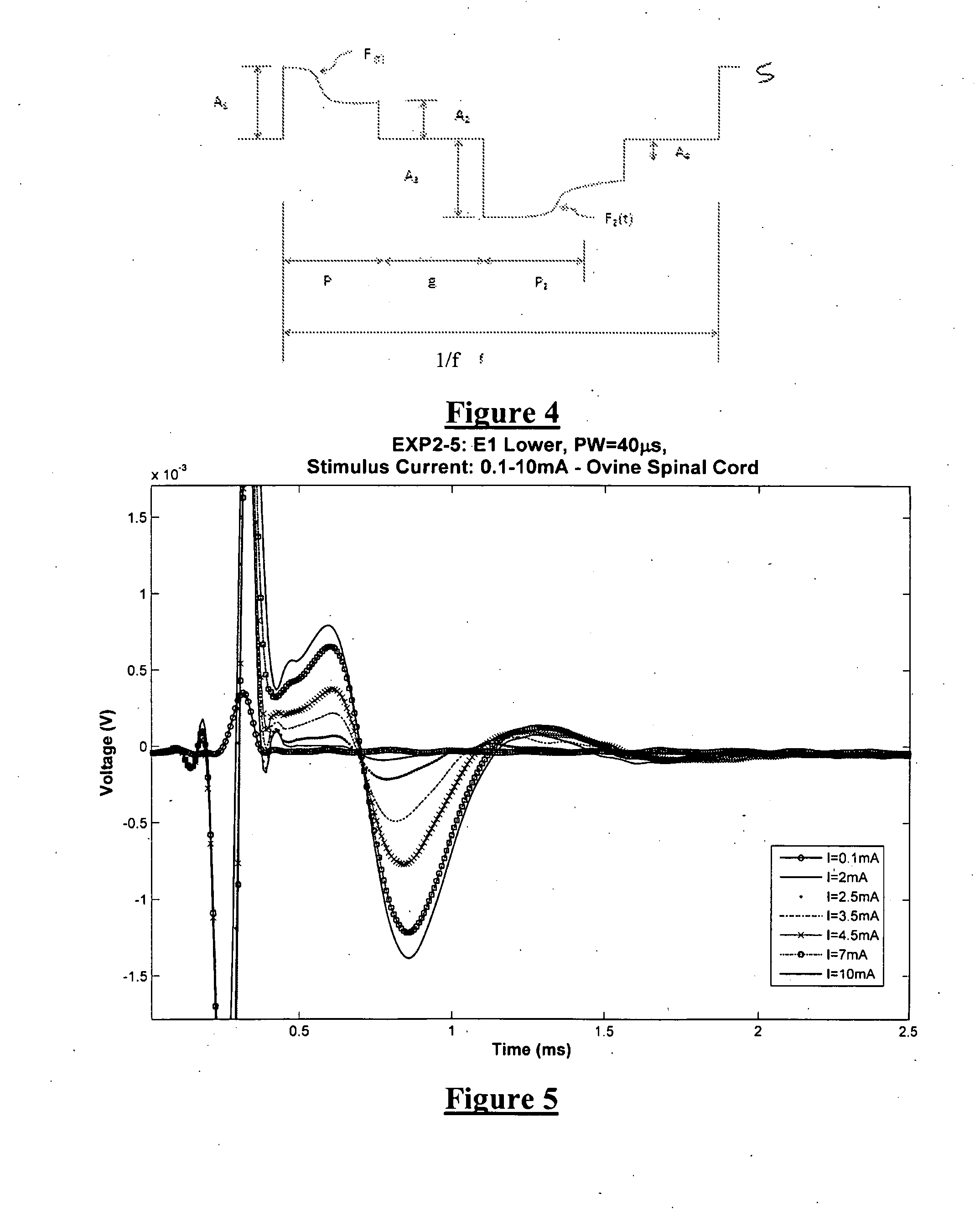
Patents
Literature
146 results about "Evoked potential recording" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
[edit on Wikidata] An evoked potential or evoked response is an electrical potential recorded from the nervous system of a human or other animal following presentation of a stimulus, as distinct from spontaneous potentials as detected by electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), or other electrophysiologic recording method.
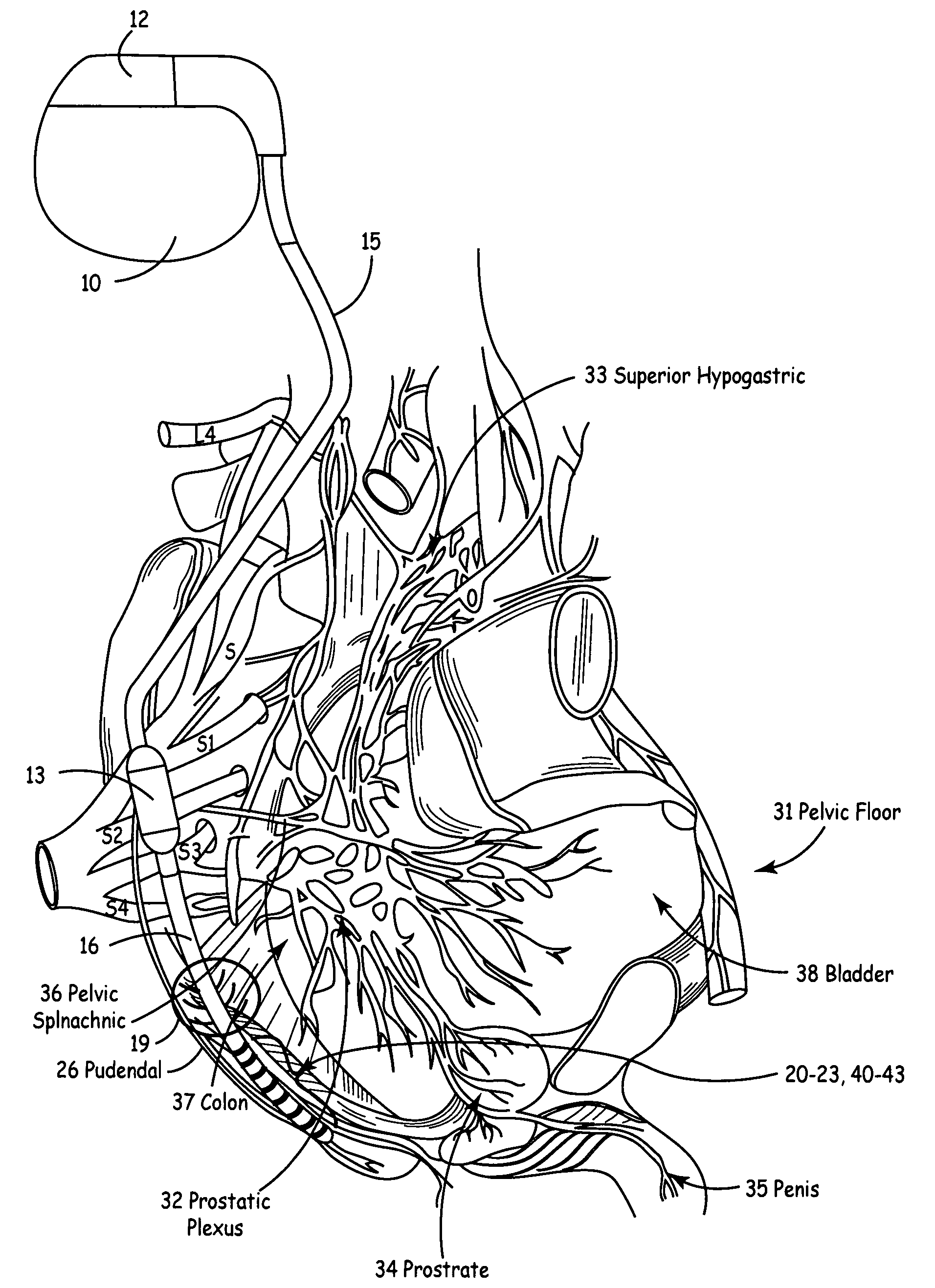
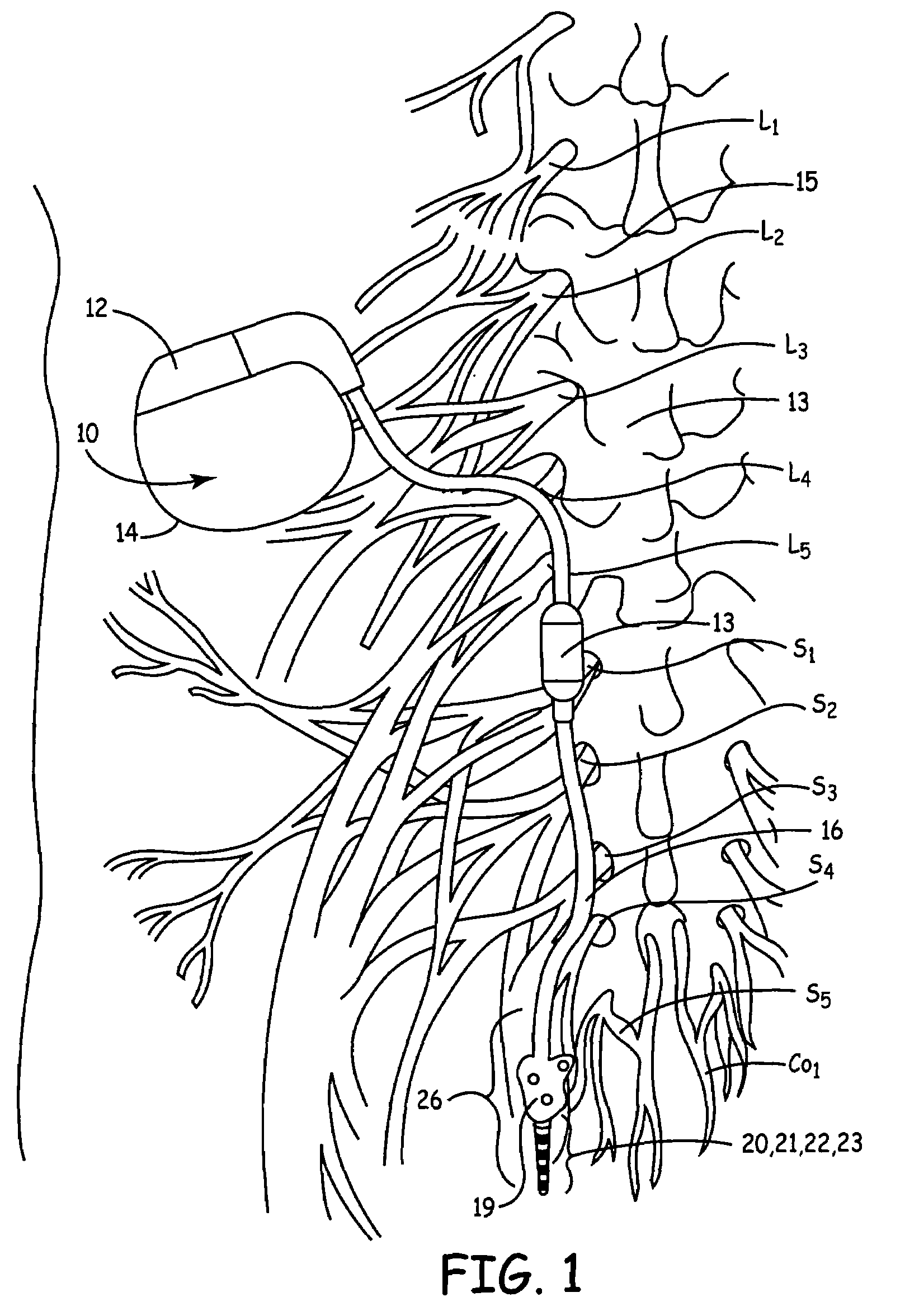
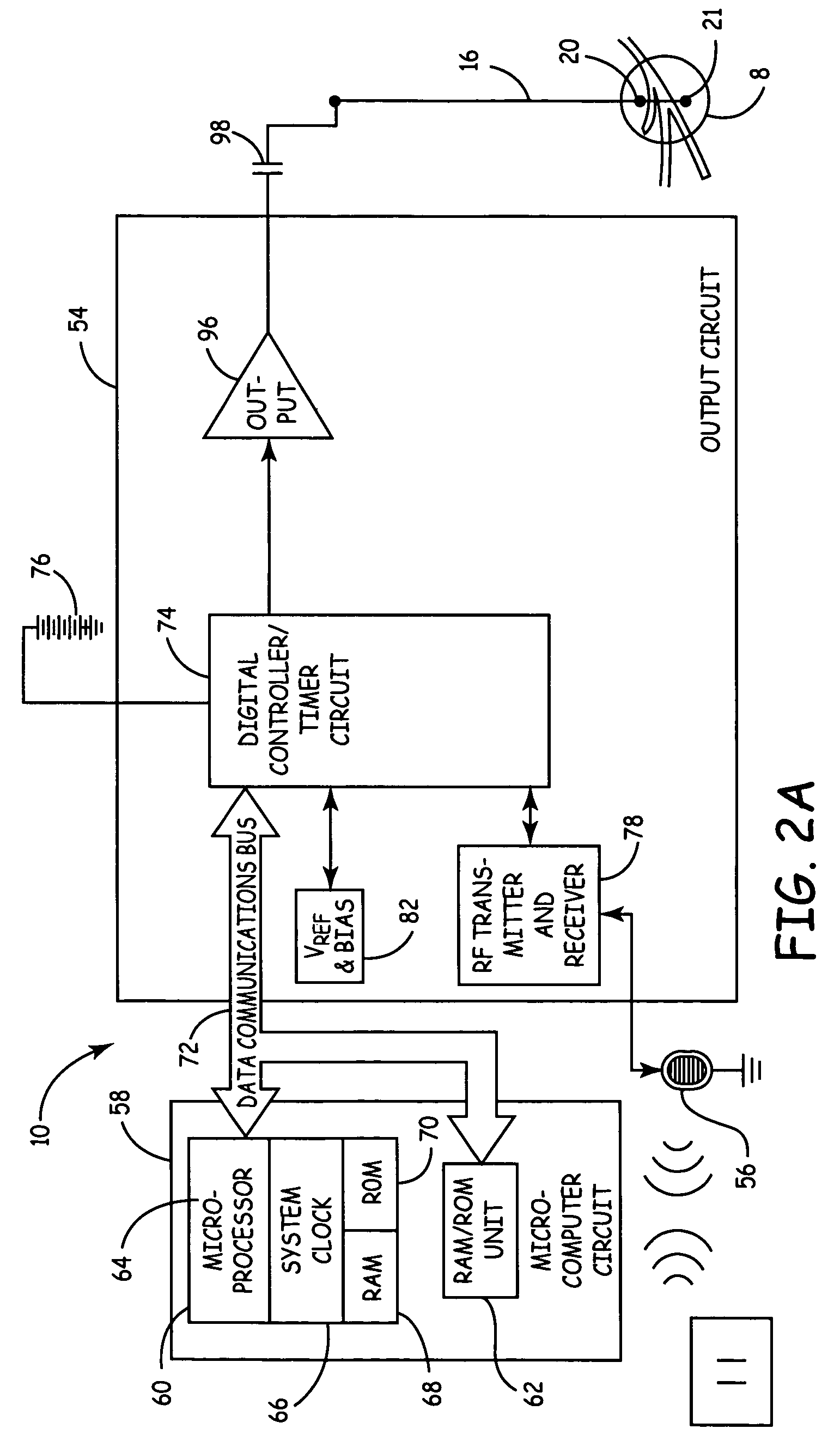
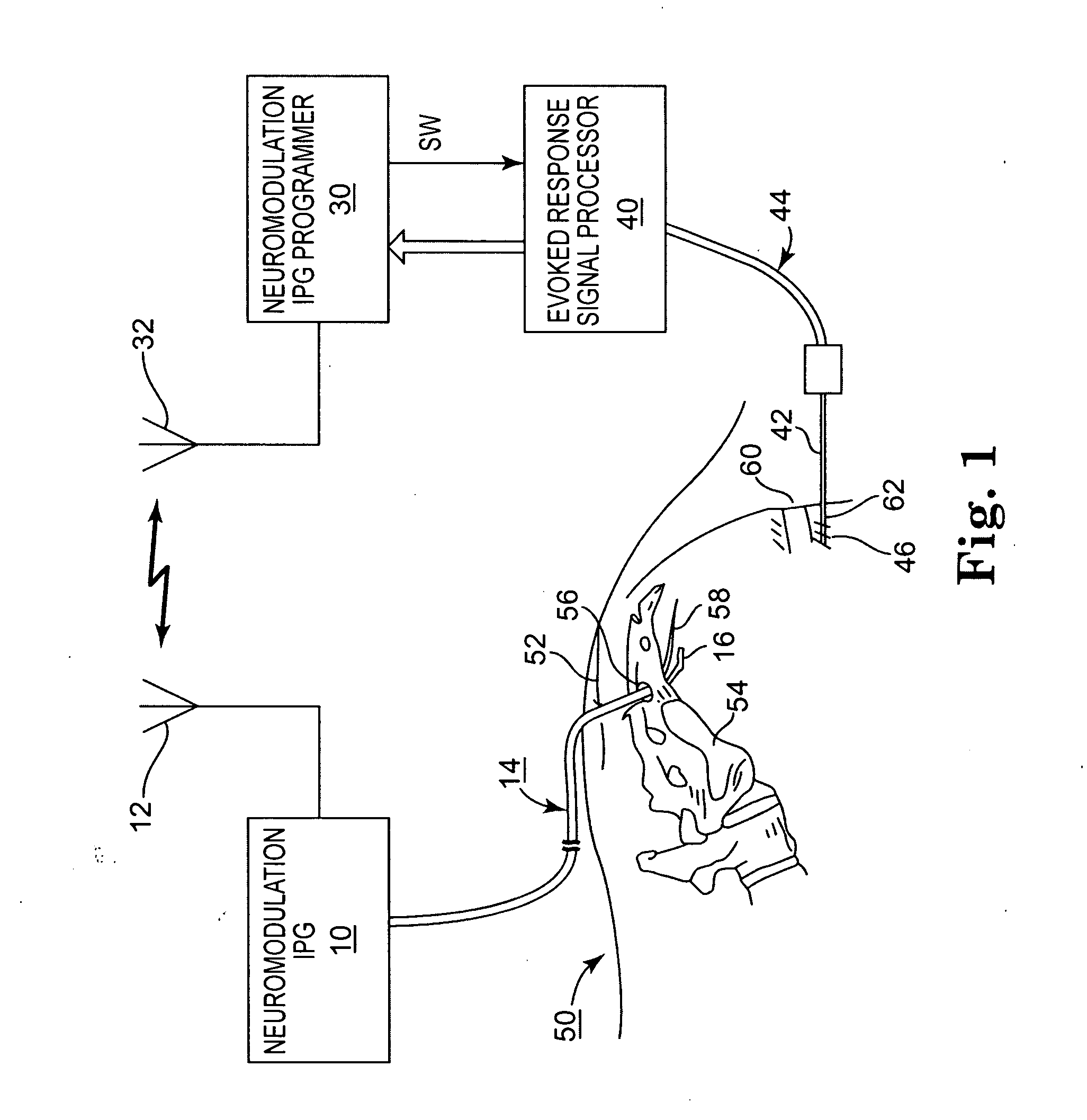
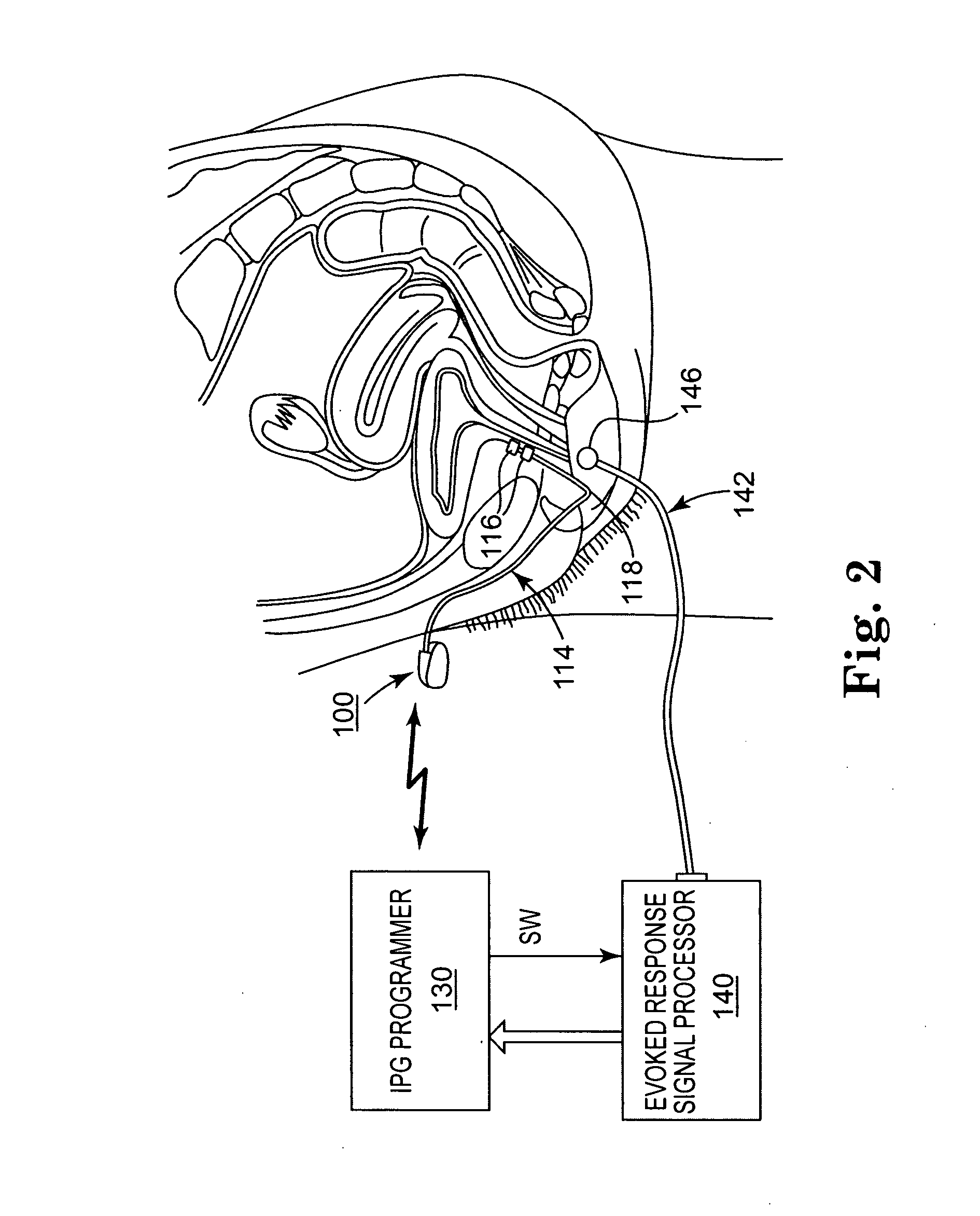
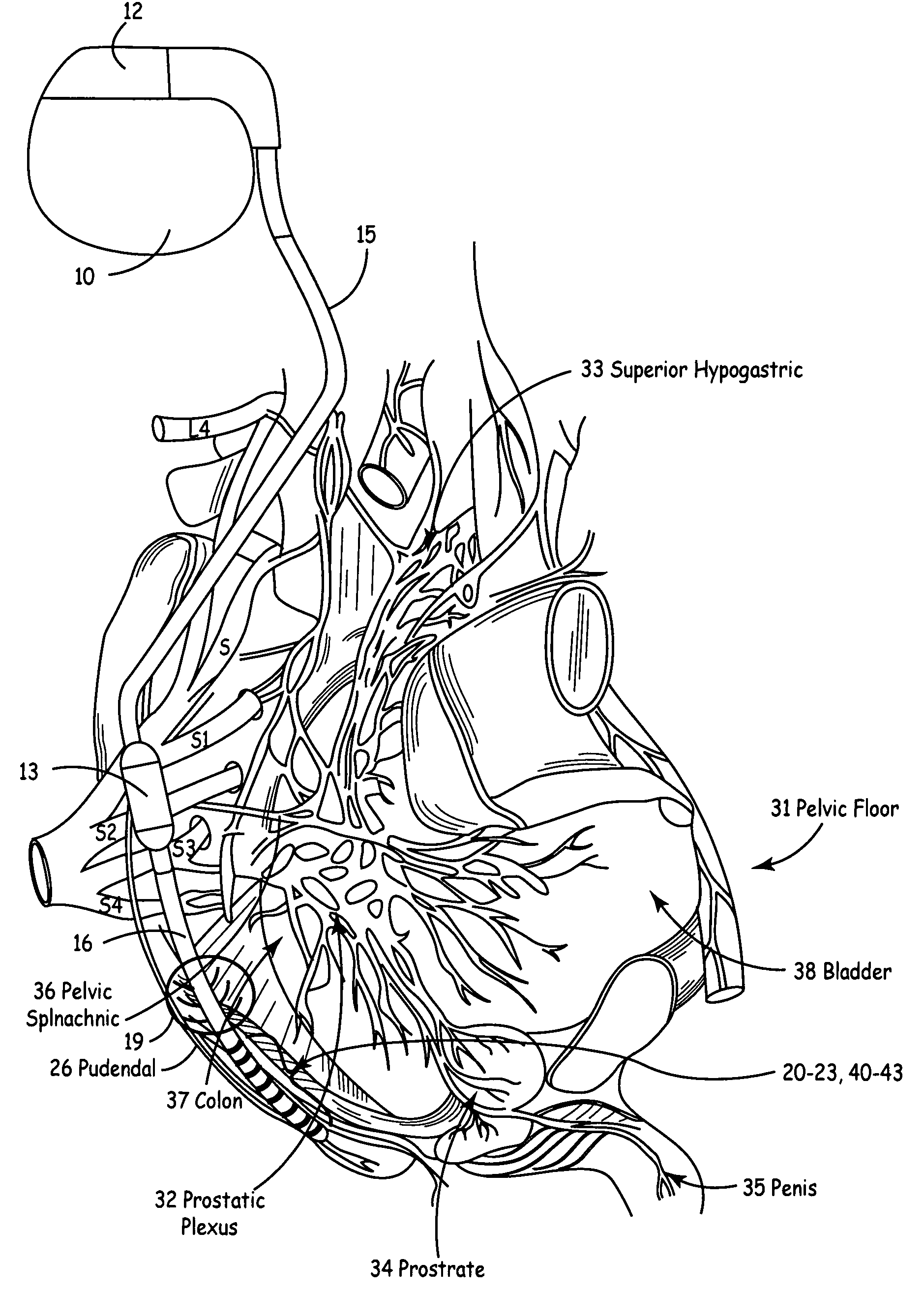
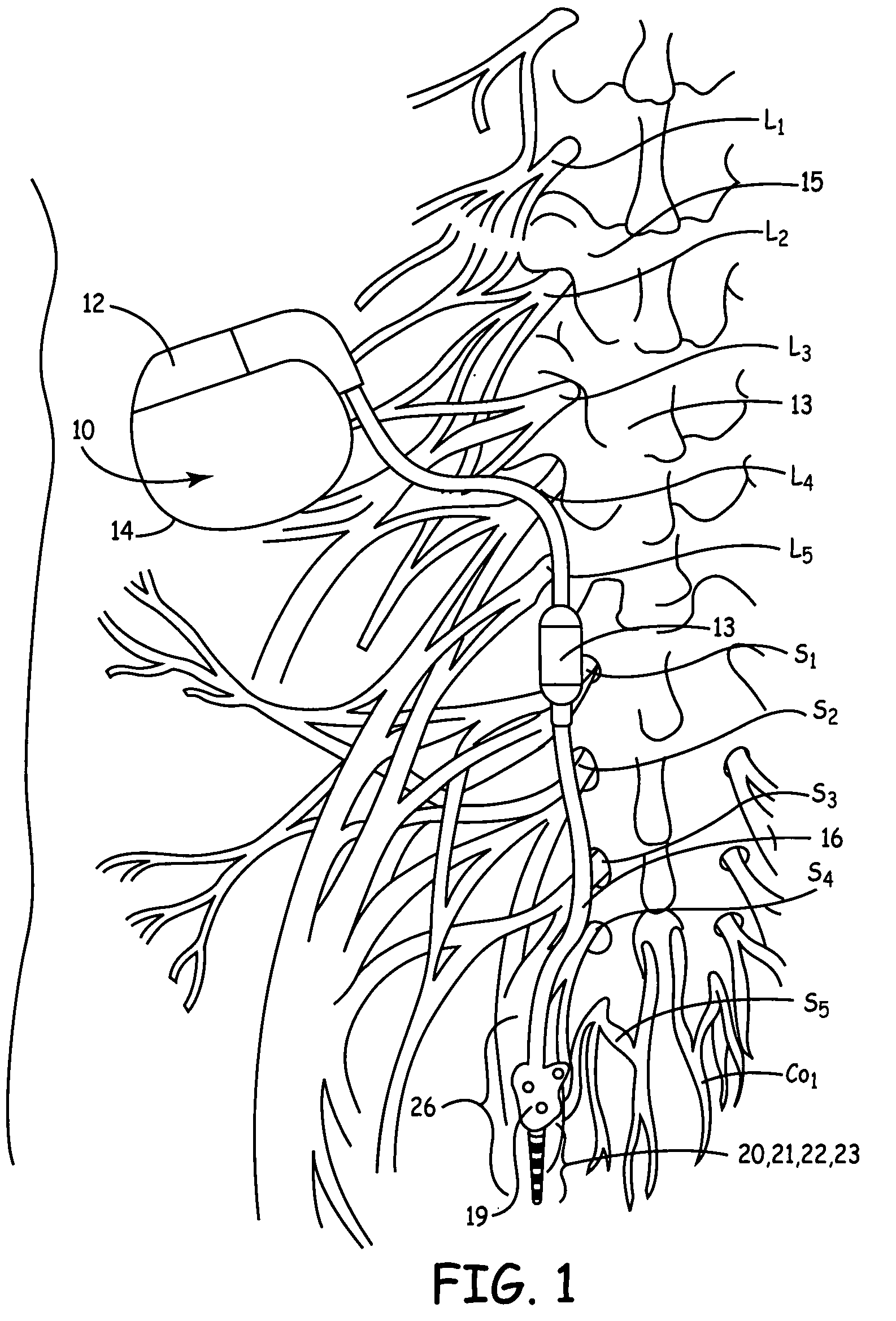
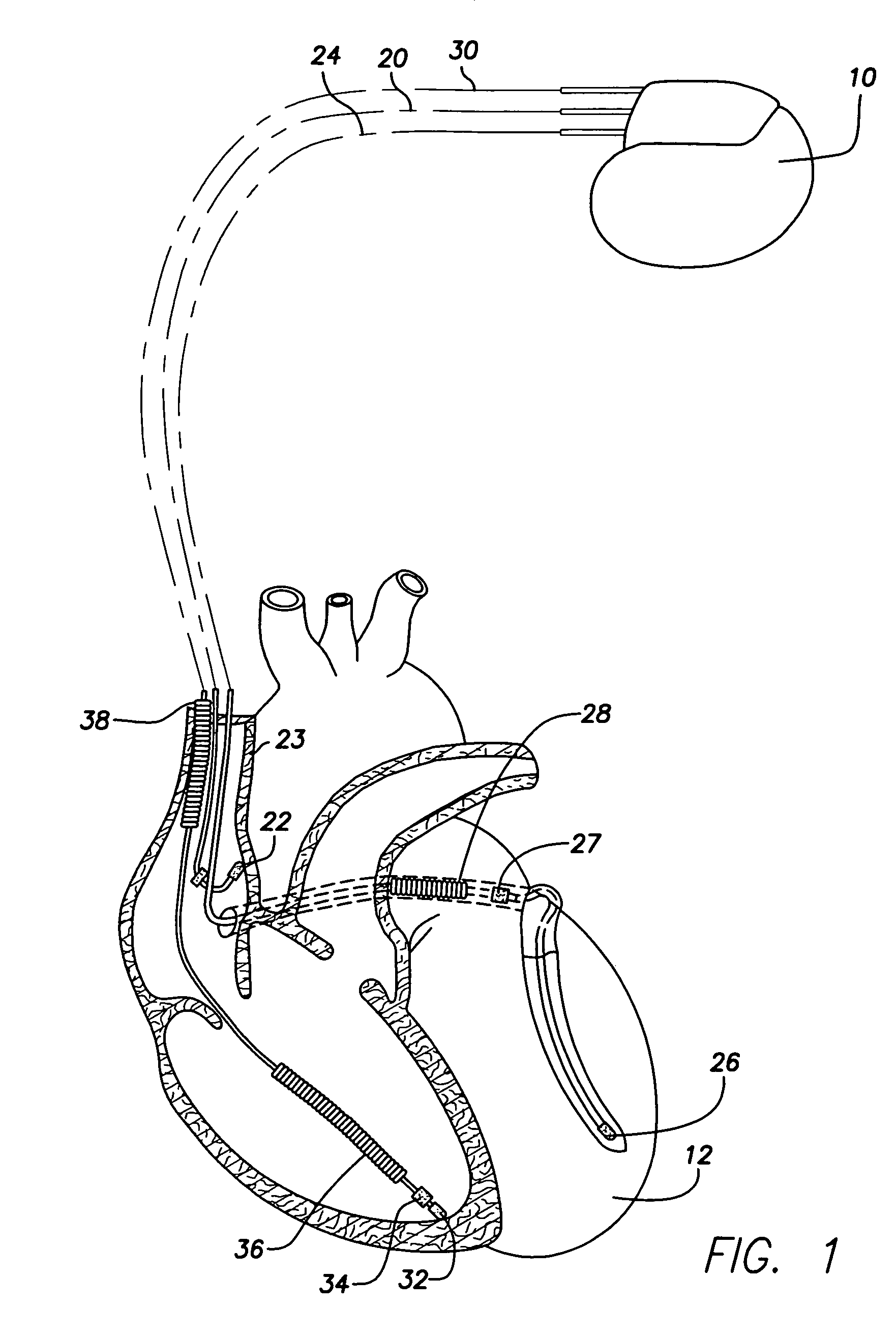
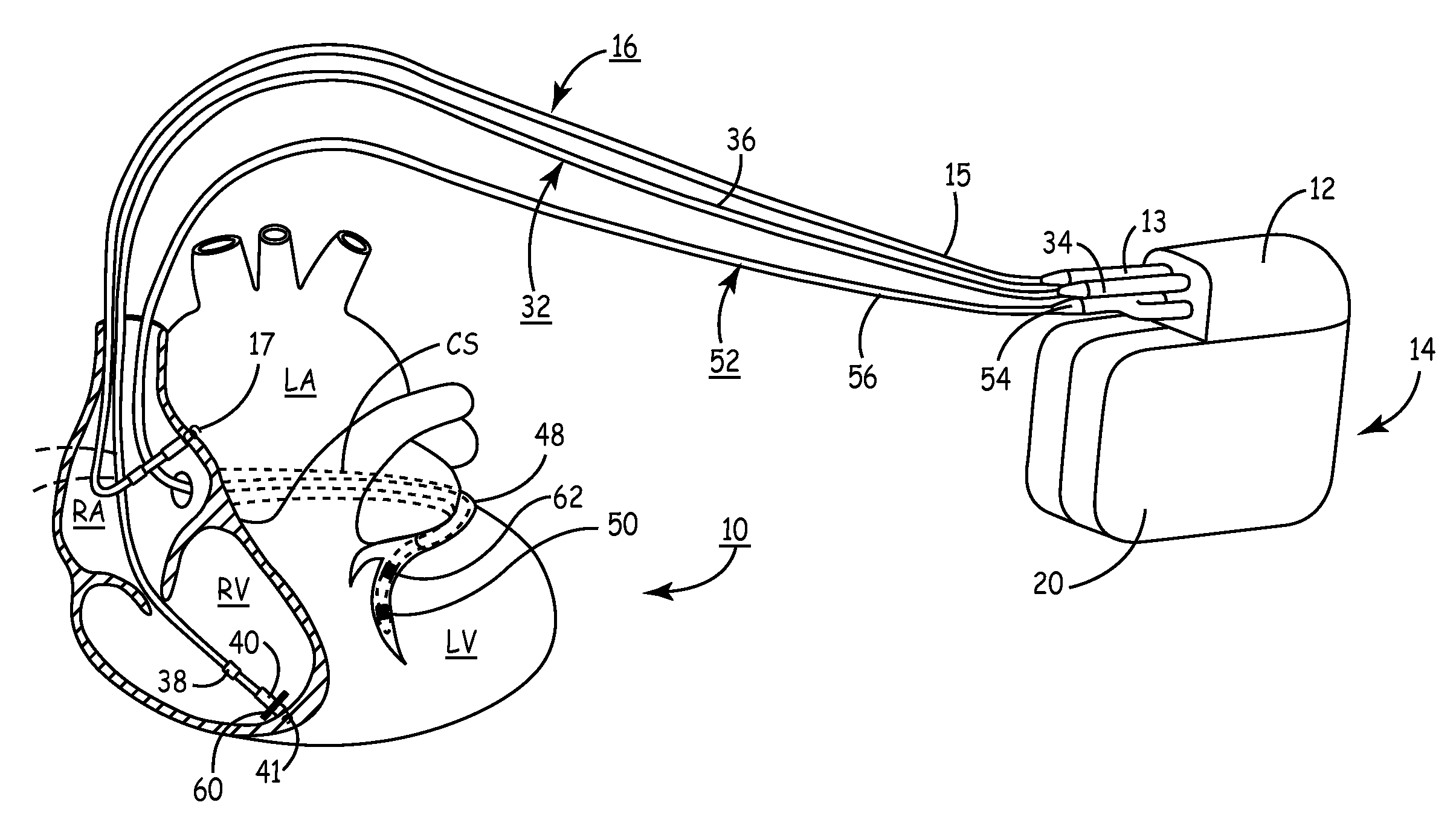
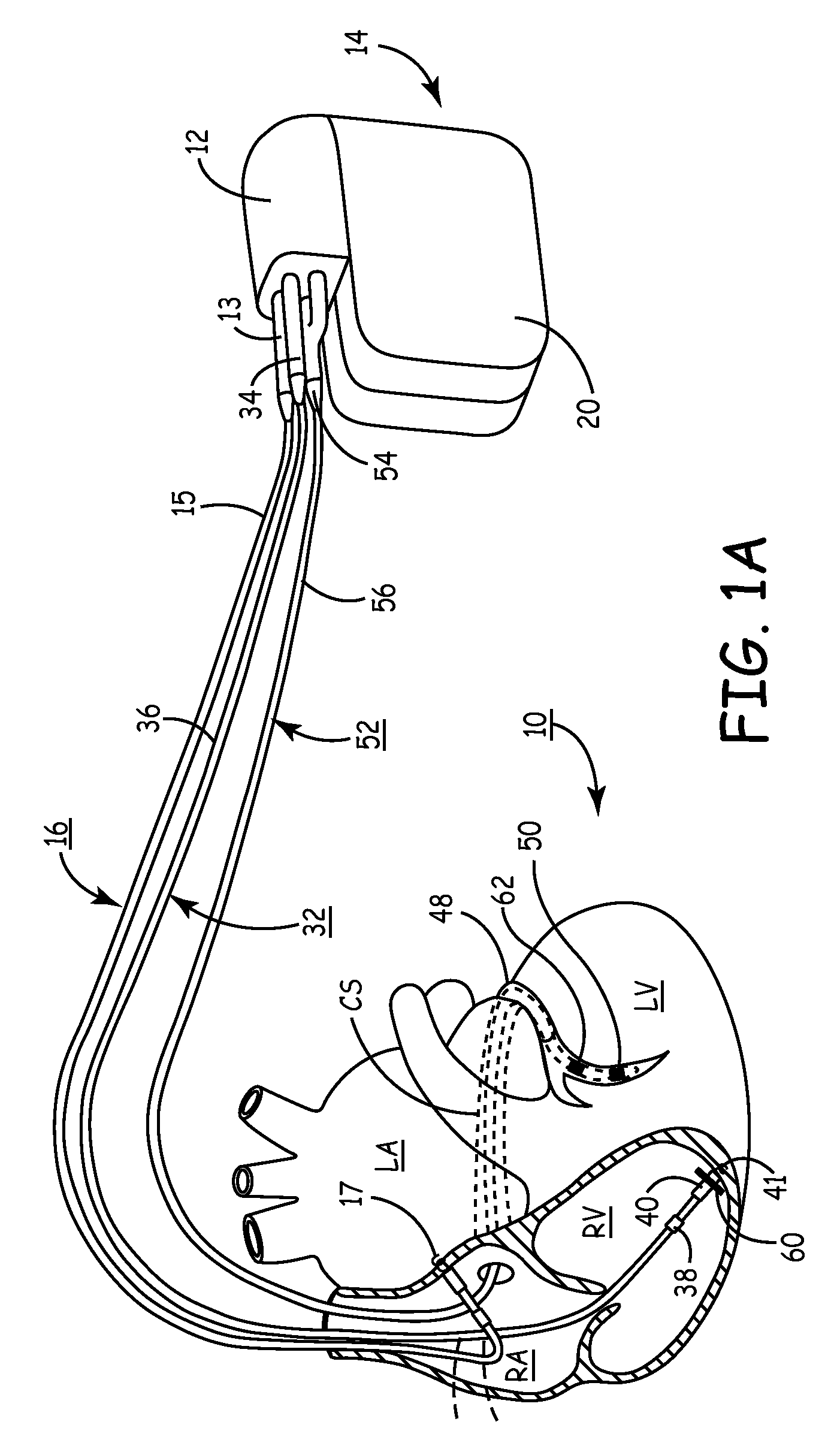
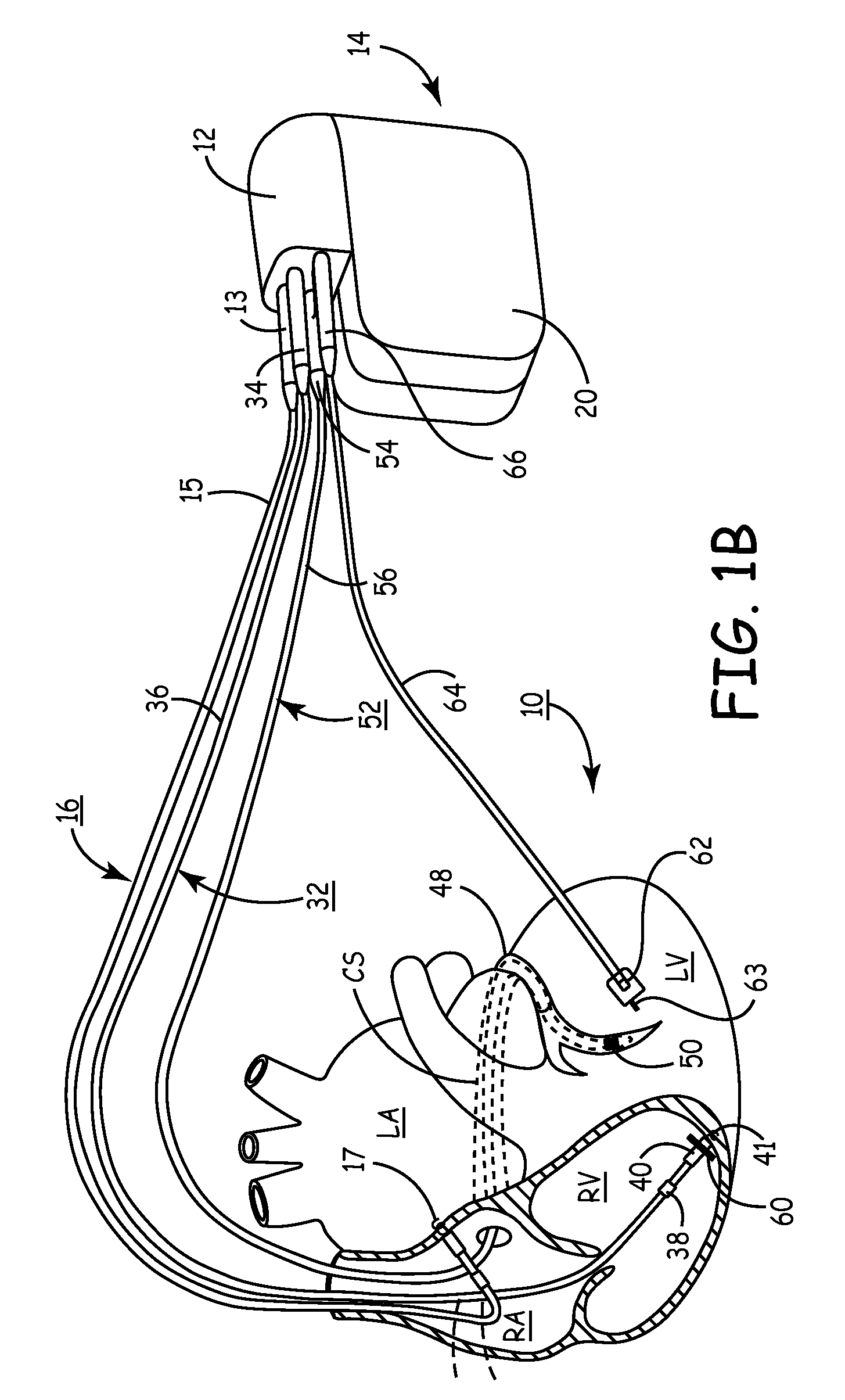
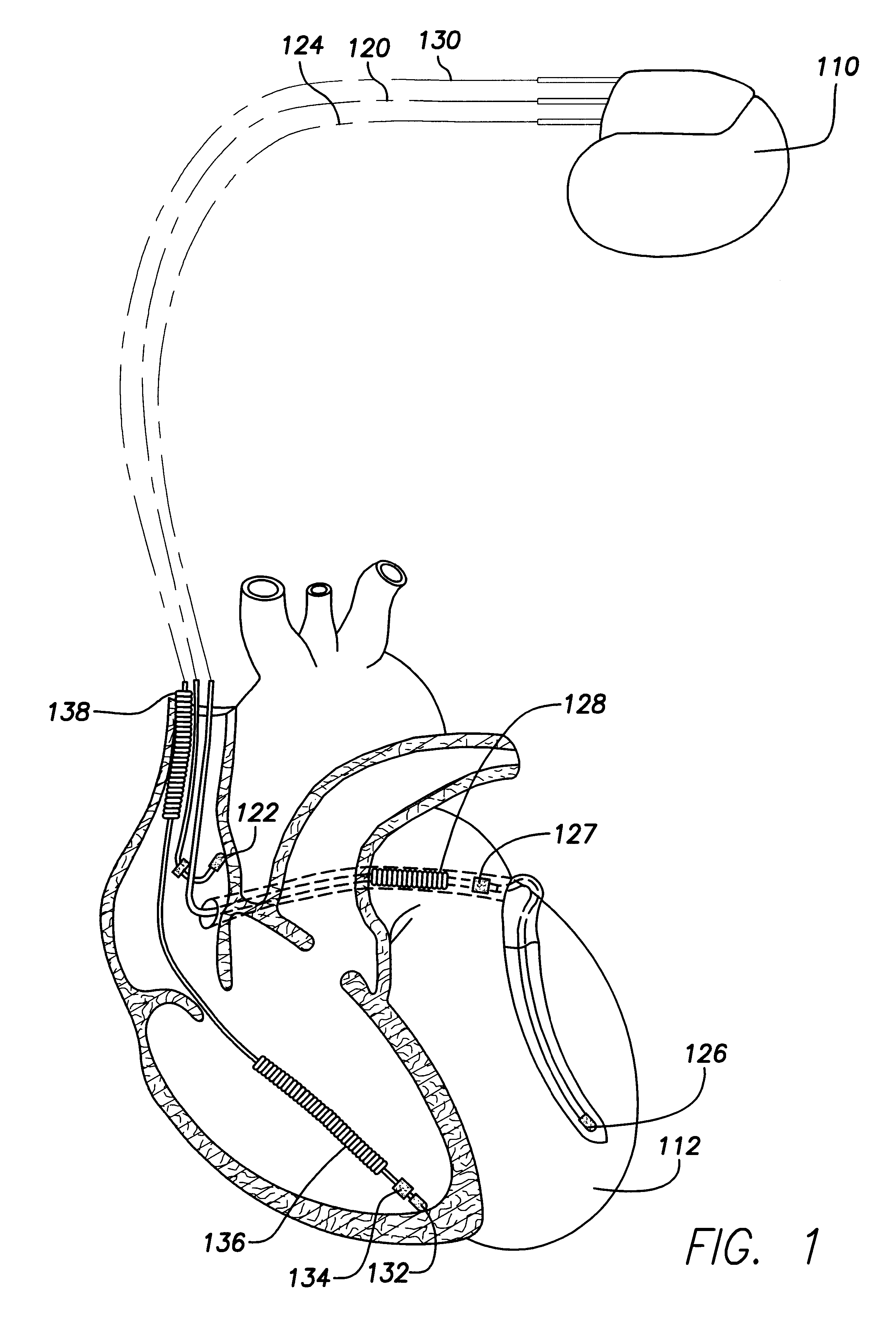
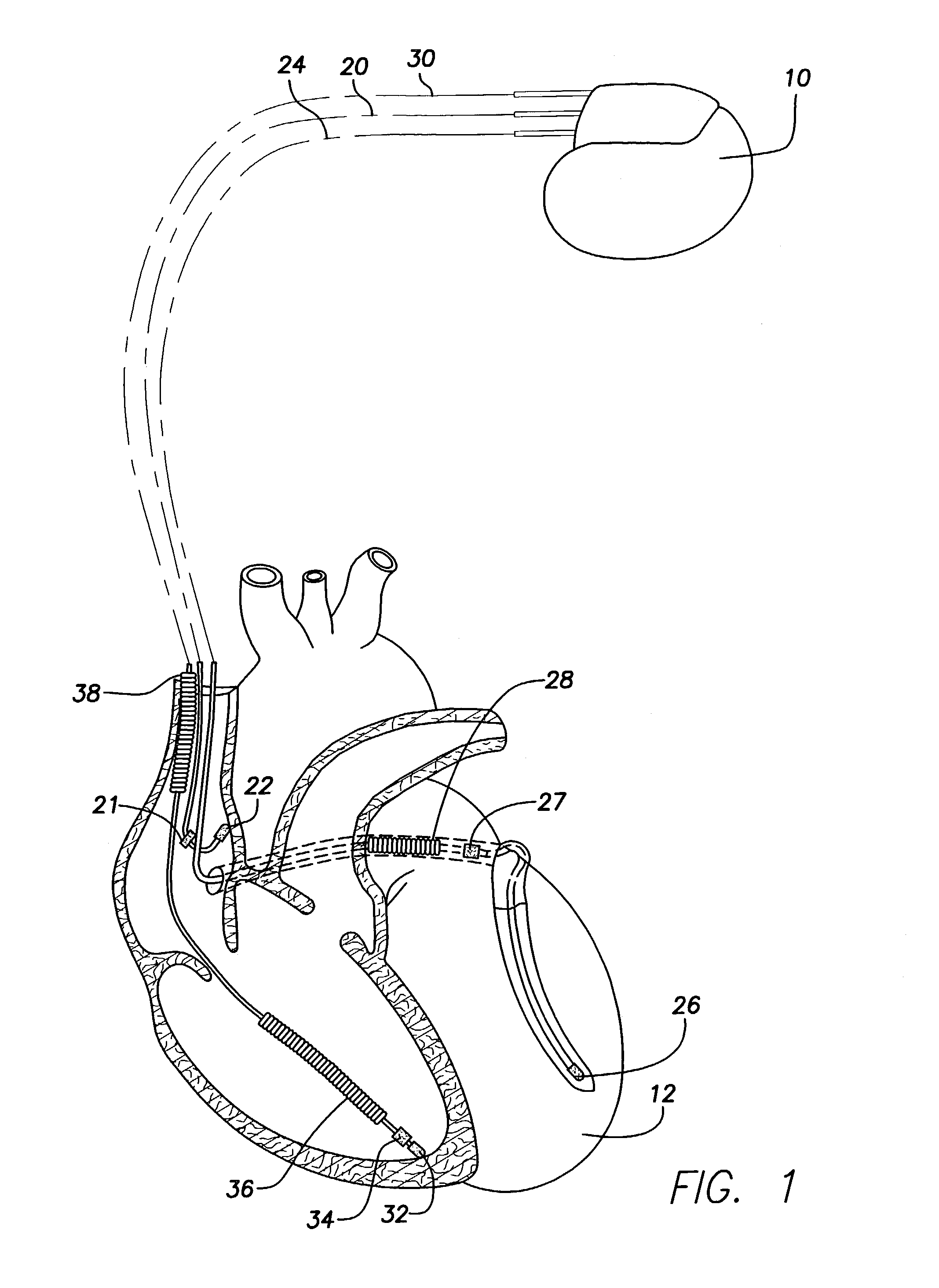
Method, system and device for treating disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal and associated nerves, and the optional delivery of drugs in association therewith
ActiveUS7328068B2Undesirable side effects of sacral nerve stimulation may be avoided or minimizedUndesirable side-effectDigestive electrodesGenital electrodesDiseaseProstatalgia
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal or other nerves, and optional means for delivering drugs in association therewith. A method of precisely positioning and implanting a medical electrical lead so as to provide optimal stimulation of the pudendal nerve or a portion thereof is also described. Placement of a stimulation lead next to or on the pudendal nerve may be performed using conventional prior art techniques through gross anatomical positioning, but usually does not result in truly optimal lead placement. One method of the present invention utilizes neurophysiological monitoring to assess the evoked responses of the pudendal nerve, and thereby provide a method for determining the optimal stimulation site. Additionally, one or more electrical stimulation signals are applied, and optionally one or more drugs are infused, injected or otherwise administered, to appropriate portions of a patient's pelvic floor and pudendal nerve or portions thereof in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Testing Efficacy of Therapeutic Mechanical or Electrical Nerve or Muscle Stimulation
InactiveUS20070265675A1Rule out the possibilityReduce complicationsElectrotherapyMuscle tissuePelvic nerve
Methods and apparatus for testing of the efficacy of therapeutic stimulation of pelvic nerves or musculature to alleviate one of incontinence or sexual dysfunction are disclosed. A therapy delivery device is operable in a therapy delivery mode and a test mode and an evoked response detector is employed in the test mode to detect the evoked response to applied test stimuli. The test stimuli parameters of the test stimulation regimen are adjusted prior to delivery of each test stimulation regimen, and the evoked responses to the applied test stimulation regimens are compared to ascertain an optimal test stimulation regimen. The therapy stimulation regimen parameters are selected as a function of the test electrical stimulation parameters causing the optimal evoked response.
Owner:AMS RES CORP
Method, system and device for treating disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudenal and associated nerves, and the optional delivery of drugs in association therewith
ActiveUS20050113877A1Reduce traumaAvoid damageDigestive electrodesArtificial respirationDiseaseProstatalgia
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal or other nerves, and optional means for delivering drugs in association therewith. A method of precisely positioning and implanting a medical electrical lead so as to provide optimal stimulation of the pudendal nerve or a portion thereof is also described. Placement of a stimulation lead next to or on the pudendal nerve may be performed using conventional prior art techniques through gross anatomical positioning, but usually does not result in truly optimal lead placement. One method of the present invention utilizes neurophysiological monitoring to assess the evoked responses of the pudendal nerve, and thereby provide a method for determining the optimal stimulation site. Additionally, one or more electrical stimulation signals are applied, and optionally one or more drugs are infused, injected or otherwise administered, to appropriate portions of a patient's pelvic floor and pudendal nerve or portions thereof in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
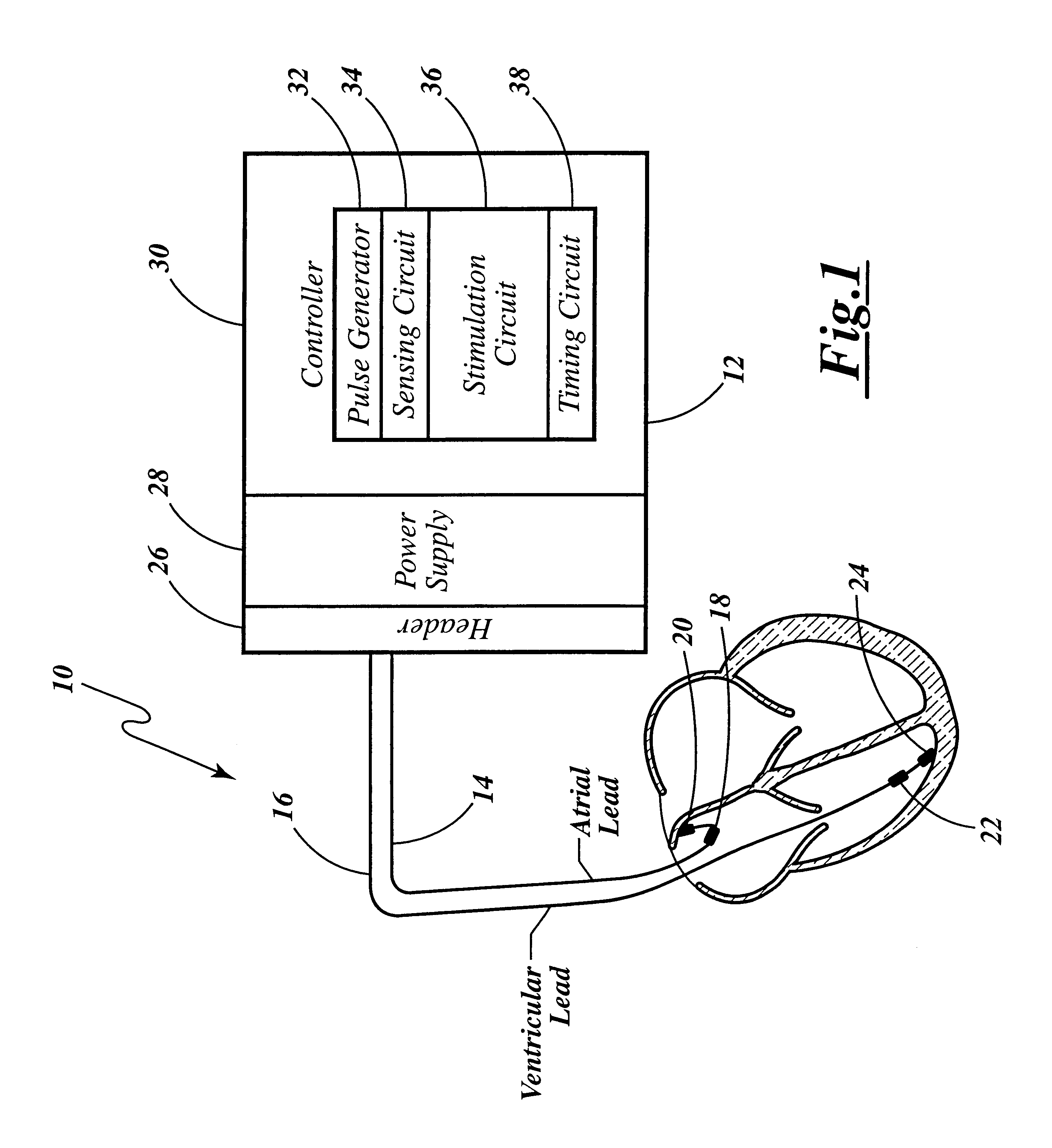
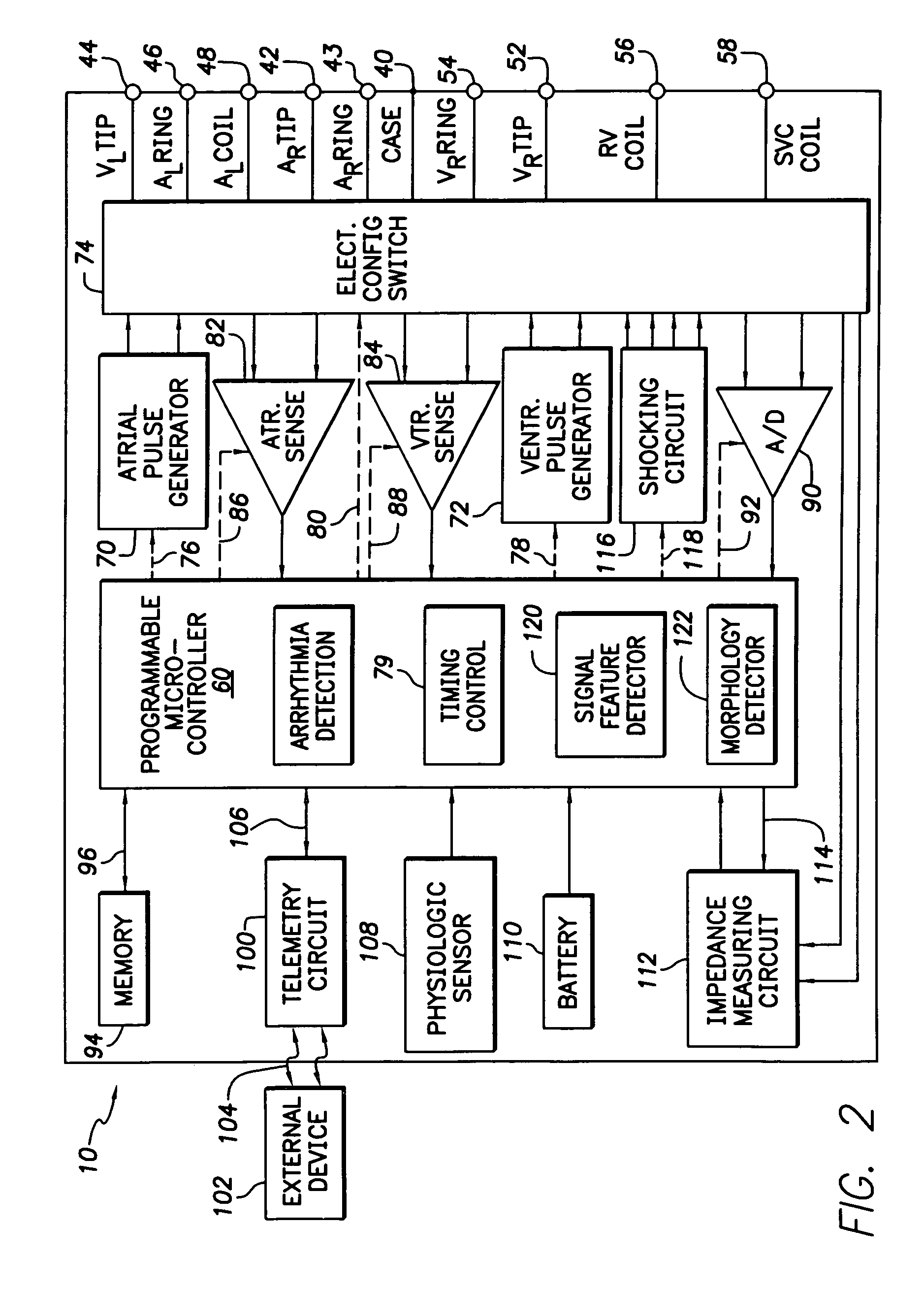
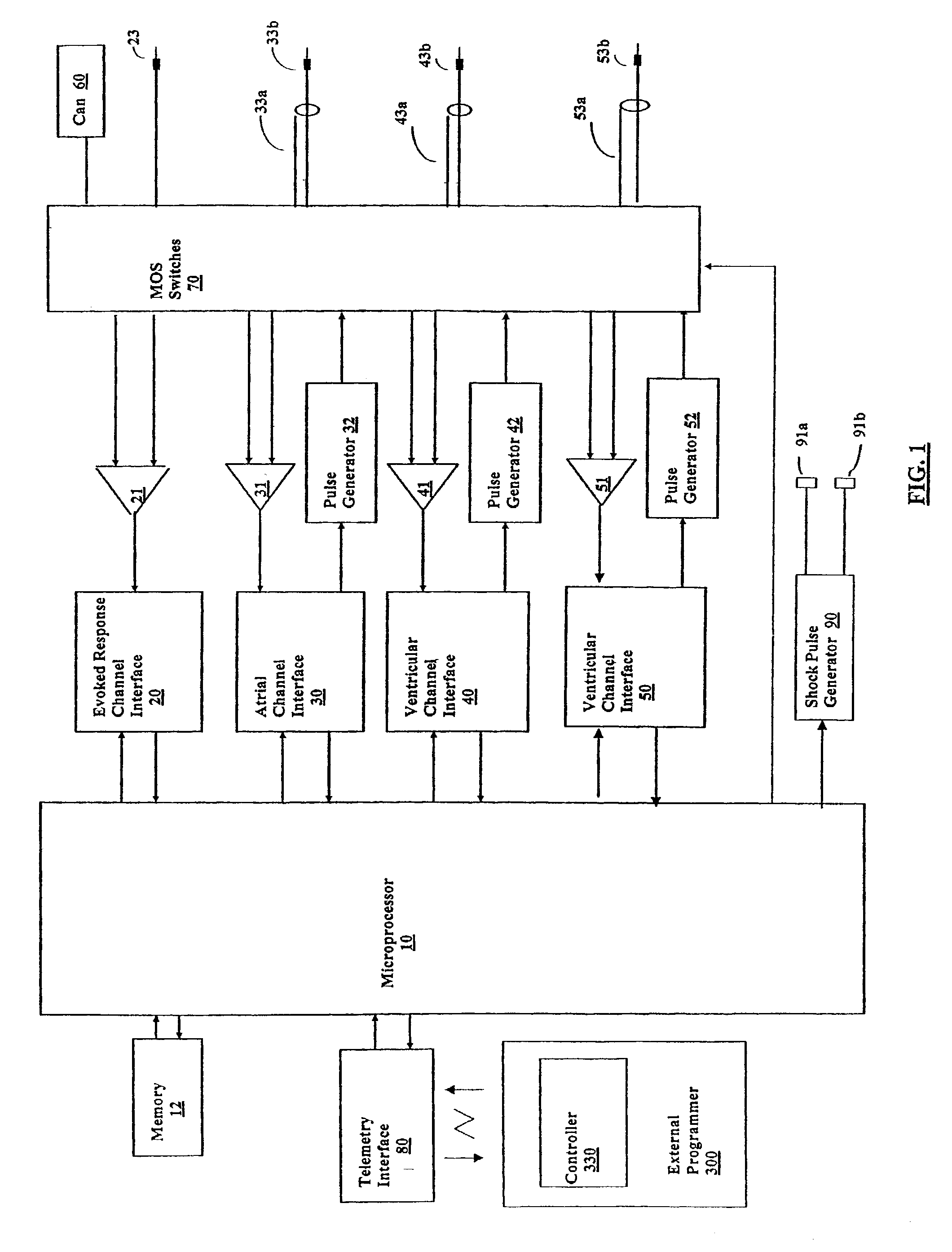
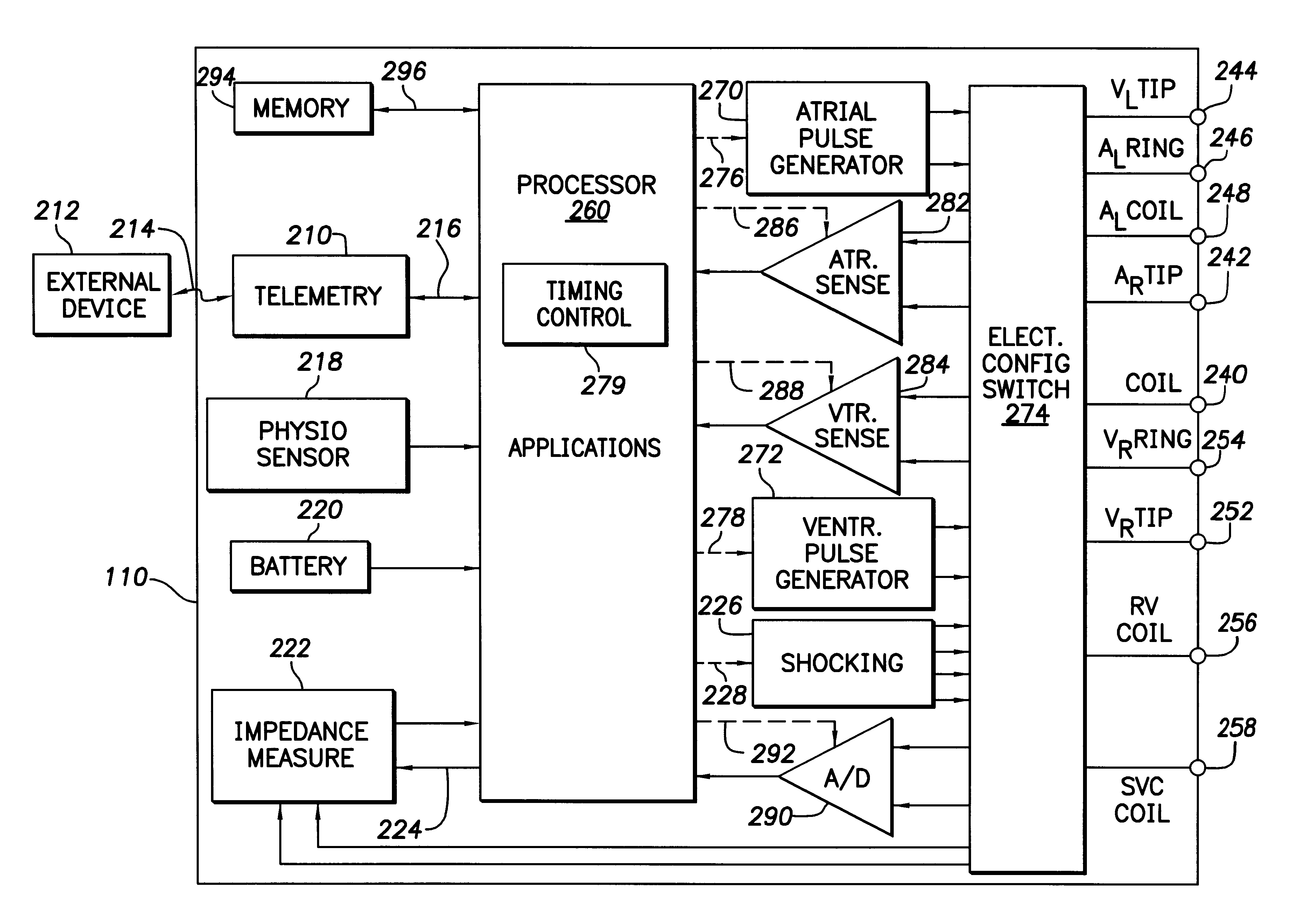
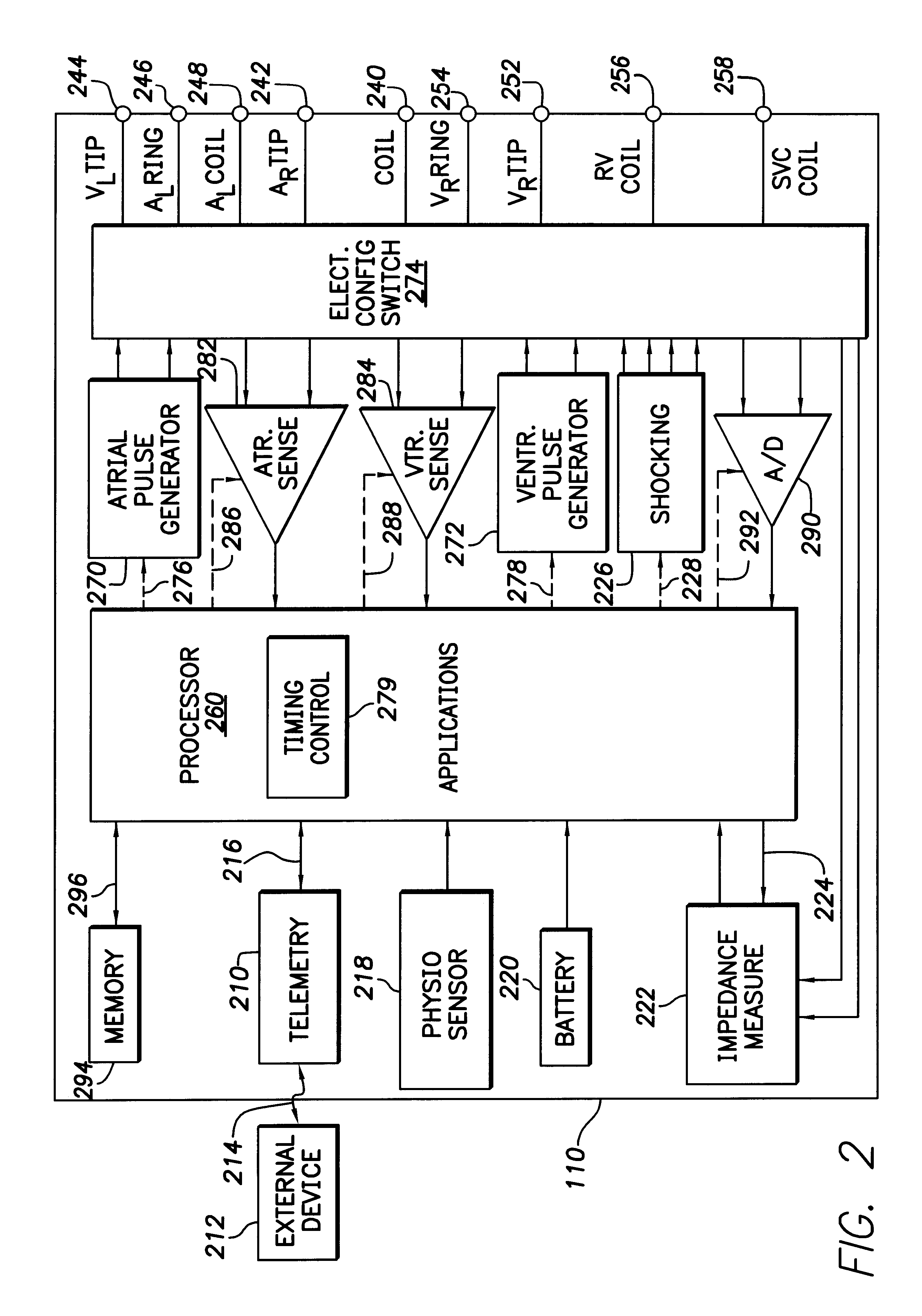
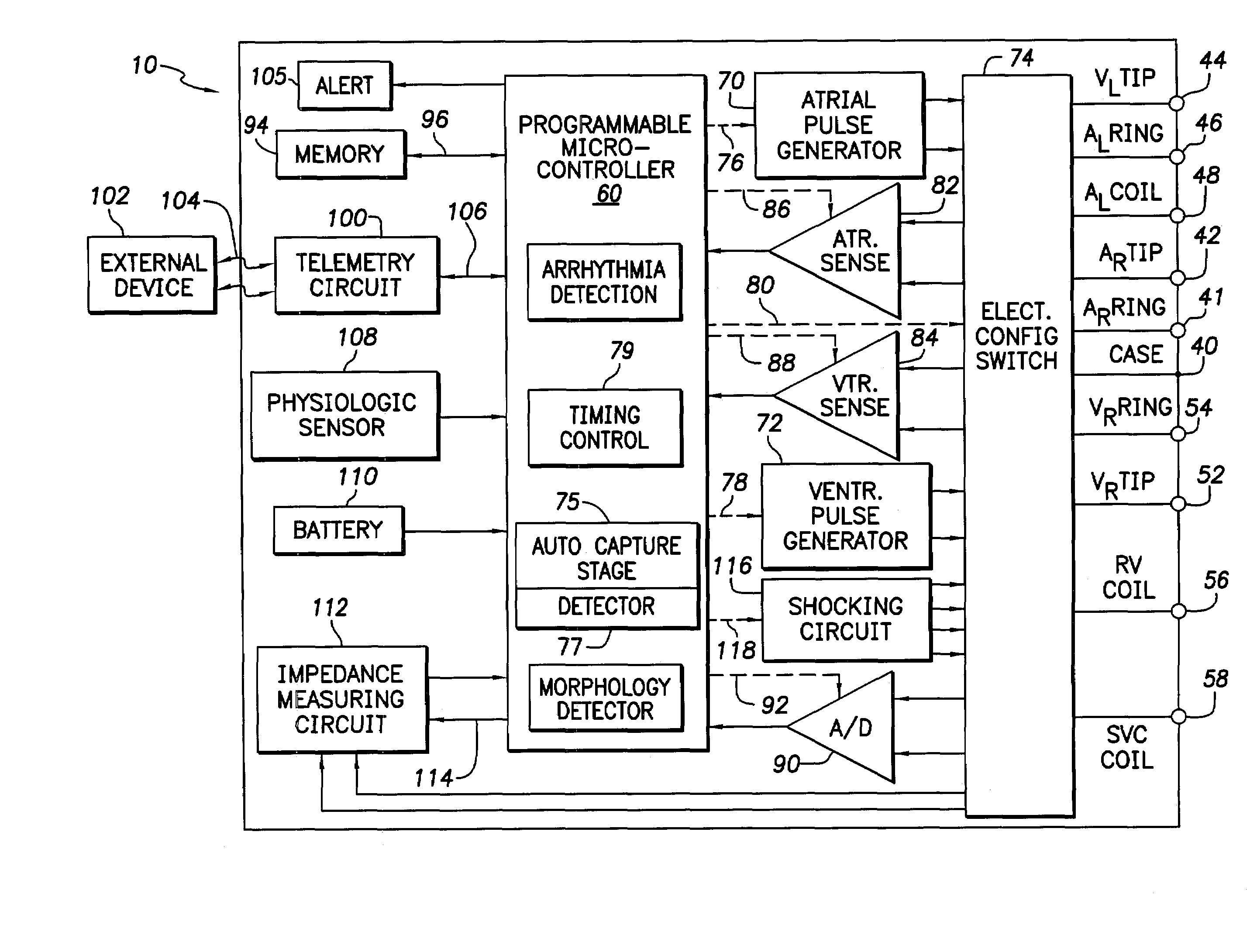
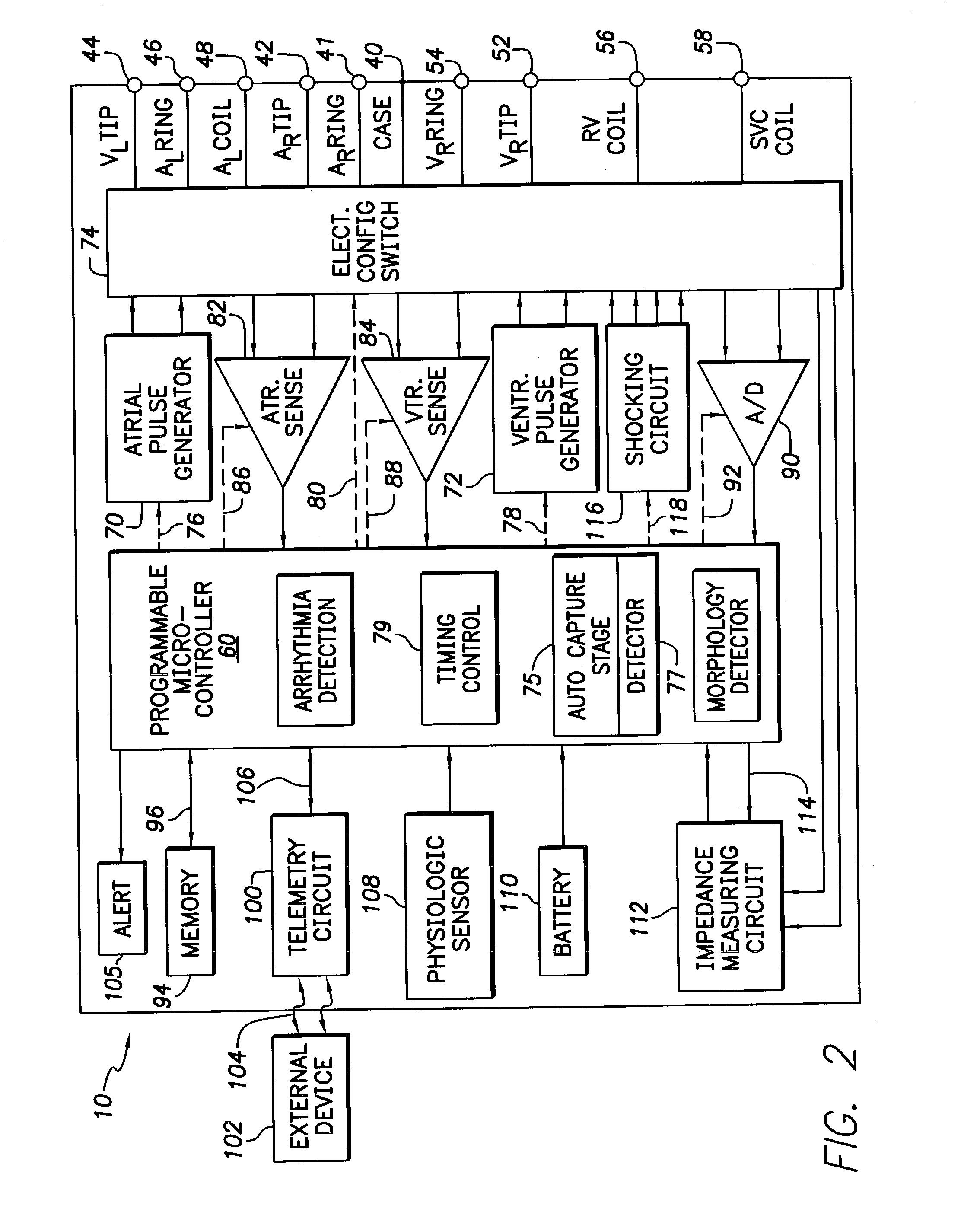
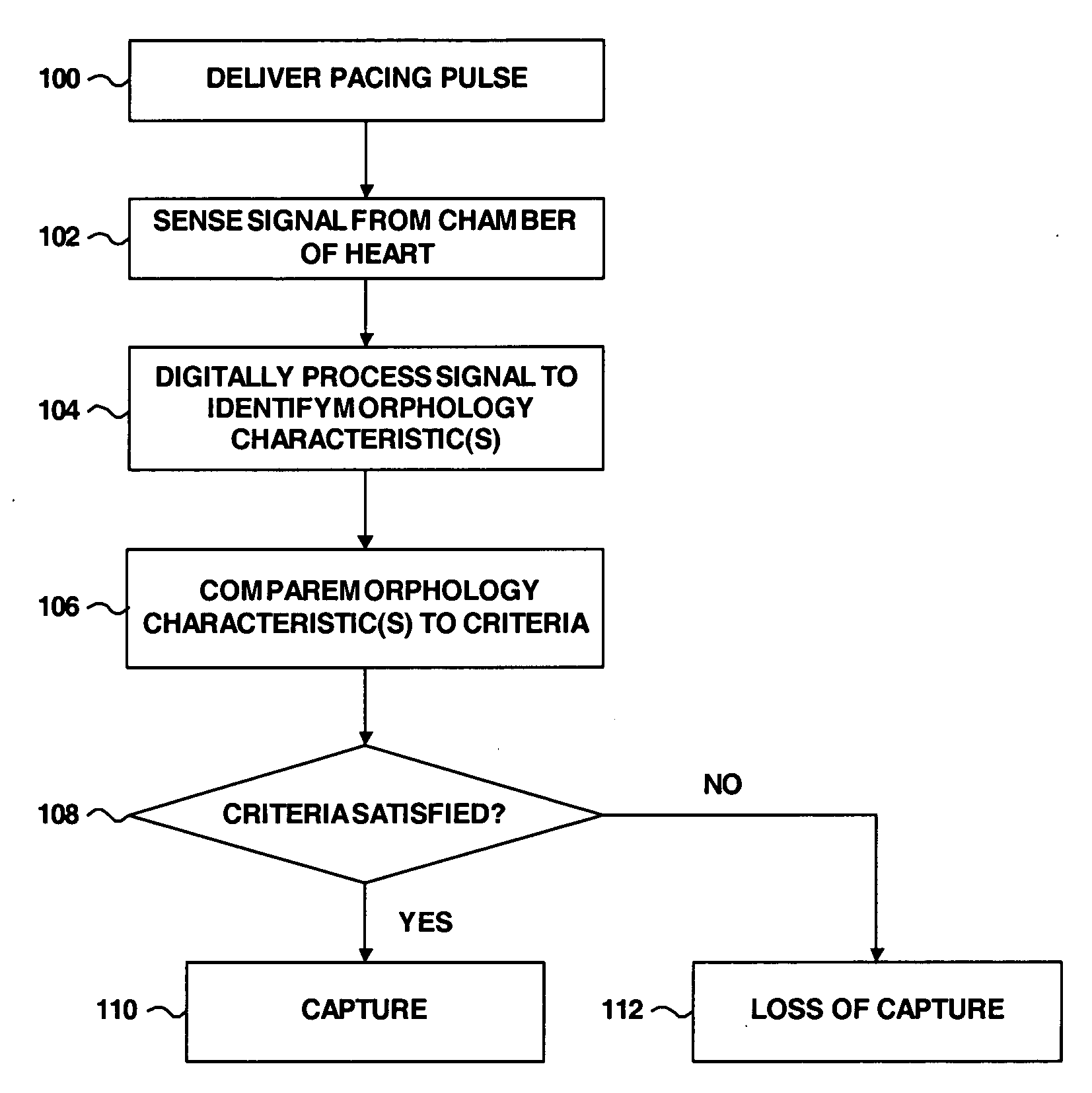
Cardiac management device with capability of noise detection in automatic capture verification
An implantable cardiac rhythm management device operable in an autothreshold or autocapture verification mode, wherein the rhythm management device is capable of detecting noise that affects signal characteristics of a sensed intracardial evoked response electrogram signal. The device includes a noise detection circuit that determines whether a minimum peak timing occurs during a predetermined time following delivery of a stimulation pulse. If a minimum peak timing occurs during the predetermined time following delivery of the stimulation pulse, then significant amounts of noise affecting the signal characteristics of the electrocardiogram signal is assumed.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Cardiac pacing apparatus and method for continuous capture management
ActiveUS7831303B2Increase the number ofIncrease incidenceHeart stimulatorsHeart chamberCardiac stimulation
An implantable cardiac stimulation system and method having continuous capture management capabilities are provided. Continuous capture management is realized by continuously monitoring for secondary effects of loss of capture, thereby effectively providing continuous capture management in any heart chamber without encountering the limitations normally associated with evoked response sensing. A pacing threshold search is triggered upon detecting a secondary indicator of loss of capture. Secondary indicators of loss of capture may be lead-related changes, changes related to the occurrence of atrial sensed events, changes related related to the occurrence of ventricular sensed or paced events, and / or changes related to a monitored physiological condition.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
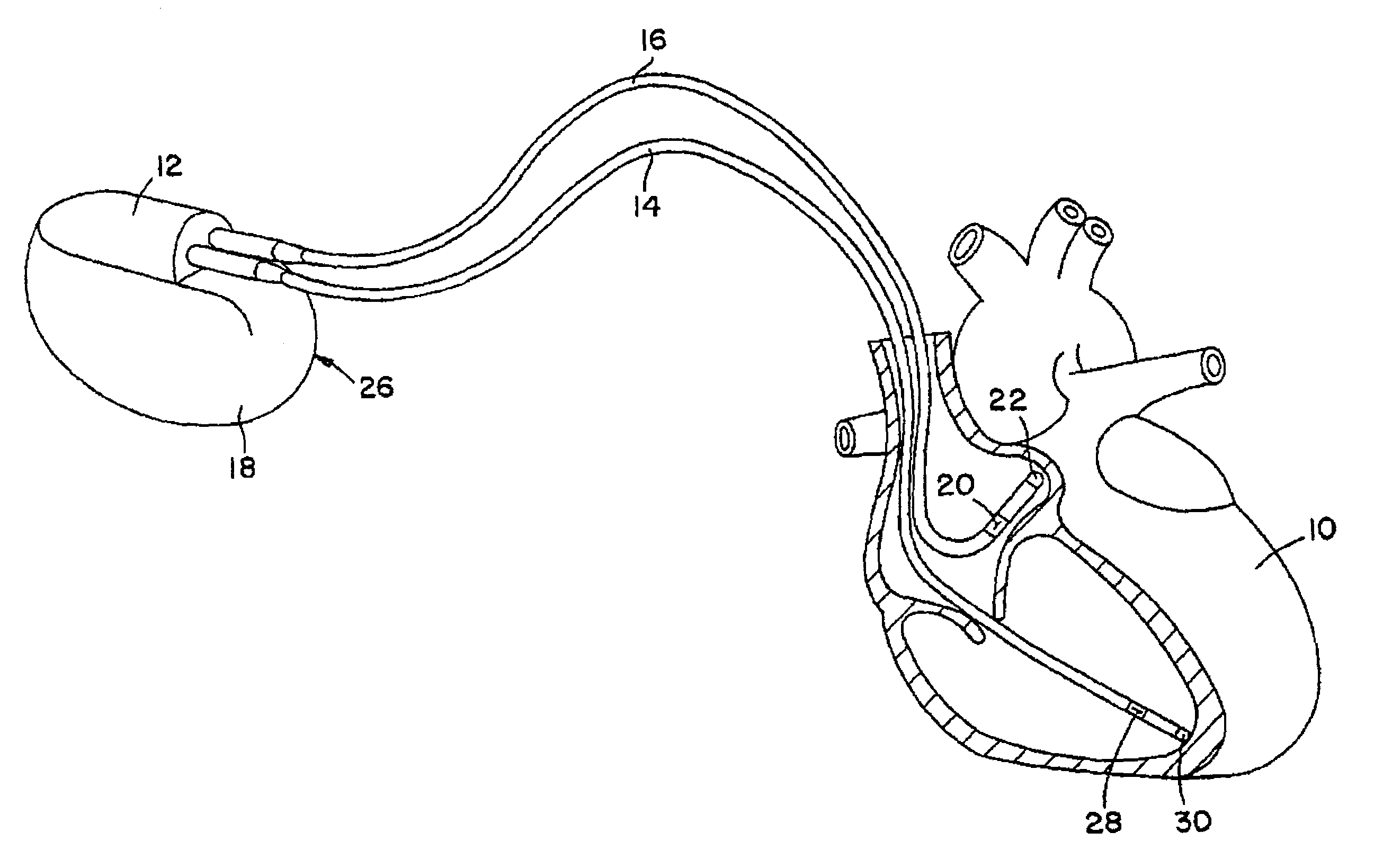
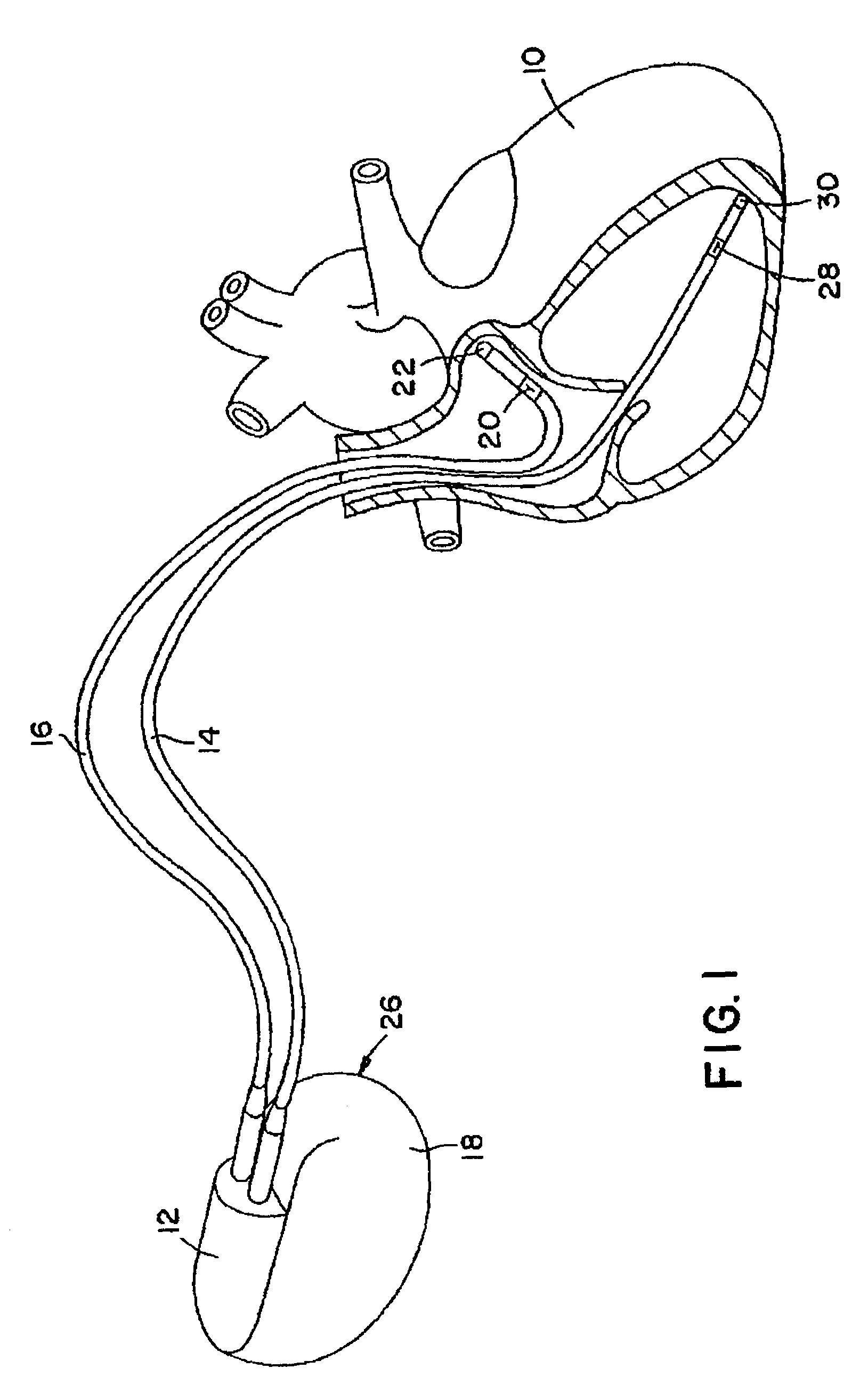
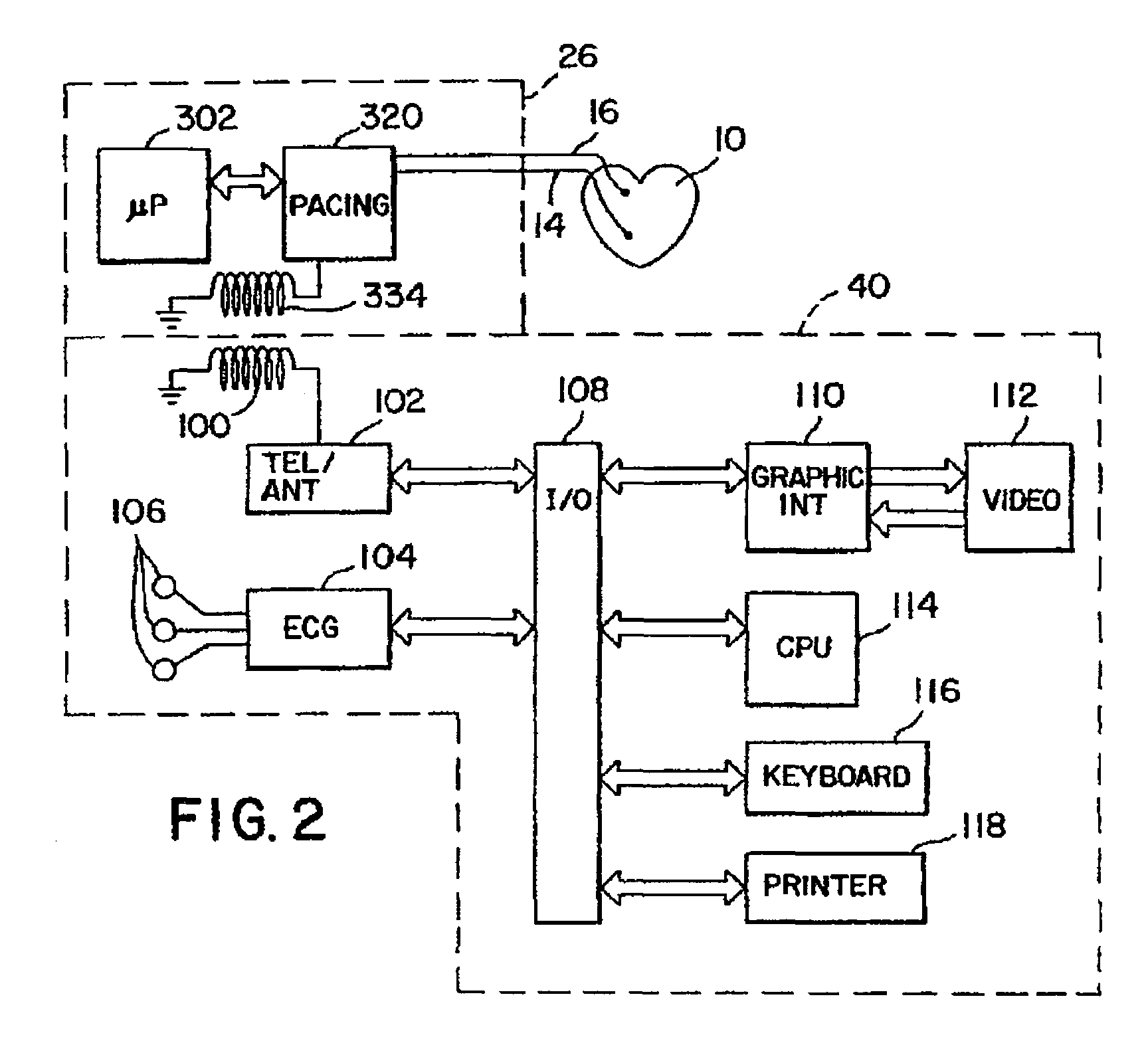
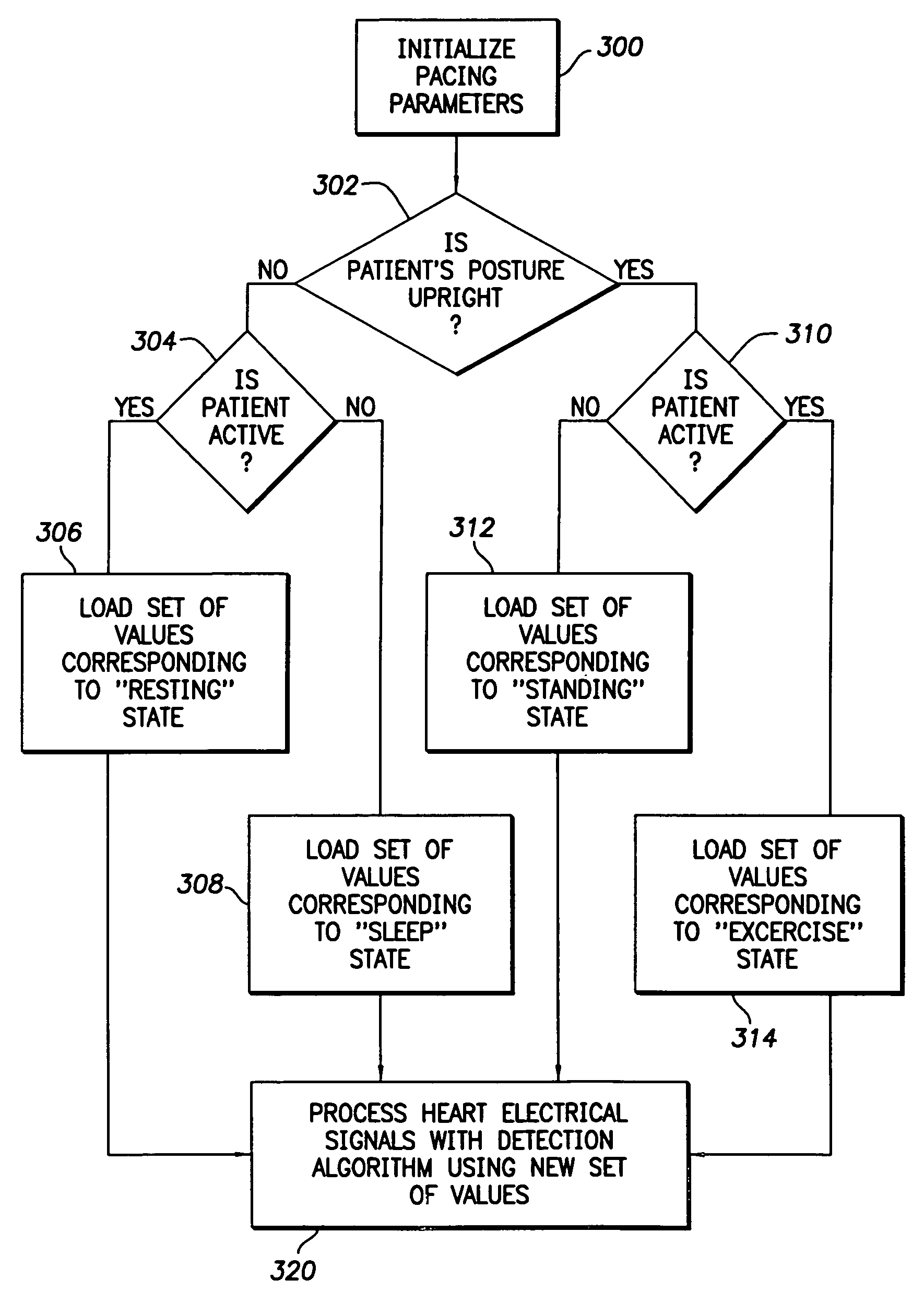
Modification of evoked response detection algorithm based on orientation and activity of patient
InactiveUS6975904B1Accurate lossAvoid captureHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringPatient statusPatient state
Optimization of evoked response detection in an automatic capture detection system employed by an implantable cardiac stimulation device is presented. Patient state information is used to determine the appropriate settings of variables that are associated with the evoked response signal detection algorithm. The variables used by the evoked response signal detection algorithm are first established for the patient in a variety of positions. During operation of the implantable cardiac stimulation device, the patient state is monitored and the variables used by the evoked response signal detection algorithm are adjusted accordingly.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
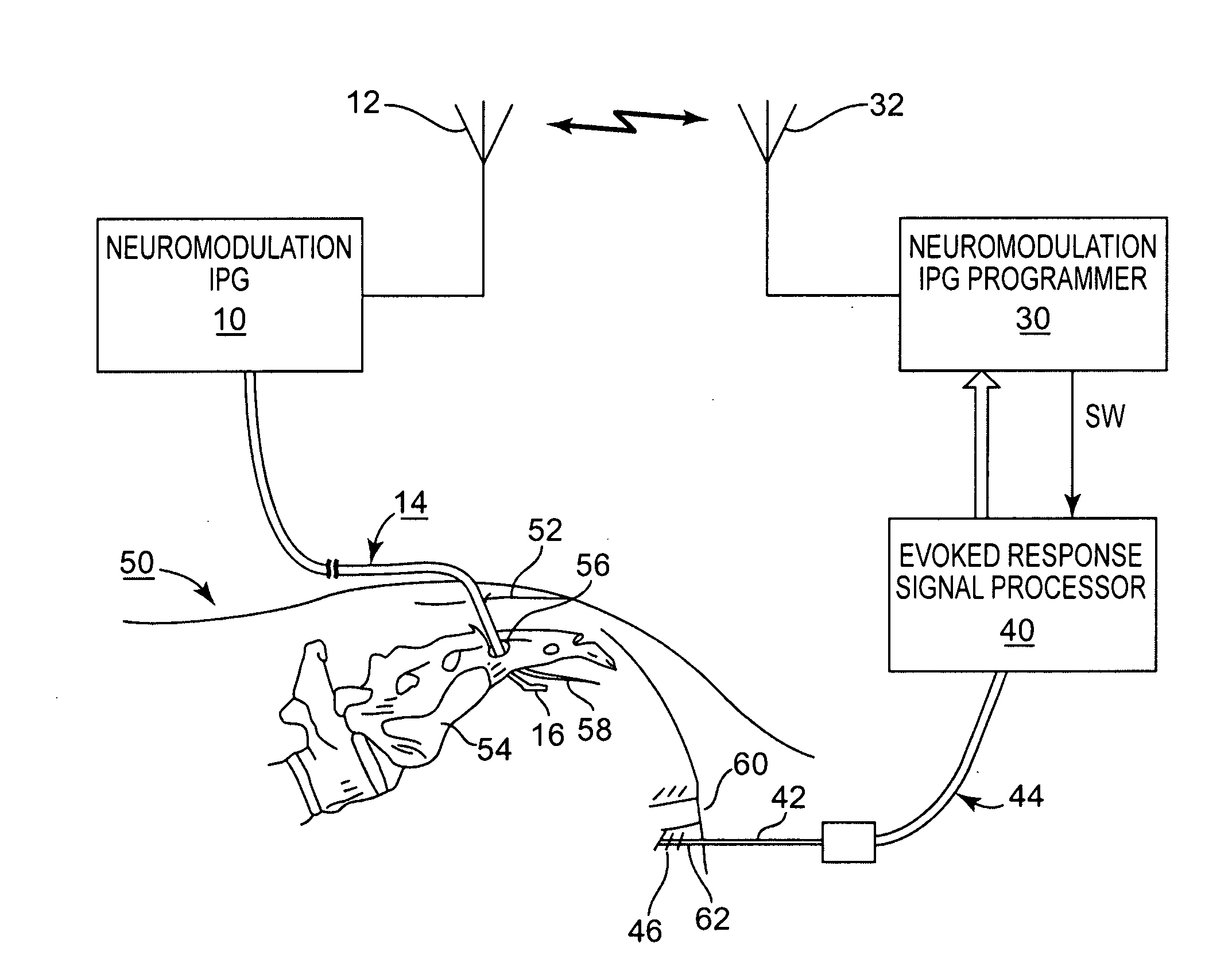
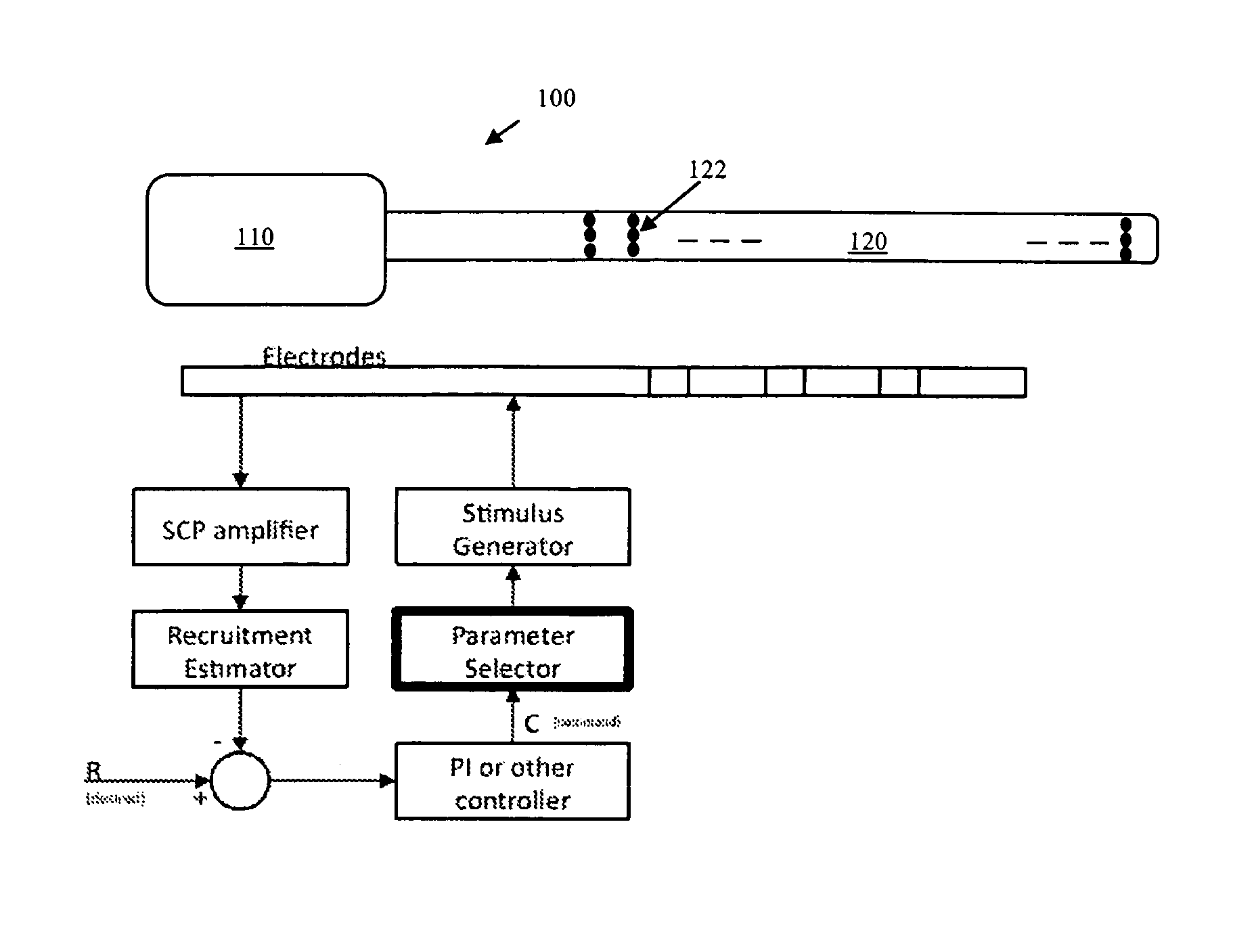
Method and apparatus for controlling a neural stimulus
ActiveUS20140236257A1Avoid misalignmentControlled levelSpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineSpinal cord
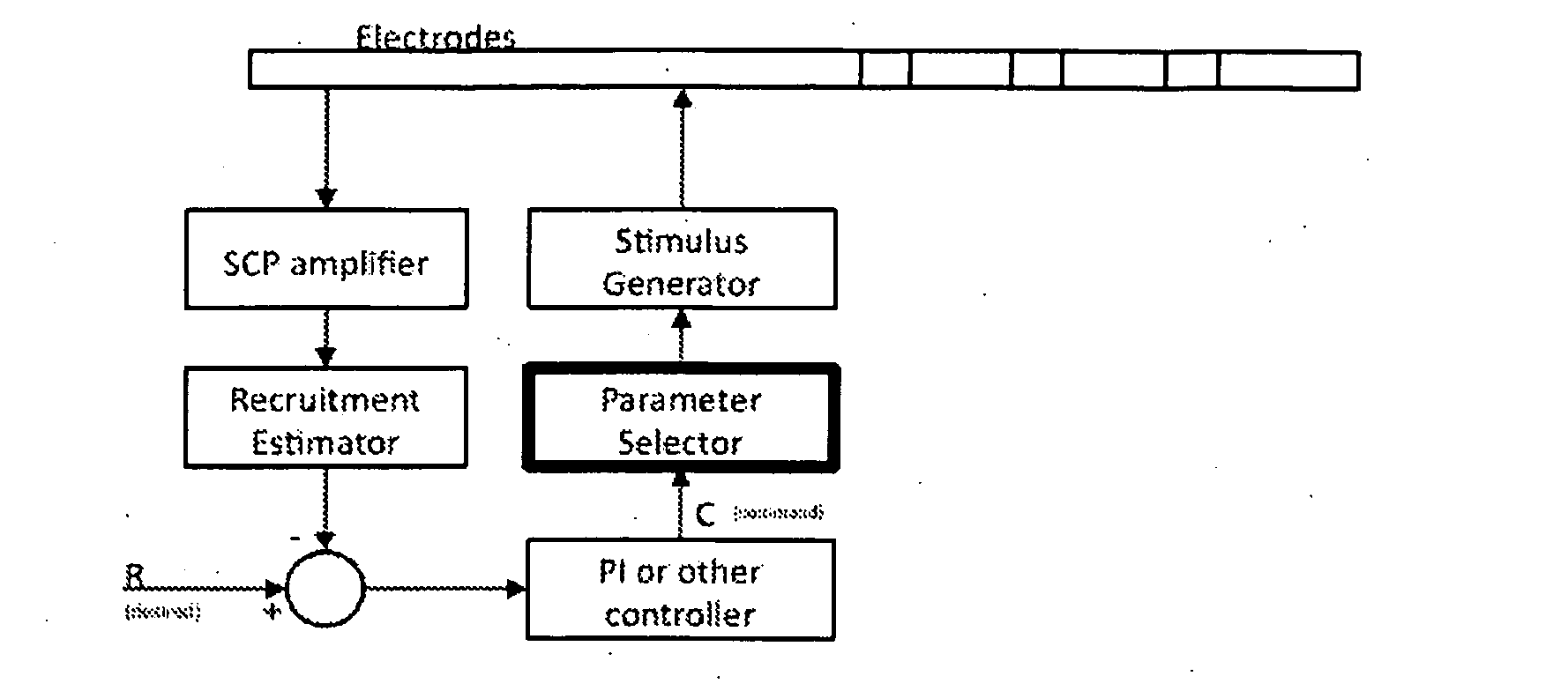
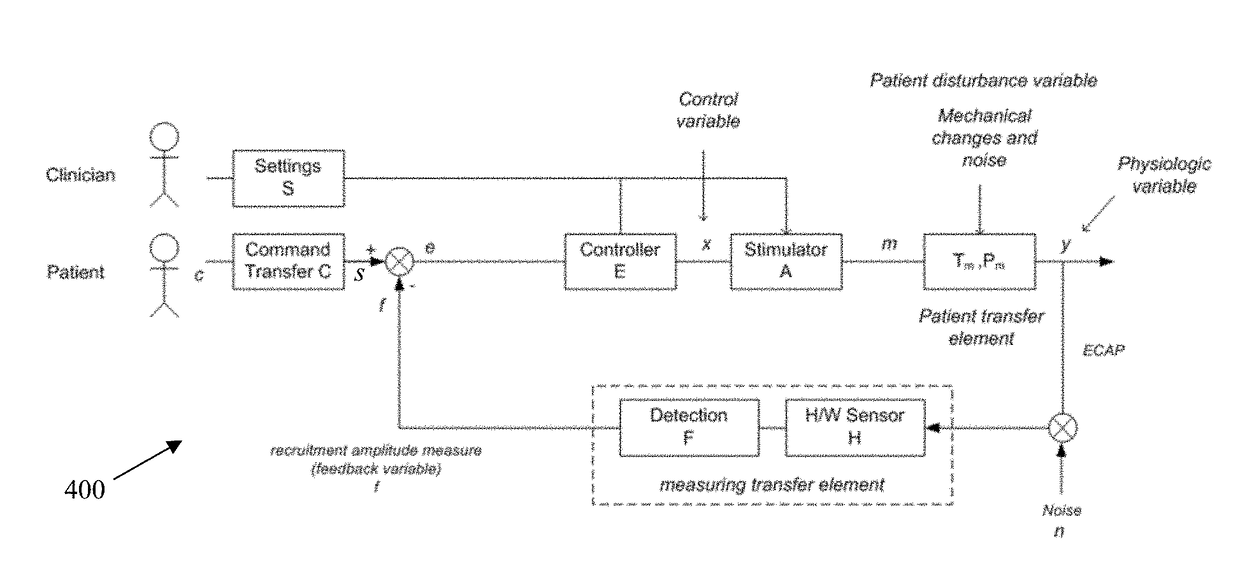
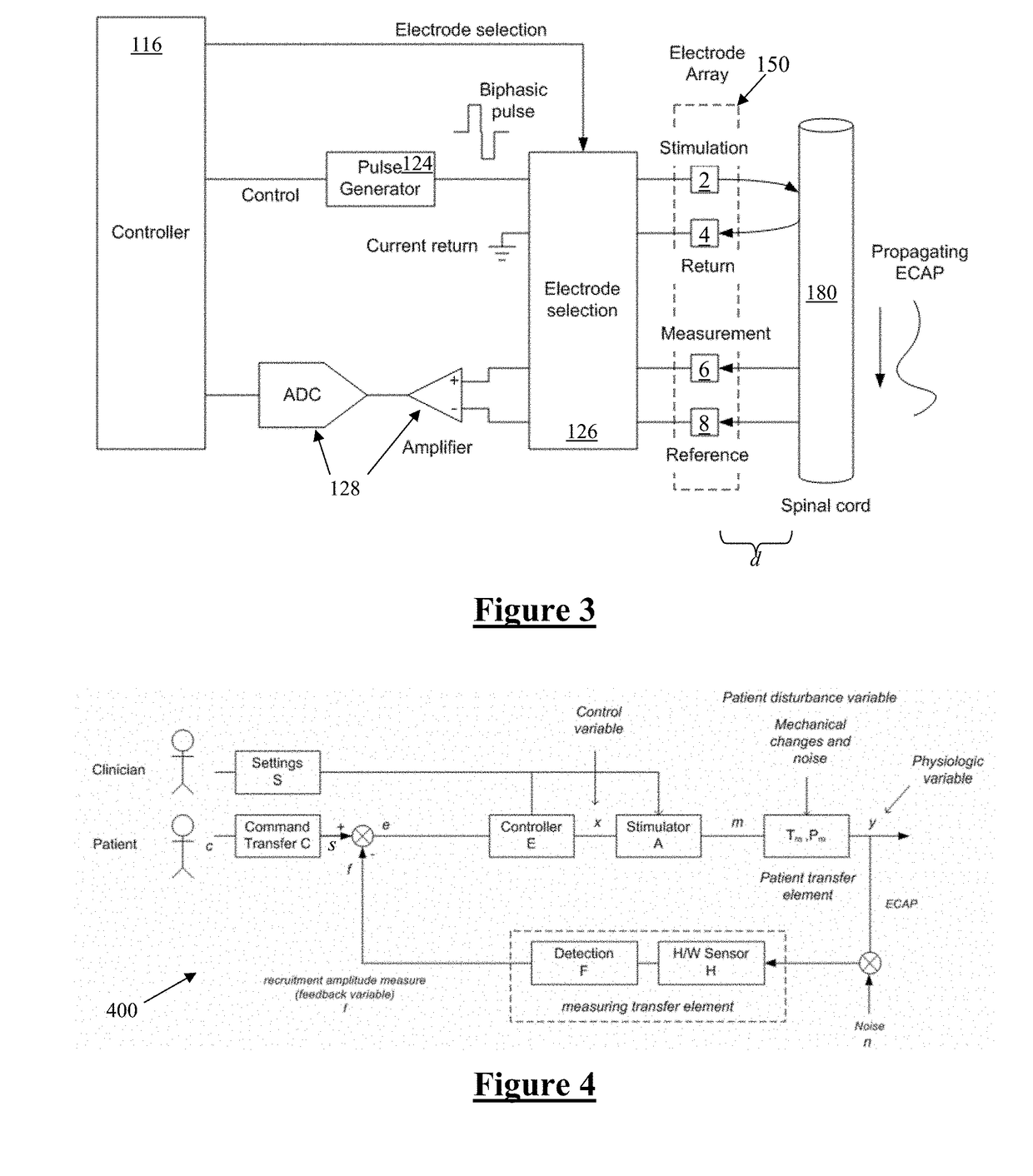
An implantable device applies and controls a neural stimulus. The device has a plurality of electrodes, and a stimulus source for providing a stimulus to be delivered from the electrodes to a neural pathway in order to evoke an action potential on the neural pathway, such as the spinal cord. A control unit controls application of a neural stimulus as defined by a set of parameter values and measures via measurement circuitry an evoked neural compound action potential response. The control unit determines from the measured evoked response a feedback variable, and compares it to a therapy map. The therapy map defines a therapeutic relationship of control variable to feedback variable. One or more of the stimulus parameter values are altered to effect the required change in the control variable. This process is performed iteratively to improve alignment of the feedback variable with the therapy map over time.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for controlling a neural stimulus
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
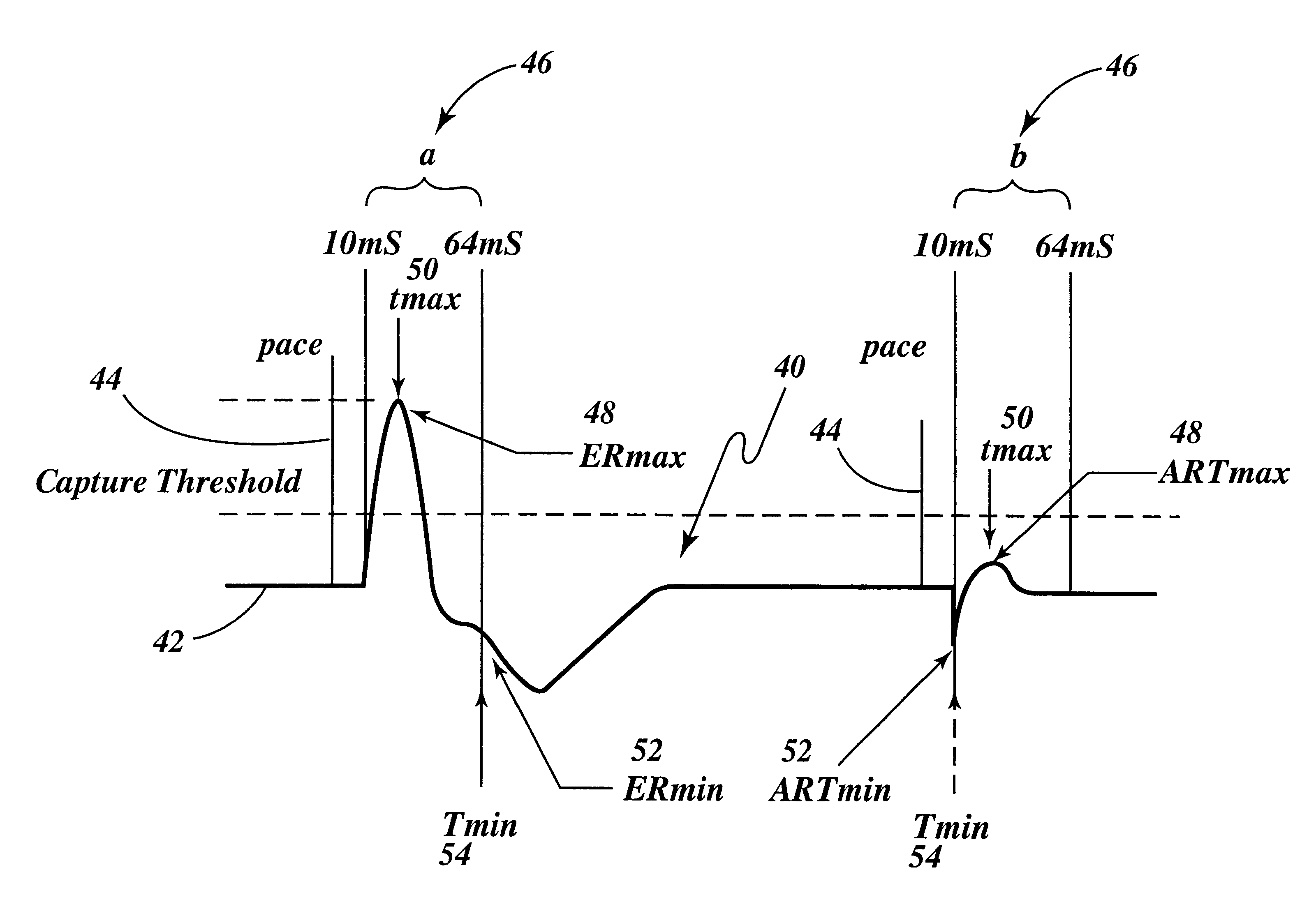
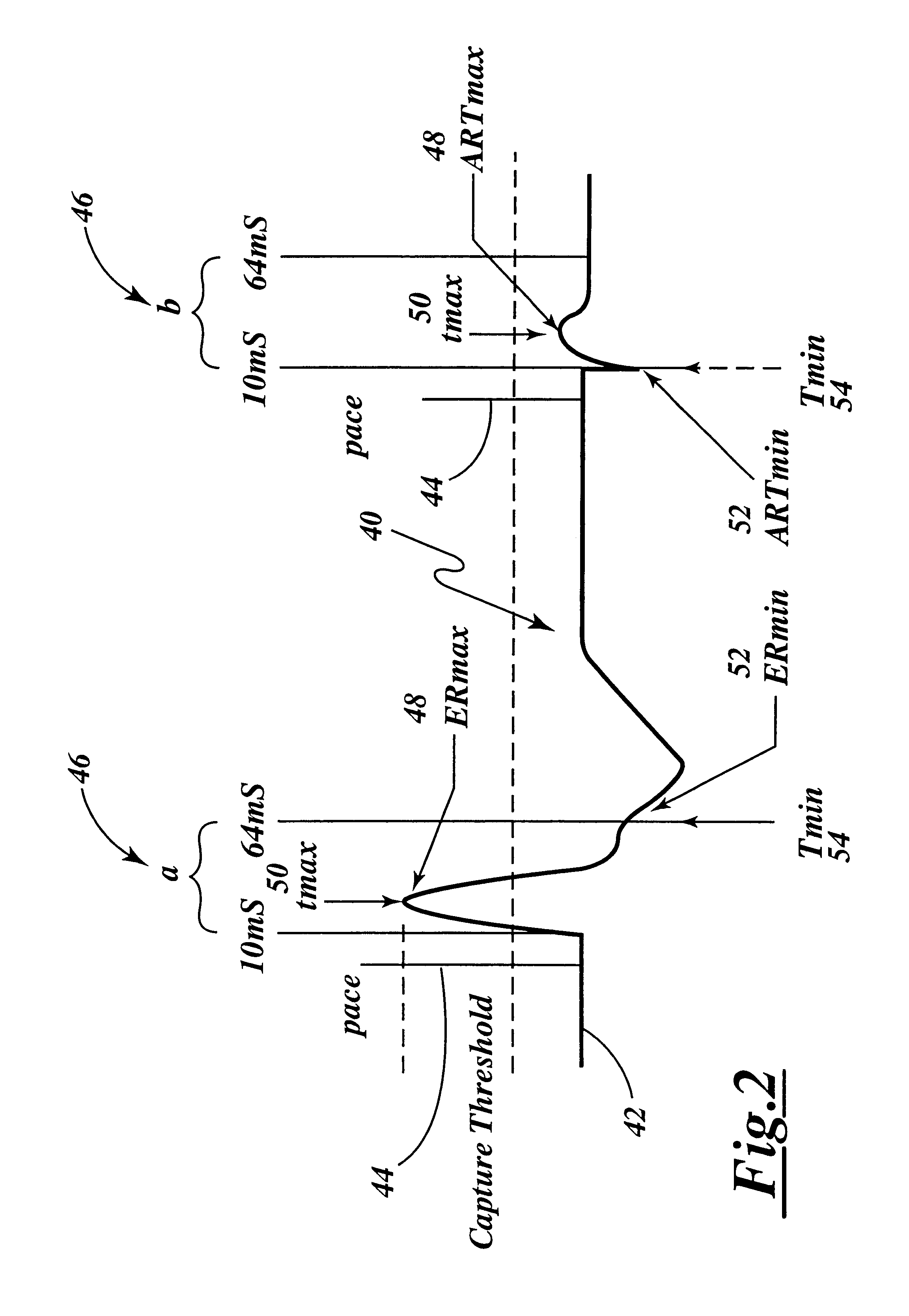
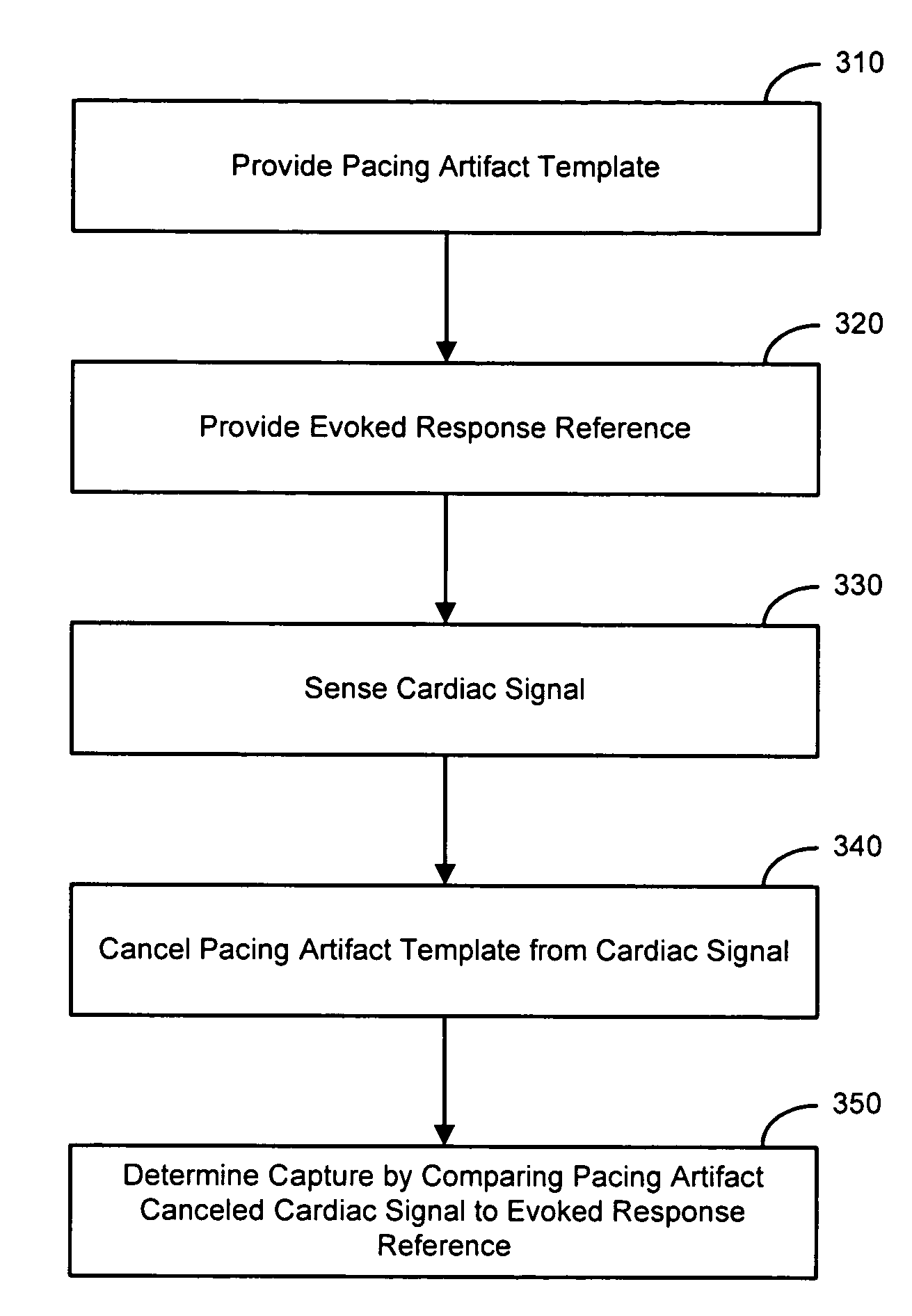
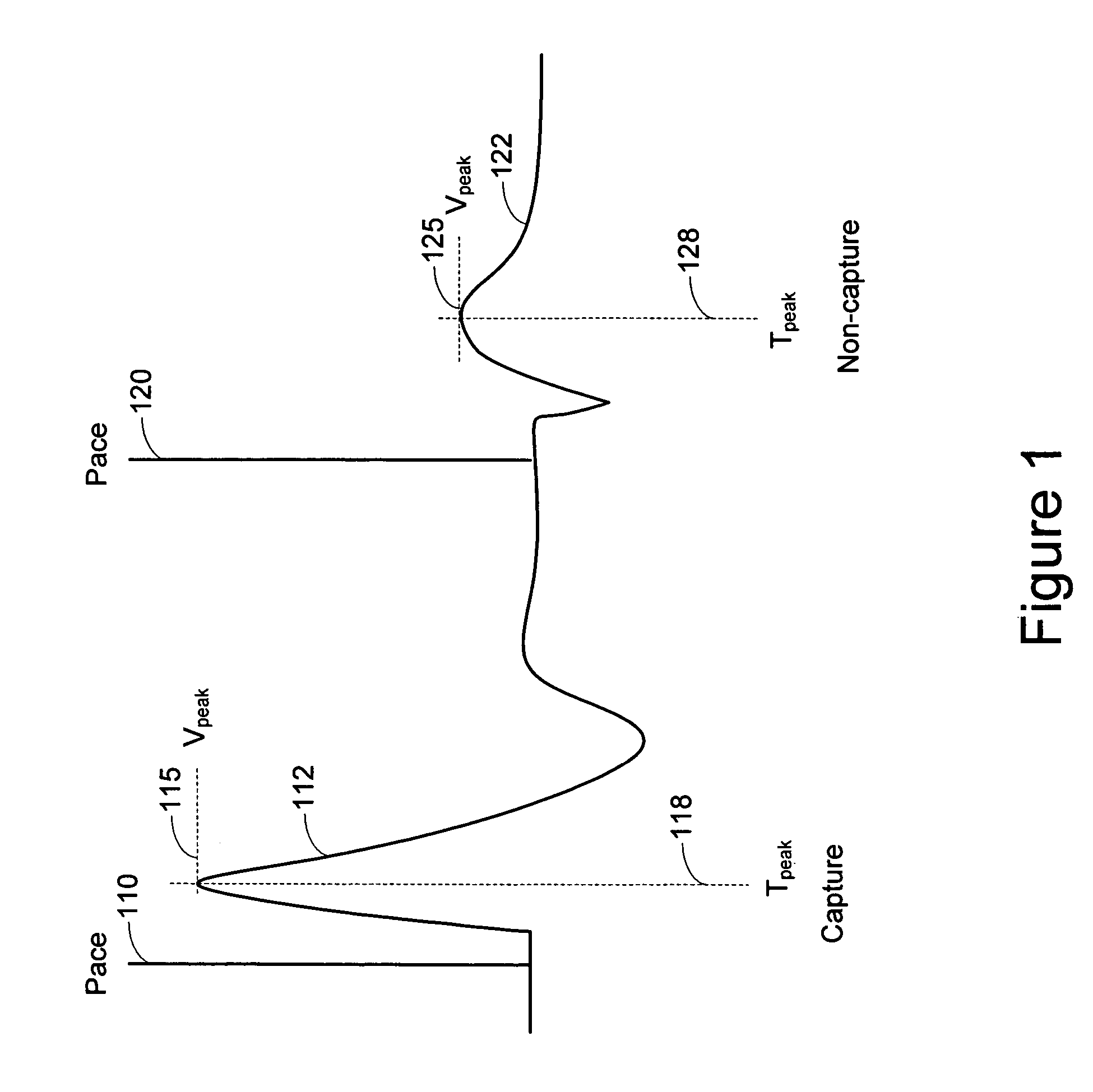
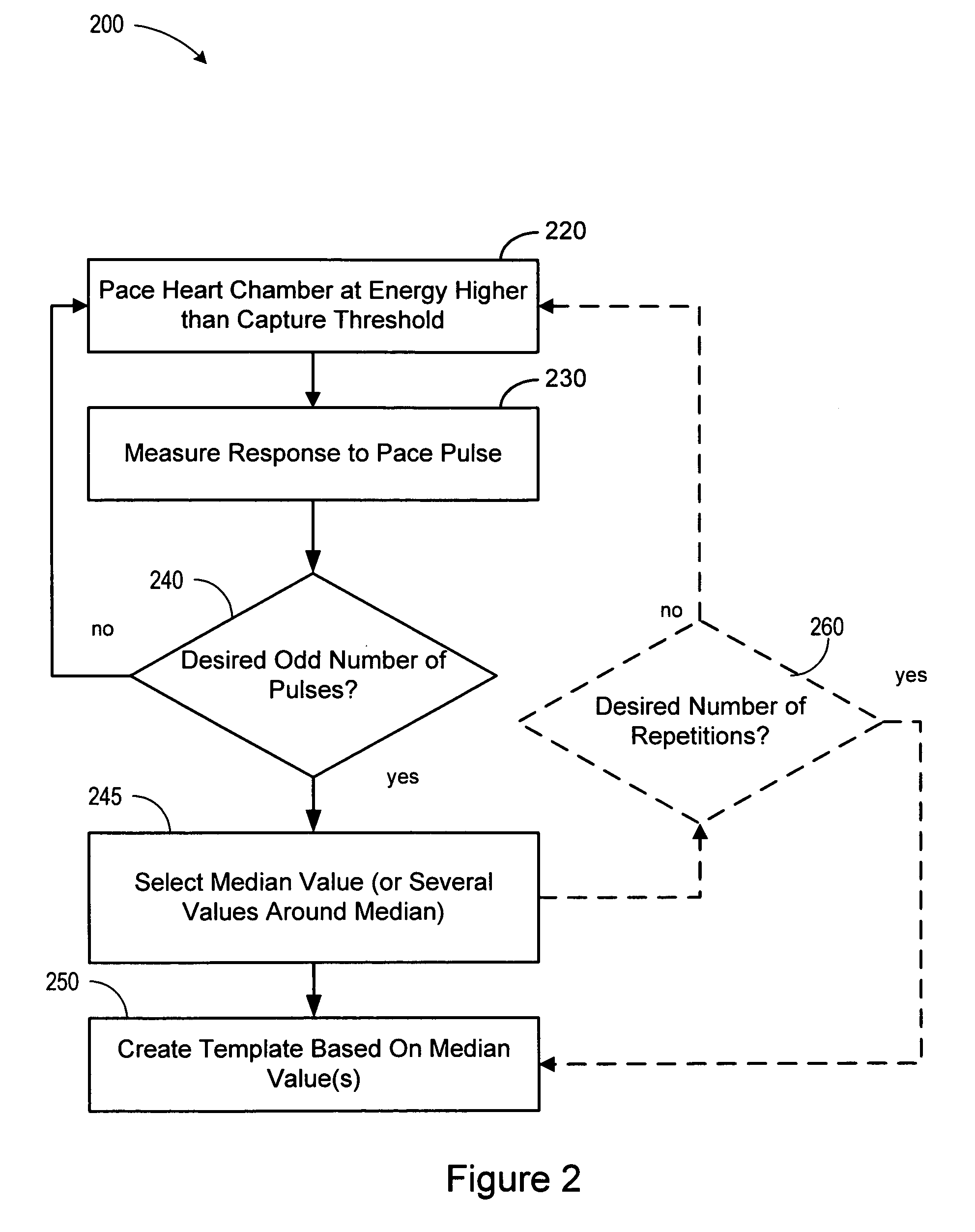
Capture verification using an evoked response reference
A method and system for verifying capture in the heart involves the use of pacing artifact templates. One or more pacing artifact templates characterizing a post pace artifact signal associated with a particular pace voltage or range of voltages are provided. A pacing artifact template is canceled from a cardiac signal sensed following a pacing pulse. Capture is detected by comparing the pacing artifact canceled cardiac signal to an evoked response reference. Fusion / pseudofusion detection involves determining a correlation between a captured response template and a sensed cardiac signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Evoked Response to Stimulation
InactiveUS20070244407A1ElectroencephalographyImplantable neurostimulatorsFunctional connectivityConfiguration design
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
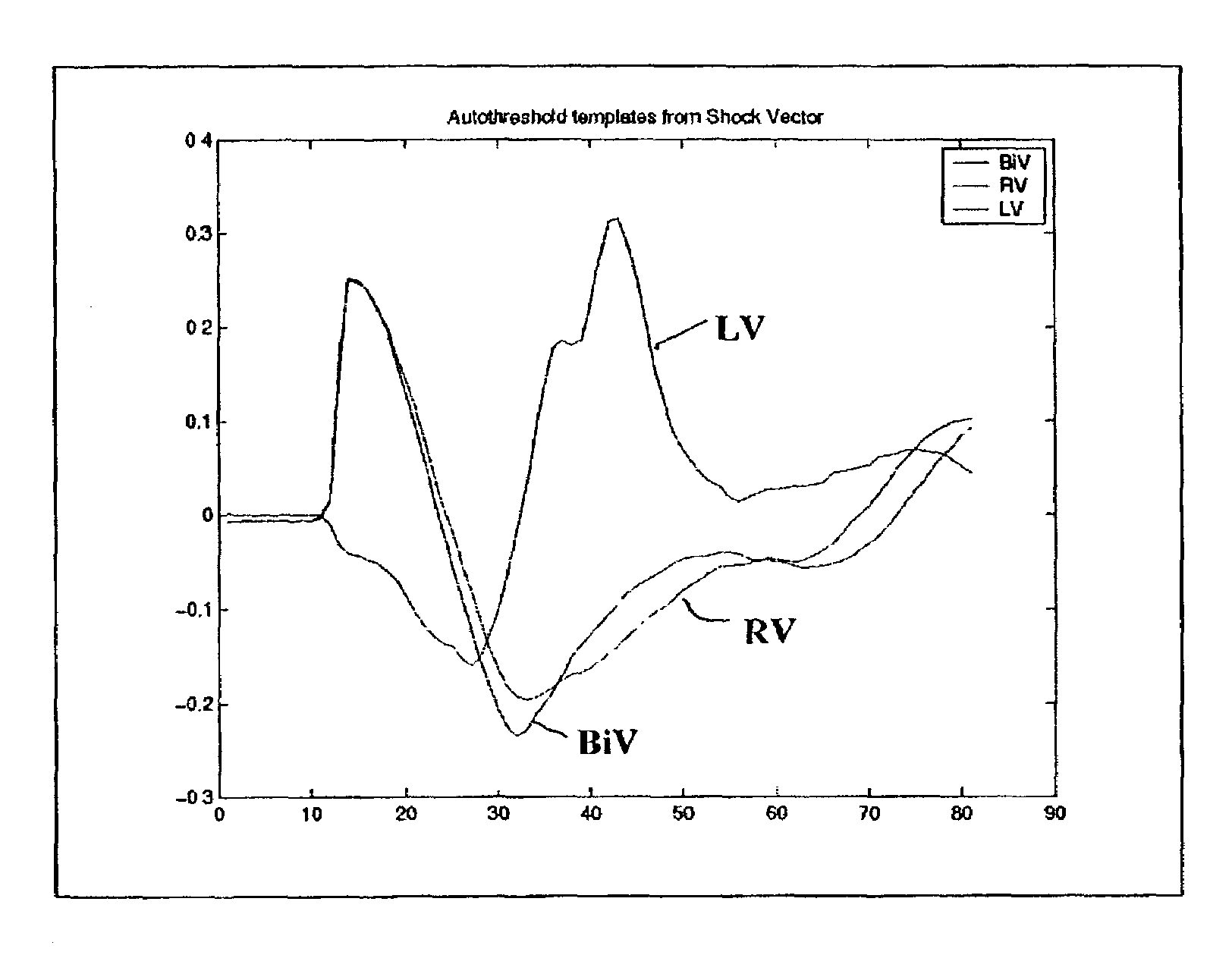
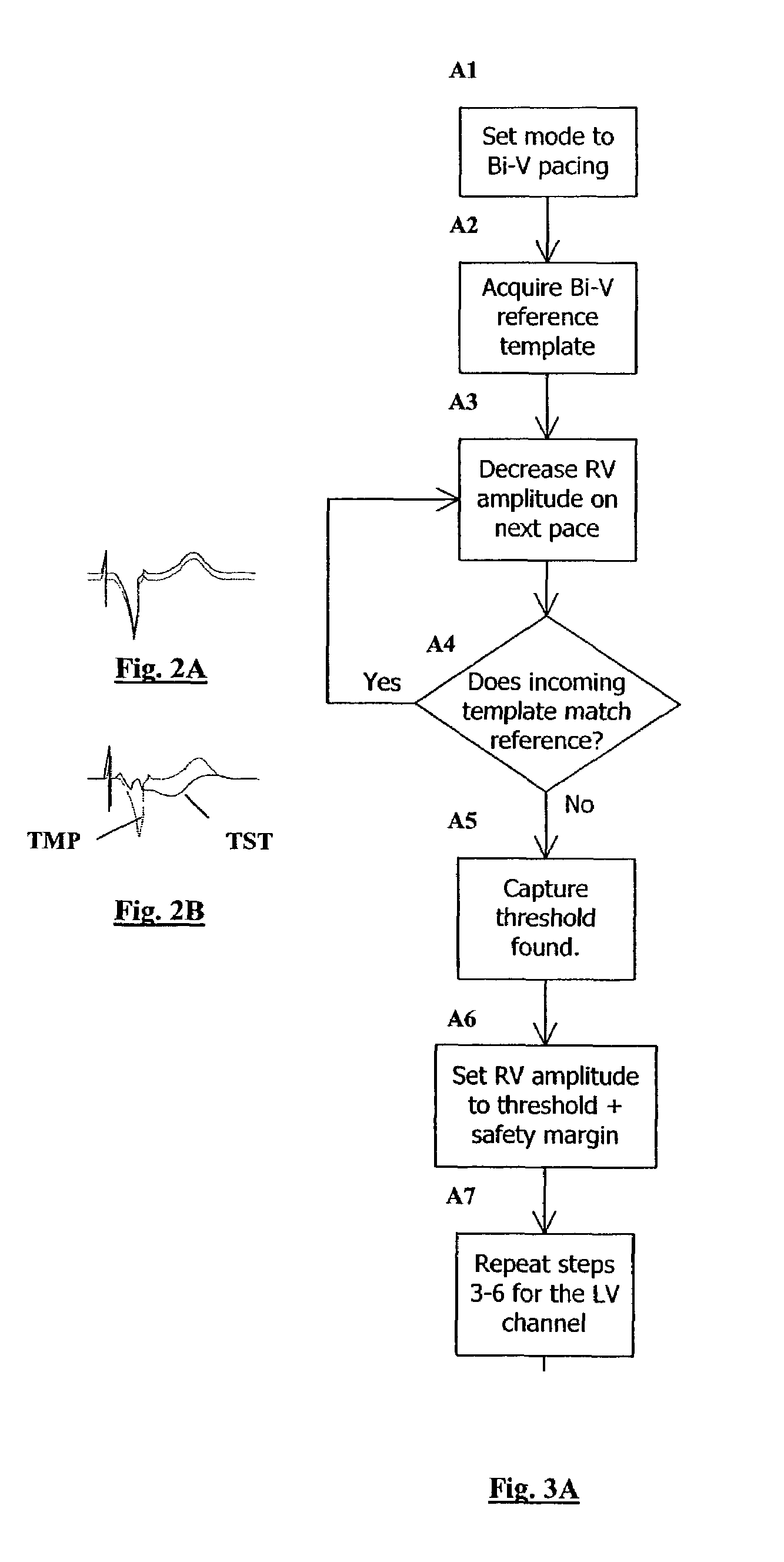
Template-based capture verification for multi-site pacing
InactiveUS7286876B2Simplified determinationElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisMulti siteTemplate based
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Mechanical Ventricular Pacing Non-Capture Detection for a Refractory Period Stimulation (RPS) Pacing Therapy Using at Least One Lead-Based Accelerometer
InactiveUS20080269825A1Increase contractilityIncrease perfusionElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerLeft ventricular size
A system and method for monitoring at least one chamber of a heart (e.g., a left ventricular chamber) during delivery of a refractory period stimulation (RPS) therapy to determine if the desired non-capture (i.e., lack of ventricular mechanical capture due to refractory period stimulation) occurs. The system includes an implantable or external cardiac stimulation device in association with a set of leads such as epicardial, endocardial, and / or coronary sinus leads equipped with motion sensor(s). The device receives and processes acceleration sensor signals to determine a signal characteristic indicative of chamber capture due to pacing stimulus delivery, non-capture due to RPS therapy delivery, and / or contractile status based on the qualities of evoked response to pacing stimulation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Evoked response variability as an indicator of autonomic tone and surrogate for patient condition
Modern implantable cardiac stimulation devices include processing and data storage capabilities that may be exploited to track myocardial condition and autonomic tone. Implantable devices have a capability to measure and store electrogram information over a period of time in a relatively large capacity memory, with advances in technology allowing increases in memory size. The evoked response varies in amplitude and morphology with changes in autonomic tone, ventricular filling, paced rate, and other parameters. The implantable cardiac device can be configured to sense and accurately quantify the evoked response, derive parameters from the quantified evoked response, store the parameters over long time periods, and derive variability statistics from the parameters to assist in tracking the patient's condition over time, and guiding the patient's therapy.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
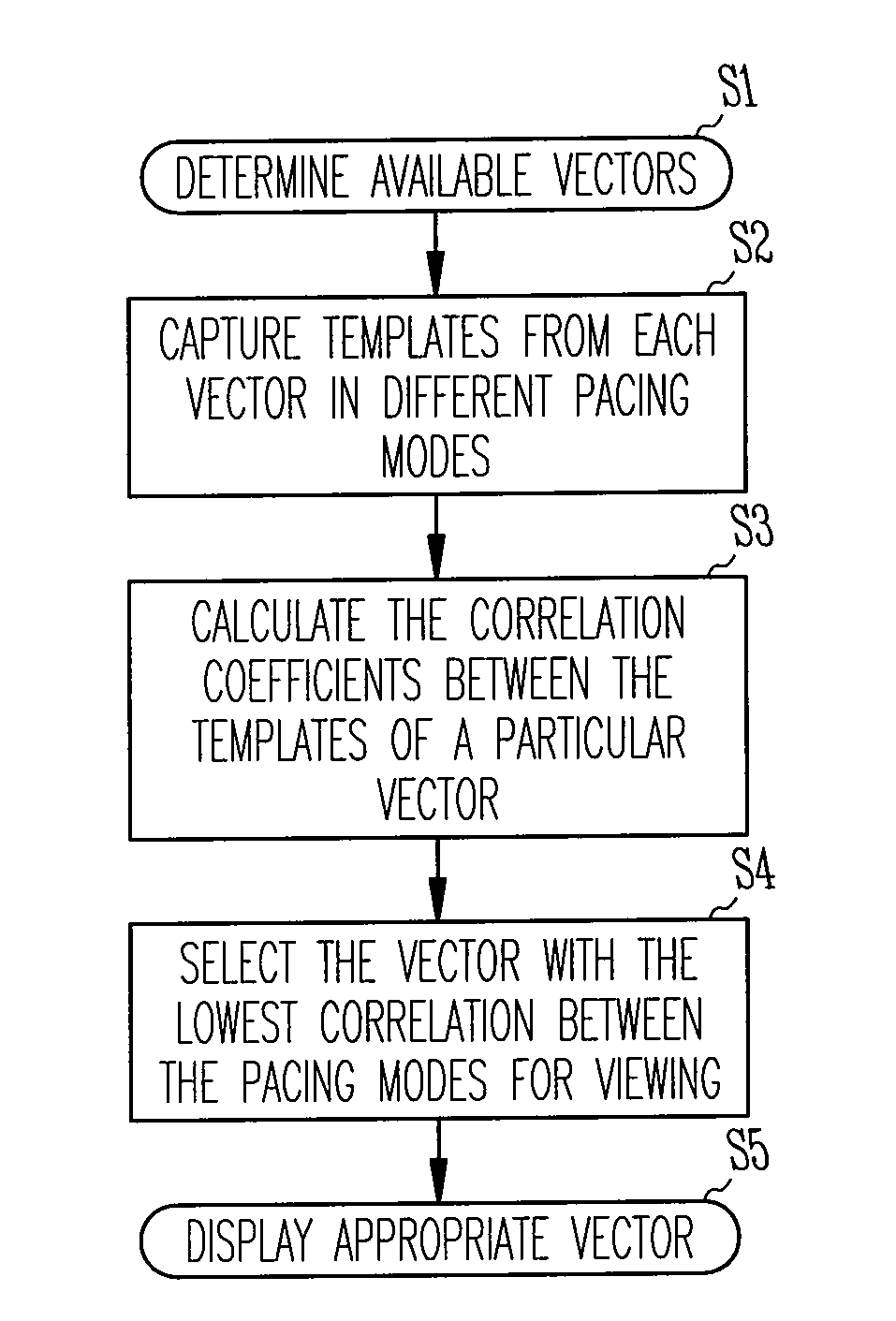
Automatic sensing vector selection for morphology-based capture verification
InactiveUS7412287B2Simplified determinationHeart stimulatorsComputer scienceEvoked potential recording
A system and method for verifying capture of the heart by one or more pacing pulses using an electrogram morphology-based technique. Capture is determined by comparing an evoked response electrogram recorded during a paced cycle with a template waveform representing a paced cycle in which capture is achieved. The comparison is facilitated and made more accurate by selecting a sensing vector in which an evoked response electrogram in which no capture occurs is most dissimilar to the template.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
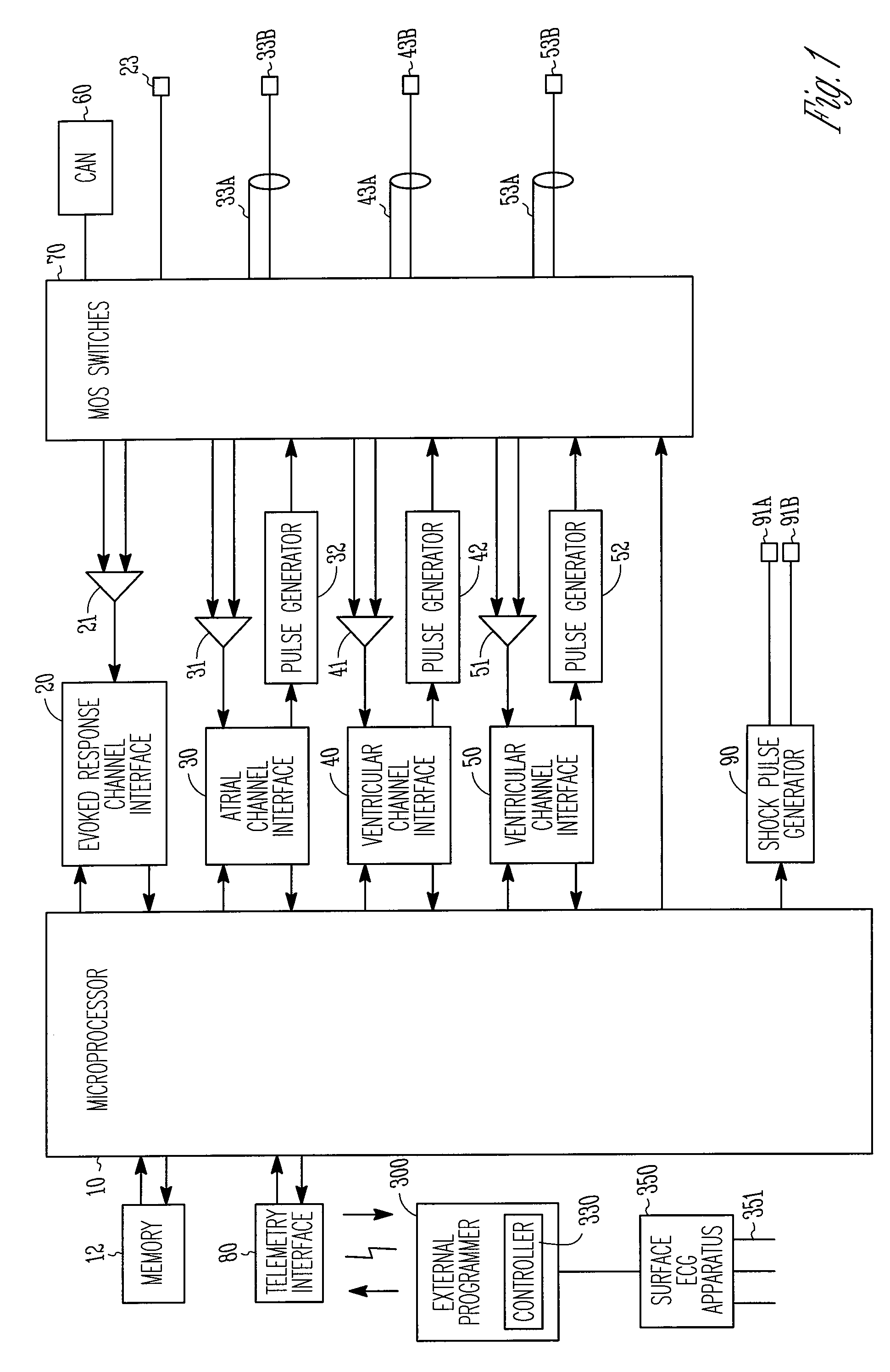
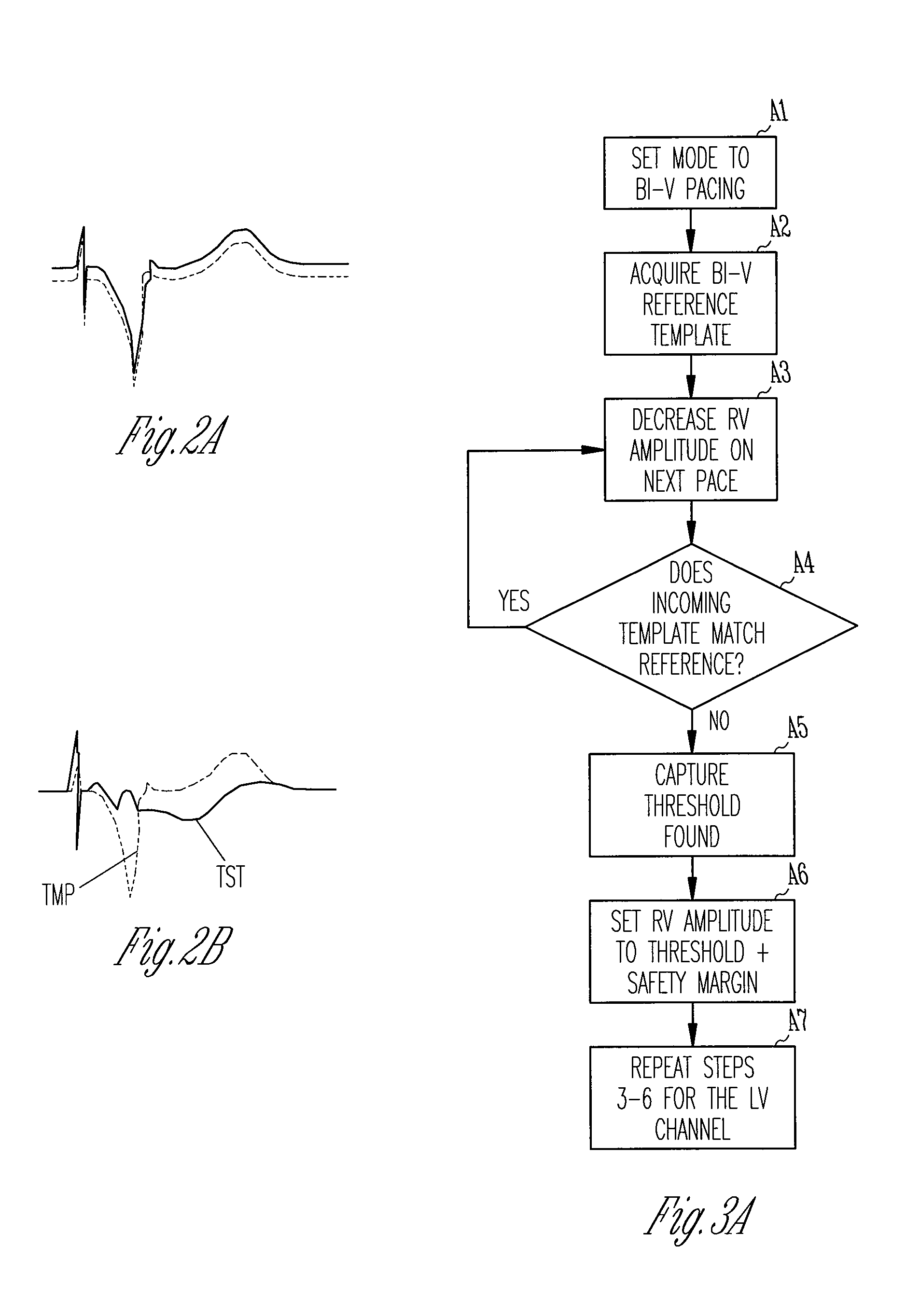
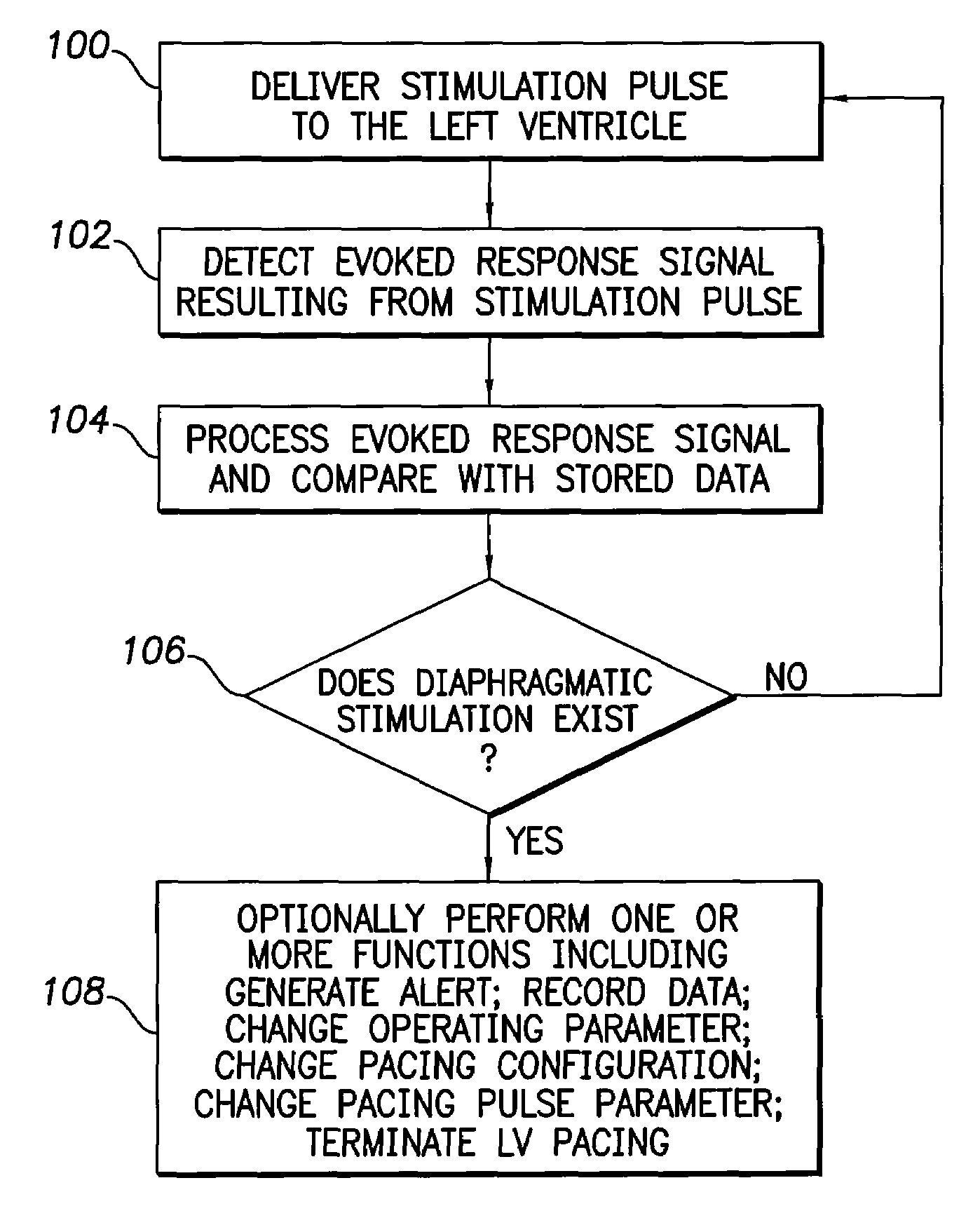
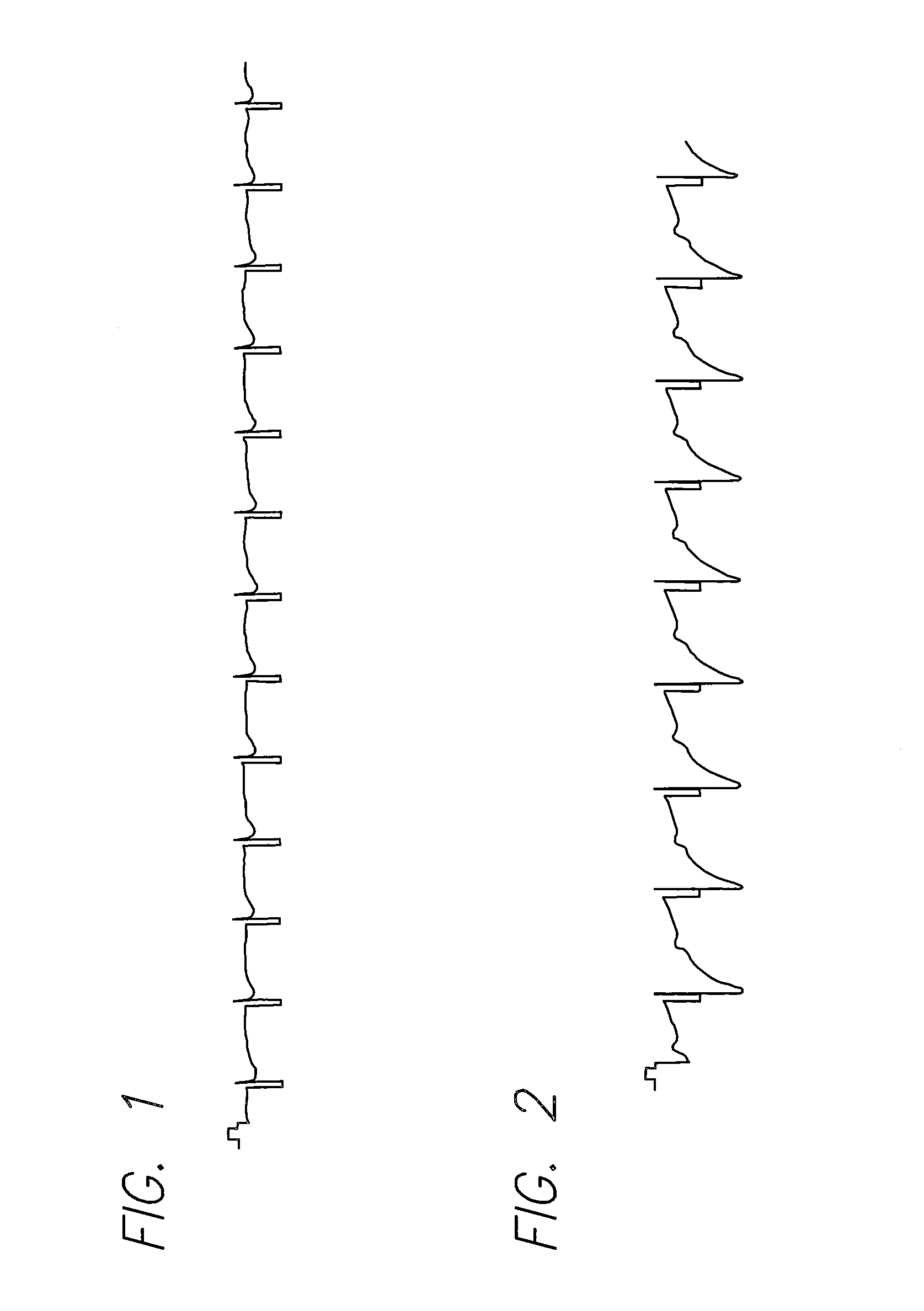
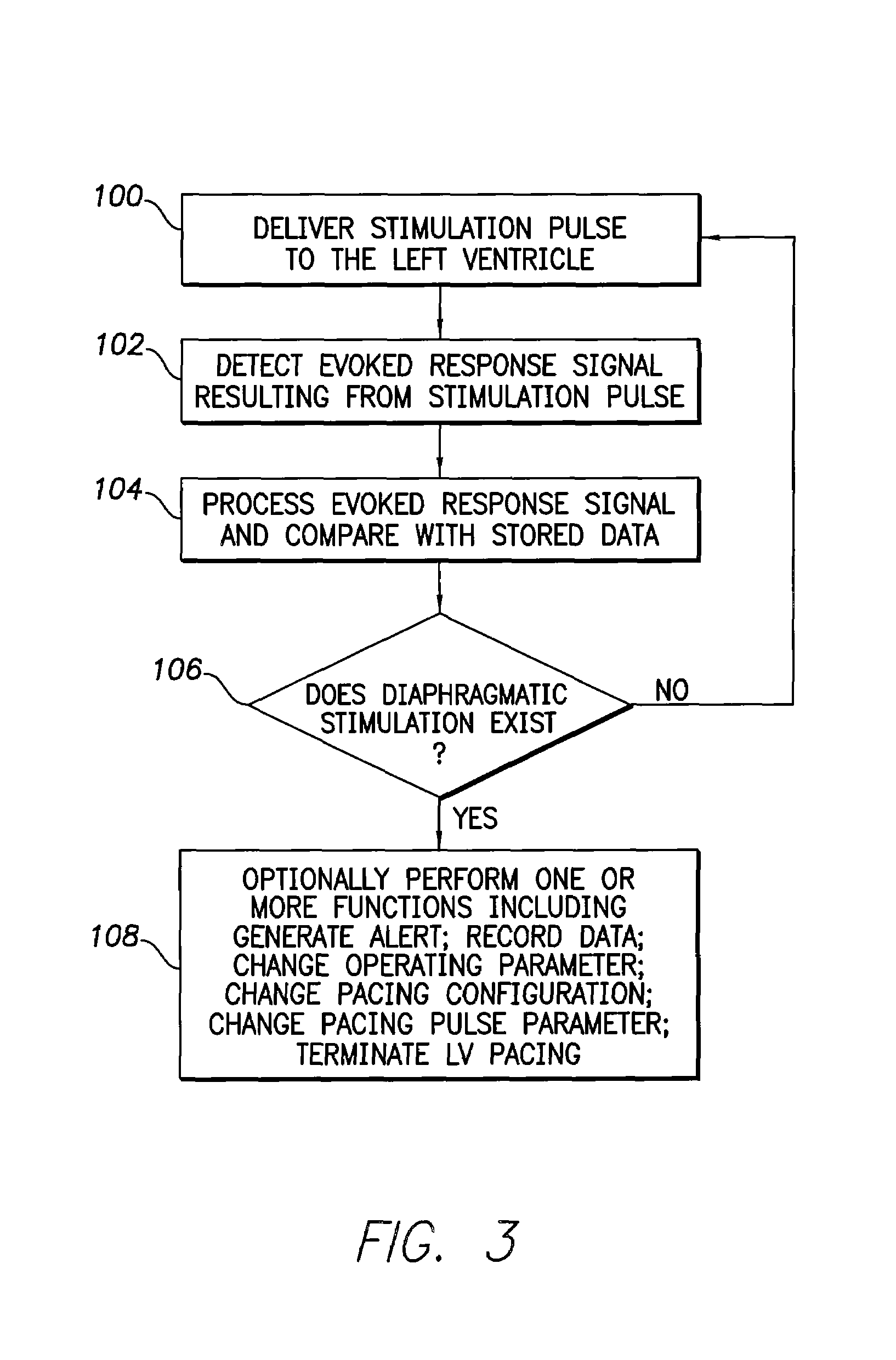
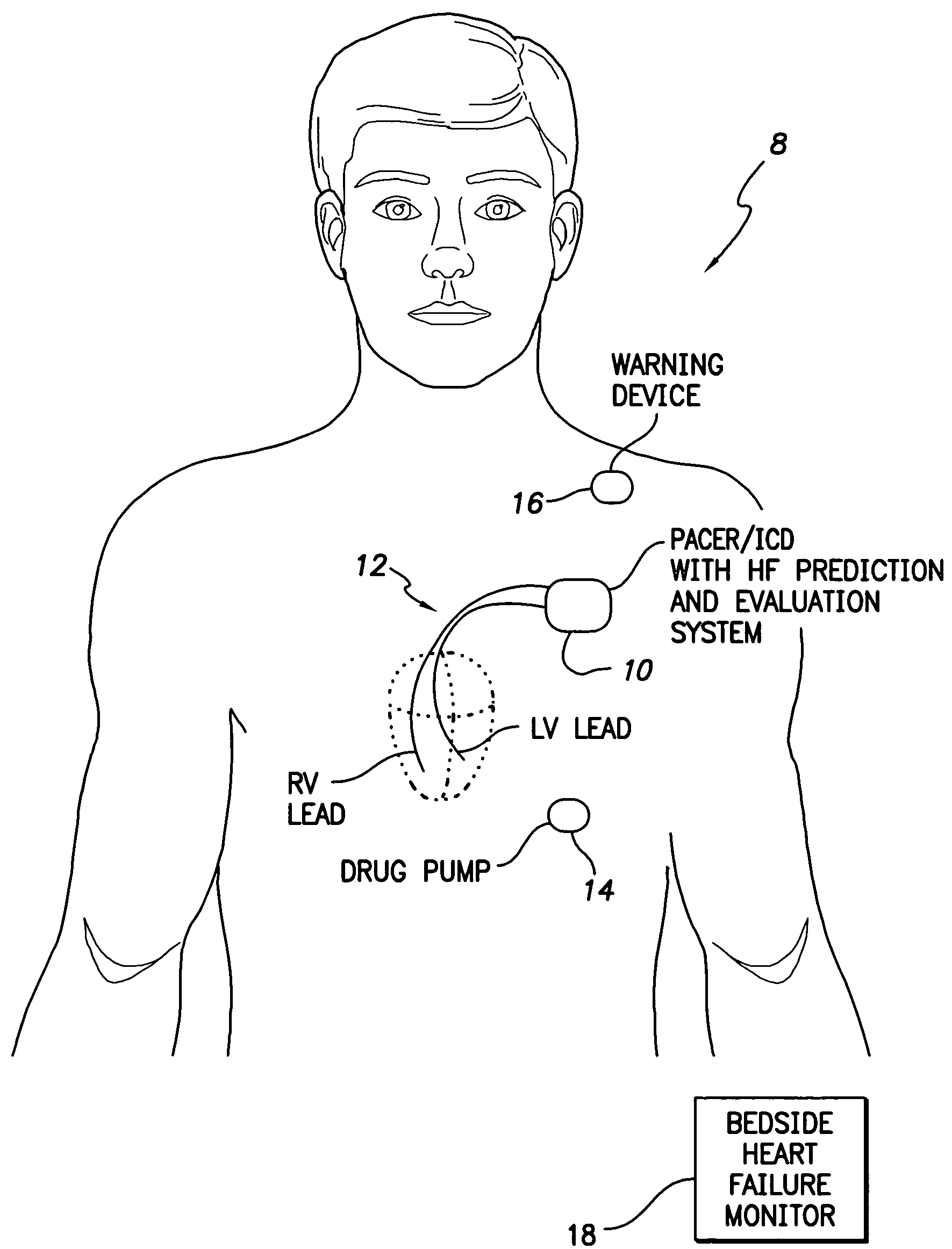
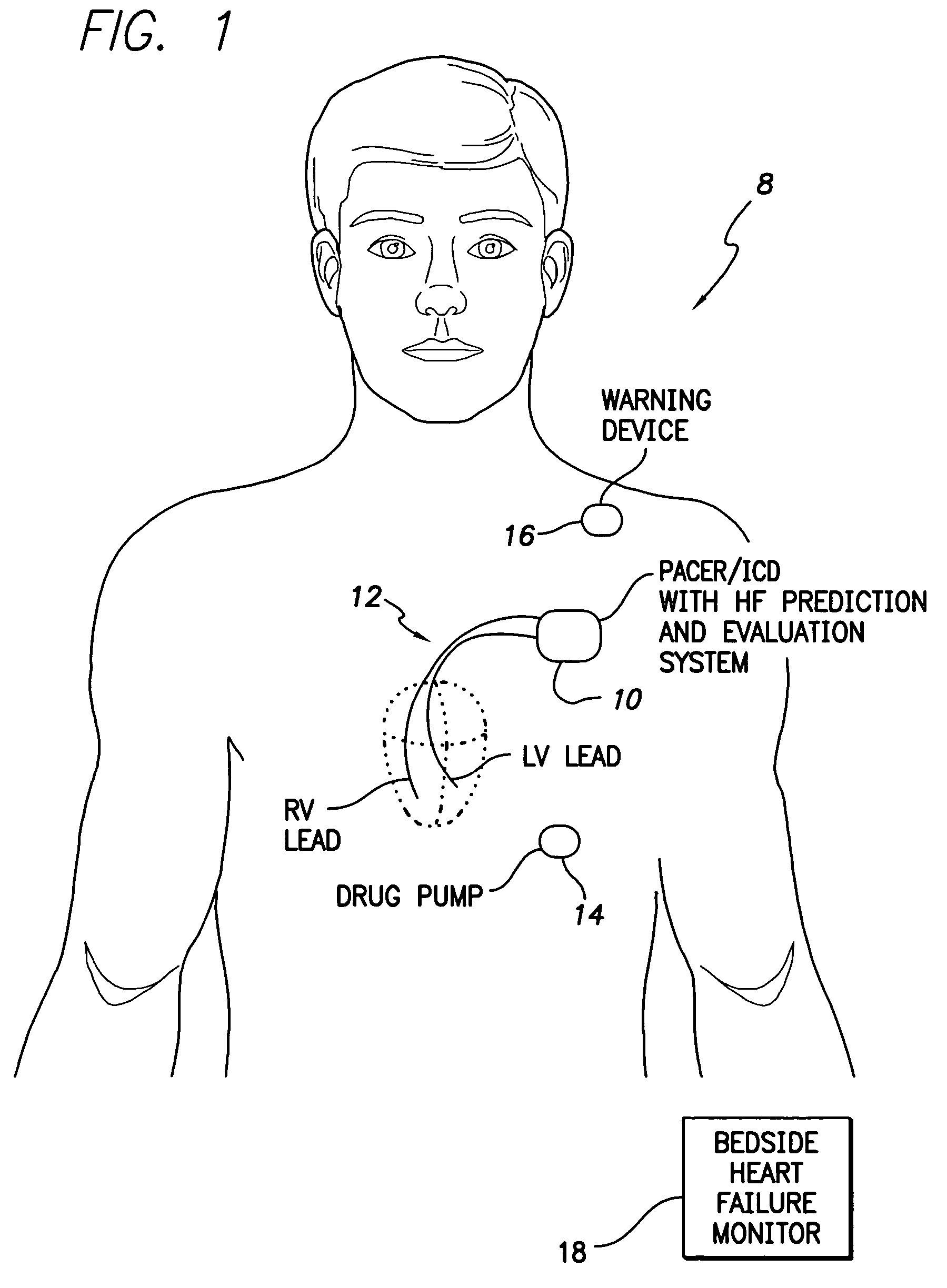
Evoked potential and impedance based determination of diaphragmatic stimulation
A system and method are described for automatically detecting diaphragmatic stimulation (DS) based on evoked response signals, electrogram data and / or thoracic impedance measurements. In addition, several optional modalities are described to circumvent this problem and alleviate symptoms related to DS while preserving LV pacing.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
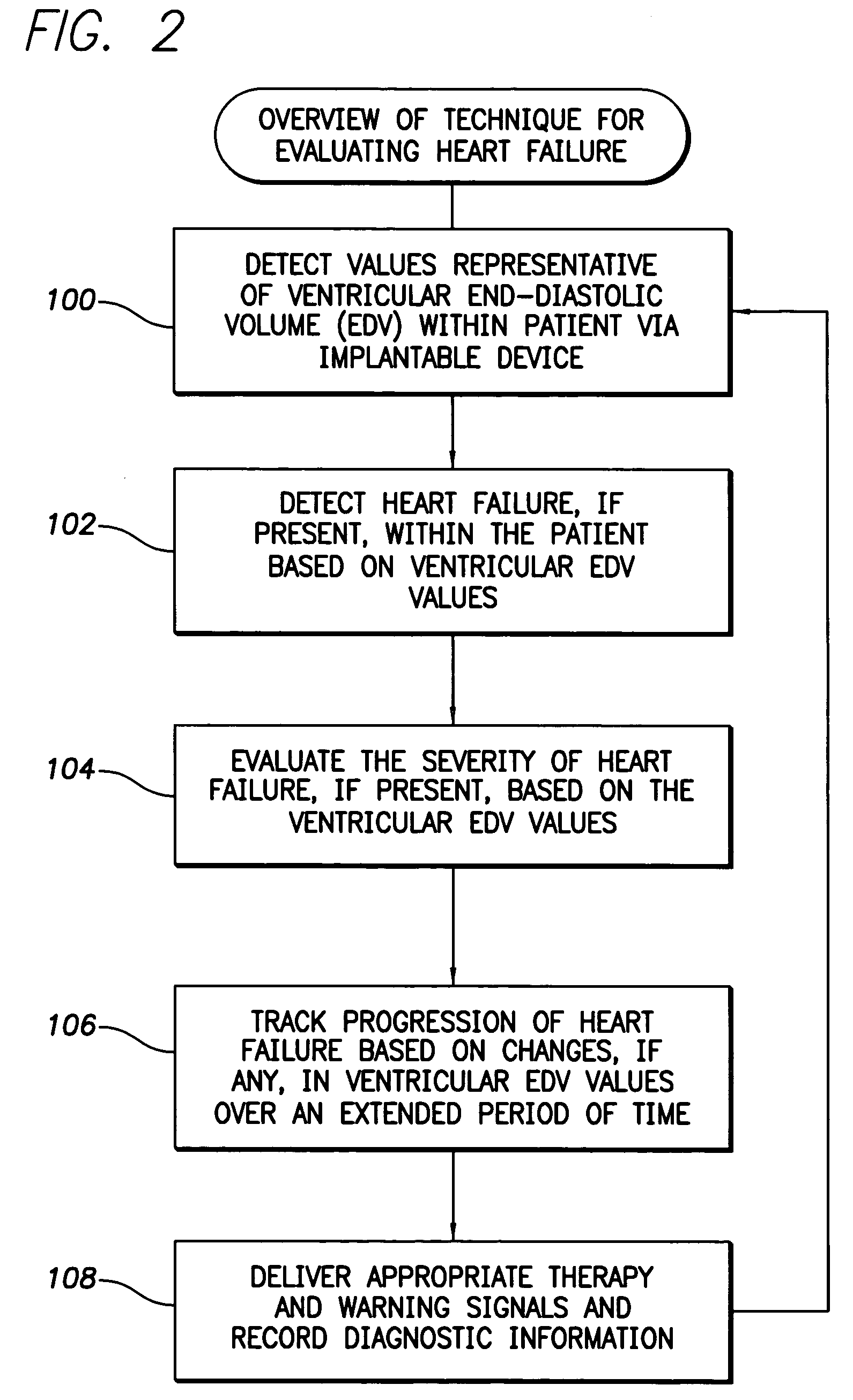
System and method for predicting a heart condition based on impedance values using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7272443B2Reliably predict onset of heart conditionHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringPulmonary edemaThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for predicting the onset of a heart condition within a patient based on impedance measurements. Briefly, overloads in fluid levels in the thorax and in ventricular myocardial mass within the patient are detected based on impedance signals sensed using implanted electrodes. The onset of certain heart conditions is then predicted based on the overloads. For example, pulmonary edema arising due to diastolic heart failure is predicted based on the detection of on-going overloads in both fluid levels and ventricular mass. Ventricular hypertrophy is detected based on an on-going ventricular mass overload without a sustained fluid overload. Various other heart conditions may also be predicted based on specific combinations of recent or on-going overloads. Evoked response is exploited to corroborate the predictions. Appropriate warning signals are generated and preemptive therapy is initiated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
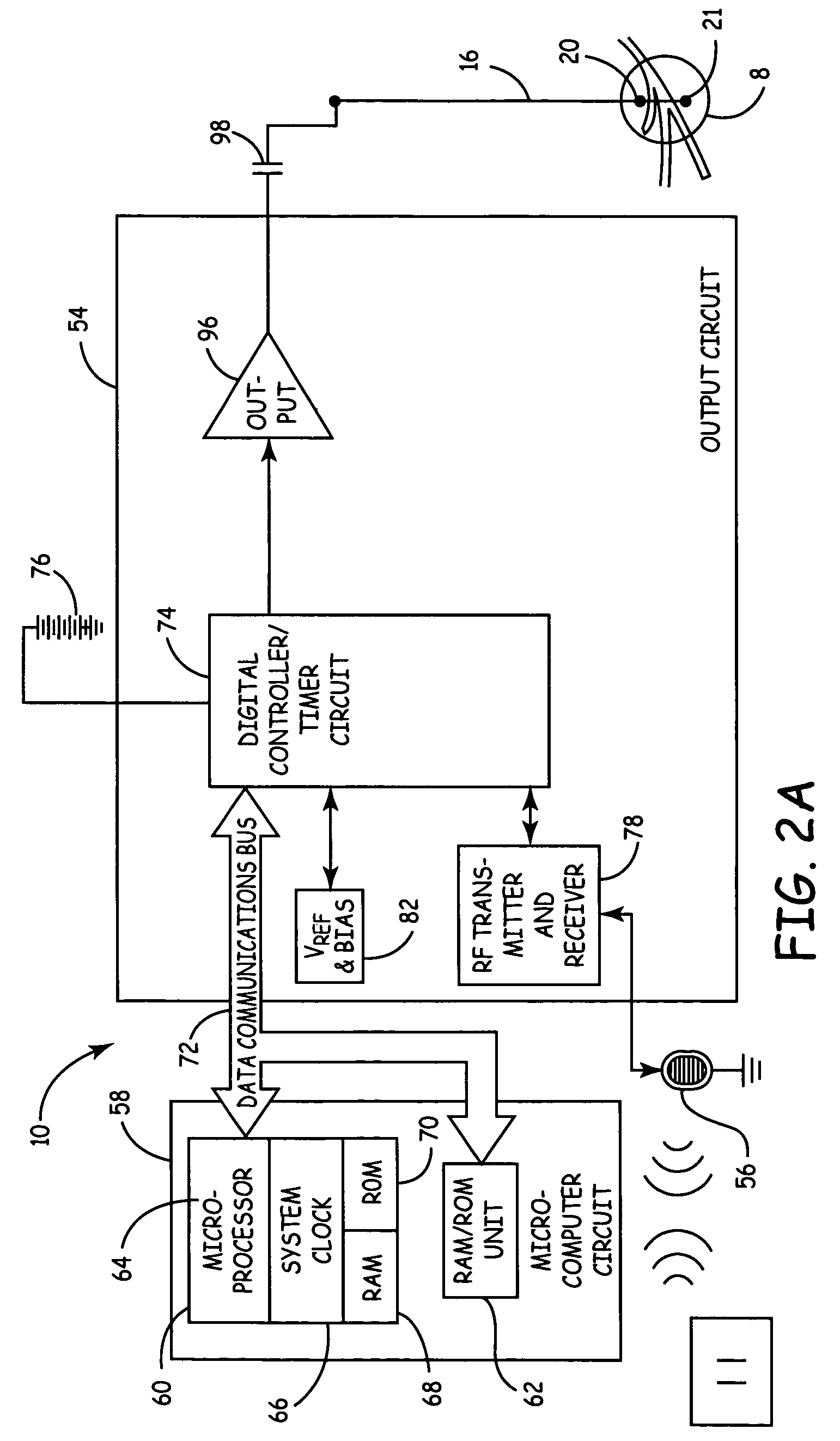
Method and system for an automated e.e.g. system for auditory evoked responses
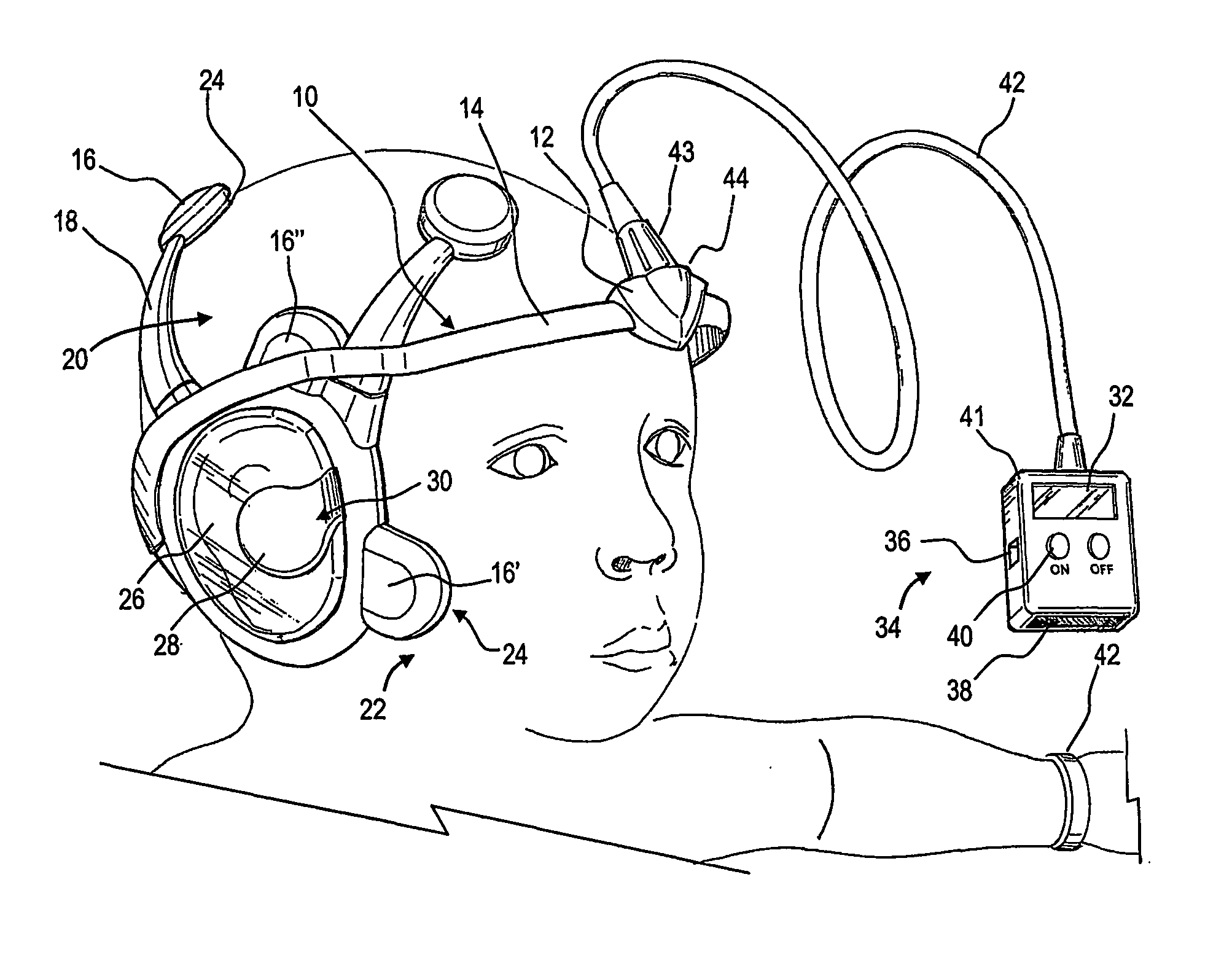
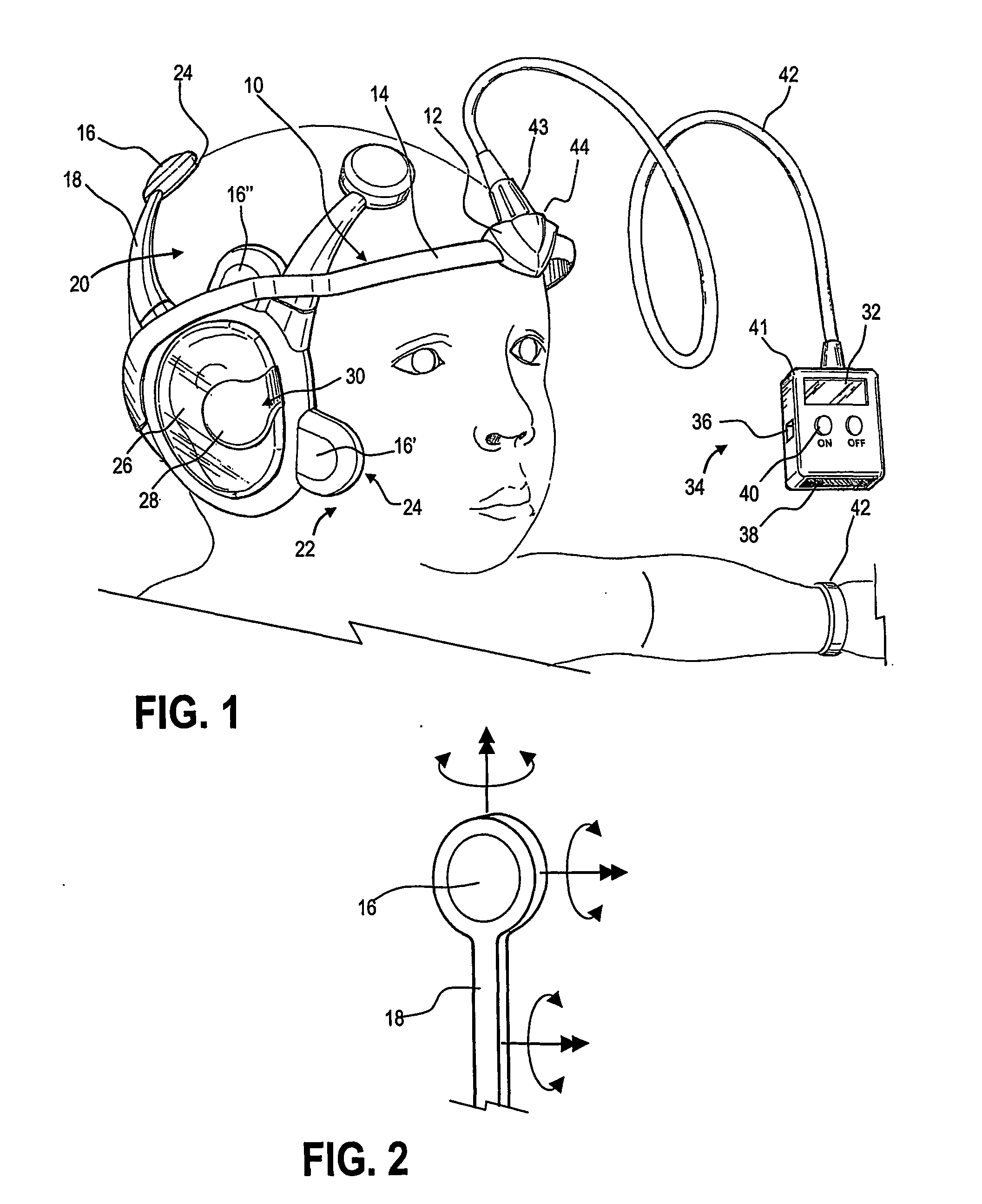
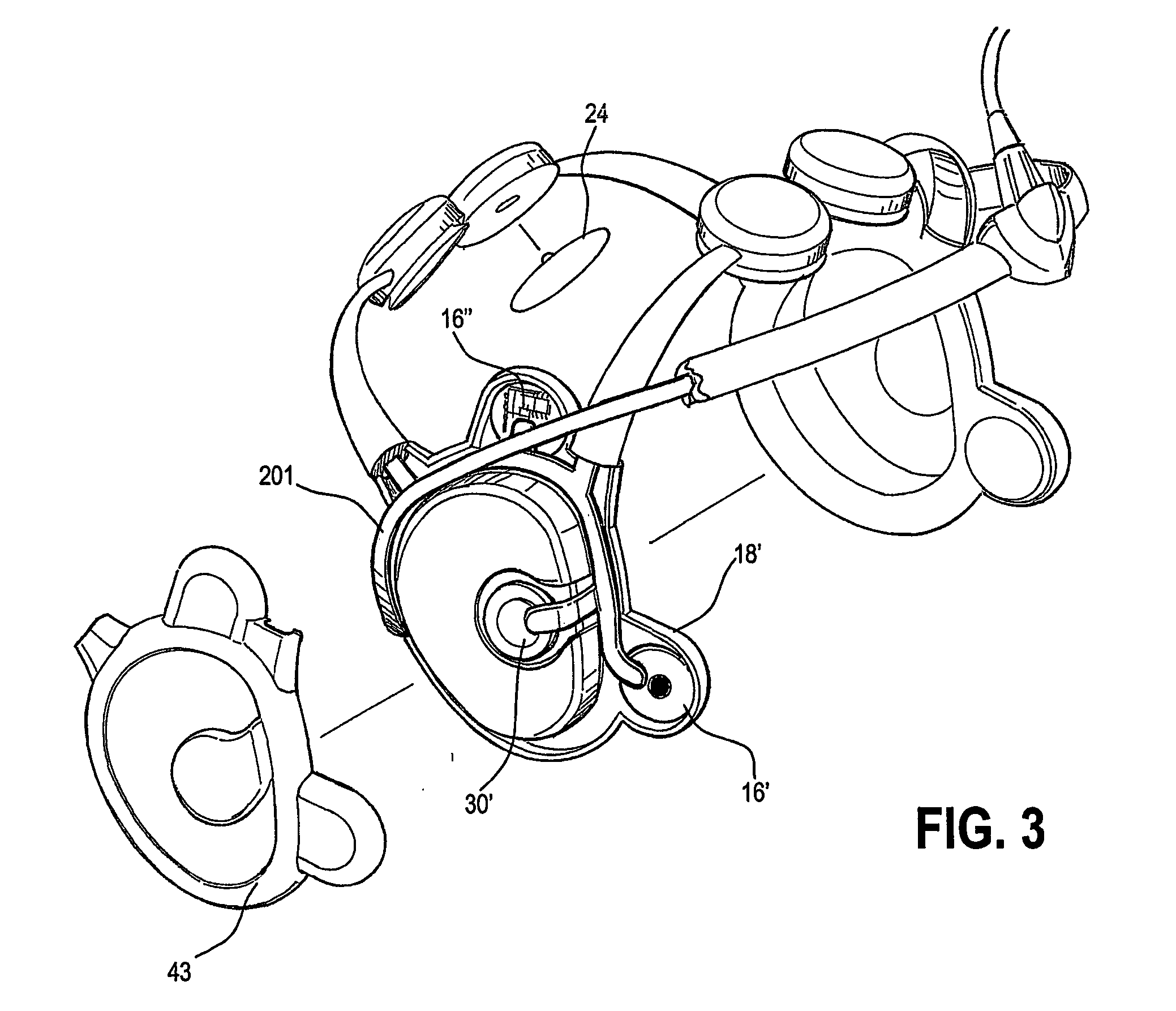
InactiveUS20070106169A1Easy to useEasily engageableElectroencephalographySensorsAuditory evoked responsesEngineering
A dyslexia screening test system suitable for clinical use includes an integrated headset that efficiently and conveniently performs an auditory evoked response (AER) test by positioning electrodes about the ears of the subject. An integral control module automatically performs the test, providing simplified controls and indications to the clinician. A number of screening tests that are stored in the headset are periodically uploaded for billing, remote analysis and result reporting.
Owner:NEURONETRIX SOLUTIONS
Implantable stimulation device and method for performing inter-chamber conduction search and conduction time measurement
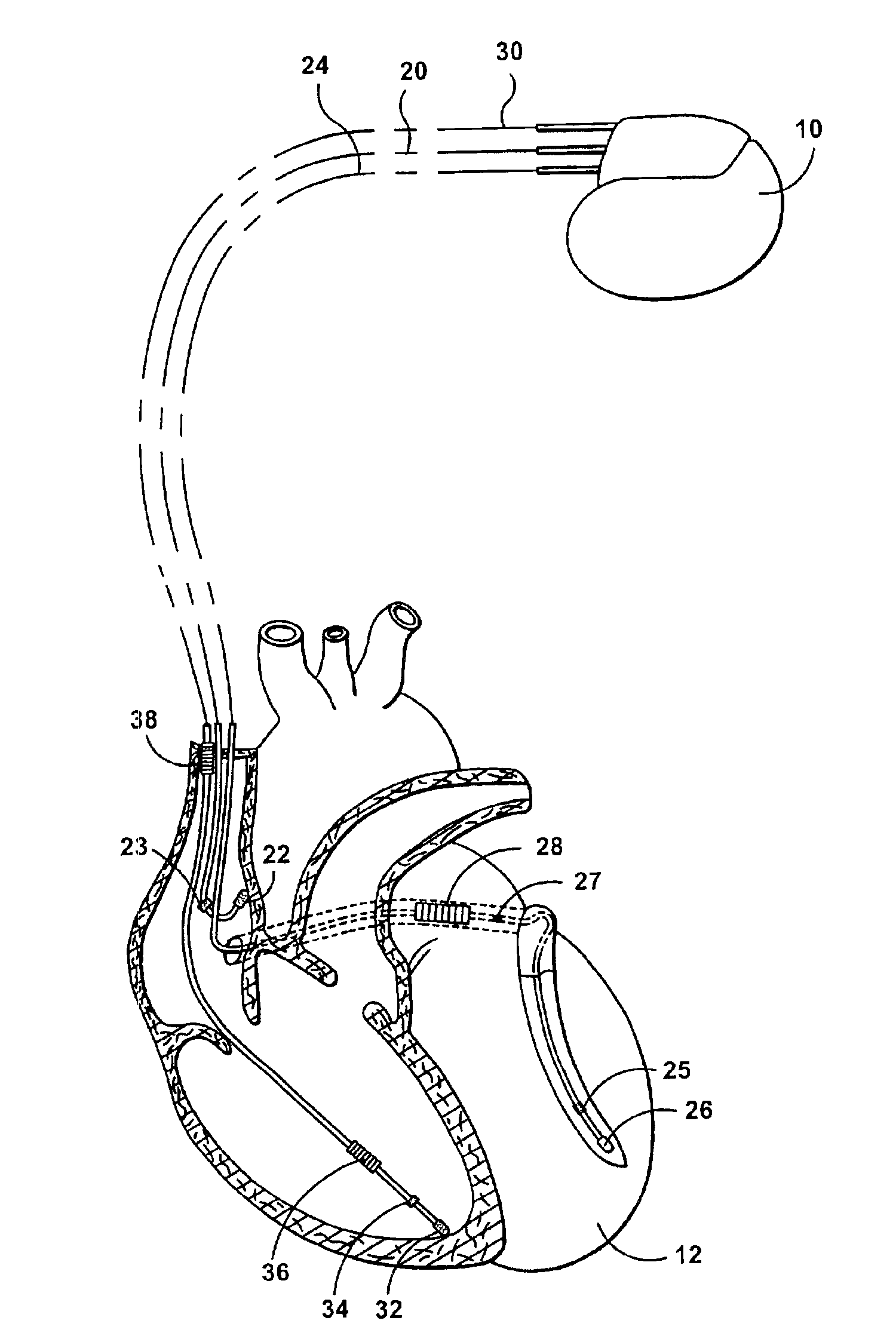
InactiveUS6885893B1Improves cardiac stimulation device performanceAvoid negative effectsHeart stimulatorsConduction timeAtrial conduction
An implantable cardiac stimulation device and associated method set an atrial capture detection window by verifying that inter-atrial conduction is intact, and then measuring the inter-atrial conduction time. The measured inter-atrial conduction time may then be used for setting the atrial capture detection window. Capture verification of a stimulated atrial site is then implemented by detecting a conducted depolarization at another atrial site or in the opposite atrial chamber. A signal received during an atrial capture detection window is compared to a depolarization signal threshold or to a depolarization signal template in order to verify detection of a conducted depolarization signal as evidence of capture at the stimulated site. By sensing depolarization signal away from the stimulated site, the negative effects of lead polarization normally encountered when detecting an evoked response are avoided.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Dual chamber heart stimulator with evoked response detector
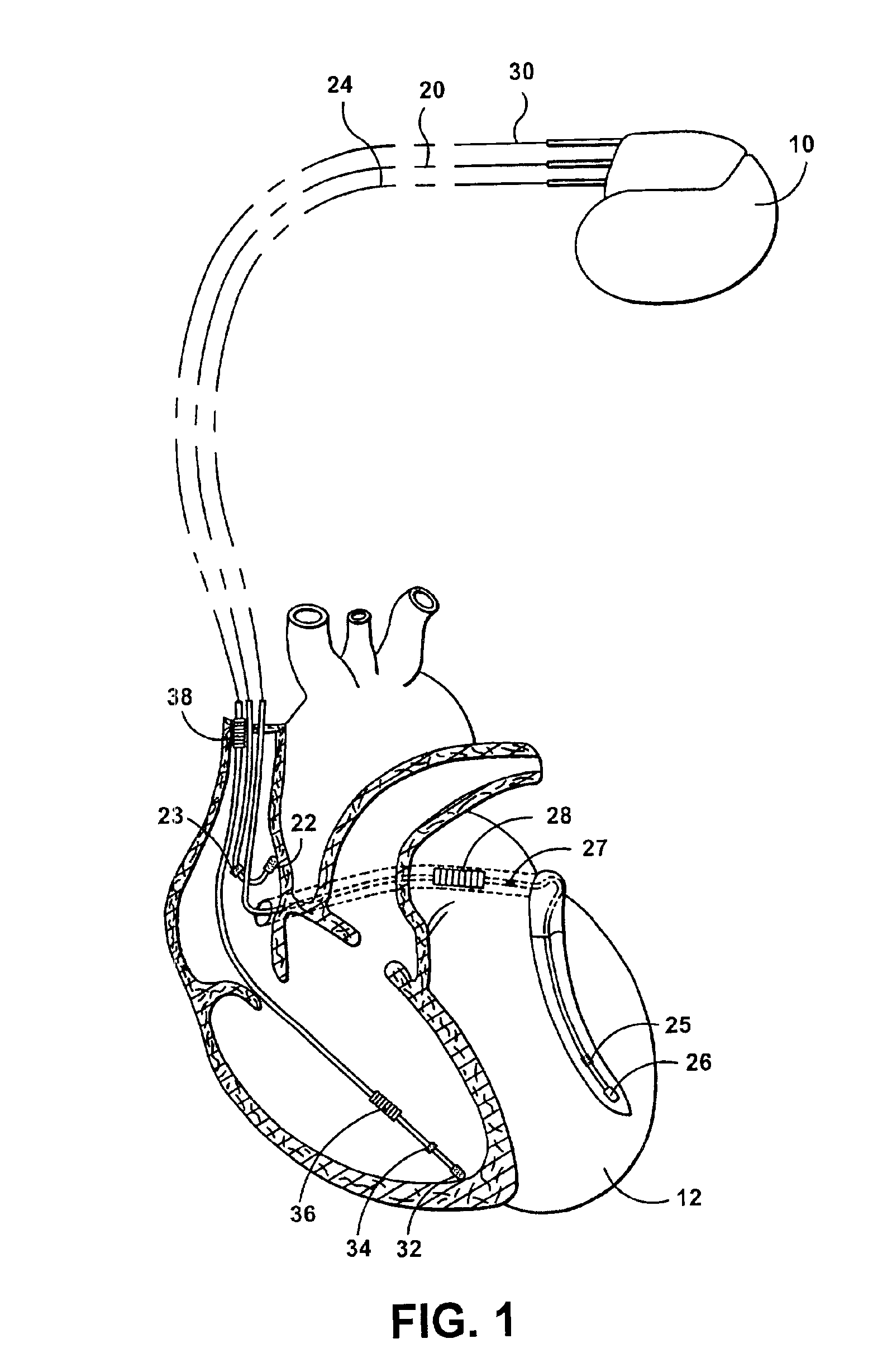
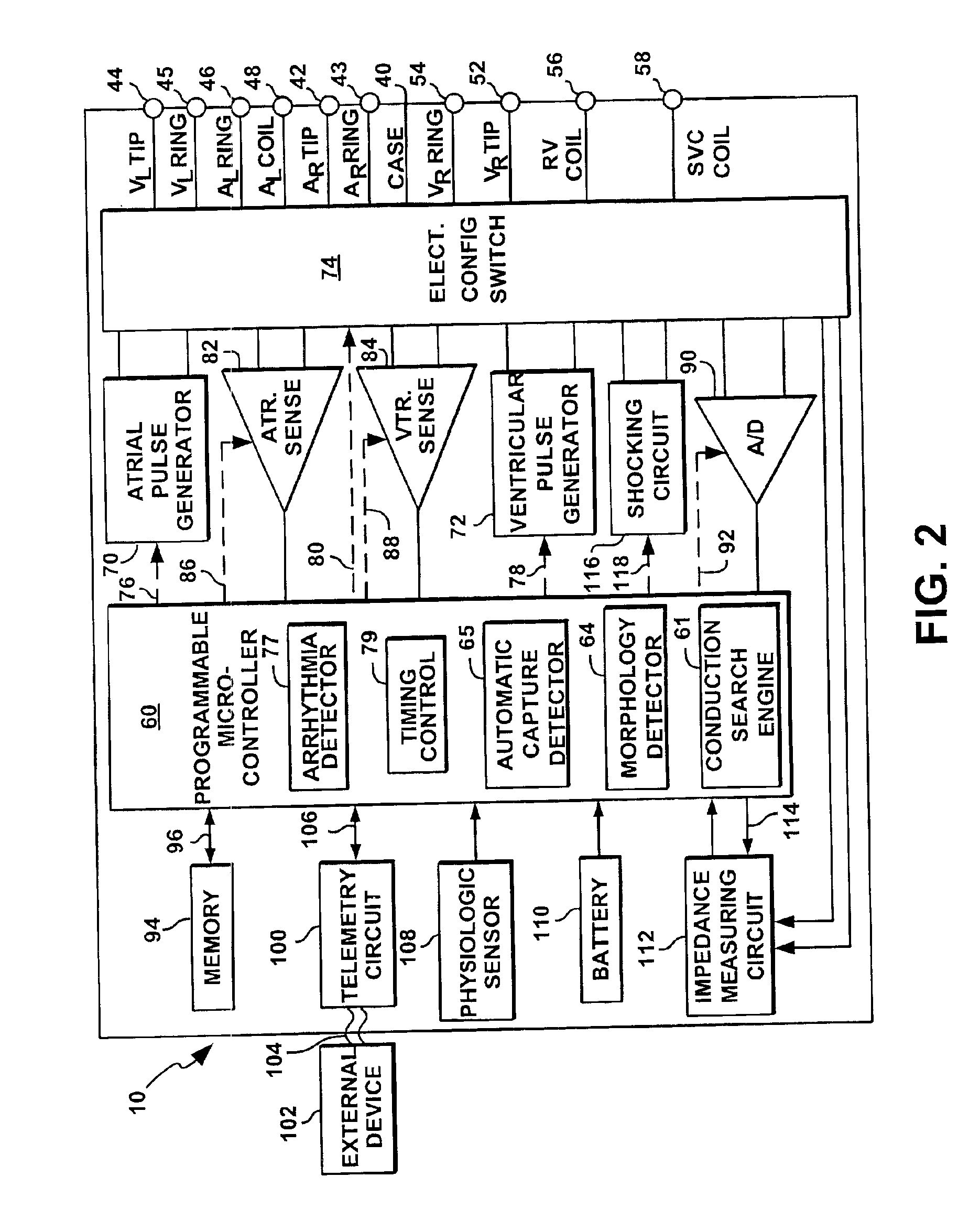
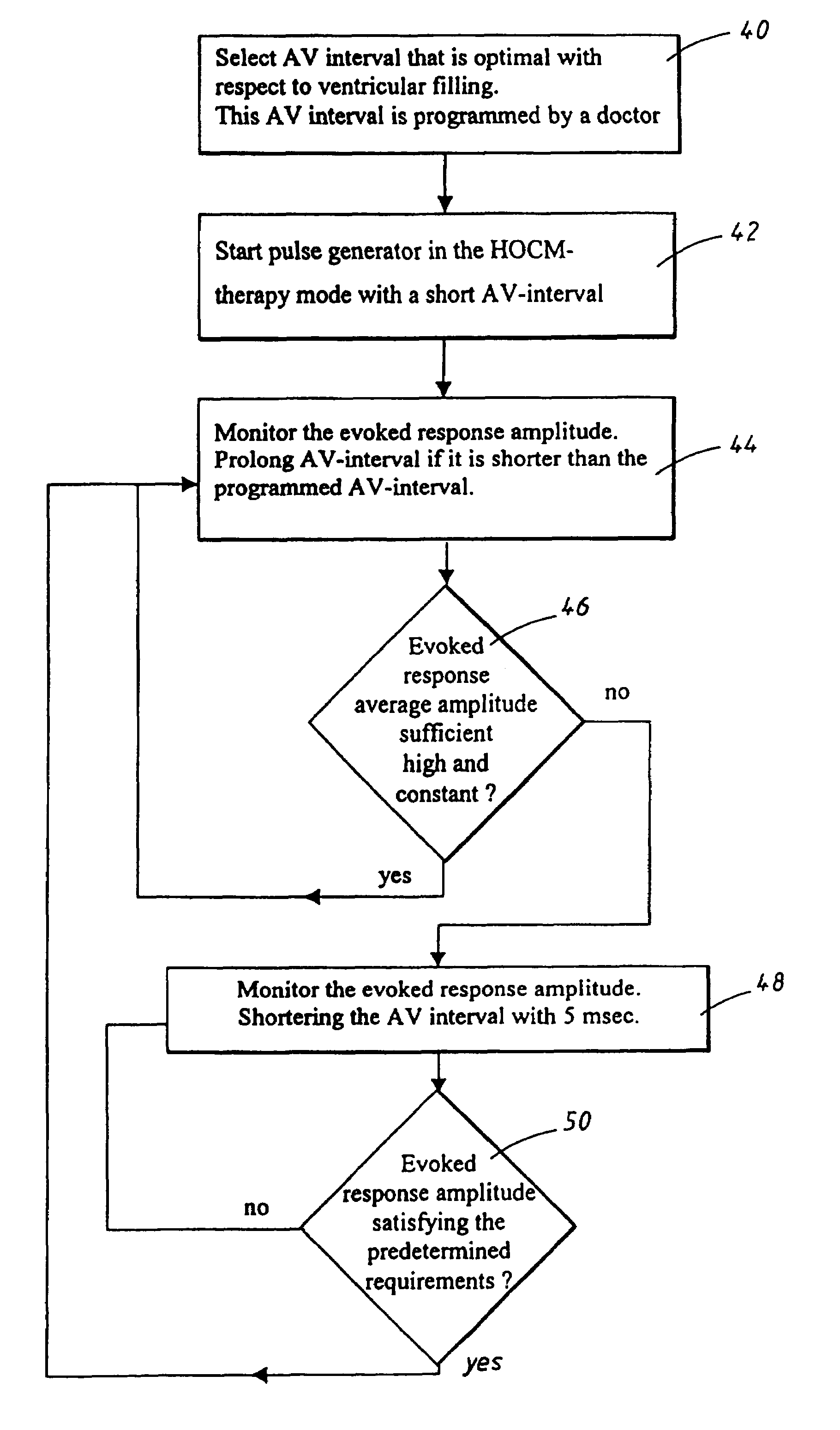
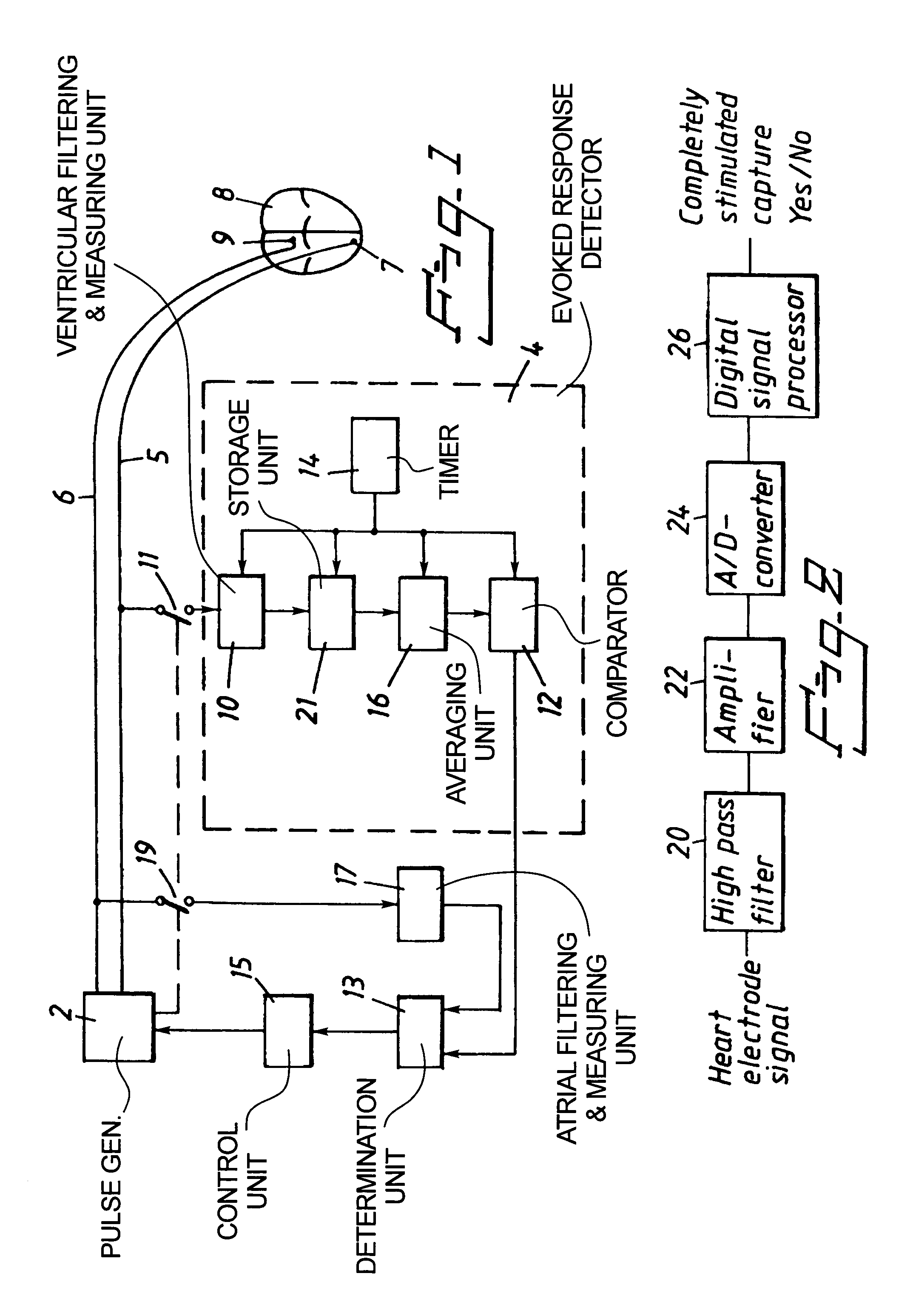
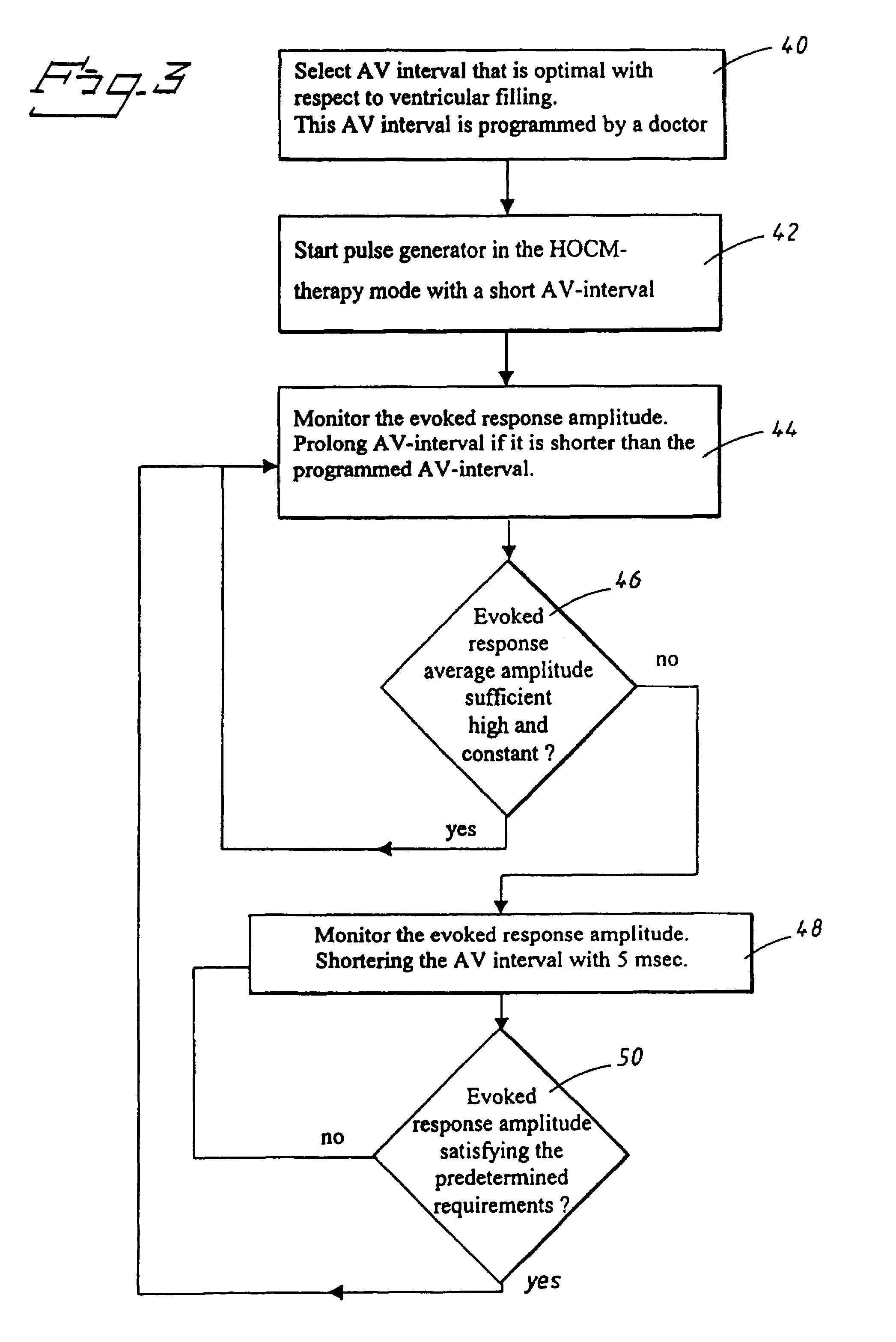
InactiveUS7020522B1The method is simple and reliableSimple and reliable processHeart stimulatorsFusion beatCardiac cycle
A heart stimulator has an atrial and ventricular pulse generator for producing atrial and ventricular stimulation pulses, an atrial sensor for sensing atrial signals and an evoked response detector for detecting the occurrence of incipient fusion beats from measured ventricular signals. A determination unit determines an incipient fusion AV-interval from the sensed atrial signals and the detected fusion beats, and a controller controls the pulse generator to deliver stimulation pulses at a controlled AV-interval which is shorter than the incipient fusion AV-interval. The evoked response detector includes an averaging unit which forms an average amplitude value of the measured ventricular signals during a predetermined time window of each cardiac cycle, and a comparator which compares the average value for each cardiac cycle with a predetermined limit criterion, and supplies the result of the comparison to the determination unit for determining a measured ventricular signal resulted from an incipient fusion beat or a completely stimulated capture.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Method and Device for Feedback Control of Neural Stimulation
ActiveUS20170361101A1Eliminate the effects ofSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesEngineeringBrain pathway
A method of controlling a neural stimulus by use of feedback. The neural stimulus is applied to a neural pathway in order to give rise to an evoked action potential on the neural pathway. The stimulus is defined by at least one stimulus parameter. A neural compound action potential response evoked by the stimulus is measured. From the measured evoked response a feedback variable is derived. A feedback loop is completed by using the feedback variable to control the at least one stimulus parameter value. The feedback loop adaptively compensates for changes in a gain of the feedback loop caused by electrode movement relative to the neural pathway.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Implantable cardiac stimulation system providing autocapture and lead impedance assessment and method
An implantable cardiac stimulation system provides autocapture assessment and lead impedance surveillance. The system includes a pulse generator that provides pacing stimulation pulses and a lead system including a plurality of electrodes that provide a plurality of different electrode configurations. The system further includes a switch that selectively couples the pulse generator to any one of the plurality of pacing electrode configurations and an autocapture circuit that performs autocapture tests with the pulse generator. The autocapture circuit includes a capture detector that detects evoked responses with an evoked response electrode configuration. When there is a failure to detect an evoked response, an impedance measuring circuit measures the lead impedance of the evoked response electrode configuration. If the measured lead impedance is outside of a given range, the switch couples the pulse generator to an electrode configuration other than the evoked response electrode configuration. Thereafter, the autocapture circuit performs a further autocapture and impedance measuring test or sets the pacing output to a level which assures capture.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and apparatus for application of a neural stimulus
A method of applying a neural stimulus with an implanted electrode array involves applying a sequence of stimuli configured to yield a therapeutic effect while suppressing psychophysical side effects. The stimuli sequence is configured such that a first stimulus recruits a portion of the fiber population, and a second stimulus is delivered within the refractory period following the first stimulus and the second stimulus being configured to recruit a further portion of the fiber population. Using an electrode array and suitable relative timing of the stimuli, ascending or descending volleys of evoked responses can be selectively synchronized or desynchronized to give directional control over responses evoked.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
System and method for predicting a heart condition based on impedance values using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20050216067A1Reliably predict onset of heart conditionHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringPulmonary edemaThoracic cavity
Techniques are provided for predicting the onset of a heart condition within a patient based on impedance measurements. Briefly, overloads in fluid levels in the thorax and in ventricular myocardial mass within the patient are detected based on impedance signals sensed using implanted electrodes. The onset of certain heart conditions is then predicted based on the overloads. For example, pulmonary edema arising due to diastolic heart failure is predicted based on the detection of on-going overloads in both fluid levels and ventricular mass. Ventricular hypertrophy is detected based on an on-going ventricular mass overload without a sustained fluid overload. Various other heart conditions may also be predicted based on specific combinations of recent or on-going overloads. Evoked response is exploited to corroborate the predictions. Appropriate warning signals are generated and preemptive therapy is initiated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
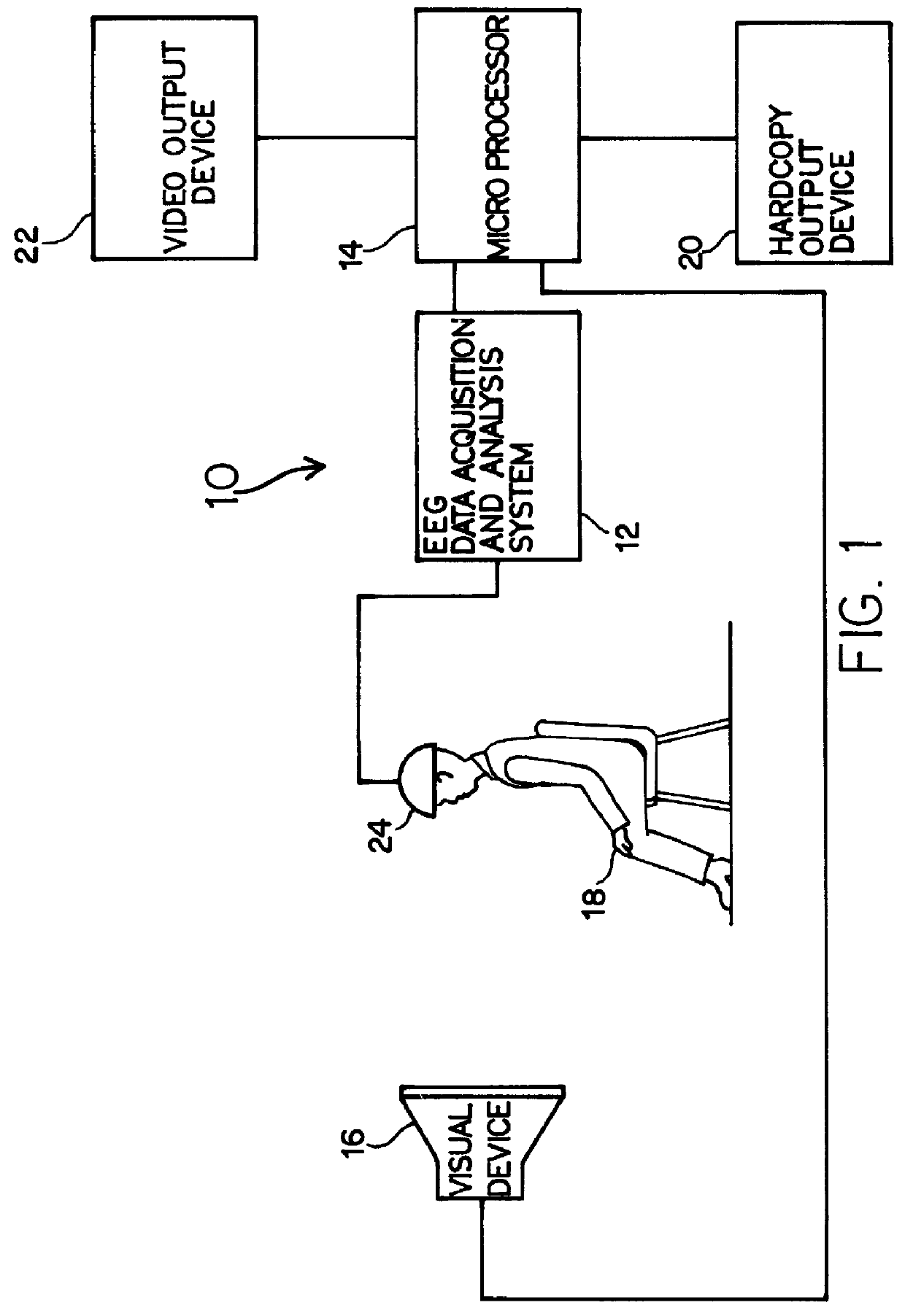
Repetitive visual stimulation to EEG neurofeedback protocols
An EEG neurofeedback and total evoked brain activity measurement methods utilize minimum ambient EEG activity as stimulant frequencies. A method of using repetitive stimulation in conjunction with EEG neurofeedback protocols is described. Electrodes, attached to a subject's scalp, transmit electroencephalographic (EEG) signals from the subject. These signals are in response to the visual and / or auditory stimuli being displayed to the subject. The resultant EEG signals are then filtered at pre-defined frequencies or frequency bands. The output from the filtered EEG signals is then analyzed and monitored for short-term state changes. The invention also uses flicker stimulation, real-time signal filtration and feedback, feedback during audio and visual stimulation derived from filtered outputs, and fundamental and integral harmonics in combination with total evoked response.
Owner:COLLURA THOMAS F
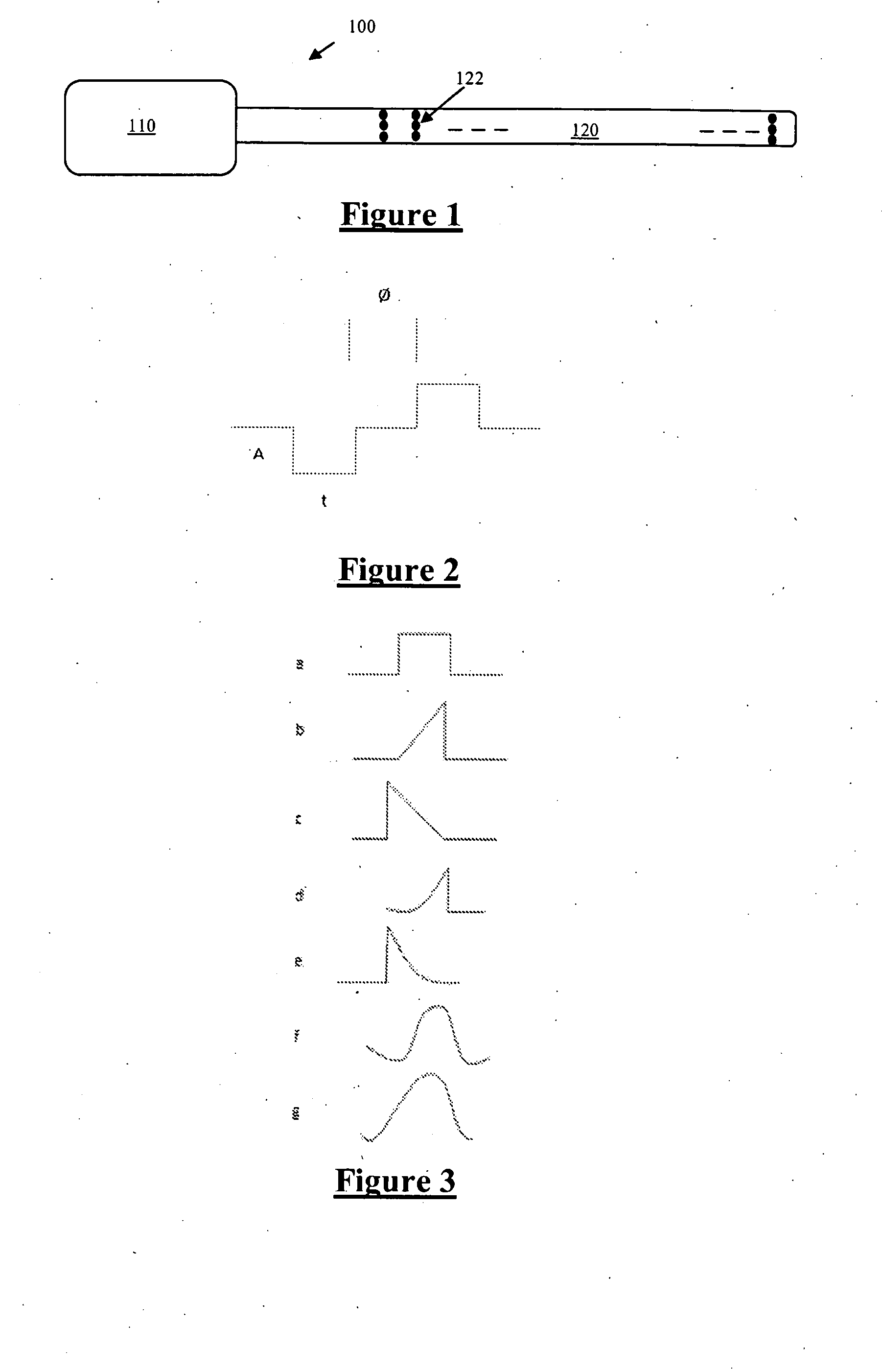
Form analysis to detect evoked response
InactiveUS20050004612A1Reliable resultsHigh selectivityElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsForm analysisHeart chamber
Method and device for determining capture status of a heart chamber that receives a pulse from an implantable pulse generator (IPG). Signal processing can be used to improve the reliability of capture detection by transforming the sensed response signal into a set of morphological characteristics. Analysis of selected morphological characteristics serves to distinguish signals indicative of capture from signals indicative of loss of capture.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
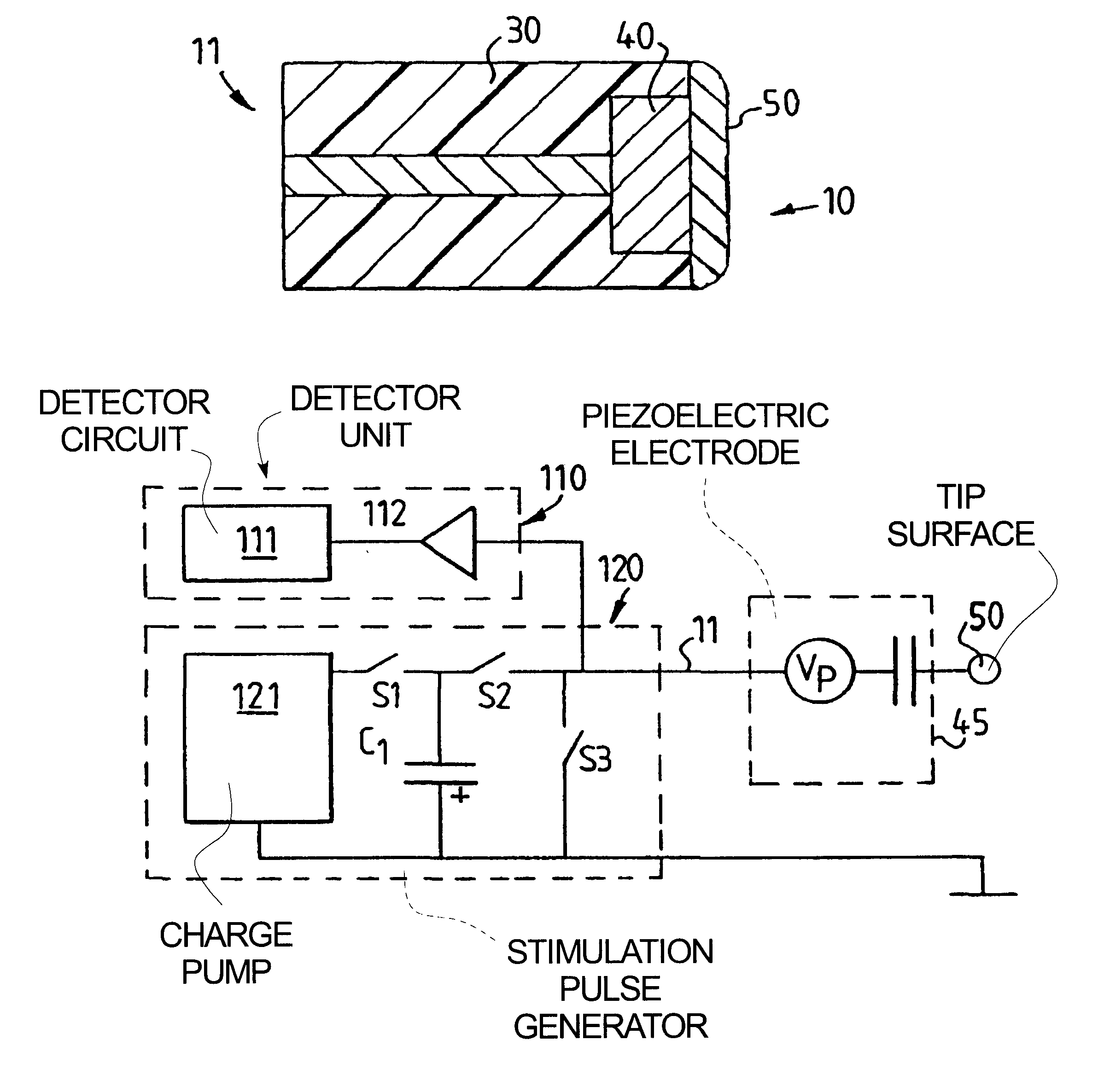
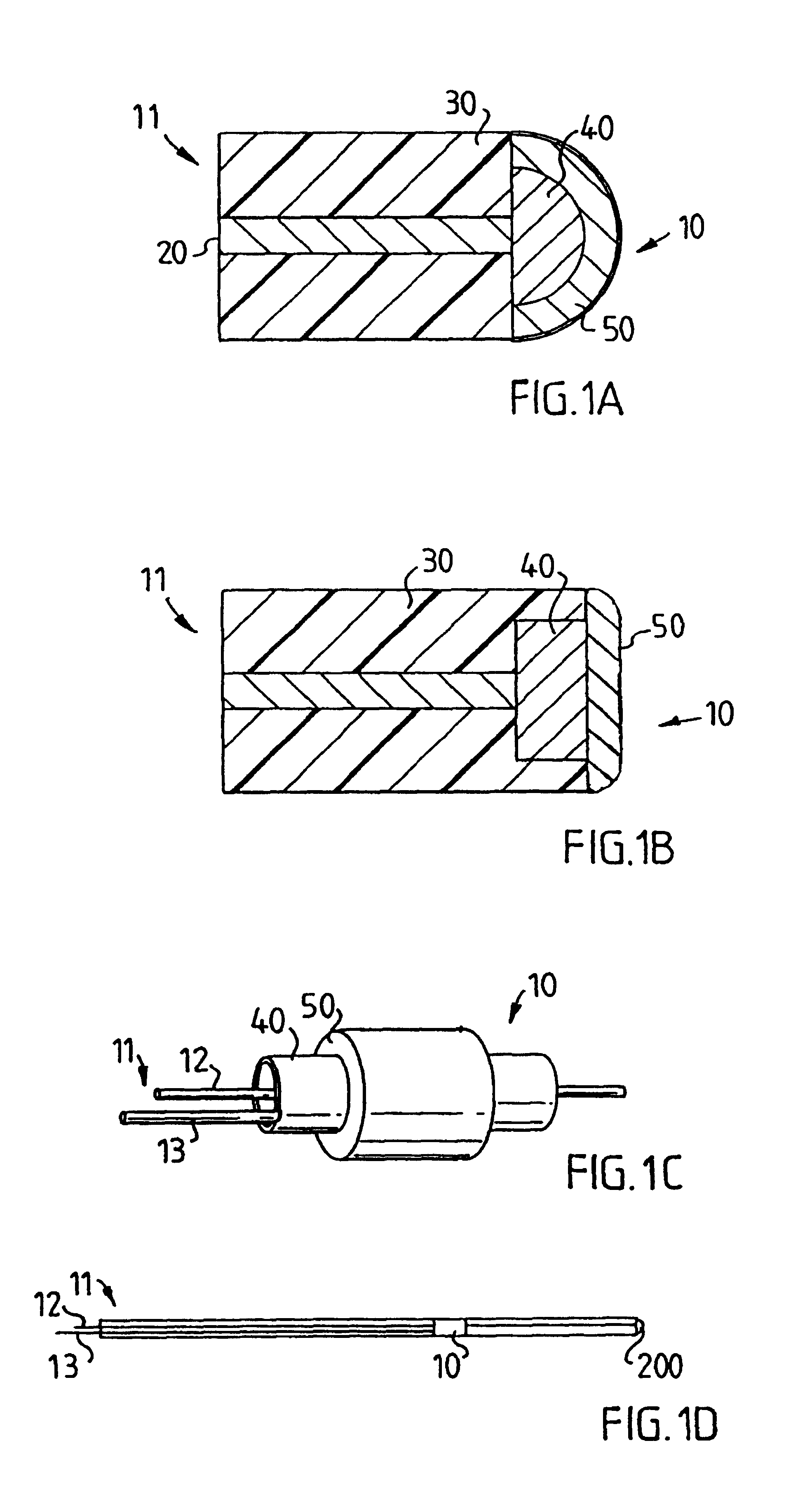
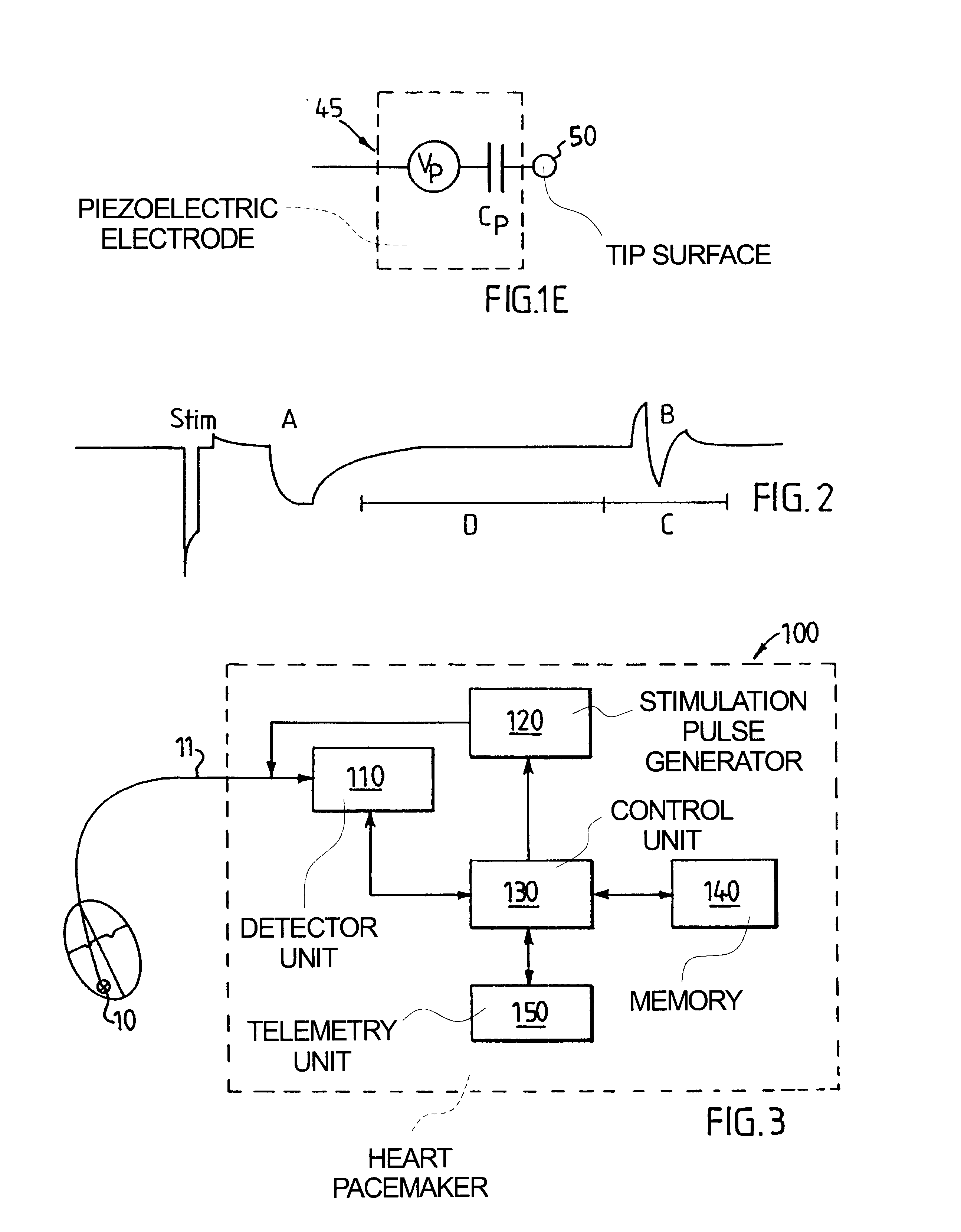
Electrode for tissue stimulation
InactiveUS6529777B1Reliably stimulateReduce energy consumptionInternal electrodesHeart stimulatorsMechanical irritationImplantable Electrodes
In an implantable electrode for an electrode lead for a stimulation device for stimulating tissue, the electrode is formed as a biocompatible piezoelectric electrode which is adapted to be in direct electrical contact with tissue for electrically and mechanically stimulating the tissue and for detecting electrical and mechanical evoked response of the stimulated tissue. The stimulation device can include circuitry for making a diagnosis of a heart condition using signals received from the implantable electrode.
Owner:PACESETTER AB
Method and apparatus for application of a neural stimulus
A method of applying a neural stimulus with an implanted electrode array involves applying a sequence of stimuli configured to yield a therapeutic effect while suppressing psychophysical side effects. The stimuli sequence is configured such that a first stimulus recruits a portion of the fibre population, and a second stimulus is delivered within the refractory period following the first stimulus and the second stimulus being configured to recruit a further portion of the fibre population. Using an electrode array and suitable relative timing of the stimuli, ascending or descending volleys of evoked responses can be selectively synchronised or desynchronised to give directional control over responses evoked.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
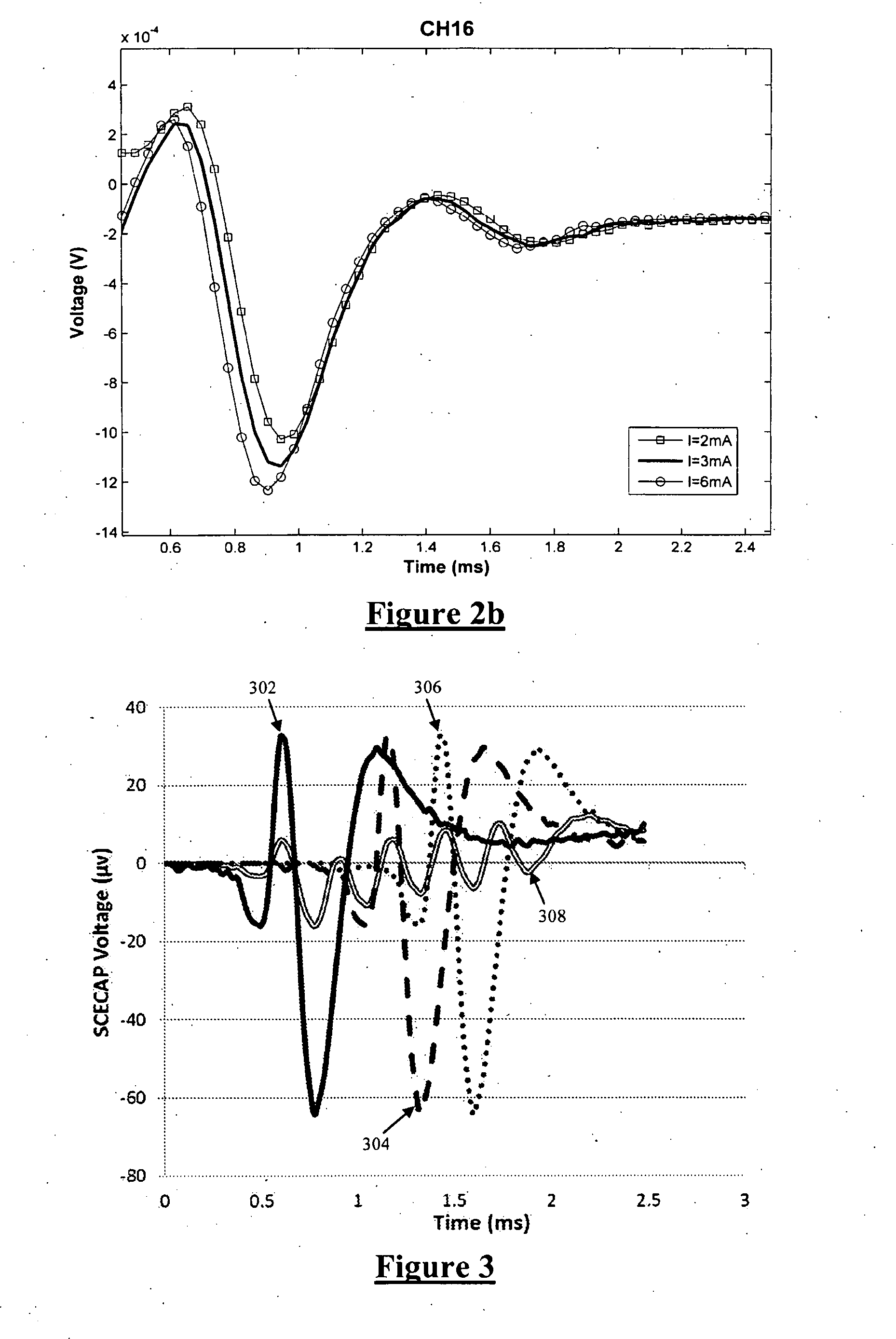
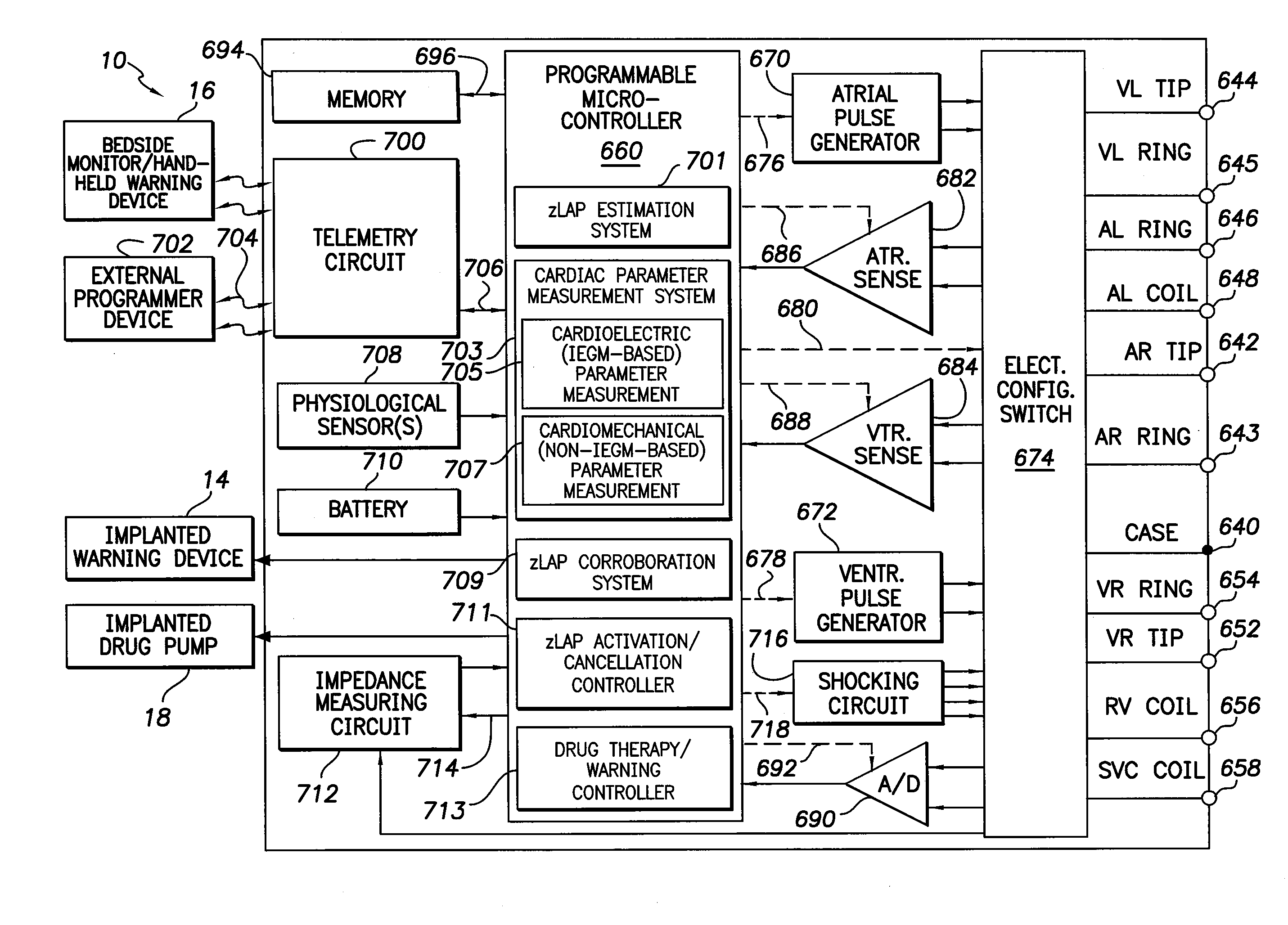
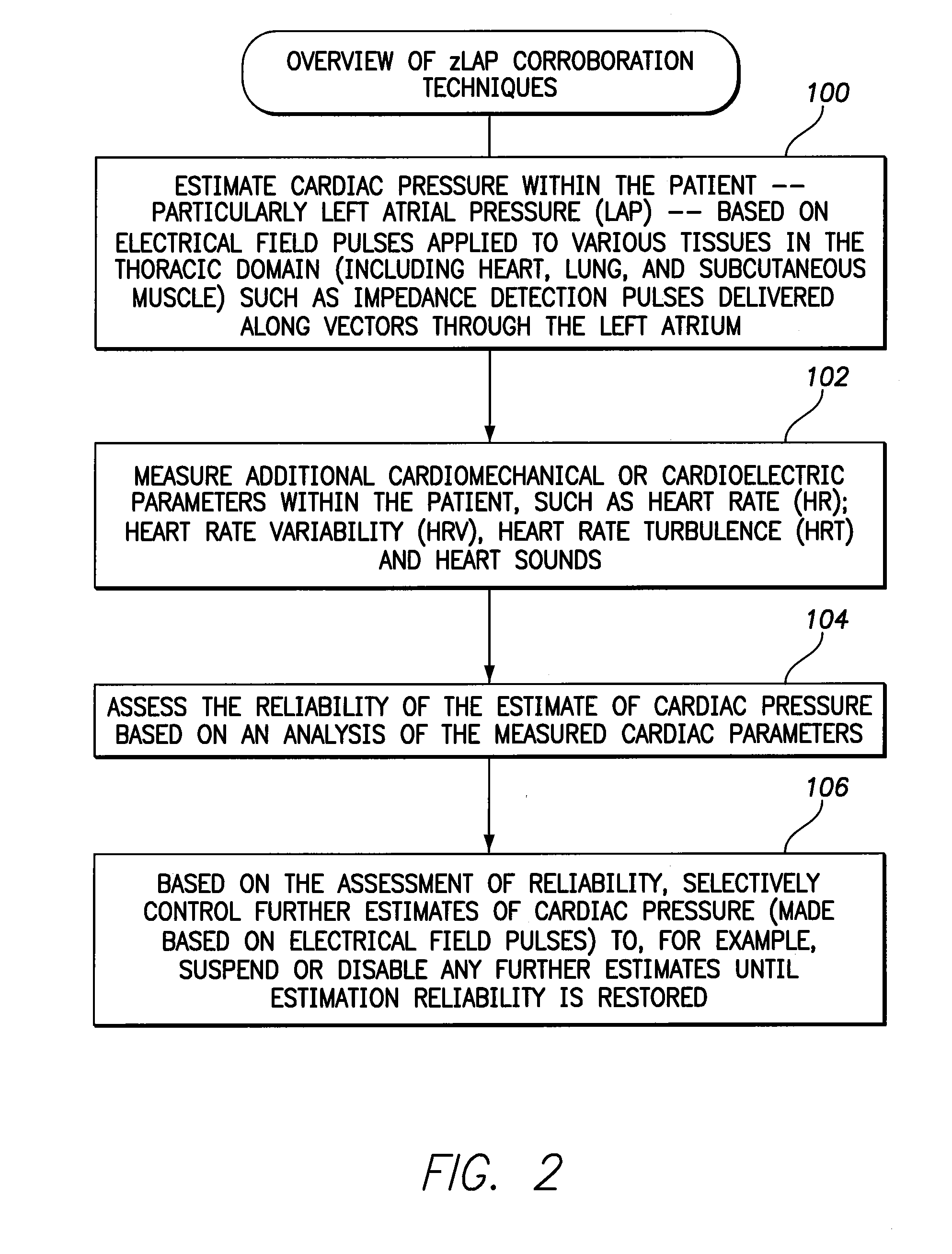
Systems and methods for corroborating impedance-based left atrial pressure (LAP) estimates for use by an implantable medical device
Various techniques are provided for assessing the reliability of left atrial pressure (LAP) estimates made by an implantable medical device based on impedance values or related electrical values. In one example, various cardioelectric and cardiomechanical parameters are used to corroborate LAP estimation in circumstances where the LAP estimates deviate from an acceptable, satisfactory or otherwise healthy range. The cardioelectric parameters include, e.g.: ST elevation; heart rate (HR); heart rate variability (HRV); T-wave alternans (TWA); QRS waveform parameters; P-wave duration; evoked response (ER) parameters; and intrinsic PV / AV / VV conduction delays. The cardiomechanical parameters include, e.g.: heart rate turbulence (HRT); cardiogenic impedance signals; heart sounds; and non-LAP blood pressure measurements, such as aortic pressure measurements. The device compares the cardioelectric and cardiomechanical parameters against corresponding baseline values to determine whether variations in the parameters corroborate the LAP estimates. If not, the LAP estimates are selectively cancelled or suspended, or the overall procedure is re-calibrated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Apparatus and method for predicting probability of explosive behavior in people
A method and apparatus for determining the probability of explosive behavior in a person of known age, sex and use of medication, is provided by generating and measuring a visually evoked response to a certain visually displayed paradigm and measuring the amplitude, in microvolts, of the evoked response at approximately 100 milliseconds after cessation of the paradigm display, and quantifying the absolute values of the delta, theta, alpha and beta frequency bands of a standard EEG, and applying this data to an algorithm to compute on the probability of explosive behavior.
Owner:HEYREND F LAMARR +1
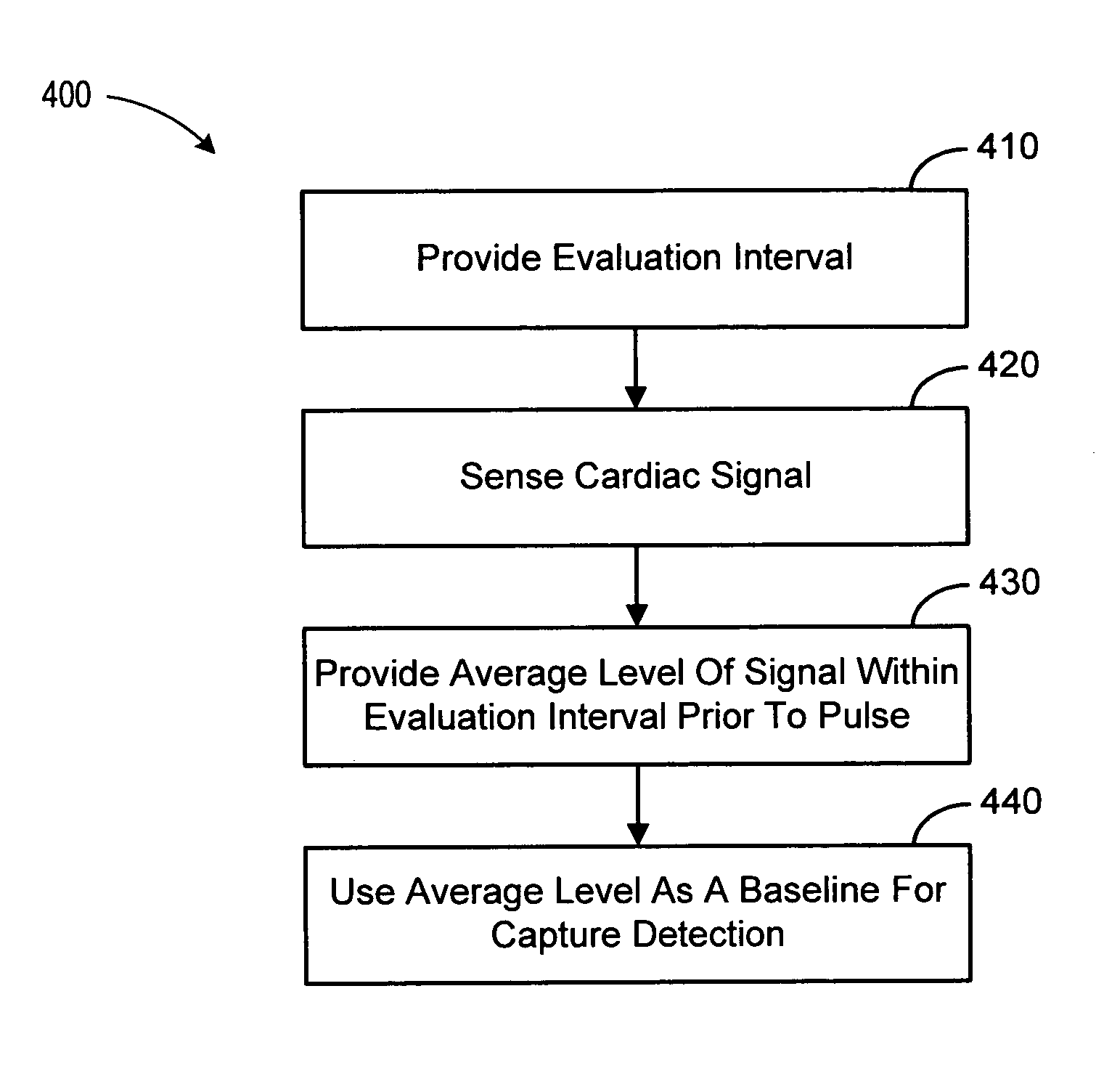
Baseline adaptation for cardiac pacing response classification
ActiveUS7330761B2Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEvaluation IntervalClassification methods
Methods and devices for establishing and using baseline for cardiac pacing response detection are described. A baseline amplitude of the cardiac signal may be established using data acquired in an evaluation interval prior to the delivery of the pacing pulse. An amplitude of the cardiac signal following delivery of the pacing pulse may be referenced using the baseline amplitude. An evoked response from the pacing pulse is detected using the referenced cardiac signal amplitude.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com