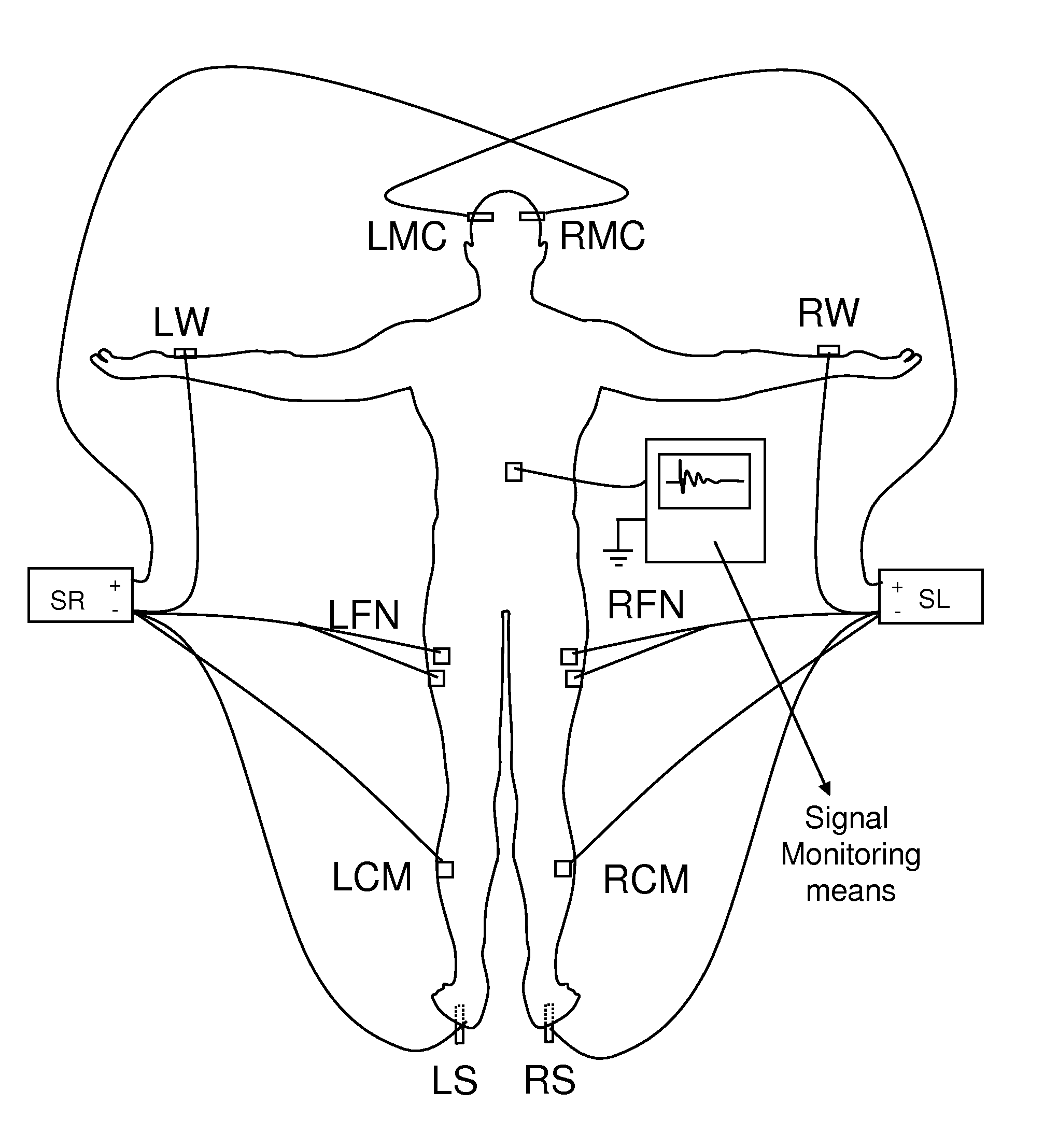
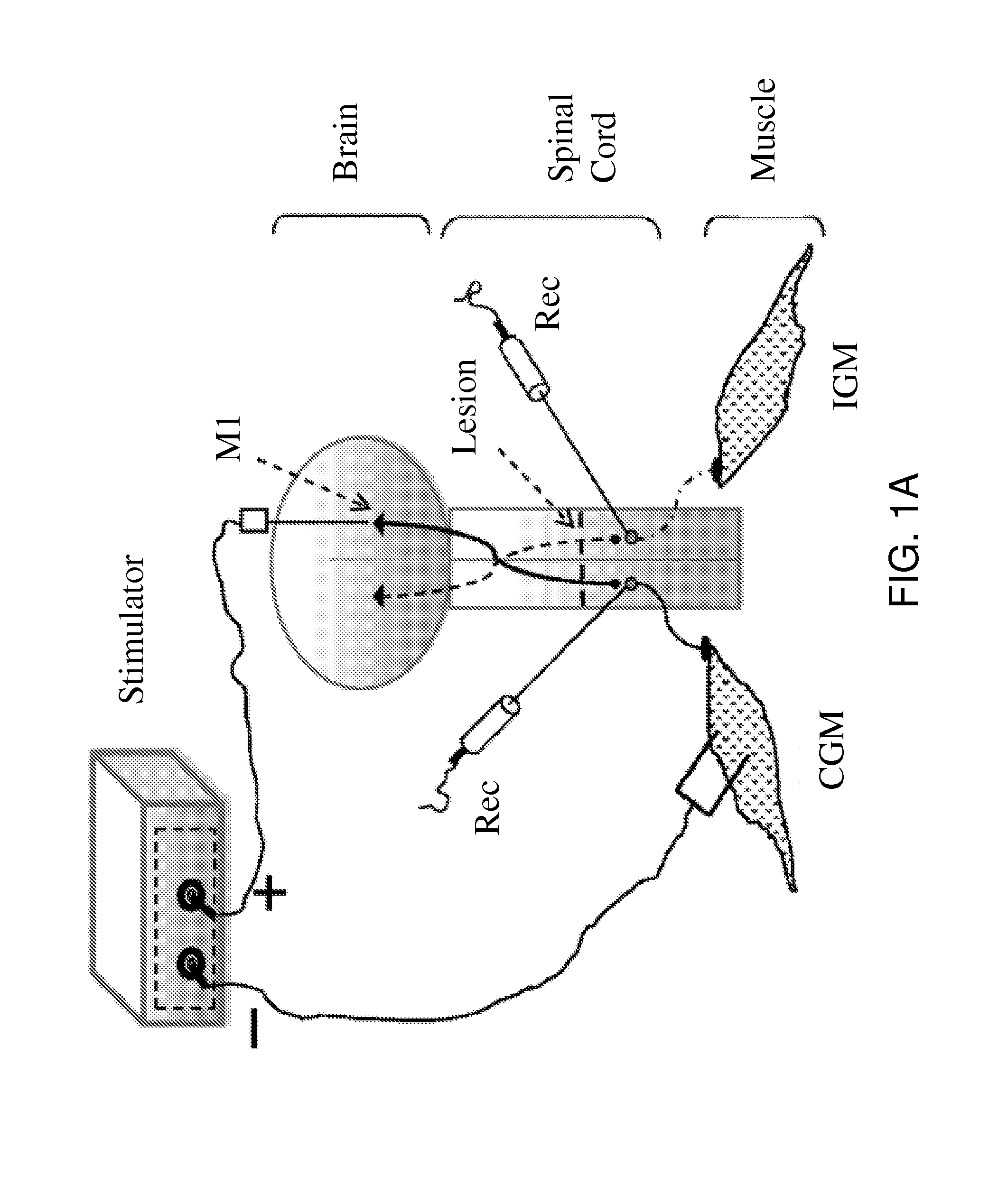
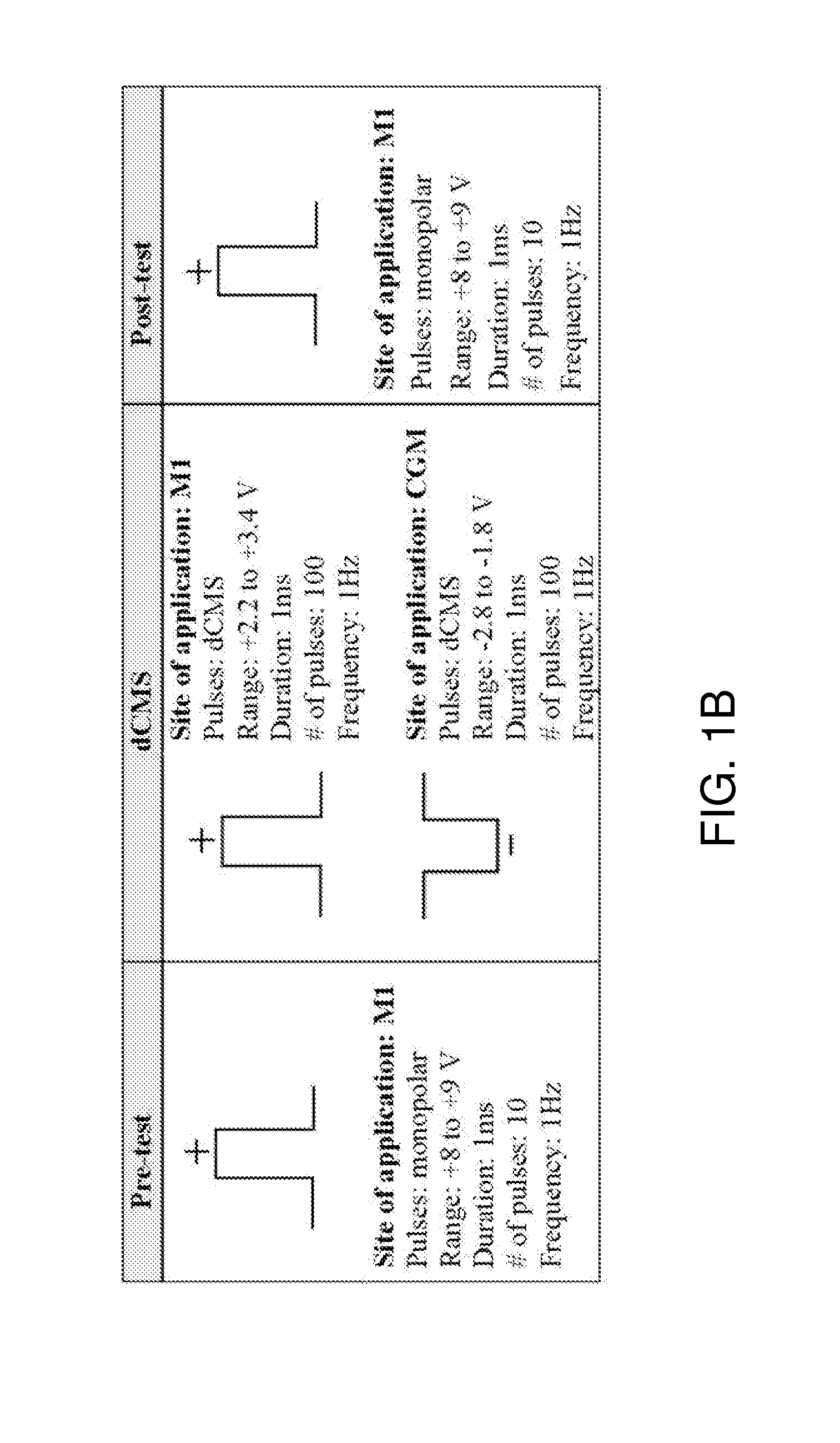
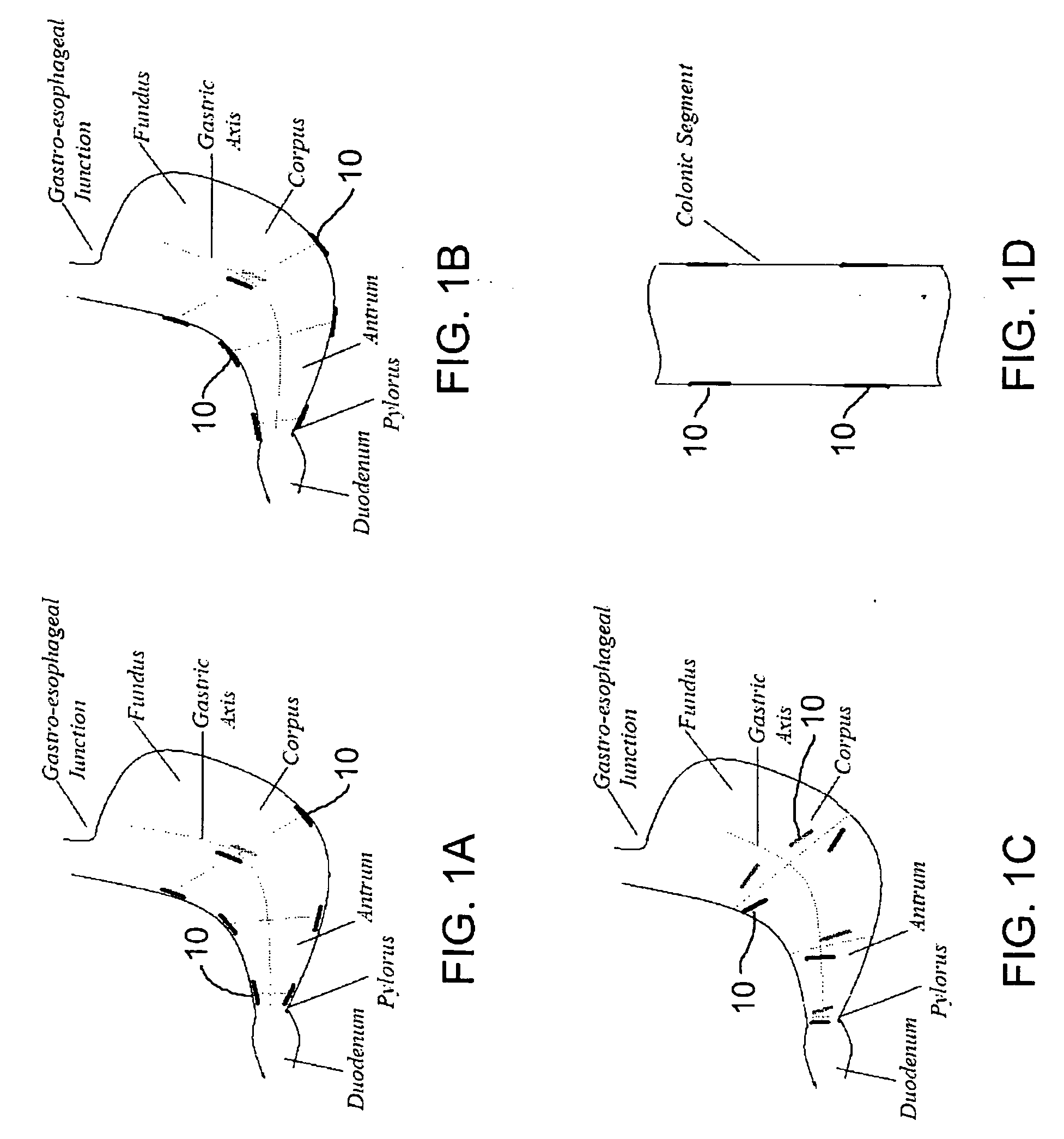
Patents
Literature
117 results about "Brain pathway" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
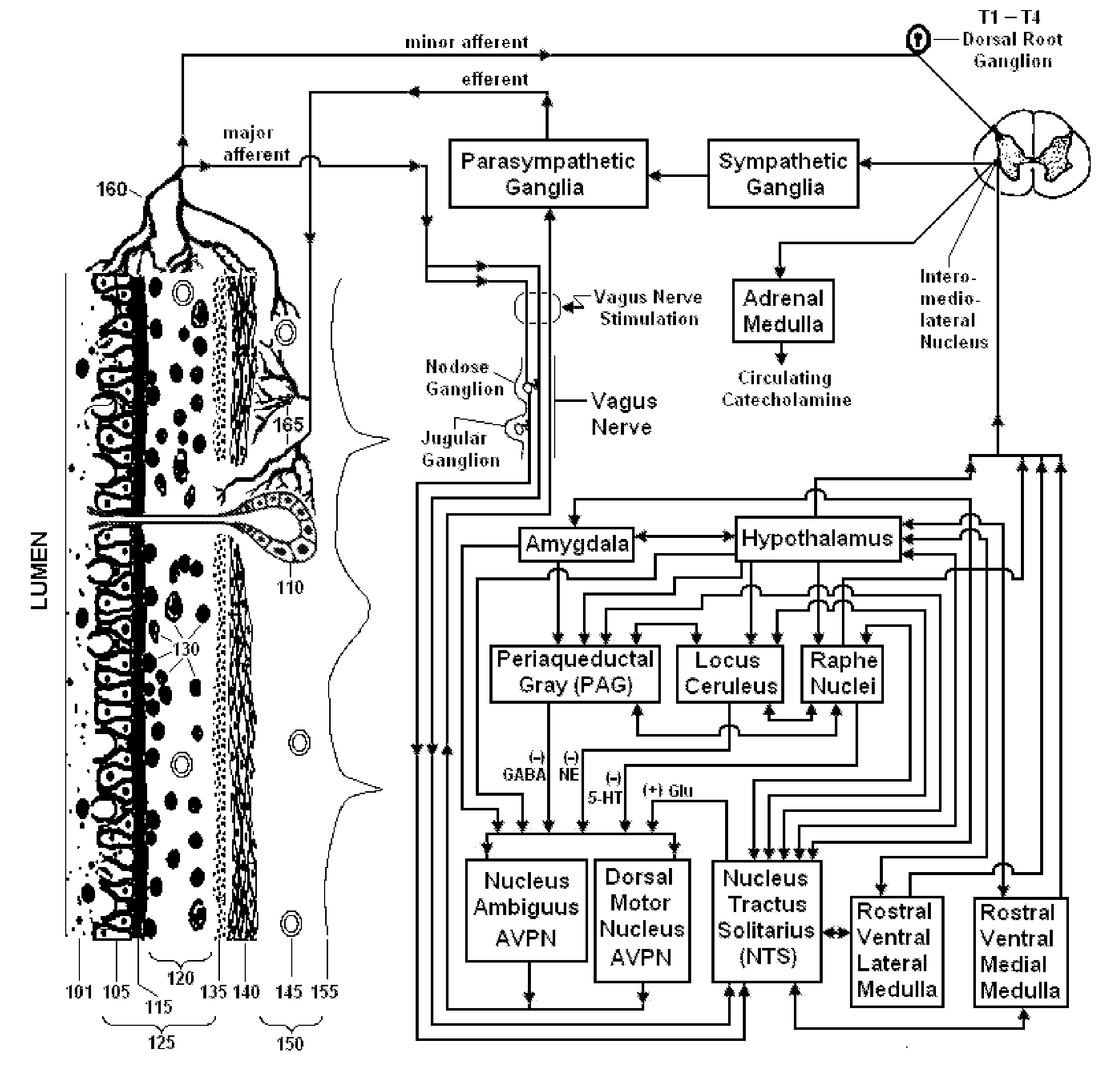
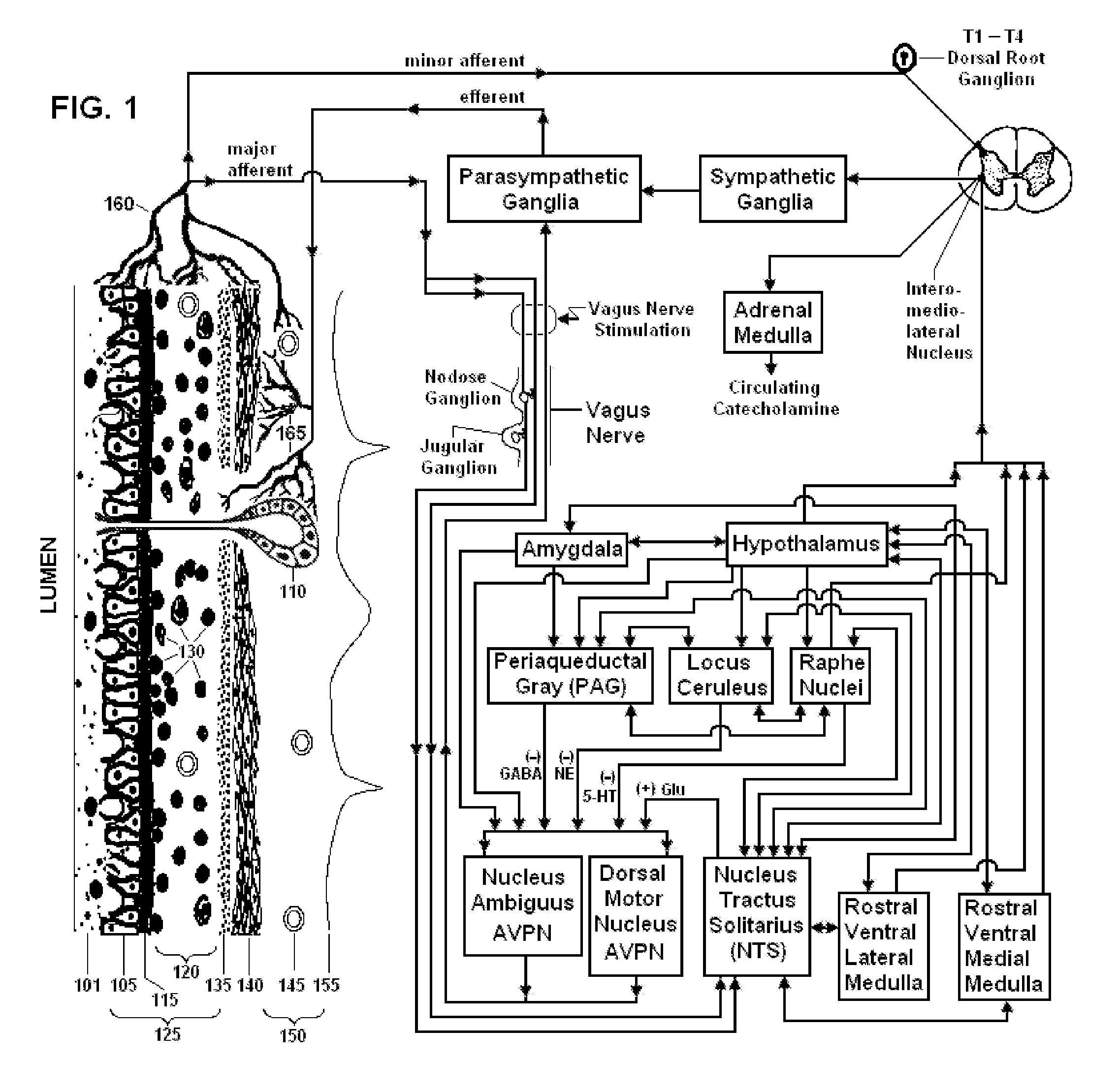
Neural pathway. A neural pathway connects one part of the nervous system to another using bundles of axons called tracts. The optic tract that extends from the optic nerve is an example of a neural pathway because it connects the eye to the brain; additional pathways within the brain connect to the visual cortex.
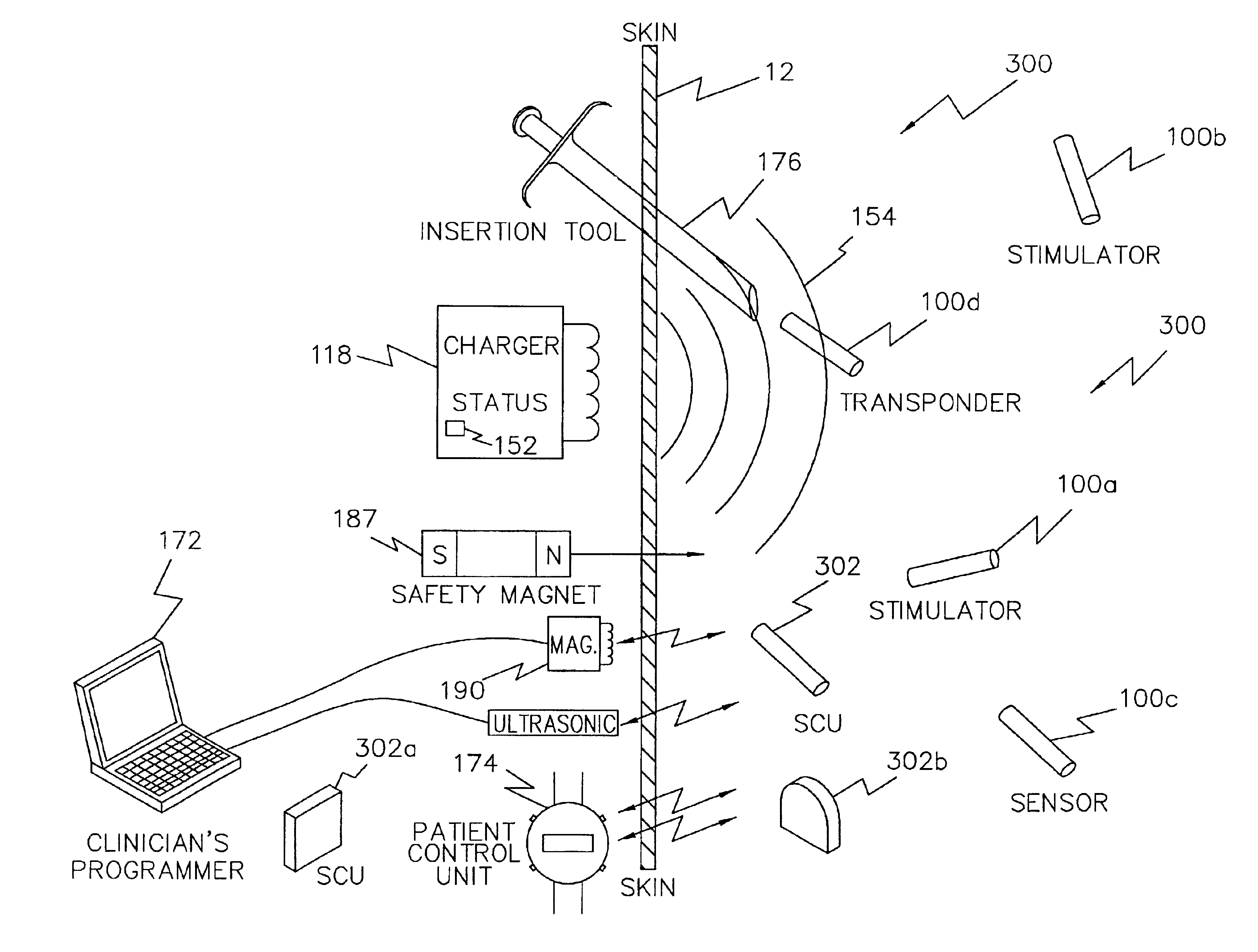
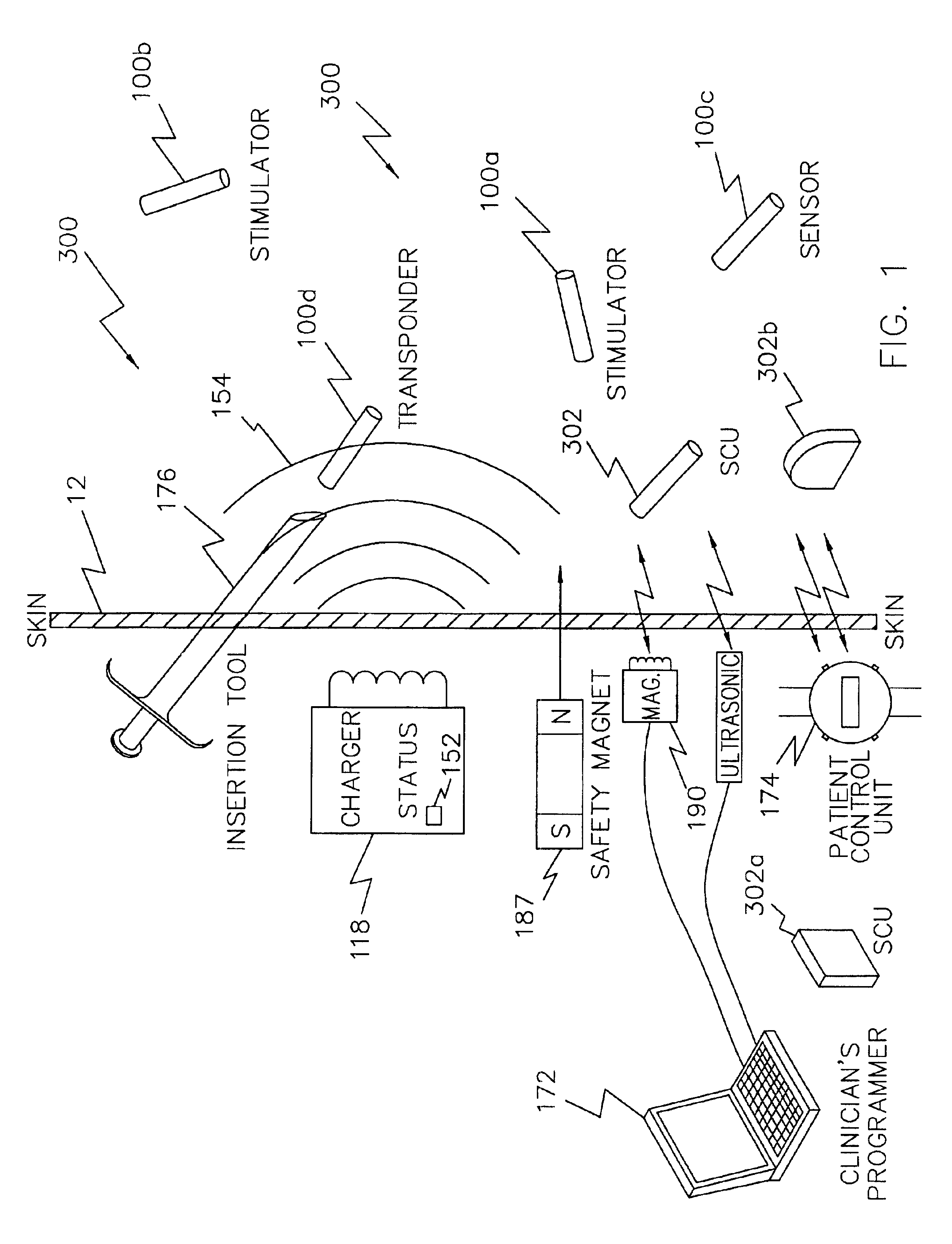
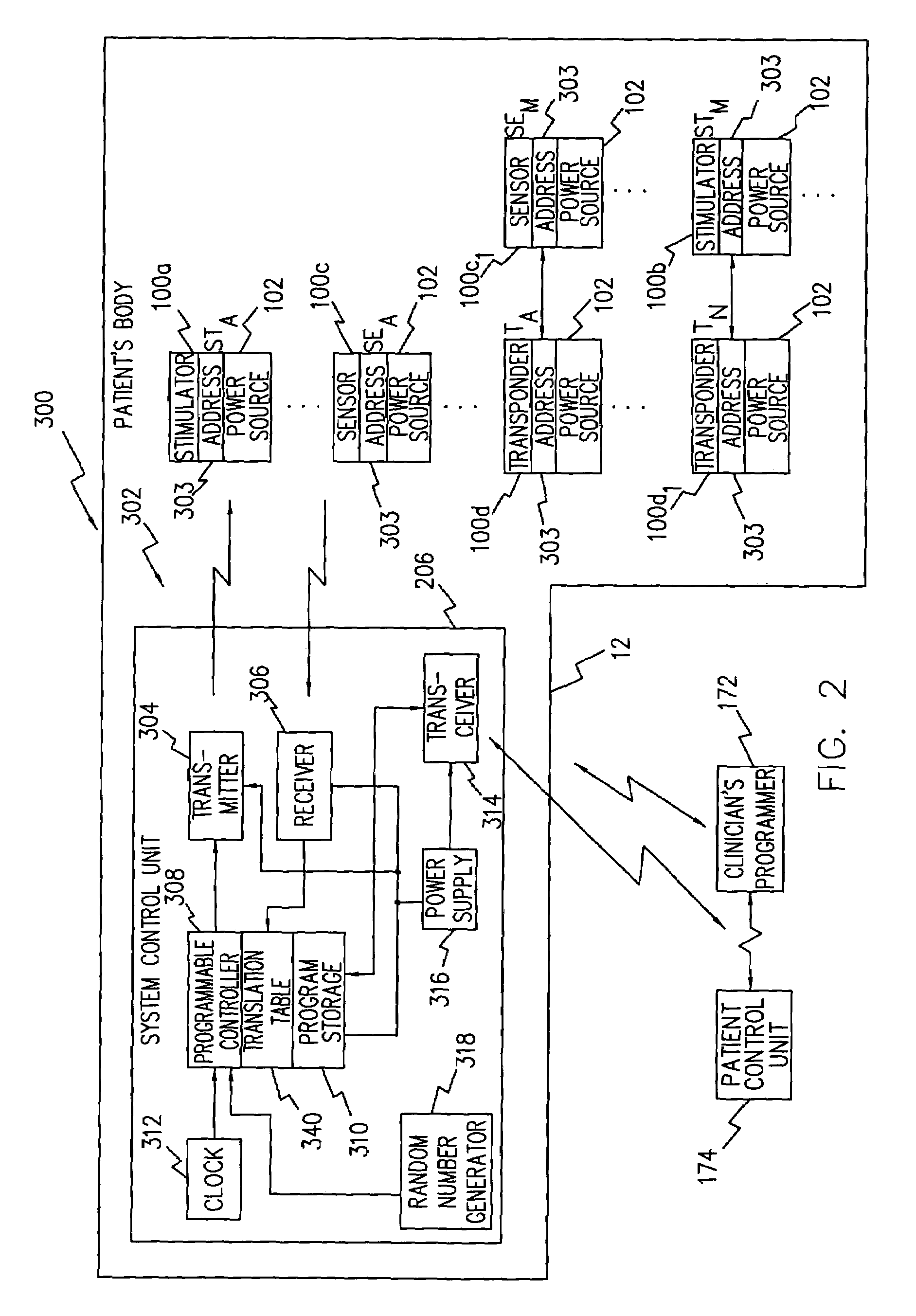
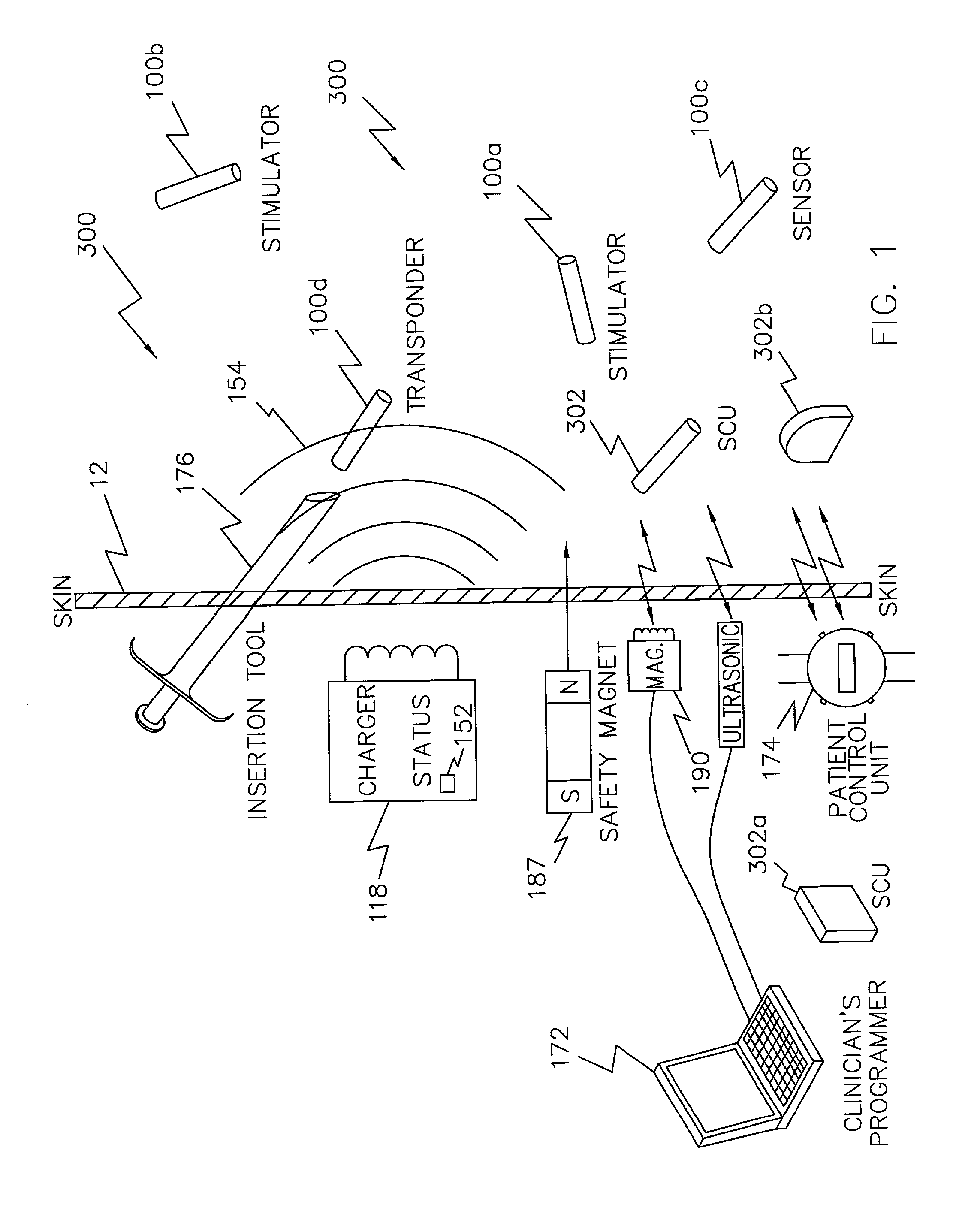
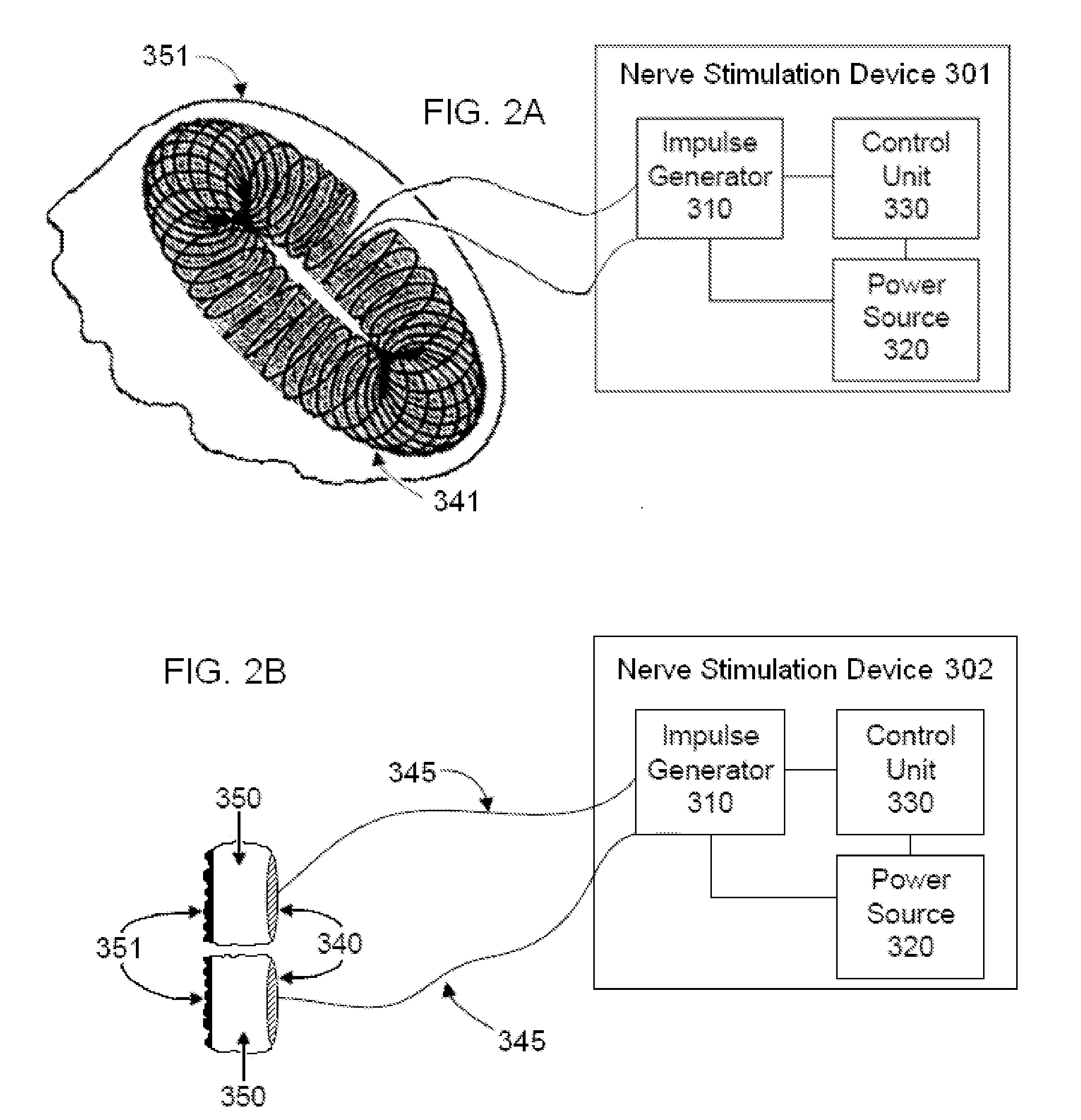
Magnet control system for battery powered living tissue stimulators
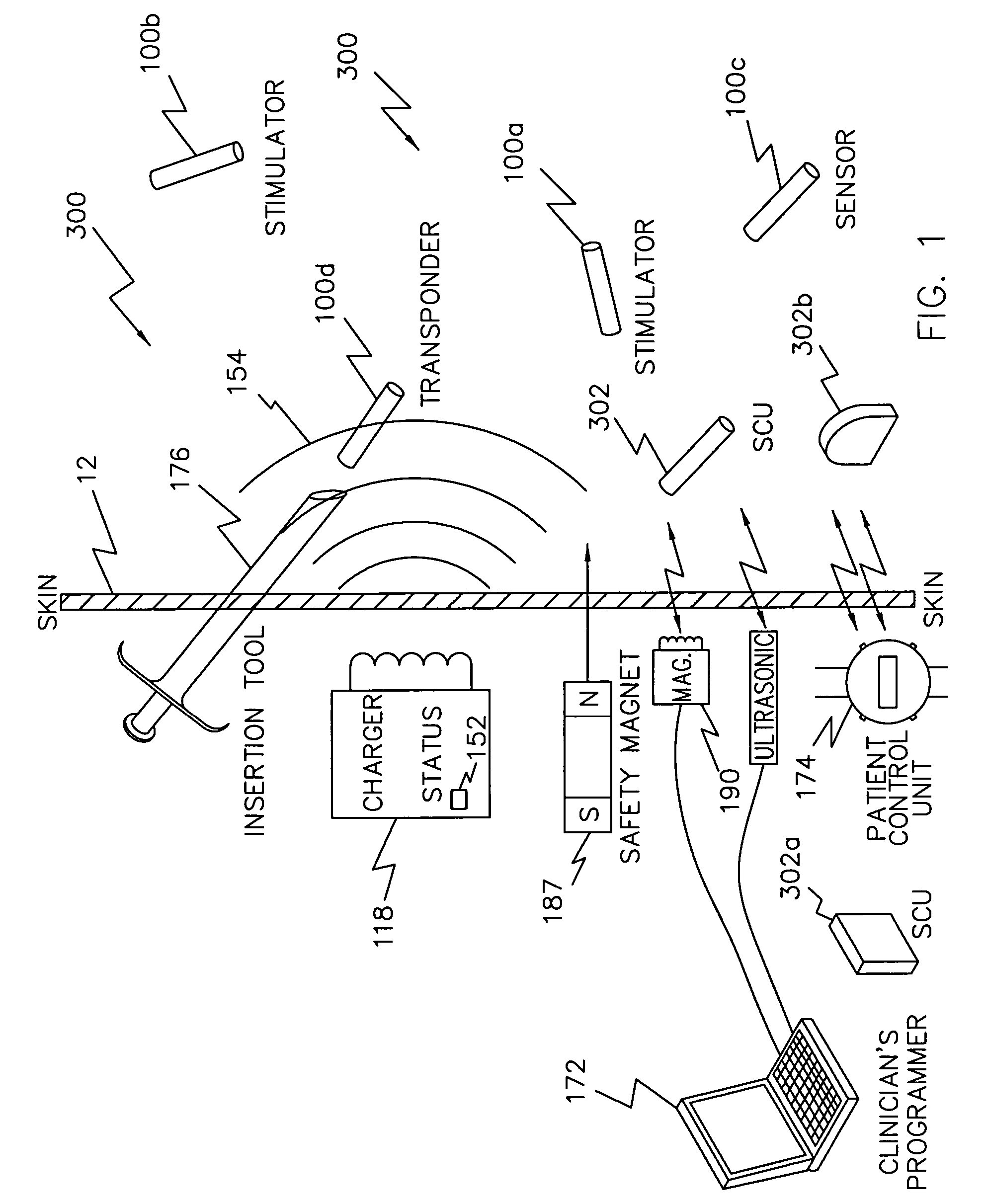
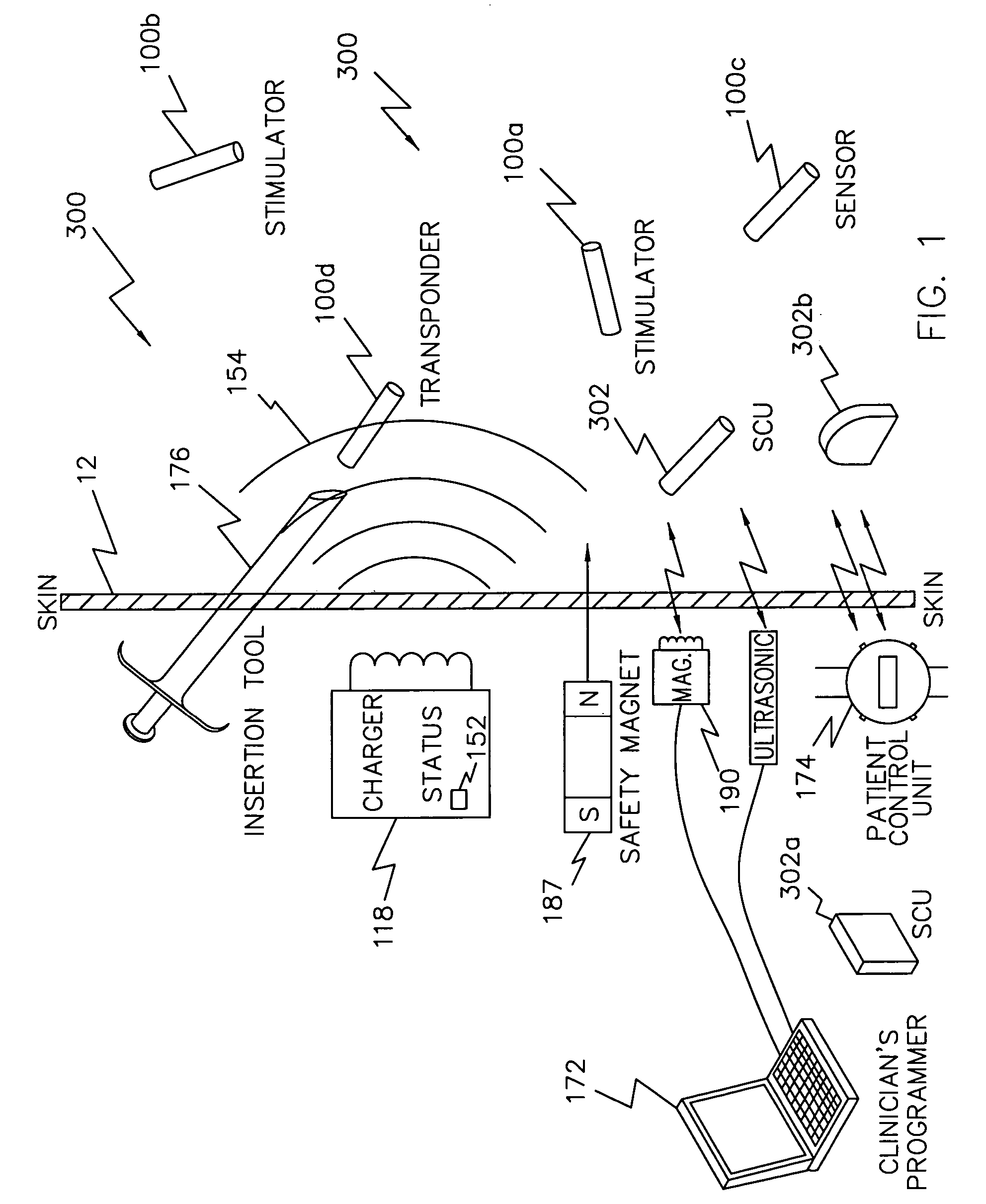
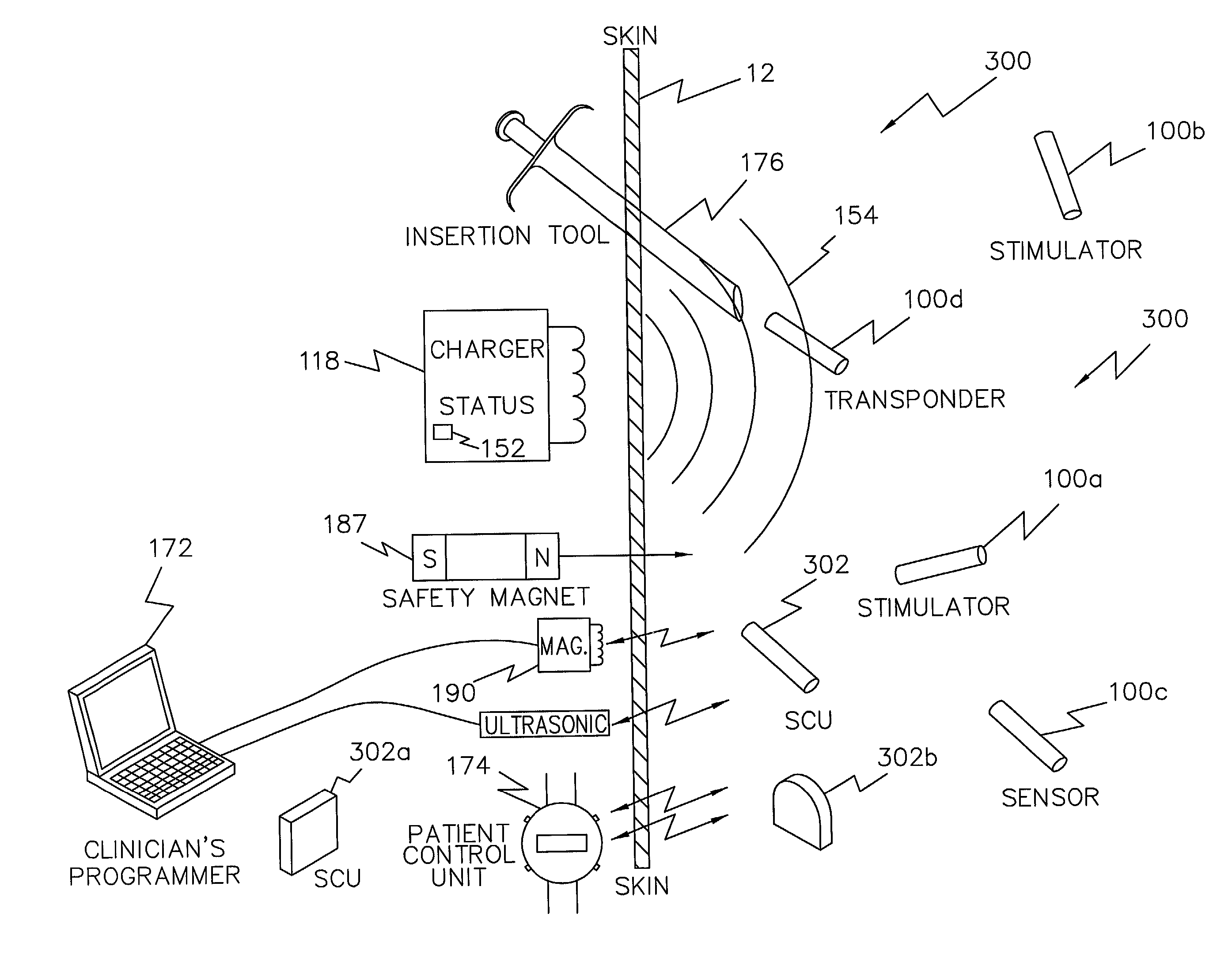
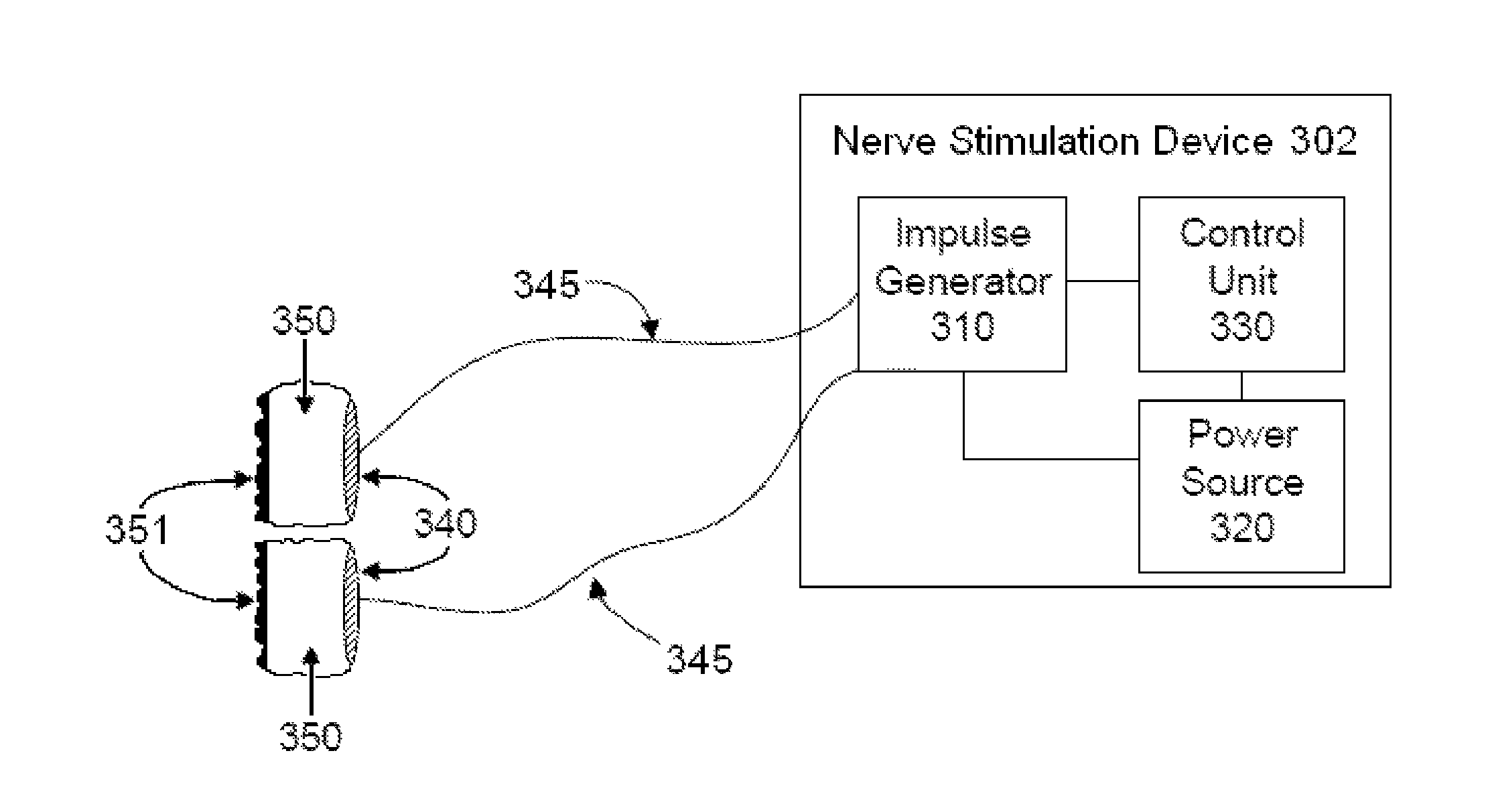
A programming system for controlling and / or altering an implantable device's operation using externally applied magnetic means, e.g., a permanent magnet or the like. Typically, such devices stimulate a neural pathway or muscle and / or block pain or muscle stimulation according to programmable settings, e.g., the amplitude, duration, frequency / repetition rates, etc., of stimulation pulses applied to the neural pathways / muscles. Preferably, once programmed from an external programmer, such implantable devices can operate “independently” using the externally provided programmed information. However, external programmers may be unavailable due to cost, size, or other constraints. Accordingly, embodiments of the present invention include a magnetic sensor, preferably a magnetoresistive, Hall effect, saturated core reactors, or the like, to sense an externally provided magnetic field. By externally applying magnetic fields in sequences of controlled polarities, durations, intensities, etc., and sensing these sequences and transitions, the operation of the implantable device may be altered, i.e., programmed.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Method and apparatus for controlling a neural stimulus
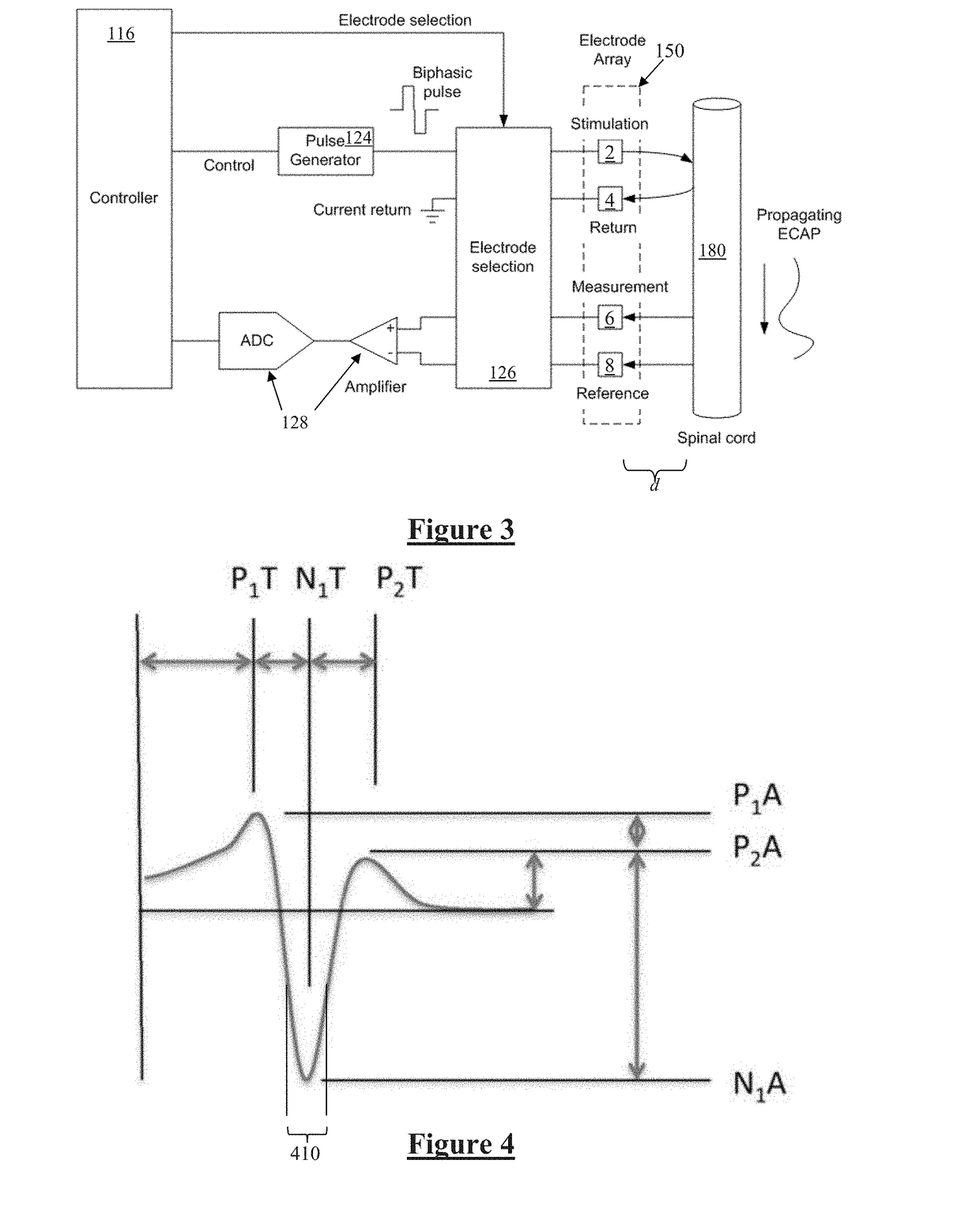
ActiveUS20140236257A1Avoid misalignmentControlled levelSpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineSpinal cord
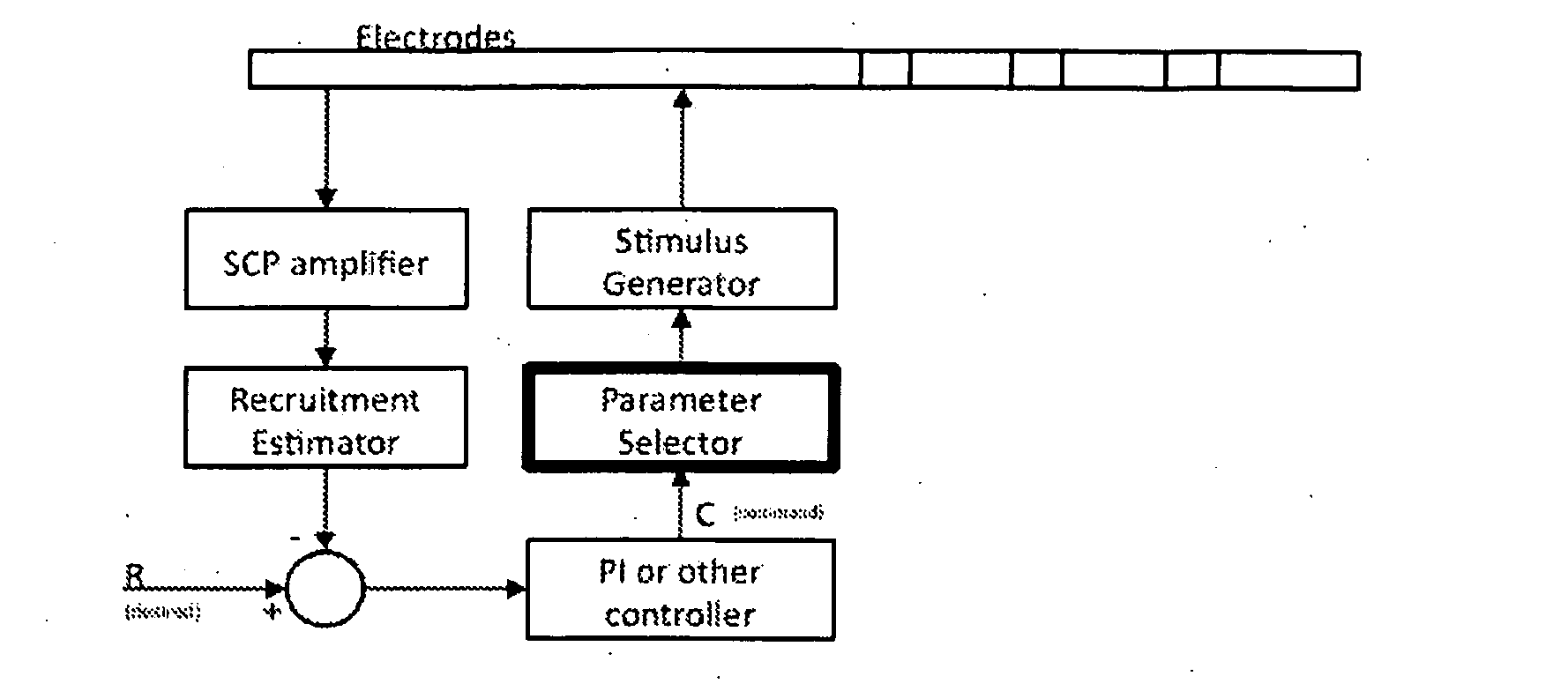
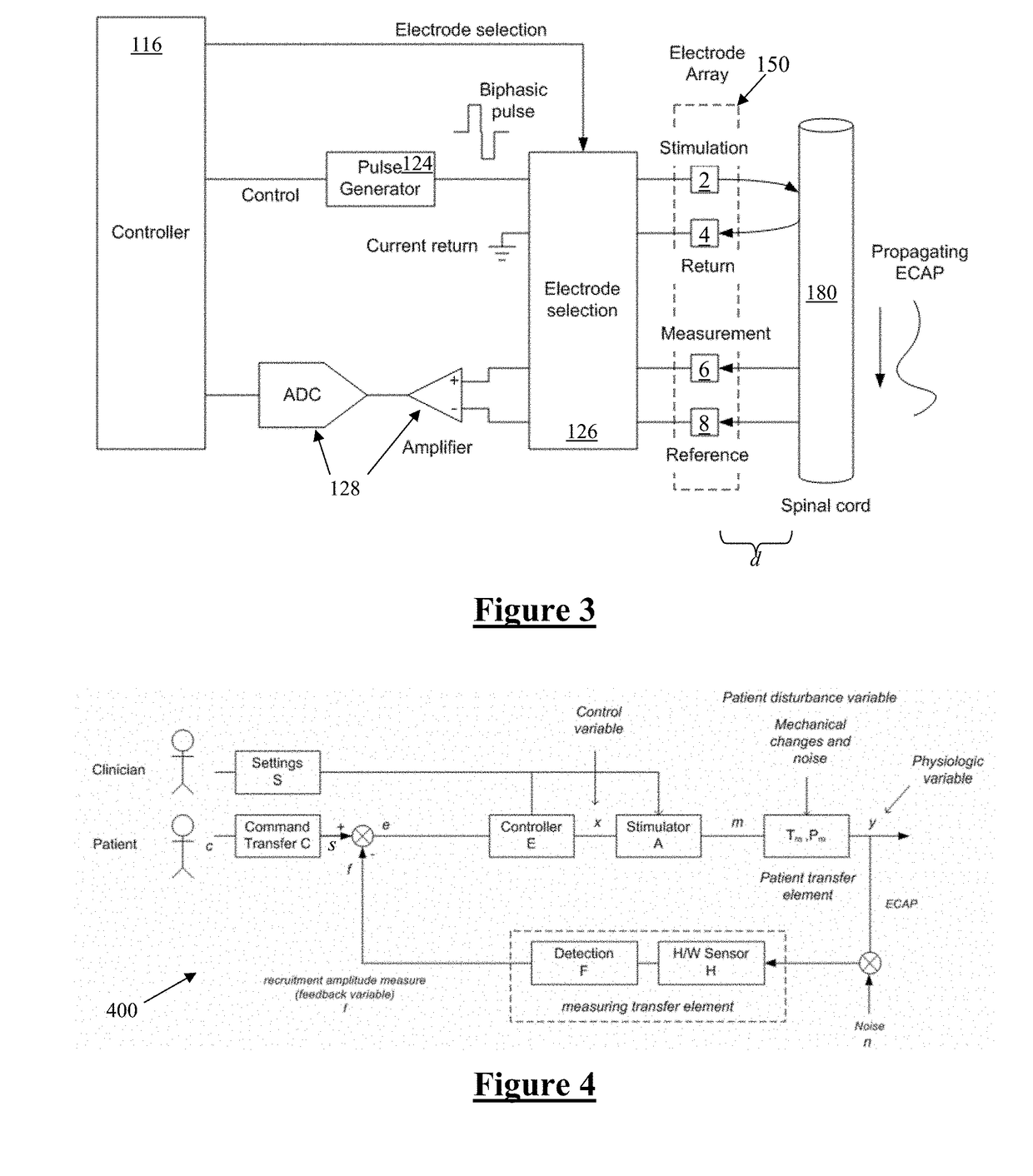
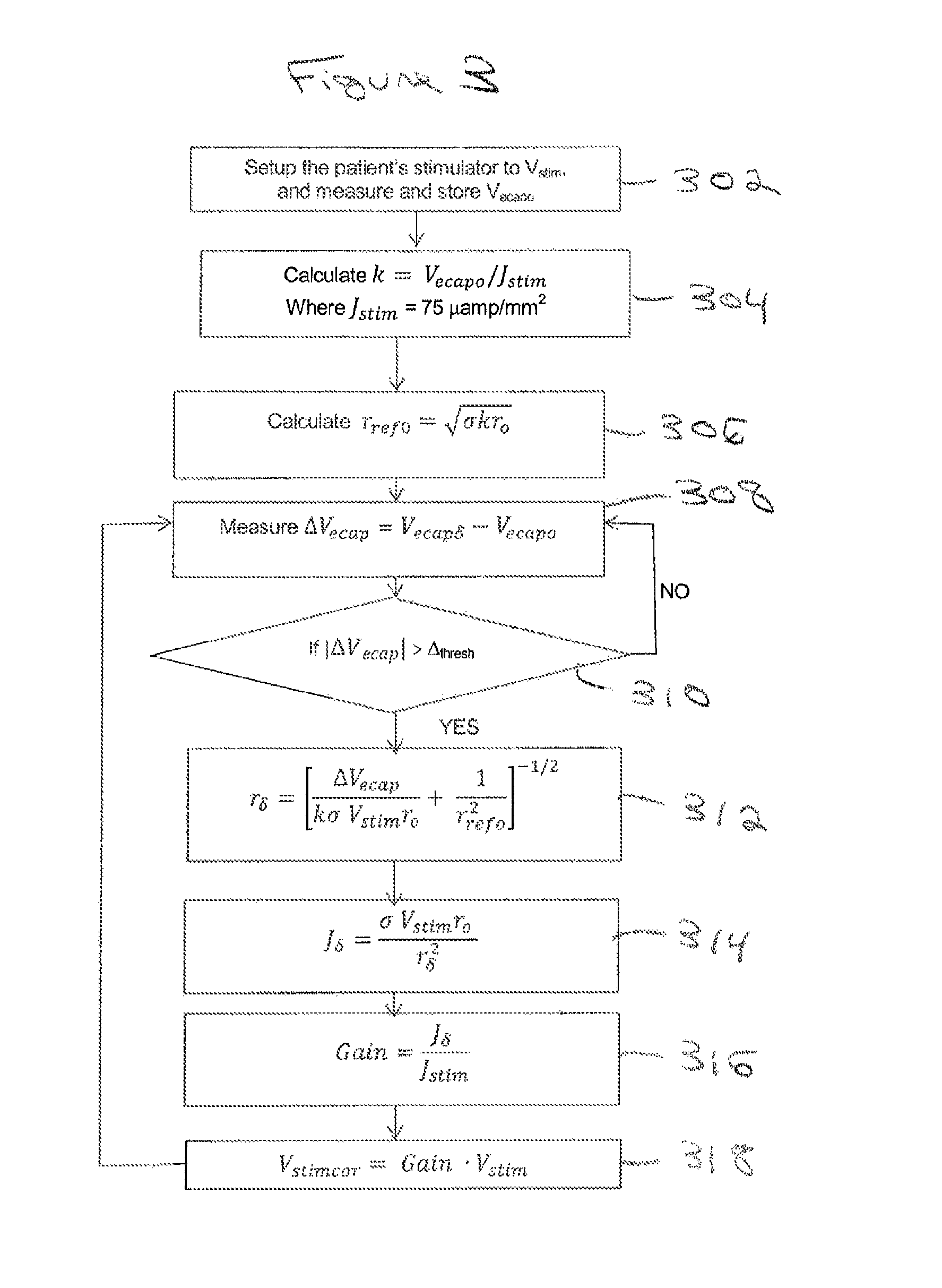
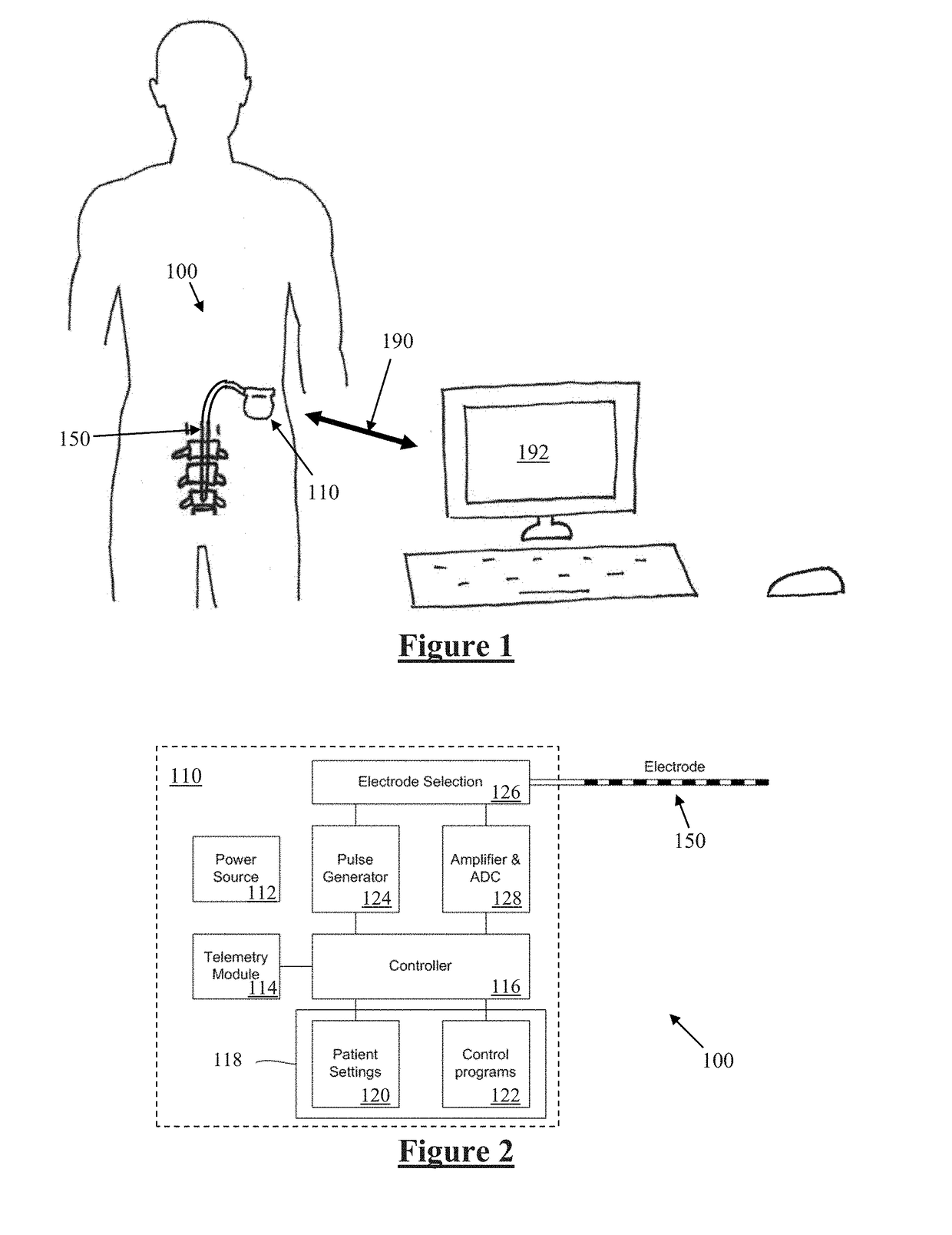
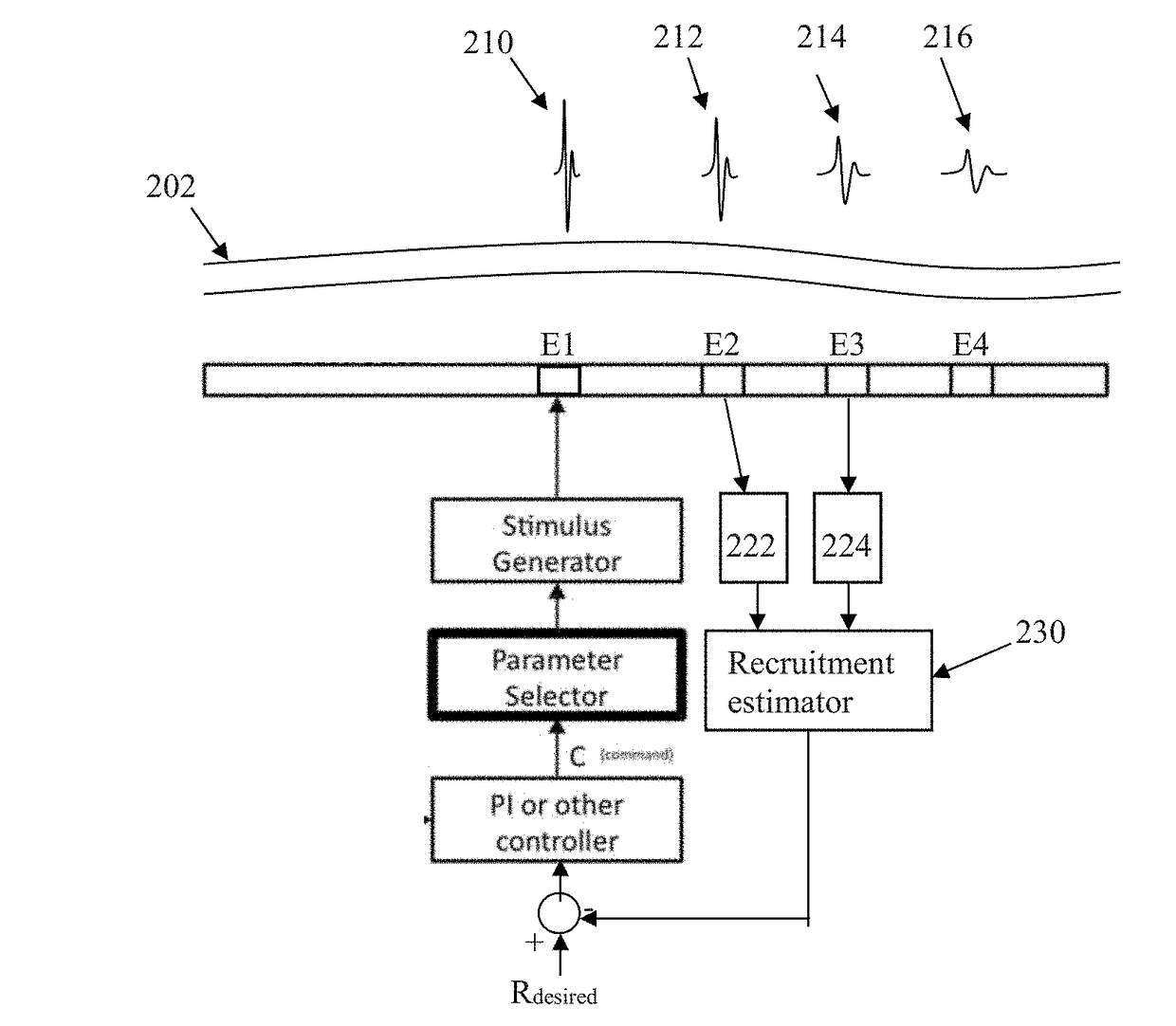
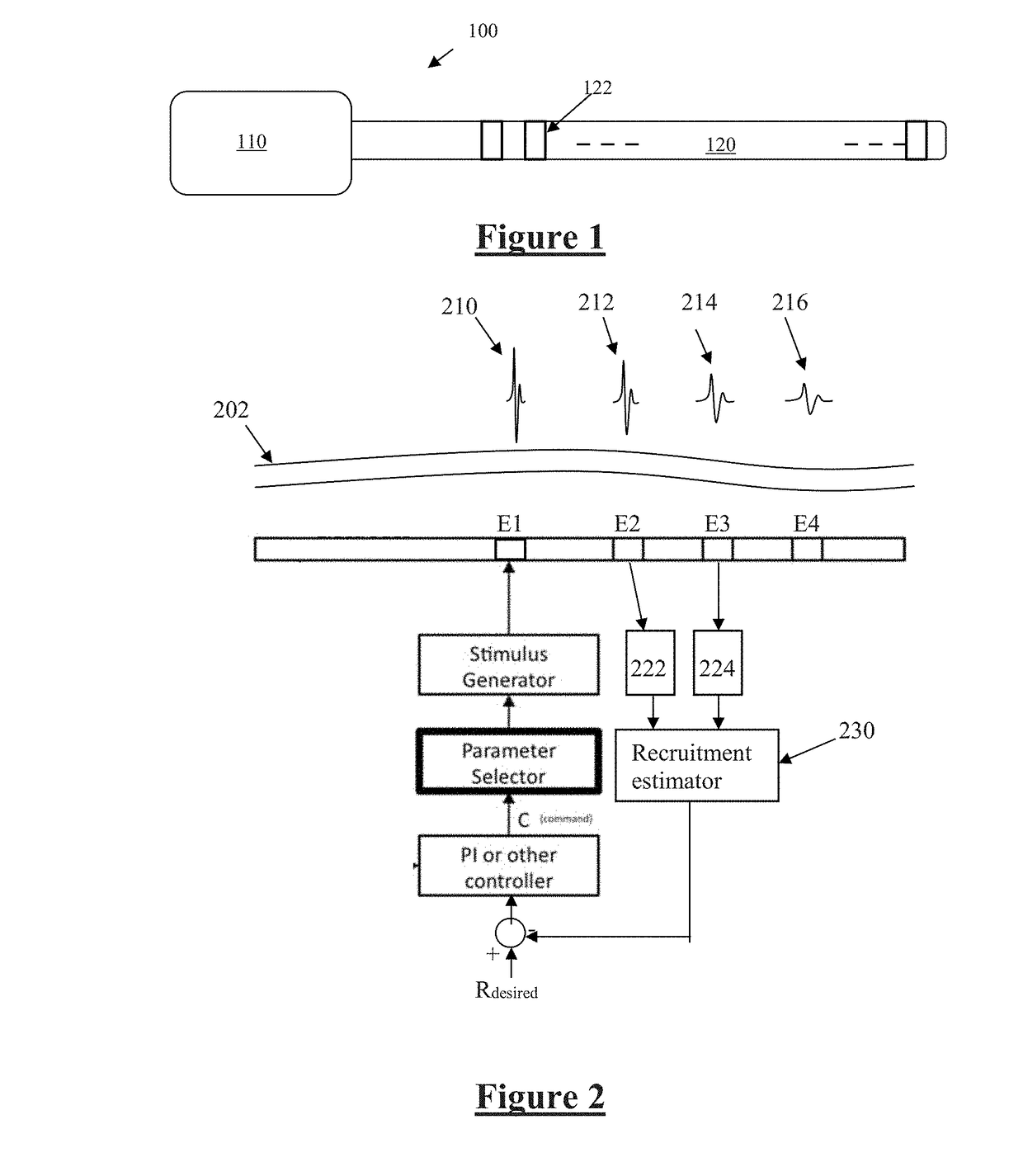
An implantable device applies and controls a neural stimulus. The device has a plurality of electrodes, and a stimulus source for providing a stimulus to be delivered from the electrodes to a neural pathway in order to evoke an action potential on the neural pathway, such as the spinal cord. A control unit controls application of a neural stimulus as defined by a set of parameter values and measures via measurement circuitry an evoked neural compound action potential response. The control unit determines from the measured evoked response a feedback variable, and compares it to a therapy map. The therapy map defines a therapeutic relationship of control variable to feedback variable. One or more of the stimulus parameter values are altered to effect the required change in the control variable. This process is performed iteratively to improve alignment of the feedback variable with the therapy map over time.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL
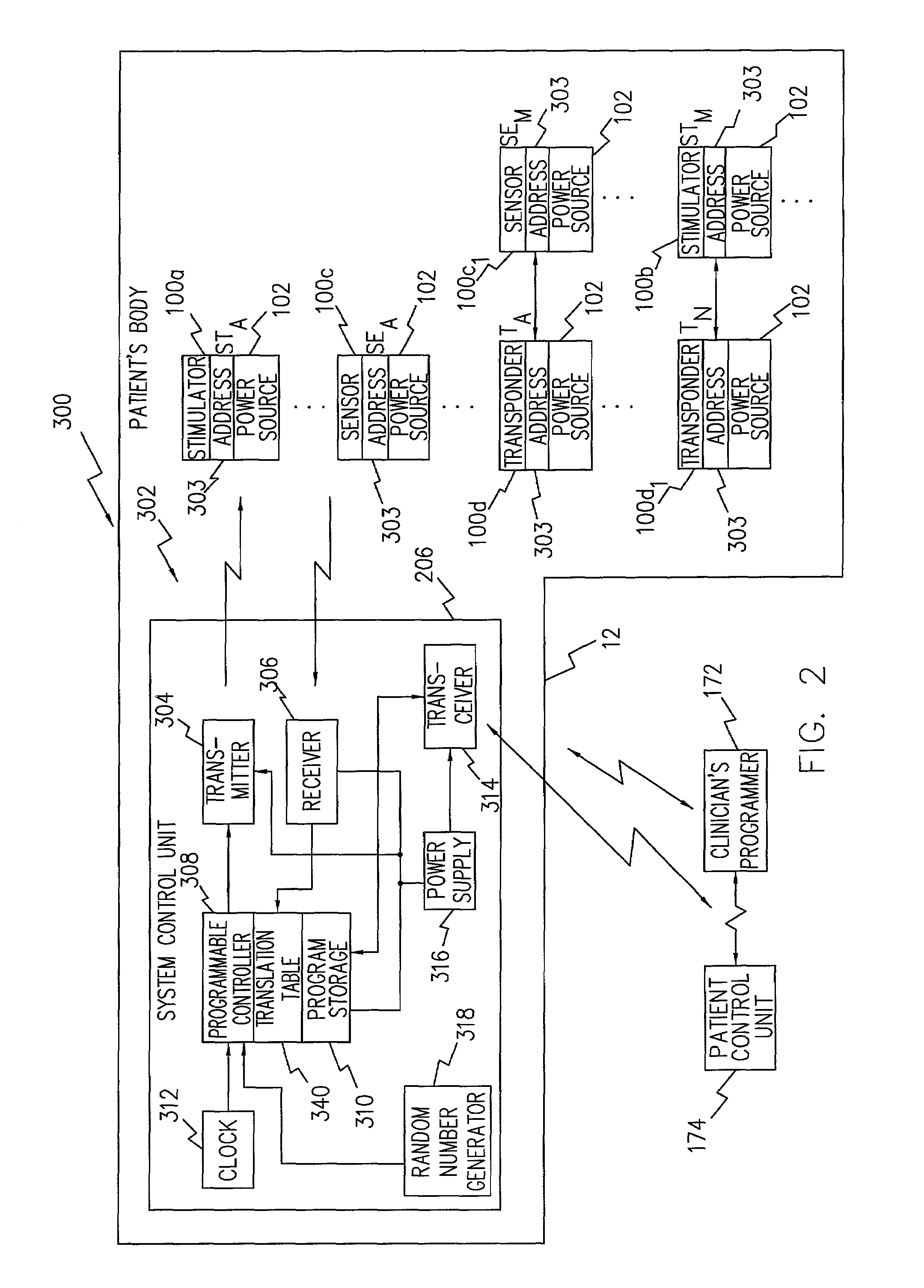
System and method suitable for treatment of a patient with a neurological deficit by sequentially stimulating neural pathways using a system of discrete implantable medical devices
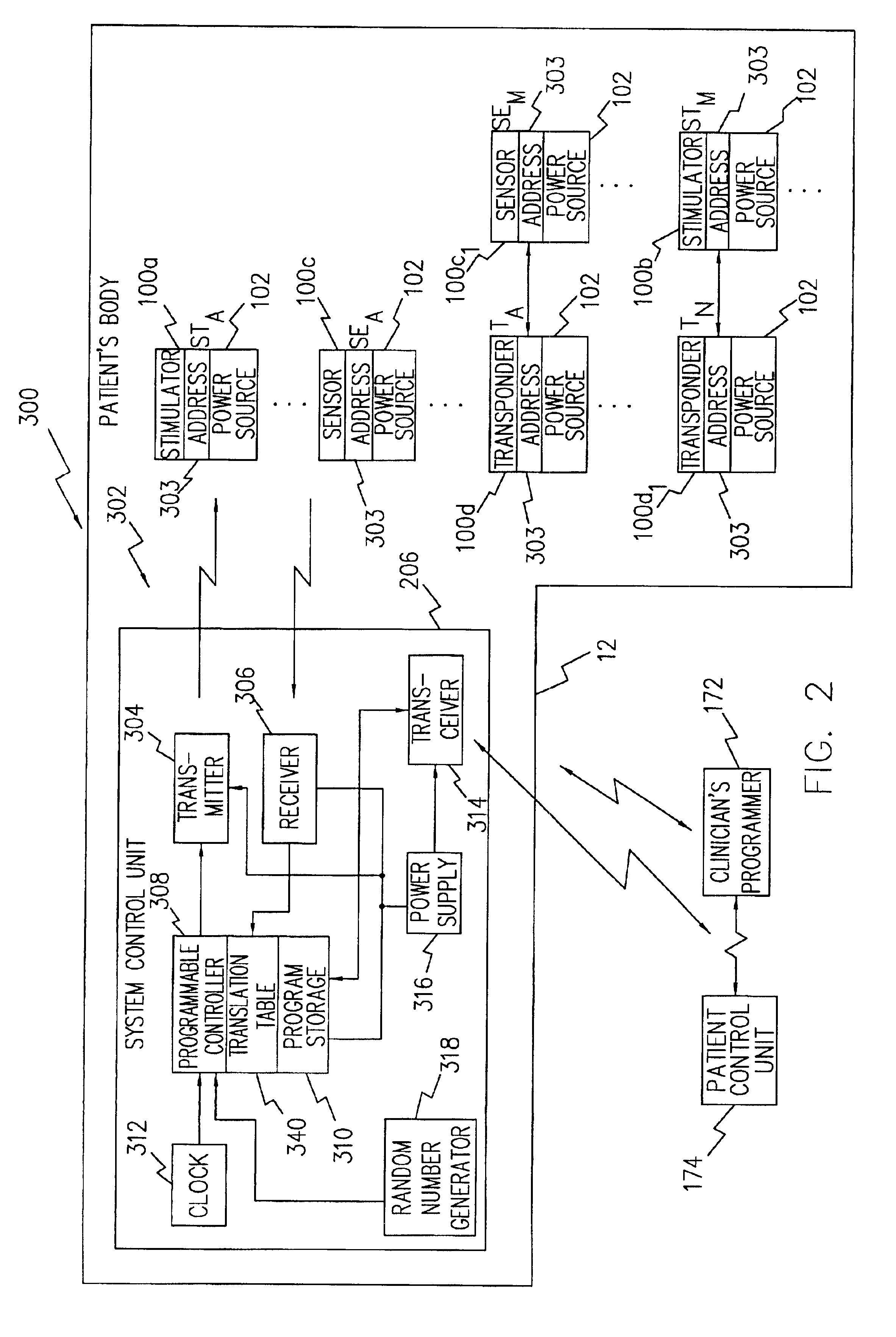
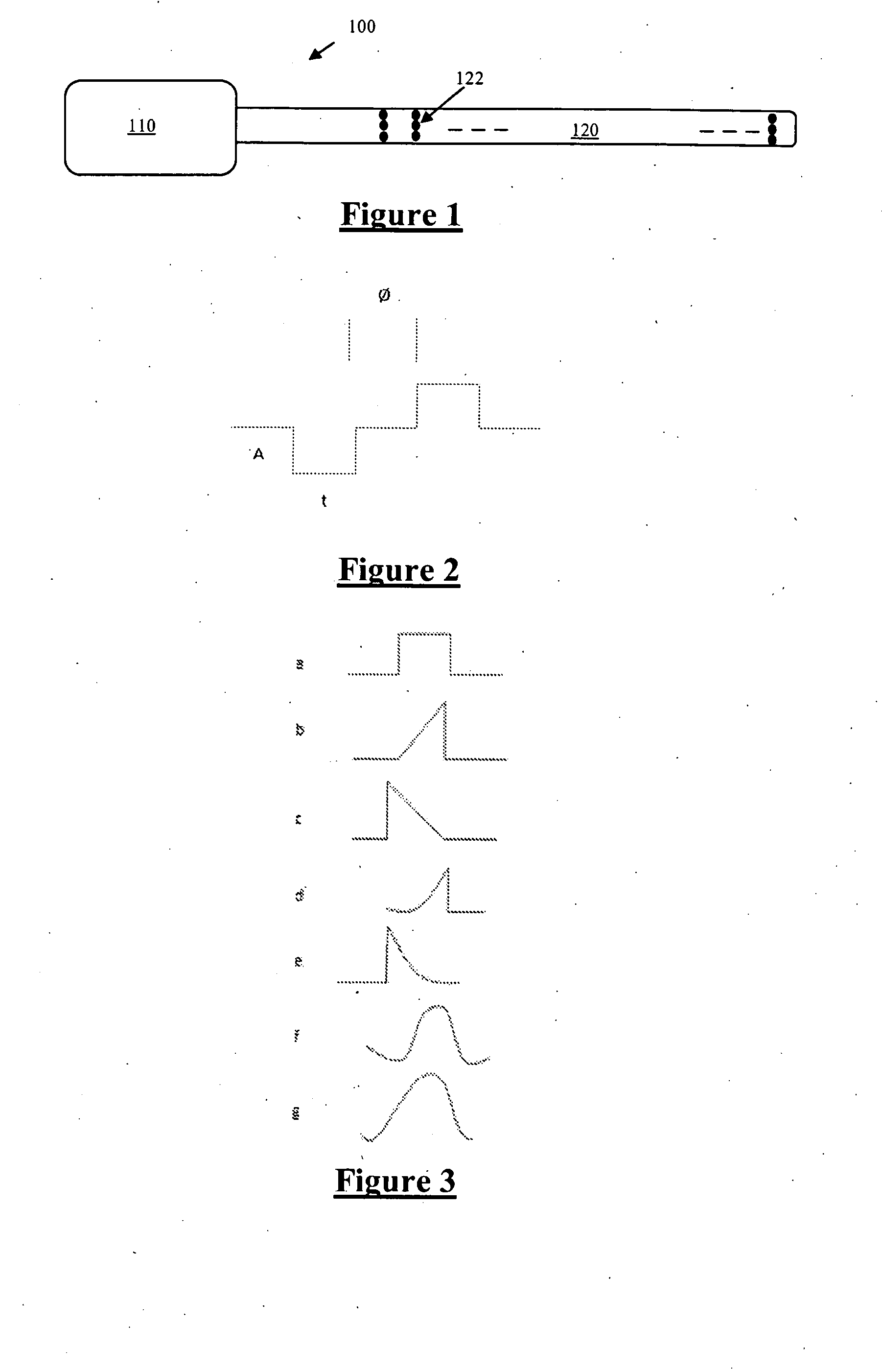
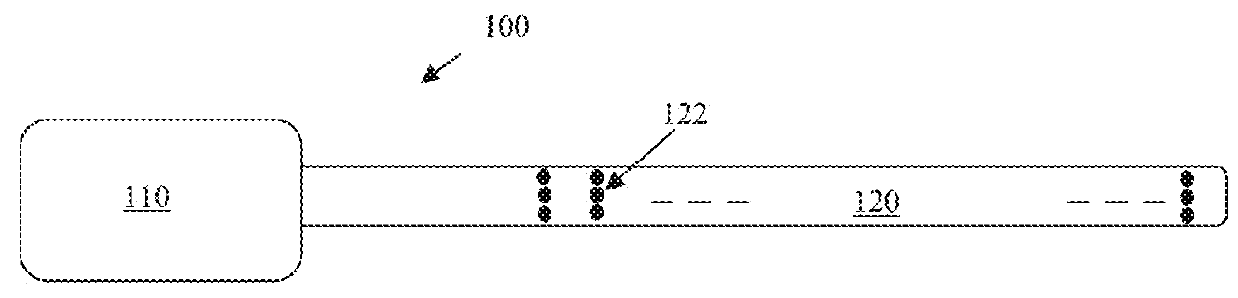
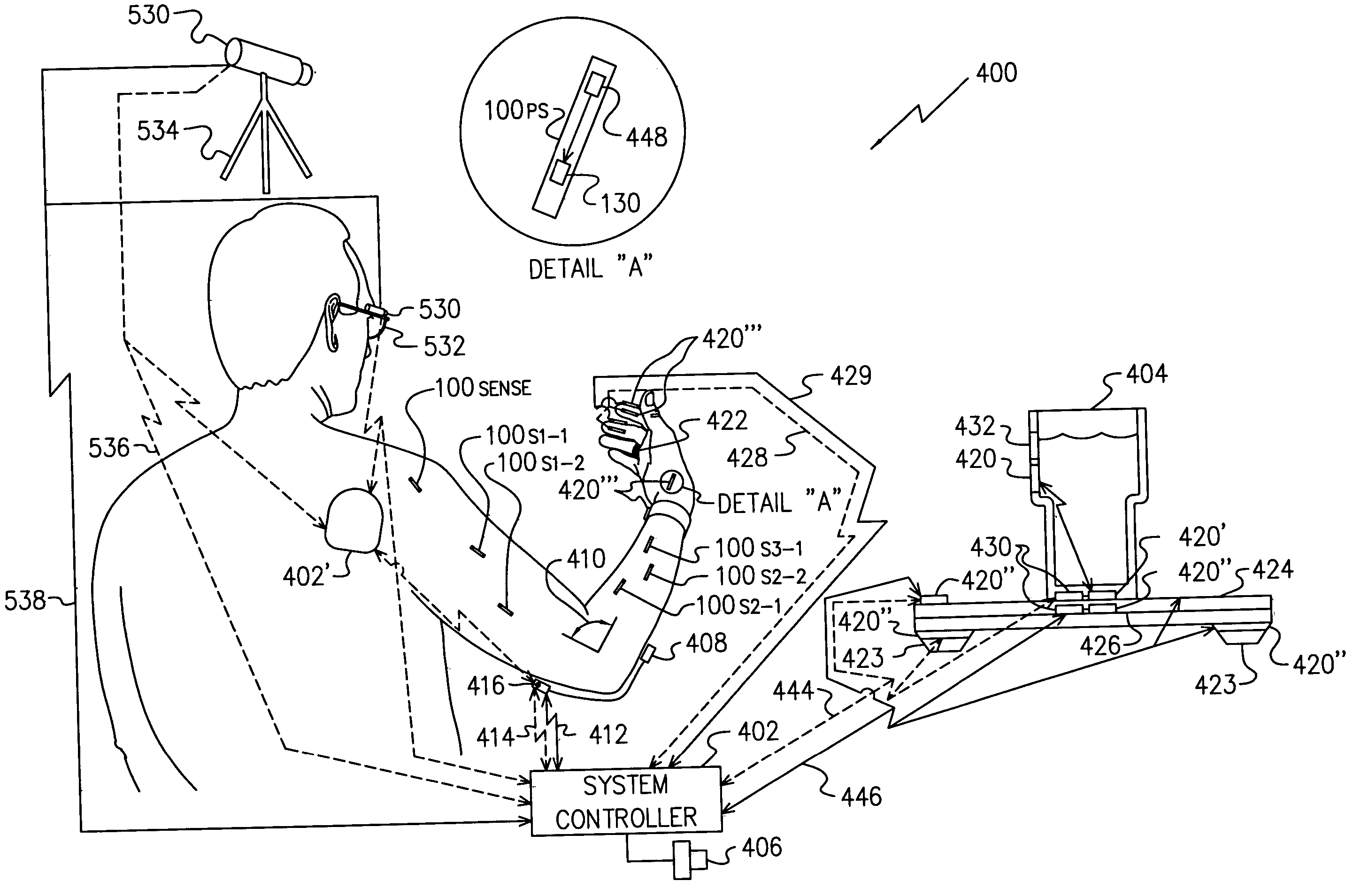
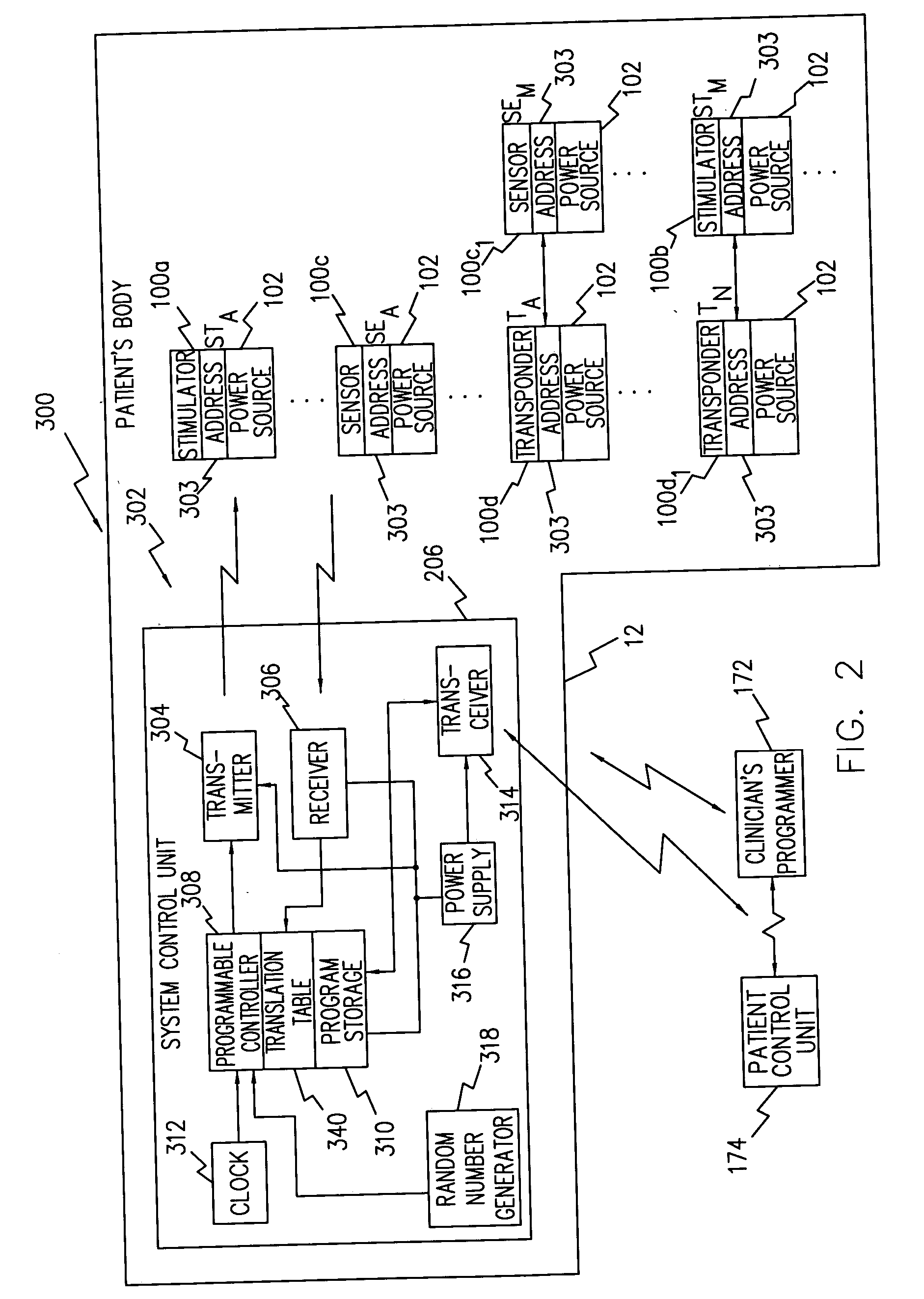
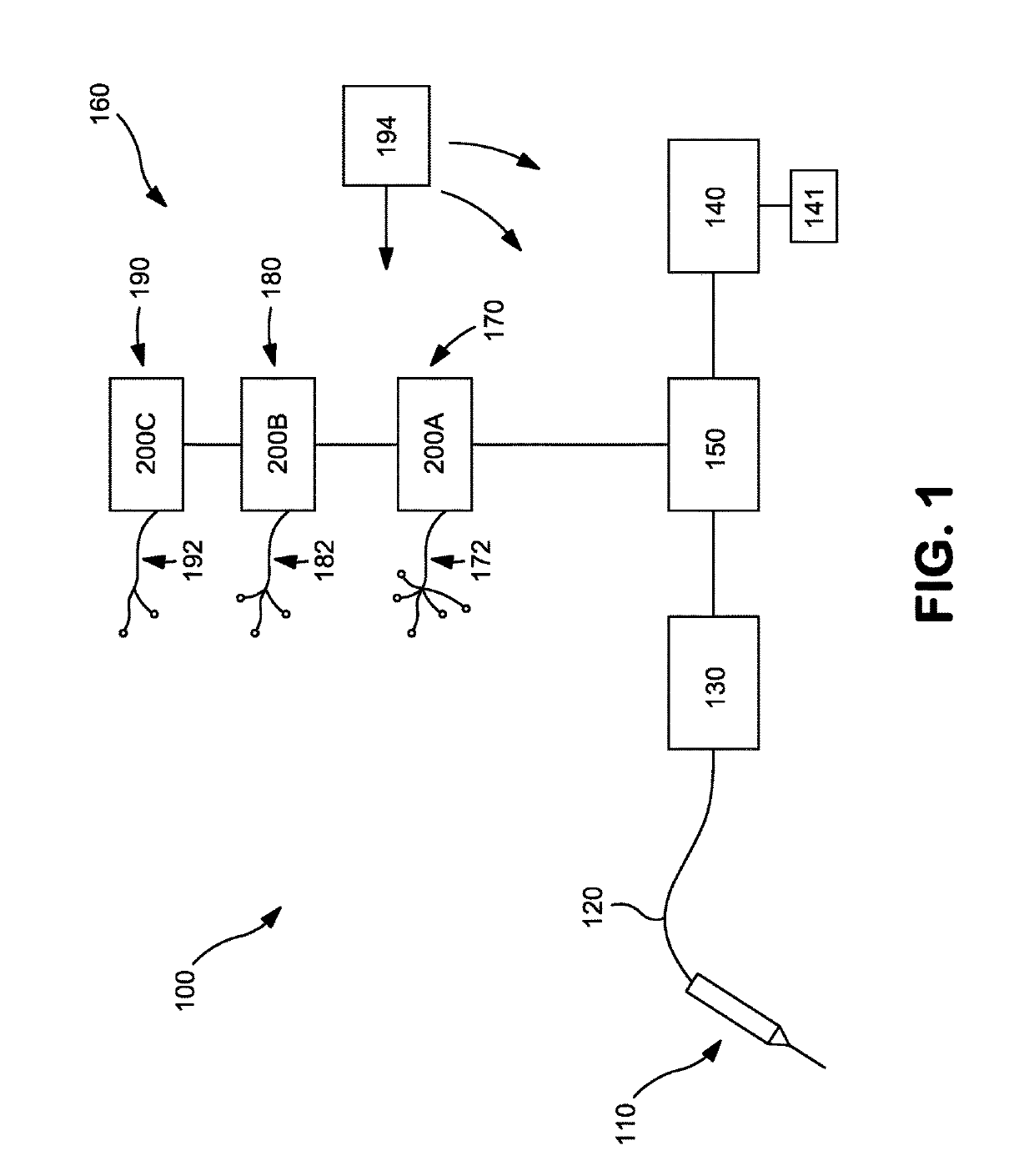
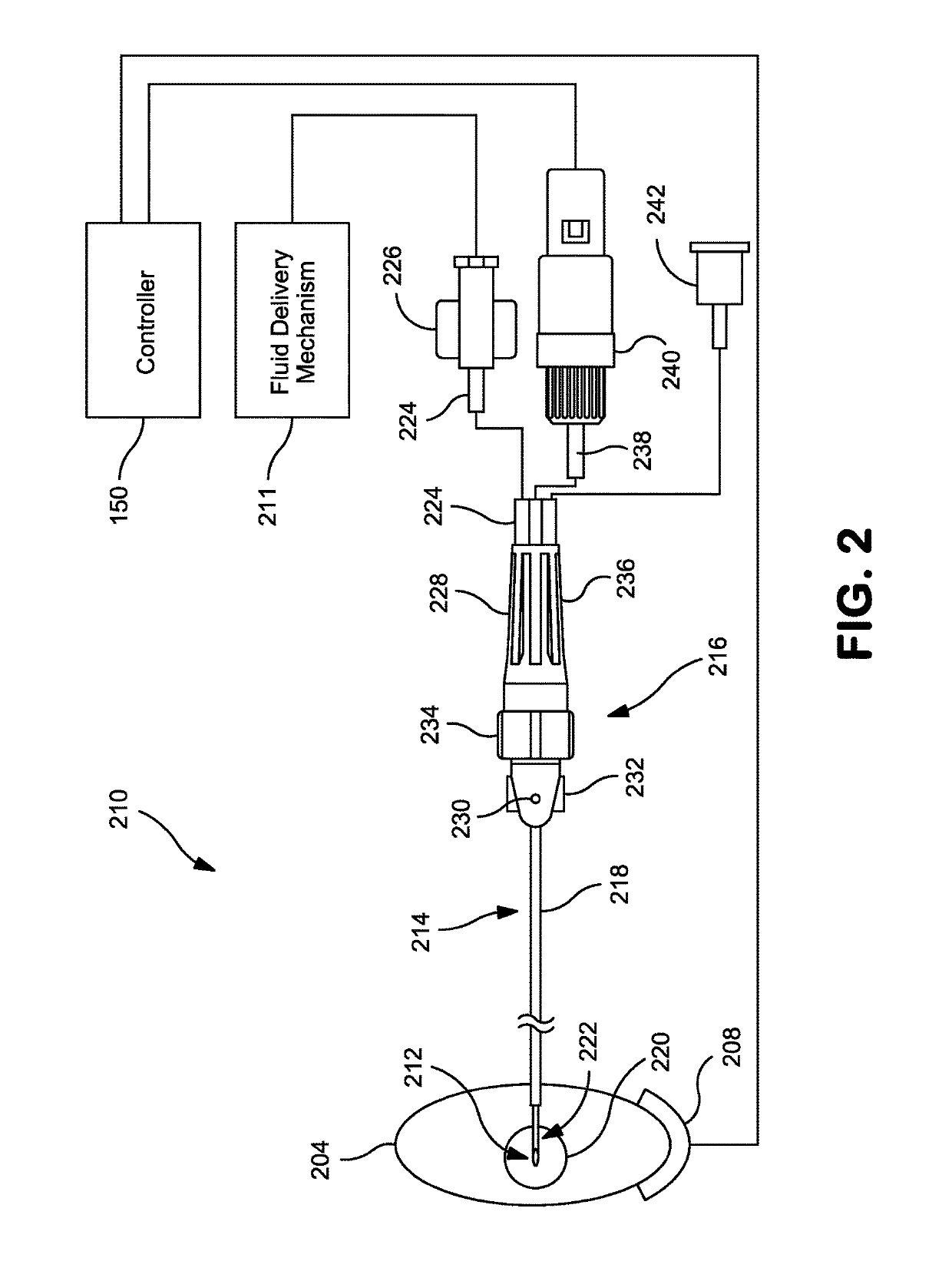
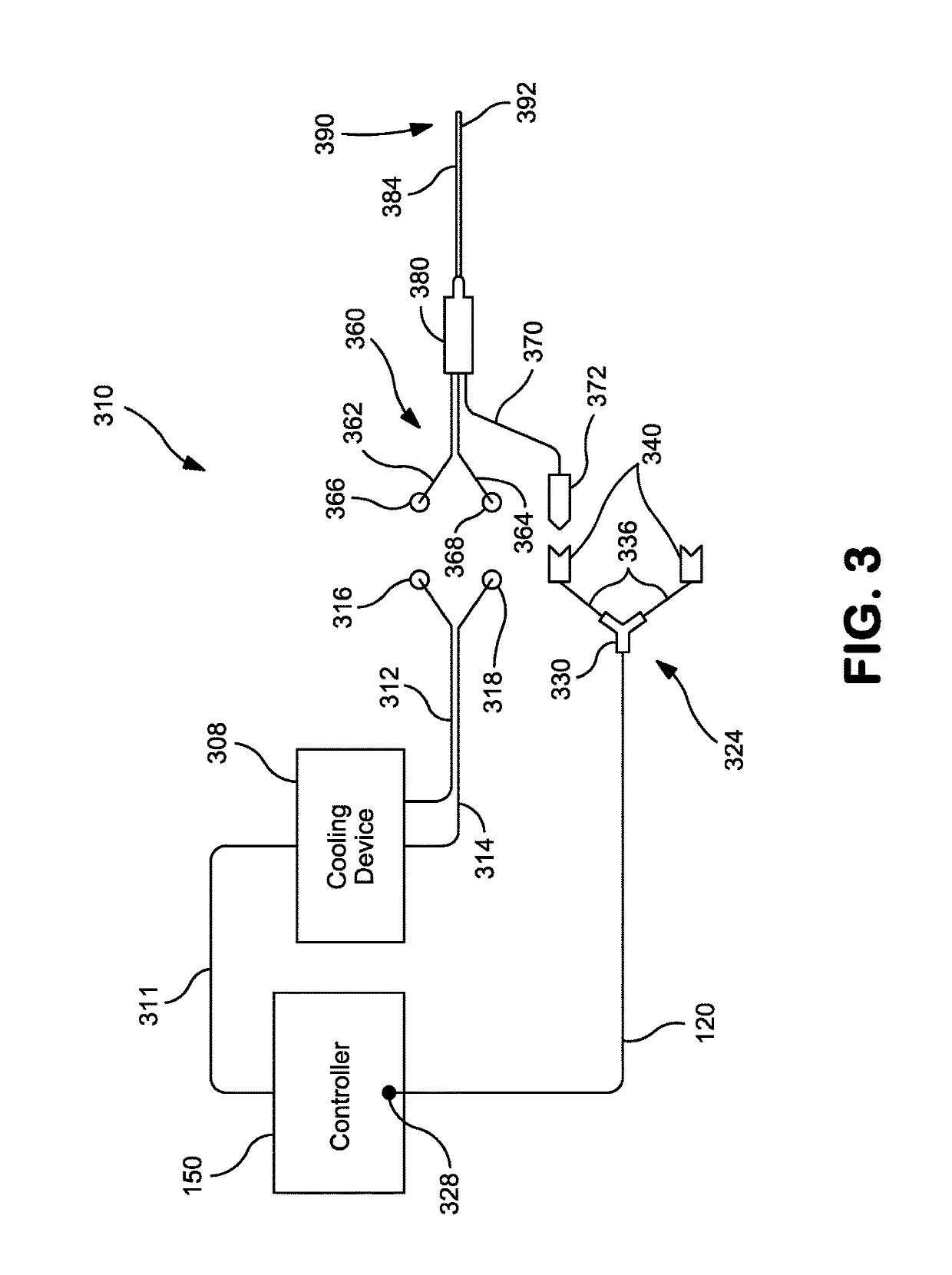
A system and method that facilitates stimulating neural pathways, e.g., muscles and / or associated nerves, of a patient's body for the purpose of therapeutic medical treatment by rehabilitating weakened muscles and using neuroplasticity to retrain sequential muscle movements and / or to provide the ability to directly deliver functional motor movements. Use of the present invention is of particular value for treating a patient following a stroke. More particularly, such systems are characterized by a plurality of discrete devices, preferably battery powered but may alternatively include RF-powered devices as well or in combination, configured for implanting within a patient's body via injection, each device being configured to affect a parameter, e.g., via nerve and / or muscle stimulation and / or to sense a body parameter, e.g., temperature, O2 content, physical position, electrical potential, etc., that operate under control of a system controller that coordinates the sequential stimulation via wireless commands to the implanted devices.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Method and apparatus for controlling a neural stimulus
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Charge-enhanced neural electric stimulation system
InactiveUS20130035745A1Stimulating effectiveness of communicationPromote effectivenessSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsElectricityElectrical polarity
A system and method to treat neural communication impairment is provided. The neural communication impairment is present in a neural pathway, which can be a cortico-neuromuscular pathway, an intra-brain neural pathway, or in a sensory-cortico pathway. A synchronized external stimulation is applied to a first point in proximity to a first neural component at one end of the neural pathway and to a second point in proximity to a second neural component at the other end of the neural pathway. Two induced neural handshake signals contemporaneously arrive at a neural communication impairment point in the neural pathway, triggering and stimulating a rehabilitation process by which the neural connection is permanently improved. The synchronized applied electrical signals applied to the first and second points may have an opposite polarity in dipolar neural stimulation, or may have identical polarity and waveform in in-phase neural stimulation.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
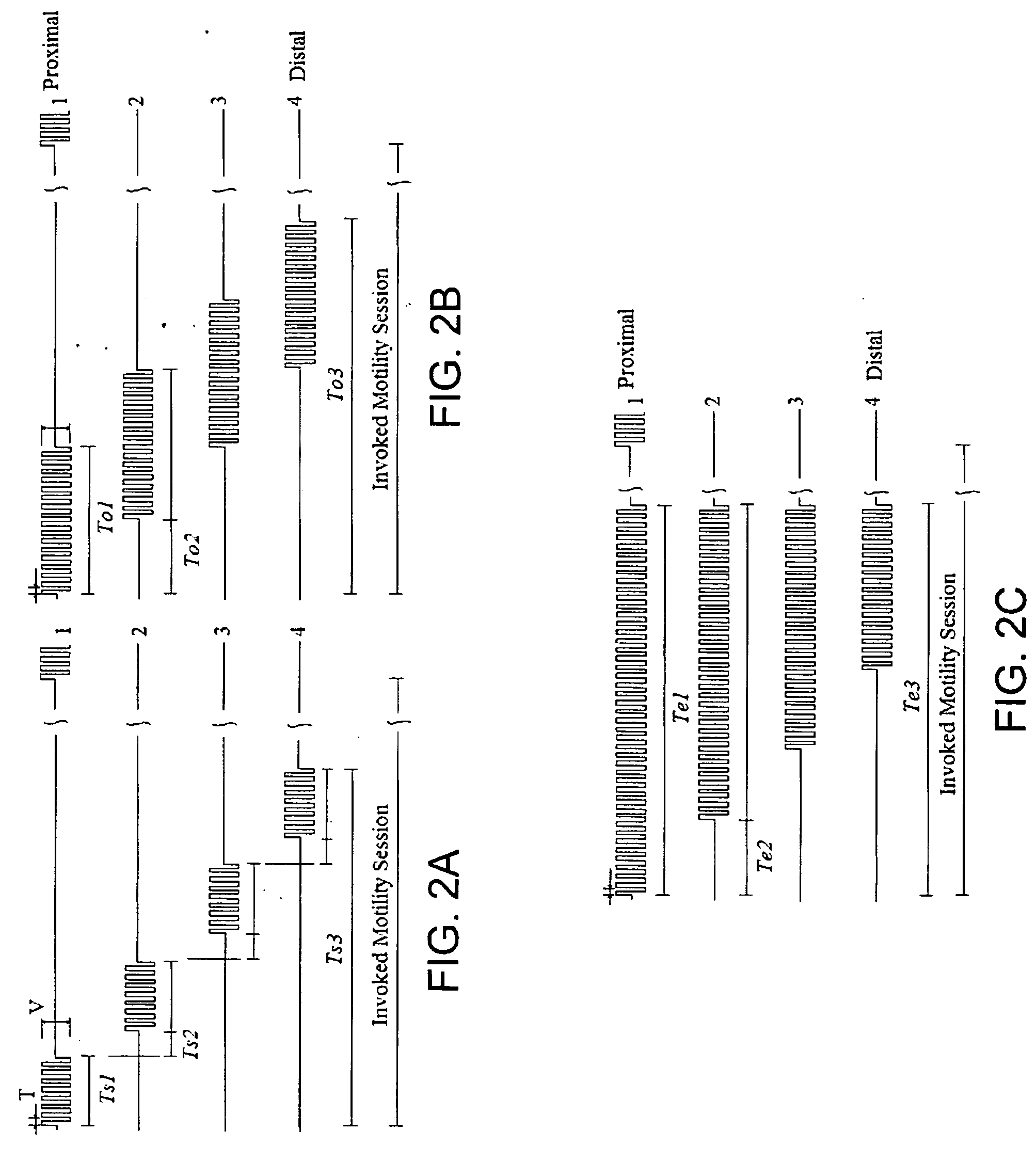
Gastrointestinal motility control
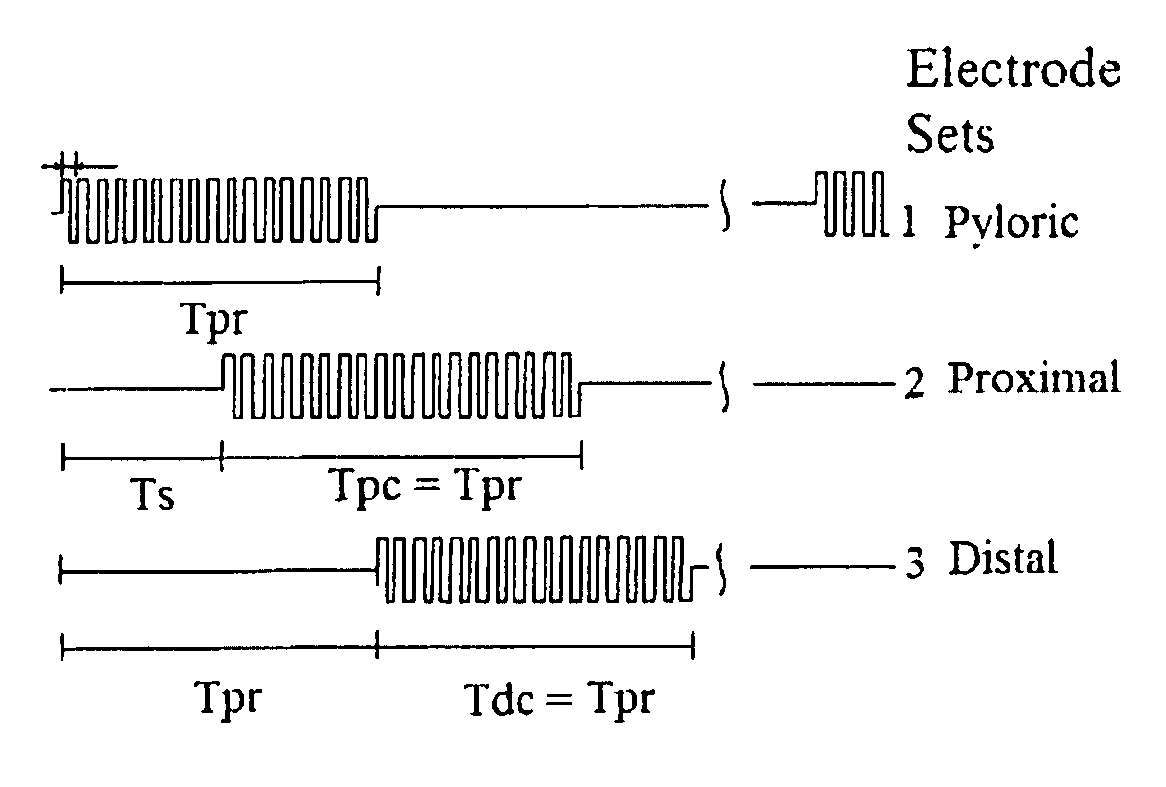
A method and a multichannel implantable device are described for partial or complete restoration of impaired gastrointestinal motility, or for disturbing and / or partially or completely blocking normal gastrointestinal motility using one or multiple microsystem-controlled channels of circumferentially arranged sets of two or more electrodes which provide externally-invoked synchronized electrical signals to the smooth muscles via the neural pathways.
Owner:UTI LLP
Method and system for non-linear feedback control of spinal cord stimulation
ActiveUS20150360031A1ElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialSpinal column
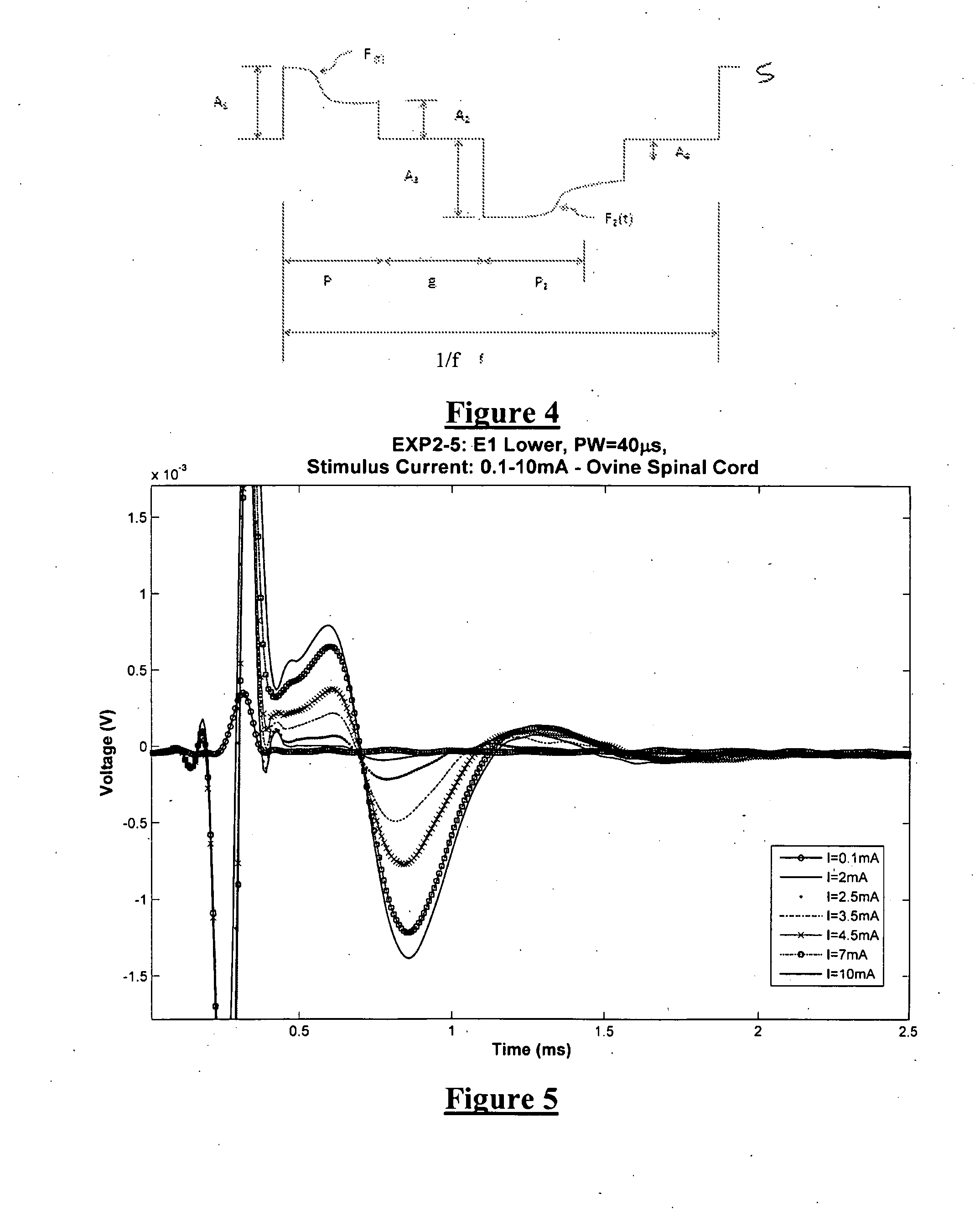
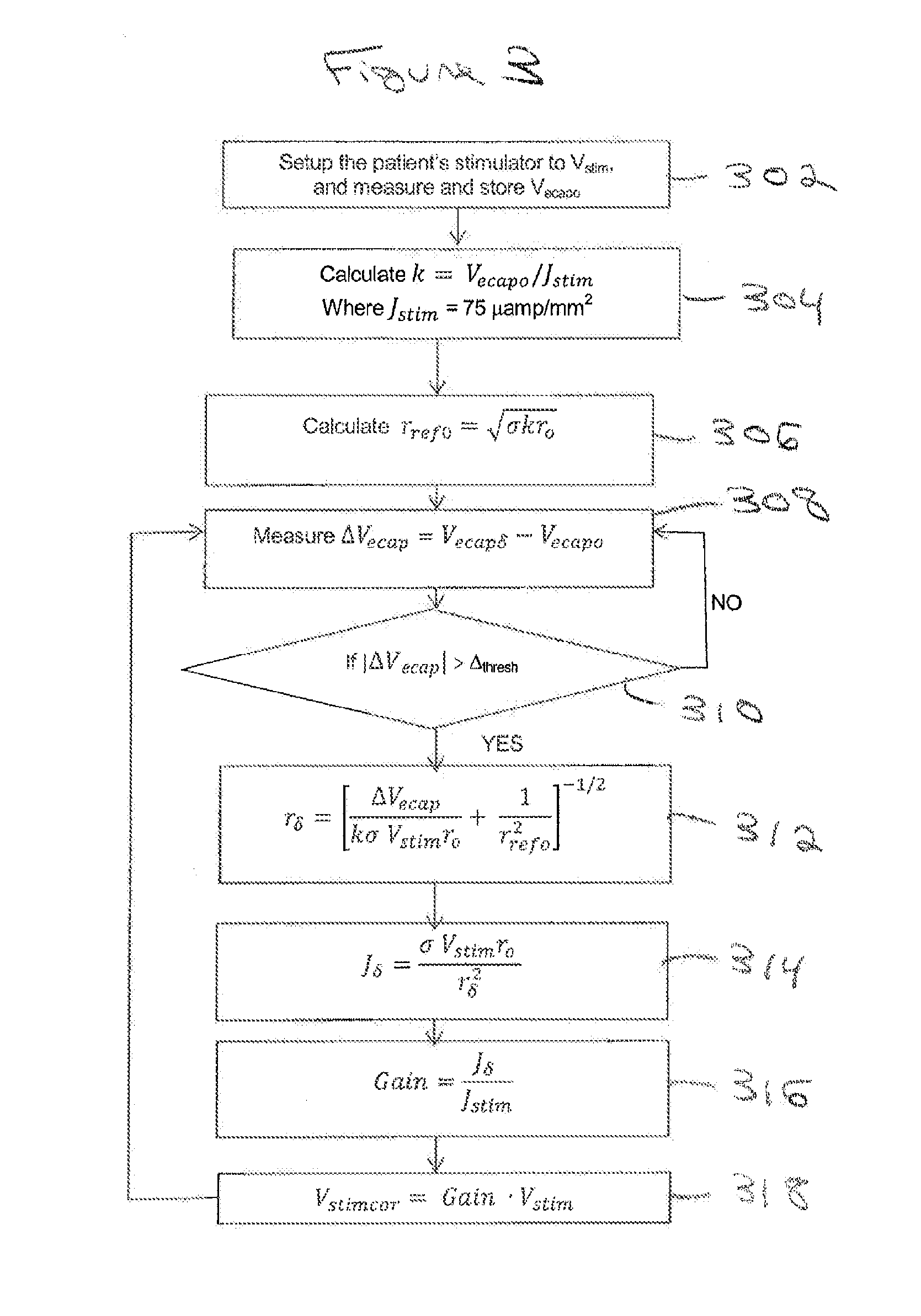
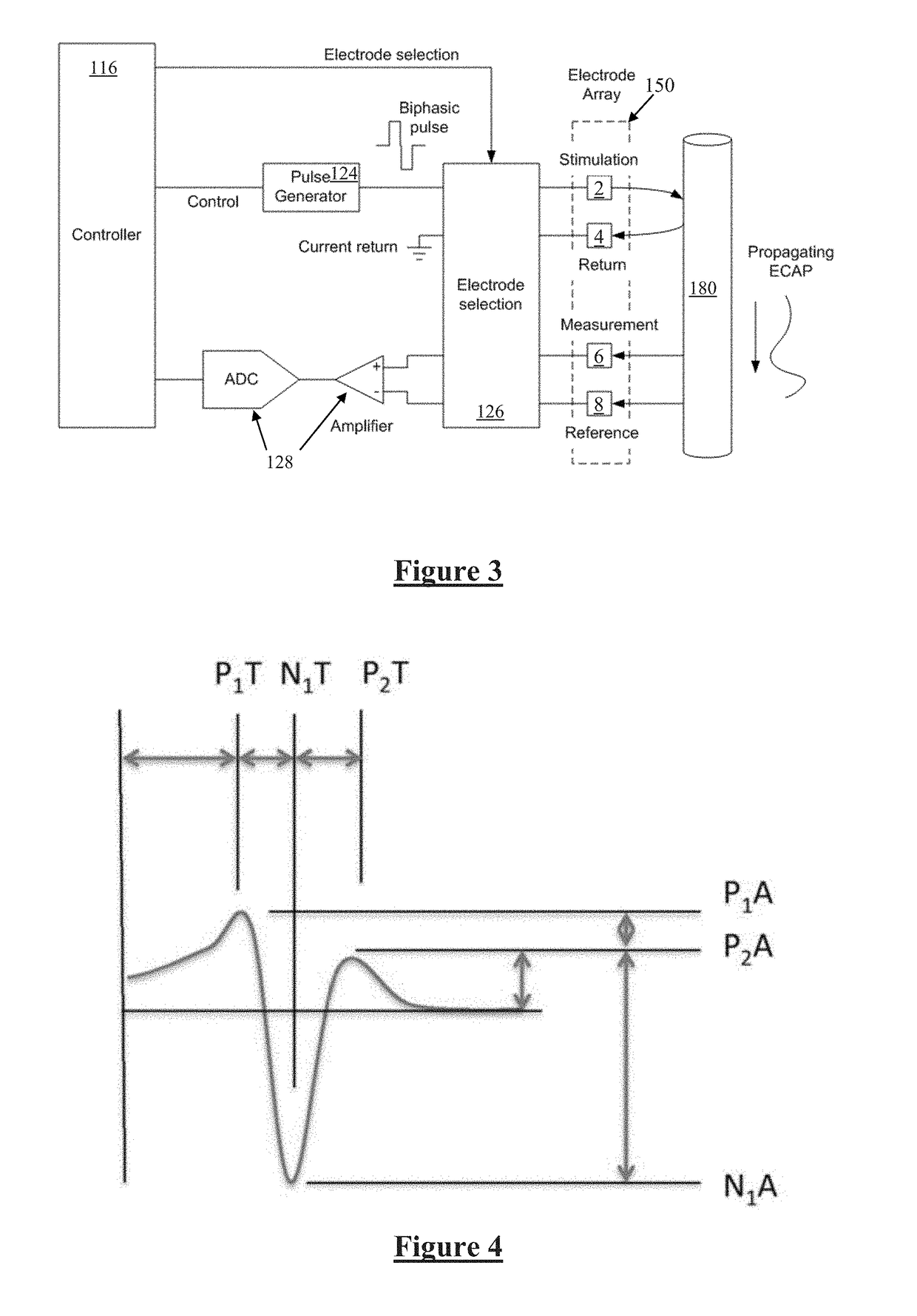
A system of non-linear feedback control for spinal cord stimulation is provided. The system comprises a lead adapted to be implanted within an epidural space of a dorsal column of a patients spine, and a pulse generator (PG) electrically coupled to the lead. The PG is configured to deliver spinal cord stimulation (SCS) therapy. The system also comprises a sensing circuitry configured to sense an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) response that propagates along the neural pathway. The system also comprises a processor programmed to operation, in response to instructions stored on a non-transient computer-readable medium, to obtain a baseline ECAP response when the lead and spinal cord tissue properties are in baseline states; analyze ECAP responses relative to the baseline ECAP response to obtain an ECAP feedback difference indicative of a change in at least one of the baseline state of the lead and the baseline state of the spinal cord tissue properties. The processor is also programmed to adjust an SCS therapy based on the ECAP feedback.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method suitable for treatment of a patient with a neurological deficit by sequentially stimulating neural pathways using a system of discrete implantable medical devices
A system and method that facilitates stimulating neural pathways, e.g., muscles and / or associated nerves, of a patient's body for the purpose of therapeutic medical treatment by rehabilitating weakened muscles and using neuroplasticity to retrain sequential muscle movements and / or to provide the ability to directly deliver functional motor movements. Use of the present invention is of particular value for treating a patient following a stroke. More particularly, such systems are characterized by a plurality of discrete devices, preferably battery powered but may alternatively include RF-powered devices as well or in combination, configured for implanting within a patient's body via injection, each device being configured to affect a parameter, e.g., via nerve and / or muscle stimulation and / or to sense a body parameter, e.g., temperature, O2 content, physical position, electrical potential, etc., that operate under control of a system controller that coordinates the sequential stimulation via wireless commands to the implanted devices.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
Method and system for identification of source of chronic pain and treatment
A method for identifying and treating a neural pathway associated with chronic pain via nerve stimulation and brain wave monitoring of a mammalian brain includes positioning a probe to stimulate a target nerve, wherein the target nerve is suspected of being a source of chronic pain; delivering a first nerve stimulation from the probe to the target nerve, wherein the first nerve stimulation is sufficient to elicit a chronic pain response in the brain; and monitoring for evoked potential activity in the brain as a result of the first nerve stimulation. The method can also include delivering second and third nerve stimulations to confirm the correct identification of the neural pathway and to treat the chronic pain, respectively. A system and apparatus for performing a procedure to identify and treat a nerve that is the source of chronic pain are also described.
Owner:AVENT INC
Pulsed magnetic control system for interlocking functions of battery powered living tissue stimulators
A magnetic control system for selectively enabling / disabling an implantable device's operation using externally applied pulsed magnetic means, e.g., a controlled electromagnet or the like. Typically, such implantable devices stimulate a neural pathway or muscle and / or block pain or muscle stimulation according to programmable settings. Preferably, once programmed from an external programmer, such implantable devices can operate “independently” using the externally provided programmed information. However, in certain circumstances, it may be desired to stop / pause the operation of such selected implanted device while not affecting other such devices. Accordingly, embodiments of the present invention include a magnetic sensor, preferably a magnetoresistive, Hall effect, saturated core reactors, or the like, to sense an externally provided magnetic field. By externally applying pulsed magnetic fields in sequences of controlled polarities, durations, intensities, etc., and sensing these identifiable sequences and transitions, the operation of the implantable device may be enabled / disabled.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
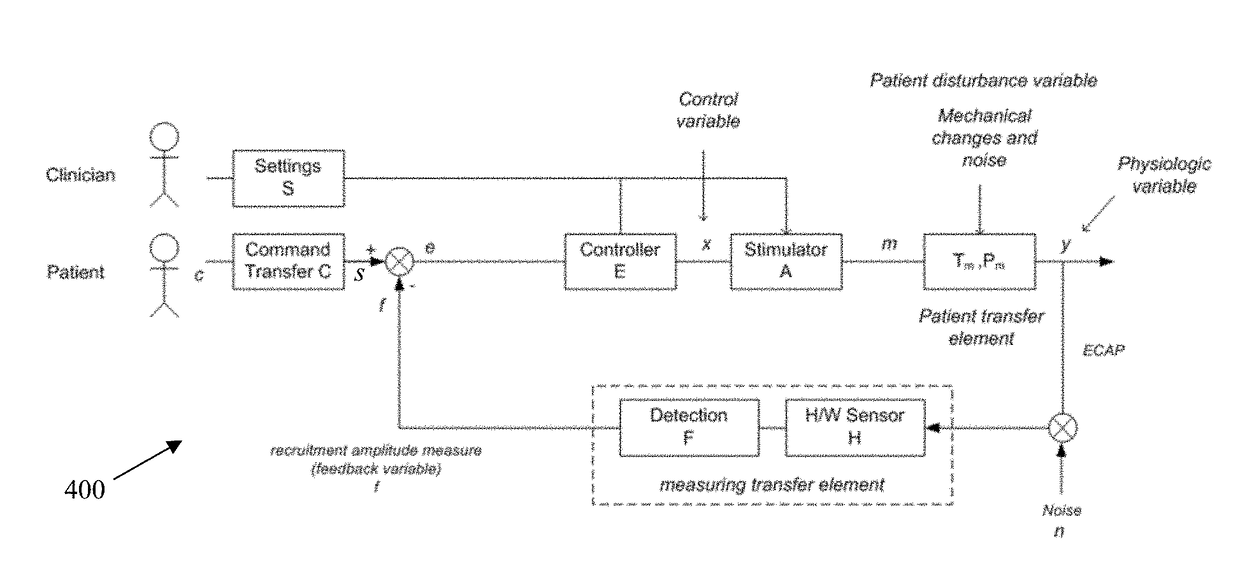
Method and Device for Feedback Control of Neural Stimulation
ActiveUS20170361101A1Eliminate the effects ofSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesEngineeringBrain pathway
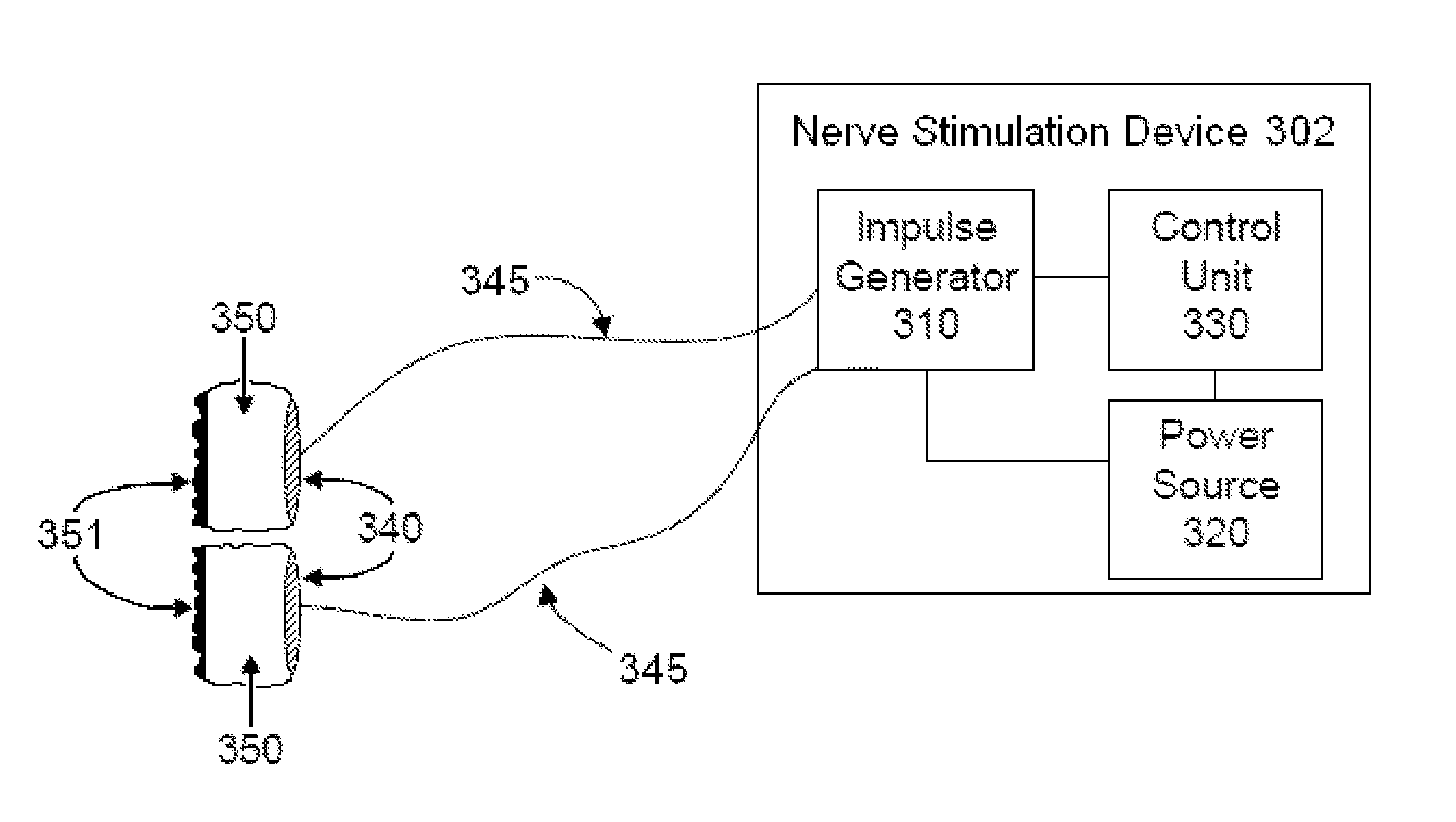
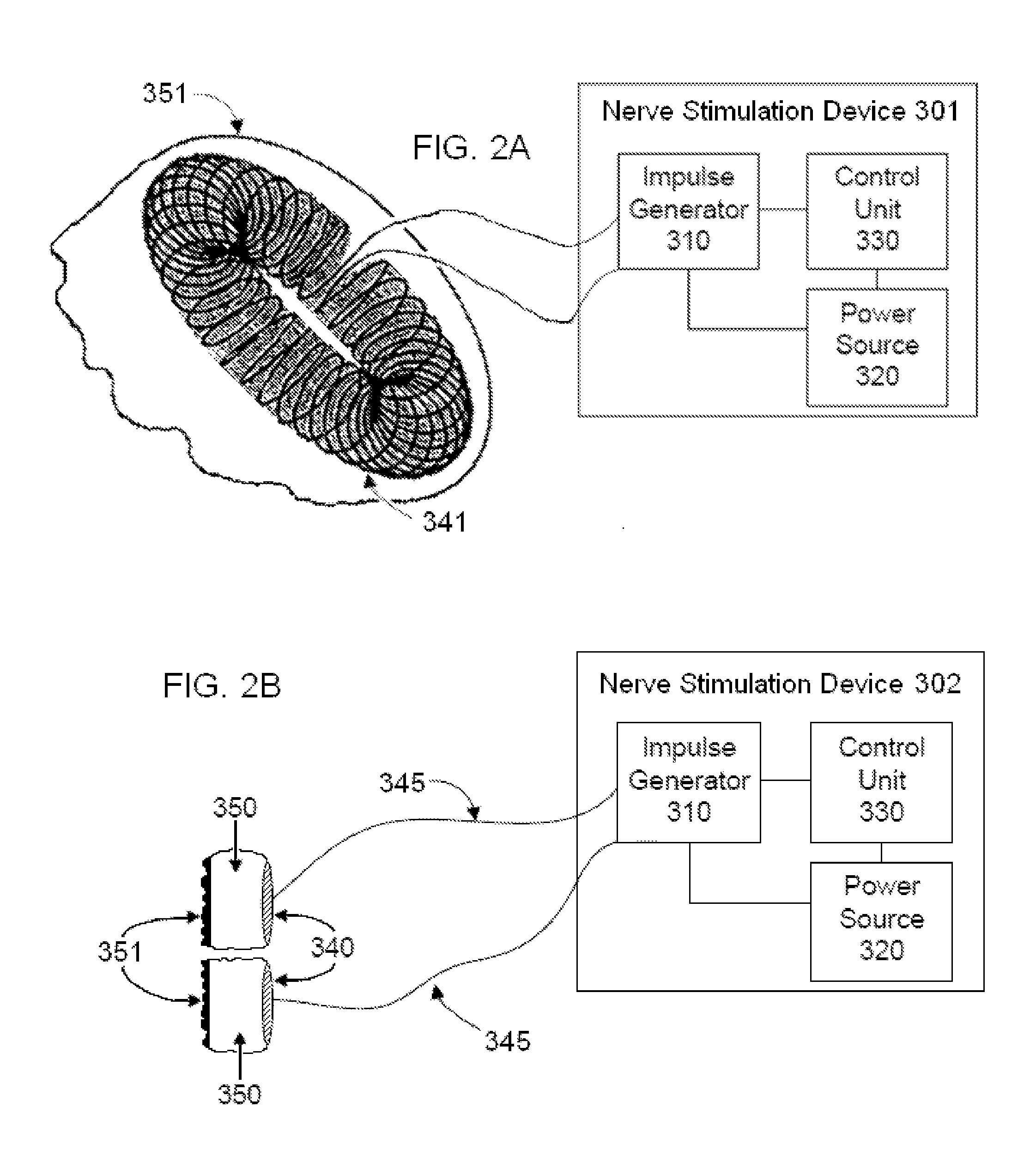
A method of controlling a neural stimulus by use of feedback. The neural stimulus is applied to a neural pathway in order to give rise to an evoked action potential on the neural pathway. The stimulus is defined by at least one stimulus parameter. A neural compound action potential response evoked by the stimulus is measured. From the measured evoked response a feedback variable is derived. A feedback loop is completed by using the feedback variable to control the at least one stimulus parameter value. The feedback loop adaptively compensates for changes in a gain of the feedback loop caused by electrode movement relative to the neural pathway.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Method and system for non-linear feedback control of spinal cord stimulation
A system of non-linear feedback control for spinal cord stimulation is provided. The system comprises a lead adapted to be implanted within an epidural space of a dorsal column of a patients spine, and a pulse generator (PG) electrically coupled to the lead. The PG is configured to deliver spinal cord stimulation (SCS) therapy. The system also comprises a sensing circuitry configured to sense an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) response that propagates along the neural pathway. The system also comprises a processor programmed to operation, in response to instructions stored on a non-transient computer-readable medium, to obtain a baseline ECAP response when the lead and spinal cord tissue properties are in baseline states; analyze ECAP responses relative to the baseline ECAP response to obtain an ECAP feedback difference indicative of a change in at least one of the baseline state of the lead and the baseline state of the spinal cord tissue properties. The processor is also programmed to adjust an SCS therapy based on the ECAP feedback.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and apparatus for measurement of neural response
ActiveUS20140194772A1Improve signal qualityIncreased signal noiseSpinal electrodesSensorsBrain pathwayNeural tract
A device for measuring a neural response evoked by a stimulus. First and second sense electrodes are positioned at distinct locations along a neural pathway. A neural stimulus is applied and first and second recordings of a neural response evoked by the stimulus are obtained from the respective sense electrodes. The first recording and the second recording are compared to determine propagation properties of the evoked neural response.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL
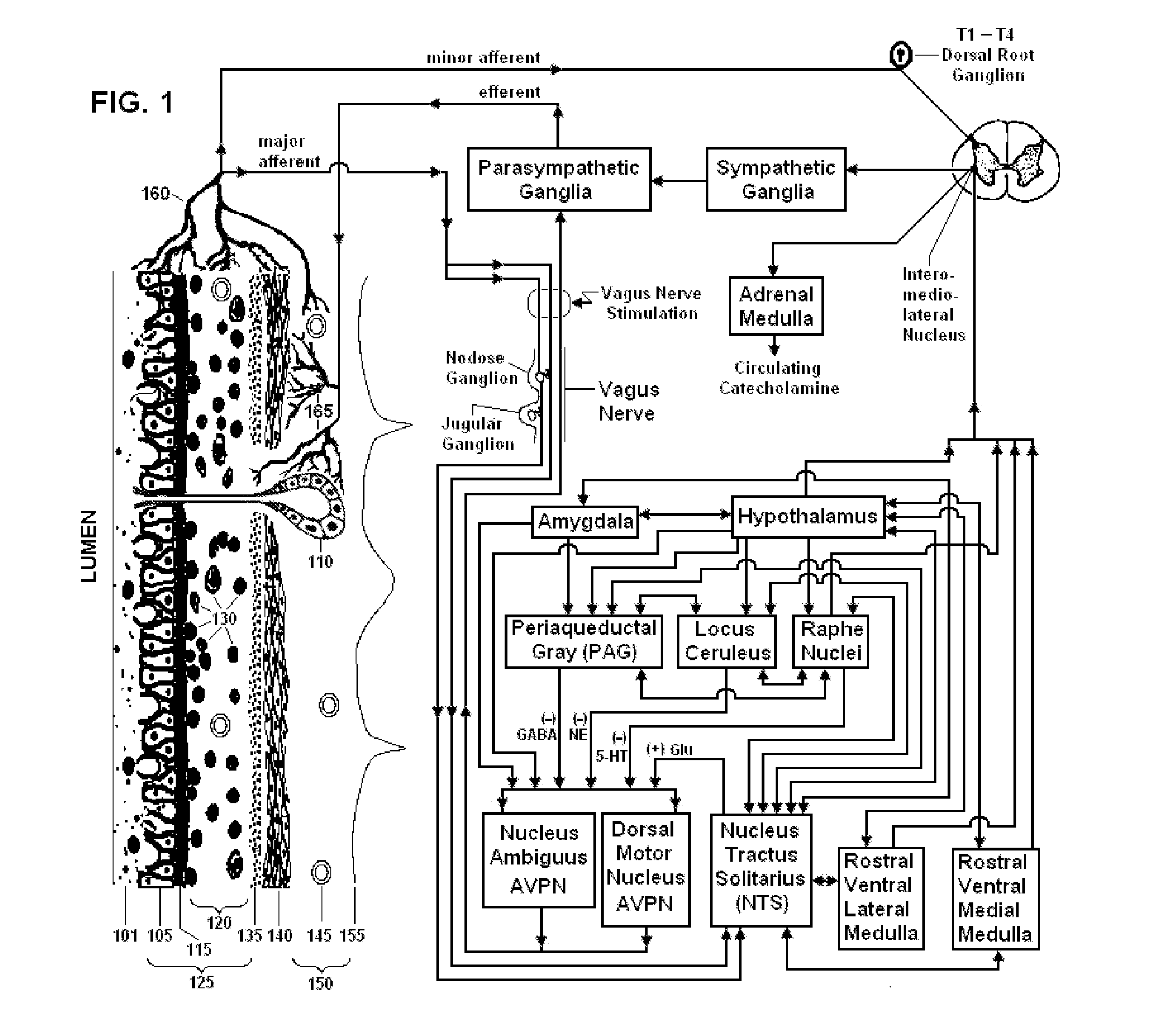
Non-invasive vagal nerve stimulation to treat disorders
ActiveUS8843210B2Excessive levelHigh activityElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiseaseNon invasive
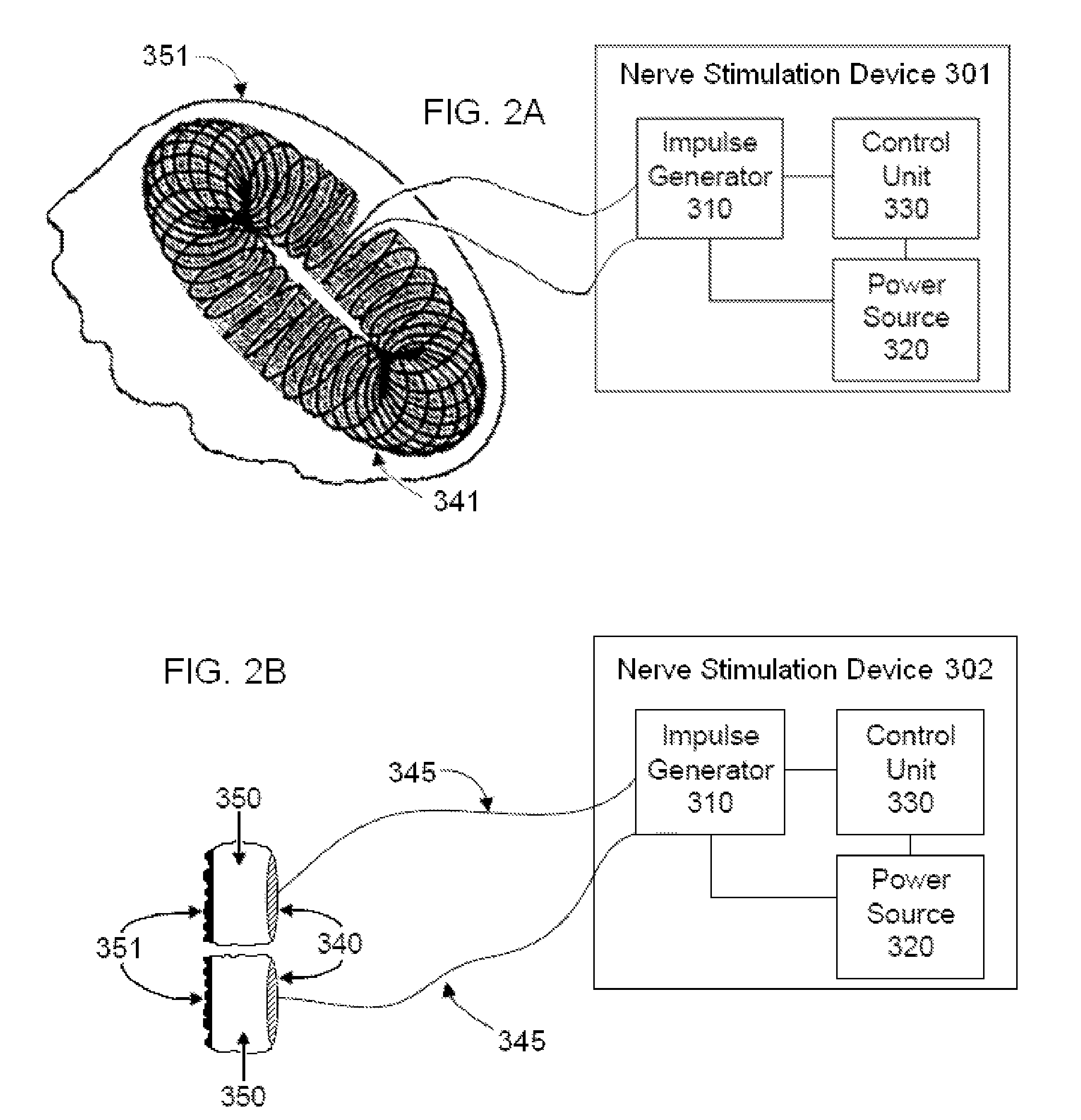
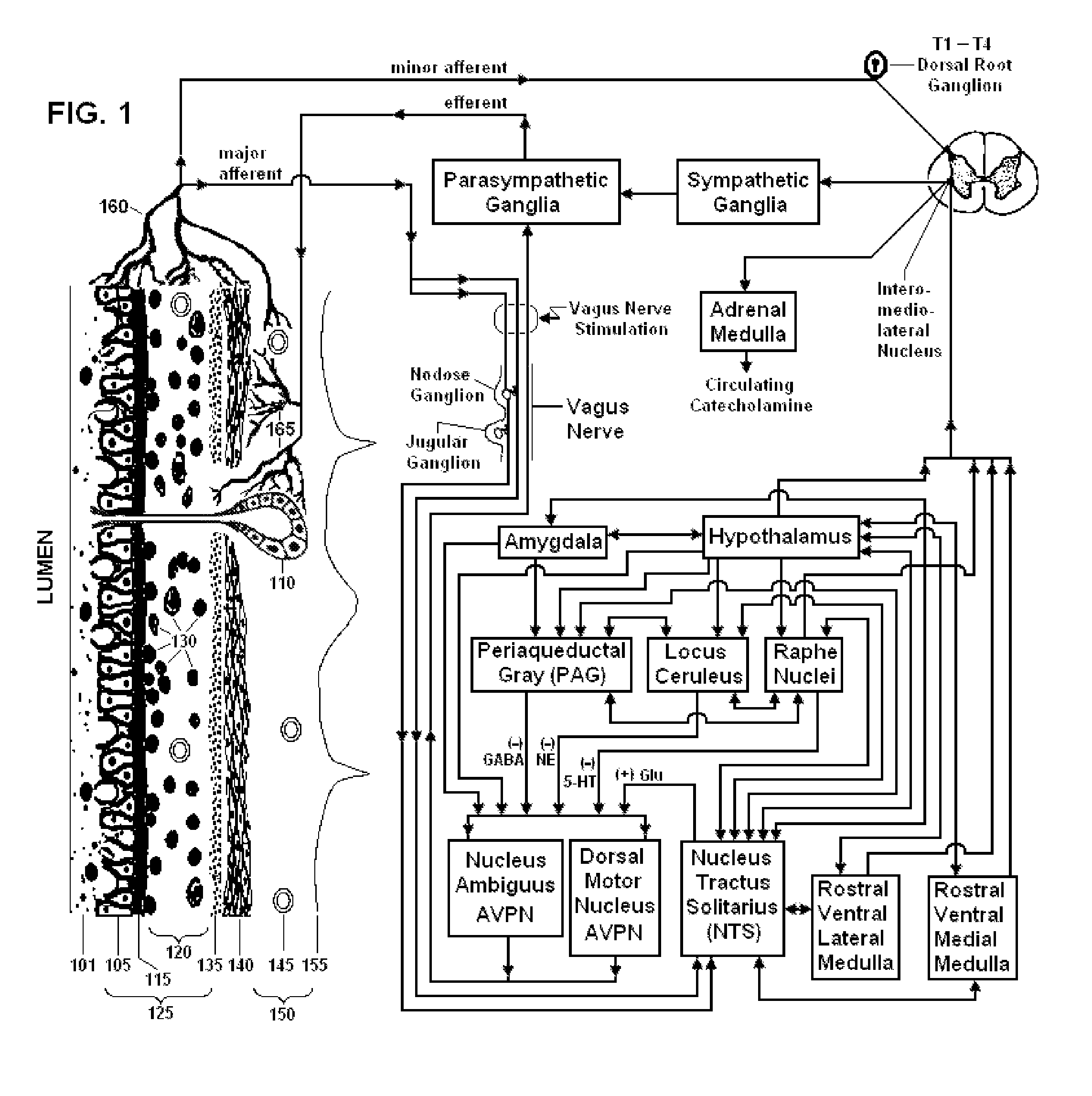
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating a variety of diseases and disorders that are primarily or at least partially driven by an imbalance in neurotransmitters in the brain, such as asthma, COPD, depression, anxiety, epilepsy, fibromyalgia, and the like. The invention involves the use of an energy source comprising magnetic and / or electrical energy that is transmitted non-invasively to, or in close proximity to, a selected nerve to temporarily stimulate, block and / or modulate the signals in the selected nerve such that neural pathways are activated to release inhibitory neurotransmitters in the patient's brain.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
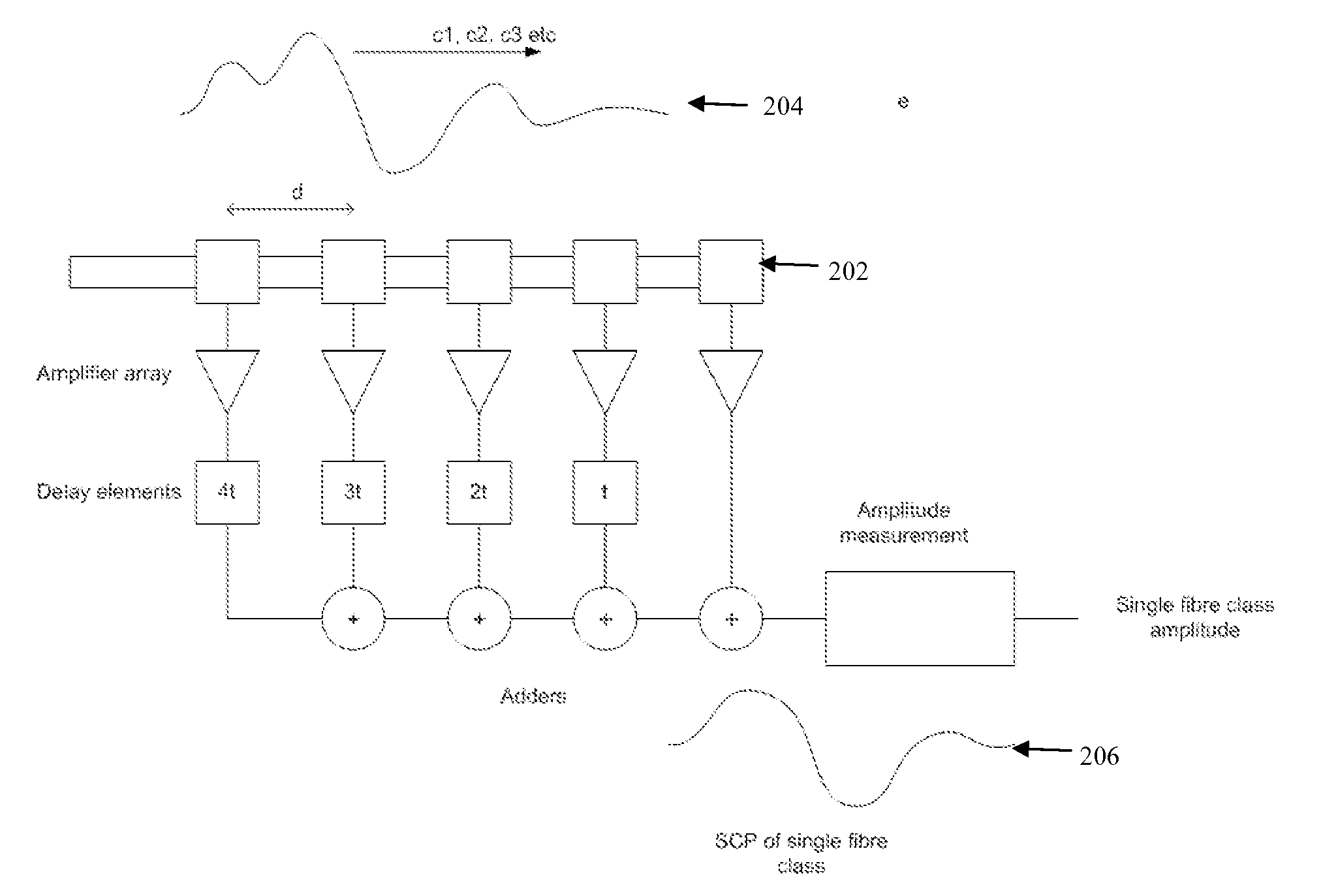
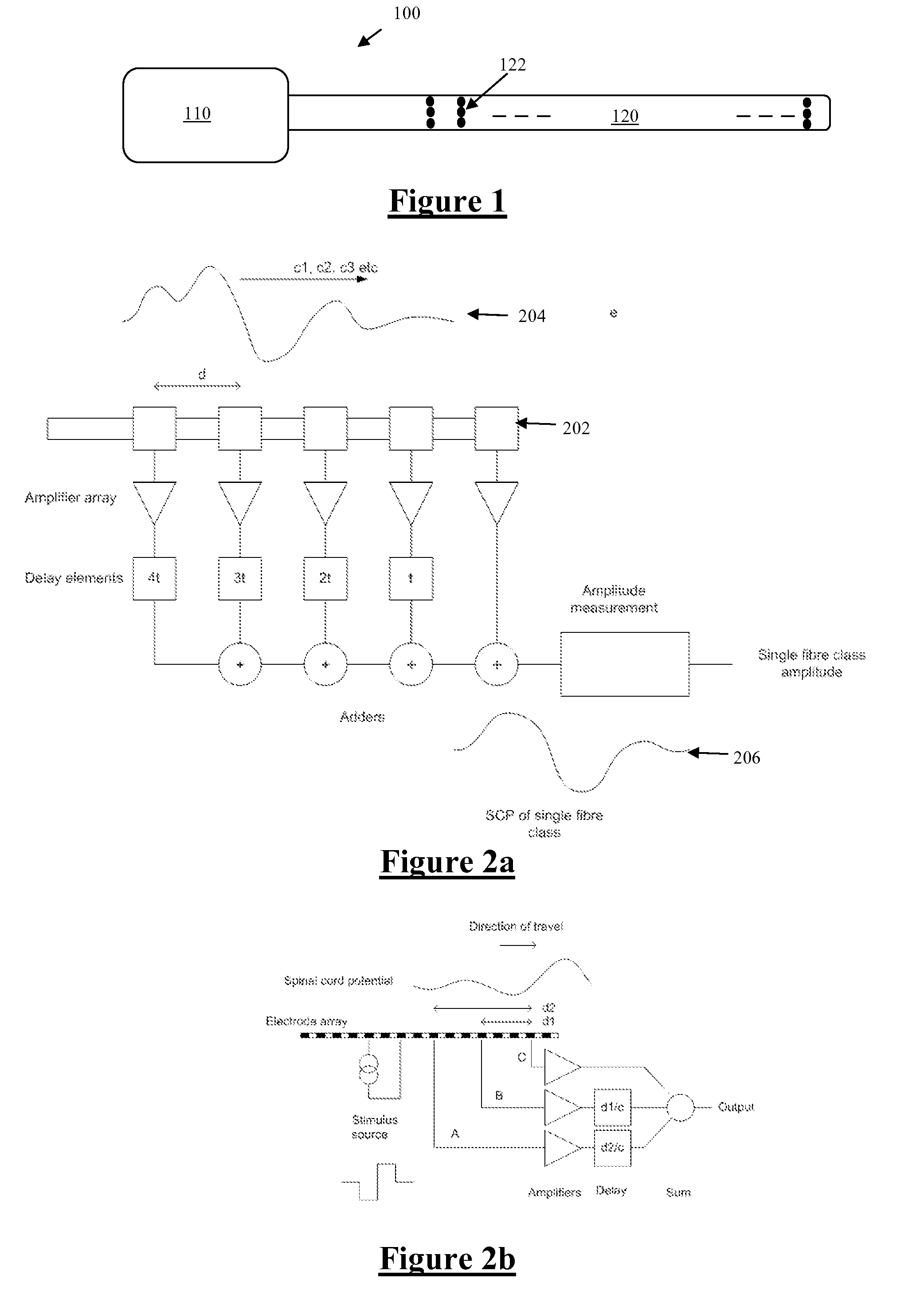
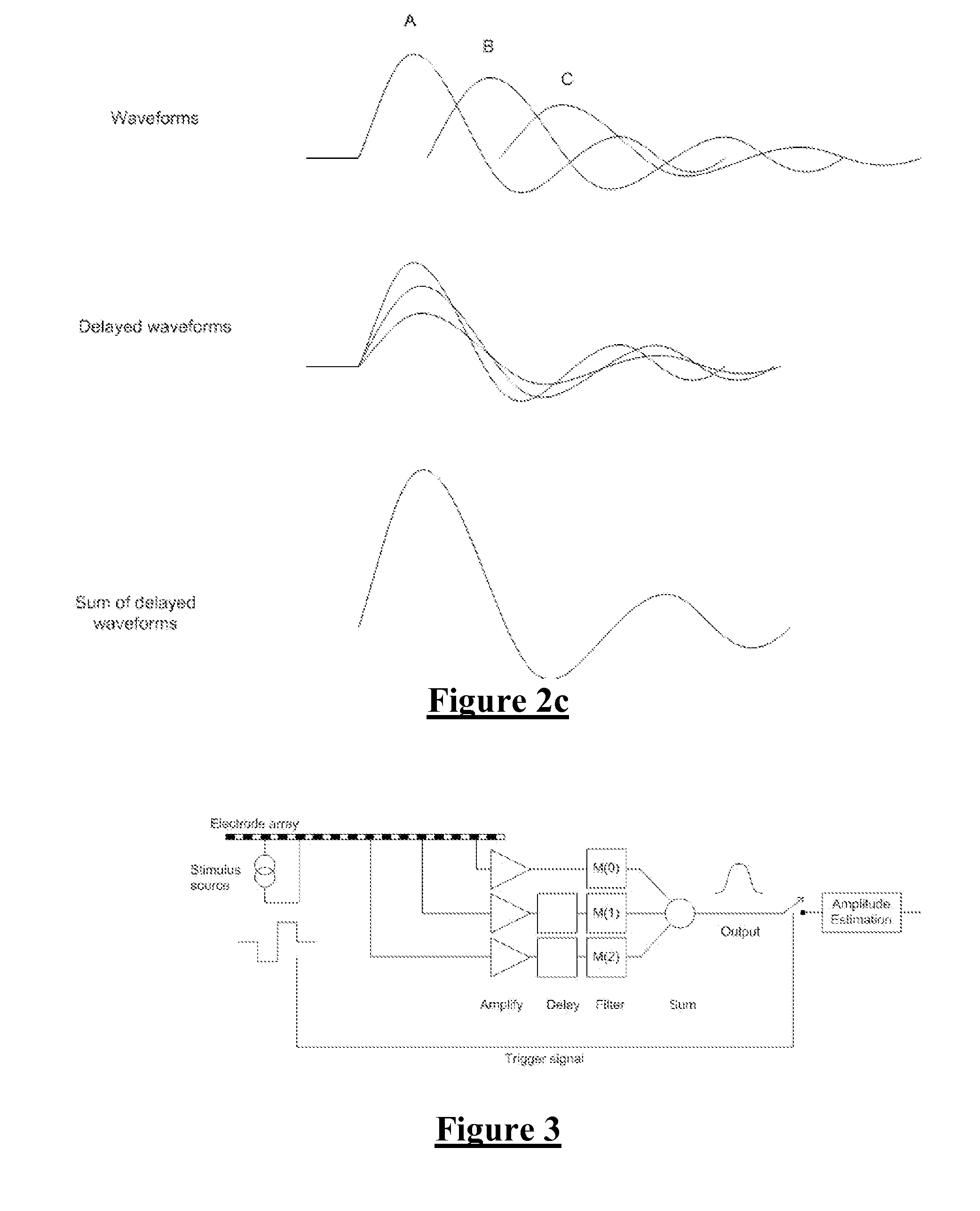
Electrode to Nerve Distance Estimation
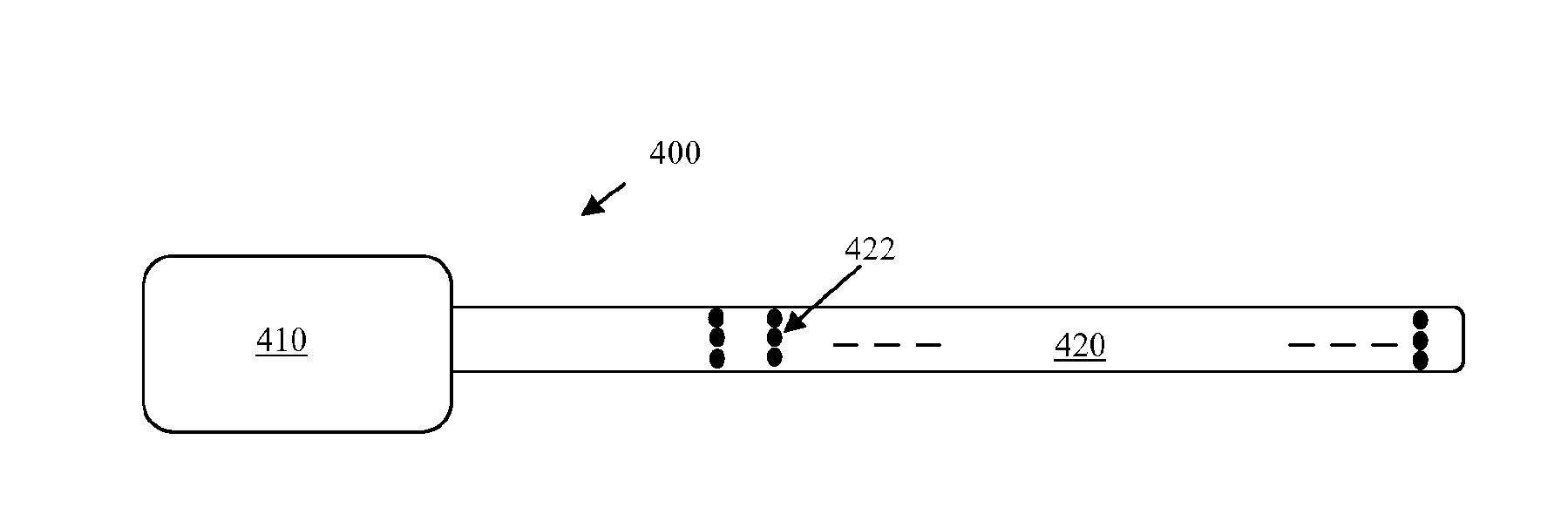
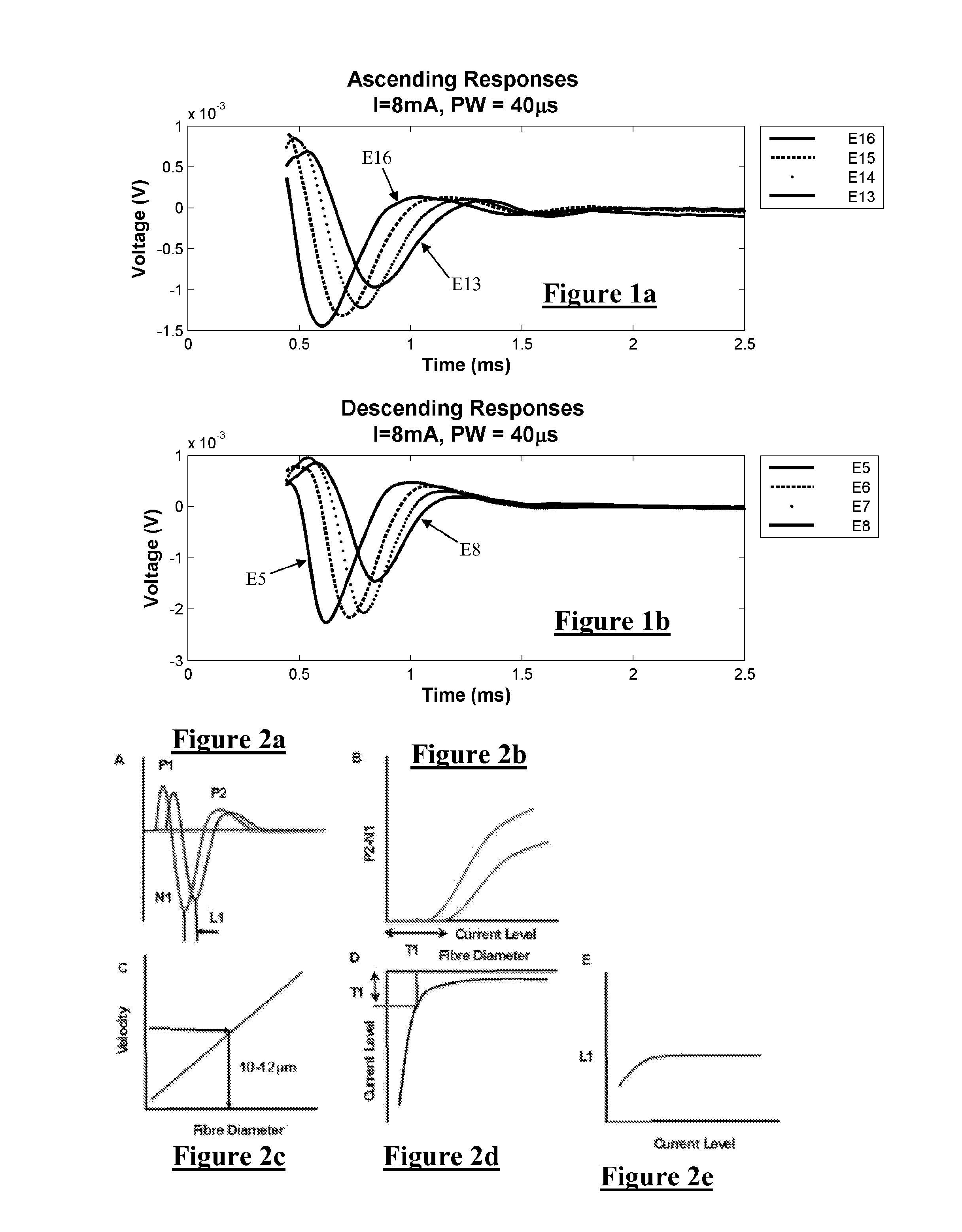
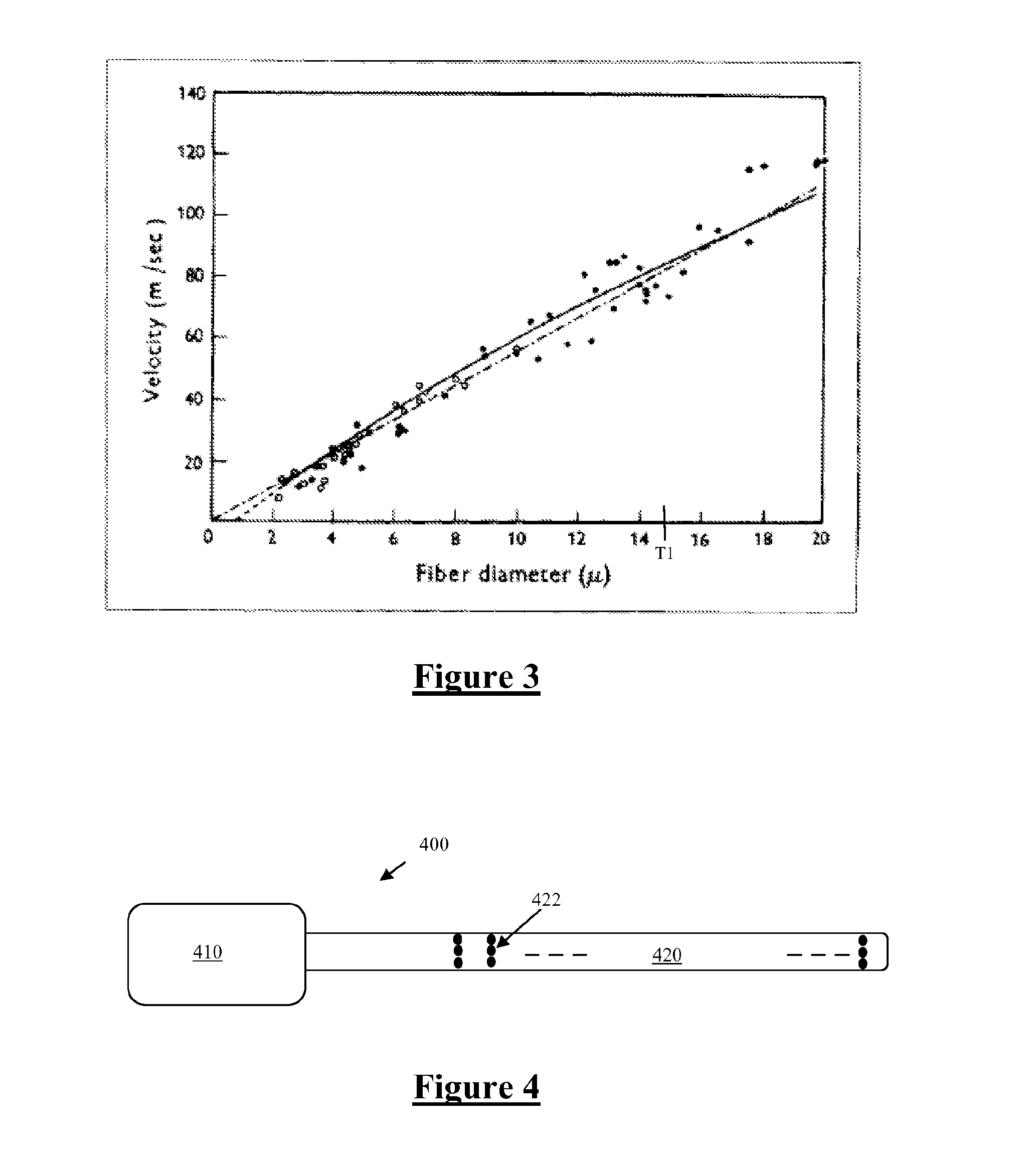
ActiveUS20180110987A1Promote resultsComplicate to effectElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialMedicine
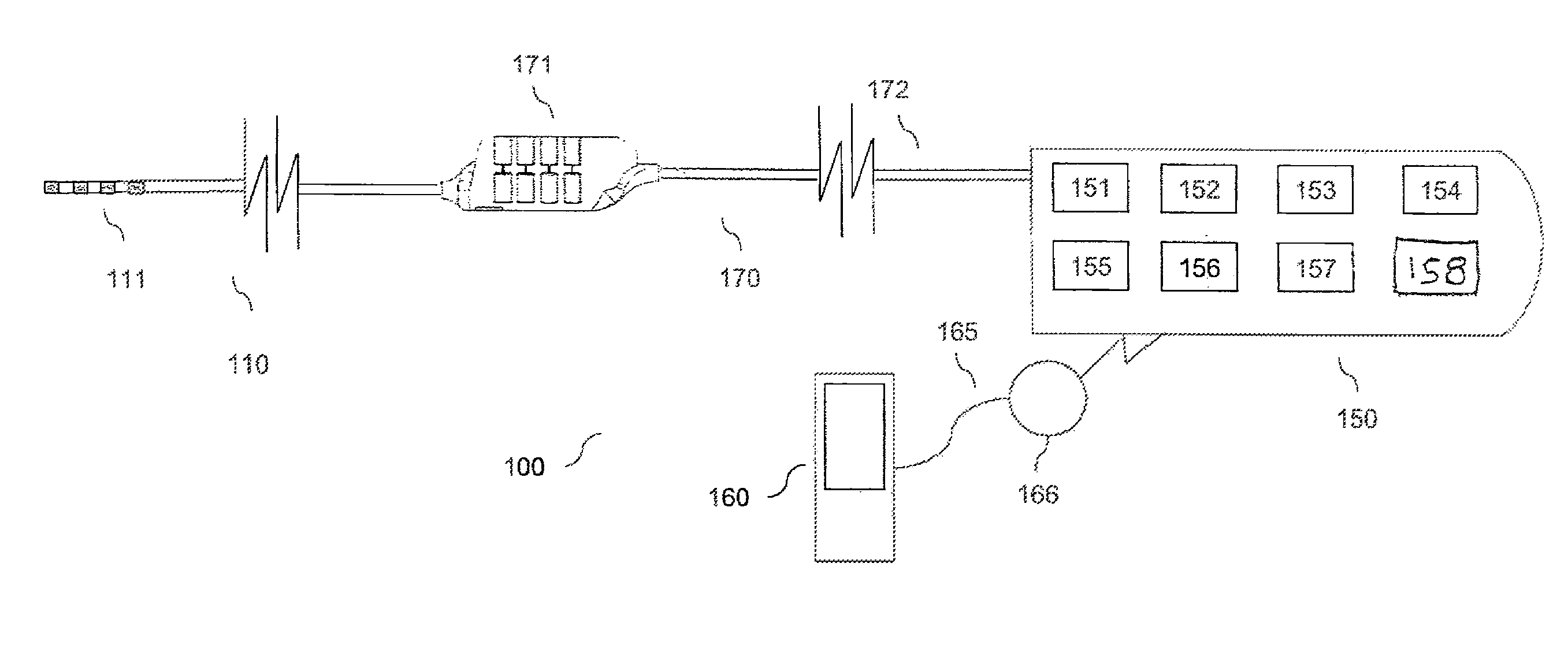
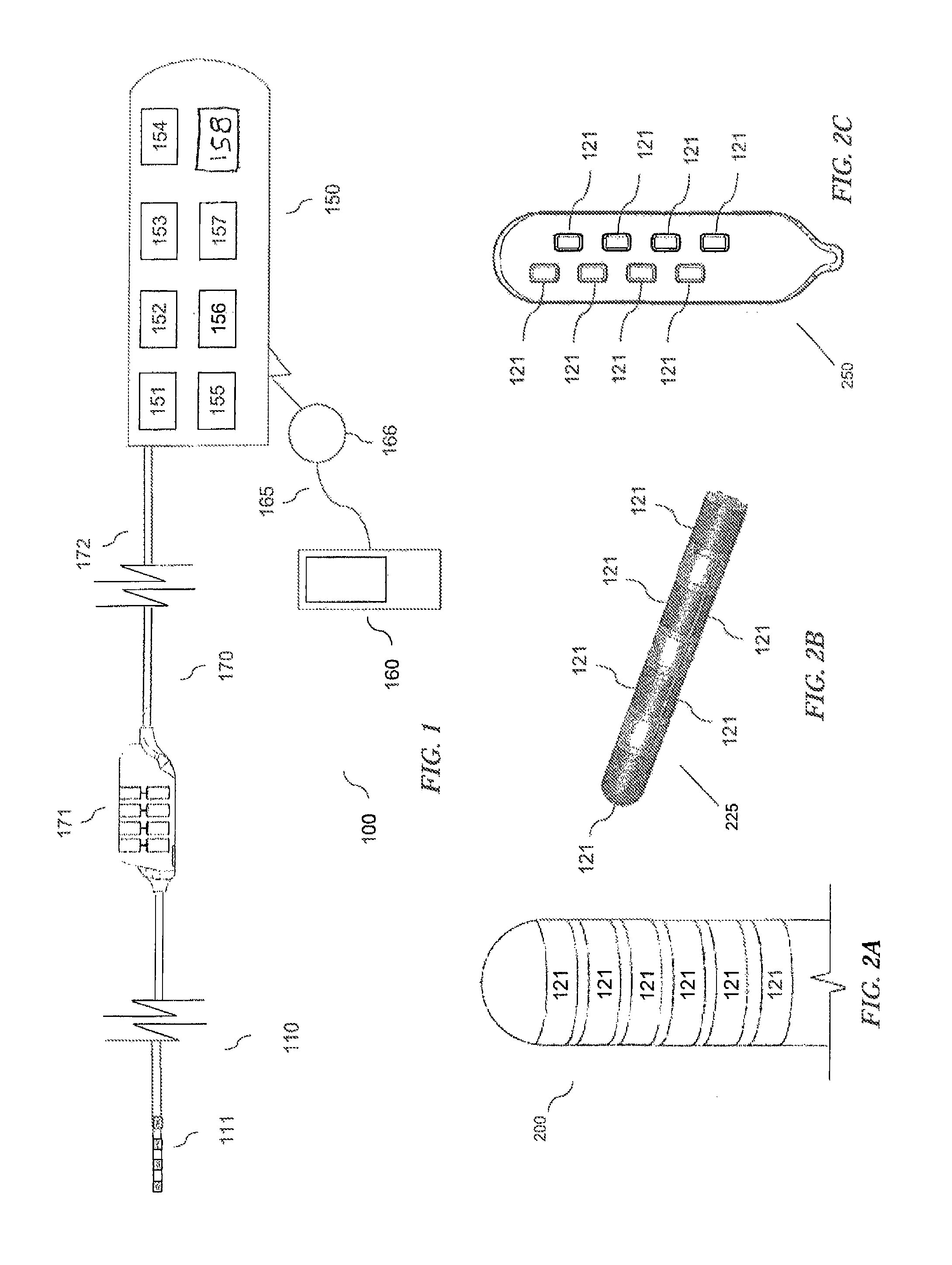
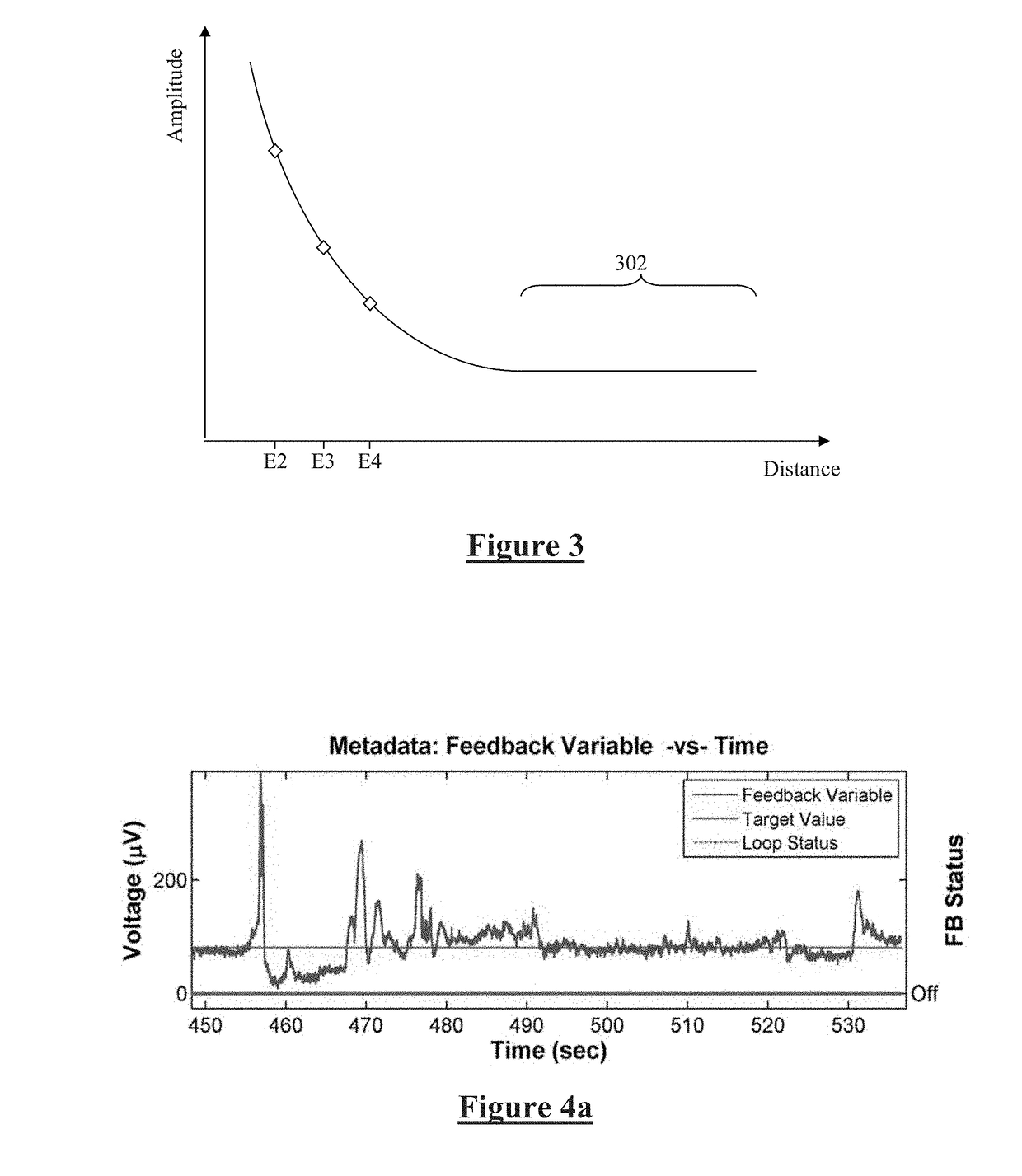
Estimating a nerve-to-electrode distance involves applying a stimulus from a stimulus electrode to a nerve. Neural measurements of at least one evoked compound action potential are obtained, and processed in order to estimate an originating state of stimulation exhibiting at least one characteristic defined by a single fibre size. A single fibre model is then applied to produce a measure of the nerve-to-electrode distance. Also provided for is estimation of a distribution of recruited fibres. Measurements of a compound action potential are obtained from sense electrodes spaced apart along a neural pathway. A conduction velocity of the compound action potential is determined from the latency between the measurements. From the conduction velocity a dominant recruited fibre diameter is determined. A rate of dispersion of the compound action potential between the sense electrodes is determined. From the rate of dispersion a distribution of diameters of the recruited fibre population is determined.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for measurement of neural response
InactiveUS20140236042A1Increase conduction velocityIncreased recruitment of large fibresSpinal electrodesSensorsBrain pathwayNeural tract
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Therapeutic method and device for rehabilitation
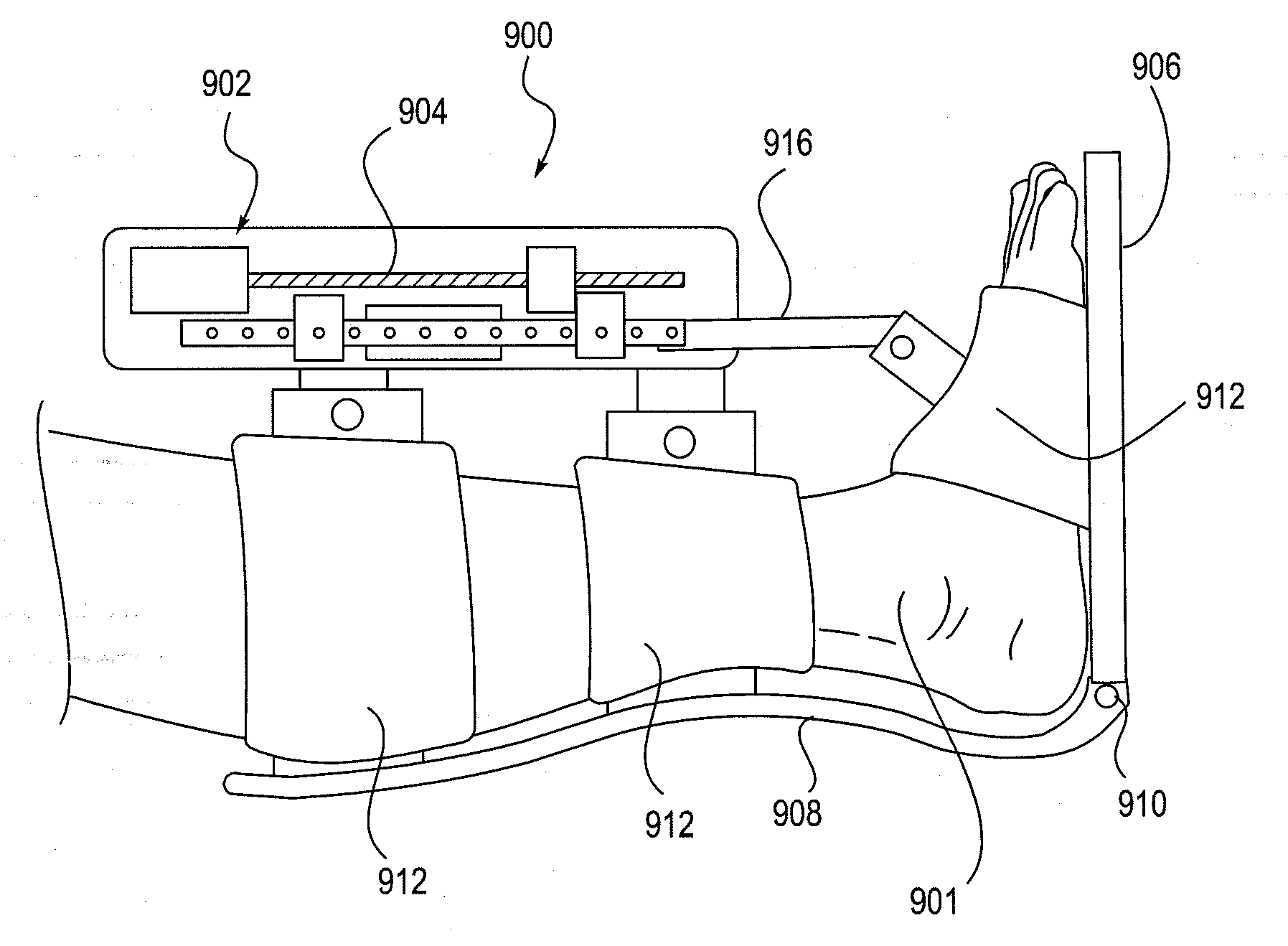
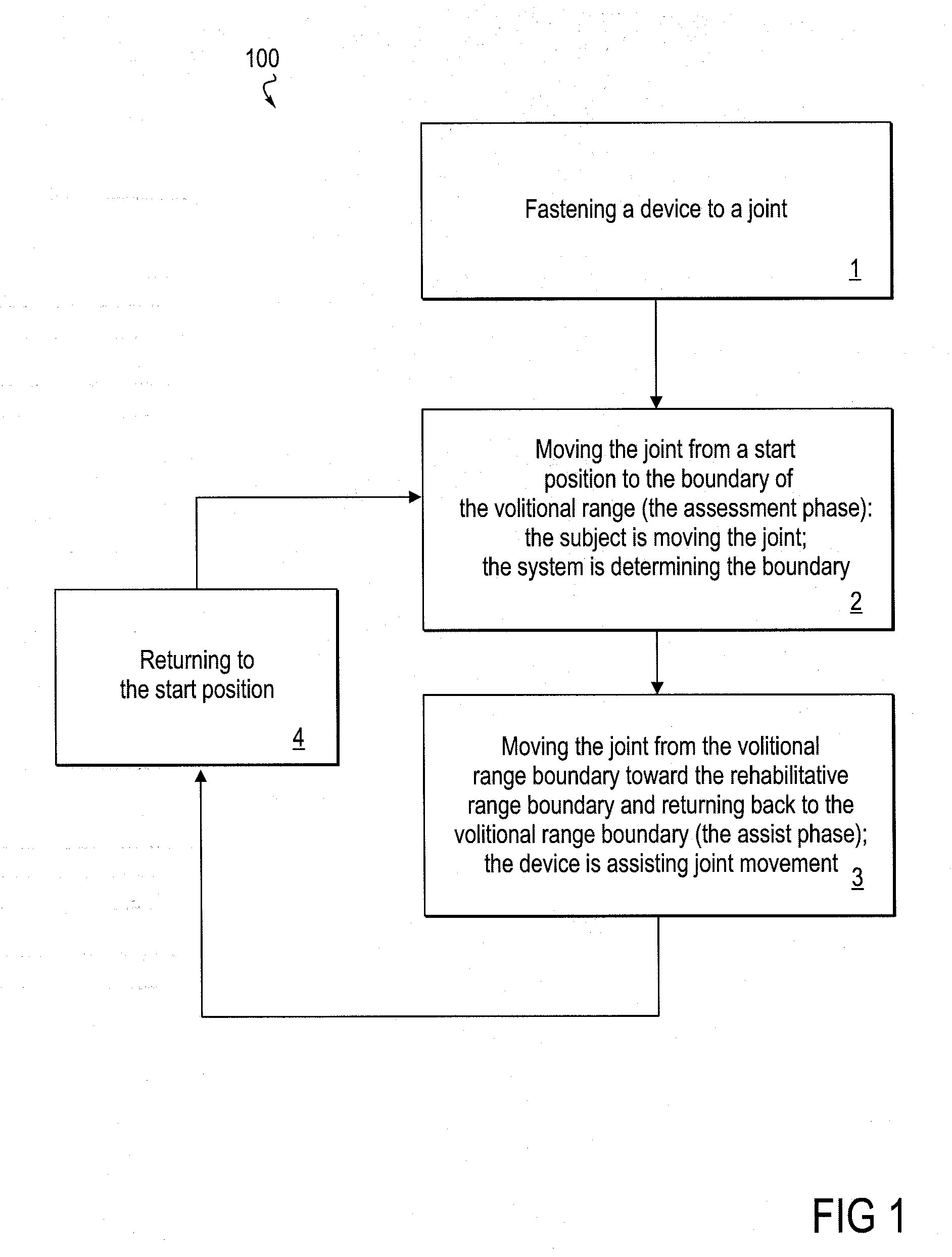
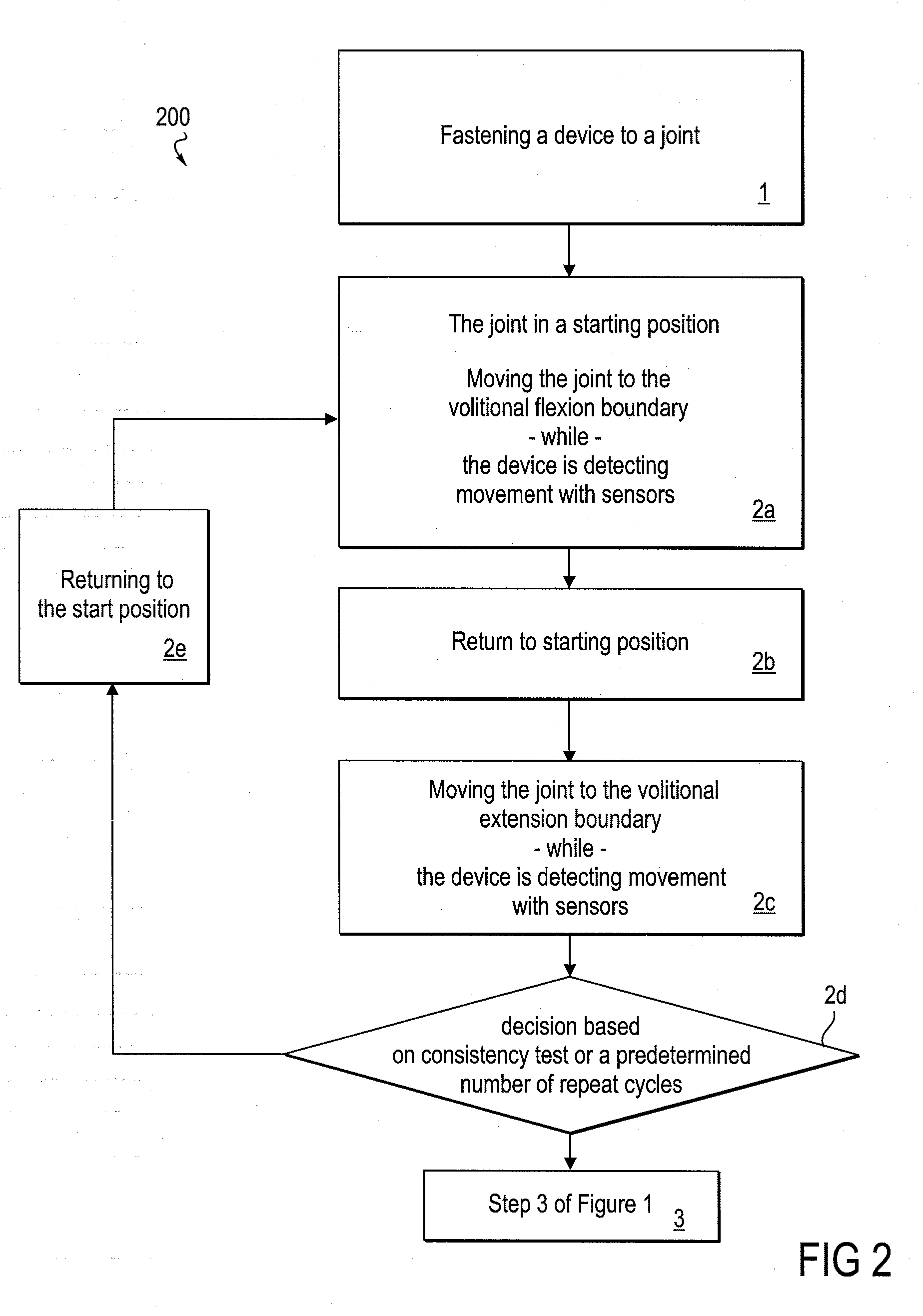
InactiveUS20090306548A1Maximum force limitImprove functionalitySurgeryPerson identificationRange of motionEngineering
The invention relates to embodiments of methods for extending a subject-controllable range of joint motion, and for increasing subject control of joint movement within a range of motion. Embodiments include fastening a powered device around a joint so as to be able to control the joint, allowing the subject to move the joint within a range of volitional motion, and then engaging the powered device to support movement of the joint into an expanded, rehabilitative range. In some embodiments, the device supports joint movement by substantially providing the force to move the joint beyond the volitional boundary. In other embodiments, supporting movement includes the subject substantially providing the force, and the device allowing movement only in a desired direction. The invention further relates to a system for increasing the functional capability of a joint by implementing embodiments of the method. By such methods and system, rehabilitation is accomplished both by building strength, and training neural pathways.
Owner:TIBION
Motor Fibre Neuromodulation
ActiveUS20180132760A1Improve responseDecrease and absenceImplantable neurostimulatorsSensorsMedicineBrain pathway
A motor response of a muscle to neural stimulation is assessed. Electrical stimuli are applied from a first electrode to a selected neural pathway to evoke an efferent neural response. A slow neural response upon the neural pathway evoked by the electrical stimuli is observed. Based on the slow neural response, a motor response of at least one muscle to the stimuli is assessed.
Owner:CLOSED LOOP MEDICAL PTY LTD
Gastrointestinal motility control
A method and a multichannel implantable device are described for partial or complete restoration of impaired gastrointestinal motility, or for disturbing and / or partially or completely blocking normal gastrointestinal motility using one or multiple microsystem-controlled channels of circumferentially arranged sets of two or more electrodes which provide externally-invoked synchronized electrical signals to the smooth muscles via the neural pathways.
Owner:UTI LLP
Focal noninvasive stimulation of the sensory cortex of a subject with cerebral palsy
InactiveUS20110270345A1Restore levelRegain healthInternal electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsCerebral paralysisNon invasive
Disclosed are methods and related devices for use with subjects with cerebral palsy or periventricular leukomalacia. In preferred embodiments, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is used to identify neural areas and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is used to stimulate neural pathways.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Morphogen-induced dendritic growth
InactiveUS6949505B1Alleviate neural pathway damageAlleviate and inhibit immunologically related responseBiocideNervous disorderMammalNeurotrophic factors
Disclosed are methods and compositions for maintaining neural pathways in a mammal including: enhancing survival of neurons at risk of dying; inducing cellular repair of damaged neurons and neural pathways; stimulating neurons to maintain their differentiated phenotype; and promoting dendritic outgrowth, including maintaining dendritic arbors and regenerating dendritic architecture. In one embodiment, the invention provides means for stimulating CAM expression in neurons. The invention also provides means for evaluating the status of nerve tissue, including means for detecting and monitoring neuropathies in a mammal. The methods, devices and compositions include a morphogen or morphogen-stimulating agent provided to the mammal in a therapeutically effective concentration. In another embodiment, the invention provides methods and compositions which include a morphogen or morphogen-stimulating agent, and a nerve trophic factor or nerve trophic factor-stimulating agent at concentrations effective for stimulating dendrite outgrowth. The morphogen and the nerve trophic factor can be admixed in combination.
Owner:MARIEL THERAPEUTICS +1
Non-invasive vagal nerve stimulation to treat disorders
ActiveUS8918178B2Effect pressureEffect rateElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiseaseNon invasive
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Method and Device for Detecting a Neural Response in Neural Measurements
ActiveUS20180228391A1Improve the immunityImprove determinationElectrotherapySensorsNeural tractBrain pathway
A method is provided for processing a neural measurement obtained in the presence of noise, in order to detect whether a locally evoked neural response is present in the neural measurement. A first neural measurement is obtained from a first sense electrode. A second neural measurement is contemporaneously obtained from a second sense electrode spaced apart from the first electrode along a neural pathway of the neural response. A neural response decay is determined, being a measure of the decay in the neural response from the first sense electrode to the second sense electrode. A ratio of the neural response decay to an amplitude normalising term is calculated. From the ratio it is determined whether a locally evoked neural response is present in the neural measurement.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Non-invasive vagal nerve stimulation to treat disorders
ActiveUS9399134B2Excessive levelHigh activityMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsExternal electrodesDiseaseNon invasive
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating a variety of diseases and disorders that are primarily or at least partially driven by an imbalance in neurotransmitters in the brain, such as asthma, COPD, depression, anxiety, epilepsy, fibromyalgia, and the like. The technology involves the use of an energy source comprising magnetic and / or electrical energy that is transmitted non-invasively to, or in close proximity to, a selected nerve to temporarily stimulate, block and / or modulate the signals in the selected nerve such that neural pathways are activated to release inhibitory neurotransmitters in the patient's brain.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Non-invasive vagal nerve stimulation to treat disorders
ActiveUS8983629B2Inhibition releaseInhibits mucous productionElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiseaseObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating bronchial constriction related to asthma, anaphylaxis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), exercise-induced bronchospasm and post-operative bronchospasm. The treatment comprises transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers that activate neural pathways to reduce the release of acetycholine from airway-related vagal preganglionic neurons within the brain of the patient. The transmitted energy impulses, comprising magnetic and / or electrical energy, stimulate the selected nerve fibers to produce the bronchodilation.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
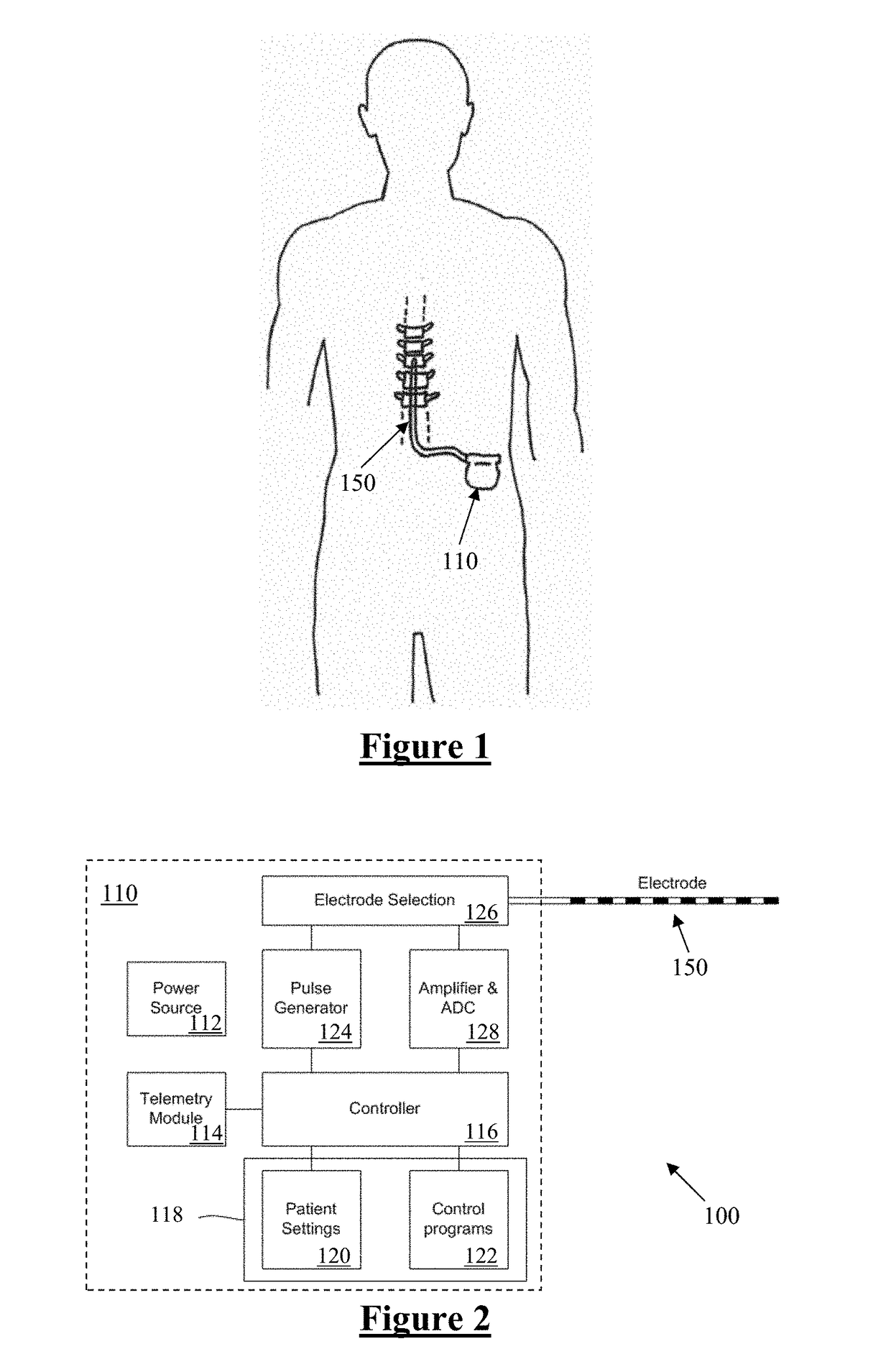
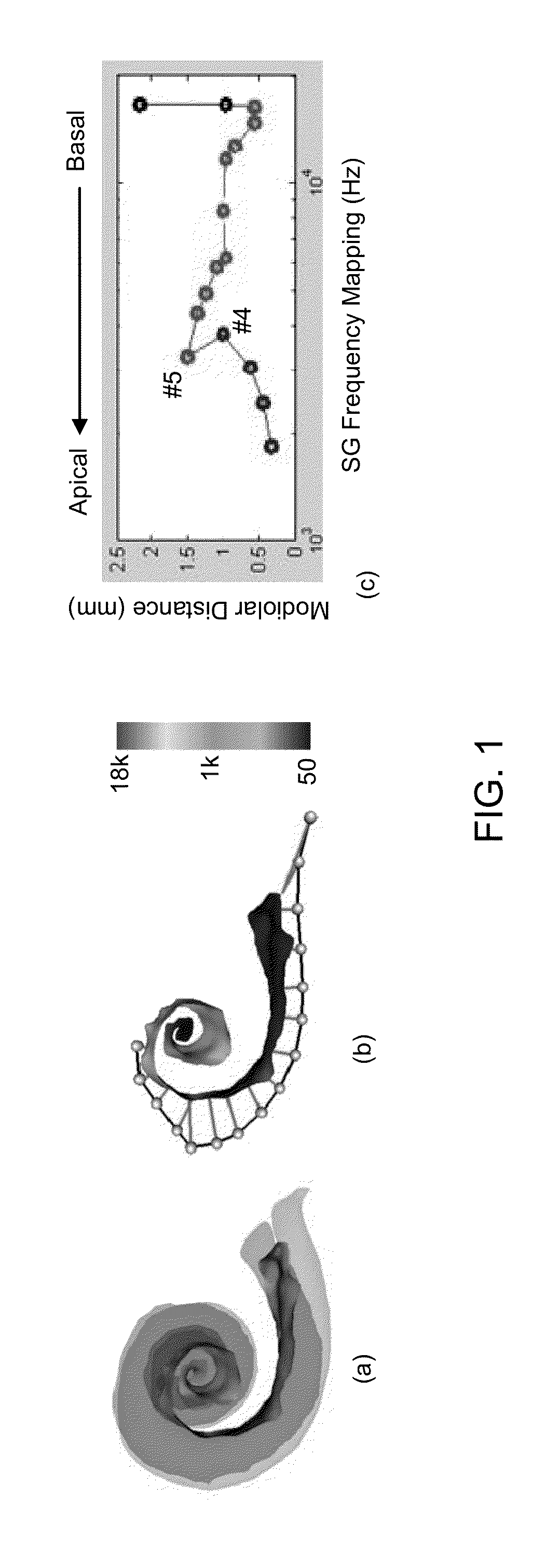
Methods and systems for customizing cochlear implant stimulation and applications of same
ActiveUS20150088225A1The result is accurateImprove efficiencyMedical simulationImage enhancementBiological bodyCochlear implantation
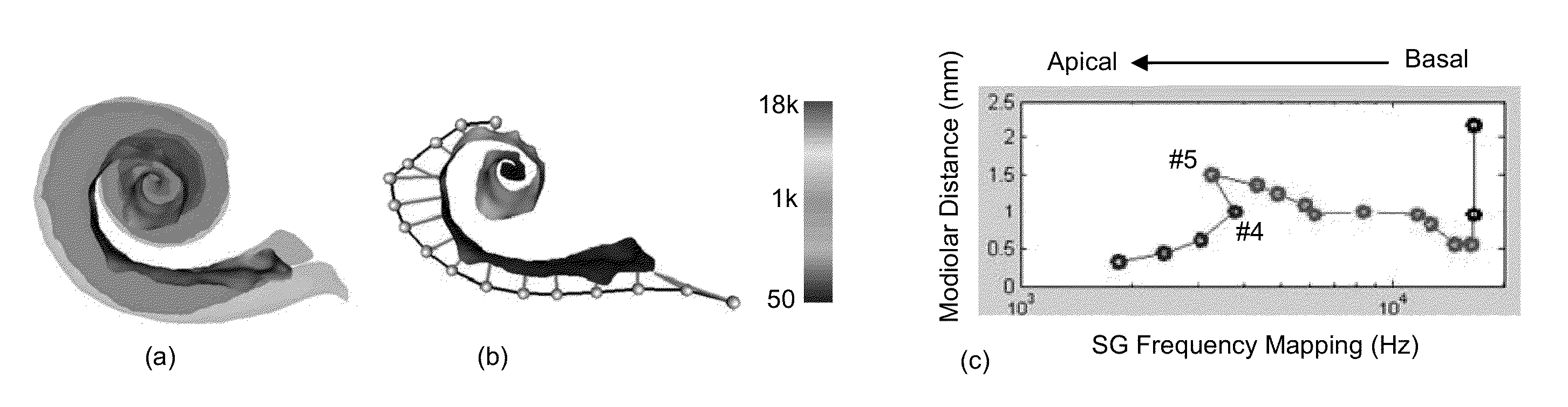
One aspect of the invention provides a method for customizing cochlear implant stimulation of a living subject. The cochlear implant includes an electrode array having a plurality of electrodes implanted in a cochlea of the living subject. The method includes determining a position for each of the plurality of electrodes and spiral ganglion nerves that the electrode array stimulates, determining a geometric relationship between neural pathways within the cochlea and the electrode array implanted therein, and using one or more electrodes of the electrode array to stimulate a group of SG neural pathways of the cochlea based on the location of the one or more electrodes and their geometric relationship with the neural pathways.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Non-invasive vagal nerve stimulation to treat disorders
ActiveUS20130238049A1Effect pressureEffect rateElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsNon invasiveBrain pathway
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating a variety of diseases and disorders that are primarily or at least partially driven by an imbalance in neurotransmitters in the brain, such as asthma, COPD, depression, anxiety, epilepsy, fibromyalgia, and the like. The invention involves the use of an energy source comprising magnetic and / or electrical energy that is transmitted non-invasively to, or in close proximity to, a selected nerve to temporarily stimulate, block and / or modulate the signals in the selected nerve such that neural pathways are activated to release inhibitory neurotransmitters in the patient's brain.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Non-invasive vagal nerve stimulation to treat disorders
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating a variety of diseases and disorders that are primarily or at least partially driven by an imbalance in neurotransmitters in the brain, such as asthma, COPD, depression, anxiety, epilepsy, fibromyalgia, and the like. The invention involves the use of an energy source comprising magnetic and / or electrical energy that is transmitted non-invasively to, or in close proximity to, a selected nerve to temporarily stimulate, block and / or modulate the signals in the selected nerve such that neural pathways are activated to release inhibitory neurotransmitters in the patient's brain.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
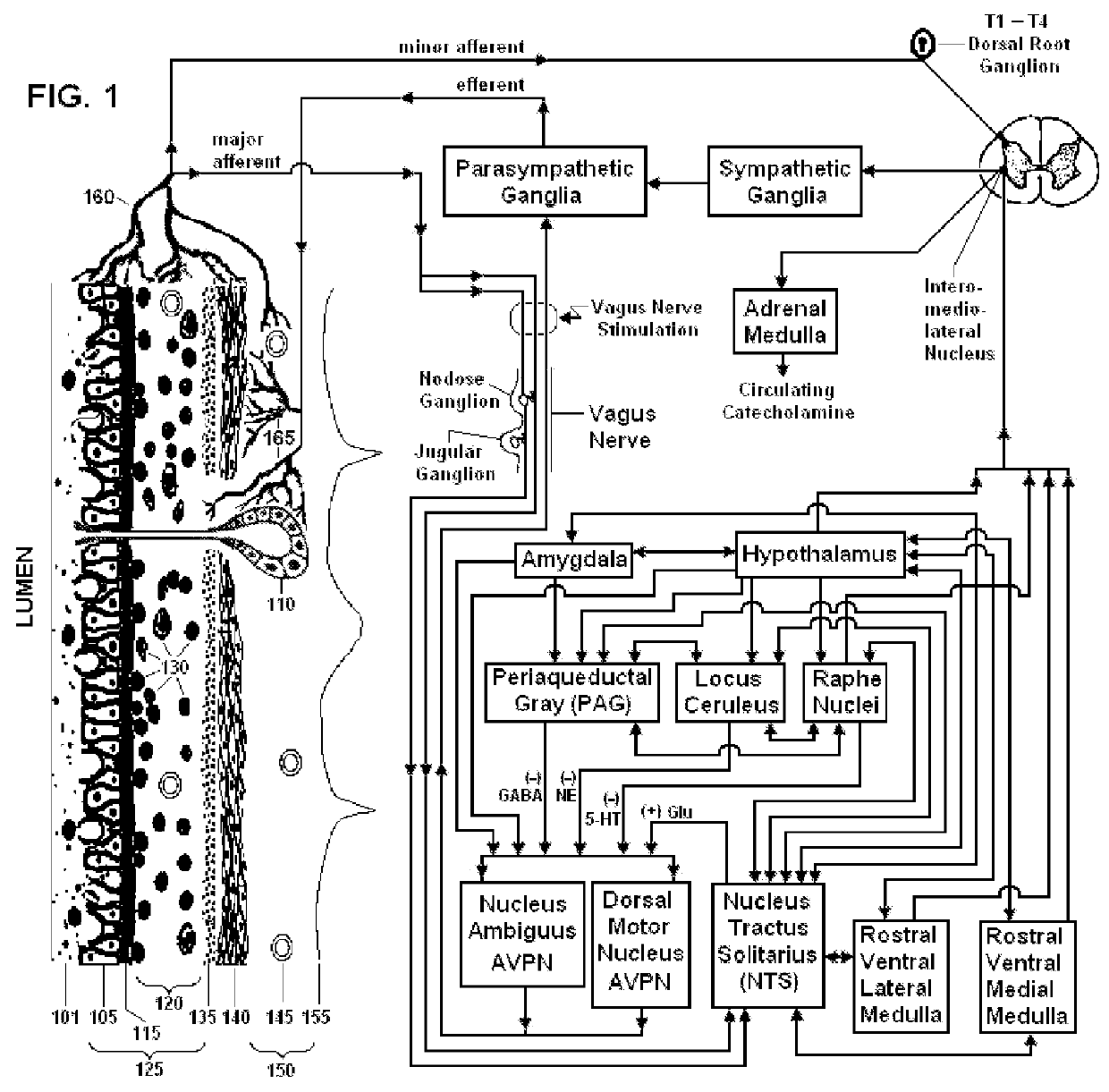
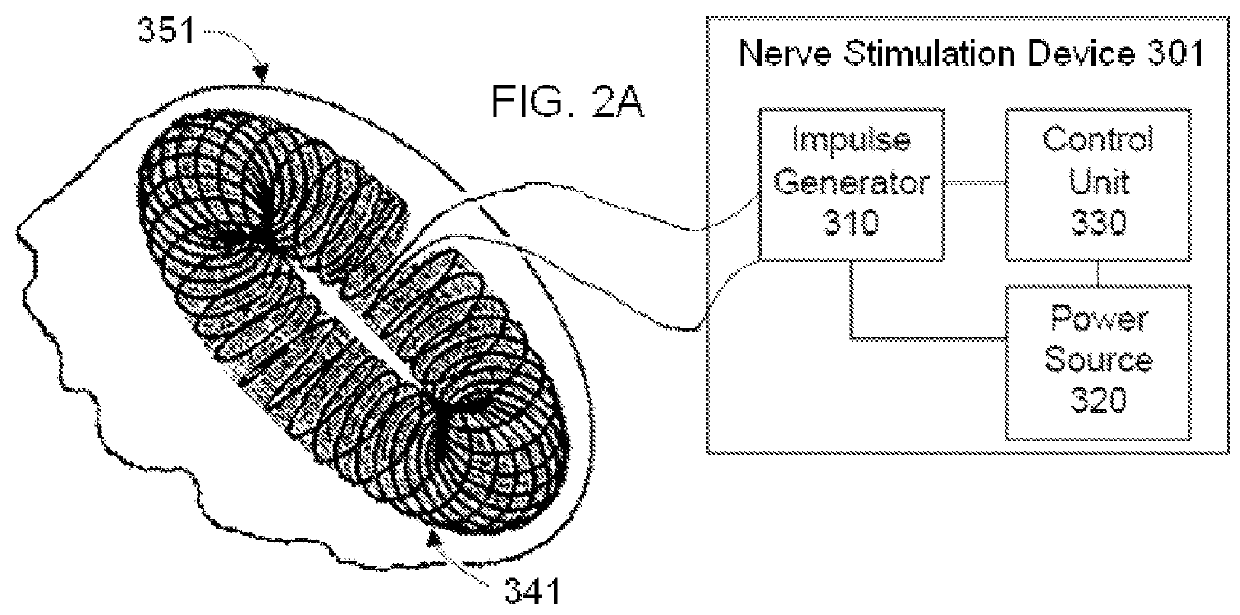
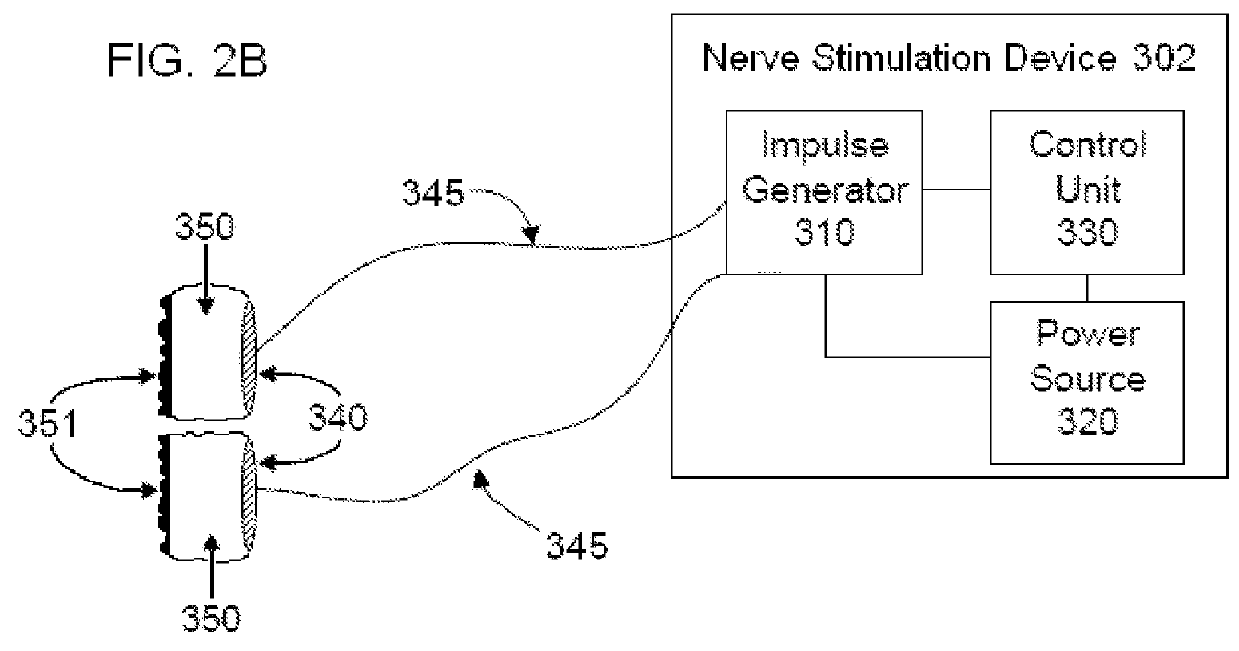
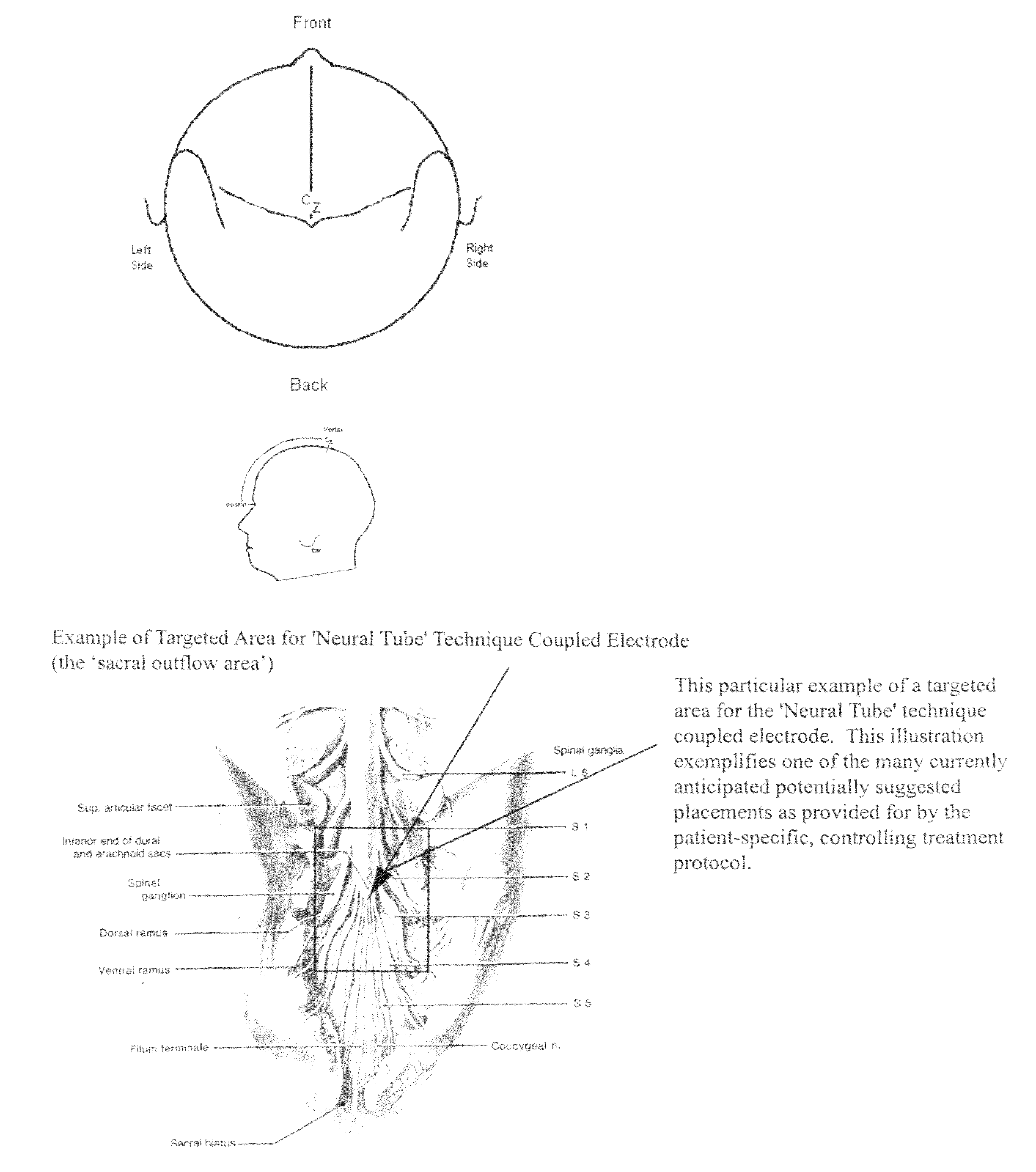
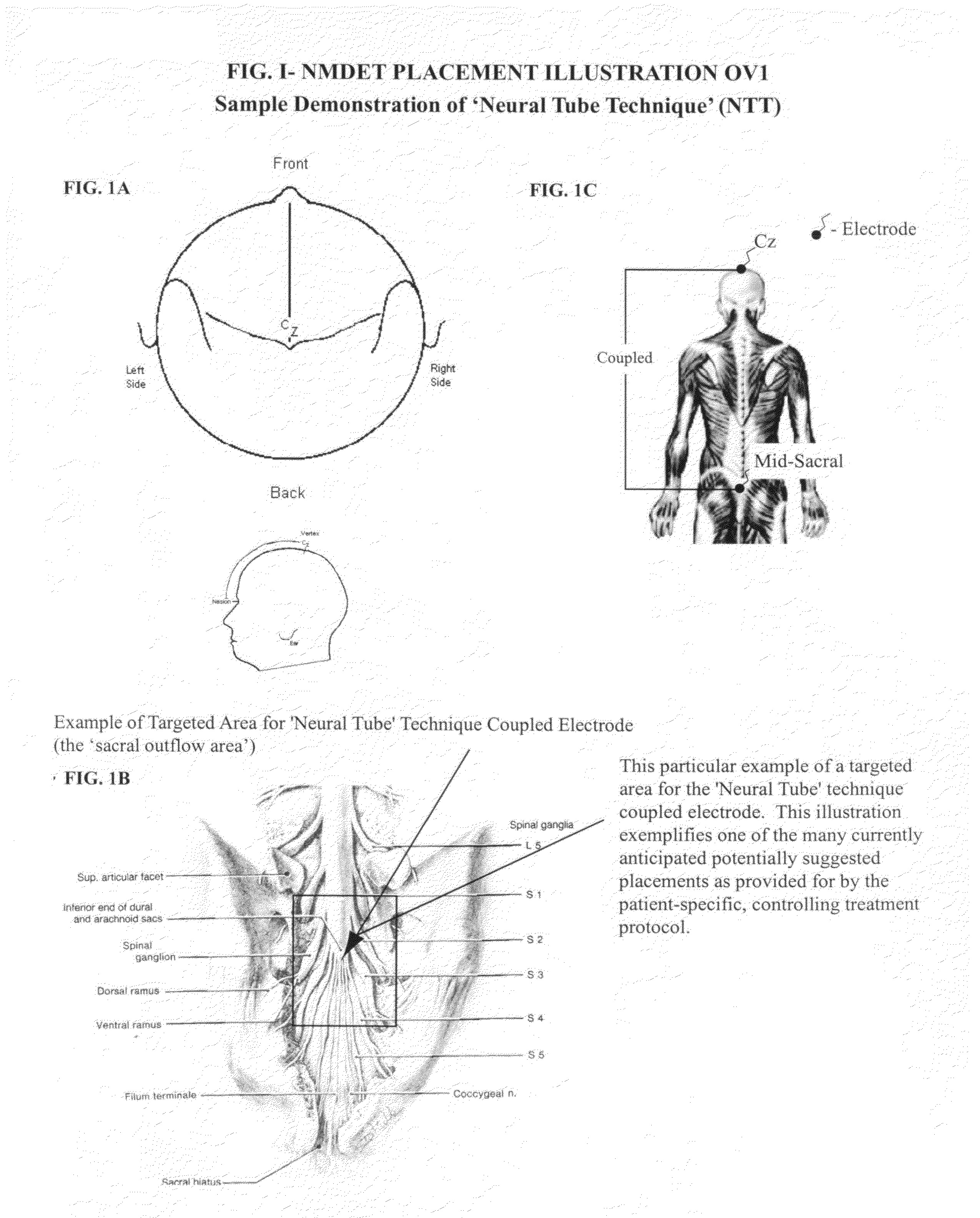
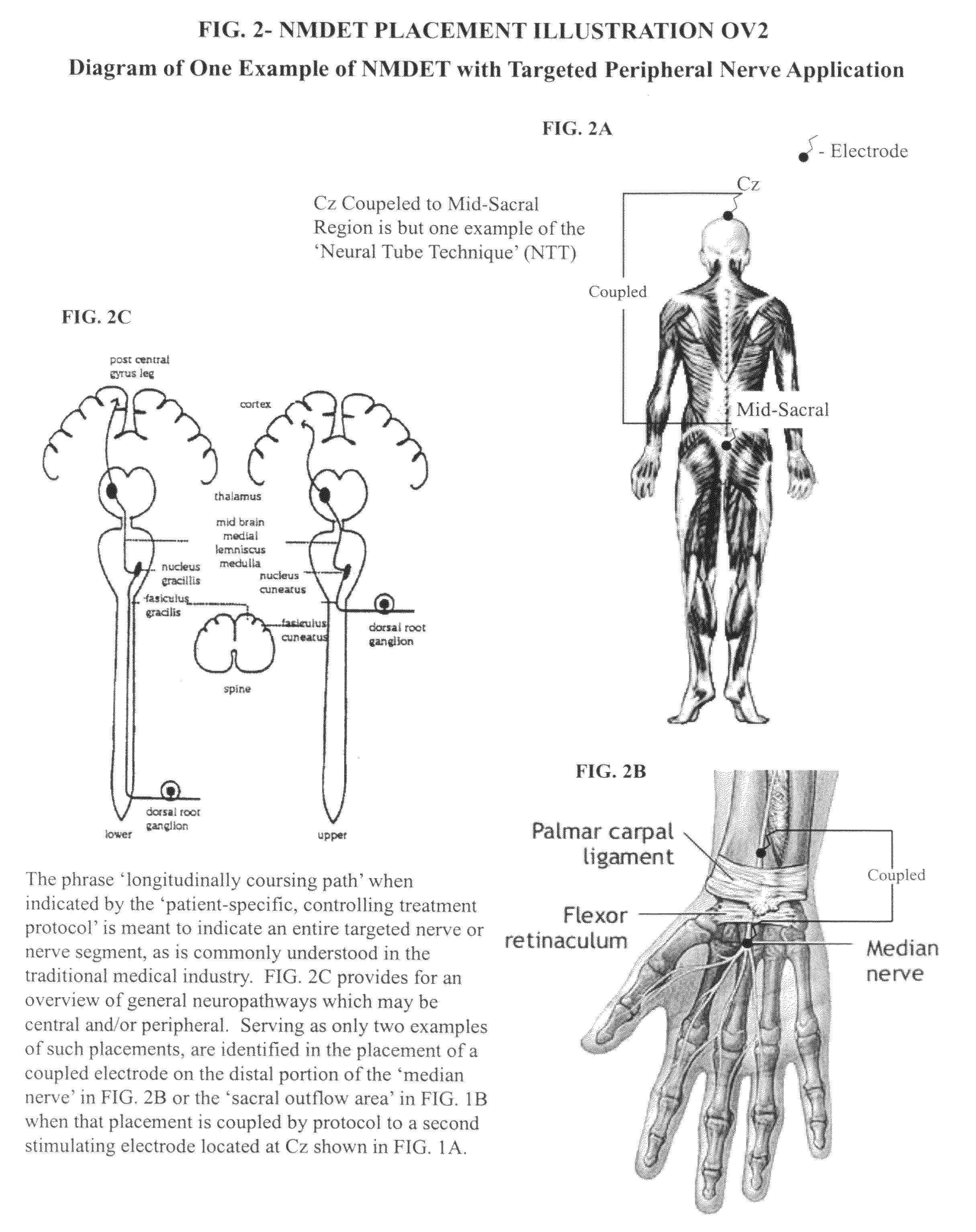
Coupled neuraxial mesoscopic desynchronization electrostimulation therapy (cNMDET) method
ActiveUS8428738B2Add supportIncrease capacityElectrotherapyElectrode placementTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
This novel therapeutic (reparative, etiotropic not merely symptomatolytic) electrostimulatory method hereinafter referred to as Coupled Neuraxial Mesoscopic Desynchronization Electrostimulation Therapy (cNMDET) is comprised of a varied combination of progressively sequenced electrode placements and its clinically targeted areas which are comprised of the CNS [regions of the brain and spinal cord including, but not limited to, the underlying clinicopathologic mechanisms of the ANS] and clinically involved components of the PNS variably coupled in such a manner as to apply this therapeutic electrostimulation (reparative modulation) along the coursing path (longitudinally) of the targeted neural pathway over a segment and / or in its entirety, as well as, the utilization of patterned applications for involved joints, muscles, fascia, ligaments, tendons and areas involved in inflammatory processes of clinical significance accomplished through the application of, preferably, but not limited to, Coupled Neuraxial Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (cNTENS) and Coupled Neuraxial Transcranial Direct Stimulation (ctDCSn).
Owner:VALENCIA ANDREW D
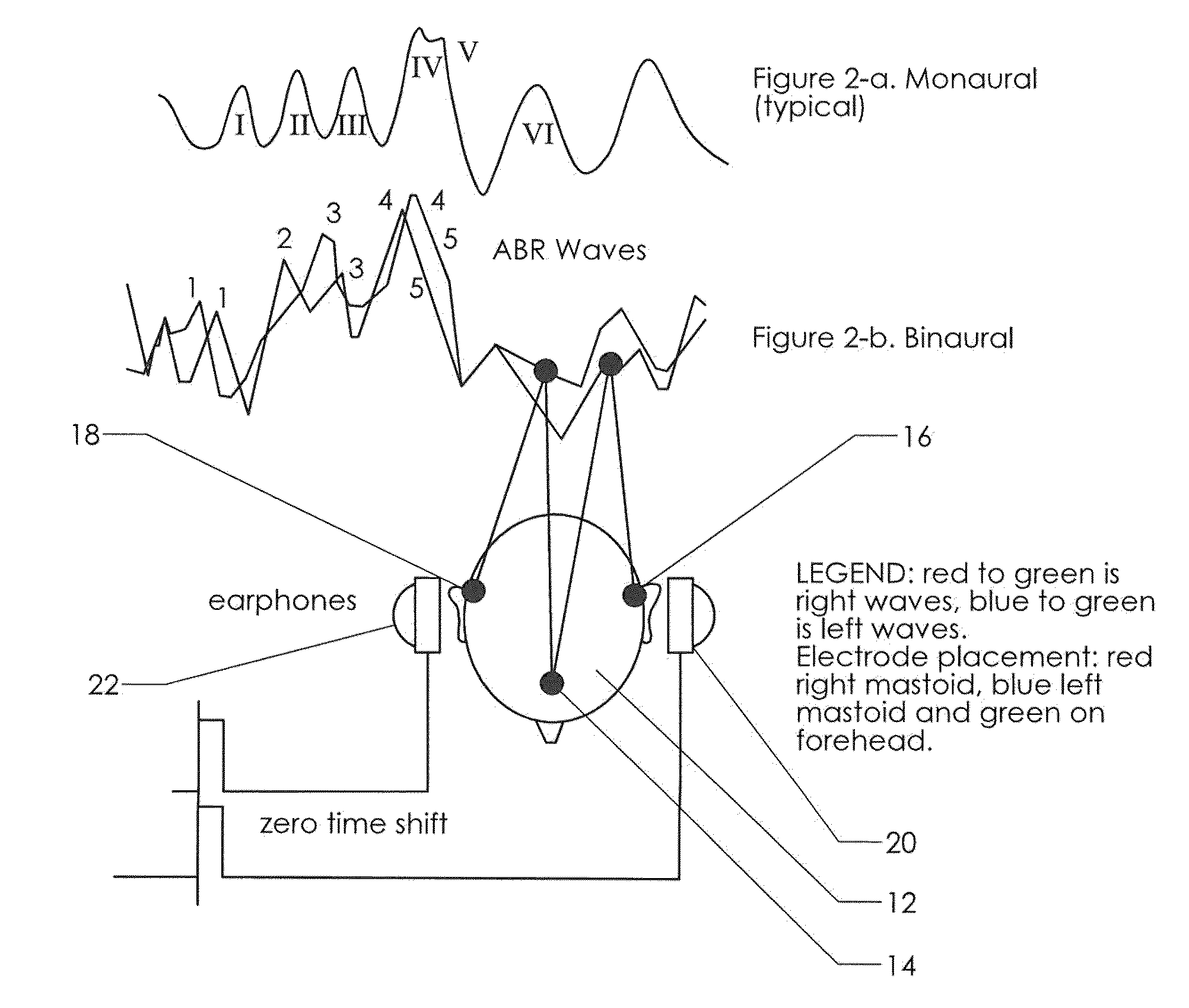
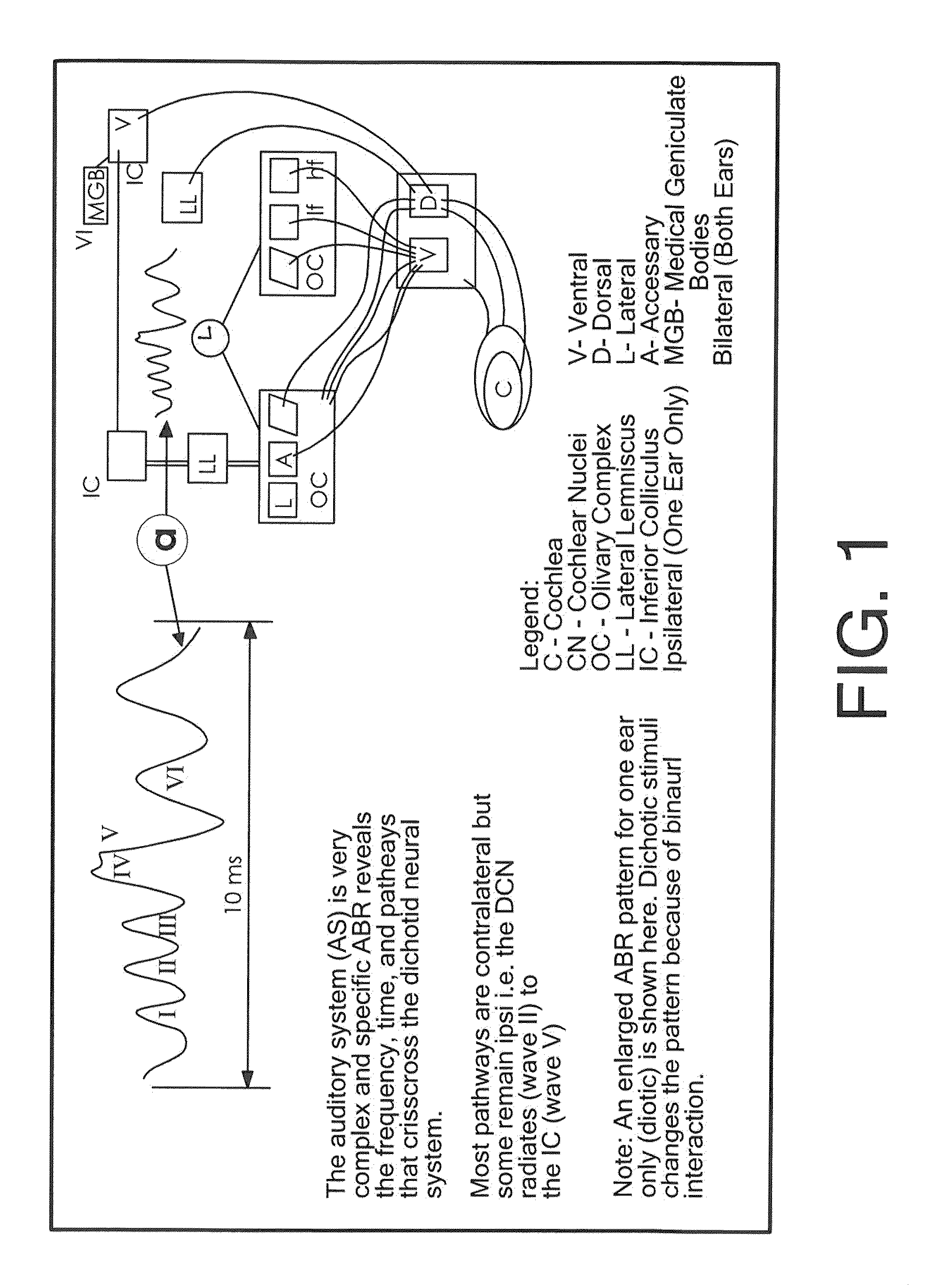
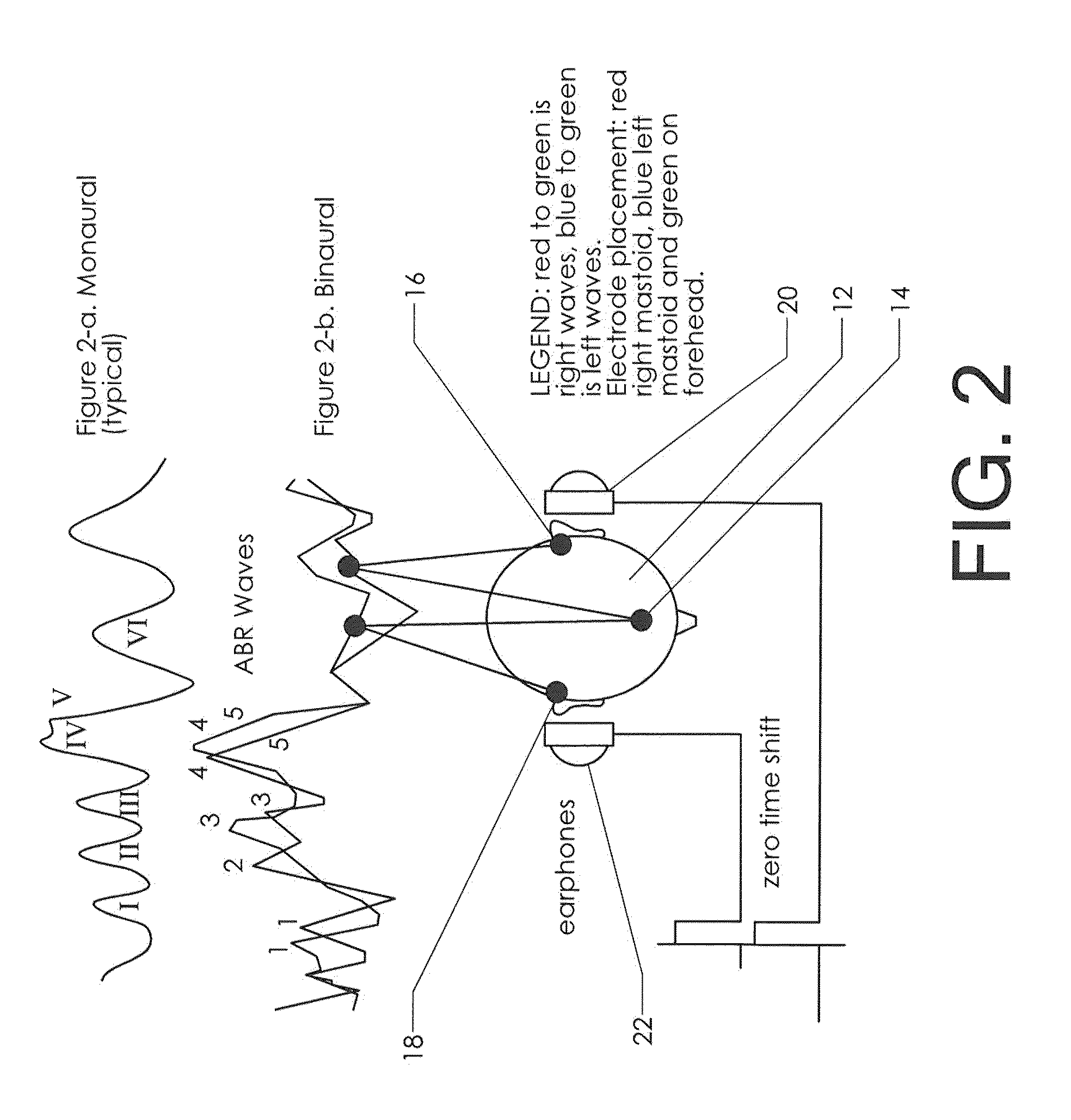
Neuroaudiological central auditory test apparatus and method of differentiation of the neural correlates in ptsd, tbi, autism, adhd, et al
An apparatus, software, procedures and technology that, beginning with a simple manipulative auditory paradigm, moves up the auditory neural pathways, modifying the basic stimulus from a unilateral routine audiology tool to a dichotic central auditory processing diagnostic tool that defines hearing loss along the entire auditory chain from the middle ear to the cortex. From the resultant data comes information related to the reduction of tinnitus employing parathreshold central procedures rather than the traditional suprathreshold masking or phase-shifting techniques. The new application modifies and applies known technology in new ways for both the top-down and bottom-up differential diagnosis of auditory disorders and the tinnitus reduction.
Owner:DICHONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com