi-Purpose Connector Guide Pin Structure
ActiveUS20160139640A1High power transmission efficiencyEnhances connector port strengthIncorrect coupling preventionCoupling device engaging/disengagingFunctional connectivityBattery charge
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Device and method for selecting and brewing the contents of a capsule to prepare a beverage
InactiveUS7673559B2Reliable and rapid mannerEasy to useLiquid flow controllersBeverage vesselsFunctional connectivityEngineering
A device for preparing drinks that incorporate a capsule selection function connected to a system for brewing the contents of the capsules to enable brewing to take place under optimal conditions. The device includes a storage system comprising capsules arranged in several sets, a mechanism for capturing a capsule individually from a set and releasing the capsule into a brewing system. The capture mechanism is able to move between the storage system and the brewing system and is designed in such a way as to adopt at least two positions, a first or reception position in which the capsule is held and is able to be transferred by the capture means and a second or release position in which the capture means can be opened to release the capsule from the capture mechanism. The device provides advantages in the handling of the capsule after its selection, in particular, its transfer, the brewing of its contents, and, optionally, the ejection of the spent capsule in a reliable, rapid and automated manner. In addition, the invention provides more reliable usage with no problems of pouring and draining the liquid extract.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Apparatus and method for the delivery of rod-shaped articles
InactiveUS7165668B2Shorten speedWithout reducing “ output ” and capacityCigarette manufactureConveyor partsFunctional connectivityEngineering
Owner:HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG
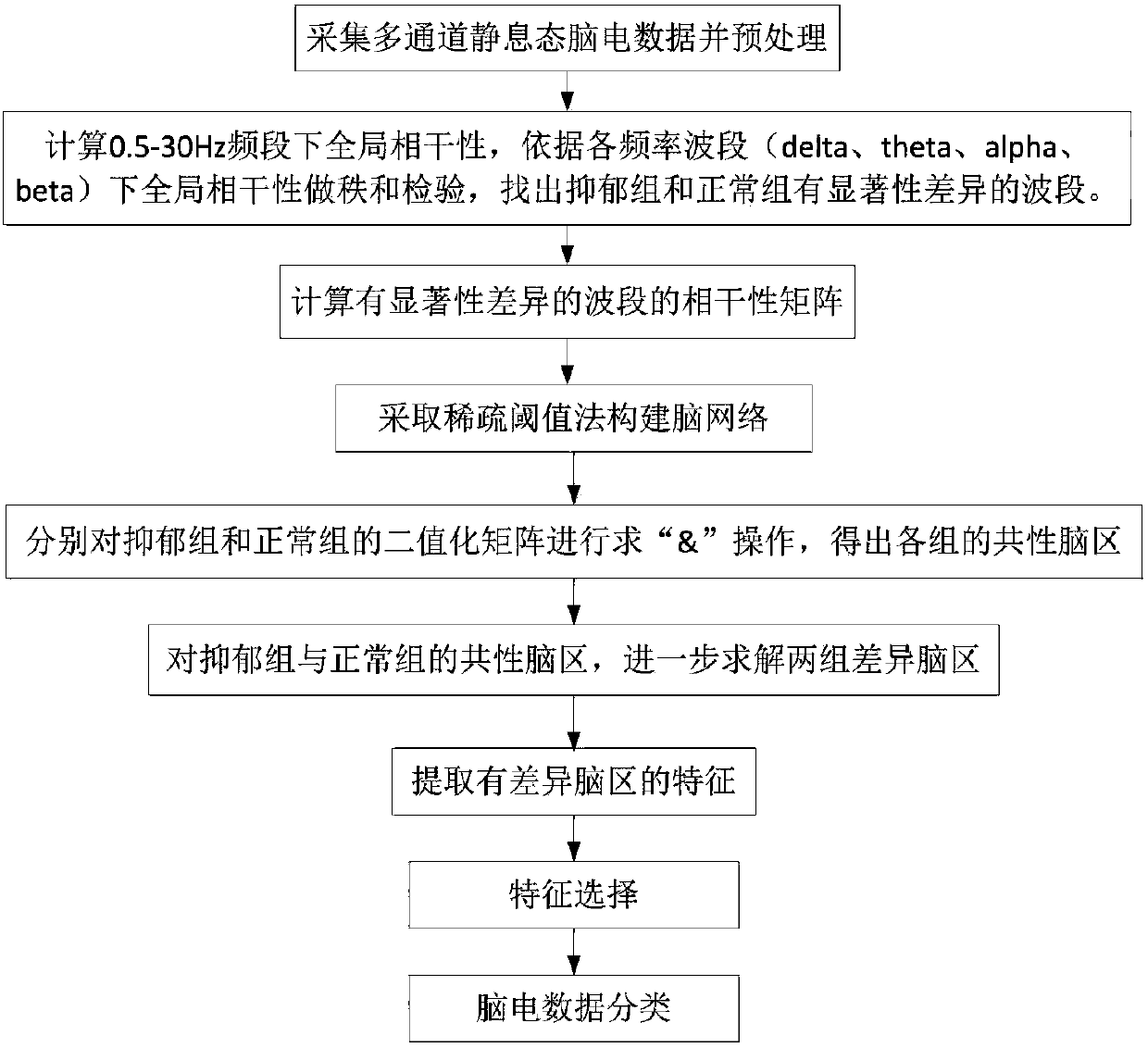
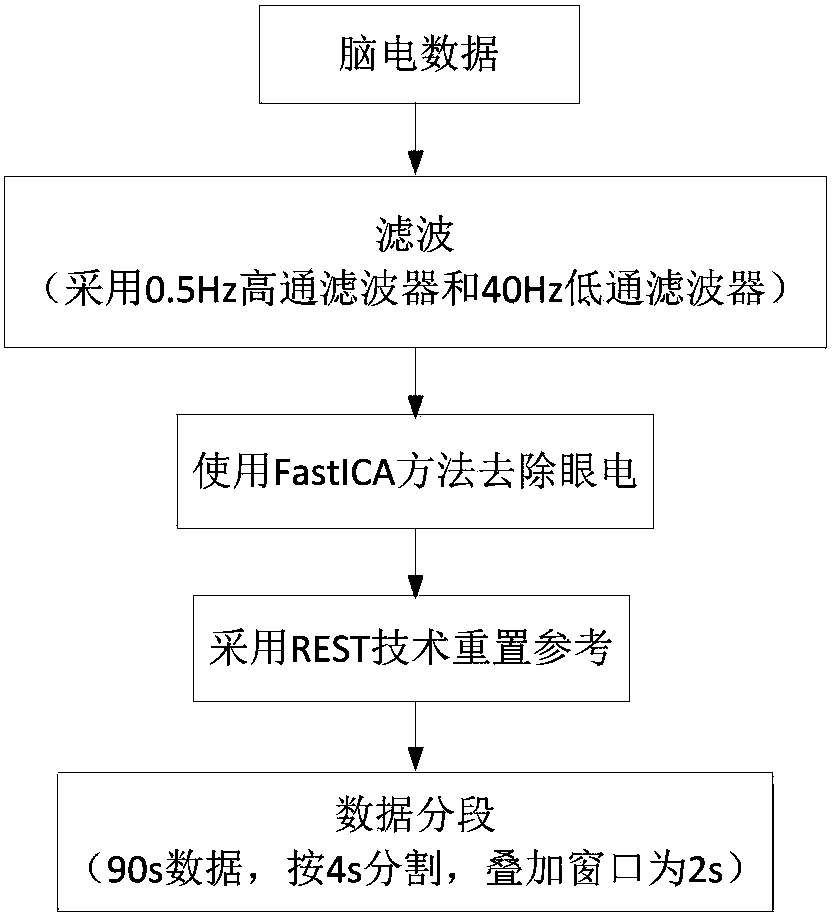
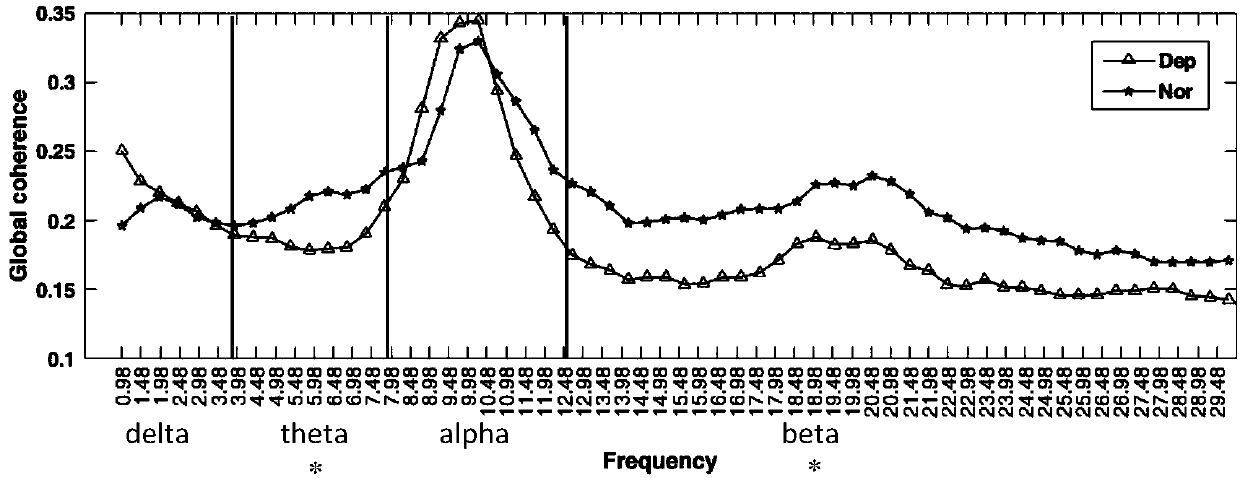
Depression recognition and analysis system based on resting state brain network
ActiveCN108427929ARealize Auxiliary DiagnosisRealize analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSensorsFunctional connectivityPersonalization
The invention provides a depression recognition and analysis system based on a resting state brain network. The depression recognition and analysis system comprises (a) a resting state electroencephalogram data acquisition and preprocessing module used for collecting resting state electroencephalogram data of subjects and preprocessing the collected resting state electroencephalogram data, (b) a brain network metric extraction module used for constructing a personalized brain network structure, respectively finding out common active brain regions of a depression group and a normal control group from the personalized brain network structure, finding out different brain regions based on the common active brain regions of the two groups and extracting brain network metrics, and (c) a classification recognition module used for conducting feature selection on the extracted brain network metrics and functional connection features and classifying the data of which features are already screened to achieve recognition of depression patients and normal subjects. The depression recognition and analysis system has the advantages that feature dimension is effectively reduced, calculation efficiency is improved, and depression recognition can be effectively achieved.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
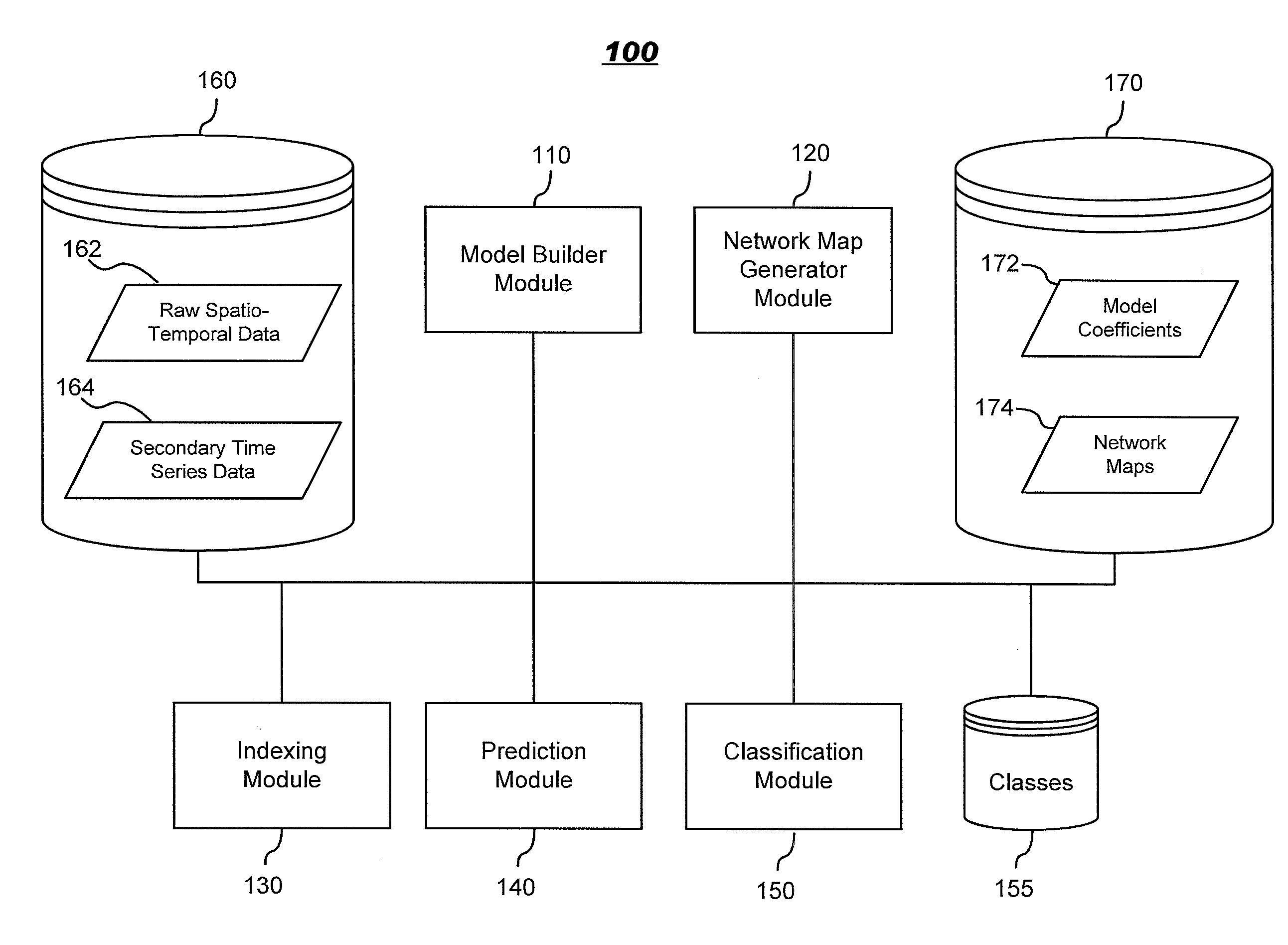
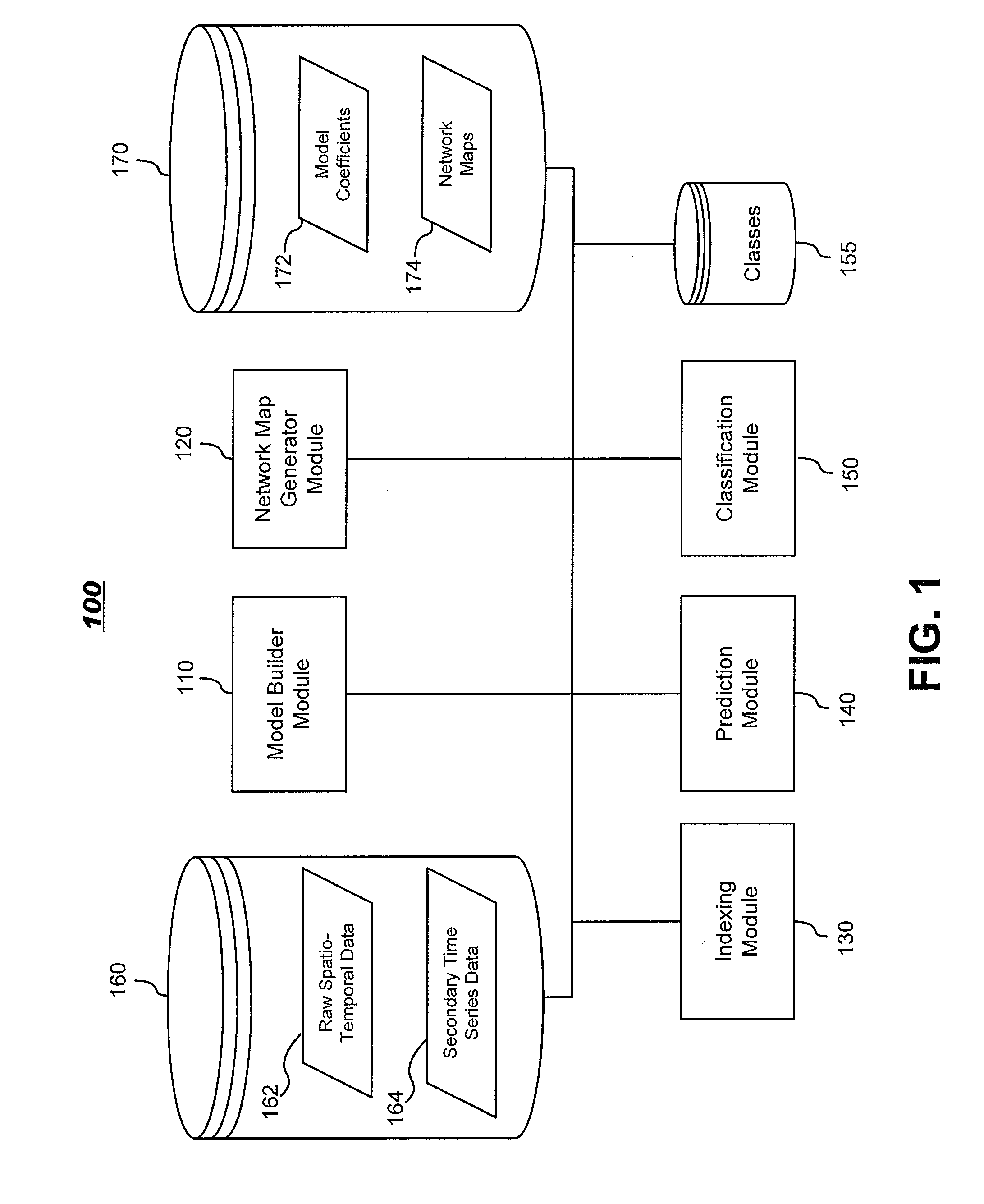
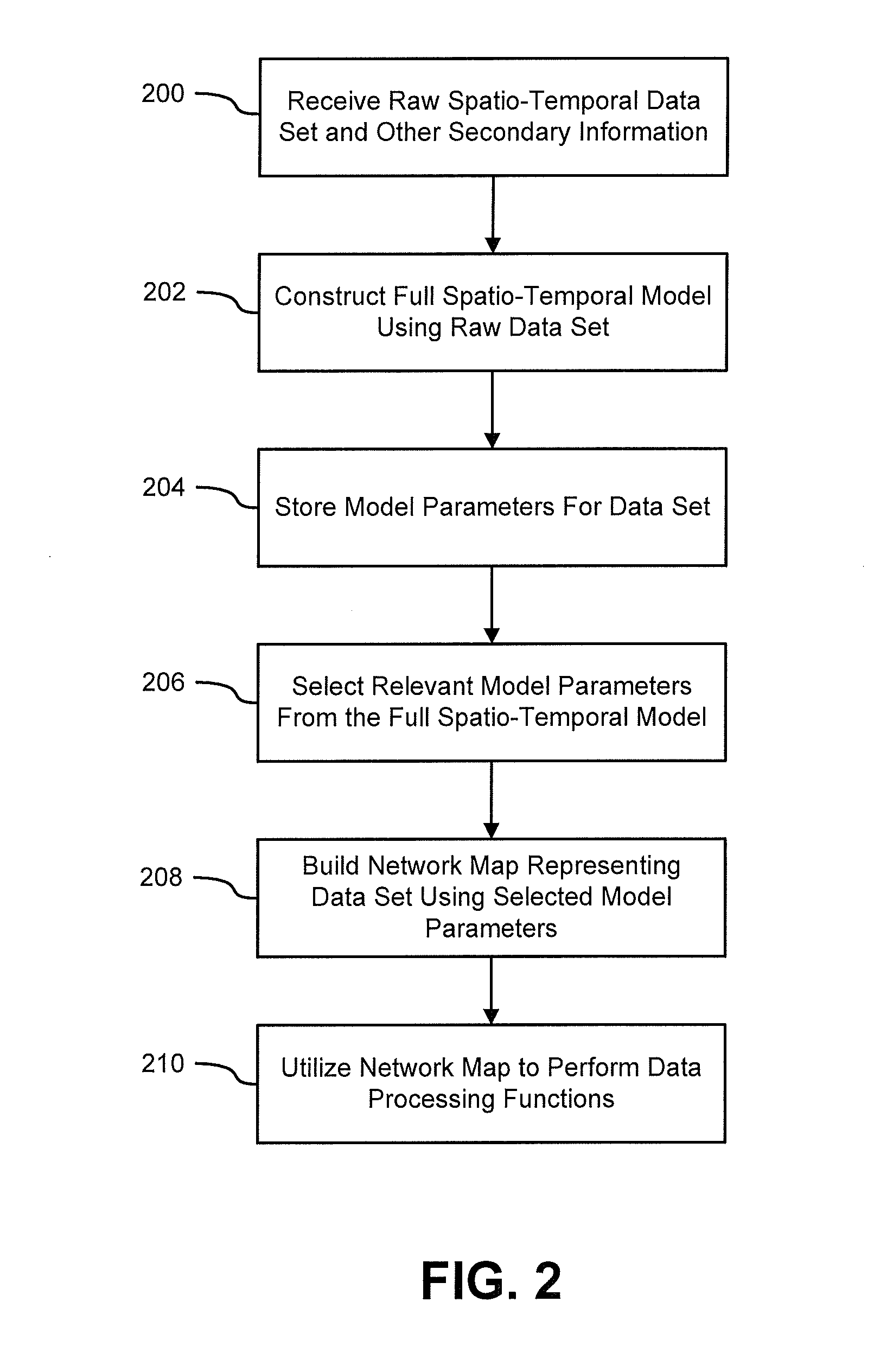
Systems and methods for modeling and processing functional magnetic resonance image data using full-brain vector auto-regressive model
InactiveUS20130034277A1Reduced representation of dataReduced representationMedical simulationImage enhancementFunctional connectivityData set
Systems and methods for modeling functional magnetic resonance image datasets using a multivariate auto-regressive model which captures temporal dynamics in the data, and creates a reduced representation of the dataset representative of functional connectivity of voxels with respect to brain activity. Raw spatio-temporal data is processed using a multivariate auto-regressive model, wherein coefficients in the model with high weights are retained as indices that best describe the full spatio-temporal data. When there are a relatively small number of temporal samples of the data, sparse regression techniques are used to build the model. The model coefficients are used to perform data processing functions such as indexing, prediction, and classification.
Owner:IBM CORP
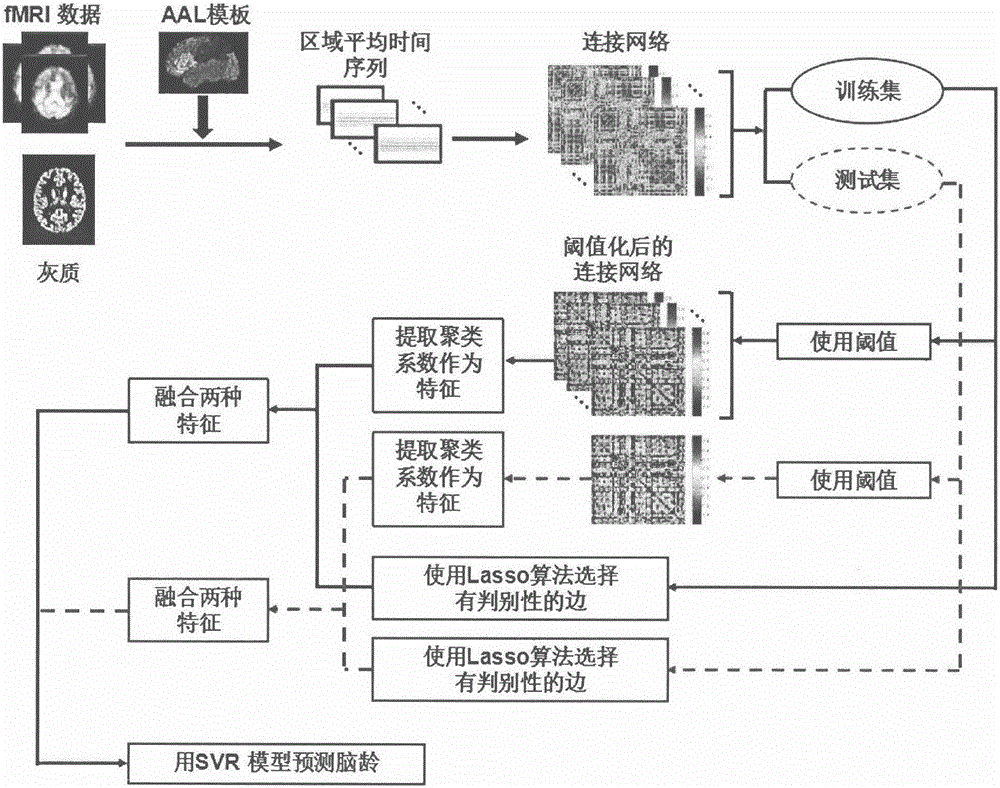
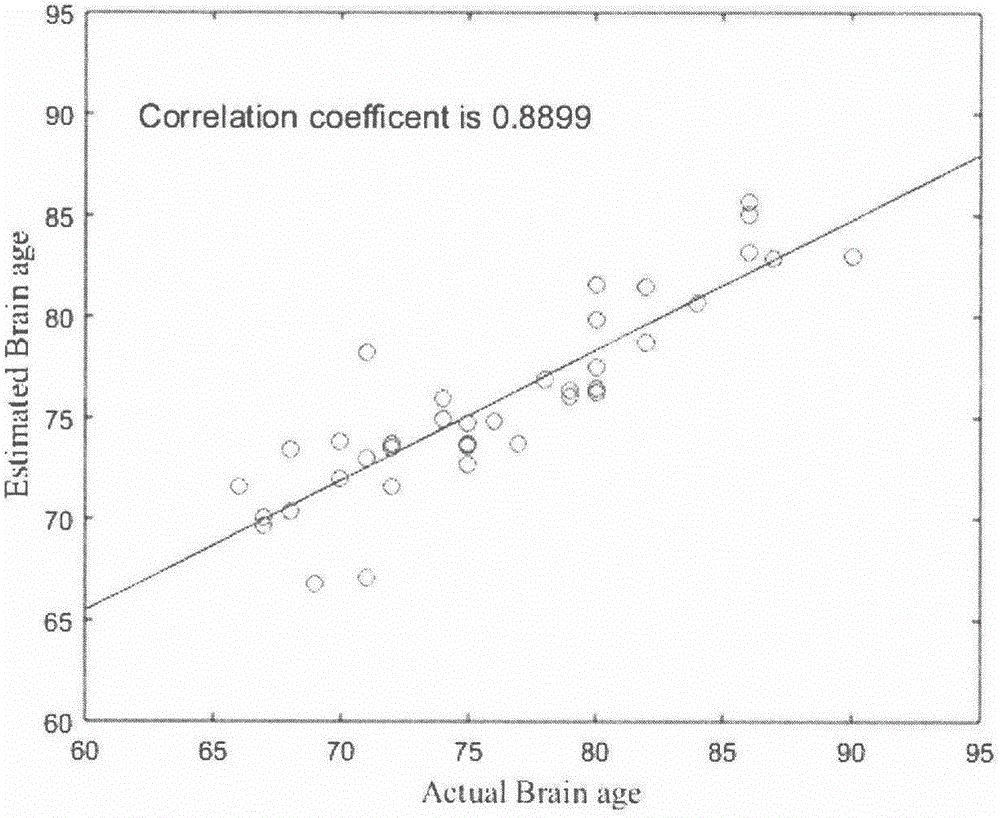
Brain age prediction method based on brain connection network
InactiveCN106127769AOptimize forecast resultsImage enhancementImage analysisFunctional connectivityMedicine
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Connectivity hub with a stationary base station and a removable second hub
InactiveUS20080133815A1Easy to transportElectric digital data processingFunctional connectivityTelecommunications
A connectivity hub enabling multiple peripheral devices to be connected with a computer includes a stationary base station functioning as a connectivity hub and a removable connectivity hub functioning by itself as a travel connectivity hub. The removable travel hub can be plugged into the stationary base station by connecting an upstream port of the removable hub to a downstream port of the base station. Thus, a user of the connectivity hub achieves the functionality of a full-featured connectivity base station as well as that of a small, easily transportable travel hub without having to purchase multiple units.
Owner:BELKIN INT
Well tool protection system and method
InactiveUS20050056429A1Reduce distractionsPromotes pressure equalizationConstructionsCleaning apparatusEngineeringFunctional connectivity
The system including a well tool having a housing forming a protection fluid chamber in fluid communication with a discharge port, a protection fluid disposed within the protection fluid chamber, and a moveable mechanism in functional connection with the protection fluid chamber in a manner to expel a portion of the protection fluid when the moveable mechanism moves.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
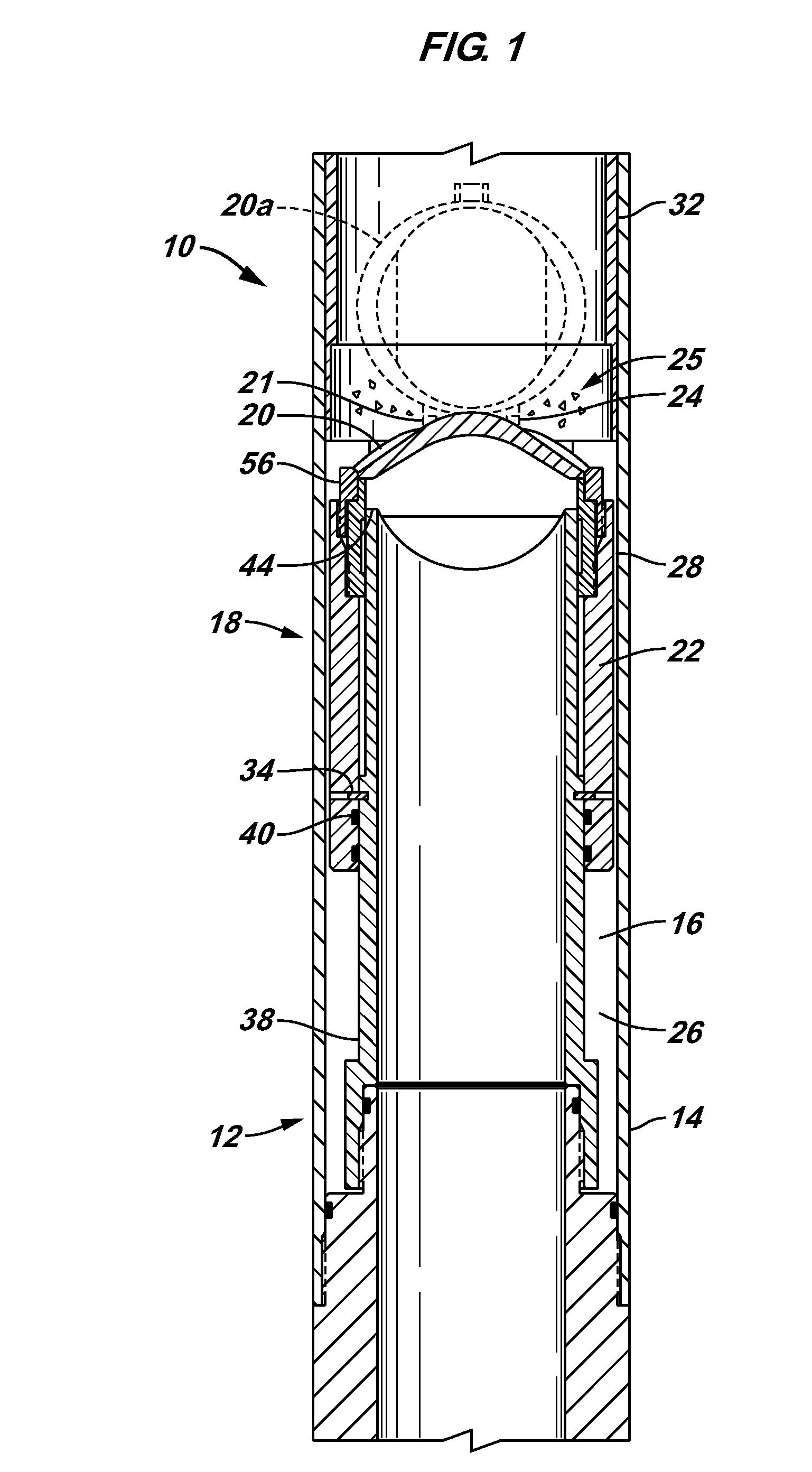
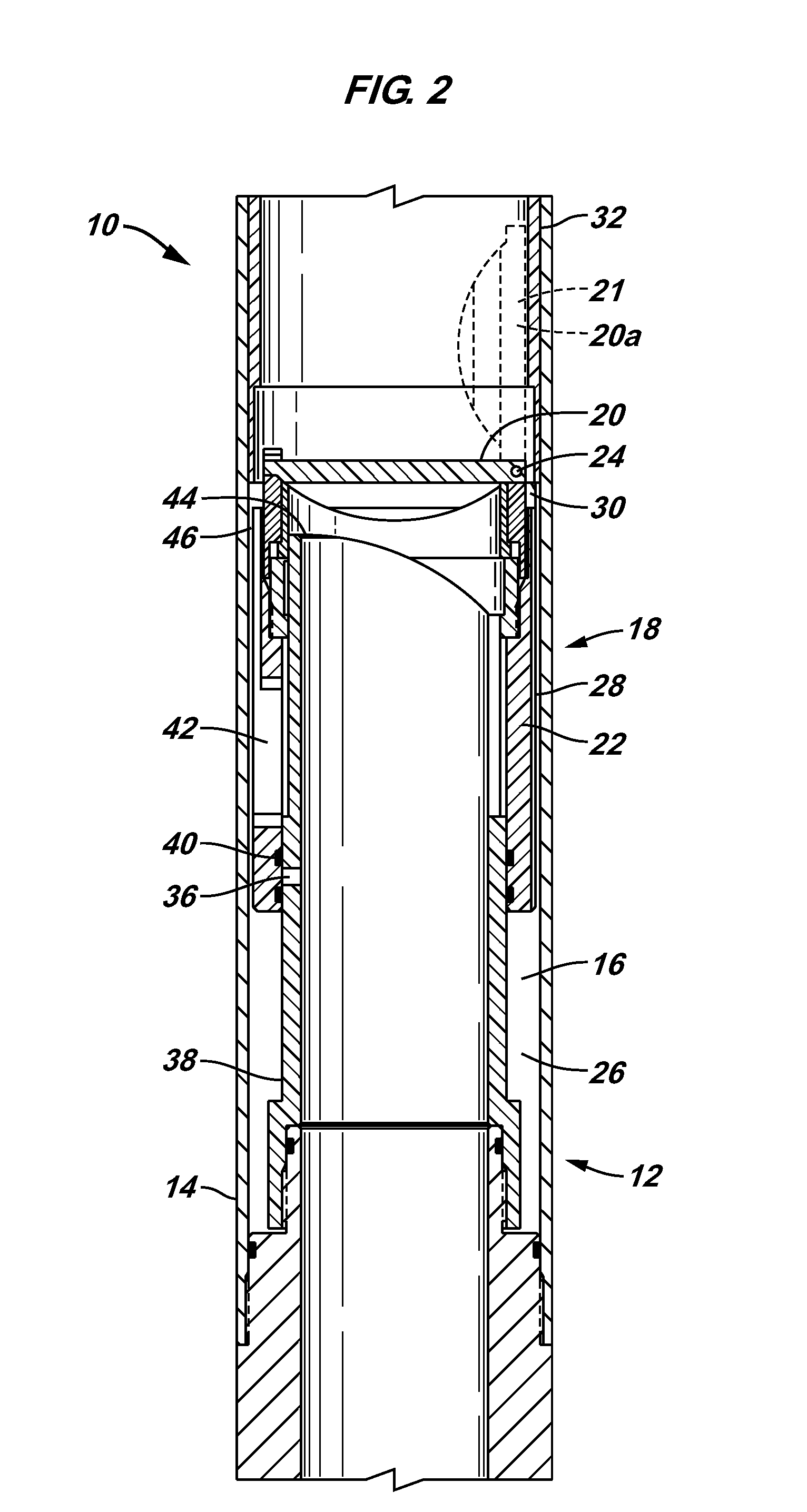
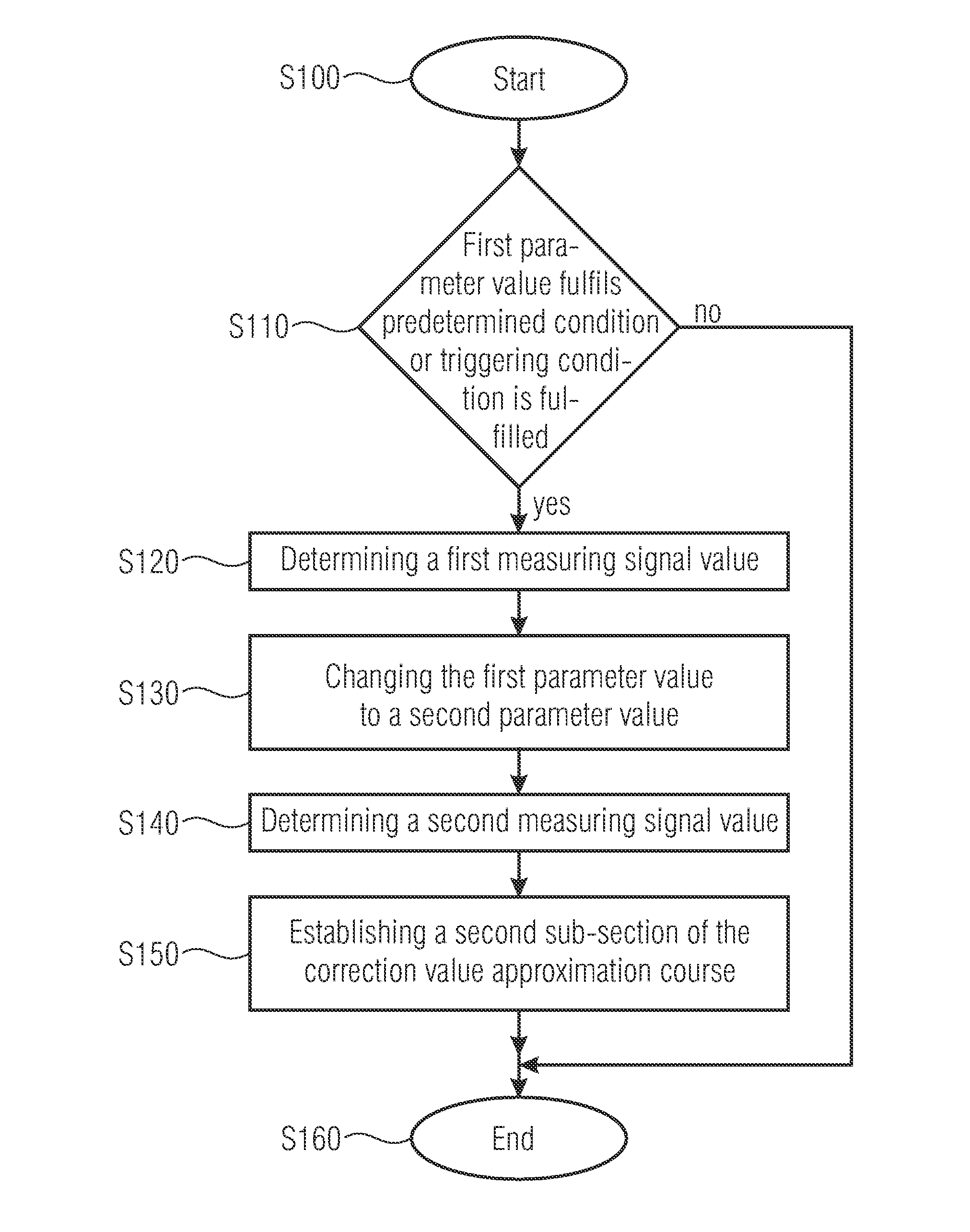
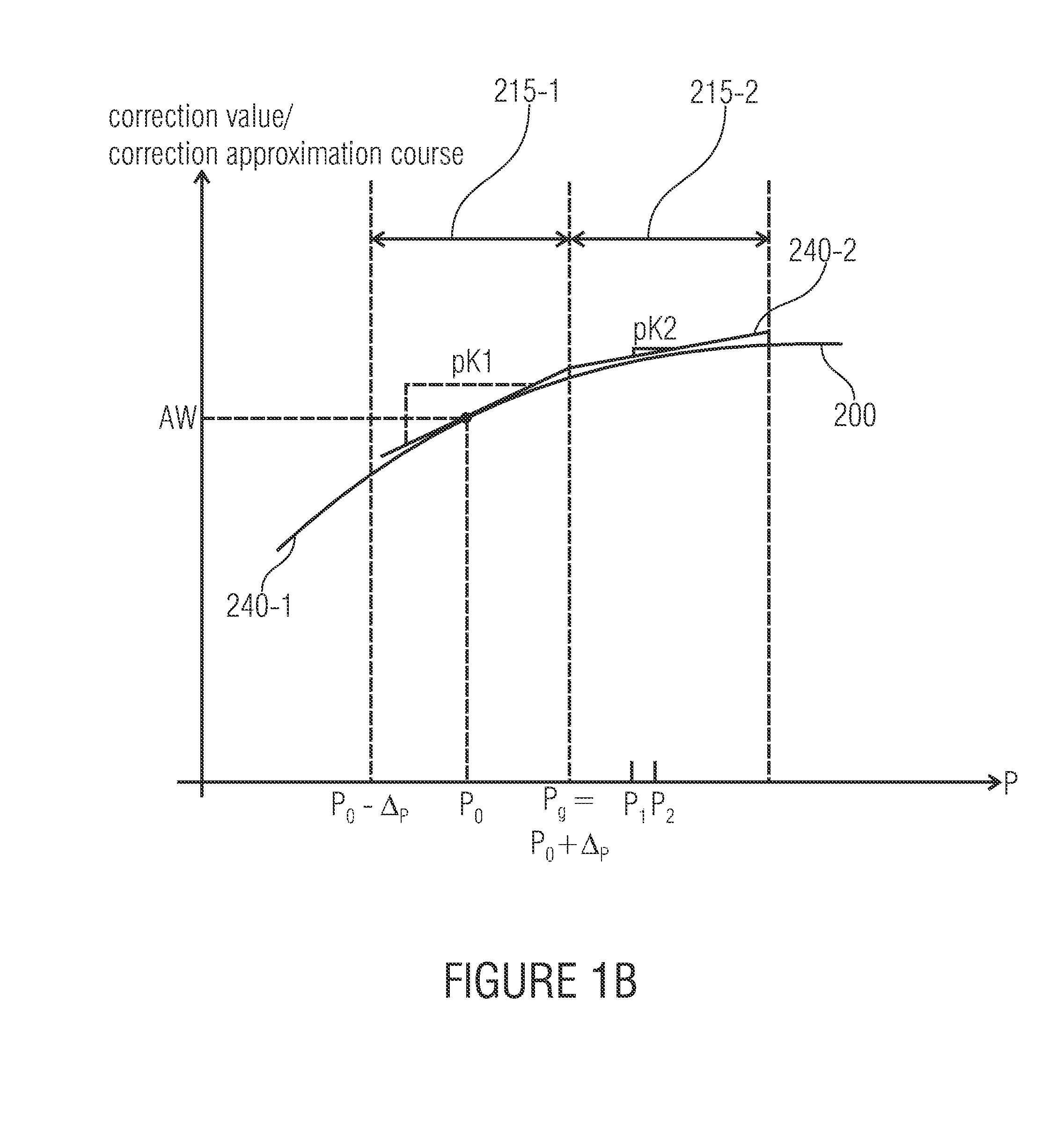
Method for determining, section after section, a parameter-dependent correction value approximation course and sensor arrangement
ActiveUS20100217556A1High measurement accuracyTesting/calibration apparatusForce measurementFunctional connectivityEngineering
An embodiment of a method for a determination, section after section, of a parameter-dependent correction value approximation course includes determining a first measurement signal value with a first parameter value associated with a sensor arrangement when the first parameter value fulfils a predetermined condition or a trigger condition is fulfilled, changing the first parameter value to obtain a second parameter value, determining a second signal value with the second parameter value and determining a second partial section of the correction value approximation course for a second parameter range based on a functional connection describing the second partial section, the first parameter value, the second parameter value, the first measurement signal value, the second measurement signal value and an initial correction value.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Novel unnatural amino acid marked antibody-drug conjugate and preparation thereof
ActiveCN106146663AEfficient modification purposeGood effectOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaFunctional connectivityIsotope
The invention provides a site-directed mutated rituximab containing unnatural amino acid markers and a method for conjugating the rituximab by site-directed mutation and site-directed micro-molecules. The method includes the steps: leading unnatural amino acid into rituximab genes by genetic codon extension technology in a site-directed manner; performing site-directed connection by the aid of the unnatural amino acid and modifiers such as poly-difunctional connecting arms DIBO-DOTA; further realizing site-directed conjugating of the rituximab and radioactive isotope such as Cu64 through DOBO-DOTA. The invention further relates to an application of site-directed conjugated micro-molecule rituximab as development, tracing and therapeutic radio-immunity conjugate.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
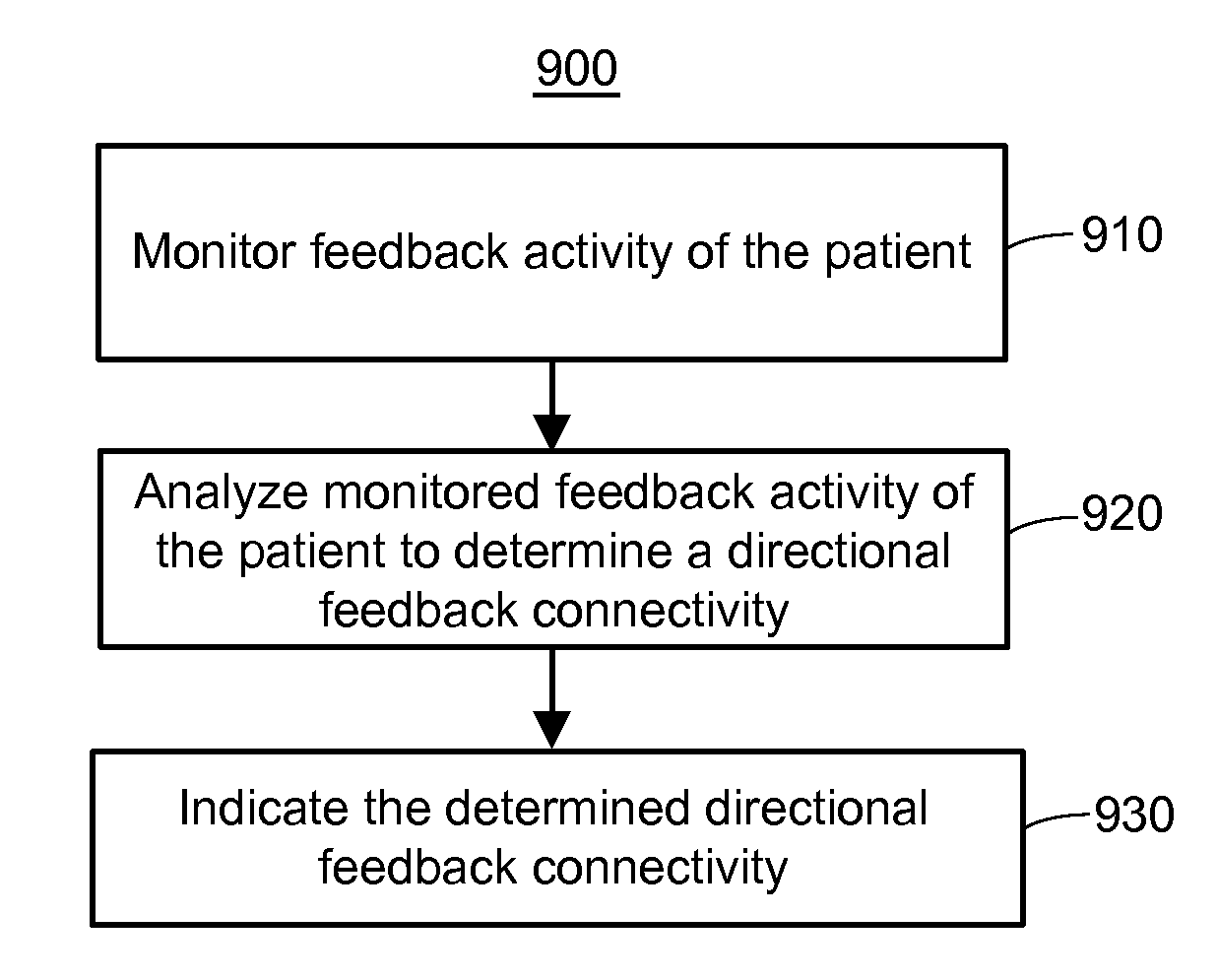
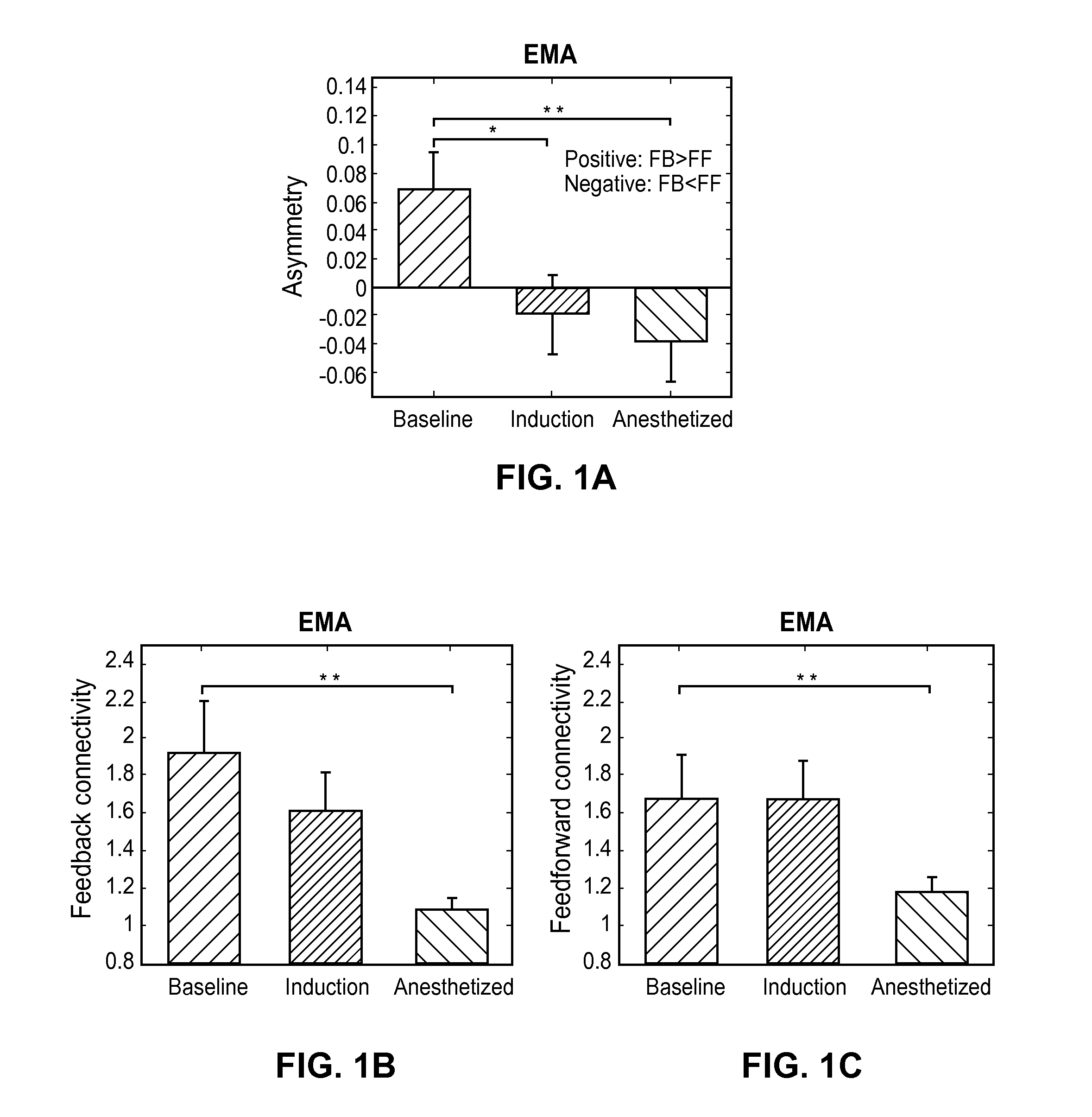
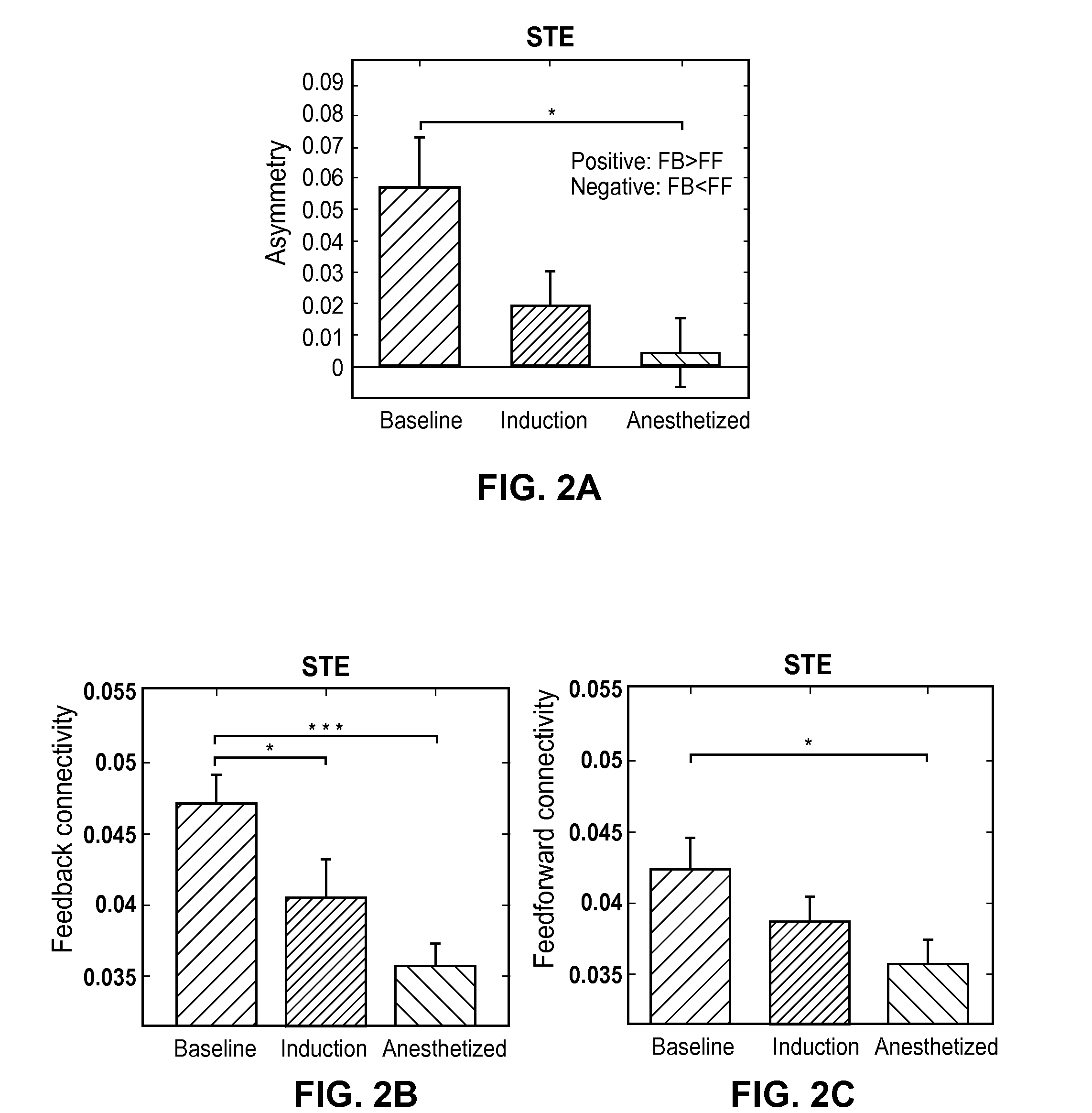
System and method to assess causal signaling in the brain during states of consciousness
InactiveUS20130245485A1ElectroencephalographyElectromyographyFunctional connectivityConsciousness states
A system and method for assessing causal signaling in the brain during states of consciousness are described. More specifically, a system and method for determining a directed functional connectivity in the brain wherein neurophysiologic correlates are analyzed with respect to feedback and / or feedforward activities to determine a directional feedback connectivity and / or a directional feedforward connectivity associated with a level of consciousness in the brain.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Aircraft and method of retrieving a rescue cradle into the aircraft fuselage
An aircraft capable of hovering, and having a fuselage defining an access opening; driving means for operating a rescue cradle; and a first wall movable between a closed position engaging a first portion of the opening, and a first open position allowing access to the first portion of the opening. The aircraft has a member connected functionally to the first wall and in turn having at least one flat surface; and the member is movable with respect to the wall into a first position, in which the flat surface defines a supporting surface for the cradle when the first wall is in the first open position.
Owner:LEONARDO FINMECCANICA SPA
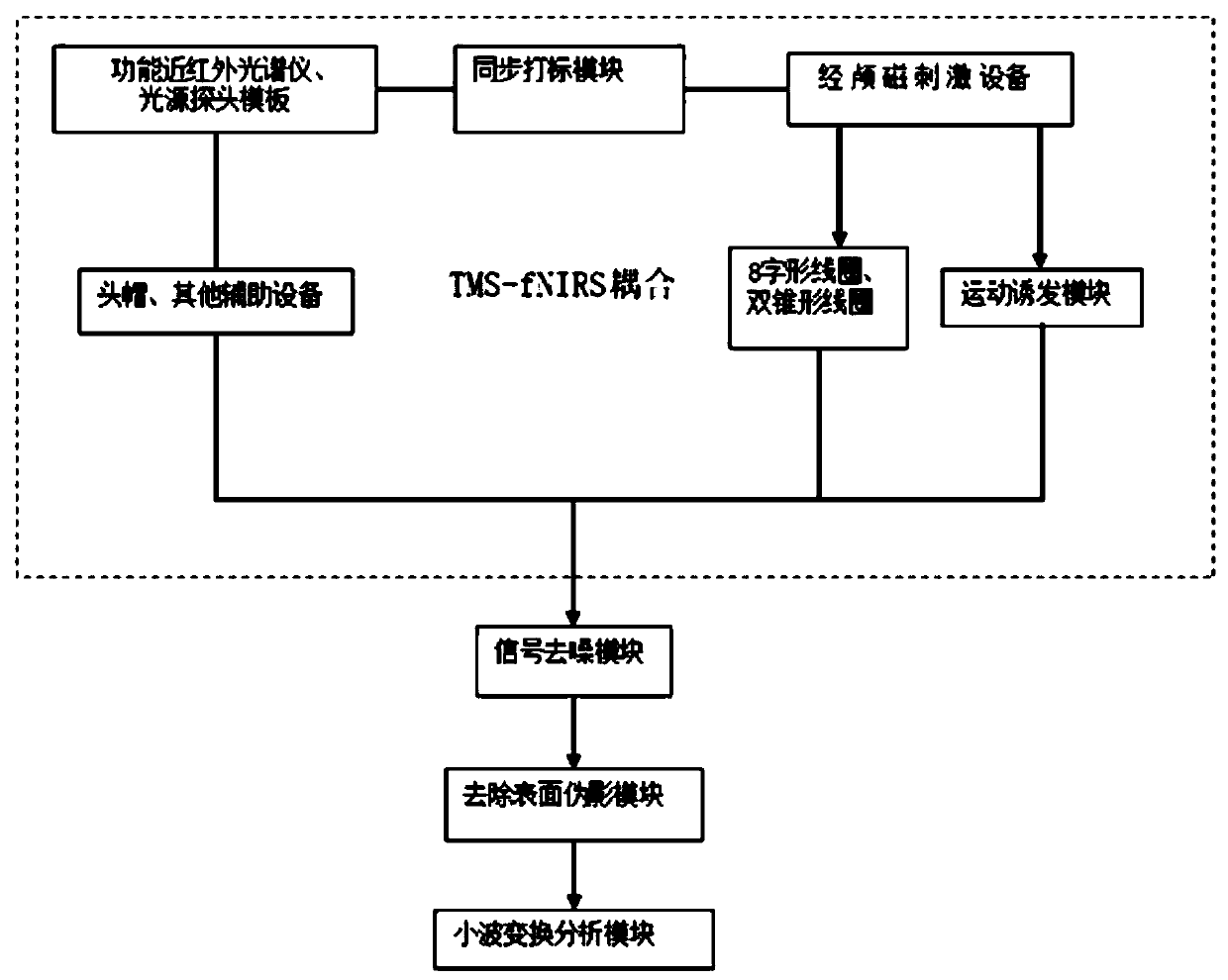
Dynamic brain function detection method and system synchronous with transcranial magnetic stimulation
PendingCN110433397AEasy to understand implementationEasy to understandElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsTime domainFunctional connectivity
The present invention relates to a dynamic brain function detection method and system synchronous with transcranial magnetic stimulation. The system comprises a transcranial magnetic stimulation device for magnetically stimulating a targeted brain region of a subject to achieve a purpose of activating or inhibiting functions of a corresponding brain region; a functional near-infrared spectrometerfor collecting brain blood oxygen signals of the targeted brain region of the subject and other function connection related brain blood oxygen signals; an analysis module for analyzing blood oxygen signals of multiple-frequency bands of the brain blood oxygen signals; and a synchronous marking module for synchronously marking a stimulation moment in near infrared time domain signals when the transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) device starts to perform magnetic stimulation so as to instantly collect changes of the blood oxygen signals when the magnetic stimulation starts. The method provides a feasible scheme for researching brain disorder and cortical changes caused by the TMS and can also objectively measure an effect of the transcranial magnetic stimulation on different regions of abrain on a premise that the effect of the transcranial magnetic stimulation on the different regions of the brain cannot be quantified.
Owner:国家康复辅具研究中心
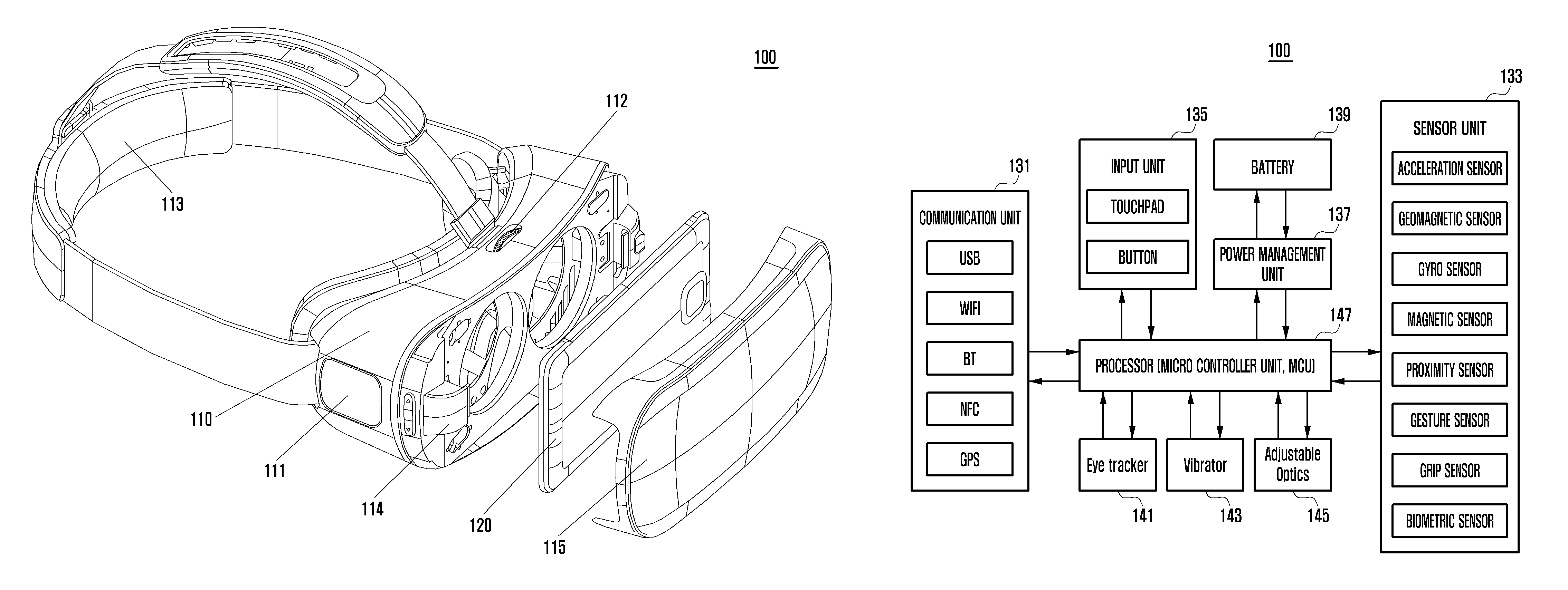
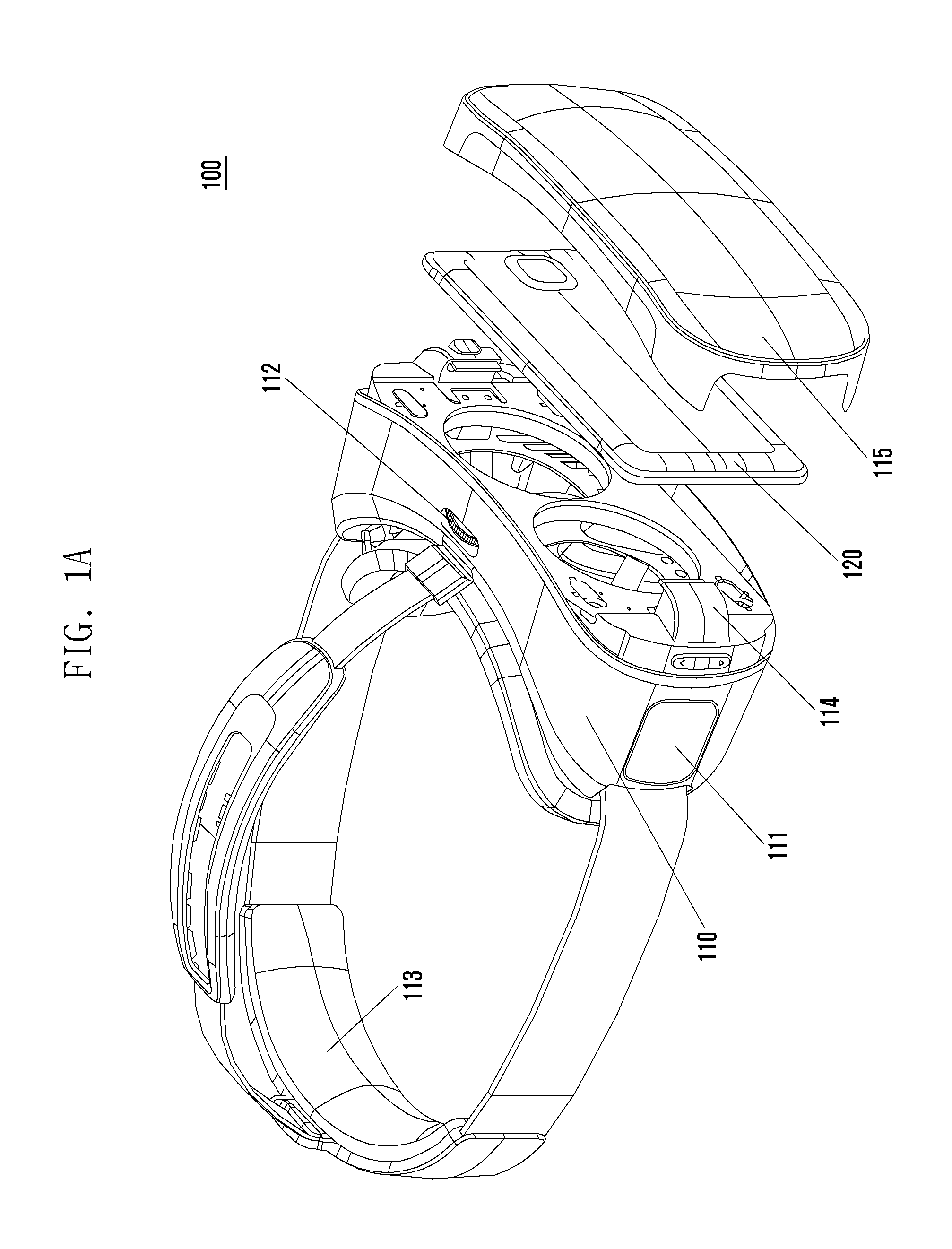
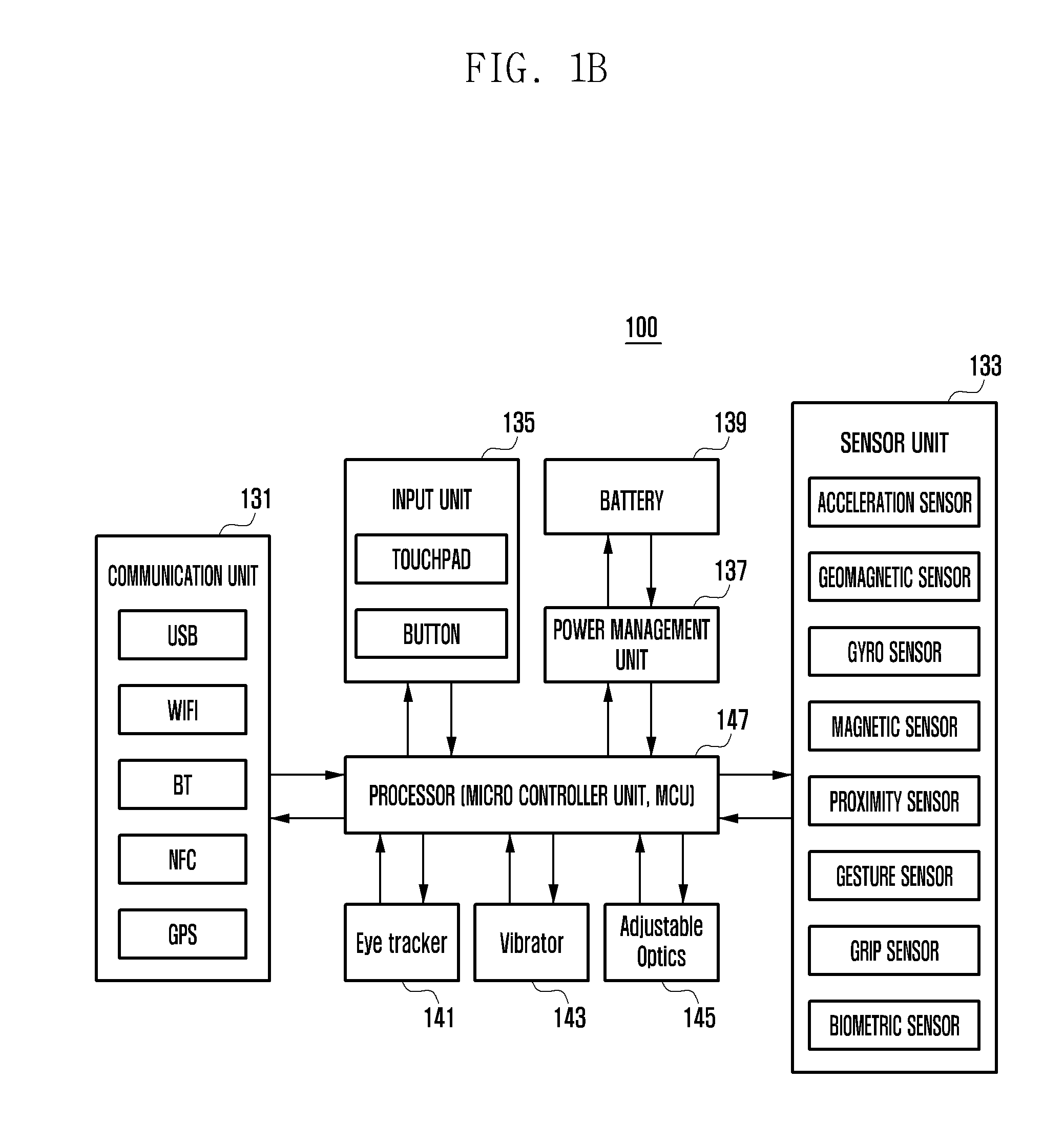
Head-mounted display apparatus
ActiveUS20170011706A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer hardwareFunctional connectivity
Provided is a head-mounted display (HMD) apparatus and a method of controlling information output for the HMD apparatus. The HMD apparatus includes a frame in which one or more devices are installable, an interface unit to functionally connect to at least one of one or more devices installed in the frame and an external device, a detection unit to detect a user input, and a processor to perform a process of determining the one or more devices installed in the frame, controlling the interface unit according to the determination result, and controlling the one or more devices installed in the frame and the external device on the basis of user input detected through the detection unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
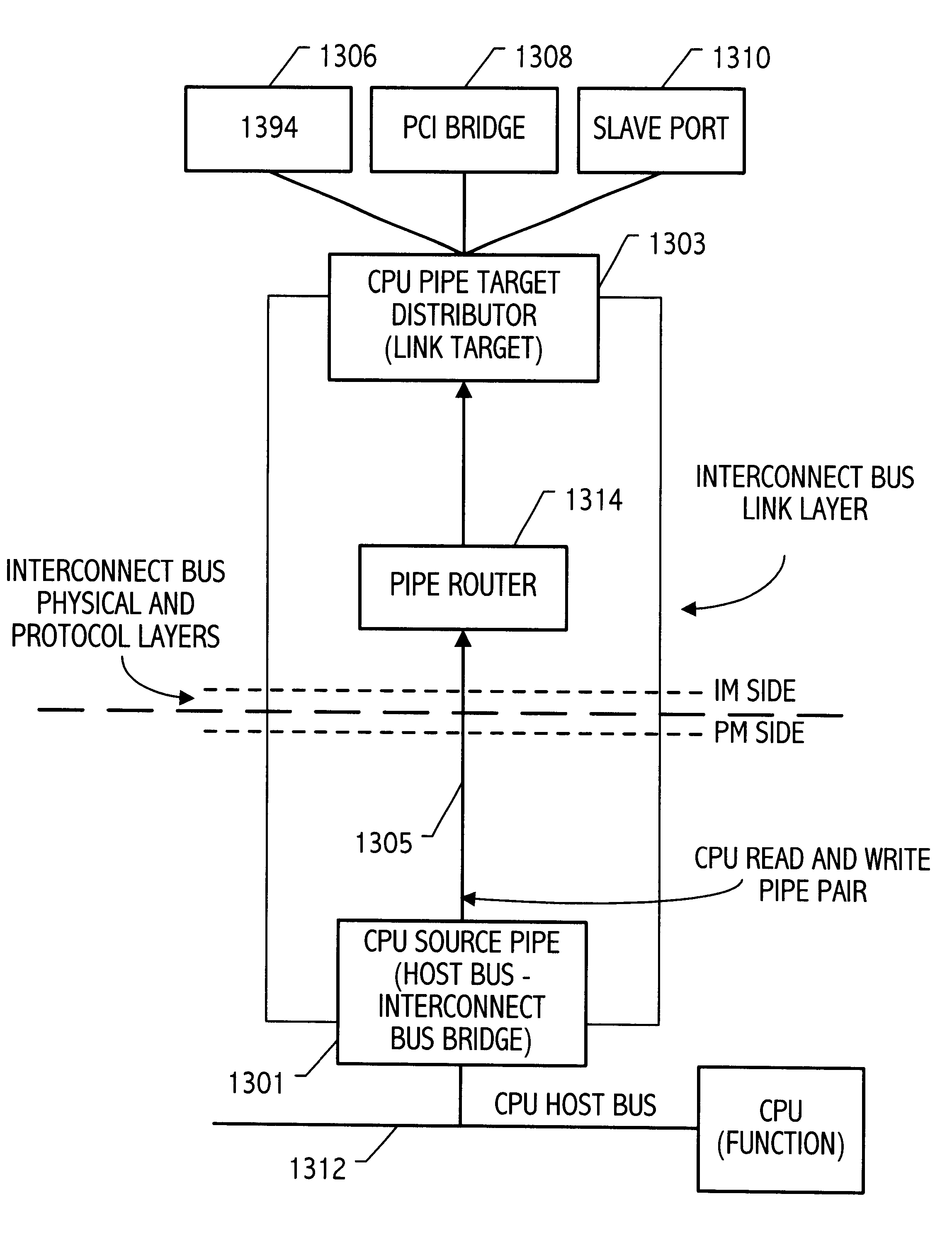
Target side distributor mechanism for connecting multiple functions to a single logical pipe of a computer interconnection bus
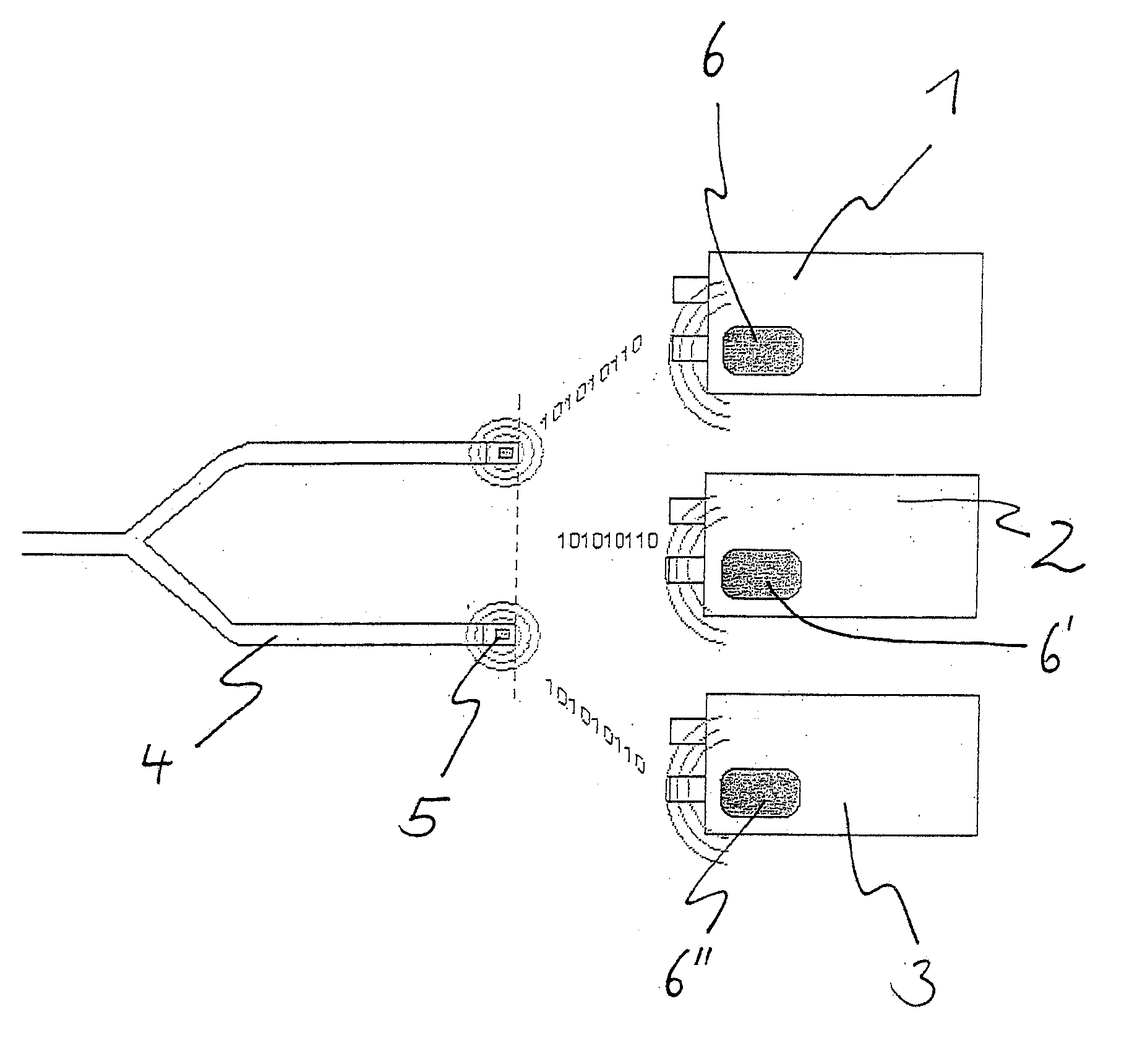
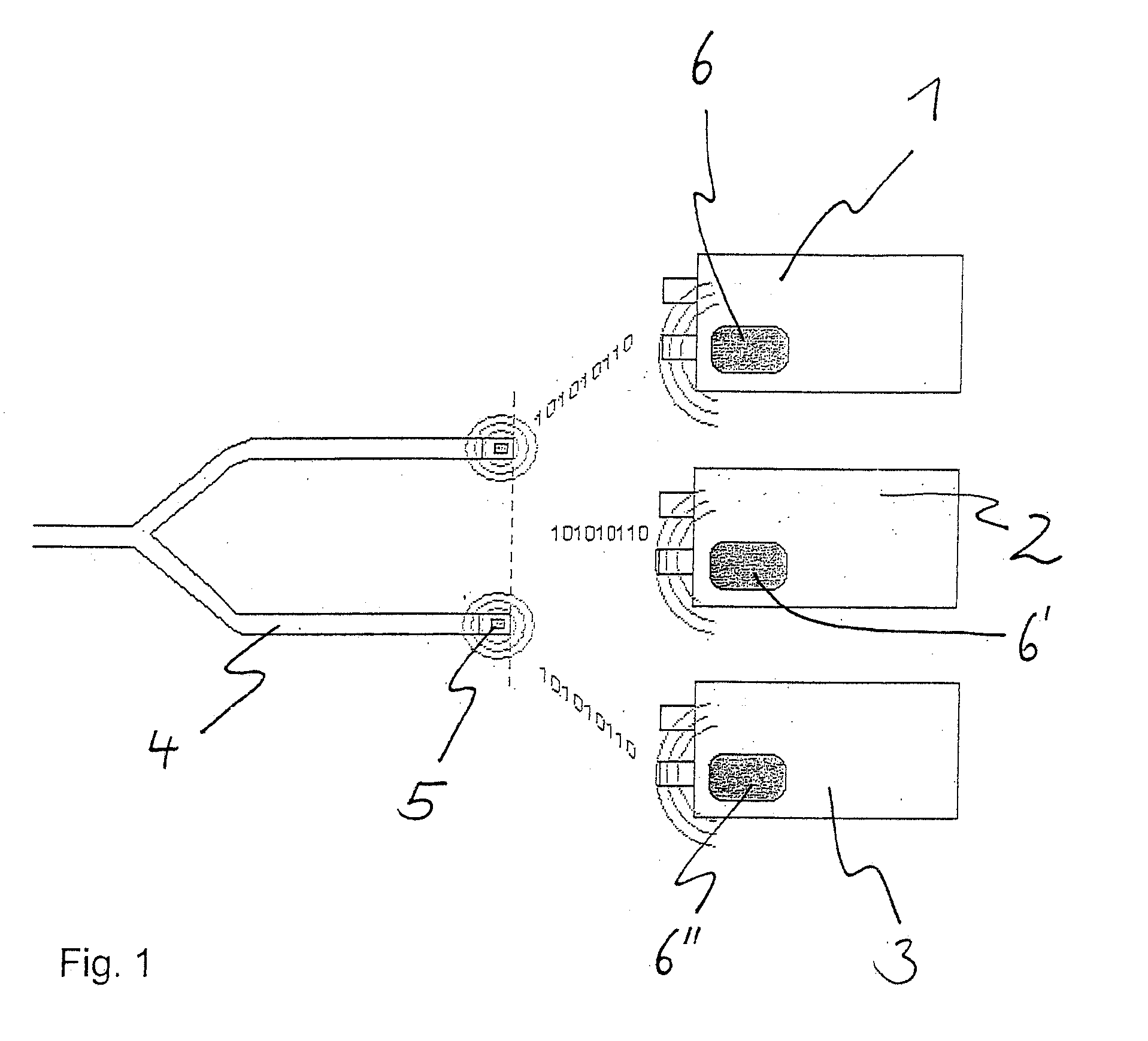
InactiveUS6457084B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationFunctional connectivityTelecommunications link
A computer system includes a first integrated circuit having a first function and a second integrated circuit having a plurality of second functions. A communication link connects the first integrated circuit and the second integrated circuit. The communication link includes at least one logical pipe having a source side on the first circuit and a target side on the second integrated circuit, the one pipe carrying transactions over the communication link between the first function and the second functions. The pipe is identified by a pipe identification carried in the transactions. A target side distributor circuit is coupled between the second functions and the communication link. The target side distributor circuit receives those transactions from the communication link having the pipe identification. The target side distributor circuit provides transactions received from the communication link having the pipe identification to respective ones of the second functions according to an address field included in the transactions.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com