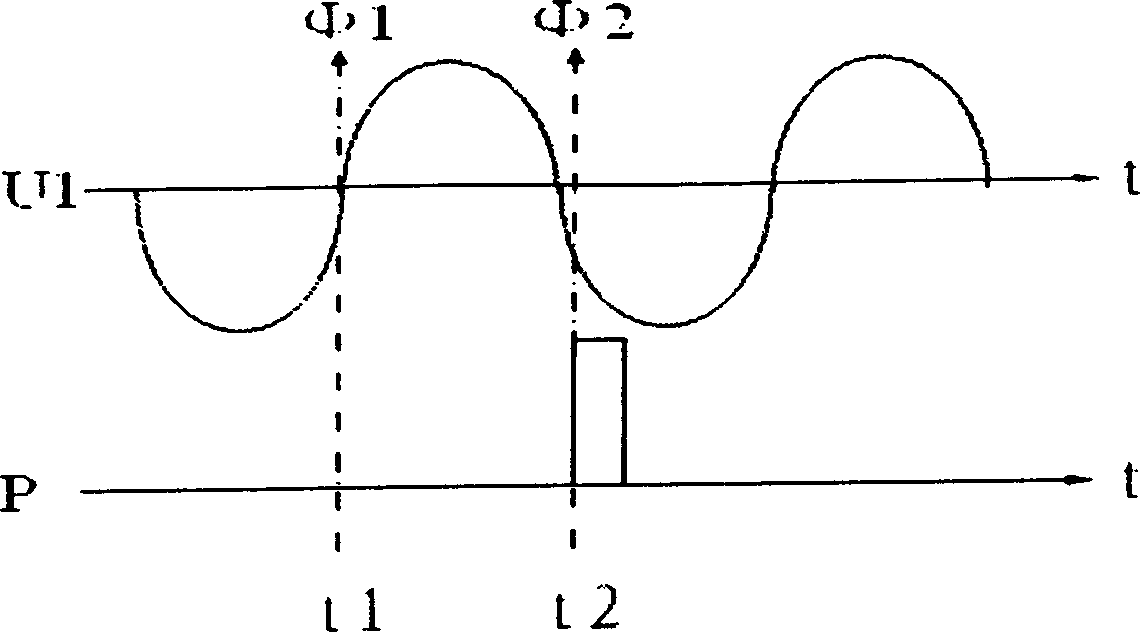Patents
Literature
108 results about "Load angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
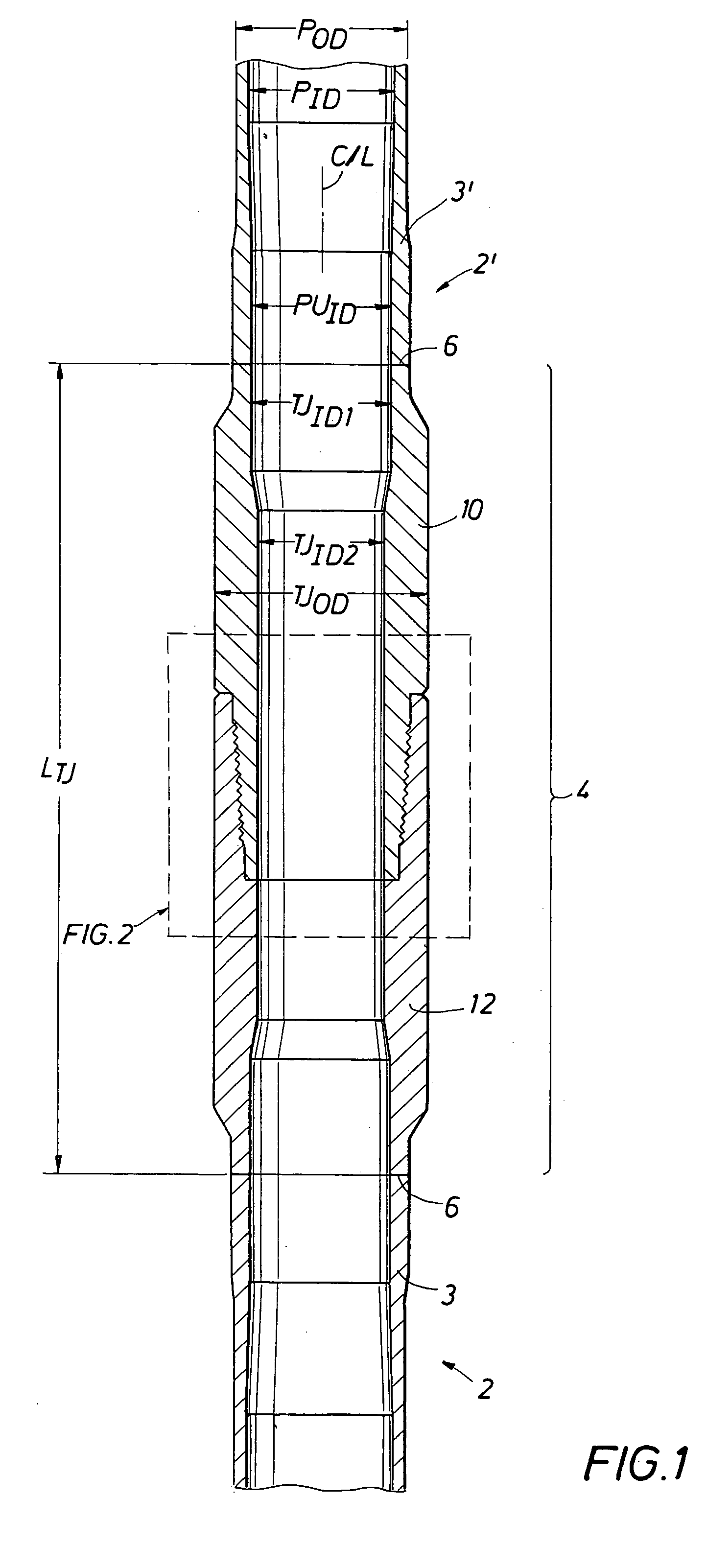
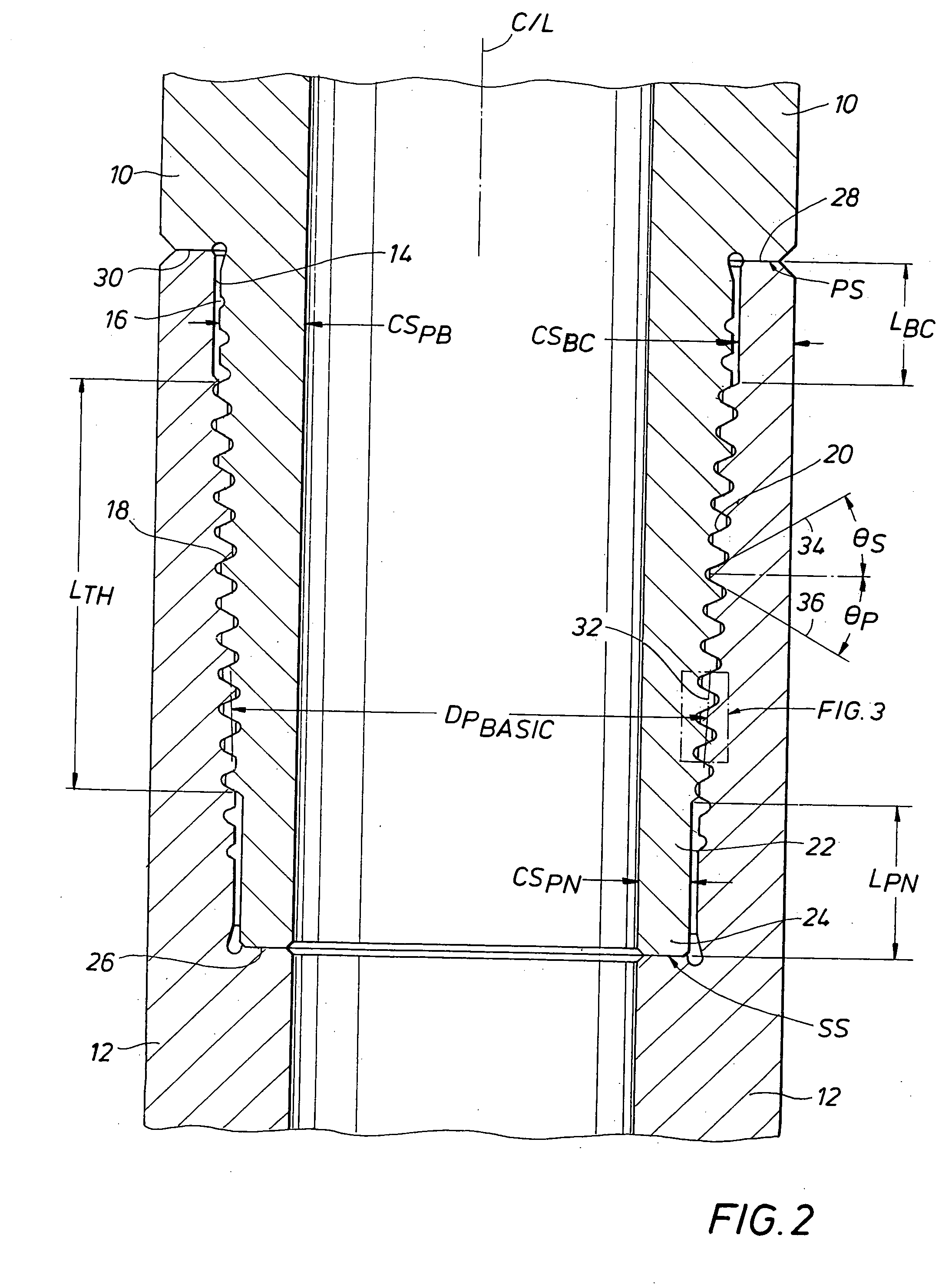
Drill stem connection
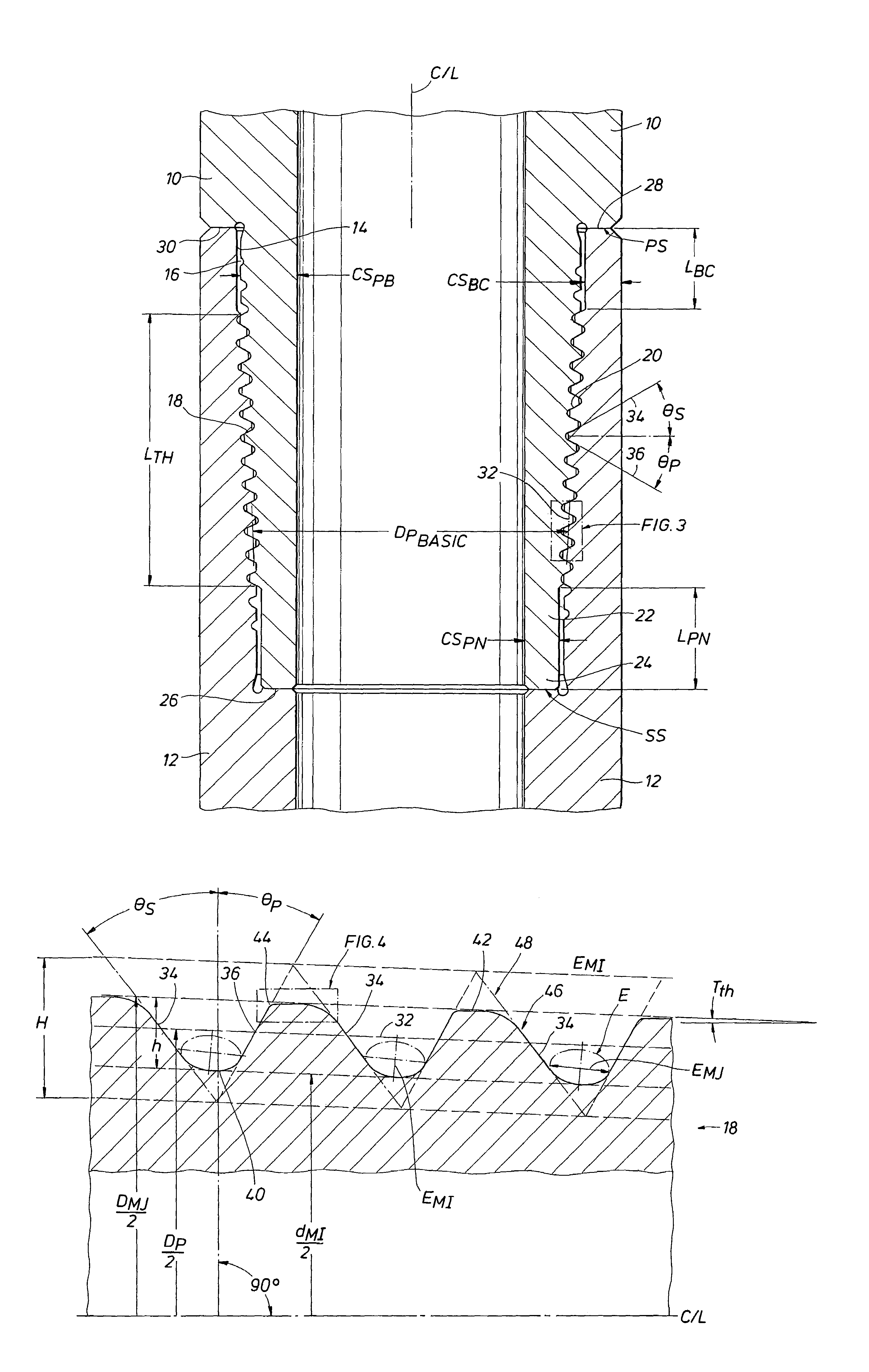
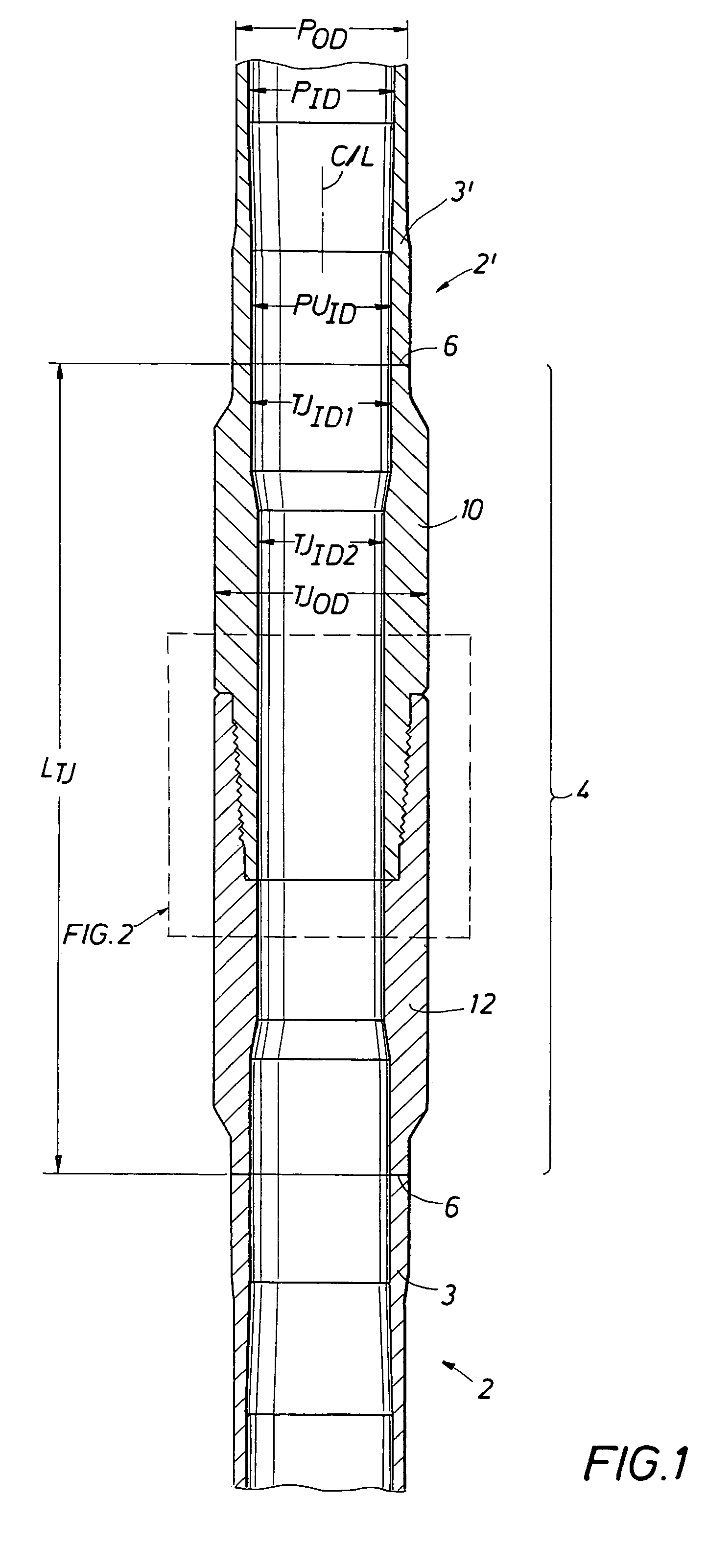
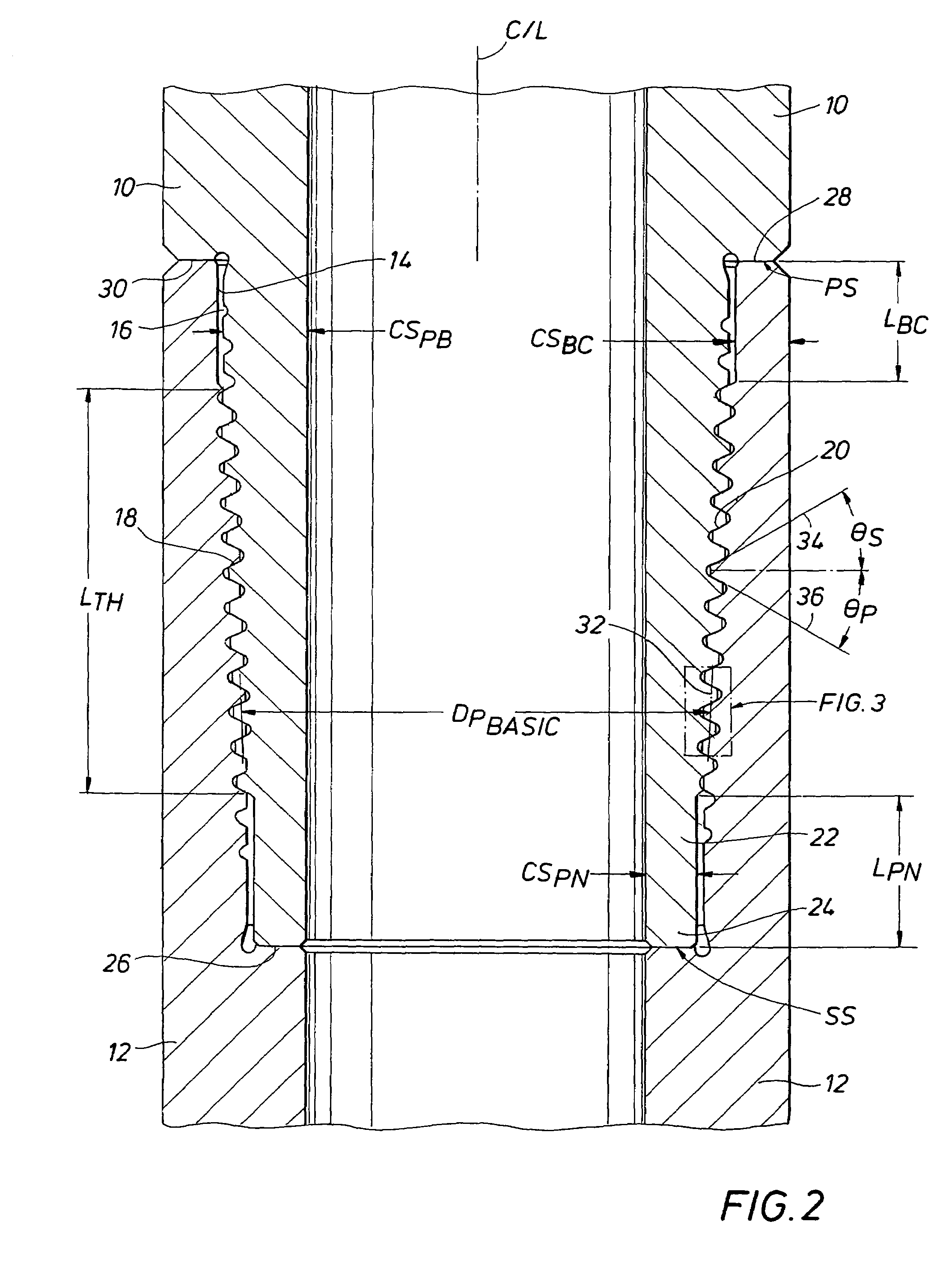
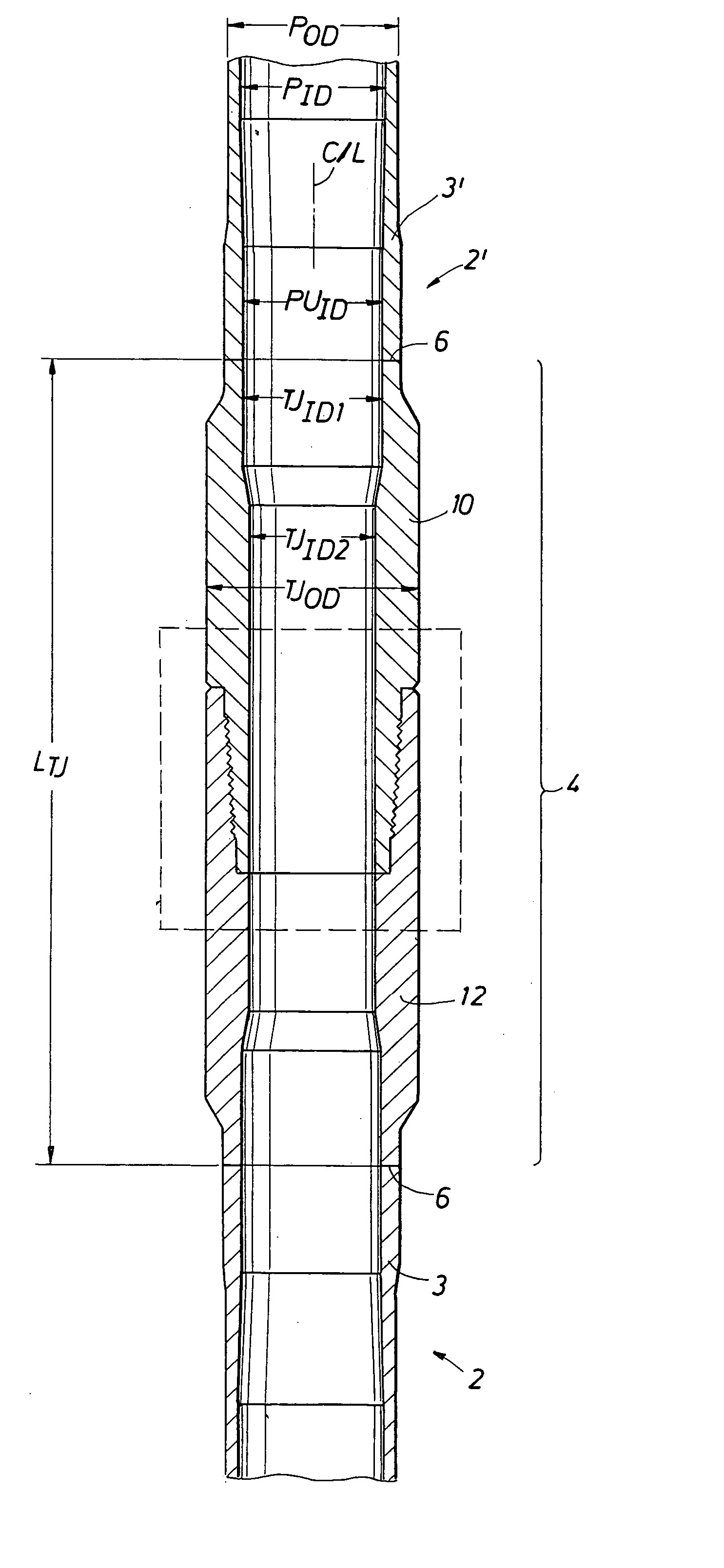
A double shoulder drill stem connection for high torque applications includes a thread taper within a range between about 1.0 and 1.2 inch per foot. The thread form is characterized by a stab angle between about 35 and 42 and a load angle between about 25 and 34 degrees and by a short thread height with elliptical roots and with crests having an angle which slopes in an opposite direction with respect to the joint centerline from the thread taper. A drill string includes a tool joint having different inner diameters for a substantial axial length to provide enhanced strength in the threaded portion of the joint.
Owner:VALLOUREC OIL & GAS FRANCE SAS
Drill stem connection
ActiveUS20050189147A1Enhanced yield torque characteristicDrilling rodsFlushingEngineeringHigh torque
A double shoulder drill stem connection for high torque applications includes a thread taper within a range between about 1.0 and 1.2 inch per foot. The thread form is characterized by a stab angle between about 35 and 42 and a load angle between about 25 and 34 degrees and by a short thread height with elliptical roots and with crests having an angle which slopes in an opposite direction with respect to the joint centerline from the thread taper. A drill string includes a tool joint having different inner diameters for a substantial axial length to provide enhanced strength in the threaded portion of the joint.
Owner:VALLOUREC OIL & GAS FRANCE SAS
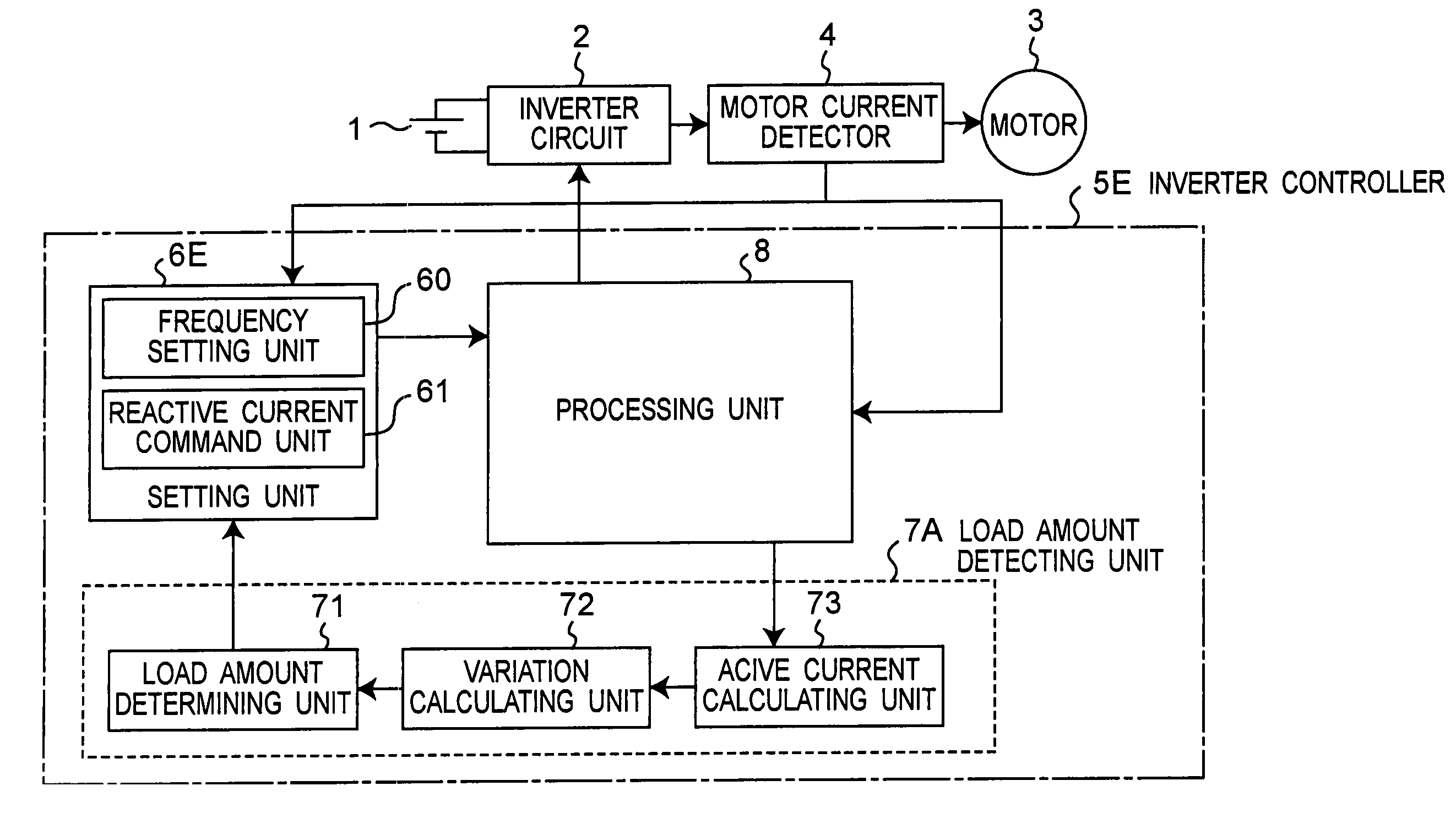
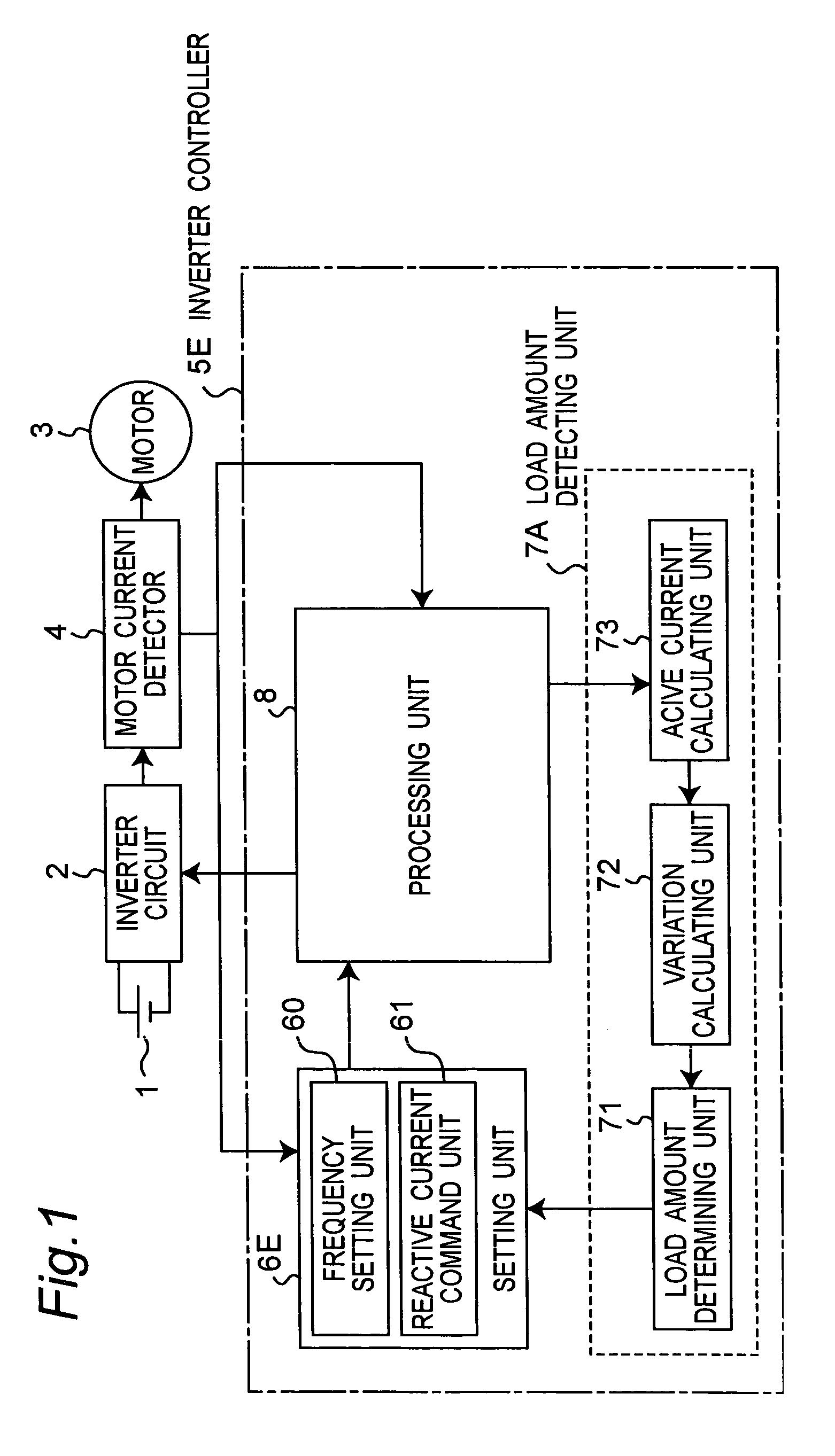
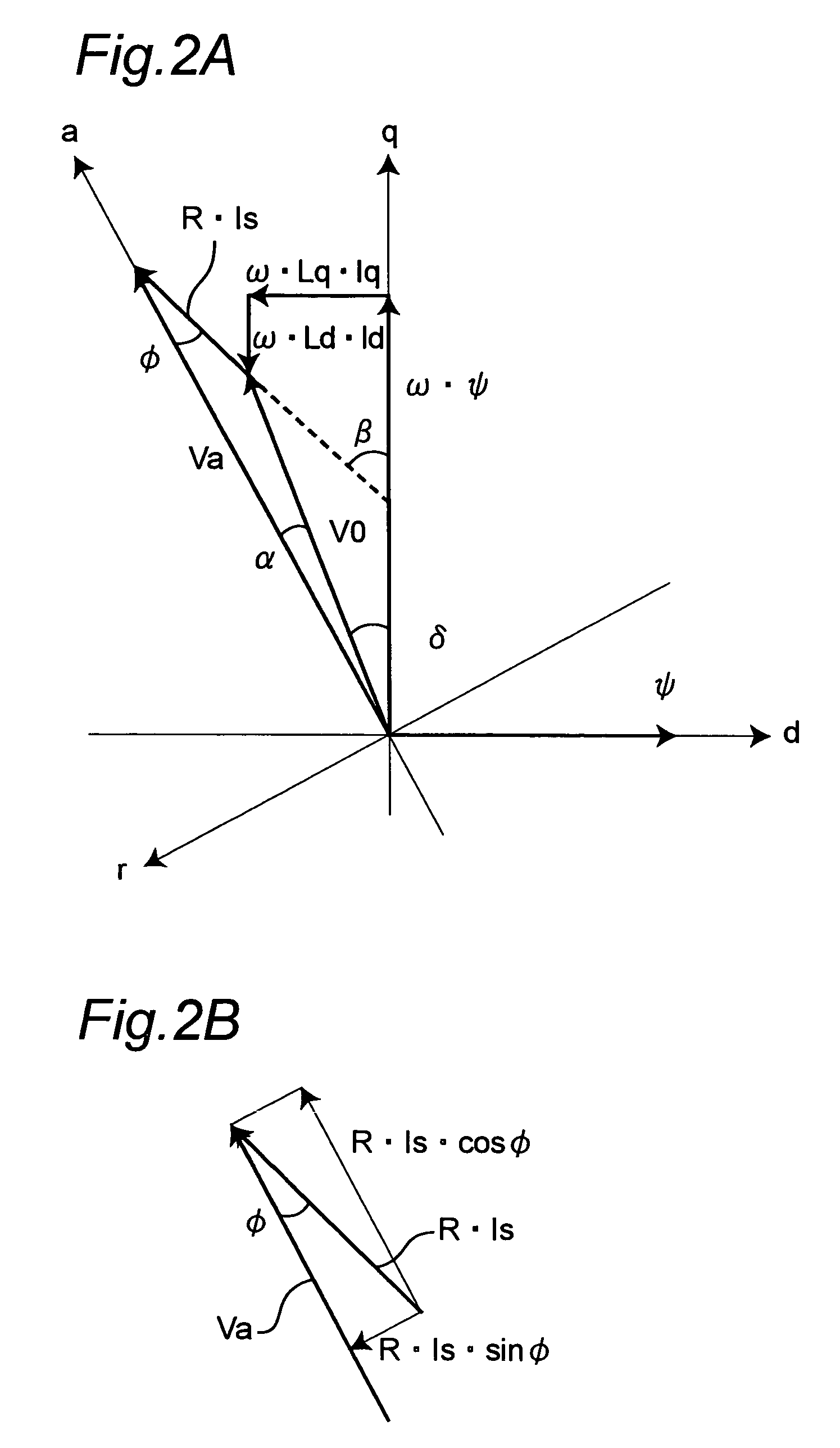
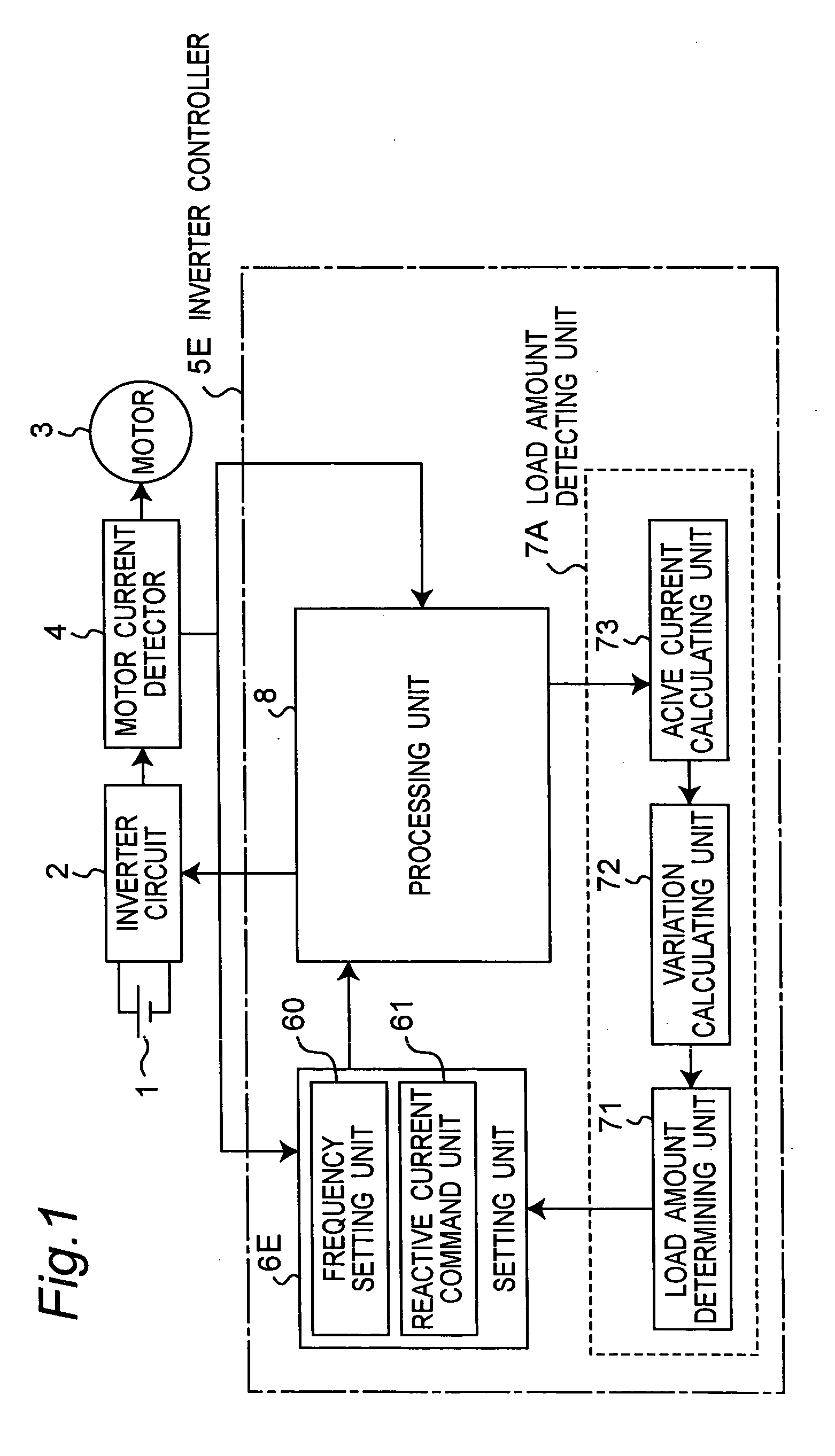
Motor control apparatus, and washing machine and drying machine using the same
InactiveUS7071641B2Small sizeLow costAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersPower inverterMotor drive
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Practical intelligent assist device
InactiveUS7461753B1Easily program and operate and monitorEasily program and operate and monitor statusDigital data processing detailsPortable liftingProgrammable logic controllerDrive motor
A practical intelligent assist device is provided that eliminates the complex use of force sensing weigh cells and vector interpreting software. By simplifying the input to a series of traditional voltage inputs, i.e. 1-4 volt signals, the use of standard available control componentry becomes available. Utilizing a series of such simplified inputs, including a load angle feedback, the processing of the vector math can be accomplished within a programmable logic controller (PLC). Outputs can then be simply generated to control a series of 0-60 Hz digital signals to drive direct drive motors.
Owner:GATTA RAYMOND P +2
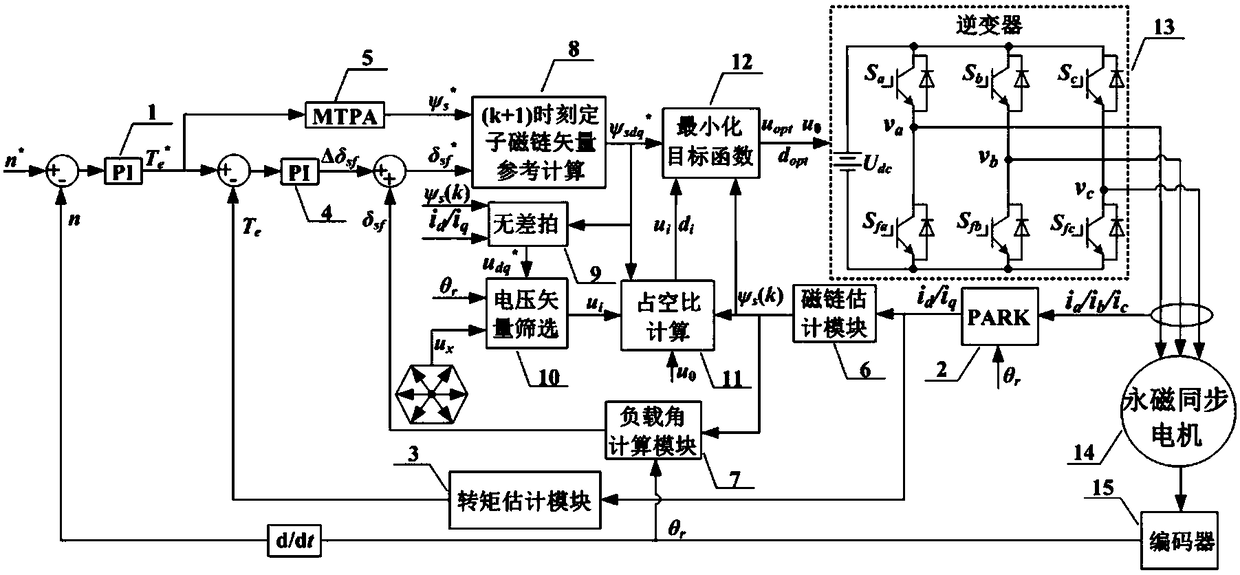
Non-weighted model predictive torque control system and method for permanent-magnet synchronous motors
ActiveCN107017810AEliminate weightsTorque ripple controlVector control systemsMaximum torqueSynchronous motor
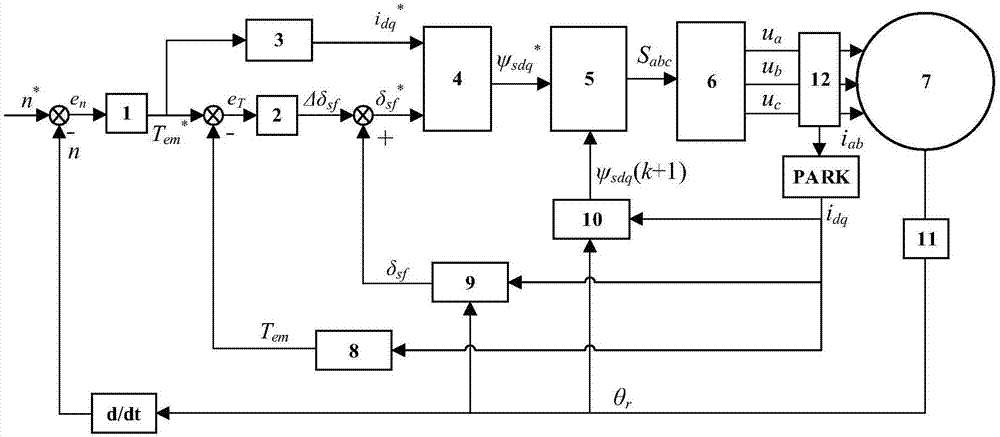
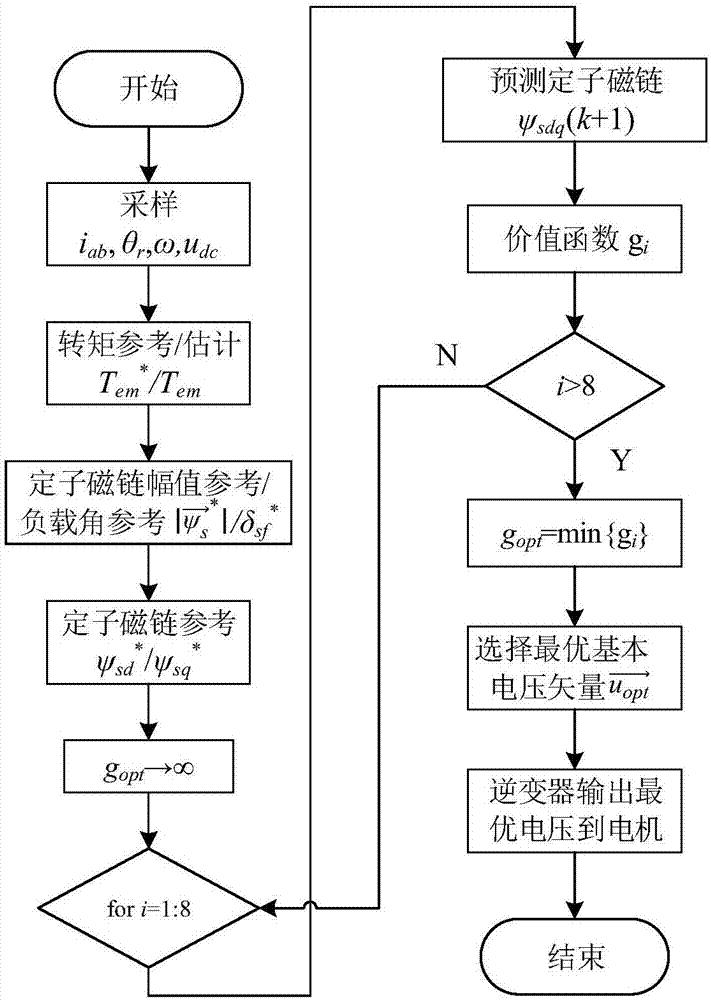
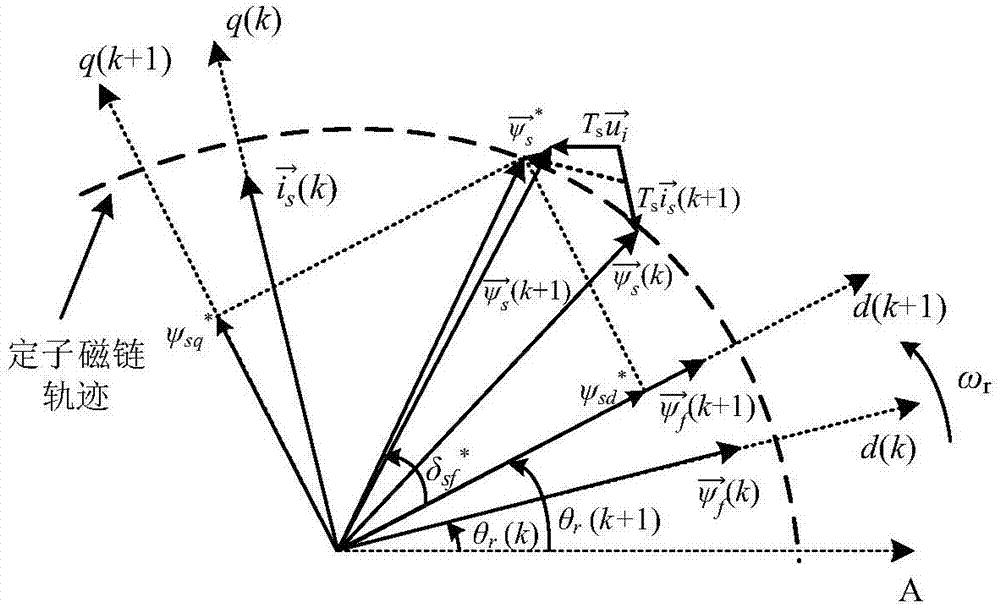
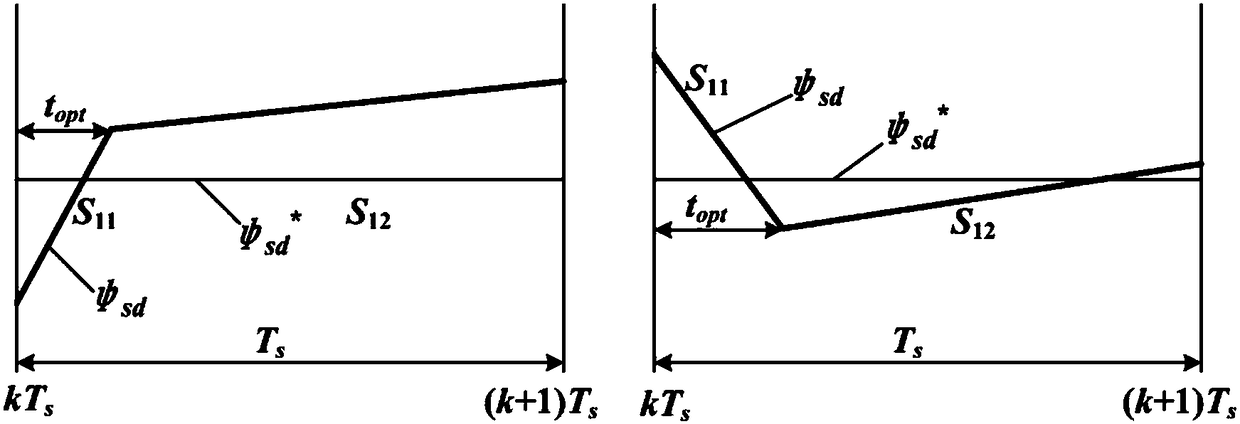
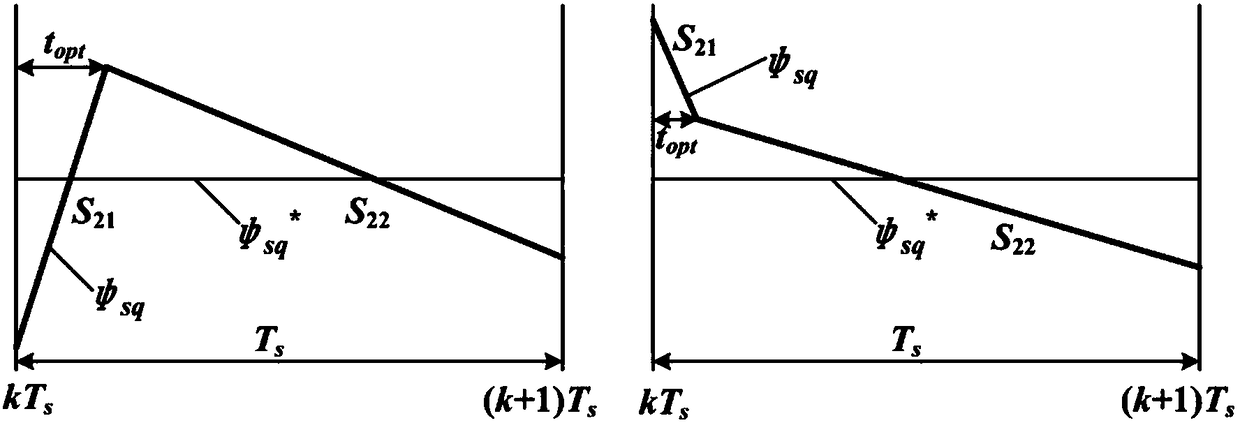
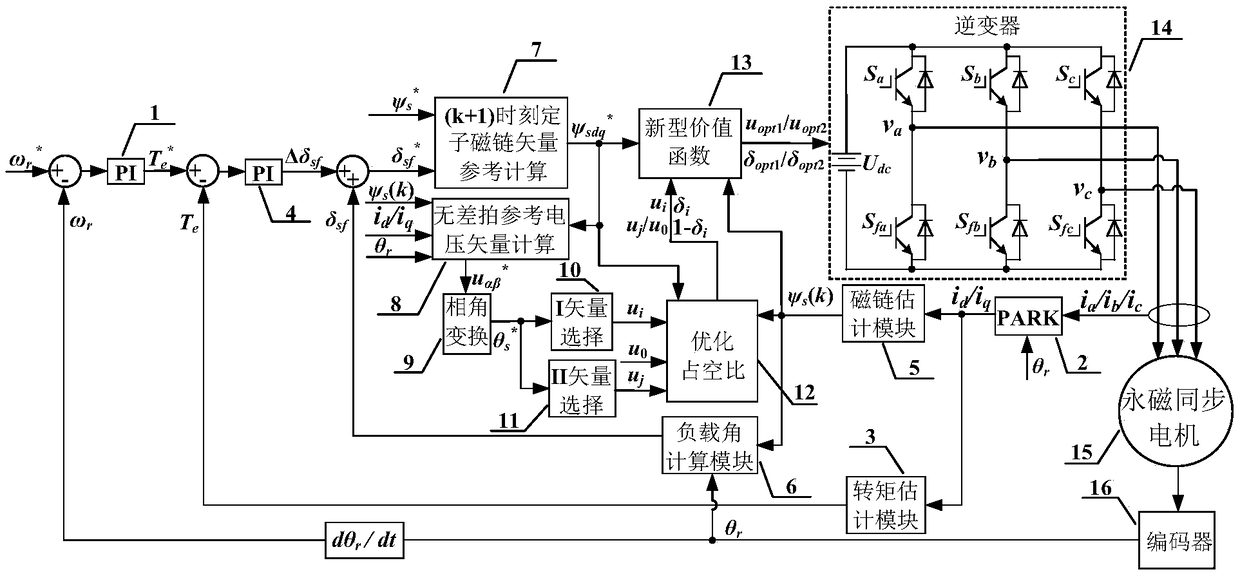
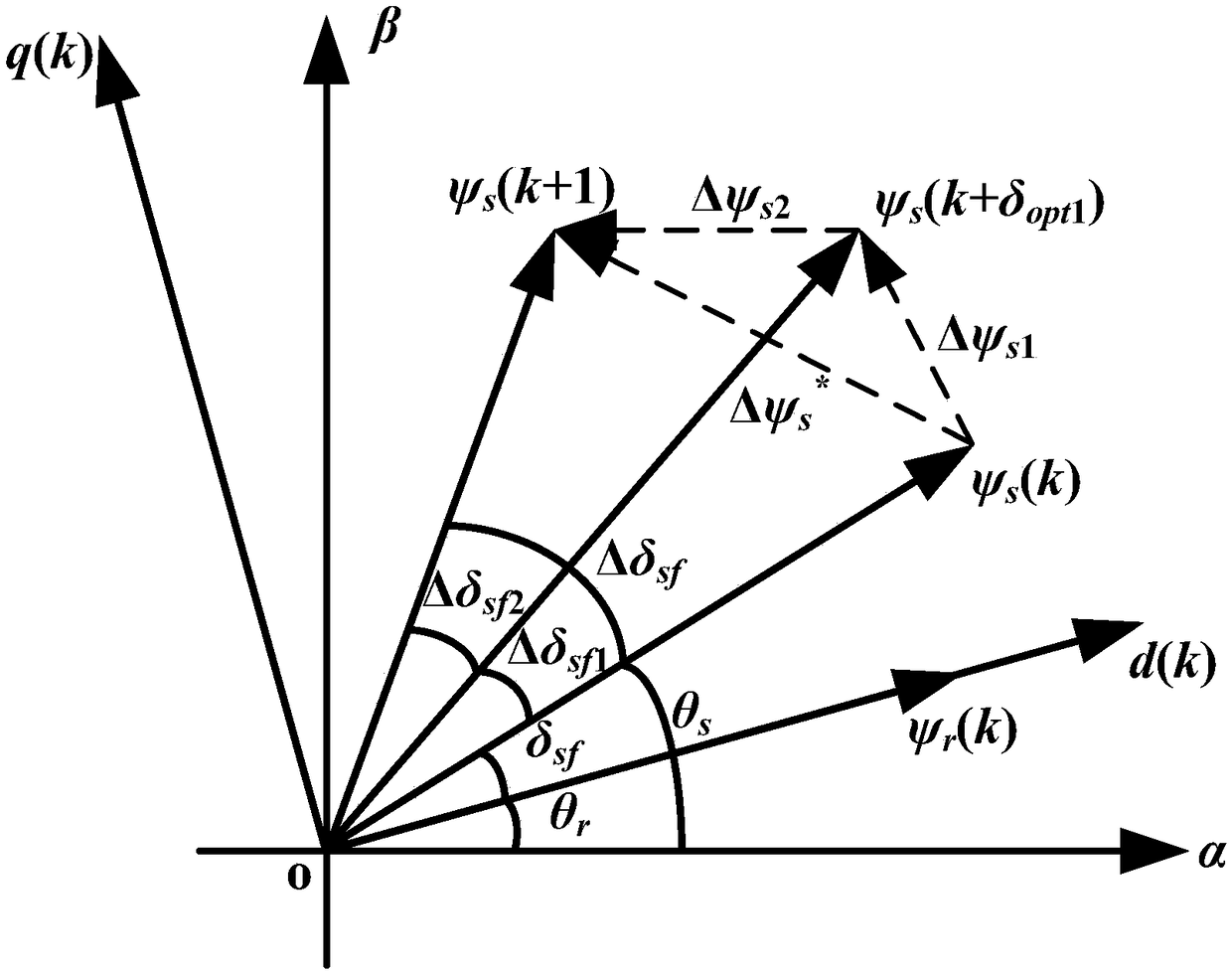
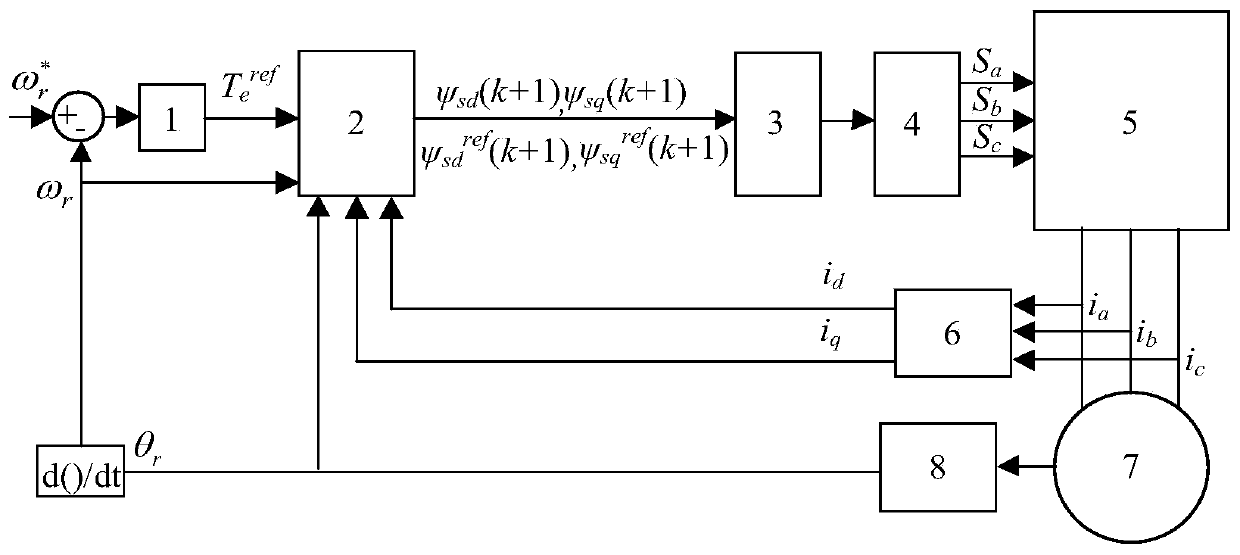
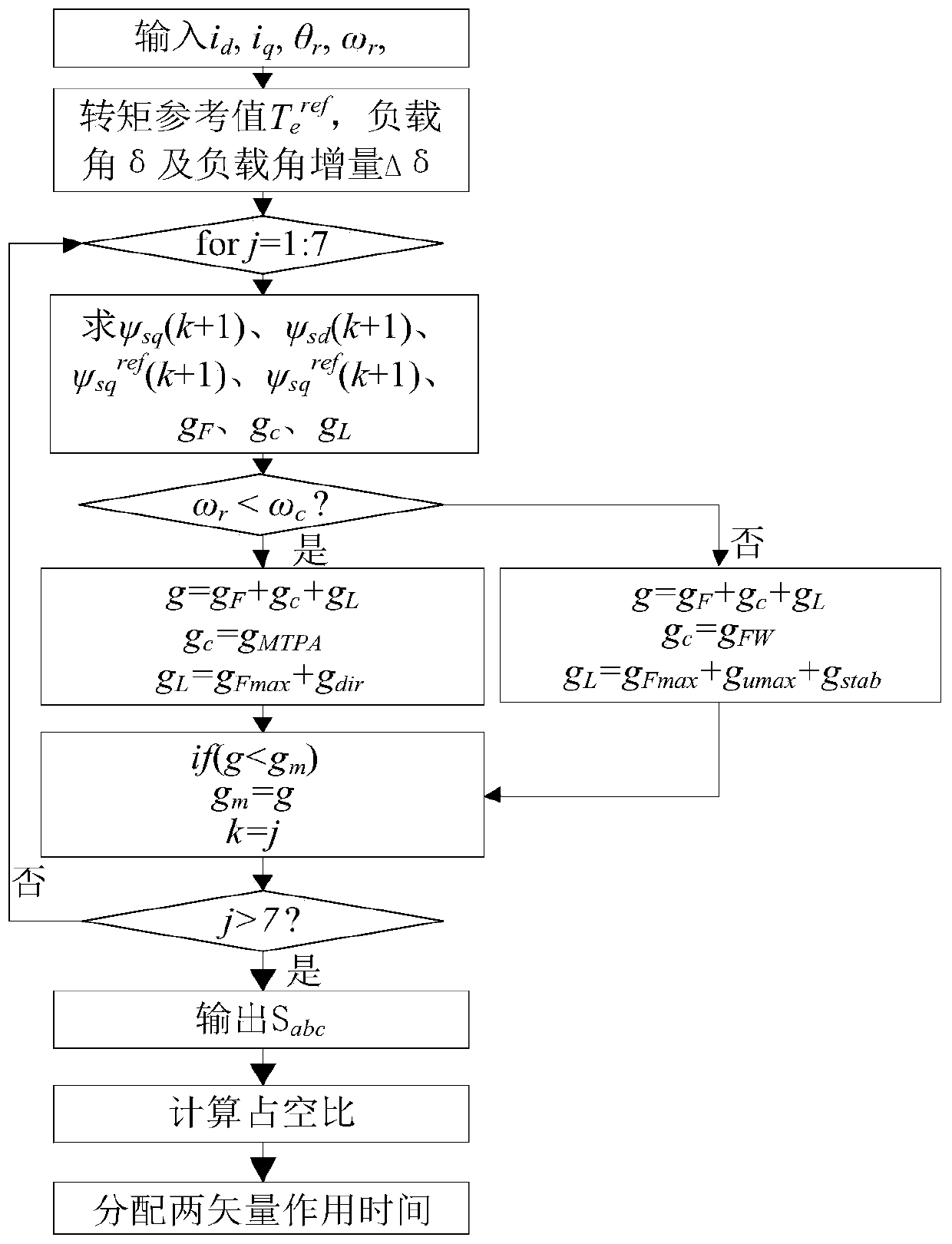
The invention discloses a non-weighted model predictive torque control system and a method for permanent-magnet synchronous motors. The method comprises the following steps: getting the reference value of torque through a speed controller, calculating the reference value of stator flux amplitude according to the principle of maximum torque-to-current ratio and a flux equation, and getting the load angle increment through a torque controller; getting the load angle at the current time through a calculated stator flux angle and a detected rotor position angle, getting the reference value of load angle at a time (k+1) according to the load angle increment and the load angle at the current time, and getting the reference value of stator flux at the time (k+1) based on the reference value of load angle and the reference value of stator flux amplitude; building a value function with use of the reference value of stator flux amplitude and a predicted value of stator flux amplitude; and getting an optimal voltage vector by optimizing the value function, and transmitting the optimal voltage vector to a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. The salient pole effect of the permanent-magnet synchronous motor is taken into account. The method can be combined with other optimization control strategies, and can be applied both to a constant-torque zone and a constant-power zone.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Permanent-magnet synchronous-motor open-winding fault-tolerant direct torque control method based on improved SVPWM
ActiveCN108418502AGuaranteed voltage utilizationGuaranteed uptimeElectric motor controlField acceleration method controlVoltage vectorControl signal
The invention discloses a permanent-magnet synchronous-motor open-winding fault-tolerant direct torque control method based on improved SVPWM. The method comprises the following steps of when an inverter switch tube has an open circuit fault, cutting off connection between a motor port and the fault inverter switch tube, connecting the motor port to a power supply midpoint, and using the remainingswitch tube to carry out fault-tolerant reconstruction on a system topology; through a PI controller, outputting a given torque; using a ''current method'' to estimate a stator flux linkage; and through the difference value of the given torque and an estimated torque, acquiring the variable quantity d delta of a load angle, using a maximum torque current ratio control method to give a reference stator flux linkage, and based on that, calculating a given reference voltage vector. Through the remaining switch tube, improved spatial voltage vector pulse width modulation reconstruction is performed. A double-inverter PWM control signal with a fixed switch frequency is output to an inverter. Under the open circuit fault of the switch tube, the safe and stable operation of a system under the fault is guaranteed, and the system has a good stable state and dynamic performance.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Online transient stability analysis method based on concise expression form of electromagnetic power of single generator in multi-machine power system
InactiveCN101794998AEasy to analyzeReliable resultsSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemMulti machine systemTransient stability analysis
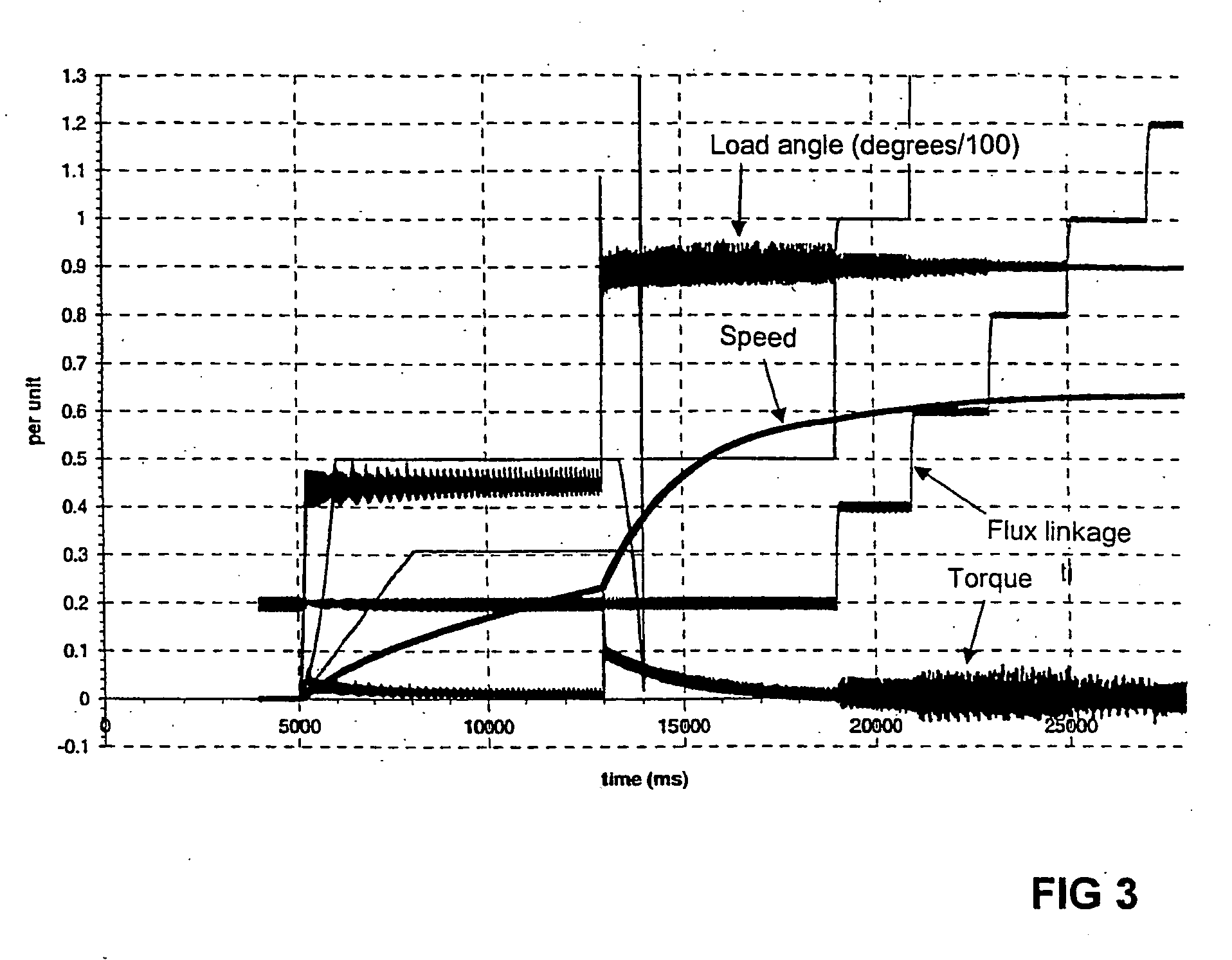
The invention discloses an online transient stability analysis method based on a concise expression form of electromagnetic power of a single generator in a multi-machine power system. Electromagnetic output power of any single generator in the power system is a multivariable nonlinear function of all generator load angles or a multivariable nonlinear function of a slip between all generator load angles and an inductor rotor, which is known by analyzing the traditional power system. A concise expression form of the electromagnetic output power of any single generator in the complex power system is obtained through expanding a Taylor series; a load angle swinging curve of a multi-machine power system and an electromagnetic power curve are obtained through time domain simulation, and a coefficient in a high-order polynomial function is obtained by using data fitting; the load angle curve obtained through the fitting is extended to obtain a predictive load angle curve of a future moment, and the stability margin of the single generator in the multi-machine system and the system can be obtained by using the obtained concise expression form of the single generator load angle curve. The invention can be used for the online transient stability analysis of the large-scale power system.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Motor driving circuit
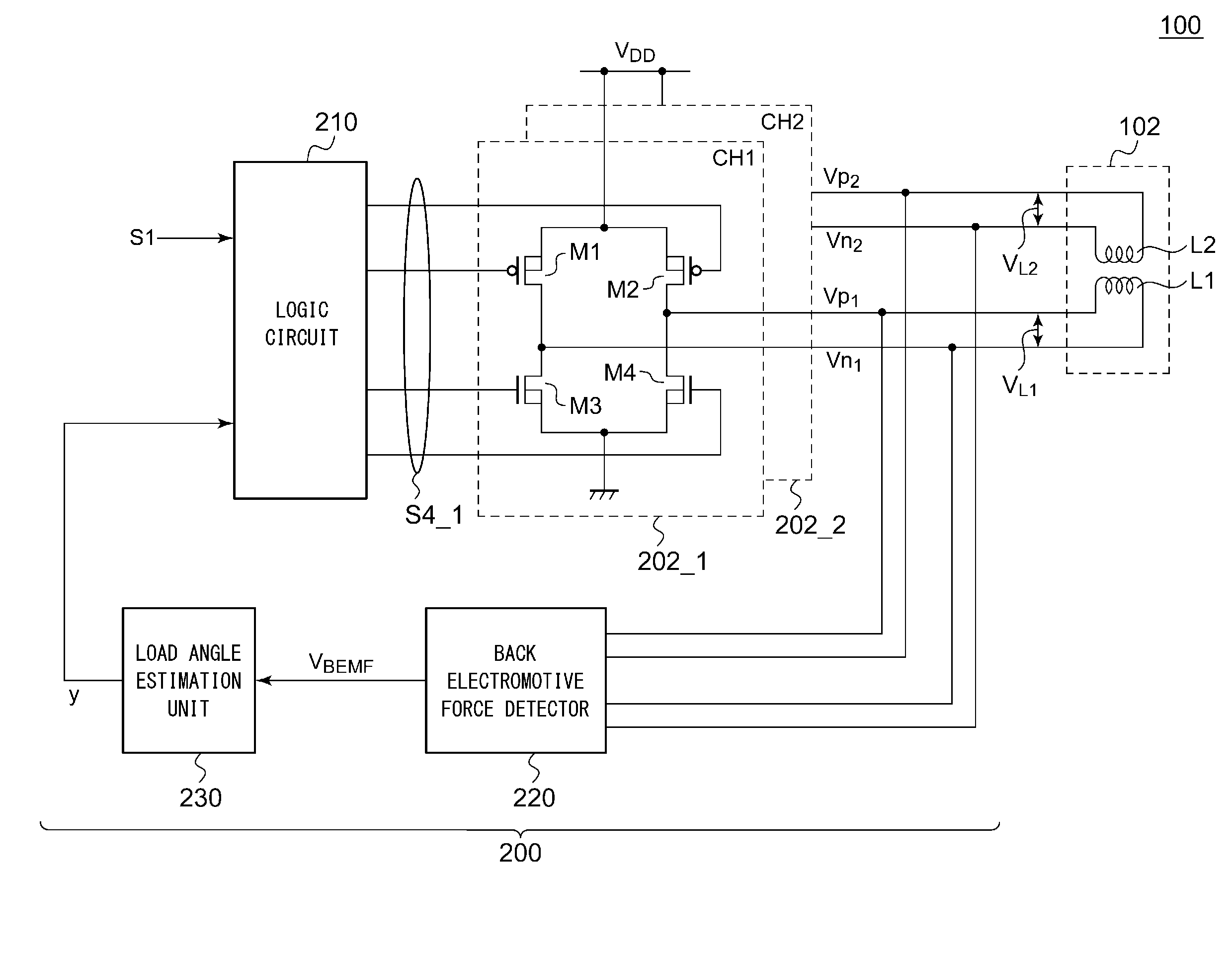
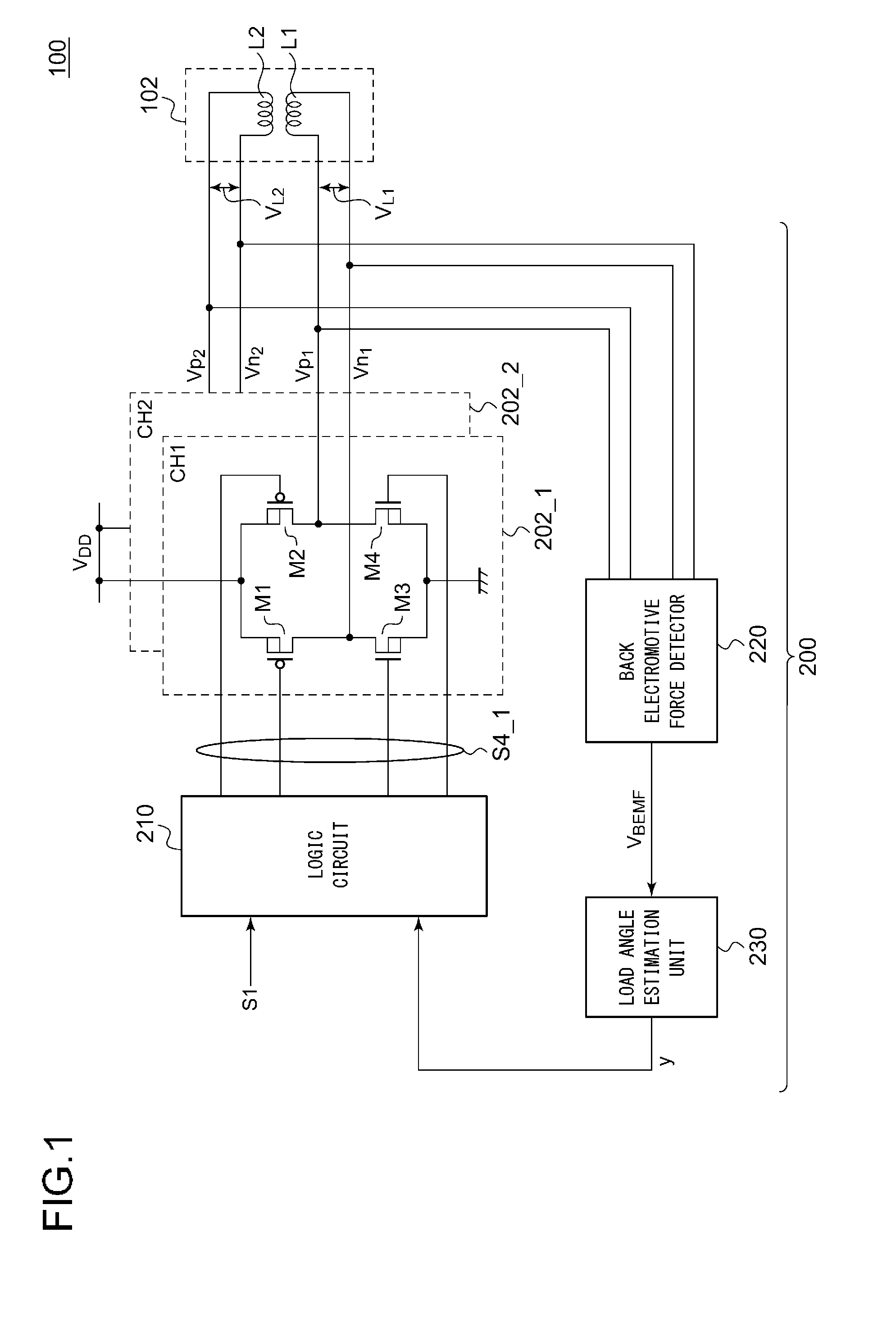
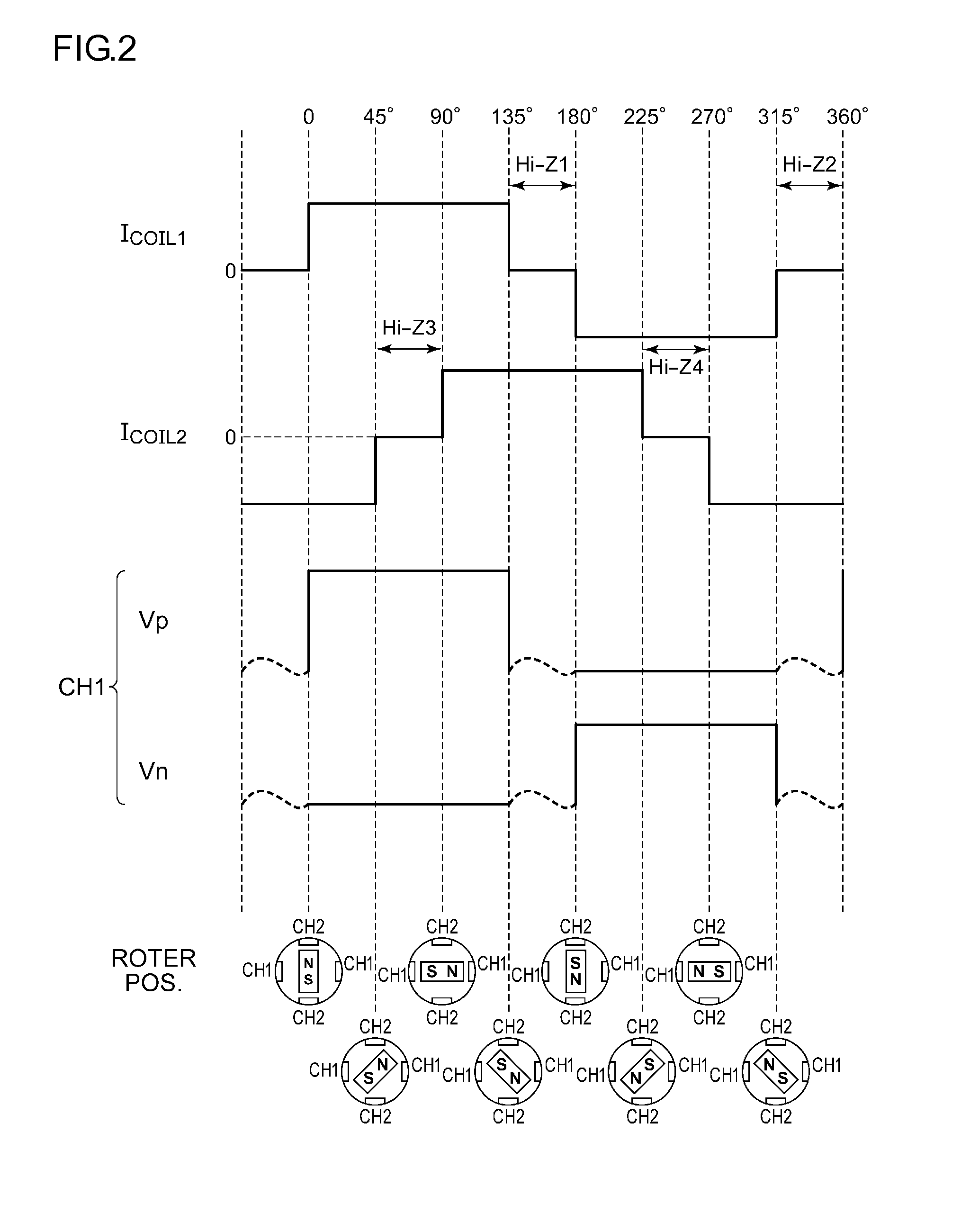
ActiveUS20150123591A1Uniform characteristicsReduce circuit areaElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlEngineeringElectromotive force
A logic circuit controls a bridge circuit connected to a coil of a stepping motor in synchronization with an input pulse, so as to control electric power supplied to the coil of the stepping motor. A back electromotive force detector detects the back electromotive force VBEMF across the coil L. A load angle estimation unit estimates the load angle φ based on the back electromotive force detected in the detection period set in the high-impedance period set for the coil L. A logic circuit is configured to adjust electric power supplied to the coil such that the estimated load angle φ approaches a predetermined target angle φREF.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Motor control apparatus, and washing machine and drying machine using the same
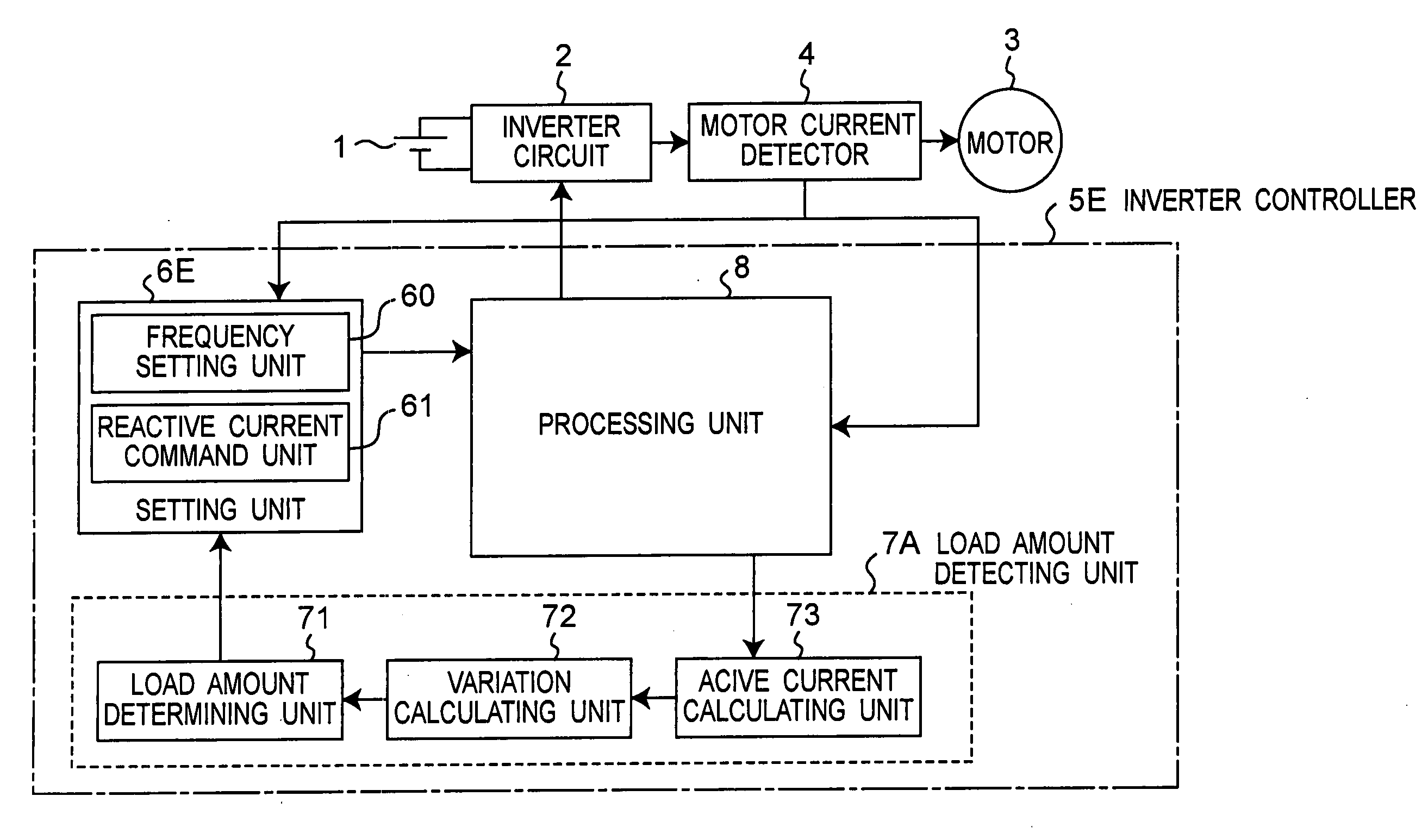
InactiveUS20050104552A1Small sizeLow costMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersMotor driveControl theory
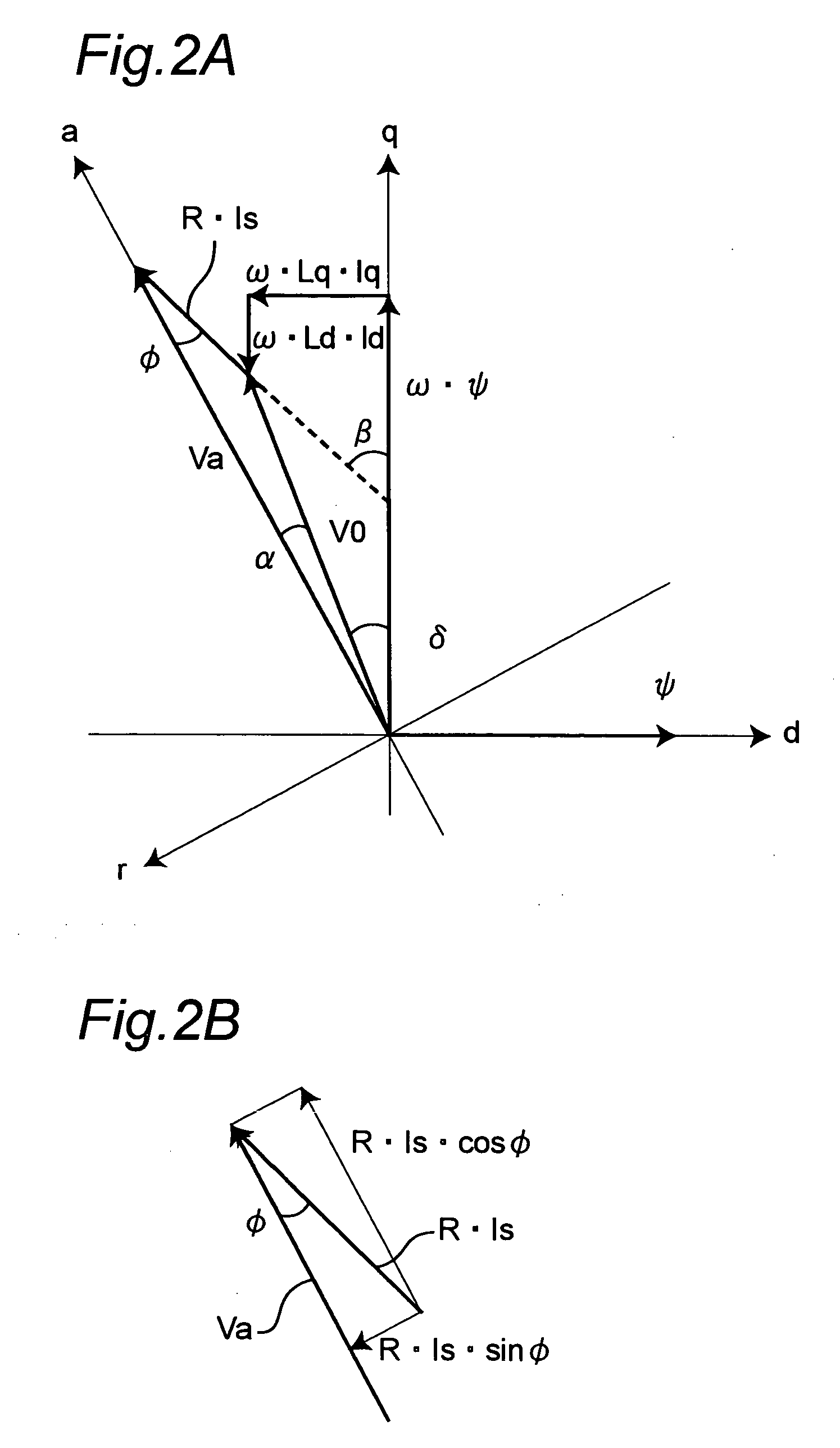
A motor control apparatus includes an inverter circuit 2 for supplying driving power to a motor 3, motor current detector 4 for detecting current flowing through the motor 3, inverter controller 5E for controlling the inverter circuit 2 based on the output of the detector 4. The inverter controller 5E has a setting unit 6E for setting various command values to control motor driving status, and processing unit 8 for controlling the inverter circuit 2 based on the setting on the setting unit 6E. The setting unit 6E sets command value so that a load angle which is an angle between rotor axis and motor applied voltage is operated on the smaller side of the angle that provides the maximum output torque in the load angle-output torque characteristics.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
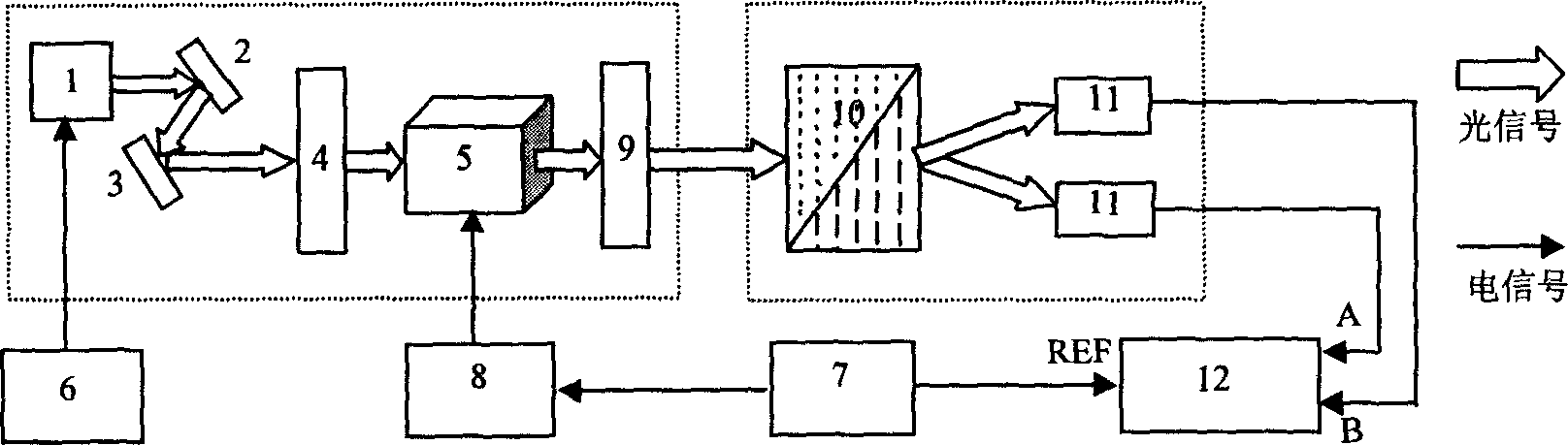
Electrooptical angle measurer
InactiveCN1527025ACompact structureStable jobUsing optical meansRadio transmissionMeasurement deviceElectric control
The present invention relates to one kind of electrooptical angle measurer and belongs to the field of electrooptical detection technology. The present invention aims at real-time monitoring coaxial relative rotation angle of emitting platform and receiving platform separated by certain distance to realize second level angle measurement. The technological scheme of the present invention includes measurer comprising three parts of emitting part, receiving part and electric control part; grating outer-cavity semiconductor laser as light source; electrooptical lithium niobate crystal for loading angle information; polarizing light splitter and light detector for demodulating information; and differential processing technology used in processing obtained electrical signal. The present invention can complete angle measurement in second level precision with an angle measurer with compact structure, high vibration resistance and high long term stability.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
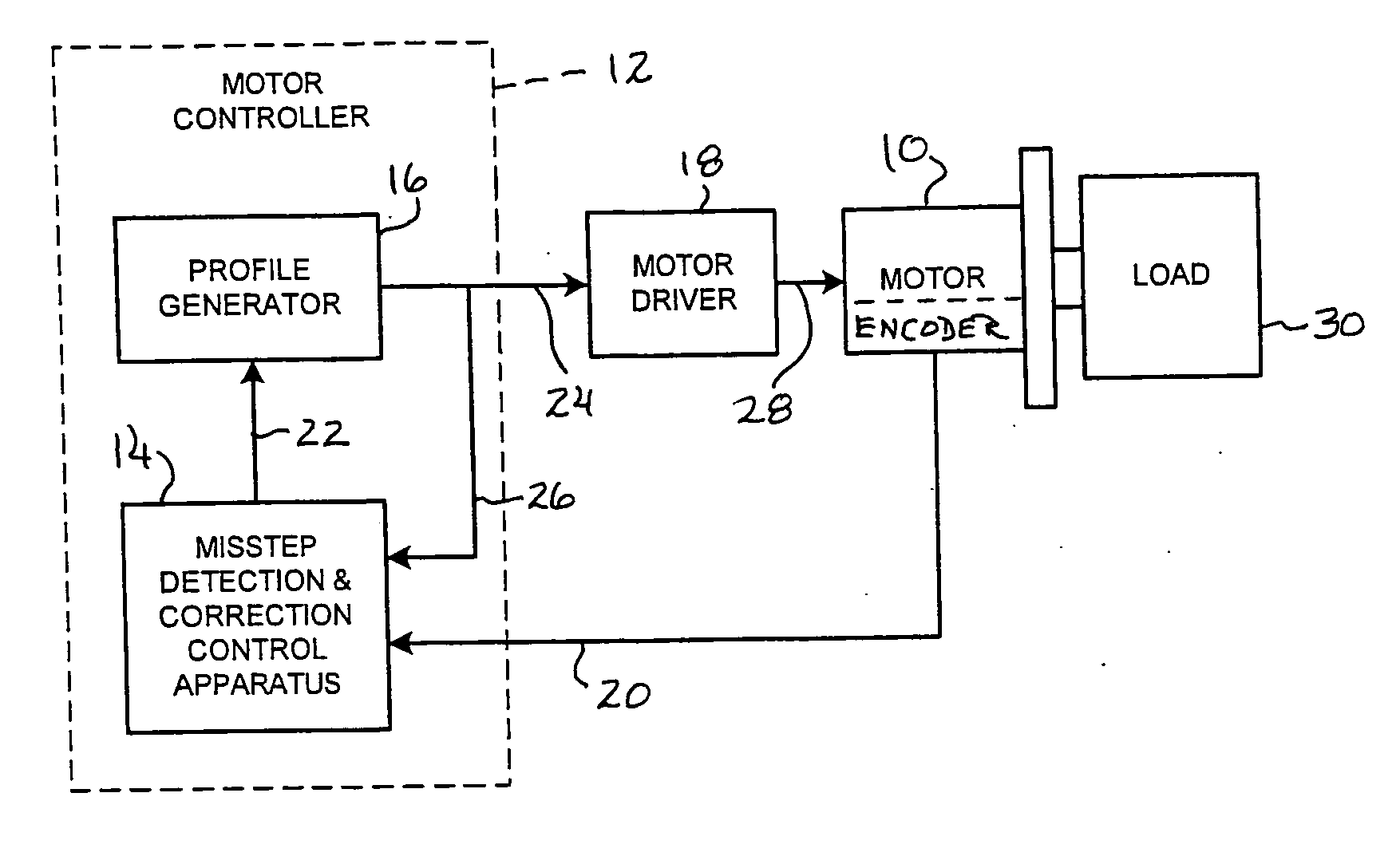
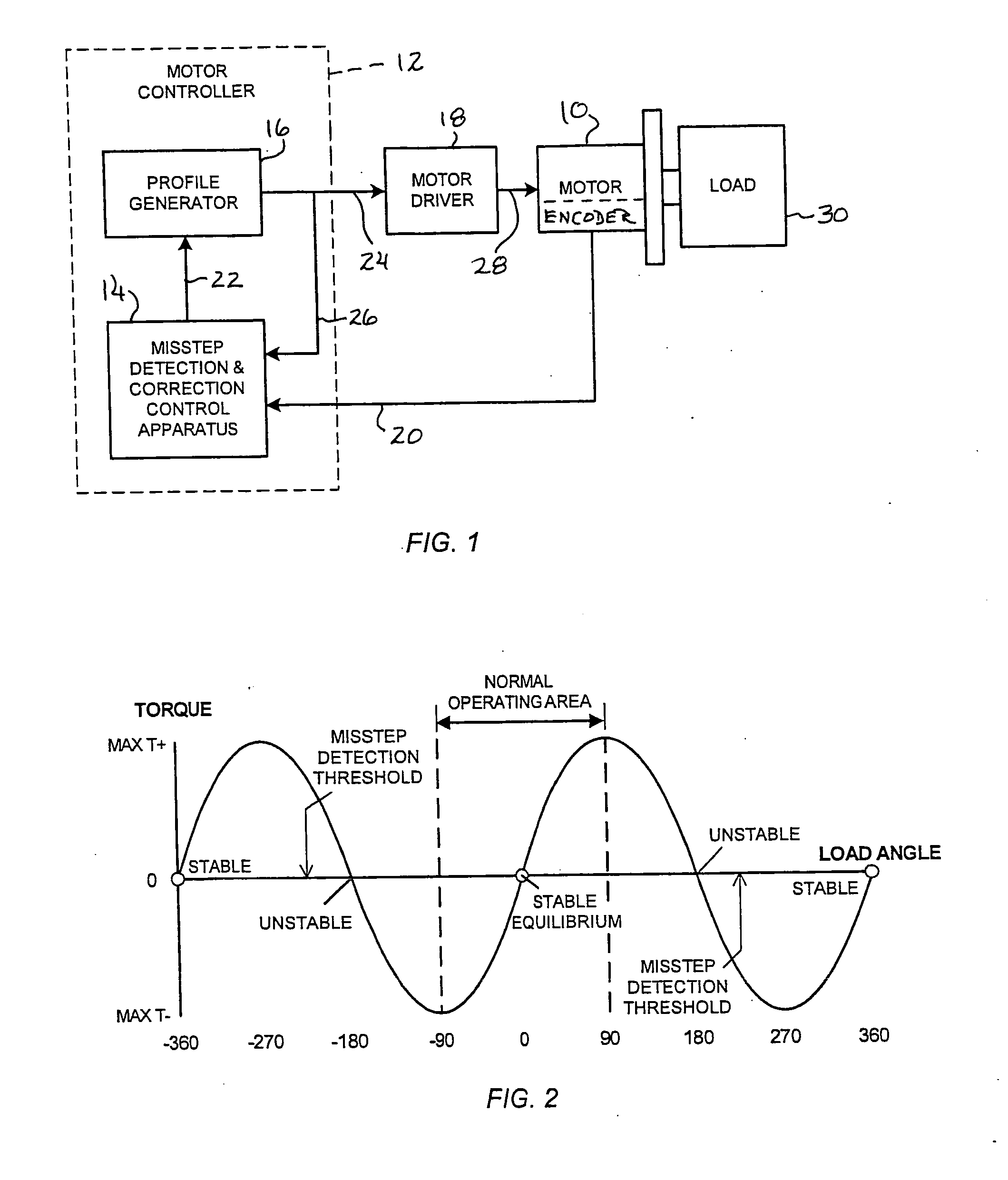
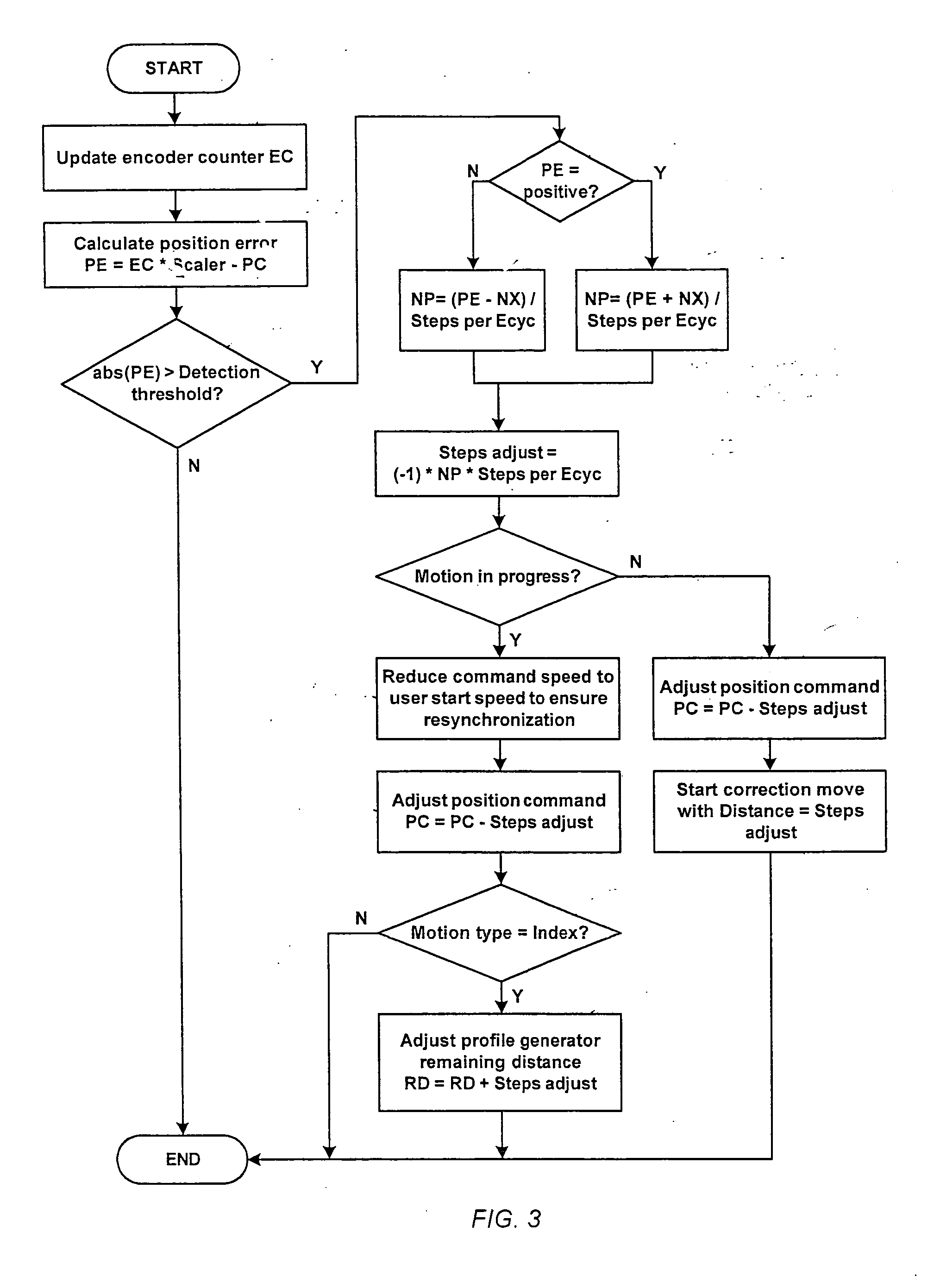
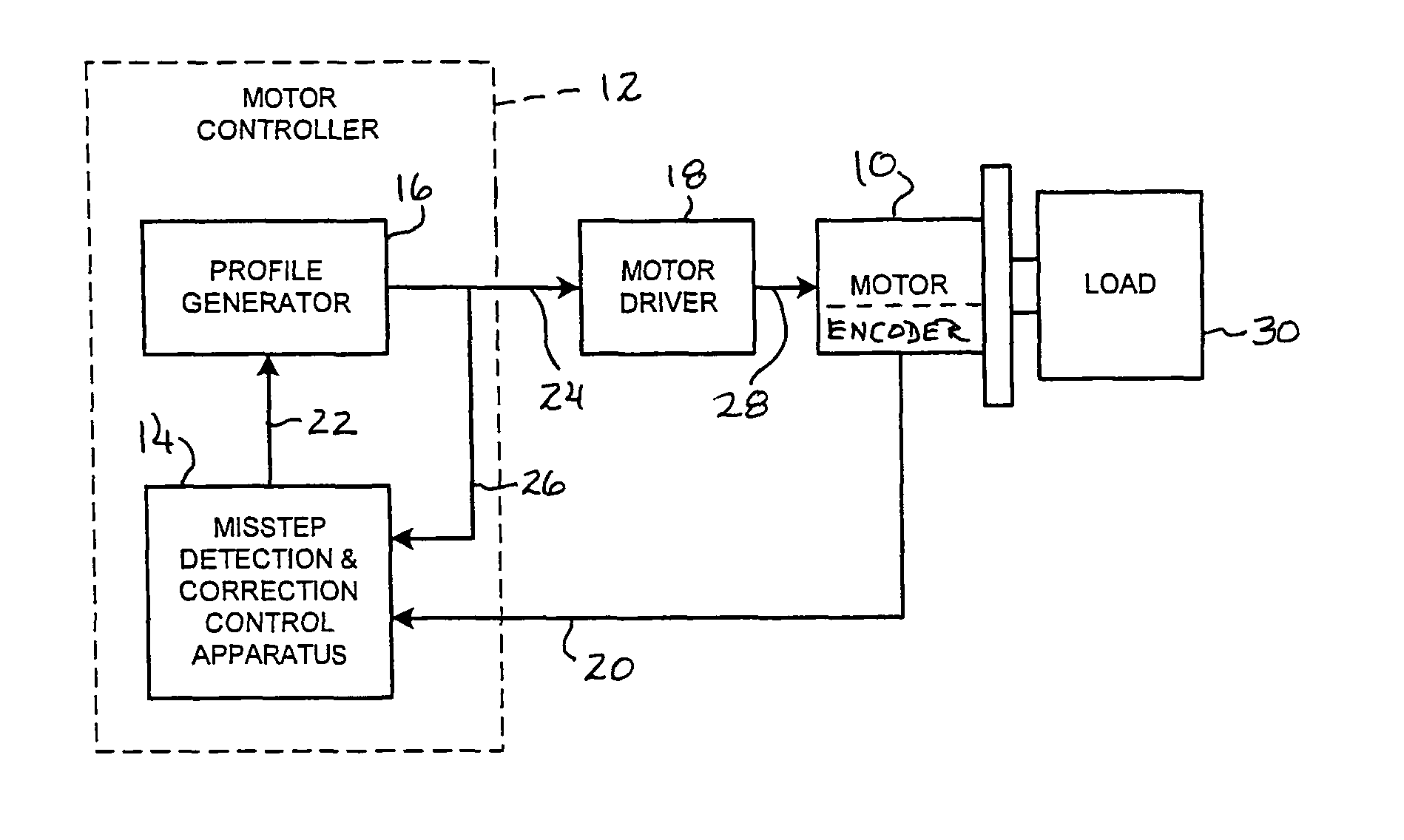
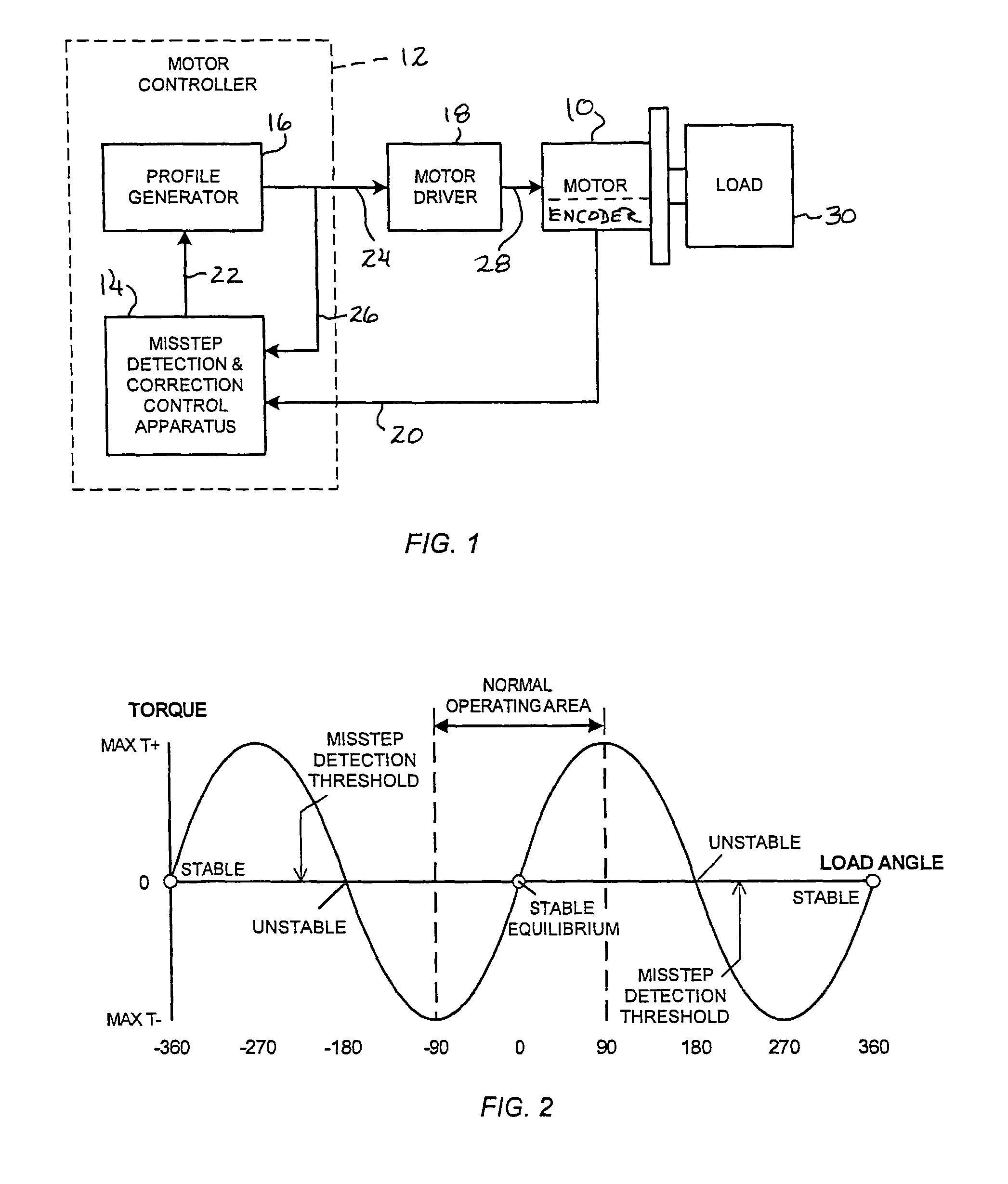
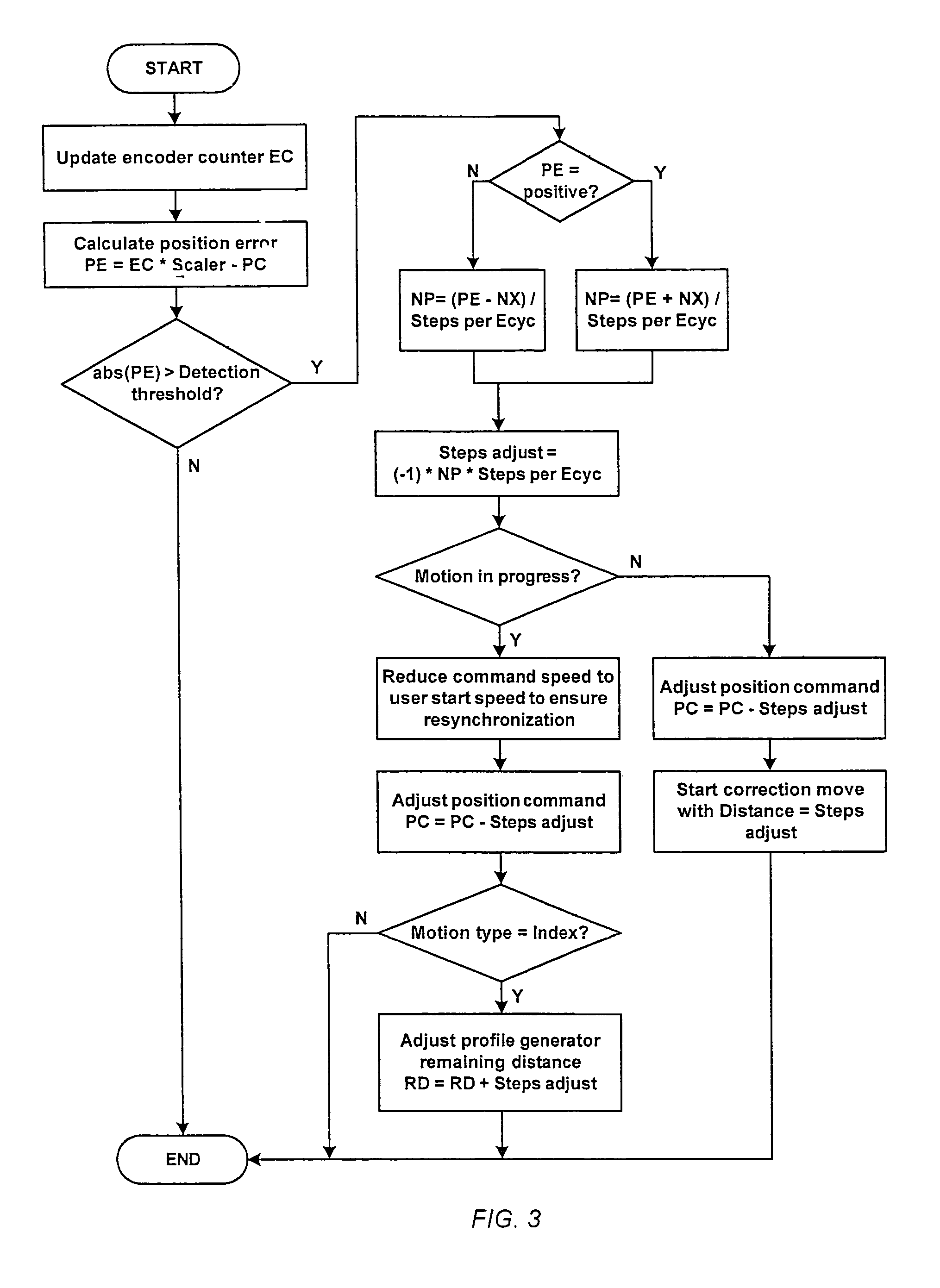
Method and apparatus for misstep detection and recovery in a stepper motor
ActiveUS20130043822A1Easy to detectLoss of timeDynamo-electric converter controlControl theorySystem controller
A stepper motor system and apparatus use a position-feedback device, which may have a resolution capability as low as 200 counts per motor shaft revolution, for misstep detection and motor step recovery. In use of the system, position deviation is computed periodically and cyclically, by subtracting the feedback position from the corresponding commanded position, to determine the load angle, implicitly, and the operating status of the motor. If the load angle is within an established allowable range of values, normal stepper operation along the programmed trajectory is maintained, without adjustment. A load angle that exceeds the limits of that range however indicates that a misstep has occurred, and the system controller initiates immediate action to recover lost motor steps, to reestablish synchronism, and to then continue toward the final target position, with minimal loss of time.
Owner:ORIENTAL MOTOR BOSTON TECH GROUP
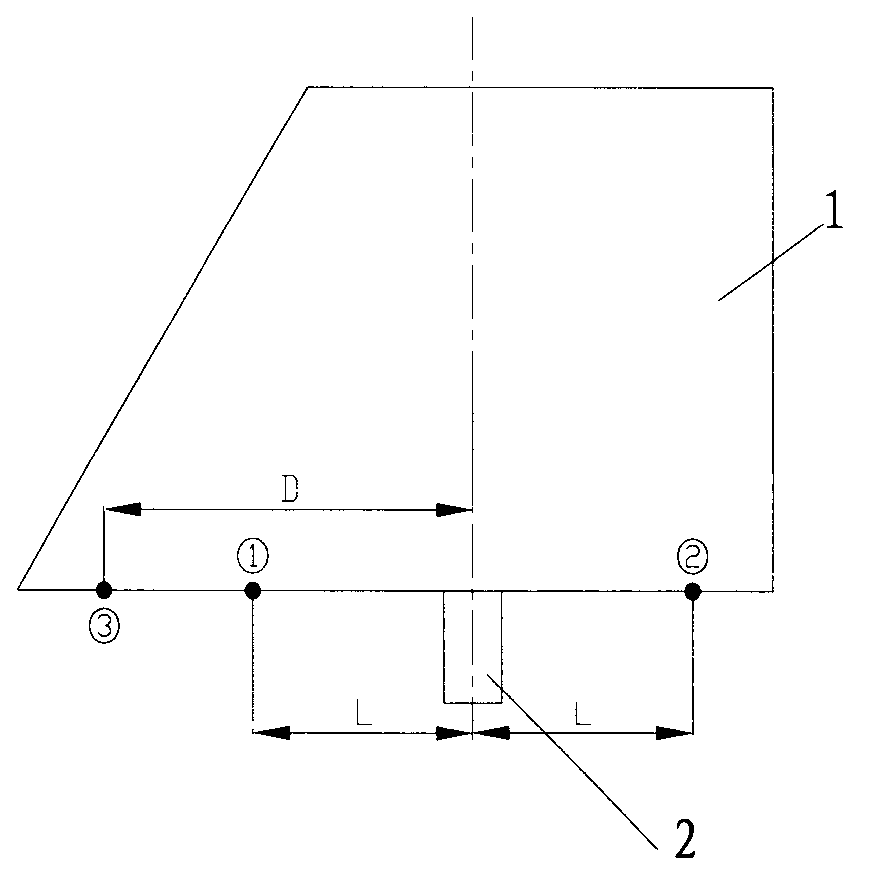
Gap measurement method suitable for nonlinear steering system
InactiveCN102829747ASolving Gap Measurement ChallengesEasy to operateMeasurement devicesPartition of unityDrift angle
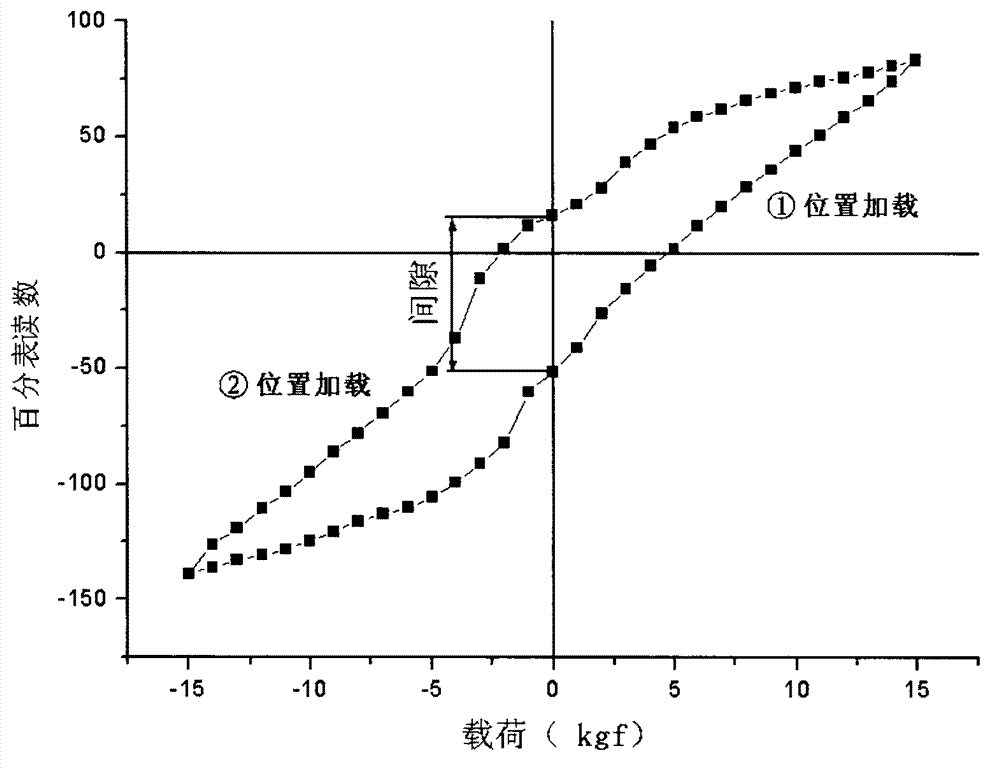
The invention provides a gap measurement method suitable for a nonlinear steering system, comprising the following steps of: arbitrarily selecting two points A and B which are symmetrical with each other by taking the centre line of a rudder axle as the center at the root of a control plane; powering off a steering engine, adjusting the control plane drift angle of the steering system to be 0 degree, and respectively carrying out load test at the point A and the point B by taking F as a loading unit, so that a rotating minimum load G' of the control plane is equal to n*F; and 3) resetting the control plane drift angle to be zero degree, loading and unloading the point A and the point B step by step by taking F as the unit, respectively recording the values of the control plane drift angles alpha under the different loads G, and drawing a 'load-angle' relation curve until two closed curves are obtained, wherein the angle difference value of the closed curves is the gap of the steering system at the place where G=0. According to the gap measurement method, the defect of the application of the conventional gap measurement method in a nonlinear system can be overcome, and the elastic deformation can be completely distinguished due to the obtained gap value.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Method and circuit arrangement for detecting motor load without sensors and for controlling motor current according to load for a stepper motor
ActiveUS20130221894A1Lower average currentCurrent consumptionProgramme controlElectronic commutation motor controlPhase shiftedElectric machine
A method and a circuit arrangement are provided in which a mechanical load applied to the motor shaft or a load angle of the motor can be detected without sensors in a stepper motor. This is achieved substantially based on the fact that the load or the load angle creates a mutually induced voltage (back EMF) in the motor coils and the load or the load angle is detected by determining the phase shift of the motor voltage at at least one of the motor coil relative to the coil current at said motor coil connection, the phase shift being caused by the mutually induced voltage. A method and a circuit arrangement are also provided wherein the motor current of a stepper motor can be controlled according to load angle in such a way that the current consumption of the motor is relatively low
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Clamp for display vibration test and installation method for same
ActiveCN105904360AEasy to installSolve the technical problem of using the same fixture for vibration testingWork holdersDisplay deviceSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a clamp for a display vibration test and an installation method for the same. The clamp comprises a baseplate which is firmly installed on the surface of a vibration test table, a supporting frame disposed on one side of the base plate, a slide rail assembly disposed on left and right sides of the supporting frame and connected between the supporting frame and the baseplate, as well as an installation panel, wherein the slide rail assembly comprises a fixation base, a first slide rail and a second slide rail, and both the first slide rail and the second slide rails are equipped with arc slideways; and the bottom of the installation panel is in a hinged connection with the joint between the supporting frame and the baseplate, and the installation panel can move along the slideways and is used for firm installation of a display. Bolts penetrate the fixation base and the slideways and are screwed into studs on inner sides of left and right edges of the installation panel; the installation panel is rotated along the slideways with a rotary fixation hole of the fixation base as the axis till the angle of the installation panel is equal to a display truck loading angle; the baseplate is installed on the surface of the vibration test table by fastening bolts; and finally a test can be implemented. The clamp and the method disclosed by the invention can solve the technical problems that an existing vibration clamp with an overall frame structure has low flexibility, low universality, the high cost and long testing duration.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
Permanent magnet synchronous motor flux linkage prediction control method taking optimal duty ratio modulation into account
ActiveCN108631672AEliminate weightsReduce the number of calculationsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor flux linkage prediction control method taking optimal duty ratio modulation into account, wherein a flux linkage vector effective value minimization principle is introduced into duty ratio calculation of a fundamental voltage vector, and in combination with a voltage vector filtering method, torque and flux linkage ripple can be restrained effectively while calculation time of a processor is reduced, and reliability and steady-state performance of a system are improved. Firstly, torque increment is converted into load angle increment, control targets are unified to be a stator flux linkage vector; then, fundamental voltage vector filtering is executed according to a dead-beat thought, and under the premise of reducing alternativevectors, working time of an effective voltage vector can be calculated quickly; thus, the duty ratio of the voltage vector can be calculated according to the flux linkage vector effective value minimization principle, the selected voltage vector and the vector duty ratio are determined according to combined error of the flux linkage vector, and torque and flux linkage ripple can be restrained effectively.
Owner:南通大学技术转移中心有限公司
Three-dimensional space variable angle loading device
InactiveCN104406777AEasy to assemblePoor adaptability to changeMachine part testingThree-dimensional spaceData acquisition
The invention discloses a three-dimensional space variable angle loading device. The three-dimensional space variable angle loading device comprises experiment test pieces, an acquisition system, a ground connection tool system, and a sensor system, a pulley system and a loading system which are connected through a steel wire a, wherein the experiment test piece comprises a test piece a, a test piece b and a test piece c, the ground connection tool system comprises multiple parallel ground grooves, the ground grooves are connected with a ground beam a and a ground beam b, the pulley system comprises a pulley a, a pulley b, a pulley c and a pulley d, the loading system comprises an MTS actuator connected with a counterforce wall, the sensor system comprises force sensors, and the acquisition system is a TDS602 data acquisition device. The three-dimensional space variable angle loading device solves problems of poor space loading angle accuracy and poor loading device adaptability existing in the prior art, the three-dimensional space variable angle loading device is suitable for random space angle loading, various parts are detachable, ground assembling is convenient and simple, end portions of the test pieces are provided with the force sensors, and the three-dimensional space variable angle loading device further has properties of accurate data and high precision.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
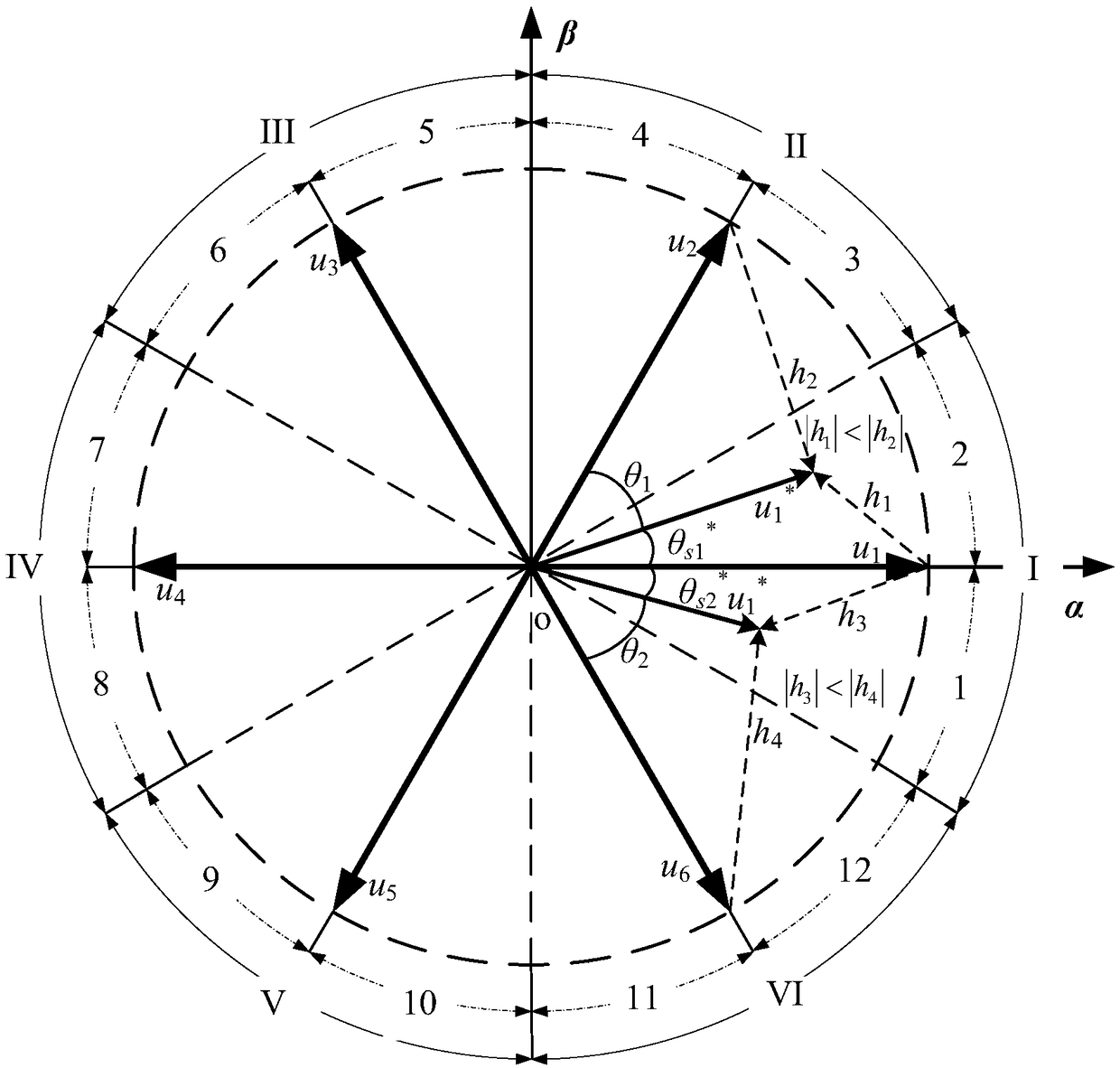
Double-vector predicted flux linkage control method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
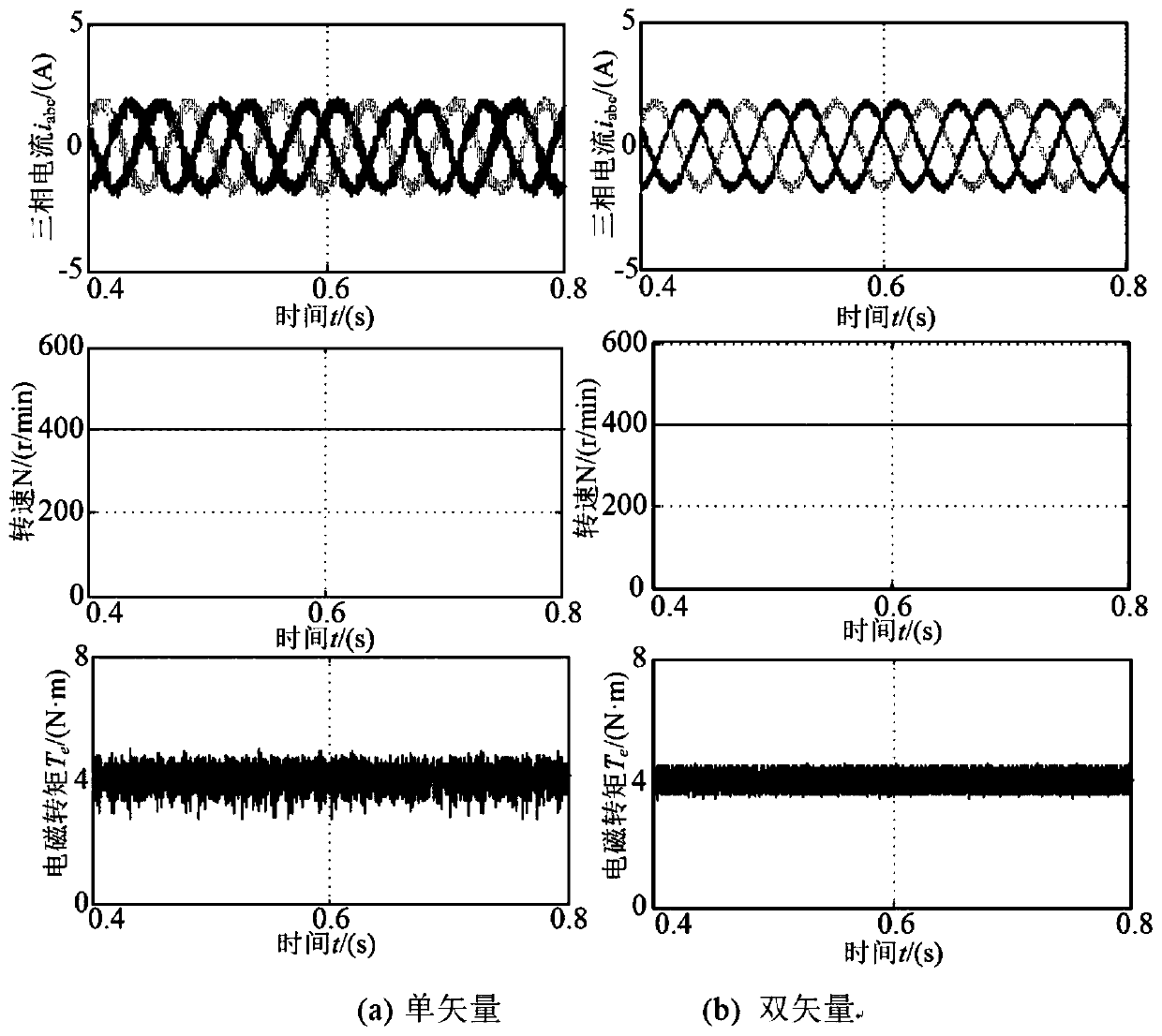
ActiveCN108736778AEliminate weightsSolve the accuracy is not highElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlReference vectorVoltage vector
The invention discloses a double-vector predicted flux linkage control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the steps of firstly converting a torque increment into a load angle increment and unifying control objectives as a stator flux linkage vector; calculating and obtaining a reference voltage vector according to a dead-beat idea, selecting a I vector through interval positions of the reference vector and selecting a II vector through subinterval positions of the reference vector; dividing a control period into two parts through optimizing a duty ratio of the voltage vector, making the I vector act on one part of the control period and selecting the II vector or a zero vector in the remaining time; and finally carrying out loop optimization calculation on the selected voltage vectors and the duty ratio to obtain an optimal voltage vector and conveying the optimal voltage vector to the permanent magnet synchronous motor. According to the double-vectorpredicted flux linkage control method for the permanent magnet synchronous motor, torque and flux linkage ripples of a system are reduced while the calculating time of a processor is shortened, and the reliability and the steady-state performance of the system are improved.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
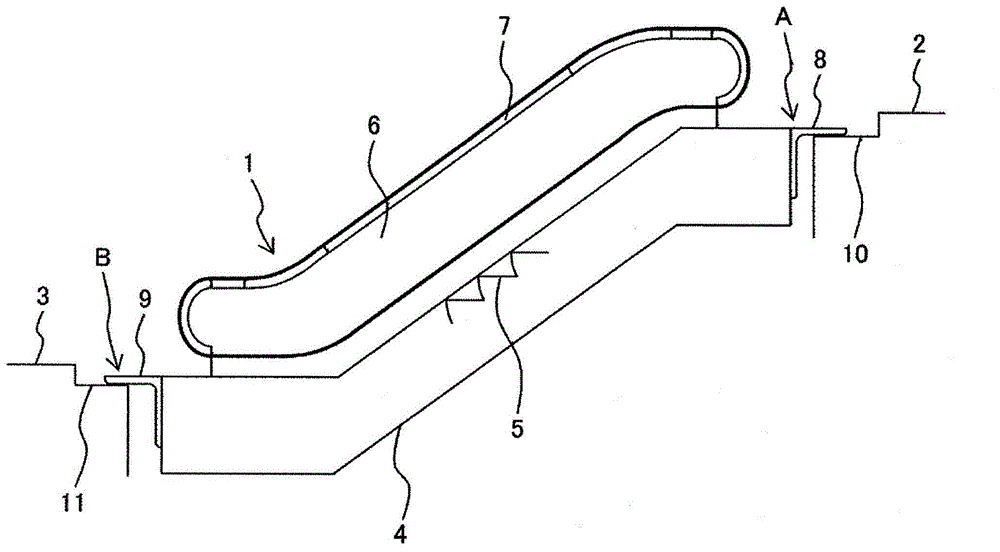
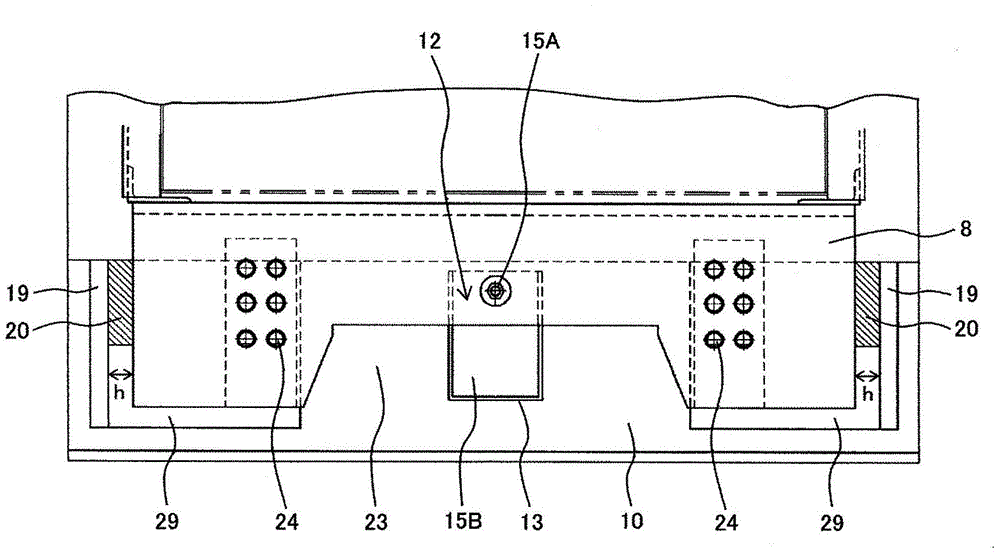
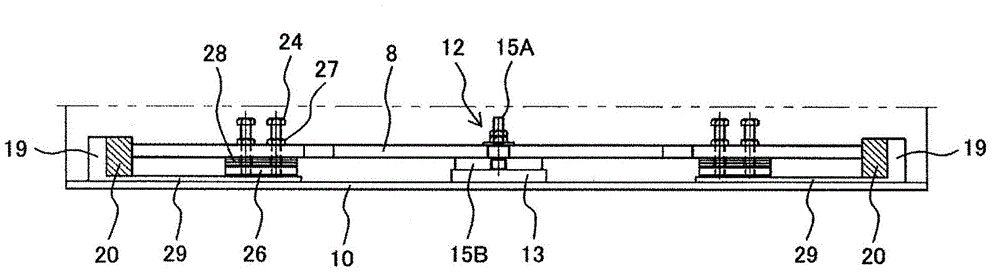
Passenger conveying equipment
The present invention provides a passenger transport equipment makes it possible to absorb the inter-layer frame width direction between the upper floor and the lower floor of the displacement, and the interlayer can absorb the longitudinal direction of the housing caused by the massive earthquake on displacement. At least one of the housing so that the housing rotatably supporting angle provided in the angle of rotation of the support bearing stage is engaged, and is located in the frame supporting the load angle and the angle of rotation of the support portion is formed between Taiwan trails section. Since the casing supporting at least one of the support angle is the angle with respect to the rotational load station, it is possible to absorb in the terminal portion of the support frame and the support frame between the upper end portion of the floor of the lower floor frame generated interlayer width direction of displacement. In addition, in the event of a large-scale earthquake in the excessive load acting on the frame when the support bearing angle and the angle between the station, the small diameter portion rotatably supported body fracture, thereby absorbing interlayer frame the length direction displacement.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
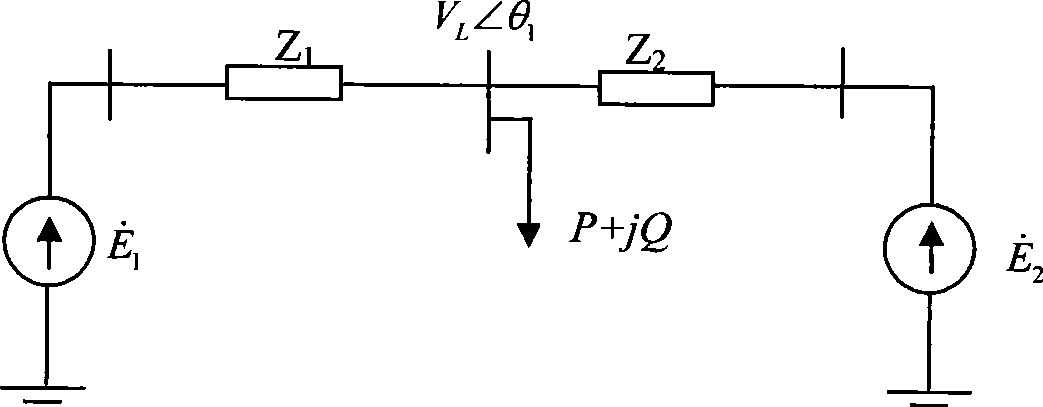
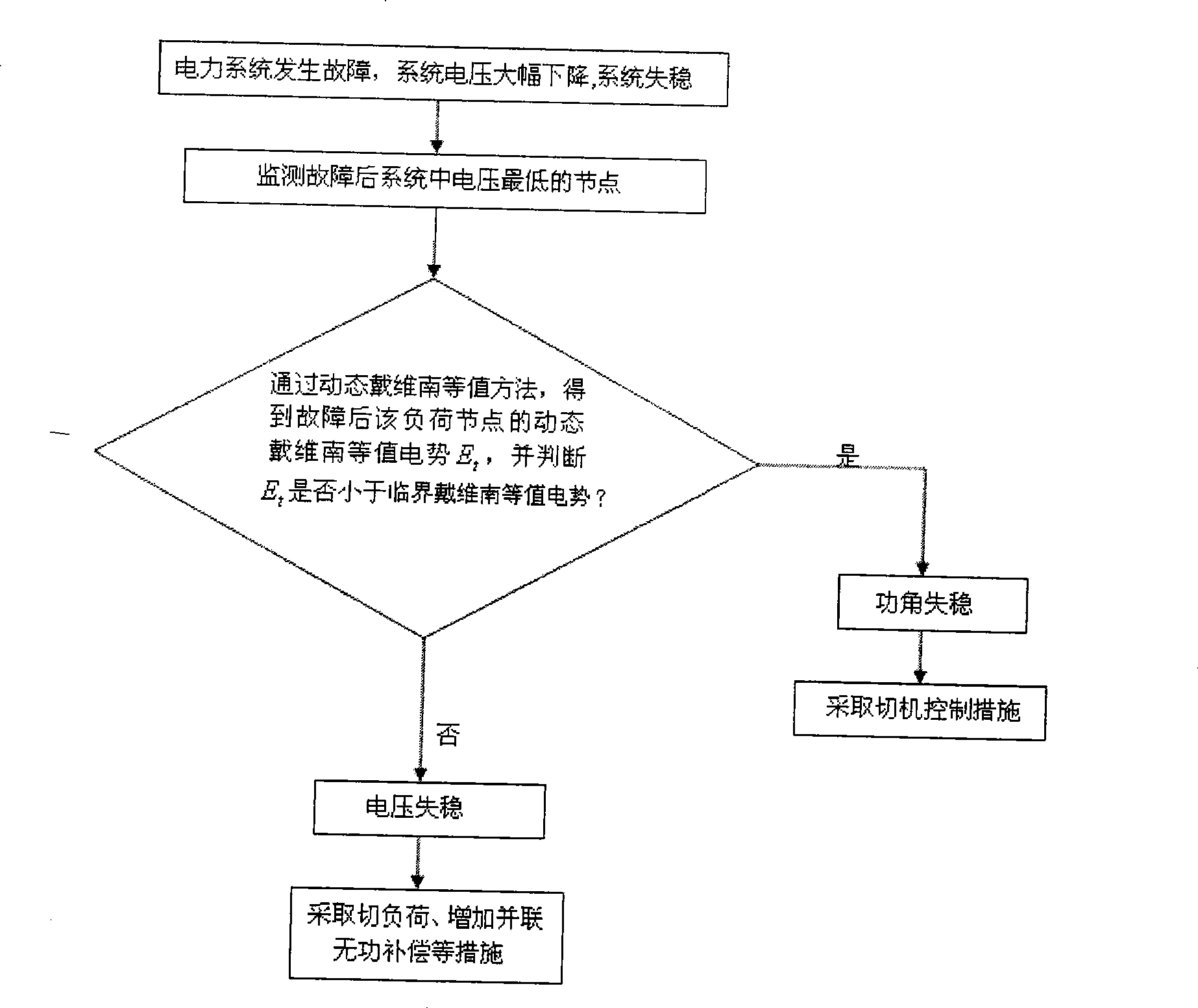
Method for discriminating voltage instability and load angle instability based on thevenin equivalent
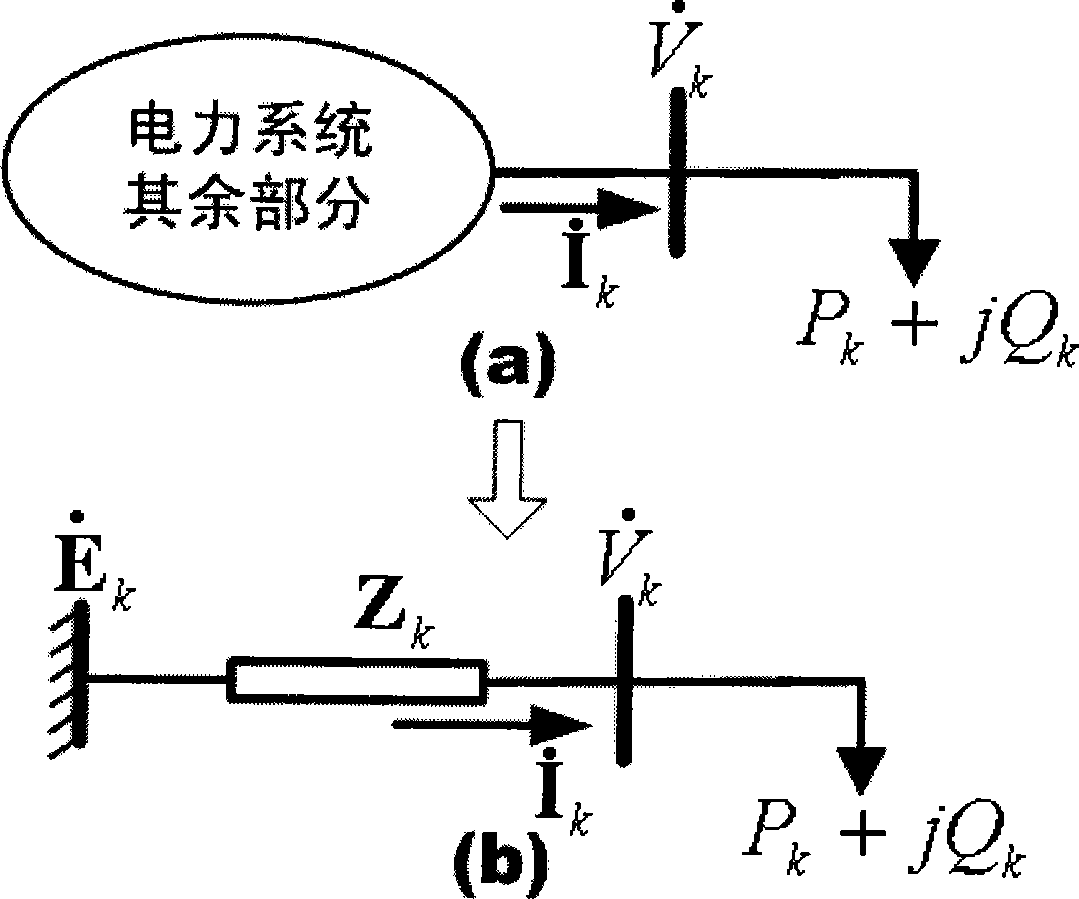
ActiveCN101363885AImprove the level of safe and stable operationReal-timeElectrical testingAc network circuit arrangementsElectric power systemInstability
The invention provides a method for judging power angle instability and voltage instability based on the dynamic Thevenin equivalence. When a power system fails and instable, and the voltage is greatly reduced, the system operation and analysts is difficult to judge whether the instable property of the system belongs to the power angle instability or the voltage instability. Based on the dynamic Thevenin equivalence method, the real-time variation of the Thevenin equivalent potential of a load node to be monitored after the failure occurs can be obtained; and compared with the Thevenin equivalent potential, the instable property of the system can be judged. The method can be applied to the on-line analysis control and the off-line emulation analysis of the power system, facilitate the system operation and the analysts to adopt the effective measure in time and improve the safe and stable operation level of the power system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Method and apparatus for misstep detection and recovery in a stepper motor
ActiveUS8810187B2Easy to detectLoss of timeMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlControl theorySystem controller
A stepper motor system and apparatus use a position-feedback device, which may have a resolution capability as low as 200 counts per motor shaft revolution, for misstep detection and motor step recovery. In use of the system, position deviation is computed periodically and cyclically, by subtracting the feedback position from the corresponding commanded position, to determine the load angle, implicitly, and the operating status of the motor. If the load angle is within an established allowable range of values, normal stepper operation along the programmed trajectory is maintained, without adjustment. A load angle that exceeds the limits of that range however indicates that a misstep has occurred, and the system controller initiates immediate action to recover lost motor steps, to reestablish synchronism, and to then continue toward the final target position, with minimal loss of time.
Owner:ORIENTAL MOTOR BOSTON TECH GROUP
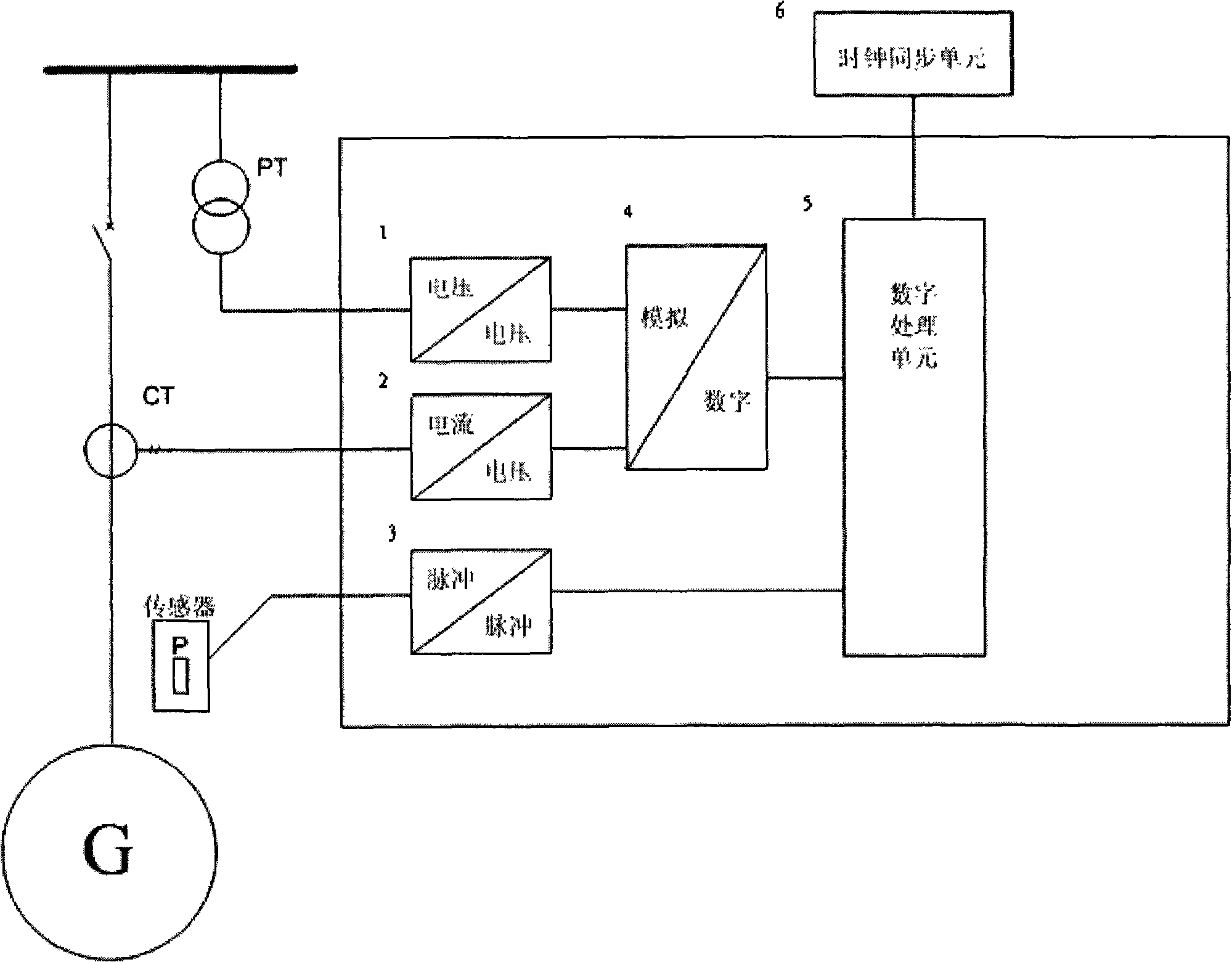
Method for directly measuring power angly and inner angle of generator
InactiveCN1786729AUnaffected by disturbing transient processesDynamo-electric machine testingElectricityTransient state
The invention discloses generator load angle and inner electric potential phase angle measuring method adopted rotating shaft key phase signal and machine end voltage phasor. While electric machine is no load, it detects frequency f0, machine end voltage zero cross t10, rotating shaft key phase signal rising edge time mark t20, machine end positive sequence voltage phase angle, inner electric potential phase angle alpha; while electric machine is running, each of them is, t1, t2; the advantages of the invention are that the measuring method has no relation with machine end current, time start point, and generator direct axis and quadrature axis synchronous reactance parameter; it does not need quadrature for machine group rotating speed; and it is not influenced by electric network and machine group disturbance transient state process.
Owner:EAST CHINA GRID +2
Dynamic calculation and control of synchronous machines
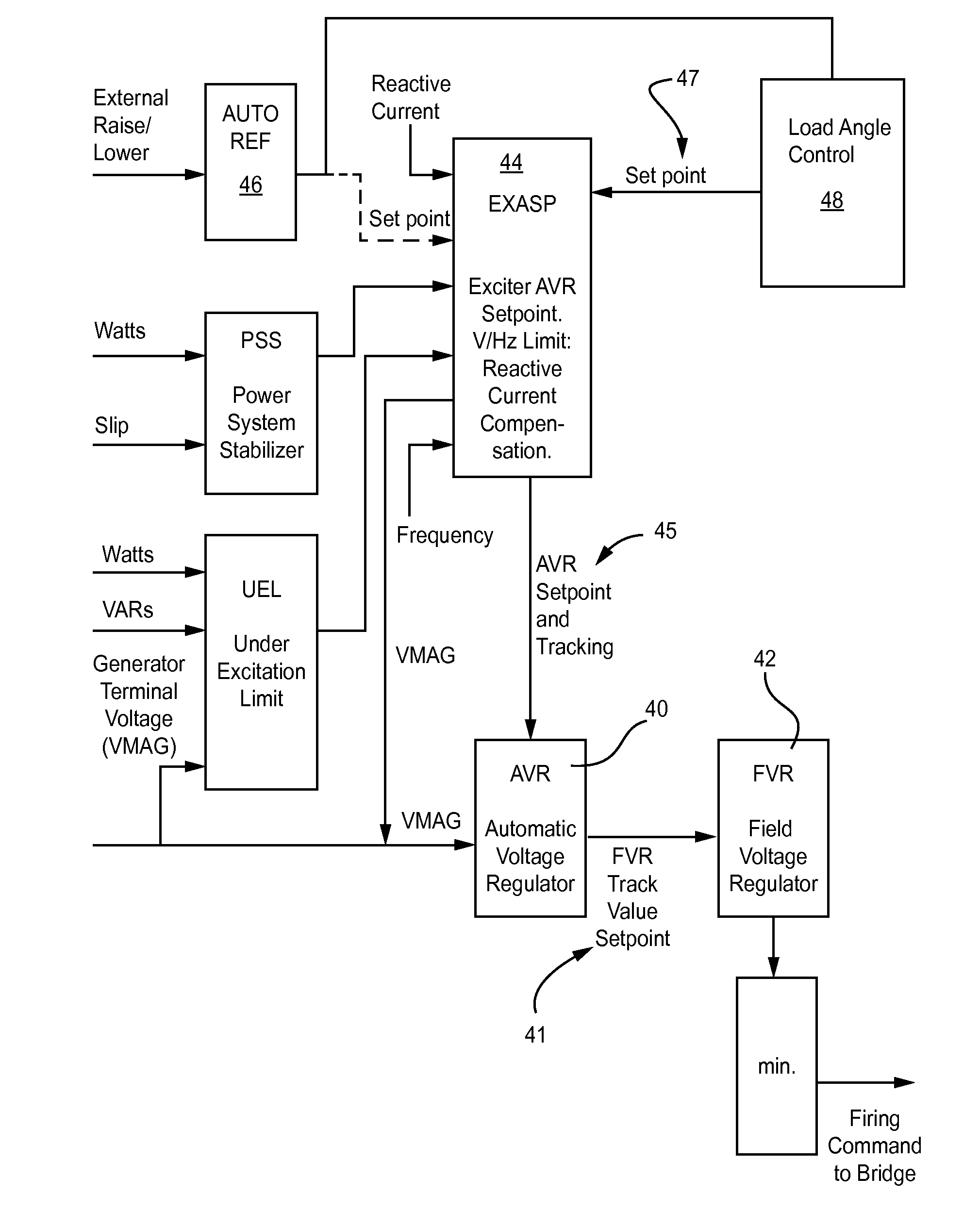
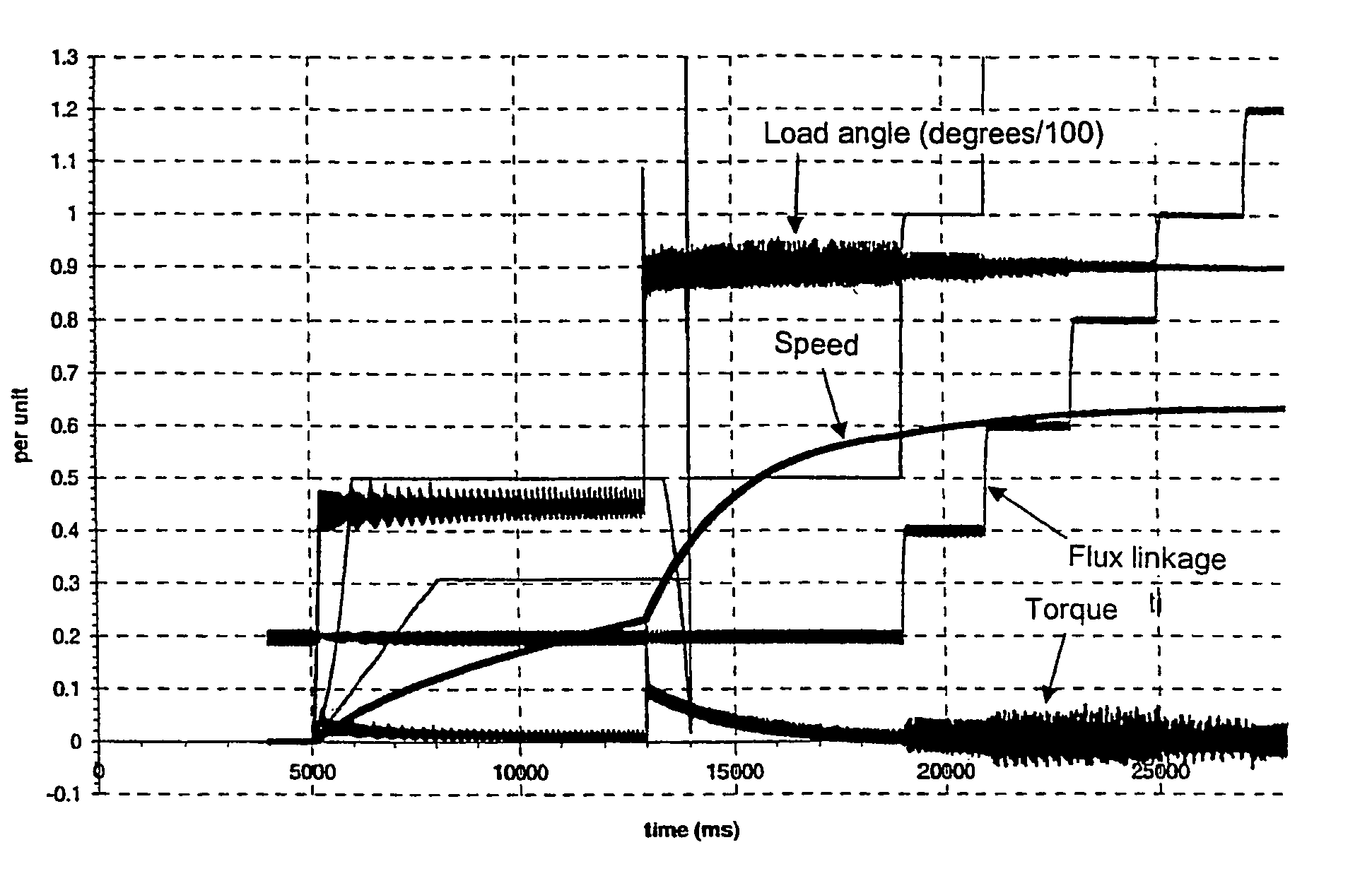
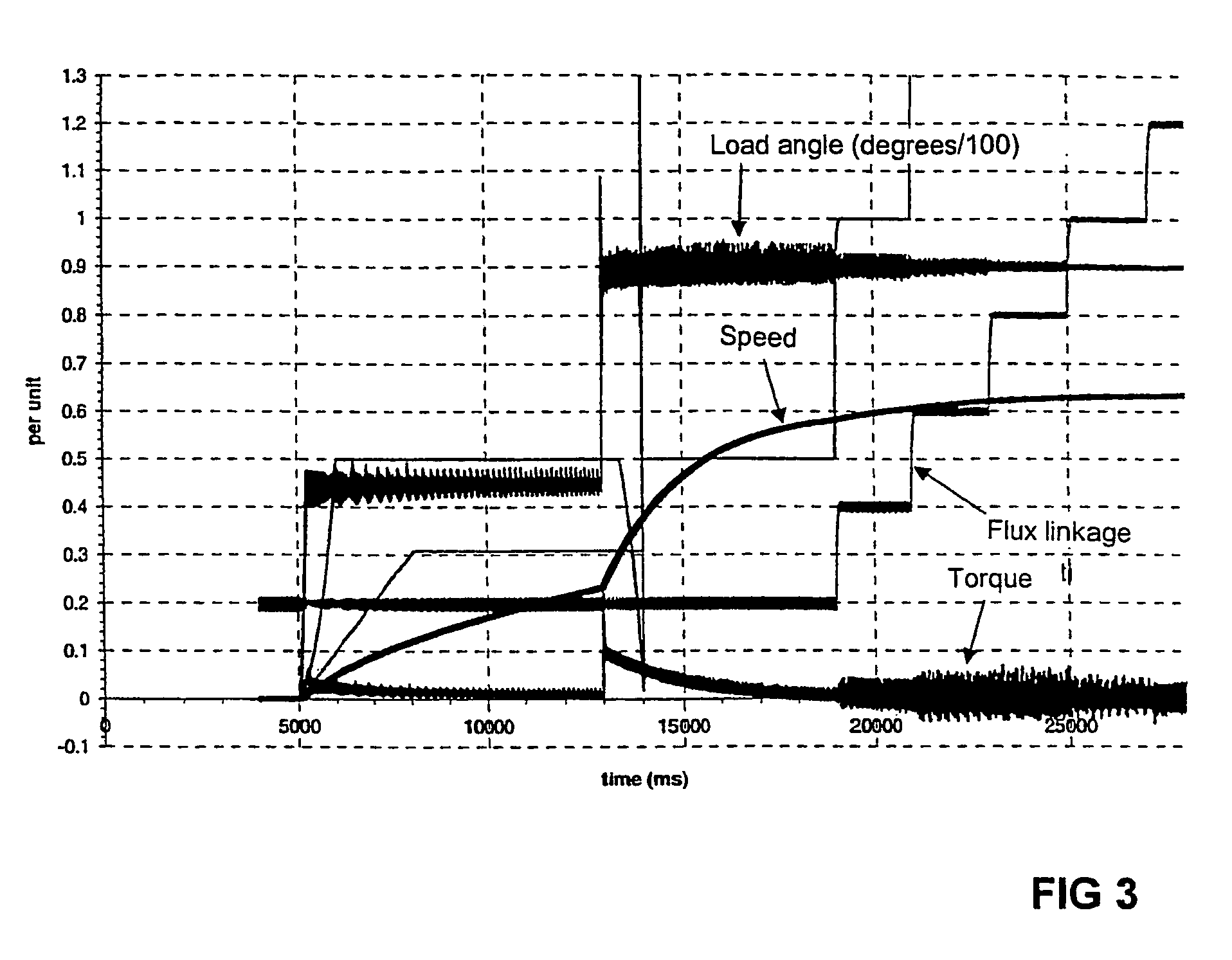
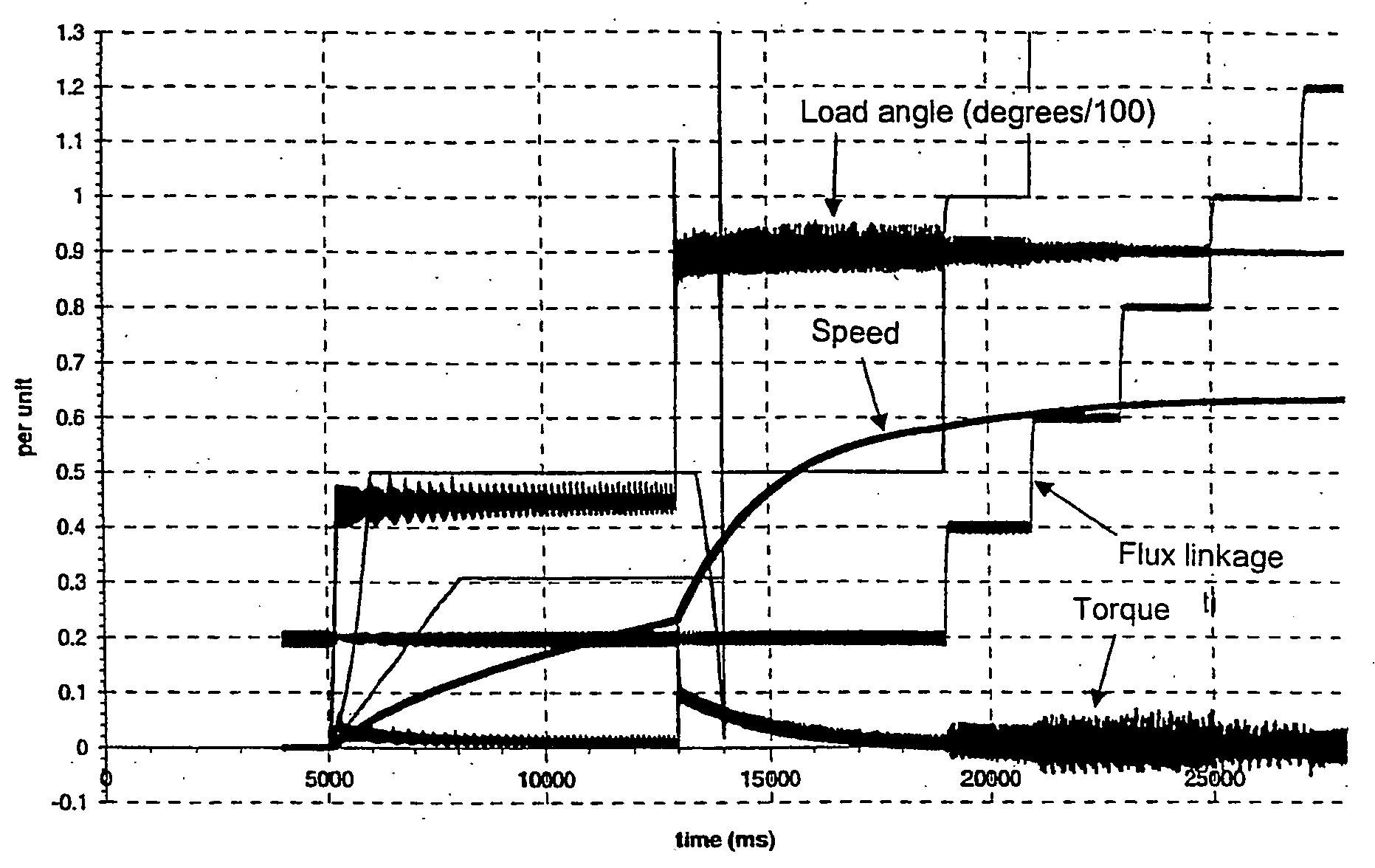
A method keeps a synchronous machine in a stable operating zone during large transient voltage excursions on a power grid to which the machine is connected. The machine's load angle, i.e., the position of the rotor flux with respect to the position of the stator flux, is calculated. If the load angle is not within a defined range of reference values for stable machine operation, the machine's field excitation is adjusted to bring the machine's load angle within the defined range of reference values for stable machine operation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Low center of gravity carrier
ActiveUS20130149084A1Lowered platform heightIncrease in payload heightHand carts with one axisItem transportation vehiclesVehicle frameMarine engineering
A carrier having a platform or deck mounted on a subframe tiltable relative to the vehicle chassis. The platform is preferably slidable relative to the subframe. Sufficient clearance is provided such that the subframe is preferably located between the vehicle chassis frame and the rear wheels, and below the top of the chassis frame. The resulting carrier has a platform with a height substantially lower than that of previous carriers, providing it with a lower center of gravity, enabling a reduction in load angle, an increase in payload height, and enhanced dynamic road stability.
Owner:MILLER IND TOWING EQUIP INC
Method and device for controlling an electric load connected to a multiphase switchable DC/AC frequency convertor
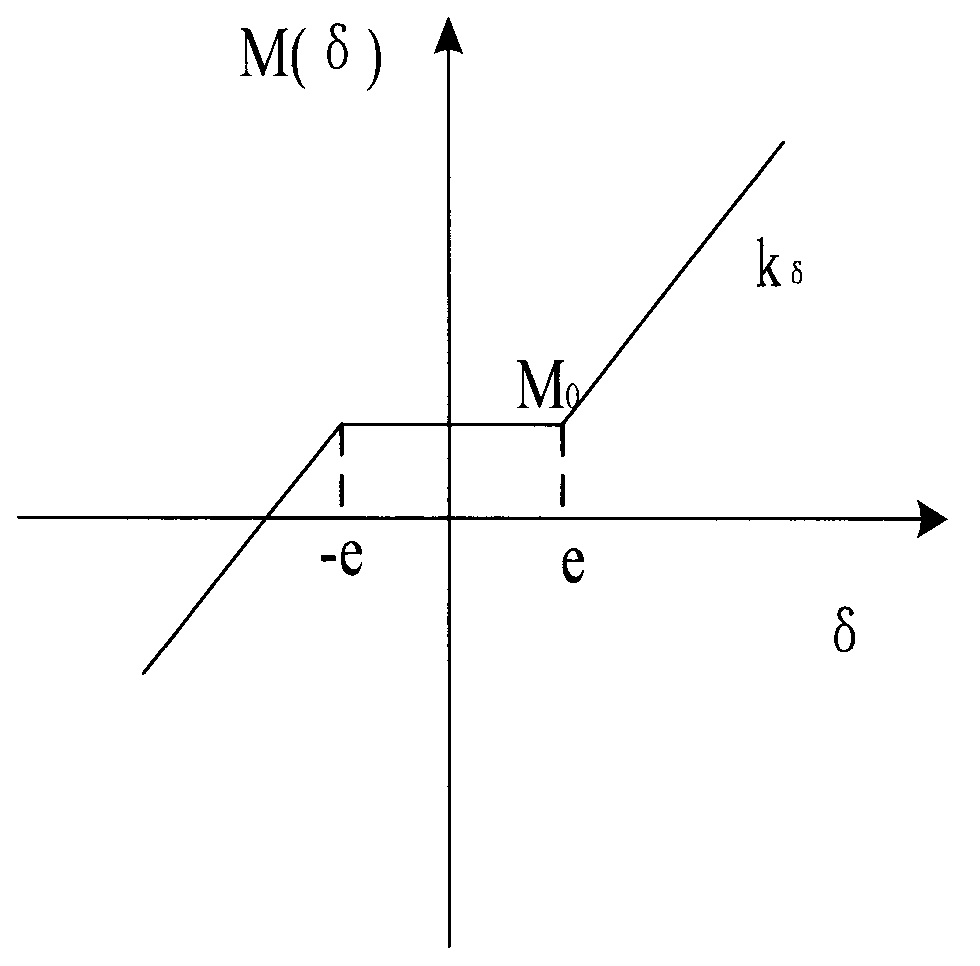
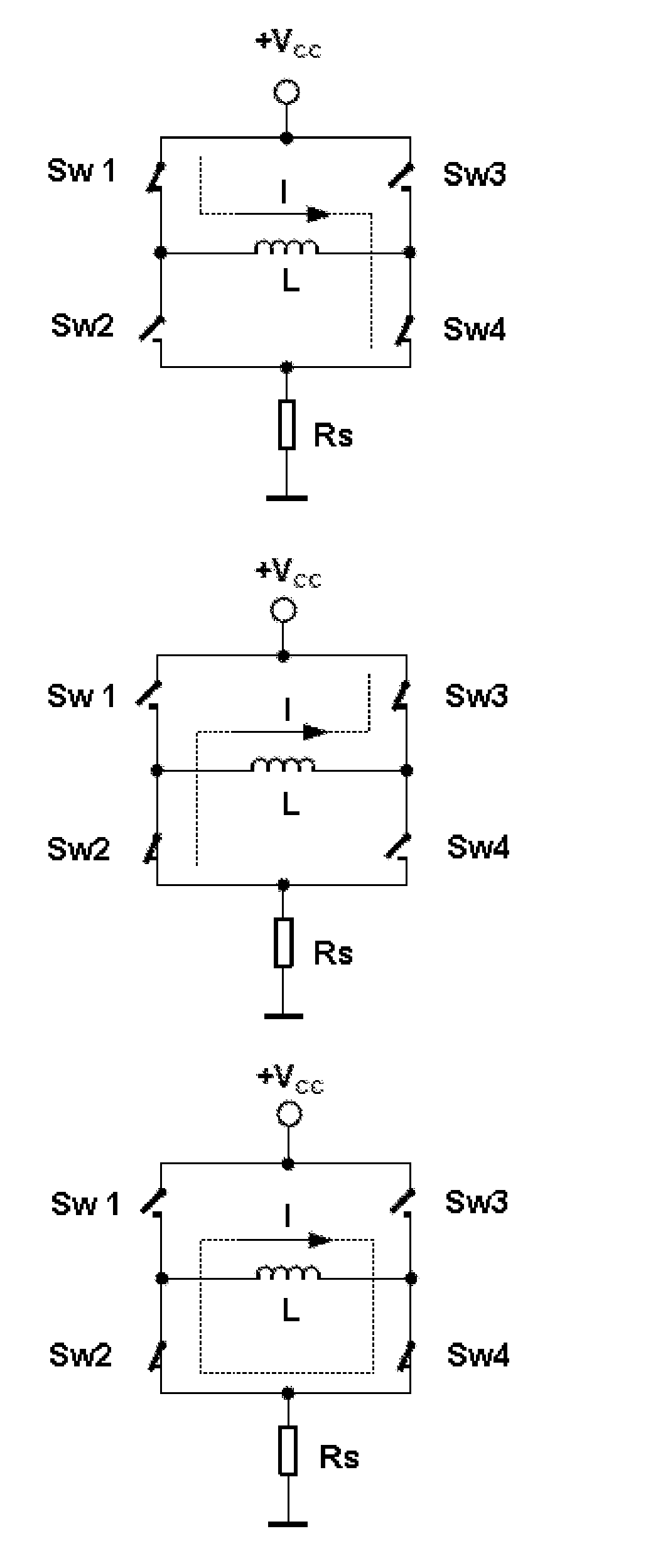
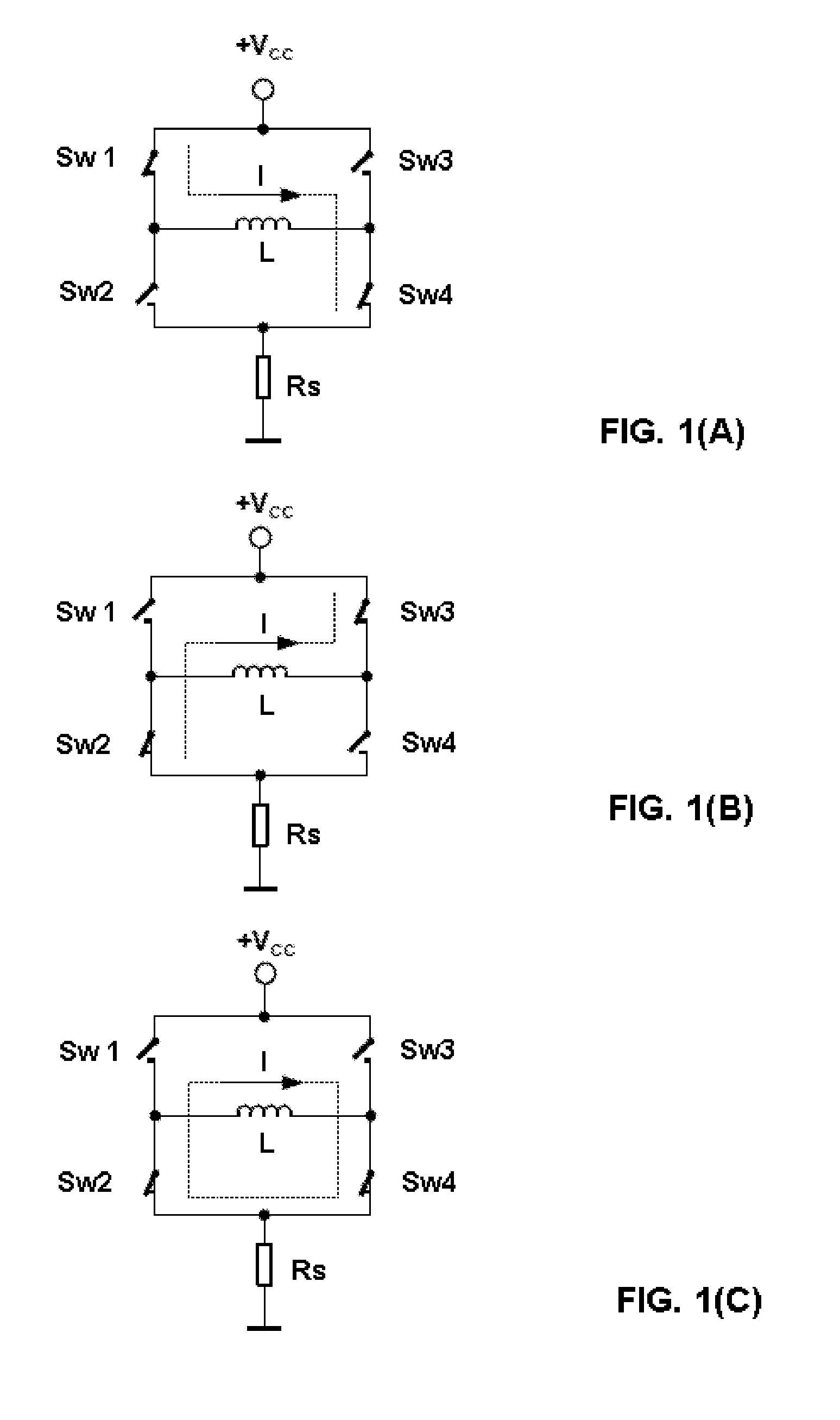
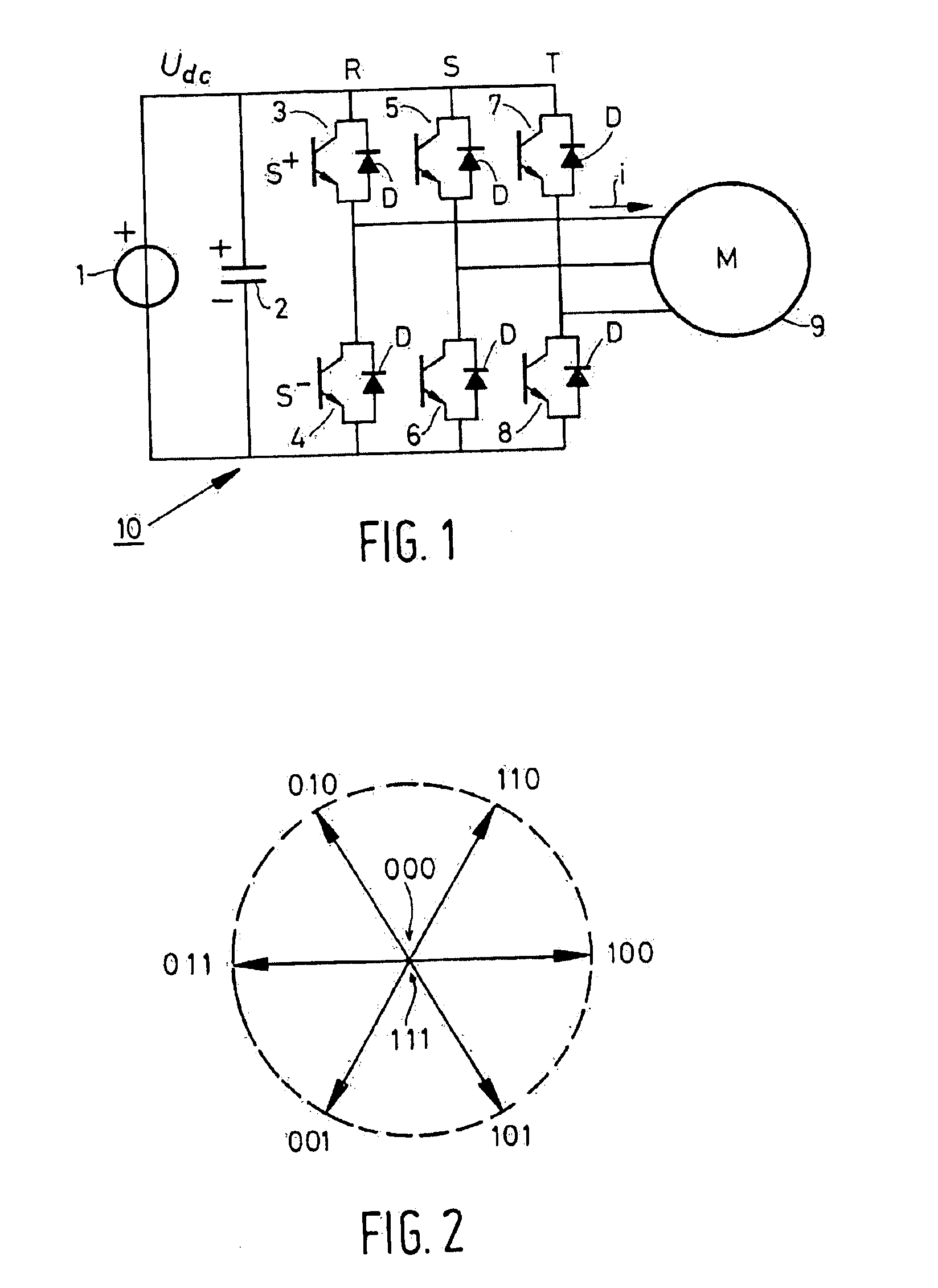
InactiveUS6864660B2Short timeEasy to implementAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlFrequency changerEngineering
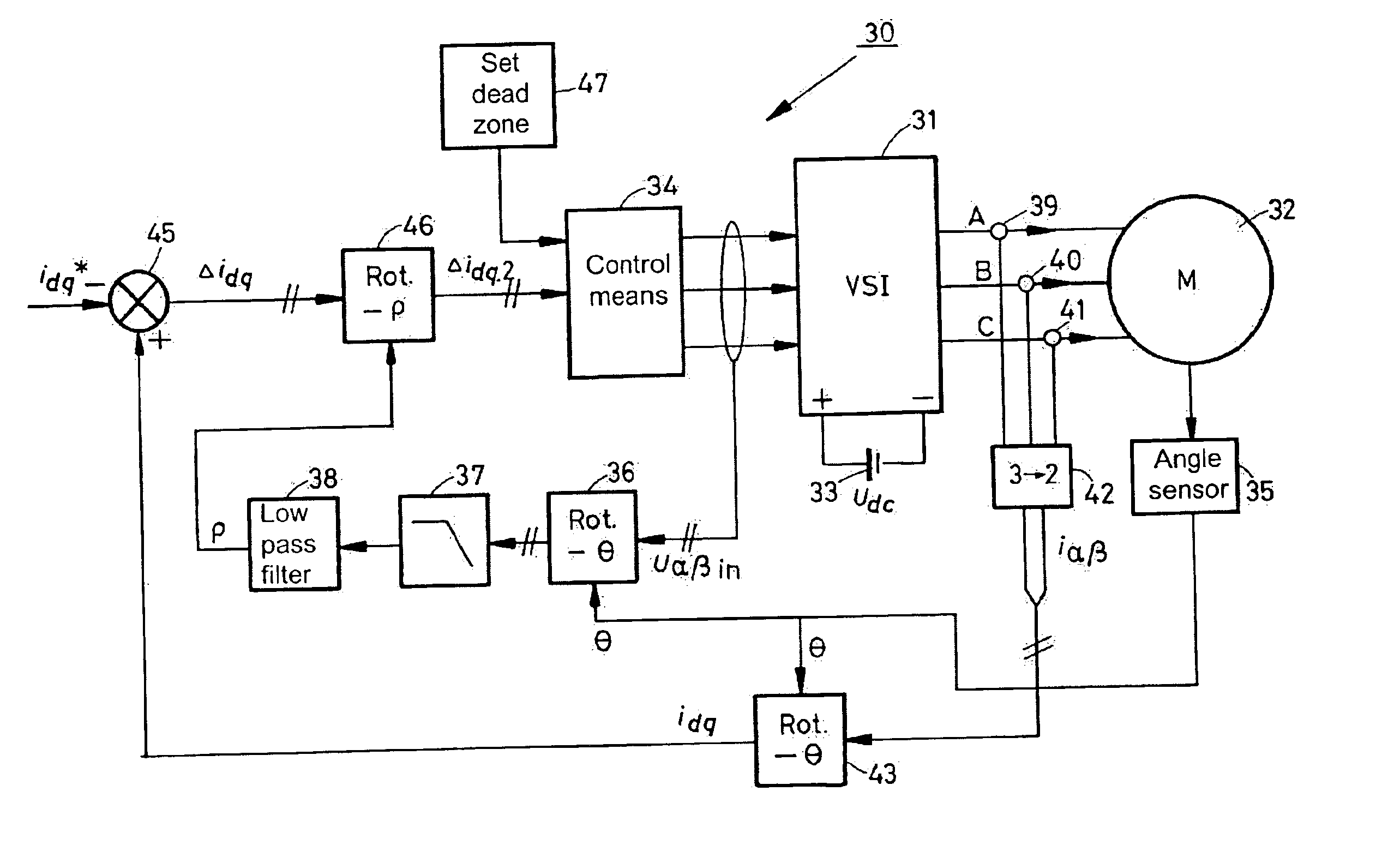
A method and a device for realizing an effective value of a quantity to be varied in an electrical load connected to a multi-phase switchable DC / AC frequency convertor comprising a plurality of controllable switches. The value is realized by varying a current or a voltage delivered by the DC / AC frequency convertor through suitable switching of the switches thereof, and wherein the quantity exhibits a load angle which, averaged in time, leads or lags the voltage or current being delivered. The method and / or the device is arranged for carrying out the steps comprising the defining of a dead zone having dimensions that are representative of an allowable amplitude and phase angle deviation in the quantity to be realized; the orienting of the dead zone with respect to the voltage or current delivered by the DC / AC frequency convertor by rotating the dead zone through the load angle in the direction of the delivered voltage or current; and the switching of one or more of the switches on the basis of the manner in which the deviation in the quantity to be realized extends beyond the dead zone, for the purpose of realizing the quantity during operation with an amplitude and phase deviation ranging within the dead zone.
Owner:ENGIE ELECTROPROJECT BV
Load angle direct measurement method of hydroelectric synchronous machine
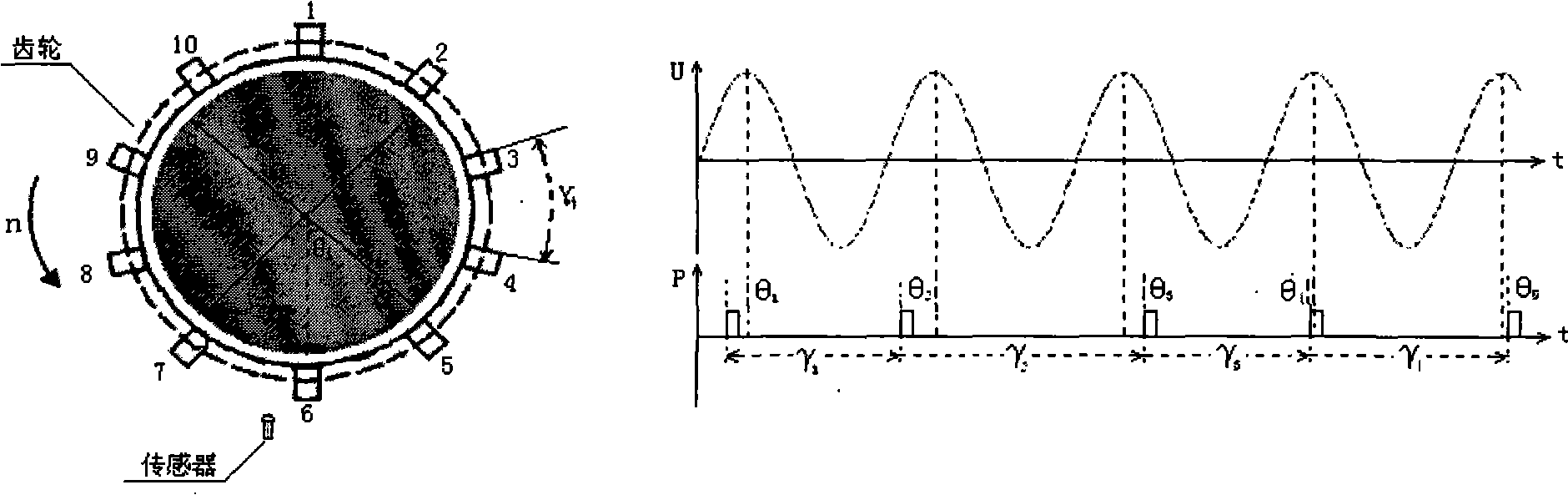
ActiveCN101299058AConvenient real-time calculationAvoid remodelingDynamo-electric machine testingFeature parameterControl theory
The present invention discloses a method for directly measuring the power angle of a hydroelectric synchronous machine, wherein the method comprises the following steps: at the state that the generator is unloaded, obtaining a preliminary phase angle and a tooth pitch characteristic parameter of the fluted disc of the generator rotor by a PMU device through a sensor; when the generator is operated with load, matching the corresponding relationship between the preliminary phase angle sequence and the tooth pitch sequence through measuring the fluted disc characteristic and tooth pitch characteristic at this time; and calculating the real-time power angle through the matching relationship. The method according to the invention can measure the initiative error angle of the position signal of the generator and directly obtain an accurate power angle of generator at the state that the existing generator gear is not improved.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +1
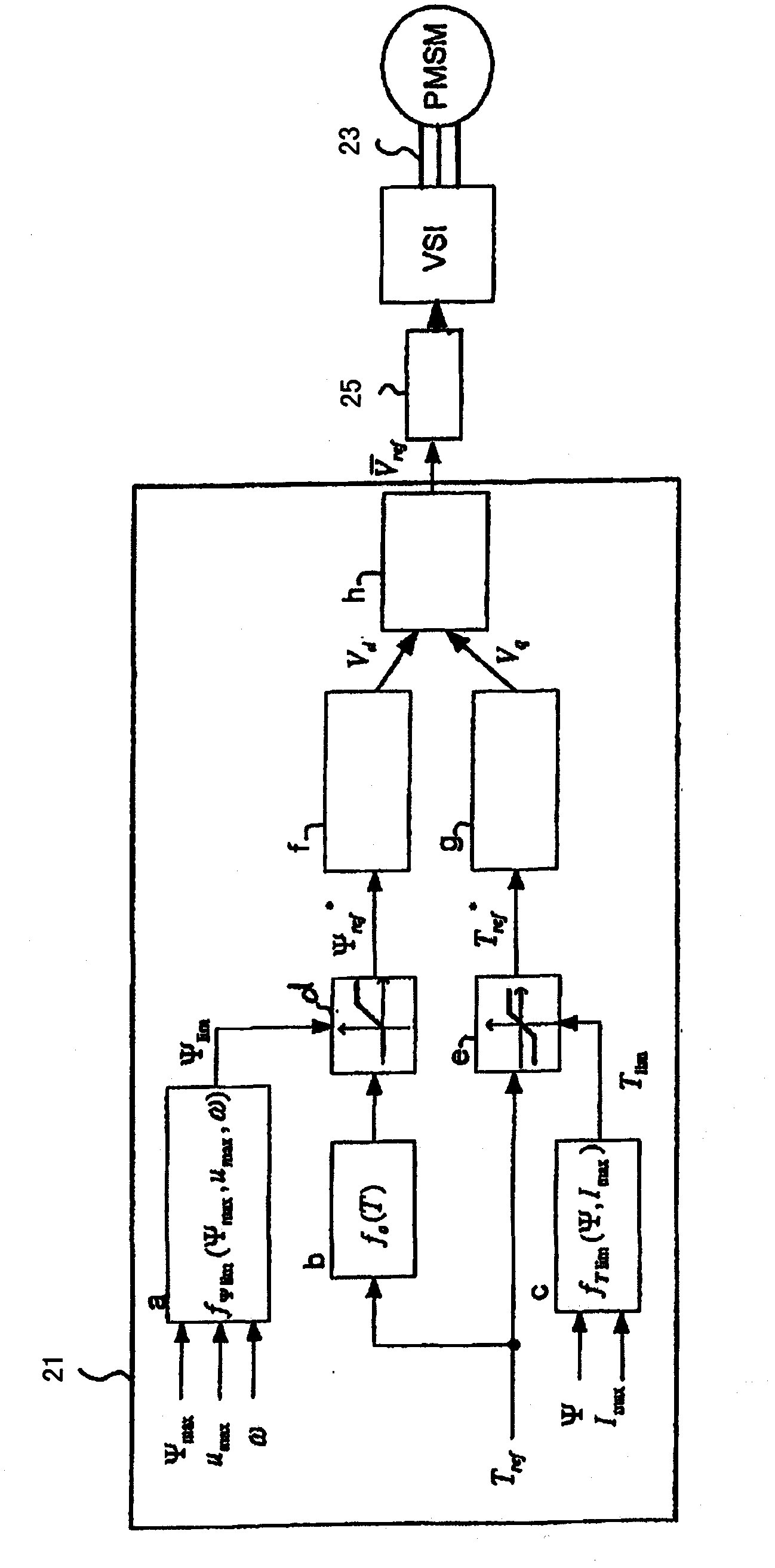
Operating a synchronous motor having a permanent magnet rotor
ActiveCN102144356AElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlPermanent magnet rotorSynchronous motor
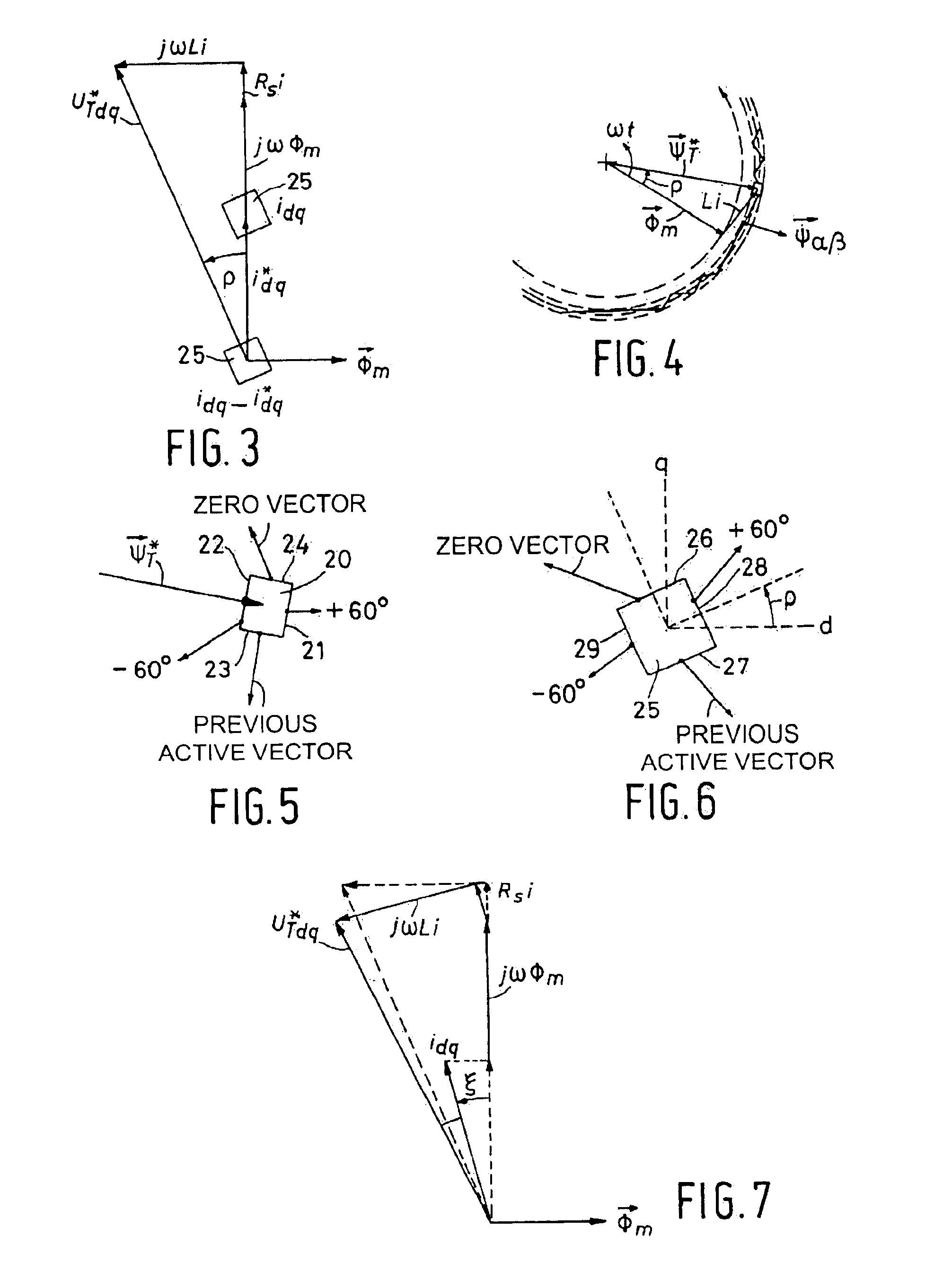
The invention relates to a method of operating a synchronous motor (1) having a stator comprising a set of electromagnets (7, 9) and having a permanent magnet rotor (5), wherein the synchronous motor (1) is controlled by calculating in a flux controller (f) a measure of a flux magnitude, which is the magnitude of the stator flux of the motor (1), and is controlled by calculating in a load angle controller (g) a measure of a load angle. Information about a desired motor torque or a reduced motor torque, which is smaller than the desired motor torque, is input to the load angle controller (g) and the load angle controller (g) calculates the measure of the load angle depending on the input motor torque. The measure of the flux magnitude is combined with the measure of the load angle to obtain commands for controlling electric currents of electromagnets of the stator, thereby directly controlling the stator flux. A flux limit value which depends on a predetermined maximum value of the stator flux allowed for the motor (1), which depends on a maximum value of an electric voltage, which is used to drive the currents through the stator electromagnets (7, 9), and which depends on the actual rotor speed is repeatedly calculated. During acceleration of the rotor (5) while the stator flux is smaller than the maximum flux allowed for the motor the measure of the flux magnitude is calculated depending on the output of a predetermined function, wherein the output of the predetermined function depends on the desired motor torque and corresponds to the magnitude of the stator flux, which results in the desired motor torque using the minimum possible stator current. The measure of the load angle is calculated depending on the desired motor torque.
Owner:BOMBARDIER TRANSPORTATION GMBH
Maritime work foundation multi-directional loading test system and method capable of simulating wind-wave effect
ActiveCN110439042AVerify reliabilityFoundation testingStructural/machines measurementControl systemWind wave
The invention provides a maritime work foundation multi-directional loading test system and method capable of simulating a wind-wave effect. The maritime work foundation multi-directional loading testsystem comprises a control system, a servo electric controller, a loading reaction frame, a model test box and a load simulation mechanism; the load simulation mechanism outputs a simulated load to afoundation model in the model test box; the load simulation mechanism comprises a vertical actuator used for simulating a vertical load, and a horizontal actuator used for simulating a marine wind load and a marine wave load; the horizontal actuator comprises first horizontal actuators fixed to rotating discs for simulating the different loading directions of the wave load, and second horizontalactuators fixed to rotating discs for simulating the different loading directions of the wind load; and different loading modes can be simulated by the rotating discs for simulating the different loading directions of the wave load and the rotating discs for simulating the different loading directions of the wind load. Under different model scales, long-term loading of a marine engineering structure foundation of the wind and wave loads with the different load frequencies and amplitudes at any loading angle and under continuous change of the loading angles can be simulated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for defining quadrature-axis magnetizing inductance of synchronous machine
InactiveUS6984958B2Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersStator voltageAngular velocity
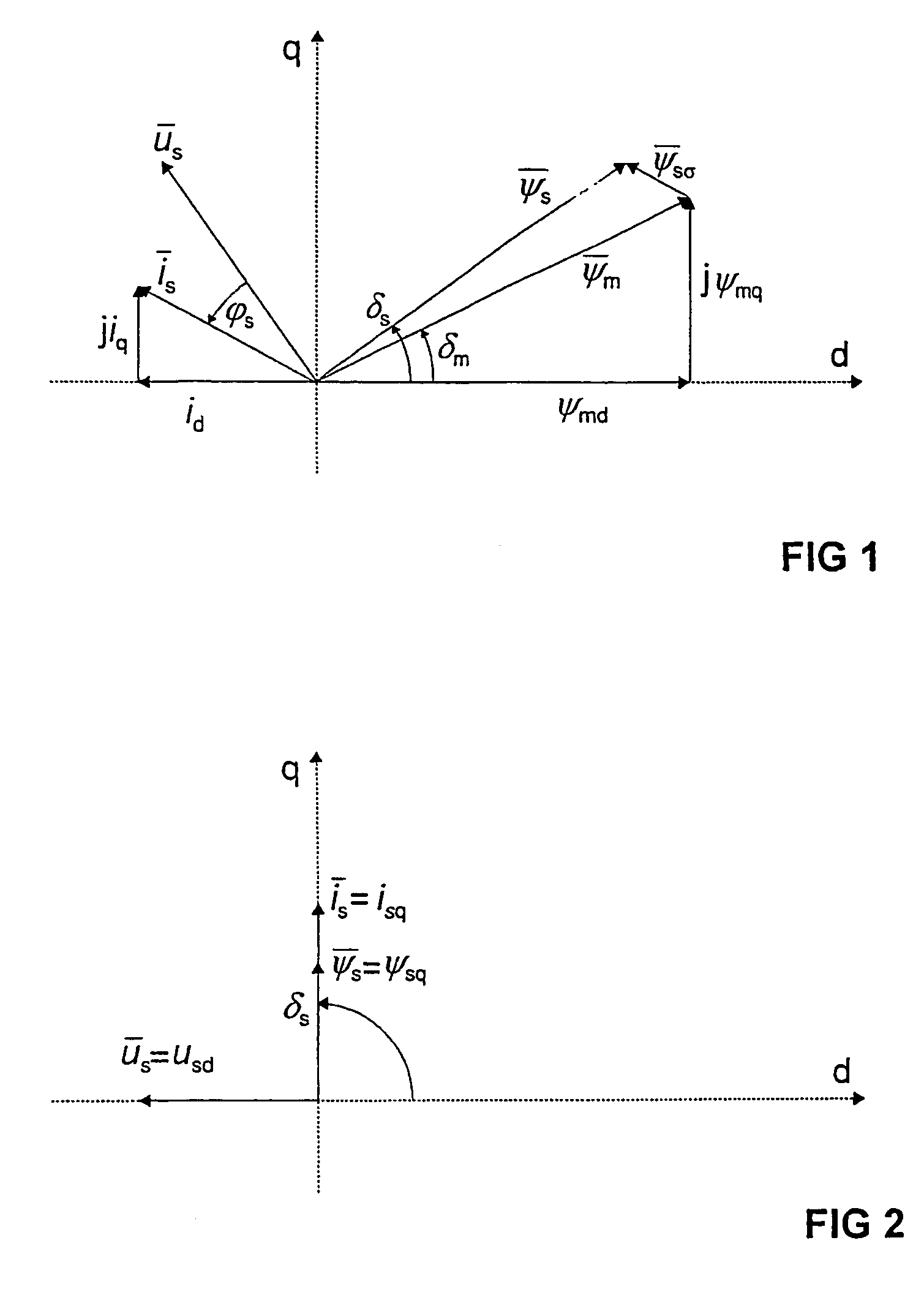
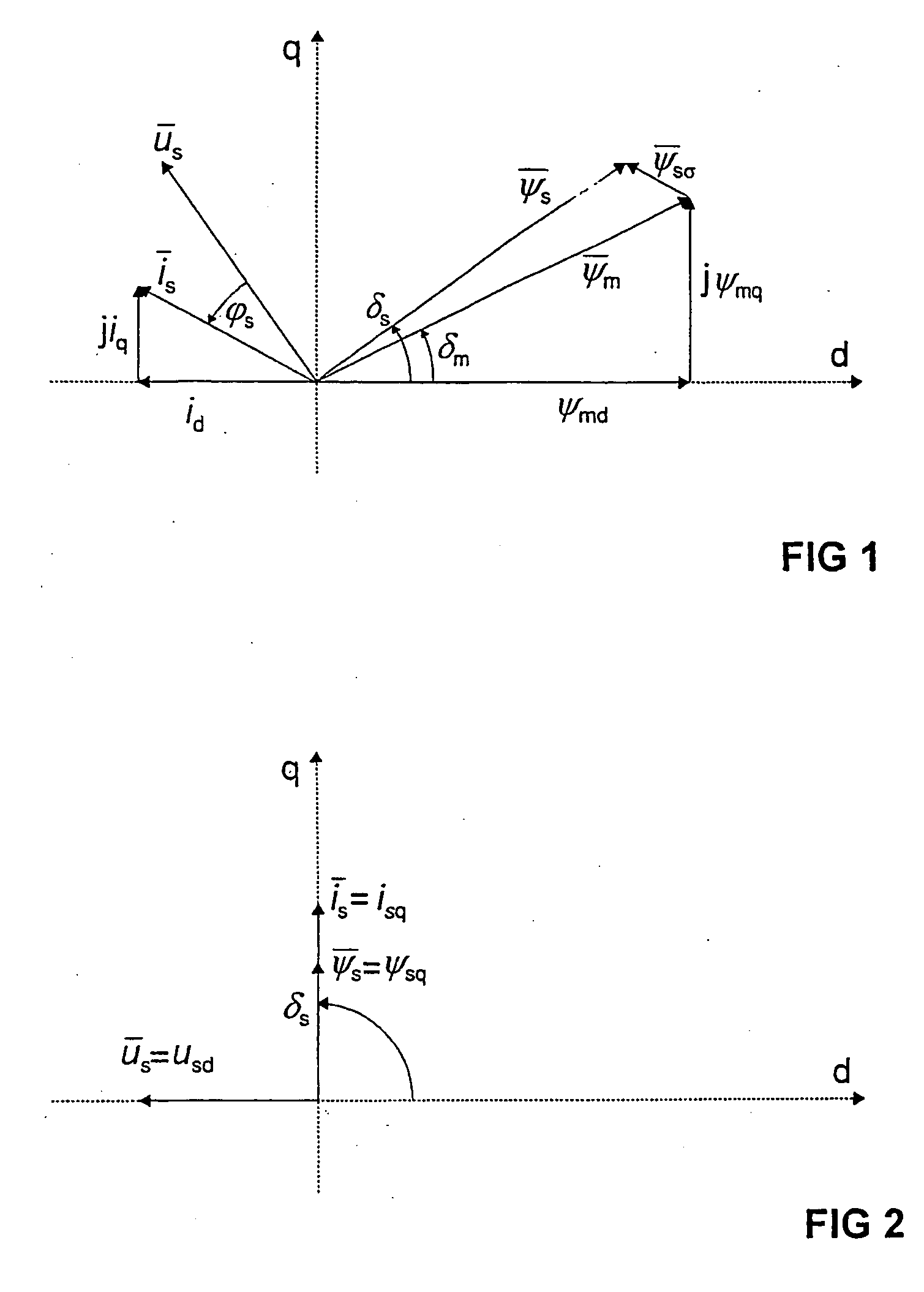
Method for defining quadrature-axis magnetizing inductance of a synchronous machine, the synchronous machine being supplied by an inverter. The method comprises steps, wherein the synchronous machine is started without load or with reduced load; the rotor current of the synchronous machine is kept substantially at zero, the synchronous machine is accelerated to initial angular velocity of measurement, the load angle (ds) of the synchronous machine is guided substantially to 90 degrees, the stator voltage (us), the stator current (is) and the electrical angular velocity (?) of the synchronous machine is defined and the quadrature-axis magnetizing inductance of the synchronous machine (lmq) is defined on the basis of the stator voltage (us), the stator current (is) and the electrical angular velocity (?) of the machine.
Owner:ABB OY
Permanent magnet synchronous motor full-speed-domain model prediction flux linkage control method
ActiveCN110784145AGood dynamic and steady state performanceTorque ripple controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorConstant power
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor full-speed-domain model prediction flux linkage control method. The method comprises the steps of firstly, acquiring a reference torque Teref through a rotating speed outer ring PI controller; obtaining an electrical angle theta r and an electrical angle speed omega r of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, obtaining a three-phase stator current at a k moment, and obtaining a d-q axis component of a stator current at the k moment after coordinate transformation; secondly, carrying out flux linkage calculation by combining a flux linkage equation and a load angle to obtain a flux linkage prediction value and a flux linkage reference value at a (k+1) moment; then, constructing a full-speed-domain value function by using the flux linkage prediction value and the reference value at the (k+1) moment, and obtaining an optimal voltage vector of an inverter by minimizing the full-speed-domain value function; and finally, calculatinga duty ratio according to a dead-beat thought of a q-axis flux linkage, and distributing time of the optimal voltage vector and a zero vector acting on the inverter. By using the method of the invention, a current and torque pulsation can be effectively reduced, good dynamic steady-state performance is possessed, and the method can be applied to a constant torque region and a constant power region.
Owner:揭阳市盛佳电机有限公司
Method for defining quadrature-axis magnetizing inductance of synchronous machine
InactiveUS20050017669A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersStator voltageAngular velocity
Method for defining quadrature-axis magnetizing inductance of a synchronous machine, the synchronous machine being supplied by an inverter. The method comprises steps, wherein the synchronous machine is started without load or with reduced load; the rotor current of the synchronous machine is kept substantially at zero, the synchronous machine is accelerated to initial angular velocity of measurement, the load angle (ds) of the synchronous machine is guided substantially to 90 degrees, the stator voltage (us), the stator current (is) and the electrical angular velocity (?) of the synchronous machine is defined and the quadrature-axis magnetizing inductance of the synchronous machine (lmq) is defined on the basis of the stator voltage (us), the stator current (is) and the electrical angular velocity (?) of the machine.
Owner:ABB OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com