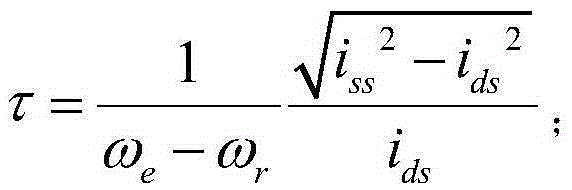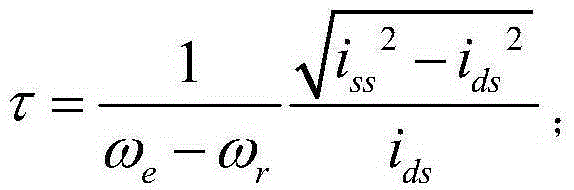Method for automatically identifying asynchronous motor rotor time constant by frequency converter
A rotor time constant, asynchronous motor technology, applied in the direction of motor generator control, control generator, electronic commutation motor control, etc., can solve the influence of motor control effect, current, voltage measurement error, rotor time constant and actual value deviation And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
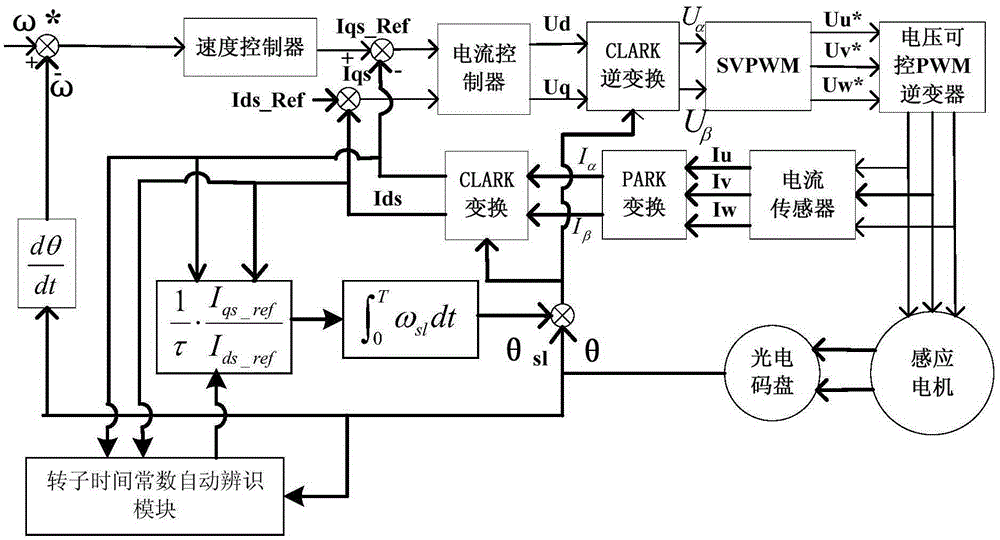
[0060] The method for automatically identifying the rotor time constant of an asynchronous motor according to Embodiment 1 includes the following steps:
[0061] Step a, calculate the approximate value τ of the rotor time constant according to the following formula;
[0062] τ = 1 ω e - ω r i s s 2 - i d s 2 i d s ;
[0063] Among them, ω e is the rated stator current angu...
Embodiment 2
[0076] The method for the inverter to automatically identify the rotor time constant of the asynchronous motor includes the following steps:
[0077] Step a, calculate the approximate value τ of the rotor time constant according to the following formula;
[0078] τ = 1 ω e - ω r i s s 2 - i d s 2 i d s ;
[0079] Among them, ω e is the rated stator current angular velocity...
Embodiment 3
[0092] The method for automatically identifying the rotor time constant of an asynchronous motor according to Embodiment 3 includes the following steps:
[0093] Step a, calculate the approximate value τ of the rotor time constant according to the following formula;
[0094] τ = 1 ω e - ω r i s s 2 - i d s 2 i d s ;
[0095] Among them, ω e is the rated stator current angu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com