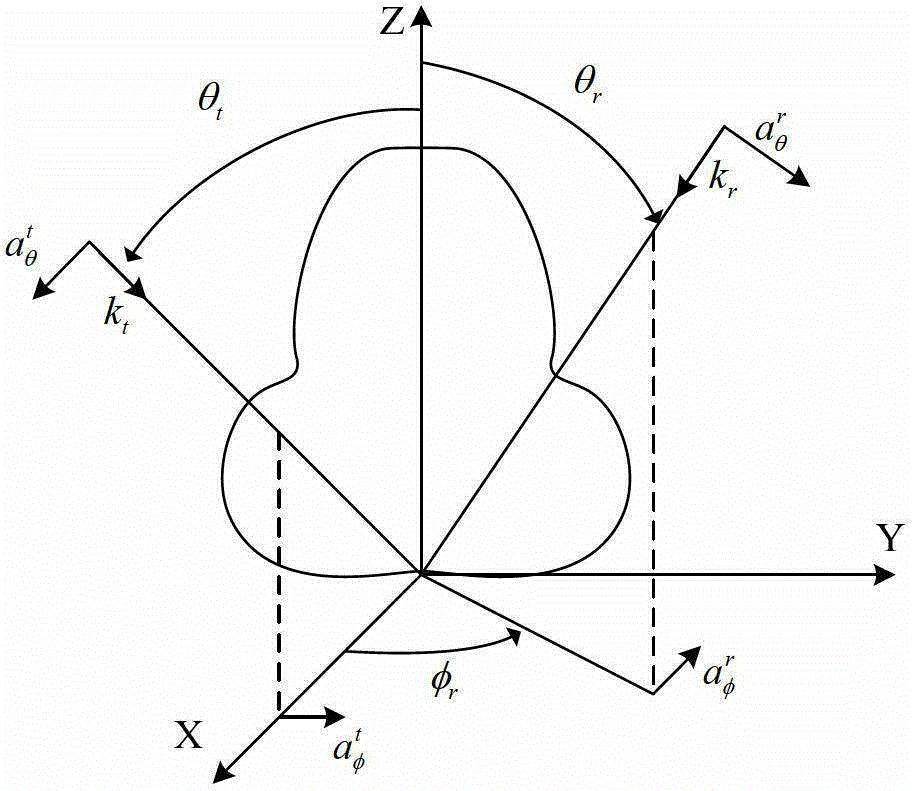
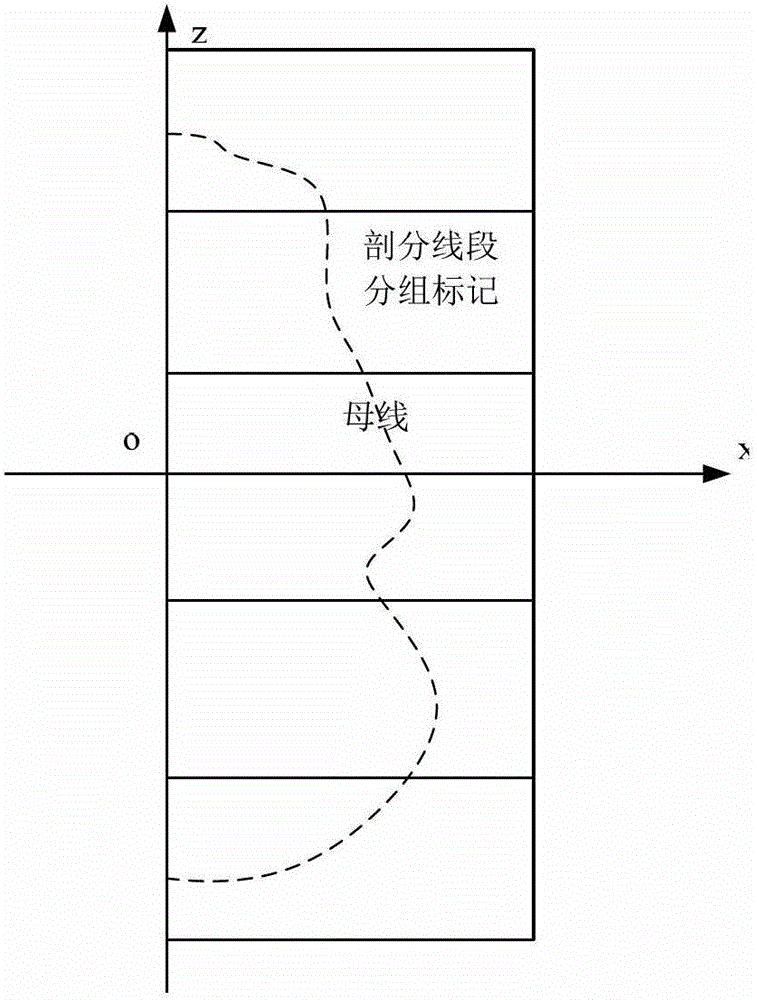
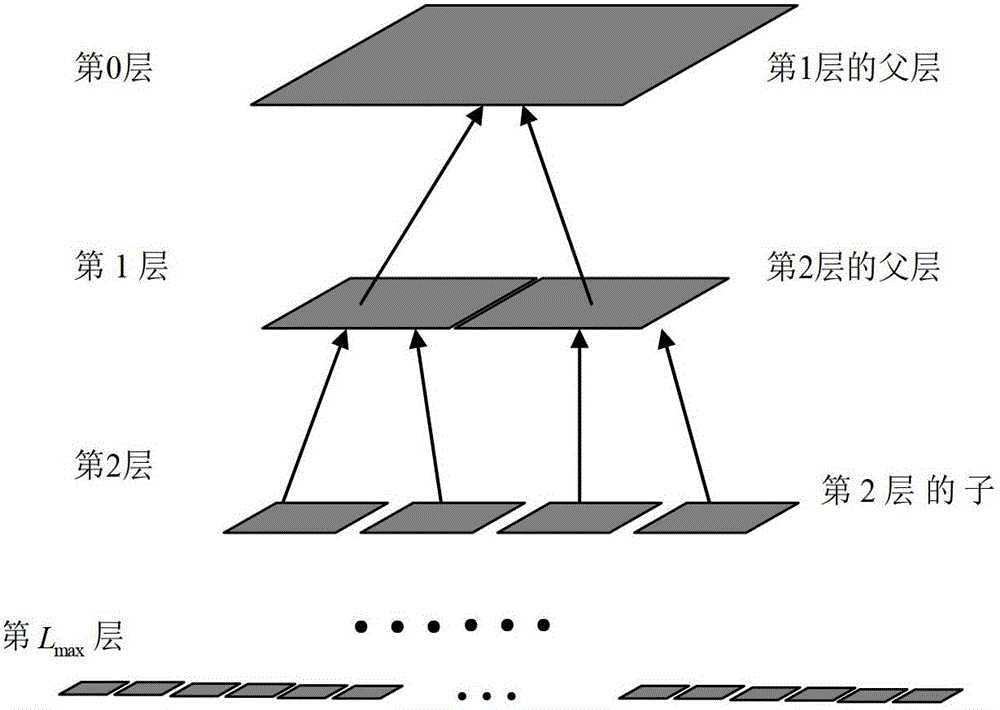
Simulation Method of Electromagnetic Scattering Characteristics of Rotationally Symmetric Body Based on Matrix Nested Compression
A technology of electromagnetic scattering characteristics and rotational symmetry, which is applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as divergence, and achieve controllable calculation accuracy, accelerated speed, and improved calculation time and calculation speed. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] According to the method of the present invention, a metal cylinder with a radius of 1m and a height of 20m is simulated. The frequency of the incident wave is 3GHz, the incident angle is (40°, 0°), a total of 43 modes are required, and the number of busbar division lines is 2200. The results are in good agreement with the original rotationally symmetric algorithm, proving the correctness of the method, such as Figure 5 shown. The present invention also provides the changes of the present invention in time consumption and memory consumption. Table 1 is a comparison between the calculation efficiency and the traditional method in Embodiment 1. As can be seen from the table, the memory consumption and calculation time are all obtained faster than the traditional method. Saved.
[0102] Table 1
[0103] method
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com