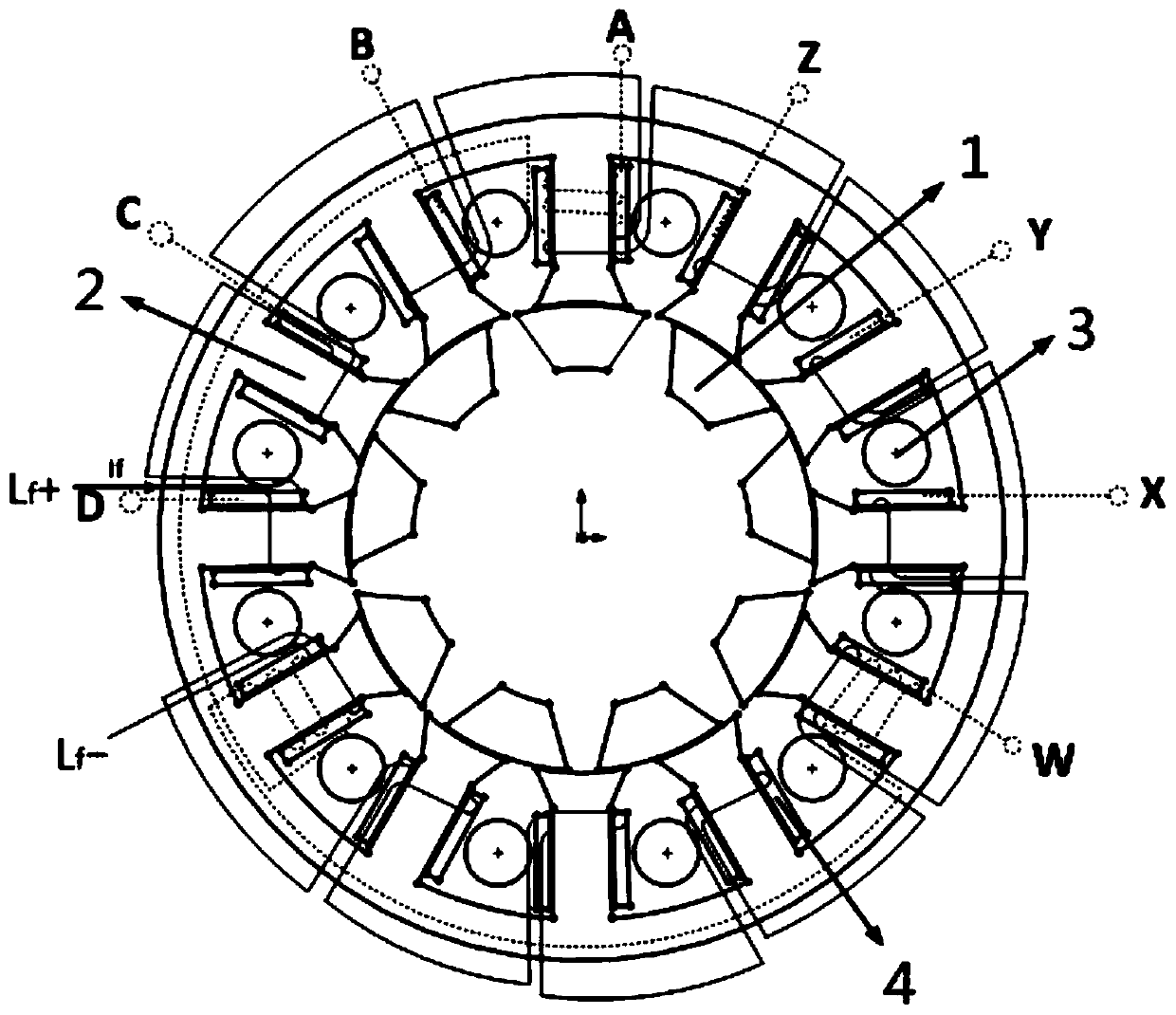
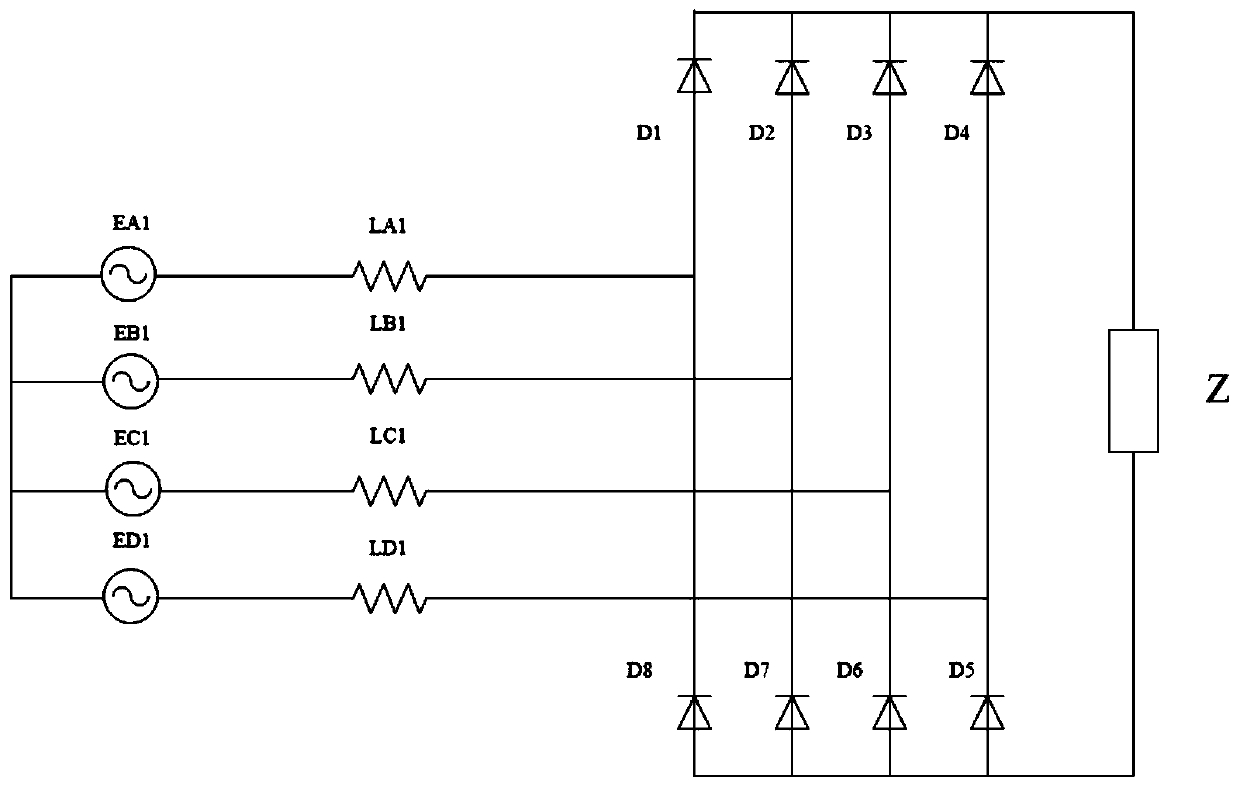
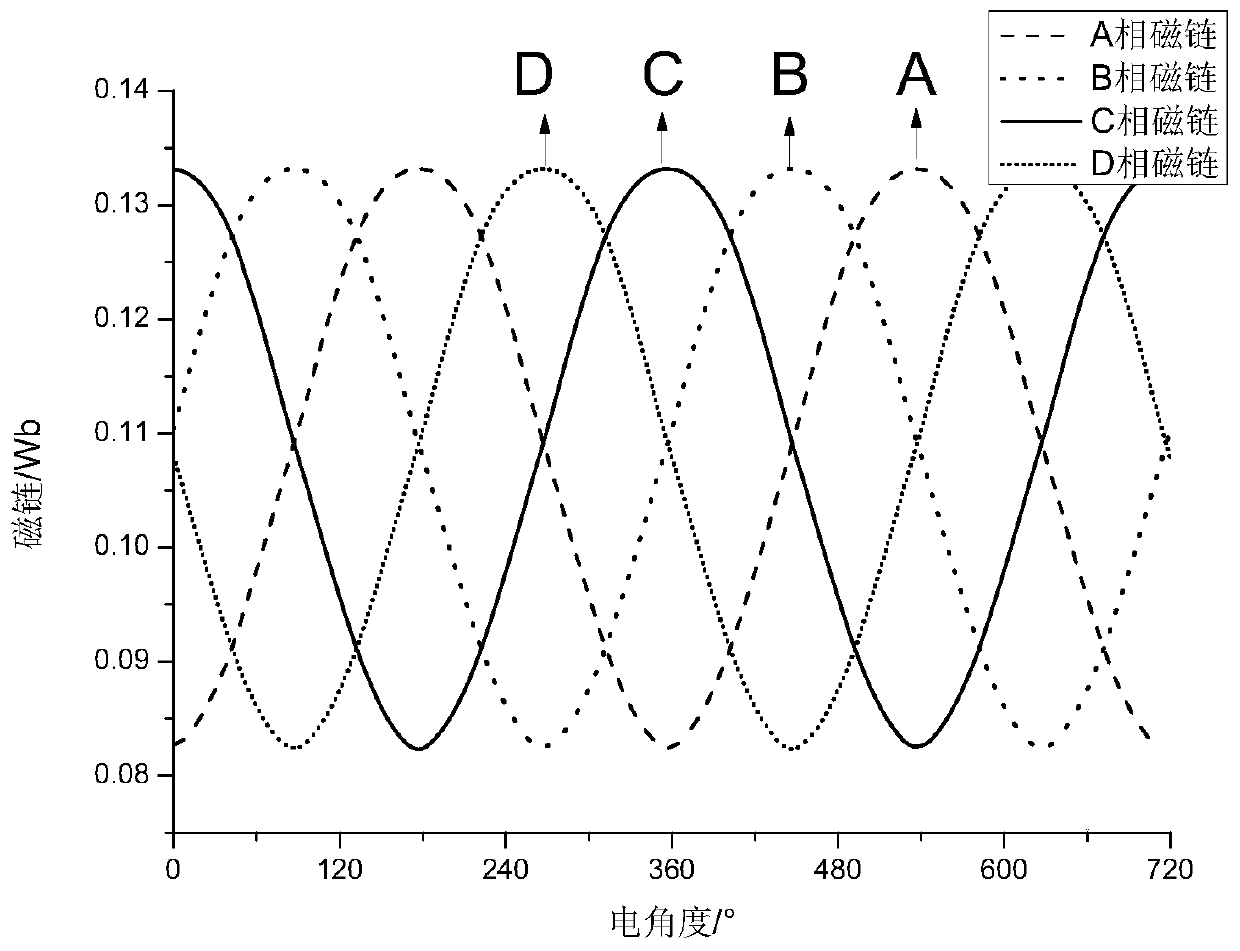
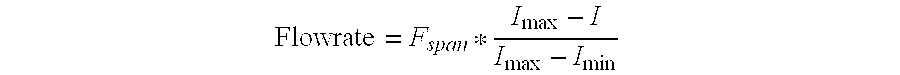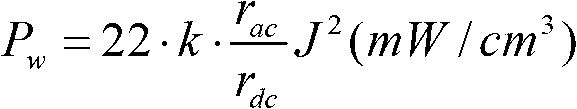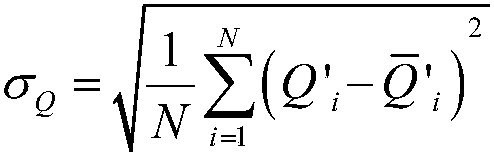Patents
Literature
48 results about "Maximum flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
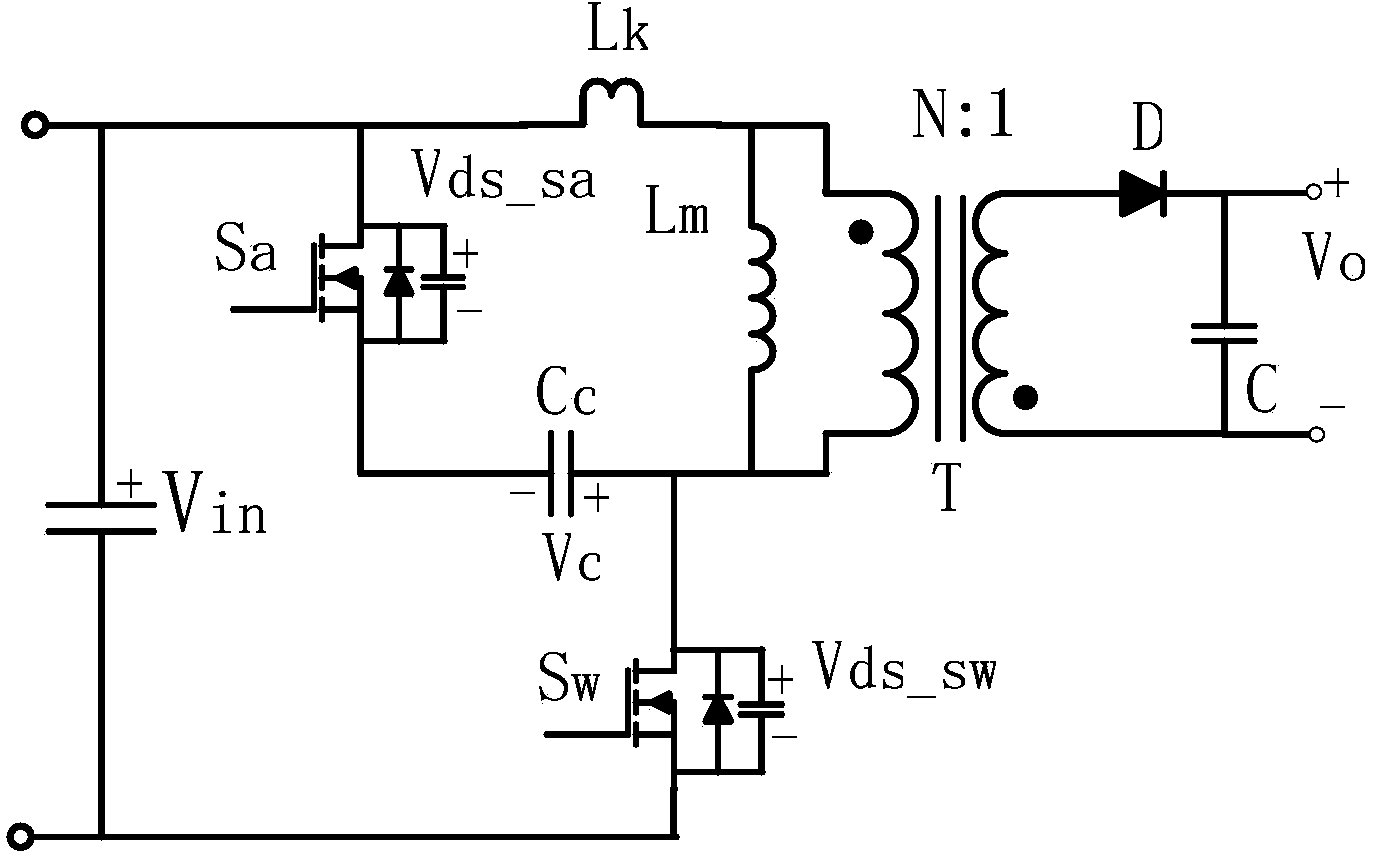
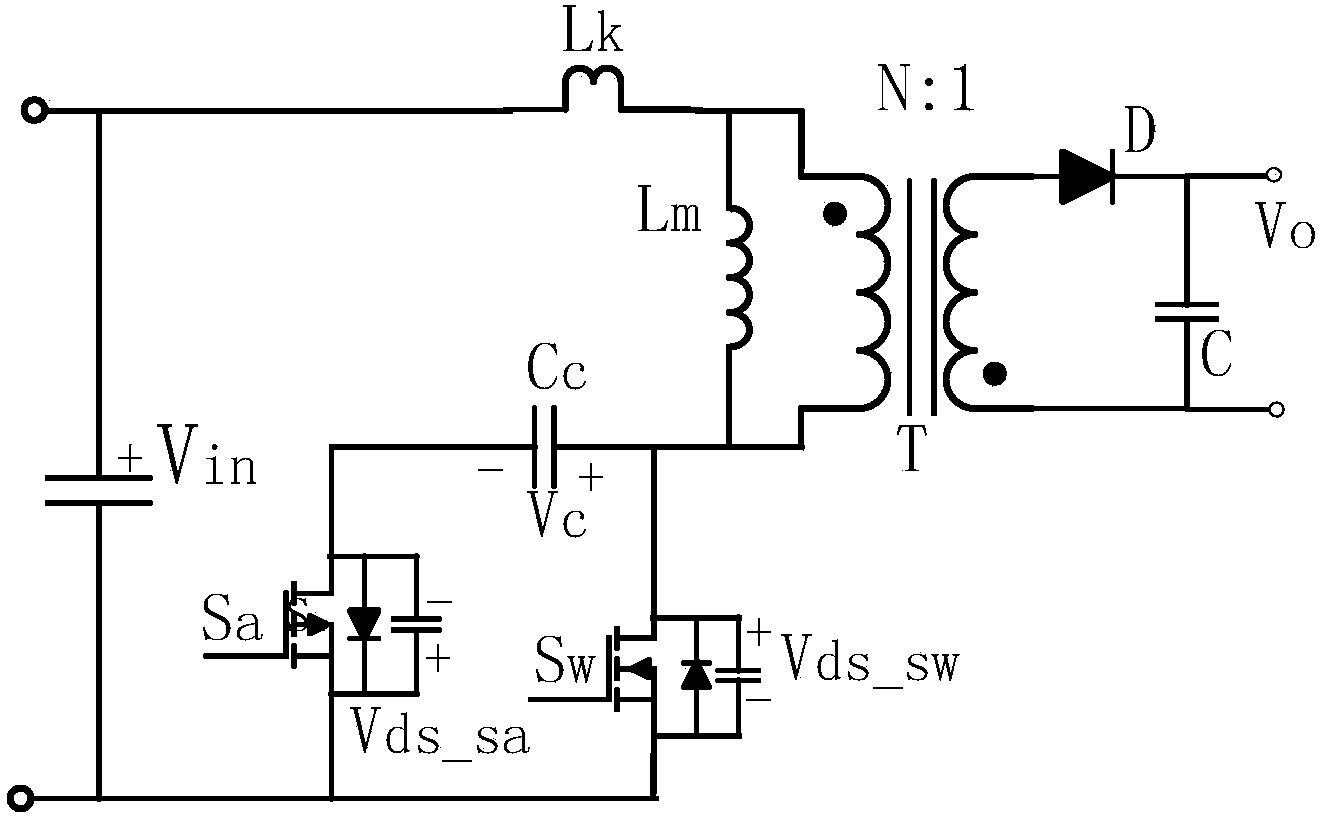
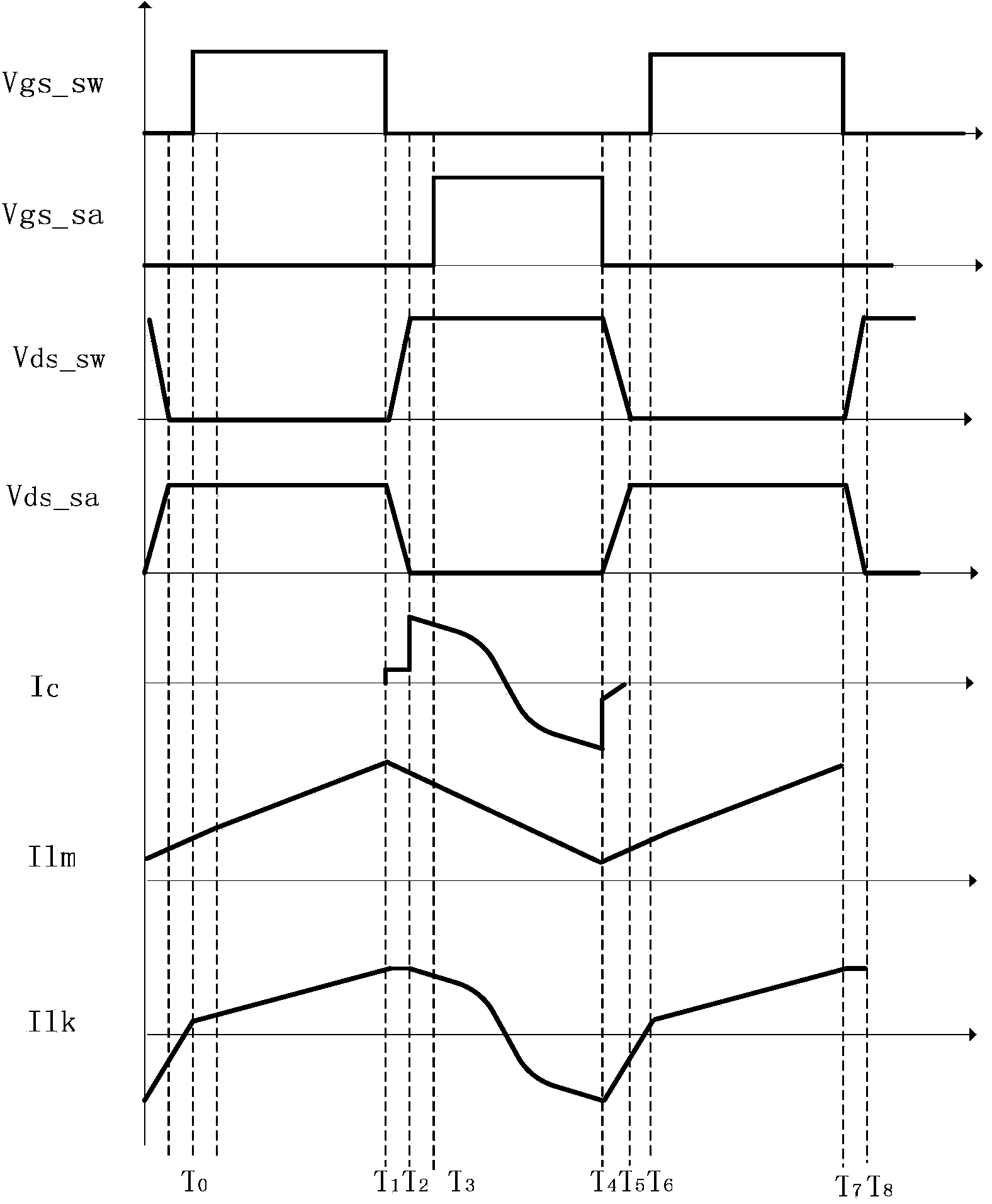
Flyback converter and control method of flyback converter
ActiveCN104300795AGuaranteed efficiencyReduce distractionsDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationClamp capacitorCapacitance
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
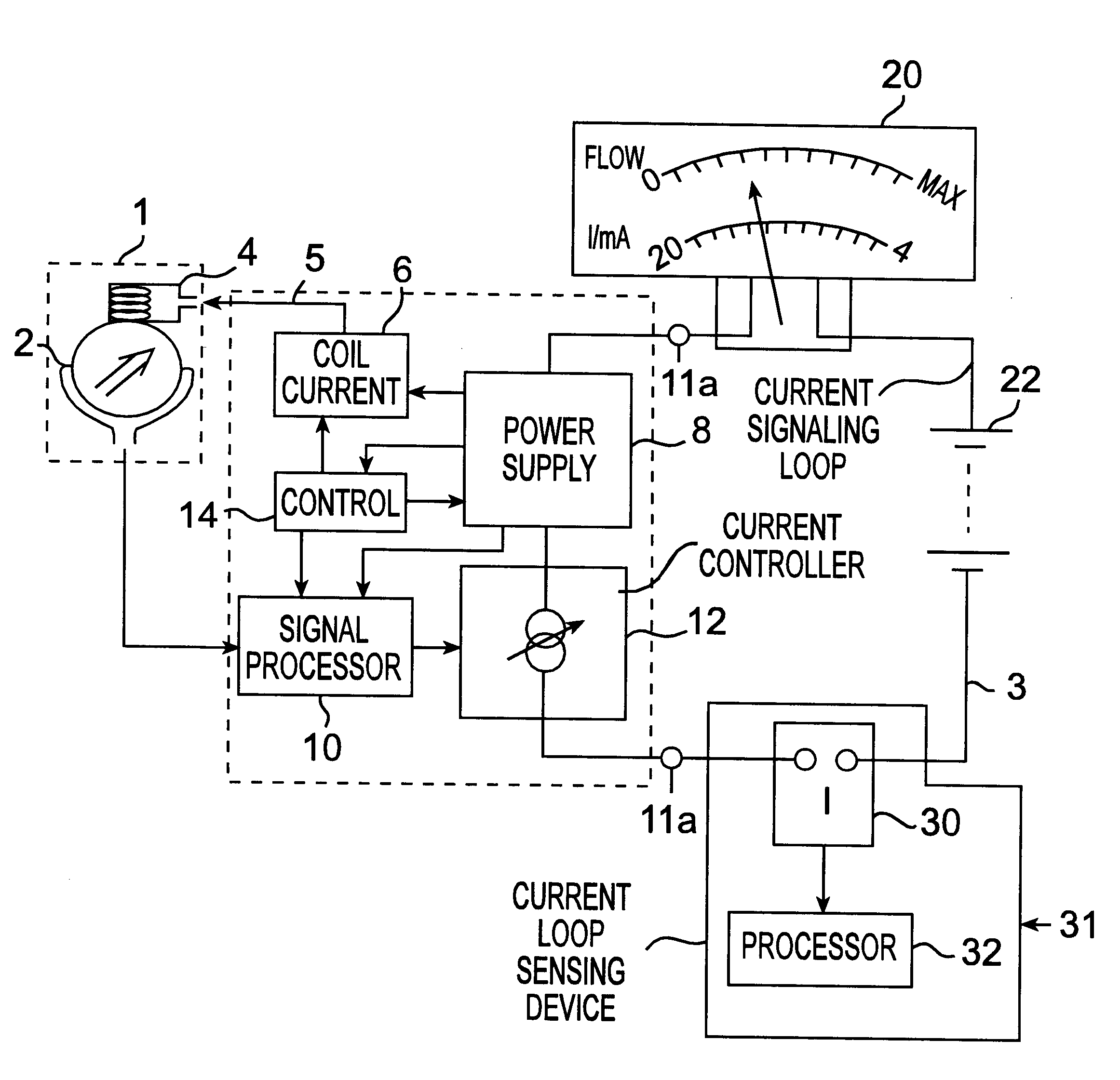
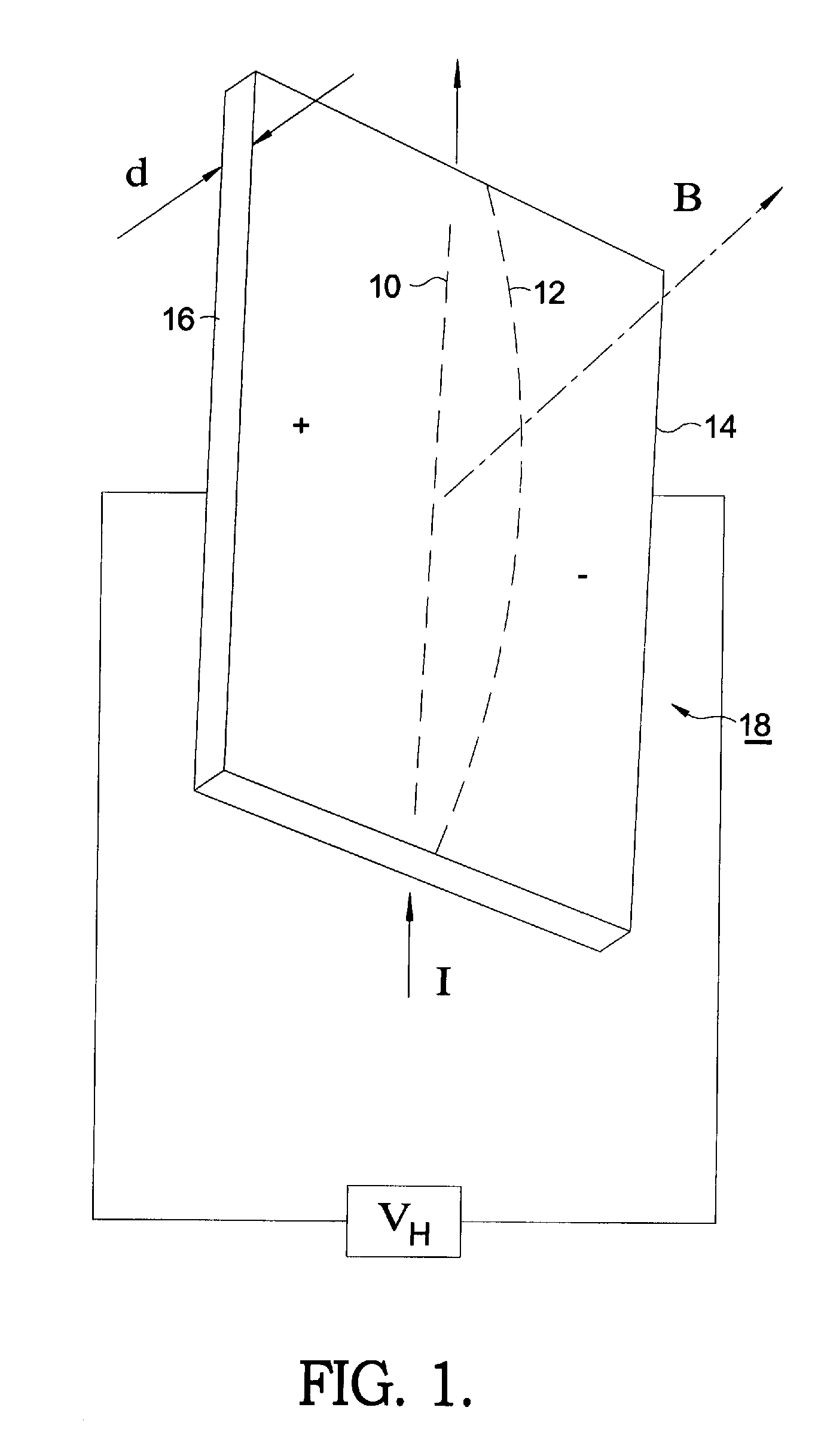
Electromagnetic flowmeter deriving power from signalling loop current
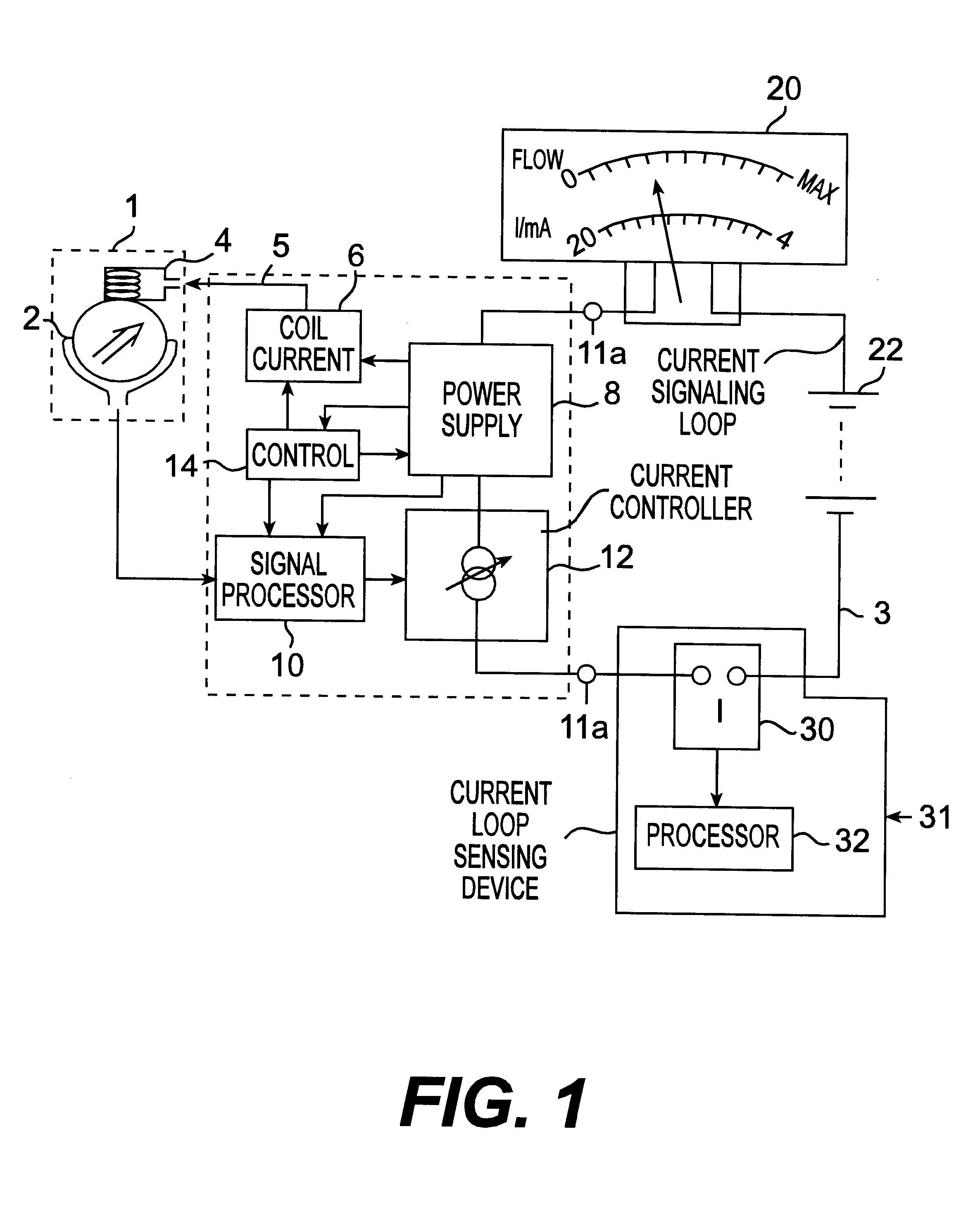
InactiveUS6269701B1Fluid speed measurementVolume/mass flow by electromagnetic flowmetersMaximum fluxCurrent range
An improvement over conventional electromagnetic flowmeters which signal a measure of flow rate by controlling the current in a current signalling loop (also known as a sensing loop) and in which power for the flowmeter is derived from the current in the signalling / sensing loop. Conventional electromagnetic flowmeters use a standard current range (typically 4-20 mA), in which zero flow is indicated by controlling the current in the loop to a minimum predeterimened value and maximum flow is indicated by controlling the current to a maximum predetermined value. In the improved flowmeter of the invention, minimum flow is signalled by maximum current in the signalling / sensing loop and maximum flow is signalled by minimum current. This has been found to enable improved accuracy to be obtained at low flow rates without requiring complex flowmeter circuitry.
Owner:ABB KENT TAYLOR
System And Method For Controlling A Matrix Of Light Emitting Diodes And Light Provided Therewith
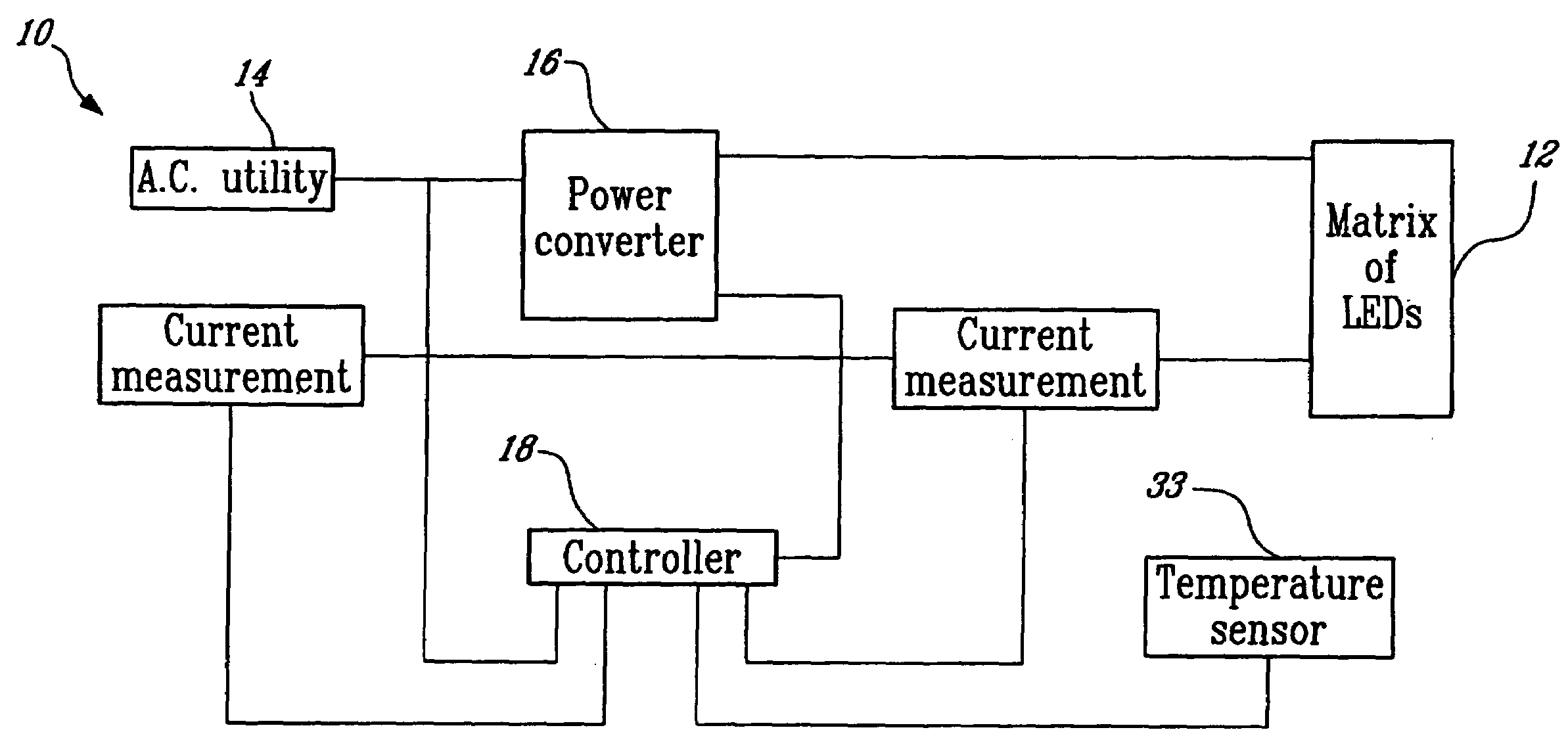
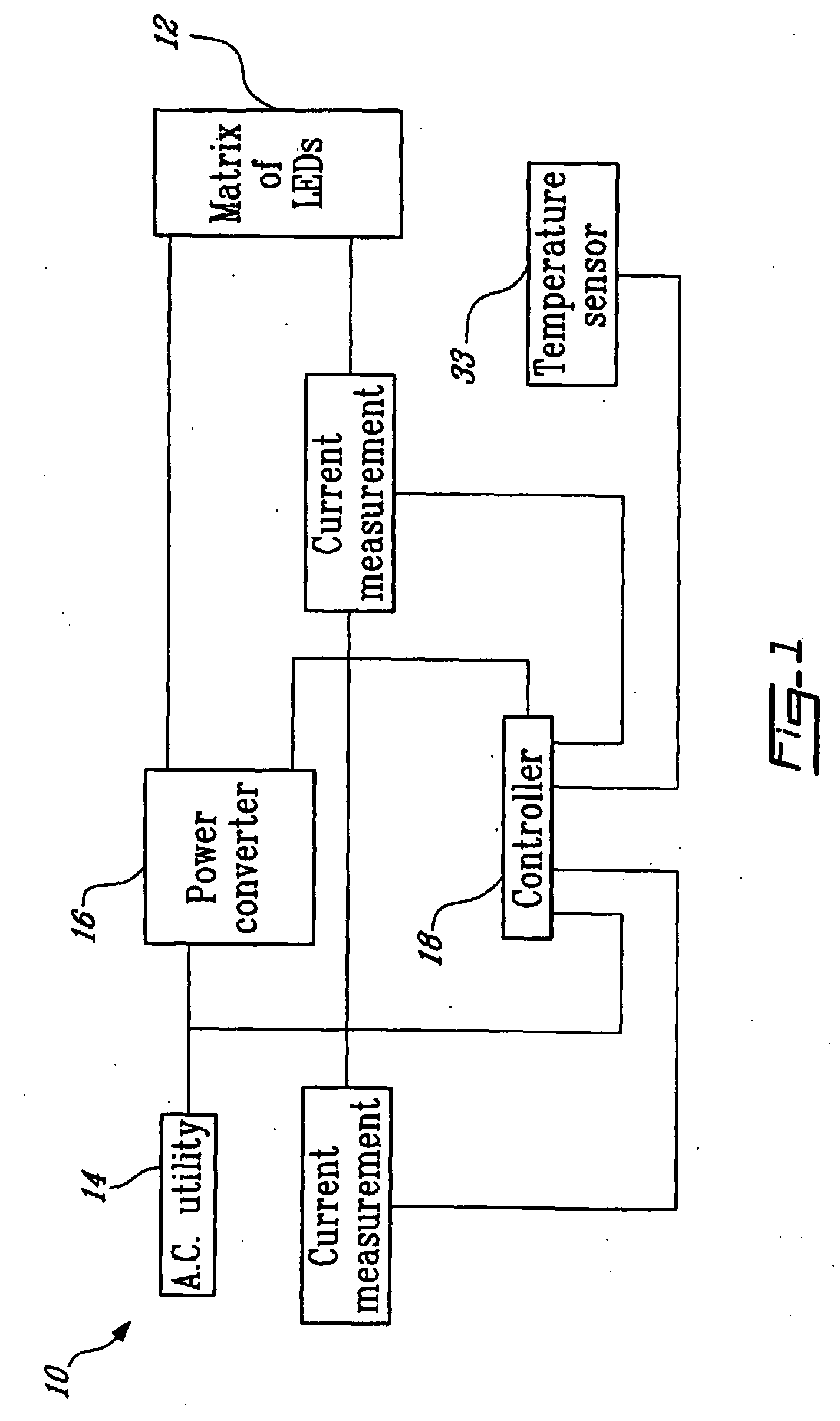
InactiveUS20100013402A1Maximize energy savingLarge fluxElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPresent methodMaximum flux
A system and method for controlling a matrix of light emitting diodes (LED) connected to an input line comprises a power converter for connecting to the matrix of LEDs and to the input line therebetween and for receiving from the input line an input current and an input voltage characterized by a shape and a frequency and for providing a direct current (D.C.) output for powering up the LEDs, yielding an operating current through the LEDs. The power converter includes a first current sensor for sensing the input current and a second current sensor for sensing the operating current. The system further comprises a controller for connecting to both the input line and to the power converter. The controller includes a voltage sensor for sensing the input voltage and a pre-regulator i) for receiving the operating current, the input current and the input voltage, ii) for biasing the operating current towards a target current value, and iii) for regulating the power converter to cause the input current to follow the shape and frequency of the input voltage, yielding a unity power factor and minimizing the input current harmonic distortion. The present method and system allows maximizing the energy savings, controlling current flowing in the diodes so as to obtain the maximum flux of light with the minimum energy and also allows meeting all safety, EMI, reliability and robustness requirements.
Owner:ELUMEN LIGHTING NETWORKS
Amorphous iron core, manufacturing method thereof and transformer with high performance, low noise and low cost
ActiveCN102360768AAvoid complex processes for separate fixationAvoid complex processesTransformers/inductances magnetic coresInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureLow noiseMaximum flux
The invention belongs to the field of transformer manufacturing and relates to an amorphous iron core, a manufacturing method thereof and a transformer with high performance, low noise and low cost. The amorphous iron core for the transformer has iron loss of less than or equal to 0.20 W / kg and excitation power of less than or equal to 0.80 VA / kg under the conditions of frequency of 50Hz and maximum flux density of 1.35T. The width of the iron core for the transformer is made of an iron-based amorphous alloy broad band with the width between 220 and 500 mm, the no-load loss of the transformer is less than or equal to 0.25 W / kg under the conditions of frequency of 50Hz and maximum flux density of 1.35T, and the noise of the transformer is reduced by 5 to 10 decibels and the copper using amount of the transformer is reduced by more than 1 percent approximately compared with those of the conventional transformer with two layers of overlaid iron cores. By the manufacturing method, a process flow of the iron core for the transformer is simplified, a complicated process for fixing the iron cores respectively under the condition of the two layers of overlaid iron cores is avoided, property deterioration caused by assembly stress of the iron cores is reduced, the noise is lowed, the total height of the iron cores is reduced, and the material cost is saved; and the operating efficiency is improved, so that the structure of the amorphous transformer is more compact and the manufacturing mode of the conventional large-capacity amorphous transformer iron cores is completely changed.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
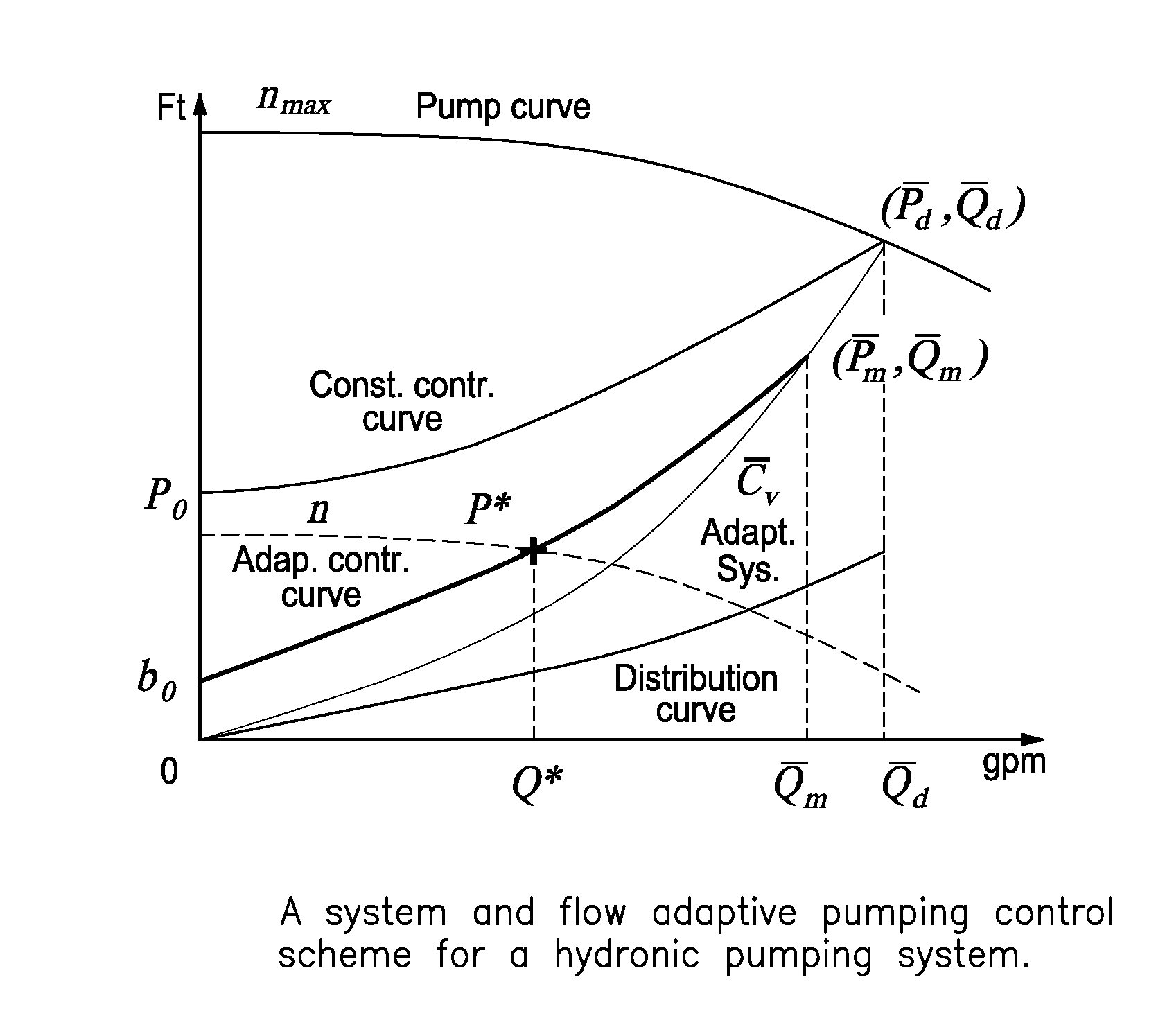
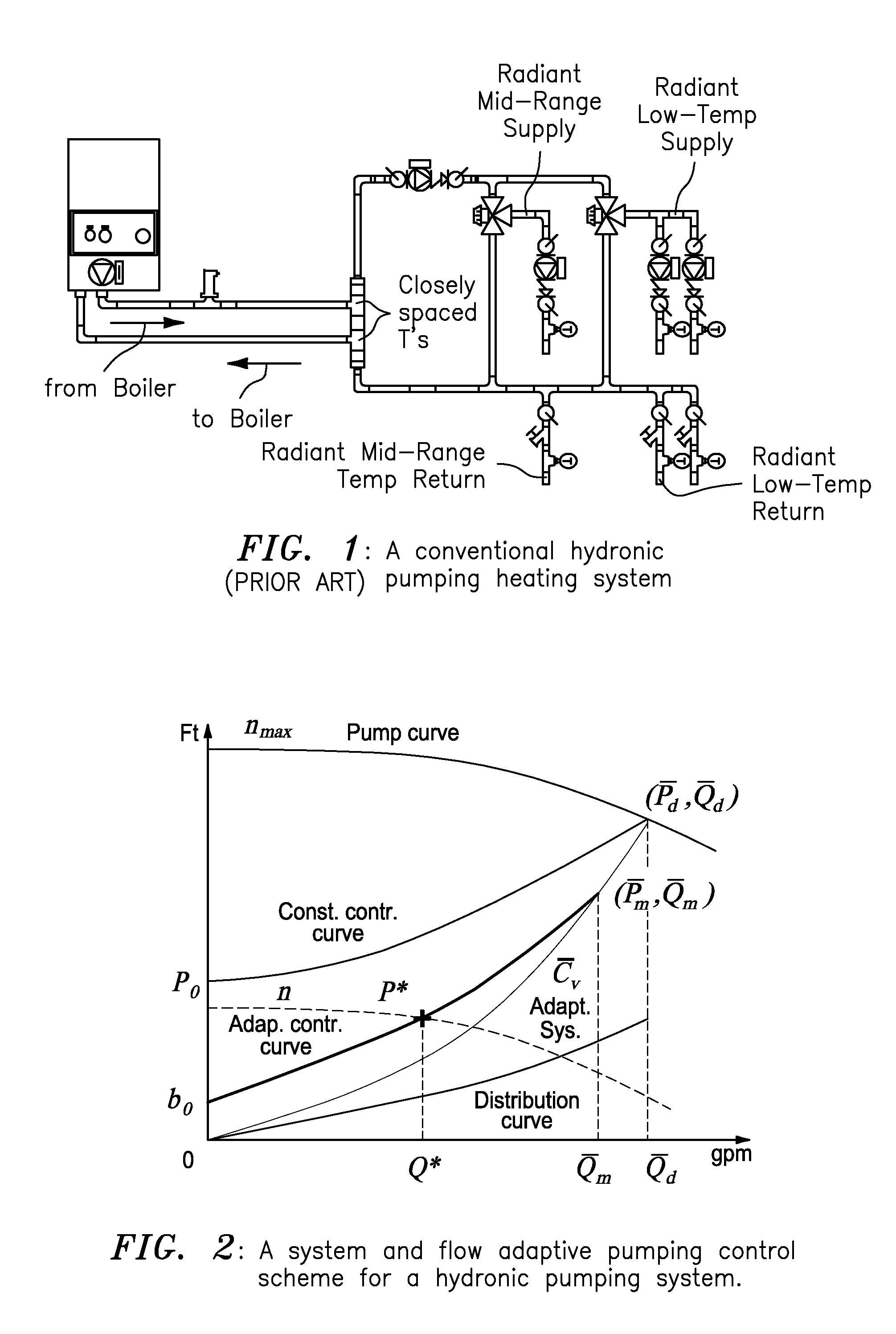
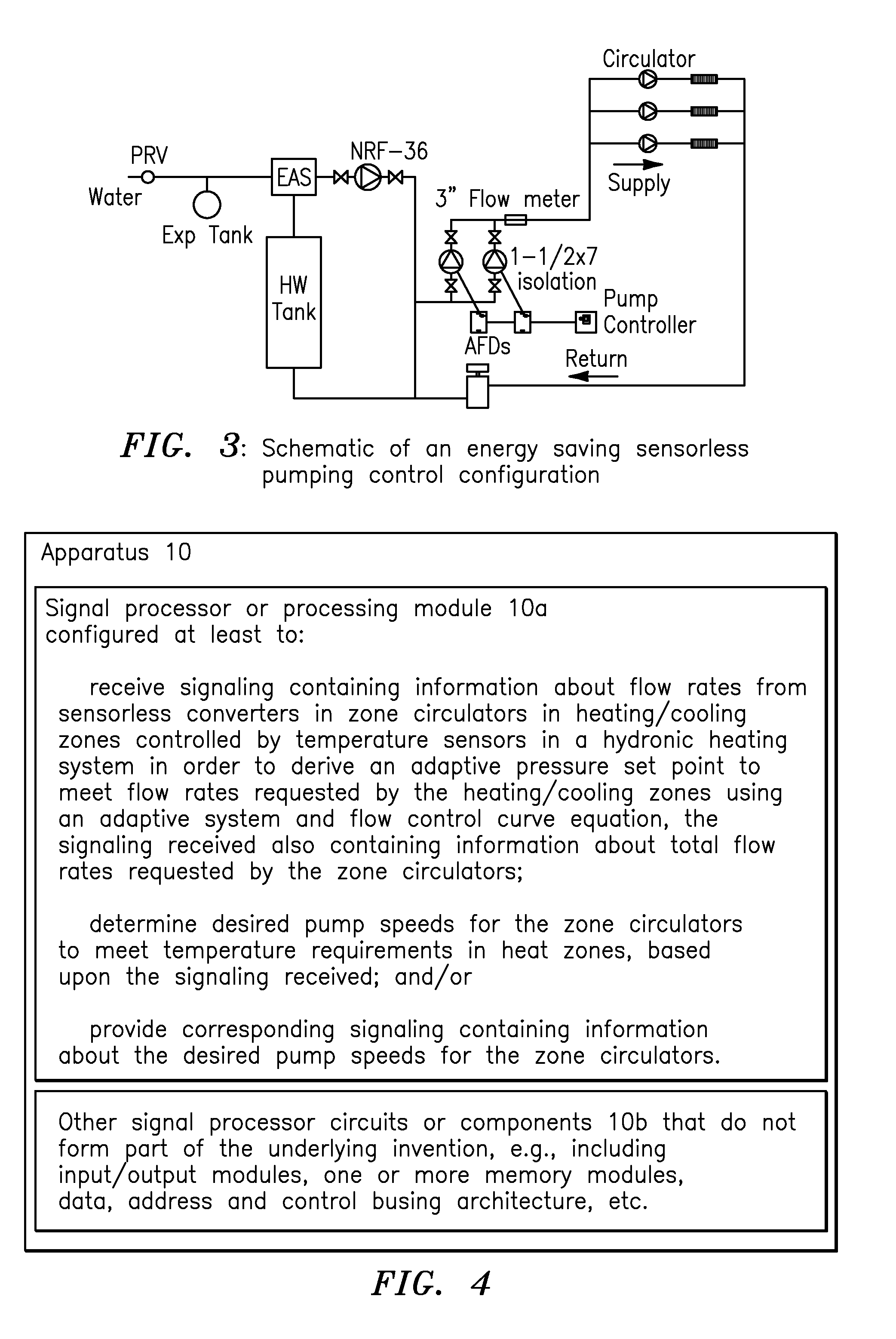
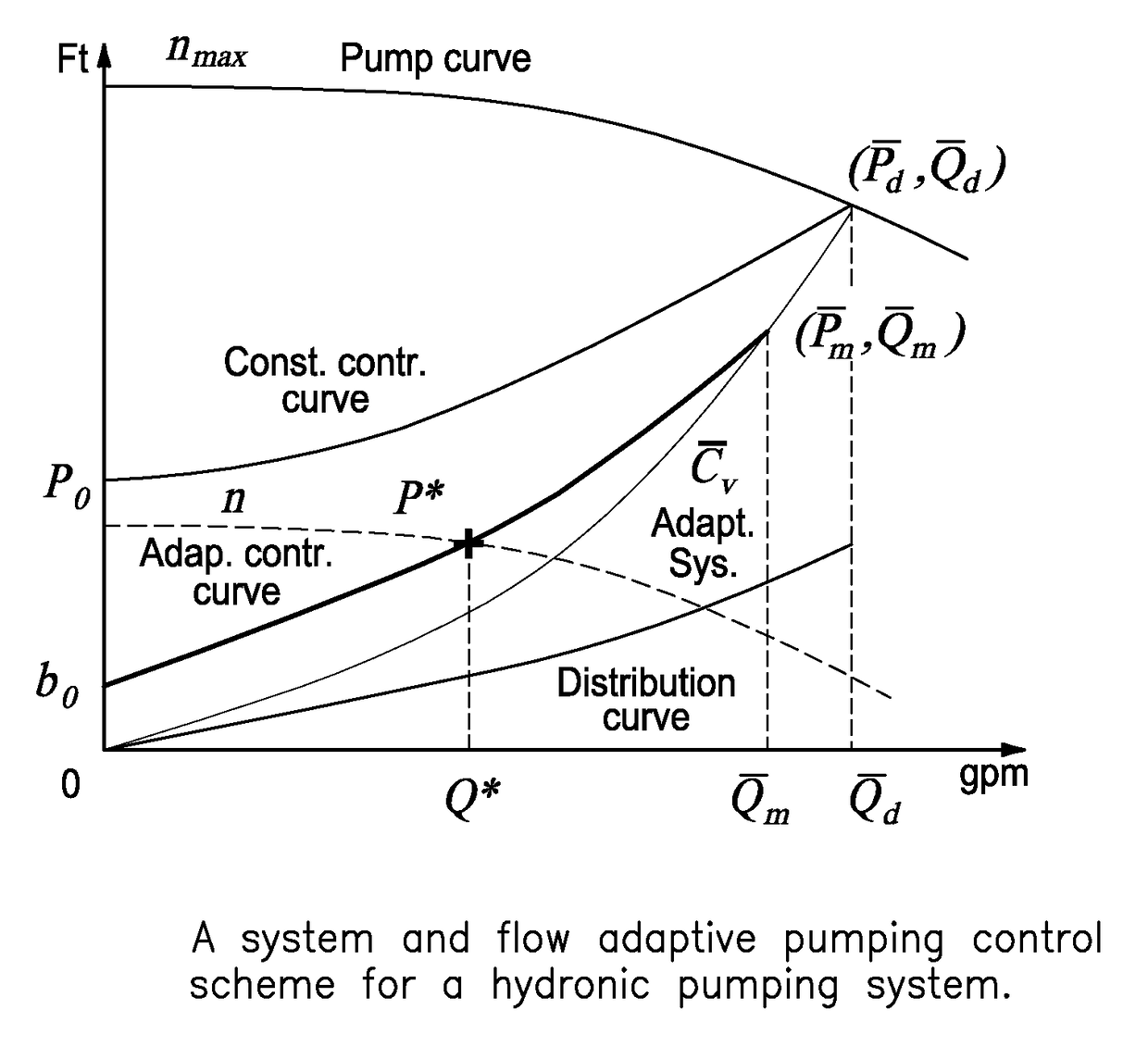
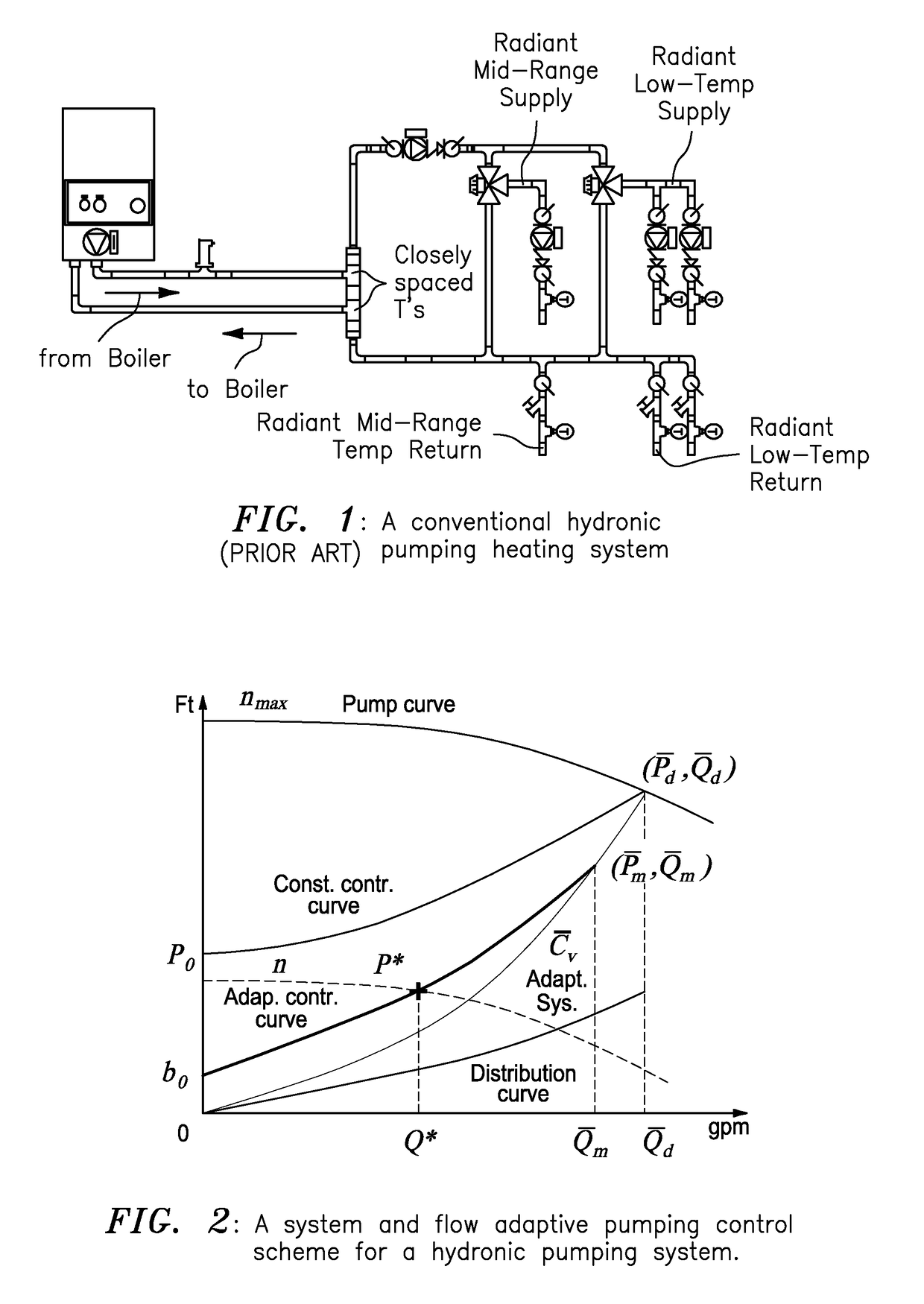
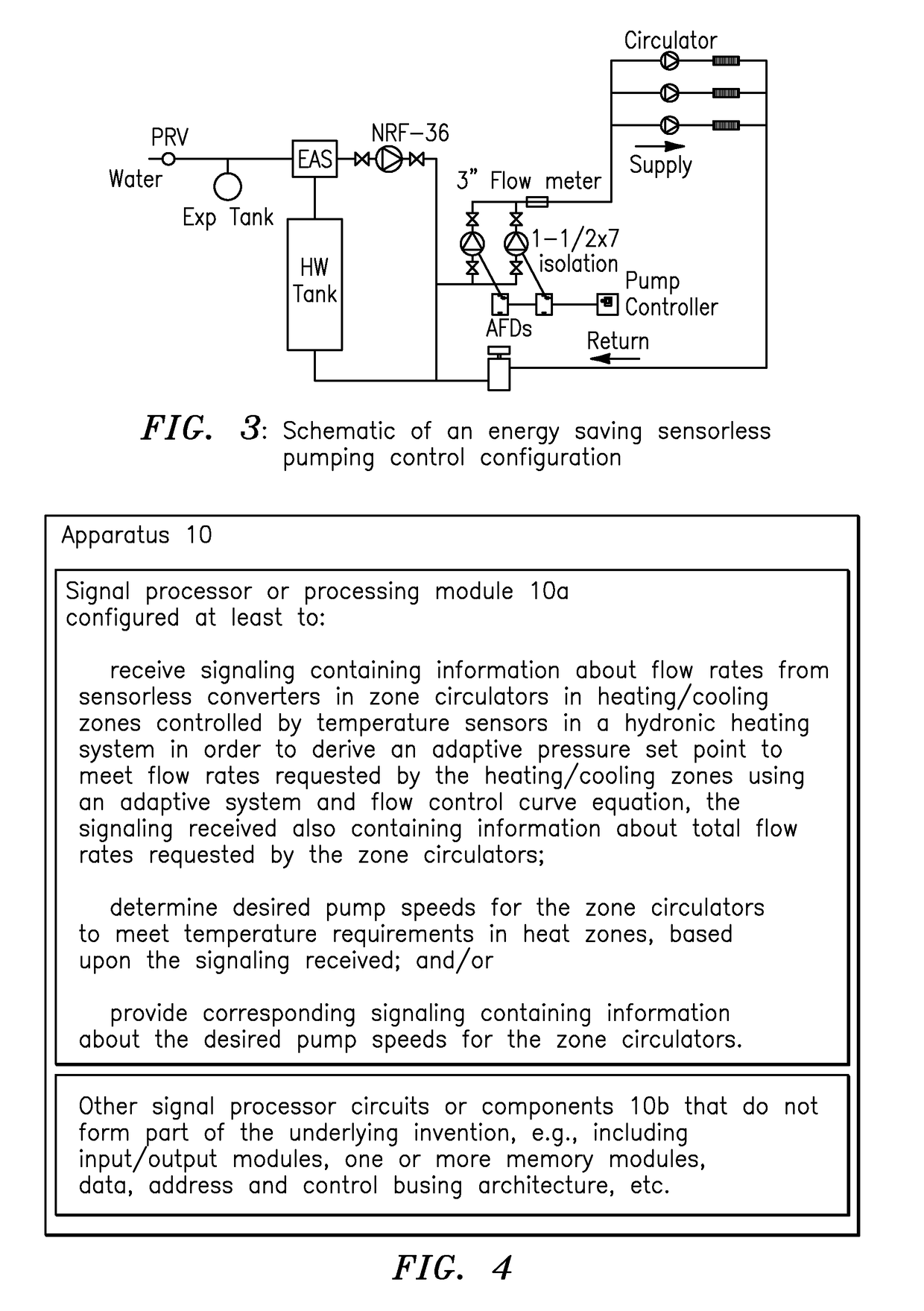
System and flow adaptive sensorless pumping control apparatus for energy saving pumping applications
ActiveUS20160017889A1Pumping energyEasy to storeSampled-variable control systemsSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsMaximum fluxEngineering
A signal processor receives signaling containing information about flow rates from sensorless converters in zone circulators in heating / cooling zones controlled by temperature sensors in a hydronic heating system in order to derive an adaptive pressure set point to meet the flow rates requested by the heating / cooling zones using an adaptive system and flow control curve equation, the signaling containing information about total flow rates requested by the zone circulators; determines desired pump speeds for the zone circulators to meet temperature requirements in heat zones; provides corresponding signaling containing information about the desired pump speeds; and / or determines the adaptive pump control curve equation based upon an adaptive system curve and as a moving maximum system flow rate depending on an adaptive pressure set point, a system flow rate requested by temperature loads, a minimum pressure at no flow, a control curve setting parameter, and an adaptive moving maximum flow and pressure.
Owner:FLUID HANDLING
Electromagnetic Lock Monitoring System
ActiveUS20090173119A1Improve reliabilityBurglar alarm by openingNon-mechanical controlsMaximum fluxElectromagnetic lock
An electromagnetic lock monitoring system for monitoring the strength of a magnetic field in an electromechanical lock which is created when a steel armature plate is closed against an electromagnet. The system utilizes dual Hall Effect devices positioned in such a way that both ends of the electromagnet and both magnetic fields are monitored, and that the resulting monitoring effectively covers the complete contact surface between the electromagnet and the armature plate. Preferably, the Hall Effect devices are disposed in series at the point of maximum flux density within the center element of an E-shaped electromagnetic core, at opposite ends of the core. If the magnetic flux is below a preset limit, a relay also in series drops out, triggering an alarm which may be sonic, electronic, and / or visual, as is known in the prior art.
Owner:HANCHETT ENTRY SYST
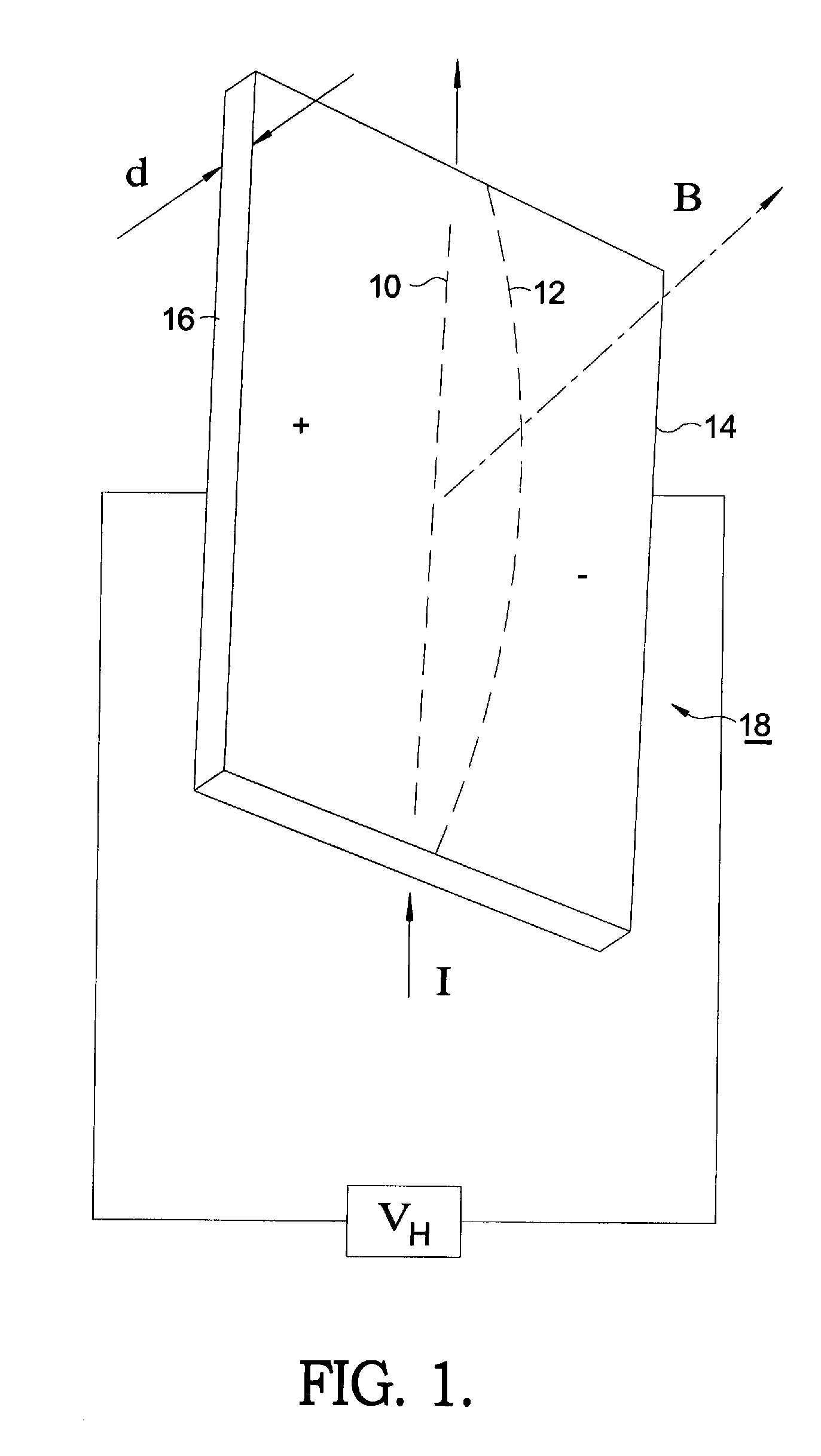
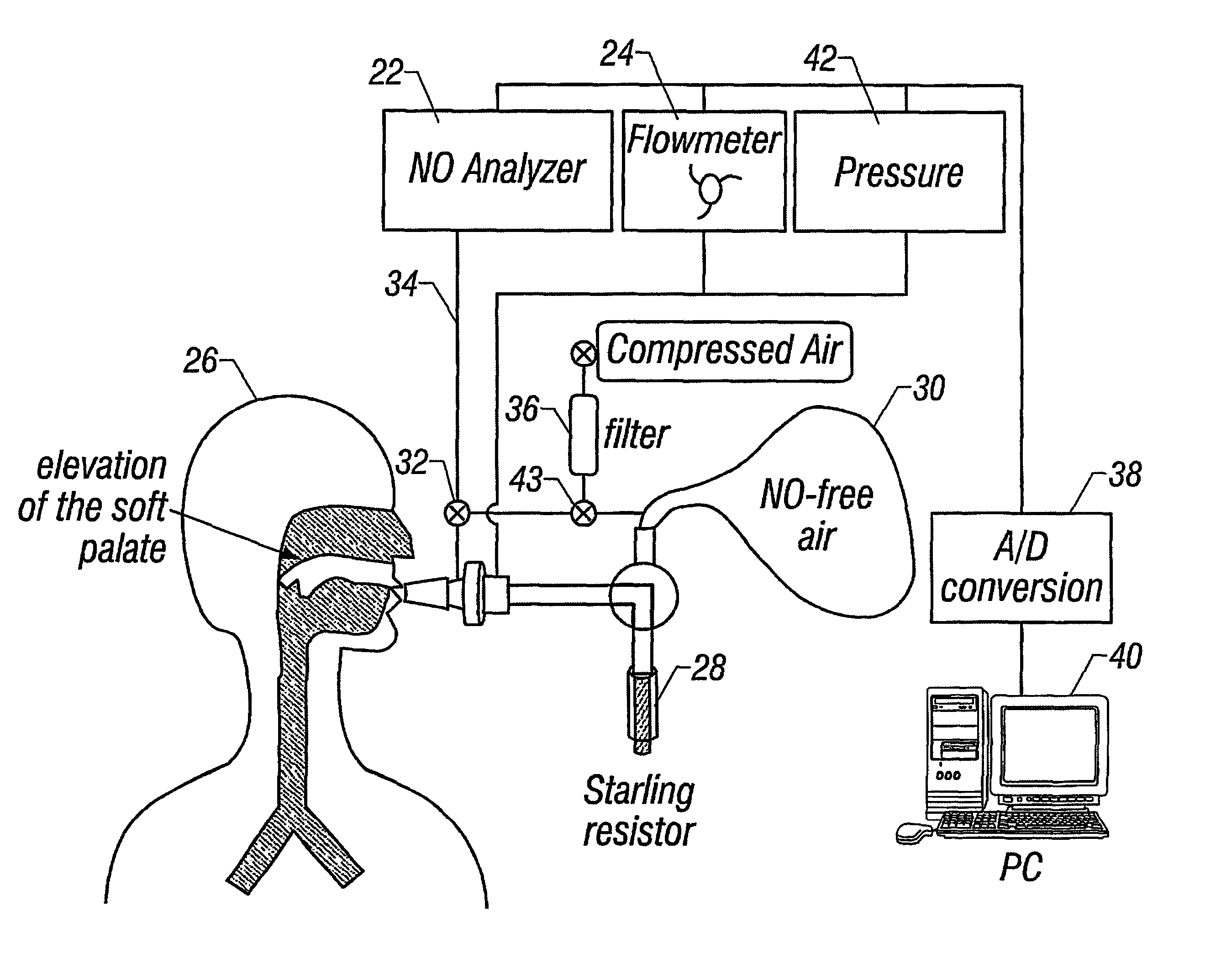
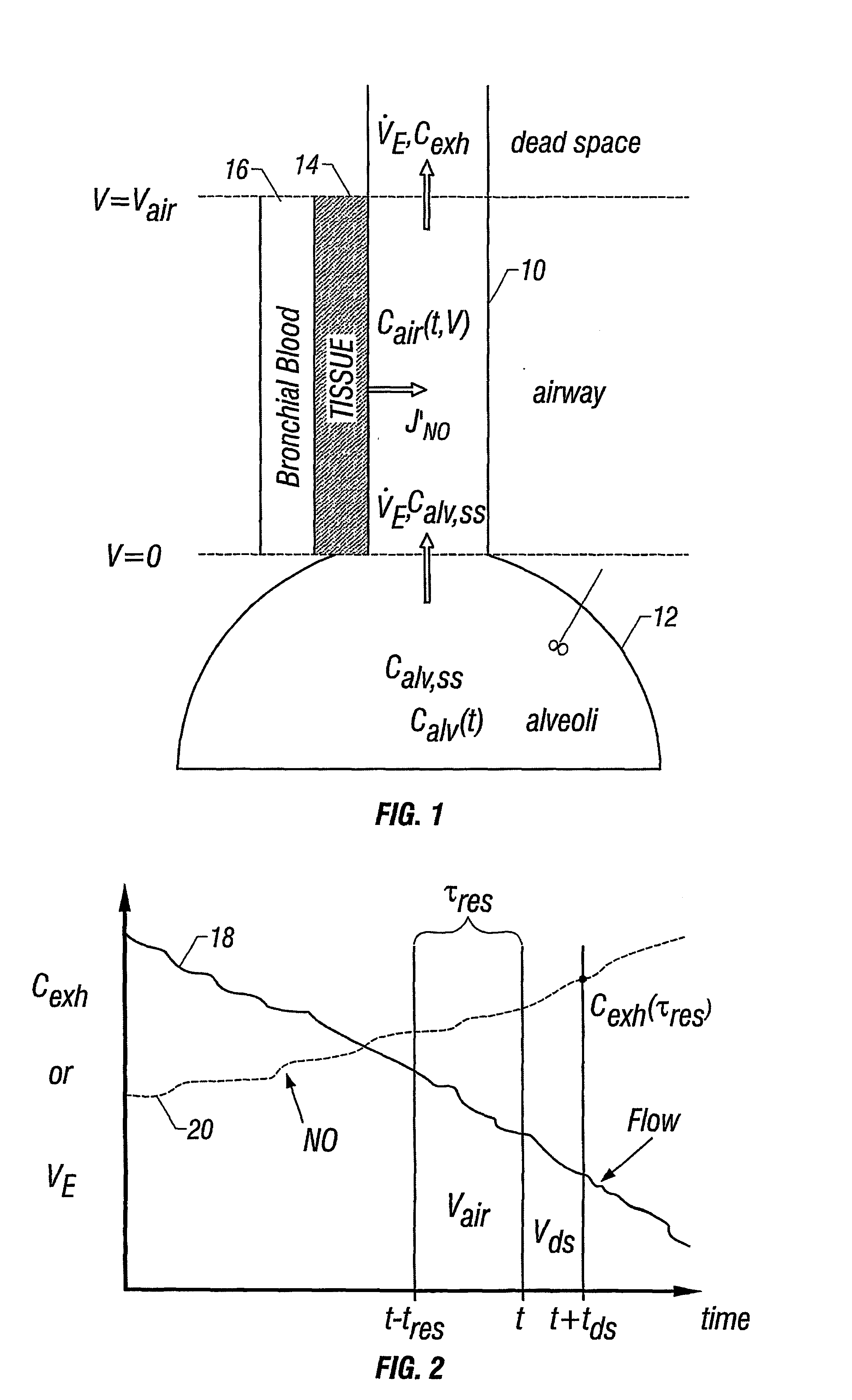
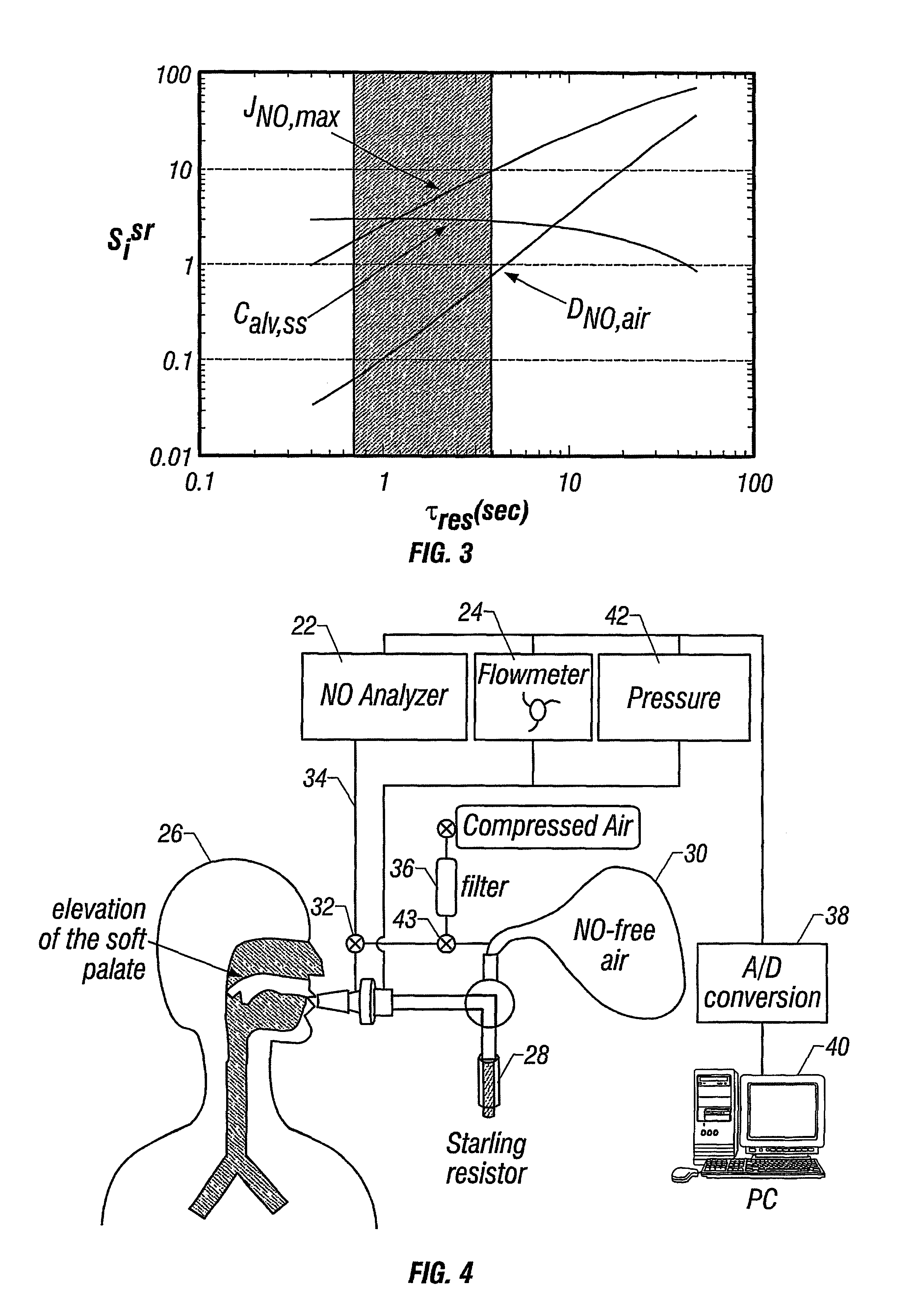
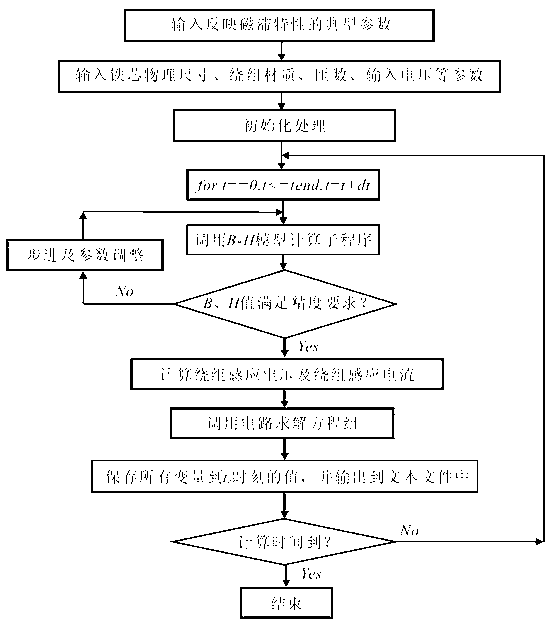
Apparatus and method for the estimation of flow -independent parameters which characterize the relevant features of nitric oxide production and exchange in the human lungs
InactiveUS6866637B2Withdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationMaximum fluxConfidence interval
The invention provides an estimation of key flow-independent parameters characteristic of NO exchange in the lungs, namely: 1) the steady state alveolar concentration, Calv,ss; 2) the maximum flux of NO from the airways, JNO,max; and 3) the diffusing capacity of NO in the airways, DNO,air. The parameters were estimated from a single exhalation maneuver comprised of a pre-expiratory breathhold, followed by an exhalation in which the flow rate progressively decreased. The mean values for JNO,max, DNO,air, and Calv,ss do not depend on breathhold time for breathhold times greater than approximately 10 seconds. A priori estimates of the parameter confidence intervals demonstrates that a breathhold no longer than 20 seconds may be adequate, and that JNO,max be can estimated with the smallest uncertainty, and DNO,air the largest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
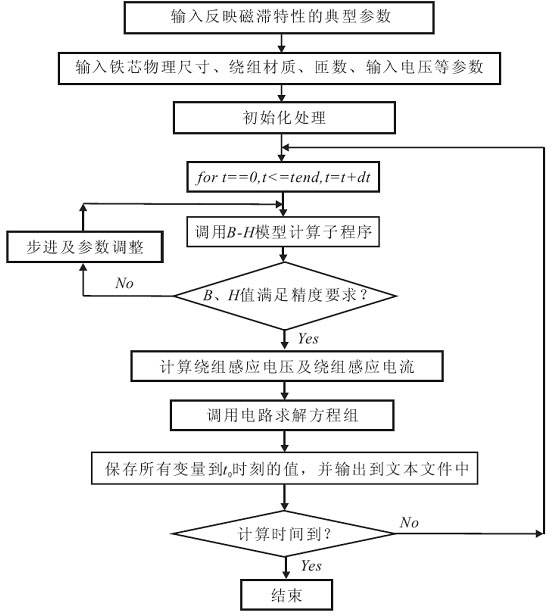
Analysis method of bias magnet characteristic of electric sheet
InactiveCN102708295AIngenious designSimple processSpecial data processing applicationsHysteresisMagnetic tension force
The invention relates to an analysis method of a bias magnet characteristic of an electric sheet. According to design parameters and power input conditions, an independent Kirchhoff voltage and current equation set of an equivalent circuit is established, and the pressure drop of a cored winding is represented by a series connection form of a change rate dB / dt of magnetic density B, leakage inductance L and a winding resistance rL. In the analog computation, according to a typical hysteresis loop and a magnetization curve of ferrous materials, the maximum flux density Bm and the maximum coercive force Hc are determined, an initial value can start from zero and stepwise perform uplink increase or downlink increase according to history operating points which reflect the hysteresis characteristic in the hysteresis loop, another hysteresis loop process is started after one cycle period, and obtained delta B / delta t and H value of corresponding current must meet the Kirchhoff voltage and current equation set. A method of numerical approximation includes that under constraint conditions limited by the maximum hysteresis loops Bm and Hc, equal interval time delta t is used for simulating B-H tracks under any bias magnet conditions. The analysis method of the bias magnet characteristic of the electric sheet is simple in process and thinking, practical and convenient.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Electromagnetic lock monitoring system
ActiveUS8094017B2Improve reliabilityBurglar alarm by openingNon-mechanical controlsMaximum fluxElectromagnetic lock
An electromagnetic lock monitoring system for monitoring the strength of a magnetic field in an electromechanical lock which is created when a steel armature plate is closed against an electromagnet. The system utilizes dual Hall Effect devices positioned in such a way that both ends of the electromagnet and both magnetic fields are monitored, and that the resulting monitoring effectively covers the complete contact surface between the electromagnet and the armature plate. Preferably, the Hall Effect devices are disposed in series at the point of maximum flux density within the center element of an E-shaped electromagnetic core, at opposite ends of the core. If the magnetic flux is below a preset limit, a relay also in series drops out, triggering an alarm which may be sonic, electronic, and / or visual, as is known in the prior art.
Owner:HANCHETT ENTRY SYST
Hierarchical porous nickel-aluminum alloy membrane with electrocatalytic performance and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108855098AEasy to handleImprove electrocatalytic performanceWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentMaximum fluxDyeing wastewater
The invention discloses a hierarchical porous nickel-aluminum alloy membrane with the electrocatalytic performance and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, a certain proportion of nickel-aluminum powder is taken, is mixed and pressed, and then is molten into a porous alloy membrane in a sintering mode, then the interior of the porous alloy membrane is enabled to form a microporous morphology through chemical corrosion, the alloy membrane forms a nano-pore structure with high specific surface area and high catalytic activity due to the fact that nickel-aluminum alloy is corroded by sodium hydroxide, so that the membrane separation and the electrocatalysis function are integrated without adding an additional supported catalyst, and therefore the processing capacity of the alloy membrane to dye wastewater is greatly improved, and the decolorization rate of the alloy membrane at the maximum flux is increased from 55% to 95% or above.
Owner:宁波杰士兄弟工具有限公司
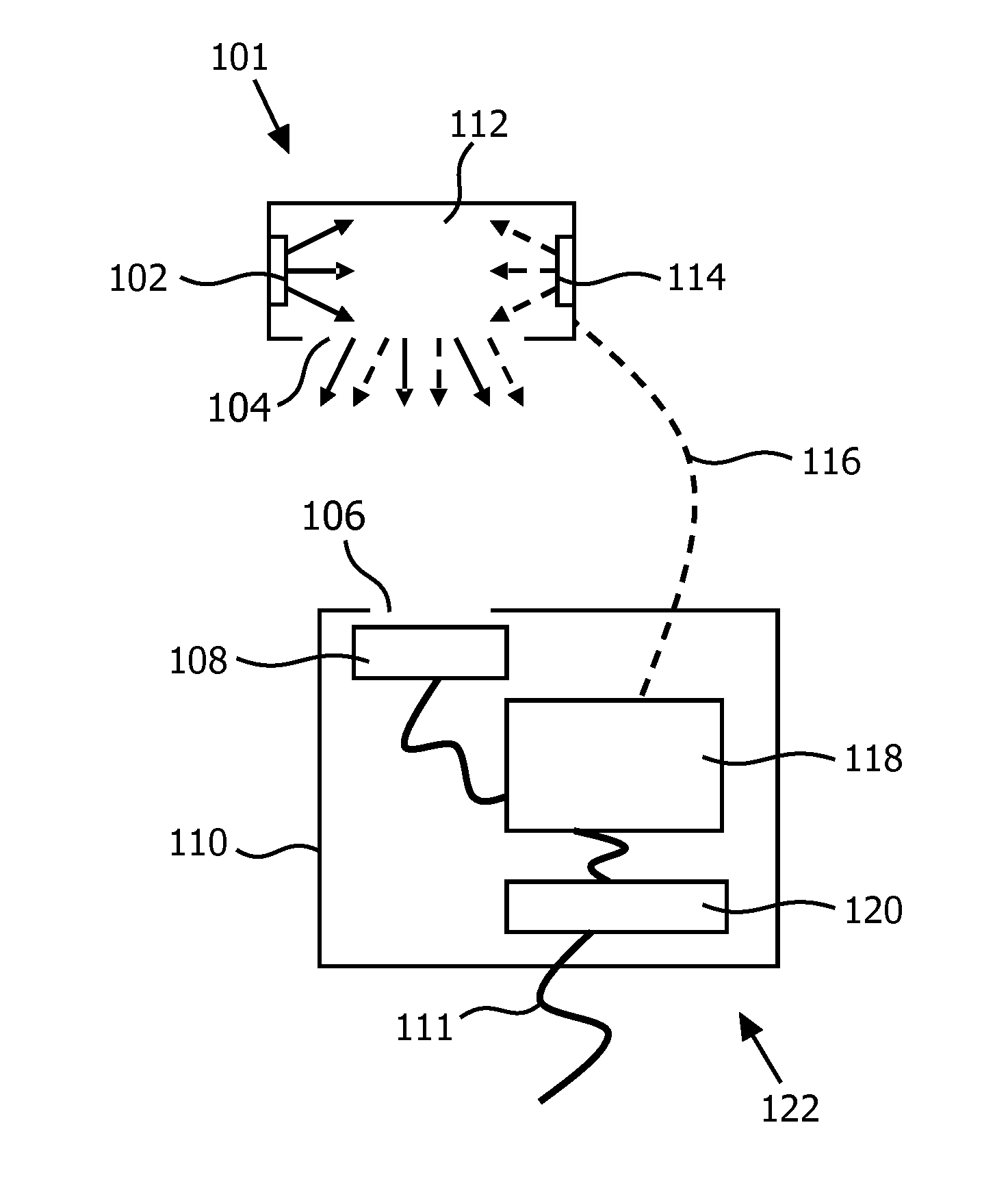
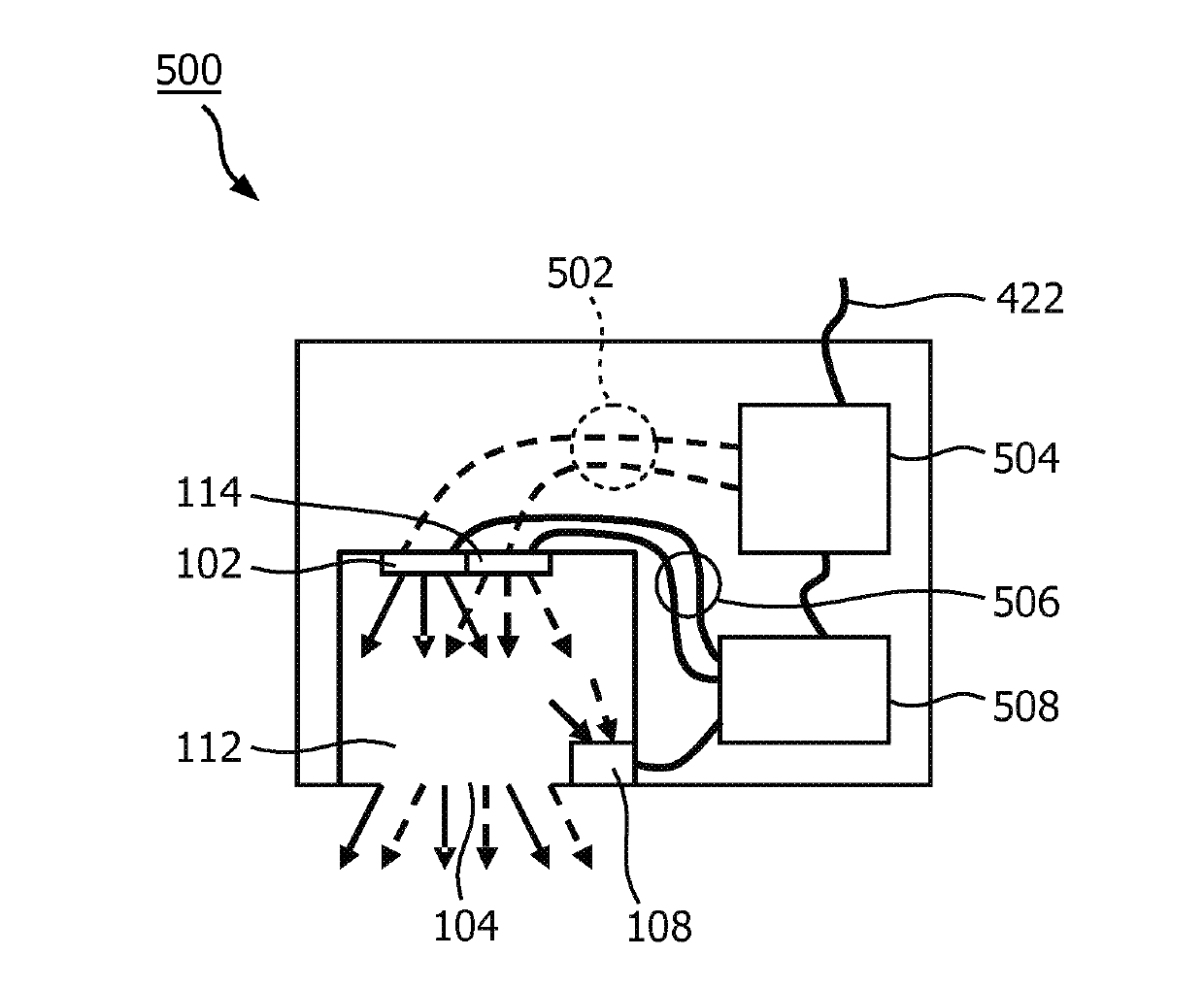
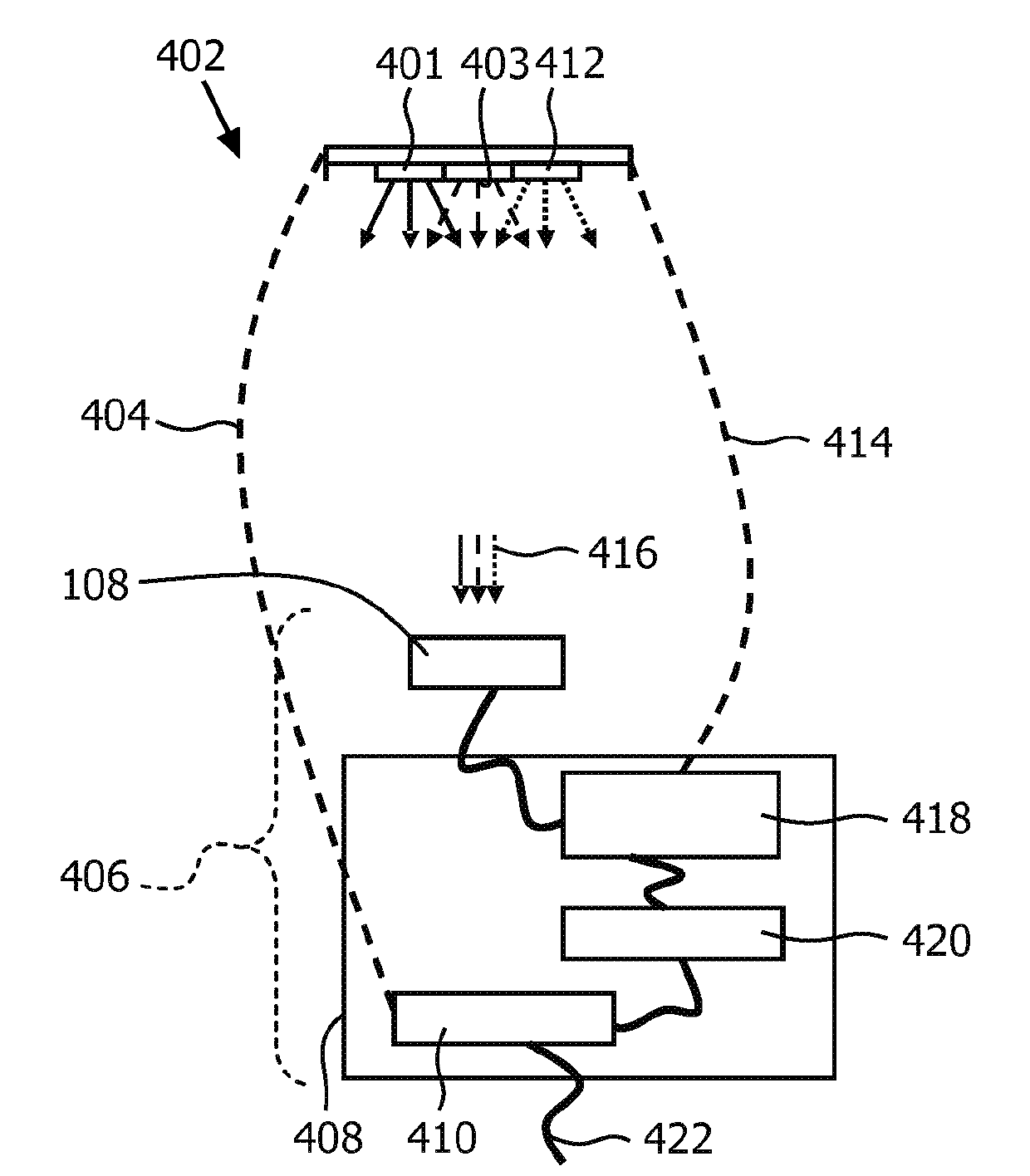
A color tunable lamp including a control device with a relative flux sensor
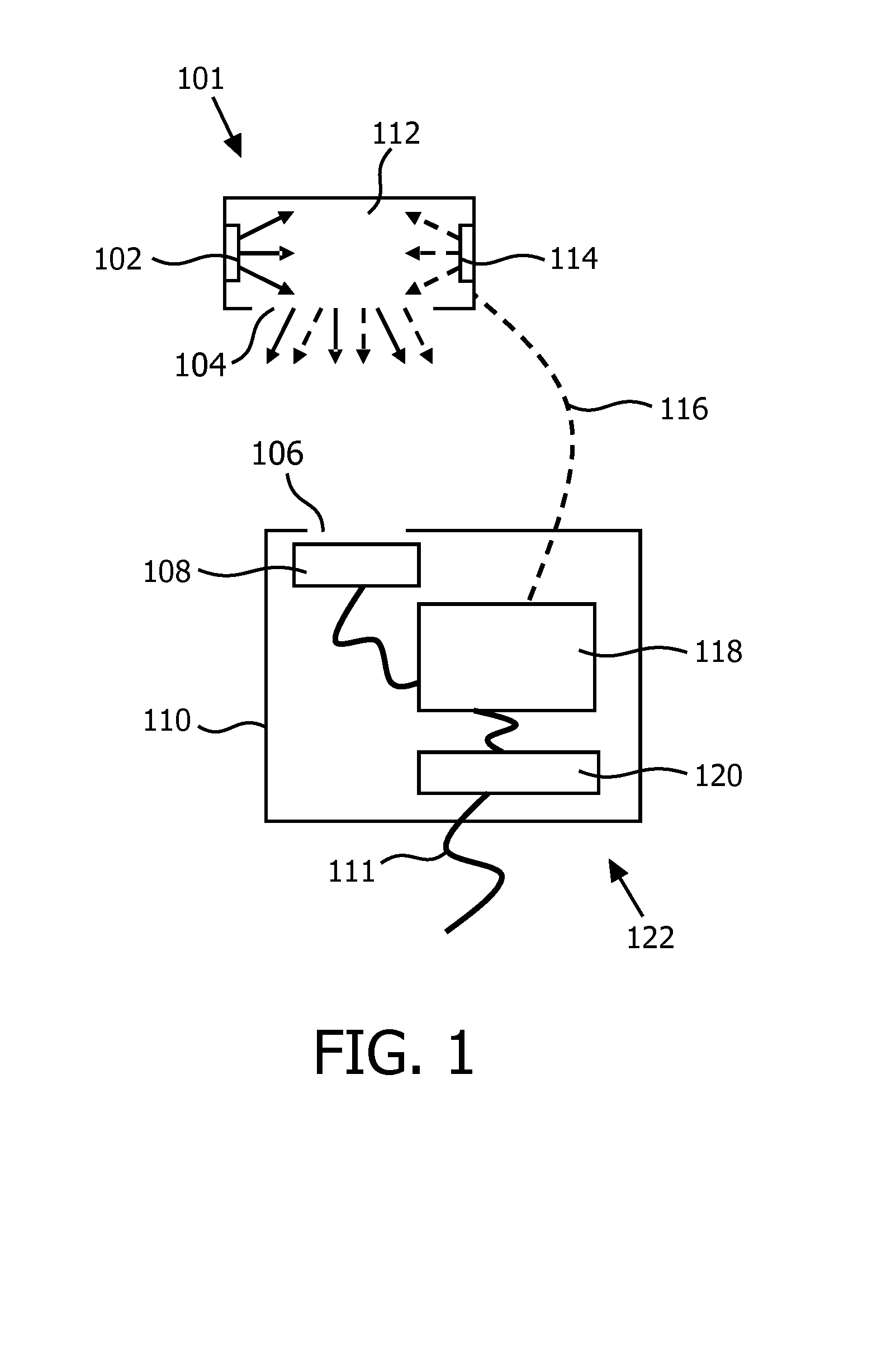
InactiveUS20130093335A1Less expensiveElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesMaximum fluxLight emitter
A relative flux sensor (122) and a method of characterizing characteristics of light emitters are provided. The relative flux sensor (122) comprises a color point sensor (108) and a sensor color (118). The color point sensor (108) measures a color point in a color space of light emitted by a light source (101) comprising a first light emitter (102) for emitting light of a first color and a second light emitter (114) for emitting light of a second color being different from the first color. The light source (101) is arranged for emitting light of a controllable color, being a mix of light of the first color and light of the second color. The sensor controller (118) is coupled to the color point sensor (108) for receiving a measuring signal and is arranged for i) providing a first signal to the light source (101), the first signal comprising a dimming factor D1 and a dimming factor D2, the dimming factor D1 and the dimming factor D2 indicating a fraction of a maximum flux of the first light emitter (102) and the second light emitter (114), respectively, and receiving the measuring signal representing a first color point when the light source (101) emits light according to the first signal, wherein at least one of the dimming factors D1 and D2 is different from 0, ii) providing a second signal to the light source (101), the second signal comprising a dimming factor D4 and a dimming factor D5, the dimming factor D4 and the dimming factor D indicating a fraction of the maximum flux of the first light emitter (102) and the second light emitter (114), respectively, and receiving the measuring signal representing a second color point when the light source (101) emits light according to the second signal, wherein both dimming factors D4 and D5 are different from 0, iii) calculating within a model of the color 20 space a ratio between a maximum flux of the first light emitter (102) and a maximum flux of the second light emitter (114) on the basis of the first color point, the second color point, the dimming factors D1, D2, D4 and D5.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
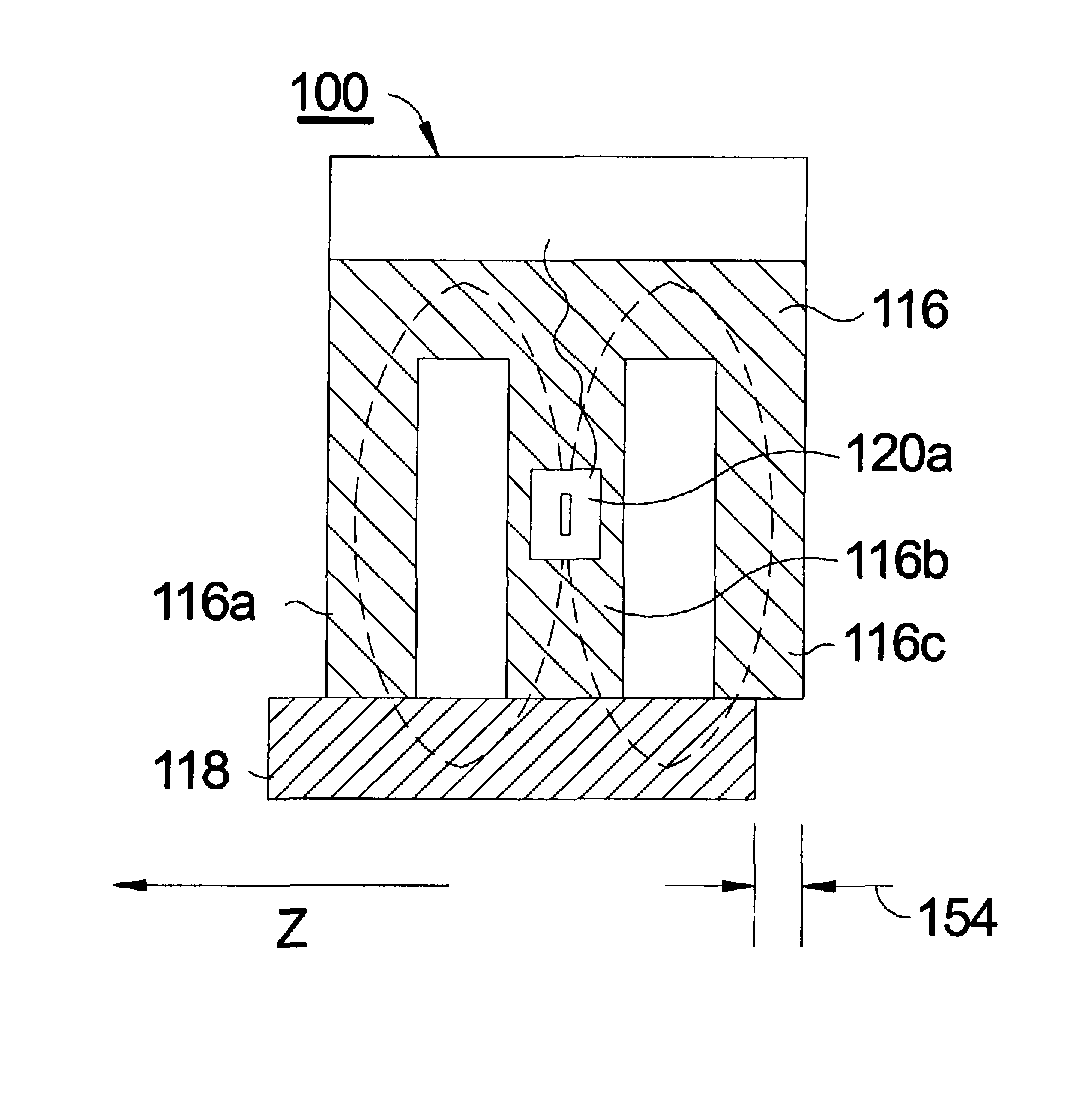
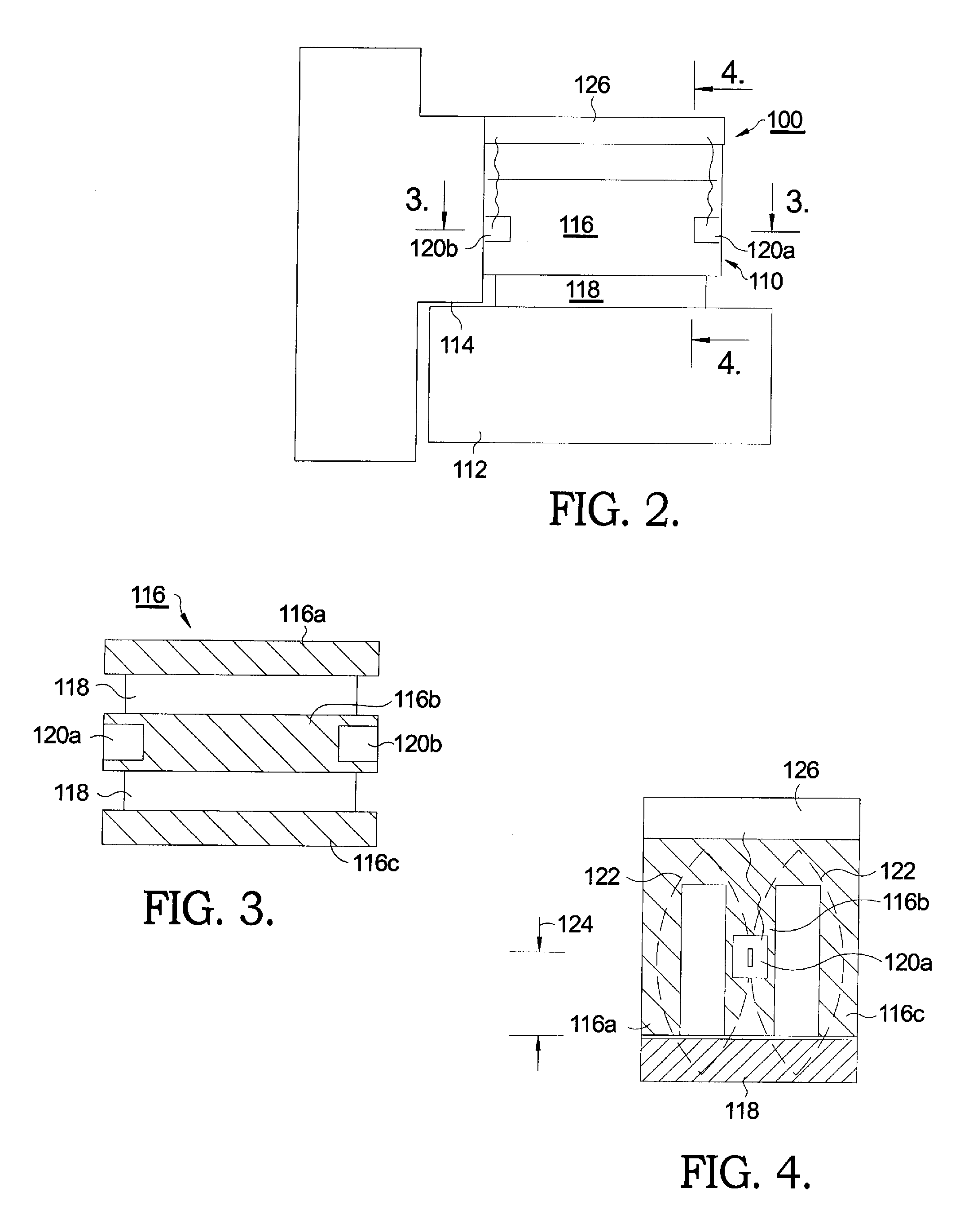
Magnetic pole position detector for rotor
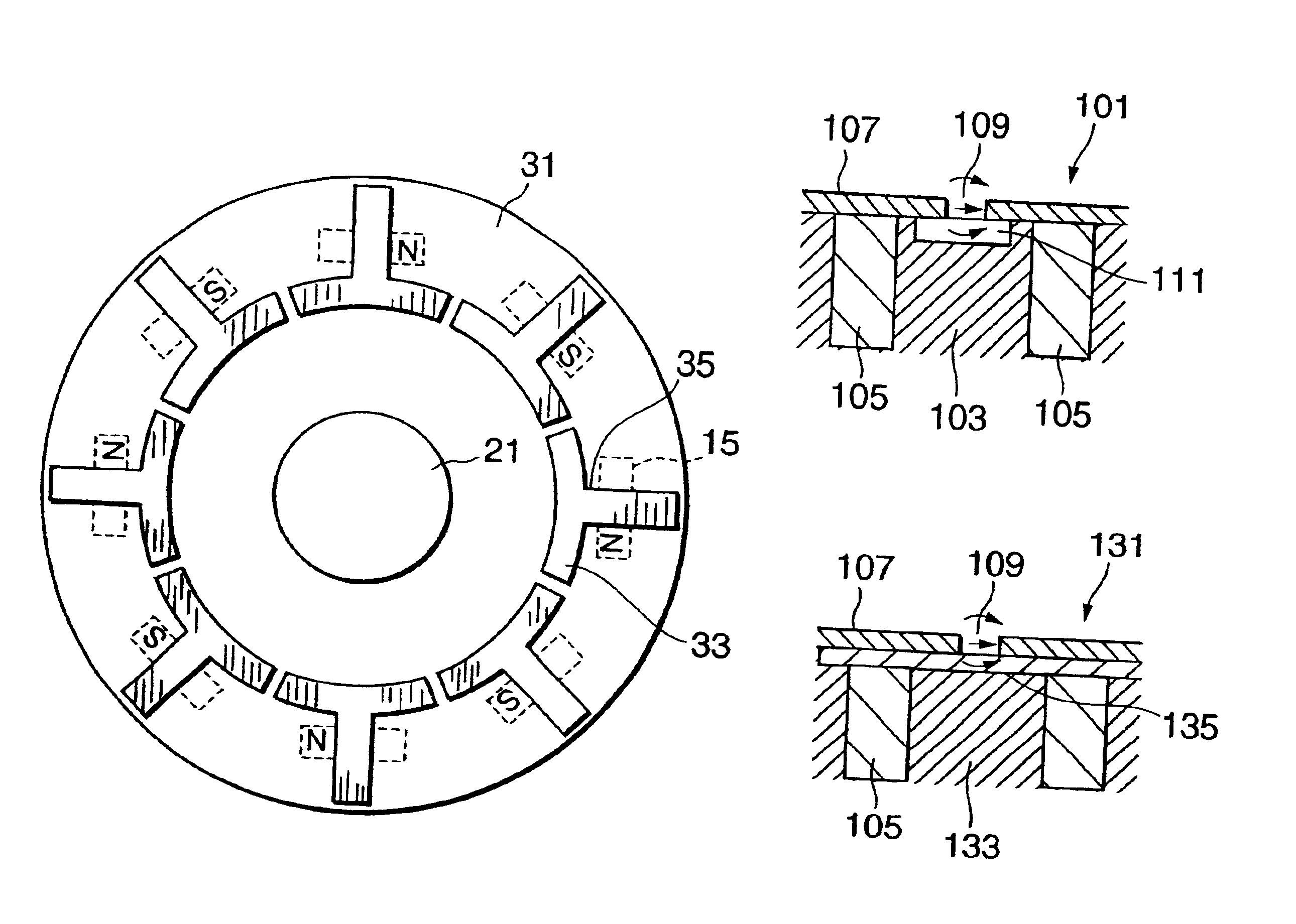
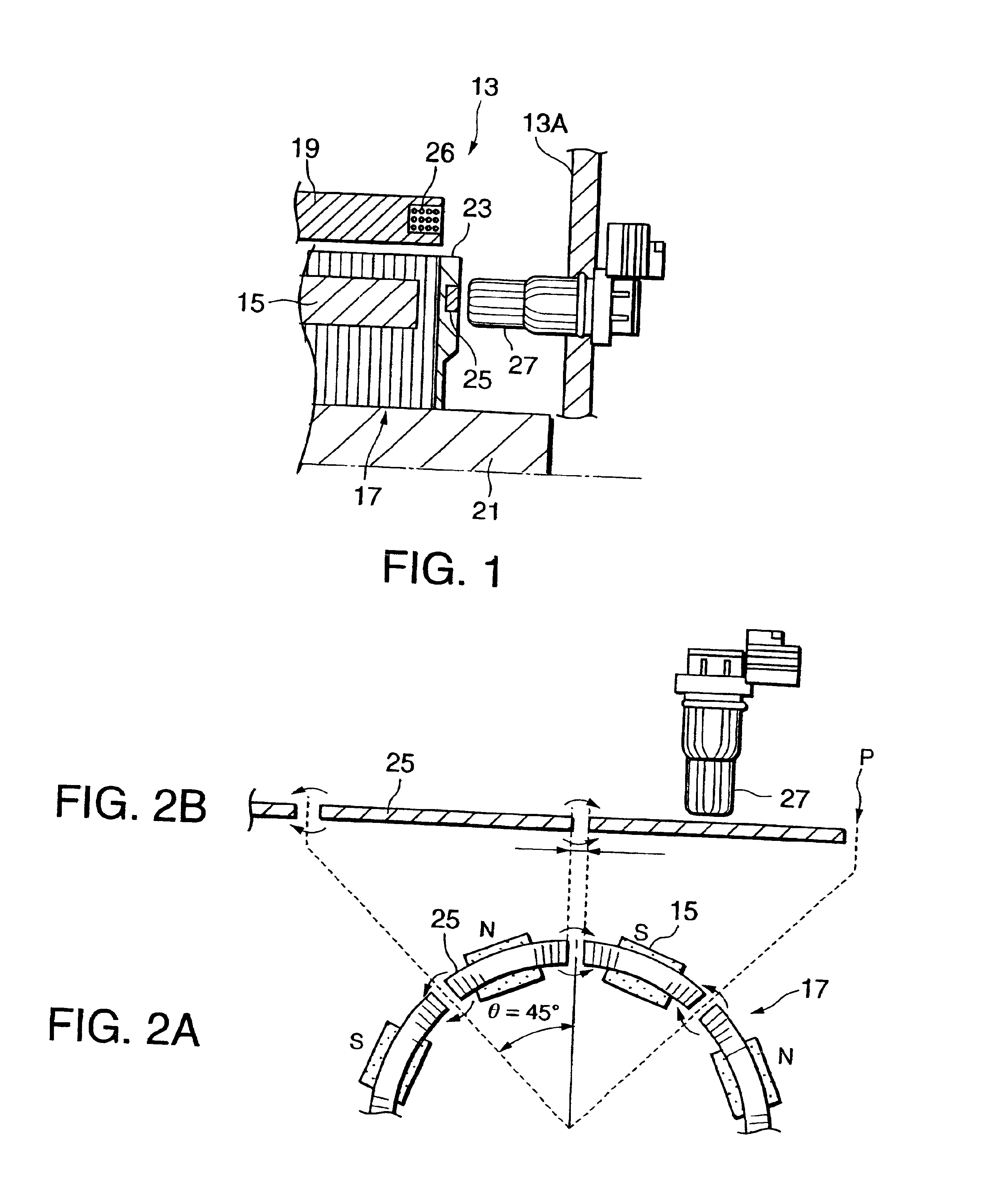
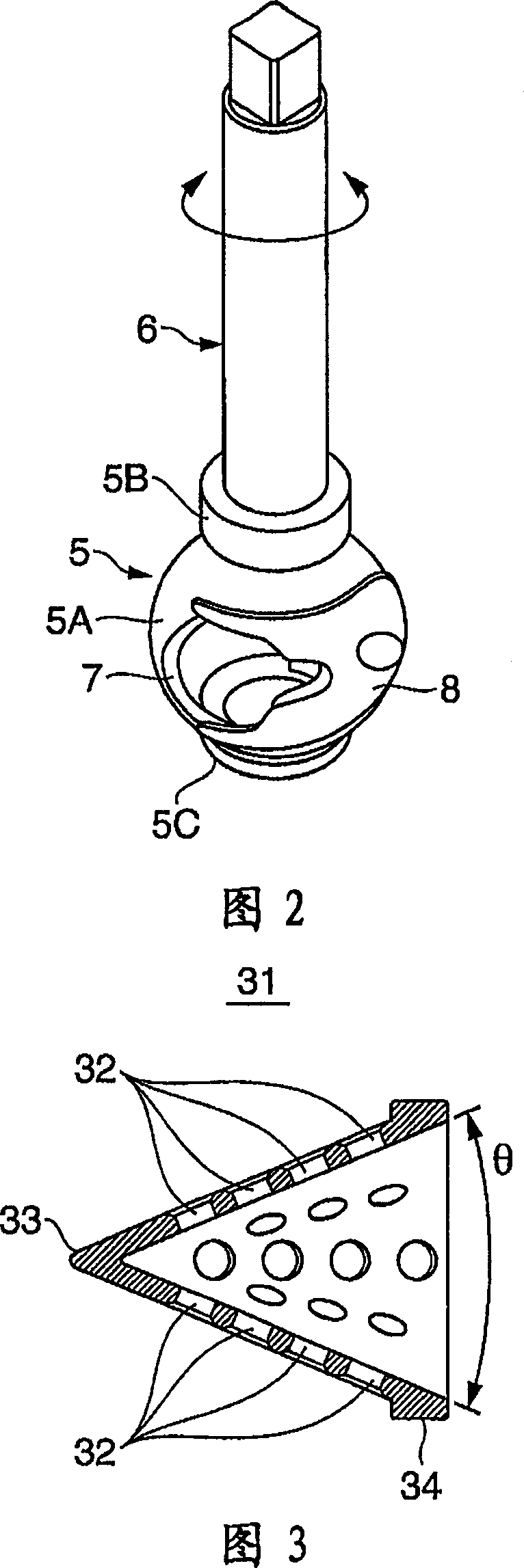
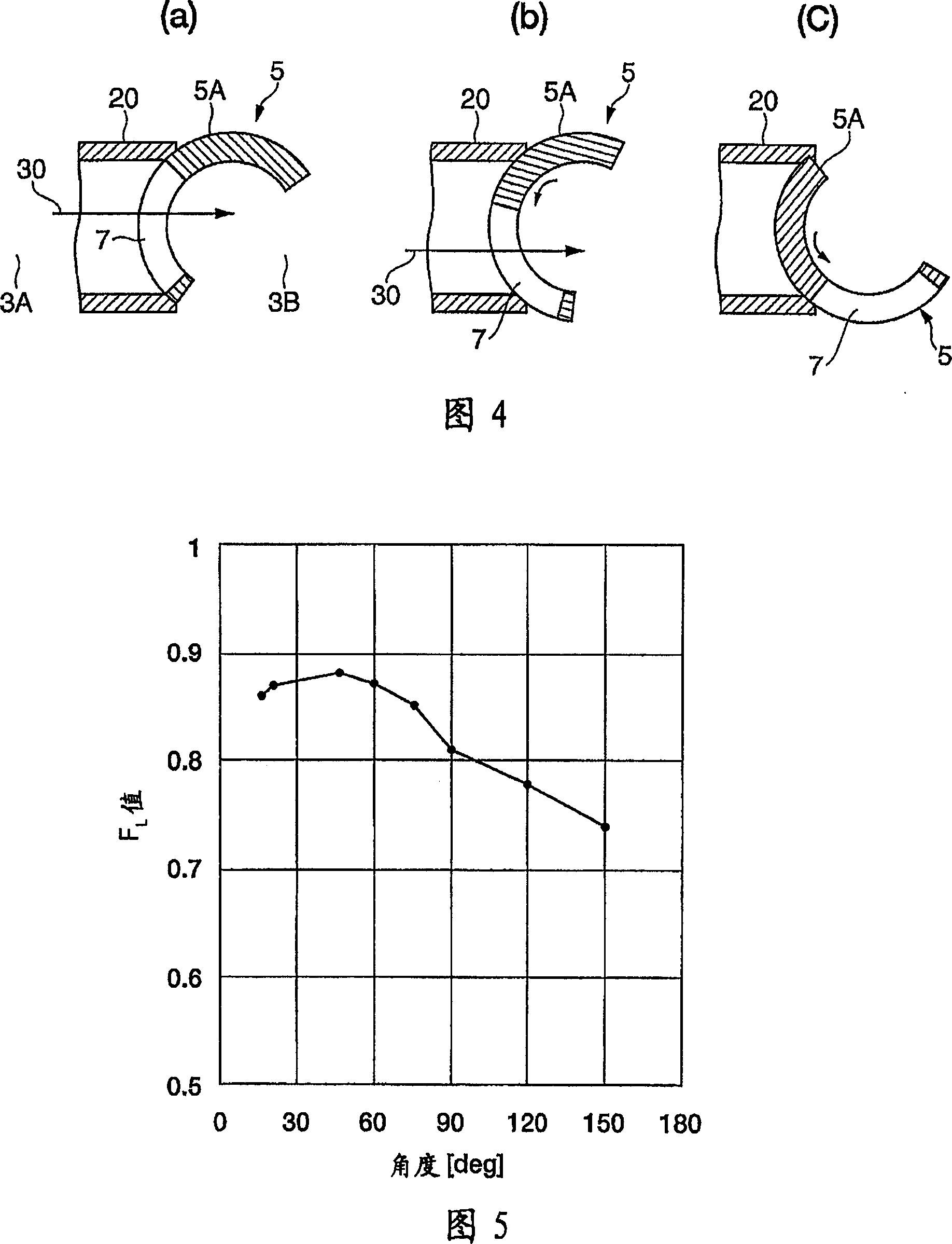
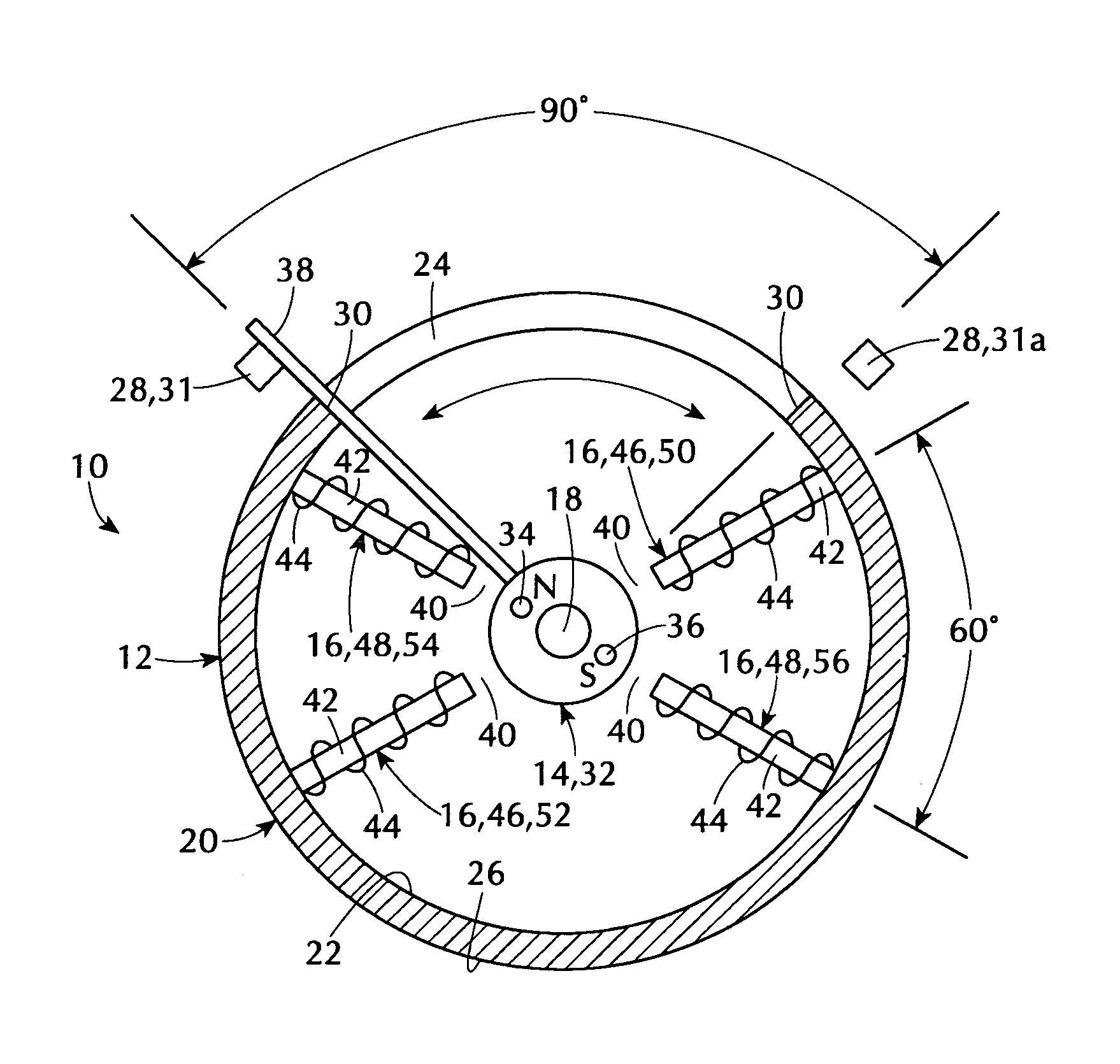
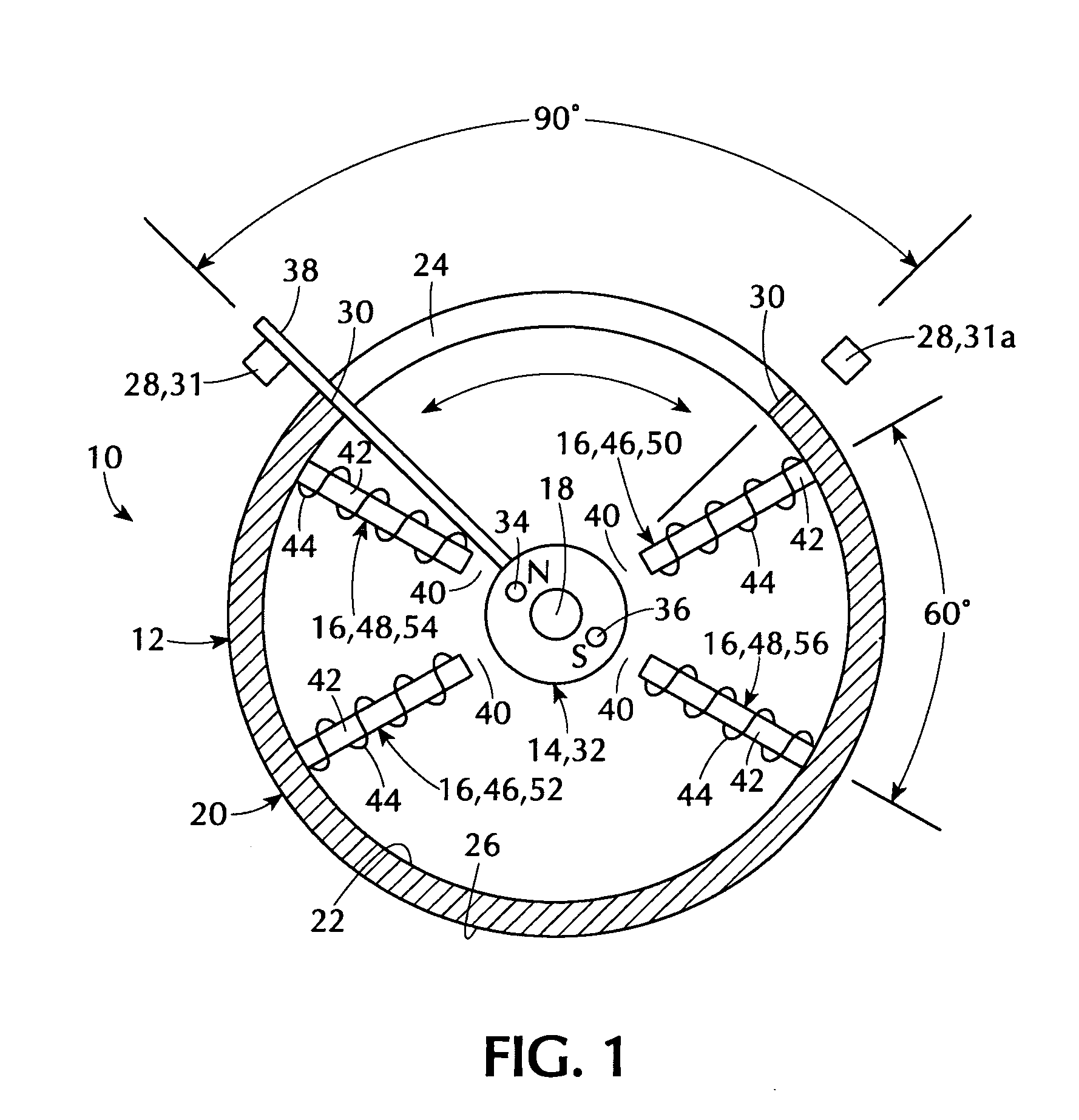
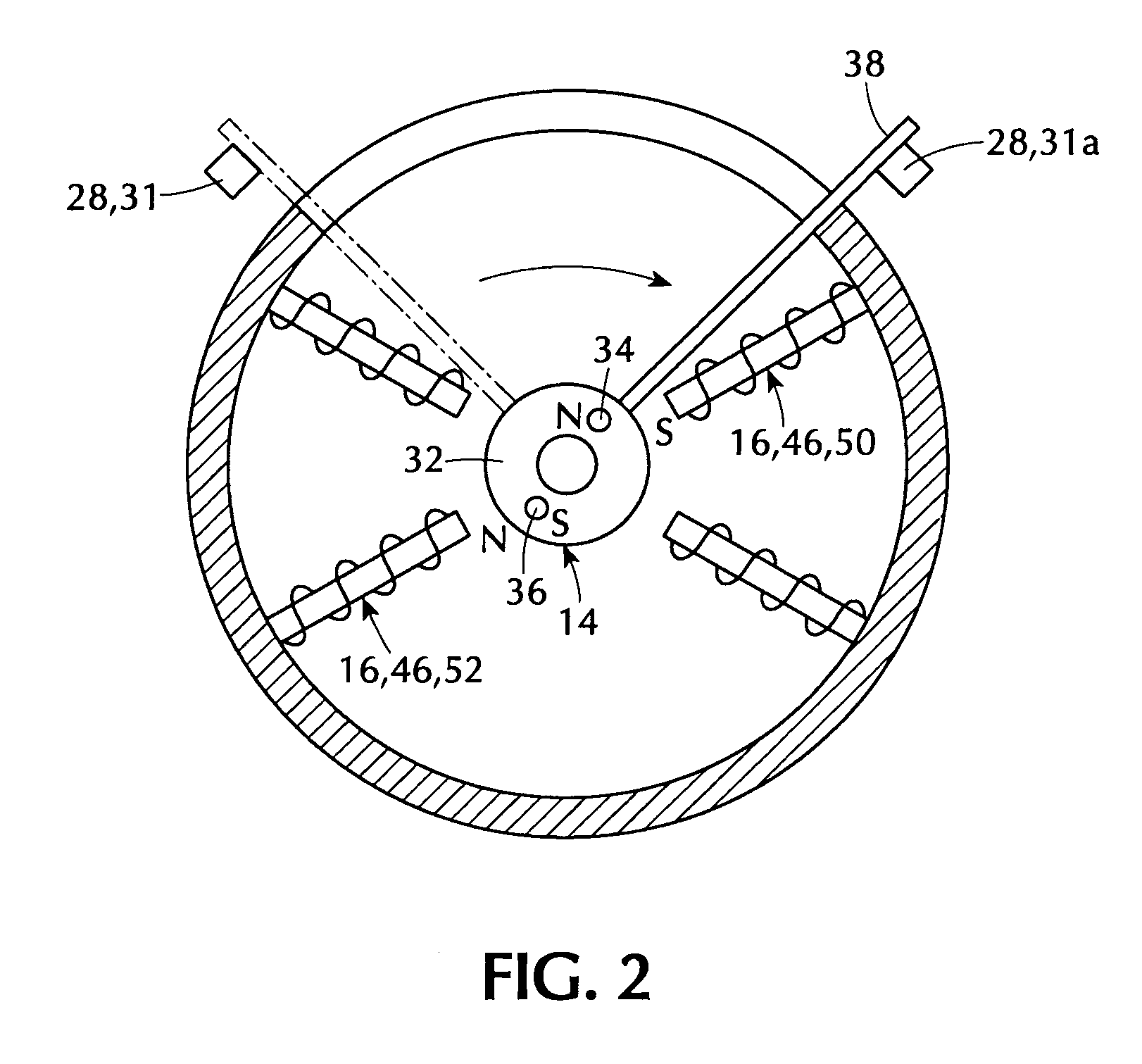
InactiveUS6858956B2Increases size of motorGuaranteed accuracySynchronous generatorsWindingsMaximum fluxMagnetic poles
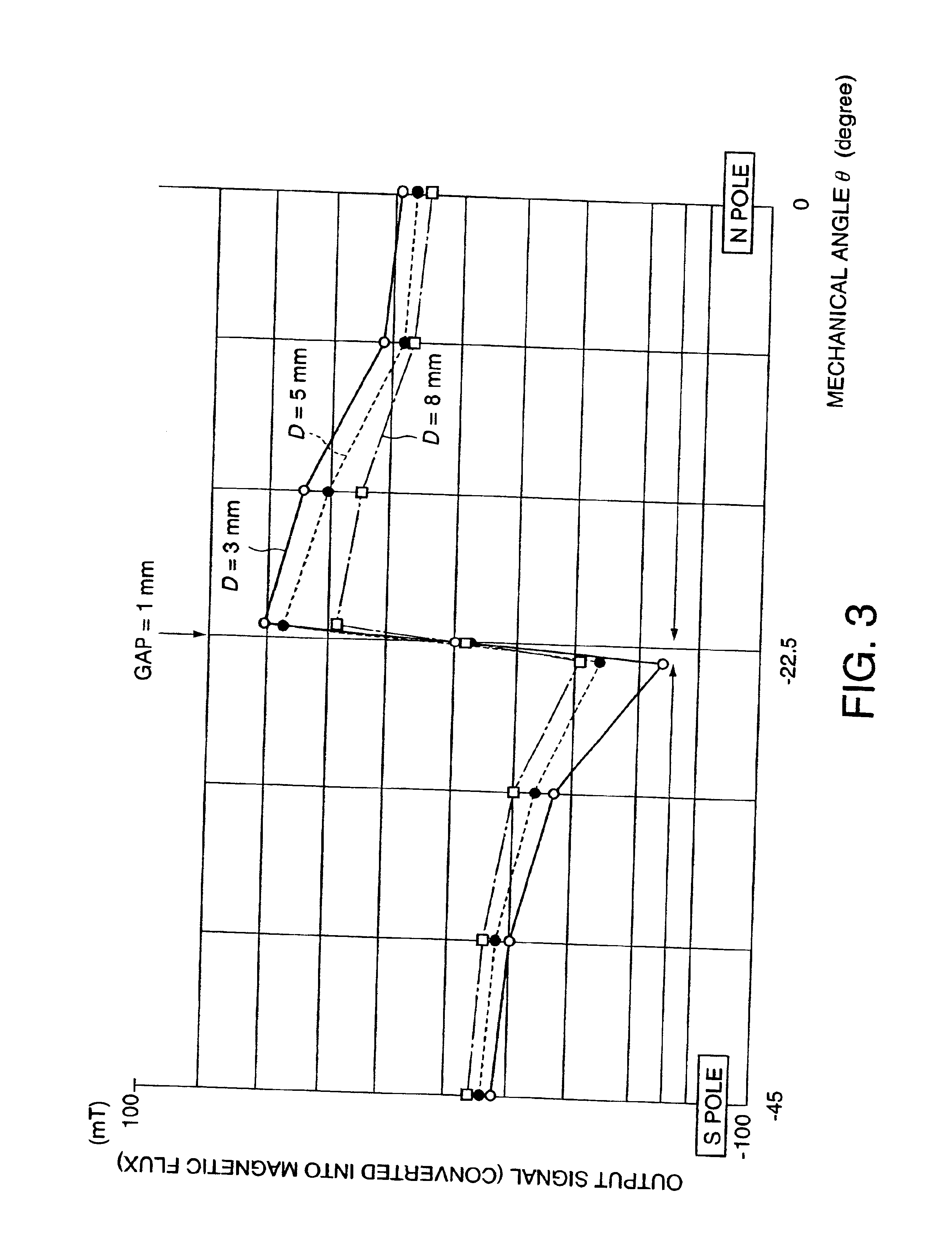
A rotor (17, 31, 71, 91, 101, 121, 131, 141, 201, 401) of a motor (13, 51) is provided with a rotation shaft (21, 59, 410) and a plurality of magnets (15, 53, 75, 105, 210A, 210B, 411) on a circular periphery. Plates (25, 25A, 25B, 25C, 63, 77, 220, 300, 430) made of magnetic materials are provided so that each of which is magnetized by leakage flux of a corresponding magnet (15, 53, 75, 105, 210A, 210B, 401). The plates (25, 25A, 25B, 25C, 33, 63, 77, 107, 220, 300, 430) are disposed along a circular path such that a maximum flux density is formed at both peripheral ends. A magnetic sensor (27) outputs a signal in response to the variation of a flux density on the circular path.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Portable oxygen concentrator
A portable oxygen concentrator includes a pressure swing absorption system defined by a relatively rigid housing adapted to generate a flow of oxygen enriched gas and a battery adapted to provide power to the pressure swing absorption system. The oxygen concentrator has a total weight of less than about 10 lbs, has a maximum flow of 100% O2 equivalent gas of about 0.9 lpm, has a total volume less than about 800 in3, and gas a battery life of at least about 8 hours. The present invention also using a liquefaction or transfill system in combination with such an oxygen concentrator.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
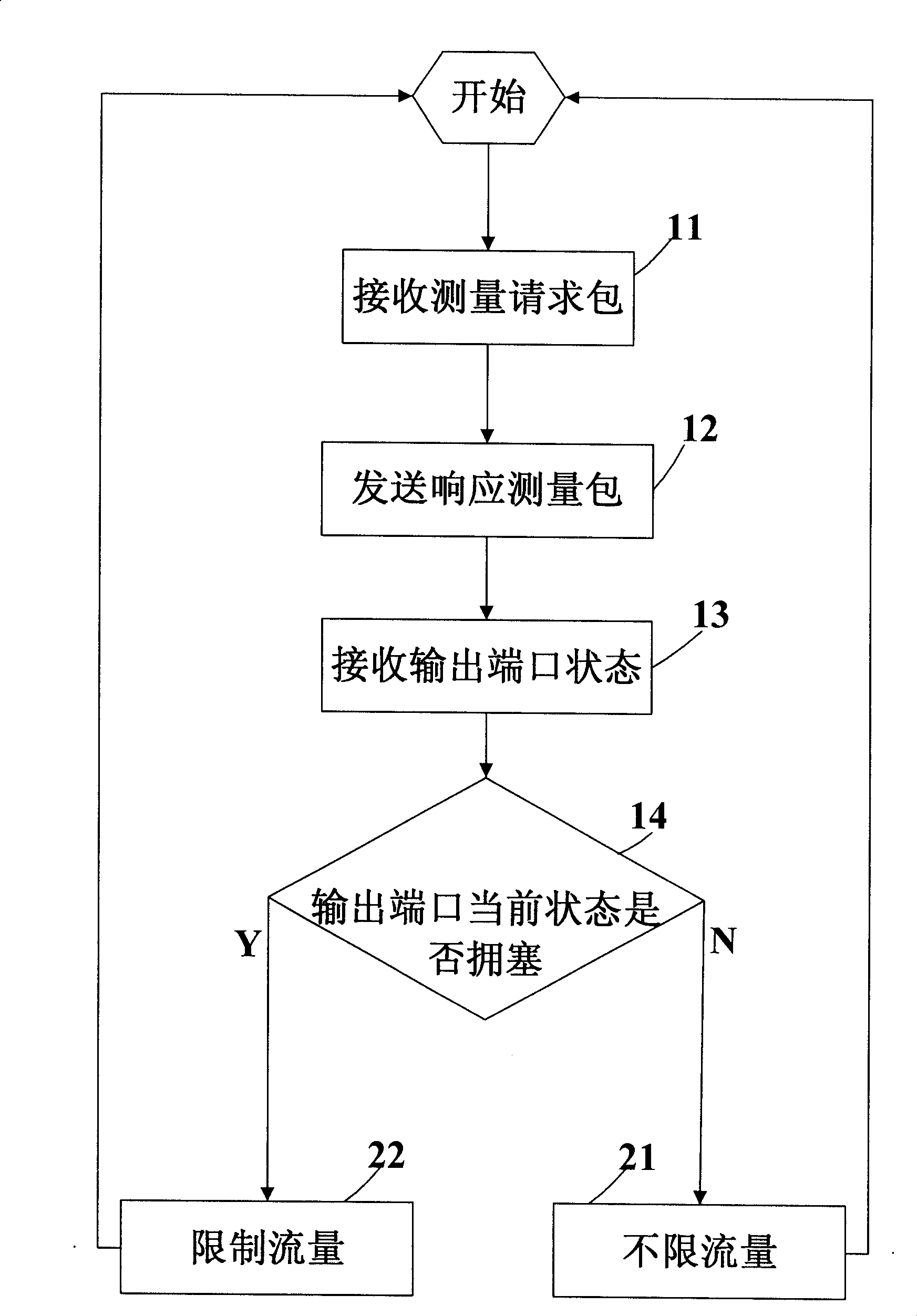
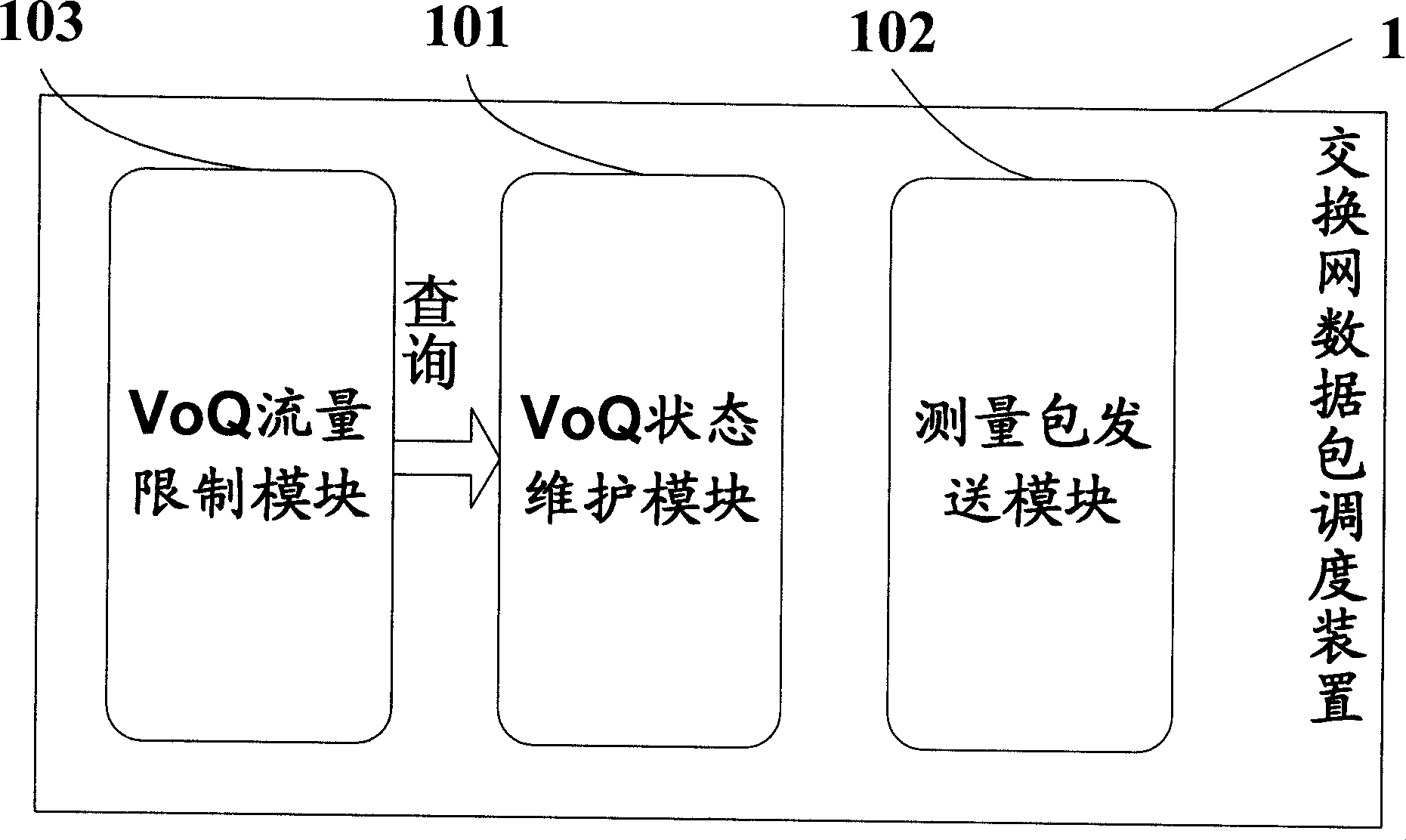
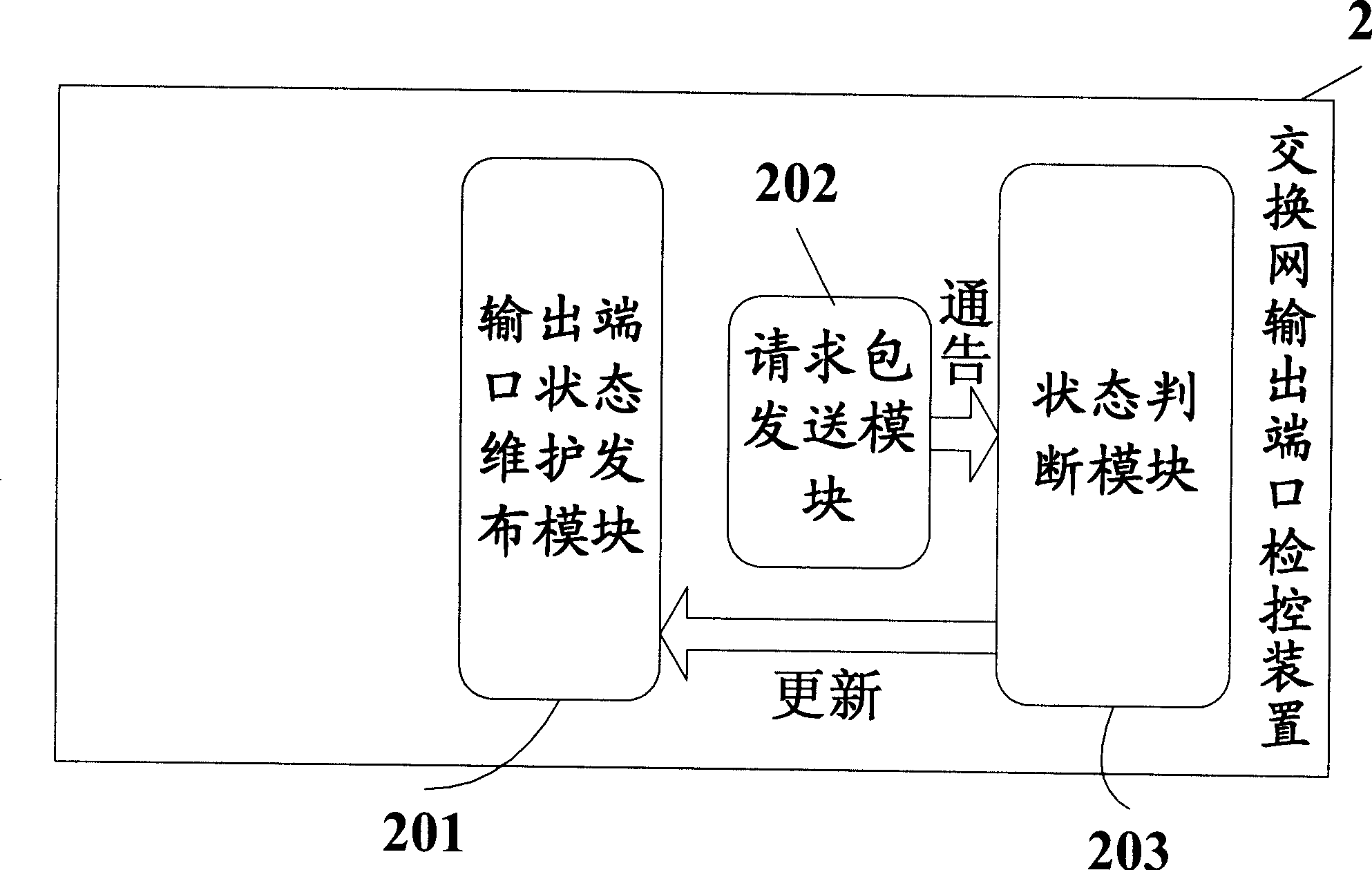
Method, device and system for scheduling exchange network data packet
InactiveCN101465806ASolve congestionError preventionData switching networksTraffic capacityMaximum flux
The invention relates to network communication field and in particular relates to a switched network management method and a system thereof. The invention provides a switched network data packet scheduling method, a device and a system thereof. The method mainly includes the steps of receiving the output port status judged by an output port of the switched network, which is the judgment to the forwarding delay time measuring result of the packet, and managing the maximum flux of a virtual output queue VoO corresponding to the output port of the switched network. The device mainly comprises a VoO status maintenance module, a measuring packet sending module and a VoO flux limiting module. A switched network output port detection and control device comprises an output port status maintenance publicizing module, a status judge module and a request packet sending module. The system mainly comprises the switched network output port detection and control device and a switched network input port managing device.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
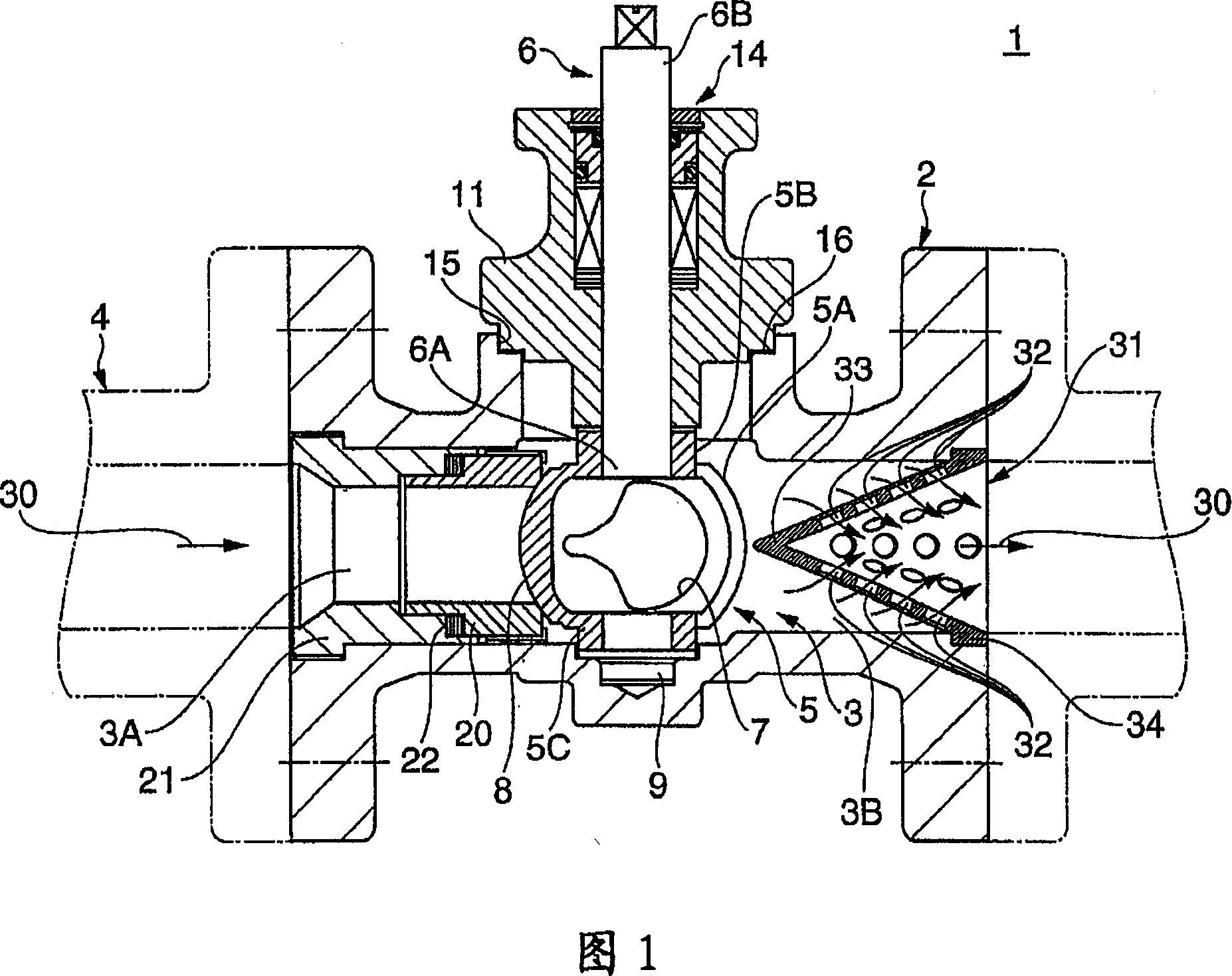
Diffuser for fluid control valve and fluid control valve
ActiveCN1952460ASuppress maximum flow reductionInhibition reduces cavitationPlug valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyFluid controlCavitation
There is provided a diffuser for fluid control valve and a fluid control valve capable of preventing or depressing cavitation phenomenon practically and depressing the reducing of the maximum flux. The diffuser 31, which is mounted inside the peristome in downstream side of the valve body 2, reduces the flow velocity of a liquid 30 and then transfers kinetic energy into pressure. The diffuser 31 is shaped as a hollow conical body with an opening bottom 34, wherein the internal angle (theta) of the top 33 is smaller than 90 DEG and a plurality of pinholes 32 is formed on side walls.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
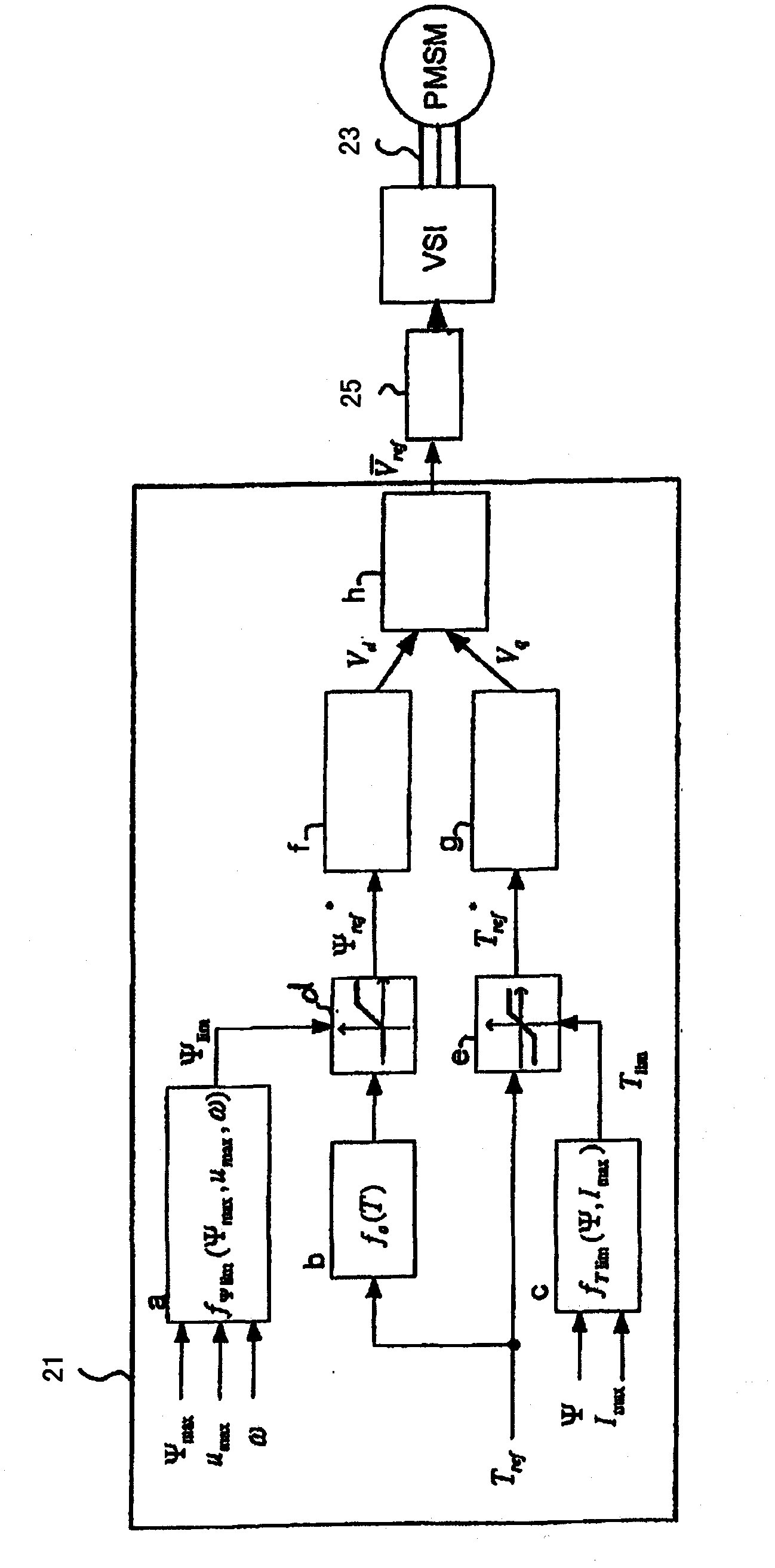
Operating a synchronous motor having a permanent magnet rotor
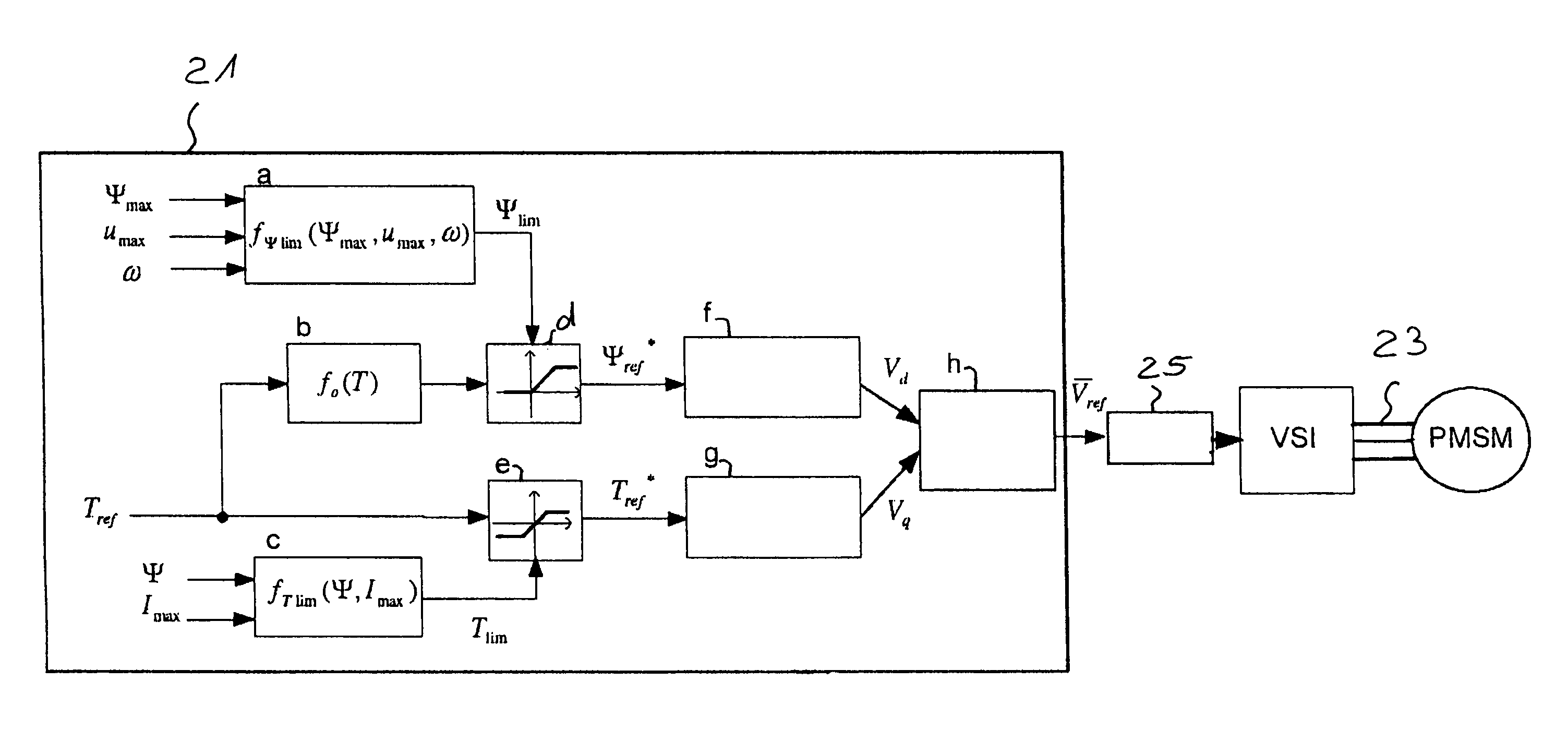
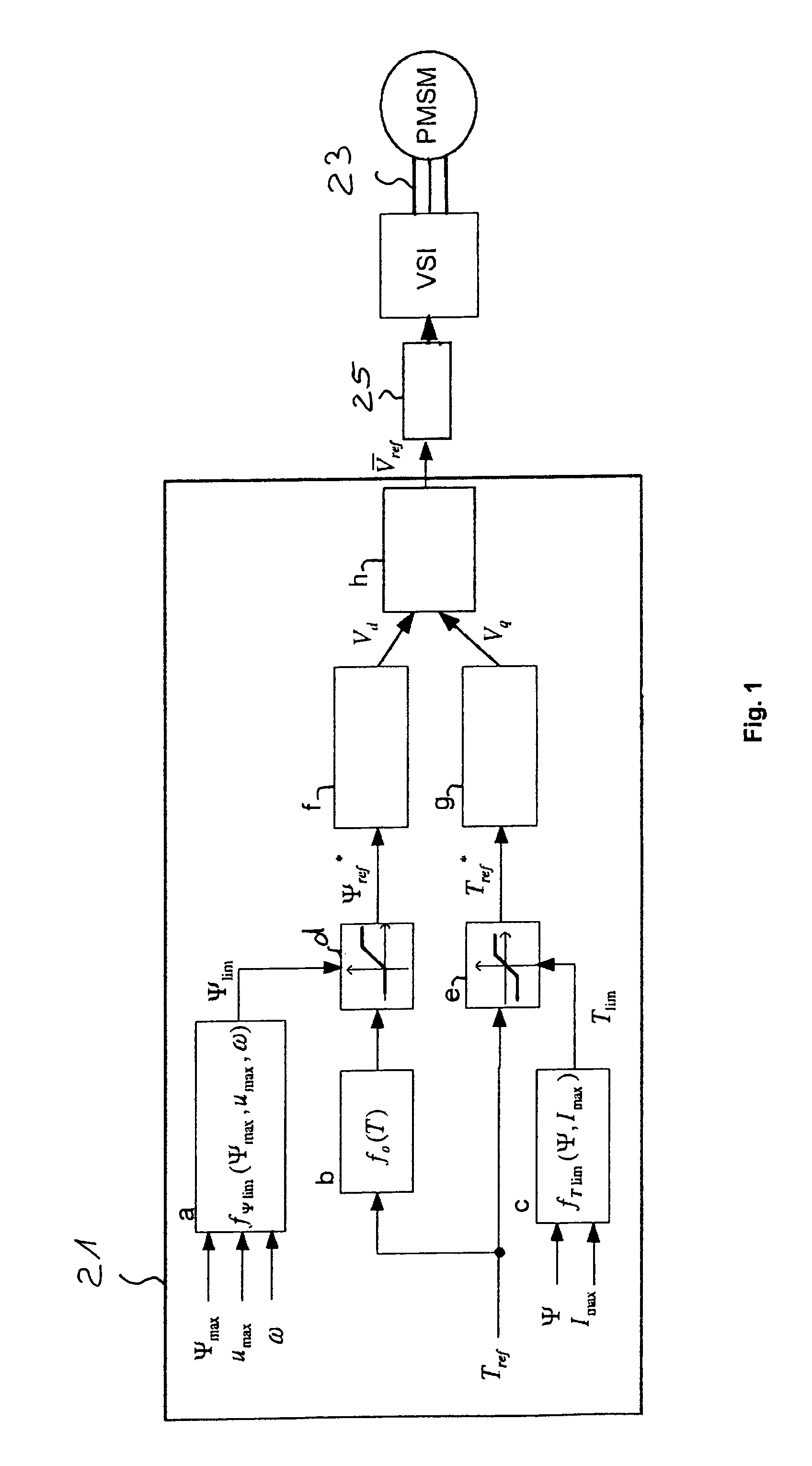
ActiveCN102144356AElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlPermanent magnet rotorSynchronous motor
The invention relates to a method of operating a synchronous motor (1) having a stator comprising a set of electromagnets (7, 9) and having a permanent magnet rotor (5), wherein the synchronous motor (1) is controlled by calculating in a flux controller (f) a measure of a flux magnitude, which is the magnitude of the stator flux of the motor (1), and is controlled by calculating in a load angle controller (g) a measure of a load angle. Information about a desired motor torque or a reduced motor torque, which is smaller than the desired motor torque, is input to the load angle controller (g) and the load angle controller (g) calculates the measure of the load angle depending on the input motor torque. The measure of the flux magnitude is combined with the measure of the load angle to obtain commands for controlling electric currents of electromagnets of the stator, thereby directly controlling the stator flux. A flux limit value which depends on a predetermined maximum value of the stator flux allowed for the motor (1), which depends on a maximum value of an electric voltage, which is used to drive the currents through the stator electromagnets (7, 9), and which depends on the actual rotor speed is repeatedly calculated. During acceleration of the rotor (5) while the stator flux is smaller than the maximum flux allowed for the motor the measure of the flux magnitude is calculated depending on the output of a predetermined function, wherein the output of the predetermined function depends on the desired motor torque and corresponds to the magnitude of the stator flux, which results in the desired motor torque using the minimum possible stator current. The measure of the load angle is calculated depending on the desired motor torque.
Owner:BOMBARDIER TRANSPORTATION GMBH
Method of Estimating Stable State Membrane Filtration Flux
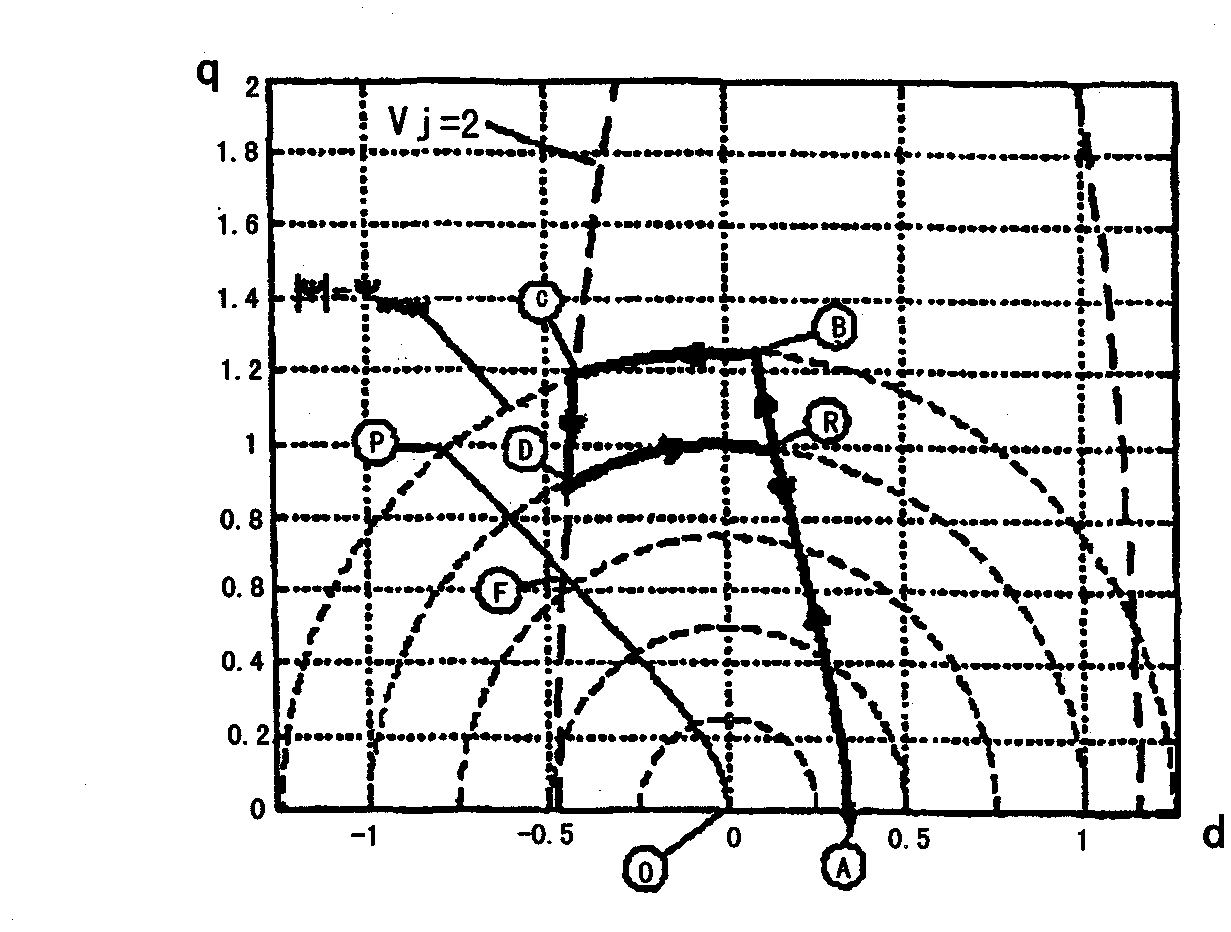
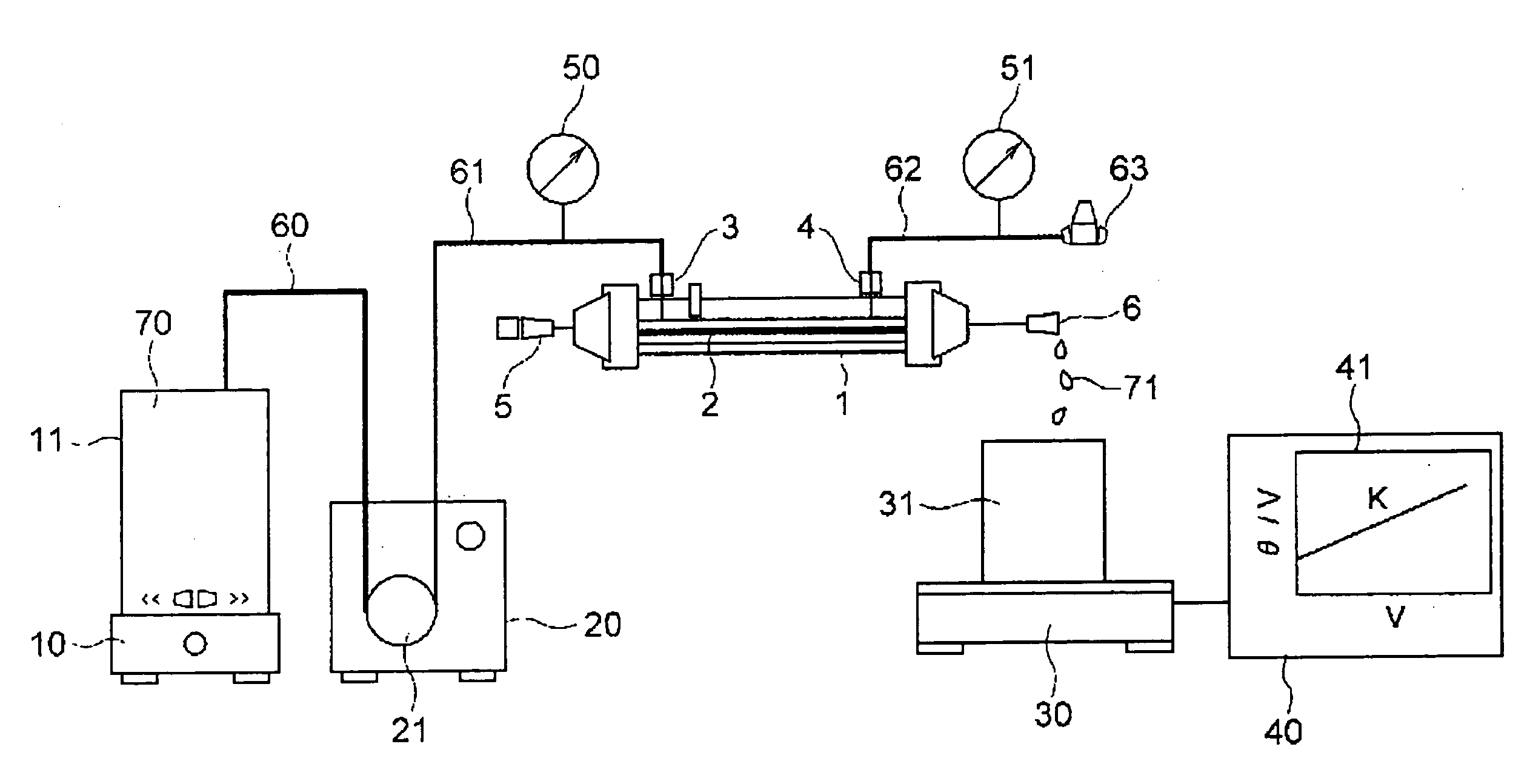
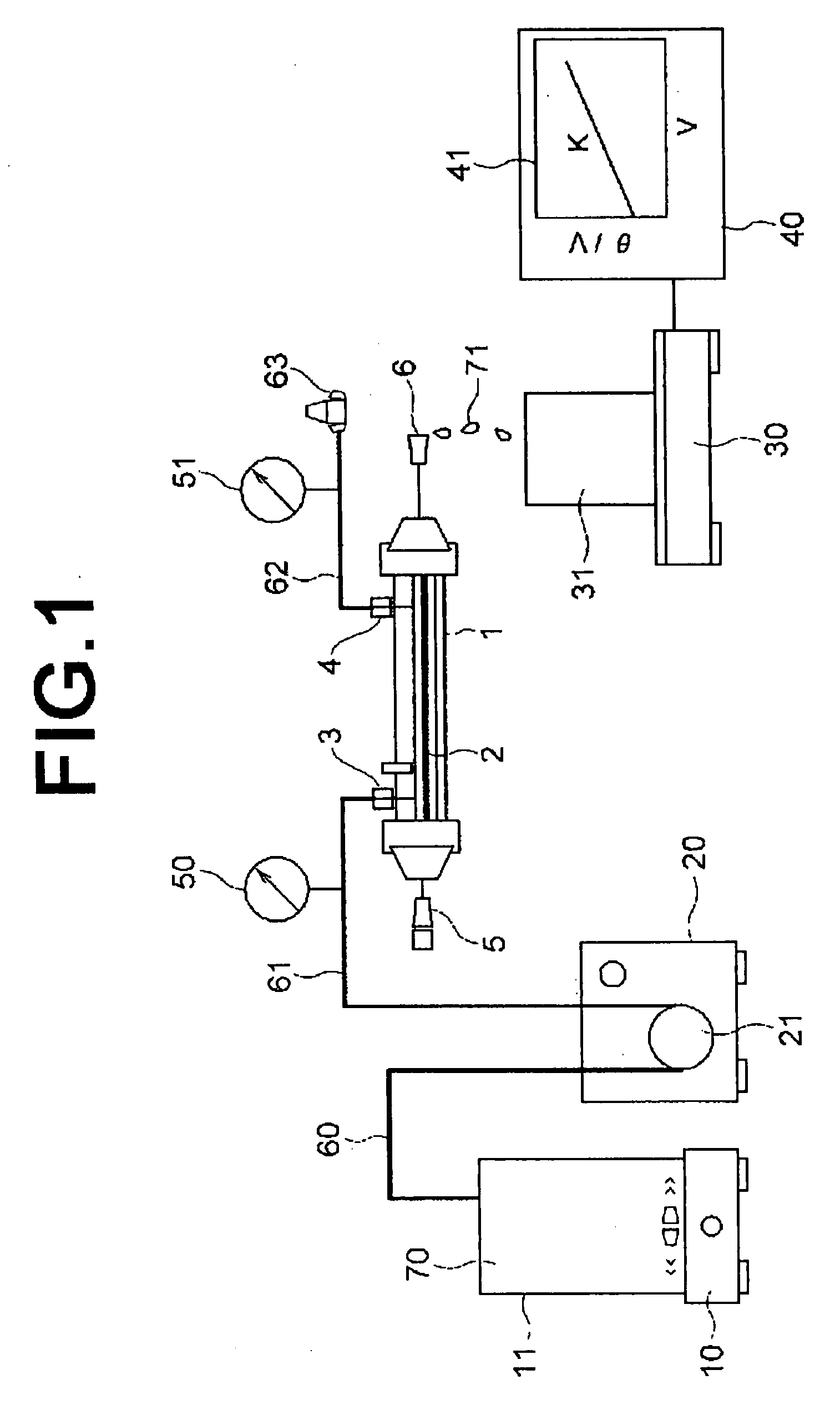
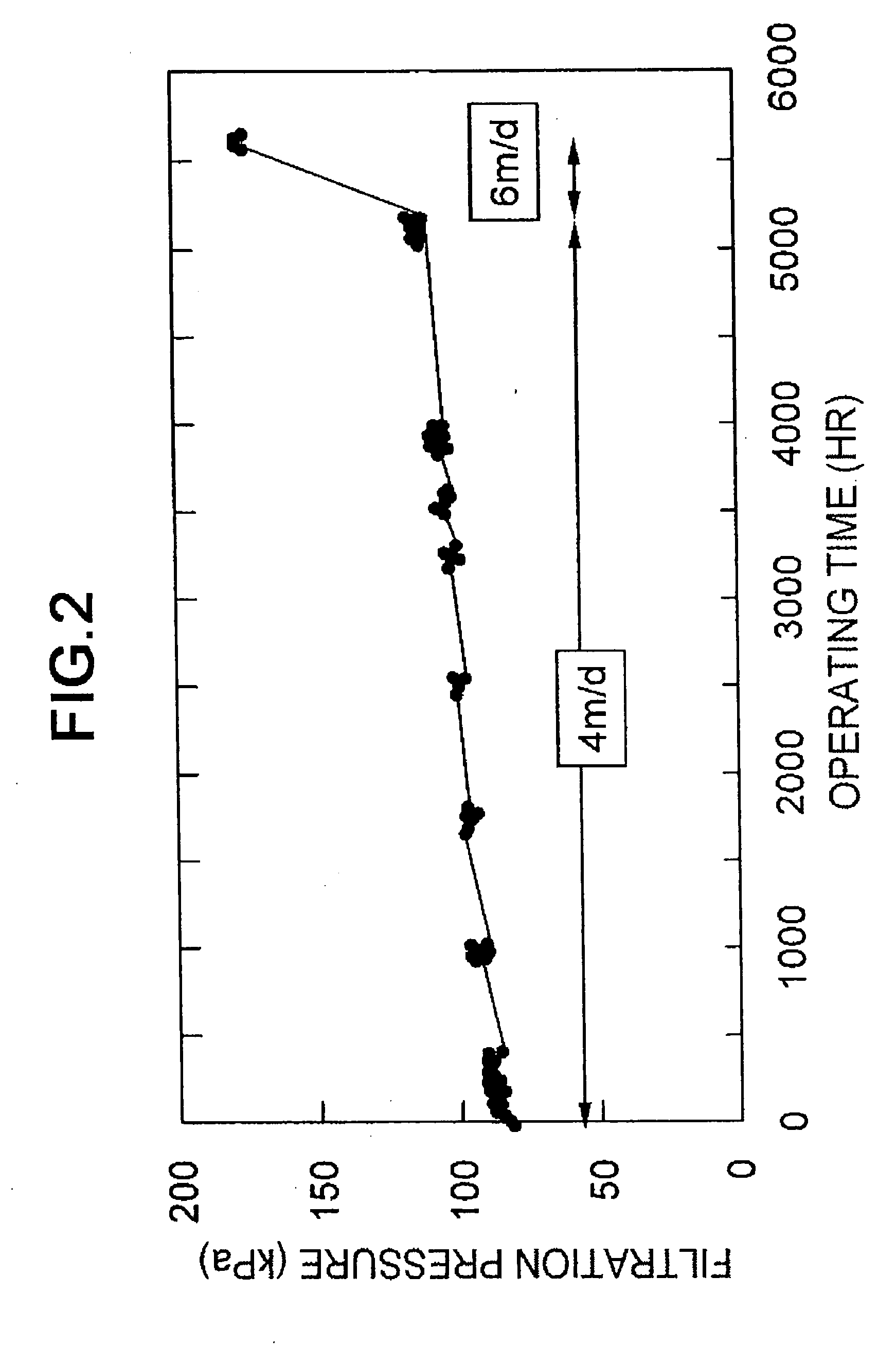
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method of estimating the maximum value of the flux during long-term stable operation including cleaning of a membrane filtration plant based on measured data of a membrane filtration characteristic during initial membrane filtration. The present invention provides a method in which the maximum flux during stable operation of a new membrane filtration plant for which a membrane module and operating conditions have been specified is estimated from a measured value A of an initial membrane filtration characteristic measured using a liquid to be treated in and a membrane of a membrane module of the new membrane filtration plant, an empirical value of a maximum flux during stable operation of each of a plurality of existing membrane filtration plants having the same or a similar membrane module and operating conditions, and a measured value B of the initial membrane filtration characteristic measured using a liquid to be treated in and a membrane of a membrane module of each of the existing membrane filtration plants.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Rapid optimization method for power battery air cooling system runner interval
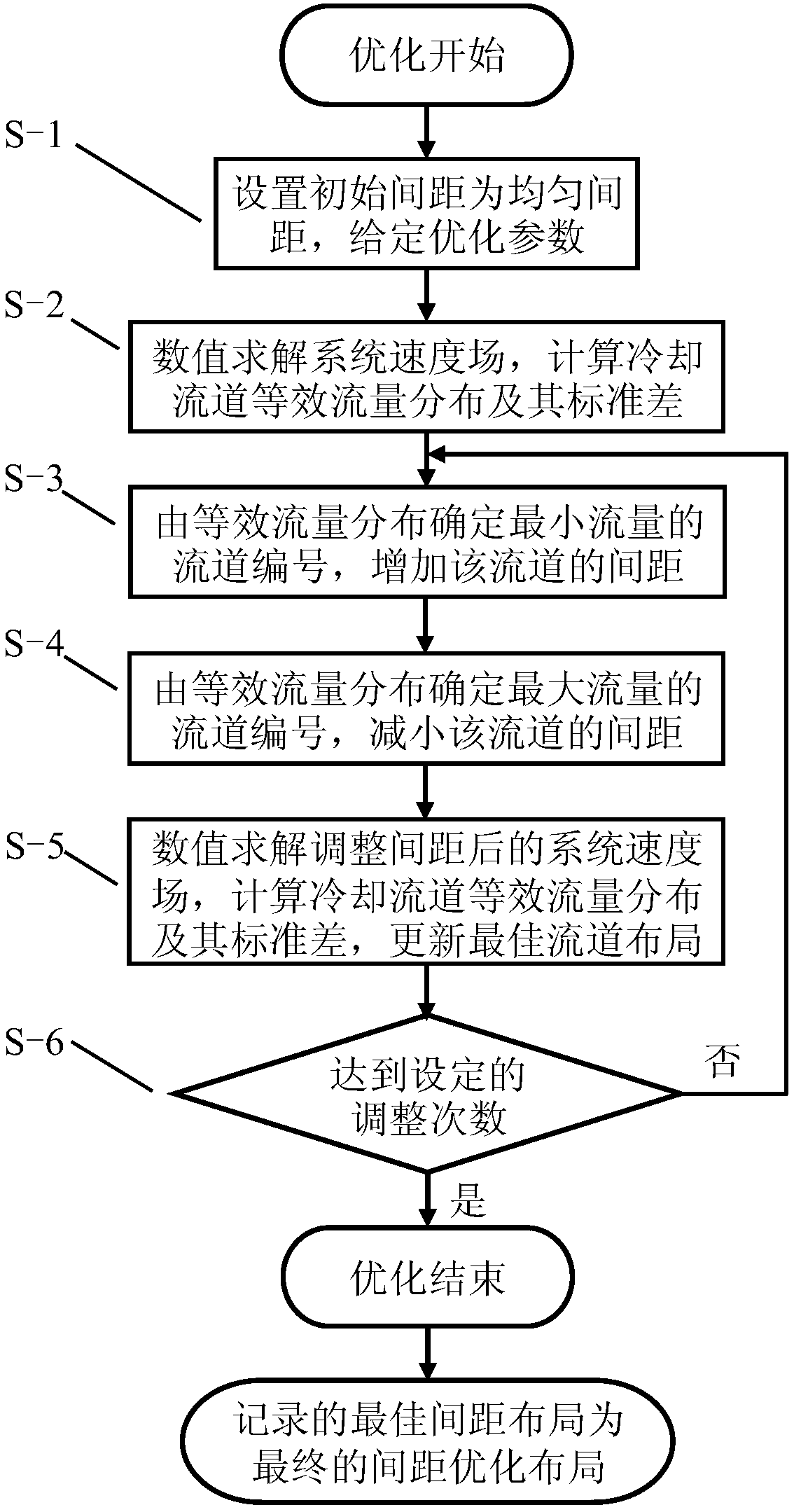
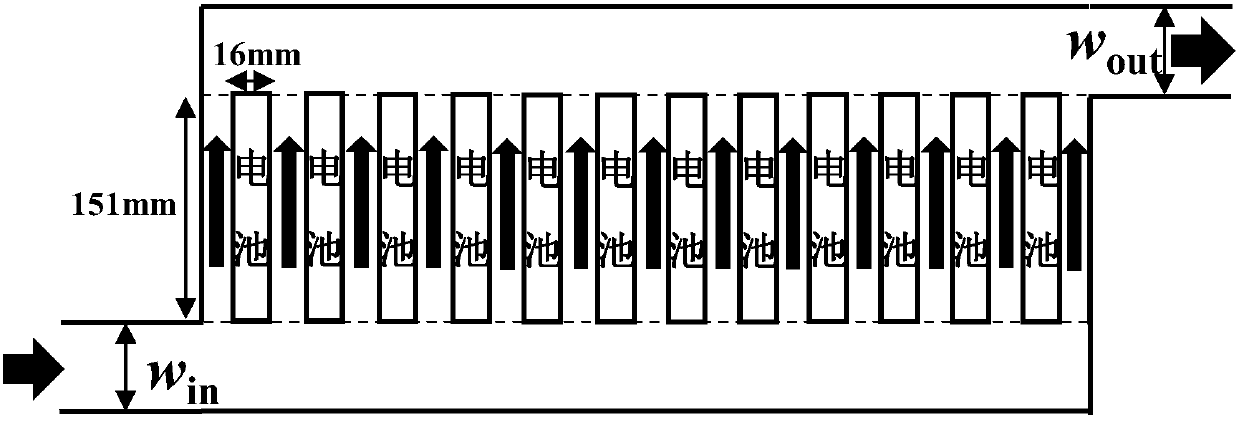
ActiveCN108038261AIncreased runner spacingReduced runner spacingSecondary cellsForecastingPower batteryMaximum flux
The invention discloses a rapid optimization method for a power battery air cooling system runner interval. The method comprises the steps that beginning from the uniform runner interval, velocity distribution of an air cooling system is solved through numerical values, by analyzing the flow distribution between cooling runners, the runner with the minimum flow and the runner with the maximum floware determined, then, the interval of the runner with the minimum flow is increased, and the interval of the runner with the maximum flow is decreased; speed distribution of the system is calculatedagain every time the runner interval is adjusted, and therefore the next runner interval adjustment is performed; when the frequency for runner interval adjustment reaches the set frequency, the layout of the runner interval with the minimum cooling runner equivalent flow standard deviation in the process is adjusted, and the final runner interval optimization result is obtained. The rapid optimization method has the advantages of being simple in optimization process, high in optimization speed, good in performance index, good in expansibility, high in practicability and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Reed pipe pulse type fluid flow meter metering method
ActiveCN104501886AAvoid "overcounting"Make up for untriggeredVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsMaximum fluxEngineering
Owner:CHONGQING SHANCHENG GAS EQUIP
A relative flux sensor and a method of determining a ratio between maximum light intensities, a control device, a color tunable lamp, a luminaire and a computer program product
A relative flux sensor (122) and a method of characterizing characteristics of light emitters are provided. The relative flux sensor (122) comprises a color point sensor(108) and a sensor color (118). The color point sensor (108) measures a color point in a color space of light emitted by a light source (101) comprising a first light emitter (102) for emitting light of a first color and a second light emitter (114) for emitting light of a second color being different from the first color. The light source (101) is arranged for emitting light of a controllable color,being a mix of light of the first color and light of the second color.; The sensor controller (118) is coupled to the color point sensor (108) for receiving a measuring signal and is arranged for i)providing a first signal to the light source (101), the first signal comprising a dimming factor D1 and a dimming factor D2, the dimming factor D1 and the dimming factor D2 indicating a fraction of a maximum flux of the first light emitter(102) and the second light emitter (114), respectively, and receiving the measuring signal representing a first color point when the light source (101) emits light according to the first signal, wherein at least one of the dimming factors D1 and D2 is different from 0, ii) providing a second signal to the light source (101), the second signal comprising a dimming factor D4 and a dimming factor D5, the dimming factor D4 and the dimming factor D indicating a fraction of the maximum flux of the first light emitter (102); and the second light emitter (114), respectively, and receiving the measuring signal representing a second color point when the light source (101) emits light according to the second signal, wherein both dimming factors D4 and D5 are different from 0, iii) calculating within a model of the color 20 space a ratio between a maximum flux of the first light emitter (102) and a maximum flux of the second light emitter (114) on the basis of the first color point, the second color point, the dimming factors D1, D2, D4 and D5.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Flow volume limiting device
ActiveUS7617949B2The method is simple and reliableSimple and reliable controlling arrangementEqualizing valvesLiquid transferring devicesImpellerTurbine wheel
A turbine wheel and gear system rotate an output shaft in response to flow, where the output shaft is connected to a clutch cup that engages a clutch and valve disk. The disk cooperates with a valve seat formed on a piston to permit / prevent flow within the piston. During flow, the clutch clamps to the disk, and the piston and disk move downstream until an associated control member hits a stop, opening the valve (as the disk stops), while the piston continues downstream. The clutch rotates the disk and control member, and if a maximum flow volume occurs, the control member rotates to an interrupt position and is released from the stop, closing the valve. Passages allow restricted flow to disengage the clutch and permit a spring to move the piston and valve upstream until engaging a reset cam that rotates the control member back to an initial position.
Owner:BROWN KEVIN
System for Preventing Transformer Saturation
ActiveUS20180191282A1Effective recoveryConversion without intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protection detectionMaximum fluxTransformer
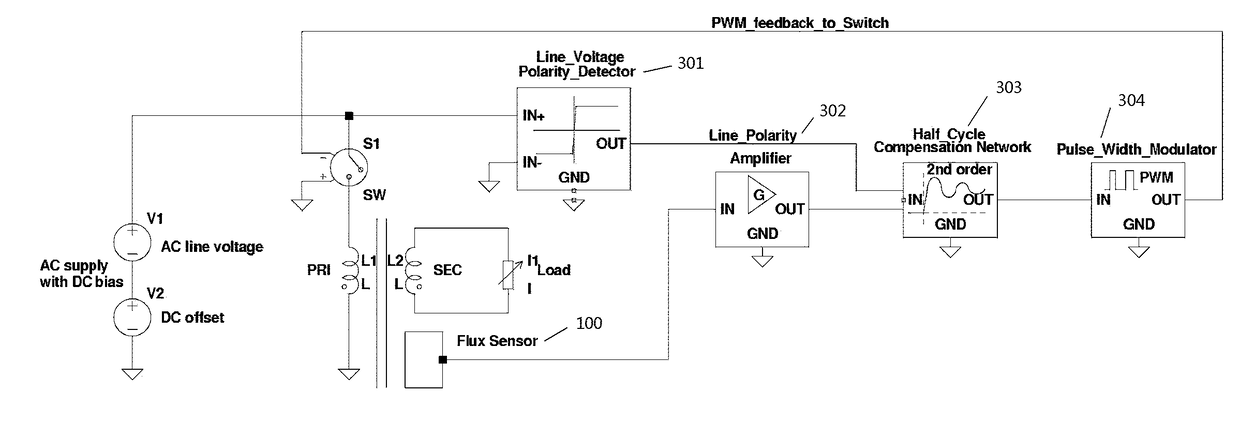
A system for preventing magnetic saturation in a transformer cores. A magnetic flux sensor is disposed within a bore in the core in a bore drilled or let into the material of a toroidal transformer core. The sensor transmits a sensor output that is continuously received by a microprocessor that is programed to process the sensor output and to also continuously compare in real time the sensor output with a stored selectable maximum flux sensor output value. Responsive to the comparison of real-time sensor output value to the stored maximum value, the microprocessor either allows, during each driving voltage half-cycle, the driving voltage to continue unabated while the sensor output remains below the selectable maximum value, or triggers a gate to modify the driving voltage for the remainder of the half-cycle when the selectable maximum value is reached.
Owner:DENT ORRIS
Four-phase block rotor pole electro-magnetic doubly salient motor
PendingCN110311487ASimple structureShort flux pathMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorsMaximum fluxElectric machine
The invention relates to a four-phase block rotor pole electro-magnetic doubly salient motor. The stator core is provided with 12 uniformly distributed salient stator poles which are identical in rootpole width. The tops of the 12 salient stator poles are widened outward to form a pole arc structure. The angle of the pole arc structure width is 22 degrees. The rotor core is provided with 9 sectorblock rotor poles. The angle of the sector top width is 32 degrees, and the angle of the bottom width is 17 degrees. A set of armature windings and a set of excitation windings are wound around the stator poles. The distributed excitation mode is used, the excitation windings are uniformly distributed on each stator pole and the generated magnetic circuit is symmetrical so that the problems of asymmetrical four-phase flux linkage, unbalanced electromagnetic force and large torque ripple in the centralized excitation mode can be solved. The rotor block structure is used and the maximum flux value is greater than that of the conventional structure doubly salient motor. The motor is externally connected with four-phase bridge current to form a DC generator so as to have the characteristics of high reliability, convenient voltage regulation and long-term operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Operating a synchronous motor having a permanent magnet rotor
ActiveUS8410742B2Good dynamic behaviourEasy to useSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlPermanent magnet rotorSynchronous motor
A method of operating a synchronous motor having a stator that includes a set of electromagnets and a permanent magnet rotor. The synchronous motor is controlled by calculating in a flux controller a measure of a flux magnitude, which is the magnitude of the stator flux of the motor and by calculating in a load angle controller a measure of a load angle. Information about a desired motor torque or a reduced motor torque, which is smaller than the desired motor torque, is input to the load angle controller and the load angle controller calculates the measure of the load angle depending on the input motor torque. The measure of the flux magnitude is combined with the measure of the load angle to obtain commands for controlling electric currents of electromagnets of the stator, thereby directly controlling the stator flux. A flux limit value, which depends on a predetermined maximum value of the stator flux allowed for the motor which depends on a maximum value of an electric voltage, which is used to drive the currents through the stator electromagnets and which depends on the actual rotor speed, is repeatedly calculated. During acceleration of the rotor while the stator flux is smaller than the maximum flux allowed for the motor the measure of the flux magnitude is calculated depending on the output of a predetermined function. The output of the predetermined function depends on the desired motor torque and corresponds to the magnitude of the stator flux.
Owner:BOMBARDIER TRANSPORTATION GMBH
Magnetic circuits of electrical machines
InactiveCN1658473ASynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMaximum fluxElectric machine
An electrical machine is provided with one or more flux plates at the end of the stator and rotor cores. On the stator side, the plate is profiled to substantially fill the void between the core and the winding. The plates are ferromagnetic and form part of the main magnetic circuit. They carry maximum flux at zero and low switching frequencies and substantially no flux at the highest operating speeds.
Owner:SWITCHED RELUCTANCE DRIVES
Electric motor valve
ActiveCN101382208AReduce volumeTroubleshoot graceful shutdown issuesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesVolume meteringMaximum fluxElectric machine
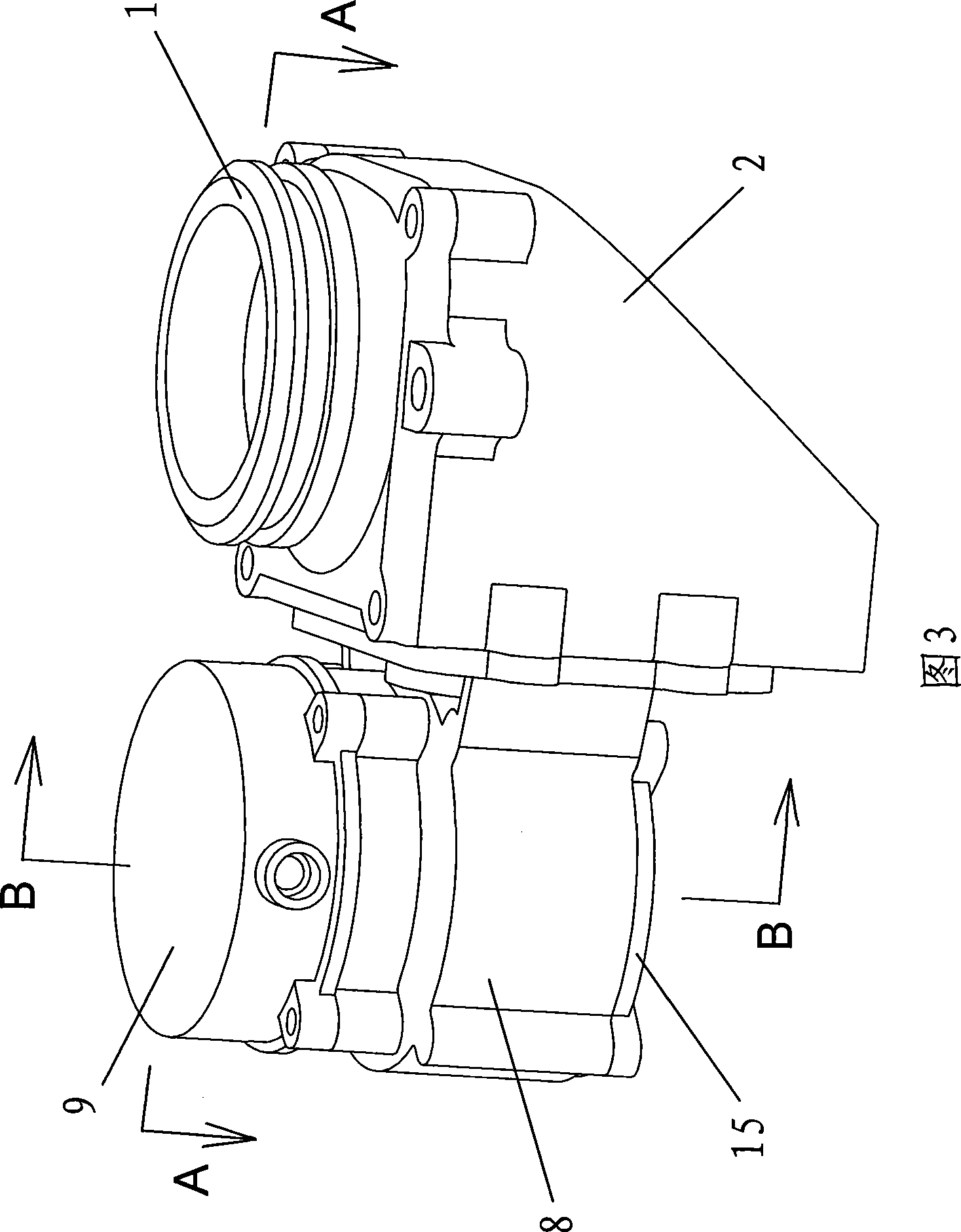
The invention discloses a motor valve which is mainly used for opening or closing control of various intelligent gas meters. The motor valve comprises a valve body, a valve cover and an execution component; the valve body is provided with an air inlet and an air outlet; the valve cover is arranged at the air outlet side; the execution component is connected with the valve cover; the motor valve is characterized in that: the valve body is an unfilled-corner rectangular valve body; the air outlet of the valve body is an oblique air outlet; the valve cover adopts a turnover typed valve cover; when the valve cover of the motor valve is opened, the airflow linearly passes through the valve body; therefore, the minimum pressure loss and maximum flux can be obtained, the motor valve overcomes the defects of large air pressure loss and unreliable switching action existing in the prior art and has the advantages of reasonable structure, reliable switching, large flux, low pressure loss, and the like.
Owner:CIXI SANYANG ELECTRONICS
Method for continuously determining air-actuated compression release valve flow characteristic
InactiveCN100573083CLow costImprove test efficiencyMachine part testingObservational errorContinuous measurement
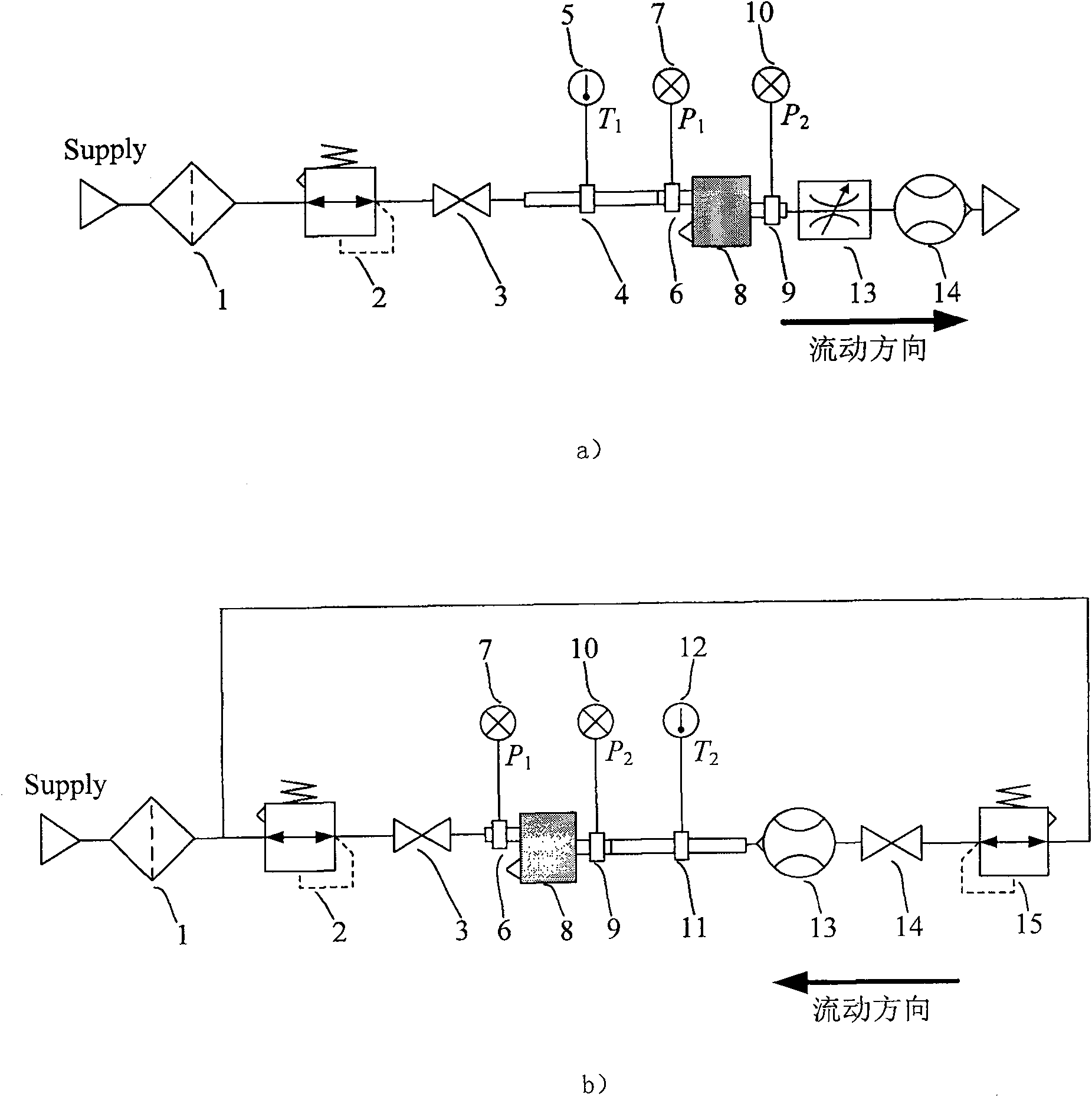
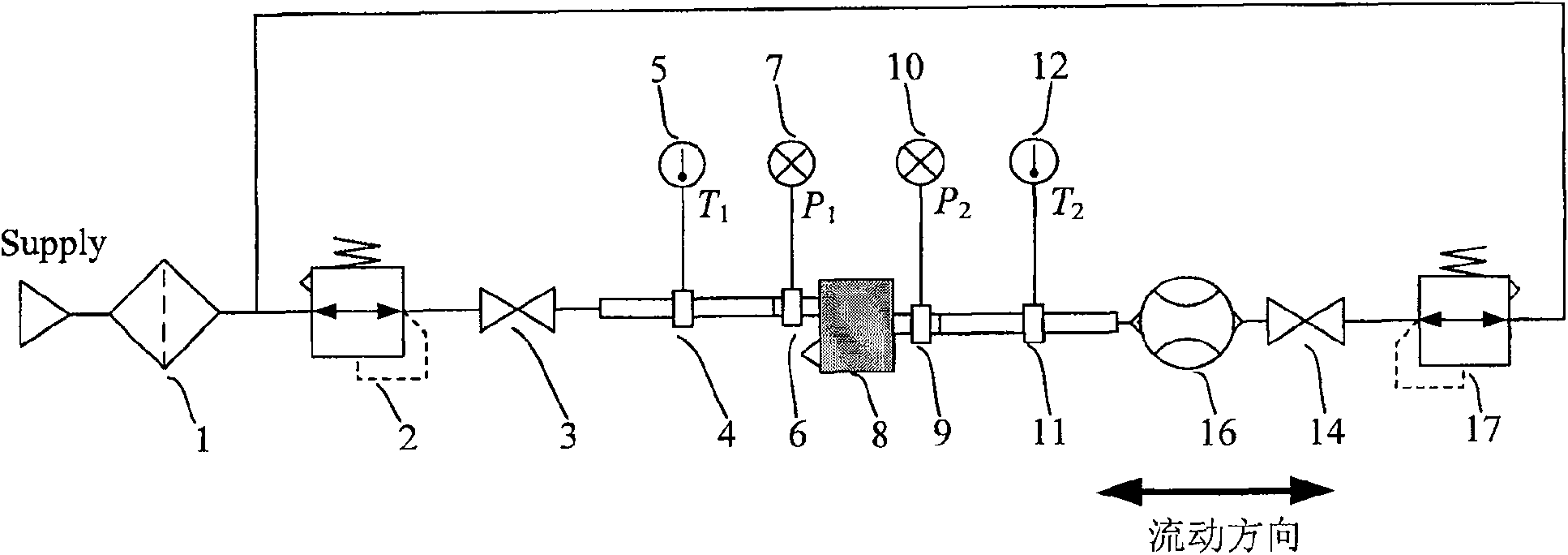
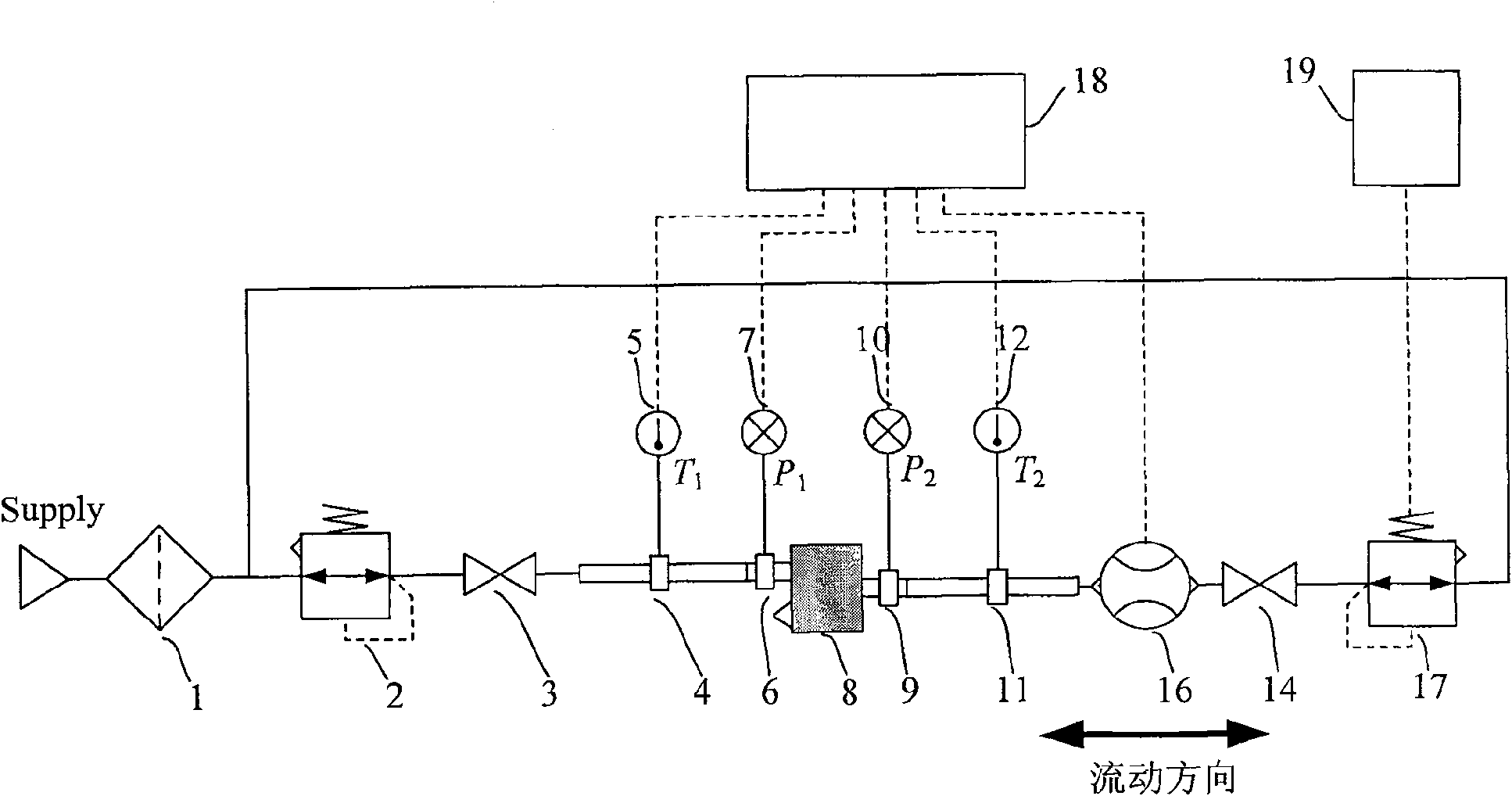
The invention relates to a device and method for continuous measurement of flow characteristics of a pneumatic pressure reducing valve. The device mainly includes: filter, air supply pressure setting pressure reducing valve, air supply side stop valve, air supply side temperature measuring tube, control side temperature measuring tube, air supply side pressure measuring tube, control side pressure measuring tube, Measure pressure reducing valve, bi-directional flowmeter, control side stop valve and control side pressure reducing valve; The flow measurement function realizes continuous measurement of pressure and flow through uninterrupted manual or automatic setting from the positive maximum flow to the overflow to the maximum flow, so as to measure the control port flow and control port pressure of the pressure reducing valve under test. Relationship, that is, the flow characteristics of the pressure reducing valve under test. The invention simplifies the experimental circuit, reduces the exchange of test equipment and the measurement error generated, improves the test efficiency and saves the air consumption.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Self-latching sector motor for producing a net torque that can be backed-up or doubled
A self-latching sector motor for producing a net torque from two integral independent sources where one can serve as a spare backup or paralleled for double net torque or used alternately for extended life operation. The self-latching sector motor includes a housing, a magnet-shaft assembly, and two pair of electromagnetic poles. The magnet-shaft assembly rotates within the housing. The two pair of electromagnetic poles extend fixedly and radially inwardly from the housing, towards the magnet-shaft assembly. The electromagnetic poles of an associated pair of electromagnetic poles are diametrically and magnetically opposed to each other, and each pair of electromagnetic poles are similarly poled to each other for North and South poles so as to provide the net torque to the magnet-shaft assembly that can be backed-up or doubled. The self-latching torque at the stops is achieved by restraining the magnet-shaft assembly from seeking a position of maximum flux.
Owner:NELSON VICTOR
Dust collector with air flow adjusting device on up flow of motor
InactiveCN101152063AHigh additional costAchieve relative motionMechanical suction controlFlow controlMaximum fluxEngineering
The present invention relates to a dust collector (1) which comprises a frame provided with an electric motor (20) connected with a fan. When the dust collector is running, at the upstream of the electric motor (20), air suction can be generated from one pipeline to a suction nozzle and to the air outlet of the frame at the downstream of the electric motor (20). A filter device is arranged on the pneumatic power path and is preferably arranged on the upstream of the motor (20). Regulating devices (200, 400) for regulating the air flux in the dust collector (1) are arranged on the pneumatic power path at the upstream of the motor (20). When the motor (20) is operating, the regulating devices (200, 400) can cause the change to the air flow area passing through under the condition that the flux is changed. The dust collector is characterized in that the change of the air flow area can be realized in a range from 80% to 100% of the predetermined maximum flux.
Owner:SEB SA
System and flow adaptive sensorless pumping control apparatus for energy saving pumping applications
ActiveUS9846416B2Pumping energyEasy to storeSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusMaximum fluxEngineering
A signal processor receives signaling containing information about flow rates from sensorless converters in zone circulators in heating / cooling zones controlled by temperature sensors in a hydronic heating system in order to derive an adaptive pressure set point to meet the flow rates requested by the heating / cooling zones using an adaptive system and flow control curve equation, the signaling containing information about total flow rates requested by the zone circulators; determines desired pump speeds for the zone circulators to meet temperature requirements in heat zones; provides corresponding signaling containing information about the desired pump speeds; and / or determines the adaptive pump control curve equation based upon an adaptive system curve and as a moving maximum system flow rate depending on an adaptive pressure set point, a system flow rate requested by temperature loads, a minimum pressure at no flow, a control curve setting parameter, and an adaptive moving maximum flow and pressure.
Owner:FLUID HANDLING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com